Patents
Literature
231 results about "Injections subcutaneous" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A subcutaneous injection is a method of administering medication. Subcutaneous means under the skin. In this type of injection, a short needle is used to inject a drug into the tissue layer between the skin and the muscle. Medication given this way is usually absorbed more slowly than if injected into a vein,...
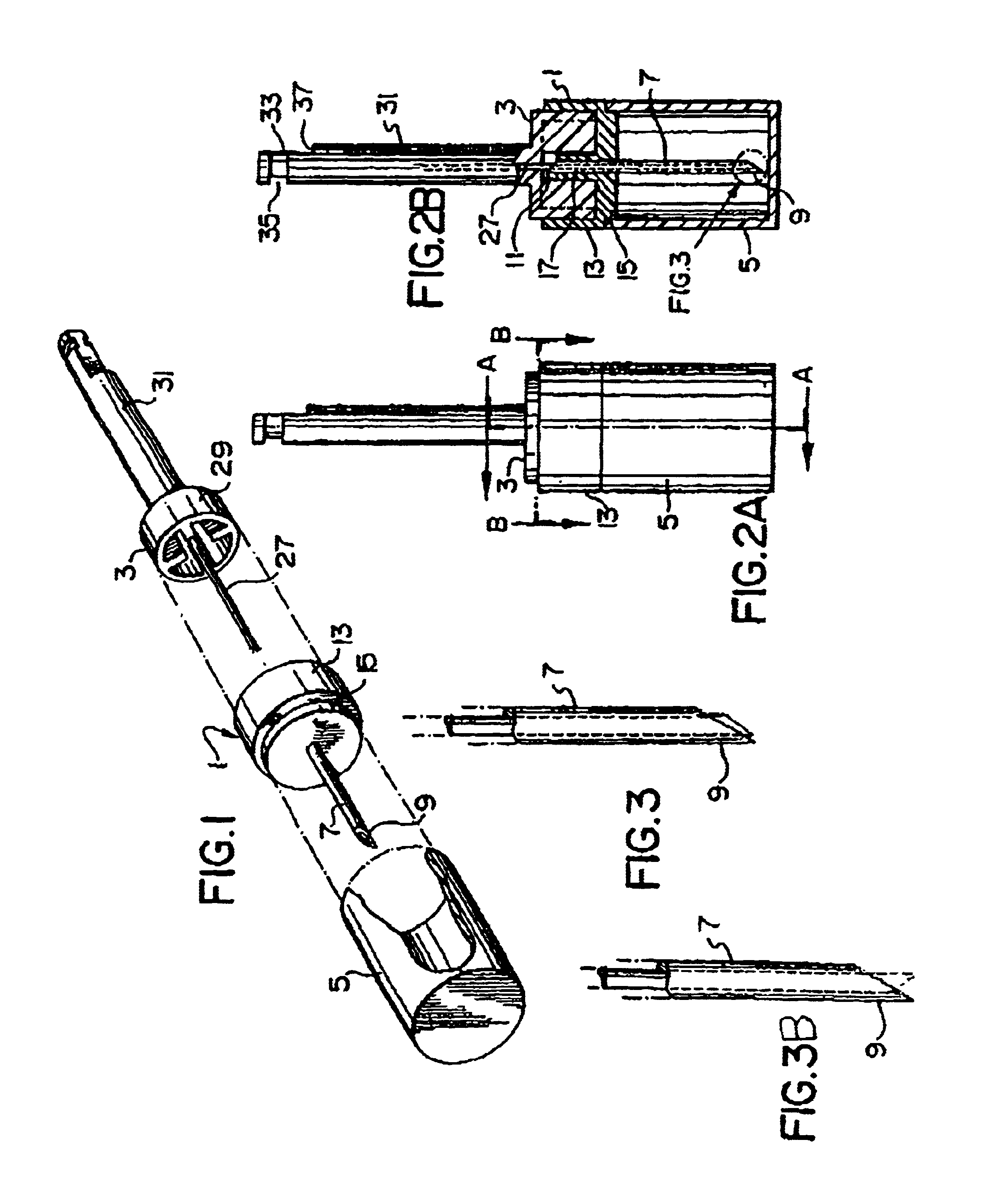
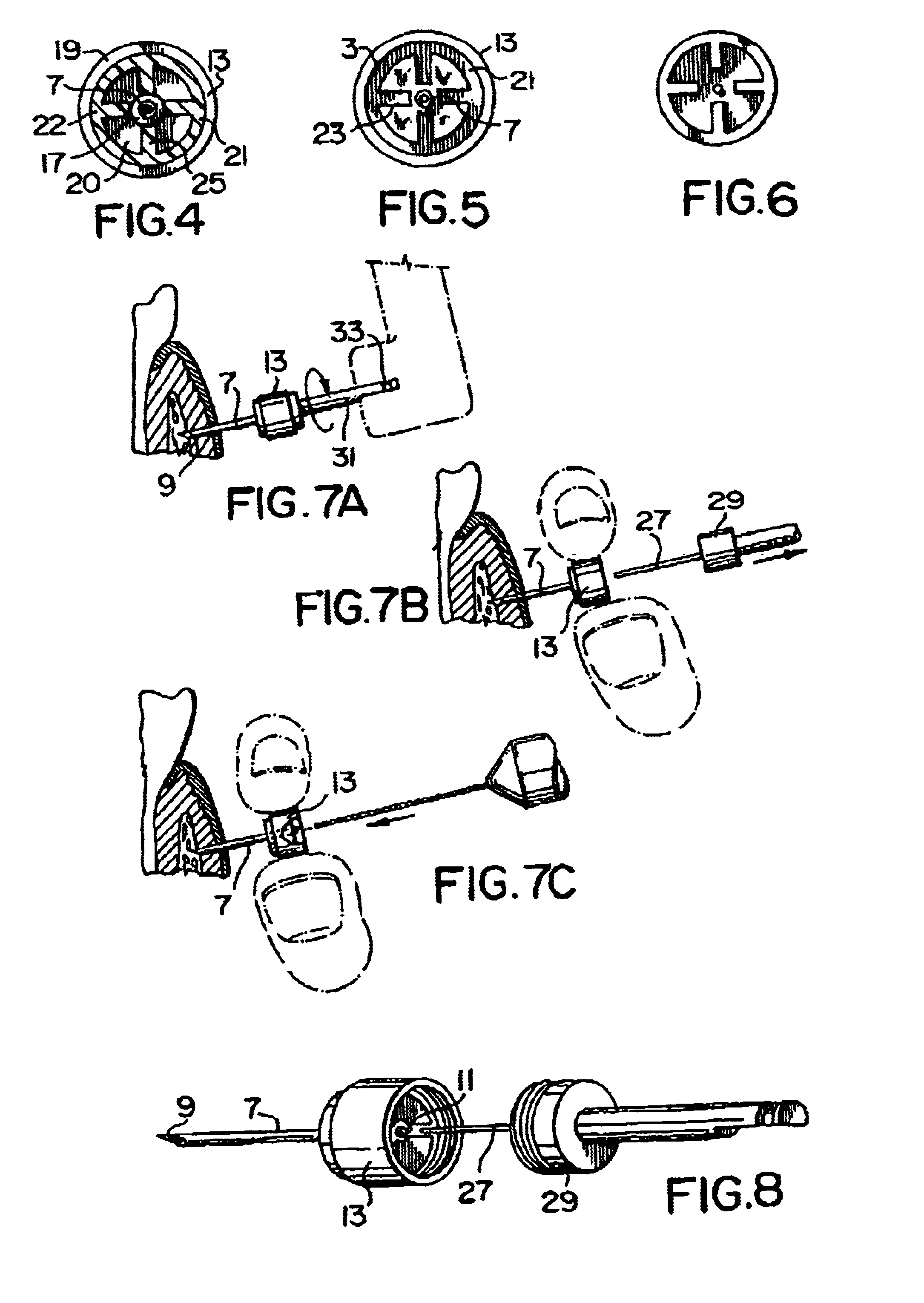
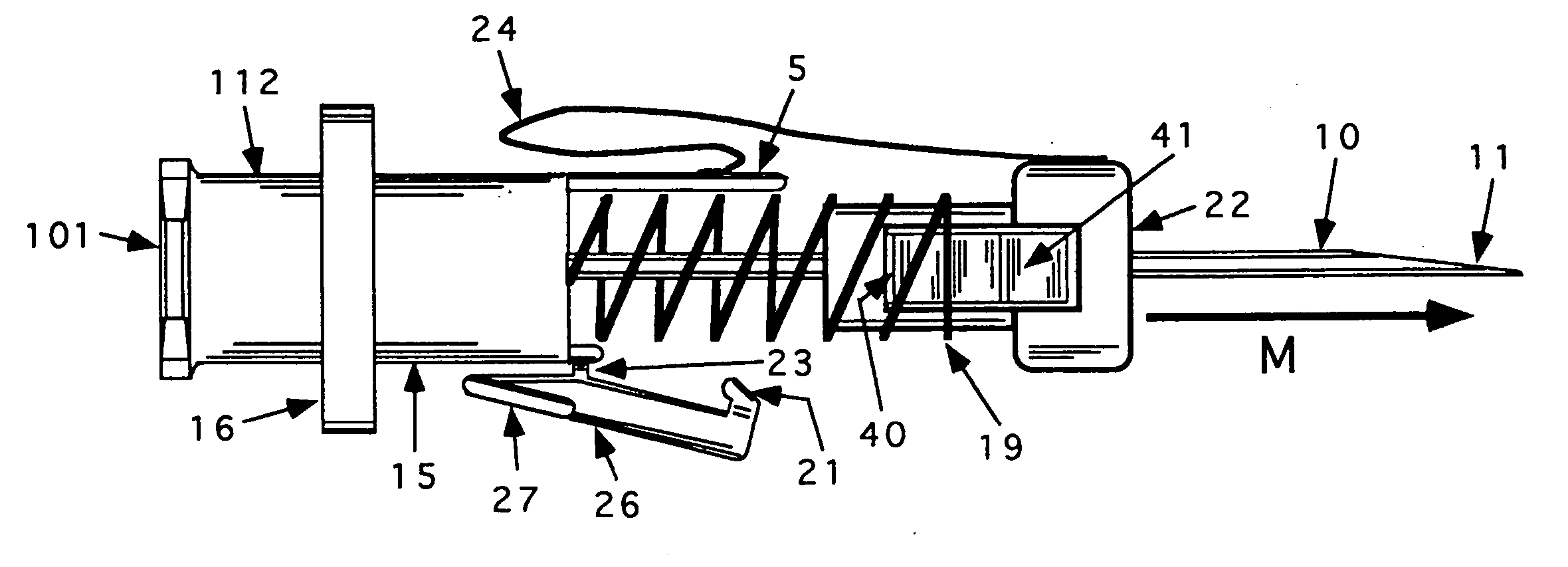
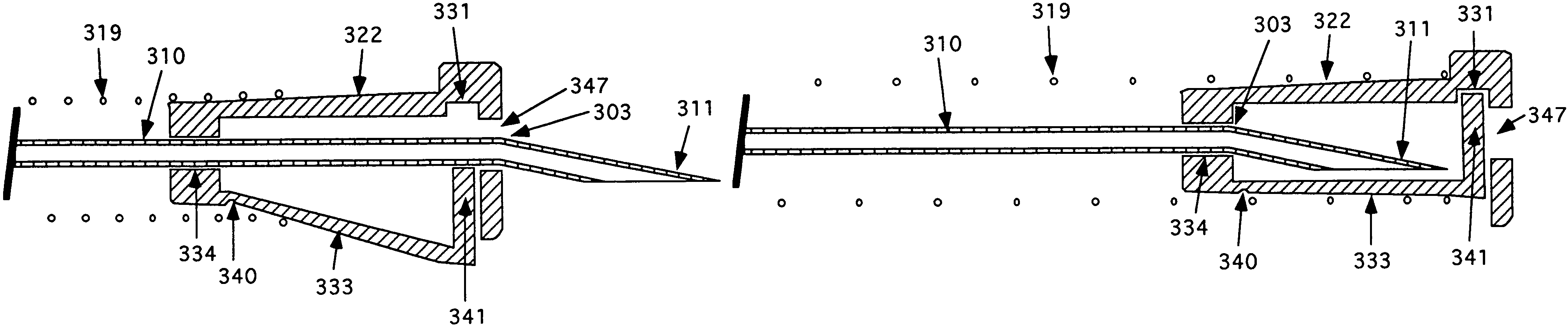
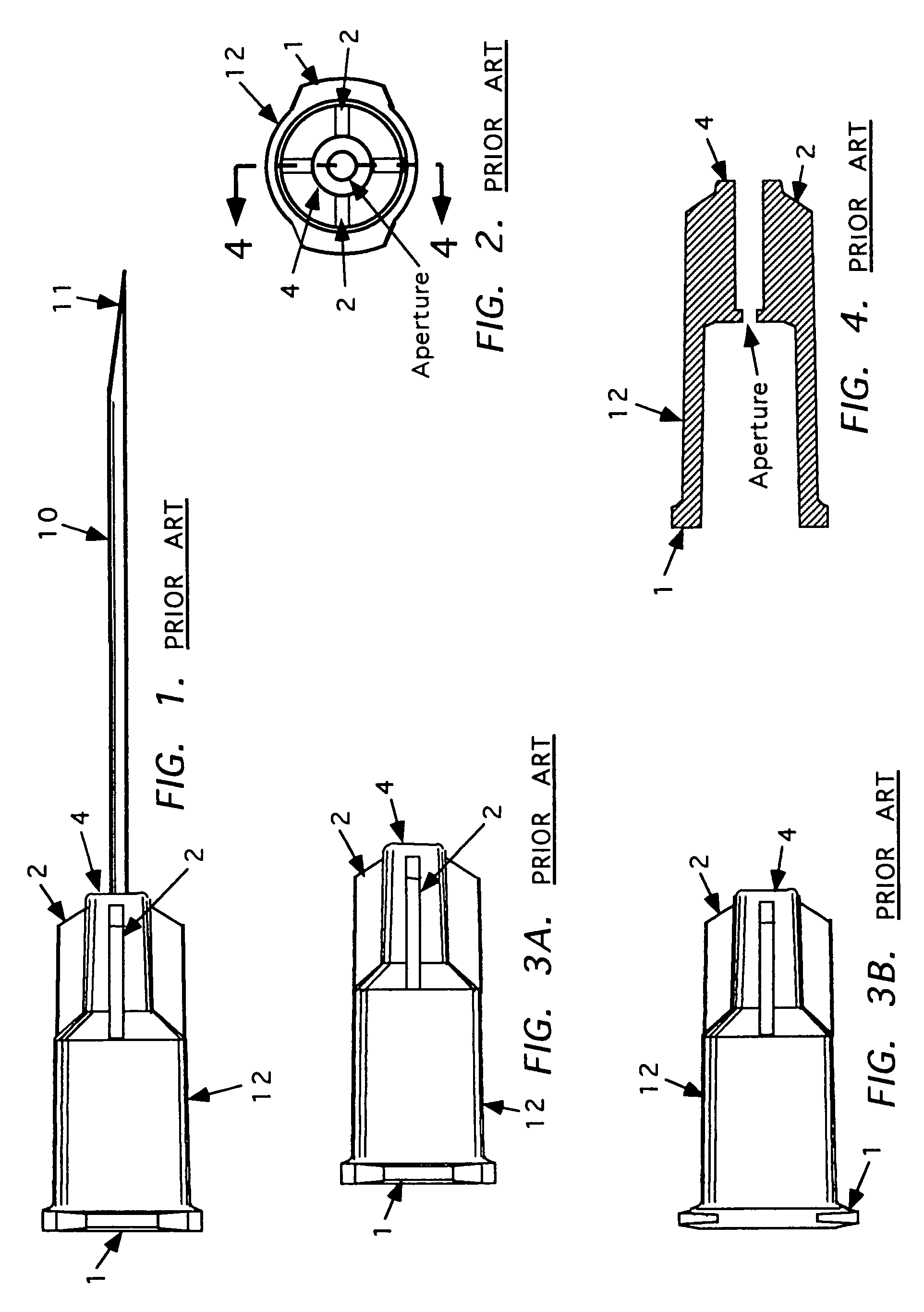
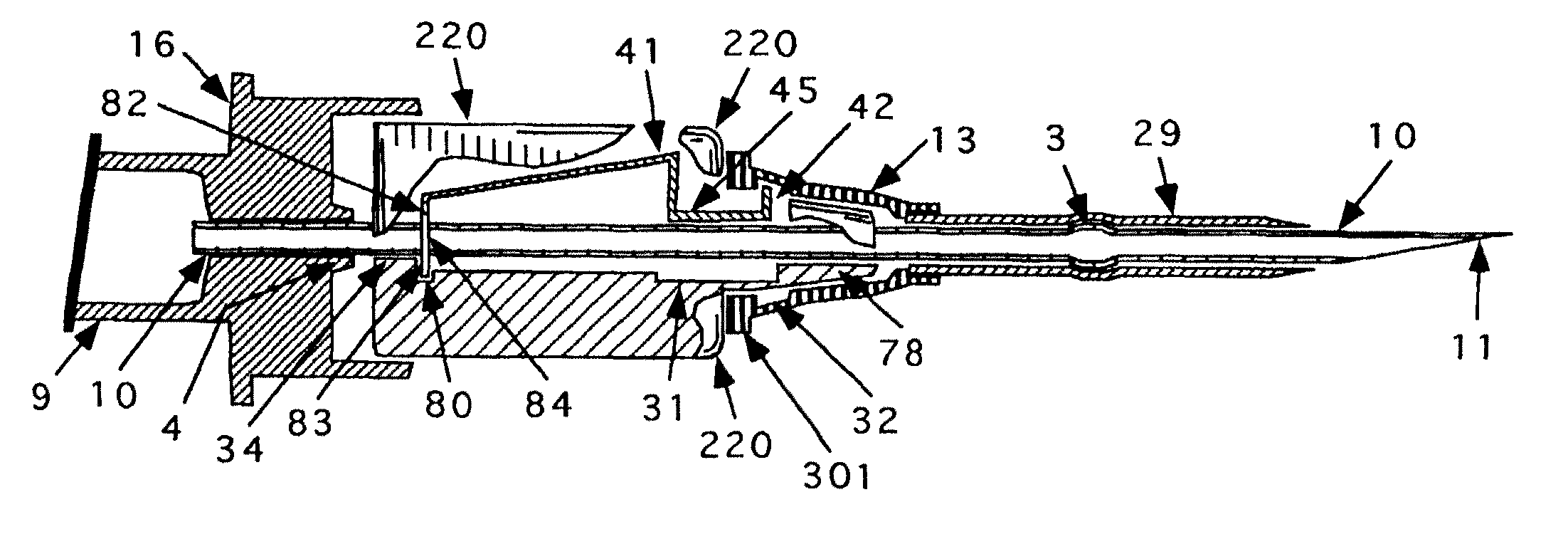
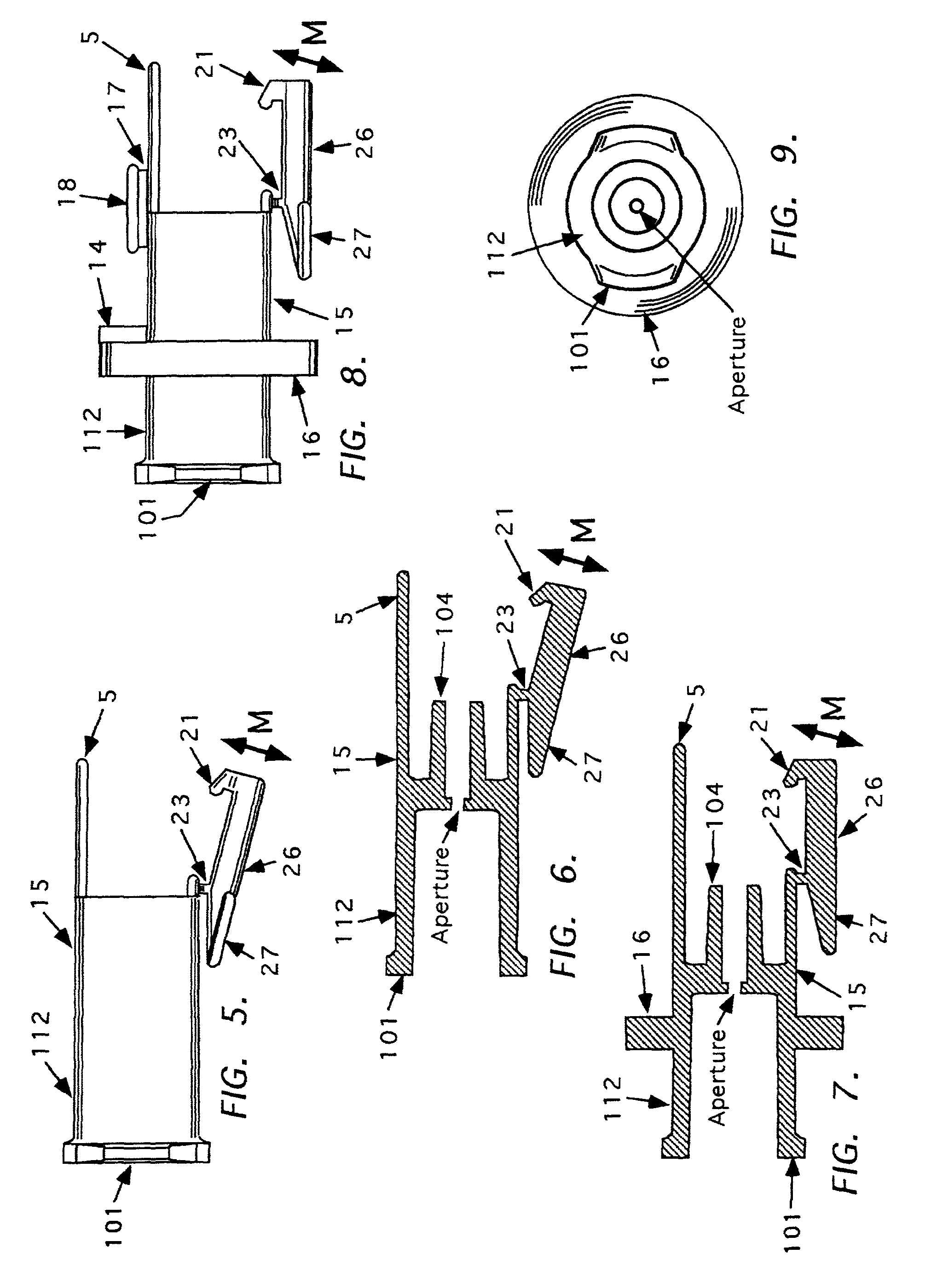
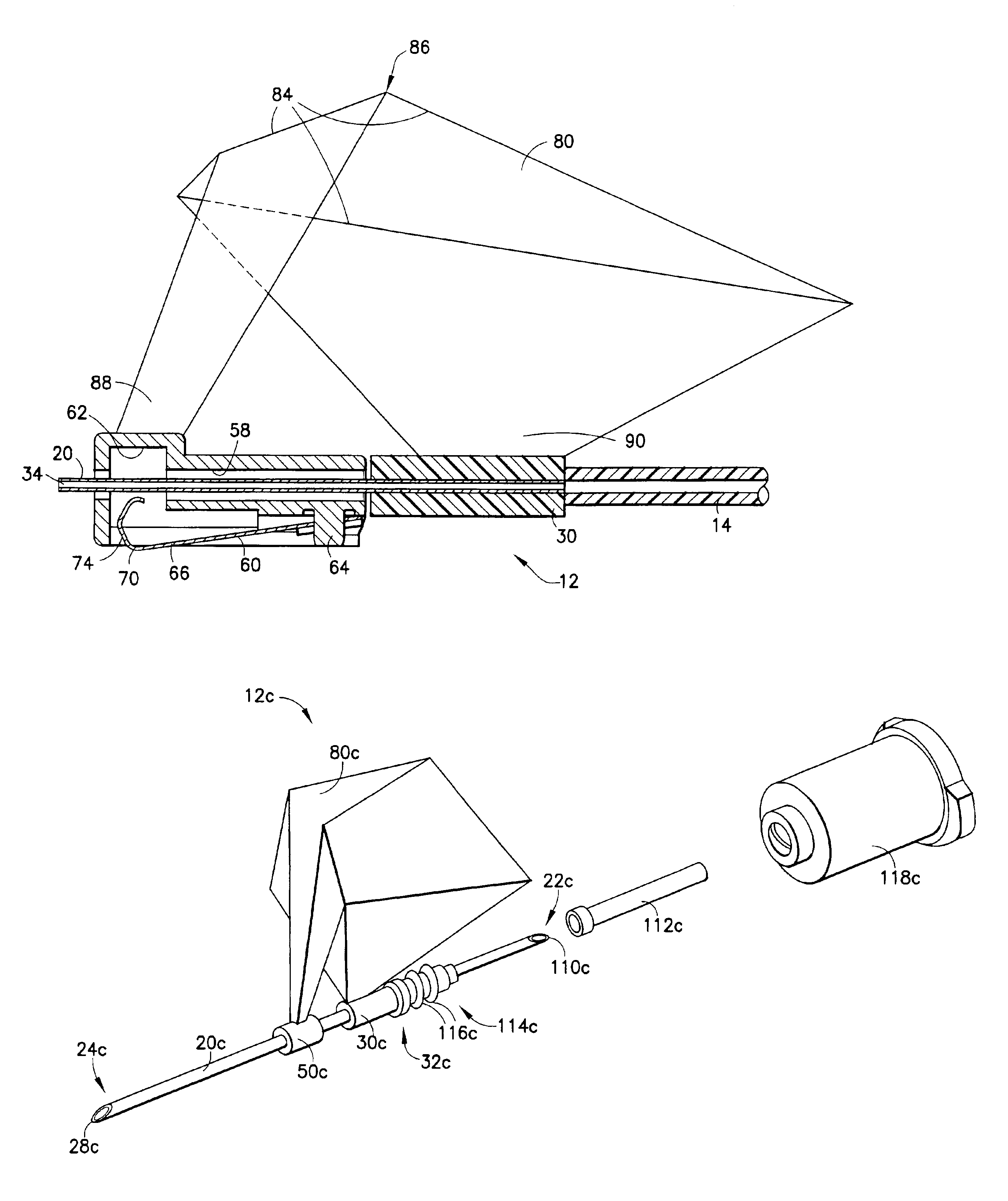
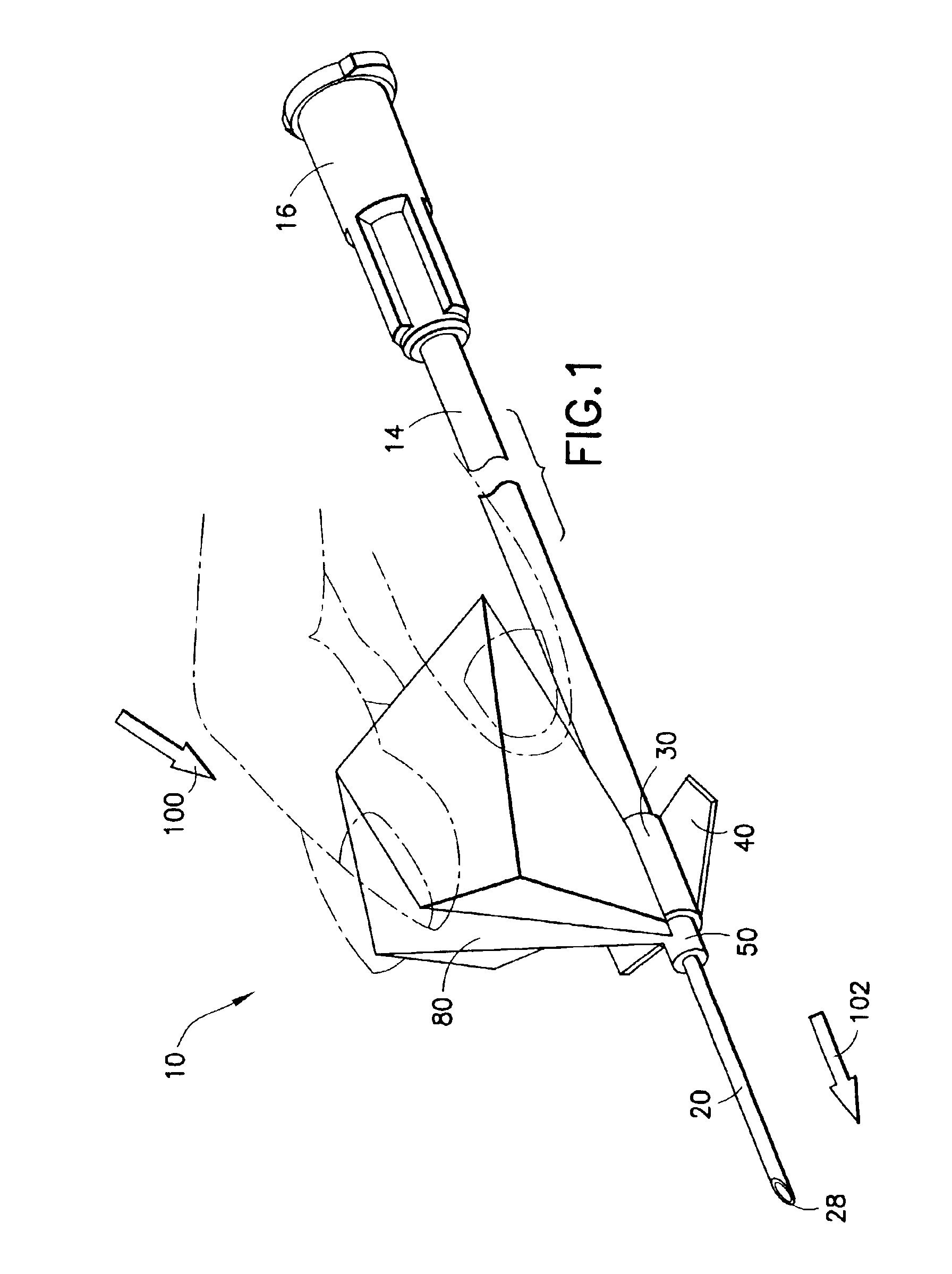
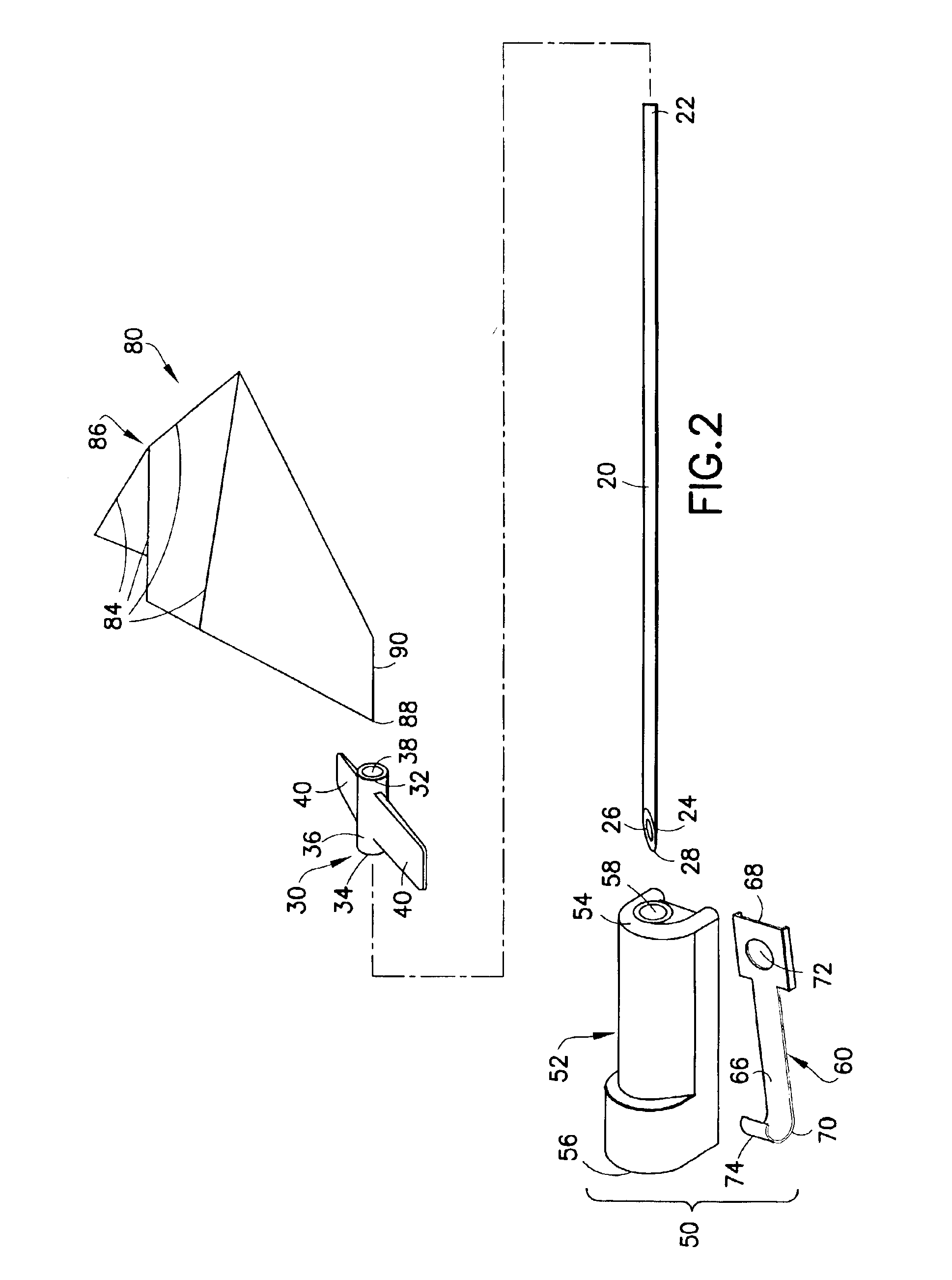
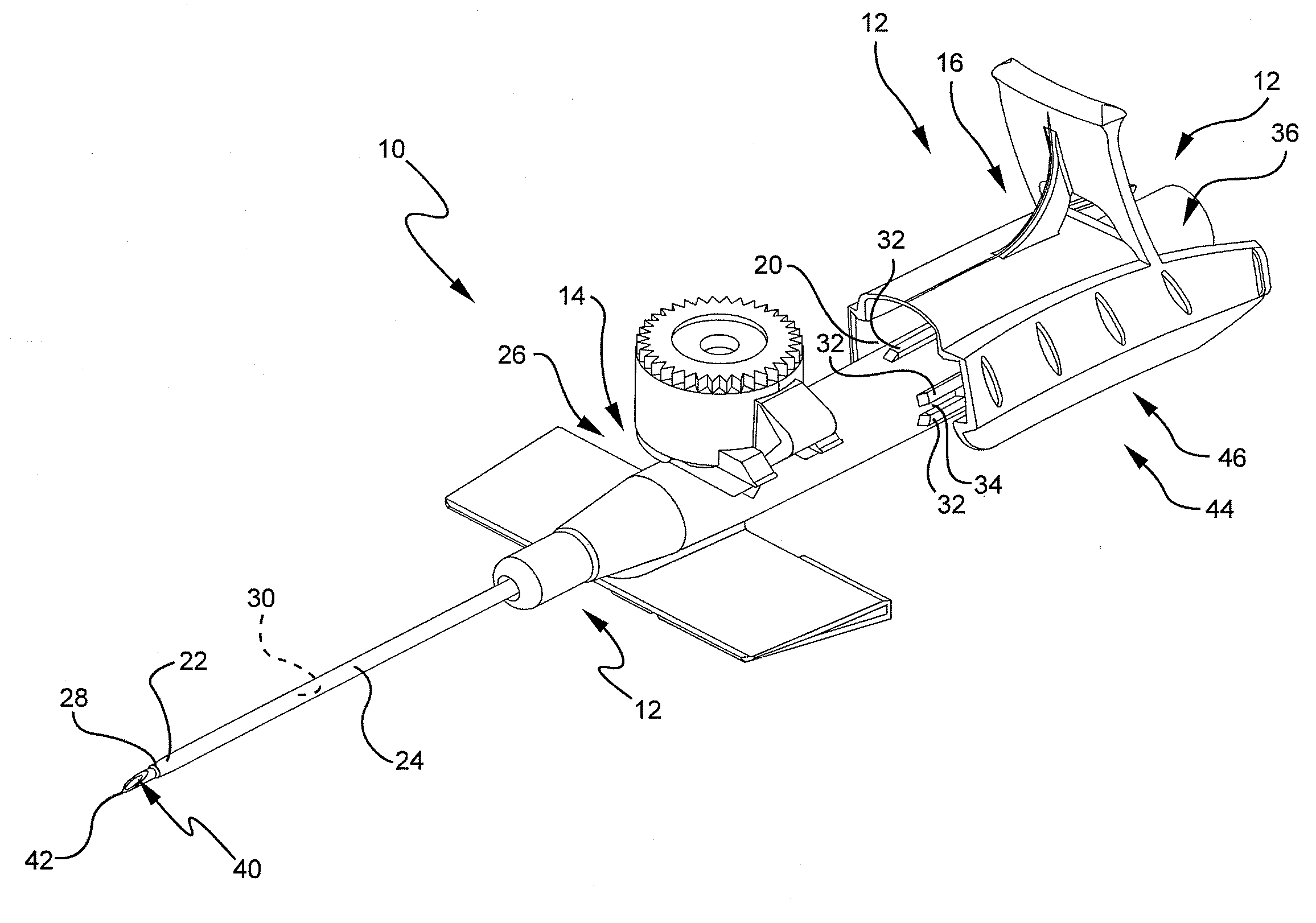
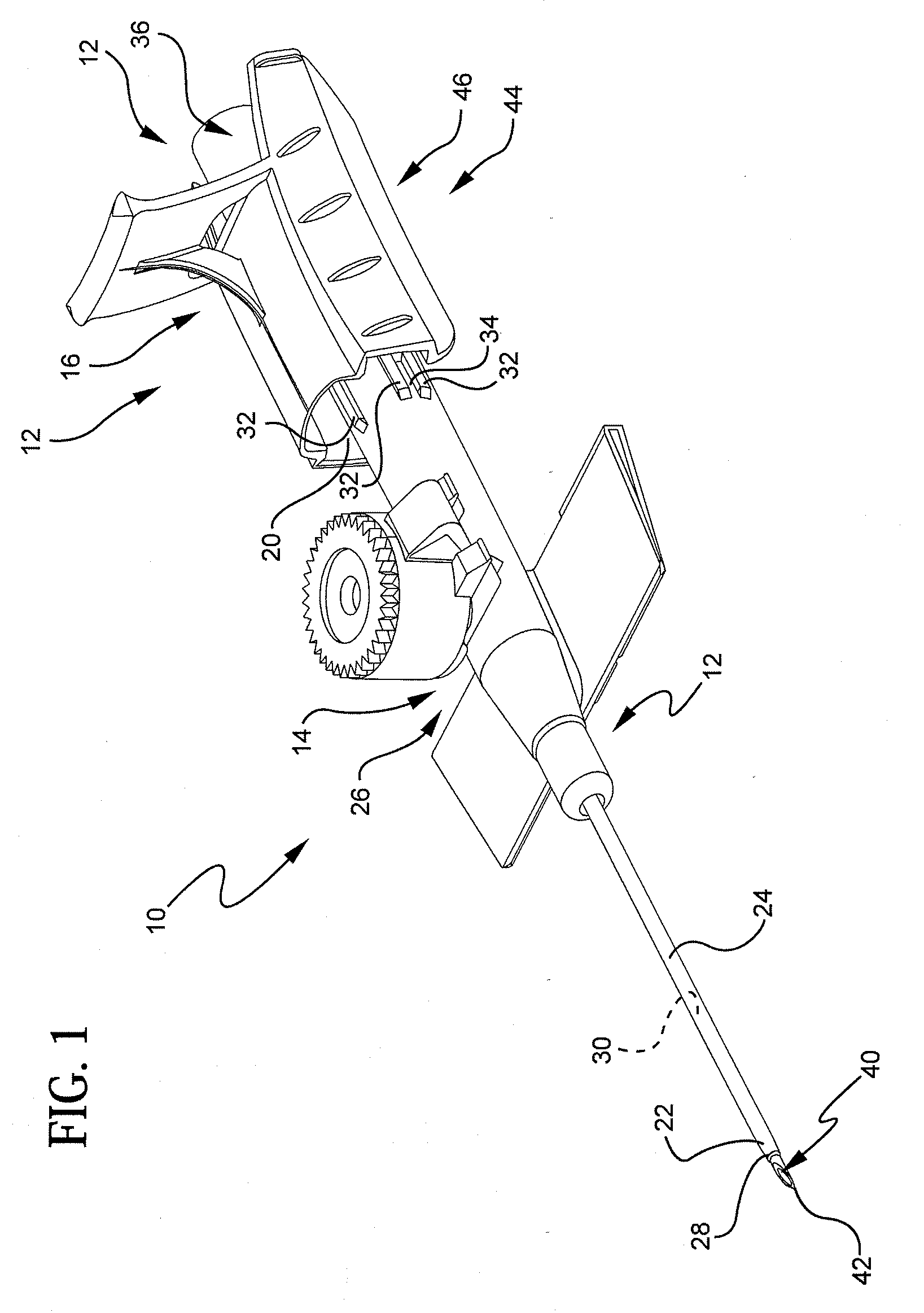
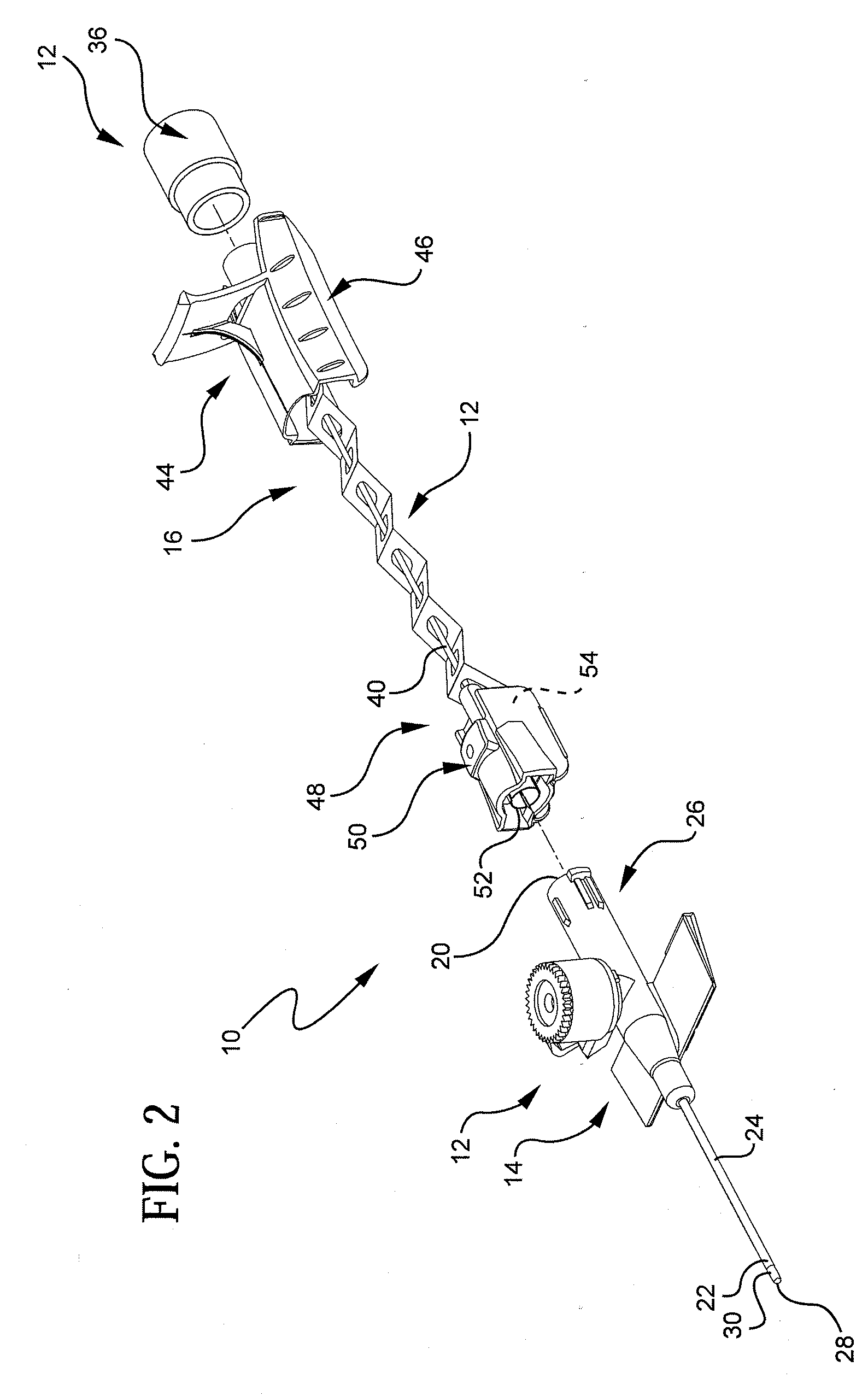
Needle tip guard for percutaneous entry needles
A needle tip protective device for use with percutaneous entry needles. In one embodiment, the needle tip protective device includes a needle guard slidably mounted on a hypodermic needle, the latter having a needle tip located at the distal end thereof, and a change of profile formed medially there along. The needle guard is movable along the hypodermic needle and engageable with the change in profile formed thereon. The engagement with the change in profile is configured to correspond with the ability of the needle trap to entrap the needle tip once the needle trap has advanced the sufficient distance distally along the hypodermic needle. In further refinements, the needle trap may be biased toward the distal needle tip of the needle.
Owner:B BRAUN MELSUNGEN AG
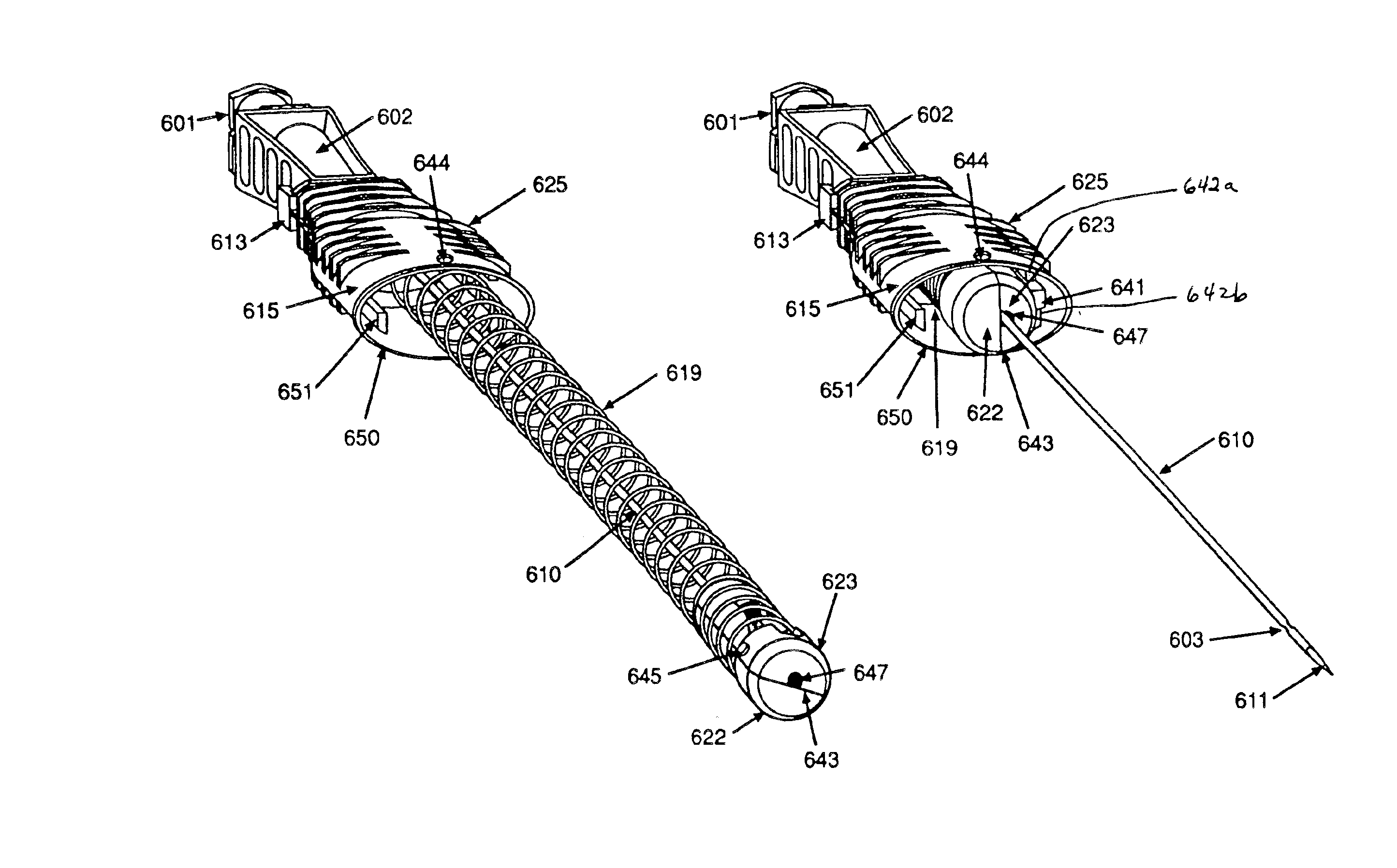
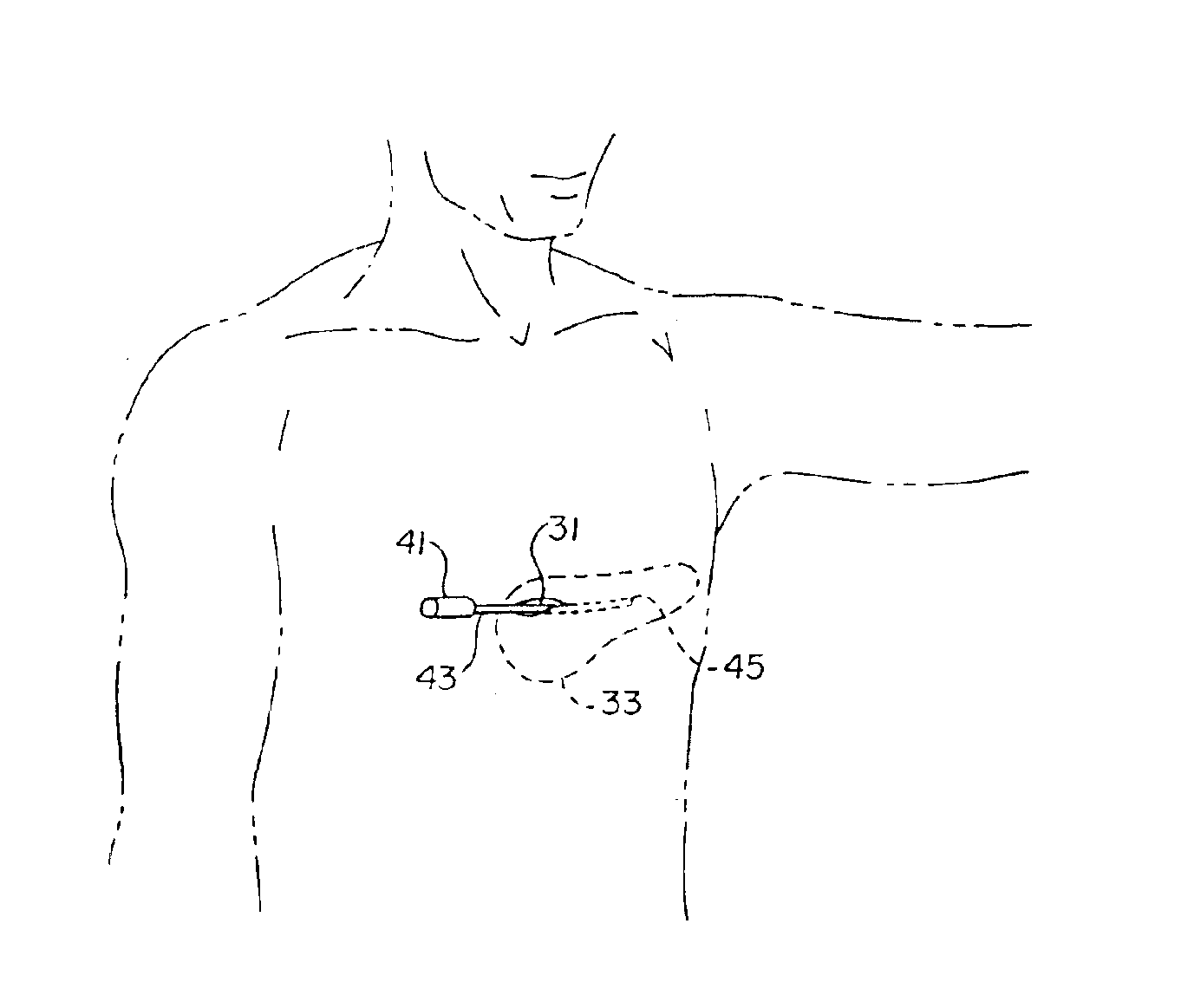
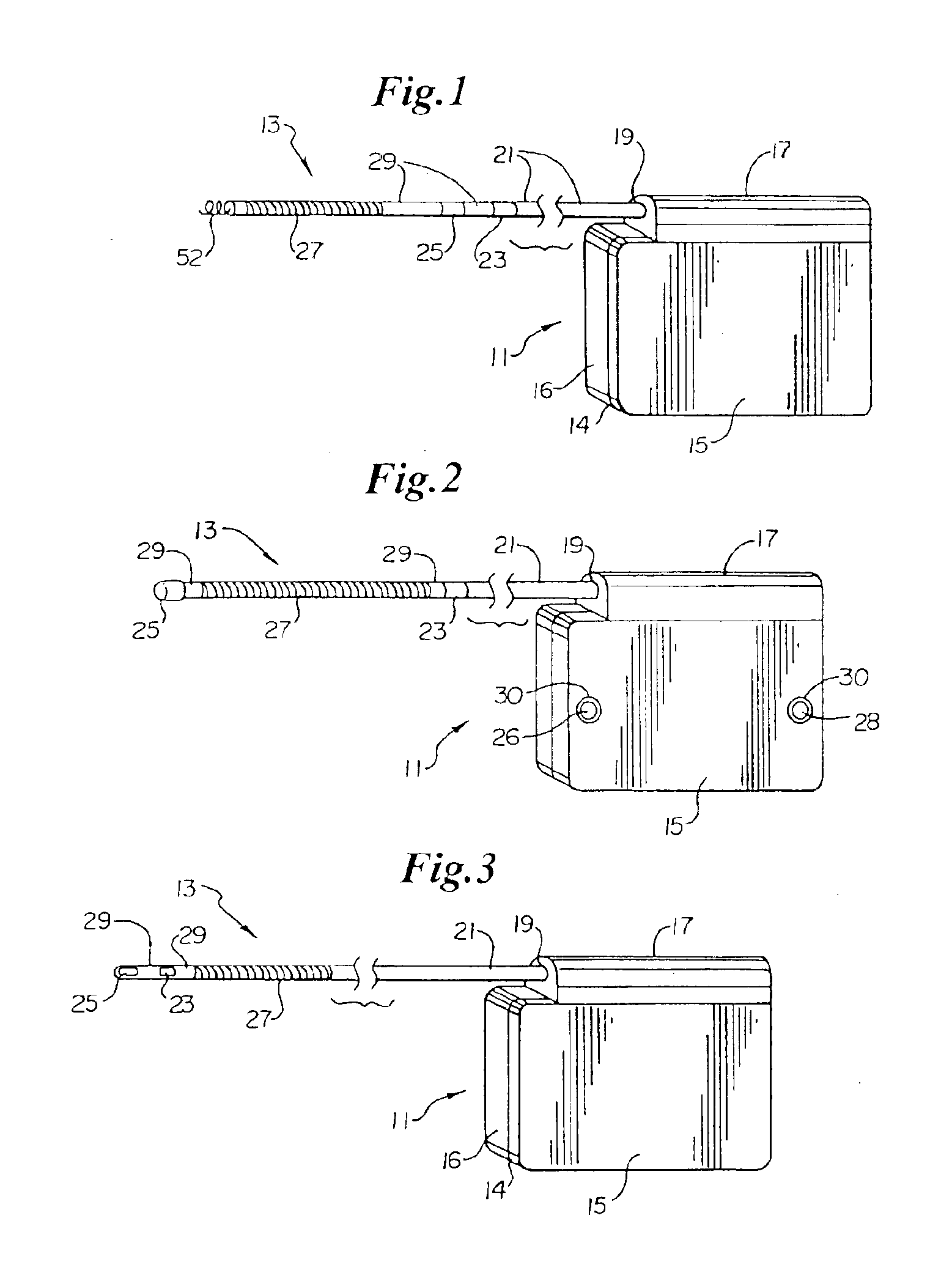
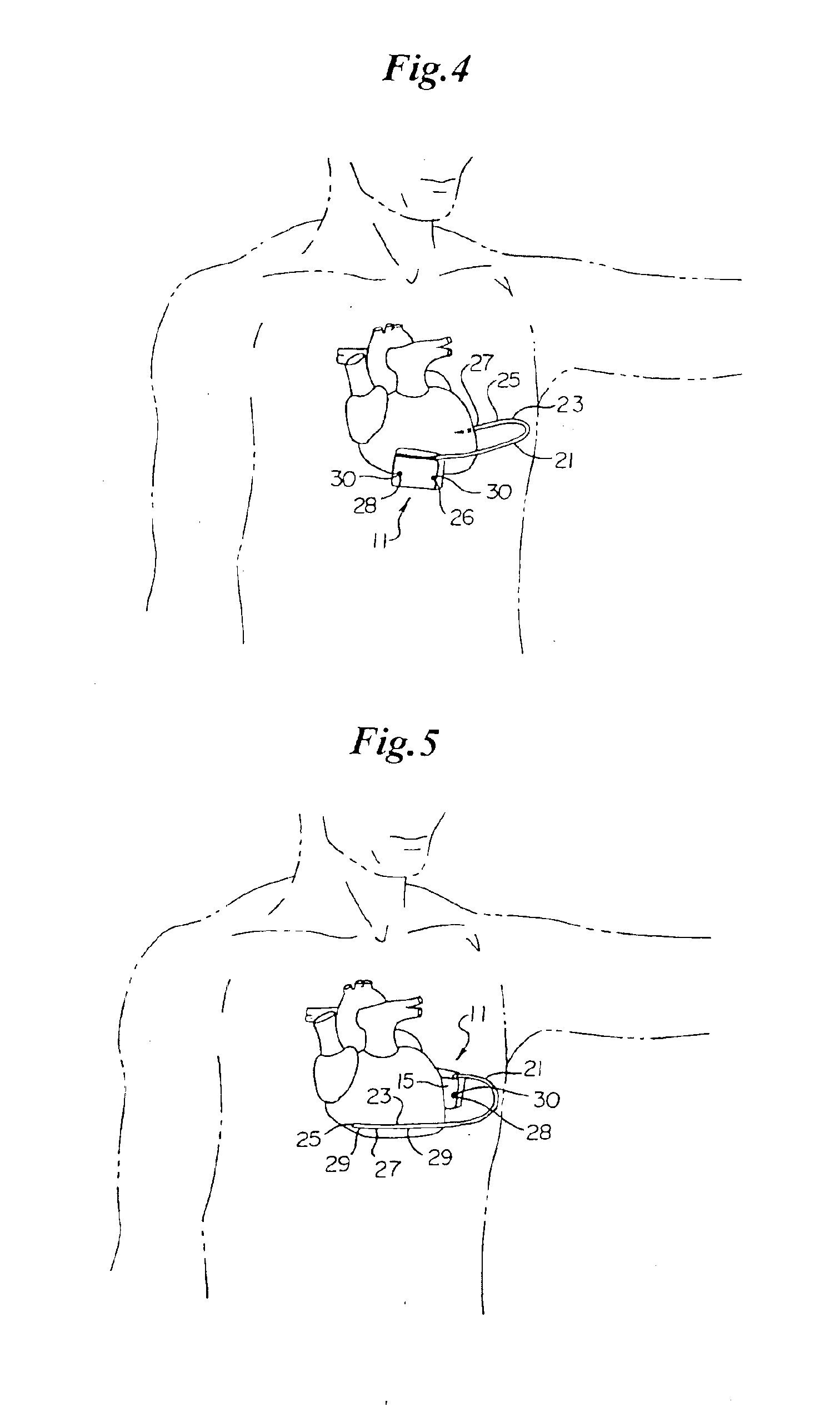
Method of insertion and implantation of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator canisters
InactiveUS6866044B2DiagnosticsHeart defibrillatorsThoracic cavityImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator
One embodiment of the present invention provides a method of inserting an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator within a patient, the method including the steps of providing a cardioverter-defibrillator canister having at least a portion of the cardioverter-defibrillator canister being non planar to maintain the cardioverter-defibrillator canister in a predetermined relationship with respect to a patient's heart, subcutaneously over a patient's ribcage; making a single incision into the patient; and advancing the cardioverter-defibrillator canister through the single incision and subcutaneously over the patient's ribcage.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
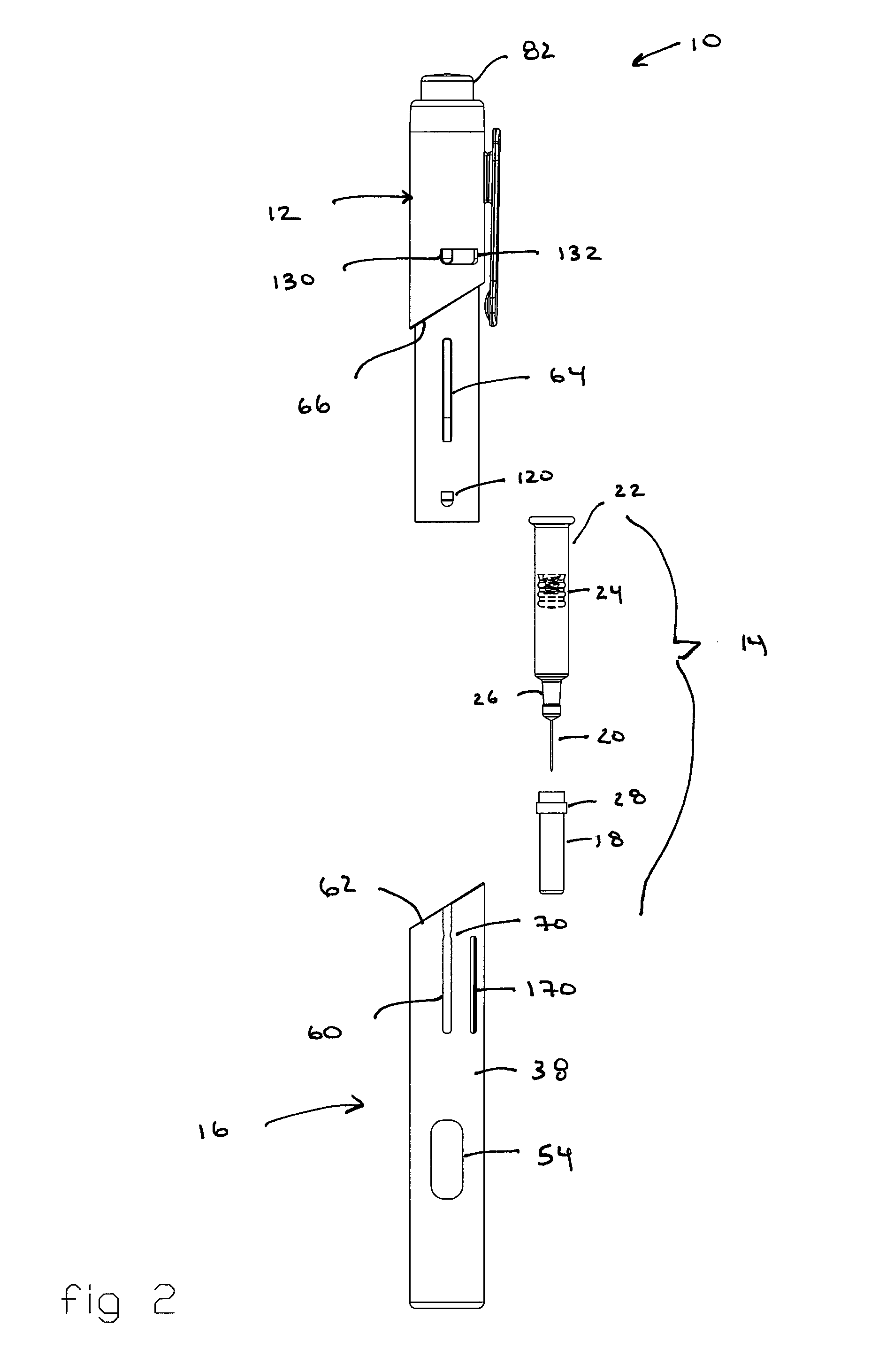
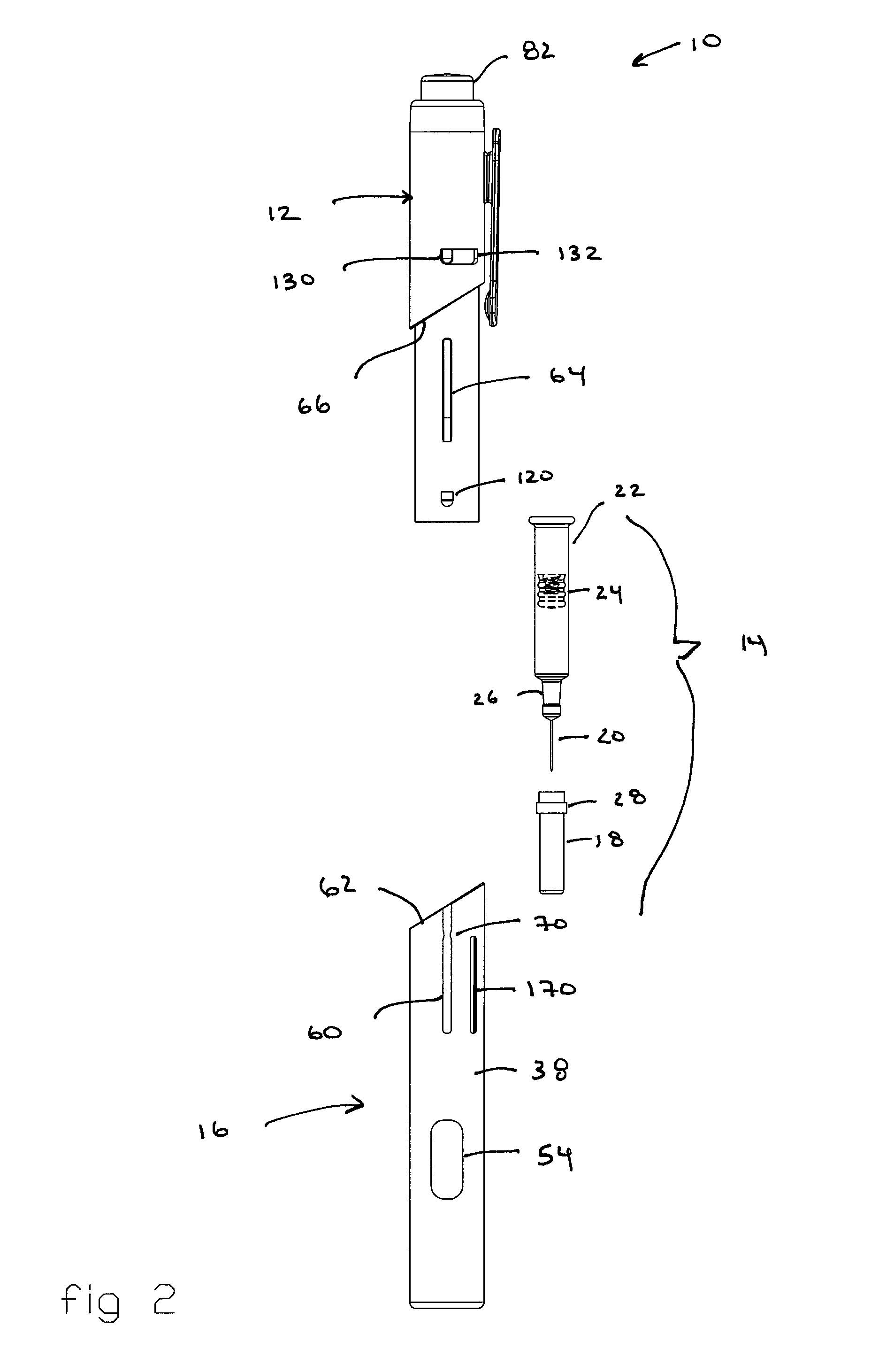
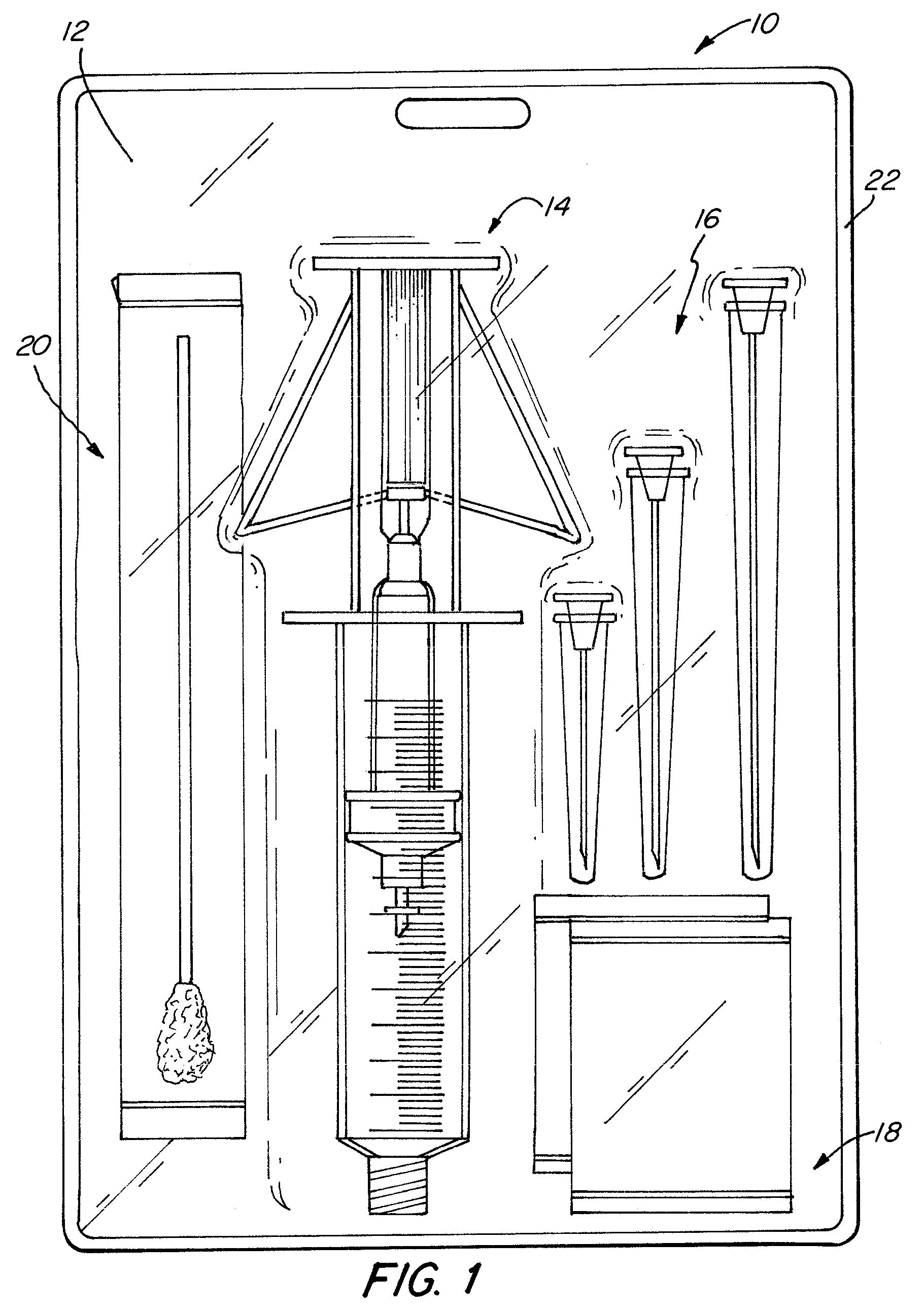
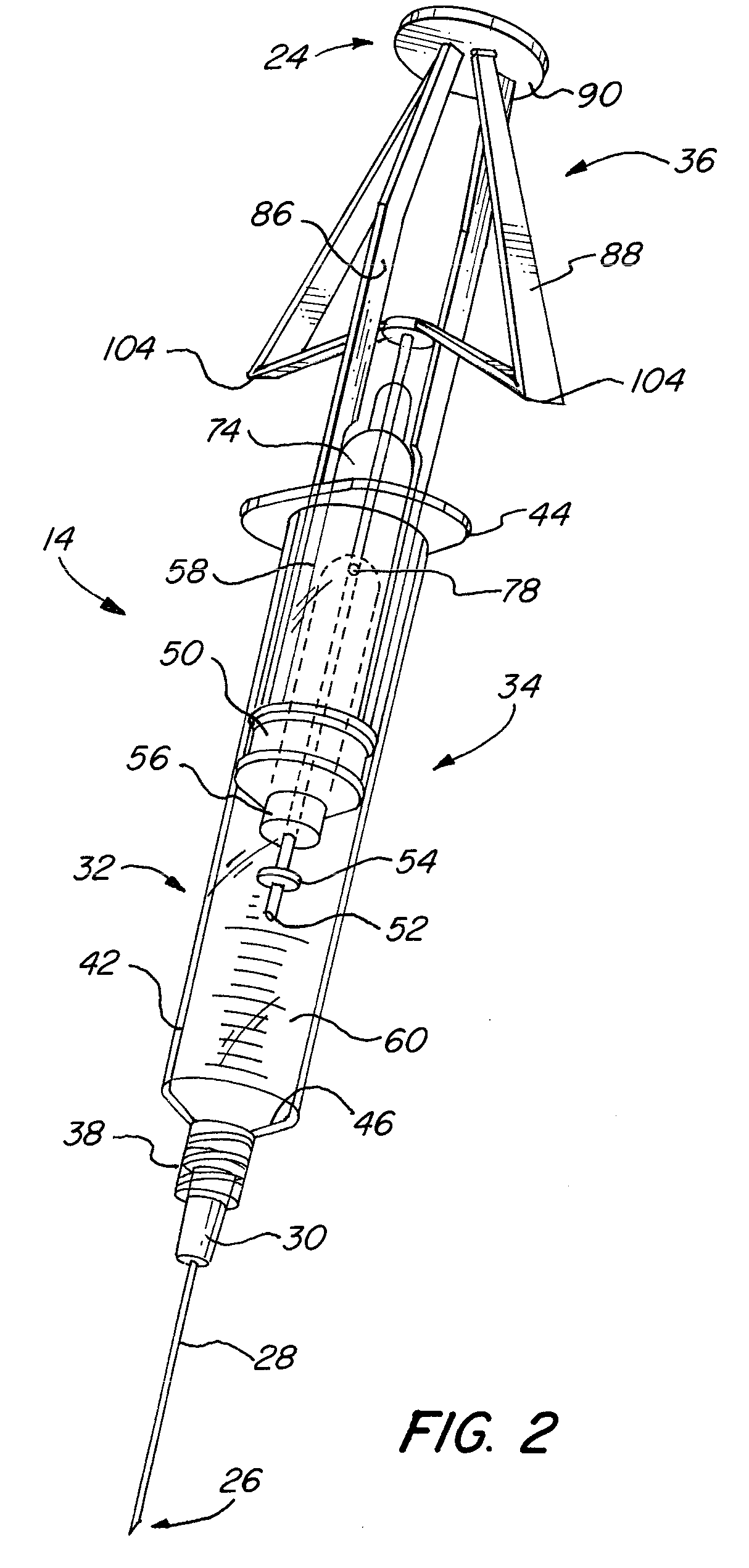
Automatic injection and retraction devices for use with pre-filled syringe cartridges
ActiveUS20070135767A1Safe disposalEasy to disassembleAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesHypodermic needleEngineering
An automatic injection and retraction device having a longitudinal axis is provided that includes an injection assembly, a retraction assembly, and a pre-filled syringe cartridge. The injection assembly has an activation-prevention feature moveable between an on position and an off position. The retraction assembly has a needle guard that is removable in a direction along the longitudinal axis upon application of a removal force. The pre-filled syringe cartridge has a hypodermic needle with a needle sheath thereon. The retraction and injection assemblies are secured to one another so that the pre-filled syringe cartridge is in the retraction assembly with the needle sheath secured to the needle guard. The retraction and injection assemblies are configured so that, upon application of a twisting torque to the injection and retraction assemblies, the activation-prevention feature moves from the on position to the off position simultaneous with applying the removal force to the needle guard.
Owner:WEST PHARMA SERVICES OF DELAWARE
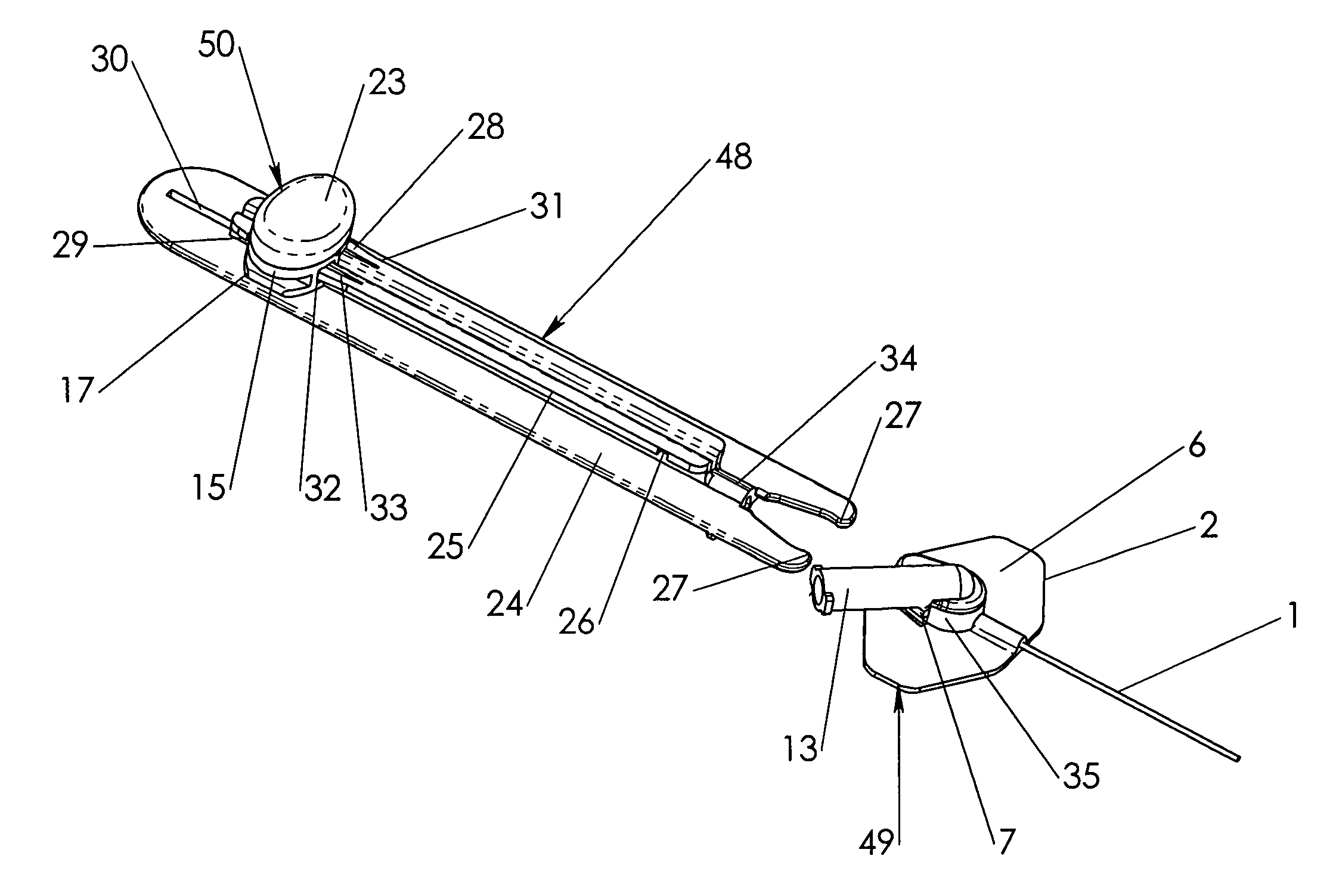
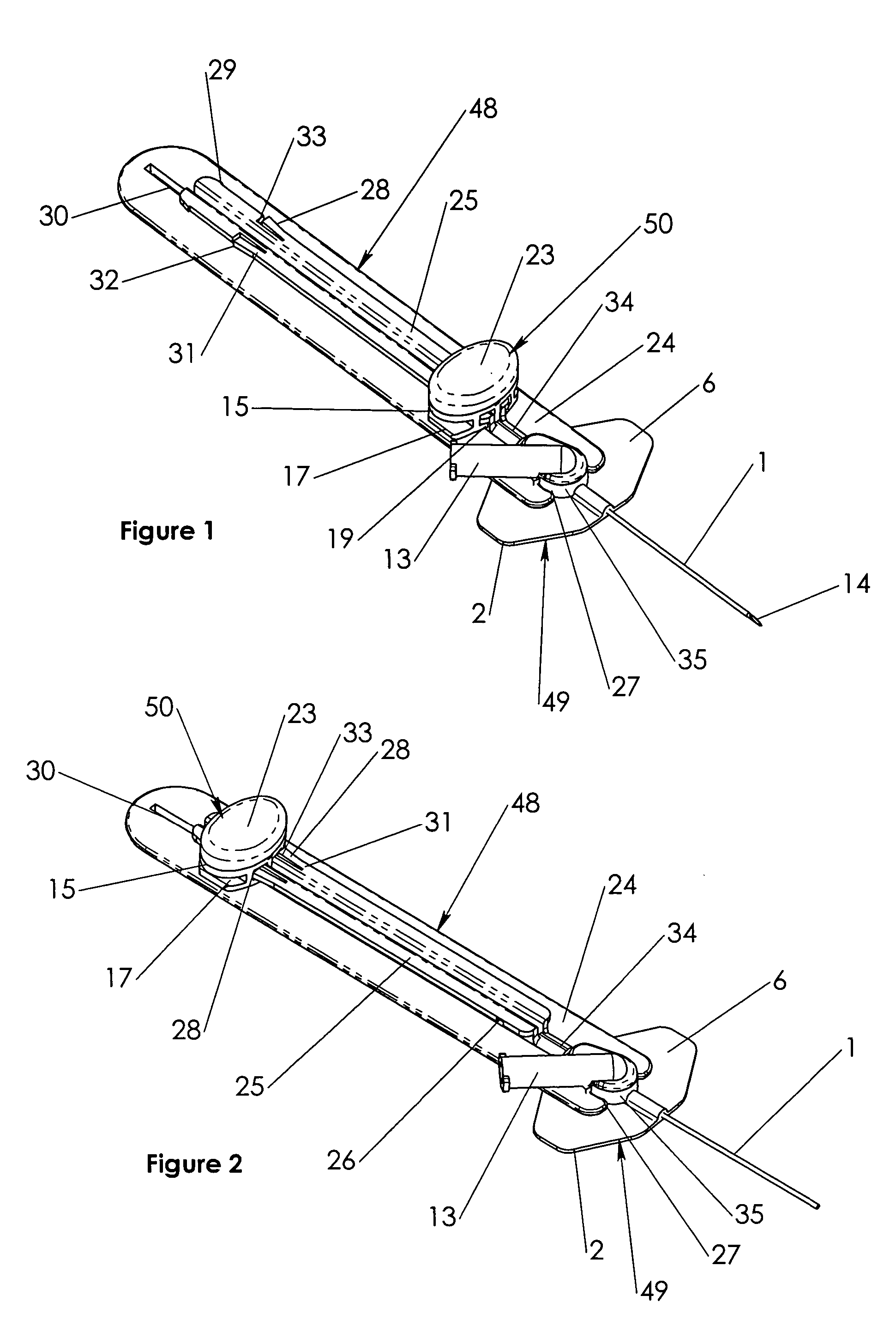
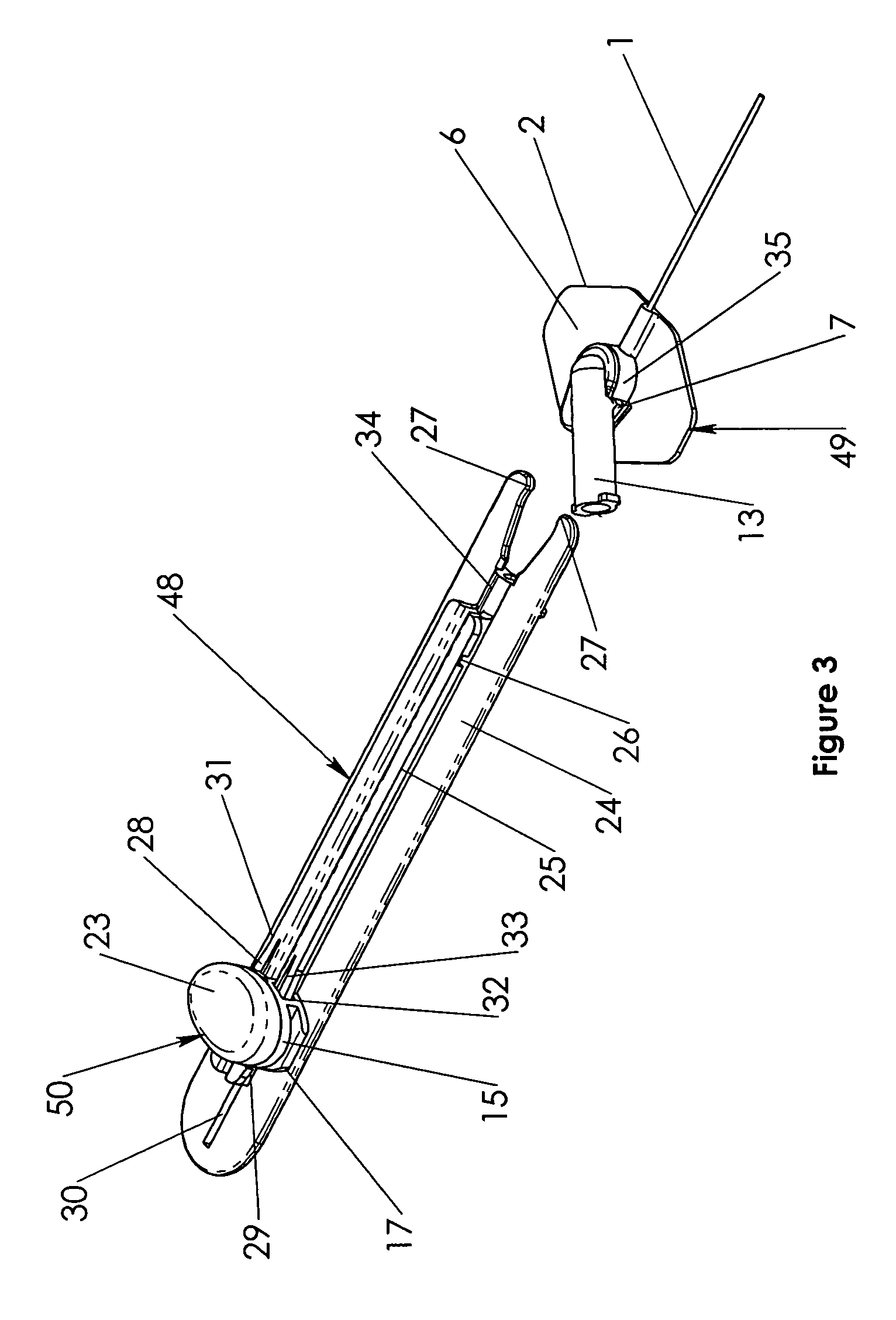
Disposable double pointed injection needle, and an insulin injection system comprising a disposable double pointed injection needle
A disposable double pointed injection needle has a needle hub to which a thin needle cannula is permanently fastened and which needle hub can be mounted on to a syringe comprising a dose setting and injection mechanism and a cartridge containing a liquid medicine to be injected subcutaneously into a human body. The needle hub is provided with a safety shield guided on the outside surface of the needle hub. The safety shield is urged in a direction away from the needle hub by a spring located between the needle hub and the safety shield. The safety shield has a number of protrusions guided in guiding tracks on the outside surface of the needle hub. The guiding tracks are designed such that the safety shield during injection is moved towards the needle hub, and after injection is moved away from the needle hub by the spring and locked in an irreversible position where the safety shield covers the needle cannula and prevents accidental needle stick injuries.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
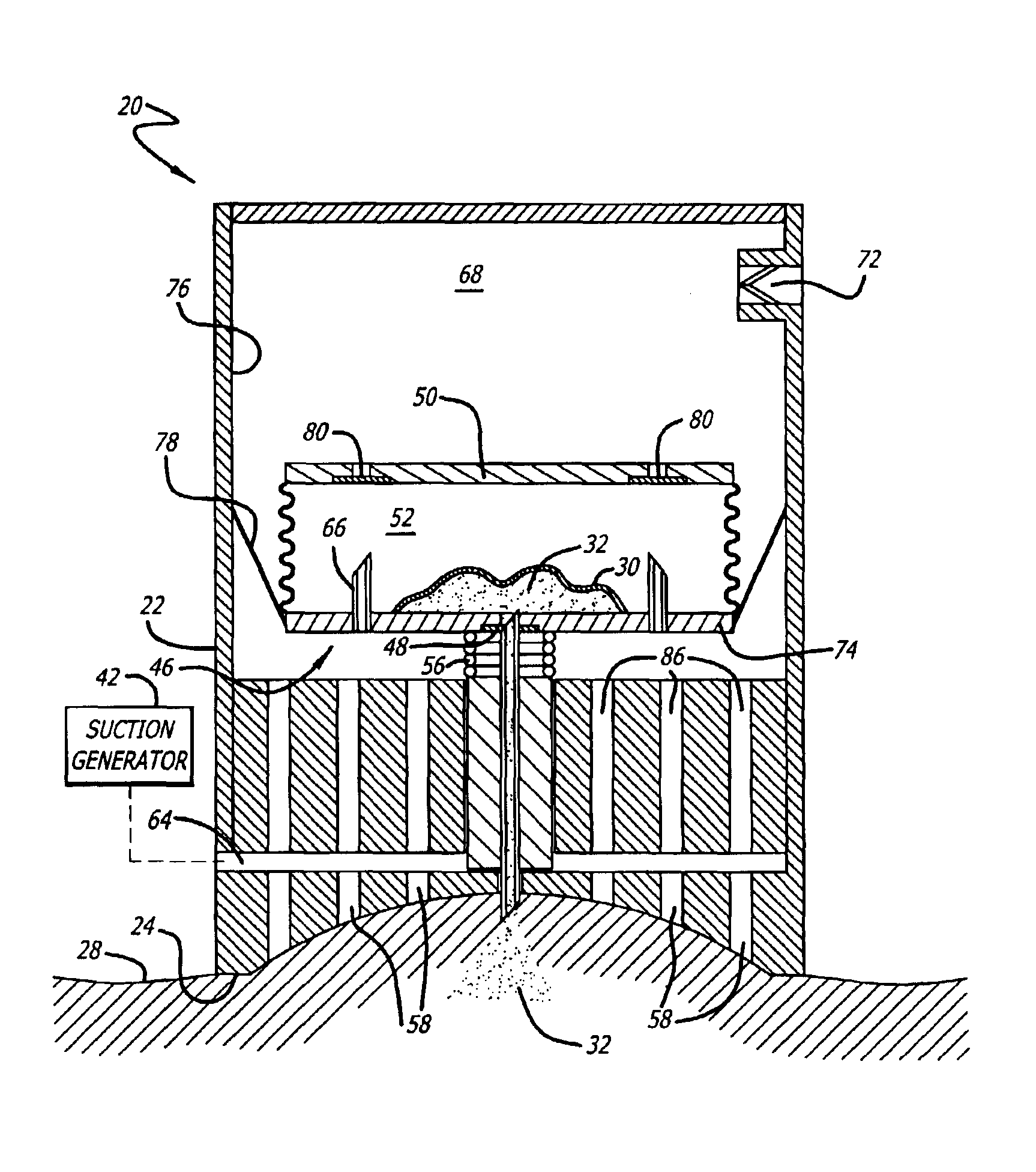
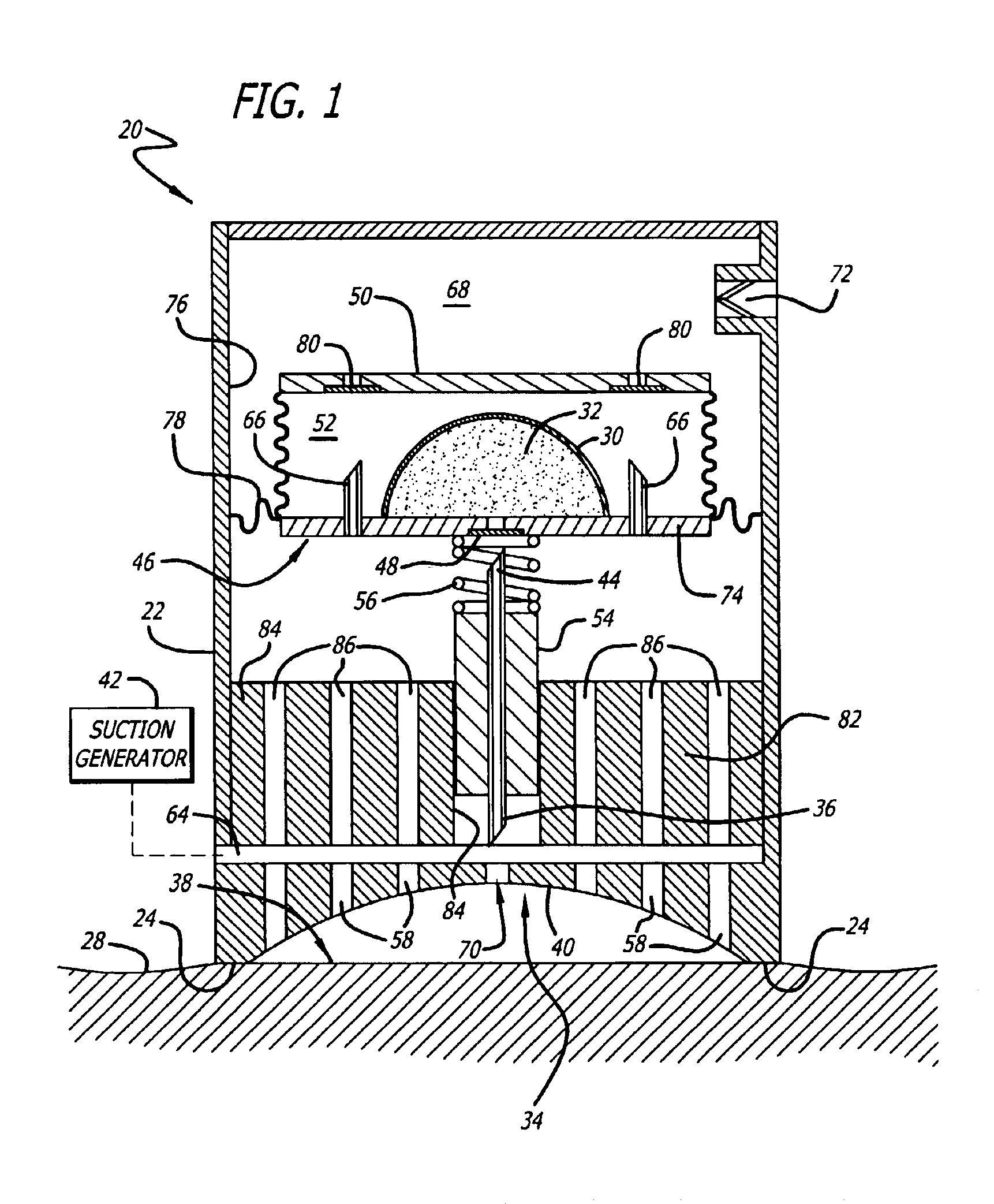
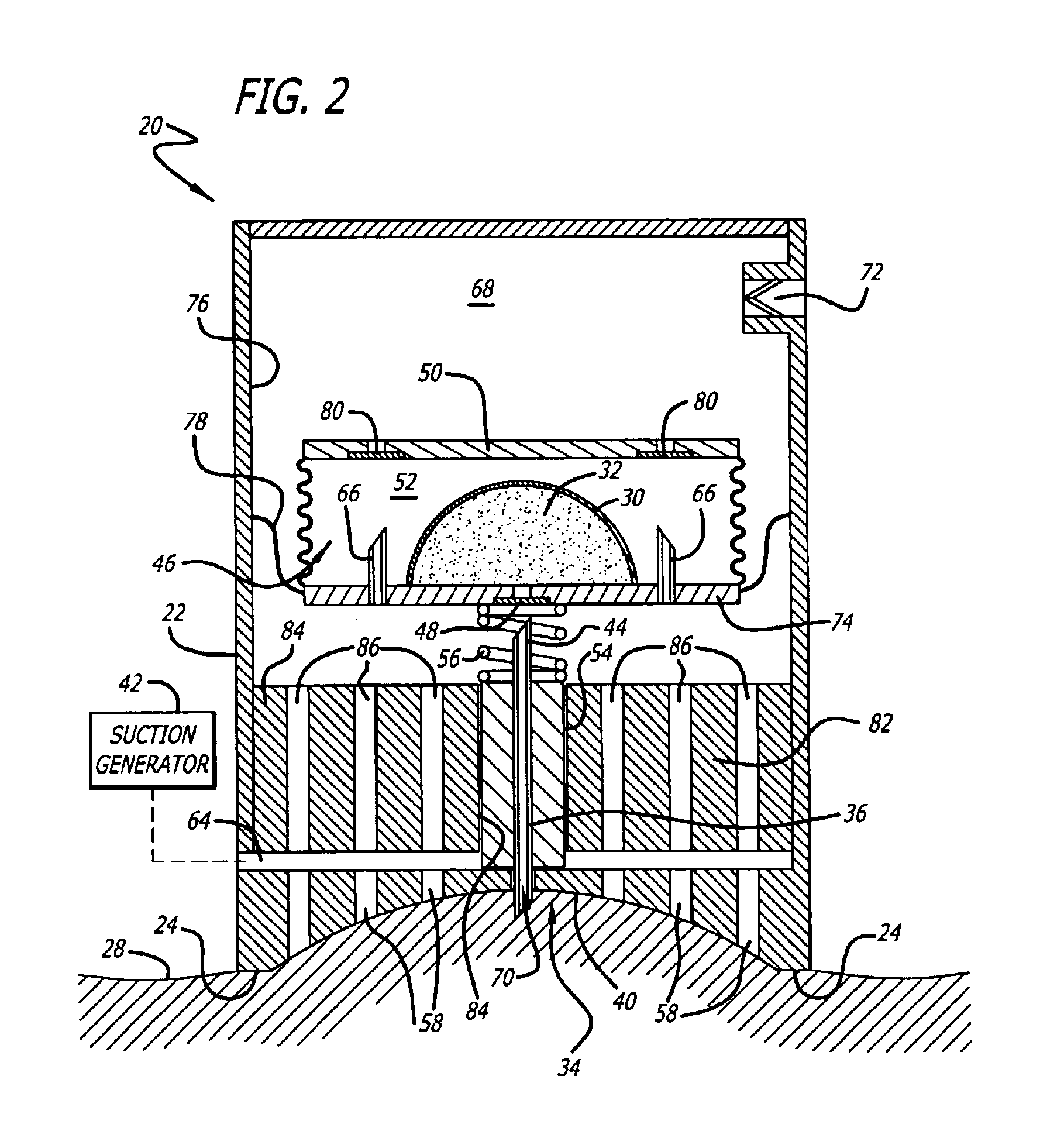
Cutaneous injection delivery under suction
The delivery of a fluid cutaneously is effected by generating a suction force on a surface of a housing. A surface of a cutaneous layer is received under the suction force about which the proximal end of a needle thereby to pierce the cutaneous surface and to effect an injection of fluid. There is generated a suction force to operate the movement of a needle in the housing. The needle is moved under the suction force from the housing thereby to permit piercing a cutaneous layer. The bladder for containing fluid is emptied under the suction into the distal end of the needle and thereby permit the expulsion of fluid through the proximal end of the needle for injection below the cutaneous layer.
Owner:KOCHAMBA FAMILY TRUST
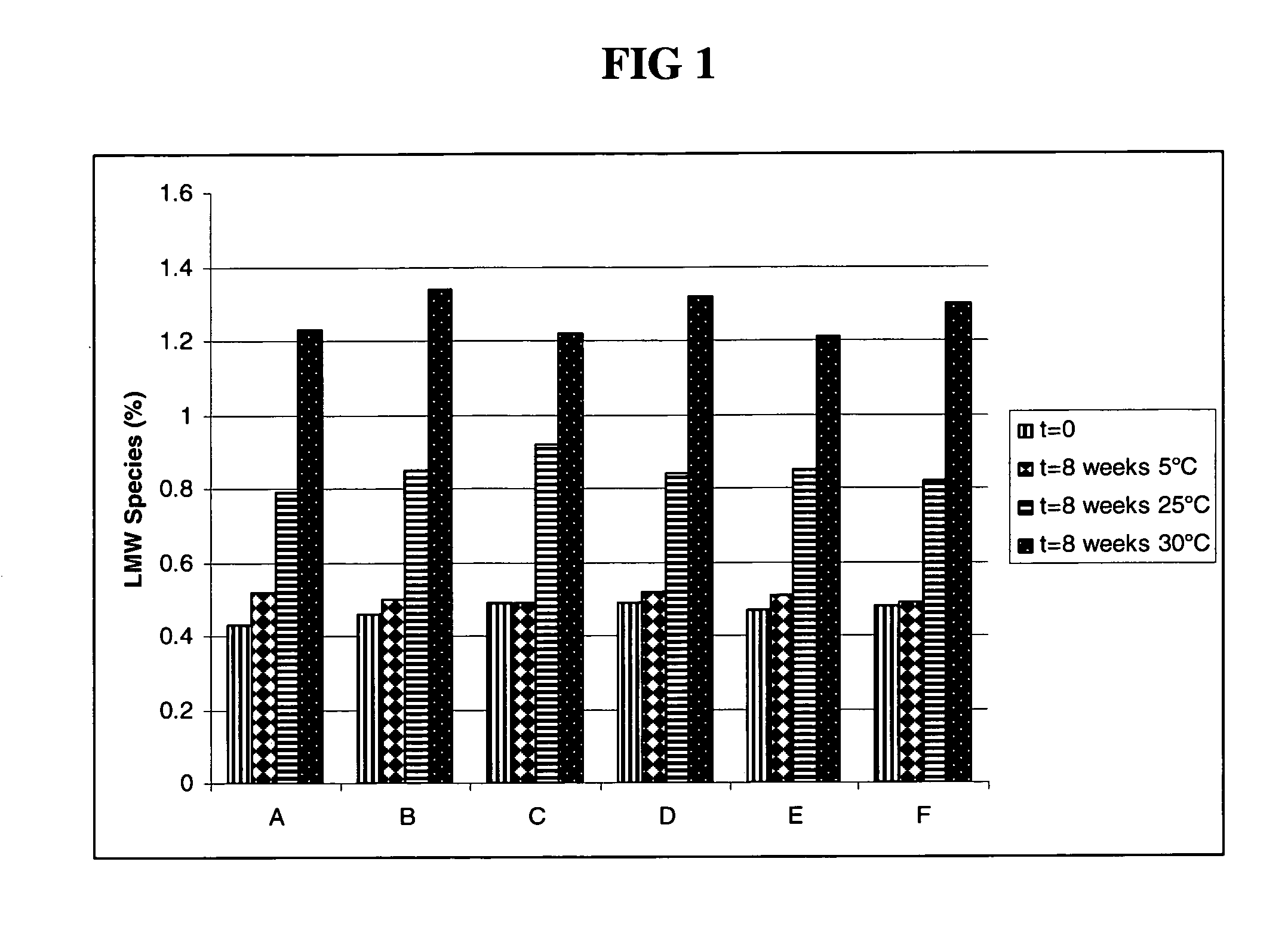
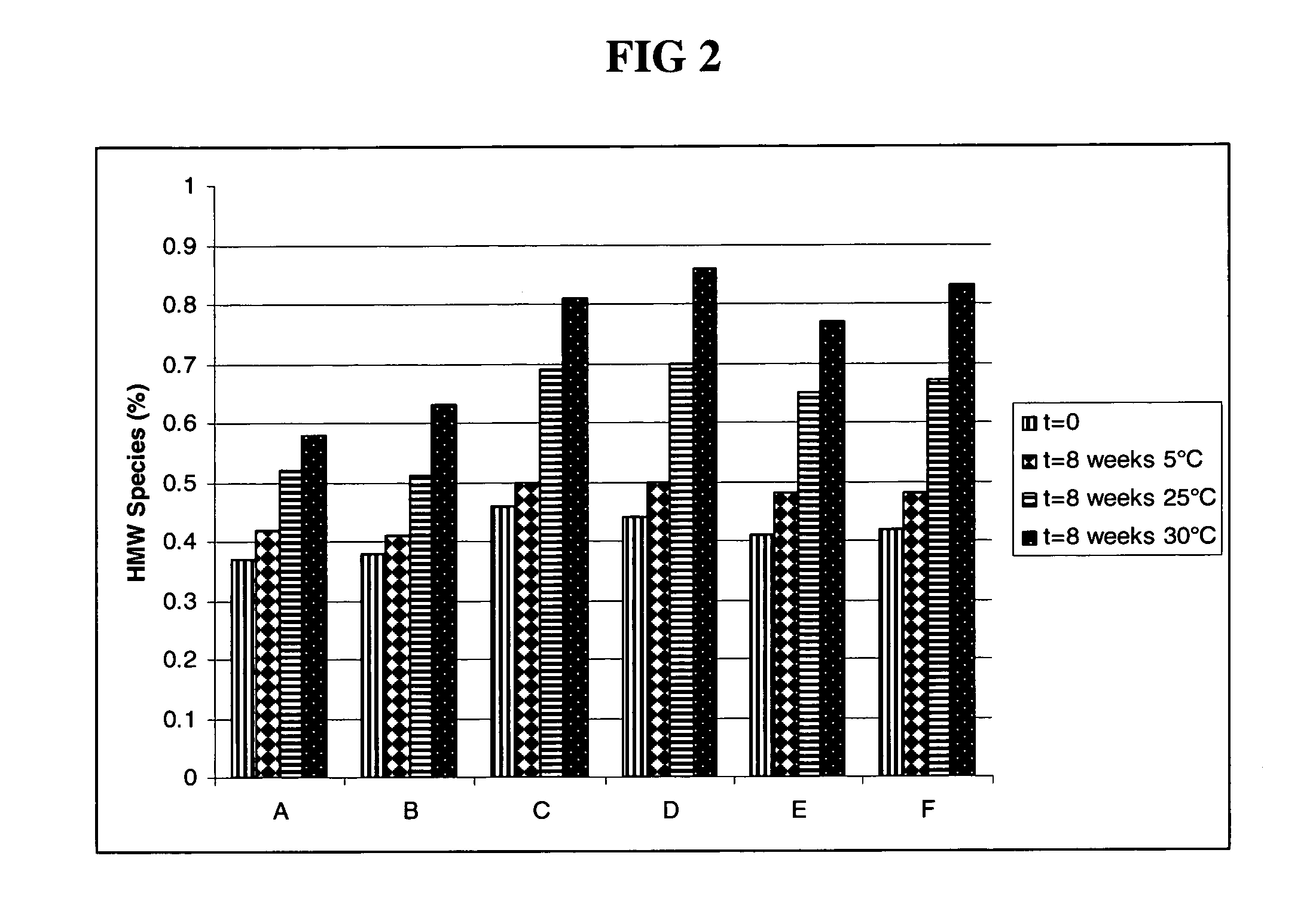
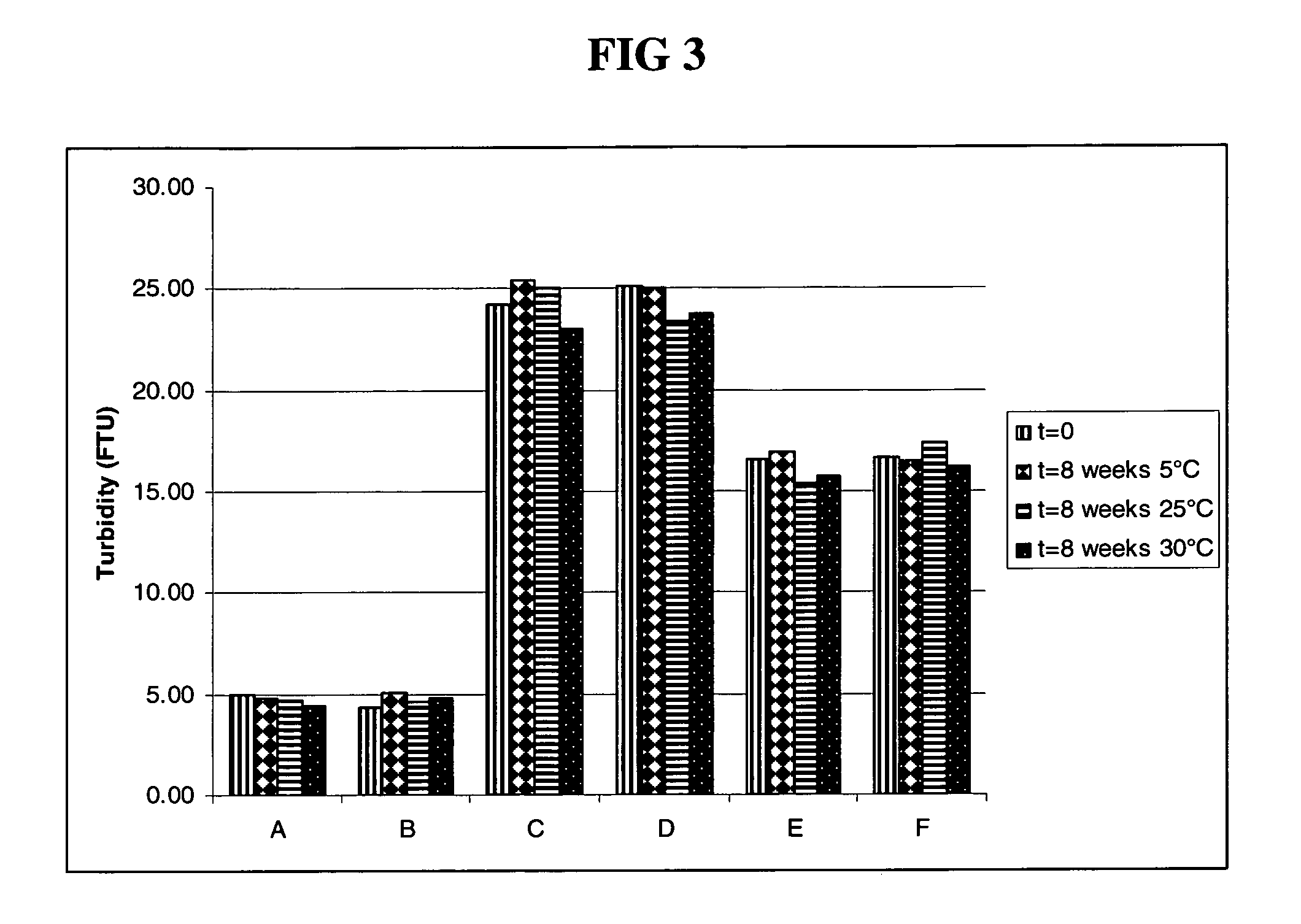
Highly Concentrated Pharmaceutical Formulations
InactiveUS20110076273A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsAntibody moleculeSubcutaneous injection
The present invention relates to a highly concentrated, stable pharmaceutical formulation of a pharmaceutically active anti-CD20 antibody, such as e.g. Rituximab, Ocrelizumab, or HuMab<CD20>, or a mixture of such antibody molecules for subcutaneous injection. In particular, the present invention relates to formulations comprising, in addition to a suitable amount of the anti-CD20 antibody, an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme as a combined formulation or for use in form of a co-formulation. The said formulations comprise additionally at least one buffering agent, such as e.g. a histidine buffer, a stabilizer or a mixture of two or more stabilizers (e.g. a saccharide, such as e.g. α,α-trehalose dihydrate or sucrose, and optionally methionine as a second stabilizer), a nonionic surfactant and an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme. Methods for preparing such formulations and their uses thereof are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Cardiac event microrecorder and method for implanting same
ActiveUS7294108B1Facilitate subcutaneous implantationElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsElectricityHypodermic needle
A cardiac event microrecorder comprising a hermetically sealed housing is shaped and dimensioned to facilitate the subcutaneous implantation of the microrecorder in a human patient by injection through the lumen of a hypodermic needle. The housing comprises a tubular central section of an electrically insulating material, the central section having spaced apart extremities. An electrically conductive sense electrode is secured to and seals each extremity. The housing may have an interior enclosing (1) electrical circuitry for processing, storing and telemetering data representing physiologic information detected by the sense electrodes; (2) a primary cell or rechargeable battery for electrically powering the electrical circuitry; and (3) an inductively couplable charger where a rechargeable battery is used. Also disclosed are a method of subcutaneously implanting a cardiac event recorder in a patient's thoracic region, and a handheld mapping device for determining an optimum location and orientation for the cardiac event microrecorder to be implanted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Tissue augmentation material and method
InactiveUS7060287B1Reduce deliveryImpression capsAnti-incontinence devicesUnilateral vocal cord paralysisSphincter
A permanent, biocompatible material for soft tissue augmentation. The biocompatible material comprises a matrix of smooth, round, finely divided, substantially spherical particles of a biocompatible ceramic material, close to or in contact with each other, which provide a scaffold or lattice for autogenous, three dimensional, randomly oriented, non-scar soft tissue growth at the augmentation site. The augmentation material can be homogeneously suspended in a biocompatible, resorbable lubricious gel carrier comprising a polysaccharide. This serves to improve the delivery of the augmentation material by injection to the tissue site where augmentation is desired. The augmentation material is especially suitable for urethral sphincter augmentation, for treatment of incontinence, for filling soft tissue voids, for creating soft tissue blebs, for the treatment of unilateral vocal cord paralysis, and for mammary implants. It can be injected intradermally, subcutaneously or can be implanted.
Owner:BIOFORM
Subcutaneous injection port with stabilizing elements
An implantable surgical injection port including a housing having a body, a closed distal end, a open proximal end and a fluid reservoir therebetween. The housing includes a needle penetrable septum attached to the housing about the opening. The injection port further includes at least one stabilizing element mounted to the housing for stabilizing the port within tissue. The stabilizing element is a member having an undeployed position and a deployed position. Wherein the element extends radially from the body in the deployed position.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
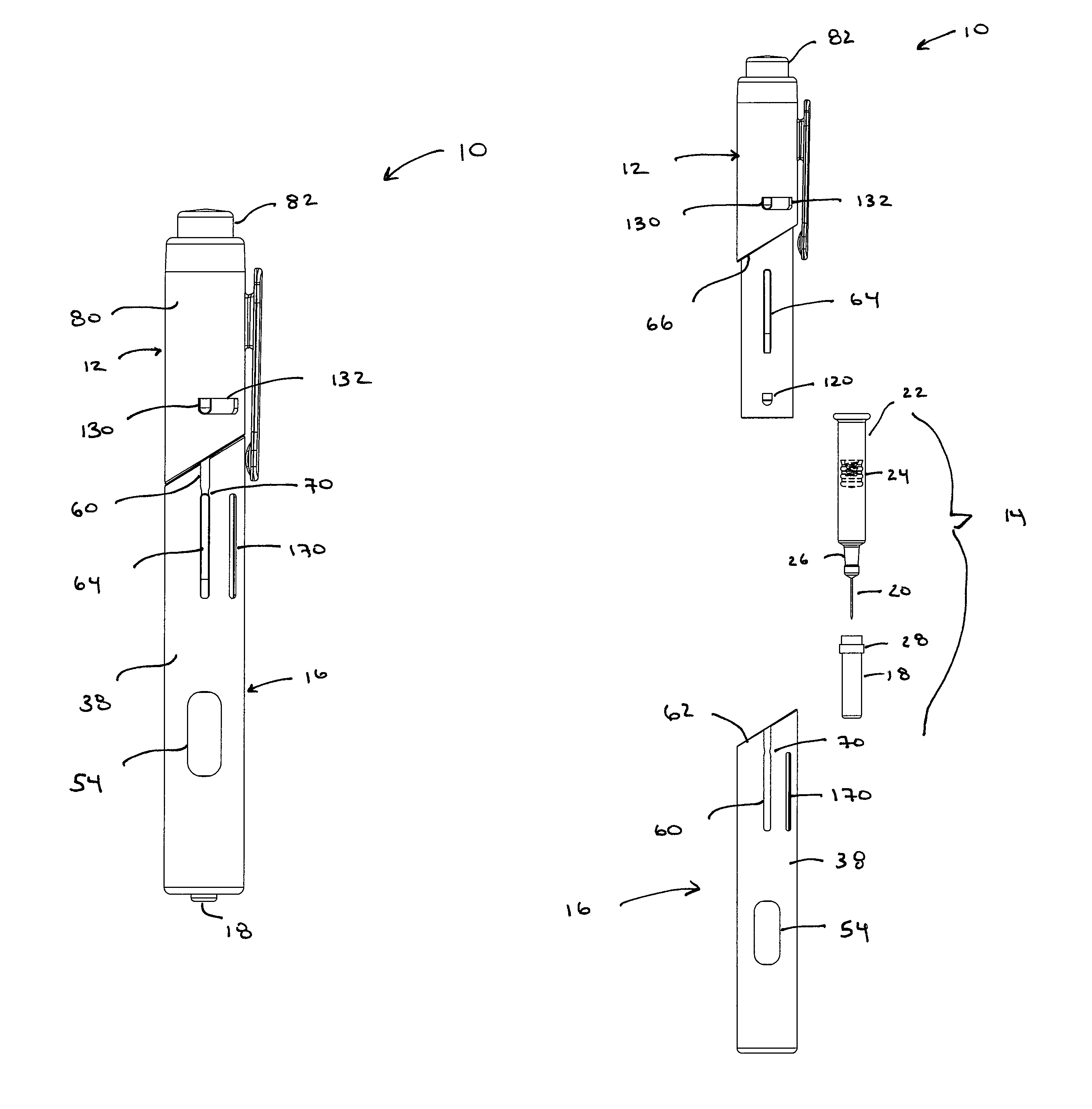
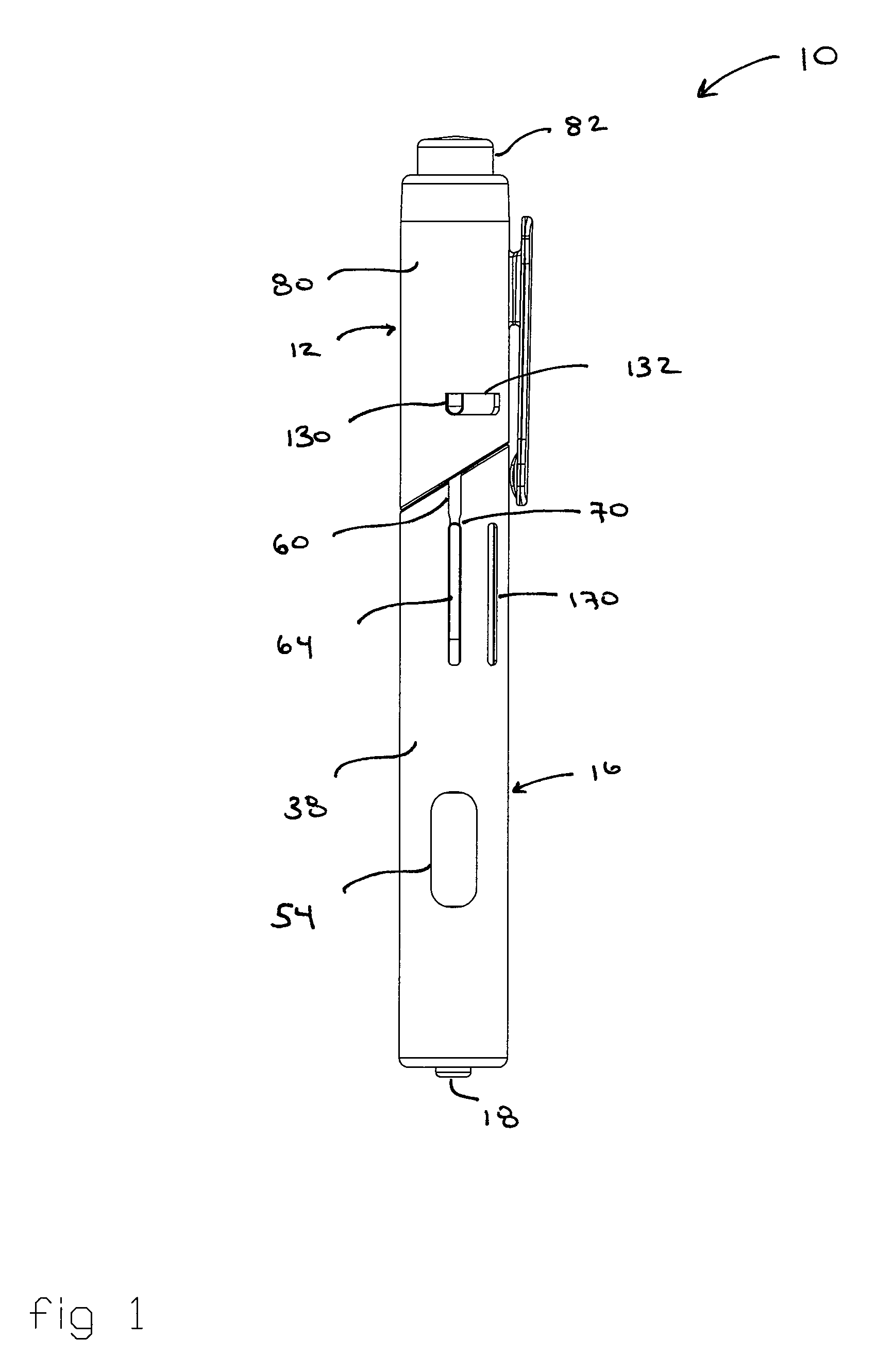
Apparatus for subcutaneous administration of an injectable product
InactiveUS7074211B1Improve securityImprove user convenienceMedical devicesInfusion needlesHypodermoclysisInjectable Product
An apparatus for subcutaneous administration of an injectable product, including a housing, a container for the product to be injected, an injection needle and a needle protection sleeve surrounding the injection needle, wherein the apparatus also includes an indicator to tell a user when the needle protection sleeve has attained its maximum distal position.
Owner:TECPHARMA LICENSING AG
Percutaneously deliverable orthopedic joint device
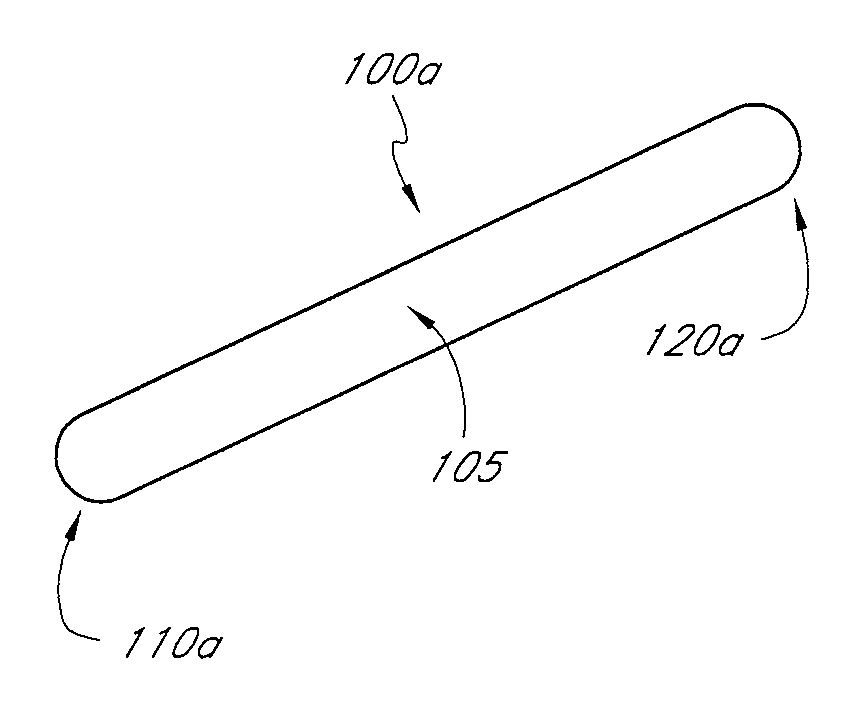
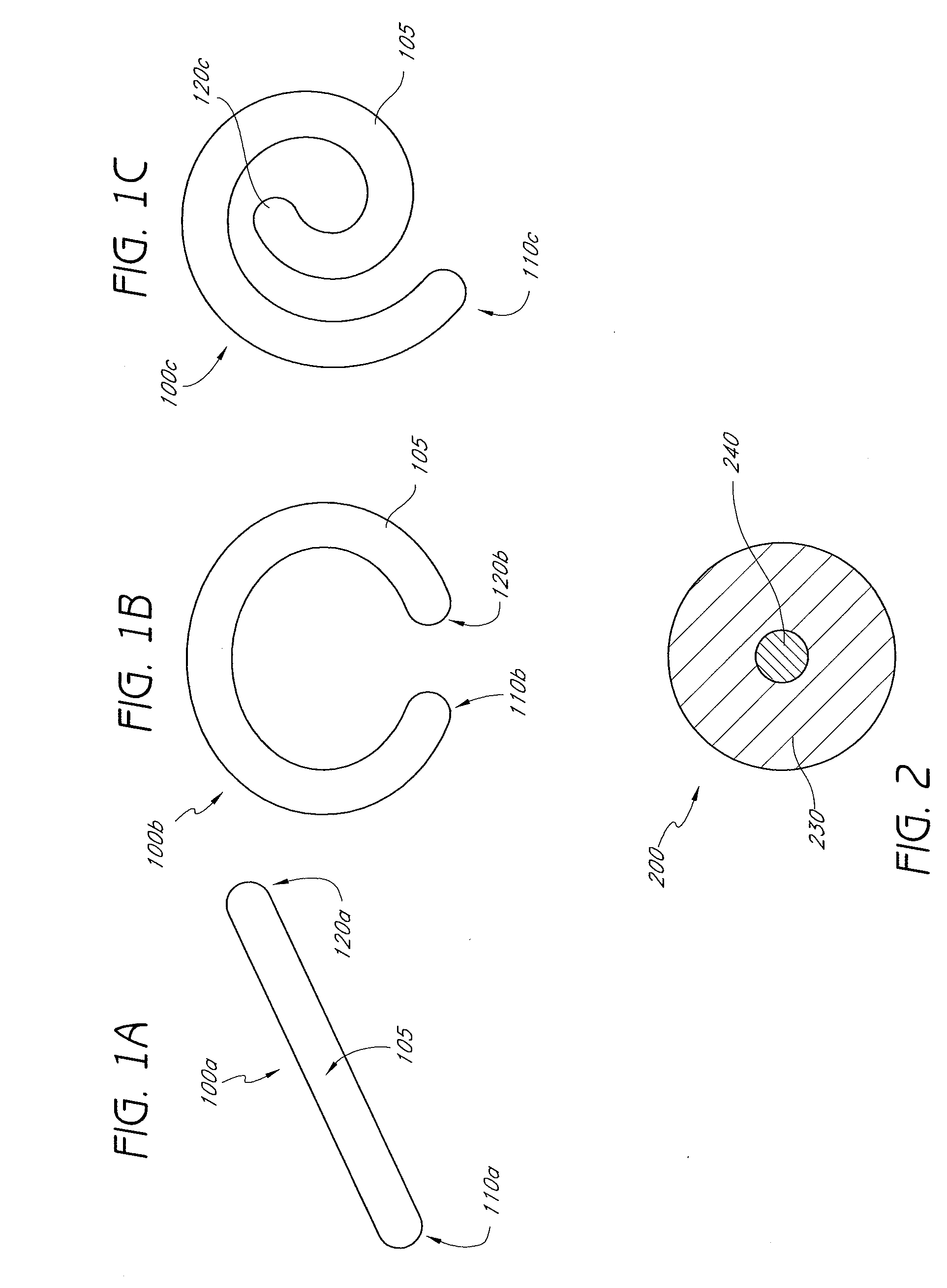
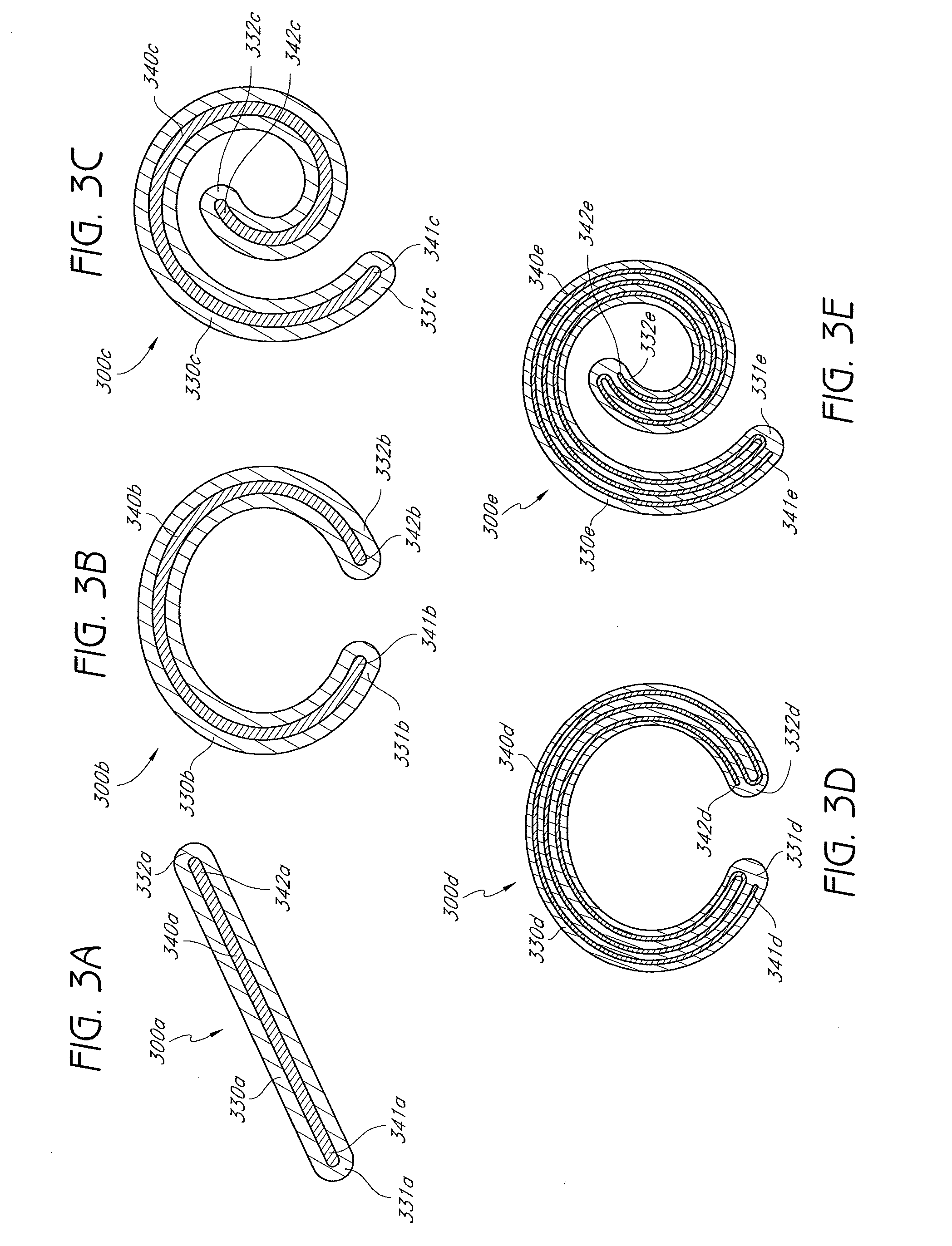
InactiveUS20080255664A1Slow deteriorationRelieve painInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsHypodermoclysisHypodermic needle
A percutaneously implantable orthopedic device is a shape-changing joint prosthesis with a generally arcuate or generally rectilinear configuration which is delivered through a delivery device in a substantially straightened or slightly curved configuration into a joint in a patient. The generally arcuate configuration may include an open ring or spiral shape. The generally rectilinear configuration may include a polygon or zig-zag shape. The delivery and retrieval device can be a syringe, hypodermic needle or cannula. The orthopedic device is moveable into its generally arcuate or generally rectilinear configuration in the joint by manipulation or a shape memory set. The orthopedic device acts as a soft compliant bearing surface or cushion that minimizes the bone-on-bone wear from articulation and loading.
Owner:ARTICULINX
Device for targeted, catheterized delivery of medications
InactiveUS6905486B2Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsSurgical needlesMedical devicesHypodermoclysisHypodermic needle
Apparatus and method for catheterized delivery or infusion of medication and anaesthesia are disclosed. The perforating catheter is first used to perforate the periodontal ligament and / or the cortical plate of bone tissue, and is then left in place and used as a catheter for insertion of a hypodermic needle of smaller gauge to deliver medication or anaesthesia to a target area. The perforator is a bevelled needle for drilling into the ligament or bone tissue. For drilling, the device comprises an adaptor which transmits the rotational movement from a dental hand piece or the like to the bevelled needle. A cap is also included for protecting the bevelled needle during storage of the device. The adaptor may have a rod which extends axially into the bevelled needle when the device is assembled for drilling. The rod is used to prevent the debris resulting from drilling from blocking the passage in the bevelled needle. As well, the rod reinforces the needle and maintains the alignment between the perforator and the adaptor for improved drilling efficiency. An adapter is disclosed which couples with the catheter once in place easing access to supply medication to difficult to reach areas.
Owner:INTROSAN DENTAL PROD
Automatic injection and retraction devices for use with pre-filled syringe cartridges
An automatic injection and retraction device having a longitudinal axis is provided that includes an injection assembly, a retraction assembly, and a pre-filled syringe cartridge. The injection assembly has an activation-prevention feature moveable between an on position and an off position. The retraction assembly has a needle guard that is removable in a direction along the longitudinal axis upon application of a removal force. The pre-filled syringe cartridge has a hypodermic needle with a needle sheath thereon. The retraction and injection assemblies are secured to one another so that the pre-filled syringe cartridge is in the retraction assembly with the needle sheath secured to the needle guard. The retraction and injection assemblies are configured so that, upon application of a twisting torque to the injection and retraction assemblies, the activation-prevention feature moves from the on position to the off position simultaneous with applying the removal force to the needle guard.
Owner:WEST PHARMA SERVICES OF DELAWARE
Needle tip guard for percutaneous entry needles
InactiveUS20060189934A1Effective shieldingGuide needlesAmpoule syringesHypodermic needleNeedle guard
A needle tip protective device for use with percutaneous entry needles. In one embodiment, the needle tip protective device includes a needle guard slidably mounted on a hypodermic needle, the latter having a needle tip located at the distal end thereof, and a change of profile formed medially there along. The needle guard is movable along the hypodermic needle and engageable with the change in profile formed thereon. The engagement with the change in profile is configured to correspond with the ability of the needle trap to entrap the needle tip once the needle trap has advanced the sufficient distance distally along the hypodermic needle. In further refinements, the needle trap may be biased toward the distal needle tip of the needle.
Owner:B BRAUN MELSUNGEN AG
Needle tip guard for percutaneous entry needles
A needle tip protective device for use with percutaneous entry needles. In one embodiment, the needle tip protective device includes a needle guard slidably mounted on a hypodermic needle, the latter having a needle tip located at the distal end thereof, and a change of profile formed medially there along. The needle guard is movable along the hypodermic needle and engageable with the change in profile formed thereon. The engagement with the change in profile is configured to correspond with the ability of the needle trap to entrap the needle tip once the needle trap has advanced the sufficient distance distally along the hypodermic needle. In further refinements, the needle trap may be biased toward the distal needle tip of the needle.
Owner:B BRAUN MELSUNGEN AG
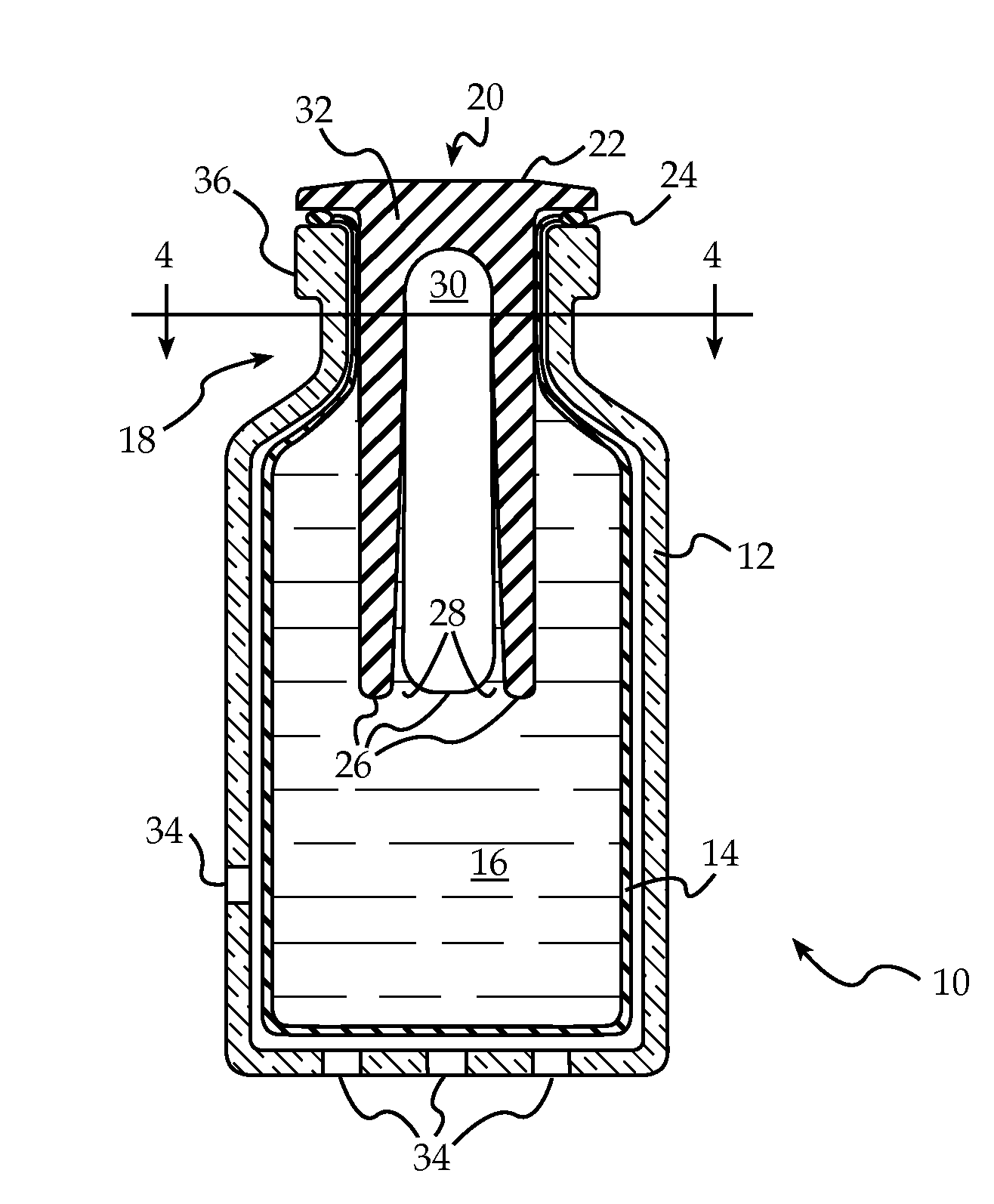
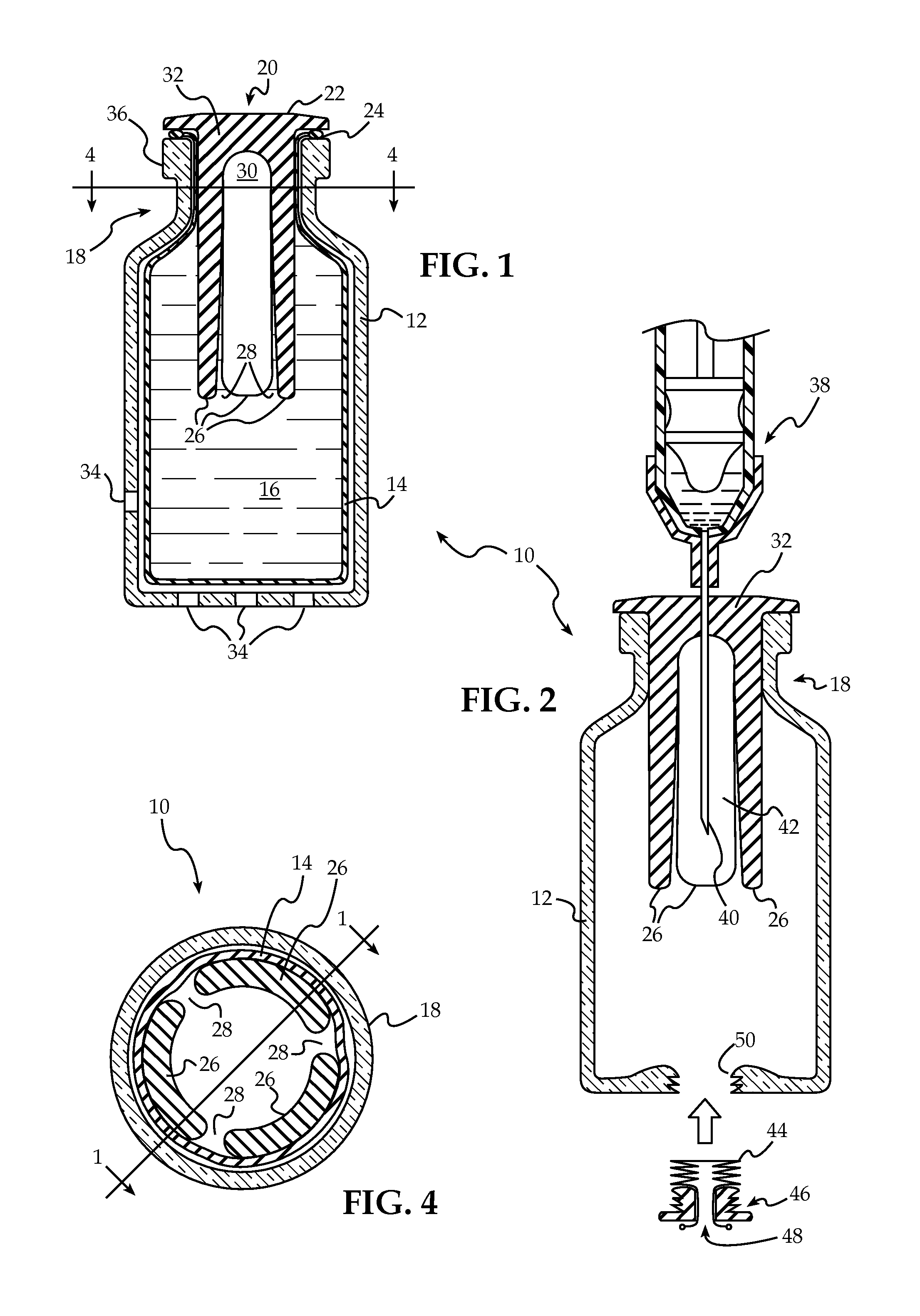
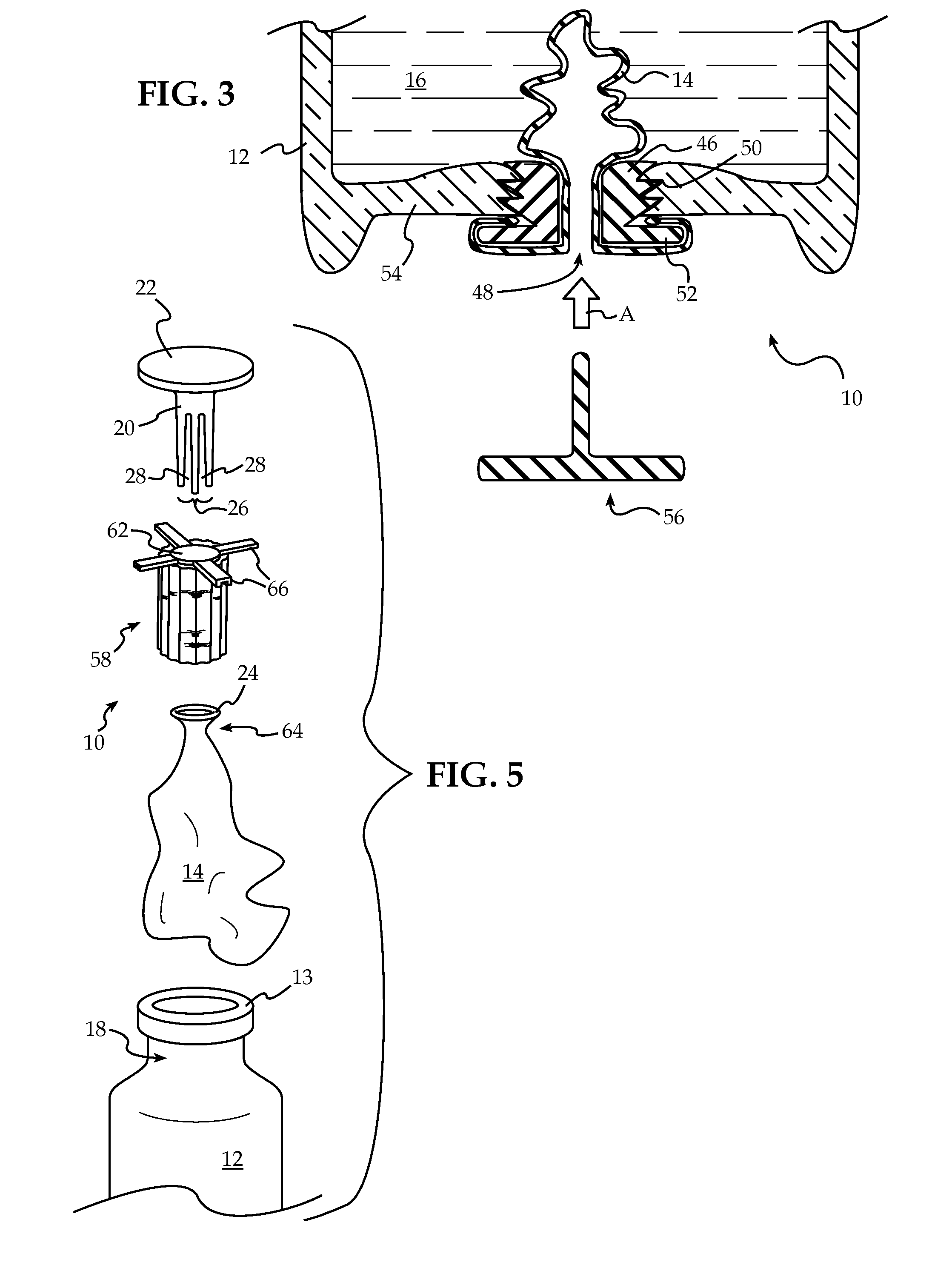
Bung assembly for anti vacuum lock medical vials
Anti-vacuum-lock assemblies for preventing vacuum lock when withdrawing medicinal fluid from a vial comprising a multi-finger bung-type stopper in which the fingers are of sufficient length to protect a collapsing or expanding bladder in the vial from being punctured by the hypodermic needle. In a first embodiment the vial includes one or more side or bottom wall holes to permit ambient air to enter in the space between an internal bladder containing a medicinal fluid and the inner wall of the vial. In another embodiment, an expanding bladder in communication with the exterior expands as fluid is withdrawn from the vial. In a third embodiment a fluted collar is inserted in the vial neck to provide air passages into the space between the medicinal fluid-containing bladder and the interior wall of the vial. The collapse of the medicinal bladder or expansion of the compensation bellows or bladder prevents vacuum lock.
Owner:YANDELL MARION E
Needle tip guard for percutaneous entry needles
A needle tip protective device for use with percutaneous entry needles. In one embodiment, the needle tip protective device includes a needle guard slidably mounted on a hypodermic needle, the latter having a needle tip located at the distal end thereof, and a change of profile formed medially there along. The needle guard is movable along the hypodermic needle and engageable with the change in profile formed thereon. The engagement with the change in profile is configured to correspond with the ability of the needle trap to entrap the needle tip once the needle trap has advanced the sufficient distance distally along the hypodermic needle. In further refinements, the needle trap may be biased toward the distal needle tip of the needle.
Owner:B BRAUN MELSUNGEN AG
Fluid delivery and extraction device and method
A fluid delivery and extraction device enables the remote transfer of fluid to or from biological tissue. The device comprises an elongated member, a syringe movable relative to the elongated member and a pair of hypodermic needles movable relative to the elongated member. The elongated member has a distal portion which is adapted to be inserted into a biological structure. A steer wire or guide wire can be used to navigate the distal portion within cavernous biological structures, particularly body lumens. The distal portion has at least one retractable hypodermic needle that is configured to pierce the interior surface of a tubular biological structure and transfer fluid to or from the walls of the tubular biological structure. A physician can use a handle or other control mechanism provided at a proximal portion of the device to remotely move the hypodermic needles. A plunger can be used to transfer fluid through the hypodermic needles to or from the syringe. In operation, the hypodermic needles are deployed simultaneously or individually from the distal portion of the device. As the hypodermic needles move, they pierce the interior surface of the tubular biological structure. The hypodermic needles can also be configured to pass beyond the exterior surface of the tubular biological structure. The plunger is then used to transfer fluid either from the syringe to the patient or from the patient to the syringe. The hypodermic needles are then moved back to their retracted positions within the distal portion, and the device is withdrawn from the patient's body.
Owner:SUTURA
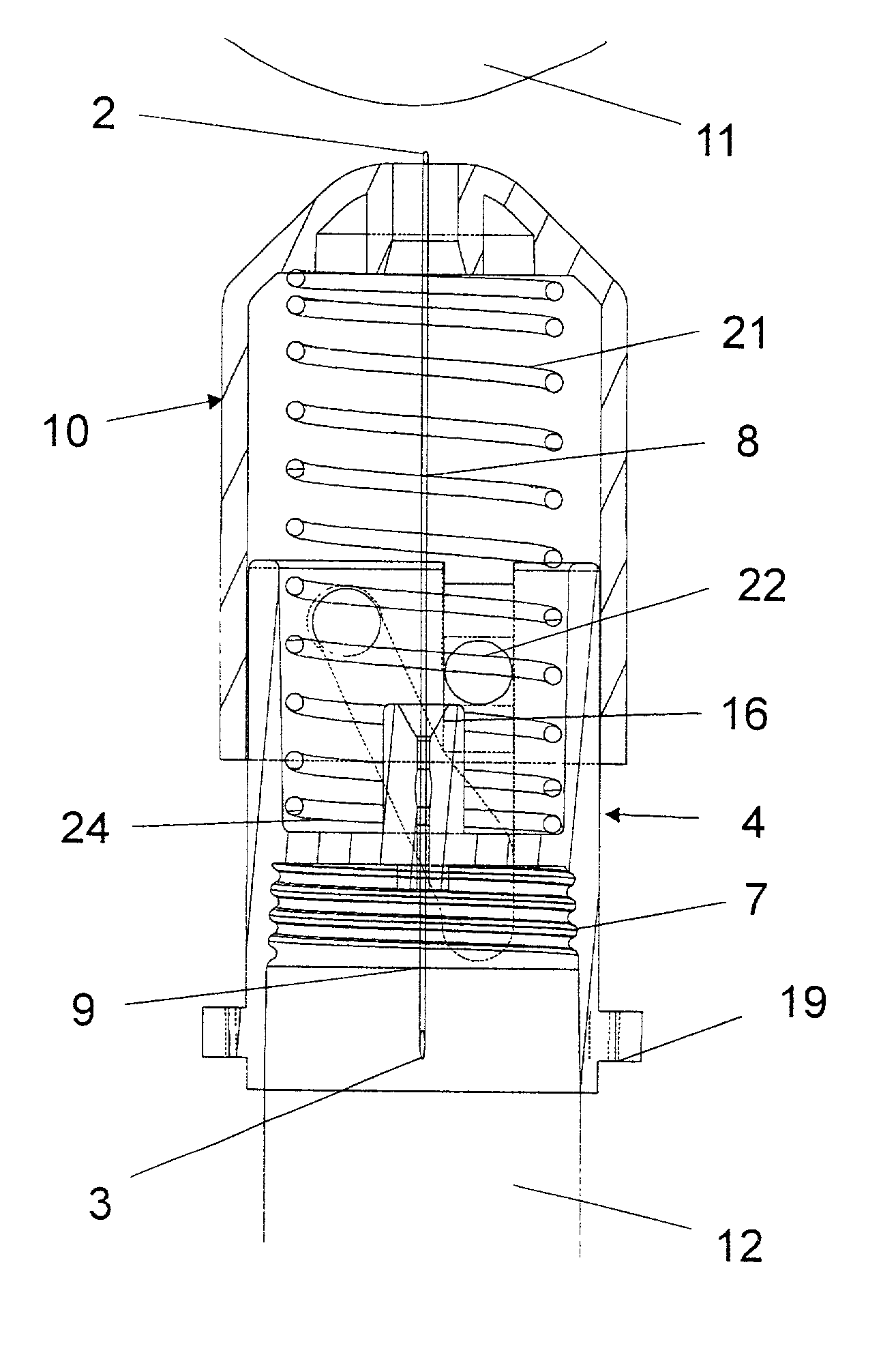
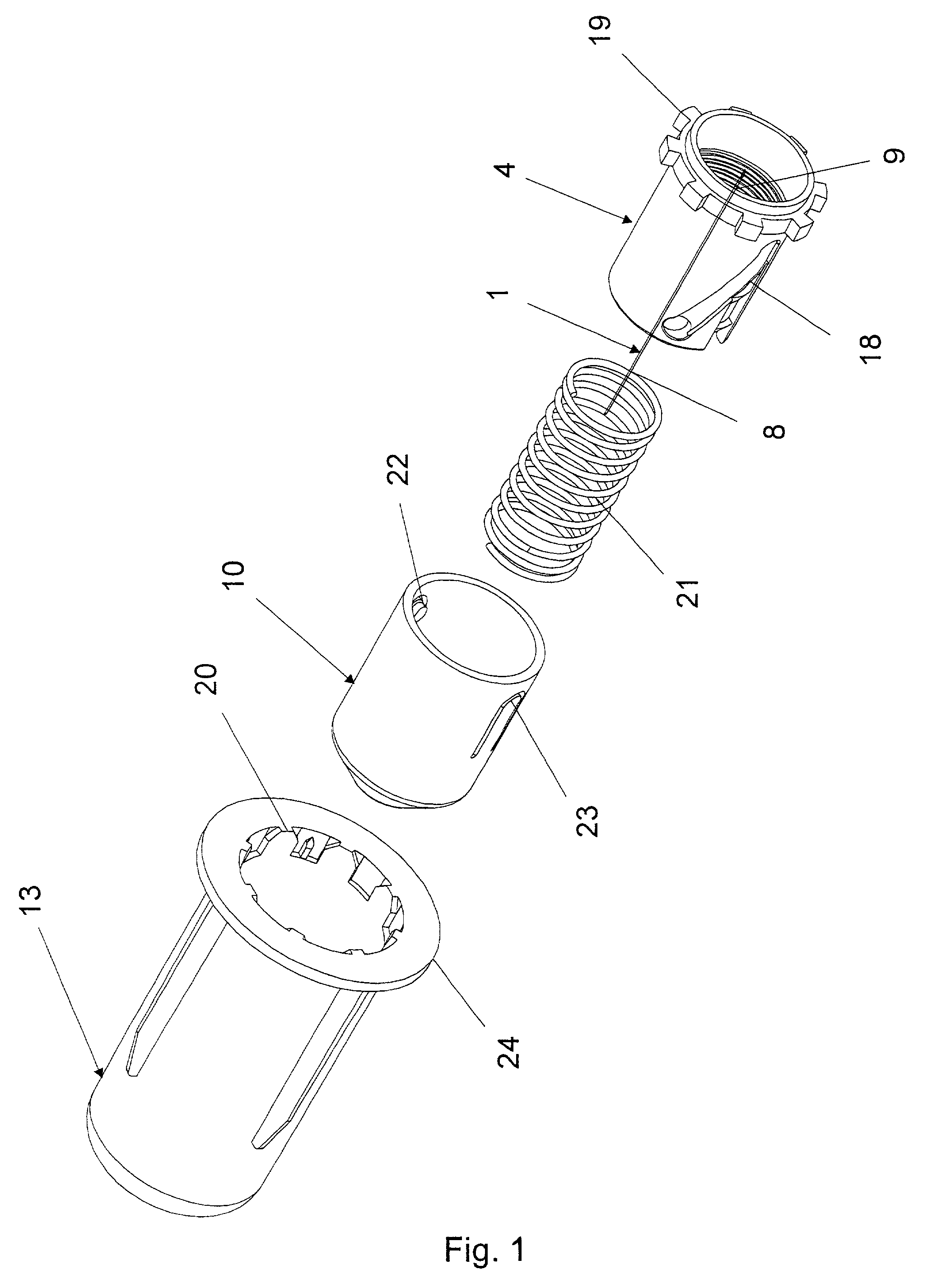
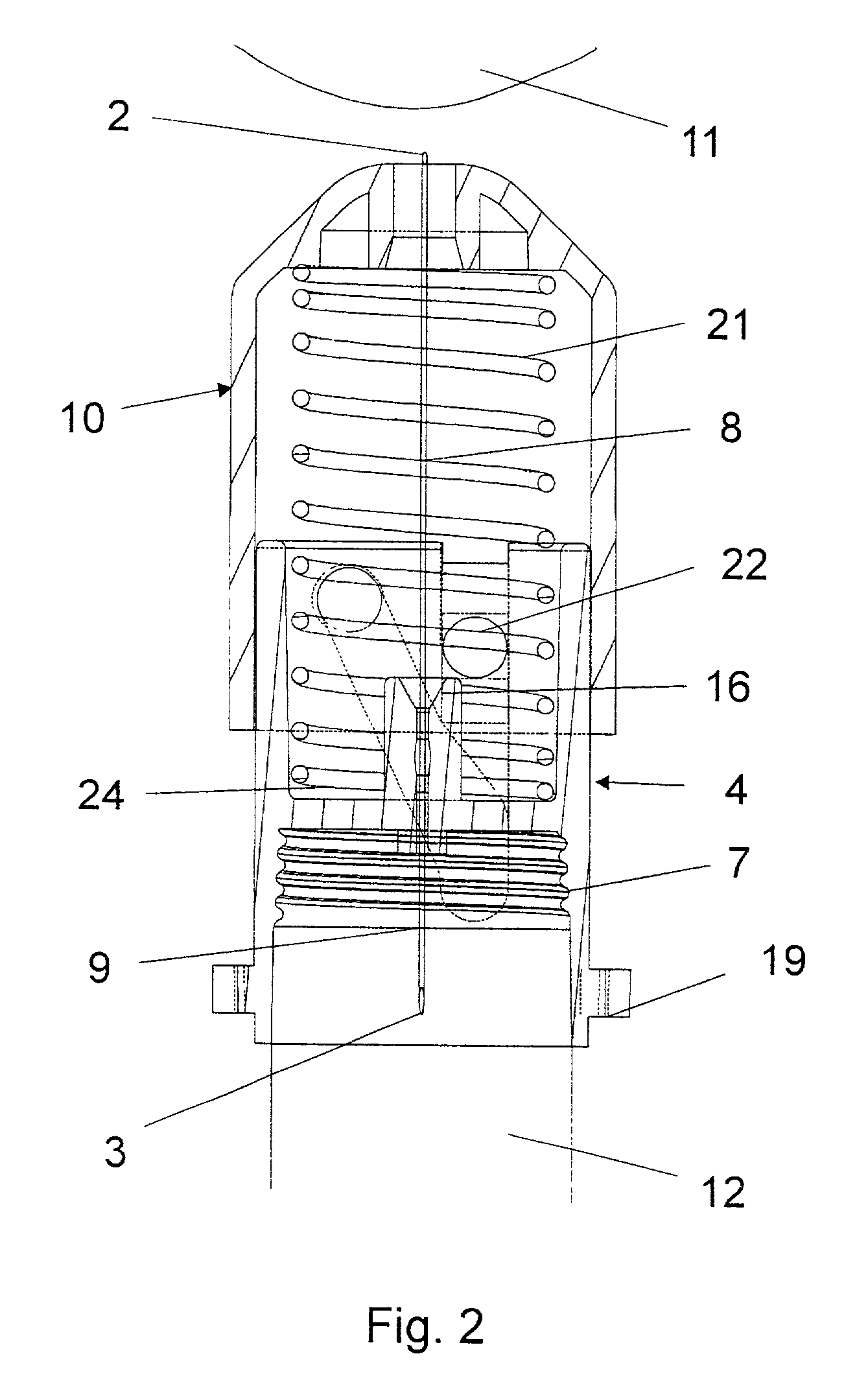
Blood collection agency
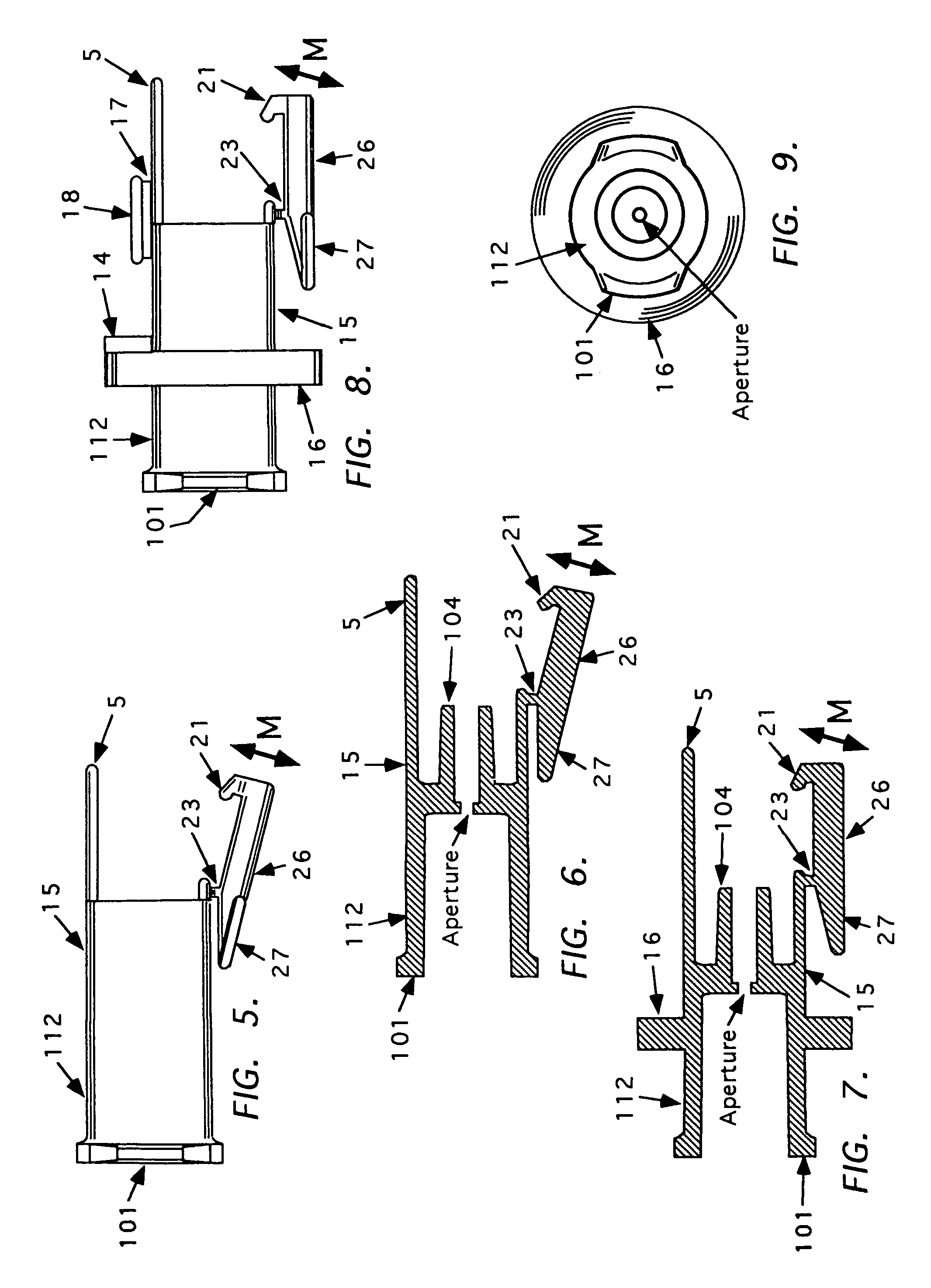
InactiveUS6936036B2Secure and effective shieldingSimple and inexpensive to manufactureSensorsPackagingBlood collectionMedical device
The present invention is directed to a low cost shieldable safety needle assembly. The assembly includes a needle cannula and a tip guard axially movable along the needle cannula through a drive mechanism. The drive mechanism may be interconnected between the tip guard and the needle cannula through a hub. The tip guard is axially movable along the needle cannula from a proximal position substantially adjacent a proximal end of the needle cannula at the hub, to a distal position in which the tip guard protectively surrounds the distal end of the needle cannula, thus effectively shielding the puncture tip of the needle. The drive mechanism is a unitary structure which is capable of maintaining a first self-supporting shape for maintaining the tip guard in the proximal position and is deflectable from the first self-supporting shape to a second extended shape in which the tip guard is moved to the distal position. The drive mechanism may be a rigid flexible planar sheet material which includes a plurality of folds for defining the self-supporting shape. The needle assembly may include structure for mating with a hypodermic syringe, a blood collection set, or other medical device.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Blood exposure prevention in vascular access devices
ActiveUS20080243086A1Reduce blood exposureReduce exposureCatheterInfusion needlesHypodermoclysisHypodermic needle
An apparatus for preventing blood exposure or contamination upon withdrawal of a hypodermic needle is provided. The apparatus may include a needle having a tip and a shield configured to at least partially entrap the needle tip upon withdrawal of the needle. The apparatus may further include a blood stabilizing material disposed such that upon withdrawal of the needle the blood stabilizing material is disposed in operative association with the needle tip such that blood carried by the needle is prevented from escaping the apparatus. In some exemplary implementations, the blood stabilizing material may be disposed on one or more surfaces of the shield. The shield of the hypodermic needle may include protective device and / or a housing for shielding the needle tip upon withdrawal. The housing may be adapted to at least partially cover the needle tip upon withdrawal of the needle. In some implementations, the housing may be adapted to allow the protective device to shield the needle before the needle is completely withdrawn.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Subcutaneous anti-HER2 antibody formulations and uses thereof
The present invention relates to a highly concentrated, stable pharmaceutical formulation of a pharmaceutically active anti-HER2 antibody, such as e.g. Trastuzumab (HERCEPTIN™), Pertuzumab or T-DM1, or a mixture of such antibody molecules for subcutaneous injection. In particular, the present invention relates to formulations comprising, in addition to a suitable amount of the anti-HER2 antibody, an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme as a combined formulation or for use in form of a co-formulation. The formulations comprise additionally at least one buffering agent, such as e.g. a histidine buffer, a stabilizer or a mixture of two or more stabilizers (e.g. a saccharide, such as e.g. α,α-trehalose dihydrate or sucrose, and optionally methionine as a second stabilizer), a nonionic surfactant and an effective amount of at least one hyaluronidase enzyme. Methods for preparing such formulations and their uses thereof are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Intravenous catheter device
A catheter appliance having a catheter in fluid communication with a luer connector is releasably secured to a catheter applicator having a track for slidably mounting a needle carrier module. The needle carrier module includes a hypodermic which extends through the catheter for insertion and which is in fluid communication with a flashback indicator on the module. The catheter applicator includes a needle cavity for containing the hypodermic needle after use.
Owner:SMITH JR P ROWAN
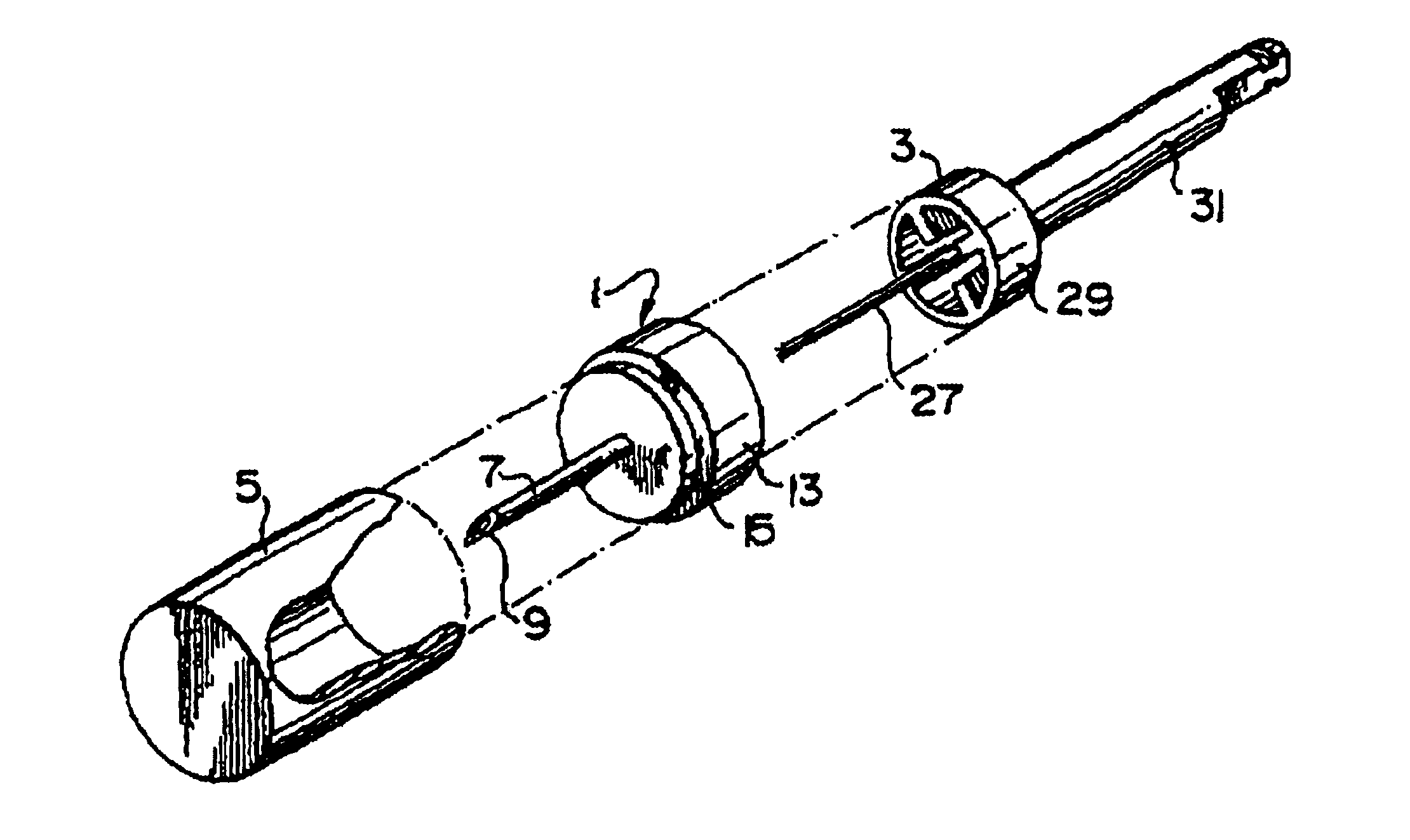
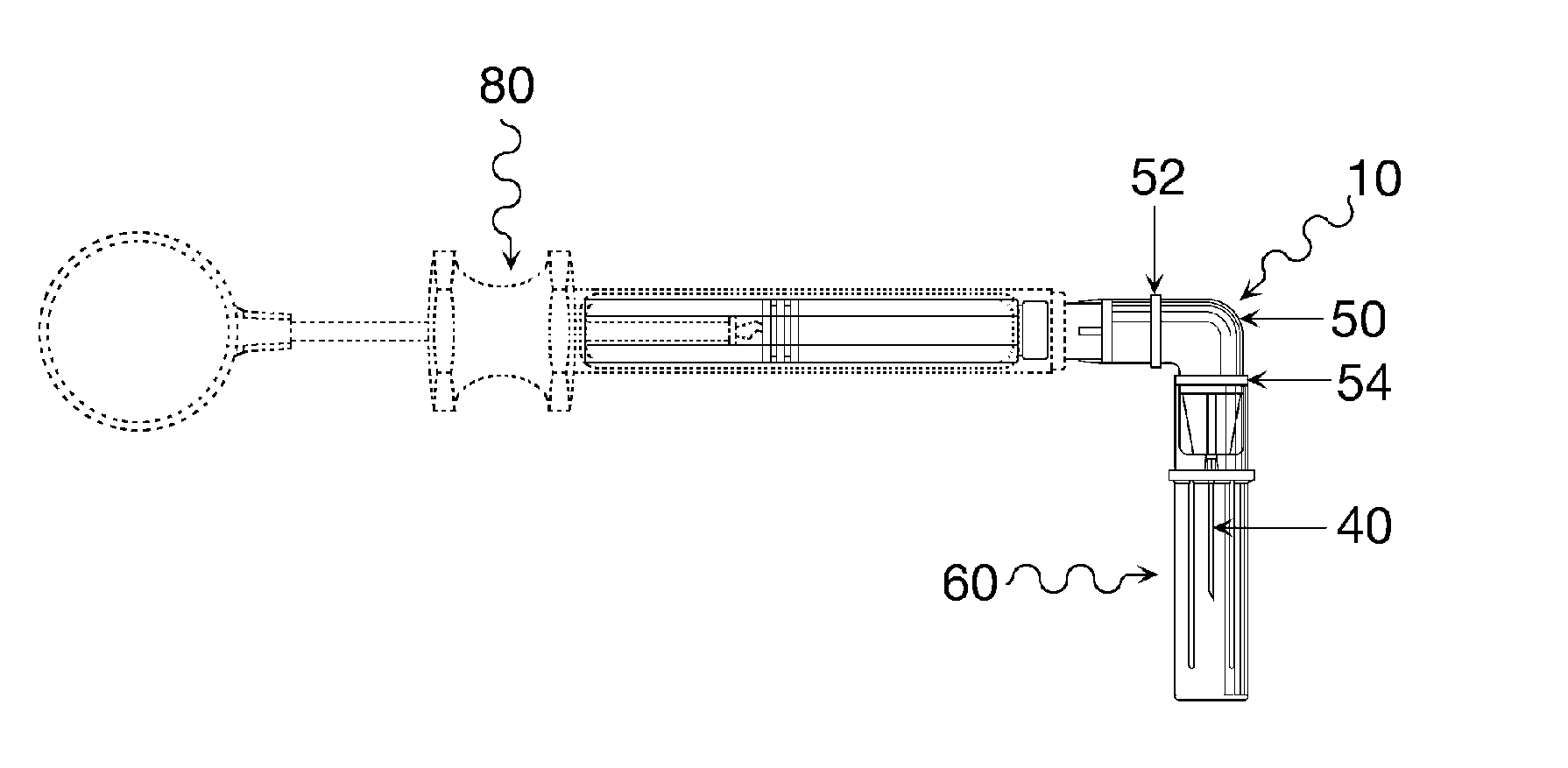
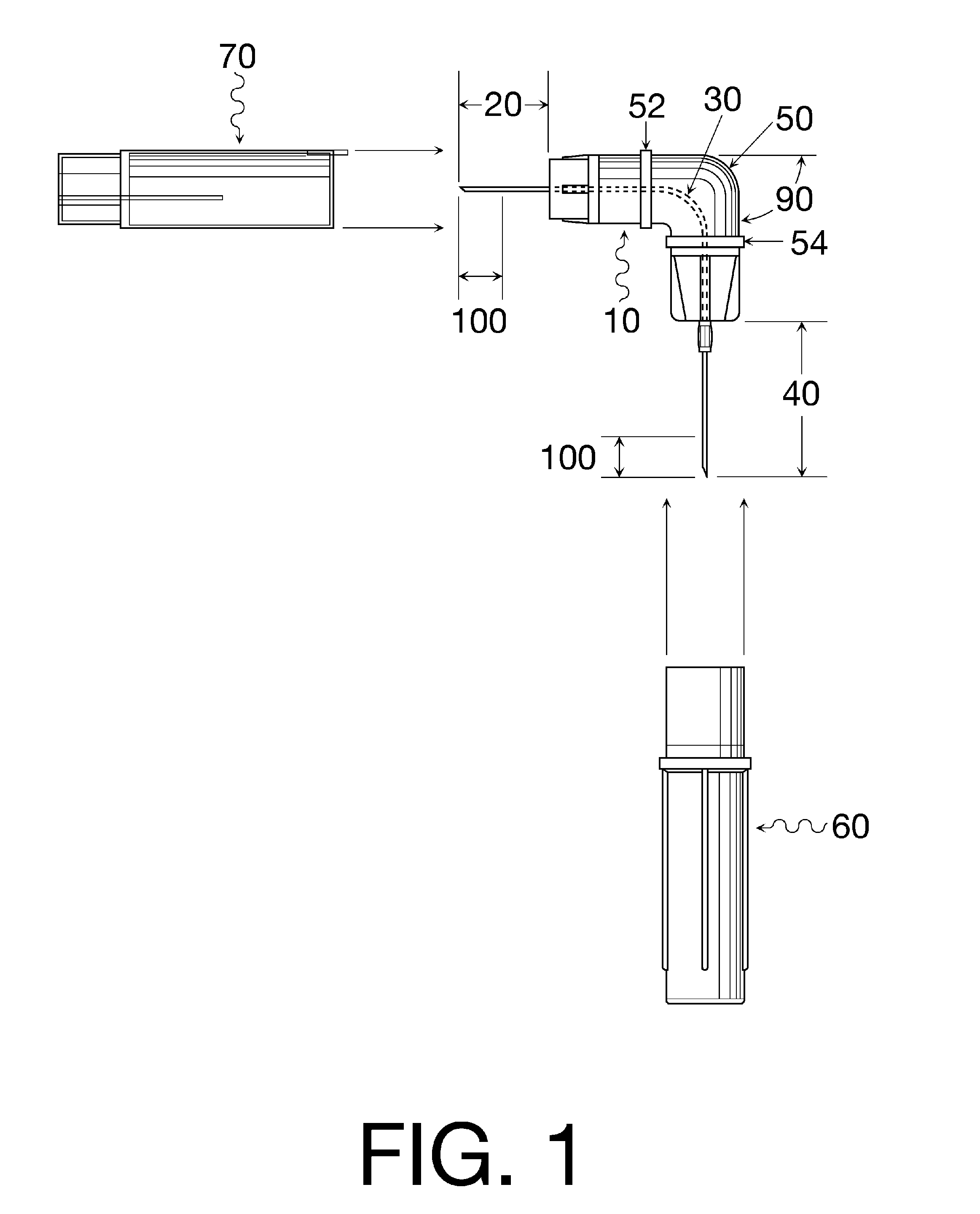
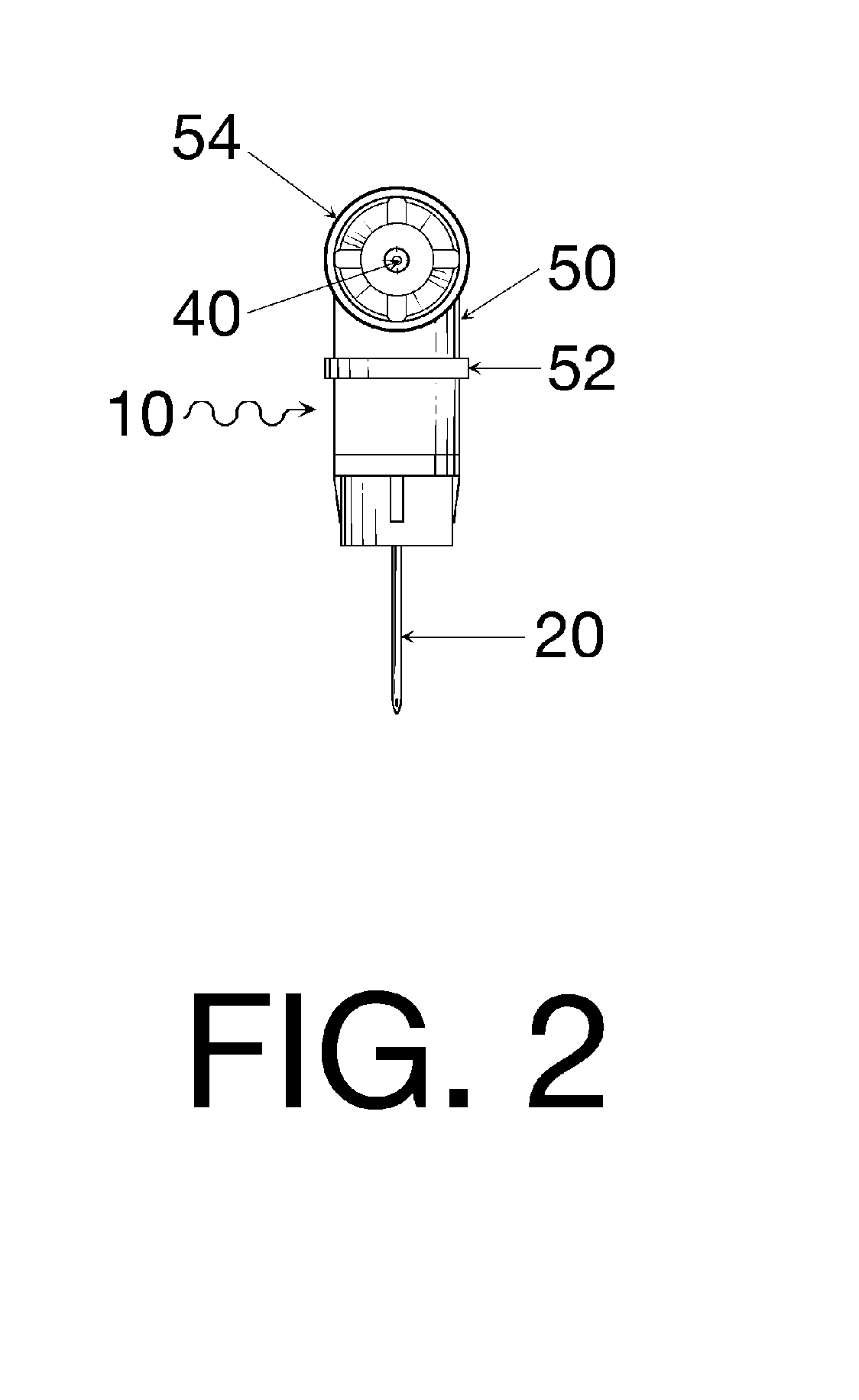
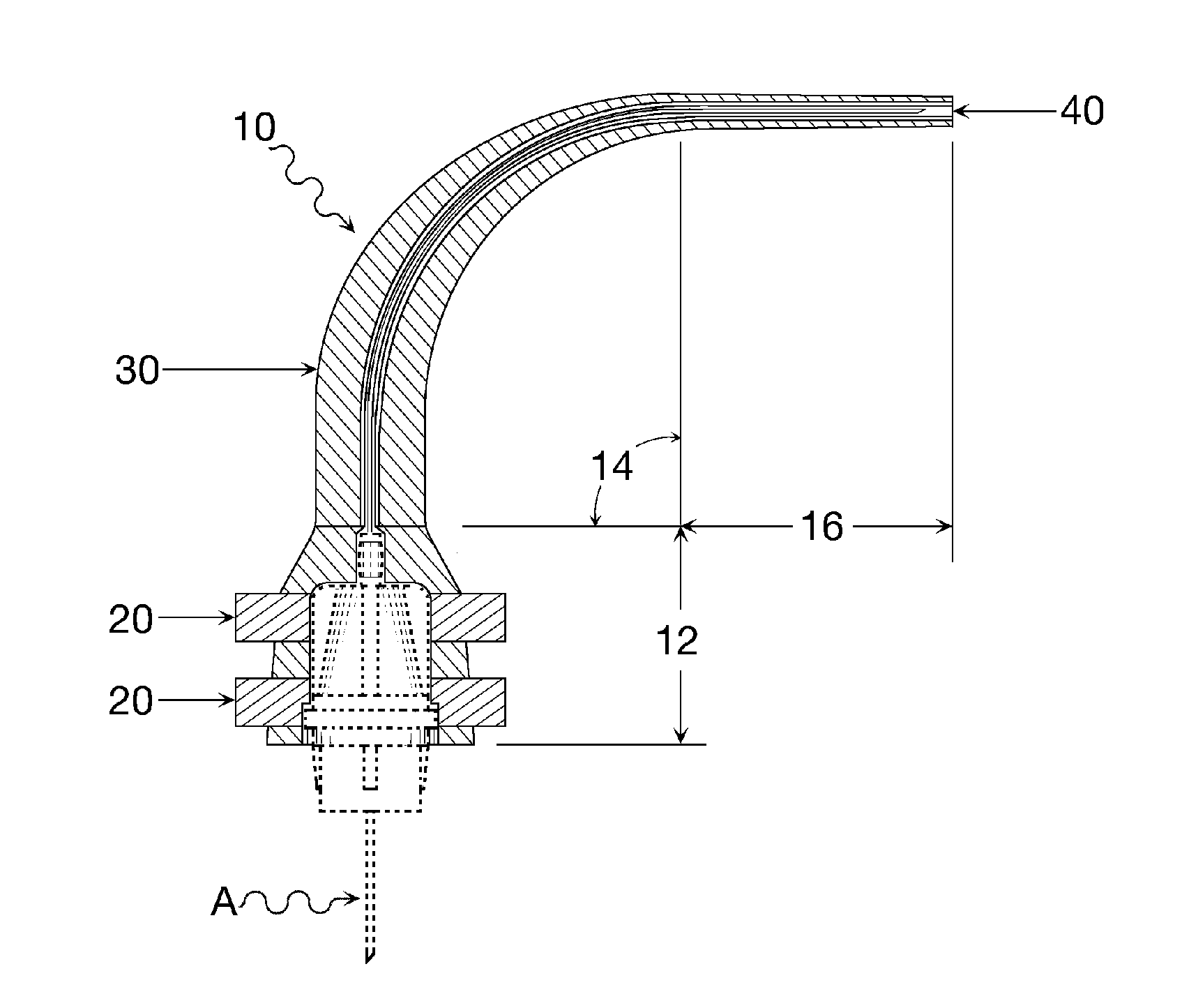
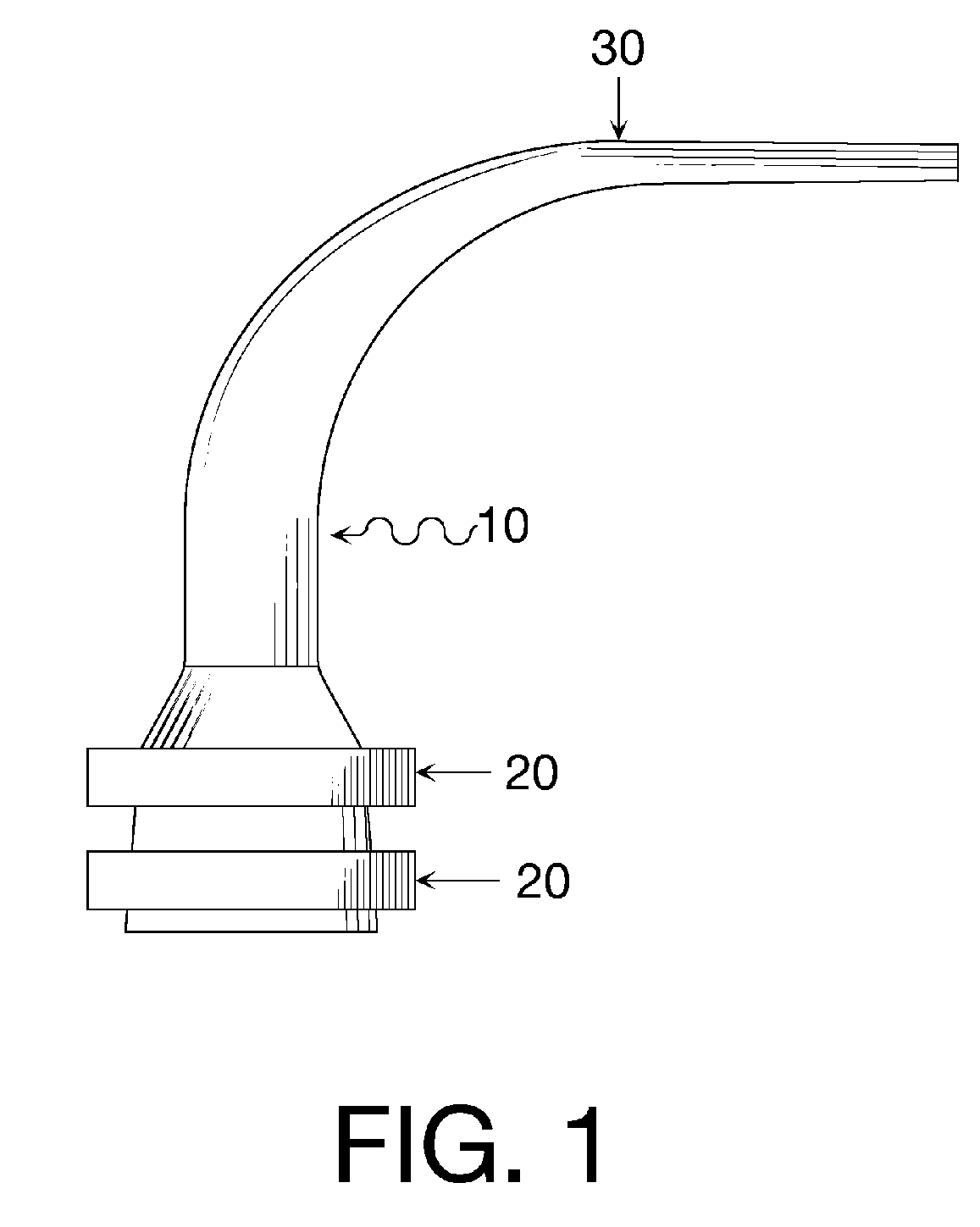
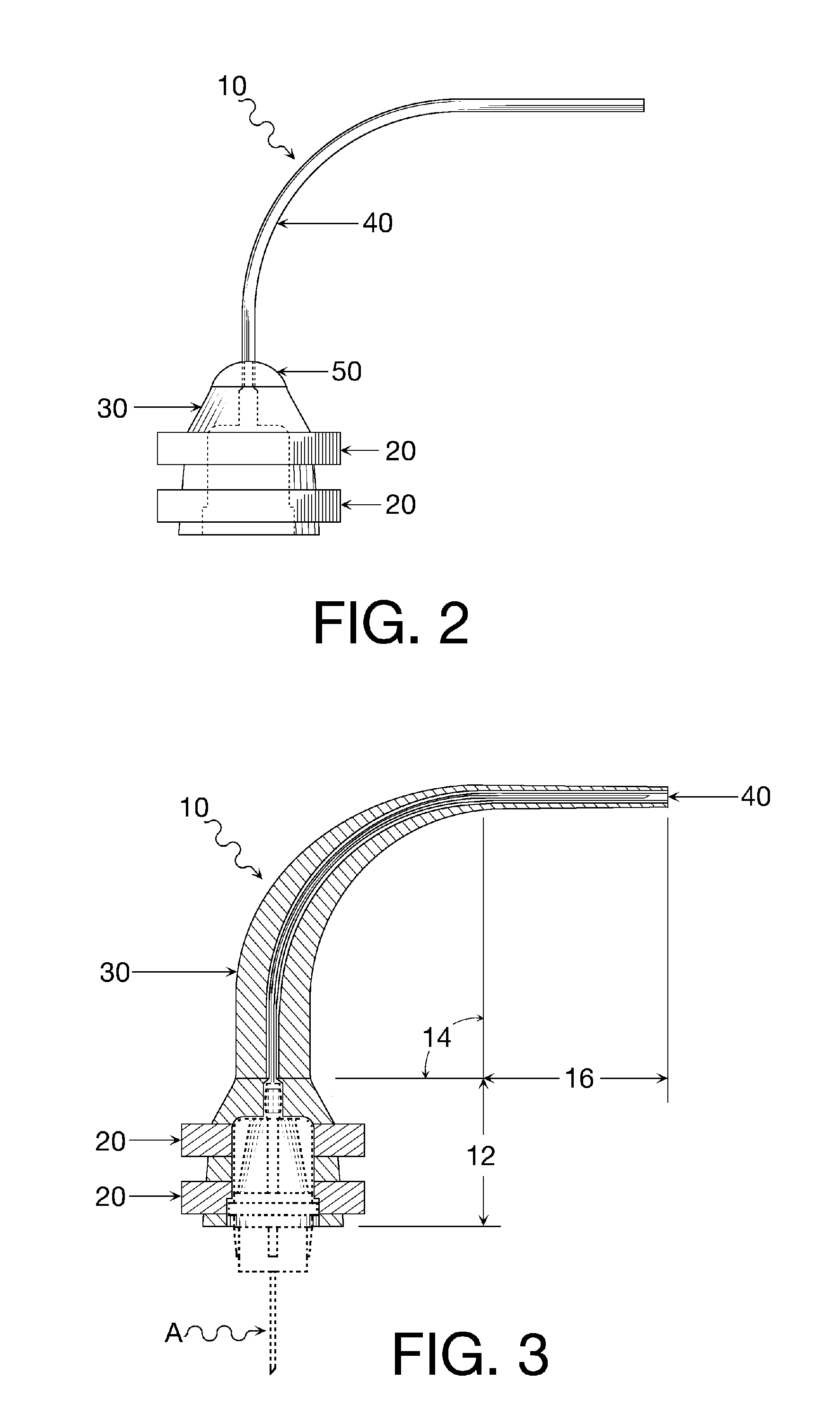
Oral cavity liquid delivery system including pre-angled needle assembly and method for using the same
A delivery system for dispensing sterile liquids into the oral cavity using a novel pre-angled needle hub assembly attached to a standard anesthetic syringe loaded with a novel cartridge ampule containing a certain liquid solution. This system substantially improves the efficiency of delivering small amounts of sterile fluid into the oral cavity by hypodermic means or by irrigation means using pre-angled needles or cannulas to reach otherwise impossible-to-reach locations within the oral cavity while also providing the ability to dispose of used needles without re-bending and thus complying with federal OSHA, state OSHA, and state regulatory disposal regulations.
Owner:SPECTOR DAVID M
Method of dispensing ready-for-use syringes having a medication dose
InactiveUS20120273087A1Reduce in quantityEasy to useMetal-working apparatusPharmaceutical containersHypodermoclysisHypodermic needle
A method of dispensing at least one syringe in real time having a medication dose comprising the steps of: loading a pumping station with at least one medication container, chosen from a plurality of standard medication containers; loading the pumping station with the at least one syringe fitted with a hypodermic needle, the hypodermic needle being covered with a needle cover, the at least one syringe selected from a plurality of syringes; drawing the medication dose through the needle of the at least one syringe from the at least one medication container; configuring an on-board computer to integrate patient real time life signs data with patient information to determine in real time the medication dose; and dispensing the at least one selected syringe to a syringe dispensing apparatus having a syringe tray which protrudes from the dosage dispensing device, the syringe having the medication dose.
Owner:STAVSKY MOR +1
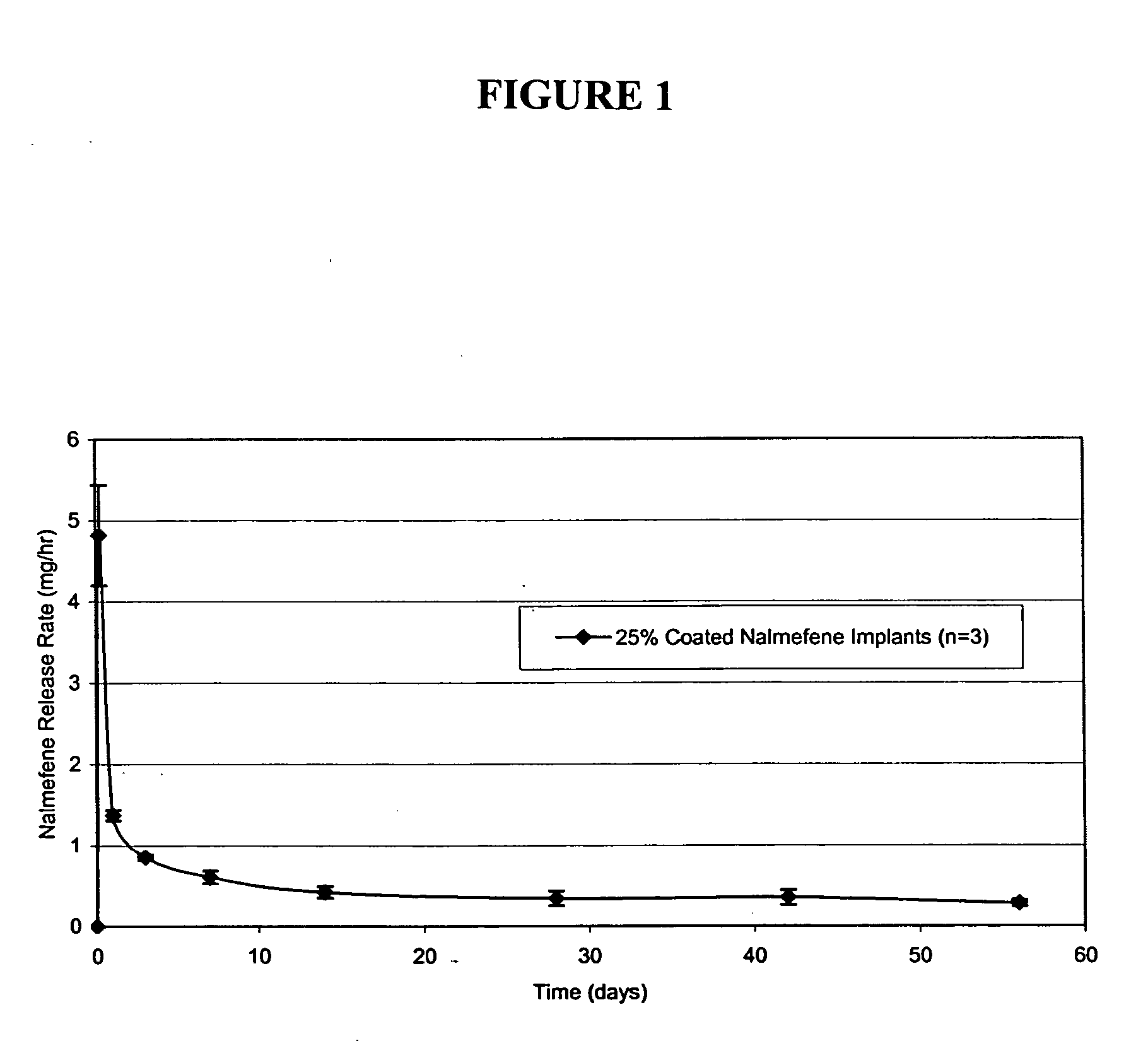
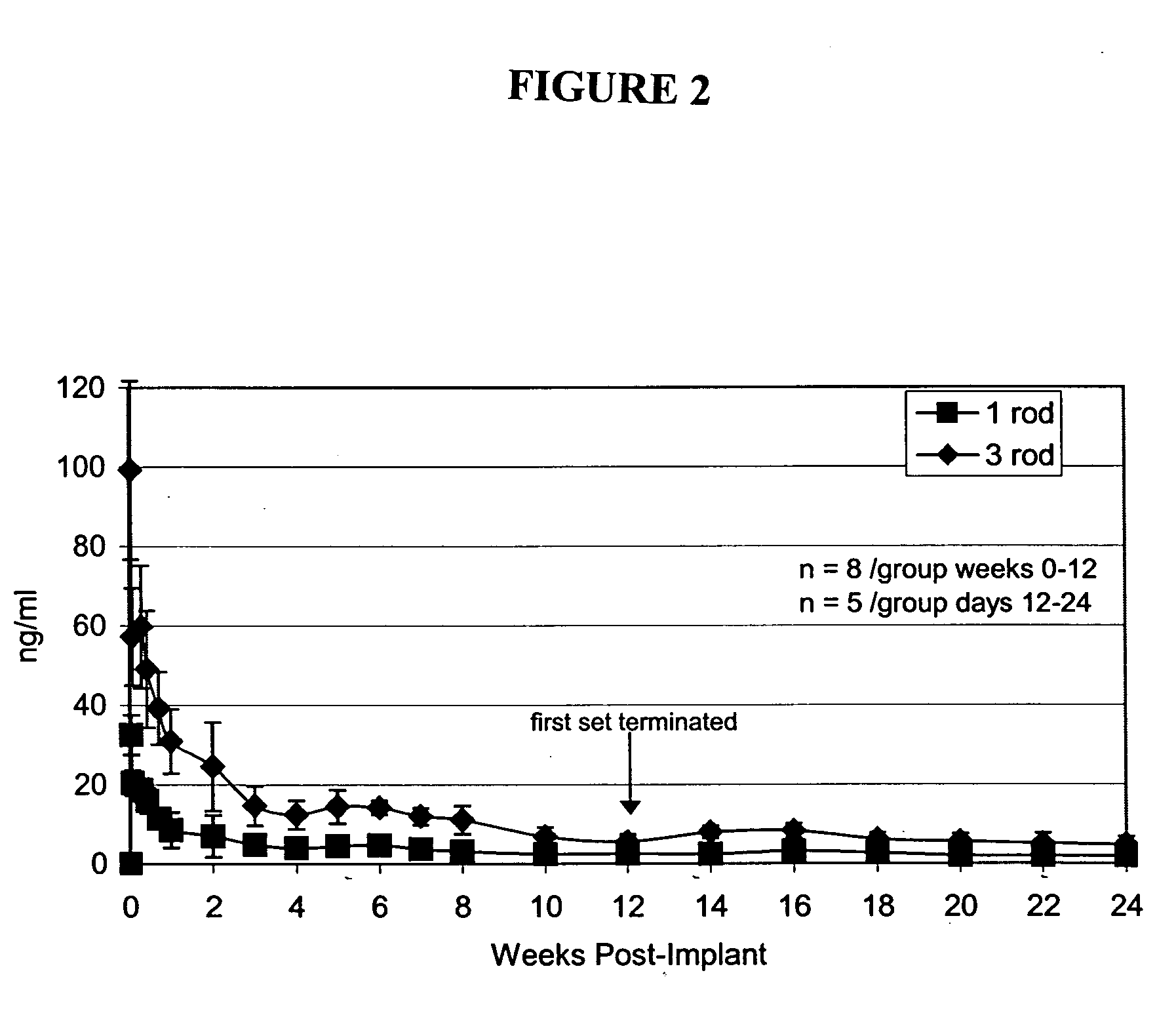
Implantable polymeric device for sustained release of nalmefene
The present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for administration of nalmefene for treatment of alcoholism, nicotine dependence, or another condition for which treatment with nalmefene is therapeutically beneficial. The invention provides a biocompatible nonerodible polymeric device which releases nalmefene continuously with generally linear release kinetics for extended periods of time. Nalmefene is released through pores that open to the surface of the polymeric matrix in which it is encapsulated. The device may be administered subcutaneously to an individual in need of continuous treatment with nalmefene.
Owner:TITAN PHARMA
Medication Delivery Device Applying A Collapsible Reservoir
The present invention relates to a medication delivery device comprising pump means and a reservoir adapted for containing a medicament. The pump means is adapted to transfer the medicament from the reservoir to an outlet arrangement, said outlet arrangement being adapted to be operatively connected to an associated hypodermic needle. The pumps means is adapted to deliver a set dose of medicament during one or more pump strokes, wherein the stroke volume(s) of said one or more pump strokes is variable. The present invention further relates to a method for adjusting stroke volumes to a set dose of medicament.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Steroid Delivery System
A steroid delivery system including a mixing syringe having a first chamber and a second chamber and at least one hypodermic needle is provided. The first chamber of the mixing syringe contains a pre-measured volume of a local anesthetic and the second chamber contains a pre-measured volume of a corticosteroid. An improved mixing syringe and a method for treating pain using the steroid delivery system of the present invention is also provided herein. The improved syringe achieves mixing without the introduction or elimination of air and without puncturing or rupturing of a membrane, diaphragm or other material. The kit concept improves the speed of the procedure, sterility, accuracy of dosing, and immediate availability of disparate items to implement the procedure in a variety of medical practice settings.
Owner:CONNAIR MICHAEL P
Oral cavity liquid delivery system including pre-angled needle guidance assembly and method for using the same
A delivery system for dispensing sterile liquids into the oral cavity using a novel pre-angled needle guidance assembly attached to a conventional anesthetic needle and conventional anesthetic syringe loaded with a novel cartridge ampule containing a certain liquid solution. This system substantially improves the efficiency of delivering small amounts of sterile fluid to the oral cavity by hypodermic means or by irrigation means using pre-angled needle guidance assemblies to temporarily bend needles or cannulas in order to reach otherwise impossible-to-reach locations within the oral cavity while also providing the ability to dispose of used needles without re-bending and thus complying with federal OSHA, state OSHA, and state regulatory disposal regulations.
Owner:SPECTOR DAVID M
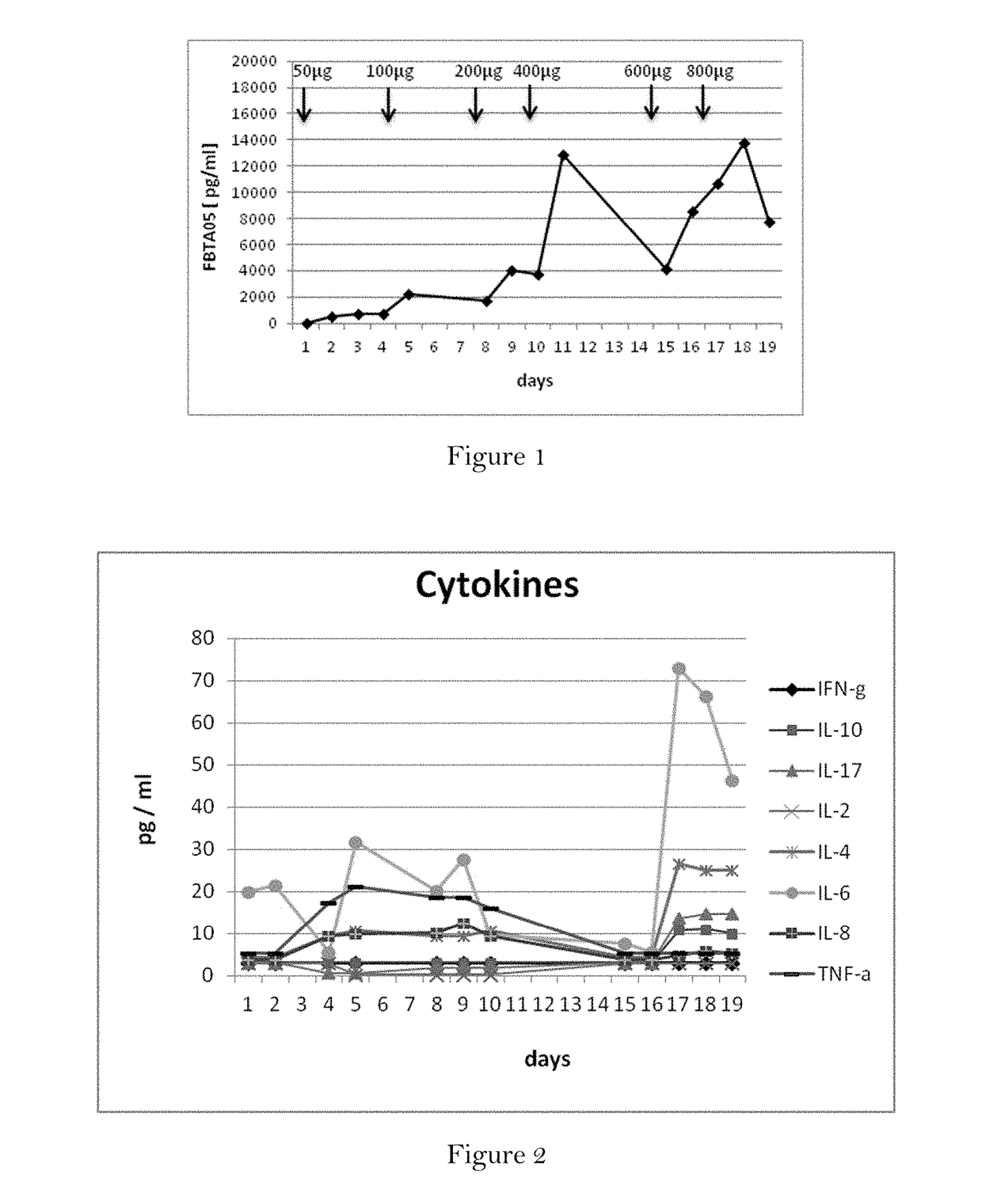
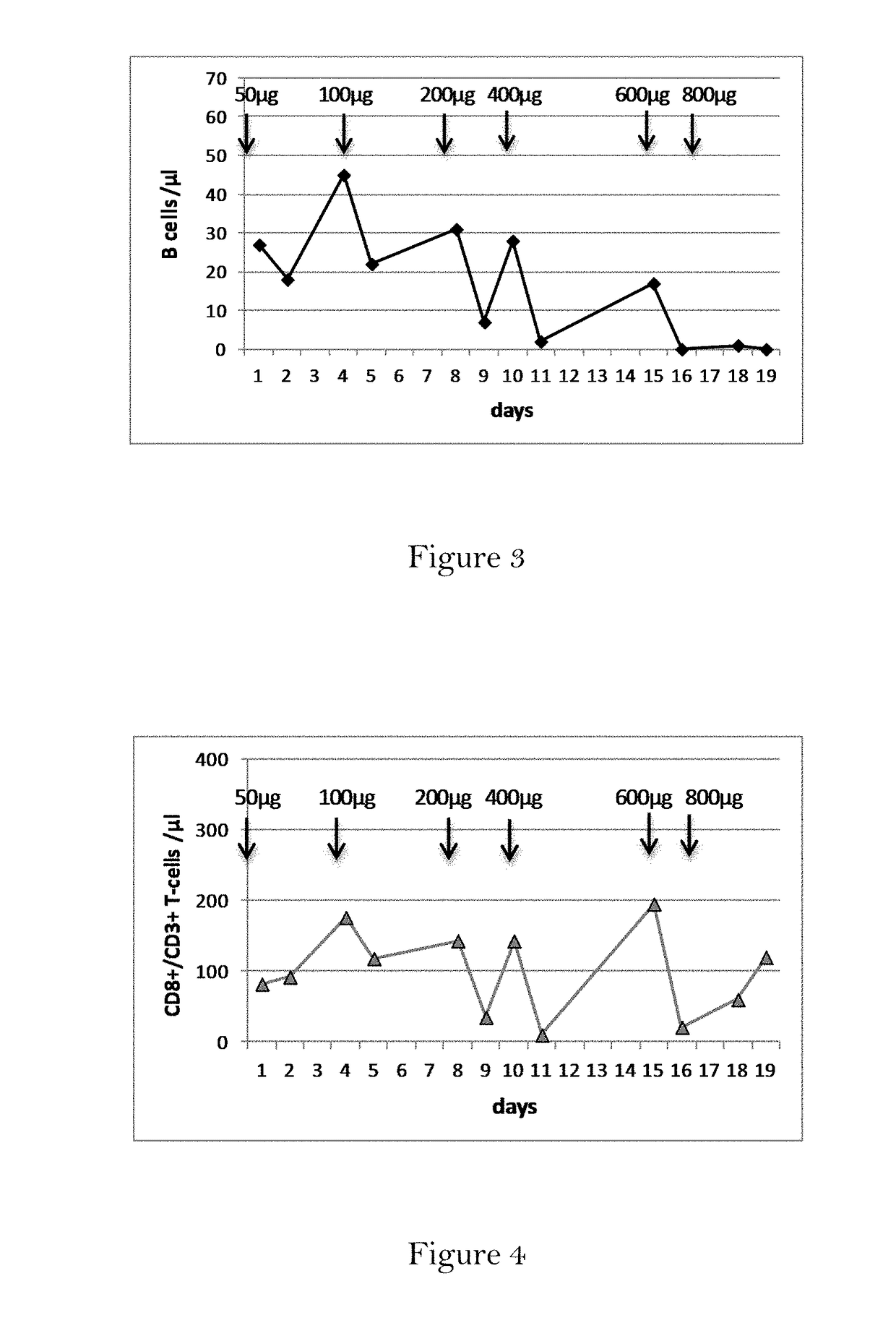
Subcutaneously administered bispecific antibodies for use in the treatment of cancer
PendingUS20170224818A1Reduce releasePrevent adverse side effectsRadioactive preparation carriersMammal material medical ingredientsBispecific antibodyTrifunctional antibody
The present invention relates to the use of T cell redirecting, bispecific, in particular trifunctional, antibodies for the treatment of a cancer disease, wherein said antibody is administered via the subcutaneous route. Thereby, the release of proinflammatory cytokines is reduced and, simultaneously, the release of inhibitory cytokines is substantially suppressed. That treatment by bispecific, in particular trifunctional, antibodies may be combined in a combination therapy with other anti-cancer drugs.
Owner:LINDIS BIOTECH GMBH
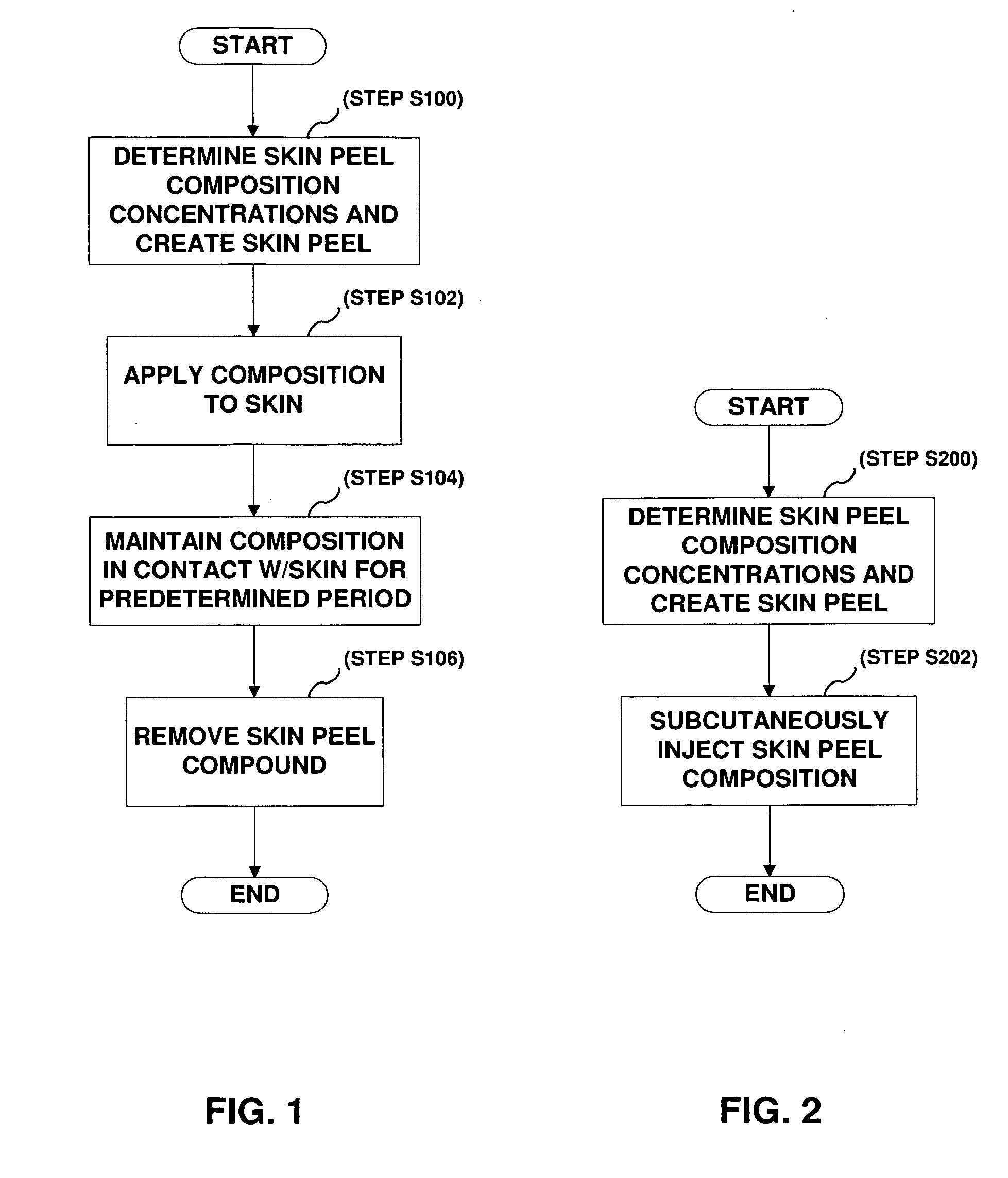
Method and compound for skin chemical peel
The present invention provides a skin peel composition including a plurality of keratolytic substances, such as trichloroacetic acid and salicylic, and a post inflammatory hyper pigmentation reducing substance such as retinoic acid. In addition, the skin peel composition may further include ascorbic acid (vitamin C), as well as vitamins A and E. Application of the skin peel composition may be either topically in the form of a cream or gel, and may further be injected subcutaneously into the skin to achieve deeper penetration of the composition within the skin layers of the area to be treated.
Owner:KALIL ENTERPRISES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com