Patents
Literature
260 results about "ABLE protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
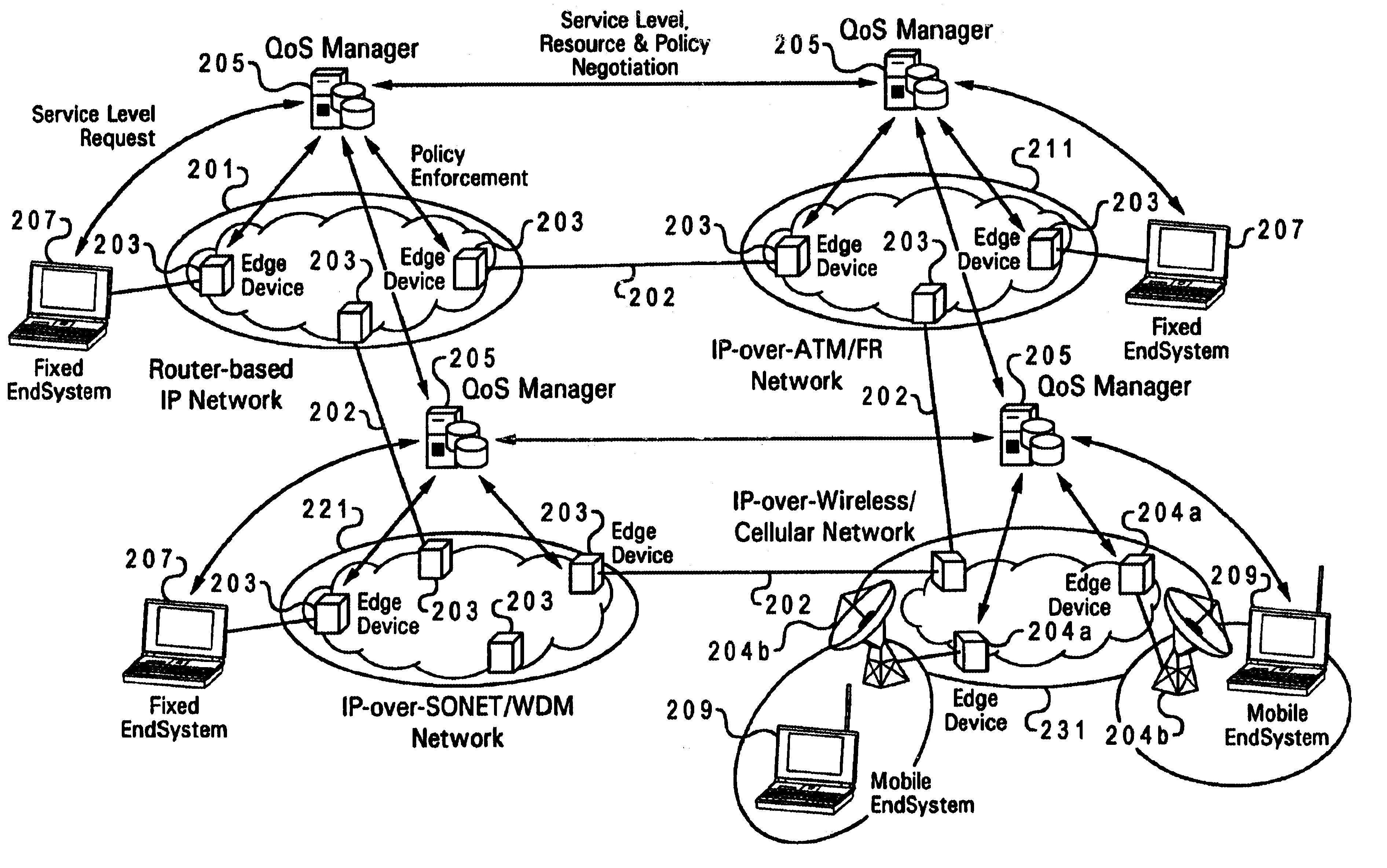
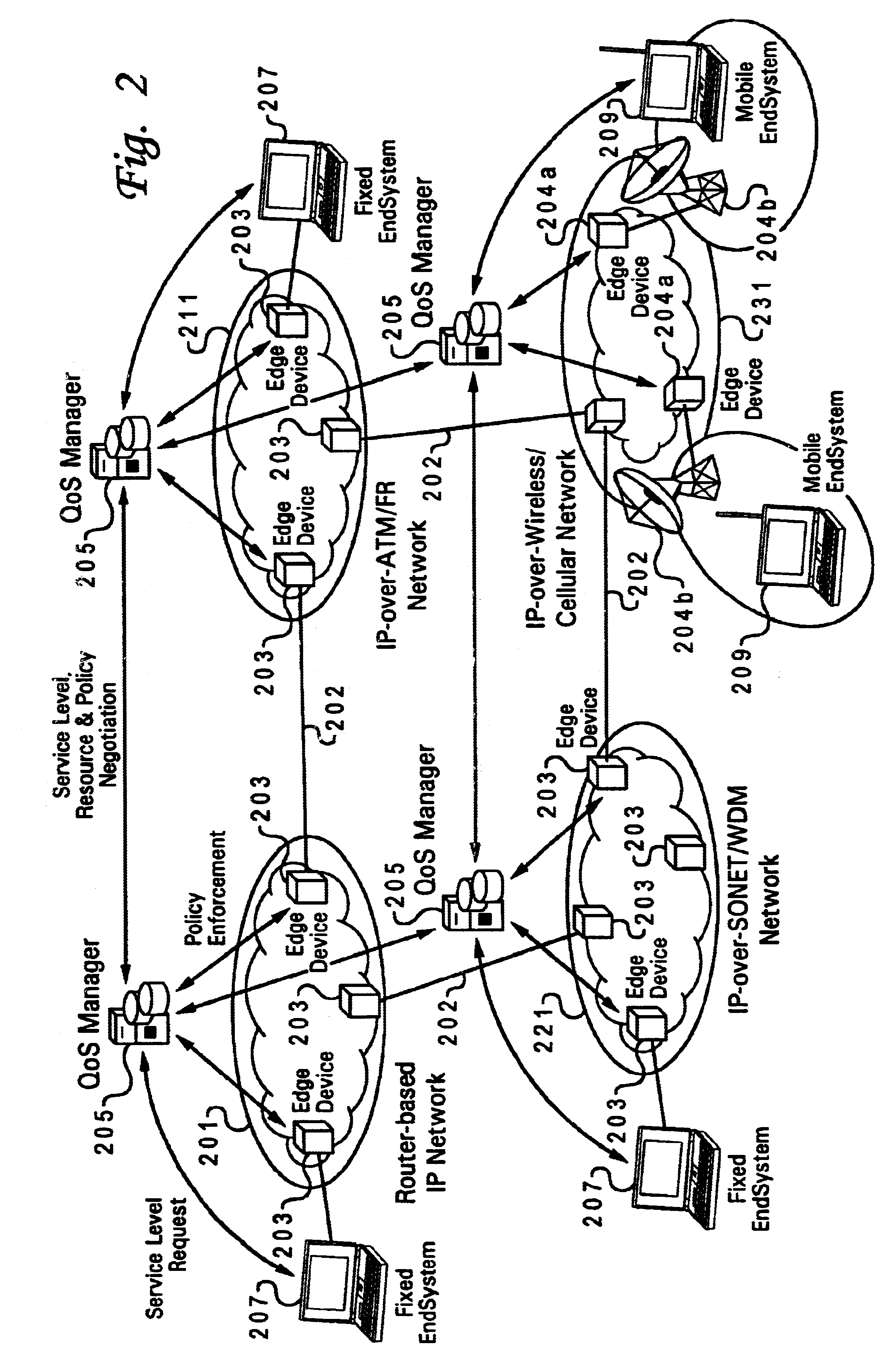
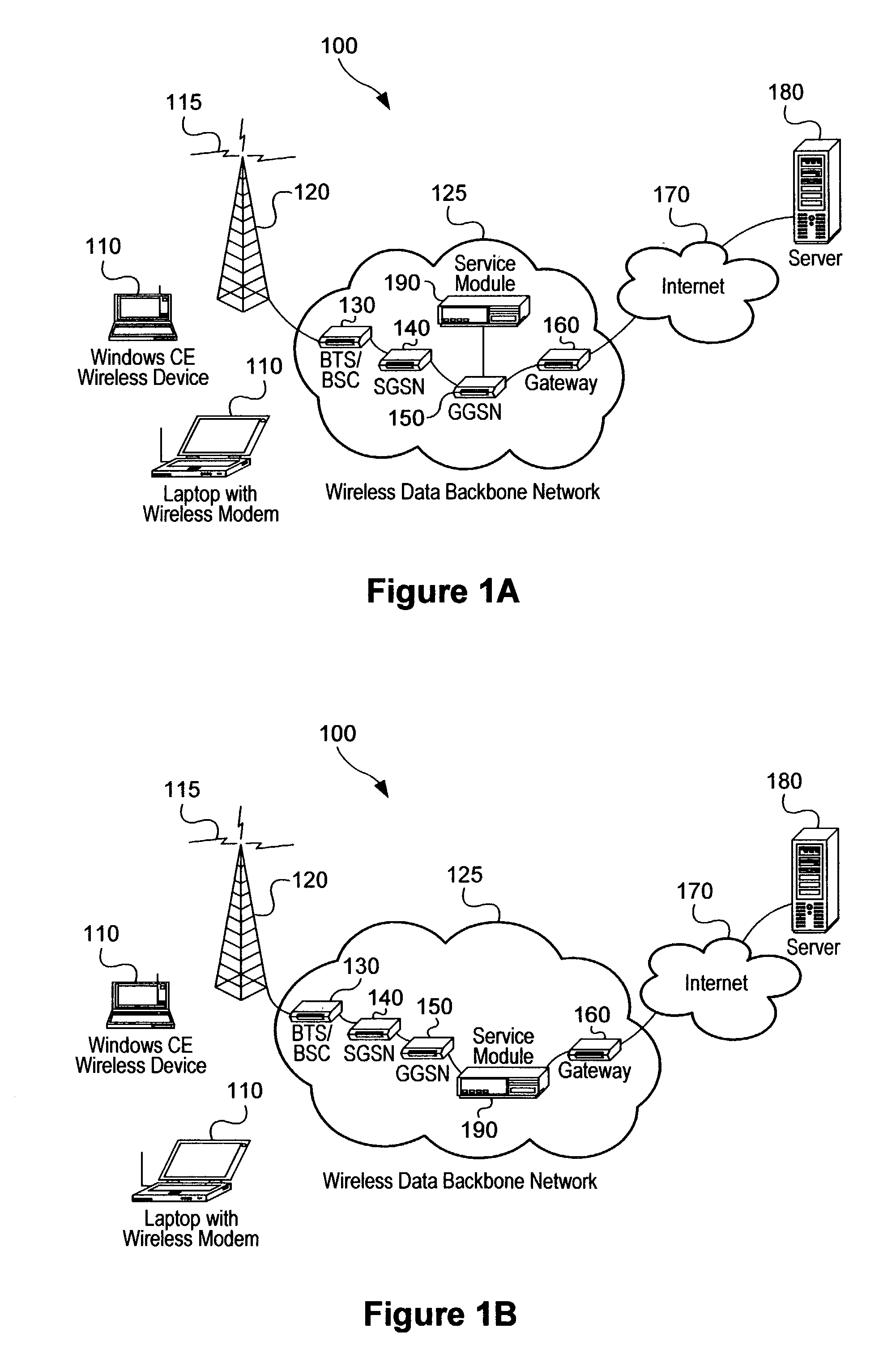
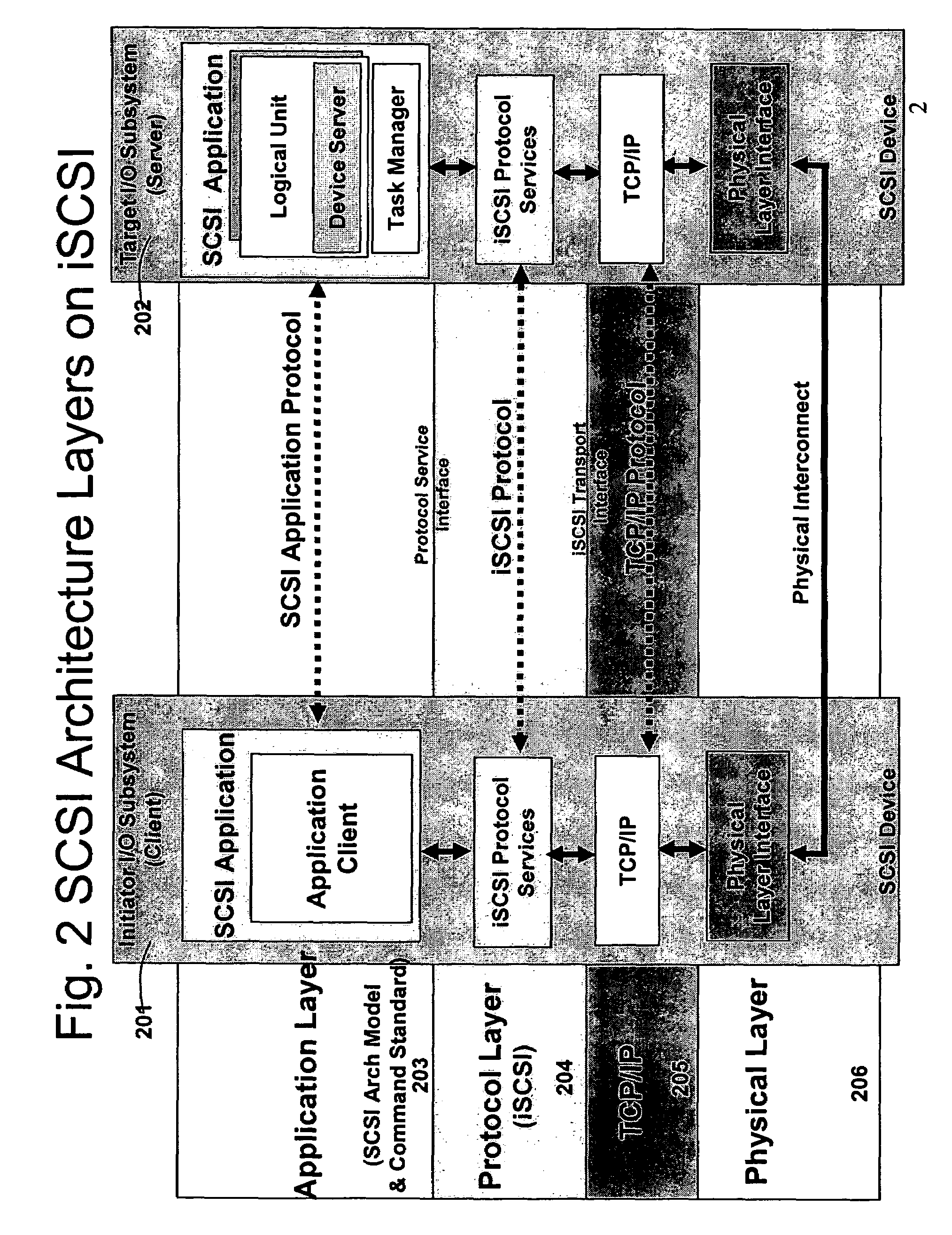
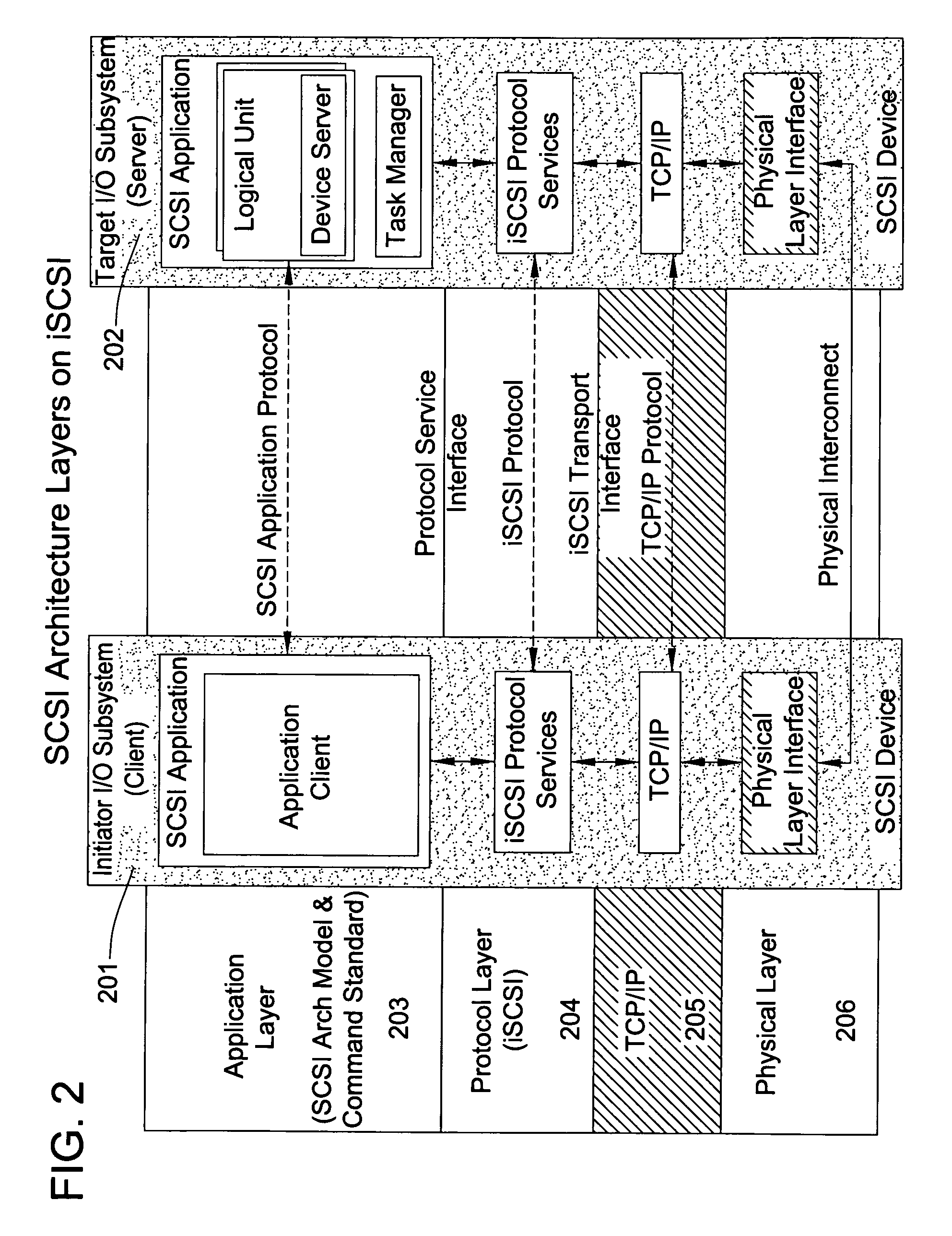
Method and system for wireless QOS agent for all-IP network
A wireless quality of service (QoS) agent for an all-Internet Protocol (IP) network. The QoS agent couples to an all-IP network. The coupling means includes communication means for transfer of information between the agent and a QoS manager of the all-IP network. The agent is also able to seamlessly extend QoS support for multimedia applications from wireline to wireless and control QoS of the multimedia applications sent over wireless connections on the all-IP network.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
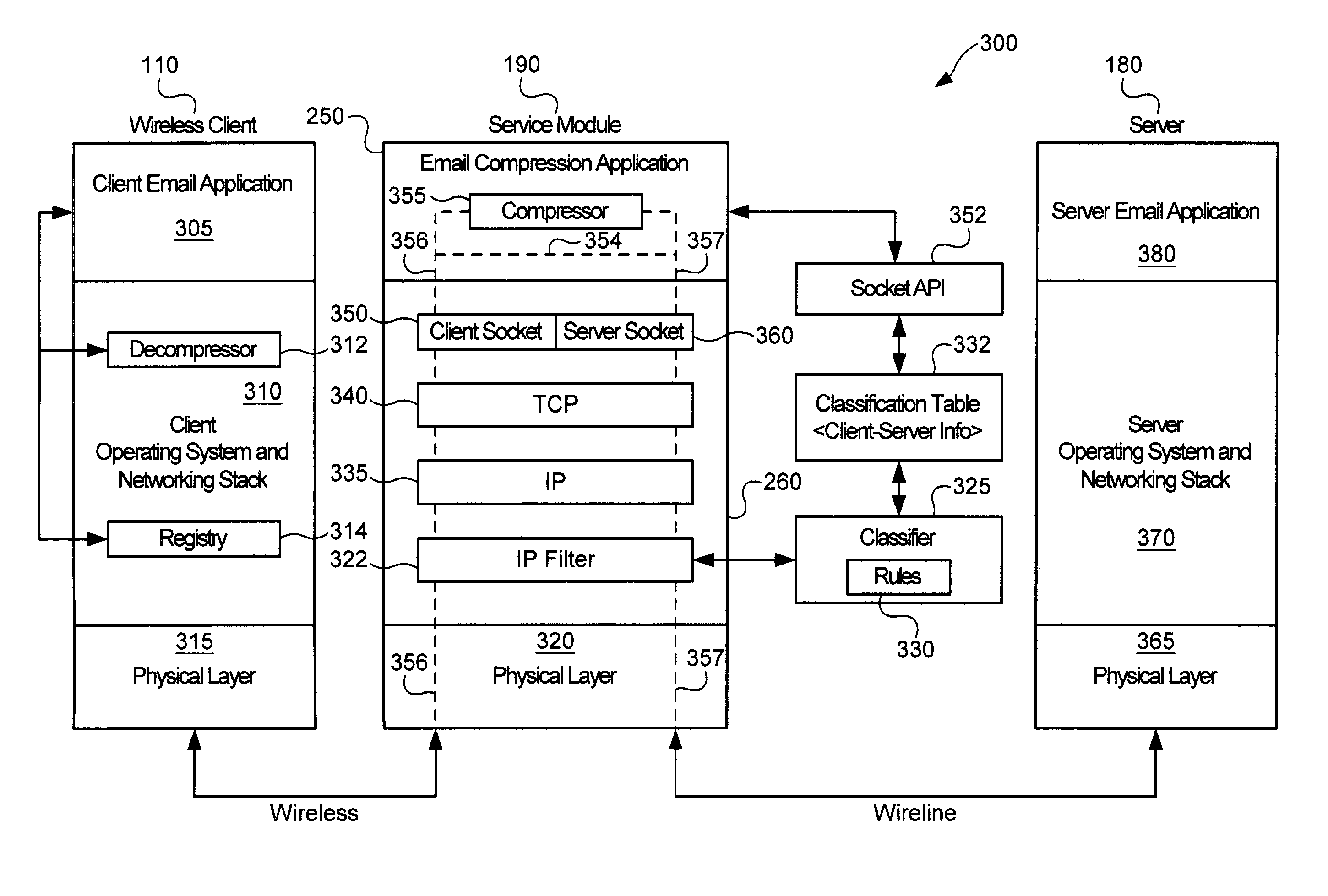
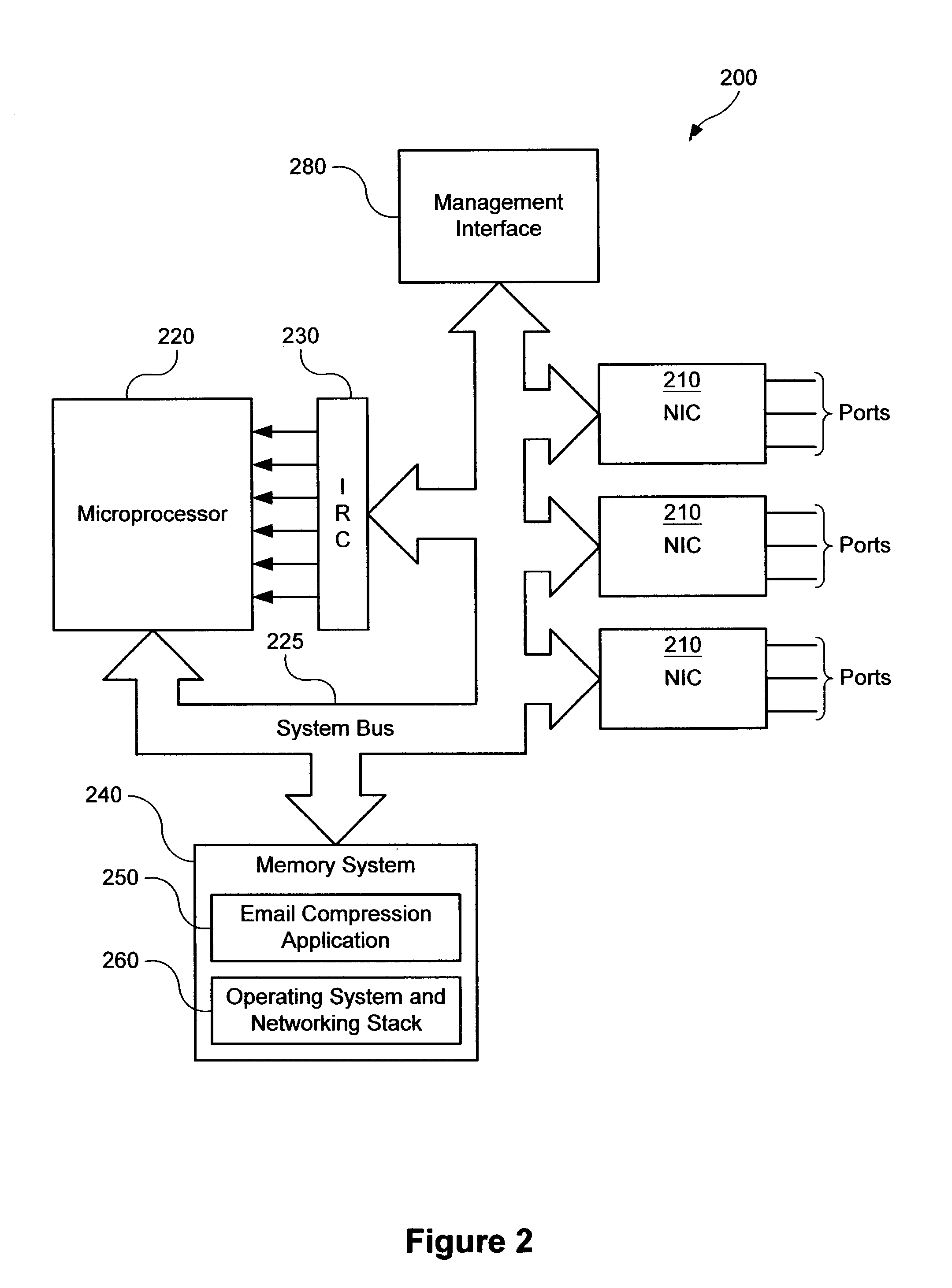
Service-based compression of content within a network communication system
ActiveUS7024460B2Easy to decompressMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksOperational systemData stream
A service module incorporated within the network infrastructure intercepts packets communicated between a client and a server to determine whether the connection corresponds to an email service. If so, the service module breaks the connection by terminating the connection with the client at the service module and opening a separate connection between the service module and the server. Packets communicated between the client and the server may then be redirected to an email compression application that monitors messages communicated between the client and the server and processes the messages in accordance with the state of the email session. For messages corresponding to connection establishment, user authentication and other protocol-specific messages, for example, the email compression application may be configured to forward the messages to the originally intended destination. Messages corresponding to an email message data, however, are buffered within the email compression application. Once the entire message has been received, the email compression application may strip the message headers and any protocol-specific data, compress the data and attach new message headers corresponding to the compressed email message. The compressed and reformatted email message is then reinserted into the data stream for transmission to the intended destination. Because compression may occur between the server and client, compression may be performed without requiring special processing by the server before email messages are sent. Furthermore, because the email messages may be compressed in a format that can be readily decompressed using decompression libraries incorporated within the operating system of client devices, such as the CAB format or GZIP format, the client may decompress received email messages utilizing software already incorporated within the operating system of the client device, without requiring download or installation of special decompression software and / or coordination of compression / decompression of email messages with the server or sending party.
Owner:OPTIMORPHIX INC
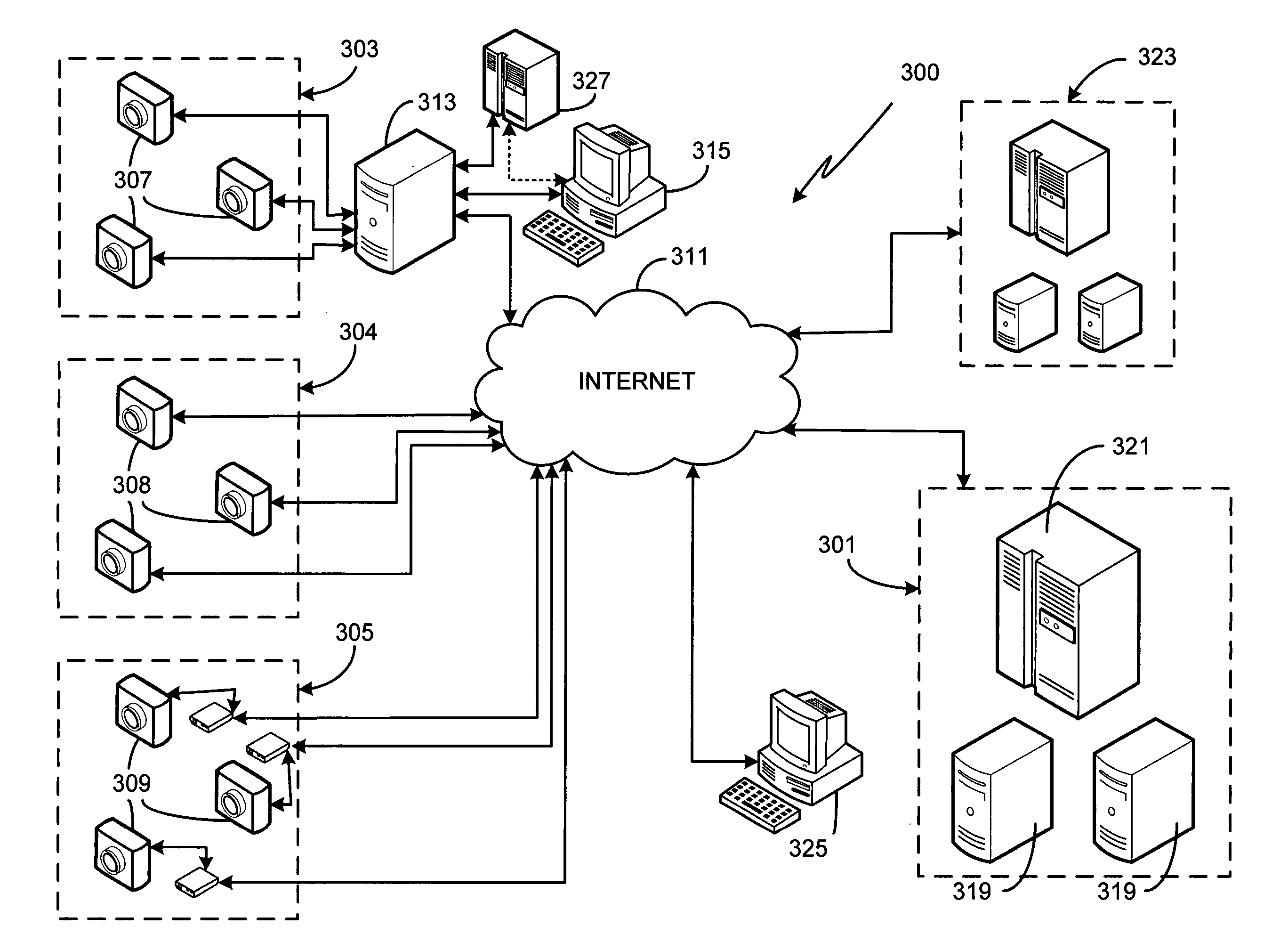
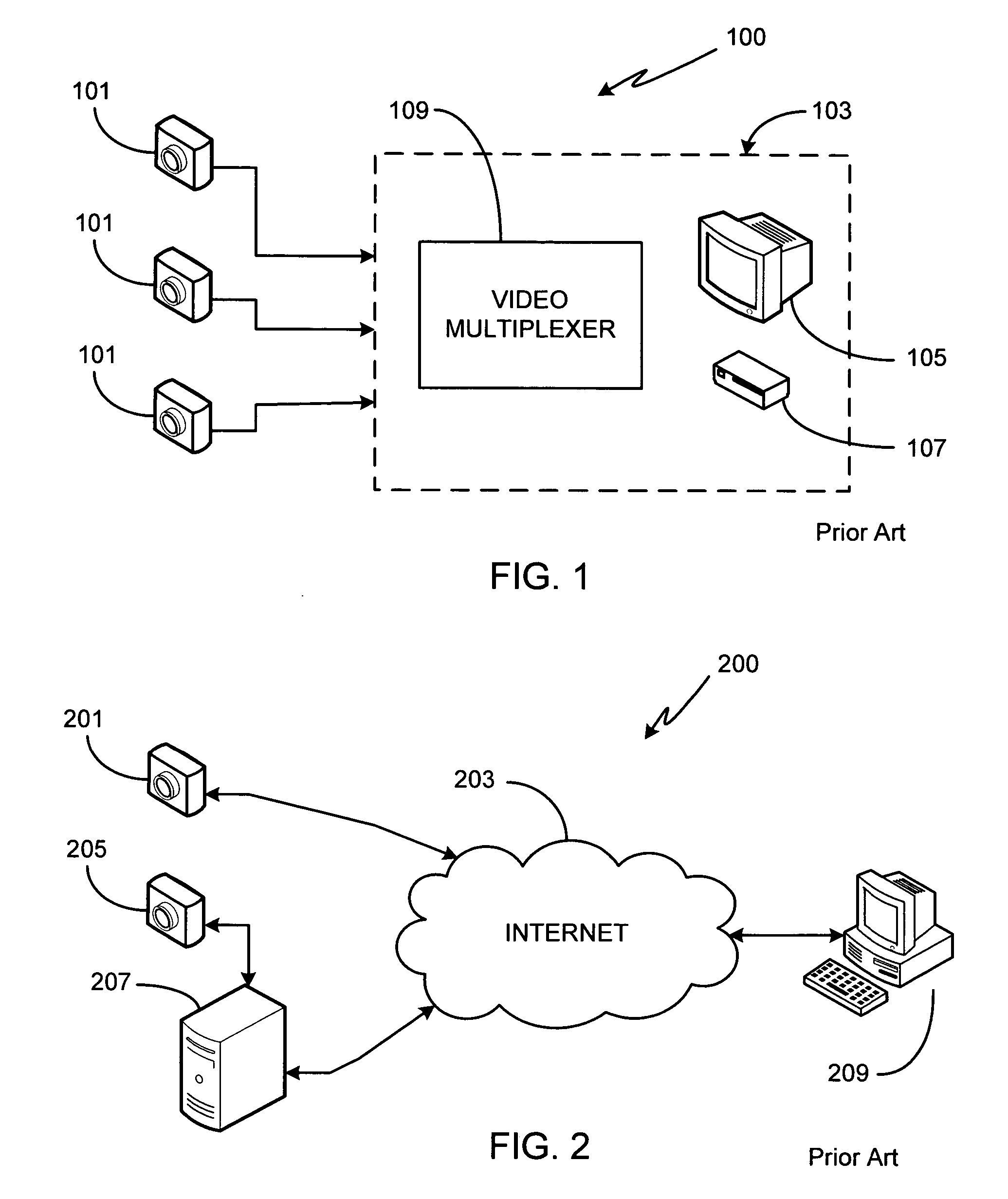
Networked video surveillance system
InactiveUS20050132414A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringGraphics
A method of storing, analyzing and accessing video data from the surveillance cameras operated by multiple, unrelated users is provided. Data storage and analysis is performed by an independent system remotely located at a third party site, the third party site and the users connected via a network. Users access stored video data using any of a variety of devices coupled to the network. In one aspect, users submit configuration instructions which govern how long their data is to be stored, the frequency of data acquisition / storage, data communication parameters / protocols, and video resolution. In another aspect, users remotely obtain from the third party system a graphical view of the video data acquired from a particular camera, the graphical view showing the activity monitored by the camera versus time. In yet another aspect, users submit zone configuration instructions to the third party system. In yet another aspect, users remotely submit rules of analysis, such as time-based and / or shaped-based rules, to be applied to their acquired video data by the third party system.
Owner:CONNEXED
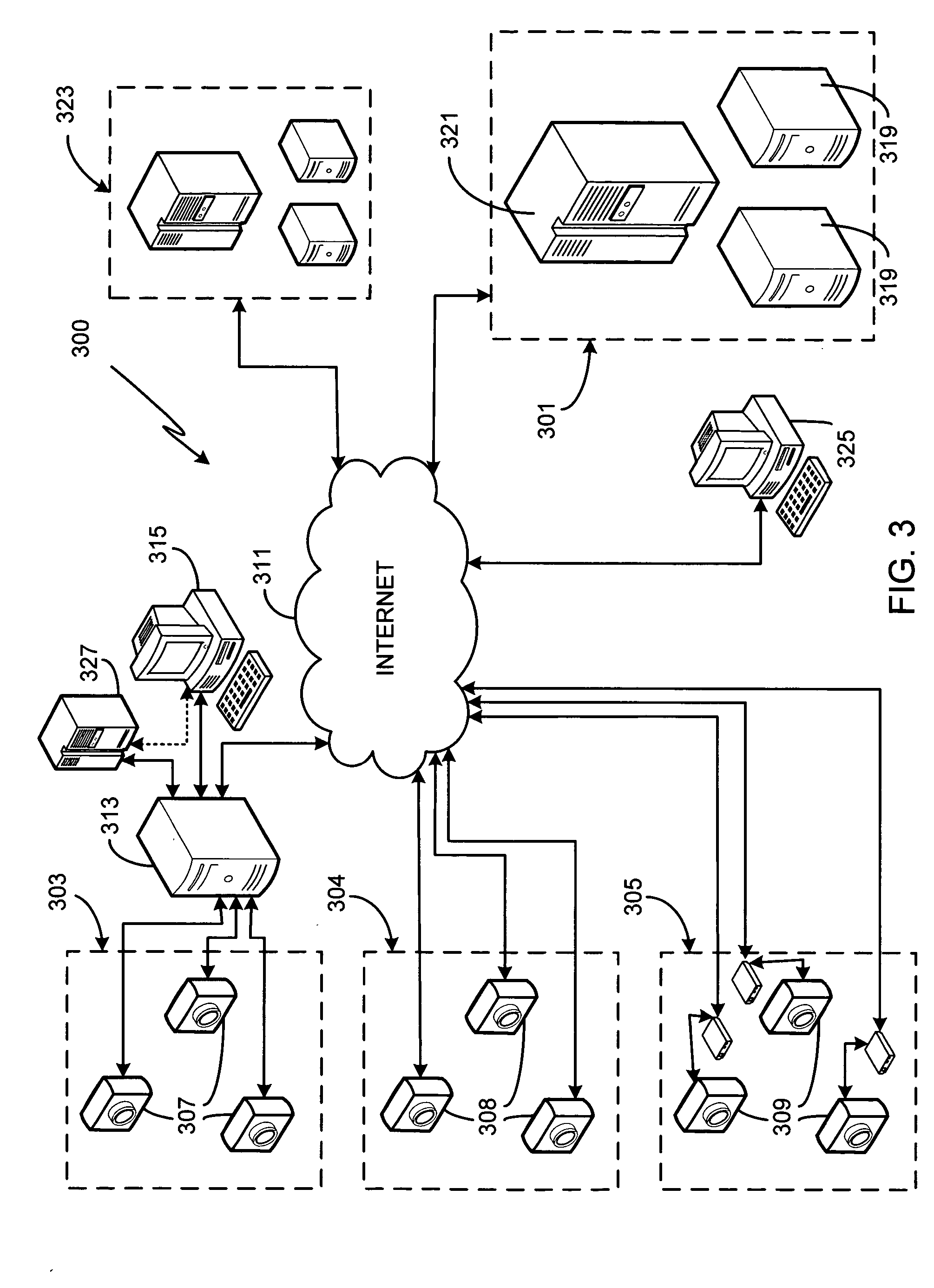
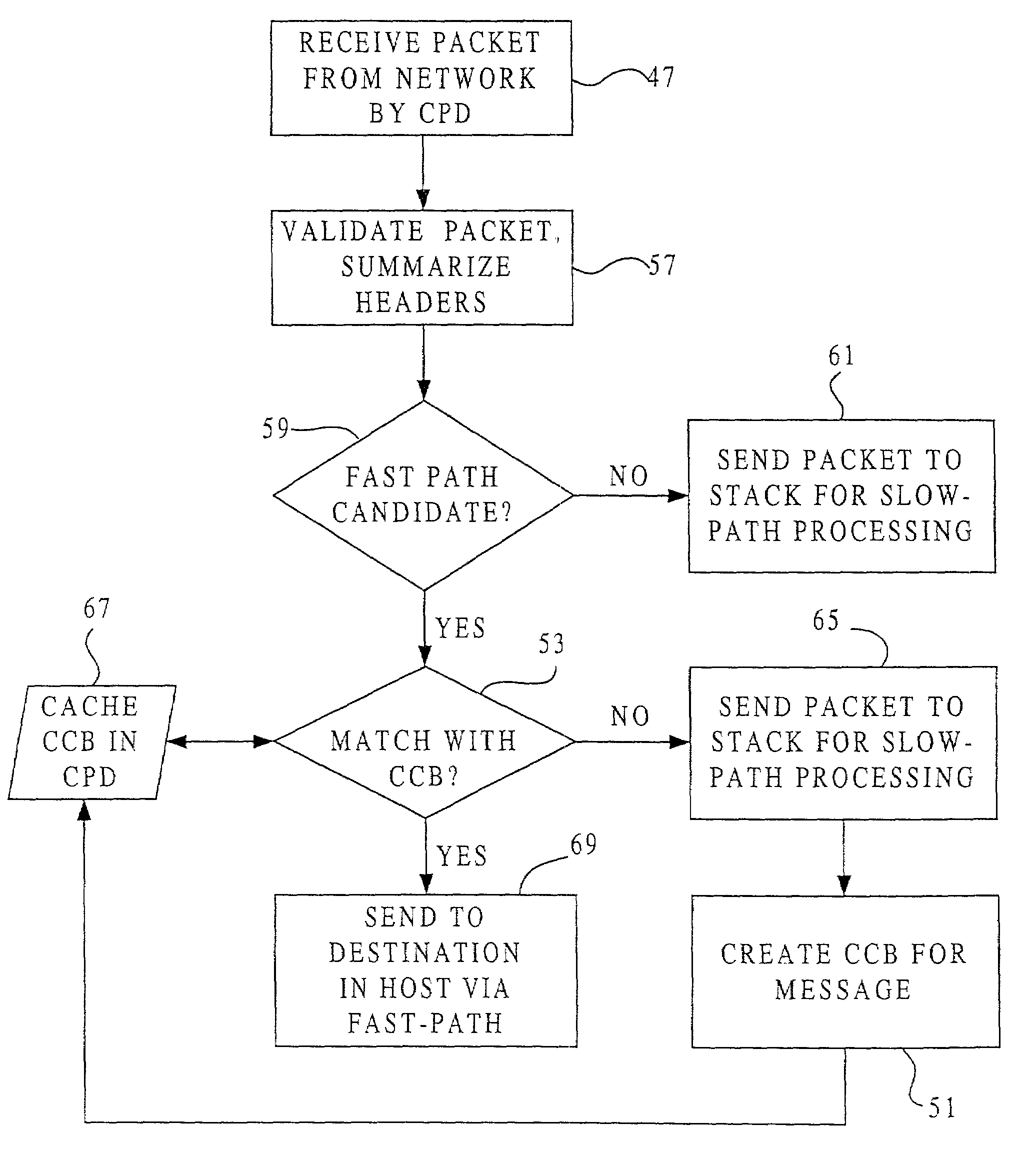
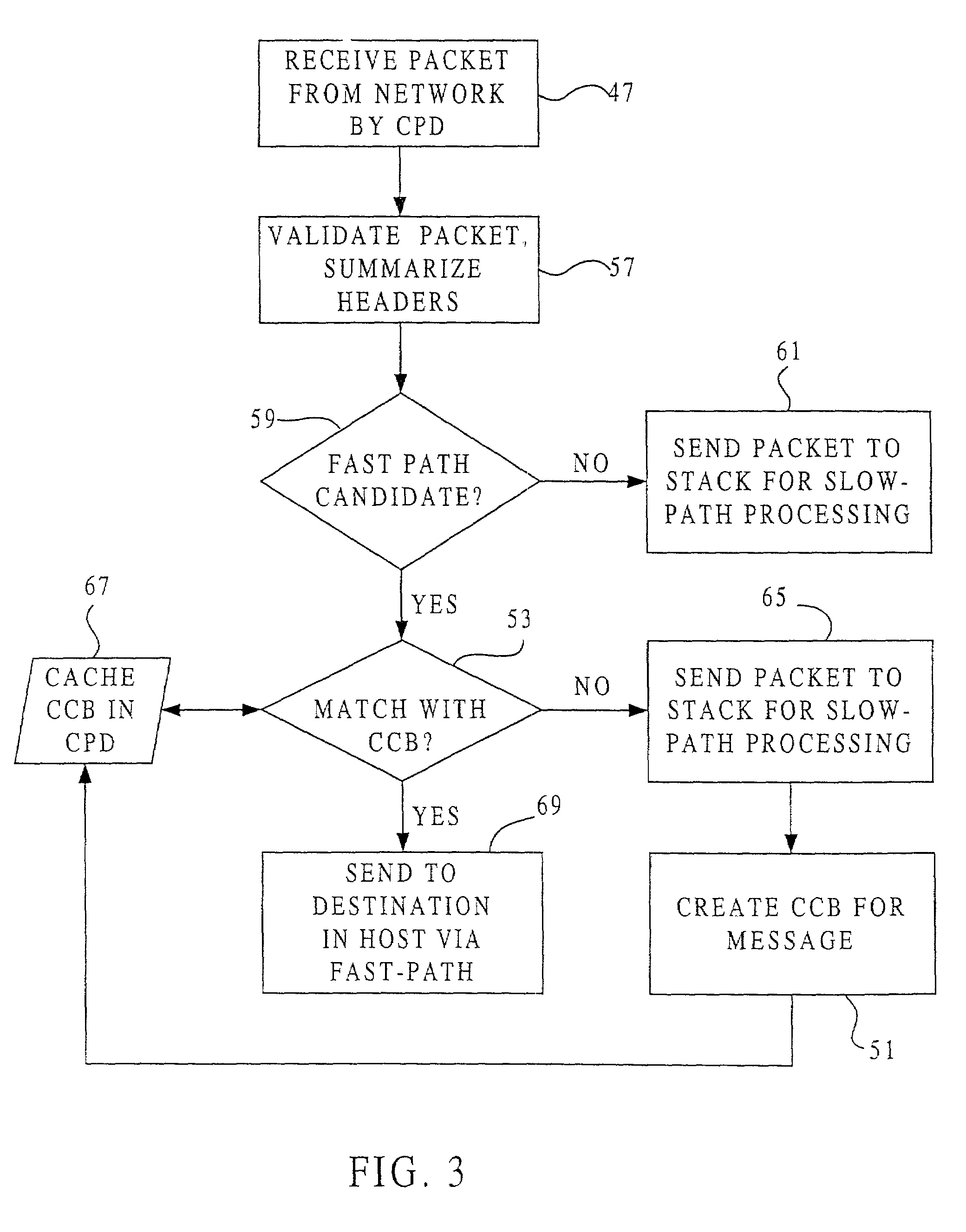
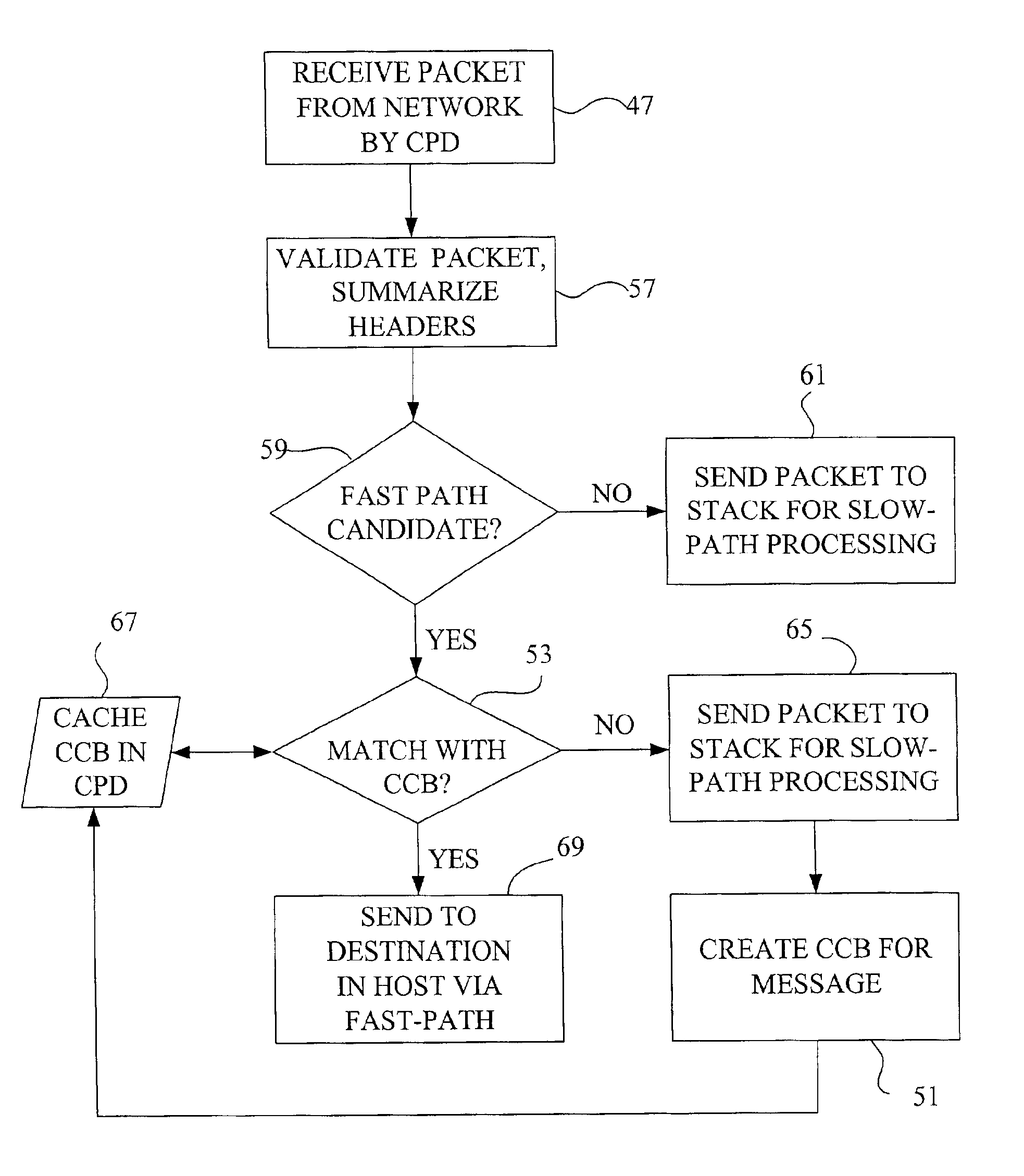
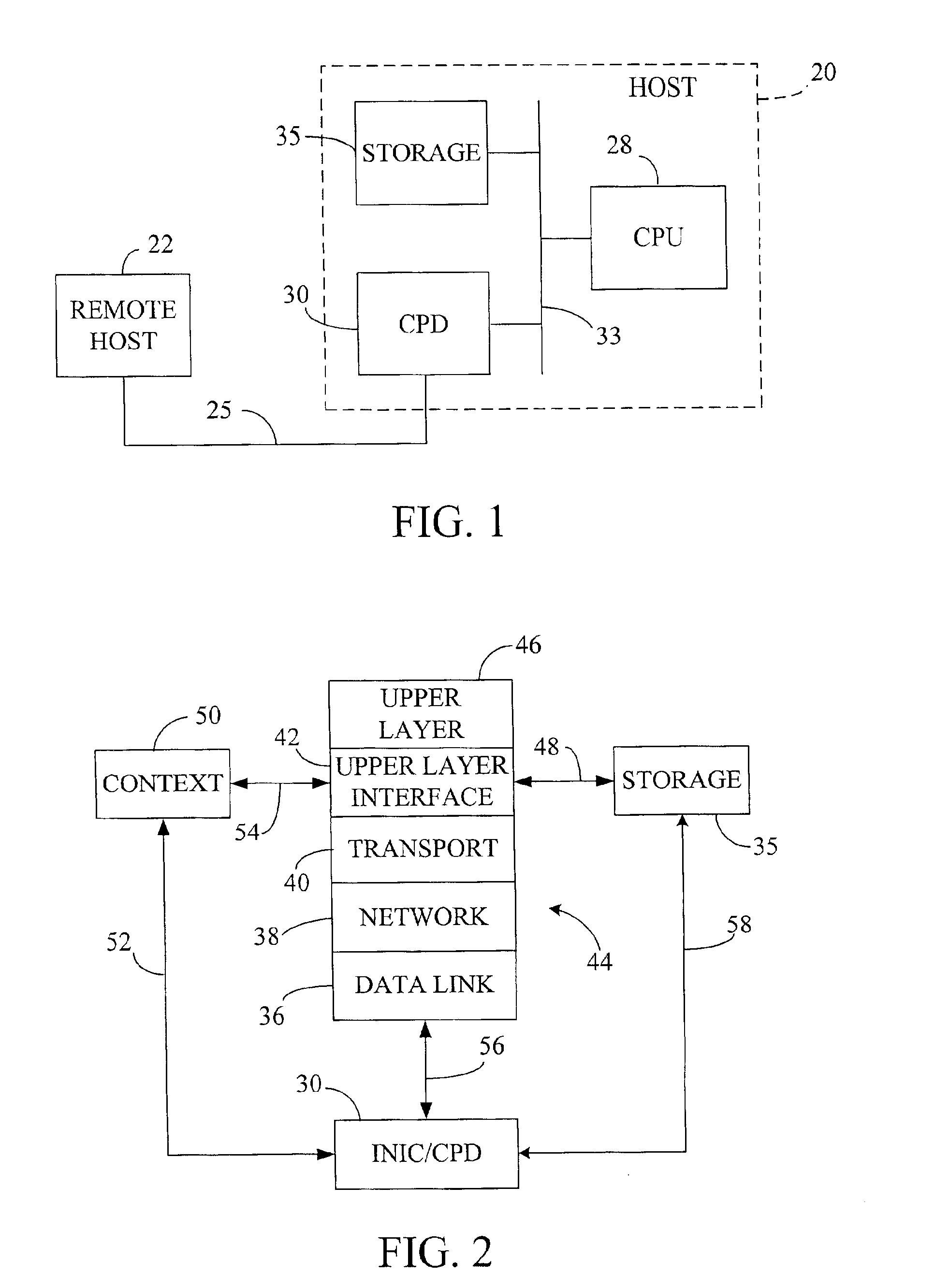
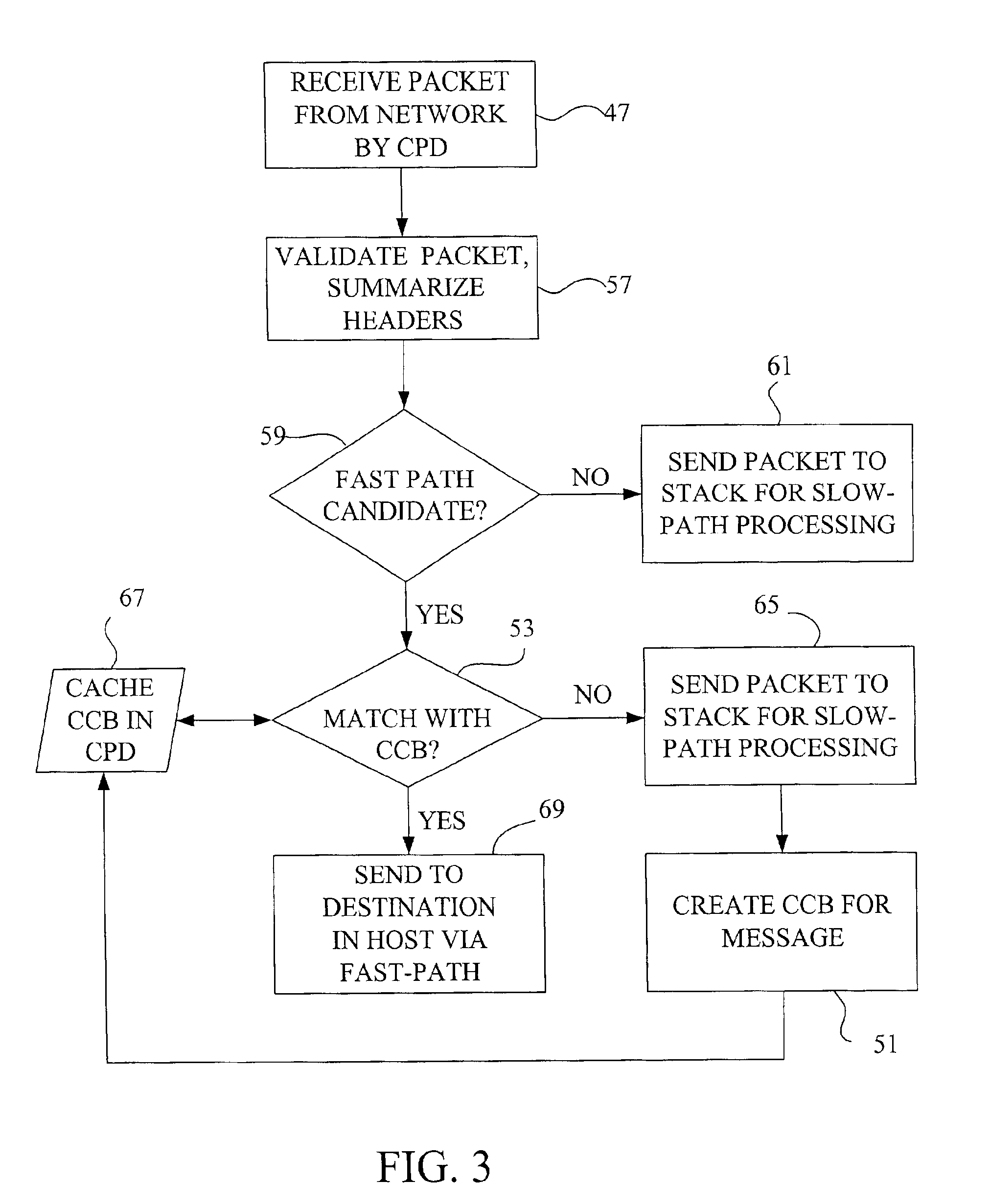
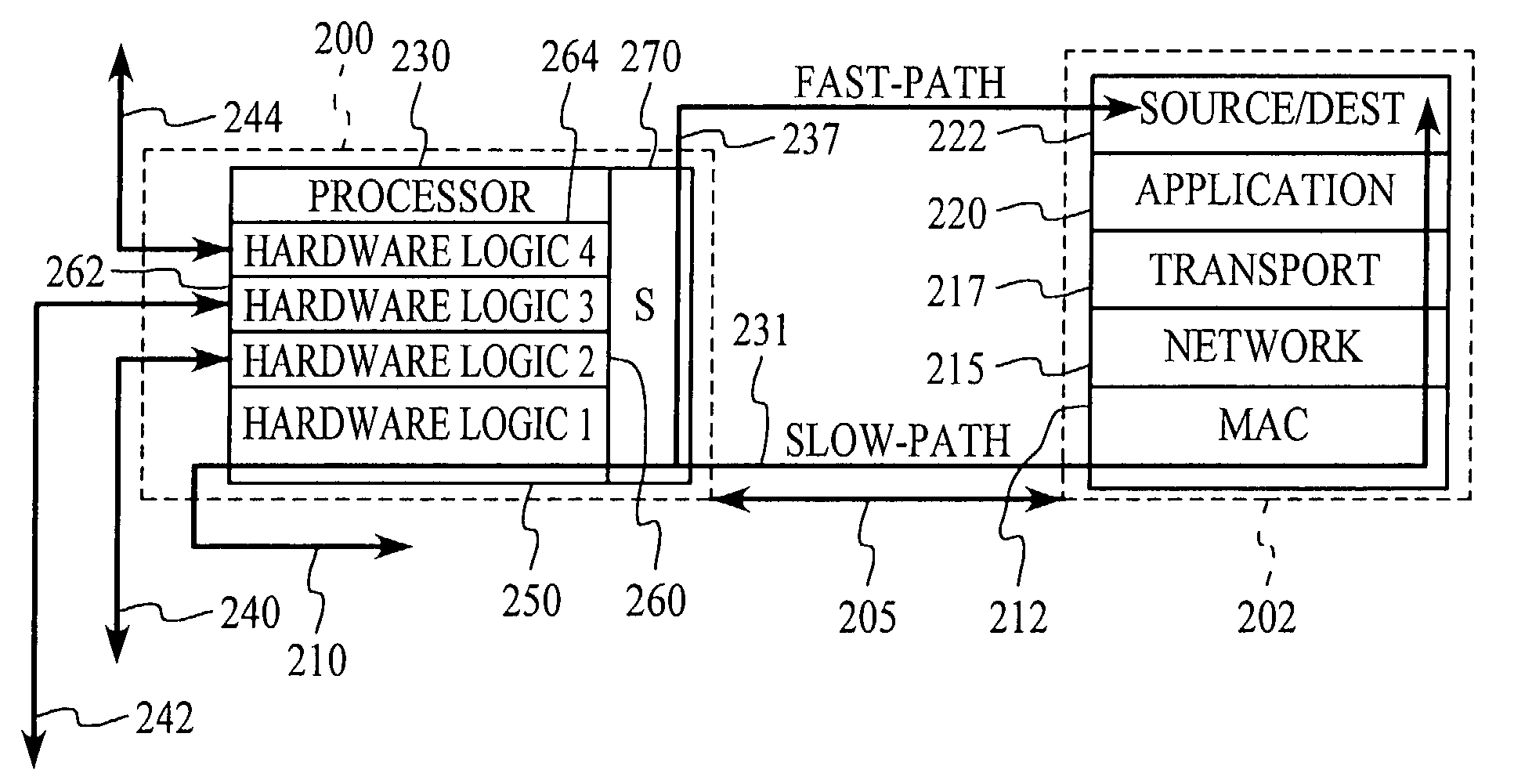
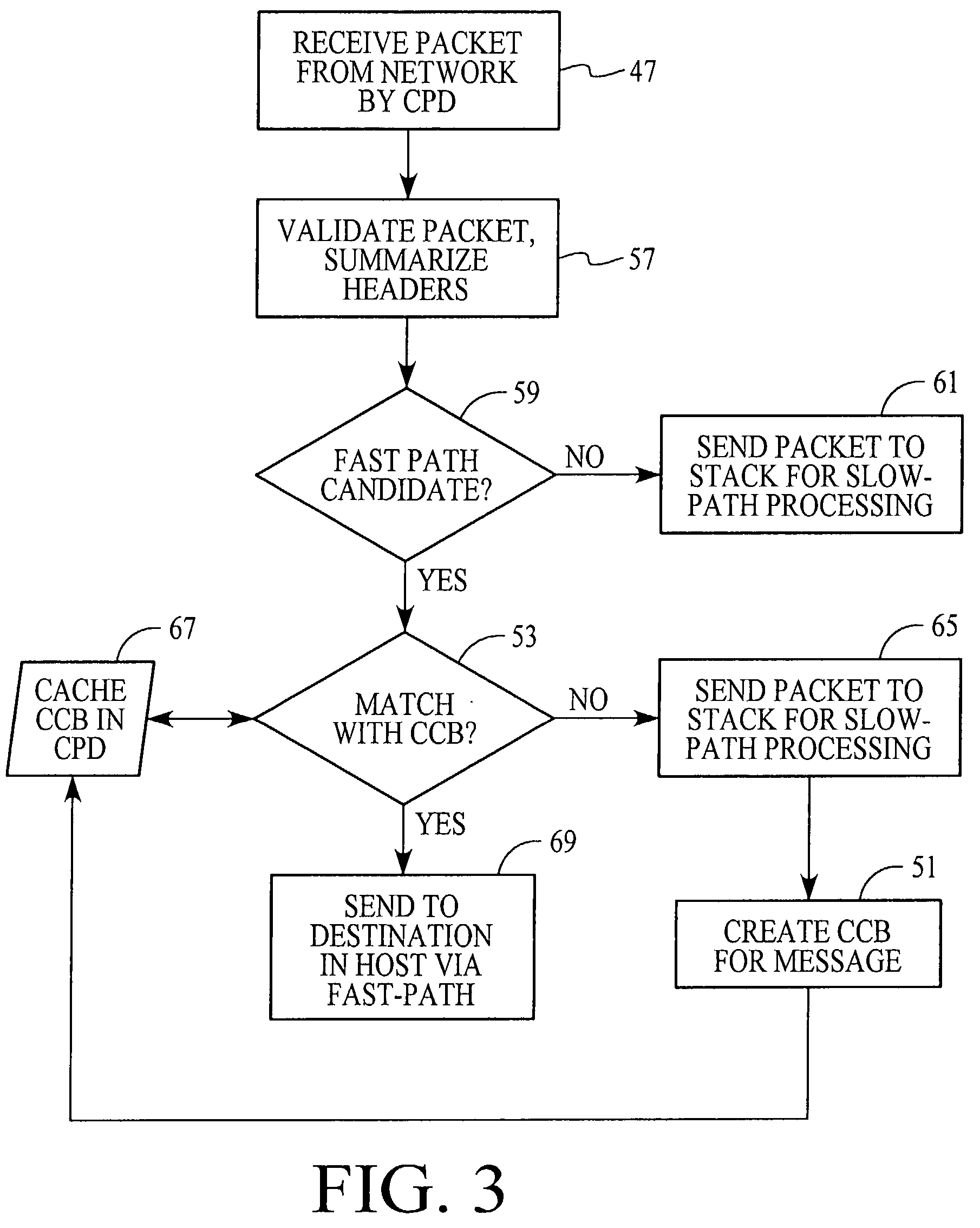
Fast-path processing for receiving data on TCP connection offload devices
ActiveUS7089326B2Negligibly effectMove quicklyMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksFast pathProtocol processing
A network interface device provides a fast-path that avoids most host TCP and IP protocol processing for most messages. The host retains a fallback slow-path processing capability. In one embodiment, generation of a response to a TCP / IP packet received onto the network interface device is accelerated by determining the TCP and IP source and destination information from the incoming packet, retrieving an appropriate template header, using a finite state machine to fill in the TCP and IP fields in the template header without sequential TCP and IP protocol processing, combining the filled-in template header with a data payload to form a packet, and then outputting the packet from the network interface device by pushing a pointer to the packet onto a transmit queue. A transmit sequencer retrieves the pointer from the transmit queue and causes the corresponding packet to be output from the network interface device.
Owner:ALACRITECH
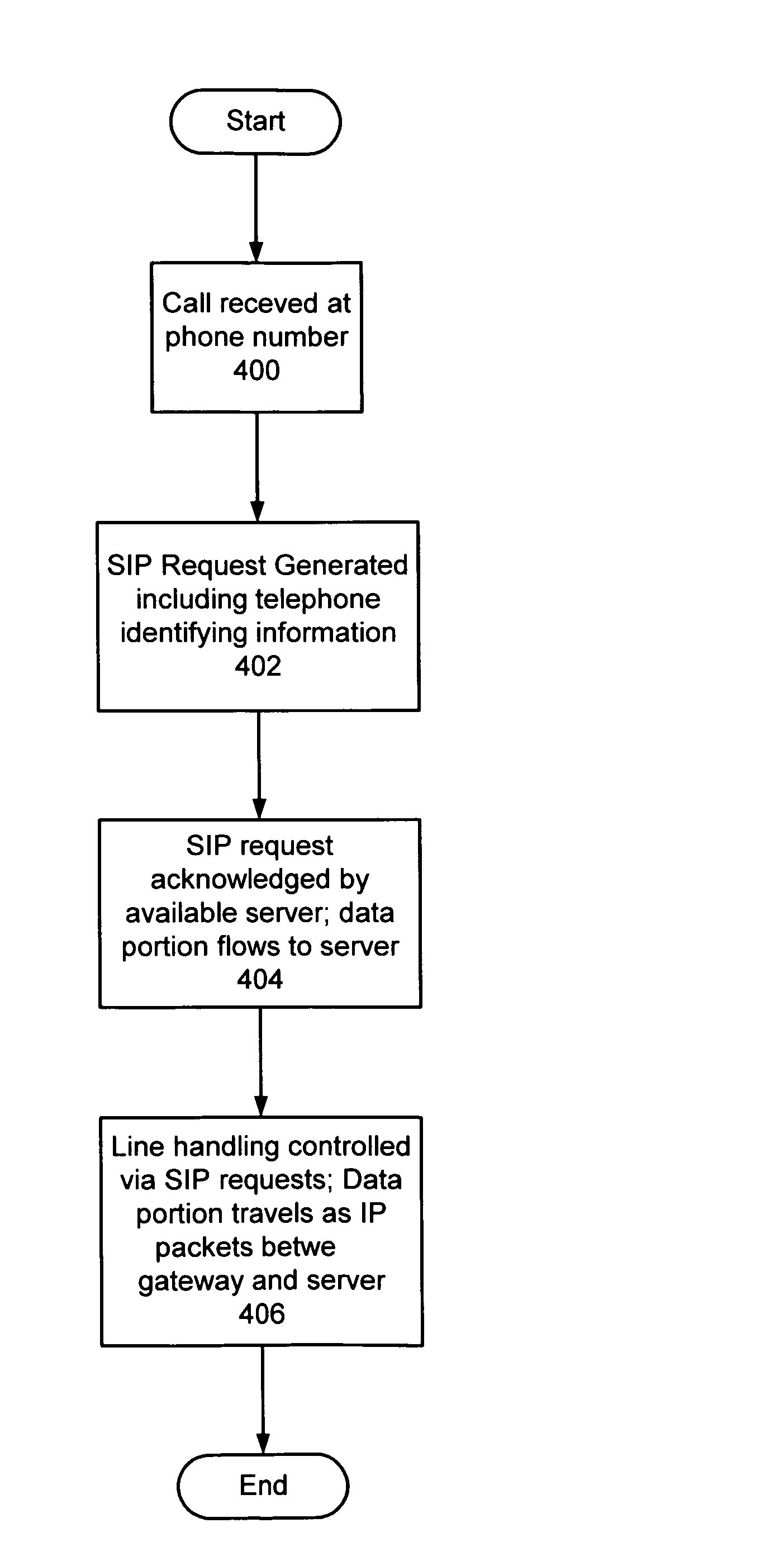
Localized voice over internet protocol communication
InactiveUS7286521B1Add supportHandled more elegantlyInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersShortest distanceSound file
An approach to abstracting the circuit switched nature of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) by using VoIP to provide voice actuated services is disclosed. By carrying a telephone call using VoIP technology for a short distance (frequently within a server room) significant benefits to call handling and capacity management can be obtained. Specifically, a PSTN-to-IP gateway is used to receive (and place) calls over the PSTN and route those calls internally to servers over an IP network in a packet switched format. A number of computer systems can receive and handle the calls in the IP format, including: translating the packets into an audio format suitable for speech recognition and creating suitable packets from computer sound files for transmission back over the PSTN.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Transmit fast-path processing on TCP/IP offload network interface device
InactiveUS6965941B2Little and no performance benefitMove quicklyMultiplex system selection arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsFast pathProtocol processing
Owner:ALACRITECH
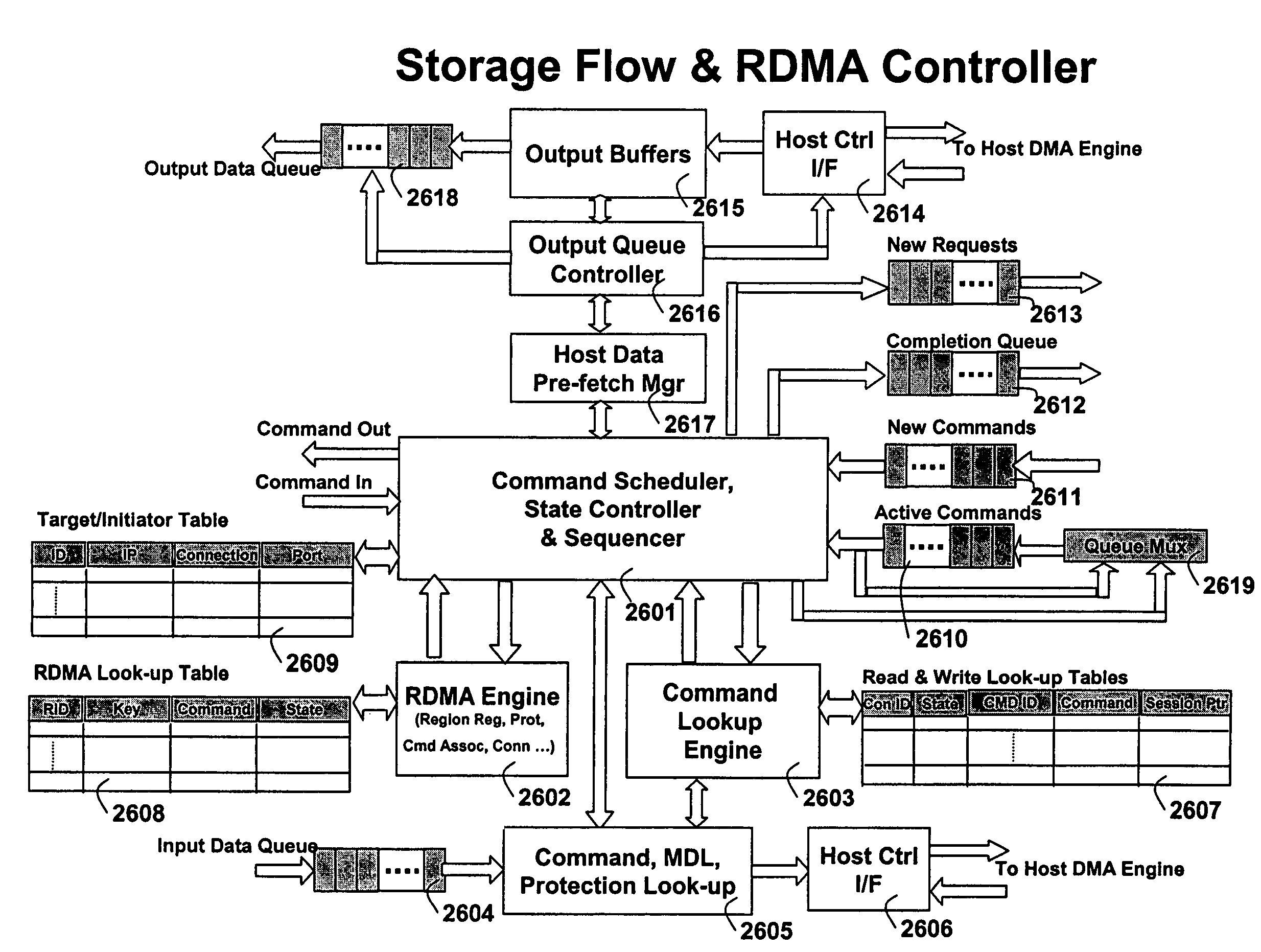
TCP/IP processor and engine using RDMA
ActiveUS7376755B2Sharply reduces TCP/IP protocol stack overheadImprove performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransmission protocolInternal memory
A TCP / IP processor and data processing engines for use in the TCP / IP processor is disclosed. The TCP / IP processor can transport data payloads of Internet Protocol (IP) data packets using an architecture that provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. The engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a TCP / IP session information database and may also store a storage information session database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
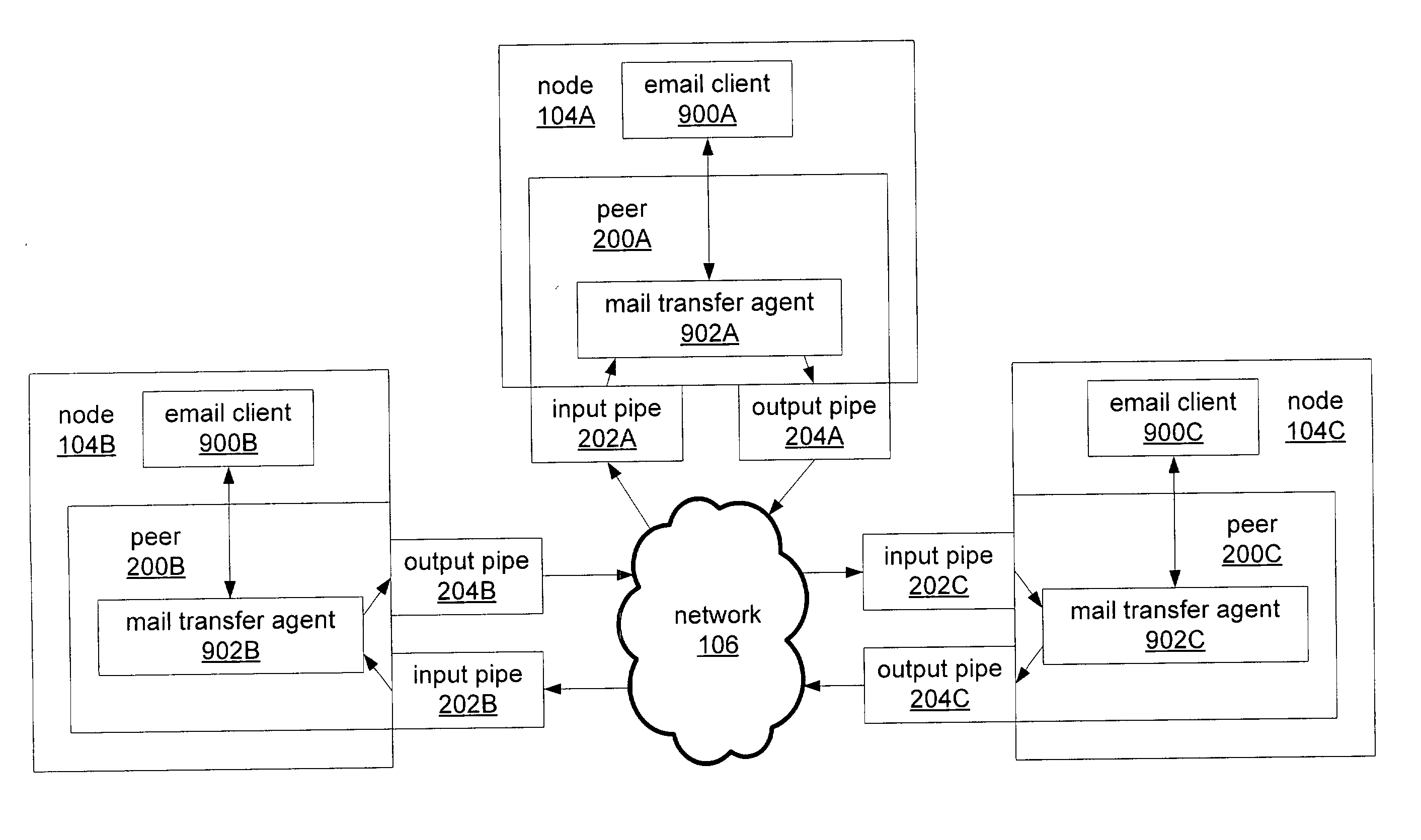
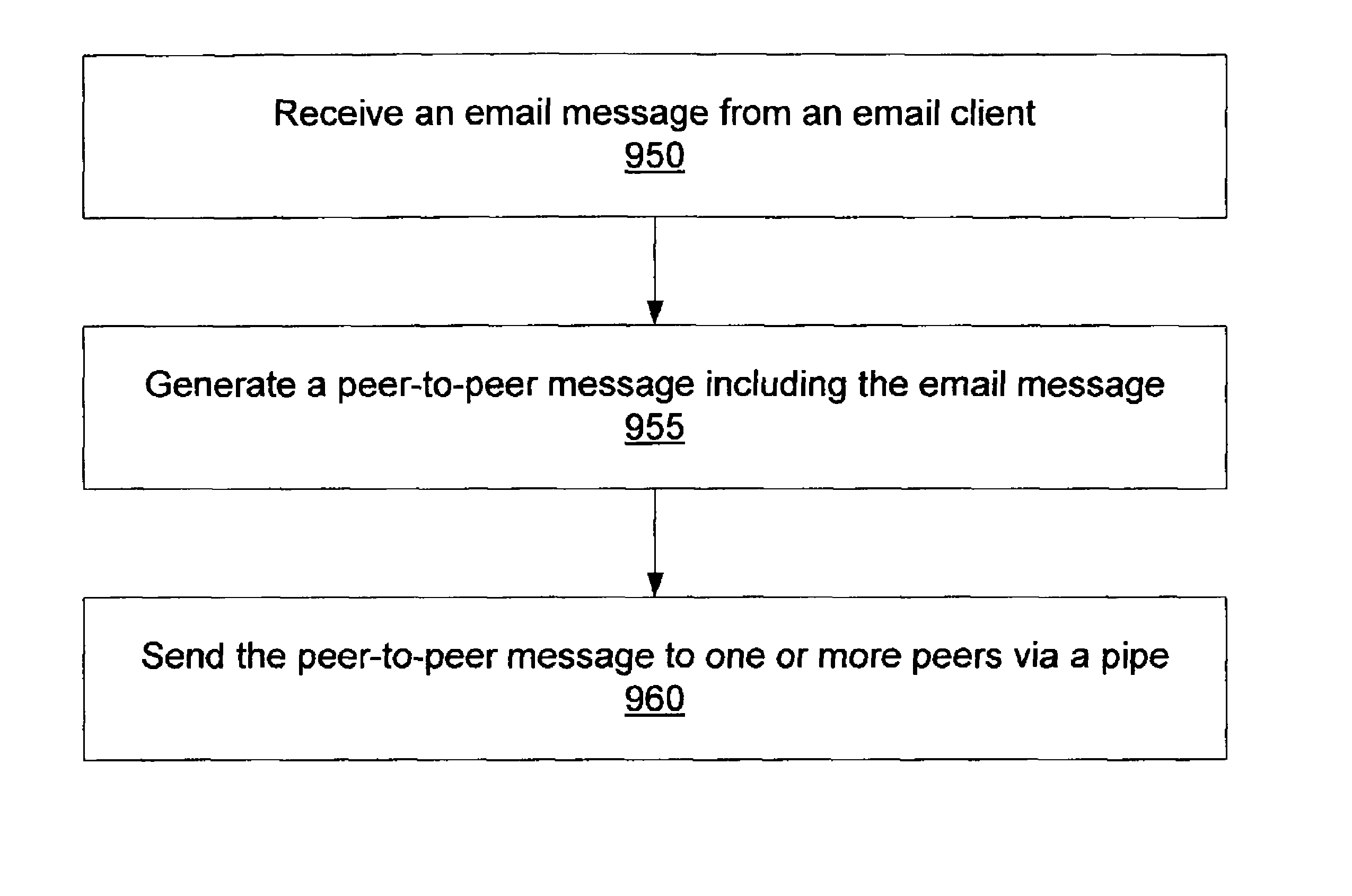
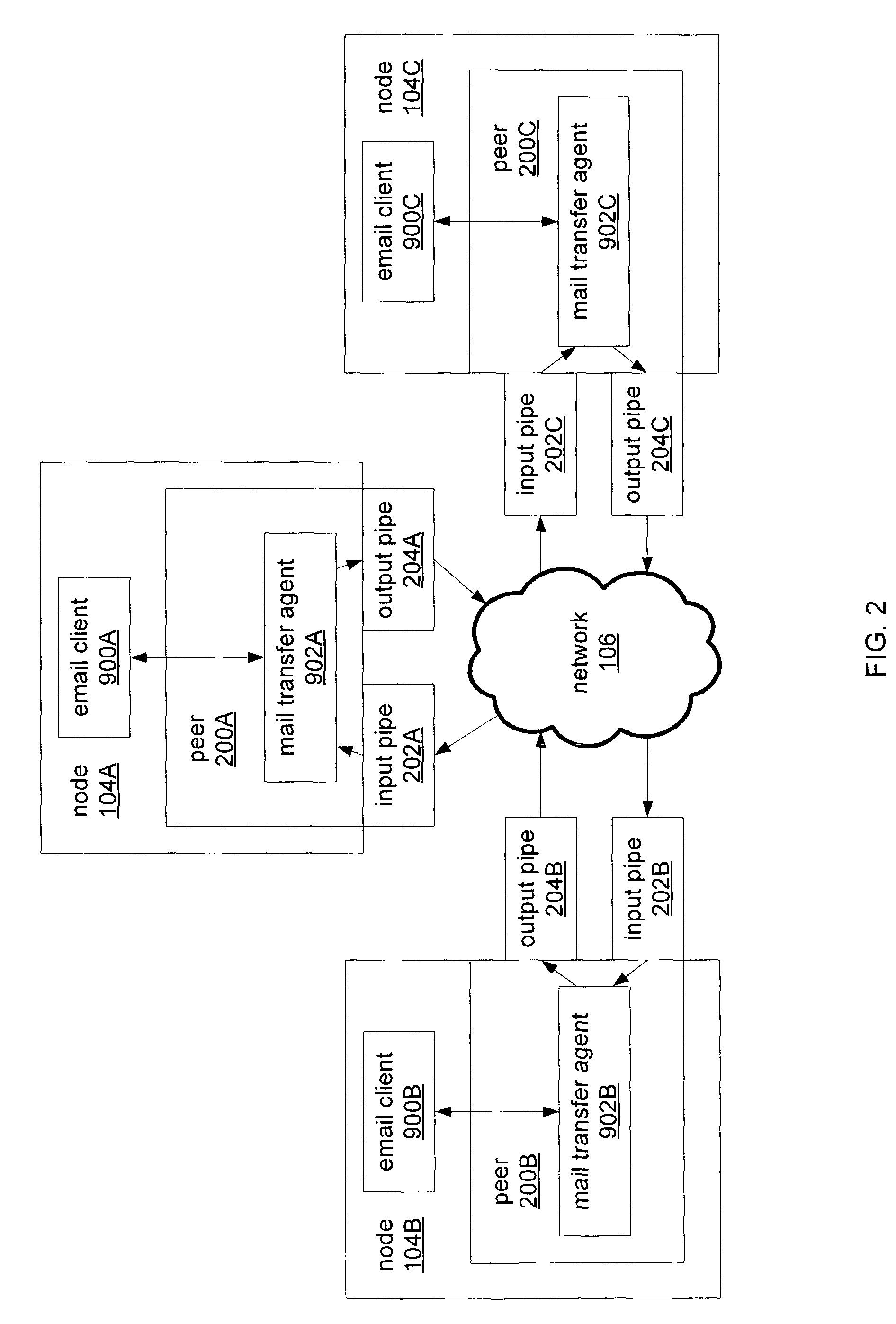
Peer-to-peer email messaging
ActiveUS20040064511A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksClient-sideDistributed computing
System and method for facilitating communications between peers in a peer-to-peer environment and network email clients. In one embodiment, network nodes including peer nodes may host mail transfer agents. The mail transfer agents may act as bridges between peer-to-peer protocols and email communication protocols. The mail transfer agents may communicate with peers according to peer-to-peer protocols and with email clients according to email communications protocols. Peers may communicate with mail transfer agents to send peer-to-peer messages to email clients. Email clients may communicate with the mail transfer agents to send email messages to and receive email messages from other email clients via the peer-to-peer network and to obtain peer-to-peer messages from peers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
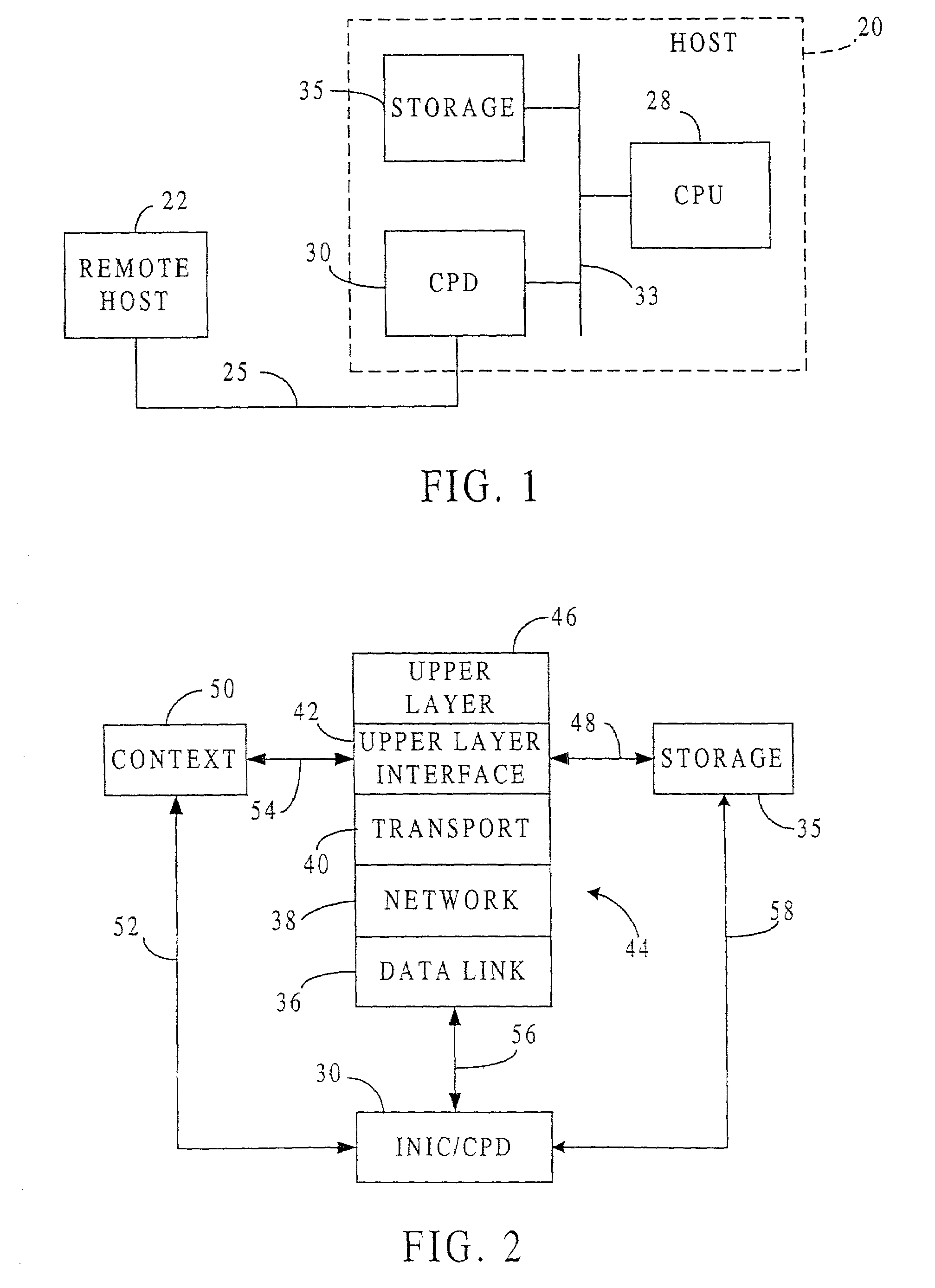
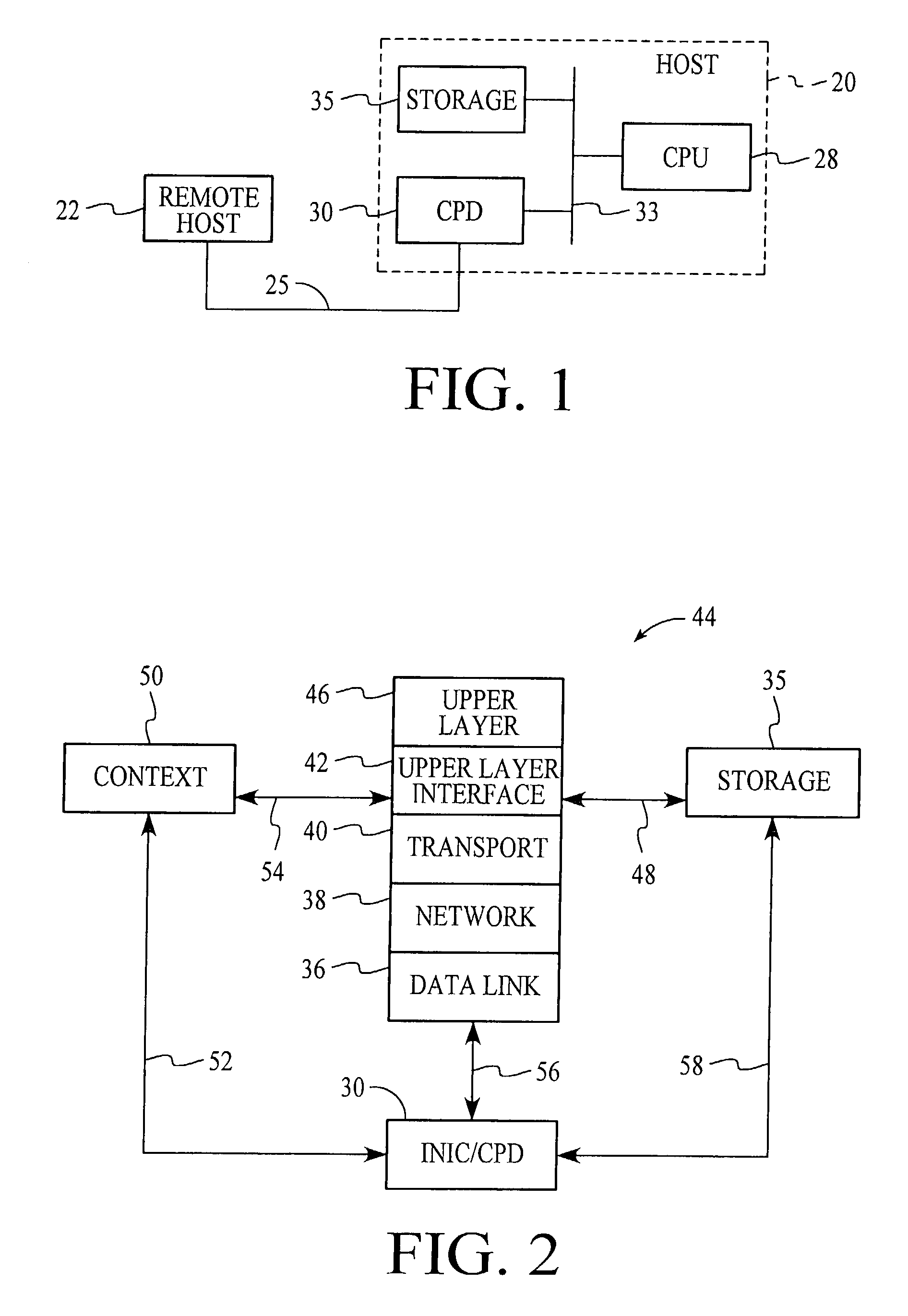
TCP/IP offload network interface device
InactiveUS7174393B2Little and no performance benefitMove quicklyMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksGeneral purposeFast path
A system for protocol processing in a computer network has a TCP / IP Offload Network Interface Device (TONID) associated with a host computer. The TONID provides a fast-path that avoids protocol processing for most large multi-packet messages, greatly accelerating data communication. The TONID also assists the host for those message packets that are chosen for processing by host software layers. A communication control block for a message is defined that allows DMA controllers of the TONID to move data, free of headers, directly to or from a destination or source in the host. The context is stored in the TONID as a communication control block (CCB) that can be passed back to the host for message processing by the host. The TONID contains specialized hardware circuits that are much faster at their specific tasks than a general purpose CPU. A preferred embodiment includes a trio of pipelined processors with separate processors devoted to transmit, receive and management processing, with full duplex communication for four fast Ethernet nodes.
Owner:ALACRITECH
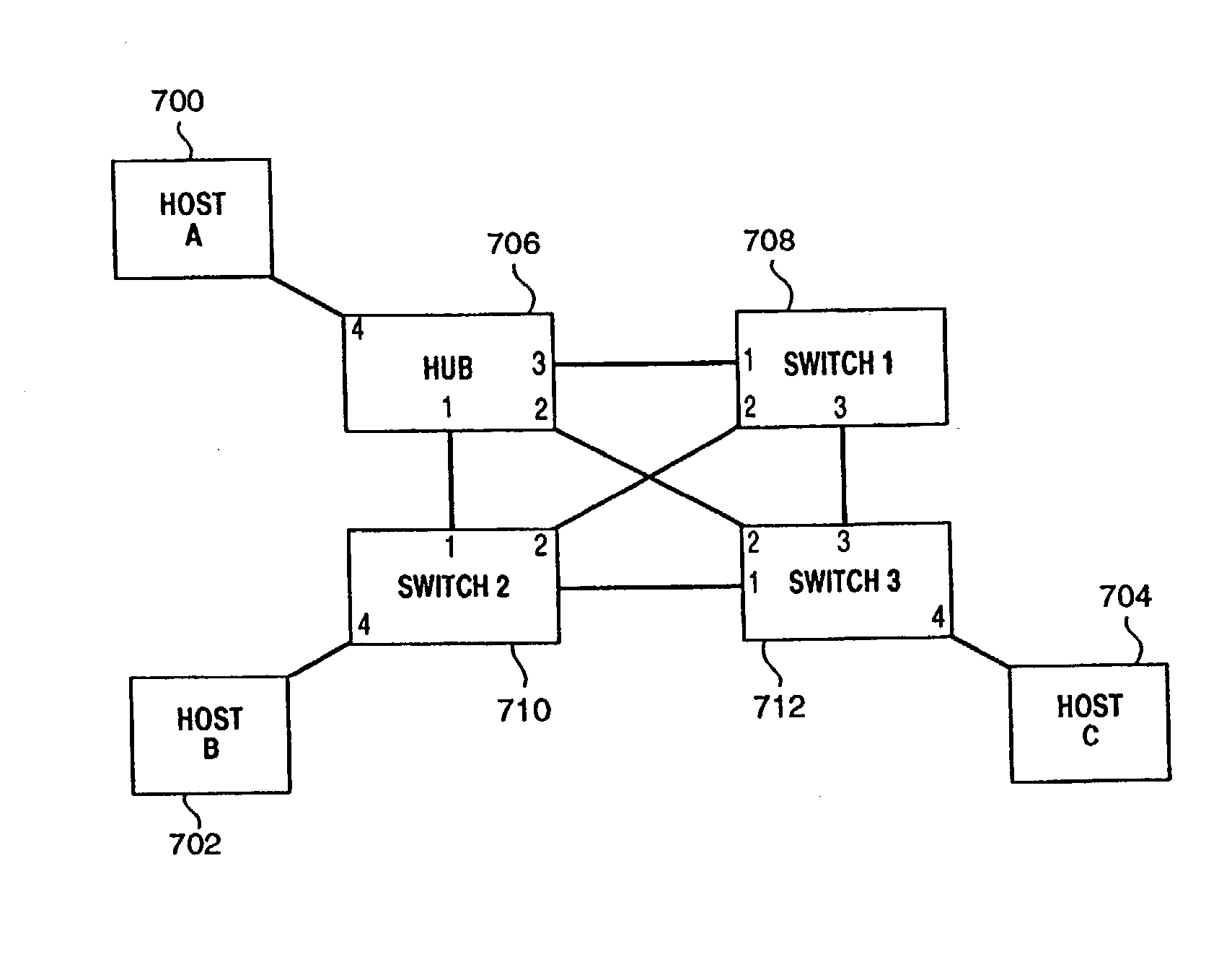
MAC address learning and propagation in load balancing switch protocols
InactiveUS20030179707A1Special service provision for substationError preventionNetwork switchBroadcasting
A method for disseminating MAC addresses for discovered network devices through a plurality of network switches which cooperate to enable maintaining multiple active paths between such devices. Where a plurality of network switches cooperate through load balancing protocols to enable simultaneous use of multiple paths between, protocols of the present invention permit newly discovered MAC addresses attached to ports of an edge switch to be disseminated through the network switches. When an edge switch detects a device having a previously unknown MAC address, a MAC address information packet is generated and disseminated from the edge switch the other switched of the same load balance domain. The packet is preferably, in effect, broadcast using the pruned broadcast tree constructed and maintained by other protocols related to the present invention. Each intermediate switch on the broadcast tree eventually receives the MAC address information packet from a neighboring switch in the load balance domain. The received MAC address information packet is used to update MAC address tables in the receiving switch. If appropriate in accordance with the pruned broadcast tree, the received MAC address packet is forwarded from each receiving intermediate switch to other neighbor switches in the load balance domain.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
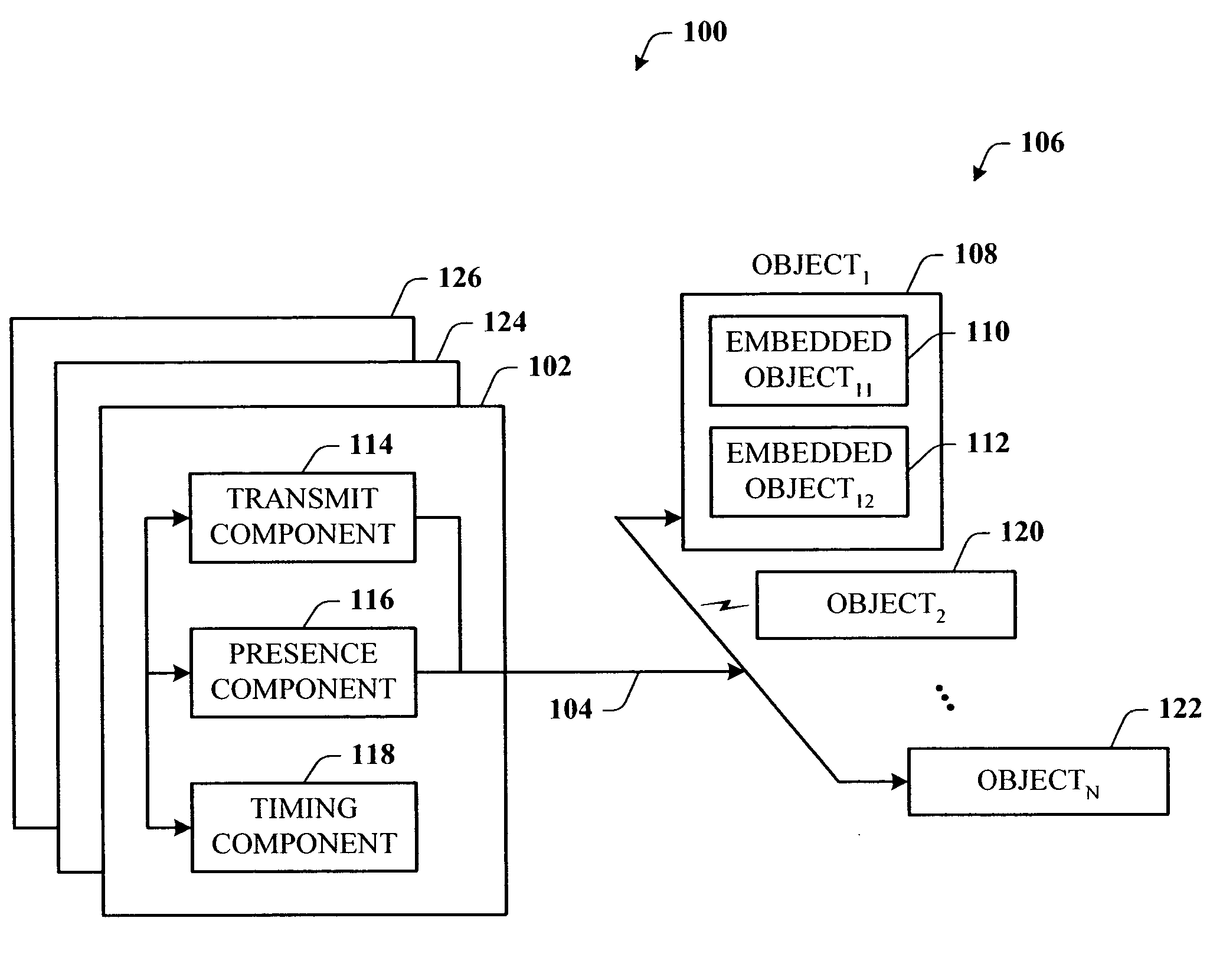
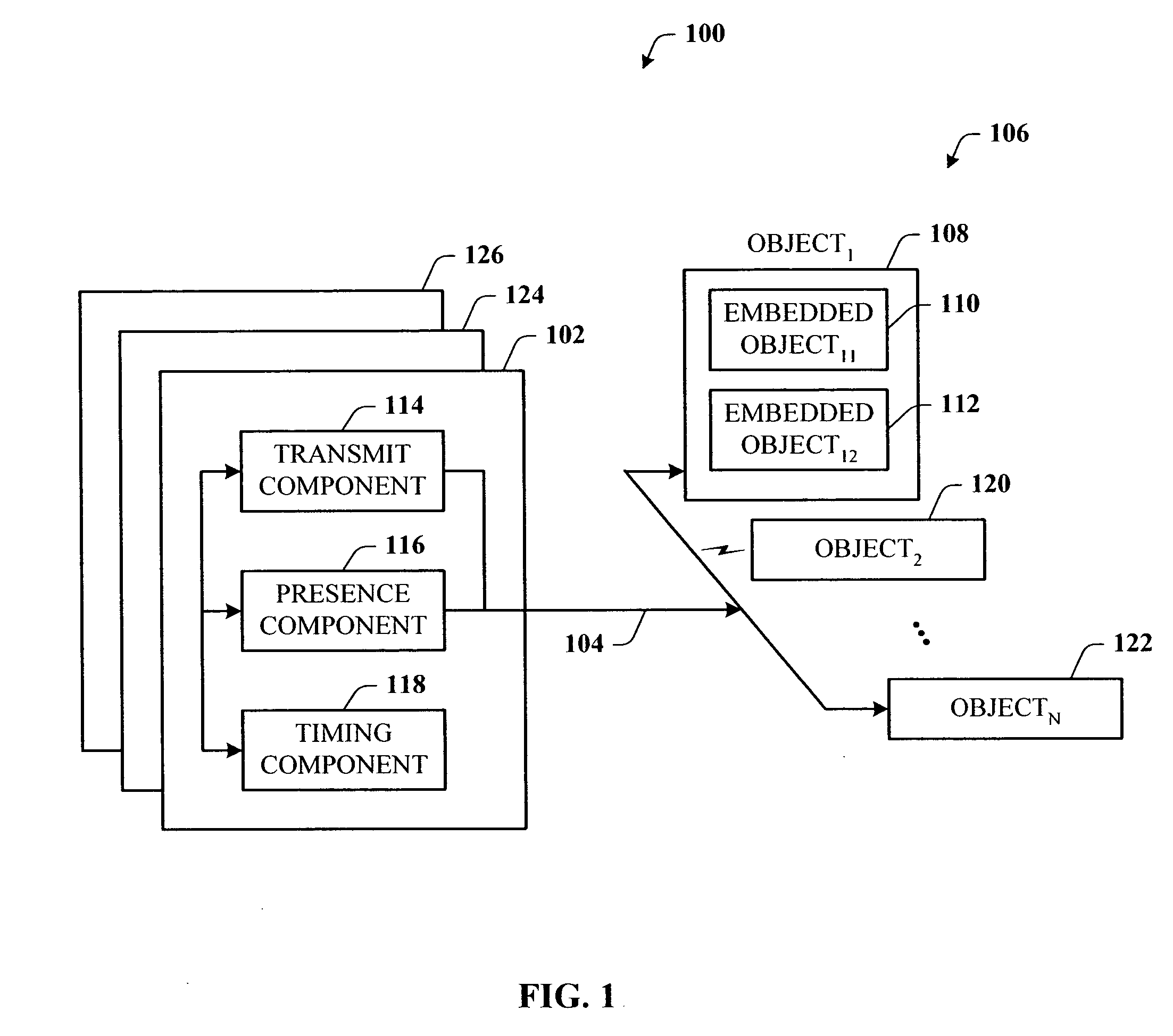
Presence tracking for datagram based protocols with search
InactiveUS20050108331A1Reduce network trafficEasy searchMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationClient-sideBroadcast multicast
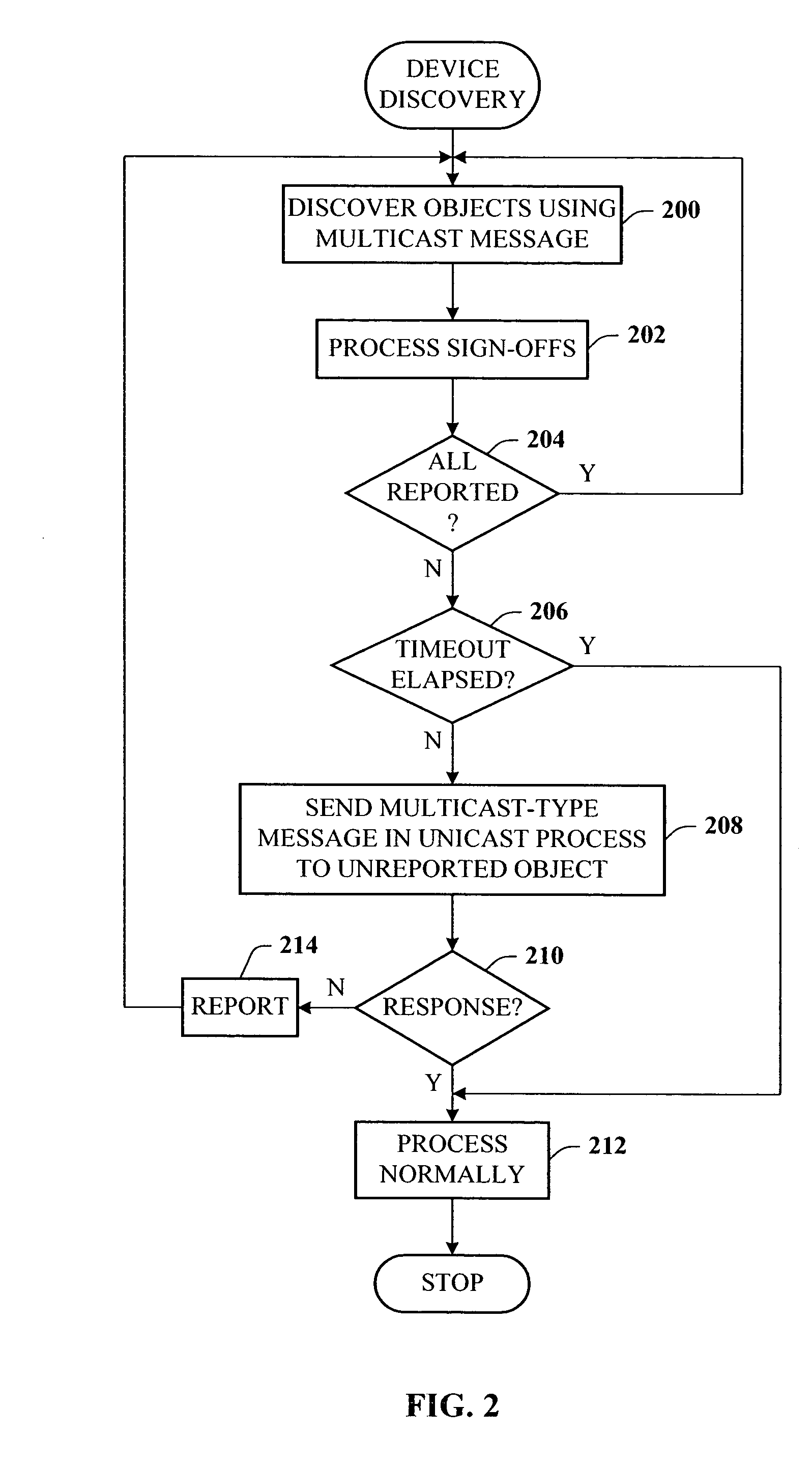
A presence tracking architecture for datagram-based protocols. A client application seeking to know the presence or lack thereof of a device and / or service utilizes a standard protocol in a non-intuitive way to trigger notification of the device and / or service before any associated timeout expires. At first presence, a multicast message is broadcast to notify all devices. Subsequently, on-demand notification may be requested by a client application by sending directly (e.g., in unicast) to the device before its timeout has expired a message that is normally only sent in multicast. If capable, the device can then respond normally with a unicast message indicating it is on-line. If the response is not received, the device and / or service is determined to be off-line.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
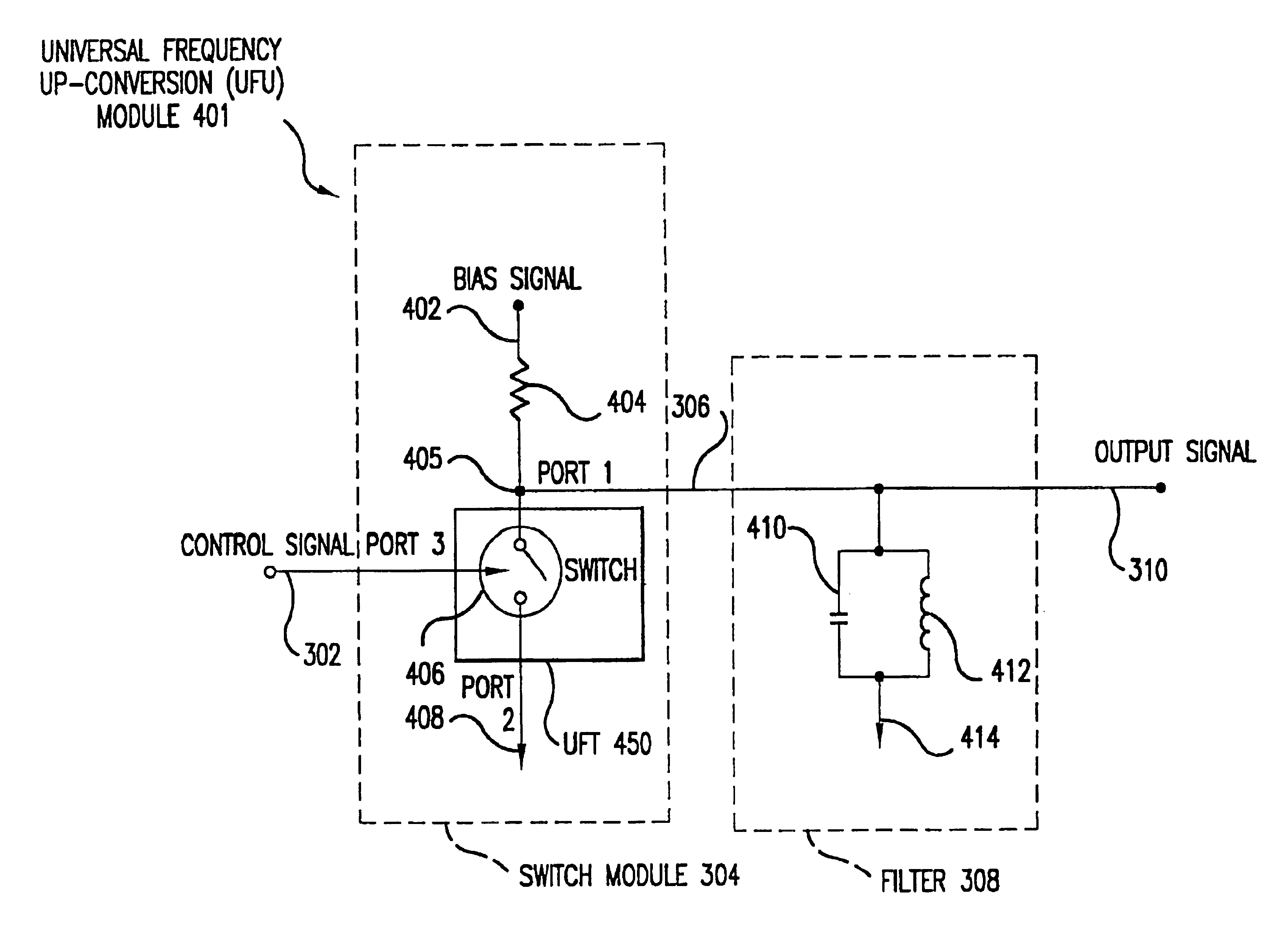
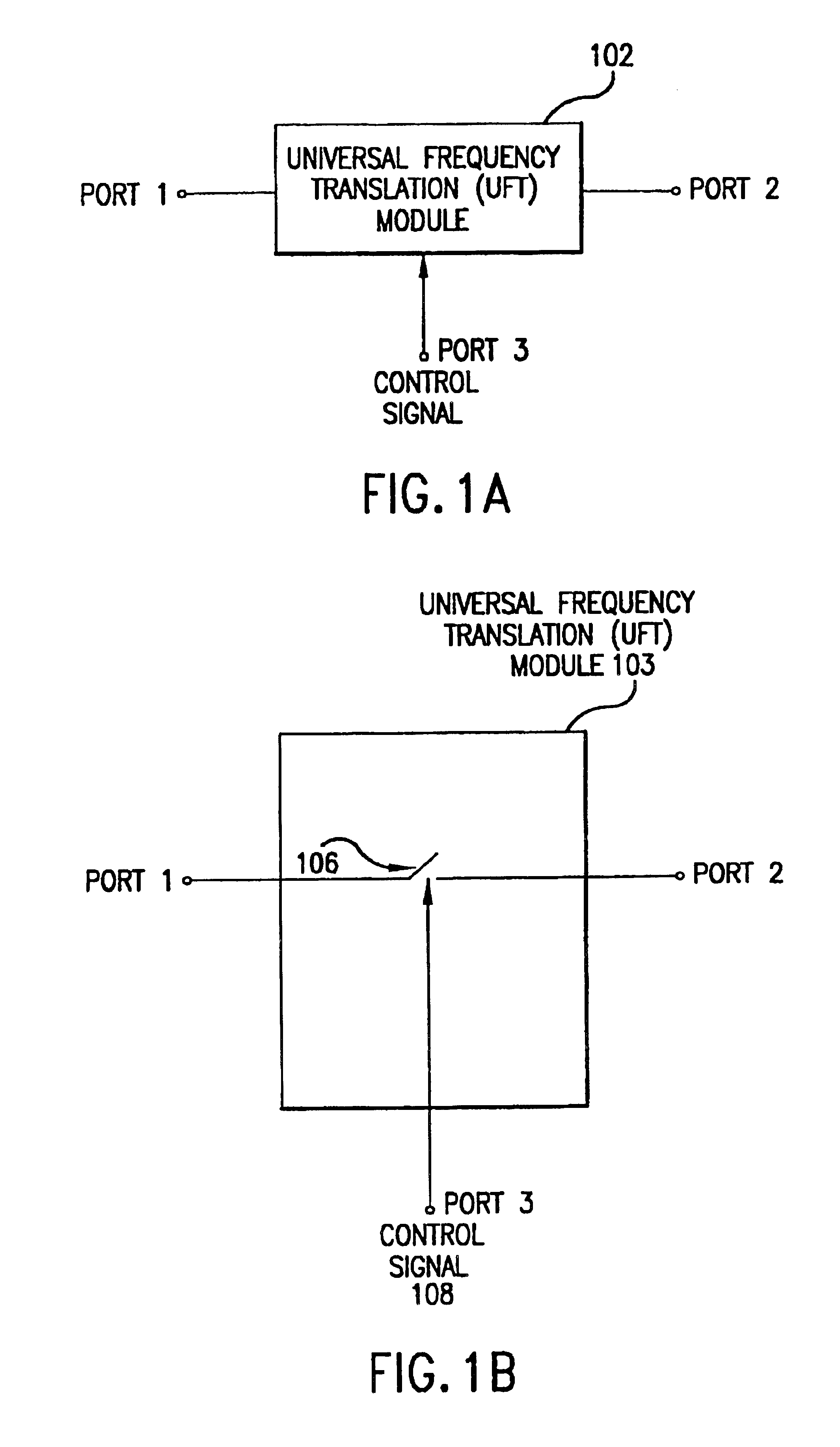
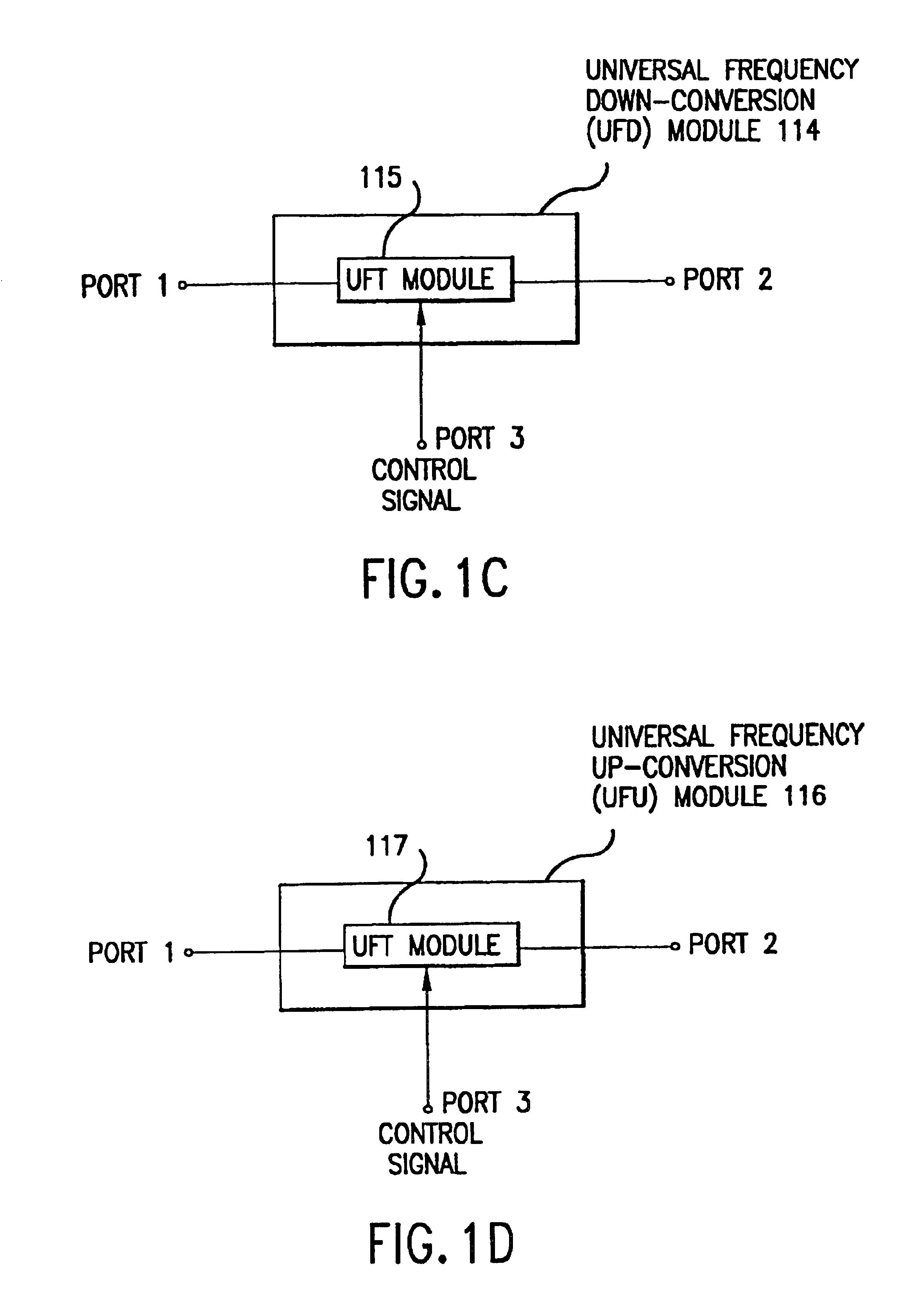
Universal platform module and methods and apparatuses relating thereto enabled by universal frequency translation technology
InactiveUS6873836B1Modulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionTransceiverCommunications system
A communication system comprising a multi-protocol, multi-bearer sub-system is described herein. The sub-system is a universal platform module that can transmit and receive one or more information signals in one or more protocols using one or more bearer services. In one embodiment, the sub-system may form a portion of a transceiver that is composed of a transmitter and a receiver, and which is a gateway server between a personal area network (PAN) and the global wireless network.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
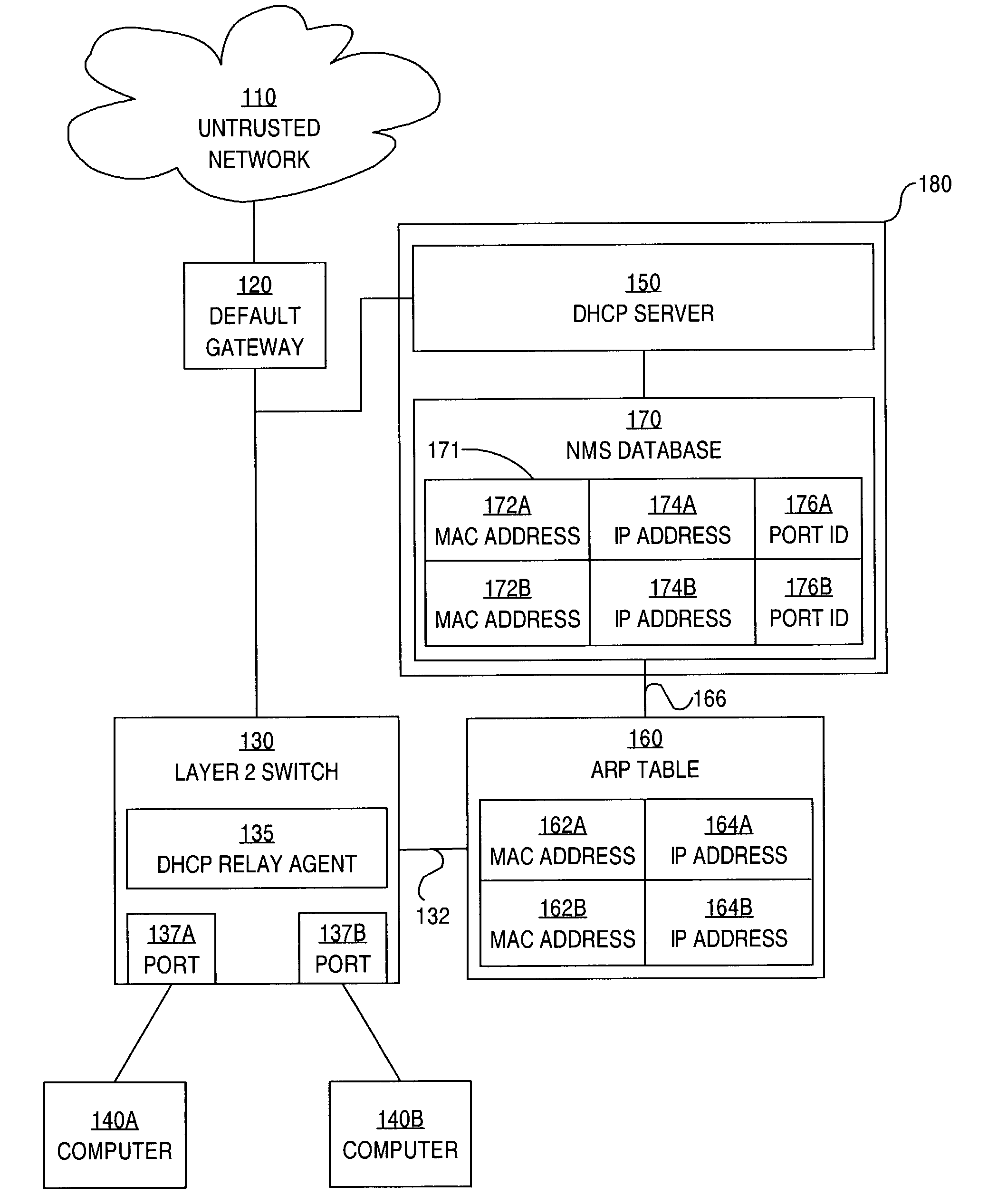
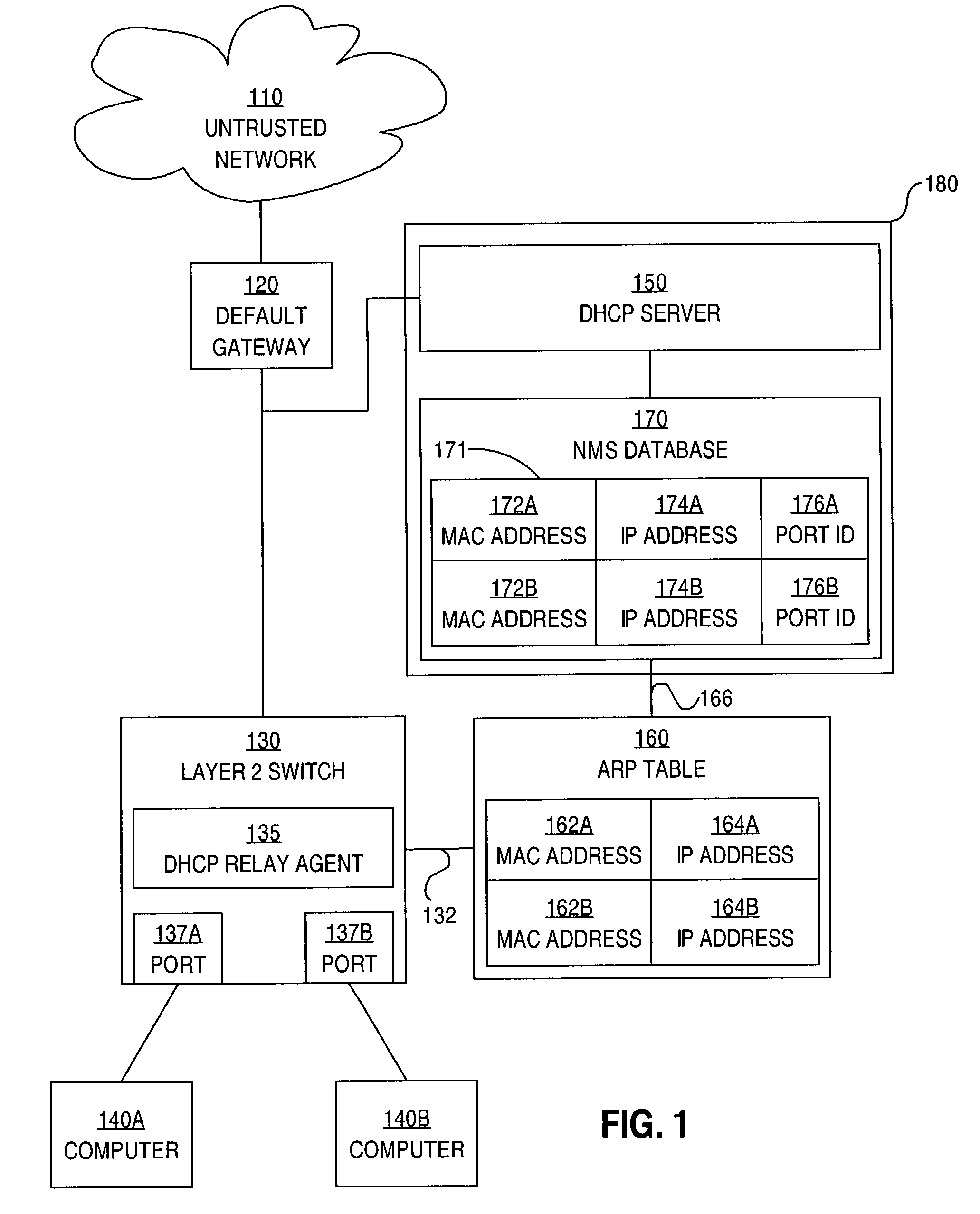
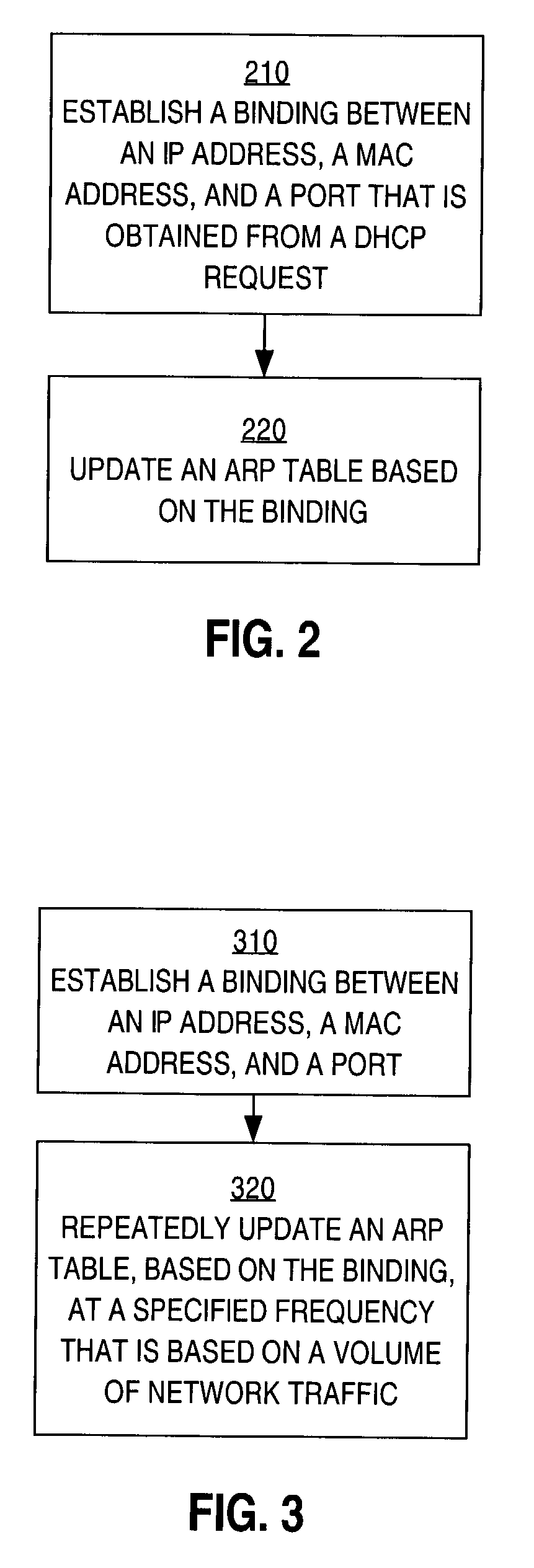
Method and apparatus for preventing spoofing of network addresses
ActiveUS7234163B1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionAddress Resolution ProtocolNetwork addressing
A method is disclosed for preventing spoofing of network addresses. A binding is established between an Internet Protocol (IP) address, a Media Access Control (MAC) address, and a port. An Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table is updated based on the binding.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
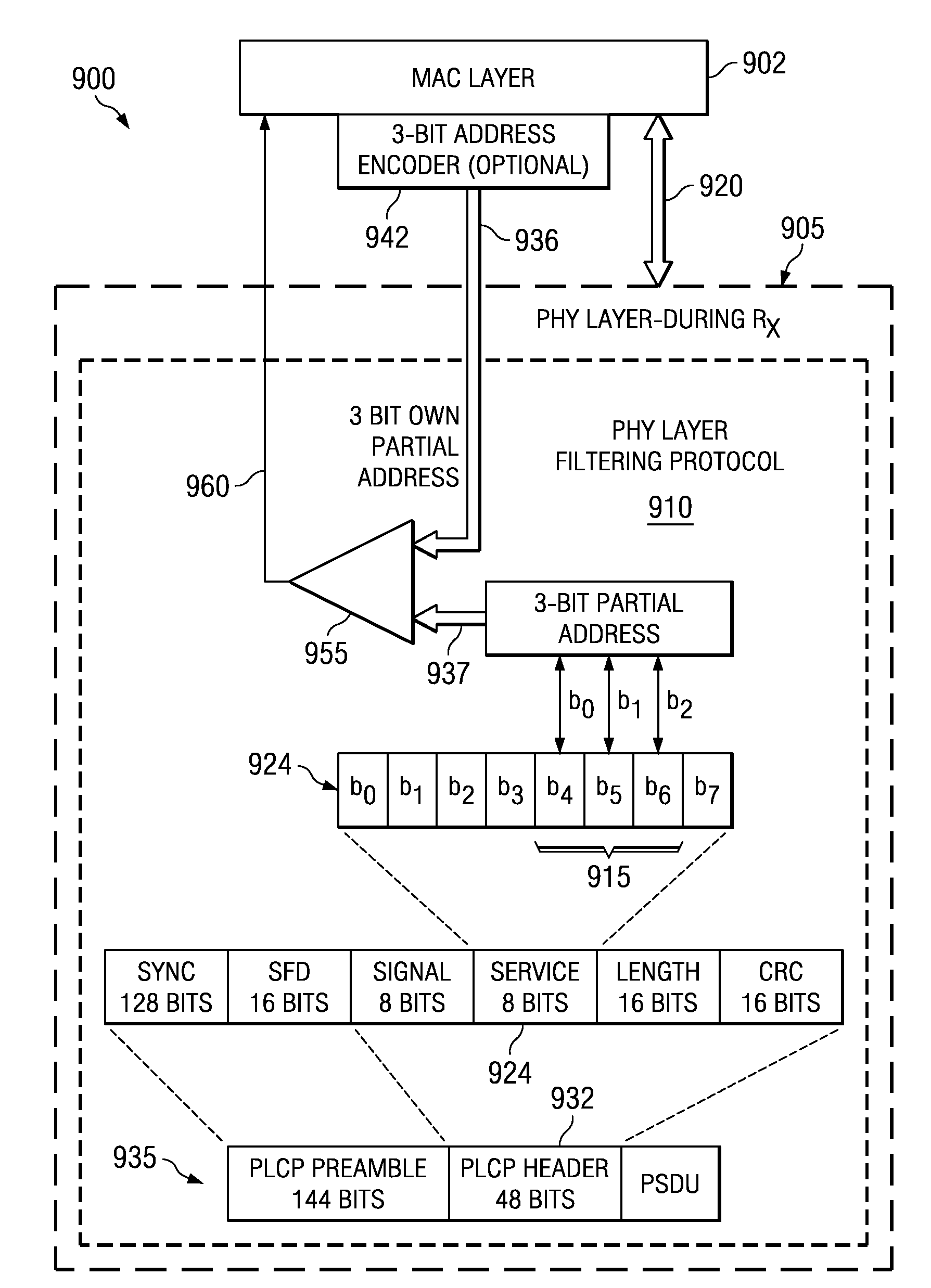
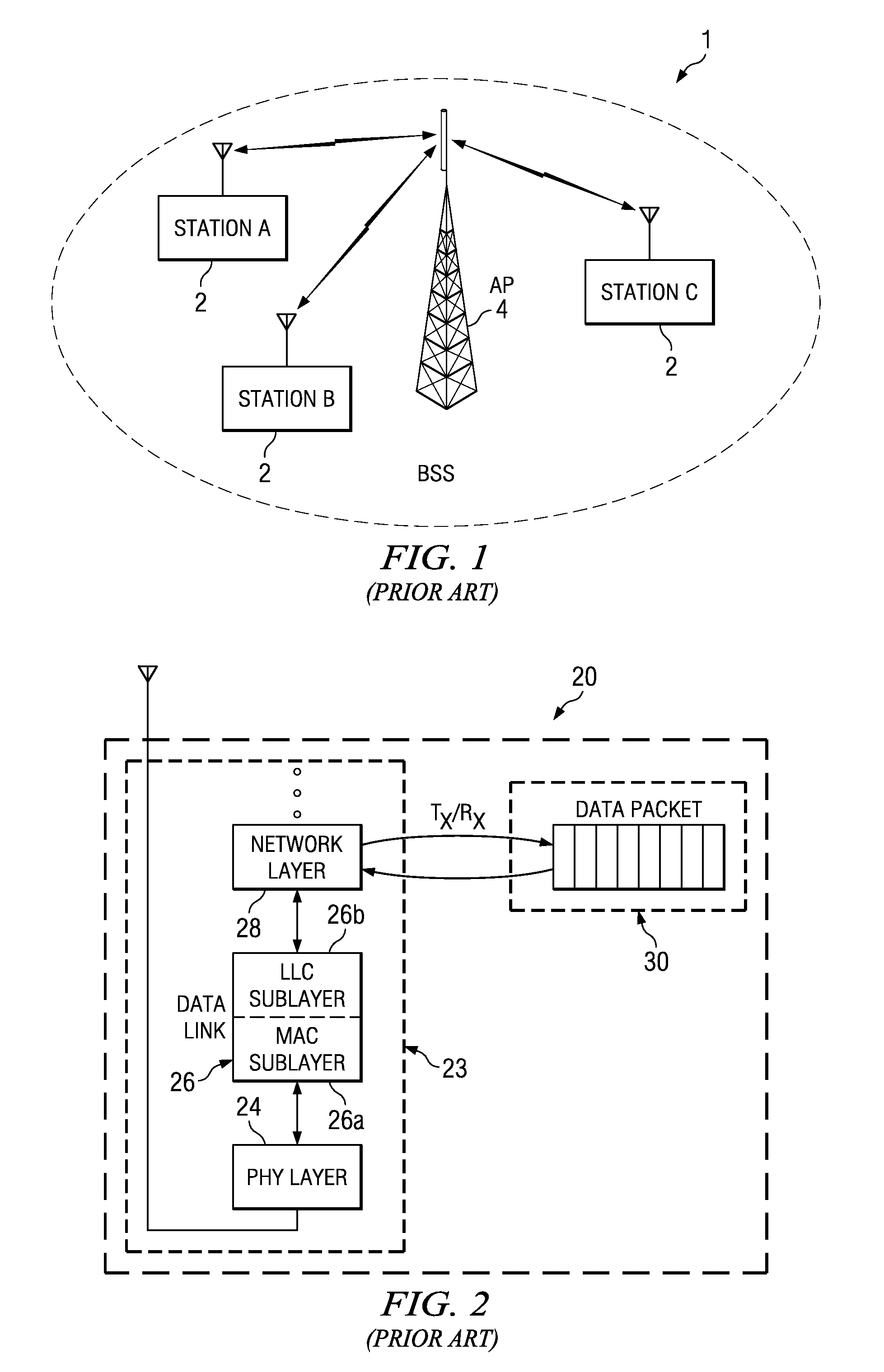
Power saving via physical layer address filtering in WLANs
ActiveUS7257095B2Save powerSolve the power is smallPower managementEnergy efficient ICTPhysical addressPhysical layer
A system and method is described for saving power in a wireless network, using a physical layer address filtering protocol based on a partial address subset of the complete destination MAC address. The system comprises a PHY layer filtering protocol for generating the partial address and writing the partial address into a PHY layer header portion (e.g., PLCP header) of a sending station, or reading the partial address from the PHY layer header portion upon transmission of each frame. A receiving station receives and decodes these PHY layer header portion bits, in accordance with the protocol, and compares whether the subset of bits match that of the stations' own partial address. If a station finds a match, the station then continues further decoding the frame at PHY layer and send the complete frame to the MAC layer for further processing. The stations that do not have a match will not activate their MAC layer components. Thus, the stations of the network will avoid wasting power decoding a significant portion of the complete frame of other stations of the wireless local area networks and unnecessary MAC layer processing. When group addressed, control / management frames or other such frames are detected at the sending station, the address filtering protocol may be “disabled” using a partial address containing a predetermined value (e.g., all zeros).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Tcp/ip processor and engine using rdma
InactiveUS20080253395A1Sharply reduces TCP/IP protocol stack overheadImprove performanceDigital computer detailsTime-division multiplexInternal memoryTransmission protocol
A TCP / IP processor and data processing engines for use in the TCP / IP processor is disclosed. The TCP / IP processor can transport data payloads of Internet Protocol (IP) data packets using an architecture that provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. The engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a TCP / IP session information database and may also store a storage information session database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
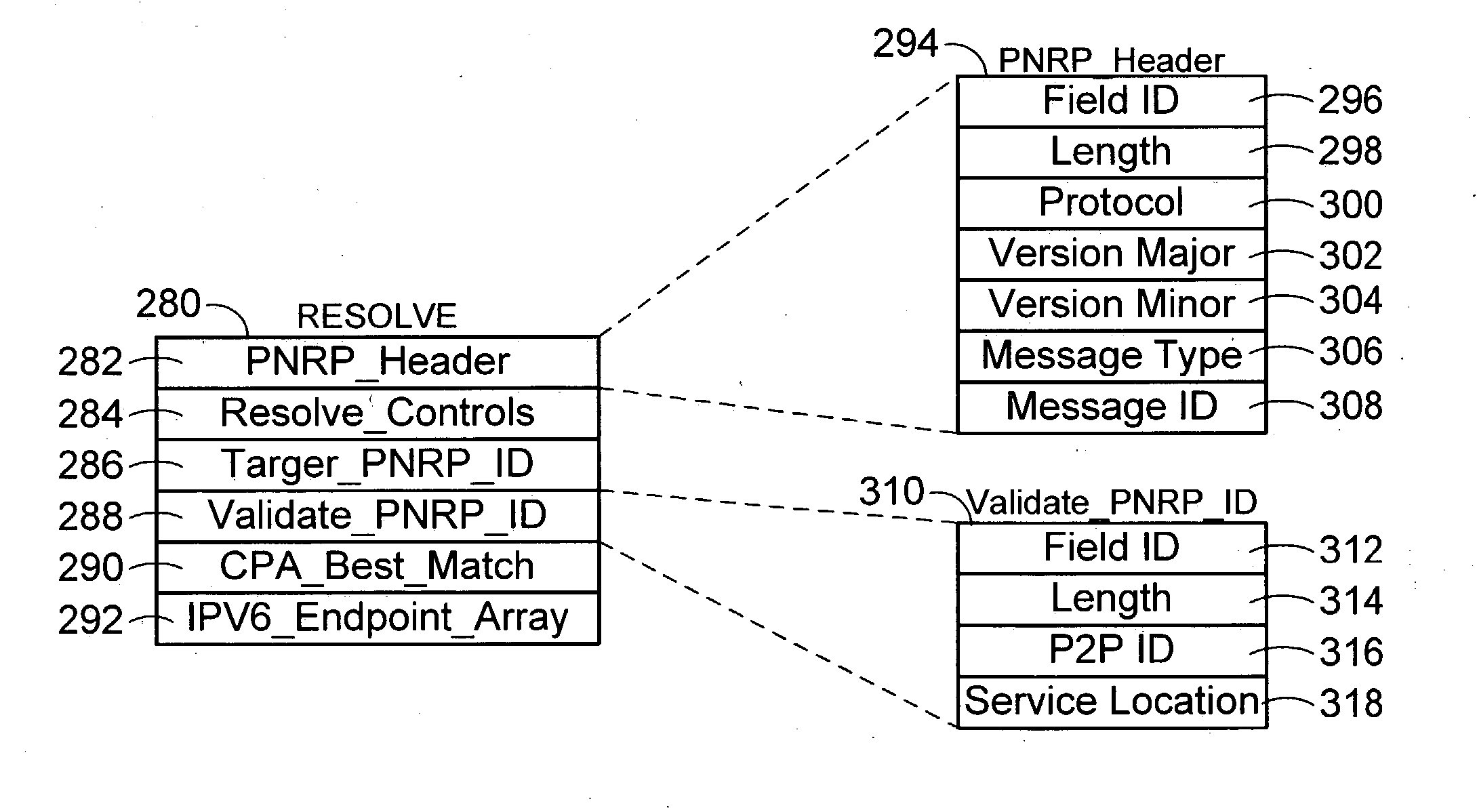
Peer-to-peer name resolution wire protocol and message format data structure for use therein
InactiveUS20050004916A1Digital data processing detailsTime-division multiplexWire protocolPeer-to-peer
An extensible data structure for messages in a peer to peer name resolution protocol is presented. This message data structure utilizes a number of fields, each containing a message element. Preferably, the first field is the message header that includes protocol information and identifies the type of message. Each message element contains a number of fields. These message element fields include a type field, a length field, and the content or payload of the message element. In one embodiment, at least ten messages are formed for proper operation of a Peer To Peer Name Resolution Protocol (PNRP), including RESOLVE, RESPONSE, SOLICIT, ADVERTISE, REQUEST, FLOOD, INQUIRE, AUTHORITY, ACK, and REPAIR messages.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Address mechanisms in internet protocol
ActiveUS20020133607A1User identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet protocol suiteComputer hardware
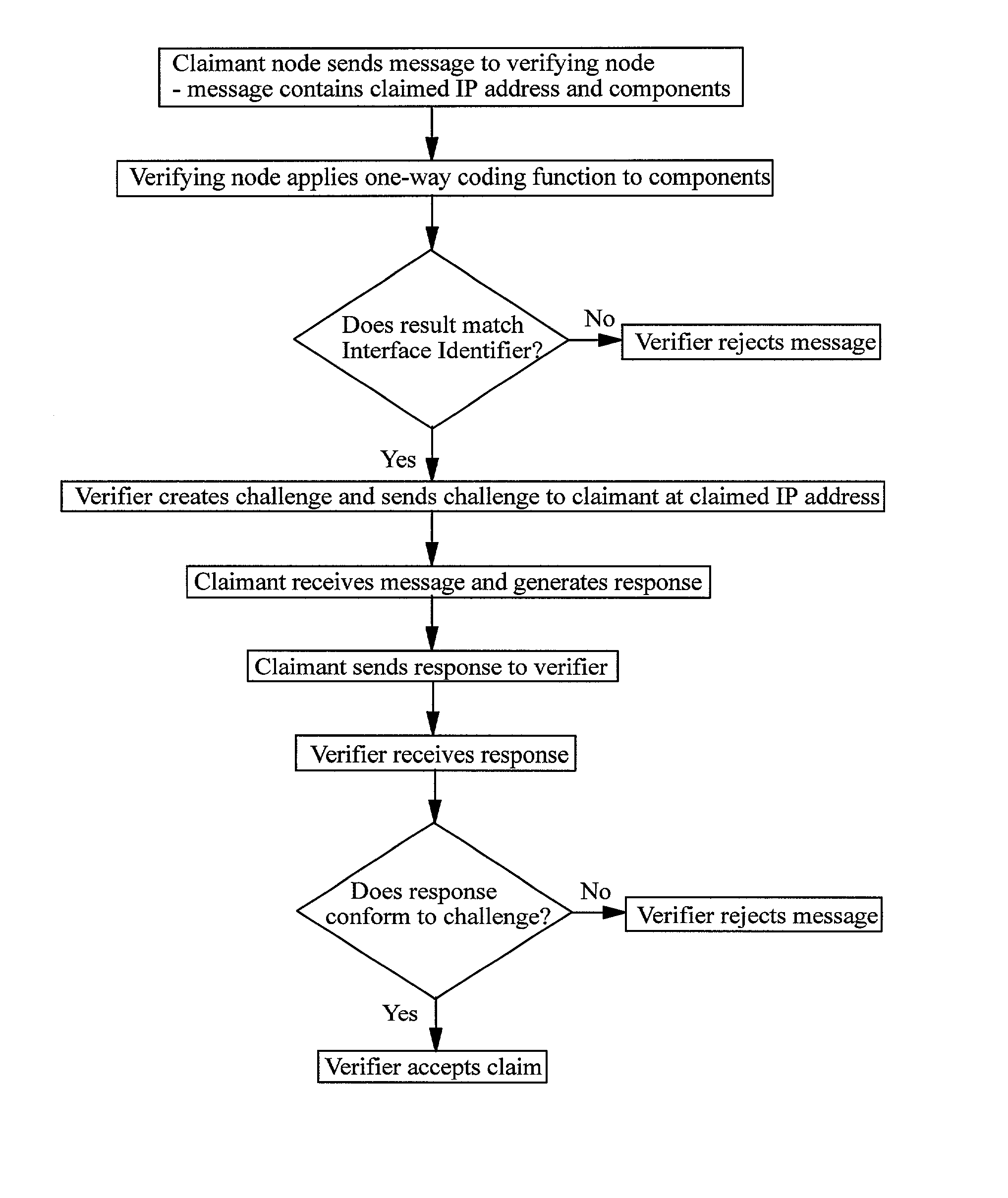
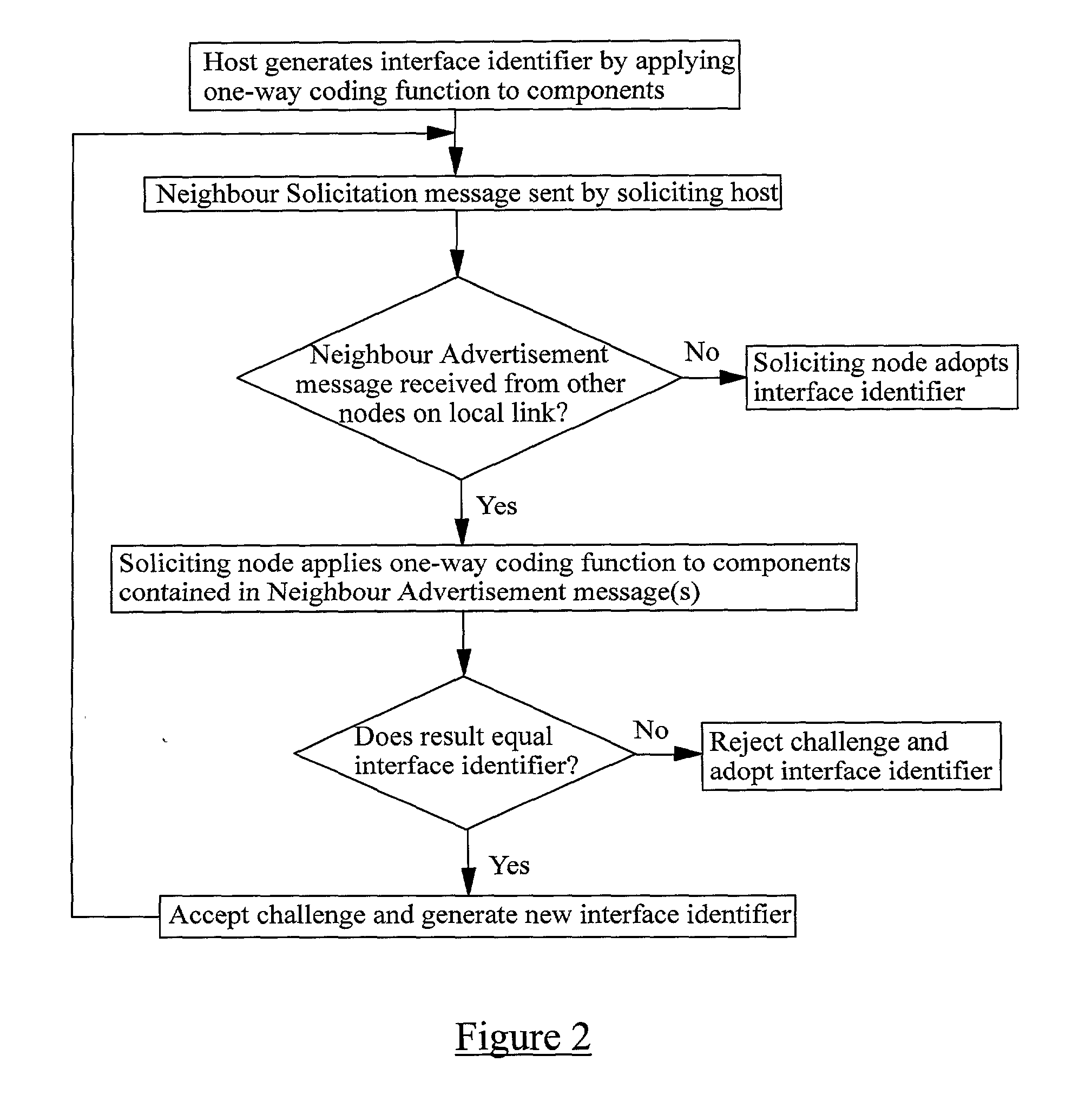
A method of verifying that a host coupled to an IP network is authorised to use an IP address which the host claims to own, the IP address comprising a routing prefix and an interface identifier part. The method comprises receiving from the host one or more components, applying a one-way coding function to the or each component and / or derivatives of the or each component, and comparing the result or a derivative of the result against the interface identifier part of the IP address. If the result or its derivative matches the interface identifier the host is assumed to be authorised to use the IP address and if the result or its derivative does not match the interface identifier the host is assumed not to be authorised to use the IP address.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
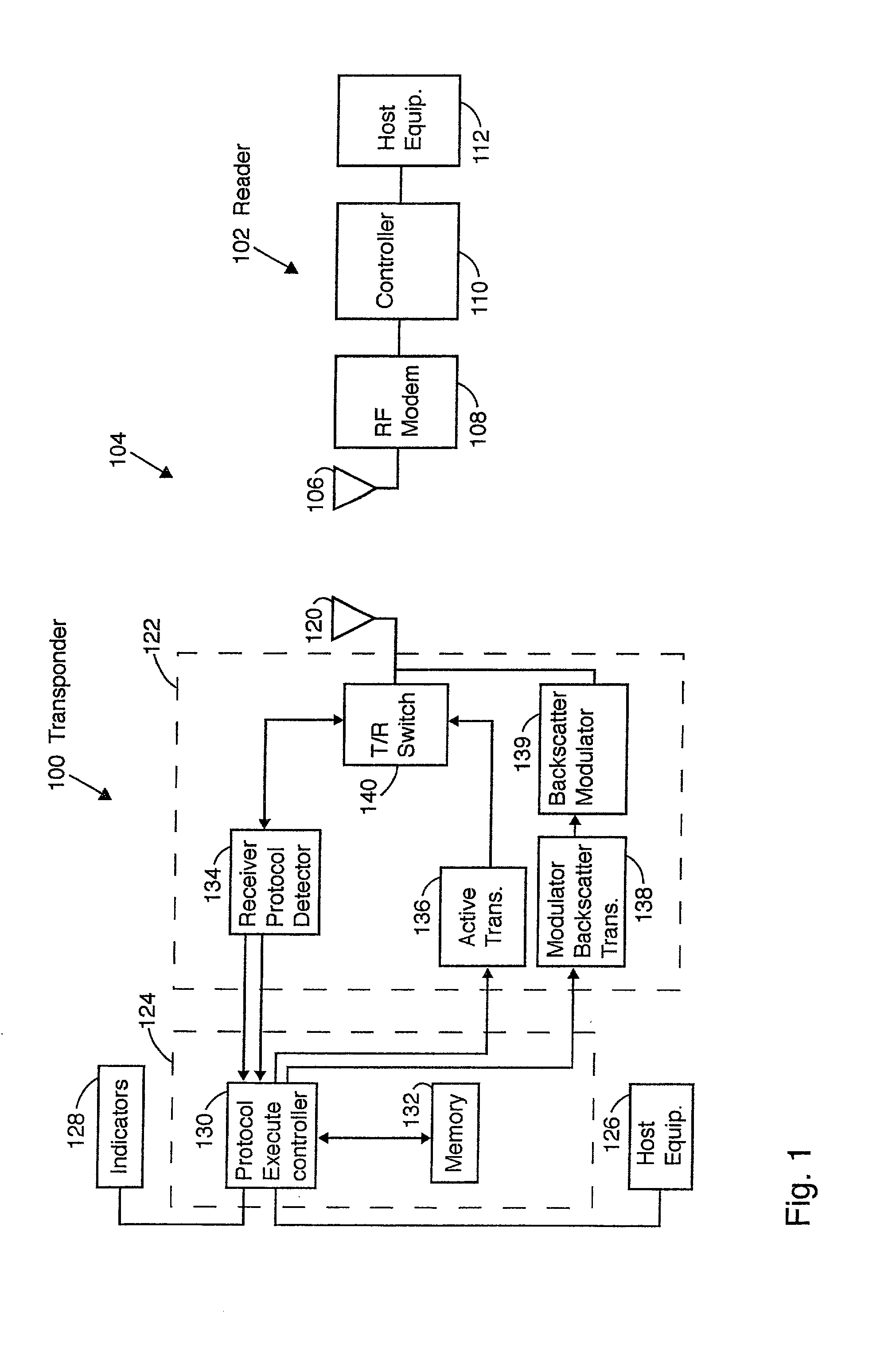
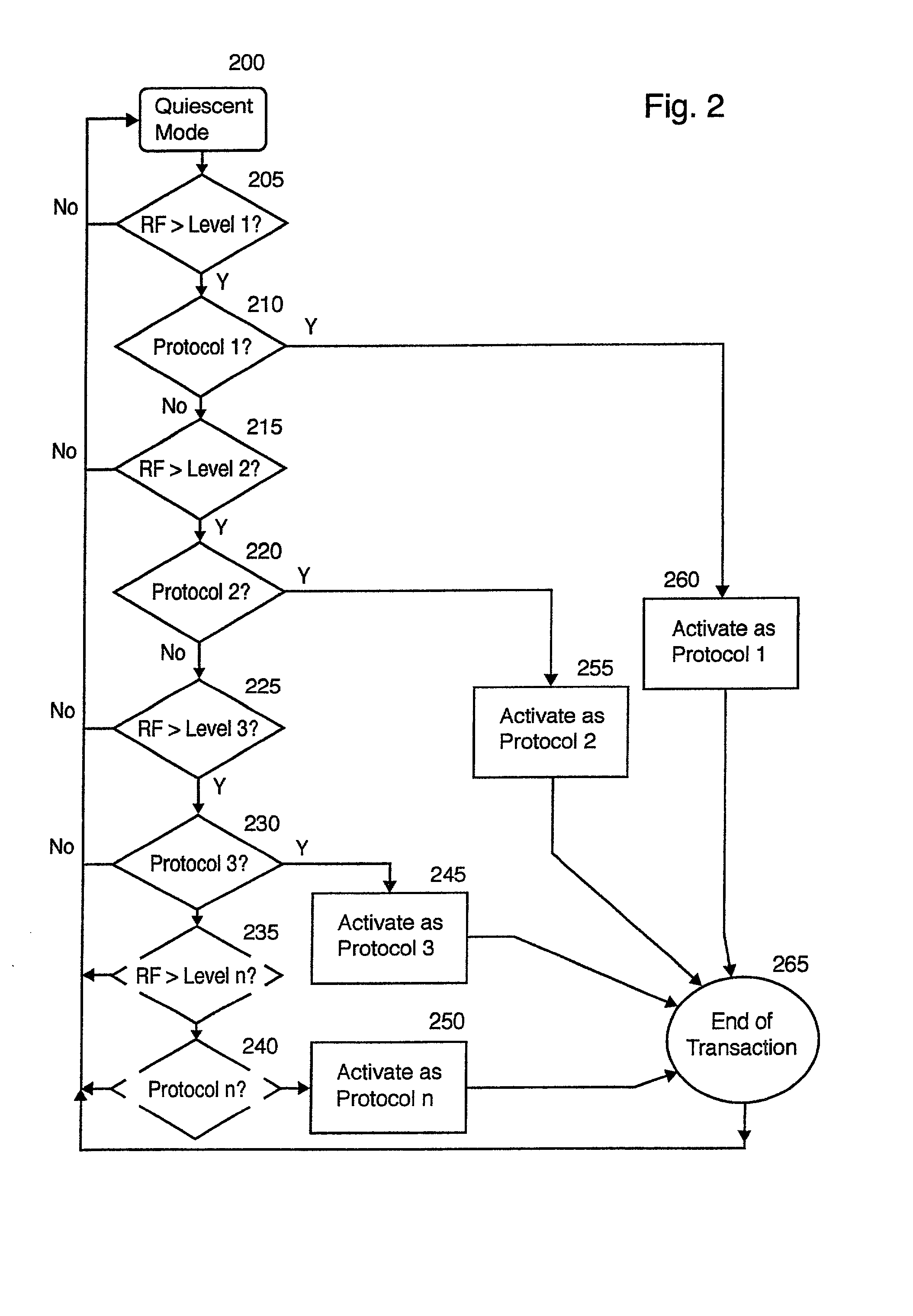
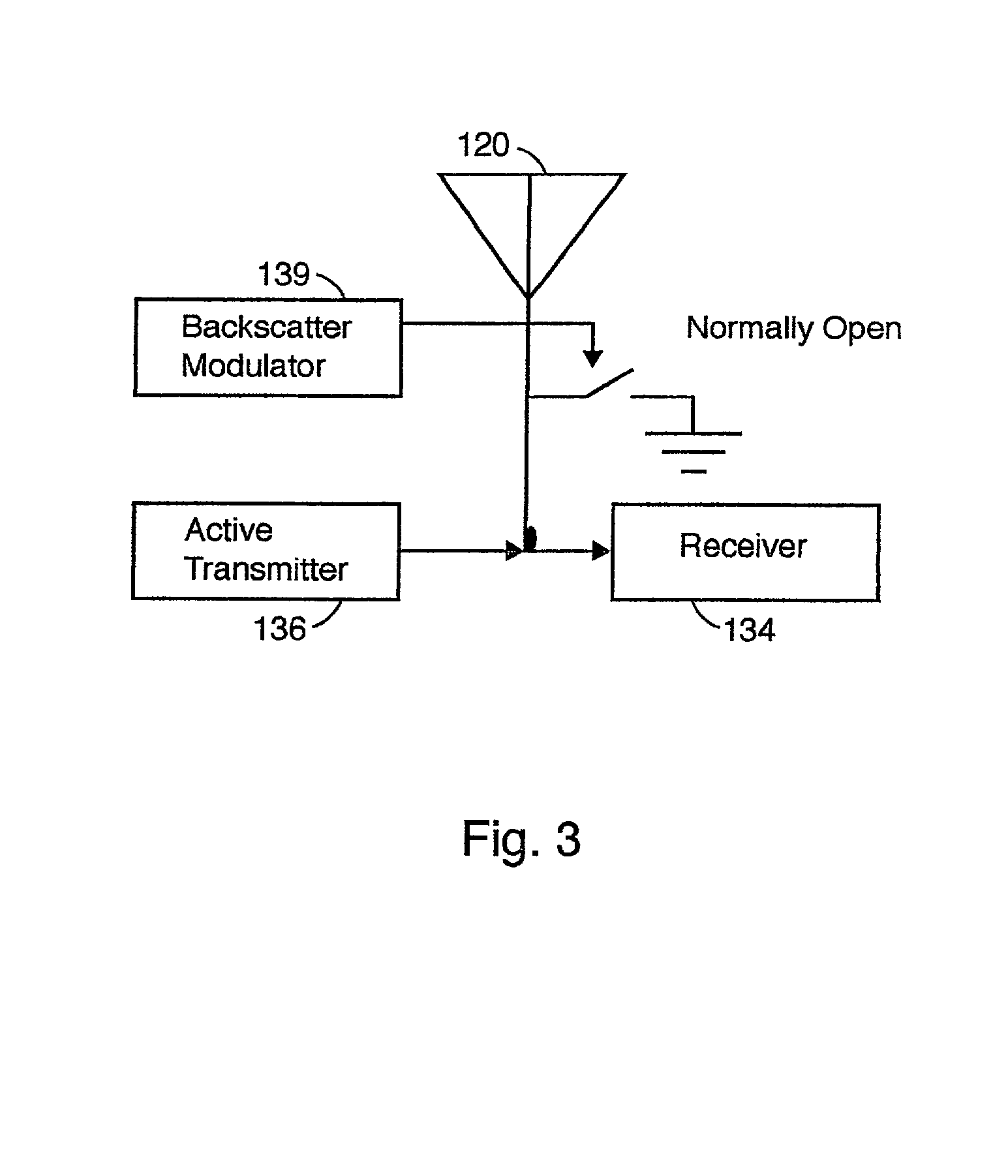
Multiple protocol transponder
InactiveUS20010050922A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork Communication ProtocolsMulti protocol
A multi protocol transponder for a communications network having a antenna for receiving a first RF signal transmitted according to a communications protocol and a detector for identifying the communications protocol from the first RF signal. A protocol controller is provided for executing the identified communications protocol to generate a second RF signal. Thereafter an antenna transmits the second RF signal according to the communications protocol either by active transmission or modulated backscatter. The transponder may implement a variety of wide area and localized lane based protocols for Automatic Vehicle Identification systems such as CVO and Toll systems.
Owner:MARK IV INDS
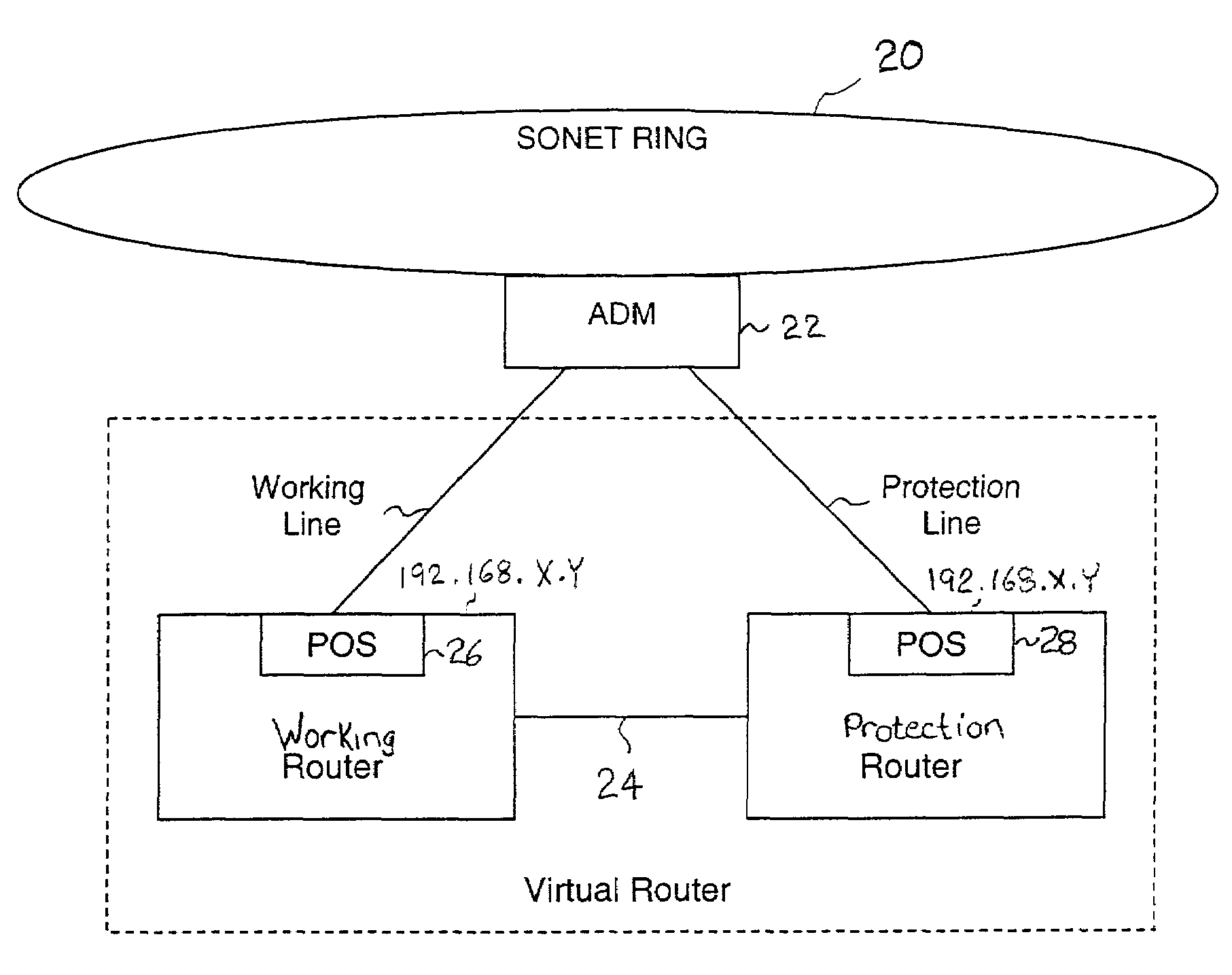
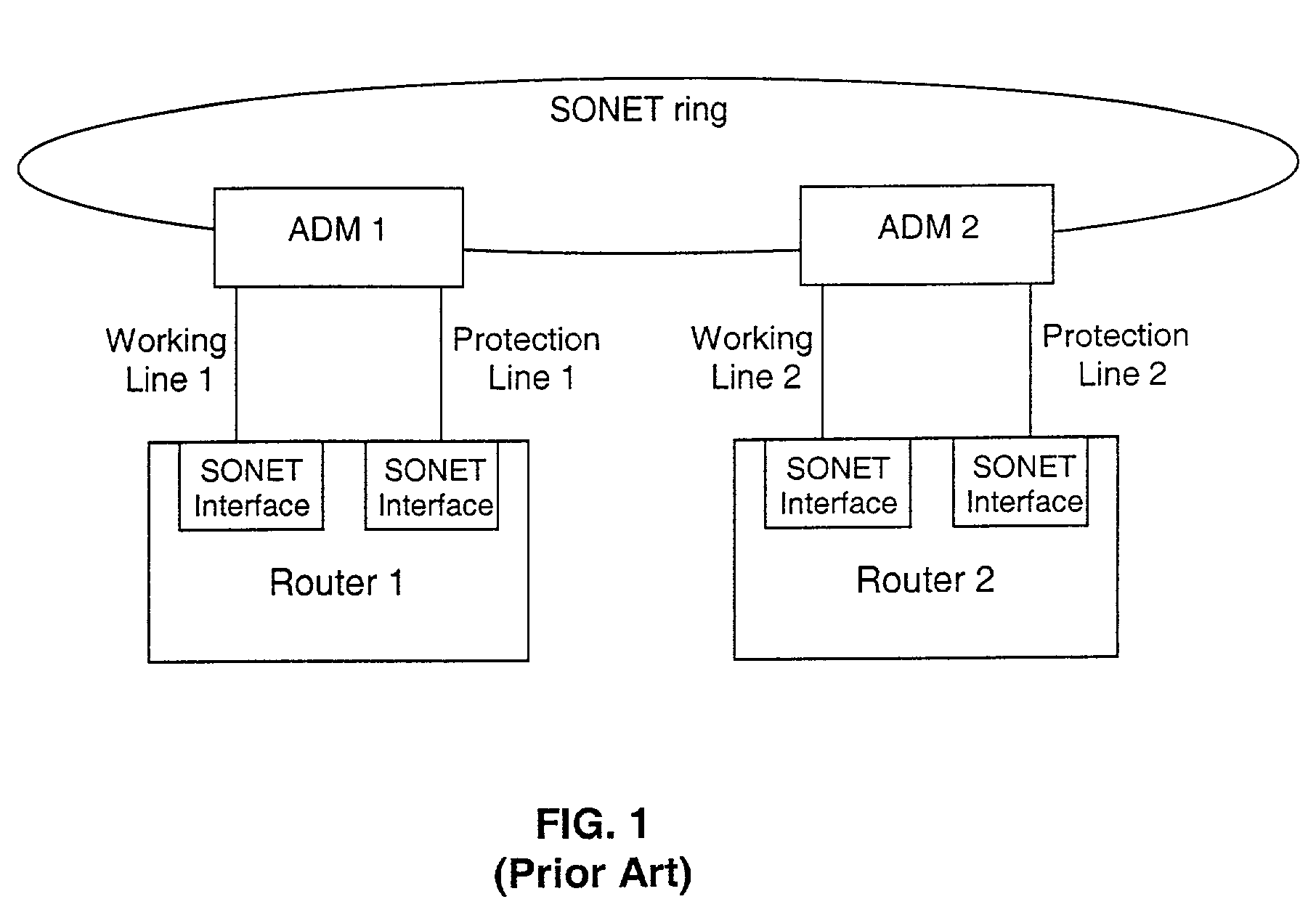
Fault tolerant automatic protection switching for distributed routers
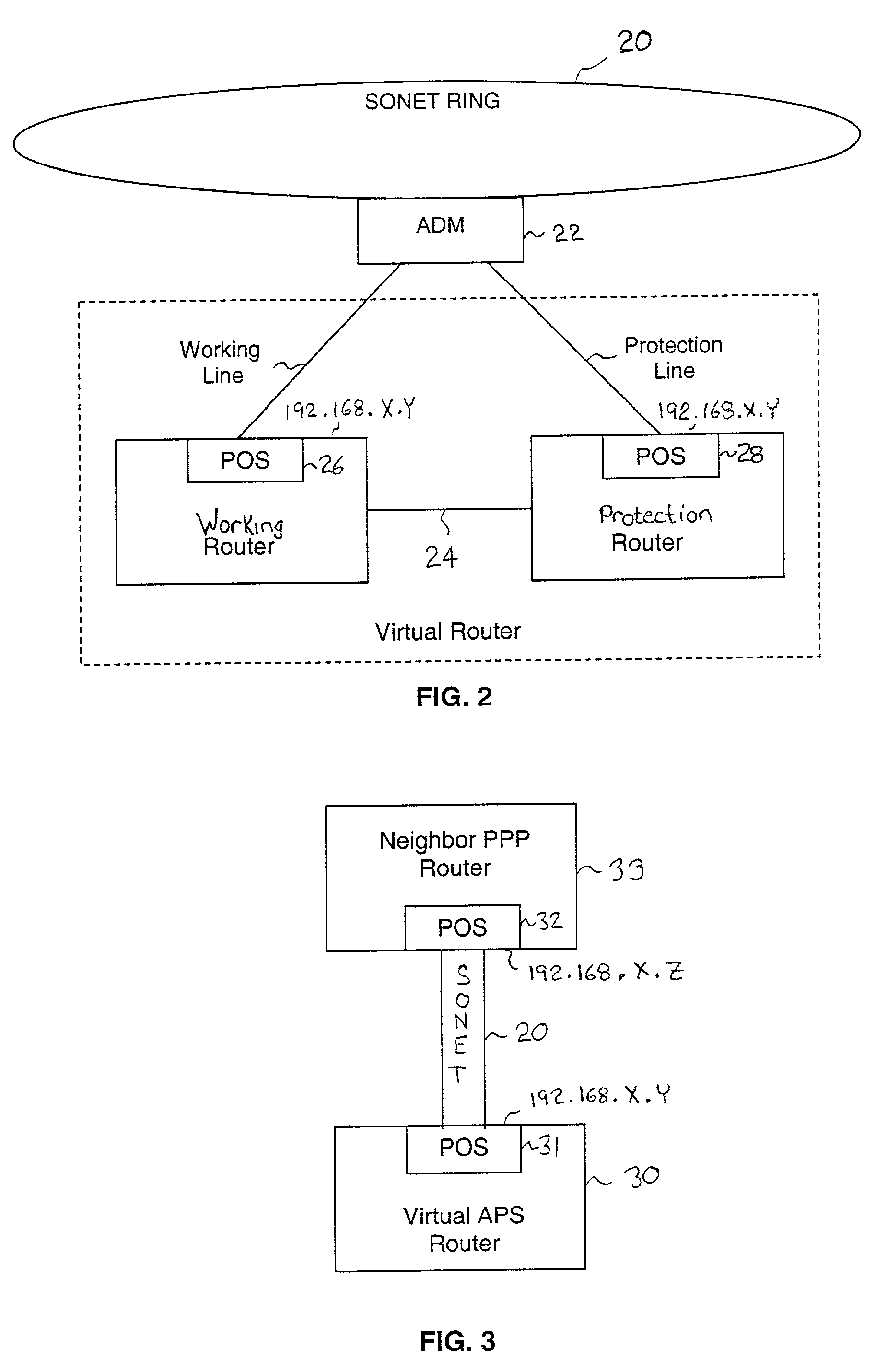
InactiveUS6956816B1Providing fault toleranceError preventionTransmission systemsPoint-to-Point ProtocolAutomatic protection switching
A working router is coupled to a SONET add-drop multiplexor (ADM) through a working line and a protection router is coupled to the ADM through a protection line. The routers are coupled to each other by a separate side-band connection and comprise a virtual router from the perspective of the neighboring router, which communicates with the virtual router over the SONET network using the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). The protection router transmits a heartbeat message to the working router over the side-band connection. If the protection router does not receive a response thereto, it initiates a line switch within the add-drop multiplexor. Once the line switch is complete, the protection router exchanges datagrams with the neighboring router, via the ADM and SONET ring to which the ADM is coupled. The protection router establishes a PPP connection between itself and the neighboring router device coupled to the SONET ring, utilizing the Link Control Protocol (LCP). The protection router includes a predetermined identifier value that identifies the originator of the request, in the LCP Identifier field of LCP request datagrams. The neighboring router includes the Identifier value received in a request datagram in the corresponding response datagram transmitted over the SONET ring to the ADM. Because datagrams received by the ADM from the SONET link are transmitted over both the working and the protect lines, the working router receives the same response as the protection router. Thus, by examining the identifier field, and recognizing the identifier value as that assigned to the protection router, the working router determines that the line switch to the protection router has occurred.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
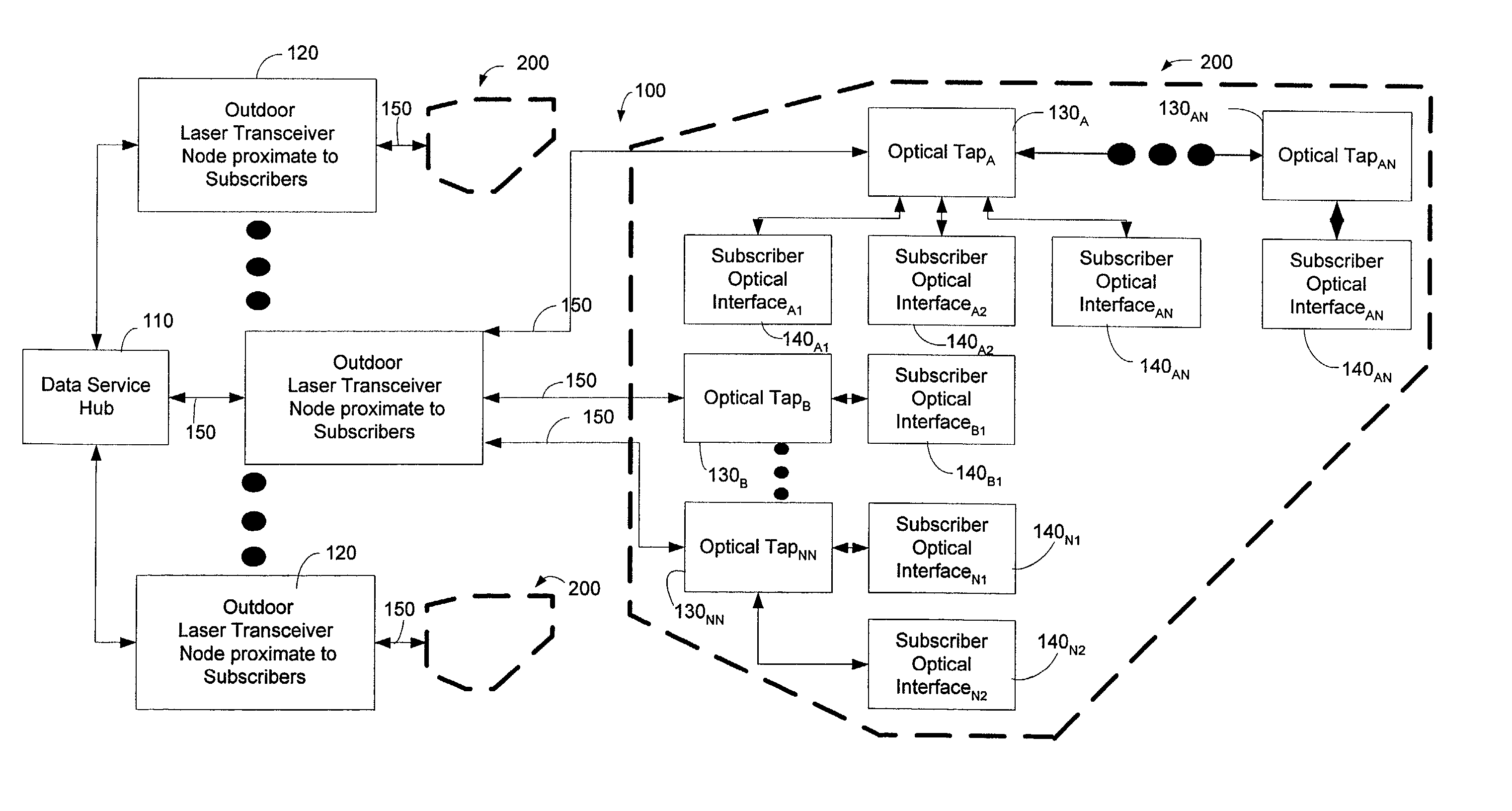
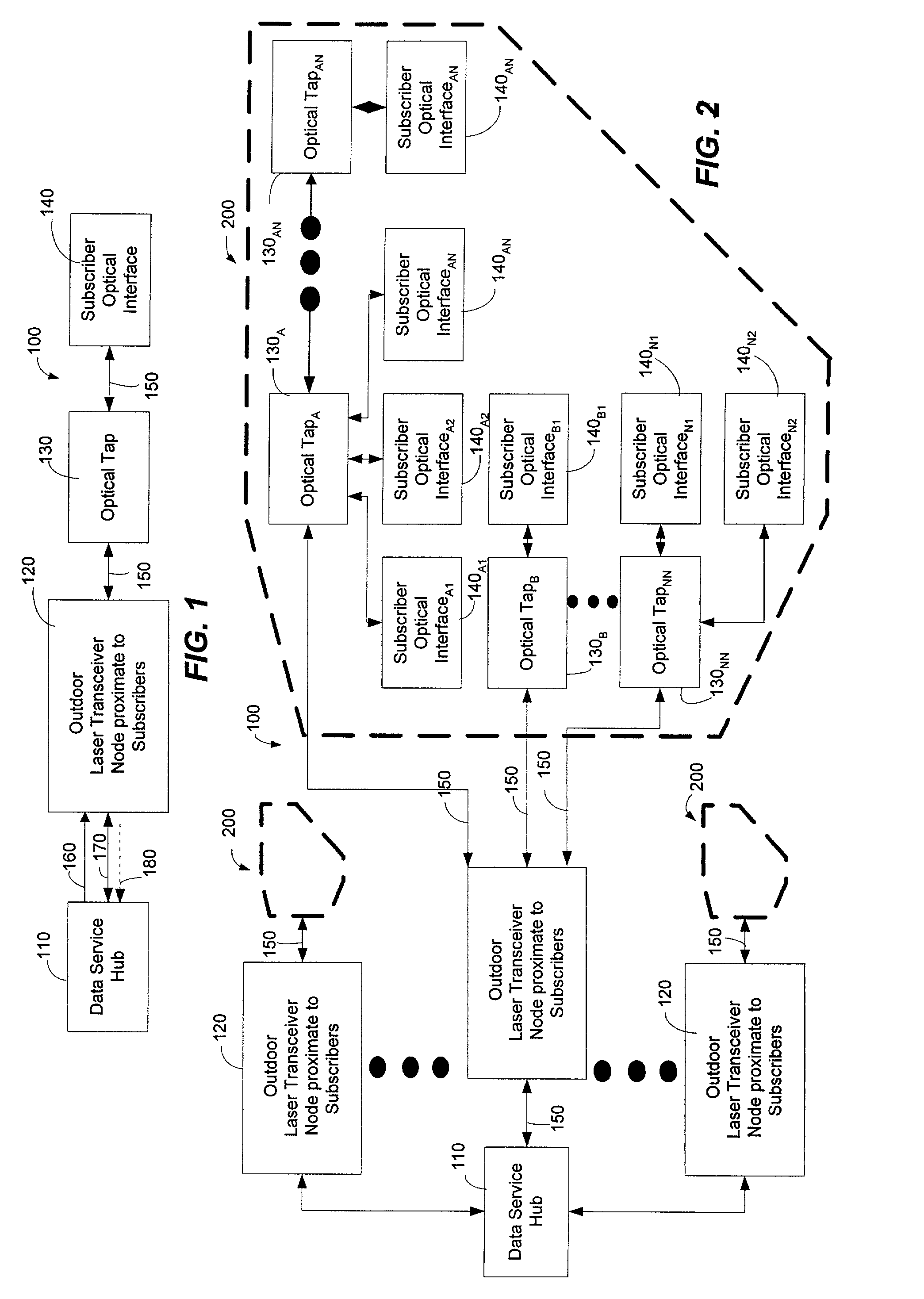
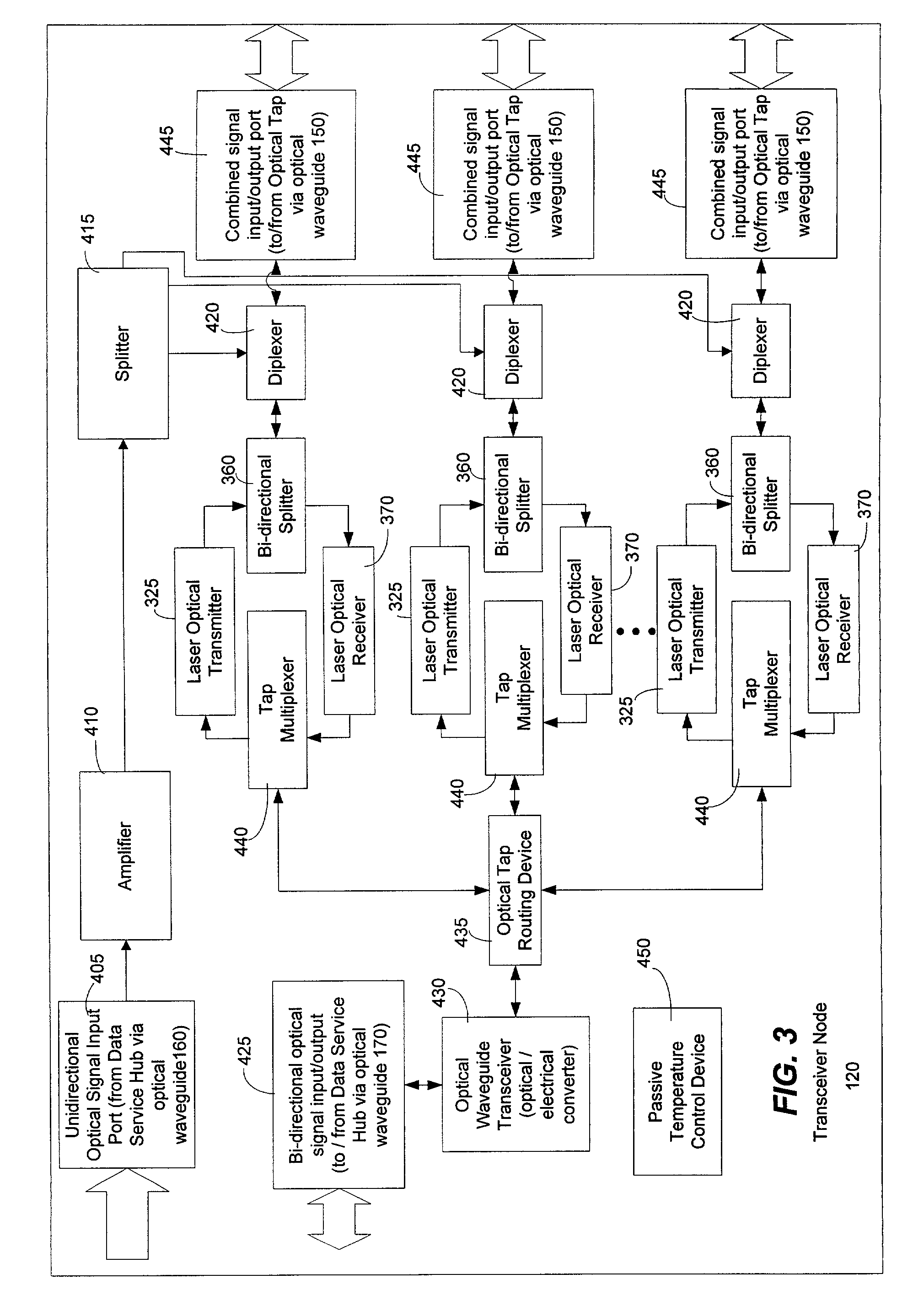
Method and system for processing upstream packets of an optical network
InactiveUS7085281B2Avoid collisionReduce performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsGeneral purposeTransceiver
A protocol for an optical network can control the time at which subscriber optical interfaces of an optical network are permitted to transmit data to a transceiver node. The protocol can prevent collisions of upstream transmissions between the subscriber optical interfaces of a particular subscriber group. With the protocol, a transceiver node close to the subscriber can allocate additional or reduced upstream bandwidth based upon the demand of one or more subscribers. That is, a transceiver node close to a subscriber can monitor (or police) and adjust a subscriber's upstream bandwidth on a subscription basis or on an as-needed basis. The protocol can account for aggregates of packets rather than individual packets. By performing calculation on aggregates of packets, the algorithm can execute less frequently which, in turn, permits its implementation in lower performance and lower cost devices, such as software executing in a general purpose microprocessor.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
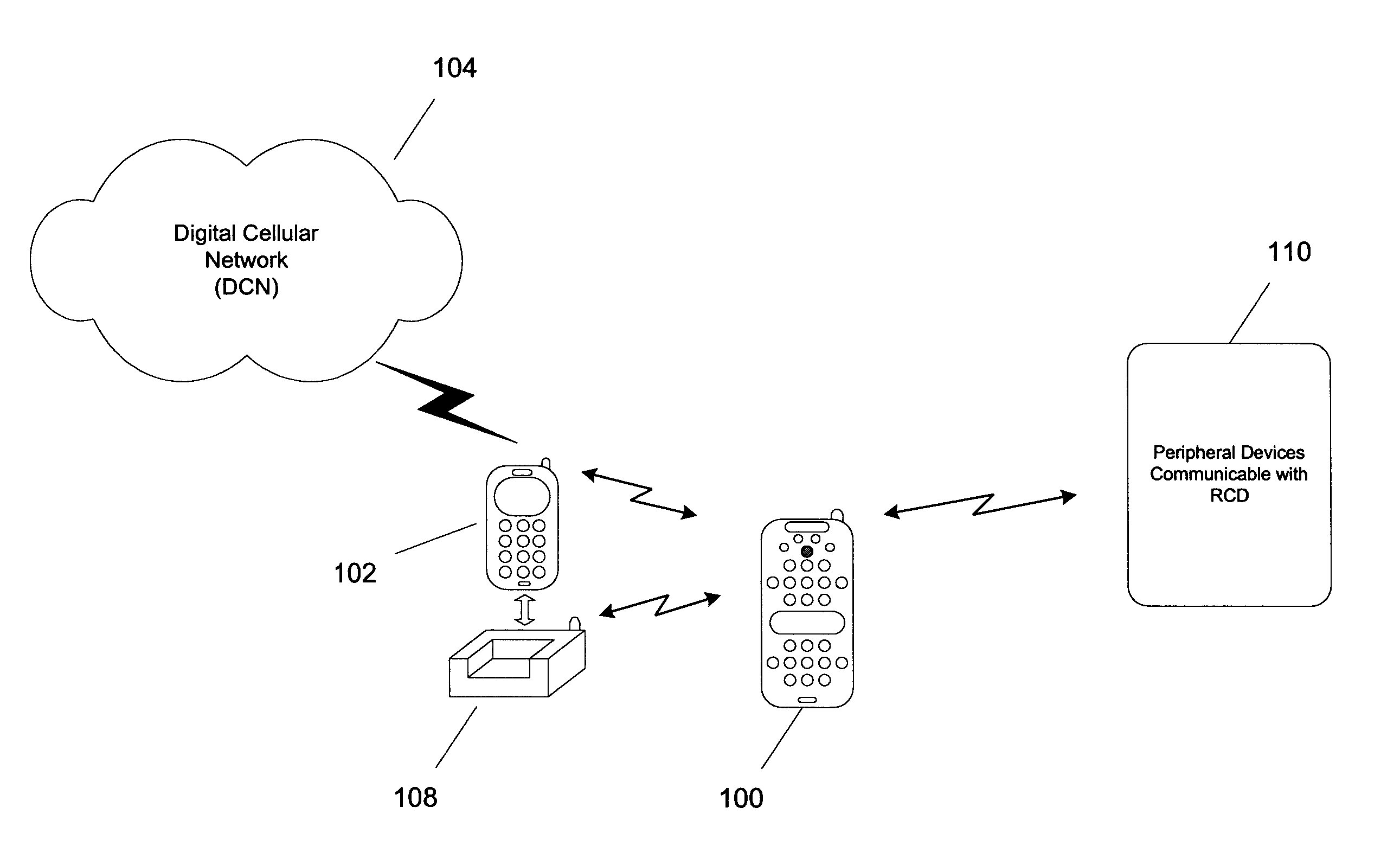
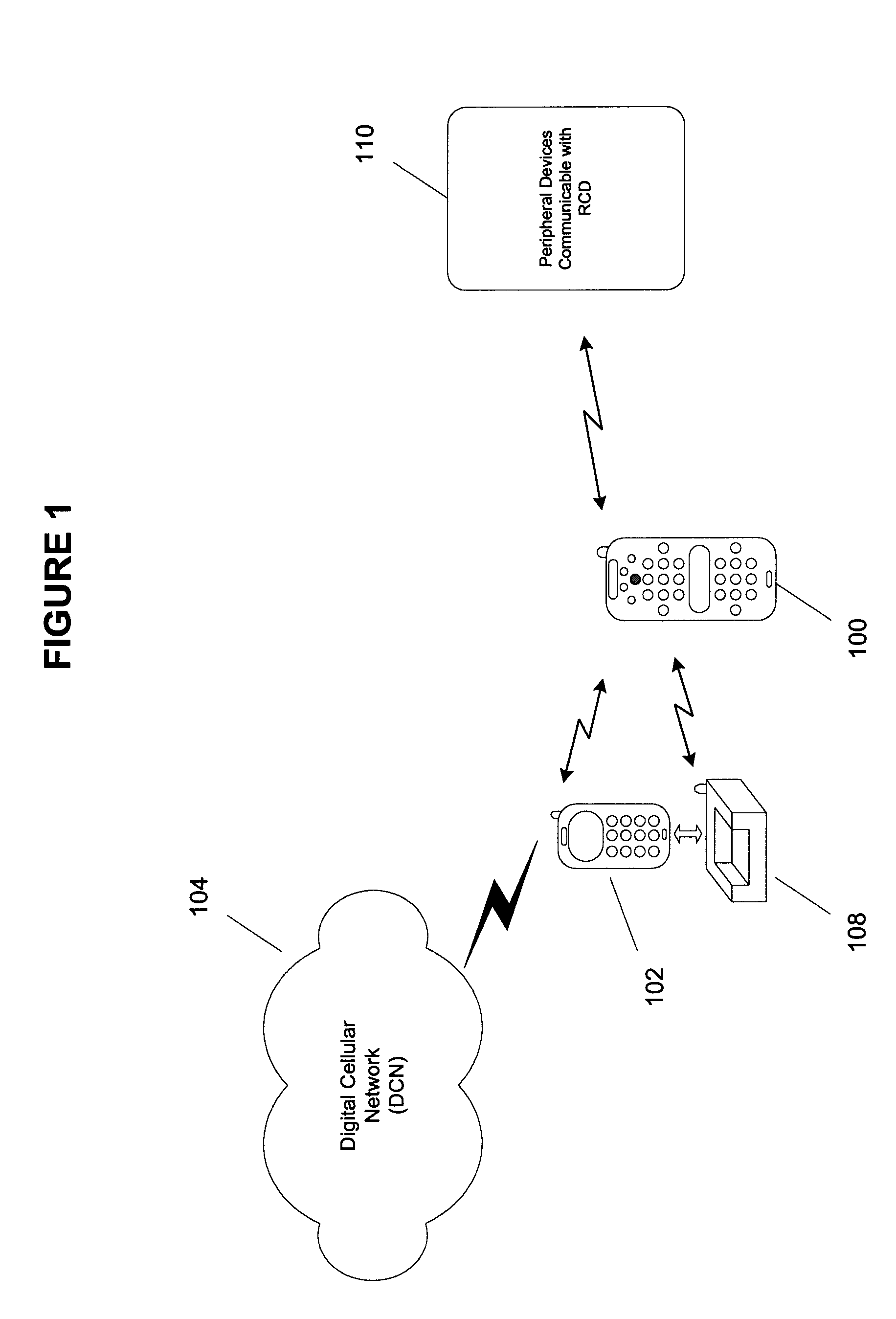
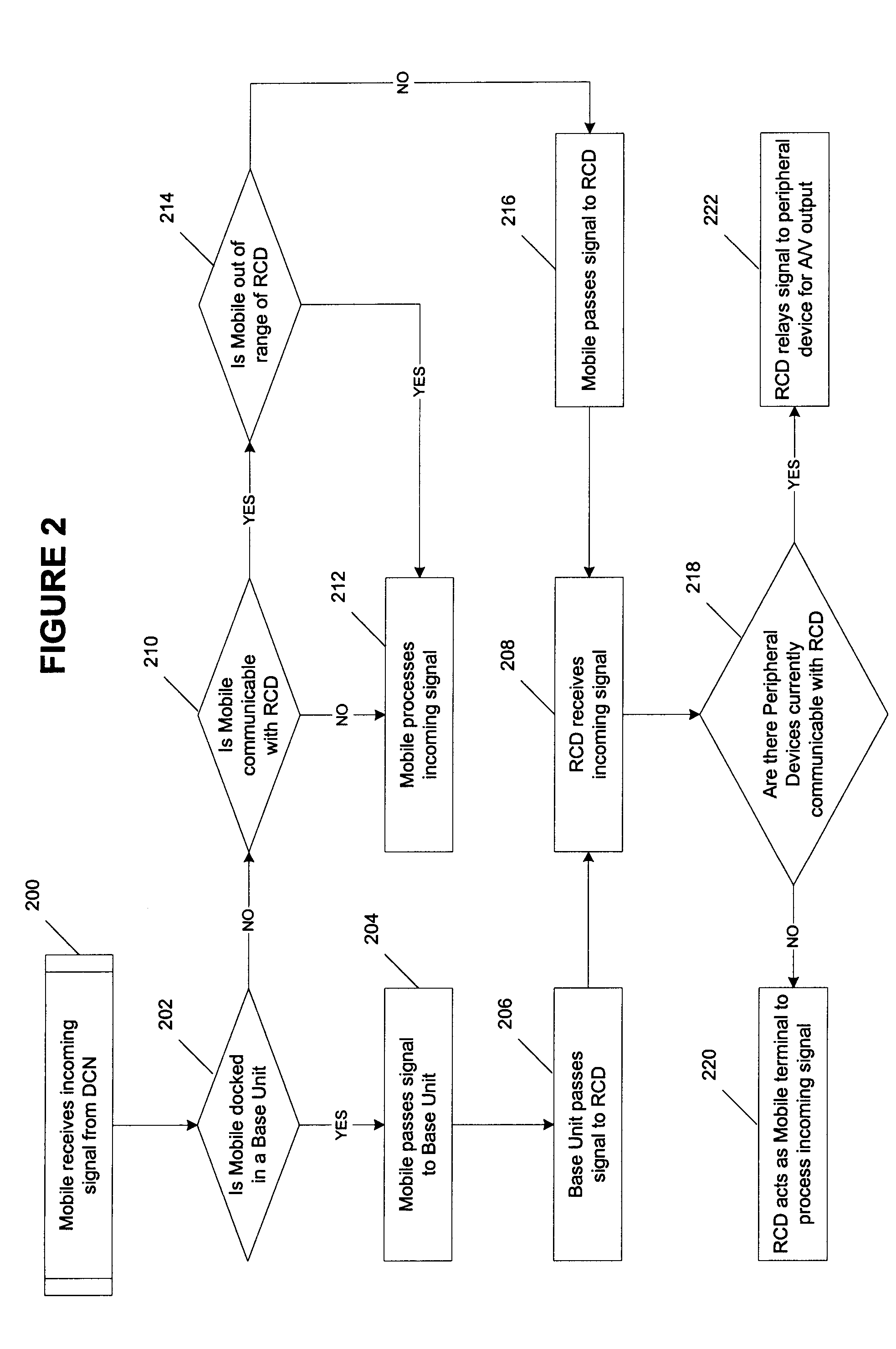
Remote control device having wireless phone interface
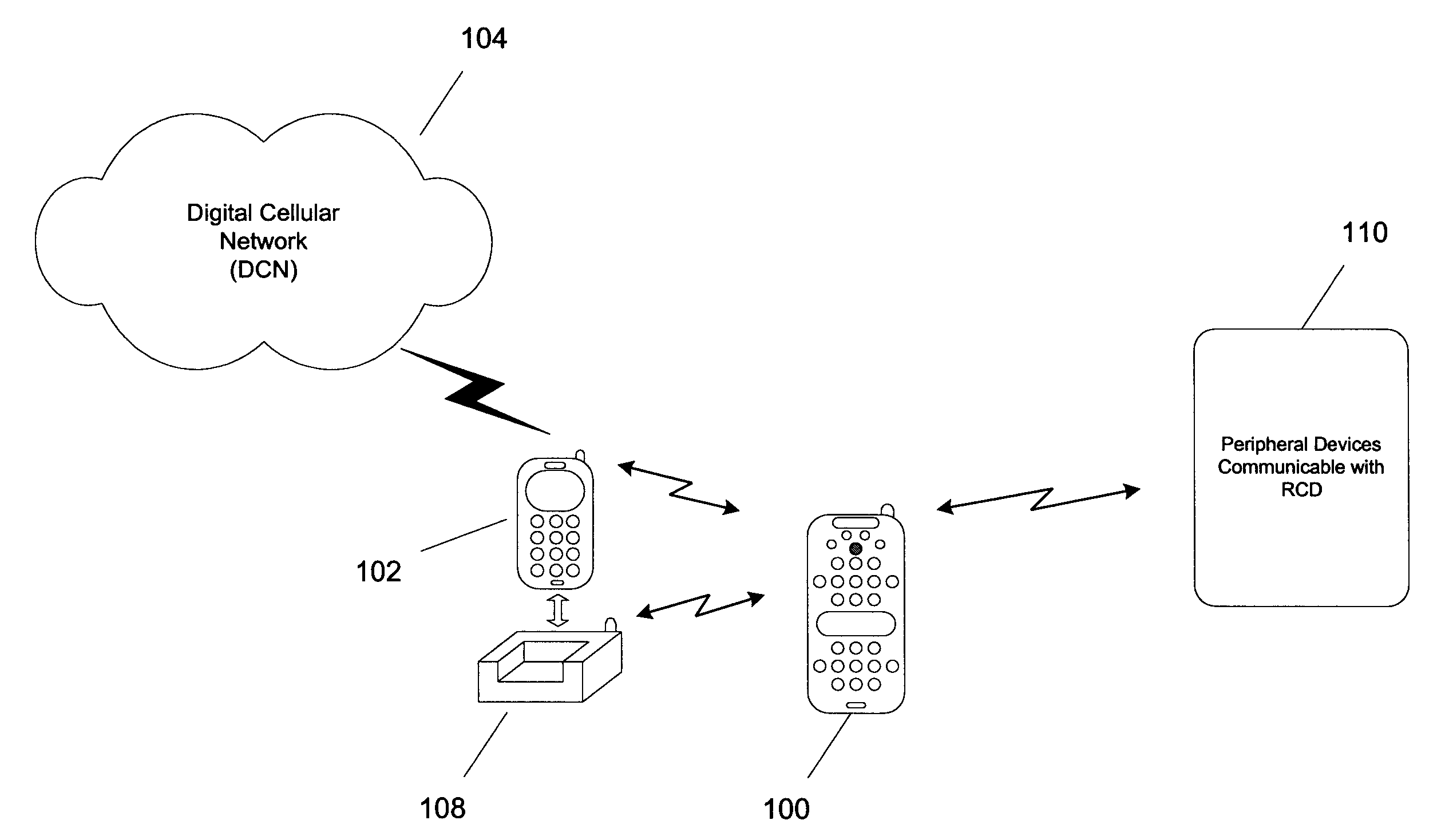
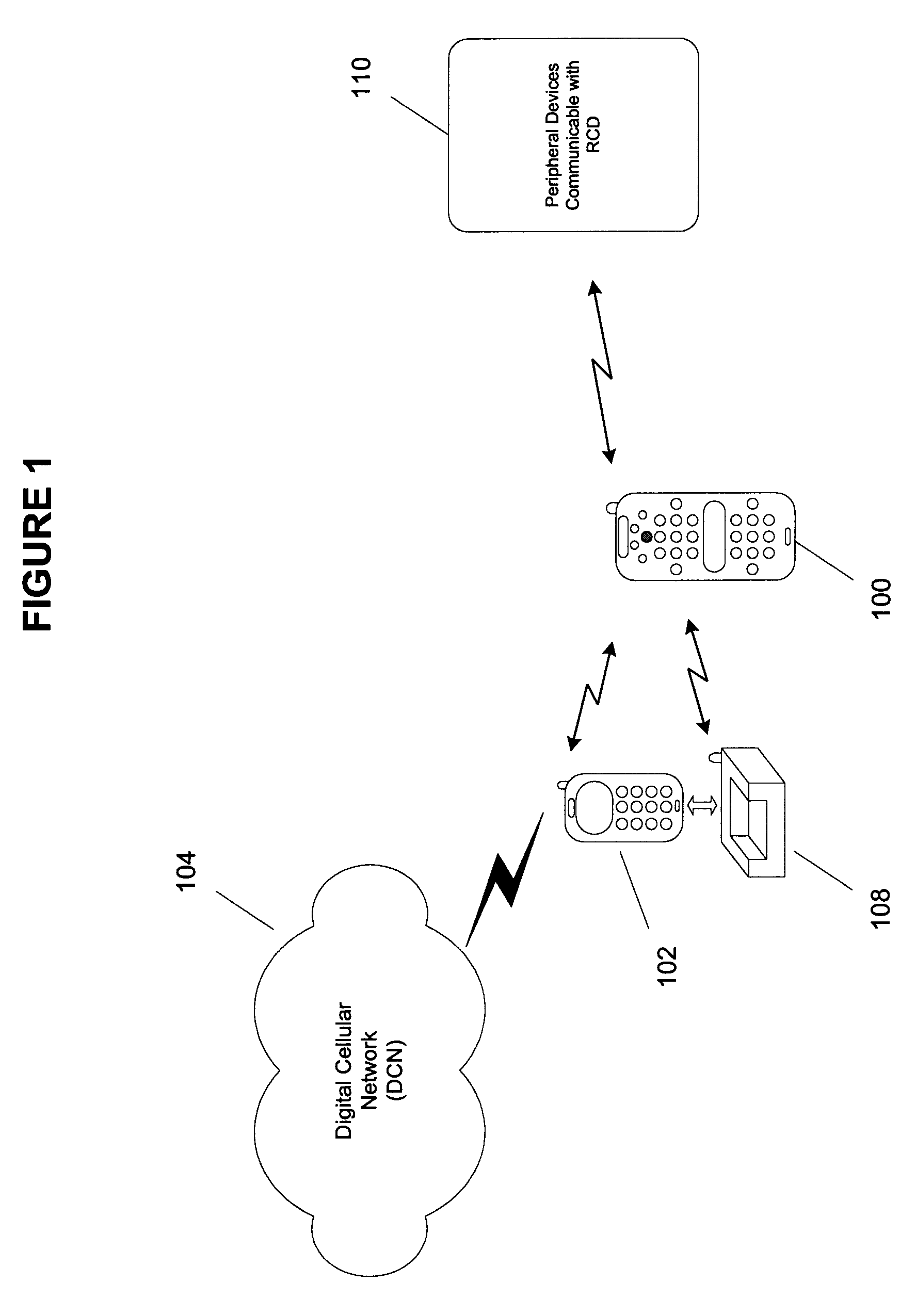
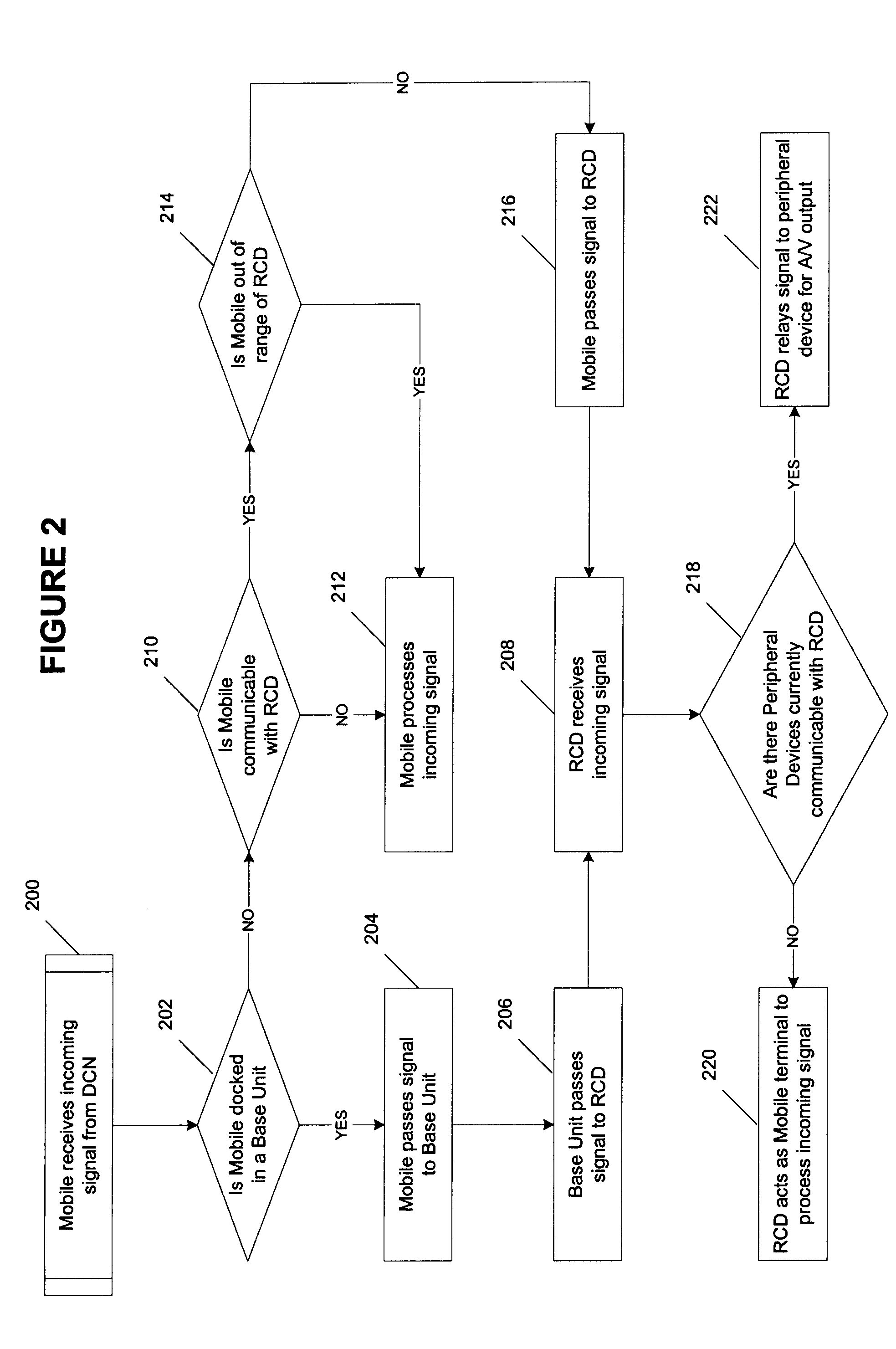
InactiveUS20050064860A1Robust audioRobust videoTelevision system detailsNon-electrical signal transmission systemsRemote controlSpeech sound
A remote control device (RCD) typical of a television or home entertainment system is adapted to be communicable with a mobile phone. When a mobile phone receives a signal in a first wireless protocol from a digital cellular network (DCN), the signal is wirelessly forwarded to the RCD in a second wireless protocol for processing such as answering a voice call or displaying message data using the RCD. In addition, the RCD is wirelessly communicable with one or more peripheral devices such as a television and / or other components of a home entertainment system. The RCD can further forward the signal or a component of the signal received from the mobile phone to one of the peripheral devices for output. Thus, if a mobile phone is not handy when a signal is received, it can be passed to the RCD to be handled in a manner deemed appropriate by a user.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
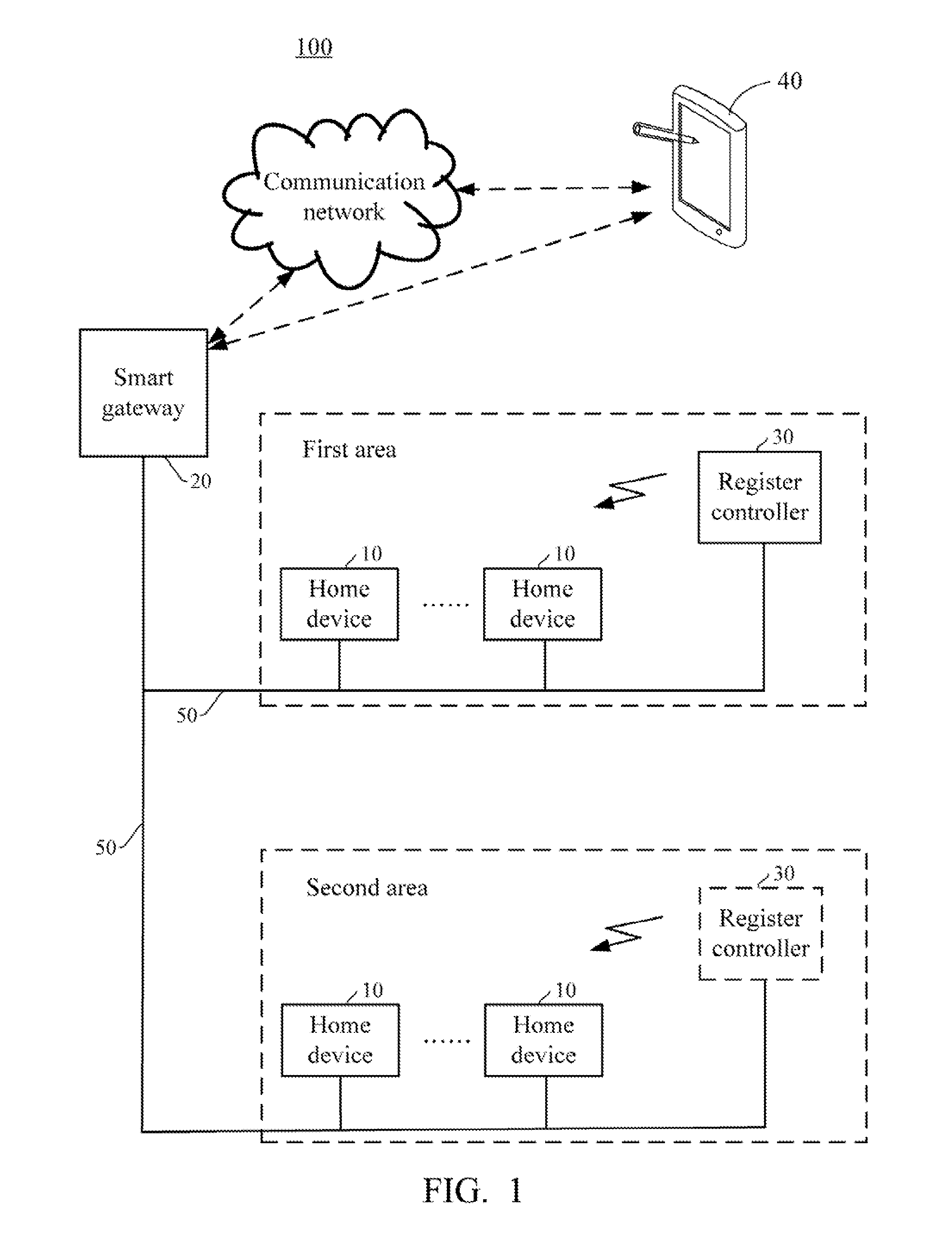
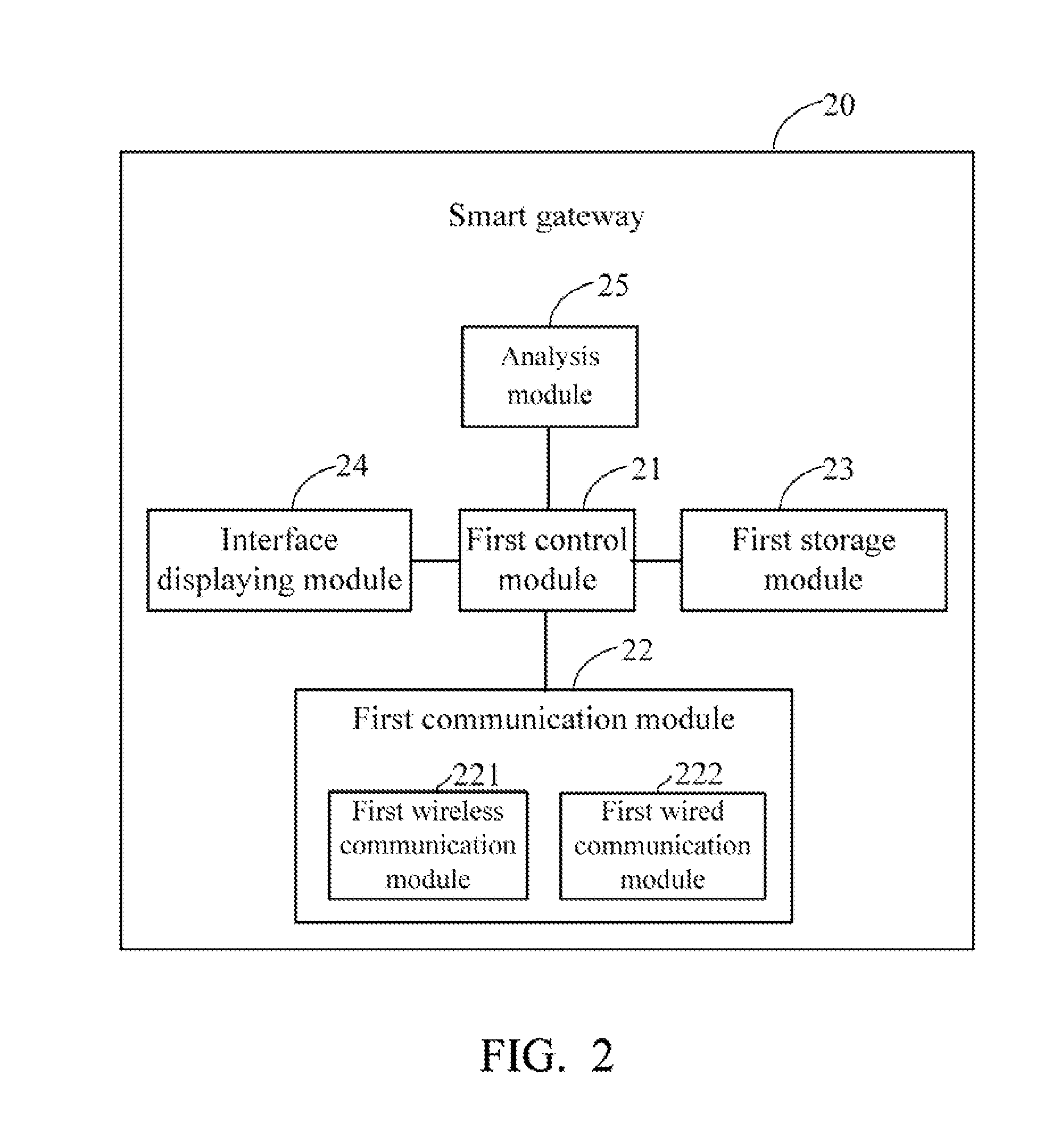
Smart gateway and smart home network system using the same
InactiveUS20140064738A1Non-electrical signal transmission systemsElectromagnetic transmissionControl signalRemote control
A smart home network system includes a number of home devices, a smart gateway, and a control device. The smart gateway stores a mapping list that records configuration information of each home device, and the configuration information contains a UID code of each home device. When received a control signal for controlling a target home device from the control device, the smart gateway analyzes the control signal and modulates the control signal with the UID of the target home device and converts network protocols, to generate an effective control command, then transmits the control command to the target home device. When received status information from the home devices, and the smart gateway sends the status information to the control device for reading status information of the home devices. Therefore, user can operate the control device anywhere to remote control each individual home device via the smart gateway.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
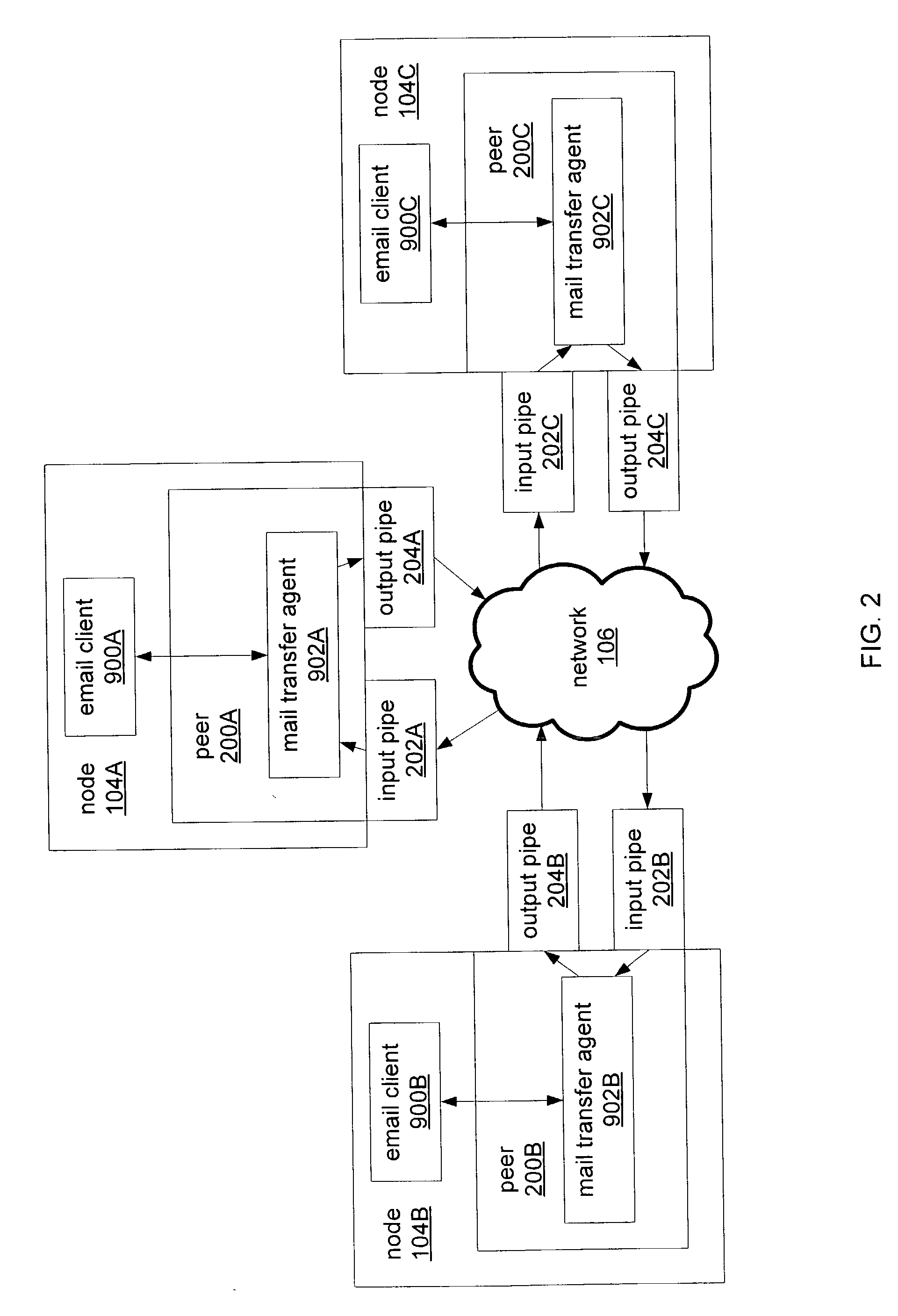
Peer-to-peer email messaging
ActiveUS7849140B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksClient-sideDistributed computing
System and method for facilitating communications between peers in a peer-to-peer environment and network email clients. In one embodiment, network nodes including peer nodes may host mail transfer agents. The mail transfer agents may act as bridges between peer-to-peer protocols and email communication protocols. The mail transfer agents may communicate with peers according to peer-to-peer protocols and with email clients according to email communications protocols. Peers may communicate with mail transfer agents to send peer-to-peer messages to email clients. Email clients may communicate with the mail transfer agents to send email messages to and receive email messages from other email clients via the peer-to-peer network and to obtain peer-to-peer messages from peers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
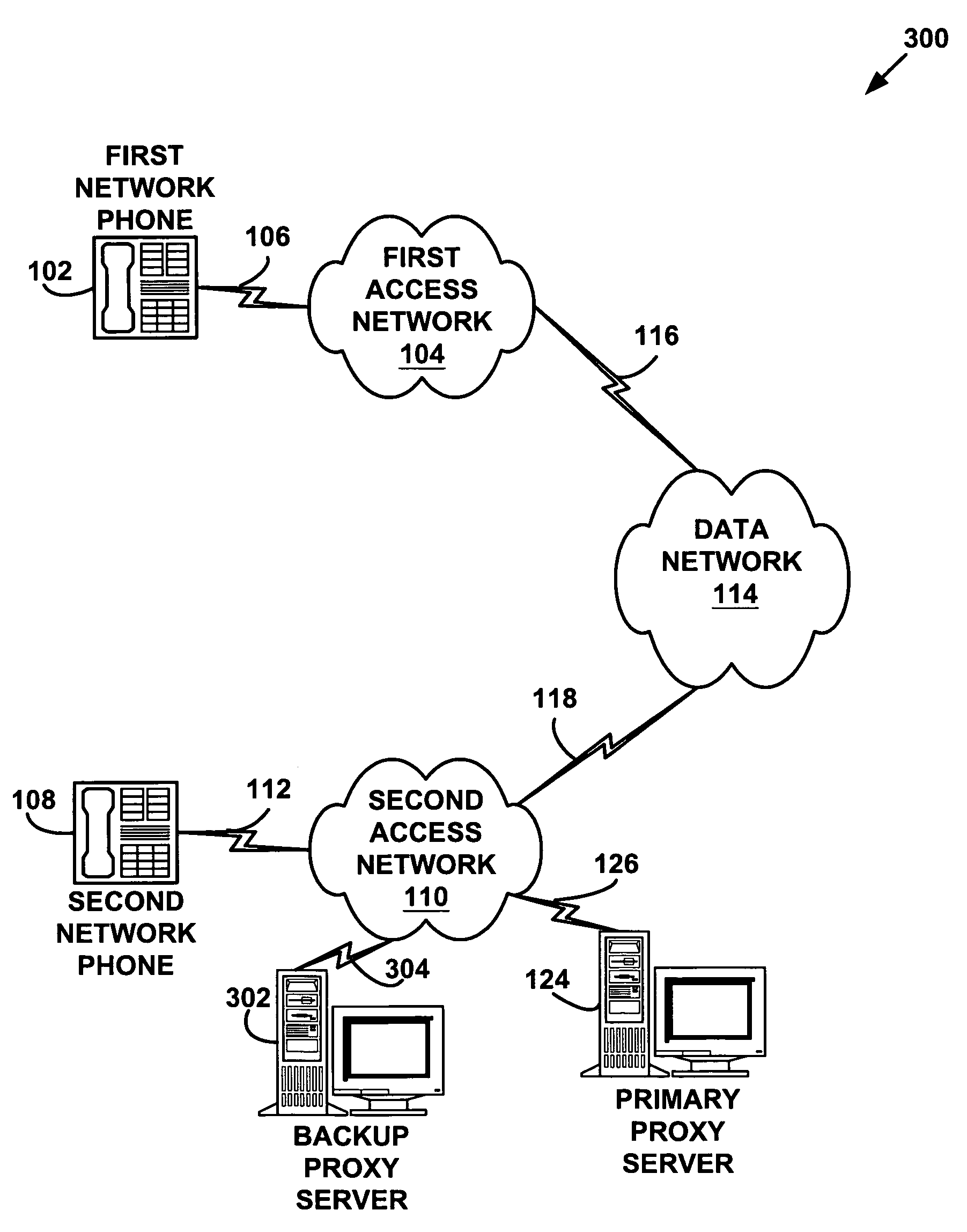
System and method for providing fault tolerance in a network telephony system
A system and method for providing fault tolerance in a network telephony system. Signaling messages according to a signaling protocol, such as the SIP protocol, are modified to include a path attribute with a network address corresponding to a backup proxy server. When a primary proxy server is supported by a backup proxy server, the primary proxy server inserts the Alternate Path tag into one or more signaling messages. When a network entity sends a message, it checks the message to identify the primary proxy server. Upon receiving a failure or timeout when attempting to send to the primary proxy server, the sending network entity should try the backup proxy server specified in the path attribute. When the backup proxy server receives the message, it may modify the message to specify the new routing path. As a result, subsequent messages get routed properly using the backup proxy server.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Remote control device having wireless phone interface
InactiveUS7194259B2Robust audioRobust videoMultiplex system selection arrangementsTelevision system detailsRemote controlSpeech sound
A remote control device (RCD) typical of a television or home entertainment system is adapted to be communicable with a mobile phone. When a mobile phone receives a signal in a first wireless protocol from a digital cellular network (DCN), the signal is wirelessly forwarded to the RCD in a second wireless protocol for processing such as answering a voice call or displaying message data using the RCD. In addition, the RCD is wirelessly communicable with one or more peripheral devices such as a television and / or other components of a home entertainment system. The RCD can further forward the signal or a component of the signal received from the mobile phone to one of the peripheral devices for output. Thus, if a mobile phone is not handy when a signal is received, it can be passed to the RCD to be handled in a manner deemed appropriate by a user.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
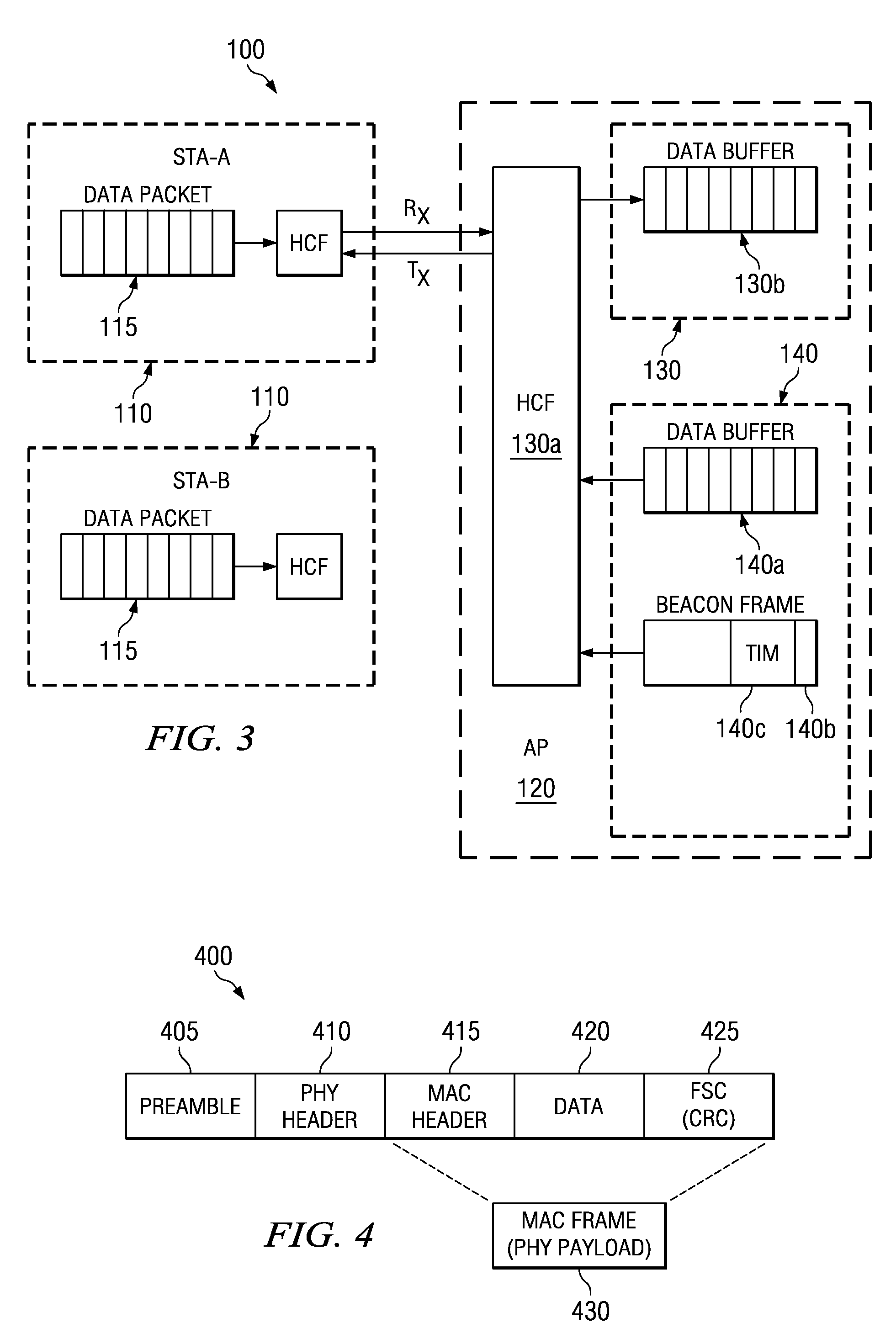
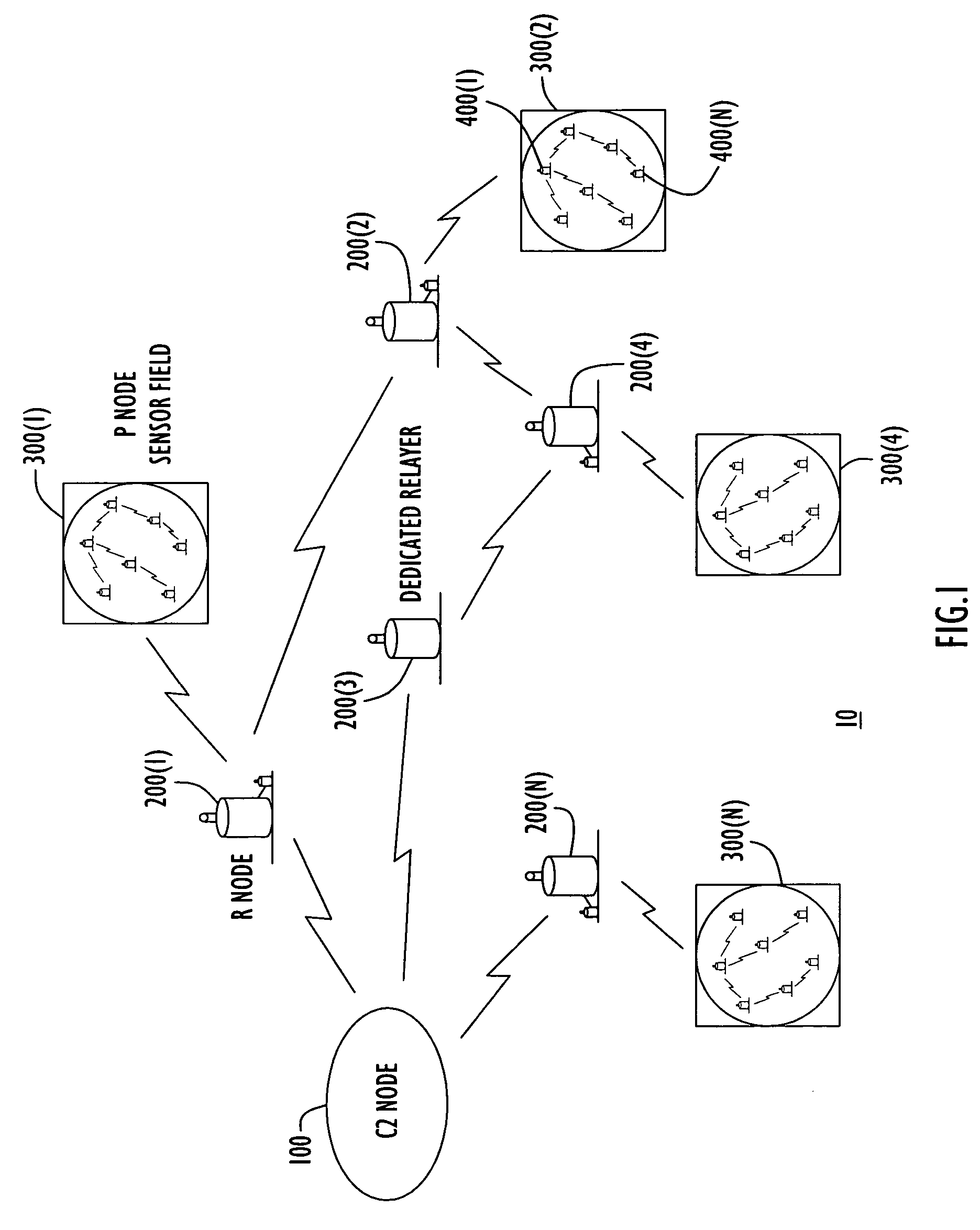
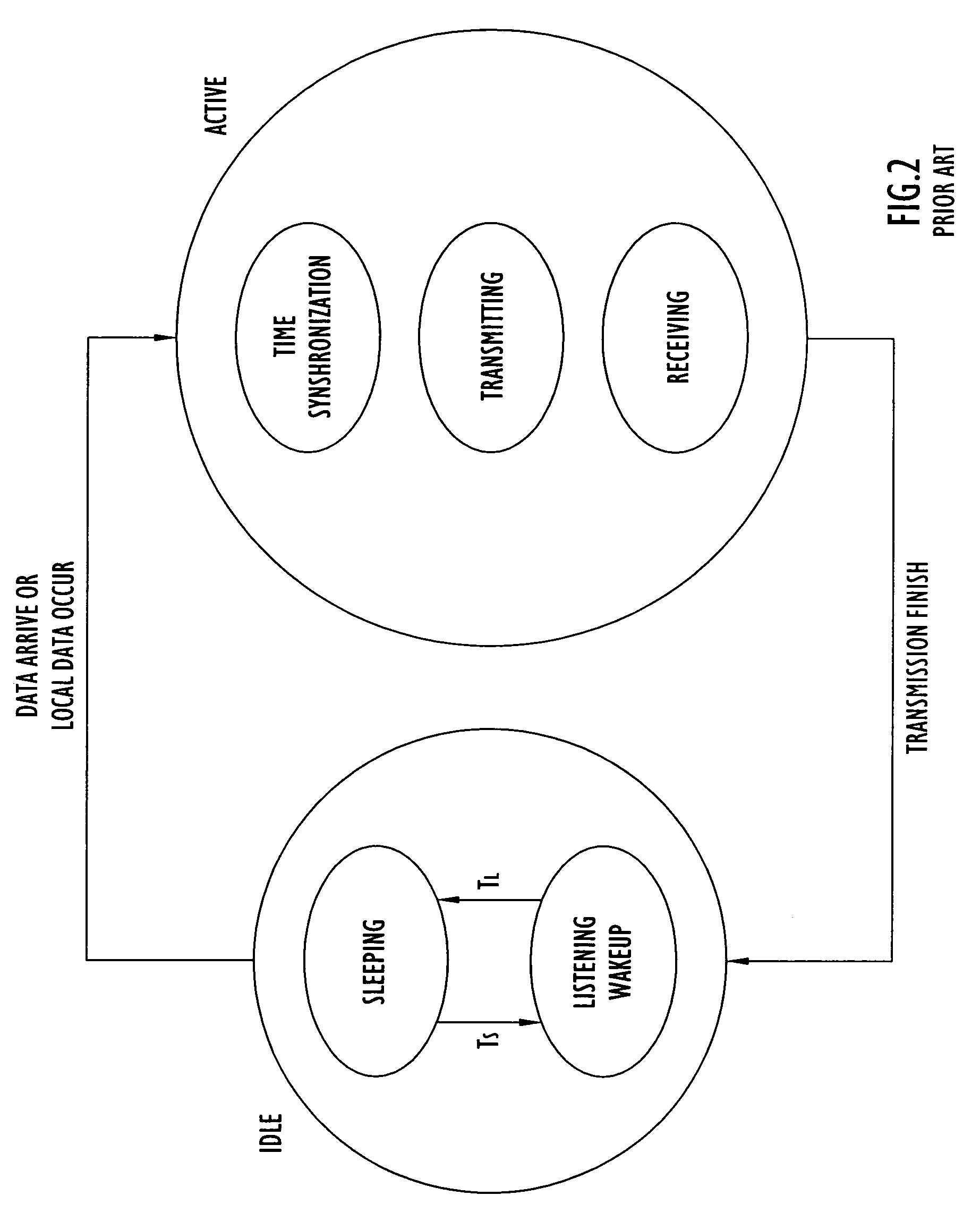
Energy-efficient medium access control protocol and system for sensor networks
ActiveUS7496059B2Extend battery lifeMore processedEnergy efficient ICTPower managementMedia access controlLife time
An energy efficient MAC protocol for a sensor network that extends the battery life of remotely located wireless nodes by employing MAC operations involving transmission of a wake-up signal with more processing gain, dynamic adjustment of a transmission rate of synchronization messages for fast time synchronization and an energy efficient neighboring node discovery technique.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
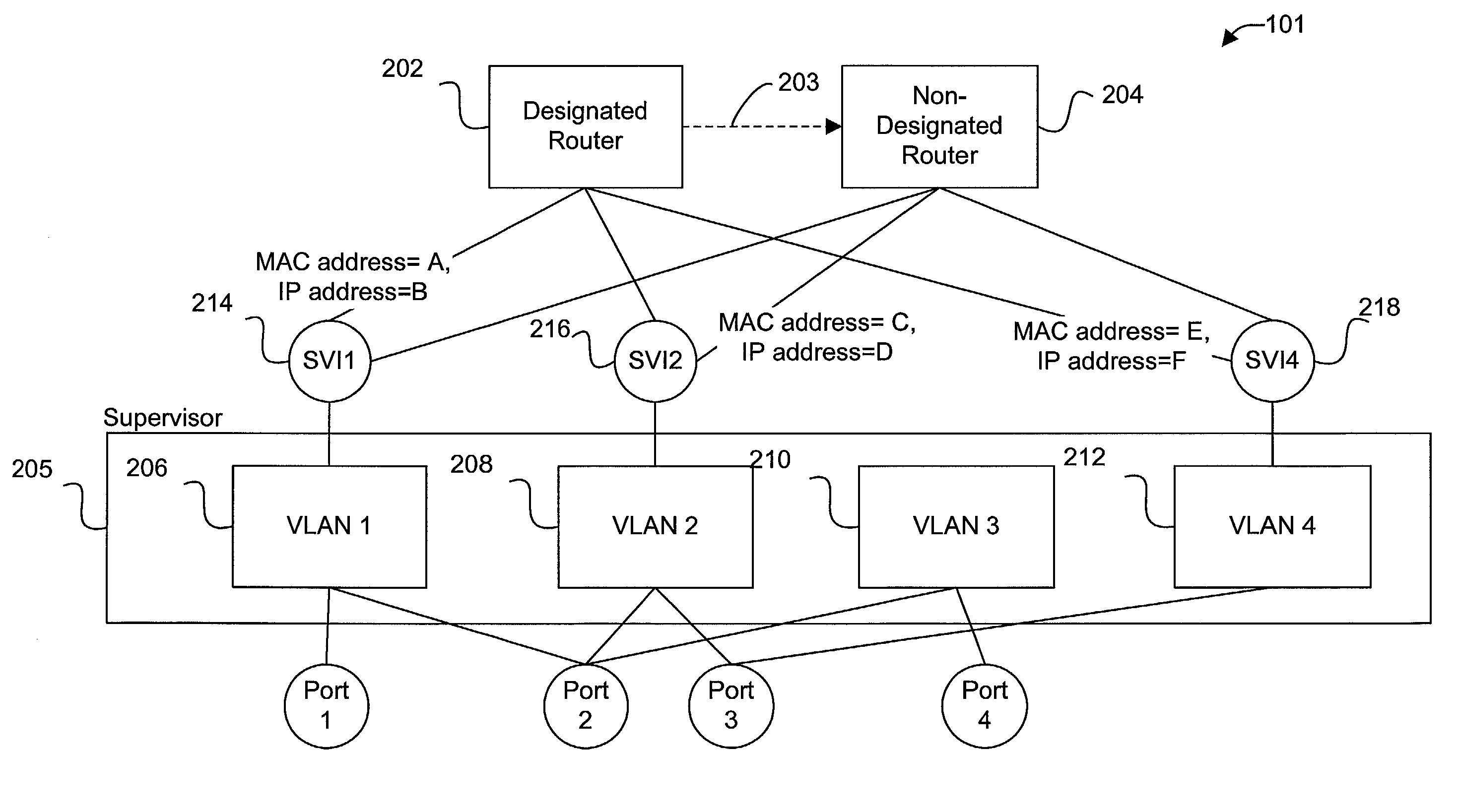
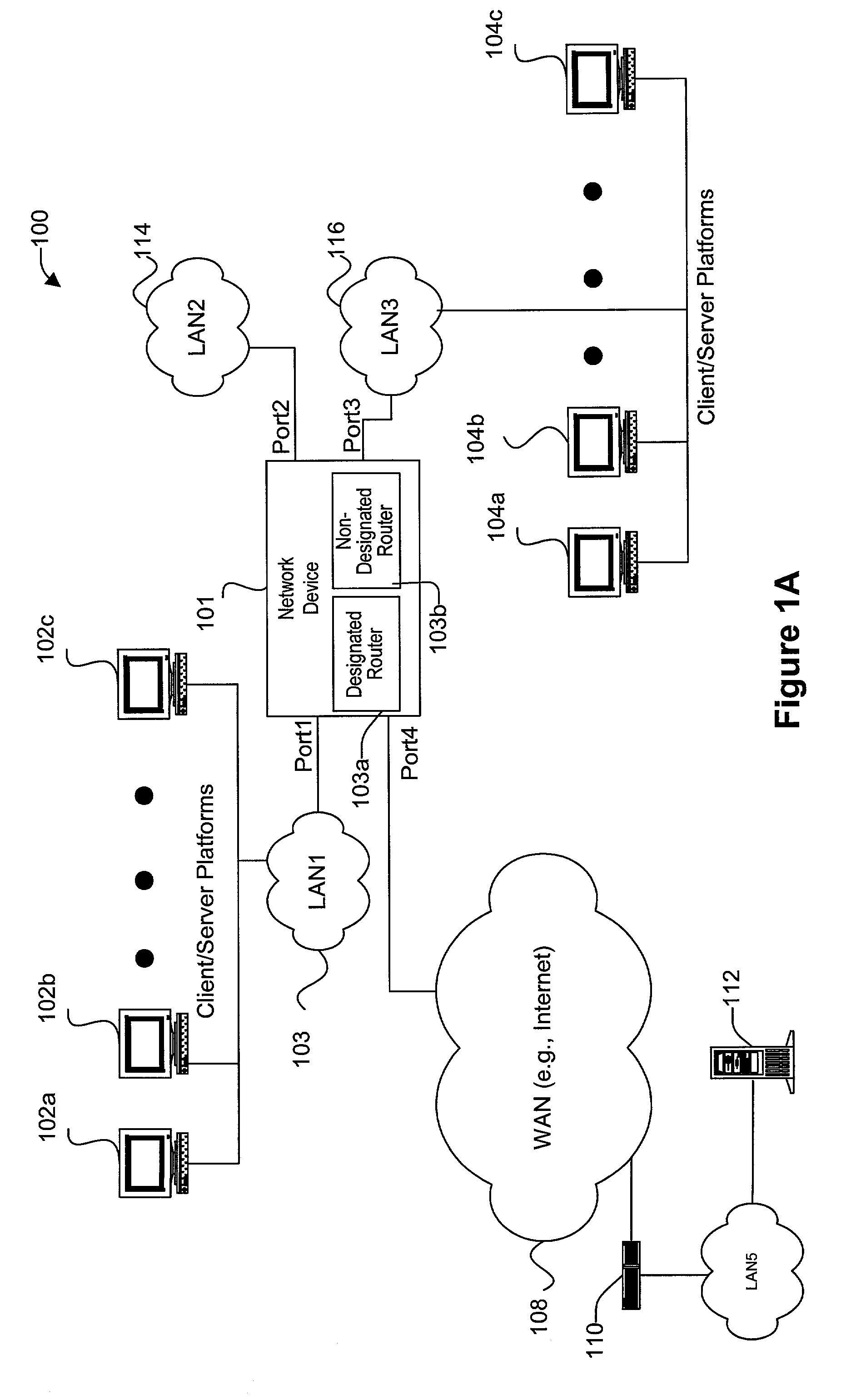
Enhanced internal router redundancy
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for providing redundant data forwarding or routing capabilities. In one embodiment, a network device includes a designated router and a non-designated router. The designated router generally provides layer 3 switching or routing for data received into the network device. Although the non-designated router is active, it generally does not provide forwarding capabilities until the designated router fails. The non-designated router's logical interfaces are disabled, while the designated router's logical interfaces are enabled. The non-designated router becomes the new designated router when the first designated router fails. In general terms, the routers of the network device provide redundancy with the network being aware of only a single router within network device. That is, the network is only aware of a single router. This is accomplished by having the routers share the same IP and MAC address on each logical interface. The routers do not each also use a unique IP and MAC address in addition to the shared IP and MAC address, in contrast to conventionally configured routers of the hot standby router protocol (HSRP).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Selectively passing network addresses through a server
A method of securely communicating a network address of a client that issues service requests to a first server that proxies the service requests for a second server. A network address of the client is received. A processor determines whether a first network address of the first server is equal to a second network address of the second server. The network address of the client is sent from the first server to the second server in a secure request message only when the first network address of the first server is equal to the second network address of the second server. Accordingly, a secure communications protocol is provided in which an address of a requesting client, e.g., an IP address, is passed in the protocol only among a responding server and its proxy, thereby preventing interception of the client IP address by unauthorized processes. By enforcing a policy that permits the network address of an originating host to pass from a first server to a second server only when the network address of the second server meets specified criteria (e.g., it is the same network address as that of the first server), the originating host address can be passed securely through a proxy server.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
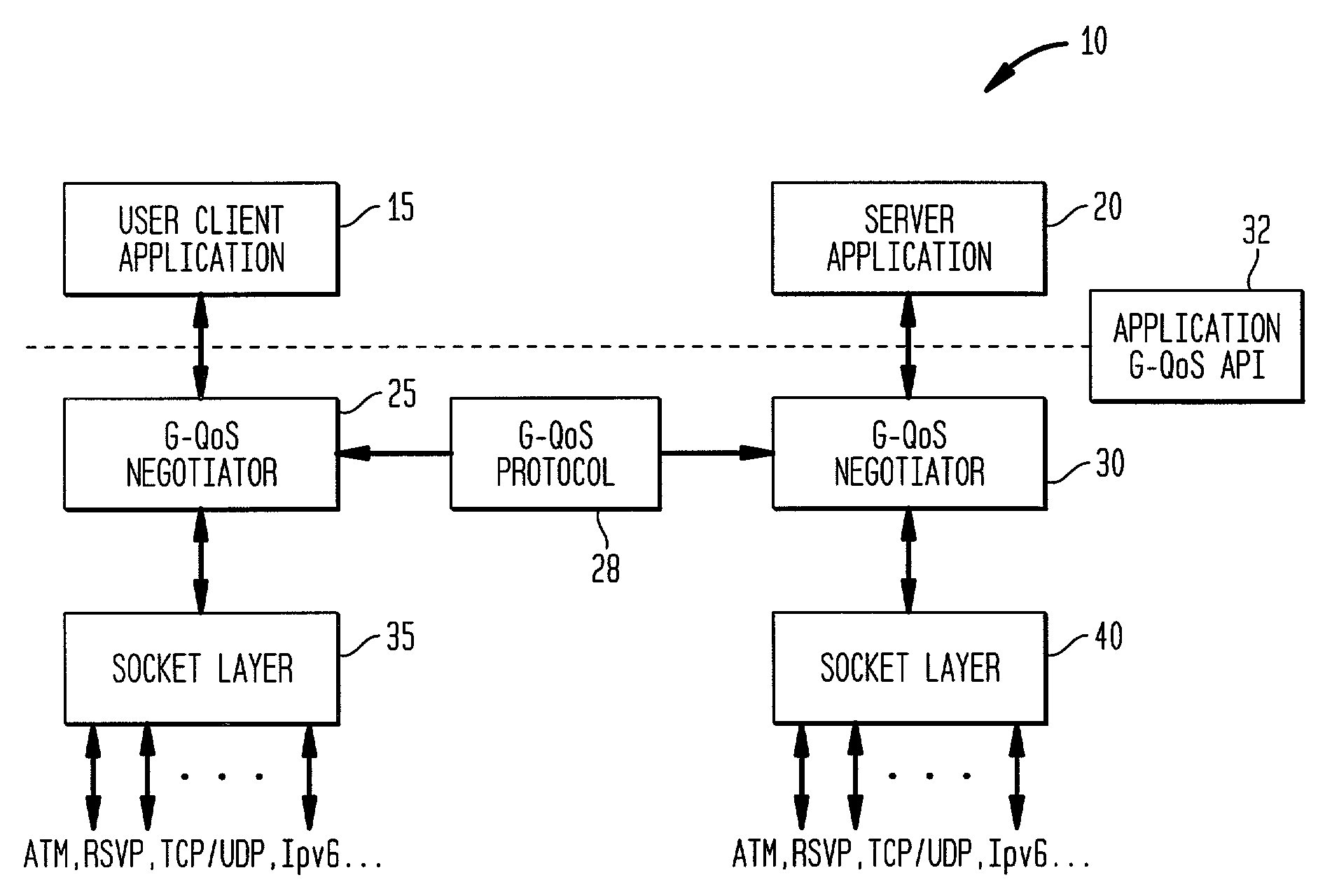
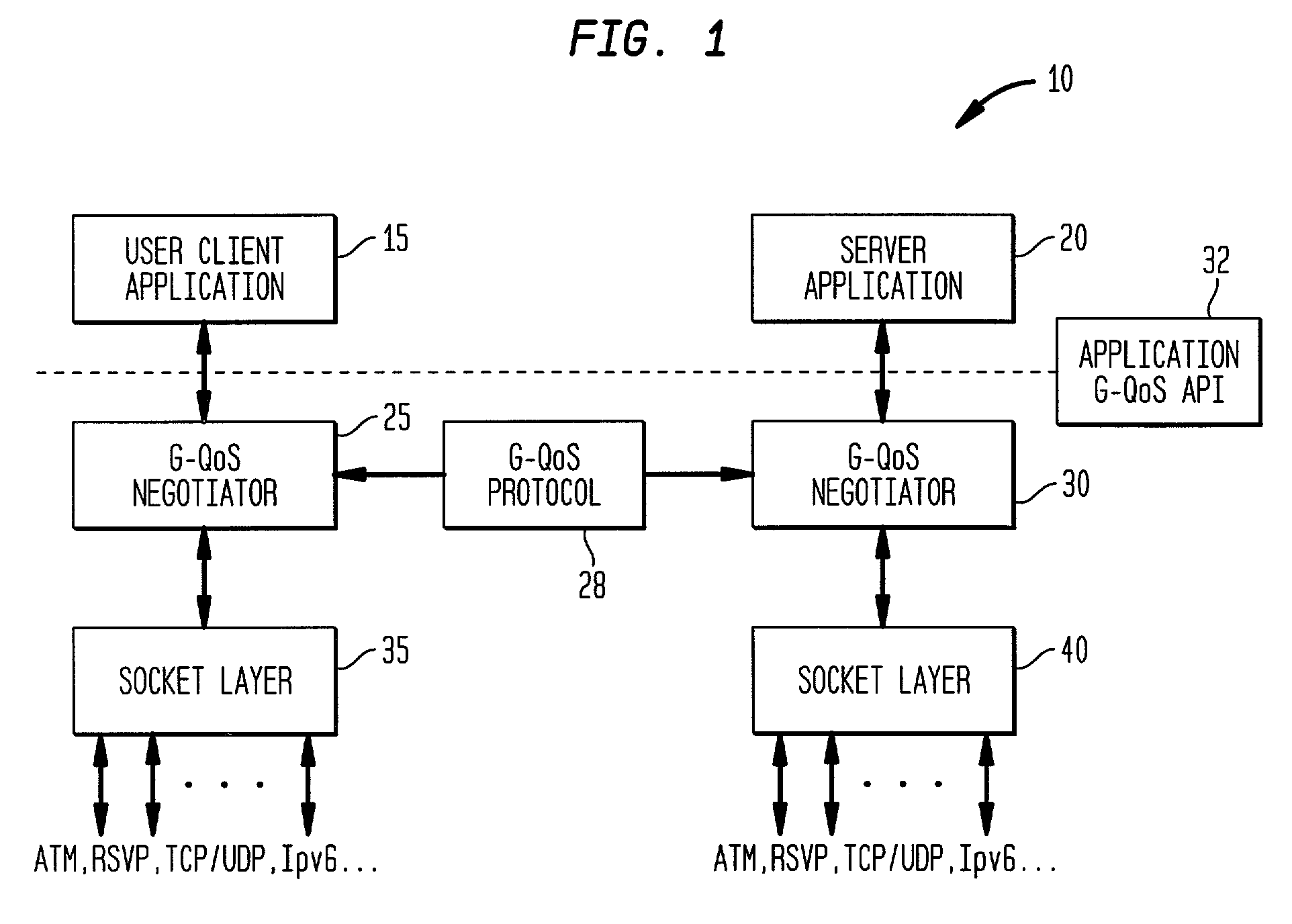
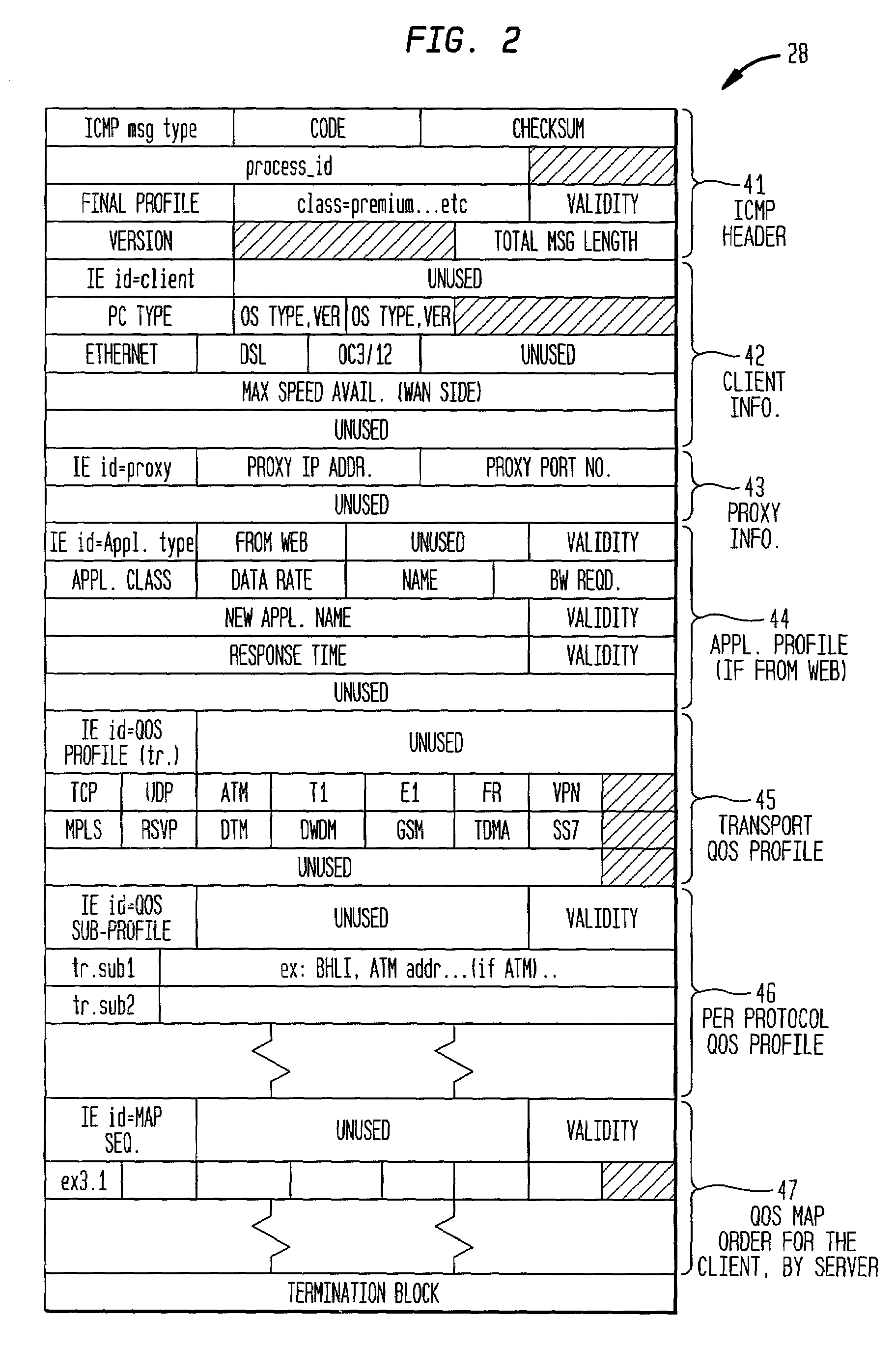
Generic quality of service protocol and architecture for user applications in multiple transport protocol environments
InactiveUS7185070B2Easy to implementEasy maintenanceData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsQuality of serviceQos architecture
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
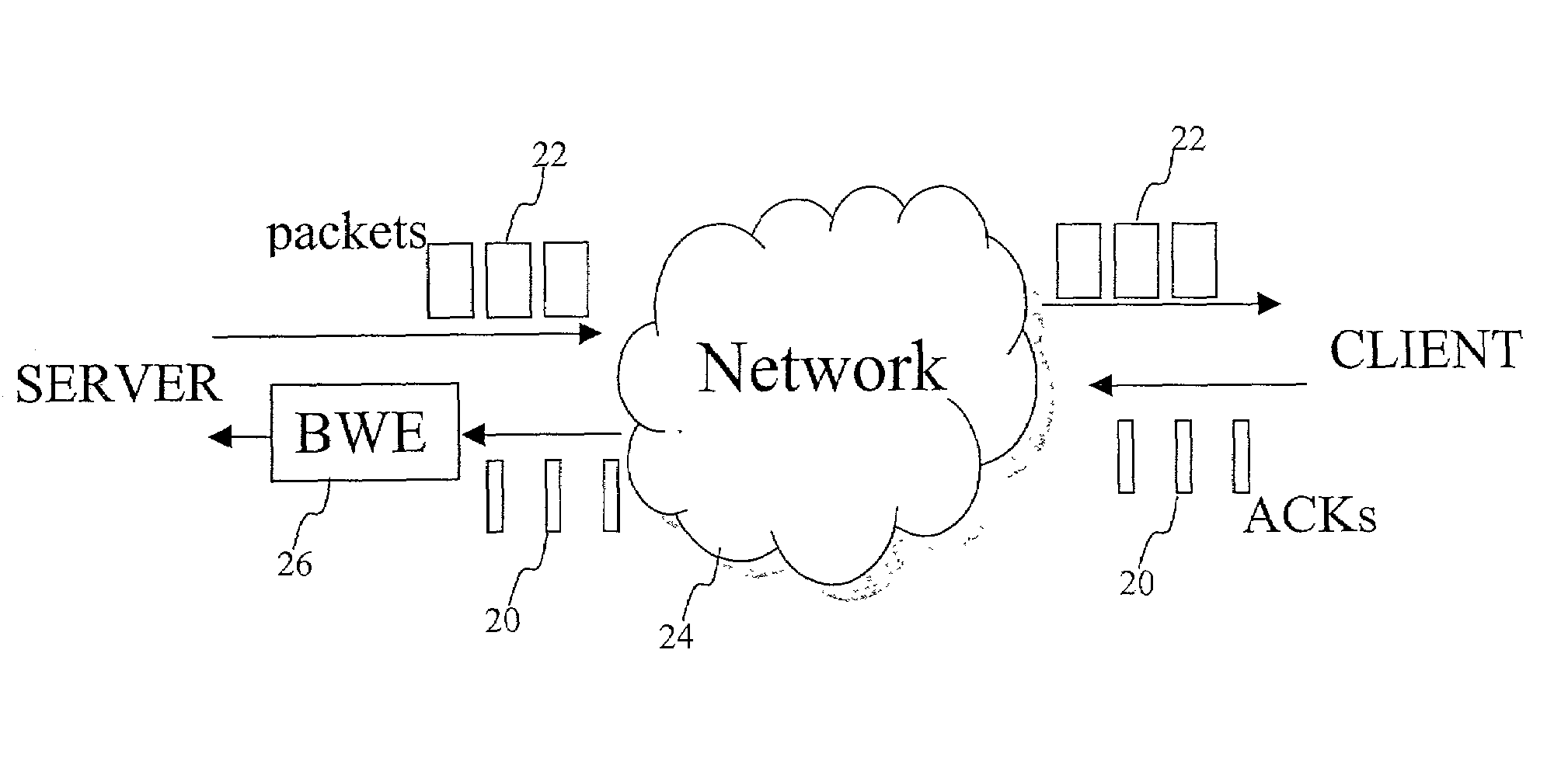
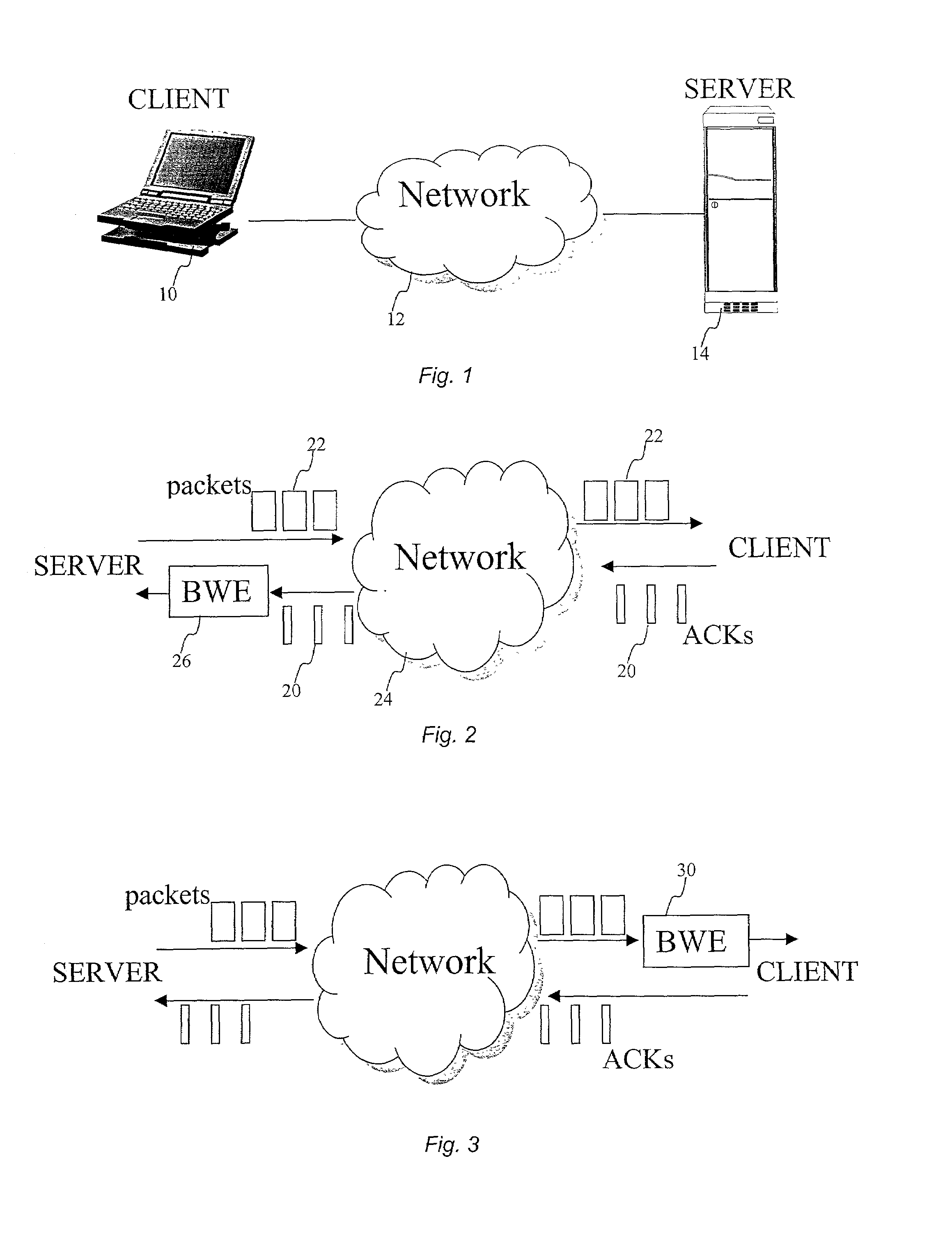
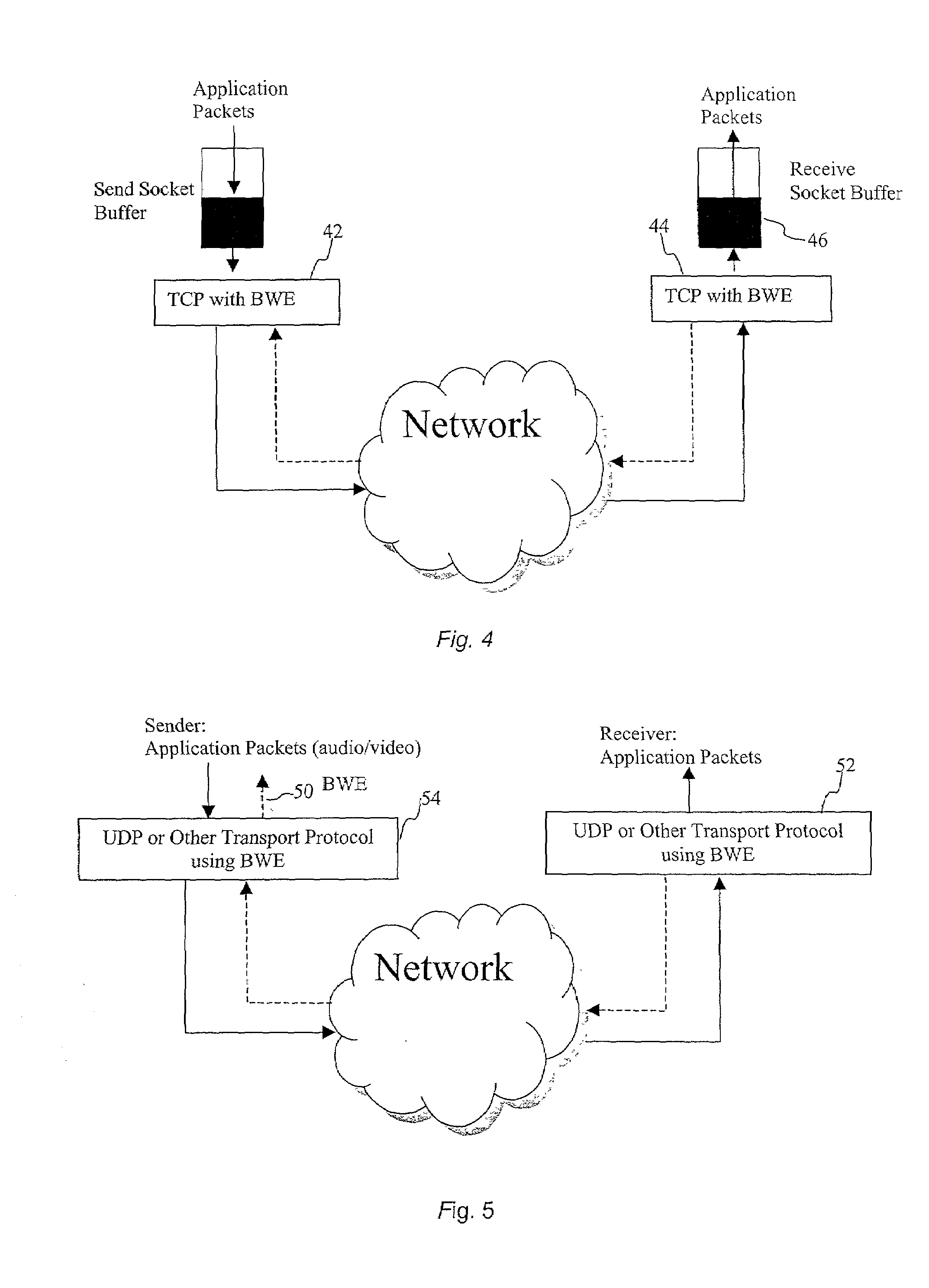
End-to-end bandwidth estimation for congestion control in packet switching networks
InactiveUS7130268B2Improve network bandwidth utilizationImprove fairnessEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTraffic capacityPacket-switching node
The invention herein described consists of an algorithm, which performs an end-to-end estimation of the bandwidth available in an end-to-end connection established between a server and a client via a packet switching network such as the Internet Protocol Network (IP). This algorithm is used to properly regulate the input rate at the send side. Typical applications are delivering best effort traffic over TCP, or audio and video traffic over RTP / UDP. The invention is particularly effective over wireless Internet and can be used in a content delivery system to dynamically choose the best server between a set of servers to satisfy the request of a client, or to select the best route in a content deliver or global hosting system.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com