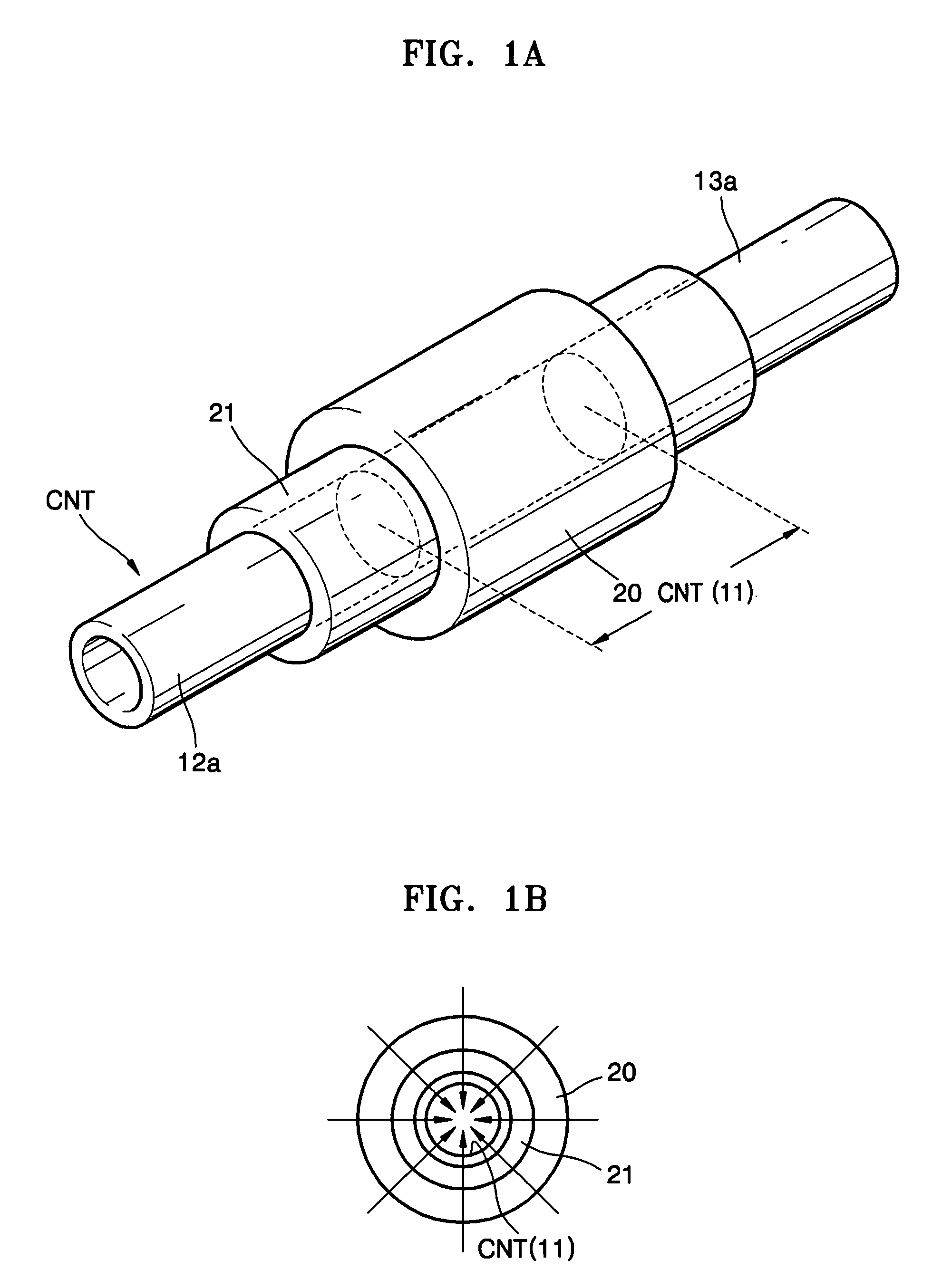
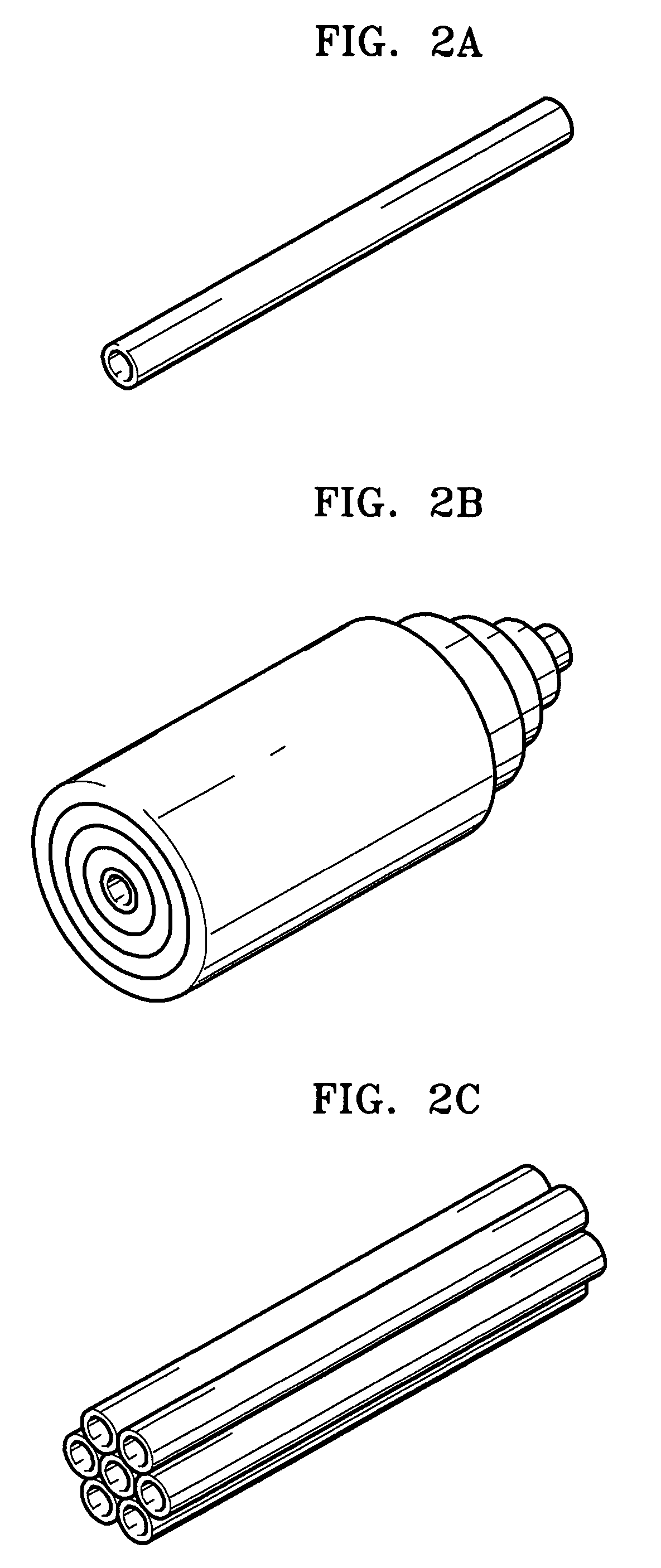
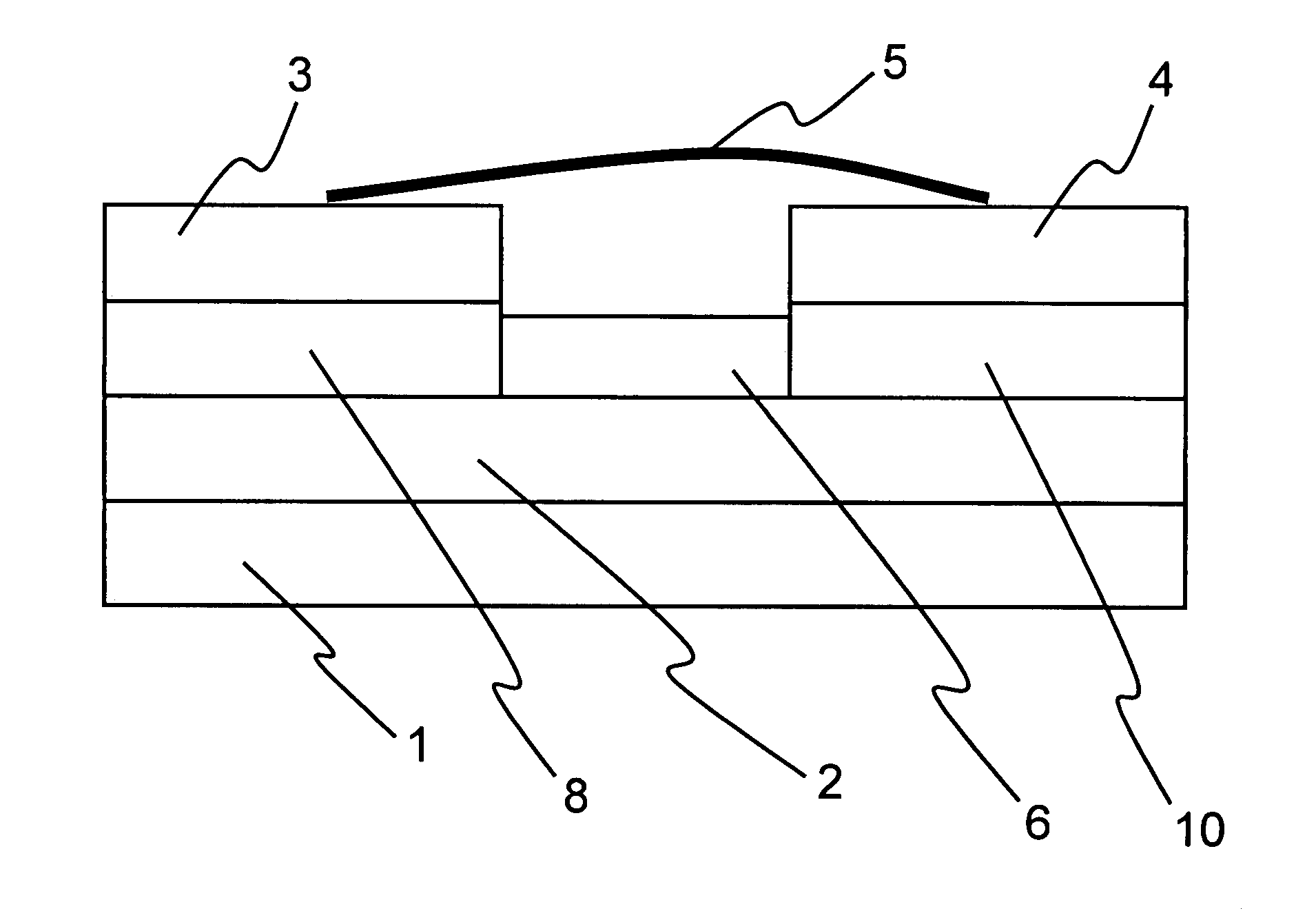
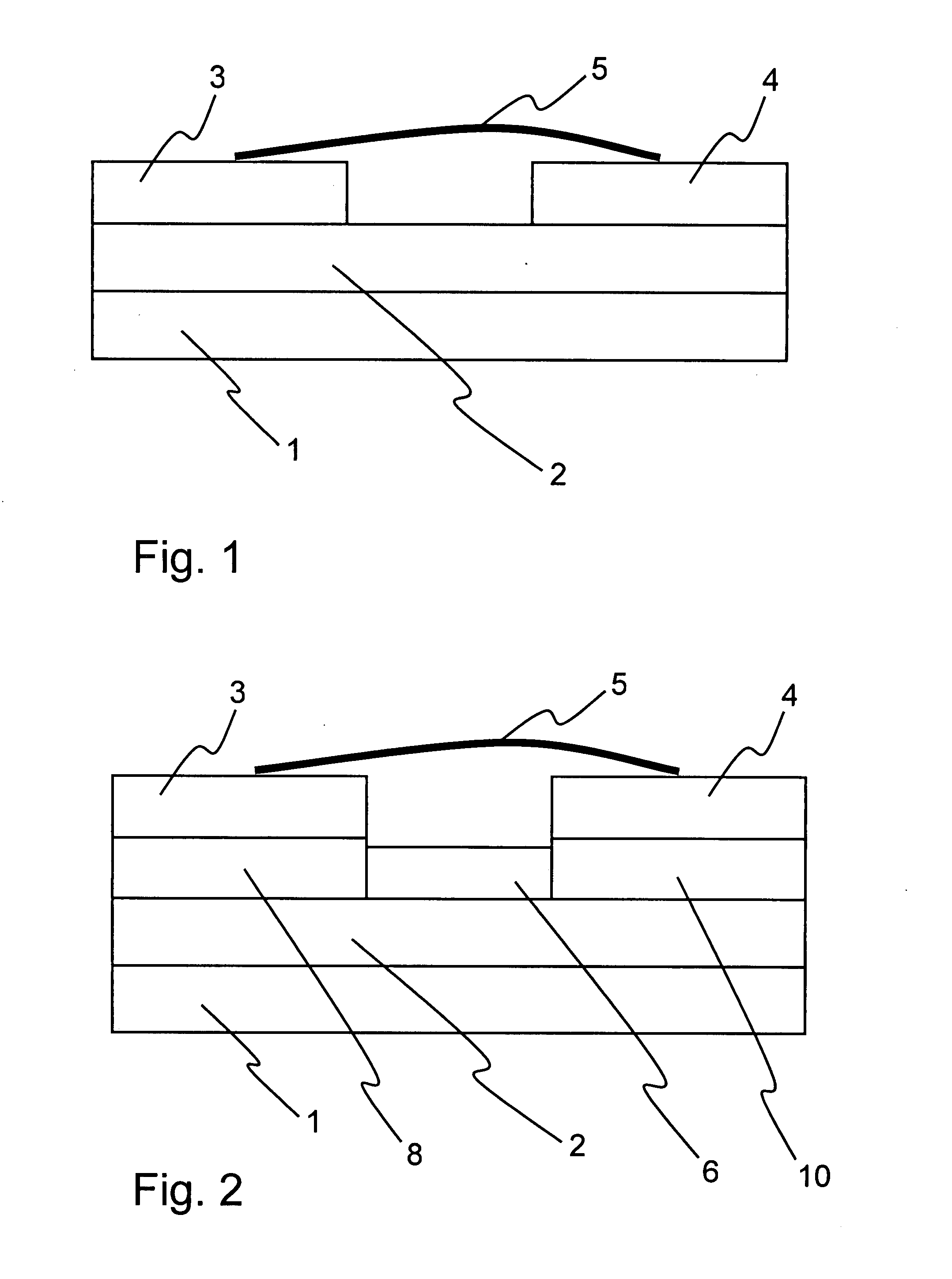
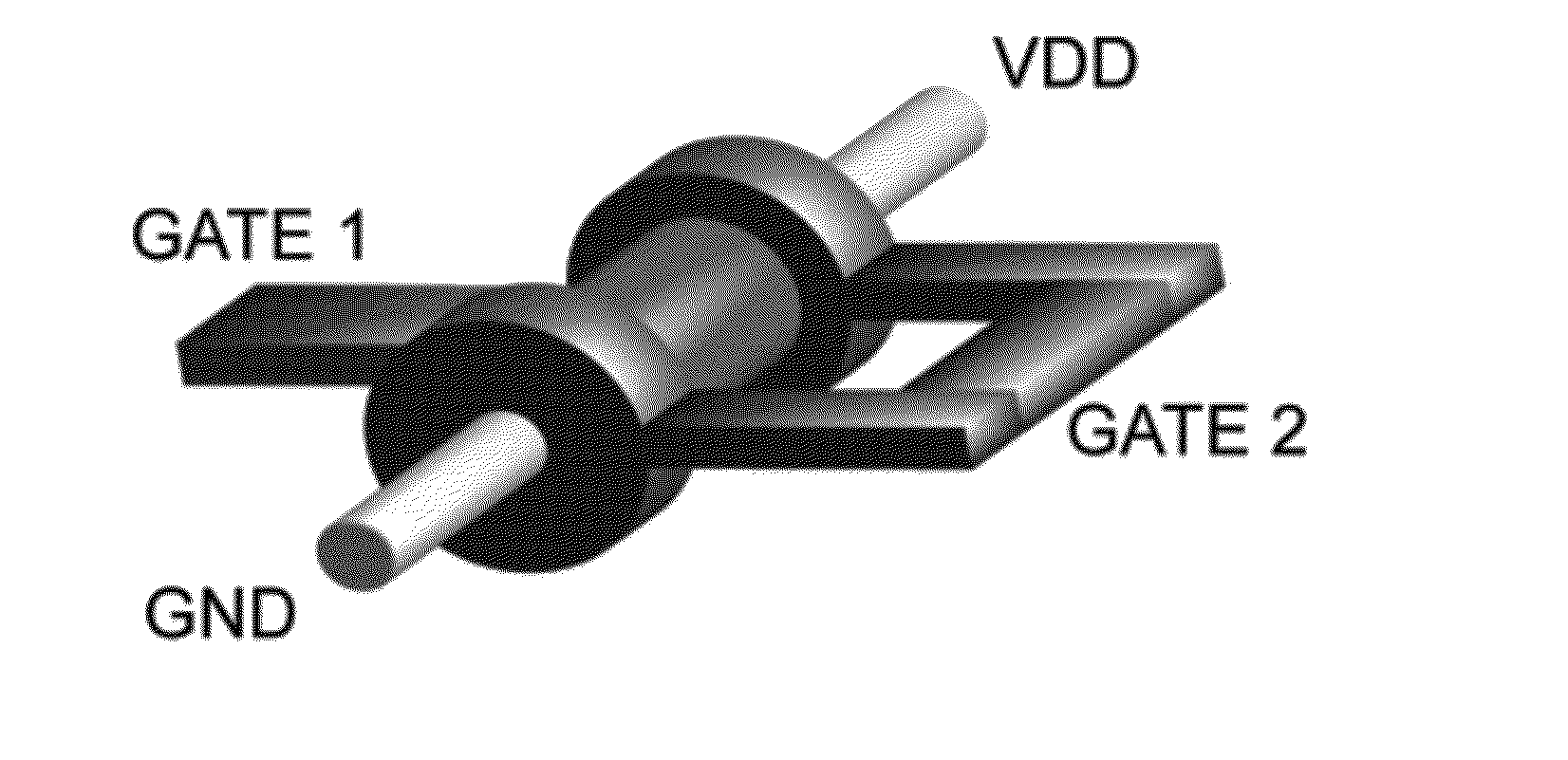Patents
Literature
83 results about "Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
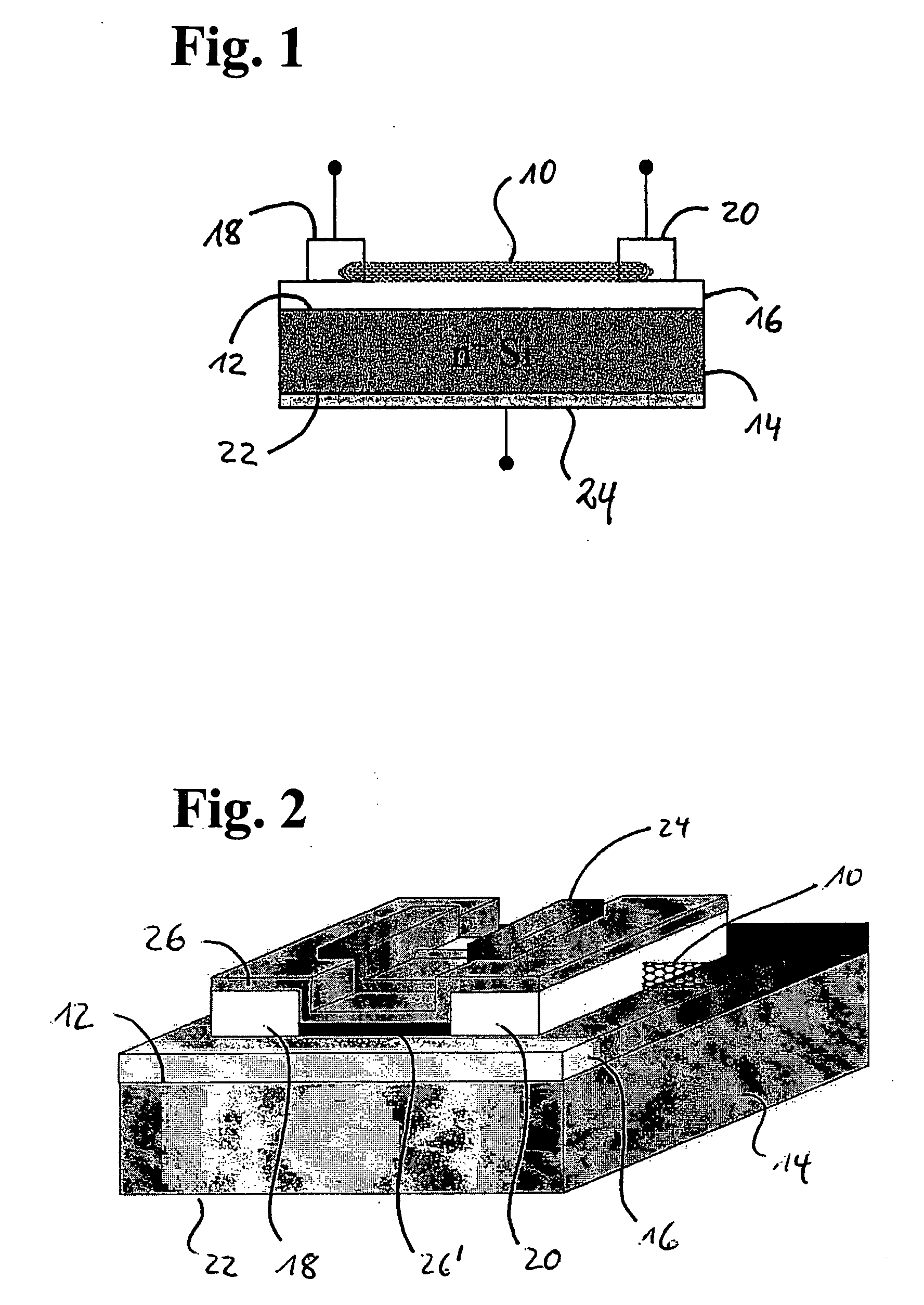
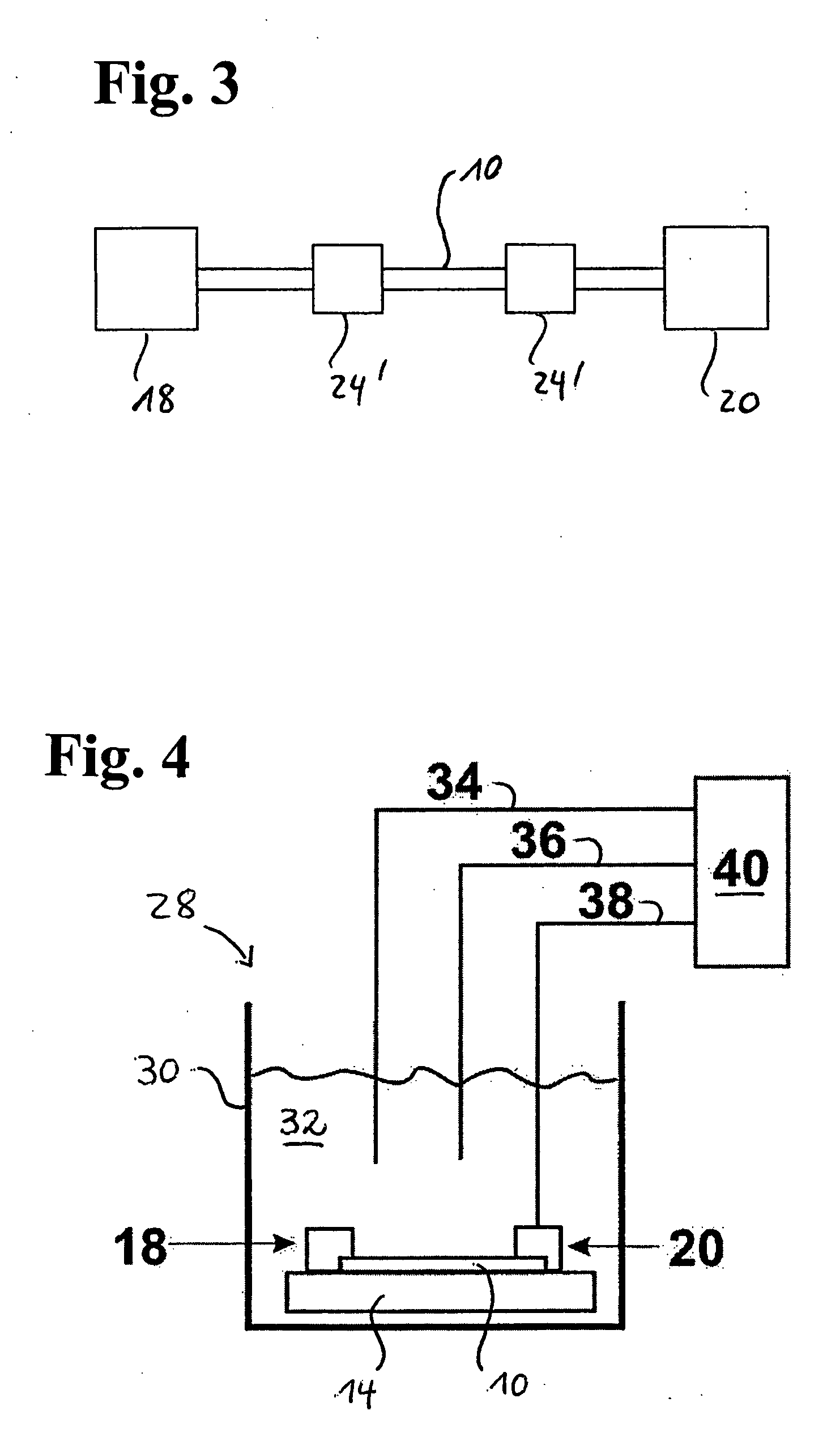
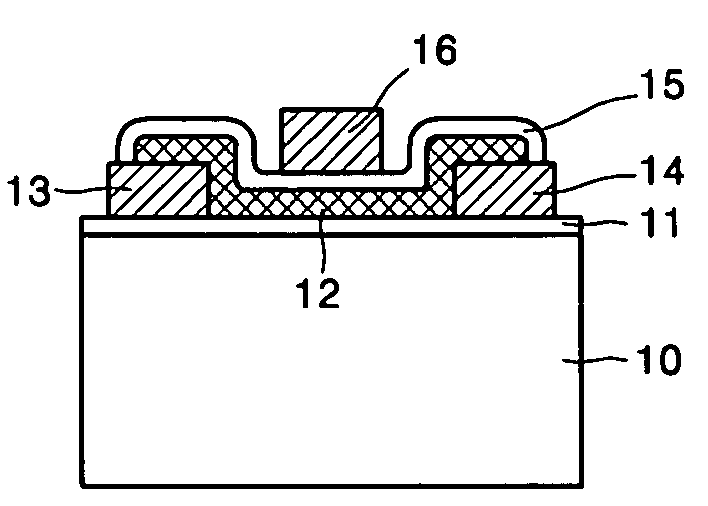
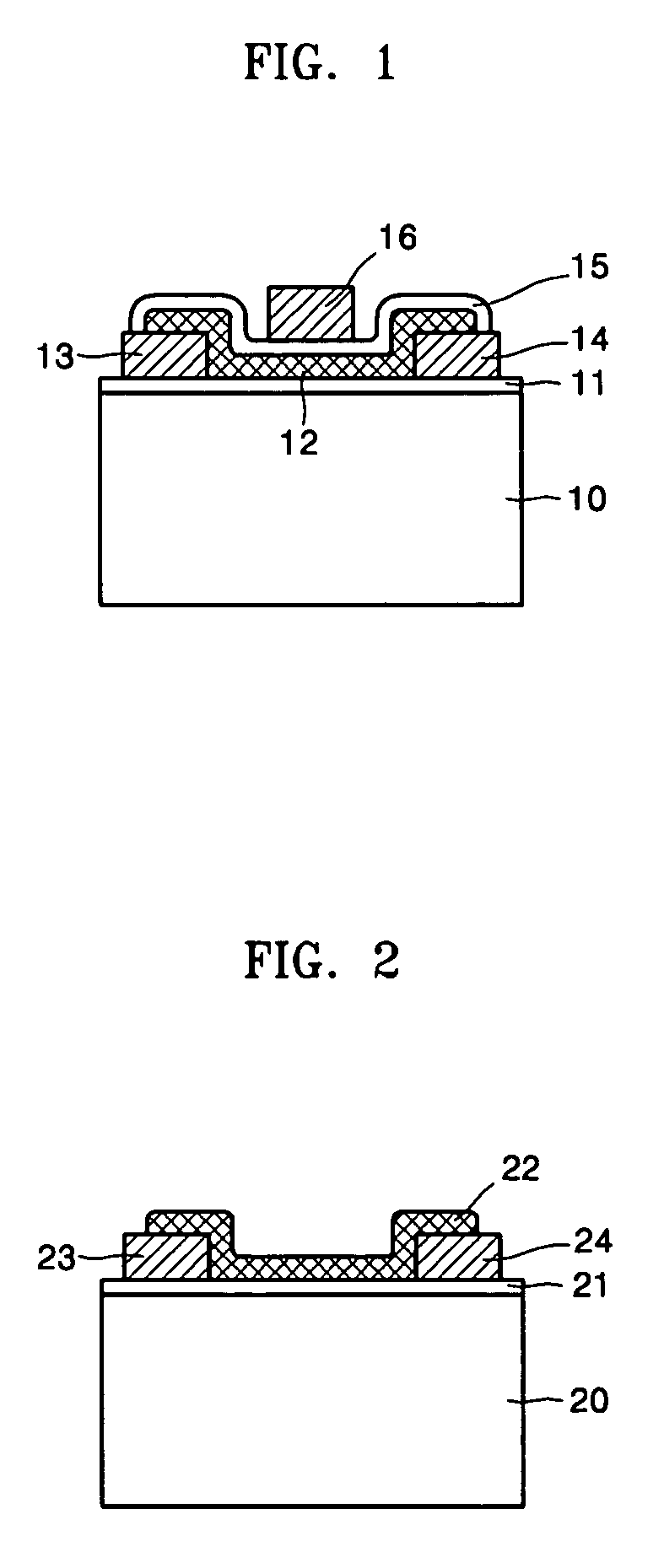
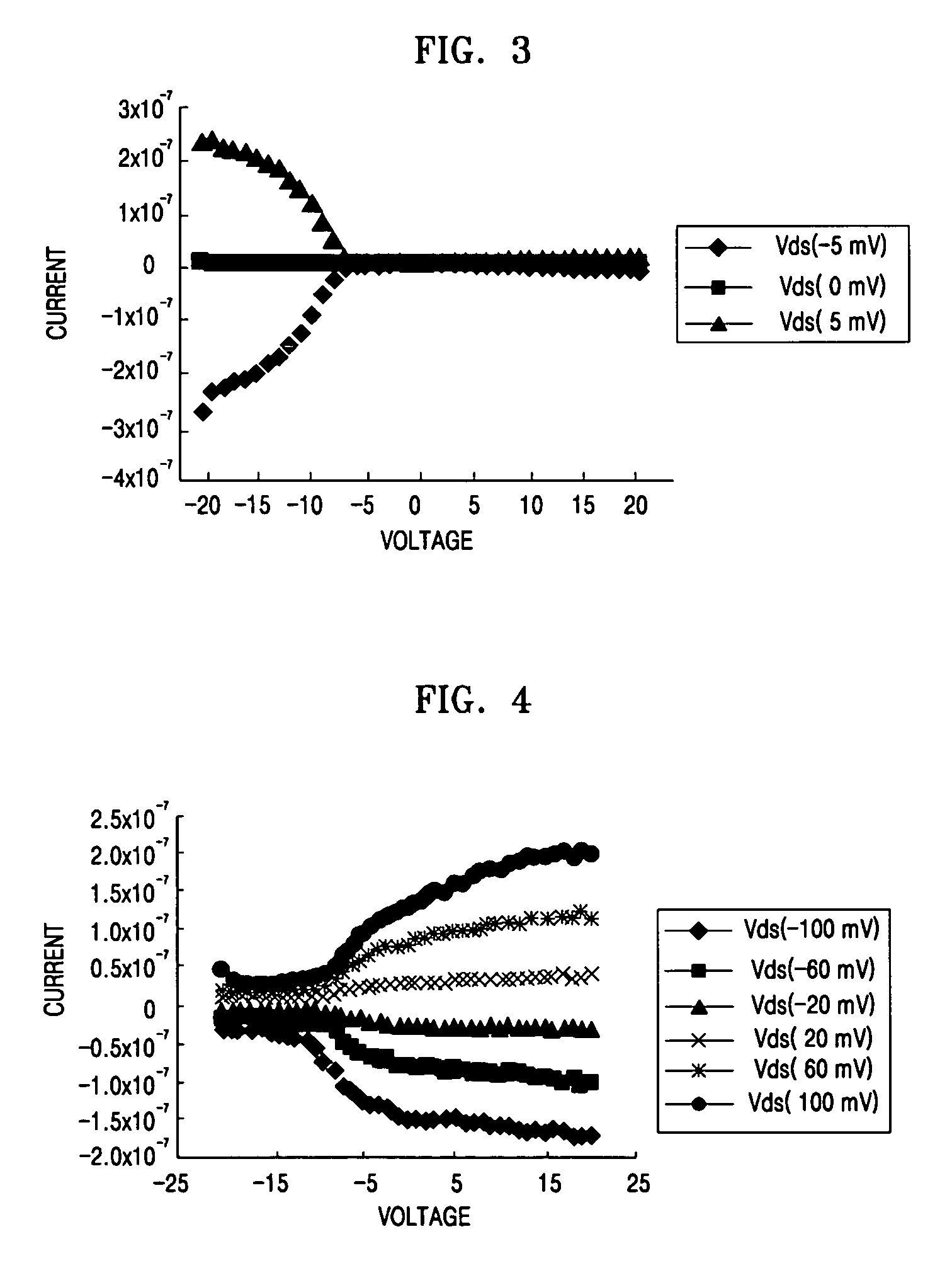
A carbon nanotube field-effect transistor (CNTFET) refers to a field-effect transistor that utilizes a single carbon nanotube or an array of carbon nanotubes as the channel material instead of bulk silicon in the traditional MOSFET structure. First demonstrated in 1998, there have been major developments in CNTFETs since.
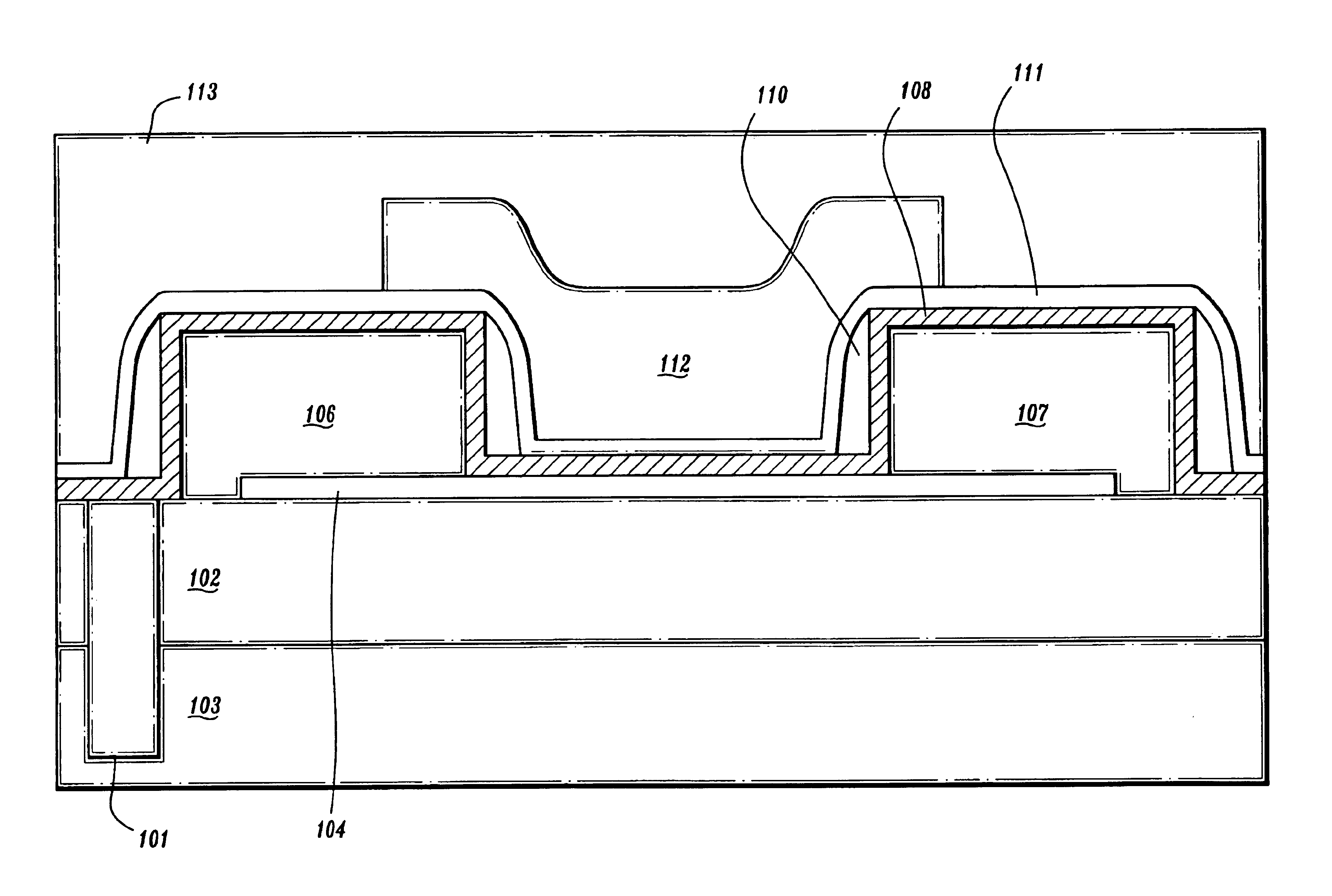
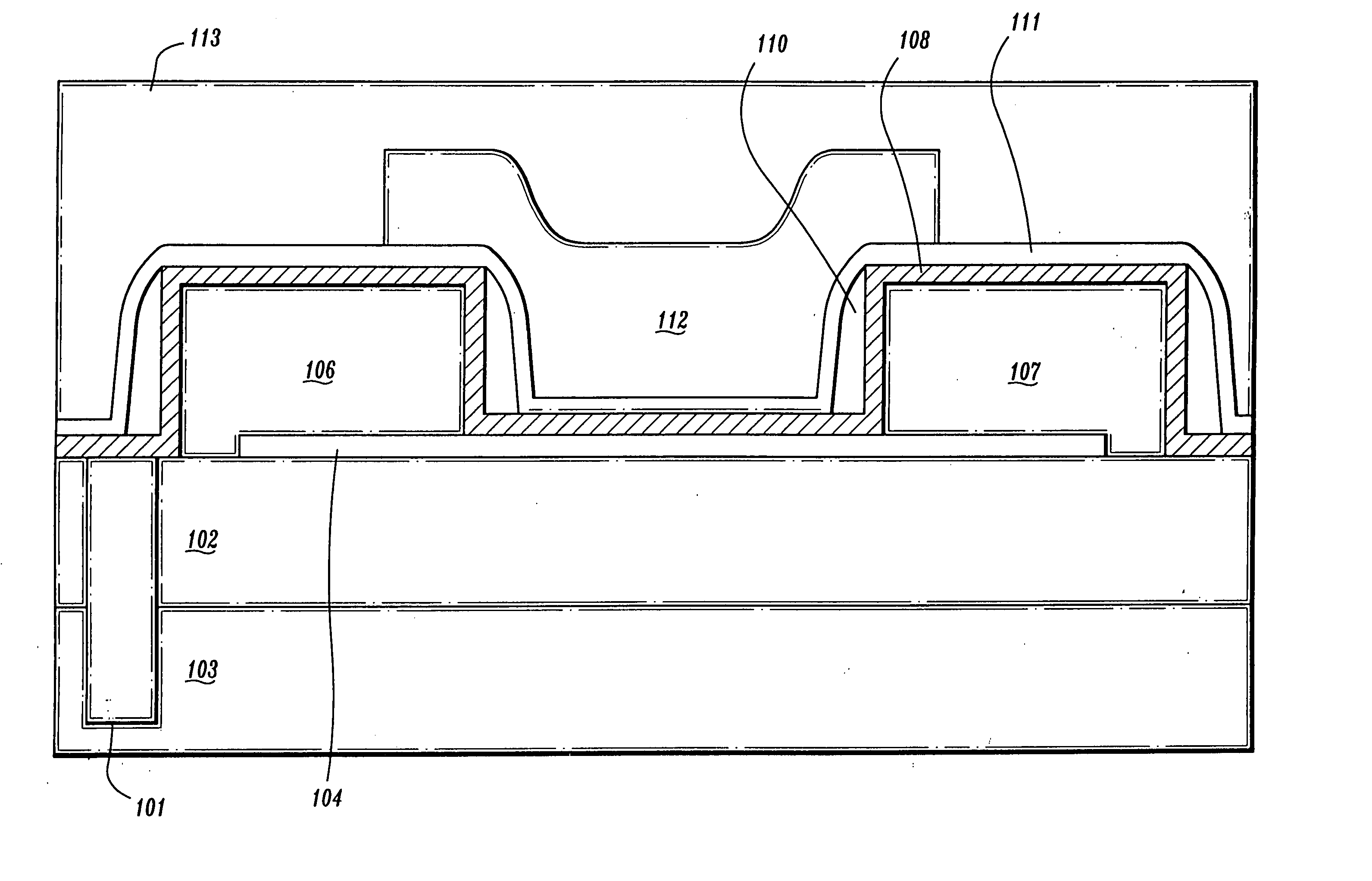
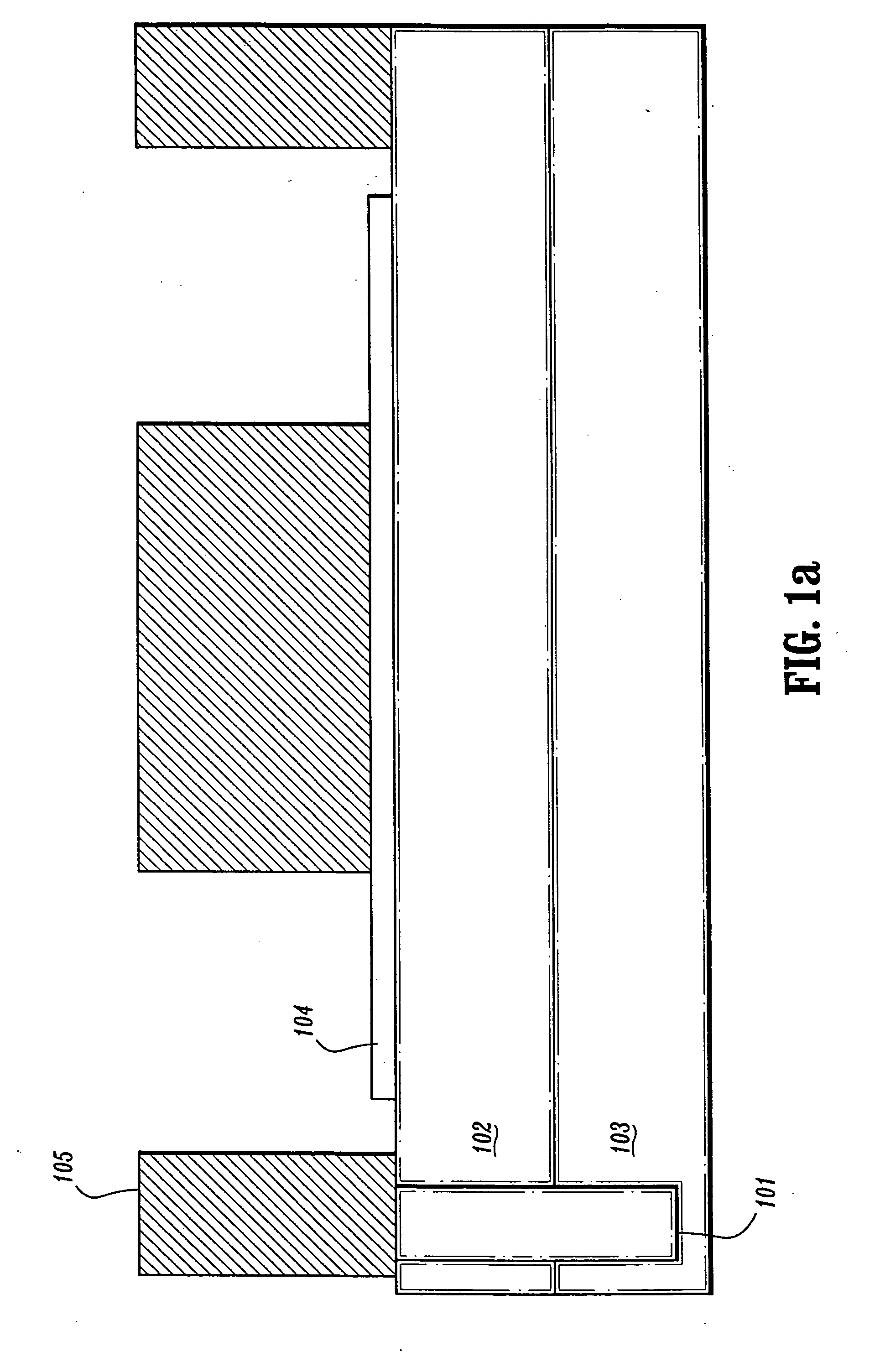
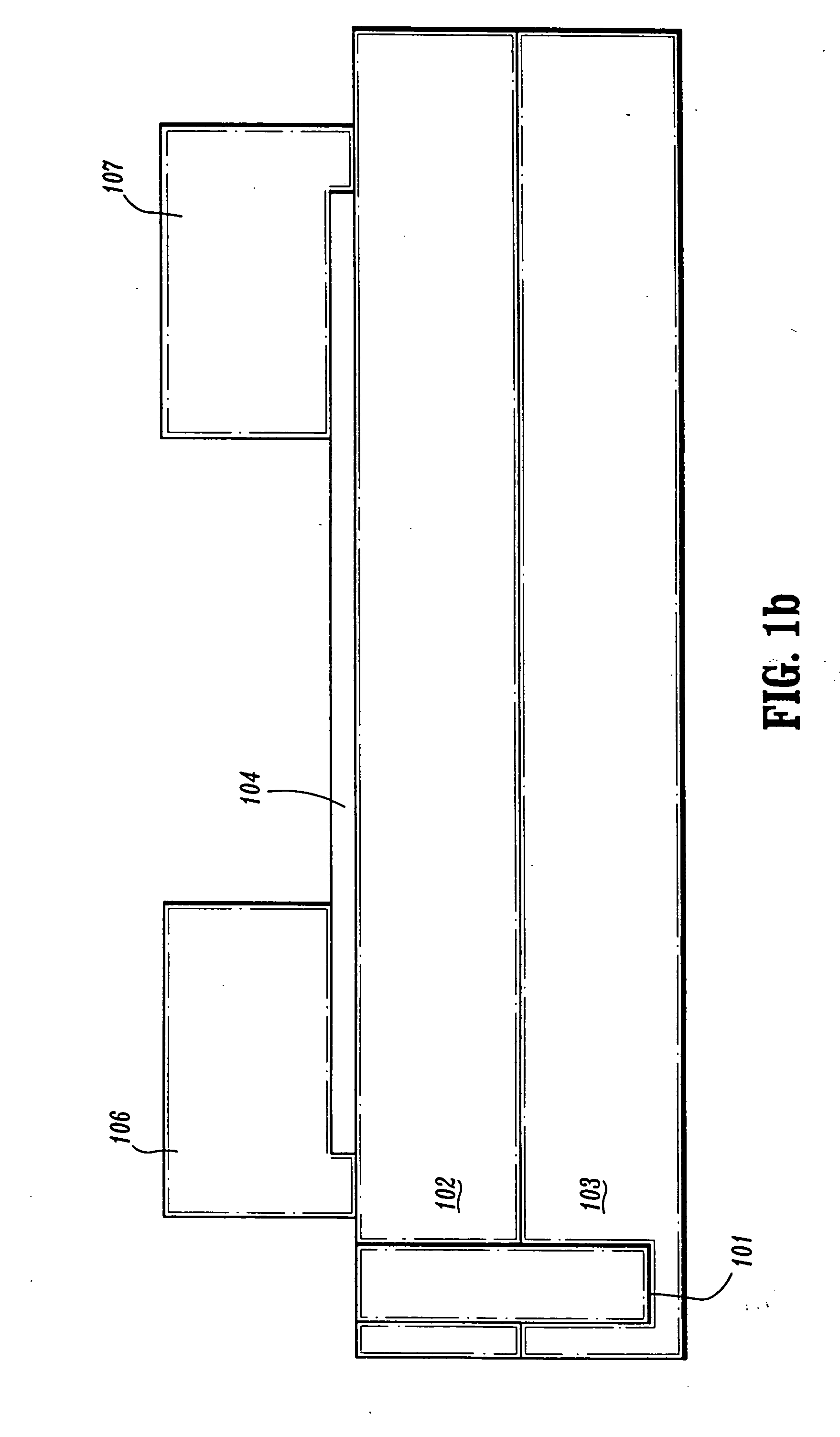
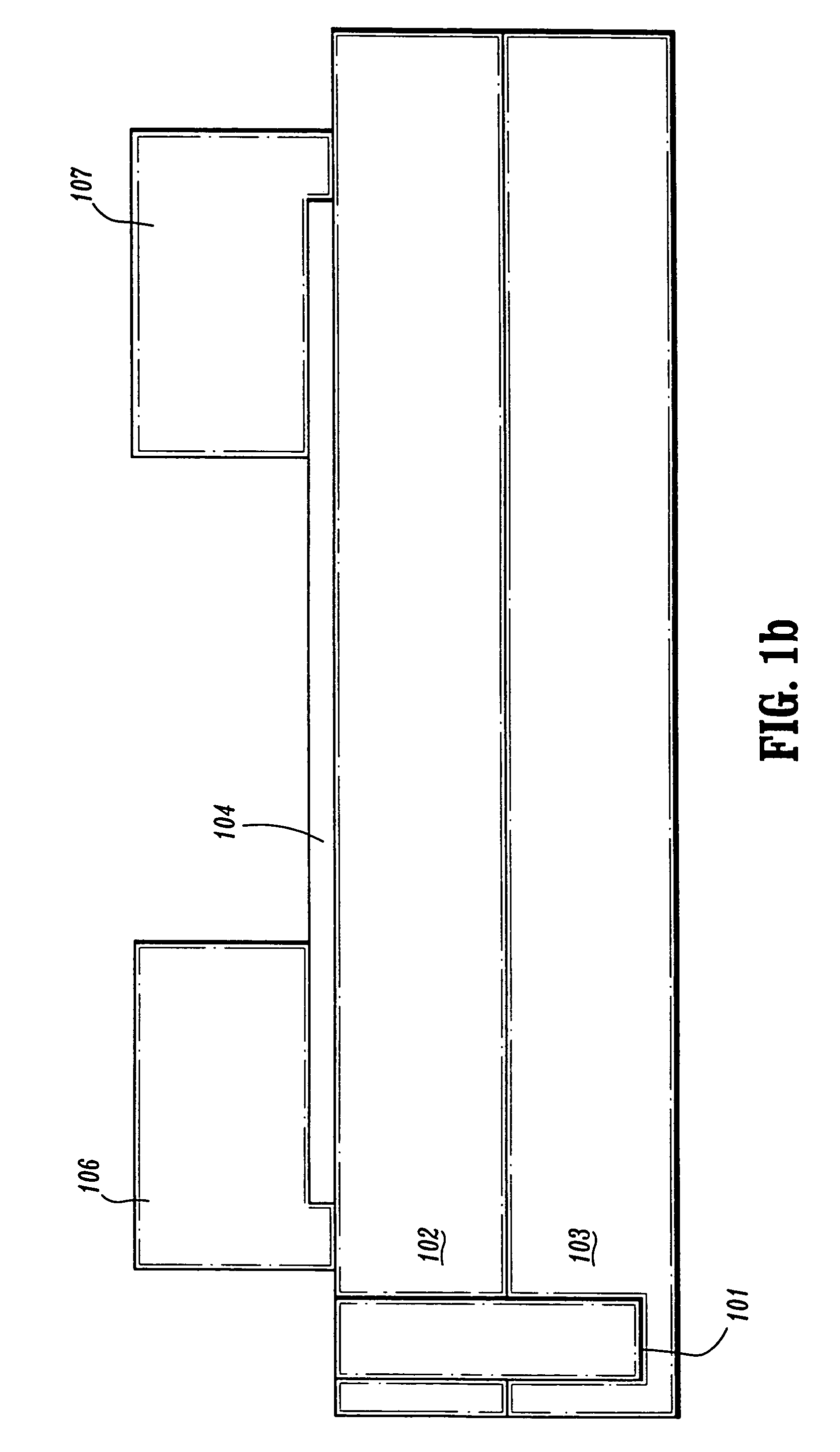
Self-aligned nanotube field effect transistor and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS6891227B2NanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesEngineeringCarbon nanotube field-effect transistor
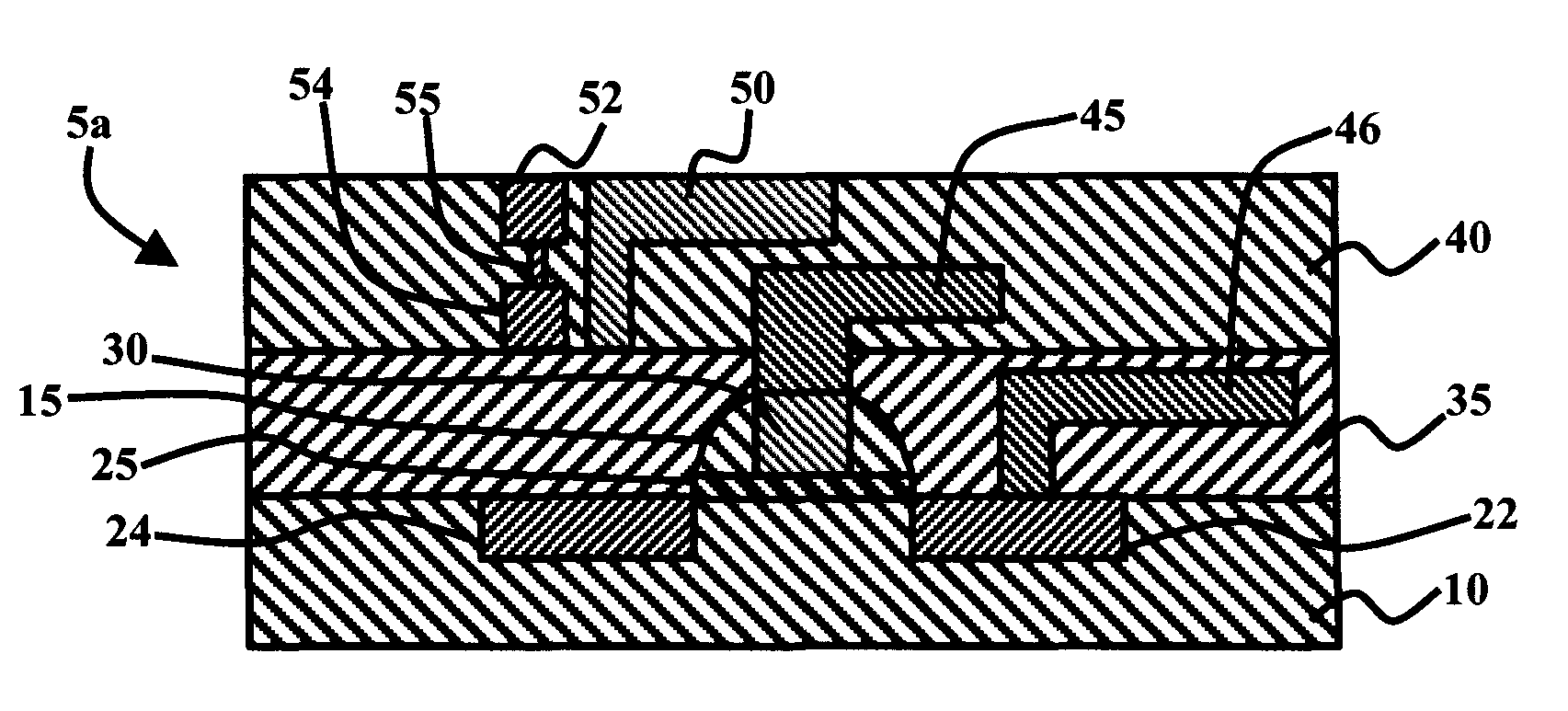
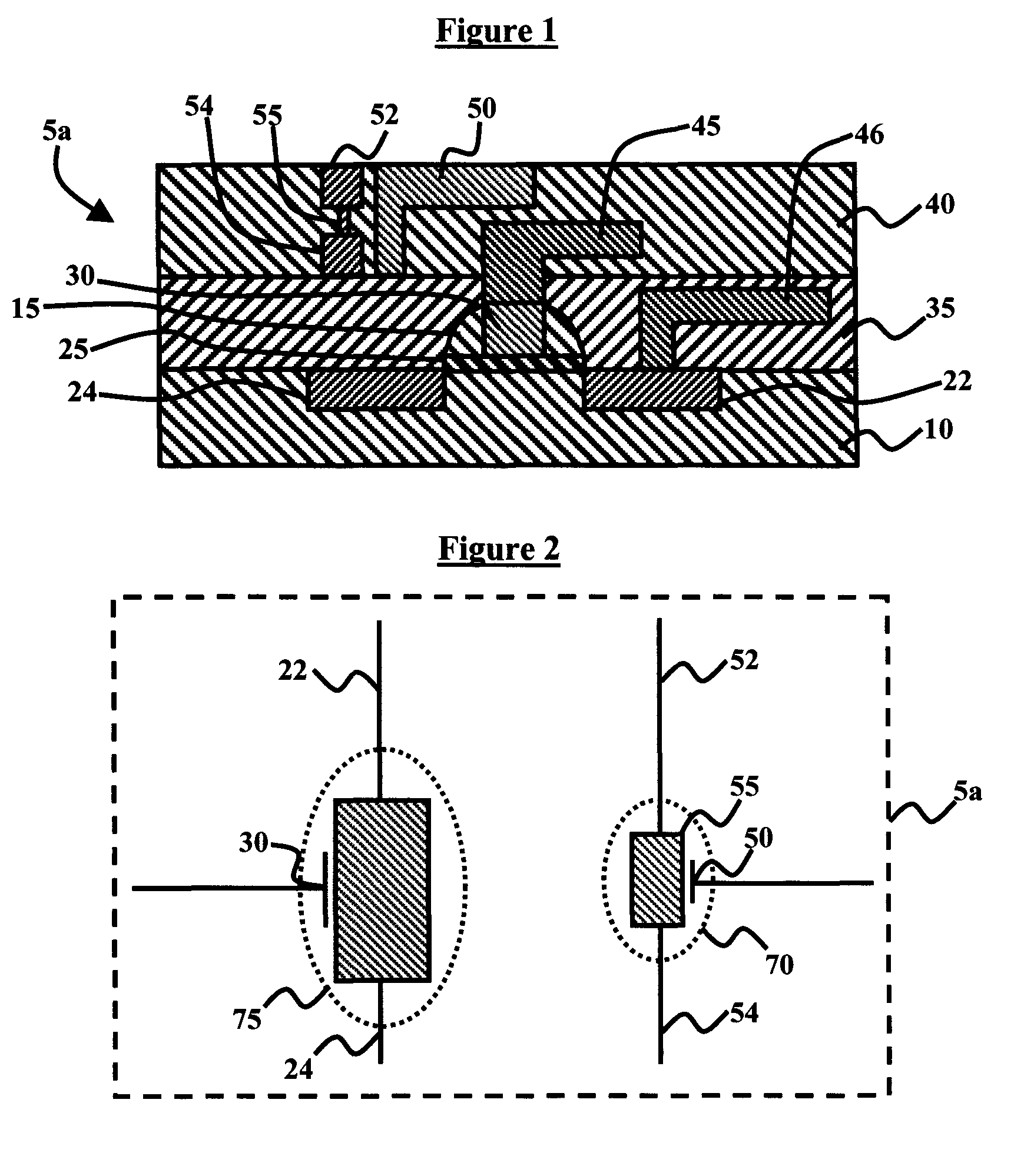
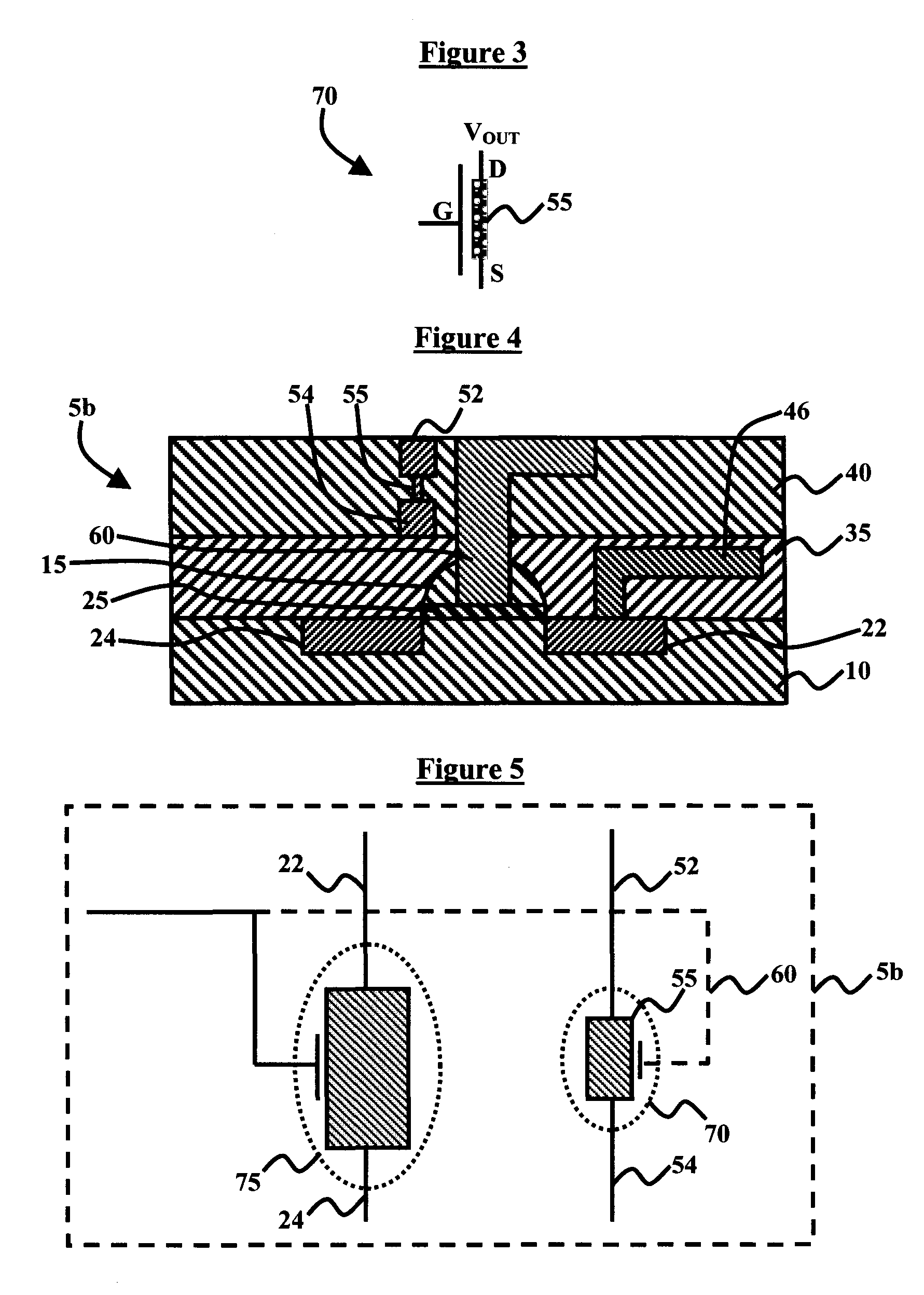
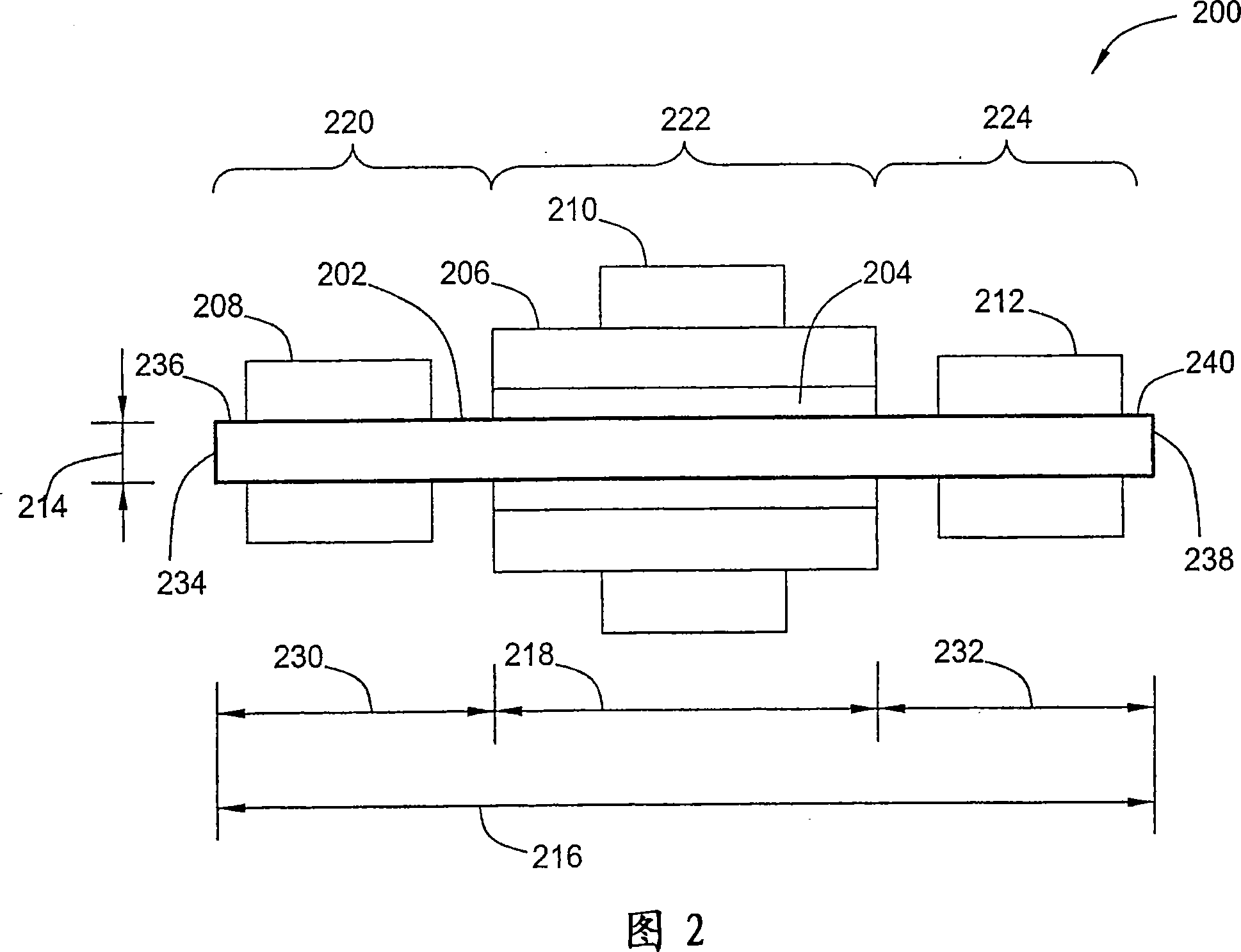
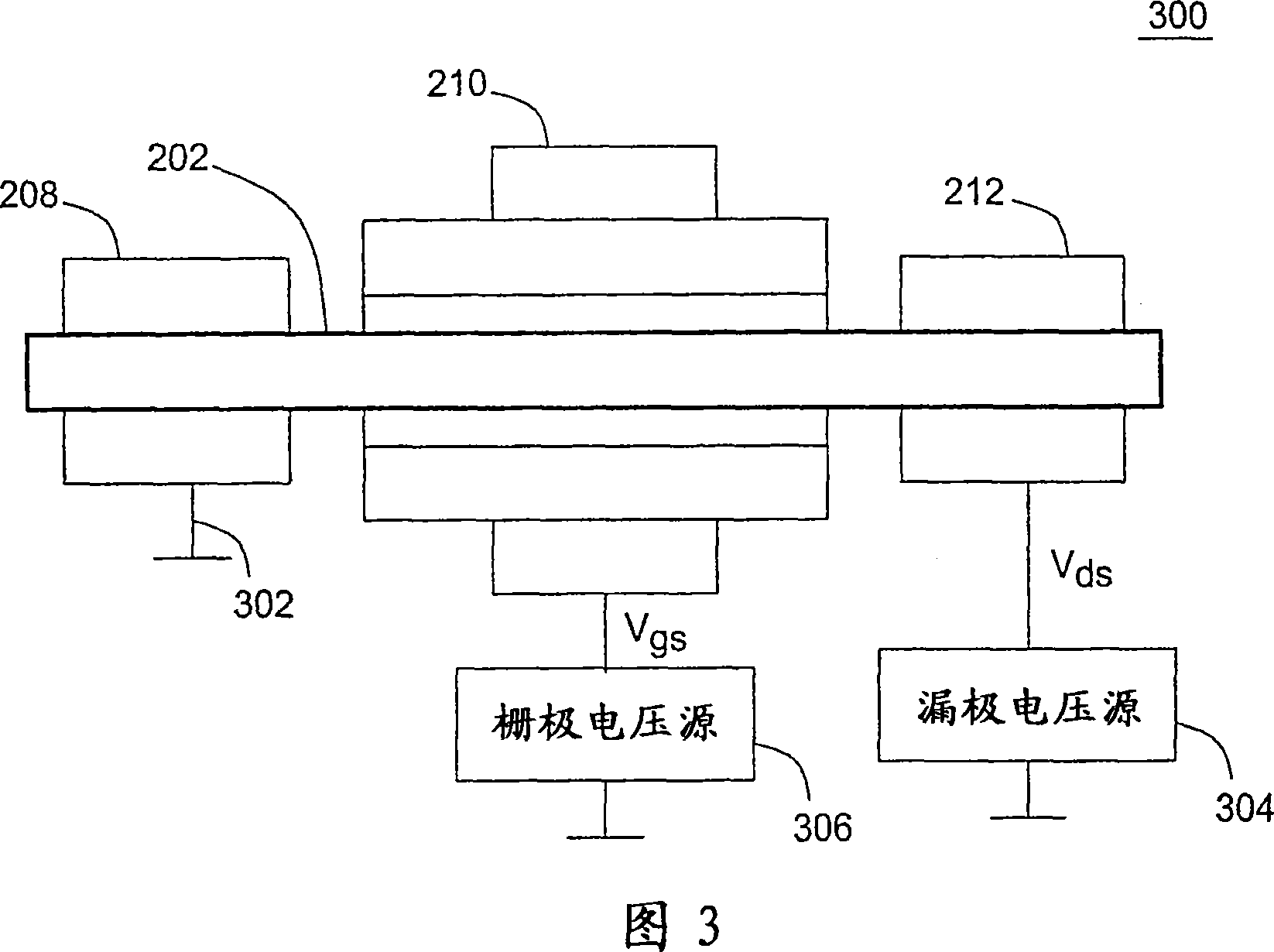
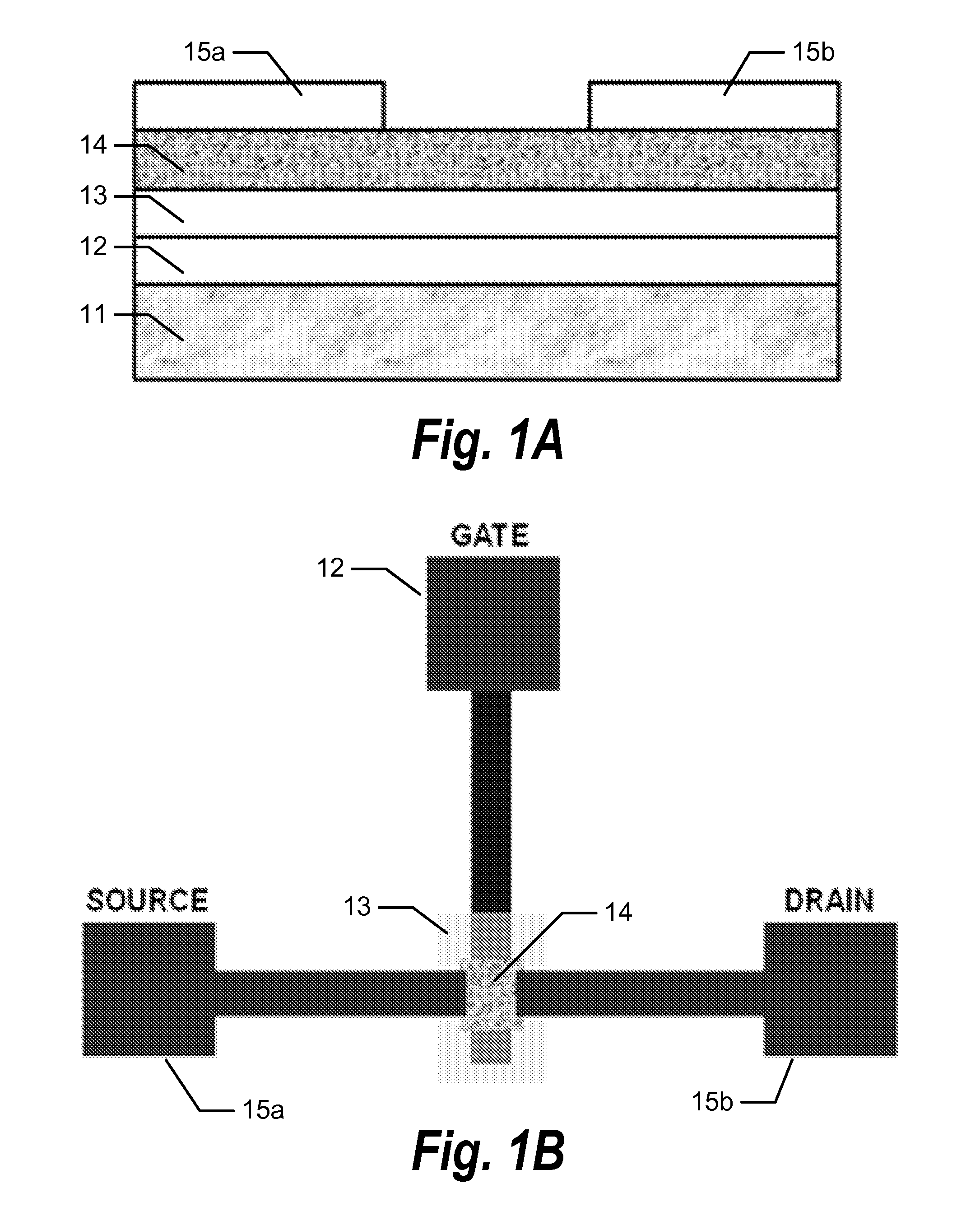
A self-aligned carbon-nanotube field effect transistor semiconductor device comprises a carbon-nanotube deposited on a substrate, a source and a drain formed at a first end and a second end of the carbon-nanotube, respectively, and a gate formed substantially over a portion of the carbon-nanotube, separated from the carbon-nanotube by a dielectric film.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Self-aligned nanotube field effect transistor and method of fabricating same
A self-aligned carbon-nanotube field effect transistor semiconductor device comprises a carbon-nanotube deposited on a substrate, a source and a drain formed at a first end and a second end of the carbon-nanotube, respectively, and a gate formed substantially over a portion of the carbon-nanotube, separated from the carbon-nanotube by a dielectric film.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
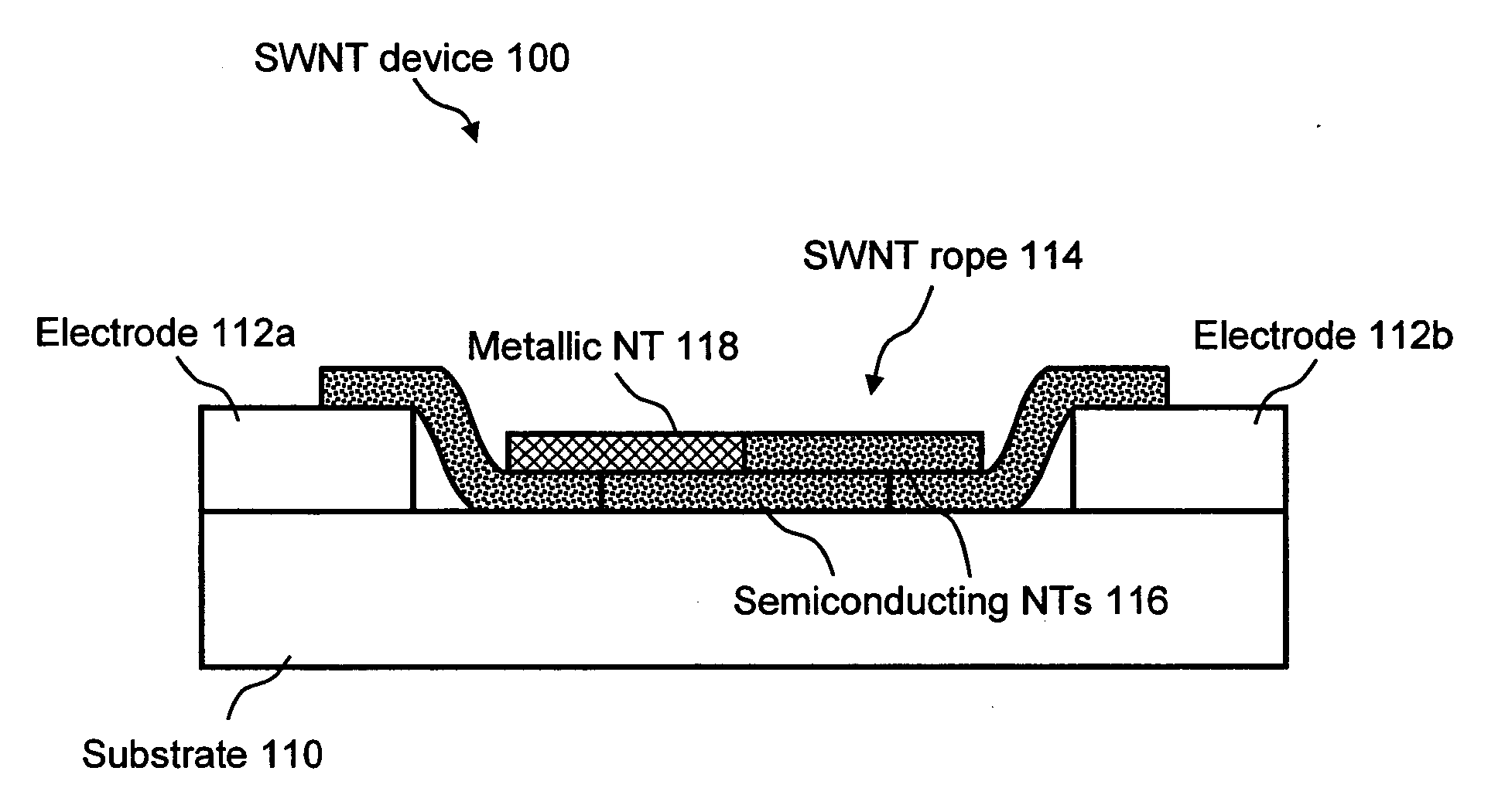
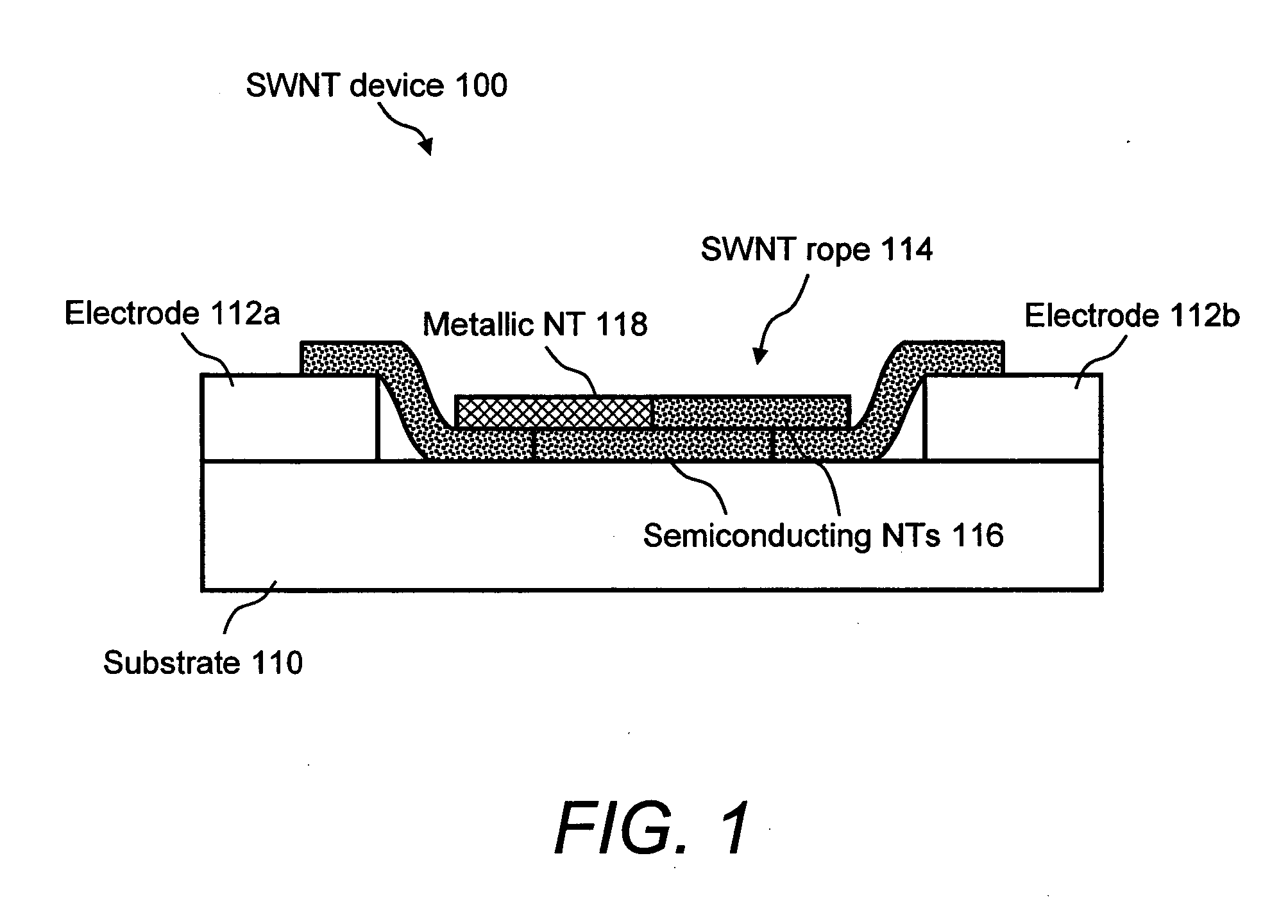
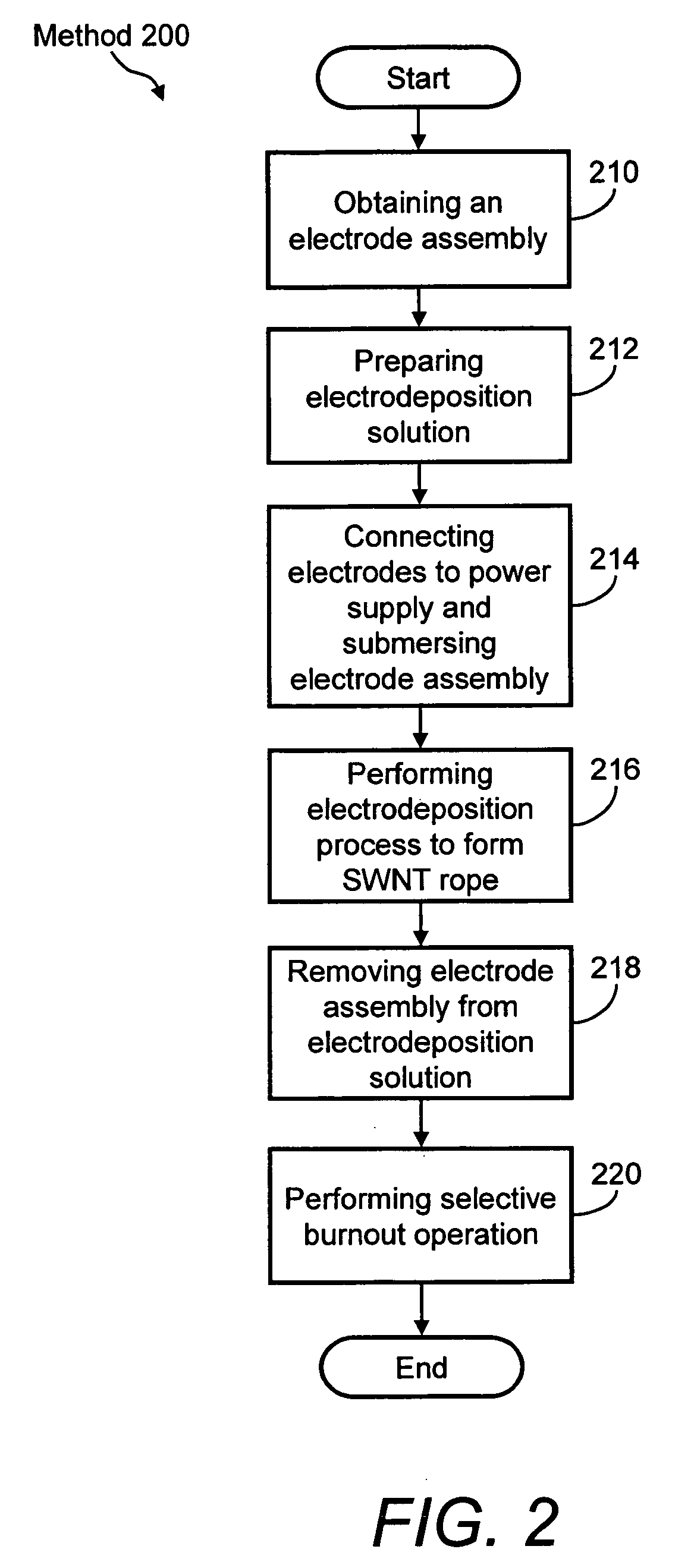
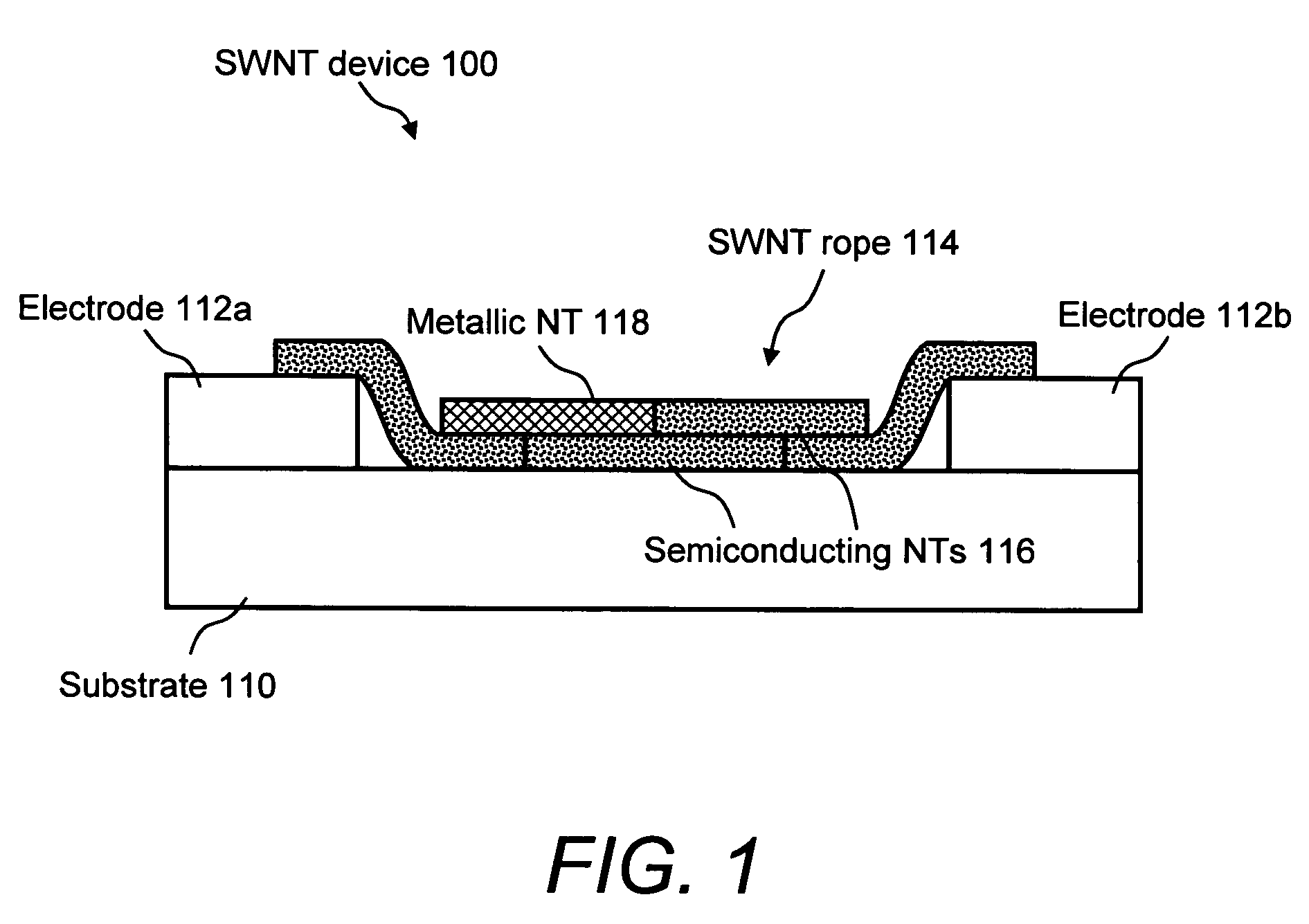
Carbon nanotube-based electronic devices made by electrolytic deposition and applications thereof
InactiveUS20060065887A1Efficient and cost-effectiveNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesDevice formMulti dimensional
Carbon nanotube-based devices made by electrolytic deposition and applications thereof are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention provides a device comprising at least one array of active carbon nanotube junctions deposited on at least one microelectronic substrate. In another preferred embodiment, the present invention provides a device comprising a substrate, at least one pair of electrodes disposed on the substrate, wherein one or more pairs of electrodes are connected to a power source, and a bundle of carbon nanotubes disposed between the at least one pair of electrodes wherein the bundle of carbon nanotubes consist essentially of semiconductive carbon nanotubes. In another preferred embodiment, a semiconducting device formed by electrodeposition of carbon nanotubes between two electrodes is provided. The invention also provides preferred methods of forming a semiconductive device by applying a bias voltage to a carbon nanotube rope. The plurality of metallic single-wall carbon nanotubes are removed (e.g., by application of bias voltage) in an amount sufficient to form the semiconducting device. The devices of the invention include, but not limited to, chemical or biological sensors, carbon nanotube field-effect transistors (CNFETs), tunnel junctions, Schottky junctions, and multi-dimensional nanotube arrays.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
Carbon nanotube gate field effect transistor
The present invention generally relates to an apparatus and method of carbon nanotube (CNT) gate field effect transistor (FET), which is used to replace the current metal gate of transistor for decreasing the gate width greatly. The carbon nanotube has its own intrinsic characters of metal and semiconductor, so it can be the channel, connector or next-level gate of transistor. Furthermore, the transistor has the structure of exchangeable source and drain, and can be defined the specificity by outside wiring.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Ambipolar silicon nanowire field effect transistor
ActiveUS20130313524A1Reduce consumptionShorten speedNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSchottky barrierNanowire
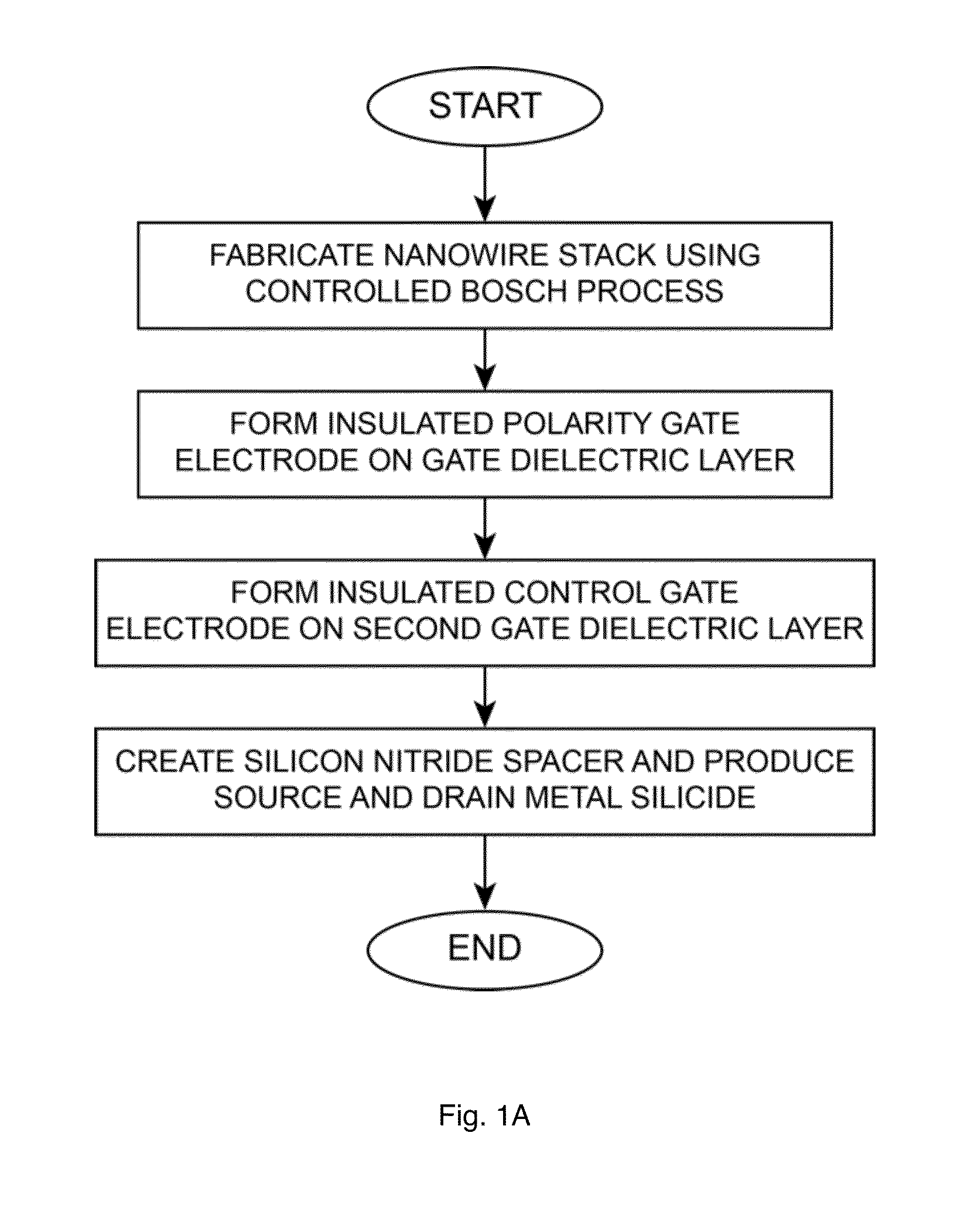
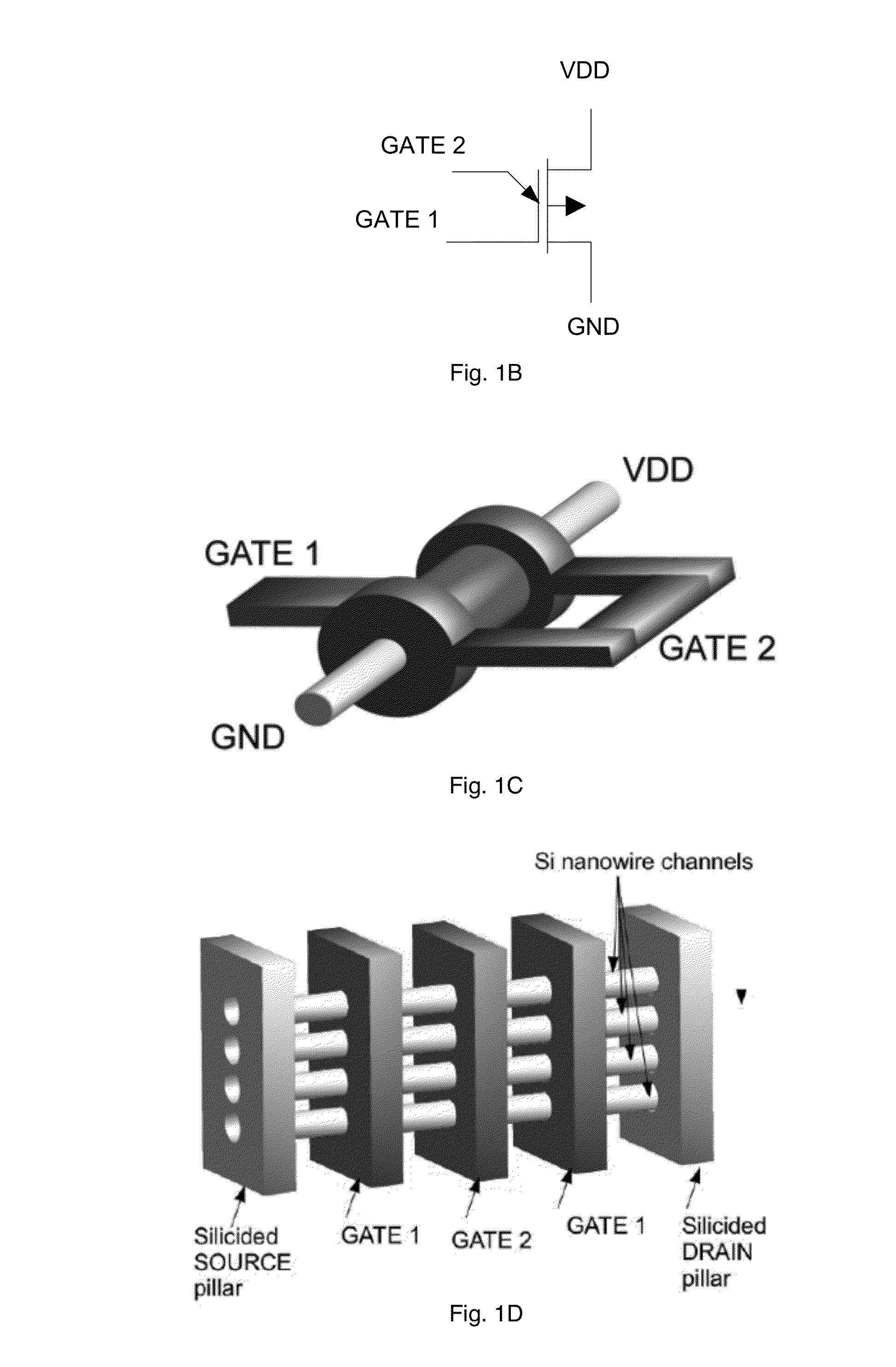
This invention describes a novel electronic device consisting of one—or more—vertically stacked gate-all-around silicon nanowire field effect transistor (SNWFET) with two independent gate electrodes. One of the two gate electrodes, acting on the central section of the transistor channel, controls on / off behavior of the channel. The second gate, acting on the regions in proximity to the source and the drain of the transistor, defines the polarity of the devices, i.e. p or n type. The electric field of the second gate acts either at the interface of the nanowire-to-source / drain region or anywhere in close proximity to the depleted region of the SiNW body, modulating the bending of the Schottky barriers at the contacts, eventually screening one type of charge carrier to pass through the channel of the transistor. This is achieved by controlling the majority carriers passing through the transistor channel by regulating the Schottky barrier thicknesses at the source and drain contacts.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Vertical carbon nanotube-field effect transistor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050156203A1Easy to makeImprove controllabilityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCarbon nanotubeCarbon nanotube field-effect transistor
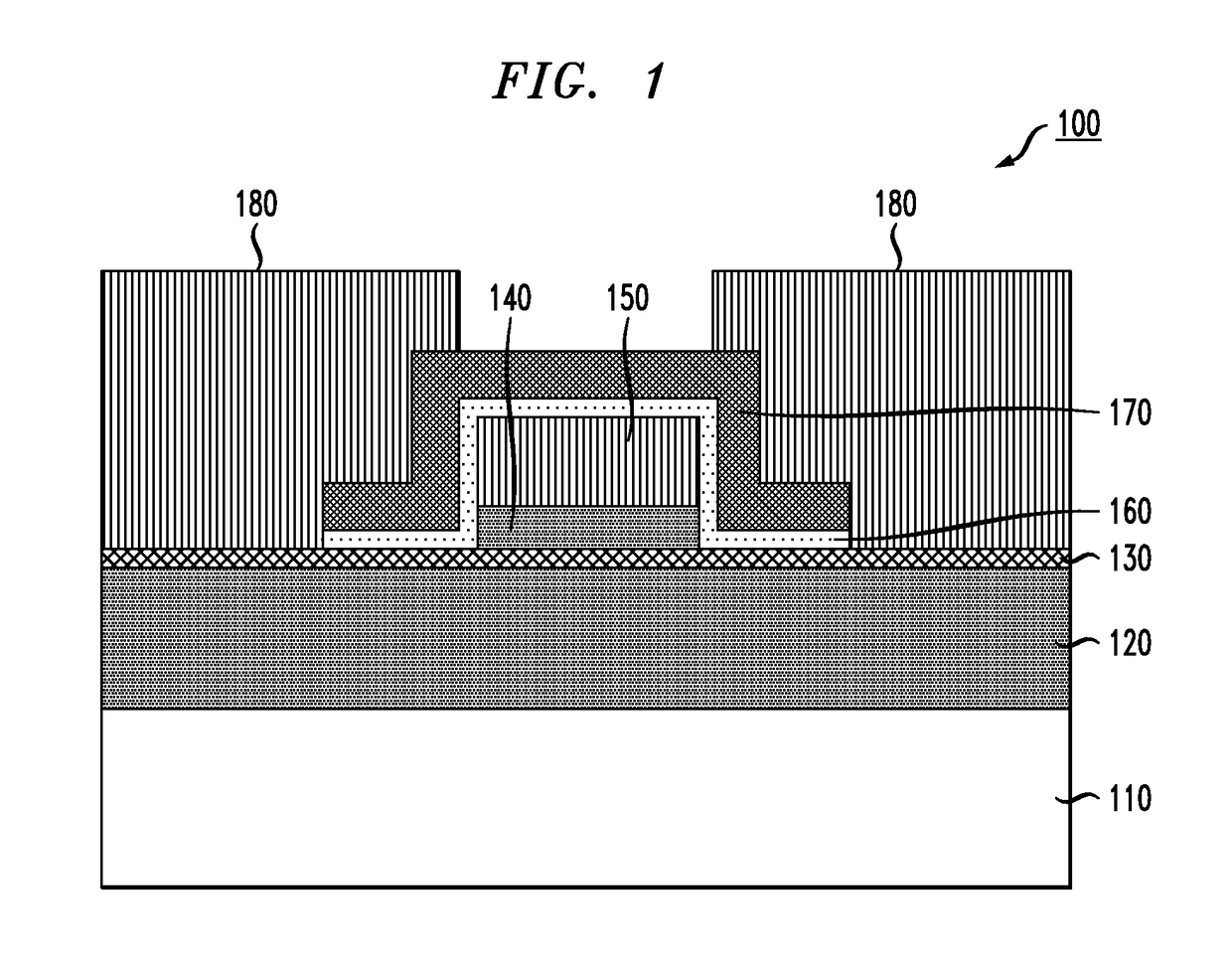
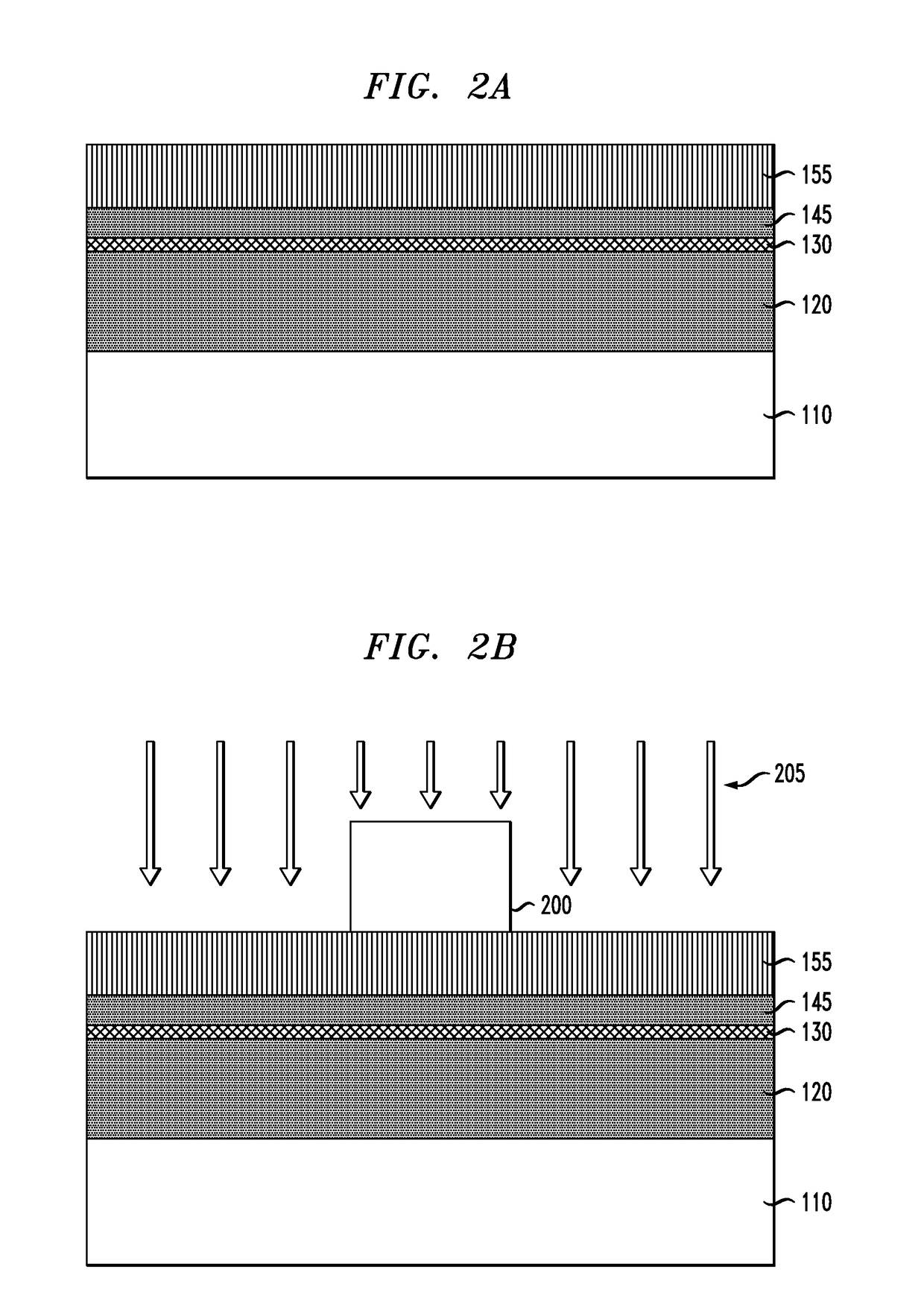
Provided are a vertical carbon nanotube field effect transistor (CNTFET) and a method of manufacturing the same. The method includes: forming a first electrode on a substrate; forming a stack of multiple layers (“multi-layer stack”) on the first electrode, the multiple layers including first and second buried layers and a sacrificial layer interposed between the first and second buried layers; forming a vertical well into the multi-layer stack; growing a CNT within the well; forming a second electrode connected to the CNT on the multi-layer stack into which the well has been formed; forming a protective layer on the second electrode; removing the sacrificial layer and exposing the CNT between the first and second buried layers; forming a gate insulating layer on the exposed surface of the CNT; and forming a gate enclosing the CNT on the gate insulating layer. The CNTFET and manufacturing method maximize the effect of electric field produced by the gate due to the channel completely enclosed by the gate while improving a ratio Ion / Ioff of on-current to off-current by fully depleting a depletion layer formed in the channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of fabricating carbon nanotube field-effect transistors through controlled electrochemical modification
InactiveUS7091096B2Poses problemImprove the immunityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCompound (substance)Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor
The invention relates to a method of fabricating a structure with field-effect transistors each comprising a source electrode, a drain electrode, a channel extending between the source and drain electrodes and at least one gate electrode associated with the channel for controlling the conductance of the channel, wherein the channel comprises one or more semiconducting single-wall carbon nanotubes. The method includes the steps ofa) depositing a plurality of single-wall carbon nanotubes on a substrate, the carbon nanotubes including a mixture of metallic carbon nanotubes and semiconducting carbon nanotubes,b) providing before or after step a) source and drain electrodes on the substrate so that one or more carbon nanotubes extend between the source and drain electrodes,c) applying a variable gate voltage to switch off the semiconducting tubes extending between the source and drain electrodes,d) wetting the surface of the structure including the transistors with a chemical to achieve a chemical bond between a radical supplied by the chemical and some carbon atoms of the metallic nanotubes, whereby these metallic nanotubes become non-conductive.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Methods of fabricating vertical carbon nanotube field effect transistors for arrangement in arrays and field effect transistors and arrays formed thereby
A method for forming carbon nanotube field effect transistors, arrays of carbon nanotube field effect transistors, and device structures and arrays of device structures formed by the methods. The methods include forming a stacked structure including a gate electrode layer and catalyst pads each coupled electrically with a source / drain contact. The gate electrode layer is divided into multiple gate electrodes and at least one semiconducting carbon nanotube is synthesized by a chemical vapor deposition process on each of the catalyst pads. The completed device structure includes a gate electrode with a sidewall covered by a gate dielectric and at least one semiconducting carbon nanotube adjacent to the sidewall of the gate electrode. Source / drain contacts are electrically coupled with opposite ends of the semiconducting carbon nanotube to complete the device structure. Multiple device structures may be configured either as a memory circuit or as a logic circuit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
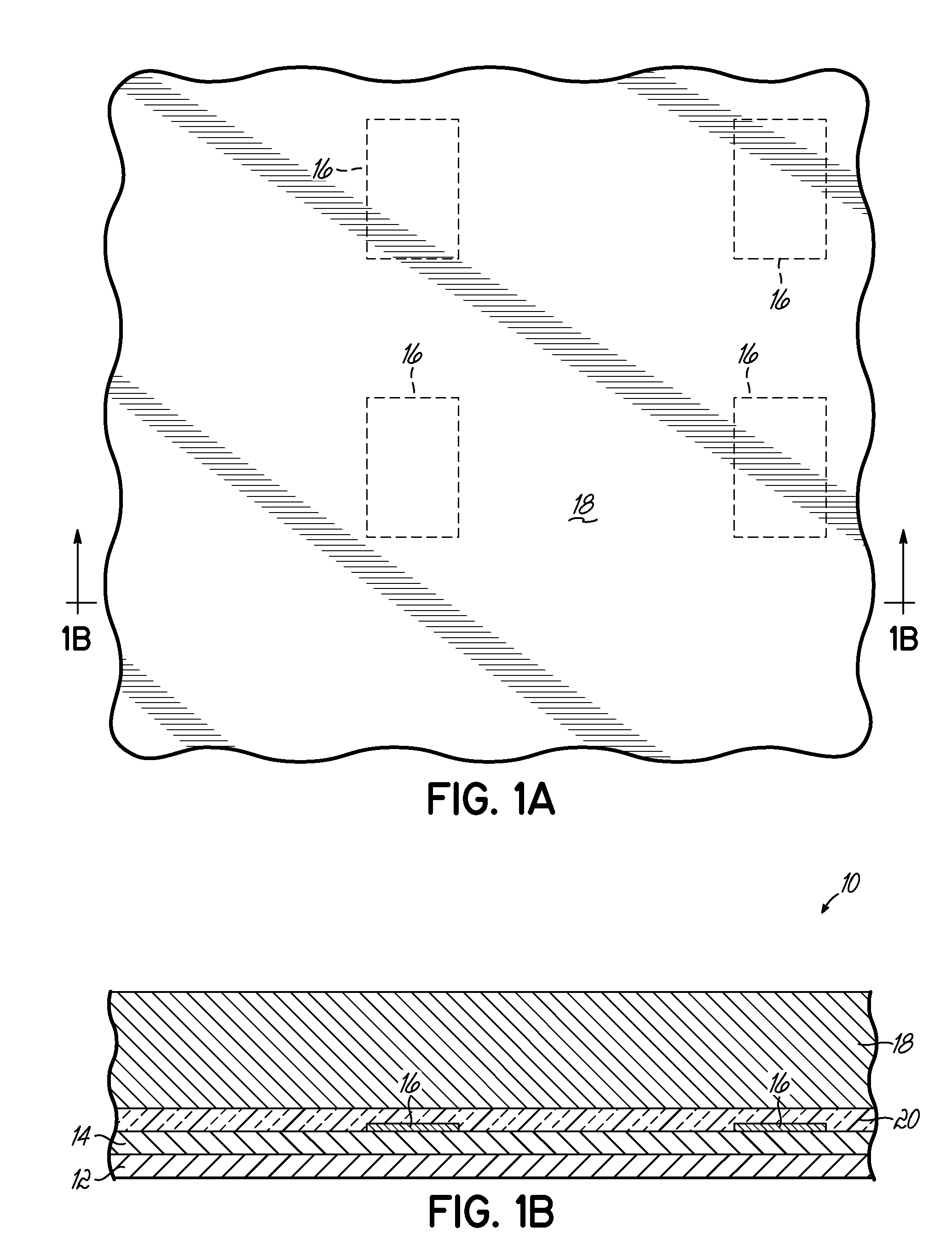
Integrated carbon nanotube sensors
InactiveUS7247877B2Improve quality resolutionNegatively impactTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCarbon nanotubeEngineering
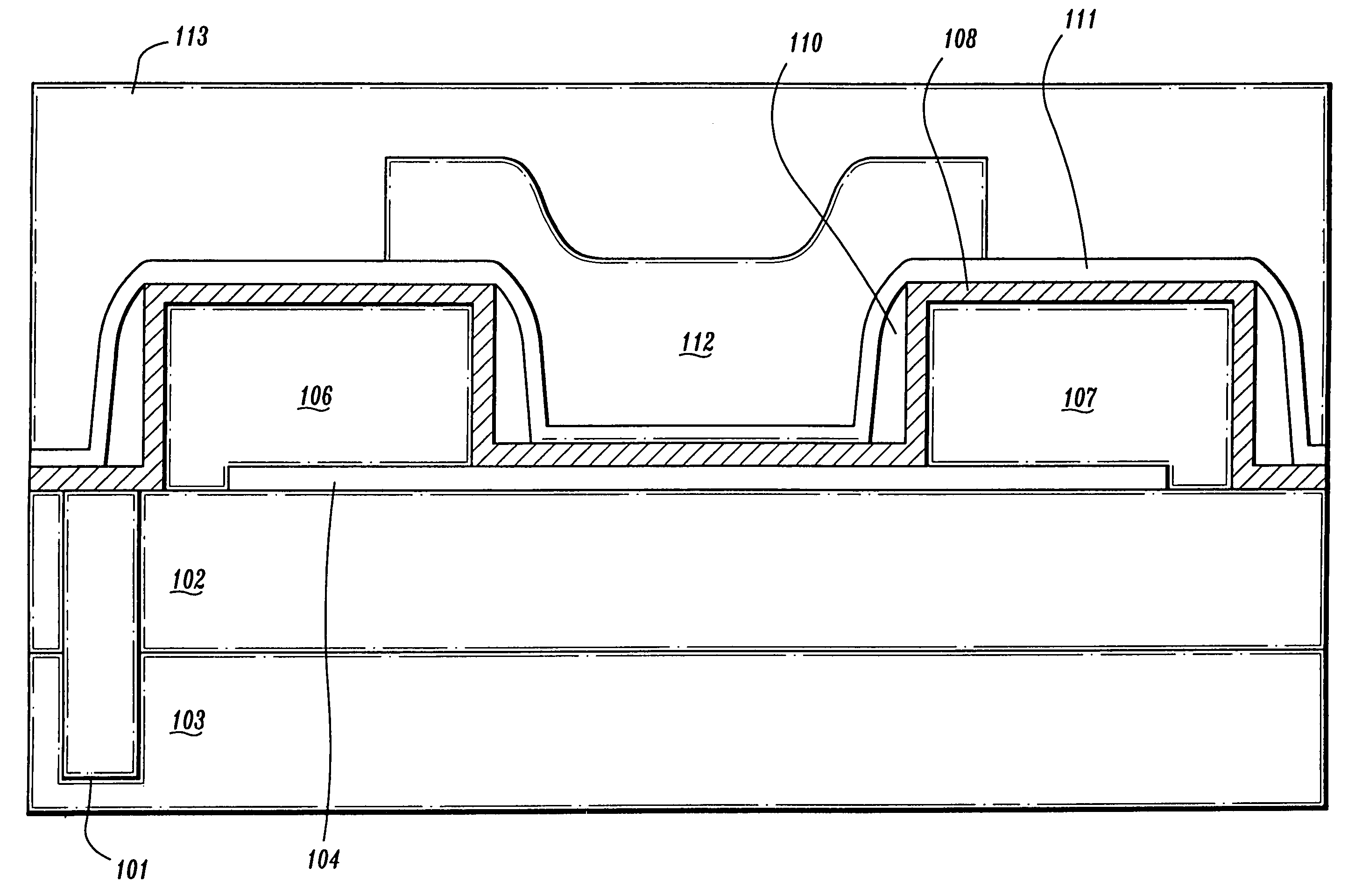
A method and structure for an integrated circuit comprising a first transistor and an embedded carbon nanotube field effect transistor (CNT FET) proximate to the first transistor, wherein the CNT FET is dimensioned smaller than the first transistor. The CNT FET is adapted to sense signals from the first transistor, wherein the signals comprise any of temperature, voltage, current, electric field, and magnetic field signals. Moreover, the CNT FET is adapted to measure stress and strain in the integrated circuit, wherein the stress and strain comprise any of mechanical and thermal stress and strain. Additionally, the CNT FET is adapted to detect defective circuits within the integrated circuit.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method of fabricating a tunneling nanotube field effect transistor
A method of fabricating a tunneling nanotube field effect transistor includes forming in a nanotube an n-doped region and a p-doped region which are separated by an undoped channel region of the transistor. Electrical contacts are provided for the doped regions and a gate electrode that is formed upon a gate dielectric layer deposited on at least a portion of the channel region of the transistor.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
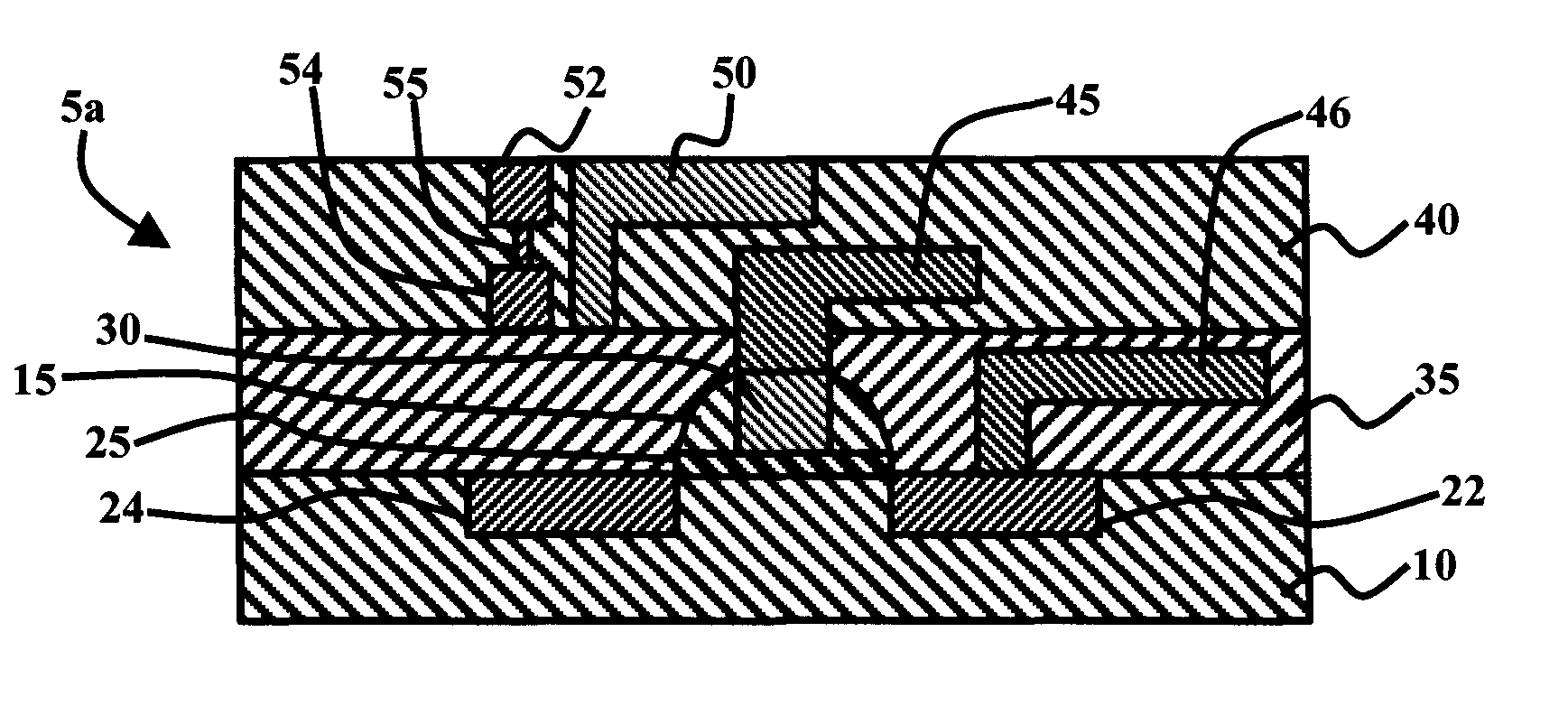
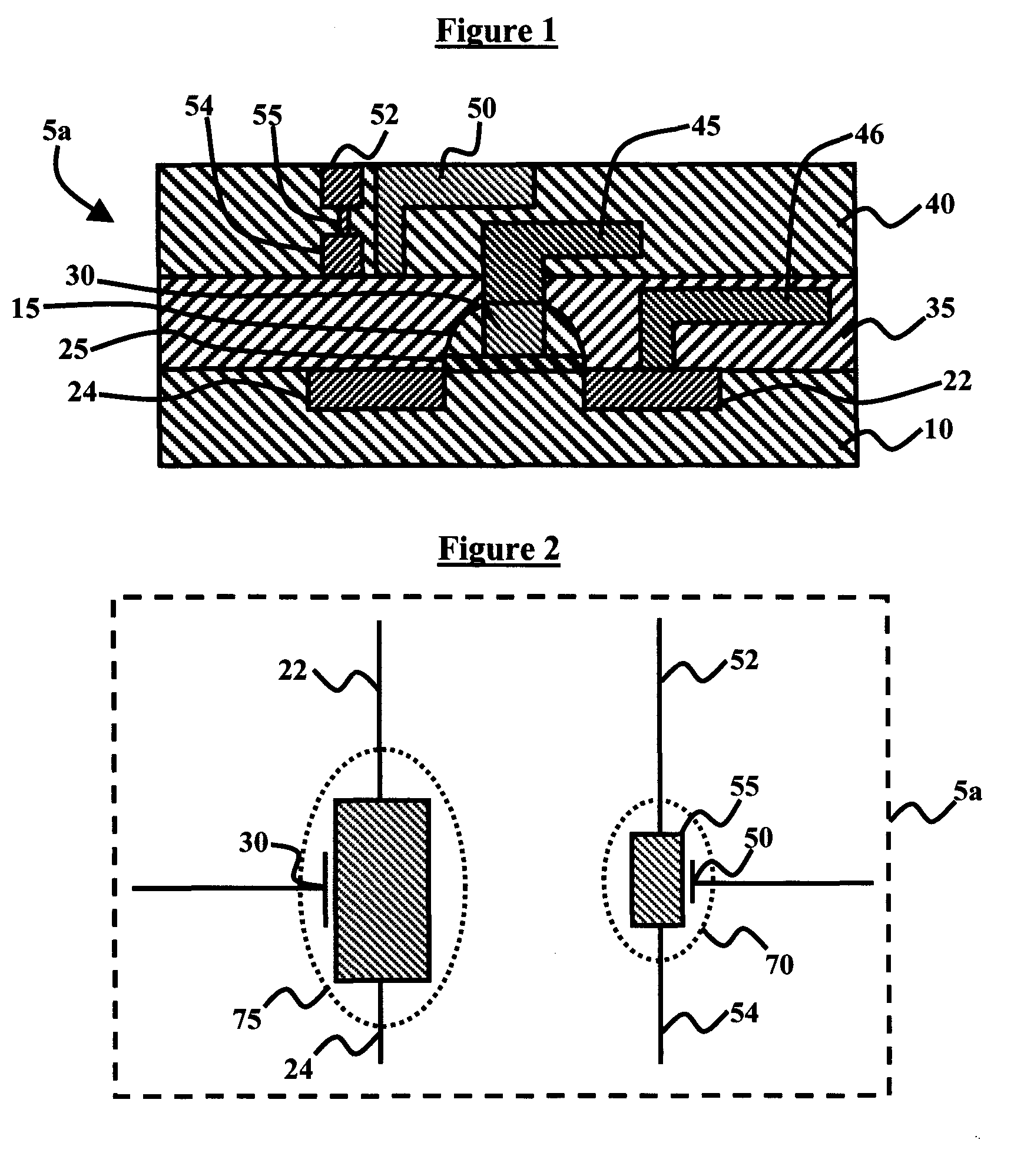
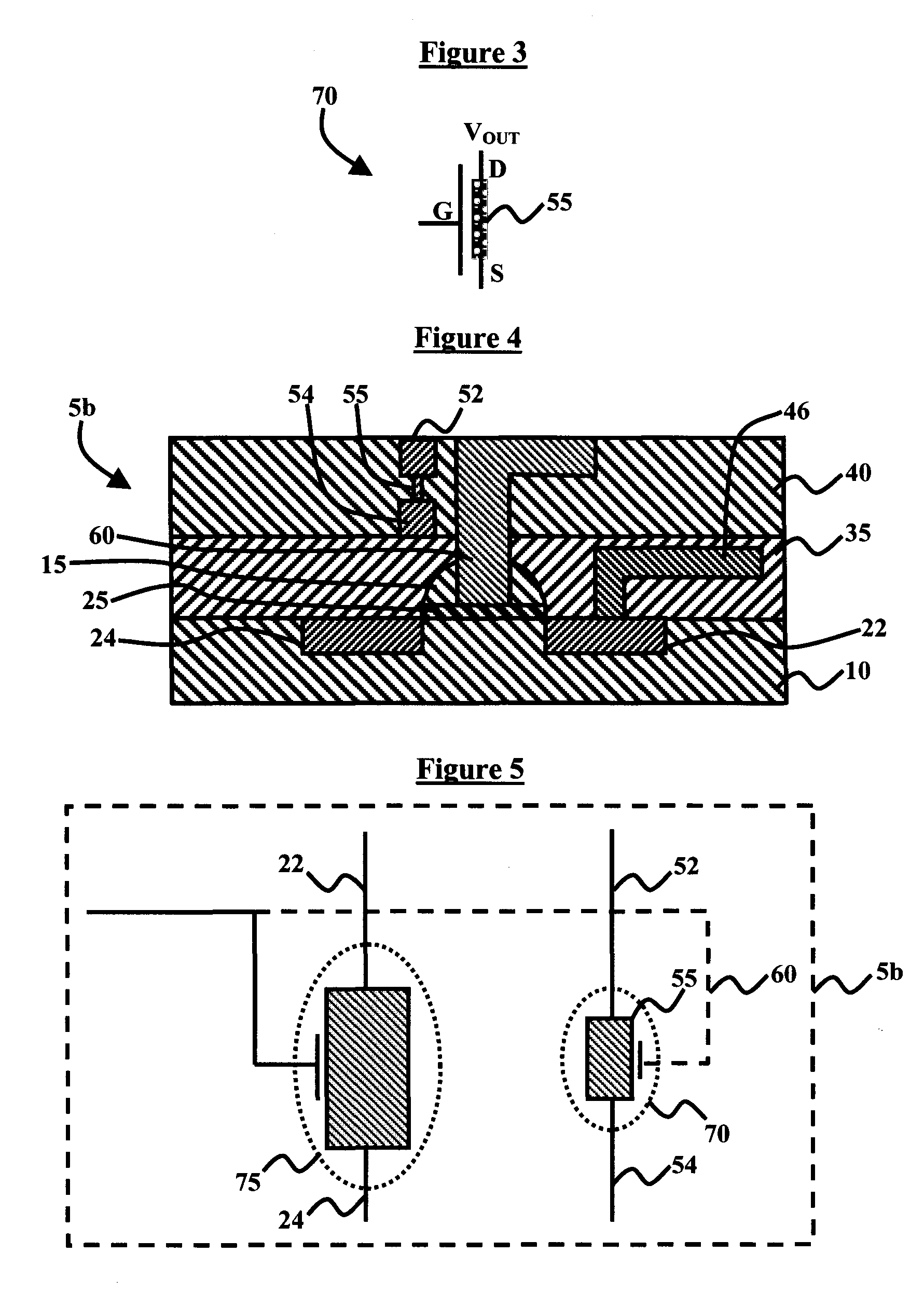
Carbon field effect transistors having charged monolayers to reduce parasitic resistance
ActiveUS8471249B2Reduce parasitic resistanceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesOrganic field-effect transistorGraphene
Carbon transistor devices having channels formed from carbon nanostructures, such as carbon nanotubes or graphene, and having charged monolayers to reduce parasitic resistance in un-gated regions of the channels, and methods for fabricating carbon transistor devices having charged monolayers to reduce parasitic resistance. For example, a carbon field effect transistor includes a channel comprising a carbon nanostructure formed on an insulating layer, a gate structure formed on the channel, a monolayer of DNA conformally covering the gate structure and a portion of the channel adjacent the gate structure, an insulating spacer conformally formed on the monolayer of DNA, and source and drain contacts connected by the channel.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
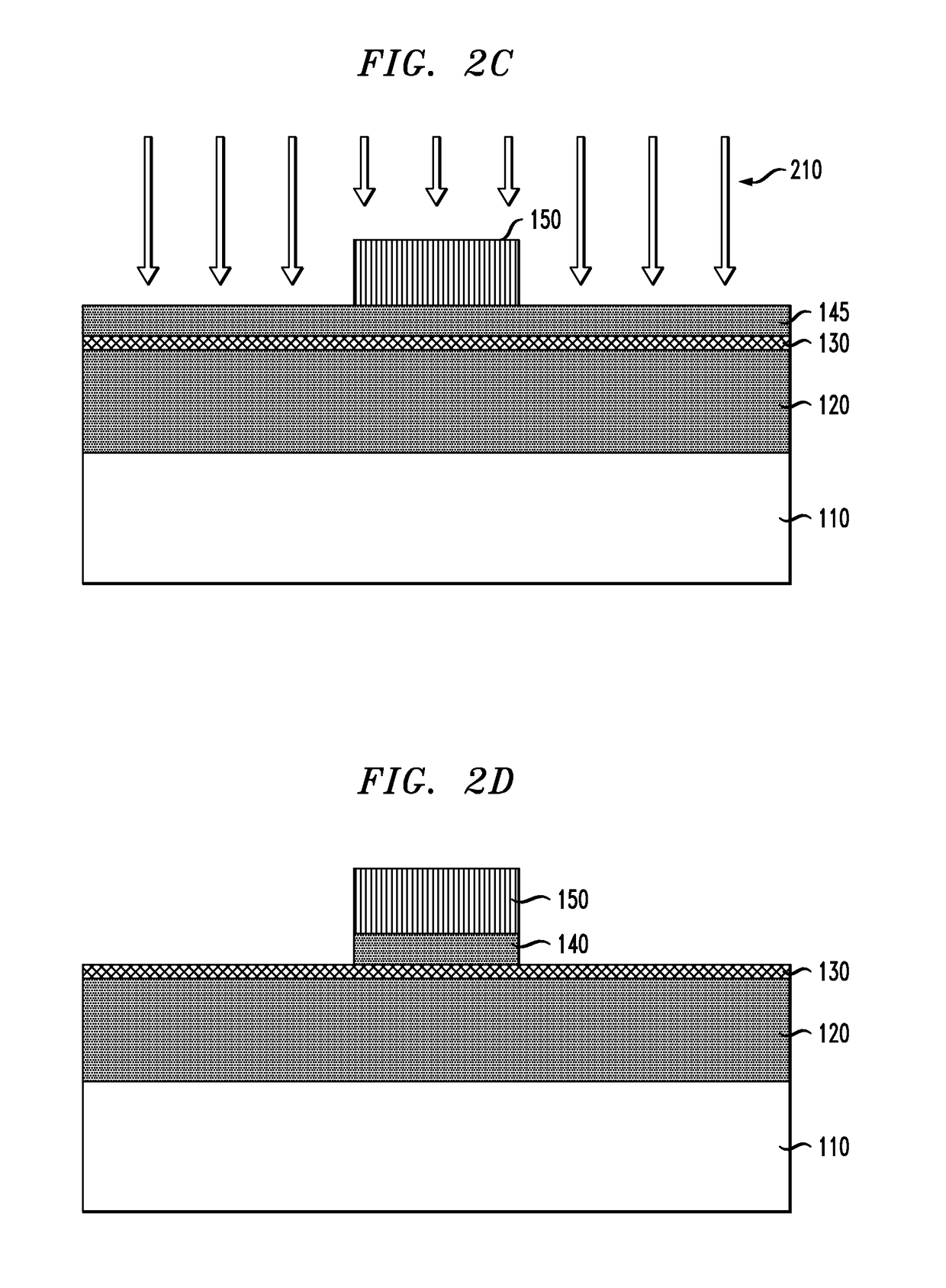
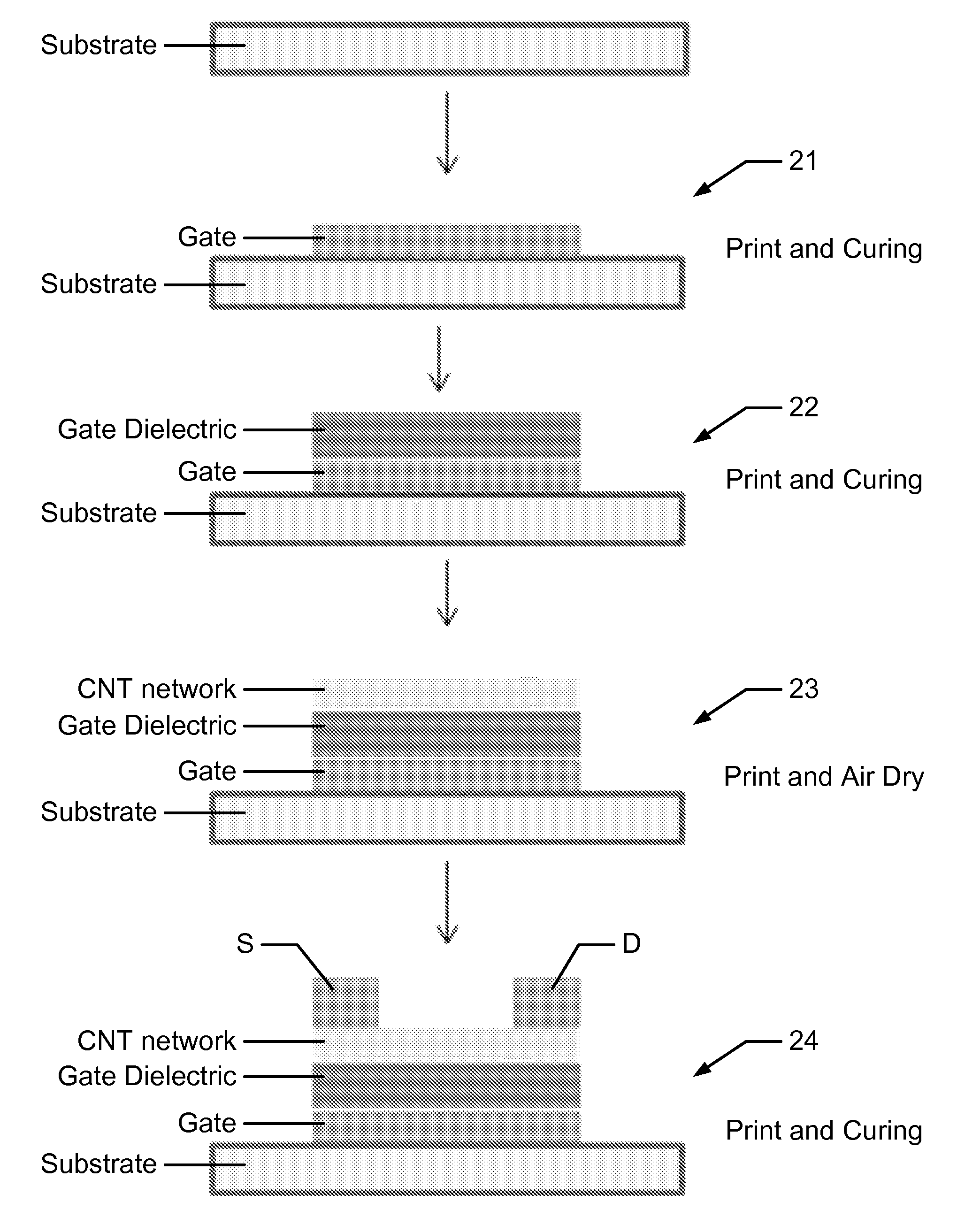
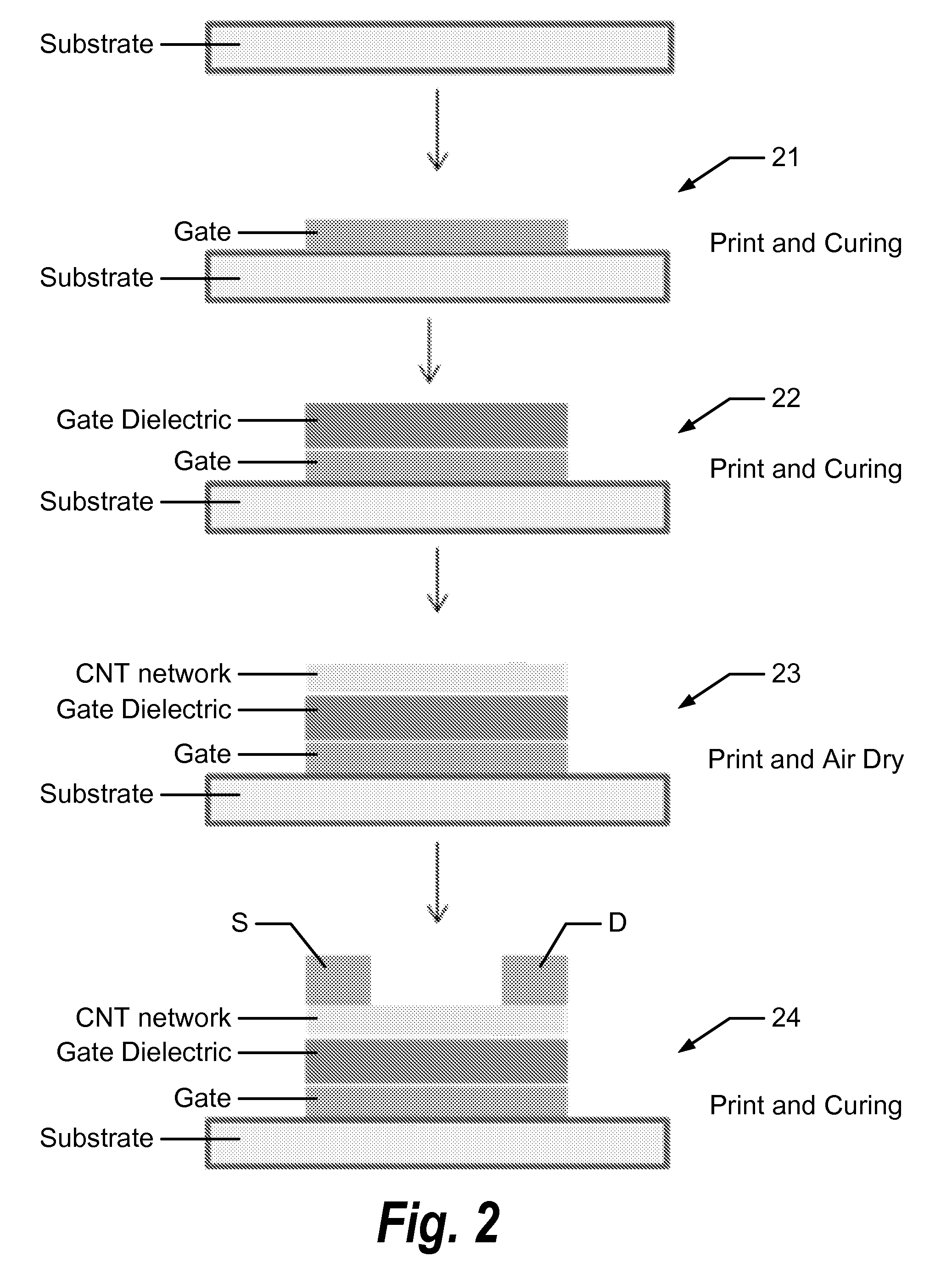
Carbon nanotube field effect transistor for printed flexible/rigid electronics
InactiveUS20110248243A1Eliminate needImprove throughputNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesUV curingIsolation layer
Methods and devices for manufacturing carbon nanotube based field effect transistors are disclosed including providing a substrate; printing a gate electrode layer onto the substrate and sintering and / or UV curing; printing a gate isolation layer onto the gate electrode and air drying and / or UV curing; printing one or more carbon nanotube channel layers onto the gate isolation layer, wherein each carbon nanotube channel layer is air dried prior to subsequent printings; and printing a source and drain electrode layer onto the one or more carbon nanotube channel layers and sintering and / or UV curing. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Integrated carbon nanotube sensors
InactiveUS20060038167A1Improve quality resolutionNegatively impactTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCarbon nanotubeEngineering
A method and structure for an integrated circuit comprising a first transistor and an embedded carbon nanotube field effect transistor (CNT FET) proximate to the first transistor, wherein the CNT FET is dimensioned smaller than the first transistor. The CNT FET is adapted to sense signals from the first transistor, wherein the signals comprise any of temperature, voltage, current, electric field, and magnetic field signals. Moreover, the CNT FET is adapted to measure stress and strain in the integrated circuit, wherein the stress and strain comprise any of mechanical and thermal stress and strain. Additionally, the CNT FET is adapted to detect defective circuits within the integrated circuit.
Owner:IBM CORP
Vertical carbon nanotube-field effect transistor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7132714B2Easy to makeImprove controllabilityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesOrganic field-effect transistorCarbon nanotube field-effect transistor
Provided are a vertical carbon nanotube field effect transistor (CNTFET) and a method of manufacturing the same. The method includes: forming a first electrode on a substrate; forming a stack of multiple layers (“multi-layer stack”) on the first electrode, the multiple layers including first and second buried layers and a sacrificial layer interposed between the first and second buried layers; forming a vertical well into the multi-layer stack; growing a CNT within the well; forming a second electrode connected to the CNT on the multi-layer stack into which the well has been formed; forming a protective layer on the second electrode; removing the sacrificial layer and exposing the CNT between the first and second buried layers; forming a gate insulating layer on the exposed surface of the CNT; and forming a gate enclosing the CNT on the gate insulating layer. The CNTFET and manufacturing method maximize the effect of electric field produced by the gate due to the channel completely enclosed by the gate while improving a ratio Ion / Ioff of on-current to off-current by fully depleting a depletion layer formed in the channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Carbon nanotube field effect transistor and method of making thereof
InactiveUS20080135892A1Simplified method of fabricatingNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCarbon nanotubeEngineering
This invention relates to field effect transistors having carbon nanotube contacts and to a method of making these field effect transistors. The field effect transistors have better contacts as the source and drains as well as the bridge are made of carbon nanotubes. The fabrication of the proposed embodiment becomes possible by using a fabrication process which involves exposing the structure to two different temperatures.
Owner:FINNIE PAUL
Logic Elements Comprising Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor (CNTFET) Devices and Methods of Making Same
ActiveUS20130181189A1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionNanoinformaticsEngineeringCarbon nanotube field-effect transistor
Inverter circuits and NAND circuits comprising nanotube based FETs and methods of making the same are described. Such circuits can be fabricating using field effect transistors comprising a source, a drain, a channel region, and a gate, wherein the first channel region includes a fabric of semiconducting nanotubes of a given conductivity type. Such FETs can be arranged to provide inverter circuits in either two-dimension or three-dimensional (stacked) layouts. Design equations based upon consideration of the electrical characteristics of the nanotubes are described which permit optimization of circuit design layout based upon constants that are indicative of the current carrying capacity of the nanotube fabrics of different FETs.
Owner:NANTERO
N-type carbon nanotube field effect transistor and method of fabricating the same
Provided are an n-type carbon nanotube field effect transistor (CNT FET) and a method of fabricating the n-type CNT FET. The n-type CNT FET may include a substrate; electrodes formed on the substrate and separated from each other; a CNT forrmed on the substrate and electrically connected to the electrodes; a gate oxide layer formed on the CNT; and a gate electrode formed on the gate oxide layer, wherein the gate oxide layer contains electron donor atoms which donate electrons to the CNT such that the CNT may be n-doped by the electron donor atoms.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of fabricating carbon nanotube field-effect transistors through controlled electrochemical modification
InactiveUS20060024871A1Poses problemImprove the immunityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCompound (substance)Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor
The invention relates to a method of fabricating a structure with field effect transistors, said transistors each comprising a source electrode, a drain electrode, a channel extending between the source and drain electrodes and at least one gate electrode associated with the channel for controlling the conductance of the channel, wherein the channel comprises one or more semiconducting single-wall carbon nanotubes. The method includes the steps of a) depositing a plurality of single-wall carbon nanotubes on a substrate, said carbon nanotubes comprising a mixture of metallic carbon nanotubes and semiconducting carbon nanotubes, b) providing before or after step a) source and drain electrodes on the substrate so that one or more carbon nanotubes extend between the source and drain electrodes, c) applying a variable gate voltage to switch off the semiconducting tubes extending between the source and drain electrodes, d) wetting the surface of the structure including the transistors with a chemical to achieve a chemical bond between a radical supplied by said chemical and some carbon atoms of the metallic nanotubes, whereby these metallic nanotubes become non-conductive.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Self-aligned nanotube field effect transistor and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS7253065B2NanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesEngineeringCarbon nanotube field-effect transistor
A self-aligned carbon-nanotube field effect transistor semiconductor device comprises a carbon-nanotube deposited on a substrate, a source and a drain formed at a first end and a second end of the carbon-nanotube, respectively, and a gate formed substantially over a portion of the carbon-nanotube, separated from the carbon-nanotube by a dielectric film.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
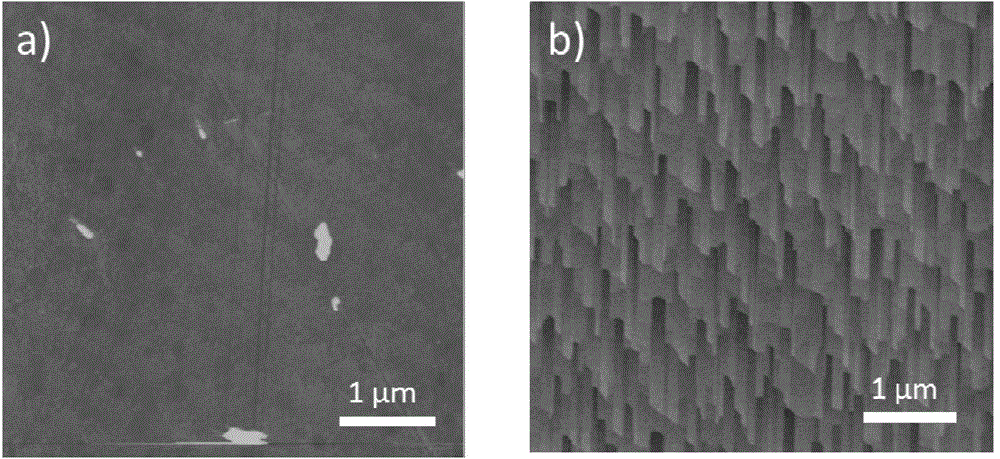
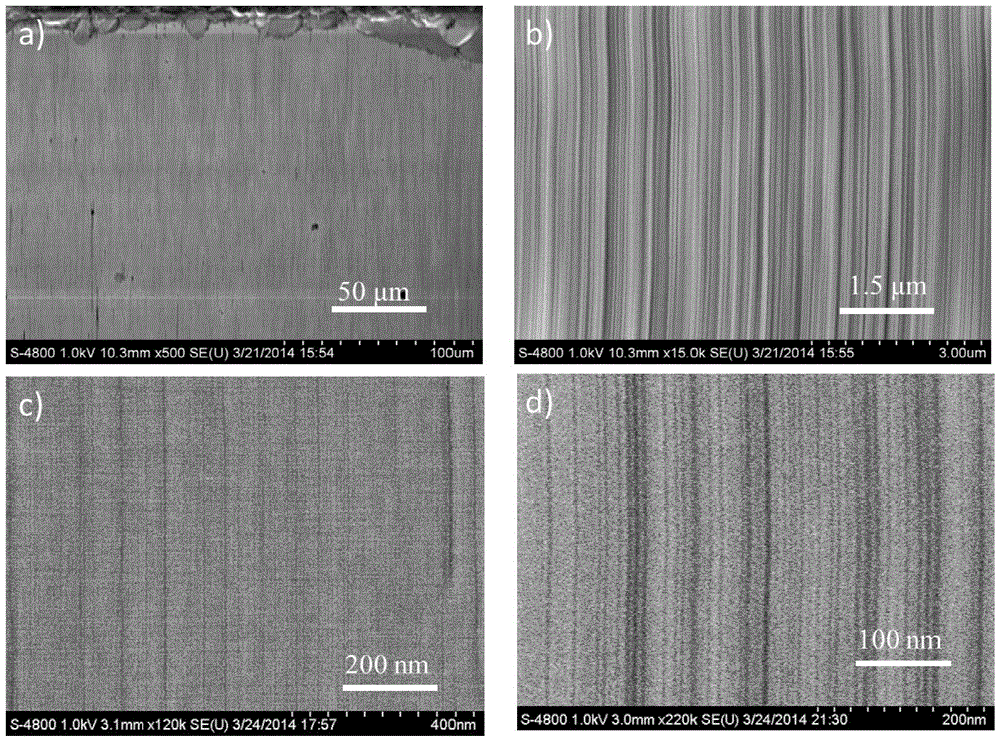
Ultra-high-density single-walled carbon nanotube horizontal array and controllable preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105565292AAchieving controllable equipmentSimple sample preparationMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystalVolumetric Mass Density
The invention discloses an ultra-high-density single-walled carbon nanotube horizontal array and a controllable preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: loading a catalyst on a single crystal growth substrate, annealing, introducing hydrogen in a chemical vapor deposition system, carrying out reduction reaction of the catalyst, maintaining introduction of hydrogen, and performing orientated growth of single-walled carbon nanotubes, thereby obtaining the horizontal array. The ultra-high-density single-walled carbon nanotube horizontal array prepared by the method has the density exceeding 130 nanotubes per micron and a single-walled carbon nanotube horizontal array with the highest direct growth density reported in the world at present. According to the test of electrical properties of the ultra-high-density single-walled carbon nanotube horizontal array prepared by the method, the horizontal array has the drain current density of 380 [mu]A / [mu]m and has the transconductance of 102.5 [mu]S / [mu]m, which are the highest level in carbon nanotube field effect transistors in the world at present.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Self-aligned T-gate carbon nanotube field effect transistor devices and method for forming the same
InactiveCN101897009AImprove performanceImprove featuresNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceCarbon nanotube
A method is provided for forming a self-aligned carbon nanotube (CNT) field effect transistor (FET). According to one feature, a self-aligned source-gate-drain (S-G-D) structure is formed that allows for the shrinking of the gate length to arbitrarily small values, thereby enabling ultra-high performance CNT FETs. In accordance with another feature, an improved design of the gate to possess a ''T''-shape, referred to as the ''T-Gate,'' thereby enabling a reduction in gate resistance and further providing an increased power gain. The self-aligned T-gate CNT FET is formed using simple fabrication steps to ensure a low cost, high yield process.
Owner:RF NANO
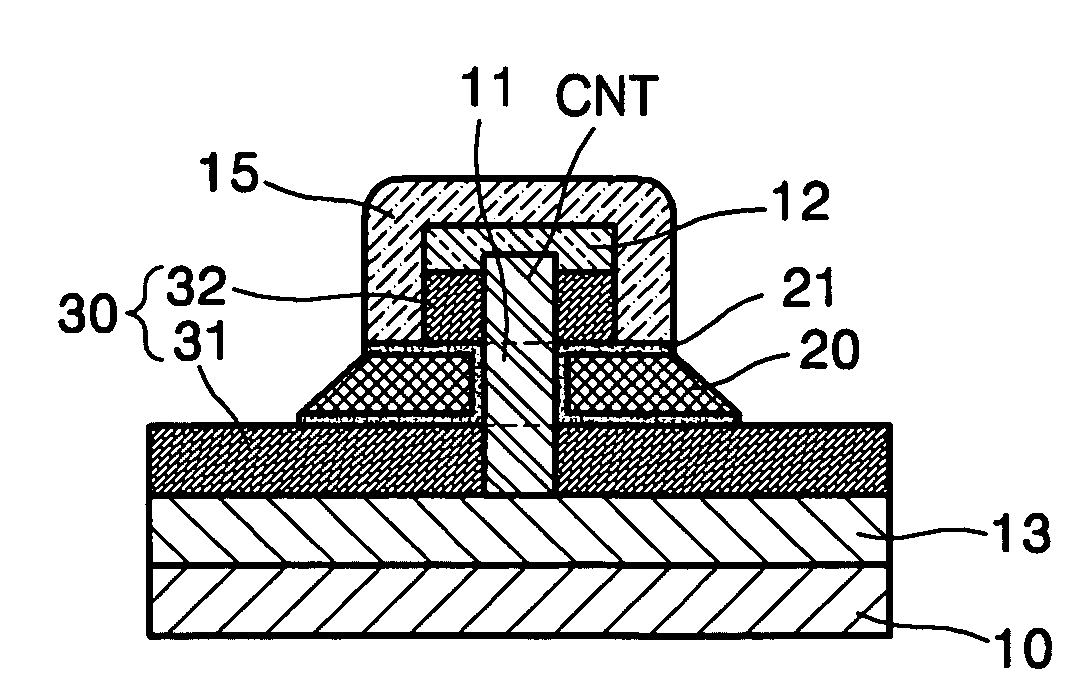
Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor with sidewall-protected metal contacts
InactiveUS9577204B1Prevent degradationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistGate dielectric
A field effect transistor includes a substrate and a gate dielectric formed on the substrate. A channel material is formed on the dielectric layer. The channel material includes carbon nanotubes. A patterned resist layer has openings formed therein. Metal contacts are formed on the channel material in the openings in the patterned resist layer and over portions of the patterned resist layer to protect sidewalls of the metal contacts to prevent degradation of the metal contacts.
Owner:IBM CORP
Biosensor and system and process for forming
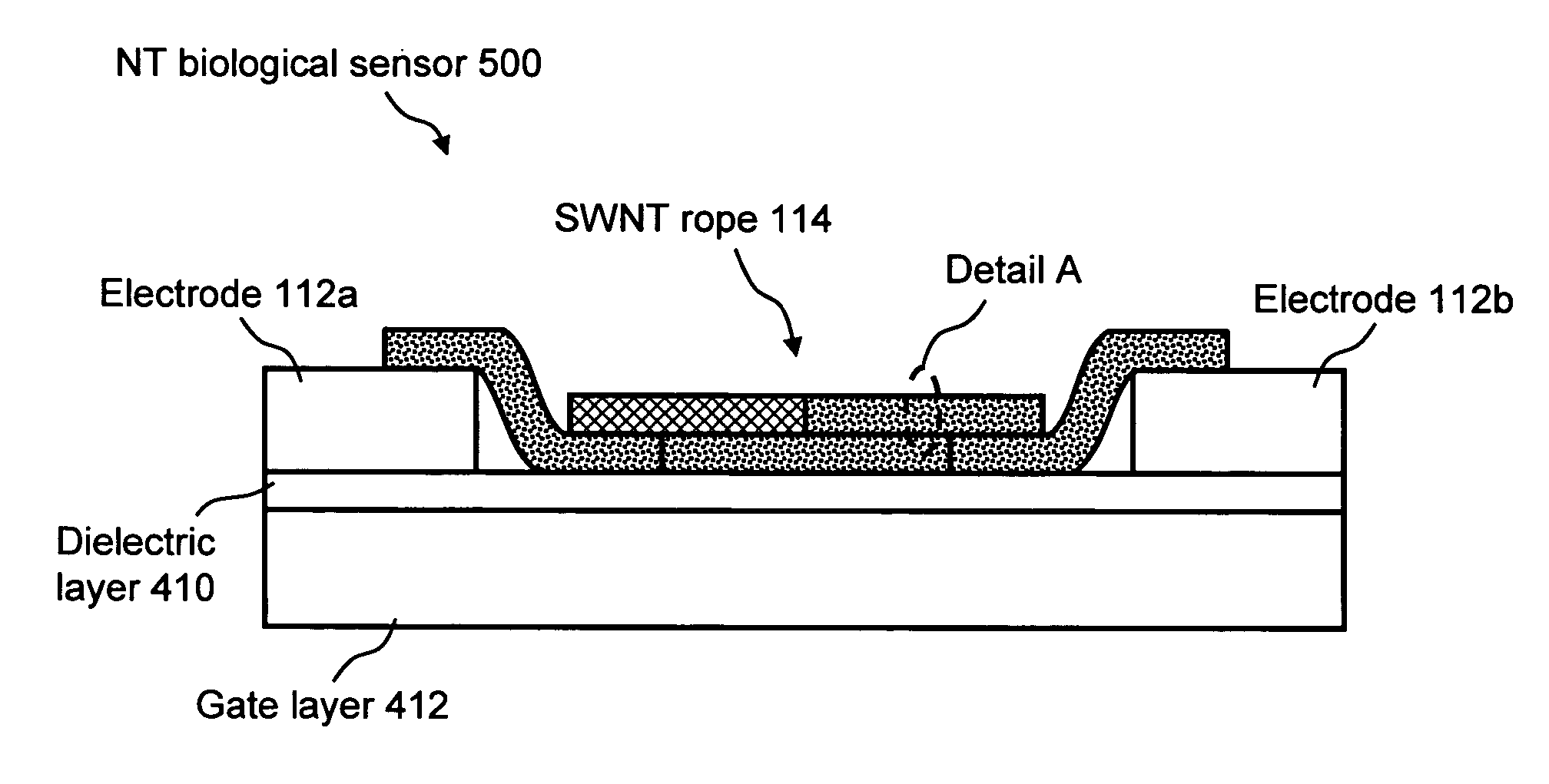
ActiveUS8895340B1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityCarbon nanotube
A process for forming a carbon nanotube field effect transistor (CNTFET) device includes site-specific nanoparticle deposition on a CNTFET that has one or more carbon nanotubes, a source electrode, a drain electrode, and a sacrificial electrode on a substrate with an interposed dielectric layer. The process includes control of PMMA removal and electrodeposition in order to select nanoparticle size and deposition location down to singular nanoparticle deposition. The CNTFET device resulting in ultra-sensitivity for various bio-sensing applications, including detection of glucose at hypoglycemic levels.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Carbon nanotube-based electronic devices made by electrolytic deposition and applications thereof
InactiveUS20070224804A1Efficient and cost-effectiveNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesDevice formMulti dimensional
Carbon nanotube-based devices made by electrolytic deposition and applications thereof are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention provides a device comprising at least one array of active carbon nanotube junctions deposited on at least one microelectronic substrate. In another preferred embodiment, the present invention provides a device comprising a substrate, at least one pair of electrodes disposed on the substrate, wherein one or more pairs of electrodes are connected to a power source, and a bundle of carbon nanotubes disposed between the at least one pair of electrodes wherein the bundle of carbon nanotubes consist essentially of semiconductive carbon nanotubes. In another preferred embodiment, a semiconducting device formed by electrodeposition of carbon nanotubes between two electrodes is provided. The invention also provides preferred methods of forming a semiconductive device by applying a bias voltage to a carbon nanotube rope. The plurality of metallic single-wall carbon nanotubes are removed (e.g., by application of bias voltage) in an amount sufficient to form the semiconducting device. The devices of the invention include, but not limited to, chemical or biological sensors, carbon nanotube field-effect transistors (CNFETs), tunnel junctions, Schottky junctions, and multi-dimensional nanotube arrays.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
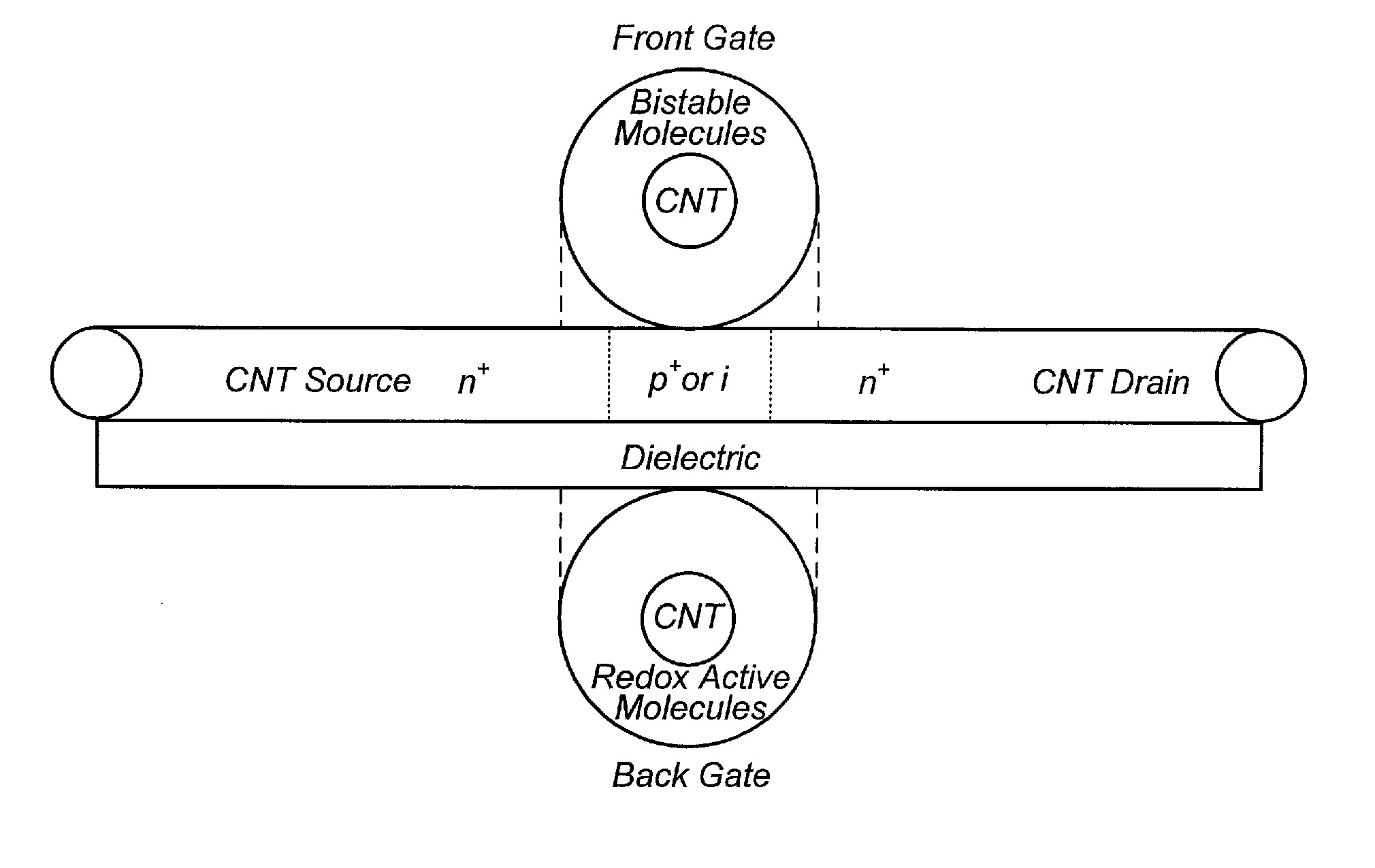
Carbon nanotube crossbar based nano-architecture
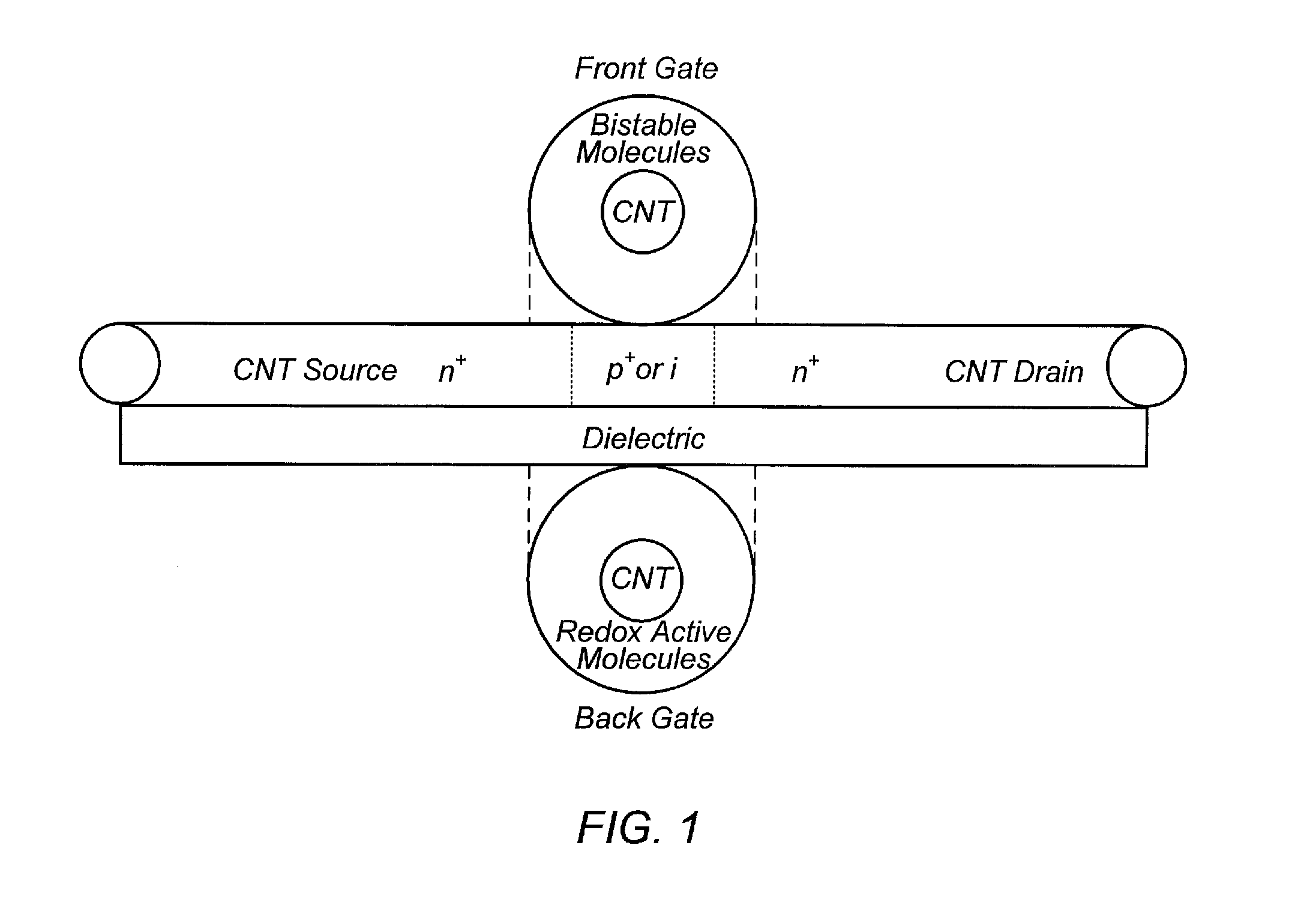
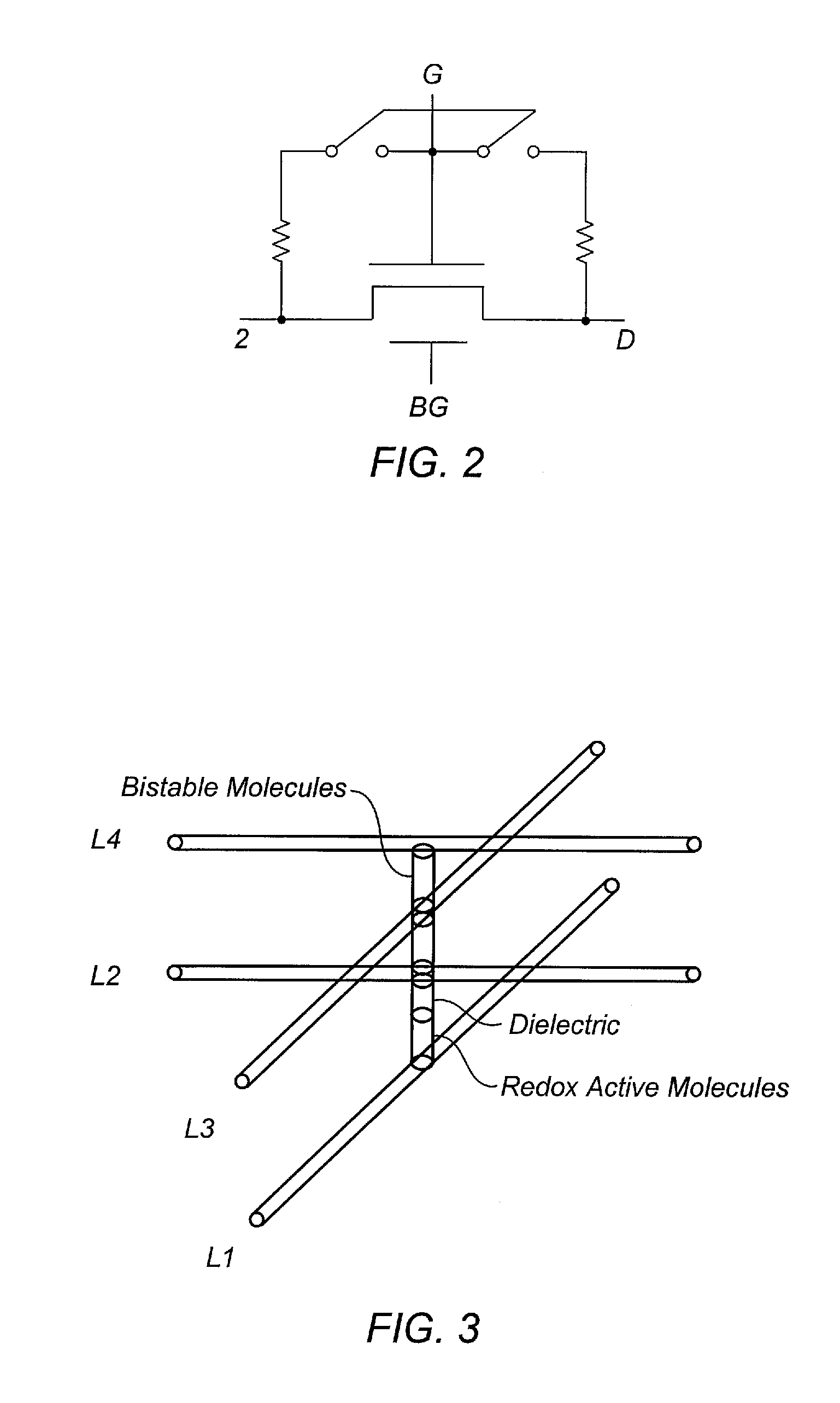
ActiveUS20130033310A1NanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCarbon nanotube field-effect transistorNanostructure
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and carbon nanotube field effect transistors (CNFETs) have demonstrated extraordinary properties and are widely accepted as the building blocks of next generation VLSI circuits. A CNT crossbar based nano-architecture, includes layers of orthogonal carbon nanotubes with electrically bistable and charge holding molecules at each crossing, forming a dense array of reconfigurable double gate carbon nanotube field effect transistors (RDG-CNFETs) and programmable interconnects, which is addressed via a voltage controlled nanotube addressing circuits on the boundaries.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
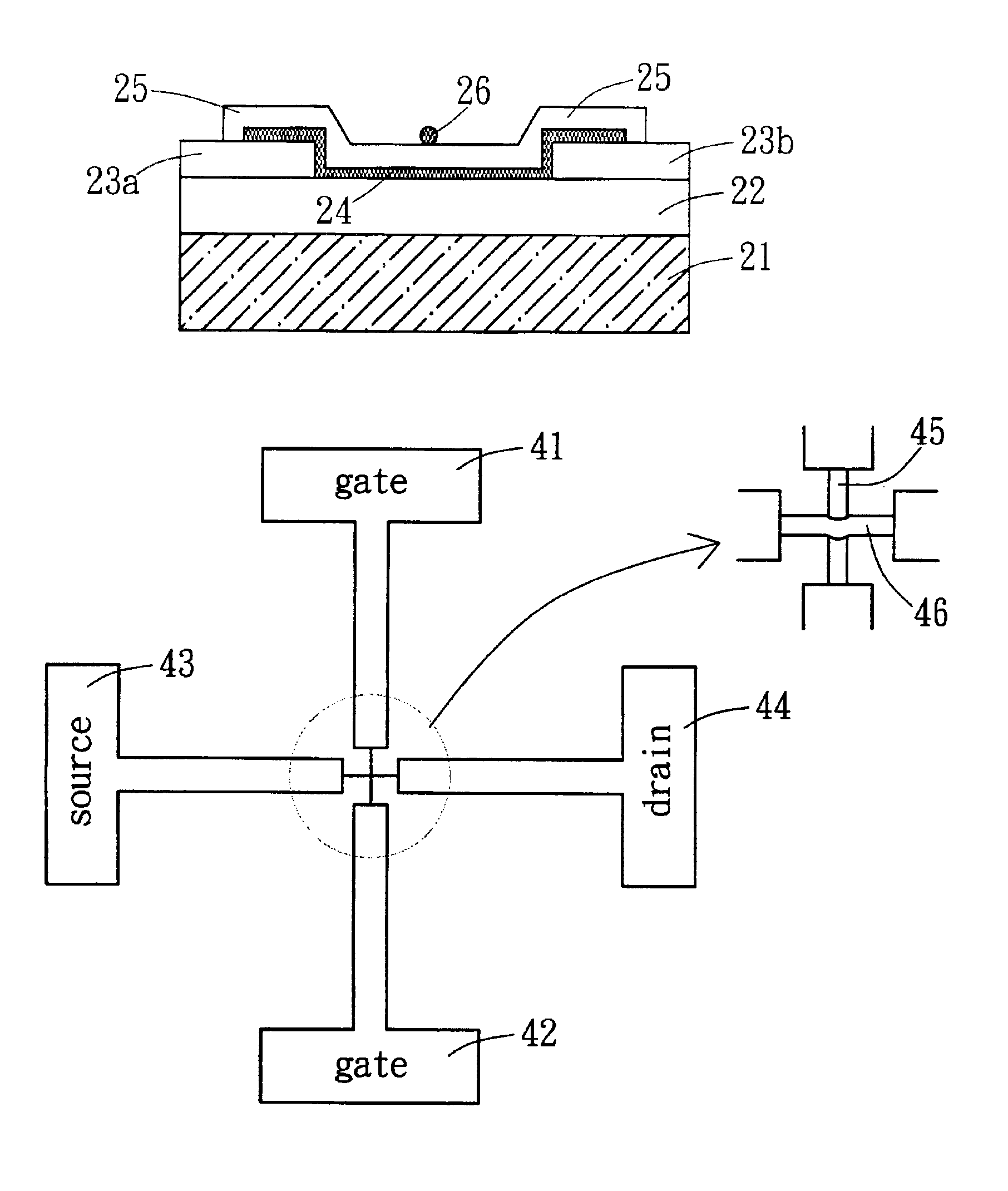
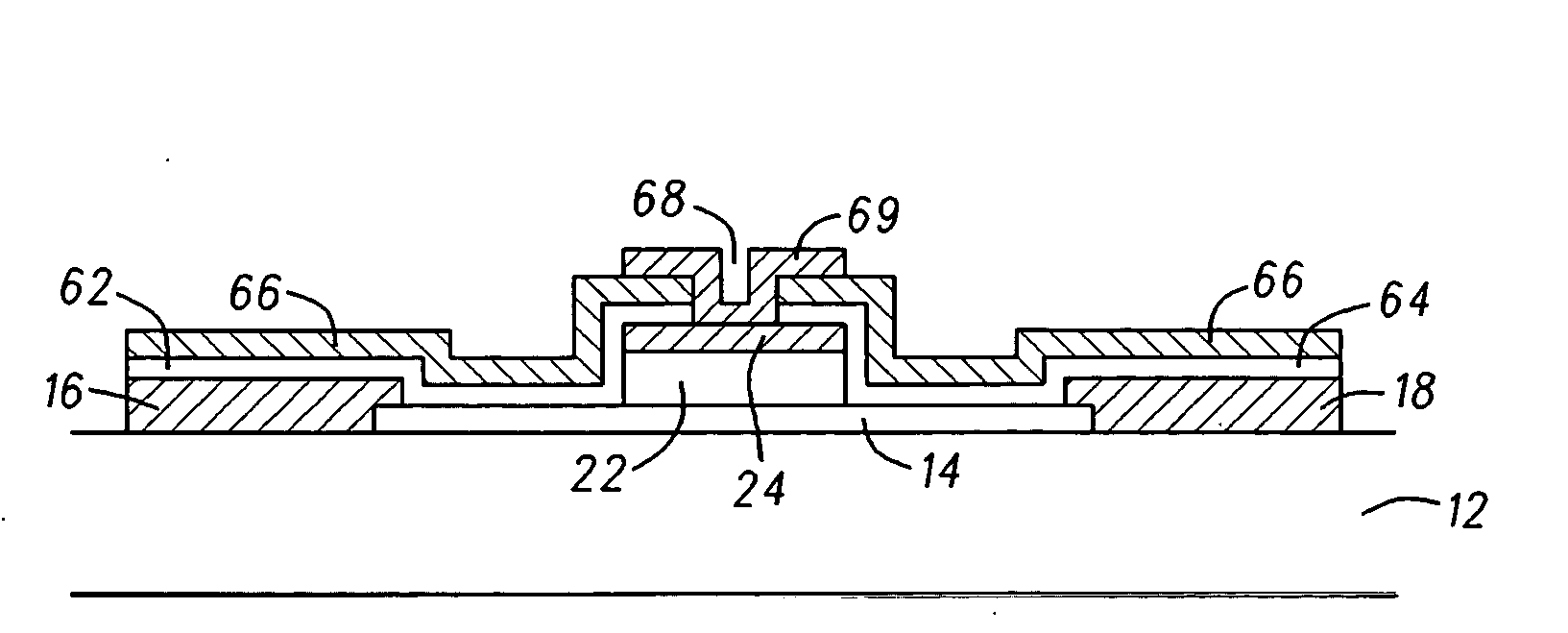
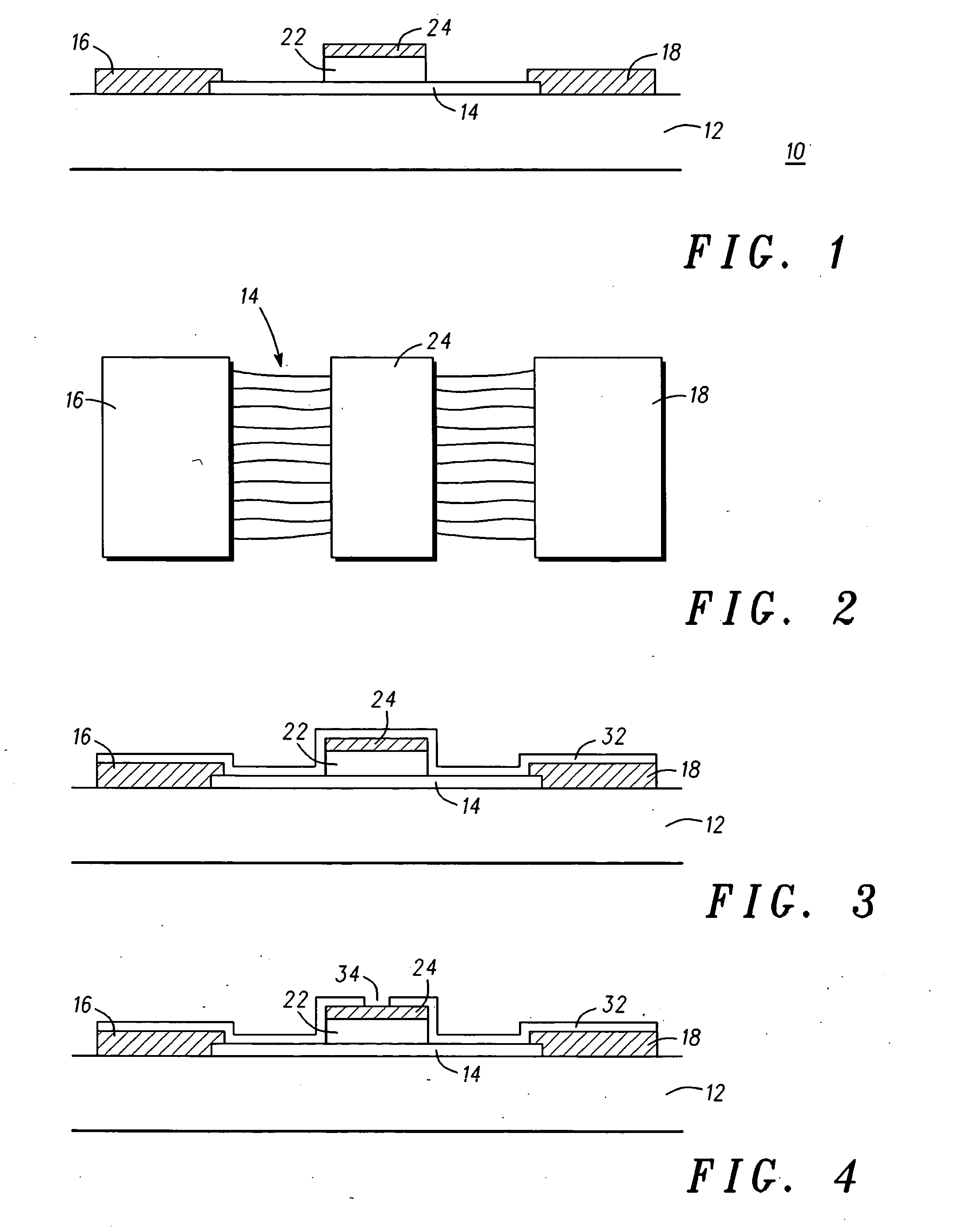
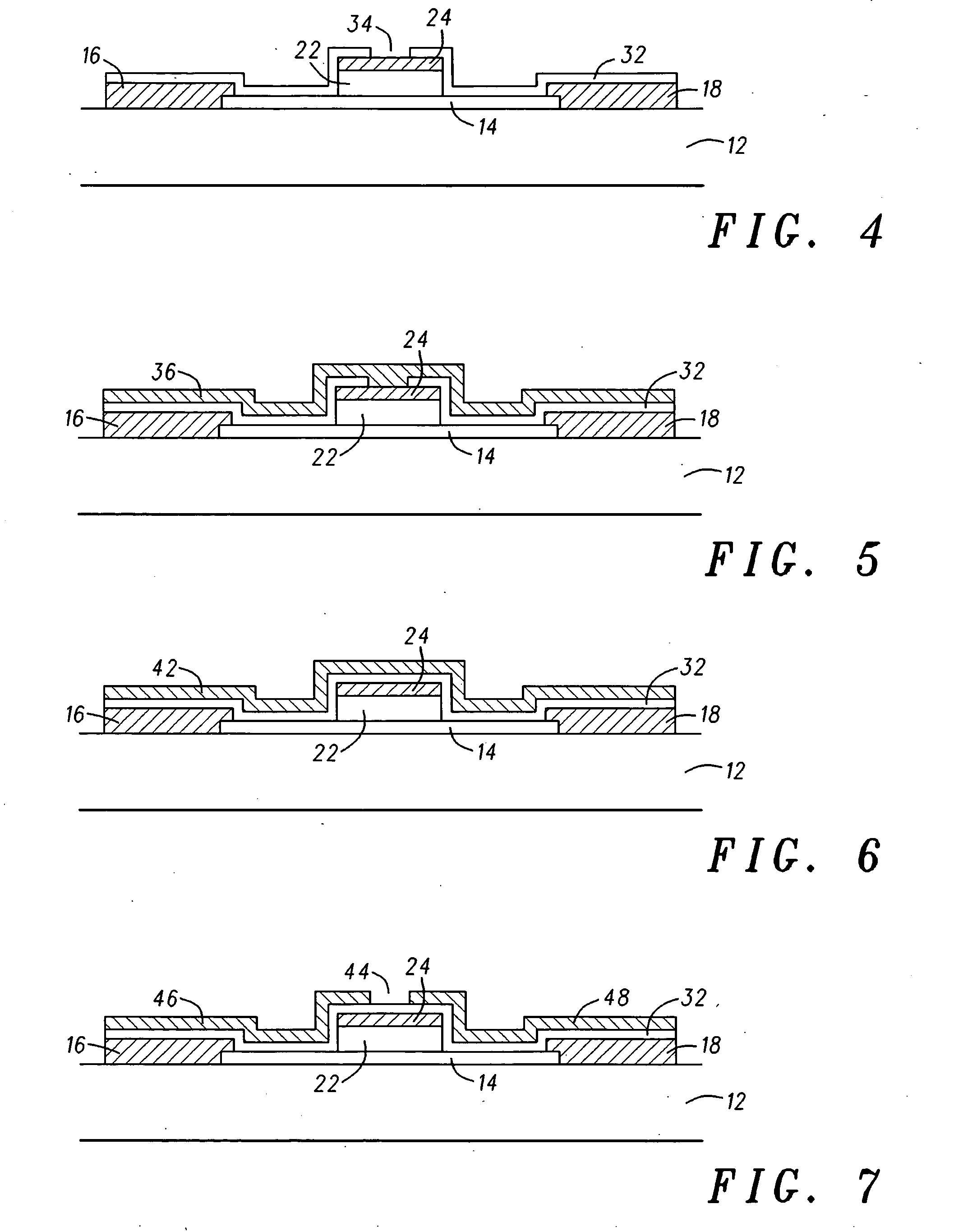
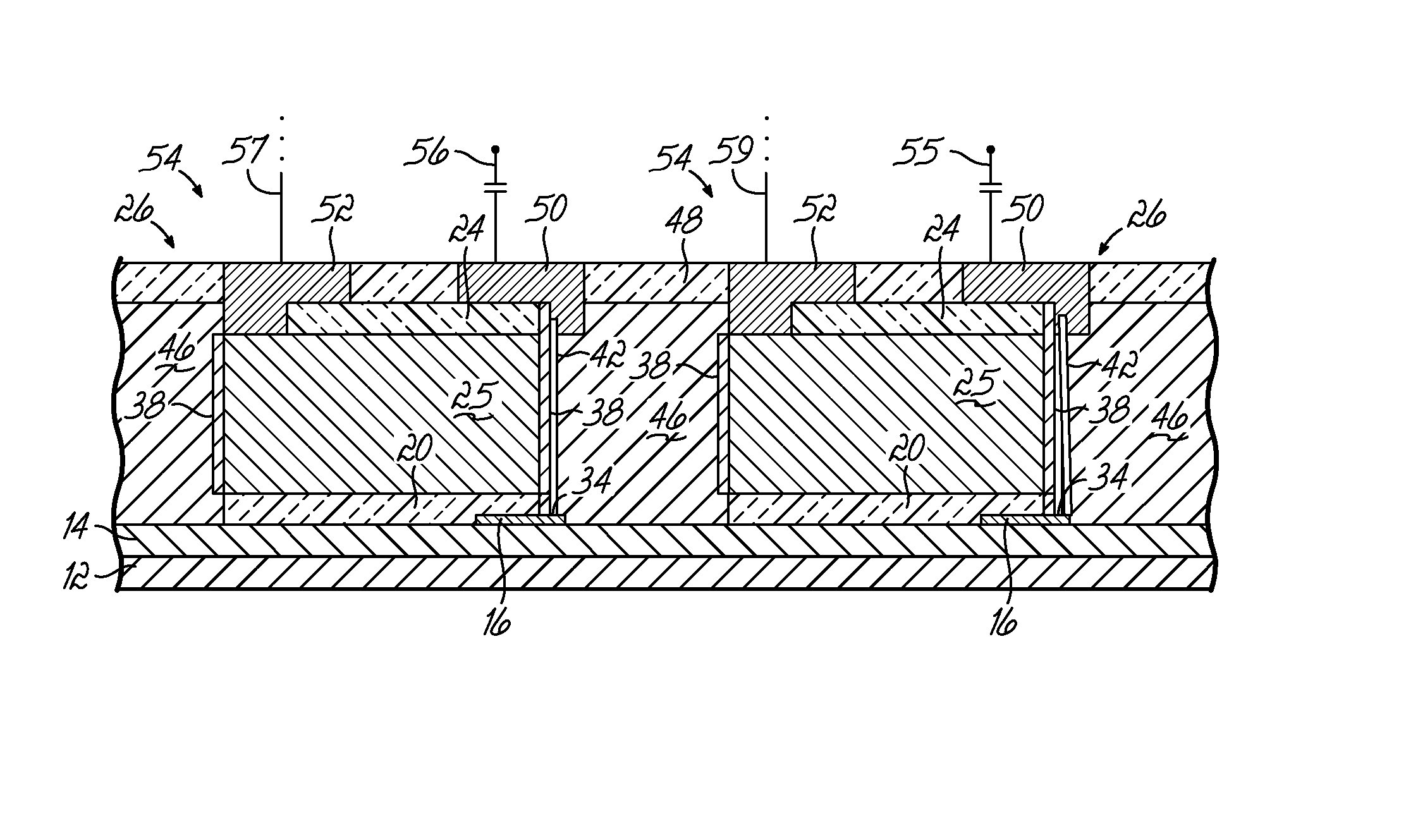
Multi-gated carbon nanotube field effect transistor
InactiveUS20080149970A1NanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCarbon nanotubeCarbon nanotube field-effect transistor
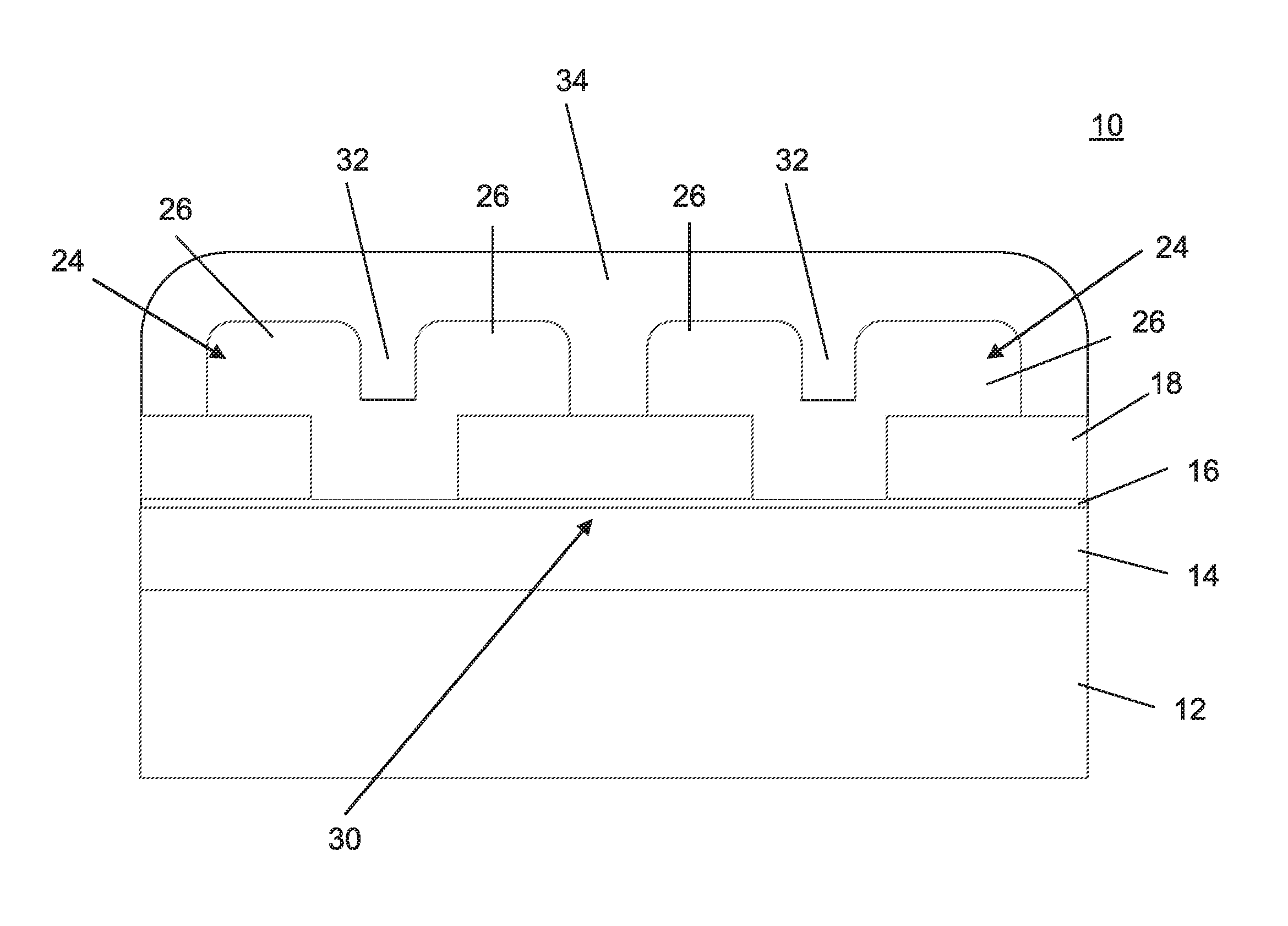
A multiple, independent top gated field effect transistor having an improved electron injection and reduced gate induced barrier lowering effects, and a method that allows for the destruction of metallic carbon nanotubes positioned between the source and drain of a top multi-gate transistor are provided. The field effect transistor comprises at least one carbon nanotube (14) coupled between the first and second electrodes (16, 18) and a first gate material (24) formed over a portion of the at least one carbon nanotube (14) and spaced apart from the first and second electrodes (16, 18). A dielectric material (32) is conformally coated on the first and second electrodes (16, 18), the at least one carbon nanotube (14), and the first gate material (24). A second gate material (36) is conformally coated on the dielectric material (32). Other exemplary embodiments include one gate (24, 36), three gates (24, 46, 48), and three gates (24, 54, 56; and 24, 66) having the dielectric layer (52, 56; and 62, 64) portioned with different material characteristics.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
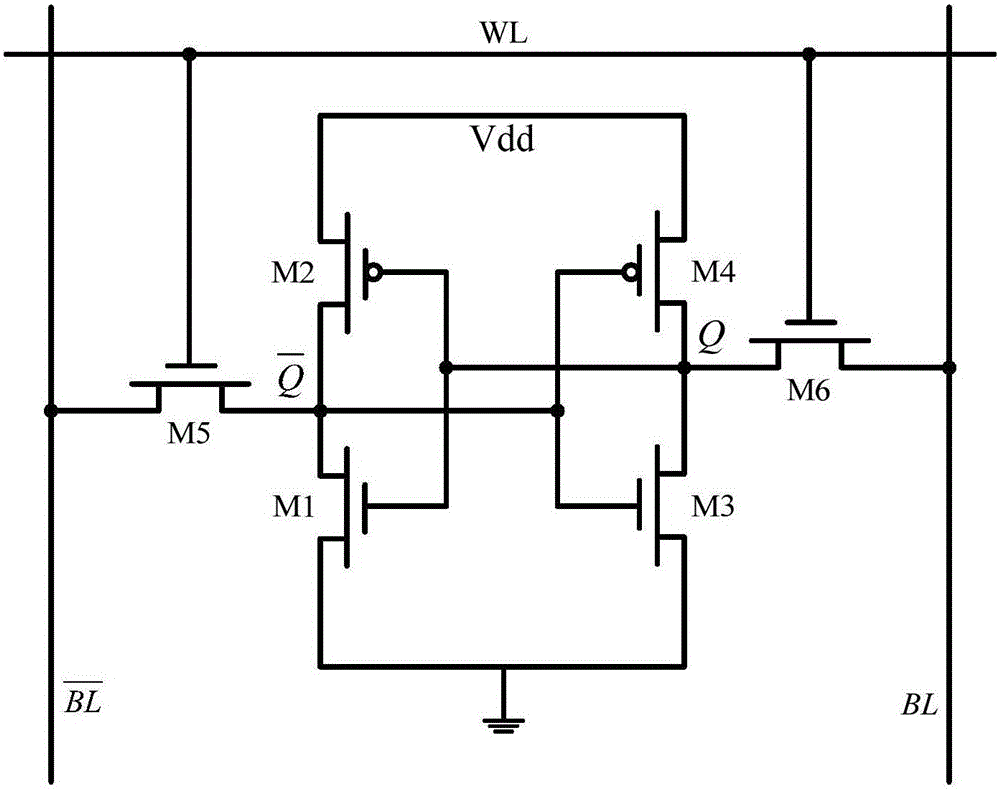
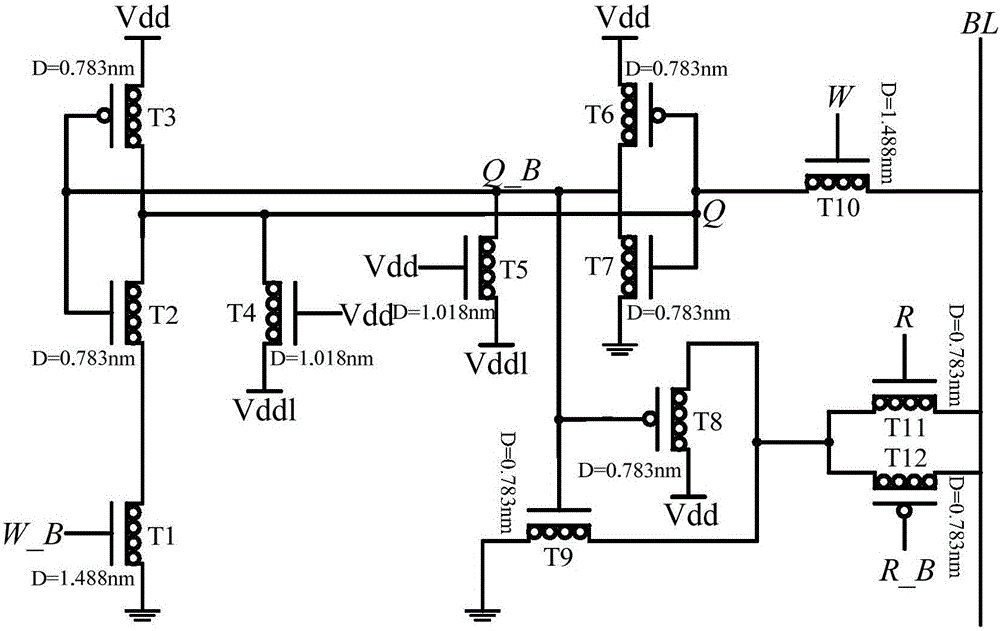
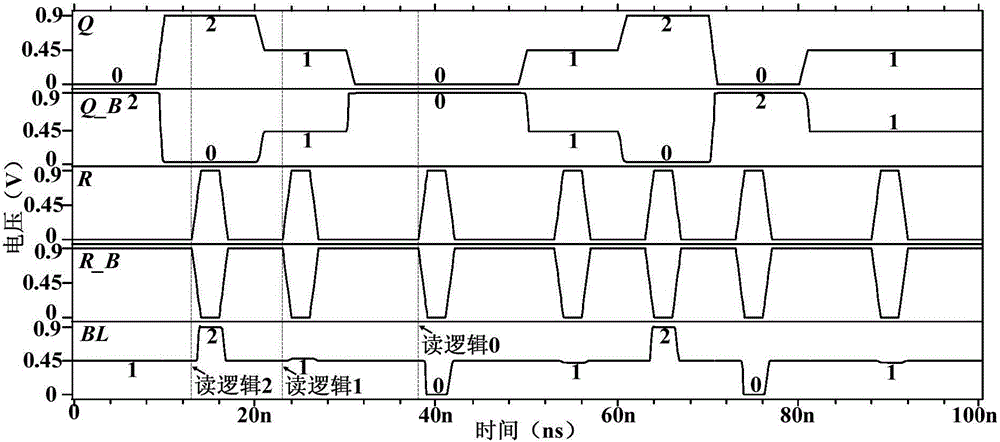
Three-valued static random access memory cell realized by utilization of carbon nanotube field effect transistor
ActiveCN106067318AWrite data fasterWork fasterDigital storageStatic random-access memoryCarbon nanotube field-effect transistor
The invention discloses a three-valued static random access memory cell realized by the utilization of a carbon nanotube field effect transistor. The three-valued static random access memory cell comprises a first CNFET tube, a second CNFET tube, a third CNFET tube, a fourth CNFET tube, a fifth CNFET tube, a sixth CNFET tube, a seventh CNFET tube, a eighth CNFET tube, a ninth CNFET tube, a tenth CNFET tube, a eleventh CNFET tube and a twelfth CNFET tube. The first CNFET tube, the second CNFET tube, the fourth CNFET tube, the fifth CNFET tube, the seventh CNFET tube, the ninth CNFET tube, the tenth CNFET tube and the eleventh CNFET tube are N-type CNFET tubes. The third CNFET tube, the sixth CNFET tube, the eighth CNFET tube and the twelfth CNFET tube are P-type CNFET tubes. The three-valued static random access memory cell has advantages of fast read-write speed, high stability of read data, small wiring area, low power consumption and large memory capacity.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
N-type carbon nanotube field effect transistor and method of fabricating the same
Provided are an n-type carbon nanotube field effect transistor (CNT FET) and a method of fabricating the n-type CNT FET. The n-type CNT FET may include a substrate; electrodes formed on the substrate and separated from each other; a CNT forrmed on the substrate and electrically connected to the electrodes; a gate oxide layer formed on the CNT; and a gate electrode formed on the gate oxide layer, wherein the gate oxide layer contains electron donor atoms which donate electrons to the CNT such that the CNT may be n-doped by the electron donor atoms.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
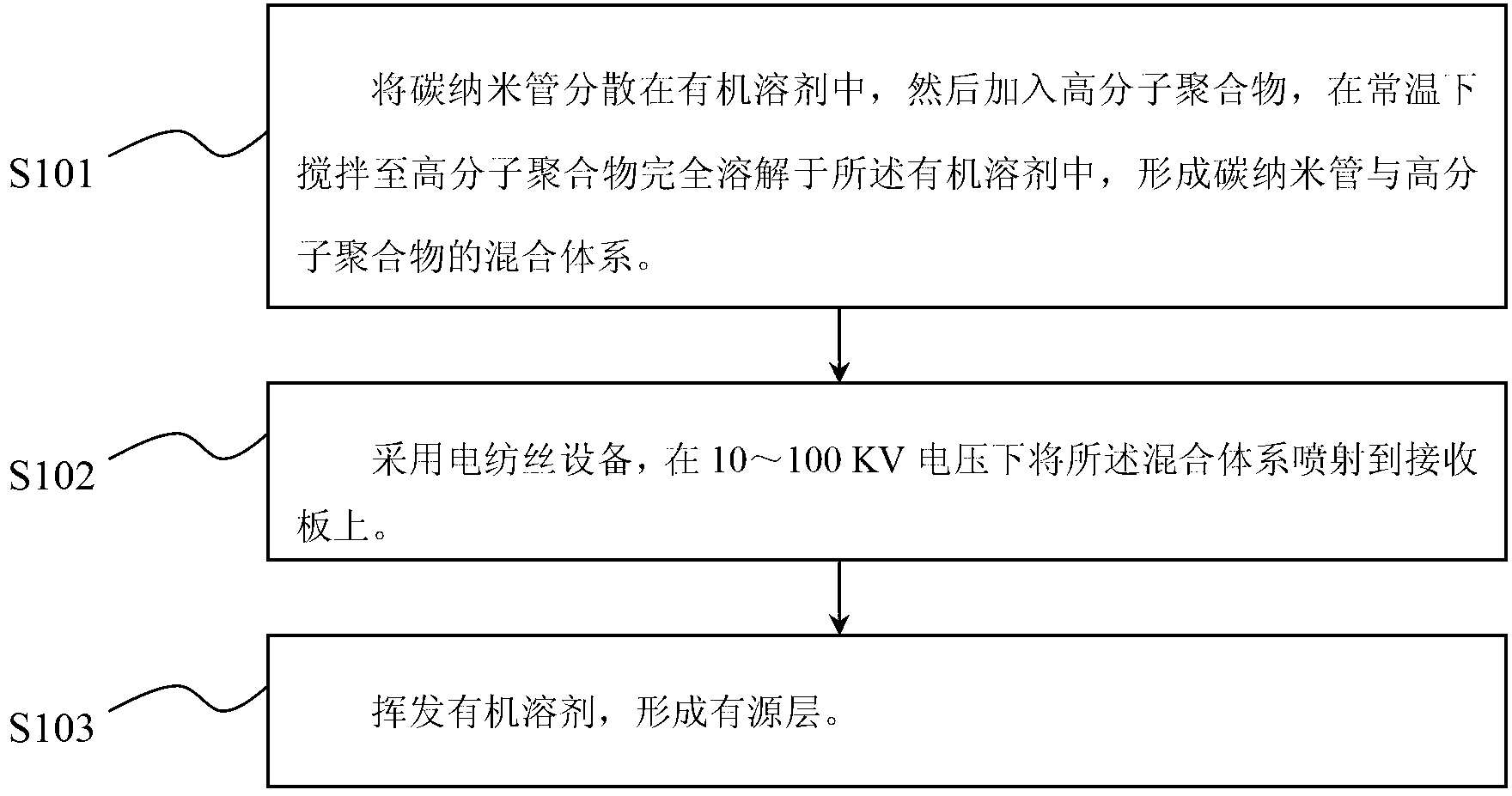
Manufacture method for active layer of carbon nano tube field effect transistor
InactiveCN102856211AImprove transmission characteristicsLow costNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyOrganic solvent
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Methods of fabricating vertical carbon nanotube field effect transistors for arrangement in arrays and field effect transistors and arrays formed thereby
A method for forming carbon nanotube field effect transistors, arrays of carbon nanotube field effect transistors, and device structures and arrays of device structures formed by the methods. The methods include forming a stacked structure including a gate electrode layer and catalyst pads each coupled electrically with a source / drain contact. The gate electrode layer is divided into multiple gate electrodes and at least one semiconducting carbon nanotube is synthesized by a chemical vapor deposition process on each of the catalyst pads. The completed device structure includes a gate electrode with a sidewall covered by a gate dielectric and at least one semiconducting carbon nanotube adjacent to the sidewall of the gate electrode. Source / drain contacts are electrically coupled with opposite ends of the semiconducting carbon nanotube to complete the device structure. Multiple device structures may be configured either as a memory circuit or as a logic circuit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com