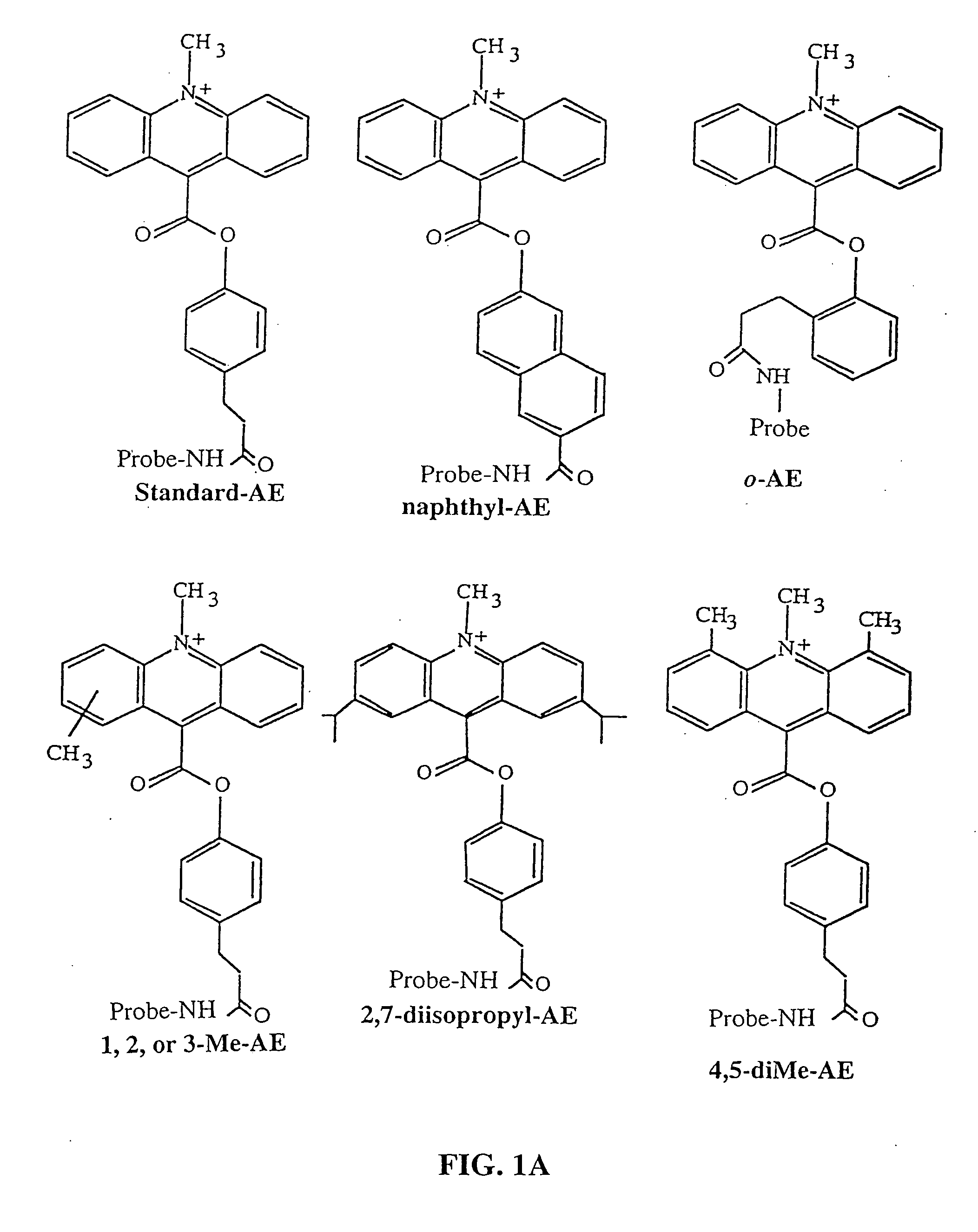
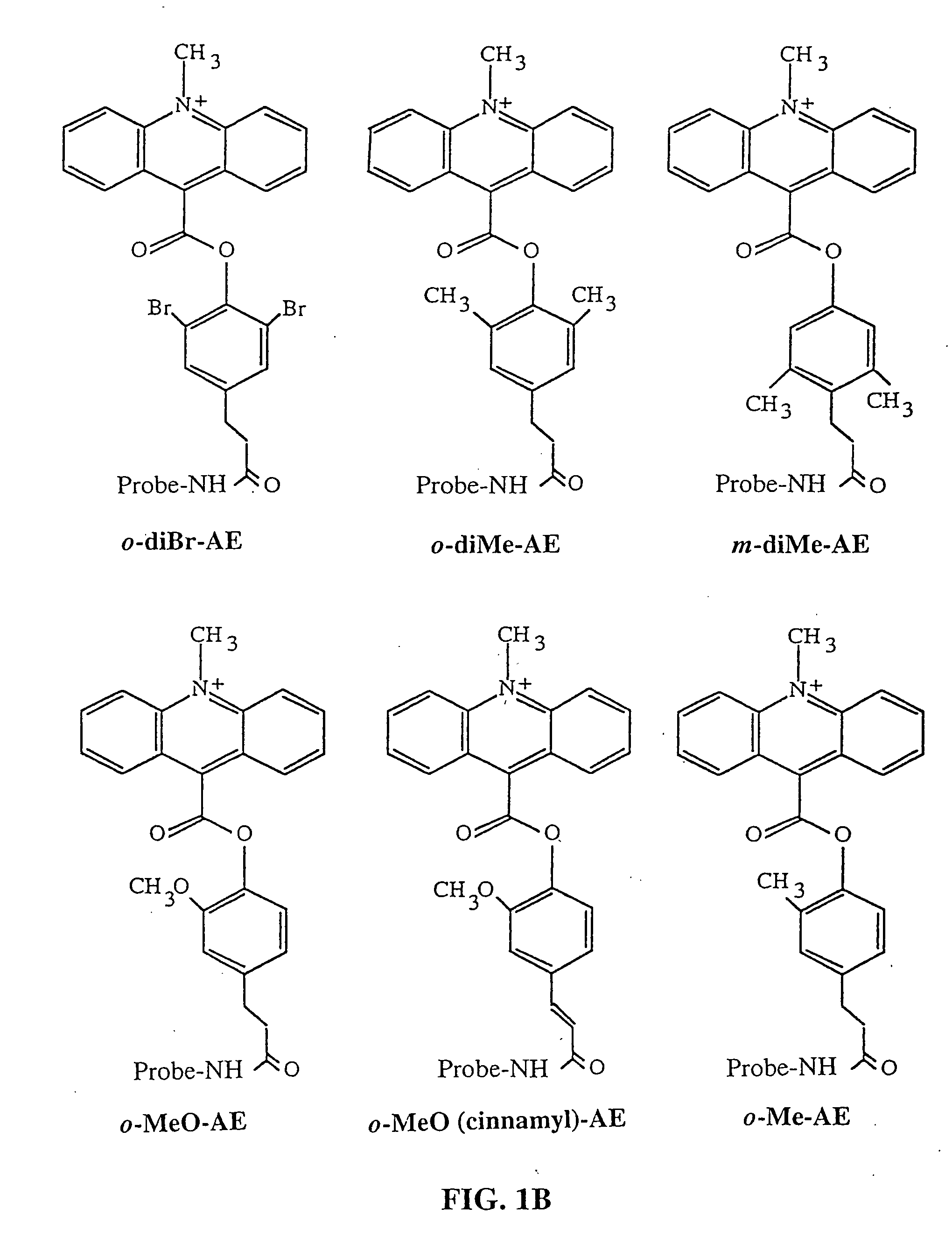
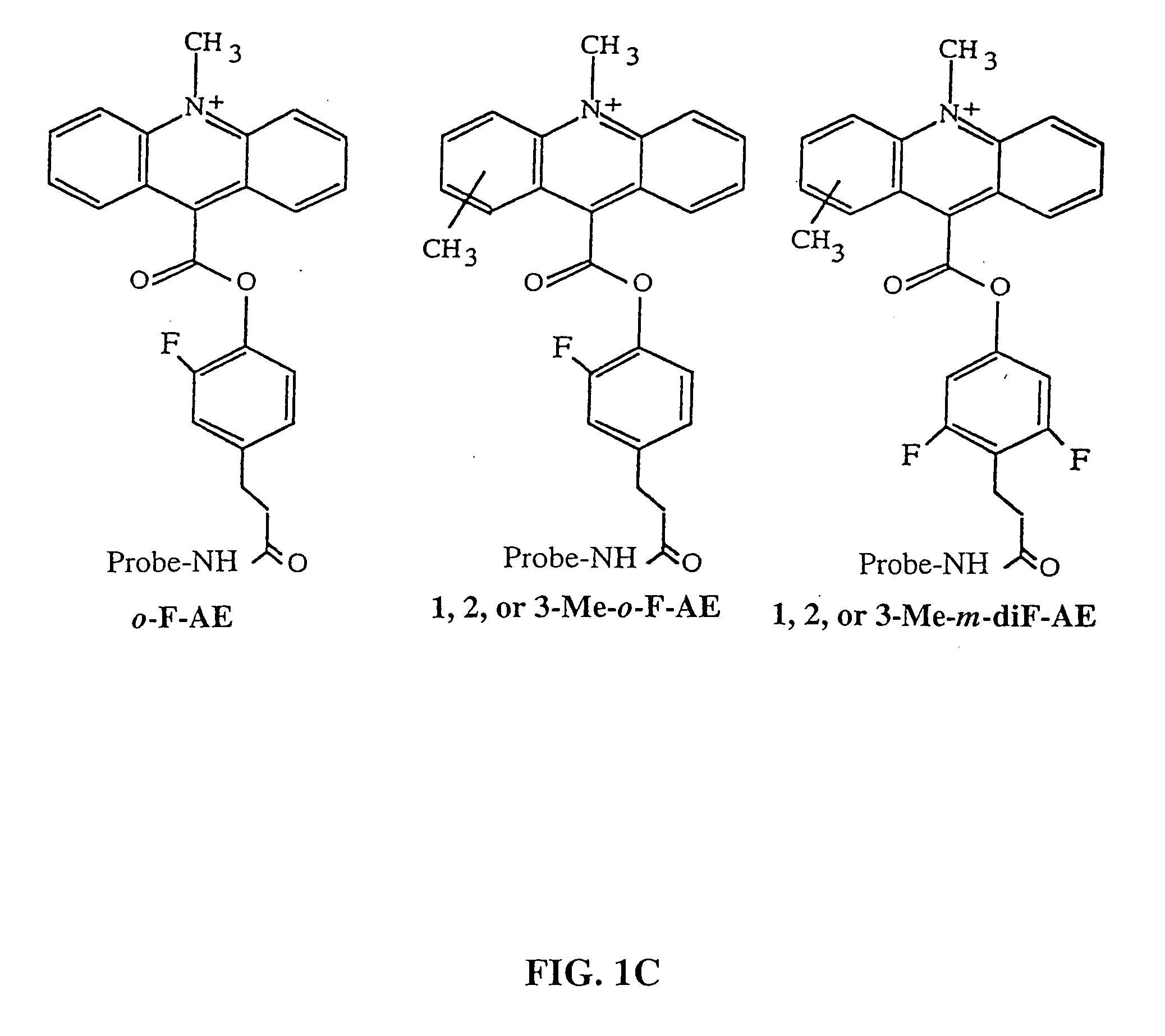
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Nucleotide base sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Base Sequence is the order of the nucleotide bases (bond pairs) in the DNA molecule. The order is where the information is stored in the molecule.
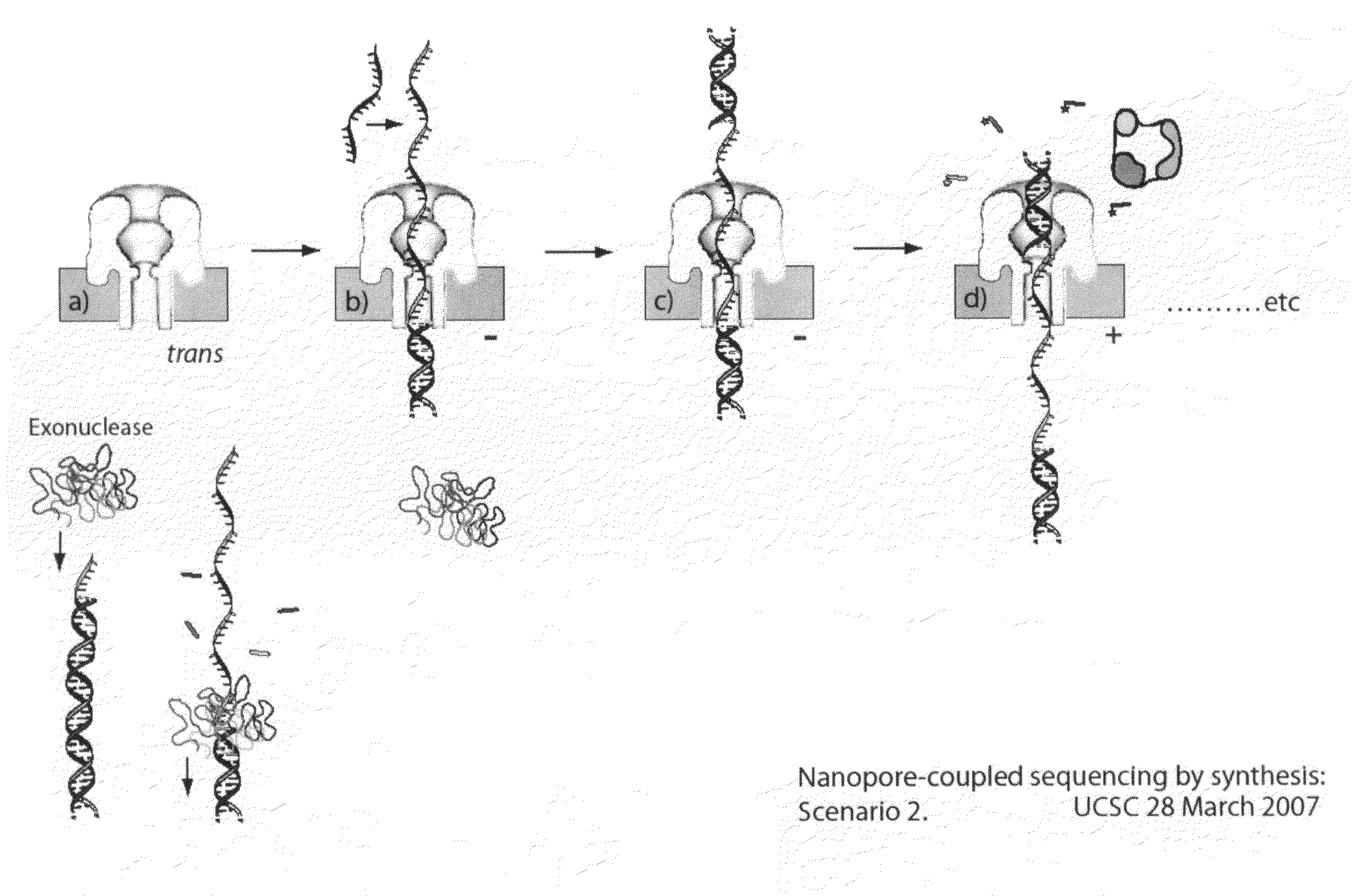
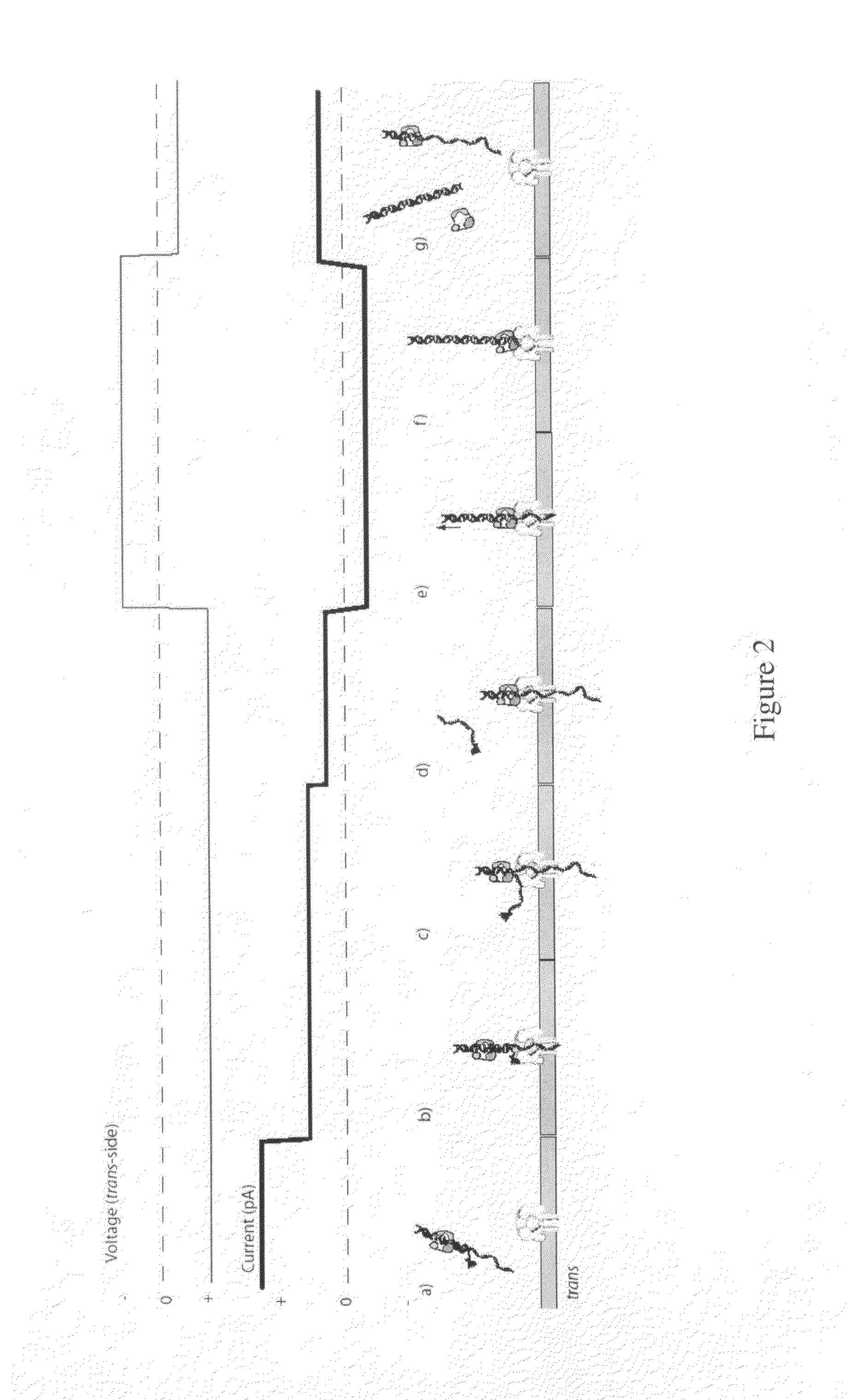
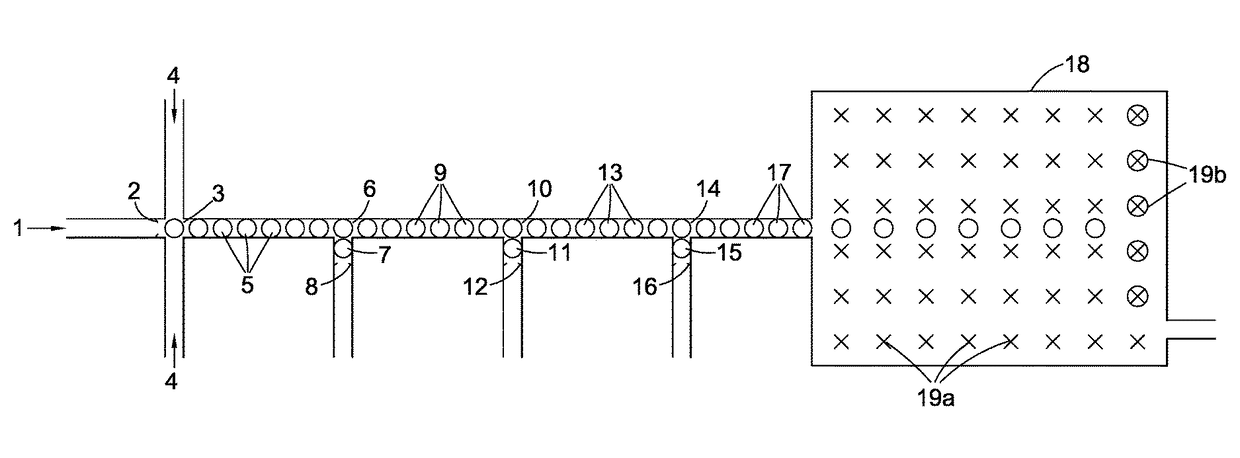
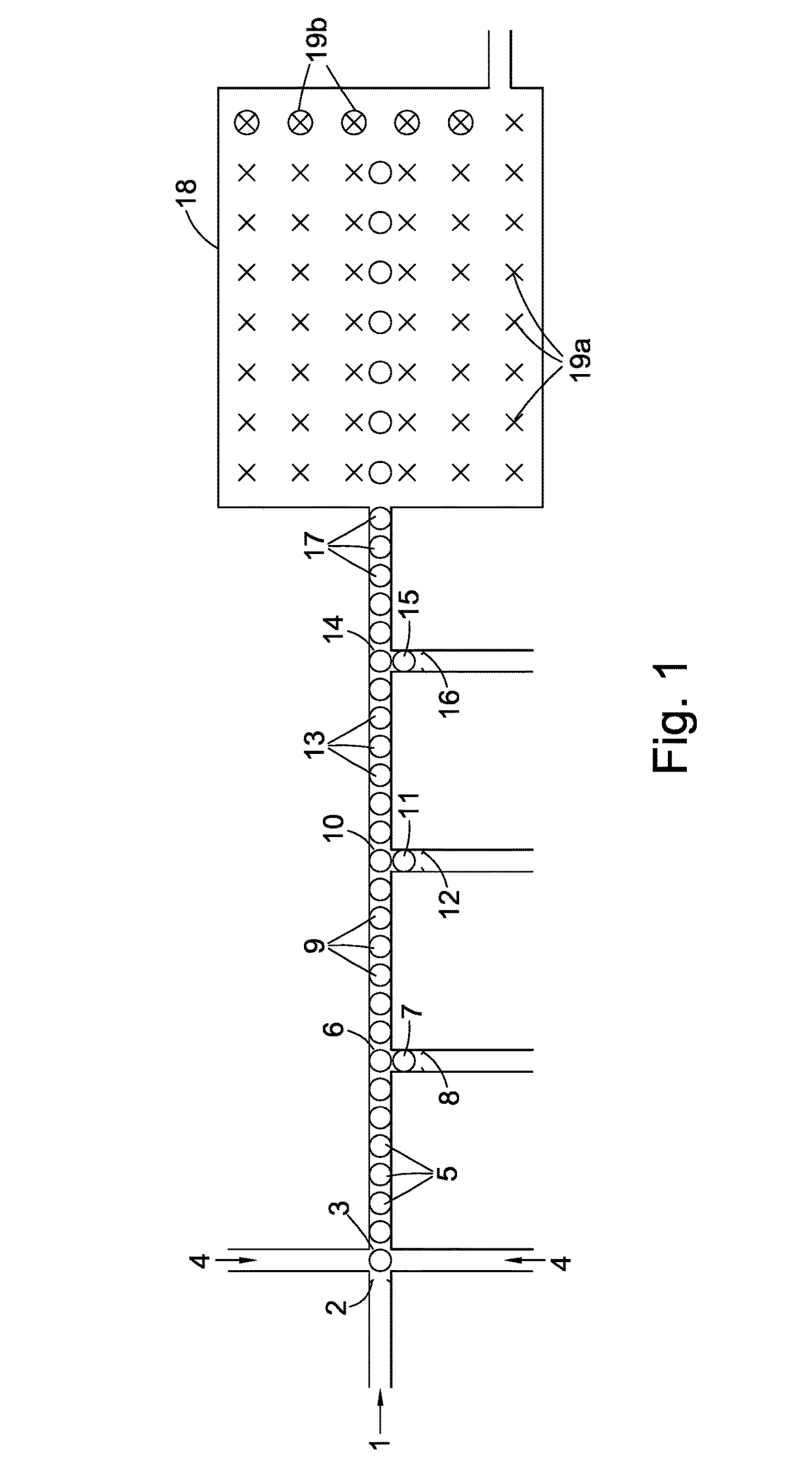
Compositions, devices, systems, for using a Nanopore
ActiveUS20100035260A1Low costRapidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsStructural biologyMolecular switch
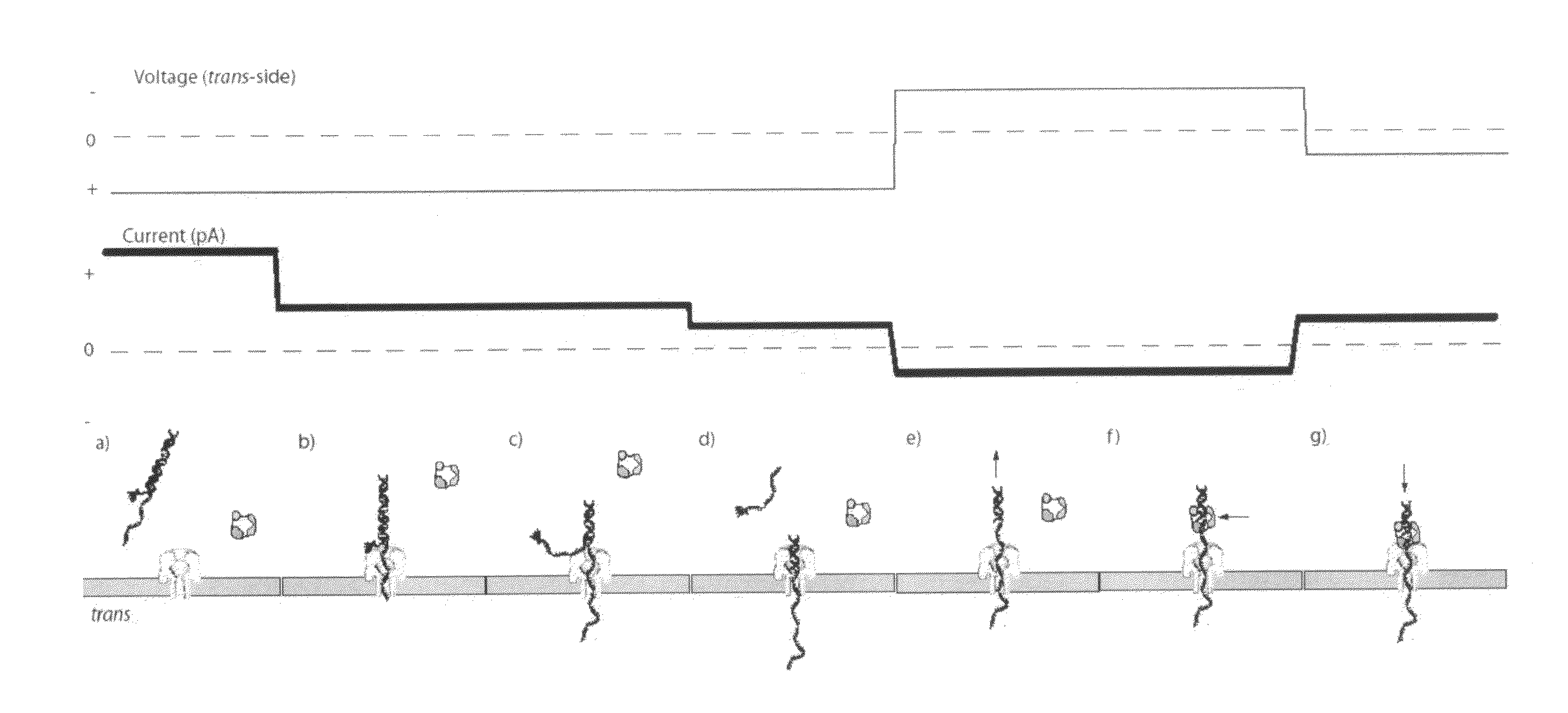
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore in the absence of requiring a terminating nucleotide. The devices and methods are also used to determine rapidly (˜>50 Hz) the nucleotide base sequence of a polynucleotide under feedback control or using signals generated by the interactions between the polynucleotide and the nanopore. The invention is of particular use in the fields of drug discovery, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions, devices, systems, and methods for using a nanopore
InactiveUS20110005918A1Low costRapidityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsStructural biologyMolecular switch
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore. The devices and methods are also used to determine rapidly (˜>50 Hz) the nucleotide base sequence of a polynucleotide under feedback control or using signals generated by the interactions between the polynucleotide and the nanopore. The invention is of particular use in the fields of molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
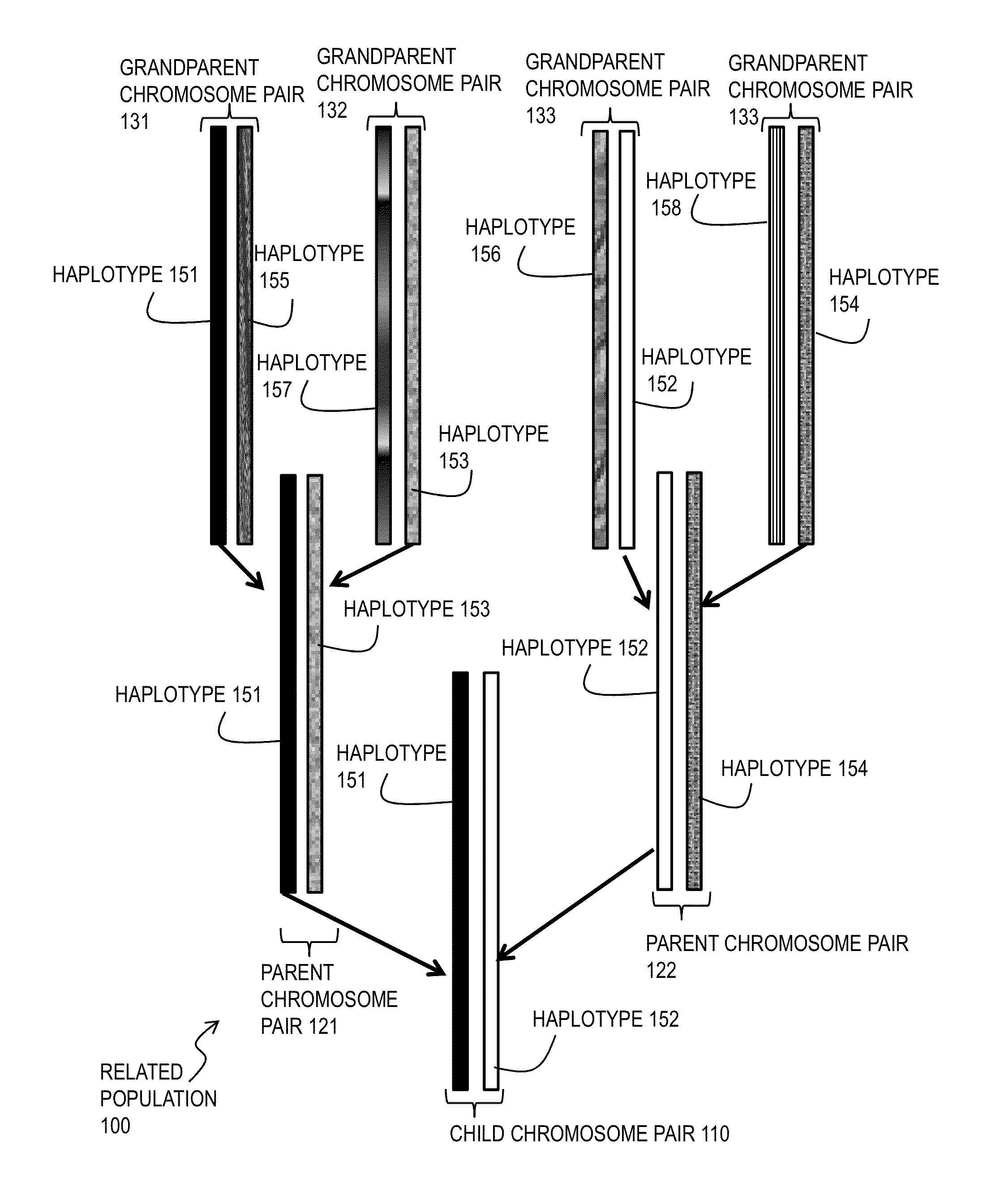
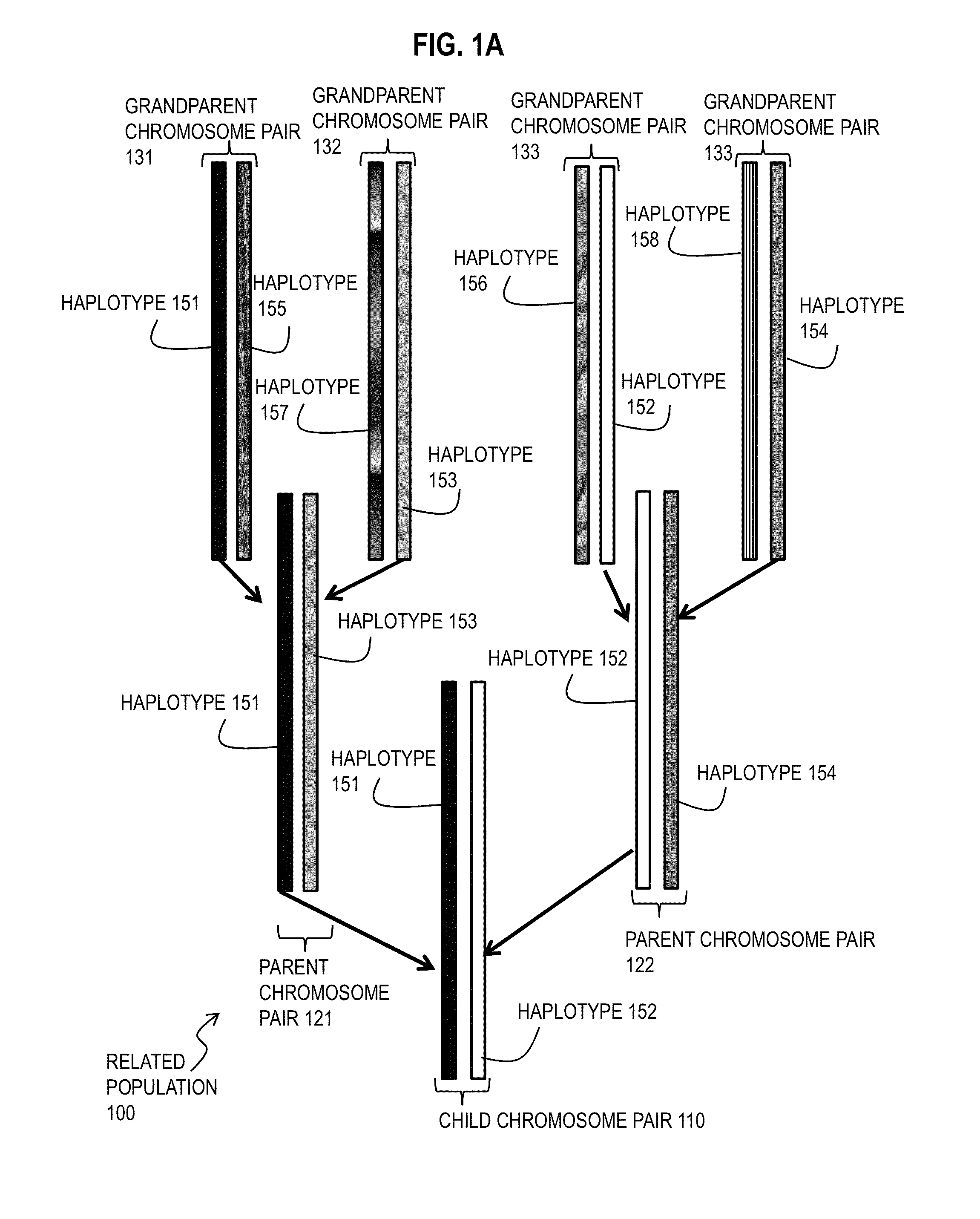
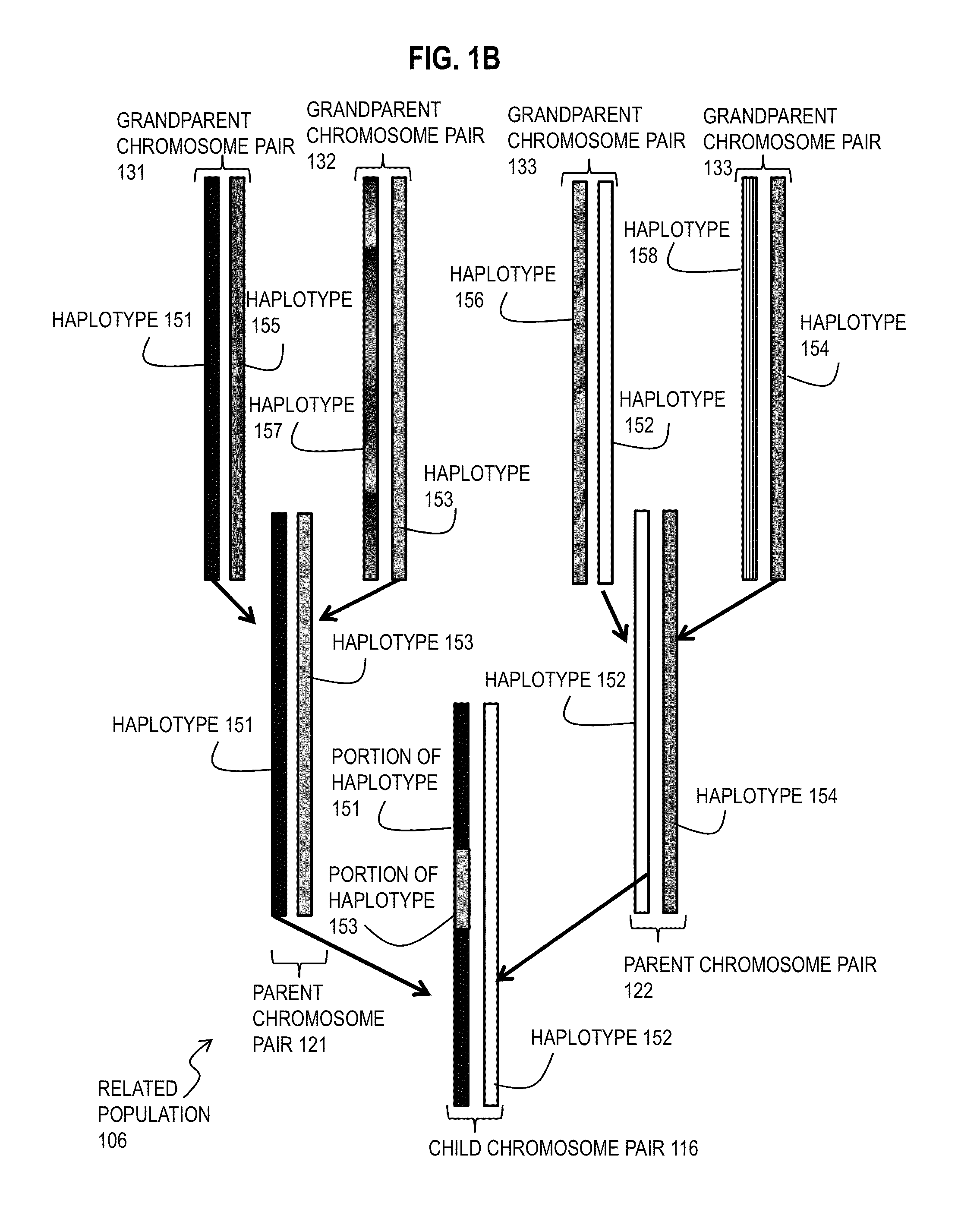
Techniques for Determining Haplotype by Population Genotype and Sequence Data
ActiveUS20140045705A1Better phasingImprove accuracyLibrary member identificationProteomicsHaplotypeSequencing data
A novel phasing algorithm harnesses sequencing read information from next generation sequencing technologies to guide and improve local haplotype reconstruction from genotypes. Techniques include determining correlated occurrences of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes of a population of individuals. A plurality of sequences of nucleotide bases in one or more individuals from the populations of individuals is determined based on ultra-high throughput sequencing of a sample from the one or more individuals. Haplotypes included in the population of individuals are determined based on both the correlated occurrences and the plurality of sequences. The inclusion of paired end read data is especially advantageous for the phasing of rare variants, including singletons.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
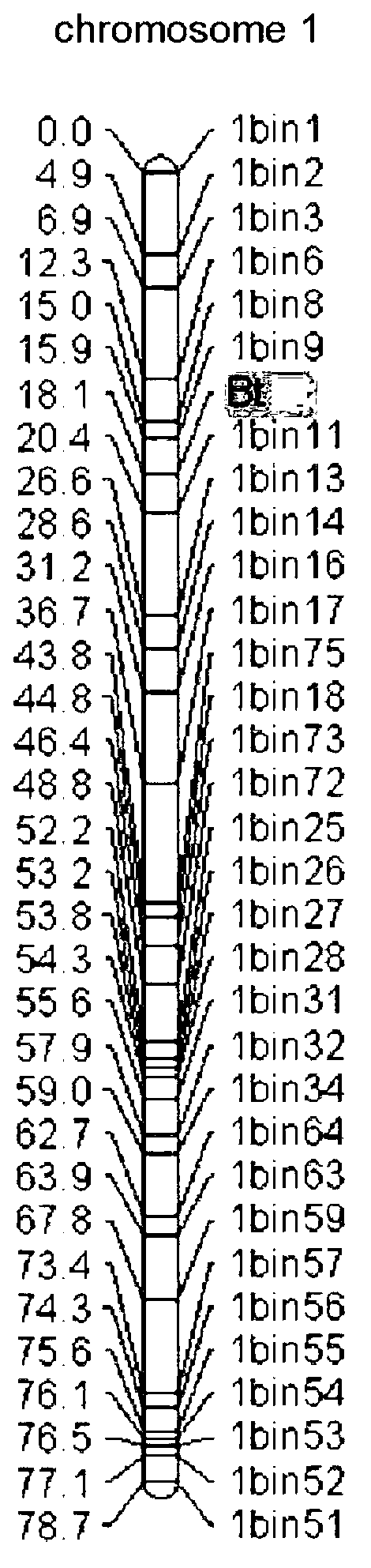
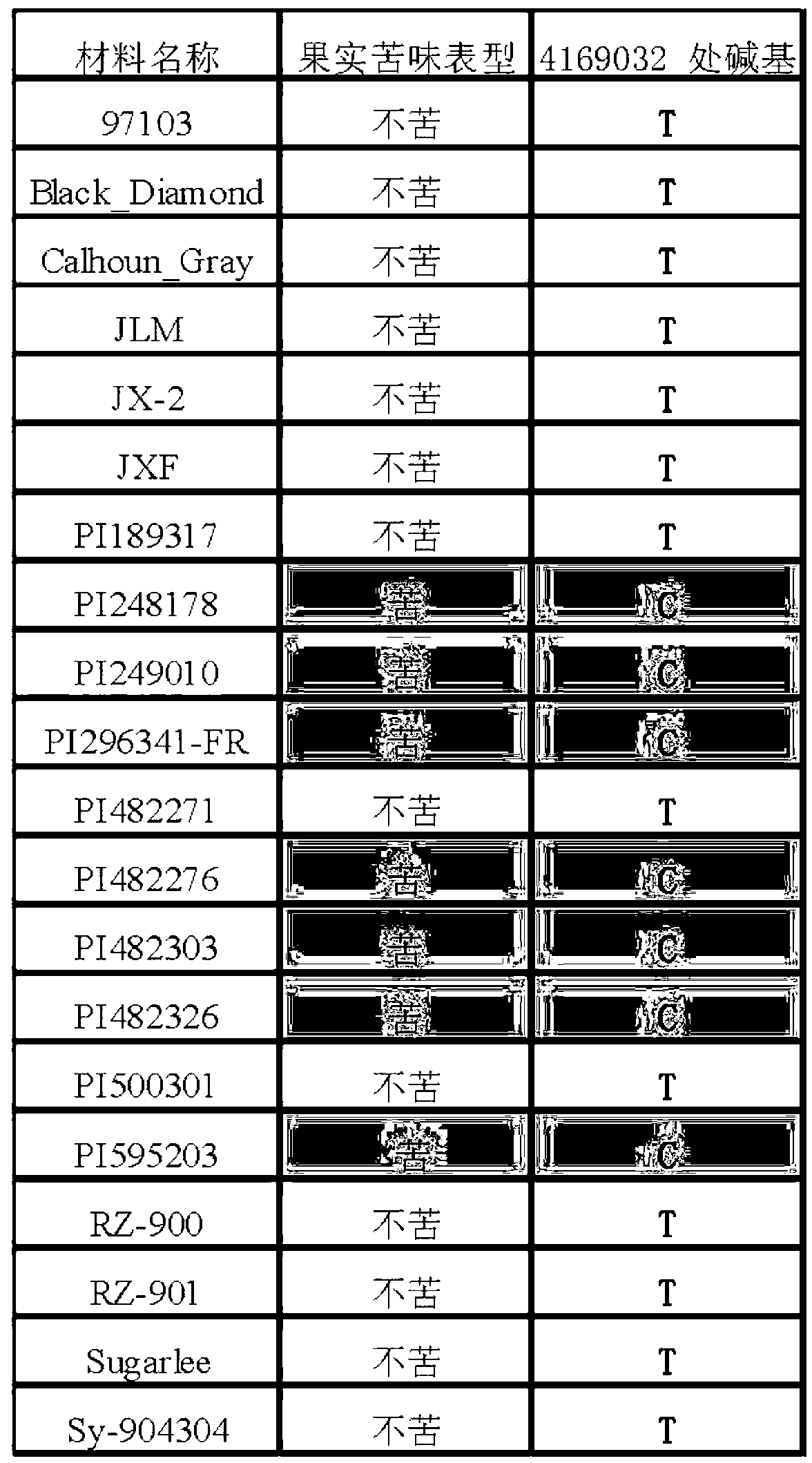
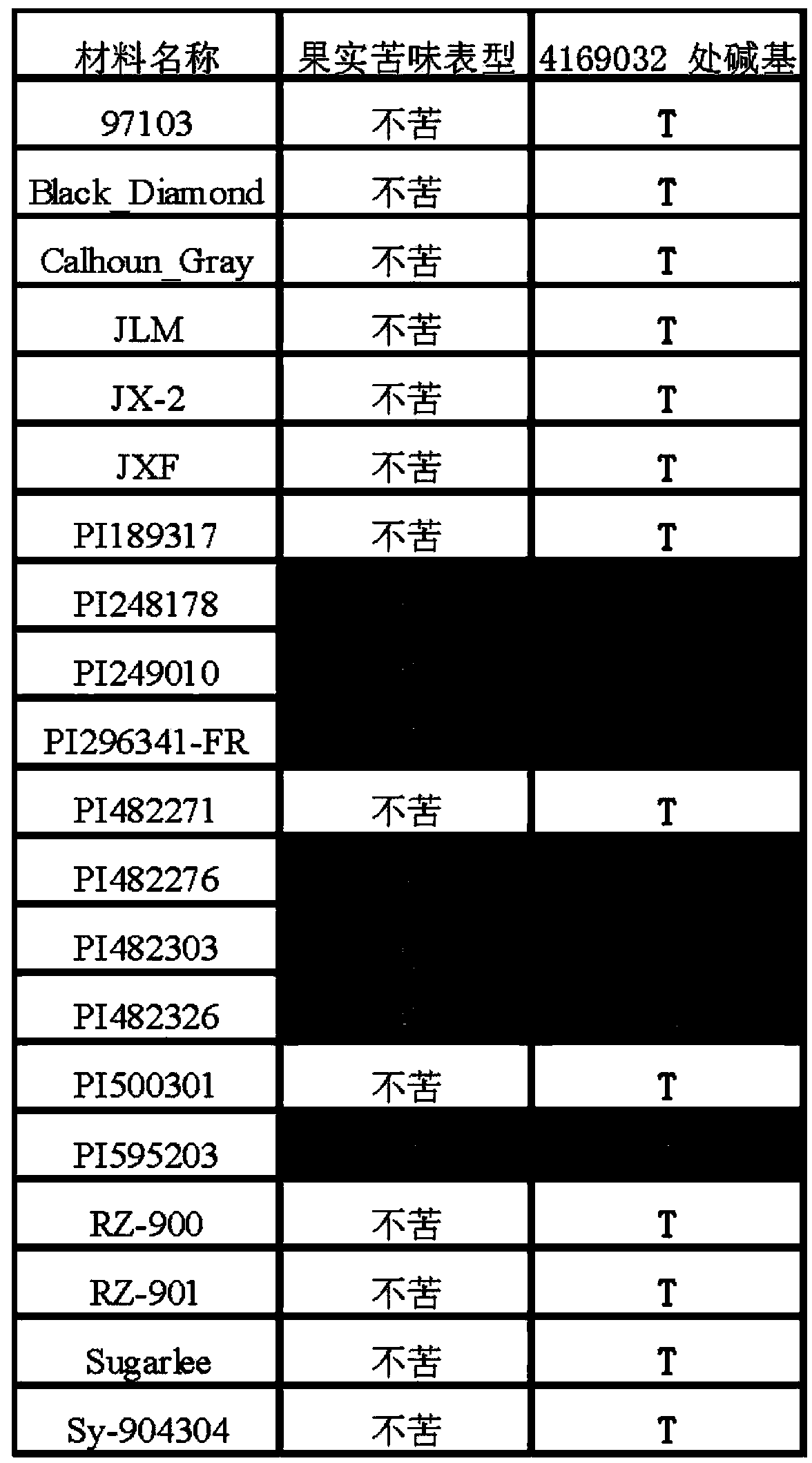
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site and CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) mark interlocked with citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste gene Bt (bitterness)
ActiveCN103194444AShorten the timeShorten the breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHigh densityMolecular breeding
The invention belongs to the fields of a gene sequence and an obtaining method of the gene sequence, and particularly relates to an obtaining method of an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site and a CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) mark interlocked with a citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste gene Bt (bitterness). The SNP site and the CAPS mark interlocked with the citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste have nucleotide base sequences in SEQ ID NO:1-2 in a sequence table. The citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste gene is primarily positioned by screening a bitter taste single plant in an RILs colony and combining with the high-density genetic map information of the citrullus lanatus; the candidate SNP site interlocked with the character is combined with separate colony verification analysis and natural colony verification analysis; the mark tightly interlocked with a target character is obtained; the SNP site and the CAPS mark can be applied to improvement of citrullus lanatus variety and molecular assisted breeding; a technical support is provided for molecular breeding of the citrullus lanatus quality; and meanwhile, the traditional gene positioning time is greatly shortened.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
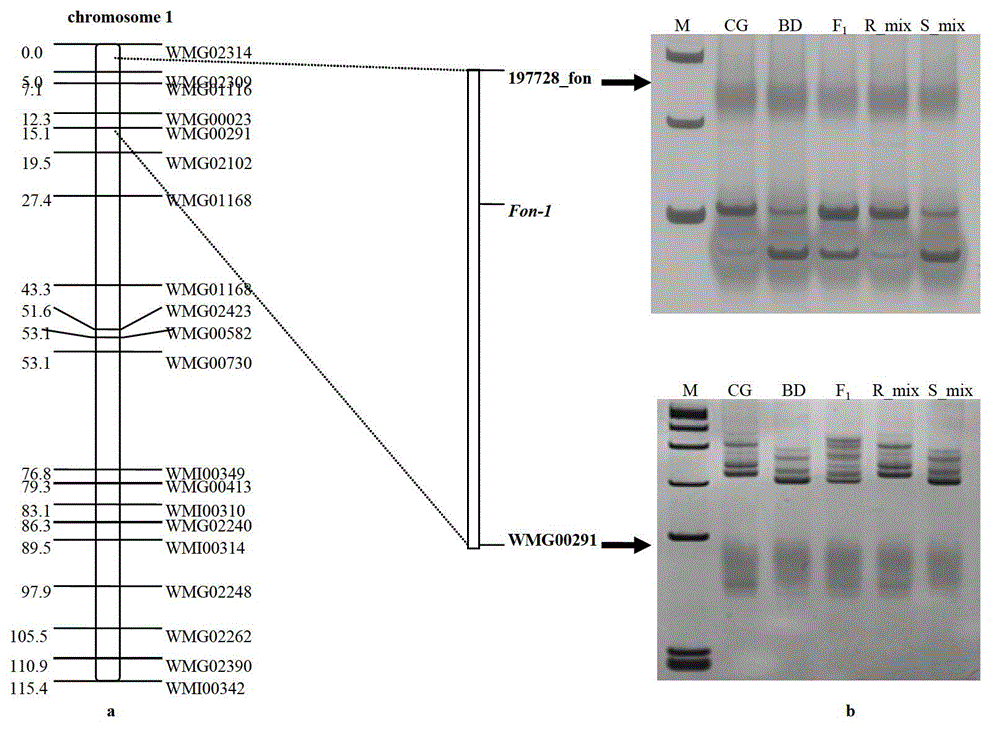
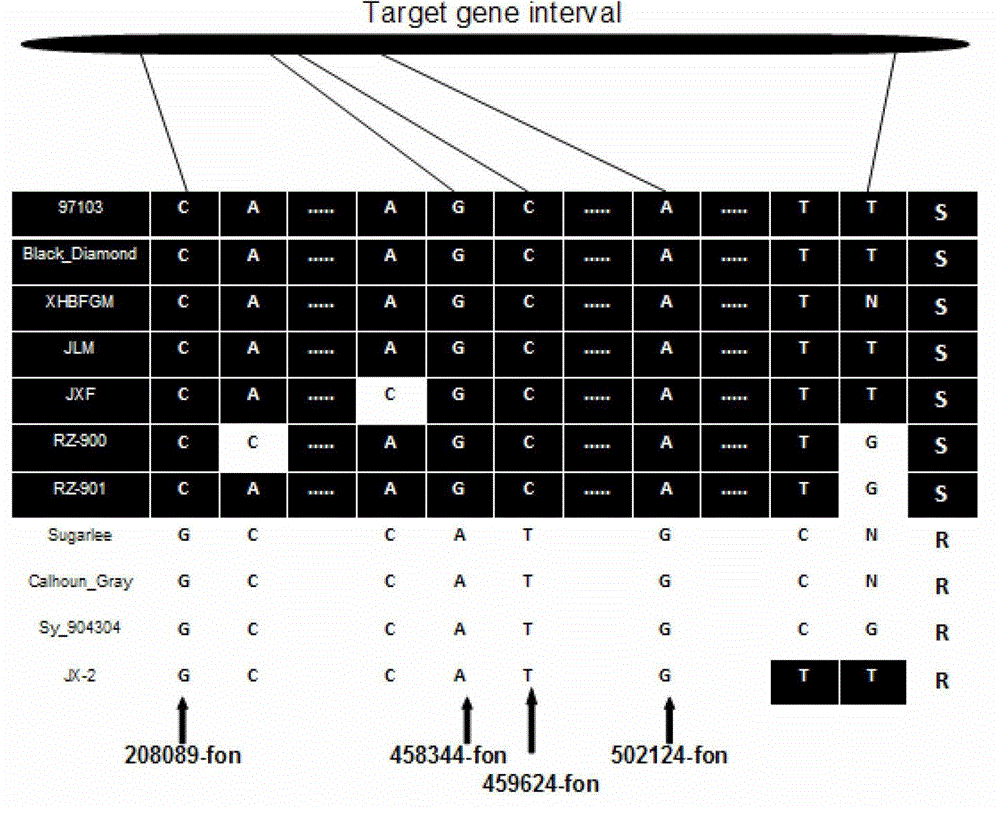
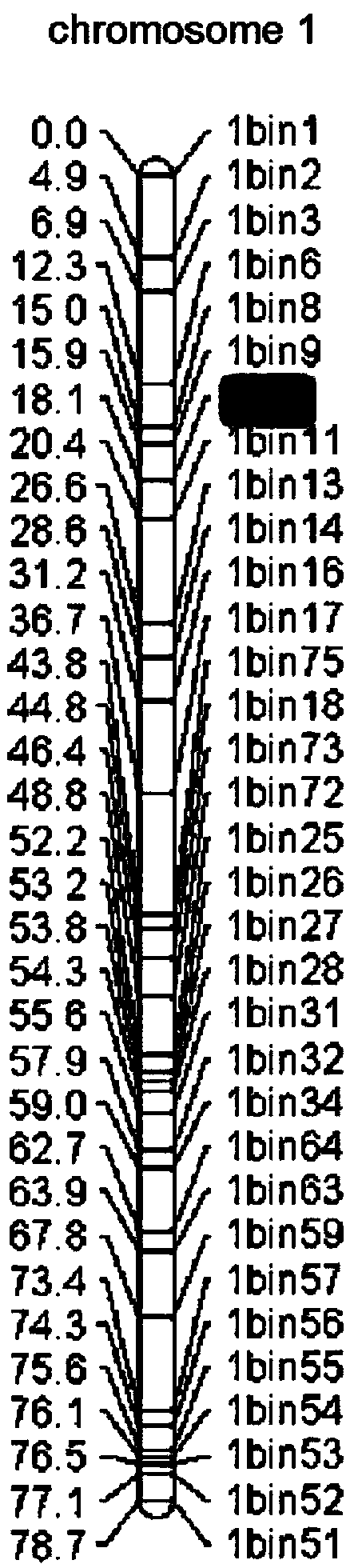
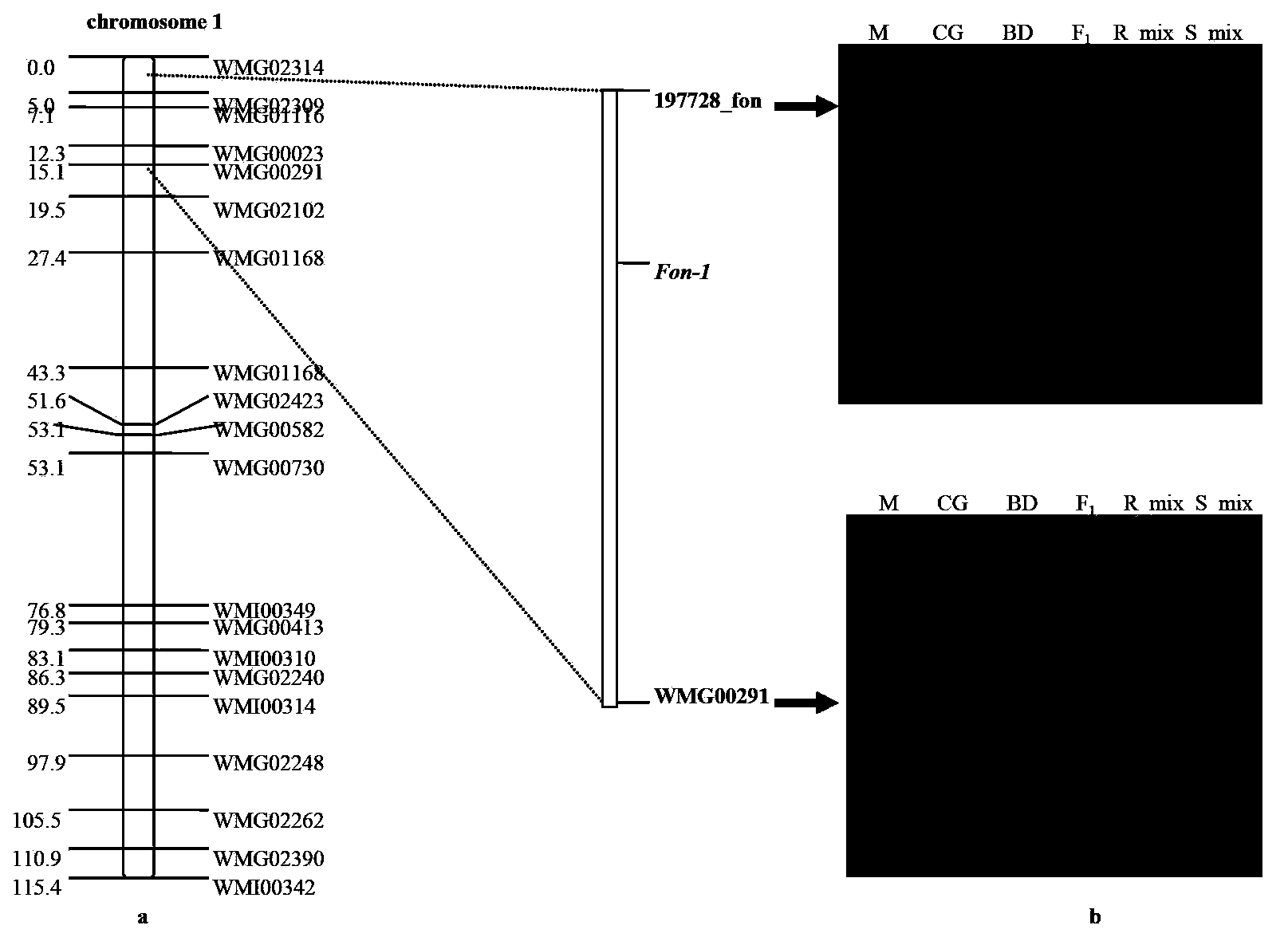
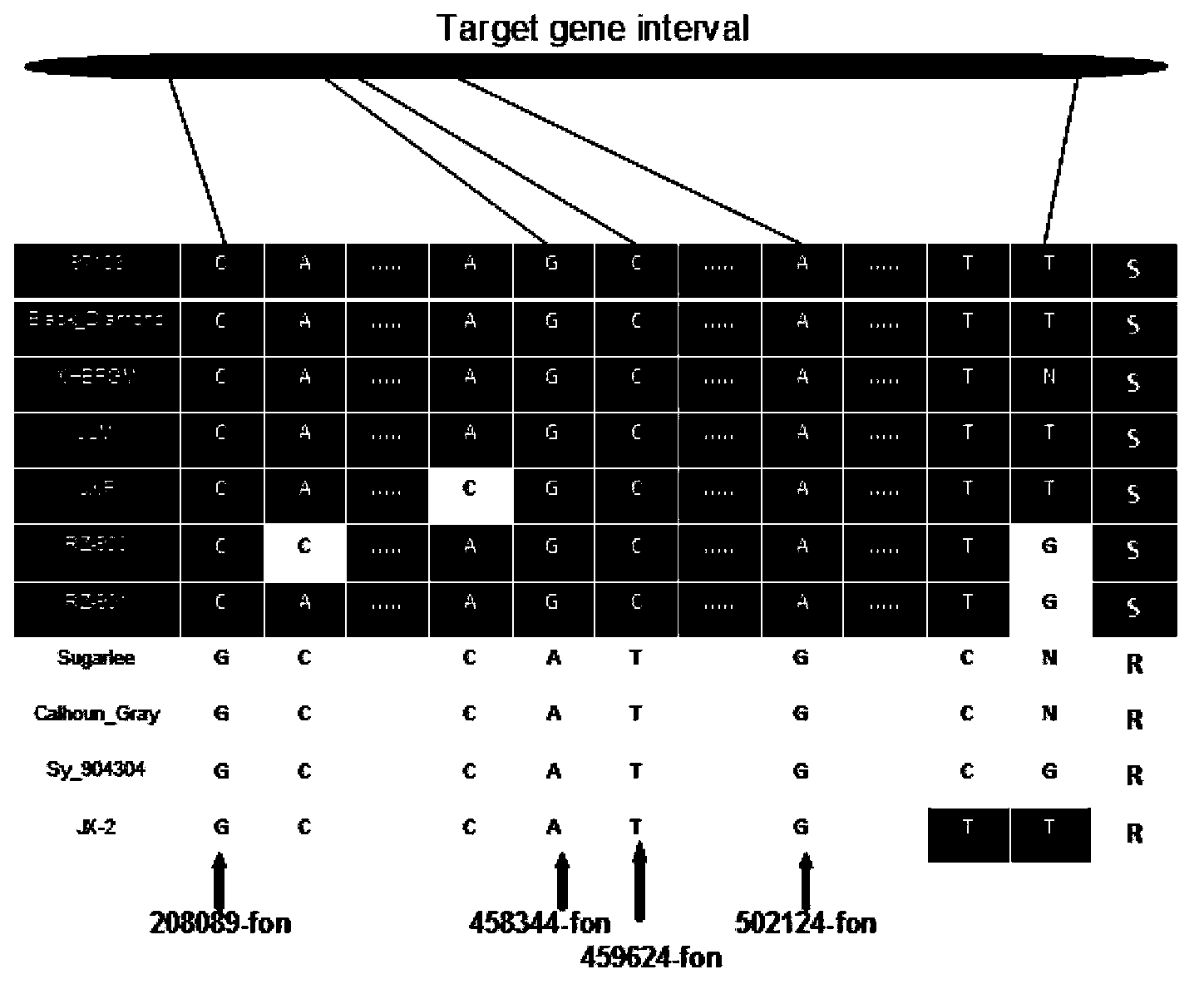
SNP loci linked with blight resistant gene Fon-1 in watermelon, and markers thereof
ActiveCN103146691AShorten the timeTo achieve the purpose of assisted breedingDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationResistant genesTest material
The invention relates to the fields of gene sequences and acquiring methods thereof, and concretely relates to SNP loci linked with a blight resistant gene Fon-1 in a watermelon, markers thereof, and acquiring methods of the loci and the markers. The SNP loci linked with a blight resistant gene Fon-1 in a watermelon and the markers thereof have nucleotide base sequences represented by SEQ ID NO:1-8 in a sequence table. The acquiring method of the loci comprises the following steps: 1, selecting a tested material; 2, carrying out preliminary positioning of the blight resistant gene Fon-1 in the watermelon; 3, acquiring candidate SNP; and 4, acquiring the SNP loci closely linked with the blight resistant gene Fon-1 in the watermelon, and verifying the candidate SNP loci. According to the invention, the phenotype identification and the molecular detection of F2 generation separation populations and natural populations are carried out through utilizing a series of markers to confirm the close linkage degree of the series of the SNP loci with target properties; and the SNP loci are utilized to design the markers respectively, and the markers can be utilized to carry out the initial-stage screening of the kind in order to reach a molecule assisted breeding purpose, so the breeding period is substantially shortened, and an important scientific research meaning is possessed.
Owner:京研益农(北京)种业科技有限公司
Kits for amplifying target nucleic acid sequences using modified oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6903206B1Increase ratingsEfficiently strand invade double-stranded regionsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNitrogenous base
The present invention concerns oligonucleotides containing one or more modified nucleotides which increase the binding affinity of the oligonucleotides to target nucleic acids having a complementary nucleotide base sequence. These modified oligonucleotides hybridize to the target sequence at a faster rate than unmodified oligonucleotides having an identical nucleotide base sequence. Such modified oligonucleotides include oligonucleotides containing at least one 2′-O-methylribofuranosyl moiety joined to a nitrogenous base. Oligonucleotides can be modified in accordance with the present invention to preferentially bind RNA targets. The present invention also concerns methods of using these modified oligonucleotides and kits containing the same.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
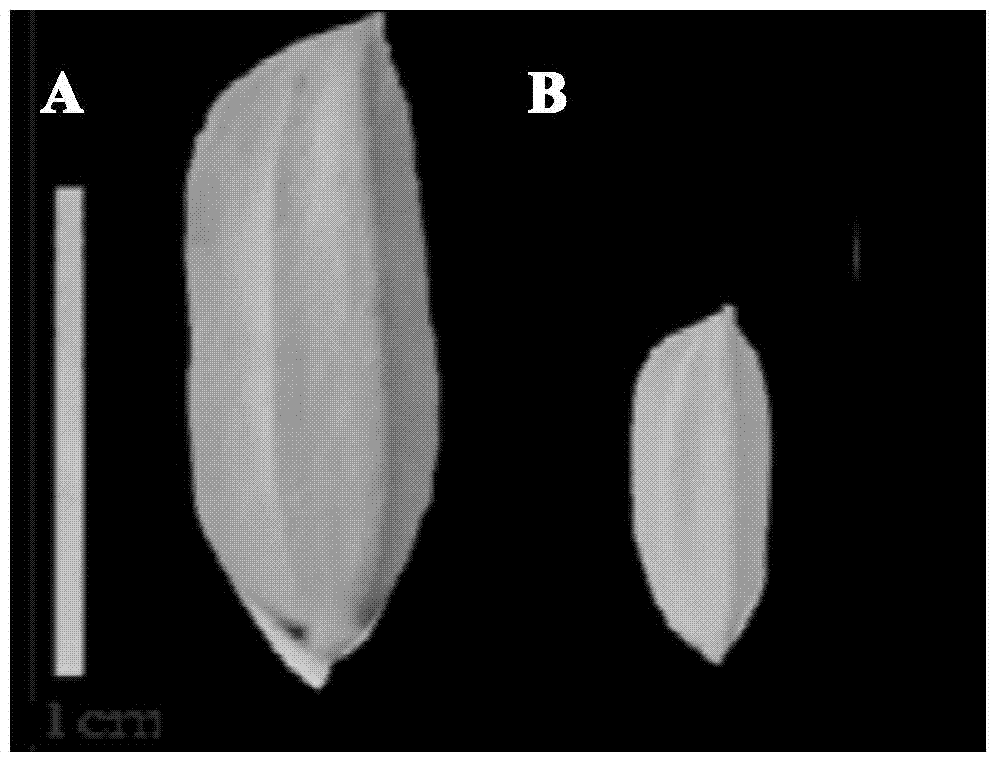
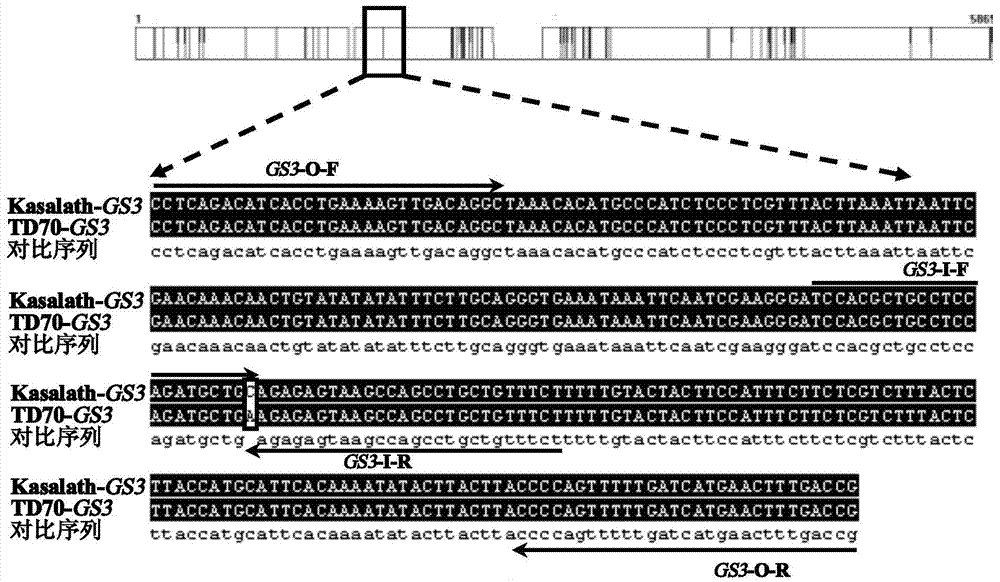
Four-primer molecular marking method for identifying different genotypes of rice grain length gene GS3
ActiveCN103882146ANo errors leading to genotypingThere is no error that caused the identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenotype
The invention relates to a four-primer molecular marking method for identifying different genotypes of a rice grain length gene GS3, belonging to the technical field of agricultural bioengineering. Four marking primers are designed and synthesized according to differences of a long and large-grain variety TD70 and a short and small-grain variety Kasalath in the nucleotide base sequence of the grain length gene GS3, and are added into the same PCR system for amplifying different rice DNA so as to distinguish different genotypes of homozygotes and heterozygotes of the GS3. The method disclosed by the invention not only can be used for rapidly and accurately identifying the different genotypes of the grain length gene GS3 in a rice genetic resource or a breeding population but also can be used for improving the selection efficiency on a long-grain genotype GS3-TGS3-T and speeding up the breeding progress of a new long-grain, high-quality and high-yield rice variety.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
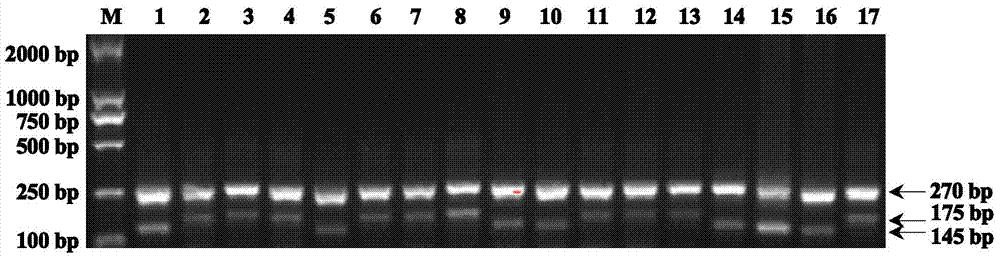
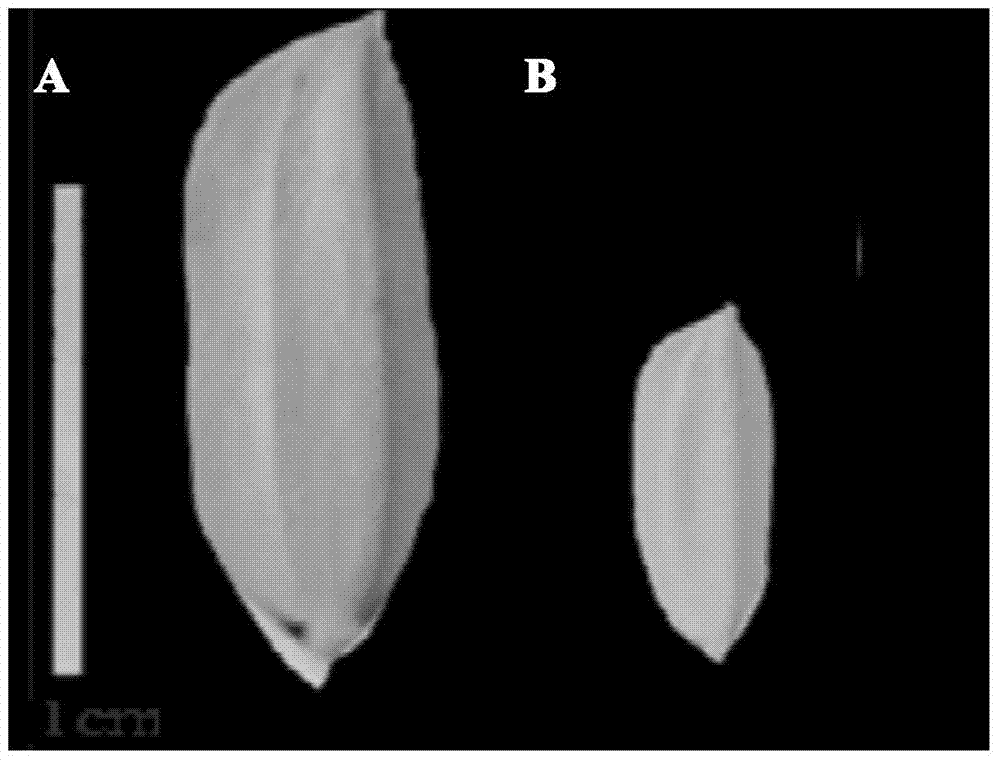
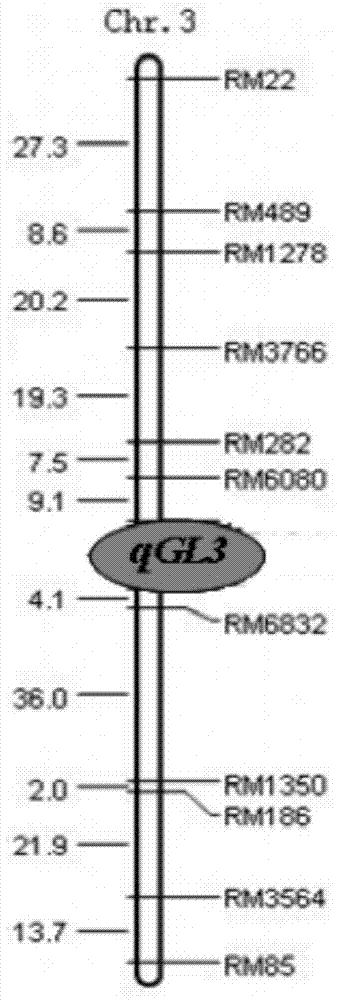
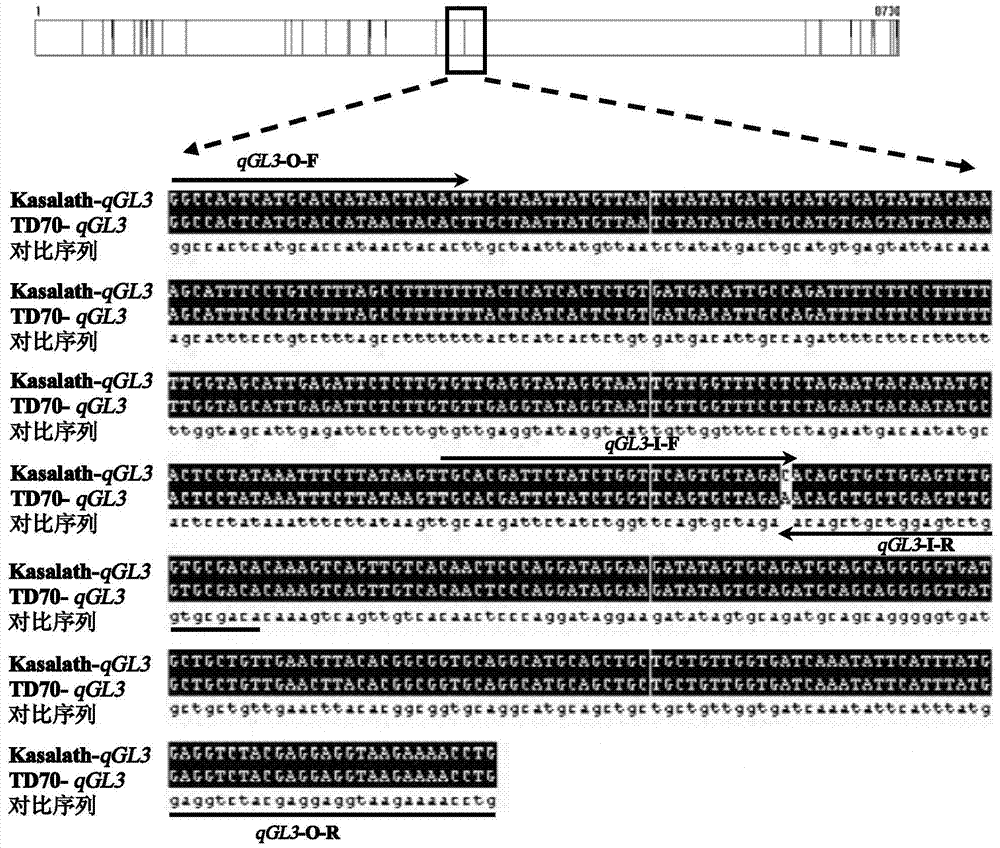
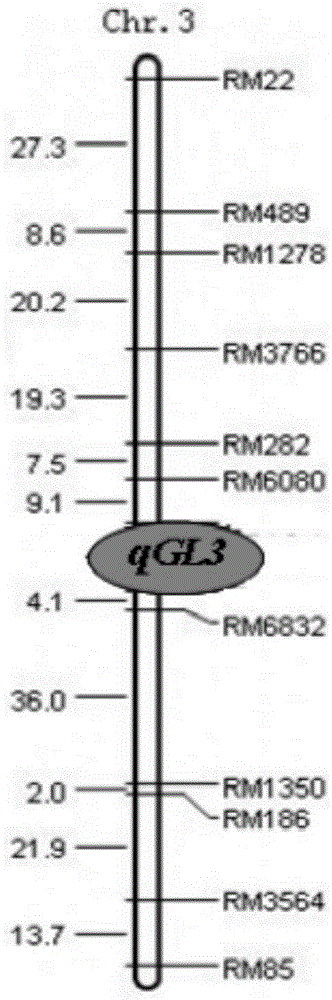
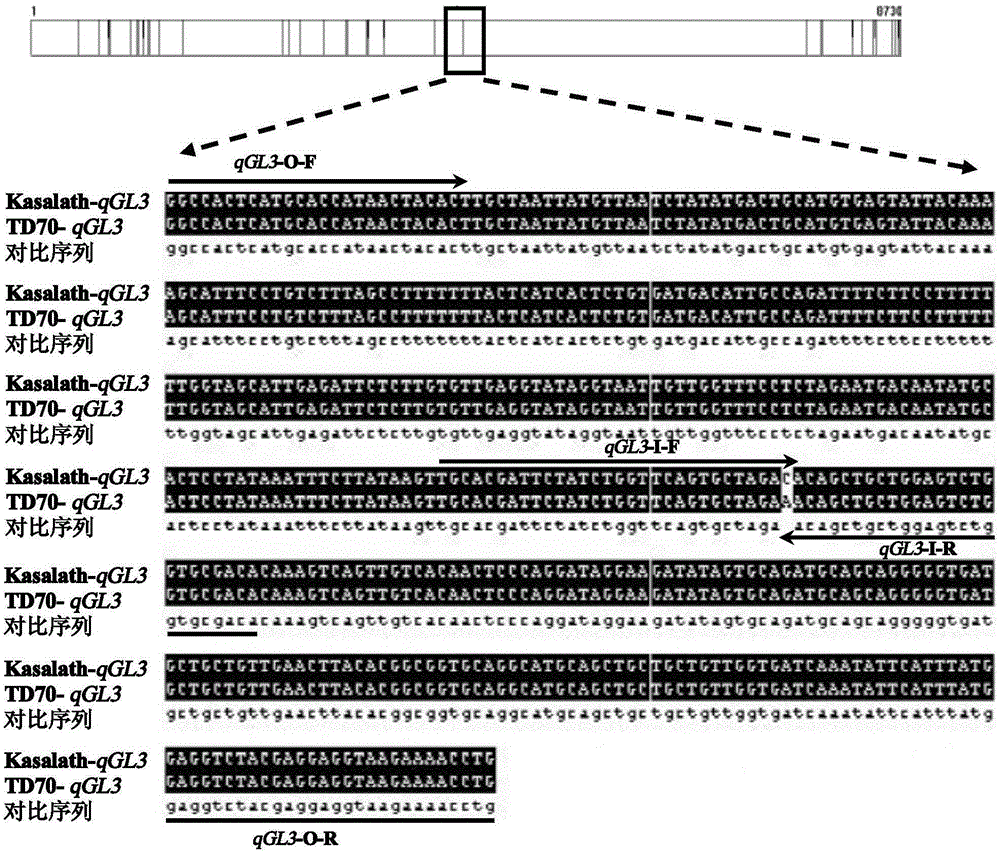
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) molecular marking method for identifying allele mutation of rice long-grain gene qGL3
ActiveCN103882145AResolving Poor Marker PolymorphismResolve accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) molecular marking method for identifying allele mutation of rice long-grain gene qGL3, and belongs to the technical field of agro-biological engineering. According to the PCR molecular marking method, four specific molecular marking primers are designed and synthesized for PCR amplification of DNA of different rice based on the difference of long-grain and large-grain variety TD70 and short-grain and small-grain variety Kasalath on the nucleotide base sequence of the long-grain gene qGL3, the amplified product is subjected to electrophoresis detection with 2.0% of agarose gel, and DNA brands of different dimension represent different allele types of qGL3 after DuRed nuclear acid developing. With the adoption of the molecular marking method, the difference of different alleles of the long-grain gene qGL3 in rice germplasm resources or breeding population can be quickly and accurately identified; in addition, the selection efficiency for the long-grain homozygous genotype qGL3-TqGL3-T is obviously improved; and therefore, the coordinative improvement of the appearance quality and output traits of rice can be realized.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
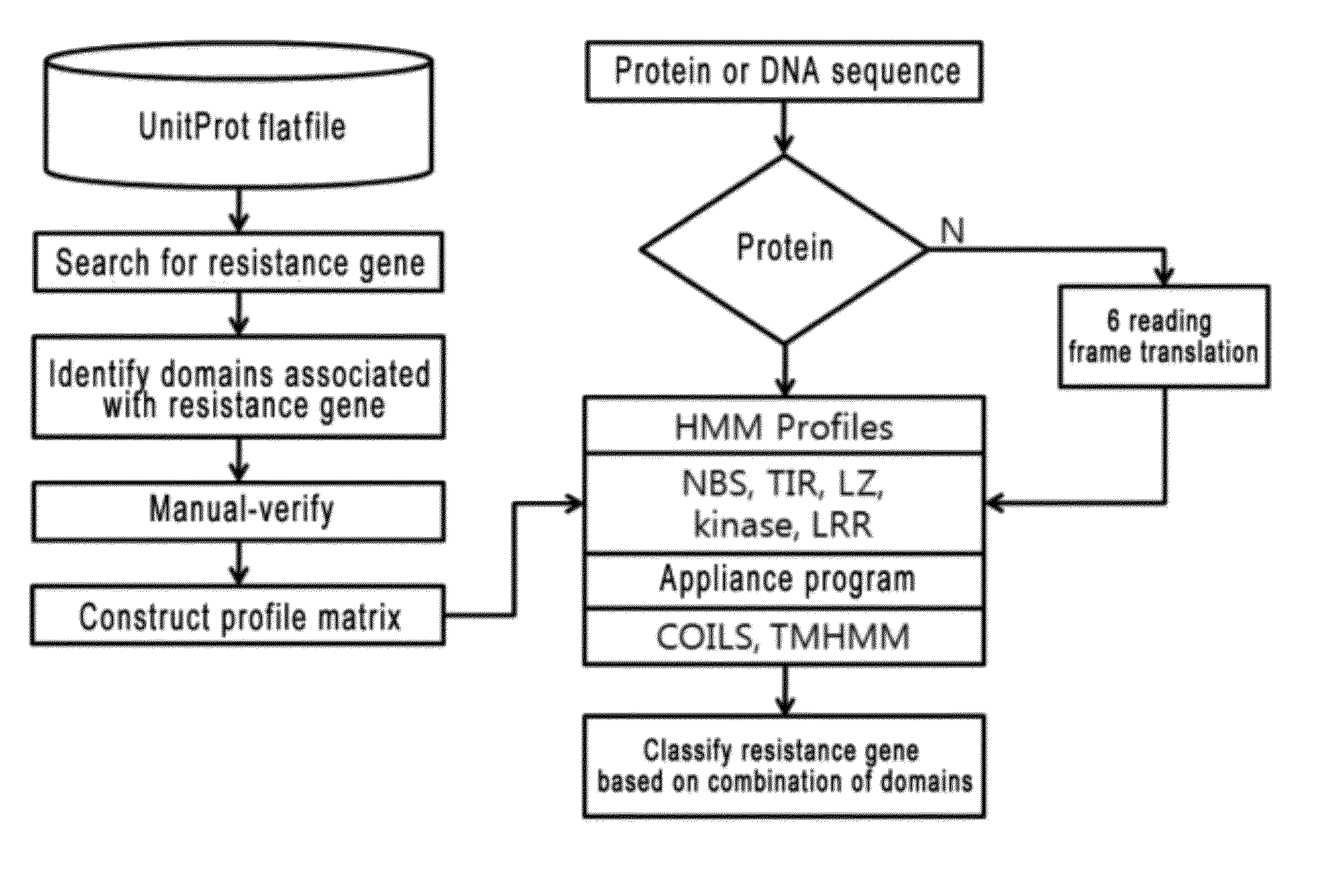
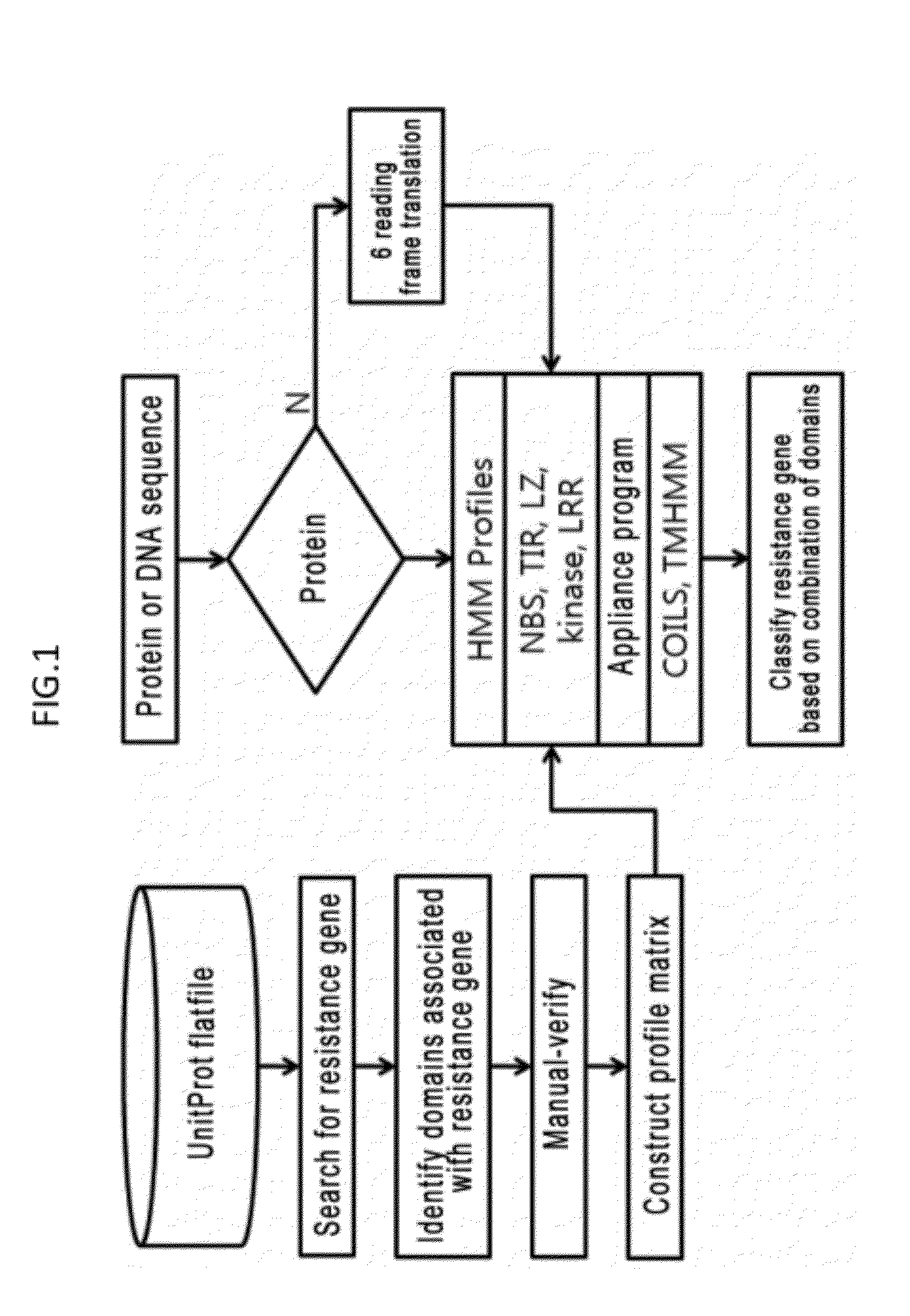
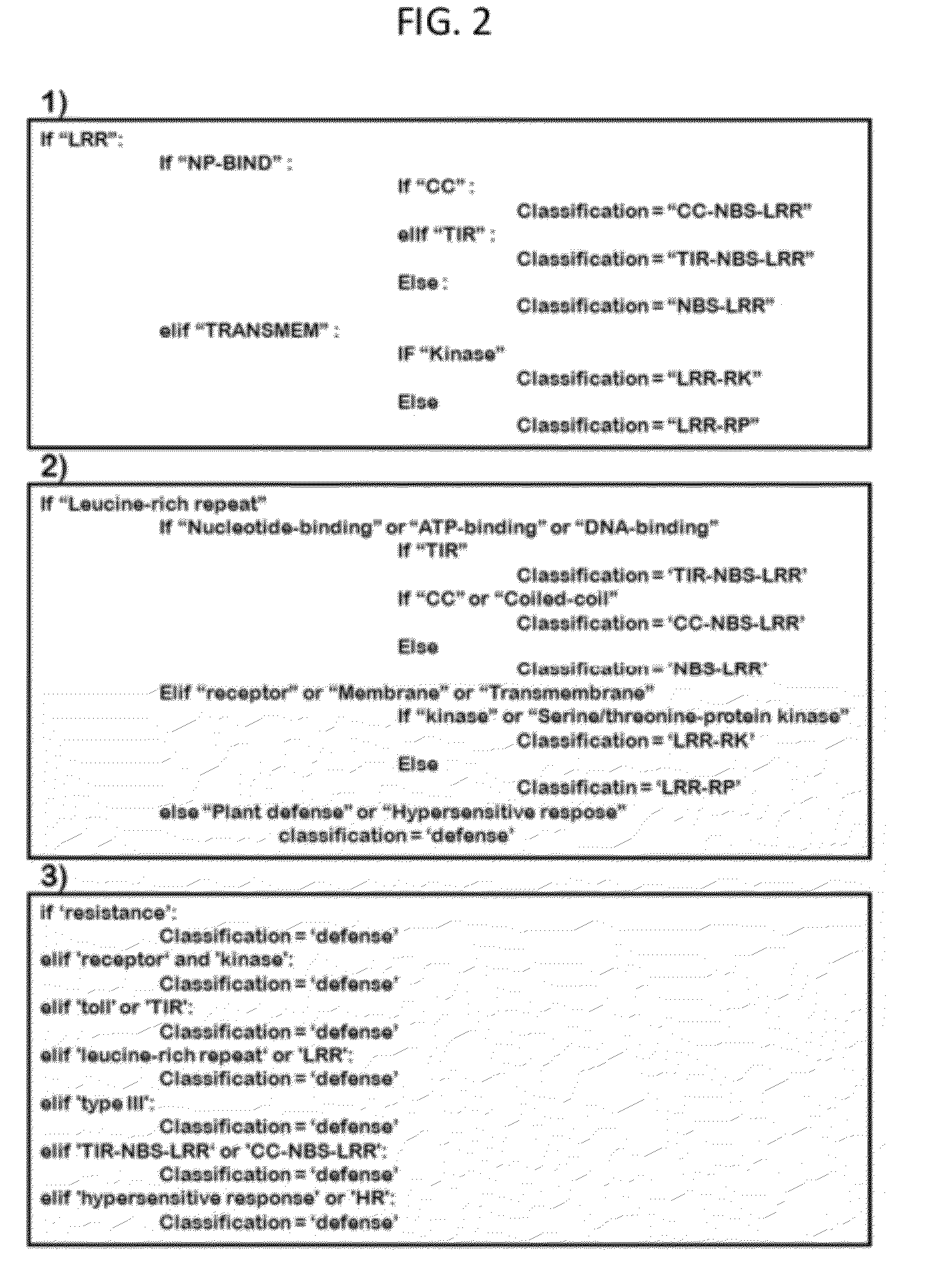
System and method for identifying and classifying resistance genes of plant using hidden marcov model
InactiveUS20120271558A1Quickly and efficiently identifiedEasy screeningBiostatisticsBiological testingResistant genesProtein insertion
The present invention relates to a system and a method for quickly and accurately identifying and classifying resistance genes of a plant from a protein or DNA sequence. In order to identify and classify resistance genes of a plant using a hidden marcov model, conceived is a profile matrix made using a protein sequence of a domain which is encoded by the resistance genes, and a system for identifying the domain of the resistance genes using the profile matrix and classifying the resistance genes by domain combination. The present invention enables effective identification and classification of the resistance genes of a plant using the profile matrix and program, of which the nucleotide base sequence or protein sequence is detected.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) molecular marking method for identifying solanum lycopersicum with purple black striped pericarp and application
ActiveCN106755357AGuaranteed accuracyAvoid the transfer stepMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGel electrophoresis
The invention discloses a CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) molecular marking method for identifying solanum lycopersicum with purple black striped pericarp and an application. The sequence of a molecular marker carried by the solanum lycopersicum with purple black striped pericarp is a nucleotide base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, PCR amplification is performed with genomic DNA of the solanum lycopersicum with purple black striped pericarp as a template, nucleotide base sequences shown as SEQ ID NO.3-4 are amplification primers, amplification and cleavage are performed, a specific band different from other solanum lycopersicum pericarp colors can be obtained after cleavage, and the molecular marking method is applied to breed improvement and breeding of the solanum lycopersicum. Compared with the prior art, the CAPS molecular marking method has the advantages that the polymorphism of a cleaved fragment is observed through PCR amplification, cleavage and gel electrophoresis separation, the step of membrane transfer in the traditional RFLP (restricted fragment length polymorphism) analysis is omitted, the operation is simplified, the precision of the RFLP technology is kept, the polymorphism detecting probability is higher, the solanum lycopersicum with purple black striped pericarp is obtained rapidly and applied to breed improvement and assisted breeding, and the method has important theoretical and practical meanings for culturing new varieties of solanum lycopersicum containing rich anthocyanidin.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
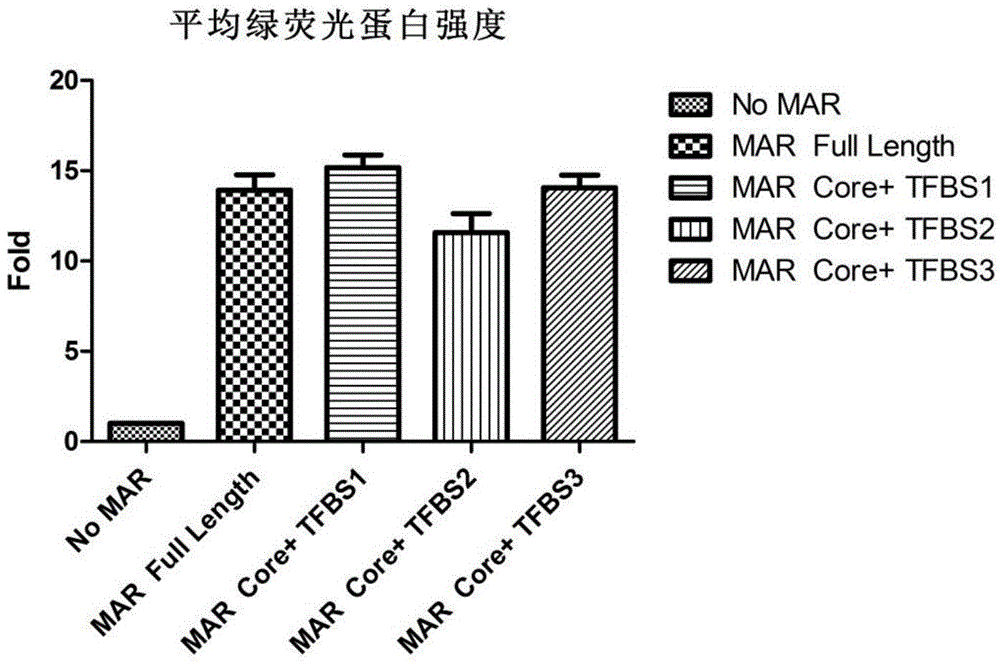
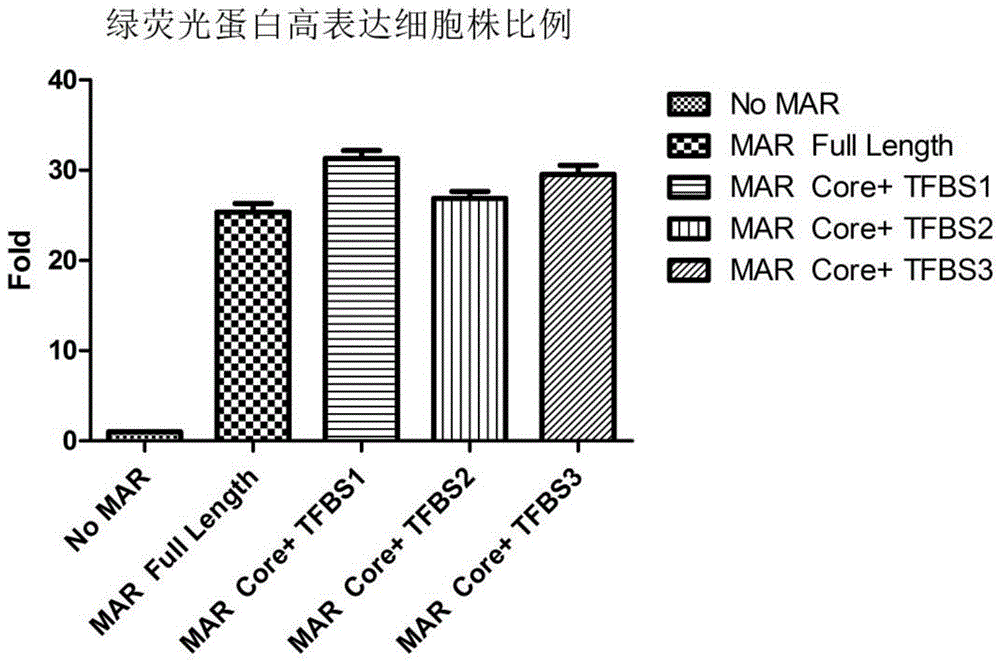
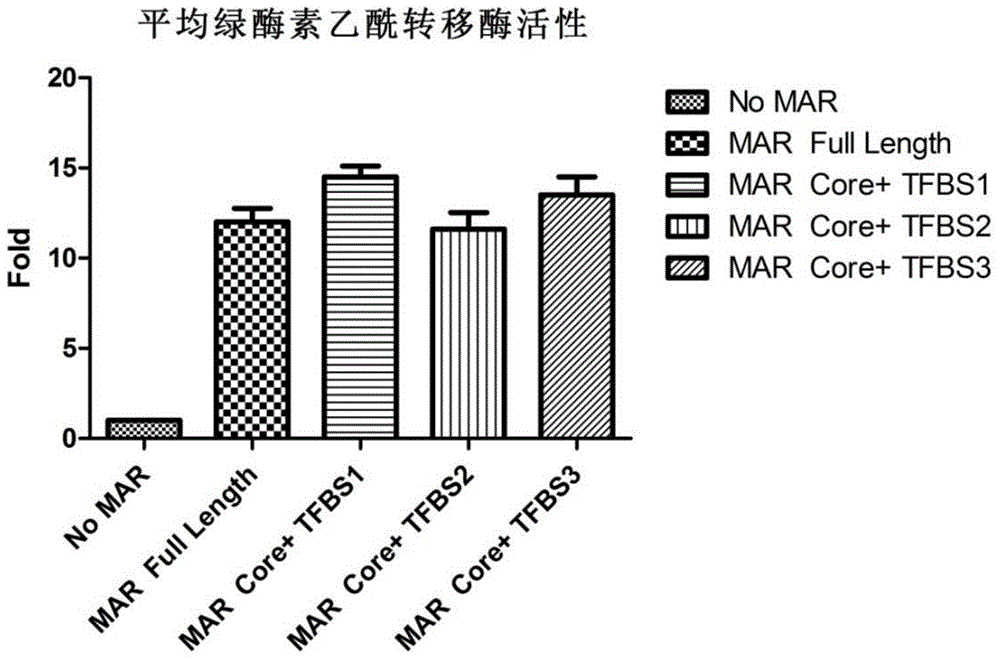
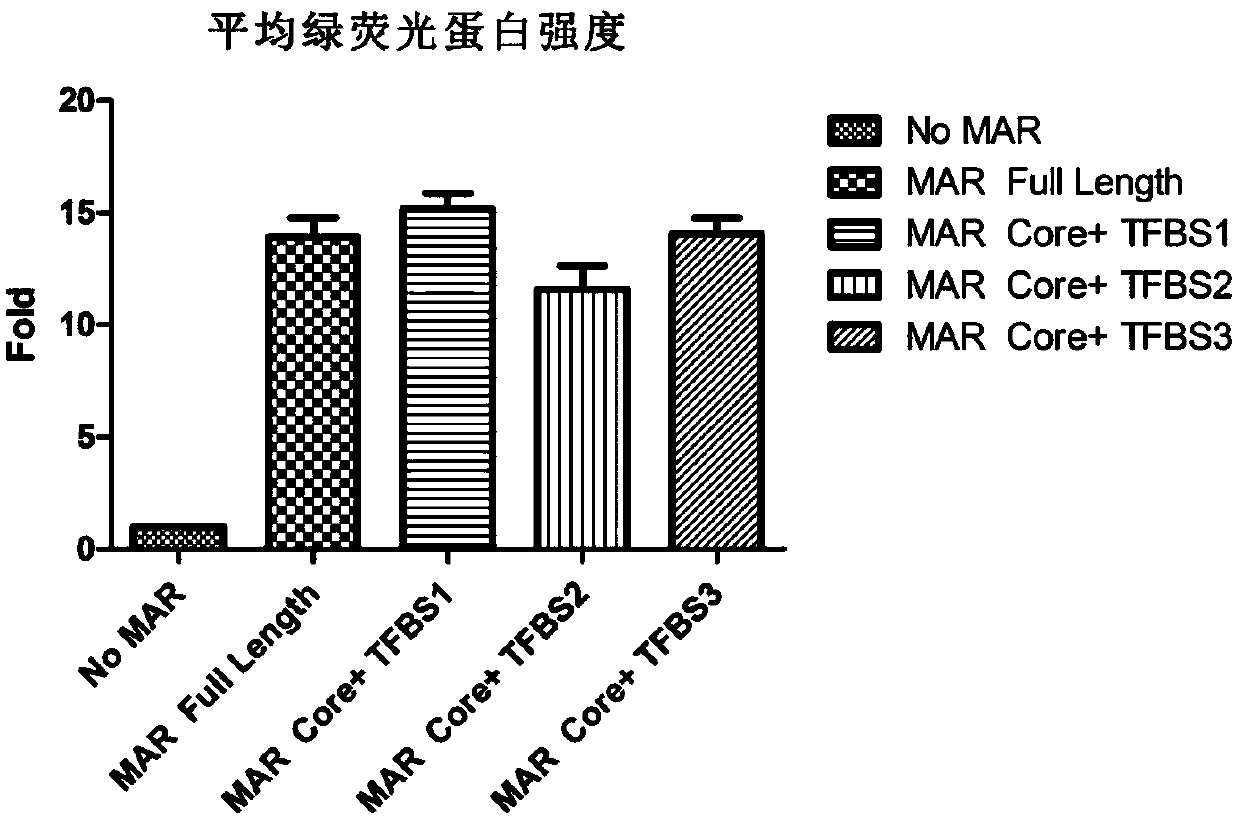
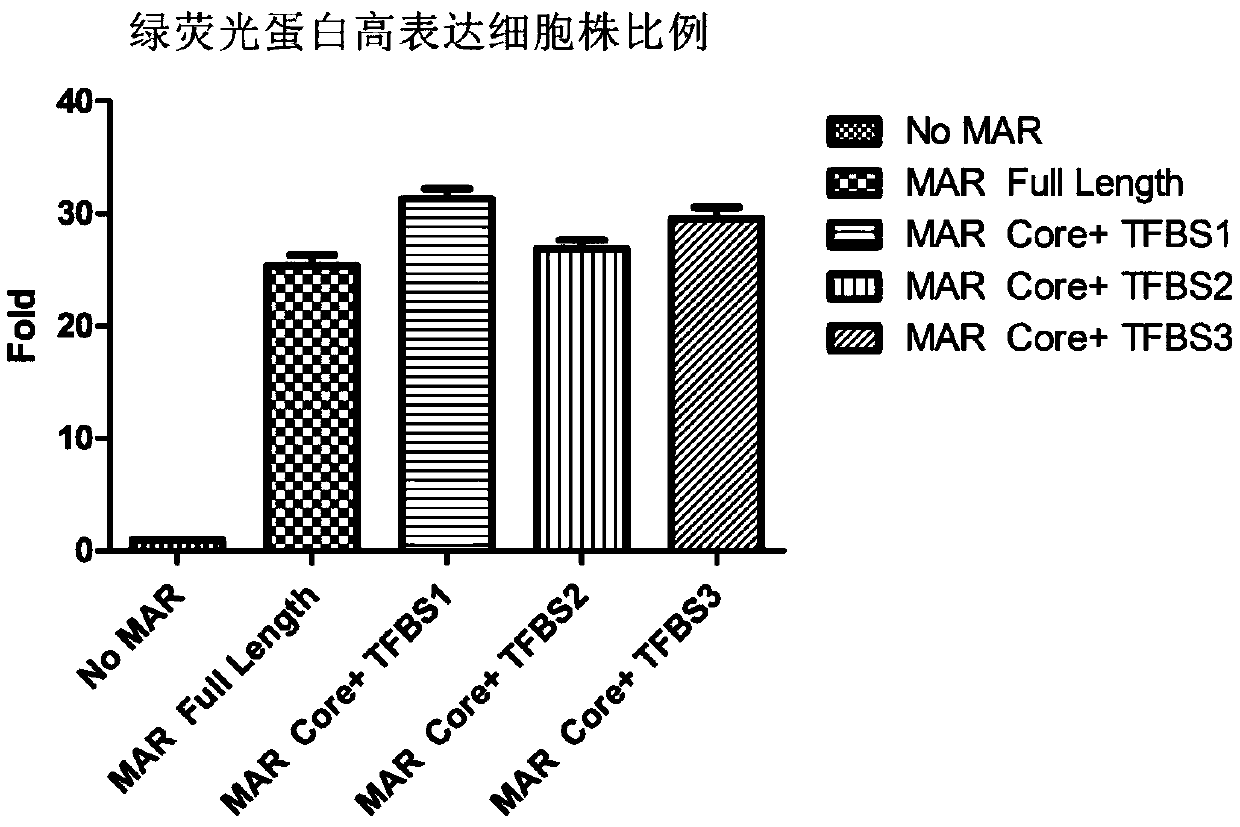
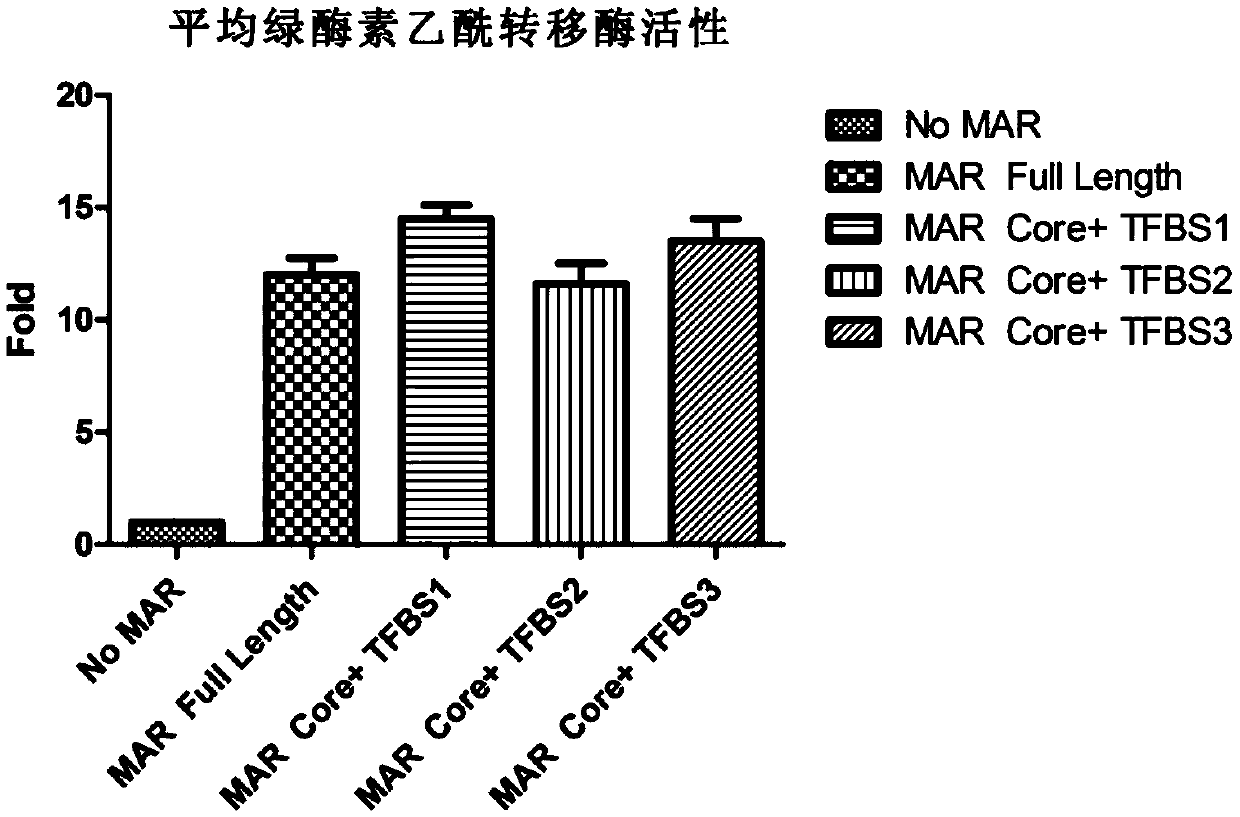
Novel MAR (matrix attachment region) core fragment-containing animal cell expression vector
ActiveCN104975009AHigh expressionImprove stabilityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceMammalian cell
The invention discloses a novel MAR (matrix attachment region) core fragment-containing animal cell expression vector. The nucleotide base sequence of the MAR core fragment of the recombinant expression vector is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, SEQ ID No.2 or SEQ ID No. 3. The expression vector disclosed by the invention can effectively increase the yield of protein in mammalian cells and reduce production cost.
Owner:SUNSHINE GUOJIAN PHARMA (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Method for determining the presence of an RNA analyte in a sample using a modified oligonucleotide probe
InactiveUS7070925B1Great ability to discriminateHigh TmSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteNitrogenous base
The present invention concerns oligonucleotides containing one or more modified nucleotides which increase the binding affinity of the oligonucleotides to target nucleic acids having a complementary nucleotide base sequence. These modified oligonucleotides hybridize to the target sequence at a faster rate than unmodified oligonucleotides having an identical nucleotide base sequence. Such modified oligonucleotides include oligonucleotides containing at least one 2′-O-methylribofuranosyl moiety joined to a nitrogenous base. Oligonucleotides can be modified in accordance with the present invention to preferentially bind RNA targets. The present invention also concerns methods of using these modified oligonucleotides and kits containing the same.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Gene sequence a for causing watermelon bisexual flower development and obtaining method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of gene sequences and obtaining methods thereof, and particularly relates to a gene sequence a for causing watermelon bisexual flower development and an obtaining method thereof. The gene sequence a has nucleotide base sequences represented by SEQ ID NO:1-6 in the sequence table. The obtaining method comprises the following steps: A, selecting a material for testing, B, extracting genome DNA, C, carrying out a long-distance PCR amplification reaction and detecting the obtained product, D, obtaining a specific amplification sequence, E, obtaining a candidate SNP, and F, verifying the candidate SNP locus, and finally obtaining the gene sequence a for causing watermelon bisexual flower development. According to the present invention, F2 generation segregation population dCAP molecule marker detection and phenotypic identification, and each core germplasm resource dCAP molecule marker detection and phenotypic identification are performed to confirm that the SNP locus is a co-segregation marker; and the obtained SNP locus can be used to develop genetic markers for assisted breeding so as to achieve a purpose of obtaining of the watermelon female line variety.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
Kits containing modified amplification oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20050106610A1Increase ratingsStrong discriminationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNitrogenous baseOligonucleotide
The present invention concerns oligonucleotides containing one or more modified nucleotides which increase the binding affinity of the oligonucleotides to target nucleic acids having a complementary nucleotide base sequence. These modified oligonucleotides hybridize to the target sequence at a faster rate than unmodified oligonucleotides having an identical nucleotide base sequence. Such modified oligonucleotides include oligonucleotides containing at least one 2′-O-methylribofuranosyl moiety joined to a nitrogenous base. Oligonucleotides can be modified in accordance with the present invention to preferentially bind RNA targets. The present invention also concerns methods of using these modified oligonucleotides and kits containing the same.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
A PCR molecular marker method for identifying allelic variation of rice grain length gene qgl3
ActiveCN103882145BRapid identificationImprove appearance qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The invention discloses a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) molecular marking method for identifying allele mutation of rice long-grain gene qGL3, and belongs to the technical field of agro-biological engineering. According to the PCR molecular marking method, four specific molecular marking primers are designed and synthesized for PCR amplification of DNA of different rice based on the difference of long-grain and large-grain variety TD70 and short-grain and small-grain variety Kasalath on the nucleotide base sequence of the long-grain gene qGL3, the amplified product is subjected to electrophoresis detection with 2.0% of agarose gel, and DNA brands of different dimension represent different allele types of qGL3 after DuRed nuclear acid developing. With the adoption of the molecular marking method, the difference of different alleles of the long-grain gene qGL3 in rice germplasm resources or breeding population can be quickly and accurately identified; in addition, the selection efficiency for the long-grain homozygous genotype qGL3-TqGL3-T is obviously improved; and therefore, the coordinative improvement of the appearance quality and output traits of rice can be realized.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker GI1354 closely linked with pepper CMV resistance gene and acquisition and application
InactiveCN105368824AAccurate detectionSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceDNA extraction
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to a molecular marker GI1354 closely linked with a pepper CMV resistance gene and an acquisition method and application. The molecular marker GI1354 has at least one of nucleotide base sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 in the sequence list. During detection of the cr gene in the molecular marker application pepper material, the steps of extraction of genome DNA of the pepper material, the PCR amplification reaction, analysis and the like are included. The screened PCR primer is directly used as the molecular marker, whether the cr gene is contained in the pepper material or not can be accurately detected, and the method is convenient to implement, rapid and capable of saving cost.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for detecting a structured target
InactiveUS20080090247A1Increase ratingsIncrease hybridization rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNitrogenous baseOligonucleotide
The present invention concerns oligonucleotides containing one or more modified nucleotides which increase the binding affinity of the oligonucleotides to target nucleic acids having a complementary nucleotide base sequence. These modified oligonucleotides hybridize to the target sequence at a faster rate than unmodified oligonucleotides having an identical nucleotide base sequence. Such modified oligonucleotides include oligonucleotides containing at least one 2′-O-methylribofuranosyl moiety joined to a nitrogenous base. Oligonucleotides can be modified in accordance with the present invention to preferentially bind RNA targets. The present invention also concerns methods of using these modified oligonucleotides and kits containing the same.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Pathogenic detection kit for lentivirus of small ruminant
PendingCN107447045ATimely and rapid test resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLentivirusGenetics
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biological detection and in particular relates to a pathogenic detection kit for a lentivirus of a small ruminant. The kit comprises (1) a genetic marker for detecting the lentivirus of the small ruminant, wherein the genetic marker has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.3 or other sequences, the sequence consistency of which is greater than 80%; (2) a specific primer pair for amplifying the genetic marker, the specific primer pair comprising an upstream primer sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and a downstream primer sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 or other sequences, the consistency of any continuous eight nucleotide base sequences of which is greater than 80%, among the upstream and downstream primer sequences; and (3) a kit for detecting the lentivirus of the small ruminant, wherein the kit comprises the specific primer pair in (2).
Owner:新疆畜牧科学院
Method for analyzing phyletic lineage of scallop
InactiveUS20020081593A1Efficient analysisQuick analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPatinopecten yessoensisCoding region
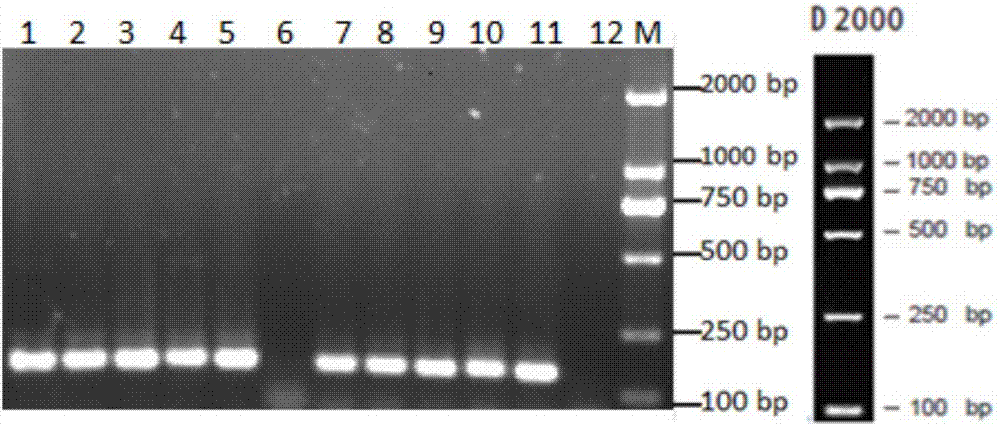
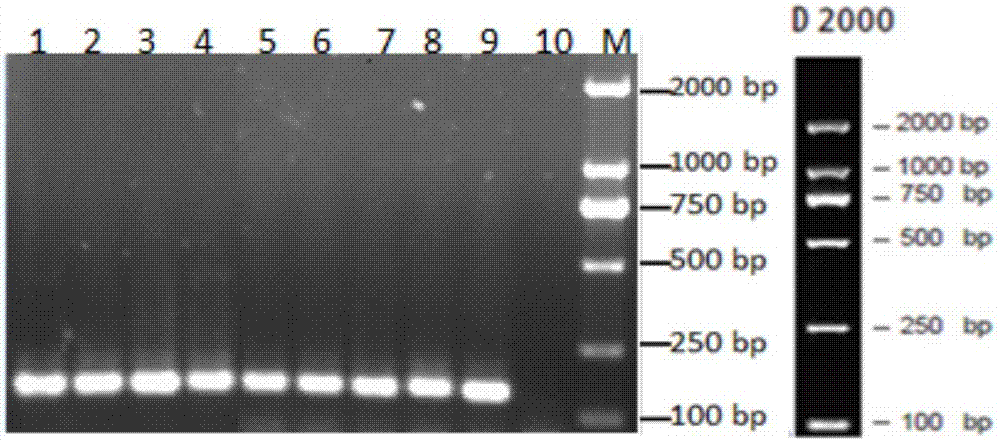
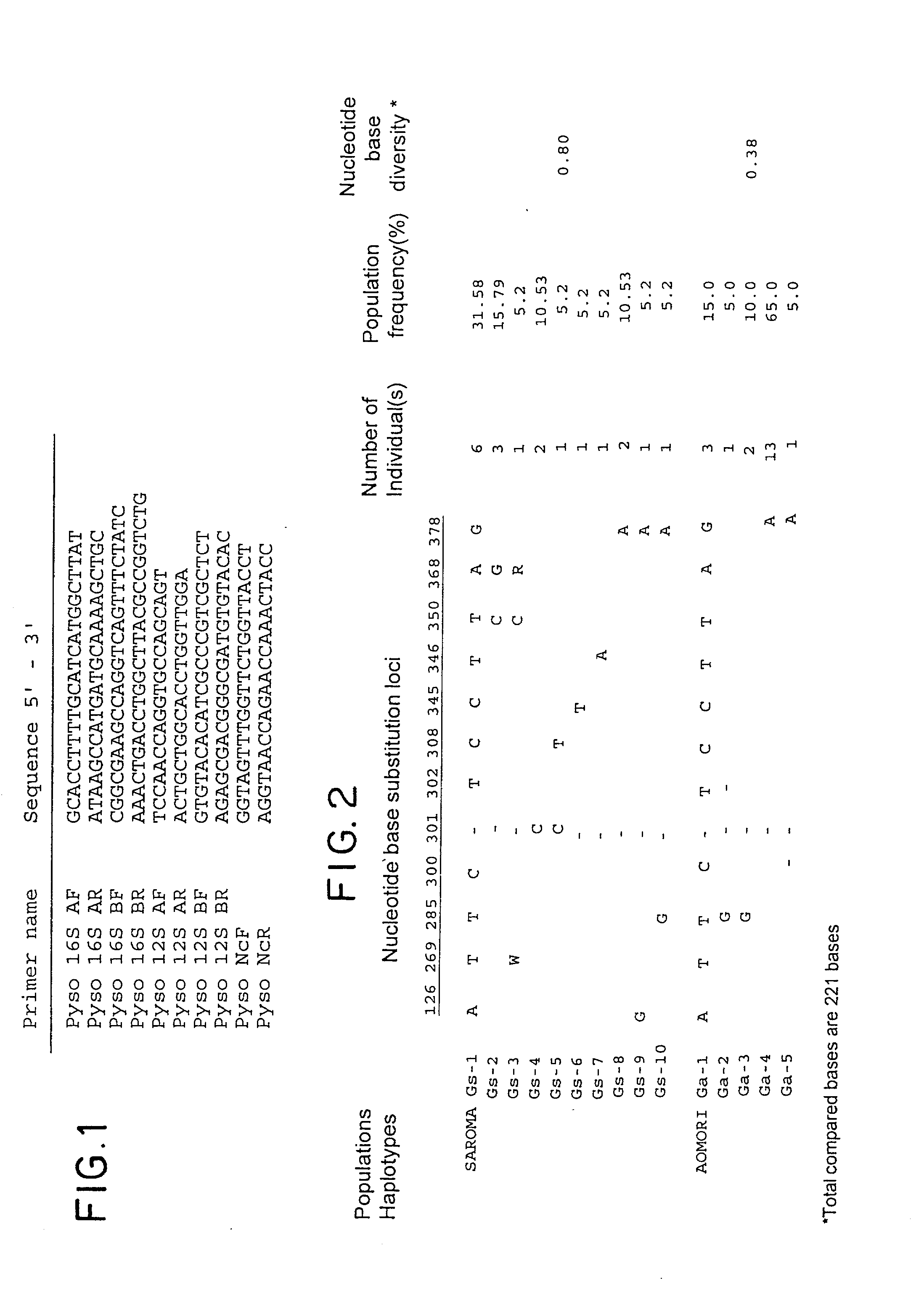
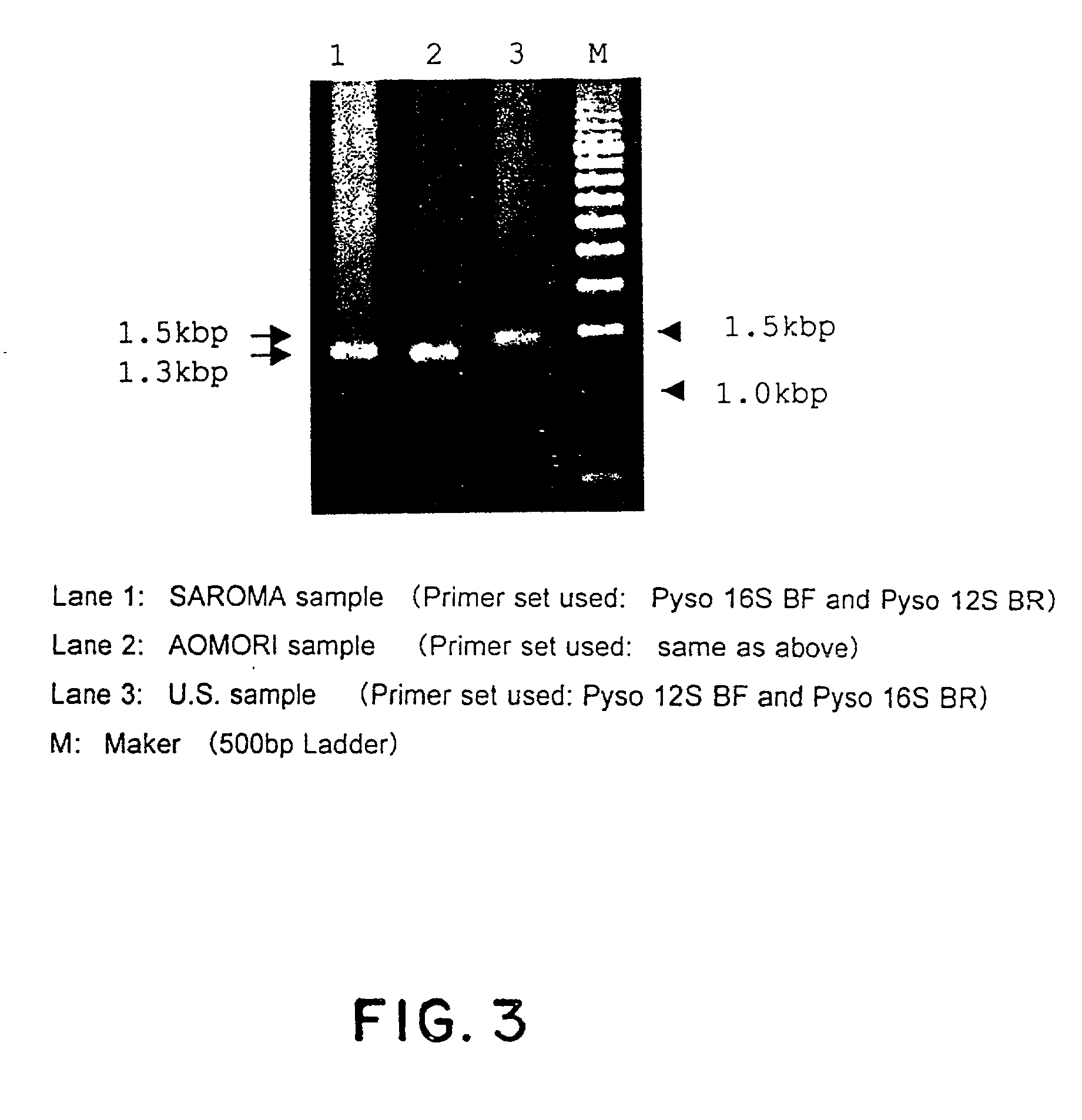
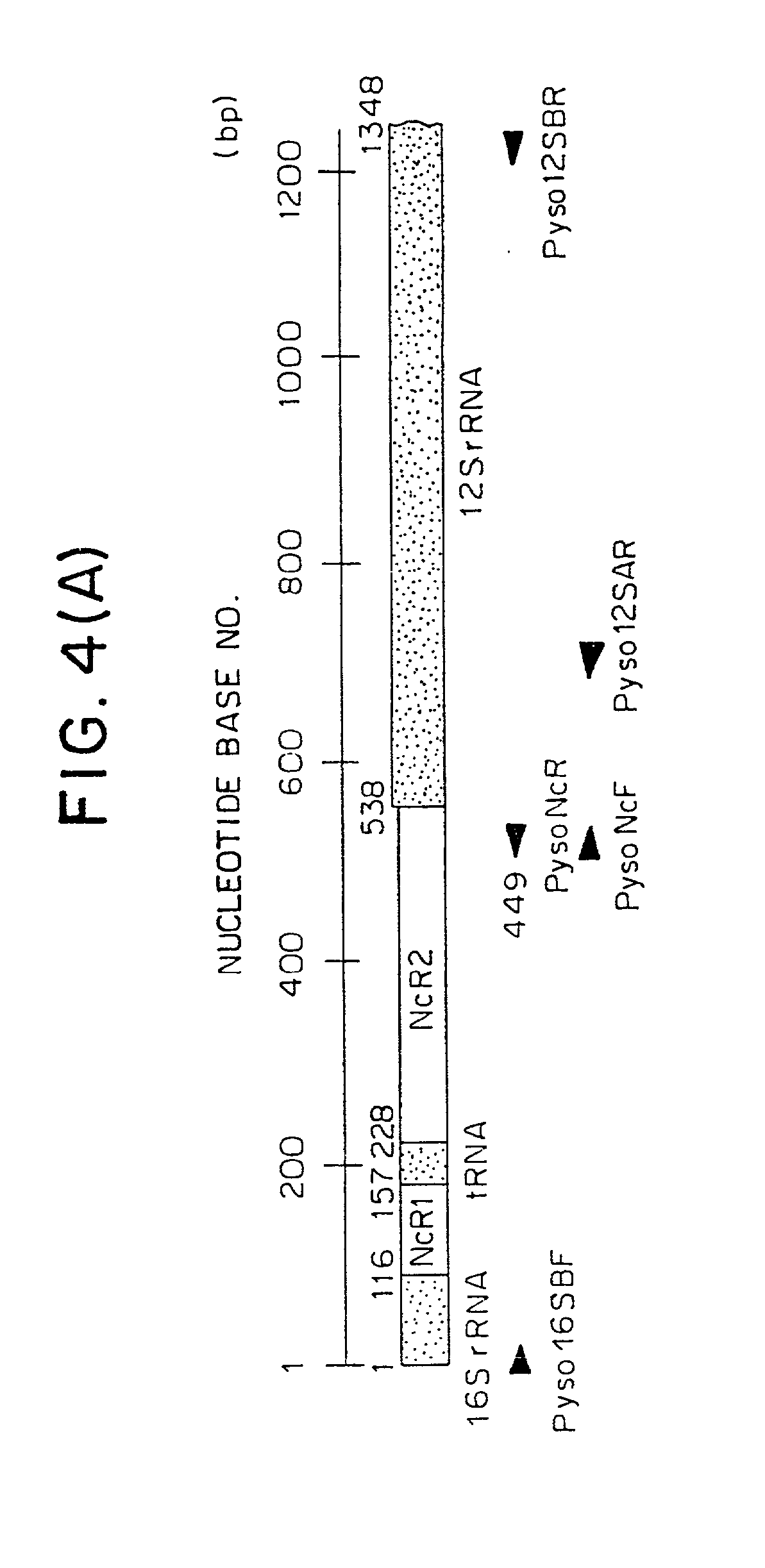
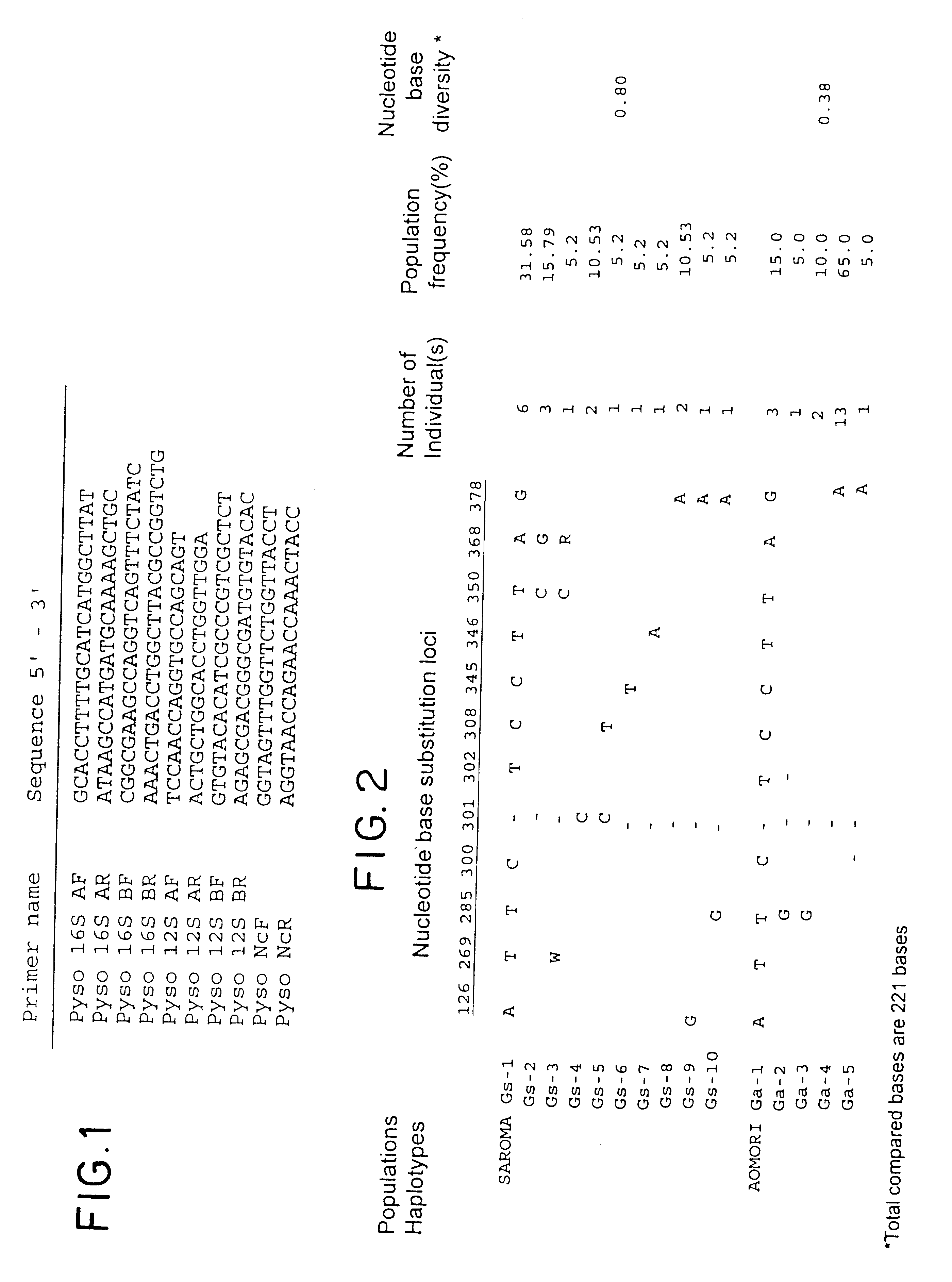
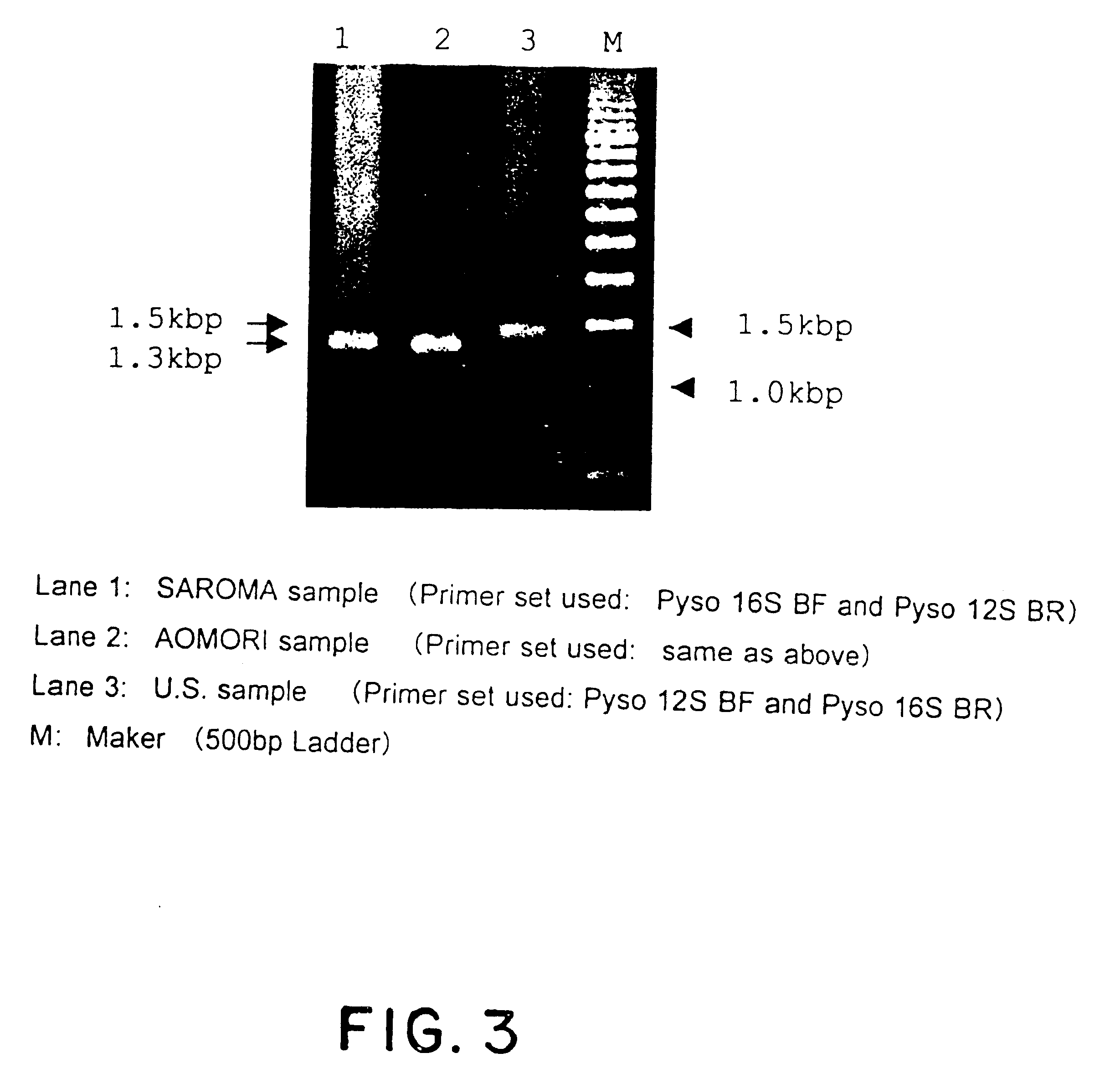
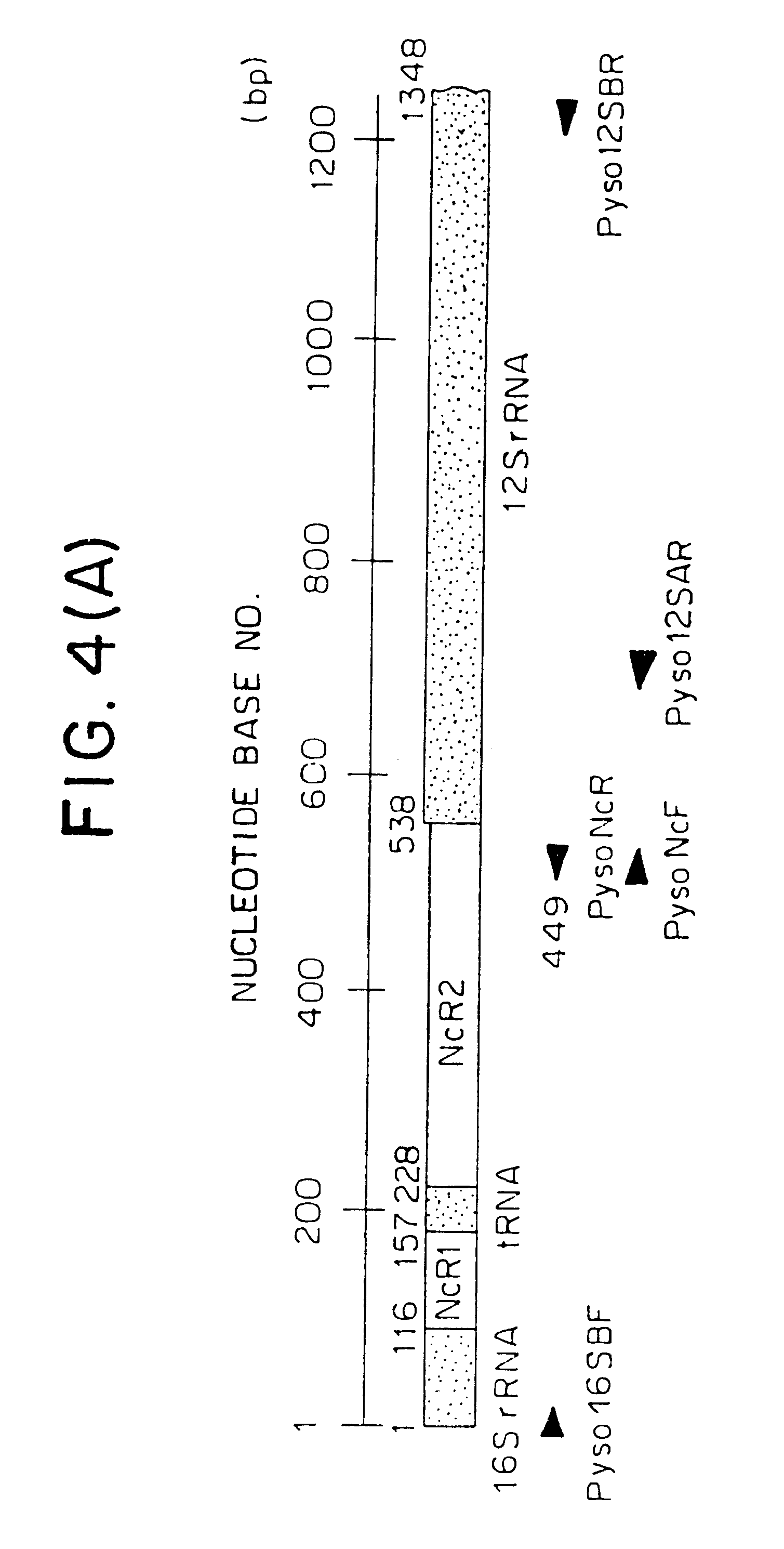
Method for analyzing a phyletic lineage of scallop, which comprises the steps of sequencing a mitochondrial DNA of the scallop to determine a nucleotide base sequence of the mitochondrial DNA, wherein the nucleotide base sequence includes a non-coding region containing a nucleotide base substitution locus which shows a sequence polymorphism indicative of a particular lineage of the scallop. Mitochondrial DNA of the scallop is amplified by PCR, using a suitable primer set designed on the basis of nucleotide base sequences conserved among known shellfish mitochondrial 16S rRNA and 12S rRNA genes, followed by sequencing to determine a non-coding region therein. In such non-coding region, a nucleotide base substitution locus is located, whereby a particular lineage of the scallop is determined. Based on those steps, a Japanese scallop, Patinopecten yessoensis, is analyzed as to the nucleotide base sequence and lineage thereof.
Owner:HOKKAIDO FEDERATION OF FISHERIES COOP ASSOCS
Amplification and detection method
InactiveUS20080090246A1Increase ratingsIncrease hybridization rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNitrogenous baseOligonucleotide
The present invention concerns oligonucleotides containing one or more modified nucleotides which increase the binding affinity of the oligonucleotides to target nucleic acids having a complementary nucleotide base sequence. These modified oligonucleotides hybridize to the target sequence at a faster rate than unmodified oligonucleotides having an identical nucleotide base sequence. Such modified oligonucleotides include oligonucleotides containing at least one 2′-O-methylribofuranosyl moiety joined to a nitrogenous base. Oligonucleotides can be modified in accordance with the present invention to preferentially bind RNA targets. The present invention also concerns methods of using these modified oligonucleotides and kits containing the same.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Method for analyzing phyletic lineage of scallop
InactiveUS6514705B2High precision and reliabilityEfficient analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPatinopecten yessoensisCoding region
Method for analyzing a phyletic lineage of scallop, which comprises the steps of sequencing a mitochondrial DNA of the scallop to determine a nucleotide base sequence of the mitochondrial DNA, wherein the nucleotide base sequence includes a non-coding region containing a nucleotide base substitution locus which shows a sequence polymorphism indicative of a particular lineage of the scallop. Mitochondrial DNA of the scallop is amplified by PCR, using a suitable primer set designed on the basis of nucleotide base sequences conserved among known shellfish mitochondrial 16S rRNA and 12S rRNA genes, followed by sequencing to determine a non-coding region therein. In such non-coding region, a nucleotide base substitution locus is located, whereby a particular lineage of the scallop is determined. Based on those steps, a Japanese scallop, Patinopecten yessoensis, is analyzed as to the nucleotide base sequence and lineage thereof.
Owner:HOKKAIDO FEDERATION OF FISHERIES COOP ASSOCS
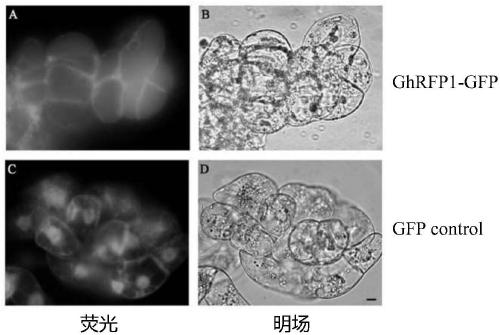
GhRFP1 gene and recombinant vector thereof
ActiveCN111218454AImprove expression levelIncrease the lengthPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyFiber
The invention discloses a GhRFP1 gene and a recombinant vector thereof. The nucleotide base sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Accordingto the novel gene GhRFP1 and the recombinant vector provided by the invention, after the gene GhRFP1 is introduced into cotton, the length of cotton fibers is increased.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
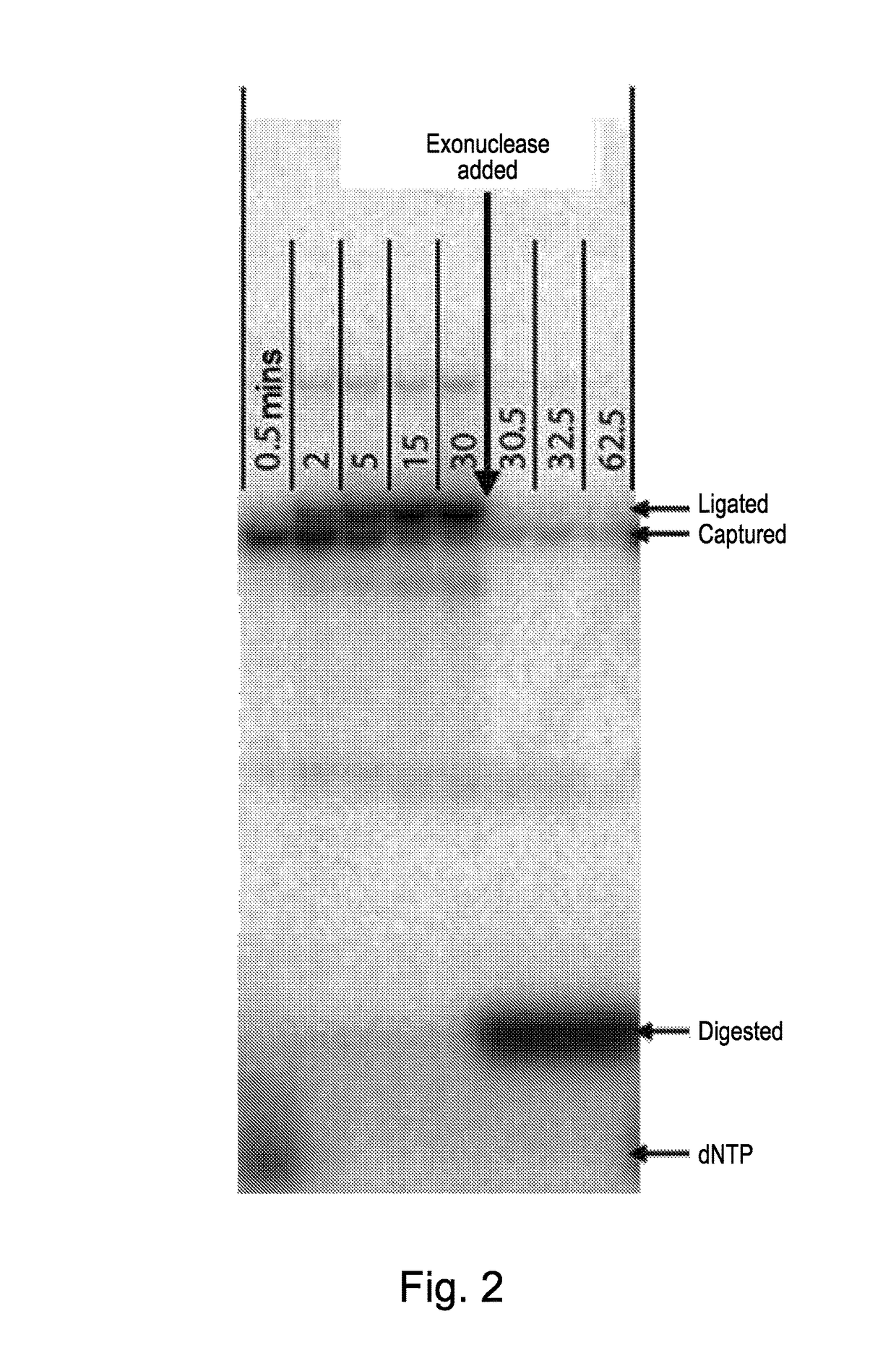
Single nucleotide detection method
ActiveUS9828631B2Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresPolynucleotideOrganic chemistry
A method for determining the sequence of nucleotide bases in a polynucleotide analyte is provided. It is characterized by the steps of (1) generating a stream of single nucleotide bases from the analyte by pyrophosphorolysis; (2) producing captured molecules by reacting each single nucleotide base with a capture system labelled with detectable elements in an undetectable state; (3) releasing the detectable elements from each captured molecule in a detectable state and (4) detecting the detectable elements so released and determining the sequence of nucleotide bases therefrom. The method can be used advantageously in sequencers involving the use of microdroplets.
Owner:LIGHTCAST DISCOVERY LTD +1
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site and CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) mark interlocked with citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste gene Bt (bitterness)
ActiveCN103194444BShorten the timeShorten the breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHigh densityMolecular breeding
The invention belongs to the fields of a gene sequence and an obtaining method of the gene sequence, and particularly relates to an obtaining method of an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site and a CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) mark interlocked with a citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste gene Bt (bitterness). The SNP site and the CAPS mark interlocked with the citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste have nucleotide base sequences in SEQ ID NO:1-2 in a sequence table. The citrullus lanatus fruit bitter taste gene is primarily positioned by screening a bitter taste single plant in an RILs colony and combining with the high-density genetic map information of the citrullus lanatus; the candidate SNP site interlocked with the character is combined with separate colony verification analysis and natural colony verification analysis; the mark tightly interlocked with a target character is obtained; the SNP site and the CAPS mark can be applied to improvement of citrullus lanatus variety and molecular assisted breeding; a technical support is provided for molecular breeding of the citrullus lanatus quality; and meanwhile, the traditional gene positioning time is greatly shortened.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
SNP loci linked with blight resistant gene Fon-1 in watermelon, and markers thereof
ActiveCN103146691BShorten the timeTo achieve the purpose of assisted breedingDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JResistant genes
The invention relates to the fields of gene sequences and acquiring methods thereof, and concretely relates to SNP loci linked with a blight resistant gene Fon-1 in a watermelon, markers thereof, and acquiring methods of the loci and the markers. The SNP loci linked with a blight resistant gene Fon-1 in a watermelon and the markers thereof have nucleotide base sequences represented by SEQ ID NO:1-8 in a sequence table. The acquiring method of the loci comprises the following steps: 1, selecting a tested material; 2, carrying out preliminary positioning of the blight resistant gene Fon-1 in the watermelon; 3, acquiring candidate SNP; and 4, acquiring the SNP loci closely linked with the blight resistant gene Fon-1 in the watermelon, and verifying the candidate SNP loci. According to the invention, the phenotype identification and the molecular detection of F2 generation separation populations and natural populations are carried out through utilizing a series of markers to confirm the close linkage degree of the series of the SNP loci with target properties; and the SNP loci are utilized to design the markers respectively, and the markers can be utilized to carry out the initial-stage screening of the kind in order to reach a molecule assisted breeding purpose, so the breeding period is substantially shortened, and an important scientific research meaning is possessed.
Owner:京研益农(北京)种业科技有限公司
Molecular marker gi1354 closely linked to pepper cmv resistance gene and its acquisition and application
InactiveCN105368824BAccurate detectionSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenomic DNA
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and in particular relates to a molecular marker GI1354 closely linked with a capsicum CMV resistance gene, an acquisition method and application. The molecular marker GI1354 closely linked with the capsicum CMV resistance gene has at least one nucleotide base sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1-2 in the sequence list. The molecular marker is used to detect the cr gene in the capsicum material, and the detection includes the steps of genome DNA extraction, PCR amplification reaction, analysis and the like of the capsicum material. The invention directly uses the PCR primer obtained by screening as a molecular marker, and can accurately detect whether the capsicum material contains the cr gene, and the method of the invention is convenient, quick and cost-saving.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Caps Molecular Marker Method and Application for Identification of Purple-black Striped Peel Tomato
ActiveCN106755357BGuaranteed accuracyAvoid the transfer stepMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGel electrophoresis
The invention discloses a CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) molecular marking method for identifying solanum lycopersicum with purple black striped pericarp and an application. The sequence of a molecular marker carried by the solanum lycopersicum with purple black striped pericarp is a nucleotide base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, PCR amplification is performed with genomic DNA of the solanum lycopersicum with purple black striped pericarp as a template, nucleotide base sequences shown as SEQ ID NO.3-4 are amplification primers, amplification and cleavage are performed, a specific band different from other solanum lycopersicum pericarp colors can be obtained after cleavage, and the molecular marking method is applied to breed improvement and breeding of the solanum lycopersicum. Compared with the prior art, the CAPS molecular marking method has the advantages that the polymorphism of a cleaved fragment is observed through PCR amplification, cleavage and gel electrophoresis separation, the step of membrane transfer in the traditional RFLP (restricted fragment length polymorphism) analysis is omitted, the operation is simplified, the precision of the RFLP technology is kept, the polymorphism detecting probability is higher, the solanum lycopersicum with purple black striped pericarp is obtained rapidly and applied to breed improvement and assisted breeding, and the method has important theoretical and practical meanings for culturing new varieties of solanum lycopersicum containing rich anthocyanidin.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Gene sequence a for causing watermelon bisexual flower development and obtaining method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of gene sequences and obtaining methods thereof, and particularly relates to a gene sequence a for causing watermelon bisexual flower development and an obtaining method thereof. The gene sequence a has nucleotide base sequences represented by SEQ ID NO:1-6 in the sequence table. The obtaining method comprises the following steps: A, selecting a material for testing, B, extracting genome DNA, C, carrying out a long-distance PCR amplification reaction and detecting the obtained product, D, obtaining a specific amplification sequence, E, obtaining a candidate SNP, and F, verifying the candidate SNP locus, and finally obtaining the gene sequence a for causing watermelon bisexual flower development. According to the present invention, F2 generation segregation population dCAP molecule marker detection and phenotypic identification, and each core germplasm resource dCAP molecule marker detection and phenotypic identification are performed to confirm that the SNP locus is a co-segregation marker; and the obtained SNP locus can be used to develop genetic markers for assisted breeding so as to achieve a purpose of obtaining of the watermelon female line variety.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
Novel animal cell expression vector containing MAR (Matrix Attachment Region) core fragment
ActiveCN109576269AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsBiologyMammalian cell
The invention discloses a novel animal cell expression vector containing a MAR (Matrix Attachment Region) core fragment. A nucleotide base sequence of the MAR core fragment of the recombinant expression vector is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2 or SEQ ID NO: 3. The expression vector can be used for effectively improving the yield of protein in mammalian cells and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:SUNSHINE GUOJIAN PHARMA (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
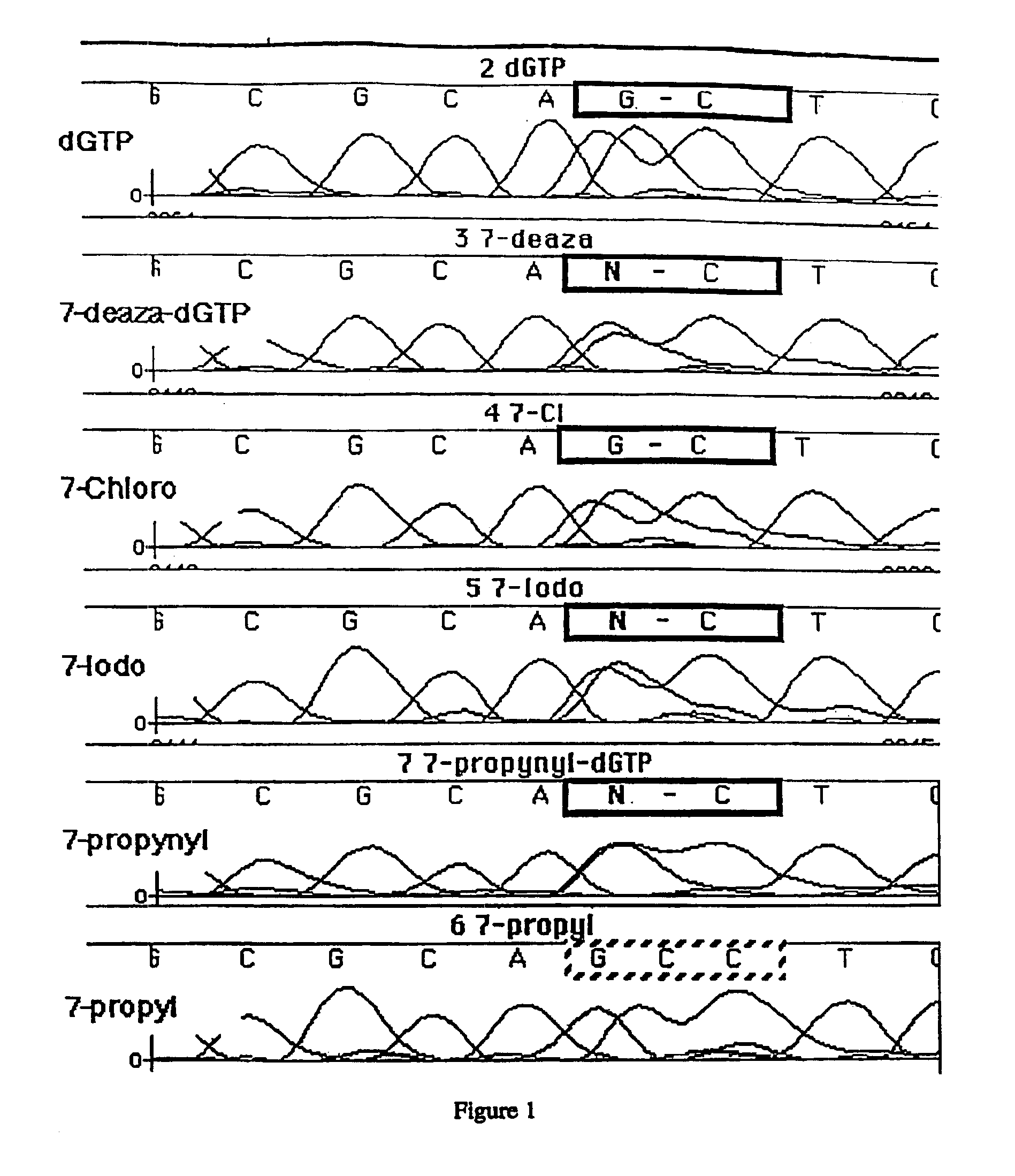
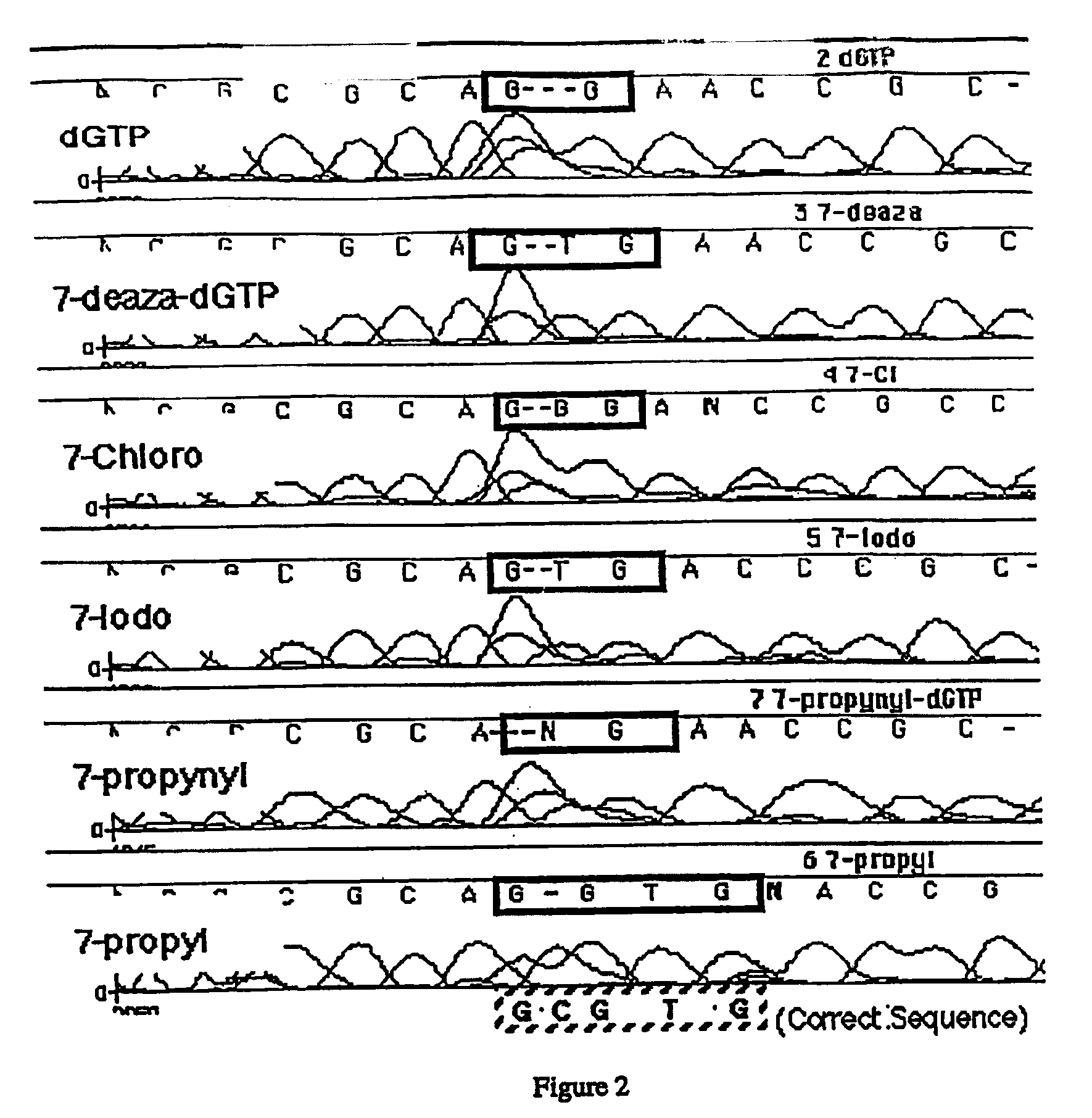
Derivatives of 7-deaza -2'-deoxyguanosine-5'-triphosphate, preparation and use thereof
Derivatives of 7-deaza-2′-deoxyguanosine are described. Also described is the use of such compounds in synthesis of nucleic acid polymers and in methods for determining a nucleotide base sequence.
Owner:CIBA VISION AG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com