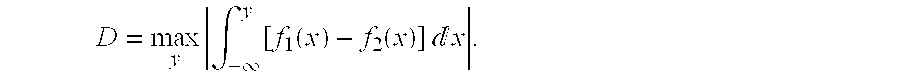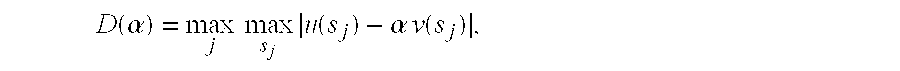Patents
Literature
62 results about "Image response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Image response (or more correctly, image response rejection ratio, or IMRR) is a measure of performance of a radio receiver that operates on the superheterodyne principle. In such a radio receiver, a local oscillator (LO) is used to heterodyne or "beat" against the incoming radio frequency (RF), generating sum and difference frequencies. One of these will be at the intermediate frequency (IF), and will be selected and amplified. The radio receiver is responsive to any signal at its designed IF frequency, including unwanted signals. For example, with a LO tuned to 110 MHz, there are two incoming signal frequencies that can generate a 10 MHz IF frequency. A signal broadcast at 100 MHz (the wanted signal), and mixed with the 110 MHz LO will create the sum frequency of 210 MHz (ignored by the receiver), and the difference frequency at the desired 10 MHz. However, a signal broadcast at 120 MHz (the unwanted signal), and mixed with the 110 MHz LO will create a sum frequency of 230 MHz (ignored by the receiver), and the difference frequency also at 10 MHz. The signal at 120 MHz is called the image of the wanted signal at 100 MHz. The ability of the receiver to reject this image gives the image rejection ratio (IMRR) of the system.
Focus adjustable head mounted display system for displaying digital contents and device for realizing the system
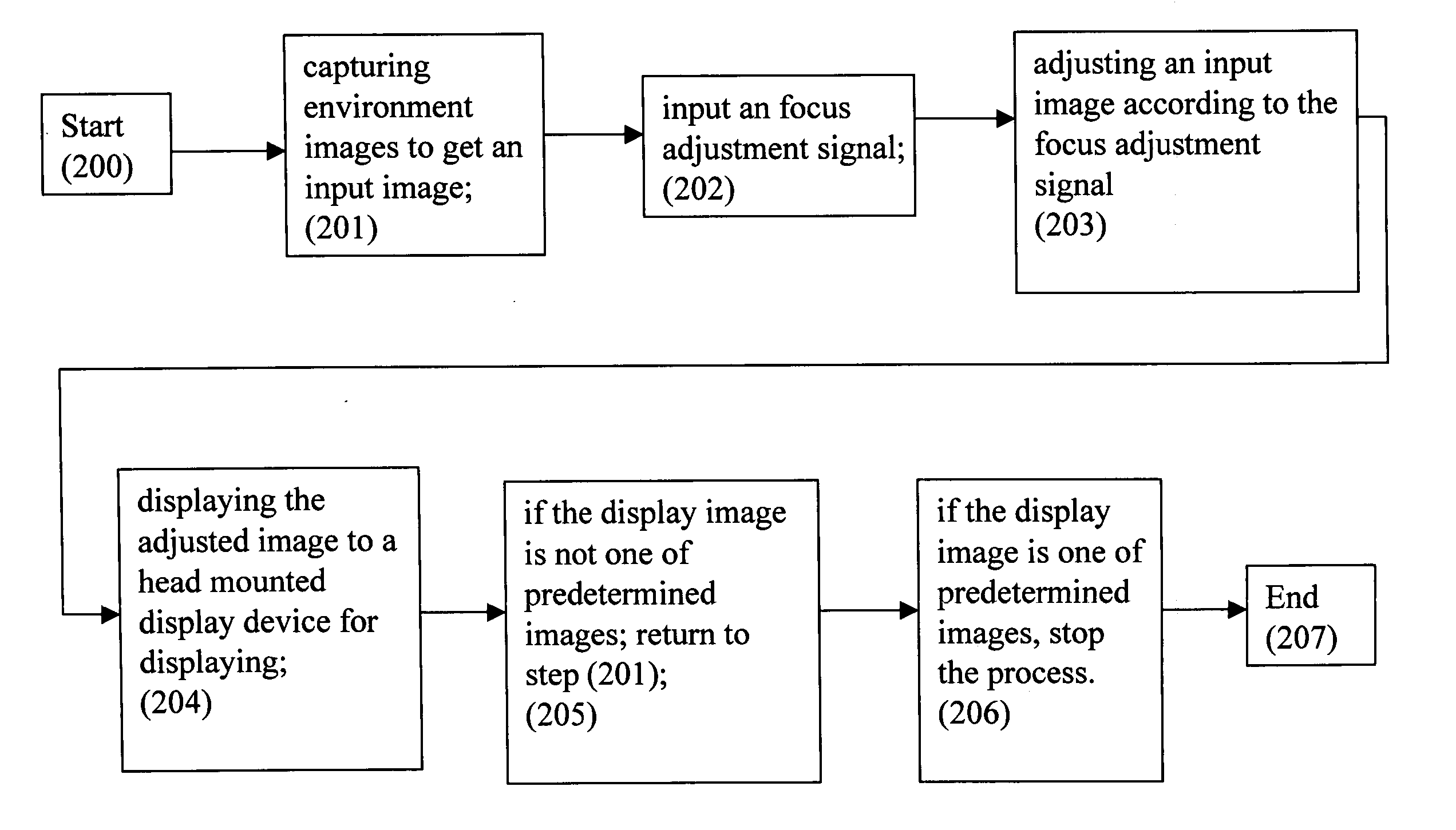
A focus adjustable head mounted display system used in a head mounted display device for displaying digital contents comprising: a digital content storage unit for storing digital data including audio data and image data; an signal processing unit for receiving image signals from the digital content storage unit and processing the received image signals; a focus adjustment unit for adjusting an input image from the digital content storage unit according an input focus adjustment signal so that the adjusted display image responses the focus adjustment signal; an image display unit installed at a head mounted display device for displaying the adjusted display image; a focus input unit being a manually operation device for generating a focus adjustment signal to the signal processing unit; and the focus input unit providing a focus value to the focus adjustment software. A head mounted display device for realizing the focus adjustable head mounted display system is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSAL VISION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
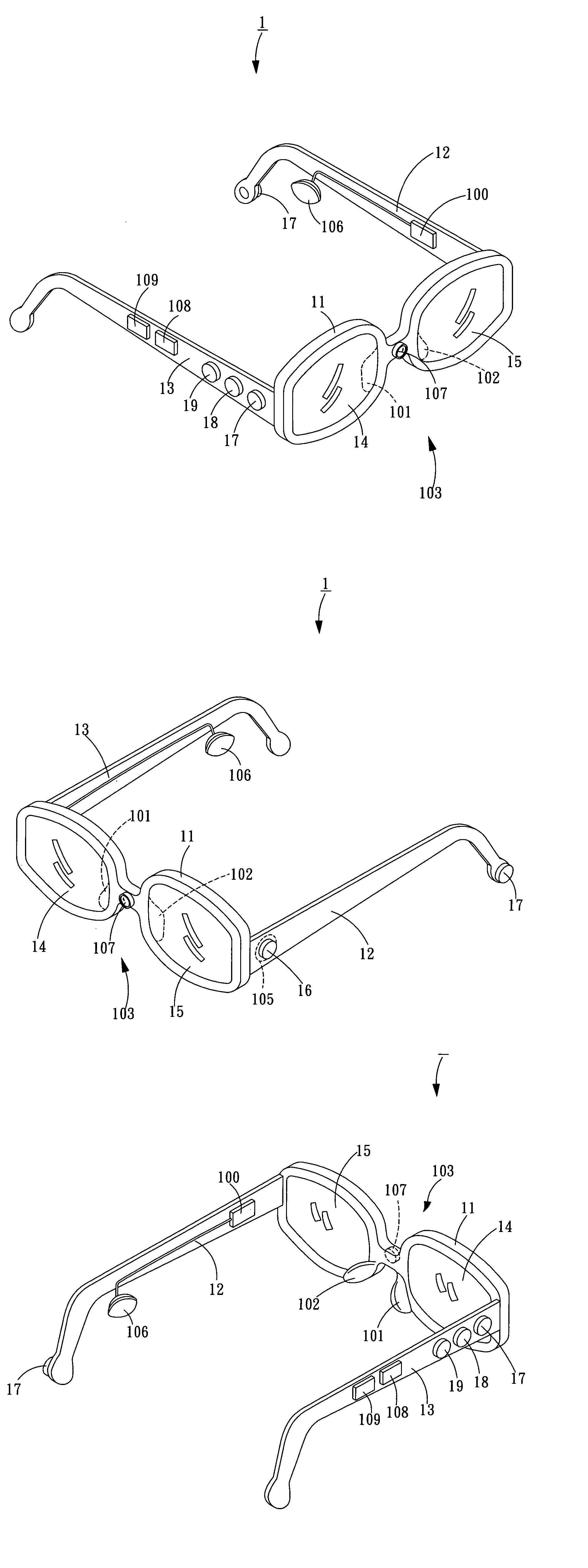
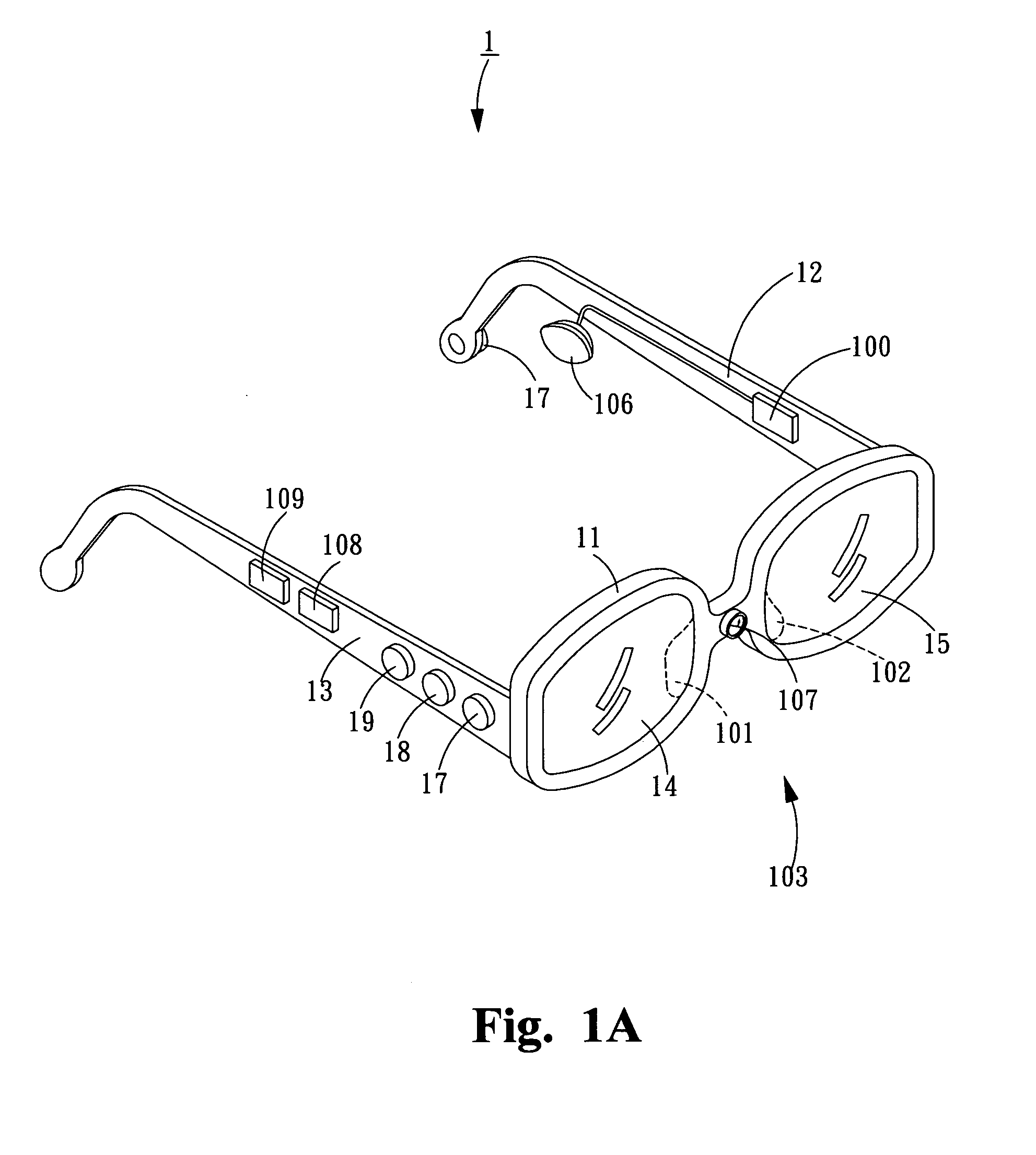
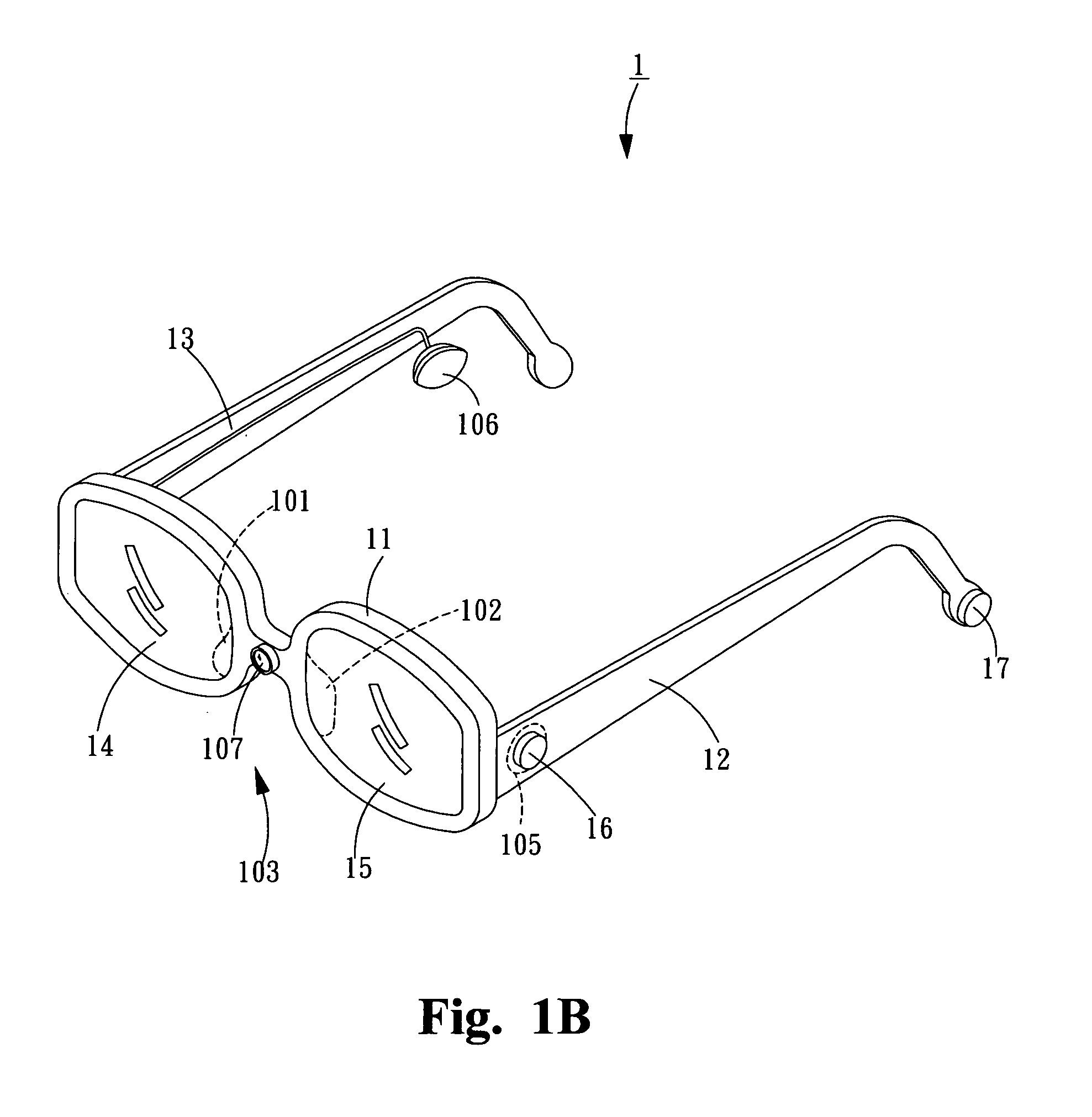
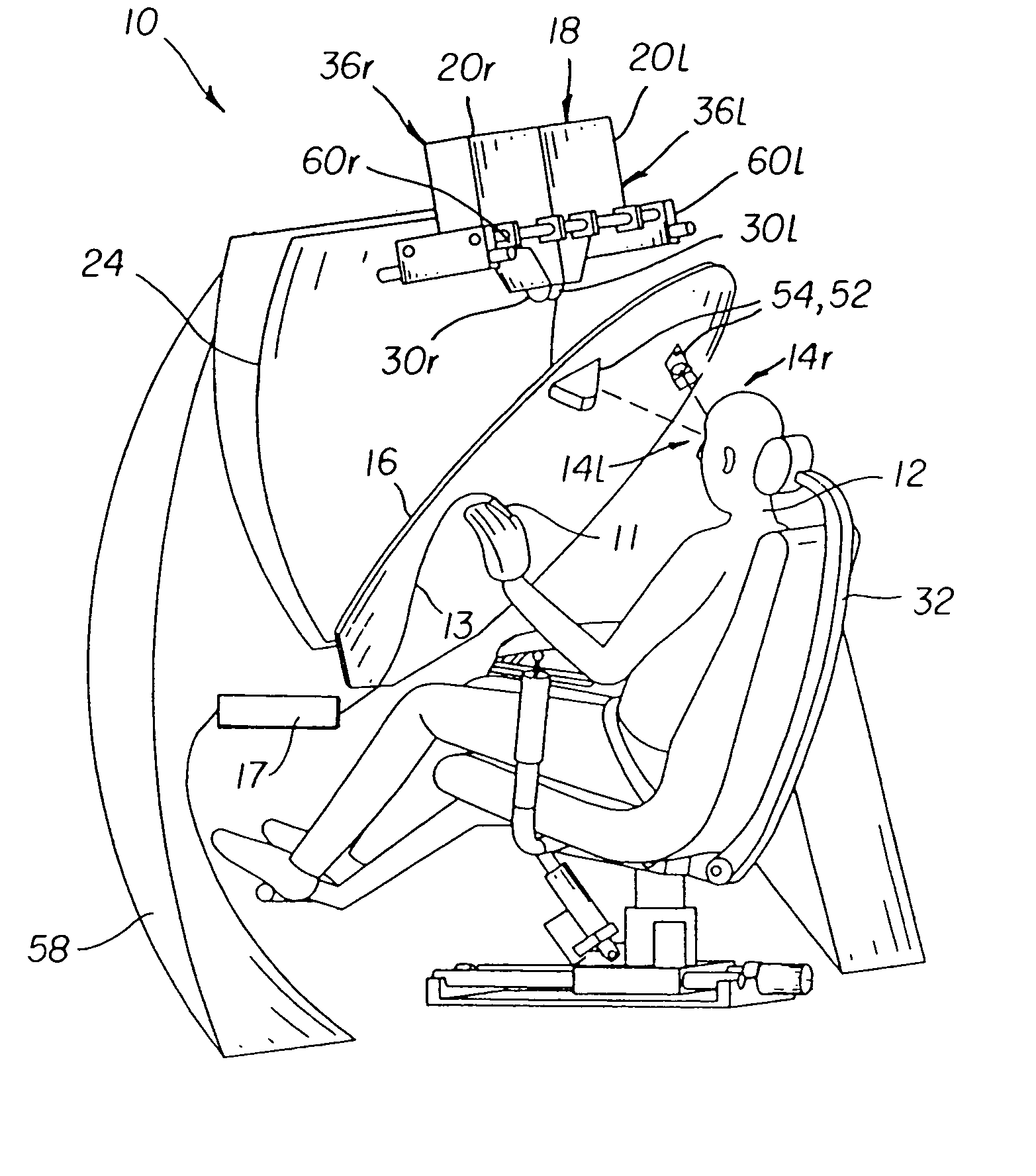
System and method for conditioning the psychological state of a subject using an adaptive autostereoscopic display
InactiveUS20050124851A1Minimize distractionOvercome disadvantagesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDisplay devicePupil
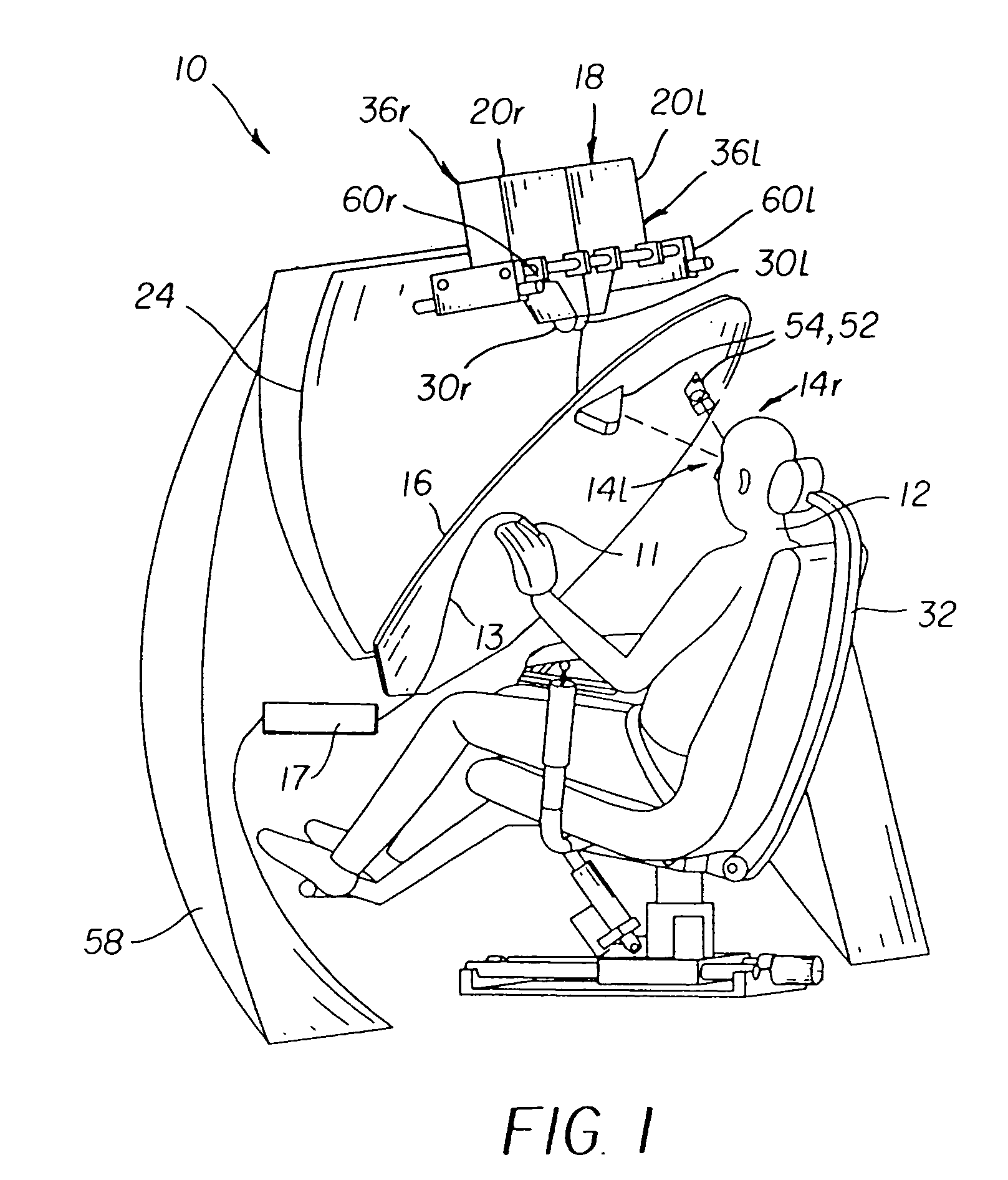
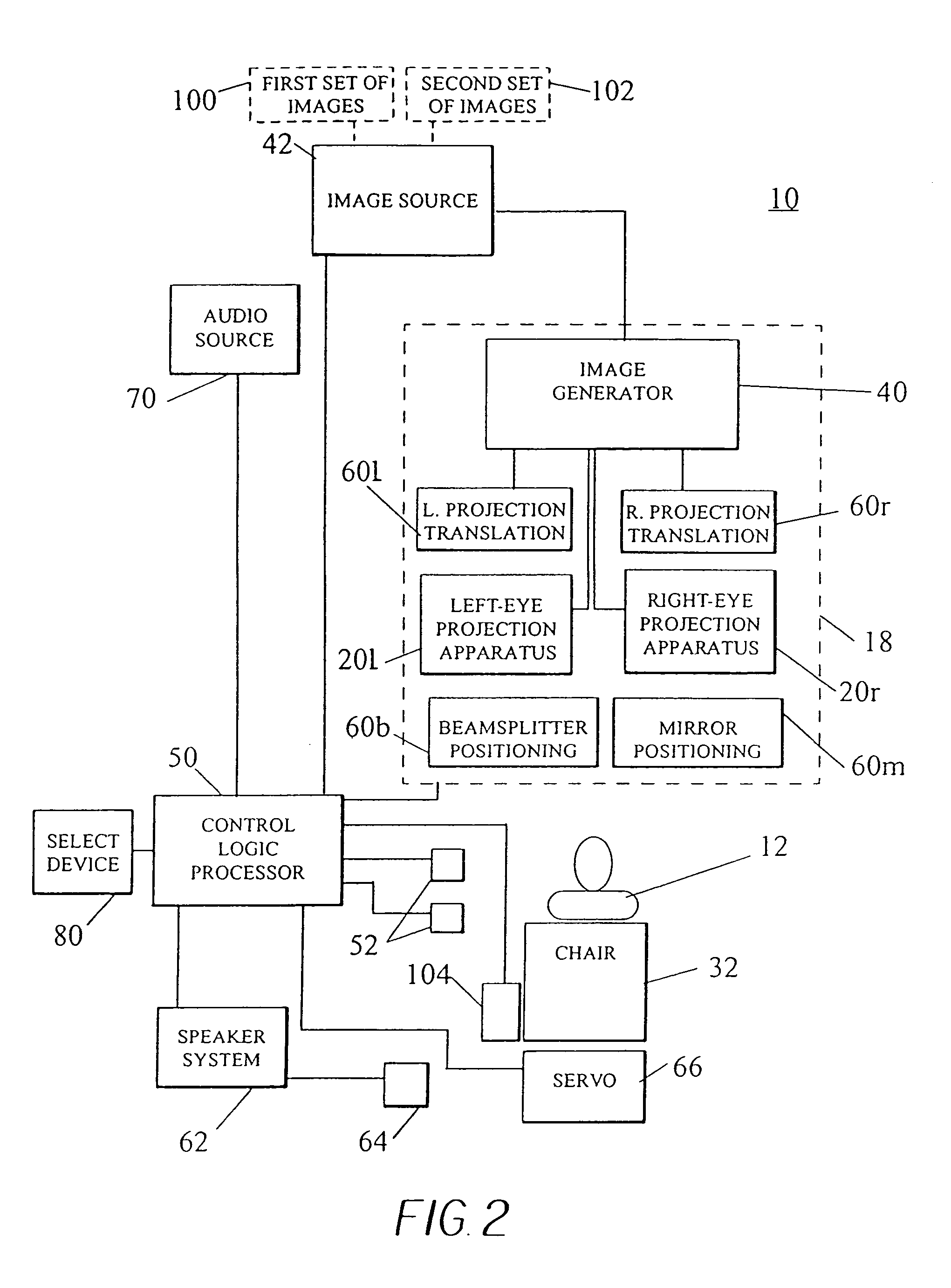
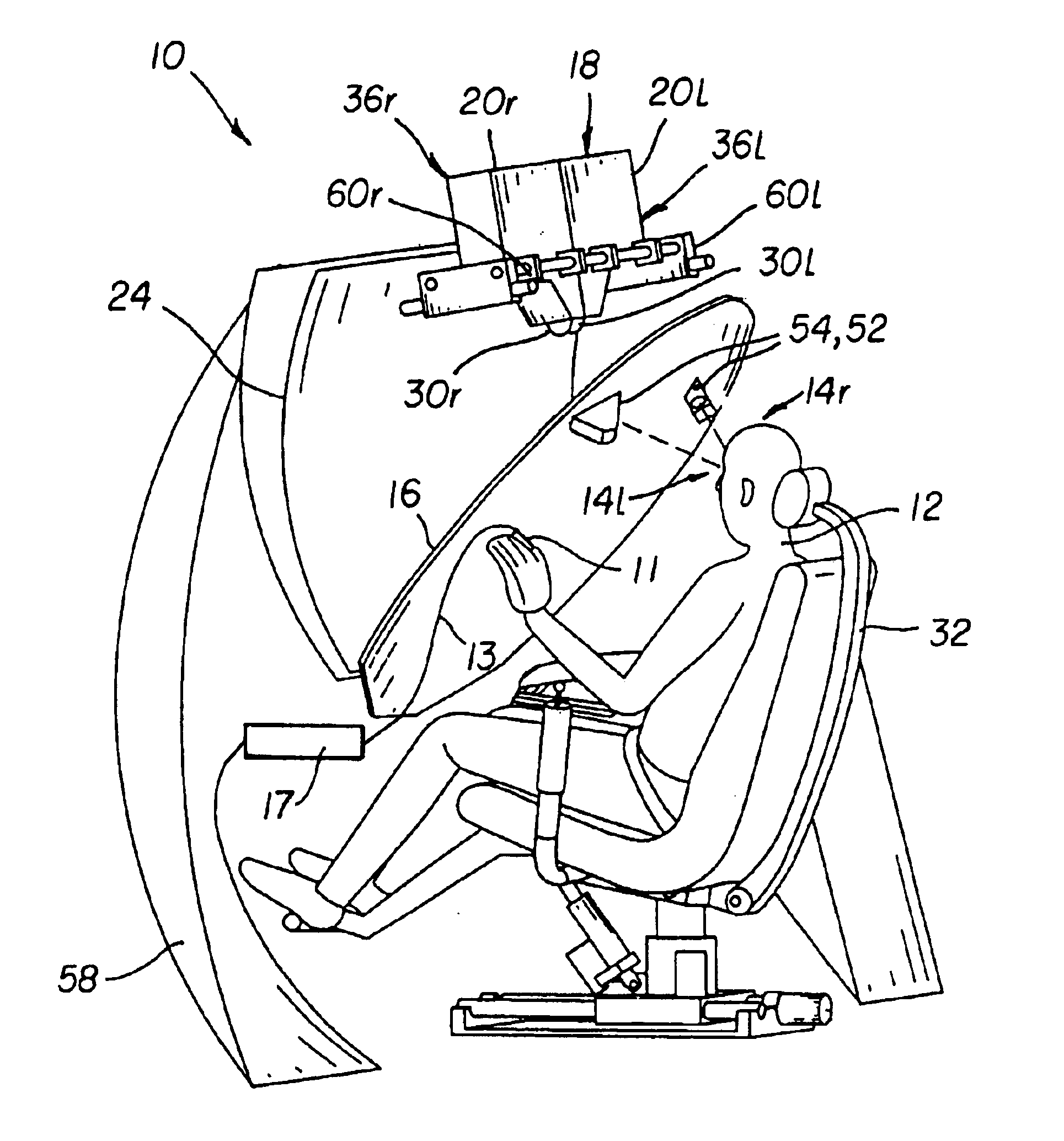
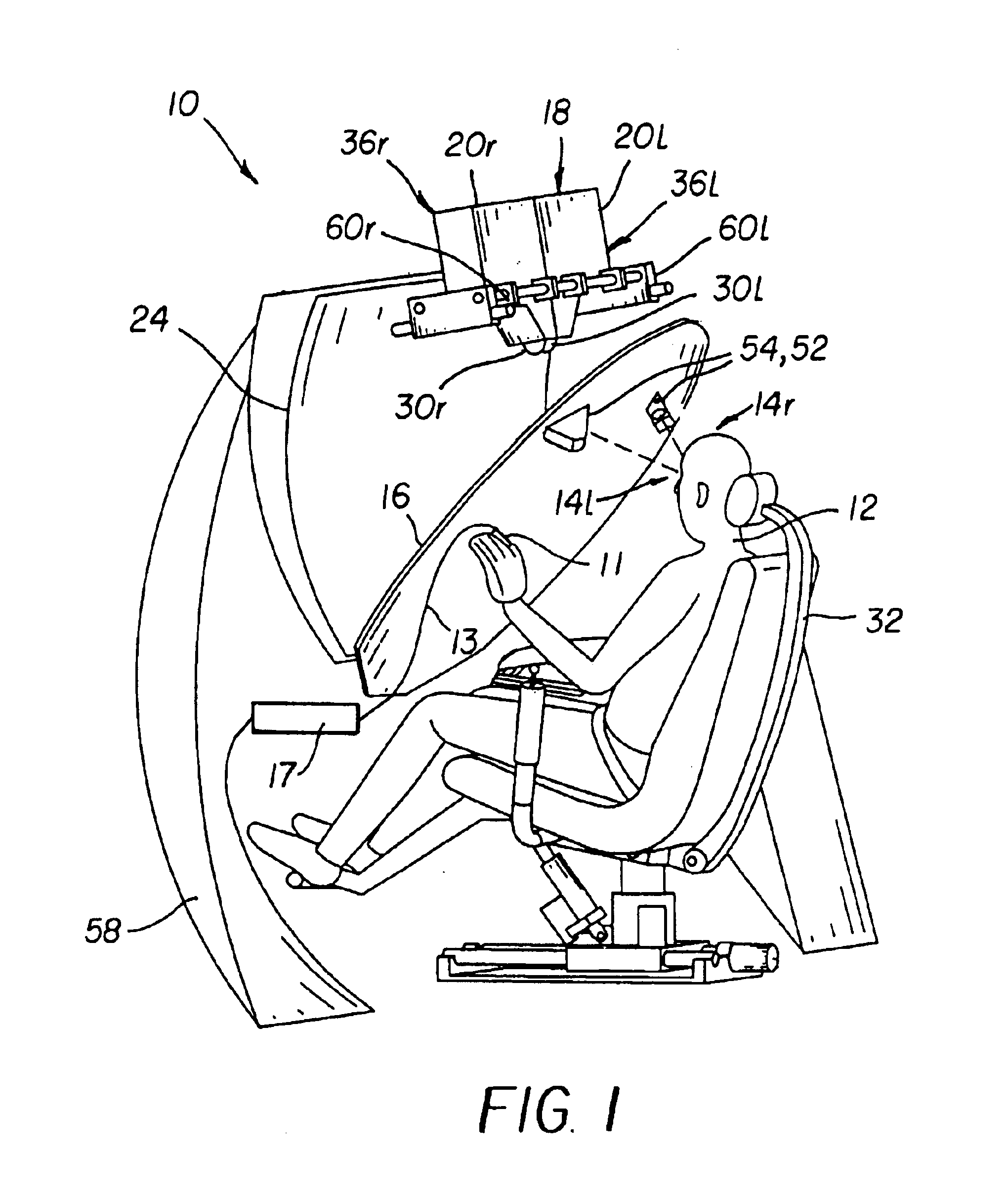
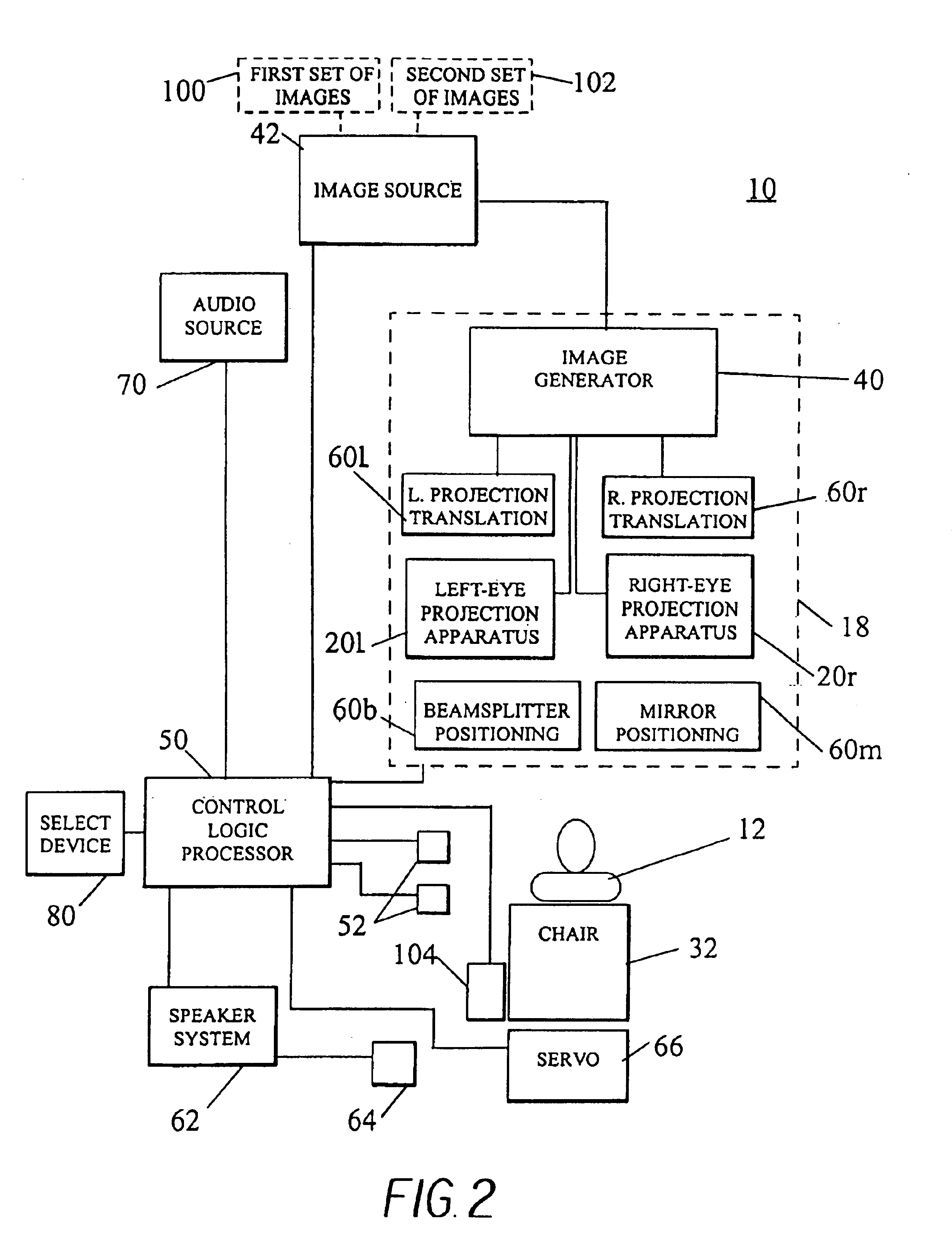
An adaptive autostereoscopic display system (10) provides an apparatus for conditioning the psychological state, physiological state, or behavior of a subject (12) by displaying a stereoscopic virtual image at a left viewing pupil (14l) and a right viewing pupil (14r). A first set of images (100) is displayed and physiological response measurements are obtained from the subject (12). Based on the response of the subject (12) a personalized image response profile is obtained. Then, in order to condition the psychological state, physiological state, or behavior of the subject (12), a second set of images (102), based on the personalized image response profile is displayed.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
System and method for conditioning the psychological state of a subject using an adaptive autostereoscopic display
InactiveUS6896655B2Minimize distractionLow stress levelDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsObject basedPhysiologic States
An adaptive autostereoscopic display system (10) provides an apparatus for conditioning the psychological state, physiological state, or behavior of a subject (12) by displaying a stereoscopic virtual image at a left viewing pupil (14l) and a right viewing pupil (14r). A first set of images (100) is displayed and physiological response measurements are obtained from the subject (12). Based on the response of the subject (12) a personalized image response profile is obtained. Then, in order to condition the psychological state, physiological state, or behavior of the subject (12), a second set of images (102), based on the personalized image response profile is displayed.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
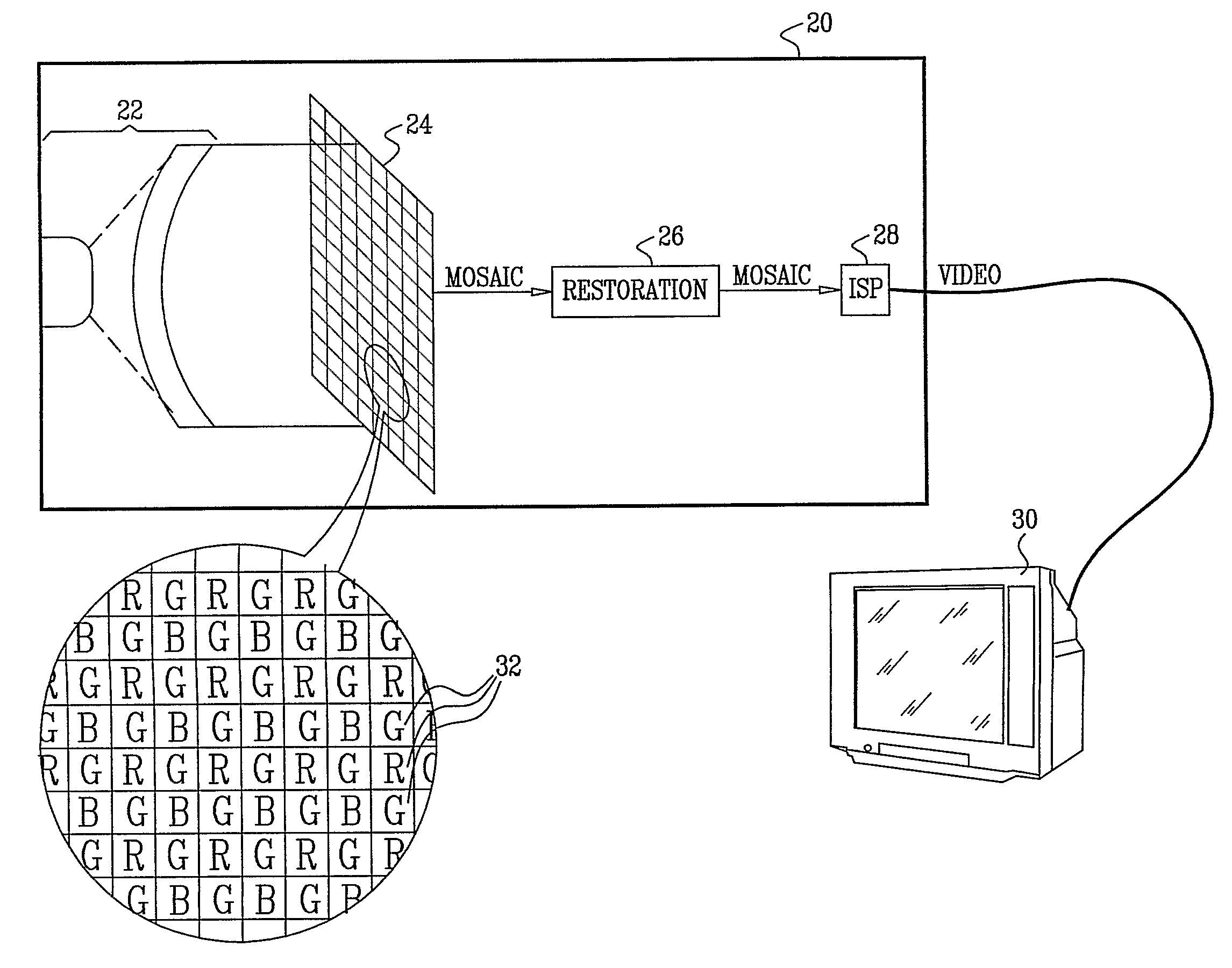
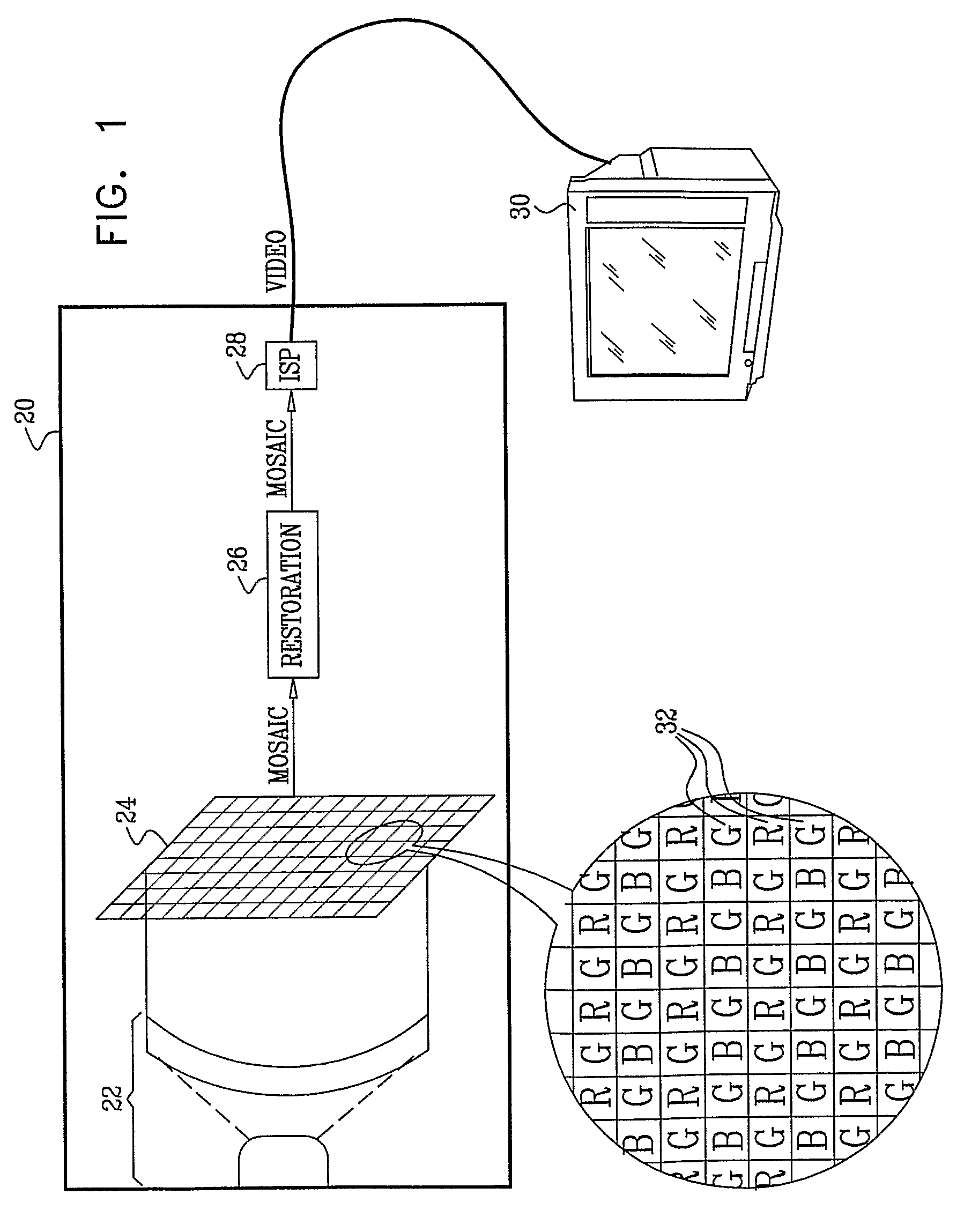
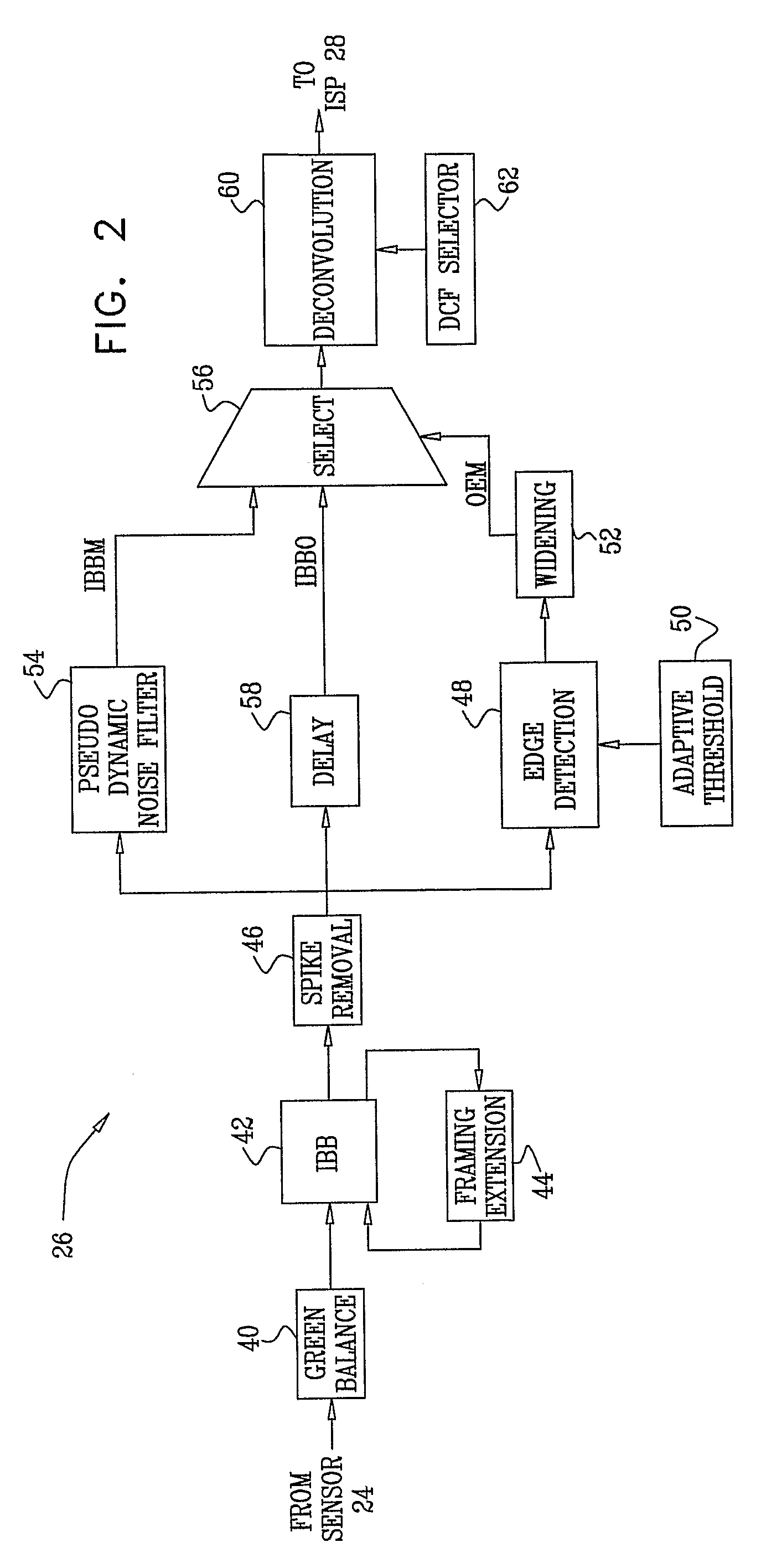
Image enhancement in the mosaic domain
ActiveUS20090147111A1Quality improvementReduce blurTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImage restorationImage signal
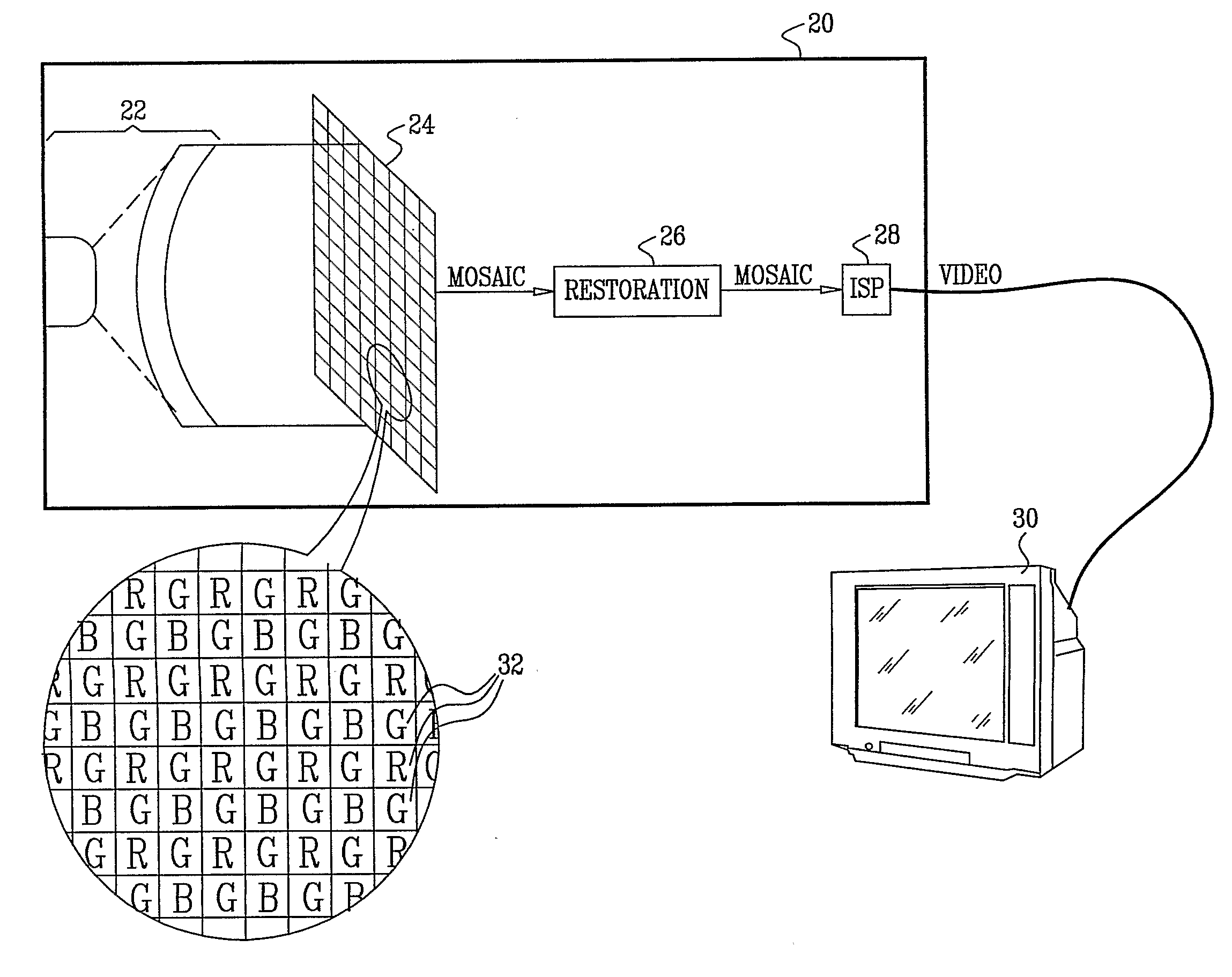
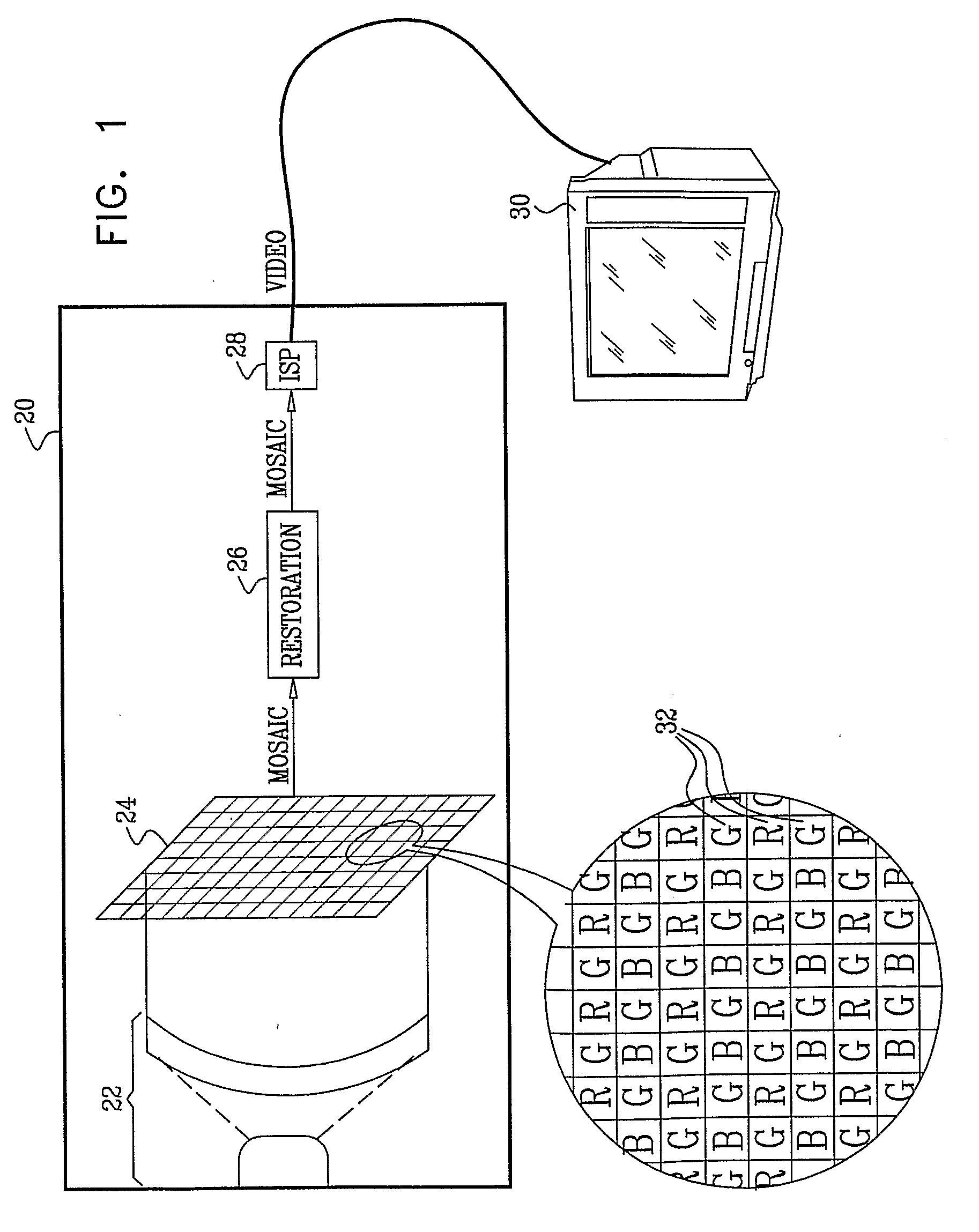
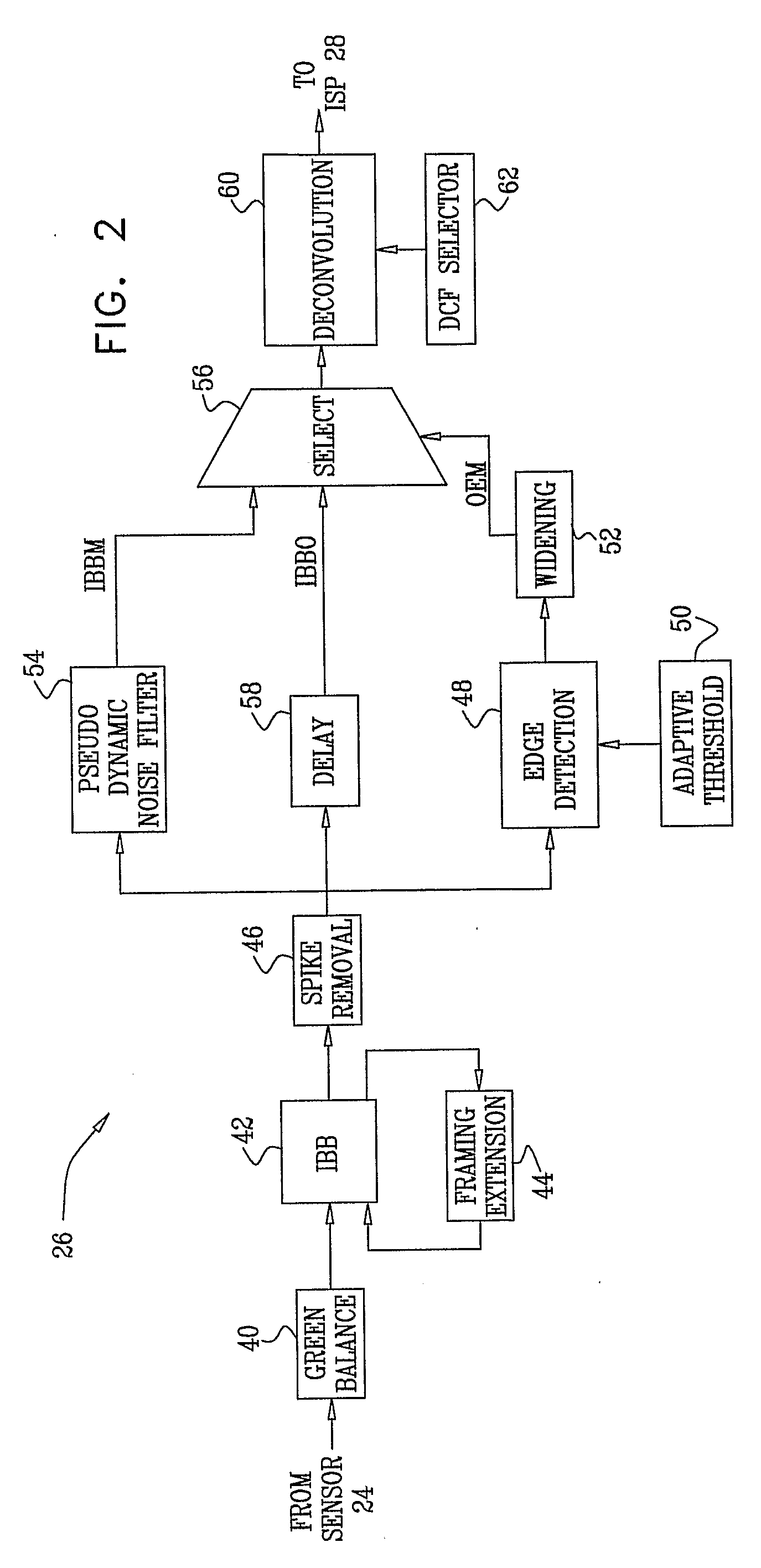
Imaging apparatus includes a mosaic image sensor (24), which is configured to generate a stream of input pixel values belonging to a plurality of input sub-images, each sub-image responsive to light of a different, respective color that is incident on the mosaic image sensor. An image restoration circuit (26) is coupled to receive and digitally filter the input pixel values in each of the input sub-images so as to generate a corresponding plurality of enhanced output sub-images. An image signal processor (ISP) (28) is coupled to receive and combine the plurality of the output sub-images in order to generate a color video output image.
Owner:DIGITALOPTICS CORPORATION
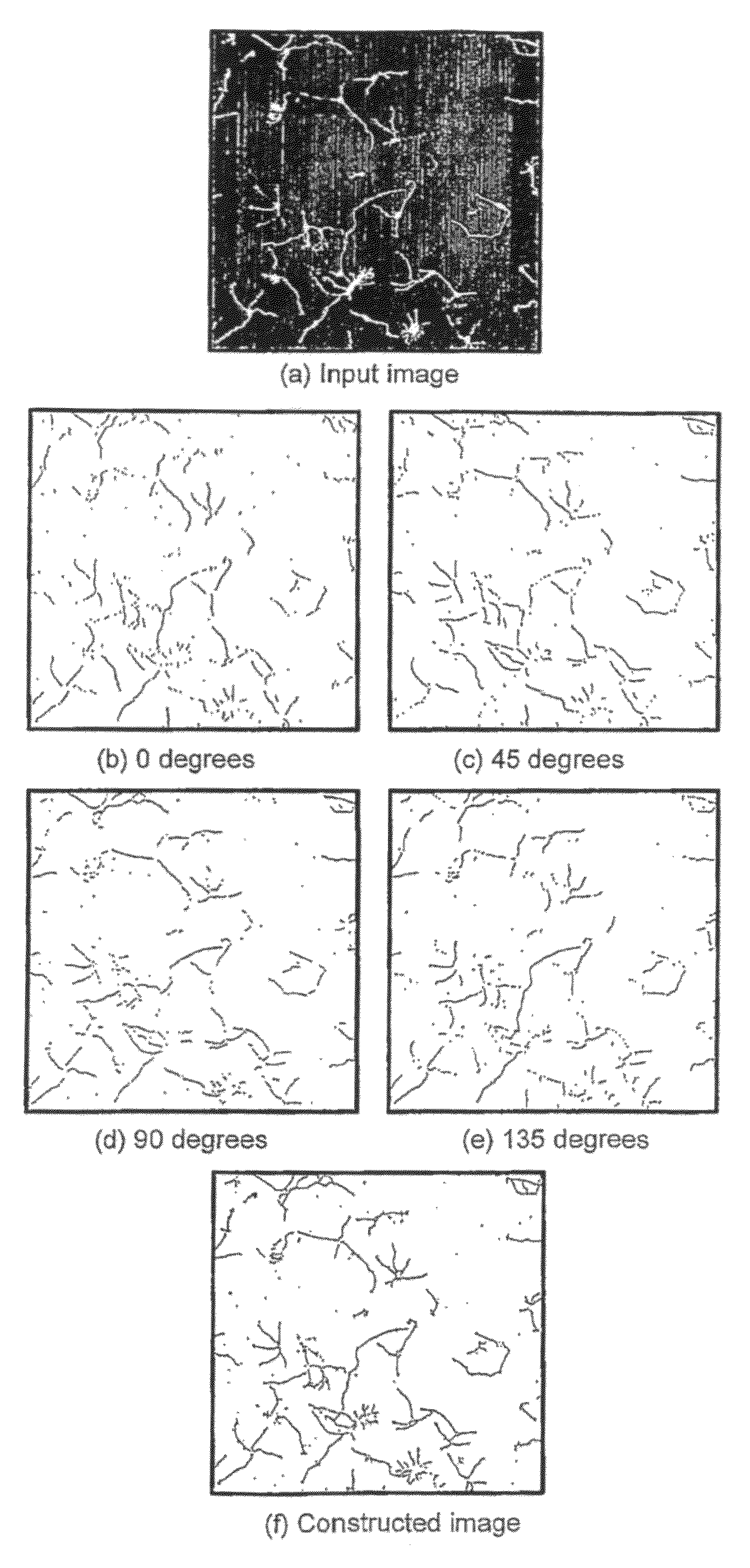
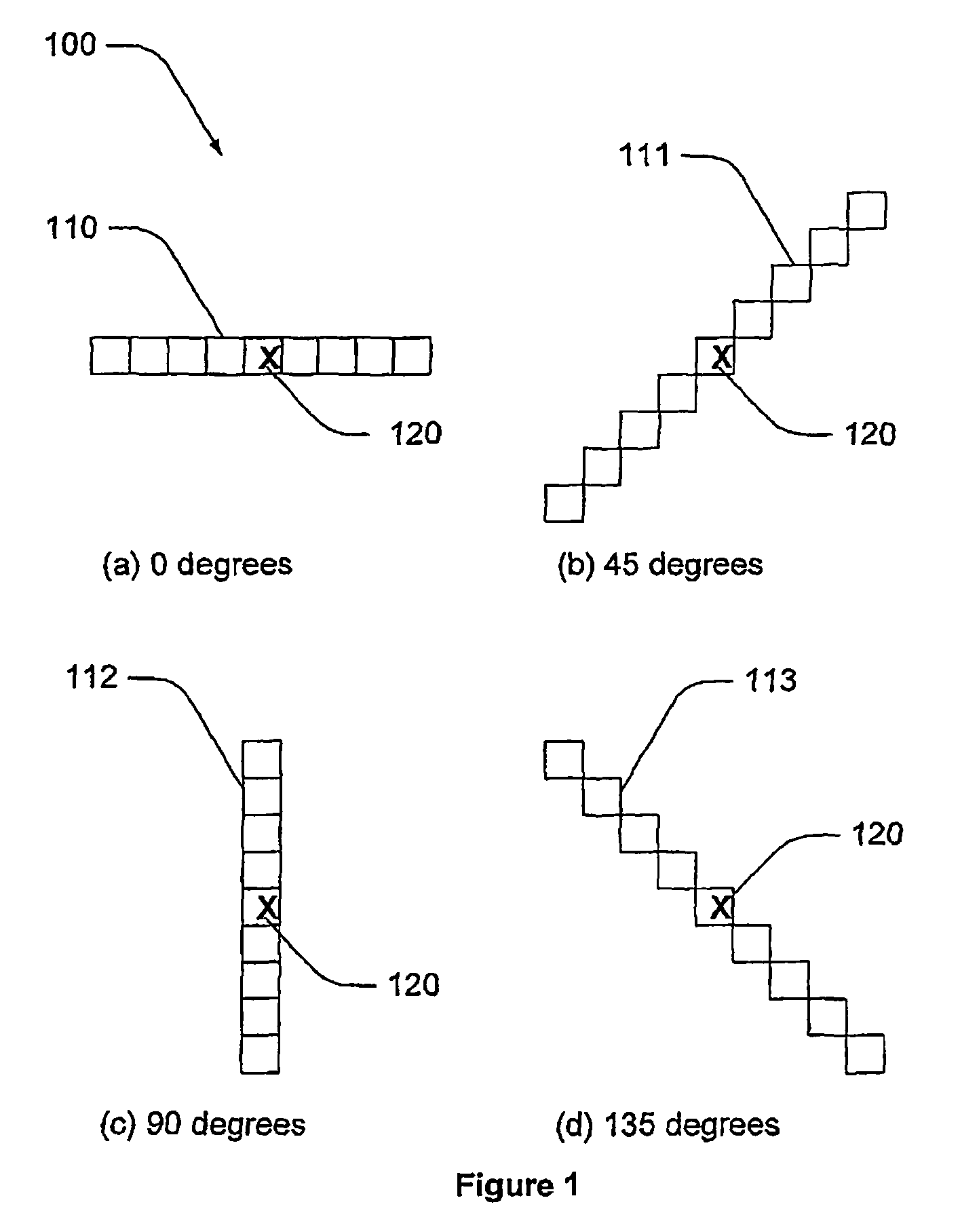
Linear Feature Detection Method and Apparatus
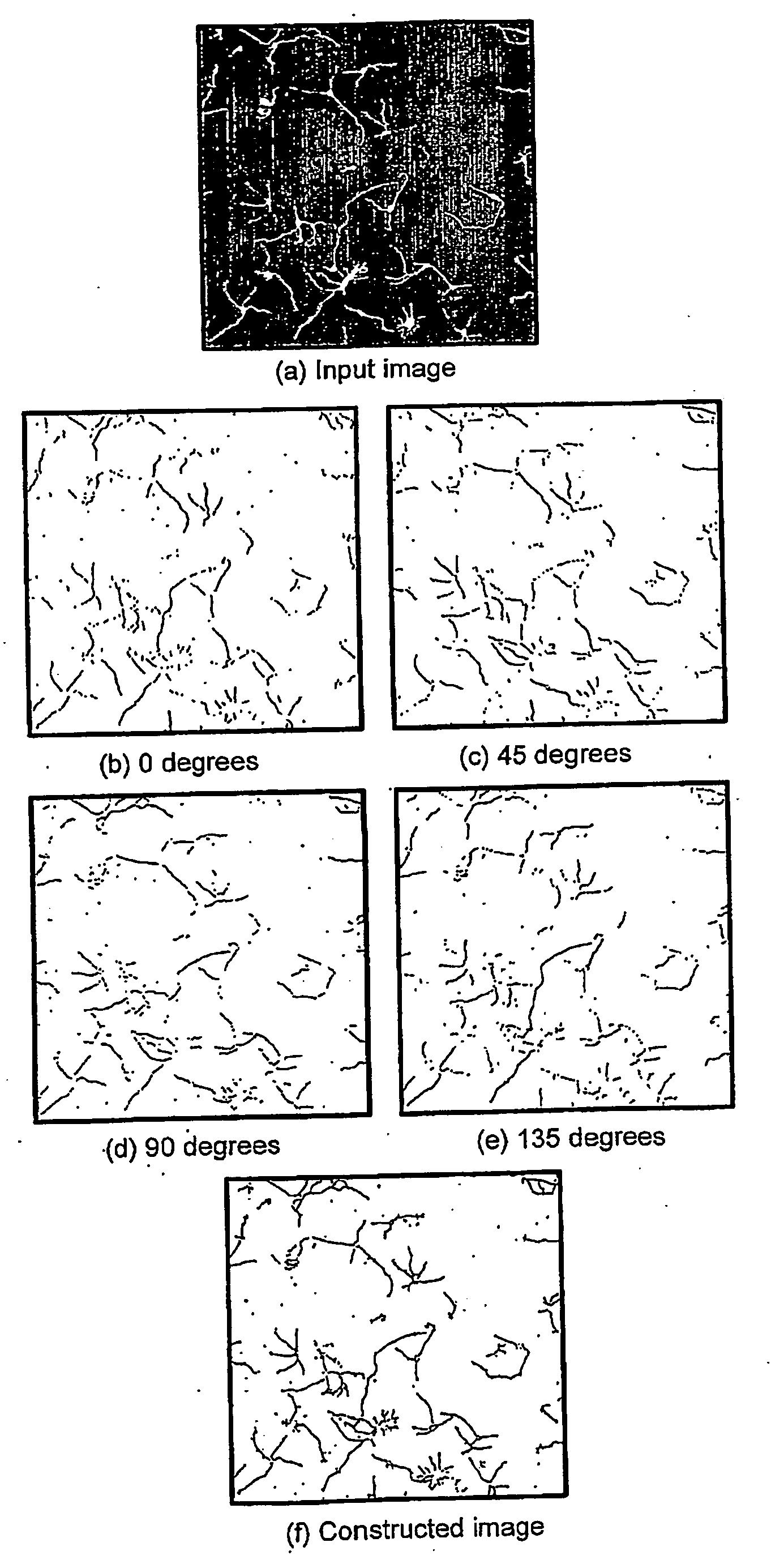
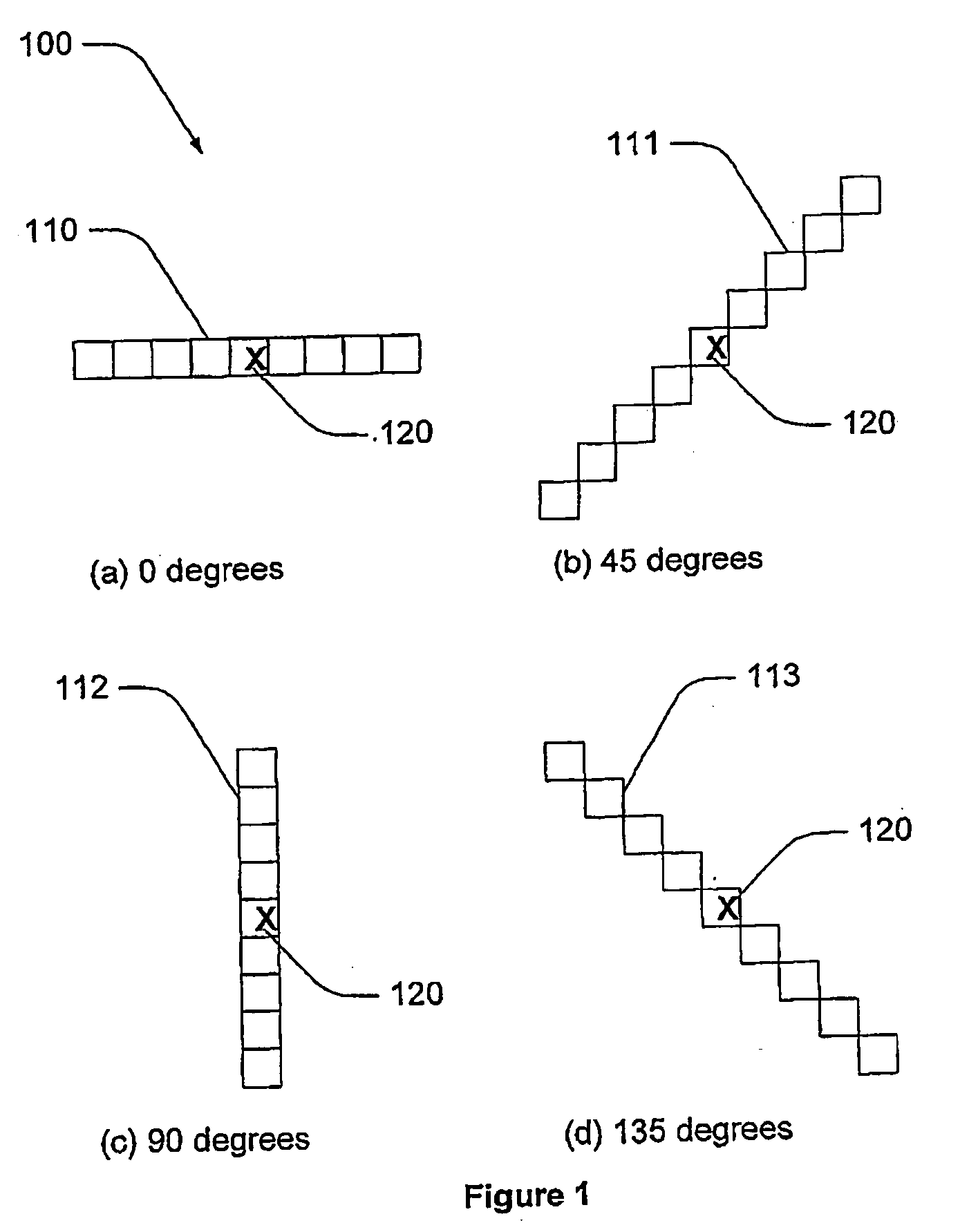
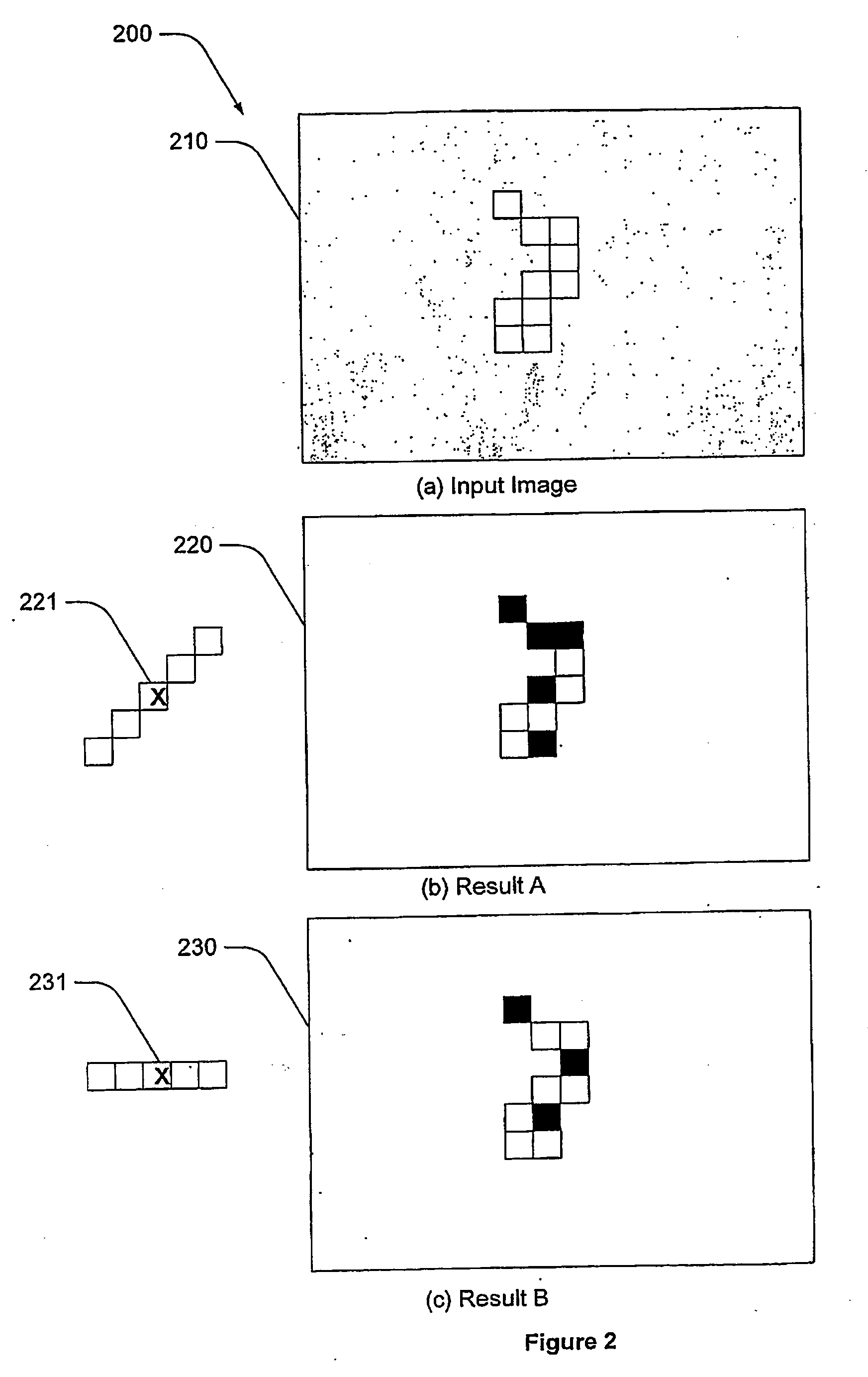
ActiveUS20090154792A1Reduce computing timeImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceNon maximum suppression
A method of extracting linear features from an image, the method including the steps of: (a) applying a non maximum suppression filter to the image for different angles of response to produce a series o filtered image responses; (b) combining the filtered image responses into a combined image having extracted linear features.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
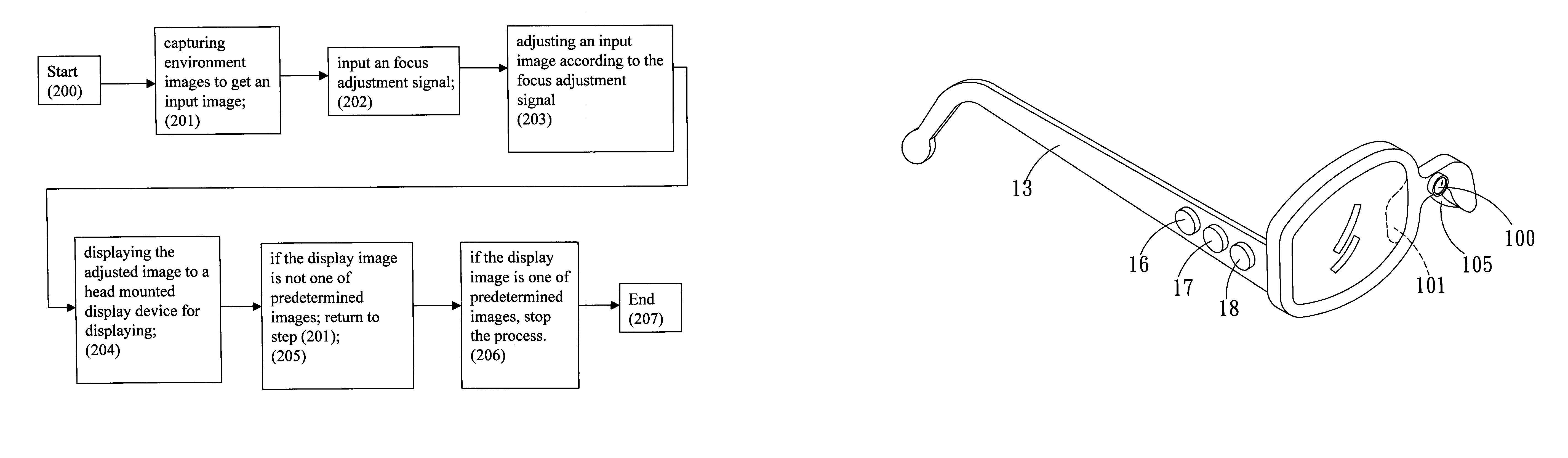
Focus adjustable head mounted display system and method and device for realizing the system
ActiveUS20050254135A1Easy to understandCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical partsImaging processingDisplay device
A focus adjustable head mounted display system used in a head mounted display device comprises an image capturing device for capturing environment images; an image processing unit for receiving image signals from the image capturing device and processing the received image signals; a focus adjustment unit for adjusting an input image from the image capturing device according an input focus adjustment signal so that the adjusted display image responses the focus adjustment signal; an image display unit installed at a head mounted display device for displaying the adjusted display image; a focus input unit being a manually operation device for generating a focus adjustment signal to the image processing unit; the focus input unit providing a focus value to the focus adjustment software. A head mounted display device and a method for realizing the focus adjustable head mounted display system is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSAL VISION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
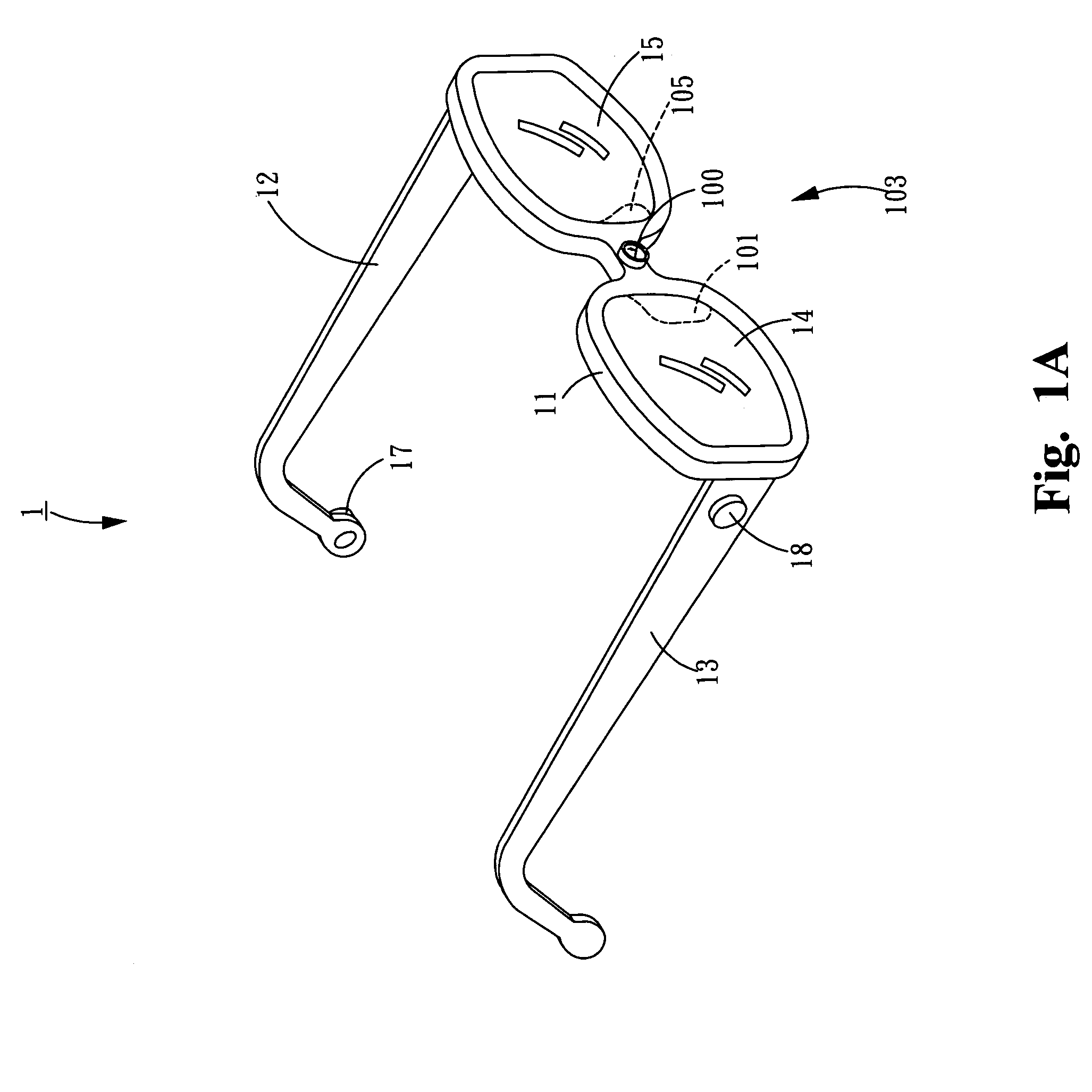
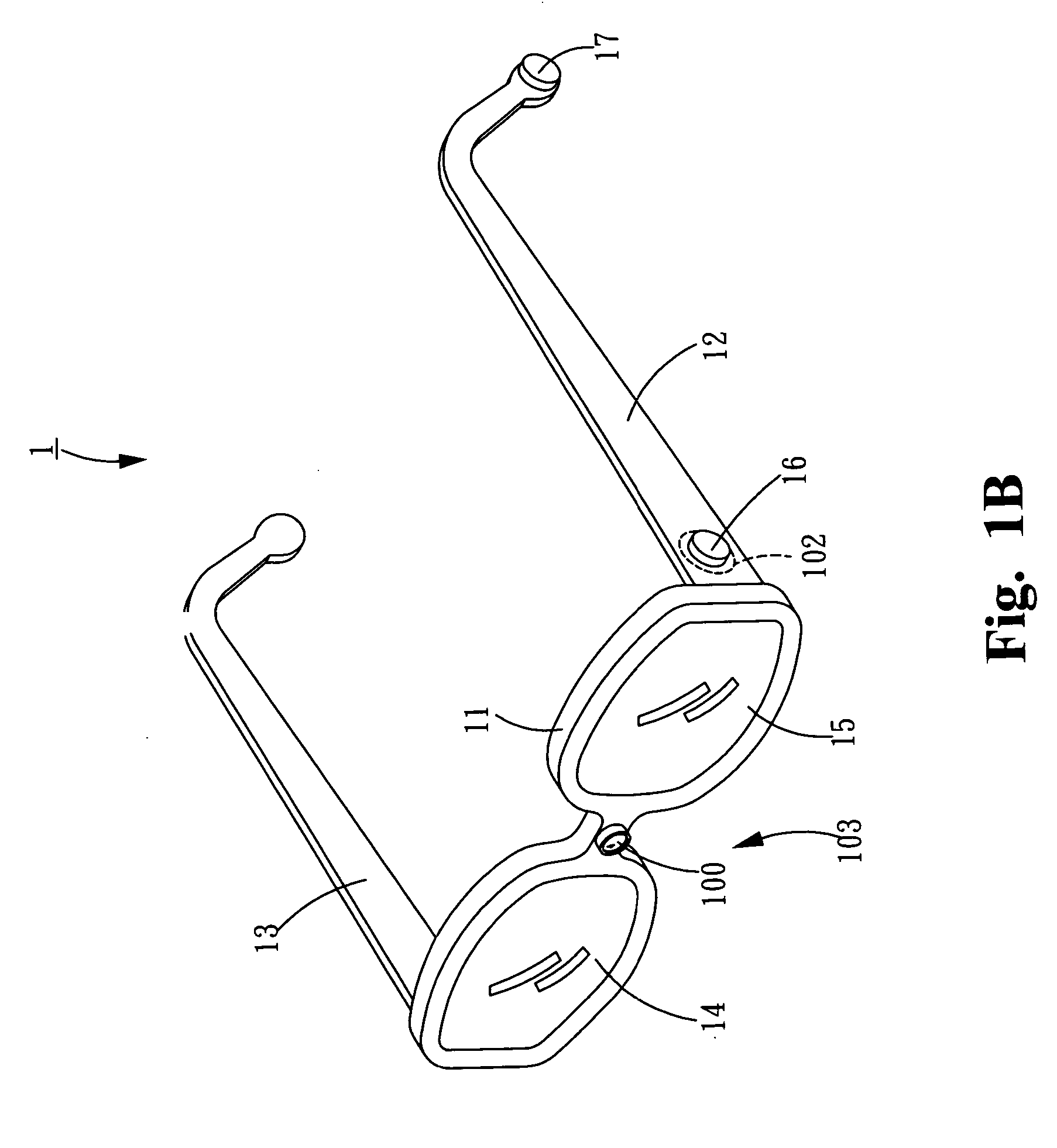
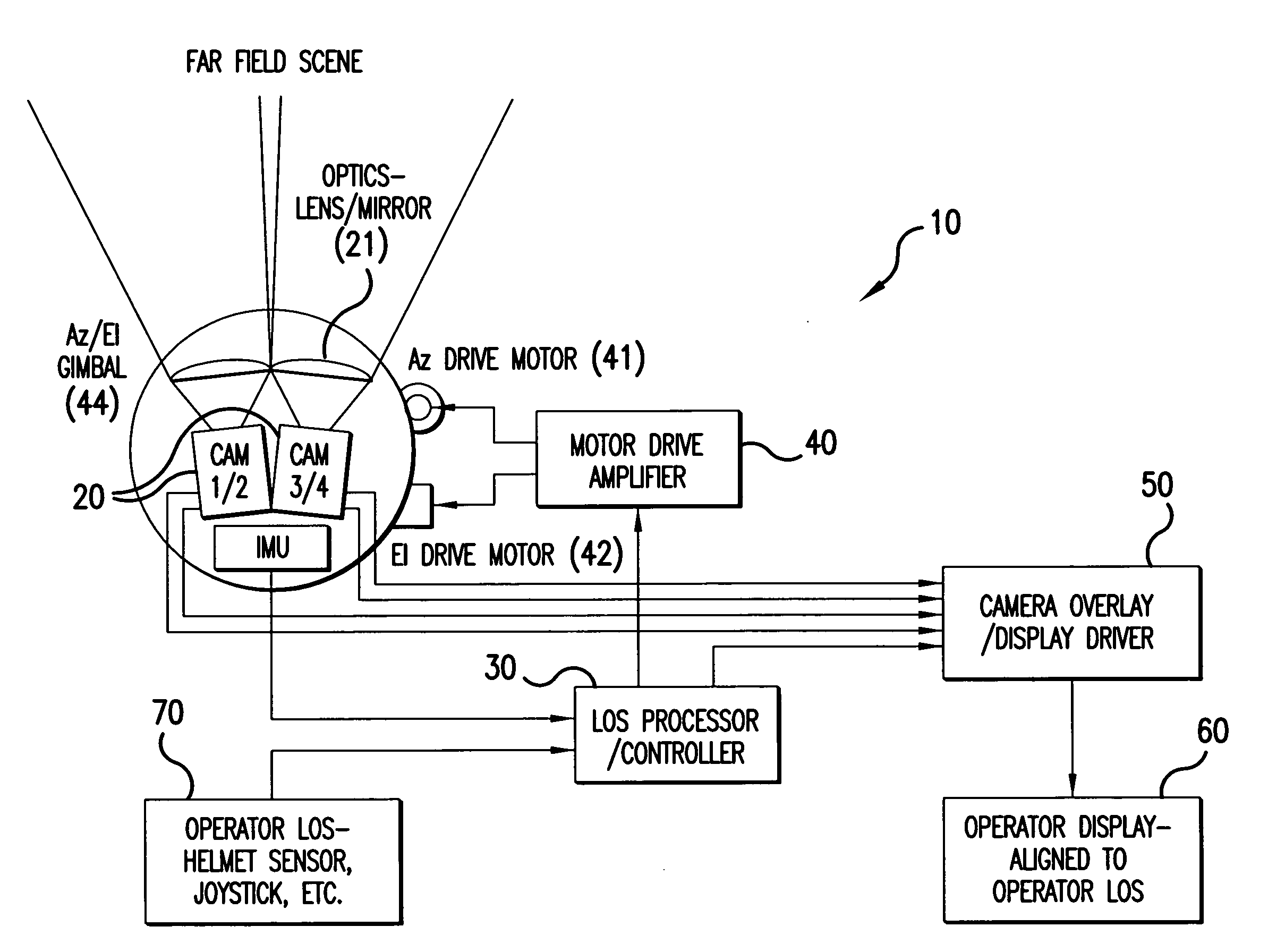
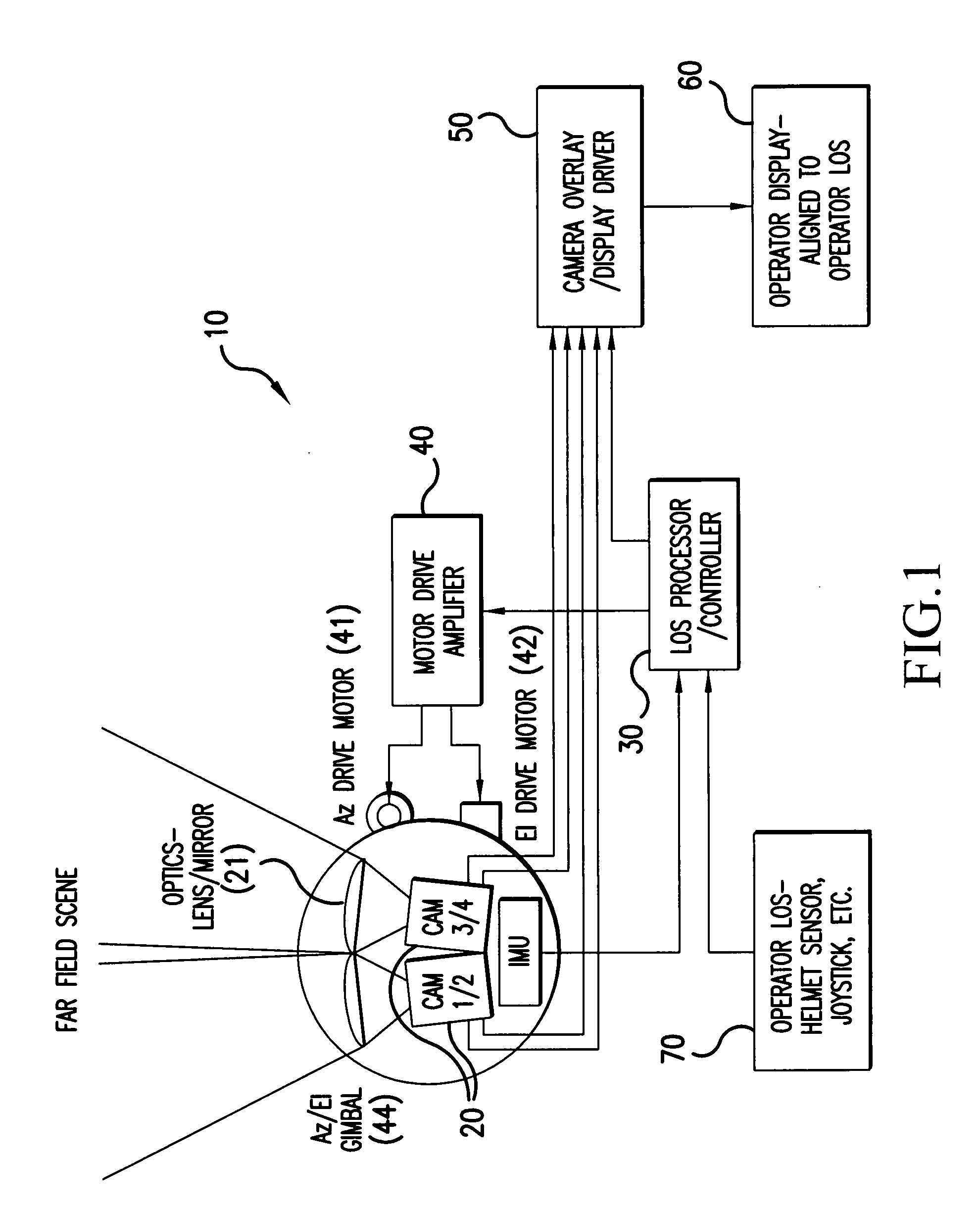
Zero-lag image response to pilot head mounted display control
ActiveUS20080218436A1Much of capabilityMore responsiveCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceLag
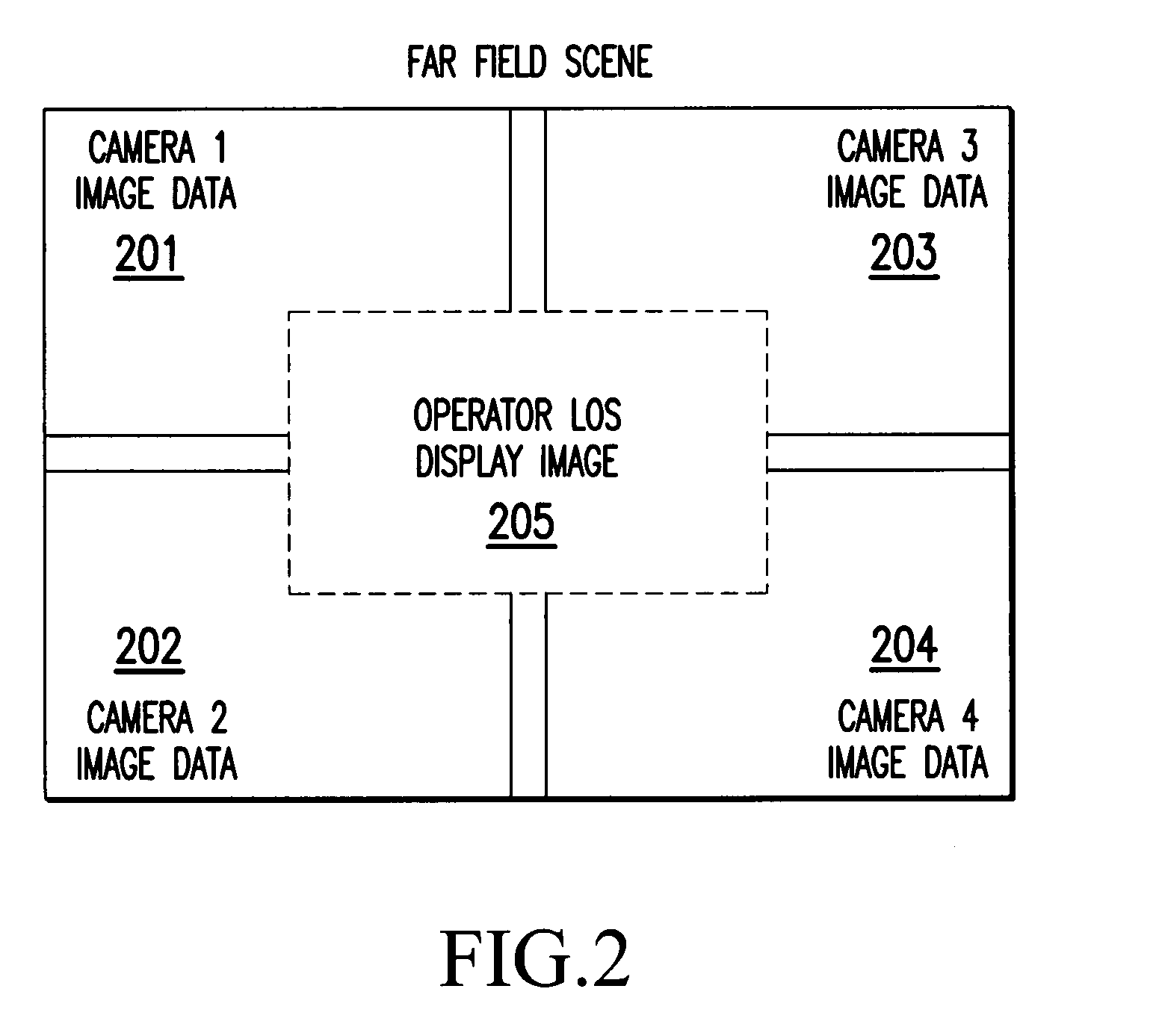
A method and a system for tracking a line-of-sight (LOS) and providing zero-lag image response to a display is disclosed. The method according to one embodiment receives image data having a filed of view (FOV) that is larger than what is displayed on the display using an initial LOS, combines the received image data to create a region of interest (ROI) image, detects a change in the LOS, creates a new ROI image using the received image data to correspond to the changed LOS, and displays the new ROI image to the display.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
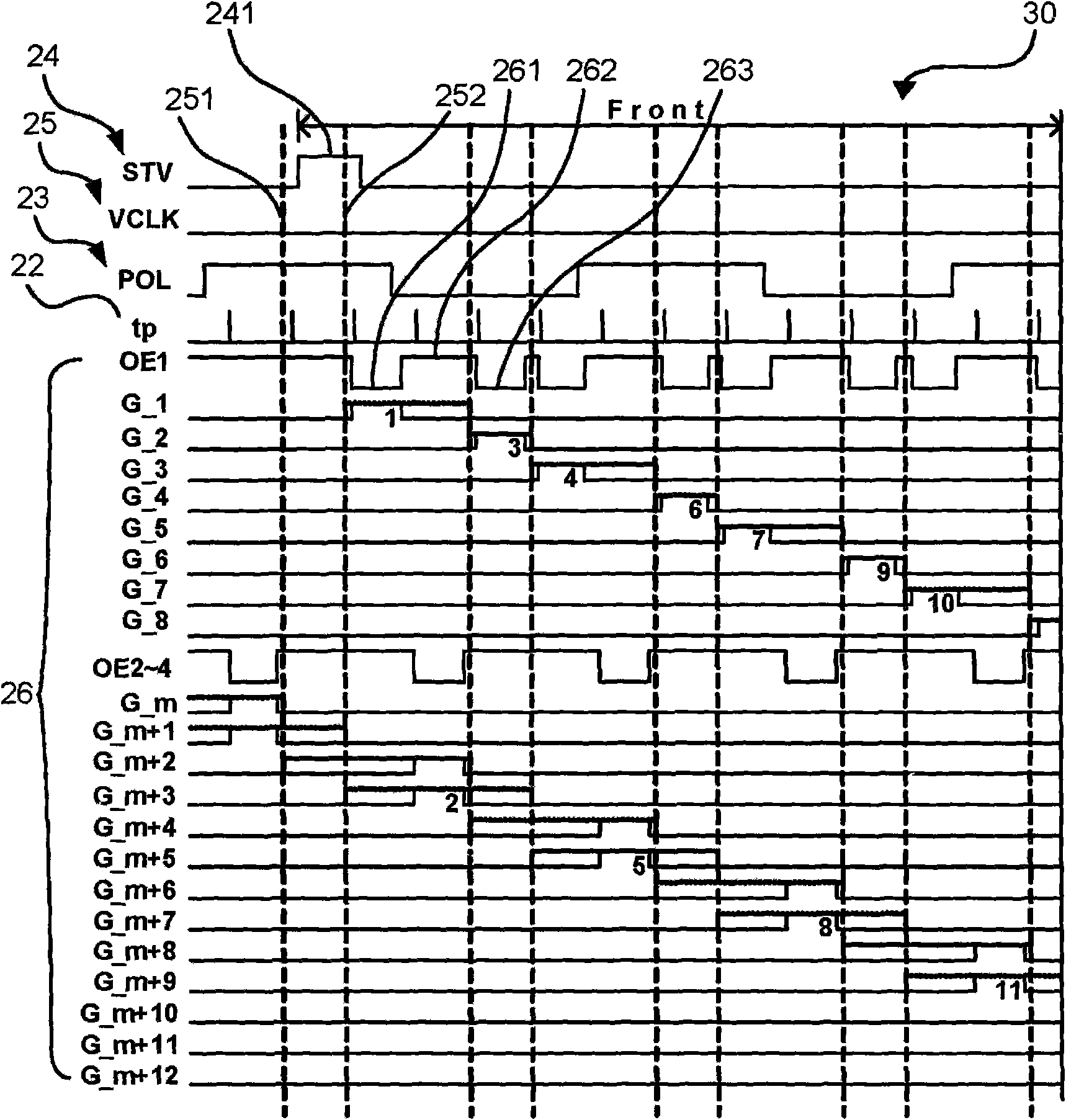
Shift register, gate drive circuit and drive method thereof
ActiveCN111599315AEnhanced Motion Picture Response TimeIncrease refresh rateStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerDriver circuit
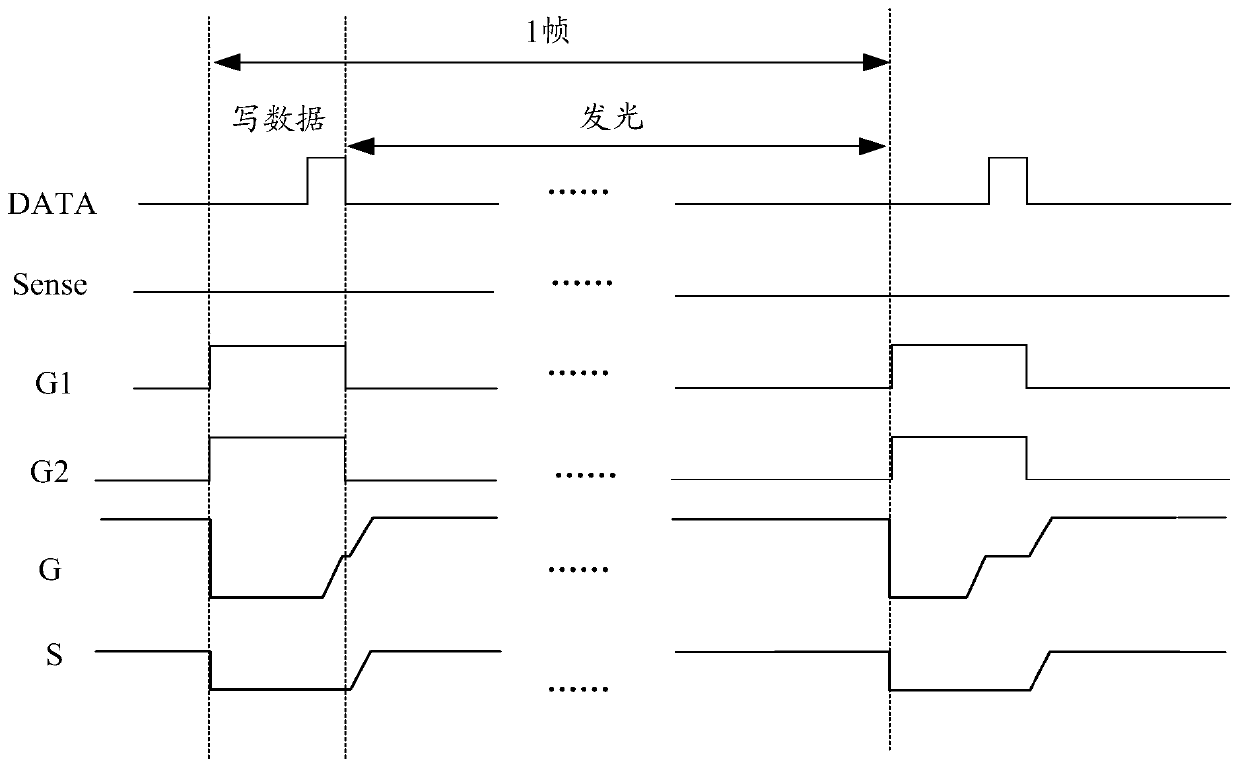
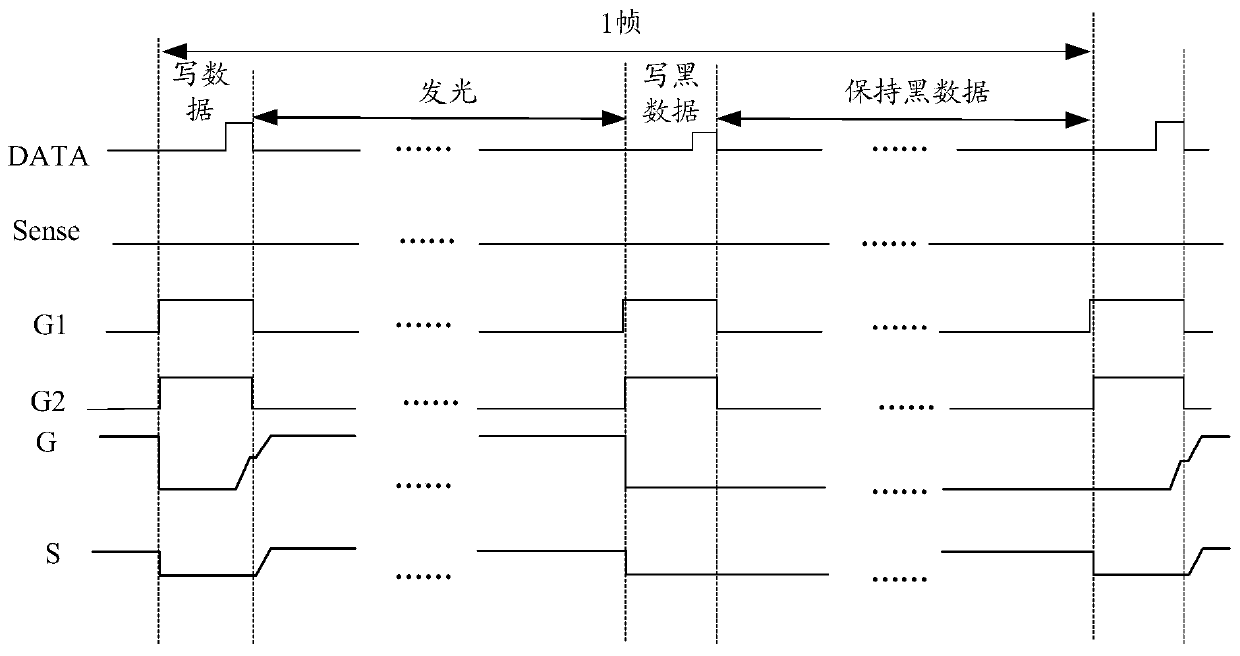
The invention discloses a shift register, a gate drive circuit and a drive method thereof. The shift register comprises a display pre-charging reset sub-circuit, a sensing pre-charging reset sub-circuit, a pull-down control sub-circuit, an output sub-circuit, a sensing cascade sub-circuit and a black insertion cascade sub-circuit, wherein the black insertion cascade sub-circuit is used for providing a signal of a second signal input end for the sensing cascade node under the control of a second random signal end. By arranging the black insertion cascade sub-circuit, black insertion can be performed on the other part of the screen of the display panel in the display gap of the part of the screen of the display panel, so that the time required for writing black data is shortened, and the high refresh rate of the display panel is ensured while the moving image response time of the display panel is prolonged.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Method of controlling digital photographing apparatus for out-focusing operation and digital photographing apparatus adopting the method
ActiveUS20060087578A1Easily perform out-focusingEasy to implementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage signalImaging data
Provided is a method of controlling a digital photographing apparatus that displays an image of a photograph region on a display panel, generates an image signal of the photograph region in response to signals generated by a shutter release button, and stores image data of the image signal in a storage medium. In an out-focusing mode, the method includes amplifying the blurriness of an out-focusing region by low-pass-filtering image data of regions excluding a setting region within the photograph region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Current mirror type TFT-OLED display image element unit circuit and its production method
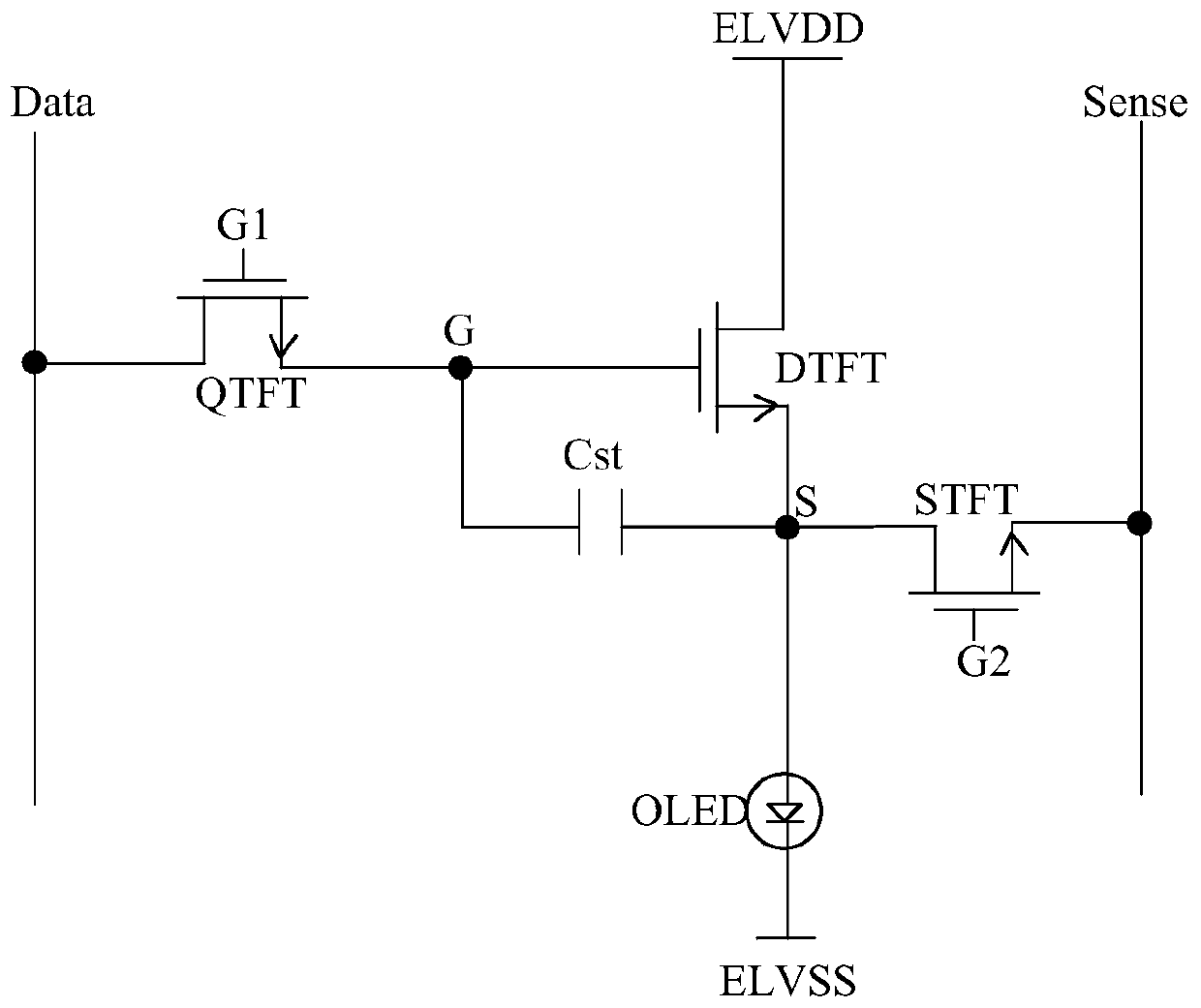
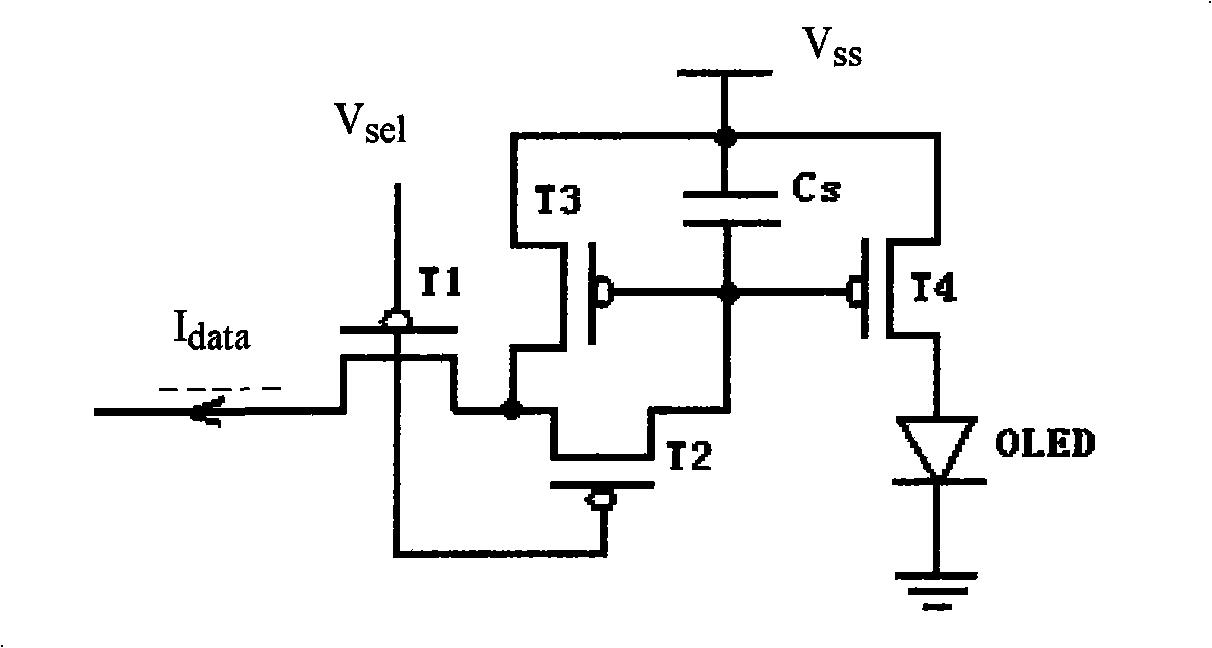
InactiveCN101404142AImprove consistencyHigh precisionStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesEngineeringMirror image
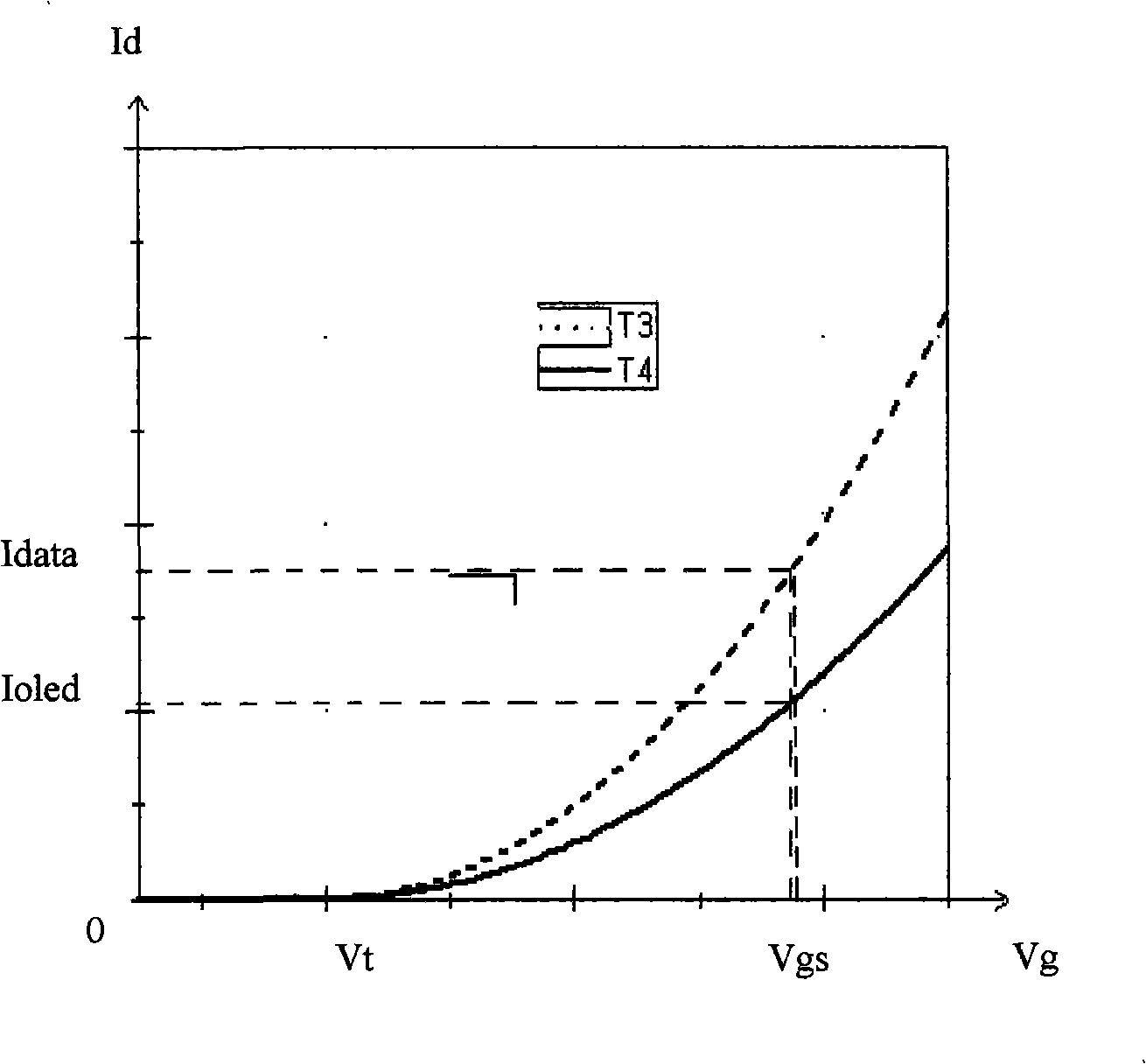
The present invention discloses a current mirror type TFT-OLED display pixel unit circuit, which comprises four polysilicon TFT tubes T1, T2, T3 and T4, an organic light emitting diode (OLED) and a capacitor Cs, wherein, the tubes T3 and T4 are completely symmetrical and form a current mirror; the tubes T1 and T2 serve as switch tubes, and line scanning signals are put in the grids of the tubes T1 and T2 to control the on-off of data current; the capacitor Cs is used for storing display data in a voltage mode, and the voltage on both ends of the capacitor Cs is loaded to the grid of the tube T4 to drive OLED to emit light; and the polysilicon TFT tubes T1, T2, T3 and T4 are all P channel devices. The present invention also provides a preparation method for transversal crystallization or laser crystallization of a mirror image TFT tube with high quality. The current mirror type TFT-OLED display pixel unit circuit and the method of the invention can enhance the consistency and precision of device properties of the TFT tube which forms mirror image current and can improve the image response speed, the image gray level and the picture display quality of an OLED screen.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Novel retina eye fundus image segmenting method
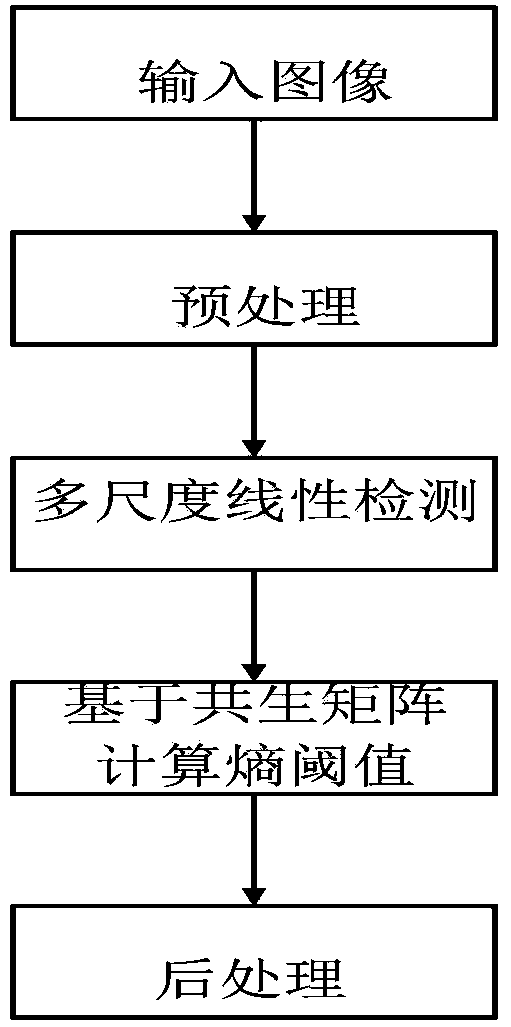
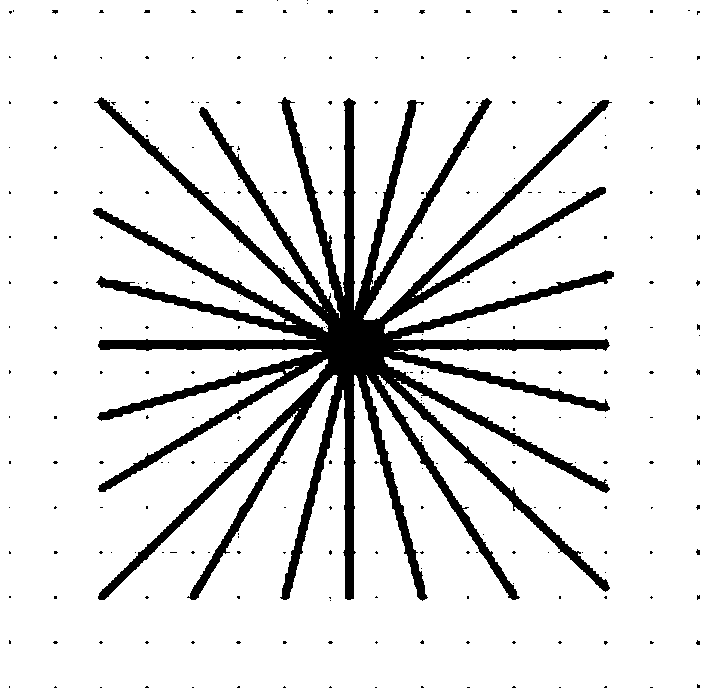
The invention provides a novel retina eye fundus image segmenting method. The method is characterized in that the best entropy threshold value is calculated by combining multi-scale linear detection and using the gray-level-gradient co-occurrence matrix of an image. Firstly, green components, containing rich blood vessel outline information, in the retina eye fundus image are extracted, and shadow correcting, noise reducing, CLAHE and other preprocessing are performed on the green components; secondly, multi-scale and multi-direction linear detection is performed on blood vessels of the retina eye fundus image according to morphological structure characteristics of the blood vessels, and image responses of different scales are fused to obtain the characteristics of the blood vessels; finally the best entropy threshold value of the image is calculated on the basis of the gray-level-gradient co-occurrence matrix of the image, and segmentation is performed. The method is high in segmenting accuracy, capable of extracting more fine blood vessels, high in calculating speed, very good in robustness and suitable for segmentation of the normal or lesion retina eye fundus image.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
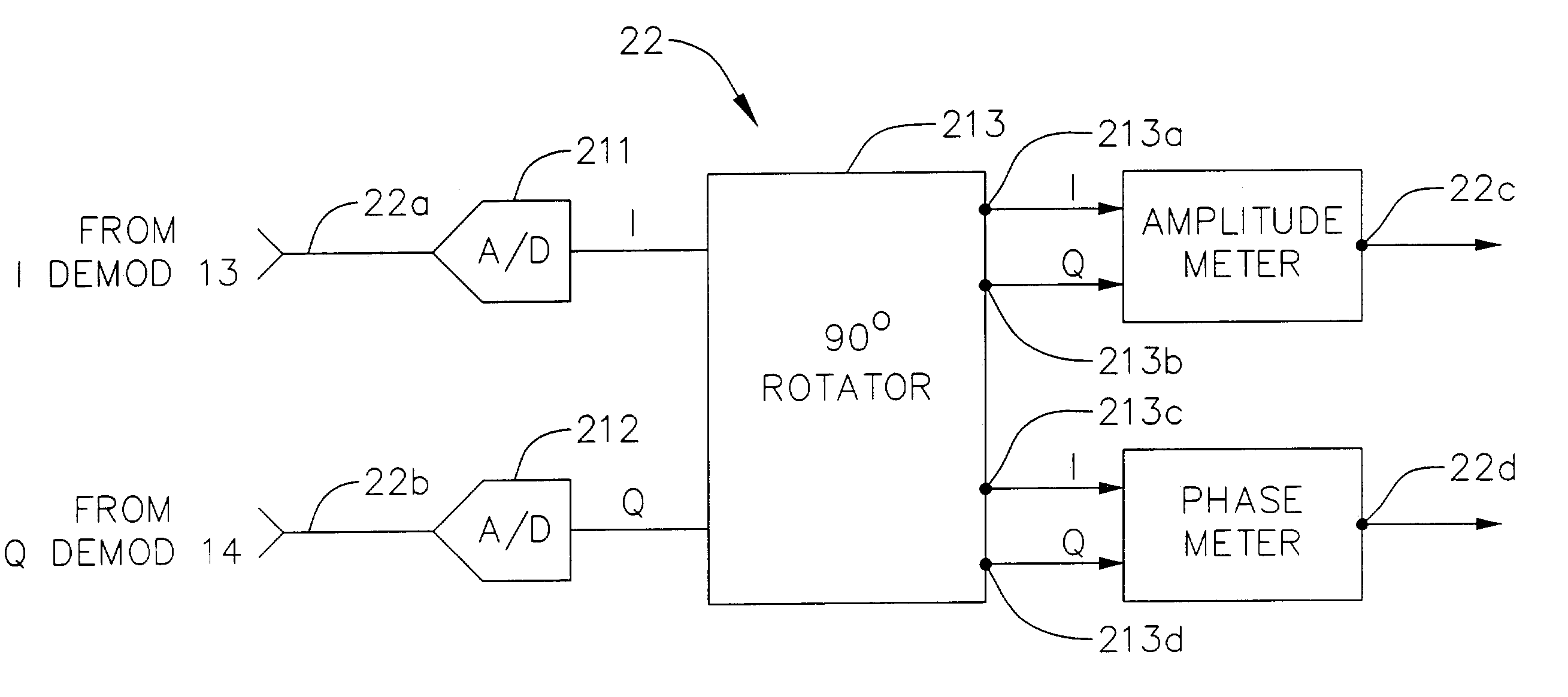
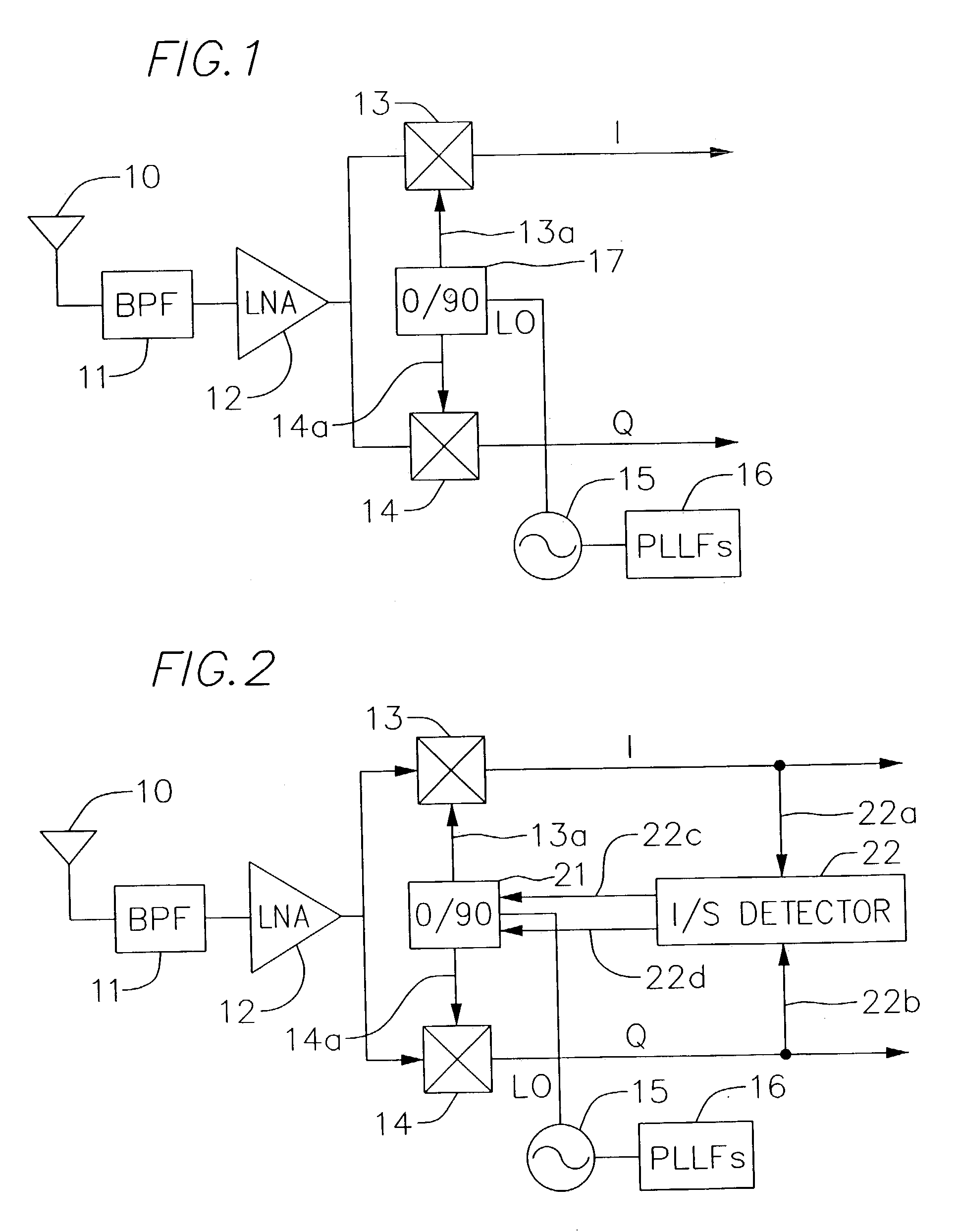
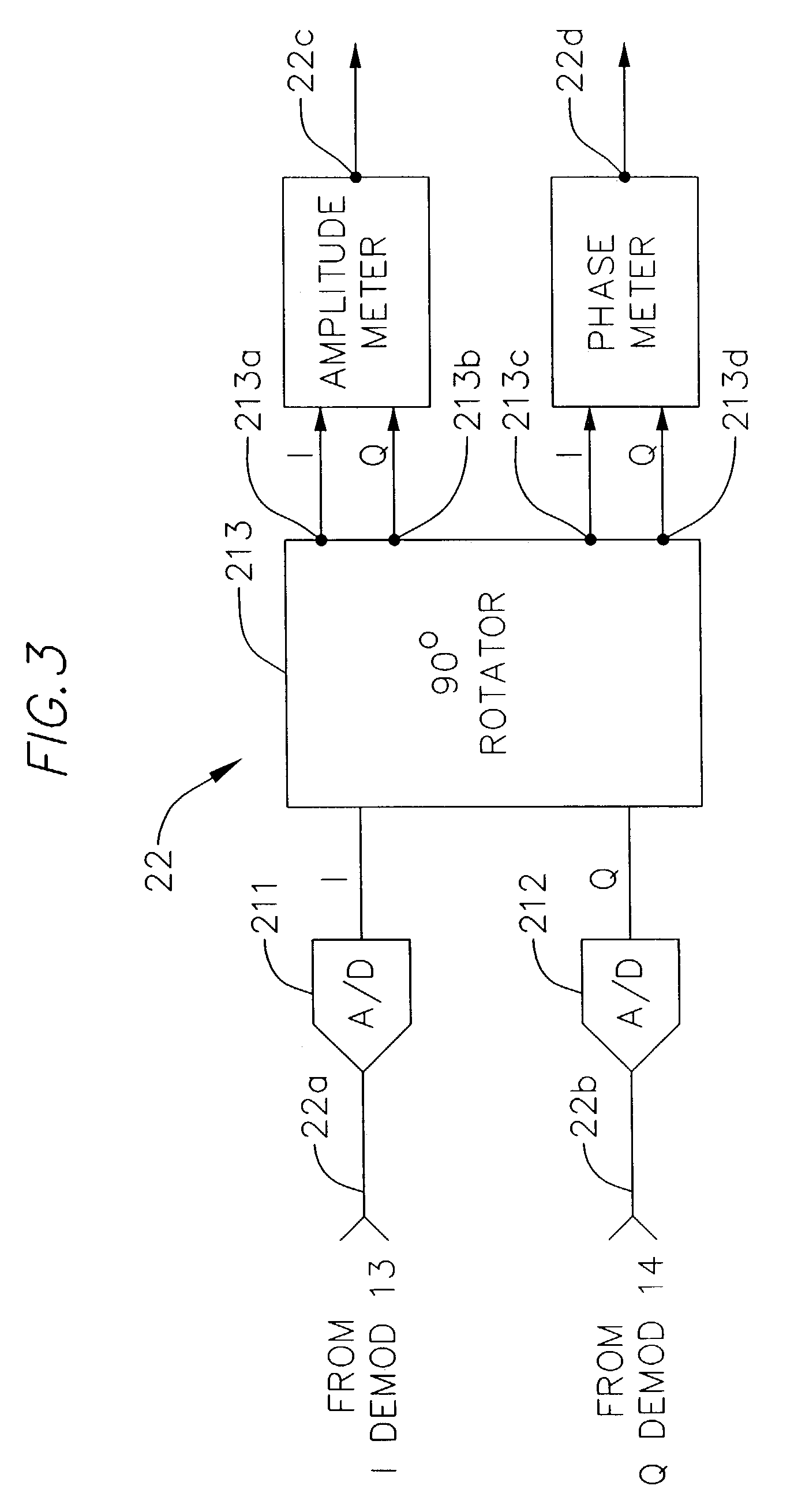
Image-rejection I/Q demodulators
InactiveUS7184737B2Reduces image responseNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsCarrier regulationControl signalRelative phase
In a communications receiver for quadrature demodulation, a feedback technique for reducing the image response of the receiver. The communications receiver includes an I demodulator and a Q demodulator. A local oscillator (LO) signal is provided by a PLL to a quadrature LO generator that provides an LO_I signal to an I demodulator and an LO_Q signal to a Q demodulator. The LO_I and LO_Q signals are amplitude and phase-controlled versions of the LO signal. An image / signal ratio (I / S) detector detects the relative phase difference and the relative amplitude difference between the respective output terminals of the I demodulator and the Q demodulator and applies an amplitude control signal and a phase control signal to corresponding amplitude control and phase control inputs of the quadrature LO generator. The I / S detector calibrates the quadrature LO generator during the interstitial interval between the reception of data packets. The control signals from the I / S detector adjust the relative amplitude and phase of the LO_I and LO_Q signals in a manner that reduces the image response of the communications receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Interpolated image response
Systems and methods are provided for characterizing a multidimensional distribution of responses from the objects in a populations subject to a perturbation. The methods enable the creation of a “degree of response” scale interpolated from non-perturbed and perturbed reference populations. The methods enables, using the interpolated degree of response scale, the quantitation of a degree of response of a test compound subject to a given level of perturbation, and enables the generation of a dose-response curve for a test compound. The methods are useful in a wide range of applications, such cellular analysis and high-content screening of compounds, as carried out in pharmaceutical research.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
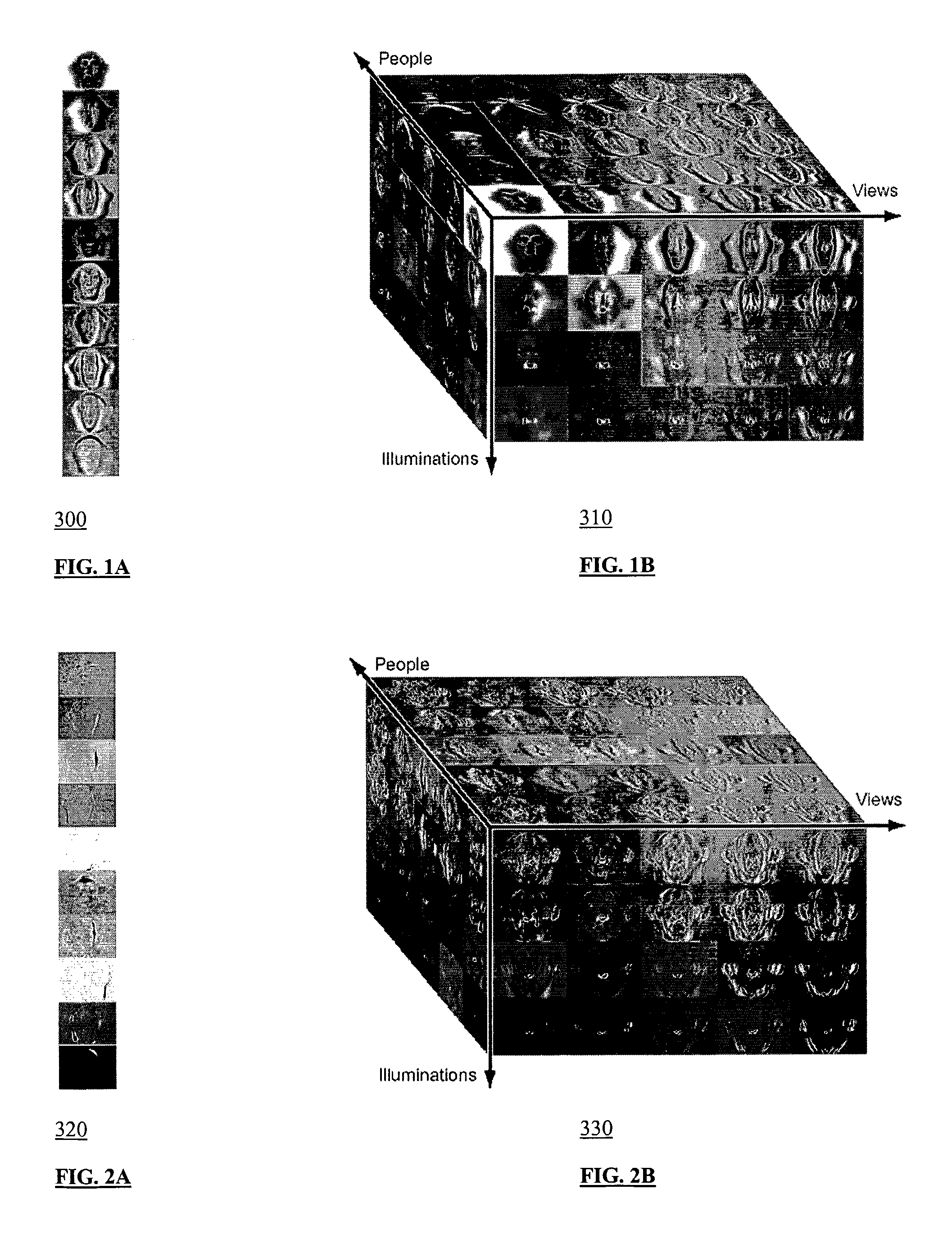
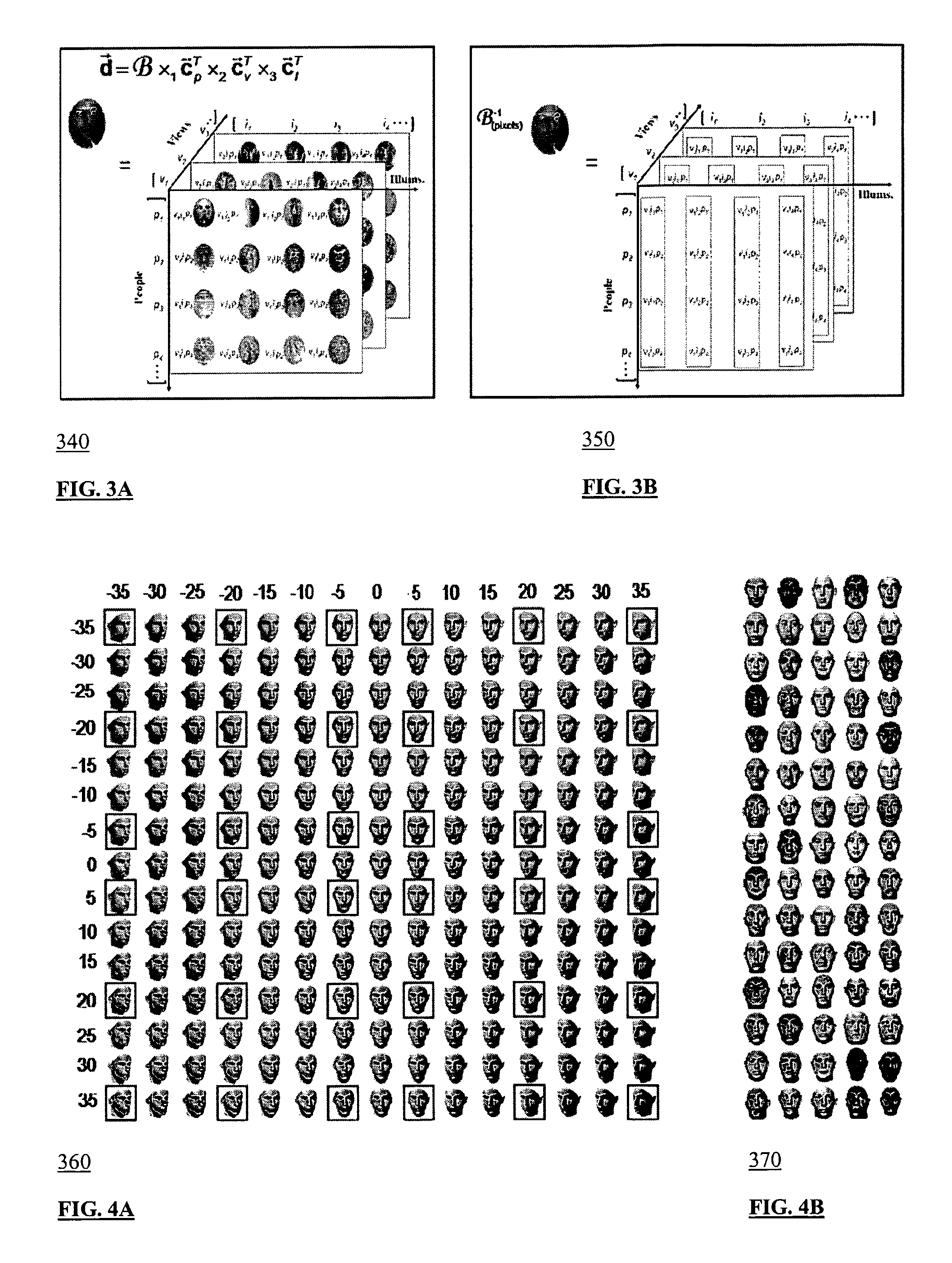
Method, System, Storage Medium, and Data Structure for Image Recognition Using Multilinear Independent Component Analysis
InactiveUS20080247608A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionIndependent component analysisImaging data
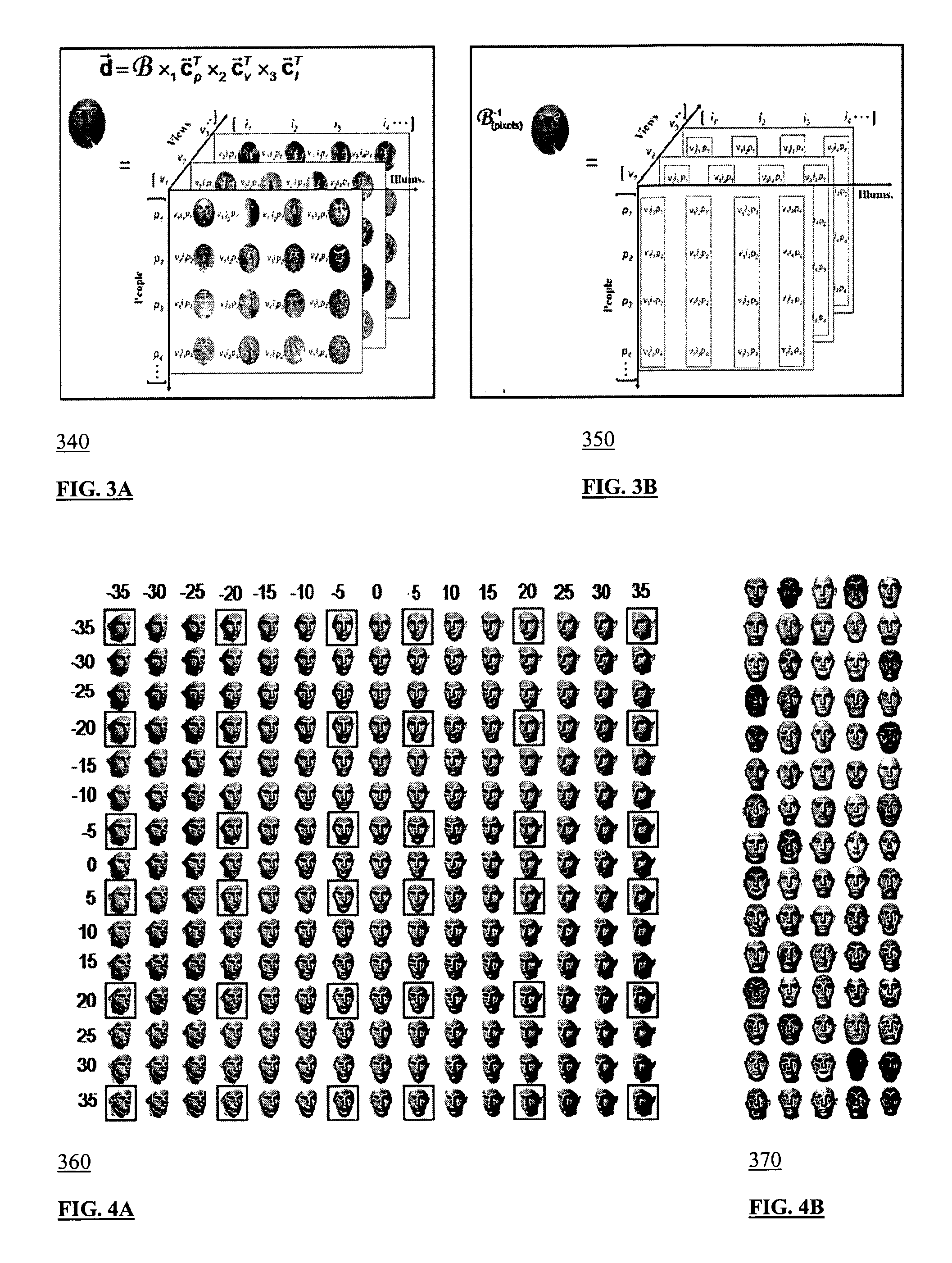
A method, system, computer-readable medium and data structure are provided for processing image data in connection with image recognition. A response of an image (FIG. 6 element 210) to a basis tensor can be determined after the image is applied thereto. The image response can be flattened (FIG. 6 element 220). A coefficient vector may be extracted from the image response (FIG. 6 element 230). The extracted coefficient vector may be compared to a plurality of different parameters stored in coefficient rows of a matrix (FIG. 6 element 240).
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
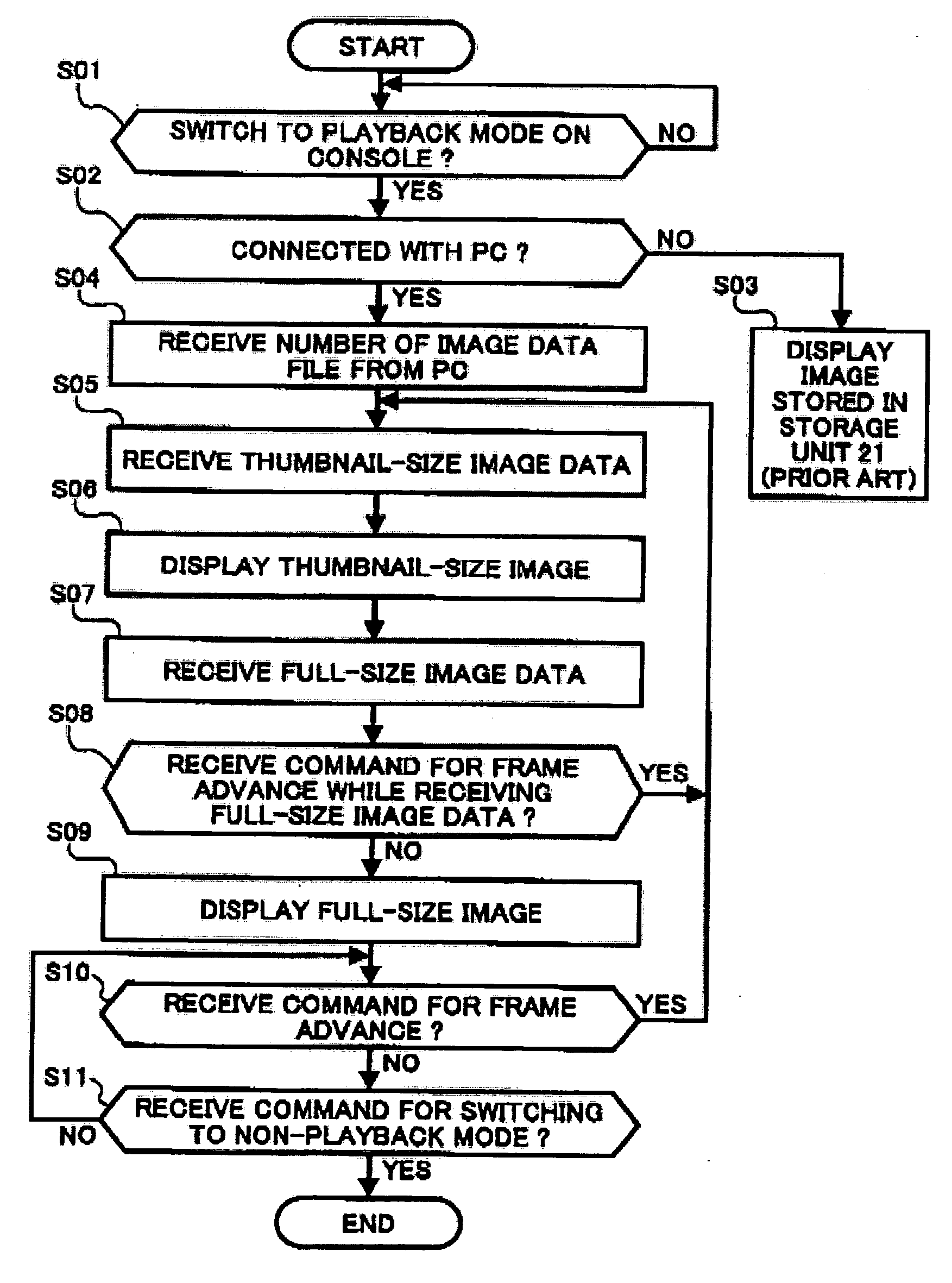
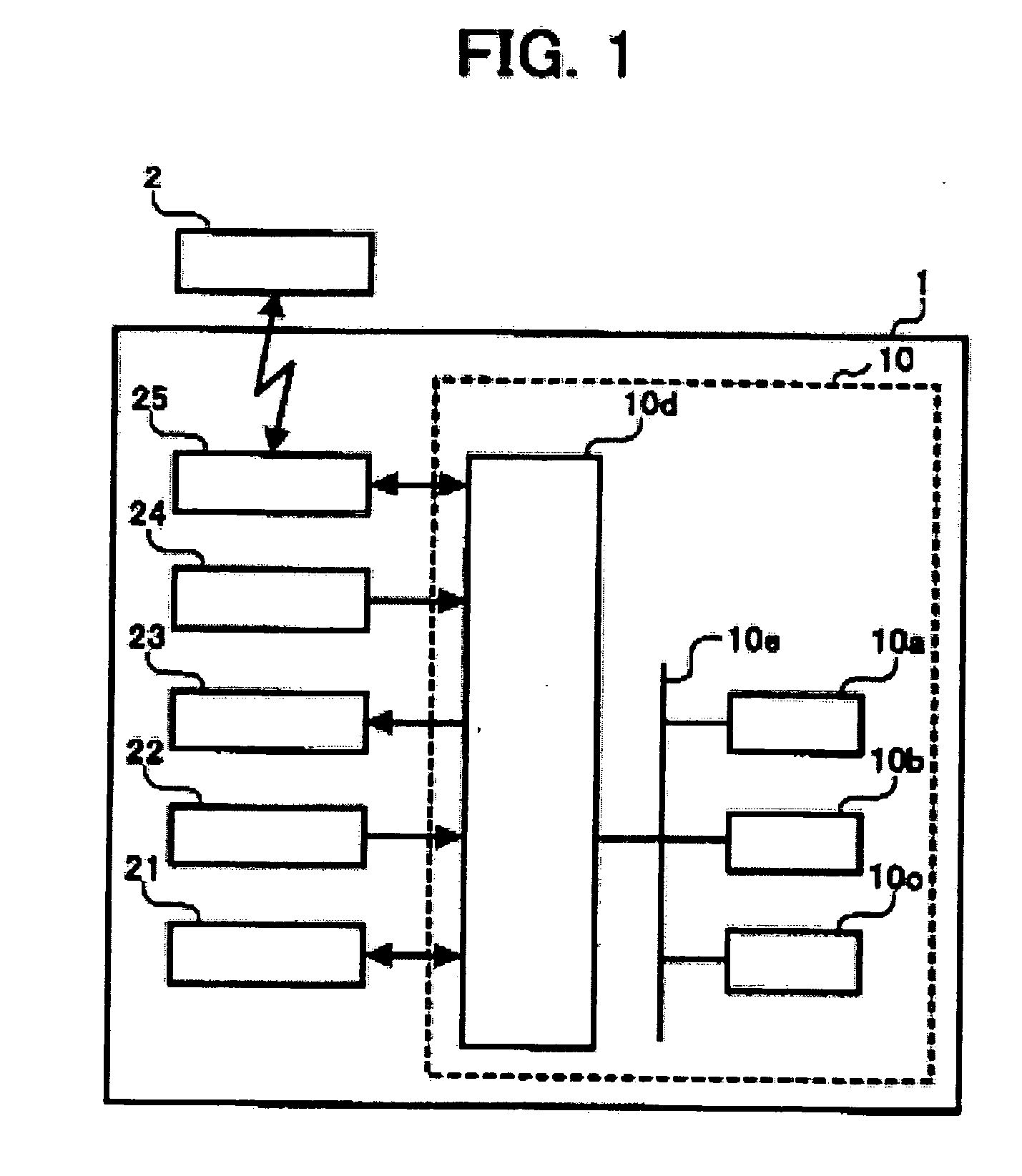
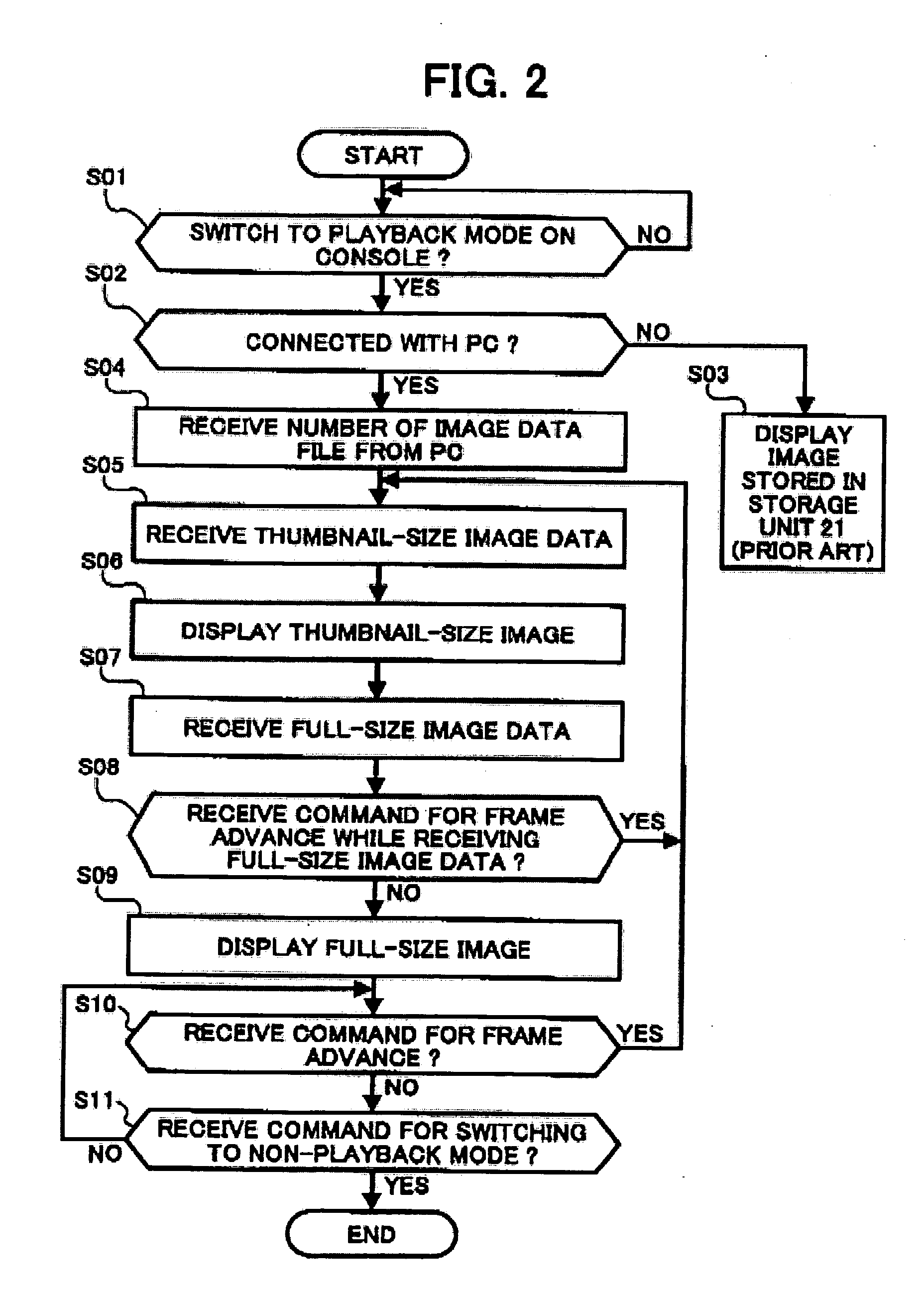
Digital camera, method for controlling digital camera, computer program for controlling a digital camera, signal for controlling digital camera and image playback apparatus
InactiveUS20050012828A1Quick switchEffective imagingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A digital camera having a temporary memory for driving a display. The temporary memory is fed image data from an external or internal non-volatile memory. The temporary memory is controlled so that it stores the image on display along with a predetermined number of previously viewed and to-be-viewed images. In response to a frame advance command, one image is deleted from temporary memory and another image is added to the temporary memory. The digital camera is configured to temporarily interrupt image uploading when the operator exercises a command, such as a frame advance command.
Owner:RICOH KK
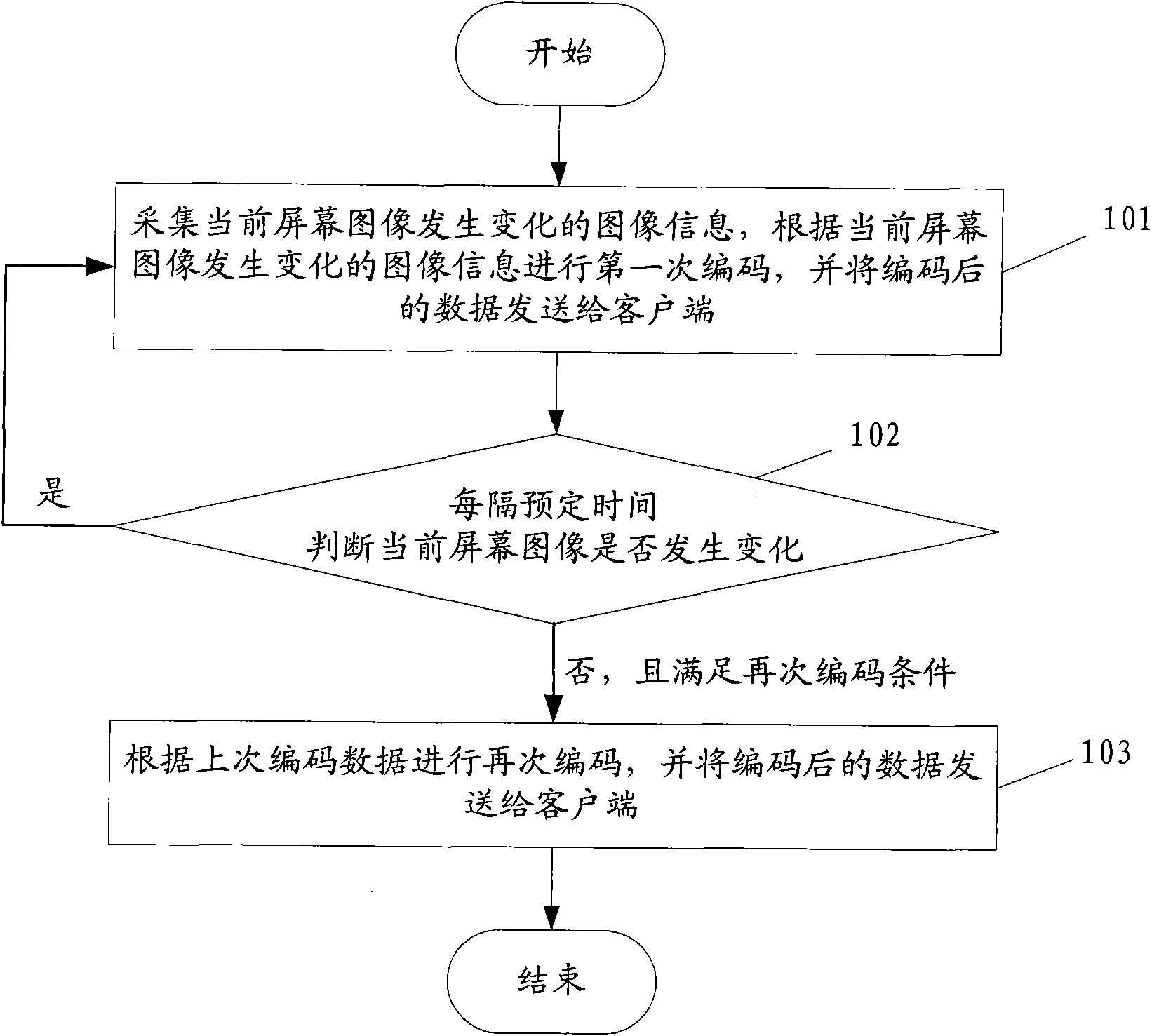
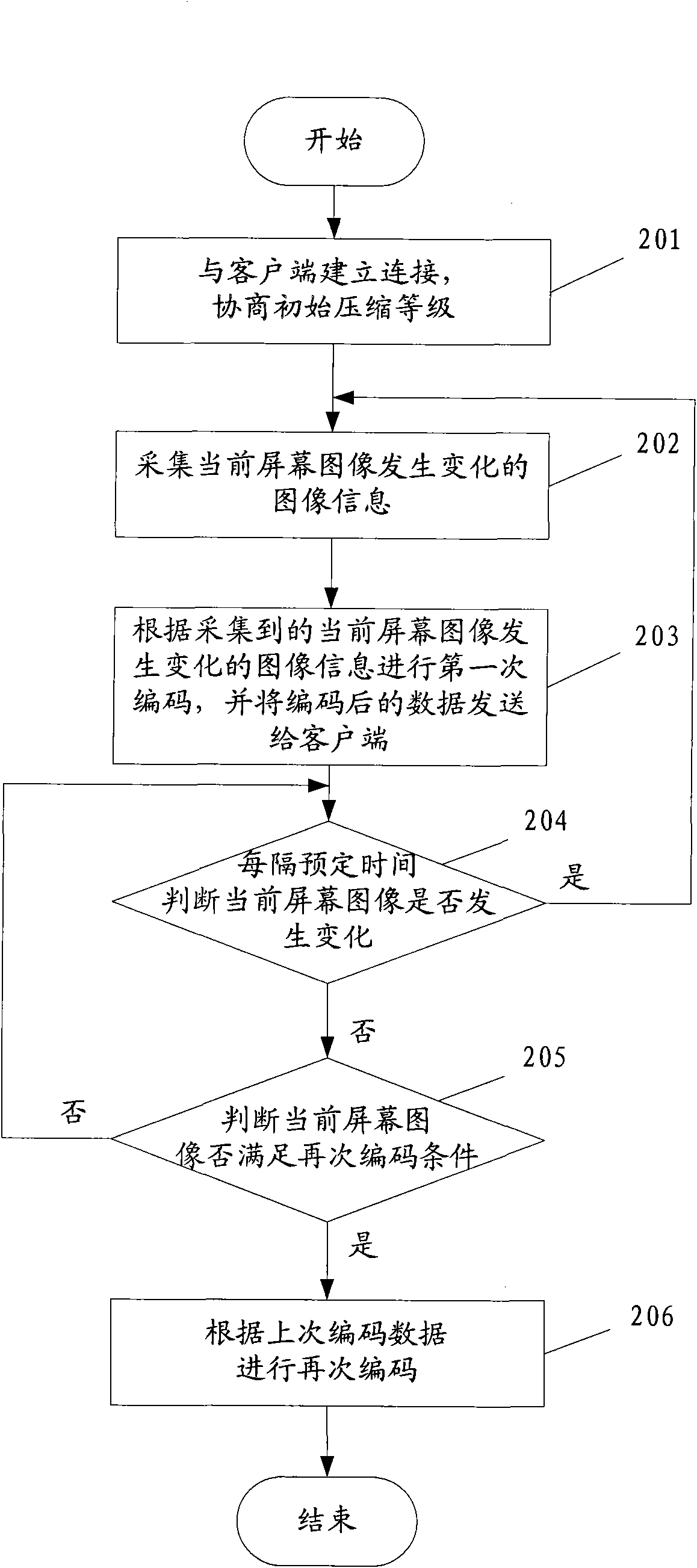
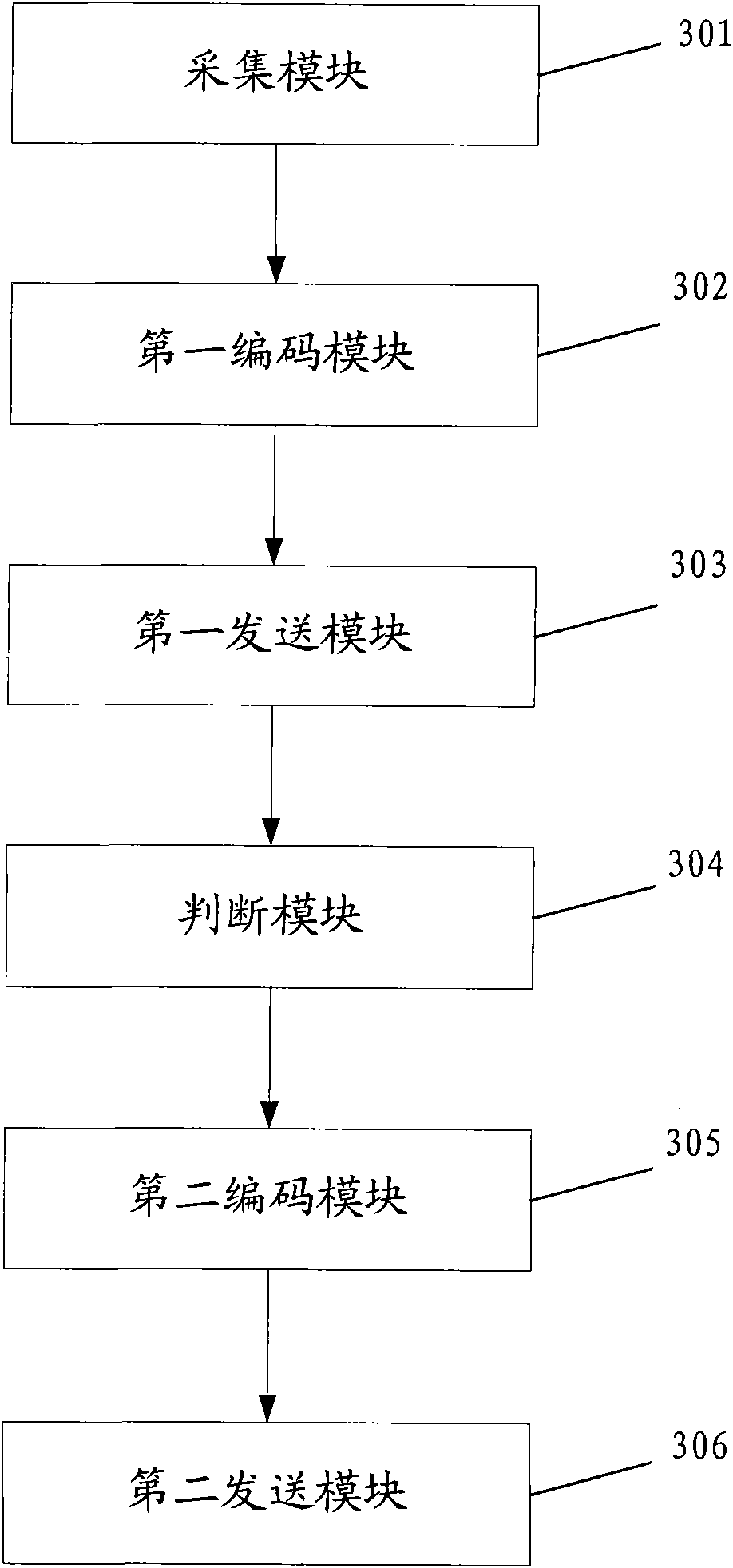
Image coding method and device
ActiveCN102143360AFast Image ResponseQuality improvementTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImaging qualityComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses an image coding method and device, belonging to the technical field of image coding. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting image information when a current screen image changes, performing first coding according to the collected image information when the current screen image changes and transmitting coded data to a client side; judging whether the current screen image changes every preset time intervals; and coding once again according to coding data in last time if the current screen image does not change and the secondary coding condition is satisfied, and transmitting the coded data to the client side. In the invention, the image information when the current screen image changes is collected, and then the first coding is performed according tothe collected image information and the coded data is transmitted to the client side, thus the client side has a relatively high image responding speed; and certain data is transmitted once again when the current screen image does not change, such that the idle band width resource can be used effectively and the image quality of the client side is further improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Linear feature detection method and apparatus
ActiveUS8463065B2Reduce computing timeImage enhancementImage analysisLinearityNon maximum suppression
A method of extracting linear features from an image, the method including the steps of: (a) applying a non maximum suppression filter to the image for different angles of response to produce a series of filtered image responses; (b) combining the filtered image responses into a combined image having extracted linear features.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Image photographing apparatus and method thereof
ActiveUS20150029379A1Television system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Image response
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
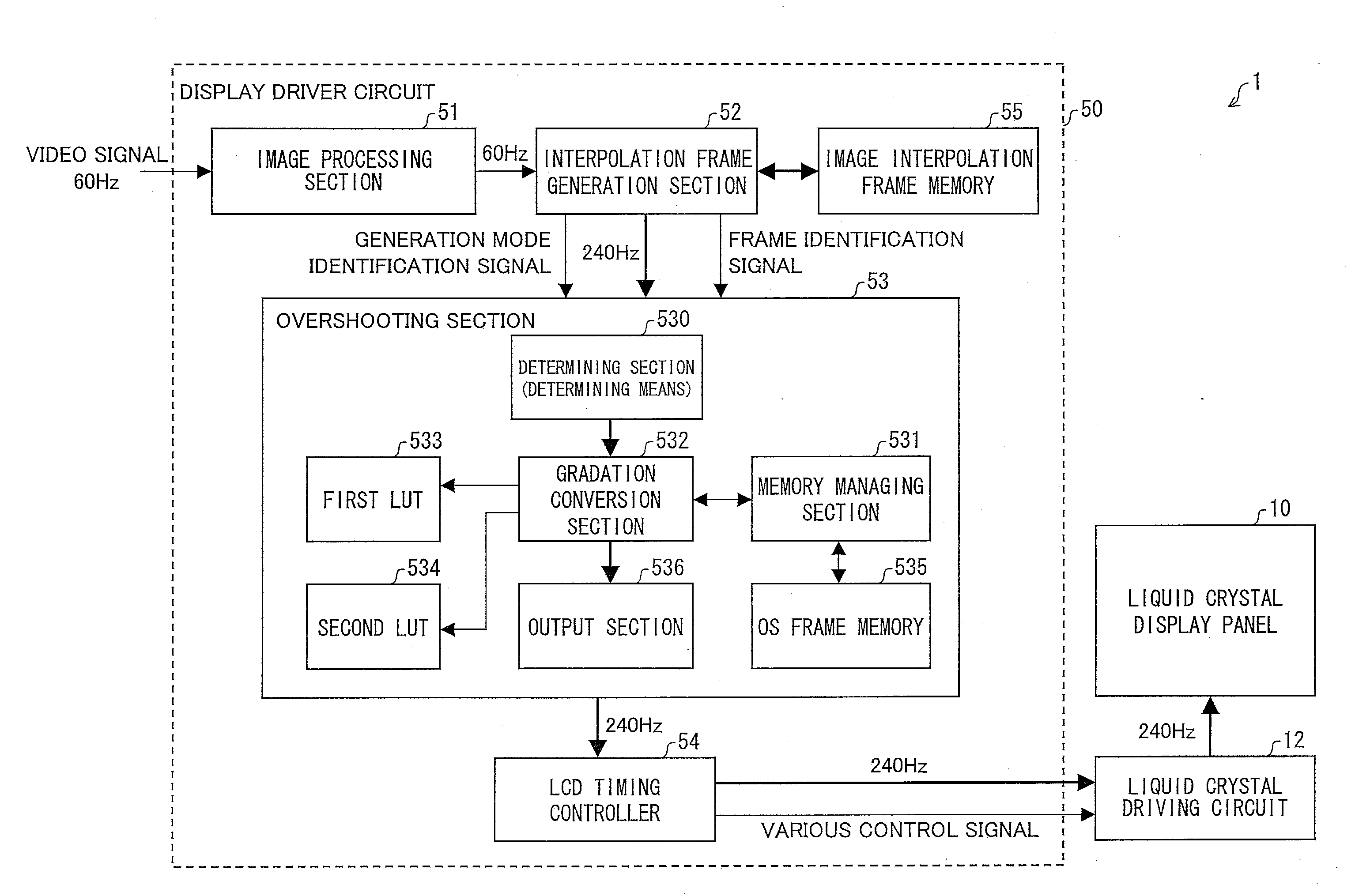
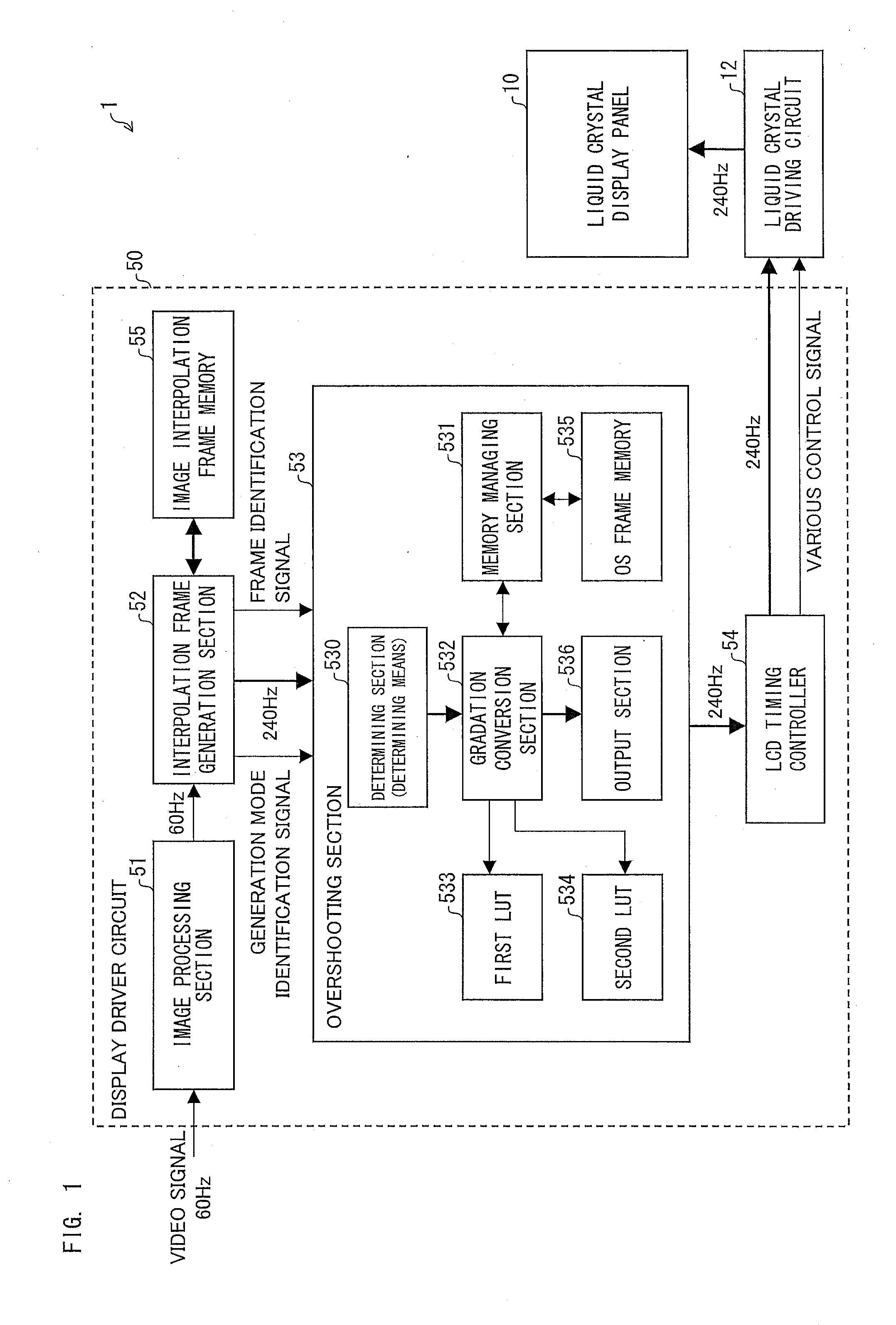
Display driver circuit, liquid crystal display device, display driving method, control program, and computer-readable recording medium having same control program recorded therein
InactiveUS20120162290A1Improve responsivenessImprove response speedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwareLiquid-crystal display
Provided is a display driver circuit which carries out frame interpolation and overshooting. An interpolation frame generation section has (i) a first generation mode of generating, based on an image of a key frame corresponding to a video signal, an interpolation frame so that a position of an object is changed with passage of time and (ii) a second generation mode of generating, based on the image of the key frame, an interpolation frame so that a display gradation of the object is changed with passage of time. An overshooting section causes an emphasis level in a tone transition for the interpolation frame generated according to the second generation mode to be different from that for the key frame. Thus, a configuration is proposed which can improve a moving image response characteristic in a display driver circuit which carries out frame interpolation and overshooting.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method, system, storage medium, and data structure for image recognition using multilinear independent component analysis
InactiveUS7693299B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionIndependent component analysisImaging data
A method, system, computer-readable medium and data structure are provided for processing image data in connection with image recognition. A response of an image (FIG. 6 element 210) to a basis tensor can be determined after the image is applied thereto. The image response can be flattened (FIG. 6 element 220). A coefficient vector may be extracted from the image response (FIG. 6 element 230). The extracted coefficient vector may be compared to a plurality of different parameters stored in coefficient rows of a matrix (FIG. 6 element 240).
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
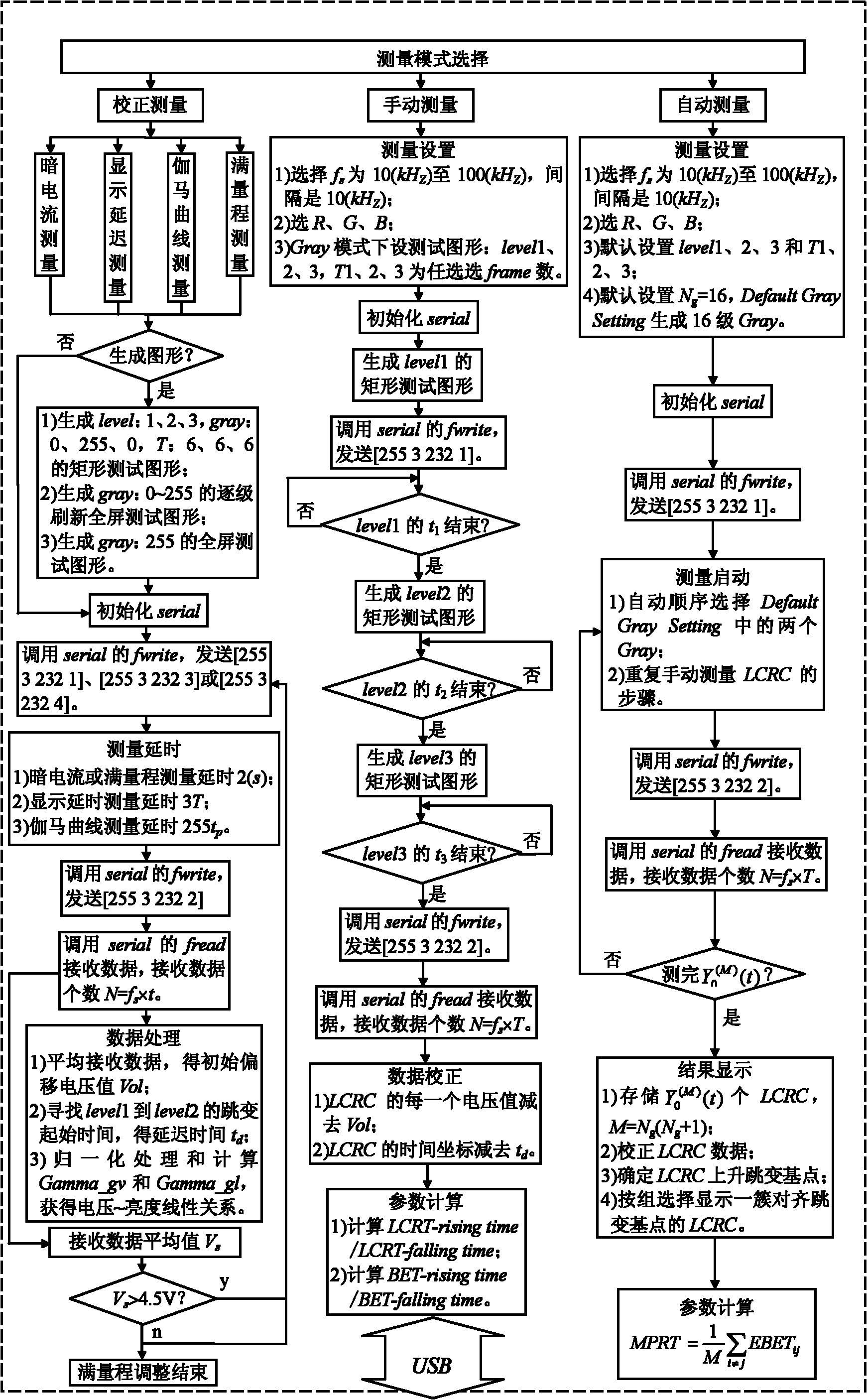
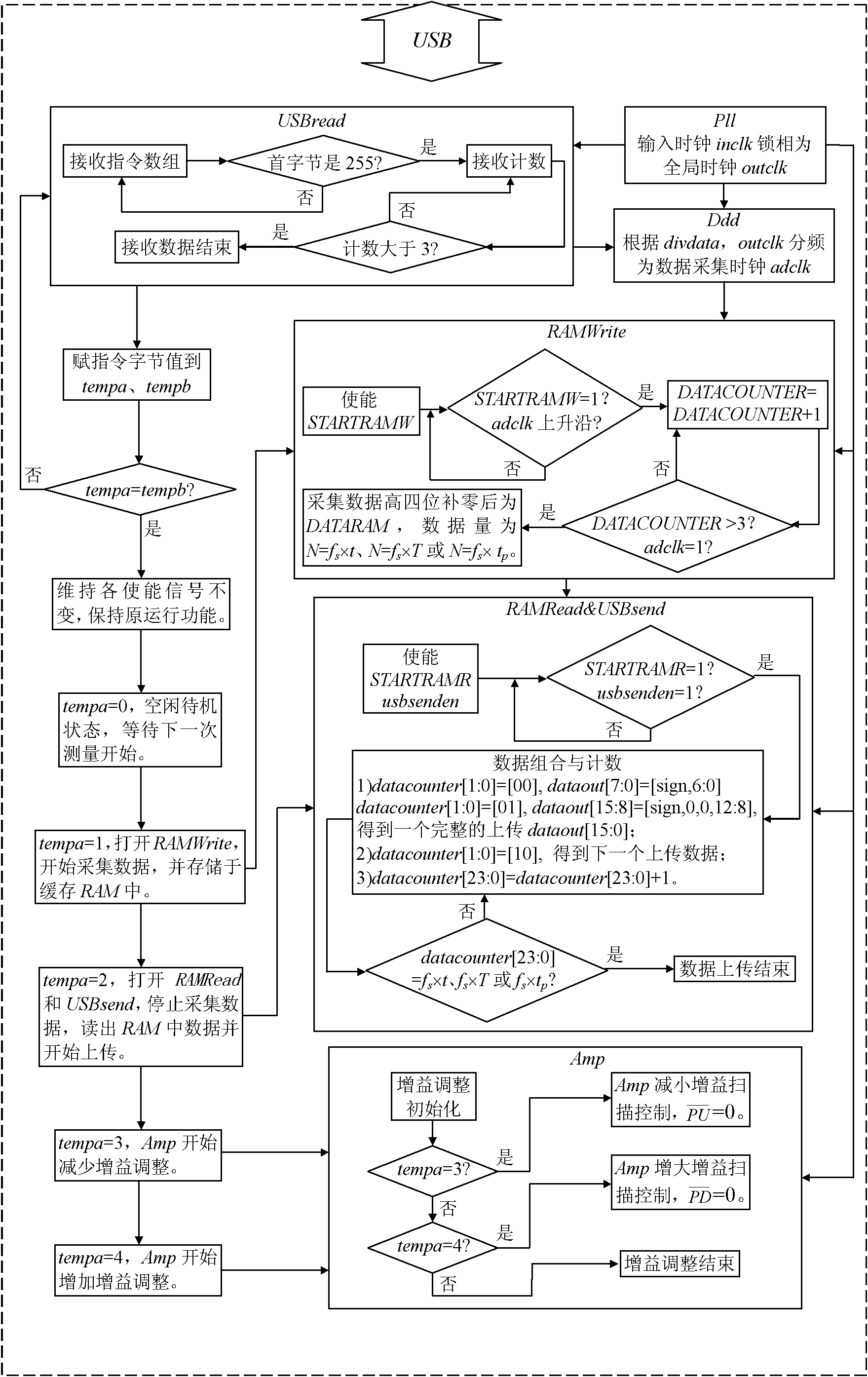
Method for measuring brightness response characteristic of display screen of notebook computer
InactiveCN102353527AEnsure accuracy andEnsure reliabilityDetecting faulty computer hardwareTesting optical propertiesImaging qualitySignal on
The invention discloses a method for measuring a brightness response characteristic of a display screen of a notebook computer. The method is used for a system for measuring the brightness response characteristic of the display screen of the notebook computer. The system comprises an upper notebook computer and a lower-computer photoelectric amplification and data acquisition device, wherein the upper notebook computer is used for generating a test pattern on the display screen of the upper notebook computer, the lower-computer photoelectric amplification and data acquisition device is used for converting, amplifying, acquiring and transmitting optical signals on the display screen of the notebook computer, the digital quantity of the optical signals is transmitted to the upper notebook computer through a serial bus interface and is processed and calculated in the upper notebook computer. The method is characterized by comprises an upper computer control method and a lower computer operation method. According to the invention, a system correction measuring flow is utilized to ensure measuring precision, and a fuzzy edge time measuring flow and a motion image response time measuring flow are used to verify the dynamic image quality of the display screen of the notebook computer.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Image processing device, image display device and image processing method
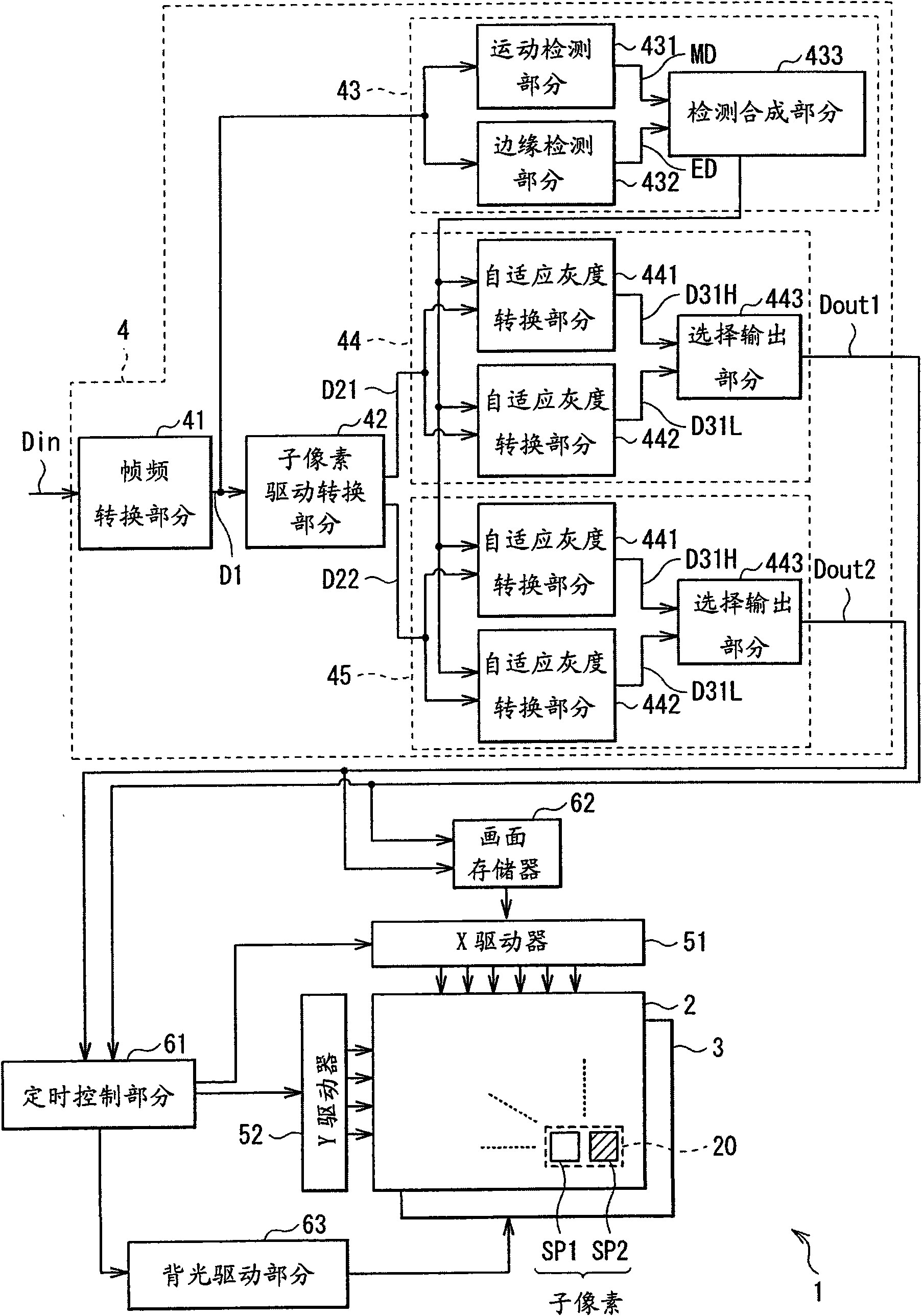
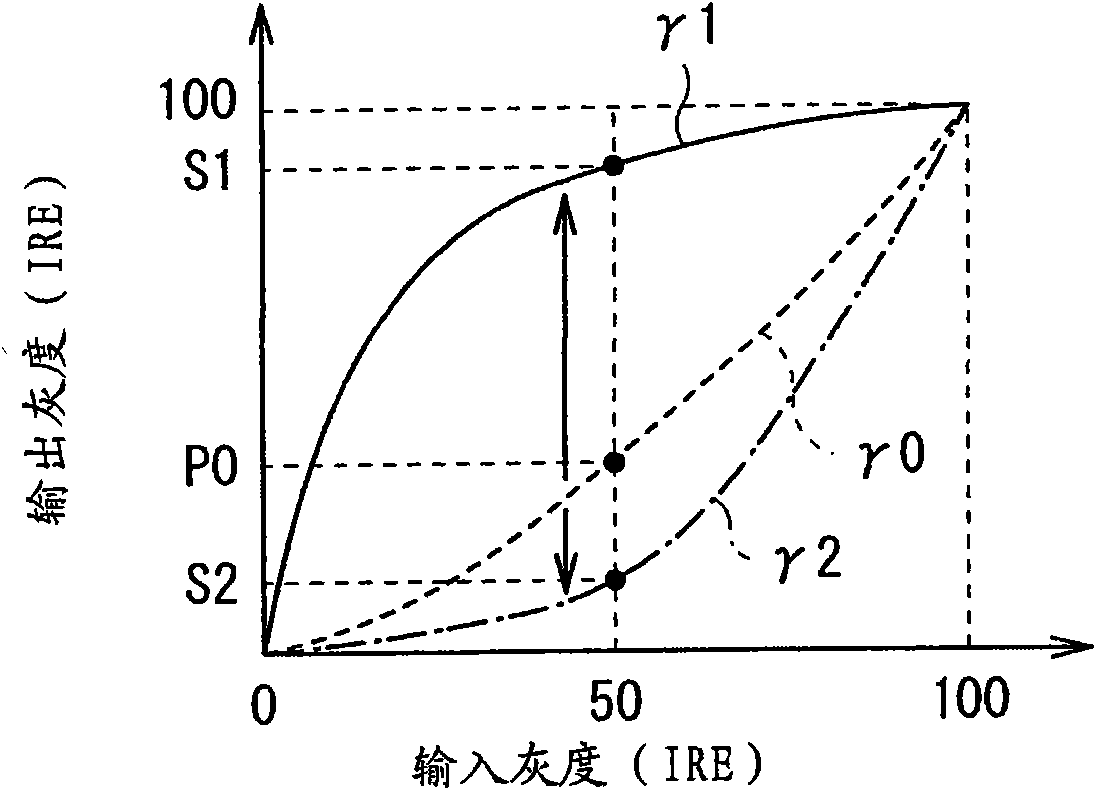
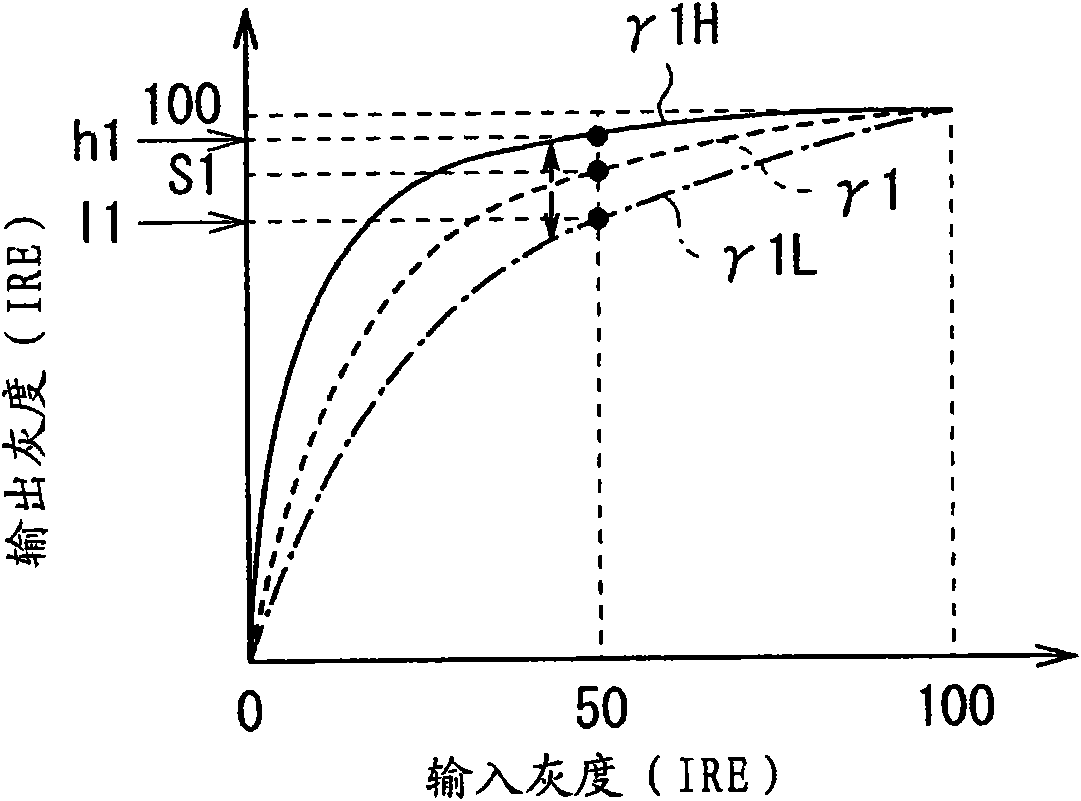
InactiveCN101647056AResponsiveImprove viewing angle characteristicsTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesImaging processingDisplay device
An image processing device is provided for making it possible to cope with both the widening of a viewing angle characteristic while reducing a feeling of flickers in an image display device with a sub-pixel structure and the improvement of a dynamic image response characteristic. The image processing device includes a detection means for detecting a motion index and / or an edge index of an input picture for each pixel; a frame division means for dividing a unit frame period of the input picture into a plurality of sub-frame periods; and a gray-scale conversion means for selectively performing adaptive gray-scale conversion on a luminance signal in a pixel region where a motion index or an edge index larger than a predetermined threshold value is detected from the luminance signal of the input picture by the detection means so that, while allowing the time integral value of the luminance signal within the unit frame period to be maintained as it is, a high luminance period having a luminance level higher than that of an original luminance signal and a low luminance period having a luminance level lower than that of the original luminance signal are allocated to sub-frame periods in the unit frame period, respectively, and performs adaptive gray-scale conversion for each sub-pixel so that the plurality of sub-pixels in each pixel have different display luminance from each other.
Owner:SONY CORP
DMC color composition image radiation re-handling method
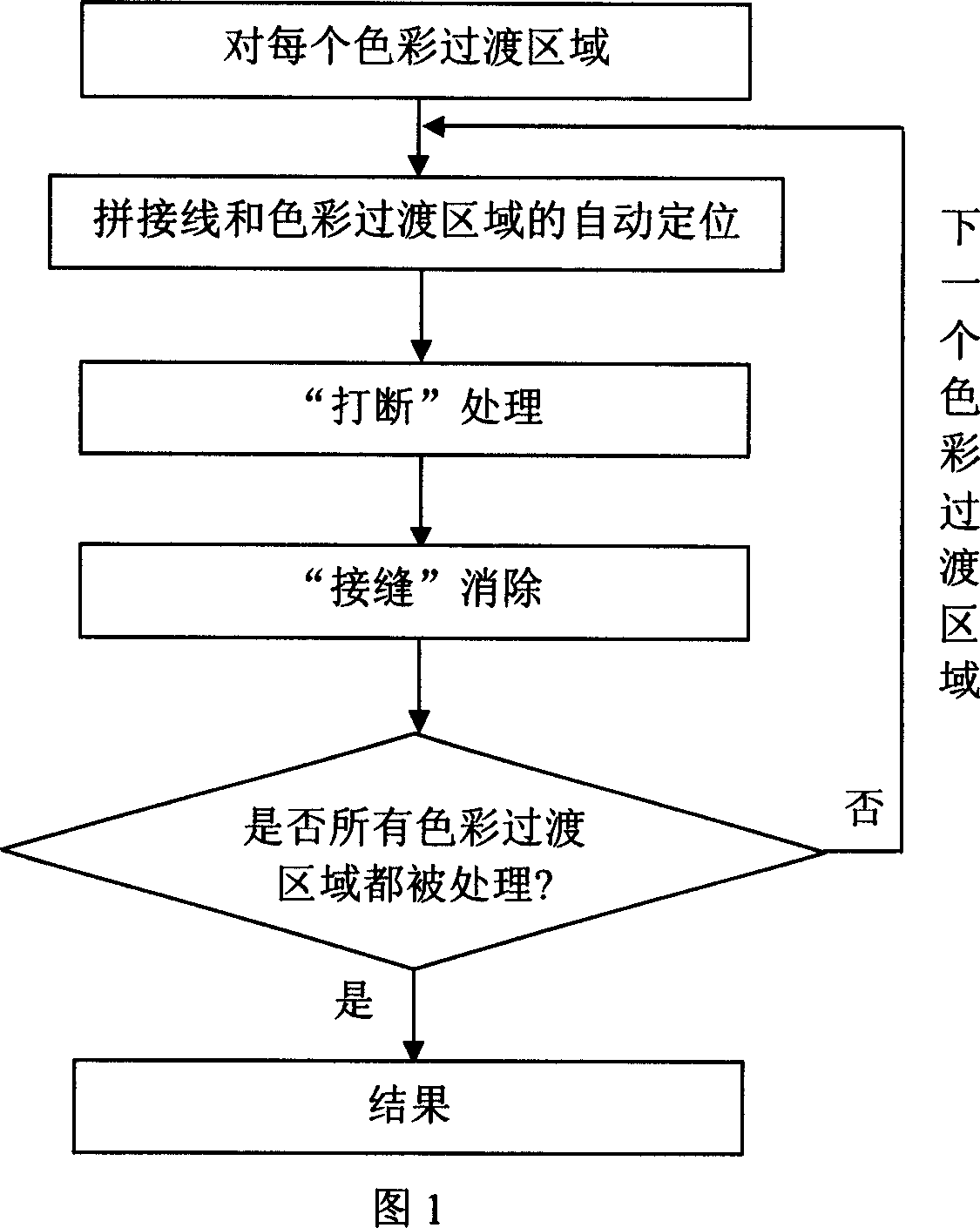
ActiveCN1924927ASolve the problem that the color transition is not smooth enoughQuality improvementImage enhancementPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryBlock methodRadiation process
This invention relates to DMC image response image radiation process method aiming at DMC color integration due to different cameral CCD difference in the image process and analysis field. This method adopts gold strategy and difference image fringe principle to automatically position matching lines and color area position and to adopt block method and voting to improve the method stability.
Owner:大连九成测绘信息有限公司
Image enhancement in the mosaic domain
ActiveUS8115840B2Quality improvementEnhance the imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage restorationImage signal
Imaging apparatus includes a mosaic image sensor (24), which is configured to generate a stream of input pixel values belonging to a plurality of input sub-images, each sub-image responsive to light of a different, respective color that is incident on the mosaic image sensor. An image restoration circuit (26) is coupled to receive and digitally filter the input pixel values in each of the input sub-images so as to generate a corresponding plurality of enhanced output sub-images. An image signal processor (ISP) (28) is coupled to receive and combine the plurality of the output sub-images in order to generate a color video output image.
Owner:DIGITALOPTICS CORPORATION
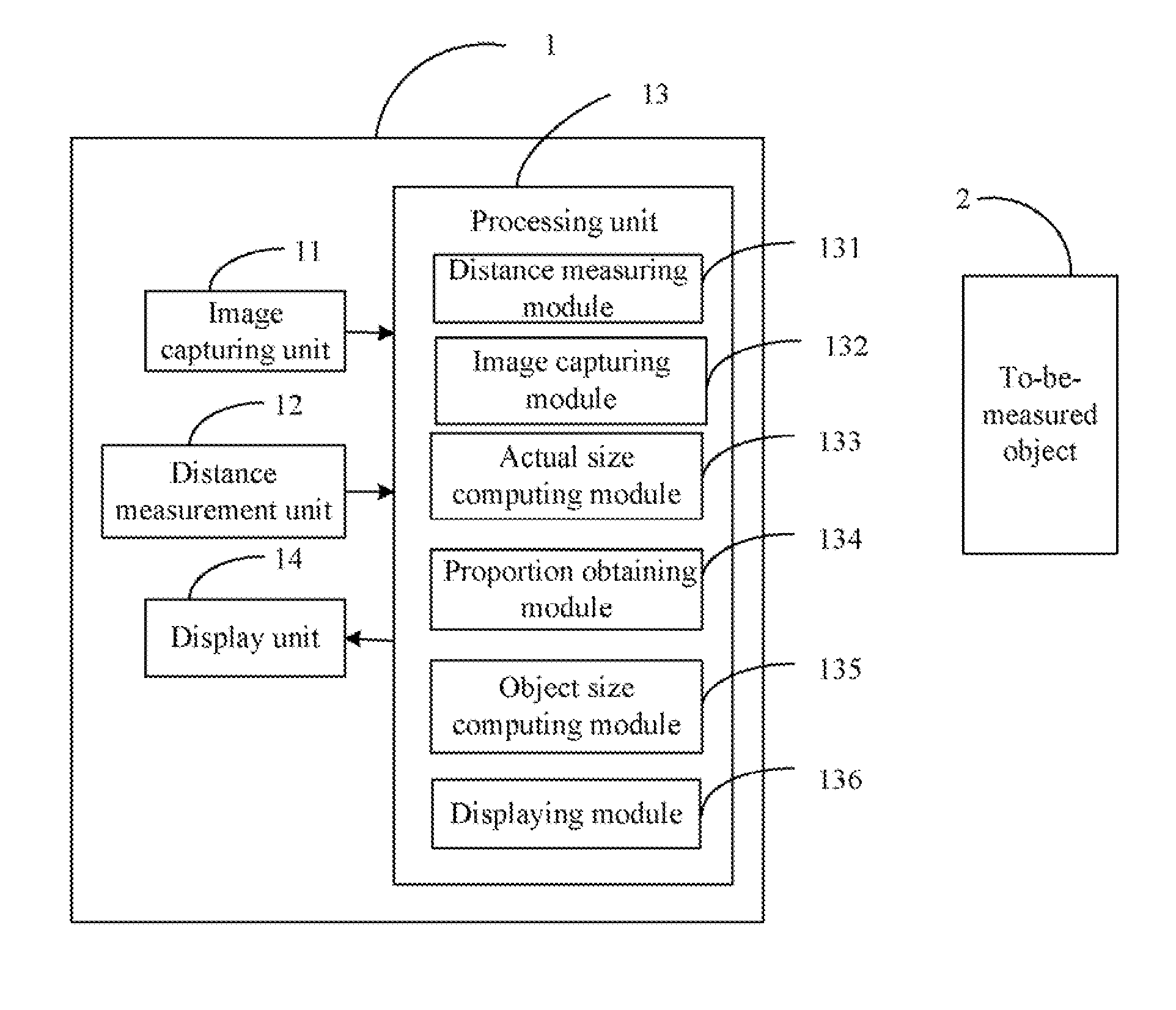
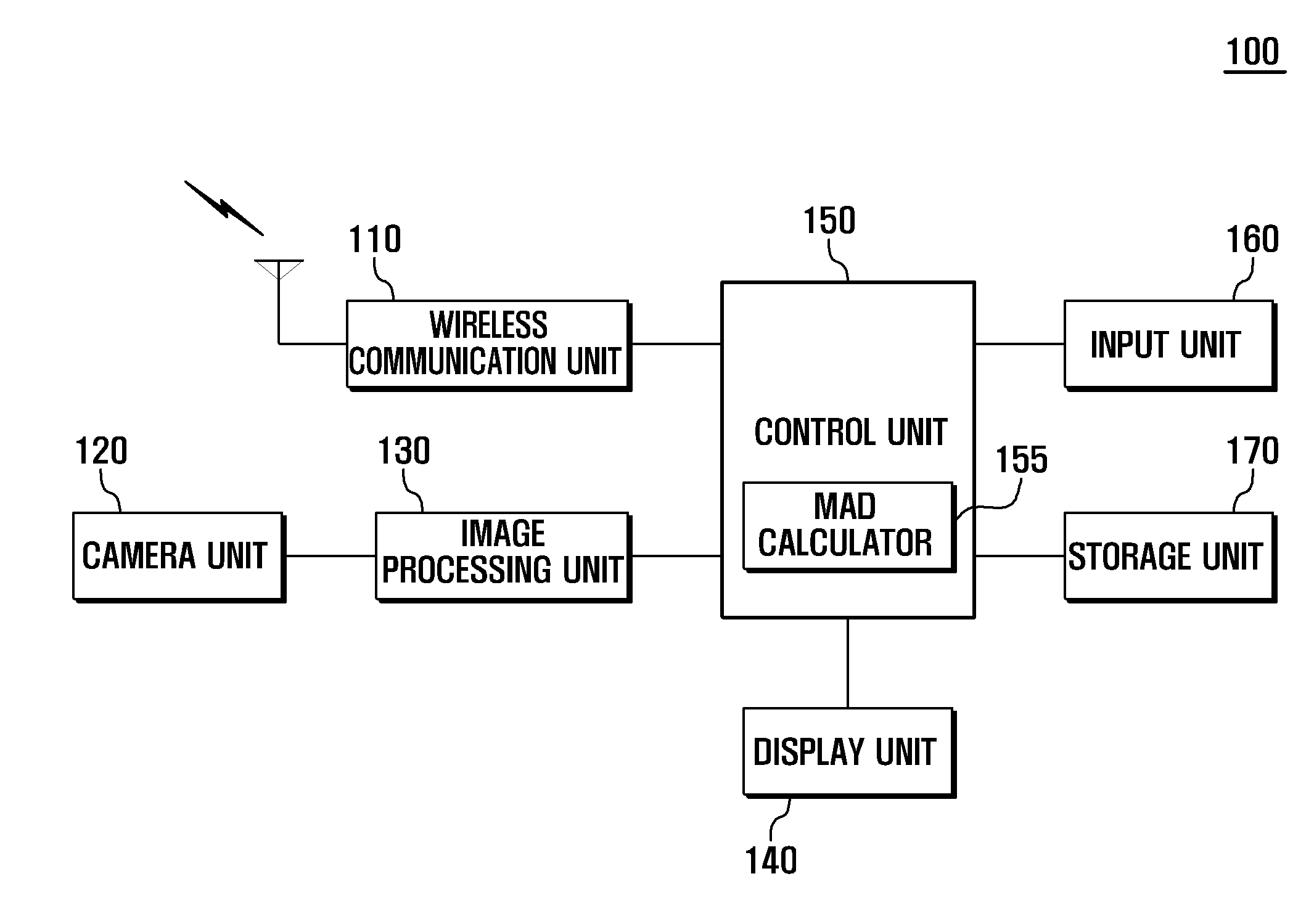
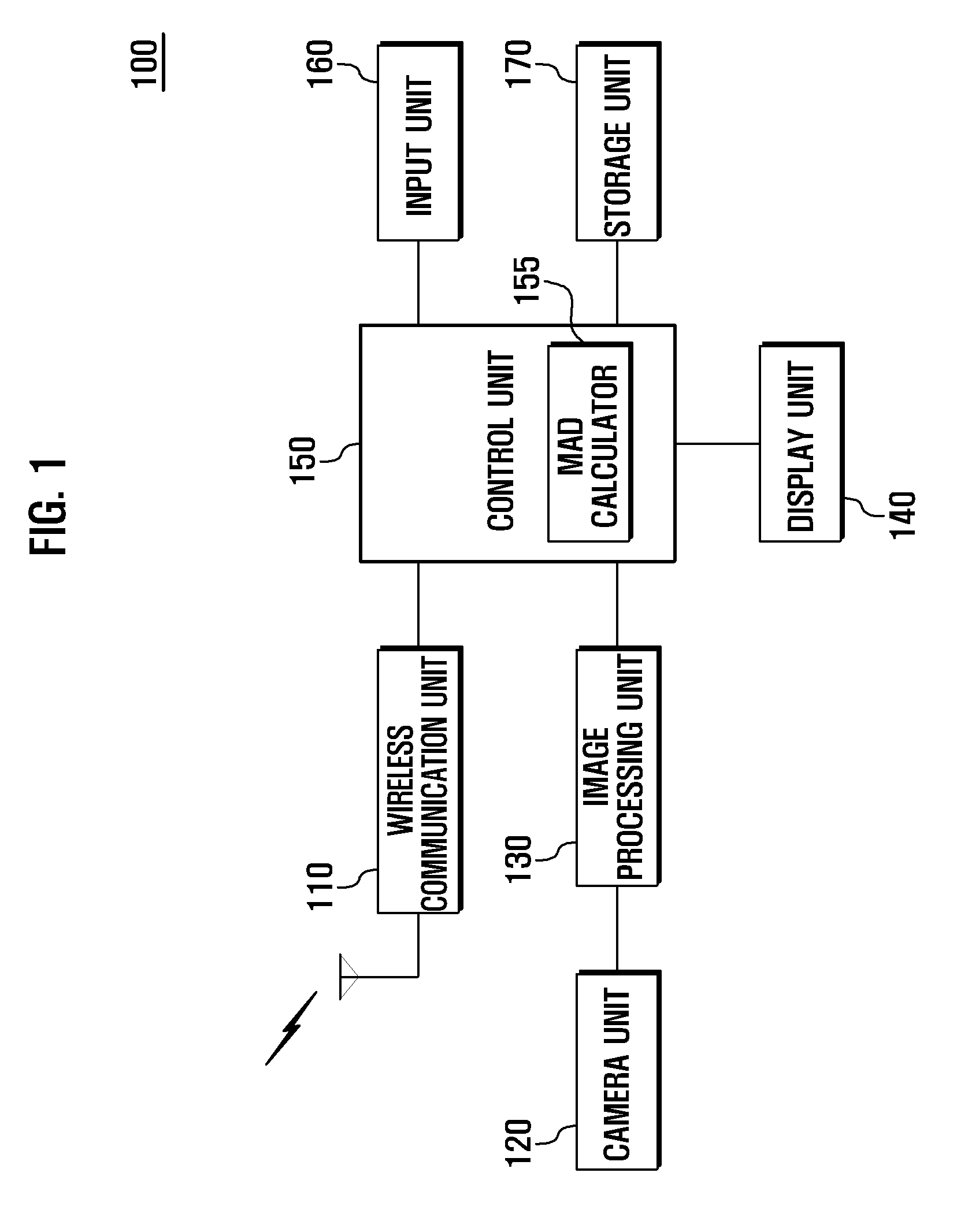
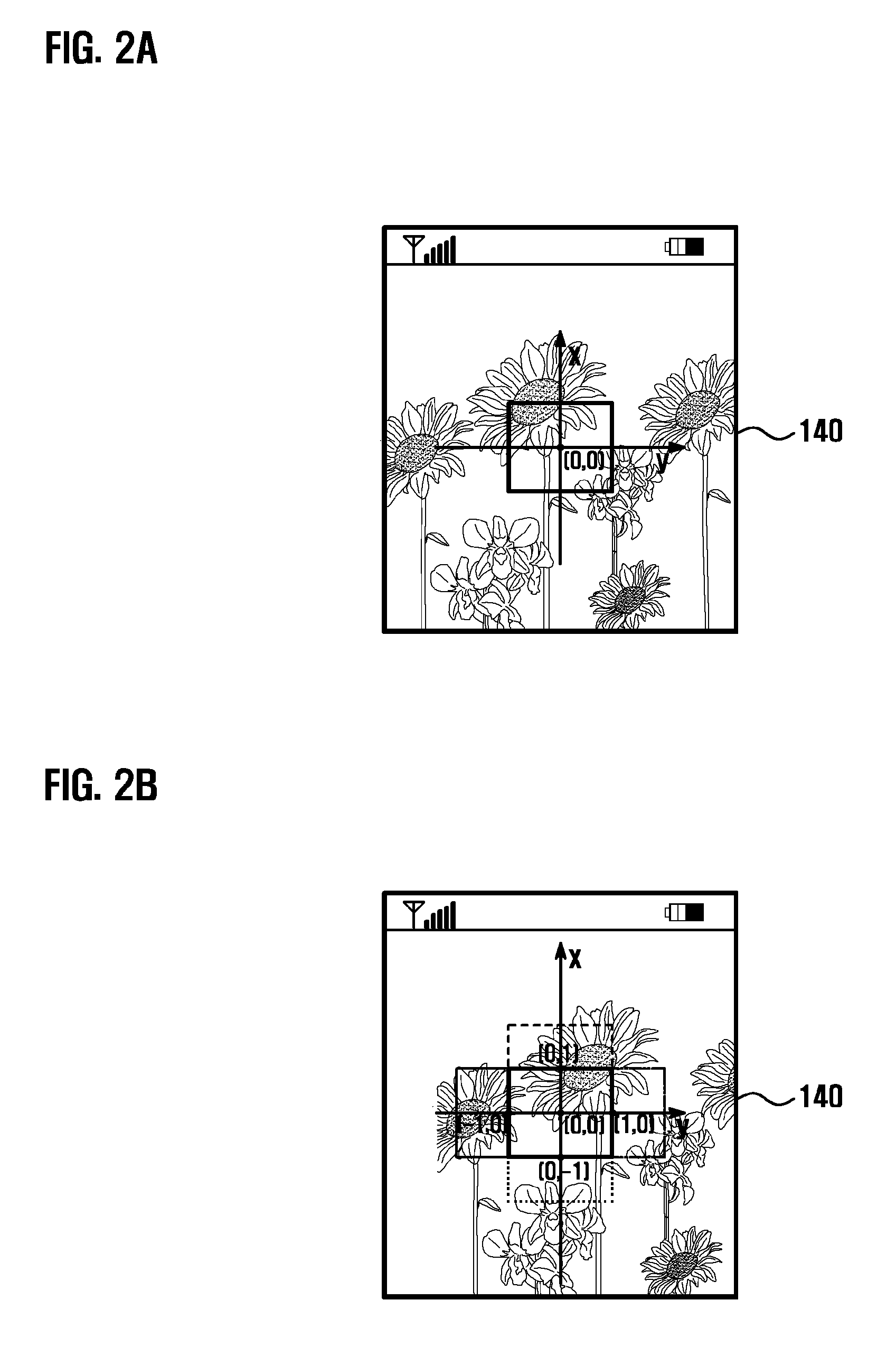
Electronic device with meaurement function and meaurement method thereof
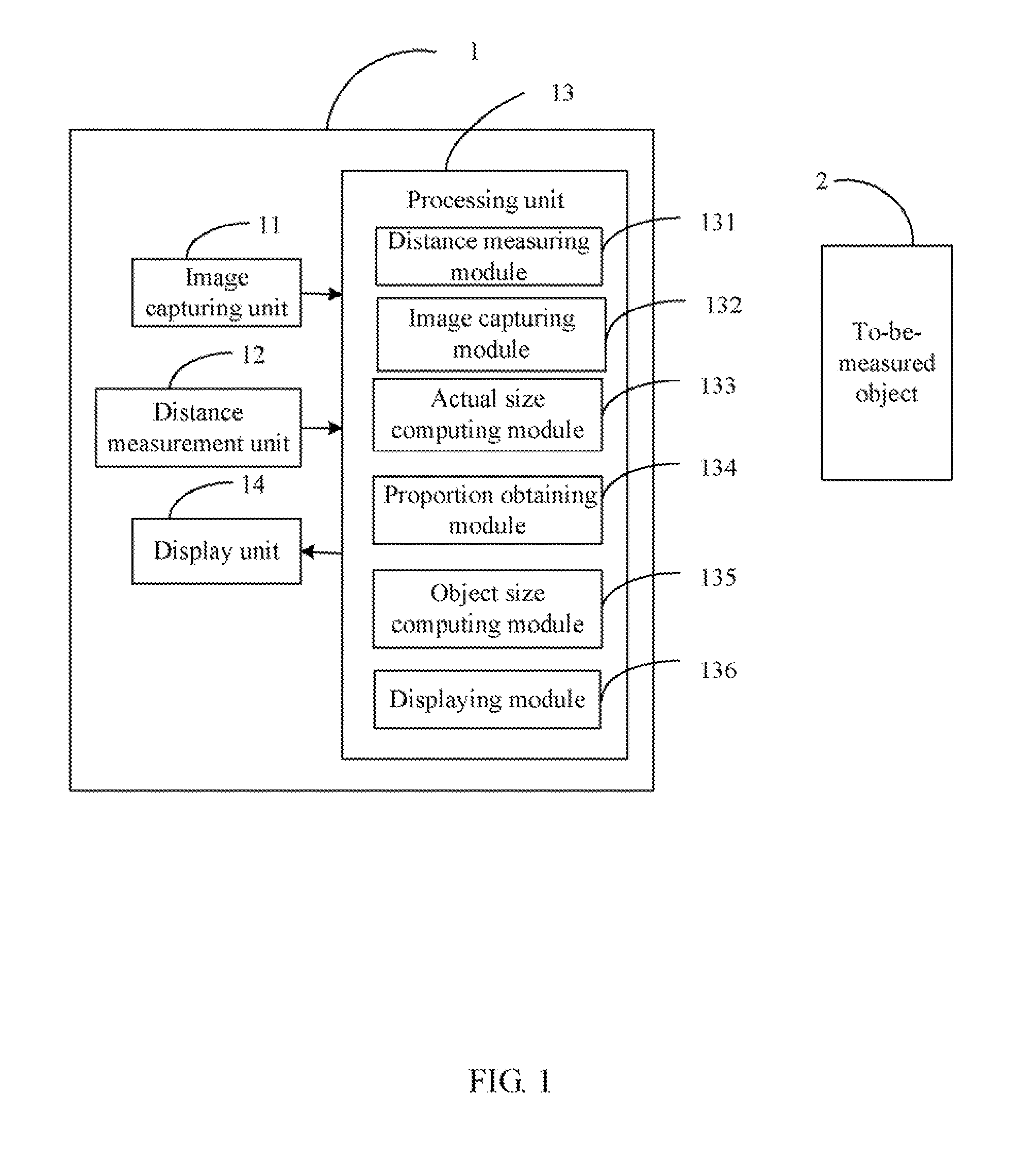
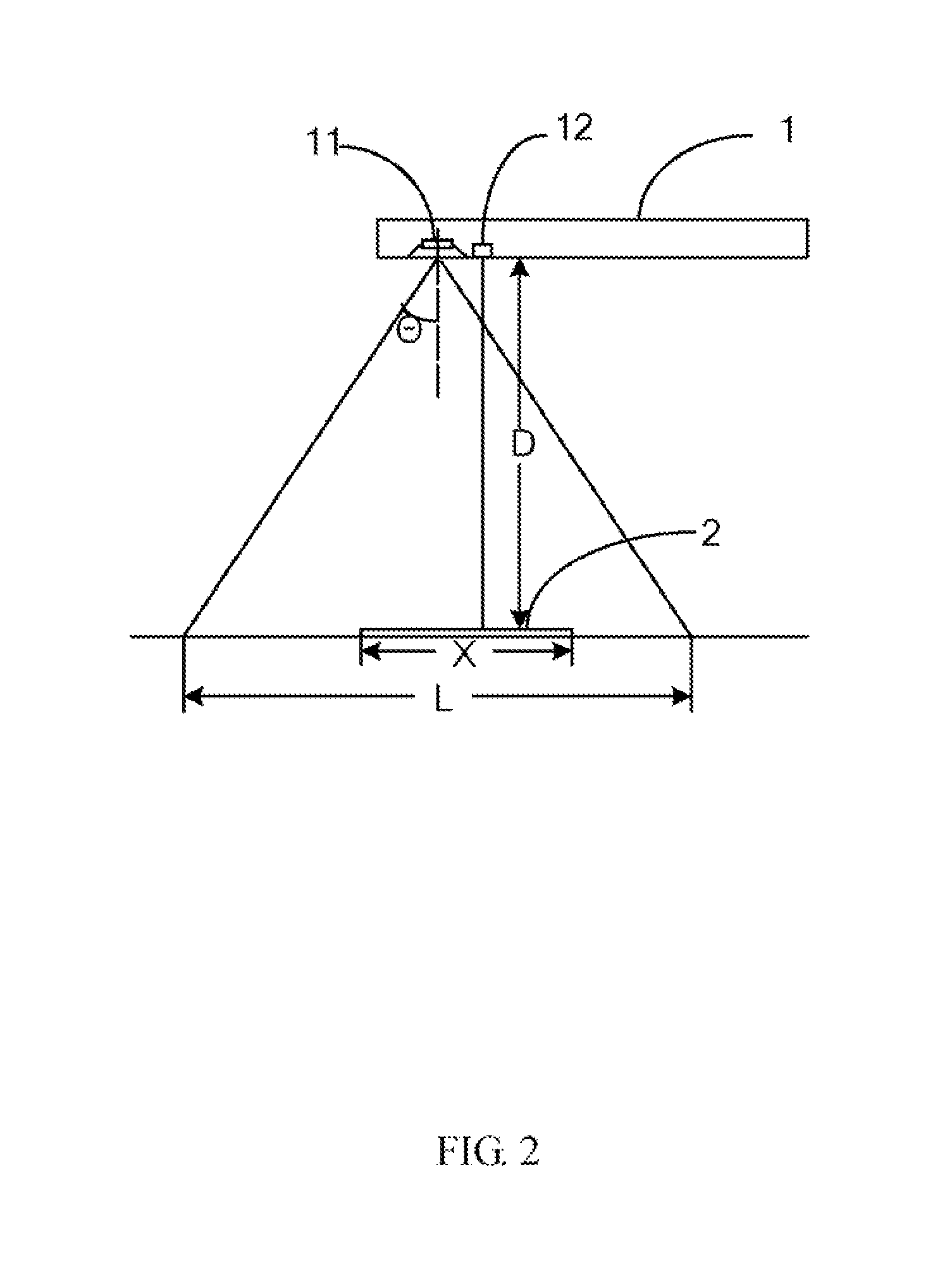
A method for measuring size of an object is provided. The method includes controlling a distance measurement unit to measure a vertical distance between an electronic device and the object in response to a measurement operation, controlling an image capturing unit to capture an image in front of the electronic device, which includes an image of the object in response to the measurement operation. Computing an actual size of the captured area according to the distance measured by the distance measurement unit and an angle of view of the image capturing unit. In addition, obtaining the image of the object from the captured image, and further computing the proportion of the image of the object in the captured image. Then computing the size of the object according to the proportion and the actual size of the captured area, and displaying the measured size of the object.
Owner:FU TAI HUA IND SHENZHEN +1
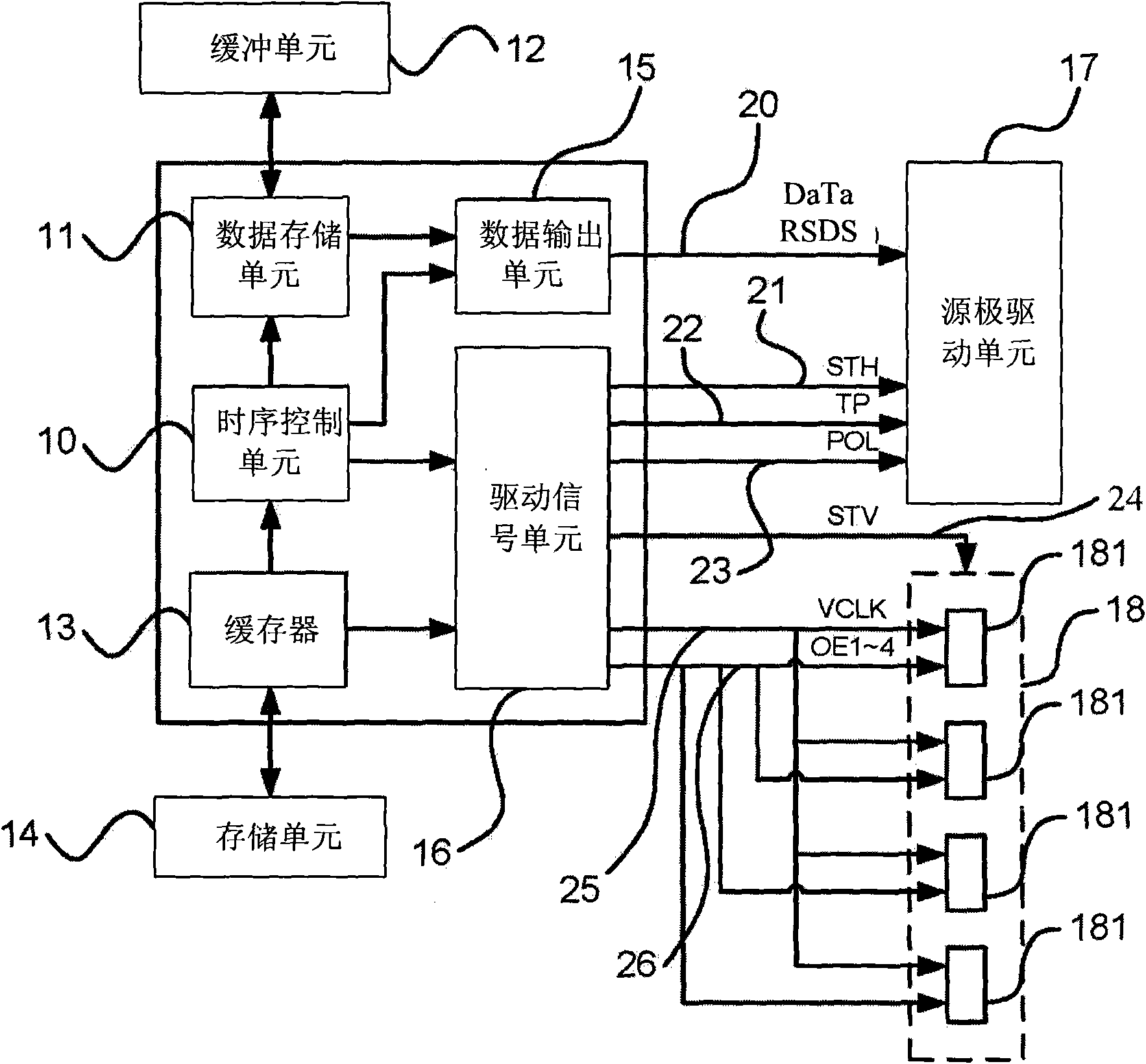
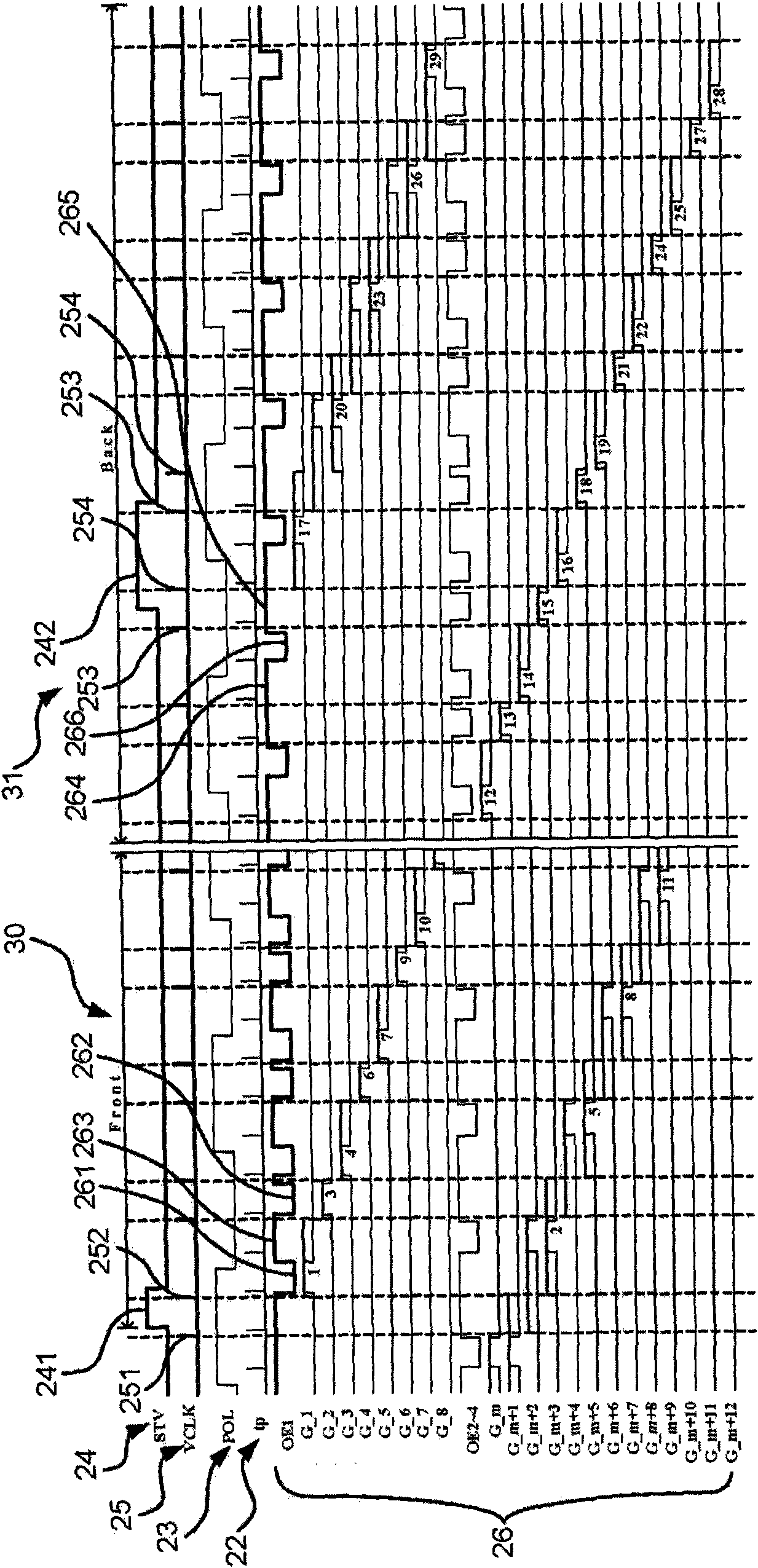
Dynamic image control device with homopolar black frame insertion signals
The invention relates to a dynamic image control device with homopolar black frame insertion signals, comprising a time-sequence control unit, a data access unit, a buffer unit, a cache, a storage unit, a data output unit and a driving signal unit. The time-sequence control unit is used for controlling the time-sequence; the data access unit is connected with the time-sequence control unit for accessing data; the buffer unit is connected with the data access unit for temporarily storing the data; the cache is connected with the time-sequence control unit for temporarily storing time-sequence data; the storage unit is connected with the cache for storing set time-sequence data; the data output unit is connected with the time-sequence control unit and the data access unit for outputting the data; and the driving signal unit is connected with the time-sequence control unit and the cache to output related driving signals. Therefore, the black frame insertion signals can be in line with the 1+2 line inversion display way, and the polarity showed by a liquid crystal can be consistent during the data display and the black frame insertion display, thereby avoiding affecting the image response time due to different response speeds.
Owner:华映视讯(吴江)有限公司 +1
Mobile terminal and panoramic photographing method for the same
ActiveUS8411133B2Television system detailsGeometric image transformationArtificial intelligenceImage response
A mobile terminal and panoramic photographing method for the same are provided. The panoramic photographing method includes displaying a preview image upon selection of a panoramic mode, successively capturing a first partial image and second partial image in response to input of a shooting start signal, setting a photographing direction through a comparison between the first partial image and second partial image, and producing a panoramic image in the set photographing direction. As a result, the user does not have to set the photographing direction to capture a panoramic image using a mobile terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
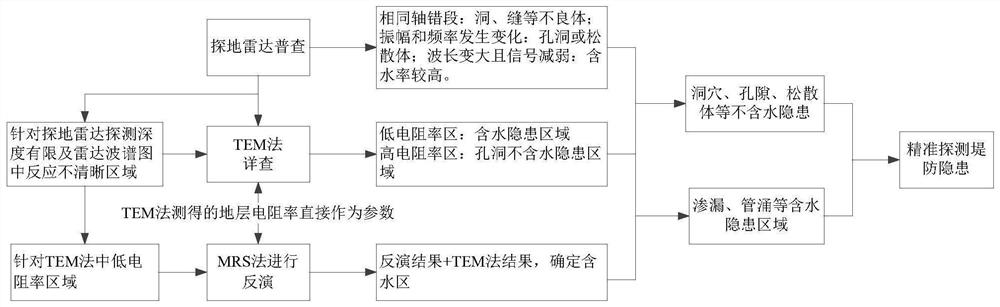
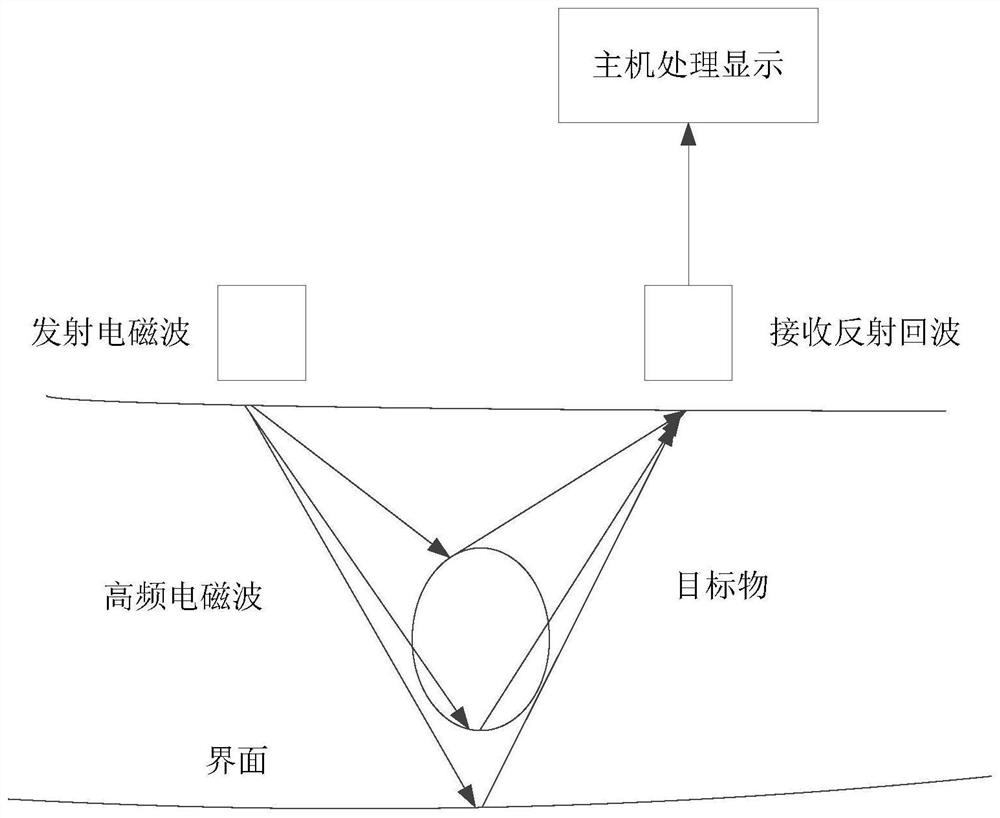
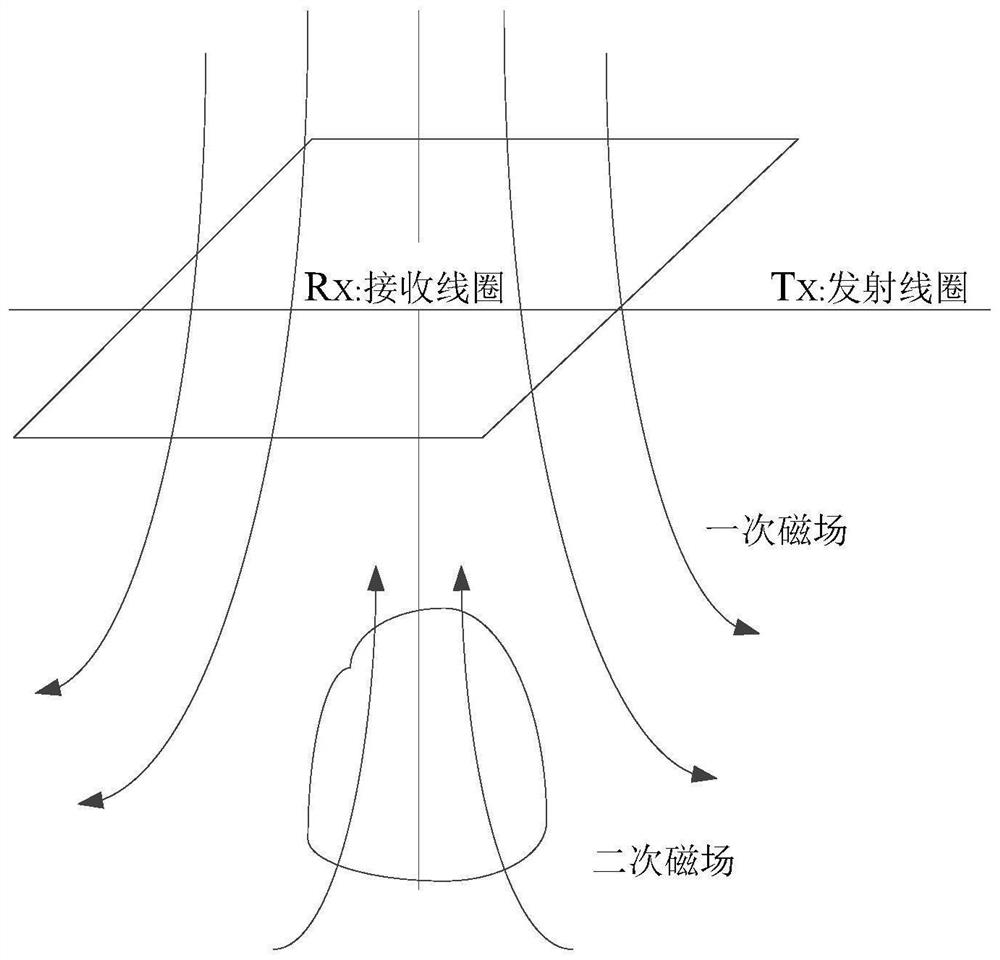
Dike hidden danger nondestructive detection method based on multi-technology cooperation
PendingCN114236621AFast, efficient and accurate detectionAvoid damageWater resource assessmentDetection using electromagnetic wavesMagnetic resonance spectrometryGround-penetrating radar
The invention relates to the technical field of embankment safety, in particular to an embankment hidden danger nondestructive detection method based on multi-technology collaboration, and the method is composed of a ground penetrating radar method, a transient electromagnetic method and a magnetic resonance technology method.For shallow embankment hidden dangers, direct image response can be achieved through the ground penetrating radar method; deep hidden dangers are checked in detail by adopting a transient electromagnetic method; for leakage and piping which are most likely to cause embankment bursting in embankment hidden dangers, underground water is directly and effectively detected by adopting a magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) method. The resistivity data of each stratum detected in the transient electromagnetic method can be directly used as a parameter for inversion of the magnetic resonance technology, so that the result is more unique. By combining a ground penetrating radar method, a transient electromagnetic method and a magnetic resonance technology, the positions of water-containing areas such as hidden dangers, leakage and piping in the deep and shallow parts of the dike can be accurately positioned, so that the hidden dangers of the dike can be timely and effectively treated.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
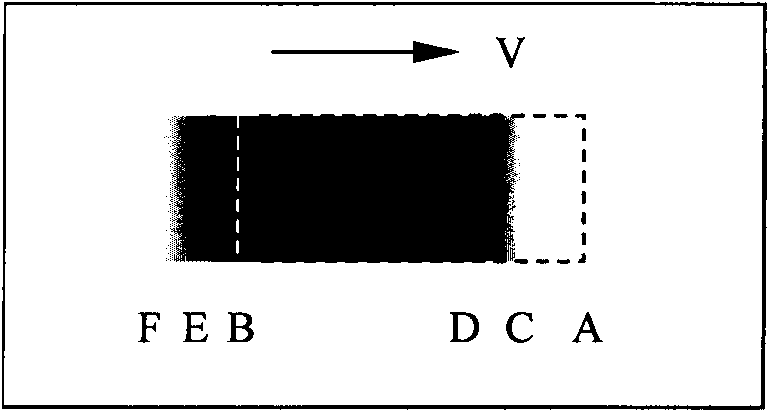
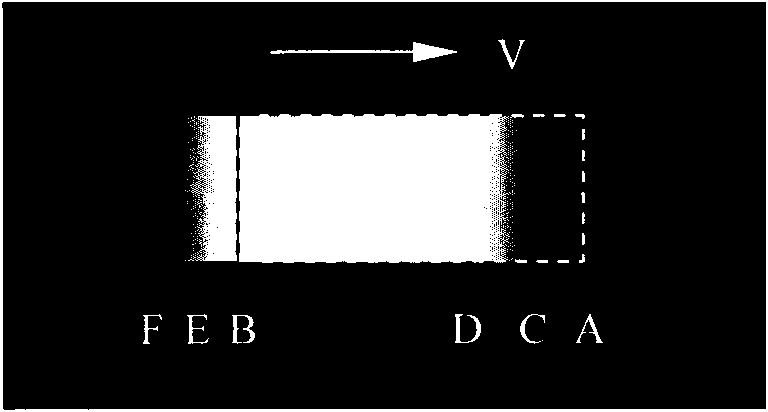
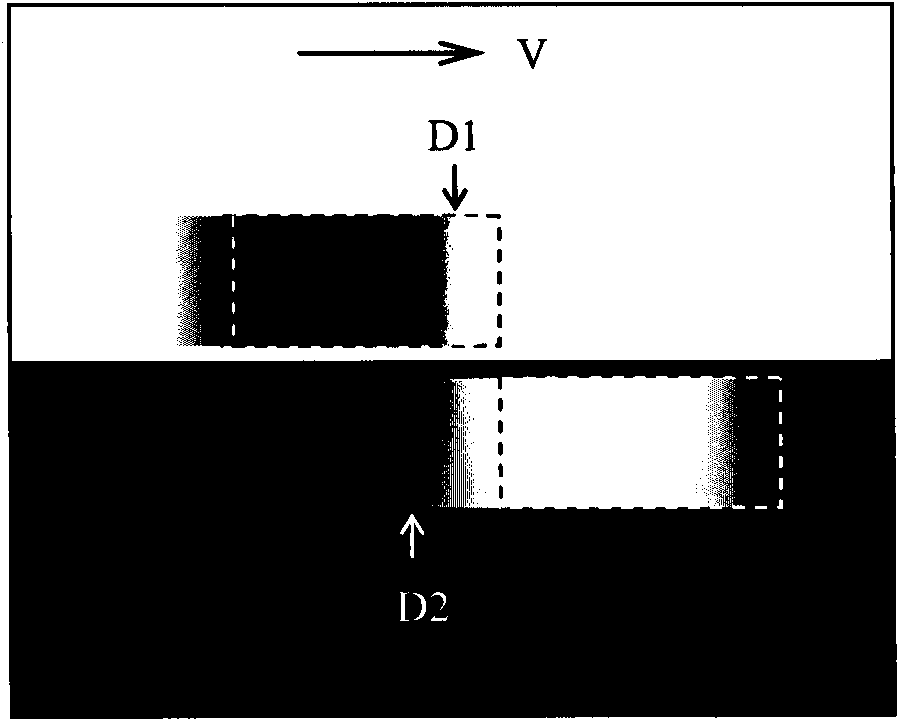
Method for measuring motion image response characteristic parameters
ActiveCN101888568ASimple calculationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsExcitation signalVisual perception
The invention provides a method for measuring motion image response characteristic parameter. The method comprises the following steps of: A, generating a dark stimulus signal and a light stimulus signal to generate a light block and a dark block which have the same movement velocity and serve as a motion image; B, observing alignment conditions of the sight front ends or the sight rear ends of the light block and the dark block in the motion image, entering the step C if the sight front ends or the sight rear ends are not aligned, and entering the step D if the sight front ends or the sight rear ends are aligned; C, regulating the actual position of the light block or the dark block in the motion imagine, and entering the step B; D, determining the relatively-regulated distance between the light block and the dark block in the motion image; and E, calculating response characteristic parameters of the motion image according to the determined relatively-regulated distance. In the method, each motion image response characteristic parameter can be calculated only according to a parameter read by a criterion, so that the method has the advantages of simple calculating process and small error.
Owner:MUDAN SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS BEIJING
Focus adjustable head mounted display system and method and device for realizing the system
A focus adjustable head mounted display system used in a head mounted display device has an image capturing device for capturing environment images; an image processing unit for receiving image signals from the image capturing device and processing the received image signals; a focus adjustment unit for adjusting an input image from the image capturing device according an input focus adjustment signal so that the adjusted display image responses the focus adjustment signal; an image display unit installed at a head mounted display device for displaying the adjusted display image; a focus input unit being a manually operation device for generating a focus adjustment signal to the image processing unit; and the focus input unit providing a focus value to the focus adjustment software. A head mounted display device and a method for realizing the focus adjustable head mounted display system are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSAL VISION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com