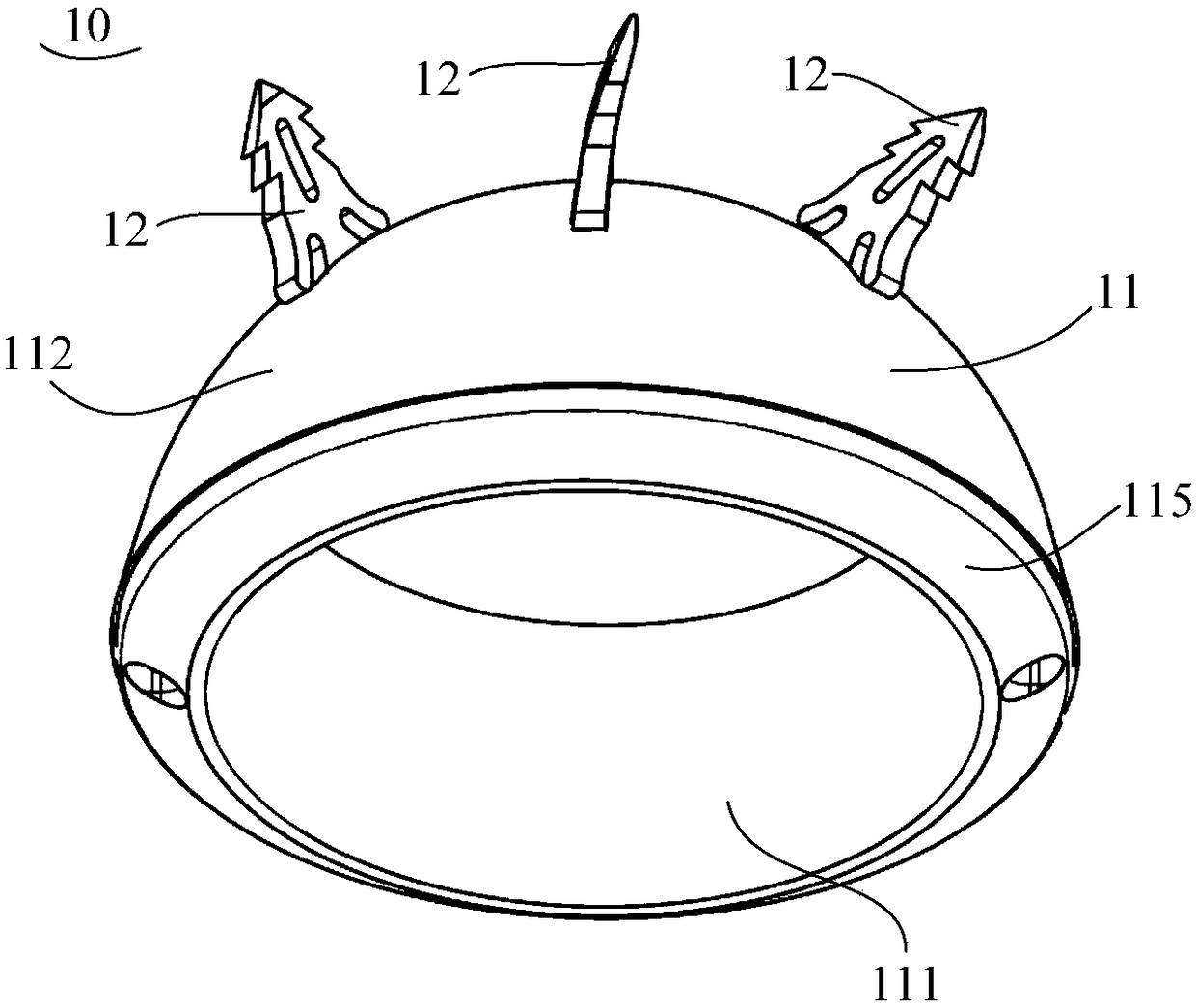
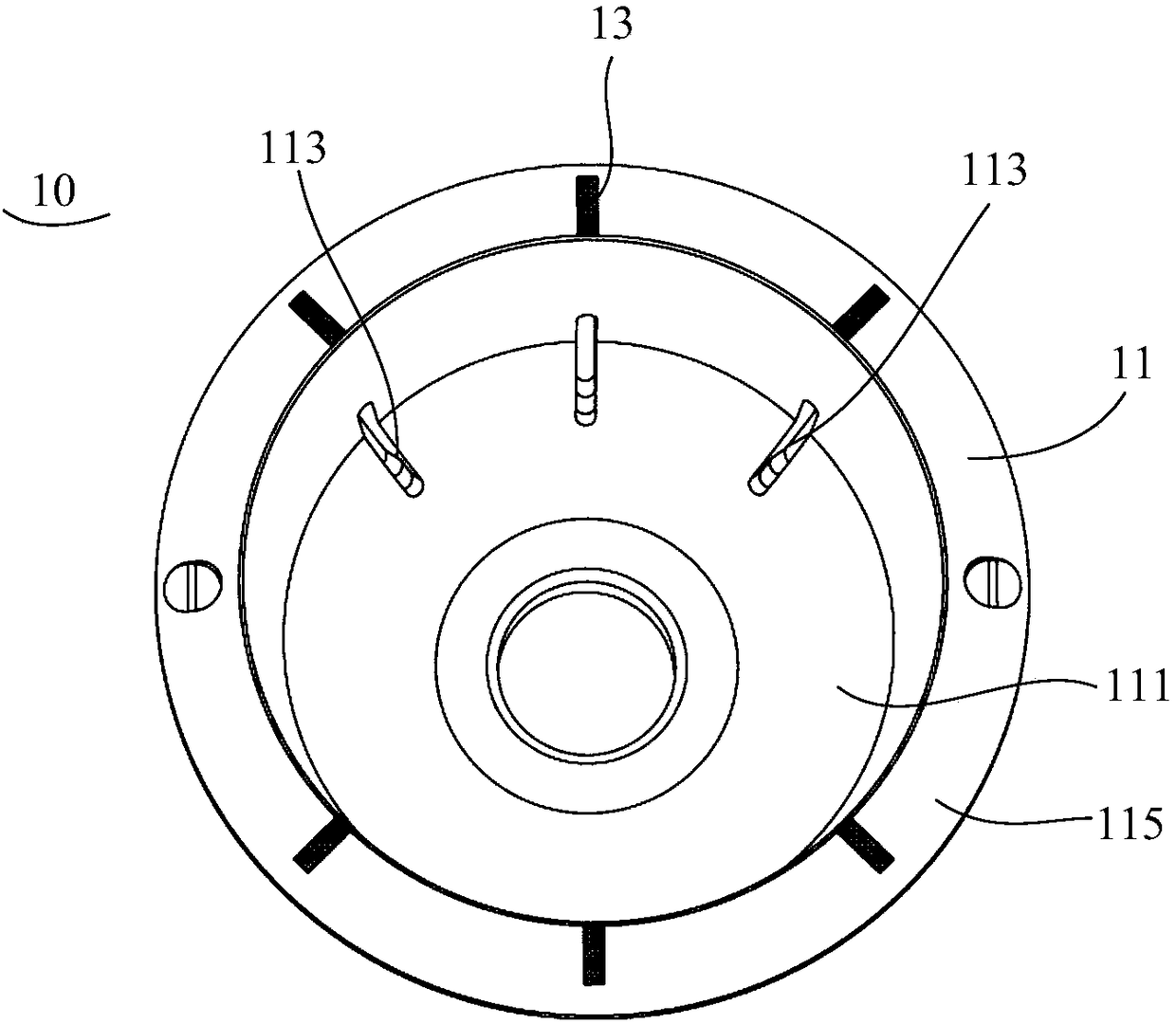
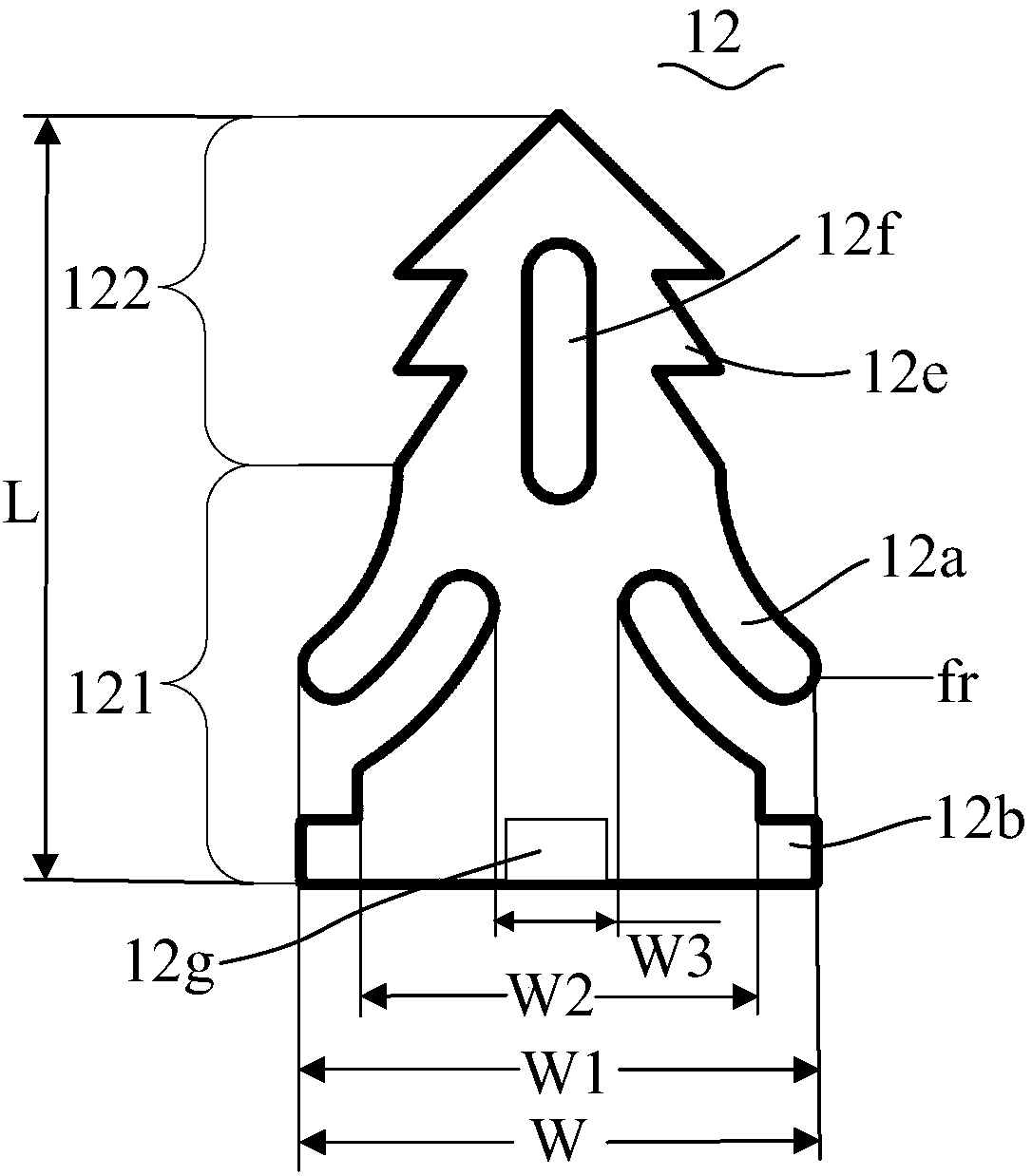
Patents
Literature
48 results about "Prosthesis Fixation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
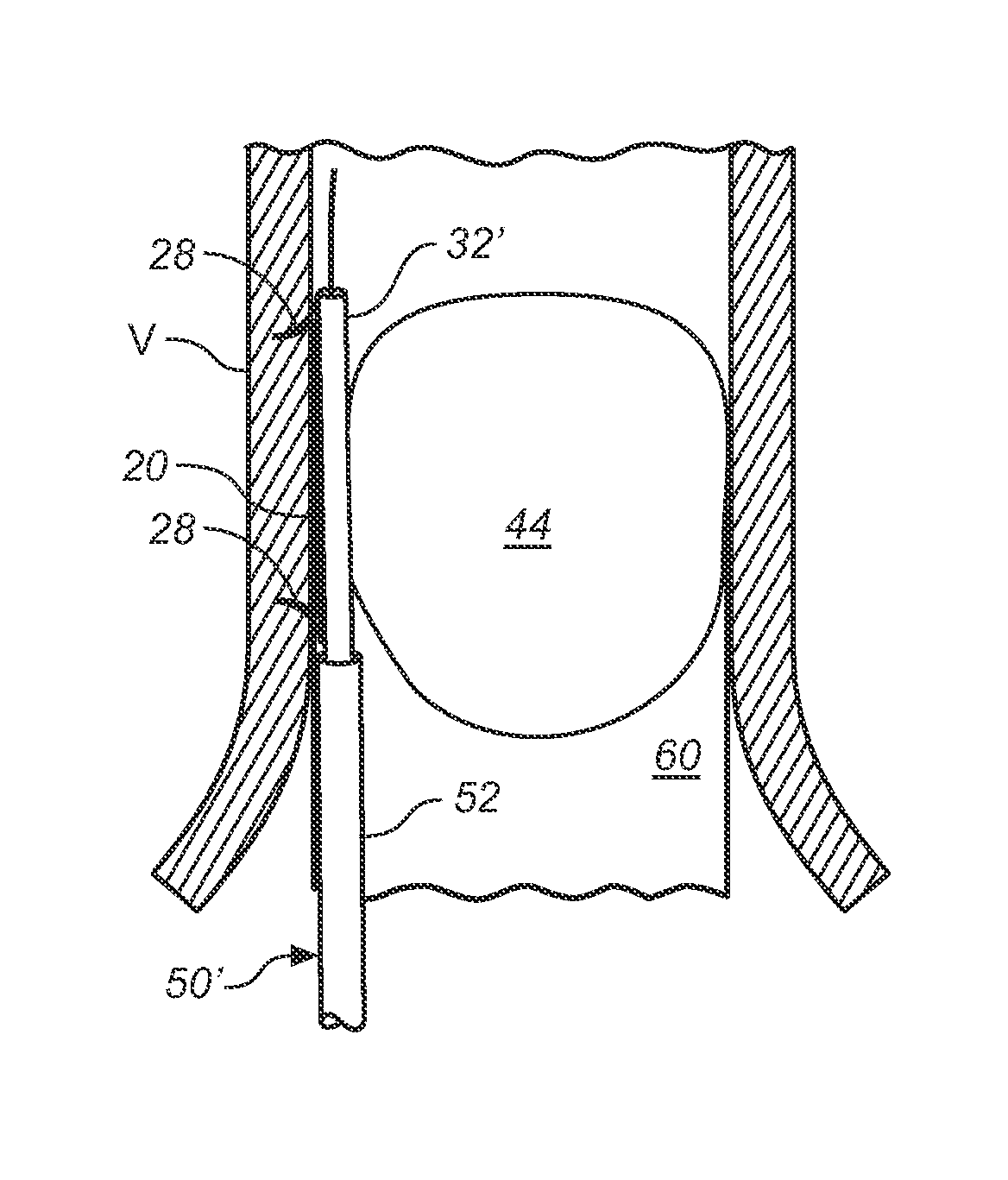
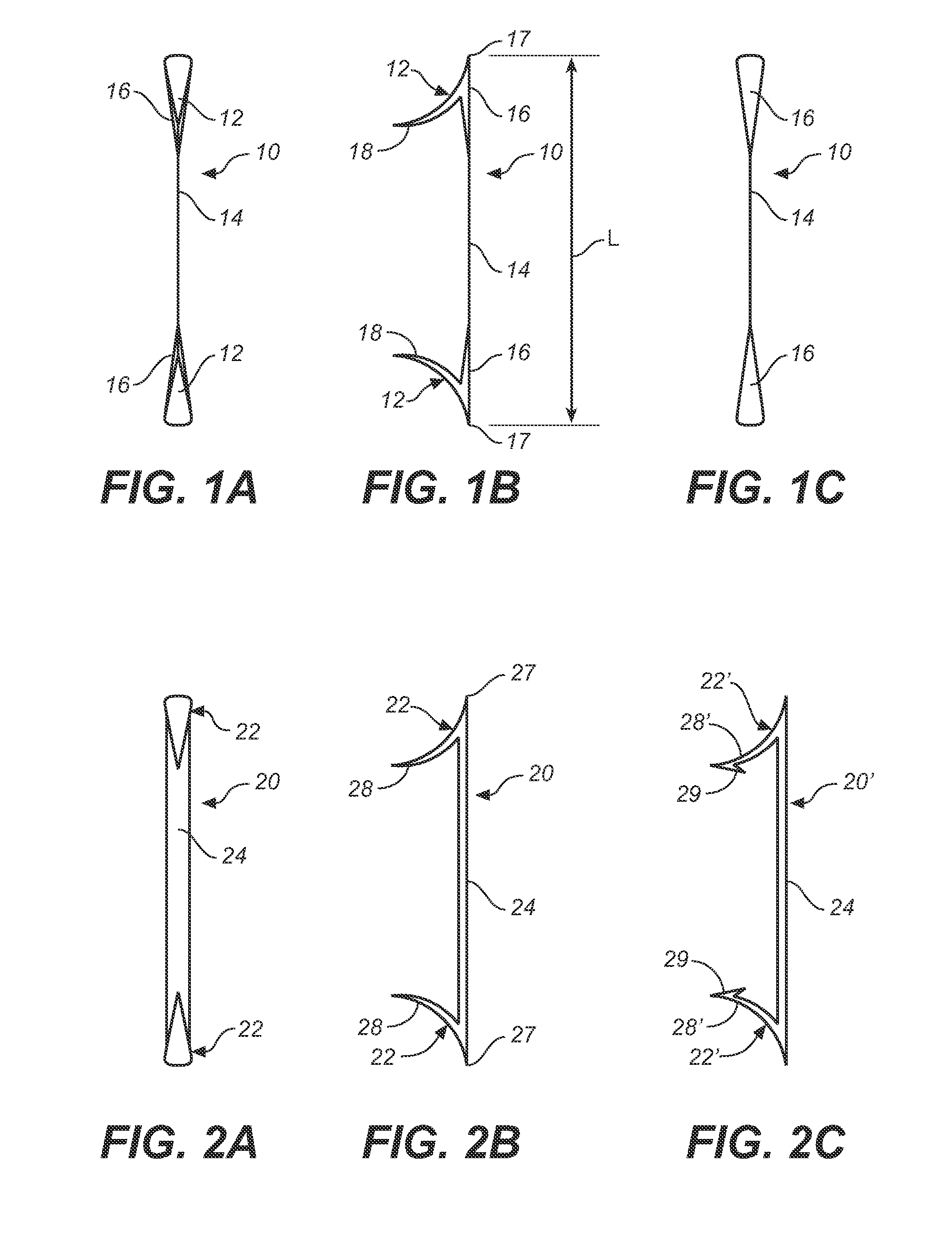
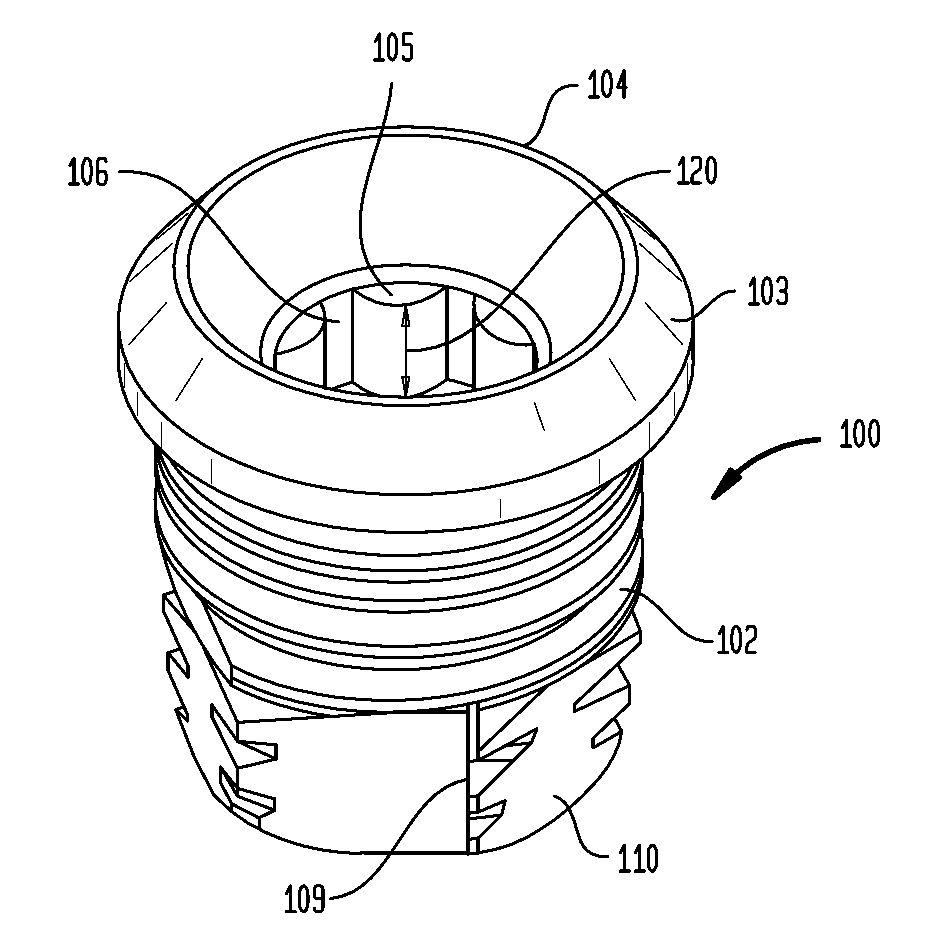
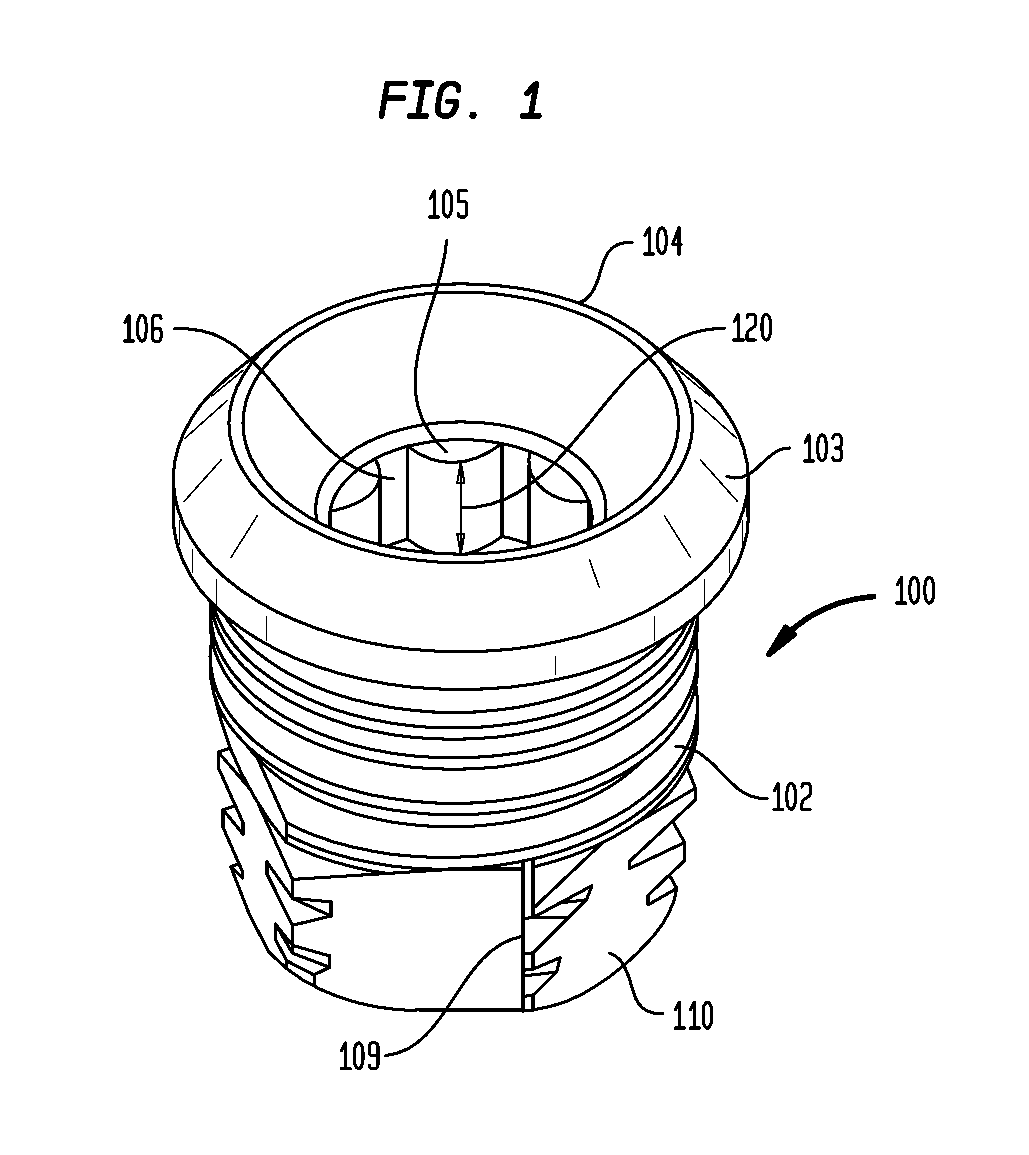
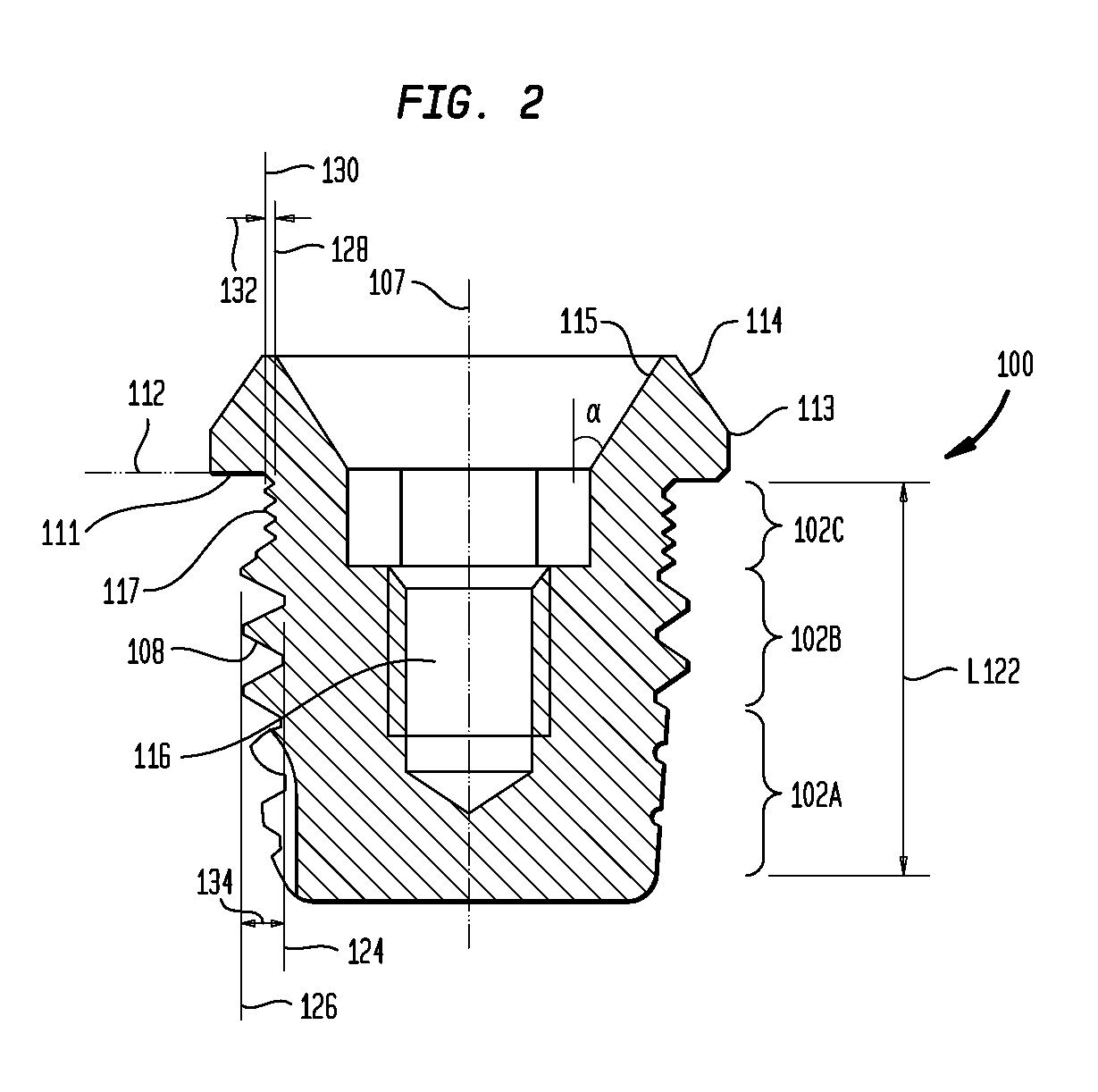
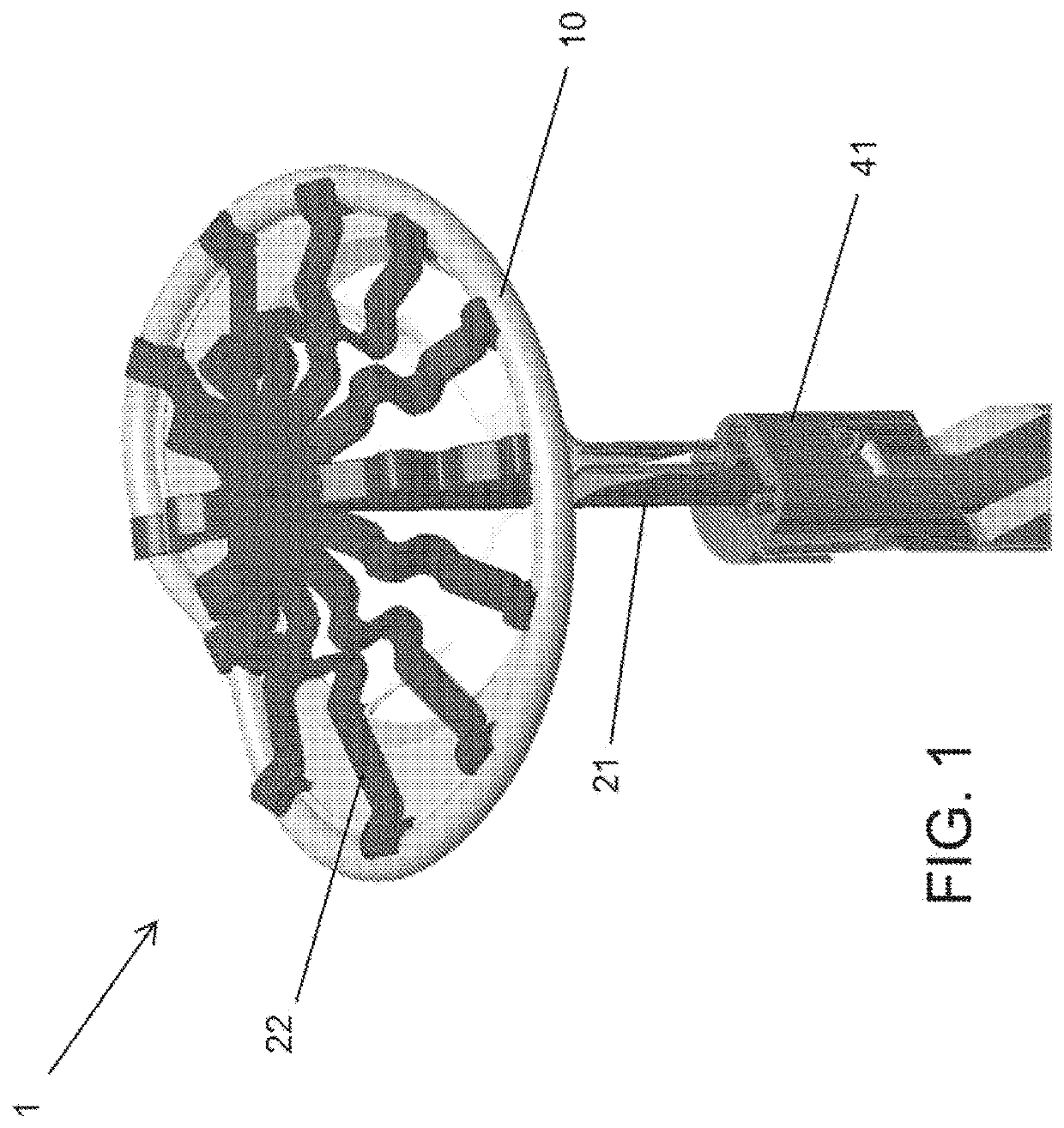
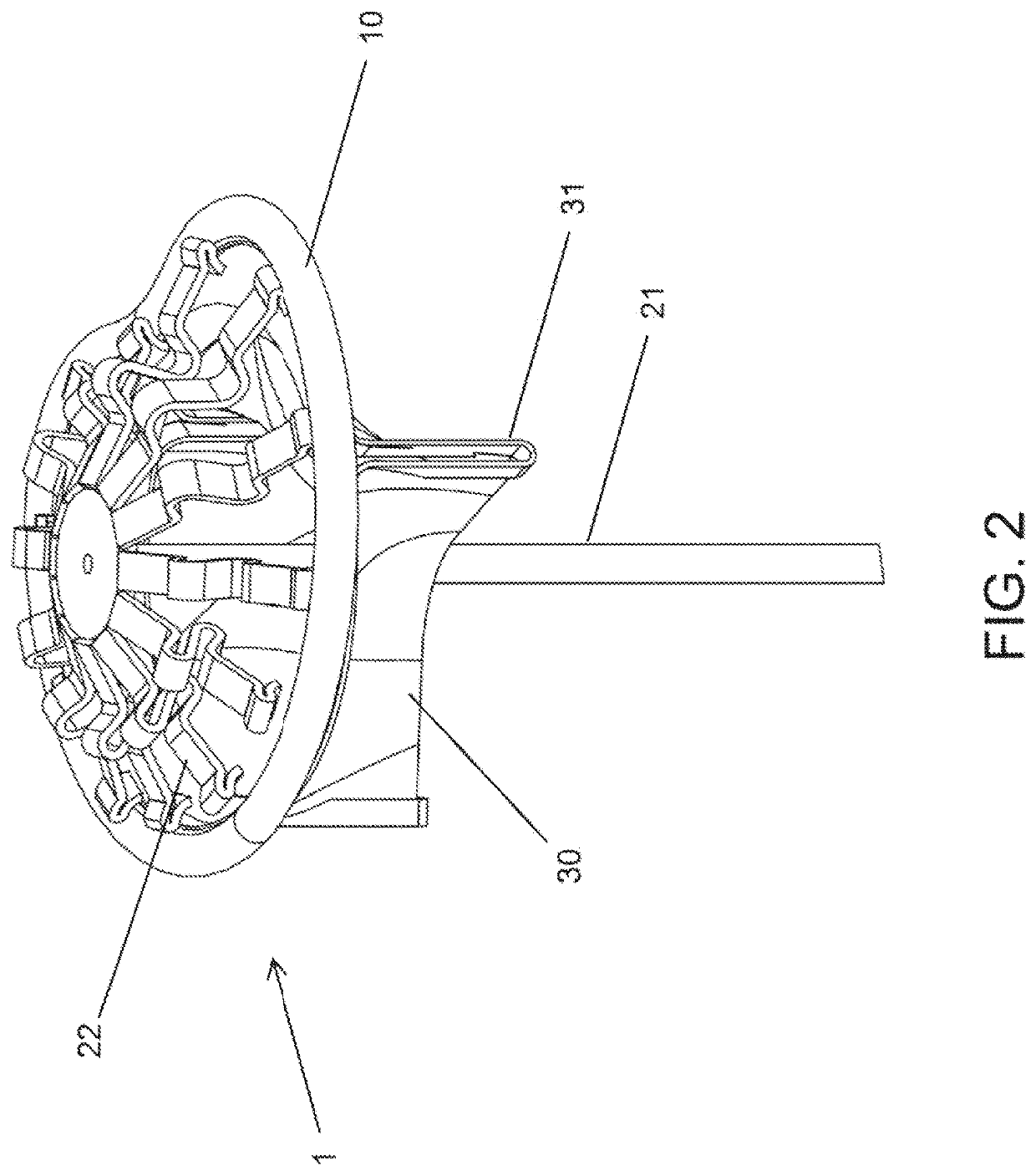
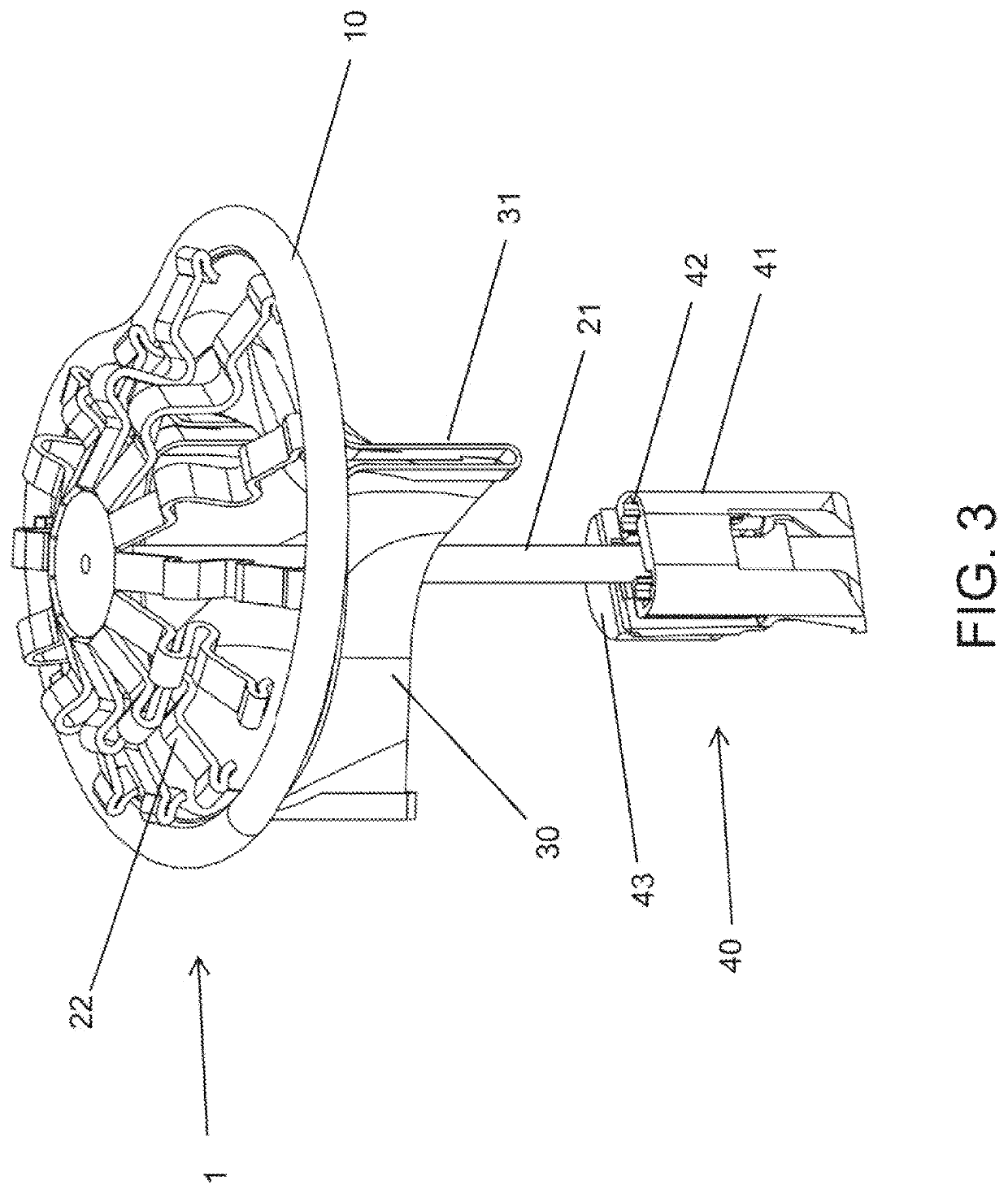
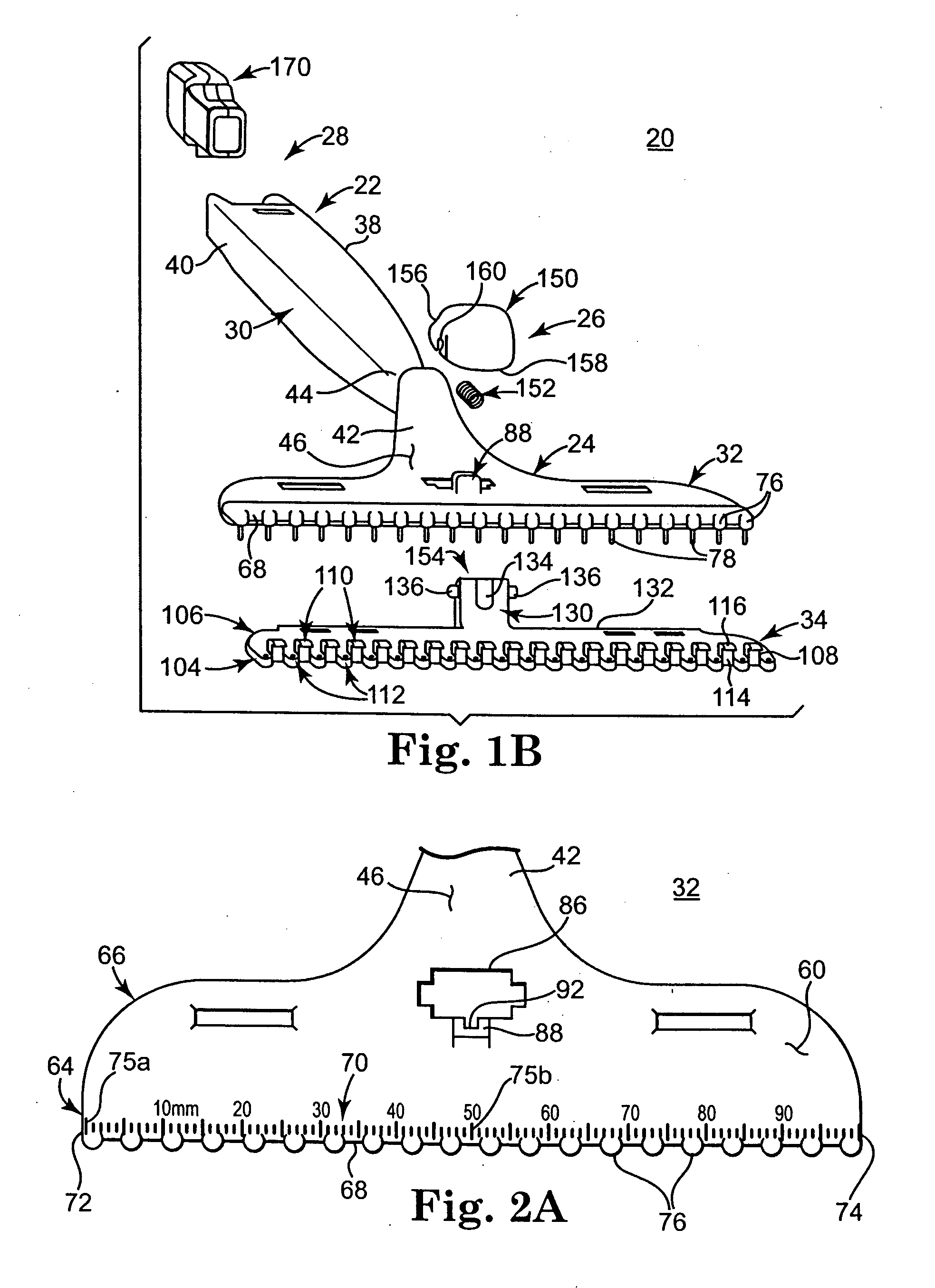
Prosthesis fixation apparatus and methods
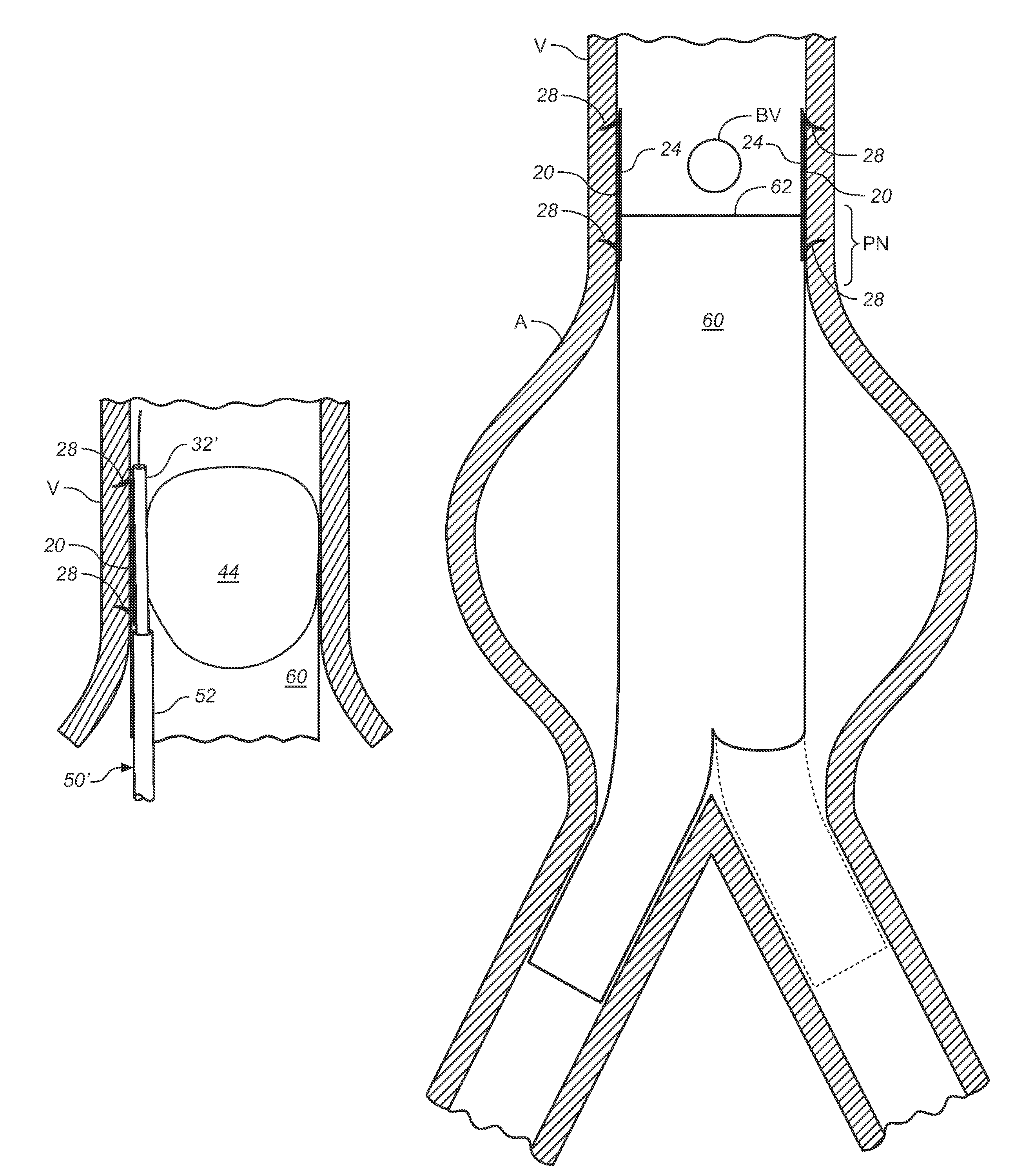
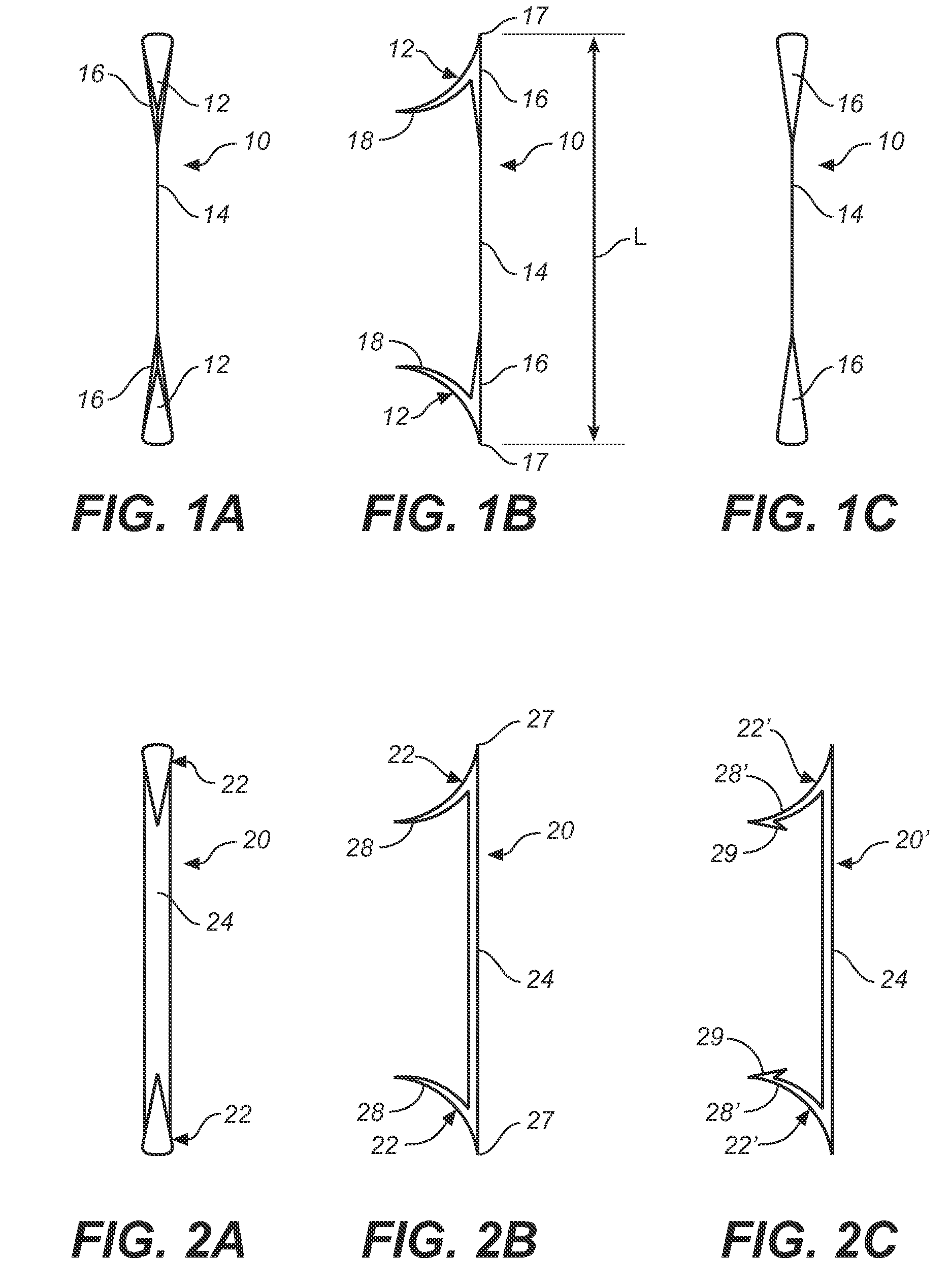
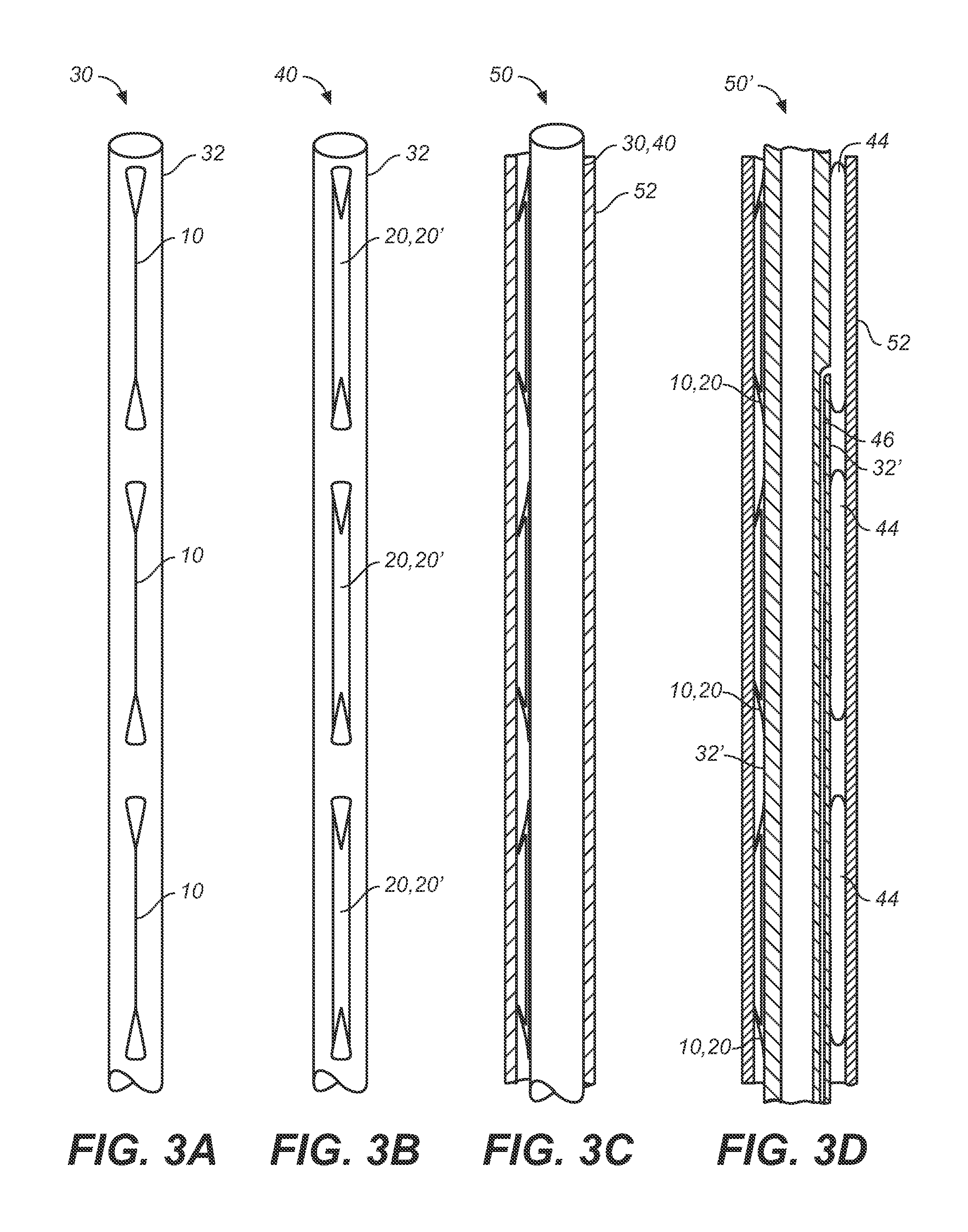
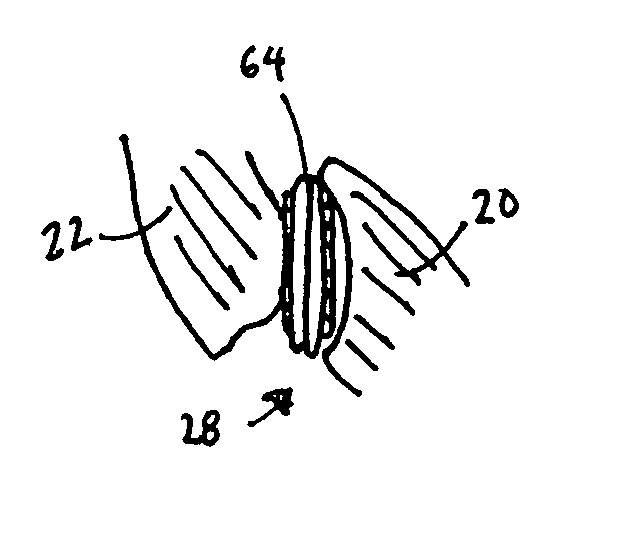
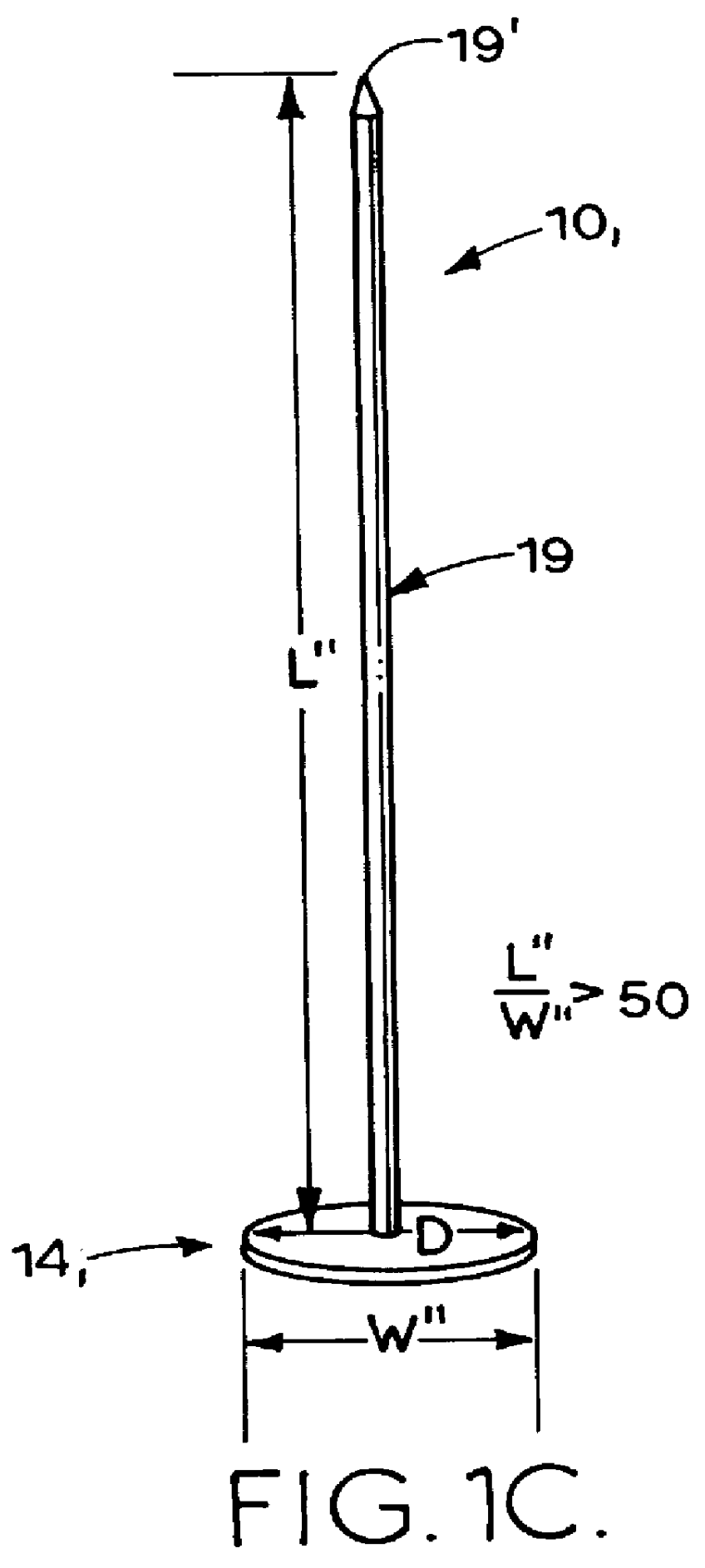
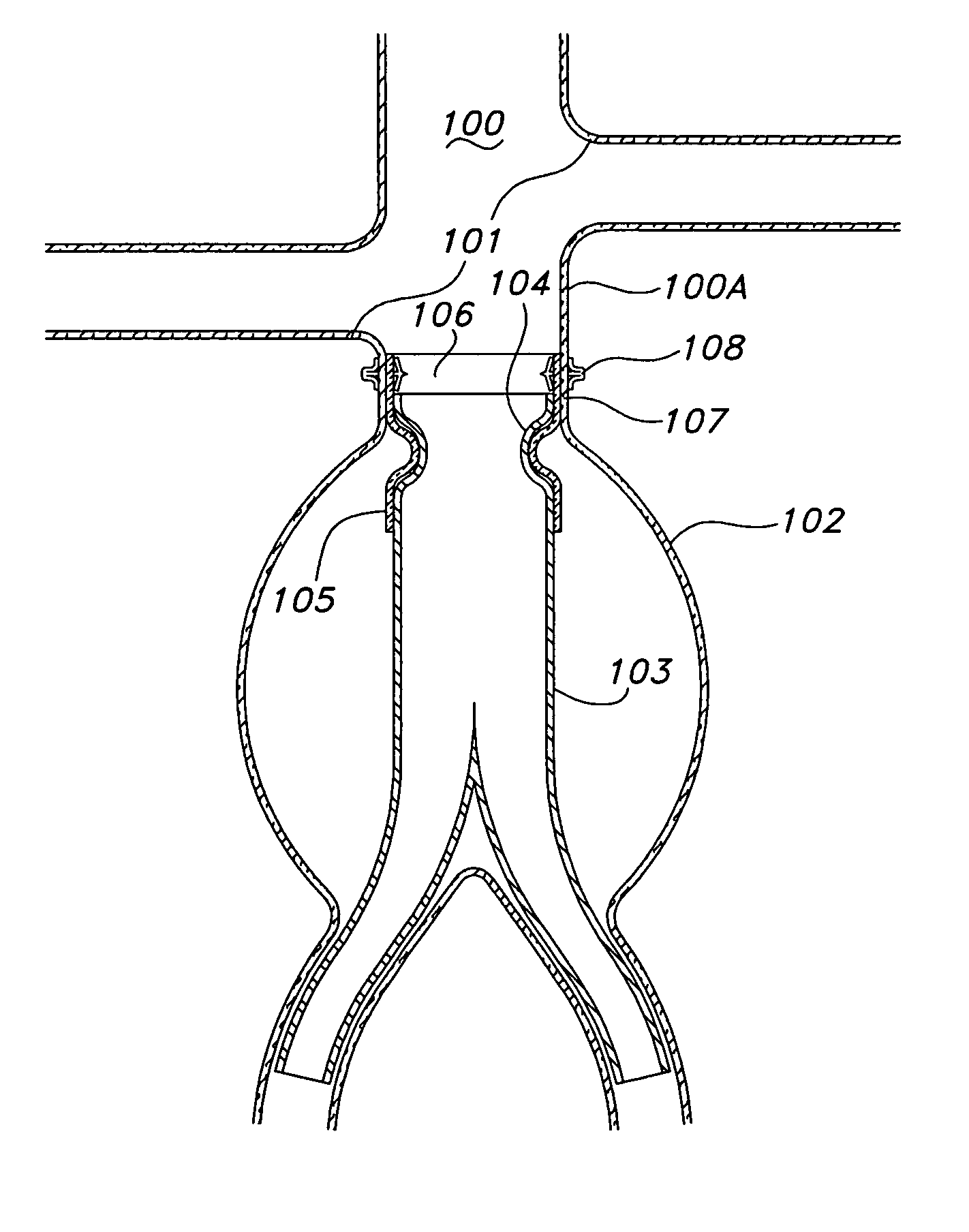
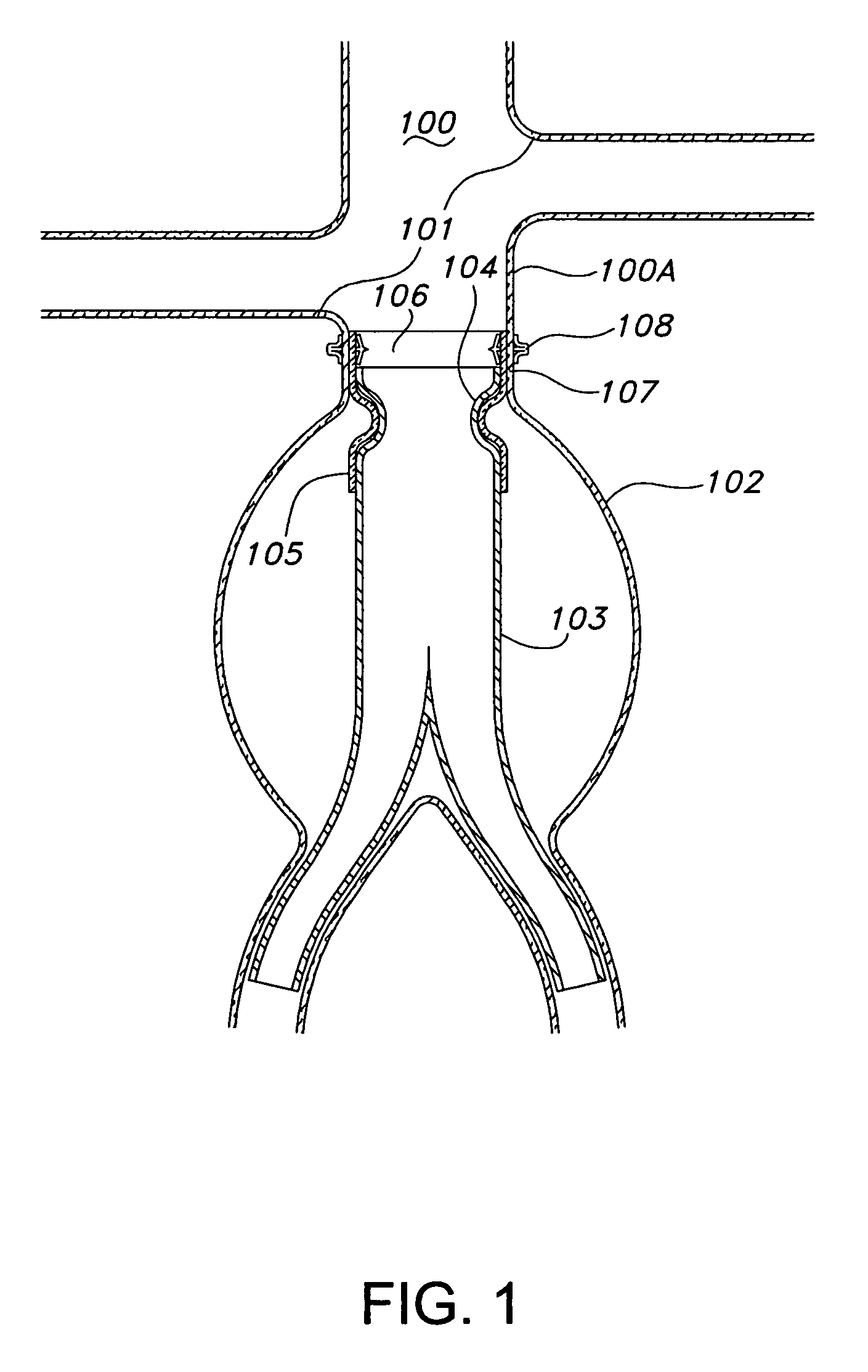
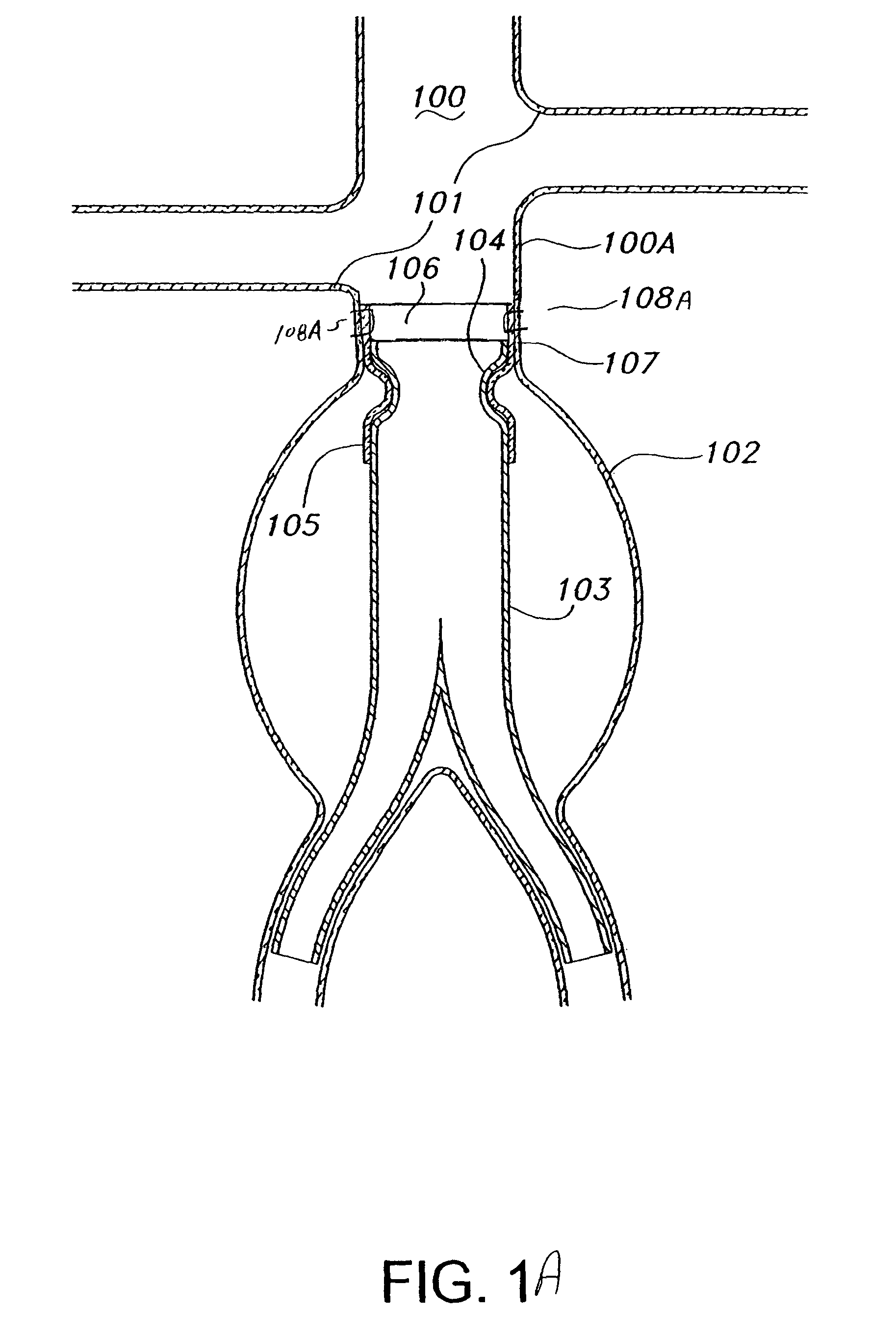
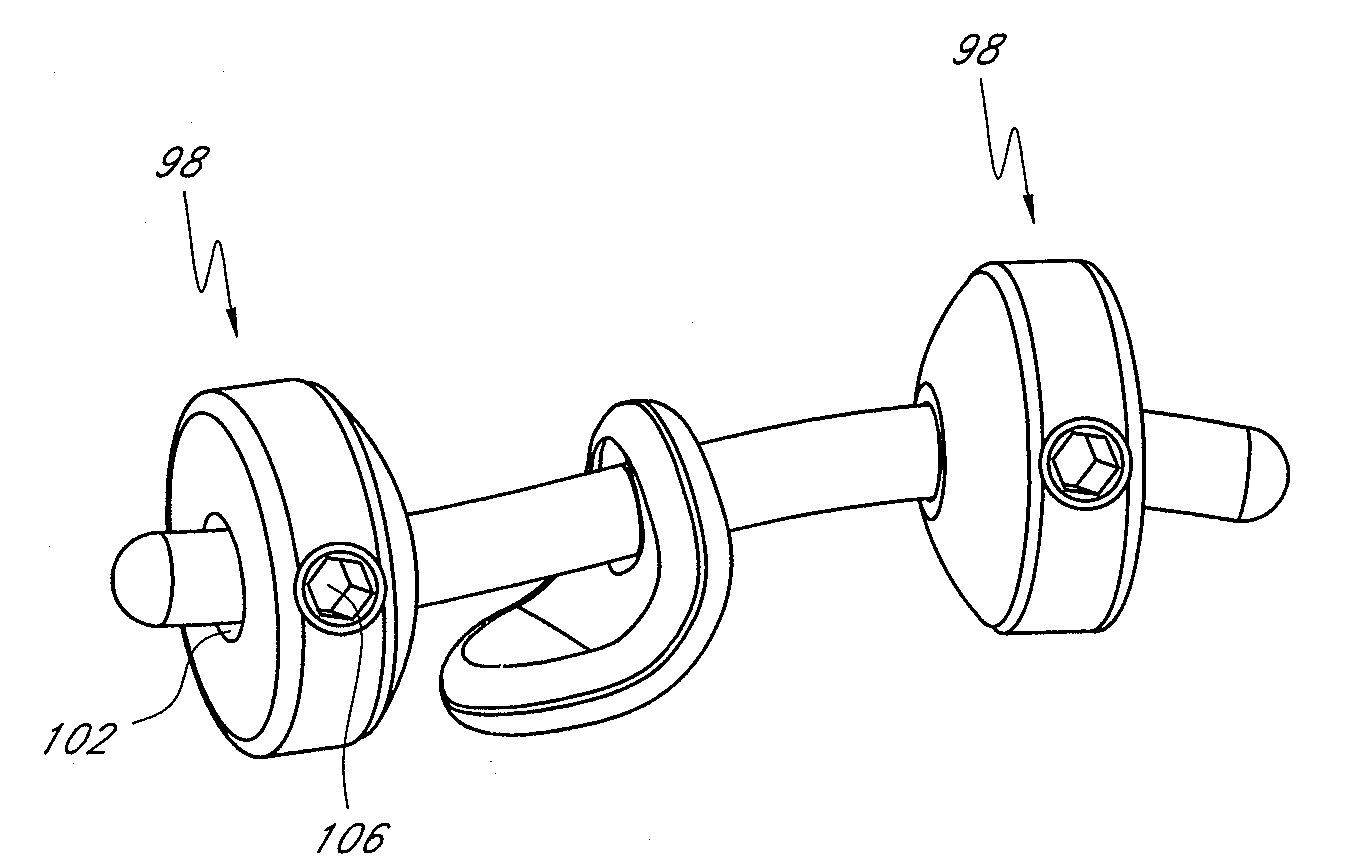
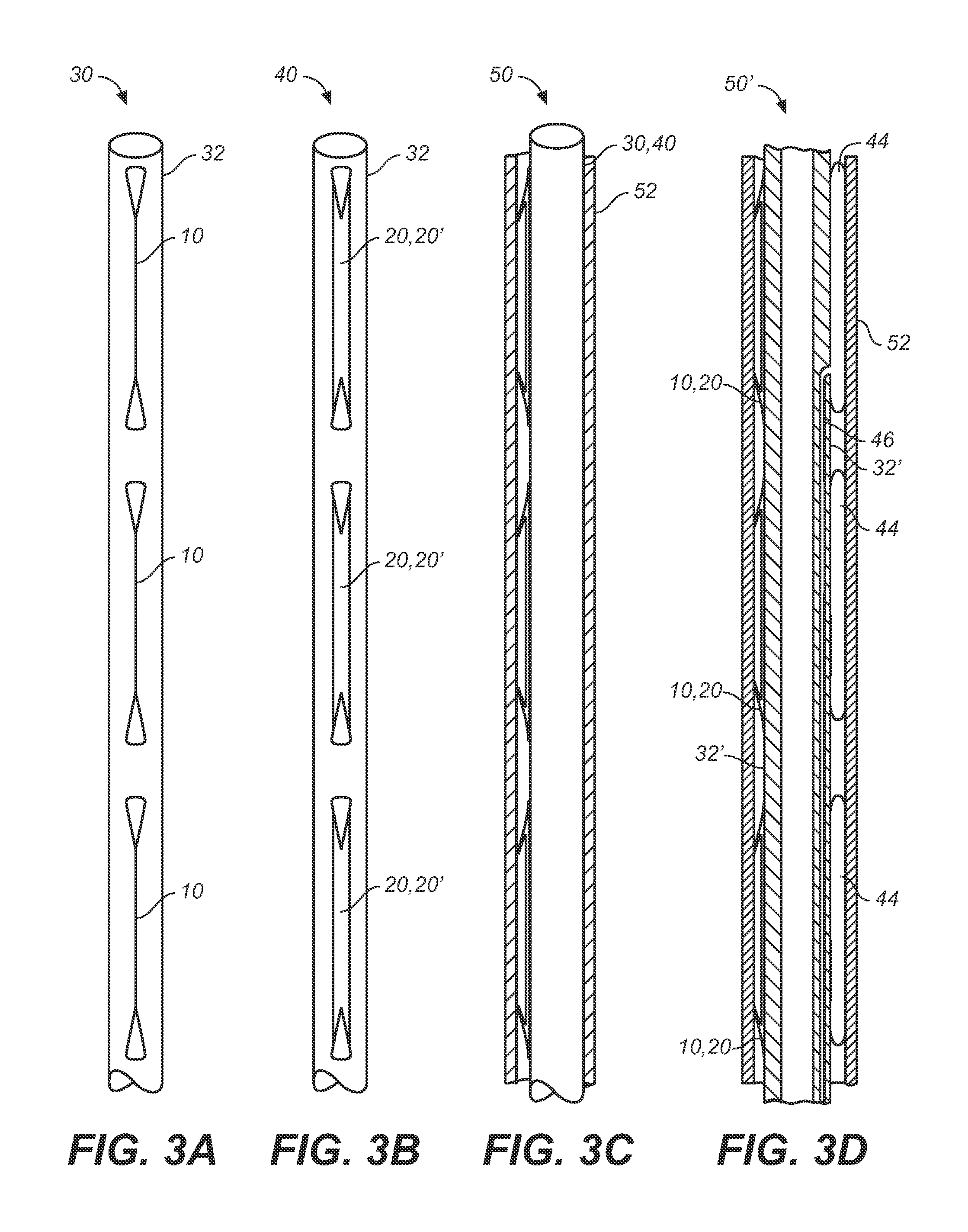
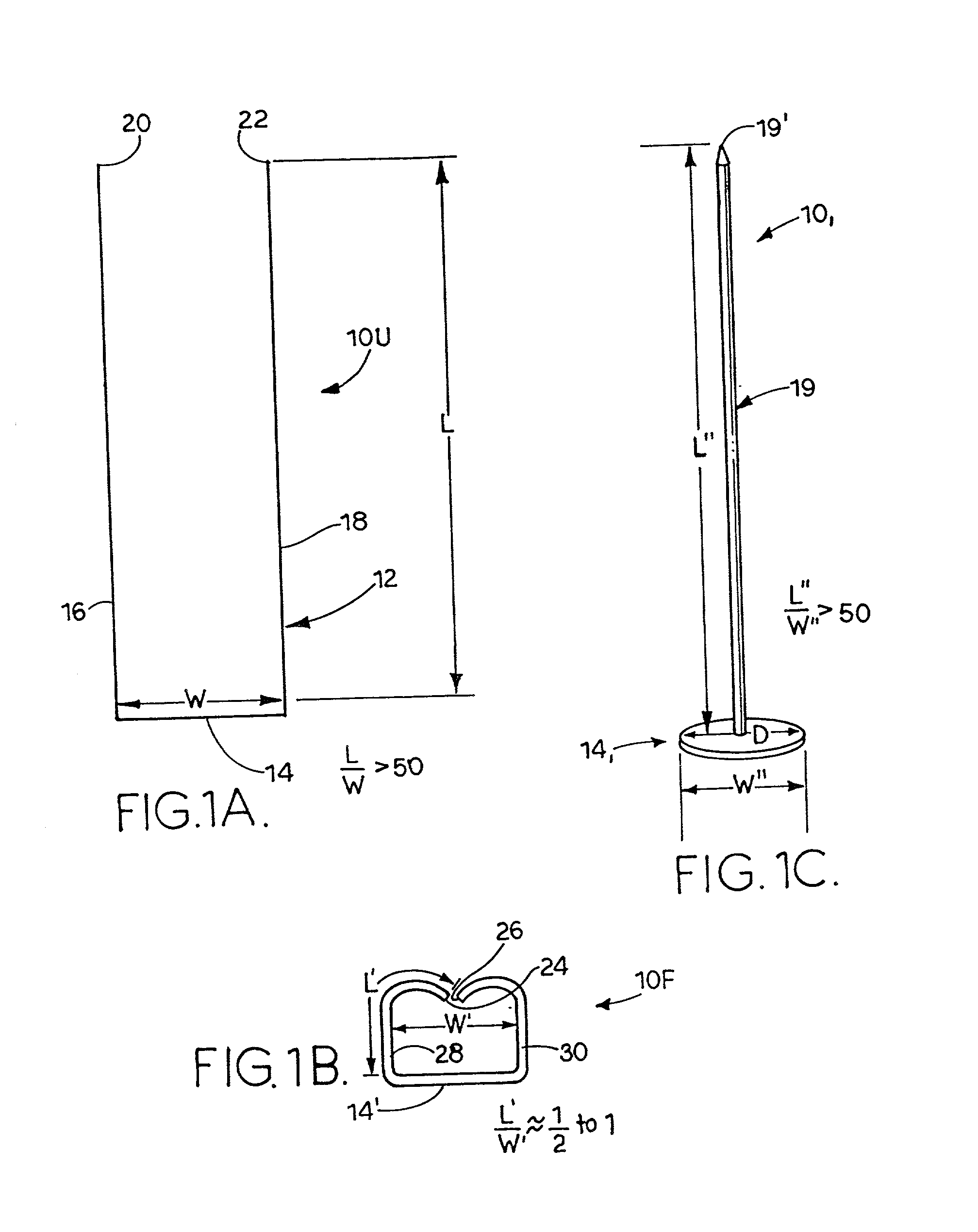
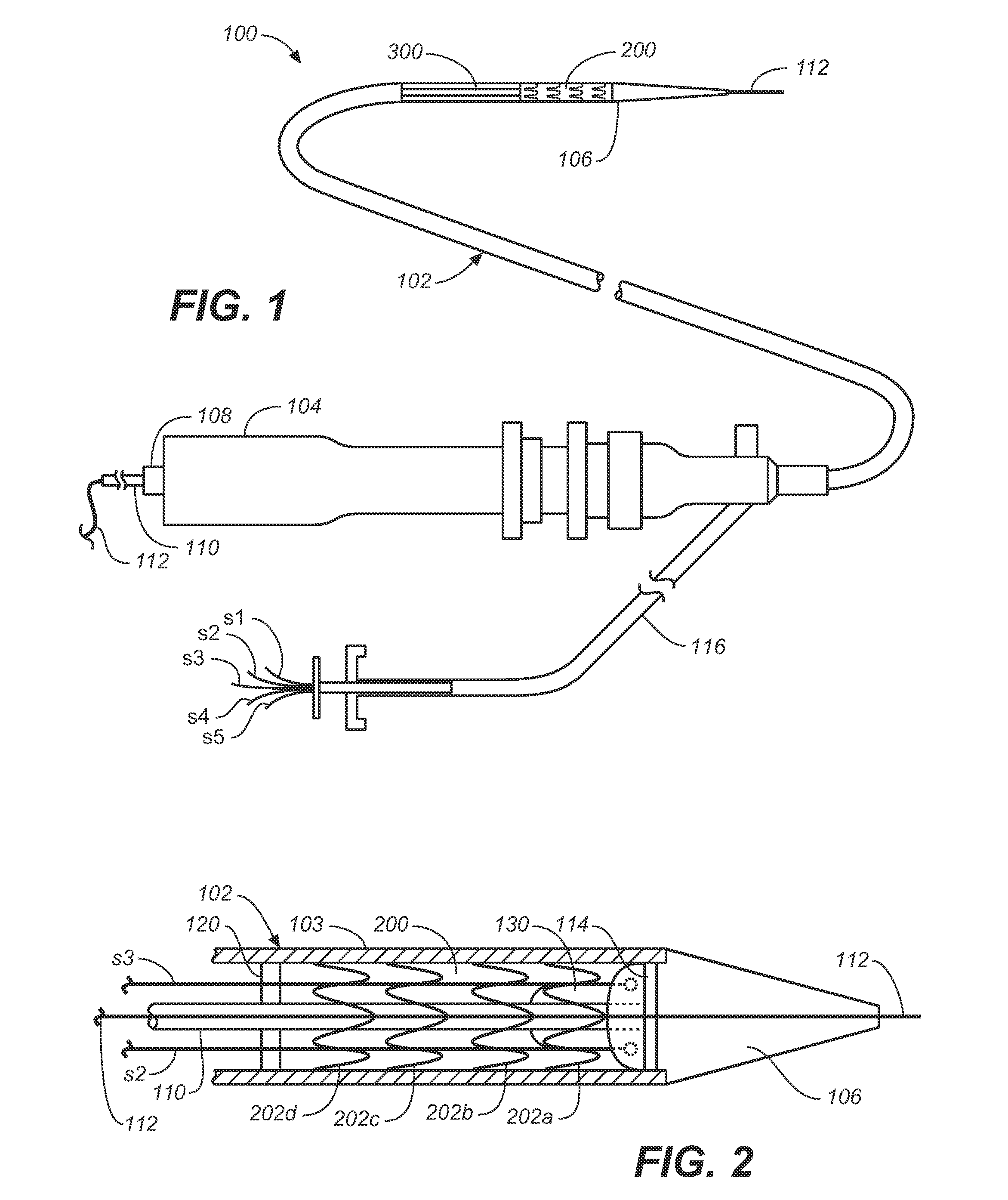
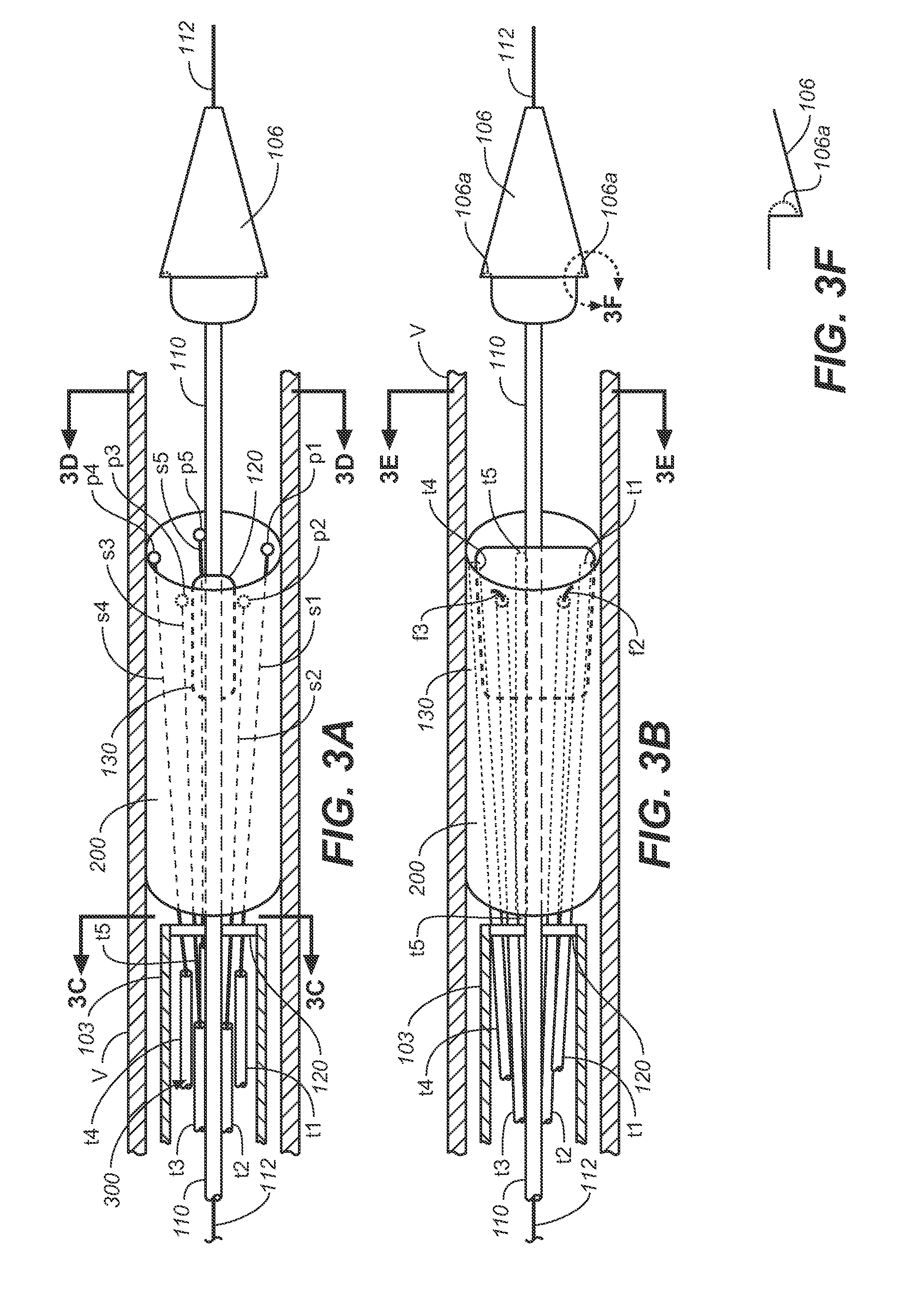
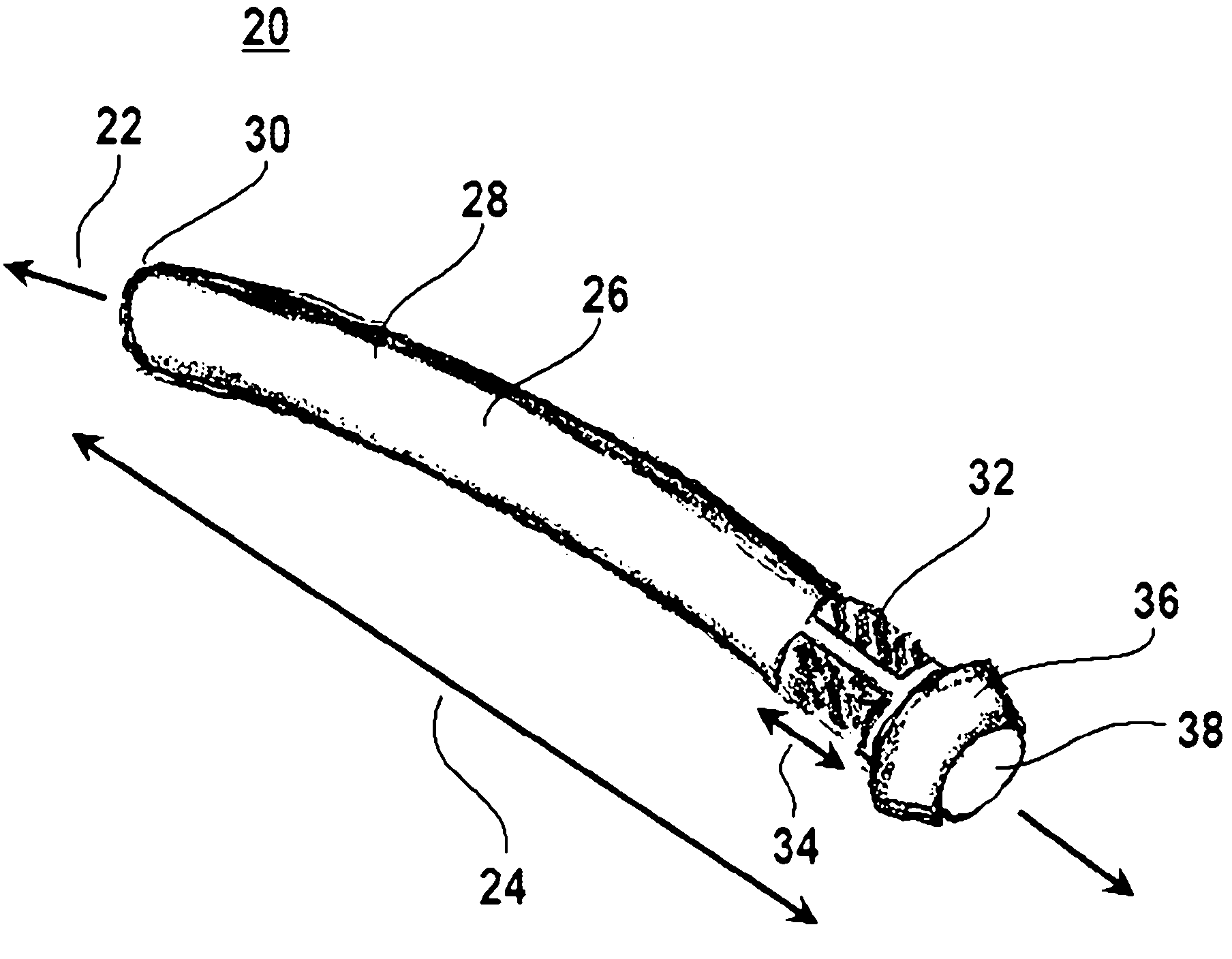
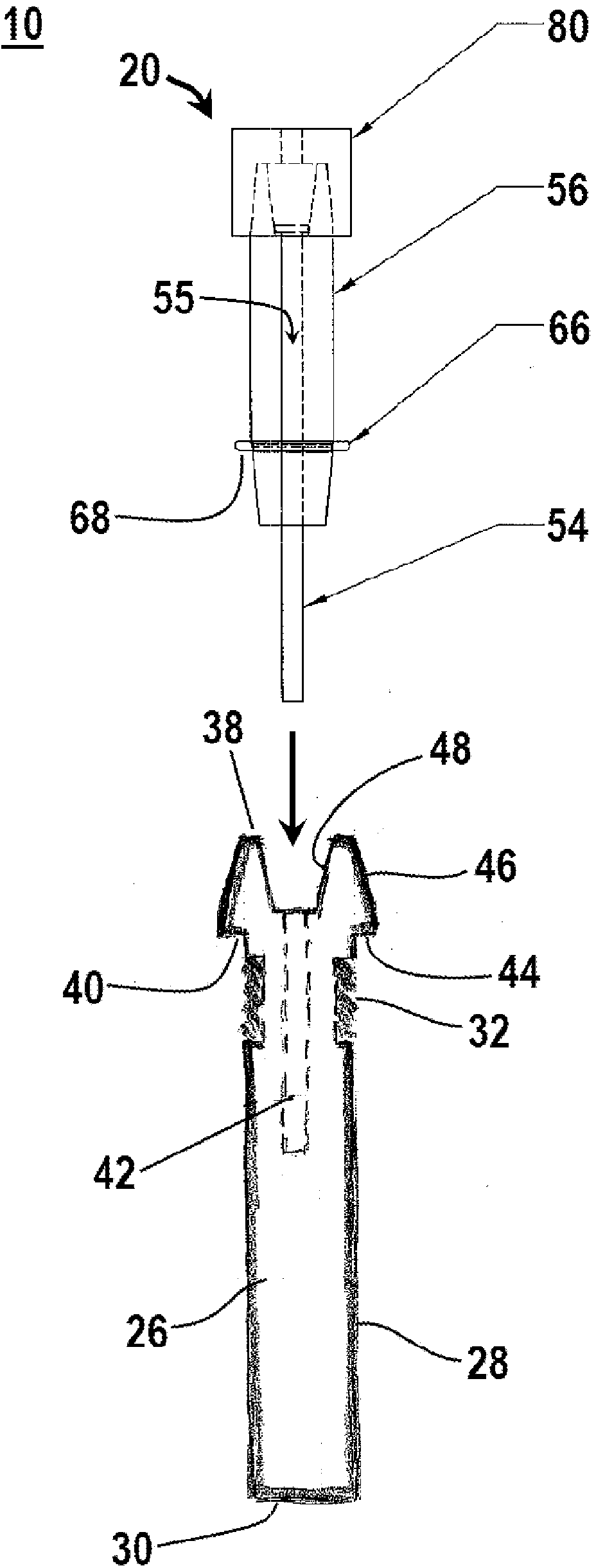
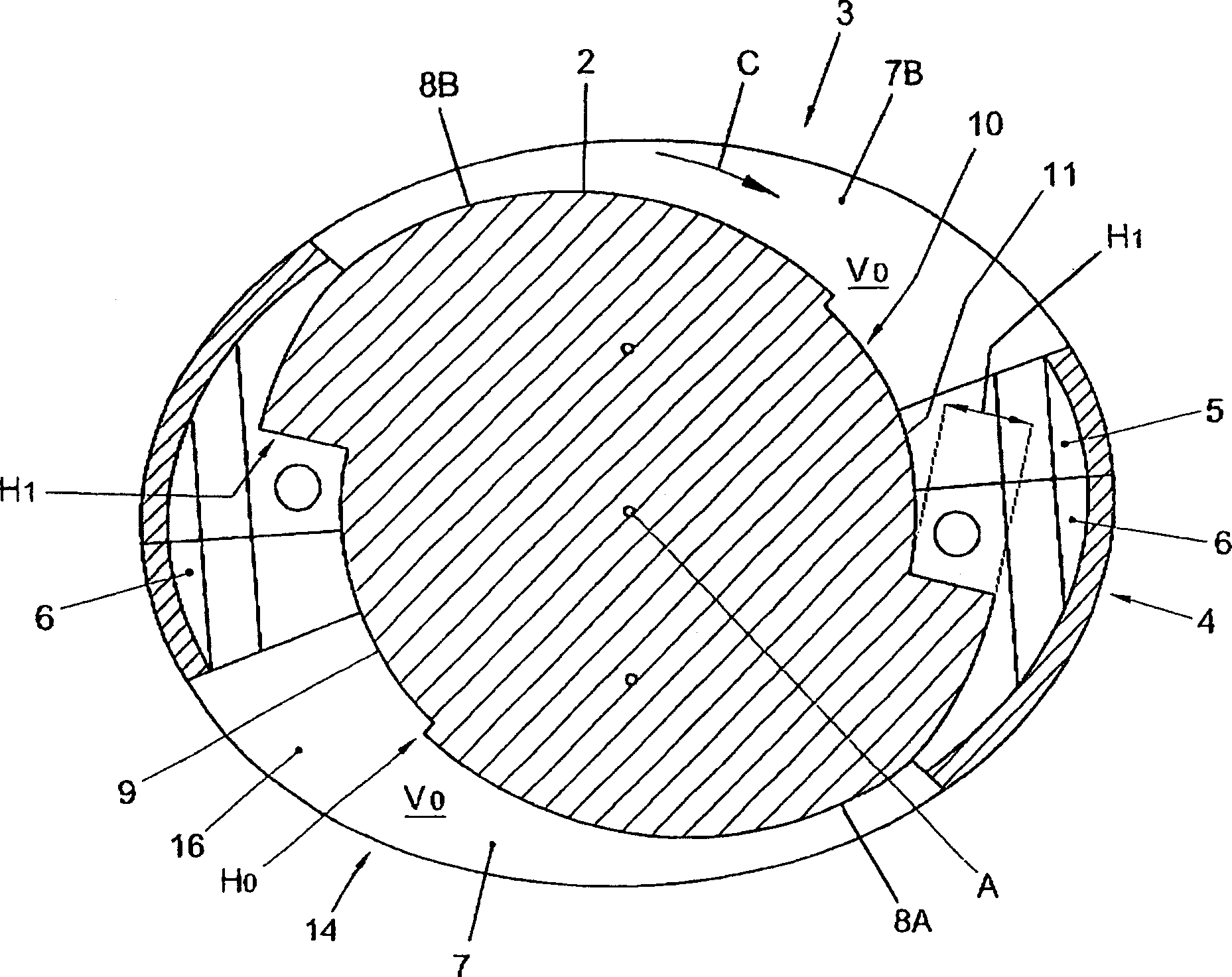
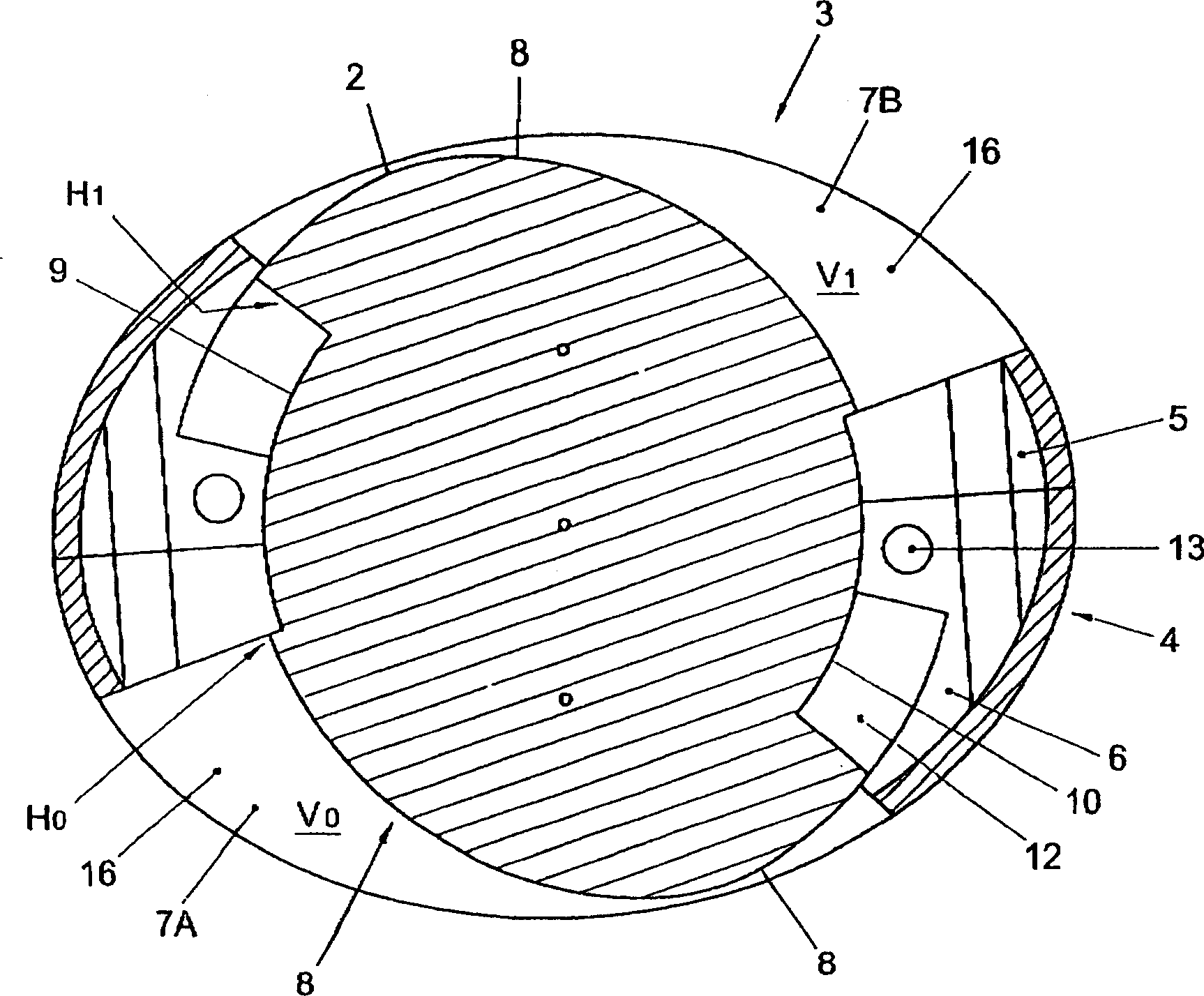
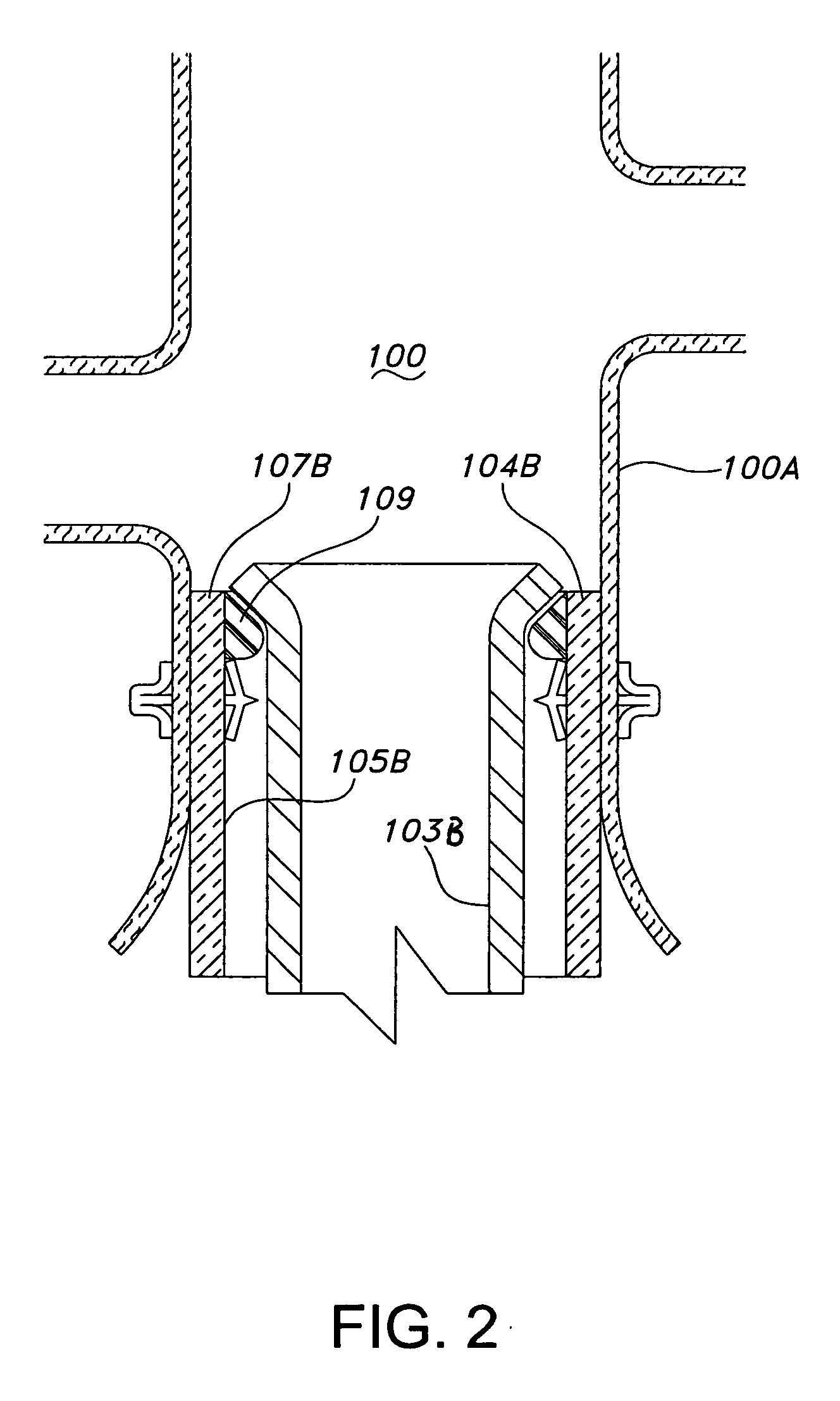
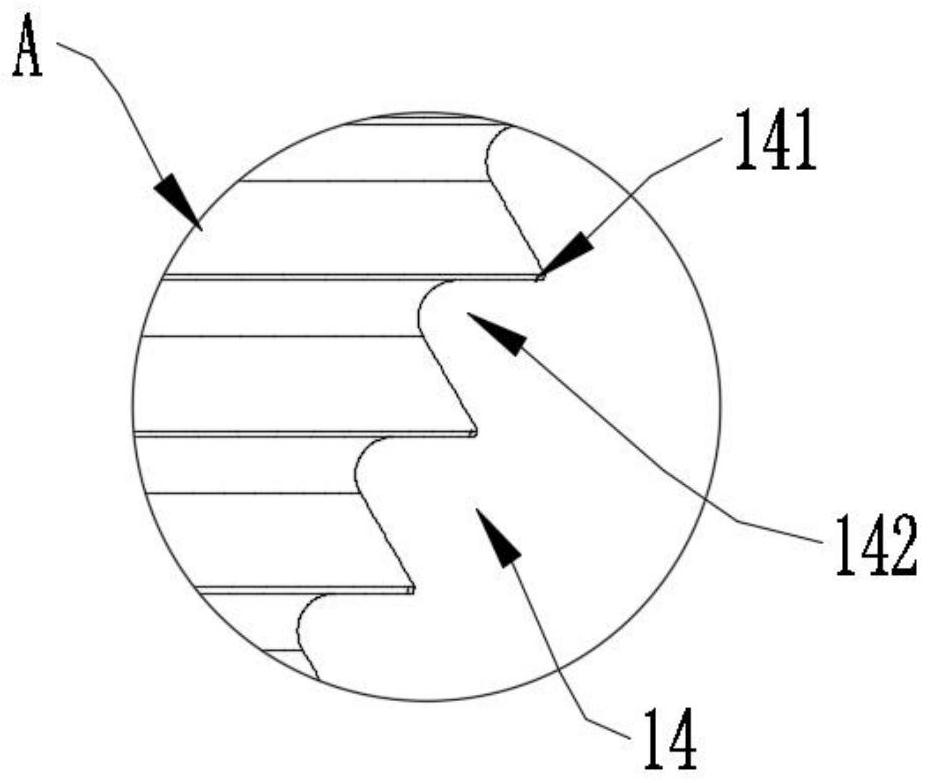
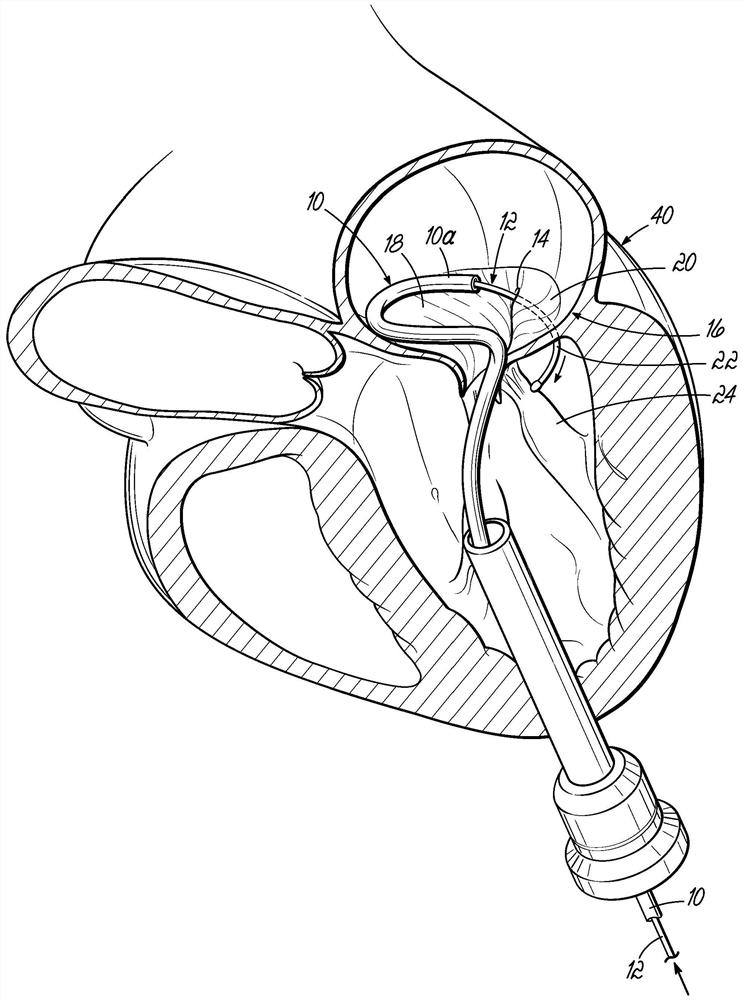
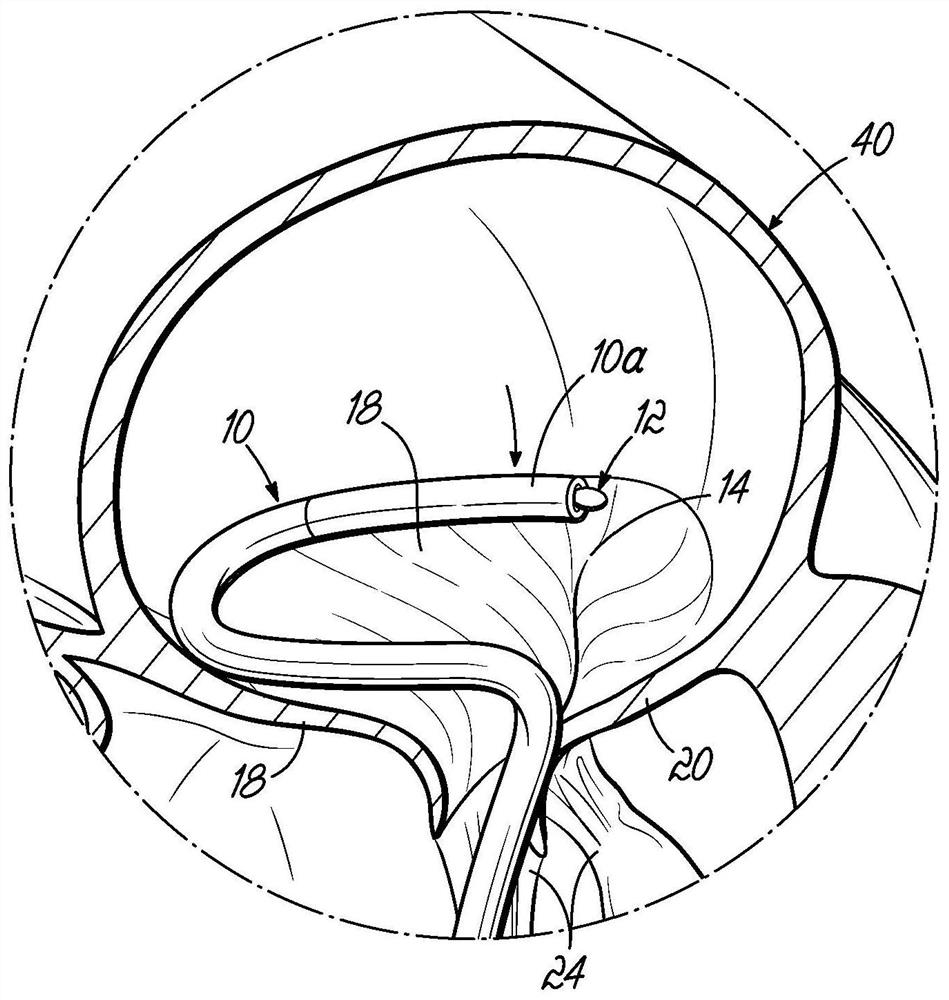
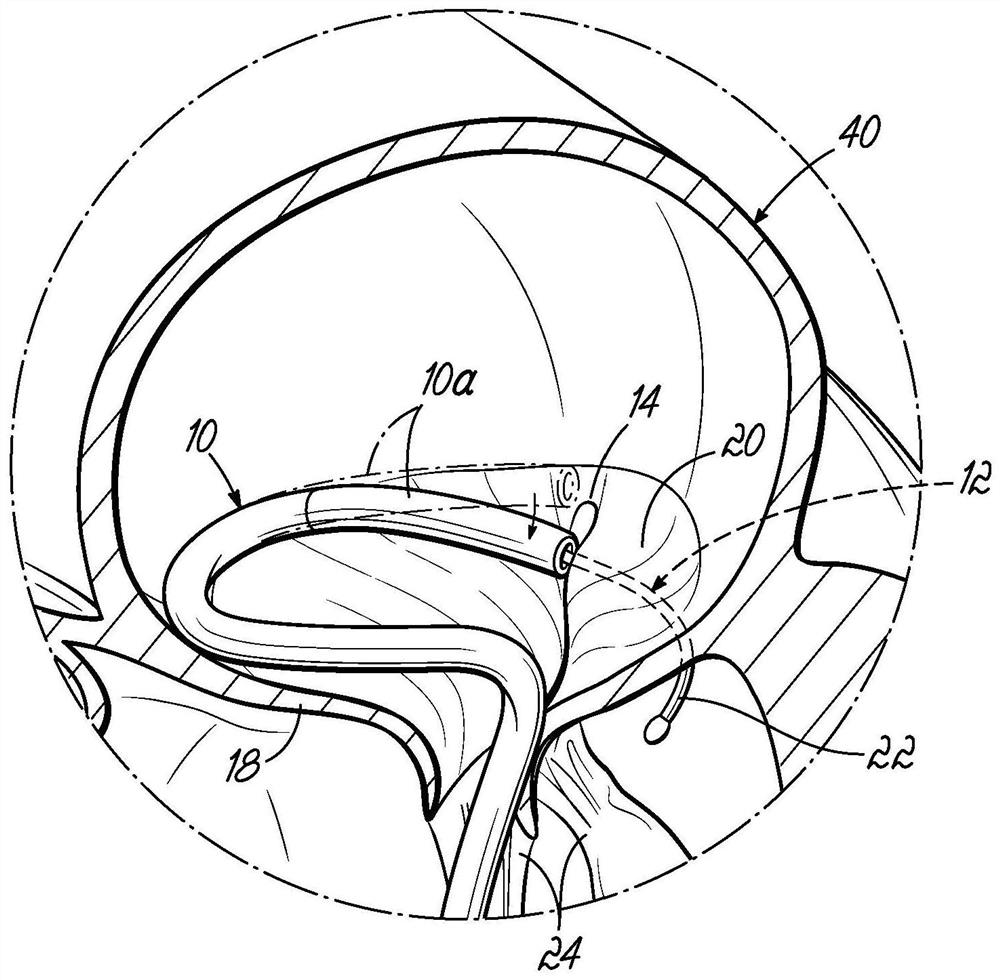
A method of securing a prosthesis placed at a desired site in a passageway of a human body comprises delivering a fastener having a proximal piercing end portion and a distal piercing end portion to a site where a prosthesis having a tubular wall has been placed in the passageway, which has a wall, advancing the proximal piercing end portion beyond the prosthesis, penetrating the proximal piercing end portion into the wall of the passageway without passing the proximal piercing end portion through the tubular wall of the prosthesis, and passing the distal piercing end portion through the tubular wall of the prosthesis and into the wall of the passageway. One surgical fastener delivery apparatus for delivering a surgical fastener to a target site comprises a support having a first end, a second end, and a longitudinal axis and being adapted for placement in a passageway in a human body. A surgical fastener having a first piercing end portion, a second piercing end portion and a central portion extending therebetween and having a longitudinal axis is releasably mounted to the support with the central portion longitudinal axis generally parallel to the support longitudinal axis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
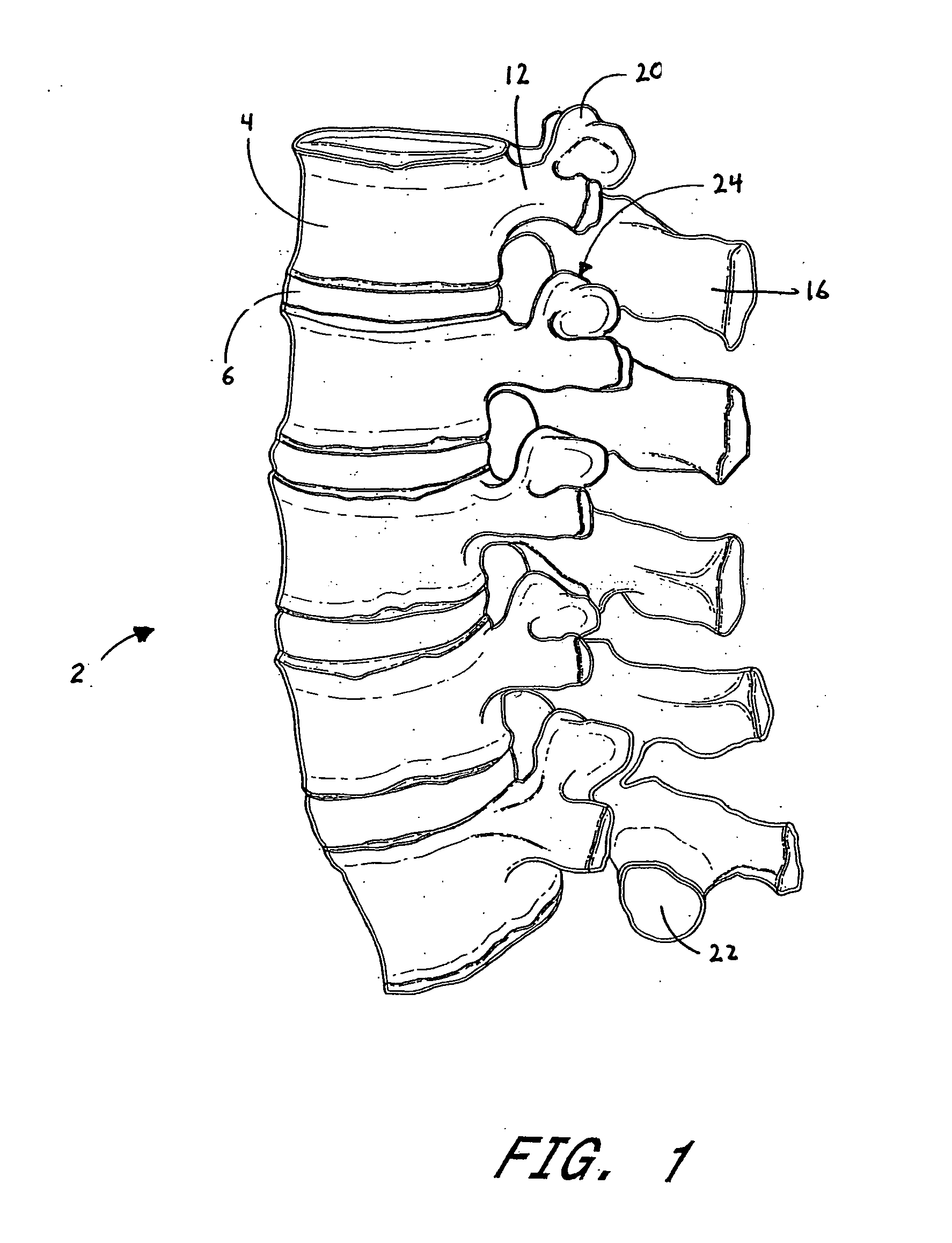
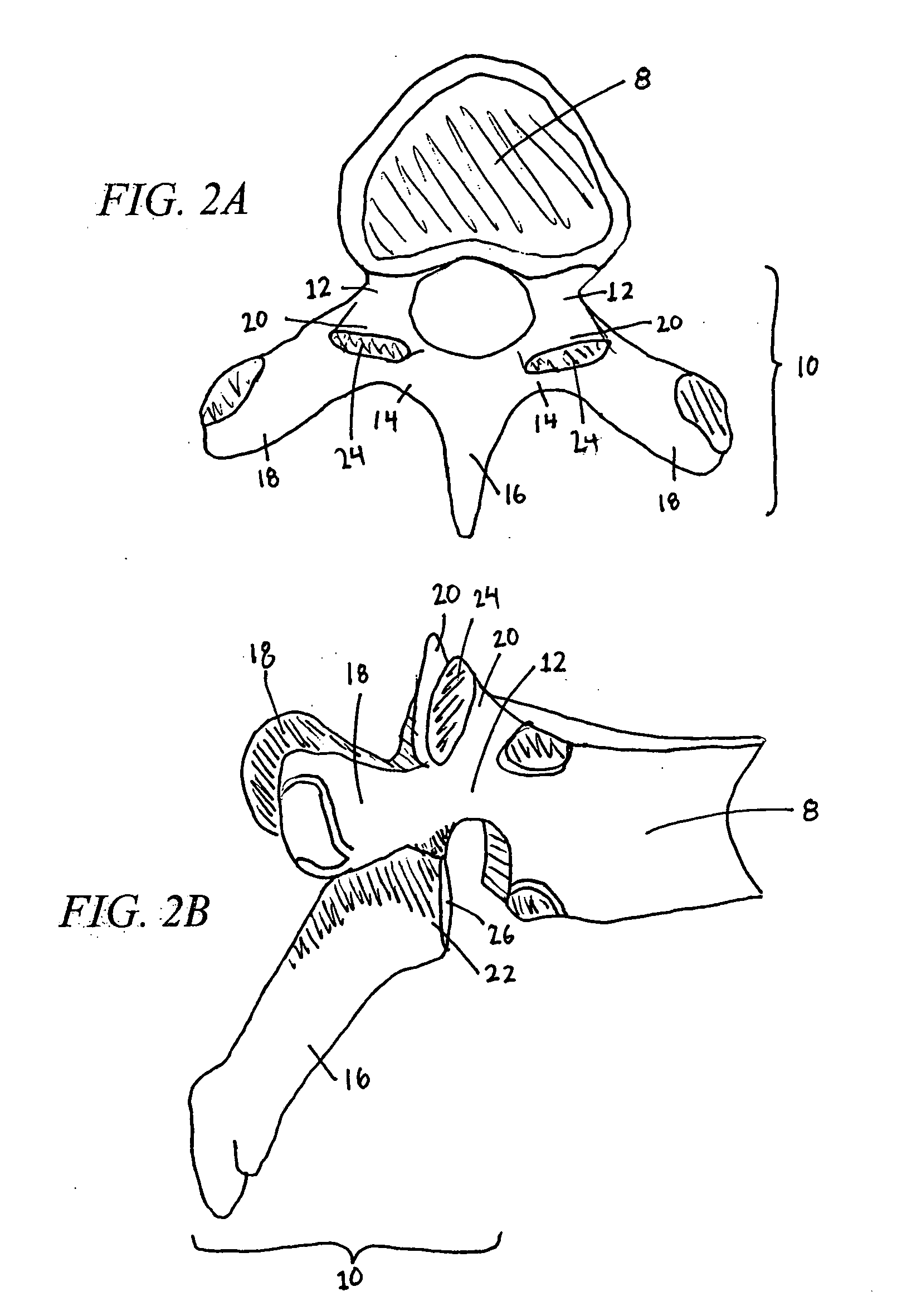
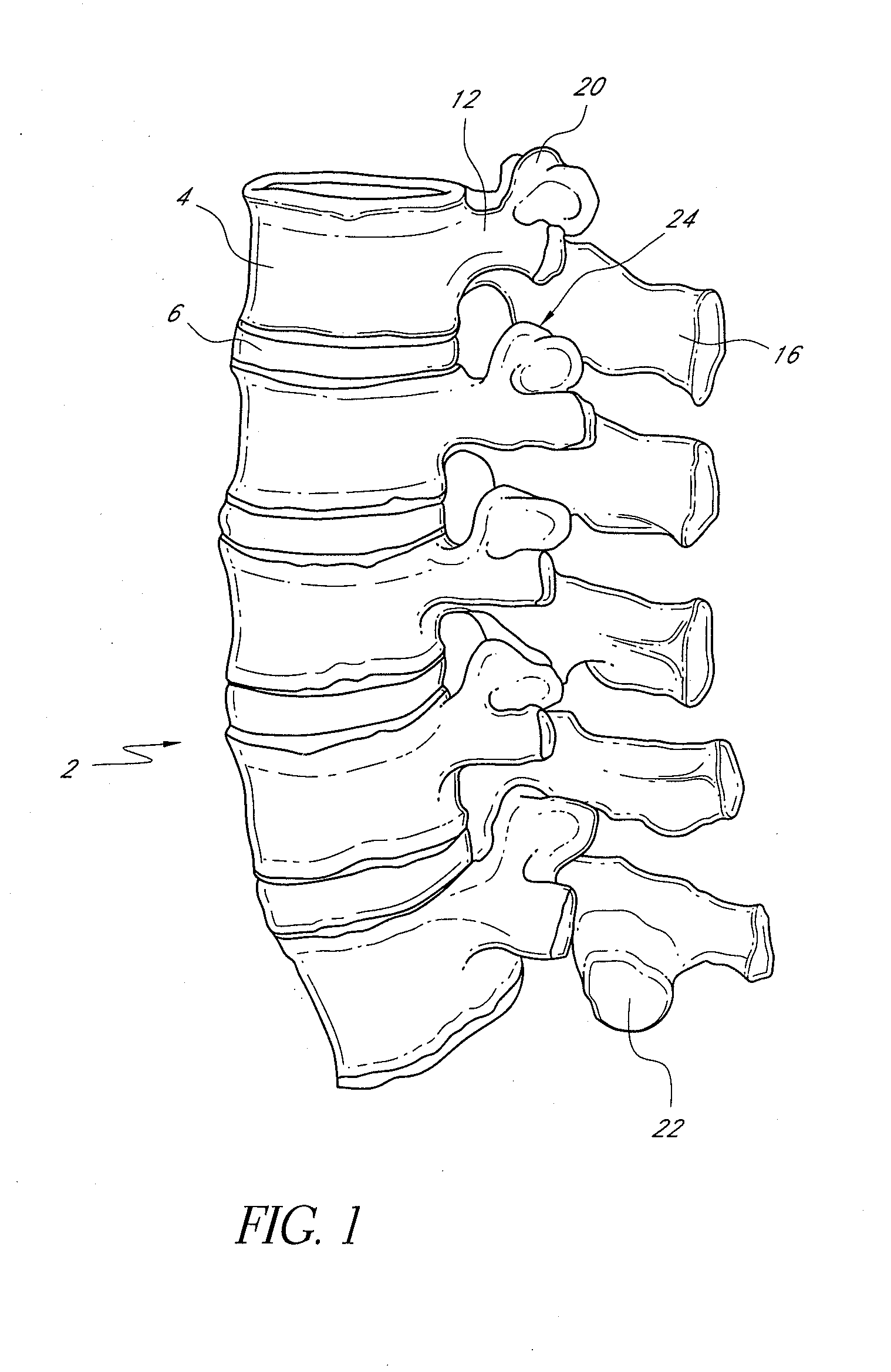
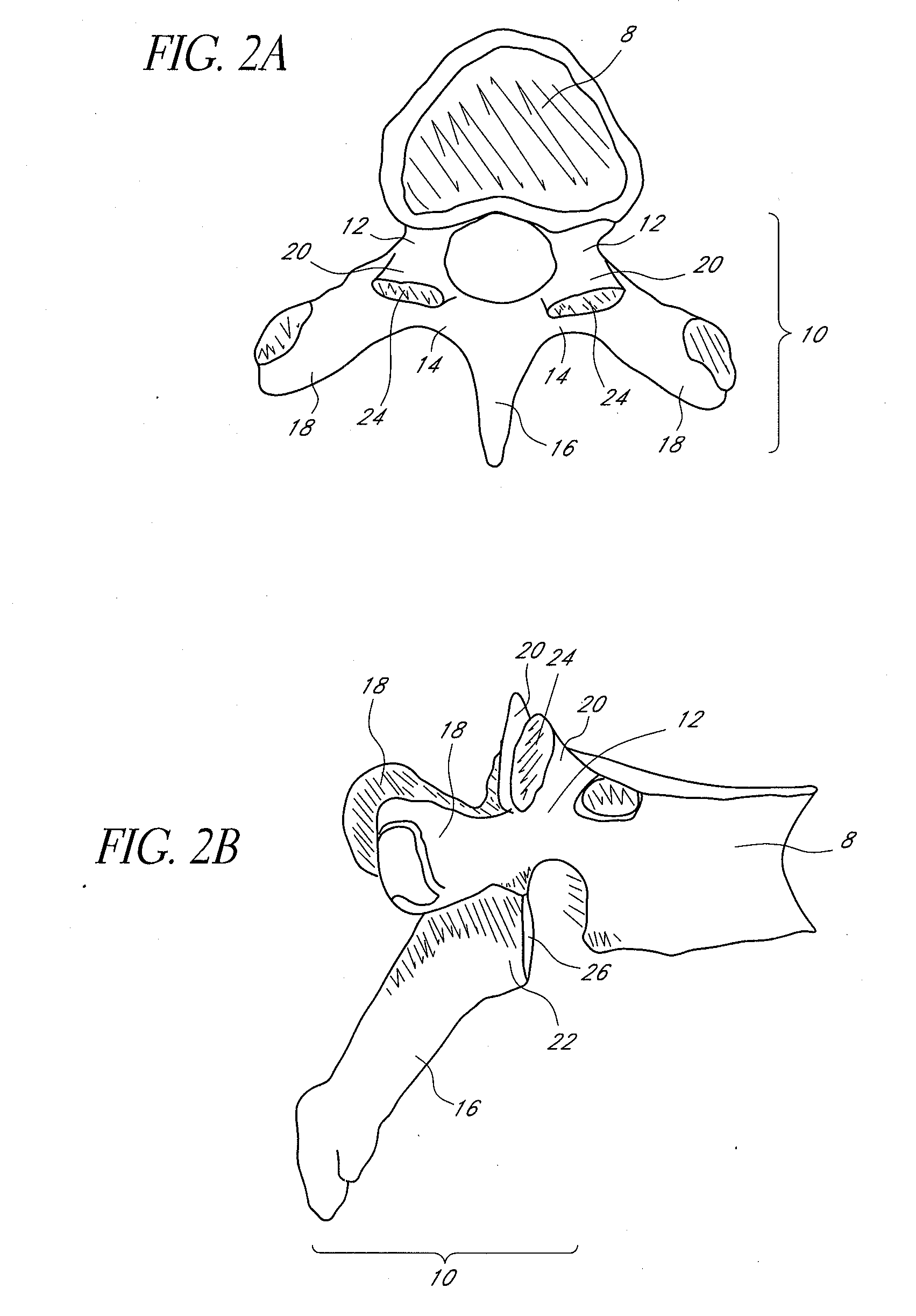
Vertebral facet joint prosthesis and method of fixation
ActiveUS20050177240A1Reduce contactMaintain liquidityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFacet joint prosthesisArticular processes
Devices and methods for altering the spacing and motion at the facet joints of the vertebral column are provided. One embodiment of the invention comprises a prosthesis with surfaces configured to articulate with the facets of the facet joint. A retaining member for anchoring the prosthesis within the facet joint is optionally included. Methods for surgically and less invasively implanting the prosthesis and securing the prosthesis to the articular processes or surrounding soft tissue are also provided.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
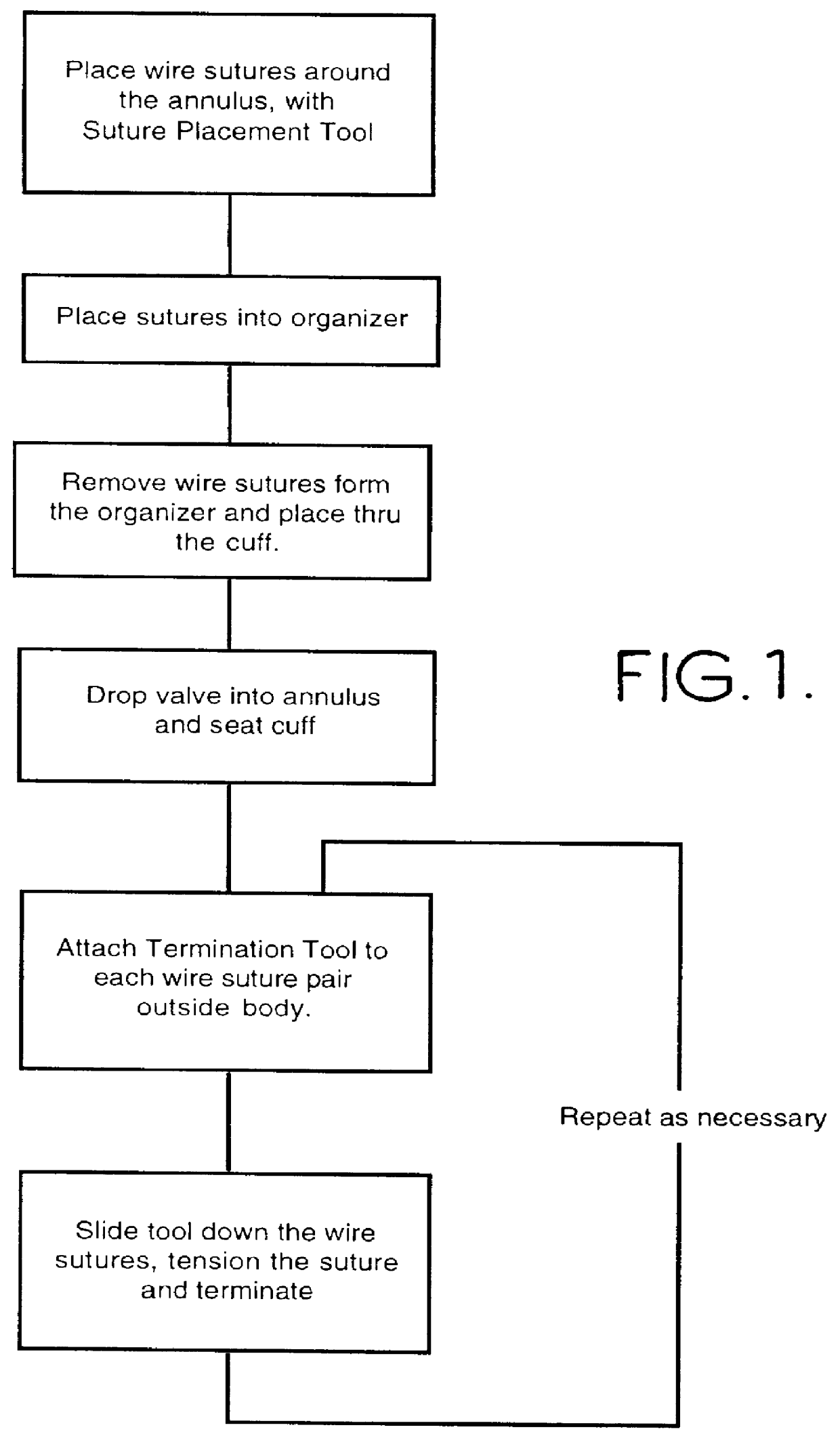
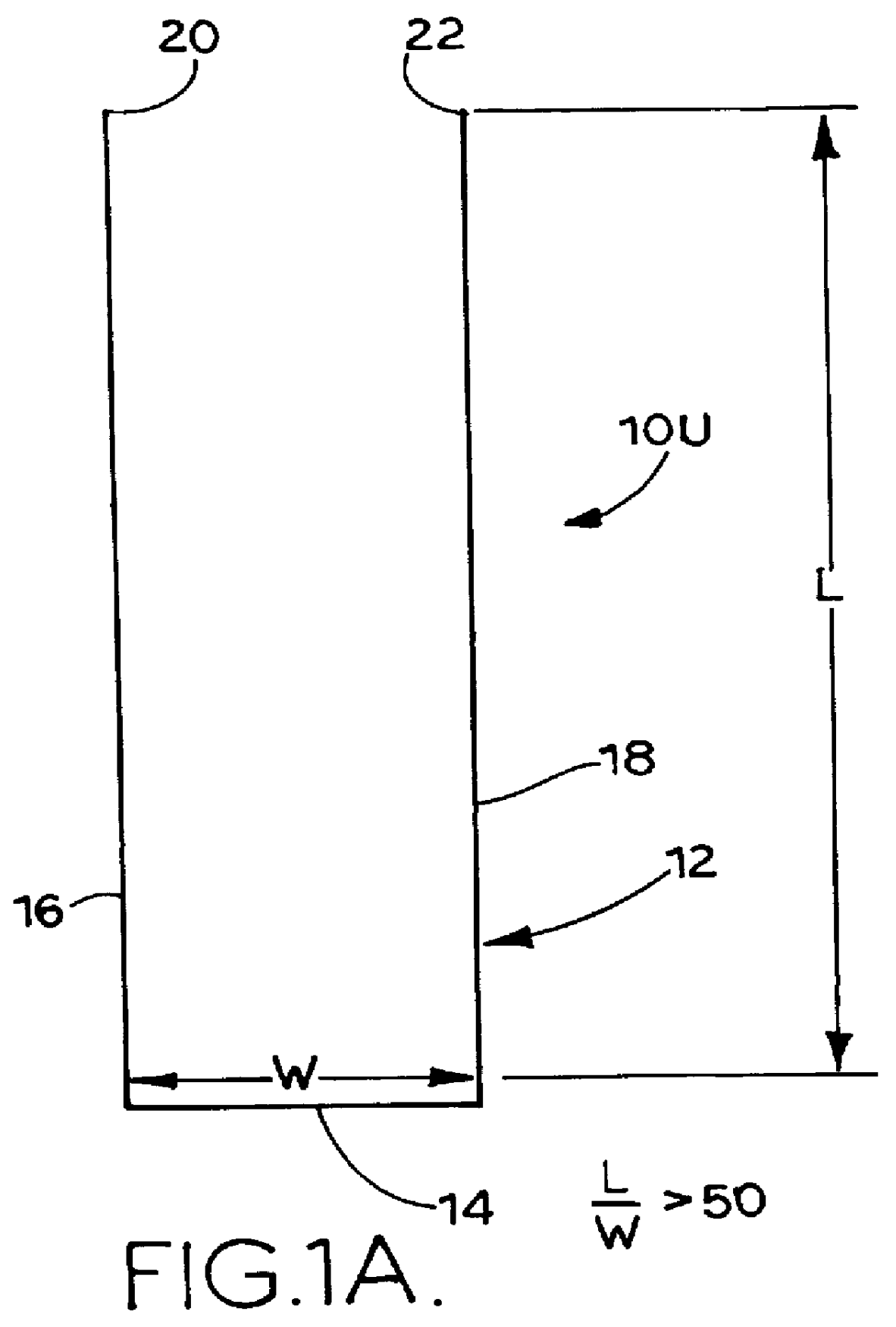
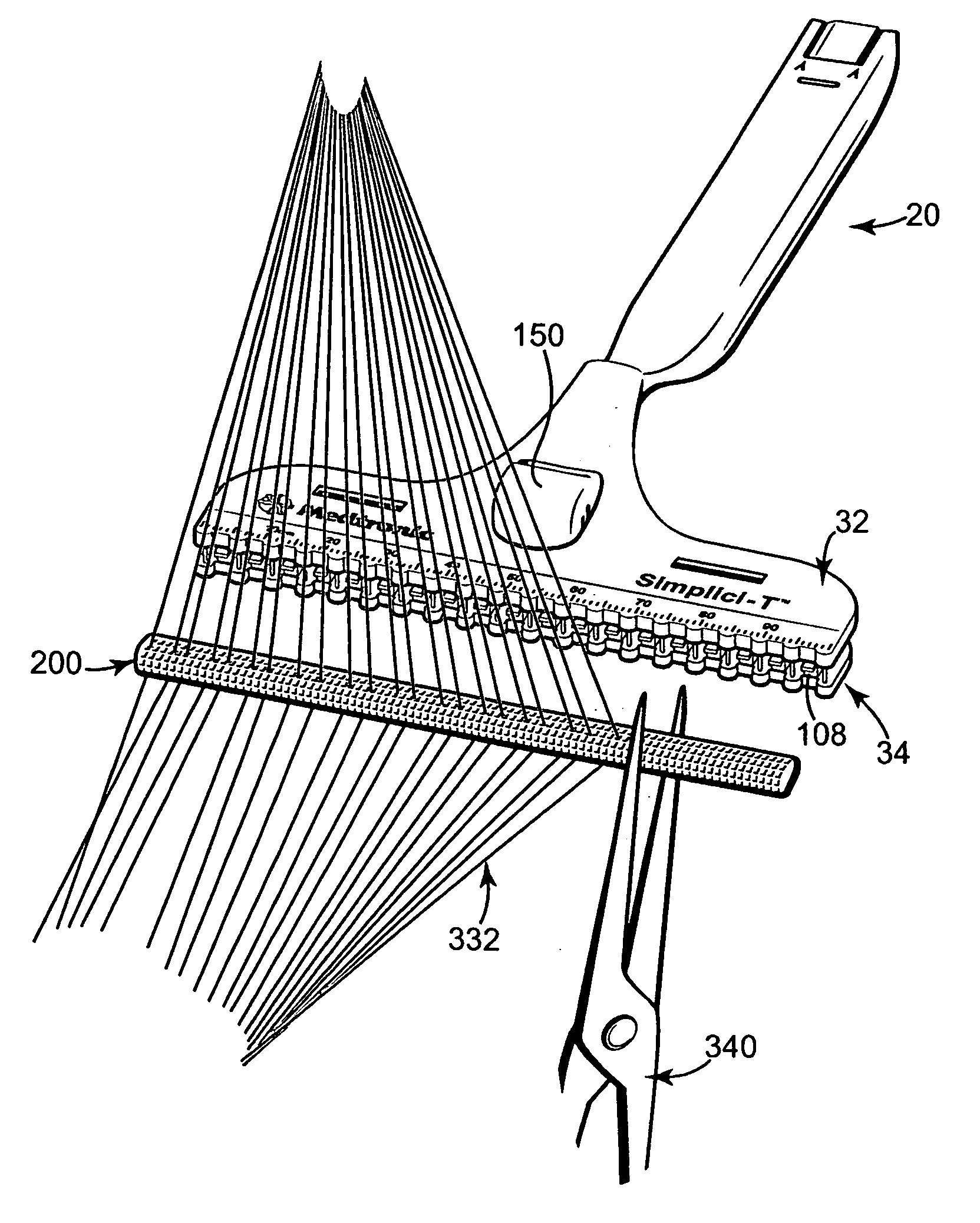
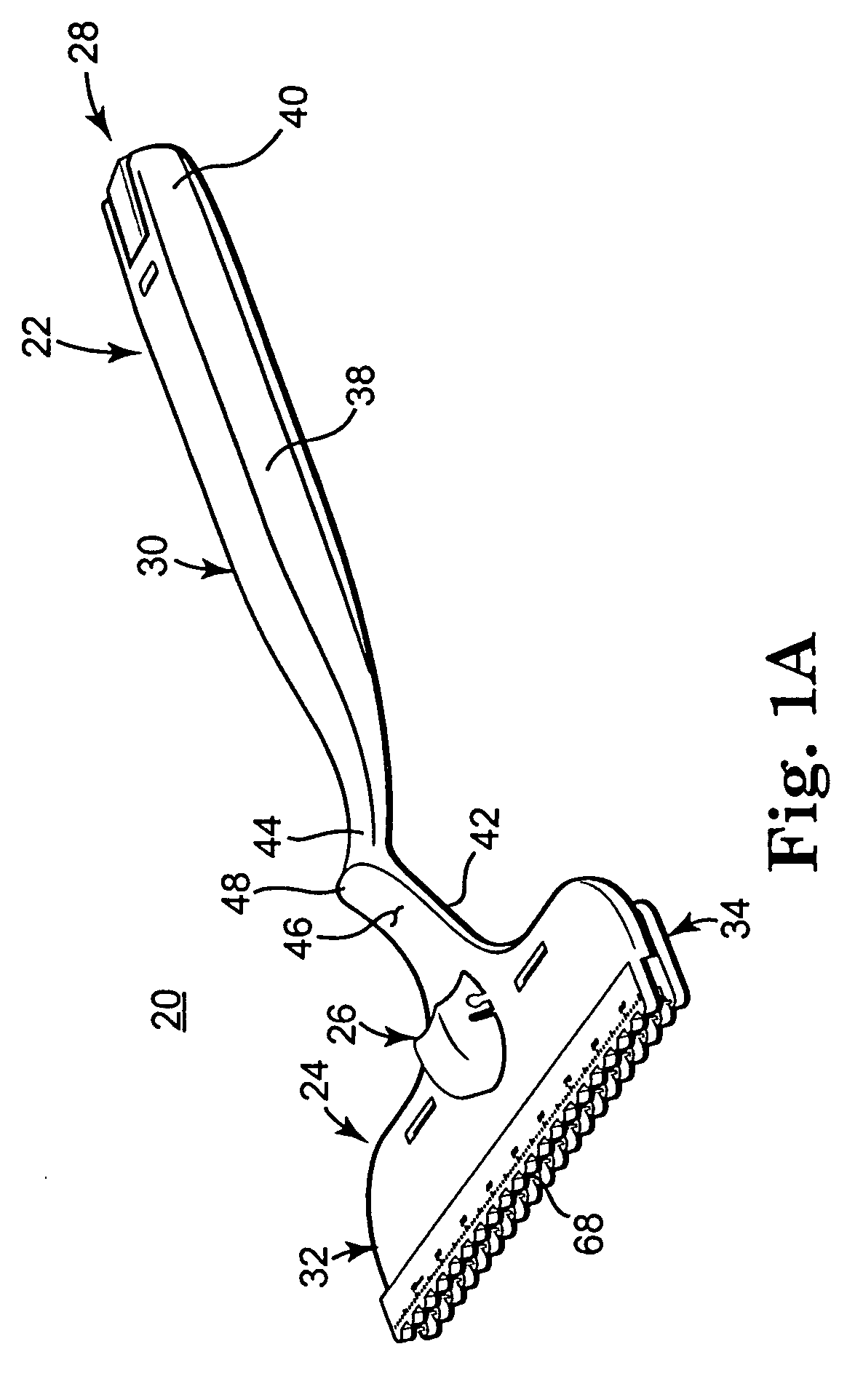
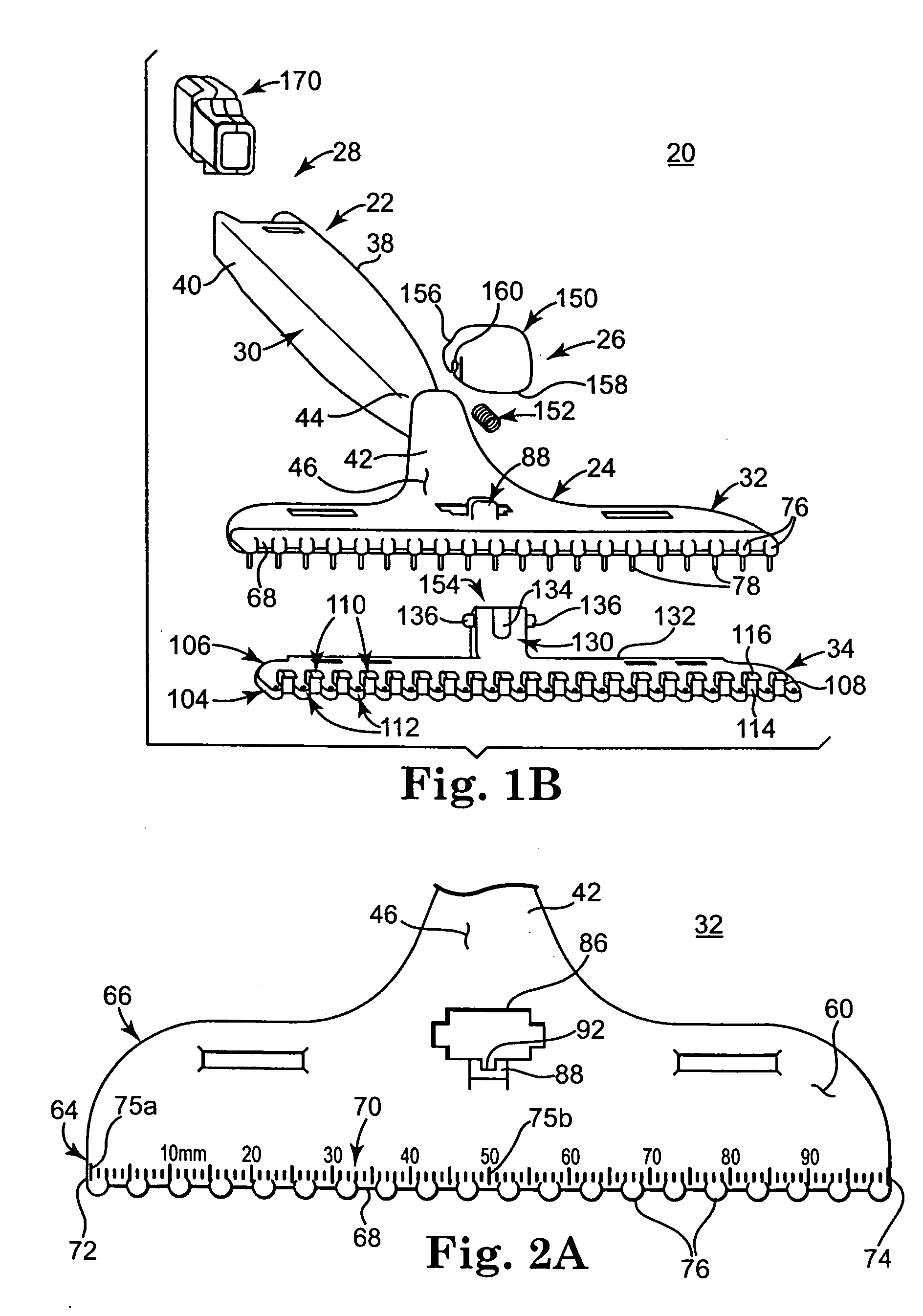
Wire fasteners for use in minimally invasive surgery and means and methods for handling those fasteners
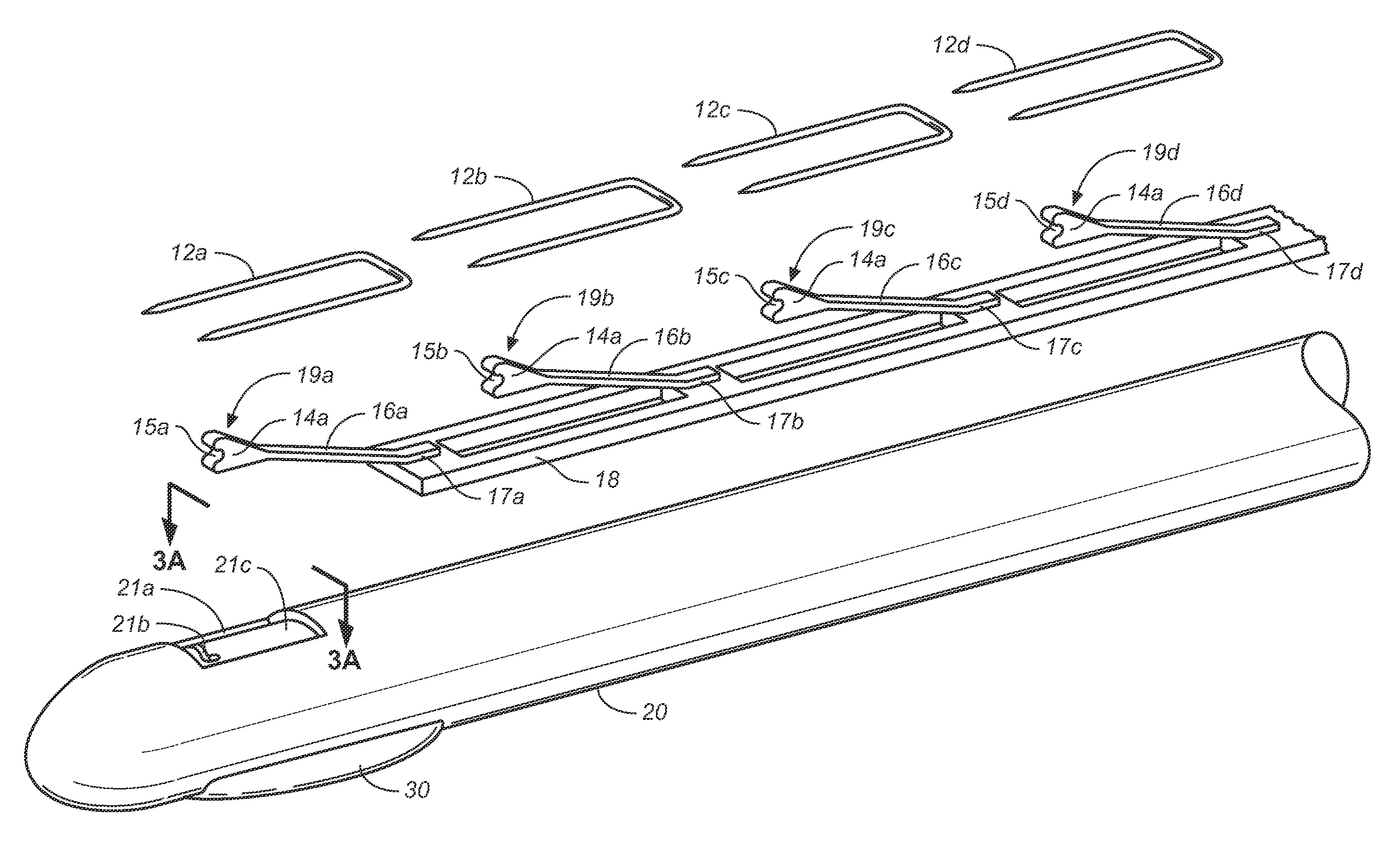
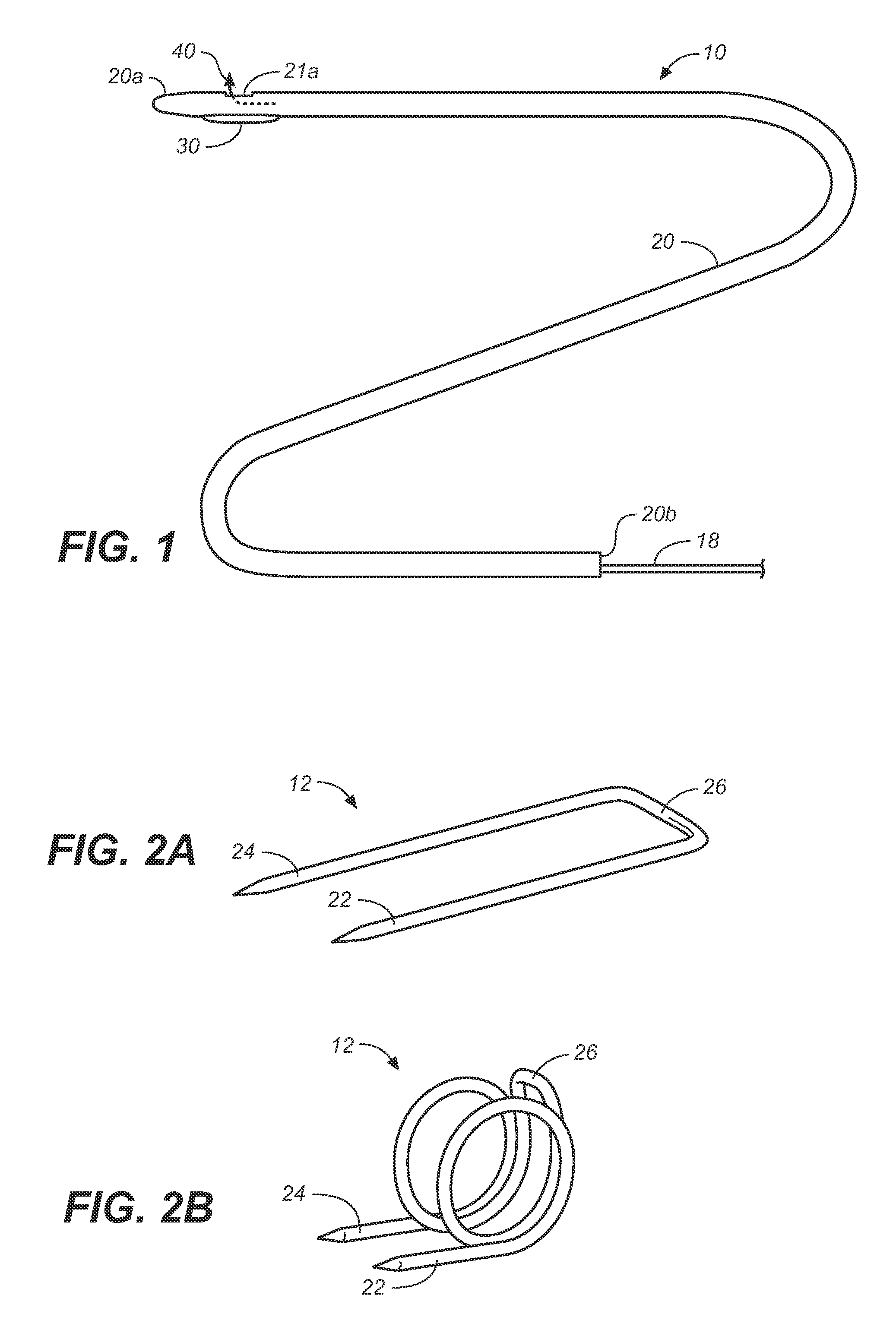
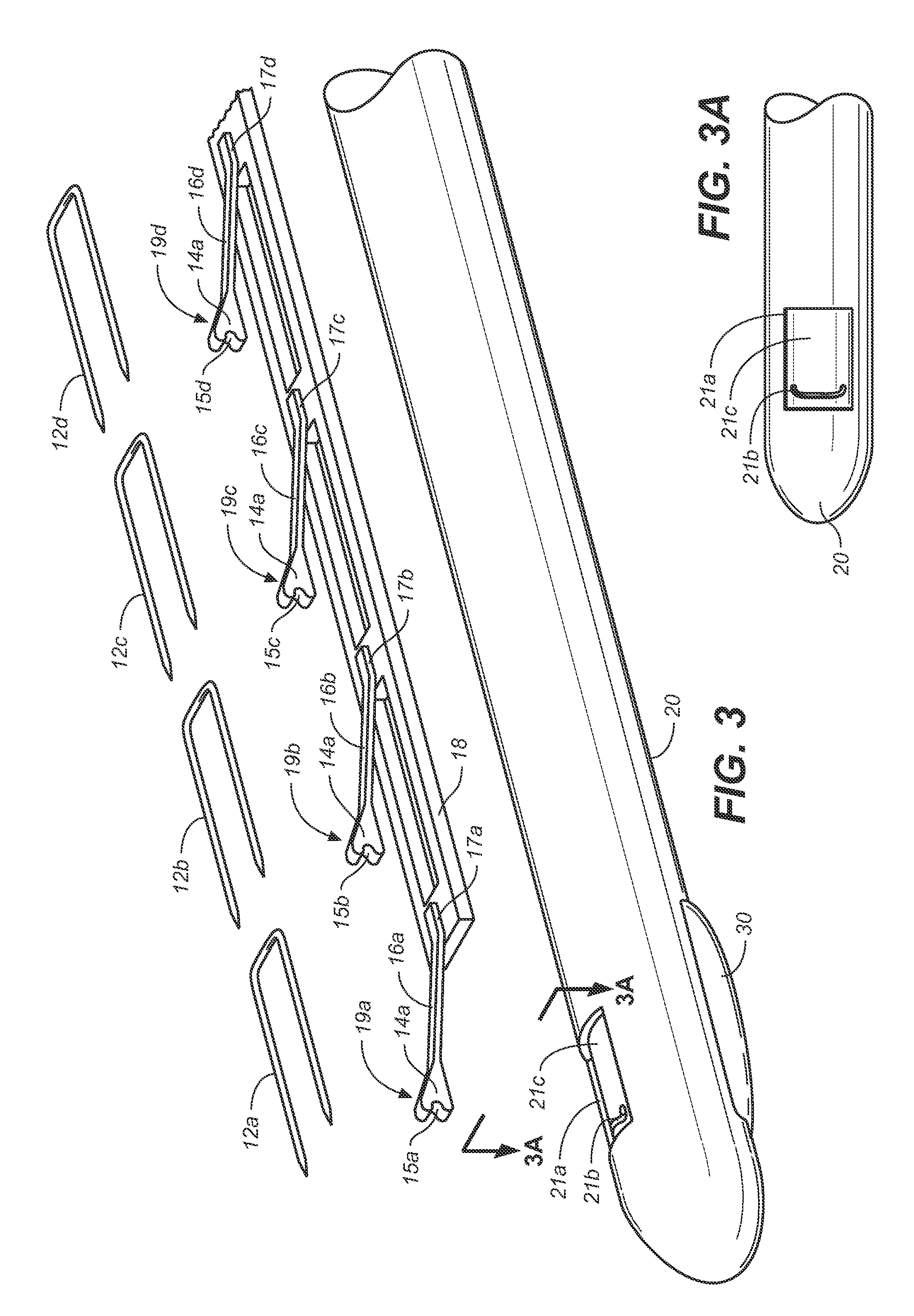
Wire fasteners having legs with lengths that can be one hundred times the width of the fastener are used to secure items, such as prosthesis valves to a patient during minimally invasive surgery. The fasteners are manipulated into position and then are immobilized by the legs thereof for tensioning, cutting and forming in situ. The fasteners are manipulated, tensioned and formed from the leg end of the fasteners. Tools for initially placing the fasteners and for immobilizing, tensioning, cutting and bending the fastener legs are disclosed. Once the fasteners are initially placed, the prosthesis is placed on the long legs of the placed fasteners and is guided into position on the legs. Once the prosthesis is in position, the legs of the fasteners are immobilized, tensioned, cut and bent into staple-like shapes to secure the prosthesis to the patient. A method for carrying out the procedure using the long fastener is also disclosed. Using the teaching of the present disclosure, a surgeon can customize a fastener to the particular surgery or even to the particular portion of surgery being performed during the surgery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Prosthesis Fixation Apparatus and Methods
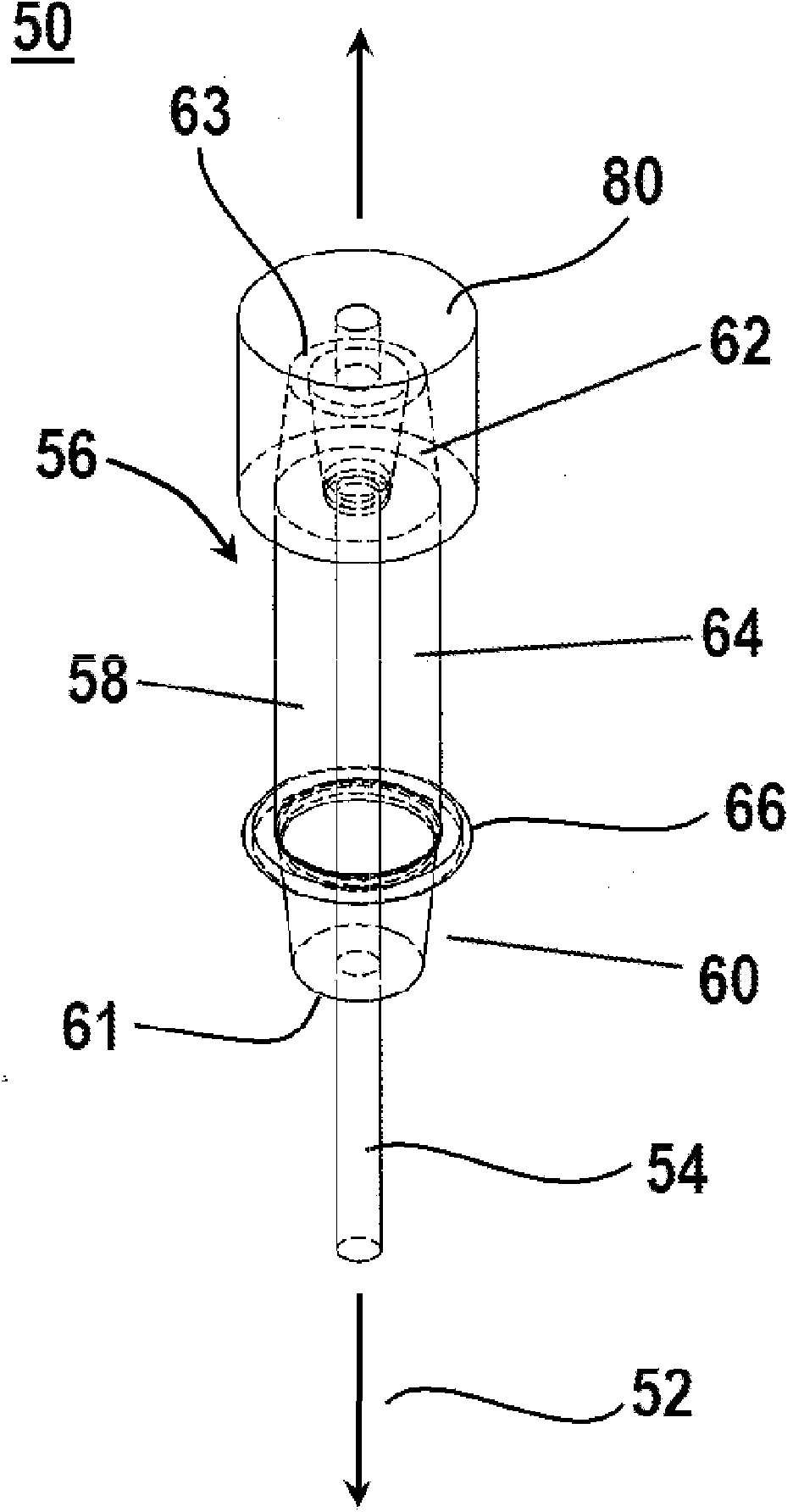
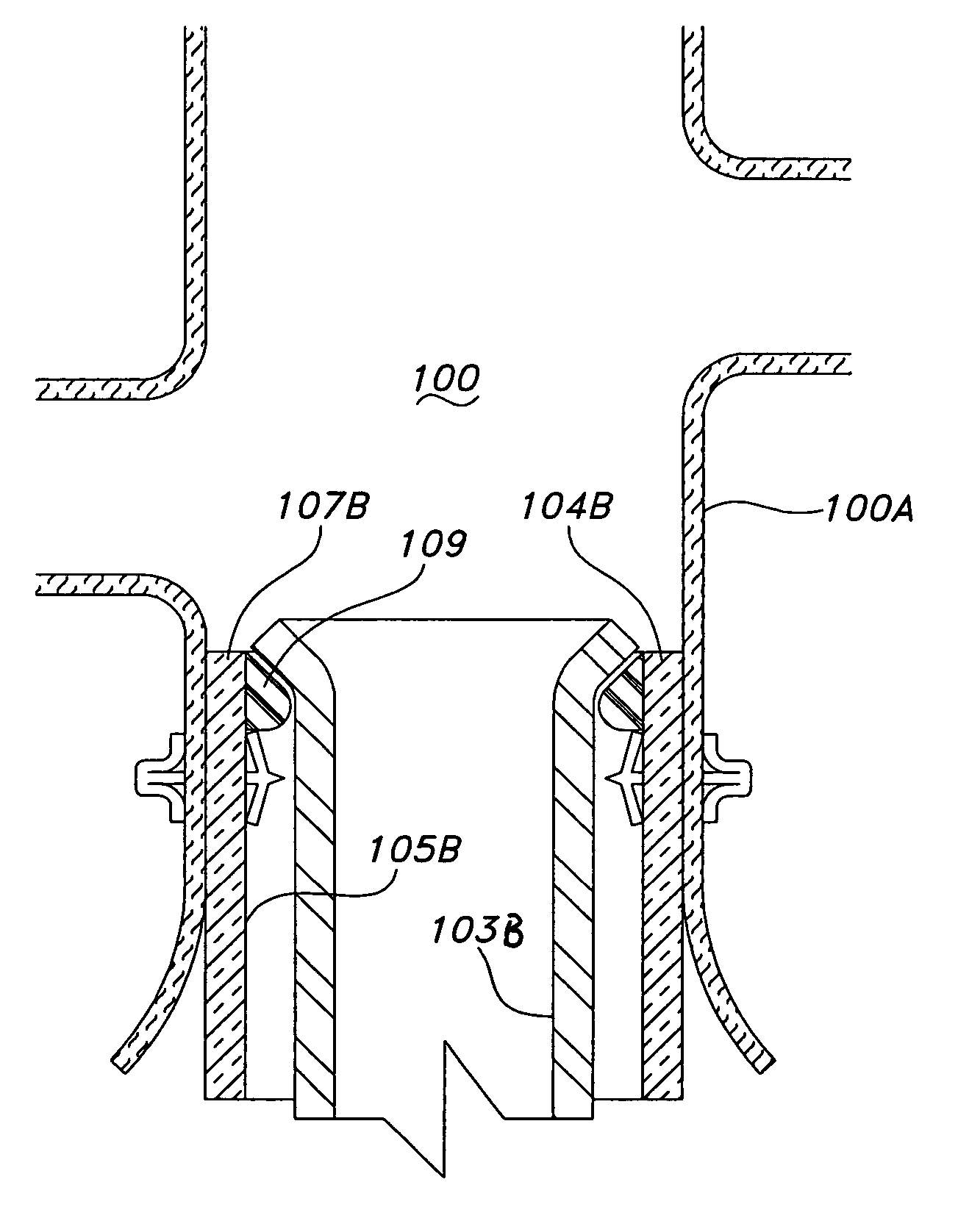
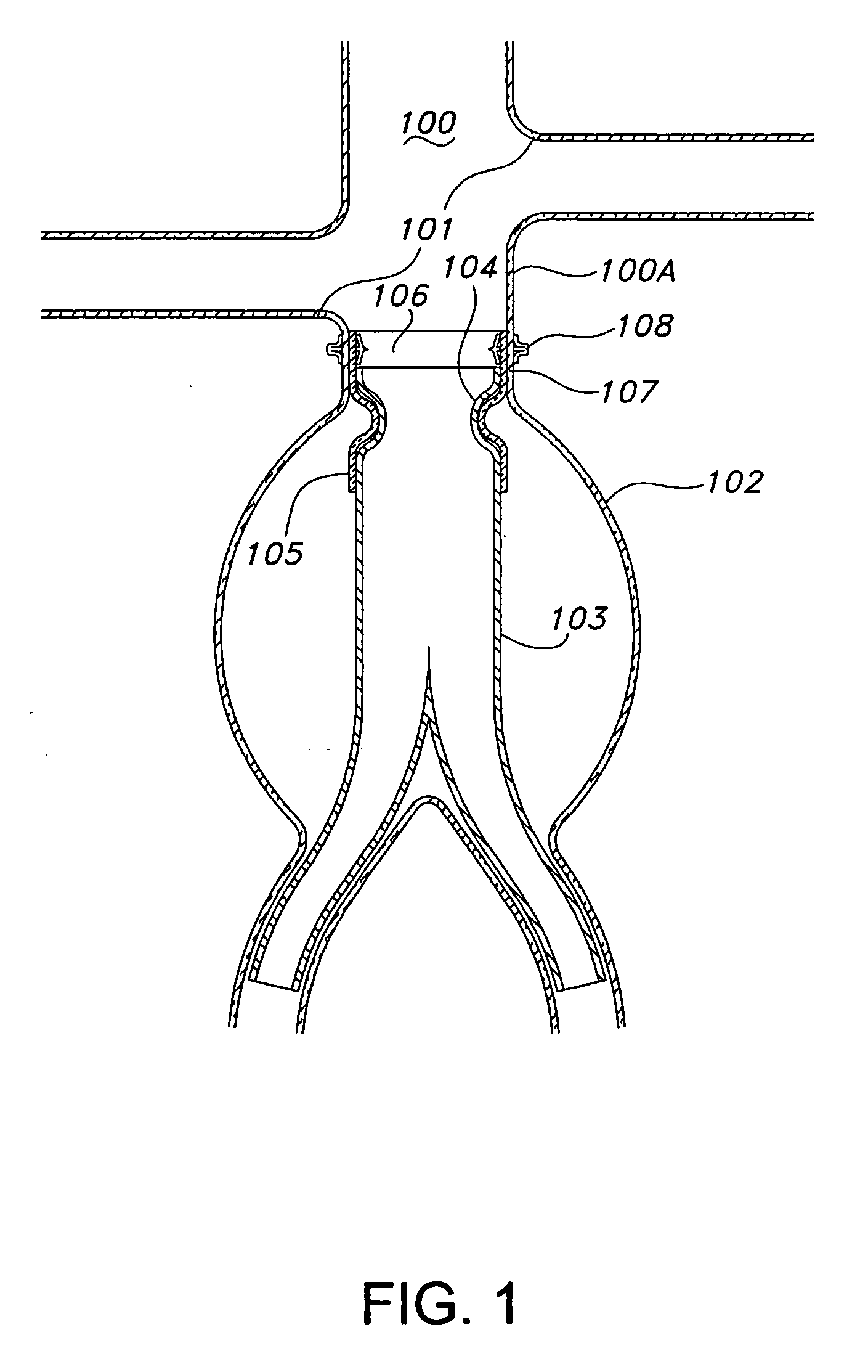
Endovascular fastener delivery apparatus comprises a flexible elongated member having a proximal end and a distal end and being configured and adapted to be endolumenally advanced through human vasculature, a flexible pusher member slidably coupled to the elongated member, and a plurality of serially aligned clip carriers secured to the pusher member, each clip carrier comprising a spring element and having a leading end adapted to seat a fastener and a trailing end fixedly secured to the pusher member. In one embodiment, a plurality of bridge clip fasteners are endolumenally advanced to a site in a lumen in a human body and the fasteners are passed from an inner surface of the prosthesis through the prosthesis and a wall of the lumen to secure the prosthesis to the lumen wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Prosthesis fixation device and method
A prosthesis anchor is adapted to convert a previously untreatable anatomy into a more typical and treatable condition. Preferably, the anchor is adapted to be transported endoluminally to a deployment site in a body lumen. The anchor includes a landing section for securing the anchor at a relatively fixed position in the lumen, and a docking section adapted to receive a mating prosthesis the landing section of the anchor may be permanently affixed to the lumen by a variety of mechanical and / or adhesive fixation means.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI +1
Vertebral facet joint prosthesis and method of fixation
ActiveUS20090204152A1Reduce contactMaintain liquidityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnFacet joint prosthesis
Devices and methods for altering the spacing and motion at the facet joints of the vertebral column are provided. One embodiment of the invention comprises a prosthesis with surfaces configured to articulate with the facets of the facet joint. A retaining member for anchoring the prosthesis within the facet joint is optionally included. Methods for surgically and less invasively implanting the prosthesis and securing the prosthesis to the articular processes or surrounding soft tissue are also provided.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Prosthesis Fixation Apparatus and Methods
A method of securing a prosthesis placed at a desired site in a passageway of a human body comprises delivering a fastener having a proximal piercing end portion and a distal piercing end portion to a site where a prosthesis having a tubular wall has been placed in the passageway, which has a wall, advancing the proximal piercing end portion beyond the prosthesis, penetrating the proximal piercing end portion into the wall of the passageway without passing the proximal piercing end portion through the tubular wall of the prosthesis, and passing the distal piercing end portion through the tubular wall of the prosthesis and into the wall of the passageway. One surgical fastener delivery apparatus for delivering a surgical fastener to a target site comprises a support having a first end, a second end, and a longitudinal axis and being adapted for placement in a passageway in a human body. A surgical fastener having a first piercing end portion, a second piercing end portion and a central portion extending therebetween and having a longitudinal axis is releasably mounted to the support with the central portion longitudinal axis generally parallel to the support longitudinal axis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
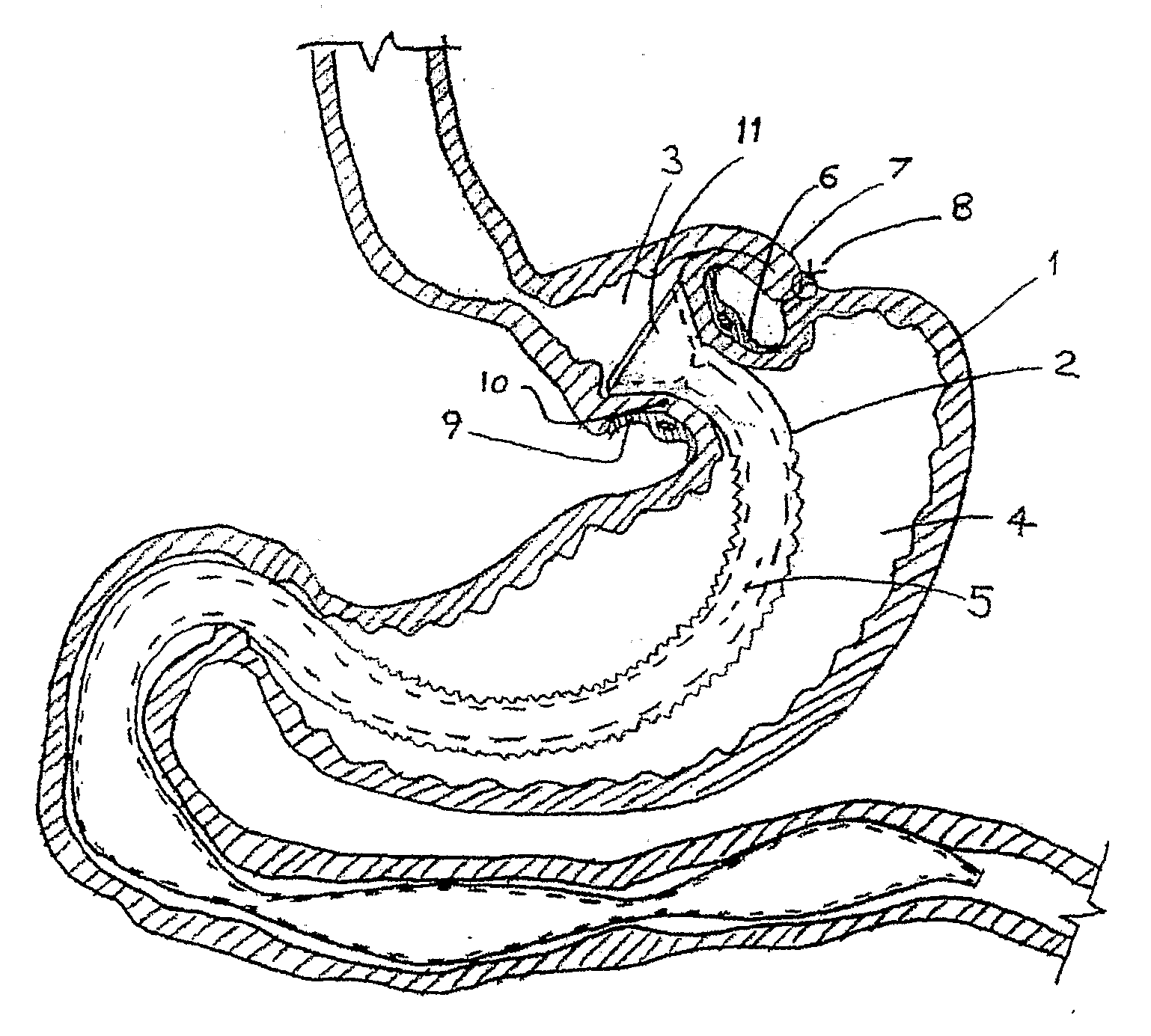
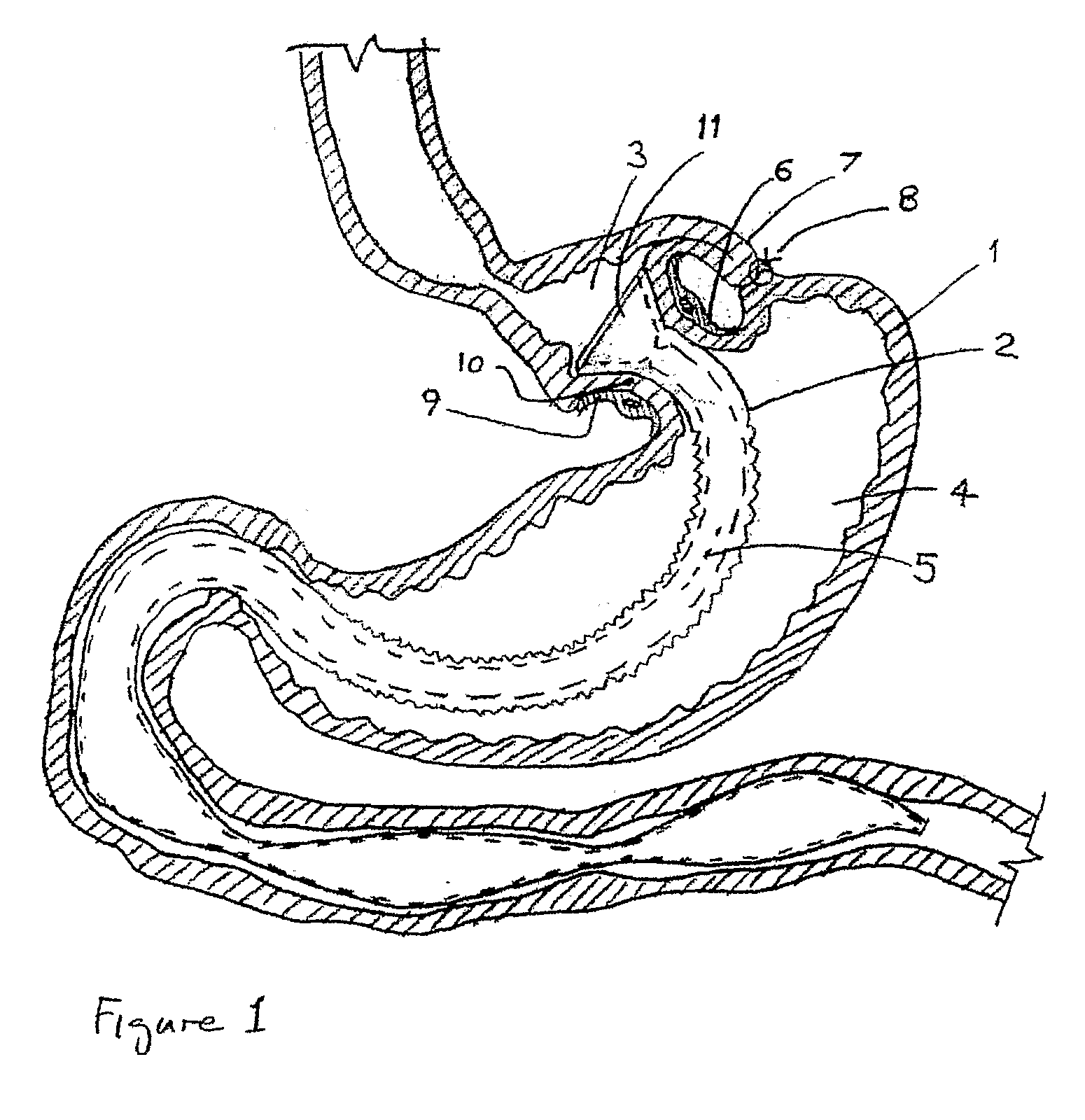
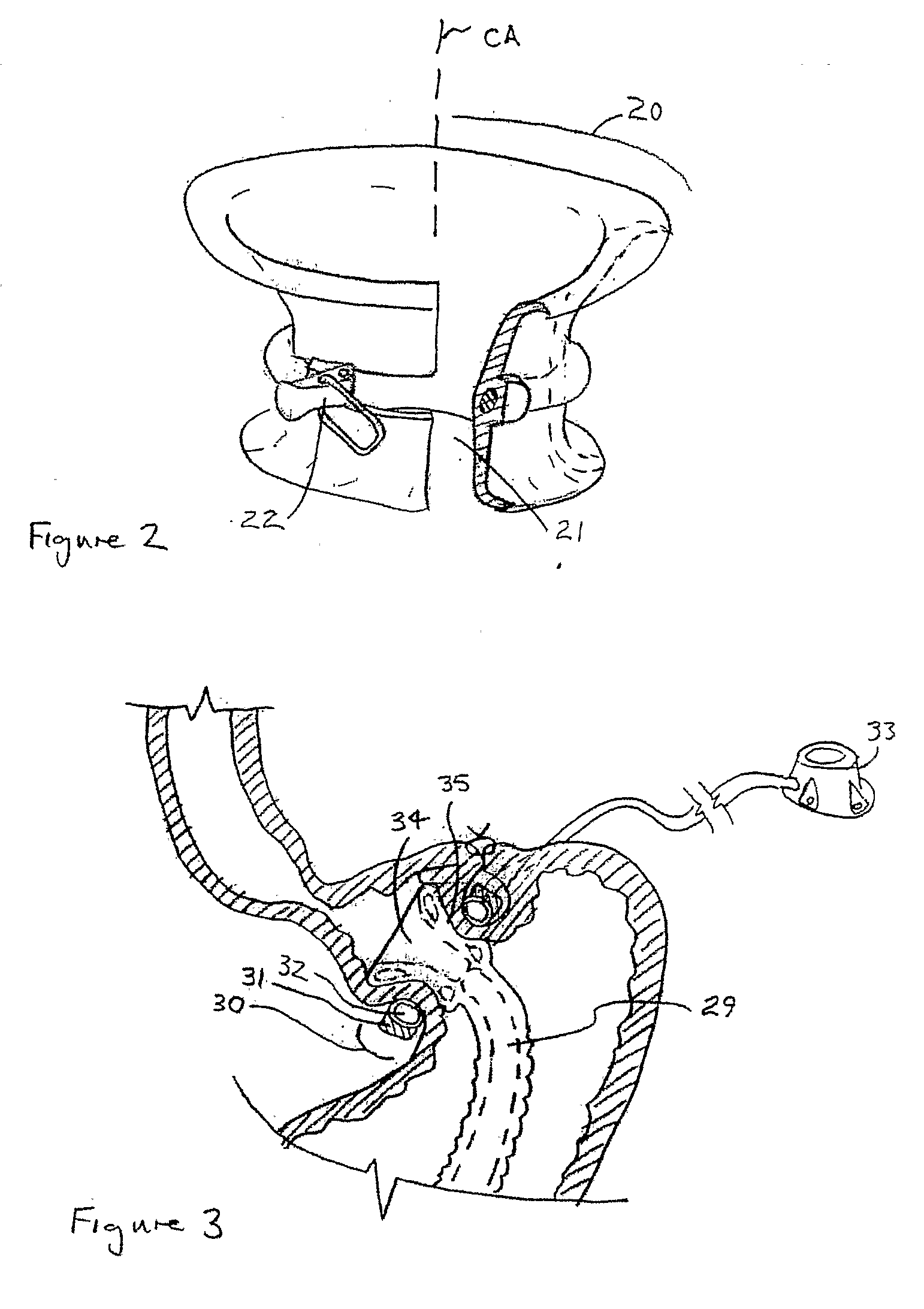
Gastric bypass prosthesis fixation system and method for treatment of obesity
InactiveUS20090216337A1Facilitate rapidFacilitate early weight lossIntravenous devicesTubular organ implantsSurgical treatmentGastric bypass
An improved gastric bypass prosthetic (GBP) device and an improved GBP fixation device, as well as a GBP kit for the surgical treatment of obesity. In one form, a gastric bypass prosthetic (GBP) device of the invention includes a optional flexible tube extending along a central axis from a proximal end to a distal end, and having a tubular tissue fixation portion at or near said proximal end. The tissue fixation portion extends along the central axis between a proximal end and a distal end of the tissue fixation portion, and has an annular outer surface between the proximal end and the distal end of the tissue fixation portion.
Owner:GASTRX MEDICAL
Bone anchor fixture for a medical prosthesis
ActiveUS20090023109A1Improve initial stabilityDental implantsBone conduction transducer hearing devicesProsthesisSkull bone
A screw-shaped anchoring fixture for anchoring a prosthesis in the skull bone. The anchoring fixture comprises a main body configured to be implanted into the bone and a flange configured to function as a stop to prevent the main body from completely penetrating through the bone. The main body comprises a distal tapered apical portion, a first portion, and a second portion. The inner diameter of the second portion is greater than the inner diameter of the first portion. The method for inserting the anchoring fixture includes providing the anchoring fixture, drilling a hole, and inserting the anchoring fixture into the hole until the flange contacts the skull bone, wherein the hole has a diameter that is greater than the inner diameter of the first portion and less than the outer diameter of the second portion.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
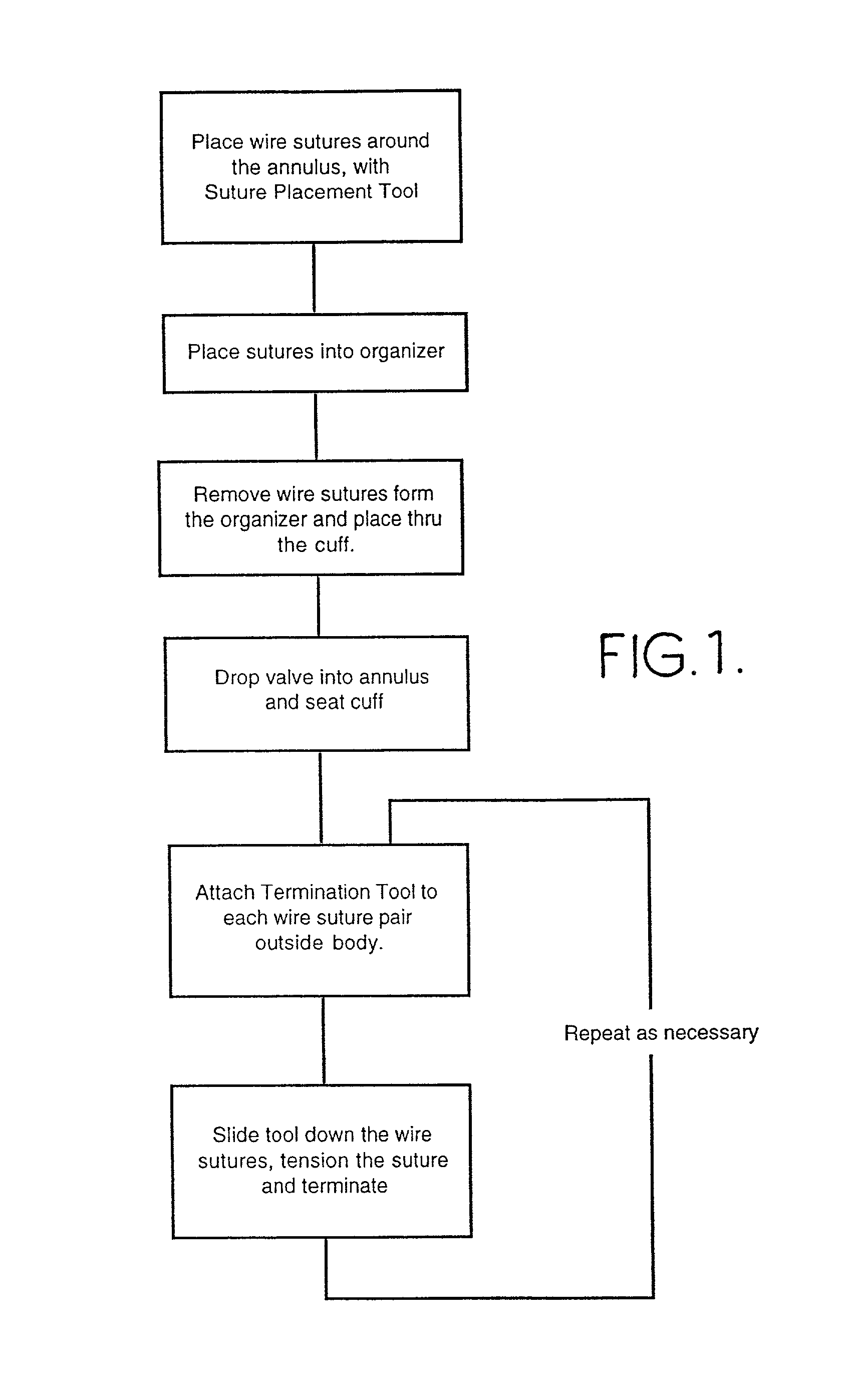
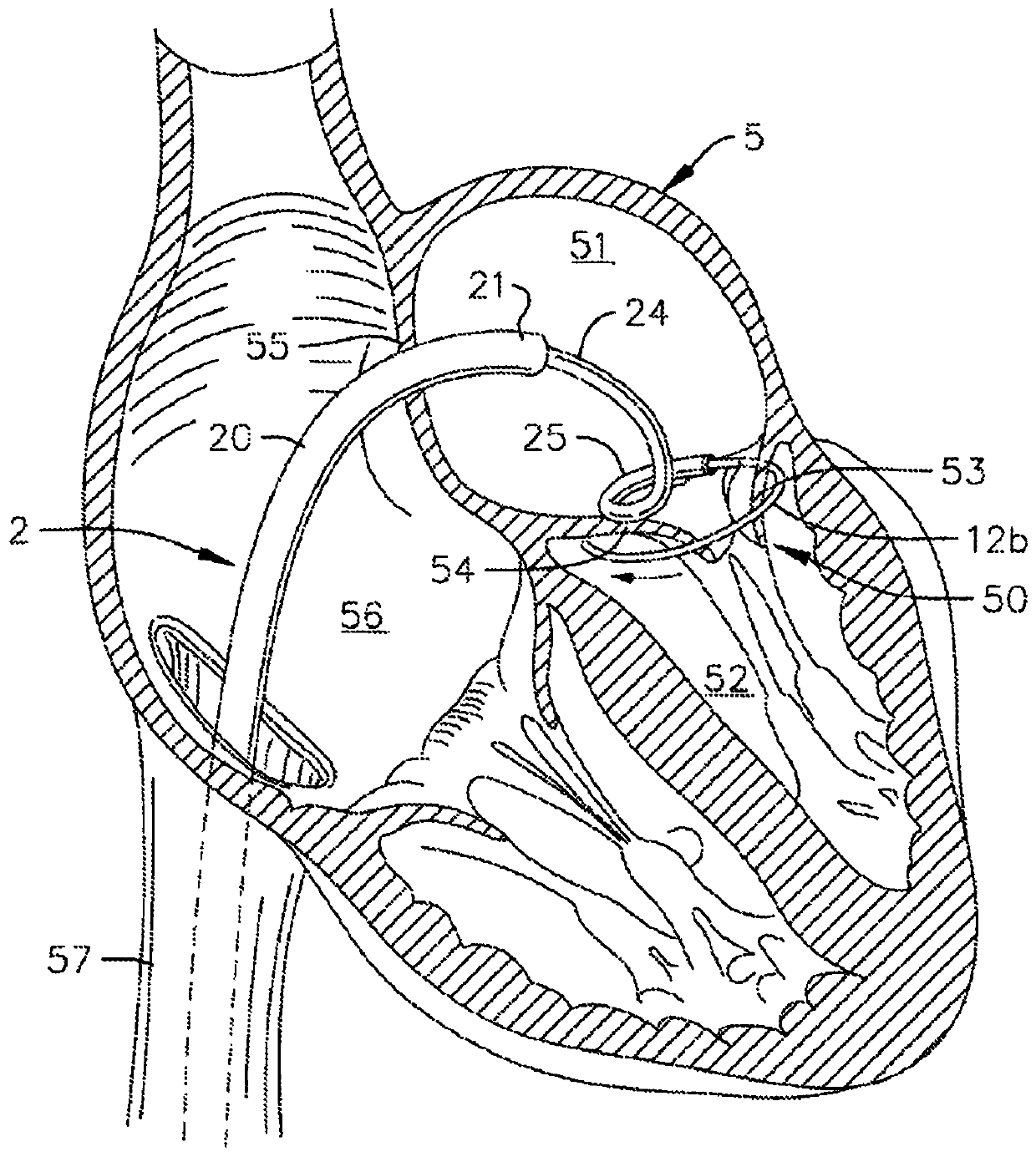
Method of implanting an annuloplasty prosthesis
ActiveUS20070078514A1Conveniently and efficiently releasingConveniently accomplishedSuture equipmentsEar treatmentSharp InstrumentsImplantable prosthesis
A simplified and more easily employed tool for holding an implantable annuloplasty prosthesis during passage of sutures through the prosthesis and for conveniently and efficiently releasing the prosthesis from the tool. Separation of the implantable prosthesis and the tool may be conveniently accomplished without requiring the use of a sharp instrument. Attachment between the prosthesis and its surgical carrying tool can be accomplished in a suture-less fashion. The tool includes a suture management device in some embodiments for selectively receiving and maintaining sutures otherwise securing the prosthesis to tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Extremely long wire fasteners for use in minimally invasive surgery and means and method for handling those fasteners
Wire fasteners having legs with lengths that can be one hundred times the width of the fastener are used to secure items, such as prosthesis valves to a patient during minimally invasive surgery. The fasteners are manipulated into position and then are immobilized by means of the legs thereof for tensioning, cutting and forming in situ. The fasteners are manipulated, tensioned and formed from the leg end of the fasteners. Tools for initially placing the fasteners and for immobilizing, tensioning, cutting and bending the fastener legs are disclosed. Once the fasteners are initially placed, the prosthesis is placed on the long legs of the placed fasteners and is guided into position on the legs. Once the prosthesis is in position, the legs of the fasteners are immobilized, tensioned, cut and bent into staple-like shapes to secure the prosthesis to the patient. A method for carrying out the procedure using the long fastener is also disclosed. Using the teaching of the present disclosure, a surgeon can customize a fastener to the particular surgery or even to the particular portion of surgery being performed during the surgery.
Owner:WILLIAMSON WARREN P IV +4
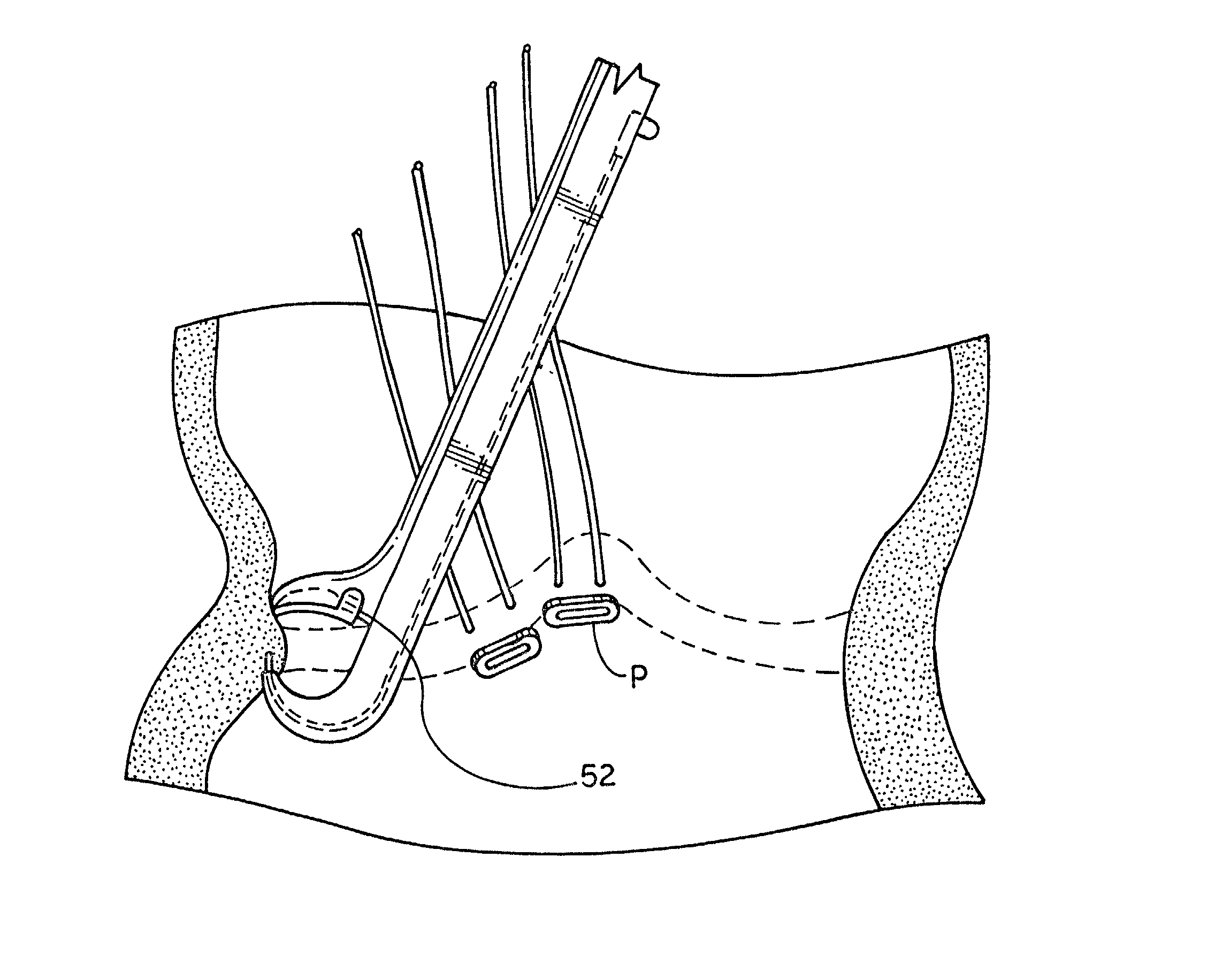
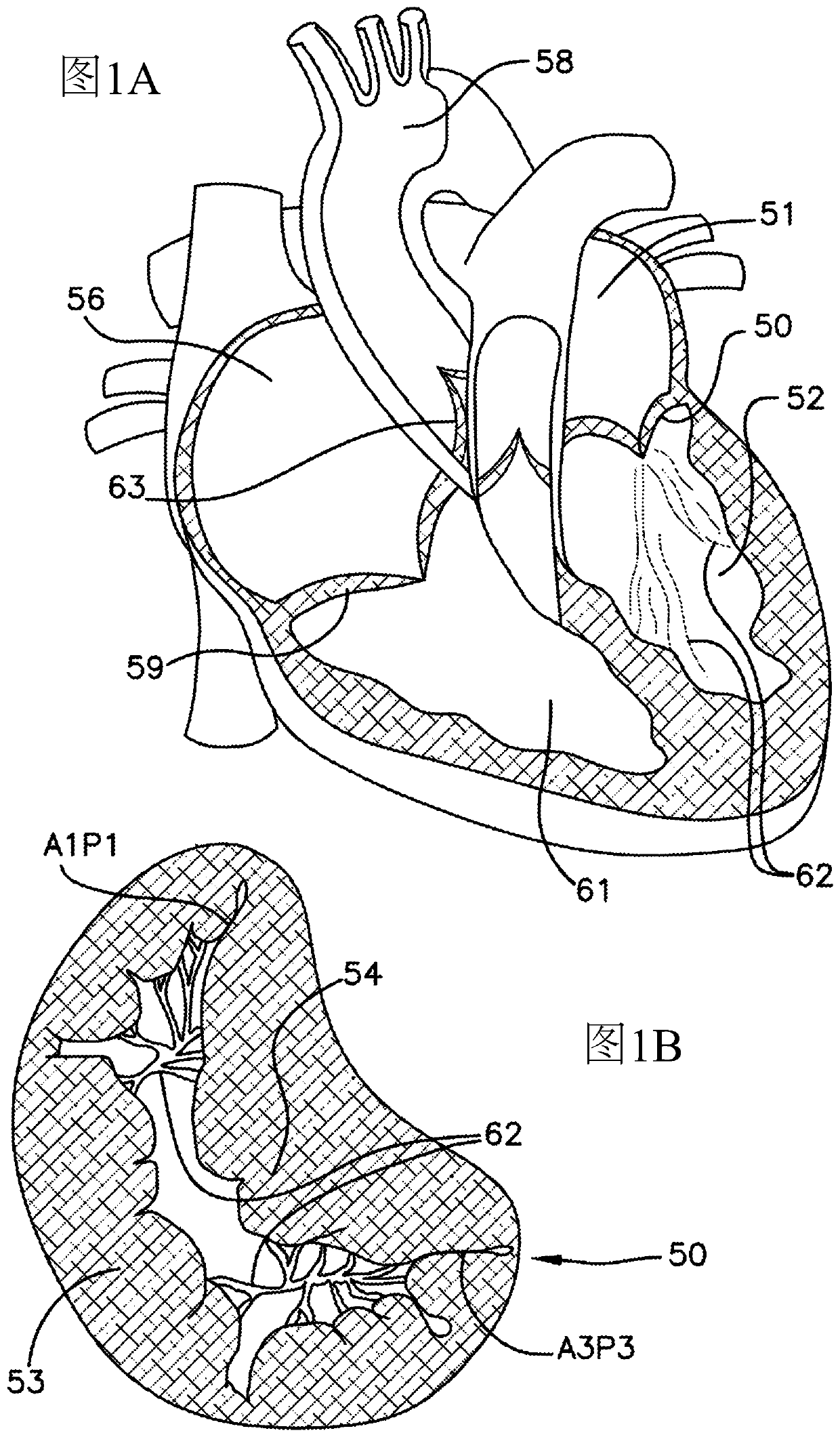
Methods for anchoring a heart valve prosthesis in a transcatheter valve implantation procedure
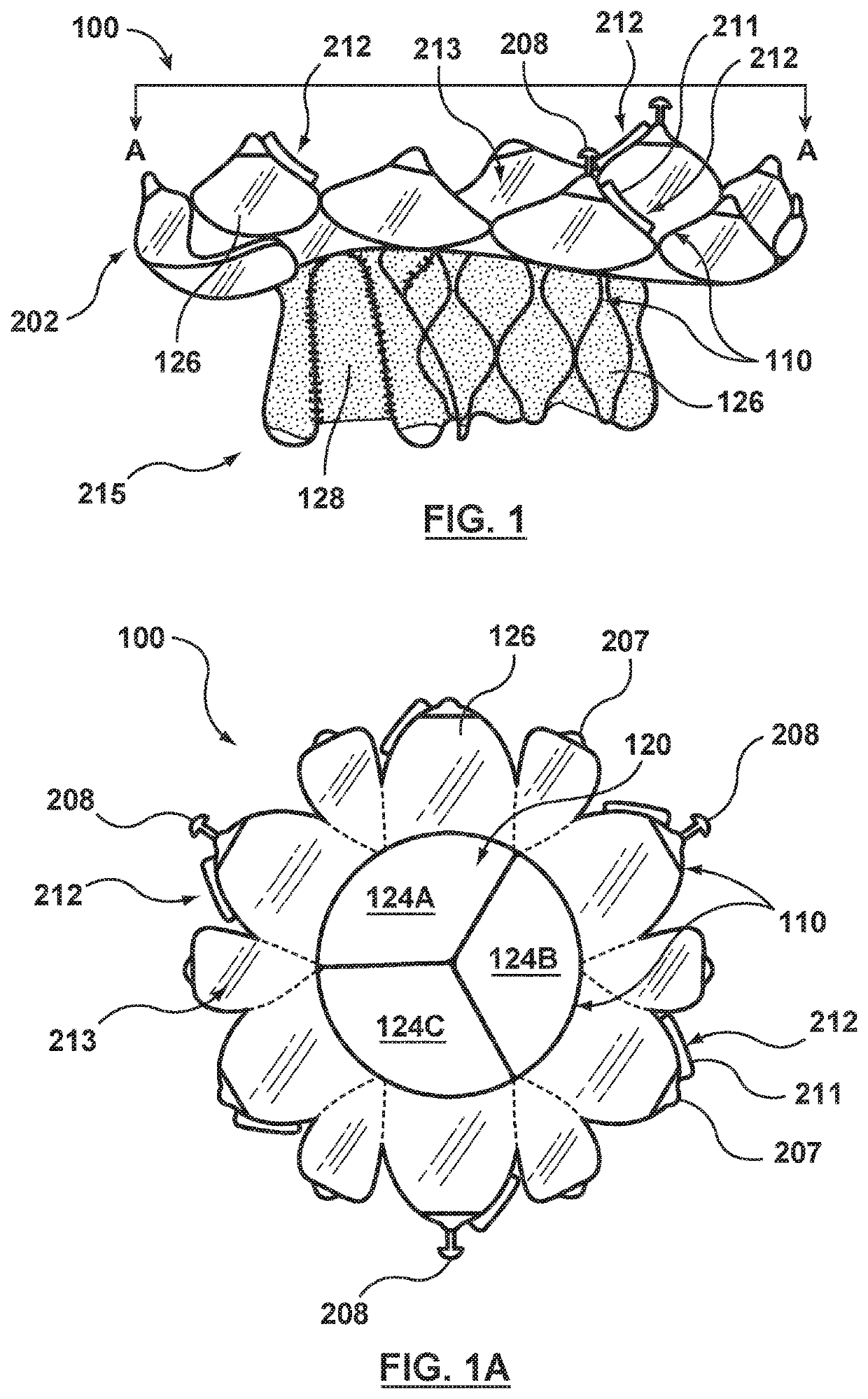
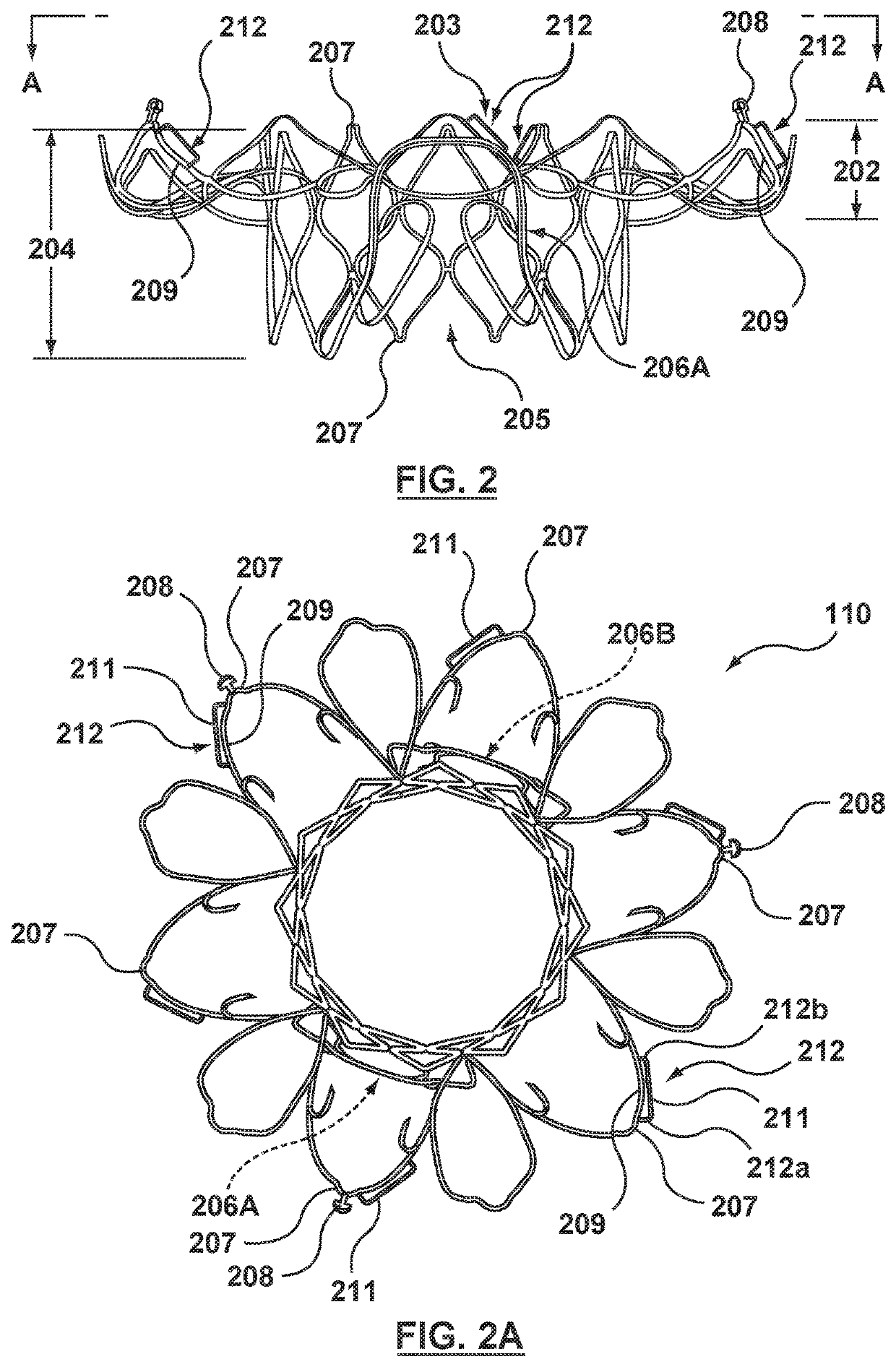
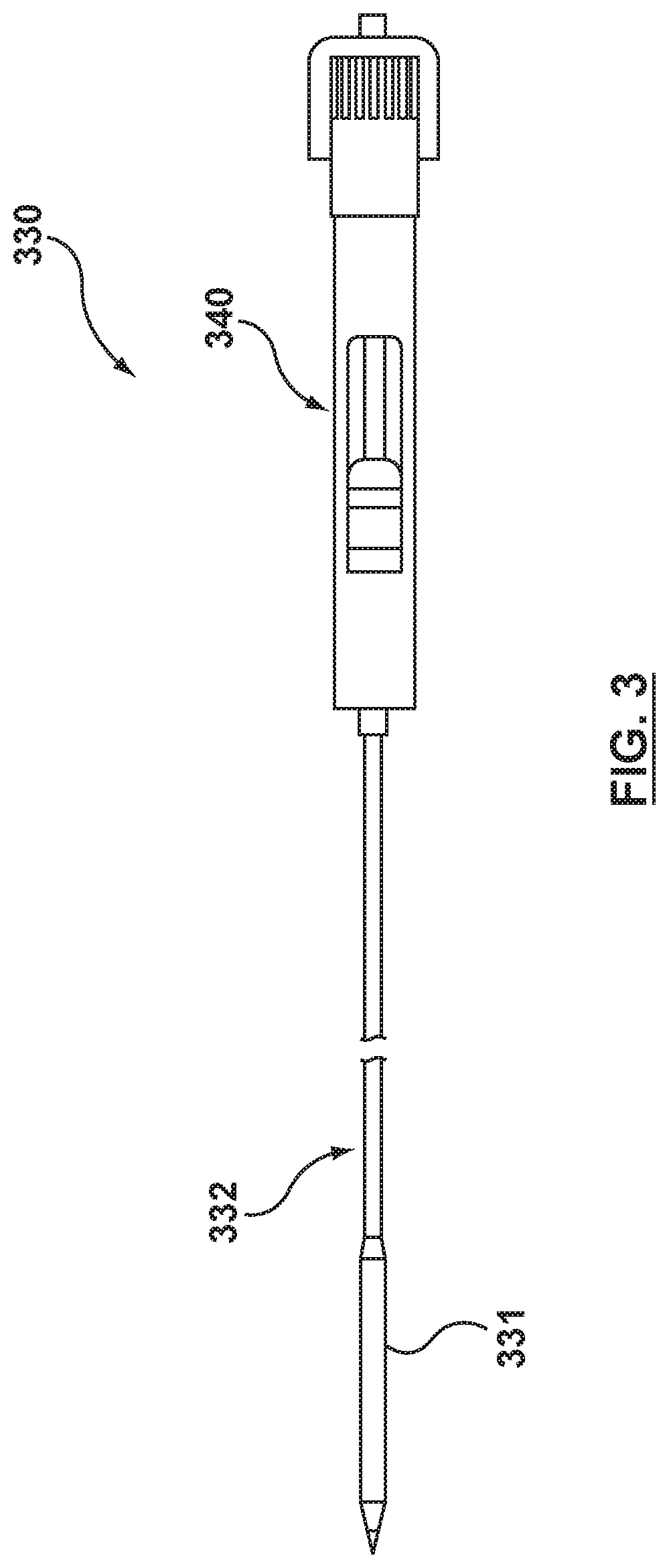
Methods of deploying and securing a heart valve prosthesis are disclosed. A heart valve prosthesis (100) having a plurality of anchor guides (212) is loaded within a catheter-based delivery device, wherein each of the anchor guides is releasably engaged by a respective elongate member (338) and wherein tensioning of the elongate members aids in collapsing the prosthesis during loading. The delivery device is advanced via a transcatheter procedure to position the heart valve prosthesis at an implantation site. The heart valve prosthesis undergoes controlled deployment by controlling the release of tension on the elongate members. After deployment of the heart valve prosthesis, an anchor tool (660) is advanced along a guide member to the anchor guide positioned at a securement site. When the securement site is reached, an anchor clip (662) is released from the anchor tool to secure the prosthesis to the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Systems and methods for affixing a prosthesis to tissue
Owner:MICRO INTERVENTIONAL DEVICES
Prosthesis Fixation Apparatus and Methods
Apparatus and methods for endoluminally advancing a tubular prosthesis and a plurality of fasteners to a site in a lumen in a human body and passing the fasteners from an inner surface of the prosthesis through the prosthesis and a wall of the lumen to secure the prosthesis to the wall. Embodiments include simultaneous deployment of fasteners using a graft alone or in conjunction with a stent graft. Another arrangement includes guide lines to guide the end of the fixation deployment device to a specific location of the wall of the prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Permanent magnet type adjustable long bone prosthesis as well as adjusting device and method thereof
InactiveCN104323876AMeet the requirements of long bone growthImprove quality of lifeProsthesisGear driveGear wheel
The invention relates to a permanent magnet type adjustable long bone prosthesis as well as an adjusting device and an adjusting method thereof. Before the length of the permanent magnet type long bone prosthesis is adjusted, a corresponding limb of a human body is put into the adjusting device of the permanent magnet type adjustable long bone prosthesis in a sleeving mode, so that outer magnetic steel of the adjusting device is aligned to inner magnetic steel on the long bone prosthesis planted into the human body; a motor is started; the rotating speed of an output shaft of the motor is reduced by a speed reducing box and then is transmitted to a first gear; the first gear is used for transmitting motion and power to a second gear by engaged transmission; the second gear drives an outer rotor base body of an outer magnetic rotor to rotate; the outer rotor base body drives the outer magnetic steel to rotate to form a rotary magnetic field; magnets have the effects of repelling of like poles and attracting of different poles, so that the outer magnetic rotor is driven to rotate after a certain phase difference is formed between the outer magnetic steel and the outer magnetic steel; the rotation of the outer magnetic rotor drives a screw rod to rotate and the rotation of the screw rod drives a prosthesis movable end to move in a prosthesis fixed end, so that the length of the long bone prosthesis is adjusted.
Owner:丁华
Artificial prosthesis of long bone diaphysis tenon and mortise structure
PendingCN107349032AImprove medium and long-term stabilityExtend your lifeFemurSkullNormal boneSurgical Manipulation
The invention relates to an artificial prosthesis of a long bone diaphysis tenon and mortise structure. A protruding face I and a rectangular protrusion I of a prosthesis proximal handle connecting part I are inserted into a strip-shaped groove II and a rectangular notch II of a prosthesis far-end handle connecting part II respectively, a protruding face II and a rectangular protrusion II of the prosthesis far-end handle connecting part are inserted into a strip-shaped groove I and a rectangular notch I of the prosthesis proximal handle connecting part I respectively, after a semicircular groove I of the prosthesis proximal handle connecting part I is in butt joint with a semicircular groove II of the prosthesis far-end handle connecting part II, a cylindrical counter bore is formed, tenon is inserted into the cylindrical counter bore formed in one end of the cylinder, and the tenon locks the connecting part I and the connecting part II together. Prosthesis fixation is firm and reliable, the operation is simple and convenient, the operation time is shortened, the operation effect and efficiency are improved, and operative complications are reduced. The artificial prosthesis can be widely applied to different defects of long bone diaphysis, the minimum osteotomy amount can reach 3.0 cm, and the maximum opportunity is provided for reserving normal bone tissue and joints as much as possible.
Owner:胡永成
Tool and method for implanting an annuloplasty prosthesis
ActiveUS20070078468A1Conveniently and efficiently releasingConveniently accomplishedSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsGeneral surgerySharp Instruments
A simplified and more easily employed tool for holding an implantable annuloplasty prosthesis during passage of sutures through the prosthesis and for conveniently and efficiently releasing the prosthesis from the tool. Separation of the implantable prosthesis and the tool may be conveniently accomplished without requiring the use of a sharp instrument. Attachment between the prosthesis and its surgical carrying tool can be accomplished in a suture-less fashion. The tool includes a suture management device in some embodiments for selectively receiving and maintaining sutures otherwise securing the prosthesis to tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
An intervertebral prosthesis
The application relates to an intervertebral prothesis. In particular, to an articulating intervertebral disc prothesis. In use, the intervertebral prosthesis is fixed to the end plates of vertebrae following the surgical excision of a degenerative or ruptured disc. The intervertebral prothesis has substantially flat bone engaging surfaces with a macro-textured surface.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Percutaneous osseointegrated prosthetic implant system
An implant system for securing a prosthesis to a selected bone of a subject including a stem and an abutment. The stem includes a porous region that promotes osseointegration of the selected bone following implantation of the stem. The abutment is secured to the stem and is configured for secure attachment to the prosthesis. The stem and the abutment include ultra-low friction and / or highly polished surfaces at select locations that inhibit bio-adhesion.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
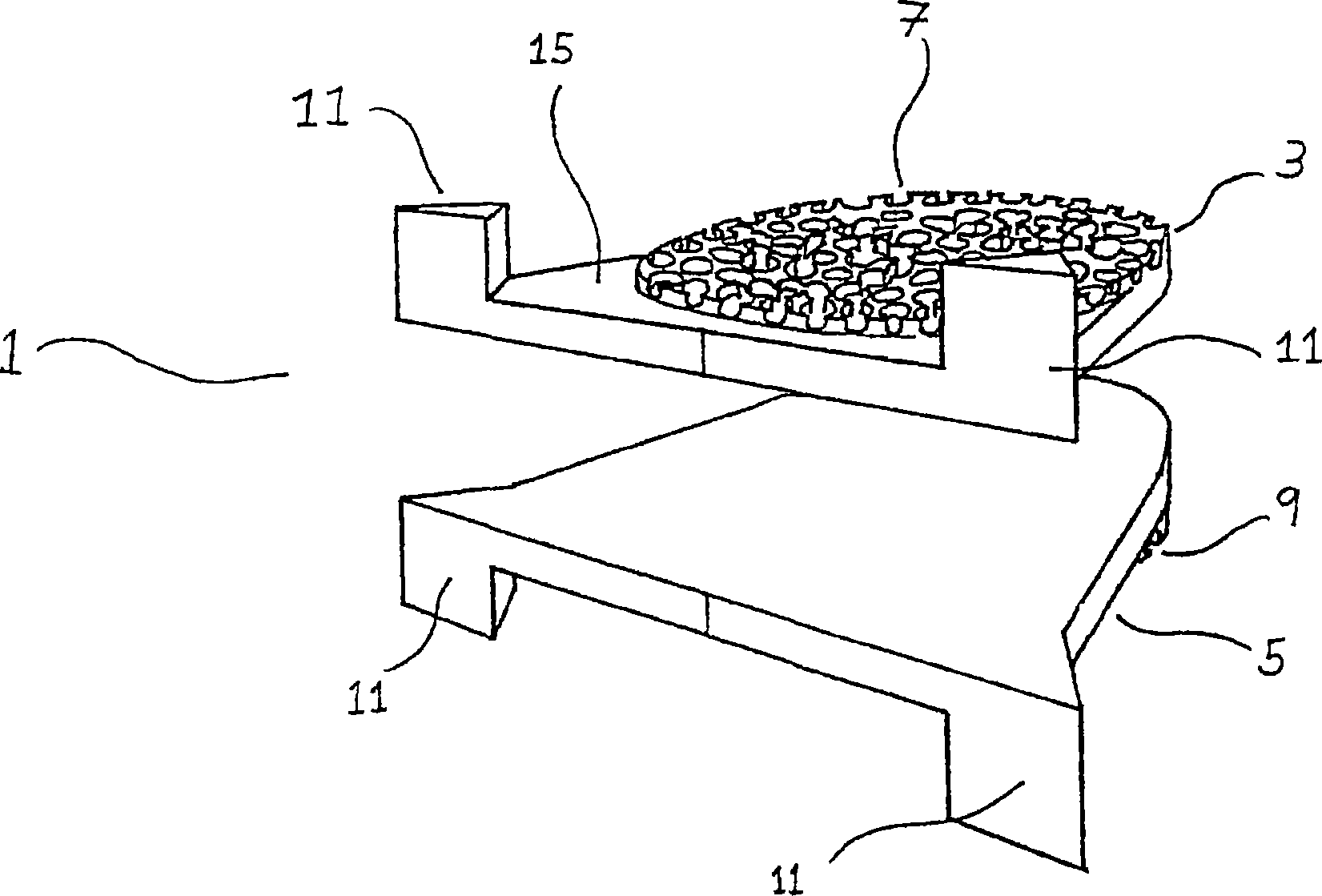
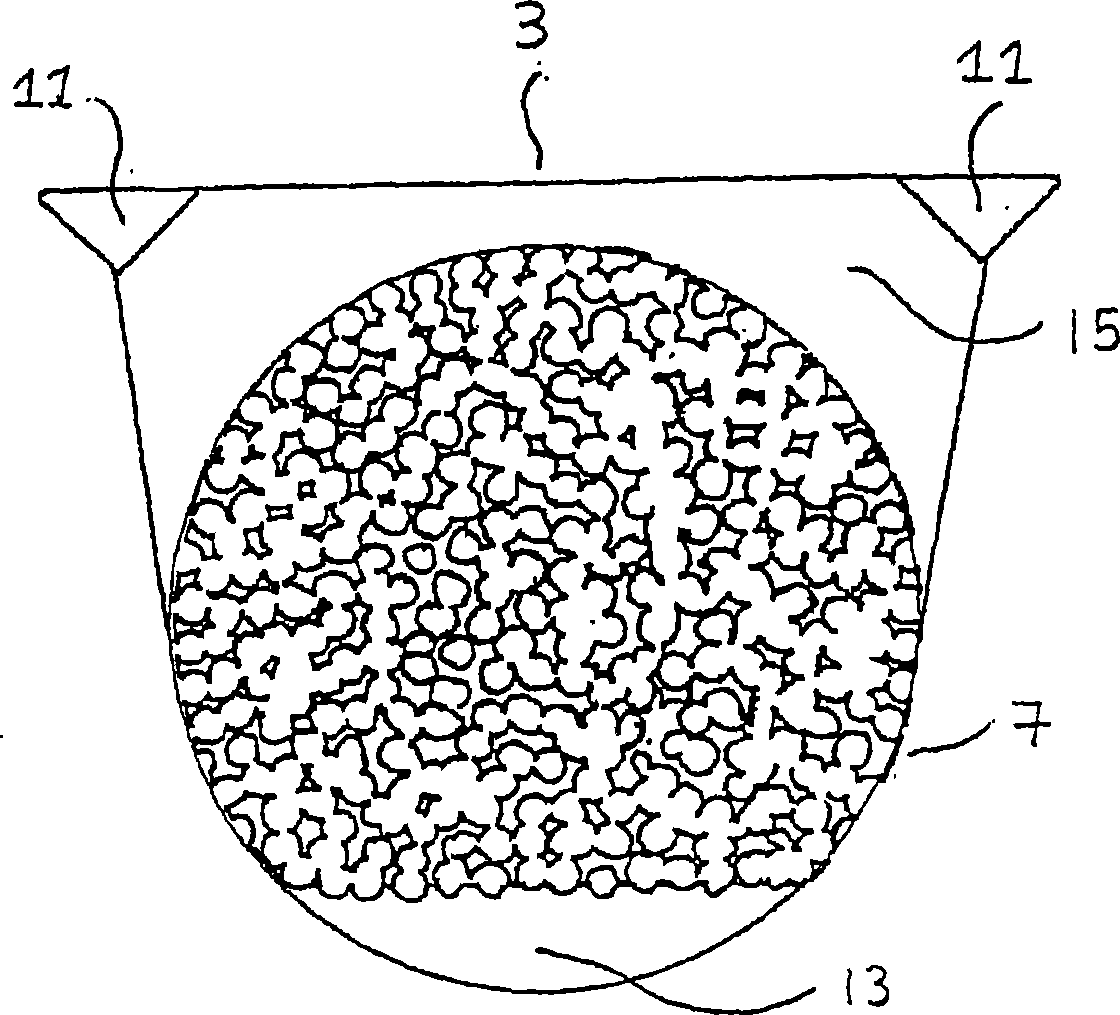
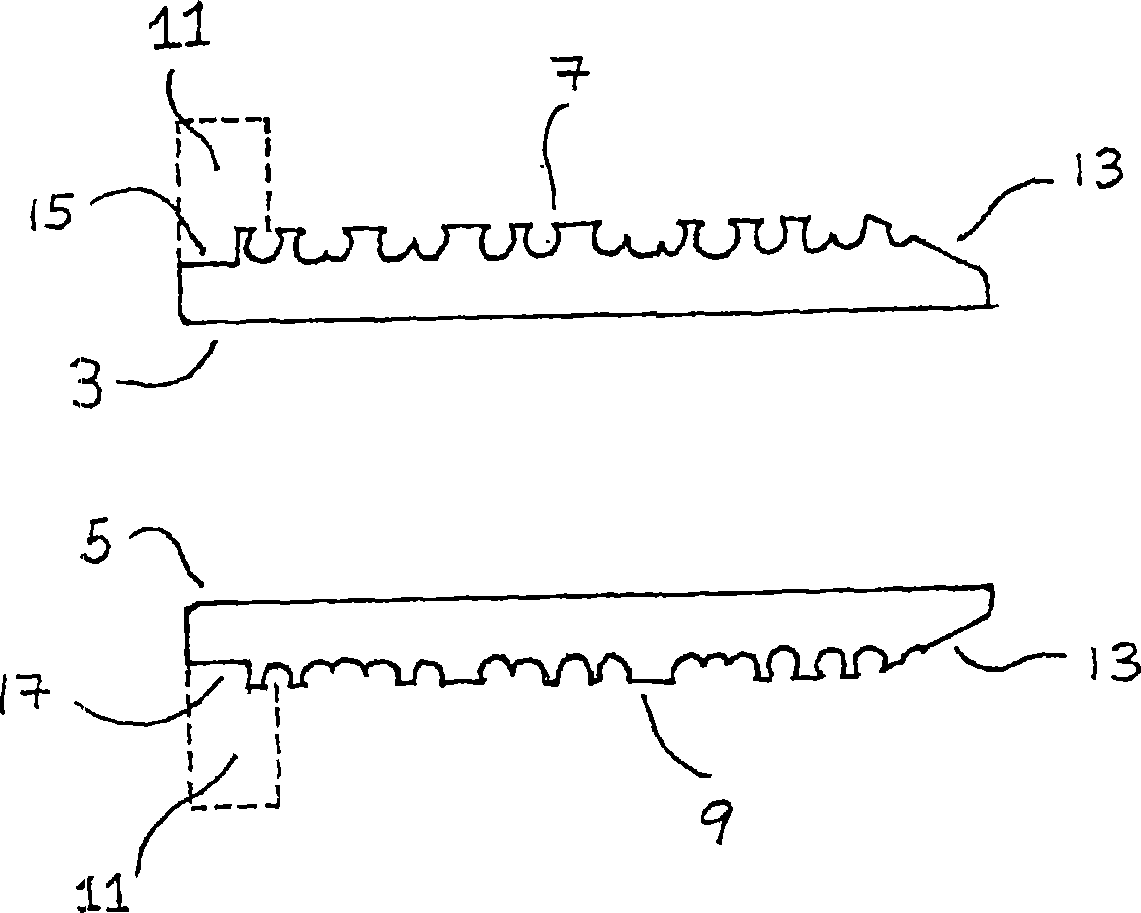
Prosthesis fixation with mechanically compacted biocompatible granules
InactiveCN1665457AEasy to controlImprove growing conditionsBone implantJoint implantsProsthesis FixationBiocompatible material
An assembly for fixating a prosthesis in body tissue such as bone of a mammal, comprising a mechanical compacting device and a mass comprising at least granules of a biocompatible material having a sponge-like structure, wherein the mechanical compacting device is designed for compacting the granules during use by insertion of the device in a hole in bone and subsequently inducing relative movement of at least a first part of the compacting device relative to a second part thereof, such that the volume of at least one space between at least part of an outer surface of the device and the adjacent inner surface of said hole is reduced.
Owner:FONDEL FINANCE BV
Prosthesis fixation device and method
A prosthesis anchor is adapted to convert a previously untreatable anatomy into a more typical and treatable condition. Preferably, the anchor is adapted to be transported endoluminally to a deployment site in a body lumen. The anchor includes a landing section for securing the anchor at a relatively fixed position in the lumen, and a docking section adapted to receive a mating prosthesis the landing section of the anchor may be permanently affixed to the lumen by a variety of mechanical and / or adhesive fixation means.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI +1
Intramedullary cannula and prosthesis with same
PendingCN111643233AEasy to fixHigh strengthBone implantJoint implantsInner CannulaBiomedical engineering
The invention provides an intramedullary cannula and a prosthesis with the same. The intramedullary cannula comprises a cannula body; the cannula body is a net-shaped cylinder formed by weaving material wires; the material wires are made of memory materials; and the prosthesis can be contained in an inner hole of the cannula body. By means of the technical scheme, the problem that in the prior art, the prosthesis fixing stability is poor can be effectively solved.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
Implant for fixing orthopedic prosthesis and acetabular cup prosthesis
InactiveCN108618873AIncrease success rateSmooth penetrationJoint implantsAcetabular cupsIliac screwBiomedical engineering
The invention provides an implant for fixing an orthopedic prosthesis and an acetabular cup prosthesis. The implant comprises a head end and a tail end, wherein the head end is provided with a top anda bottom, the thickness from the bottom to the top decreases progressively to enable the implant to enter a preset area, and the ratio of the maximum width to the maximum thickness of the implant isgreater than 1.155. The implant is in a thin shape on the one hand and can reduce bone defects during implantation; and on the other hand, punching holes in an acetabulum and measuring the depth of the holes are not needed, and the implant can be inserted without alignment. The operation process of fixing the acetabular cup prosthesis is simplified, and the problem of loosening of the acetabular cup prosthesis caused by inaccurate screw implantation position does not occur.
Owner:MICROPORT ORTHOPEDICS SUZHOU CO LTD +1
Elastic bionic artificial temporomandibular zygopophysis prosthesis and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113491600AIncrease elasticityFirmly connectedJoint implantsTissue regenerationAnatomyEngineering
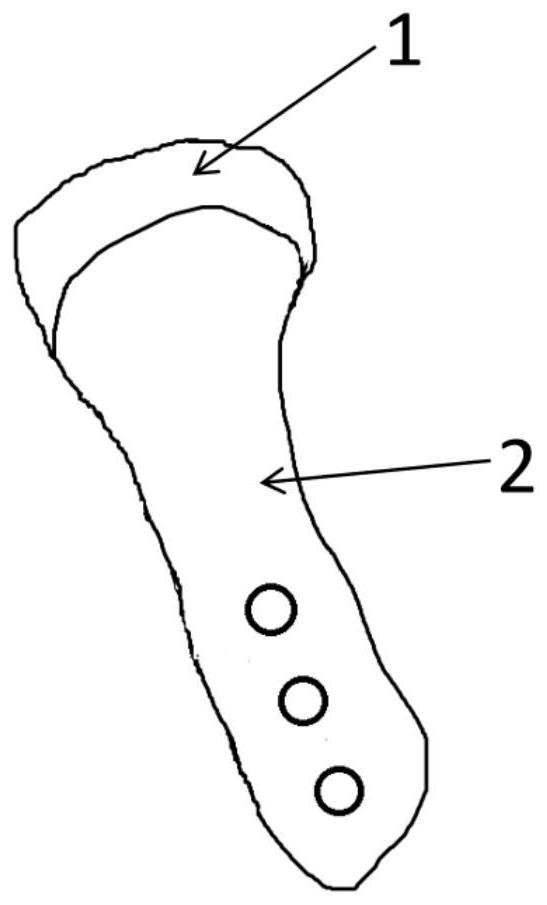
The invention provides an elastic bionic artificial temporomandibular zygopophysis prosthesis and a preparation method thereof. The zygopophysis prosthesis comprises a bionic articular cartilage (1) and a mandibular branch metal prosthesis (2). The bionic articular cartilage is made of a high polymer material, and the mandibular branch metal prosthesis (2) is made of a metal material. The bionic articular cartilage (1) is arranged at the top end of the mandibular branch metal prosthesis (2), and the bionic articular cartilage (1) is fixedly connected with the mandibular branch metal prosthesis (2). The articular cartilage of the elastic bionic artificial temporomandibular zygopophysis is prepared from a combined material comprising ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, and a certain connecting structure is designed to realize heterogeneous material integrated connection with a mandibular branch metal prosthesis, so that stable connection between artificial temporomandibular zygopophysis metal and an organic polymer surface structure is realized. The interior of the bionic articular cartilage is provided with an elastic structure, so that the elastic performance of a zygopophysis functional surface is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY
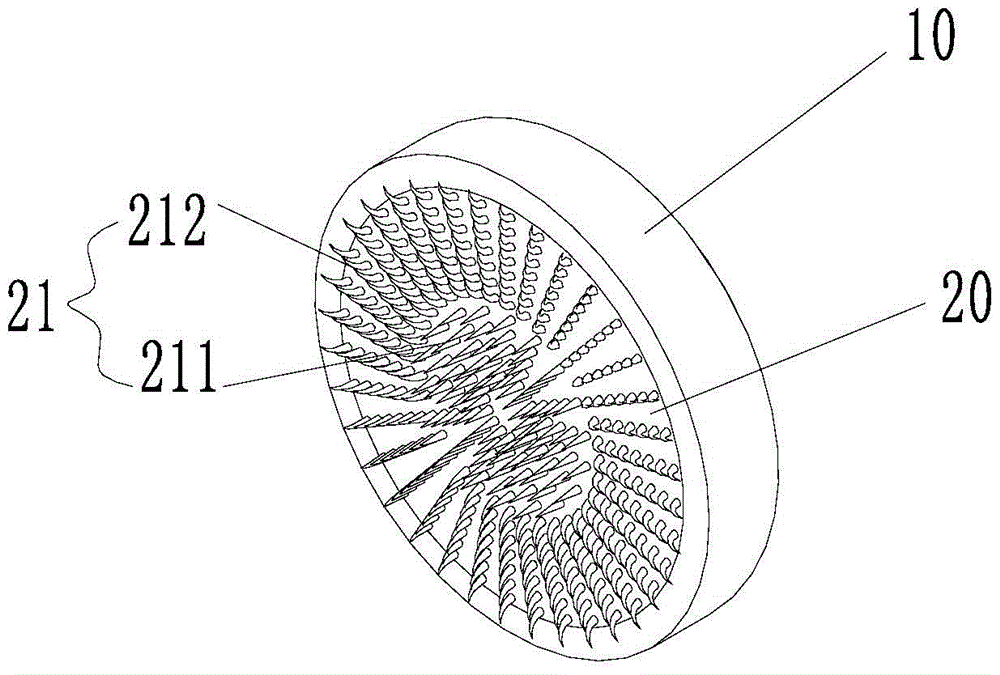
Patellar prosthesis
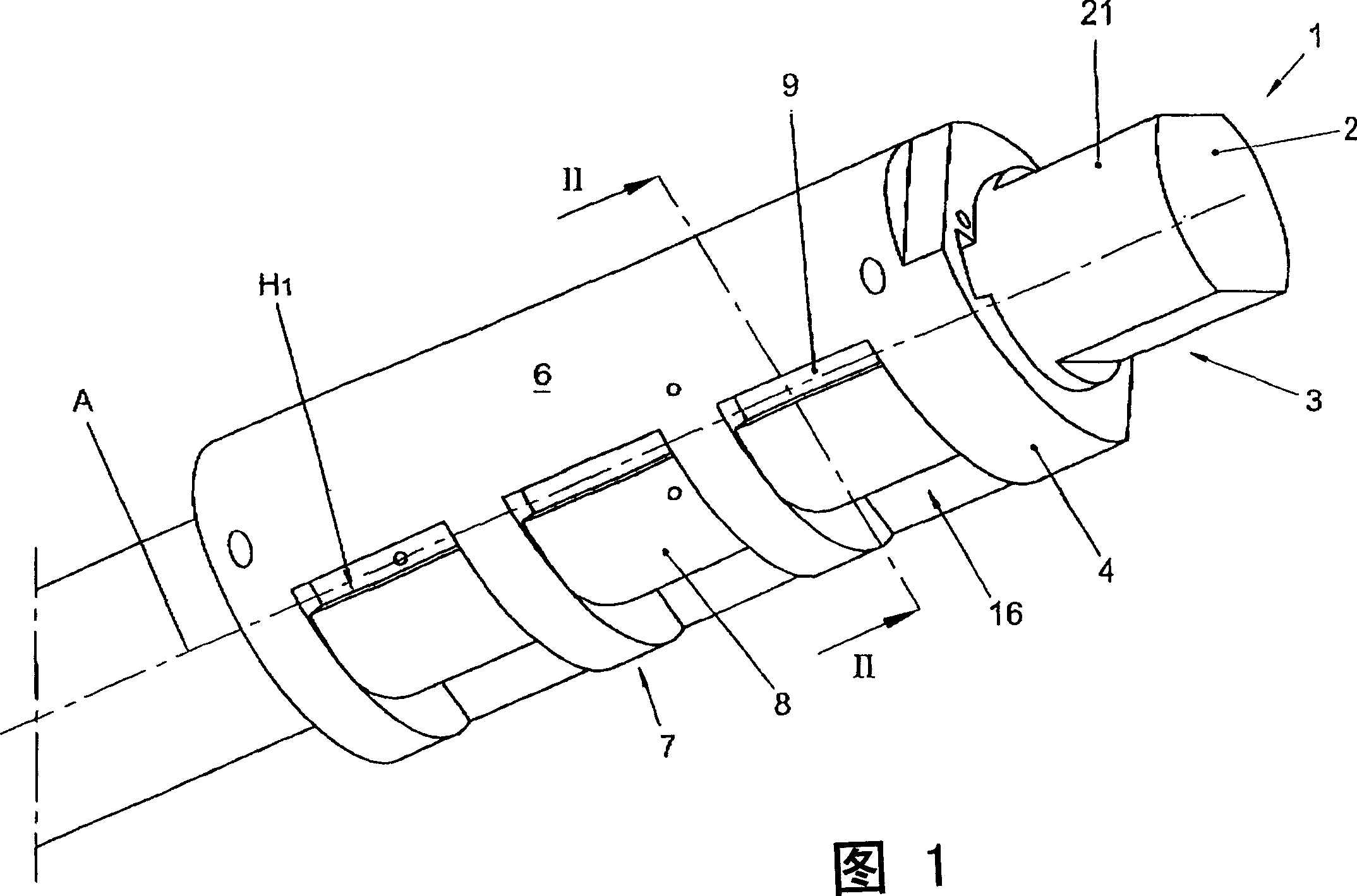
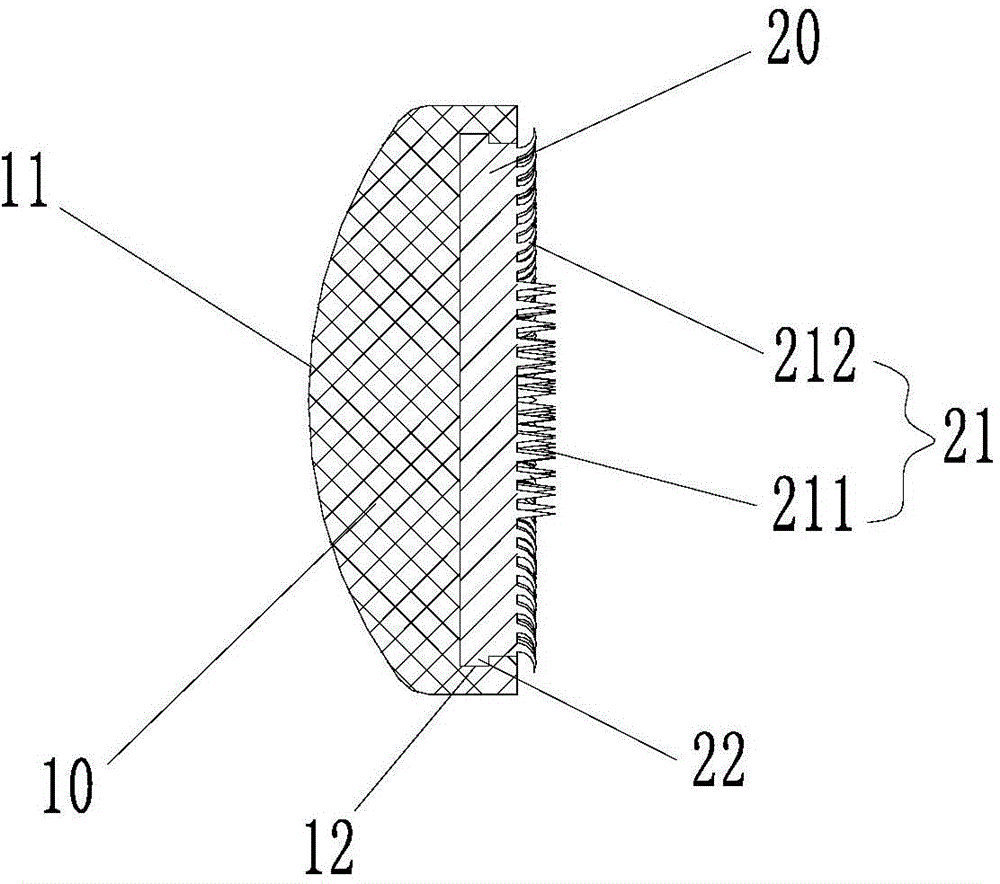
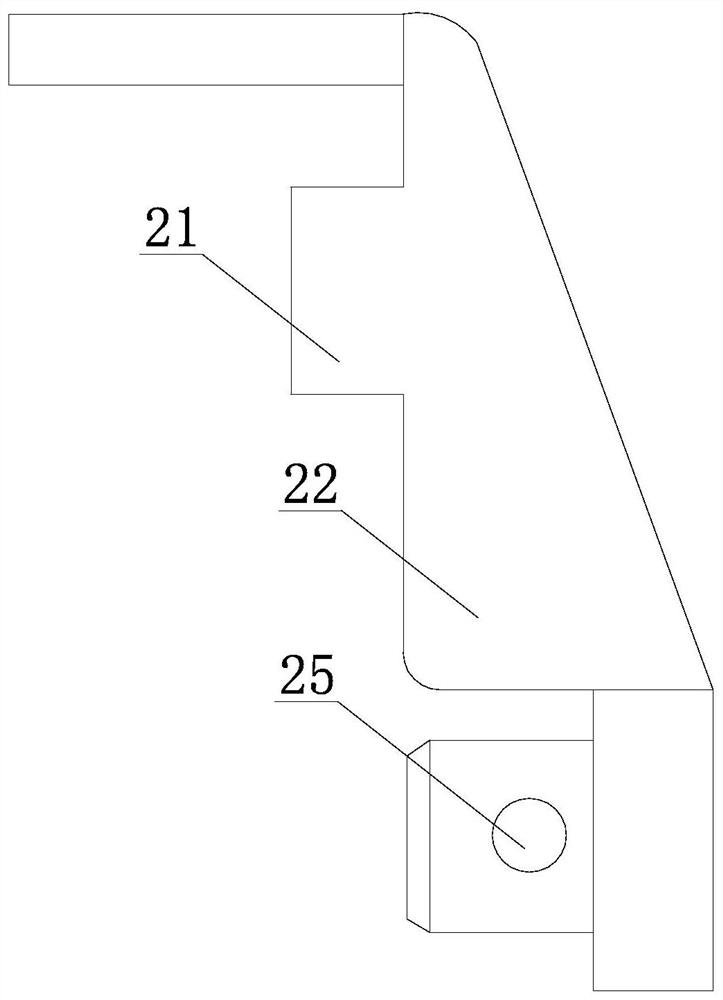
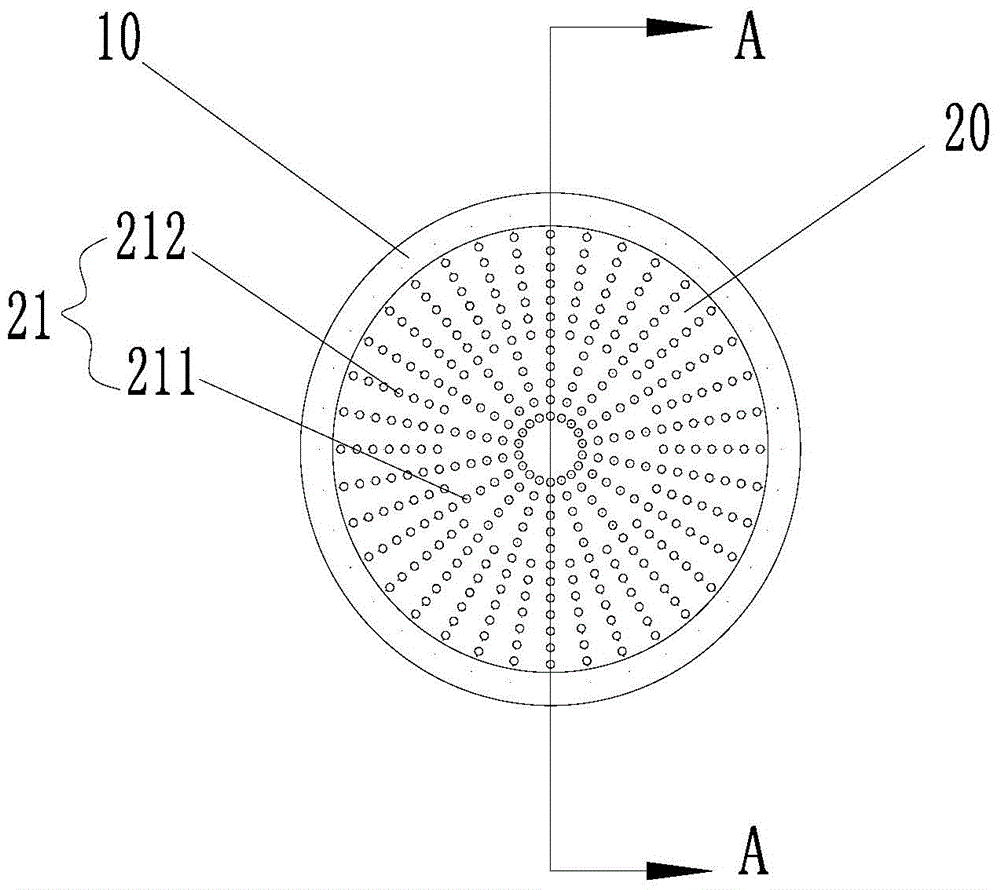
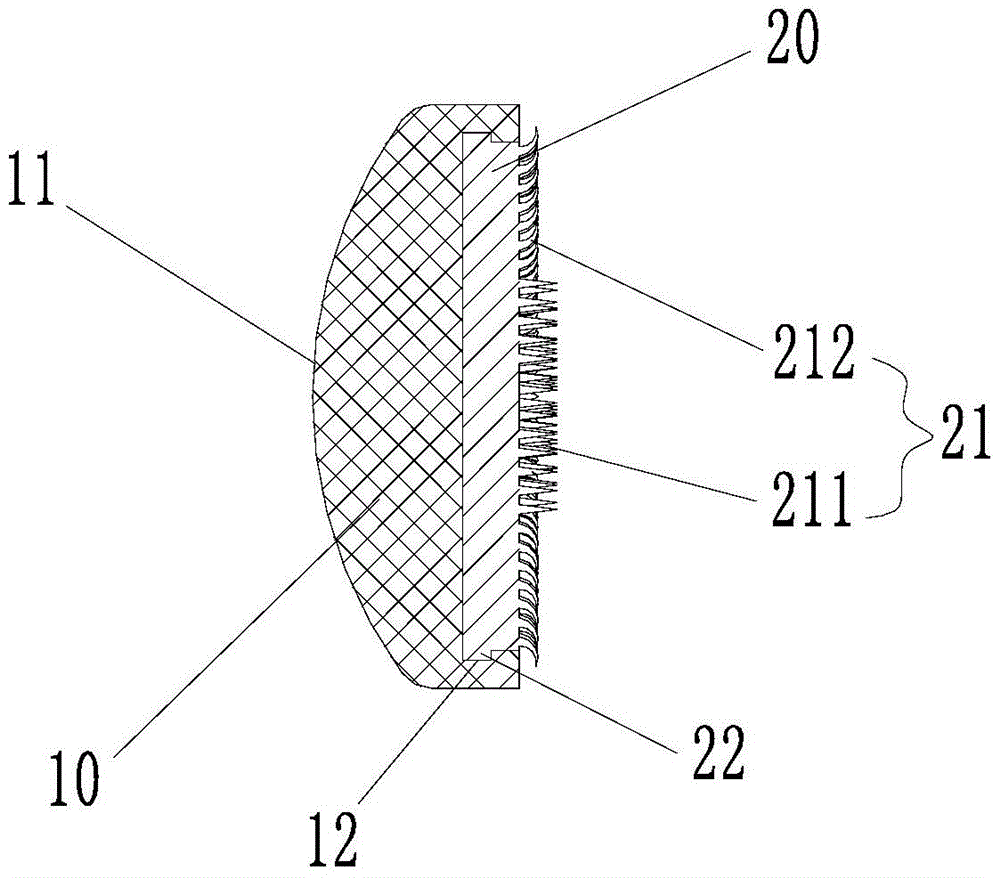
ActiveCN104799979AReplacement effect is goodAffect thicknessJoint implantsKnee jointsMedicineKnee surface
The invention provides a patellar prosthesis, which comprises a metal basal body, the metal basal body is provided with a mating surface, and after the mating surface is processed by laser texturing, a plurality of pointed structures (21) are formed. The technical scheme of the invention effectively solves the problems that patellar prosthesis-fixing bolts in the prior art cannot take both patellar blood supply and prosthesis fixation into consideration and the patellar replacement effect is not good.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
Assembly-adjustable four-in-one osteotomy plate
PendingCN113662618AAvoid prosthetic instabilityOptimal osteotomy positionSurgeryKnee JointFEMORAL CONDYLE
The invention discloses an assembly-adjustable four-in-one osteotomy plate which comprises a four-in-one osteotomy plate main body and anterior and posterior condyle osteotomy blocks, the four-in-one osteotomy plate is designed to be of a split structure, a knee joint knee bending gap can be measured through a posterior condyle plane and a tibial plateau plane before osteotomy, the anterior condyle osteotomy amount of the femoral condyle of a knee joint can be measured through an anterior condyle plane, and the situation that the prosthesis is not stably fixed due to anterior condyle Notch appearance or insufficient osteotomy is avoided; two positioning columns are designed on the four-in-one osteotomy plate main body, and the up-down position of the four-in-one osteotomy plate main body is adjusted according to the measured knee bending gap of the knee joint and the osteotomy amount of the femoral condyle and the anterior condyle of the knee joint, so that the four-in-one osteotomy plate main body reaches the optimal osteotomy position and selects the optimal specification; and the four-in-one osteotomy plate main body is provided with a taking-out structure, so that a doctor can conveniently and quickly take down the four-side osteotomy plate main body in an operation, the operation time is shortened, infection is reduced, resection of bone mass caused by poor matching is avoided, and damage to a soft tissue balance system is reduced.
Owner:北京中安泰华科技有限公司
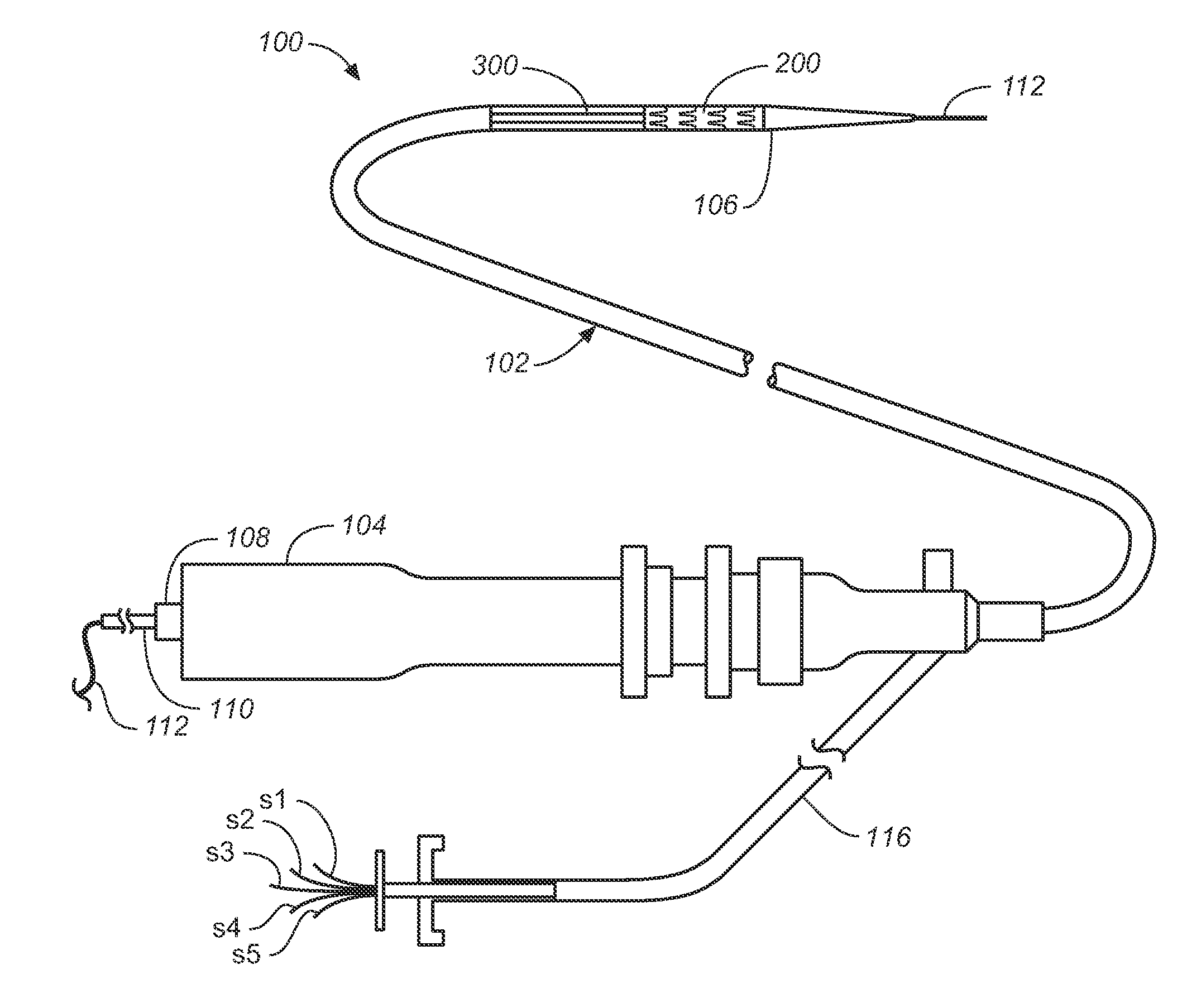
Deployment systems, tools, and methods for delivering an anchoring device for a prosthetic valve
A delivery catheter is in various embodiments configured to deliver an anchoring device to a native valve annulus of a patient' s heart, where the anchoring device can better secure a prosthesis at the native annulus. The delivery catheter can includes a distal section that includes one or more spines or is laser cut to assume a particular shape for better facilitating delivery of the anchoring device at the implant site and can include a flexible tube, a first pull wire, and a second pull wire. The flexible tube can comprise a bore extending between the first end and the second end sized forpassing the anchoring device therethrough. The distal portion can comprise a first flexing section and a second flexing section. Actuation of the first pull wire and the second pull wire can cause theflexible tube to move from a first configuration to a second configuration.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Patella prosthesis
ActiveCN104799979BReplacement effect is goodAffect thicknessJoint implantsKnee jointsPatella prosthesisMedicine
The invention provides a patellar prosthesis, which comprises a metal basal body, the metal basal body is provided with a mating surface, and after the mating surface is processed by laser texturing, a plurality of pointed structures (21) are formed. The technical scheme of the invention effectively solves the problems that patellar prosthesis-fixing bolts in the prior art cannot take both patellar blood supply and prosthesis fixation into consideration and the patellar replacement effect is not good.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
Knee joint revision file
The invention discloses a knee joint revision file which comprises a file body, the file body is of an ellipse-like cylinder structure extending towards the two ends and can also serve as a mold testing tool, and the file body comprises a first end face and a second end face; the side ring surface is a conical surface, and the two ends of the side ring surface extend to be connected with the first end surface and the second end surface respectively; and the plurality of filing teeth are distributed on the side ring surface. The knee joint revision file is designed to be of the structure consistent with the shape of the middle part, implanted into the medullary cavity, of the revision prosthesis, stability and accuracy of revision bone grafting can be promoted, and on the basis, due to the fact that the shape of the revision file is consistent with the shape of the middle part, implanted into the medullary cavity, of the revision prosthesis, after hole filing is completed, the revision bone grafting is completed. In addition, the revision file can be used as a test mold for revision of the prosthesis to simulate the fixing state of the prosthesis in the medullary cavity, so that the time for searching a test mold with a proper specification can be shortened, meanwhile, the material consumption of a test mold tool can be reduced, and the revision operation can be smoothly carried out.
Owner:天衍医疗器材有限公司
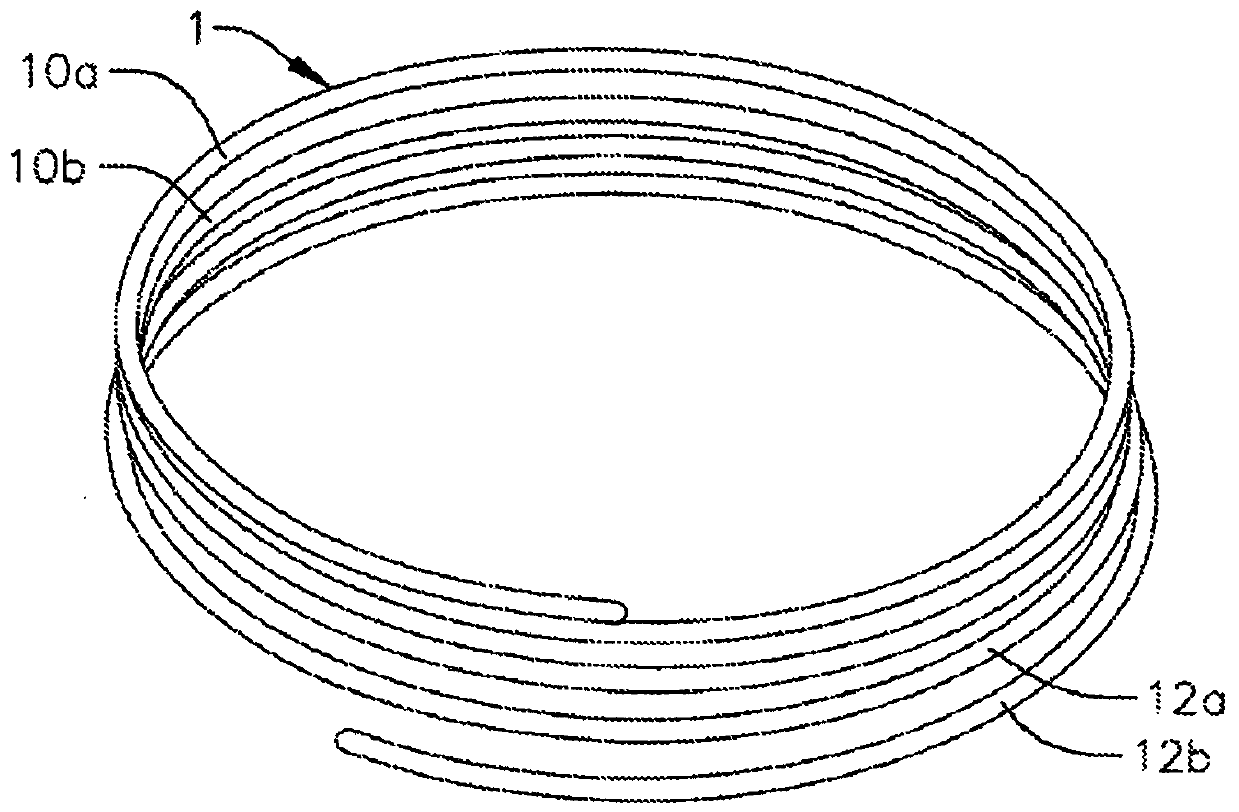
Heart valve replacement device and method
The present application relates to heart valve replacement devices and methods, and provides a system and method for heart valve replacement. The expandable helical anchor is formed as a plurality of coils that support the valve prosthesis. At least one of the coils is expandable to a second, larger diameter upon application of force from within the anchor. A gap is defined between adjacent coils sufficient to prevent engagement of at least one of the adjacent coils with the native heart valve. An expandable heart valve prosthesis is provided and configured to be delivered into the anchor and expand into engagement within the coil. This progresses the coil from a first diameter to a second diameter while holding the anchor and prosthesis together. The system further includes a seal on the expandable heart valve prosthesis configured to engage the helical anchor and prevent blood past the heart valve prosthesis following implantation of the heart valve prosthesis in the helical anchor leakage.
Owner:MITRAL VALVE TECHNOLOGIES SARL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com