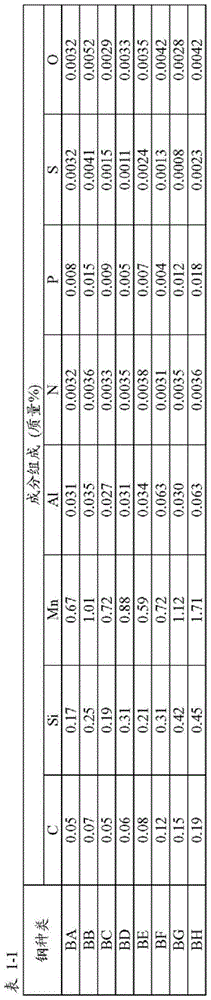
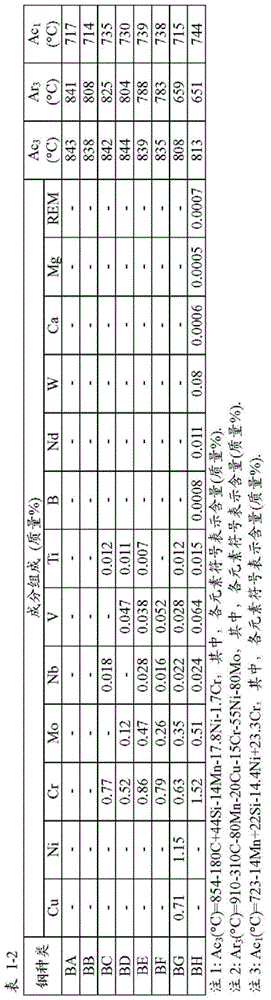
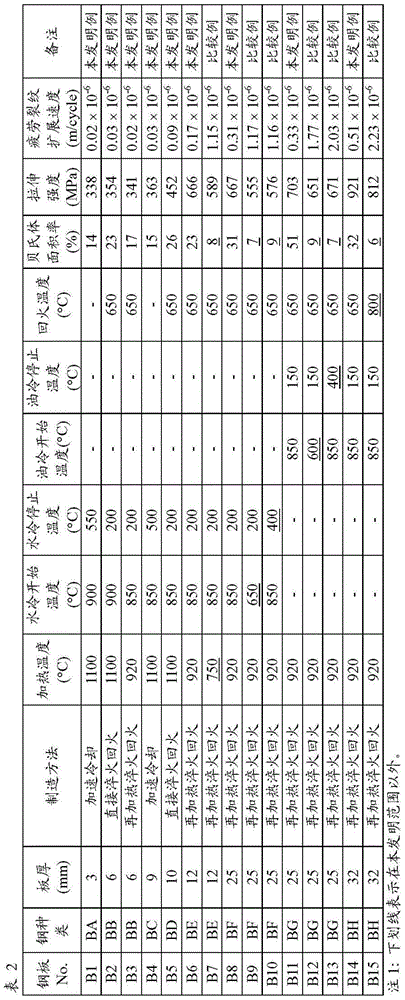
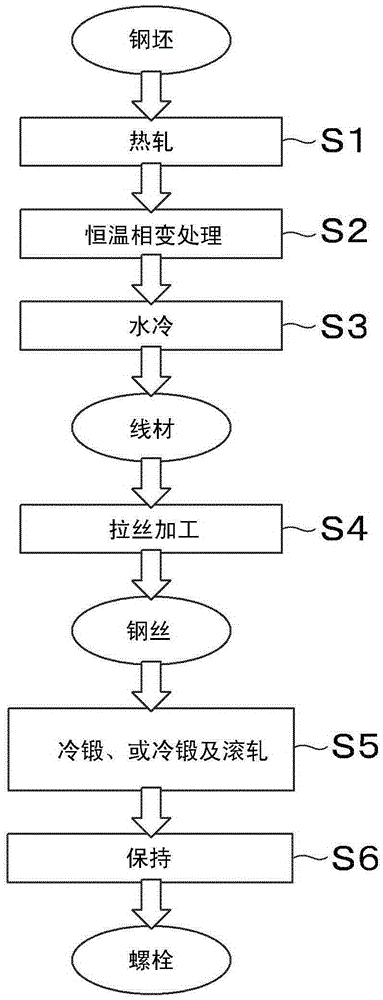
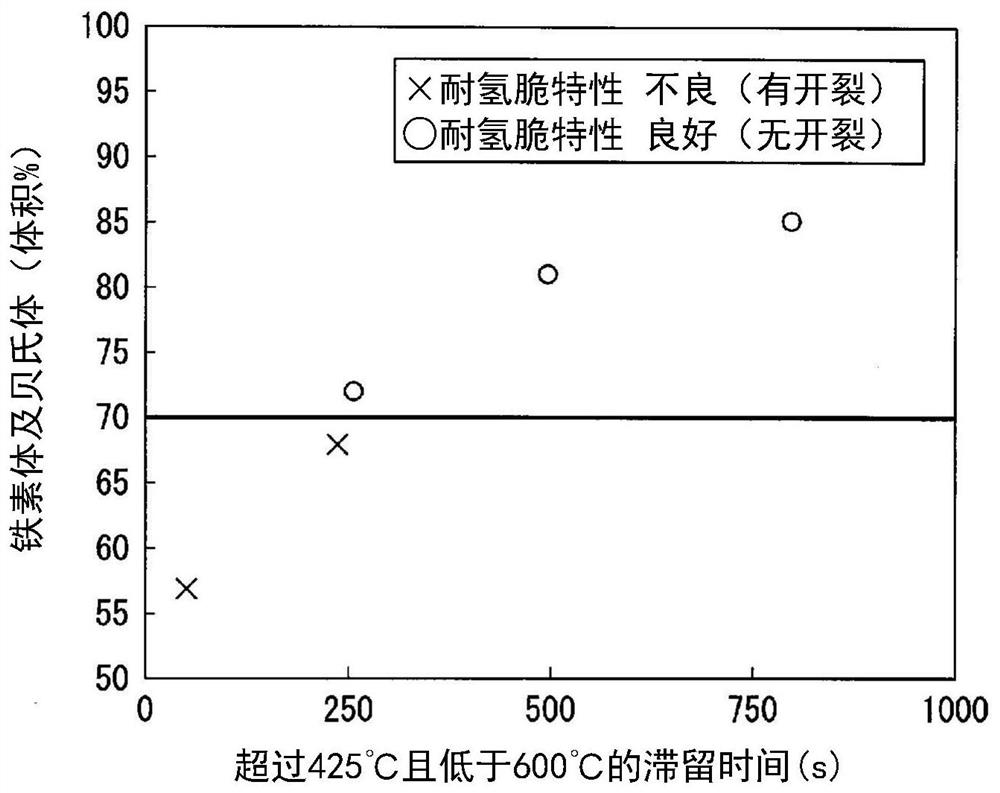
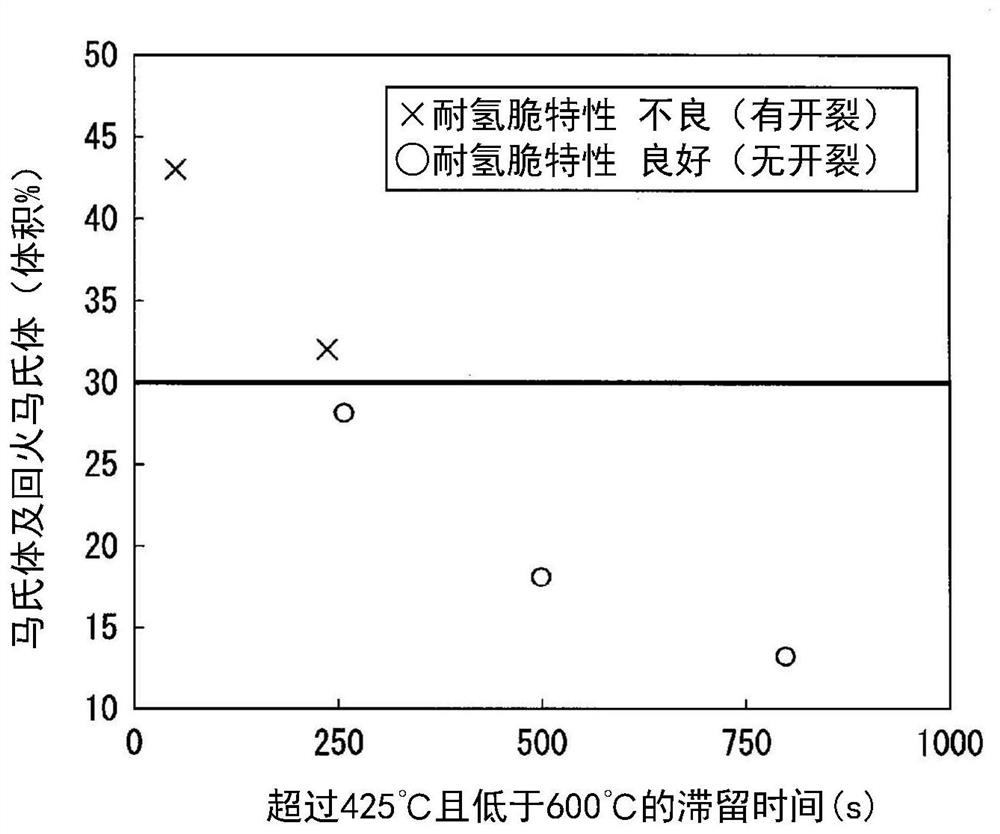
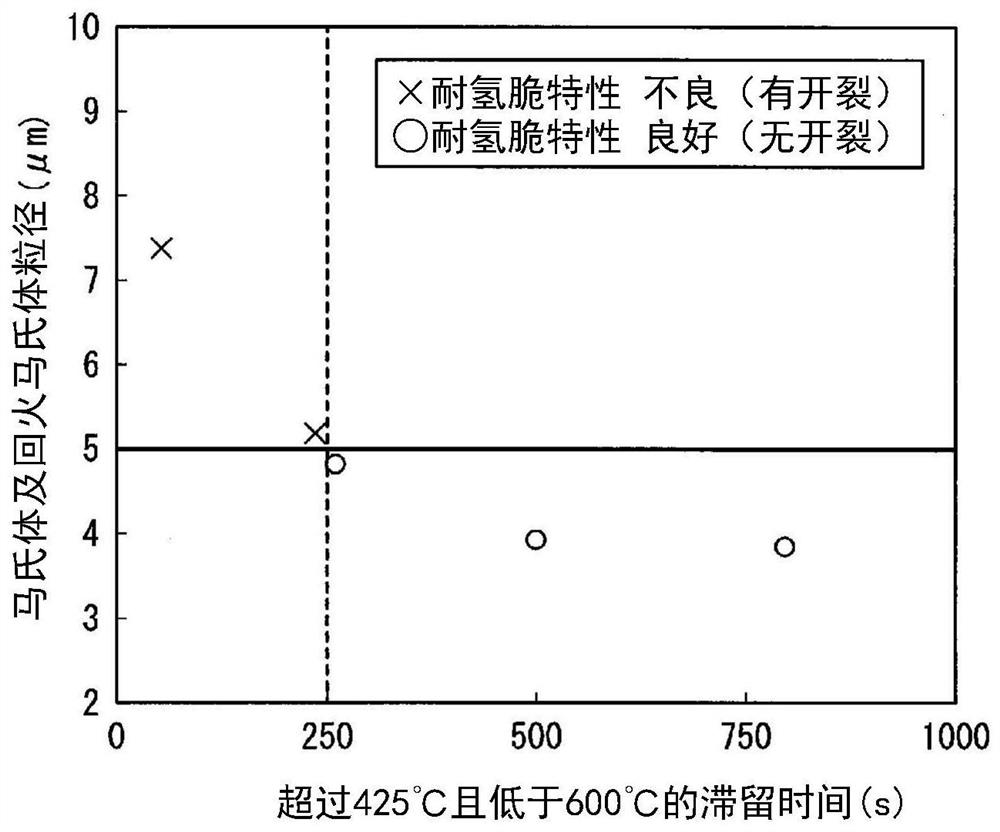
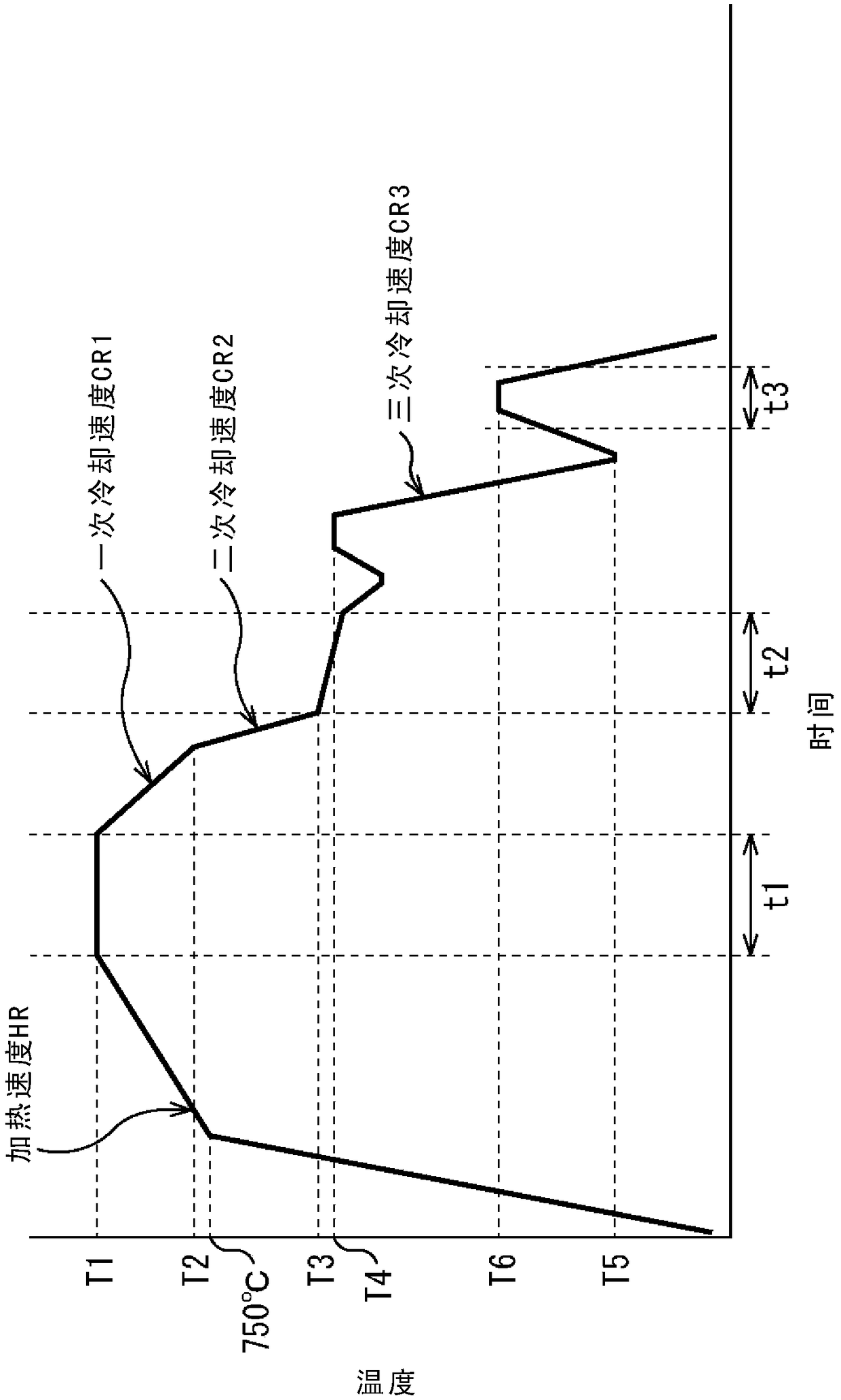
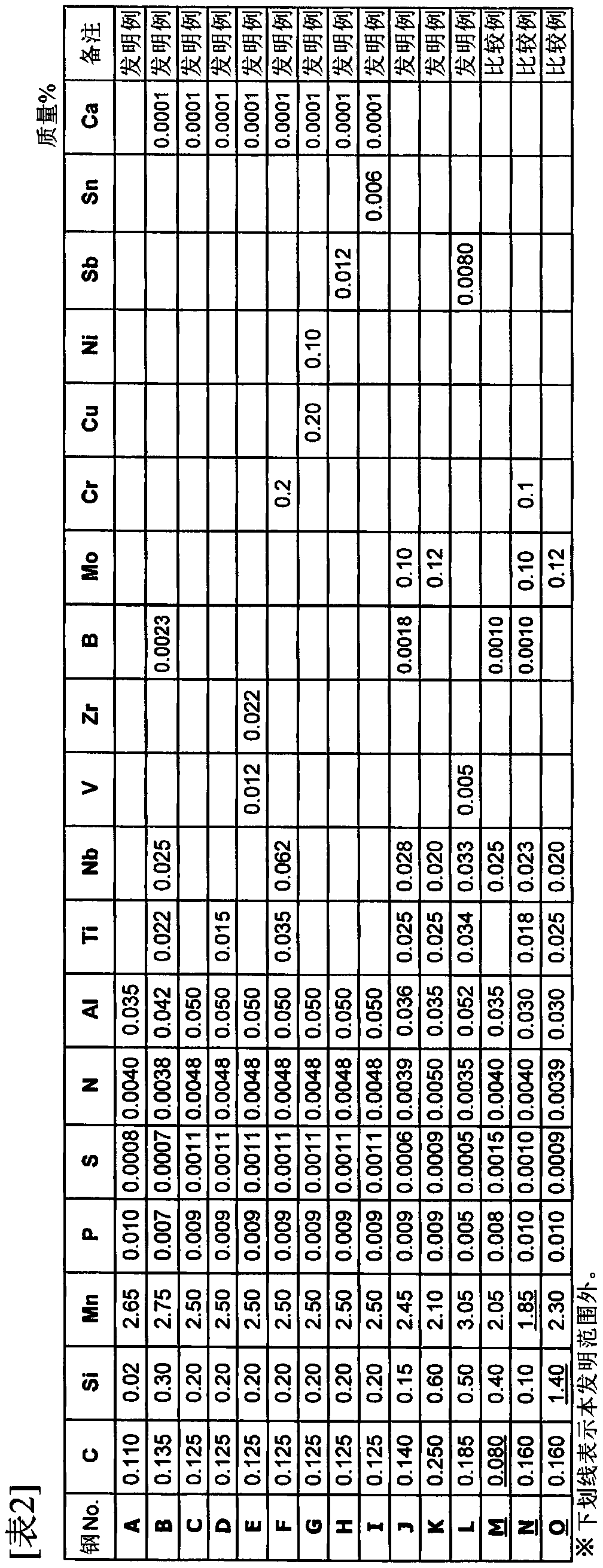
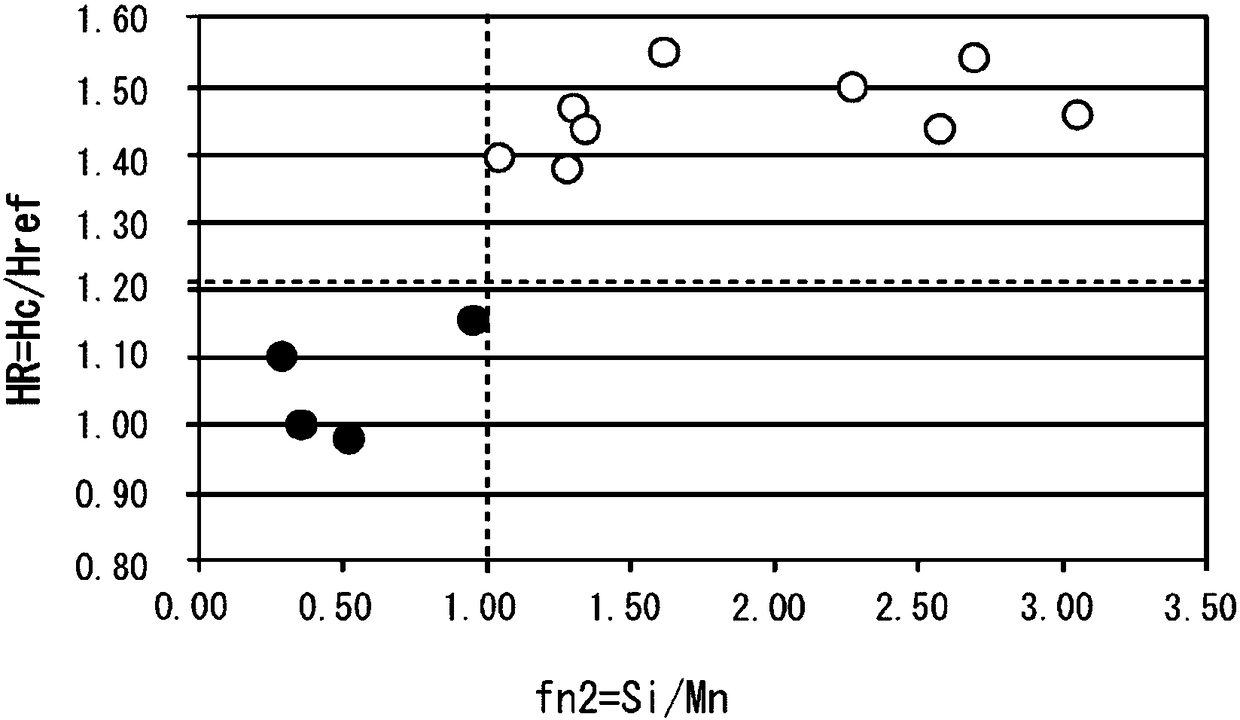
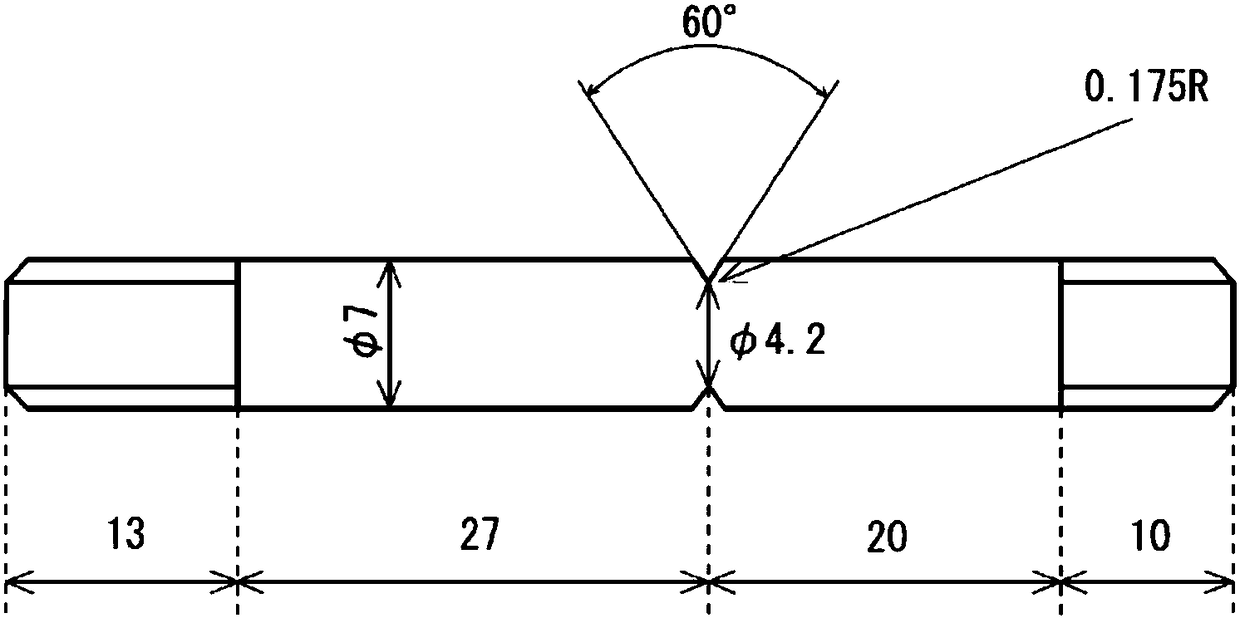
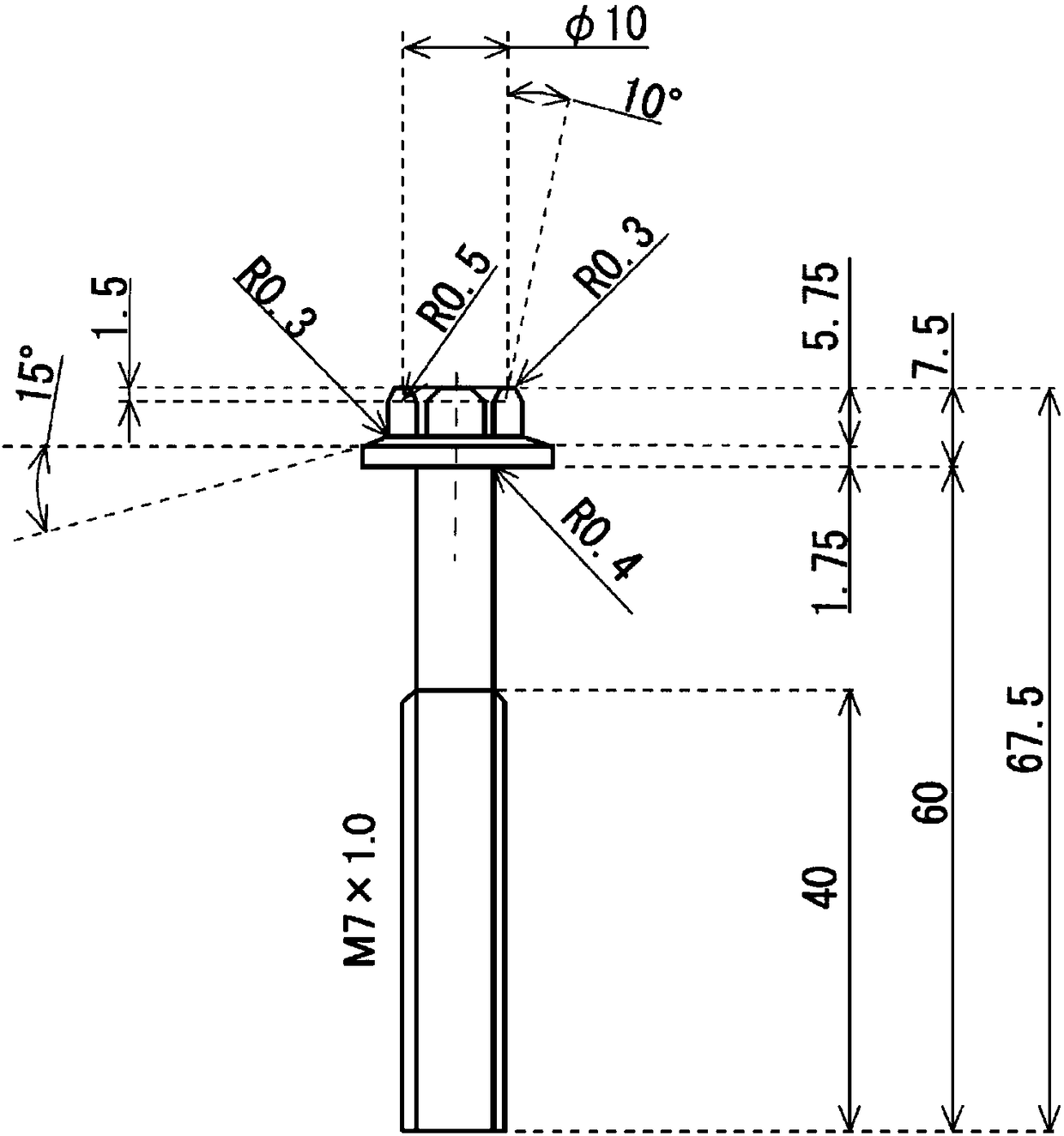
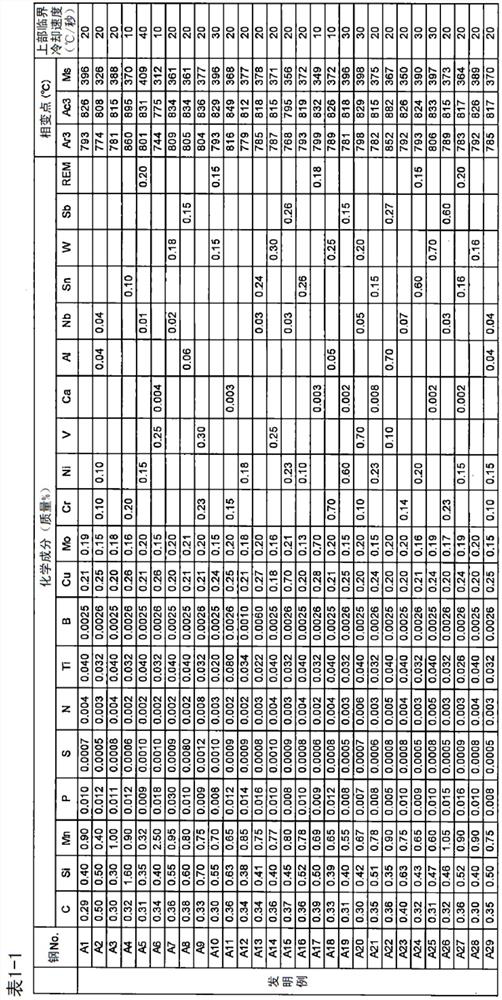
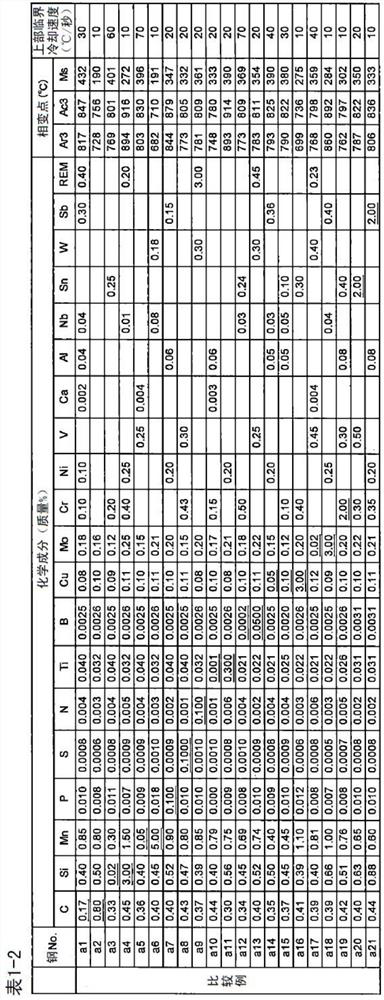
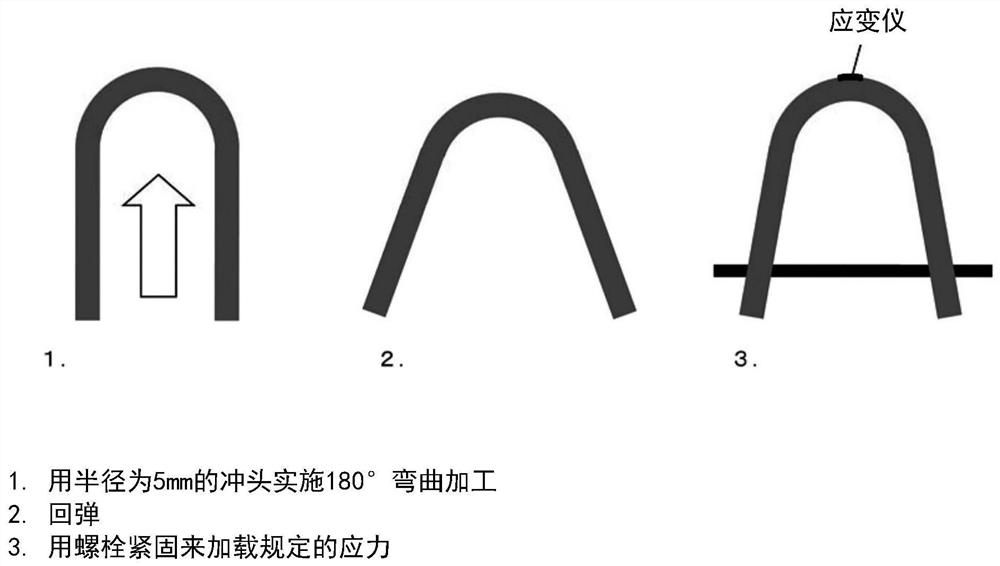
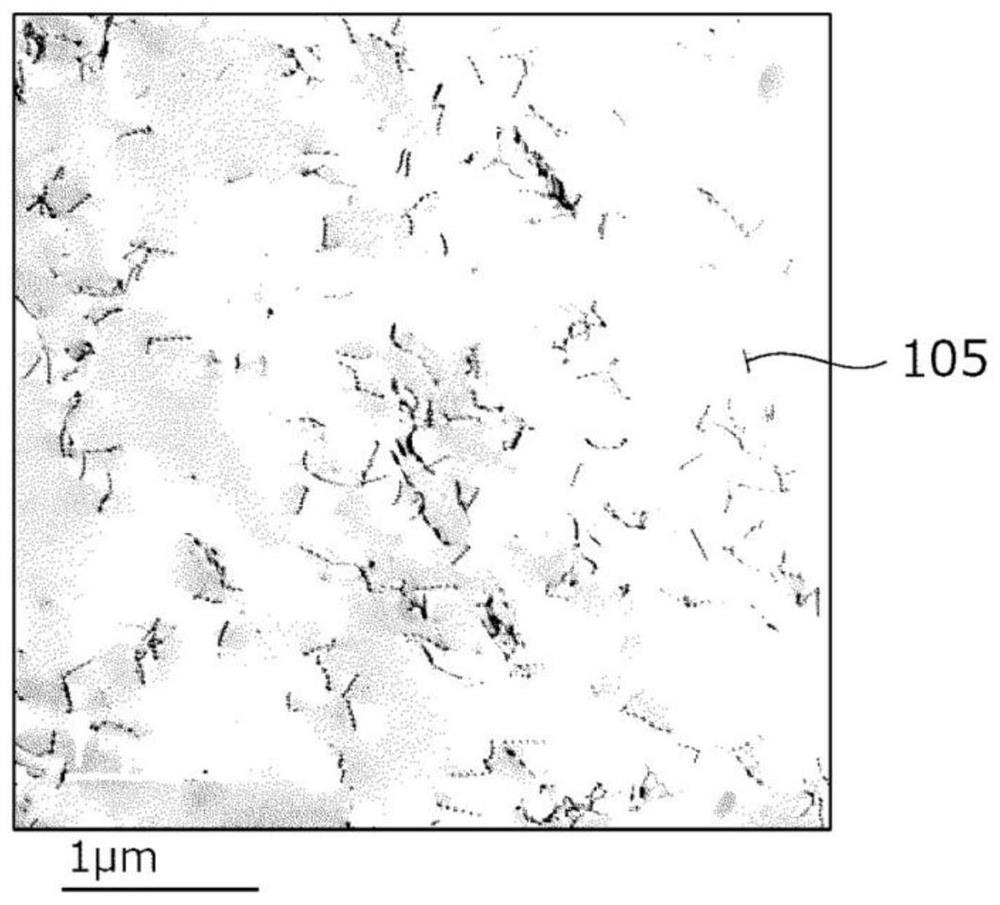
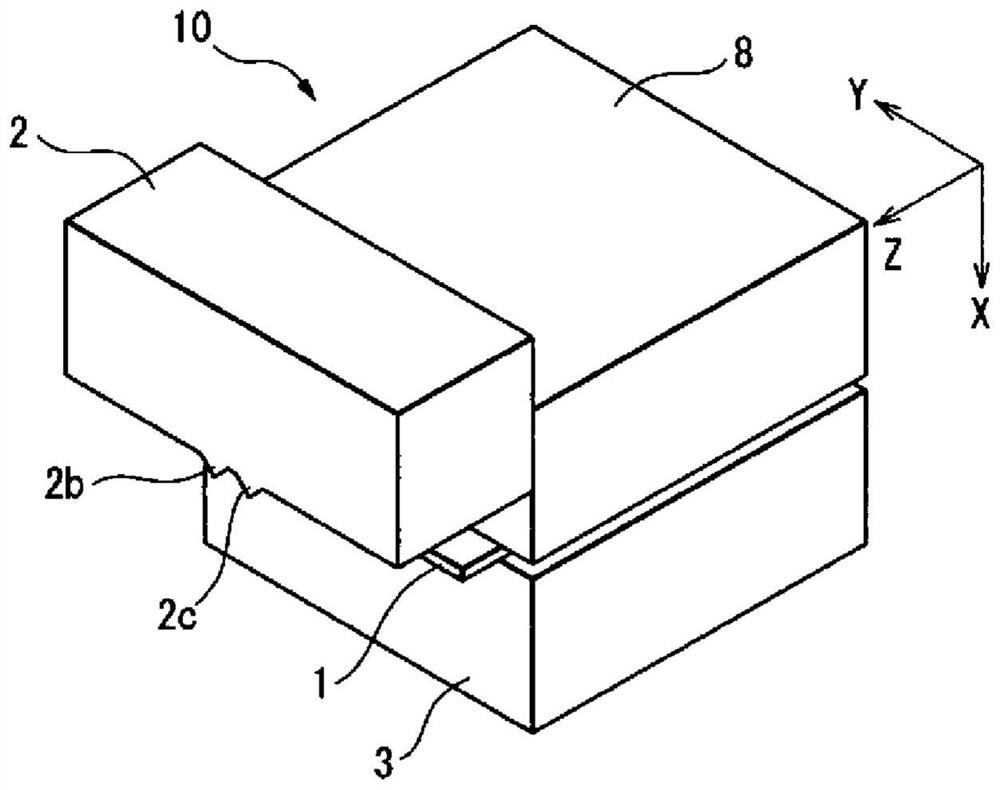
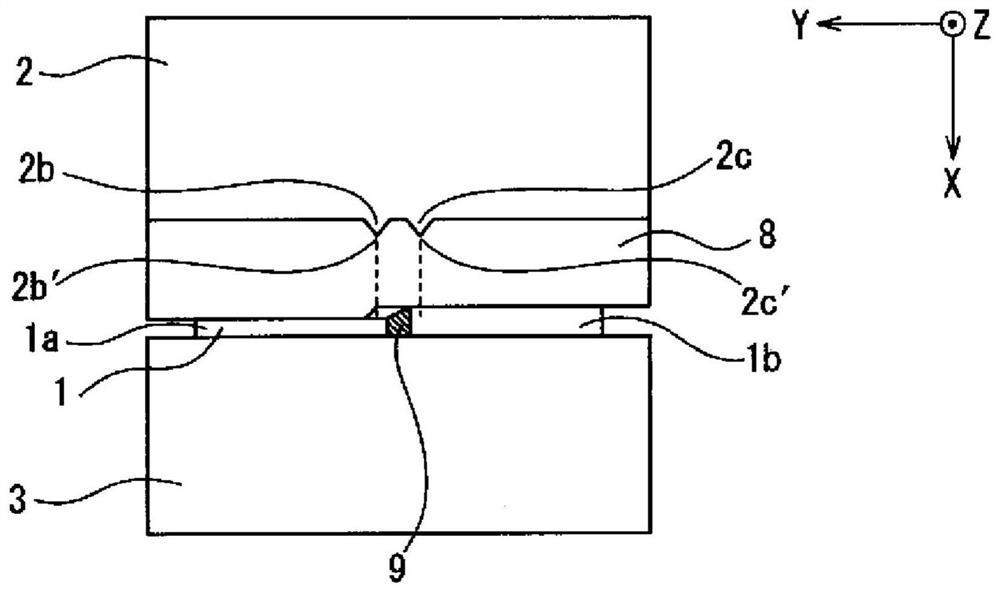
Patents
Literature
59results about How to "Excellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultrahigh-strength thin steel sheet
ActiveCN101351570AImprove corrosion resistanceReduce contentFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSheet steelUltimate tensile strength
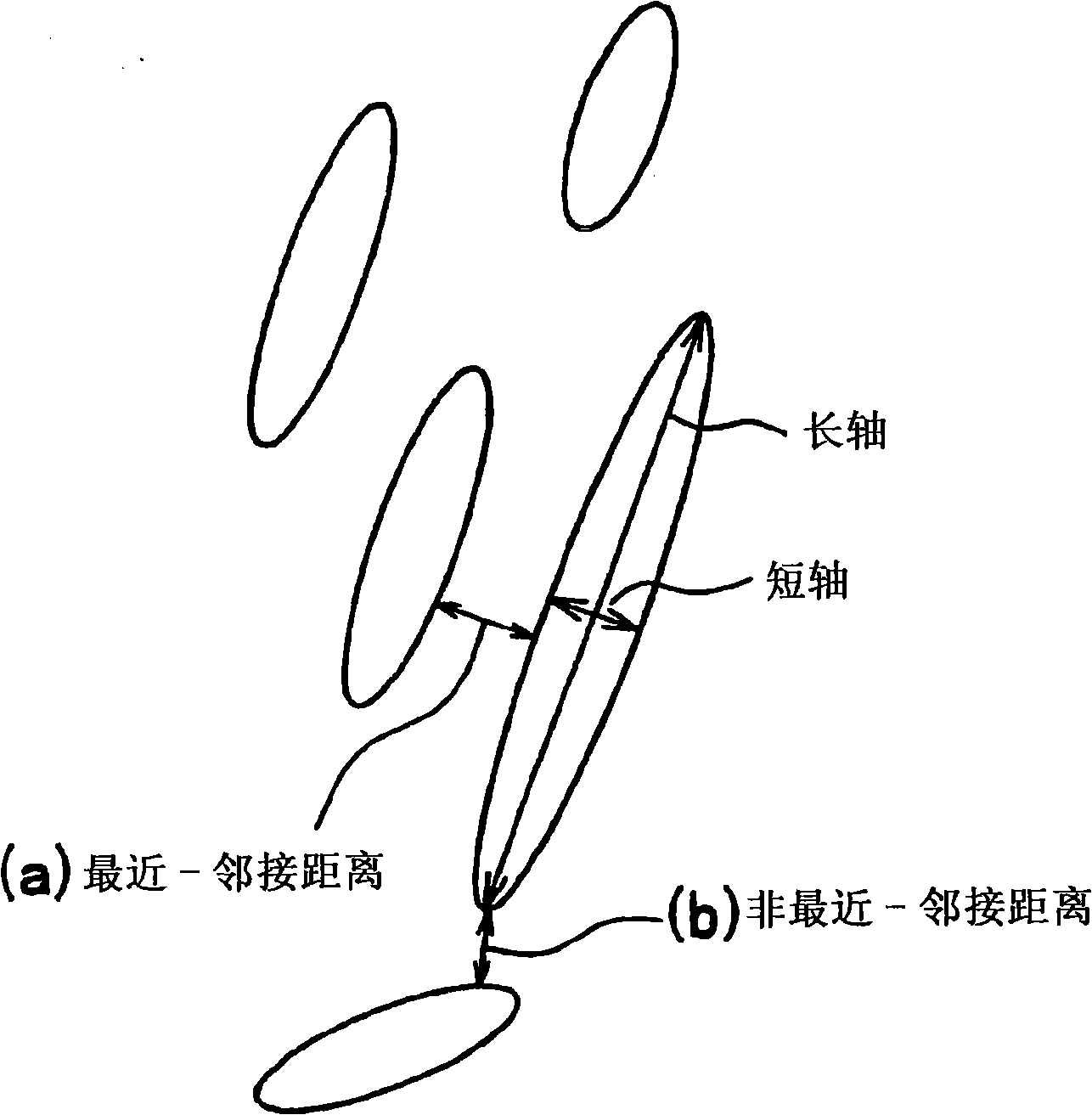
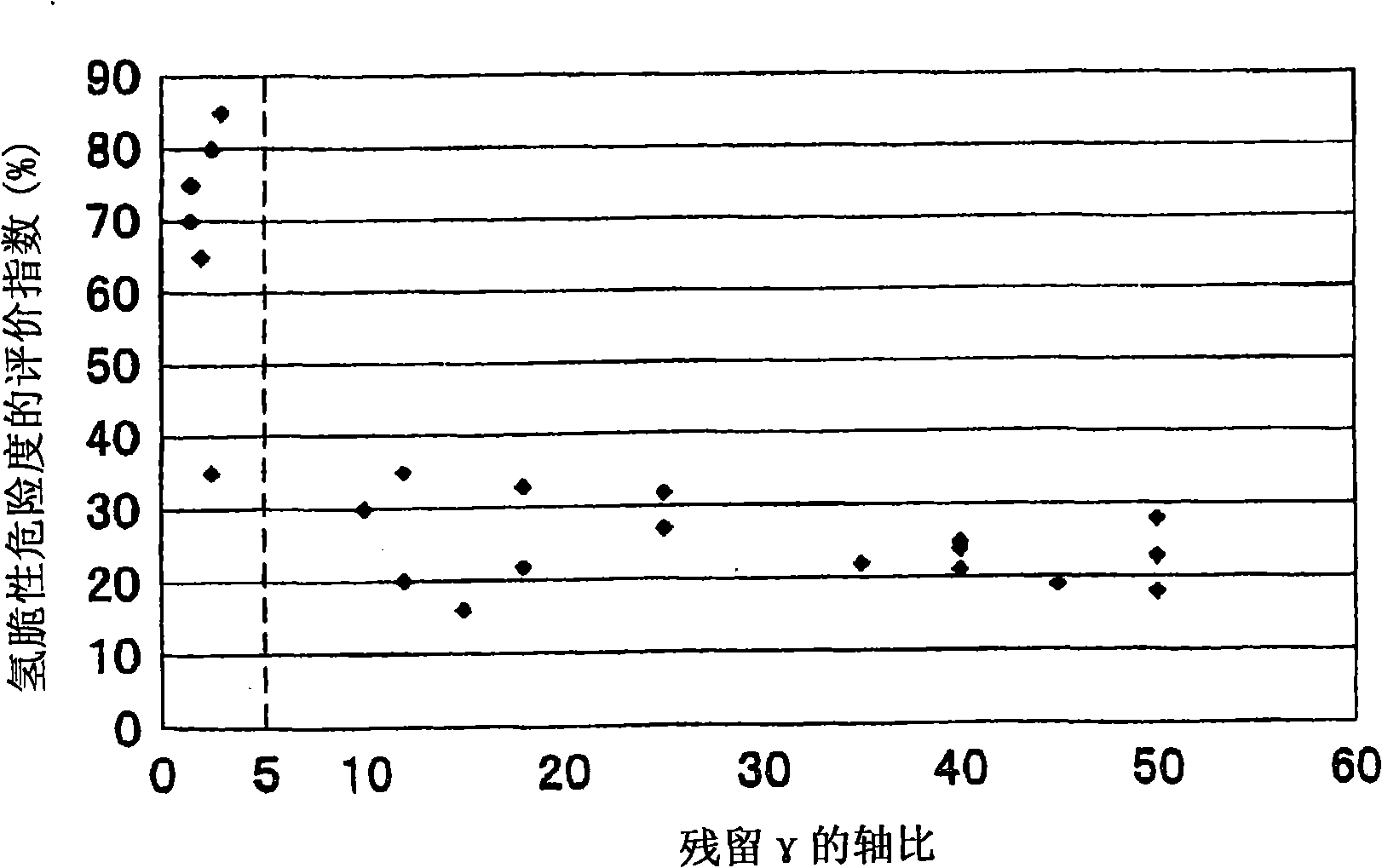
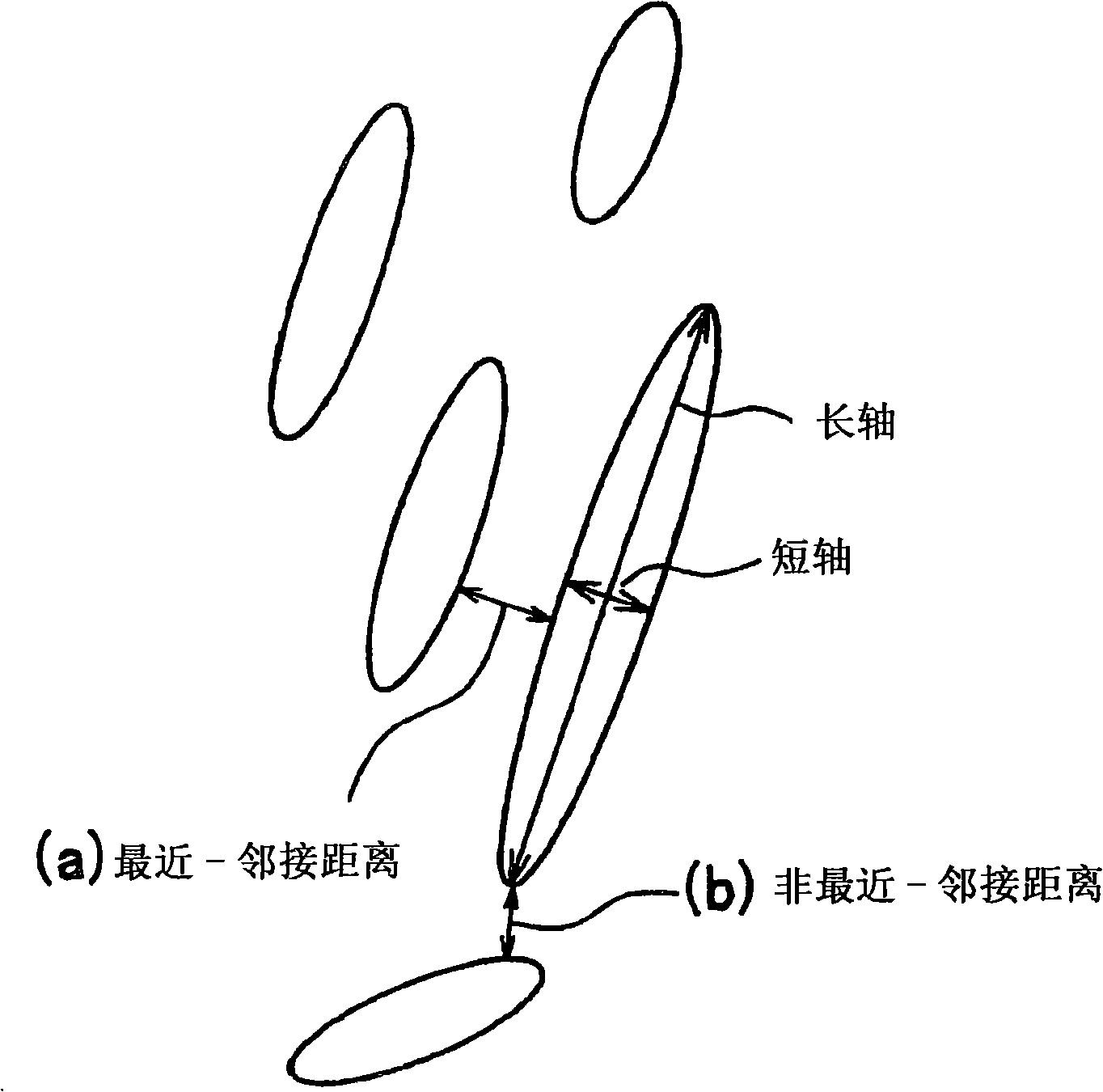
The present invention relates to an ultrahigh-strength steel sheet, which comprises, in terms of wt.%, 0.10-0.60% C, 1.0-3.0% Si, 1.0-3.5% Mn, up to 0.15% P, up to 0.02% S, up to 1.5% Al, and 0.003-2.0% Cr, with the remainder being iron and unavoidable impurities, and in which the crystal grains of residual austenite have an average aspect ratio (major axis / minor axis) of 5 or higher, an average minor-axis length of 1 [mu]m or shorter, and a minimum grain-to-grain distance of 1 [mu]m or shorter. It has excellent unsusceptibility to hydrogen embrittlement.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
High-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and process for producing same
ActiveCN102482753AImprove fatigue durabilityExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSoft layerHigh intensity
Disclosed is a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet which comprises a steel sheet part and a deposit formed on the surface of the steel sheet part and has a tensile strength of 770 MPa or higher, wherein the deposit is a zinc layer formed by hot-dip plating or an alloyed zinc layer formed by hot-dip plating, the steel sheet part comprises a soft layer, which is in direct contact with the deposit, and an inner layer, which is the part other than the soft layer, and the thickness (D) of the soft layer is 0.001 to 5% of the thickness (t) of the steel sheet part. In a cross-section along the thickness direction of the steel sheet part, when the hardness of the soft layer measured by a nanoindentation method is expressed by H1 and the representative hardness of the steel sheet part measured by the nanoindentation method is expressed by Ha, then H1 is 5-75% of Ha.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
High-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and process for producing same
ActiveCN104245999AImprove corrosion resistanceExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementHot-dipping/immersion processesSolid state diffusion coatingSheet steelCarbide
A hot-dip galvannealed steel sheet which comprises a steel sheet that has a composition containing, in terms of mass%, 0.02-0.30% C, 0.01-2.5% Si, 0.1-3.0% Mn, 0.003-0.08% P, up to 0.01% S, 0.001-0.20% Al, and 0.03-0.40% Ti, with the remainder comprising Fe and unavoidable impurities, and a zinc coating layer formed on each of the surfaces thereof in an amount of 20-120 g / m2 per surface, wherein each coating layer contains carbide grains having an average grain diameter of 10 nm or smaller in a number of 5-50 per section and oxide grains having an average grain diameter of 50 nm or larger in a number of 5-50 per section. The section means an area (t11 ([mu]m2)) defined by the coating-layer thickness (t1 [mu]m) and segments obtained by dividing a cross-section of the coating layer in the direction perpendicular to the thickness direction at an interval of 1 [mu]m.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Steel wire for high-strength spring having exceptional coiling performance and hydrogen embrittlement resistance, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN104321454AHigh strengthImprove the winding effectSpringsFurnace typesGranularityHigh intensity
The present invention provides a spring steel wire that demonstrates high strength without being doped with large quantities of alloy elements, and makes it possible to obtain a cold winding spring having exceptional coiling performance and improved hydrogen embrittlement resistance. The spring steel wire is characterized in comprising 0.40 to 0.65 percent by mass of C, 1.0 to 3.0 percent by mass of Si, 0.6 to 2.0 percent by mass of Mn, 0.015 mass percent or less (excluding 0%) of P, 0.015 percent by mass or less (excluding 0%) of S, and 0.001 to 0.10 percent by mass of Al, the balance being made up of iron and impurities; 70% or more of the area of the entire structure being tempered martensite, and 6 to 15% of the area of the entire structure being residual austenite, the old austenite crystal grain size number as determined using the method defined in JIS G 0551 being 10.0 or higher and the tensile strength being 1900 MPa or higher.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Steel structure for hydrogen, and method for manufacturing pressure accumulator for hydrogen and line pipe for hydrogen
ActiveCN105102653AExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesHigh pressure hydrogenMetallurgy
Provided is a steel structure for hydrogen, such as a pressure accumulator for hydrogen or a line pipe for hydrogen, which has a reduced fatigue crack growth rate, and superior hydrogen embrittlement resistance in a high-pressure hydrogen environment compared to conventional steel. The steel structure for hydrogen, which has excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance in high-pressure hydrogen gas, has a steel composition having either 10-95% bainite by surface area, 10-95% martensite by surface area, or 10-95% pearlite by surface area, with the remainder substantially comprising ferrite.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Wire rod for manufacture of steel wire for pearlite structure bolt having tensile strength of 950-1600 mpa, steel wire for pearlite structure bolt having tensile strength of 950-1600 mpa, pearlite structure bolt, and methods for manufacturing same
ActiveCN105308202AExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementImproved cold working propertiesNutsBoltsChemical structureWire rod
This wire rod for the manufacture of a steel wire for a pearlite structure bolt having a tensile strength of 950-1600 MPa has a predetermined chemical structure and is manufactured by performing an isothermal transformation process directly after hot rolling. If the C content is represented as [C] in unit mass%, then in a region 4.5 mm from the surface of the wire rod, the metal structure has a pearlite structure of 140 * [C] area% or more. In the region 4.5 mm from the surface of the wire rod, the mean block particle size of pearlite blocks as measured in a cross-section of the wire rod is 20 Mum or less. In the region 4.5 mm from the surface of the wire rod, the average lamellar spacing of the pearlite structure is more than 120 nm and not more than 200 nm.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
Steel wire for non-thermal-refined machine component, and non-thermal-refined machine component
ActiveCN108474073AImproved cold working propertiesExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementNutsBoltsImpurityMetal
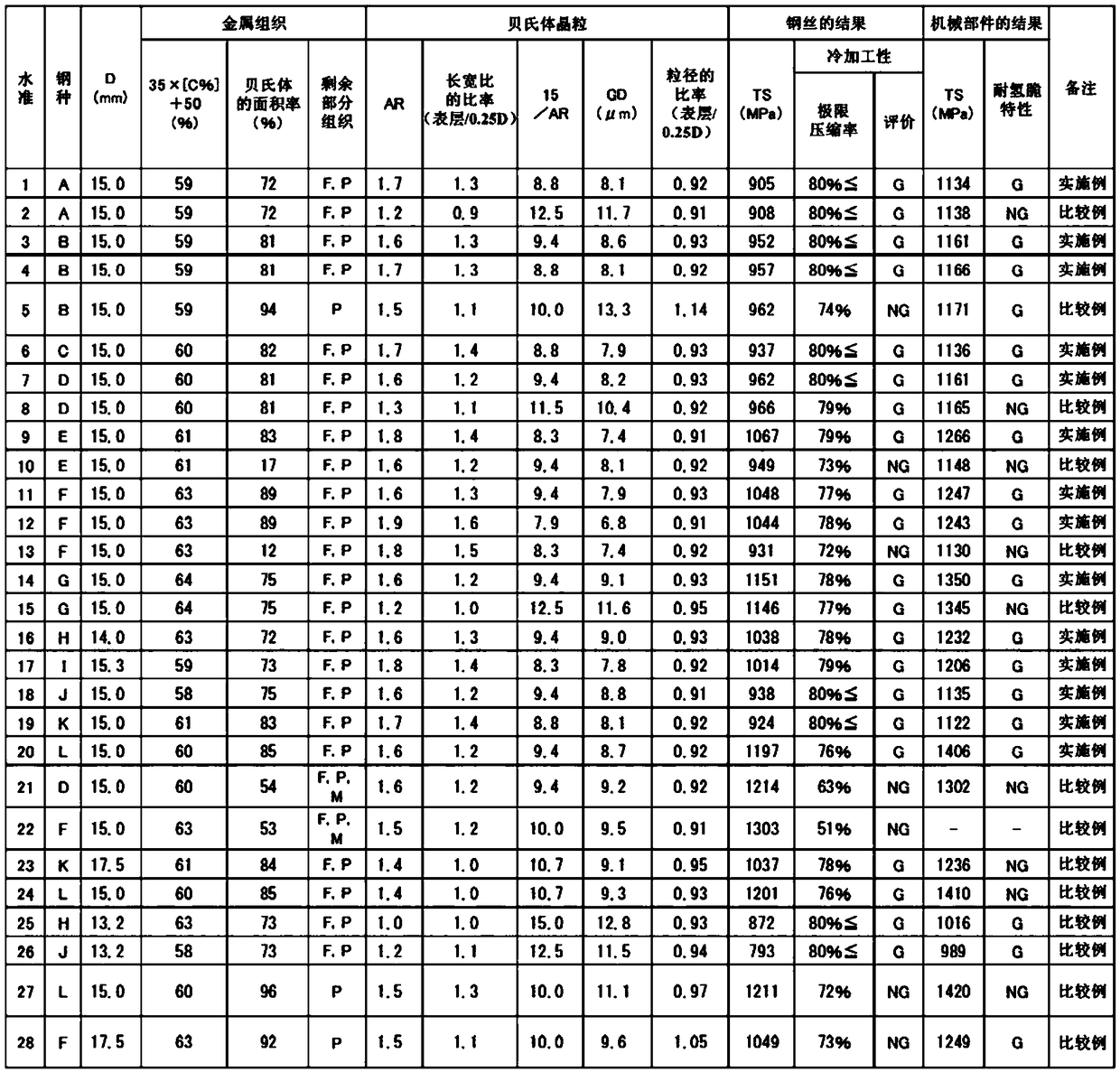
A steel wire for a non-thermal-refined machine component, the steel wire including, in terms of mass%, 0.20-0.40% C, 0.05-0.50% Si, 0.50-2.00% Mn, and 0.005-0.050% Al, the remainder including Fe and impurities, the metallographic structure including (35 x [C%] + 50)% or more of bainite, and AR being 1.4 or greater, (AR) / (average aspect ratio of bainite particles at a position a depth of 0.25 D inthe L cross-section) being 1.1 or greater, GD being (15 / AR) [mu]m or less, and (GD) / (average particle diameter of bainite particles at a position a depth of 0.25 D in the C cross-section) being less than 1.0, where D is the diameter of the steel wire, AR is the average aspect ratio of bainite particles at a position a depth of 50 [mu]m in the L cross-section, and GD is the average particle diameter of bainite particles at a position a depth of 50 [mu]m in the C cross-section.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hydrogen permeation alloy material and preparation thereof
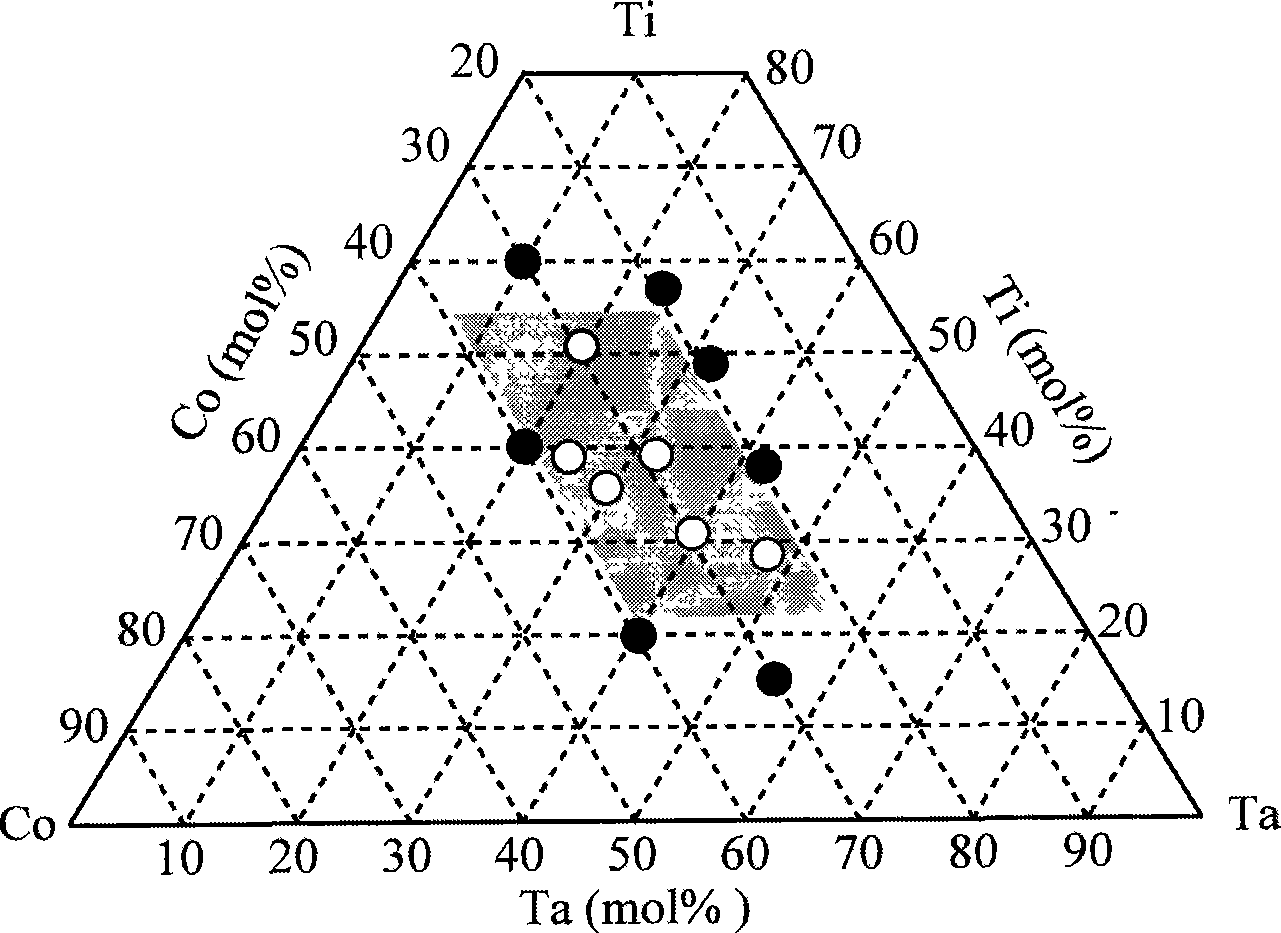
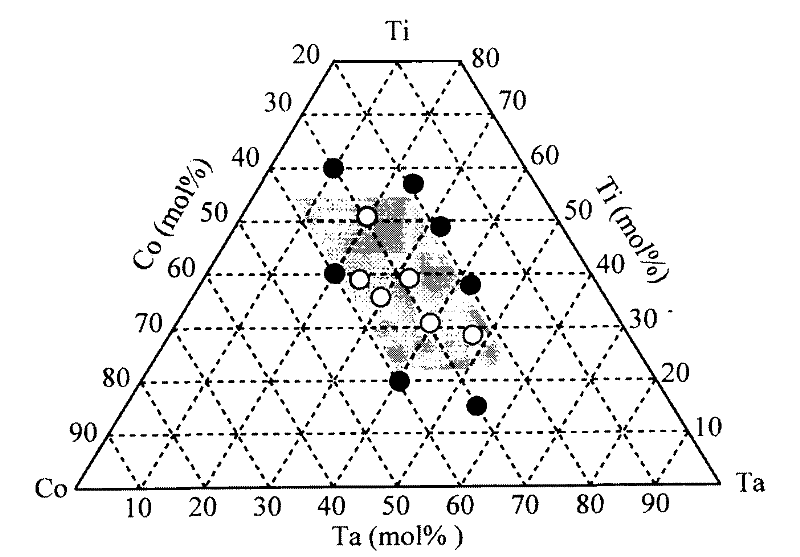
The invention discloses a hydrogen permeating alloy material and a method for preparing the same, and the alloy comprises the following components by molar percentage: titanium of 23mol%-54mol%, cobalt of 21mol%-39mol% and tantalum, titanium, cobalt and tantalum of which the total content is of 98-100mol%.The manufacturing of the alloy material comprises steps of putting titanium, cobalt and tantalum with a purity of more than 99% into a non-consumable vacuum arc furnace, vacuumizing to a pressure below 3*10 3 Pa, filling in argon of high purity to a pressure of 4*10 Pa, and then smelting. The alloy material of the invention has the hydrogen permeability and excellent hydrogen brittleness resistance ability higher than pure palladium under 573-673K, while the cost of the alloy material is only about 1 / 100 of that of the pure palladium, thus, the alloy material can be used for hydrogen gas isolation and purification, and can also be used for a catalytic-reformed compact membrane reactor and the like.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Austenitic stainless steel and method for producing same
ActiveCN106170576AExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementHigh strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMetallurgyMachinability
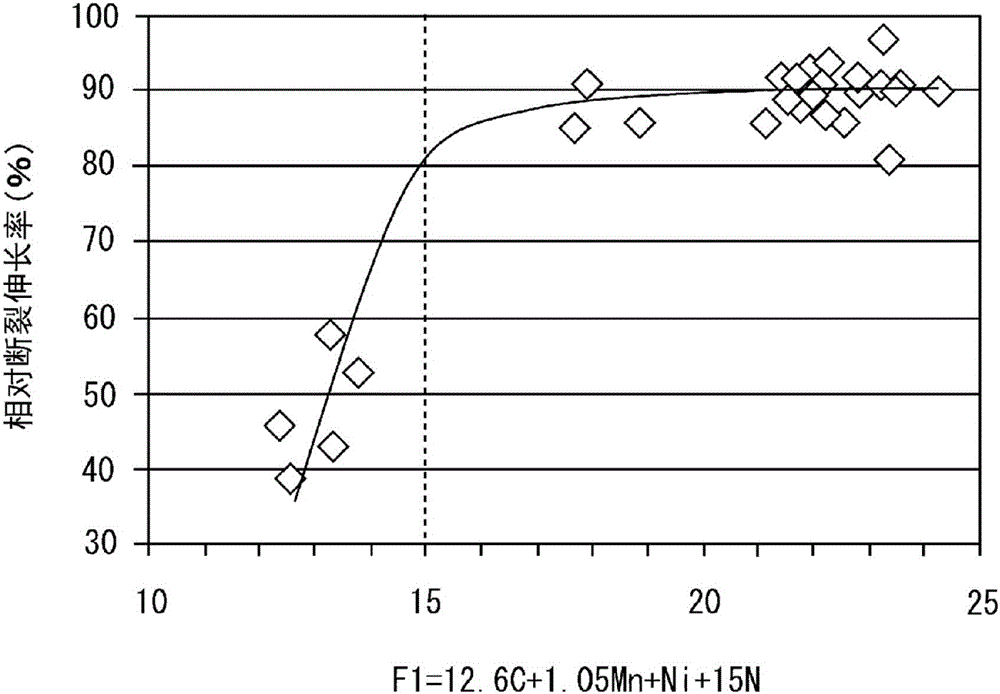
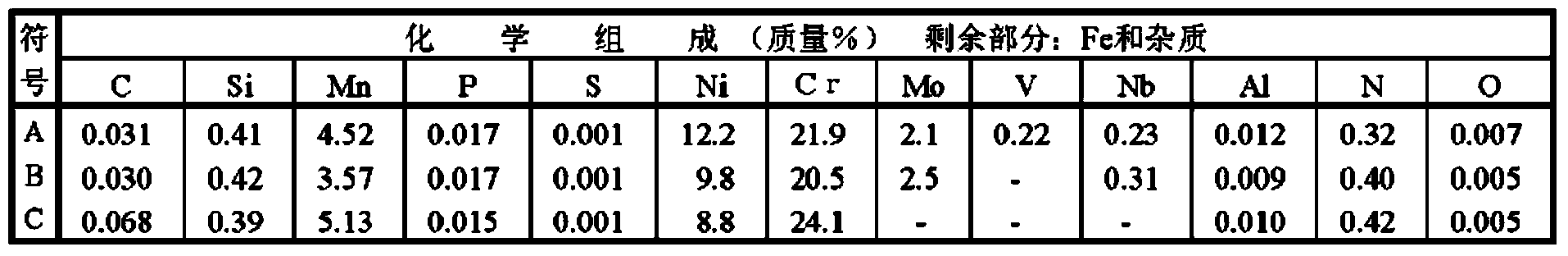
Provided is austenitic stainless steel which has high strength and excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance, and which additionally has excellent machinability. Austenitic stainless steel according to one embodiment of the present invention has a chemical composition which contains, in mass%, 0.10% or less of C, 1.0% or less of Si, 2.1-6.0% of Mn, 0.045% or less of P, 0.1% or less of S, 8.0-16.0% of Ni, 15.0-30.0% of Cr, 1.0-5.0% of Mo, 0.05-0.45% of N, 0-0.50% of Nb and 0-0.50% of V with the balance made up of Fe and impurities, and which satisfies formula (1). This austenitic stainless steel has a crystal grain size number of less than 8.0 and a tensile strength of 690 MPa or more. 15<=12.6C + 1.05Mn + Ni + 15N (1).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
High strength thin steel sheet having high hydrogen embrittlement resisting property and high workability
InactiveCN1796588AEasy to processTensile strength for excellent processabilityRoll mill control devicesHeat treatment process controlAustenite grainSheet steel
The present invention provides an ultrahigh strength steel sheet that has high hydrogen embrittlement resisting property and high workability. The ultrahigh strength steel sheet comprises: C: more than 0.25-0.60 wt%, si: 1.0-3.0 wt%, Mn: 1.0-3.5 wt%, P: less than 0.15 wt%, S: less than 0.02 wt%, Al: less than 1.5 wt% (excluding 0%), the residual consists of Fe and unavoidable impurity, has a metallurgical structure after stretch forming process with 3% working rate, which comprises: 1% or more residual austenite; 80% or more in total of bainitic ferrite and martensite; and 9% or less (may be 0%) in total of ferrite and pearlite in terms of proportion of area to the entire structure, wherein the mean axis ratio (major axis / minor axis) of the residual austenite grains is 5 or higher; and the steel sheet has tensile strength of 1180 MPa or higher.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Steel structure for hydrogen which exhibits excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance properties in high-pressure hydrogen gas, and method for producing same
InactiveCN108026619AImproved resistance to hydrogen embrittlementExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesLine tubingHigh pressure hydrogen
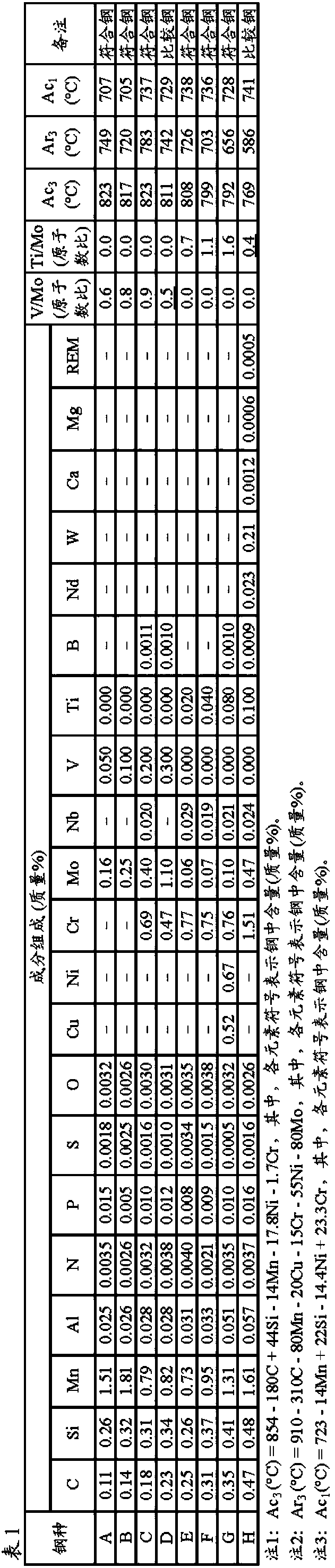
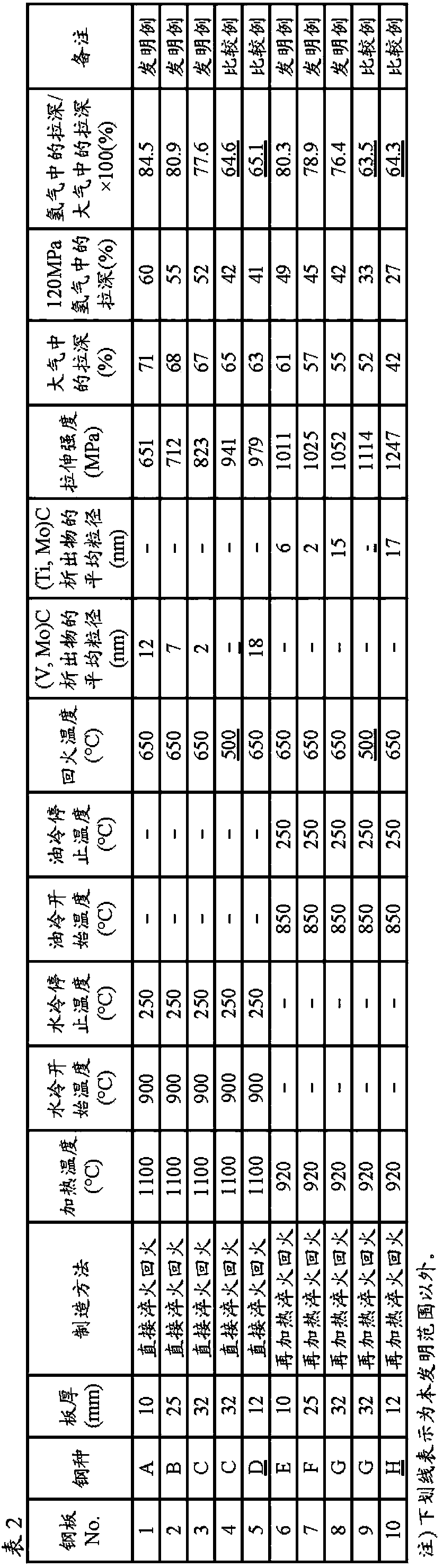
A steel structure for hydrogen, which can exhibit excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance properties in a high-pressure hydrogen environment and therefore can be used as a pressure accumulator forhydrogen, a line pipe for hydrogen and the like. The steel structure can be produced by: providing a steel composition containing, in % by mass, 0.02 to 0.50% of C, 0.05 to 0.50% of Si, 0.5 to 2.0% of Mn, 0.05% or less of P, 0.01% or less of S, 0.01 to 0.10% of Al, 0.0005 to 0.008% of N and 0.01% or less of O and also containing V and Mo in amounts that meet such requirements that the content ofV is 0.05 to 0.30%, the content of Mo is 0.05 to 1.13% and the (number of atoms of V) / (number of atoms of Mo) ratio becomes 0.6 to 2.0, with the remainder being made up by Fe and unavoidable impurities; and adjusting the average particle diameter of a composite fine carbide composed of V and Mo to 1 to 20 nm.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Austenite steel welded joint
ActiveCN103648708AHigh strengthExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementArc welding apparatusFurnace typesPipeAustenite
This austenite steel weld joint is welded by a gas tungsten arc welding method using an austenite steel base material that has a specific chemical composition and using an austenite steel welding material that has a specific chemical composition. The chemical composition of the welding metal contains C <= 0.1%, Si <= 0.8%, Mn: 1.5-5.5%, Ni: 8-15%, Cr: 18-24%, Al<0.05%, and N: 0.15-0.35% and, as necessary, contains one or more of V <= 0.5%, Nb <= 0.5%, and Mo <= 4.5%, with the remainder being formed from Fe and impurities. The impurities are O <= 0.02%, P <= 0.05%, and S <= 0.03%, the chemical composition satisfies [413-462(C + N)-9.2Si-8.1Mn-13.7Cr-9.5Ni-18.5Mo=-70], and an austenite steel weld joint in which the amount of ferrite in the welding metal is 20% or less by area ratio is provided with both high strength and excellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlement, which are characteristics required for high-pressure hydrogen gas pipes, even when post weld heat treatment is not carried out.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
High strength thin steel sheet having high hydrogen embrittlement resisting property and high workability
InactiveCN100410409CEasy to processTensile strength for excellent processabilityRoll mill control devicesHeat treatment process controlAustenite grainSheet steel
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
High-strength cold-rolled steel sheet and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveCN111868284AFull formabilityExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesChemical compositionBend radius
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet
ActiveCN109154044AExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementHigh tensile strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesChemical compositionCarbide
This hot-dip galvanized steel sheet has a specific chemical composition and a steel structure that is represented as: containing, in terms of area ratio, polygonal ferrite in an amount not more than 10%, upper bainite in an amount not more than 20%, residual austenite in an amount not more than 5%, and martensite in an amount not less than 70%; and a martensite that includes Fe carbides at a number density not less than 1*106 / mm2, that is contained in an amount not less than 50% of the entire amount of martensite, and that has an average effective crystal grain size of not more than 5.0 [mu]m.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
High-strength galvanized steel sheet, and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN111433380AHigh strengthExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesHydrogen contentUltimate tensile strength
Provided are: a high-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet that has a material quality meeting the high yield strength highly demanded for ultra-high-strength plated steel sheets for which hydrogenembrittlement is a concern, has an excellent plating appearance and excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance, and has high yield strength suitable for building materials and automotive impact-resistant parts; and a method for manufacturing the same. This high-strength galvanized steel sheet comprises: a steel sheet having a specific component composition and a steel structure that contains at least 70% (including 100%) martensite and bainite, less than 20% (including 0%) ferrite, and less than 5% (including 0%) residual austenite, and having an in-steel diffusible hydrogen content of no more than 0.20 mass ppm; and a galvanized layer formed on the surface of the steel sheet and having an Fe content of 8 to 15%, in mass%, and a plating adhesion amount per surface of 20 to 120 g / m2, wherein the amount of Mn oxide contained in the galvanized layer is no more than 0.050 g / m2, the tensile strength is at least 1,100 MPa, and the yield ratio is at least 0.85.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High-strength bolt
InactiveCN108291284AHigh strengthExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementFurnace typesScrewsChemical compositionHigh intensity
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Austenitic stainless steel having improved hydrogen embrittlement resistance, and high-pressure hydrogen gas container comprising same
InactiveCN110191972AReduce manufacturing costExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementVessel wallsSecondary cellsHigh pressure hydrogenHigh pressure
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Steel member, steel sheet, and methods for producing same
ActiveCN111801436AHigh tensile strengthExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionToughness
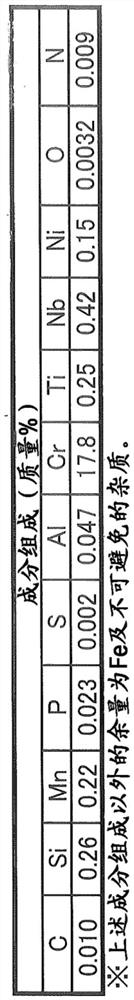
The objective of the present invention is to provide a steel member and a steel sheet that have high tensile strength and toughness, and also have excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance in corrosive environments, and to provide methods for producing the same. A steel member according to the present invention is characterized by having a predetermined chemical composition, wherein the maximumCu content at a depth range within 0-30 [mu]m from the surface is at least 1.4 times greater than the Cu content at a depth of 200 [mu]m from the surface.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Steel sheet and manufacturing method therefor
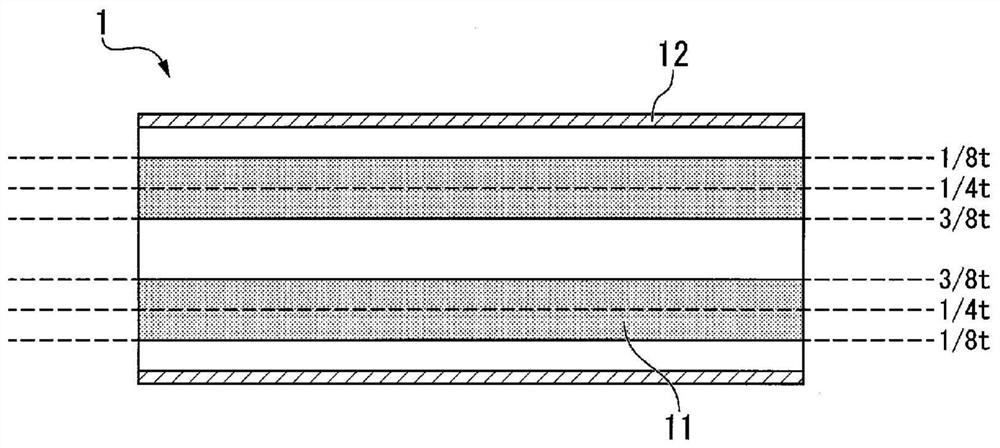
ActiveCN111902554AImprove ductilityExcellent hole expandabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSoft layerChemical composition
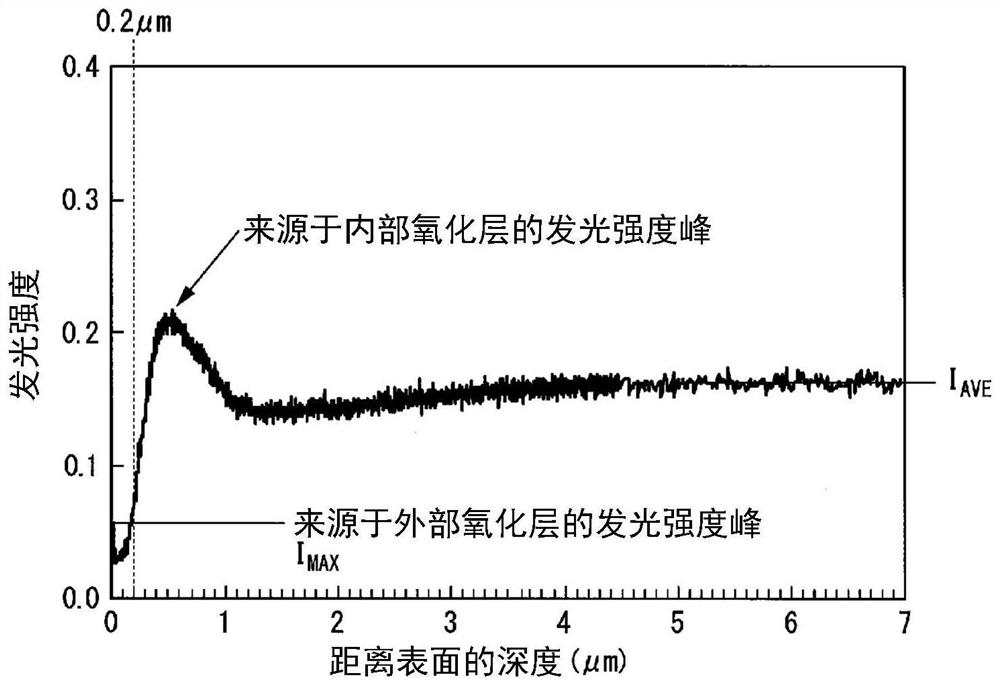
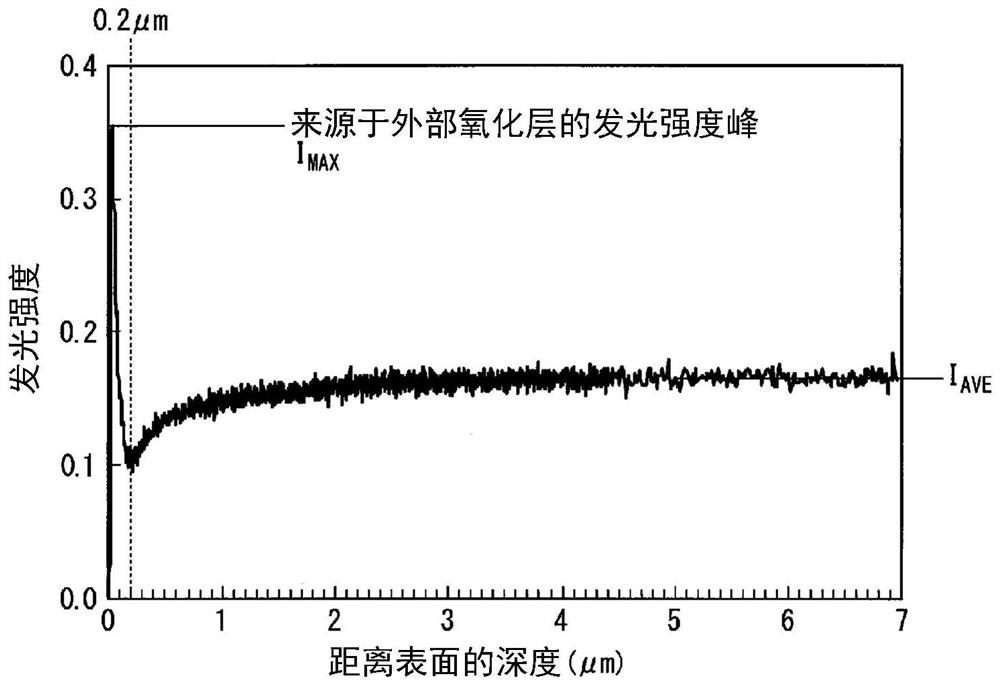
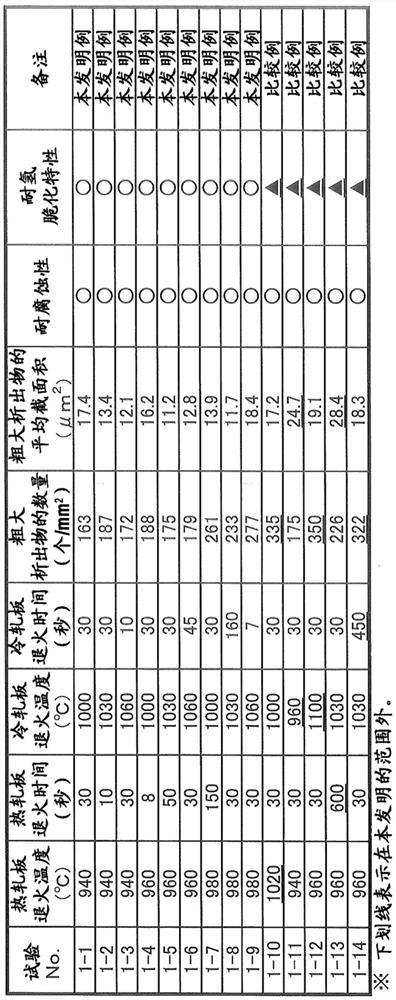
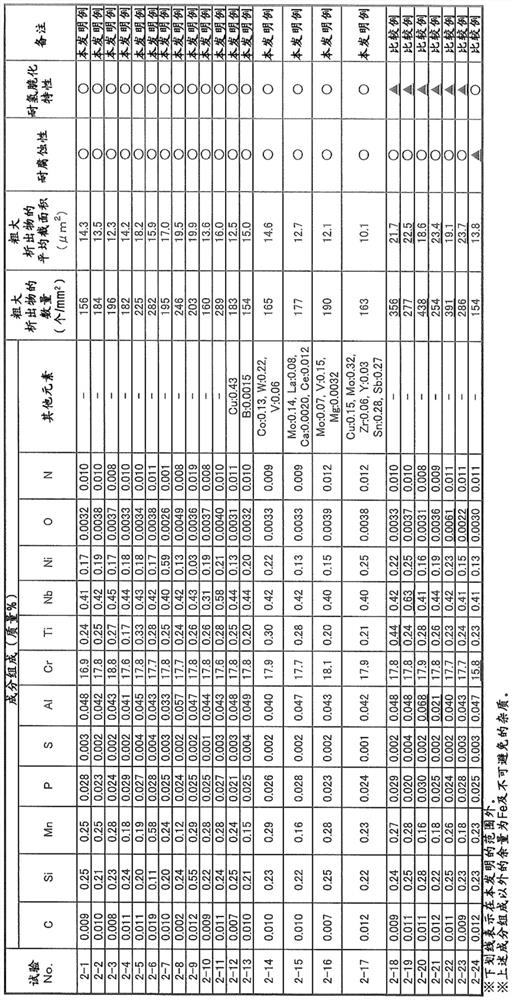
This steel sheet has a prescribed chemical composition, wherein a steel structure in the interior of the steel sheet contains, by volume fraction, 0-30% soft ferrite, 3-40% residual austenite, 0-30% fresh martensite, and a total of 0-10% pearlite and cementite, the remainder including hard ferrite. The number percentage of residual austenite with an aspect ratio of 2.0 or greater included among all of the residual austenite is 50% or greater, a soft layer having a thickness of 1-100 [mu]m in the sheet thickness direction from the surface exists, of the ferrite contained in the soft layer the volume fraction of crystal grains with an aspect ratio of 3.0 or greater is 50% or greater, the volume fraction of the residual austenite in the soft layer is 80% or less of the volume fraction of theresidual austenite in the interior of the steel sheet, and the peak emission intensity of a wavelength representing Si appears in a range of greater than 0.2 [mu]m from the surface and 10.0 [mu]m or less from the surface.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Ferritic stainless steel sheet and method for producing same
ActiveCN113614269AExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementImprove corrosion resistanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesDehydrogenationSS - Stainless steel
Provided is a ferritic stainless steel sheet which does not require a dehydrogenation treatment for the production thereof and has excellent corrosion resistance and hydrogen embrittlement resistance properties in spite of the fact that Ni, Cu and Mn are not contained in larger amounts. The ferritic stainless steel sheet has a component composition comprising, in % by mass, 0.001 to 0.020% of C, 0.10 to 0.60% of Si, 0.10 to 0.60% of Mn, 0.040% or less of P, 0.030% or less of S, 0.030 to 0.060% of Al, 16.5 to 19.0% of Cr, 0.15 to 0.35% of Ti, 0.30 to 0.60% of Nb, 0.01 to 0.60% of Ni, 0.0025 to 0.0050% of O (oxygen), 0.001 to 0.020% of N and a remainder made up by Fe and unavoidable impurities, and is so configured that the number of precipitates each having a cross-sectional area of 5.0 [mu]m2 or more in a 1-mm2 zone is 300 or less and the average cross-sectional area of precipitates each having a cross-sectional area of 5.0 [mu]m2 or more is 20.0 [mu]m2 or less.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Steel sheet
ActiveCN112969804AHigh strengthExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionMetallurgy
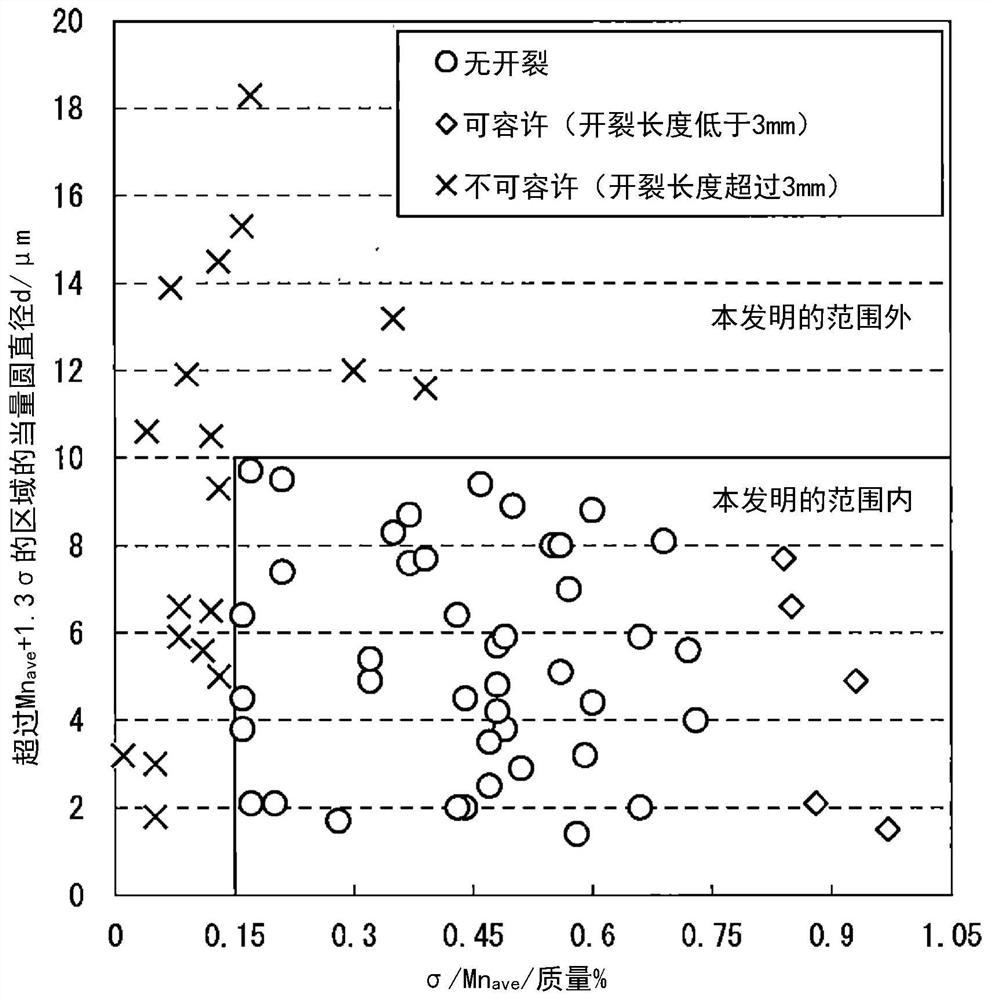
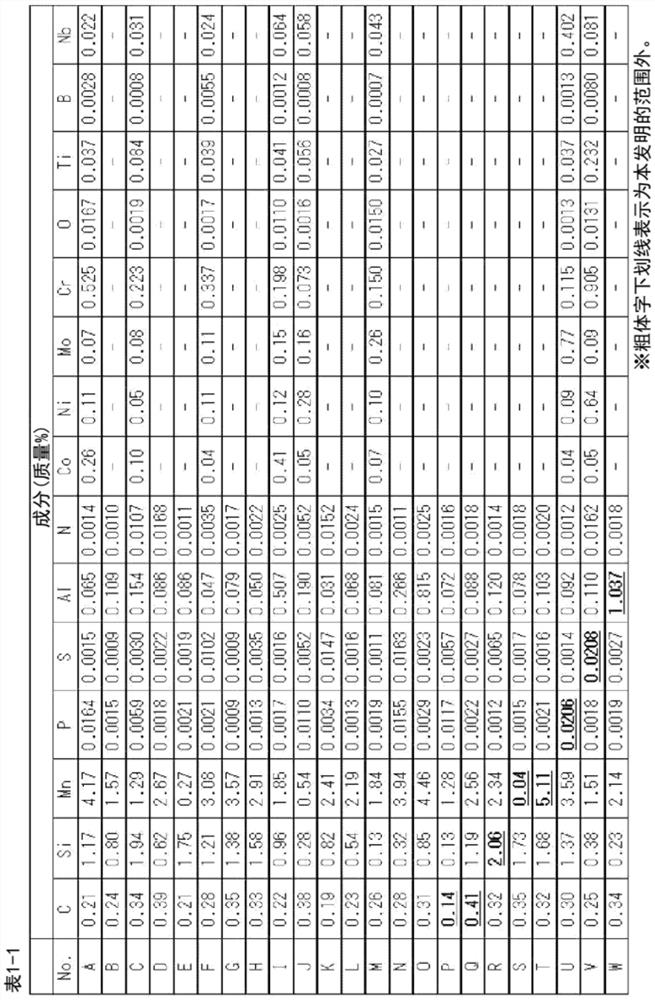
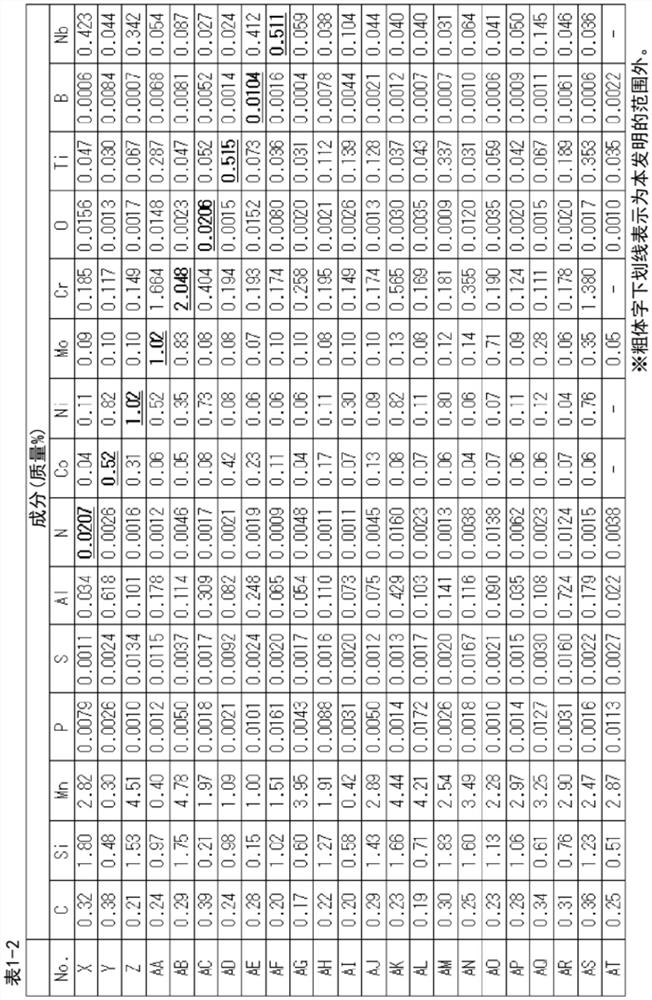
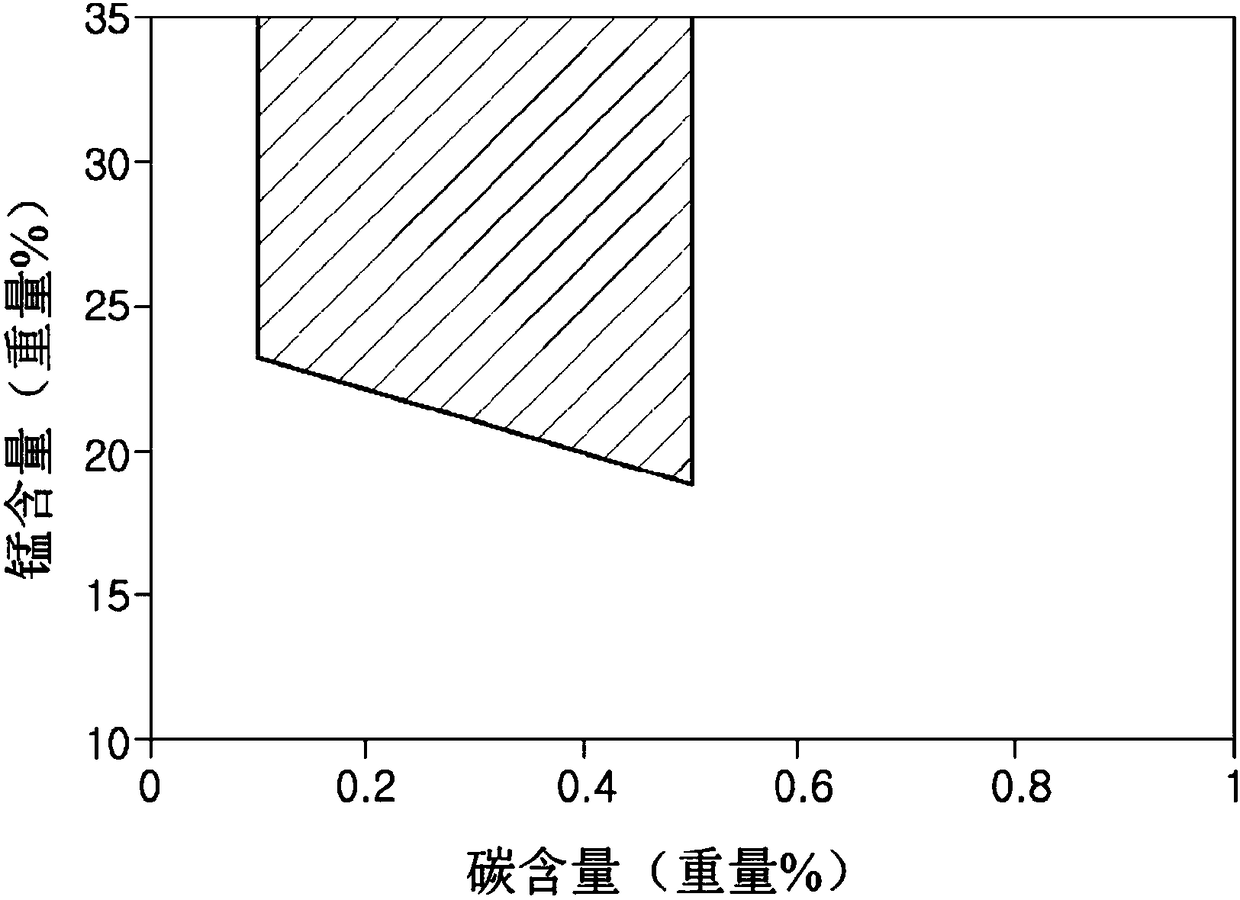
Provided are: a steel sheet having high strength and excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance; and a method for manufacturing the steel sheet. Provided is a steel sheet having a specified chemical composition and a specified structure, wherein the standard deviation sigma of the Mn concentration satisfies the formula: sigma >= 0.15 Mnave (wherein Mnave represents an average Mn concentration), and the equivalent circle diameter of a region having an Mn concentration of more than Mnave + 1.3 sigma is less than 10.0 microns. Also provided is a method for manufacturing a steel sheet, the method comprising: a hot rolling step including performing the finish rolling of a steel piece having a specified chemical composition under specific conditions; a step of winding up the hot-rolled steel sheet at a winding temperature of 450 to 700DEG C ; and a step of cold-rolling the hot-rolled steel sheet and then annealing the cold-rolled steel sheet at 800 to 900DEG C.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Austenitic steel material having excellent hydrogen-embrittlement resistance
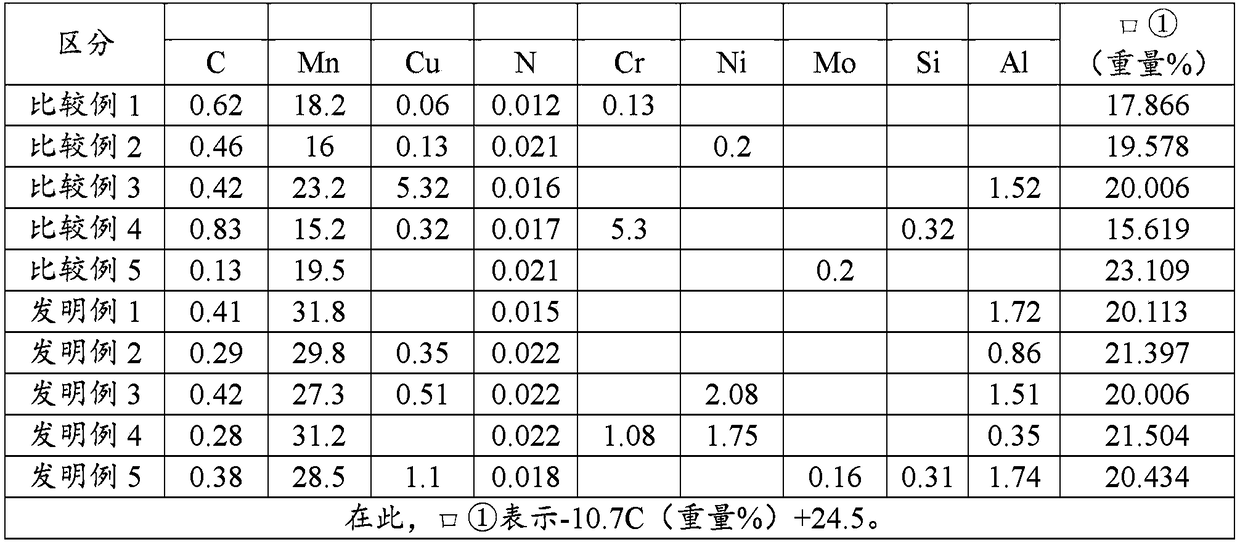
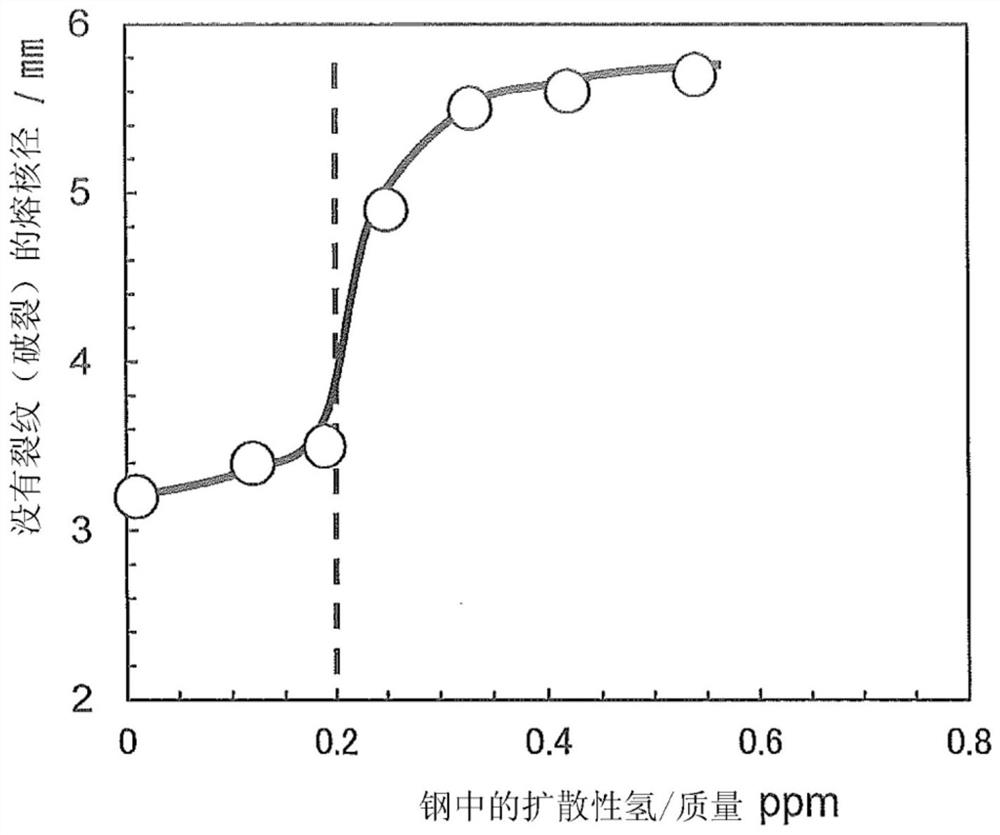
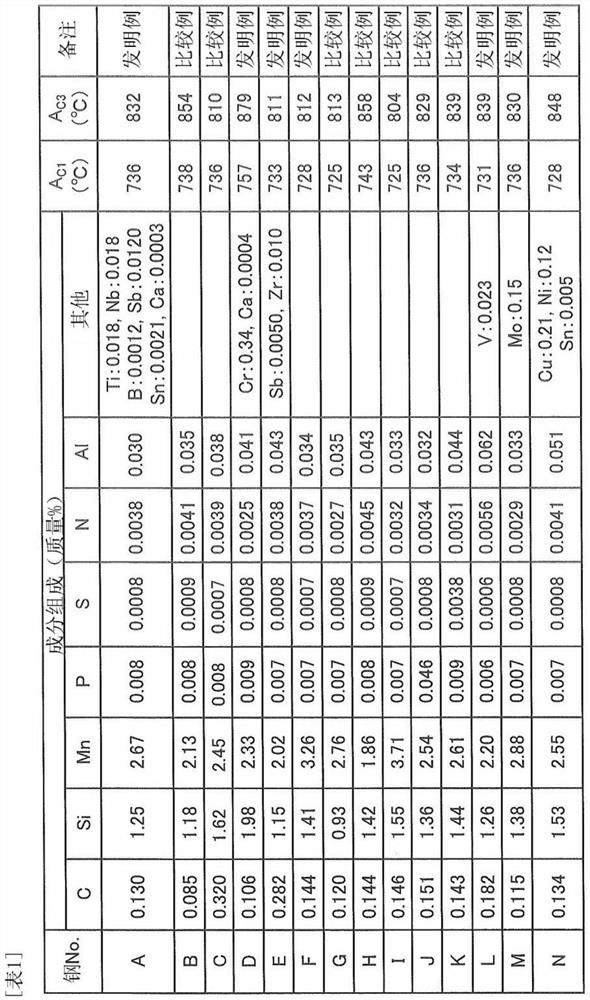
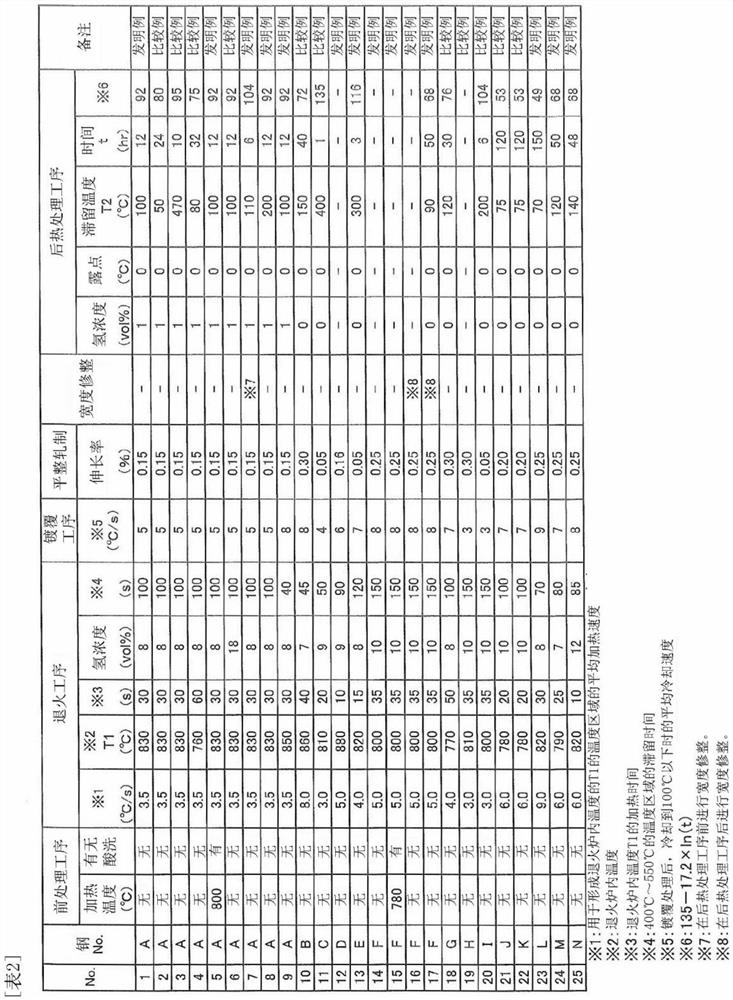
Disclosed is an austenitic material having excellent hydrogen-embrittlement resistance, comprising, by weight, 0.1-0.5% of C, 5% or less (0% exclusive) of Cu, 1% or less (0% exclusive) of N, a contentof [Mn] satisfying [Mn]>=-10.7C+24.5, 10% or less of Cr, 5% or less of Ni, 5% or less of Mo, 4% or less of Si, 5% or less of Al, and a balance amount of Fe and inevitable impurities, with a T-El2 / T-El1 ratio of 0.5 or higher, wherein T-El1 is an elongation at break according to a tensile test at 25oC under an atmospheric condition of 1 atm and T-El2is an elongation at break according to a tensiletest at 25 DEG C under a hydrogen condition of 70 MPa.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-strength galvanized steel sheet, high-strength member, and manufacturing methods therefor
PendingCN111936651AHigh strengthImprove surface propertiesHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesUltimate tensile strengthHydrogen embrittlement
The present invention addresses the problem of providing, with regard to a high-strength galvanized steel sheet for which hydrogen embrittlement is a concern, a high-strength galvanized steel sheet which has excellent plating appearance and the material of which has excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance, and a high yield strength suitable for impact-resistant parts of construction materialsand automobiles, and providing a high-strength member, and manufacturing methods therefor. This high-strength galvanized steel sheet comprises: a steel sheet having a prescribed component compositionand a steel structure containing 4-20% residual austenite, 30% or less (including 0%) ferrite, 40% or greater martensite, and 10-50% bainite, and a zinc plating layer on the steel sheet. The amount ofdiffusible hydrogen in the steel is less than 0.20 mass pmm, and the tensile strength is 1100 MPa or greater. The relationship between the tensile strength TS (MPa), the elongation El (%), and the sheet thickness t (mm) satisfies formula (1), and the yield ratio YR is 67% or greater. TS*(El+3-2.5t)>= 13000 (1)
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Low Alloy Steel
InactiveCN104040005AExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesHydrogenStress corrosion cracking
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and method for producing the same
ActiveCN113330133BExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesAustenite grainPearlite
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Austenitic stainless steel material
ActiveCN113924378AHigh tensile strengthExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAustenite grainChemical composition
Provided is an austenitic stainless steel material having excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance and high strength. This austenitic stainless steel material has a chemical composition in terms of mass% of no more than 0.100% C, no more than 1.00% Si, no more than 5.00% Mn, 15.00-22.00% Cr, 10.00-21.00% Ni, 1.20-4.50% Mo, no more than 0.050% P, no more than 0.050% S, no more than 0.100% Al, no more than 0.100% N, and 0-0.70% Cu, the remainder comprising Fe and impurities, the austenitic grain size number based on ASTM E112 of the austenitic stainless steel material is 5.0 to less than 8.0, the dislocation cell structure ratio in a cross section perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the austenitic stainless steel material is 50% to less than 80%, and the number density of deposits having a major axis of 1.0 um or greater is 5.0 / 0.2 mm2 or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Shearing method
ActiveCN109641294BReduce residual stressImprove surface propertiesPerforating toolsShearing machinesStructural engineeringUltimate tensile strength
The present invention provides a shearing processing method. For a workpiece obtained by welding a steel plate with a large step width at the welded portion and / or with a strength of 1000 MPa or more and other steel plates, the shearing line crossing the welded portion is In the shearing process in which the shearing process is performed, a sheared surface with less residual stress and excellent surface properties is formed, and the life of the punch is prolonged. The shearing method of the present invention is to use a punch and a die to shear a workpiece having a welded portion, wherein two protrusions are provided on the tip of the punch, and the two protrusions are clamped from both sides. Hold all or part of the welded part of the workpiece, and shear the workpiece along the cutting line intersecting the welded part.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hydrogen permeation alloy material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101476076BImprove hydrogen permeabilityExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementTitaniumHydrogen permeation
The invention discloses a hydrogen permeating alloy material and a method for preparing the same, and the alloy comprises the following components by molar percentage: titanium of 23mol%-54mol%, cobalt of 21mol%-39mol% and tantalum, titanium, cobalt and tantalum of which the total content is of 98-100mol%.The manufacturing of the alloy material comprises steps of putting titanium, cobalt and tantalum with a purity of more than 99% into a non-consumable vacuum arc furnace, vacuumizing to a pressure below 3*10 3 Pa, filling in argon of high purity to a pressure of 4*10 Pa, and then smelting. The alloy material of the invention has the hydrogen permeability and excellent hydrogen brittleness resistance ability higher than pure palladium under 573-673K, while the cost of the alloy material isonly about 1 / 100 of that of the pure palladium, thus, the alloy material can be used for hydrogen gas isolation and purification, and can also be used for a catalytic-reformed compact membrane reactor and the like.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Steel material
ActiveCN113260717AHigh limit processing rateImprove fatigue strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionCarburizing
The present invention provides a steel material which has a high critical working ratio during cold forging and exhibits high fatigue strength and excellent hydrogen embrittlement resistance characteristics after being formed into a carburized steel component. A steel material according to one embodiment of the present invention has a chemical composition that contains, in mass%, 0.07-0.13% of C, 0.15-0.35% of Si, 0.60-0.80% of Mn, 0.005-0.050% of S, 1.90-2.50% of Cr, 0.0005-0.0100% of B, 0.010% or more but less than 0.050% of Ti, 0.010-0.100% of Al, 0.0002-0.0030% of Ca, 0.0080% or less of N, 0.050% or less of P and 0.0030% or less of O, with the balance being made up of Fe and impurities, while satisfying the formula (1) to formula (5) that are described in the description.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com