Patents
Literature
35 results about "Platelet product" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
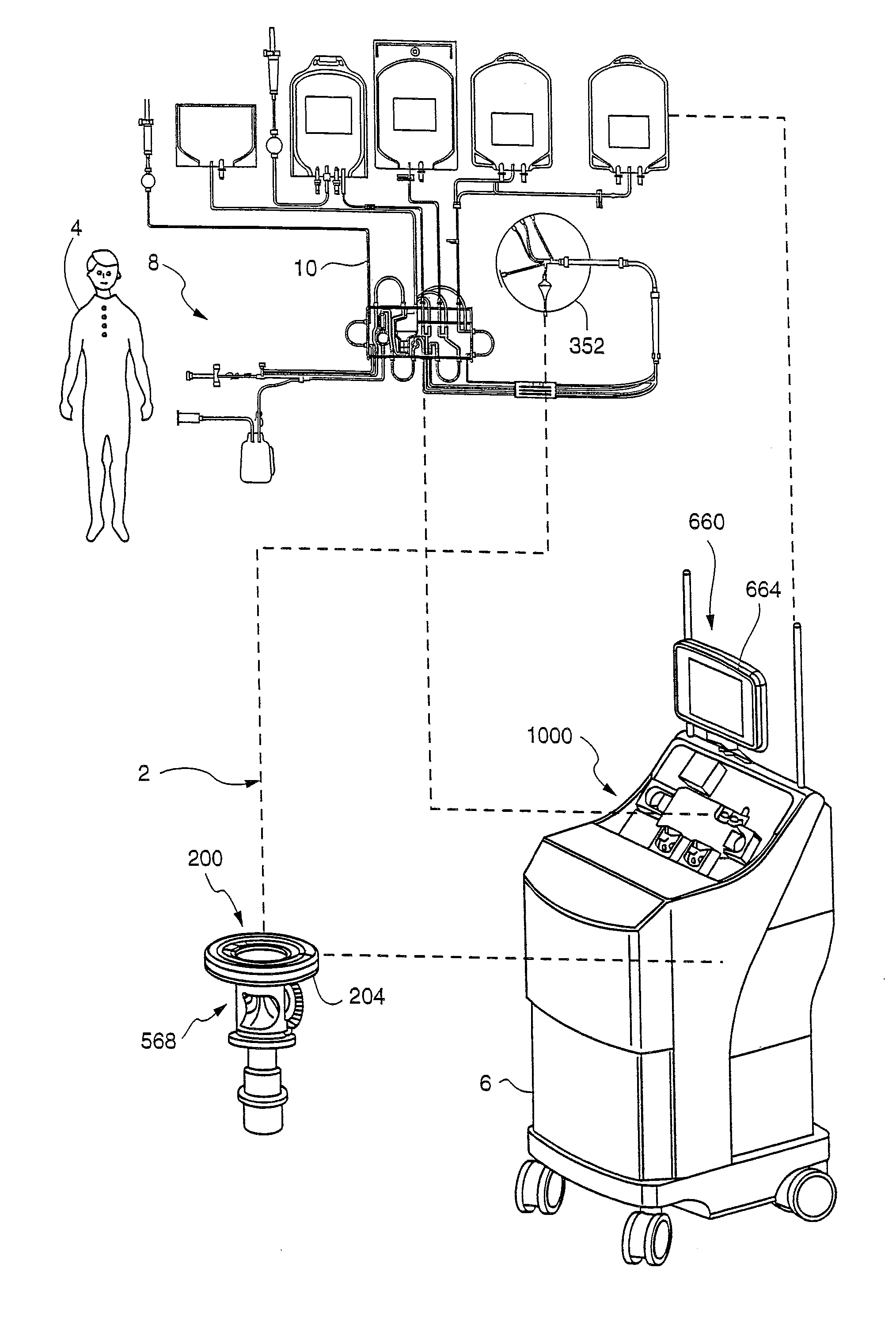
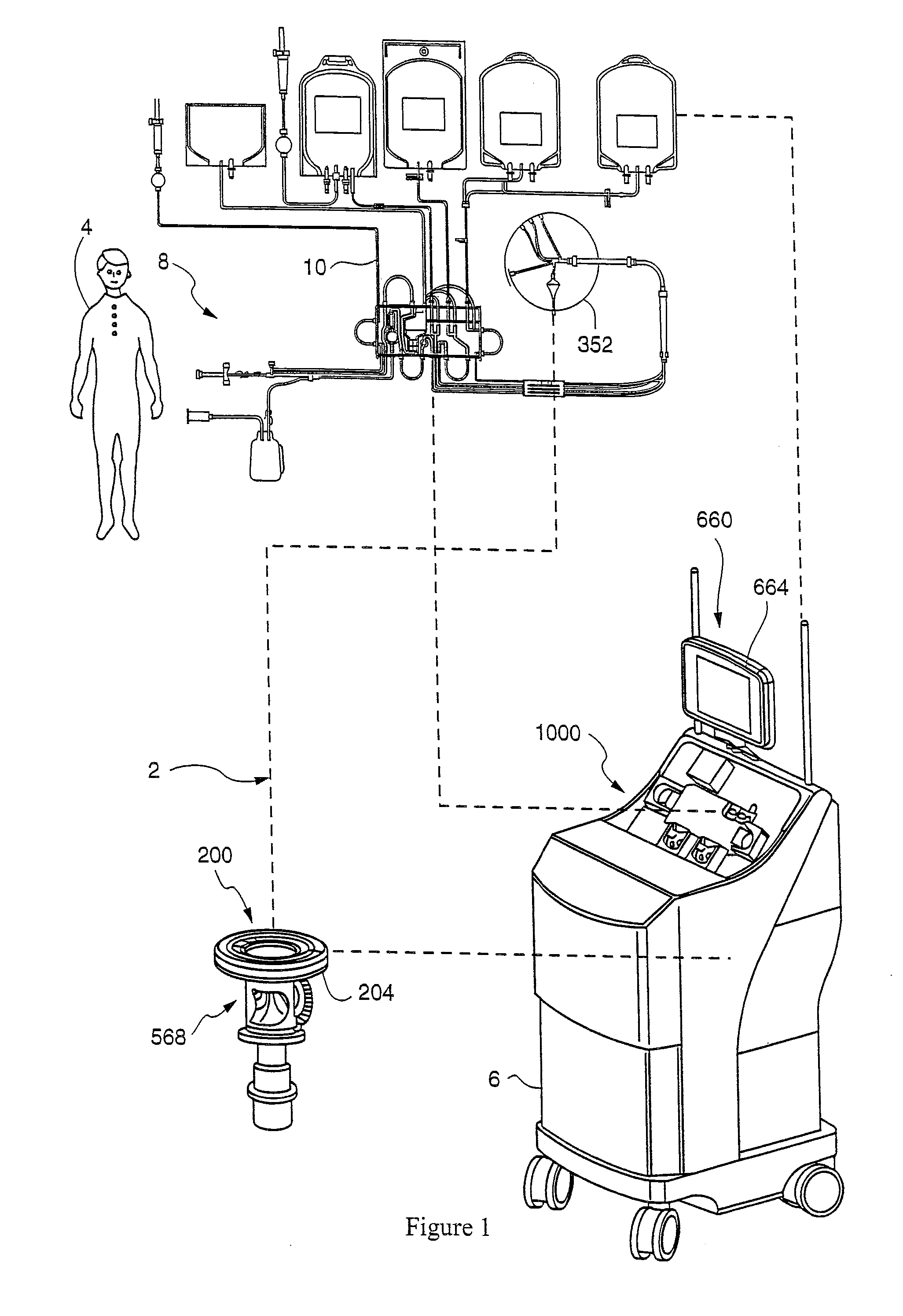
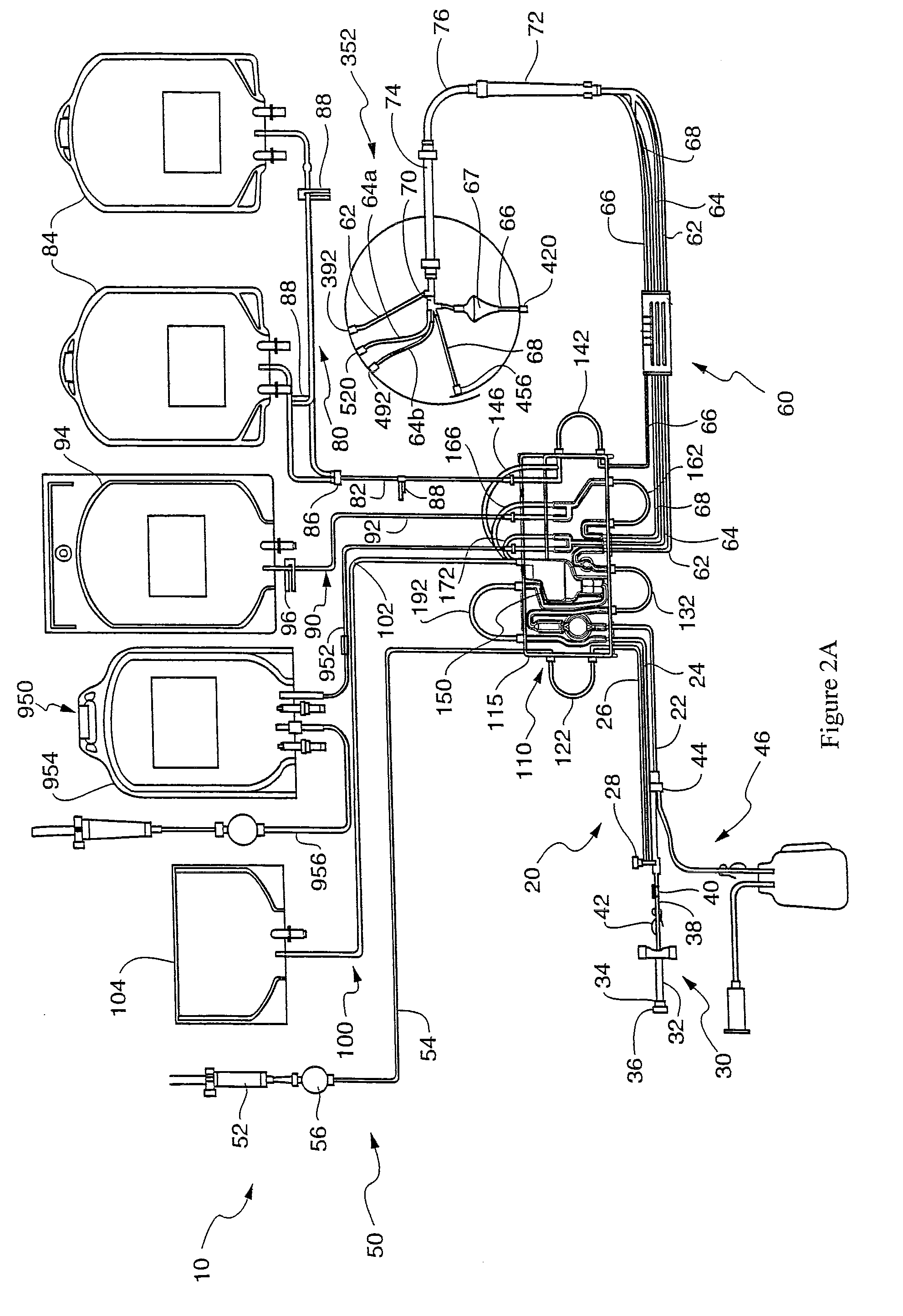
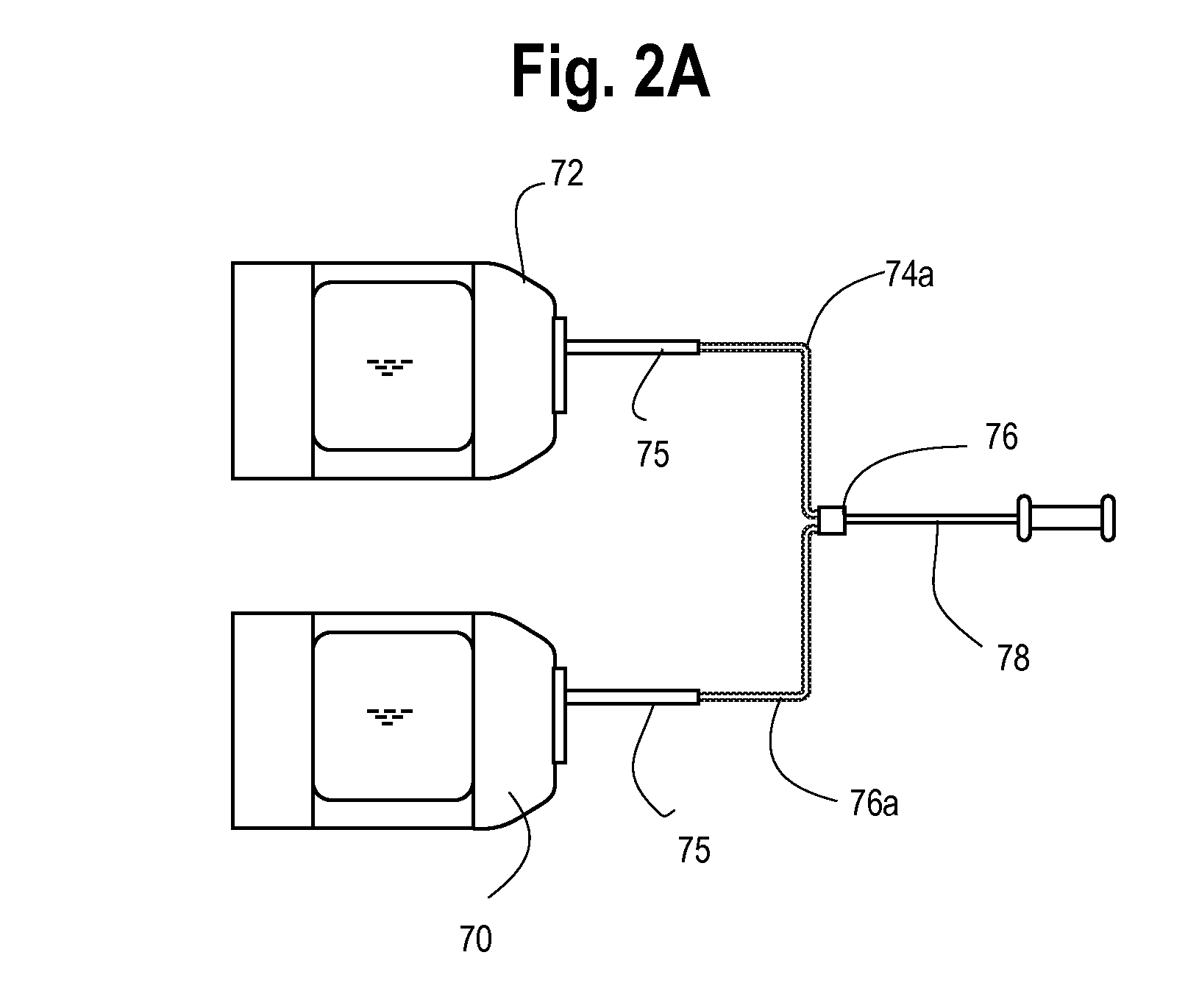
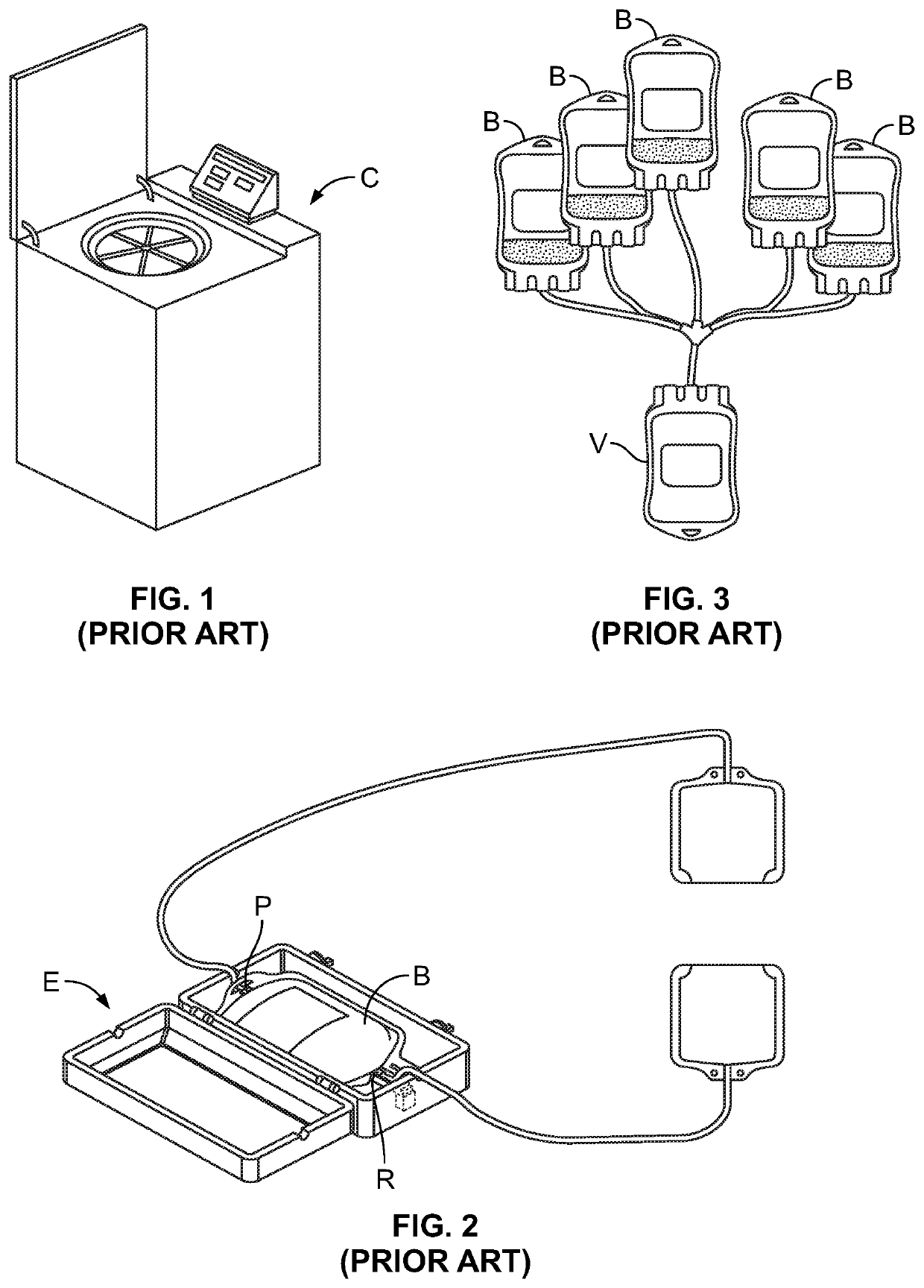
Method and apparatus for collecting hyperconcentrated platelets
InactiveUS6022306AOther blood circulation devicesDispersed particle separationParticle flowPlatelet product
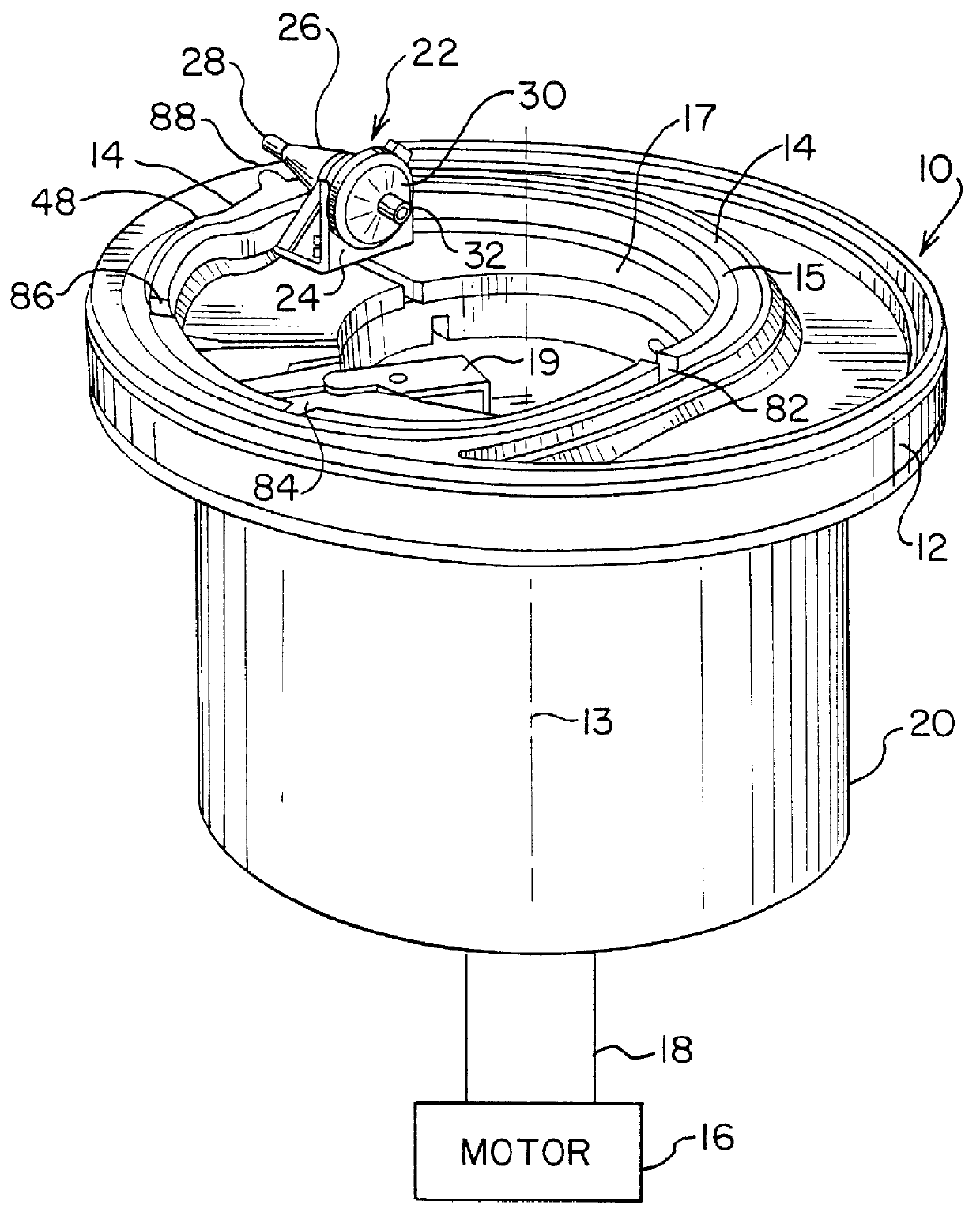
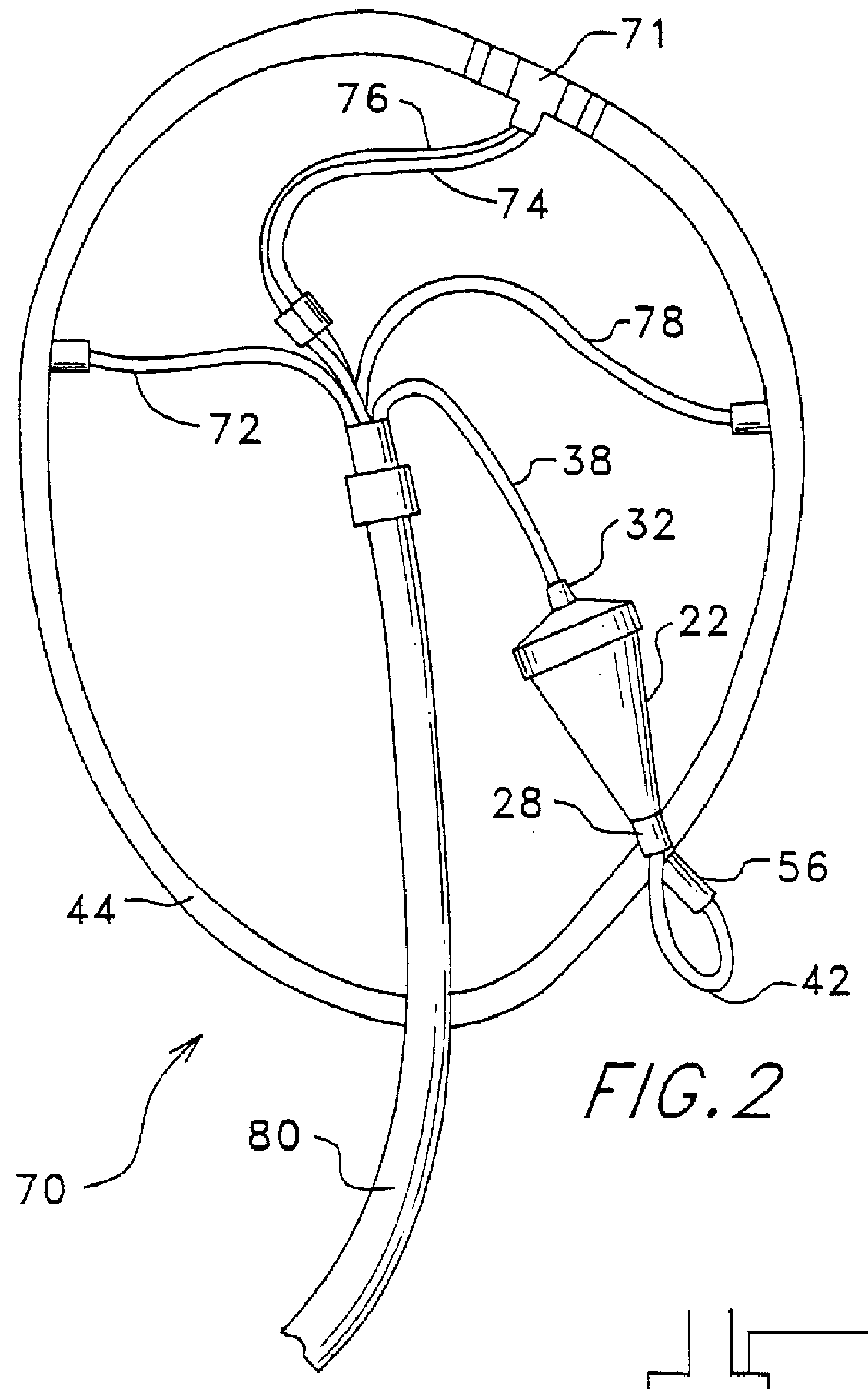
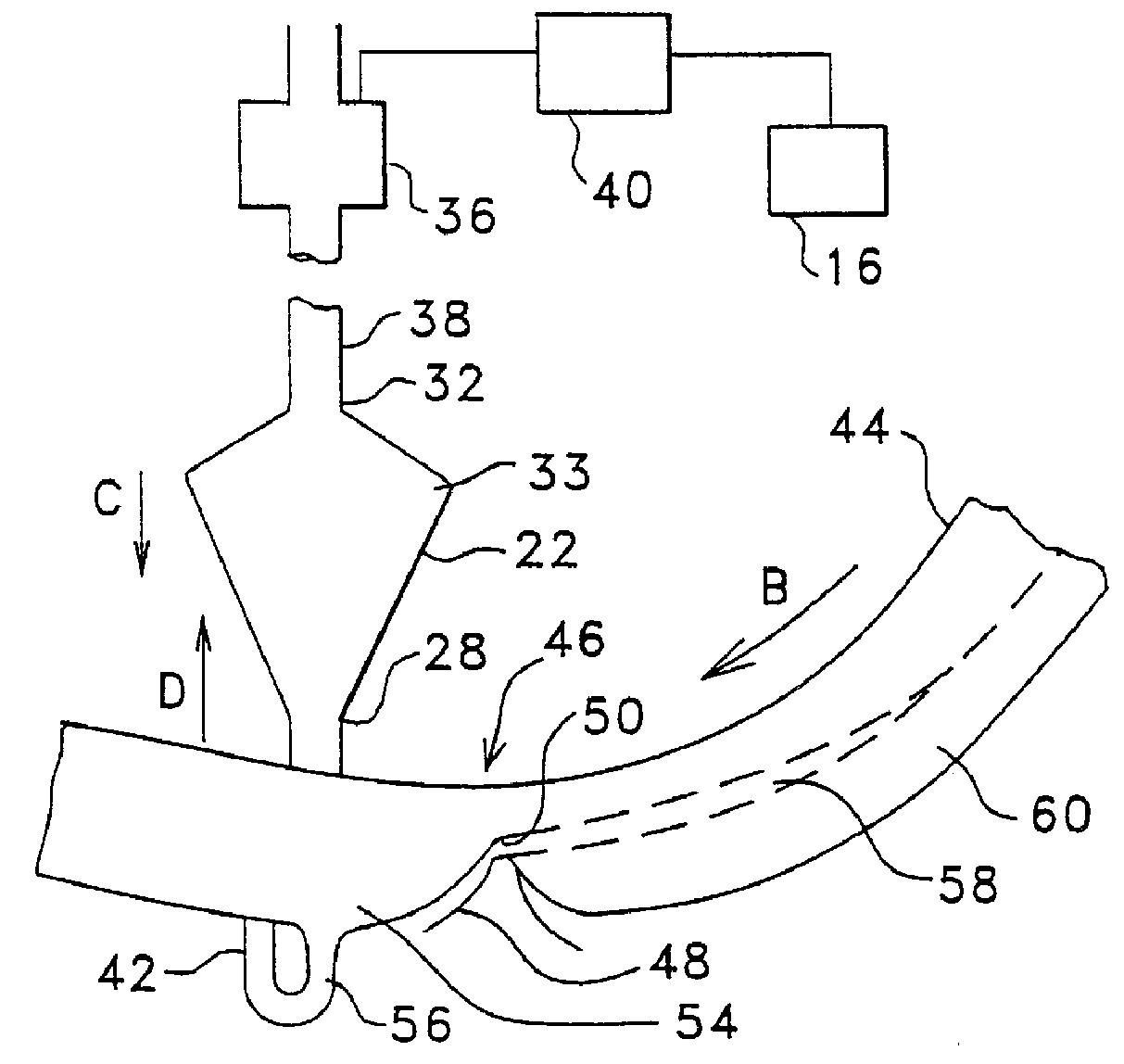
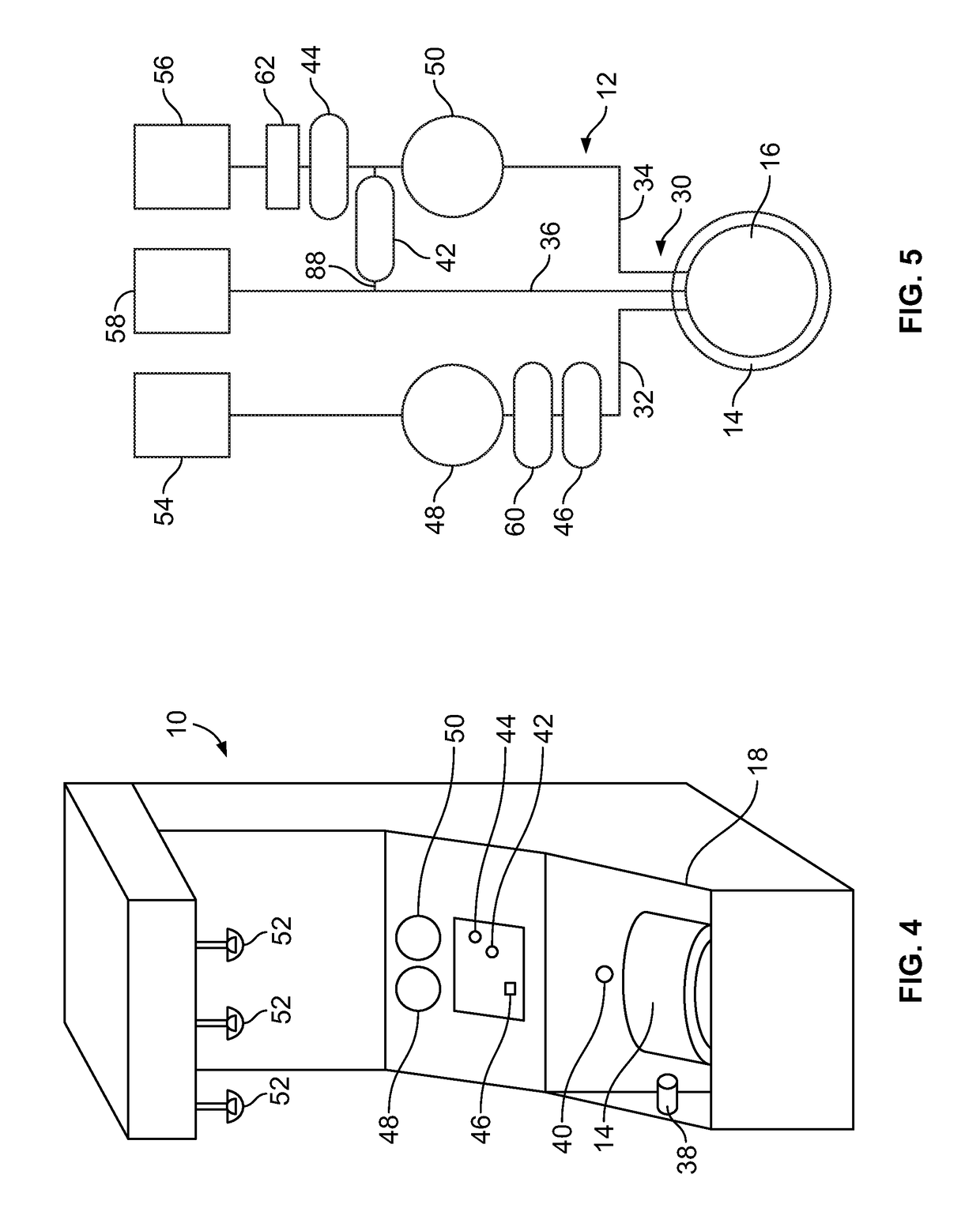
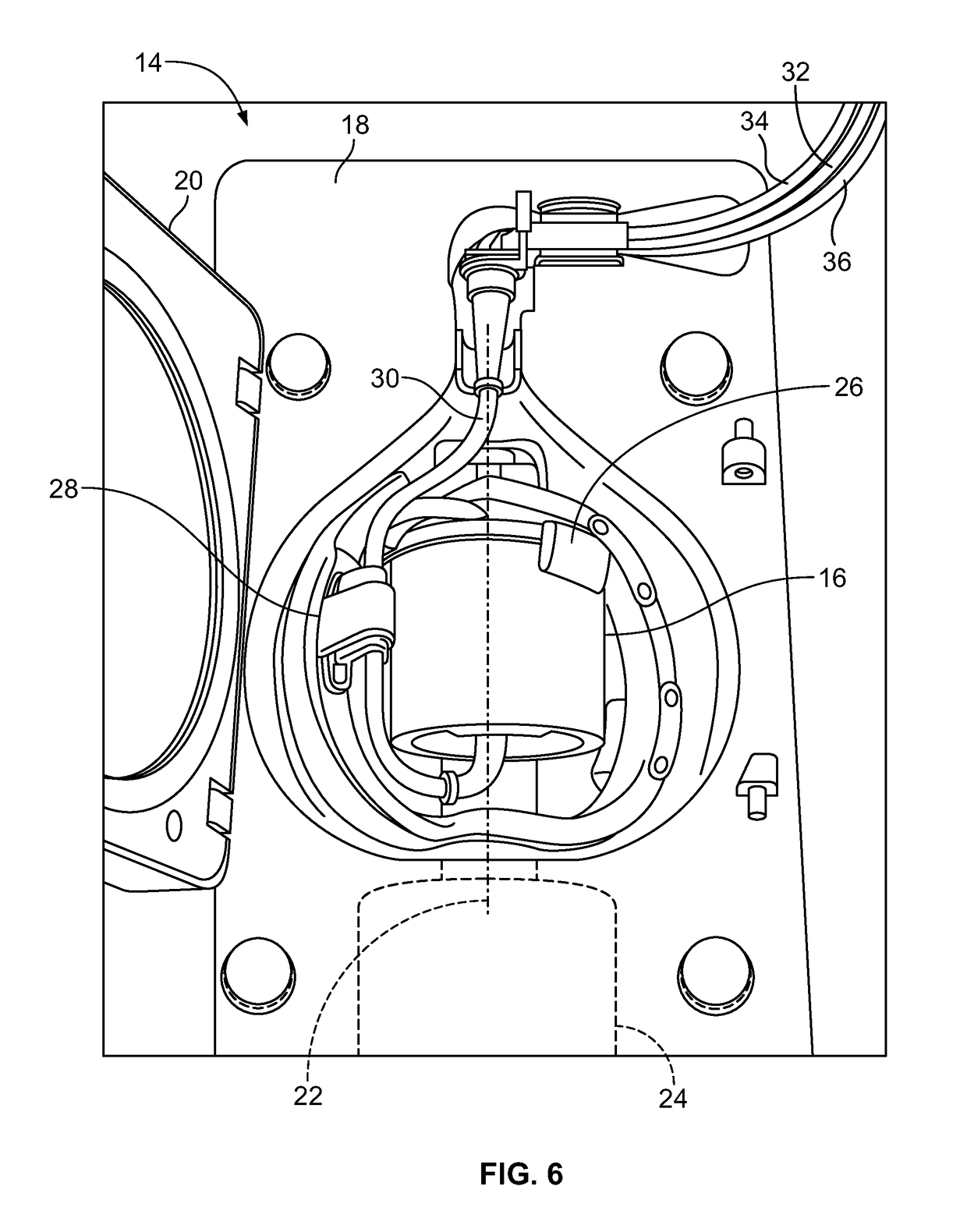
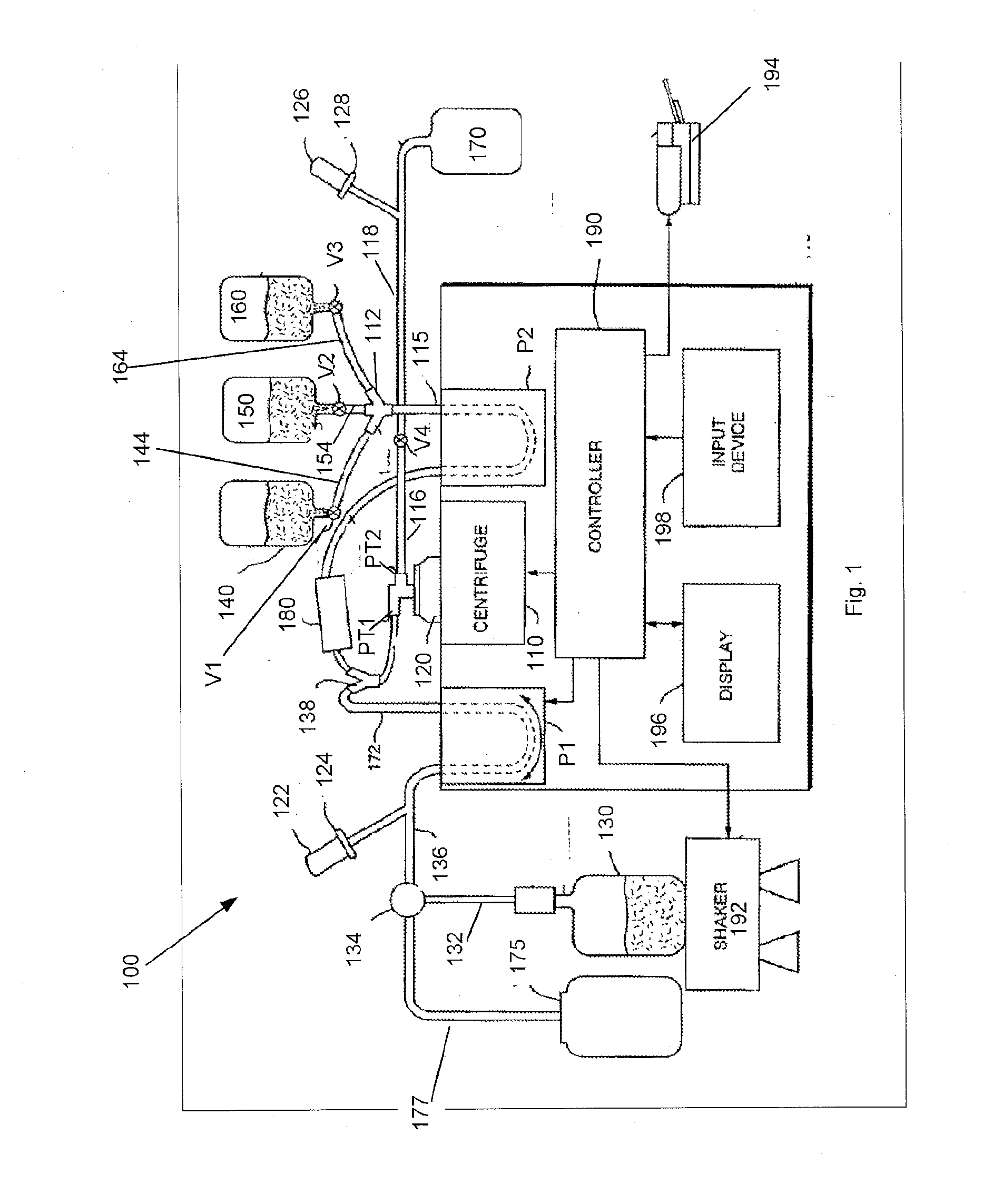
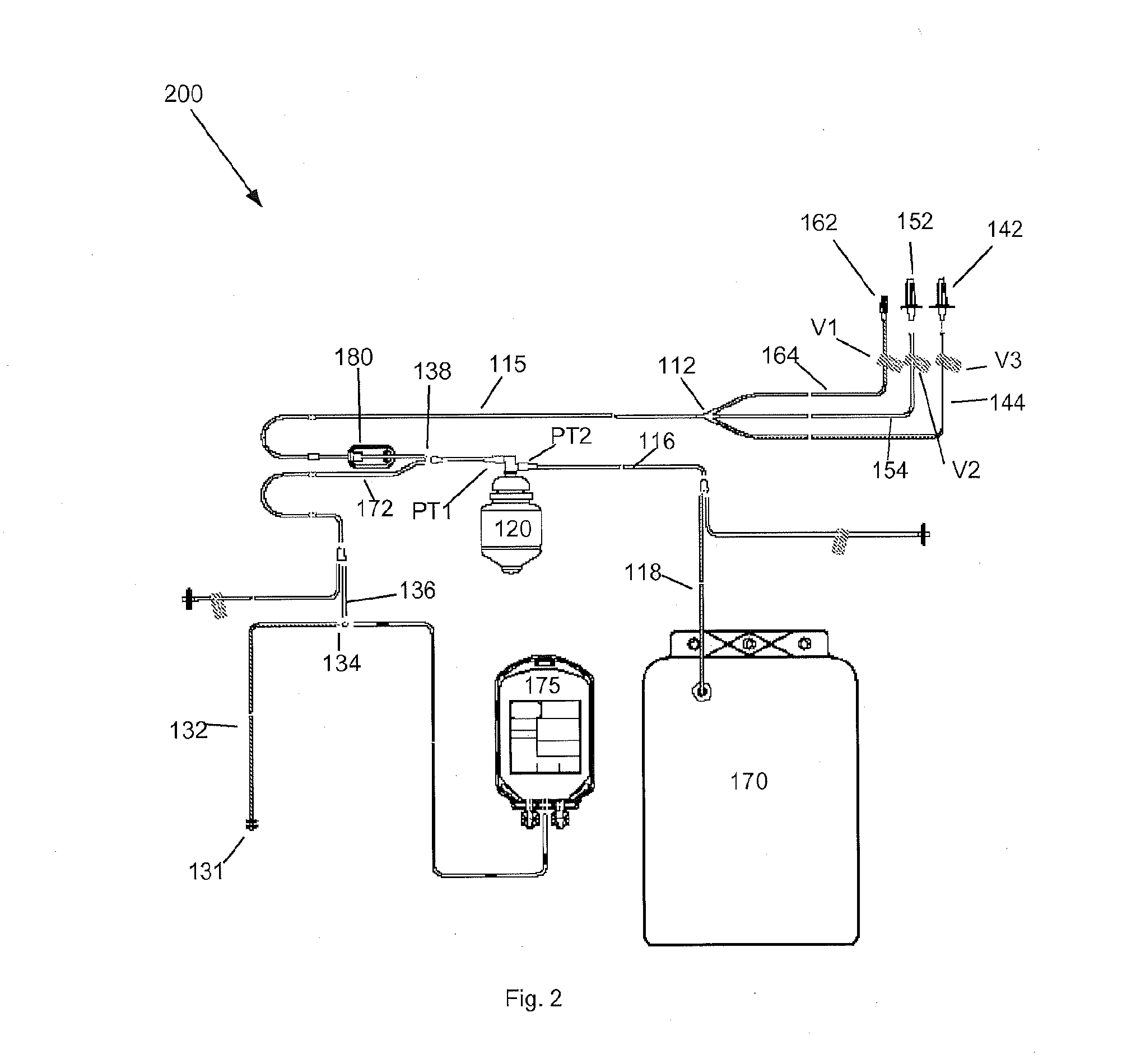
The instant invention relates to a method and the apparatus for collecting a hyperconcentrated platelet product. A fluid containing platelets and other particles flows into a fluid chamber at a flow rate. The flow rate of the fluid is selected to retain the majority of the platelets in the fluid chamber in a saturated bed. The platelets are collected from the fluid chamber without collecting the other particles to form a hyperconcentrated other particle reduced platelet product.
Owner:CARIDIANBCT
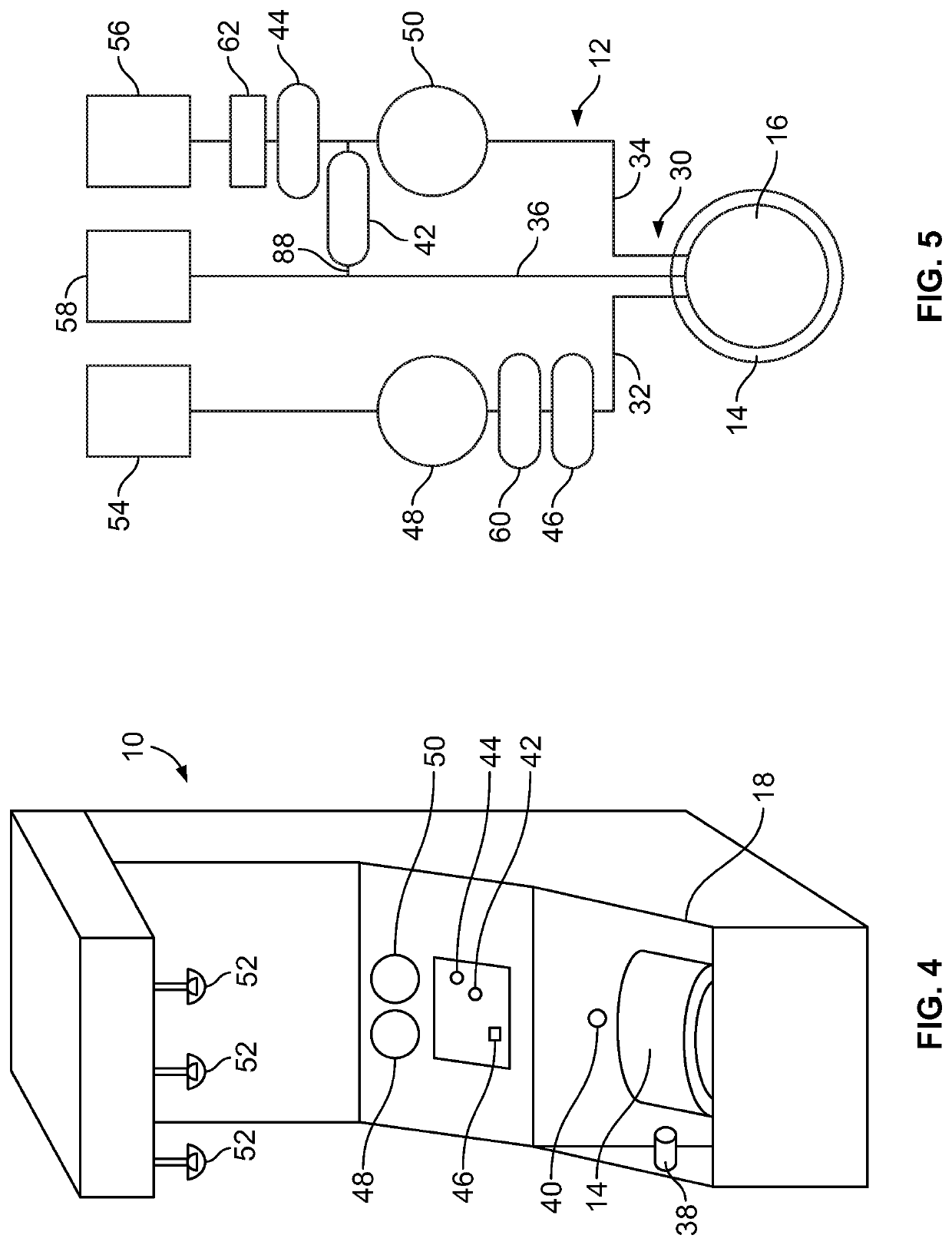
System and Method for Plasma Reduced Platelet Collection
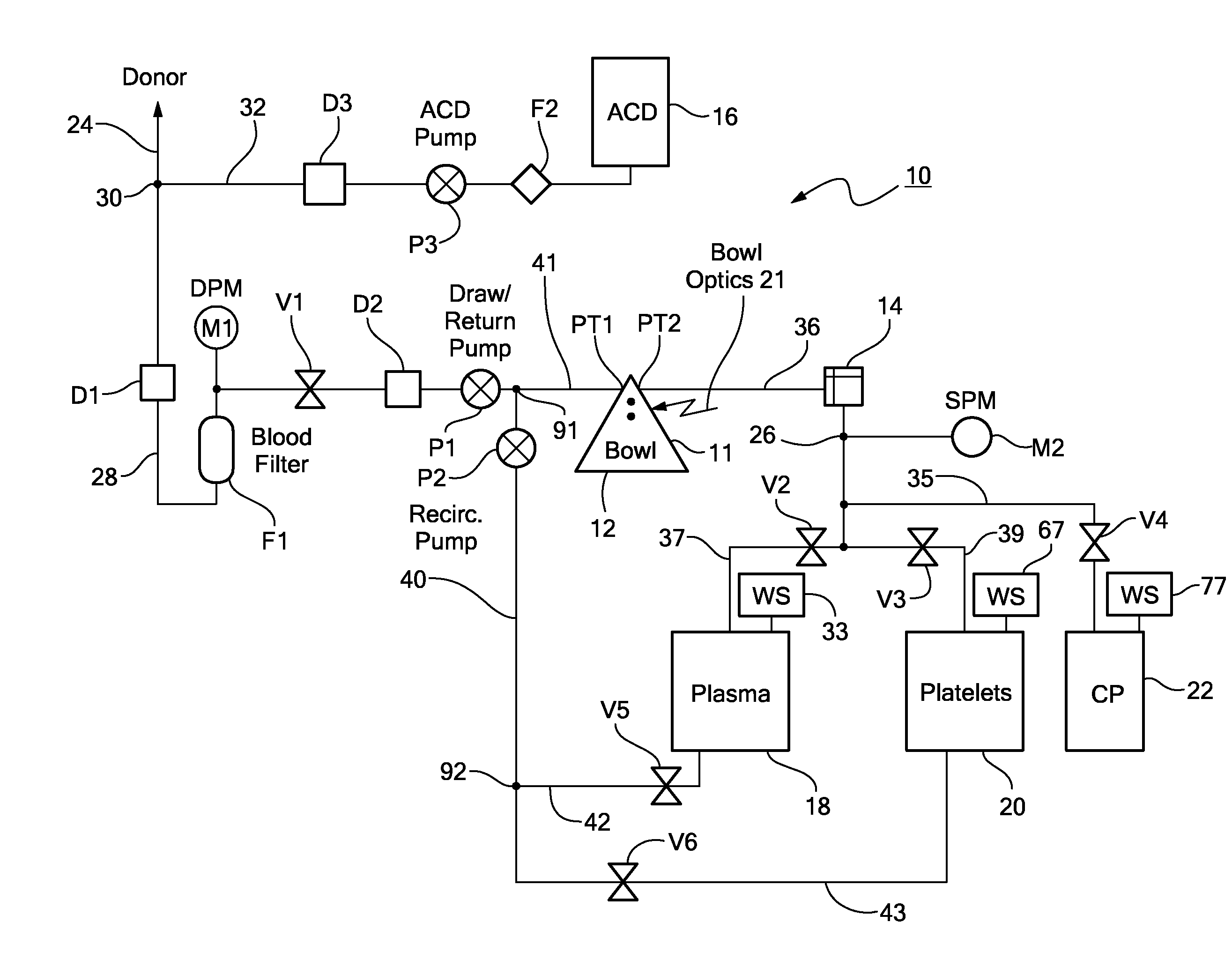
A method and apparatus for collecting plasma reduced platelets potentially suspended in a synthetic solution from a donor. Whole blood is drawn from the donor and introduced into a separation chamber. Platelets are extracted from the separation chamber into a container, using, for example, surge (with anticoagulated plasma or a synthetic solution) or push methodologies. The remaining blood components in the separation chamber are returned back to the donor. The steps of drawing whole blood and introducing the whole blood into the separation chamber, extracting platelets from the separation chamber into the container, and returning the remaining components in the chamber back to the donor are repeated. The sequestered platelets in the container are reintroduced into the separation chamber, whereupon a plasma reduced platelet product is extracted.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
Selective deleukocytation unit for a platelet product
InactiveUS7140497B2Increase capacityImprove hydrophilicityOther blood circulation devicesSolvent extractionBlood componentWhite blood cell
The invention includes a filtration unit for the selective deleukocytation of a fluid containing blood platelets such as blood or a blood component. The unit includes a medium for deleukocytation by adsorption and / or filtration of the leukocytes. The medium is formed by at least one layer of non-woven polyurethane fabric which has been treated by gas plasma.The invention also includes bag systems containing such a unit, including closed filtration systems.
Owner:MACO PHARMA SA
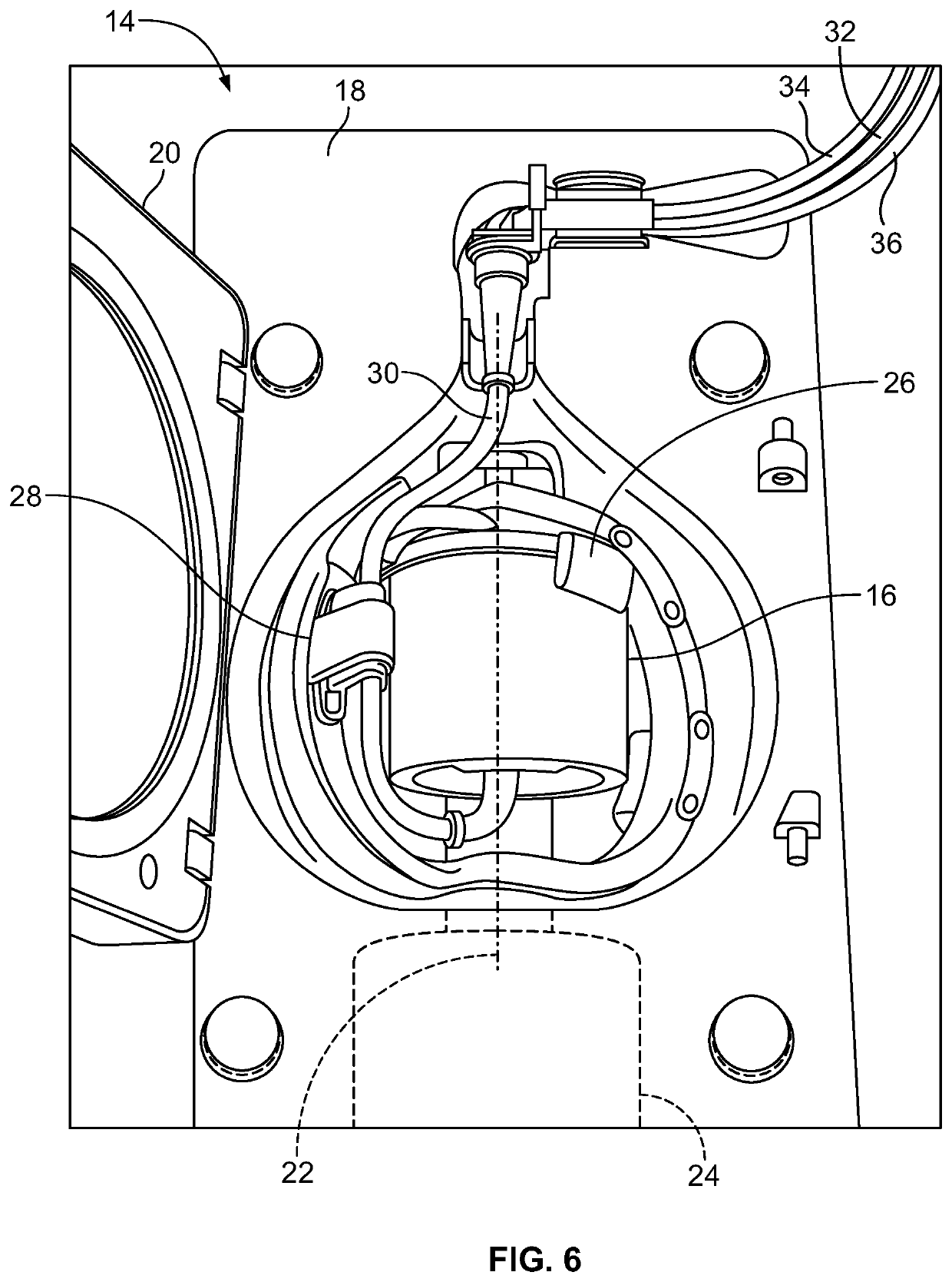
Blood processing apparatus and method with automatically adjusted collection targets
InactiveUS20120010062A1Optimize collection of reliableIncrease probabilityOther blood circulation devicesDispersed particle separationSurgeryIntensive care medicine
A method and apparatus for collecting a maximum amount of platelets for a selected blood separation procedure without collecting excess platelets above those required for a selected platelet product, whether that product was one unit of platelets, two units of platelets (a double platelet), or more. The method and apparatus will continue to adjust the platelet yield target for platelet collection throughout the procedure without operator intervention, unless the selected procedure cannot be completed successfully, and the operator is required to select another allowed procedure.
Owner:TERUMO BCT
System and method for plasma reduced platelet collection
A method and apparatus for collecting plasma reduced platelets potentially suspended in a synthetic solution from a donor. Whole blood is drawn from the donor and introduced into a separation chamber. Platelets are extracted from the separation chamber into a container, using, for example, surge (with anticoagulated plasma or a synthetic solution) or push methodologies. The remaining blood components in the separation chamber are returned back to the donor. The steps of drawing whole blood and introducing the whole blood into the separation chamber, extracting platelets from the separation chamber into the container, and returning the remaining components in the chamber back to the donor are repeated. The sequestered platelets in the container are reintroduced into the separation chamber, whereupon a plasma reduced platelet product is extracted.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
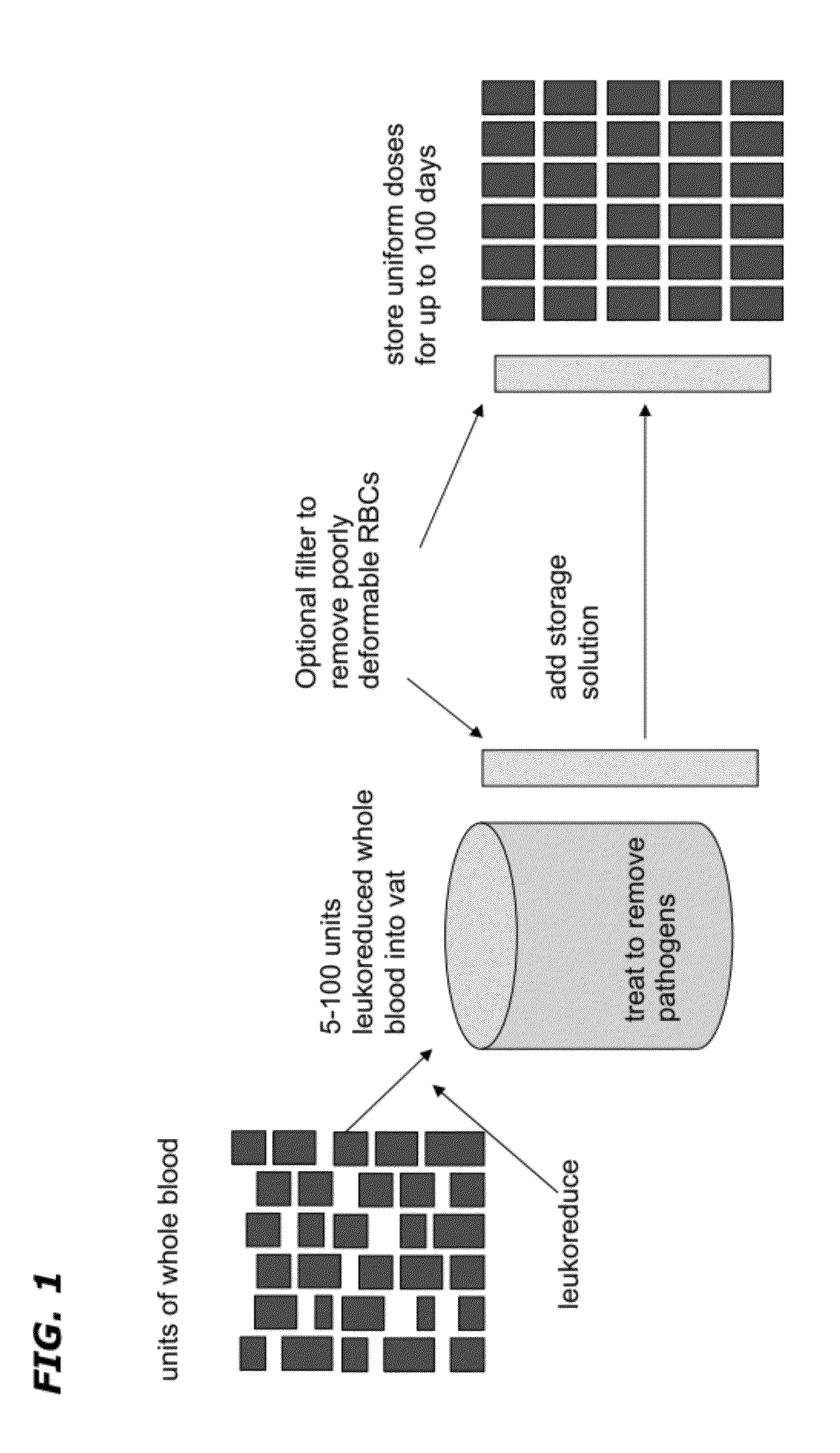
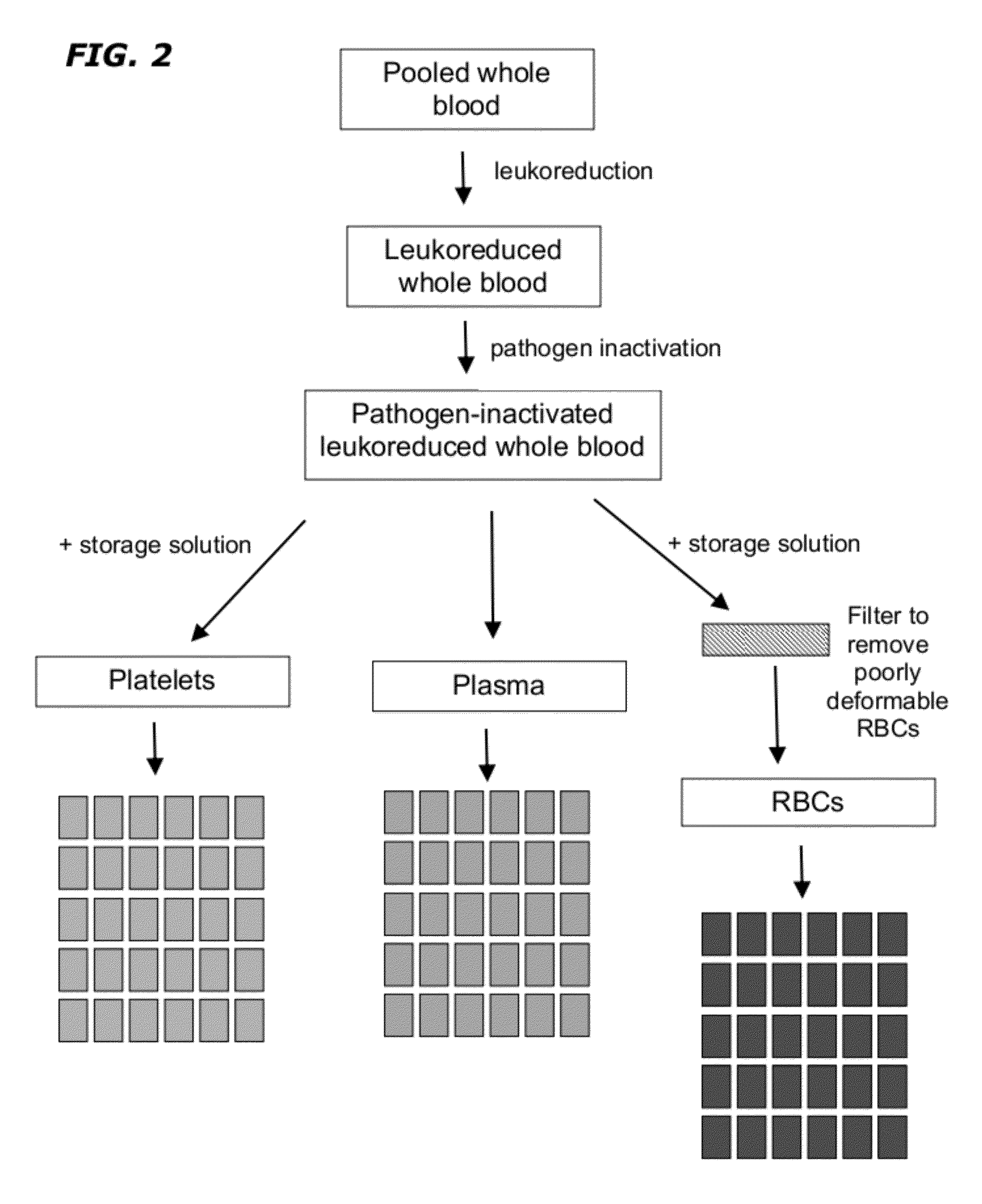
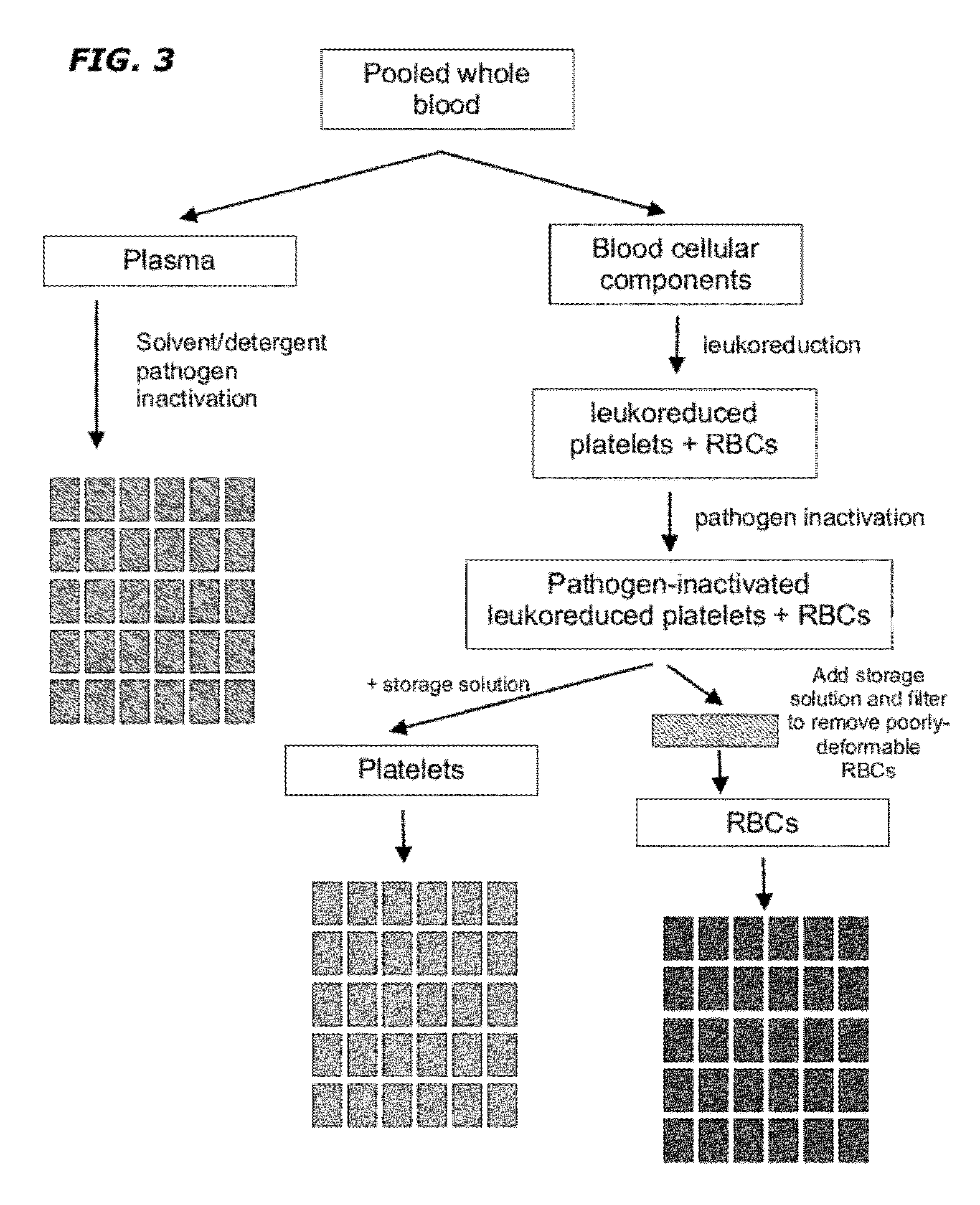
Method of Blood Pooling and Storage
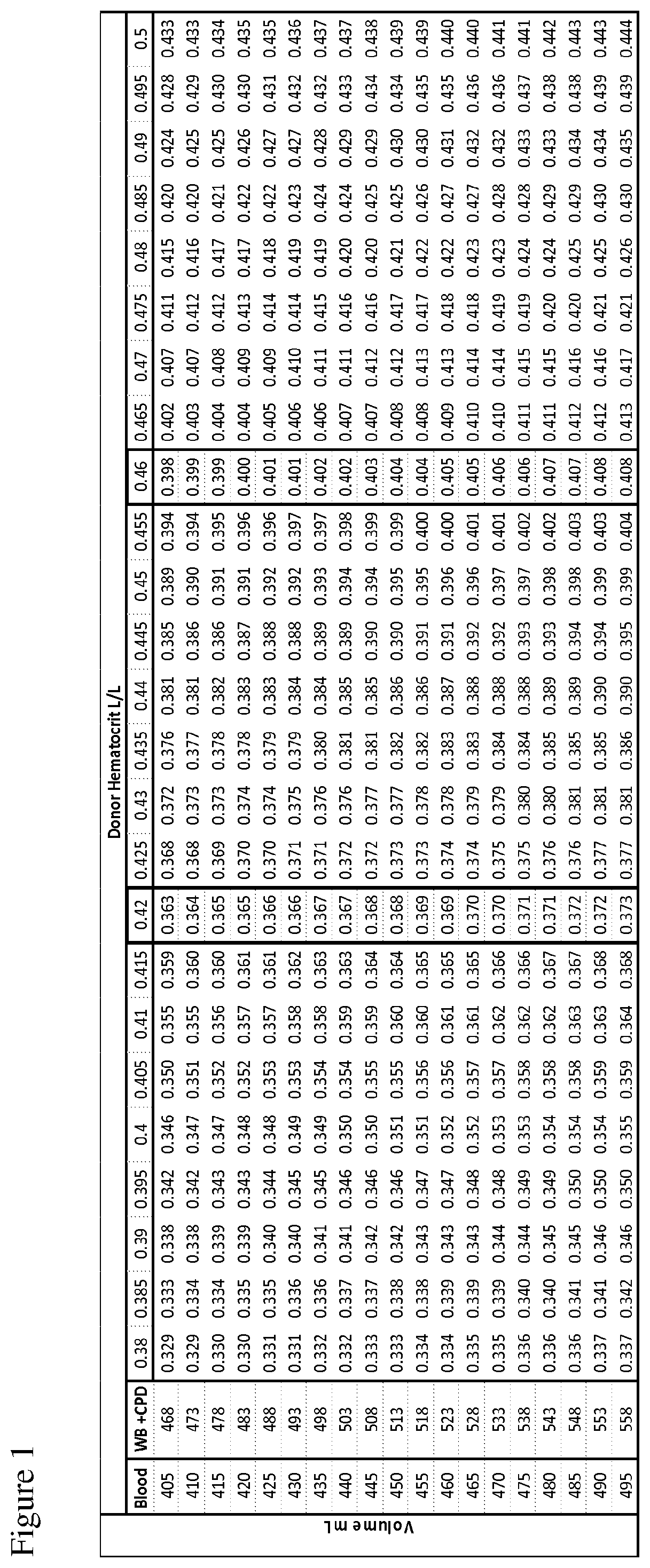
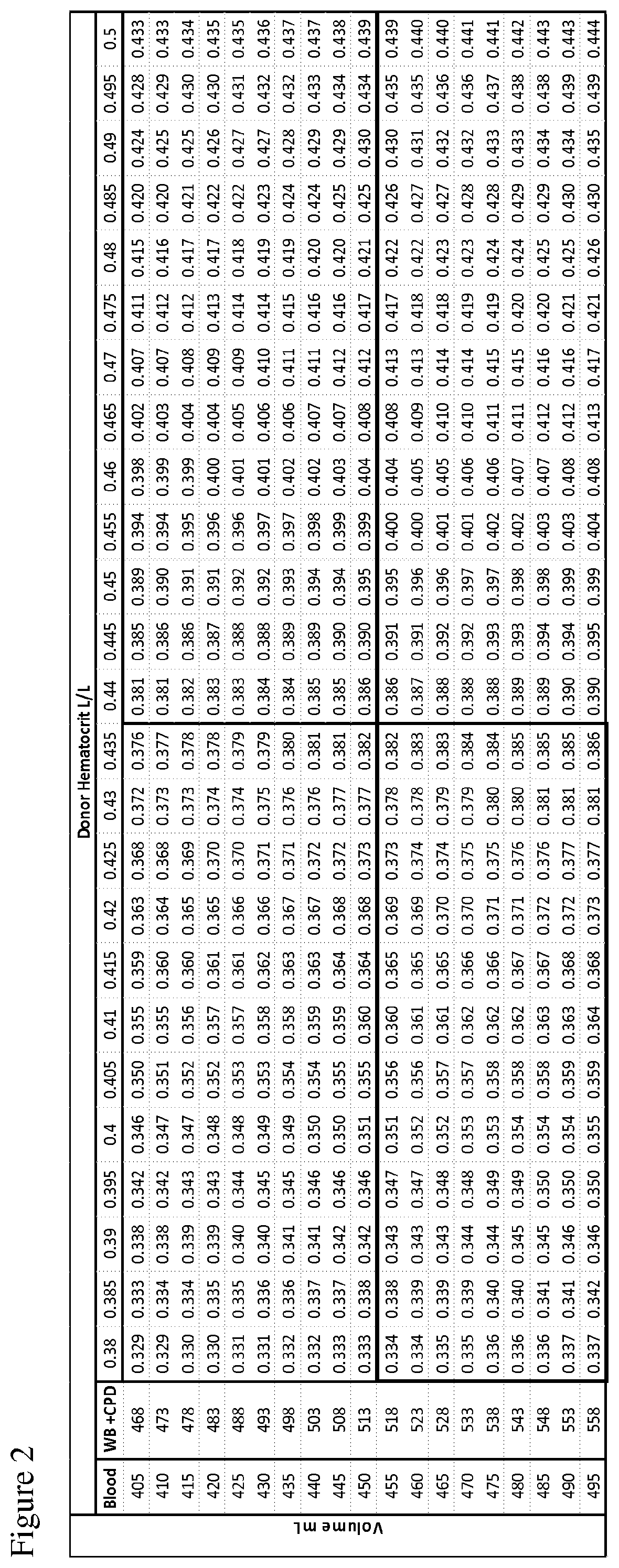
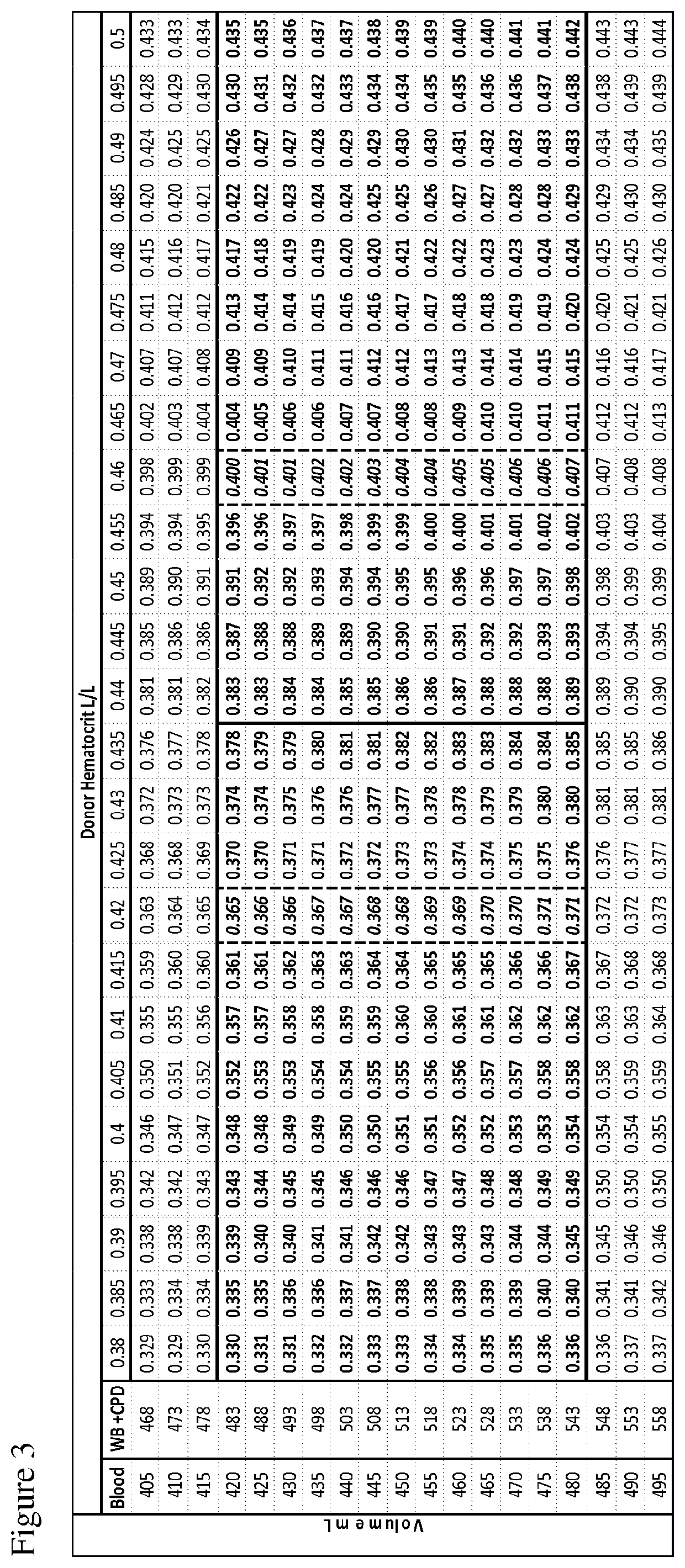
The disclosure provides methods of making a red blood cell, plasma, and platelet products having a uniform dose and volume. The method comprises pooling a plurality of blood units, leukoreducing the blood and inactivating any pathogen contained therein. Plasma, RBCs, and platelets are then divided into uniform dose and volume units which have an extended shelf life.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
Automated methods and systems for providing platelet concentrates with reduced residual plasma volumes and storage media for such platelet concentrates
Automated systems and methods for providing platelet concentrates and synthetic storage media with reduced residual plasma volumes are disclosed. The disclosed systems and methods reduce the residual volume of plasma in platelet concentrate to obtain a platelet product having a volume of plasma that is approximately 5% or less of the total platelet product volume. The disclosed systems and methods also reduce the residual volume of plasma in platelet concentrate to obtain a washed platelet product, wherein the volume of plasma in the washed platelet product is approximately 1% or less of the total washed platelet product volume. Storage media for platelets including less than approximately 10% plasma are also disclosed.
Owner:FENWAL
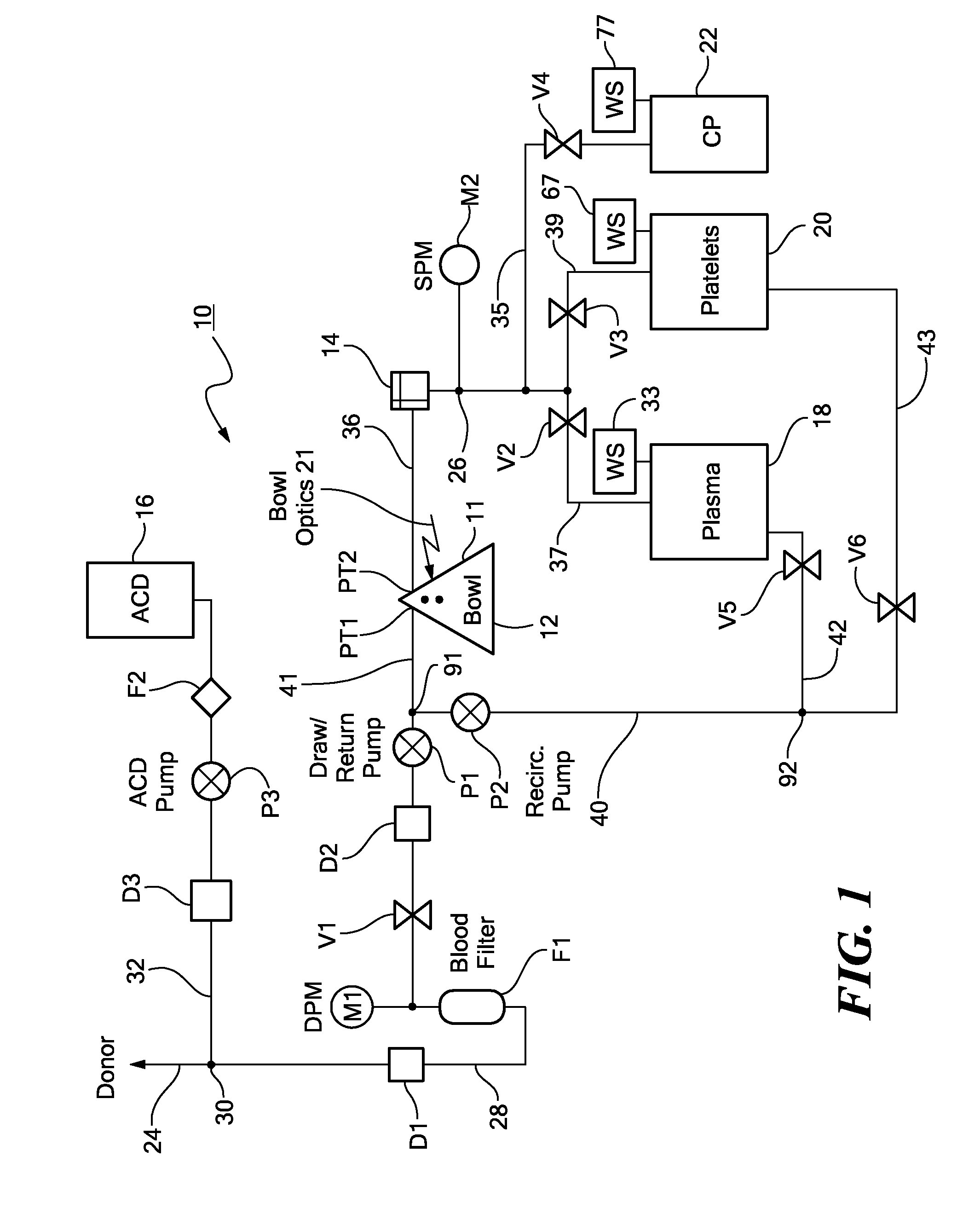
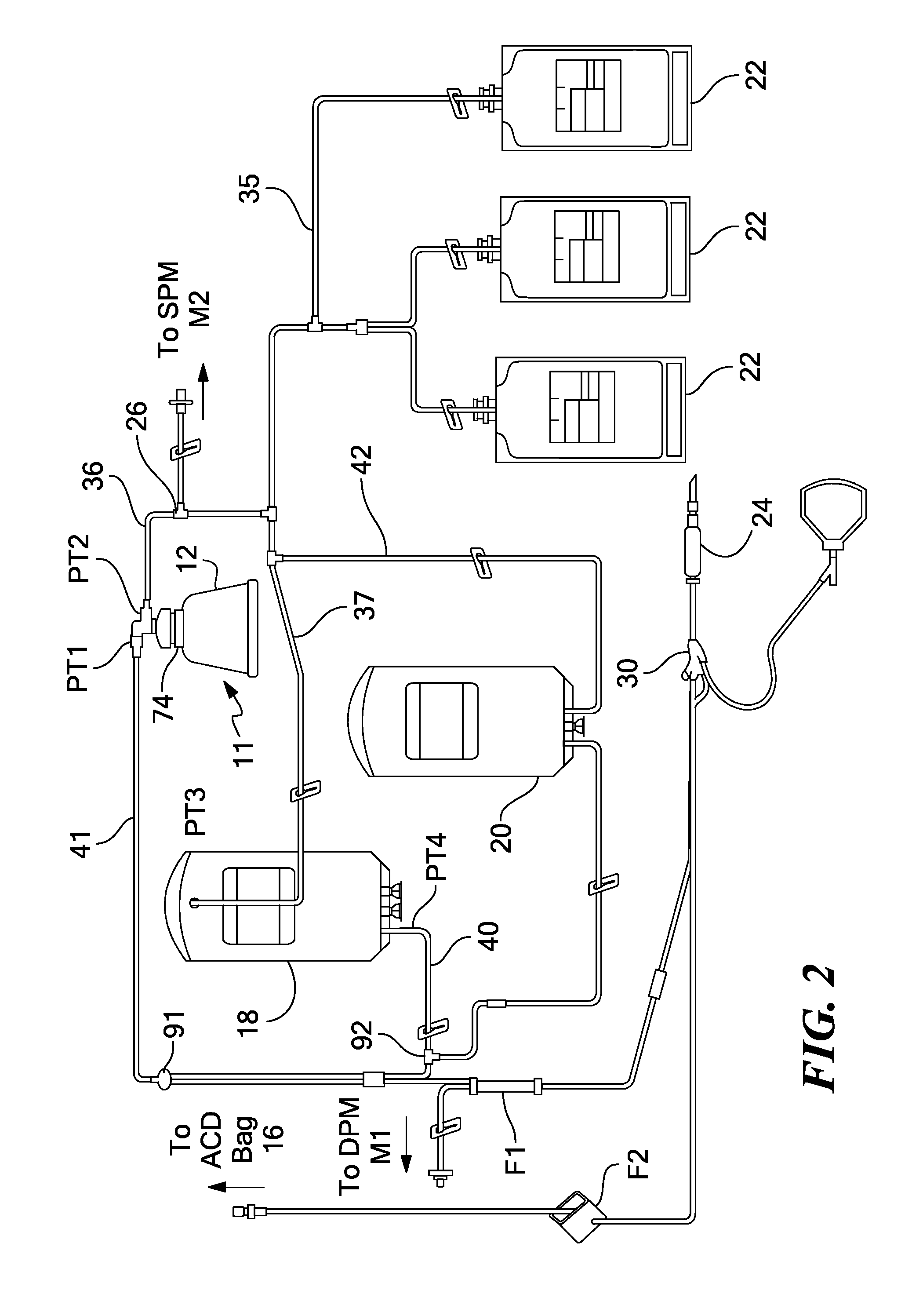
System and method for automated platelet wash
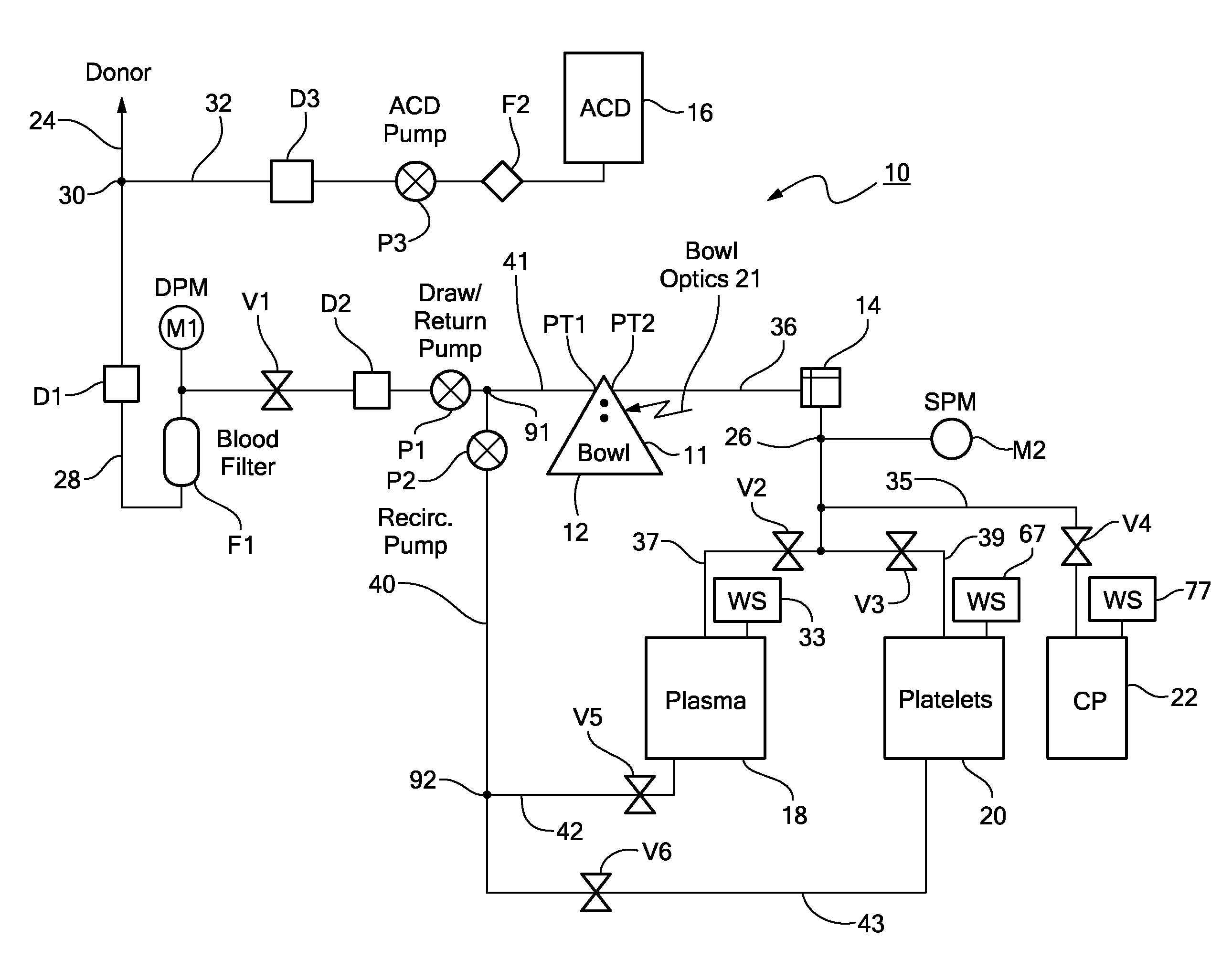
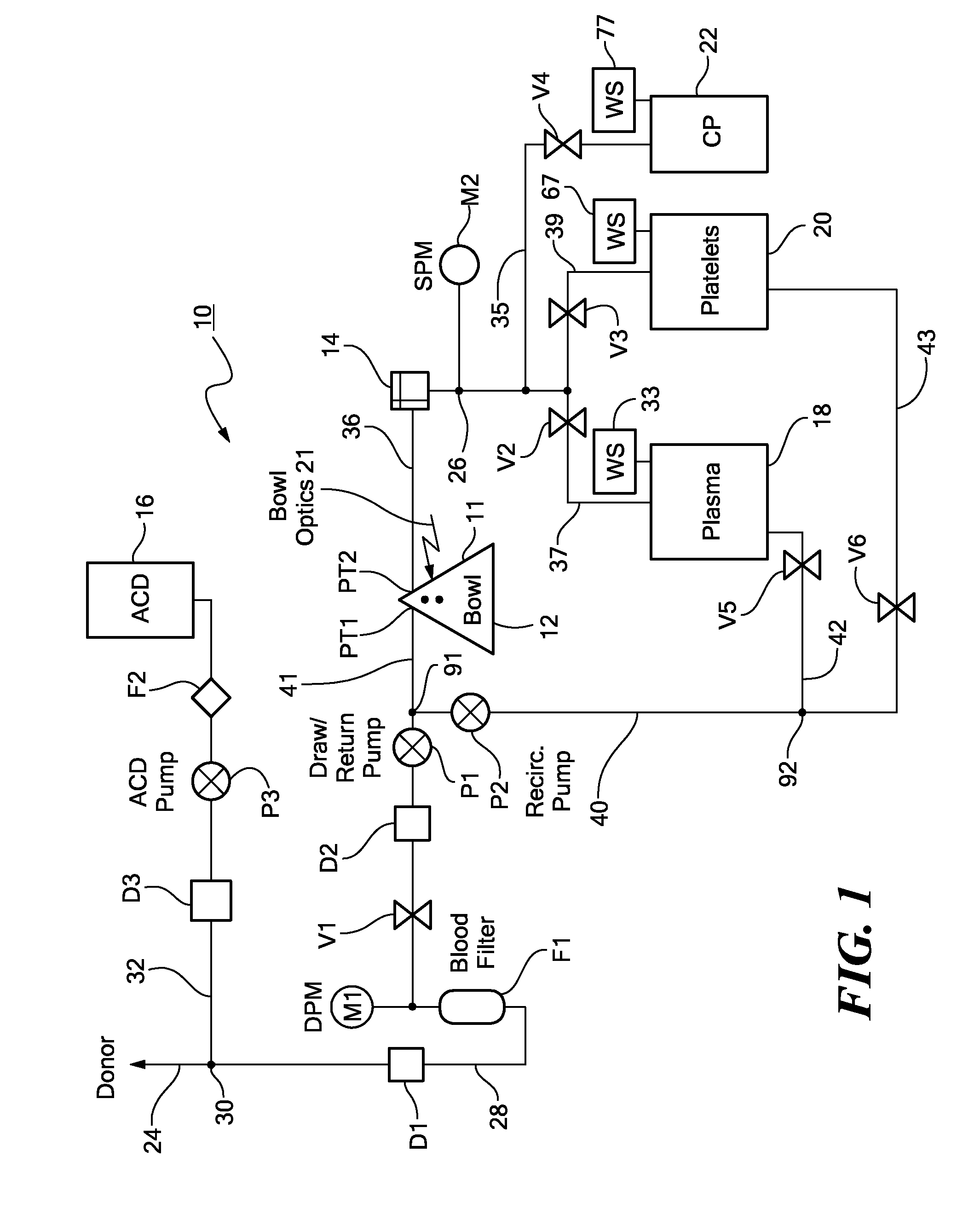
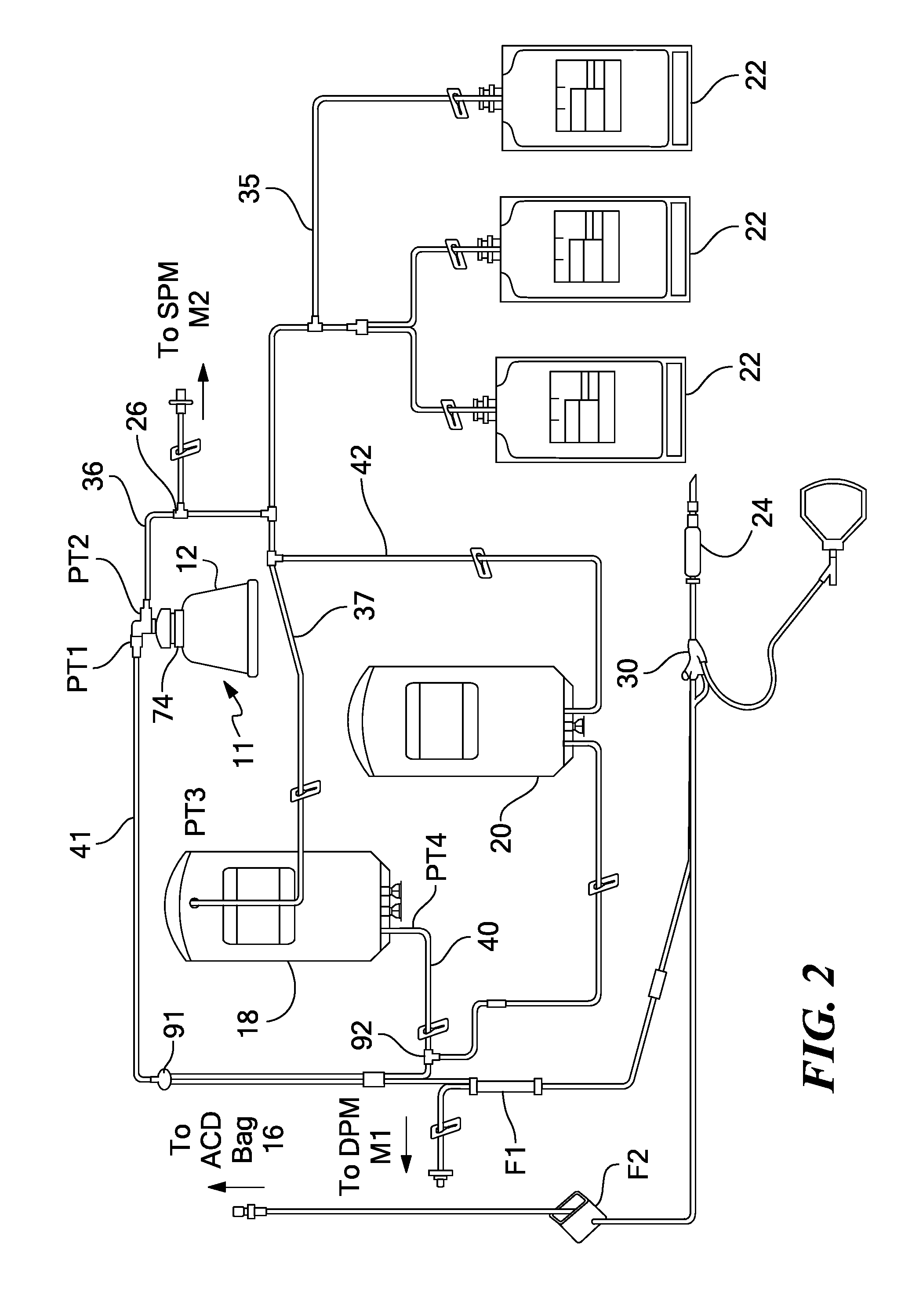
ActiveUS8808978B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnticoagulantEngineering
A method for washing platelets includes introducing anticoagulant into a platelet product container, drawing re-anticoagulated platelet product from the platelet product container, and introducing it into a centrifuge bowl. The centrifuge bowl separates the platelets from the supernatant in which they are suspended. The method then washes the platelets by introducing wash solution into the centrifuge bowl. As the wash solution is introduced into the bowl, it displaces the supernatant from the bowl and into a waste container. The method then introduces platelet additive solution into the centrifuge bowl, which displaces the wash solution from the centrifuge bowl and into the waste container and further wash the platelets. The method then repeatedly accelerates and decelerates the centrifuge bowl to resuspend the platelets in the platelet additive solution.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
Platelet Additive Solution For Leukoreducing White Blood Cells In Apheresed Platelets
InactiveUS20100081985A1Reducing residual white blood cellOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesWhite blood cellPlatelets blood
Owner:TERUMO BCT
Methods for preparing platelet products
ActiveUS20170202882A1Speed up the processEfficient preparationMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsPlatelet productChemistry
Owner:CERUS CORP
Automated methods and systems for providing platelet concentrates with reduced residual plasma volumes and storage media for such platelet concentrates
ActiveUS20140037750A1Plasma-reduced plateletBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsBlood plasmaWashed platelet
Automated systems and methods for providing platelet concentrates and synthetic storage media with reduced residual plasma volumes are disclosed. The disclosed systems and methods reduce the residual volume of plasma in platelet concentrate to obtain a platelet product having a volume of plasma that is approximately 5% or less of the total platelet product volume. The disclosed systems and methods also reduce the residual volume of plasma in platelet concentrate to obtain a washed platelet product, wherein the volume of plasma in the washed platelet product is approximately 1% or less of the total washed platelet product volume. Storage media for platelets including less than approximately 10% plasma are also disclosed.
Owner:FENWAL
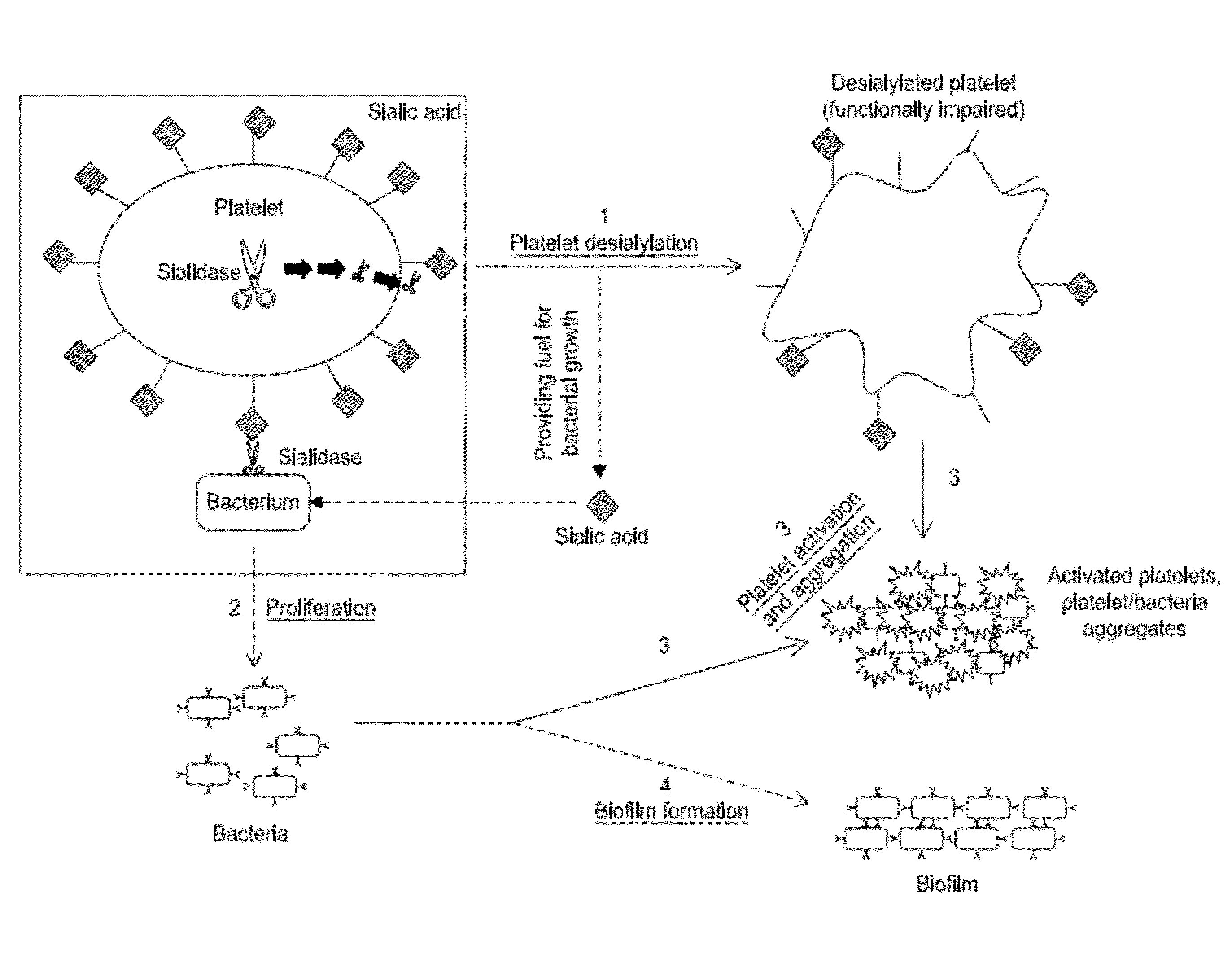
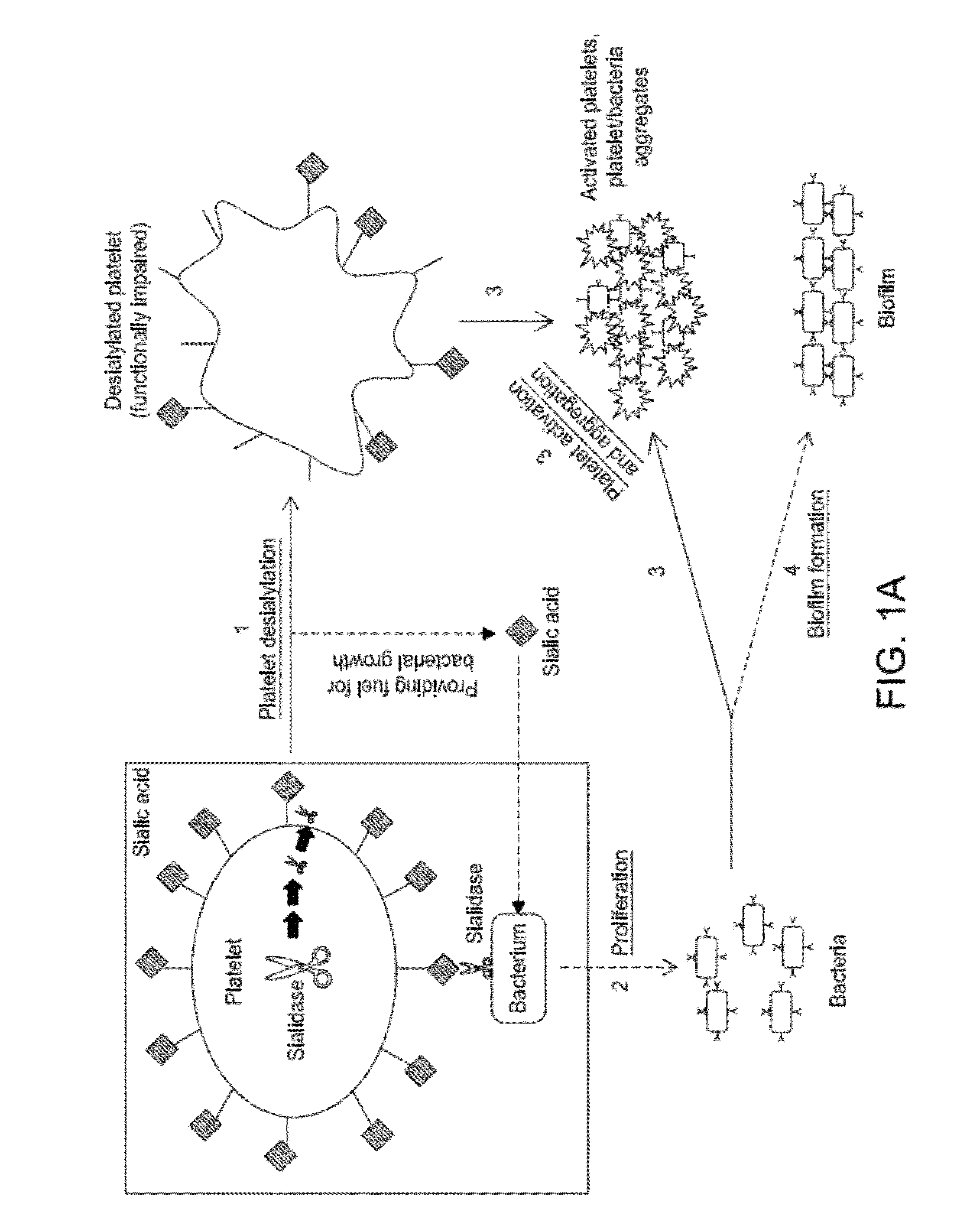
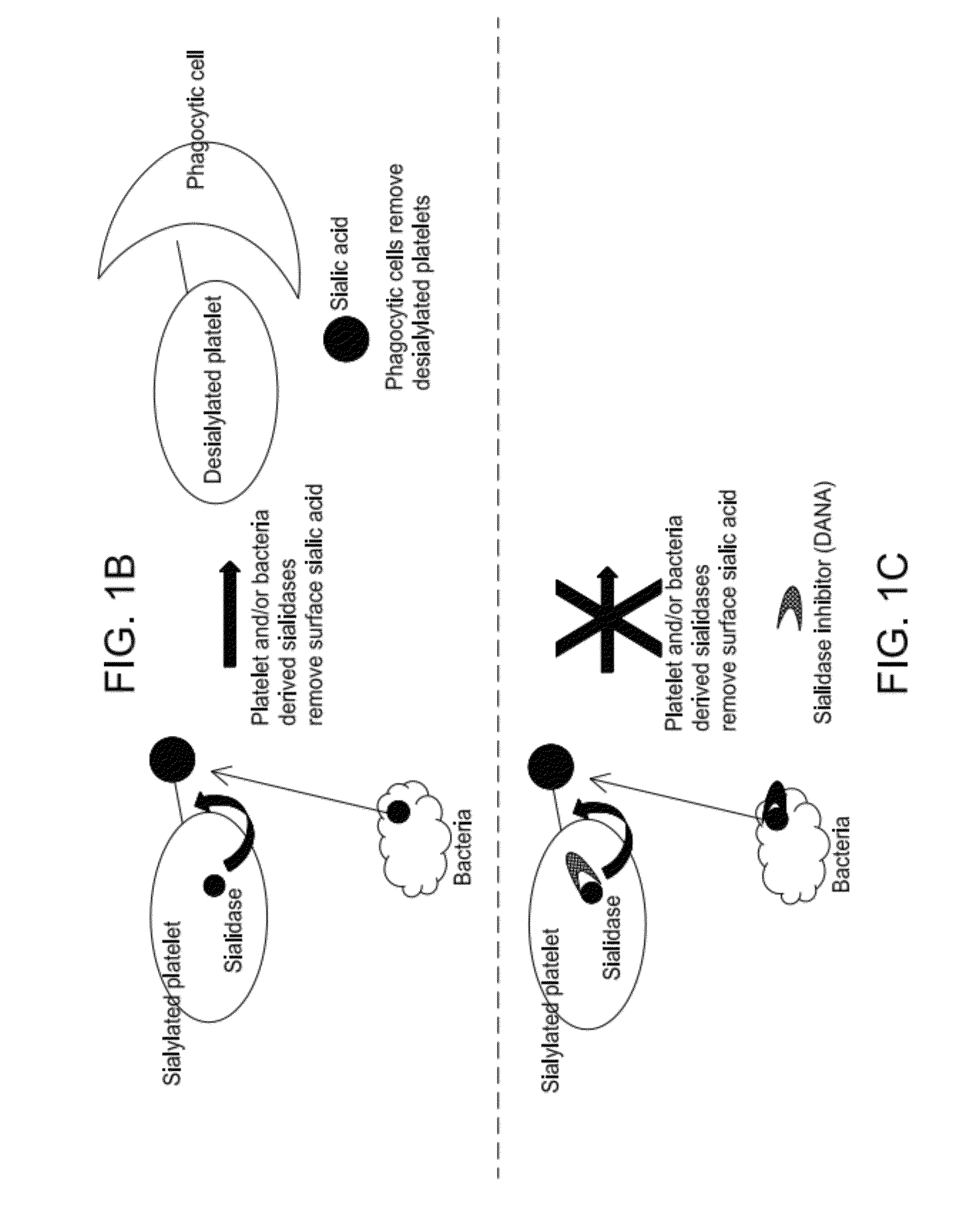
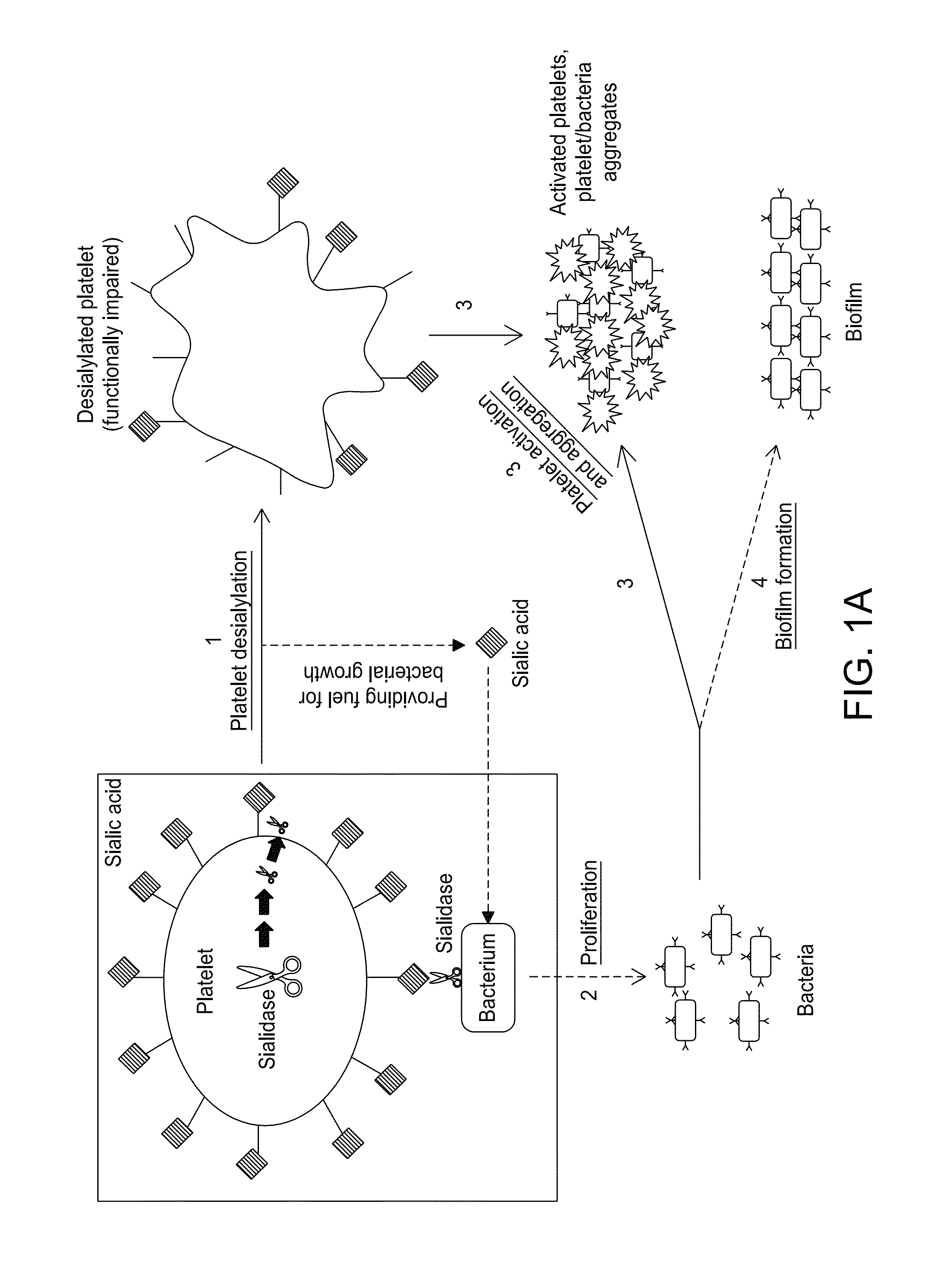
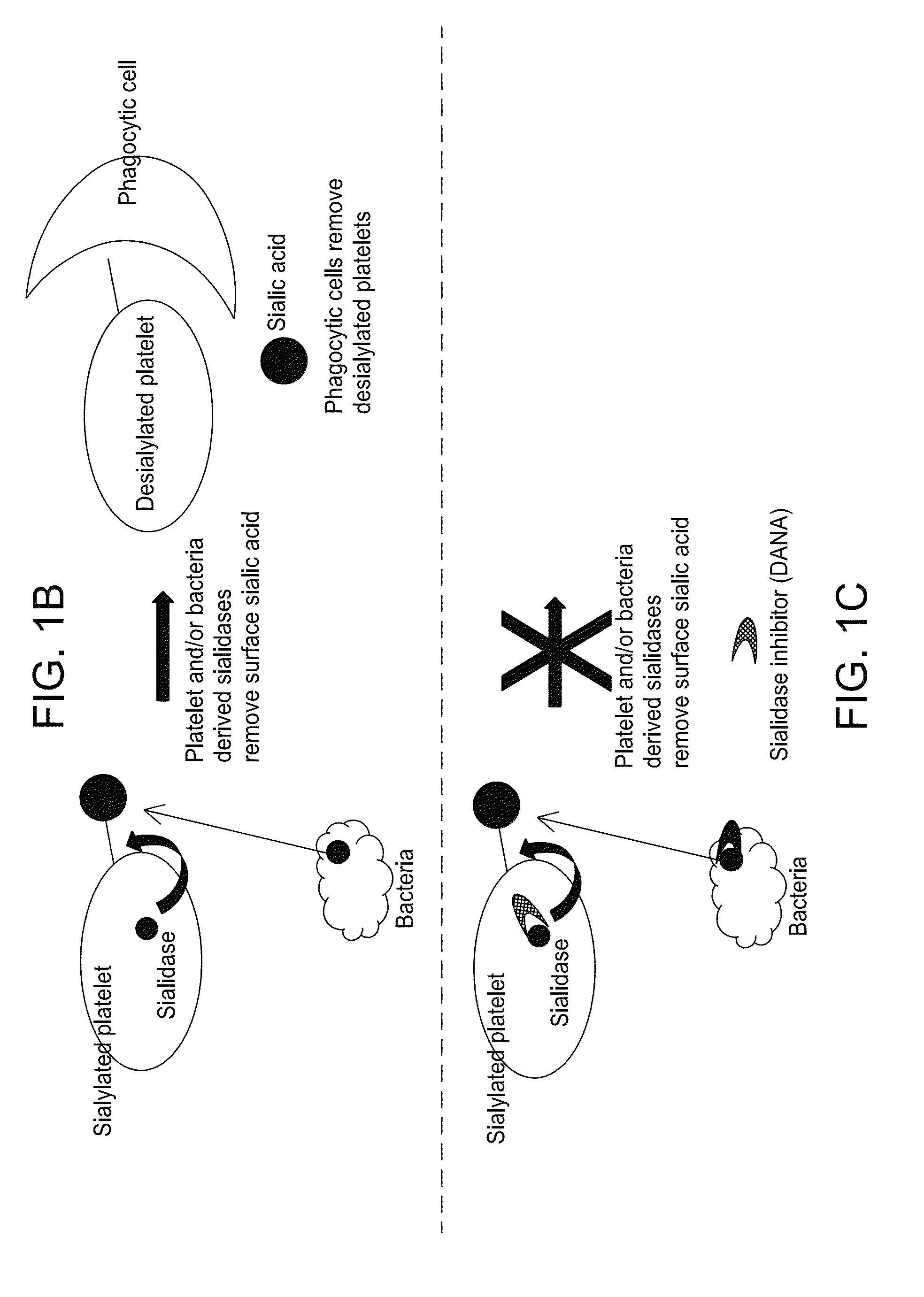
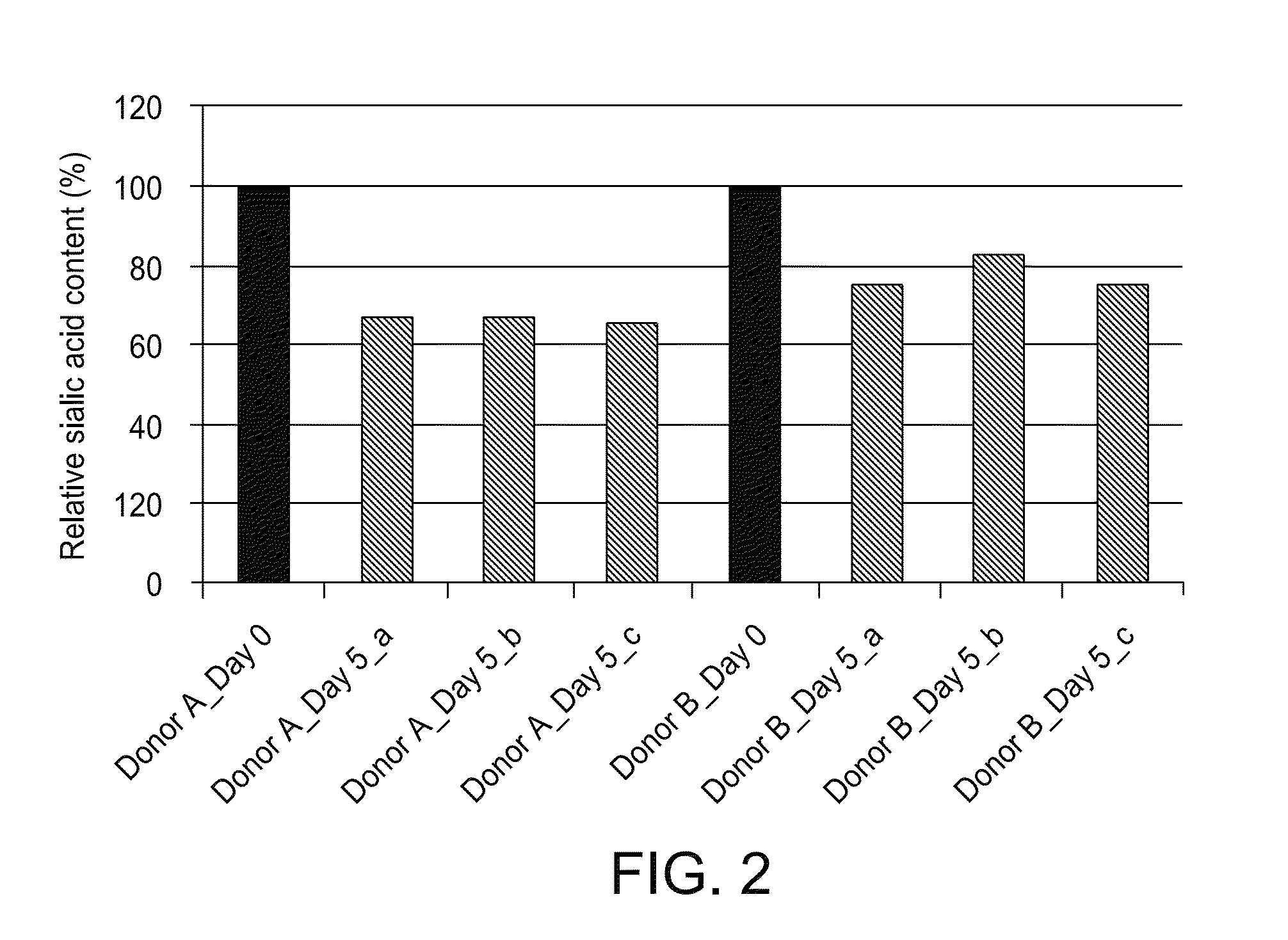
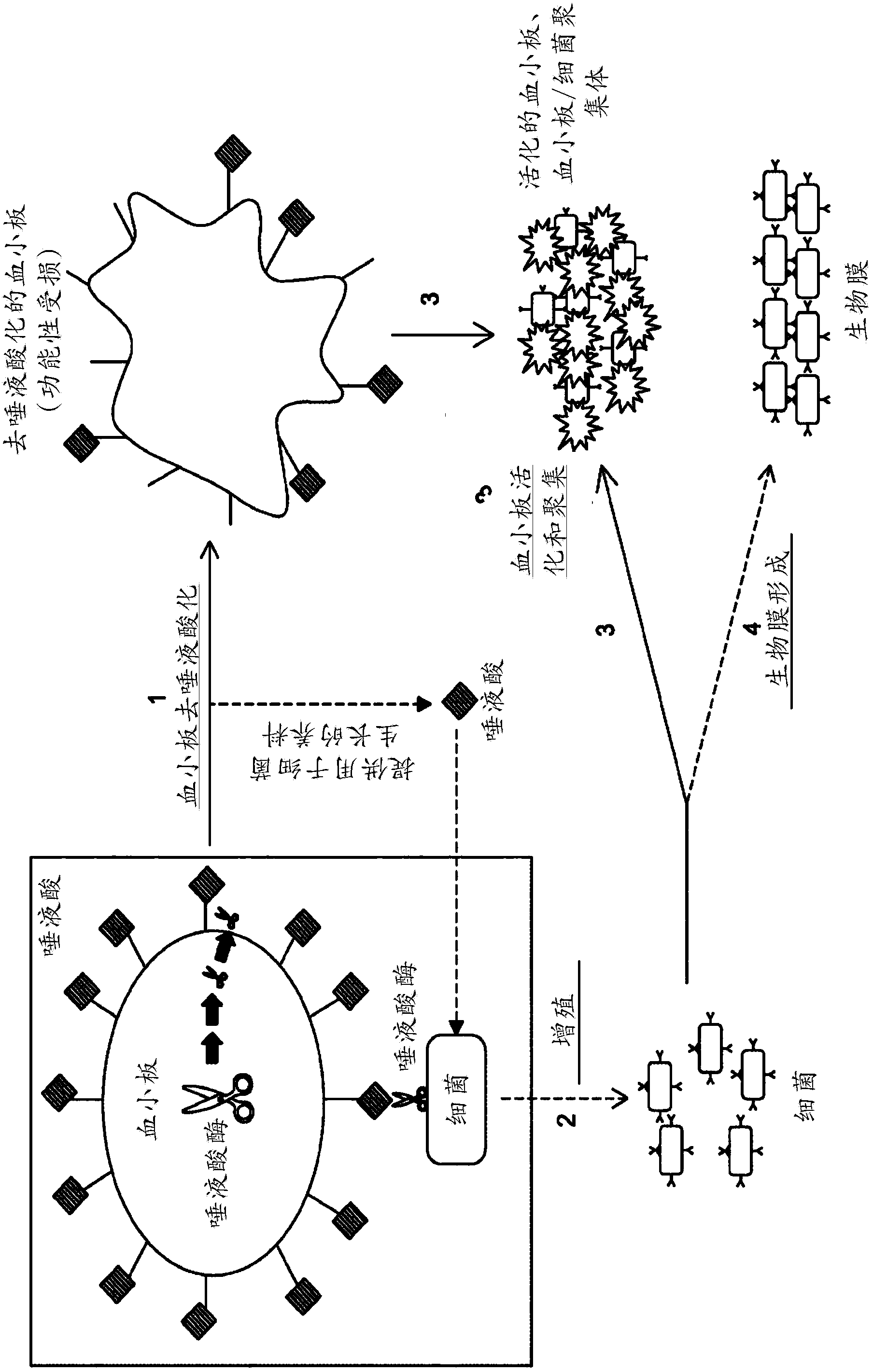
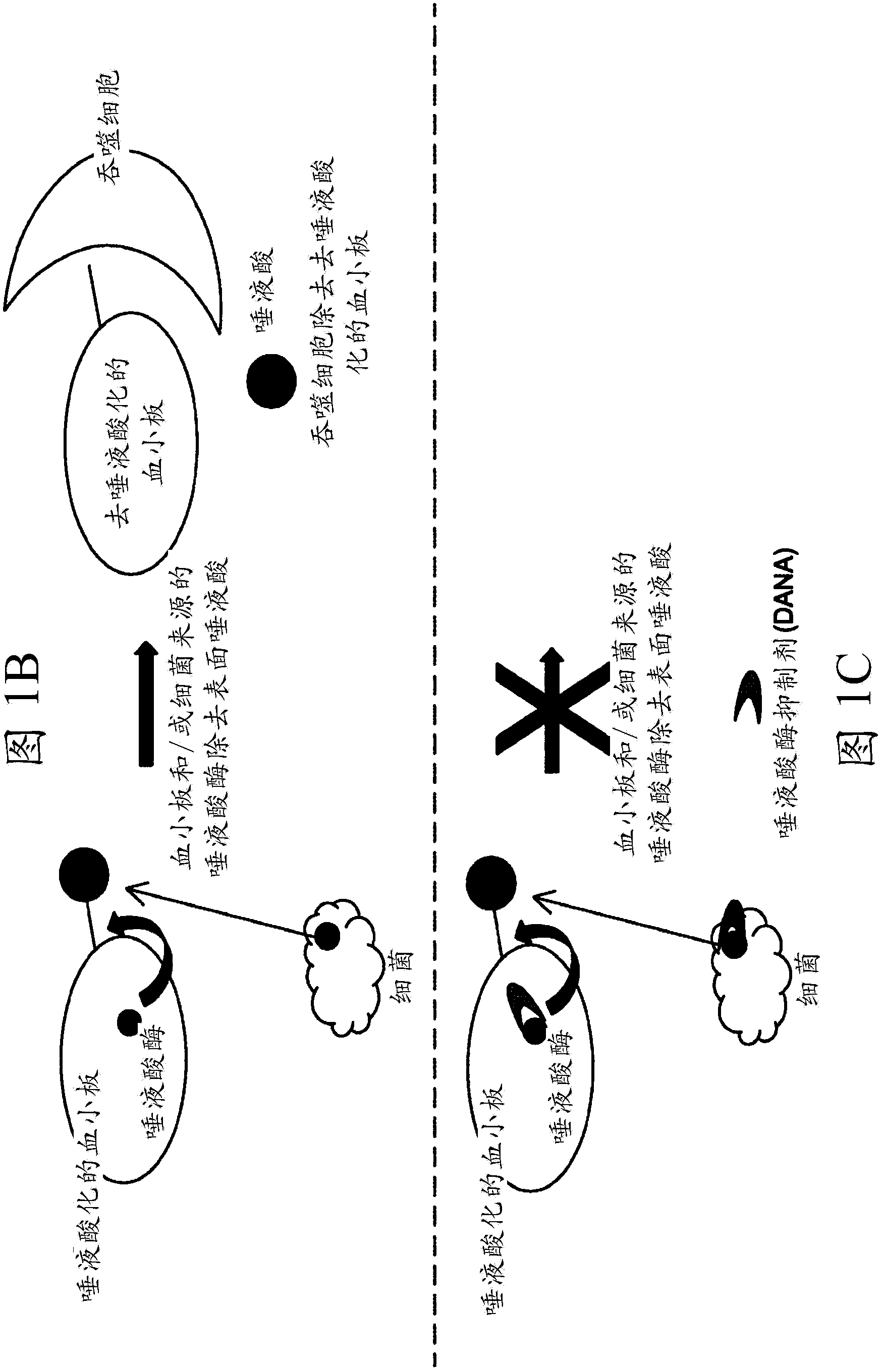
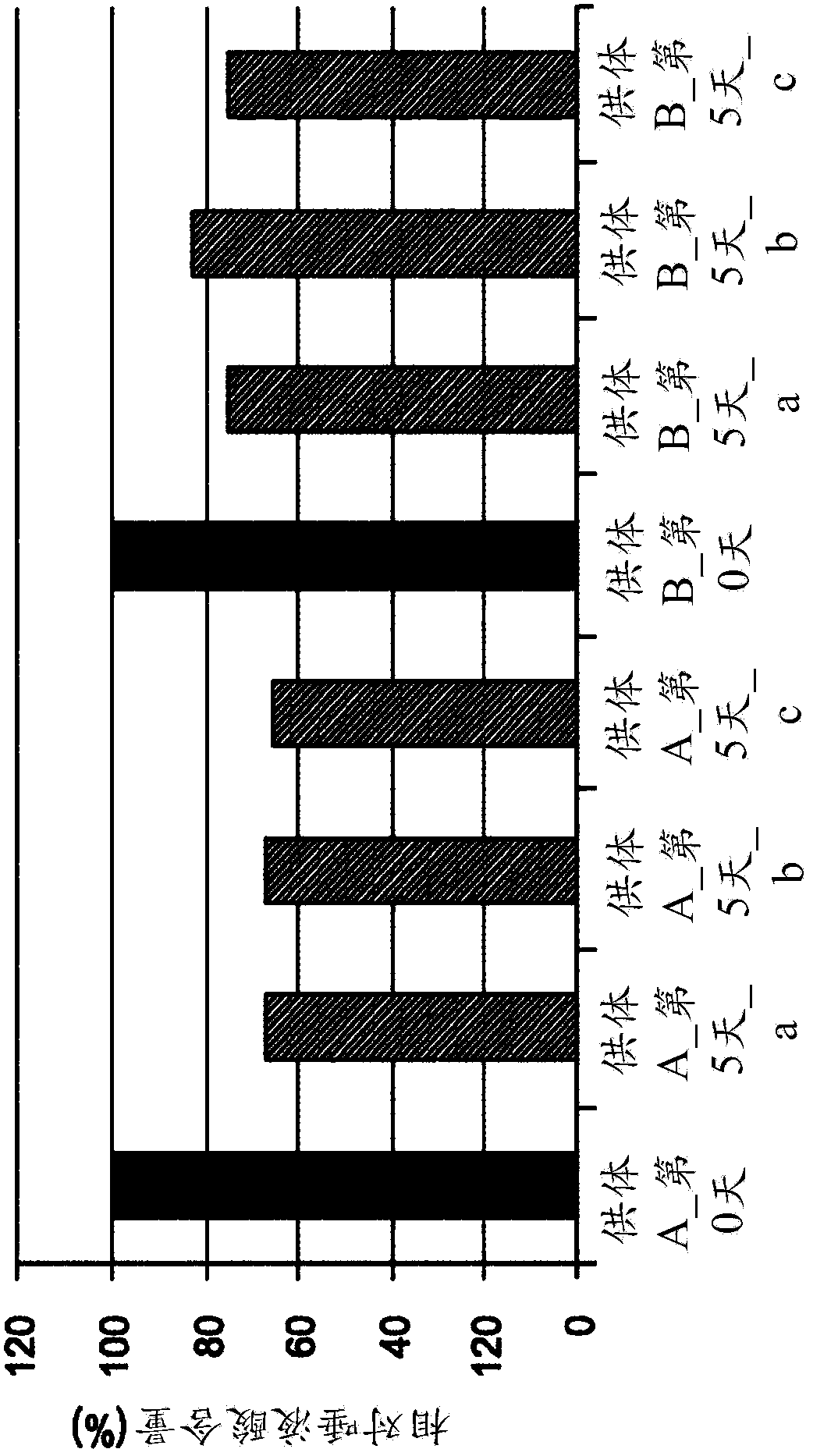
Platelet Storage and Reduced Bacterial Proliferation In Platelet Products Using A Sialidase Inhibitor
InactiveUS20120321722A1Reducing sialidase activityExcess proliferationAntibacterial agentsMammal material medical ingredientsPlatelet productPlatelet storage
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing sialidase activity and inhibiting bacterial proliferation of one or more bacteria in a platelet product preparation from one or more donors. In general, the method includes contacting the platelet product preparation with an amount of a sialidase inhibitor, to thereby obtain a sialidase inhibitor-treated platelet product preparation. Sialidase activity is reduced and the proliferation of one or more bacteria is inhibited, as compared to a platelet product preparation not subjected to the sialidase inhibitor treatment.
Owner:VELICO MEDICAL +1
Chromatographic test strip for detecting platelet product bacterial pollution and detection method
InactiveCN104502589ASave resourcesSimple and fast operationMaterial analysisLife qualityPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a chromatographic test strip for detecting platelet product bacterial pollution and a detection method. The test strip consists of a sample pad, reaction films and an absorption pad which are mutually lapped on a bottom plate, wherein two ends of the sample pad are respectively lapped with two reaction films; each reaction film is fixedly provided with an inner quality control band and at least one detection band; the two reaction films are capable of respectively detecting the gram positive bacterium and negative bacterium in the platelet pollution; the sample in the sample pad can simultaneously diffuse toward the reaction films at two sides. Through the manner, the chromatographic test strip is capable of solving the technical problem that the traditional detection technology of the platelet product bacterial pollution is long in time, tedious to operate and low in sensitivity, so that the detection of conventional platelet product bacterial pollution before blood transfusion can be carried out clinically so as to avoid the blood transfusion diseases caused by bacterial pollution, improve the life quality of the patients and guarantee the clinically safe, effective and scientific blood transfusion.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
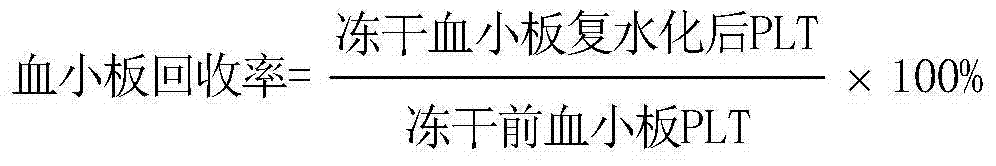
Novel platelet freeze-drying treating fluid
ActiveCN104771412AMeet the needs of useGood effectMammal material medical ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsFreeze-dryingRoom temperature
The invention discloses a novel platelet freeze-drying treating fluid. The fluid is composed of two parts: (1) a platelet freeze-drying pretreatment liquid, which is prepared by adding mycose and PGE1 into a basic buffer liquid; (2) a platelet freeze-drying buffer liquid, which is prepared by adding blood plasma into a freeze-drying pretreatment liquid. Preferably 30%v / v-40%v / v blood plasma is adopted to replace human serum albumin, a good effect is achieved, and the blood plasma is taken as the platelet protein protective agent to replace the pricy albumin and is economic. The osmotic pressure of the pretreatment liquid is 311.6 mOsm, is similar to the blood plasma osmotic pressure, and thus will not generate adverse effect on platelet. The weight concentration of the freeze-drying buffer liquid is 29%w / v, and the obtained freeze-dried platelet has a qualified appearance. The freeze-dried platelet can be stably preserved at a room temperature for at least 6 months, and the platelet can be used to prepare hemostatic or platelet products used in operation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENERAL HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MILITARY COMMAND
Platelet Storage and Reduced Bacterial Proliferation in Platelet Products Using a Sialidase Inhibitor
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing sialidase activity and inhibiting bacterial proliferation of one or more bacteria in a platelet product preparation from one or more donors. In general, the method includes contacting the platelet product preparation with an amount of a sialidase inhibitor, to thereby obtain a sialidase inhibitor-treated platelet product preparation. Sialidase activity is reduced and the proliferation of one or more bacteria is inhibited, as compared to a platelet product preparation not subjected to the sialidase inhibitor treatment.
Owner:VELICO MEDICAL +1
Bacteria genome DNA extraction liquid, preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN101319213AEasy to makeEasy to storeFermentationPlant genotype modificationChelex 100DNA extraction
The invention discloses a bacteria genome DNA extracting solution in a blood and platelet product and a preparation method and an application method thereof. The bacteria genome DNA extracting solution consists of chelex-100, tween, NP-40, SDS, lysostaphin, a wall-breaking enzyme, a protease K and water. The extracting solution can be effectively used for extracting a bacteria genome DNA with high extraction efficiency. The preparation method and the application method are simple and convenient for operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI BLOOD CENT
Systems And Methods For Deriving And Collecting Platelet Products
ActiveUS20180078582A1Mammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsBlood componentWhite blood cell
Systems and methods are provided for deriving a platelet product from a plurality of buffy coats. A plurality of buffy coats are separately collected, for example, using a conventional floor centrifuge. Plasma and / or a platelet additive solution may be added to the buffy coats. The buffy coats are pooled into a container and conveyed into a centrifuge or are sequentially conveyed into the centrifuge without being pooled, where they are continuously processed to separate platelets from the other cellular blood components. The separated platelets are conveyed out of the centrifuge as a platelet product, which may be passed through a leukocyte removal filter to reduce the white blood cell content of the platelet product. By continuously separating the buffy coats, fewer buffy coats are required to produce a single-dose platelet product, while also allowing for the derivation and collection of a plurality of single-dose platelet products.
Owner:FENWAL
Methods for preparing platelet products
ActiveUS10842818B2Speed up the processEfficient preparationMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsBiochemistryPlatelet product
Owner:CERUS CORP
Improved platelet storage using a sialidase inhibitor
InactiveCN103702556ADead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsIn vivoPlatelet preservation
The present invention relates to a platelet additive solution (PAS) having an amount of one or more sialidase inhibitors and optionally one or more glycan-modifying agents; and one or more of PAS components that includes a salt, a citrate source, a carbon source, and any combination thereof. The present invention also relates to methods, compositions and kits for increasing the in vivo circulation time of isolated platelets by storing the platelets with one or more sialidase inhibitors. Additionally, the present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing sialidase activity and inhibiting bacterial proliferation of one or more bacteria in a platelet product preparation from one or more donors.
Owner:VELICO MEDICAL +1
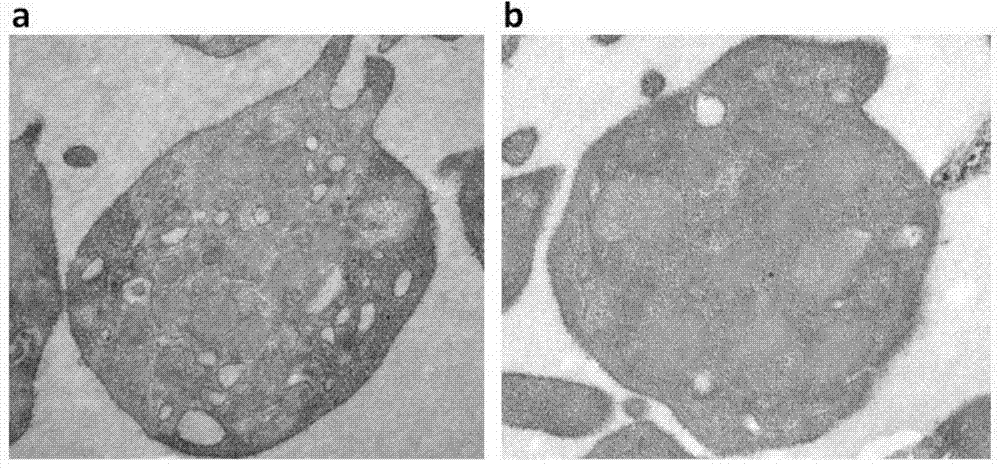
Methods to reduce clot formation in cold-stored platelet products
InactiveUS20200060262A1Reduce formation of clotSuitable for storageMedical devicesDead animal preservationClot formationPlatelet product
Methods to significantly reduce clot formation in cold-stored platelet samples are described. The methods include collecting platelet samples at defined yields and / or concentrations and allowing collected platelet samples to rest at room temperature without agitation for a period of time before being moved into cold storage.
Owner:BLOODWORKS
Method for detecting bacterial contamination of platelet product
PendingCN110456049AEnhance the visibility of color changesReduce the impactMaterial analysisAptamerMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention relates to the technical field of medical examination, in particular to a method for detecting bacterial contamination of a platelet product. The method comprises the following steps: enriching and separating to-be-detected bacteria from a to-be-detected sample by using magnetic nanoparticles that have surfaces coupled with monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies or aptamers bound with the to-be-detected bacteria; resuspending the magnetic nanoparticles with the to-be-detected bacteria captured by using a buffer solution; inserting a piece of chromatography test paper into the buffersolution and carrying out reaction; taking out the chromatography test paper after reaction and immersing the chromatography test paper into a substrate capable of being catalyzed for color development by the magnetic nanoparticles to carry out secondary color development reaction; and taking out the paper, terminating the color development reaction, and observing results at a test strip and a quality control strip. With processing of the secondary color development reaction, the obviousness of the color change at the detection line can be enhanced, so that the detection sensitivity is improved and thus the detection result becomes accurate.
Owner:苏州市中心血站
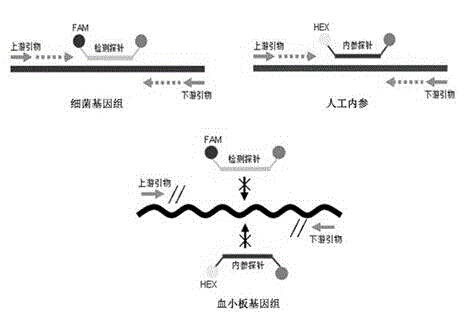
Universal type fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting platelet bacterial pollution
InactiveCN104372072ASolve the problem of pollution and lack of standard productsWhether to solveMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnosis methodsPcr method
The invention discloses a universal type fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting platelet bacterial pollution. The fluorescent quantitative PCR method employs a pair of universal type primers detecting bacteria, an artificial internal interference of the universal type primers, a first fluorescently-labeled fluorescent probe and a second fluorescently-labeled fluorescent probe; the two fluorescent probes employ different fluorescent labels; the first fluorescently-labeled fluorescent probe is a universal type fluorescent probe used for detecting bacteria, and the second fluorescently-labeled fluorescent probe is an internal reference probe used for detecting the artificial internal interference; and a routine PCR amplification technology is employed for detection. According to the above technical scheme, the detection method is suitable for screening on bacteria pollution of platelet products, is capable of fully solving the bacteria existence, bacteria content, bacteria survival state and other problems in bacteria pollution of the platelet products, satisfies rapid, accurate and reliable detection requirements, and provides a scientific effective auxiliary diagnosis method for safe infusion of platelet.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Apheresis platelet disaggregation device
InactiveCN107349483AReduce labor intensityLow costShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingControllabilityPlatelet product
The invention relates to an apheresis platelet disaggregation device. The apheresis platelet disaggregation device comprises a machine frame. An oscillation device for platelet disaggregation is arranged above the machine frame and is a circumferential movement device. The labor intensity of workers in a blood station can be effectively reduced; cost is low; rotating speed is adjustable; a motor is good in controllability, and a timing device can be additionally arranged; a platelet product is good in disaggregation effect, and the quality is far higher than that of an artificial disaggregation platelet product.
Owner:张方亮
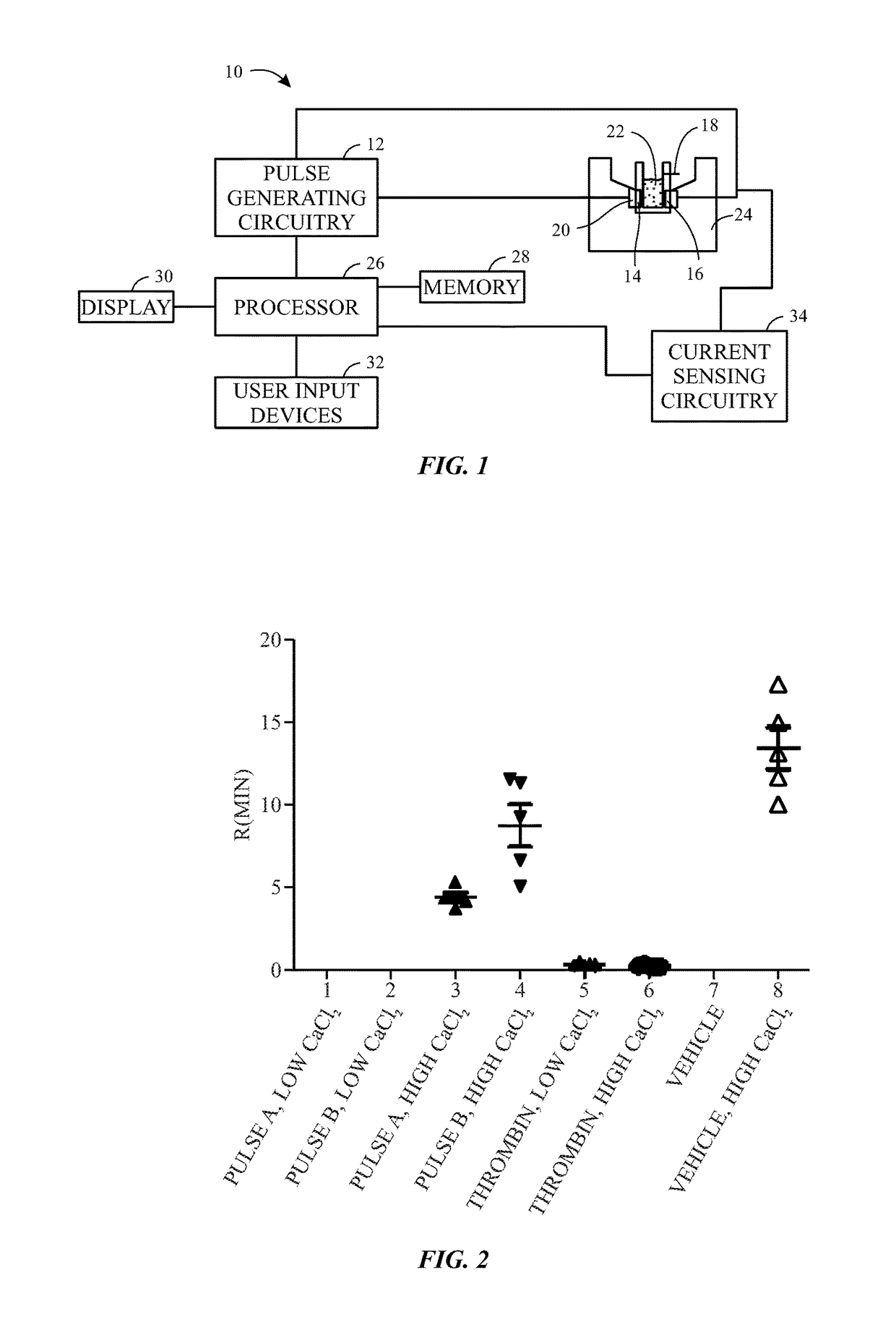
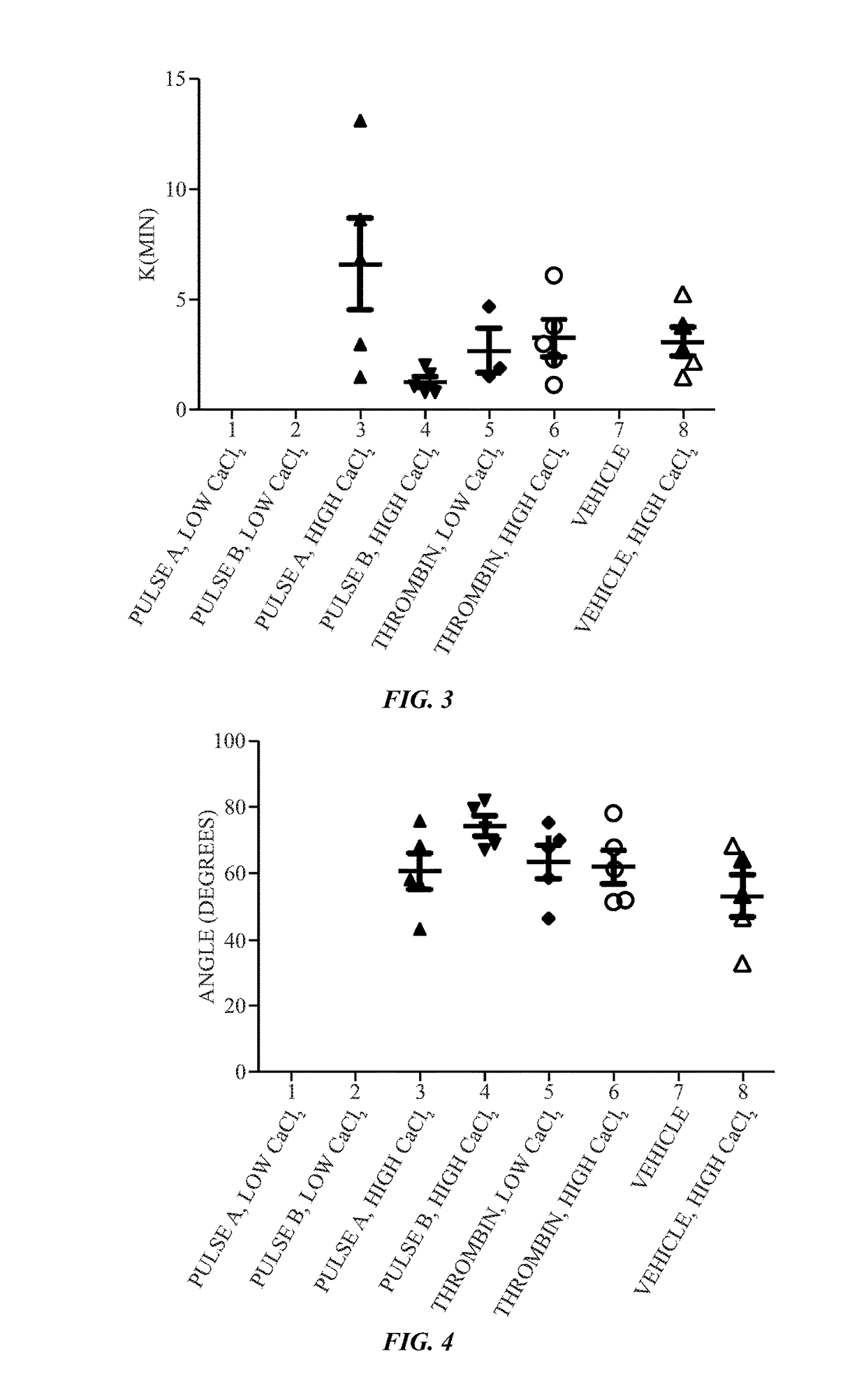
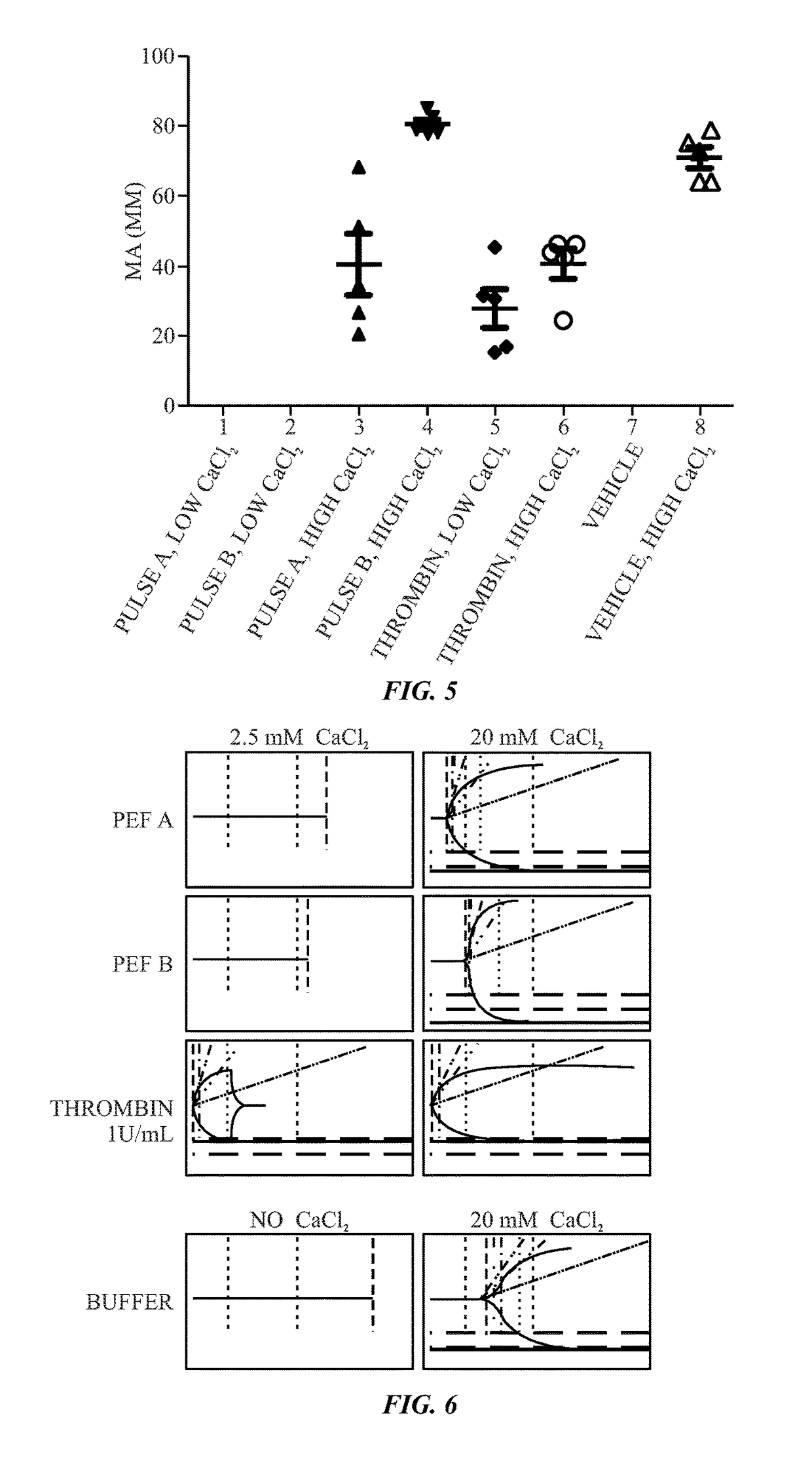
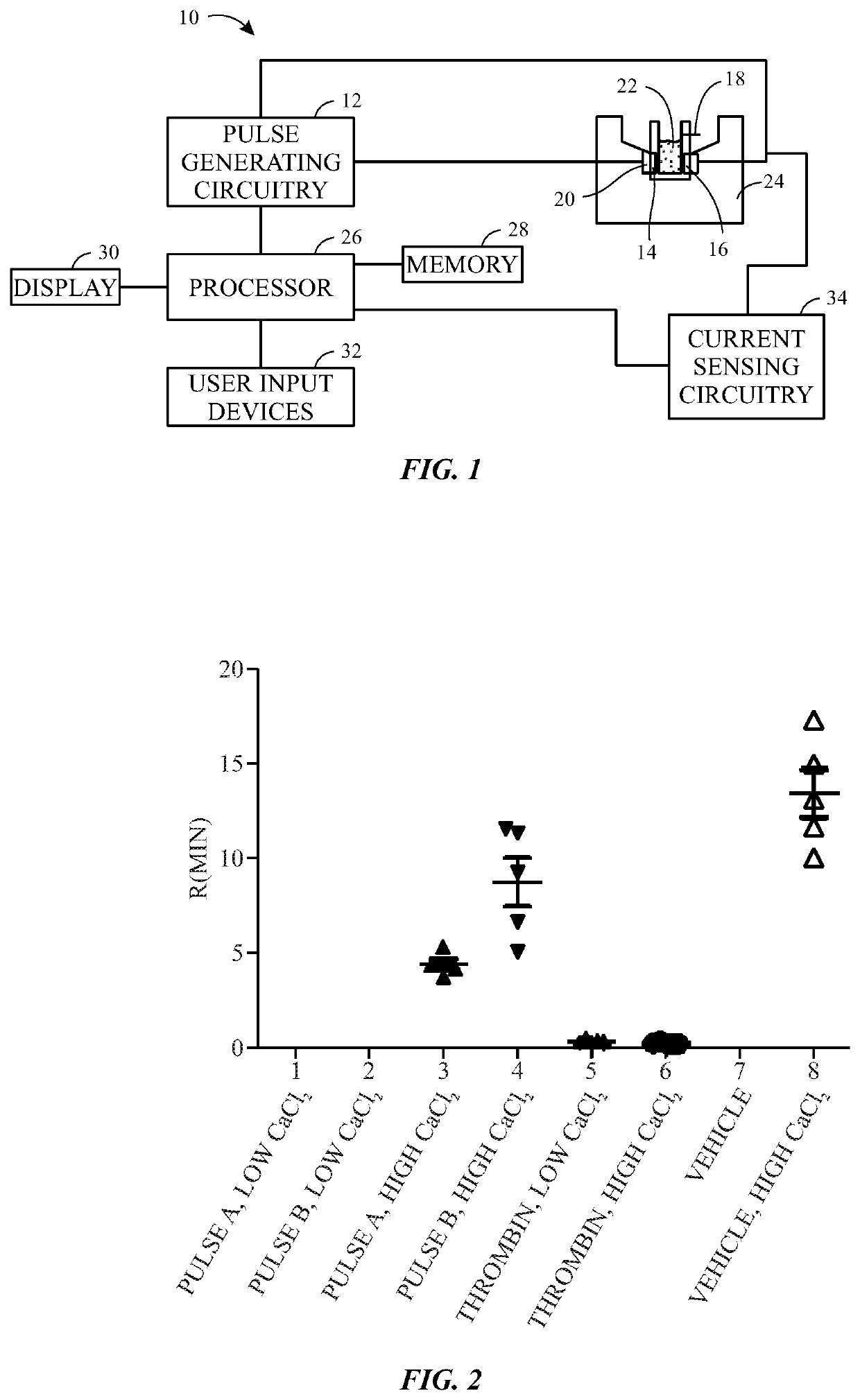
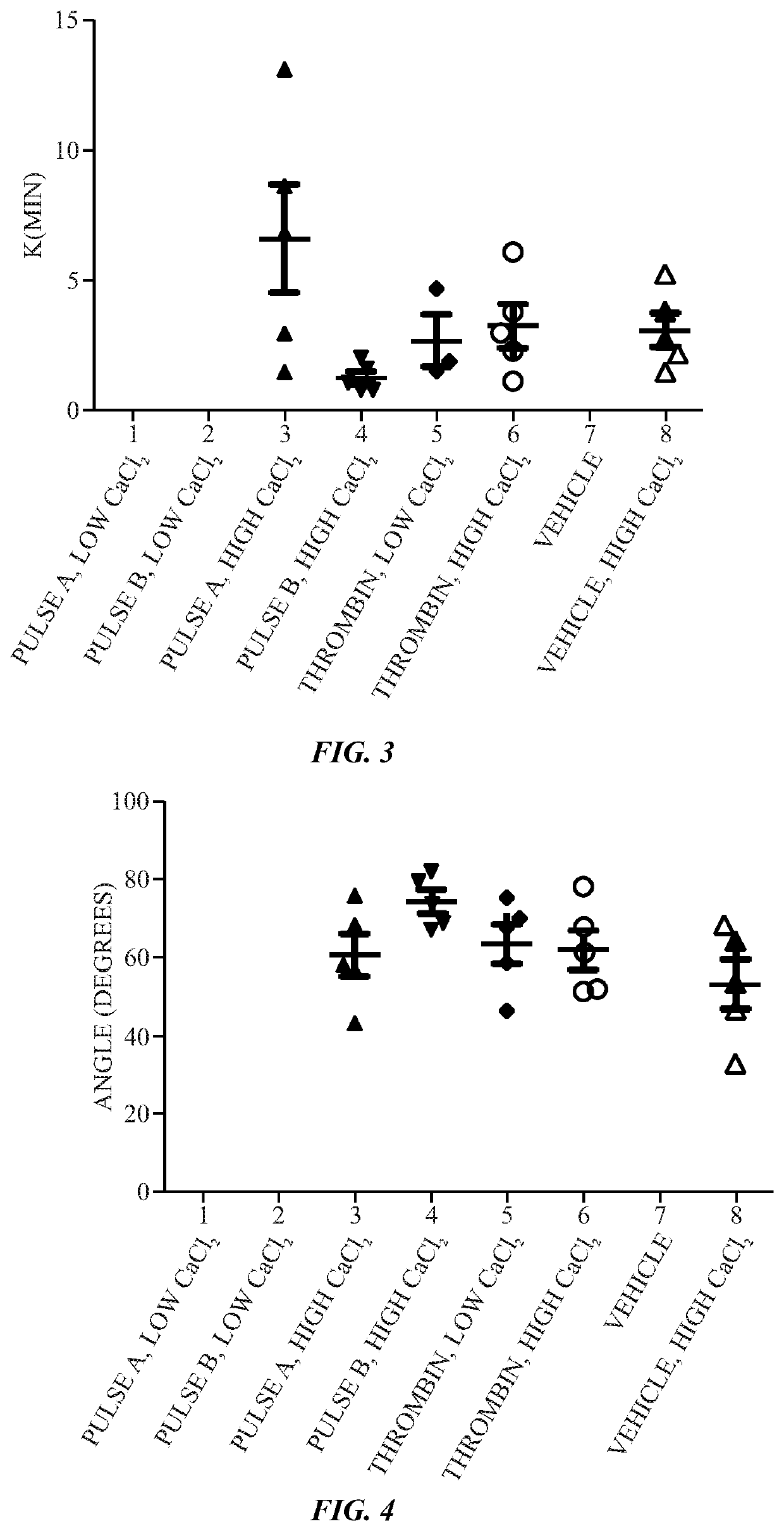
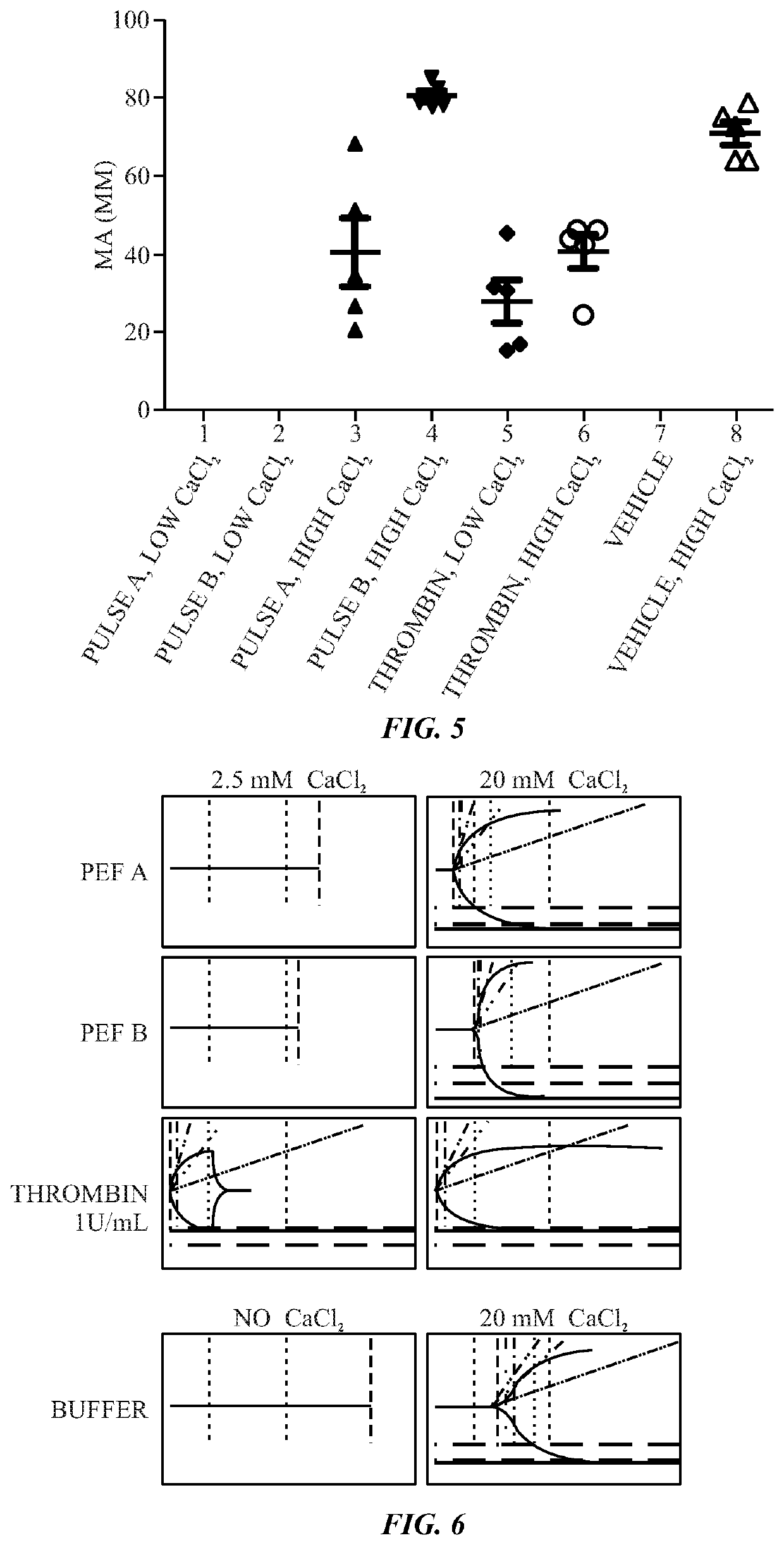
Calcium controlled activation of platelets via electrical stimulation
ActiveUS20170191052A1Peptide/protein ingredientsEnergy modified materialsClot formationBiological activation
The present disclosure relates to the generation of an activated platelet product in which one or more of the presence or absence of clots, the timing of clot formation (if present), and / or the mechanical strength of clots (if present) is controlled by the presence or concentration of calcium ions during the activation process. In certain embodiments, the calcium ion concentration is controlled in the presence of pulsed electric fields or a chemical activator (e.g., thrombin) as part of the activation process.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for deriving and collecting platelet products
ActiveUS10772916B2Other blood circulation devicesMammal material medical ingredientsBlood componentWhite blood cell
Systems and methods are provided for deriving a platelet product from a plurality of buffy coats. A plurality of buffy coats are separately collected, for example, using a conventional floor centrifuge. Plasma and / or a platelet additive solution may be added to the buffy coats. The buffy coats are pooled into a container and conveyed into a centrifuge or are sequentially conveyed into the centrifuge without being pooled, where they are continuously processed to separate platelets from the other cellular blood components. The separated platelets are conveyed out of the centrifuge as a platelet product, which may be passed through a leukocyte removal filter to reduce the white blood cell content of the platelet product. By continuously separating the buffy coats, fewer buffy coats are required to produce a single-dose platelet product, while also allowing for the derivation and collection of a plurality of single-dose platelet products.
Owner:FENWAL
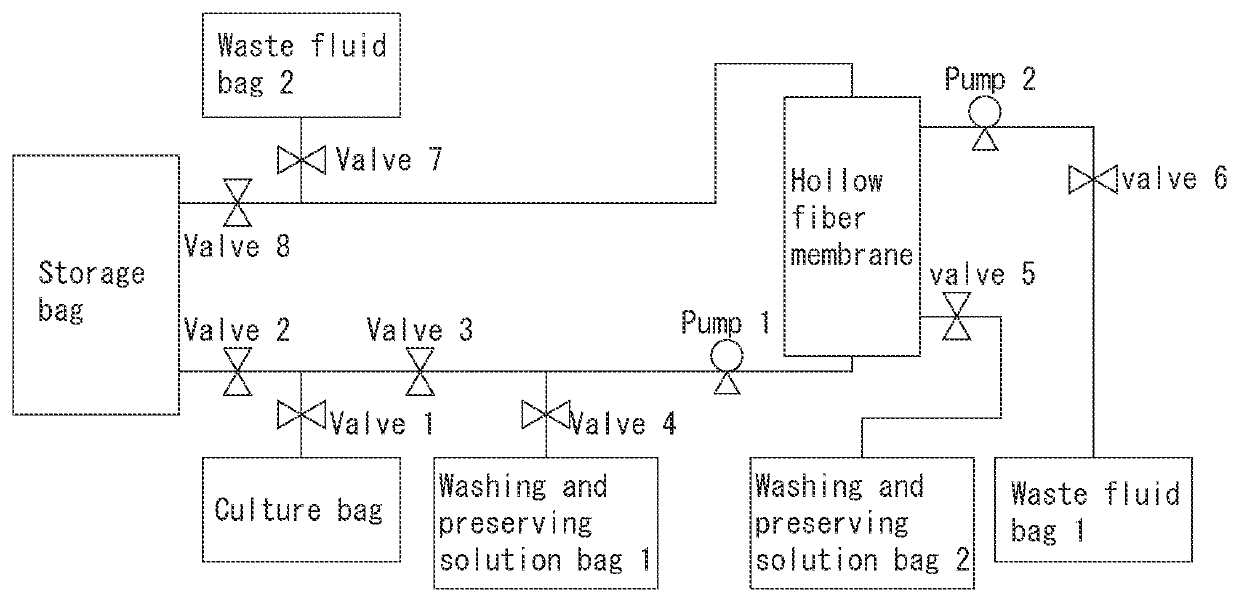
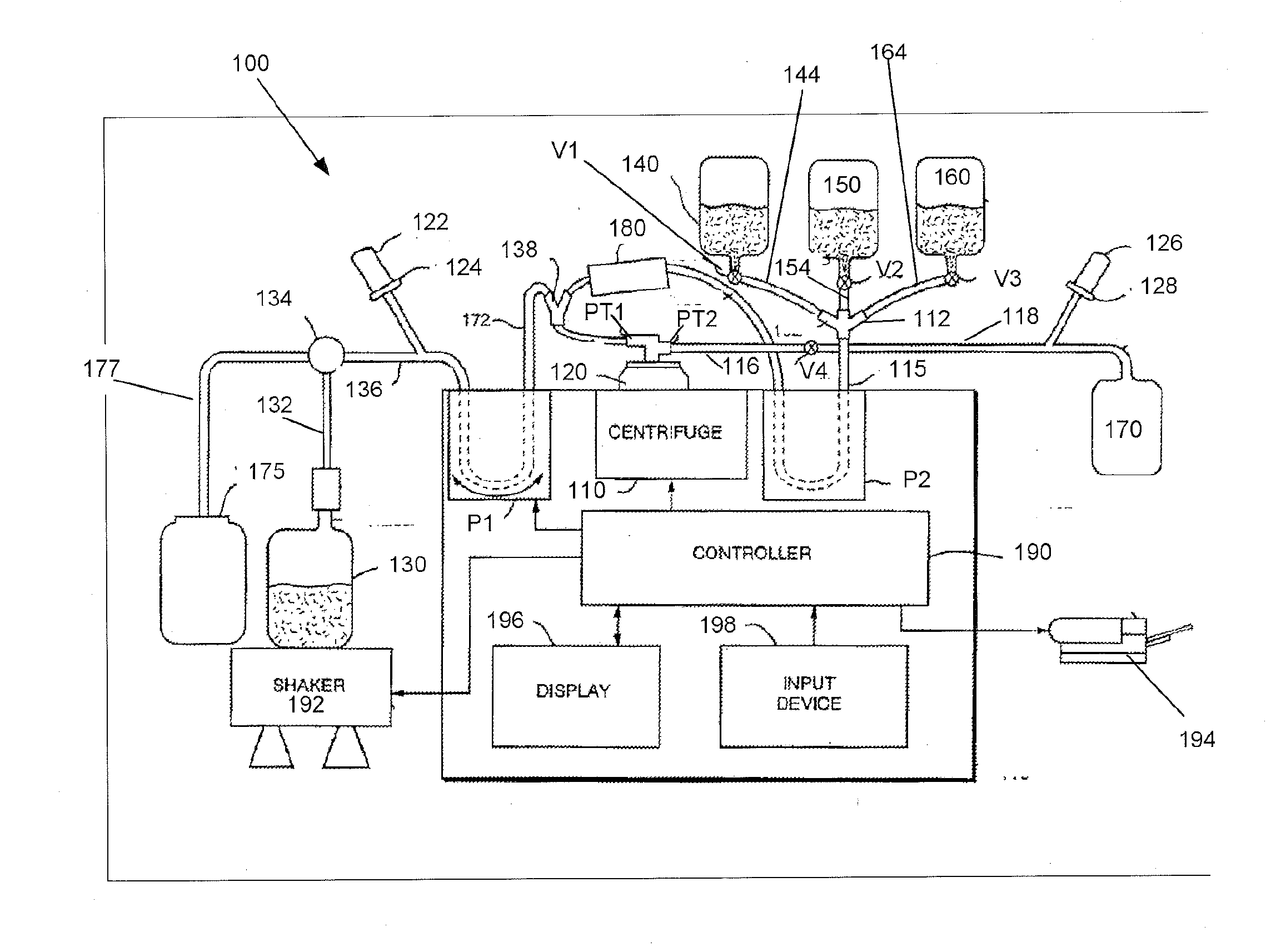
Method for producing purified platelets, method for producing platelet product, method for producing blood product, platelet preserving solution, platelet preserving agent, and method for preserving platelets
PendingUS20200216809A1Short timeReduce harmUltrafiltrationMedical devicesWhole blood productMedicine
Provided is a method for producing platelets, in which damage to platelets is suppressed compared with a method in which platelets are separated using a filter from a megakaryocyte culture, and then the platelets are concentrated using a hollow fiber membrane and are further washed using the hollow fiber membrane, and purified platelets can be produced in a shorter period of time compared with the time that is taken to perform the above-described method so as to reduce damage to platelets. The method for producing purified platelets of the present invention includes a concentrating step of concentrating a megakaryocyte culture, and a centrifuging step of centrifuging platelets from an obtained concentrate.
Owner:MEGAKARYON CORP
Method for producing platelets, method for producing platelet product, and method for producing blood product
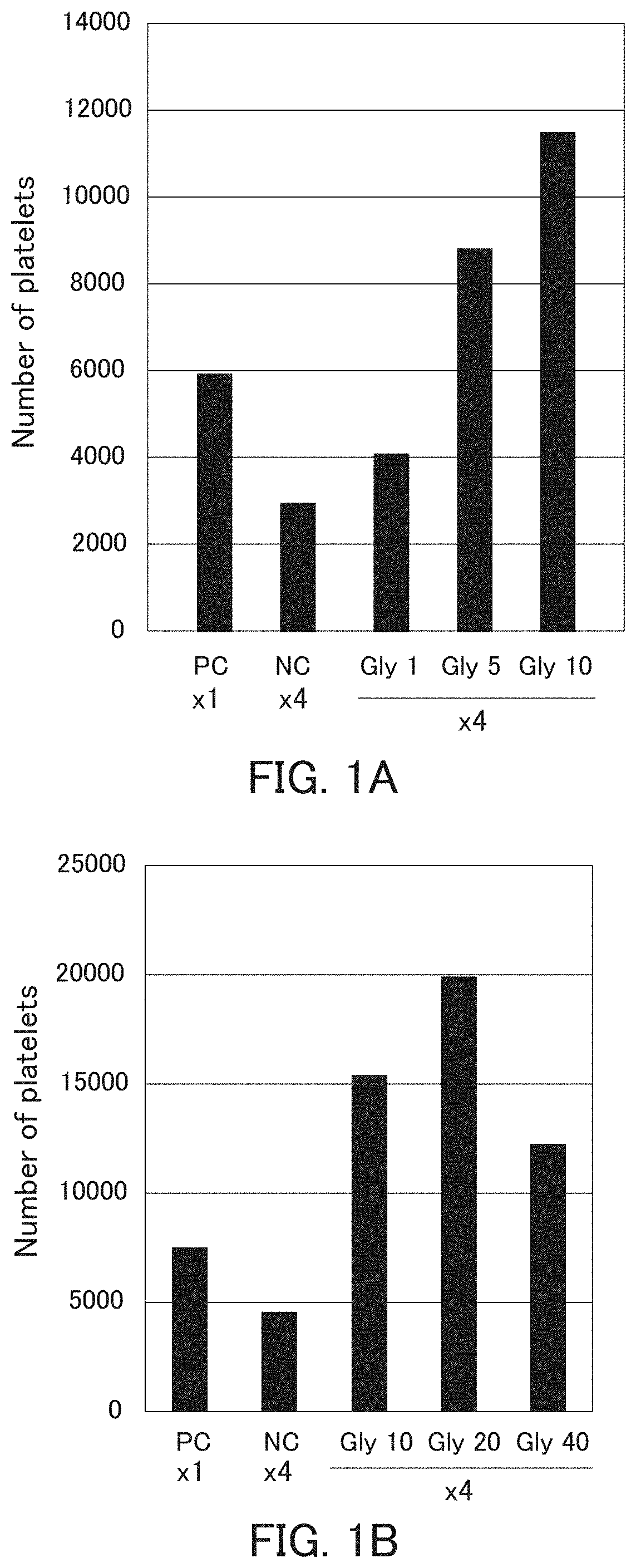
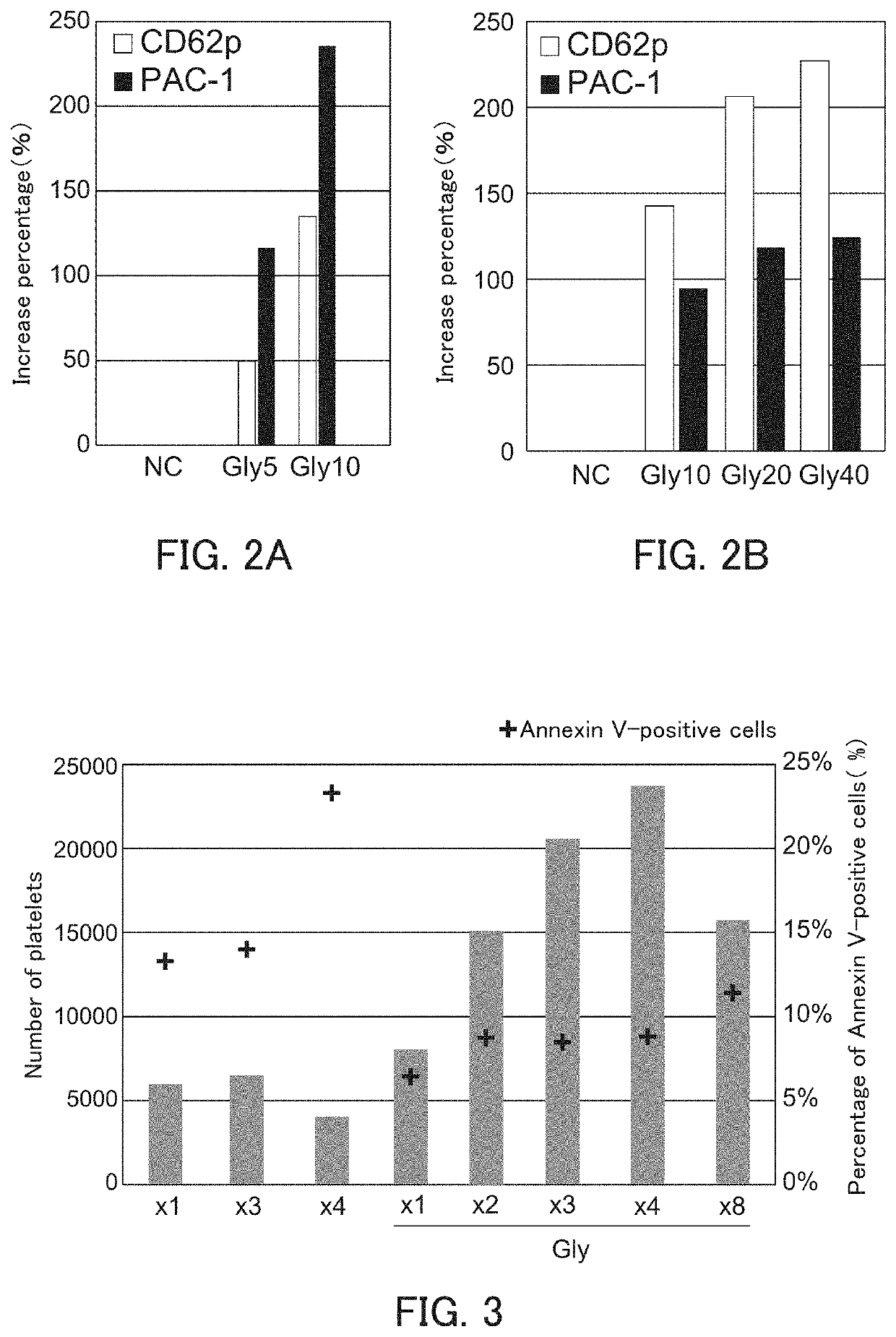
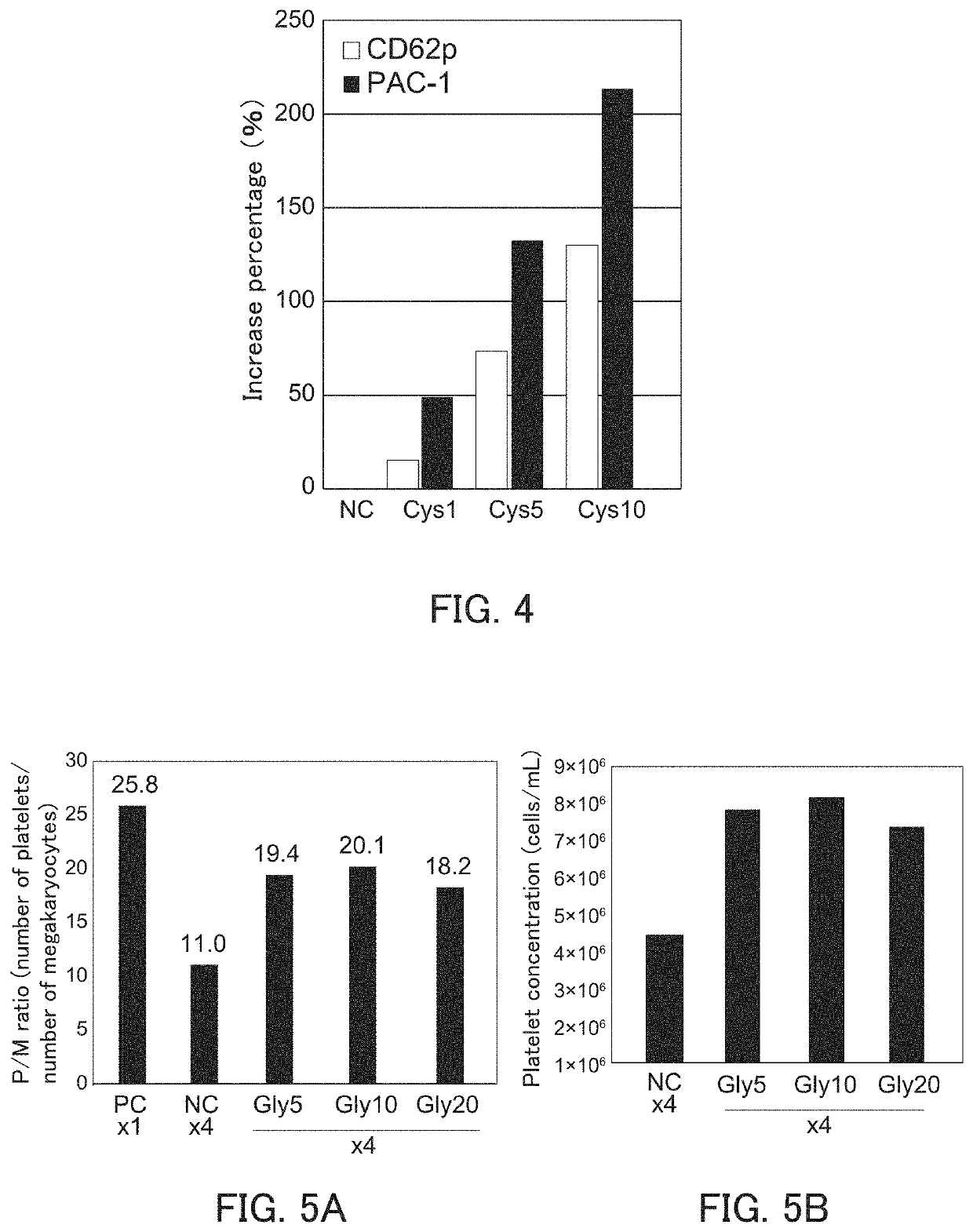
PendingUS20200216808A1Improve biological activityImprove at least oneGenetically modified cellsCulture processGlycineWhole blood product
The present invention provides a method for producing platelets that can improve at least one of the ability of megakaryocyte to produce platelets and the bioactivity of platelets produced even in high-density culture, for example. The method for producing platelets of the present invention includes a platelet producing step of producing platelets from megakaryocytes, wherein the platelet producing step is performed in the presence of at least one of glycine and cysteine.
Owner:MEGAKARYON CORP
System and Method For Automated Platelet Wash
ActiveUS20130309652A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnticoagulantEngineering
A method for washing platelets includes introducing anticoagulant into a platelet product container, drawing re-anticoagulated platelet product from the platelet product container, and introducing it into a centrifuge bowl. The centrifuge bowl separates the platelets from the supernatant in which they are suspended. The method then washes the platelets by introducing wash solution into the centrifuge bowl. As the wash solution is introduced into the bowl, it displaces the supernatant from the bowl and into a waste container. The method then introduces platelet additive solution into the centrifuge bowl, which displaces the wash solution from the centrifuge bowl and into the waste container and further wash the platelets. The method then repeatedly accelerates and decelerates the centrifuge bowl to resuspend the platelets in the platelet additive solution.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
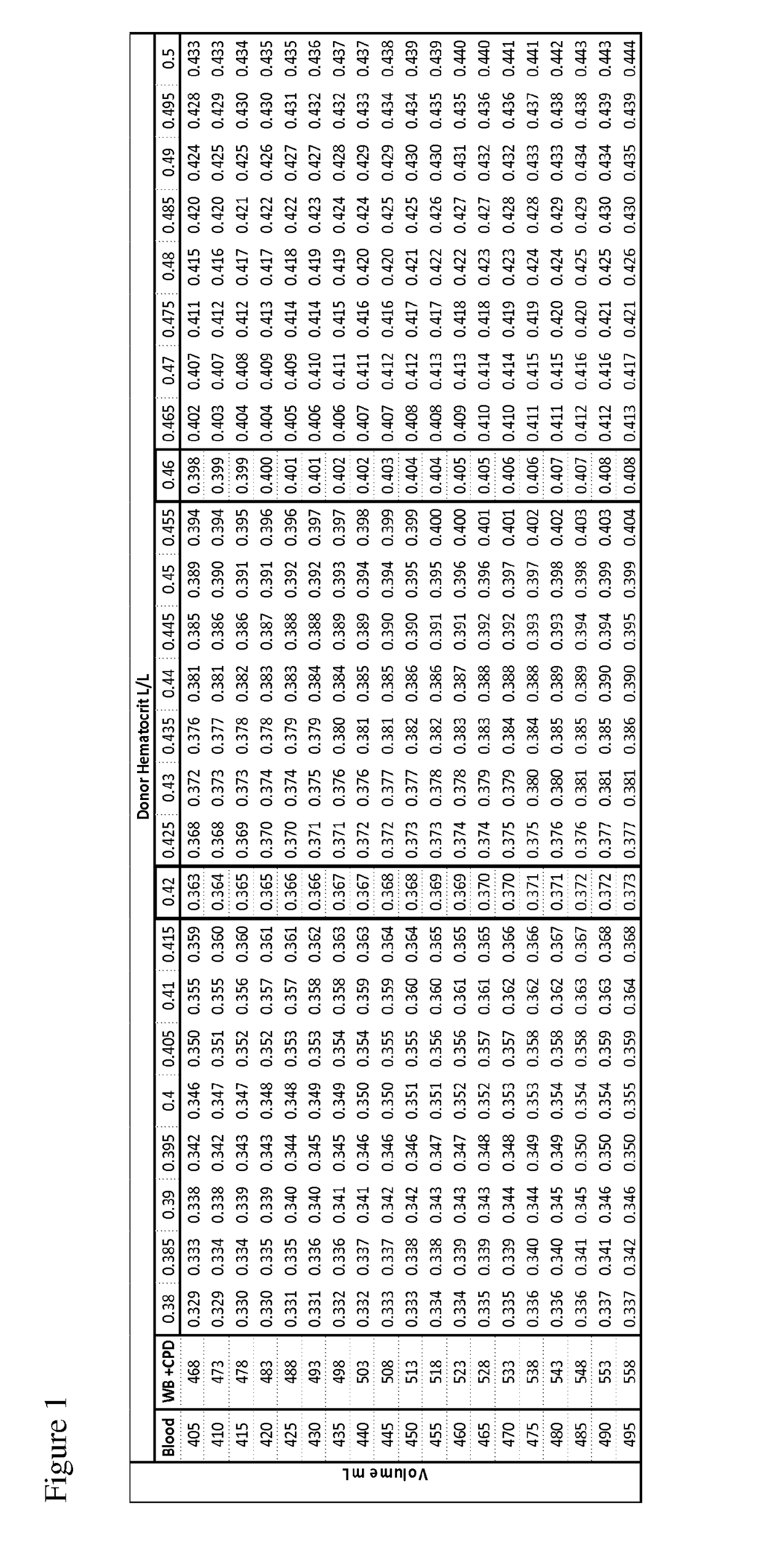
Platelet quantitative separation method applied to automatic blood component separator
ActiveCN107080869AConstant weightOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesBlood Collection TubeBlood component separator
The invention discloses a platelet quantitative separation method applied to an automatic blood component separator and can provide a more optimized operation method for platelet separation. The automatic blood component separator comprises a front extrusion plate, a hanging arm, a heat sealing head and an inductive head. The separation method comprises the following steps: centrifuging series of blood collection bags containing constant plasma weight D and different red blood cell weight Gn, extruding the blood collection bags to enable a red blood cell level to reach an inductive head position, recording a front extrusion plate moving distance as an absolute distance Hn, setting extruded plasma volume D1 (D1=D-E) according to the platelet quantity demanded E, sequentially enabling the front extrusion plate to continuously extrude all the blood collection bags till the D1 volume of plasma is extruded, recording a change value relative distance delta n of each of the blood collection bags corresponding to the moving distance at the moment and enabling a corresponding relation among the blood bag specification, the absolute distance and the relative distance to form a program to guide into software for invoking during separation operation. The platelet quantitative separation method disclosed by the invention has the benefits that prepared platelet products are consistent in weight, and the platelet density difference is smaller.
Owner:深圳市爱康生物科技股份有限公司
Calcium controlled activation of platelets via electrical stimulation
The present disclosure relates to the generation of an activated platelet product in which one or more of the presence or absence of clots, the timing of clot formation (if present), and / or the mechanical strength of clots (if present) is controlled by the presence or concentration of calcium ions during the activation process. In certain embodiments, the calcium ion concentration is controlled in the presence of pulsed electric fields or a chemical activator (e.g., thrombin) as part of the activation process.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com