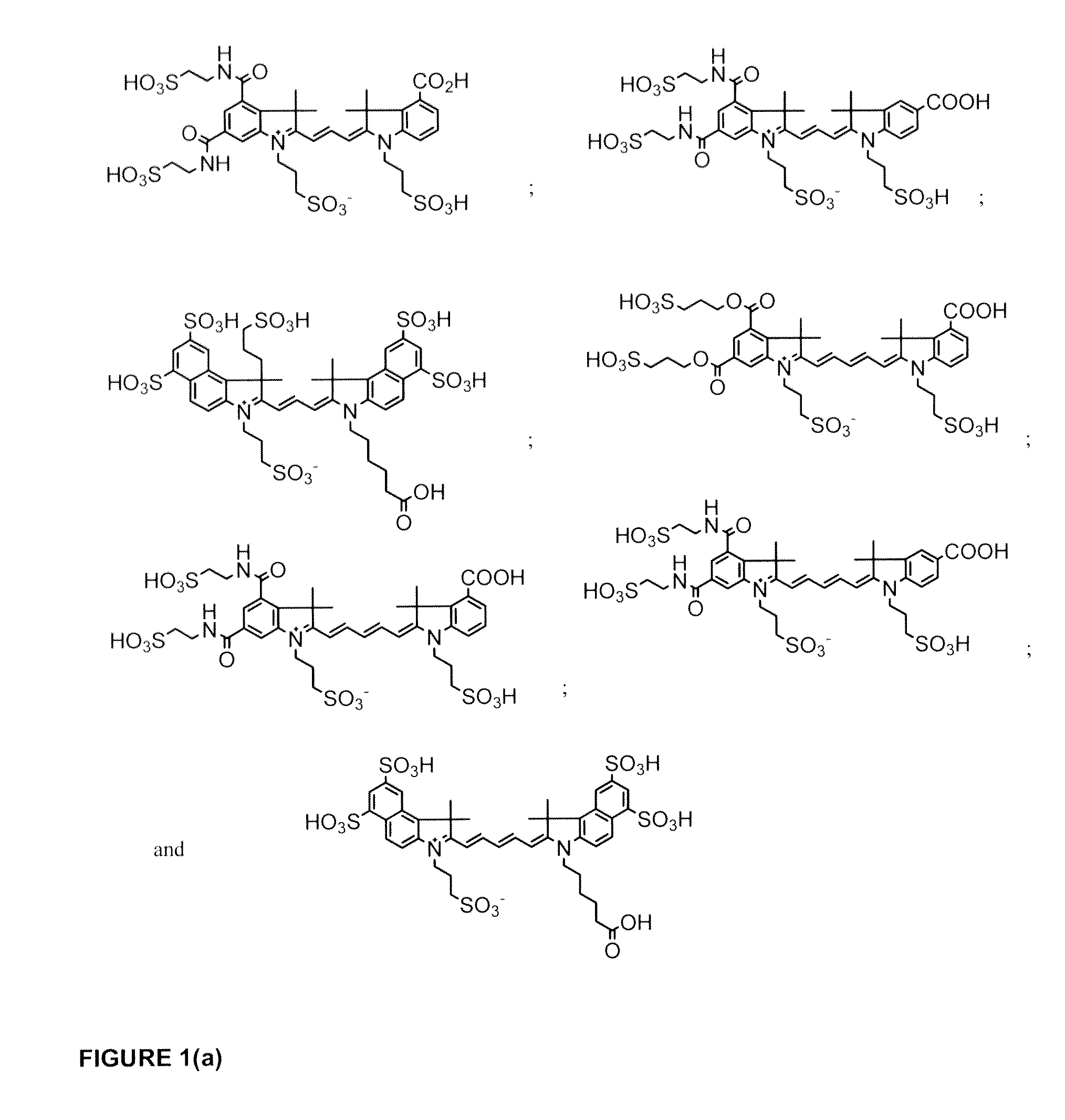
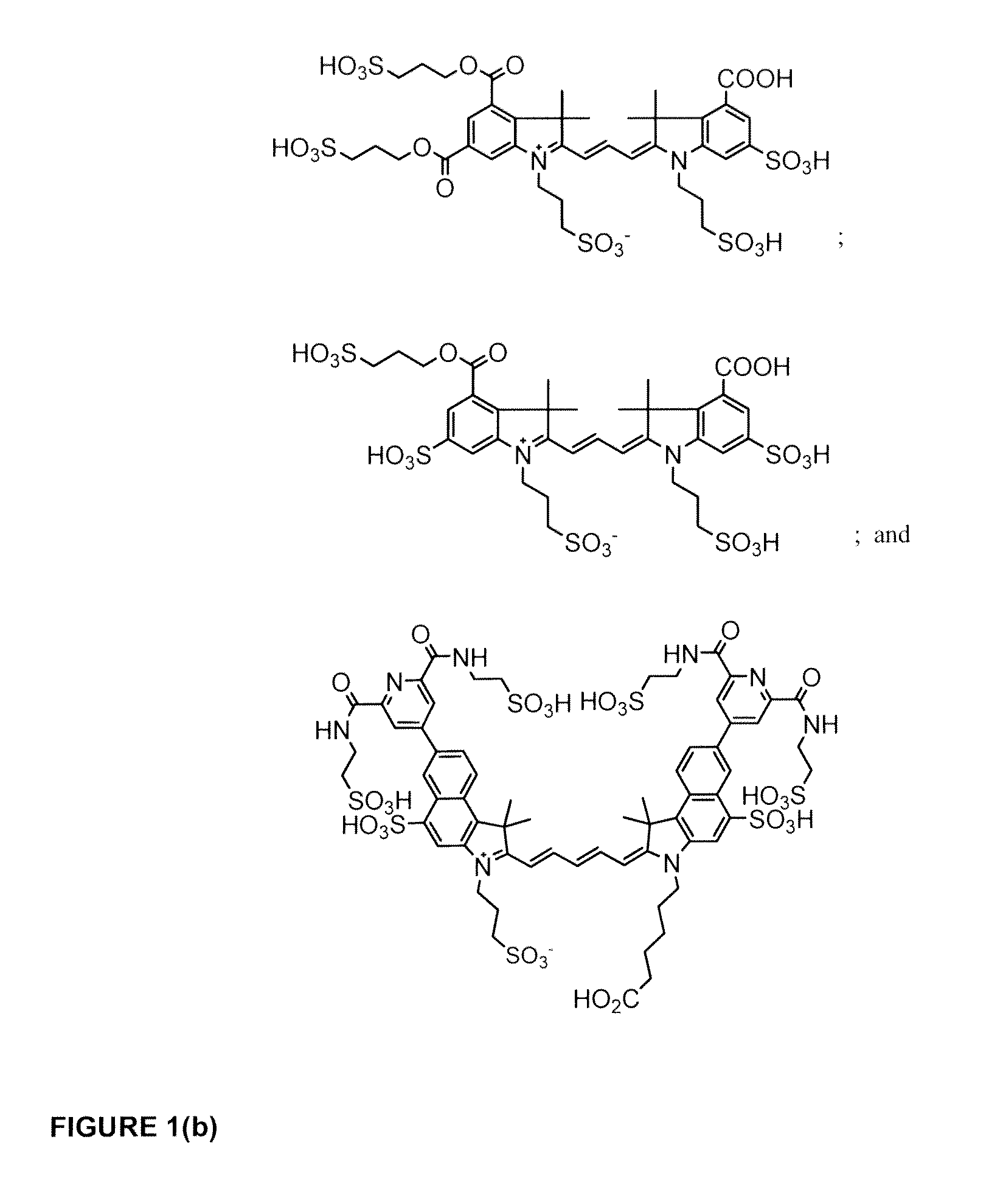
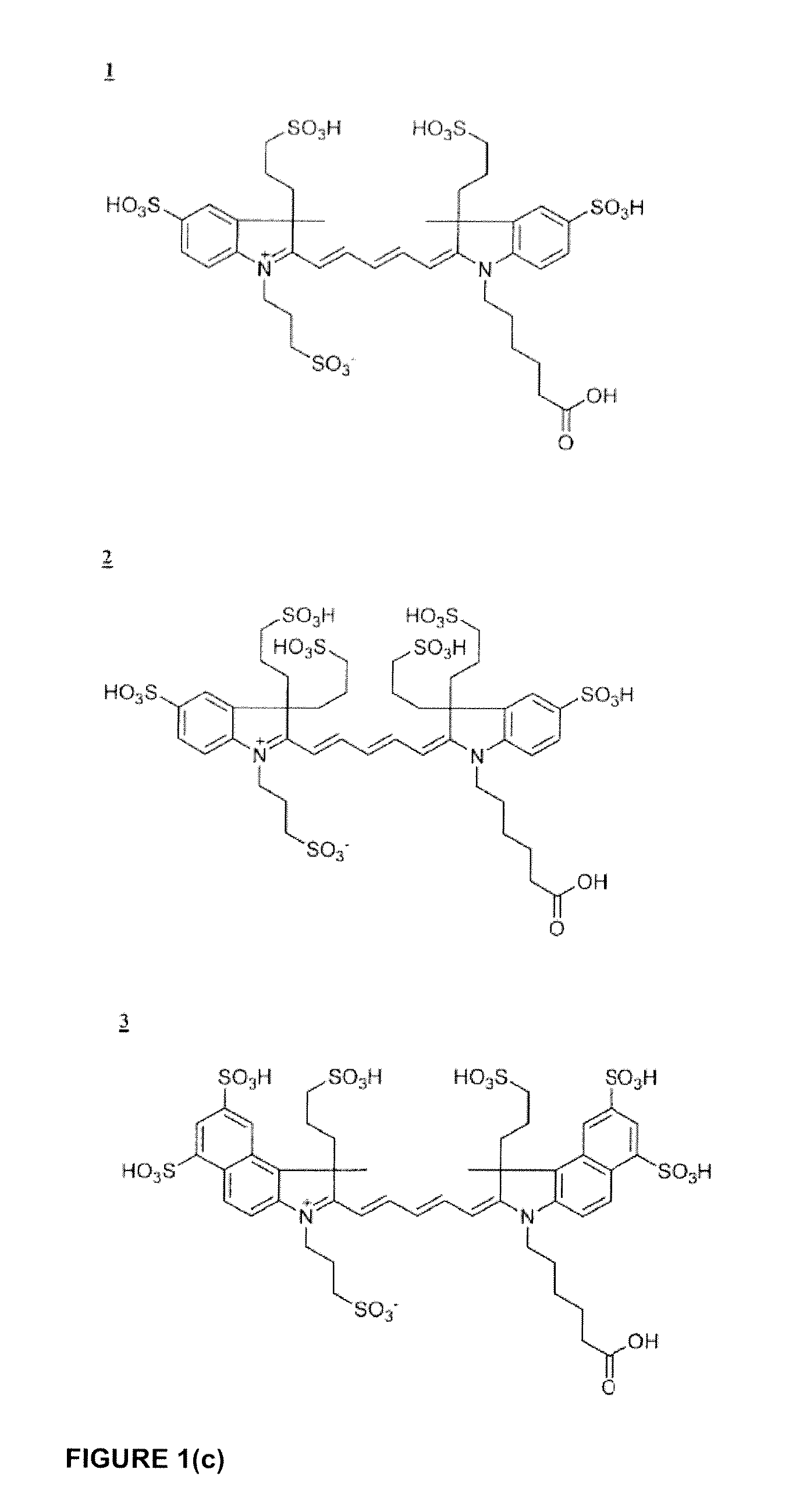
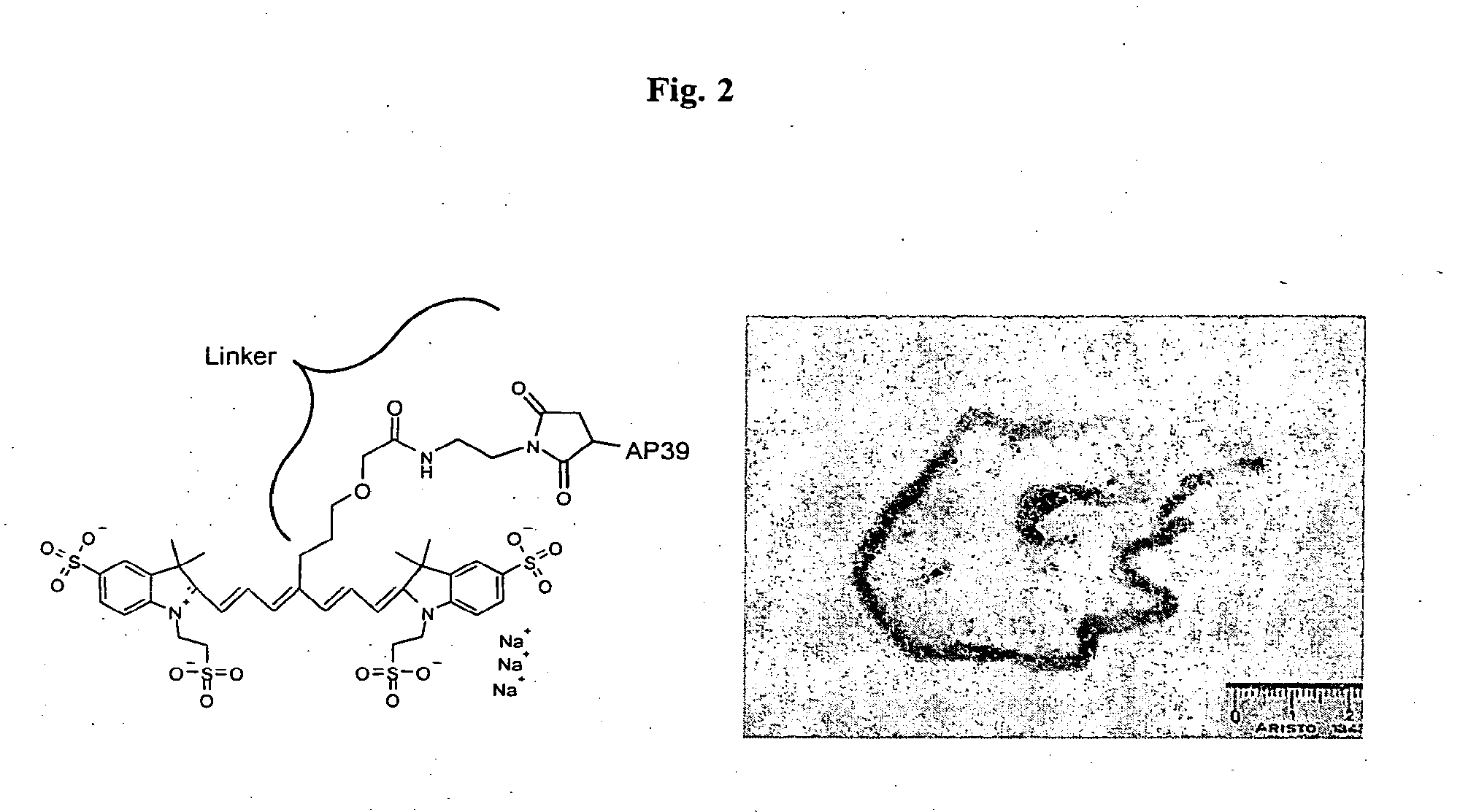
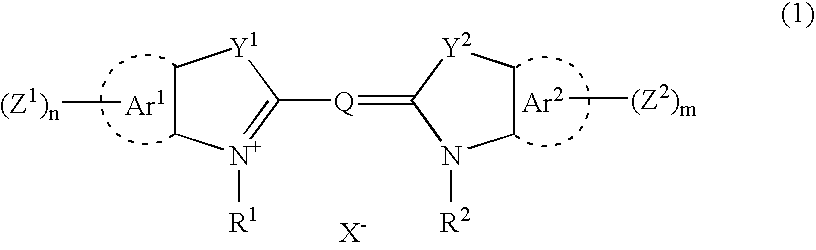
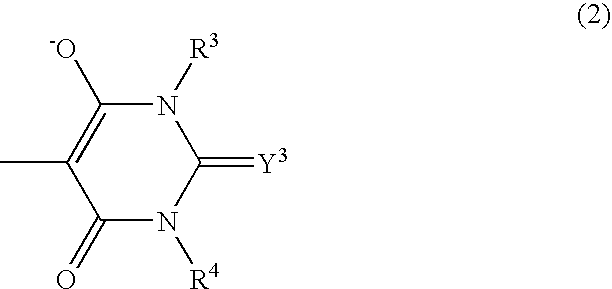
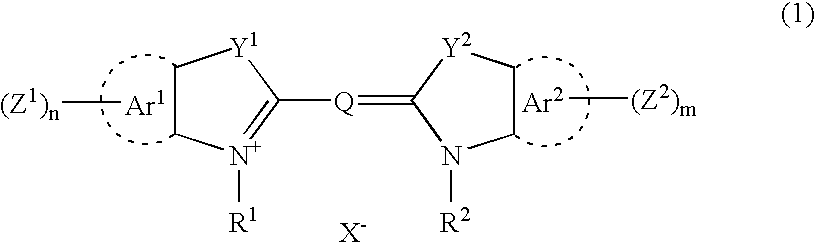
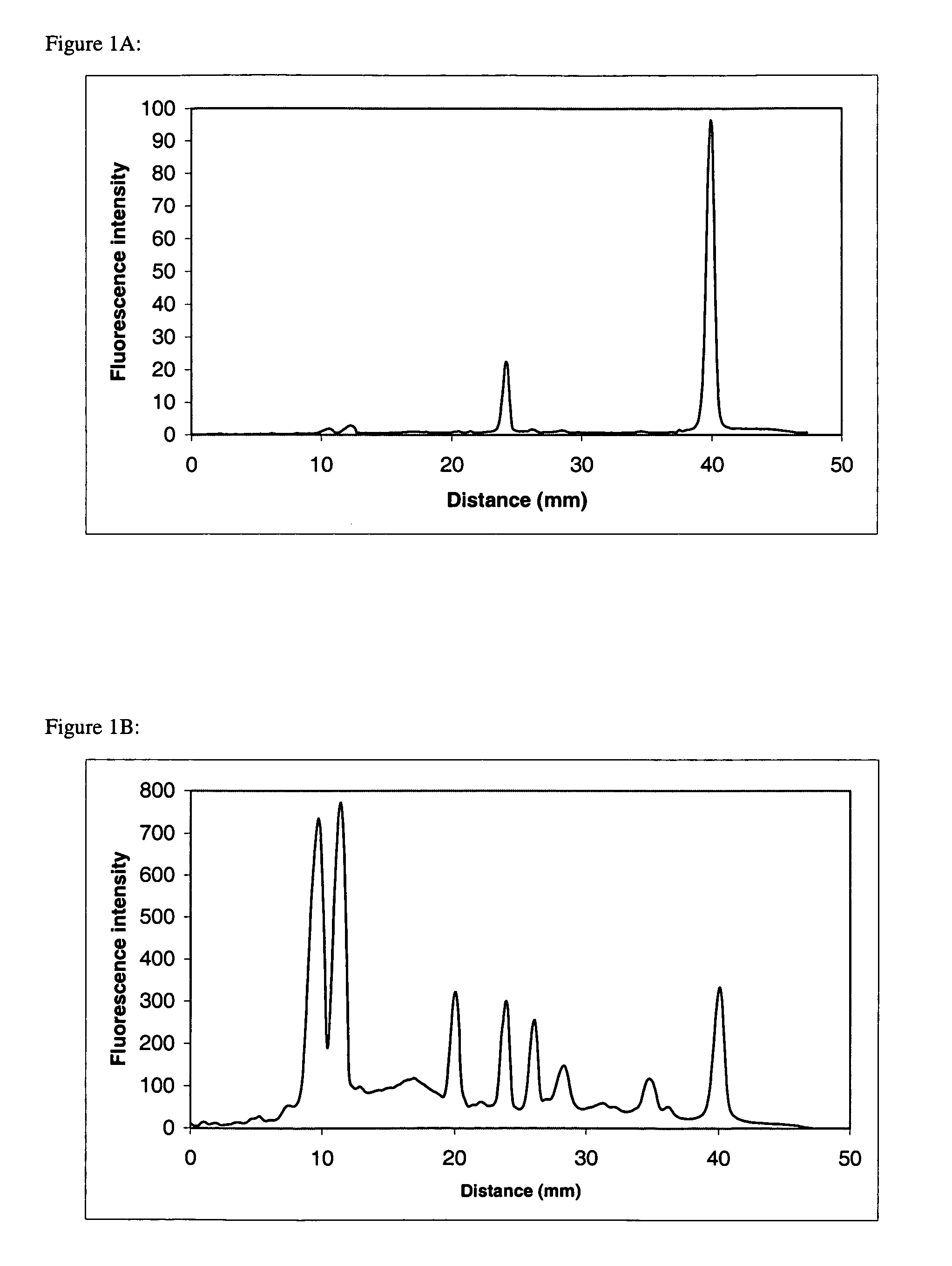
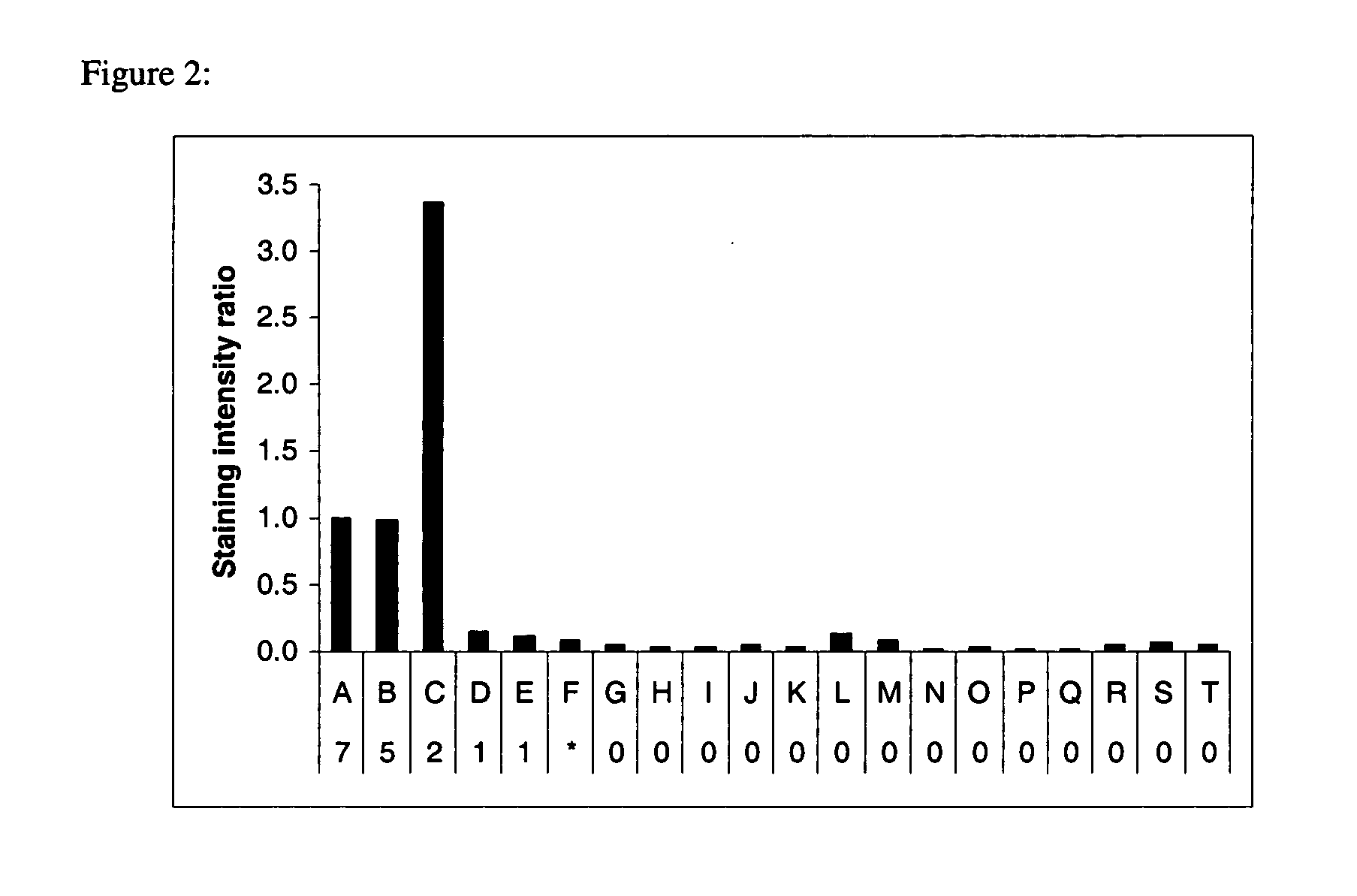
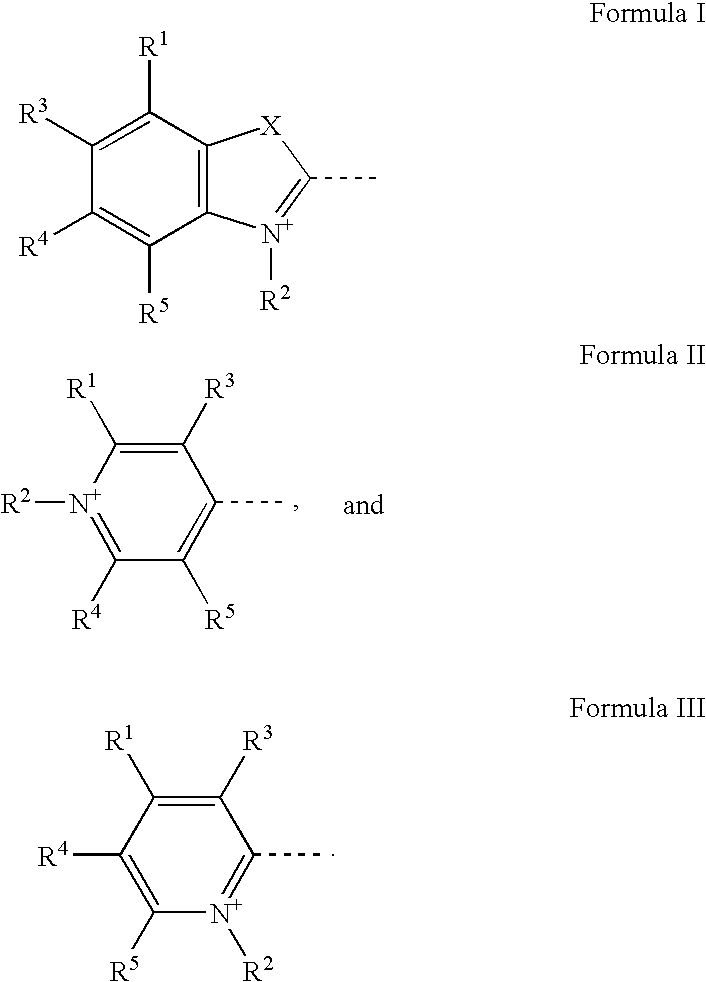
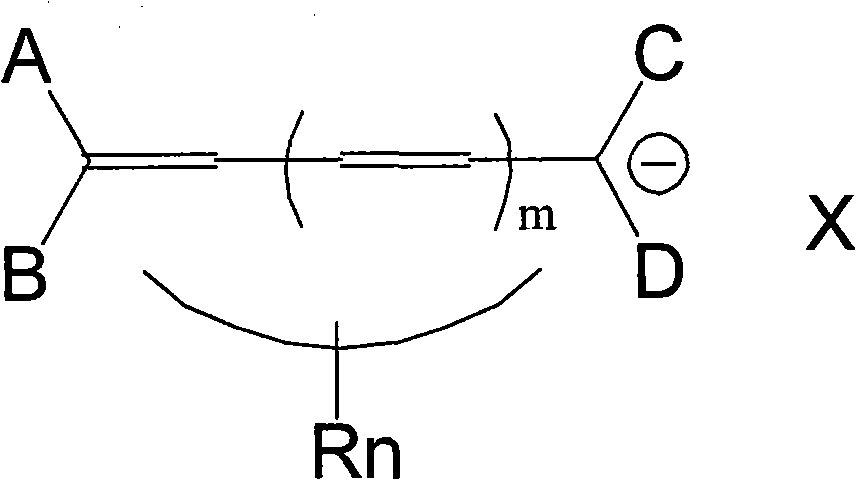
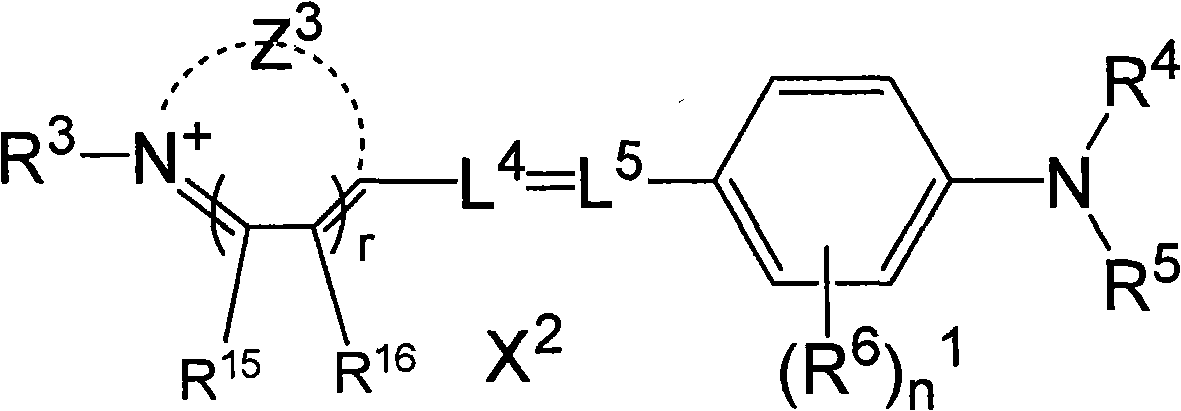
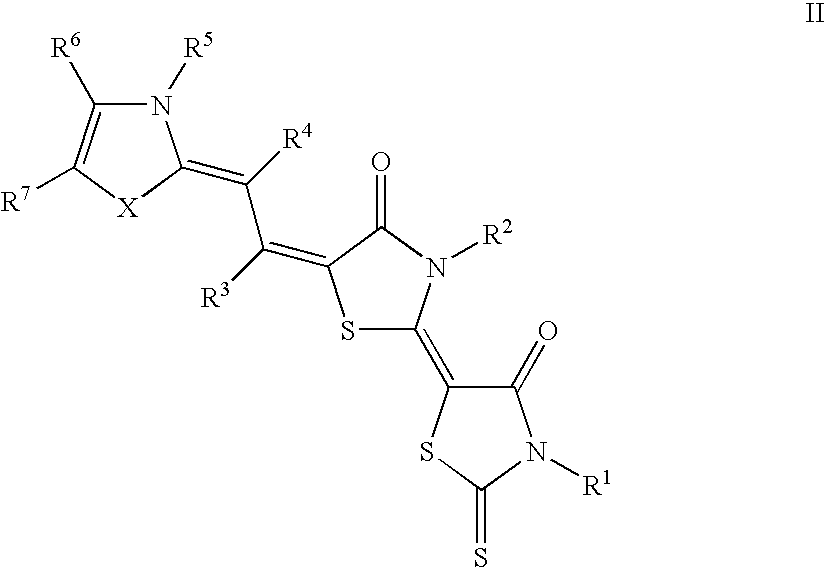
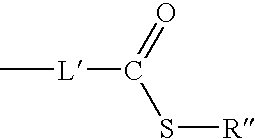
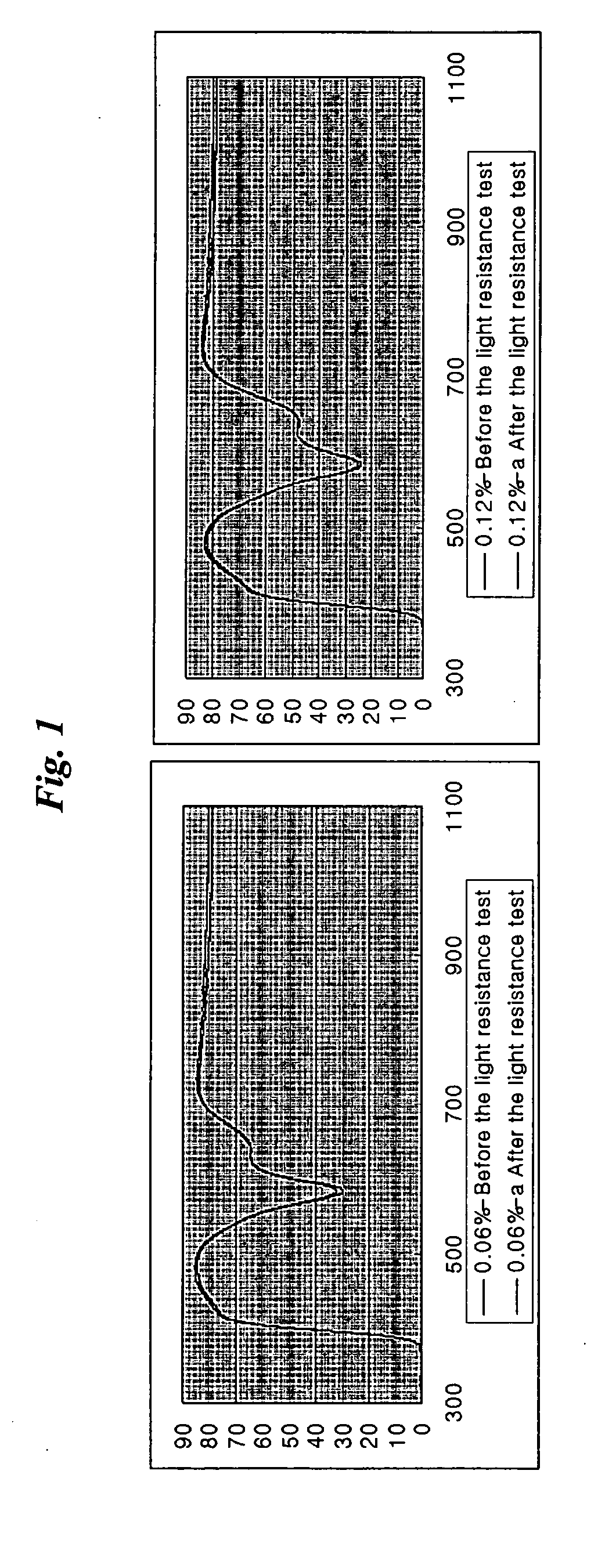
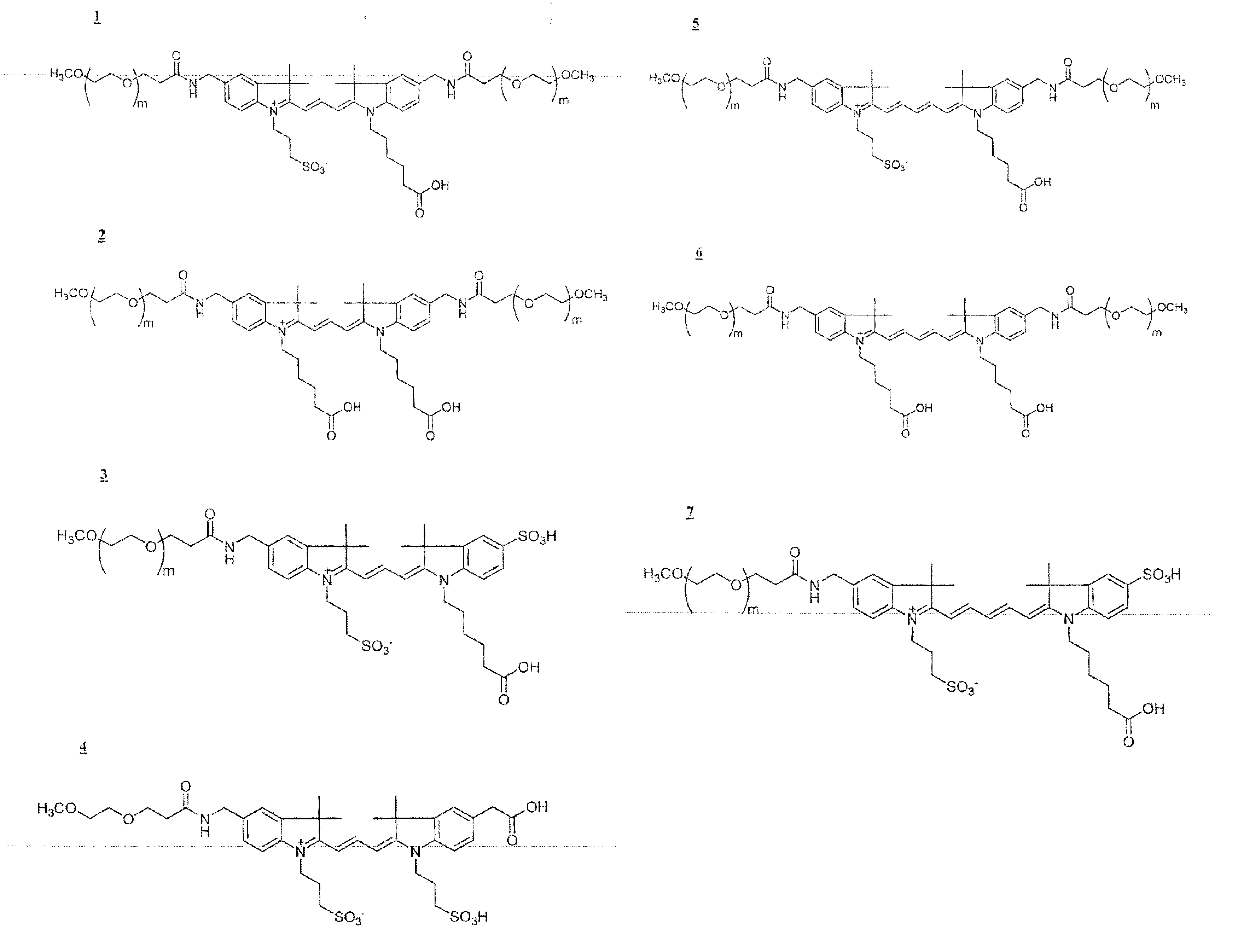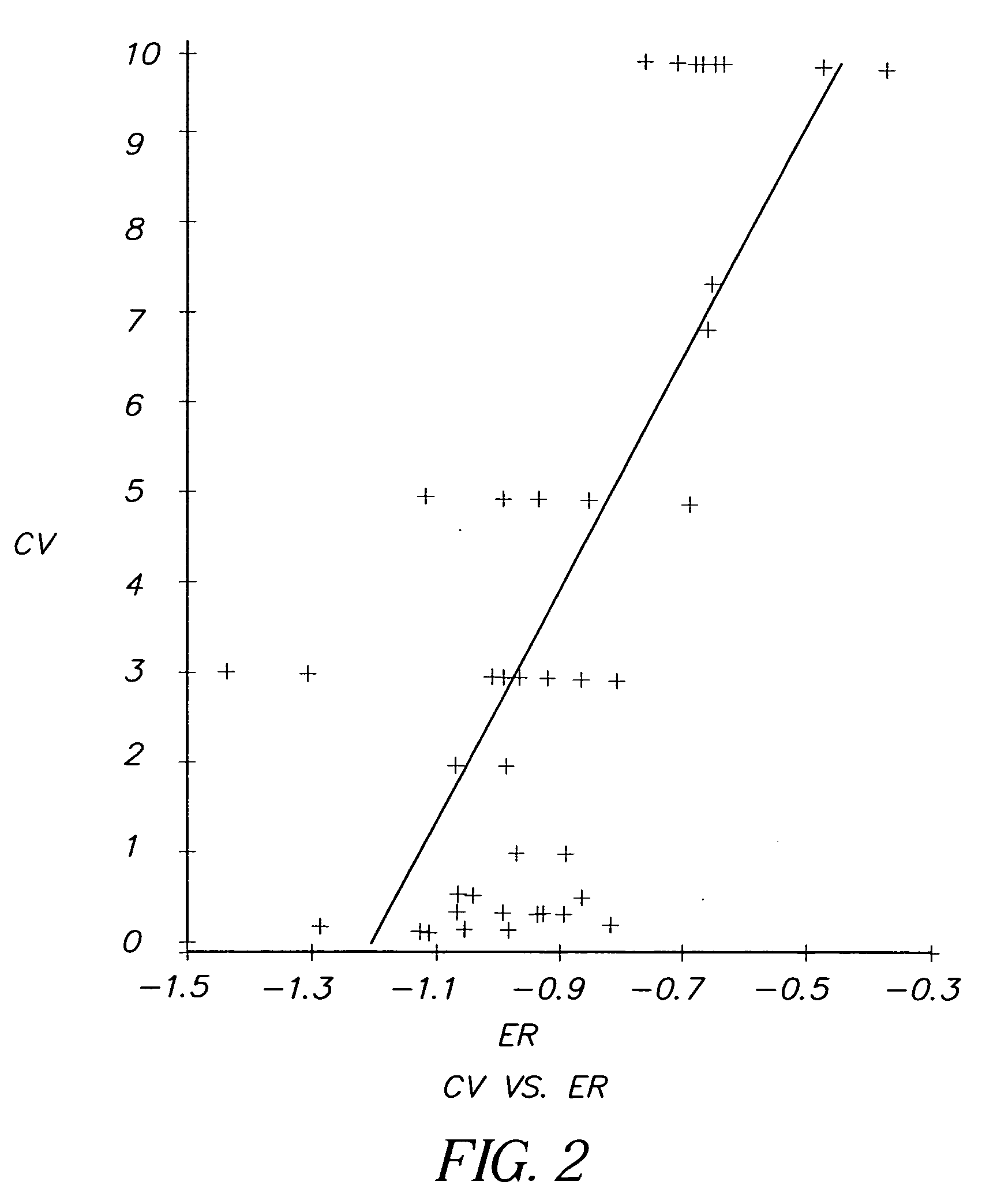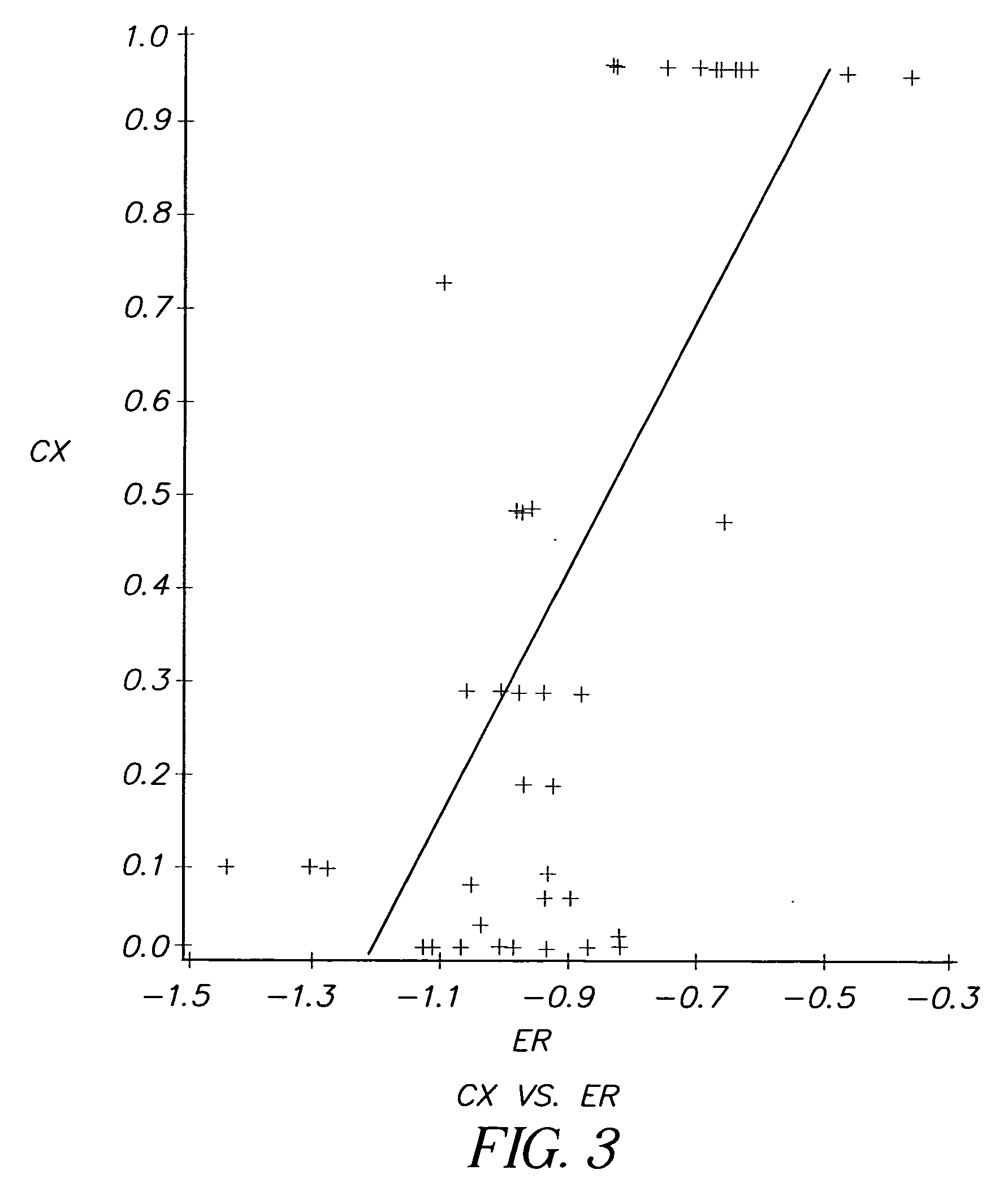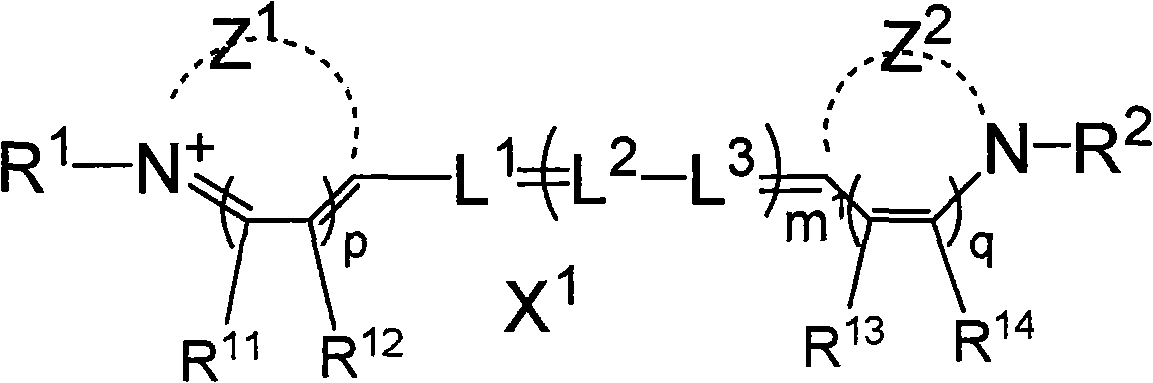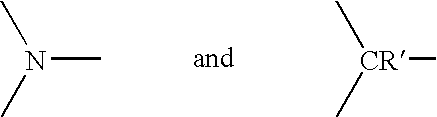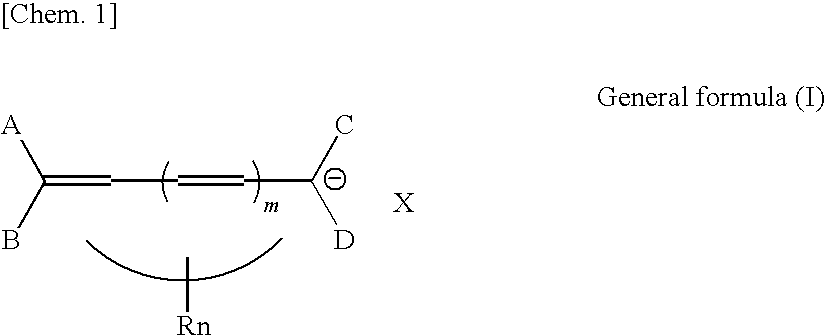Patents
Literature
70 results about "Merocyanine dye" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cyanine dyes
ActiveUS20120052506A1Versatile assay designImprove analytical performanceMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesSolubilityCyanine
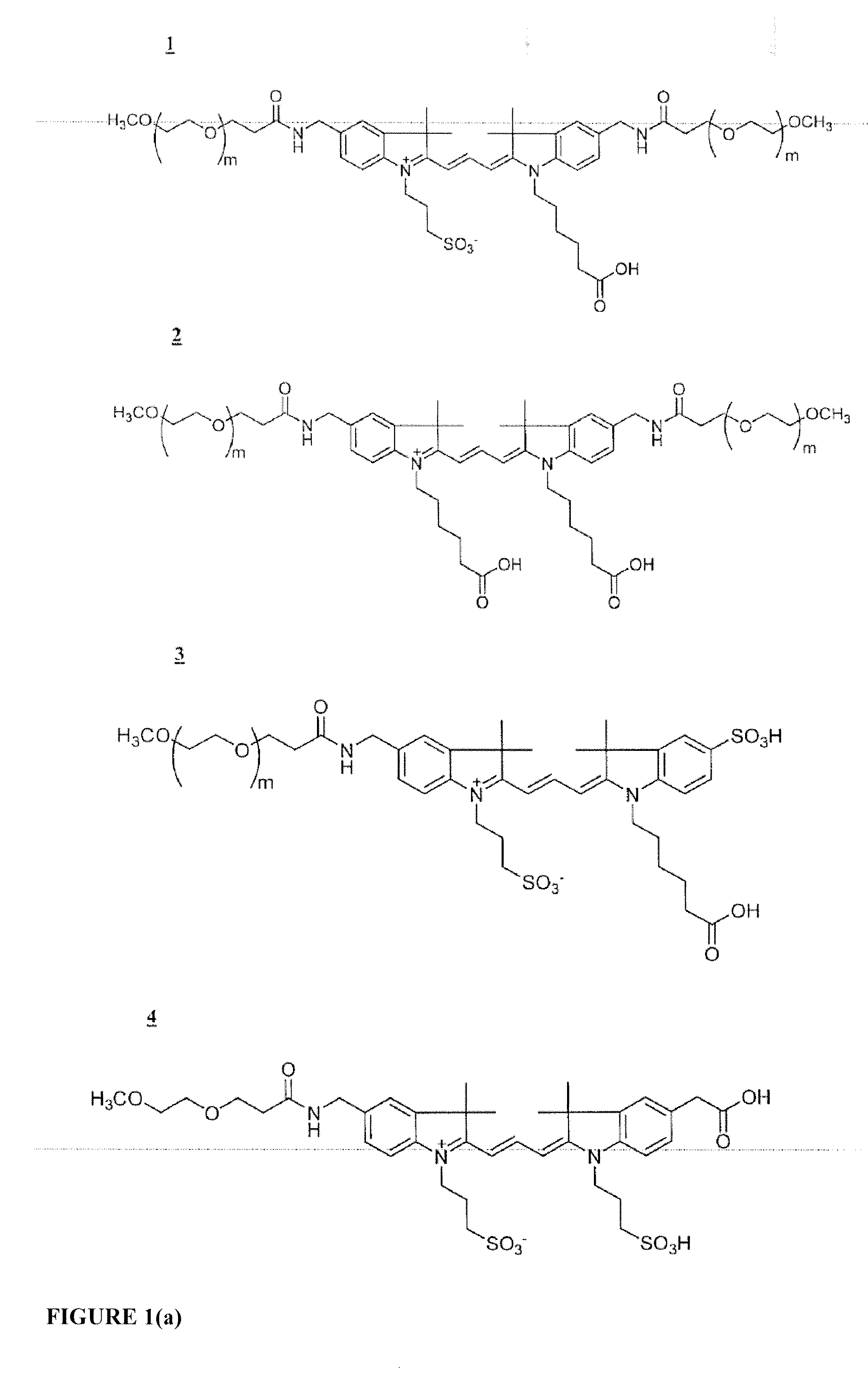
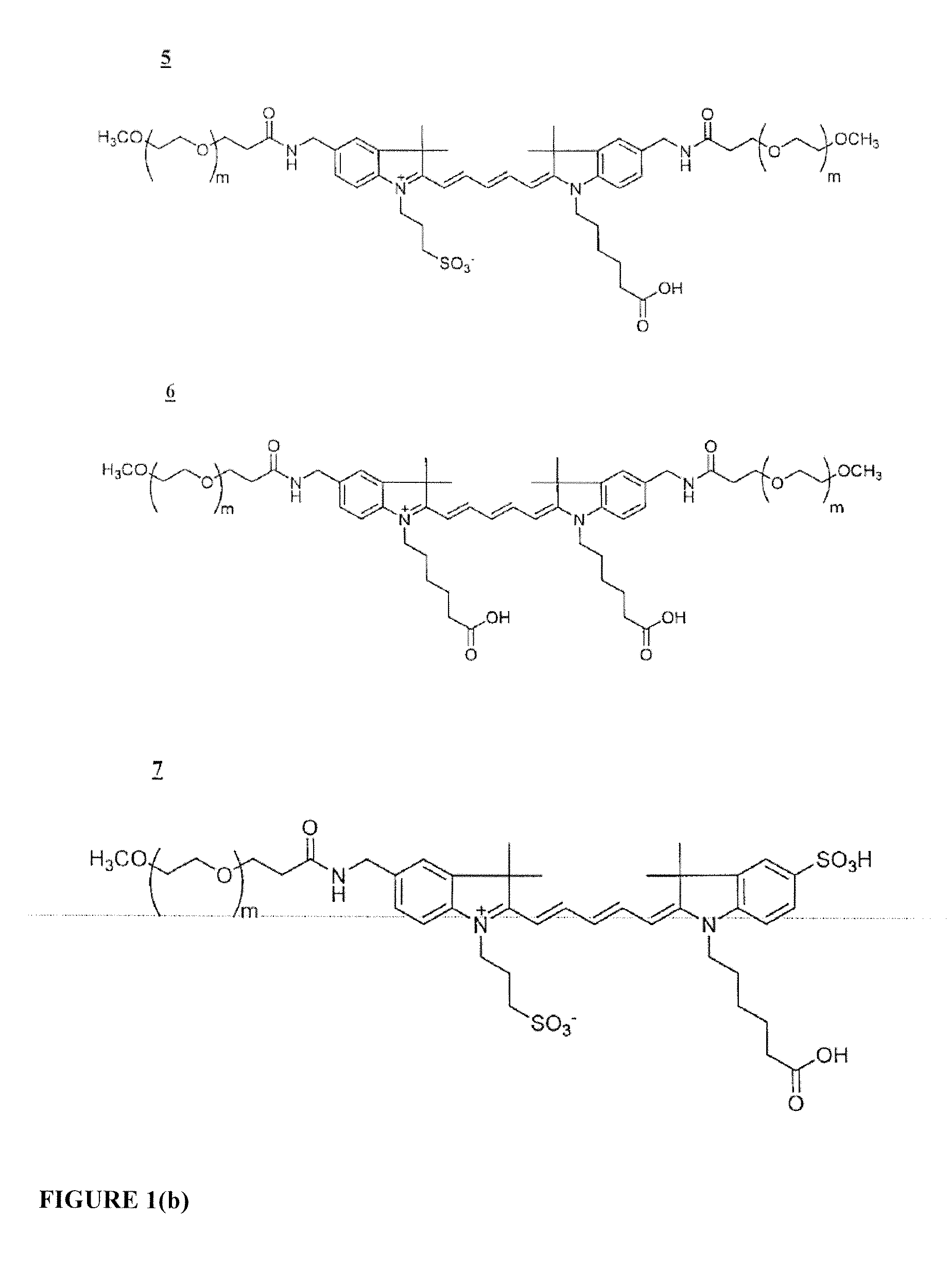
The invention provides a novel class of cyanine dyes that are functionalized with sulfonic acid groups and a linker moiety that facilitates their conjugation to other species and substituent groups which increase the water-solubility, and optimize the optical properties of the dyes. Also provided are conjugates of the dyes, methods of using the dyes and their conjugates and kits including the dyes and their conjugates.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Functionalized cyanine dyes (PEG)
ActiveUS20120058469A1Good adhesionVersatile assay designMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesCyanineMerocyanine dye
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Photoelectric conversion device, imaging device, and method for driving photoelectric conversion device
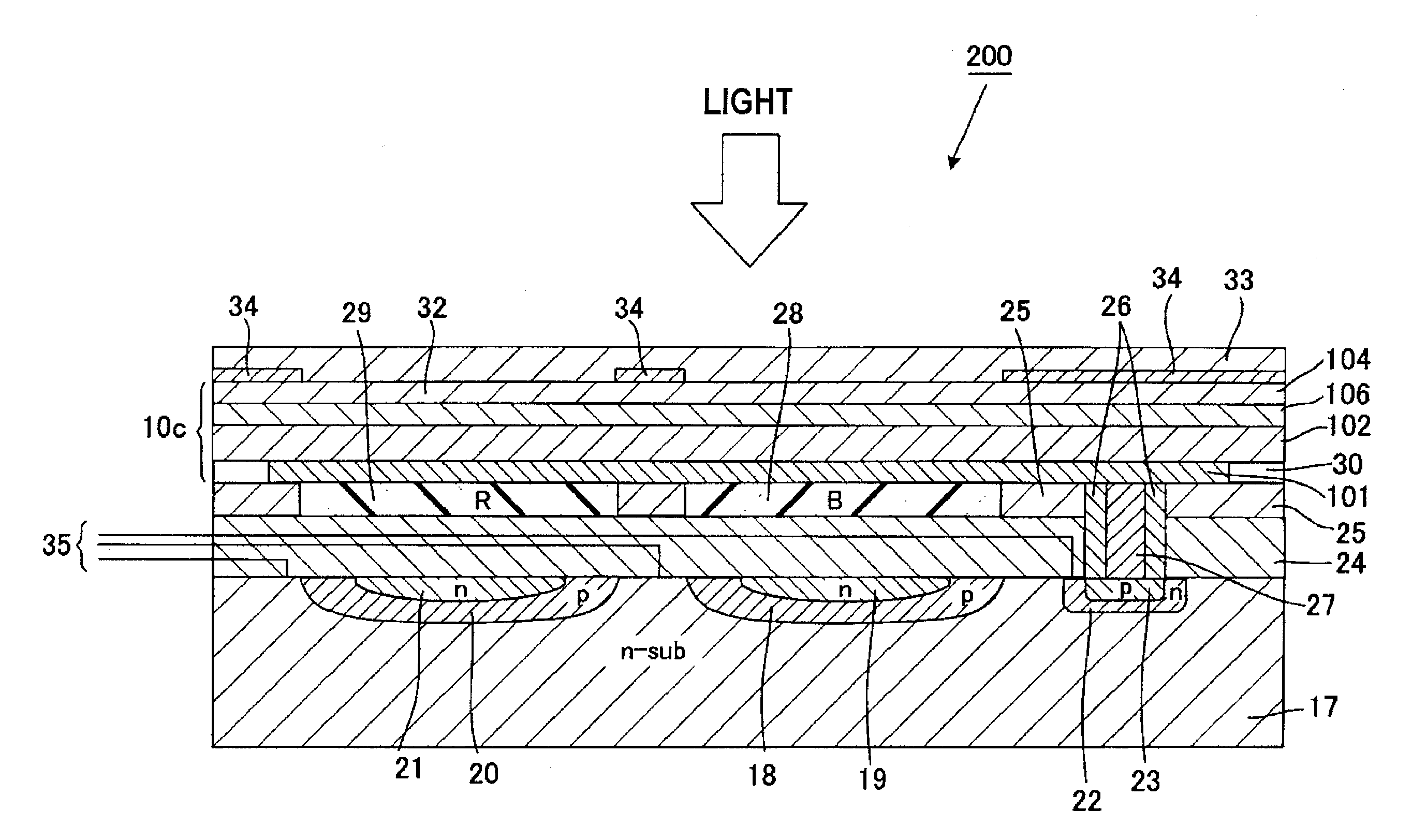
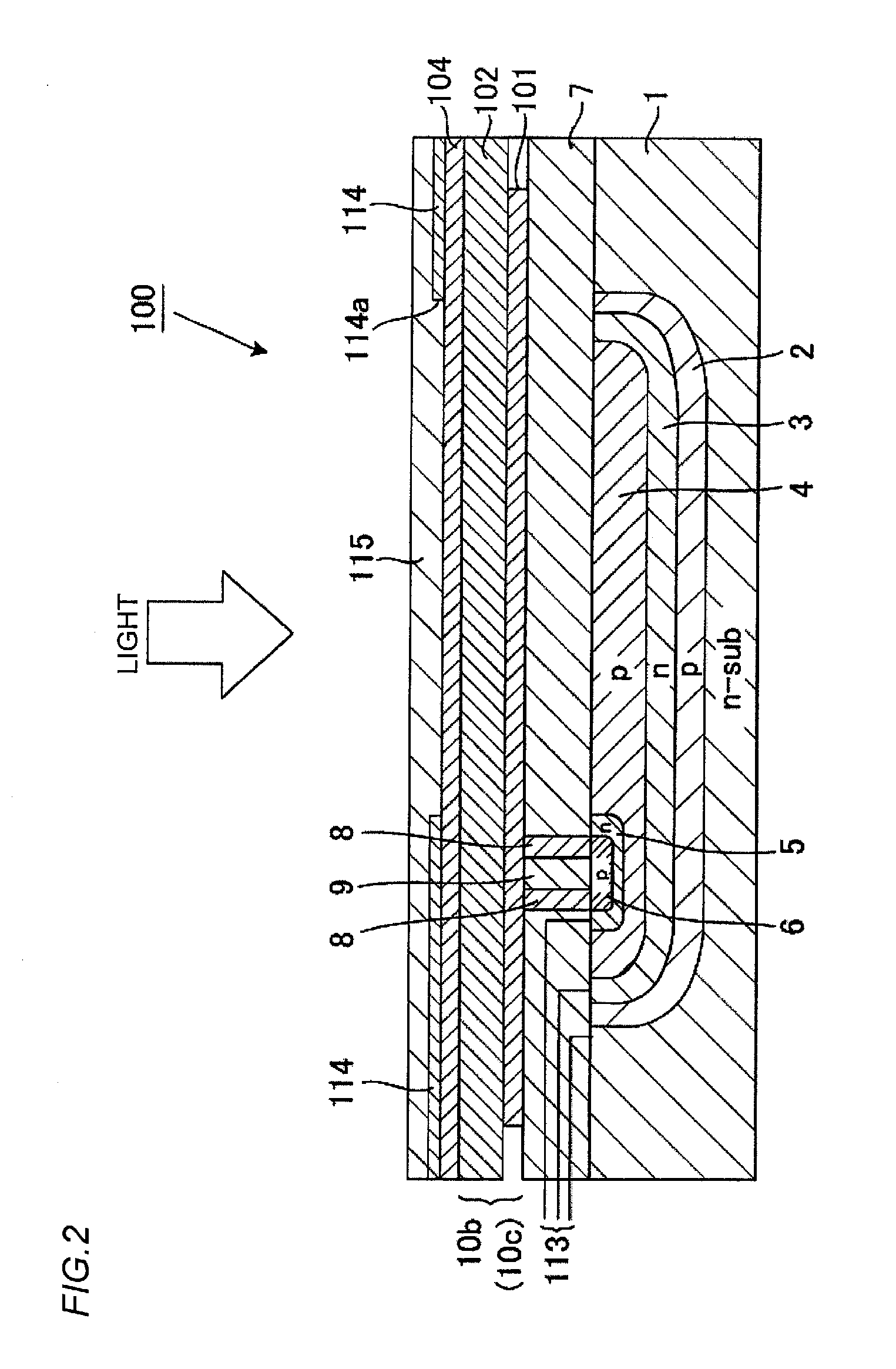
InactiveUS20130087682A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce dark currentMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionLength wave
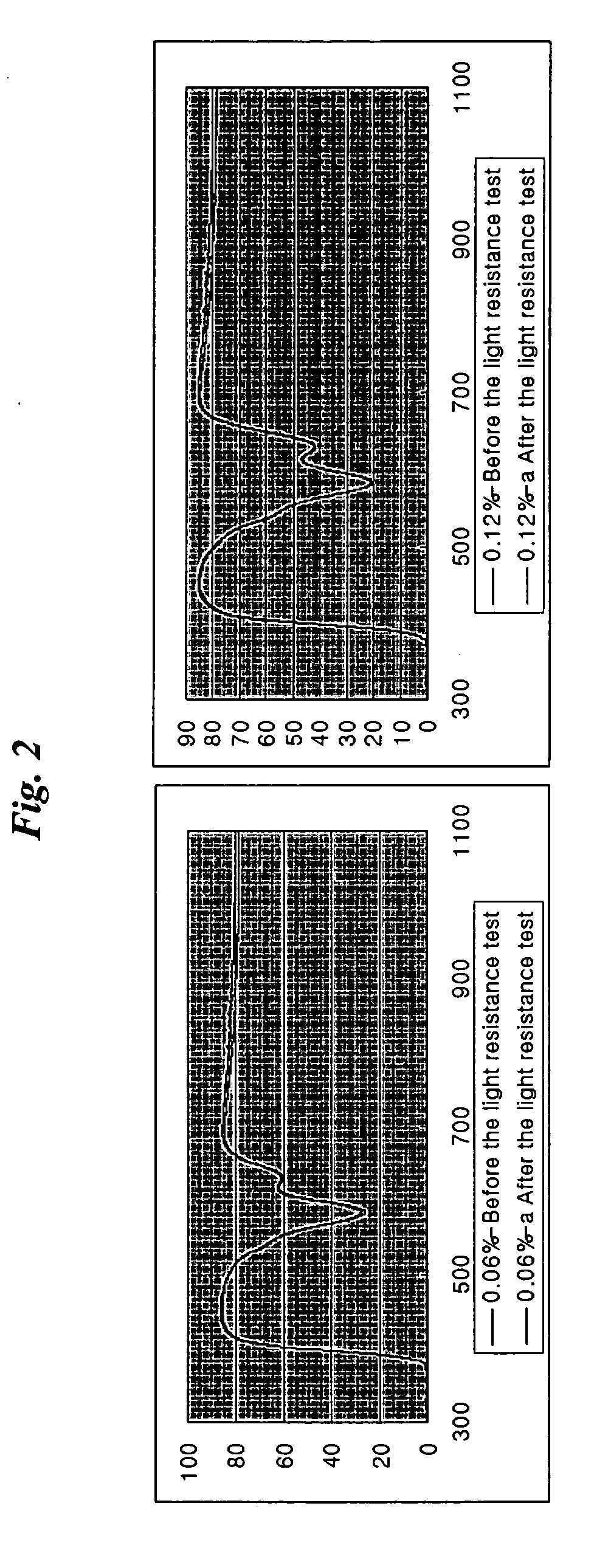
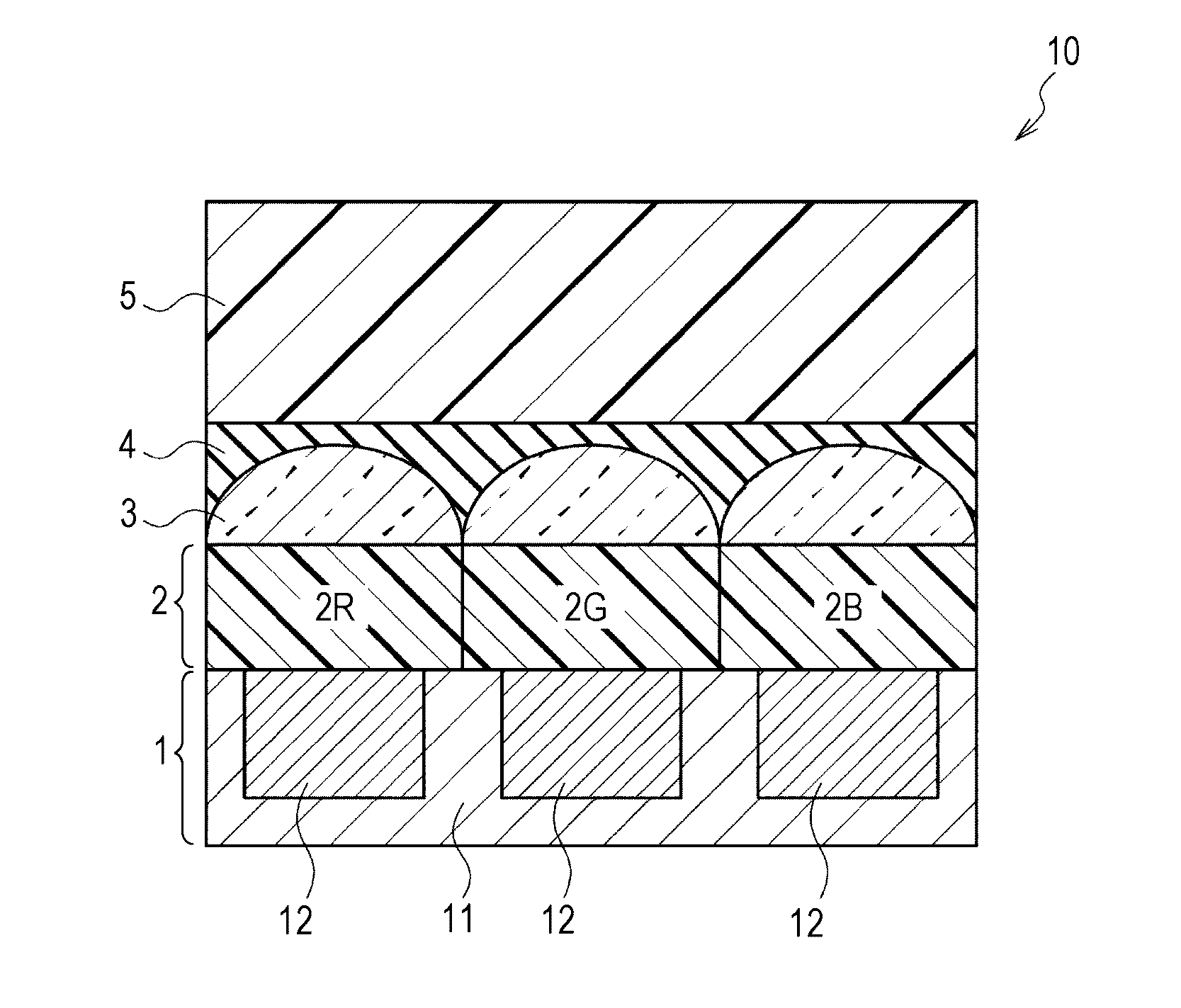
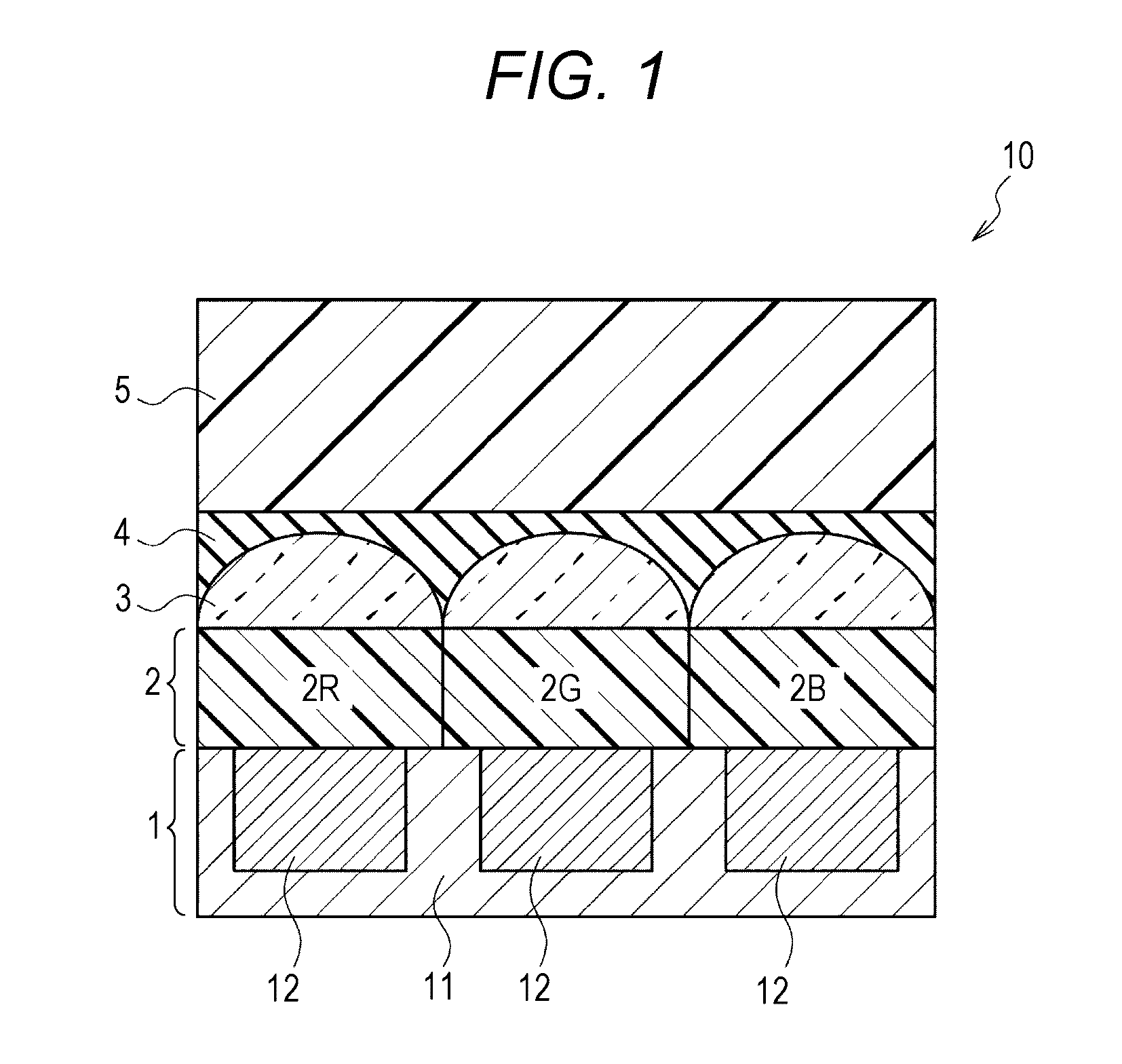
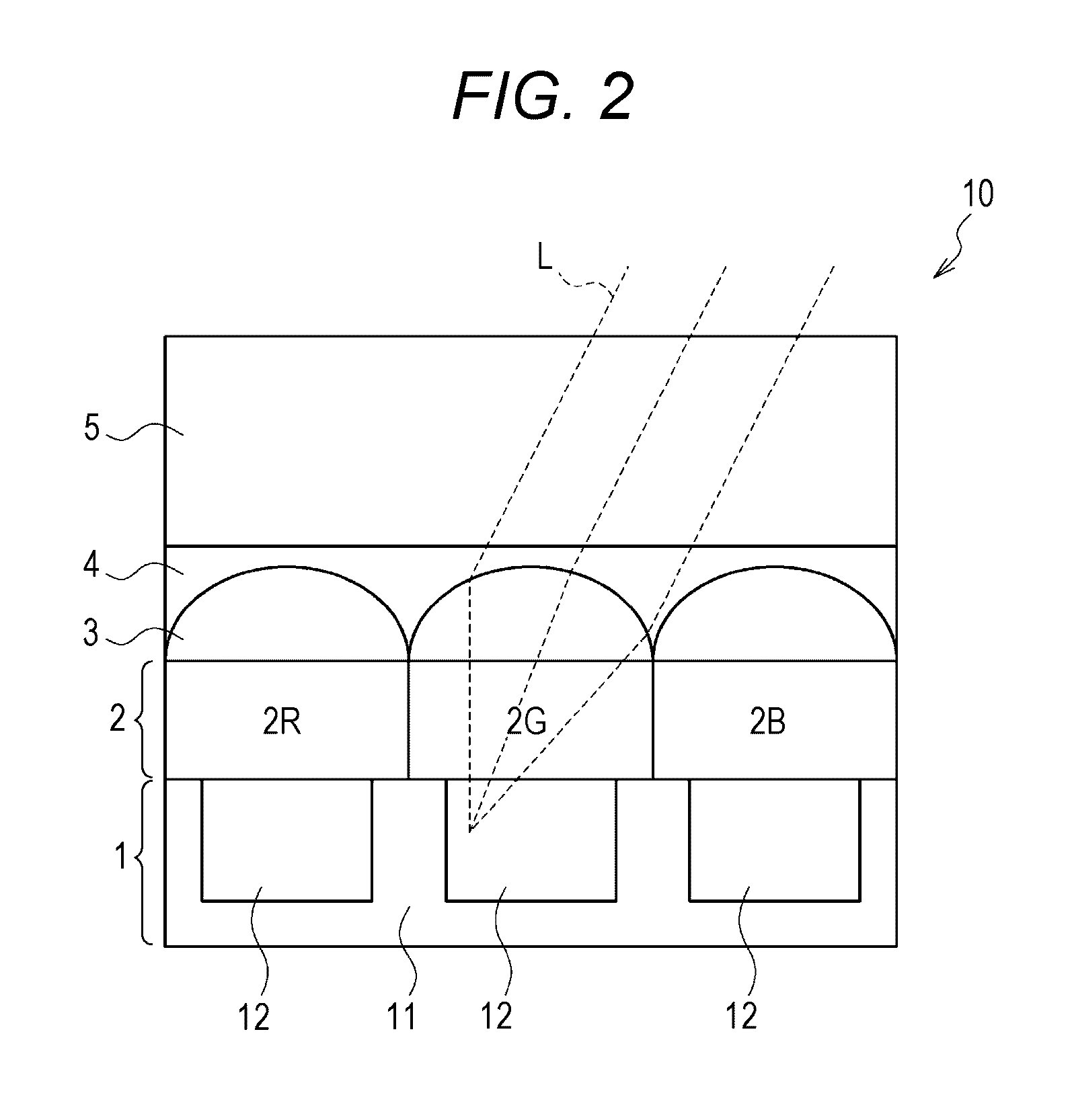
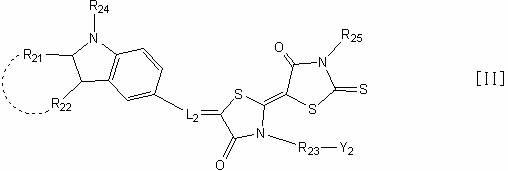
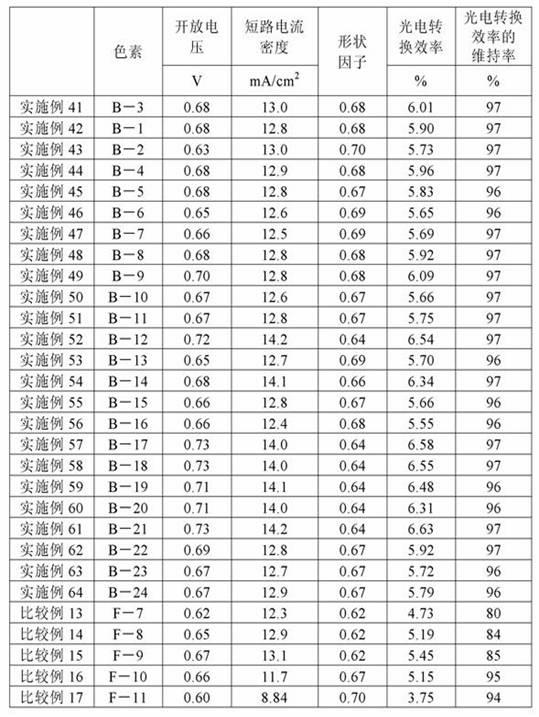
A photoelectric conversion device includes, in the following order: a first electrode; an electron blocking layer; a photoelectric conversion layer containing a merocyanine dye; a hole blocking layer; and a transparent electrode as a second electrode, and an absorption maximum wavelength in a thin film absorption spectrum of the photoelectric conversion layer containing a merocyanine dye is within a range of from 400 to 520 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Functionalized cyanine dyes (PEG)
ActiveUS20120058482A1Good adhesionVersatile assay designMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesCyanineMerocyanine dye
The invention provides a novel class of cyanine dyes that are functionalized with a linker moiety that facilitates their conjugation to other species and substituent groups which increase the water-solubility, and optimize the optical properties of the dyes. Also provided are conjugates of the dyes, methods of using the dyes and their conjugates and kits including the dyes and their conjugates.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Lithographic printing plate precursor, lithographic printing method, and novel cyanine dye
InactiveUS20070056457A1Improve visibilityExcellent in on-machine development propertyMethine/polymethine dyesPlate printingCyanineImage recording
A lithographic printing plate precursor comprising a support and an image-recording layer which contains (A) a cyanine dye including a solvent-soluble group and having an absorption maximum in an infrared wavelength region and is capable of being removed with at least one of printing ink and an aqueous component.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for making positive working printing plates from a heat mode sensitive image element
InactiveUS6060218AEasy to prepareIncrease the lengthPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsEngineeringMerocyanine dye
According to the present invention there is provided a method for making lithographic printing plates including the following steps a) preparing a heat mode imaging element consisting of a lithographic base with a hydrophilic surface and a top layer which top layer is sensitive to IR-radiation, comprises a polymer, soluble in an aqueous alkaline solution and is unpenetrable for an alkaline developer containing SiO2 as silicates; b) exposing imagewise said heat mode imaging element to IR-radiation; c) developing said imagewise exposed heat mode imaging element with said alkaline developer so that the exposed areas of the top layer are dissolved and the unexposed areas of the top layer remain undissolved characterized in that said top layer includes an IR-dye selected from the group consisting of indoaniline dyes, cyanine dyes, merocyanine dyes, oxonol dyes, porphine derivatives, anthraquinone dyes, merostyryl dyes, pyrylium compounds, diphenyl and triphenyl azo compounds and squarylium derivatives.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Use of cyanine dyes for the diagnosis of proliferative diseases
InactiveUS20100166659A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityIn-vivo testing preparationsCyanineBody weight
The present invention concerns the use of the cyanine dye SF64 for the diagnosis of proliferative diseases upon administration of less than 5 mg / kg body weight.
Owner:SCHERING AG
Lithographic printing method and presensitized plate
ActiveUS20040197701A1Practical amount of energyIncrease impressionRadiation applicationsPhotomechanical apparatusDigital dataNitrogen
Disclosed is a presensitized plate composed of a support having thereon an image recording layer which includes: an infrared absorber (A) that is a cyanine dye having at least one fused ring composed of a nitrogen-containing heterocycle in combination with an aromatic ring or a second heterocycle, and having on the aromatic ring or second heterocycle an electron-withdrawing group or a heavy atom-containing group, a radical generator (B), and a radical-polymerizable compound (C), and which is removable with printing ink and / or dampening water. The presensitized of the present invention can be imaged with an infrared light-emitting laser to directly record an image from digital data on a computer or the like and is then subjected to on-machine development without carrying out a development step, which is capable of providing a large number of good impressions with a practical amount of energy.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Selective detection of proteins that contain two or more alpha-helical transmembrane domains
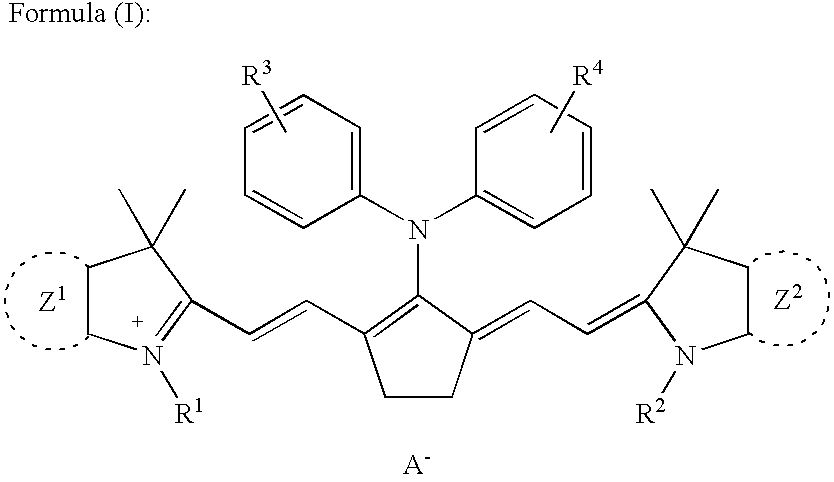
Embodiments of the present invention provide a staining solution and of method of using the staining solution for selectively detecting proteins that contain two or more α-helical transmembrane domains. The staining solution comprises a lipophilic dyes and at least about a 30% hydrophobic solvent. The dyes of the present are represented by the general formula A-B-E wherein A is a nitrogen heterocycle, B is a bridge moiety and E is an electron pair accepting moiety that comprises either a carbonyl or nitrogen atom. In one embodiment these lipophilic dyes are merocyanine dye, a cyanine dye, a styryl dye or a carbazolylvinyl dye.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for making positive working printing plates from a heat mode sensitive image element
InactiveUS6235451B1Increased durabilityIncrease run lengthRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMerocyanine dye
According to the present invention there is provided a method for making lithographic printing plates including the following stepsa) preparing a heat mode imaging element having on a lithographic base with a hydrophilic surface a first layer including a polymer, soluble in an aqueous alkaline solution and a top layer on the same side of the lithographic base as the first layer which top layer is sensitive to IR-radiation and is unpenetrable for an alkaline developer containing SiO2 as silicates;b) exposing imagewise said heat mode imaging element to IR-radiation;c) developing said imagewise exposed heat mode imaging element with said alkaline developer so that the exposed areas of the top layer and the underlying areas of the first layer are dissolved and the unexposed areas of the first layer remain undissolved characterized in that said top layer includes an IR-dye in an amount between 1 and 100% by weight of the total amount of said IR-sensitive top layer selected from the group consisting of indoaniline dyes, cyanine dyes, merocyanine dyes, oxonol dyes, porphine derivatives, anthraquinone dyes, merostyryl dyes, pyrylium compounds, diphenyl and triphenyl azo compounds and squarylium derivatives.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Correlation of anti-cancer activity of dyes with redox potentials
InactiveUS20060099712A1High anticancer activityReduce the amount requiredMethine/polymethine dyesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCancer cellCyanine
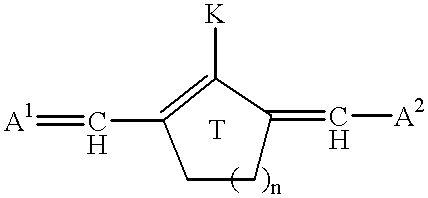
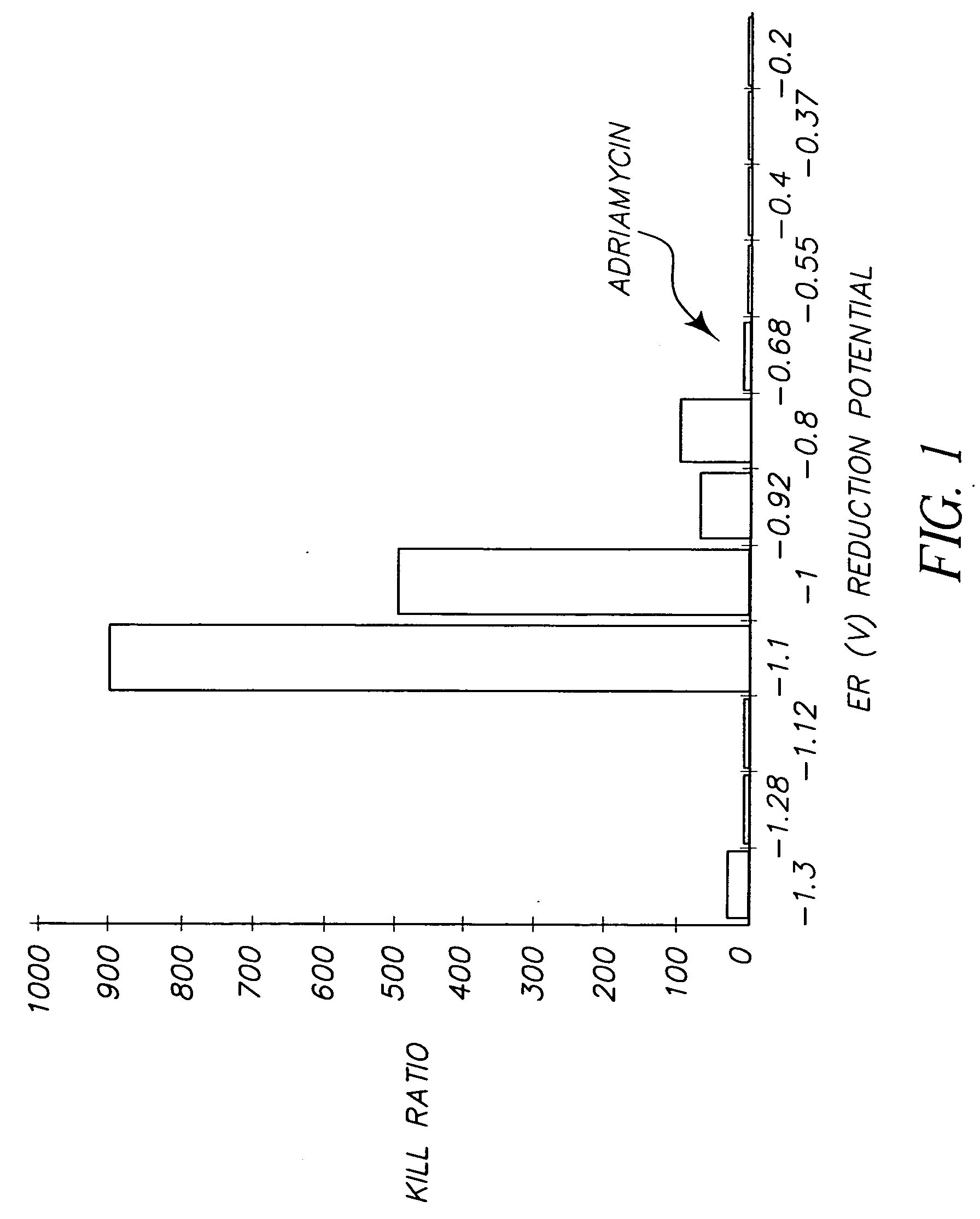
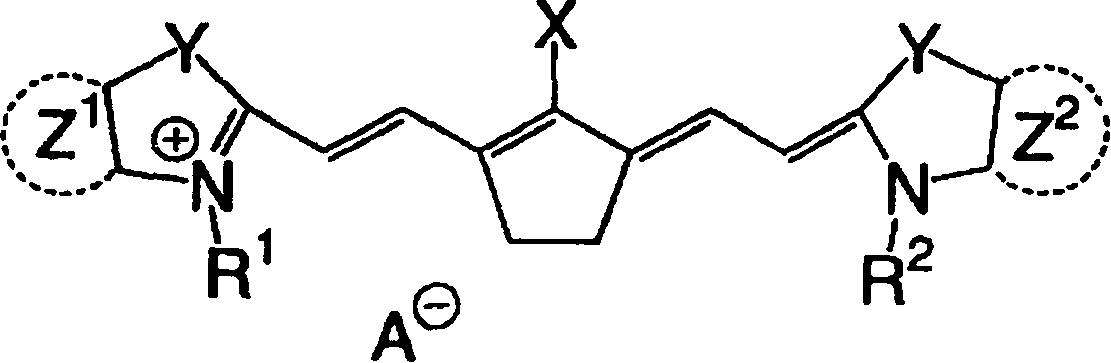
The present invention relates to a method for selecting pharmacological compounds for selective inhibition of cancer cells comprising identifying a compound, determining the reduction potential (ER) of the compound, and selecting the compound which has a reduction potential from −1.1 to −0.8 volts. The invention also relates to a pharmacological compound comprising at least one cyanine dye or merocyanine dye, wherein the dye has at least one cationic substituent, wherein the dye has a reduction potential of from—1.1 to 0.8 volts, and wherein the pharmacological compound demonstrates selective inhibition of cancer cells.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Thermally reactive infrared absorption polymers and their use in a heat sensitive lithographic printing plate
InactiveUS8632947B2Improve stabilityPhotosensitive materialsDuplicating/marking methodsCyanineNear infrared laser
The invention provides a near infrared absorption polymer comprising at least two different pendent infra-red chromophoric moieties covalently bonded to the backbone of an alkali-soluble resin, at least one of which is an indole cyanine dye and the other of which is a benz[e]-indole cyanine dye. When used in the coating of a heat sensitive positive working lithographic printing plate precursor the stabilization time needed after manufacture is significantly reduced, avoiding further conditioning processes before use. The precursors are preferably imagewise exposed with a near-infrared laser emitting at between 780 nm and 850 nm.
Owner:IPAGSA IND
Lithographic printing plate precursor, lithographic printing method, and novel cyanine dye
ActiveCN1924703AImprove visibilityInhibit coloringMethine/polymethine dyesPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusCyanineImage recording
A lithographic printing plate precursor comprising a support and an image recording layer, the image recording layer containing (A) a cyanine dye and removable with at least one of printing ink and an aqueous component, the cyanine dye containing a solvent removable Soluble groups and have maximum absorption in the infrared wavelength region.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Aggregates of plural transition metal nanoparticles and plural cyanine dye molecules
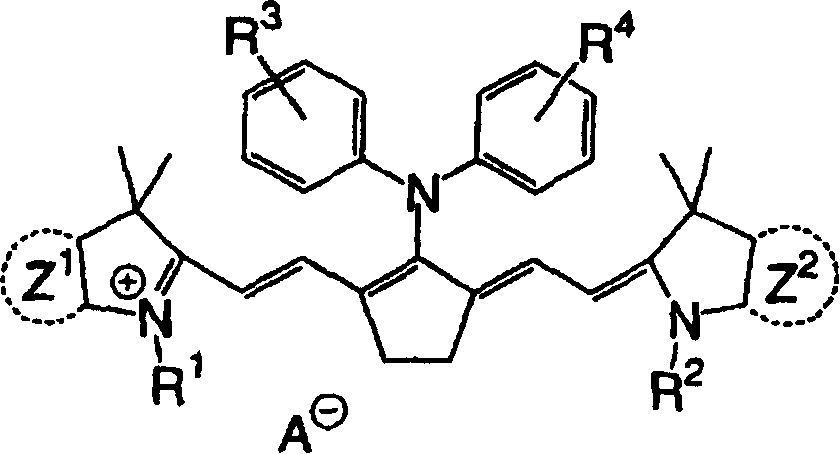
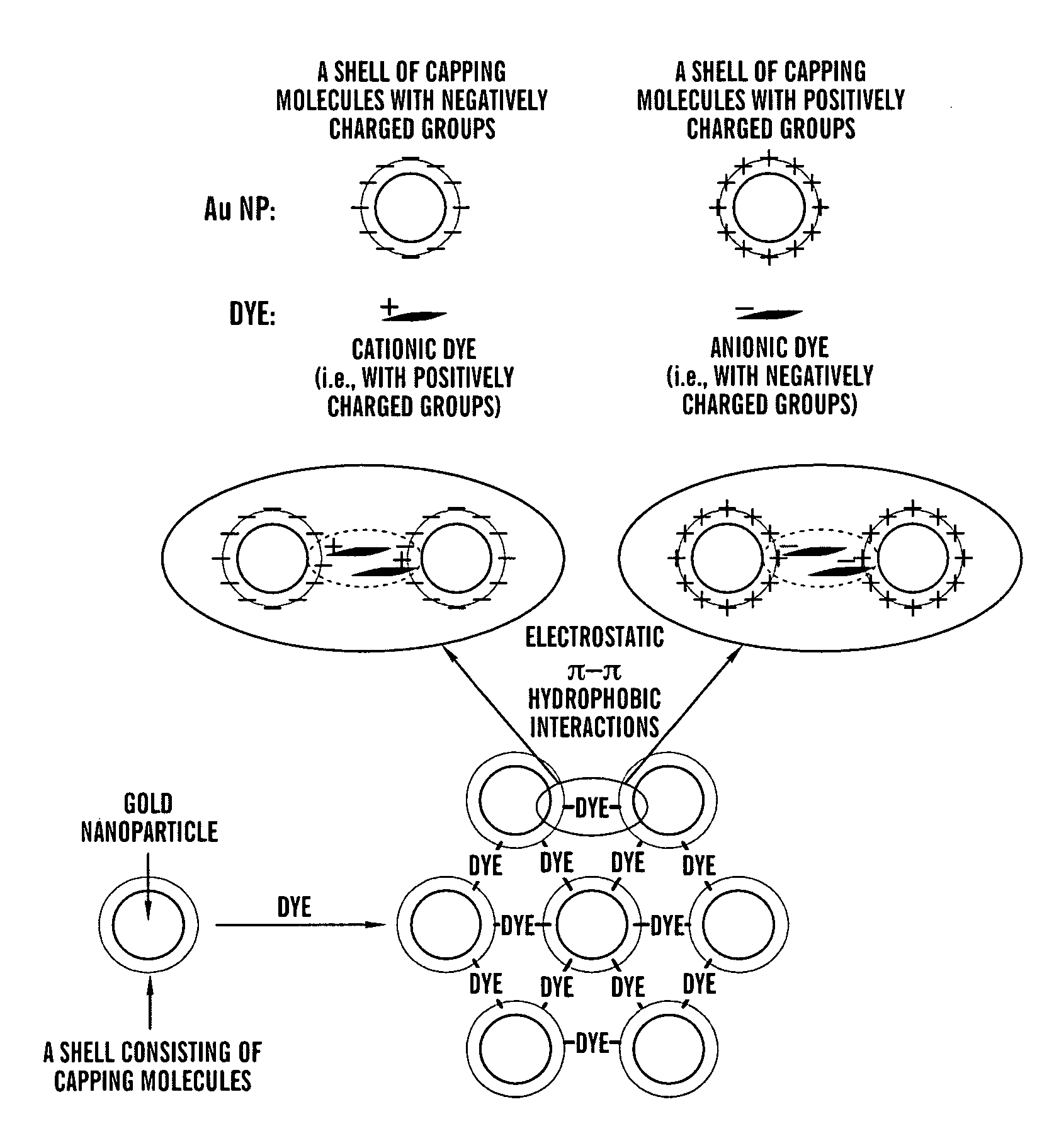
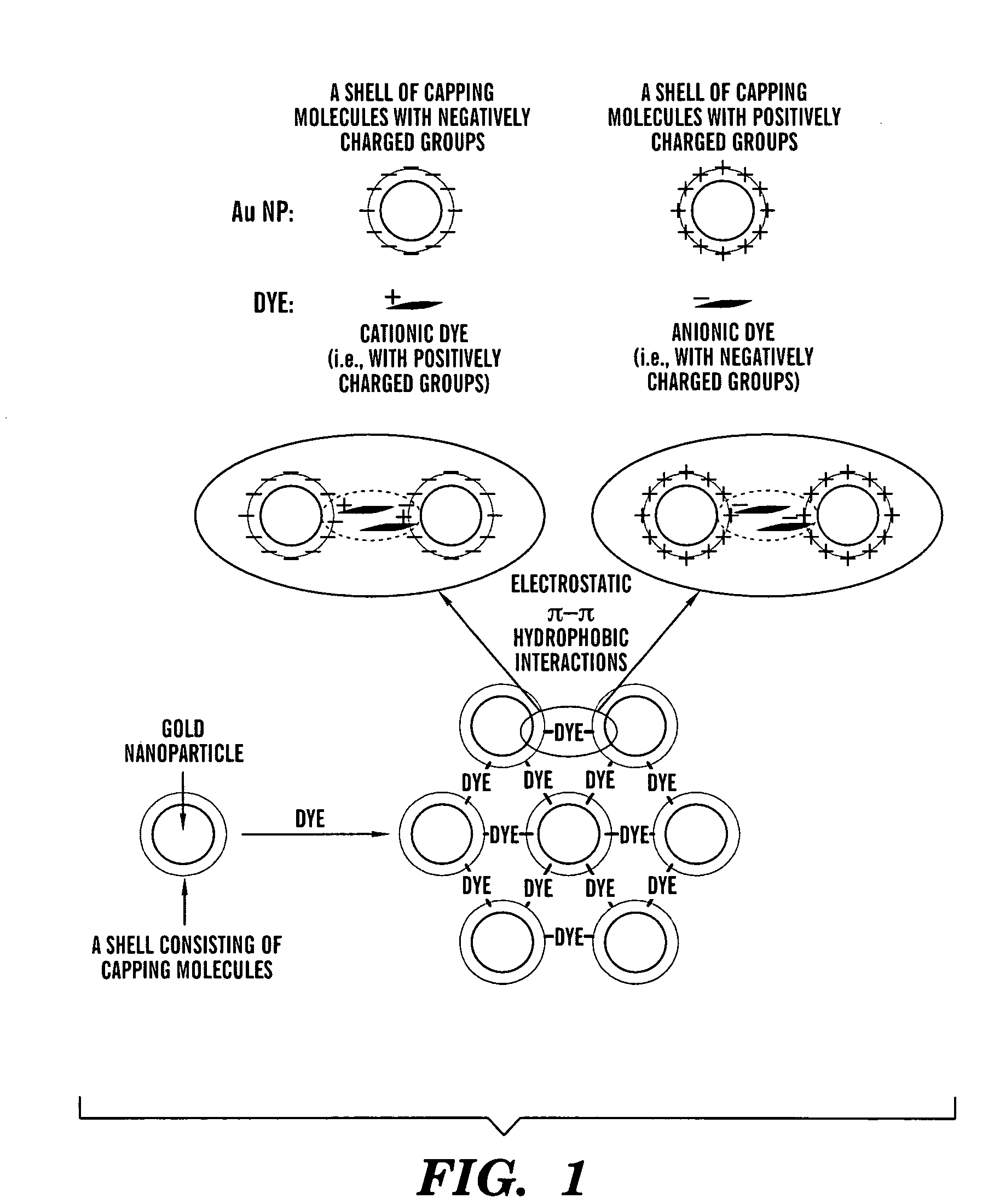
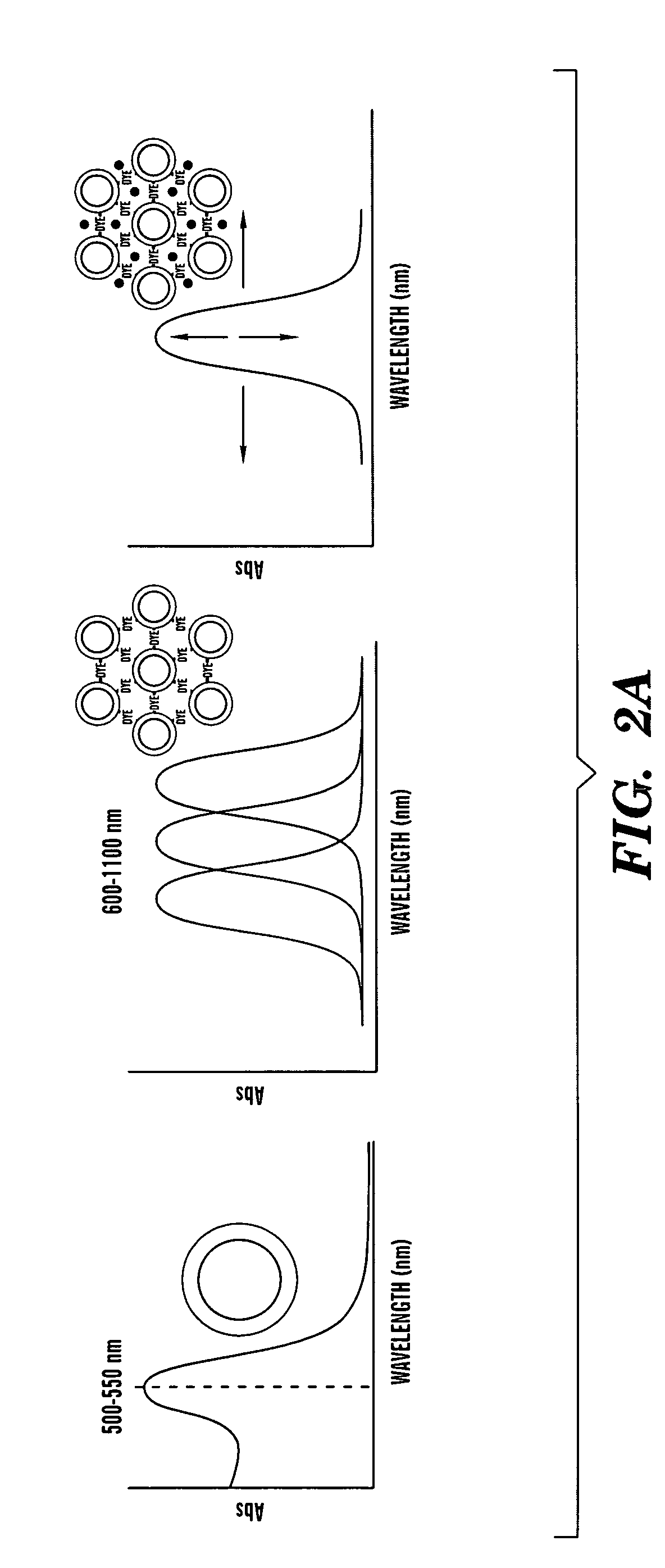
The present invention is directed to an aggregate composed of a plurality of nanoparticles of a transition metal and a plurality of cyanine dye molecules that are interacting non-covalently. The nanoparticles are capped with a capping molecule, while the cyanine dye molecule can be cationic, anionic, or neutral cyanine dye. Methods of making such aggregates and for using them in detection of an analyte are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
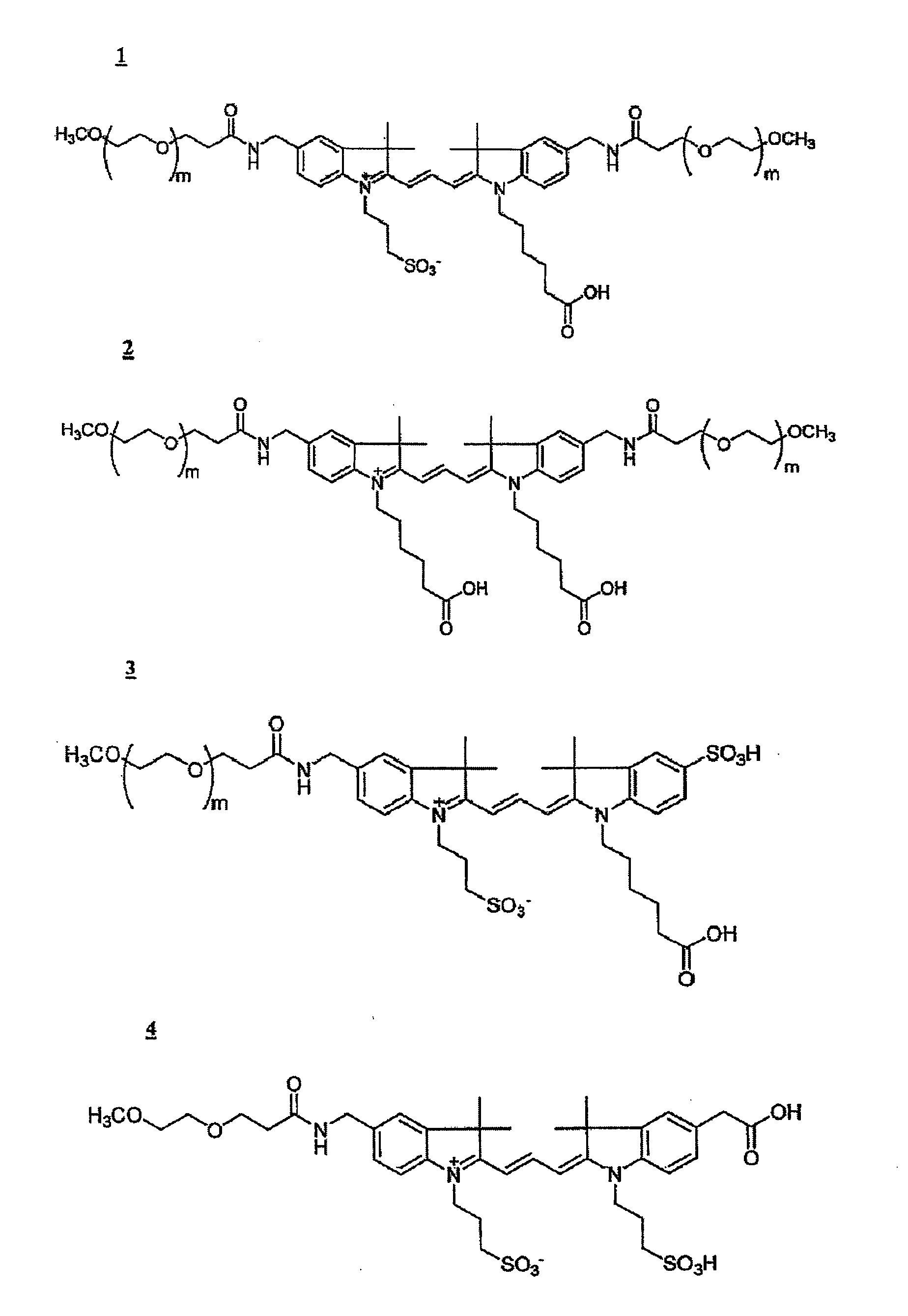
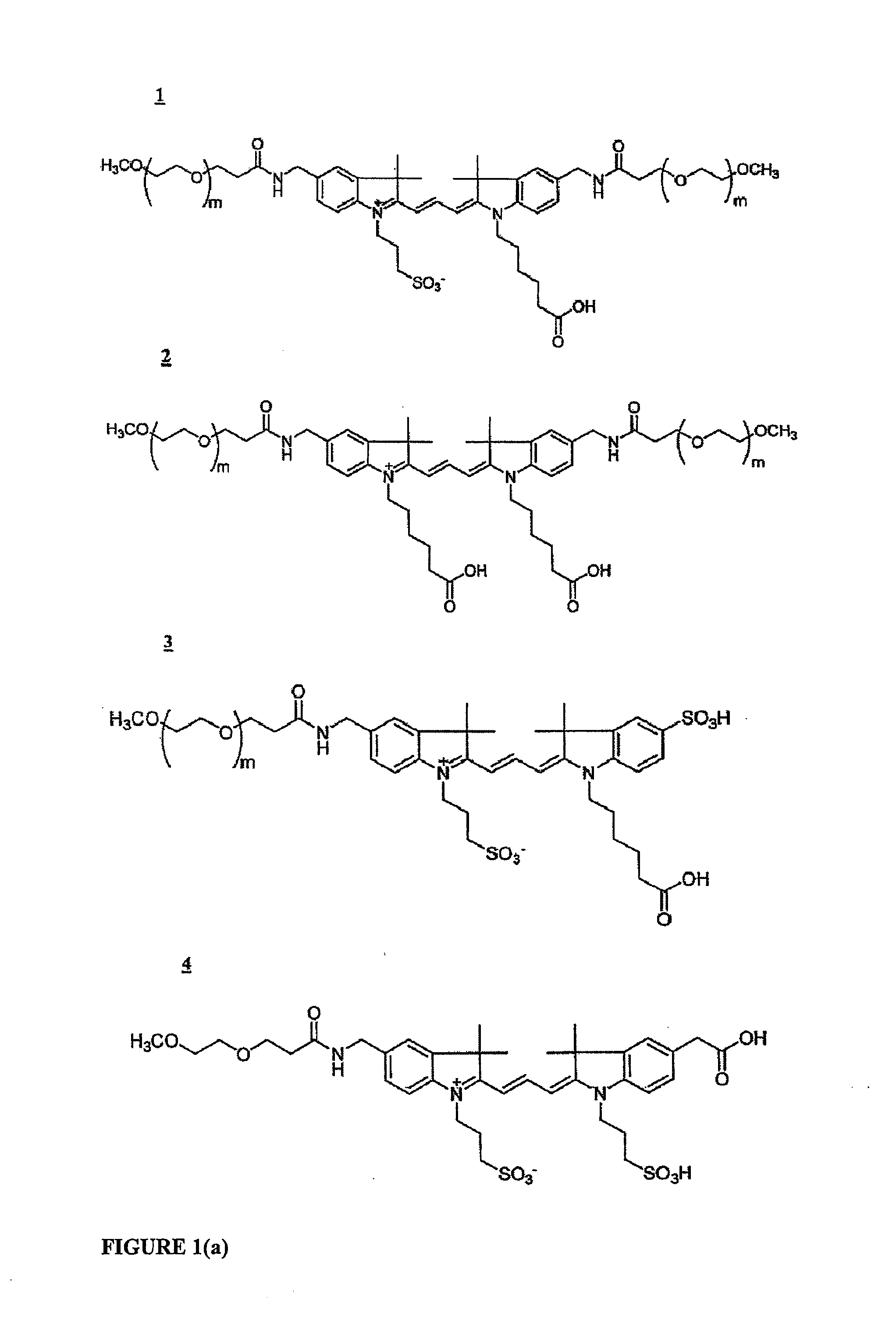
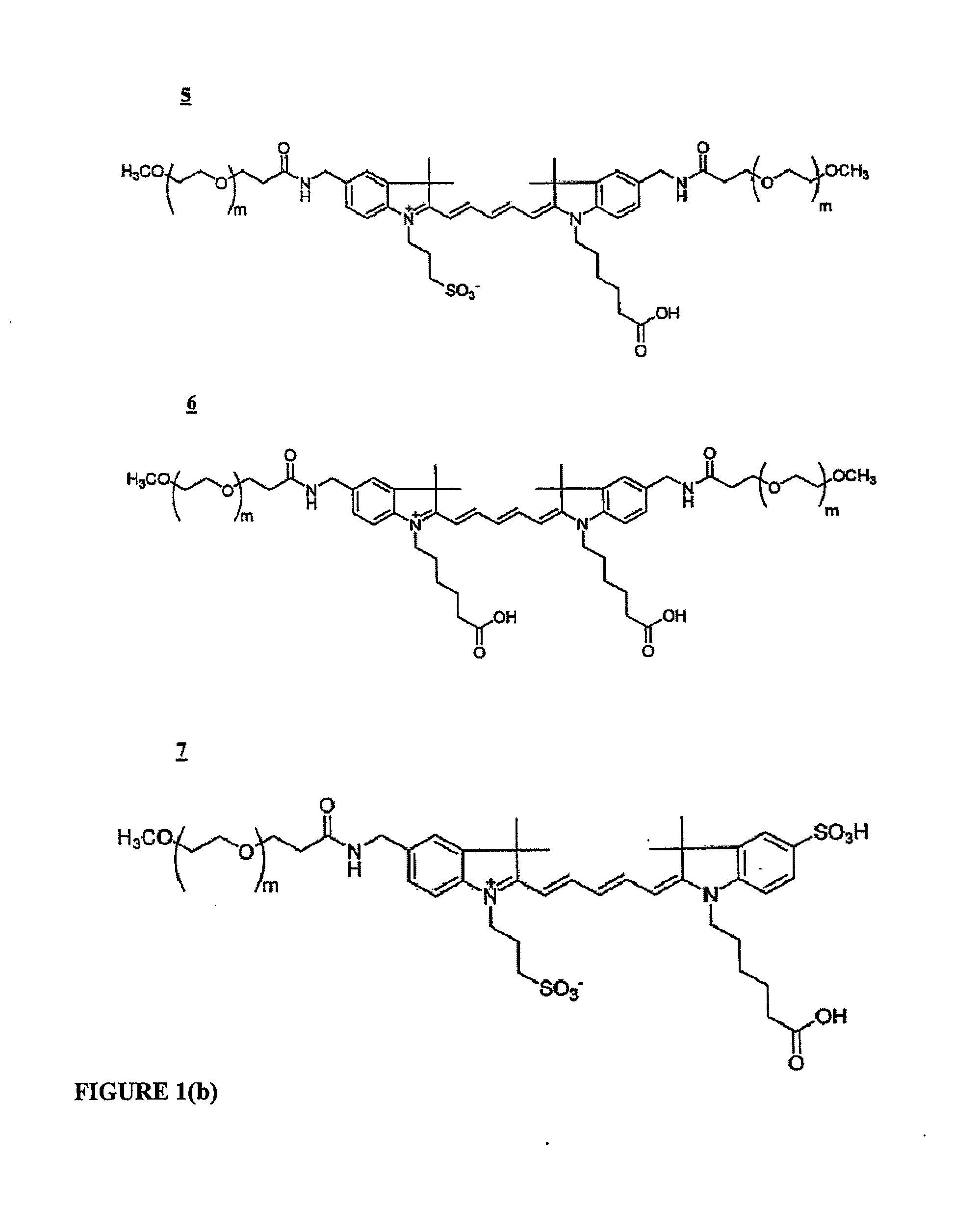
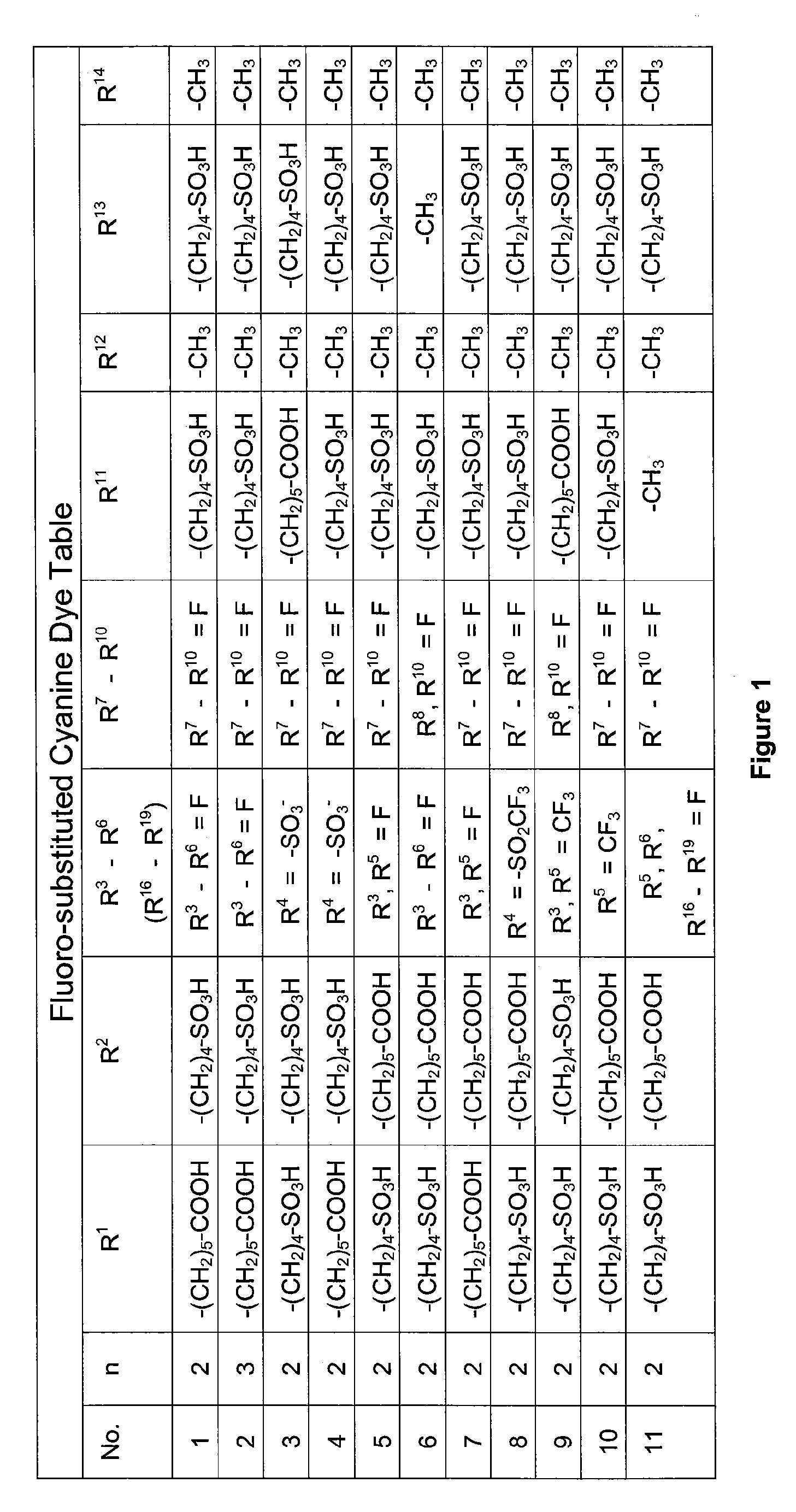
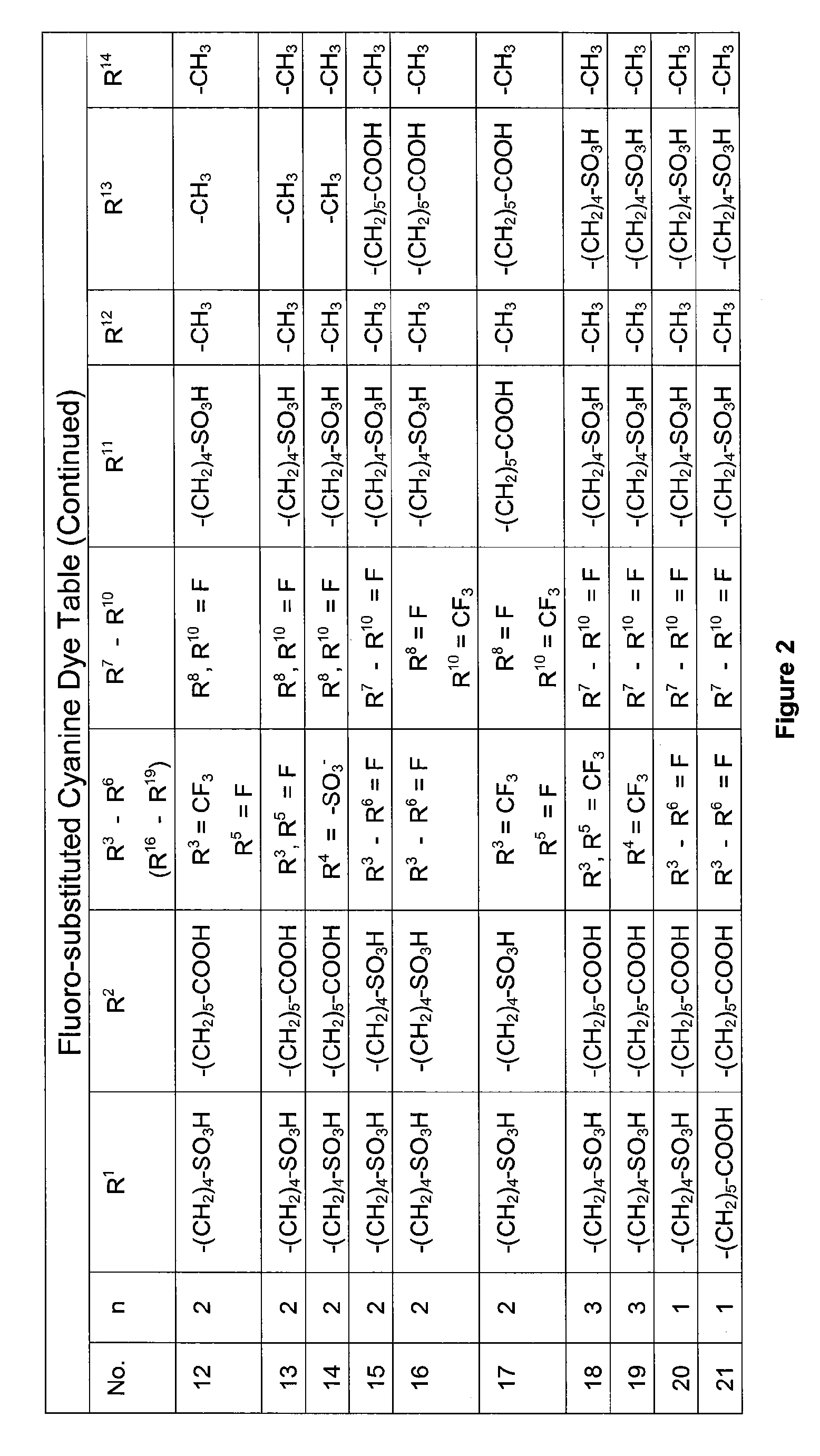
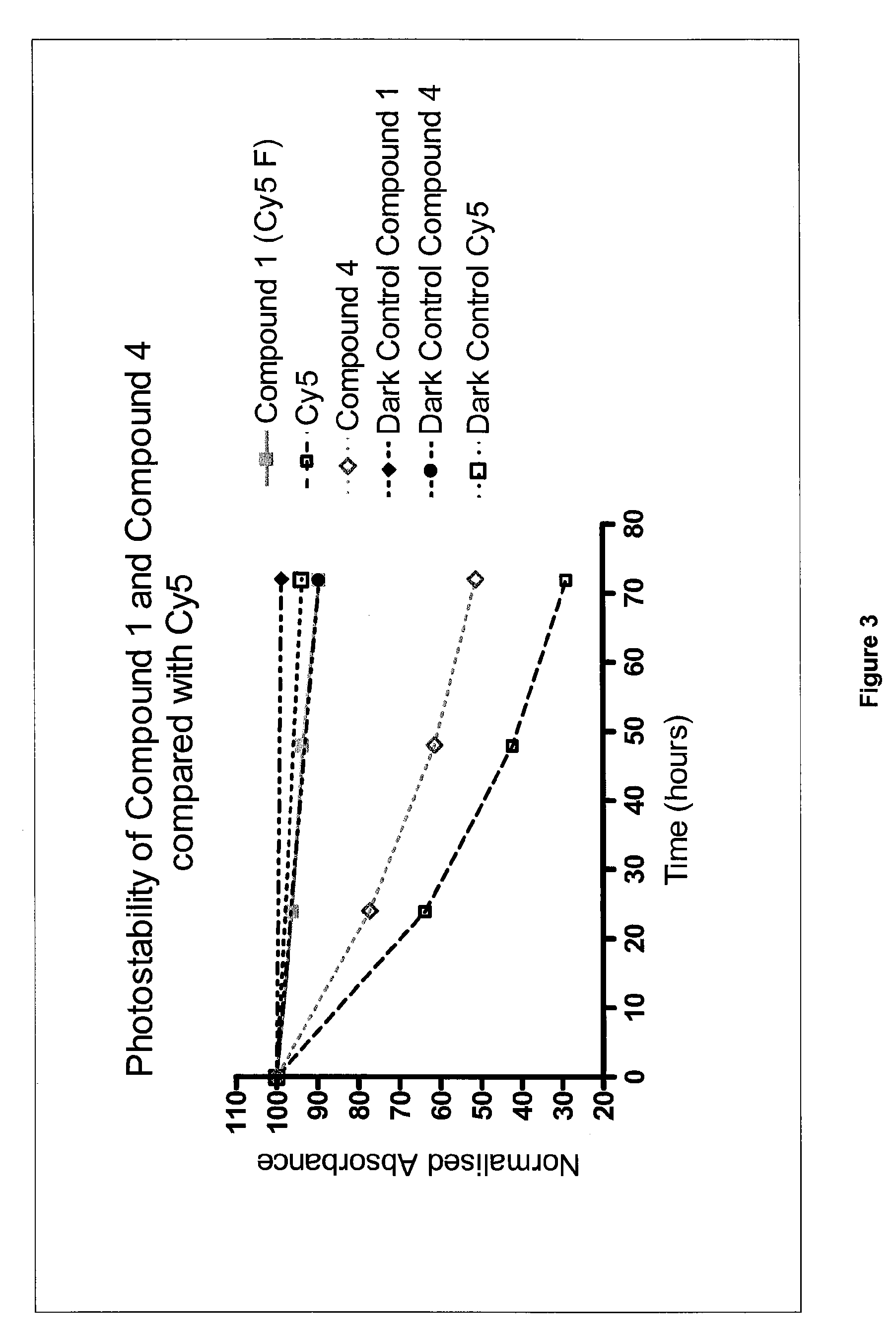
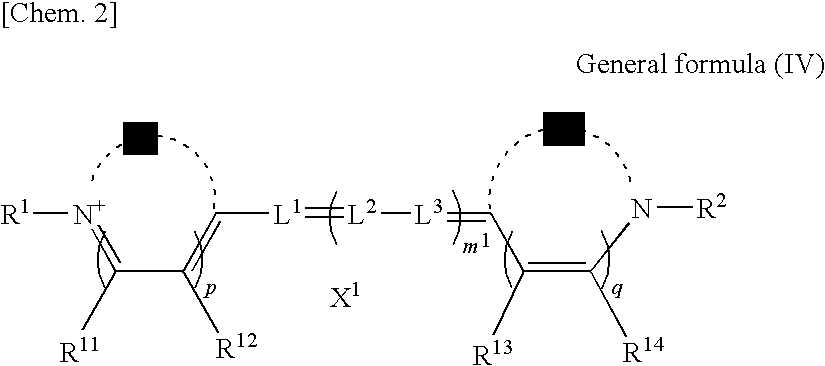
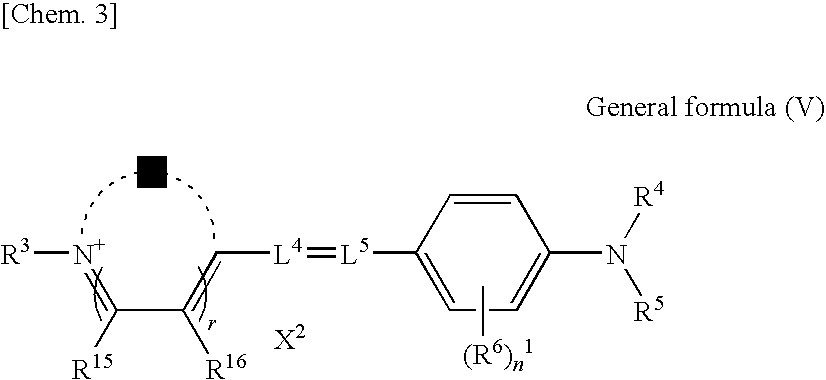
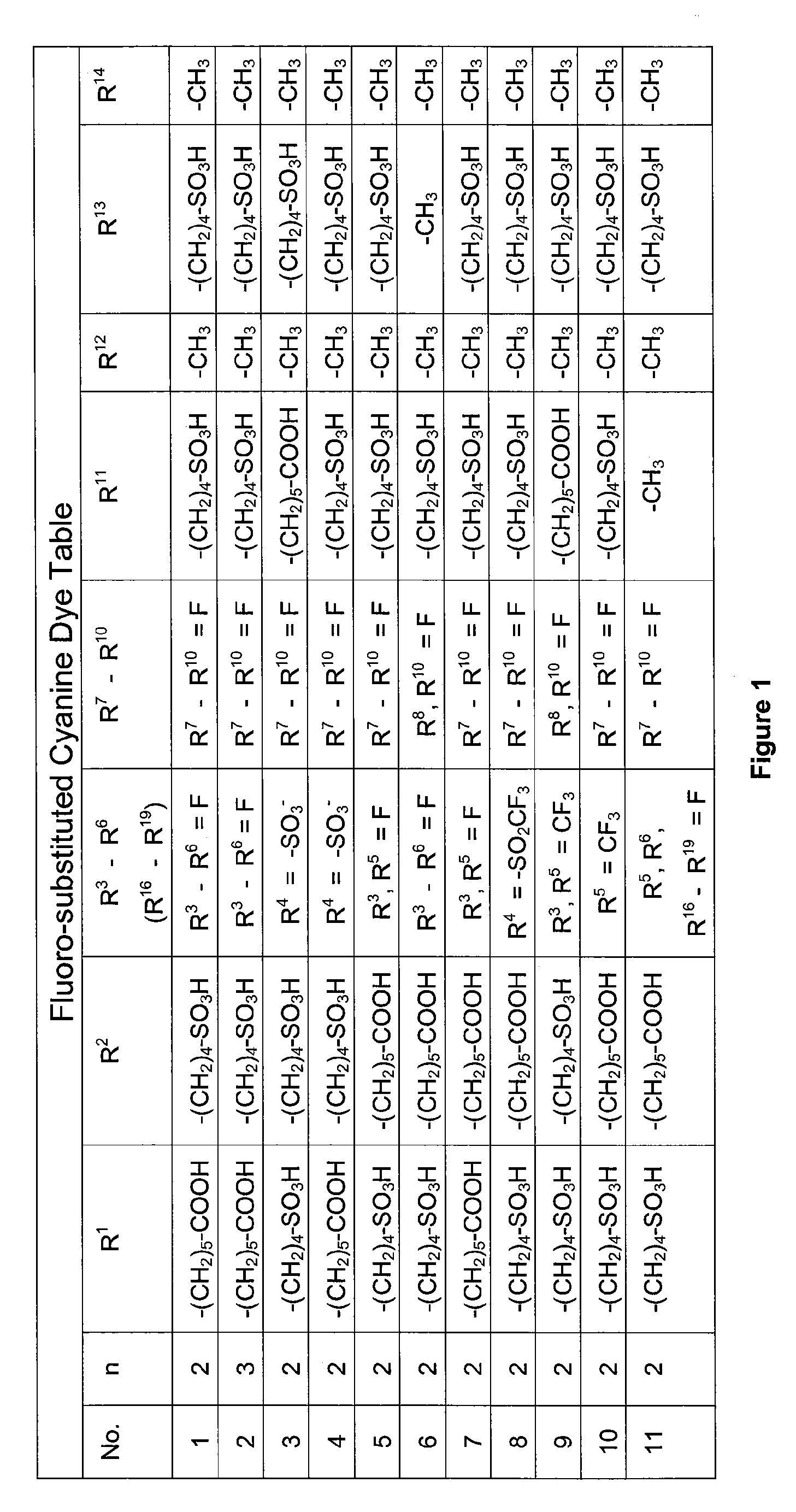
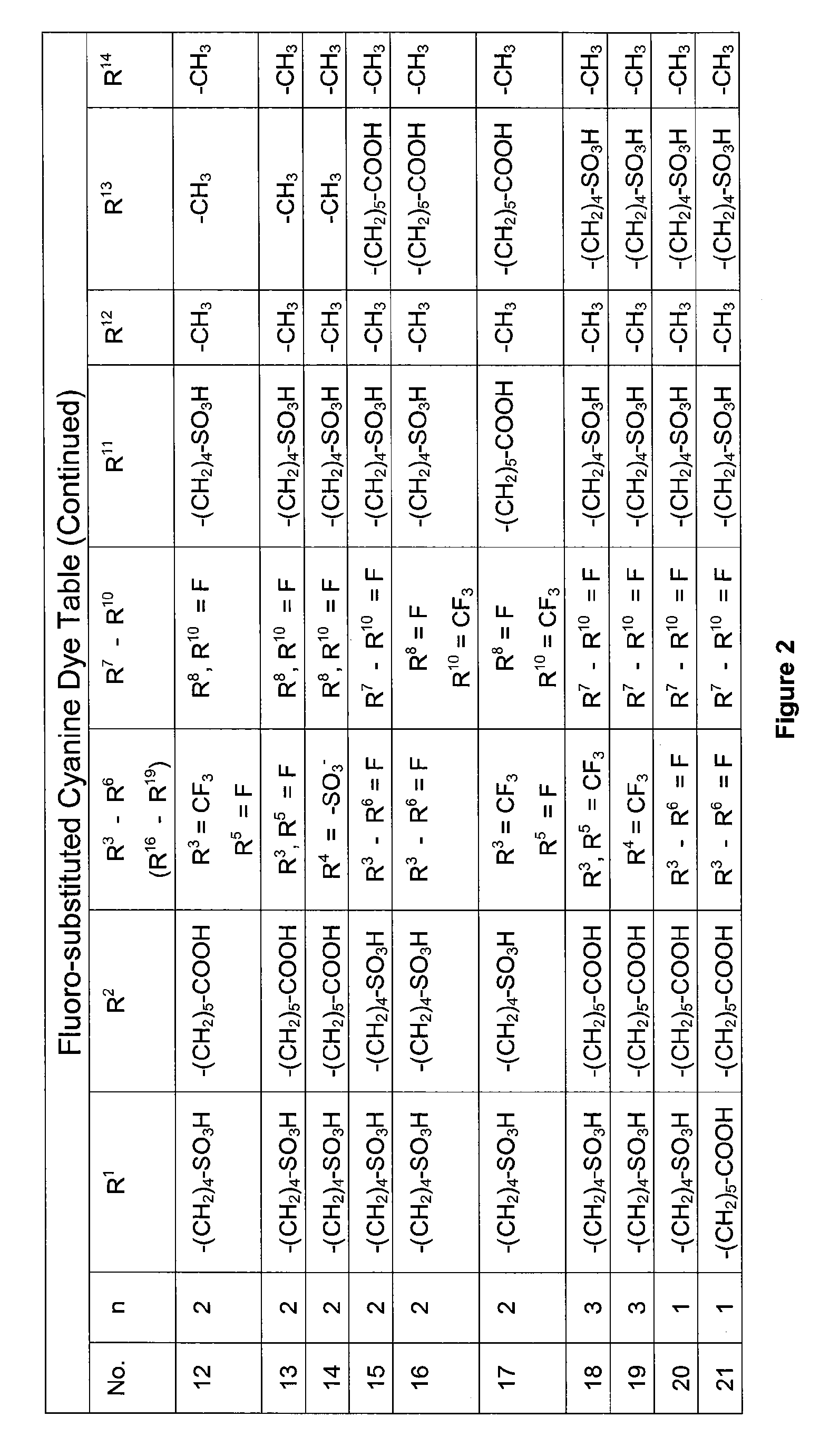
Water-soluble fluoro-substituted cyanine dyes as reactive fluorescence labelling reagents
ActiveUS20060239922A1Reduced dye-dye interactionImprove light resistanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMethine/polymethine dyesCyanineBiological target
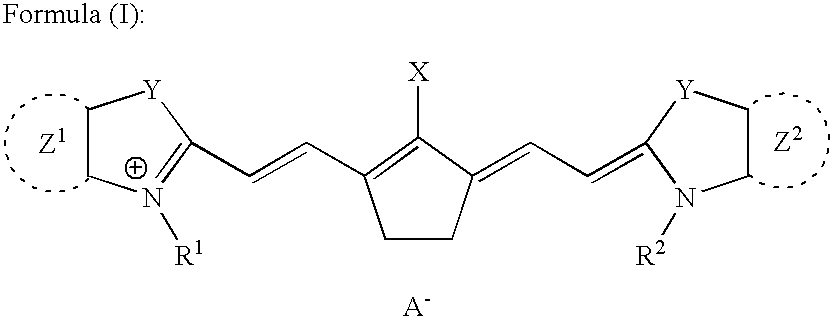
Disclosed are cyanine dyes that are useful for labelling and detecting biological and other materials. The dyes are of formula (I): in which at least one of groups R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10 R11, R12, R13 and R14 is -L-M or -L-P, where L is a linking group, M is a target bonding group and P is a conjugated component, and at least one of groups R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9 and R10 comprises fluorine. The use of cyanine dyes substituted by fluorine and having additional substitution with three or more sulphonic acid groups for labelling biological target molecules results in a labelled product in which there is reduced dye-dye aggregation and improved photostability, compared with cyanine dyes having no such substitutions. The dyes of the present invention are particularly useful in assays involving fluorescence detection where continual or repeated excitation is a requirement, for example in kinetic studies, or in microarray analyses where microarray slides may need to be reanalysed over a period of days.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS GERMANY GMBH
Heteroarylcyanine dyes
ActiveUS20140080127A1Useful level of resolutionMitigate one or more of these factorsMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesMoietyMerocyanine dye
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Use of cyanine dyes for the diagnosis of proliferative diseases
InactiveUS20060239916A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCyanineBody weight
The present invention concerns the use of the cyanine dye SF64 for the diagnosis of proliferative diseases upon administration of less than 5 mg / kg body weight.
Owner:BAYER SCHERING PHARMA AG
Compound for photoresist, photoresist solution, and etching method using the photoresist solution
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Photographic materials having improved keeping properties
InactiveUS7351523B2Prevent speedingShorten speedPhoto-taking processesPhotomechanical apparatusDopantSulfur
The use of a red-sensitising trinuclear merocyanine dye and an osmium dopant according to formula (I): [Os(NZ)L5]r wherein Z is sulphur or oxygen, L is a ligand and r is 0, −1, −2 or −3, in photographic silver halide emulsions for use in photographic materials, result in a reduction and / or prevention of speed gain in the emulsion over time without significant speed loss.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Hydrophilizable and hydrophilic cyanine dyes
ActiveUS7138391B2Mild conditionsSuitable for detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideArylCyanine
The present invention provides an IR-absorbing dye of formula (I) or (II):whereinQ1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 are the same or different and are independently selected from a C3-20 heteroarylene group comprising at least one N atom;M is selected from Si(A1)(A2), Ge(A1)(A2), Ga(A1), Mg, Al(A1), TiO, Ti(A1)(A2), ZrO, Zr(A1)(A2), VO, V(A1)(A2), Mn, Mn(A1), Fe, Fe(A1), Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Sn, Sn(A1)(A2), Pb, Pb(A1)(A2), Pd and Pt;A1 and A2 are axial ligands, which may be the same or different, and are selected from —OH, halogen, —OR3, a hydrophilic ligand and / or a ligand suitable for reducing cofacial interactions;R3 is a selected from C1-12 alkyl, C5-12 aryl, C5-12 arylalkyl or Si(Rx)(Ry)(Rz); andRx, Ry and Rz may be the same or different and are selected from C1-12 alkyl, C5-12 aryl, C5-12 arylalkyl, C1-12 alkoxy, C5-12 aryloxy or C5-12 arylalkoxy.Dyes of this type are especially suitable for use in netpage and Hyperlabel systems.
Owner:BASF SE
Hydroxamate substituted azaindoline-cyanine dyes and bioconjugates of the same
ActiveUS9012643B2High sensitivityReduce distractionsMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryEnergy transferAnalyte
Hydroxamate substituted azaindoline cyanine dyes, conjugates thereof and methods of using the same are provided. The subject cyanine dyes include an azaindoline ring having a hydroxamate substituent. The dyes may further include a reactive group moieties (RGM) and / or a water soluble group. Also provided are conjugates of the subject dyes. Also provided are tandem conjugates including a fluorescent protein capable of energy transfer to the dye. Methods of detecting an analyte in a sample by contacting the sample with a detection reagent are provided. The detection agent may be a dye-conjugate that specifically binds the analyte, or may be a reactive dye which conjugates to the analyte. Also provided are compositions, e.g., kits, etc., incorporating such dyes which facilitate use in such methods.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Site-specific labelling of proteins using cyanine dye reporters
InactiveUS20040023408A1Methine/polymethine dyesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCyanineRecombinant peptide
The present invention therefore provides new cyanine dye reagents and methods that afford direct attachment of the cyanine dye reporter to either the N-terminus or C-terminus of a synthetic or recombinant peptide or protein and their derivatives, in a site-specific manner, coupled with purification of the resultant labelled molecule.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Nir absorption and color compensating compositions
InactiveUS20060292462A1Avoid failureMethine/polymethine dyesOther chemical processesCyanineLength wave
Disclosed herein is a composition for use as a film on an image display filter. In some embodiments, the composition includes a cyanine dye exhibiting an absorption maximum in the wavelength region from about 830 to about 880 nm or from about 580 to about 600 nm and an anthraquinone dye comprising an anthraquinone compound substituted with an amino group in one or more positions selected from the 1-, 4-, 5-, and 8-position.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Image device and imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20170023713A1Reduces thickness of moduleLow infrared light transmittanceMethine/polymethine dyesOptical filtersCarbonyl groupPhenyl group
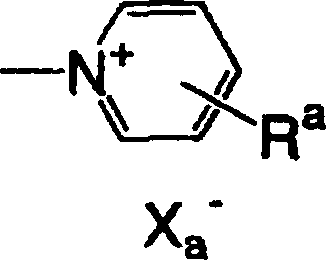
An imaging device, comprising: an infrared light absorption layer including a cyanine dye represented by Chemical Formula (A) below: wherein R1 and R2 are selected from the group consisting of: a chain alkyl group,a cyclic alkyl group, a phenyl group, and a benzyl group; wherein the chain alkyl group and the cyclic alkyl group including at least one group member selected from the group consisting of: 1) a first group having one or more hydrogen atoms in a first alkyl group substituted with at least one functional group selected from the group consisting of: a halogen atom, an alkoxy group, an alkanoloxy group, an amino group, a thiol group, and a mercapto group; 2) a second group having at least one reactive group selected from the group consisting of: a vinyl group, an acrylic group, a carbonyl group, a carboxyl group, an alkenyl group, an alkenyloxy group, an alkoxycarbonyl group, a nitrile group, a carboxyl group, a carbonyl group, a sulfonyl group, a sulfamoyl group, a carbamoyl group, a benzoyloxy group, and a cyano group,wherein the reactive group is any one of introduced at a terminal alkyl group of at least one of the chain alkyl group and the cyclic alkyl group and positioned two or more carbon atoms away from an indoline ring; 3)an unsubstituted chain alkyl group; and 4) an unsubstituted cyclic alkyl group; and wherein X− represents an anion.
Owner:SONY CORP
Dye for dye-sensitized solar cell, semiconductor electrode, and dye-sensitized solar cell
InactiveCN102171885AReduce hindranceImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyOrganic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesSemiconductor electrodeElectron donor
Disclosed is a dye for dye-sensitized solar cells that is composed of a compound classified as a merocyanine dye, has a structure wherein electron donor units and electron acceptor units are joined with a conjugated double bond, and has excellent photoelectric conversion and durability. With the dye, it is possible to provide a semiconductor electrode that is sensitized by the dye as well as a dye-sensitized solar cell made by using the semiconductor electrode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PAPER MILLS LTD
Compound for photoresist, photoresist liquid, and etching method using the same
InactiveUS20100104985A1Significant simplificationMonoazo dyesMethine/polymethine dyesPhthalocyanine dyeMerocyanine dye
The present invention relates to a compound for photoresist, selected from the group consisting of a compound comprising an oxonol dye skeleton, a cyanine dye, a styryl dye, a compound comprising a merocyanine dye skeleton, a compound comprising a phthalocyanine dye skeleton, an azo compound, and a complex compound of an azo compound and a metal ion. The present invention further provides a photoresist liquid comprising at least one of the compound for photoresist and a method of etching a surface being processed using the photoresist liquid.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Water-soluble fluoro-substituted cyanine dyes as reactive fluorescence labelling reagents
ActiveUS7767829B2Reduced dye-dye interactionImprove light resistanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMethine/polymethine dyesFluorescenceBiological target
Disclosed are cyanine dyes that are useful for labelling and detecting biological and other materials. The dyes are of formula (I):in which at least one of groups R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10 R11, R12, R13 and R14 is -L-M or -L-P, where L is a linking group, M is a target bonding group and P is a conjugated component, and at least one of groups R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9 and R10 comprises fluorine. The use of cyanine dyes substituted by fluorine and having additional substitution with three or more sulphonic acid groups for labelling biological target molecules results in a labelled product in which there is reduced dye-dye aggregation and improved photostability, compared with cyanine dyes having no such substitutions. The dyes of the present invention are particularly useful in assays involving fluorescence detection where continual or repeated excitation is a requirement, for example in kinetic studies, or in microarray analyses where microarray slides may need to be reanalysed over a period of days.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS GERMANY GMBH
Methods of using cyanine dyes for the detection of analytes
InactiveUS20120178171A1Reduce problem sizeEfficient systemAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAnalyteAqueous solution
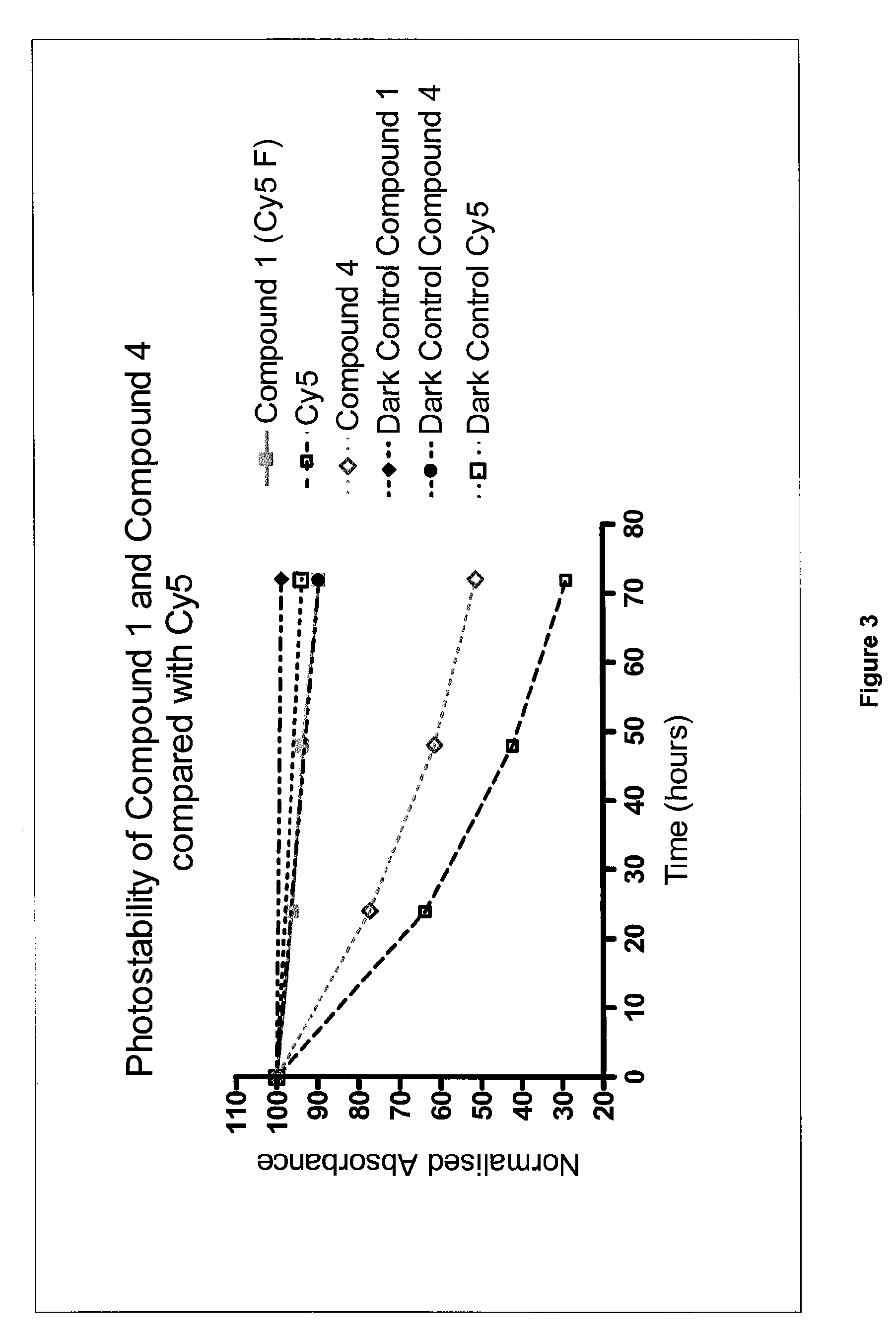
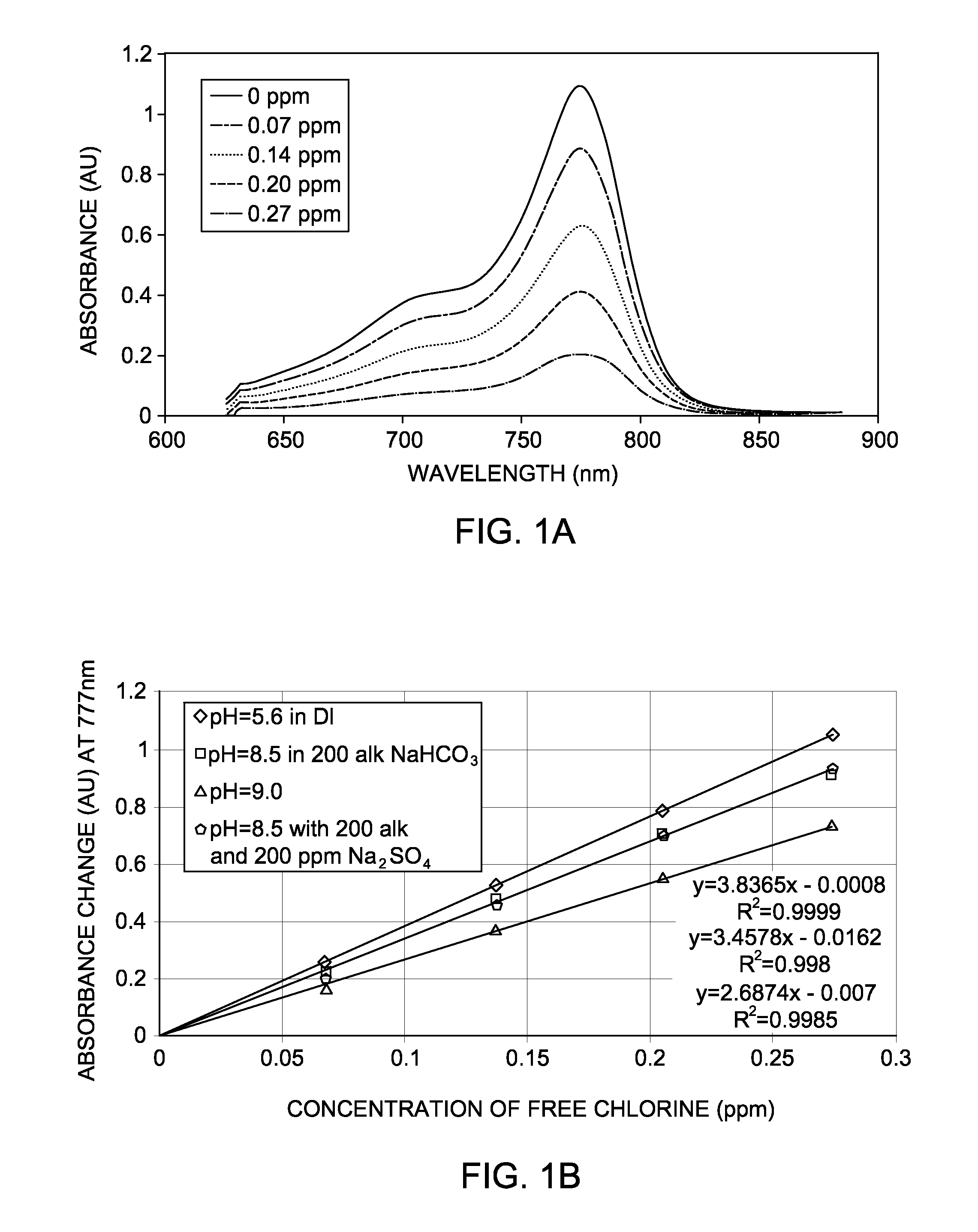
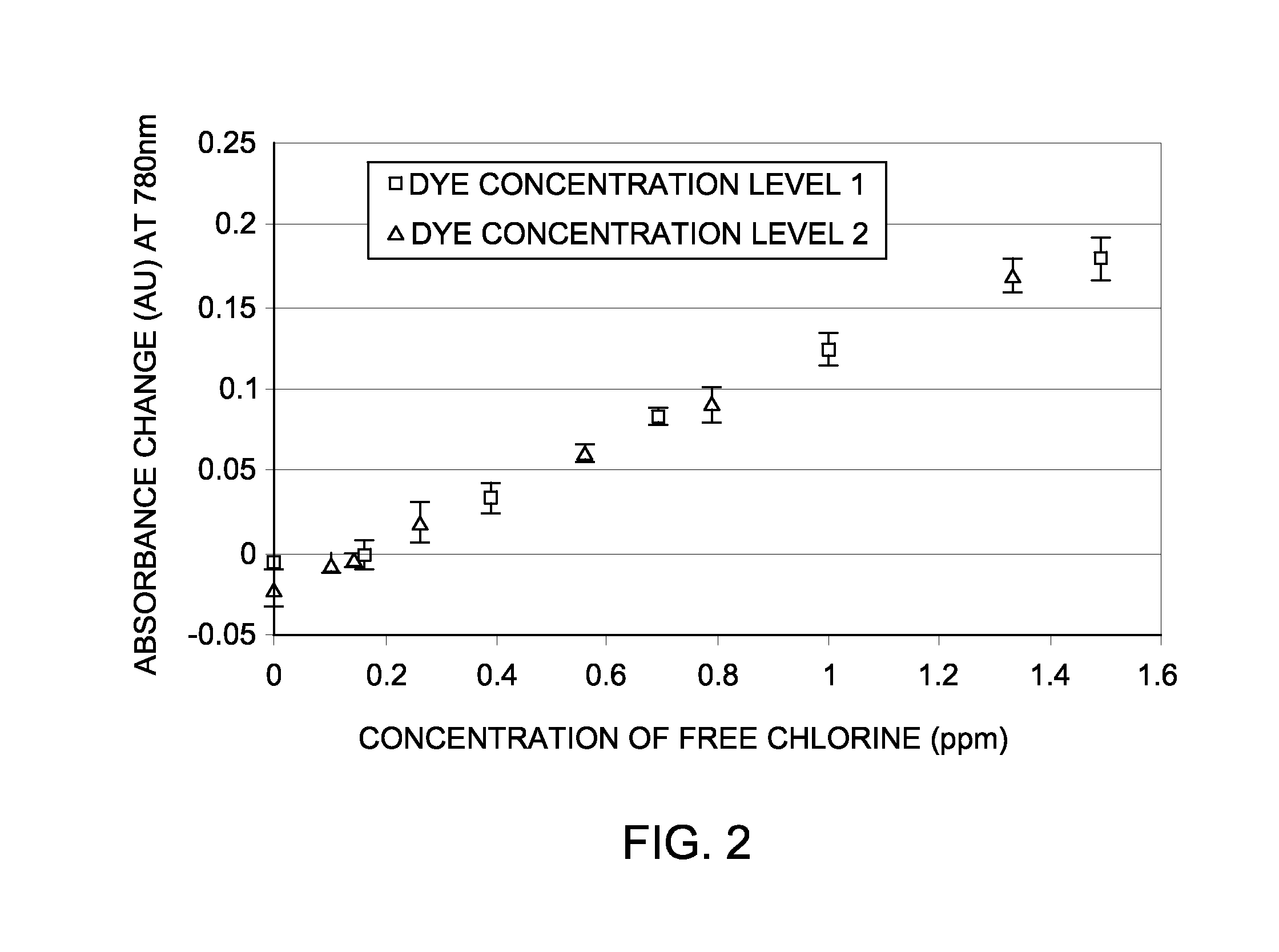
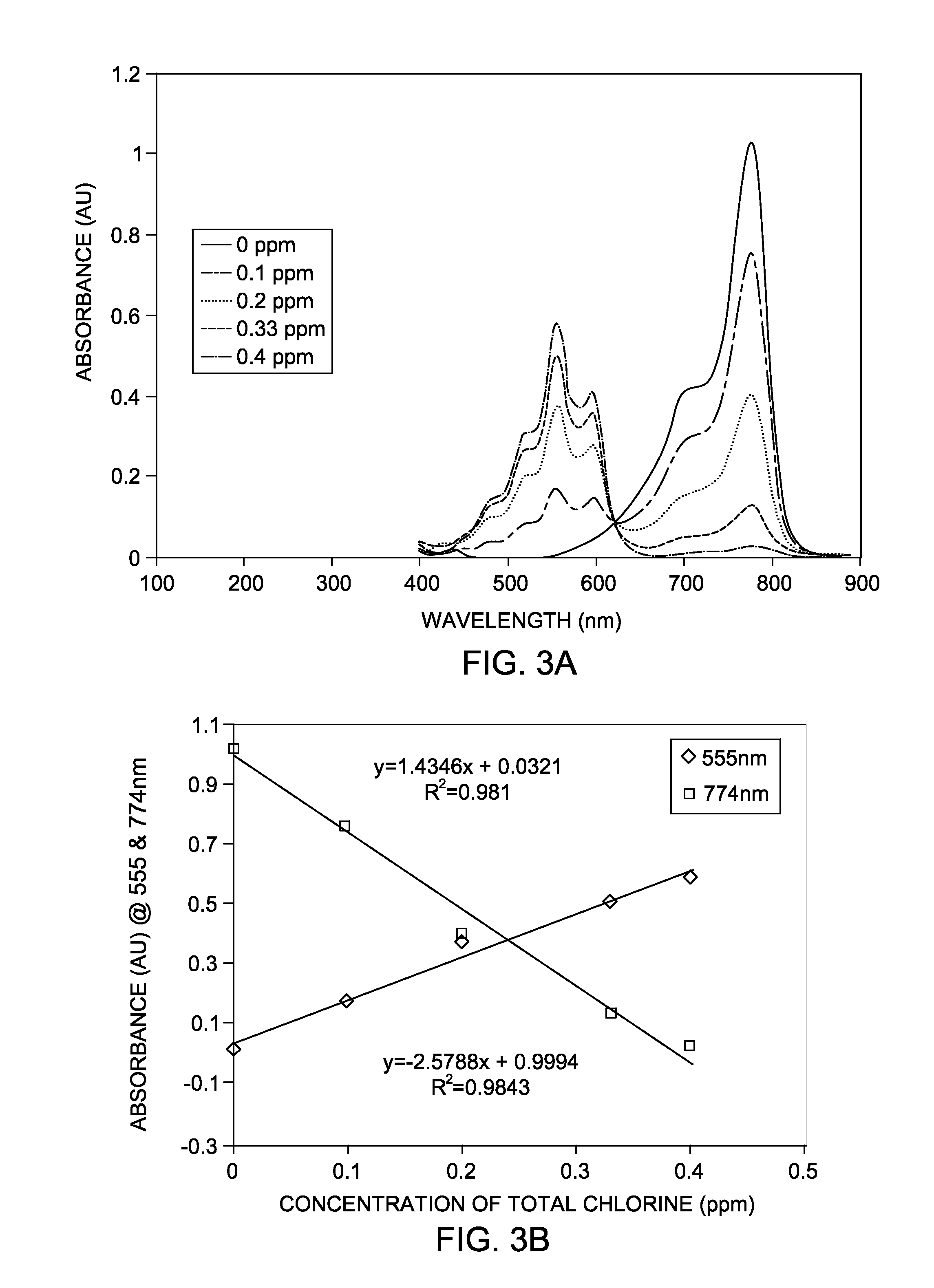
The present invention concerns a method of measuring the concentration of an analyte in an aqueous solution that comprises the steps of: obtaining an aqueous solution containing an analyte, providing a cyanine indicator, placing the aqueous solution in fluid communication with the cyanine indicator, measuring a detectable property change of the cyanine indicator, and comparing the detectable property change of the cyanine indicator with a calibration curve of the detectable property change of samples containing known concentrations of the analyte to determine the concentration of the analyte, wherein the detectable property change is proportional to the concentration of the analyte in said aqueous solution.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cyanine dye having reduced visible absorption
ActiveUS20060030703A1Reducing intermolecular interactionMinimize absorptionReactive dyesInksCyanineMerocyanine dye
Owner:BASF AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com