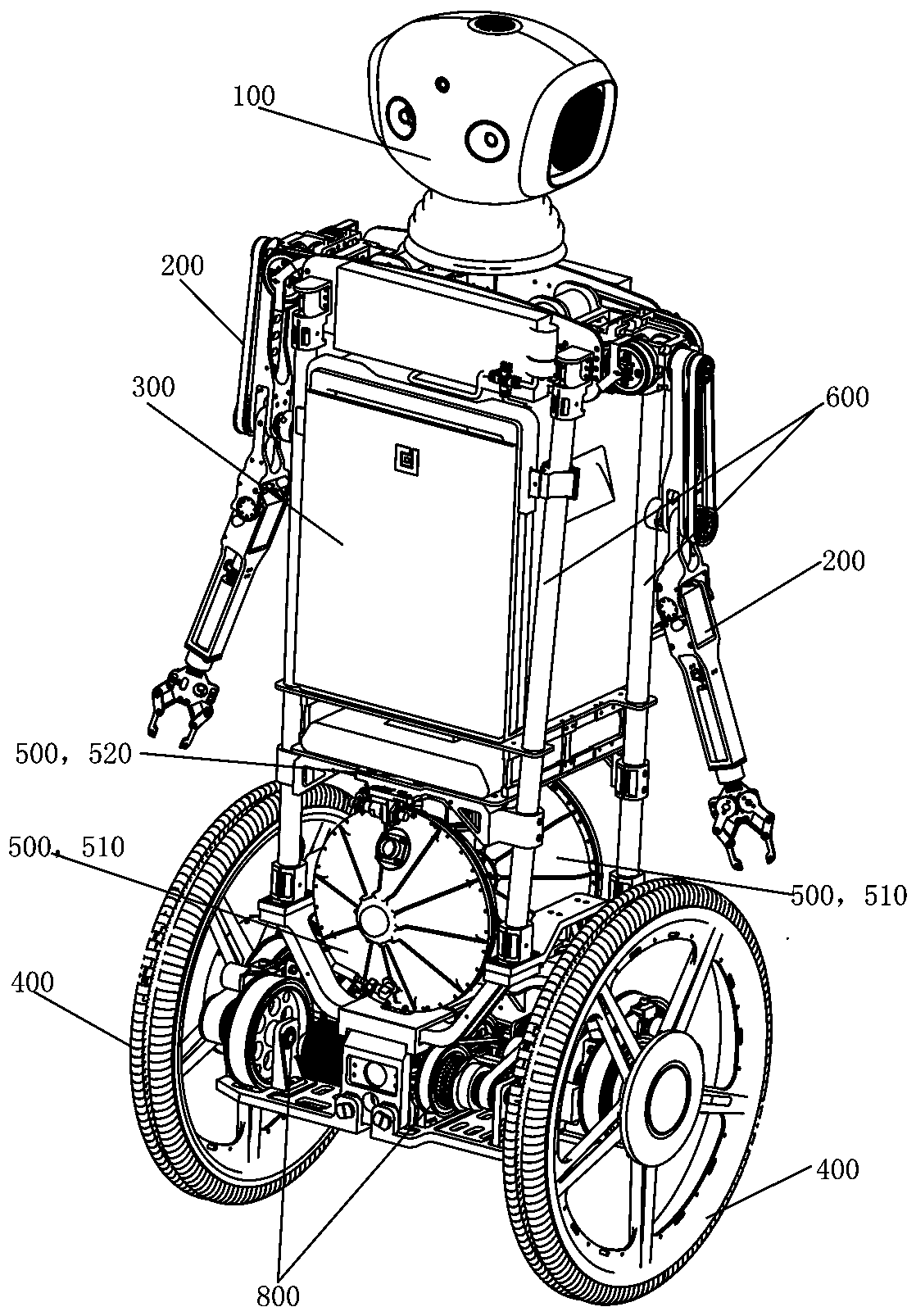
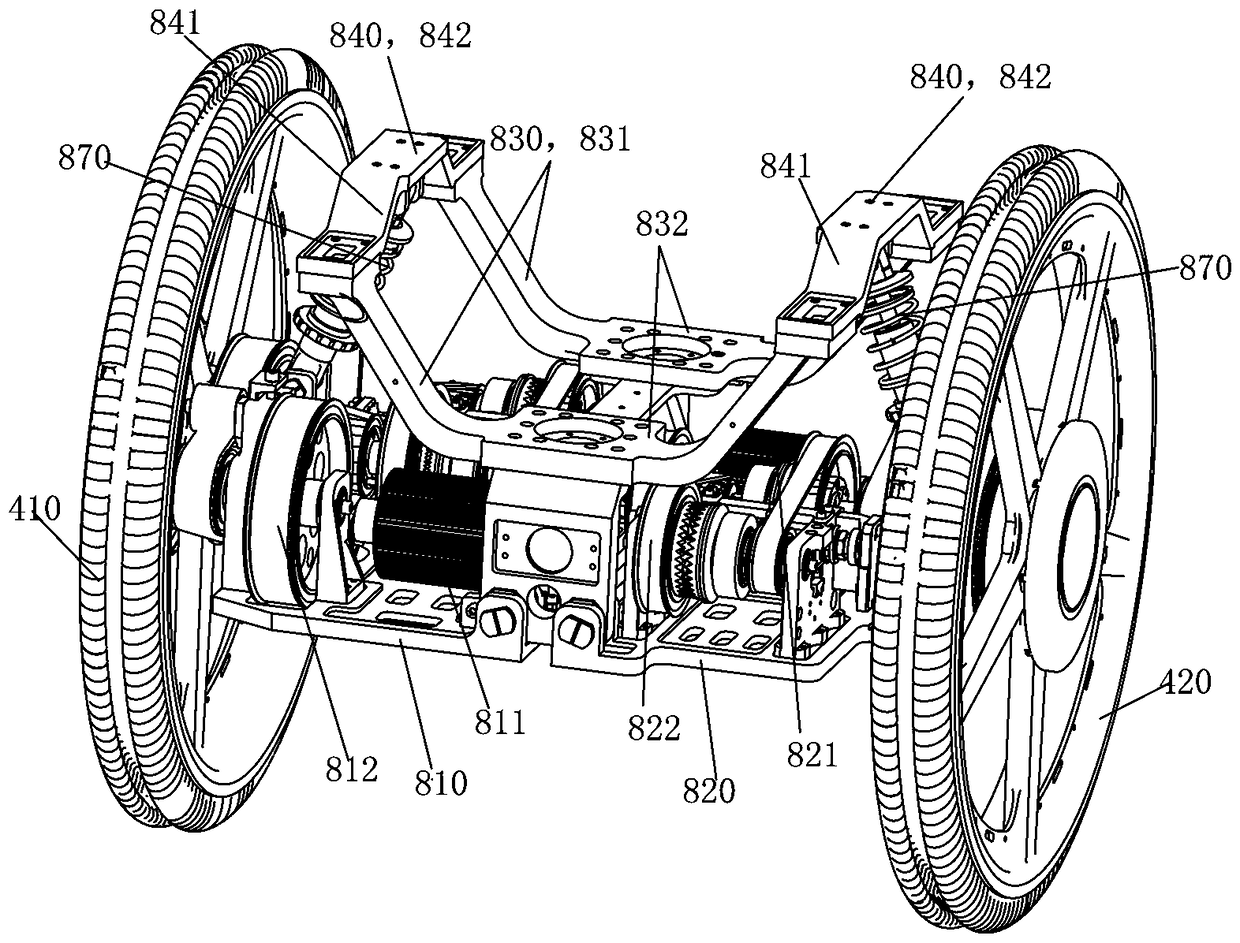
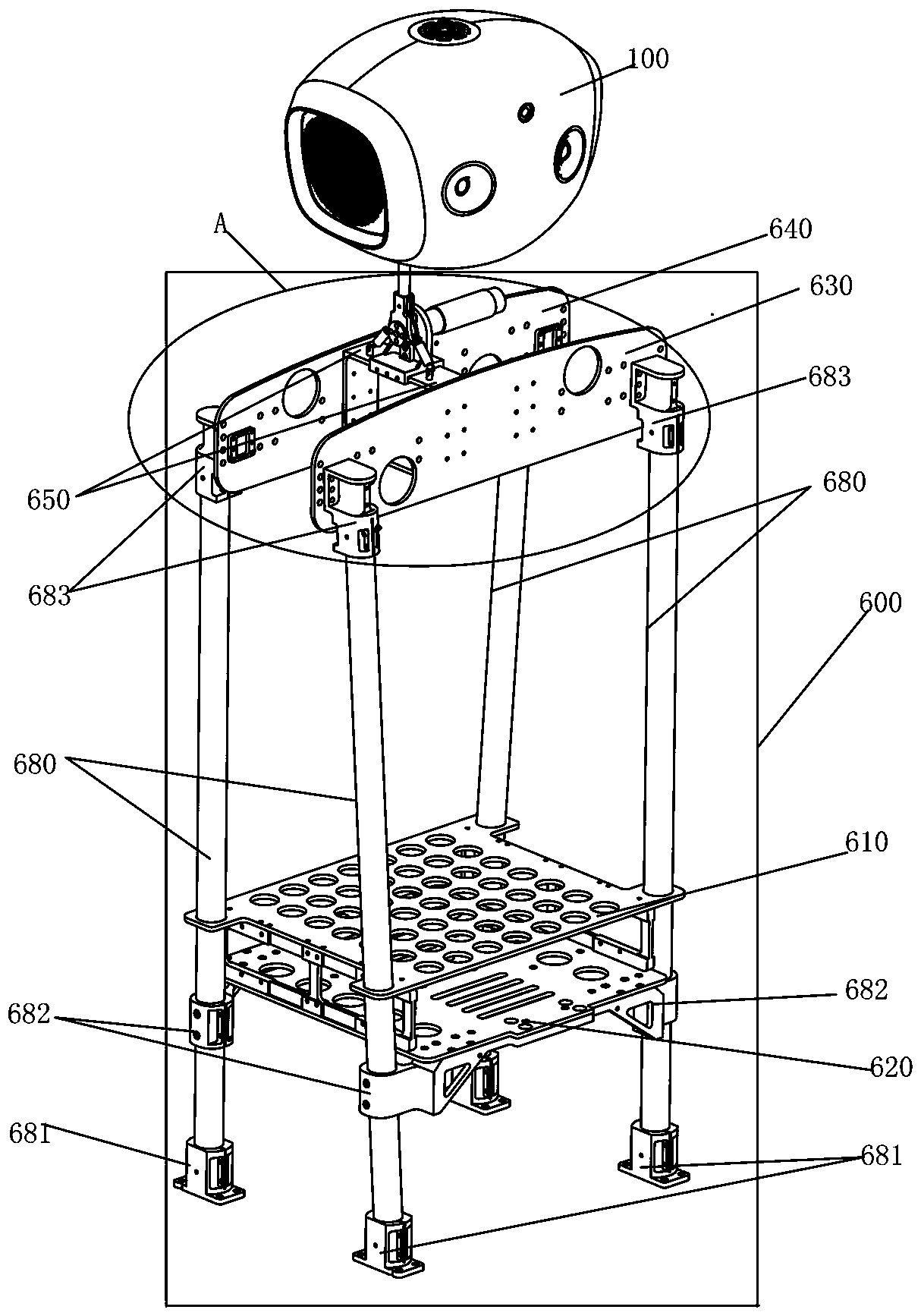
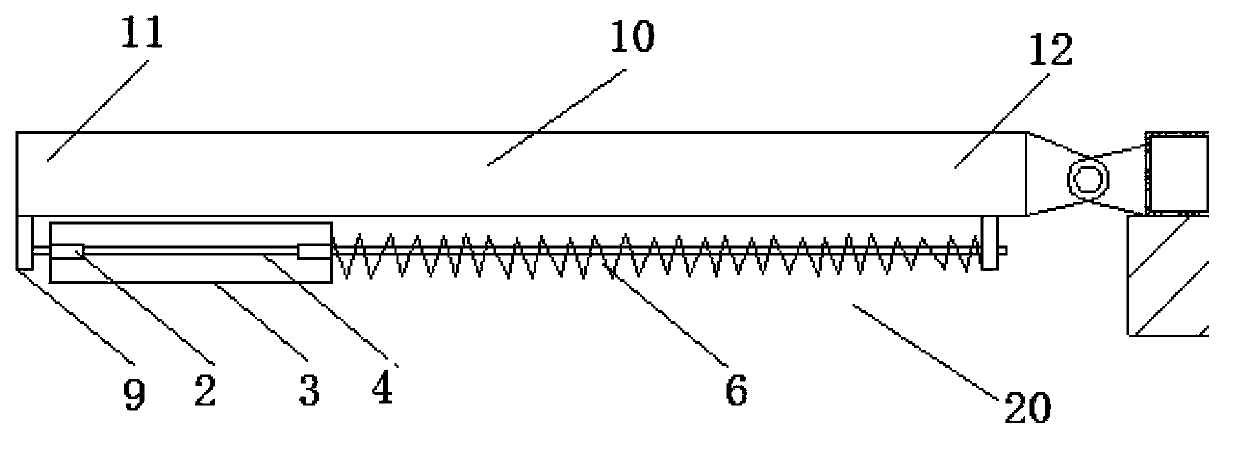
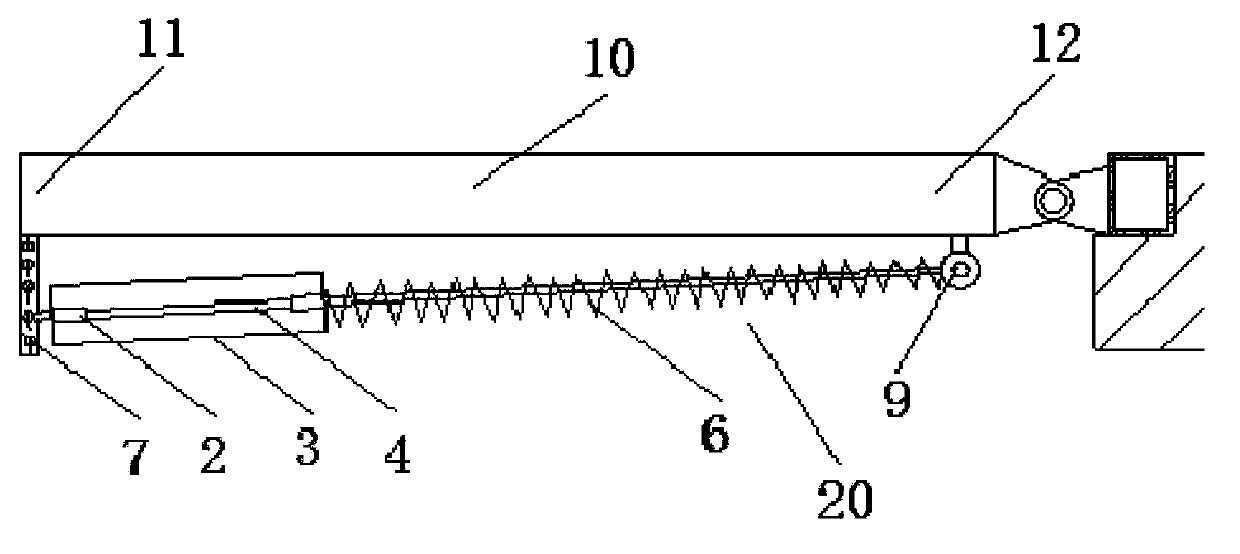
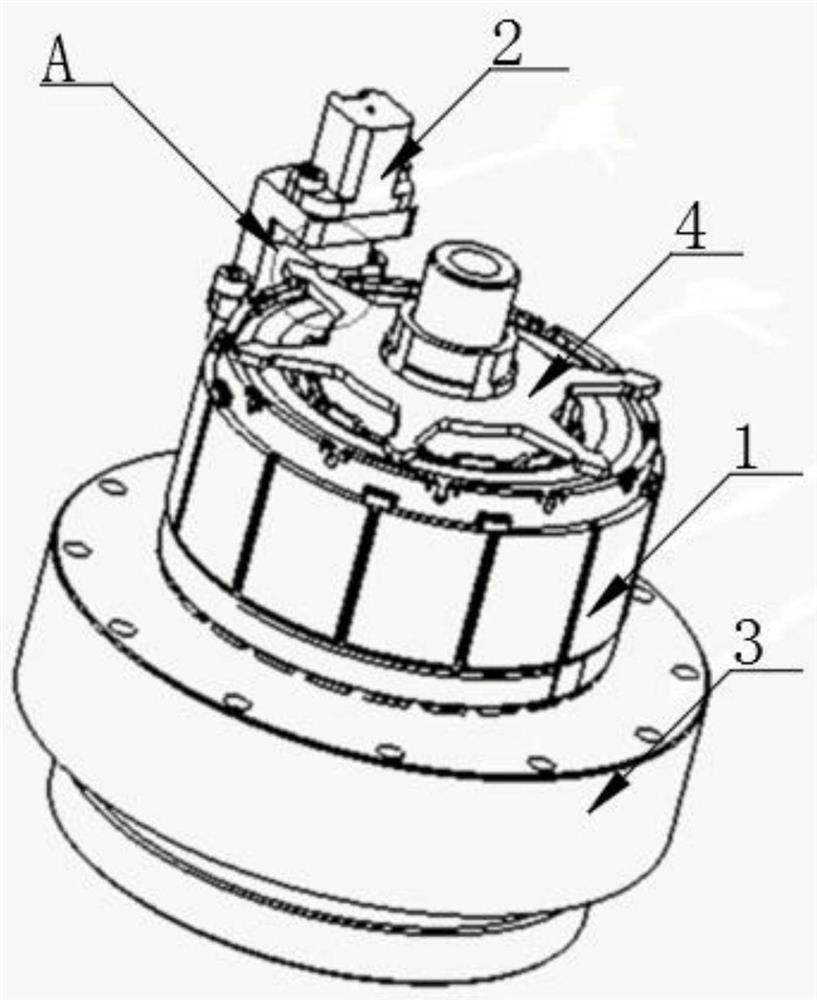
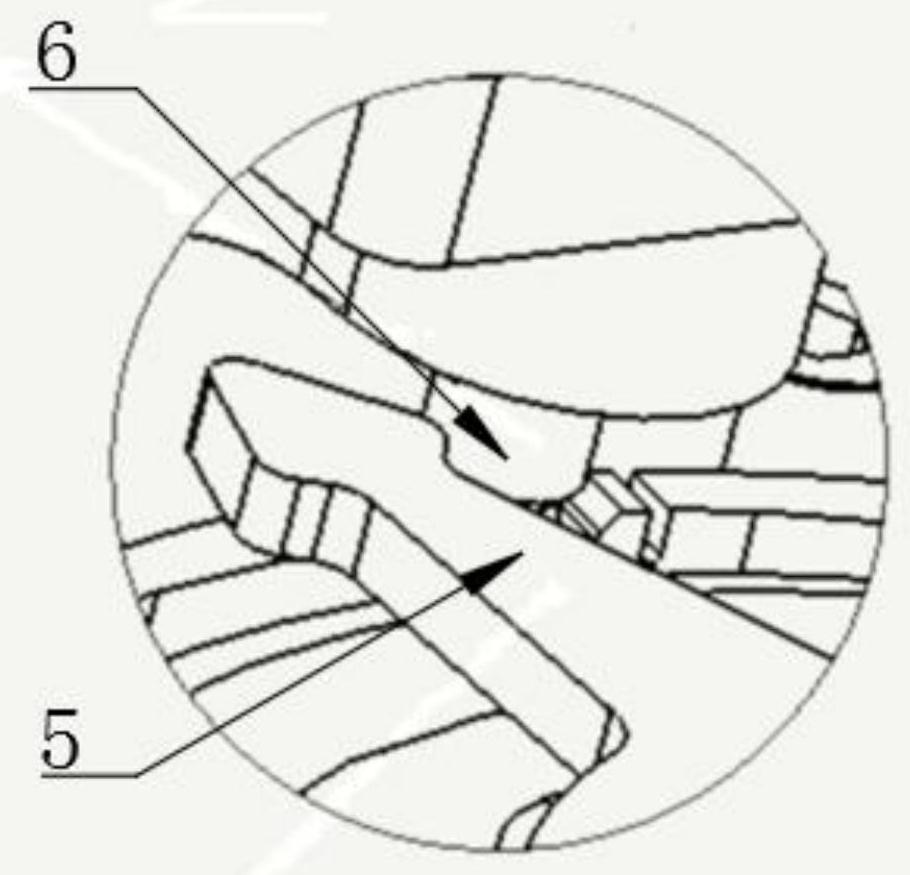
Patents
Literature
115 results about "Gravitational torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
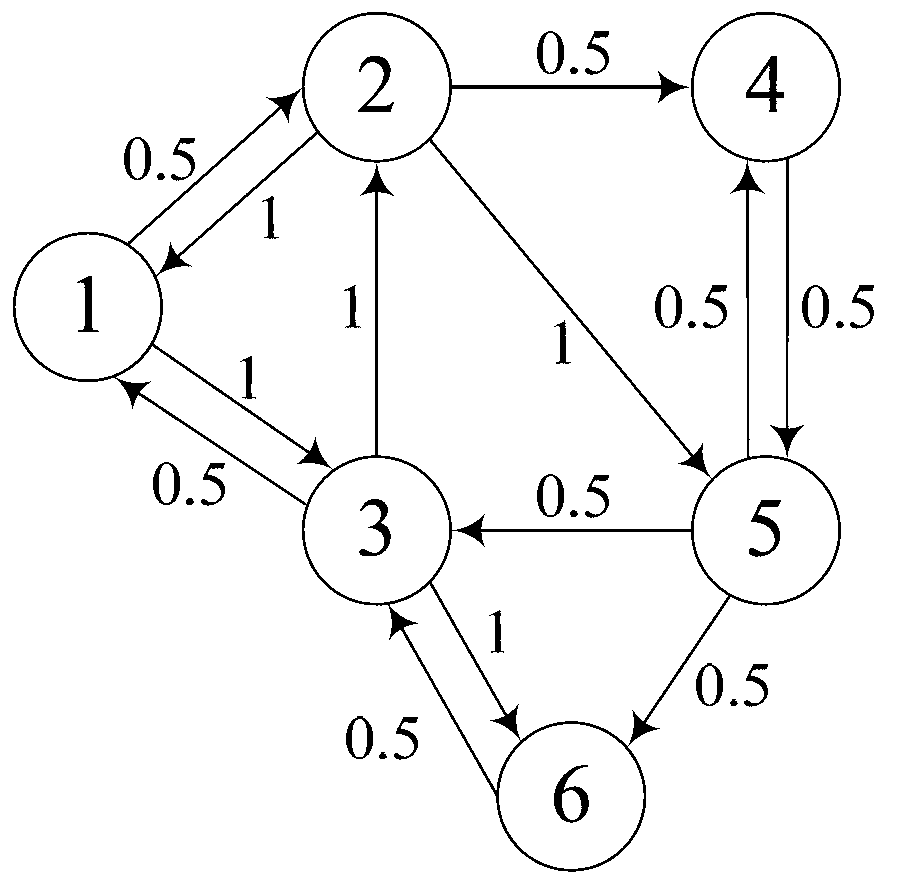
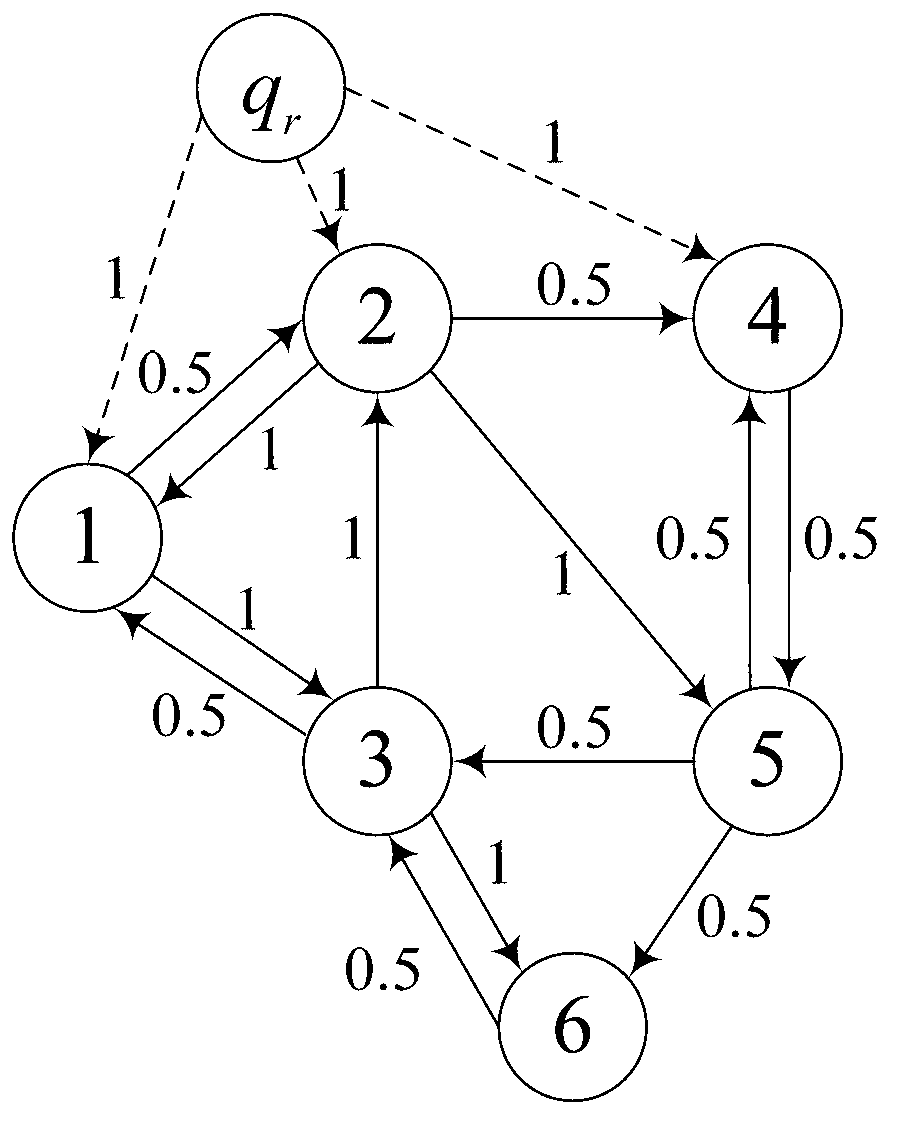
Gravitational torque. torque on the body caused by its weight; it occurs when the center of gravity of the body is not located on the axis of rotation. Keyboard Shortcuts Previous Card.
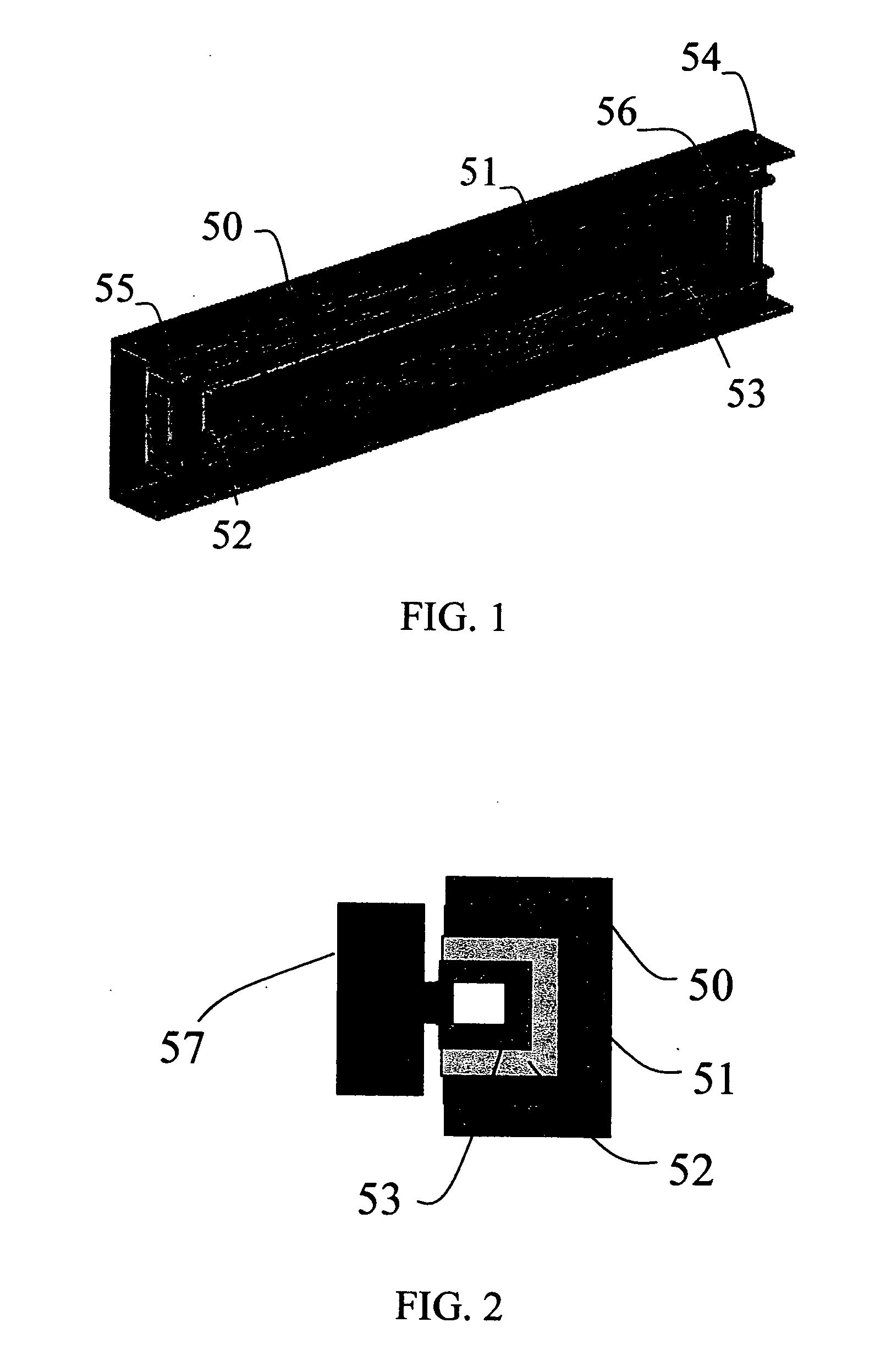
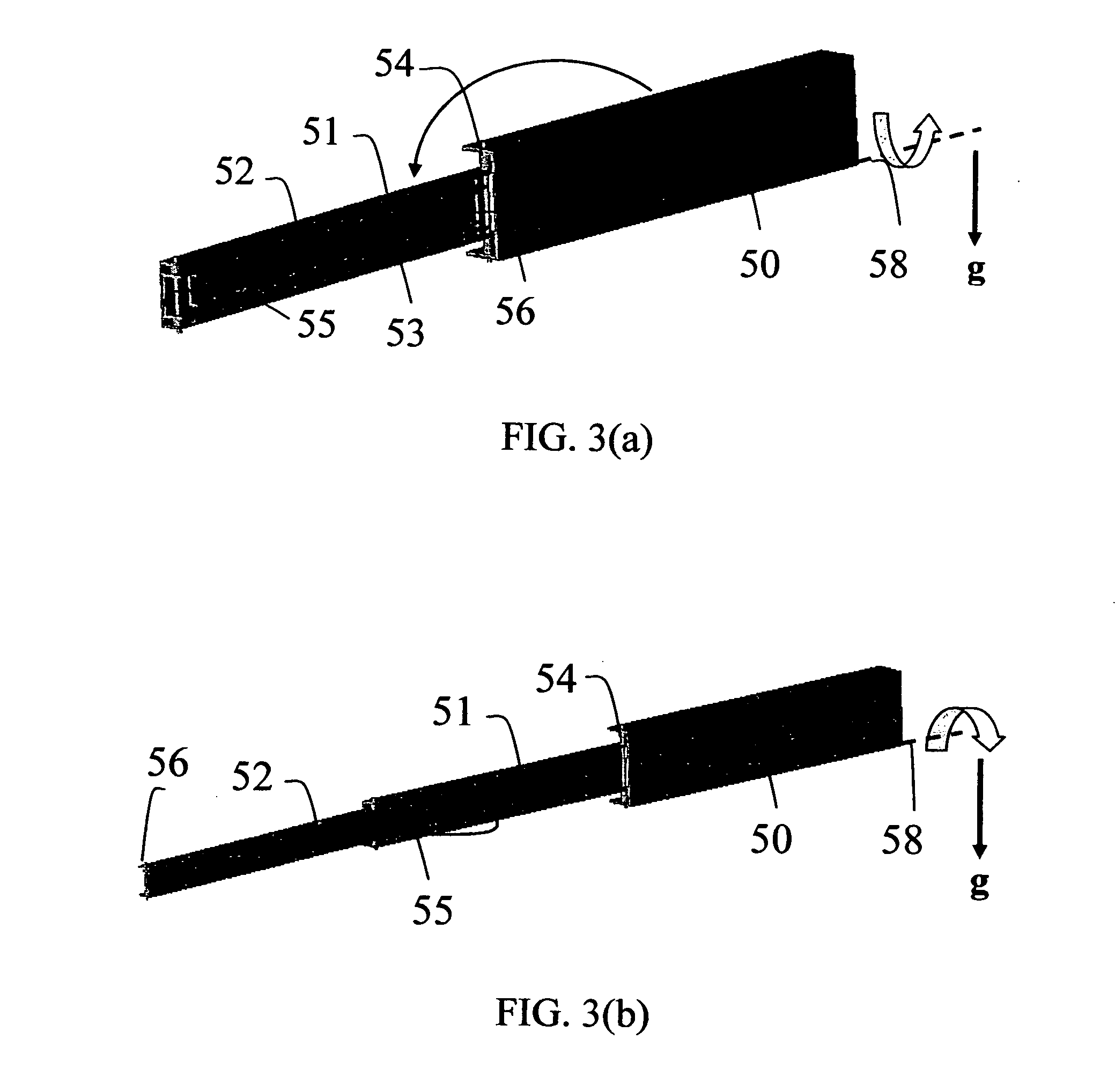
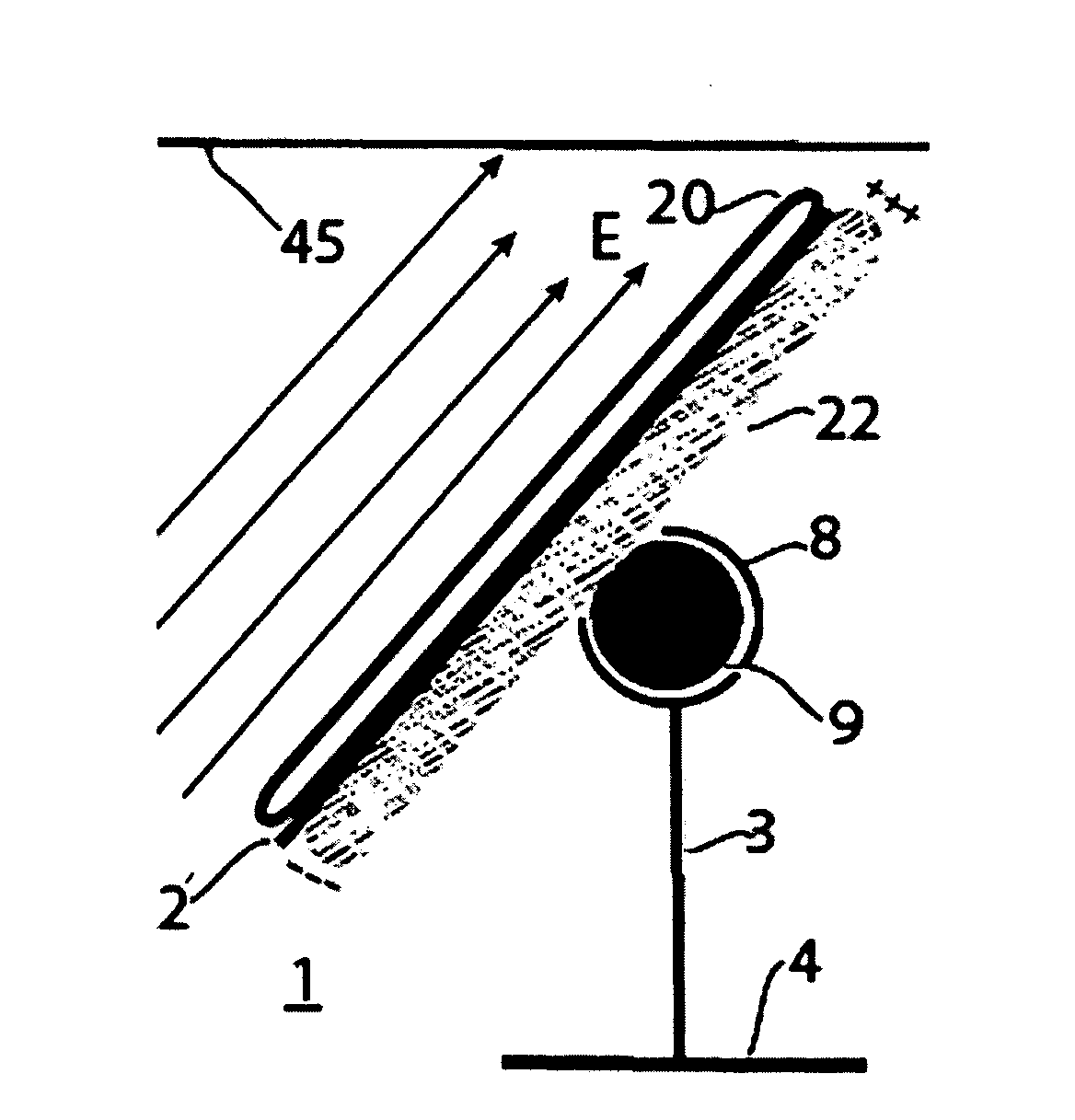
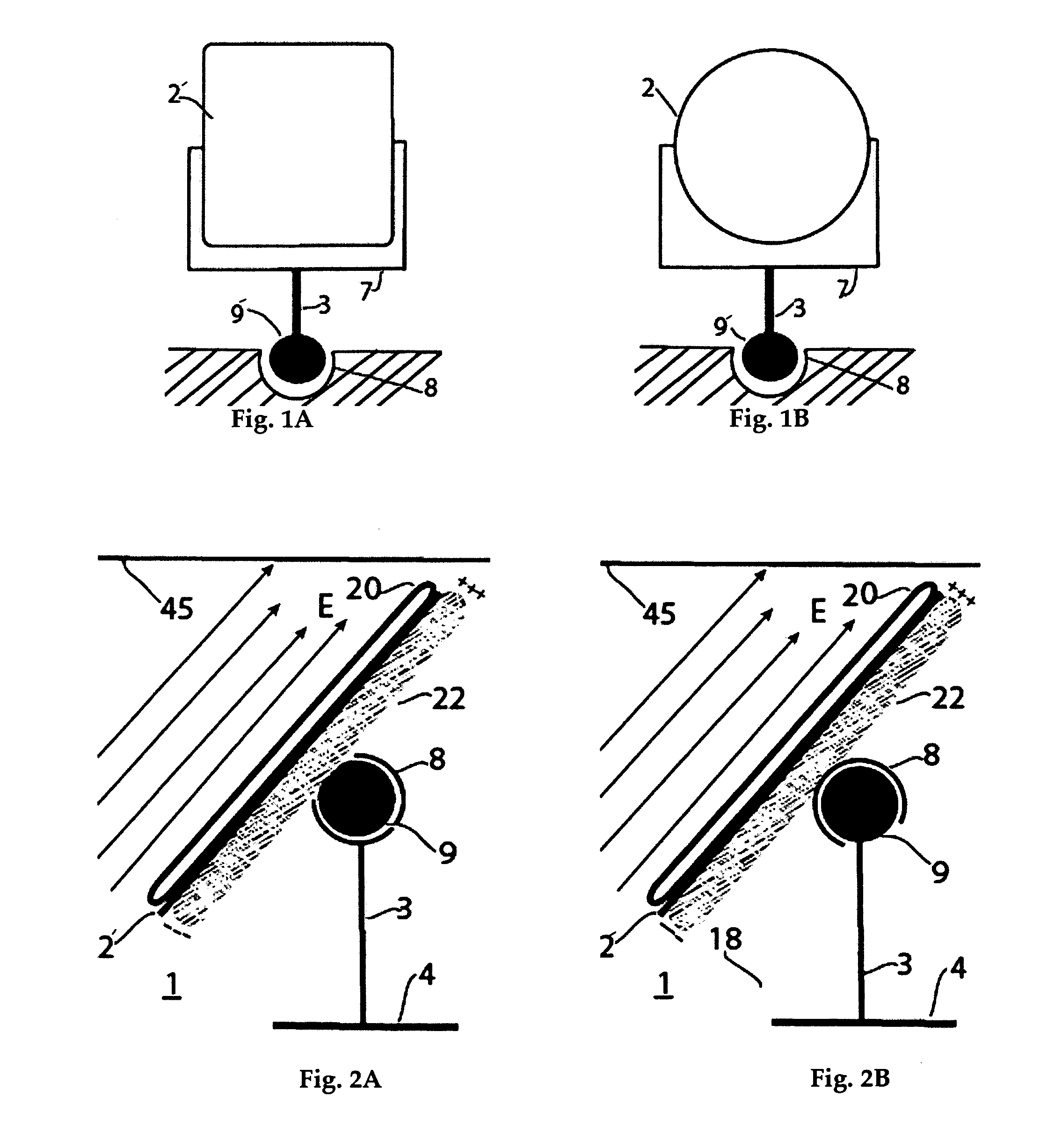
Fresnel solar concentrator array with centered universal pivots
InactiveUS7866836B2Easy to operateMinimum power consumptionSolar heating energyMirrorsDipole couplingSolar concentrator
This invention deals with novel method and apparatus for positioning and motion control of the optical elements (mirrors and lenses) of a Fresnel solar concentrator tracking array which approximately eliminates gravitational torque by use of a central universal pivot or gimbals. Linkage torque is produced by induced and / or permanent dipole coupling to an electronic grid to produce angular deflection, and rotational motion that is enhanced by the presence of highly polarizable material. This system is ideally suited for maximization of solar energy focused by the array onto a receiver. Since there are no mechanical linkages, the instant invention is applicable for fabrication from the mini- to the nano-technology realm. The elimination of gravitational torque by balancing the optical elements on a universal pivot or gimbals greatly reduces the power required for the optical elements to track the sun and focus sunlight onto a receiver.
Owner:RABINOWITZ MARIO
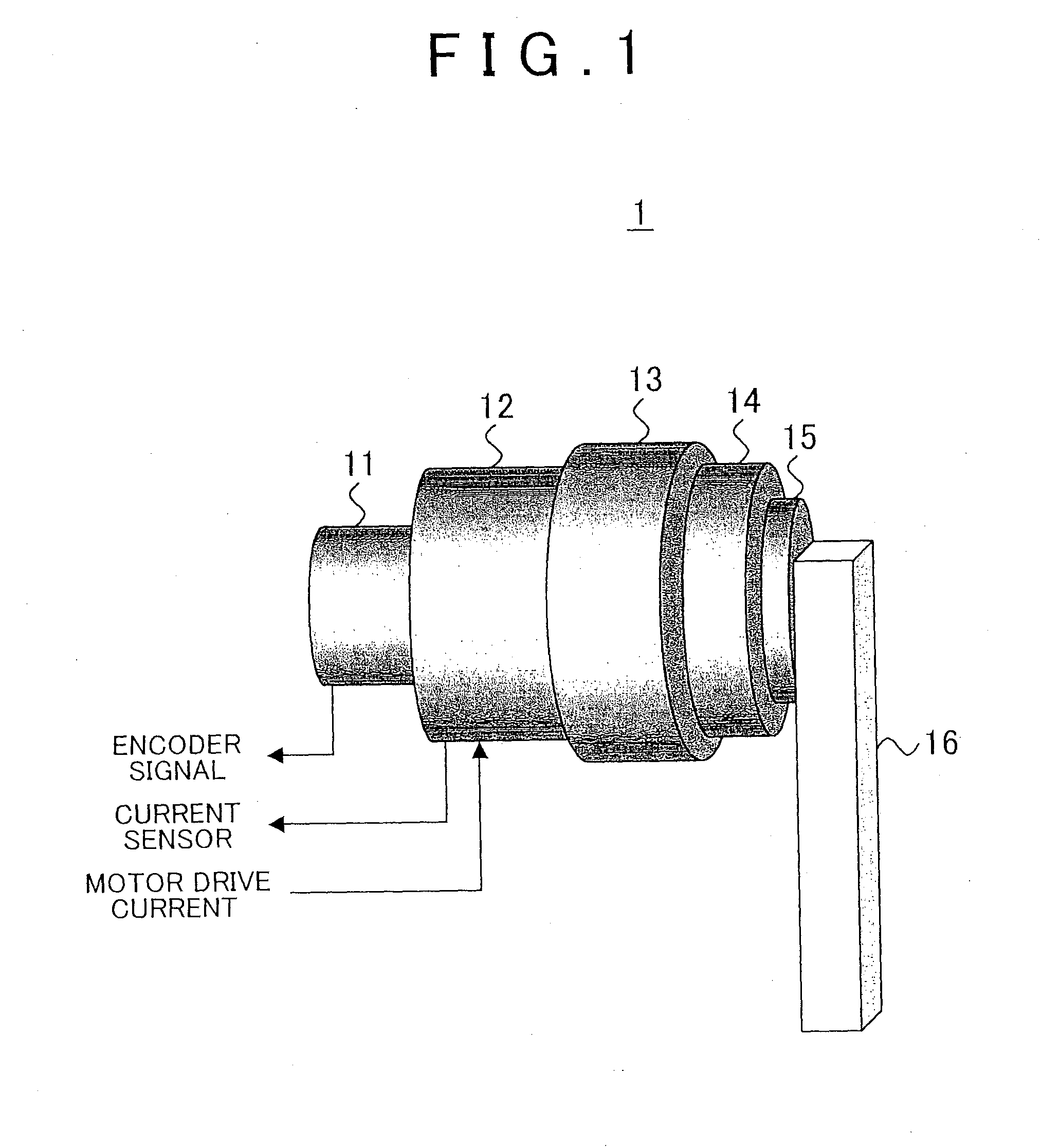
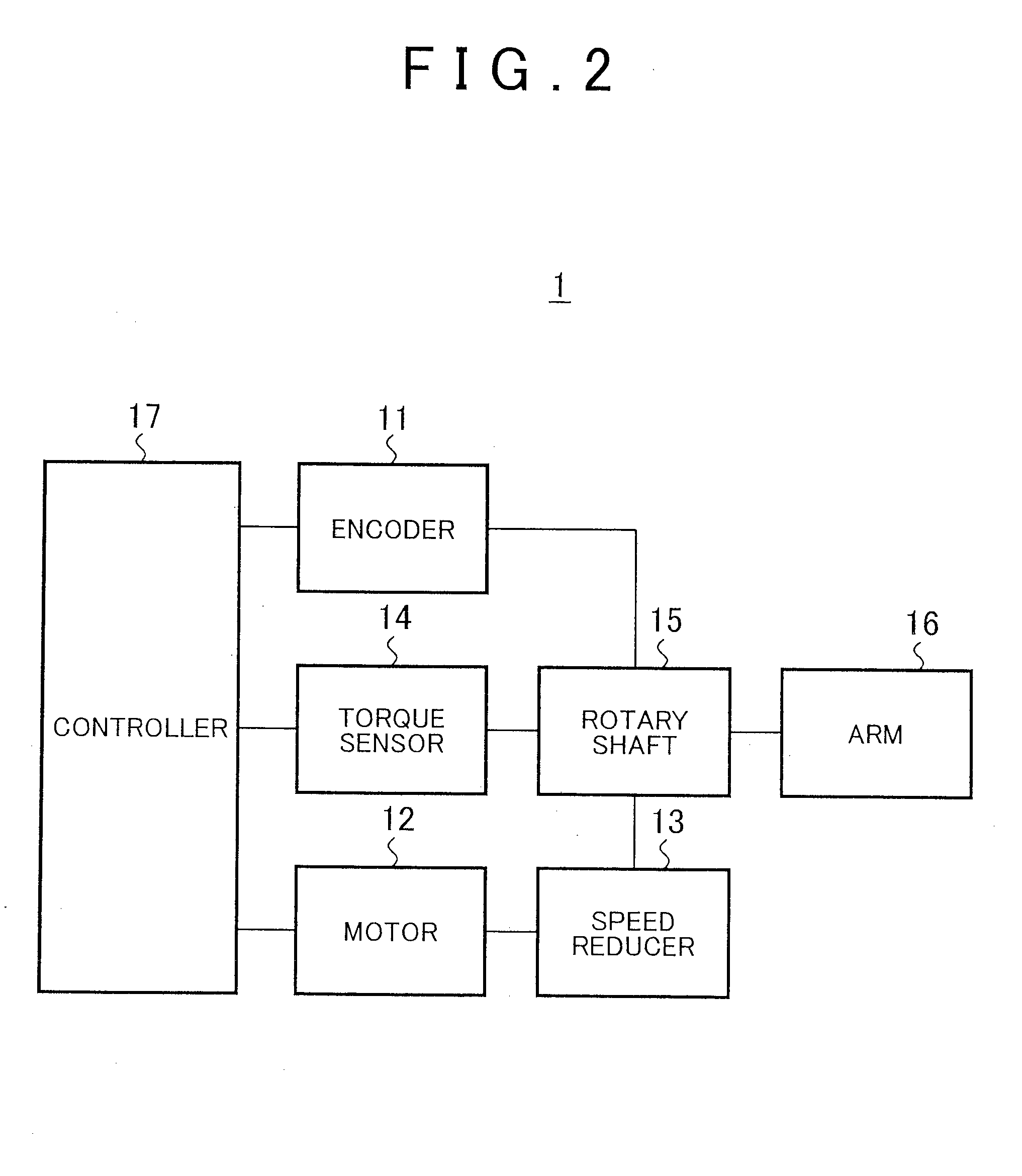
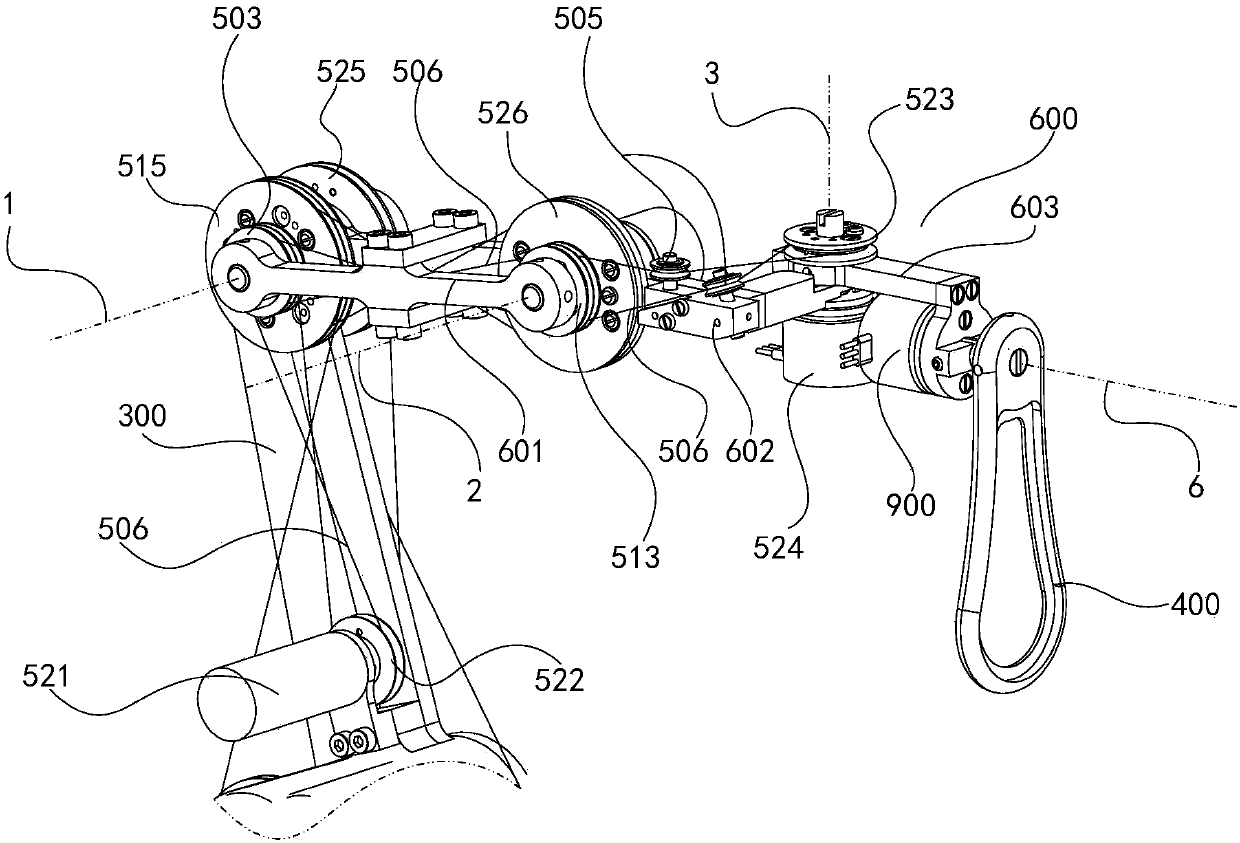
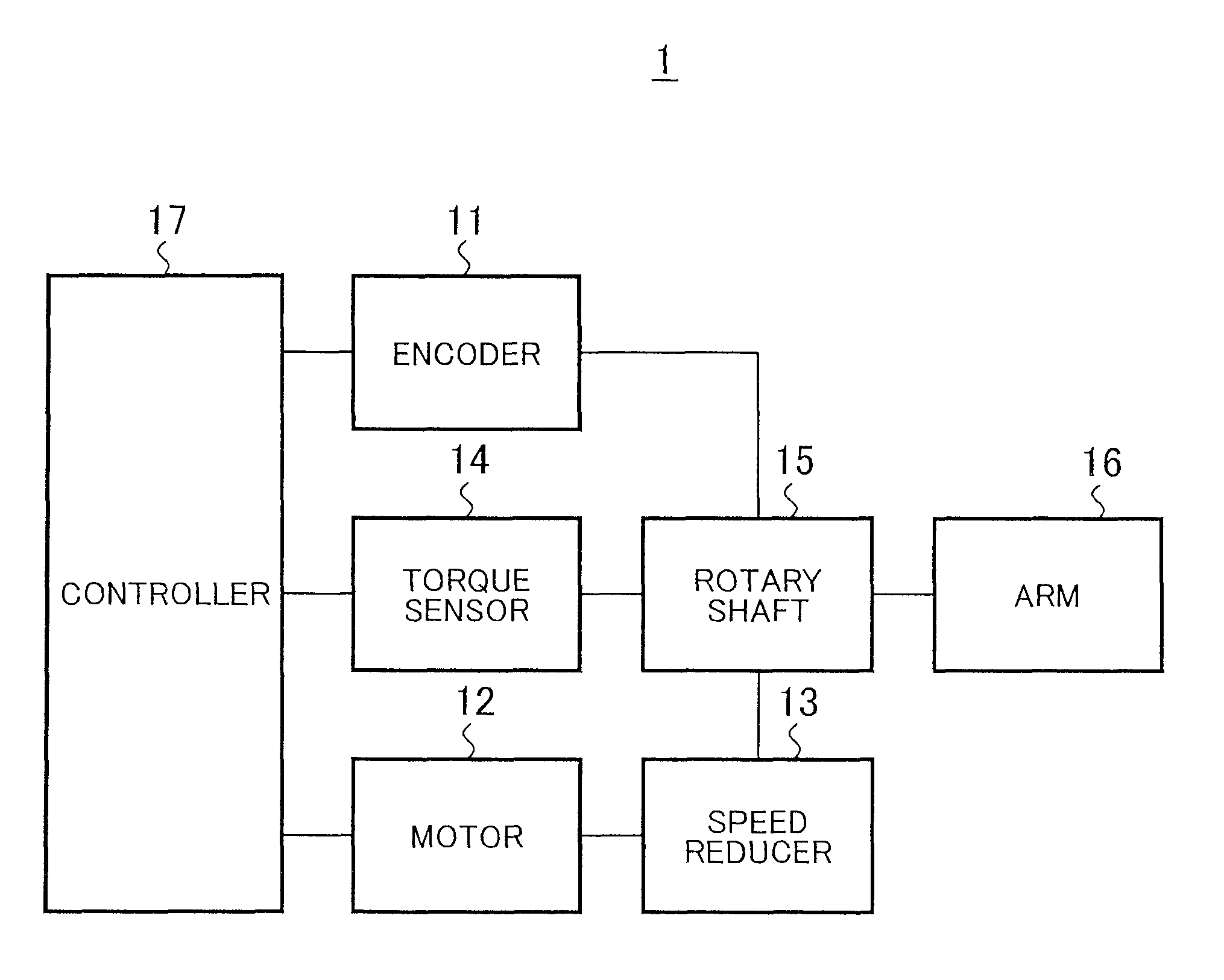
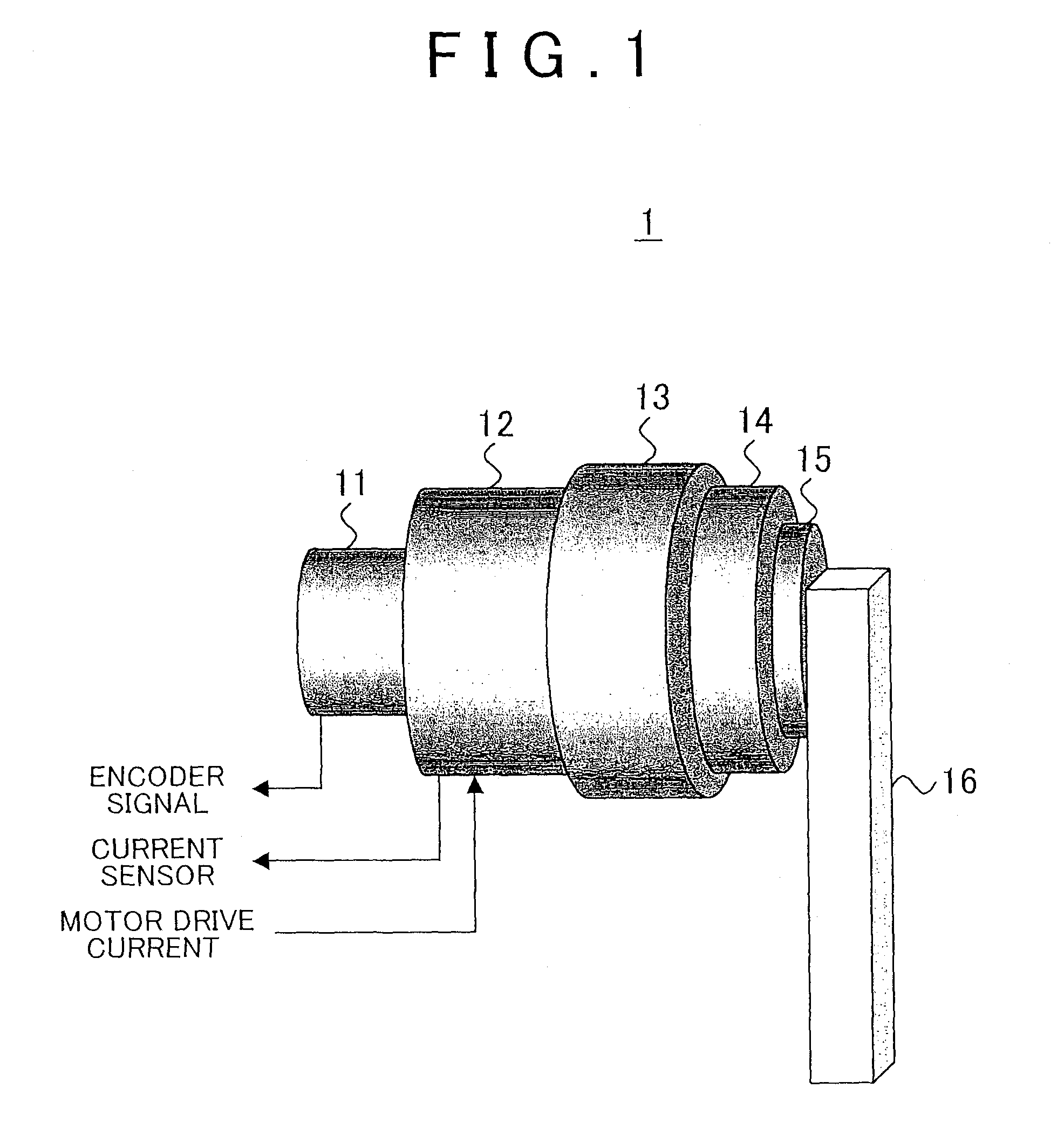
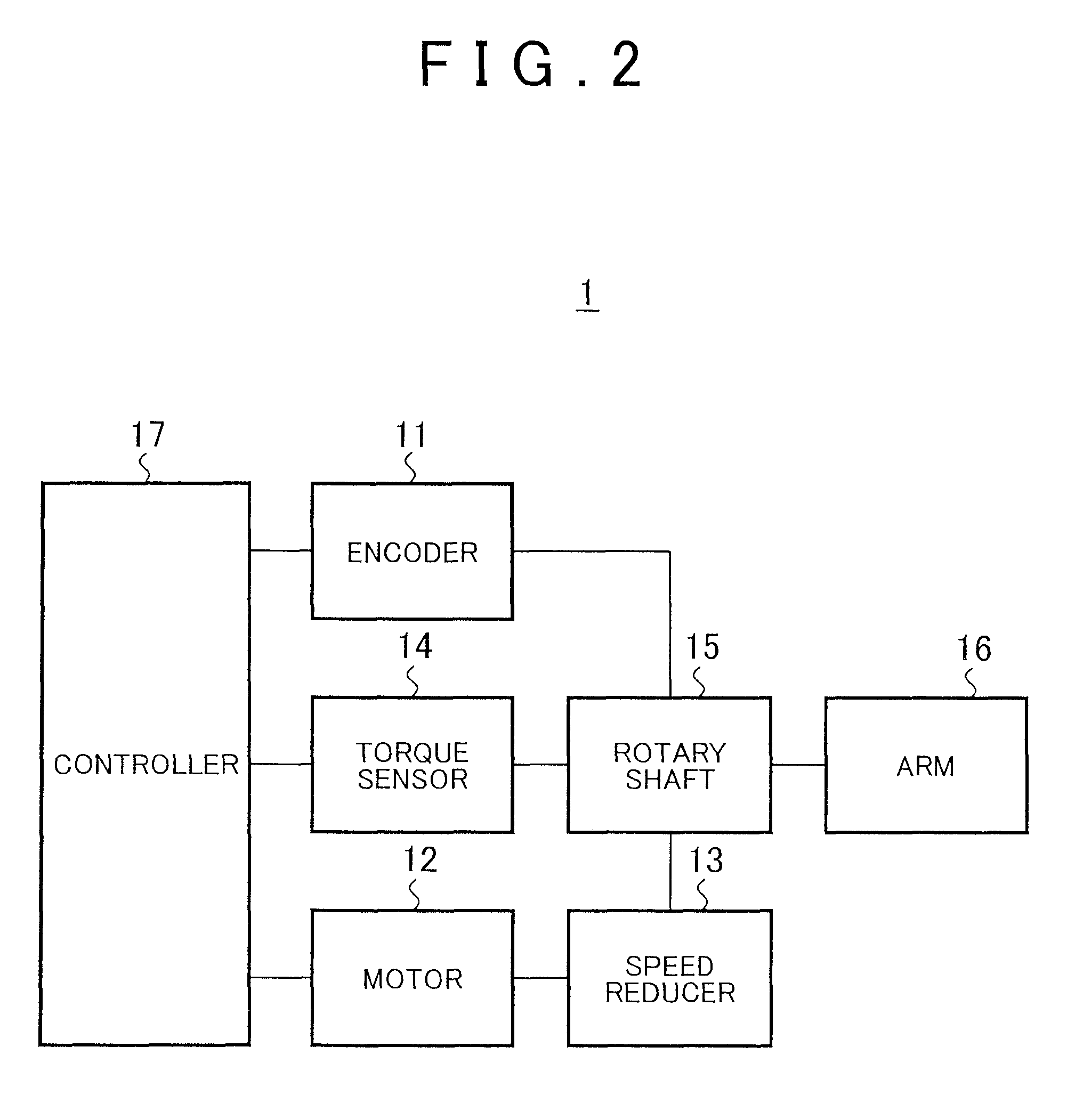
Torque detecting method and arm device
ActiveUS20150045952A1Good compensationImprove accuracyProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorGravitational forcePosition control
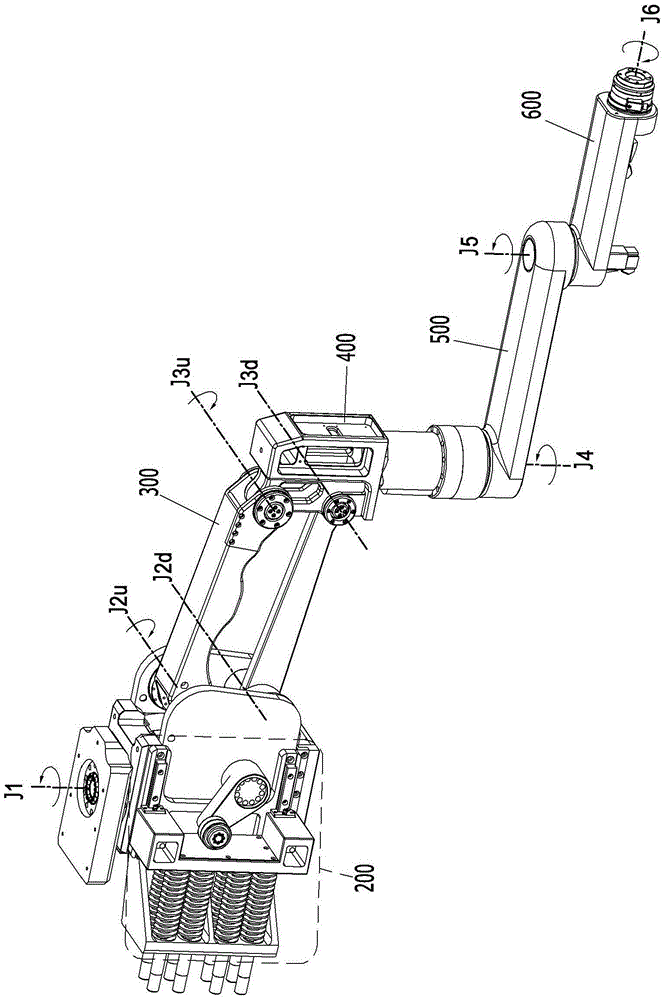
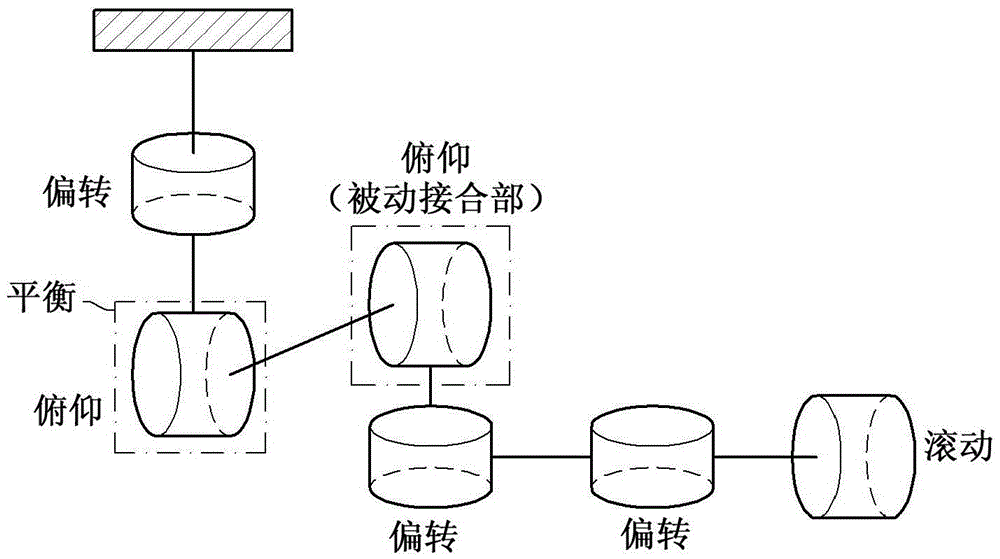
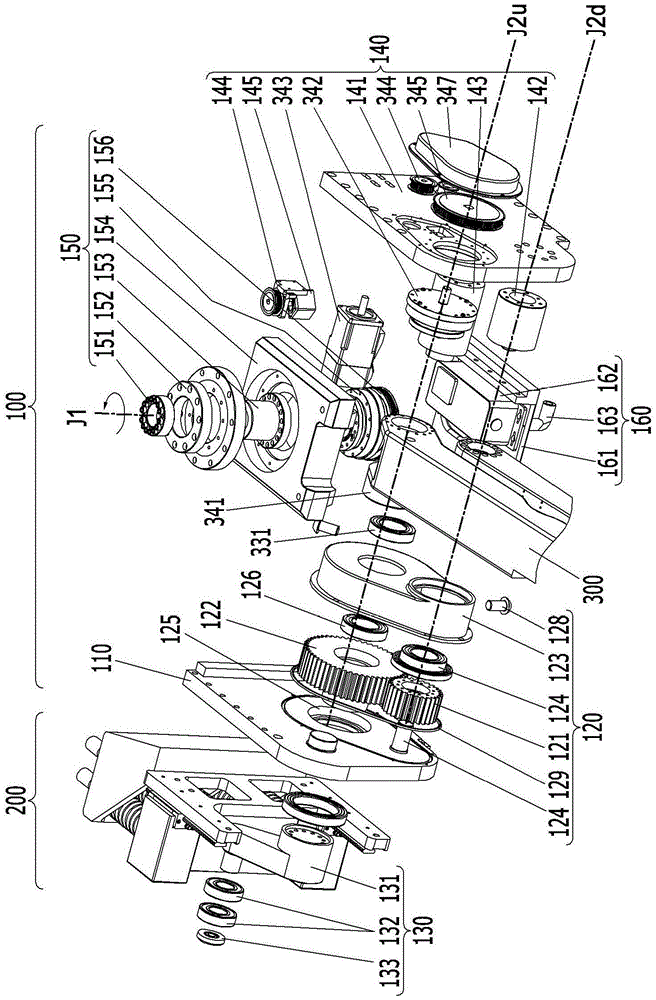
According to a torque detecting method, gravitational torque applied to a rotary shaft of an arm is detected in a condition where position control of the arm is stopped, when the arm is located at a first position at which the arm is oriented in a direction different from a direction of gravitational force. Then, a gravity coefficient used for calculating gravitational torque corresponding to a position of the arm is calculated, based on the gravitational torque and the first position. Then, gravitational torque during position control is calculated, based on the position of the arm detected during the position control, and the gravity coefficient. Further, an actual output torque during the position control is calculated, based on operating torque applied to the rotary shaft and detected during the position control, and the gravitational torque calculated during the position control.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Power transmission monitoring and maintenance systems and methods
ActiveUS20110316525A1Negates needMachine part testingDevices using electric/magnetic meansElectric power transmissionAerodynamic drag
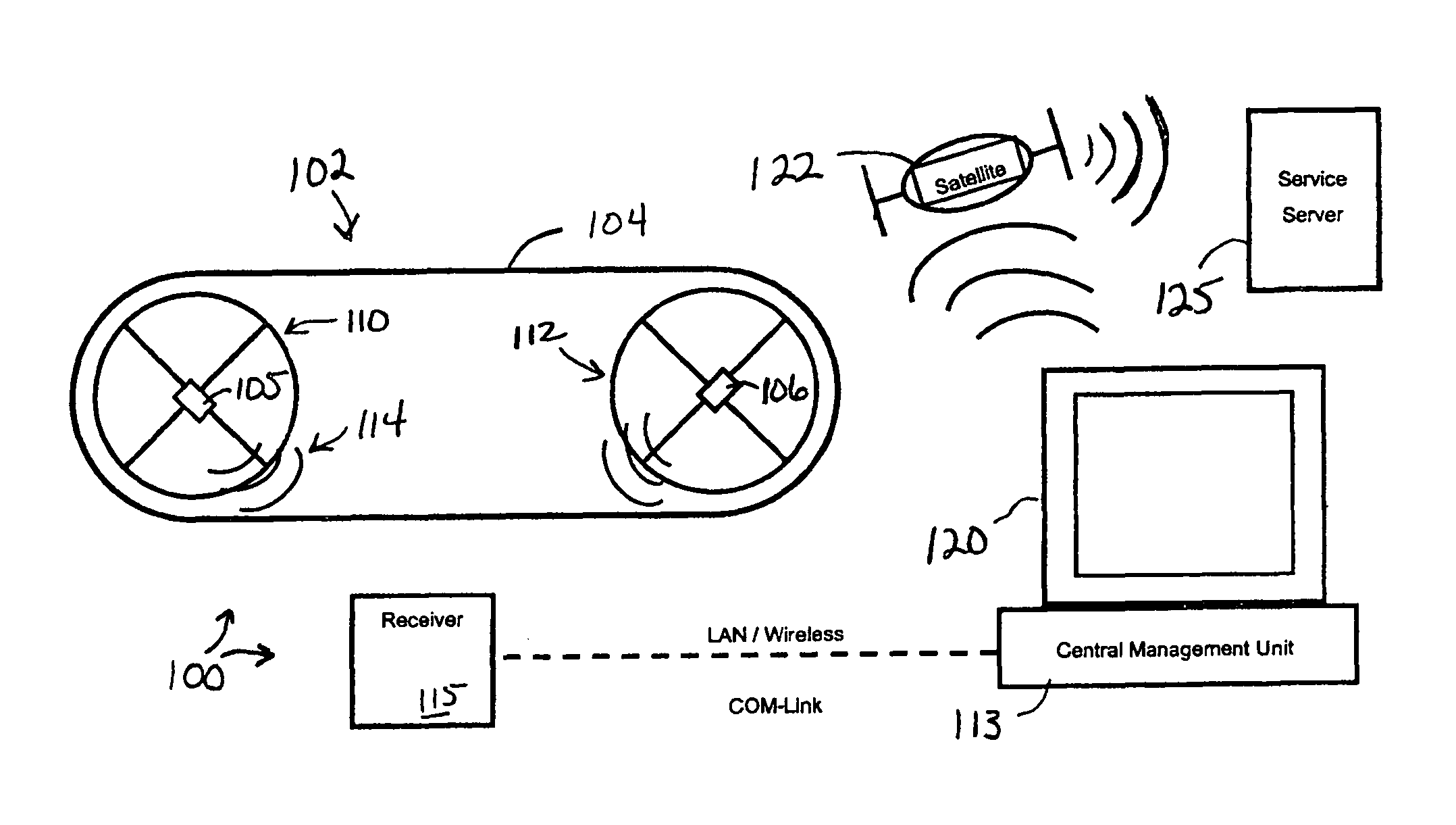
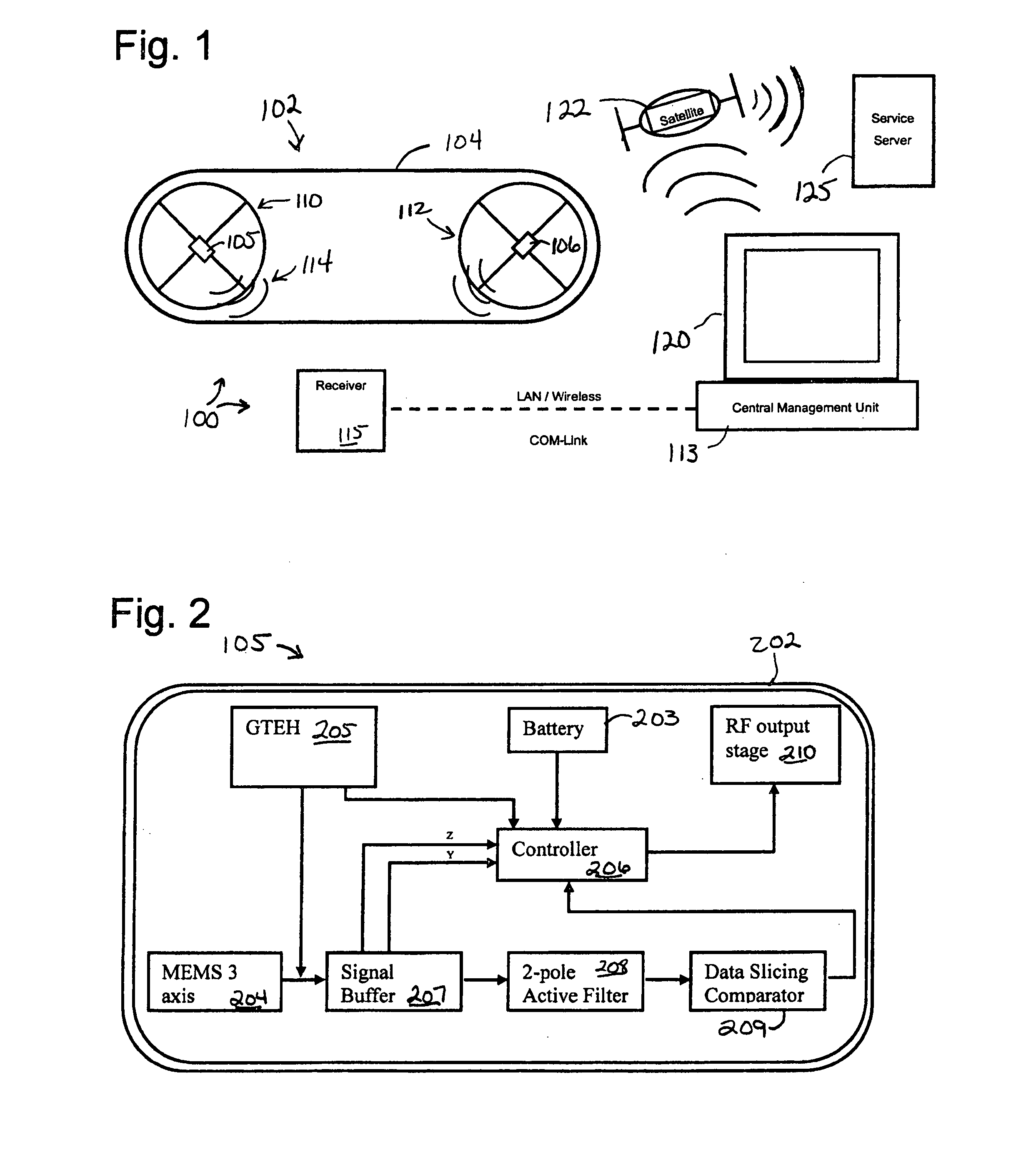
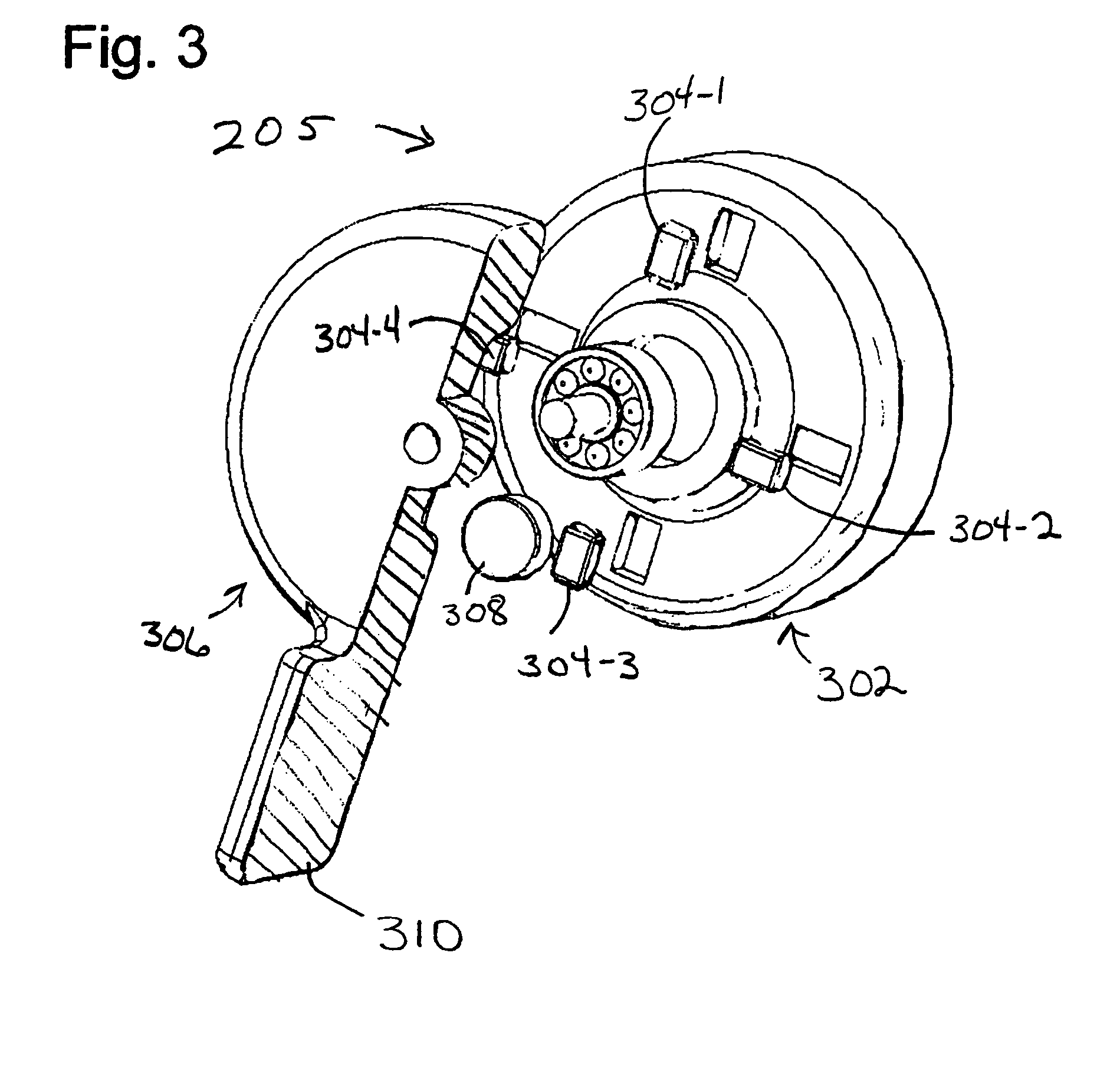
Power transmission monitoring systems includes rotation speed sensors mounted to hubs of a power transmission pulley. A sensor comprises a rotation sensing device, and a controller receiving rotation data therefrom and determining rotation speed of the pulley. A transmitter transmits rotational speed of the pulley to a receiver, which may include or be connected to a device that compares the rotational speed to rotational speed in transmissions from other sensors to determine slip in the power transmission system. The rotation speed sensing device may be an accelerometer, or a gravitational torque harvester. A harvester might include a rotor body rotating with the pulley and mounting induction coils, and a gravitational torque stator mounting an induction magnet and including an air vane damper maintaining the stator stationary with respect to the rotor, through air resistance. The transmissions may be employed to monitor, maintain and repair the power transmissions system.
Owner:SCHRADER ELECTRONICS LTD
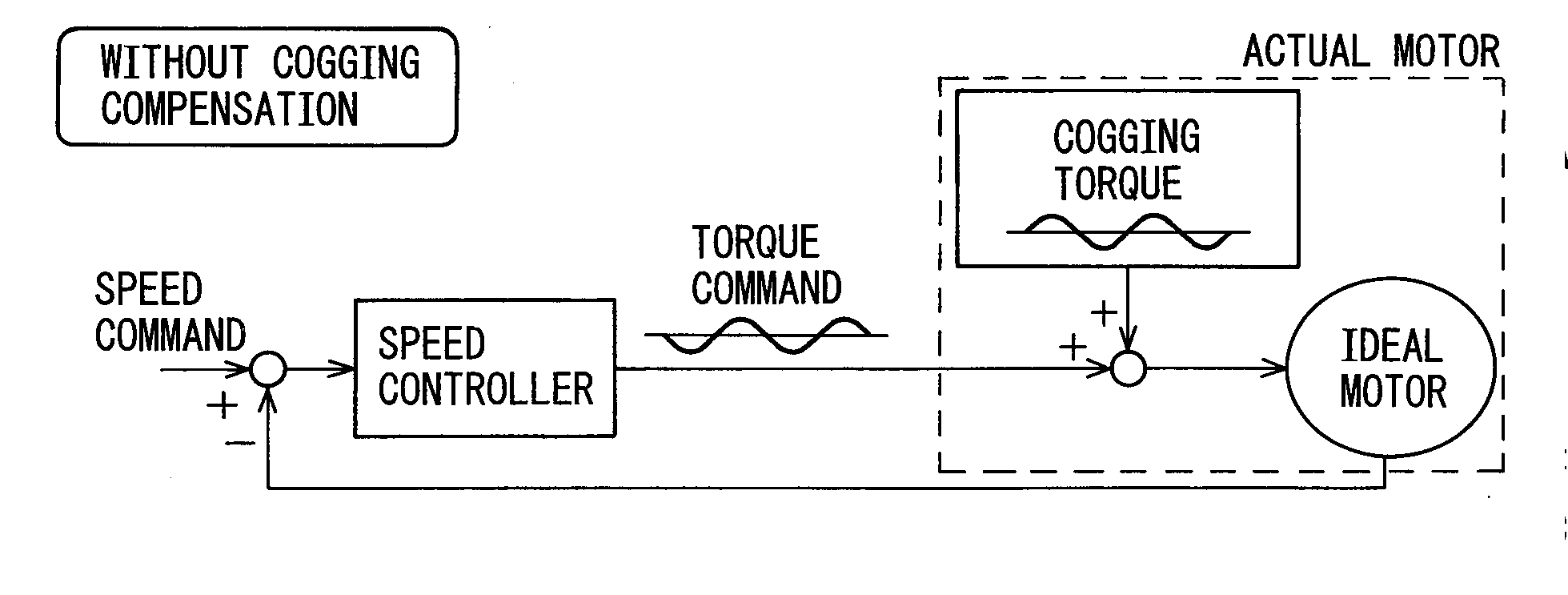
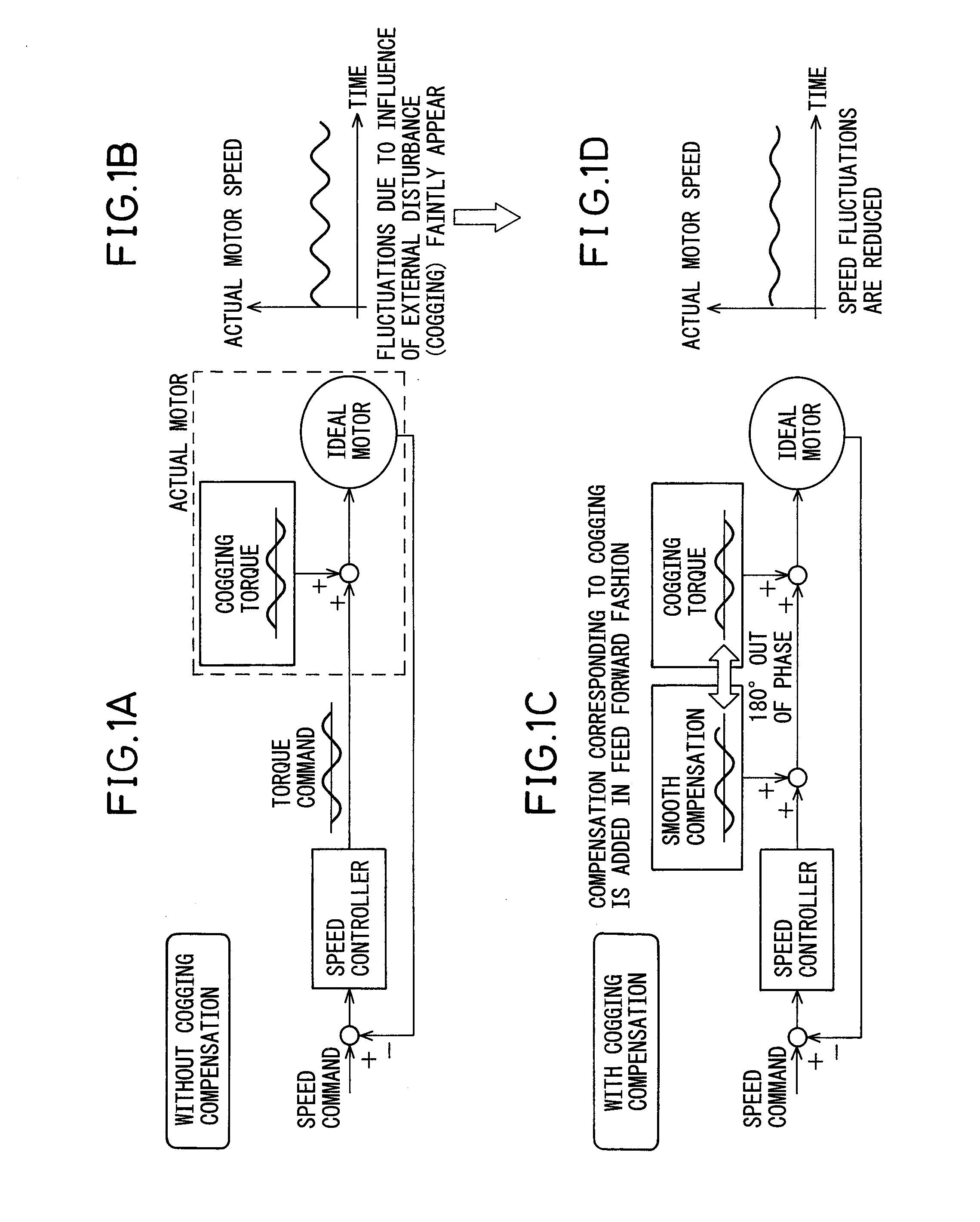
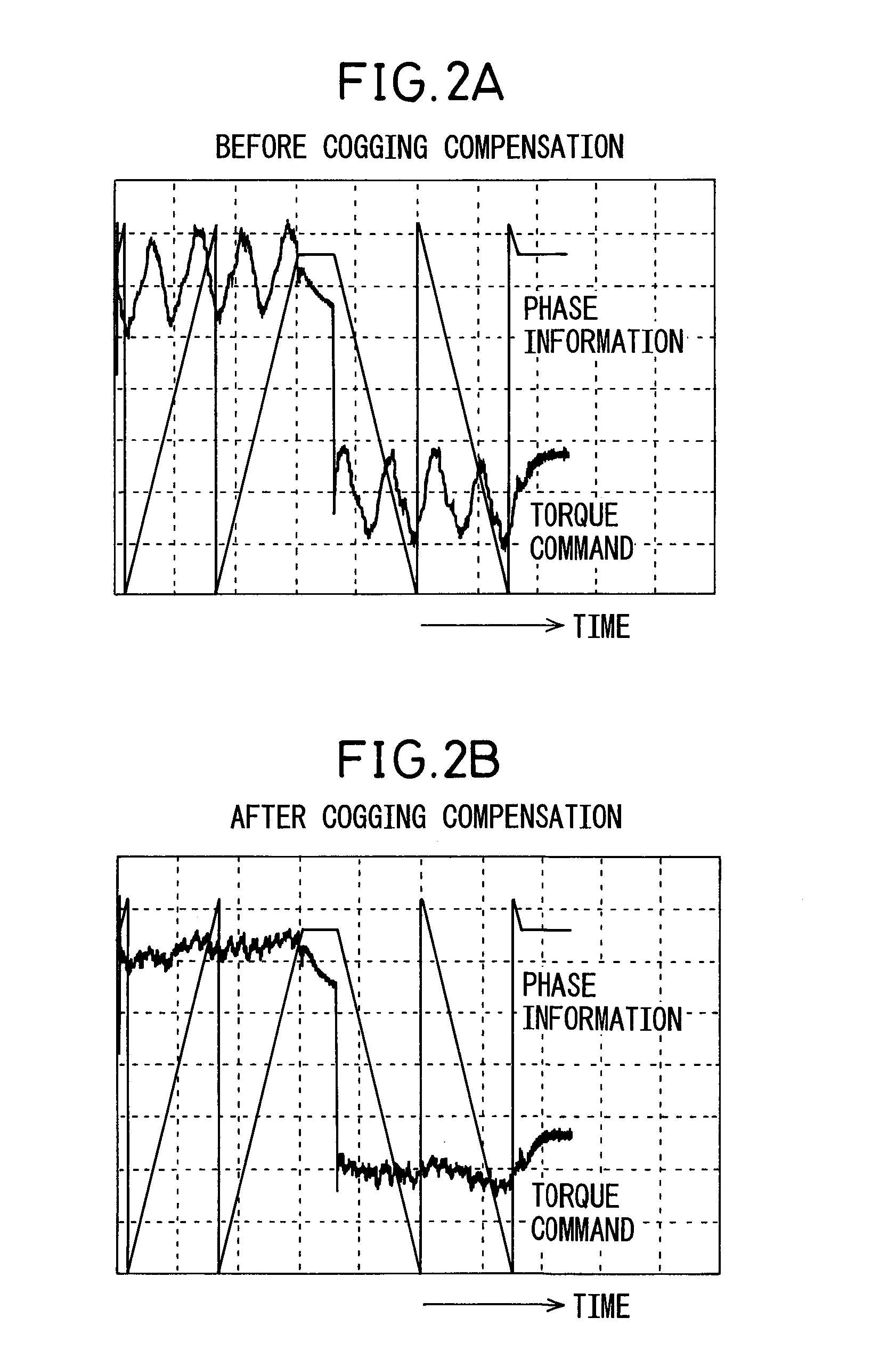
Motor control apparatus having a function to calculate amount of cogging torque compensation
ActiveUS20110147028A1Fluctuation in motor speedProgramme controlTorque ripple controlFundamental frequencyMotor control
A motor control apparatus that can calculate a proper amount of cogging torque compensation even in cases where components due to other factors than cogging torque (for example, components due to gravitational torque, etc.) are superimposed on a torque command being output during constant slow-speed feed operation. The motor control apparatus includes: a torque command monitoring unit which monitors a torque command when the motor is caused to operate at a constant speed; an approximation calculation unit which calculates a torque command approximation component by approximation from the torque command monitored over an interval equal to an integral multiple of the cogging torque period of the motor; a second torque command calculation unit which calculates a second torque command by subtracting the torque command approximation component from the torque command; a second torque command frequency analyzing unit which extracts frequency components, each at an integral multiple of the fundamental frequency of the cogging torque, by performing frequency analysis on the thus calculated second torque command; and a cogging compensation amount calculation unit which calculates the amount of cogging compensation from the amplitude and phase of the extracted frequency components.
Owner:FANUC LTD
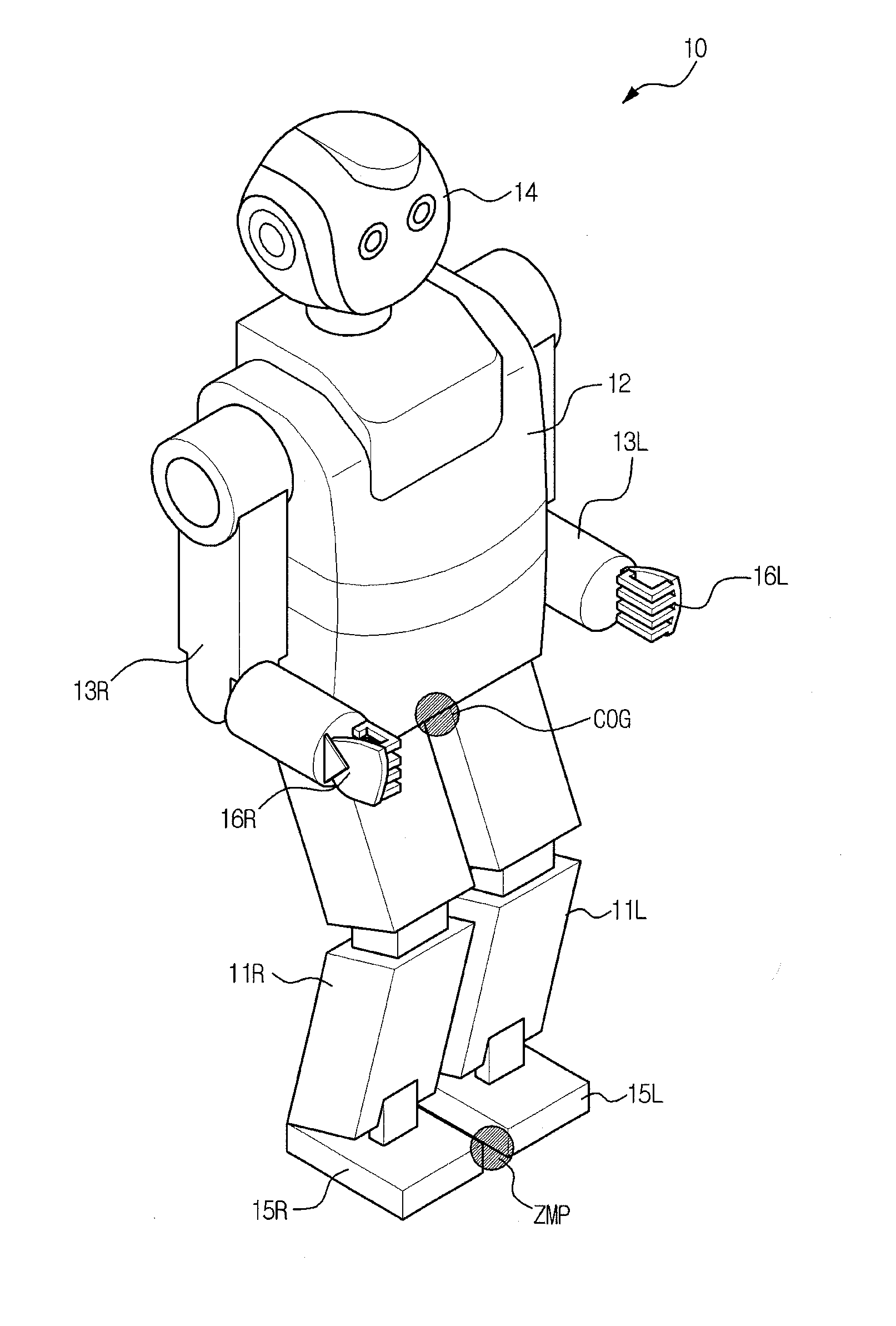
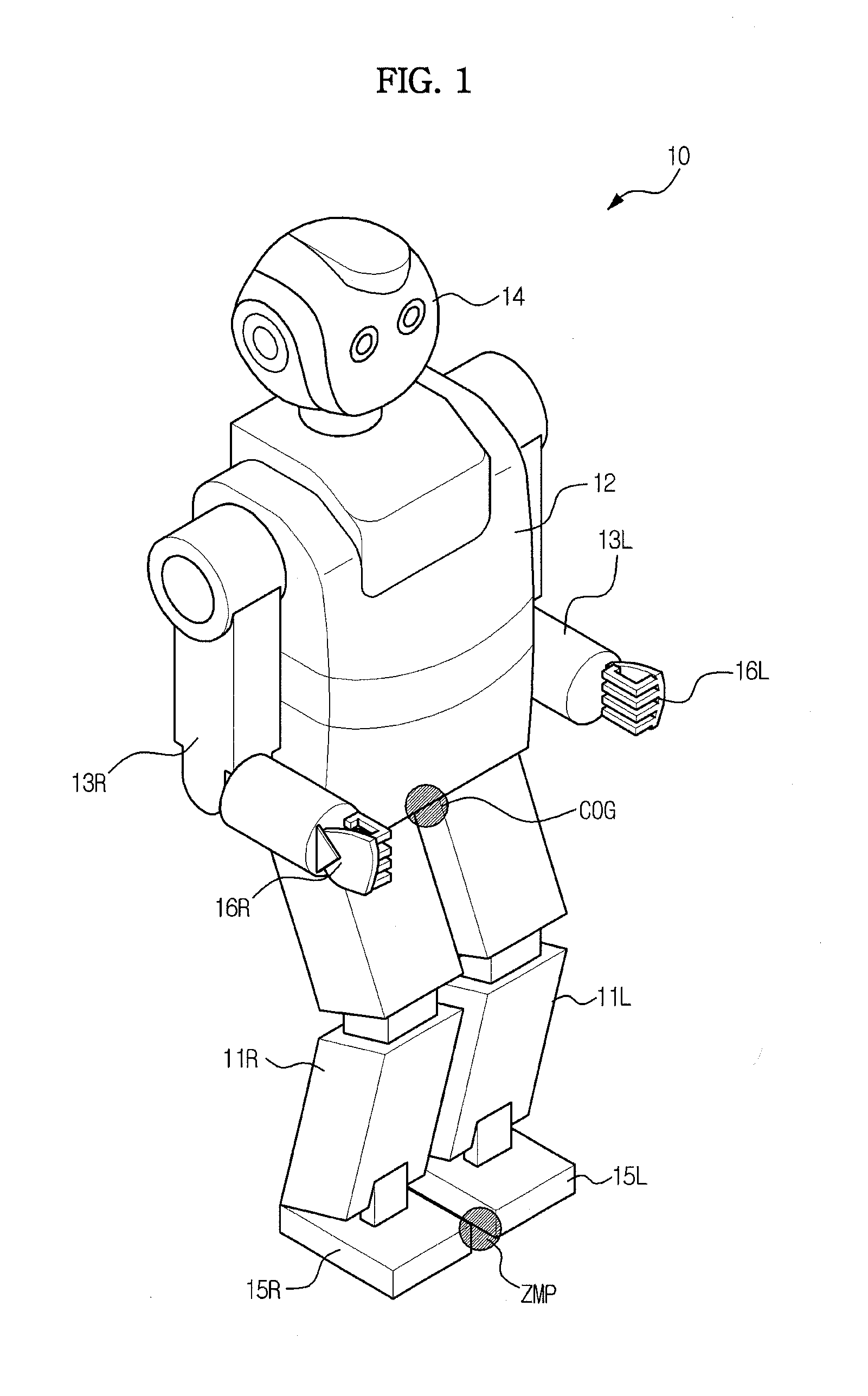
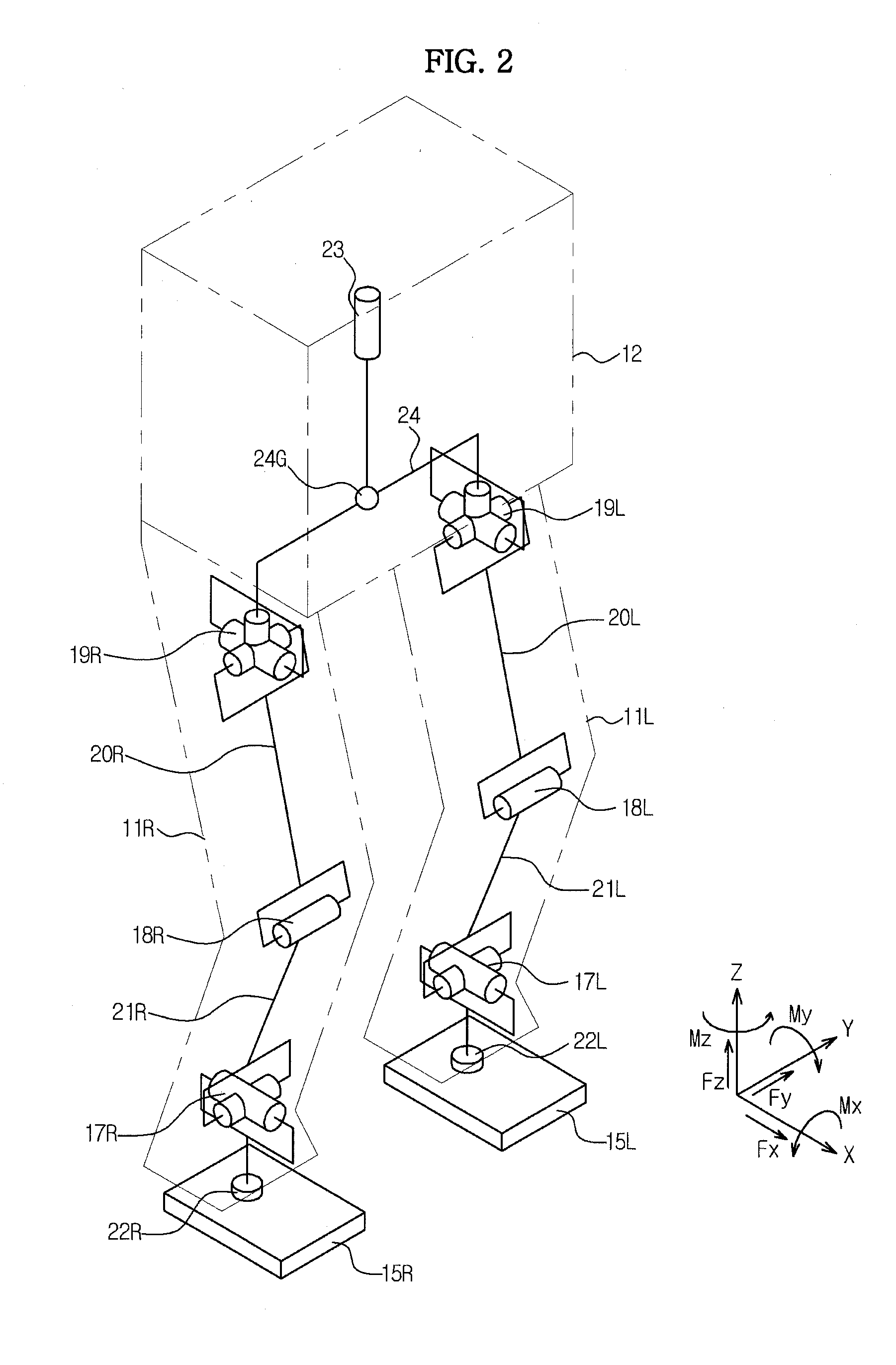
Walking robot and control method thereof
ActiveUS20120165987A1Reduce energy consumptionProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationClassical mechanics
A walking robot and a control method thereof. The control method of the walking robot which walks using two legs includes applying first virtual gravity torque including a vector component in the anti-gravity direction to respective joints of a support leg from among the two legs during walking, and applying second virtual gravity torque including a vector component in the gravity direction to respective joints of a swing leg from among the two legs during walking. Thereby, the walking robot implements a natural walking motion having a low energy consumption rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Gravity driven underactuated robot arm for assembly operations inside an aircraft wing box
InactiveUS20080028880A1Programme-controlled manipulatorControlling membersUnderactuated robotsDegrees of freedom
The invention proposes a design and deployment scheme for a hyper-articulated manipulator for assembly operations inside an aircraft wing box. The manipulator comprises nested C-channel structures connected by 1 degree of freedom rotary joints. The wing box has a large span, but is only accessible through multiple small portholes along its length. The manipulator is compact enough to enter the wing-box through the portholes, yet capable of subsequent reconfiguration so as to access multiple assembly points inside the wing-box. Traditional electromechanical actuators powering the rotary joints are unsuitable for this purpose, because of limited space and large payload requirements. The manipulator is an underactuated system which uses a single actuator at the base for the deployment of the C-channel serial linkage structure. The deployment scheme modulates gravitational torques in the system dynamics to rapidly deploy the system to a desired final configuration starting from any initial configuration.
Owner:ASADA H HARRY +1
Fresnel solar concentrator array with centered universal pivots
InactiveUS20080170312A1Minimum power consumptionEasy to operateSolar heating energyMirrorsMovement controlSolar concentrator
This invention deals with novel method and apparatus for positioning and motion control of the optical elements (mirrors and lenses) of a Fresnel solar concentrator tracking array which approximately eliminates gravitational torque by use of a central universal pivot or gimbals. Linkage torque is produced by induced and / or permanent dipole coupling to an electronic grid to produce angular deflection, and rotational motion that is enhanced by the presence of highly polarizable material. This system is ideally suited for maximization of solar energy focused by the array onto a receiver. Since there are no mechanical linkages, the instant invention is applicable for fabrication from the mini- to the nano-technology realm. The elimination of gravitational torque by balancing the optical elements on a universal pivot or gimbals greatly reduces the power required for the optical elements to track the sun and focus sunlight onto a receiver.
Owner:RABINOWITZ MARIO
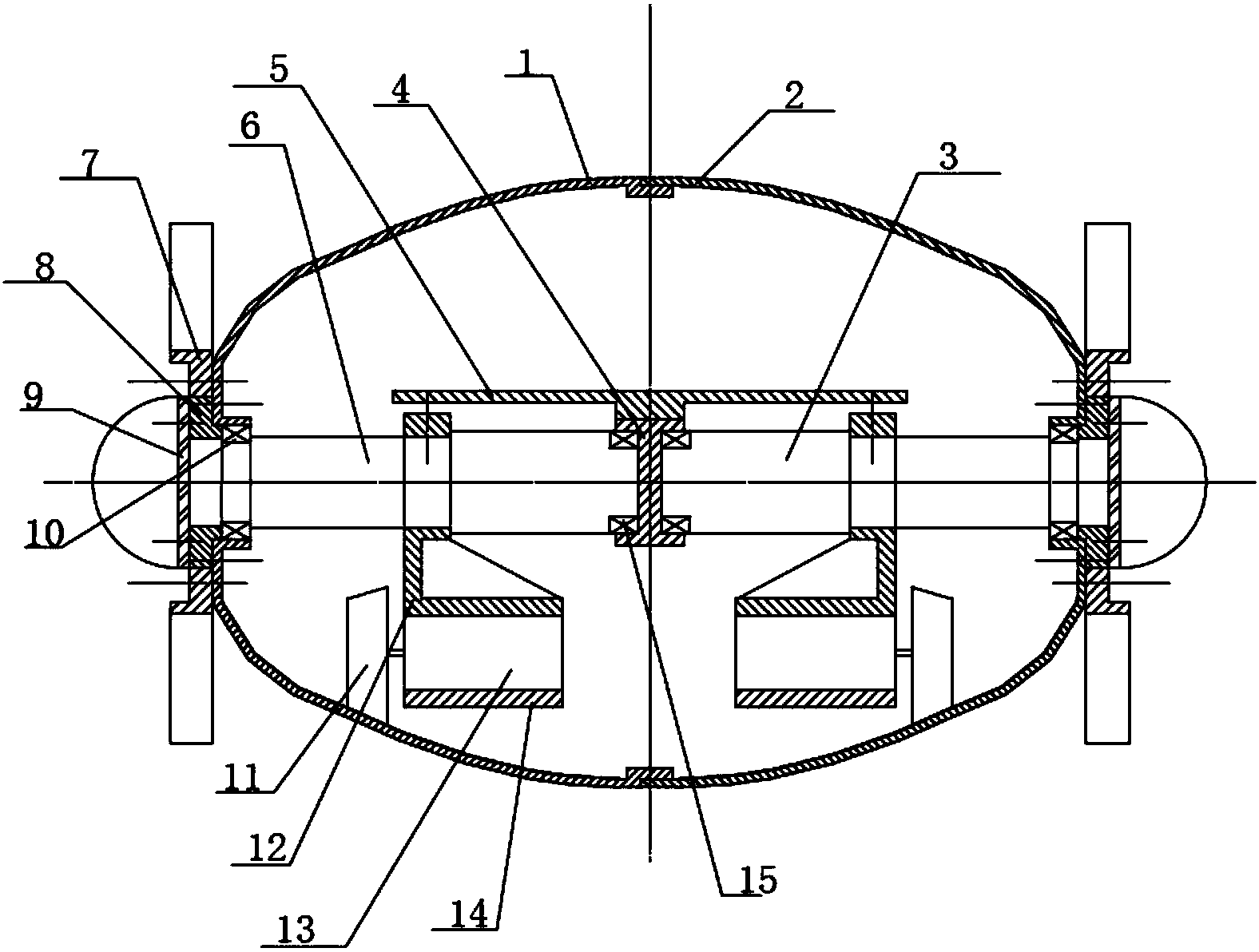
Displayer turning device, gravity balancing mechanism thereof and displayer device
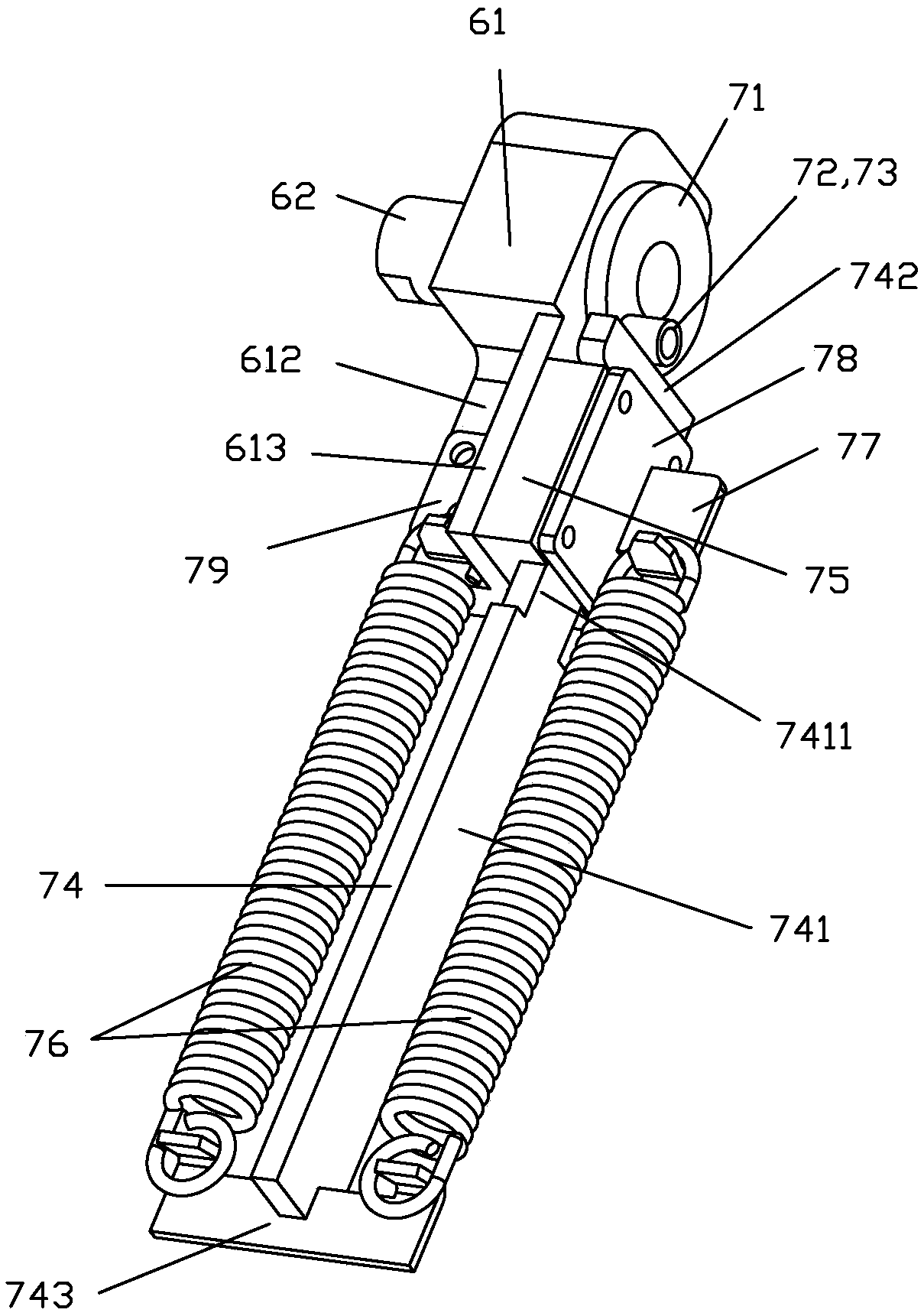
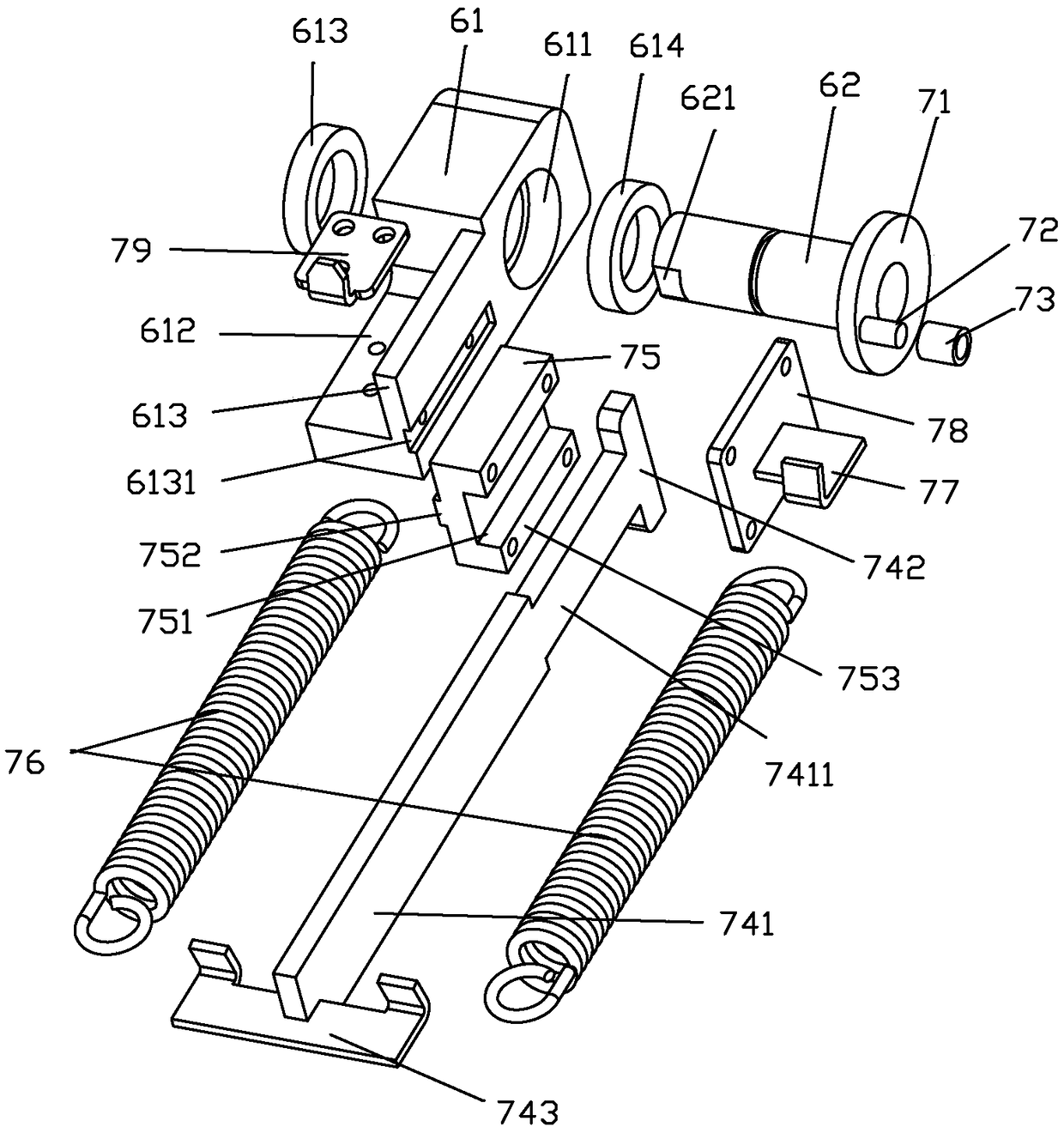
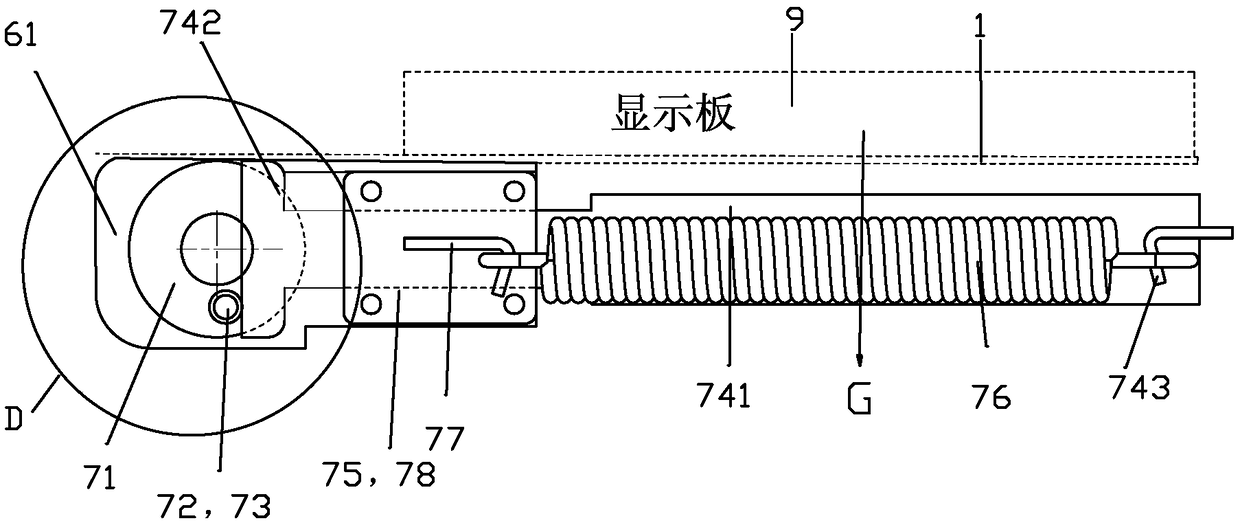
ActiveCN109236945ACounteract negative effectsImprove impact resistanceSpringsSprings/dampers design characteristicsDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention discloses a gravity balancing mechanism of a displayer turning device. The gravity balancing mechanism comprises a rotary frame part, a rotating part, a sliding part and an elastic mechanism; the rotating part can be rotatably connected to the rotary frame part with the rotating axis being an axis X, an eccentric part is fixedly connected to the rotating part and is eccentrically arranged relative to the axis X, the sliding part is slidably connected to the rotary frame part, and the elastic mechanism is connected with the sliding part and the rotary frame part and can generate elastic force applied to the sliding part, wherein the elastic force makes the sliding part abut against the eccentric part. The gravity balancing mechanism can offset gravitational torque generated bythe gravity of a display panel and a pallet in time to protect a gear motor.
Owner:XIAMEN XINSHENYUE ELECTROMECHANICAL
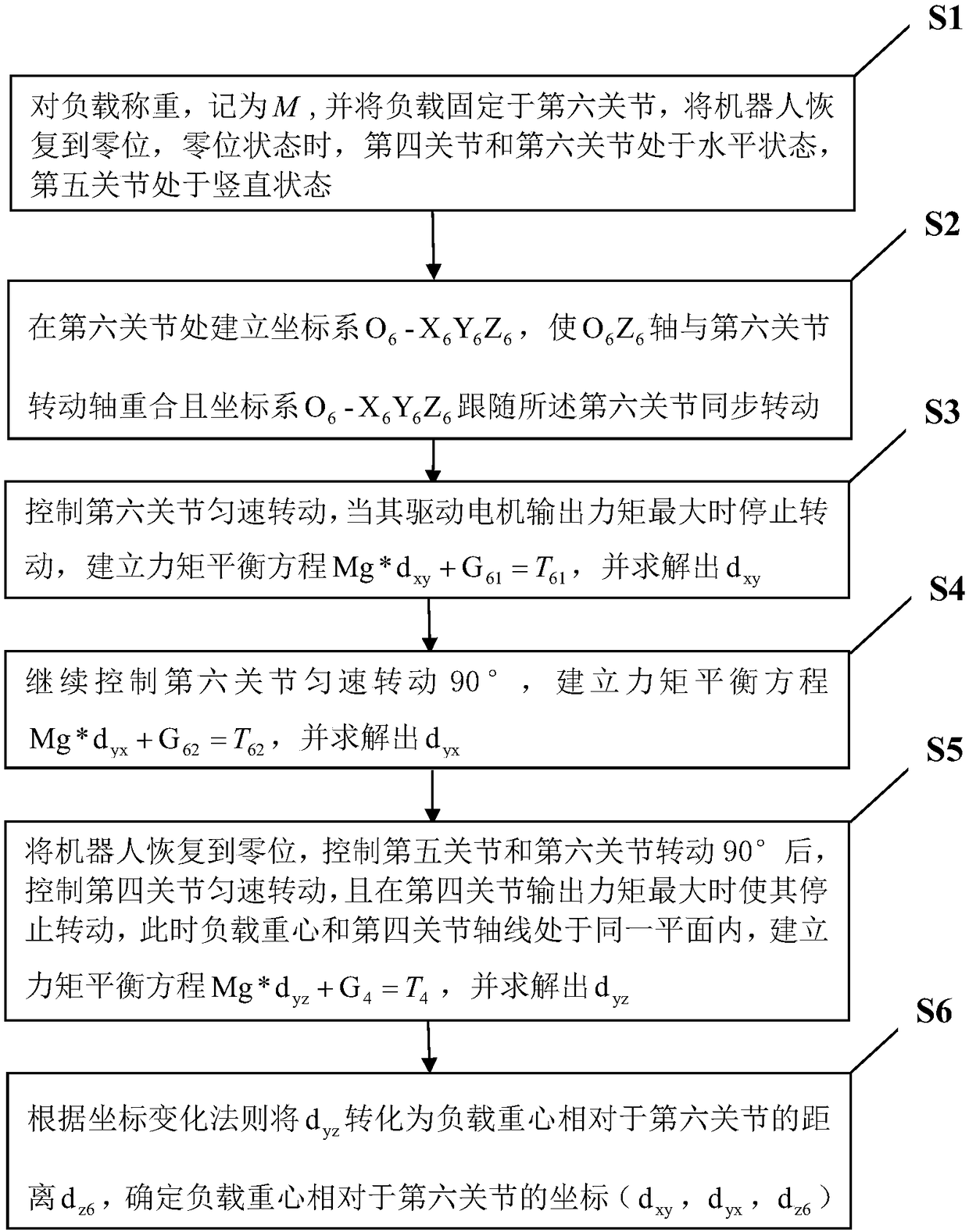
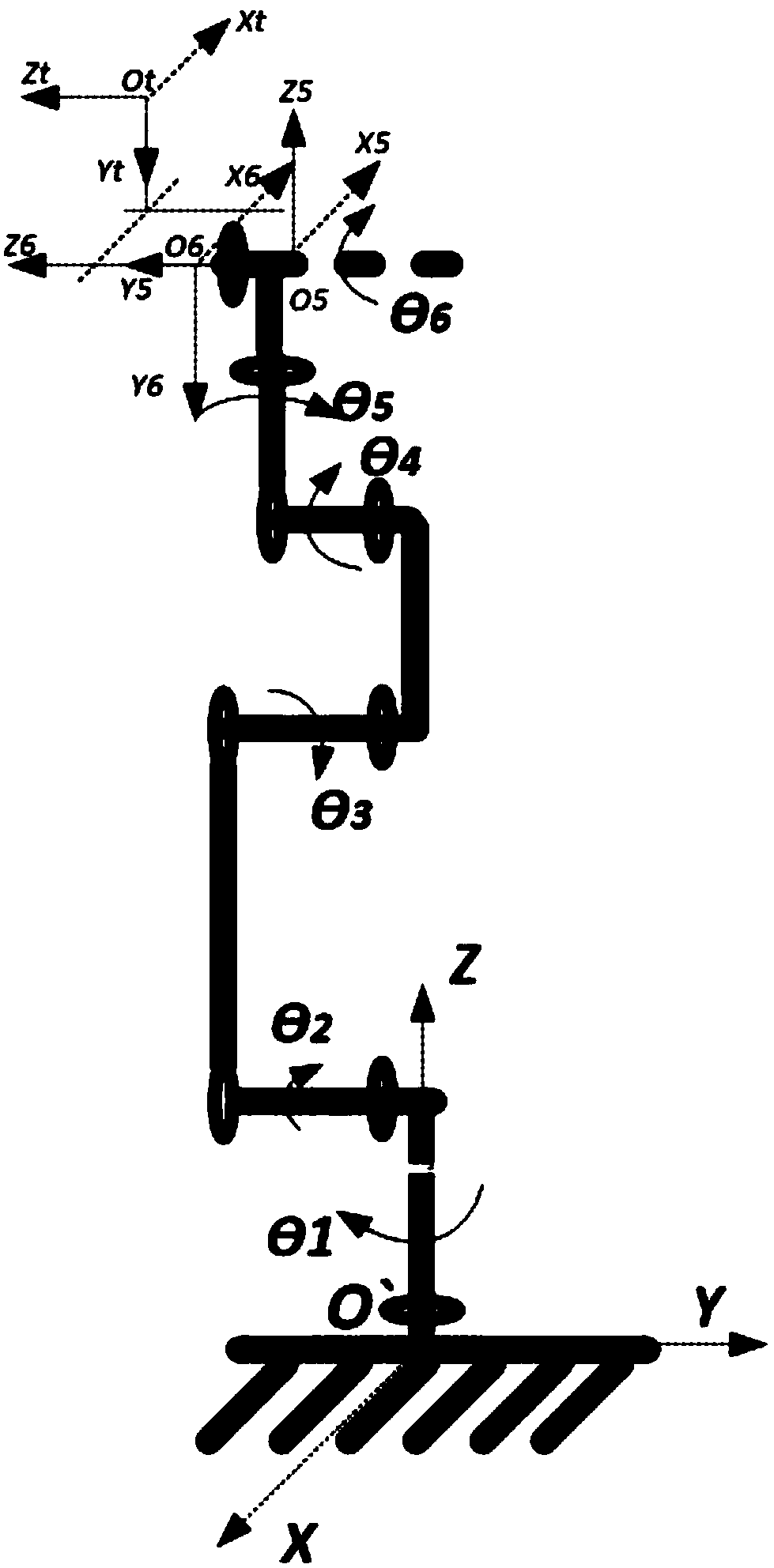
Test method of load of tool end of robot
ActiveCN109483596AHigh measurement accuracyAvoid deriving computationally difficult problemsManipulatorAngular degreesGravity center
The invention provides a test method of a load of a tool end of a robot. According to the test method, three joints at the tail end of the robot are controlled to rotate by a certain angle to measurethe gravity center of the load and the rotational inertia, the sixth joint is rotated to enable the axis of the sixth joint and the gravity center of the load to be located on the same plane; after the robot is stable, the maximum gravitational torque is applied to the sixth joint by the load, the motor output toque is read, and a force arm length is worked out to serve as the absolute value of the position of the load in one direction relative to the origin of coordinates of the sixth joint; and similarly, the three joints at the tail end of the robot are rotated to work out the gravity centers of the load in the other two directions; or, one or two of the joints are rotated by a certain angle, and the other joints are controlled to rotate to enable the axes of the joints and the gravitycenter of the load to be located on the same horizontal plane, so that the position of the gravity center is worked out; and on this basis, the three joints at the tail end of the robot are controlledto rotate in a uniform acceleration mode, so that the rotational inertias of the load in the three directions are worked out. The test method has the beneficial effects that the gravity center and rotational inertia of the load are accurately detected, and the test method is universal.
Owner:库曼机器人(武汉)有限公司
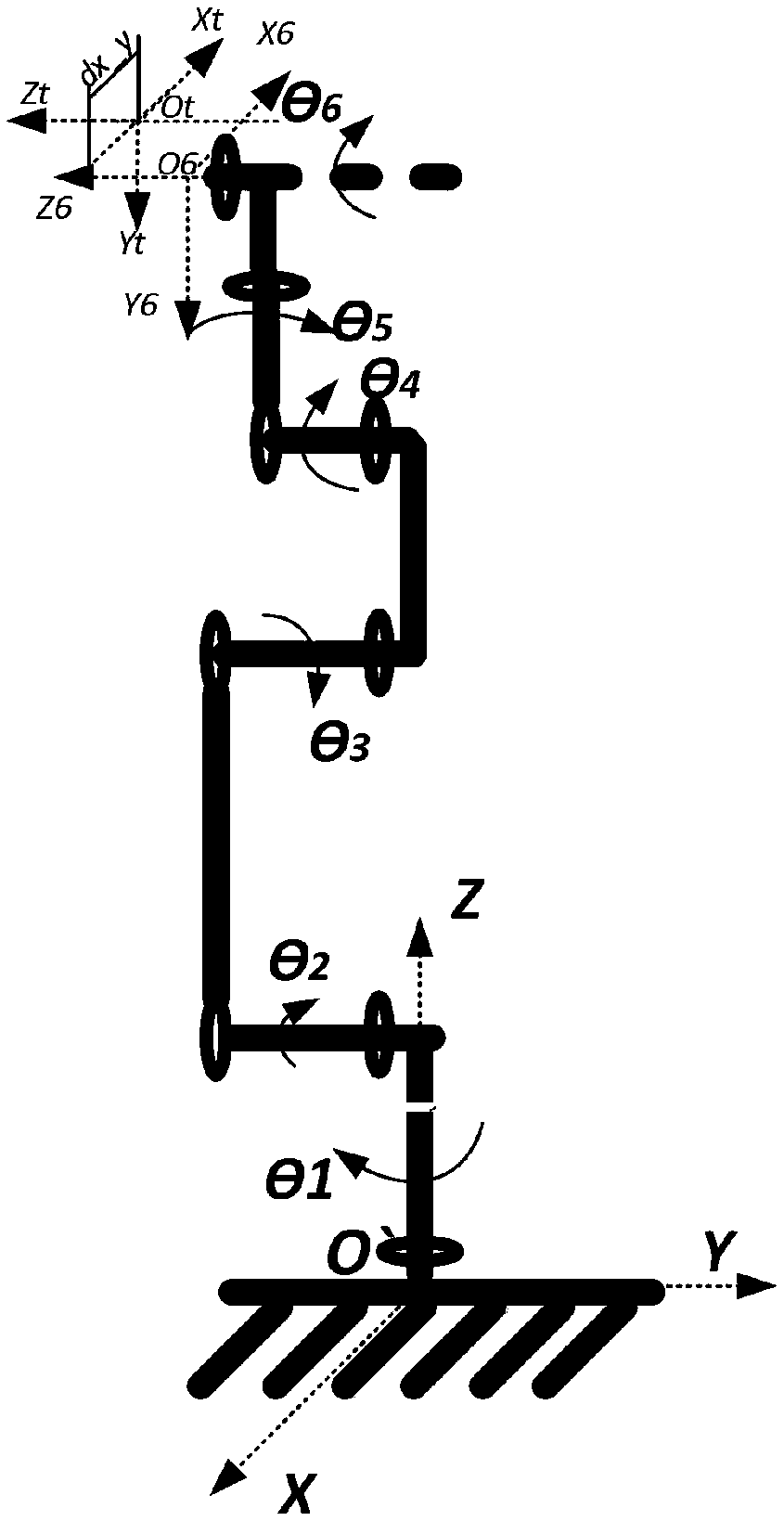
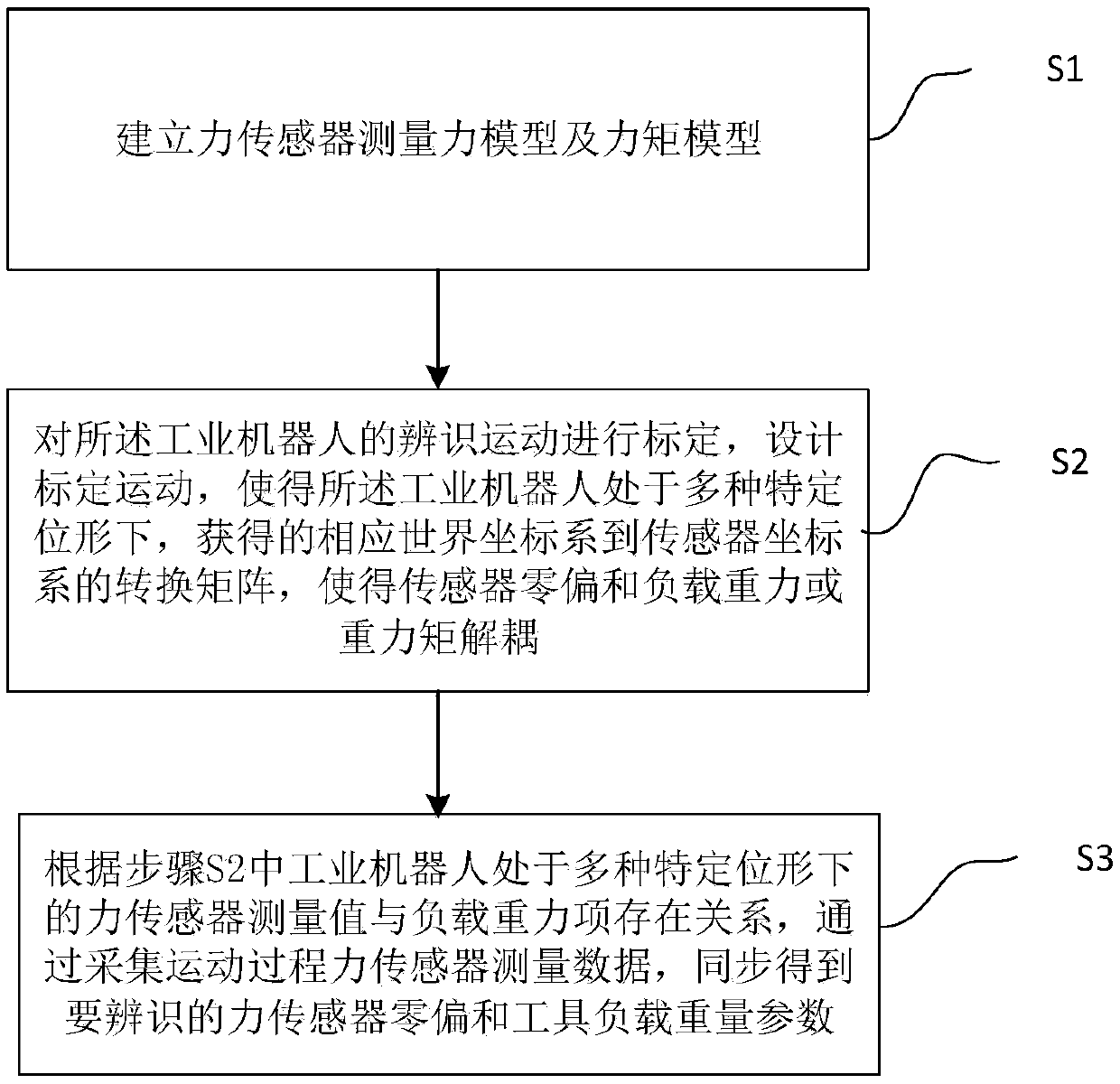
Synchronous calibration method for zero deviation and load parameters of robot end force sensor
InactiveCN108716962ARecognition time is shortCutting costsForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingControl theoryForce sensor
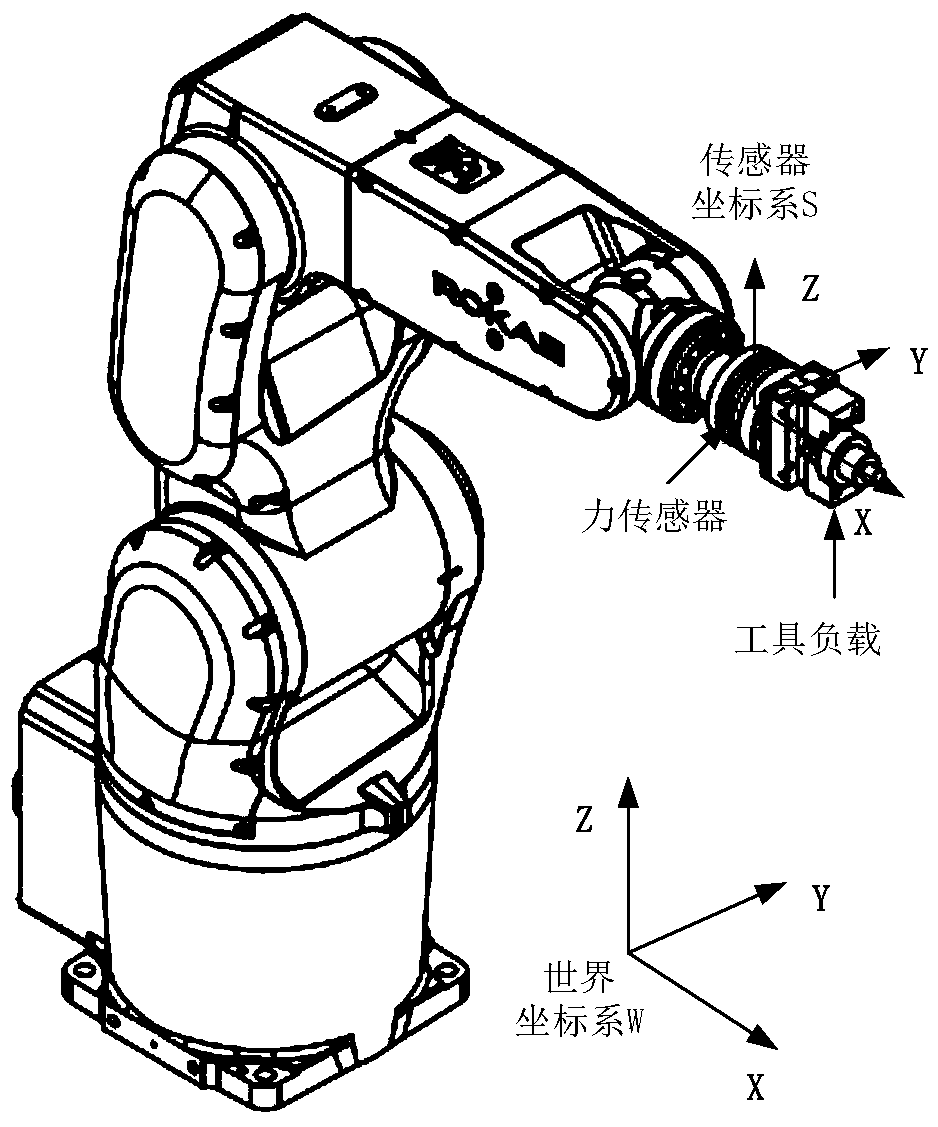
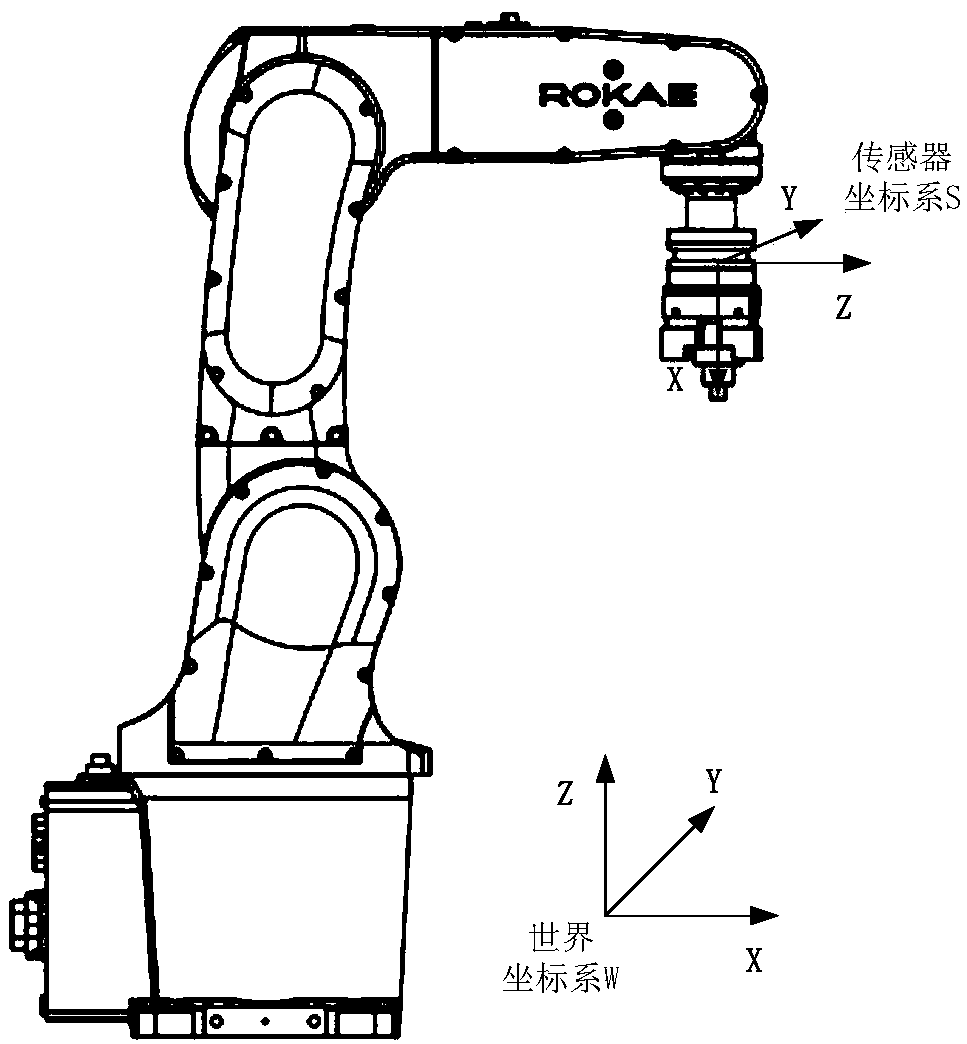
The invention provides a synchronous calibration method for zero deviation and load parameters of a robot end force sensor. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a force sensor measuring force model and a torque model; calibrating the identification movement of an industrial robot, designing a calibration motion, and making the industry robot is in a variety of specific configurations, and obtaining the transformation matrix of the corresponding world coordinate system to the sensor coordinate system, so that the sensor zero deviation and the load gravity or gravitational torque are decoupled; according to the relationship between the measured values of the force sensor and the load gravity of the industrial robot in various specific configurations, by collecting the measured values of the force sensor during the motion process, obtaining the force sensor zero deviation and the tool load gravity parameter to be identified synchronously. The method utilizes the specific shape of the robot to obtain a transformation matrix for decoupling the force sensor zero deviation and the load gravity parameter, which is applicable not only to the robot ground installation, but also to the wall installation, the hoisting and the oblique installation.
Owner:ROKAE SHANDONG INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Multifunctional master manipulator device with low center of gravity
PendingCN107553467AImprove stabilityEasy to operateProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsPartial gravityWire wheel
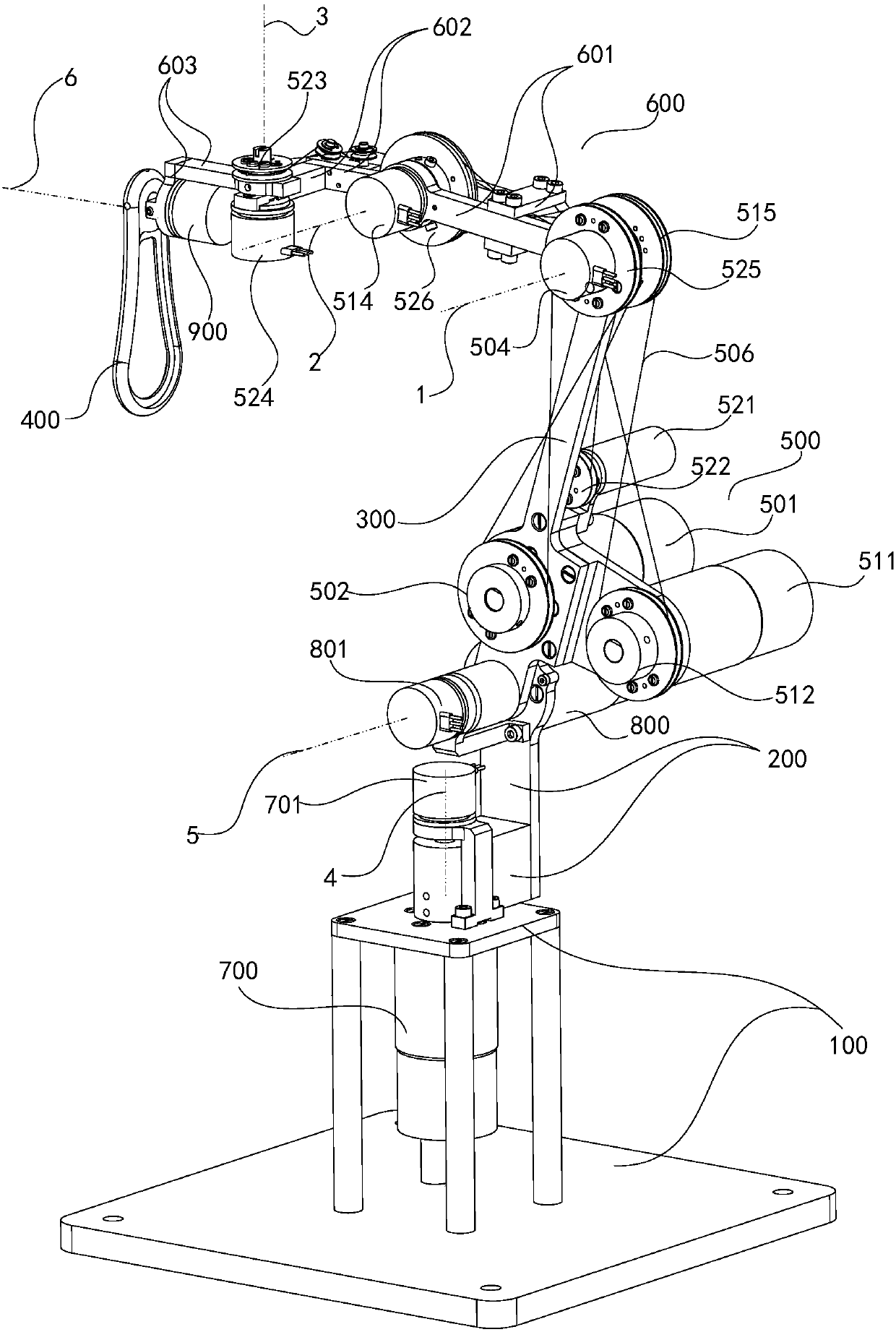
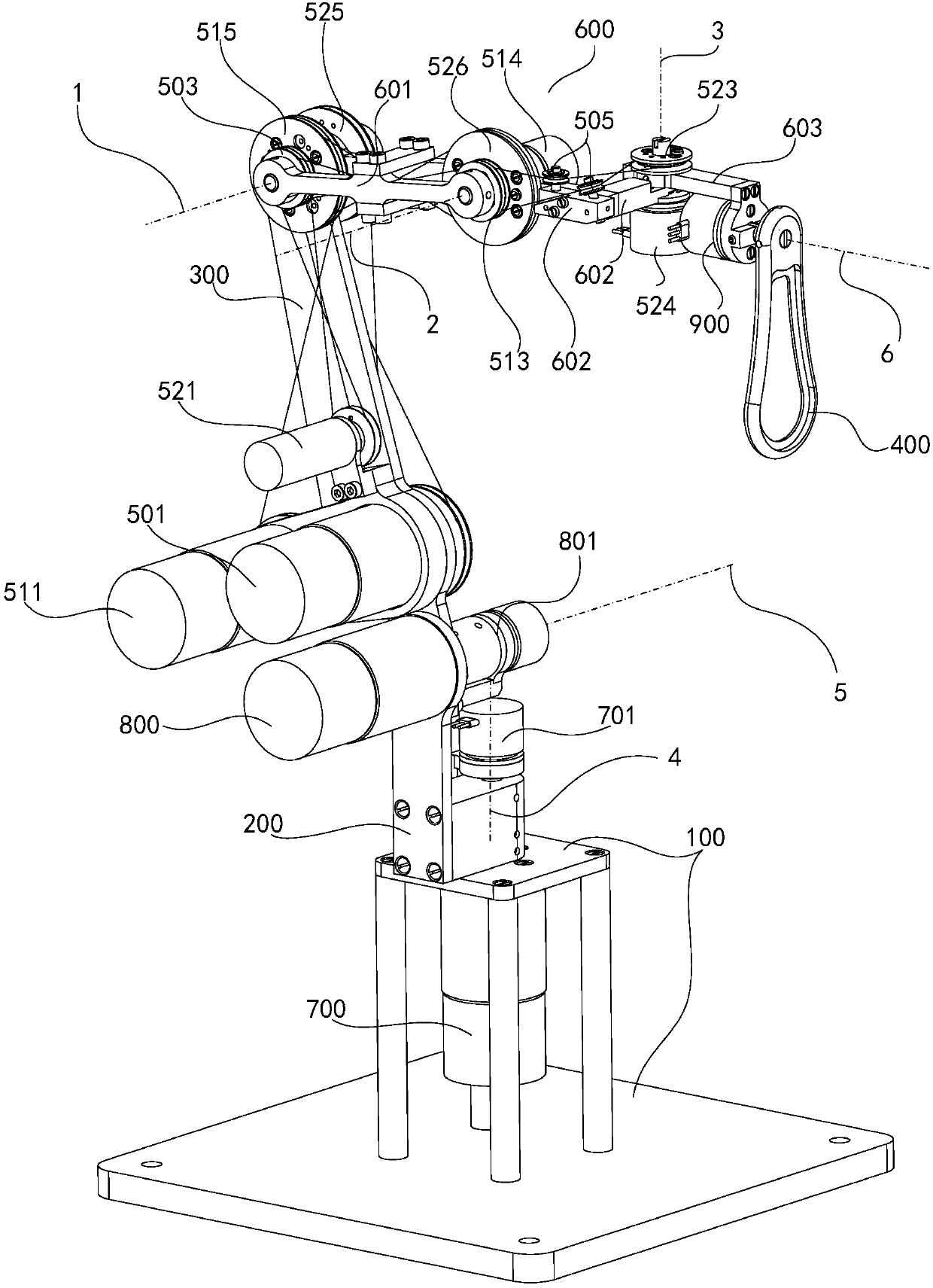
The invention relates to a multifunctional master manipulator device with the low center of gravity. The multifunctional master manipulator device comprises a pedestal, a supporting rod, a connectingrod, a plurality of joint connecting rods, a plurality of transmission assemblies and a handle. The pedestal is in transmission connection with one end of the supporting rod, and the other end of thesupporting rod is in transmission connection with one end of the connecting rod. The multiple joint connecting rods are in transmission connection end to end to form a connecting arm. The connecting arm extends to the side deviating from the tilting direction of the connecting rod. The two ends of the connecting arm are in transmission connection with the other end of the connecting rod and the handle. The transmission assemblies comprise first drivers and steel wire wheel components. The first drivers are arranged on the connecting rod and get close to the supporting rod. The steel wire wheelcomponents are arranged on the joint connecting rods to be driven, and the first drivers drive the steel wire wheel components to drive the corresponding joint connecting rods to move. According to the multifunctional master manipulator device with the low center of gravity, the first drivers are arranged at the position, close to the supporting rod, of the connecting rod in a skewing mode, partof gravitational torque of the connecting arm can be compensated for, the center of gravity of the whole master manipulator device can get close to the pedestal, and thus the whole master manipulatordevice can be better stabilized.
Owner:国机智能技术研究院有限公司
Torque detecting method and arm device
ActiveUS9533414B2Good compensationImprove accuracyProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorGravitational forceEngineering
According to a torque detecting method, gravitational torque applied to a rotary shaft of an arm is detected in a condition where position control of the arm is stopped, when the arm is located at a first position at which the arm is oriented in a direction different from a direction of gravitational force. Then, a gravity coefficient used for calculating gravitational torque corresponding to a position of the arm is calculated, based on the gravitational torque and the first position. Then, gravitational torque during position control is calculated, based on the position of the arm detected during the position control, and the gravity coefficient. Further, an actual output torque during the position control is calculated, based on operating torque applied to the rotary shaft and detected during the position control, and the gravitational torque calculated during the position control.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Ellipsoidal robot
The invention provides an ellipsoidal robot. The movement of the ellipsoidal robot is controlled through gravitational torque and friction torque. The ellipsoidal robot mainly comprises a semi-ellipsoidal case I, a semi-ellipsoidal case II, a center shaft I, a center shaft II, a center shaft connector, a center shaft carrying platform, two driving motors, two driving wheels, two motor installation parts, two motor fastening parts, two shaft end covers, two cameras, camera fixing parts, two paddles and a bearing. When the two motors are the same in rotation speed and direction, the two driving wheels climb along the inner walls of the cases synchronously and drive the ellipsoidal robot to move forward or backward. When the two driving motors are different in speed or opposite in direction, the friction force on the cases from the driving wheels forms the friction torque and drives the ellipsoidal robot to turn. When the two paddles are installed, the ellipsoidal robot can be operated in water. The ellipsoidal robot is provided with the stable platform, the internal space of the semi-ellipsoidal cases is large so that many devices can be carried, and differential steering is adopted, so that control is simple and stable.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Mechanism for compensating gravitational torque generated by vertical rotary component
ActiveCN106454222AThe drive control circuit is simpleExtended service lifeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectric machineTerminal equipment
The invention discloses a mechanism for compensating gravitational torque generated by a vertical rotary component and relates to the technical field of video terminal equipment. The mechanism is composed of a main shaft, a crankshaft and a power-assisted part. One end of the crankshaft is vertically connected with one end of the main shaft, and the other end of the crankshaft is hinged to the power-assisted part. The mechanism can generate varying elastic force. Elastic torque for the output shaft of a motor is generated by the elastic force and can balance gravitational torque for the main shaft of the motor, wherein the gravitational torque is generated because the direction where the vertical rotary component bears gravity is not on the same straight line with the direction of the main shaft of the motor, and the varying range of the elastic torque is large, so that problems that the service life of the motor is reduced due to gravitational torque, and the drive control circuit of video terminal equipment is complicated are effectively solved.
Owner:CHINA FORESTRY STAR BEIJING TECH INFORMATION CO LTD
Power transmission monitoring and maintenance systems and methods
ActiveUS8604776B2Machine part testingDevices using electric/magnetic meansElectric power transmissionAccelerometer
Power transmission monitoring systems includes rotation speed sensors mounted to hubs of a power transmission pulley. A sensor comprises a rotation sensing device, and a controller receiving rotation data therefrom and determining rotation speed of the pulley. A transmitter transmits rotational speed of the pulley to a receiver, which may include or be connected to a device that compares the rotational speed to rotational speed in transmissions from other sensors to determine slip in the power transmission system. The rotation speed sensing device may be an accelerometer, or a gravitational torque harvester. A harvester might include a rotor body rotating with the pulley and mounting induction coils, and a gravitational torque stator mounting an induction magnet and including an air vane damper maintaining the stator stationary with respect to the rotor, through air resistance. The transmissions may be employed to monitor, maintain and repair the power transmissions system.
Owner:SCHRADER ELECTRONICS LTD
Counterbalancing Linkage Mechanism
ActiveCN105881585AReduce capacityMaximize load capacityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGearingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A counterbalancing linkage mechanism includes a base link including a first joint; a second link forming a second joint to be rotatably connected to the base link; and a counter balancer having one portion disposed at the second joint and another portion movably disposed at the base link along a length direction of the second link. The counter balancer compensates a gravitational torque generated due to a weight of the second link when the second link rotates on the second joint. A third link is connected to the second link. The counter balancer comprises a counter balancer delivery portion connected to the second link and rotating by the rotation of the second link. A counter balancer driving portion is in contact with the counter balancer delivery portion, linearly moves by the rotation of the counter balancer delivery portion, and compensates the gravitational torque and a load capacity due to interaction with the counter balancer delivery portion.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND +2
Self-adaptive coordination control method of multi-robot-arm system
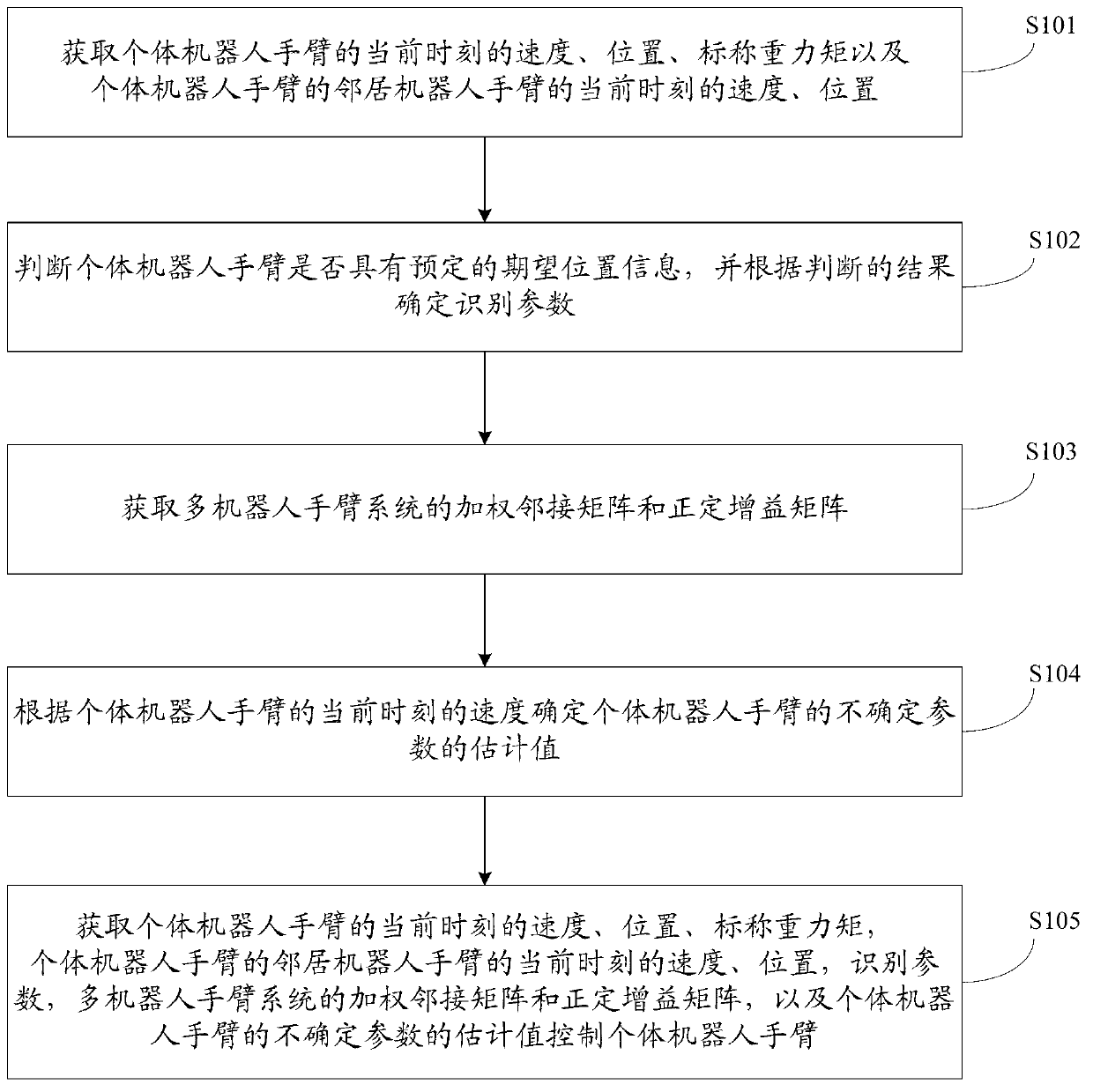
The invention provides a self-adaptive coordination control method of a multi-robot-arm system. The self-adaptive coordination control method comprises the steps that the position, the speed and nominal gravitational torque of an individual robot arm at the current moment and the position and the speed of an adjacent robot arm at the current moment are obtained; recognition parameters are determined according to whether the individual robot arm has a judgment result of reserved expecting position information or not; a weighing adjacent matrix and a positive definite gain matrix of the multi-robot-arm system are obtained; estimated values of uncertain parameters of the individual robot arm are determined according to the speed of the individual robot arm at the current moment; the individual robot arm is controlled according to the position, the speed and nominal gravitational torque of the individual robot arm at the current moment, the position and the speed of the adjacent robot arm at the current moment, the recognition parameters, the weighing adjacent matrix, the positive definite gain matrix and the estimated values of the uncertain parameters. The self-adaptive coordination control method guarantees that the multi-robot-arm system can complete given tasks in the environment where uncertain external interference exists, and is high in control precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
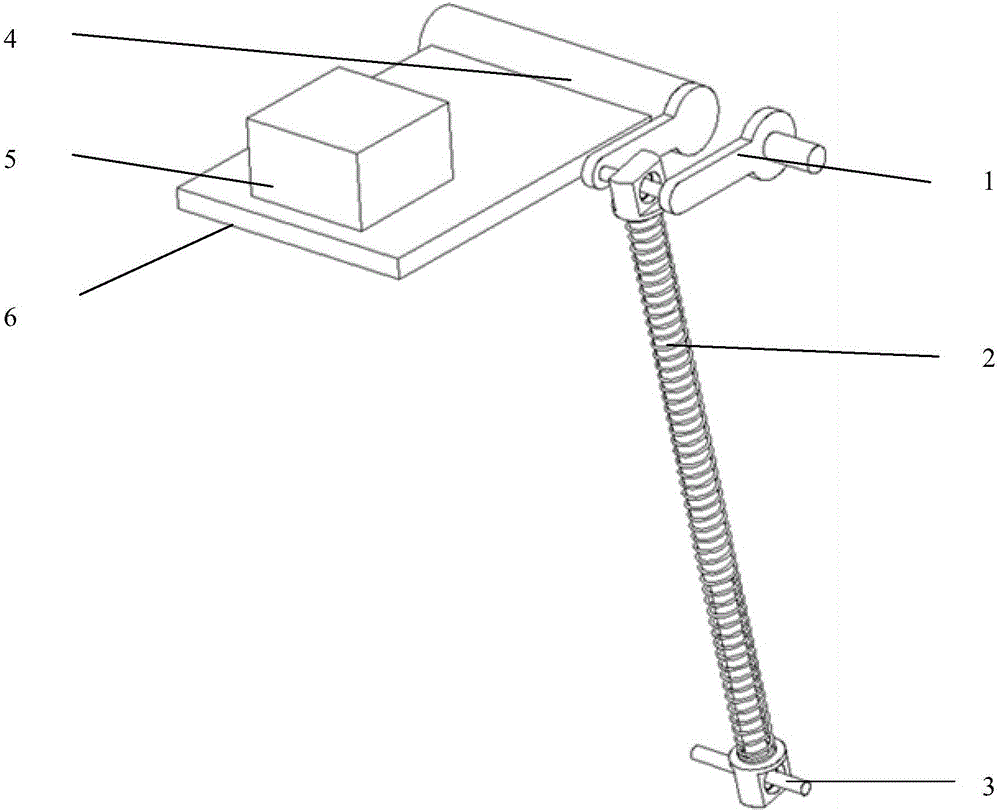
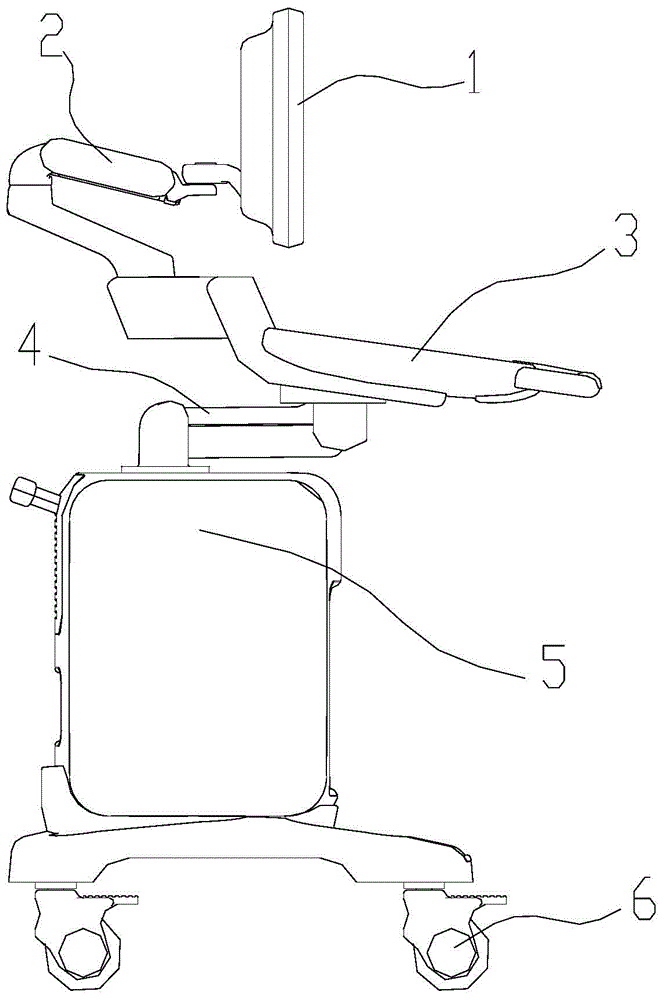
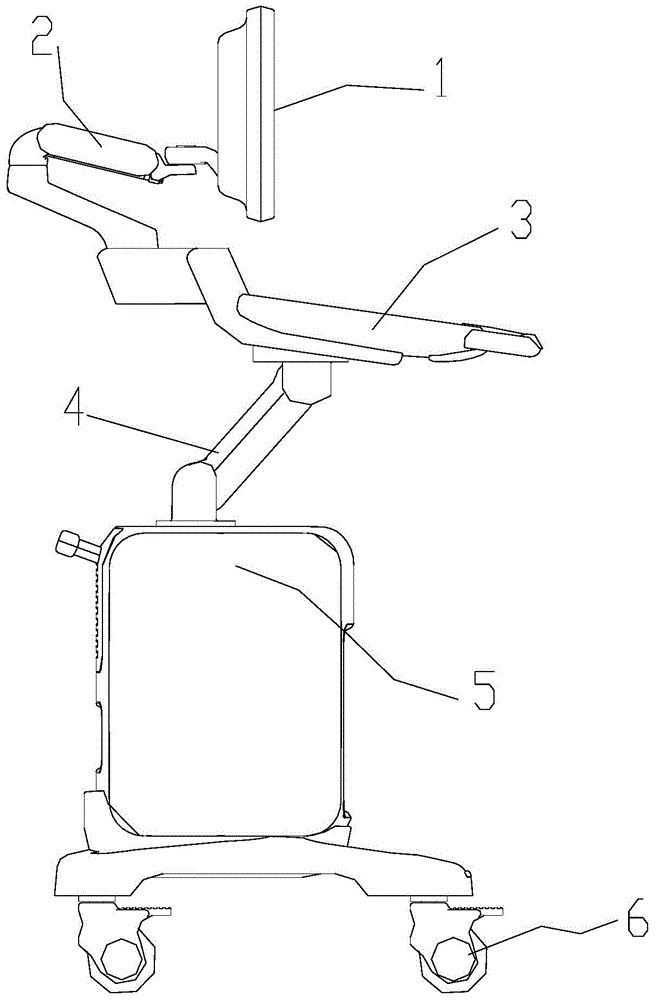
Lifting support device and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
ActiveCN105078508AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsEngineeringGravitational torque
The invention discloses a lifting support device and an ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus. The lifting support device is capable of supporting and lifting a carrier and comprises a base, an upper support and a spring assist; one end of the upper support is rotatably connected with the base, and the other end thereof can support the carrier; the spring assist comprises at least two springs disposed in a same direction; one end of every spring is abutted to the base, and the other end thereof is abutted to the upper support; acting torque that the springs apply to the upper support to balance gravitational torque that the upper support bears. By providing the spring assist with the multiple springs, the acting torque of the springs is used to balance the gravitational torque; since the springs are generally good in stability and rarely fail during long-term using, force values of the springs rarely attenuate, the lifting support device is more reliable, and maintenance cost is lower; owing to the multiple springs, great supporting force can be provided in small space, and applicable range of the lifting support device is widened.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rotational gravitational torque-generating system and method
A rotational gravitational machine including a rotatable structure and a set of movable weight assemblies carried by the rotatable structure and jointly rotatable with the rotatable structure about a rotation axis. The movable weight assemblies are arranged radially spaced apart from the rotation axis and angularly spaced apart from each other. Each movable weight assembly includes a movable magnetic weight that can reciprocally and radially move between radially innermost and outermost positions relative to the rotation axis. A first magnetic biasing system is provided, including a radially movable, first magnetic piston which magnetically biases the movable magnetic weight between the radially innermost position and the radially outermost position in order to unbalance the assembly formed by the rotatable structure and movable weight assemblies. This unbalancing allows gravity to produce a torque arm that promotes rotation of the assembly about the rotation axis.
Owner:JENKINS ROBERT E
Non-Power Driven Window Capable Of Adjusting Ventilation Rate
InactiveUS20200240188A1Stable air volumeOpening of the window decreasesBuilding braking devicesVentilation arrangementSash windowEngineering
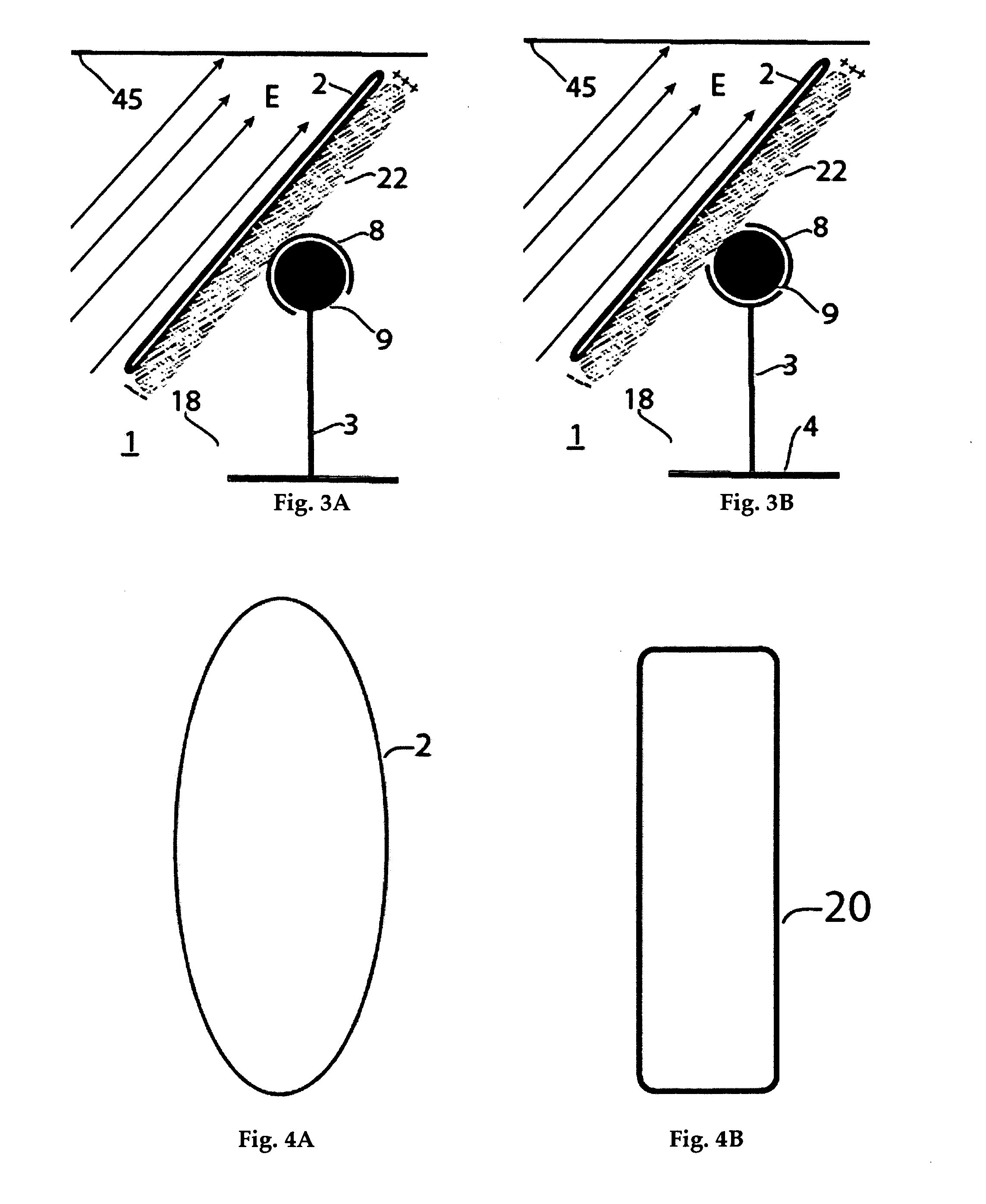
The present invention discloses anon-power driven window capable of adjusting ventilation rate. When the sash is unlocked, due to combined action of the sash's gravitational torque and the expansion of a torsion spring against the sash, the window keeps open. The window is designed having a bigger size in the lower section below the pivot than that in the upper section. Subject to the outdoor wind blowing, the moment by the outdoor wind tends to shut the window. In addition, the upper screen is installed in the outer side of the pane above the pivot, while lower screen is installed to the inner side of the pane below the pivot. Thus the lower sash is exposed into the outdoor air and can be easily blown by the outdoor wind. Consequently, the stronger is the outdoor wind, the smaller is the effective opening of the window for ventilation, and vice versa.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Grounding switch for direct-current valve hall and grounding conducting rod mechanism of grounding switch
ActiveCN102832073ASmall operating forceThe opening and closing process is stableSwitches with movable electrical contactsHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesEngineeringGravitational torque
The invention relates to a grounding switch for a direct-current valve hall and a grounding conducting rod mechanism of the grounding switch. The grounding conducting rod mechanism comprises a grounding conducting rod, a transmission base and a counterweight structure, the grounding conducting rod can swing back and forth relative to a corresponding wall surface of the valve hall, the transmission base is used for being mounted on the corresponding wall surface of the valve hall, a conducting rod rotary shaft which is in running fit with the transmission base is fixedly arranged at one end of the grounding conducting rod, the rotation axis of the conducting rod rotary shaft extends along the left-right direction, and the counterweight structure is in transmission connection with the conducting rod rotary shaft by a balance transmission mechanism so as to apply torque for overcoming gravitational torque of the grounding conducting rod. The problem that a grounding conducting rod in the prior art cannot be switched on or off stably is solved.
Owner:HENAN PINGGAO ELECTRIC +2
Automatic light mechanical arm
InactiveCN106113003ALightweightBrisk movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic armControl engineering
The invention discloses an automatic light mechanical arm which comprises a base, a driving fixed seat and a mechanical arm. A control main center is fixed on the base. A power line interface is mounted on one side of the control main center. The driving fixed seat is connected with the control main center. A fixed cover fixed through a driving device is arranged on the driving fixed seat. The mechanical arm is connected with the driving fixed seat through a third rotating structure. A first rotating structure is connected to the upper part of the mechanical arm through a buckle. An expansion link is arranged at the front part of an expansion structure. A rotating shaft is mounted at the front end of the expansion link. A second rotating structure is arranged at the front part of the rotating shaft. A front end device is fixed on the second rotating structure. The automatic light mechanical arm is compact in structural design, the moving arm with the expansion structure is adopted, the gravitational torque is reduced, the flexibility of the mechanical arm is improved, an arm and a vertical column are prevented from being stuck, machine manufacturing can be conducted well, and development of the mechanical arm industry is promoted.
Owner:WUXI XINGUANG COMP INSTALLATION
Platform perpendicular lifting mechanism with unchanged gravitational torque
InactiveCN107055382ASmooth motionSolve the problem of changing the gravity momentLifting framesHydraulic cylinderGear wheel
The invention discloses a platform vertical lifting mechanism with constant gravity moment, which belongs to the technical field of lifting equipment. It consists of a front lifting mechanism, a rear lifting mechanism, a platform and a base. The top of the platform is used to carry goods and the lower part is used to install related gears and pins. The structures of the front lifting mechanism and the rear lifting mechanism are exactly the same as the corresponding dimensions, which belong to virtual constraints. Application, jointly used to realize the motion transformation and force support of platform lifting, the front lifting mechanism is driven by the front hydraulic cylinder, the rear lifting mechanism is driven by the rear hydraulic cylinder, the two sets of hydraulic cylinders act synchronously, and the base is used to support related components and pins , can be used in a single section or in multiple sections. Whether it is a single-section mechanism or a multi-section combined mechanism, the degree of freedom of the present invention is always 1, and only one active part is needed to realize the vertical lift of the platform. When the platform is vertically lifted The moment of cargo gravity remains constant.
Owner:JIANGSU VOCATIONAL INST OF ARCHITECTURAL TECH
Rotating magnetic field device
InactiveCN105655089AEasy to adjustAdjustable rotation speedElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetic variable regulationControl theoryGravitational torque
A rotating magnetic field device comprises an electromagnet, bearing pedestals, a coupling wheel, a speed reducer, a rotating shaft, a balance weight, a support, a power source control cabinet and a motor. The electromagnet is in a capital C shape, is composed of two sets of electromagnetic coils and electrical iron magnetic conductive loops and provides a direct-current magnetic field at intervals after being powered on. The two bearing pedestals symmetrically support the electromagnet. The electromagnet is connected with the speed reducer through the rotating shaft and the coupling wheel; the speed reducer is connected with the motor, and power is supplied to rotation of the electromagnet after the rotating speed of the motor is reduced; the balance weight and the electromagnet are symmetrically distributed on the two sides of the rotating shaft, the gravitational torque of the balance weight and the gravitational torque of the electromagnet are equal when the balance weight and the electromagnet rotate, and unbalance caused to the system when the electromagnet rotates can be eliminated; the power source control cabinet is connected with the motor and provides energy for the system, and operation parameters can be set conveniently; the support is located on the lowest position of the whole device and used for supporting all the other structural components. The magnetic field intensity can be adjusted conveniently by adjusting currents, rotation movement perpendicular to the magnetic field direction can be achieved, and the rotation speed is adjustable.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
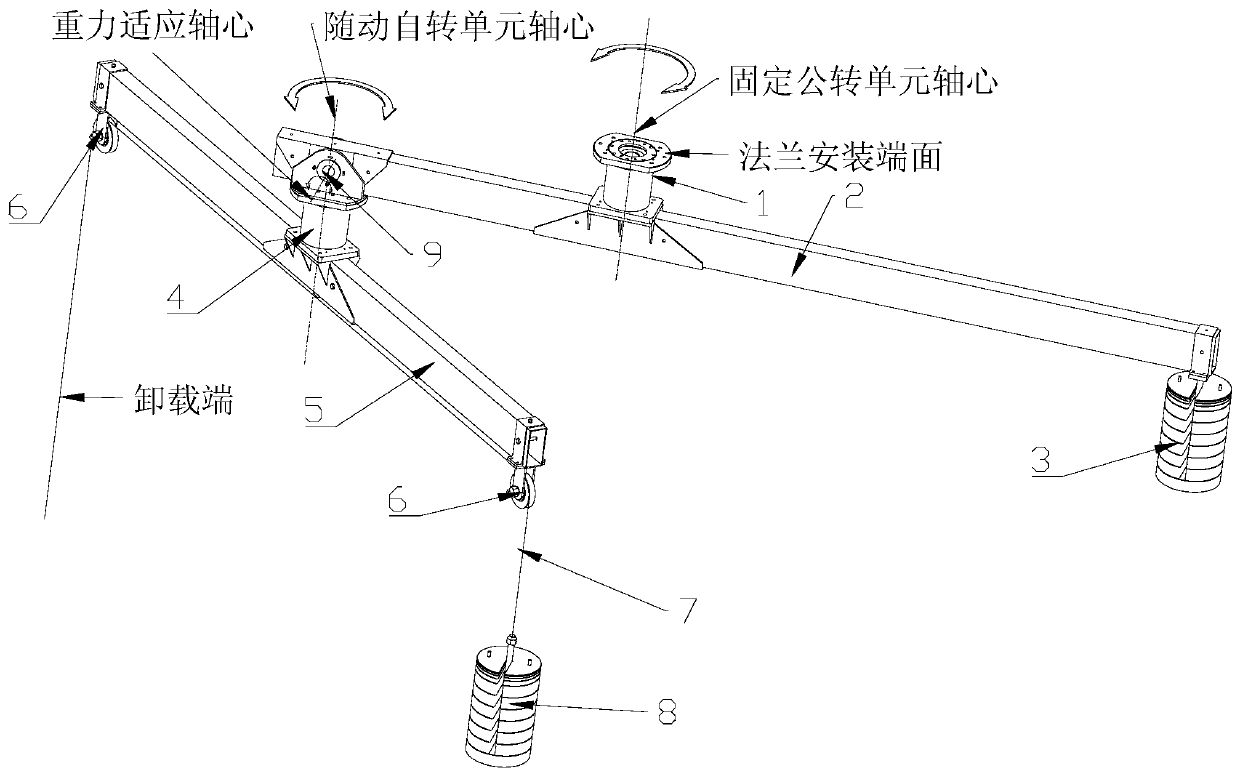
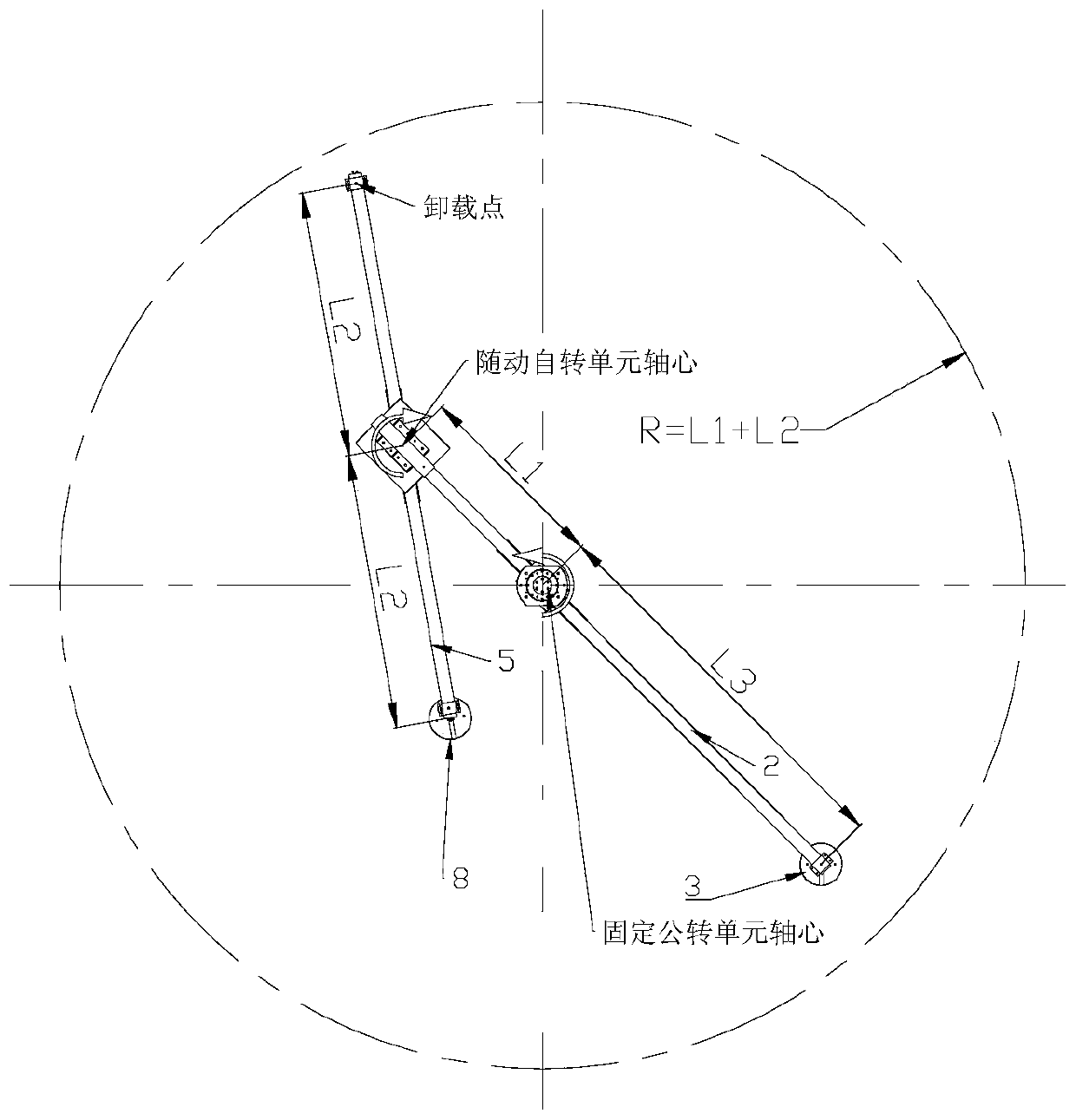
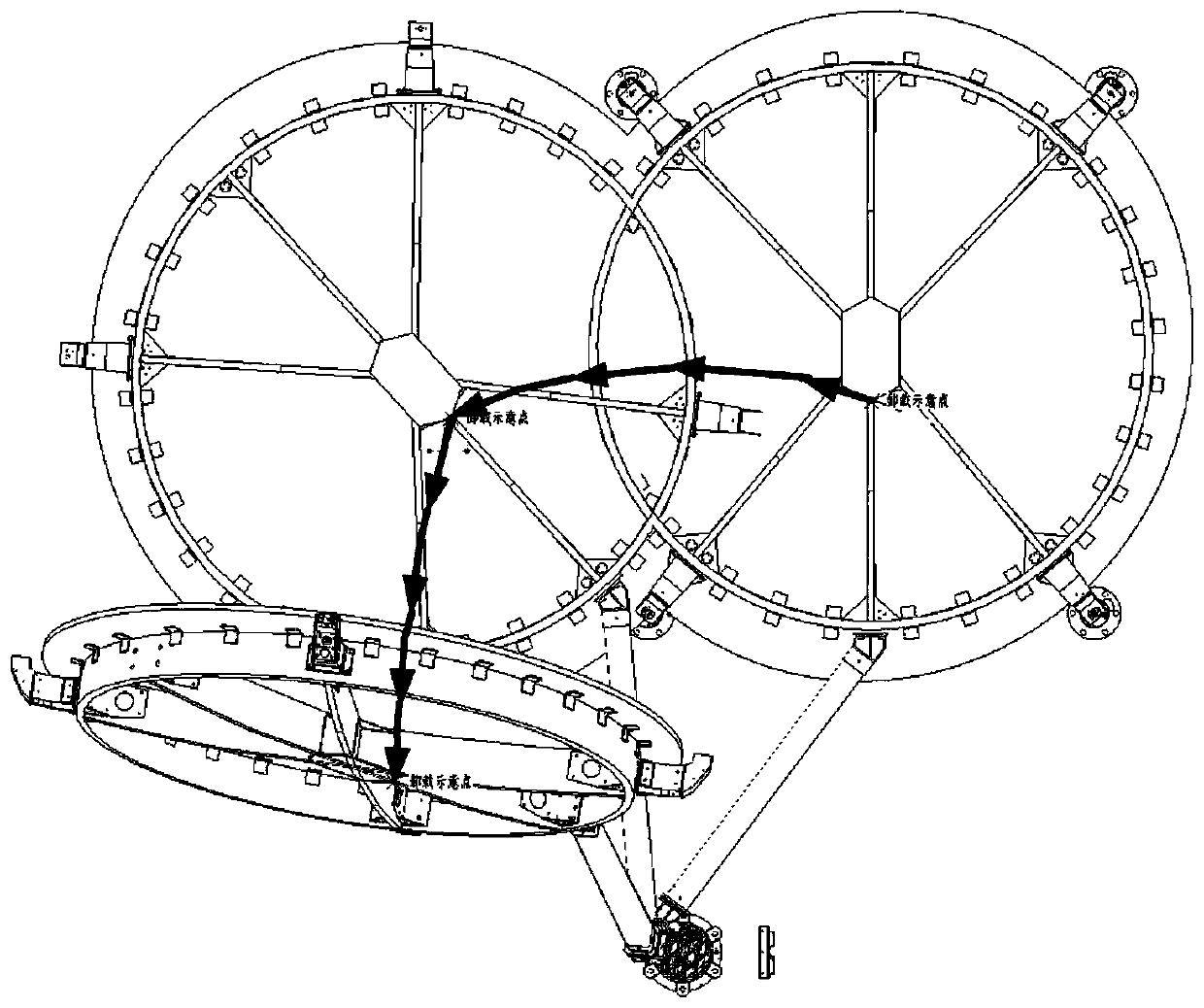
Universal zero-gravity unloading device
ActiveCN110395415AImprove stabilityEasy to transportCosmonautic condition simulationsThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
The invention relates to a universal zero-gravity unloading device. The universal zero-gravity unloading device is used for realizing satellite-borne antenna ground-based simulation deployment and isdeveloped aiming at meeting the requirements of large antenna unloading capacity and high unloading precision requirements, rotating is adopted to replace sliding, a balance weight is adopted to pre-balance the gravitational torque of a revolution bearing beam relative to the center of a fixed revolution unit, so that it is guaranteed that the device is always in a vertical state, a gravity adaptive shaft is designed to guarantee that the axis of a servo autorotation unit is automatically vertical, and therefore the unloading stability is remarkably improved; by means of the planetary double-rotation motion self-adaptive unloading point two-dimensional motion, three-dimensional space motion is completed through cooperation of vertical motion of an unloading cable, overlapping type antennascan be realized, simulation zero-gravity deployment of overlapped antennas and other antennas meeting the track can be realized, and the universality is good; and the device is simple to install anddebug, convenient to transport and suitable for fast use in various occasions.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Double-wheel distribution robot
The invention provides a double-wheel distribution robot. The double-wheel distribution robot comprises a robot body and two wheels. A storage box for storing distributed objects is arranged in the robot body. A control torque gyroscope device comprises two control torque gyroscopes, a deflection motor for controlling the gyroscopes to actively deflect, and a reverse synchronization mechanism forcontrolling the two gyroscopes to be in the same deflection speed but in opposite deflection directions. Axles are arranged on the robot body, a main driving module is connected with the axles throughtransmission mechanisms, and then the robot body can rotate around the axles at the two ends of the robot body. During driving of the main driving module, wheels are driven to rotate around the axles, or the robot body is driven to rotate around the axles, then all parts arranged on the robot body are driven to bend forwards or lean back, thus, gravitational torque is generated to enable the gyroscopes to naturally deflect to generate gyroscope torque, and / or the deflection motor is controlled to drive the gyroscopes to enable the gyroscopes to actively deflect to generate the gyroscope torque, the posture balancing and obstacle climbing capacity of the double-wheel distribution robot in the movement process is greatly improved, and the double-wheel distribution robot can be suitable formultiple working conditions.
Owner:湖南坎德拉创新科技有限责任公司
Device for adjusting curve characteristic of gravitational torque of cover plate of hanging hole of torsional spring structure
InactiveCN103967370ASolve the problem of warped headSmooth motionWing openersWing closersEngineeringGravitational torque
The invention discloses a device for adjusting a curve characteristic of gravitational of a cover plate of a hanging hole of a torsional spring structure. The device is arranged on the cover plate of the hanging hole and comprises a counter weight, an elastic device and a pulley, and the counter weight and the elastic device move between a free end and a hinge end of the cover plate along the pulley. The device is simple in structure and convenient to implement, the problem that the cover plate of the hanging hole turns up is solved, and opening and closing of the cover plate of the hanging hole are facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI TAIBIYA POWER EQUIP
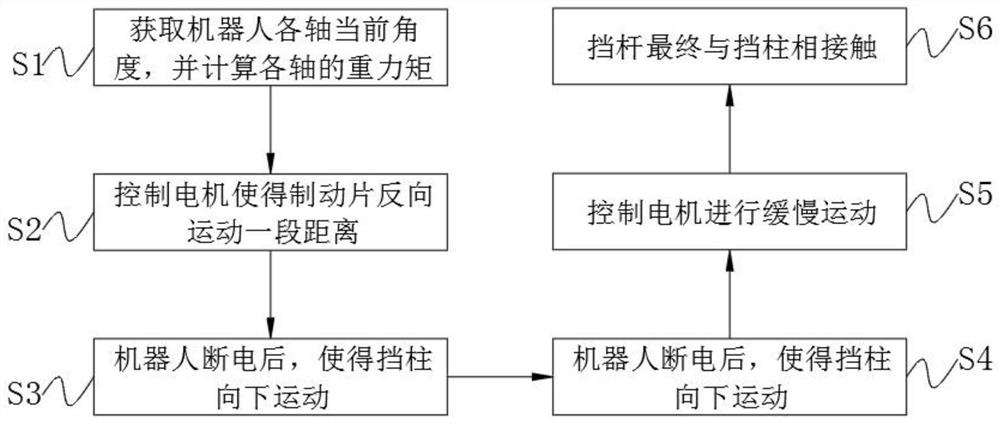
Robot contact pin type brake and control method thereof
PendingCN111993463AReduce shockAffect stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl engineeringElectric machinery
The invention discloses a robot contact pin type brake and a control method thereof. The robot contact pin type brake comprises a motor, an electromagnetic push rod and a speed reducer, the outer surface of the output end of the motor is fixedly connected with a brake pad, the outer surface of the brake pad is fixedly connected with gear levers, and a plurality of the gear levers are arranged andevenly distributed on the outer surface of the brake pad. The invention relates to the technical field of robot contact pin type brakes and control methods thereof. According to the robot contact pintype brake and the control method, when the robot is powered on, the motor is controlled to reversely move for a certain distance according to the gravitational torque, and then a bumping post is pulled up, so that the friction between the bumping post and the gear levers can be prevented; and when the robot is powered off, a torque is applied to the motor, so that the motor is powered off after slowly moving for a certain period of time, the influence on the running stability of the robot due to collision between the bumping post and the gear levers can be reduced to a great extent, the motorcan be prevented from being started repeatedly, and the stability is further enhanced.
Owner:武汉海默机器人有限公司
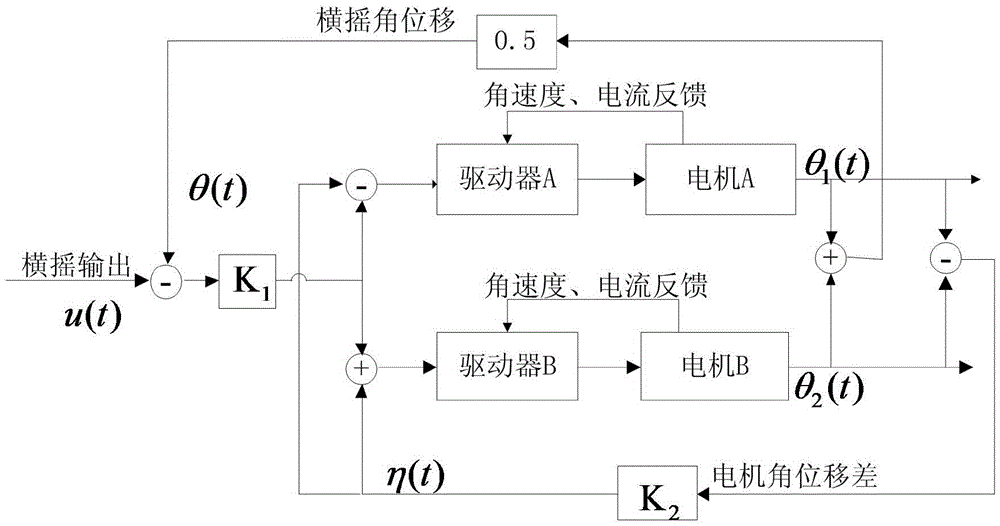
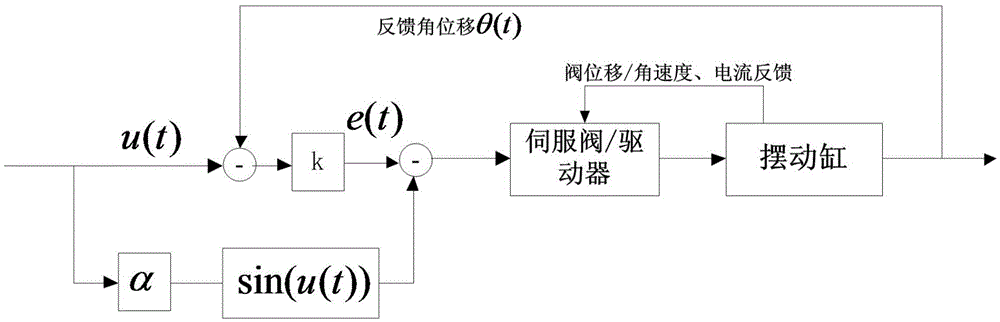
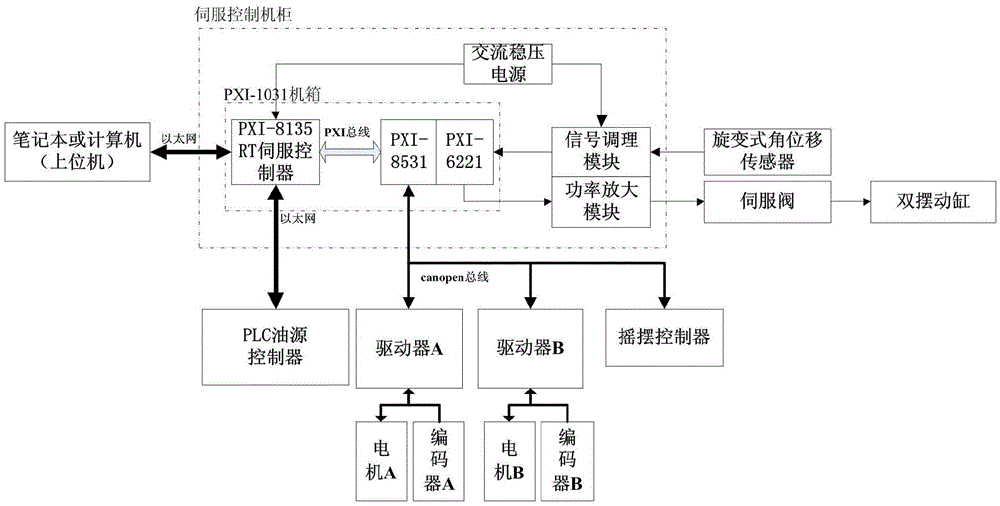
Dual-driving servo control device of large-torque serial swing table, and control methods
ActiveCN105676885ARealize full digital communicationImprove anti-interference abilityControl using feedbackDifferential inhibitionSignal conditioning
The invention discloses a dual-driving servo control device of a large-torque serial swing table. A rolling outer frame of the swing table is driven by double motors, and a pitching inner table top of the swing table is driven by double swing cylinders. A control device comprises an upper computer, a lower computer, a servo control cabinet and a rotary angular displacement sensor. The servo control cabinet is internally provided with a servo controller, a bus communication card, a data collection card, a signal conditioning module and a power amplification module. Control methods include a dual-driving control method of the double motors and a dual-driving control method of the double swing cylinders. According to the invention, the dual-driving servo control methods of the large-torque serial swing table comprises the dual-driving control method of the double motors and the dual-driving control method of the double swing cylinders, and an angular displacement feedback differential inhibition method and a gravitational torque compensation method are utilized, so that the control stability is effectively ensured, and the control precision and the angular displacement waveform distortion degree are improved.
Owner:GENERAL ENG RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Supporting module
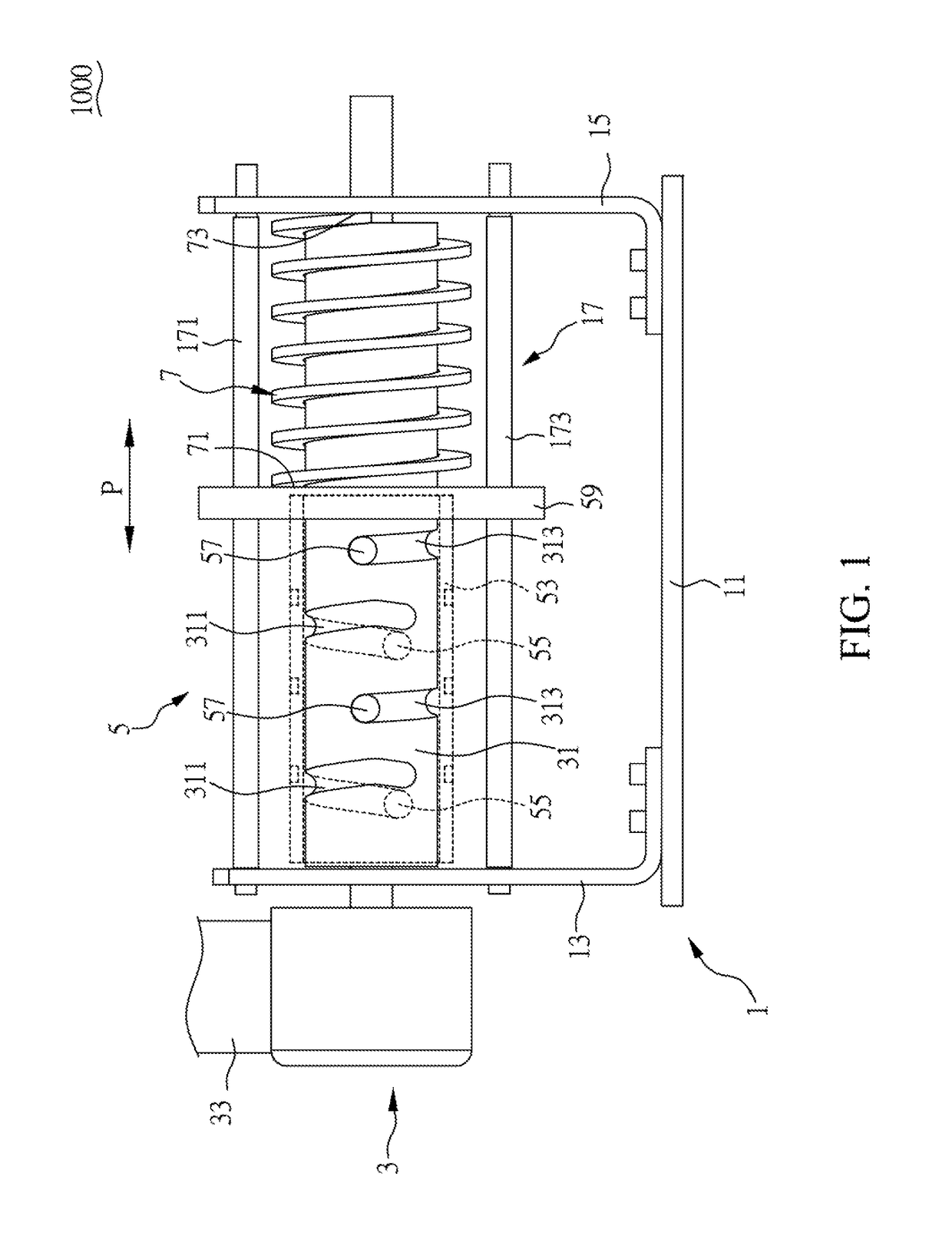
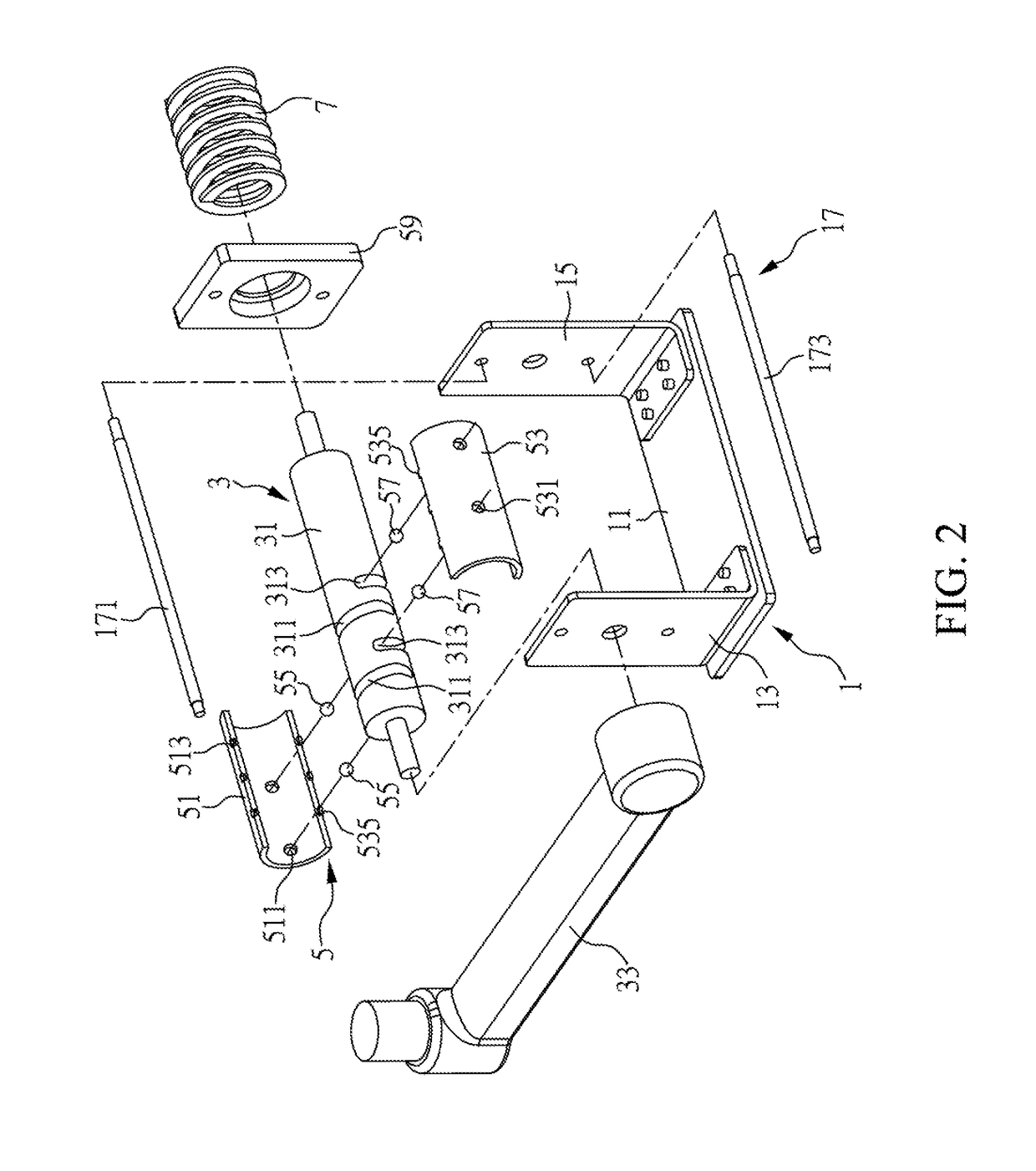
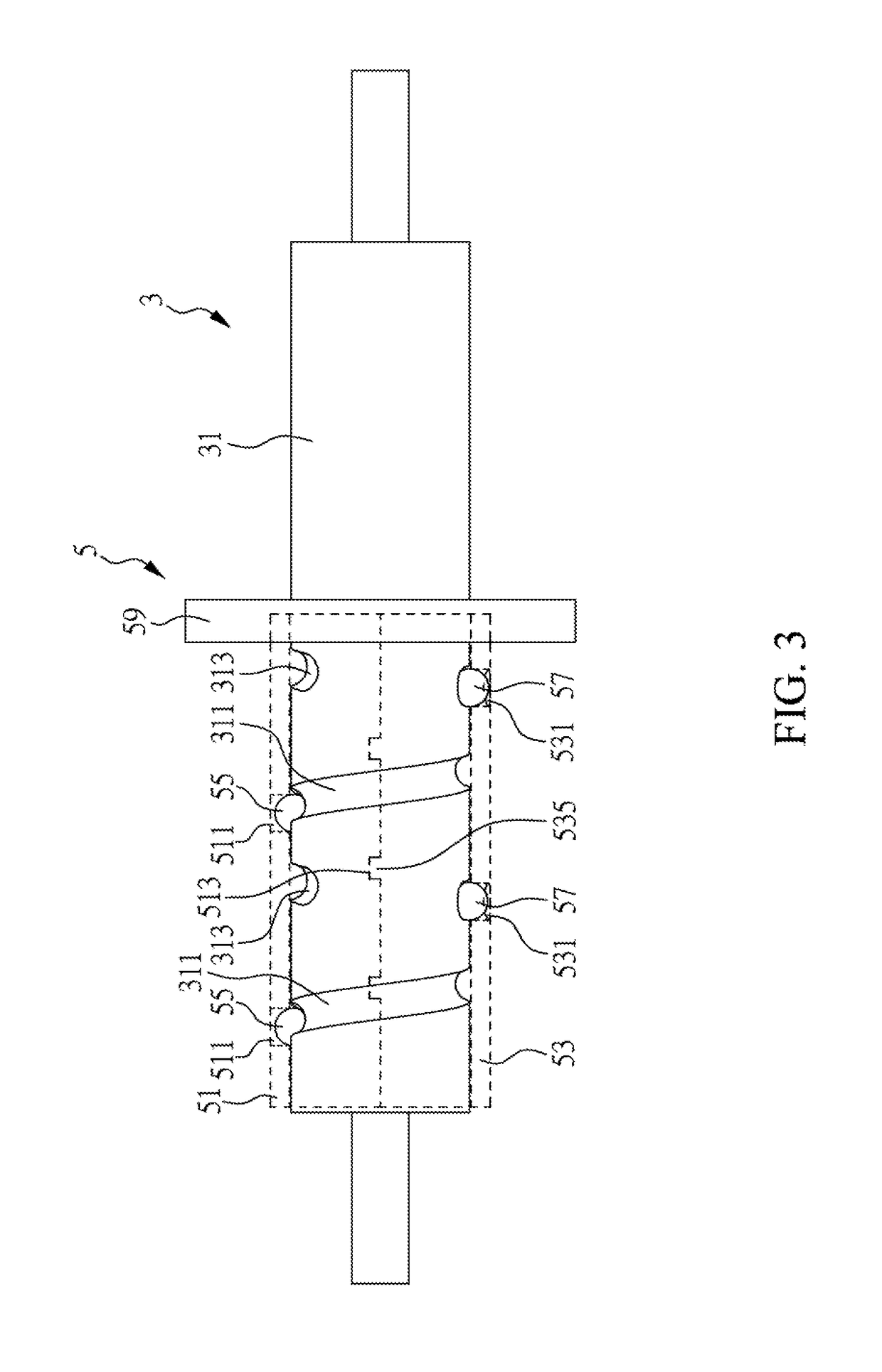
ActiveUS20180372266A1Avoid separationCasings with display/control unitsGearingLinear motionComputer module
Disclosed is a supporting module for a display device, which includes a fixing seat, a pivot lever, a slider and a spring. The pivot lever and the slider constitute a screw transmission mechanism with a varied helix angle. The lifting and lowering of the display device can cause screw motion between the pivot lever and the slider and thus induces the linear movement of the slider according to the axial advance of the varied helix angle. Accordingly, the displacement of the slider causes different degrees of deformation in the spring, resulting in different spring resilience forces on the slider. By the screw transmission mechanism with the varied helix angle, different spring resilience forces can be further converted into different resistance torques to provide appropriate supporting force in coordination with the variation of the gravity torque of the display device.
Owner:SYNCMOLD ENTERPRISE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com