Patents
Literature
182results about How to "Degree of freedom is lowered" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
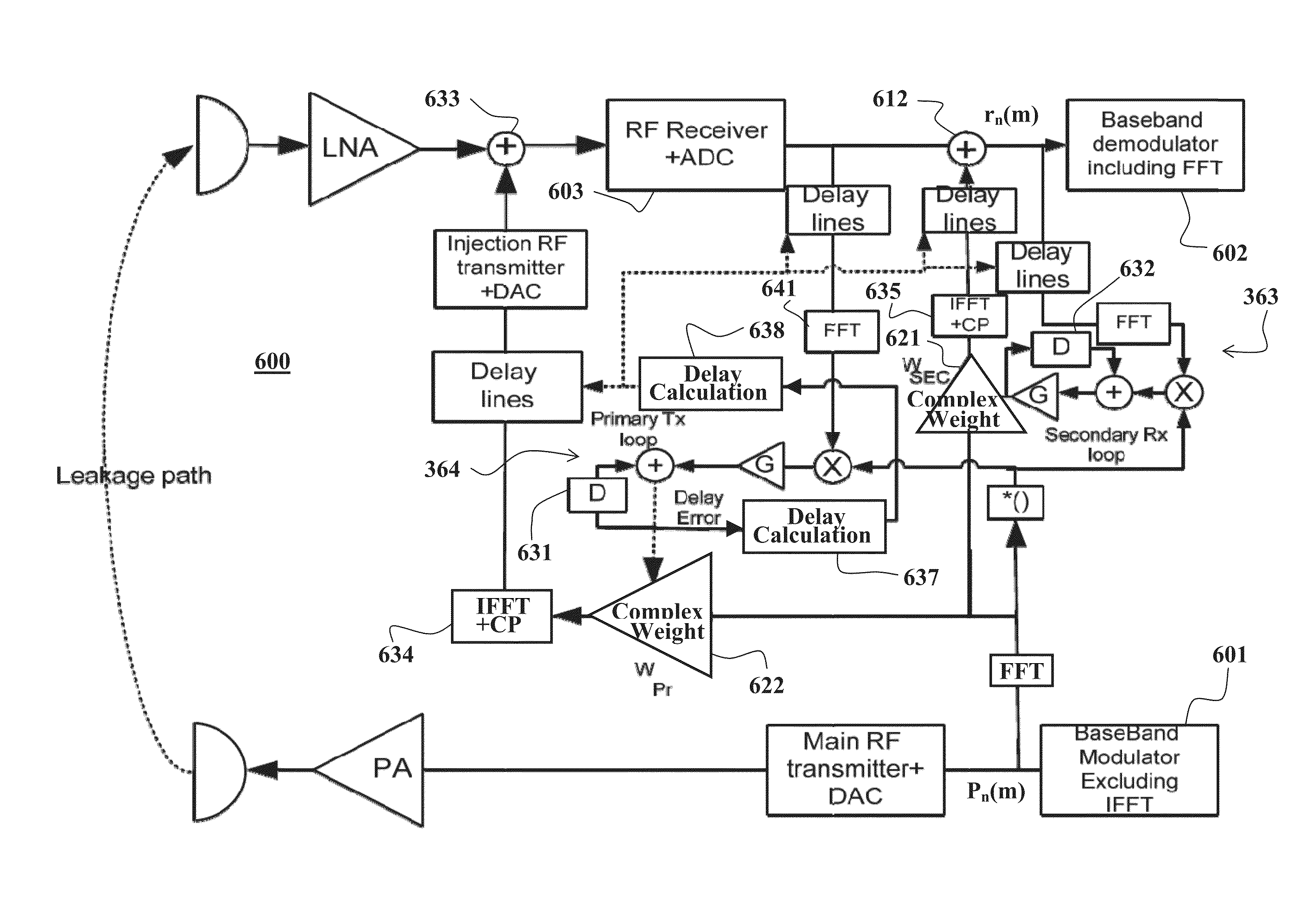
Method and system of interference cancelation in collocated transceivers configurations
ActiveUS20130102254A1Reduce distractionsDegree of freedom is loweredTransmission noise suppressionVIT signalsTransceiver
The present invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to a method of cancelling interference in a wireless system, wherein the interference introduced by an interfering signal causing reception of an interfered signal responsive to transmission of a desired signal, the method comprising acquiring the interfering signal from a transmitter during or before transmission thereof, generating an analog cancellation signal based on the acquired interfering signal, and injecting said analog cancellation signal into an interfered receiver receiving said interfered signal to reduce said interference therefrom.
Owner:UBIQAM
Mobile communication terminal
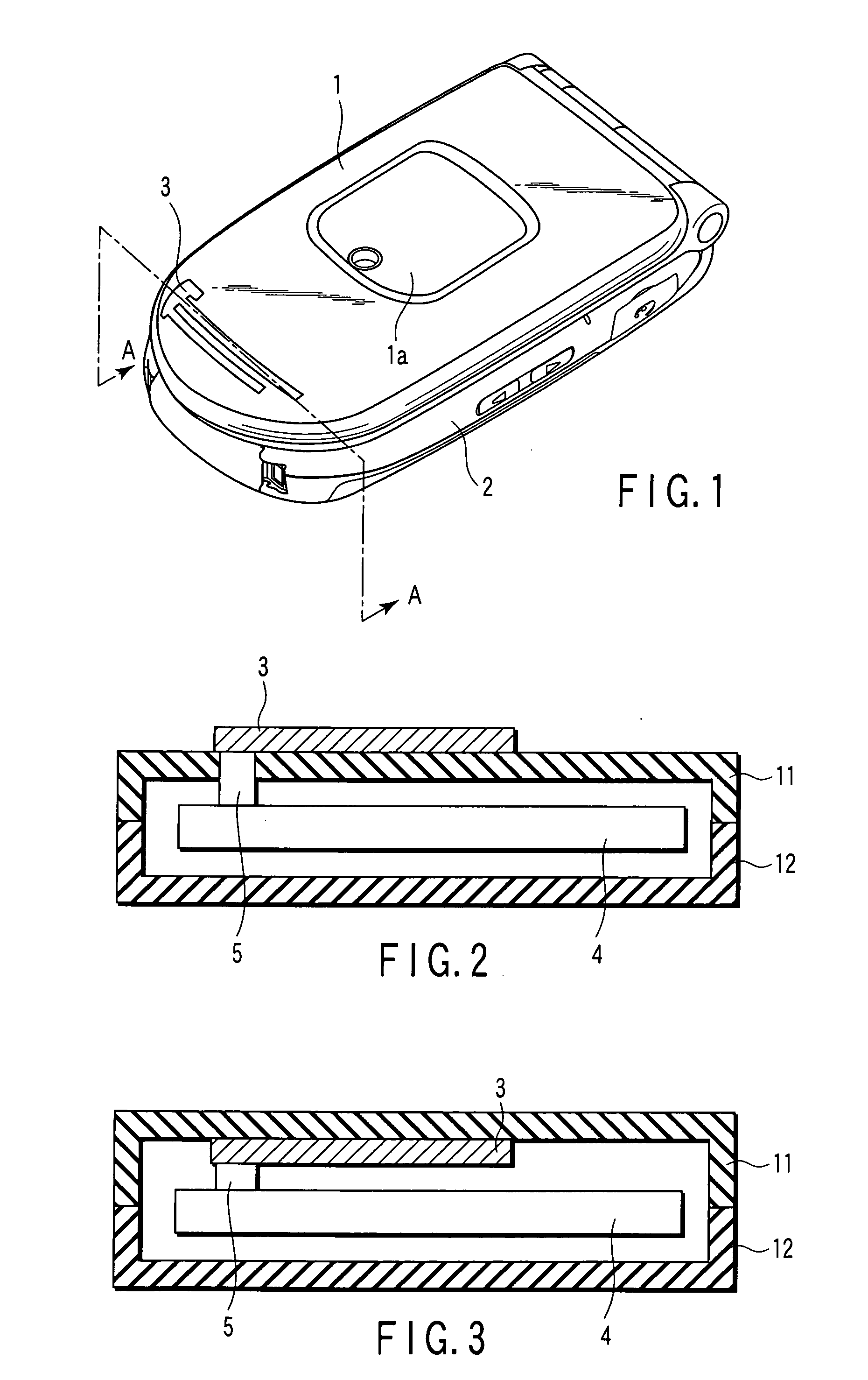
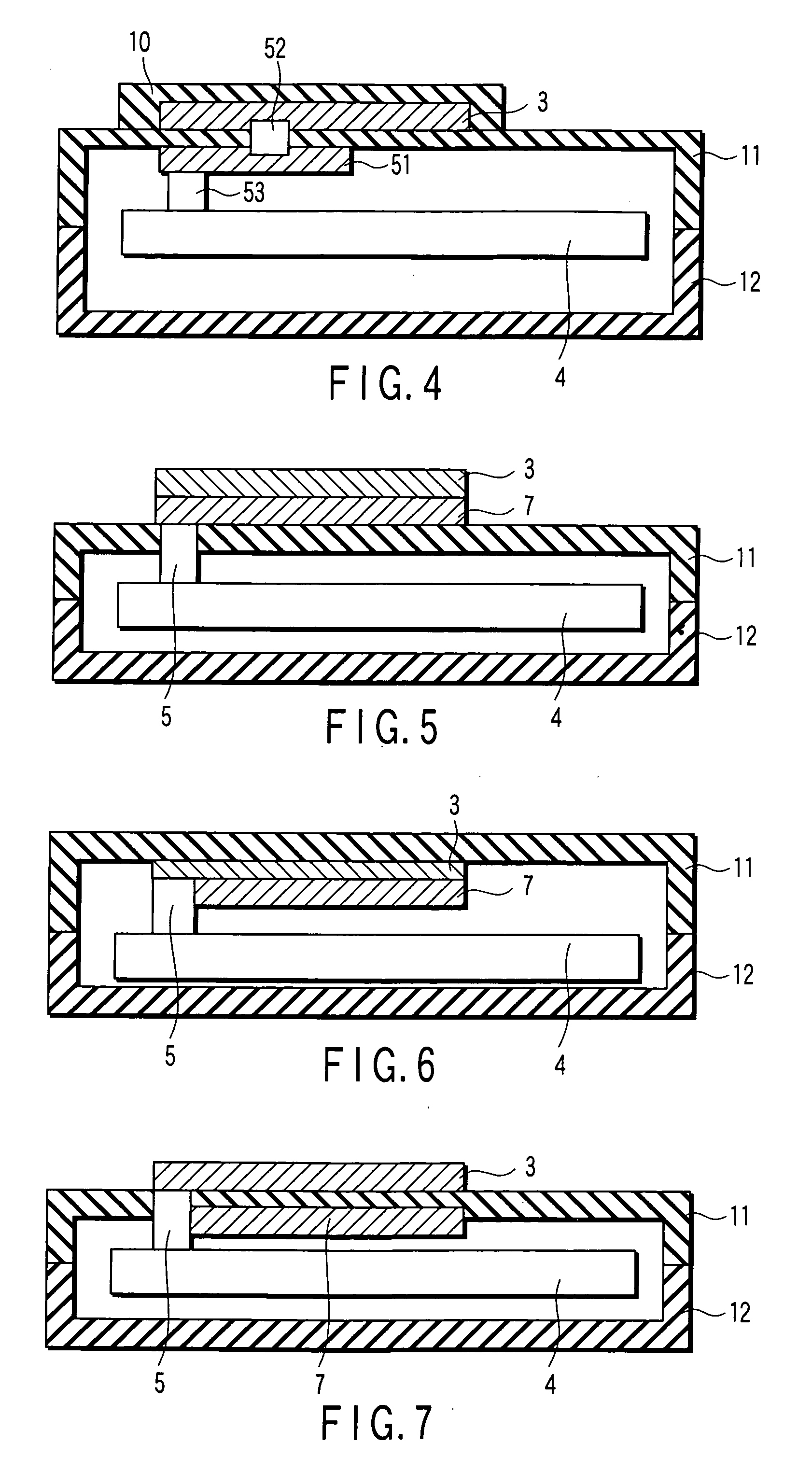
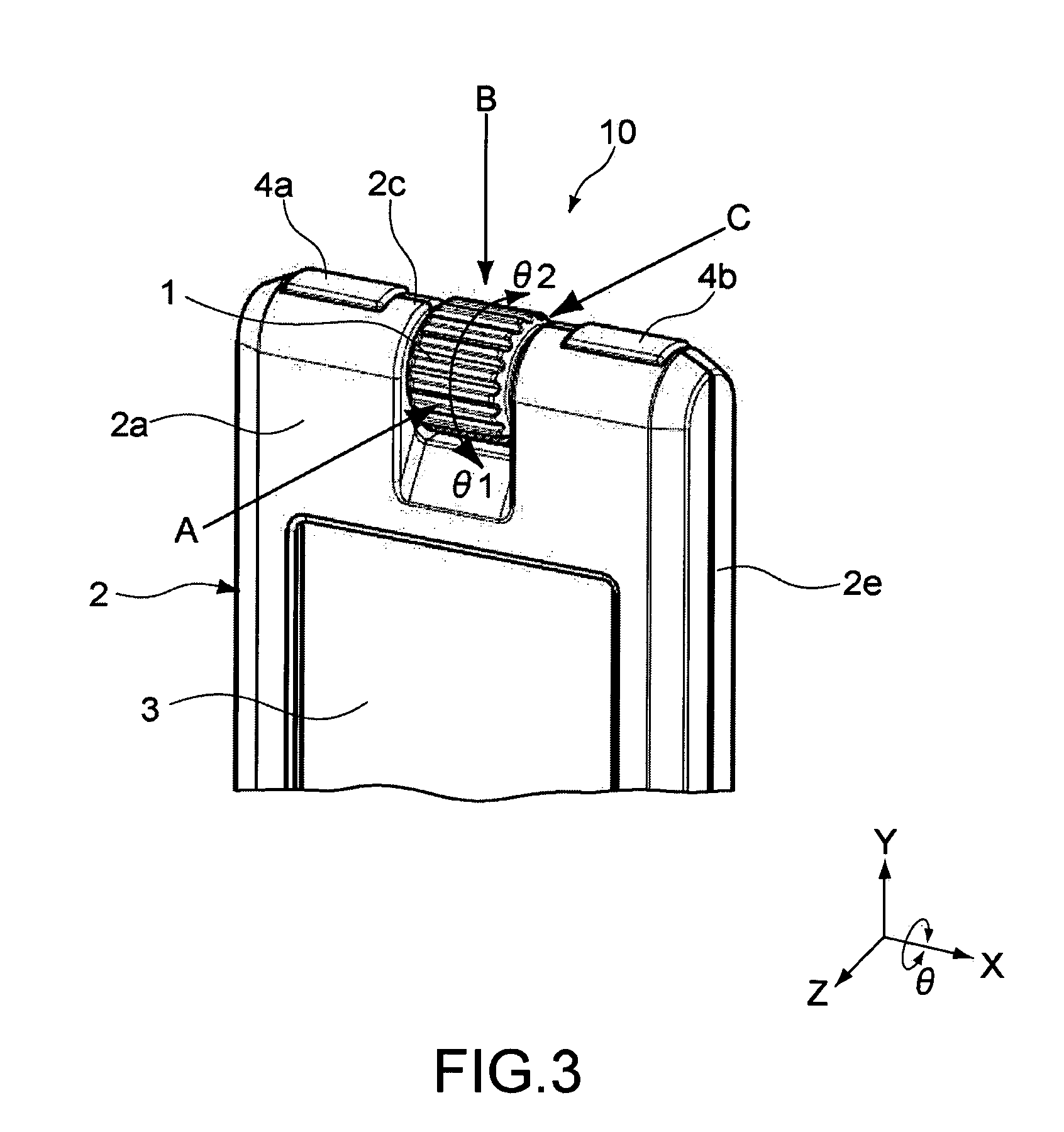
InactiveUS20070241971A1Easily and inexpensively integrationIncrease freedomAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna connectorsEngineeringAntenna element
An antenna element made of an electrically conductive material pattern is printed and formed on a face of a casing made of an electrically nonconductive material having a circuit board housed therein, and the antenna element and the circuit board are electrically connected to each other by a connecting element.
Owner:TOSHIBA CLIENT SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Electronic apparatus
InactiveUS7856255B2Increase the number ofDegree of freedom is loweredInput/output for user-computer interactionInterconnection arrangementsEngineeringElectron device
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and Apparatus for Measuring a Structure on a Substrate, Computer Program Products for Implementing Such Methods and Apparatus
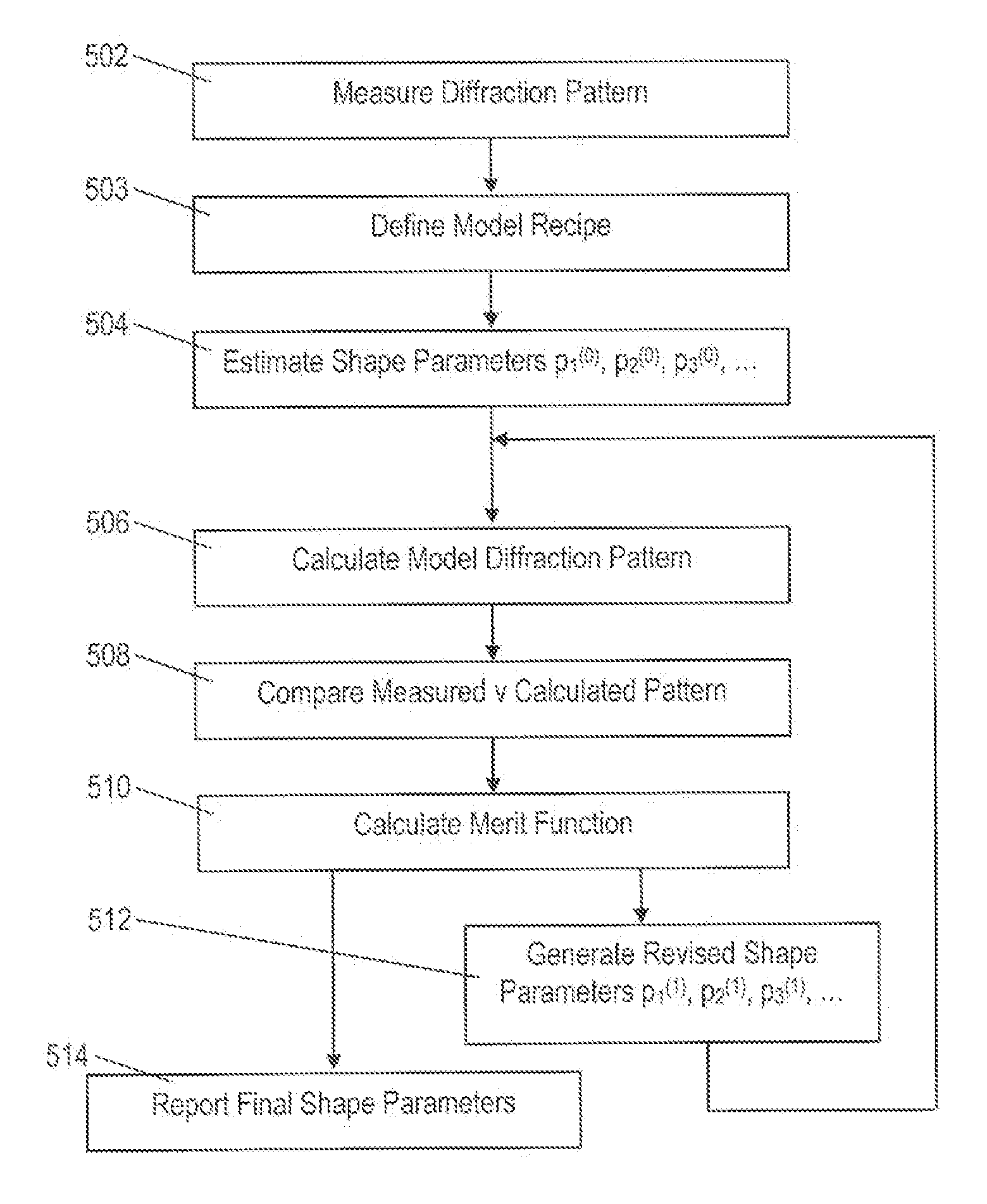
ActiveUS20120123748A1Degree of freedom is loweredReduce in quantityMaterial analysis by optical meansComputation using non-denominational number representationAlgorithmUser input
Diffraction models and scatterometry are used to reconstruct a model of a microscopic structure on a substrate. A plurality of candidate structures are defined, each represented by a plurality of parameters (p1, p2, etc.)). A plurality of model diffraction signals are calculated by simulating illumination of each of the candidate structures. The structure is reconstructed by fitting one or more of the model diffraction signals to a signal detected from the structure. In the generation of the candidate structures, a model recipe is used in which parameters are designated as either fixed or variable. Among the variable parameters, certain parameters are constrained to vary together in accordance with certain constraints, such as linear constraints. An optimized set of constraints, and therefore an optimized model recipe, is determined by reference to a user input designating one or more parameters of interest for a measurement, and by simulating the reconstruction process reconstruction. The optimized model recipe can be determined automatically by a parameter advisor process that simulates reconstruction of a set of reference structures, using a plurality of candidate model recipes. In the generation of the reference structures, restrictions can be applied to exclude unrealistic parameter combinations.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
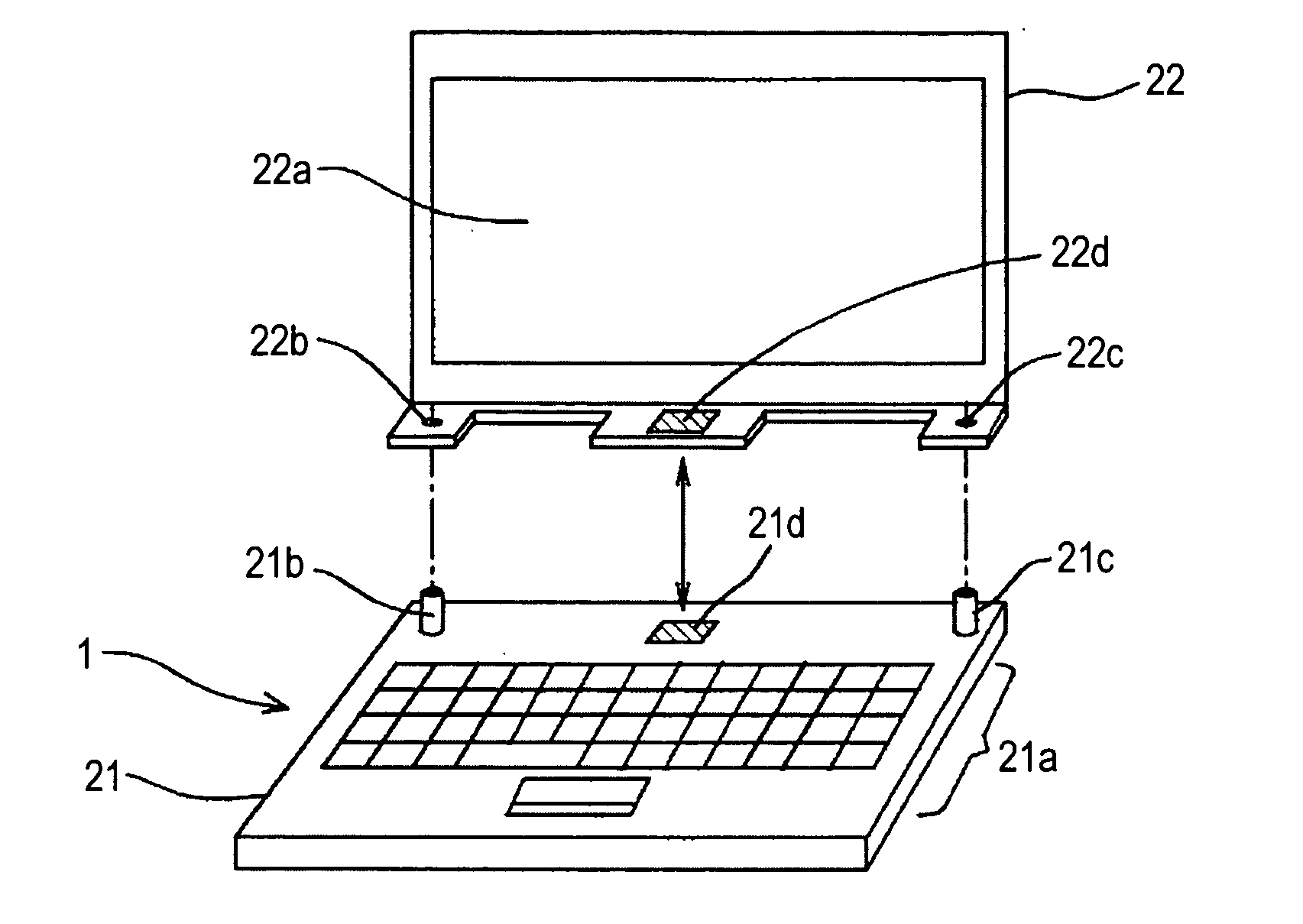
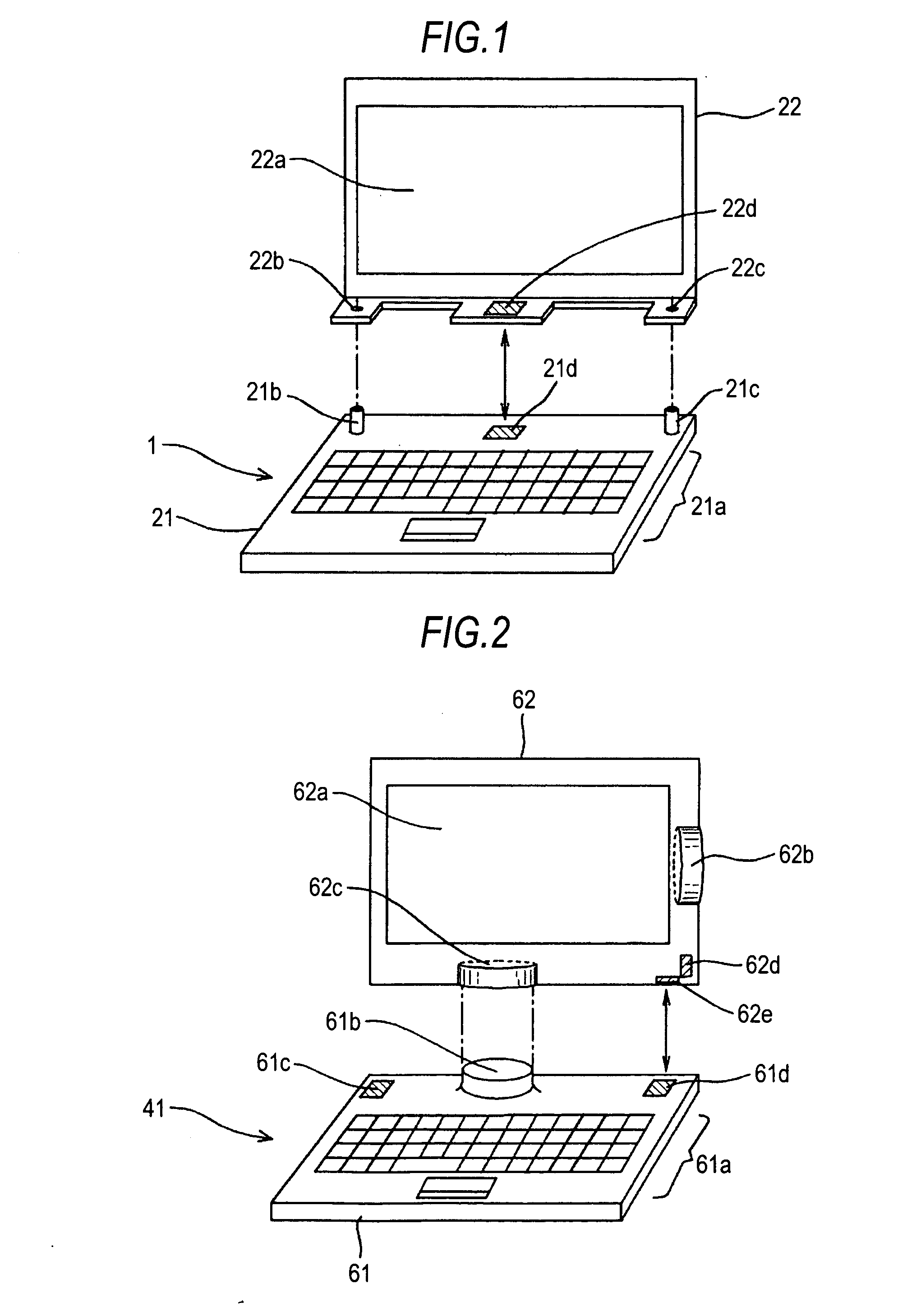
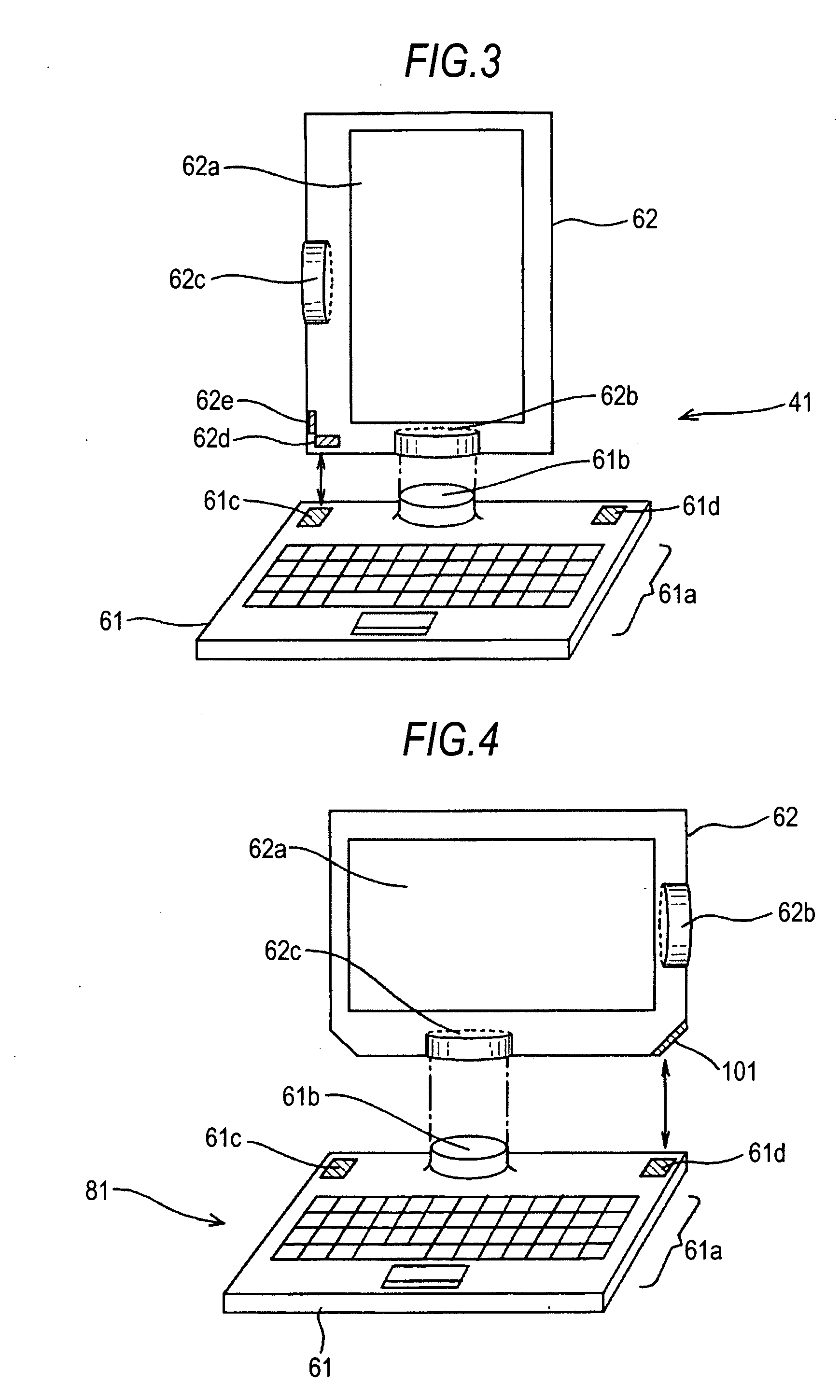
Information processing device
InactiveUS20100265648A1Angle and orientation of the displayDegree of freedom is loweredDetails for portable computersIdentification meansTelecommunicationsInformation processing
An information processing device, includes: a display means including a receiving surface for receiving data transmitted by wireless communication; and a supporting means including a transmitting surface for transmitting the data by the wireless communication and supporting the display means, wherein the supporting means supports the display means in a position in which the wireless communication can be performed.
Owner:SONY CORP
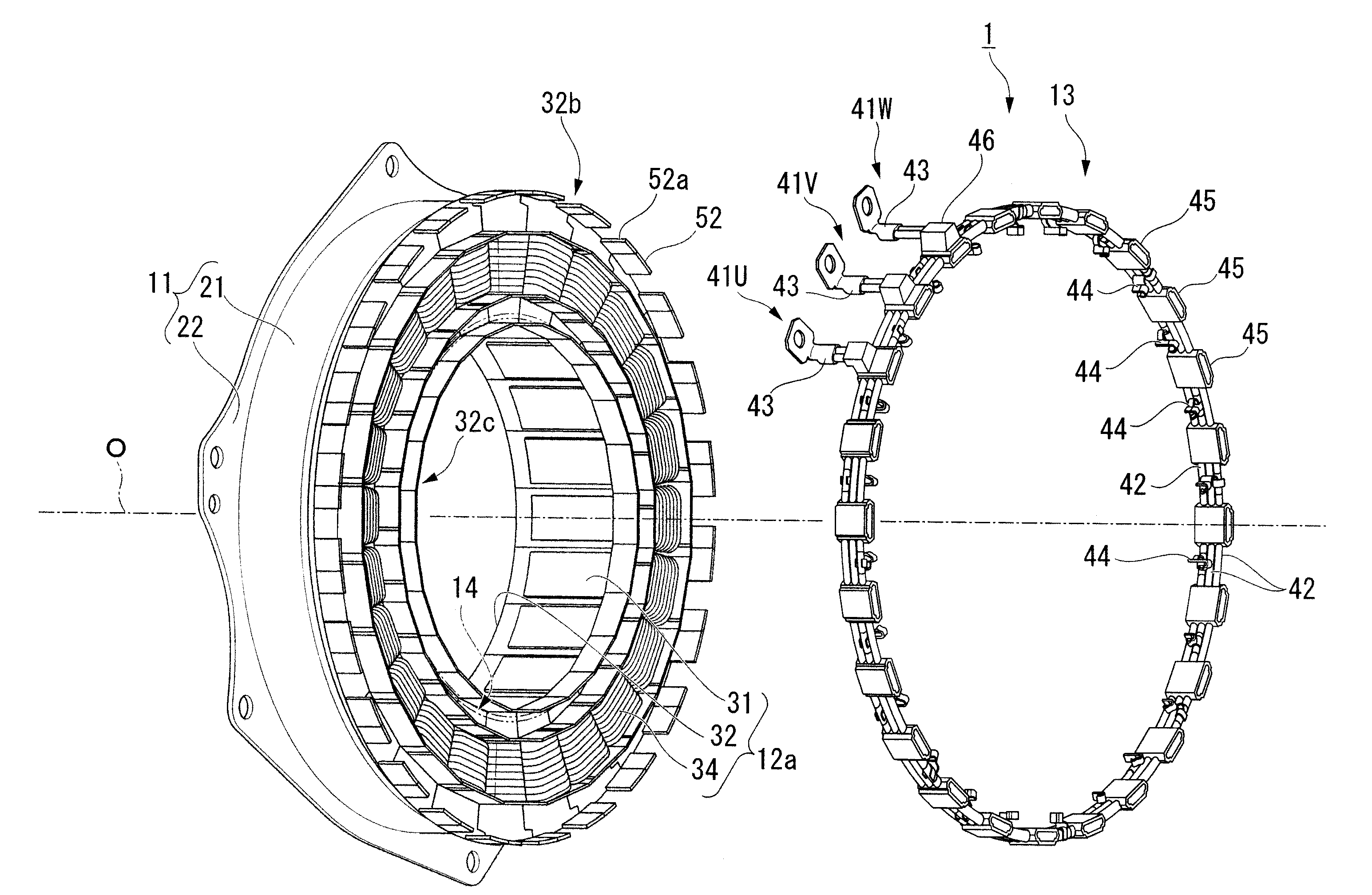
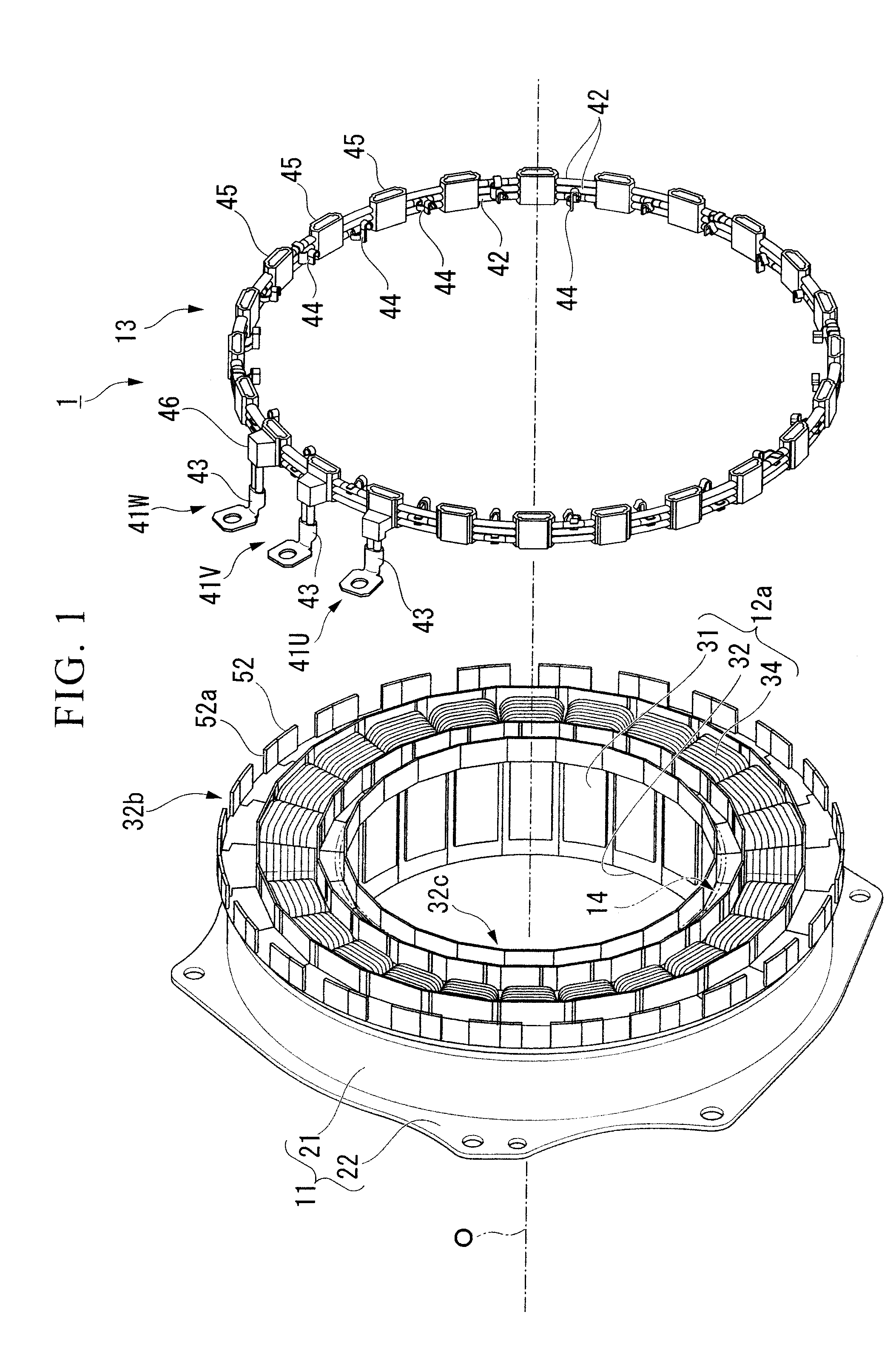
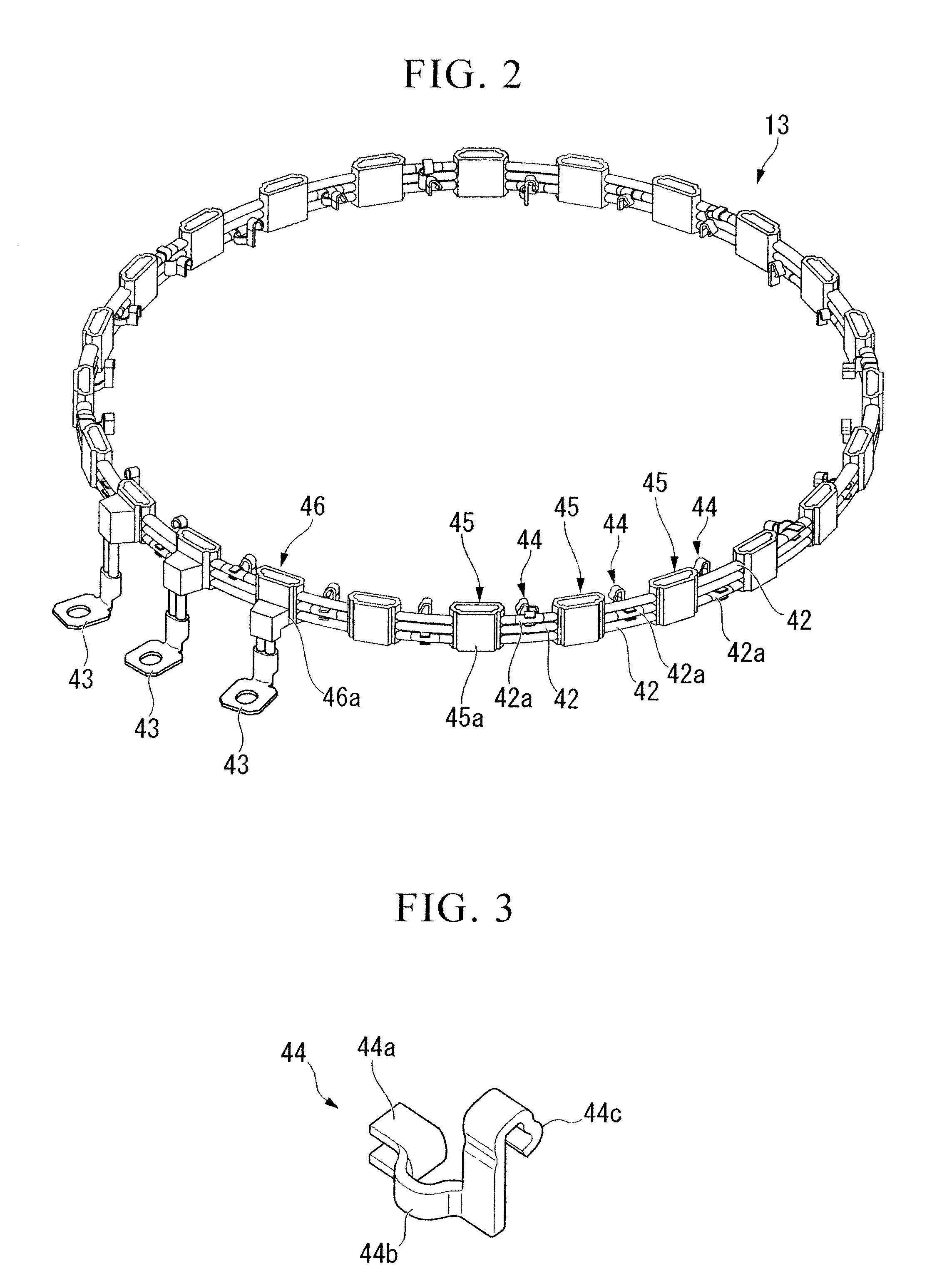
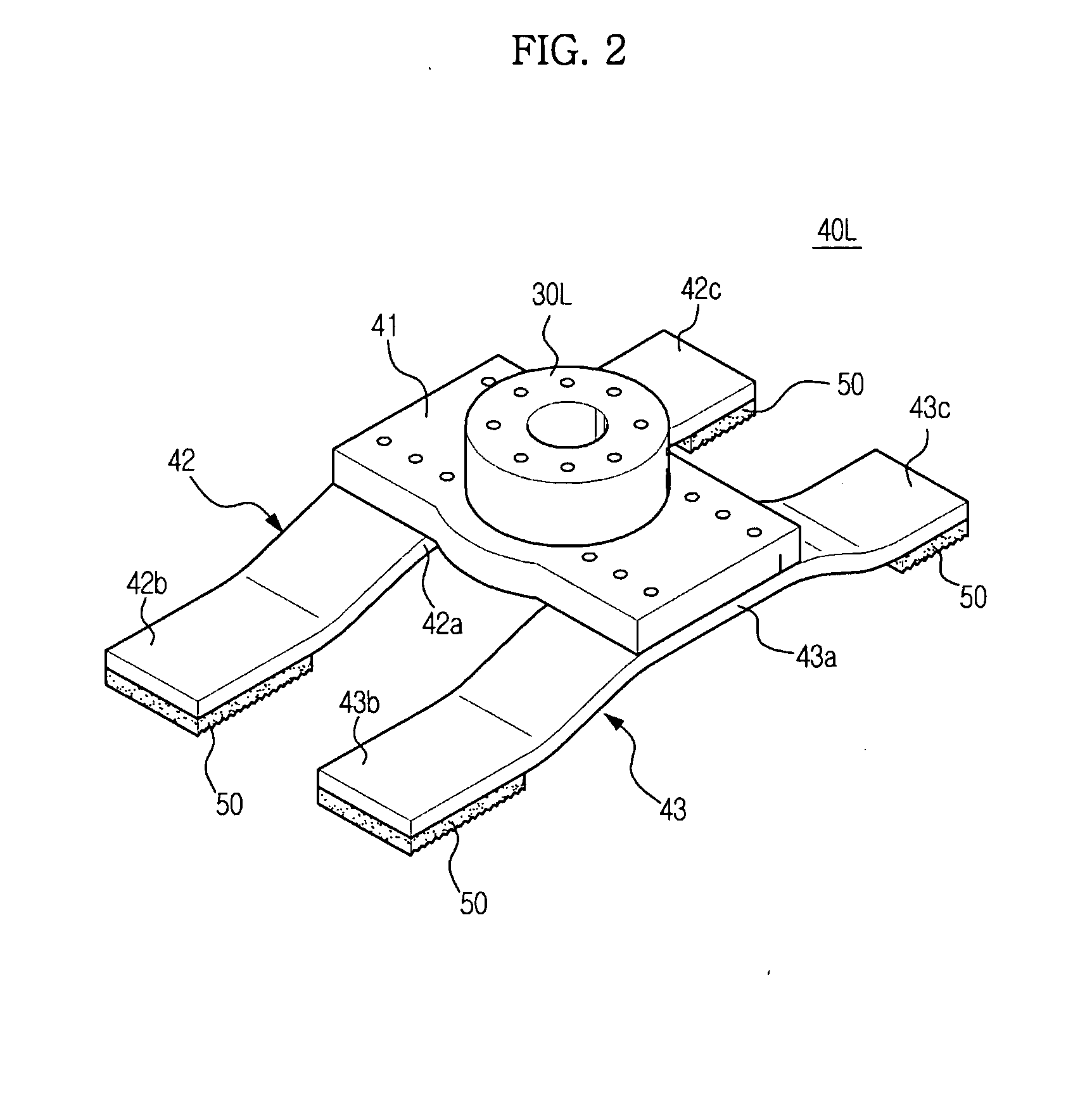
Electric power collection/distribution ring of rotary electric machine
An electric power collection / distribution ring of a rotary electric machine including: a plurality of ring shaped bus rings each of which is to be connected to one of a plurality of coils provided in the rotary electric machine, the coils each corresponding to phases of the rotary electric machine; a plurality of fixing member which are fixed to the bus rings and arranged along the circumferential direction thereof; and a plurality of connection terminals which are fixed to the bus rings and arranged along said circumferential direction, and which can be connected with one of leader line sections of the coils.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
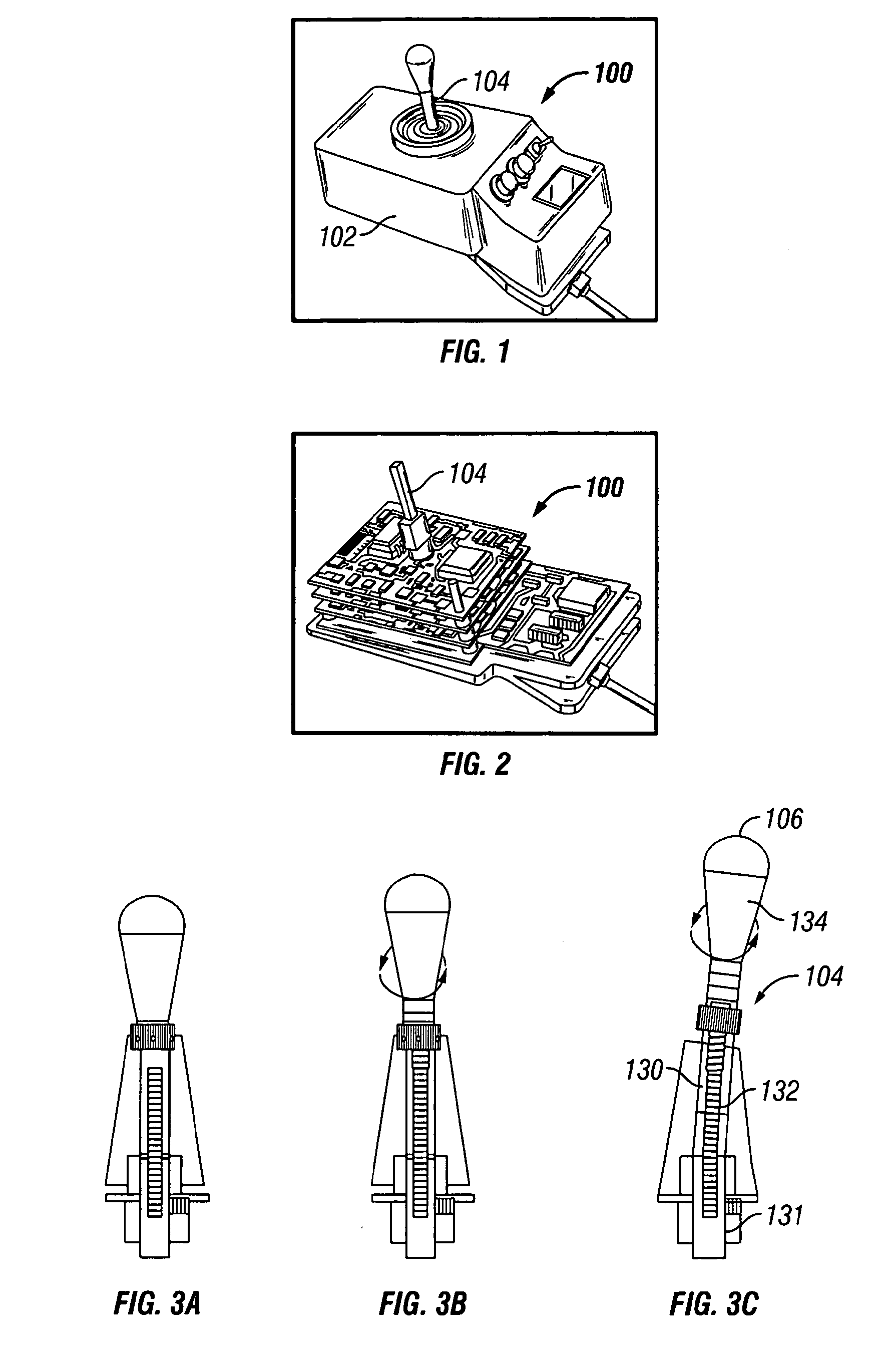
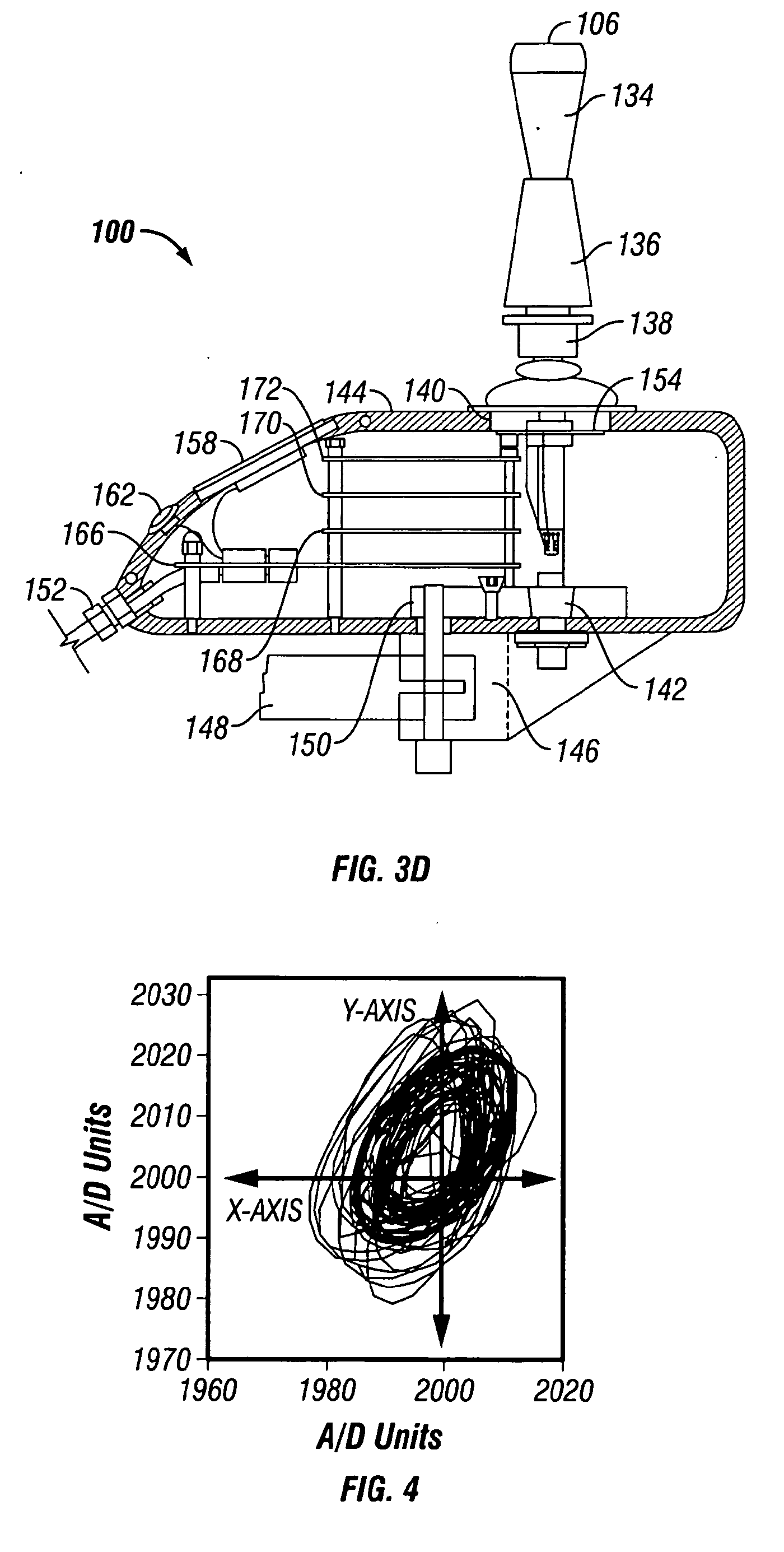
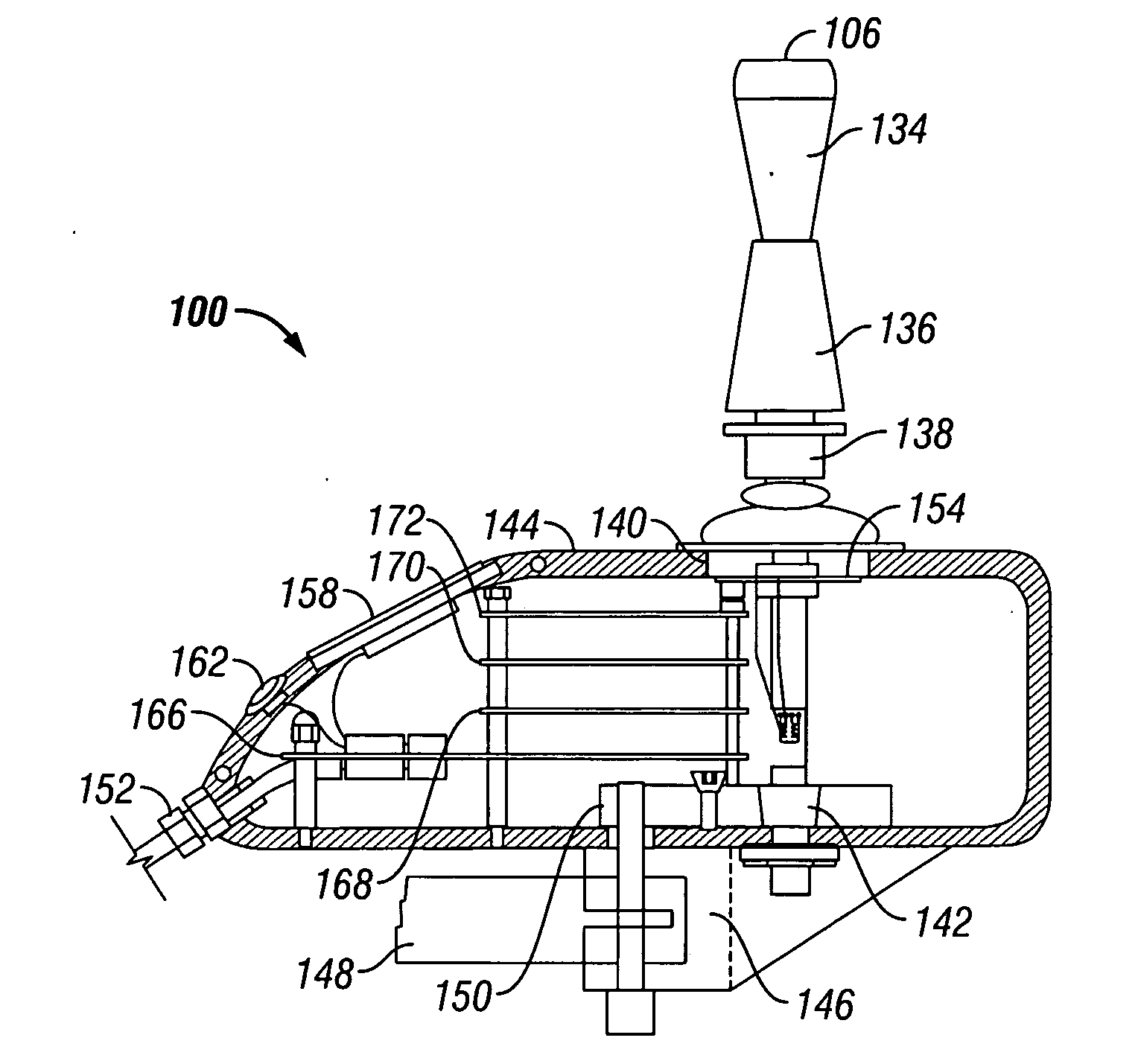
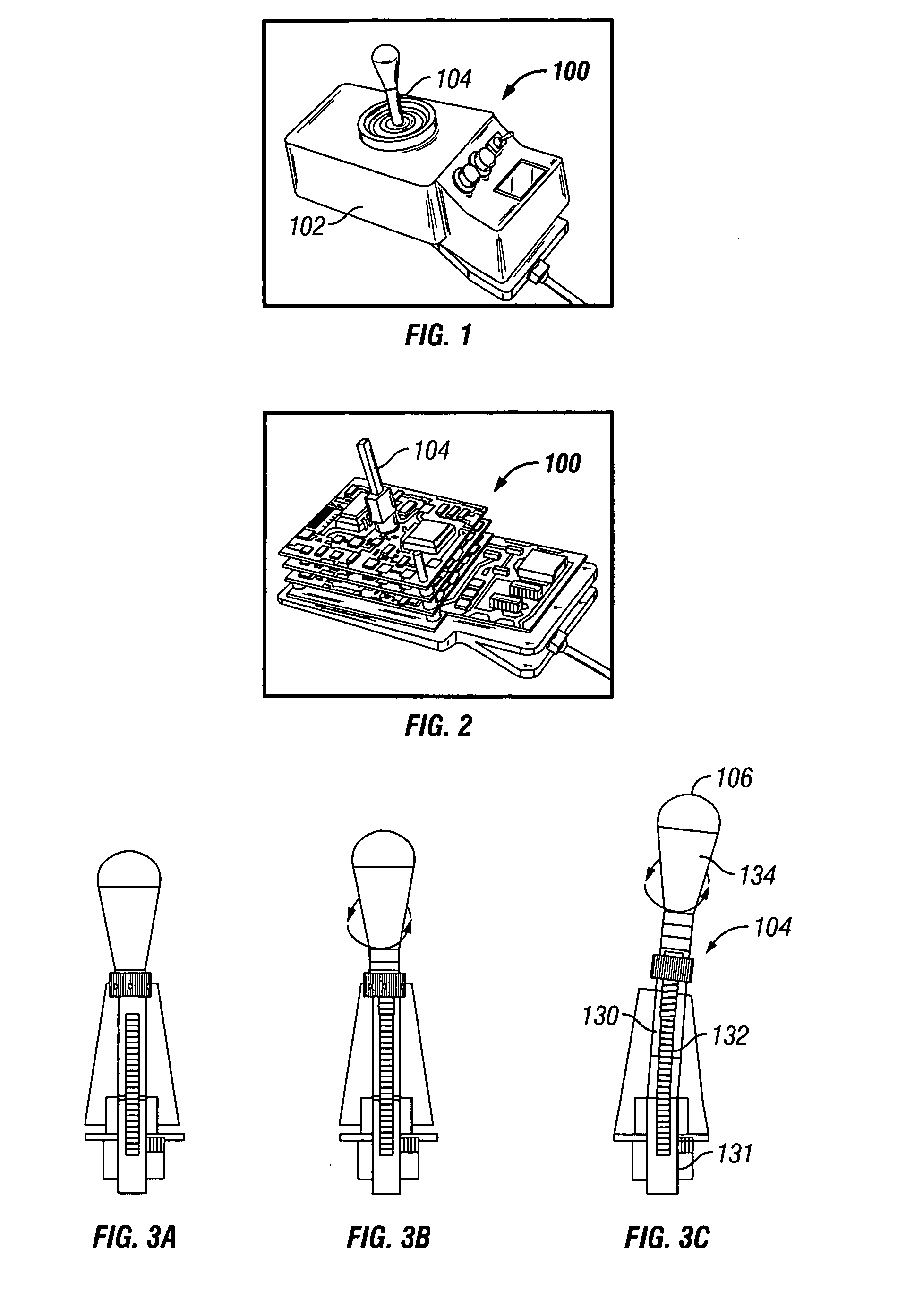
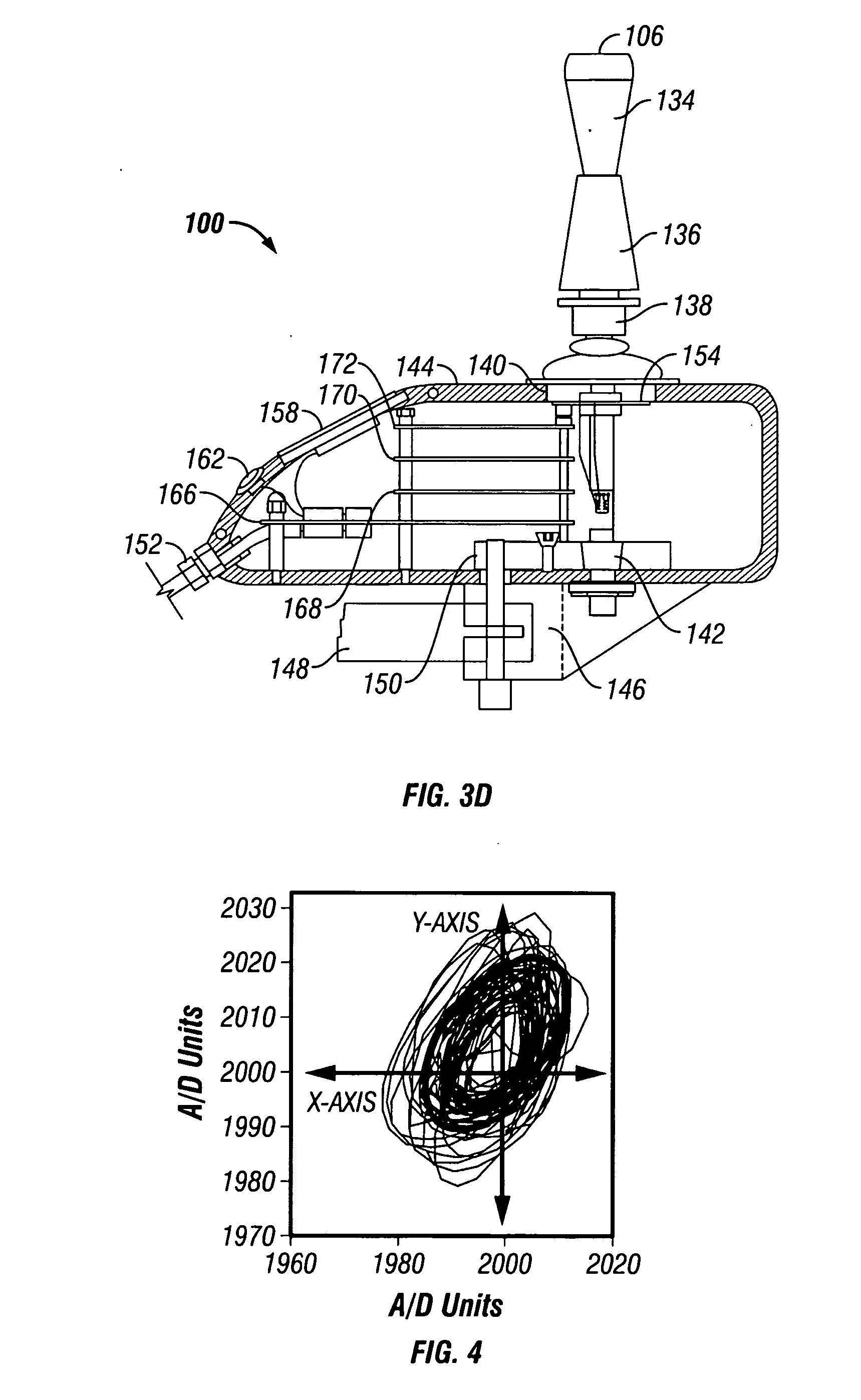
Variable compliance joystick with compensation algorithms
ActiveUS20090153370A1Reduce throwDegree of freedom is loweredManual control with multiple controlled membersMechanical apparatusJoystickEngineering
The present invention provides variable compliance joysticks with mechanical and software customization, and with an integrated control capability, and a method of systematically determining the best mechanical settings and compensatory algorithms to embed in the joysticks to offer an individual with substantial upper extremity motor impairments a personal fit and maximum function. The joysticks may include components for varying the compliance and dampening of the joystick shaft. The method may include providing the user access to operate the joysticks, operatively connecting the joysticks to a driving simulator, displaying an icon on the driving simulator, controlling movement of the icon by the joysticks, evaluating performance of the user based upon the user's ability to control movement of the icon, and modifying hardware settings and software algorithms for the joysticks based upon the evaluation.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
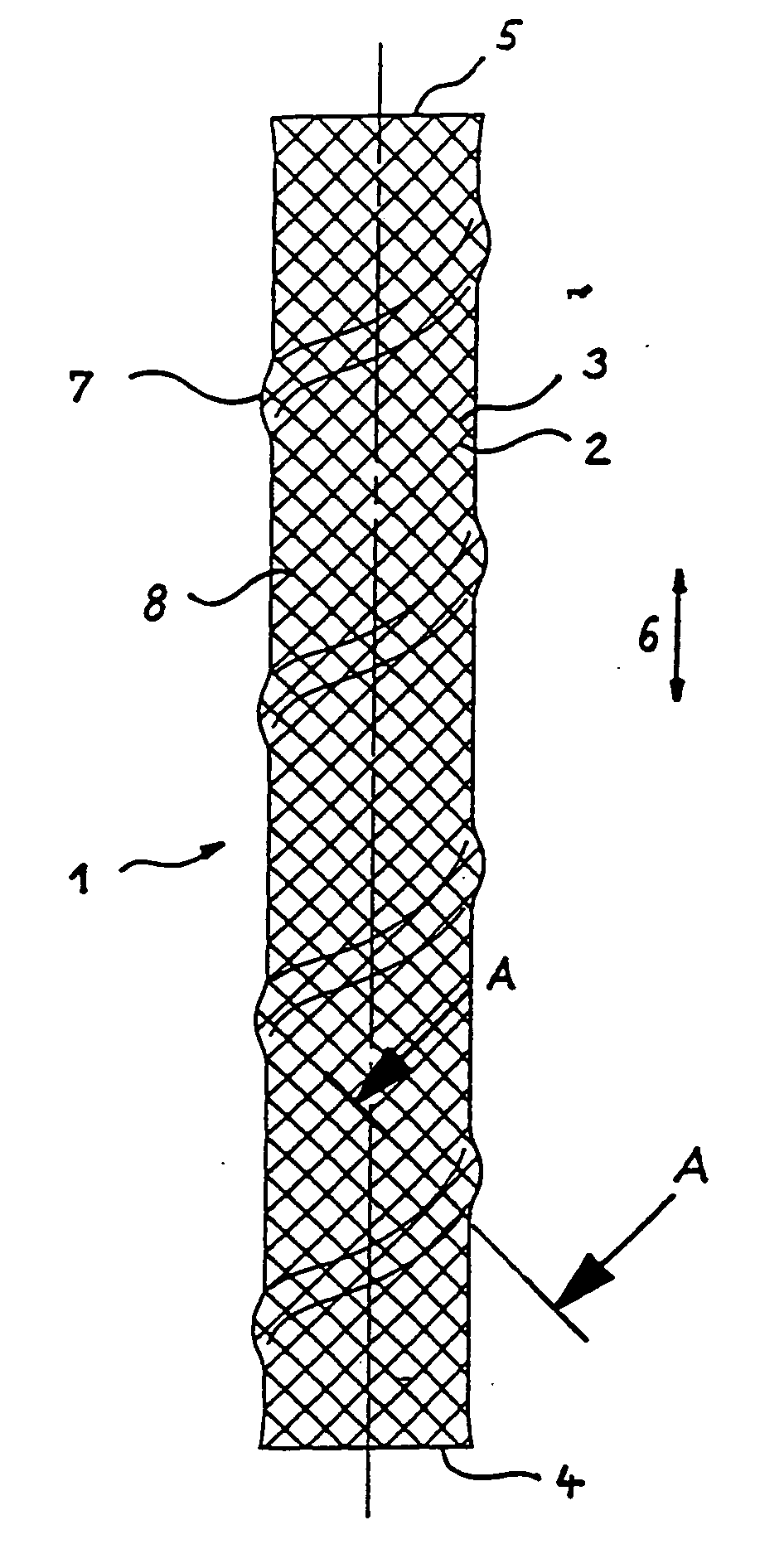
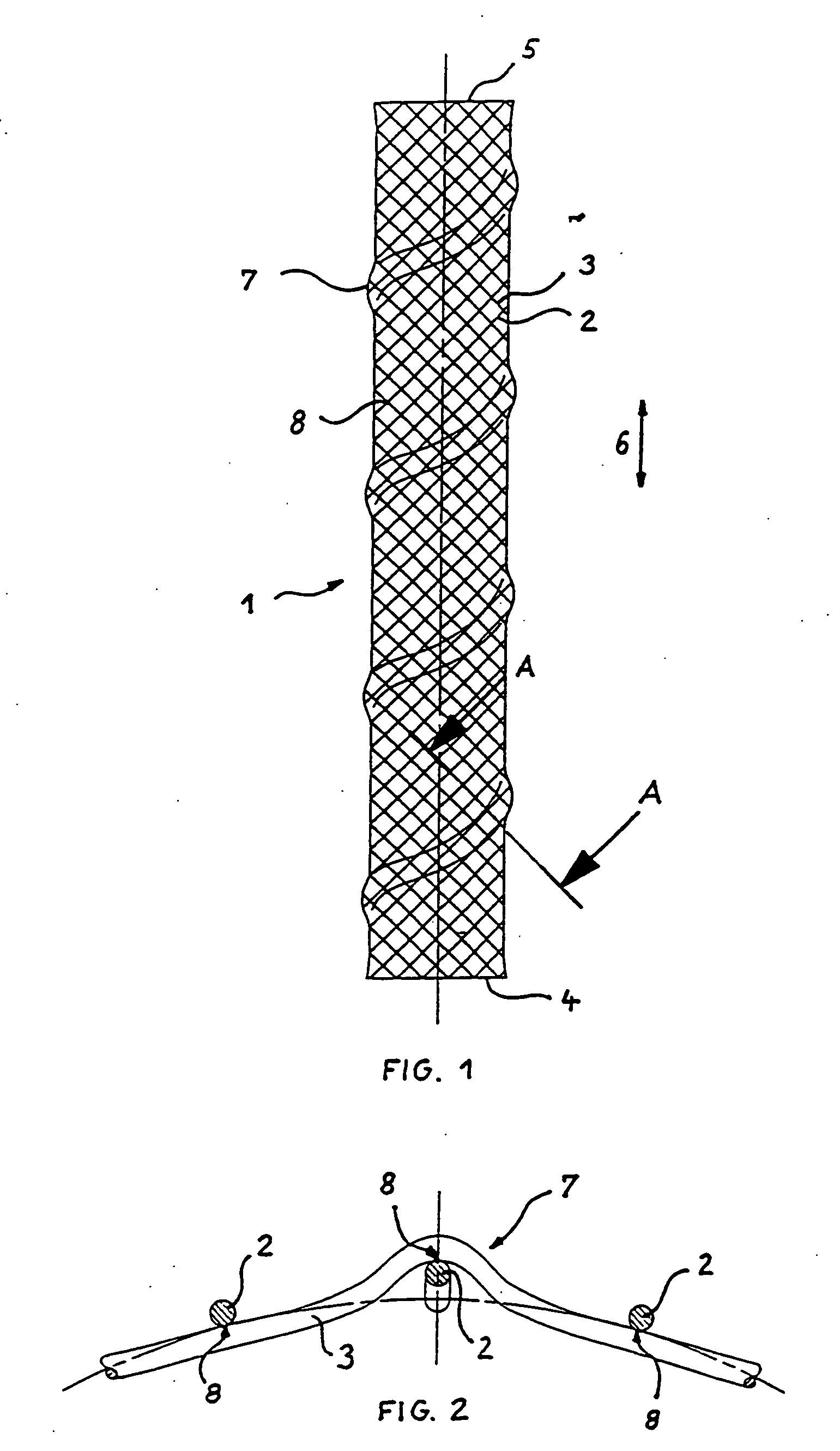
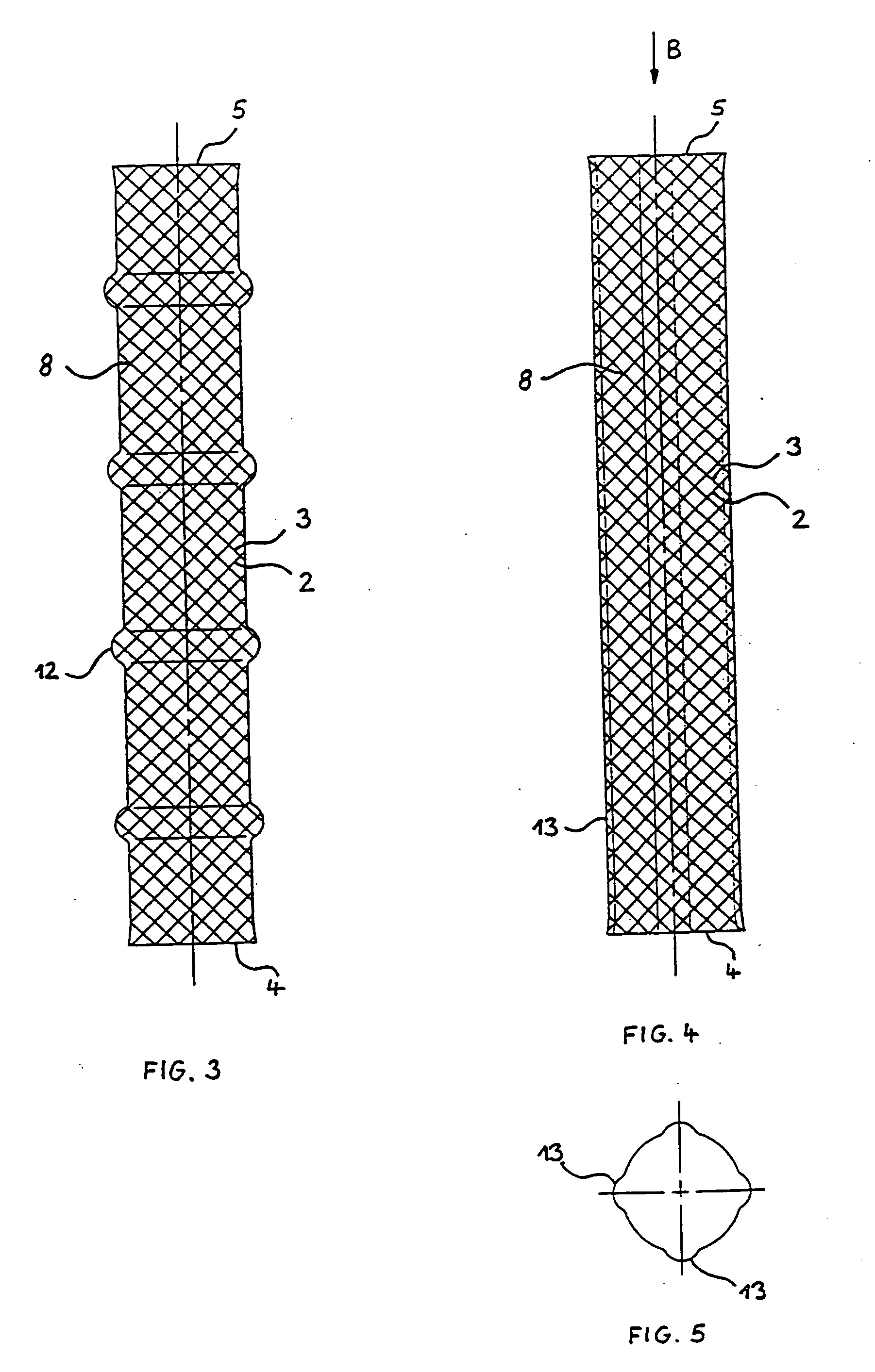
Braided stent
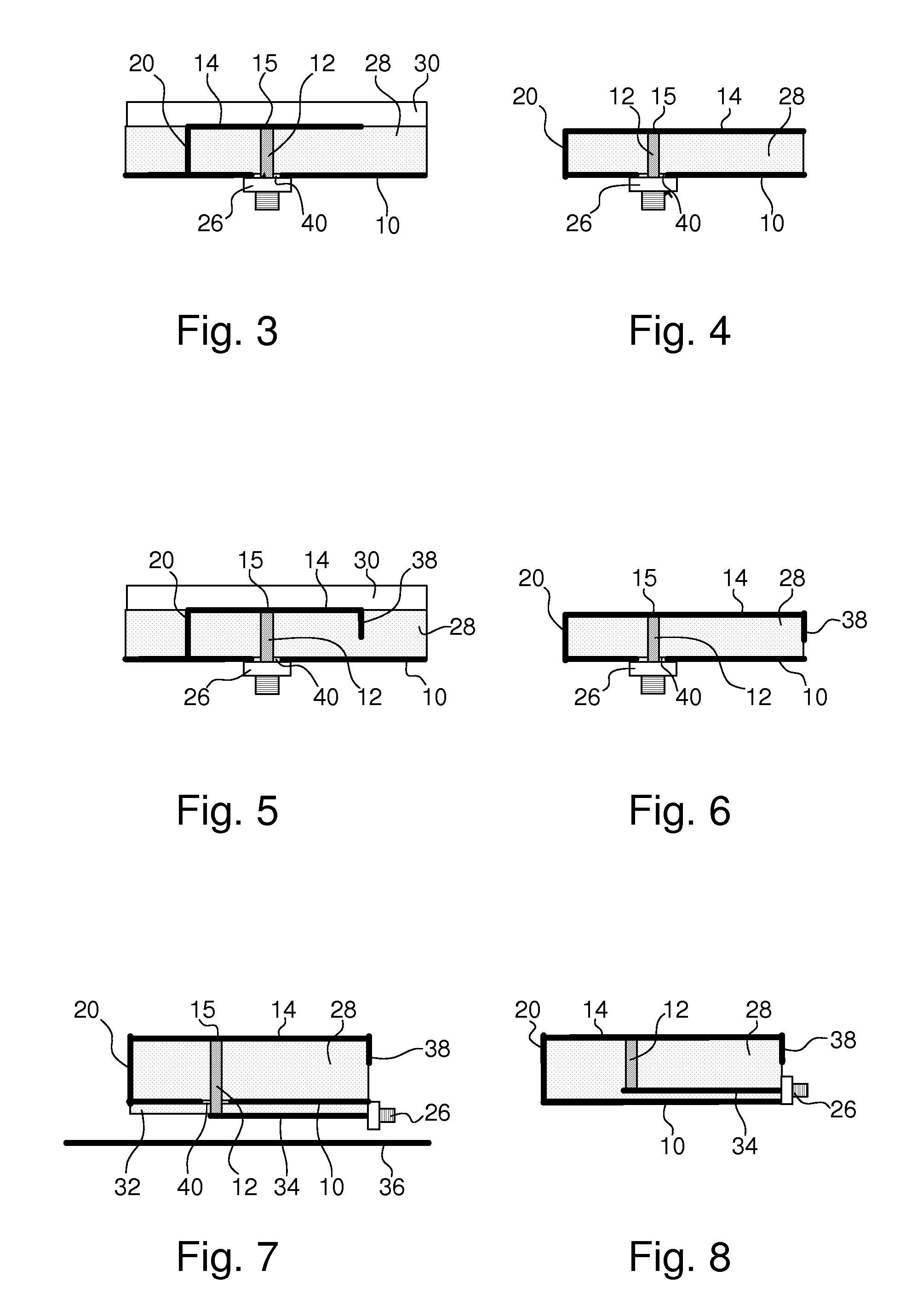
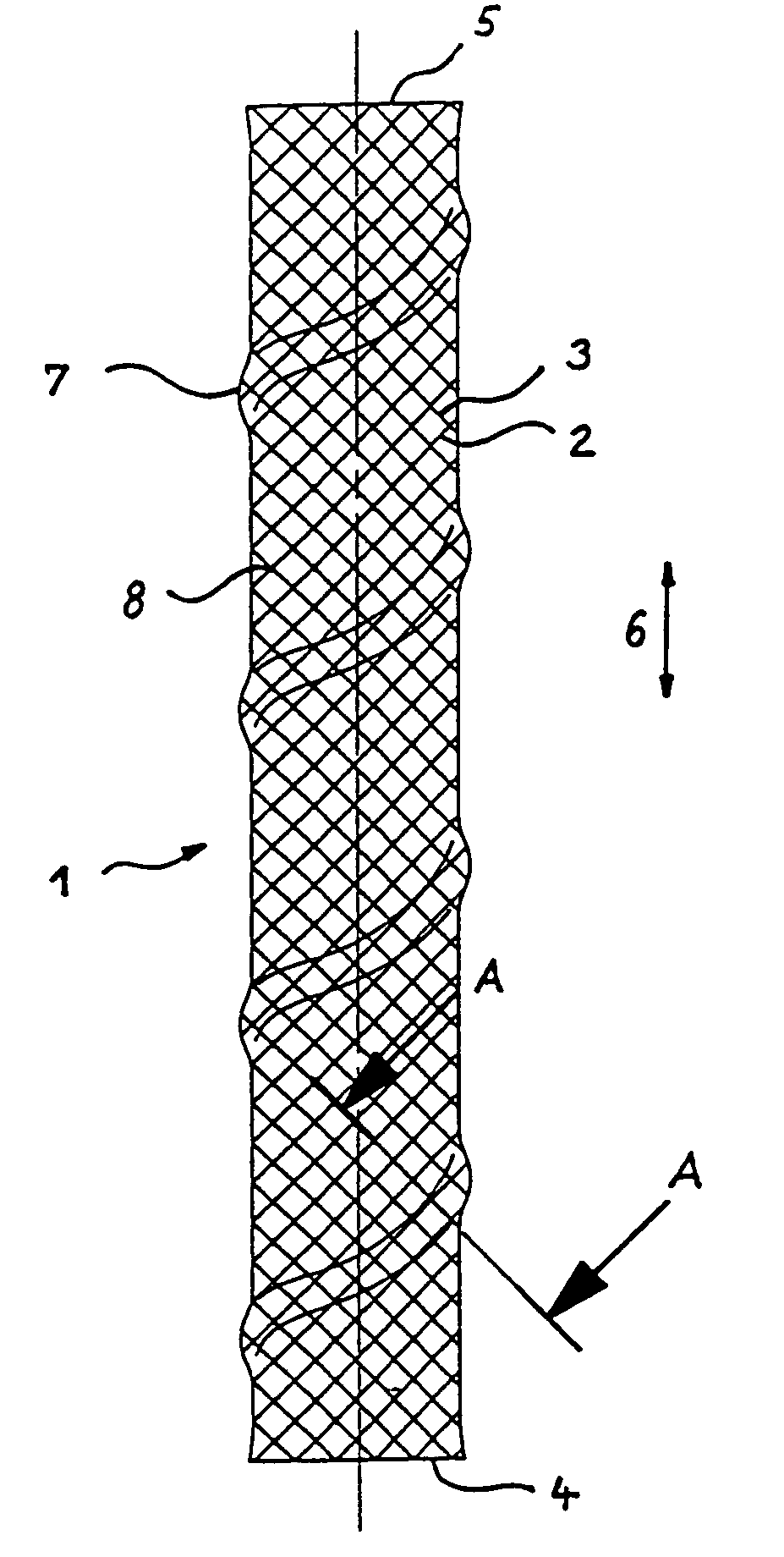
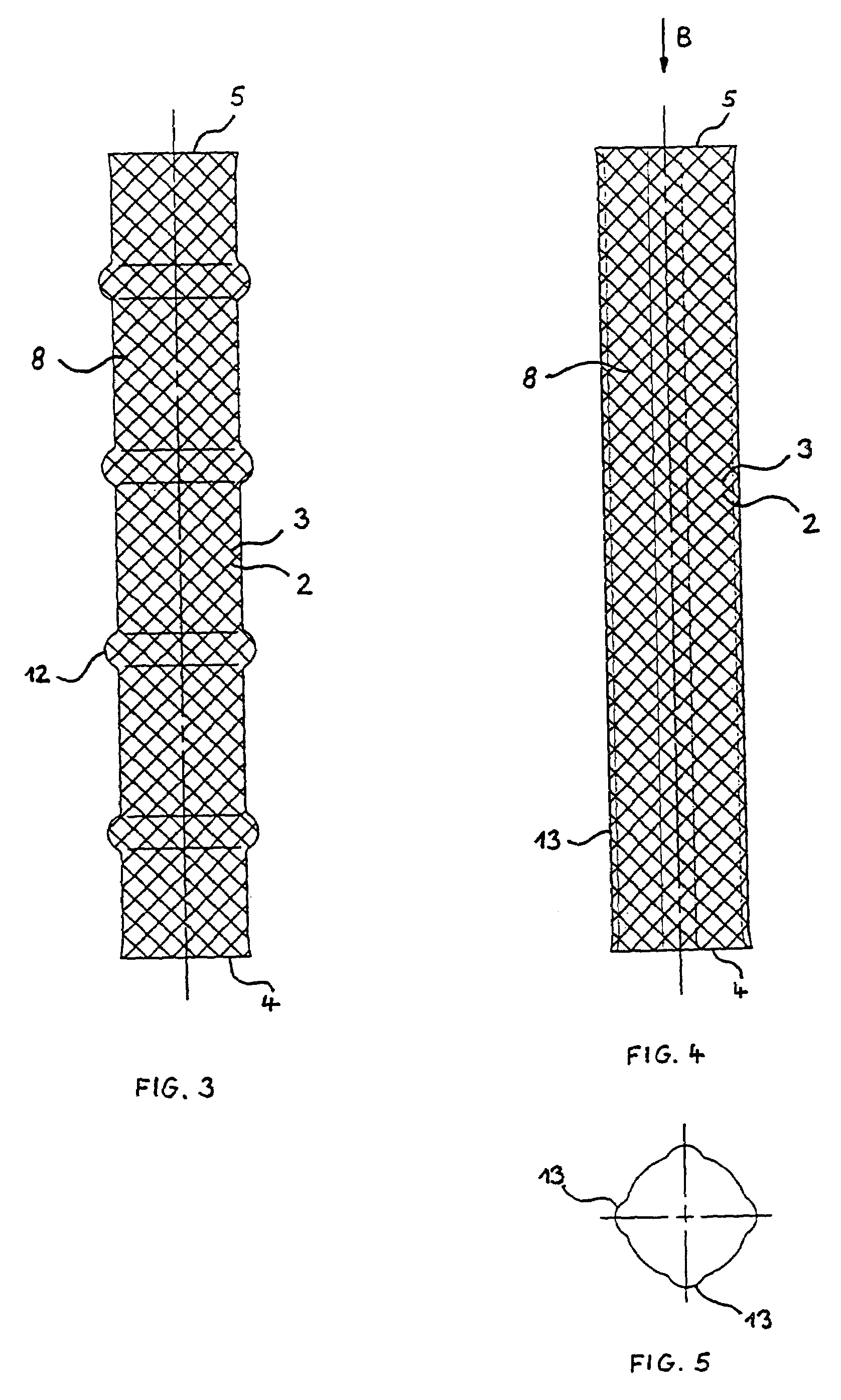
InactiveUS20070123969A1Less-shorteningEasy to manufactureStentsOrnamental textile articlesBraided stentInsertion stent
A stent for use in a body passageway includes a plurality of wires braided to form a self-expanding braided tubular structure. The braided wires form braiding angles along a length of the tubular structure. A portion of the wires are plastically deformed to reduce foreshortening of the braided structure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
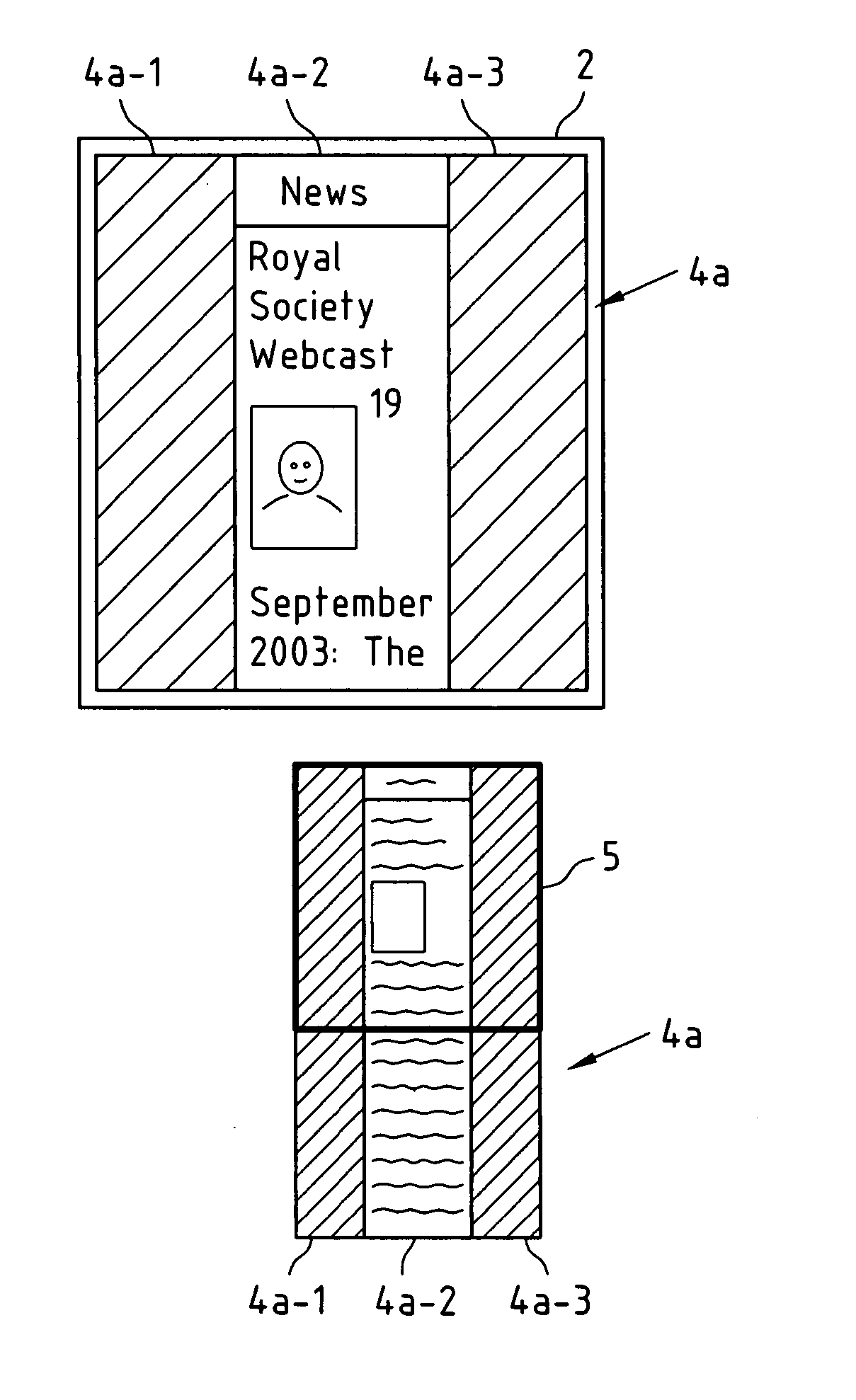
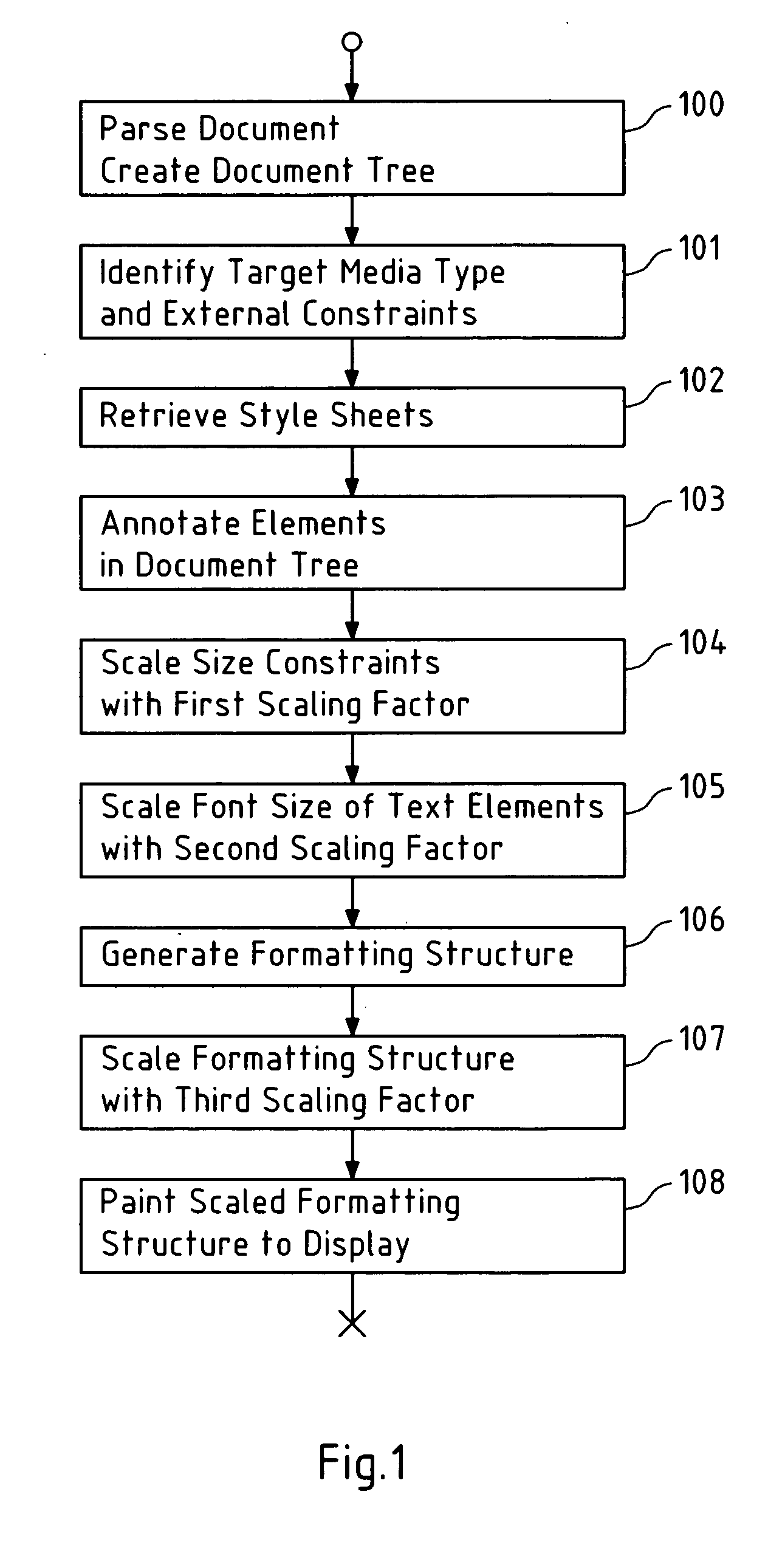
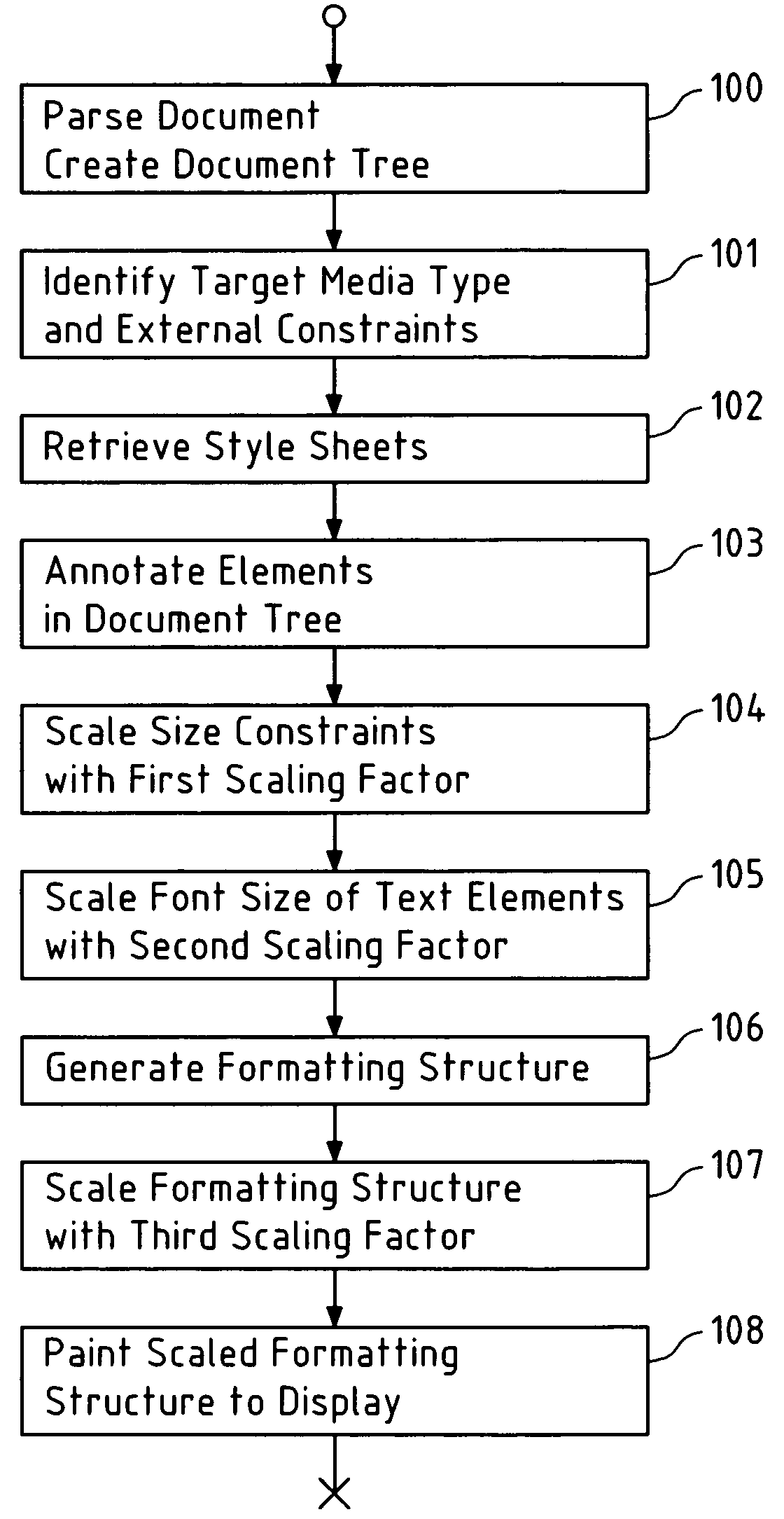
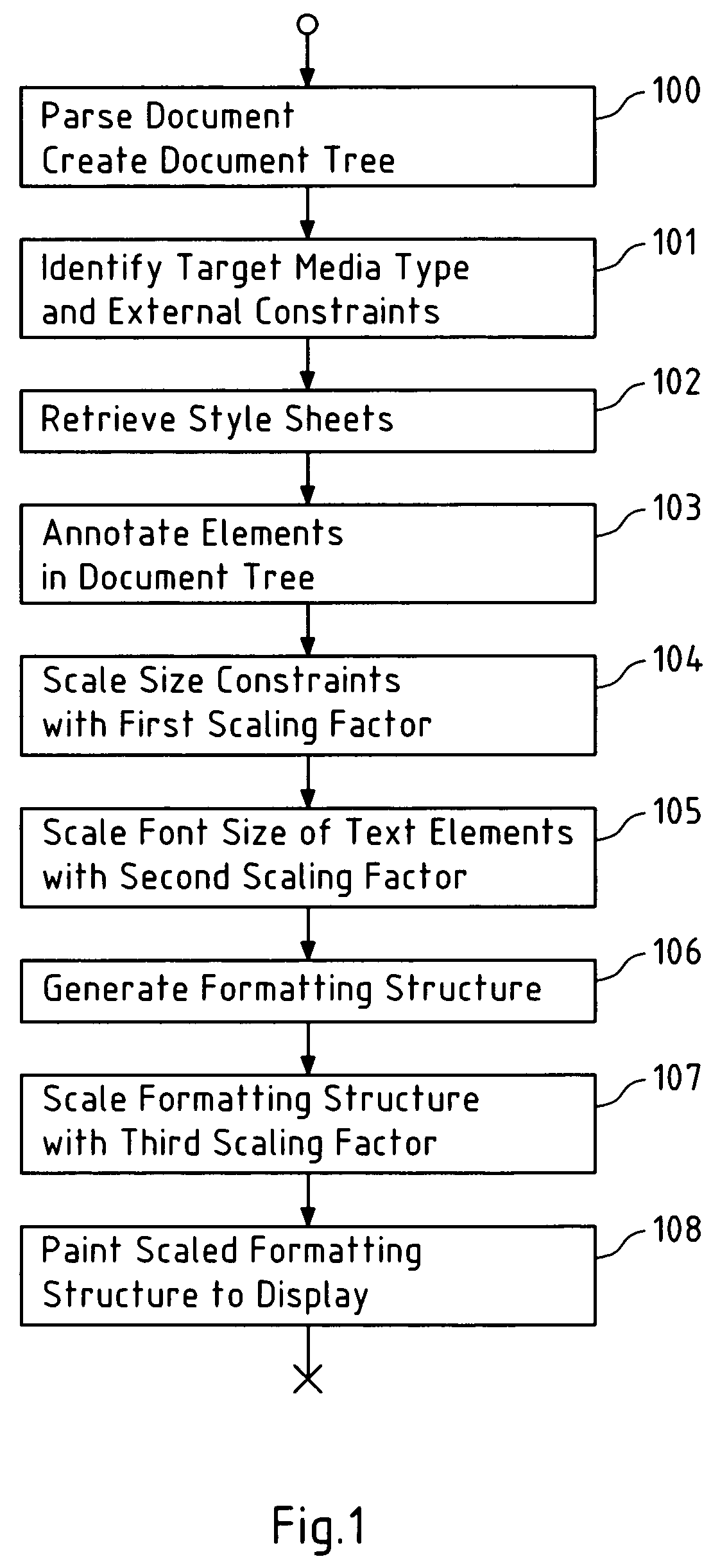
Presentation of large objects on small displays
ActiveUS20060195784A1Reduce layout areaIncrease display areaDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsDisplay deviceComputer vision
This invention relates to a method, a computer program product, a device and a system for formatting an object to obtain a formatted object, wherein the object comprises a plurality of elements, and wherein the formatted object is affected by at least one constraint, wherein the constraint is scaled by a first scaling factor to obtain a scaled constraint; wherein at least one of the elements is scaled by a second scaling factor to obtain a scaled element; wherein a layout structure is generated for the plurality of elements including the scaled element under consideration of the scaled constraint; and wherein the layout structure is scaled by a third scaling factor to obtain the formatted object.
Owner:TEENSHARE LTD
Method and system of interference cancelation in collocated transceivers configurations
ActiveUS9065519B2Reduce distractionsDegree of freedom is loweredTransmission noise suppressionTransceiverInterference cancelation
The present invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to a method of cancelling interference in a wireless system, wherein the interference introduced by an interfering signal causing reception of an interfered signal responsive to transmission of a desired signal, the method comprising acquiring the interfering signal from a transmitter during or before transmission thereof, generating an analog cancellation signal based on the acquired interfering signal, and injecting said analog cancellation signal into an interfered receiver receiving said interfered signal to reduce said interference therefrom.
Owner:UBIQAM
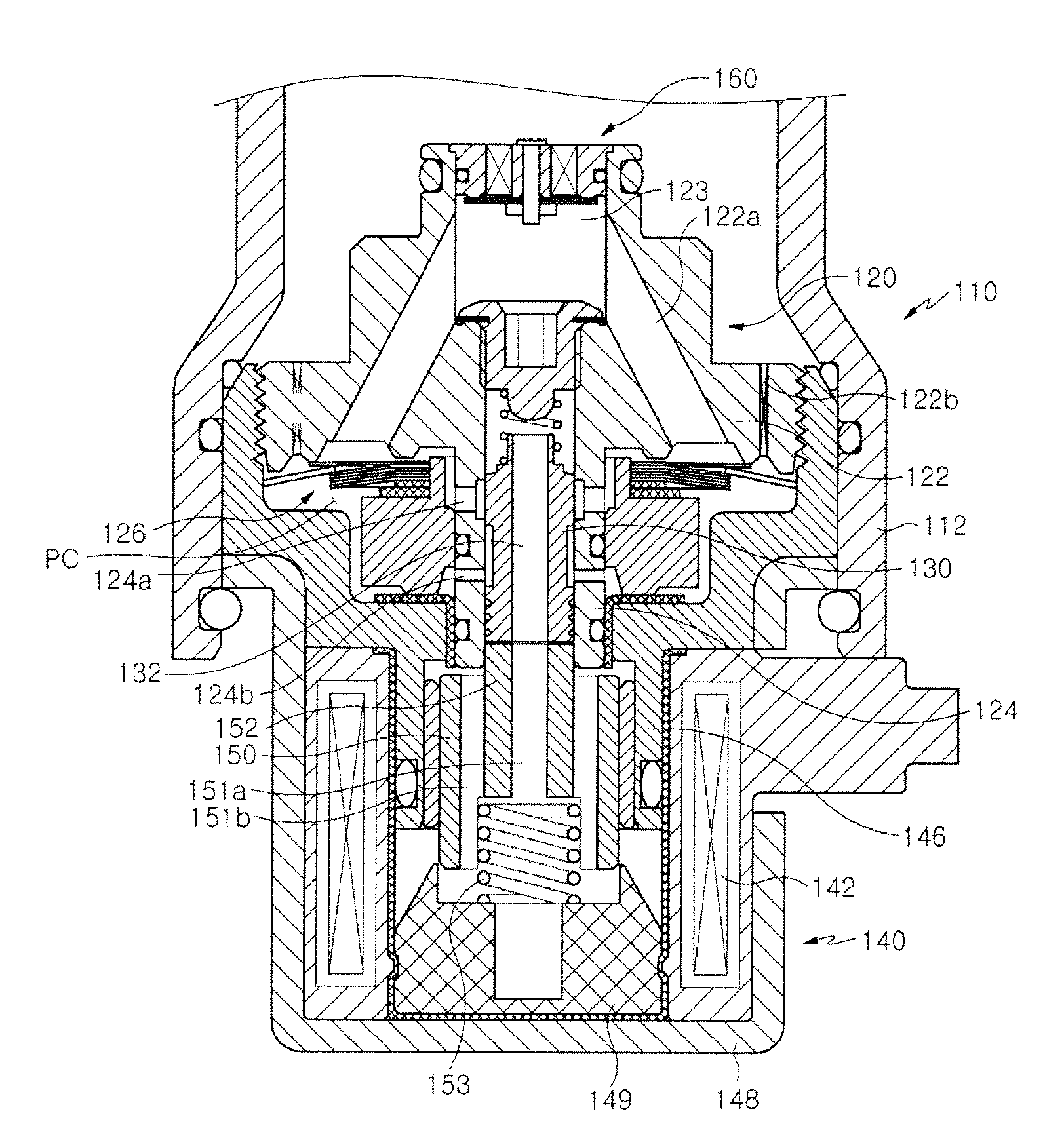
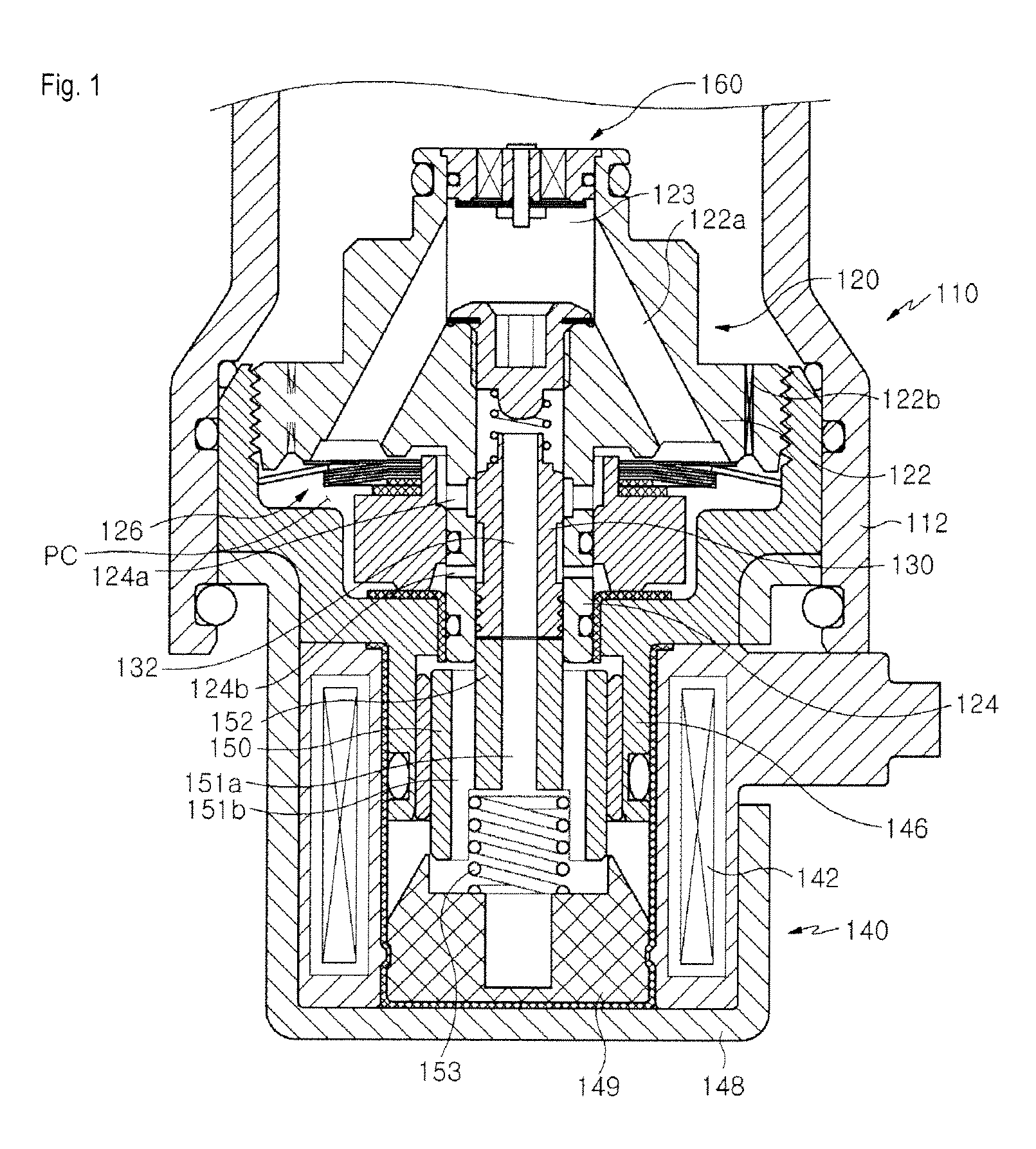
Damping force controlling valve assembly for shock absorber
ActiveUS8556049B2Improving ride comfort of a vehicleIncrease forceOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSpringsWorking fluidLow speed
A damping force controlling valve assembly for a shock absorber is provided. The damping force controlling valve assembly includes: a main body part of a retainer having an inlet passage connected to a high pressure side of the shock absorber; a main valve generating a damping force while resisting a working fluid flowing in through the inlet passage; a spool rod part interacting with a spool inserted thereinto and supplying a working fluid through a connection port to a back-pressure chamber provided at the rear of the main valve; a solenoid part controlling a position of the spool to adjust a pressure of the back-pressure chamber; and an auxiliary valve disposed at an upstream of the main valve to generate a damping force in an extremely low speed section in advance of the main valve.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
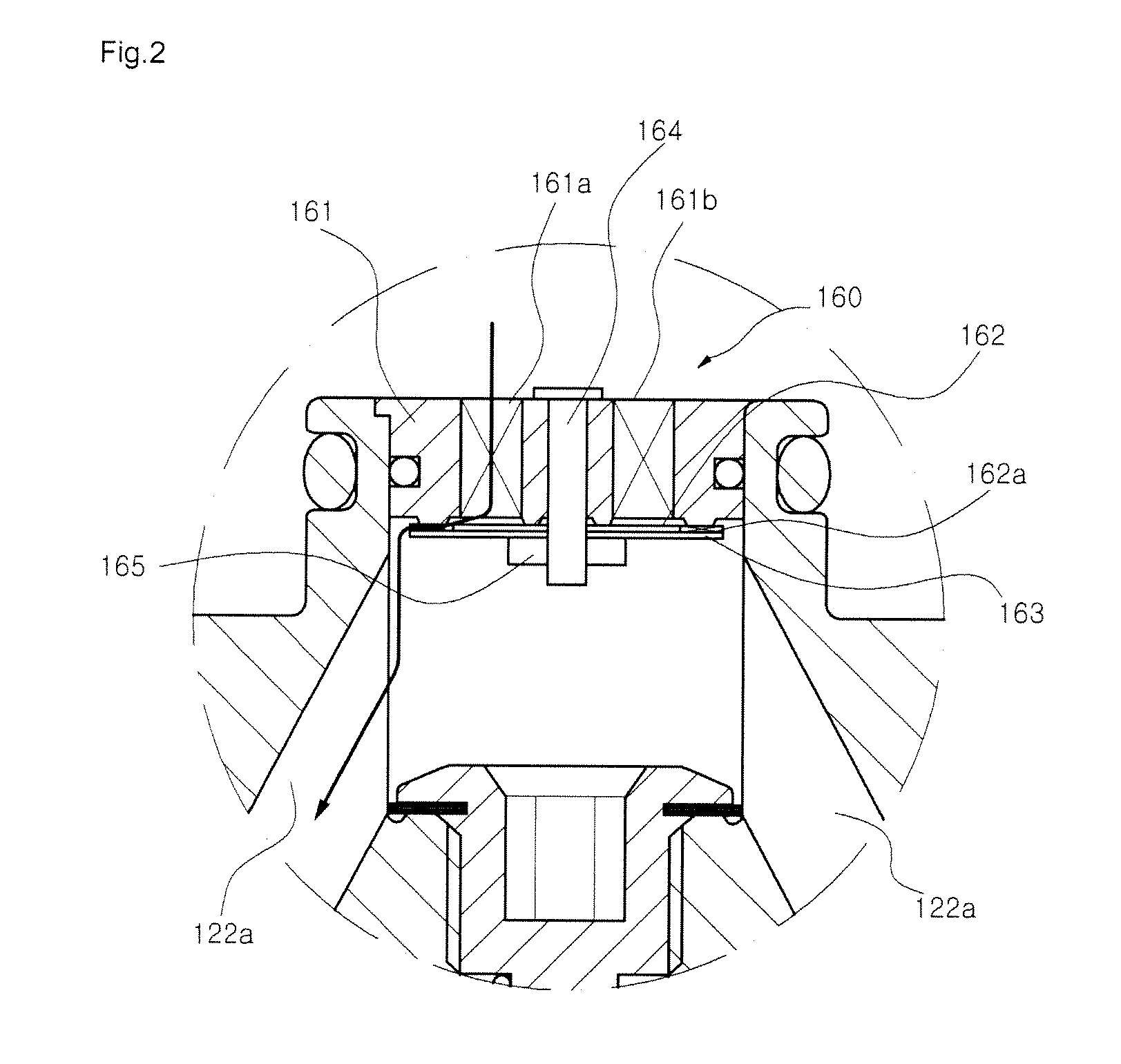
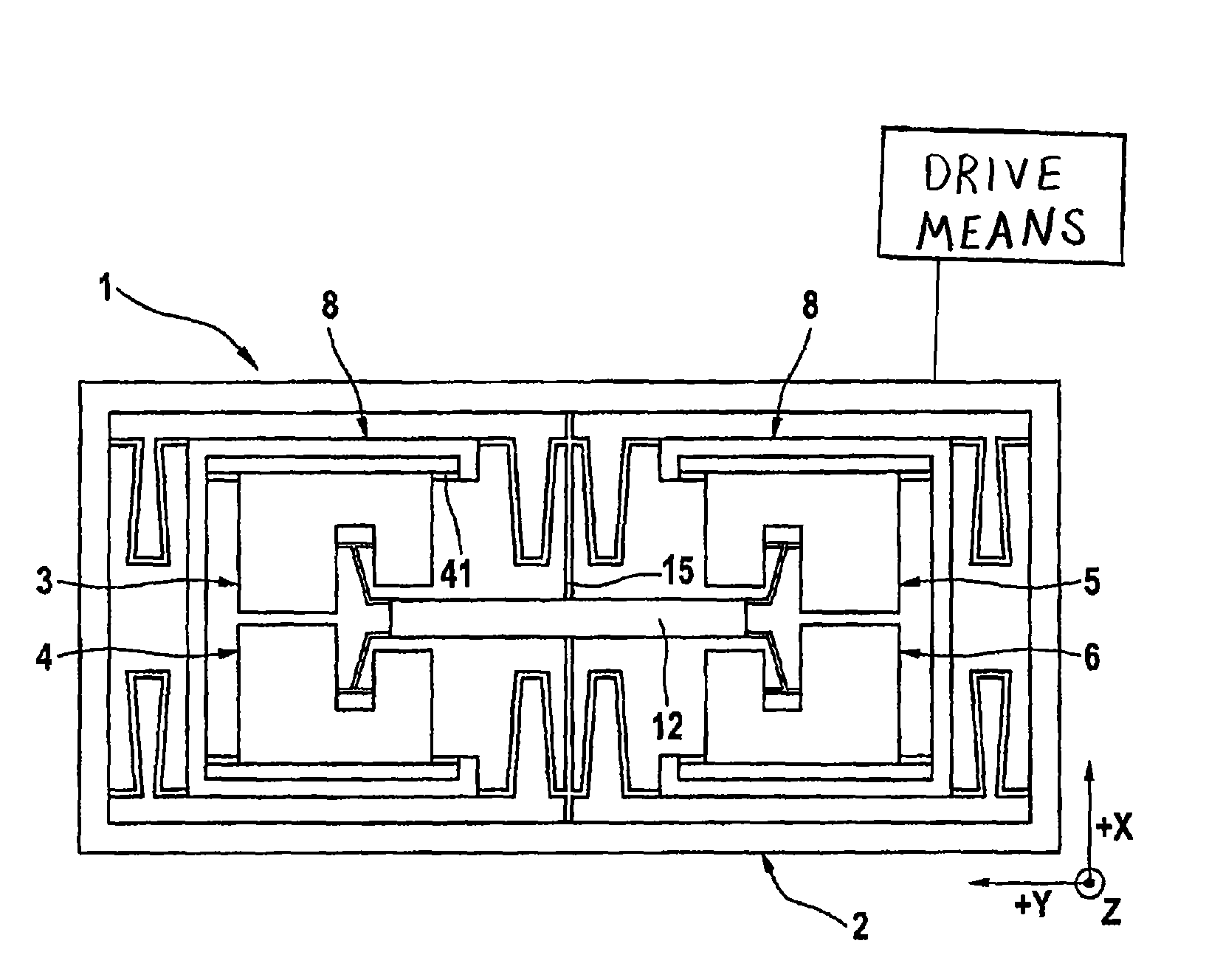
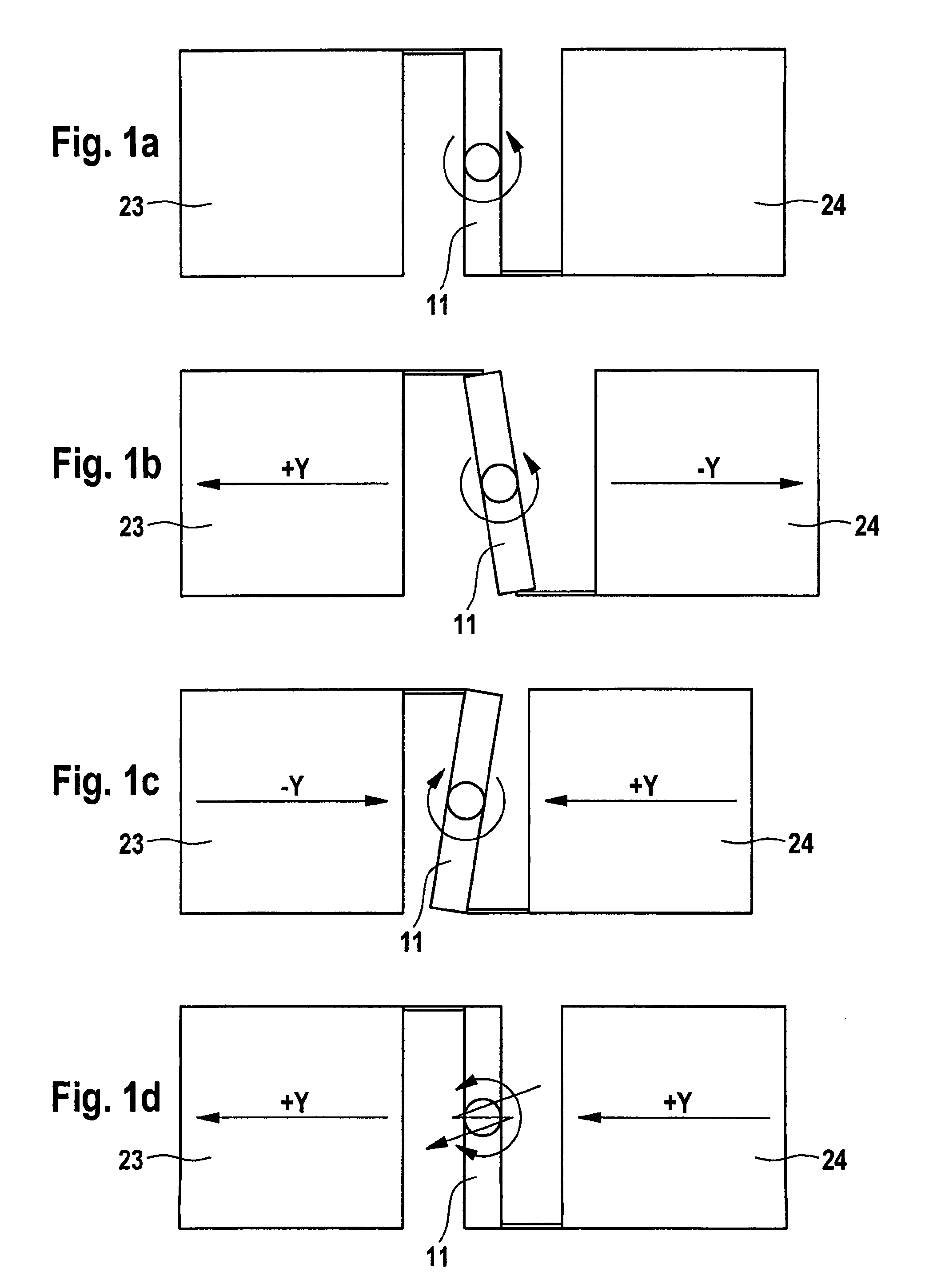
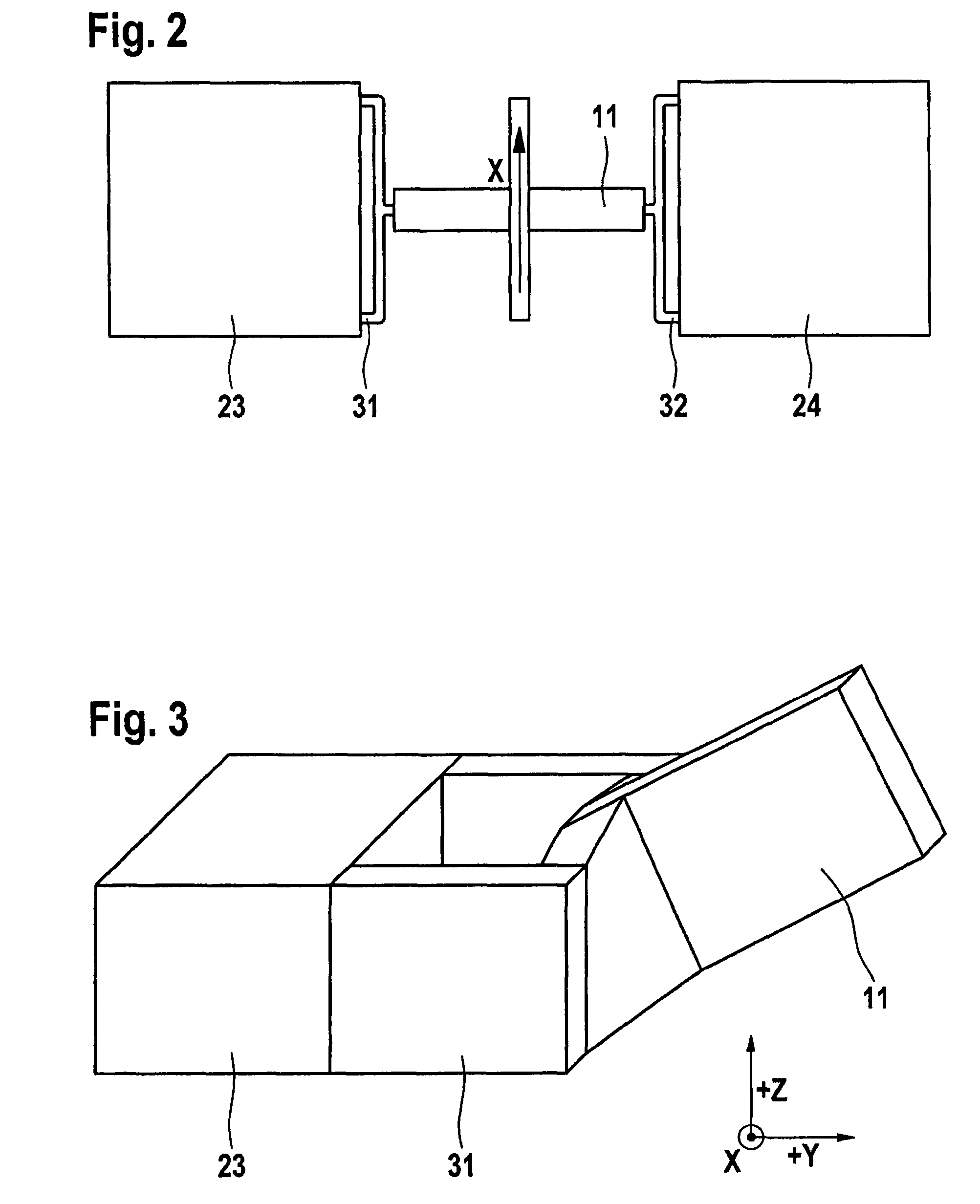
Rotational speed sensor having a coupling bar
ActiveUS8261614B2Avoid and reduce parasitic mode and interference deflectionAvoid couplingAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSeismic massMechanical engineering
A rotational speed sensor including at least one substrate, at least two base elements which each have a frame, a means for suspending the frame from the substrate, at least one seismic mass and one means for suspending the seismic mass from the frame. One or more drive means are provided for driving one or more base elements and one or more reading devices. The at least two base elements are coupled to one another by means of at least one coupling bar.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Variable compliance joystick with compensation algorithms
InactiveUS20050195166A1Shorten the lengthVarying complianceManual control with multiple controlled membersMechanical apparatusJoystickEngineering
The present invention provides variable compliance joysticks with mechanical and software customization, and with an integrated control capability, and a method of systematically determining the best mechanical settings and compensatory algorithms to embed in the joysticks to offer an individual with substantial upper extremity motor impairments a personal fit and maximum function. The joysticks may include components for varying the compliance and dampening of the joystick shaft. The method may include providing the user access to operate the joysticks, operatively connecting the joysticks to a driving simulator, displaying an icon on the driving simulator, controlling movement of the icon by the joysticks, evaluating performance of the user based upon the user's ability to control movement of the icon, and modifying hardware settings and software algorithms for the joysticks based upon the evaluation.
Owner:COOPER RORY A +2
Rotational Speed Sensor Having A Coupling Bar
ActiveUS20100037690A1Avoid and reduce parasitic modeAvoid and reduce and interference deflectionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSeismic massEngineering
A rotational speed sensor including at least one substrate, at least two base elements which each have a frame, a means for suspending the frame from the substrate, at least one seismic mass and one means for suspending the seismic mass from the frame. One or more drive means are provided for driving one or more base elements and one or more reading devices. The at least two base elements are coupled to one another by means of at least one coupling bar.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Method and system for improving the efficiency of state information transfer over a wireless communications network
InactiveUS20060004874A1Improve efficiencyEfficiency in updating stateSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications networkApplication server
The present invention is directed to a system and method for managing state information related to an interactive application to accommodate one or more users participating in an interactive application session, wherein the state information comprises local state information specific to each of the one or more user's unique view of the interactive application and global state information. The system of the present invention may comprise a telecommunications network; an application server in communication with the telecommunications network for managing the global state information relative to all of the users participating in the interactive application session; and at least one mobile client device in communication with the application server over the telecommunications network for managing the local state information for each of the one or more users. The method of the present invention may comprise the steps of structuring the state information for optimized delivery over the telecommunications network; and transferring the state information over the telecommunications network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Lamb wave device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140009032A1Degree of freedom is loweredLimit on characteristicPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringSupport surface
A Lamb wave device according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a piezoelectric function member and a supporting member. The piezoelectric function member has a piezoelectric substrate, IDT electrodes, and a cutout portion. The IDT electrodes are disposed on the upper surface of the piezoelectric substrate. The cutout portion is formed in the piezoelectric substrate, and includes a step face provided between the upper surface and the lower surface of the piezoelectric substrate. The supporting member has a supporting surface and a cavity. The supporting surface is bonded to the lower surface of the piezoelectric substrate, and is exposed in the cutout portion toward the upper surface of the piezoelectric substrate. The cavity is formed adjacent to the supporting surface, and faces the IDT electrodes through the piezoelectric substrate.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Presentation of large objects on small displays
ActiveUS7516402B2Reduce layout areaIncrease display areaDigital data information retrievalNatural language data processingDisplay deviceComputer vision
This invention relates to a method, a computer program product, a device and a system for formatting an object to obtain a formatted object, wherein the object comprises a plurality of elements, and wherein the formatted object is affected by at least one constraint, wherein the constraint is scaled by a first scaling factor to obtain a scaled constraint; wherein at least one of the elements is scaled by a second scaling factor to obtain a scaled element; wherein a layout structure is generated for the plurality of elements including the scaled element under consideration of the scaled constraint; and wherein the layout structure is scaled by a third scaling factor to obtain the formatted object.
Owner:TEENSHARE LTD
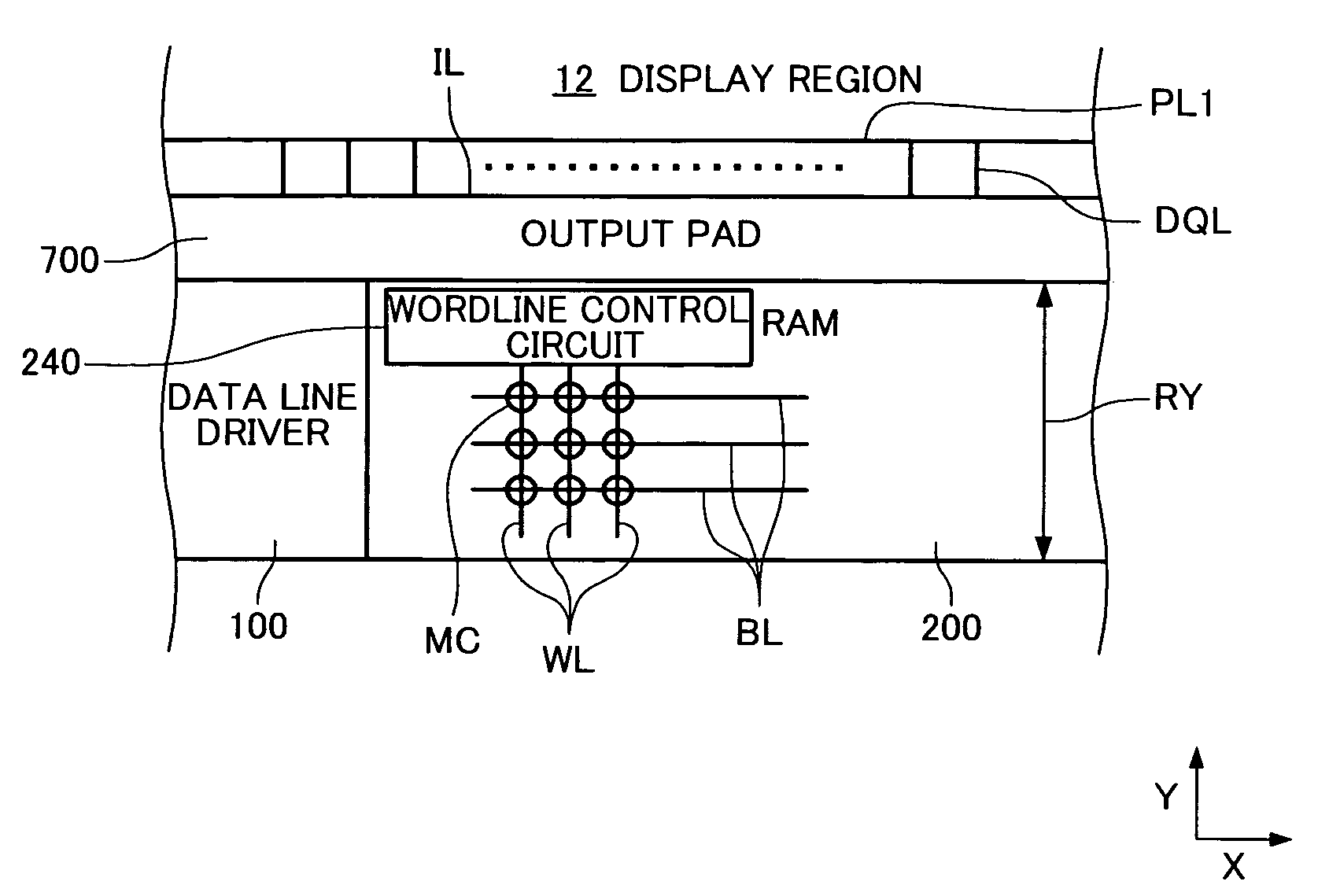
Integrated circuit device and electronic instrument
InactiveUS20070001969A1Degree of freedom is loweredStatic indicating devicesDigital storageDisplay memoryIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit device has a display memory which stores data for at least one frame displayed in a display panel which has a plurality of scan lines and a plurality of data lines. The display memory includes a plurality of RAM blocks, each of the RAM blocks including a plurality of wordlines WL, a plurality of bitlines BL, a plurality of memory cells MC, and a data read control circuit. Each of the RAM blocks is disposed along a first direction X in which the bitlines BL extend. The data read control circuit controls data reading so that data for pixels corresponding to the signal lines is read out by N times reading in one horizontal scan period 1H of the display panel (N is an integer larger than 1)
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Recording system, information processing apparatus, storage apparatus, recording method, and program
InactiveUS20090089593A1Safe storageDegree of freedom is loweredUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringInformation processingComputer hardware
Disclosed herein is a recording system including a storage apparatus incorporating a storage medium, and an information processing apparatus which is connectable to the storage apparatus and which holds a content to be recorded to the storage apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
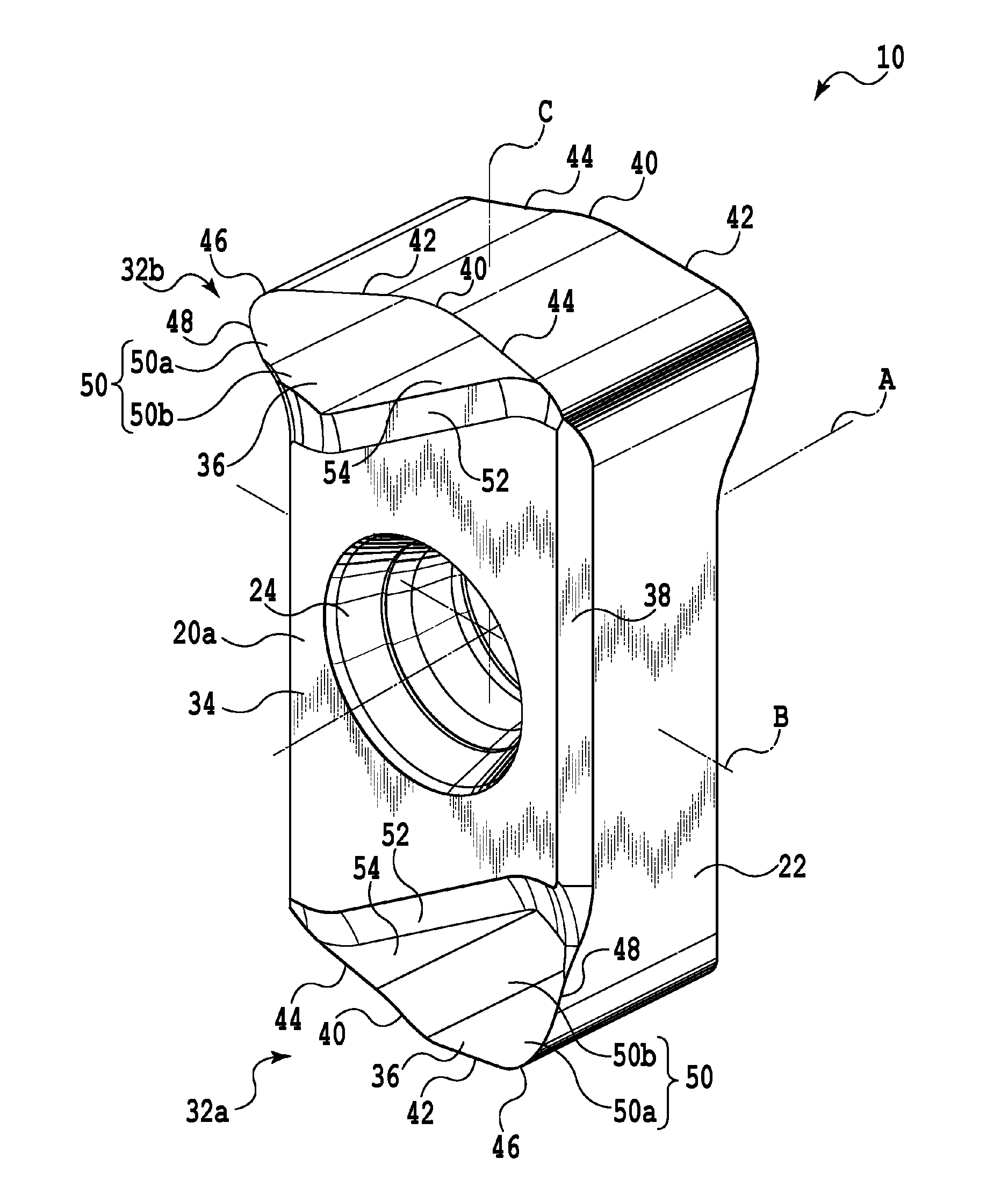
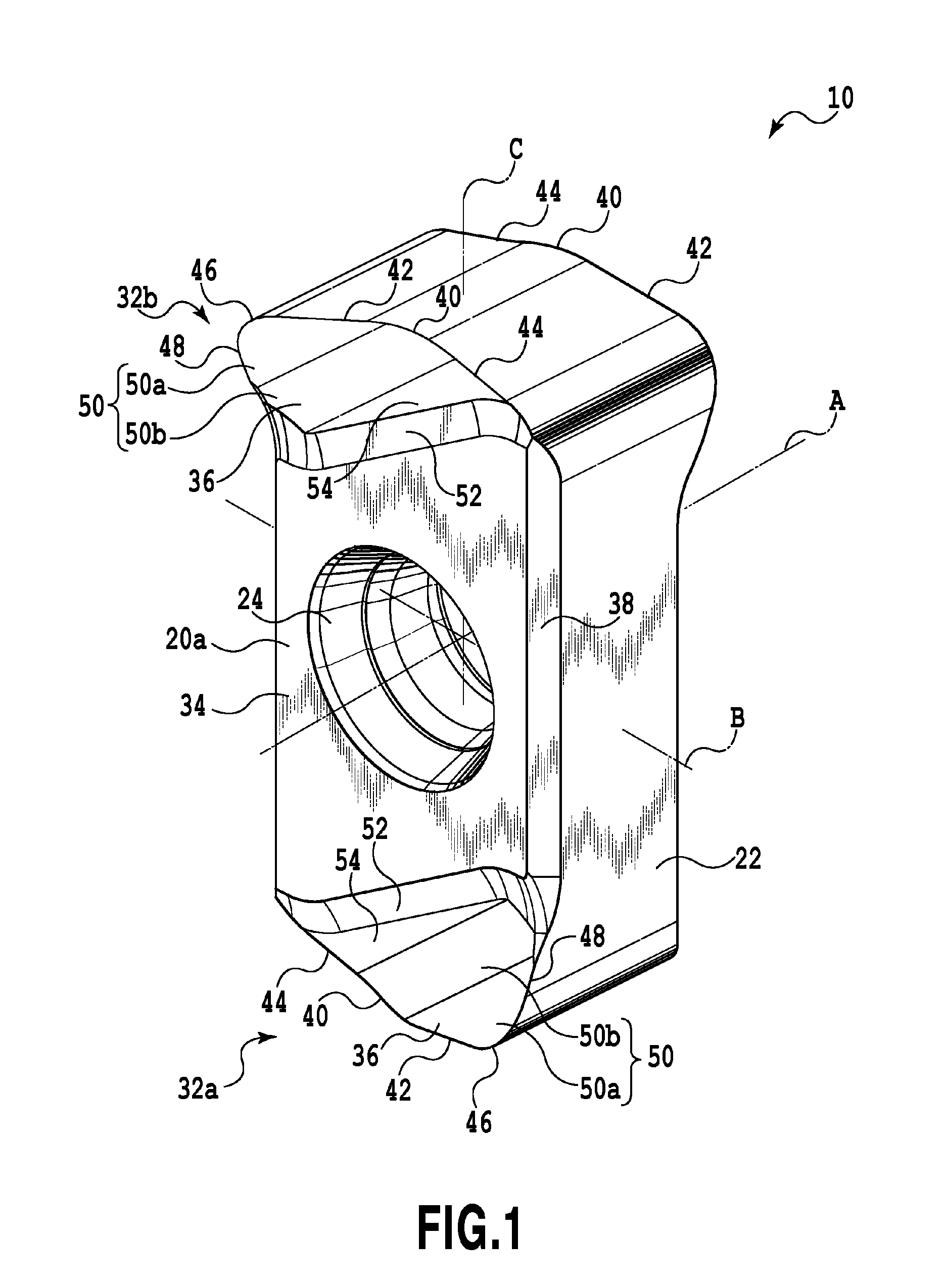
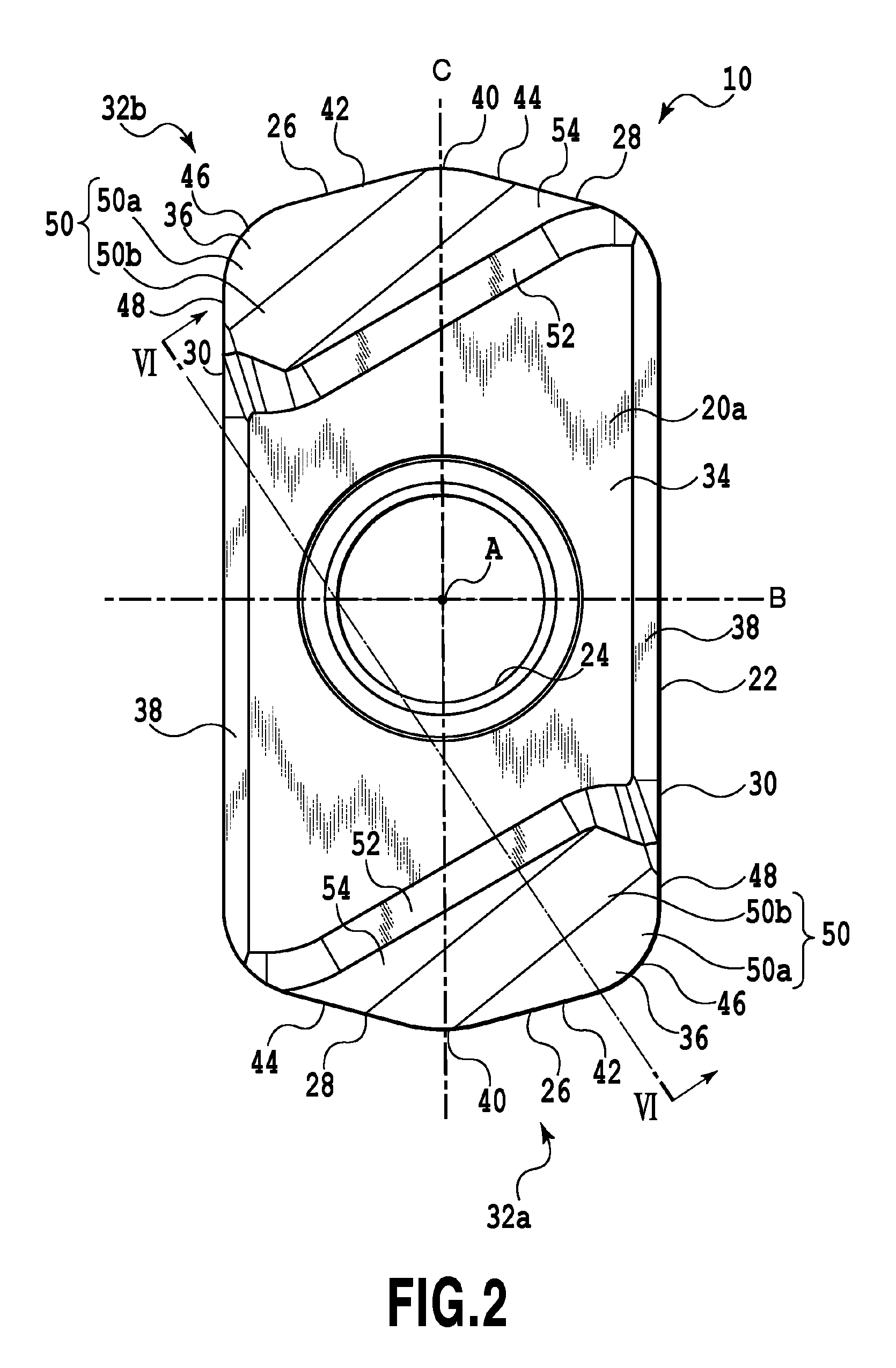
Cutting insert and cutting edge replaceable cutting tool
ActiveUS8696263B2Degree of freedom is loweredHigh strengthMilling cuttersTurning toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A cutting insert includes two end surfaces each having a main surface usable as an attachment surface to a tool body, a peripheral side surface extending between the two end surfaces and a plurality of cutting edge portions each formed at an intersection between each end surface and the peripheral side surface. Each cutting edge portion includes a corner edge formed at a corner of a related end surface, a major cutting edge extending from one end of the corner edge and extending so as to depart from an intermediate plane defined to be perpendicular to the first axis and to include the second axis, and a minor cutting edge extending from the other end of the corner edge and extending in a direction to approach the intermediate plane.
Owner:TUNGALOY CORP
Vibration isolator
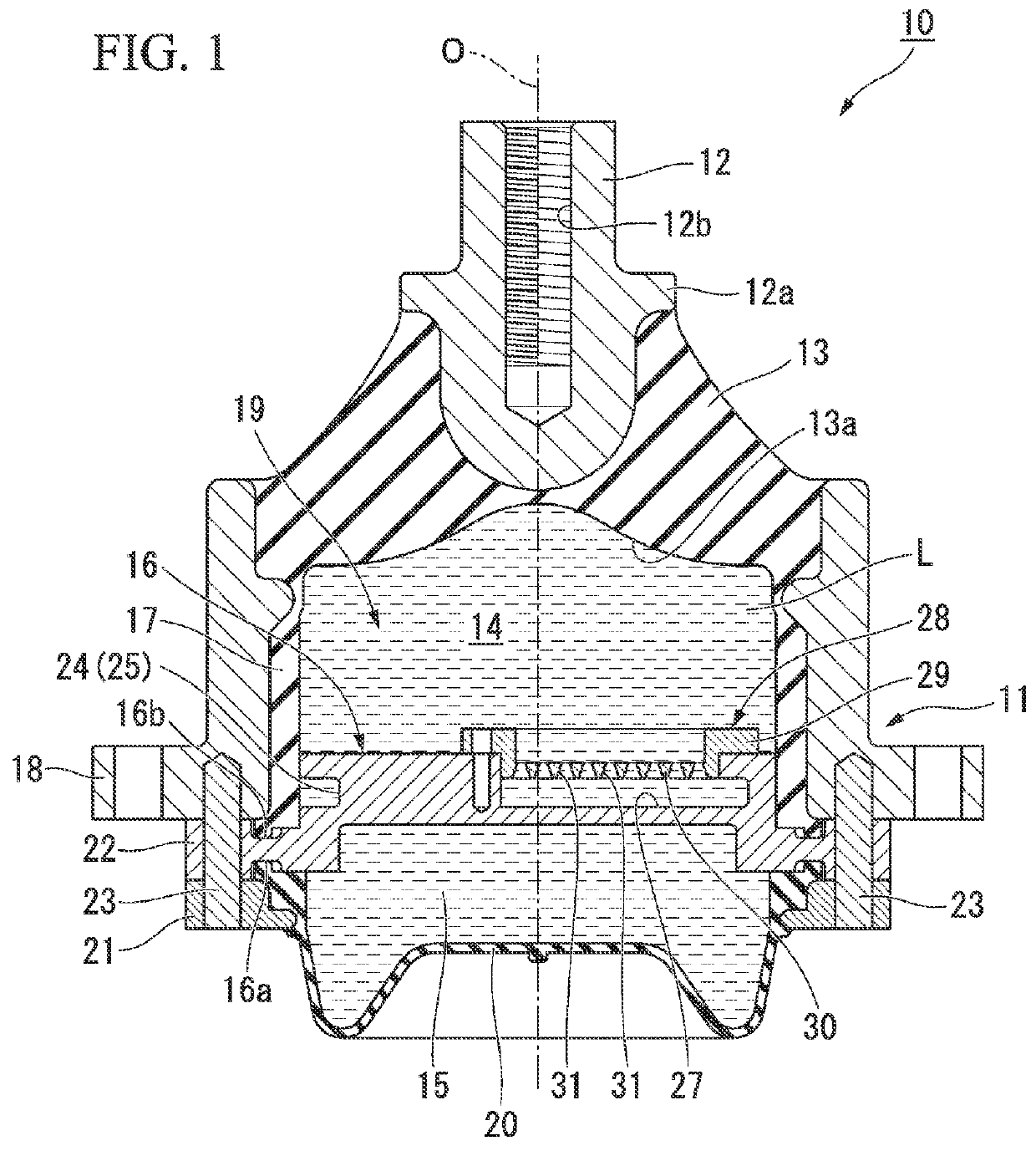
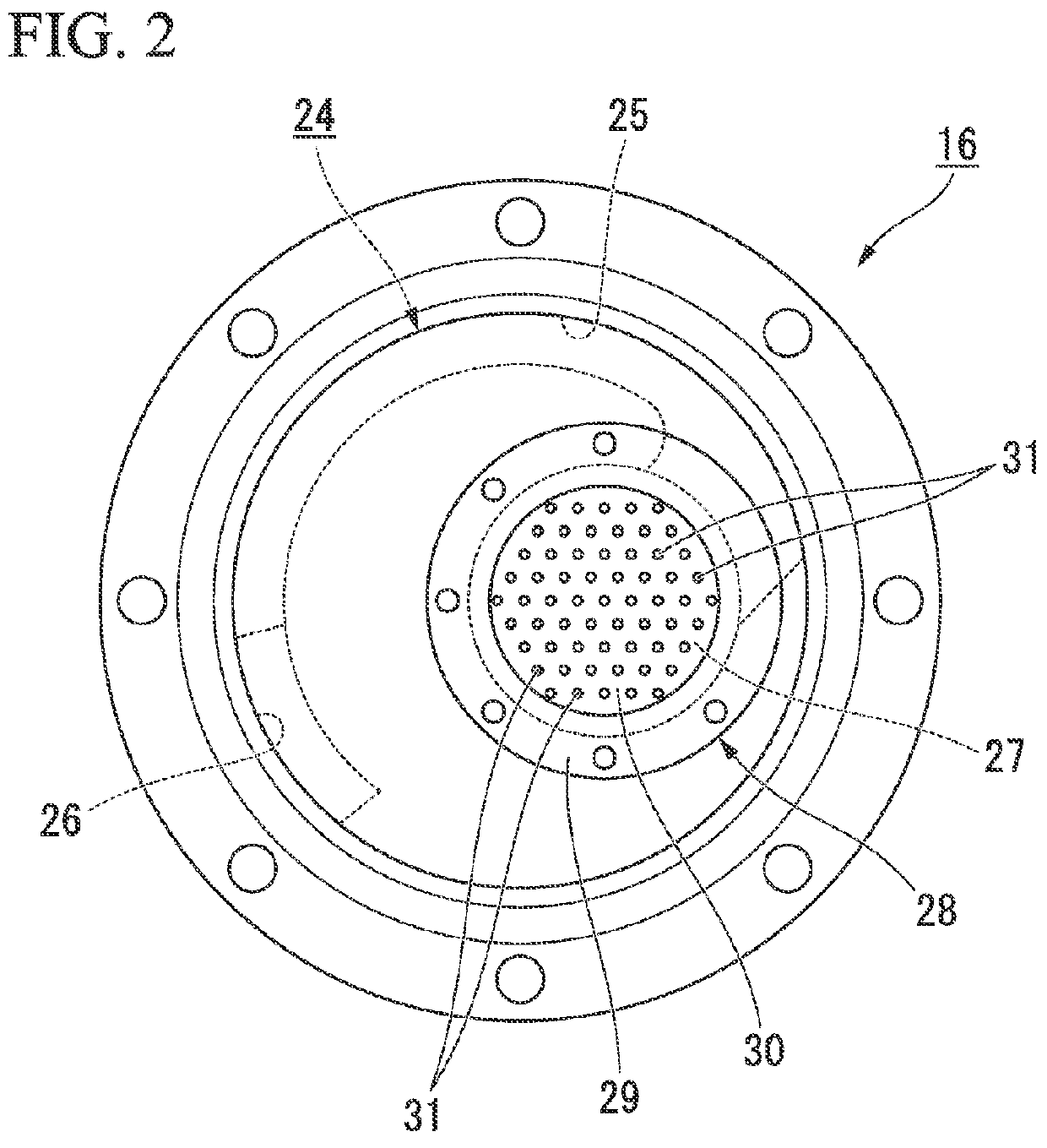
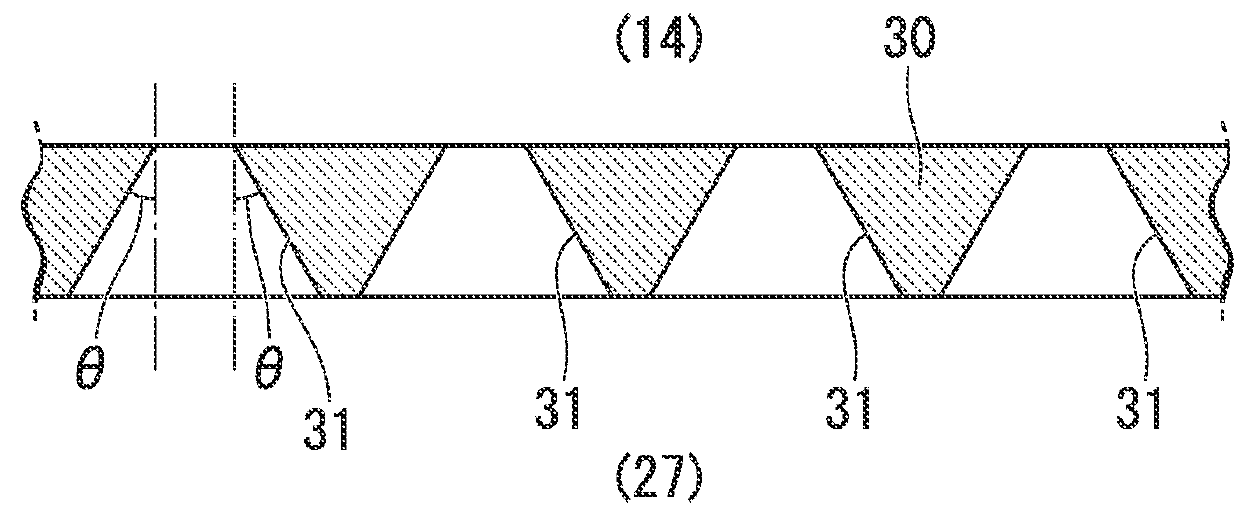
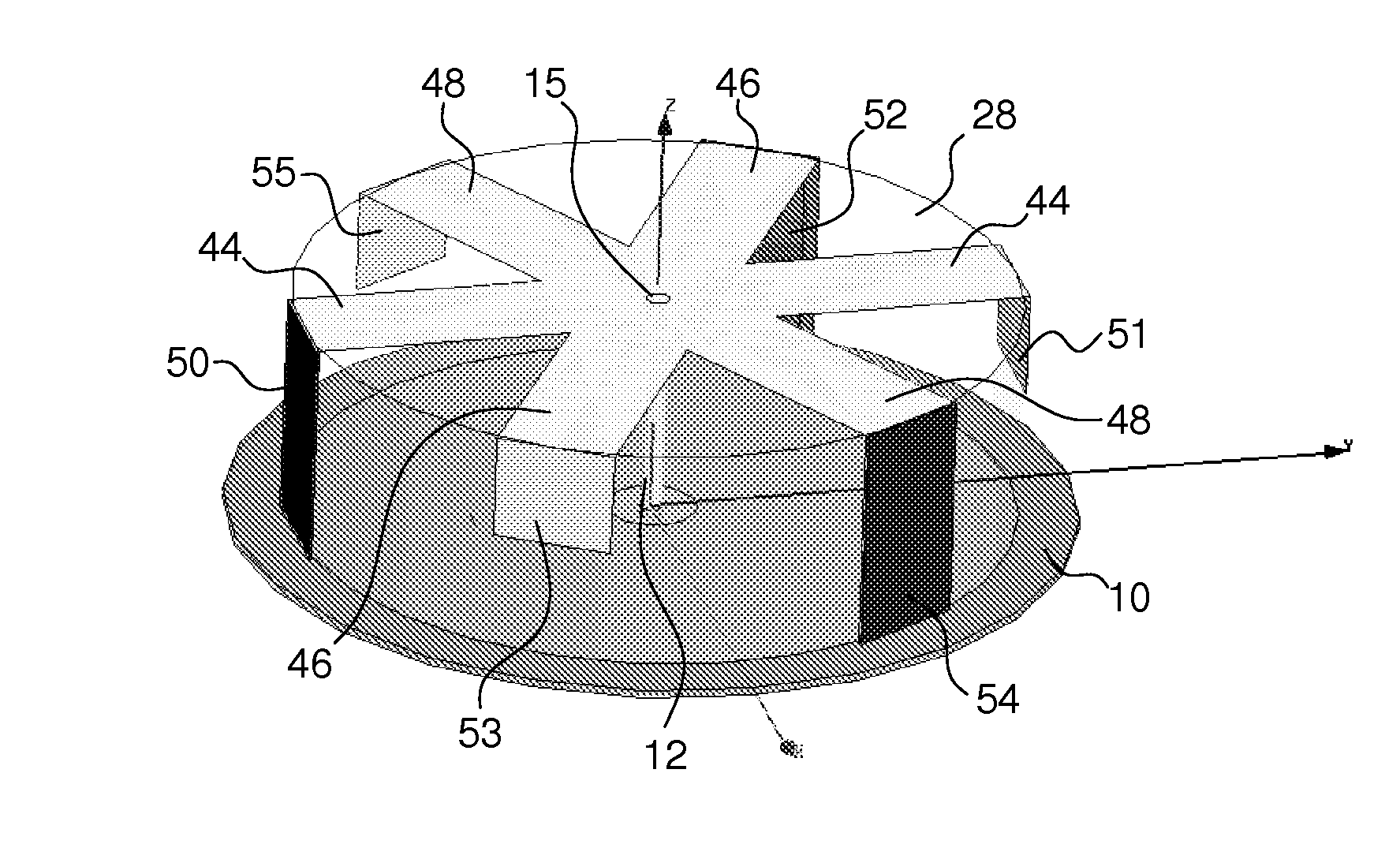
ActiveUS20160053845A1Increase manufacturing costDegree of freedom is loweredMachine framesLiquid springsElastomerEngineering
A vibration isolator (10) is a liquid-enclosed vibration isolator and includes: a tubular first mounting member (11) connected to one of a vibration generator and a vibration absorber, and a second mounting member (12) connected to the other; an elastic body (13) elastically connecting the mounting members; and a partition member (16) partitioning a liquid chamber (19) in the first mounting member (11) within which a liquid (L) is enclosed into a primary liquid chamber (14) that uses the elastic body (13) as a part of a wall surface thereof and a secondary liquid chamber (15), wherein the partition member (16) is formed with a restriction passage (24) communicating the primary and secondary liquid chambers (14, 15) with each other, and a porous body (28) having numerous pores (31), which are disposed in parallel so as to communicate a side of the primary liquid chamber (14) and a side of the secondary liquid chamber (15) with each other, is arranged in the restriction passage (24).
Owner:PROSPIRA CORP
Omni-directional antenna for mobile satellite broadcasting applications
InactiveUS20090027294A1Reduce in sizeLoss in efficiencyAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsOmnidirectional antennaPhysics
An antenna for mobile satellite communication is disclosed. The antenna may include an electrically conducting ground plane and at least a first and a second radiating element. Each one of the radiating elements may be electrically coupled to a feed line, whereby each one of said at least first and second radiating elements may be electrically connected to the ground plane at one end and being open-circuit at an opposite end, whereby the at least first and second radiating elements may intersect at a feeding point of the feed line and extend radially with respect to the elongation of the feed line.
Owner:JAST
Stents with proximal and distal end elevations
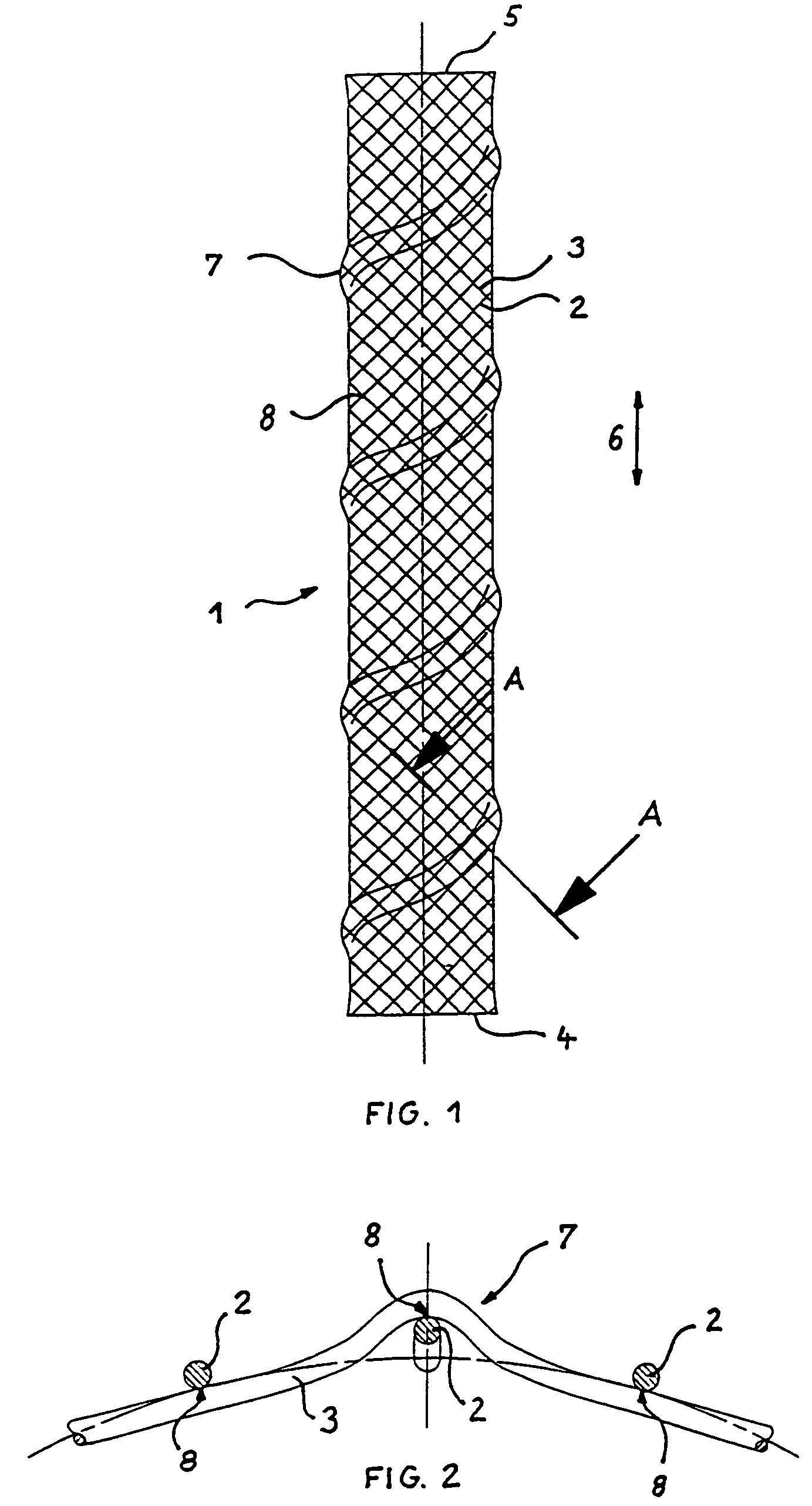
InactiveUS7331990B2Improve a less-shortening stentAvoid deformationStentsOrnamental textile articlesMedicineMechanical stability
A prosthetic stent with a tubular wall having local inwardly or outwardly formed elevations. Stents having such elevations have a higher mechanical stability if bent according to the curvature of the body vessels to be supported or repaired. Also a method for manufacturing a stent with such elevations is described.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
Planar package structure for high power light emitting diode
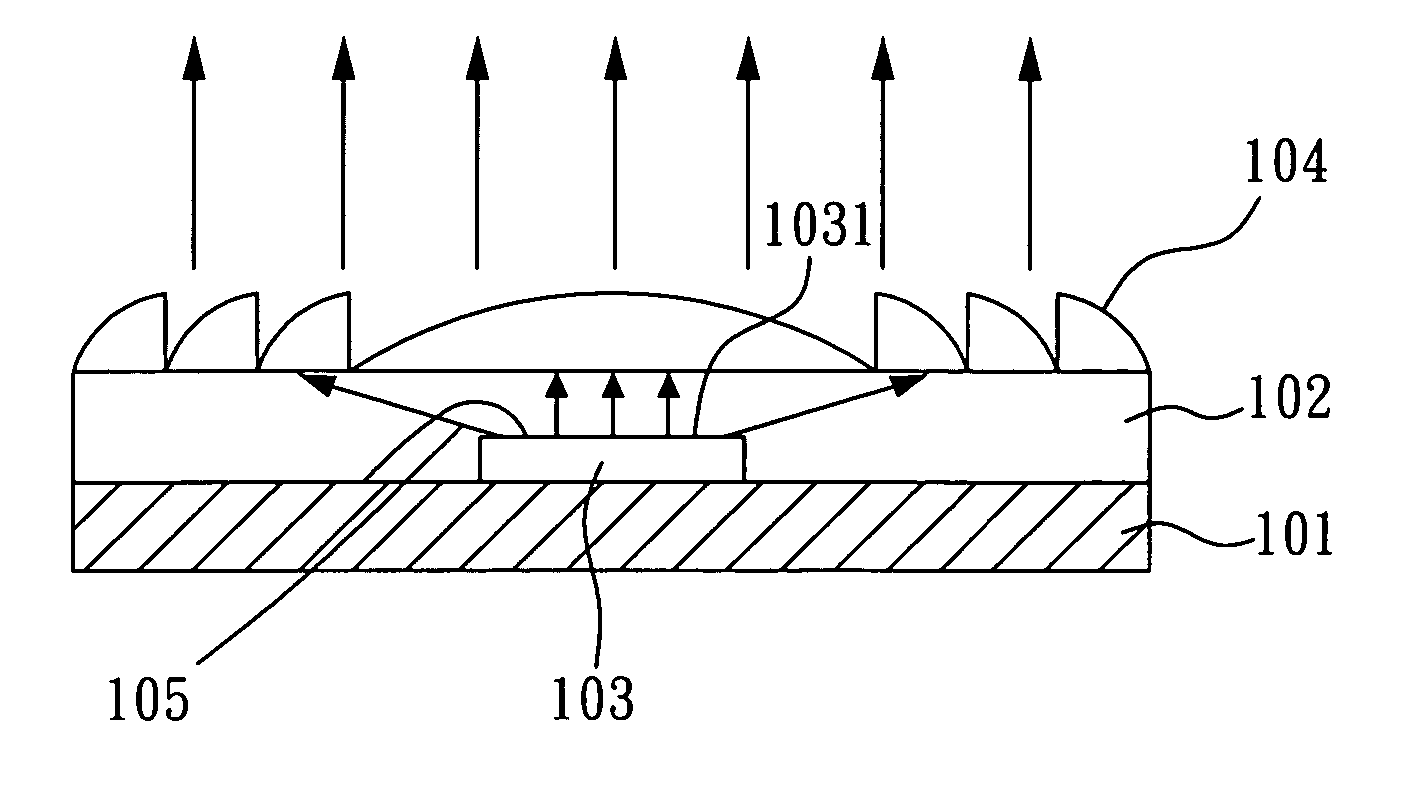
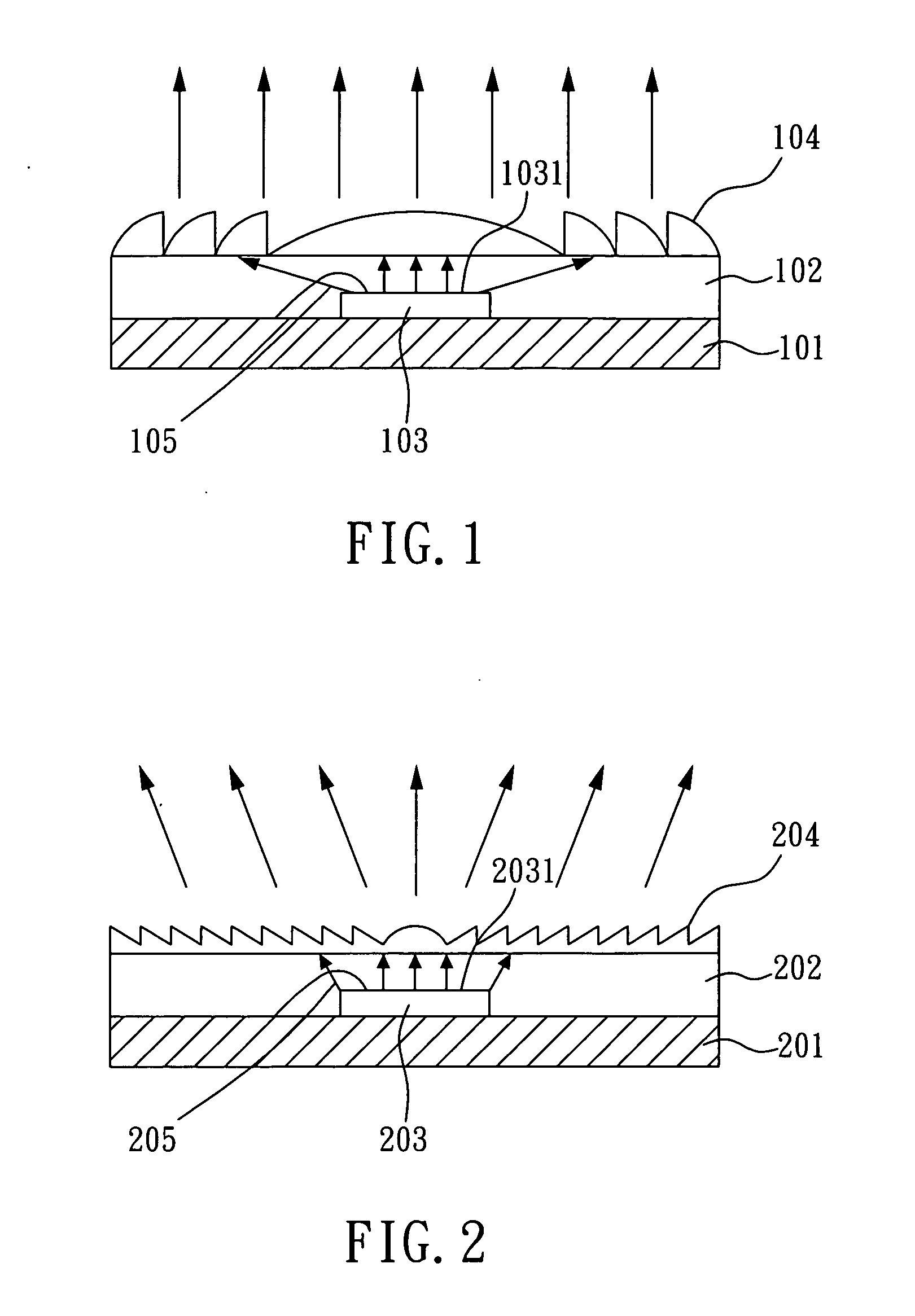
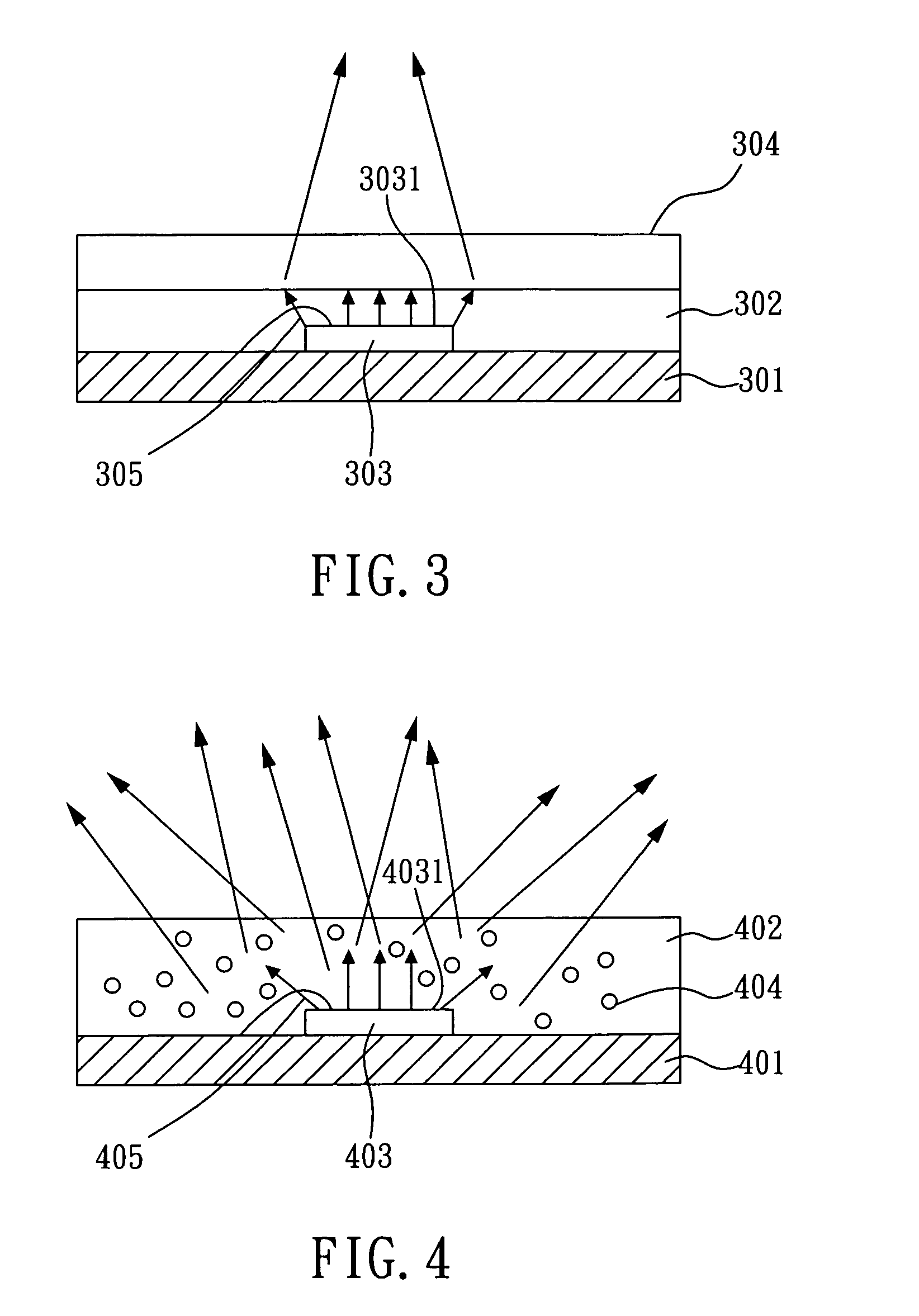
InactiveUS20050145867A1Package volume is largeDegree of freedom is loweredSemiconductor devicesLight-emitting diodePhase modulation
A planar package structure for high power light emitting diode, comprising: a substrate; a package material; a light emitting diode chip disposed on the substrate, having a main light emitting surface served as a light source; and a planar optical modulation unit disposed on the package material, so that the planar optical modulation unit is above the main light emitting surface, and utilized for modulating the optical phase of the light source. The planar optical modulation unit can perform a refractive optical phase modulation or a diffractive optical phase modulation such that a thin and planar high power light emitting diode package element with function of optical phase modulation is obtained.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Toy building set
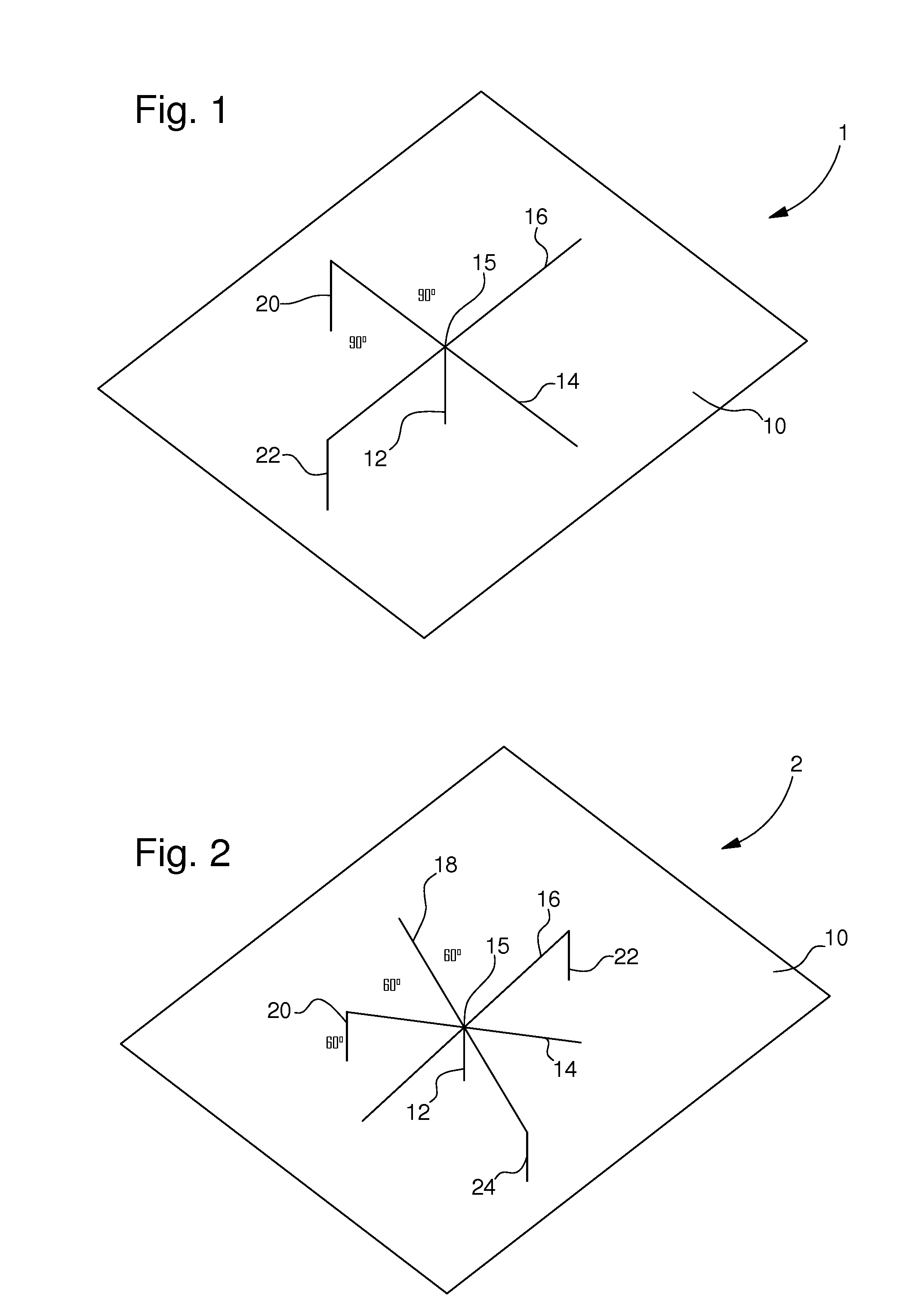
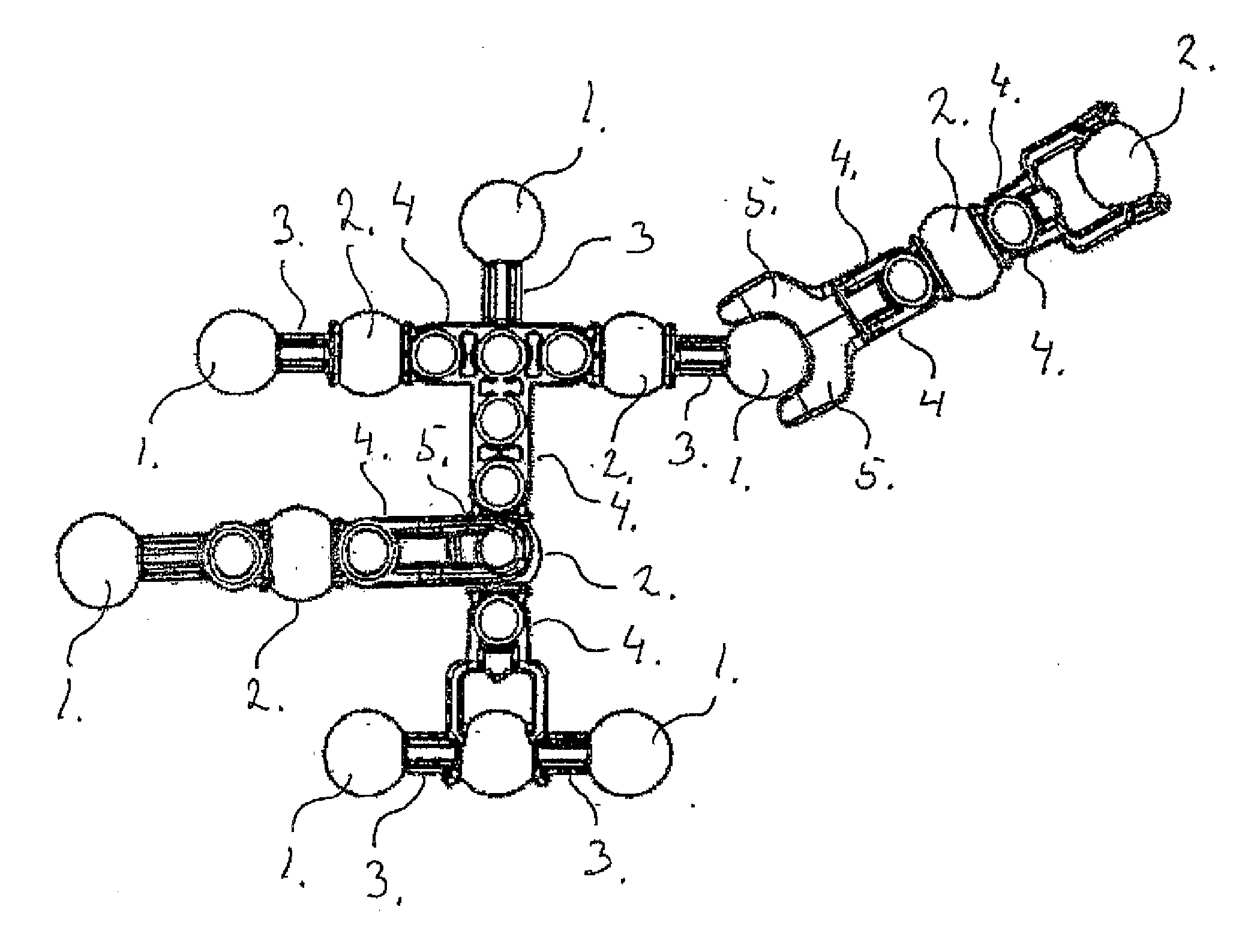
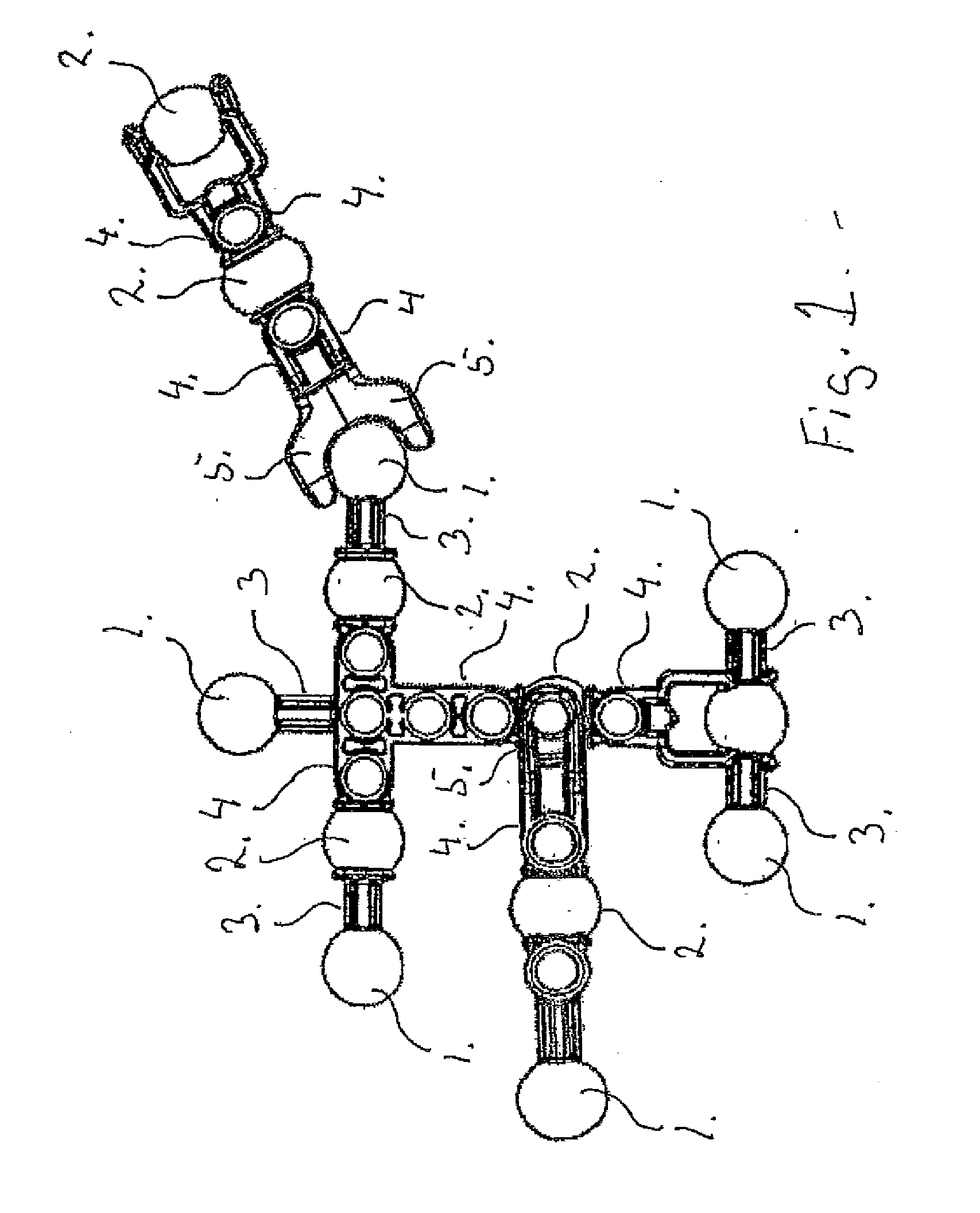
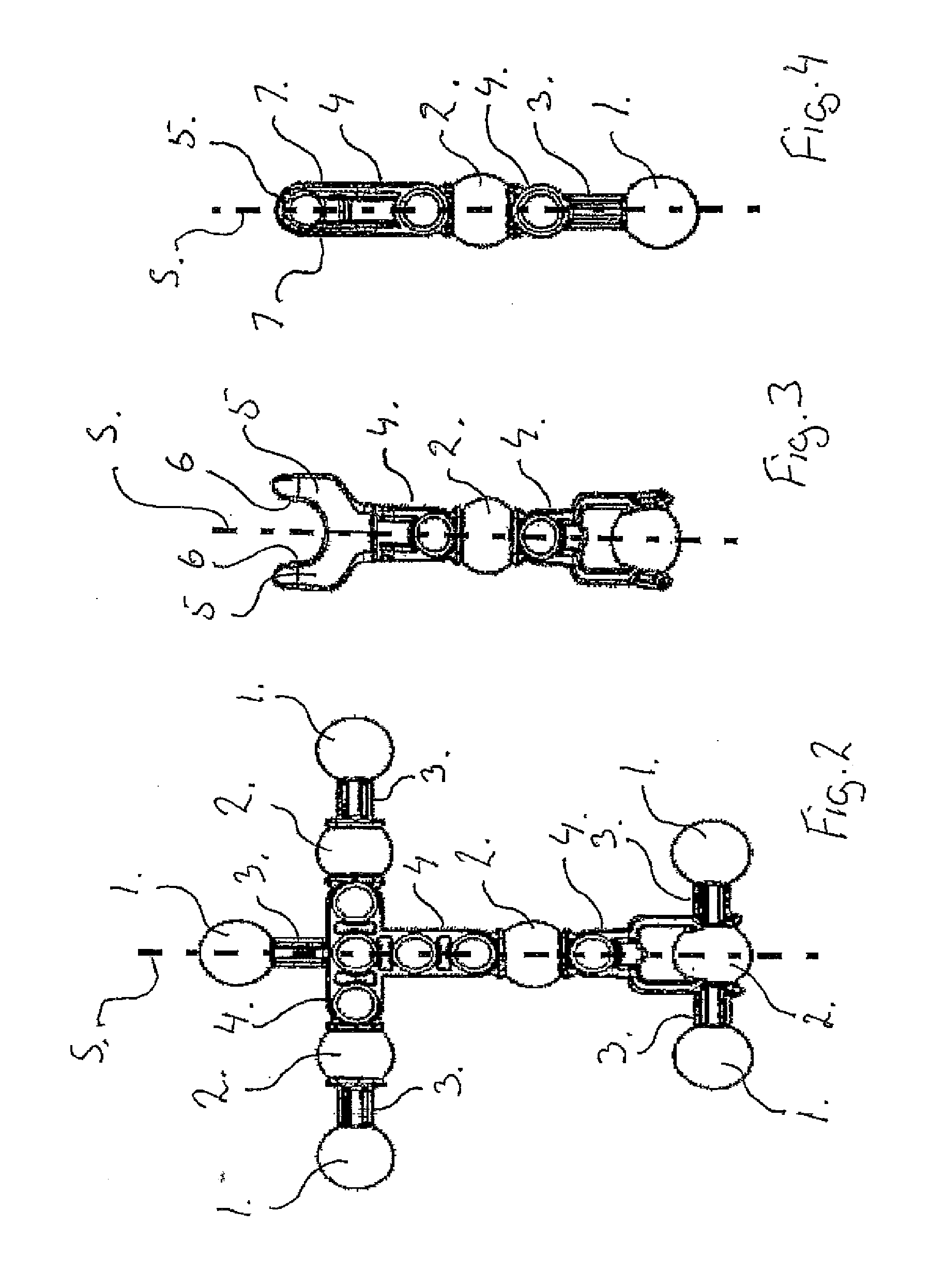
A toy building set comprising a group of building elements, each having at least one ball 1, 2 arranged on the building element, and where the ball 1, 2 is connected to other parts of the building element via a connection rod 3, 4, and where the toy building set further comprises at least one element having a socket formed by two jaws 5, being arranged and adapted for receiving said ball 1, 2 in order to form a ball and socket joint, and where the cross section of the connection rod 3, from where it is connected to the ball 1 and at least a distance away from the ball 1, is smaller than the cross section of the ball 1, so that it gives a certain degree of freedom for the socket to rotate around the ball 1. The connection rods 3, 4 also comprise connections rods 4 having a relatively large cross section, so that the connection rods 4 with a relatively large cross section reduces the degree of freedom for the socket to rotate around the ball 2.
Owner:LEGO AS
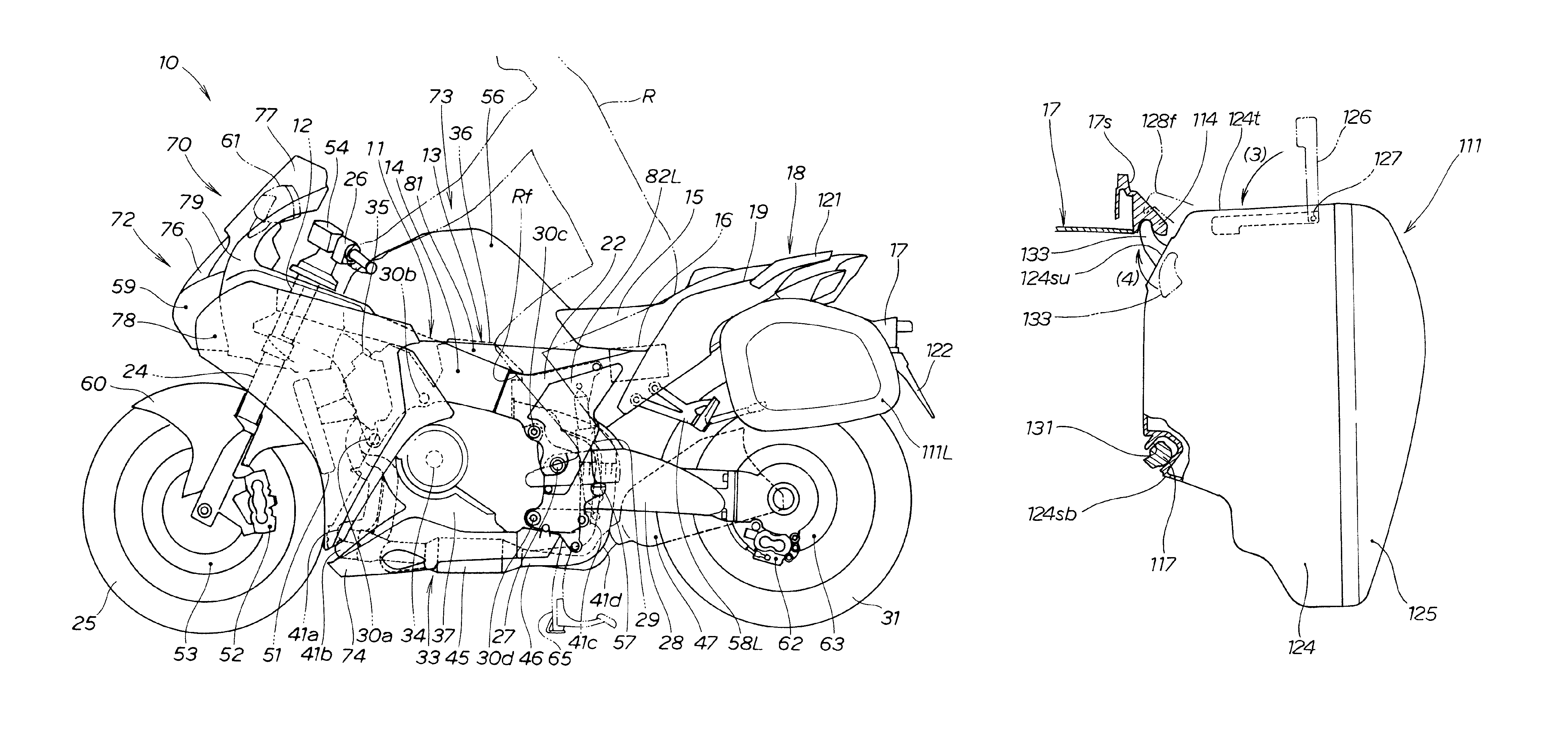
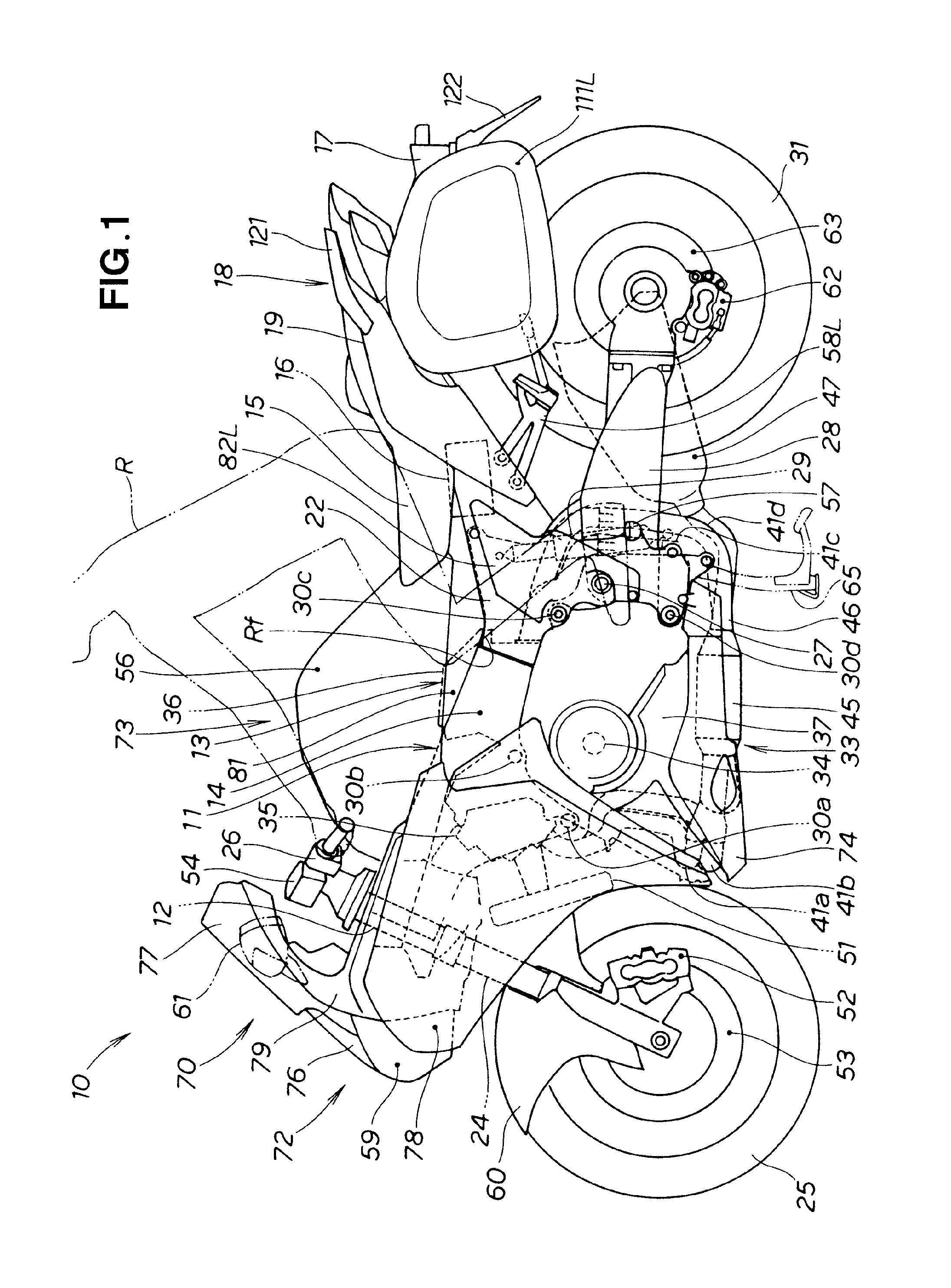
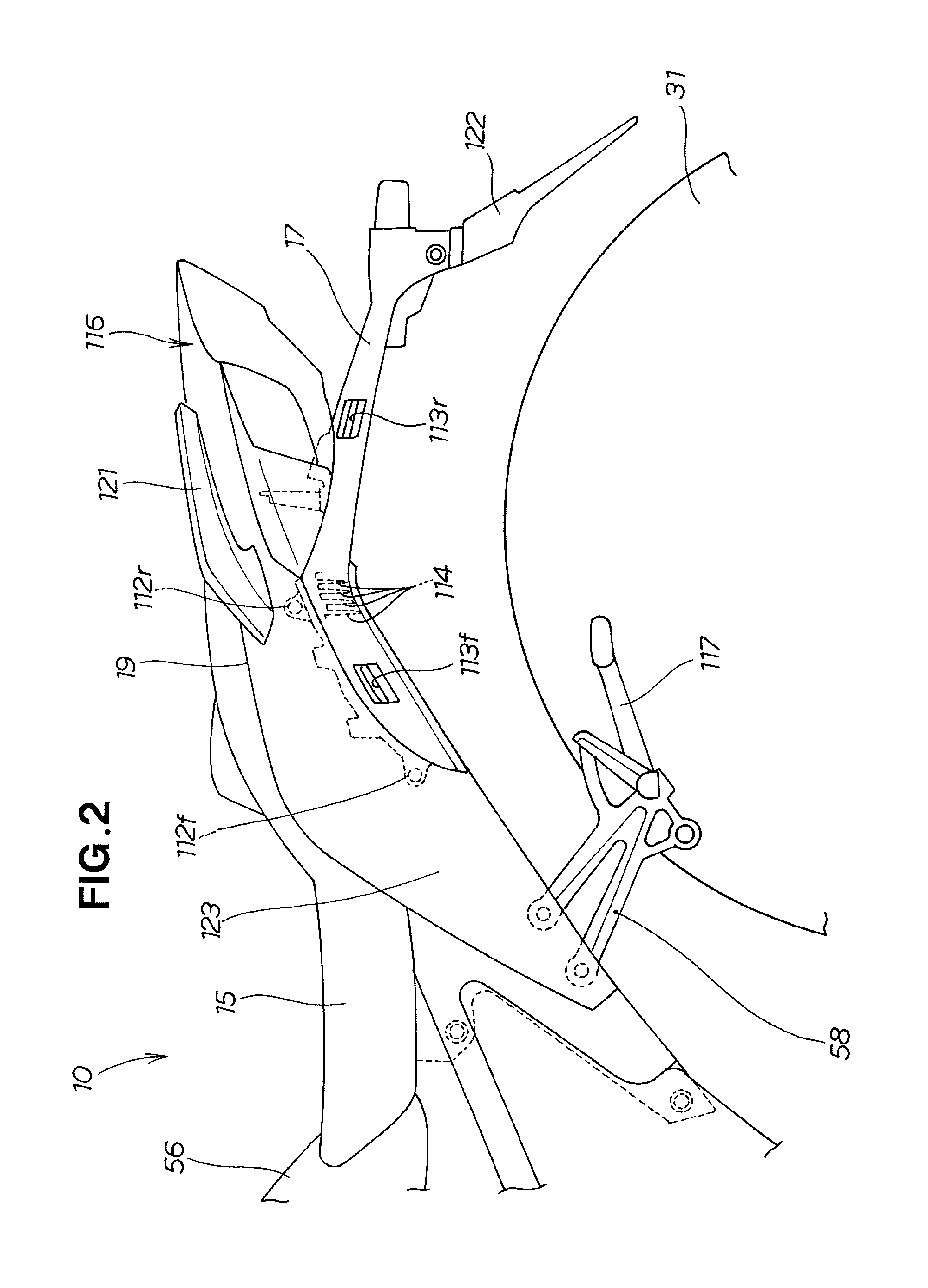
Side trunk mounting structure for two-wheeled motor vehicle
ActiveUS8864002B2External appearance is compromisedDegree of freedom is loweredLuggage carriersSupplementary fittingsEngineeringMotorized vehicle
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Foot of walking robot and walking robot having the same
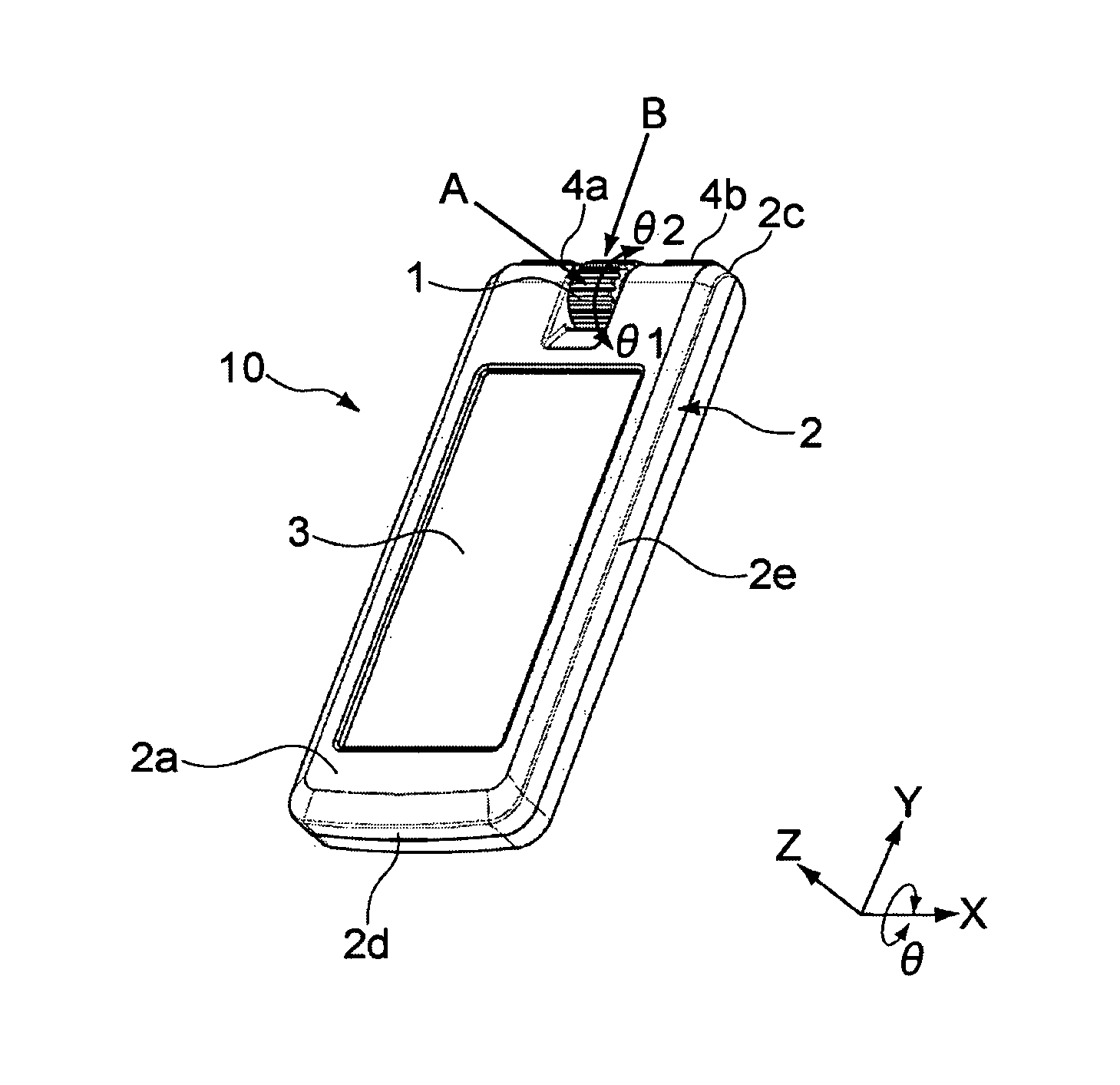
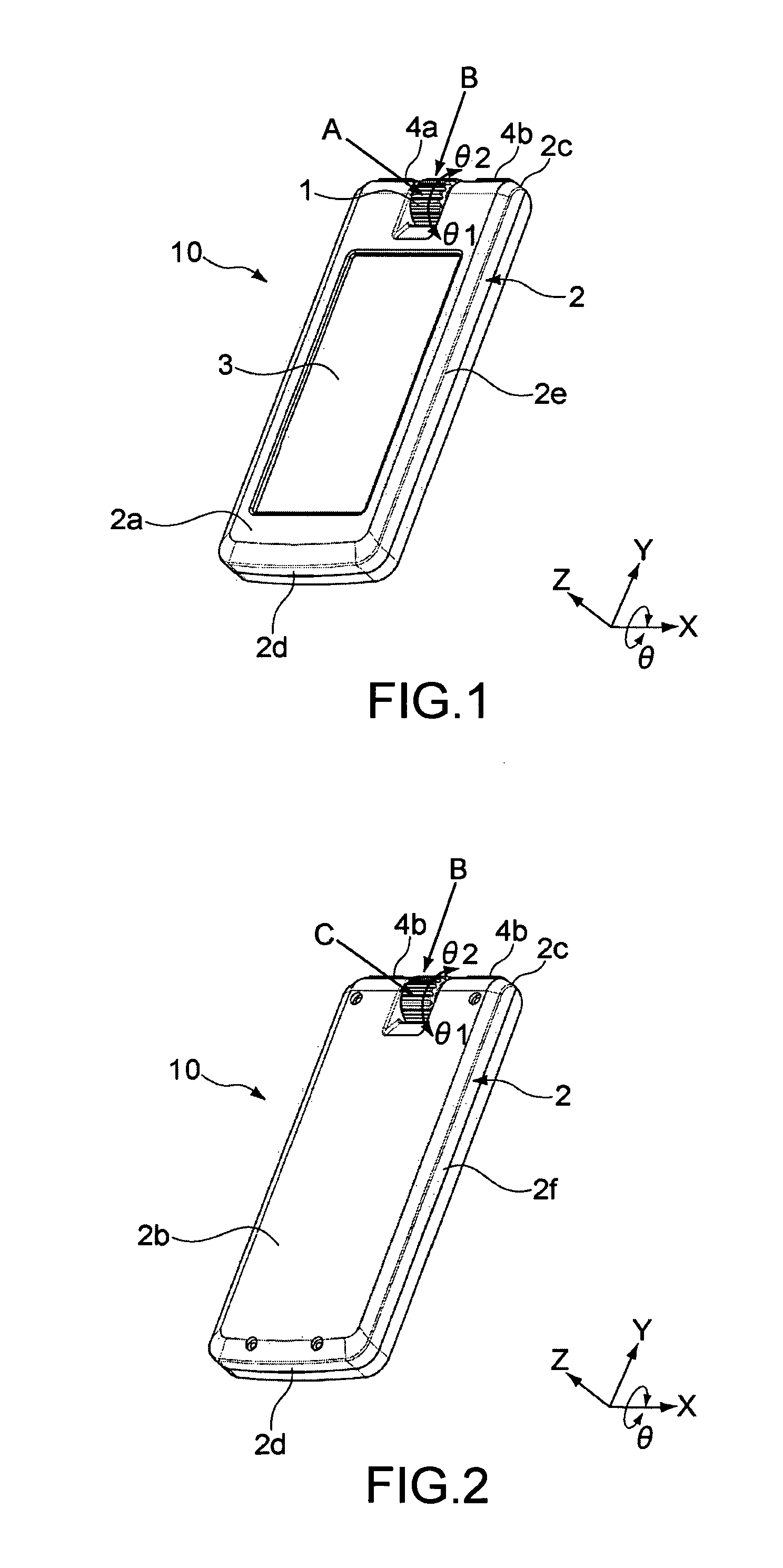
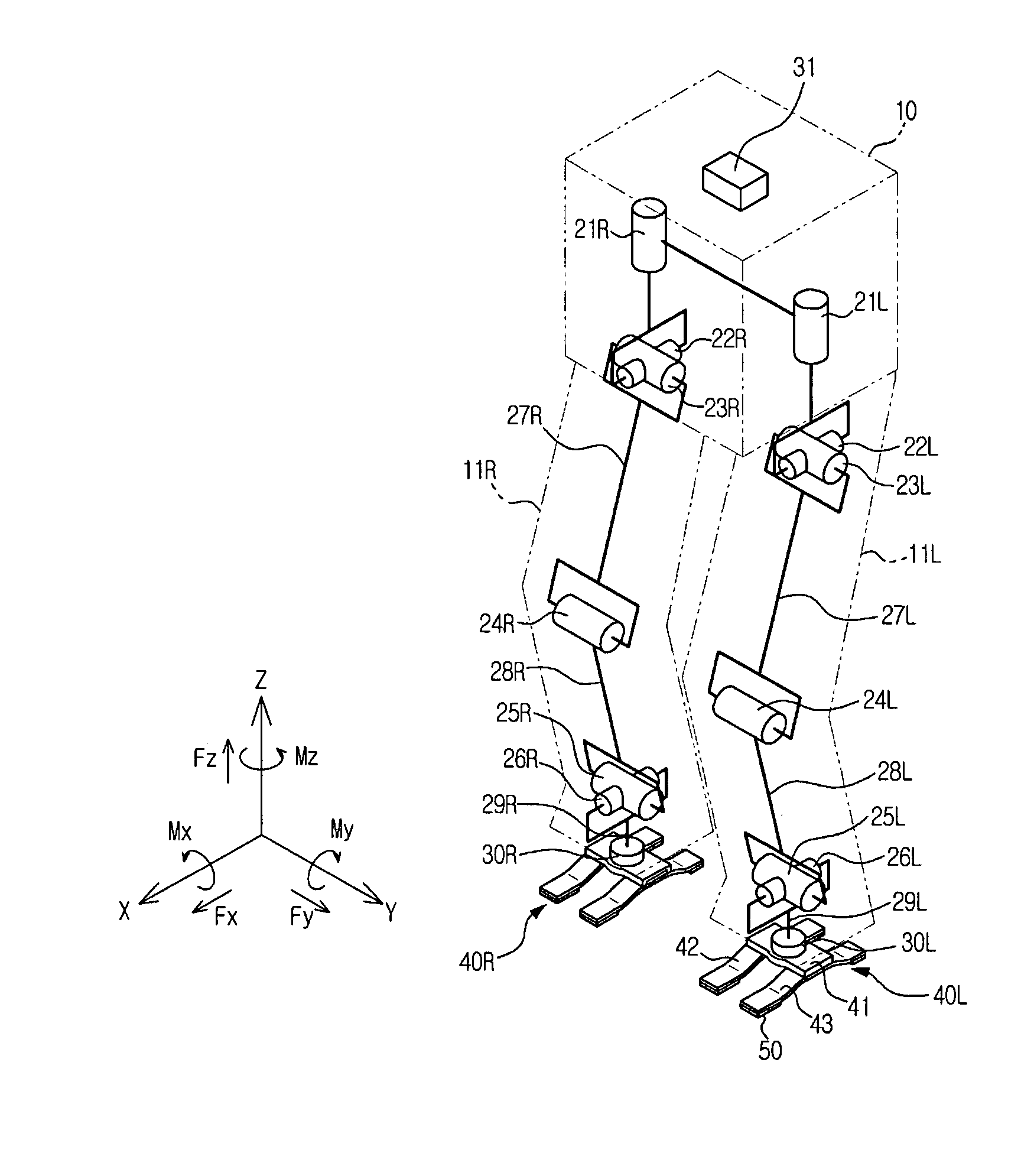
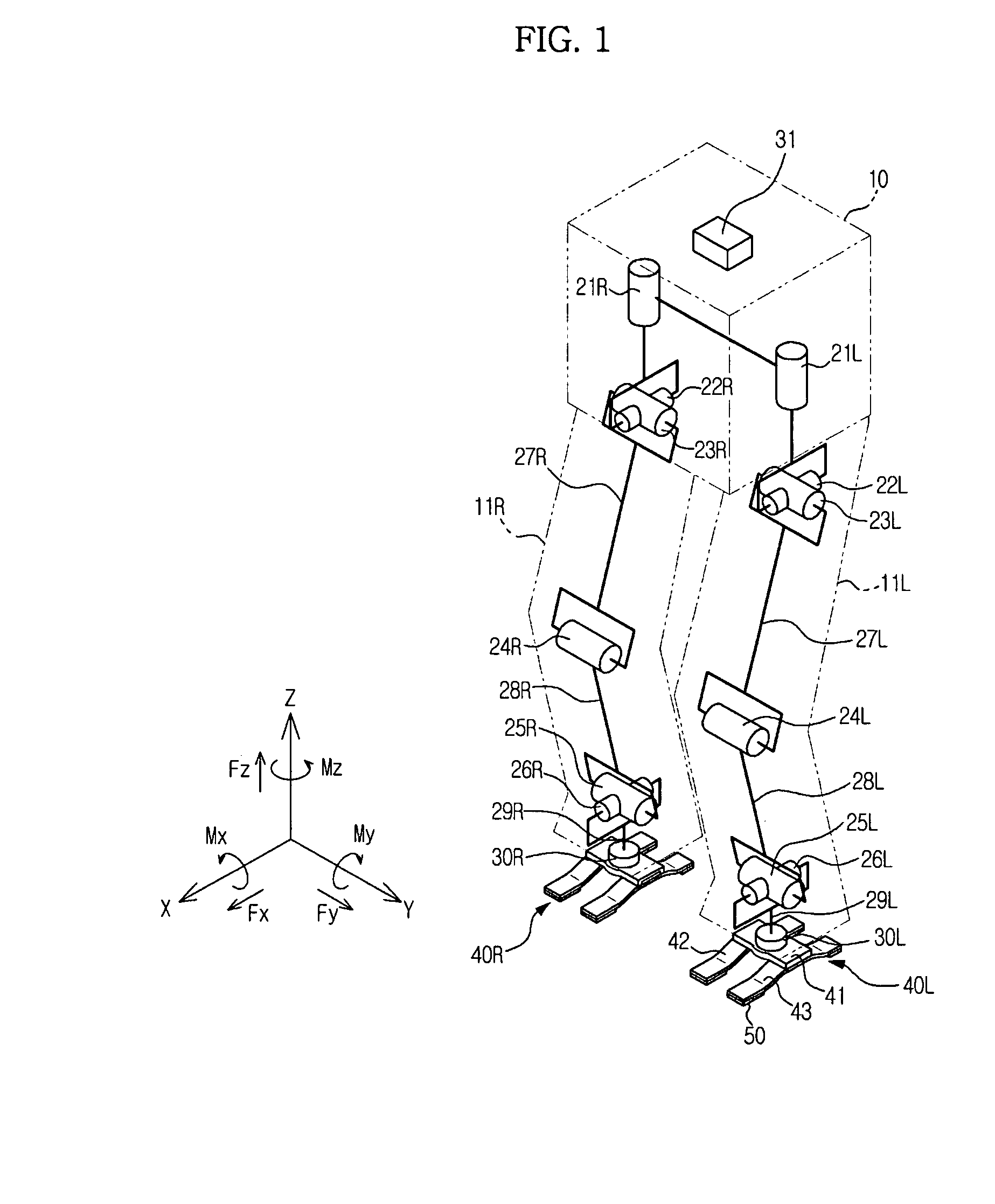
InactiveUS20080297091A1Minimize tiltDegree of freedom is loweredManipulatorVehiclesDegrees of freedomEngineering
Disclosed are a foot of a walking robot, which minimizes tilting of a sole of the foot and reduces a degree of freedom to easily control the walking of the robot, and a walking robot having the same. The foot includes a frame connected to a lower portion of a leg of the walking robot; and a plurality of impact absorbing plates having elasticity respectively connected to two sides of the frame such that the impact absorbing plates are separated from each other. Each of the impact absorbing plates includes a separation part connected to the frame and separated from a ground surface, a front ground part extended forward from the separation part and contacting the ground surface, and a rear ground part extended backward from the separation part and contacting the ground surface.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Resin-coated glove
Provided is a glove which has good adhesiveness to a rubber or resin coating material and excellent durability and further fits a hand well enabling good work efficiency. The glove is knitted from a covered yarn obtained by winding a sheath yarn around a core yarn and at least a part of the surface thereof is coated with a rubber or resin coating material, wherein the sheath yarn is a crimped yarn made of a high strength fiber having, as a property of a raw yarn, a tensile strength of 1.75 N / tex or more as measured according to JIS L 1013 8.5, and the crimped yarn simultaneously satisfies the following (1) to (3): (1) a degree of bulkiness of 40 cm3 / g or more as measured according to JIS L 1013 8.16 A method after hot water treatment at 90° C. for 20 minutes, (2) a bulk compression modulus of 80% or more as measured according to the same method, and (3) a shrinkage / elongation ratio of 20% or more as measured according to JIS L 1013 8.11 A method.
Owner:DUPONT TORAY CO LTD
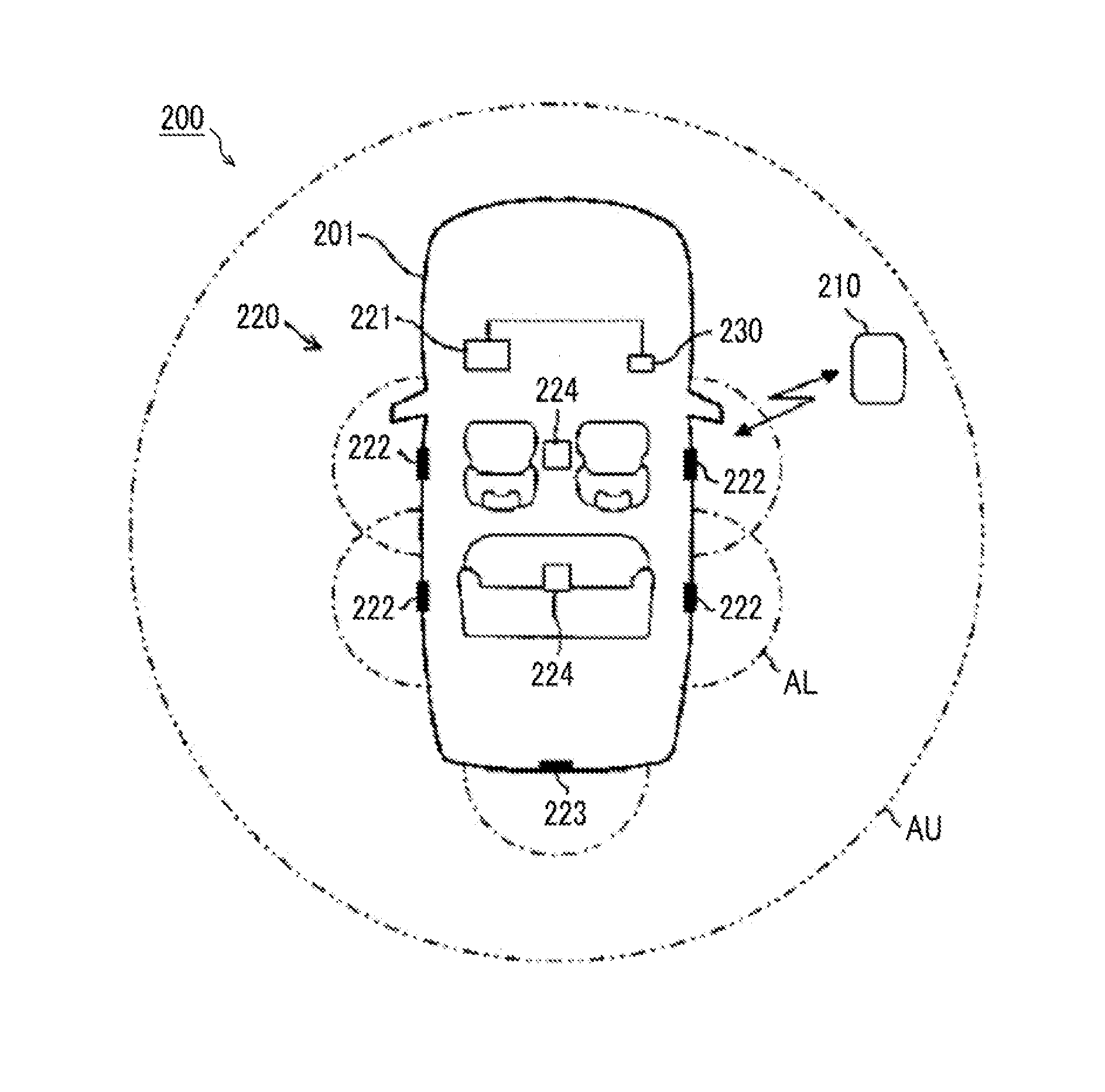
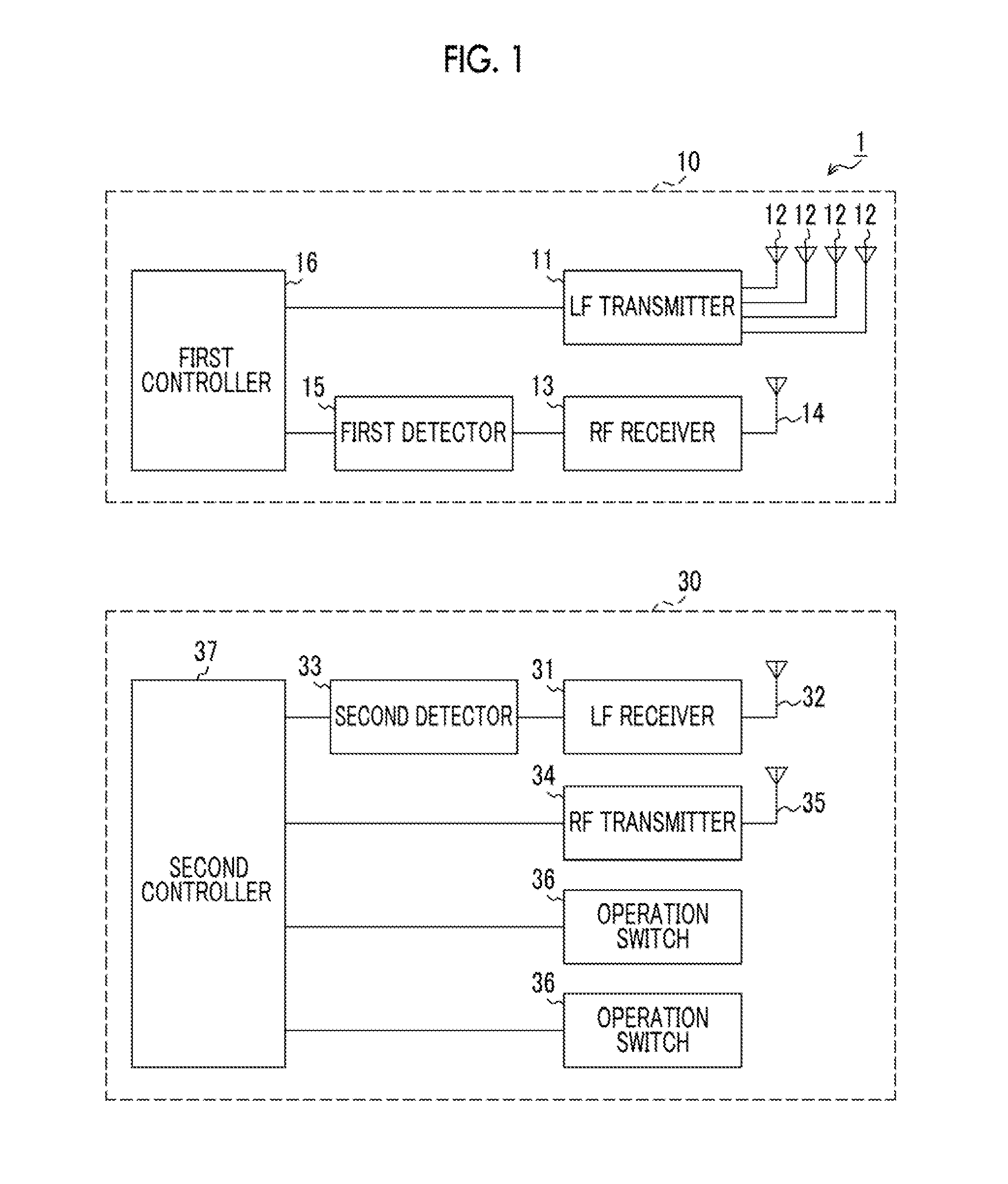
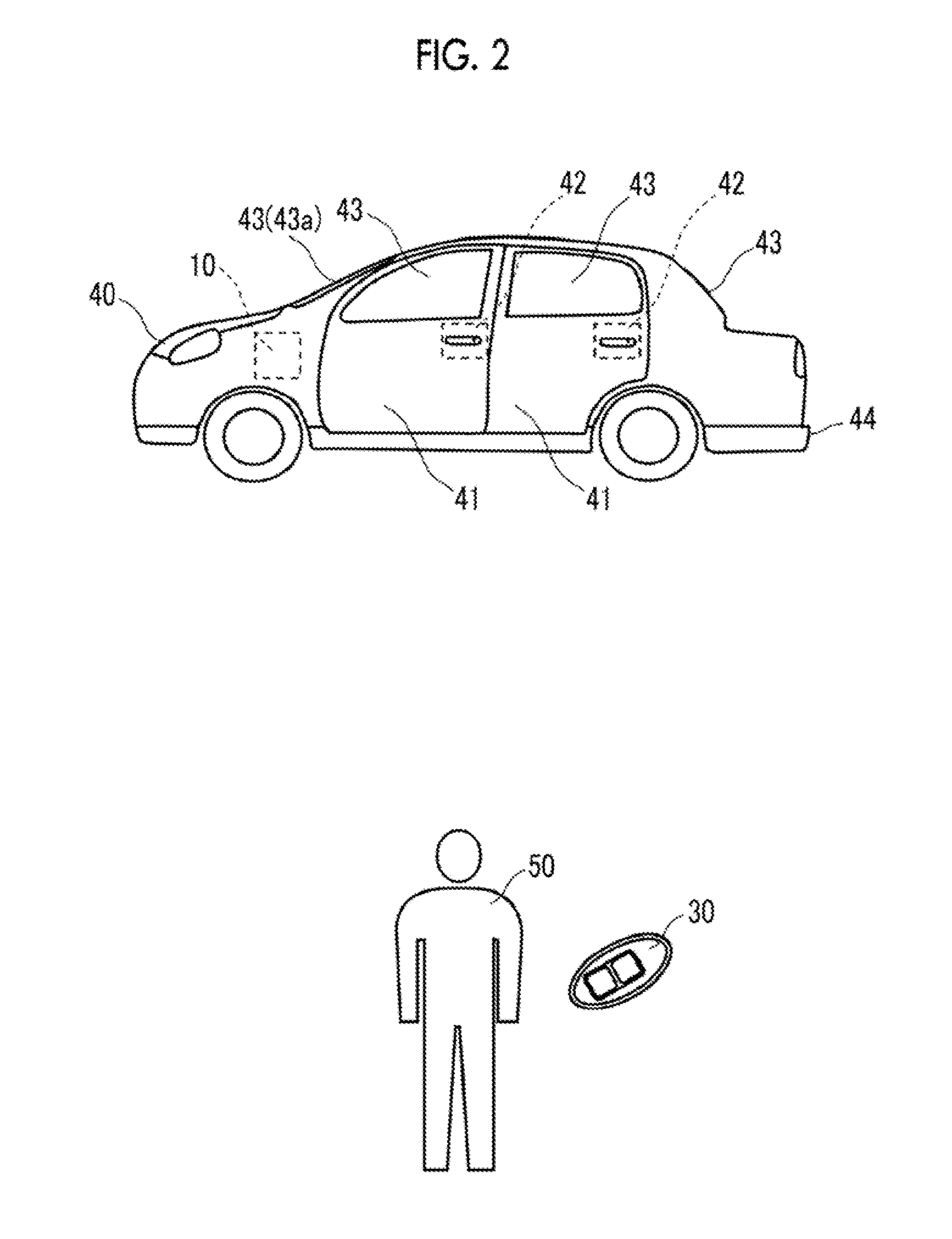
Keyless entry system
ActiveUS20150145646A1Increase volumeEasy to liftProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsMobile deviceEmbedded system
A keyless entry system includes an on-vehicle unit which is mounted in a vehicle, and a mobile device which is able to perform radio communication with the on-vehicle unit. The keyless entry system controls on-vehicle equipment mounted in the vehicle through radio communication between the on-vehicle unit and the mobile device. The on-vehicle unit has a plurality of LF transmission antennas (transmission antennas) for radio-transmitting a signal to the mobile device, and at least one of the plurality of LF transmission antennas is arranged in the vehicle interior of a door of the vehicle and is attached such that radiating magnetic flux passes through the window of the vehicle.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
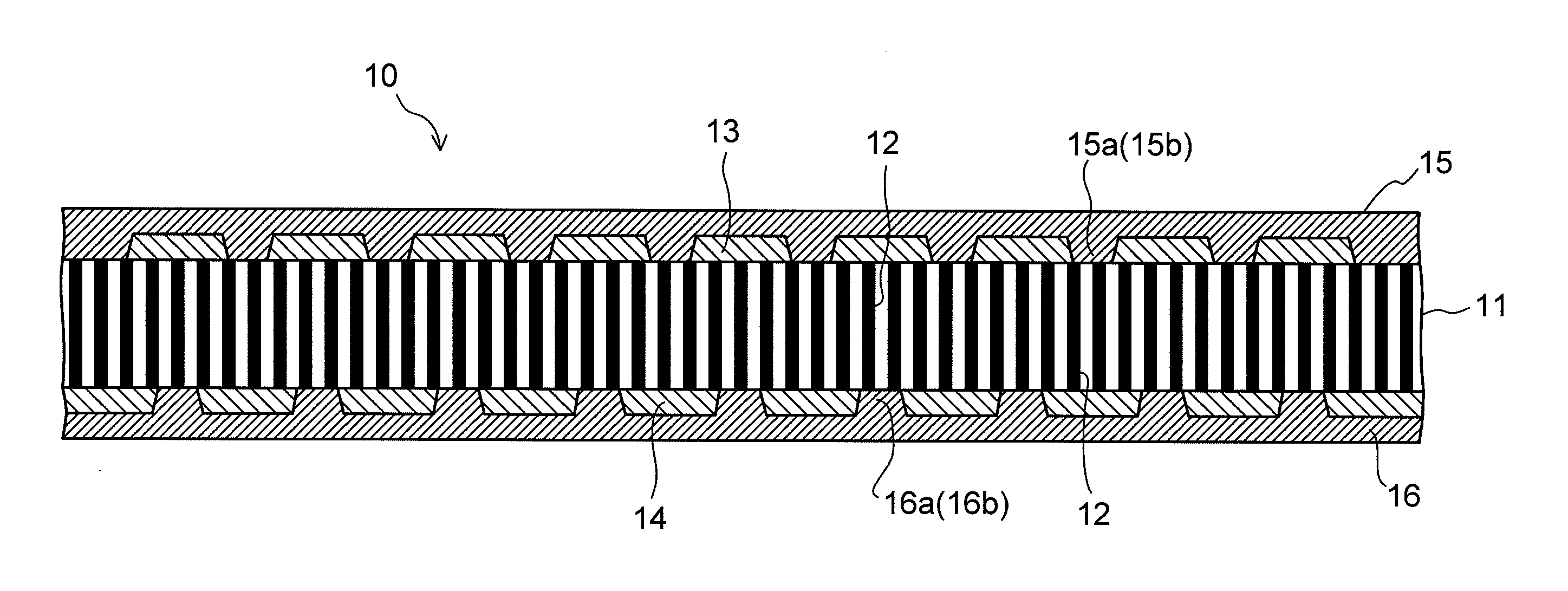
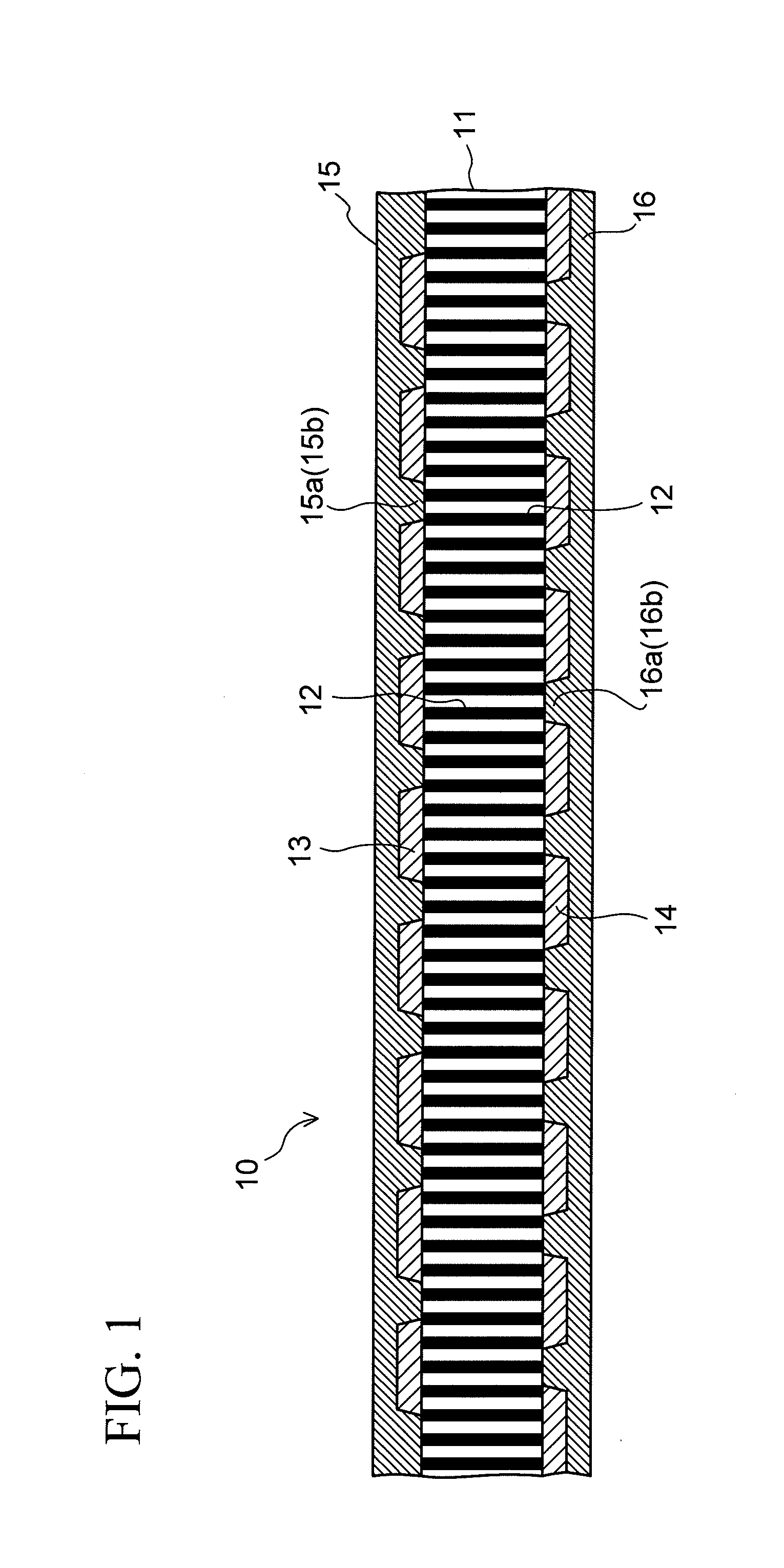
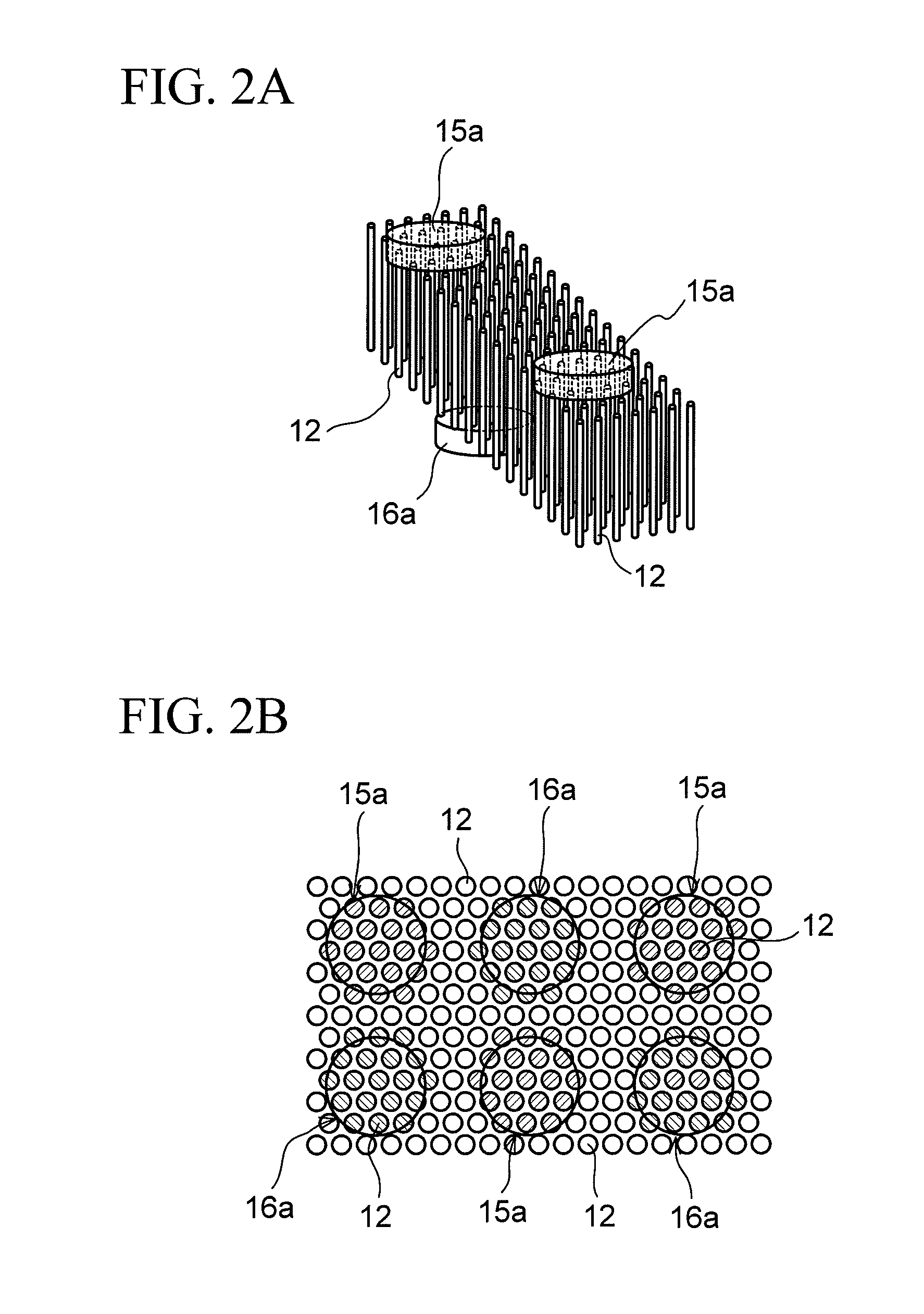
Capacitor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110013340A1Increase capacitanceEasy to changePrinted circuit assemblingFixed capacitor electrodesElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
A capacitor includes a dielectric substrate and a large number of filamentous conductors formed to penetrate through the dielectric substrate in a thickness direction thereof. An electrode is connected to only respective one ends of a plurality of filamentous conductors constituting one of groups each composed of a plurality of filamentous conductors. The electrode is disposed in at least one position on each of both surfaces of the dielectric substrate, or in at least two positions on one of the surfaces. Further, an insulating layer is formed on each of both surfaces of the dielectric substrate so as to cover regions between the electrodes, and a conductor layer is formed on the corresponding insulating layer integrally with a desired number of electrodes.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com