Patents
Literature
1186results about "Tidal stream/damless hydropower" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
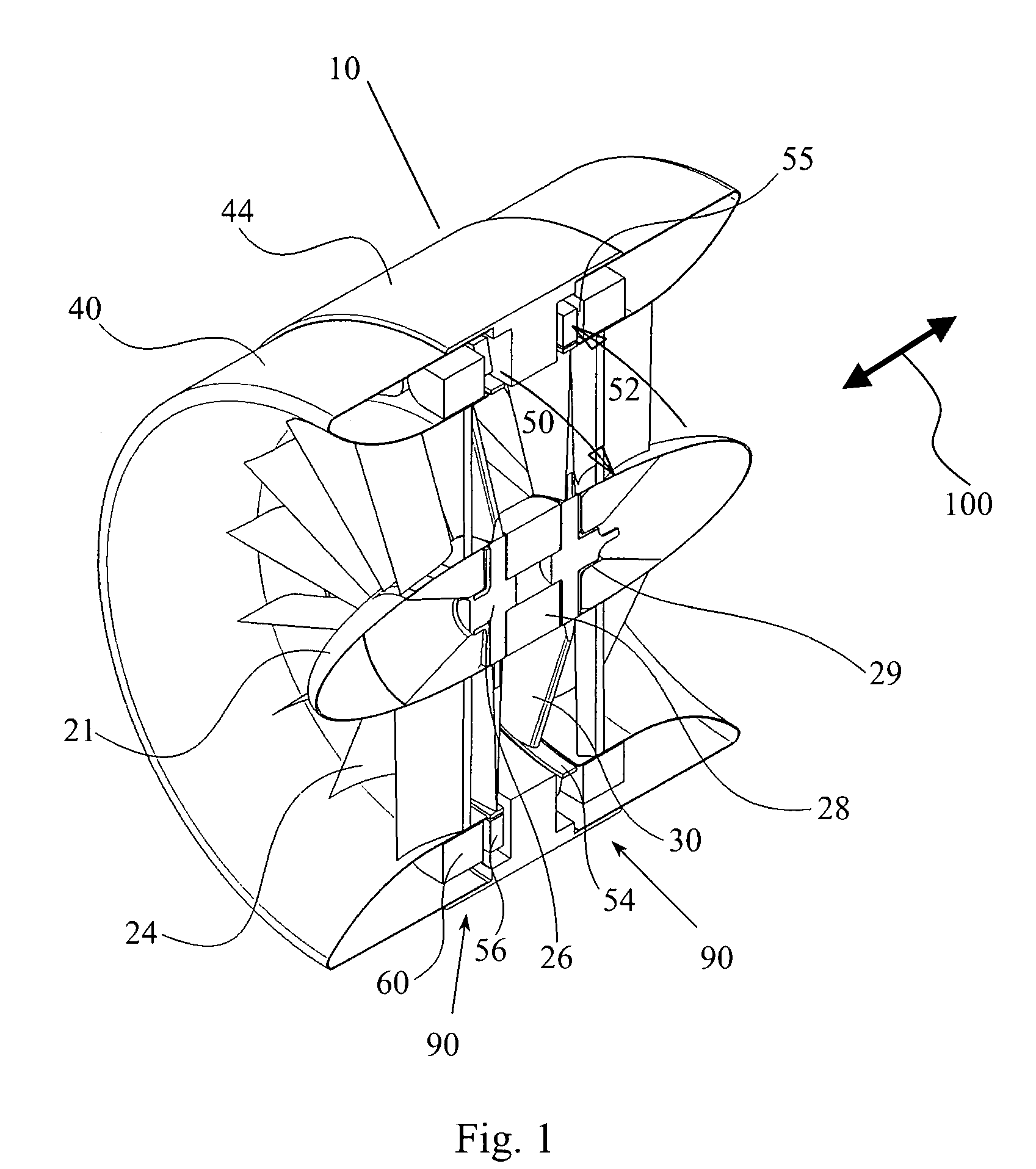
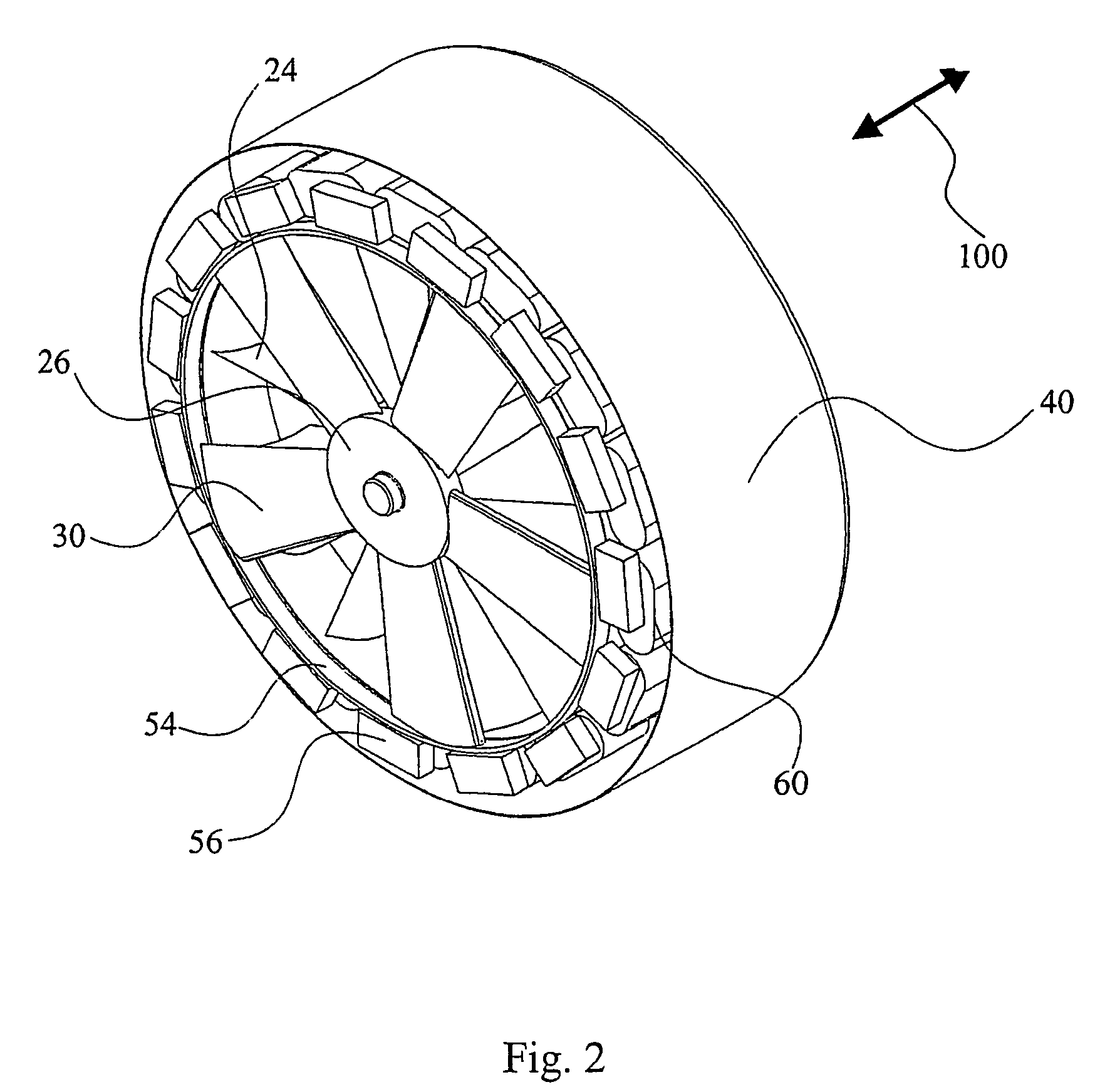
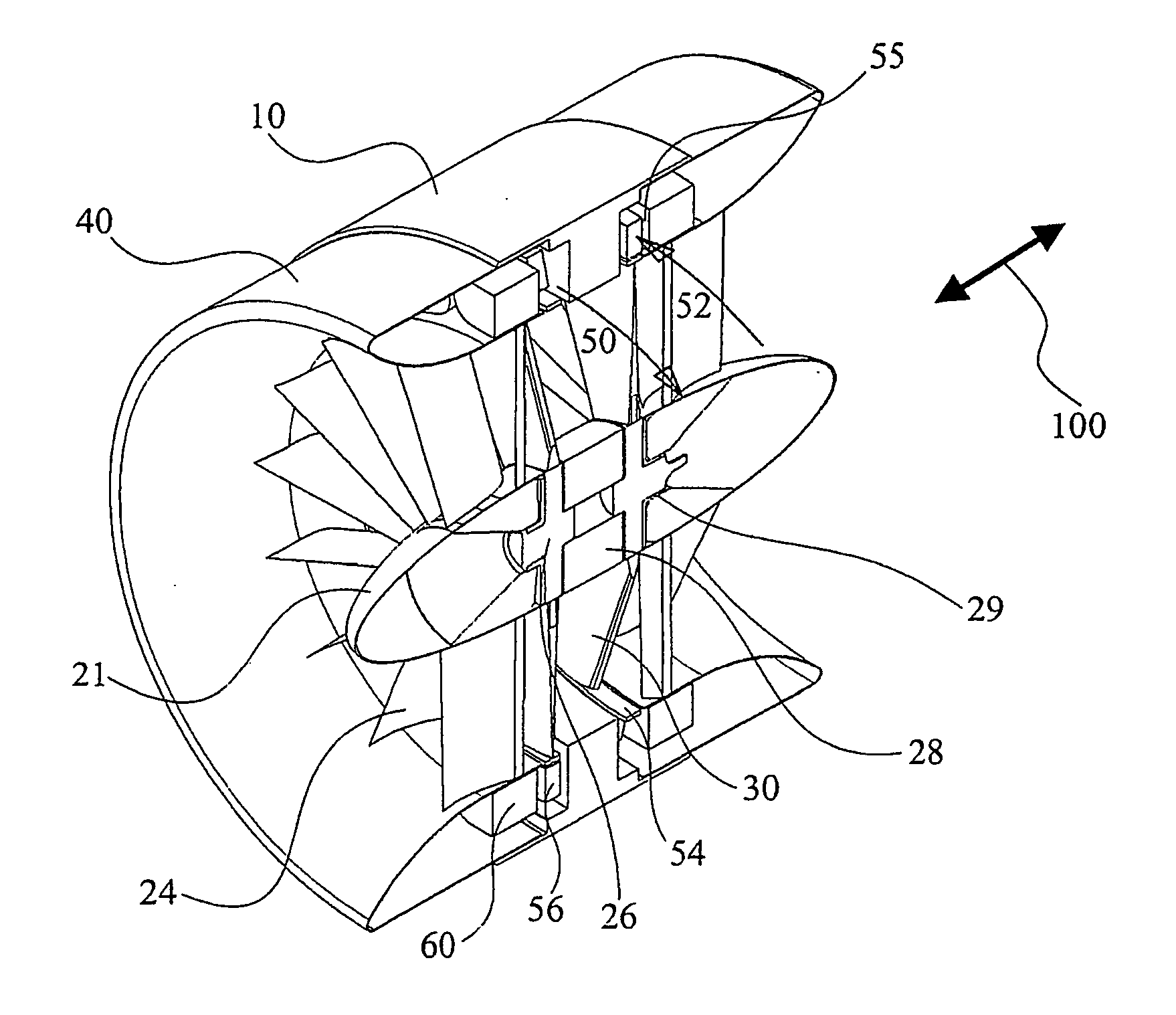
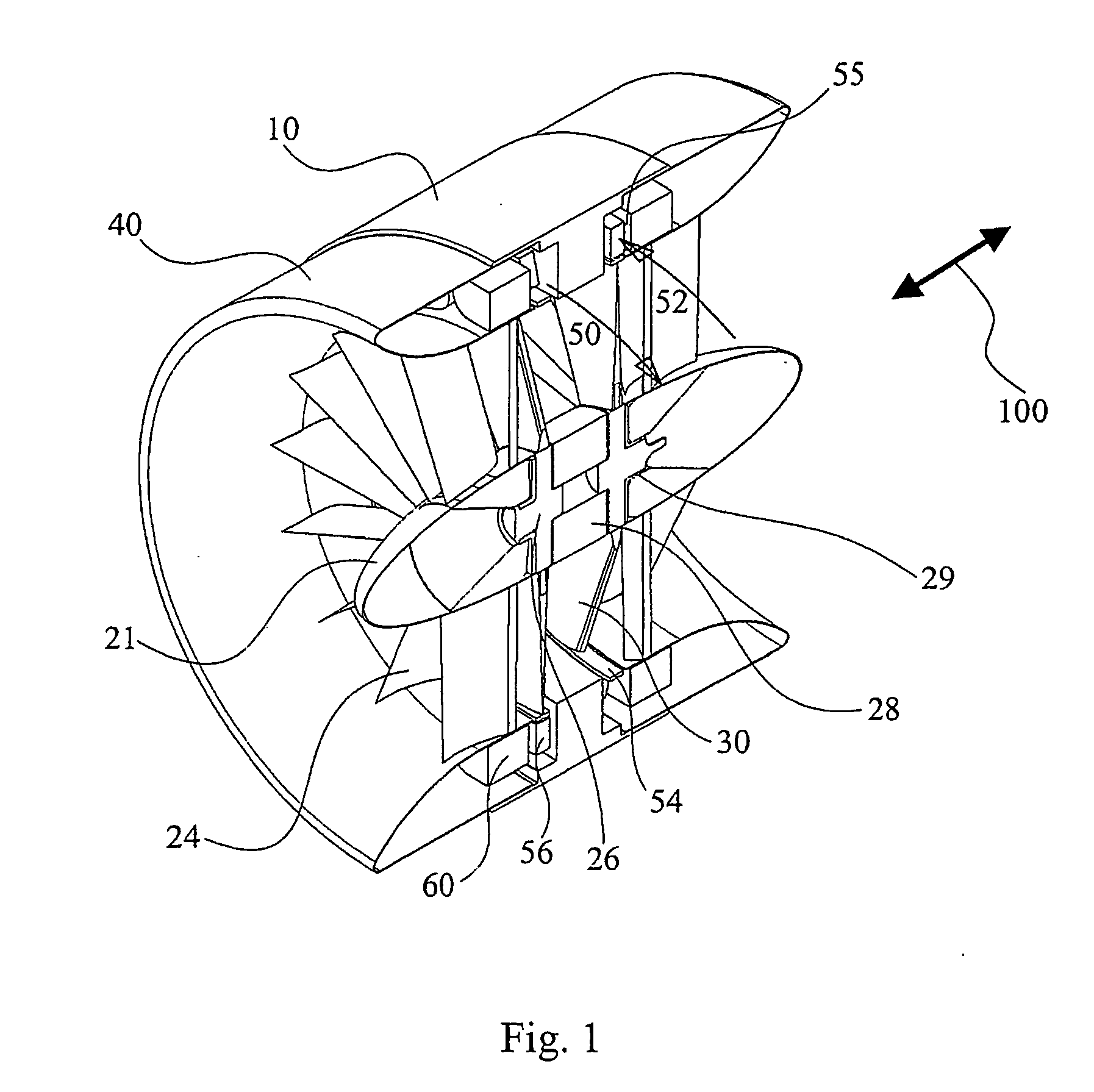
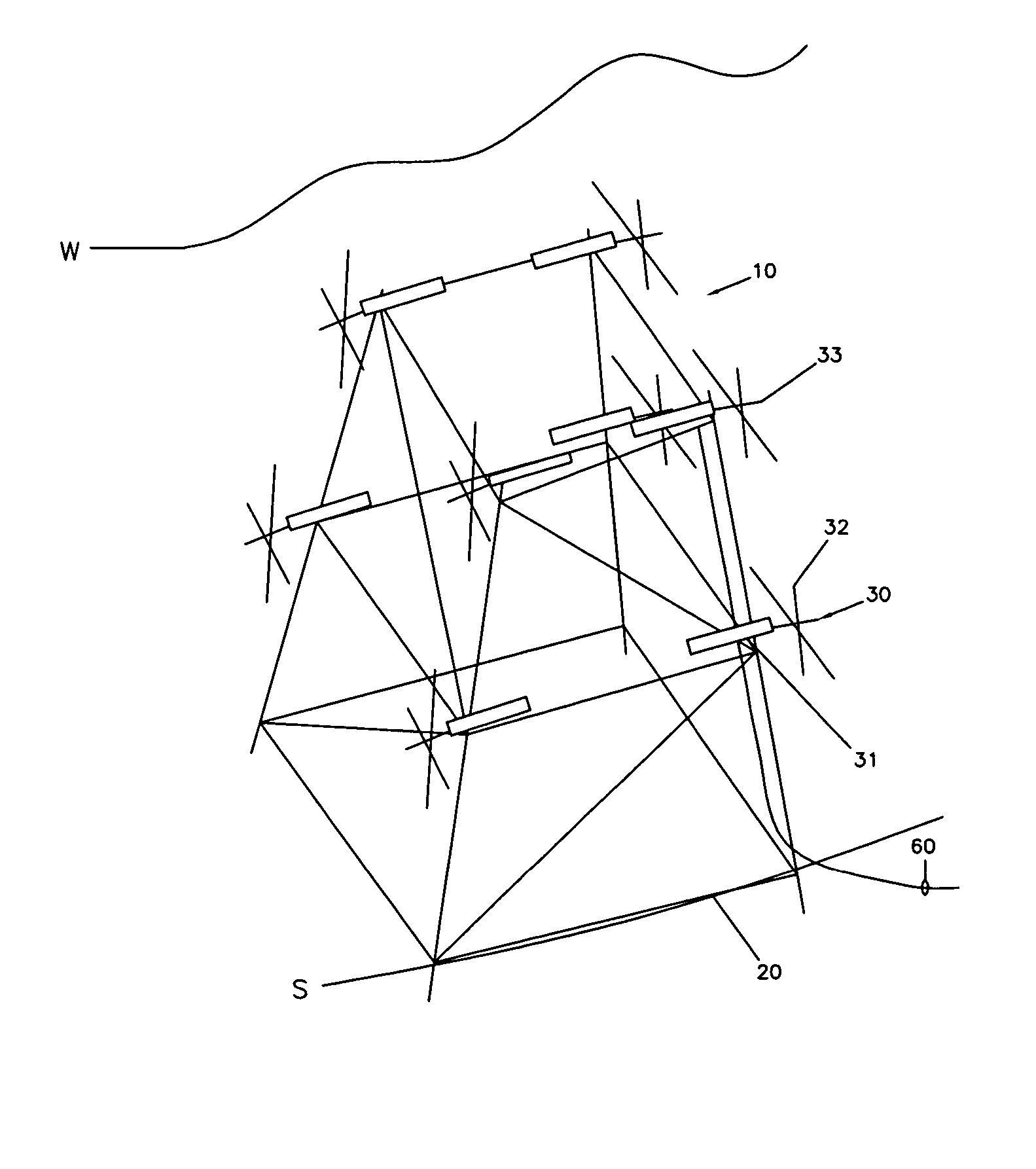
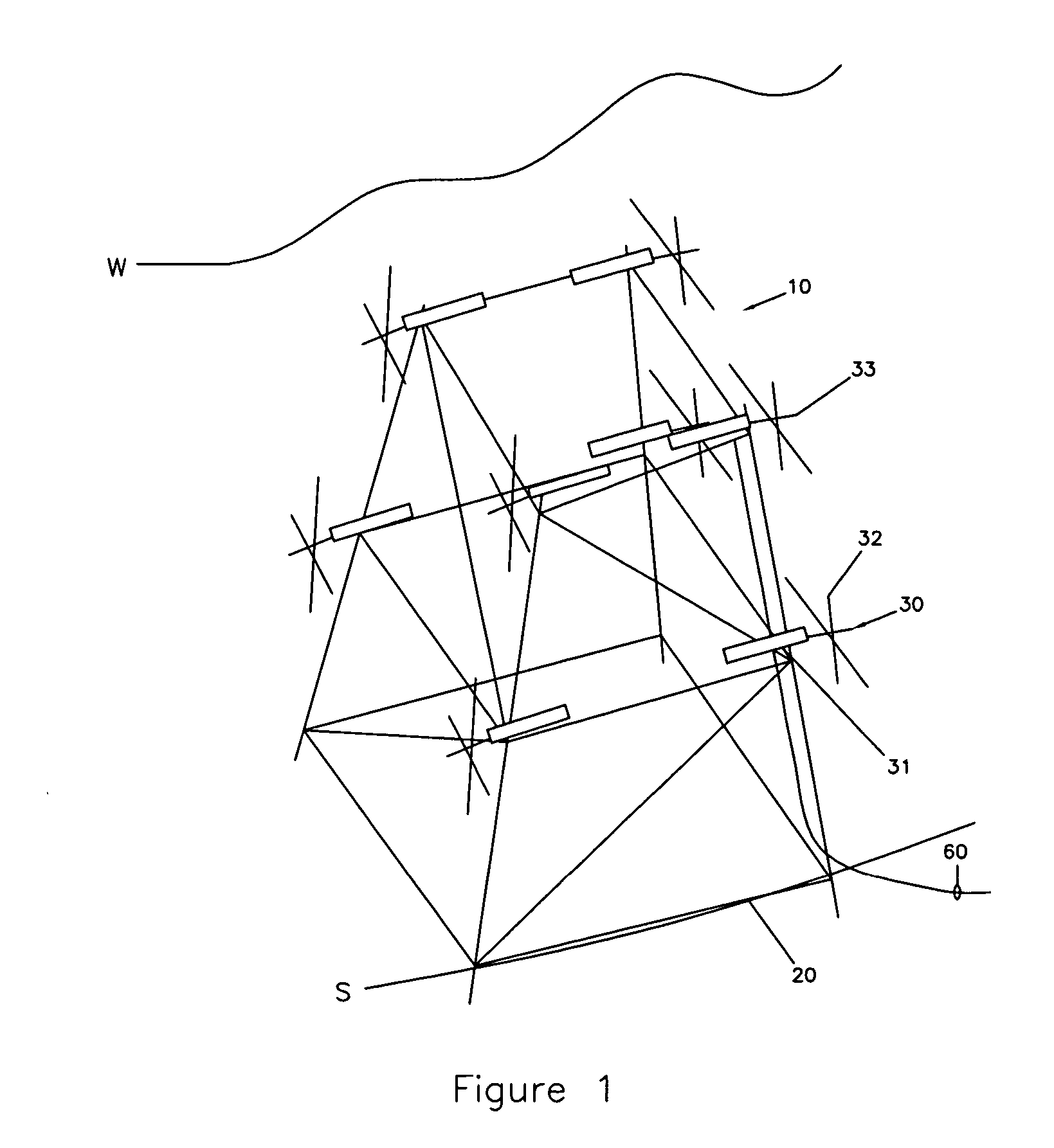
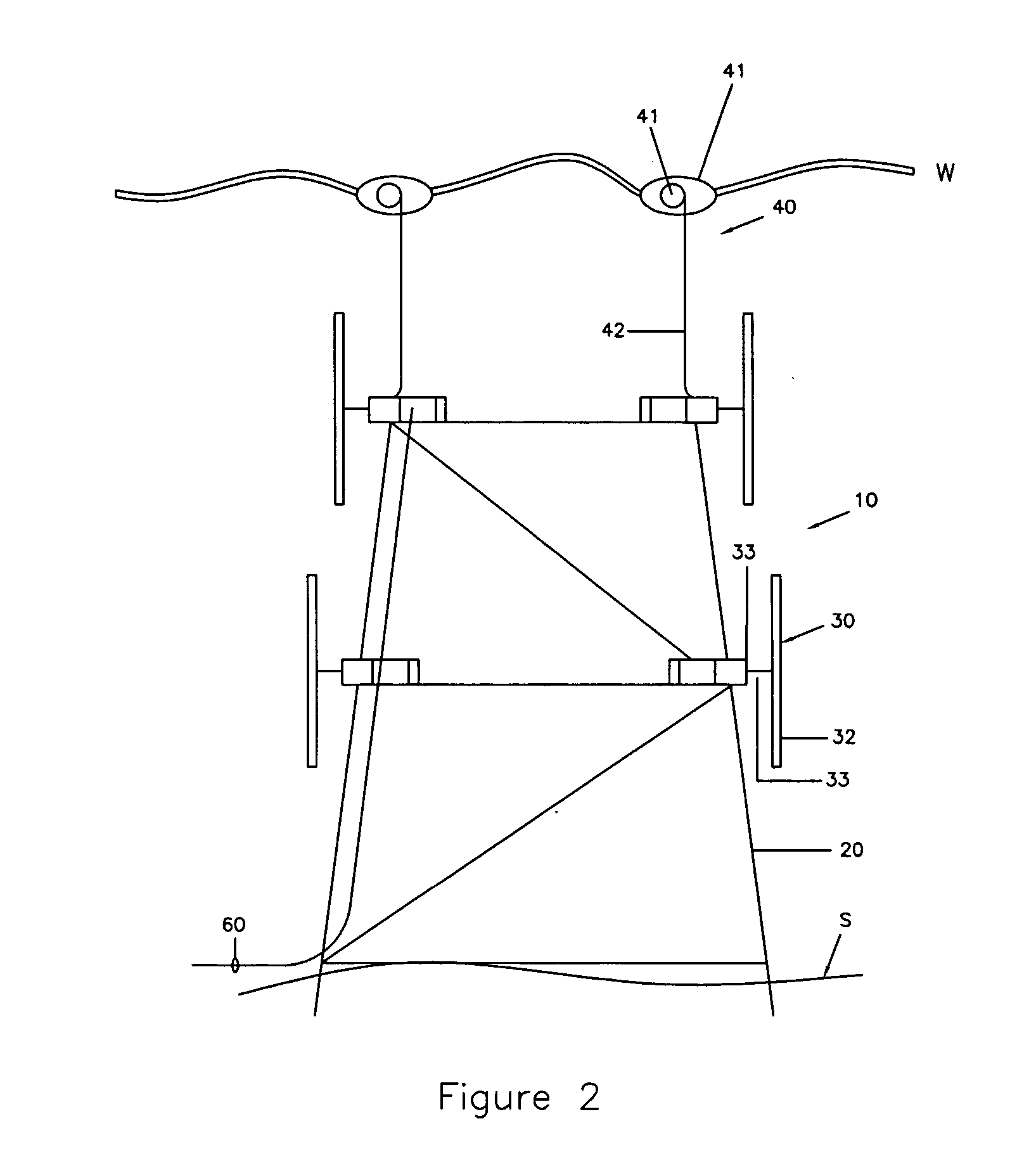
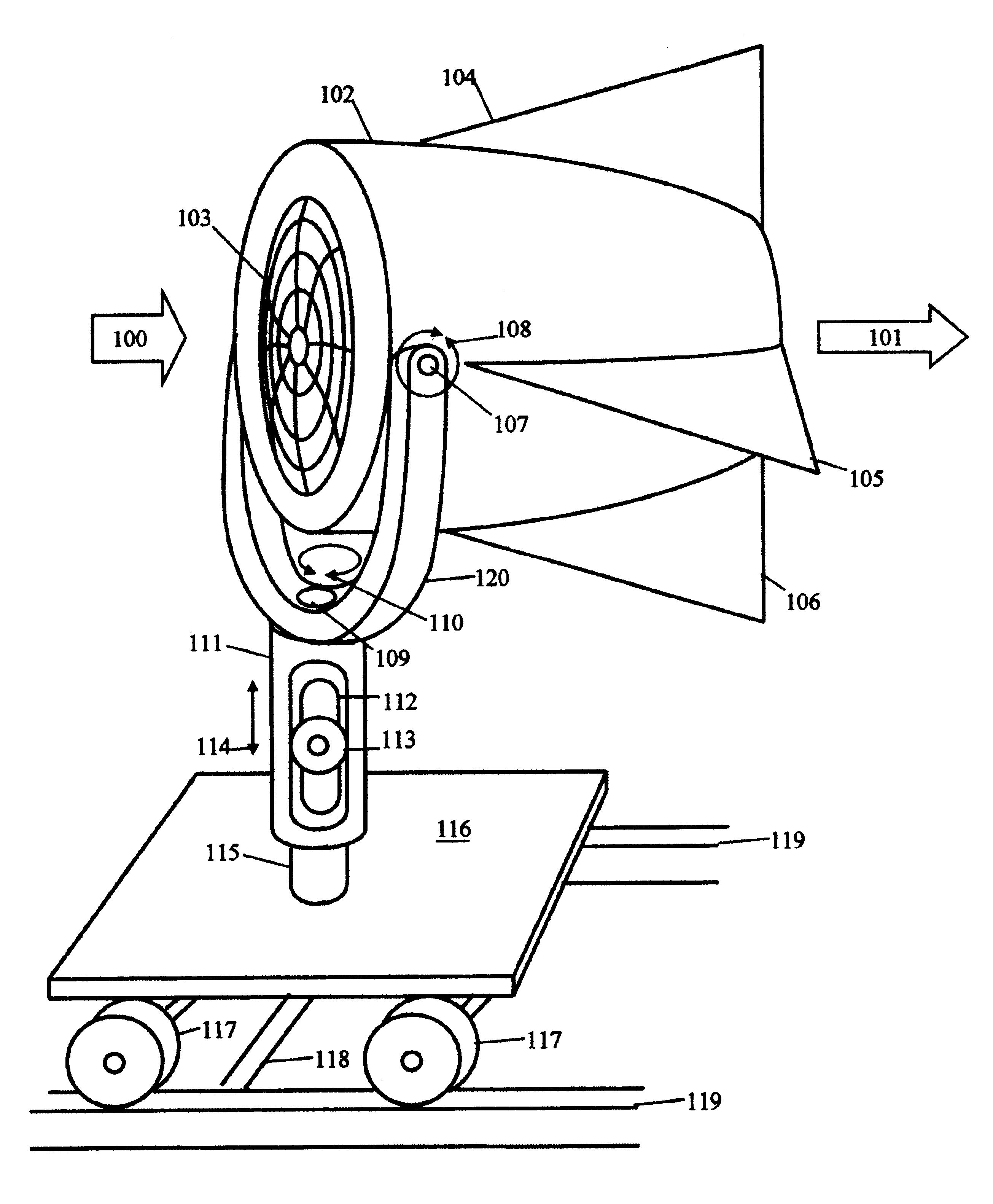
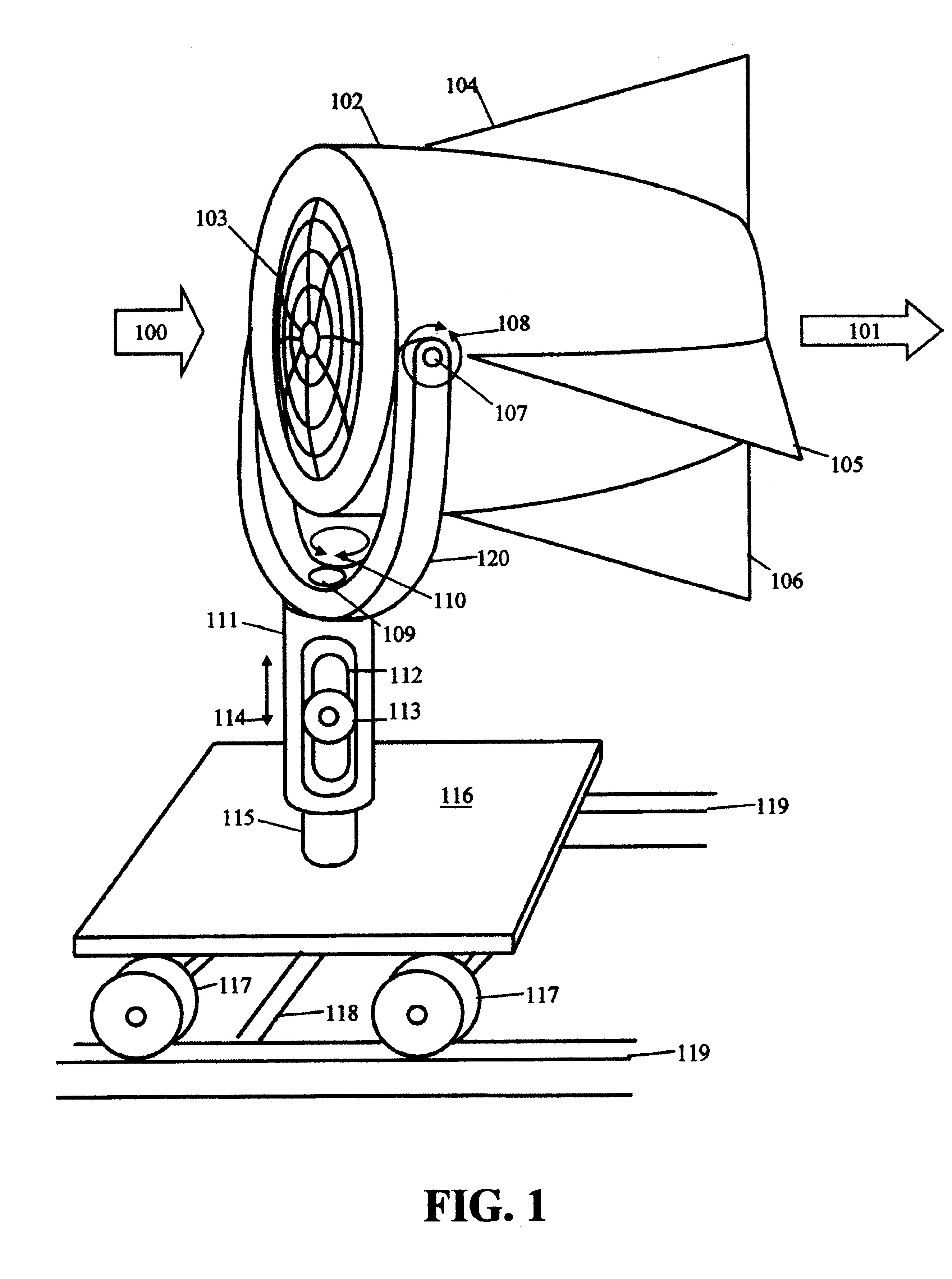
Submersible appartus for generating electricity and associated method
InactiveUS6109863AReduce the impactReduce impactCircumferential flow pumpsWind motor controlElectricityMarine engineering
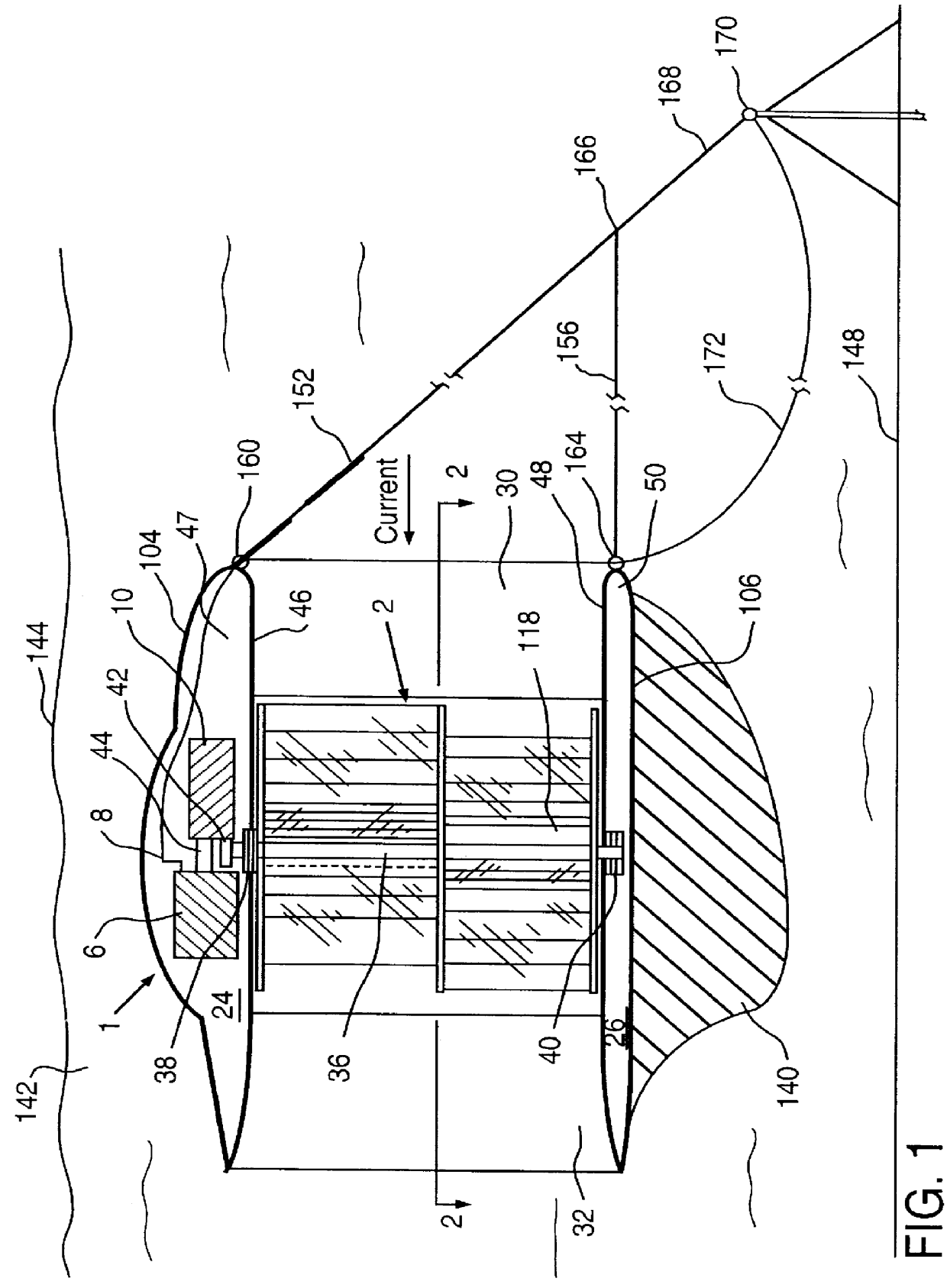
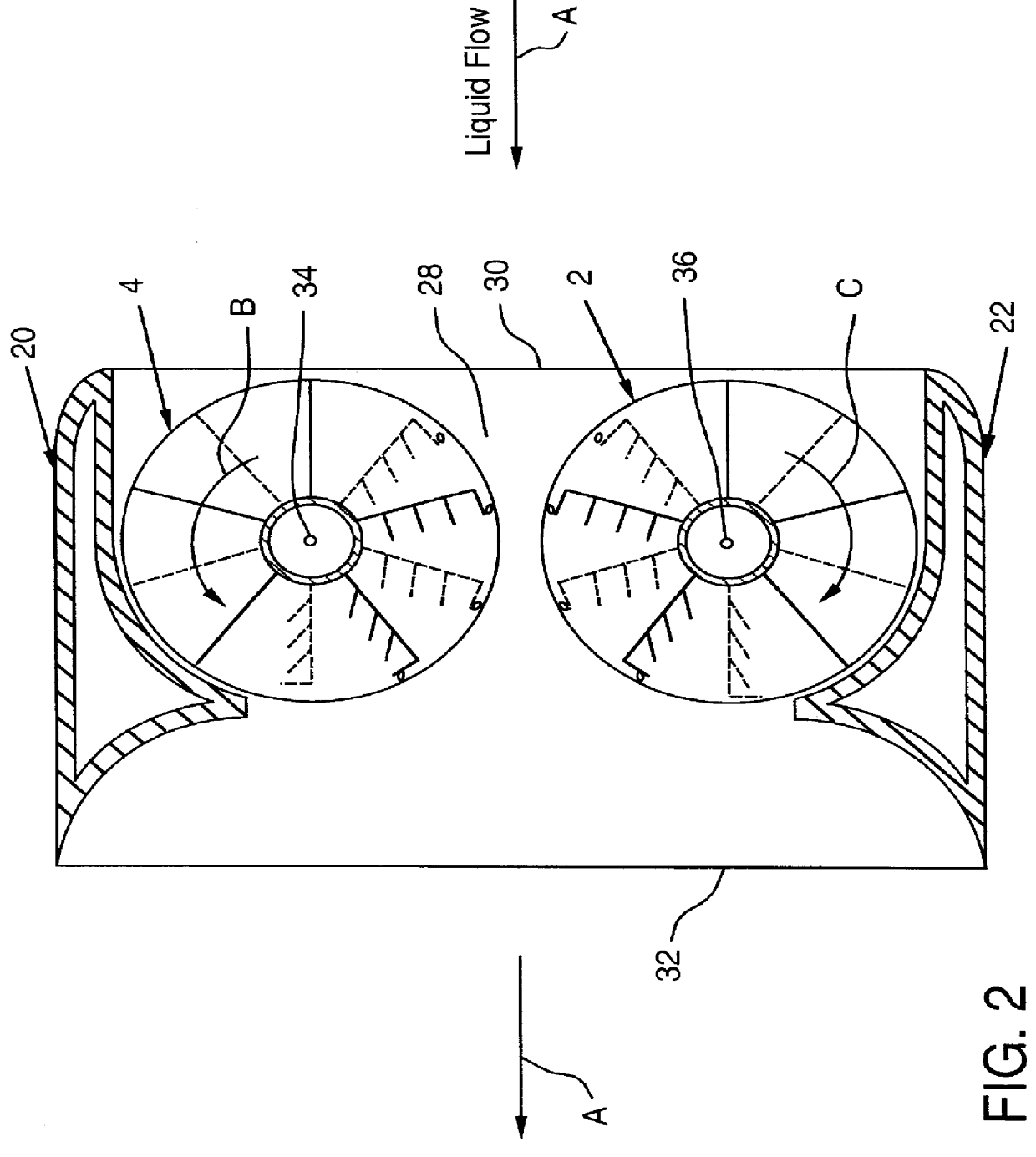
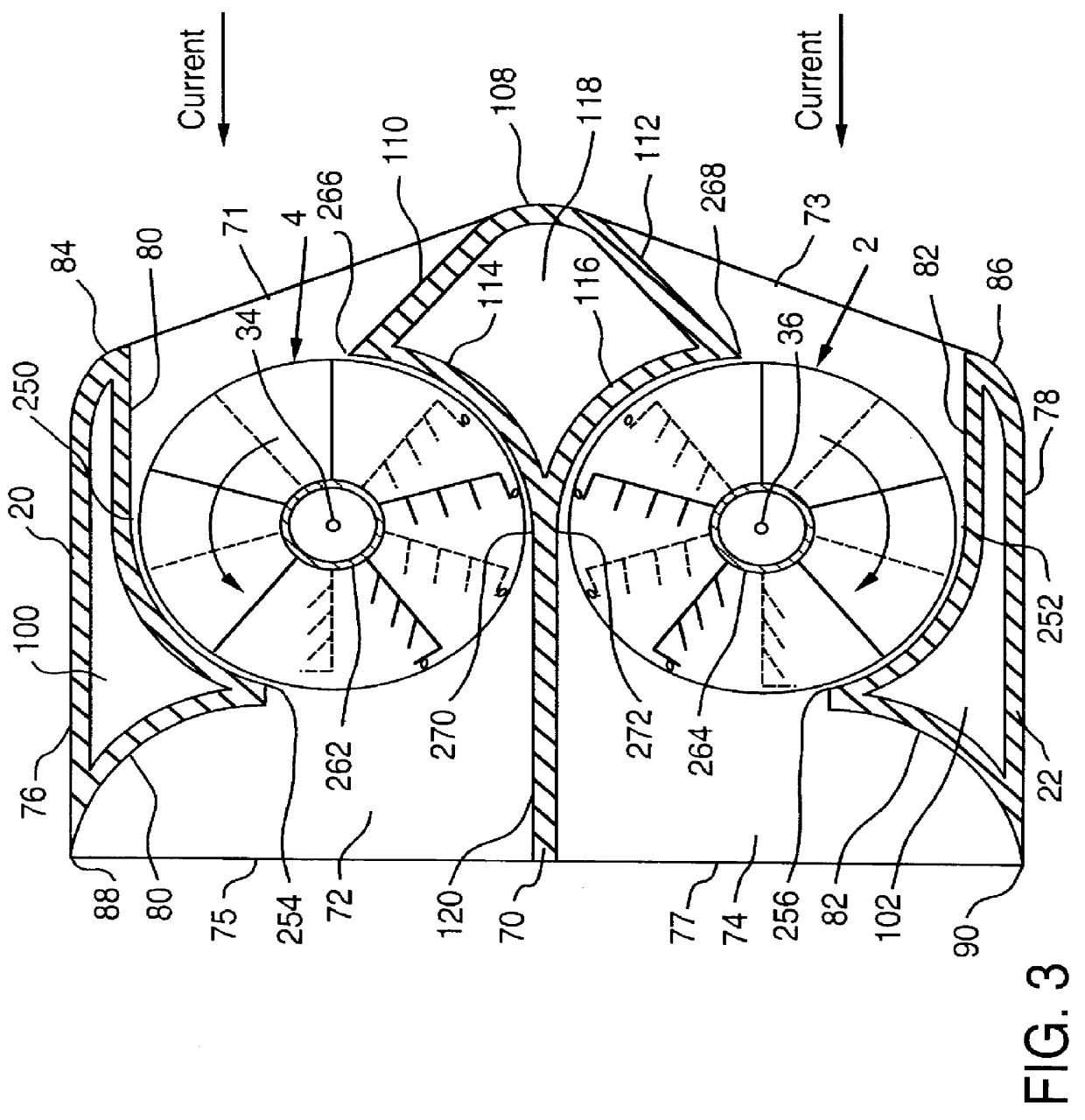
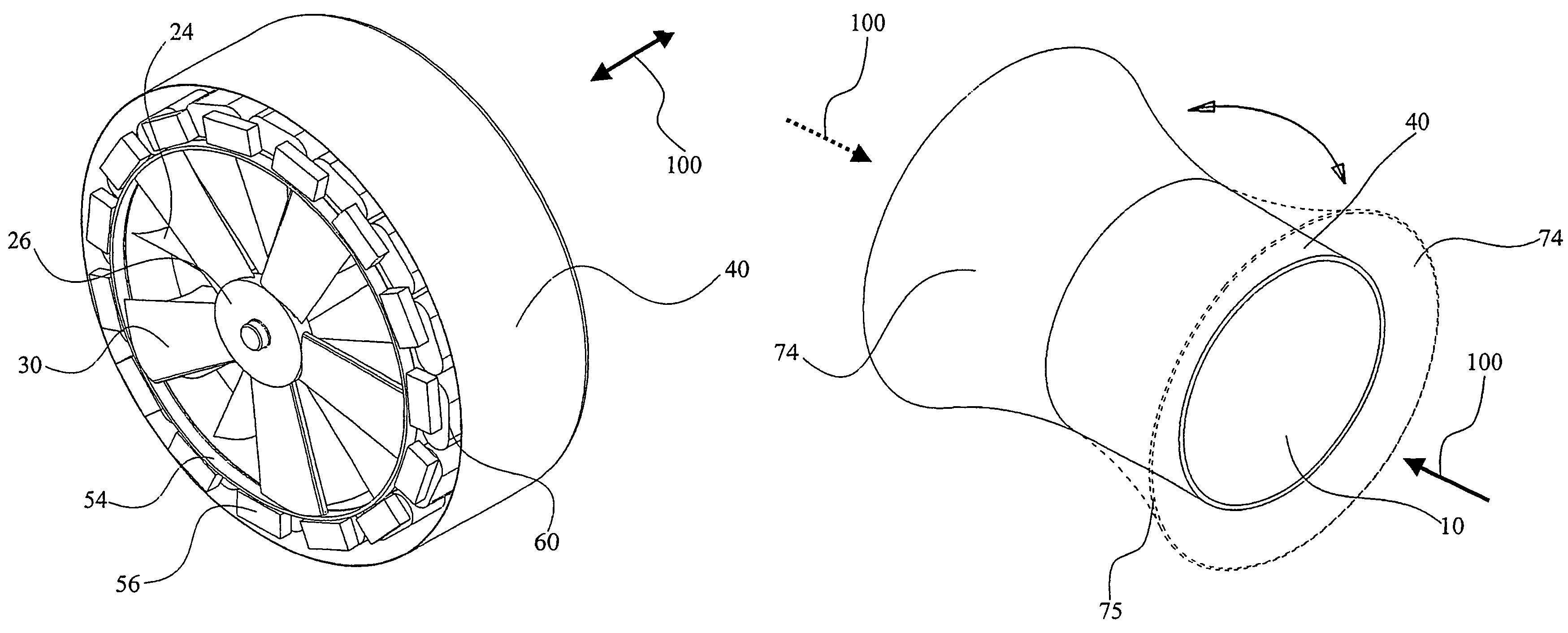
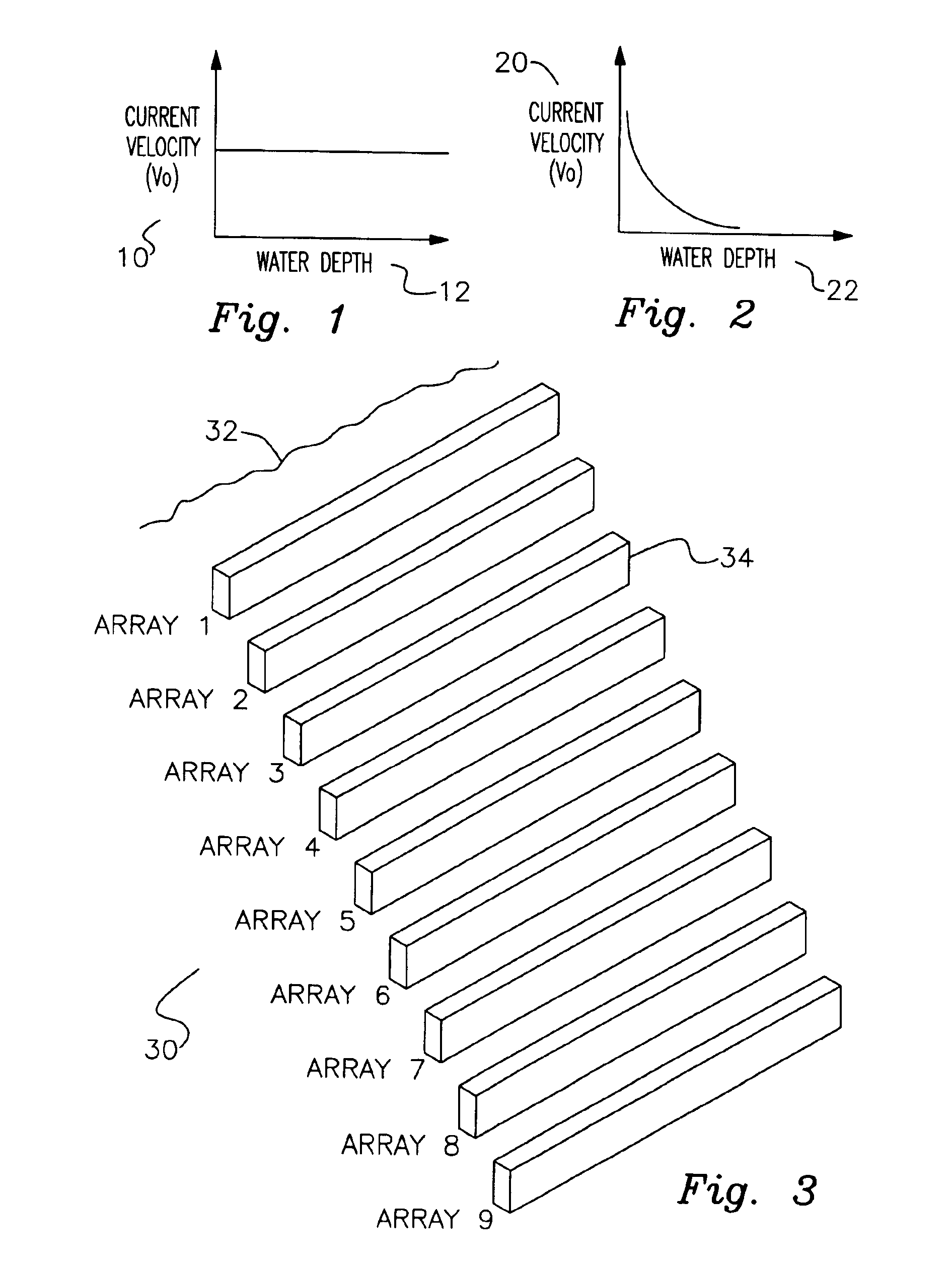
A fully submersible apparatus for generating electricity from liquid flow as in an ocean or river current. A buoyant structure is fully submersible and has at least one pair of counter-rotating side-by-side motors with a plurality of angularly spaced radial vanes each having a plurality of rotatable subvanes such that current impinging upon the motor will impinge on a closed or solid vane to effect rotation of the motor and its shaft during a first phase of the rotational cycle and will impinge on open vanes for free passage therethrough on the return or second phase of rotation of the motor. Motors may also be provided with vanes in overlying and underlying relationship. An associated method is provided.
Owner:MILLIKEN LARRY D
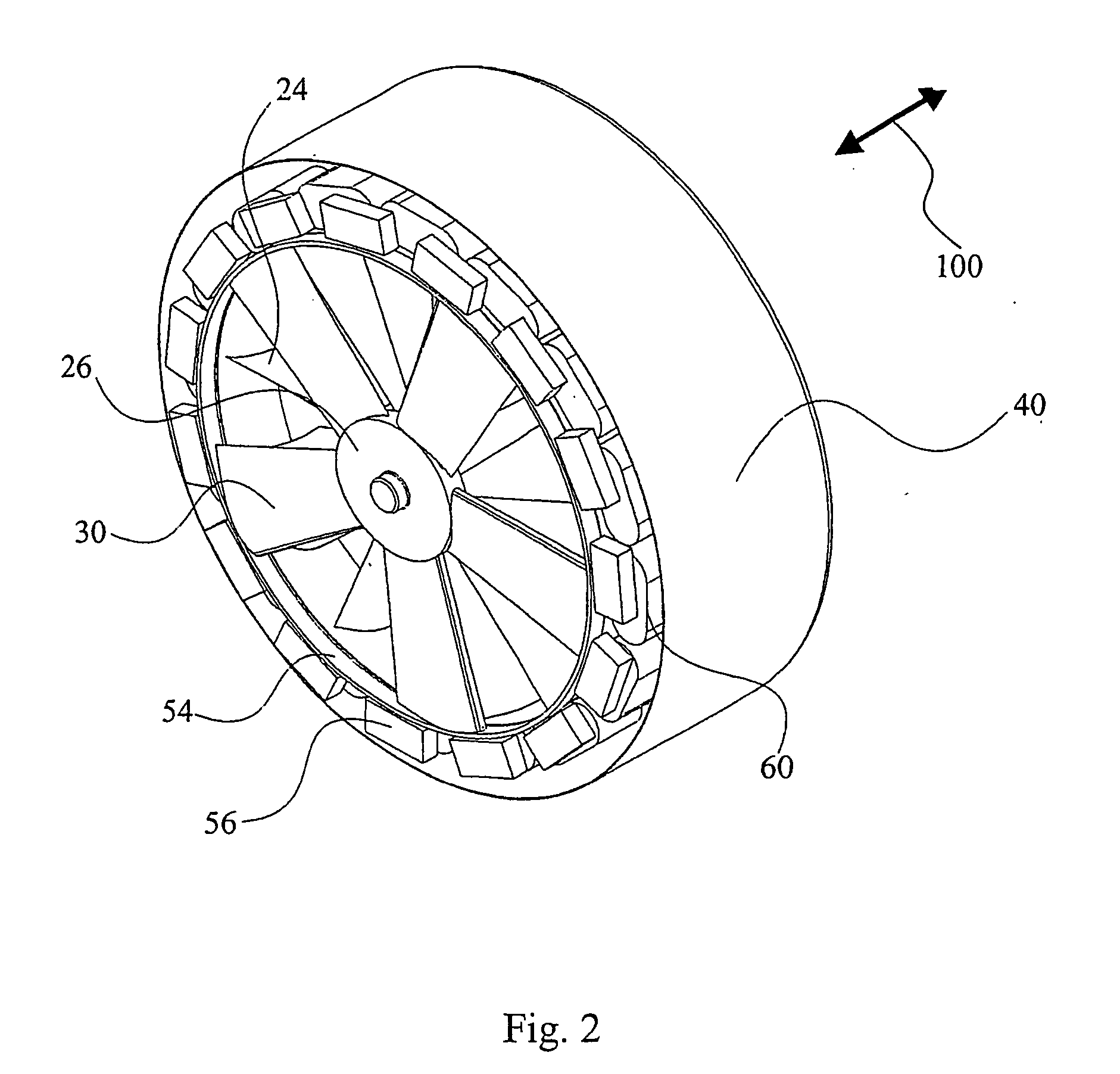
Underwater ducted turbine
InactiveUS7471009B2Minimize loss of efficiencyThe process is stable and efficientEngine fuctionsWorking fluid for enginesUnderwaterStator coil
An apparatus is disclosed for a turbine for generating electrical power from water or air flow comprising at least one rotor disk having a plurality of hydrofoil blades, a guide vanes, a cylindrical housing, and a generator means. A rim generator comprising a magnet race rotor rim and fixed stator coils in the housing is used. The apparatus is fitted with a screen to stop the ingress of debris and marine life, and a skirt augmenter device to reduce the Betz effect. The apparatus is preferably for sub-sea deployment and driven by tidal currents, but may be powered by river current or wave driven air or by wind. The apparatus may be deployed on at least one telescoping pole, tethered to the sea-bed and kept buoyant by buoyant concrete in the housing, inserted in a dam, under a barge or in a tidal power array.
Owner:CLEAN CURRENT PARTNERSHIP
Hydro turbine generator
InactiveUS20050285407A1Minimize downstream efficiency lossMinimizing swirl lossEngine fuctionsWorking fluid for enginesStator coilEngineering
An apparatus is disclosed for a turbine for generating electrical power from water or air flow comprising at least one rotor disk having a plurality of hydrofoil blades, a guide vanes, a cylindrical housing, and a generator means. A rim generator comprising a magnet race rotor rim and fixed stator coils in the housing is used. The apparatus is fitted with a screen to stop the ingress of debris and marine life, and a skirt augmenter device to reduce the Betz effect. The apparatus is preferably for sub-sea deployment and driven by tidal currents, but may be powered by river current or wave driven air or by wind. The apparatus may be deployed on at least one telescoping pole, tethered to the sea-bed and kept buoyant by buoyant concrete in the housing, inserted in a dam, under a barge or in a tidal power array.
Owner:CLEAN CURRENT PARTNERSHIP
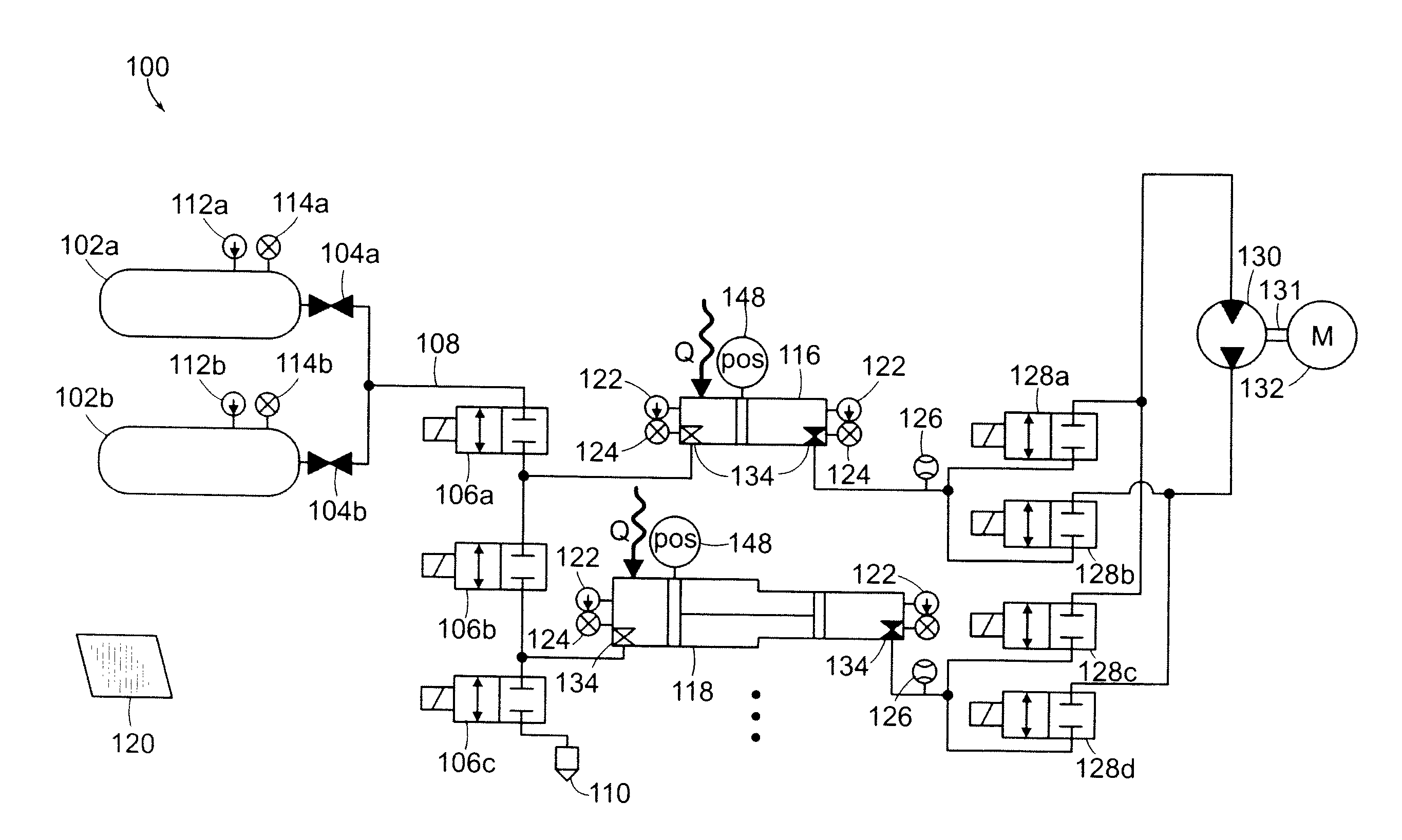
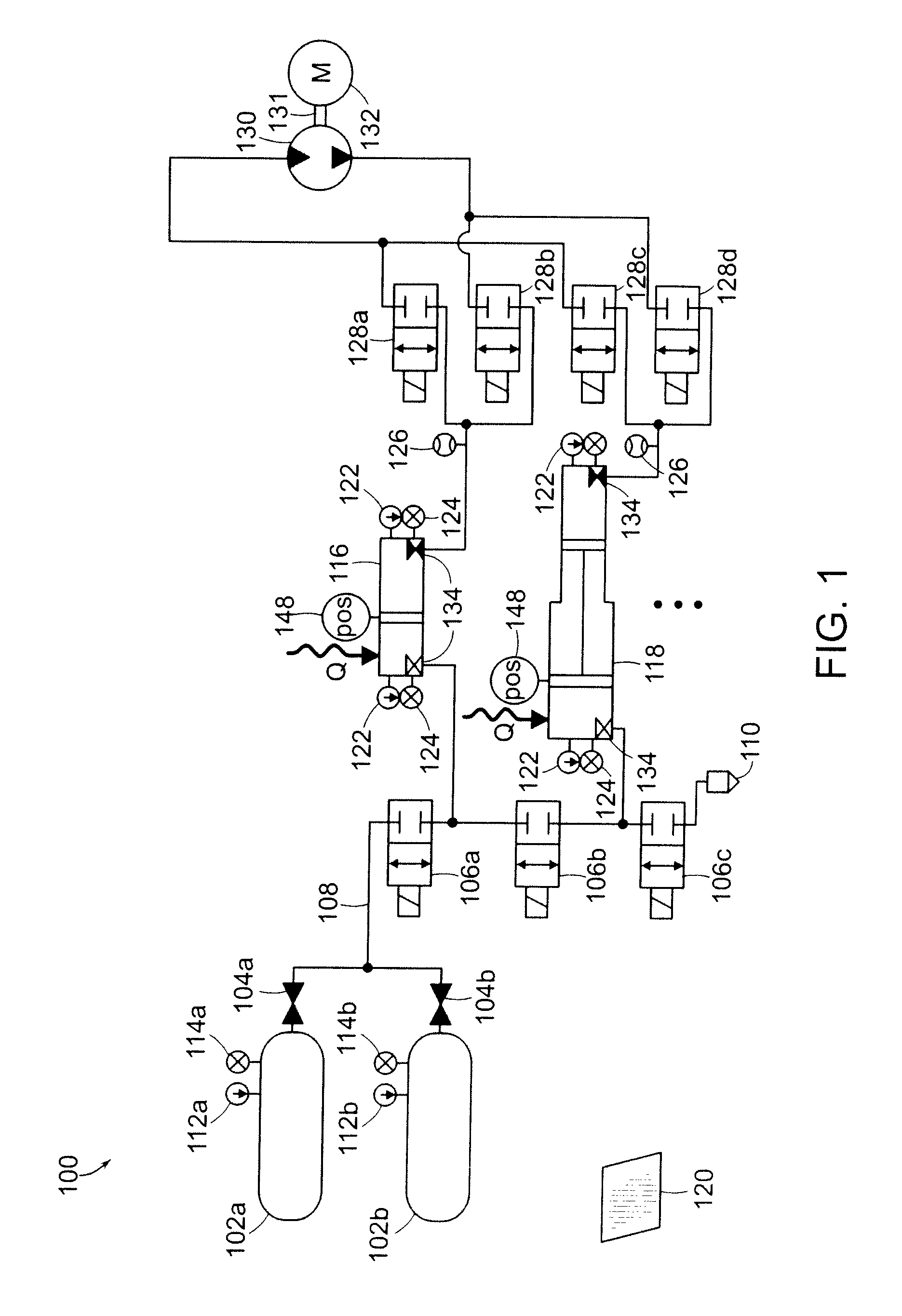
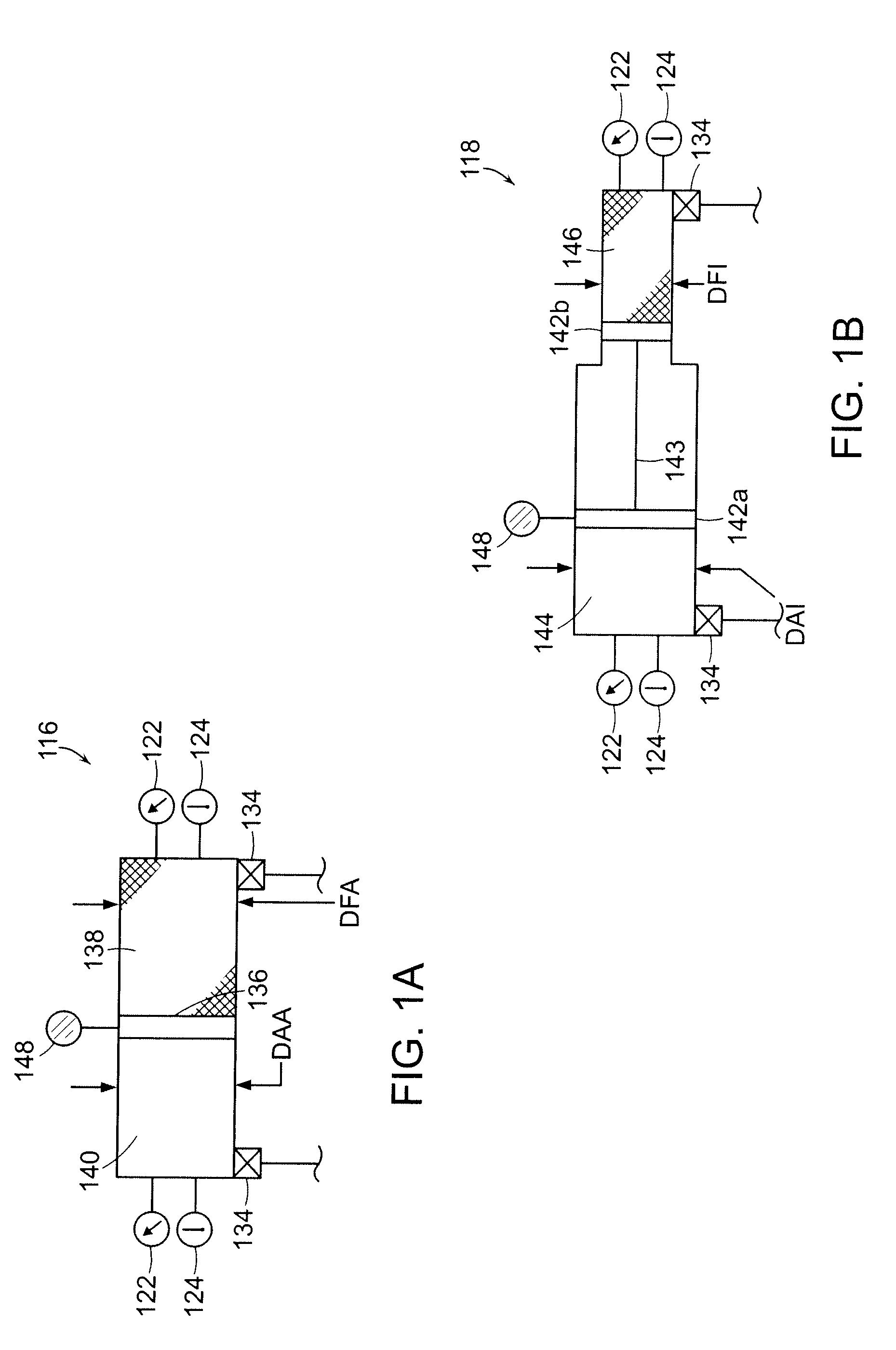
Systems and Methods for Energy Storage and Recovery Using Rapid Isothermal Gas Expansion and Compression
InactiveUS20100089063A1Increase energy densityHigh outputElectrical storage systemInternal combustion piston enginesProduct gasEngineering
The invention relates to systems and methods for rapidly and isothermally expanding and compressing gas in energy storage and recovery systems that use open-air hydraulic-pneumatic cylinder assemblies, such as an accumulator and an intensifier in communication with a high-pressure gas storage reservoir on a gas-side of the circuits and a combination fluid motor / pump, coupled to a combination electric generator / motor on the fluid side of the circuits. The systems use heat transfer subsystems in communication with at least one of the cylinder assemblies or reservoir to thermally condition the gas being expanded or compressed.
Owner:SUSTAINX
Fan blade modifications
Owner:DELTA T
Installation for harvesting ocean currents (IHOC)
Installation for harvesting kinetic energy of ocean currents in deepwaters is based on utilization of a semisubmersible platform and the multiple of vertically oriented Darrieus type hydraulic turbines with funnels. The turbines are located bellow sea level on distance sufficient to exclude them from being affected by wave actions. The electric power generators are located on a structure above water and transmit electric power to the shore utilizing flexible cable from semisubmersible to the sea bottom and underwater cable going to the shore, where it connected to the power distributing network. One of the Embodiments of this invention is designed to harvest energy of tides in deepwaters.
Owner:BELINSKY SIDNEY IRVING
Submersible electrical power generating plant
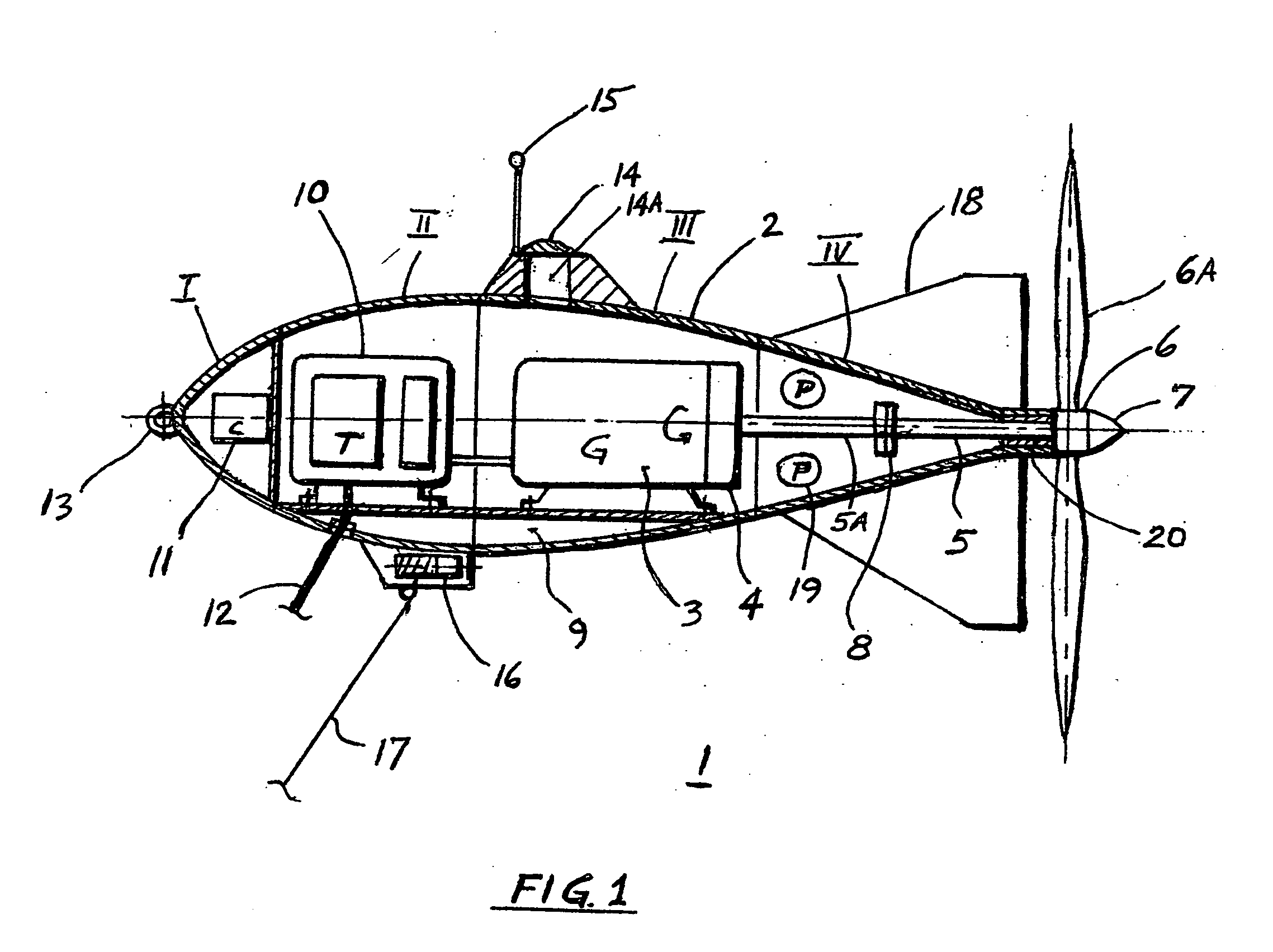
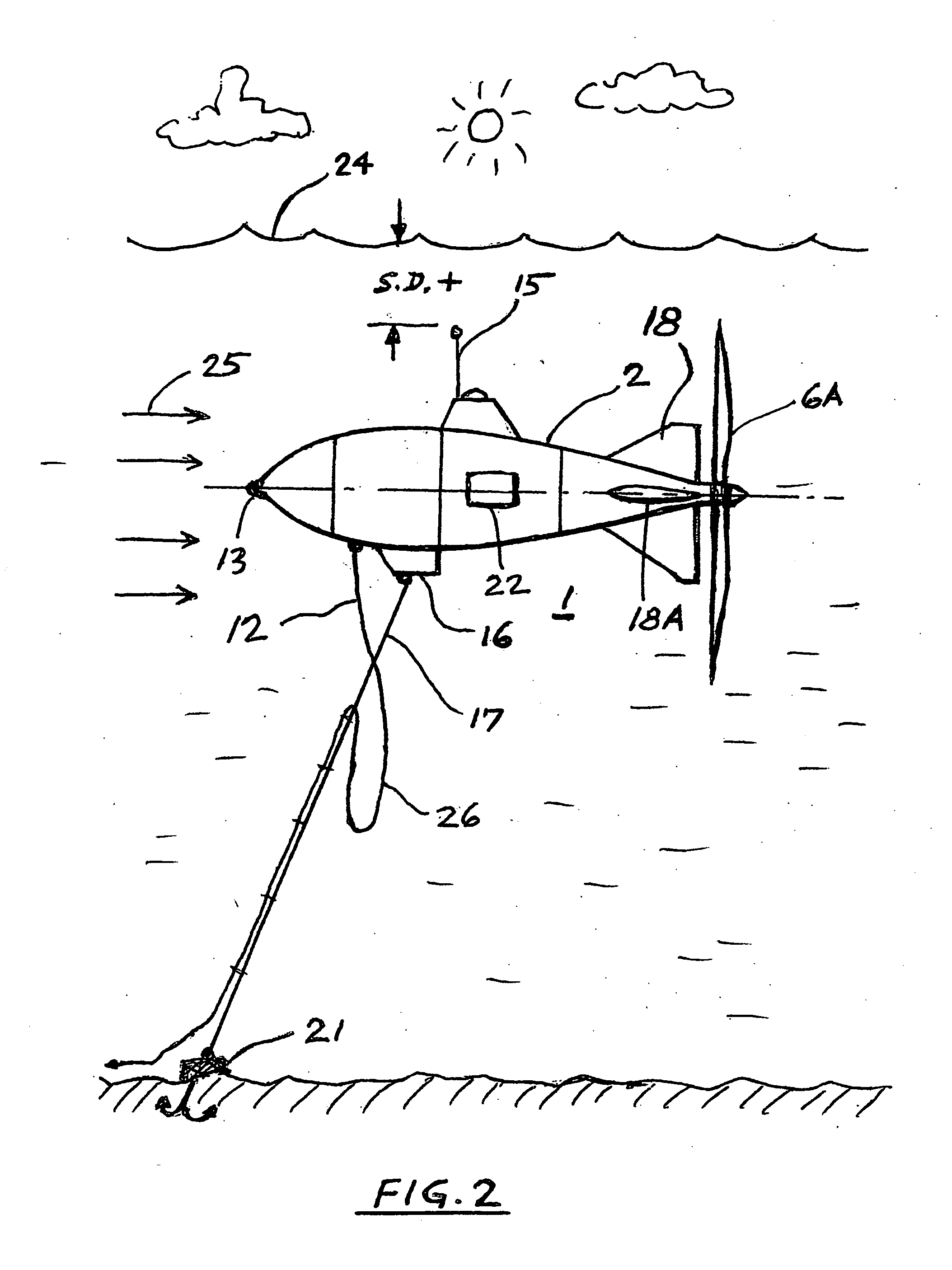
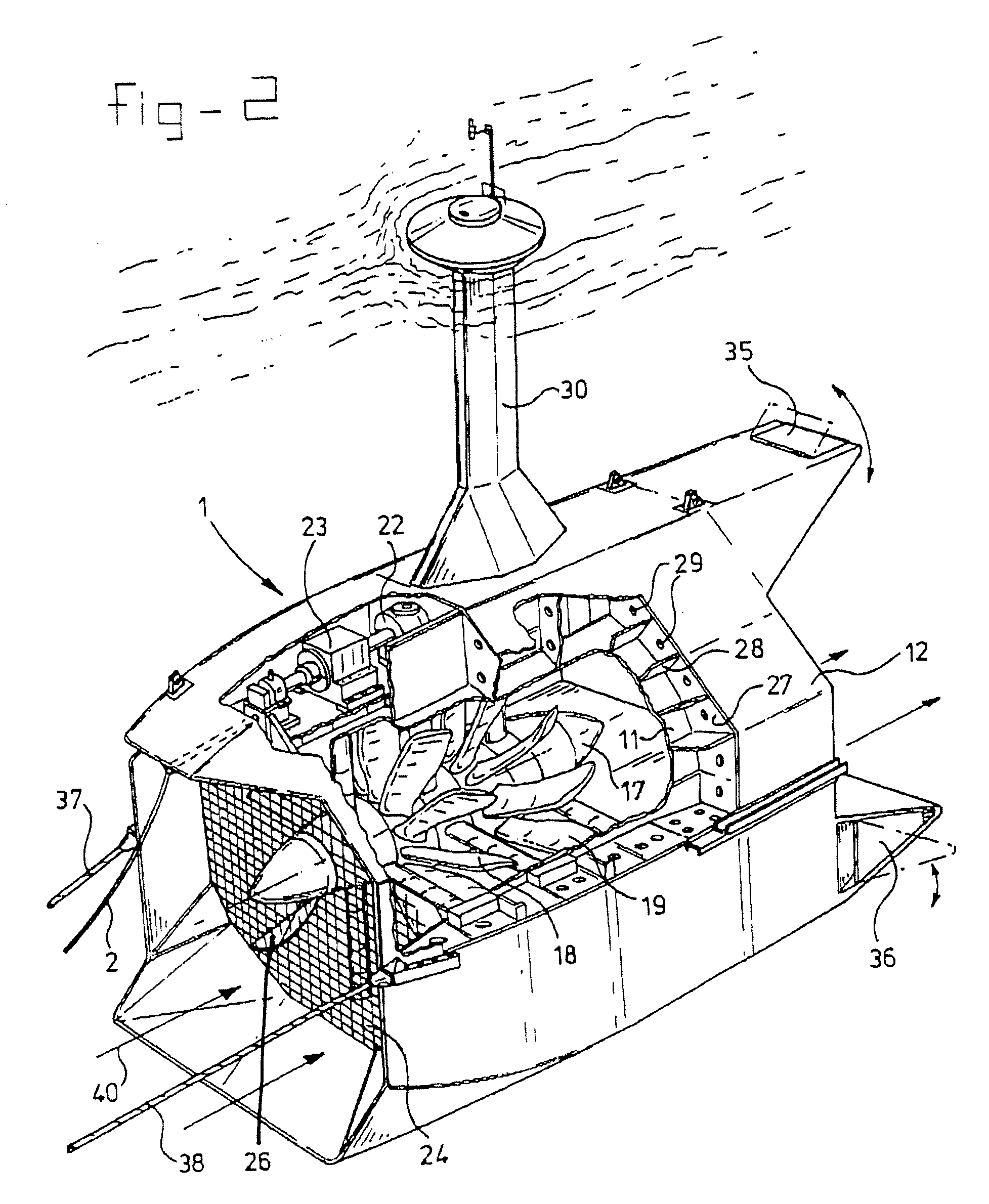
InactiveUS7291936B1Prevent siphonImproved directional stabilityEnergy industryWind motor combinationsNacelleHorizontal axis
A self-supporting, submersible generating plant for producing electricity from ocean currents, consisting of two counter-rotating, rear-facing turbines with a plurality of rotor blades extending radially outward from two separate horizontal axis that convey the kinetic energy from the two side-by-side, counter-rotating turbine rotors through separate gearboxes to separate generators that are housed in two watertight nacelles that are located sufficiently far apart to provide clearance for the turbine rotors. The two generators and their gearboxes serve as ballast and are located far below a streamlined buoyancy tank that extends fore and aft above and between them. A combination of a leverage system and a pressure-controlled system adjusts the hydrodynamic lifting forces to maintain constant depths. There are systems to purge the ballast water to facilitate the recovery of both individual submersible power plants and a group of many submersible power plants.
Owner:ROBSON JOHN H
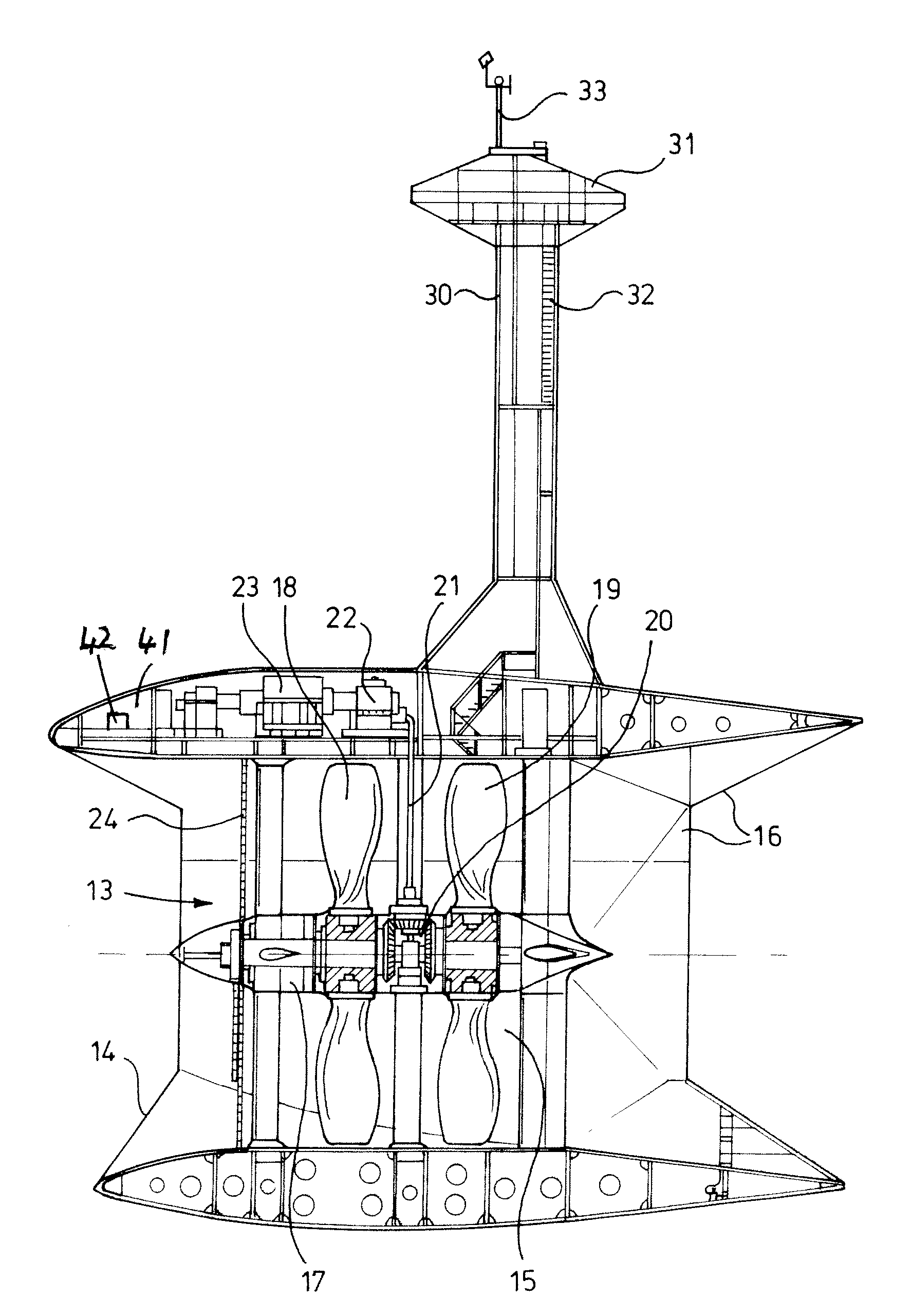
Plant, generator and propeller element for generating energy from watercurrents
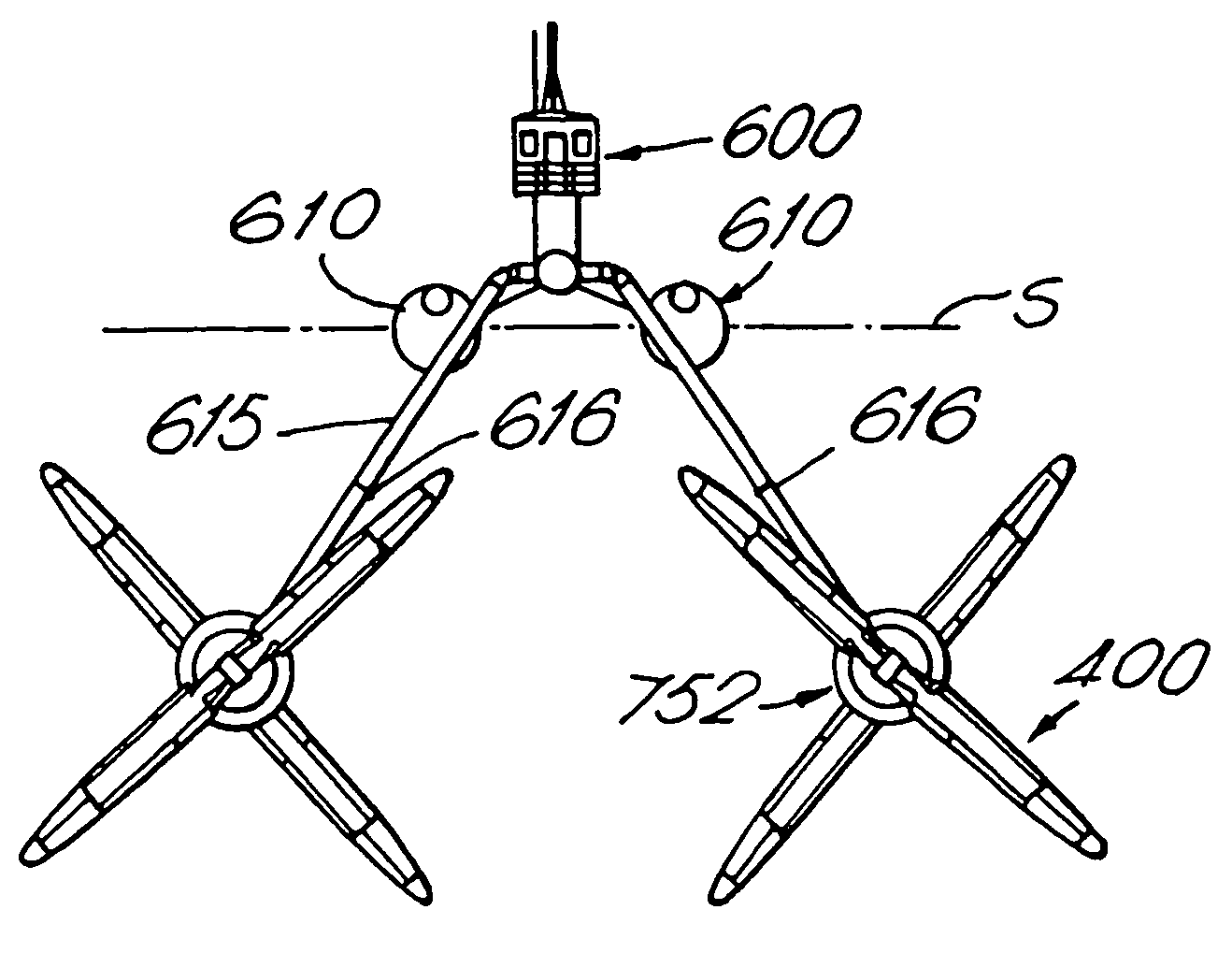
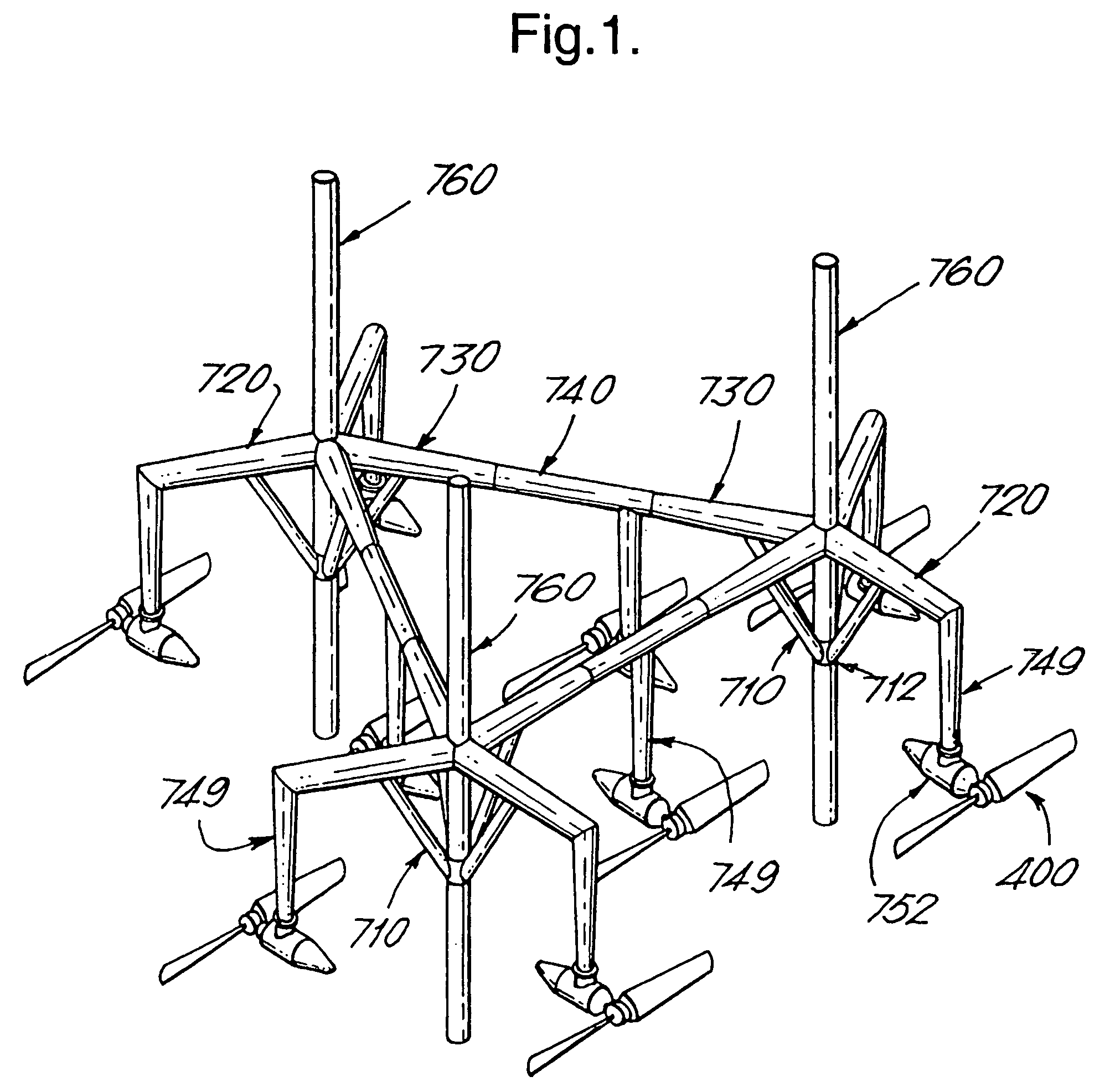
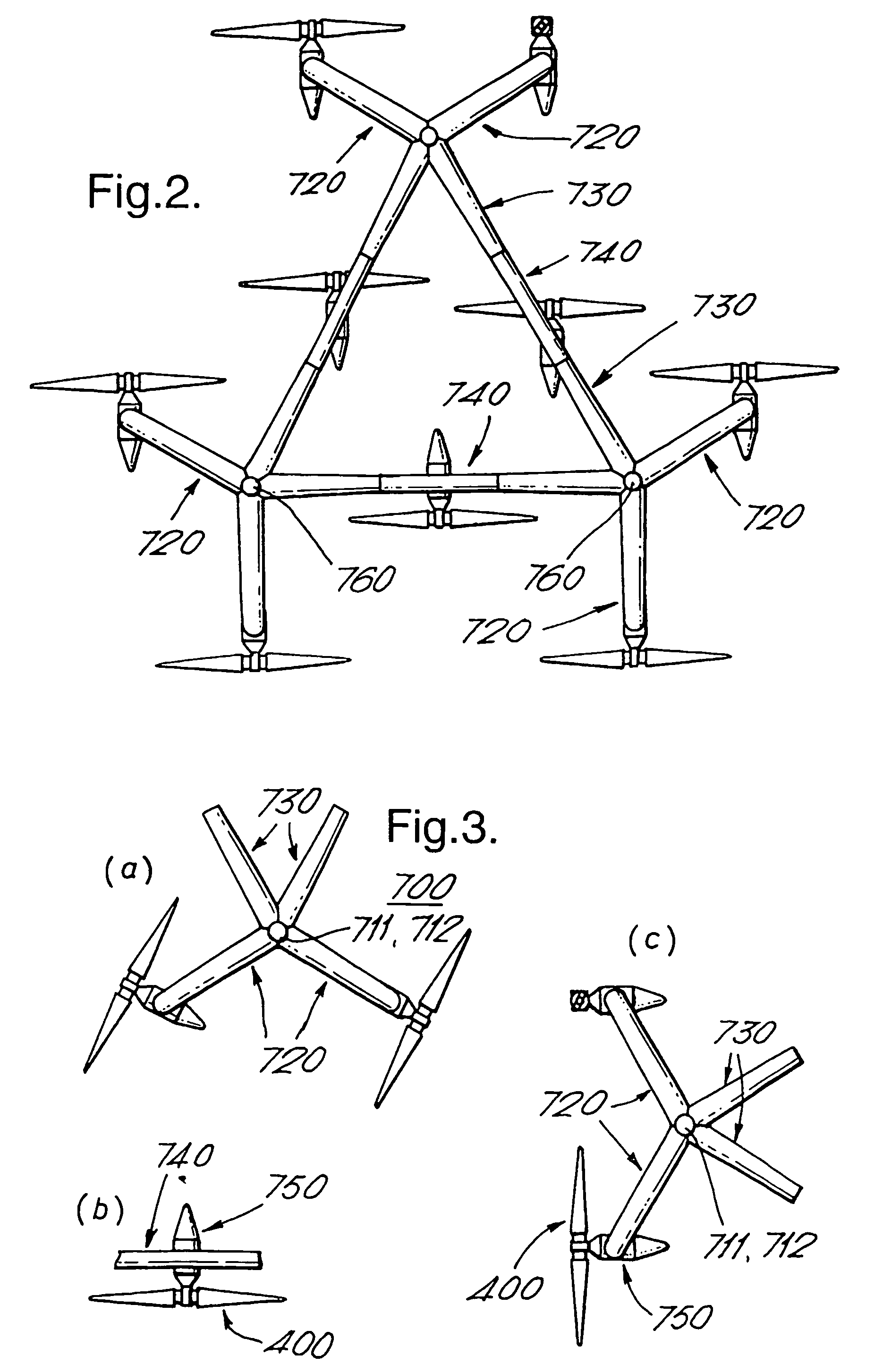
A plant, generator and rotating member for the production of power from currents in a body of water, comprising a fixedly mounted of floating structure, and a plurality of replaceable generator units (750) supported by the structure and which are driven by the water currents. The structure comprises arms (615, 720, 730). The rotating member (400) comprises a plurality of member sections (410) rotatably mounted on a shaft (405) between an end piece (407) and a tip (406). The generator comprises a contra-rotating rotor (550) and stator (800) connected to respective shafts (500, 820) and bearings, where the stator frame (800) is axially supported (810) on the first shaft (500) and the first shaft (500) at one end thereof is axially supported (810) on the stator frame. The generator according to the invention can be used for the production of electric power, and as an electromotor for the production of mechanical rotational energy.
Owner:HYDRA TIDAL ENERGY TECH
System and method for extracting power from fluid using a tesla-type bladeless turbine
InactiveUS20100129193A1Reduce lossesOptimal longitudinal spacingWind motor controlPump componentsSurface oceanViscous shear
Smooth, preferably variable-sweep fluid collection device surfaces disposed into opposition with wind, river, surf, ocean or tidal currents generate enhanced velocity fluid flows at length driven into onboard work-extracting disc turbines at advantageous angles of attack. Keyed to shafts turning freely through optionally extendable volutes, disc turbines comprising a dense population of smooth, axially fixed or adjustably spaced discs conducting preferably laminar flow between adjacent elements develop significant torque through boundary layer adhesion and viscous shear-stress between fluid layers. Exhaust of disc turbine throughput into divergent channels drafting into external currents of initially higher than ambient velocity and lower pressure may reduce turbine discharge backpressure, rapidly clear system throughput, and allow normally disadvantageous drag to be utilized to develop greater work generation. Gainfully turning with, instead of at odds to natural or anthropogenic currents provided, disc turbines utilized as disclosed may provide unprecedented renewable energy from fluids in motion.
Owner:SHERRER GORDON DAVID
River and tidal power harvester
InactiveUS20090230686A1Reduce buildReduce installationWater resource protectionWaterborne vesselsMooring systemFluvial
An energy module comprising an energy absorber; and a mooring system, comprising a wing-shaped polymer shell attached to the energy absorber, the wing-shaped polymer shell designed to utilize the force of a passing current to create a downward force and thereby reduce any upward motion in the energy module; and a mooring cable housed inside the wing-shaped polymer shell and anchored to maintain the energy module in a fore and aft and a side-to-side position to provide stability, and to negate a rotational force on the energy module.
Owner:CATLIN CHRISTOPHER S
Method and apparatus for generating hydro-electric power
ActiveUS7084521B1Small sizeSmoother power generationMachines/enginesEngine componentsElectricityElectric power system
A hydroelectric power generating method and / or apparatus provides one or more inlet pipes perpendicular to a flow of water in a stream or river. The inlet pipes have a length and plural apertures along the length of the at least one inlet pipe. A feedline and a turbine generator combination are interconnected with the inlet pipes. One or more outlet pipes are interconnected with the feedline and the turbine generator combination. The outlet pipes have an elevation lower than the inlet pipe. A flow of water passes through the inlet pipes, the feedline, the turbine generator combination, and the outlet pipes, and generates electricity from the flow of water passing through the turbine generator combination. The hydroelectric power generating method also provides a pressure dissipation device that causes a reduction in the pressure of the water so that the water can be released safely back into the stream or river.
Owner:MARTIN GERALD G
Apparatus for generating electricity from flowing fluids
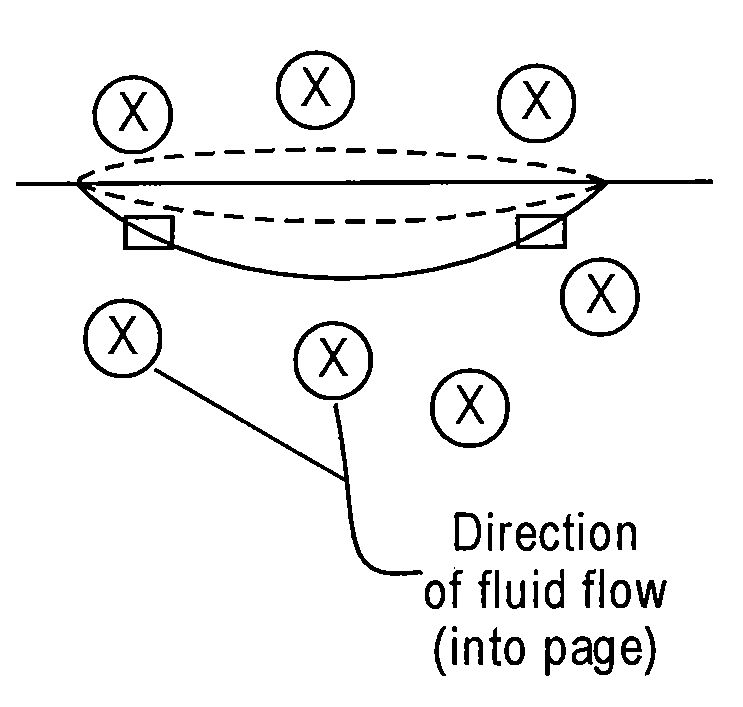
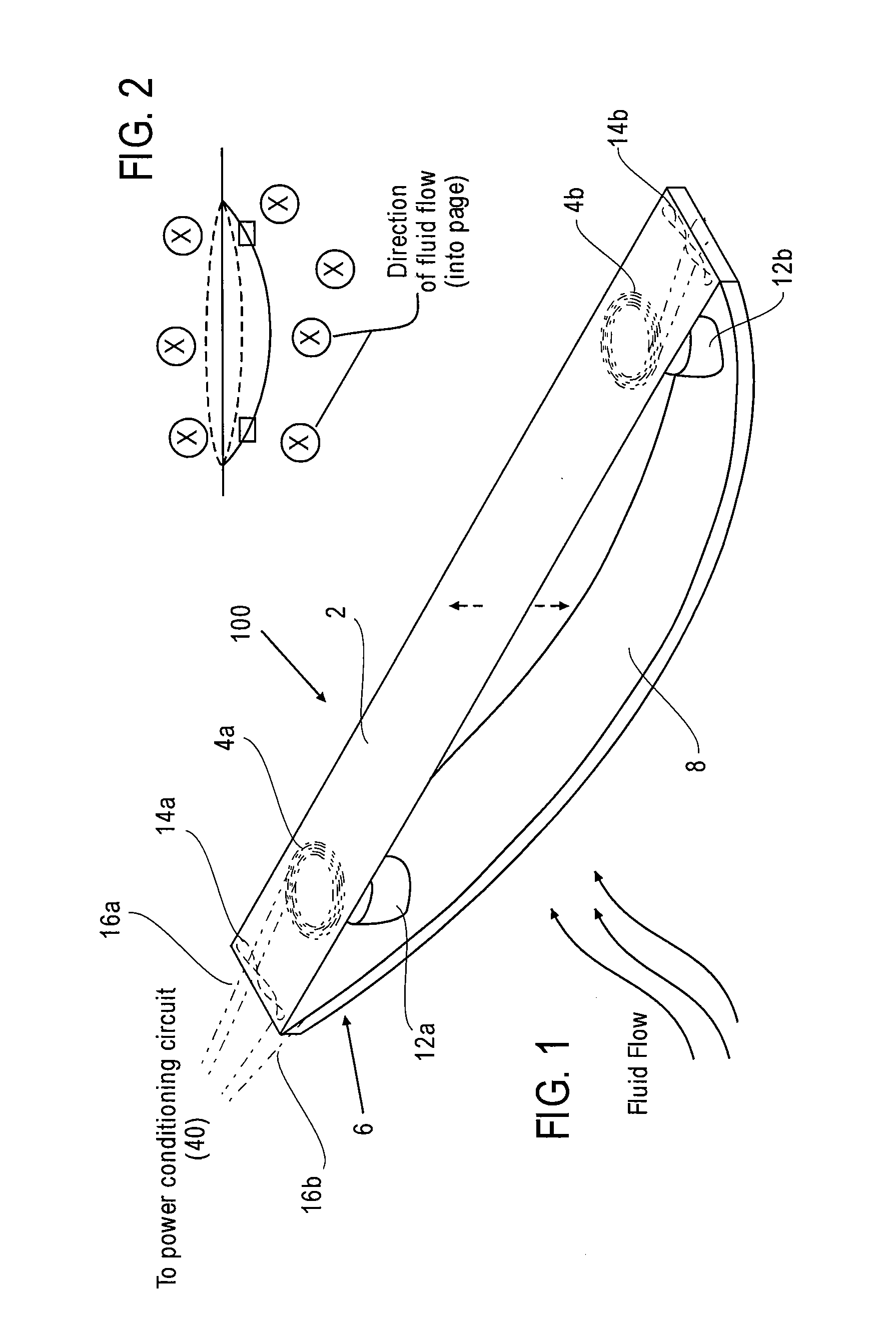
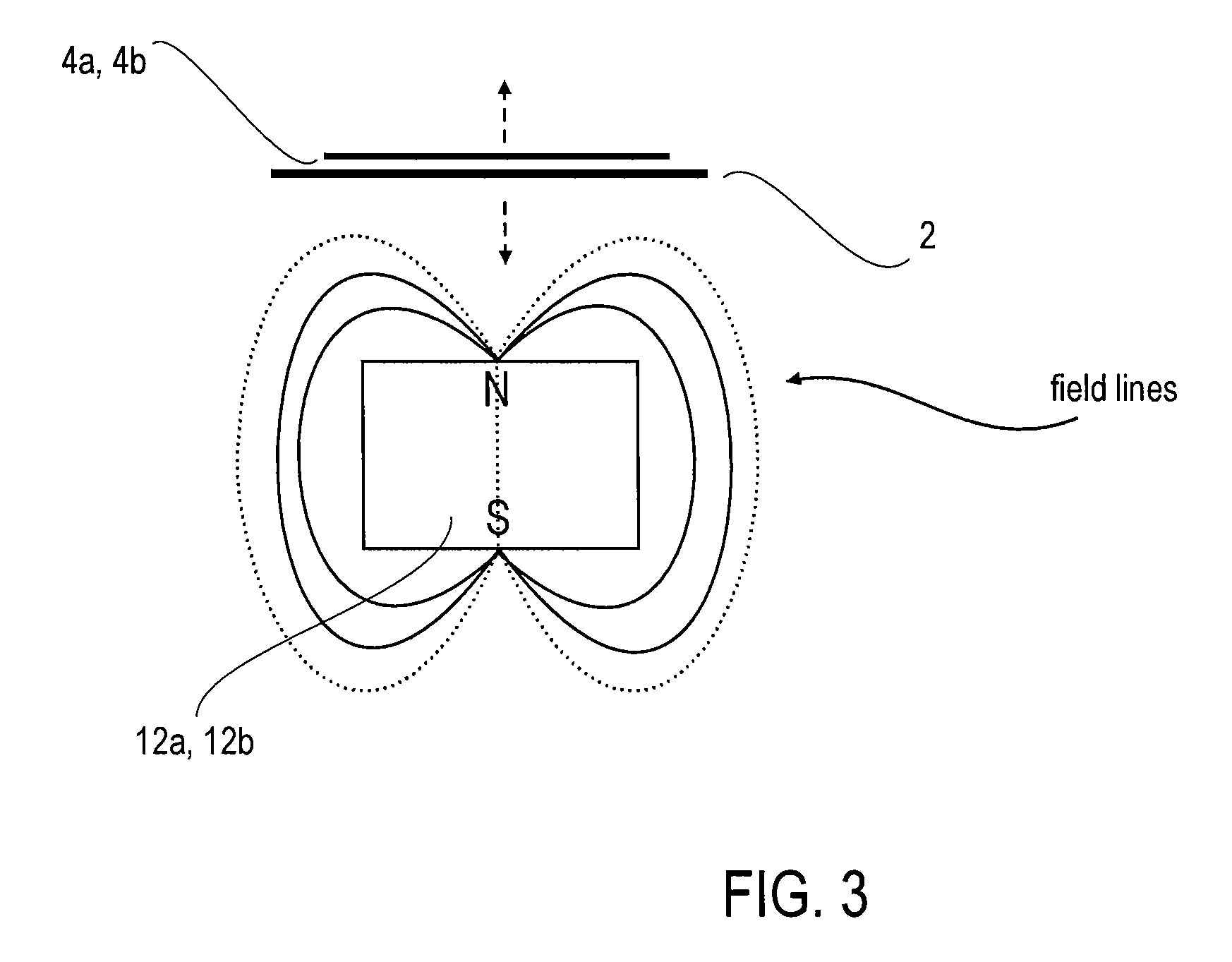
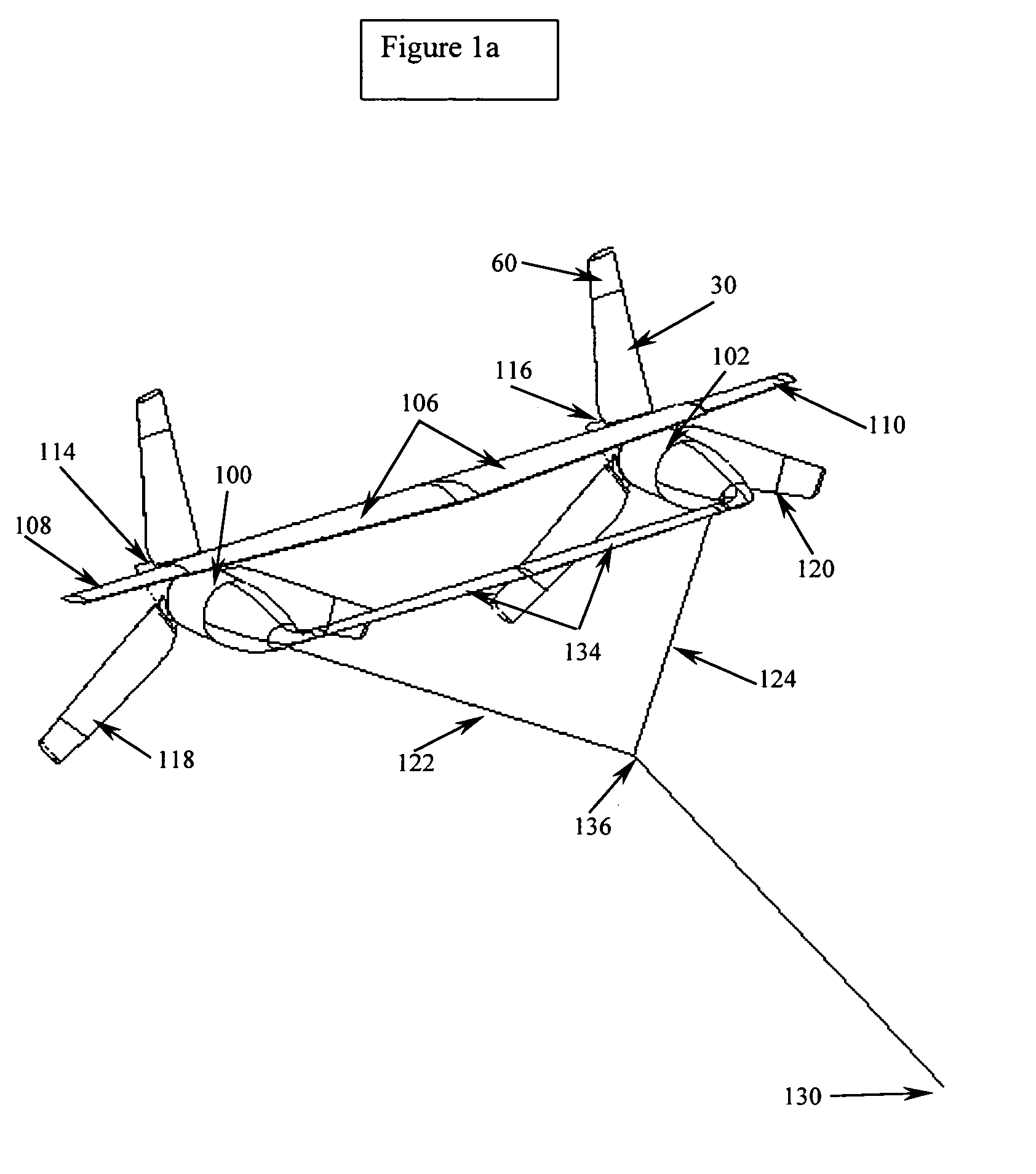
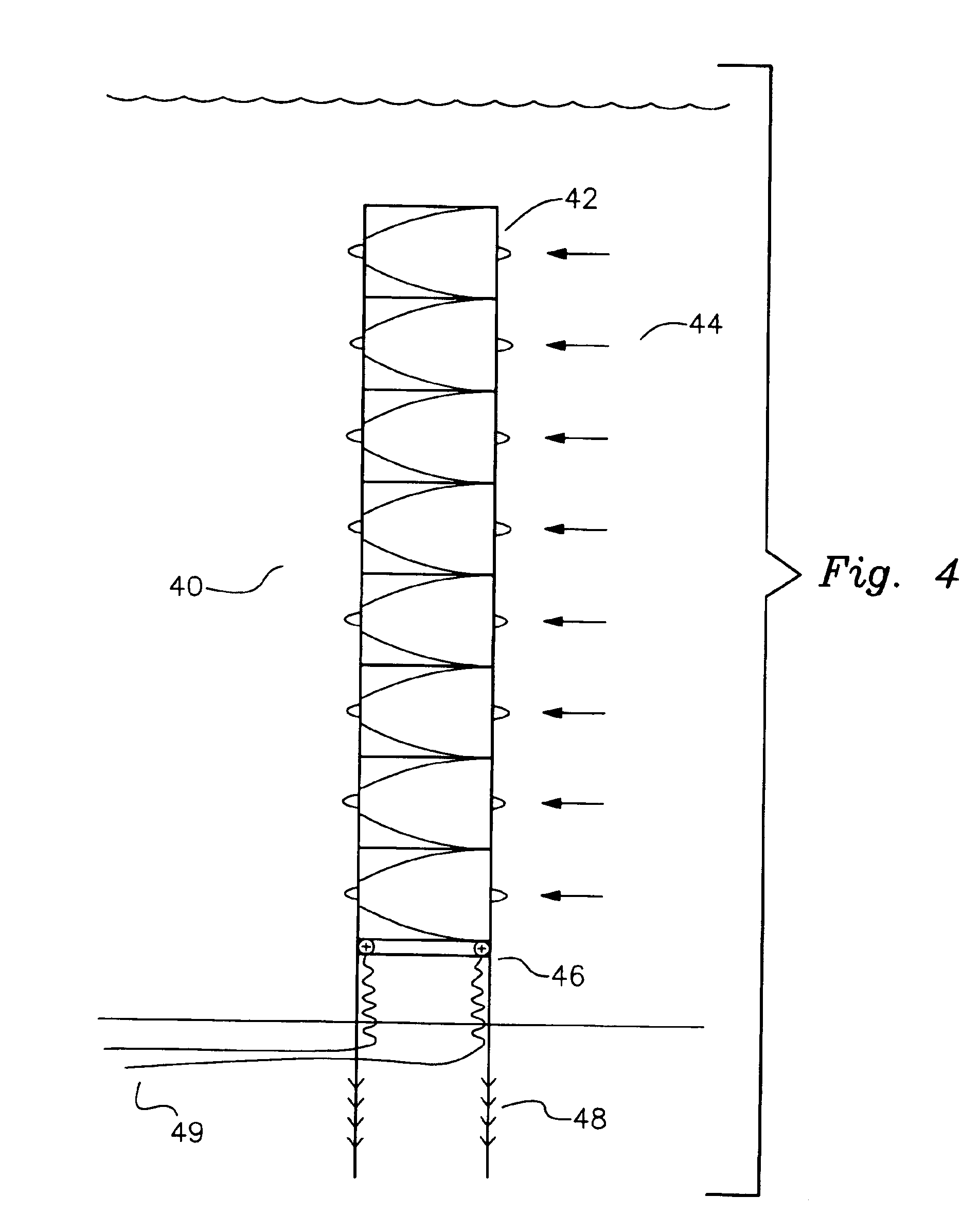
An apparatus for generating electricity from aeolian oscilaltions caused by the flow of a fluid such as wind or water. An immobile beam extends between two piers, and a movable vane is disposed around the beam in parallel relation thereto. The vane is generally tubular, having a generally cylindrical or foil-shaped cross section. The movement of a fluid, such as wind or deep ocean tidal flow, past the vane induces aeolian oscillation in the vane, so that the vane moves to-and-fro, with respect to the beam, in a direction generally perpendicular to the direction of fluid flow. Rods and a crankshaft may connect the vane to a generator mounted upon the beam, so that the movement of the vane is converted into electricity. Alternatively, electricity can be generated from the movement of the vane by a field coil on the vane inducing electrical current in induction wires mounted upon the immobile beam.
Owner:CLARK ROBERT O
Generator utilizing fluid-induced oscillations
InactiveUS20080129254A1Batteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectrical conductorInduced oscillations
An electrical generator including a magnetic field generator and at least one energy converter for converting energy present in fluid flows into vibrations or oscillations. The converter includes a flexible membrane having at least two fixed ends. The membrane vibrates when subject to a fluid flow. One of the electrical conductor and the magnetic field generator is attached to the membrane and configured to move with the membrane. The vibration of the membrane caused by the fluid flow causes a relative movement between the electrical conductor and the applied magnetic field. The relative movement causes a change in the strength of the magnetic field applied to the electrical conductor, and the change in the strength of the magnetic field applied to the electrical conductor induces a current flowing in the conductor.
Owner:HUMDINGER WIND ENERGY
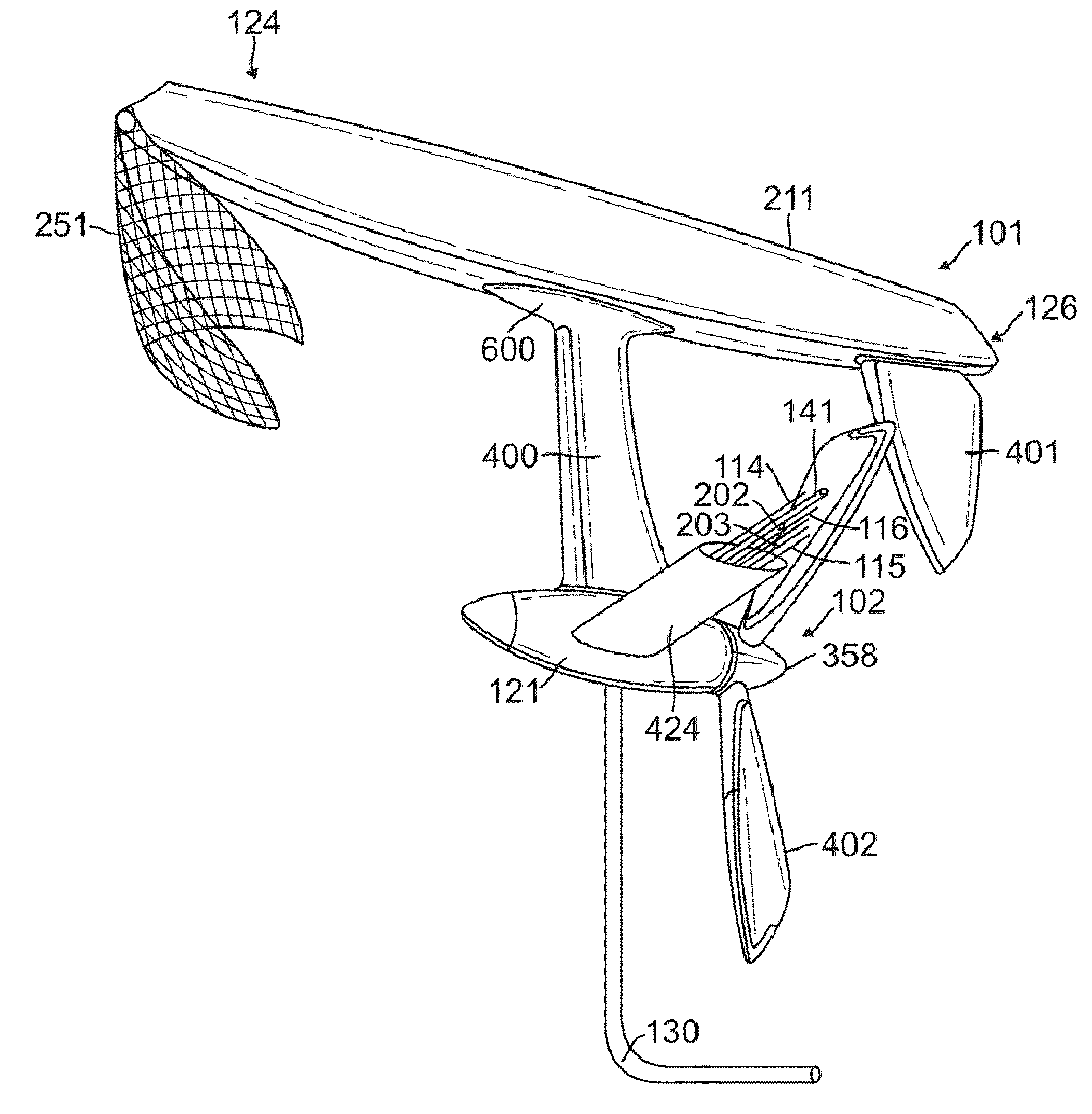
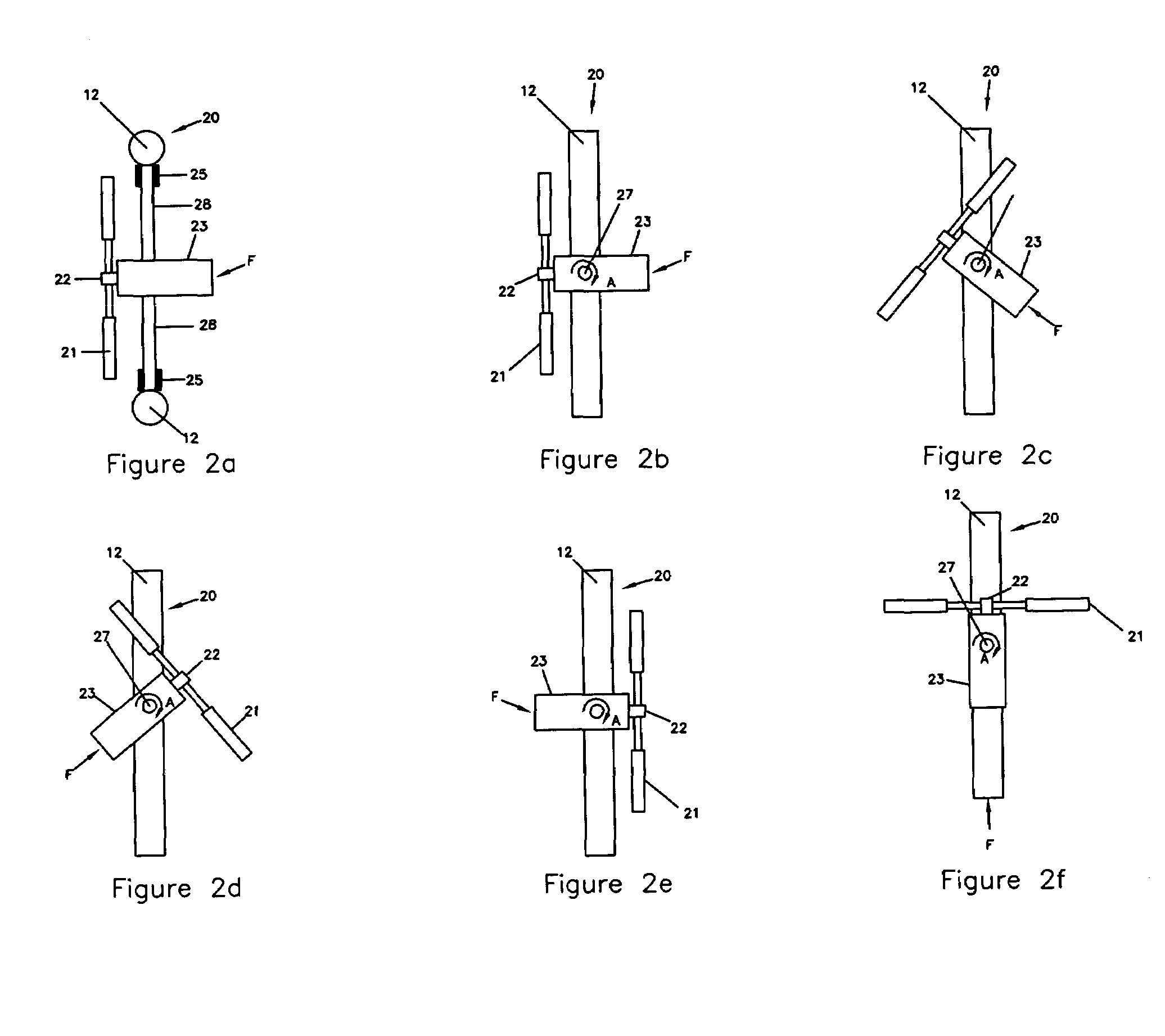
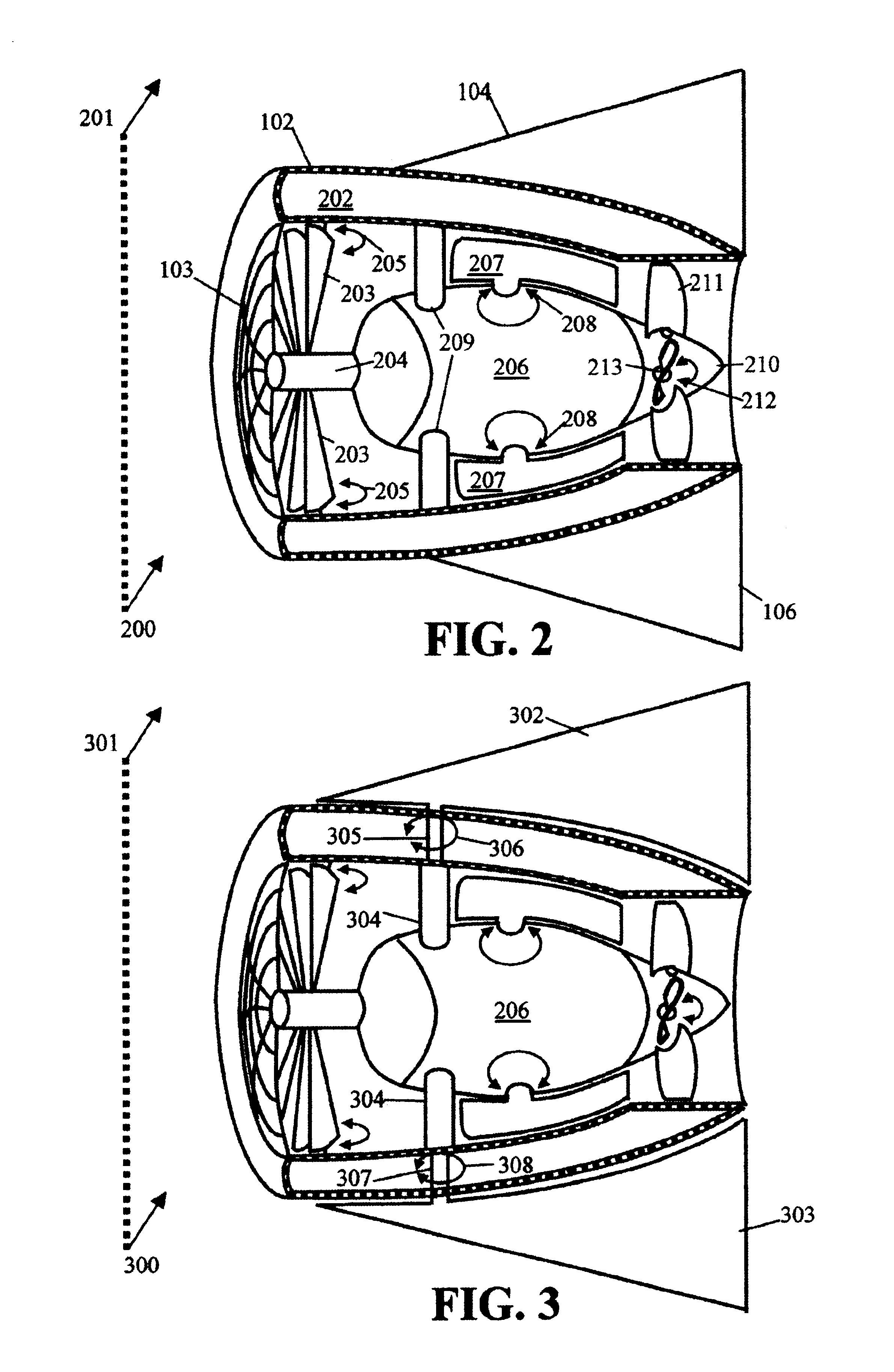
Mechanism for extendable rotor blades for power generating wind and ocean current turbines and means for counter-balancing the extendable rotor blade
A power generating system wherein a turbine is mounted on top of a tower or tethered underwater. The turbine includes a rotor having a main blade section connected to a rotor hub and an extender section. An adjusting device positions the extender section between a retracted position within the main blade section and to an extended position to expose more or less of the rotor to the fluid flow. The adjusting device includes a first web-engaging wheel anchored at a hub end of the main blade section and a second web-engaging wheel anchored at a distal end of the main blade section. A web is wound around the first and second web-engaging wheels. The extender section is attached to the web at a hub end of the extender section. A generator is connected to the turbine for generating electrical energy.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
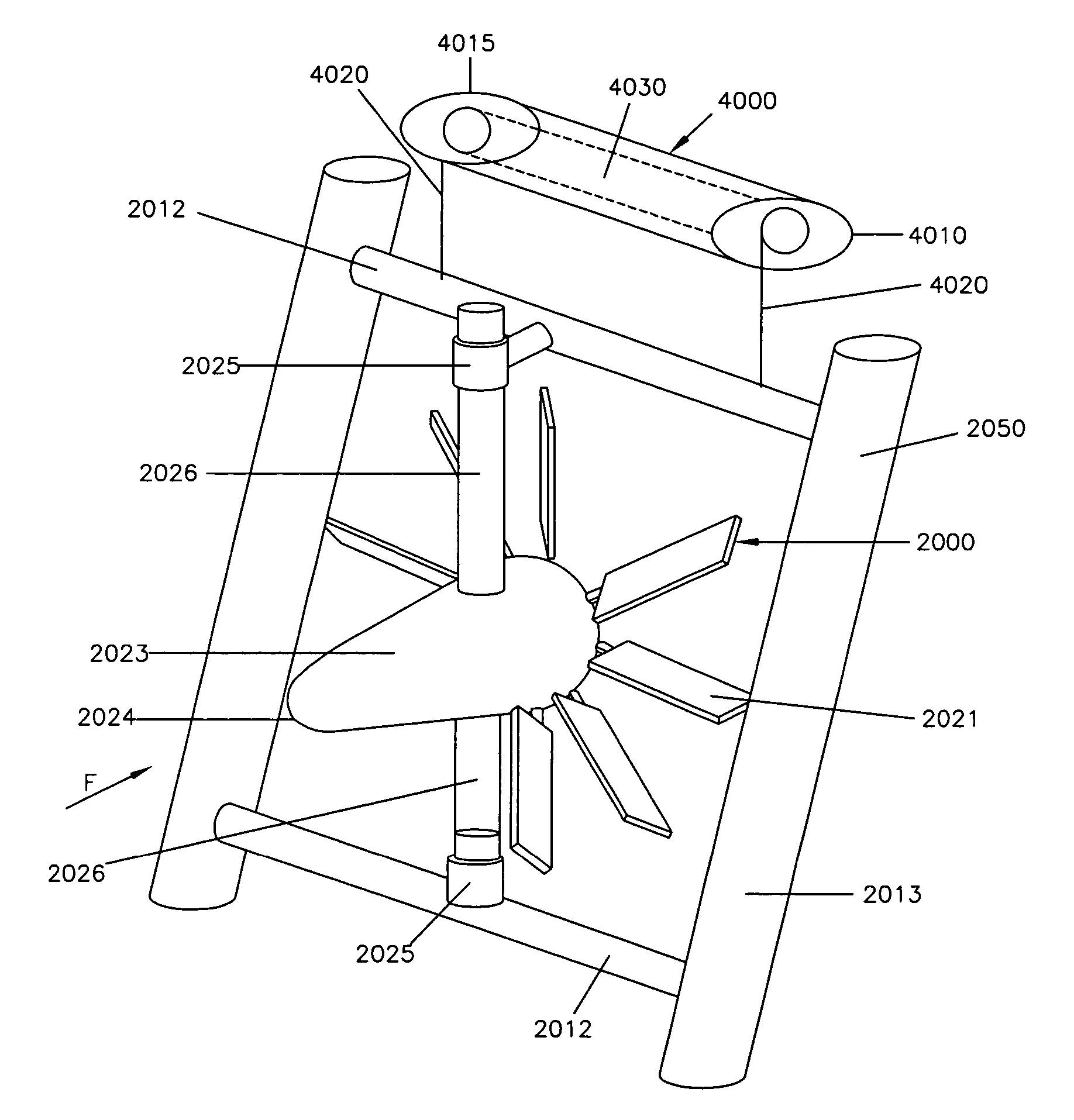
Current power generator
A current power generator includes a vertical support member mounted to the seabed and horizontal support members mounted to the vertical support member. Generators are mounted between the horizontal support members. A rotatable shaft is operatively connected to each of the generators such that when the shaft rotates, the generator generates electricity. Blades mounted to the shaft are capable of rotation in response to water current. The generators are pivotal relative to the horizontal support members in response to changing current flow direction.
Owner:GEHRING DONALD HOLLIS
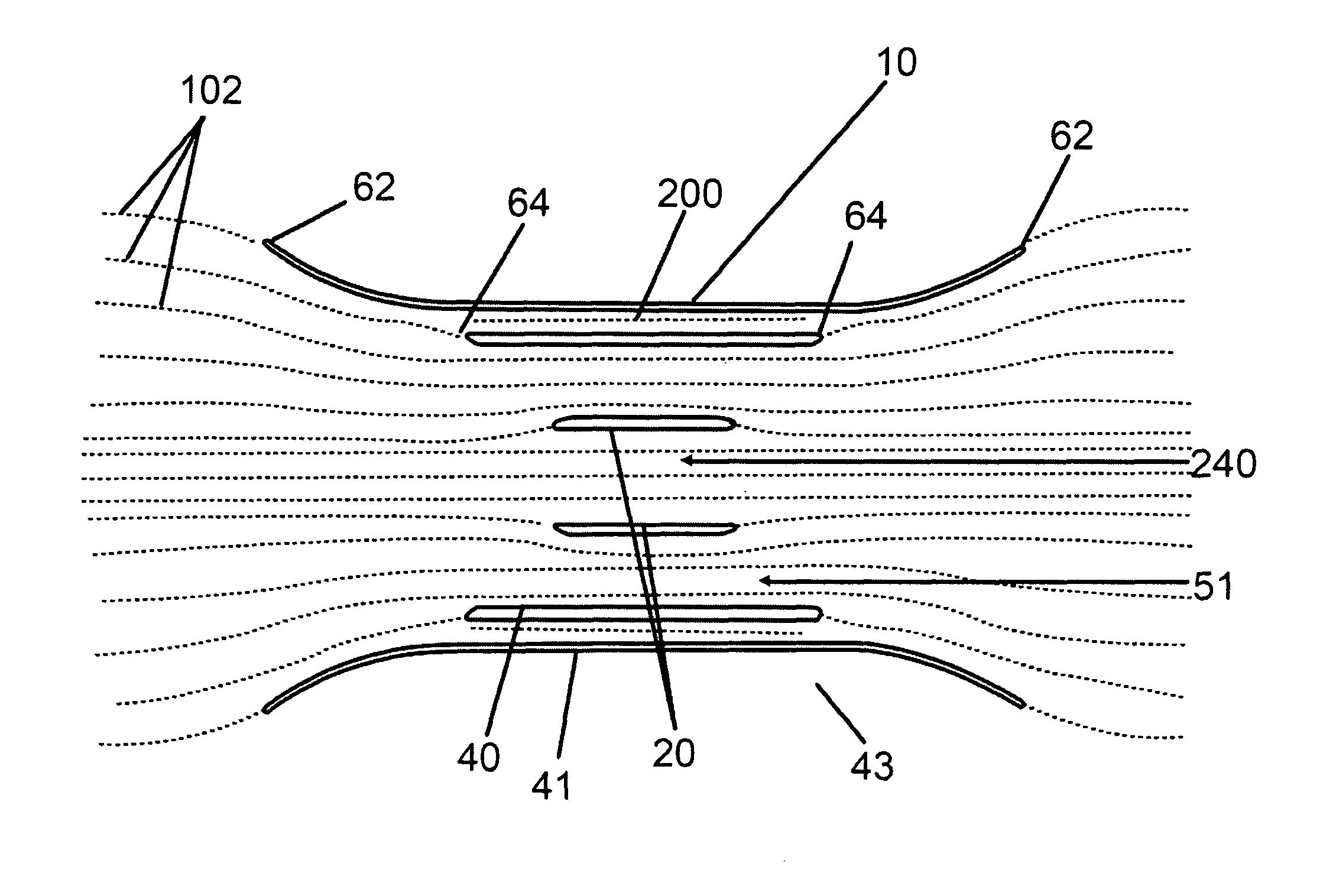
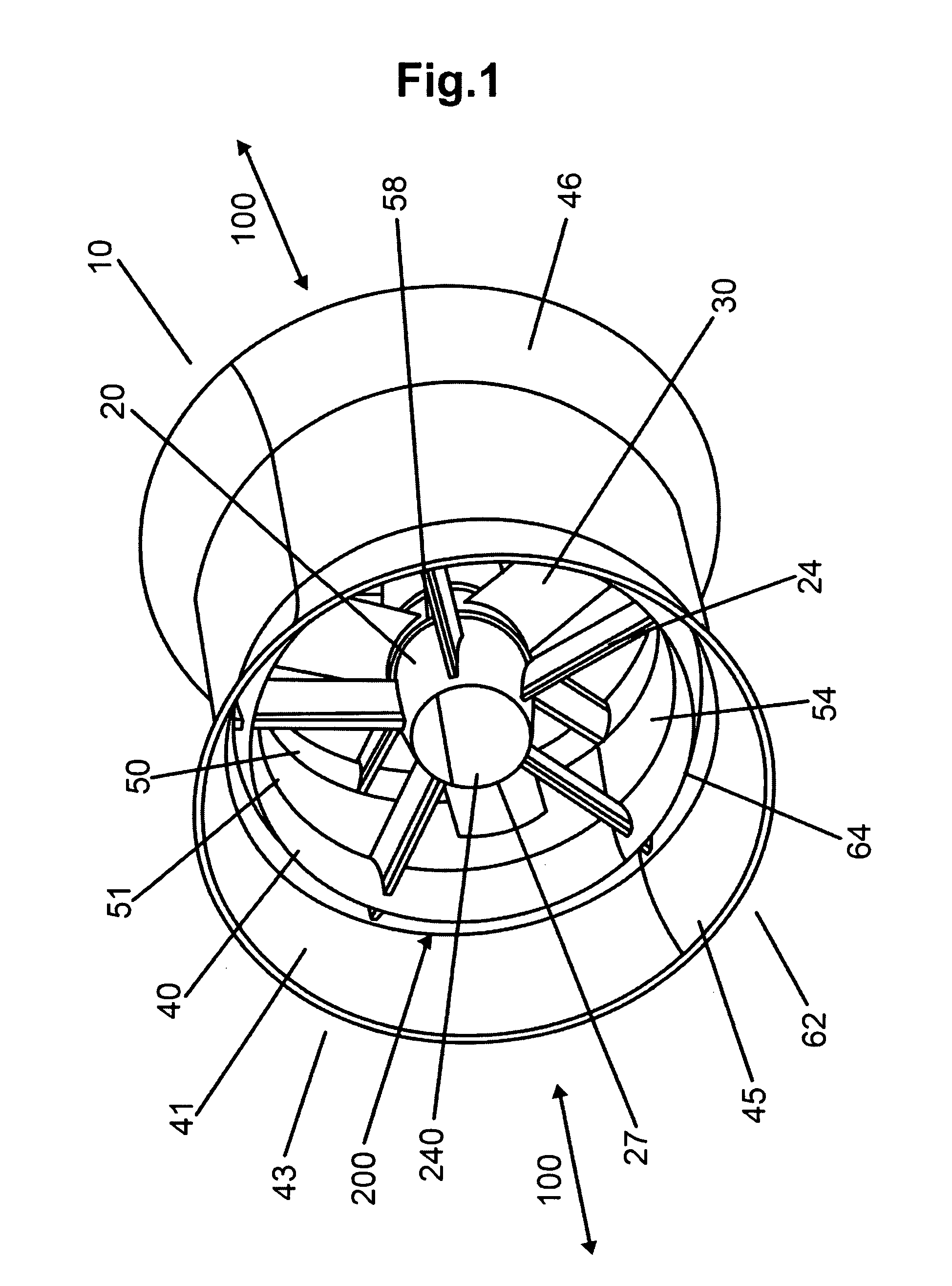
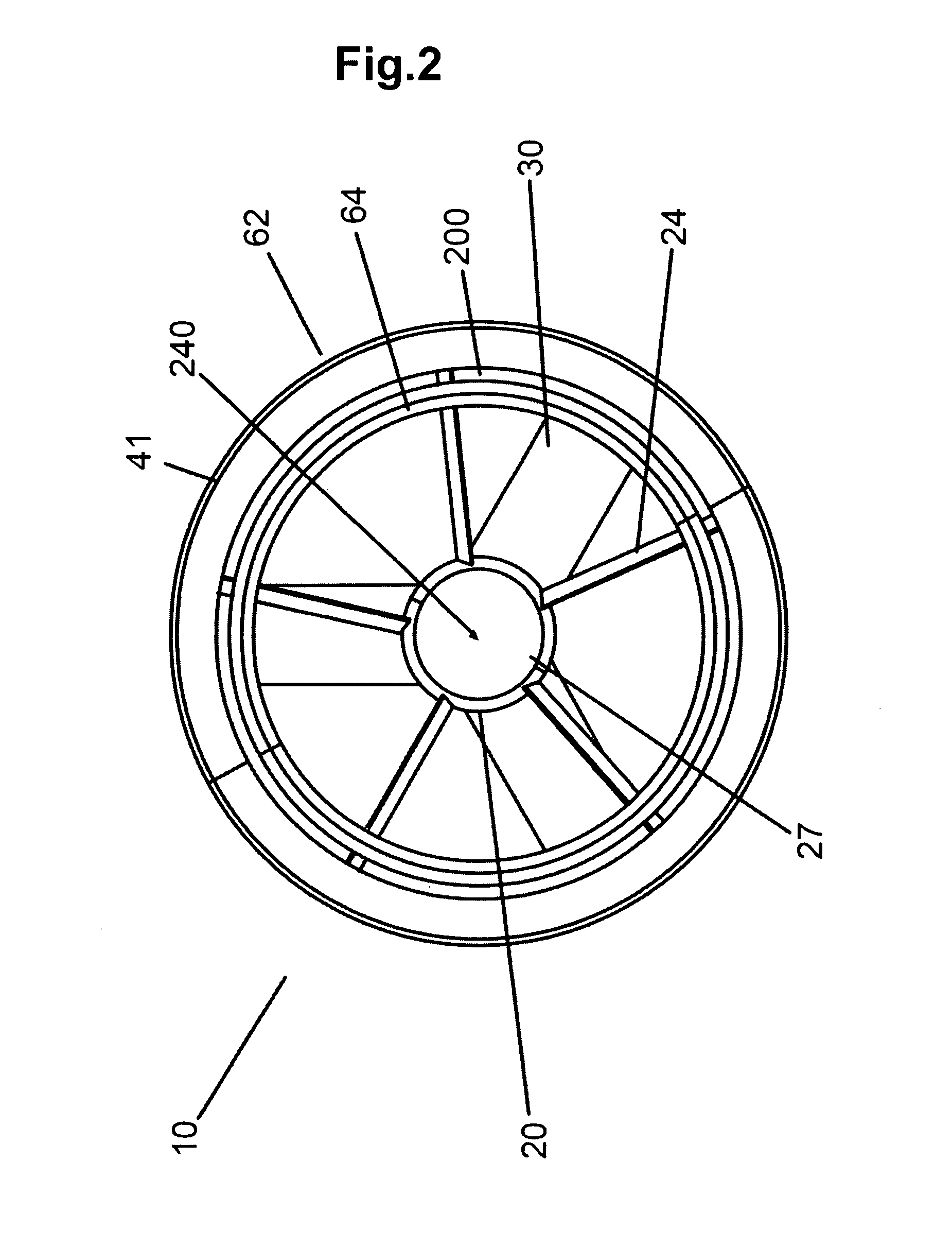
Flow enhancement for underwater turbine
InactiveUS7874788B2Improve turbine efficiencyImprove efficiencyWind motor controlPump componentsLeading edgeMarine engineering
A flow enhancement improvement for an underwater turbine generator (10) is disclosed wherein a longitudinal hole (240) is disposed in the central area (26), typically a hub (20) of the generator (10), and a second, augmentor duct (41), preferably rigid, is disposed about the outer duct (40) or housing of the unit to create a slot (200) area. The slot (200) and hollow hub (20) create areas of smooth, laminar fluid flow. The leading edges of the hub (20) or central ring and the augmentor (41) and outer ducts (40) are elliptical to enhance the fluid dynamics of the structure.
Owner:CLEAN CURRENT PARTNERSHIP
Ocean wave generation
An ocean wave generator includes a buoy for floating on the surface of the ocean. A generator is mounted to the buoy. A pulley is mounted on the generator for turning the generator. An anchor cable has a first end wrapped around the pulley and an anchored second end. Upward movement of the buoy and generator due to a wave causes the cable to unwind from the pulley, which turns the generator. A spring connected to the pulley rewinds the anchor cable when the buoy and generator drop into the trough of a wave.
Owner:GEHRING DONALD HOLLIS
Machine and system for power generation through movement of water
ActiveUS6955049B2Light weightCheap manufacturingWind motor controlPump componentsElectricityImpeller
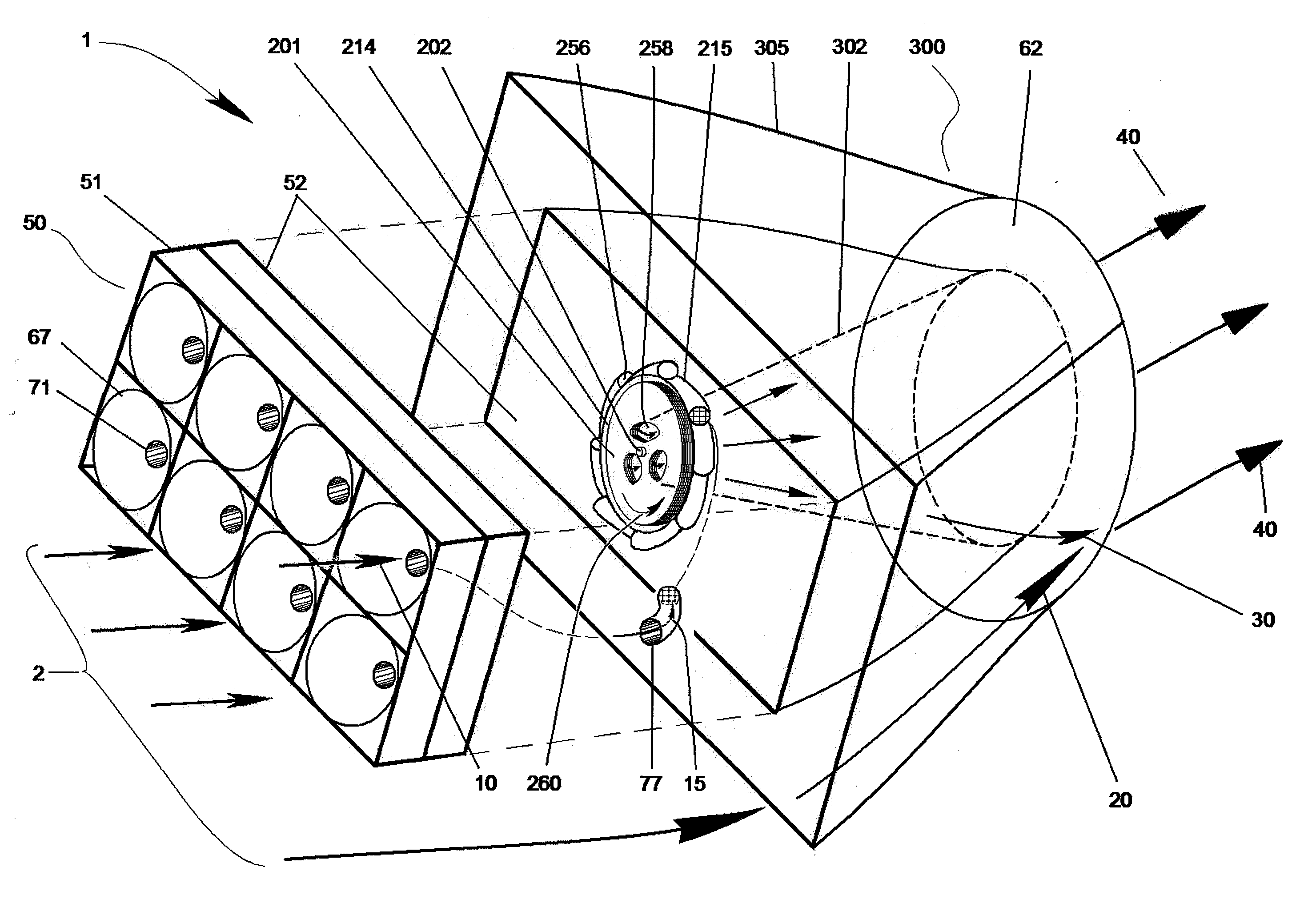
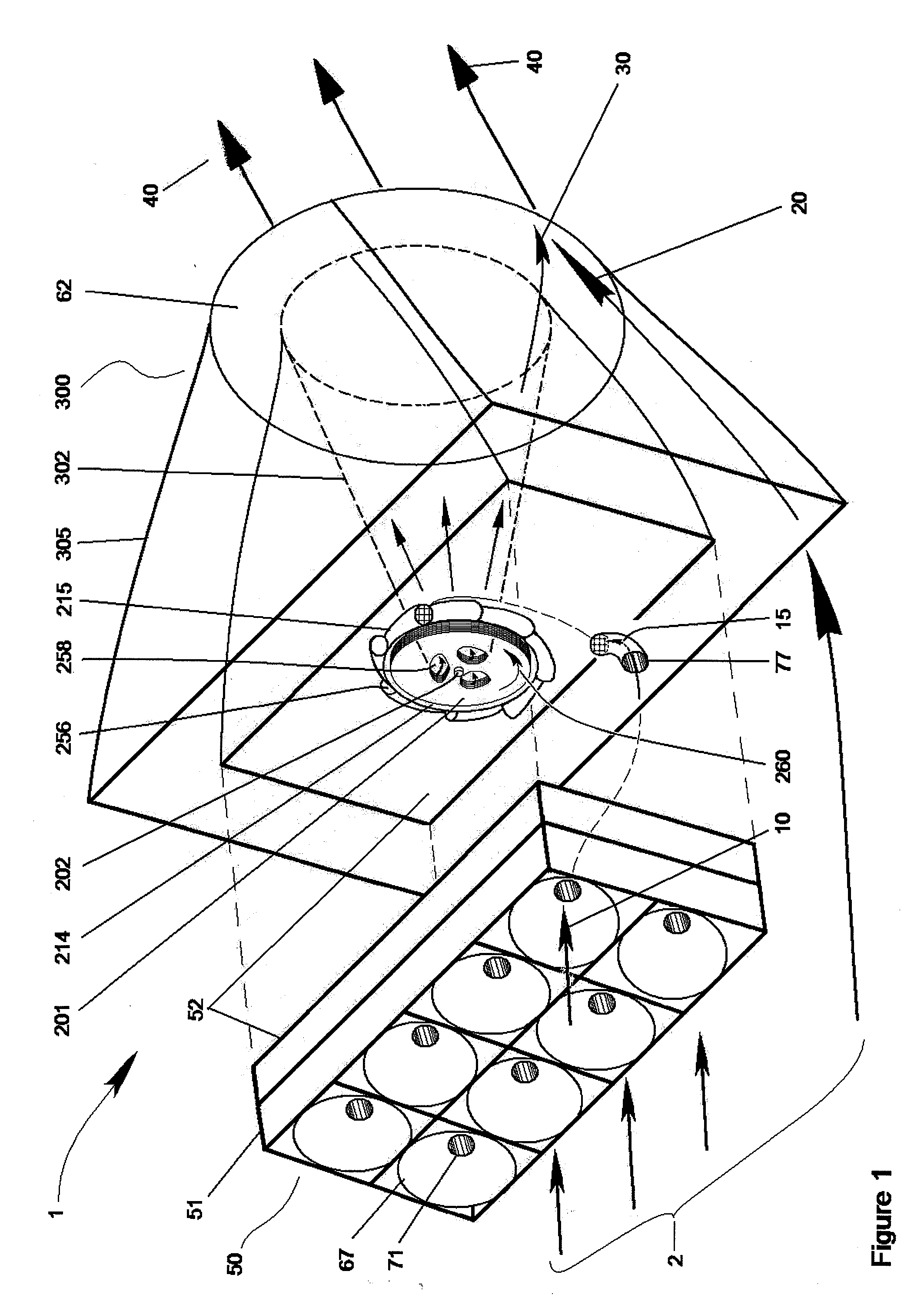
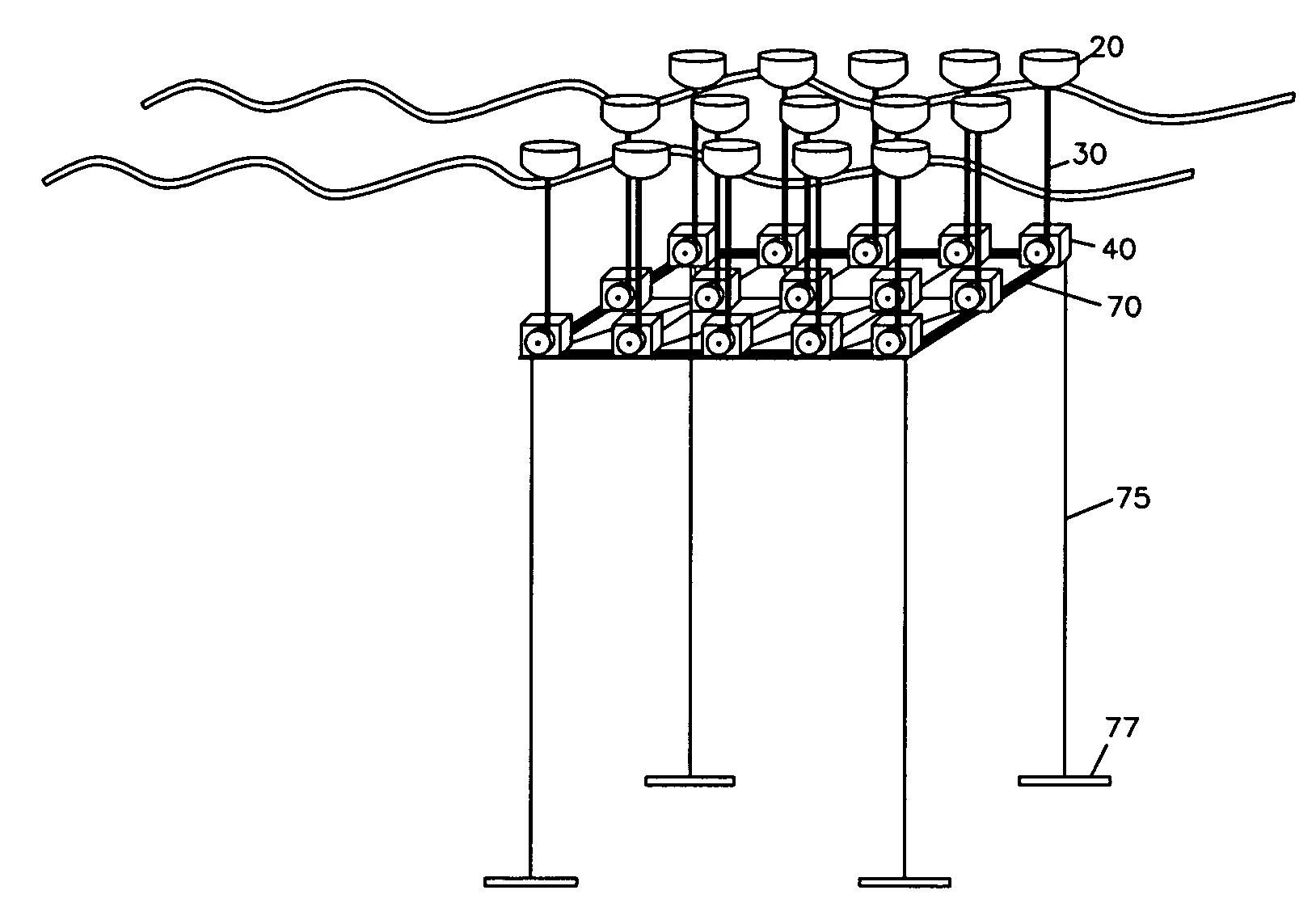
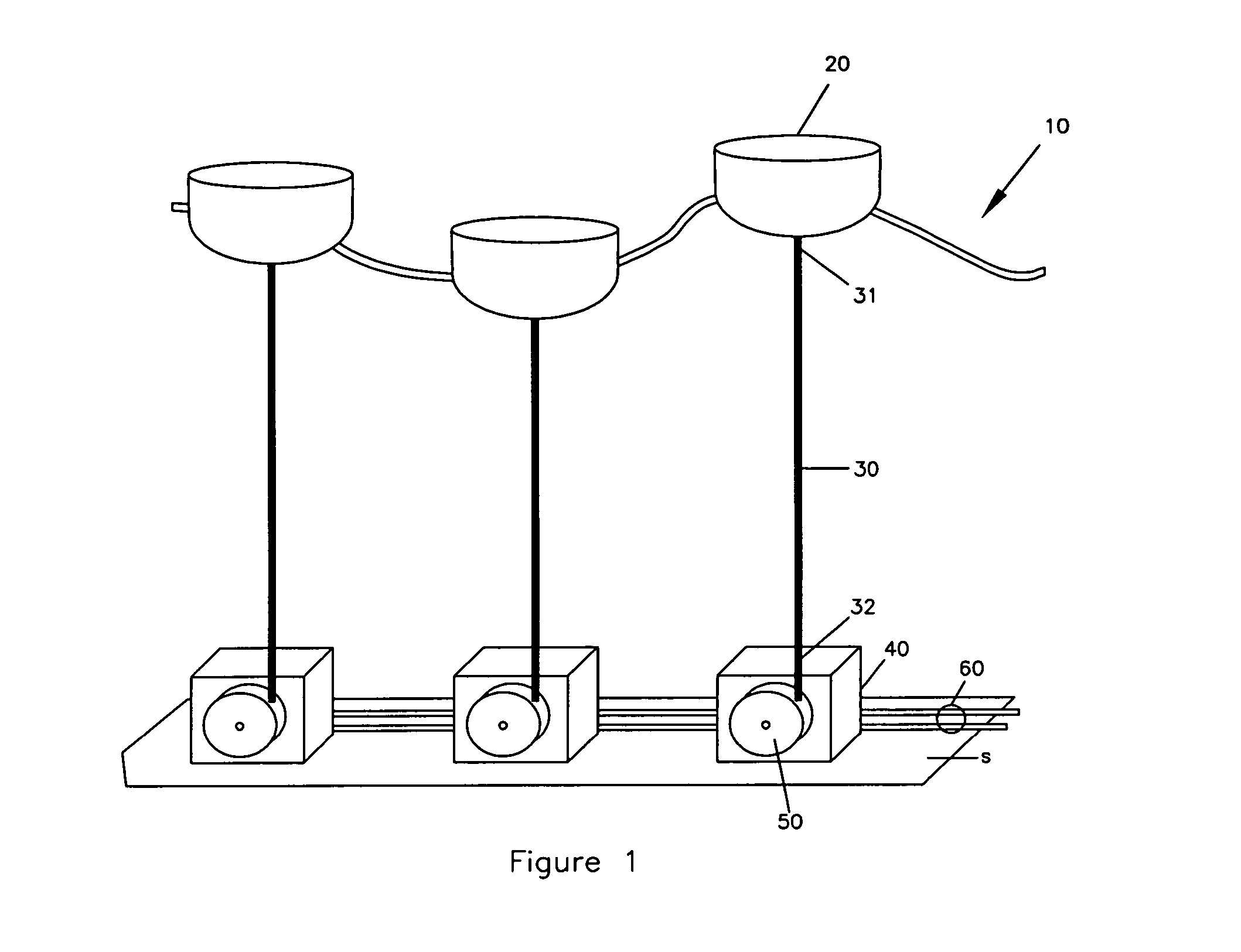
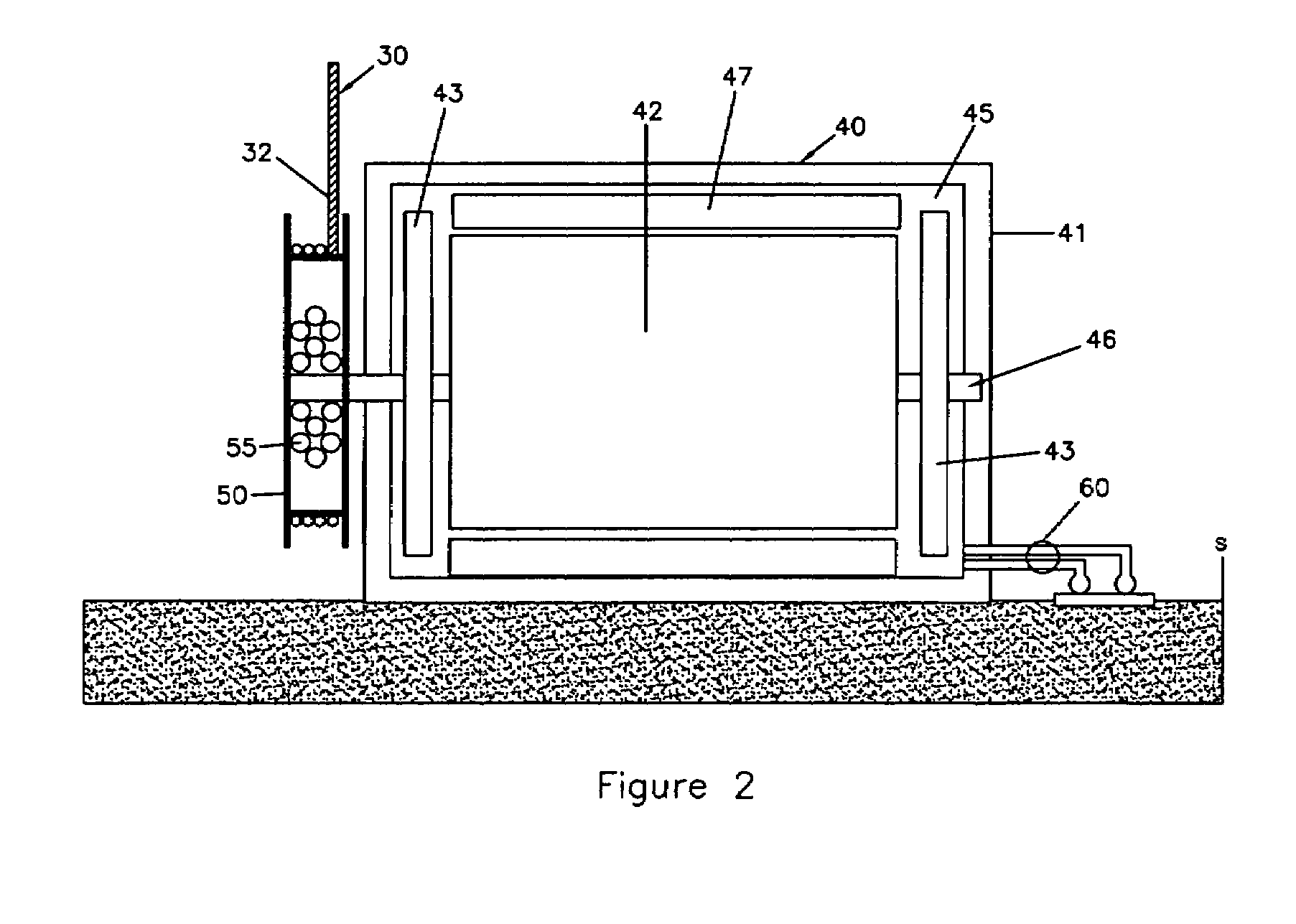
A machine and system for power generation through movement of water having an array of power generating cells electrically interconnected, where the array is configured in an interchangeable modular fashion and the cells are positioned to receive kinetic energy from the movement of water to generate electricity through the movement of an electrical turbine within each cell. The individual turbines and cells may generate relatively small amounts of electricity and use polymer magnetics in the impellers and windings in the turbine to withstand ocean environments and are stacked on electrically conductive trays for ease of installation and replacement.
Owner:HYDRO GREEN ENERGY LLC
Miniature hydro-power generation system
InactiveUS20080136191A1High speedShorten speedGeneral water supply conservationGas turbine plantsEngineeringKinetic energy
A miniature hydro-power generation system includes an outer housing and an inner housing. The outer housing may receive a flow of liquid flowing in a first direction at a predetermined range of pressure. The flow of liquid may be decreased by a predetermined amount of pressure and increased by a predetermined amount of velocity and channeled to a hydro-generator included in the inner housing with an inlet nozzle. The flow of liquid may be channeled with the inlet nozzle to flow in a second direction that is substantially perpendicular to the first direction. Upon transfer of kinetic energy in the flow of liquid to the hydro-generator, the inner housing may rotate in the second direction. The flow of liquid may then be channeled back to the first direction and out of the housing with an outlet nozzle. The outlet nozzle configured to increase the pressure and decrease the velocity of the flow of liquid to minimized non-laminar flow characteristics.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
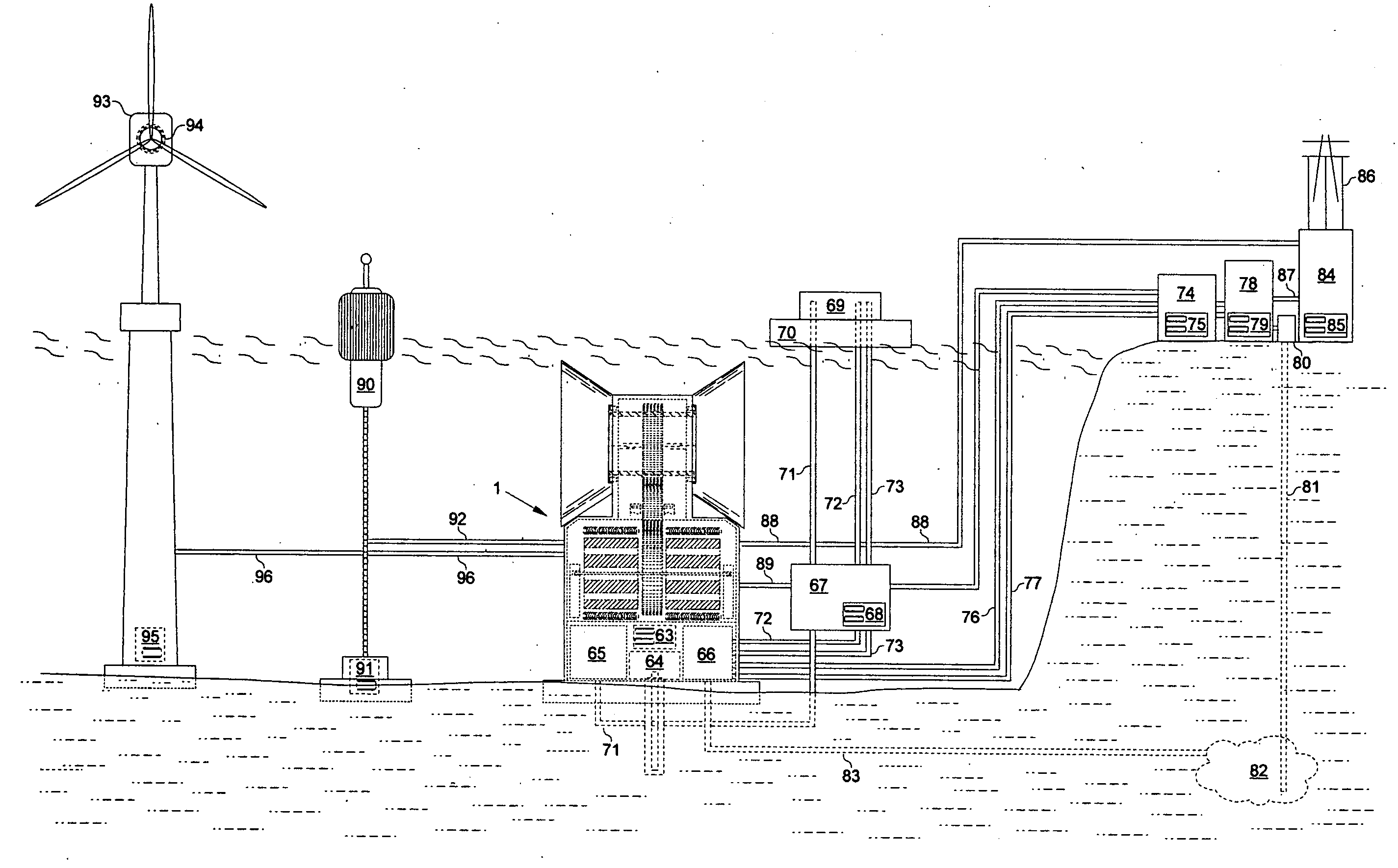
Offshore power generator with current, wave or alternative generators
An offshore power generator is disclosed. The offshore power generator includes an offshore platform, which can be a new, existing, abandoned, removed, dumped or relocated fixed or floating offshore platform; one or more types of current, wind, wave and other renewable energy generators mounted to the offshore platform; and interconnecting power cables, in electrical communication with the current generators for distribution from the generators to end users.
Owner:GEHRING DONALD HOLLIS
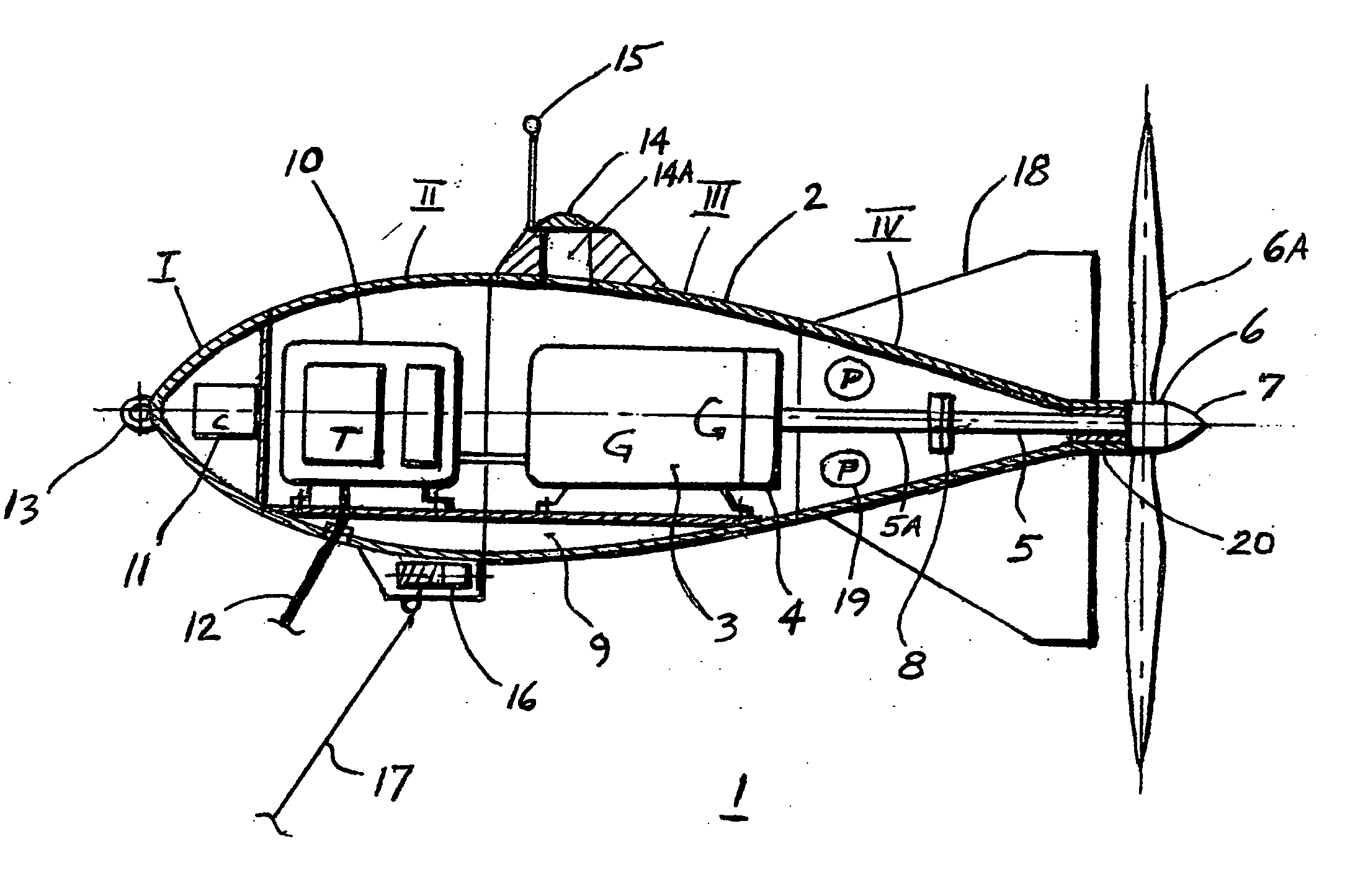
Deployable submarine-hydroelectric generator for sea currents energy harvesting
InactiveUS20090140524A1Easy to harvestReduce global warmingFinal product manufactureGas turbine plantsOcean bottomElectrolysis
Deployable submarine hydroelectric generator for conversion of kinetic energy of deep ocean currents into electricity by having an electric generator mounted in a sealed hydrodynamic, buoyant vessel with tail fins, and connected by a shaft to a rotary turbine blades at the tail end of the submarine vessel, which vessel is anchored at desired depth to the bottom of the ocean by a cable. The drag of the turbine blades causes the vessel to self-steer against the direction of the ocean current. An electric cable is also provided, connecting said electric generator with electric grid on the land. Such generator is out of sight, unlike windmills, and is environmentally friendly to the sea life, due to slow rotating blades. This clean electricity can also be used for production of low cost hydrogen by electrolysis of sea water.
Owner:KEJHA JOSEPH B
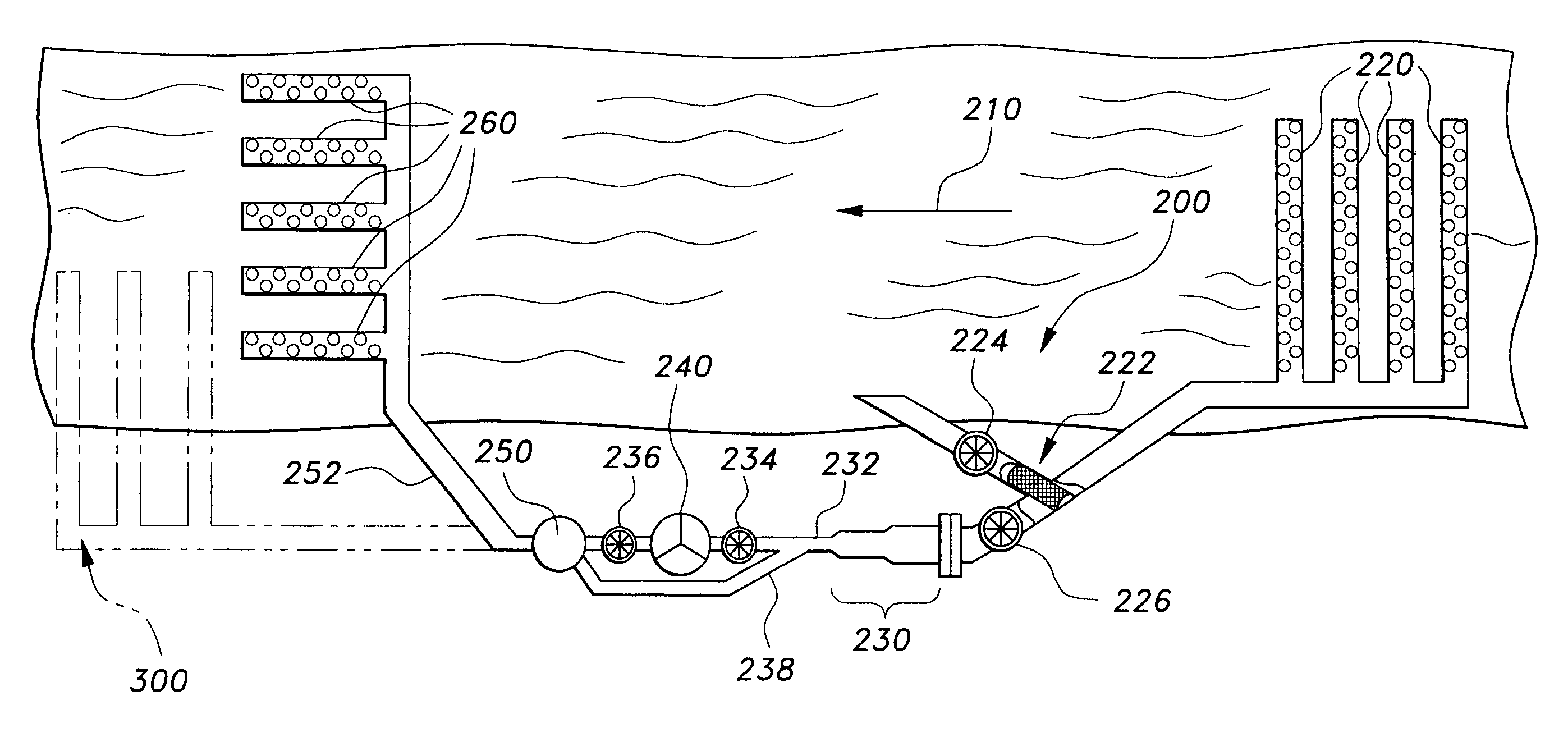
System for producing hydrogen making use of a stream of water
A system for producing hydrogen from water, making use of a stream of water such as a gulf stream or tidal stream, includes a number of submerged modules, each having a turbine that can be driven by the stream of water. The turbine is coupled to a generator for generating electrical energy. Each module may have submerged decomposition means for decomposing water into hydrogen and oxygen using the electrical energy generated. The modules are provided with means to control the depth of the modules below water level, and furthermore with means for automatically orienting the front of the modules—viewed in the longitudinal direction of the turbines—to the direction of flow of the water or an angular position deviating therefrom.
Owner:PAS PETER ALEXANDER JOSEPHUS
Energy conversion systems and methods
An energy conversion system may include a stationary structure, a rotatable structure configured to rotate relative to the stationary structure, wherein the rotatable structure defines an axis of rotation. The system may further include at least one blade member mounted to and extending radially outward from the rotatable structure, the at least one blade member being configured to interact with fluid currents flowing in a direction substantially parallel to the axis of rotation to cause the rotatable structure to rotate about the axis of rotation, and at least one bearing mechanism disposed to provide at least one of a radial and axial bearing between the rotatable structure and the stationary structure as the rotatable structure rotates about the stationary structure. The system may be configured to convert rotation of the rotatable structure to at least one of electricity and hydrogen production.
Owner:OCEANA ENERGY
Hydrokinetic generator
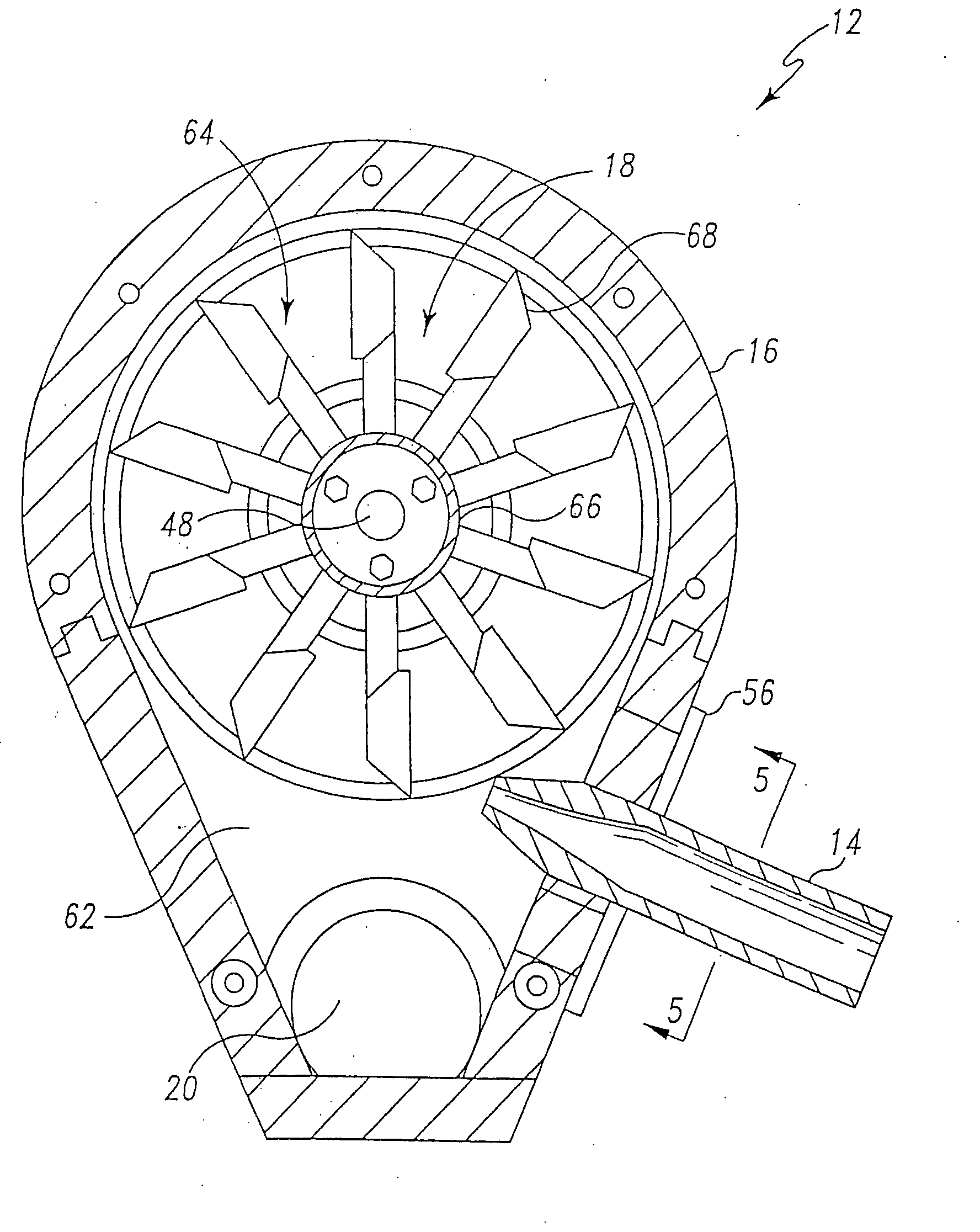
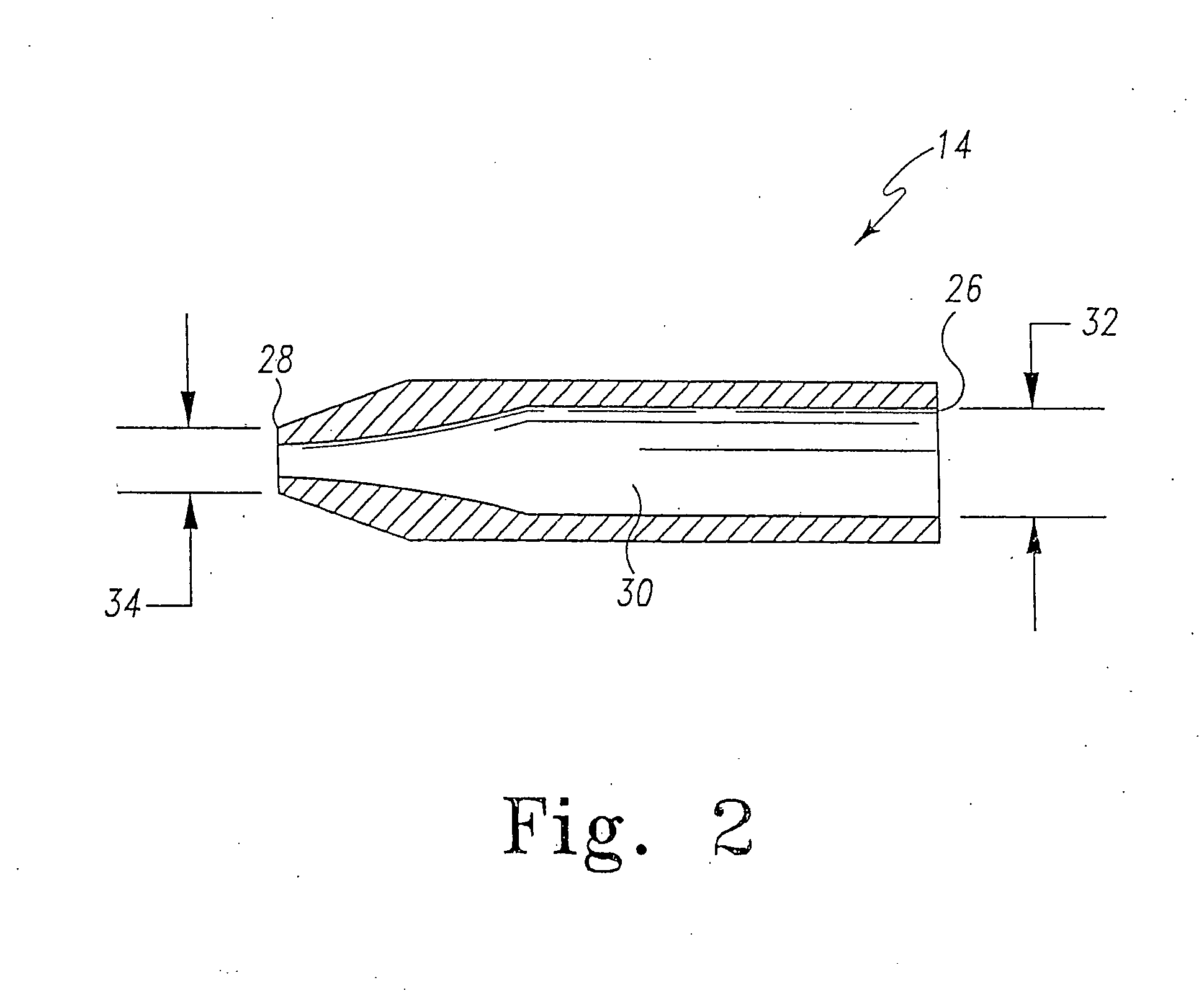
An improved method and means for transforming kinetic energy into mechanical energy to generate hydroelectric power. A submersible scoop-like composite structure (10) with a hollow, tapered, inner chamber to funnel moving water through a turbine (22). The structure (10) has a hydrodynamically clean outer hull with cambered surfaces to increase the velocity of moving water to enhance the turbine's (22) efficiency. The structure (10) has a large orifice with a protective grill (14). The body of the structure (10) contains a vertical stabilizer petition (13) to keep the structure (10) parallel with the direction of the moving water. The detachable turbine (22) is housed in a tube (11) attached aft of the structure (10). The detachable generator (25A, 25B, 25C) is housed in a protective housing (12A, 12B, 12C) and attached to the turbine housing (11). The turbine (22) is coupled to the generator (25A, 25B, 25C) by a turbine drive shaft (24) through a gear box (23) to a generator drive shaft (26A, 26B, 26C). The turbine drive shaft (24) is supported by a front vertical support (27) and a rear vertical support (28). The generator drive shaft (26A, 26B, 26C) is protected by a generator drive shaft housing (29A, 29B, 29C). The entire structure is attached to an anchor base (16A, 16B, 18A, 18B, 21) by legs (15A, 15B, 17A, 19A, 19B, 20) The anchor base is fixed to a submerged medium. The scoop-like composite structure is formed from rigid material and submerged, whereby it cannot be seen from the surface. The structure is cost effective, efficient, produces no known pollution, and is not susceptible to weather related damage.
Owner:SALLS DARWIN ALDIS
Offshore power generator with current, wave or alternative generators
An offshore power generator includes an offshore platform. Current, wind, wave and other renewable energy generators are mounted to the offshore platform. Each current generator has a shroud enclosing a set of blades. A hub member is located within the shroud and extends in an upstream direction from the blades. The flow area between the interior of the shroud and the hub member converges from the shroud inlet to the blades.
Owner:GEHRING DONALD HOLLIS
Self-sufficient hydrogen generator
InactiveUS20100258449A1Photography auxillary processesGeneral water supply conservationWave power generationOrchestration
A self-sustaining, fully automated, hydrogen generator that utilizes the ocean's currents, tides, and water to produce vast amounts of hydrogen and oxygen. Additional electricity may be supplied by locally generated means including offshore wind, offshore geothermal, as well as wave powered generation. Hydrogen is exported as well as the oxygen not consumed by the life support systems. Residue collected from the ocean water purification process is collected and exported for use elsewhere or dispersed locally around the underwater facility. Systems orchestration is achieved by control systems that operate independently of one another with no single point of failure.
Owner:FIELDER WILLIAM SHERIDAN
Systems and Methods for Energy Storage and Recovery Using Rapid Isothermal Gas Expansion and Compression
InactiveUS20100139277A1Increase energy densityHigh outputElectrical storage systemInternal combustion piston enginesProduct gasEngineering
Owner:SUSTAINX
Direct Current Brushless Machine and Wind Turbine System
InactiveUS20100148515A1Improve efficiencyHigh relative moving magnetPump componentsReaction enginesElectrical conductorPressure difference
A direct current brushless electric machine is described that comprises a sequence of permanent magnets where the N and S magnetic poles being alternately arranged adjacent to each other, each exerting a magnetic field; phase coils are composed of a group of conductors, each conductor being laid essentially in parallel with each other, each coil being displaced by a full range of a single magnetic pole of the permanent magnet, such that each phase coil is alternately disposed adjacent to each other; and magnetic field or every other coil is in the same orientation to form an armature positioned opposite to the permanent magnet movable with respect to the armature with a predetermined amount of air gap provided between the phase coils and the permanent magnets. The electric machine operates as a generator when the power is flowing from a prime mover, such as the turbine blade extracting energy from the wind or water. The electric machine operates as a motor when the current is applied to the coils in a sequence to move the rotor when the turbine blades move the wind or water.Also described is an aerodynamic system comprising inner and outer annulus disposed driving fans, with a pressure differential flow enhancing aerodynamic housing, able to concentrate and make laminar rough and turbulent intake air molecule flows, creating a smooth rotationally organized downstream vortex field, with maximum power extraction from building structure directed velocity flow enhancements.
Owner:GEDDRY MARY +1
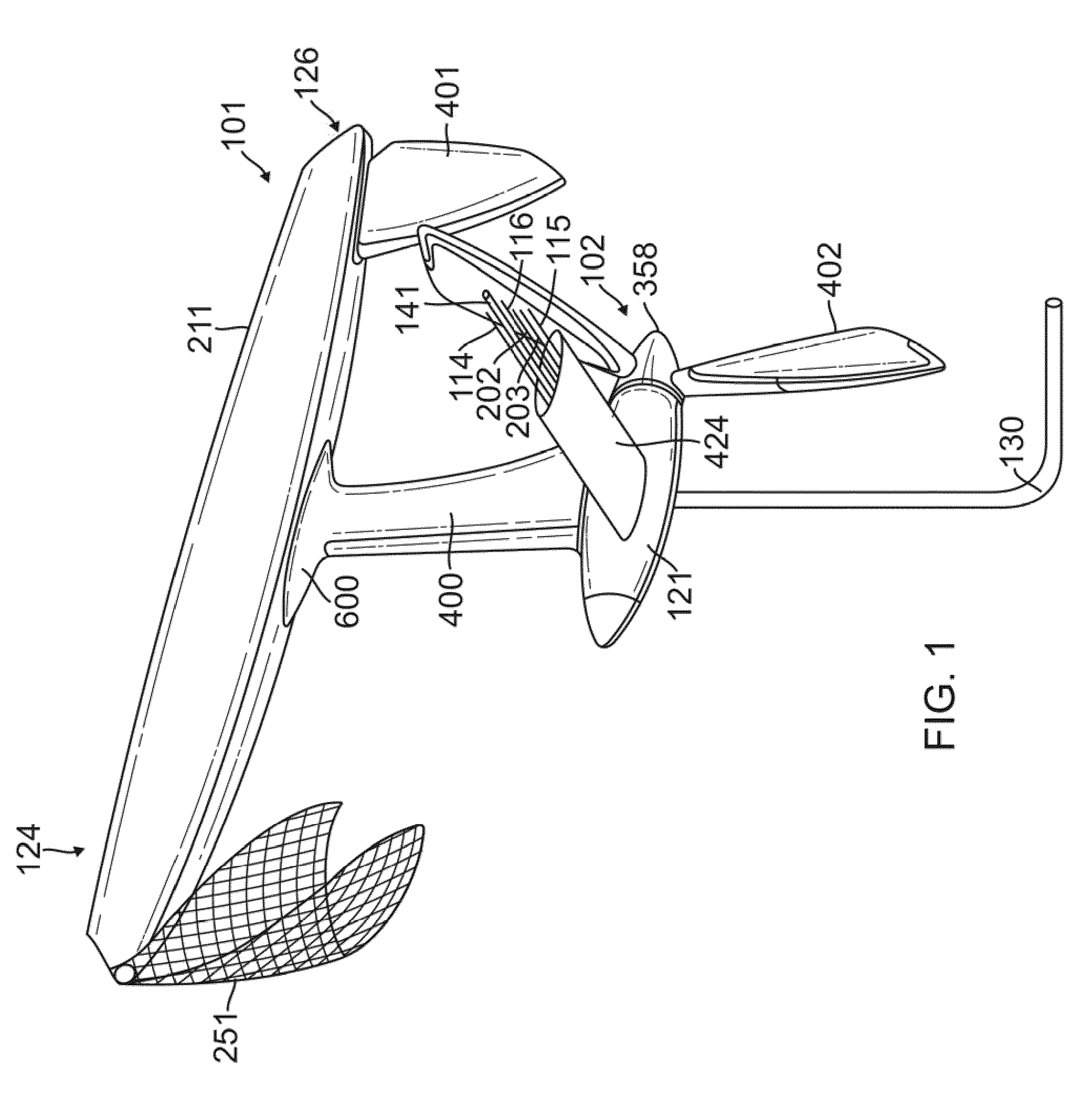
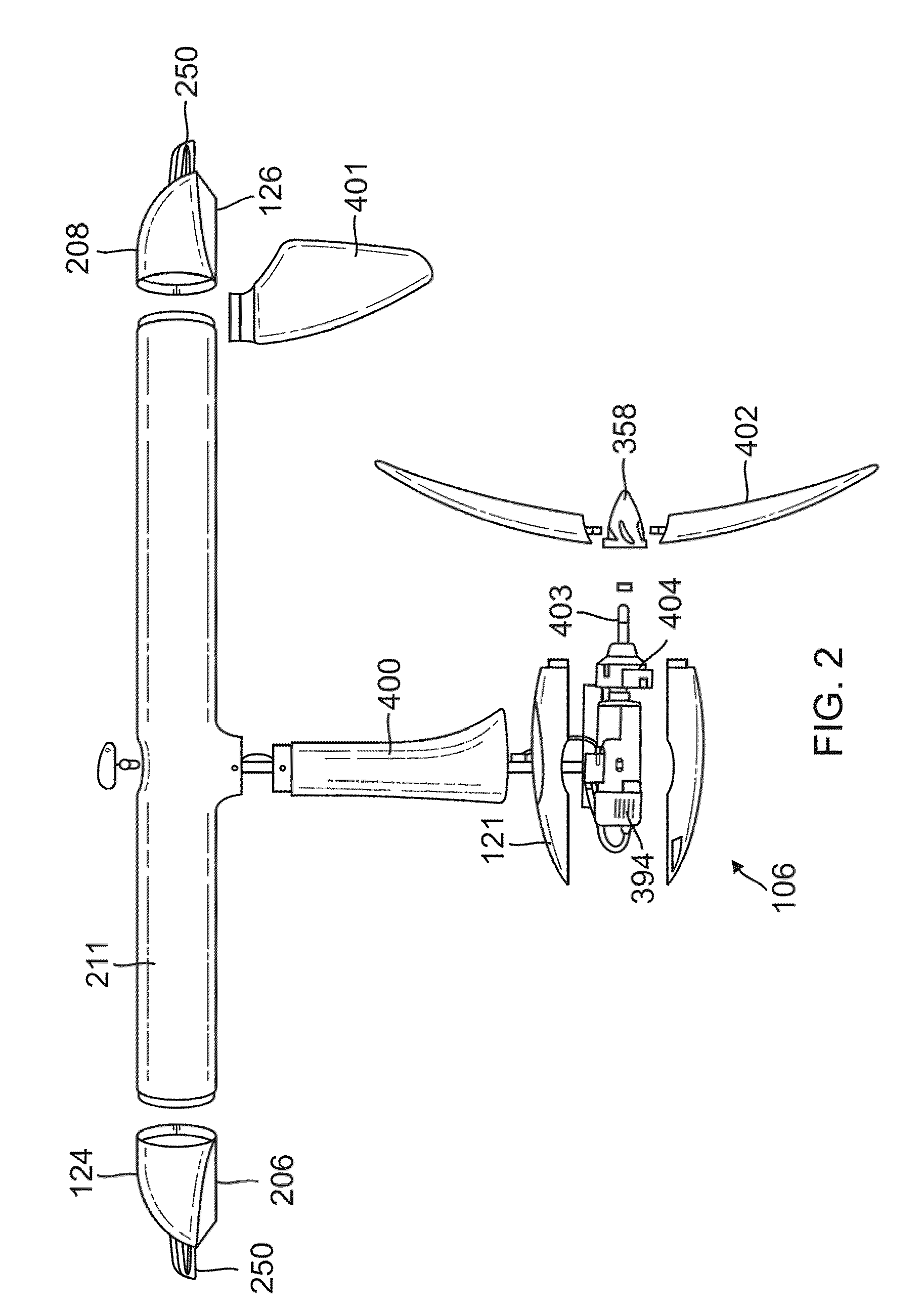
Gimbal-mounted hydroelectric turbine
InactiveUS6956300B2Reduce environmental impactPositive net energyFluid couplingsWind energy with electric storageFluid intakeEngineering
A power plant extracts energy from a free flowing motive fluid by means of a turbine mounted on a gimbal. The shroud element of the fluid intake has external rudders, in conjunction with the gimbal mounting, enabling the enclosed turbine to instantaneously respond to changes in the direction of the free flowing motive fluid thus ensuring the face area of the intake is always physically orthogonal to the direction of the motive fluid streamlines. The shroud element may also be buoyant so as to optimally extract energy from an upper non-turbulent and higher velocity layer of the free flowing motive fluid. To function within an inherently unsteady source of energy, the preferred embodiment of the turbine is coupled to a DC generator which may further be coupled to a voltage and current regulating circuit which either charges a battery, performs electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen fuel, or is further coupled to a DC motor coupled to an AC generator. Alternatively an AC induction generator may be coupled to the turbine. Other mechanical, electrical, electronic, or electromechanical features may optionally be implemented to perform such tasks as adaptively locating the turbine in the maximum velocity flow, adapting internal vane and runner blade pitches for various flow rates and loads, keeping the intake free of obstructions, preventing loss of aquatic life, controlling and communicating the state of charge of the battery, or gauging and controlling the electrolysis process and communicating the fullness of the hydrogen gas output tanks.
Owner:INTEGRATED POWER TECH CORP
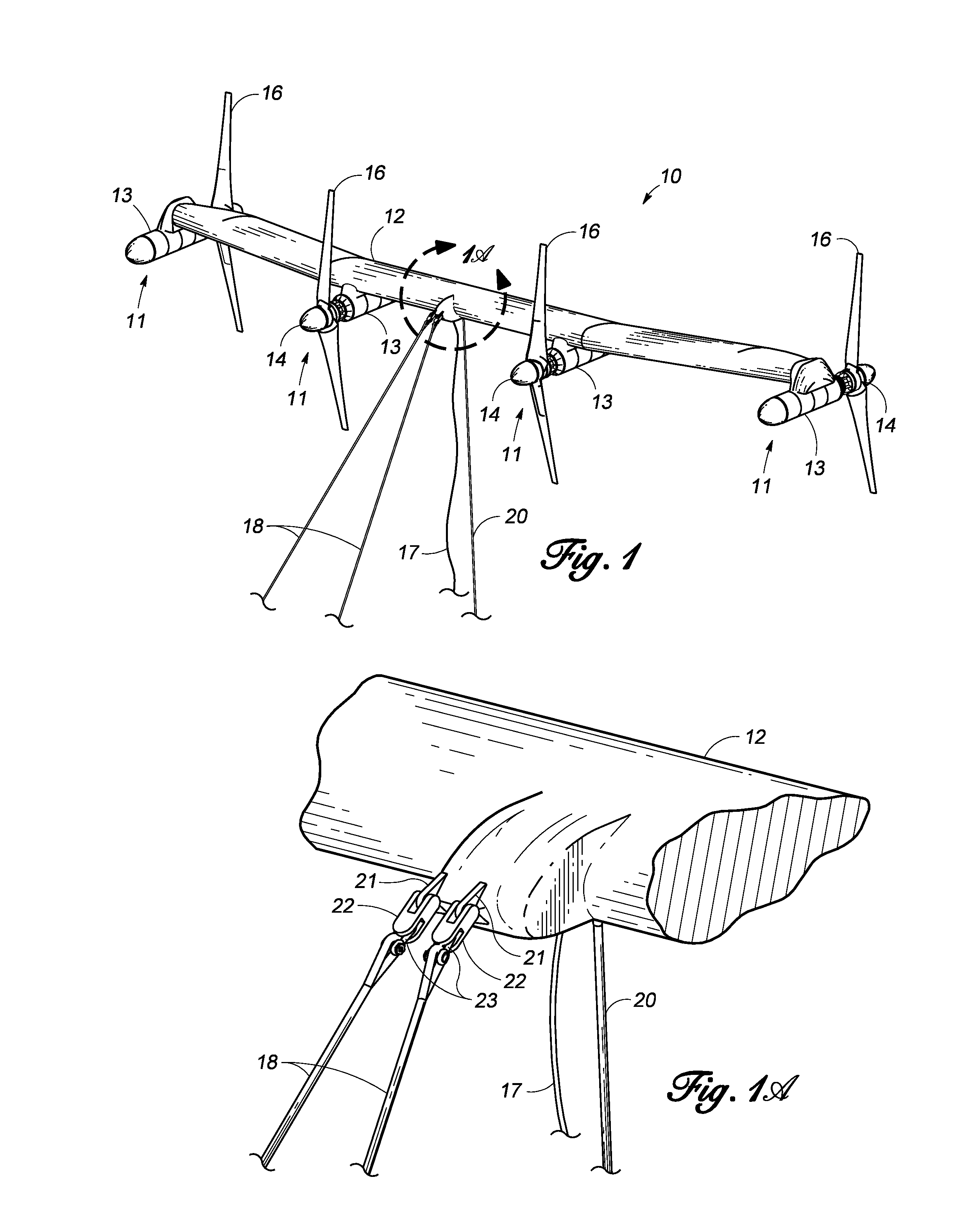
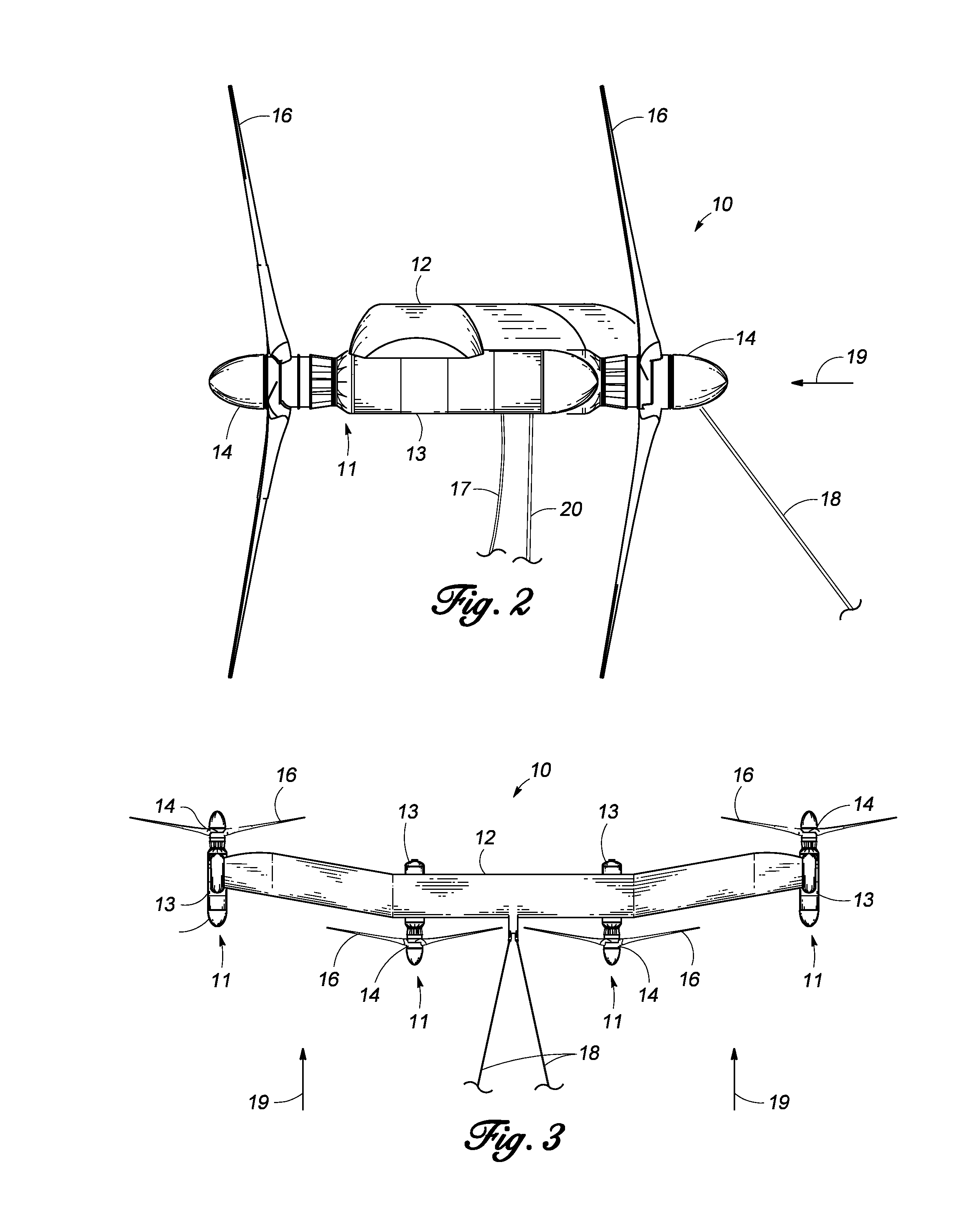
Multi-Megawatt Ocean Current Energy Extraction Device
InactiveUS20130106105A1Counteract buoyancyReduce the average velocityEngine fuctionsBuoyancy controlOcean bottomDrivetrain
An underwater apparatus for generating electric power from ocean currents and deep water tides. A submersible platform including two or more power pods, each having a rotor with fixed-pitch blades, with drivetrains housed in pressure vessels that are connected by a transverse structure providing buoyancy, which can be a wing depressor, hydrofoil, truss, or faired tube. The platform is connected to anchors on the seafloor by forward mooring lines and a vertical mooring line that restricts the depth of the device in the water column. The platform operates using passive, rather than active, depth control. The wing depressor, along with rotor drag loads, ensures the platform seeks the desired operational current velocity. The rotors are directly coupled to a hydraulic pump that drives at least one constant-speed hydraulic-motor generator set and enables hydraulic braking. A fluidic bearing decouples non-torque rotor loads to the main shaft driving the hydraulic pumps.
Owner:AQUANTIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com