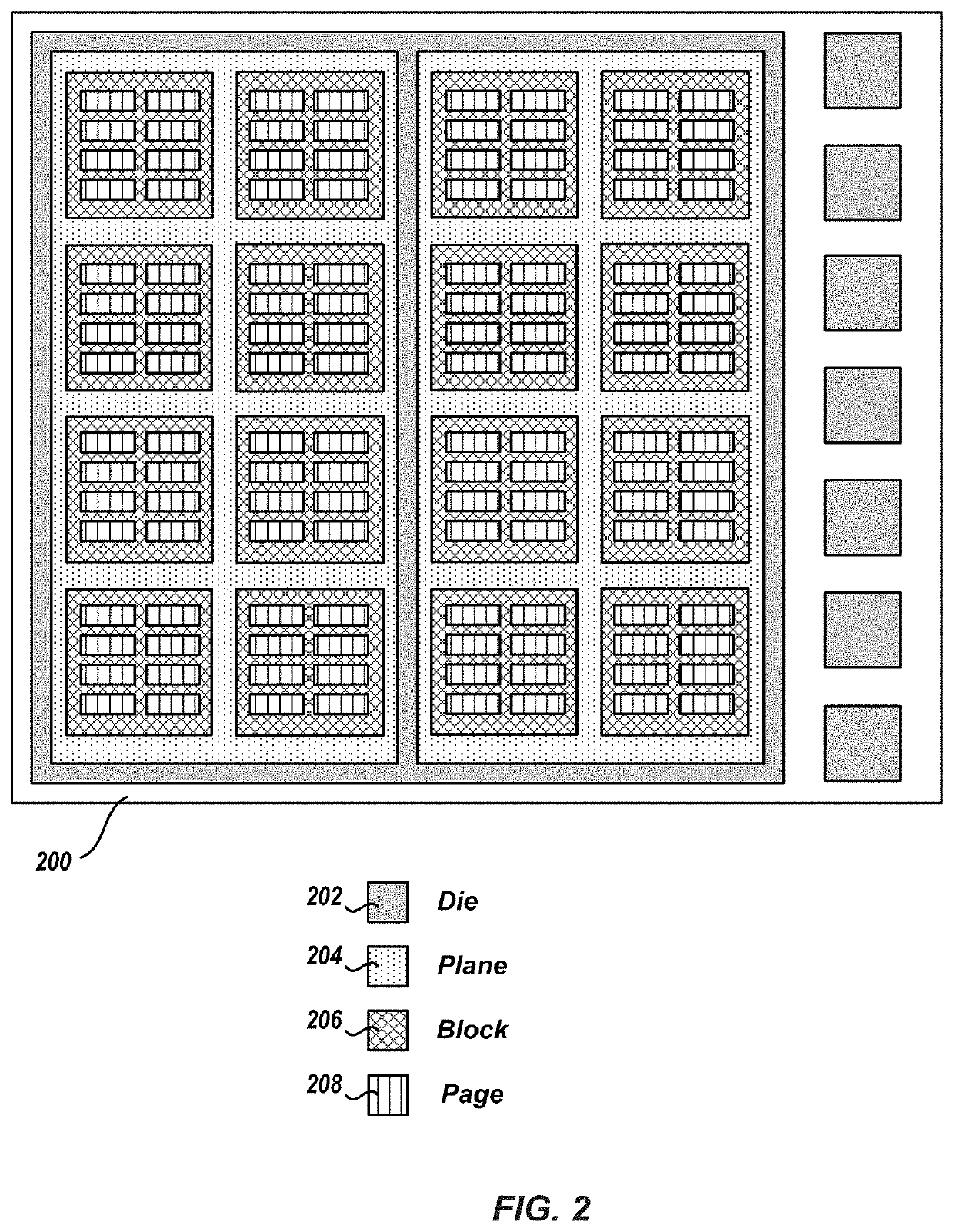
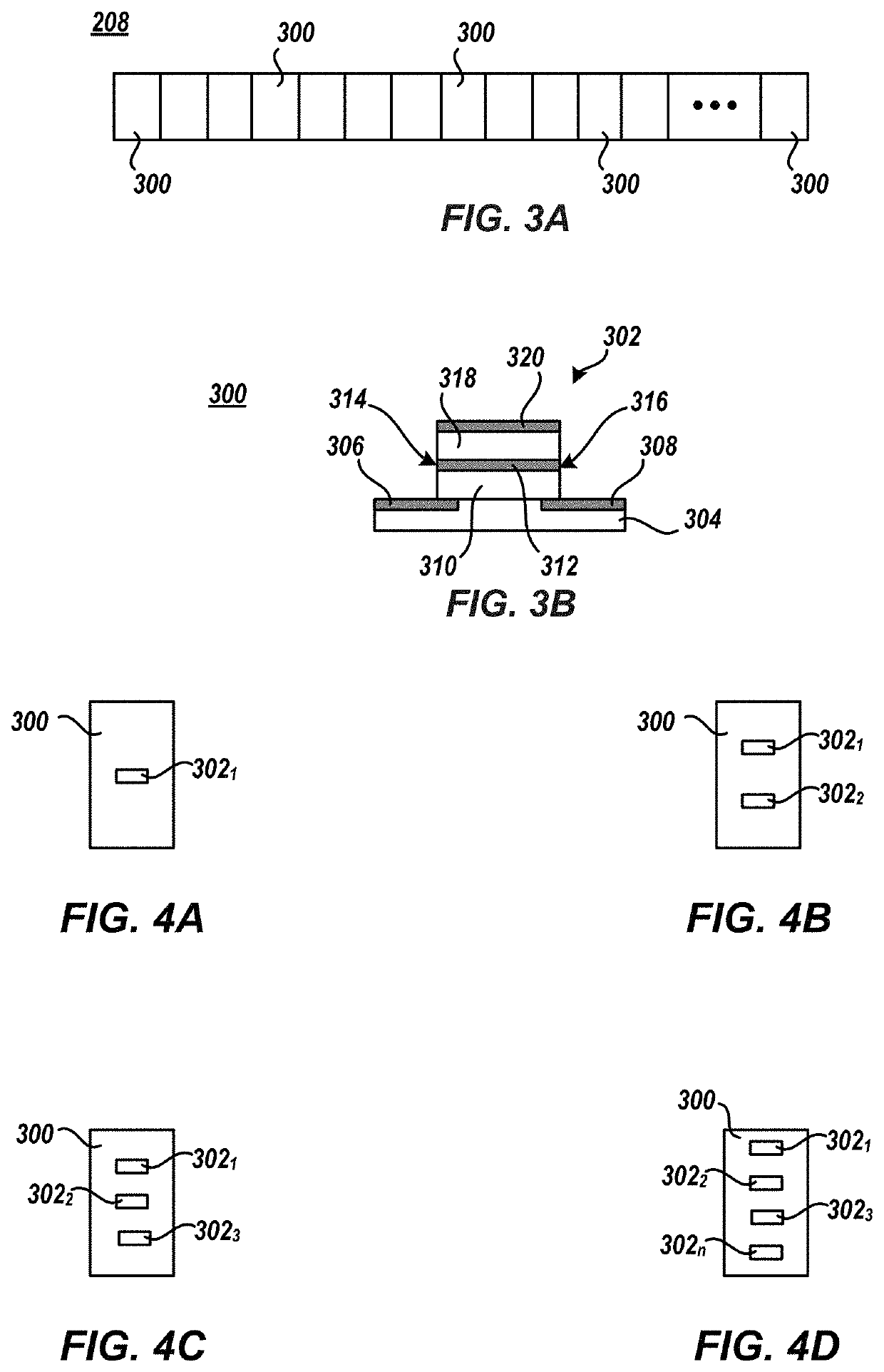
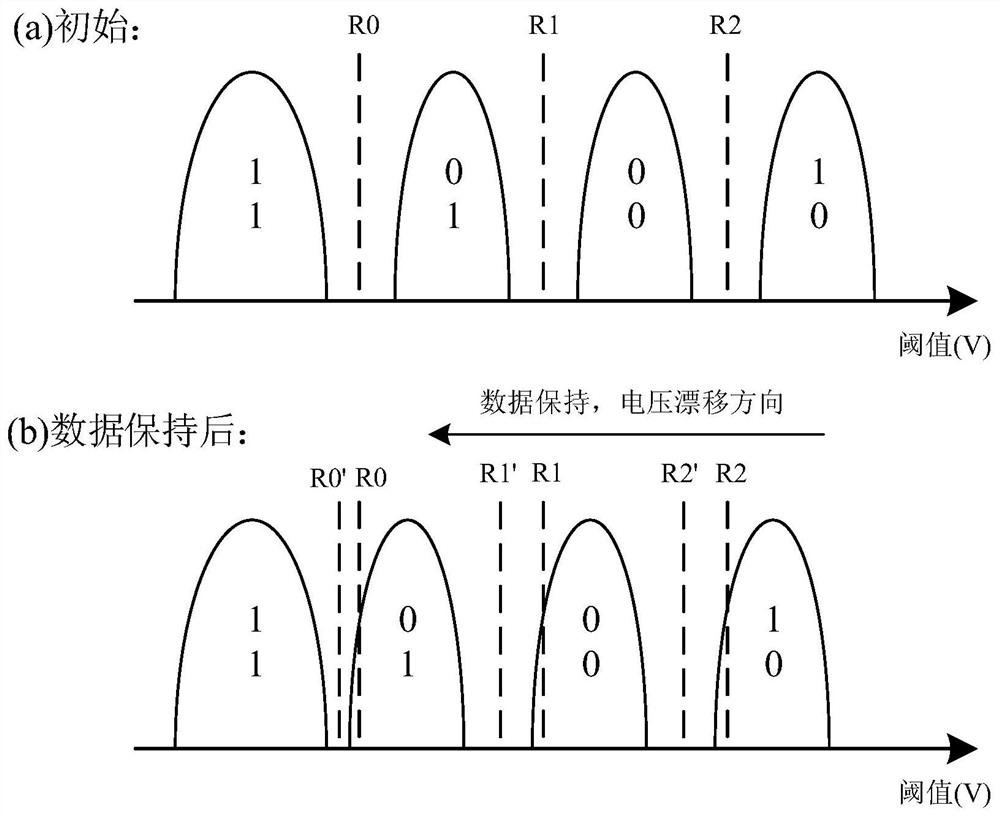
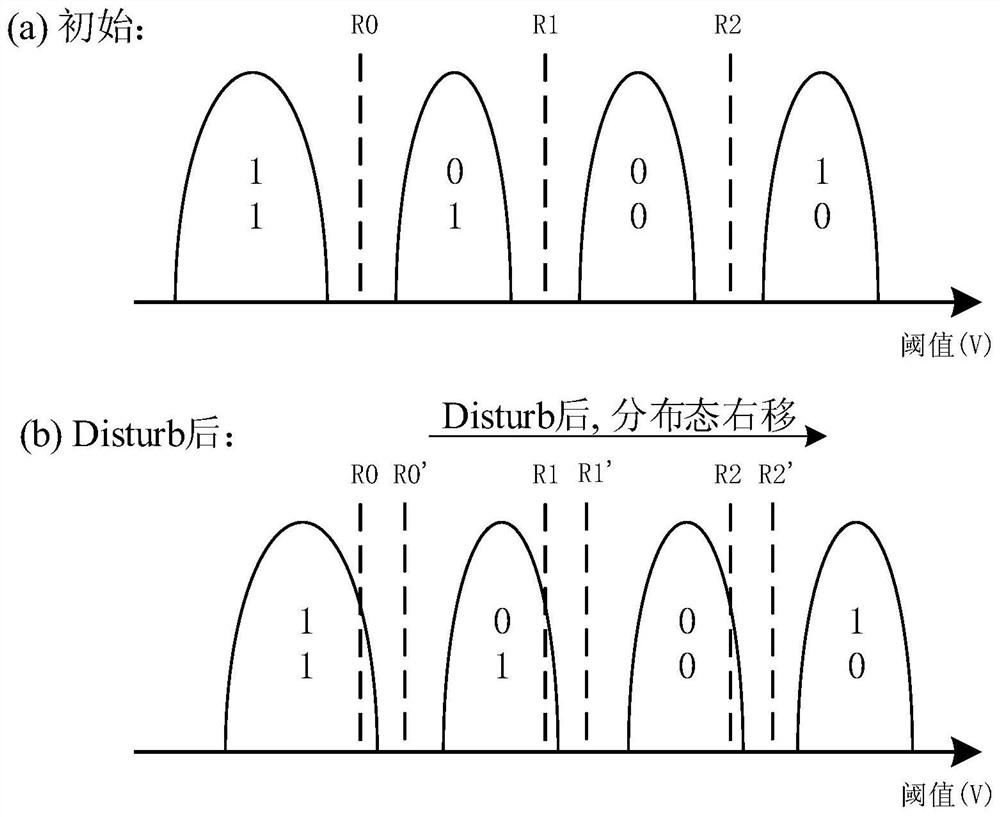
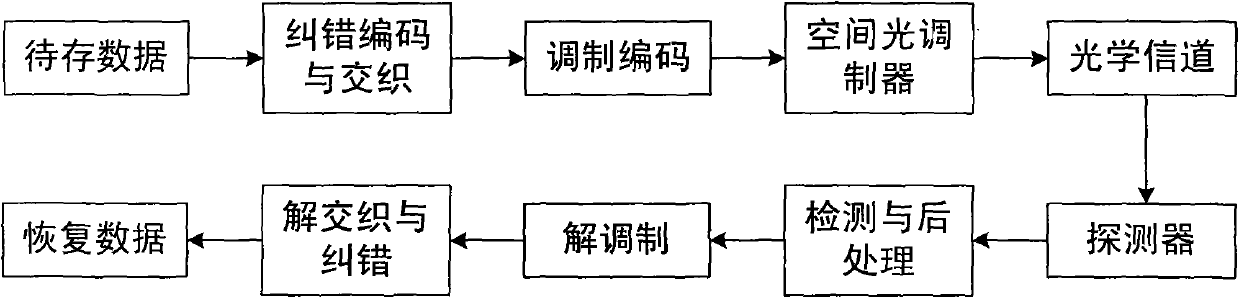
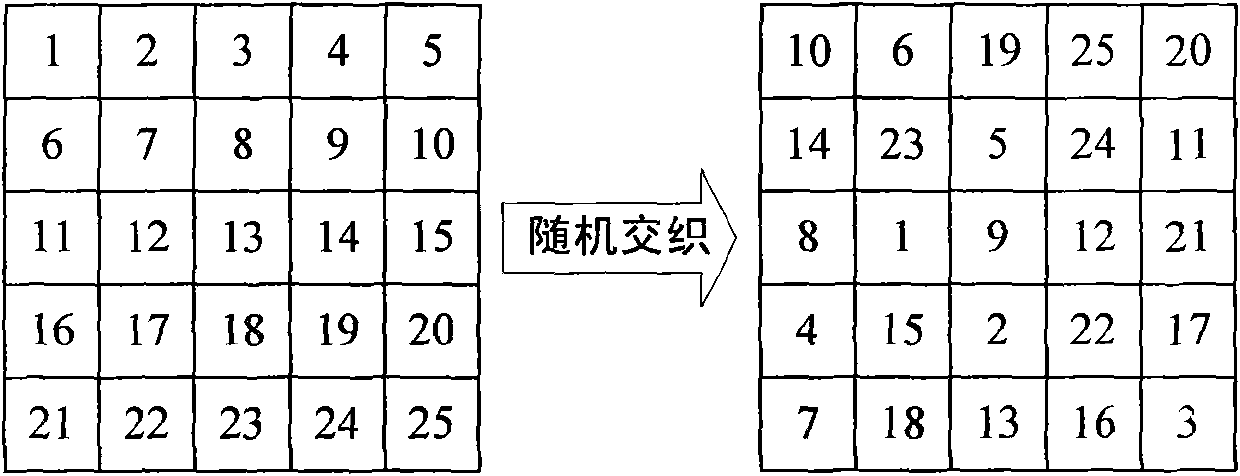
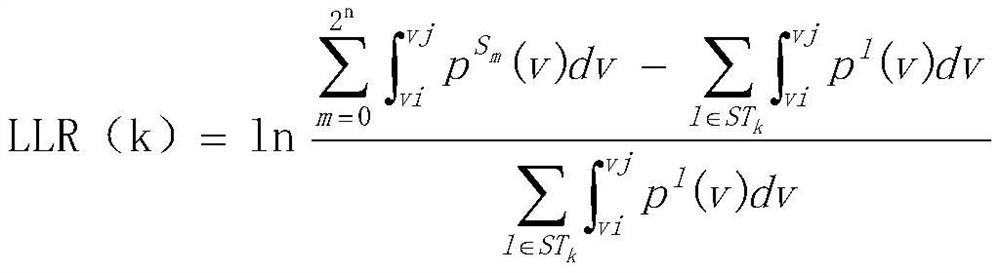Patents
Literature
38 results about "Raw bit error rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
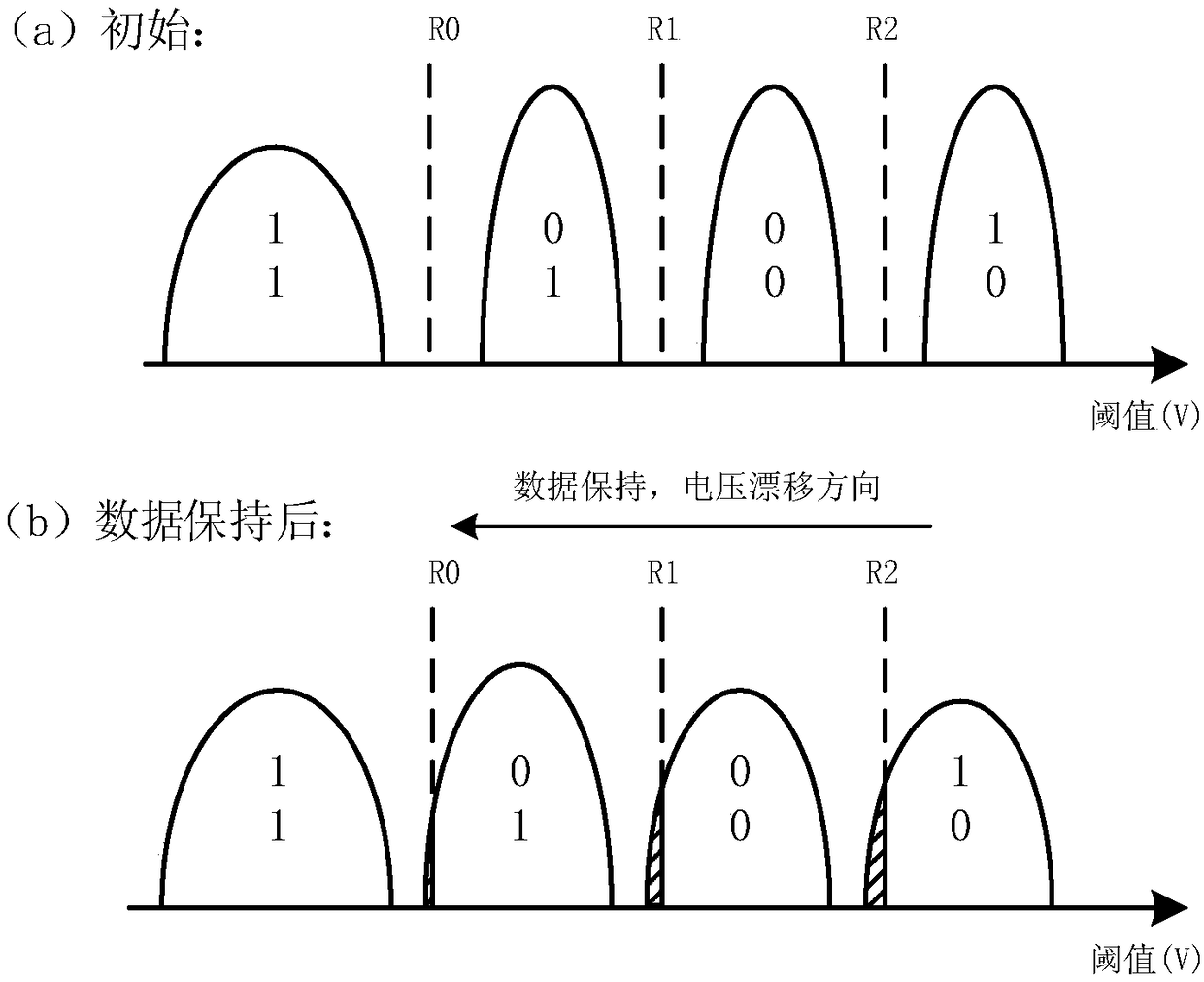
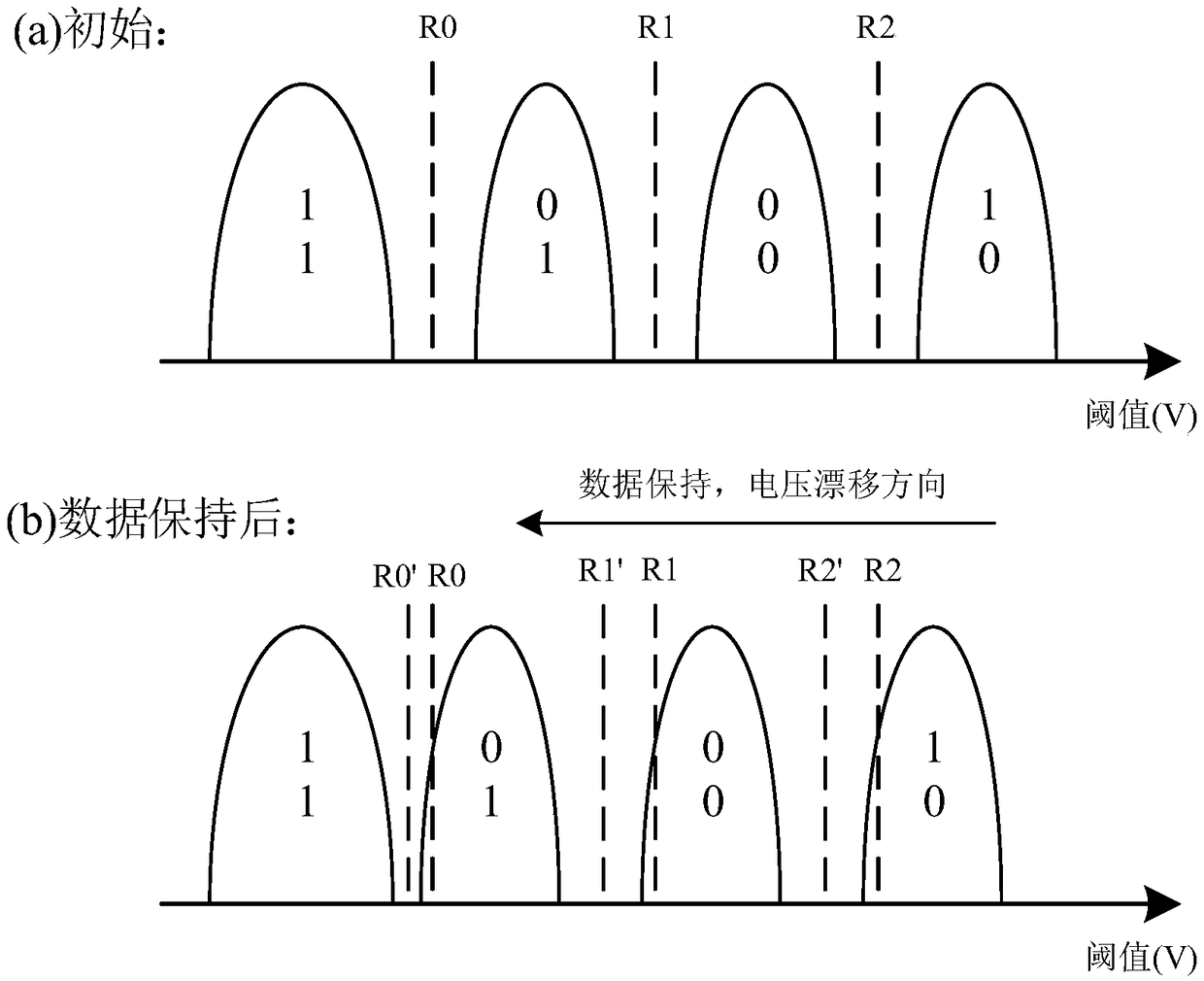
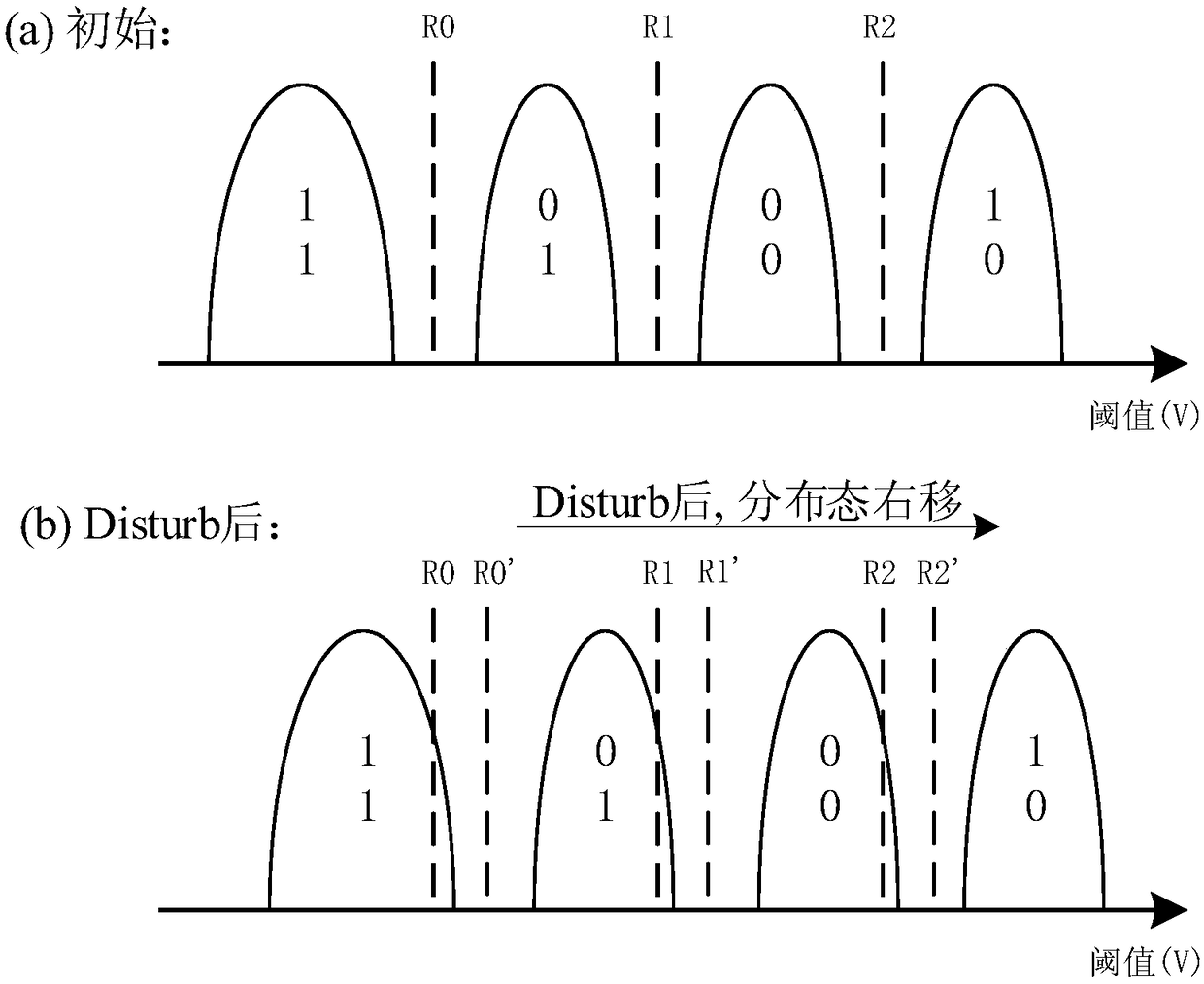
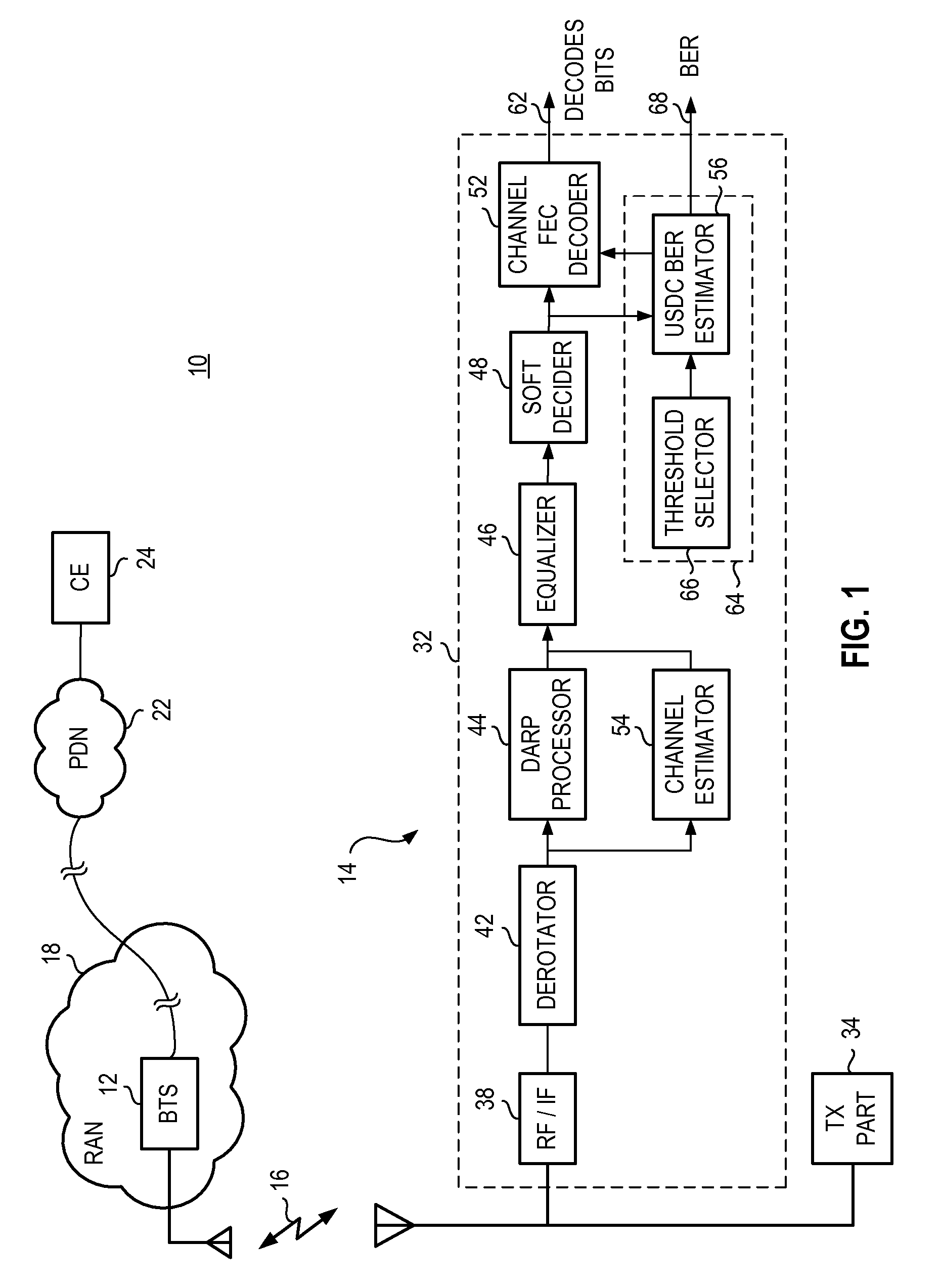
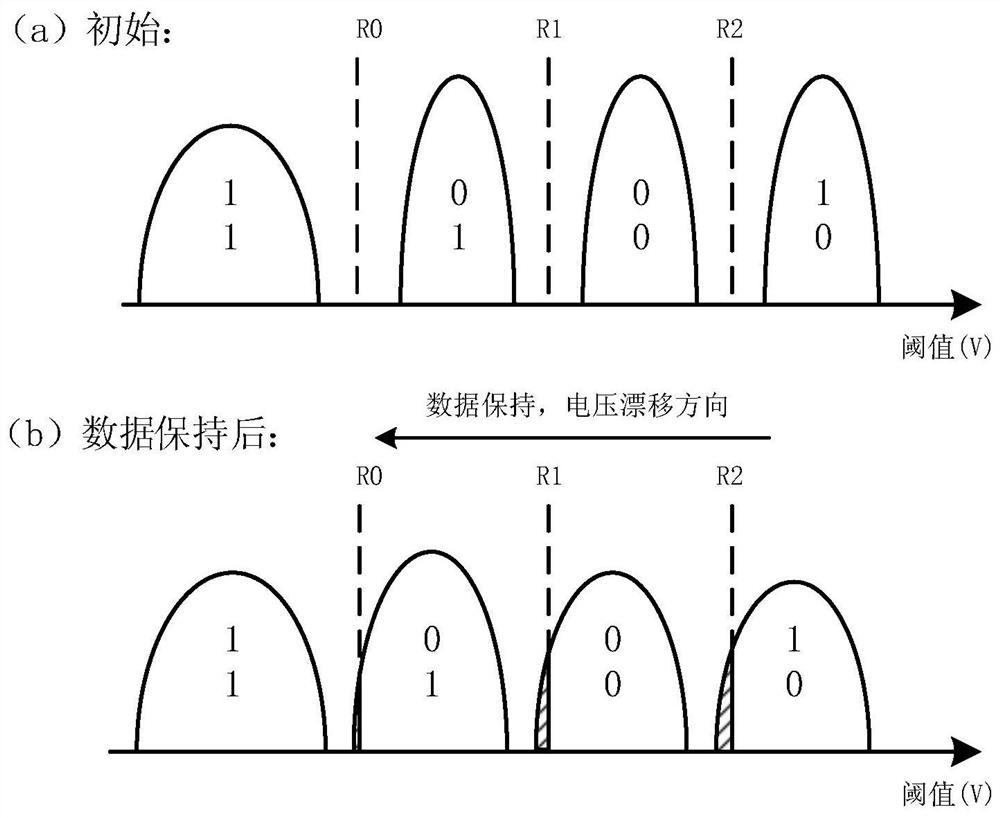
The bit error rate (BER) is the number of bit errors divided by the total number of bits transferred. The data transfer error is usually corrected with ECC in computing, and thus keeping the data more safe and accurate. The raw bit error rate (RBER) is the number of bit errors without ECC checksum divided by the total number of bits transferred.
Communications system, receiver, and method of estimating received signal quality by using bit error rate
ActiveUS7496804B2Improve performanceImprove throughputError preventionError detection/correctionCommunications systemSignal quality
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
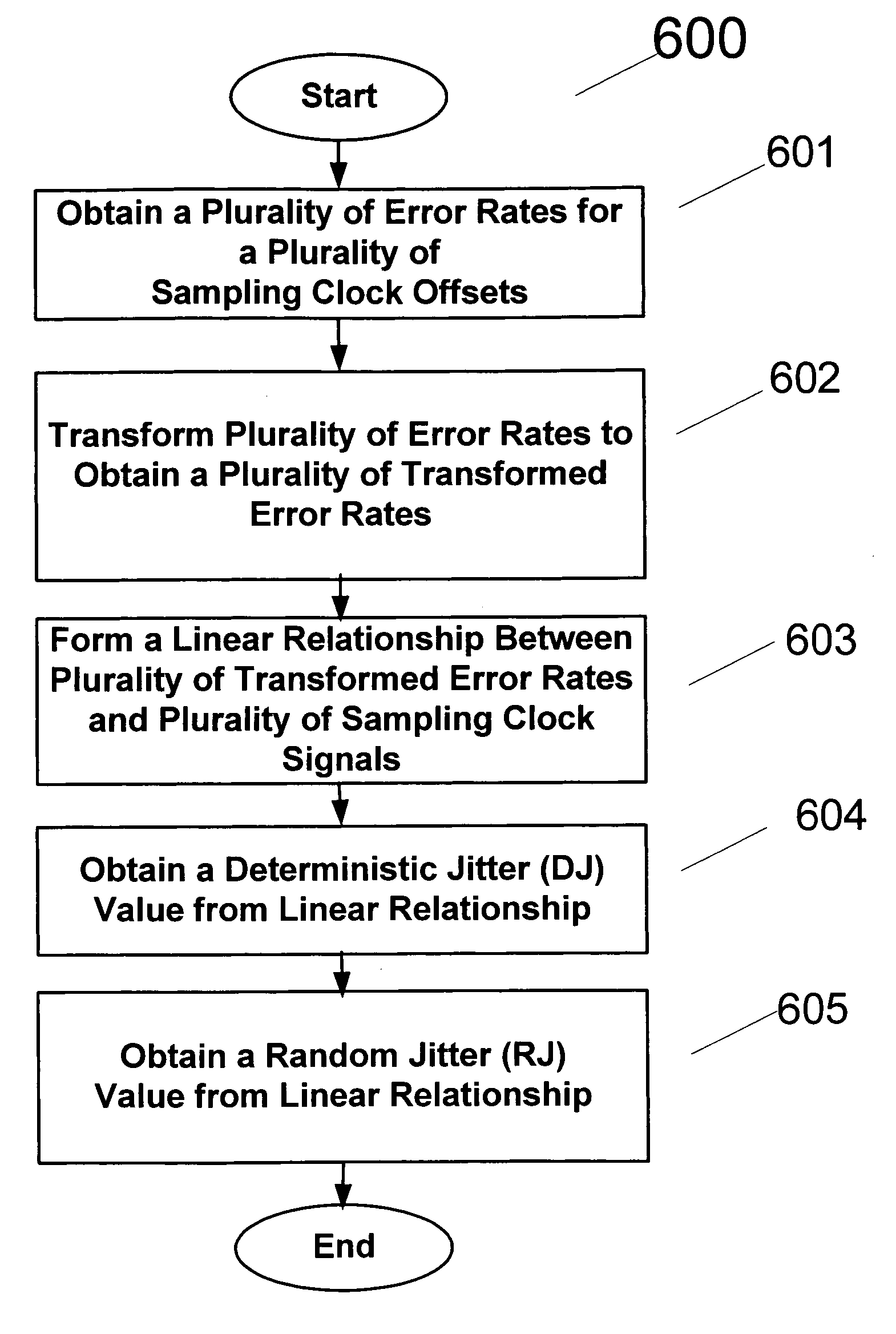
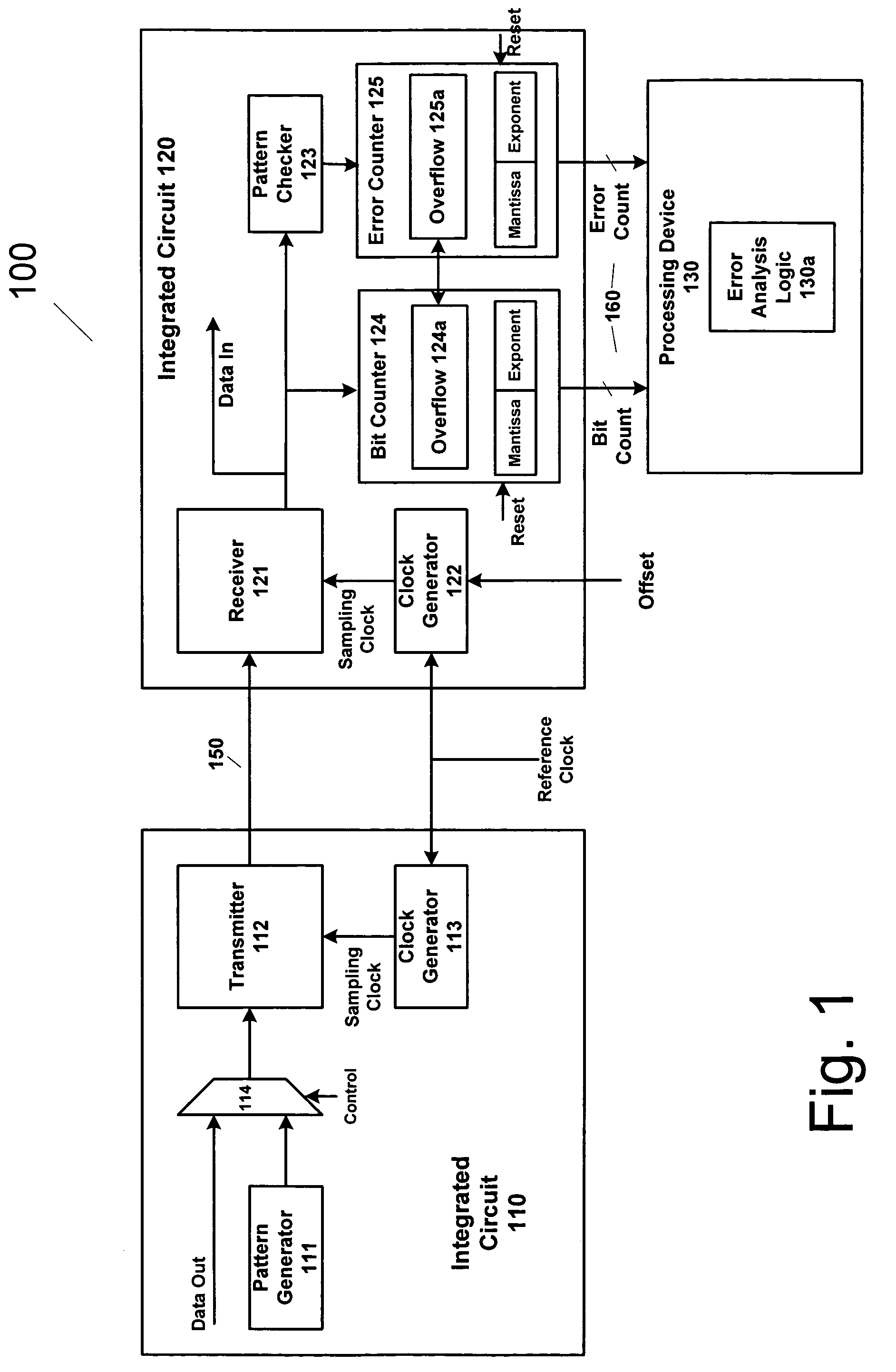
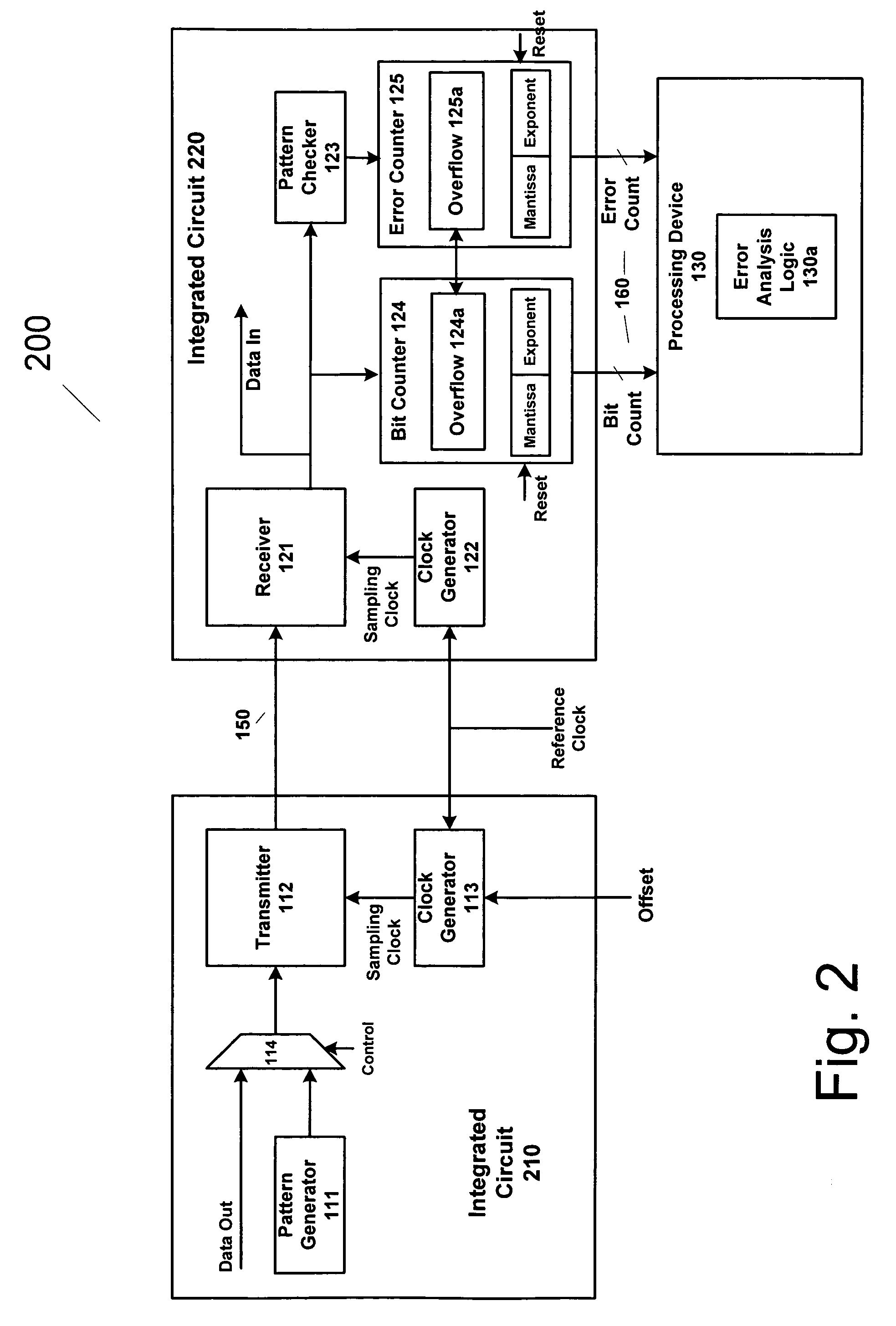
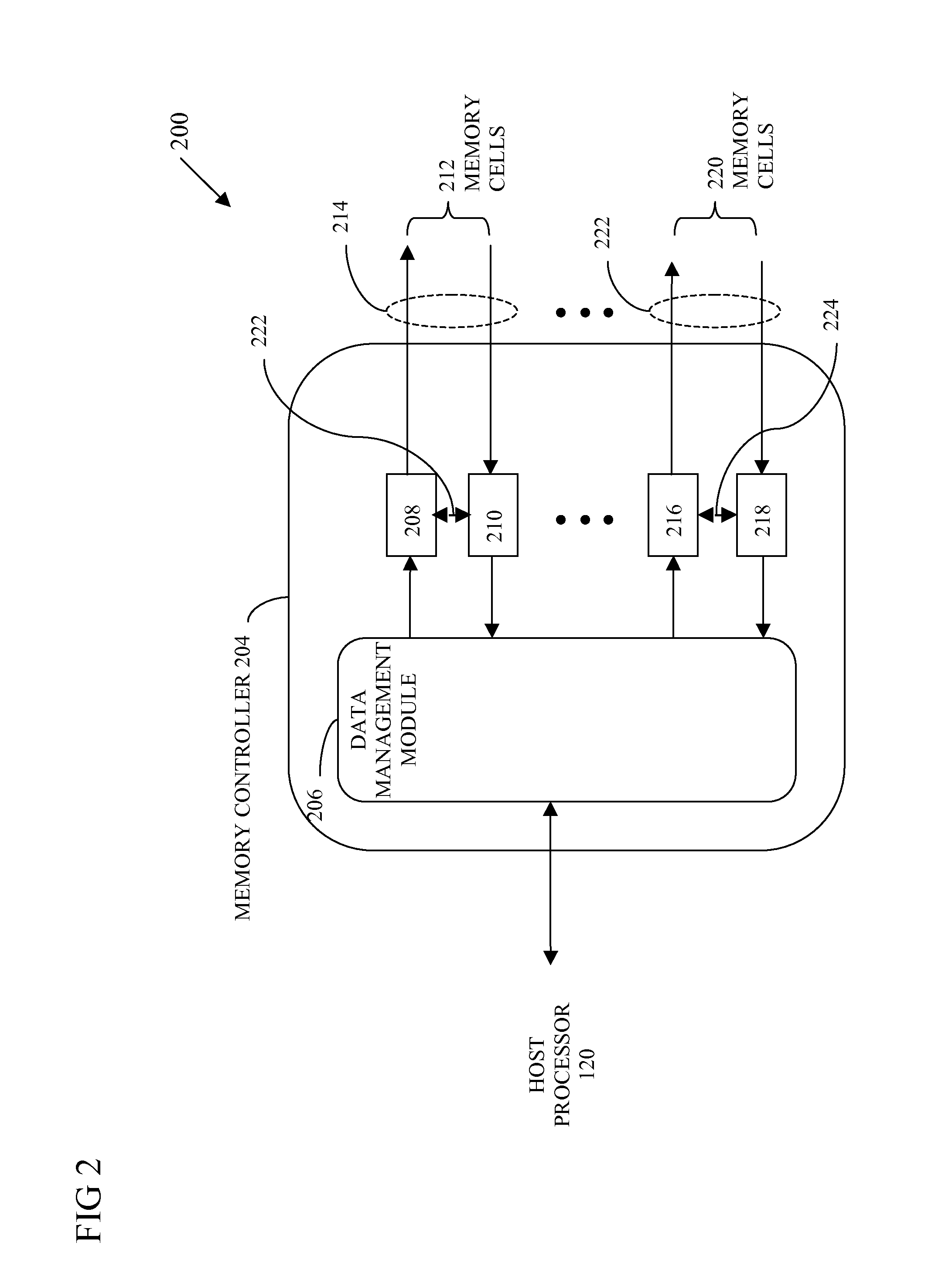
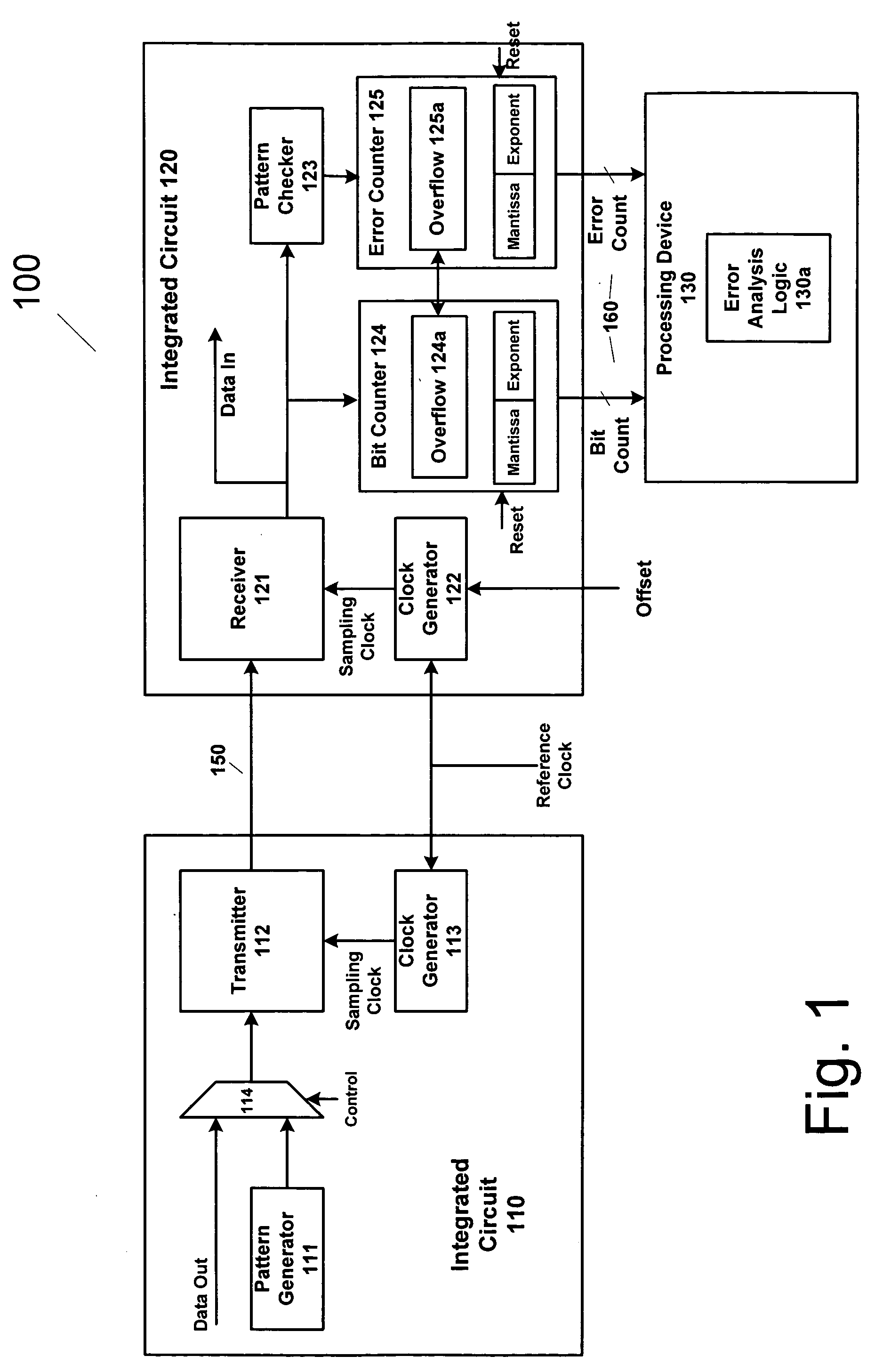
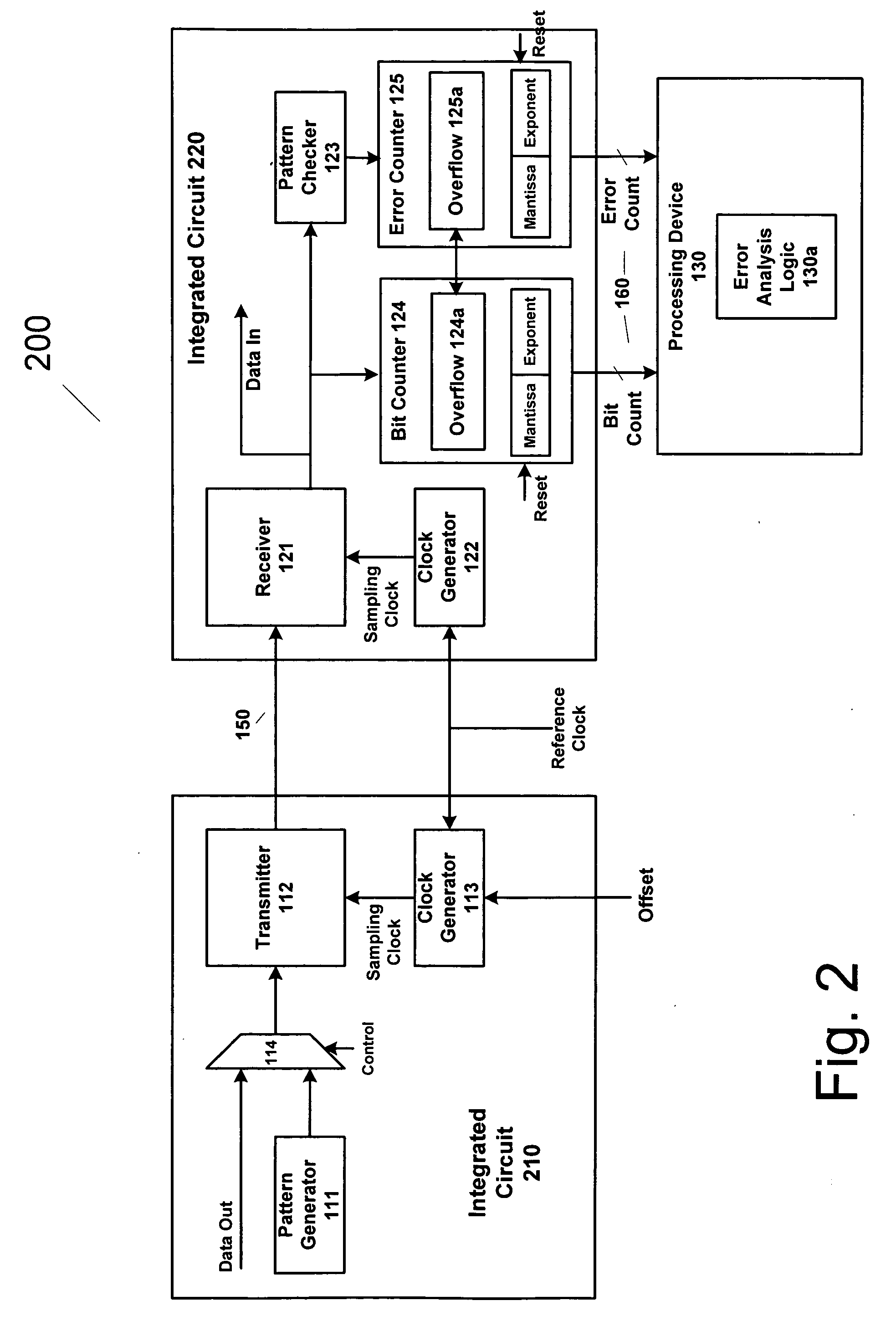
Method and apparatus for estimating random jitter (RJ) and deterministic jitter (DJ) from bit error rate (BER)
An apparatus and method provides prediction of BER for an interface between ICs, such as a processor and a memory device, without using special test equipment. A known data pattern or PRBS is transmitted to a receiver, which compares the received data values with expected data values to determine if a bit error has occurred in an embodiment of the present invention. A center of data eye and the edge of the data eye are sampled (over sampled) in order to determine if a bit error has occurred in an alternate embodiment of the present invention. A first counter is used to count the total number of bits sampled and the second counter is used to count the number of errors that occurred in the total number of bits sampled.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
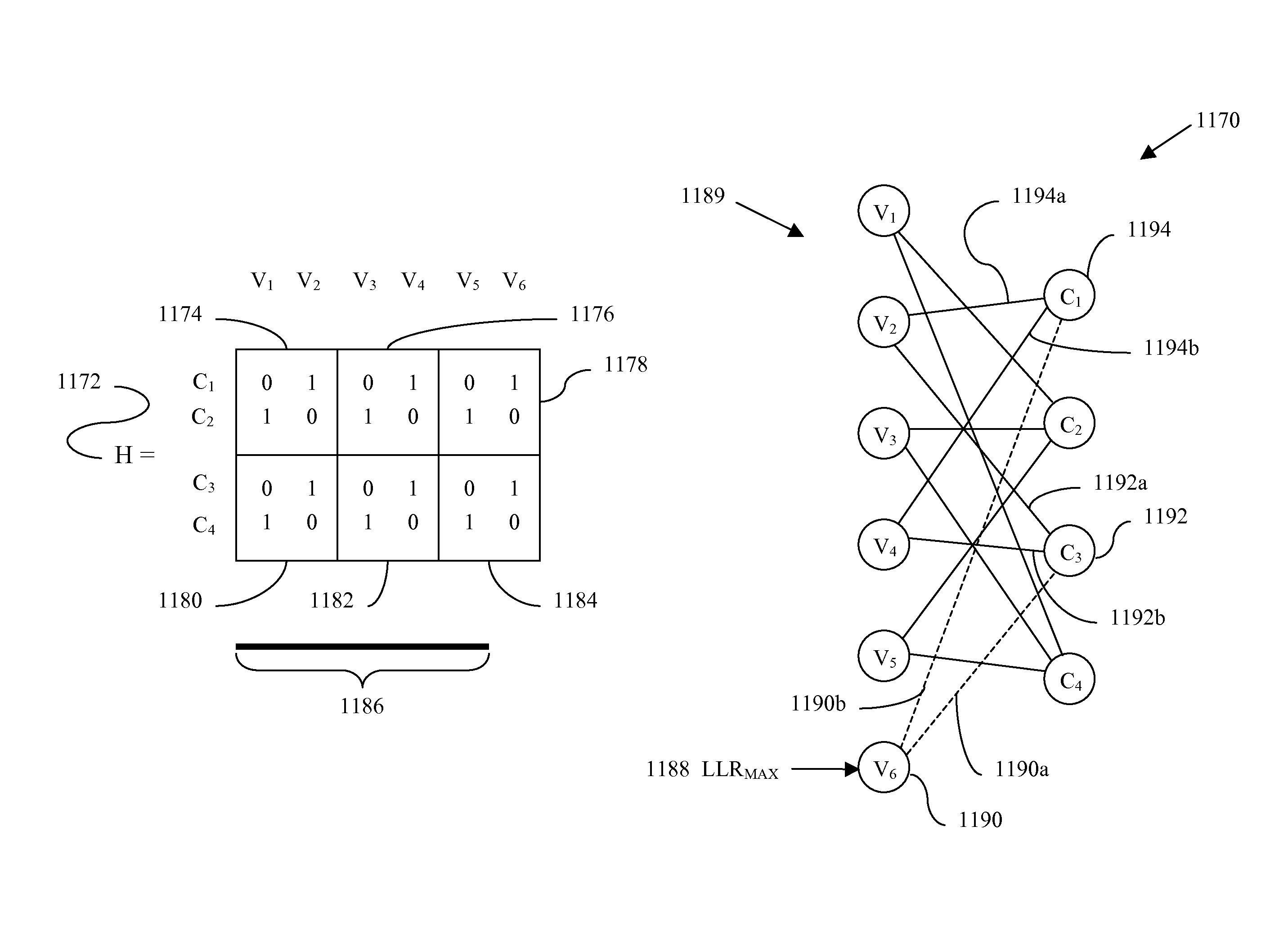
Apparatus and method for adjusting a correctable raw bit error rate limit in a memory system using strong log-likelihood (LLR) values
ActiveUS9128858B1Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresSingle parity checkComputer hardware
Apparatuses and methods for correcting errors in data read from memory cells of an integrated circuit device includes an encoder. The encoder is configured from a single parity check matrix and the encoder is configured to be virtually adjustable by setting a number of bits in the encoder to zero. A decoder is configured from the single parity check matrix and the decoder is configured to be virtually adjustable by setting a log-likelihood ratio (LLR) for a number of bits in the decoder to a strong value. A code-rate that the encoder and decoder uses can be changed by adjusting the number of bits in the encoder that are set to zero and the number of bits in the decoder that are set to the strong LLR value.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
Method and apparatus for estimating random jitter (RJ) and deterministic jitter (DJ) from bit error rate (BER)
An apparatus and method provides prediction of BER for an interface between ICs, such as a processor and a memory device, without using special test equipment. A known data pattern or PRBS is transmitted to a receiver, which compares the received data values with expected data values to determine if a bit error has occurred in an embodiment of the present invention. A center of data eye and the edge of the data eye are sampled (over sampled) in order to determine if a bit error has occurred in an alternate embodiment of the present invention. A first counter is used to count the total number of bits sampled and the second counter is used to count the number of errors that occurred in the total number of bits sampled. In an embodiment of the present invention, the first and second counters are logarithmic counters that include overflow protection. The counter values are output to a processing device to perform the BER calculation in an embodiment of the present invention. A plurality of BER values is then obtained for corresponding offsets. A subset of the plurality of BER values corresponding to the plurality of offsets is selected. An inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution (NormSlnv) function for respective BER values is calculated. Two linear fits on the transformed BER values and offsets are performed to obtain the x-intercepts that correspond to a DJ component and the slopes corresponding to a RJ component. The DJ and RJ components are used with the Fibre Channel jitter model equation to predict BER as a function of transition density and offset value.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
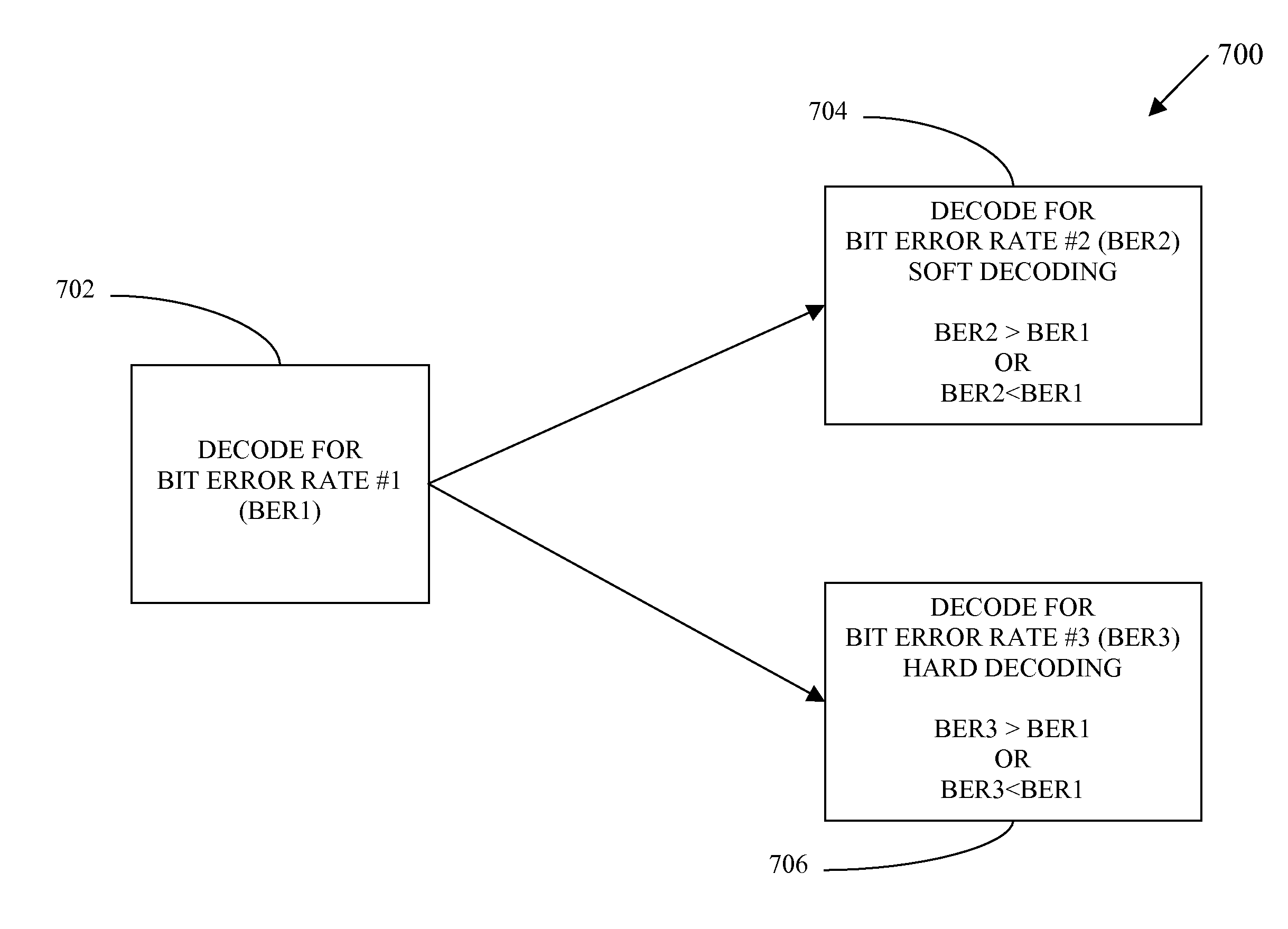
Apparatus and method based on LDPC codes for adjusting a correctable raw bit error rate limit in a memory system
ActiveUS9092353B1Reduce in quantityOther decoding techniquesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputer hardwareMemory controller
Systems and methods for correcting errors in data read from memory cells include a memory controller, which includes an encoder, and a decoder. The memory controller is configured to adjust a correctable raw bit error rate limit to correct different bit error rates occurring in data read from the memory cells. The correctable raw bit error rate limit is adjusted by switching the decoding between hard-decision decoding and soft-decision decoding, wherein a number of soft bits allocated for message values can be changed during soft-decision decoding. The correctable raw bit error rate is adjusted by changing the code-rate within the memory system while making virtual adjustments to the same encoder and decoder.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
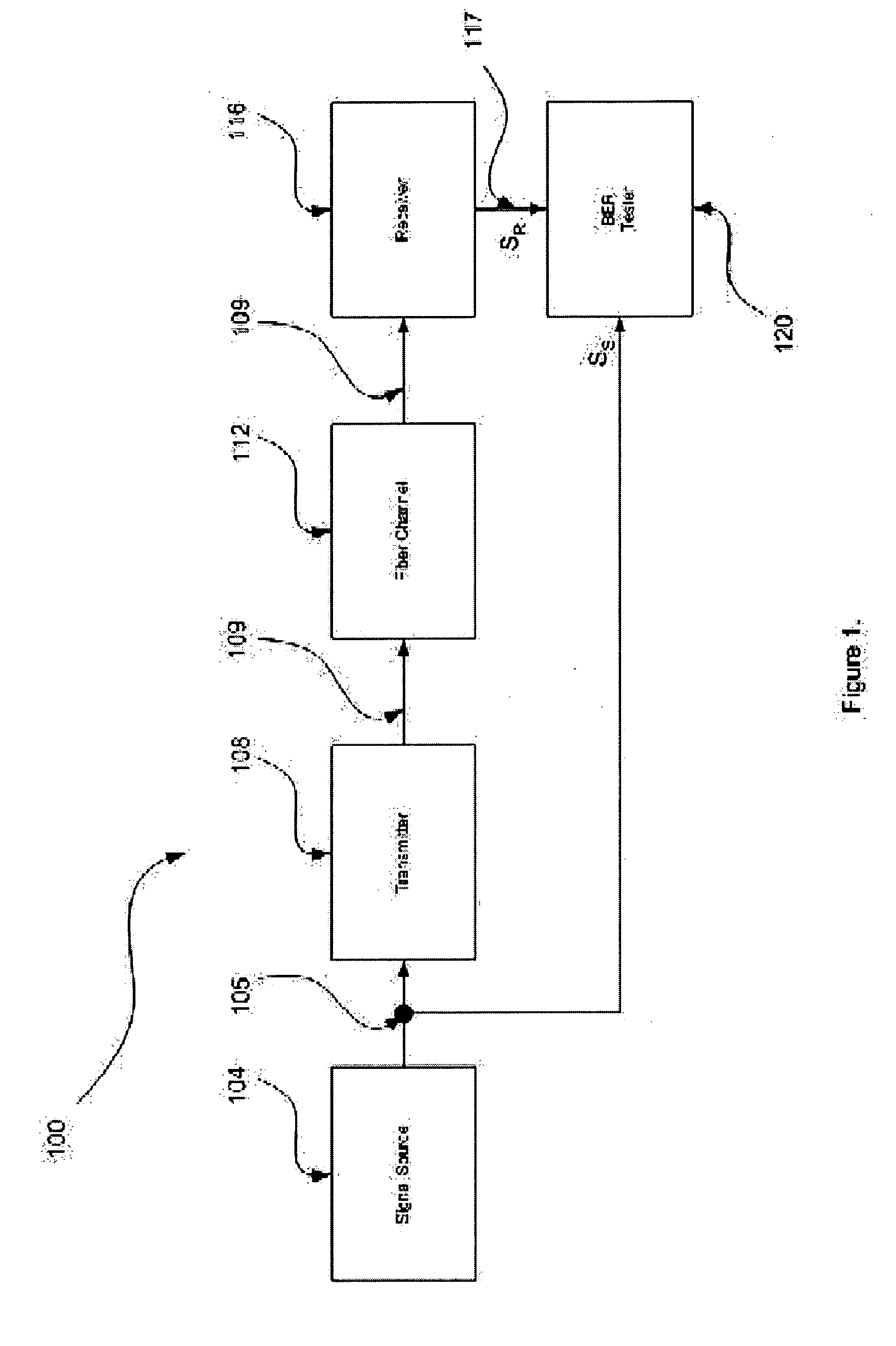
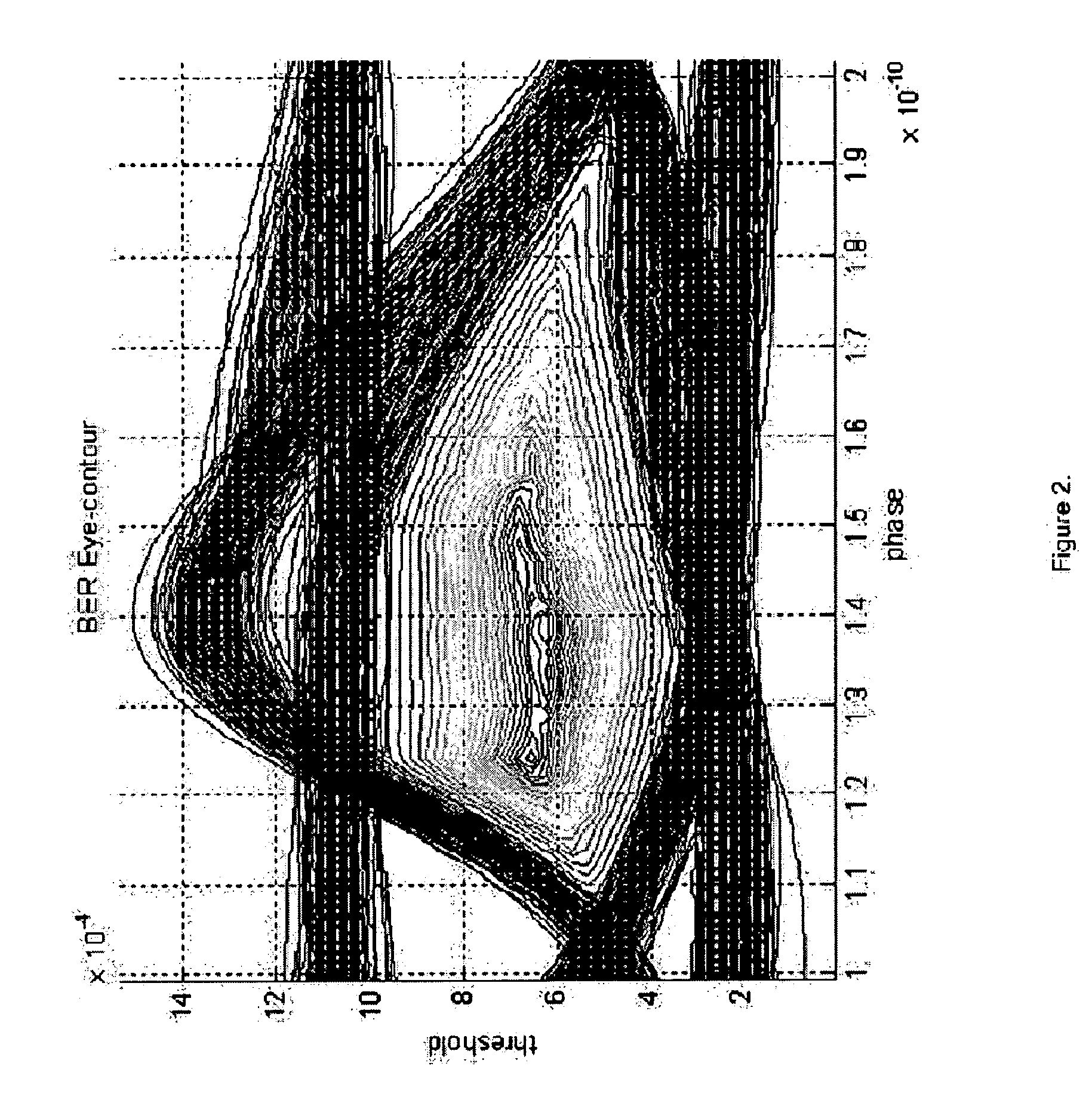
Method and system for determining receiver power for required bit error rate
InactiveUS20070003280A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsCommunications systemContour diagram
A method and system for determining a receiver power for a required bit error rate (BER) in an optical communication systems is disclosed. A signal is transmitted using an initial transmitter power and is received at a receiver. A BER contour diagram is created by measuring high BER values and approximating low BER values from the high BER values. The optimum decision threshold and / or sampling phase is determined from the contour diagram and the BER is calculated at the optimum decision threshold and / or at the optimum sampling phase. If the calculated BER is not close to or equal to the required BER, the transmitter power is adjusted until the calculated BER is close to or equal to the required BER. The receiver power is then calculated from the transmitter power or directly measured from the received signal.
Owner:MINDSPEED TECH INC
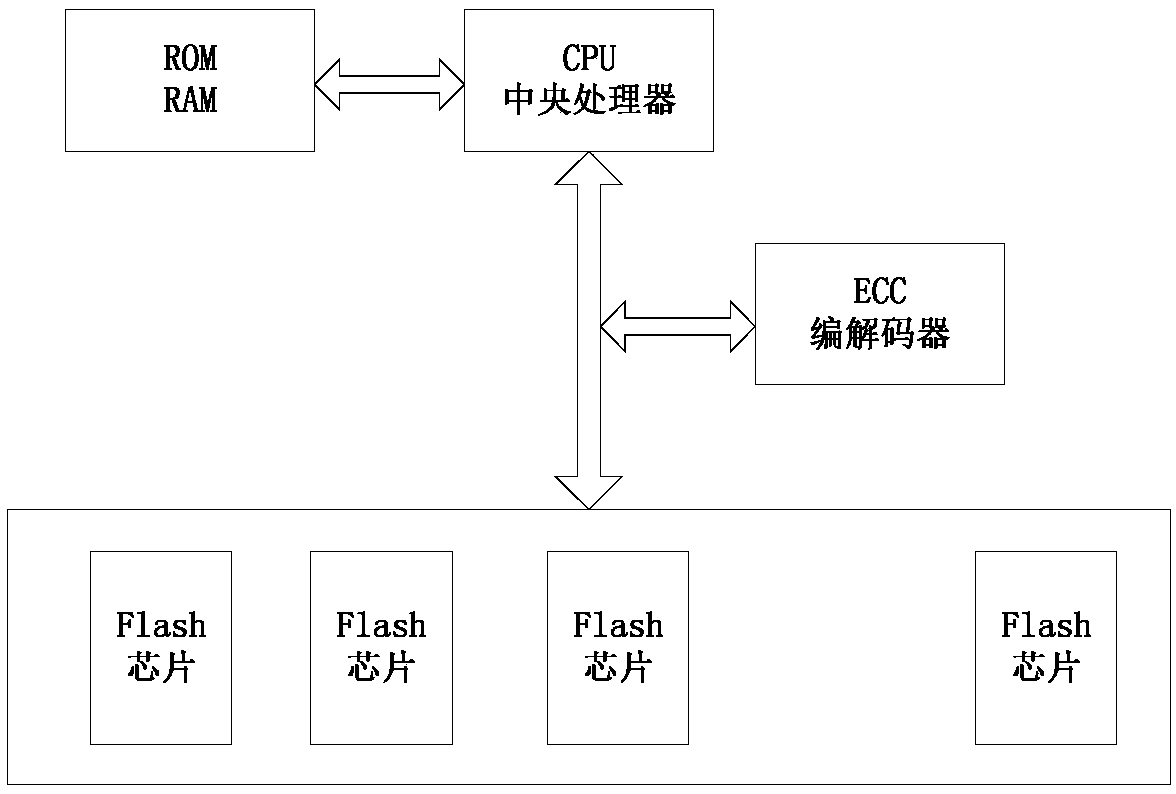
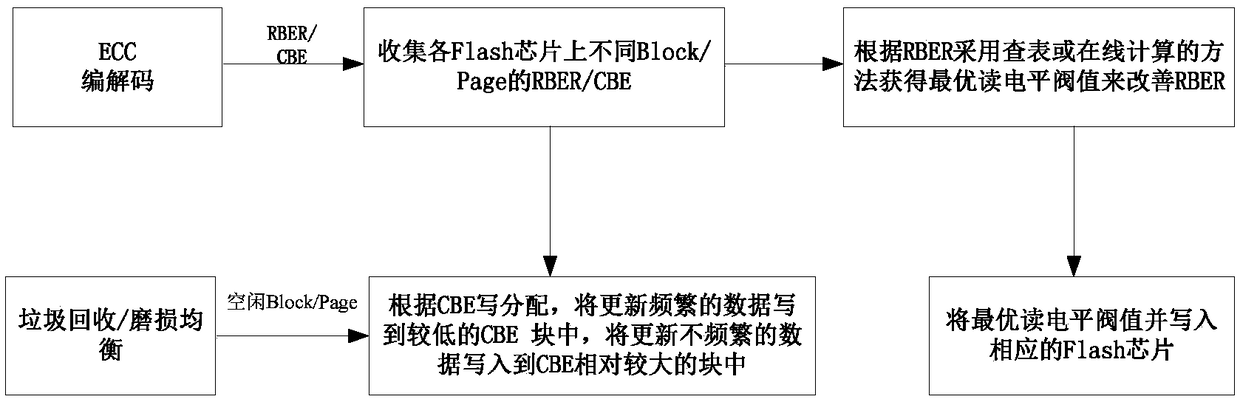
Method for prolonging Flash abrasion life, control device and storage system
ActiveCN108628552ADelay the speed of damageIncreased wear lifeMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersReading levelEmbedded system
The invention discloses a method for prolonging Flash abrasion life, a control device and a storage system. The method includes the steps that the original error rates RBER and the correction error rates CBE of different Blocks / Pages on all Flash chips are collected; when the RBER is increased to a certain degree, the optimal reading level threshold values of the corresponding Blocks / Pages are calculated and written in the corresponding Flash chips; the vacant Blocks / Pages are classified according to the CBE, the Blocks / Pages with the low CBE are distributed to data with high update frequency,and the Blocks / Pages with high CBE are distributed to data with low update frequency. On one hand, by adjusting the reading level threshold values, the RBER is reduced, on the other hand, the damagespeeds of the blocks can be reduced through the update characteristics of matched data and Endurance abrasion of Flash, and the abrasion life of the Flash is prolonged. The method, the control deviceand the storage system can be applied to multiple fields such as solid state disks, disk arrays, solid state caches, distributed storage systems and big data application, and have wide application prospects.
Owner:南京道熵信息技术有限公司
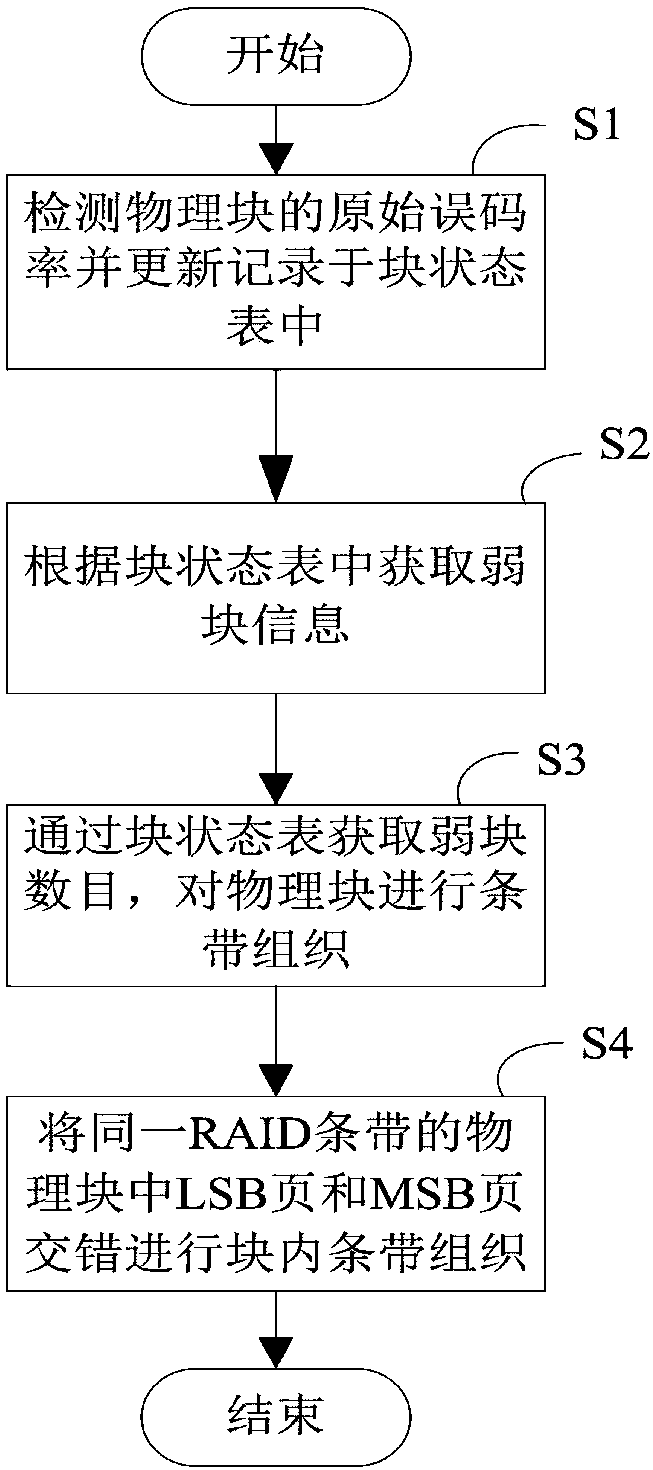
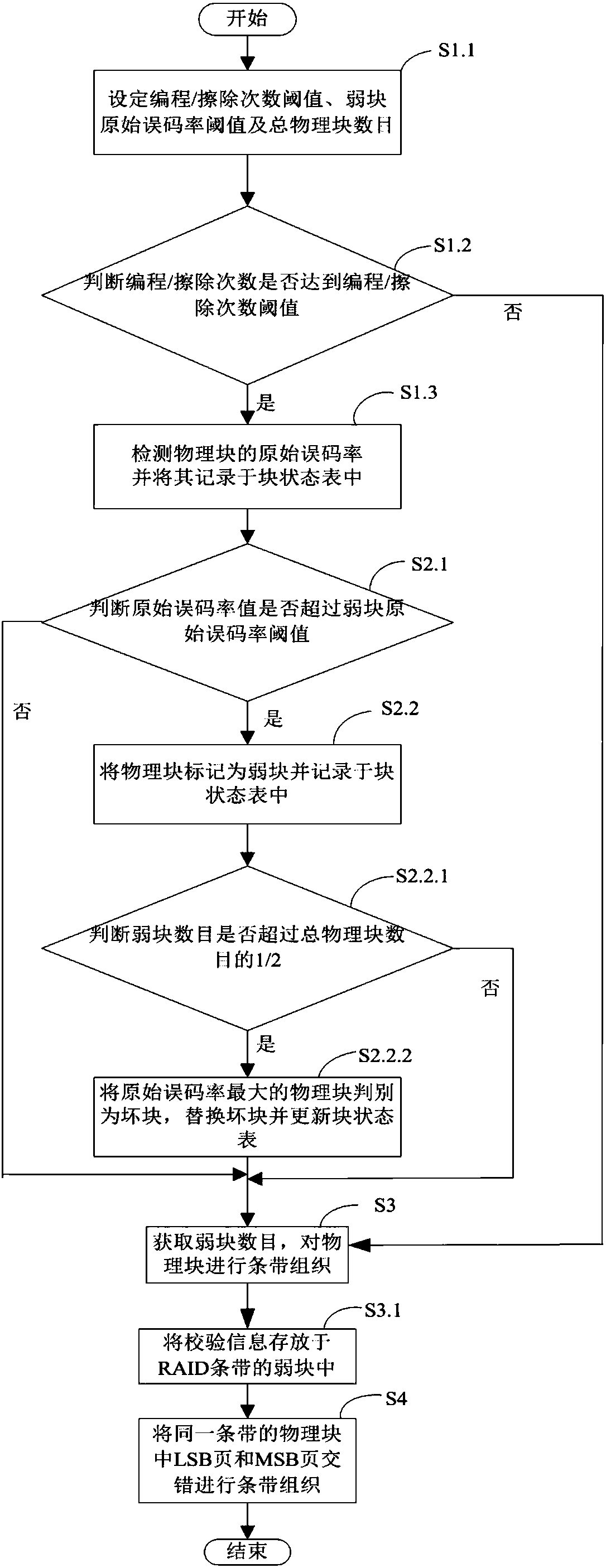
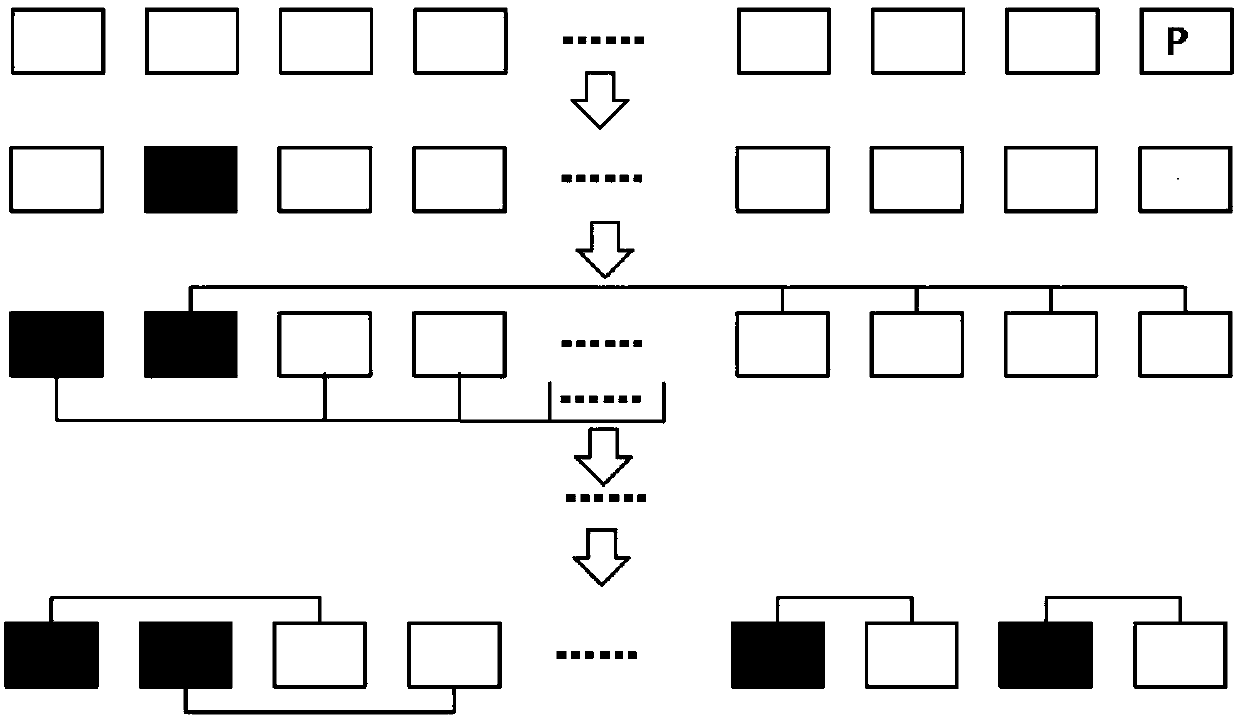
RAID stripe reconstruction method and solid state disk
ActiveCN107678694AImprove reliabilityExtend your lifeInput/output to record carriersRAIDReconstruction method
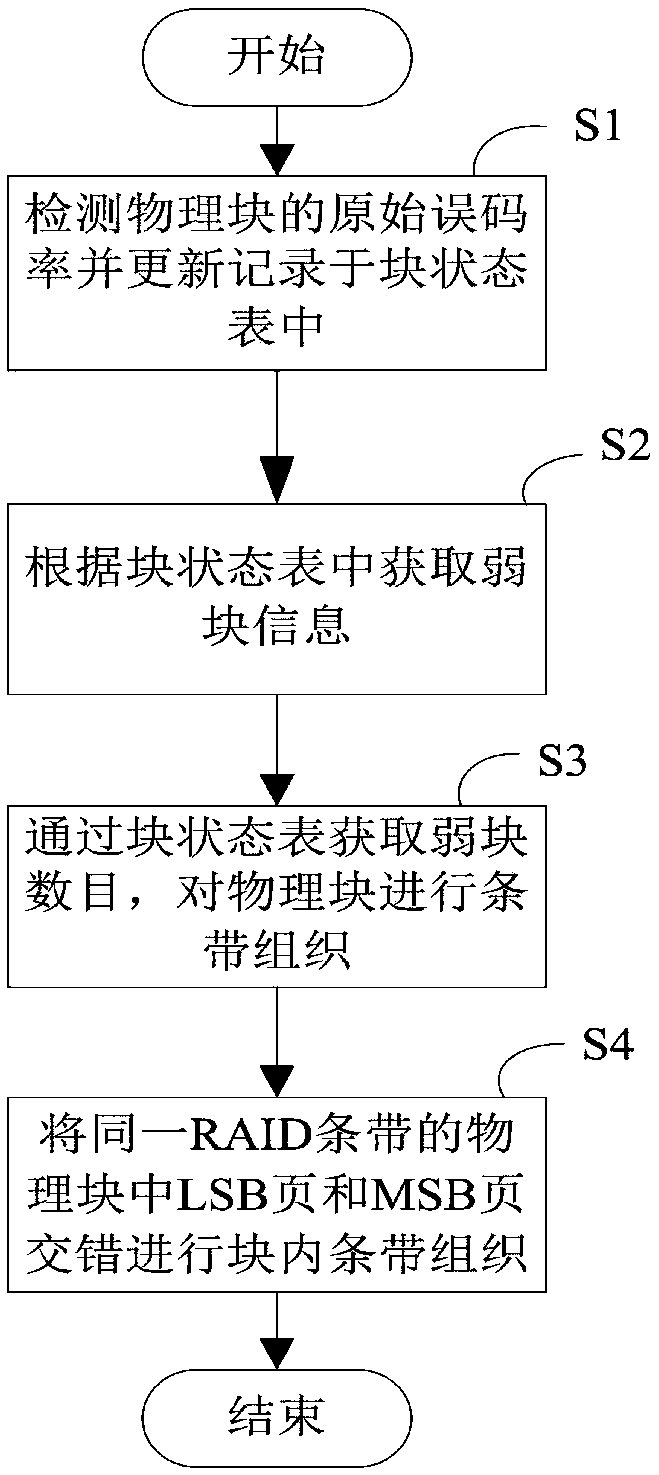
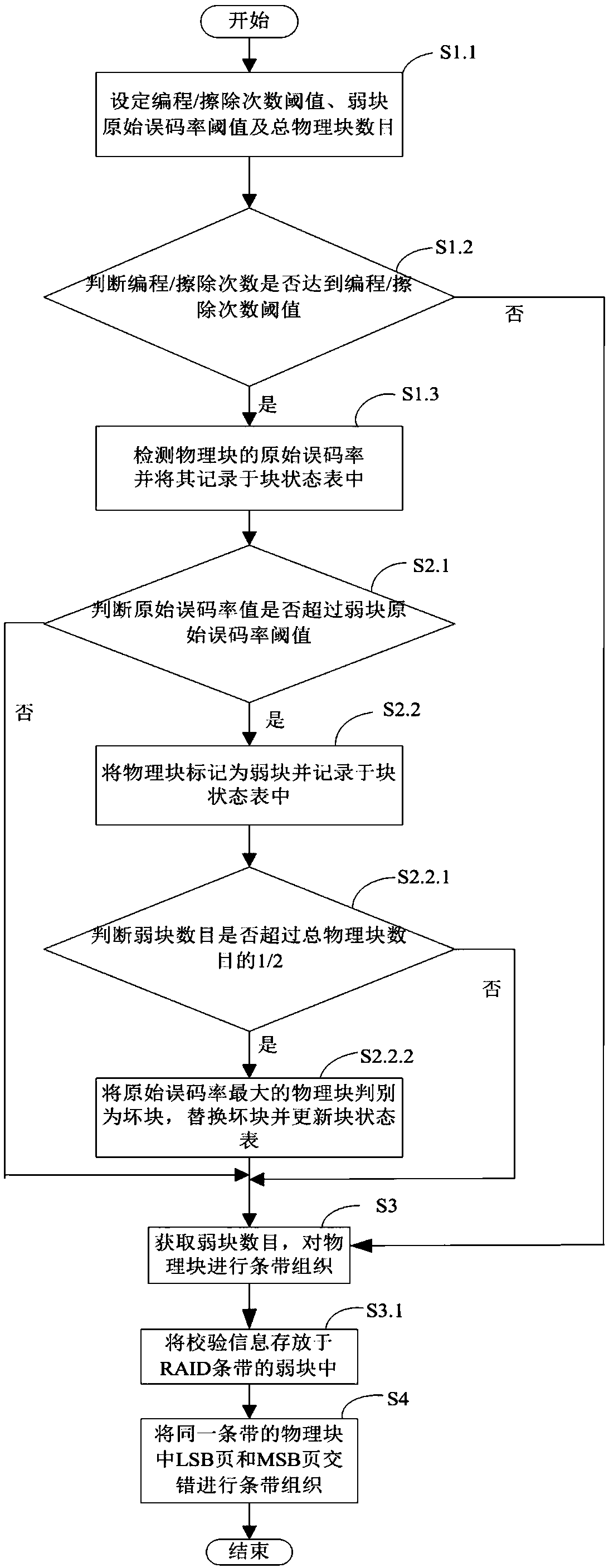
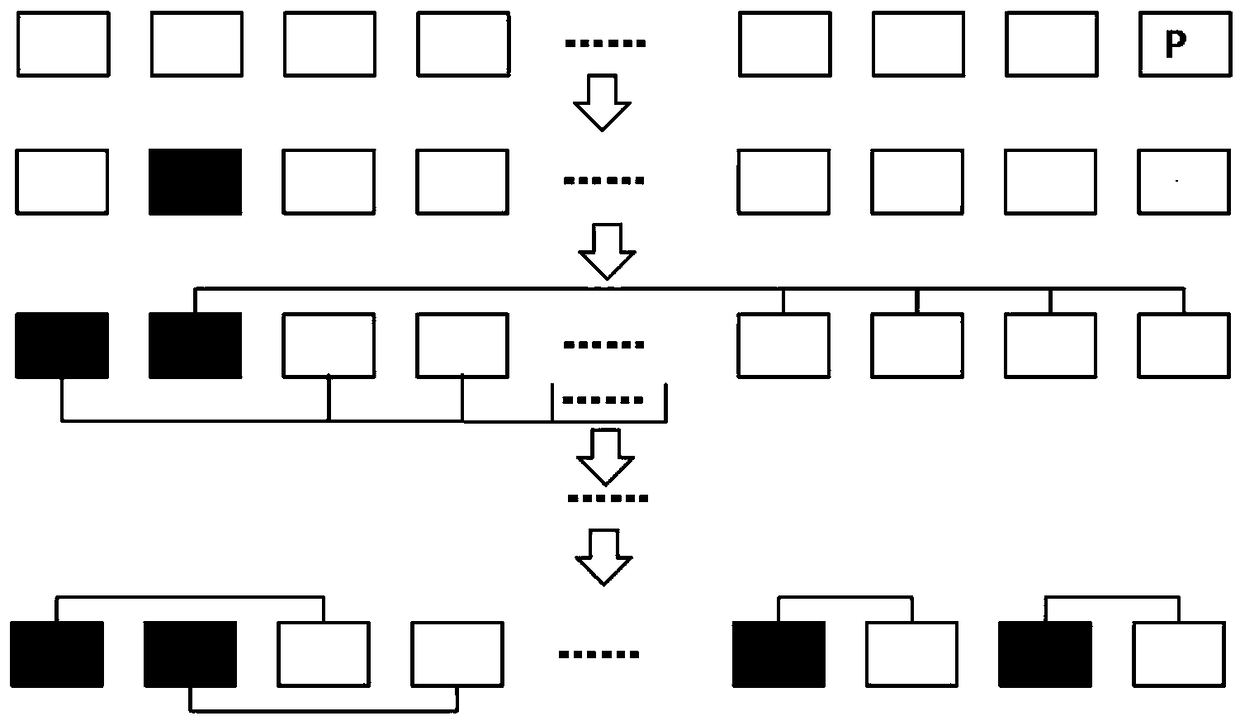
The invention discloses an RAID stripe reconstruction method applied to a solid state disk. The method is used for recombining physical block groups of an RAID memory array to form a new RAID stripe.The method comprises the steps of S1, detecting original error rates of physical blocks and updating and recording the original error rates in a block state table; S2, according to the original errorrates in the block state table, obtaining weak block information; S3, obtaining a weak block quantity through the block state table, and performing stripe organization for the physical blocks; and S4,performing block internal stripe organization in a staggered way for LSB pages and MSB pages of the physical blocks in a same RAID stripe. According to the RAID stripe reconstruction method, dynamicadjustment of the RAID stripe of the solid state disk is realized; data loss is avoided; storage space waste is avoided; the reliability of the solid state disk is improved; and the service life of the solid state disk is prolonged. Meanwhile, the invention furthermore discloses the solid state disk. The solid state disk comprises the RAID memory array and a controller used for performing adaptiveadjustment on the RAID memory array and managing data stored in the array.
Owner:SHENZHEN DAPU MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and device for calculating bit error rate of received signal
InactiveUS7607053B2Reduce the amount of calculationGood estimateData representation error detection/correctionError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorDigital radioData field
System and method of estimating radio channel bit error rate (BER) in a digital radio telecommunications system wherein the soft output of the turbo decoder is used as pointer or index to look-up-tables containing the bit-wise BER of a certain bit in the data field of the received frame. A quantizer quantizes the received data frame and the quantized bit operates on a switch which selects the appropriate look-up-table. By means of accumulation and scaling the average BER of a certain amount of bits are calculated. Decoding bit-errors may occur but as they are submitted to posterior probability estimation, systematic errors which normally happen at low SNR are avoided.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
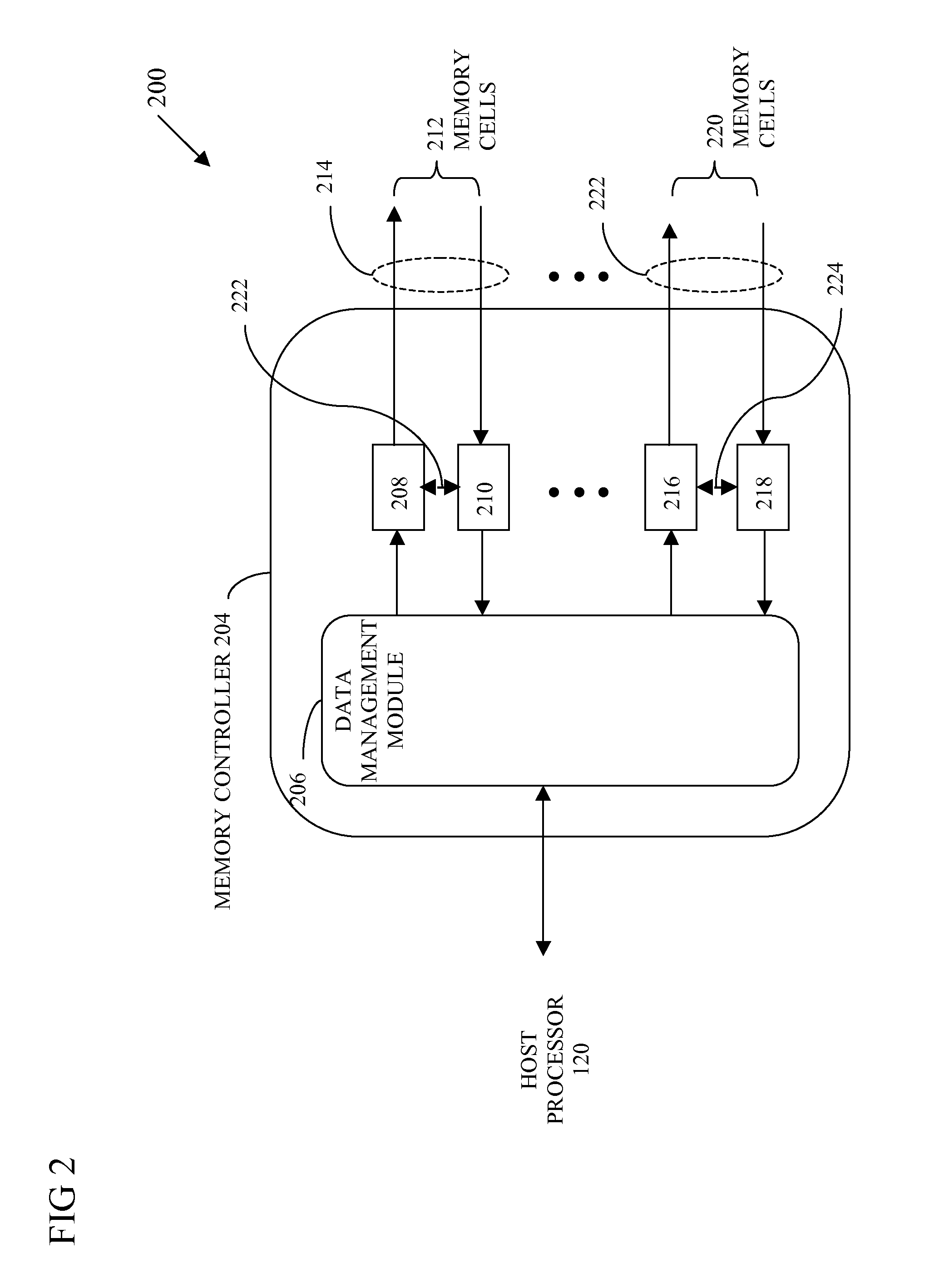
Memory controller and integrated circuit device for correcting errors in data read from memory cells
ActiveUS9448881B1Reduce in quantityOther decoding techniquesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsControl storeData management
An integrated circuit device for correcting errors in data read from memory cells includes a decoder, an encoder and a data management module. The data management module is configured to select a correctable raw bit error rate limit from a plurality of raw bit error rate limits by changing a code-rate used by the encoder, wherein a virtual change to the decoder and the encoder occur to change the code rate.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
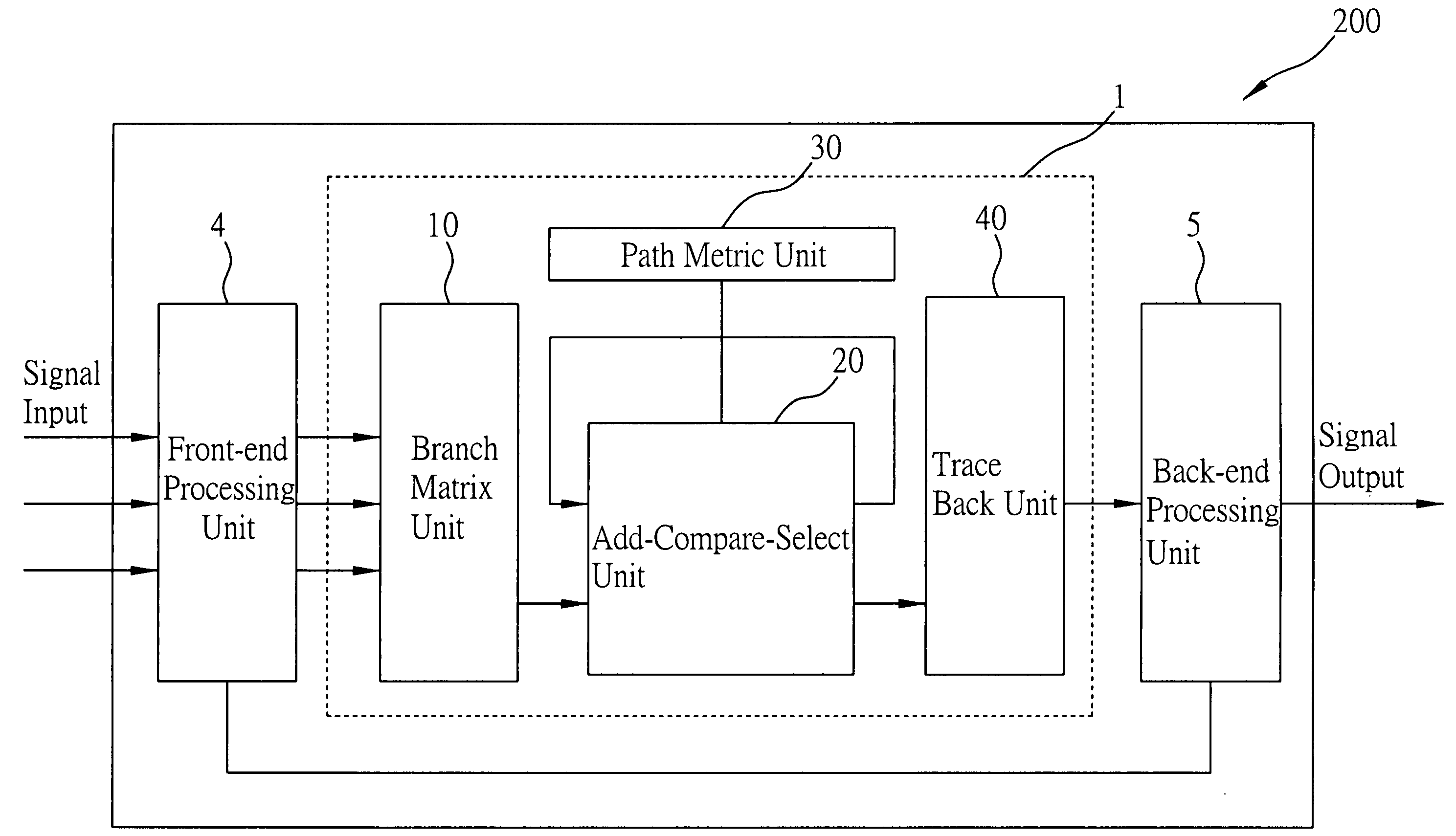
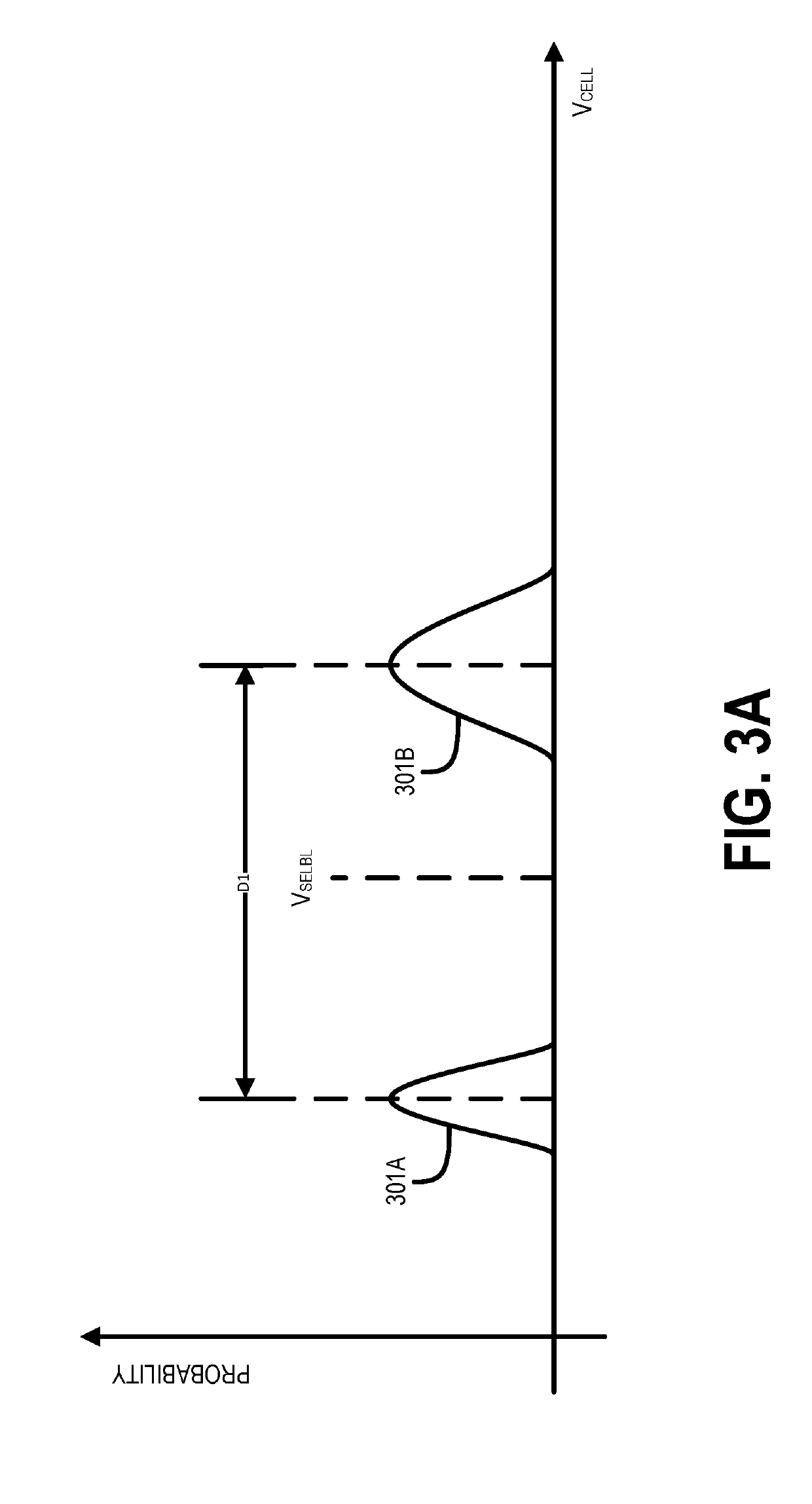
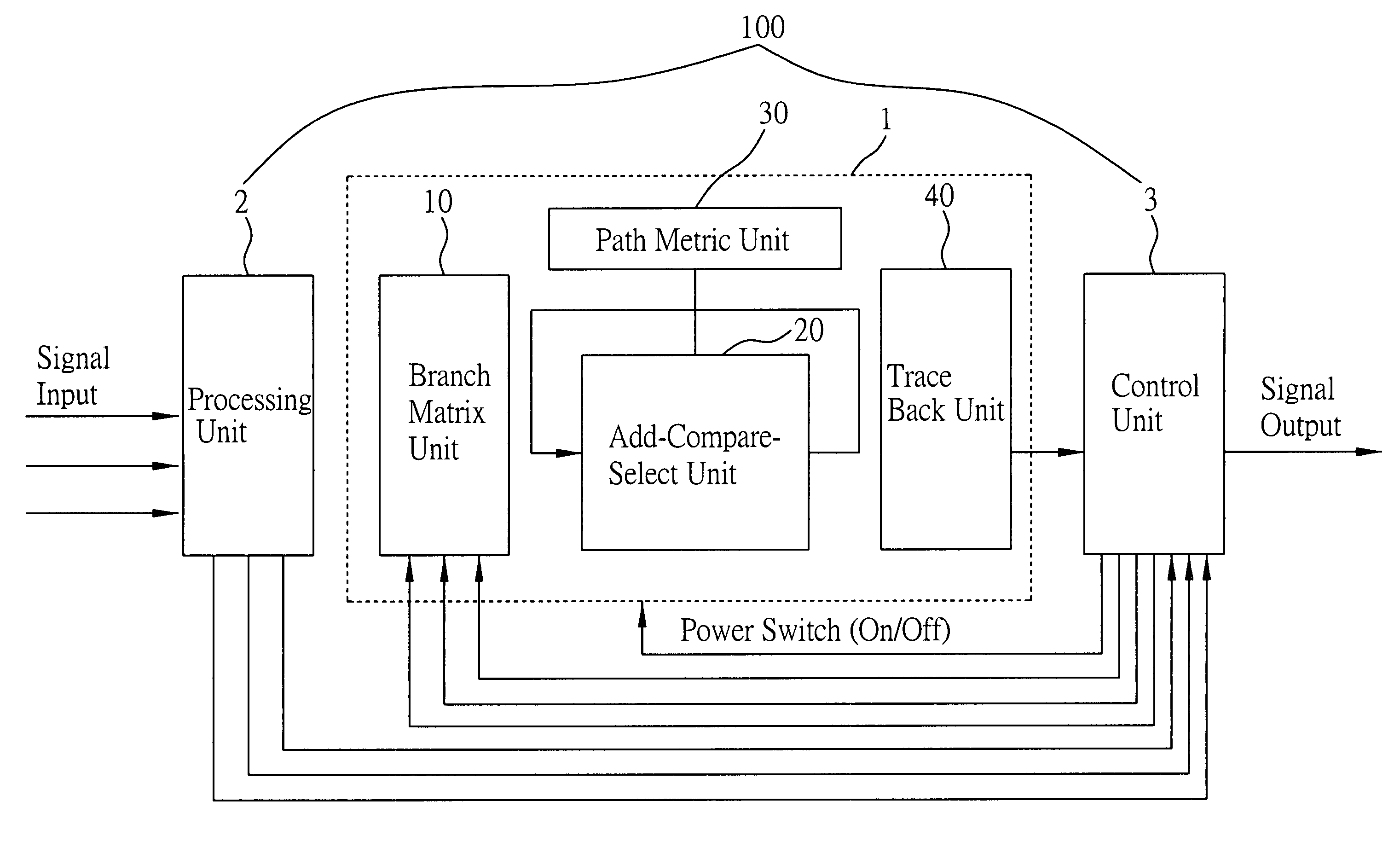
Dynamic power adjusting device for viterbi decoder
ActiveUS20070277081A1Reduce bit error rateLess powerError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwareViterbi decoder
A dynamic power adjusting device for a Viterbi decoder is disclosed. The device includes a processing unit for receiving a plurality of data to be decoded, detecting whether the data to be decoded have any bit errors, and estimating a number of the bit errors of the data. The device further includes a control unit for receiving the bit errors and the number of the bit errors of the data detected by the processing unit, so as to enable the Viterbi decoder to perform decoding, and disable the Viterbi decoder after the Viterbi decoder has performed the decoding the number of times equivalent to the number of the bit errors. By way of the dynamic adjustment technique, coupled with the bit-error detection and estimation, workload of the Viterbi decoder in operation is capable of being adjusted according to bit error rate (BER) such that less power is consumed in a decoding process.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Data recovery method and system used for flash memory
ActiveCN108717385AReduce raw bit error rateRedundant data error correctionRedundant operation error correctionRecovery methodOriginal data
The application discloses a data recovery method and system used for a flash memory. The method includes: reading original data on the basis of default reading voltage when the flash memory receives areading command; carrying out ECC (Error Correcting Code) checking on the original data, and judging whether a first error number is greater than maximum ECC error-correction capability; when the first error number is greater than the maximum ECC error-correction capability, determining rereading voltage by rereading error-correction, carrying out ECC checking on data read by the rereading voltage, and judging whether a second error number is greater than the maximum ECC error-correction capability; and when the second error number is greater than the maximum ECC error-correction capability,carrying out compensation on threshold voltage of a storage unit, and obtaining optimal reading voltage by rereading error-correction until a third error number after ECC checking on data read by theoptimum reading voltage is less than or equal to the maximum ECC error-correction capability. The method is capable of recovering flash memory data by combining data rereading and compensation, and effectively reduces an original bit error rate as compared with the prior art.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Combiner/TMUX simulated B1 transparency in fiber optic networks running SONET
InactiveUS6826200B1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommon baseFiber
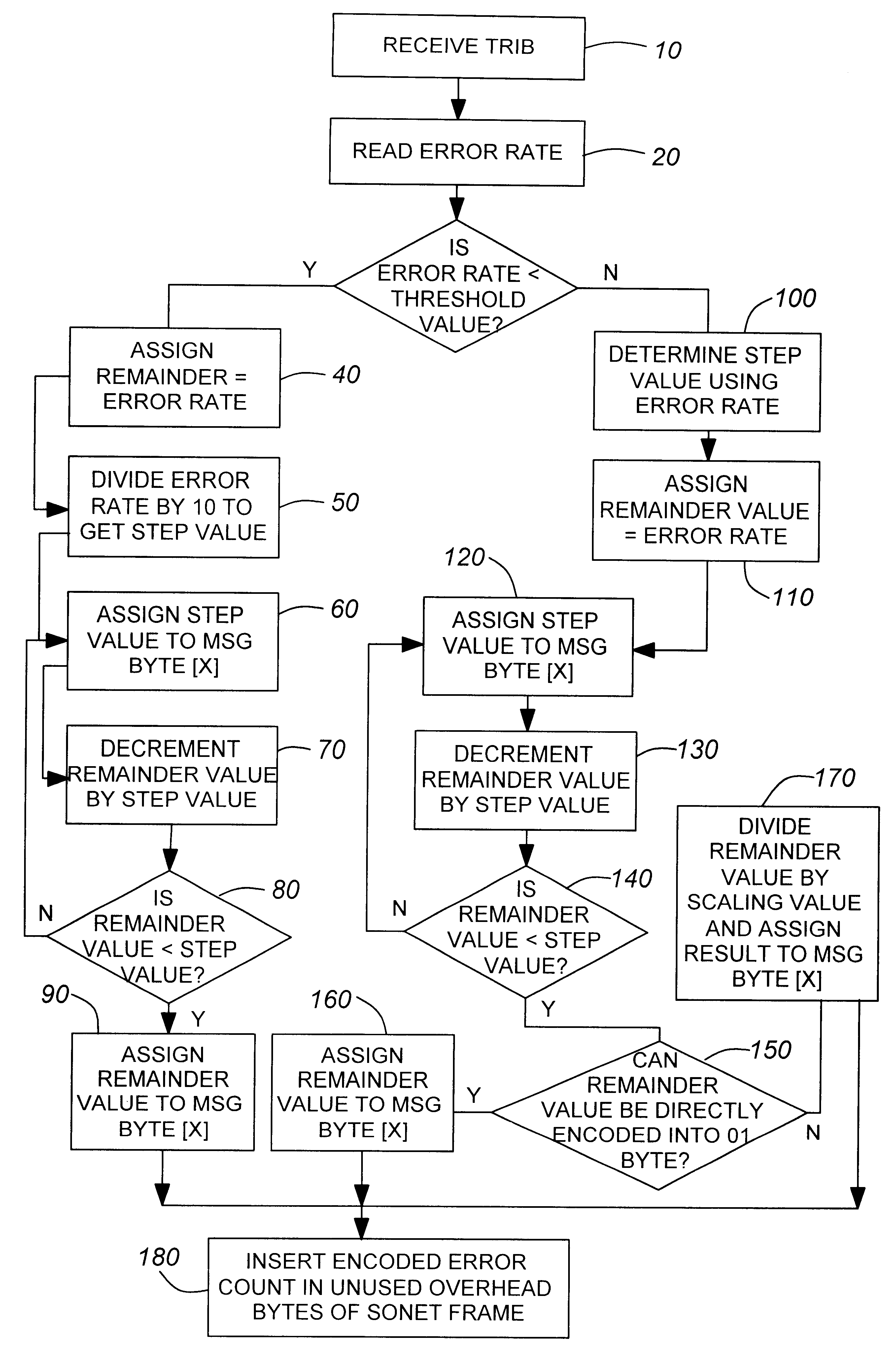
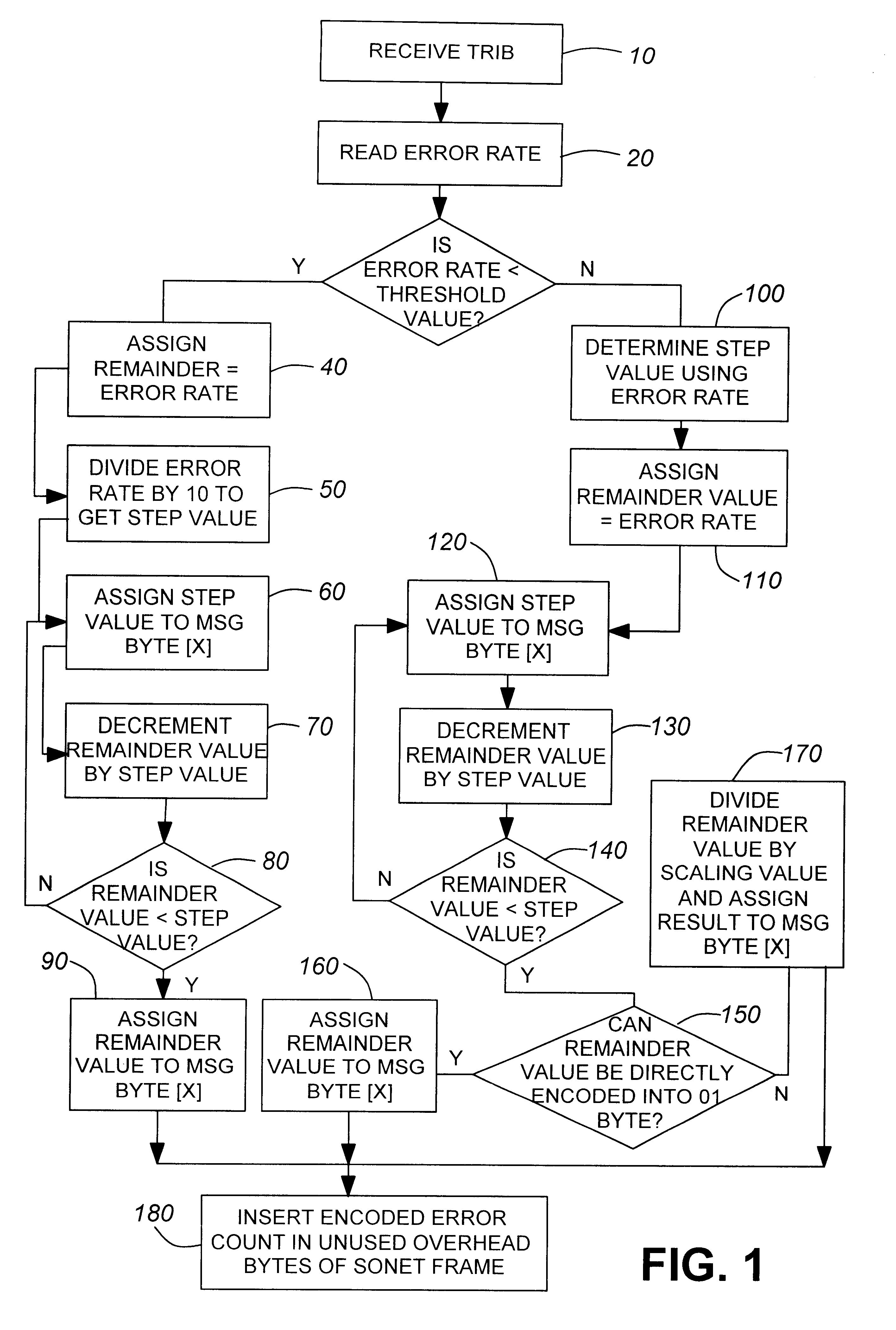
The present invention overcomes the shortcomings of the prior art by providing a method of encoding bit error rates using a two-tiered system. If the bit error rate is less than a threshold value, the bit error rate is directly encoded in binary into substantially equal portions. However, if the error rate is equal to or greater than the threshold value, the error rate is encoded into equal valued amounts using a common step value. A remainder amount is also formulated to account for any remainders. Multiplying the equal valued amounts that are scaled by a common base value and then adding it all up along with the remainder amount results in a value which is at worst, within 0.2% of the original bit error rate value.
Owner:CIENA
Hierarchical buffering scheme to normalize non-volatile media raw bit error rate transients
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Dynamic power adjusting device for viterbi decoder
ActiveUS7810019B2Addressing slow performanceReduce bit error rateError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwareViterbi decoder
A dynamic power adjusting device for a Viterbi decoder is disclosed. The device includes a processing unit for receiving a plurality of data to be decoded, detecting whether the data to be decoded have any bit errors, and estimating a number of the bit errors of the data. The device further includes a control unit for receiving the bit errors and the number of the bit errors of the data detected by the processing unit, so as to enable the Viterbi decoder to perform decoding, and disable the Viterbi decoder after the Viterbi decoder has performed the decoding the number of times equivalent to the number of the bit errors. By way of the dynamic adjustment technique, coupled with the bit-error detection and estimation, workload of the Viterbi decoder in operation is capable of being adjusted according to bit error rate (BER) such that less power is consumed in a decoding process.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Storage system with data reliability mechanism and method of operation thereof
PendingCN109471808AMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesComputer hardwareOriginal data
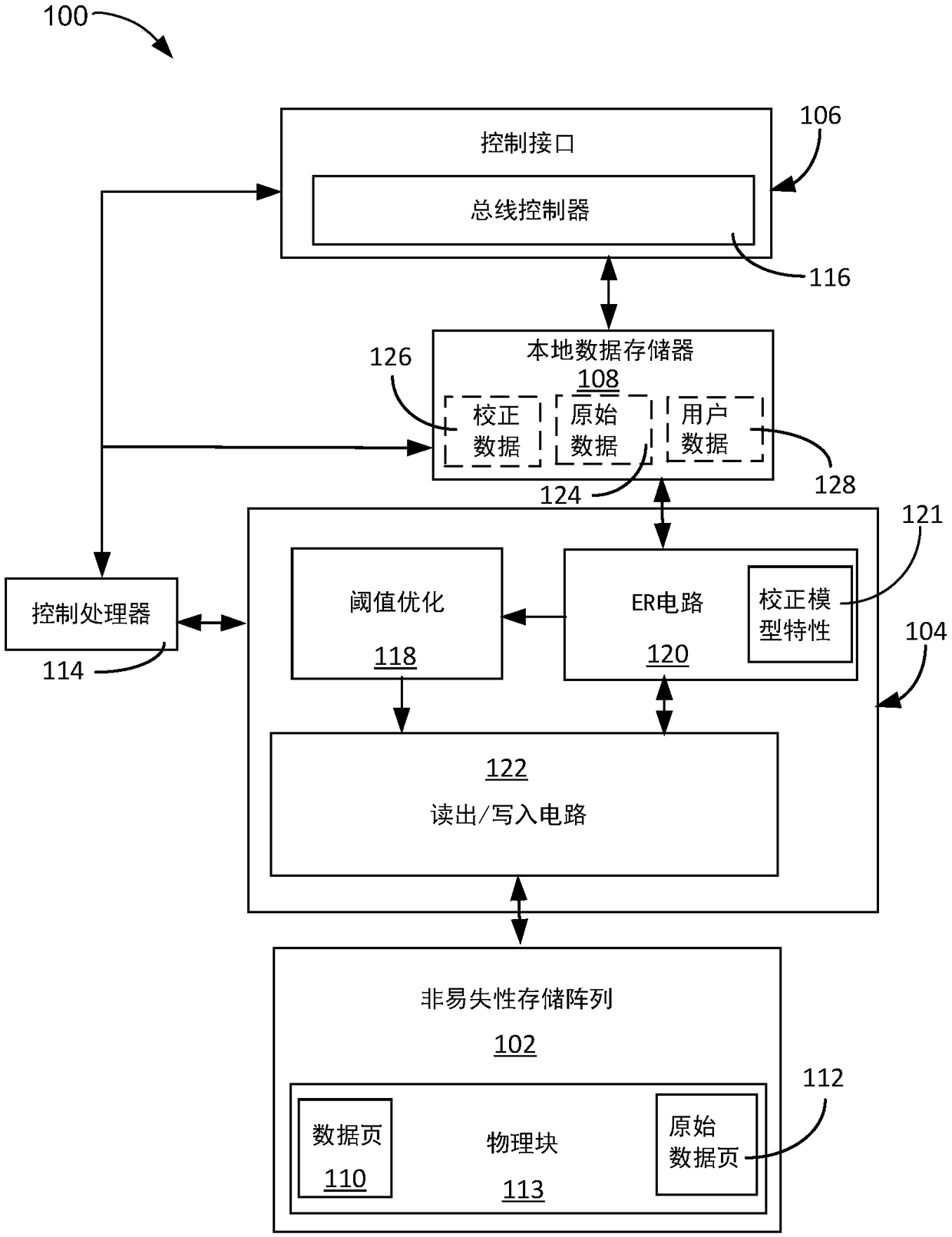
A storage system includes: a control processor unit, configured to: initiating a read of a raw data page, having correctable errors, calculating a raw bit error rate (RBER) (EQ1) by correcting the correctable errors to become corrected data and comparing raw data with the corrected data, and calculating a correction model characterization based on the RBER (EQ1); and a non-volatile storage array,coupled to the control processor unit, configured to store a processed data page in a physical block with the raw data page; and wherein the control processor unit is further configured to apply the correction model characterization to the raw data page in the physical block.
Owner:CNEX LABS
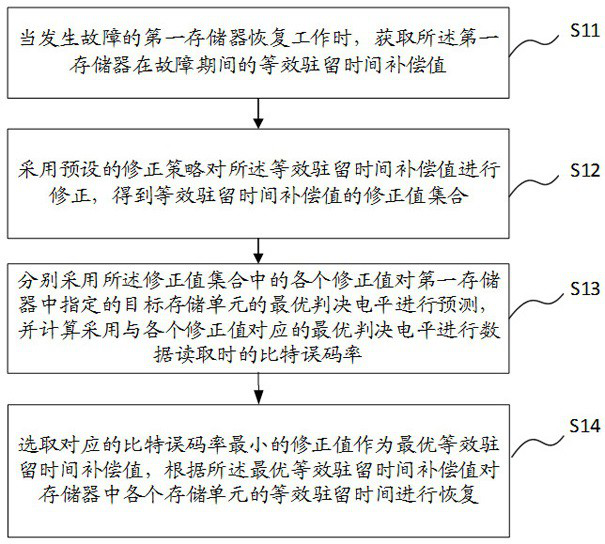
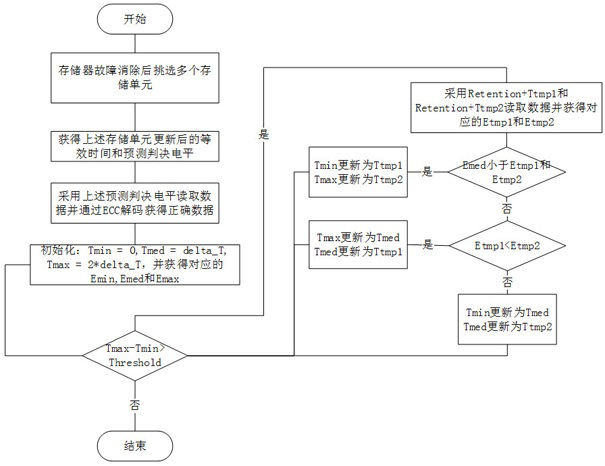
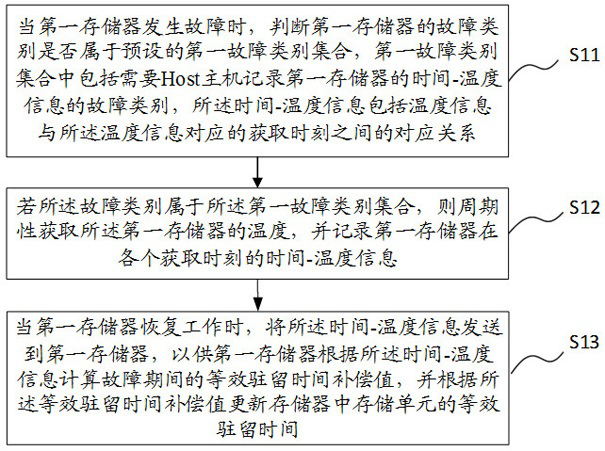
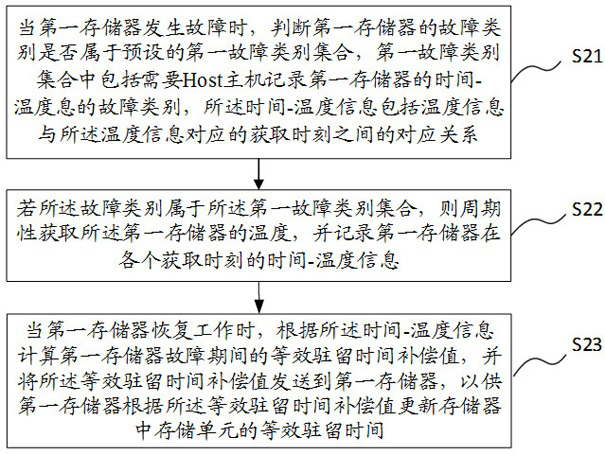
Equivalent residence time recovery method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment
ActiveCN114816836AEquivalent dwell time recoveryImprove reading speedRead-only memoriesRedundant data error correctionData storeIndustrial engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of data storage, and provides an equivalent residence time recovery method and device, a storage medium and electronic equipment, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an equivalent residence time compensation value during a fault when a first memory with a fault recovers to work; correcting the equivalent residence time compensation value by adopting a preset correction strategy to obtain a corresponding correction value set; predicting an optimal judgment level of a target storage unit in the first memory by adopting each correction value in the correction value set, and calculating a bit error rate when the optimal judgment level corresponding to each correction value is adopted to perform data reading; and selecting the correction value with the minimum corresponding bit error rate as the optimal equivalent residence time compensation value, so as to recover the equivalent residence time of each storage unit in the memory. According to the invention, the equivalent residence time during the fault period of the memory can be accurately recovered, and the original bit error rate is reduced while the reading speed of the memory is improved.
Owner:DERA CO LTD
Morphic storage device
ActiveCN107526543ABenefits performanceBenefit lifeInput/output to record carriersRead-only memoriesSolid-state driveData storing
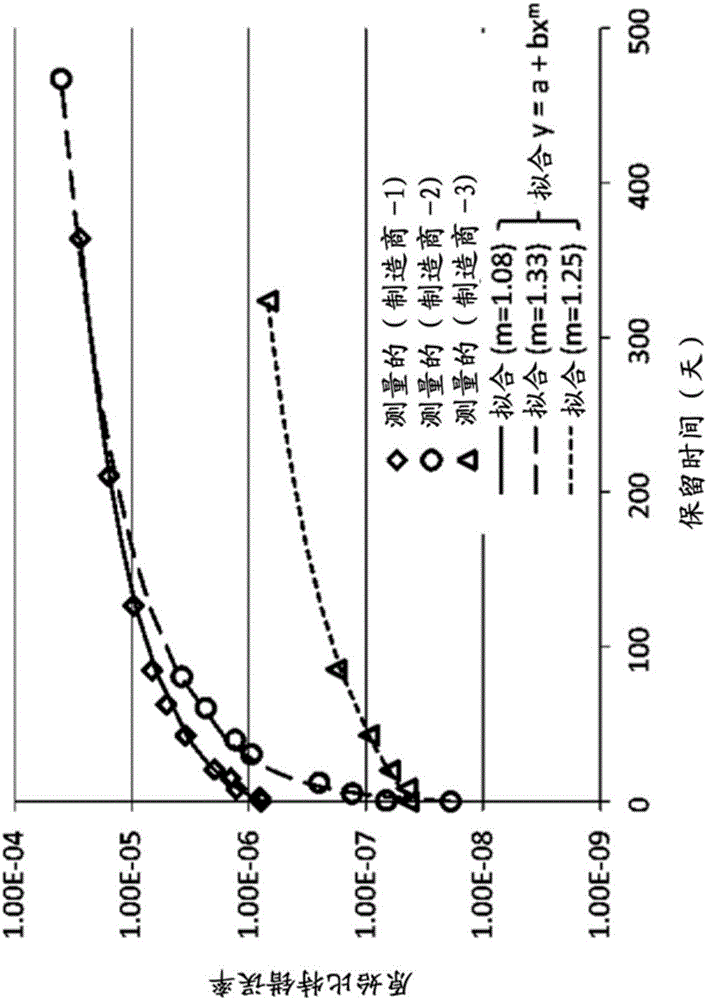
A solid state drive with a capability to select physical flash memory blocks and erasure and programming methods according to requirements of an application using storage in the solid state drive. A wear-out tracker in the solid state drive counts programming and erase cycles, and a raw bit error rate tracker in the solid state drive monitors raw bit errors in data read from the solid state drive. The application provides, to the solid state drive, requirements on an allowable retention time, corresponding to the anticipated storage time of data stored by the application, and on an average response time corresponding to programming and read times for the flash memory. The solid state drive identifies physical flash memory blocks suitable for meeting the requirements, and allocates storage space to the application from among the identified physical flash memory blocks.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
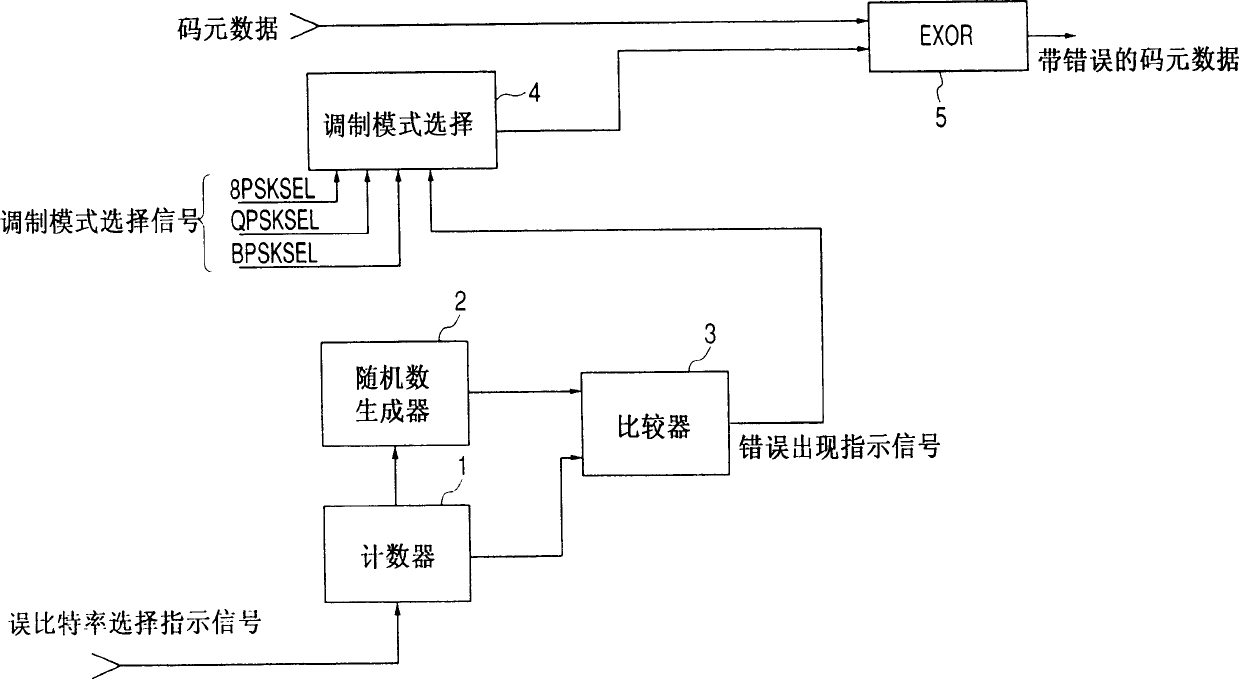
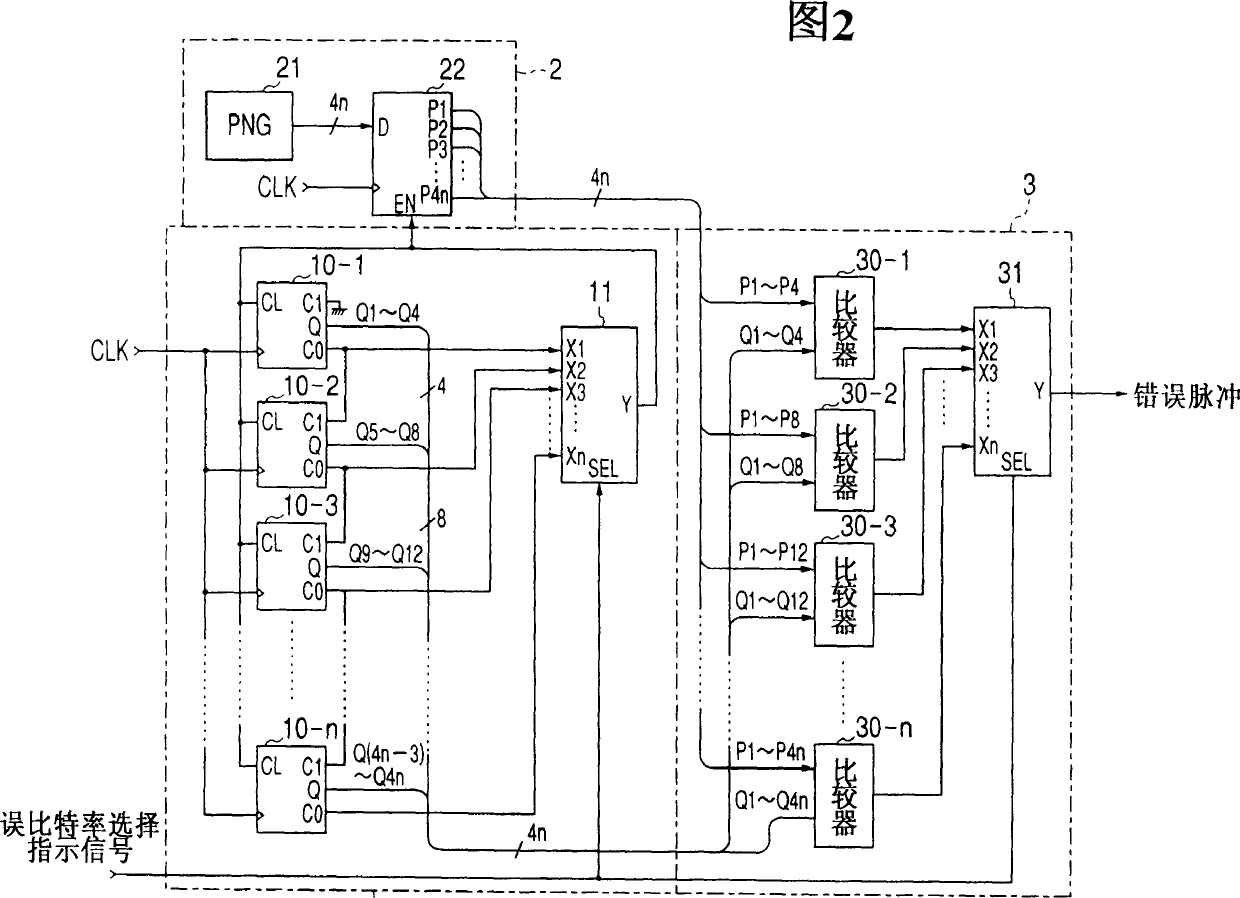
Dummy error addition circuit
InactiveCN1325582ACorrect operation testingPhase-modulated carrier systemsShift registerQuadrature modulation
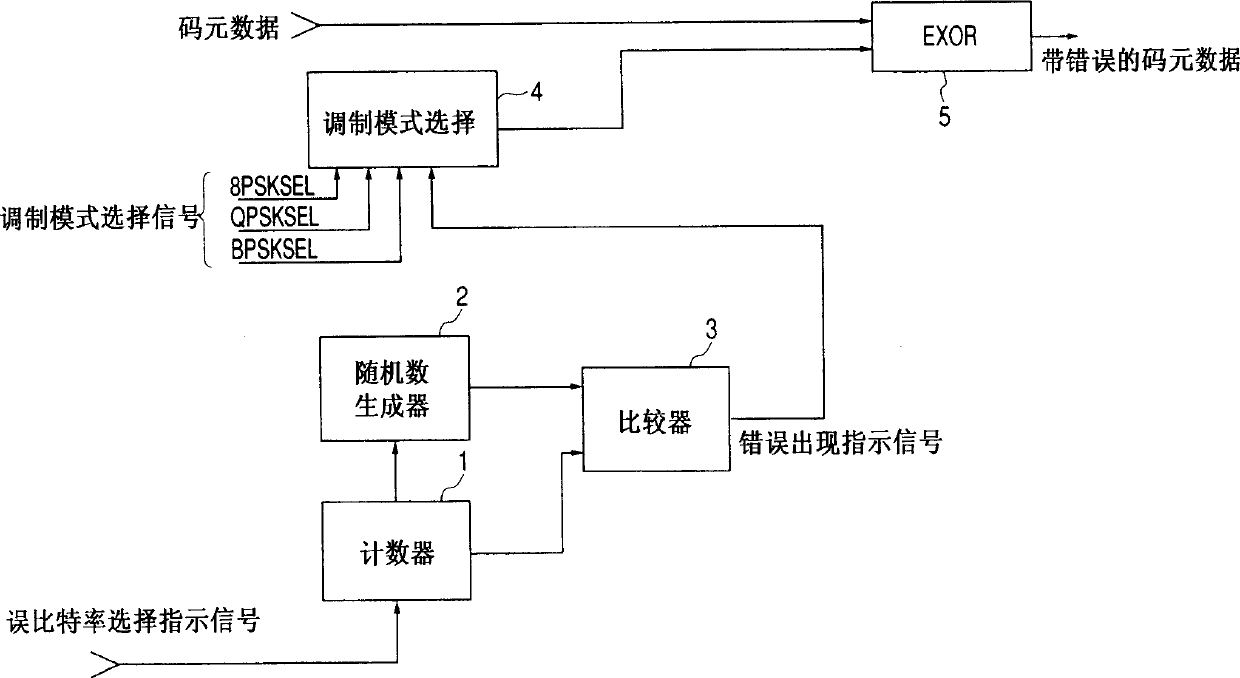
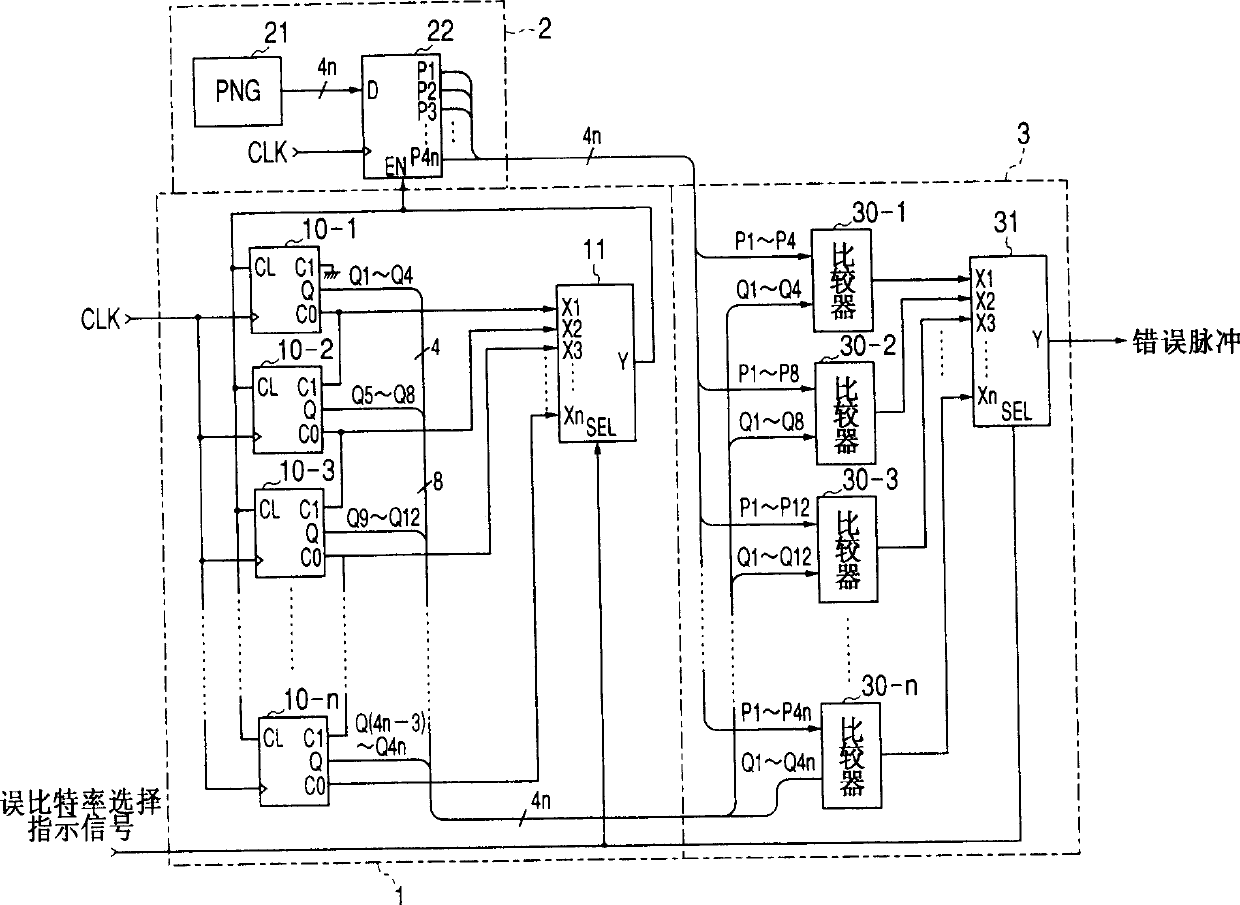
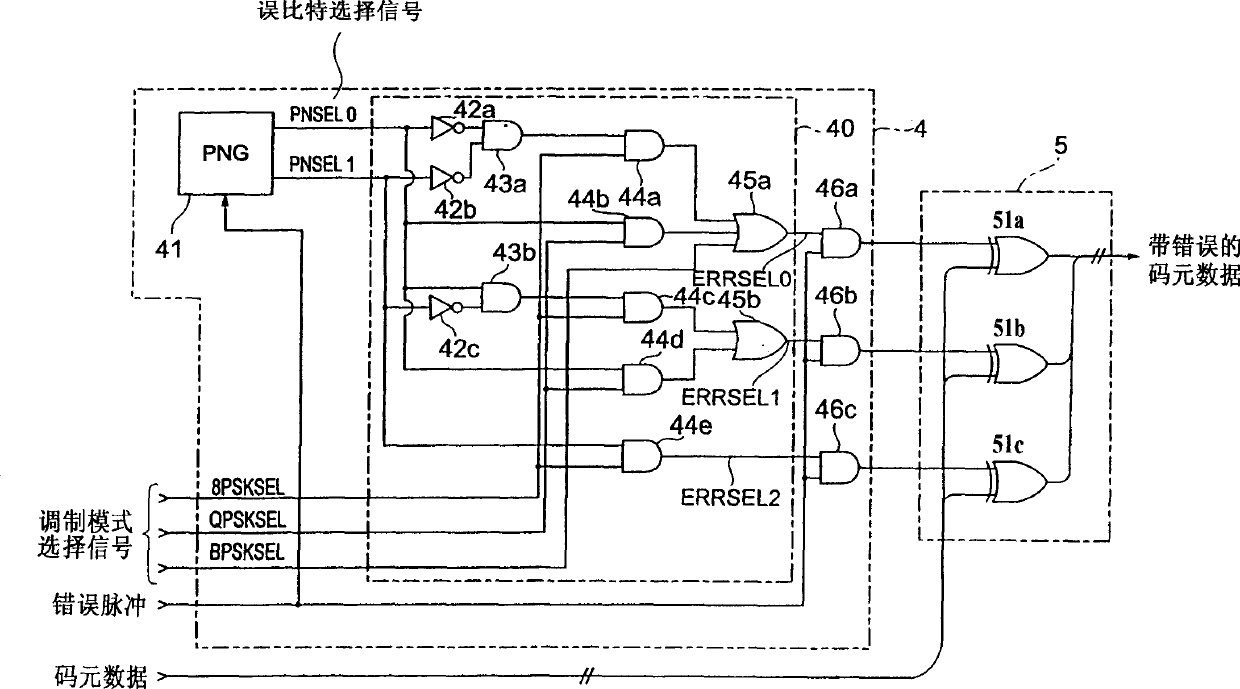
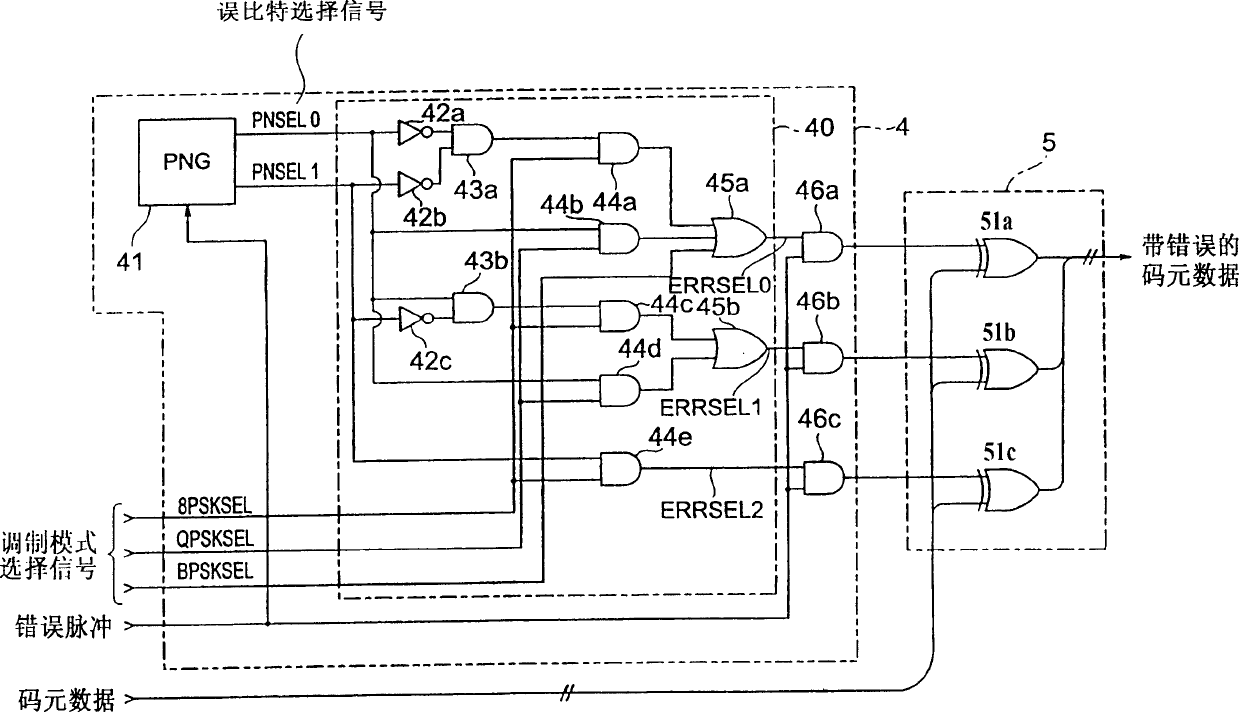
A dummy error addition circuit for adding a dummy error to an orthogonal modulation symbol data, wherein a value based on a specified bit error rate is loaded to count clock signals at a counter(11), a carrier of the counter(11)stores outputs from a PN data generator(21)in a shift register(22), outputs from a PN comparison circuit(3)when stored data agree with count values of the counter(11)are recognized as error pulses, a bit selector(40)randomly selects, on receiving error pulses and based on outputs from a PN data generator(41), bits to which to add errors in an orthogonal modulation data, e.g. a PSK modulation symbol data, at intervals based on a bit error rate, and bits selected from the orthogonal modulation data are inverted in a bit inversion circuit(5)for outputting to thereby add errors.
Owner:KENWOOD CORPORATION +1
NAND flash memory error control code structure and error code control method thereof
InactiveCN104932952AGuaranteed long-term stabilityRedundant data error correctionBit rateError control coding
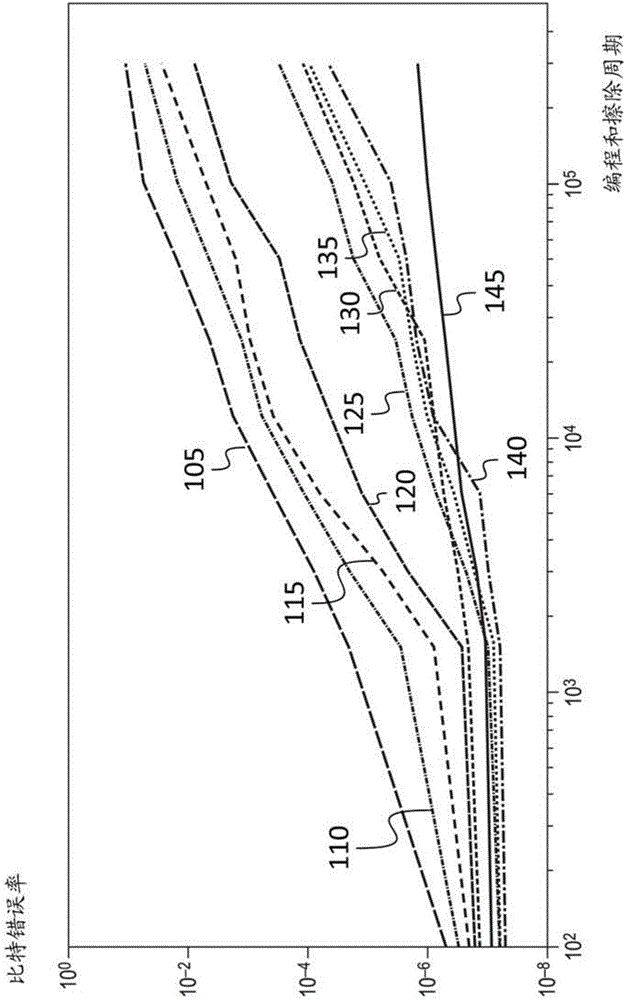
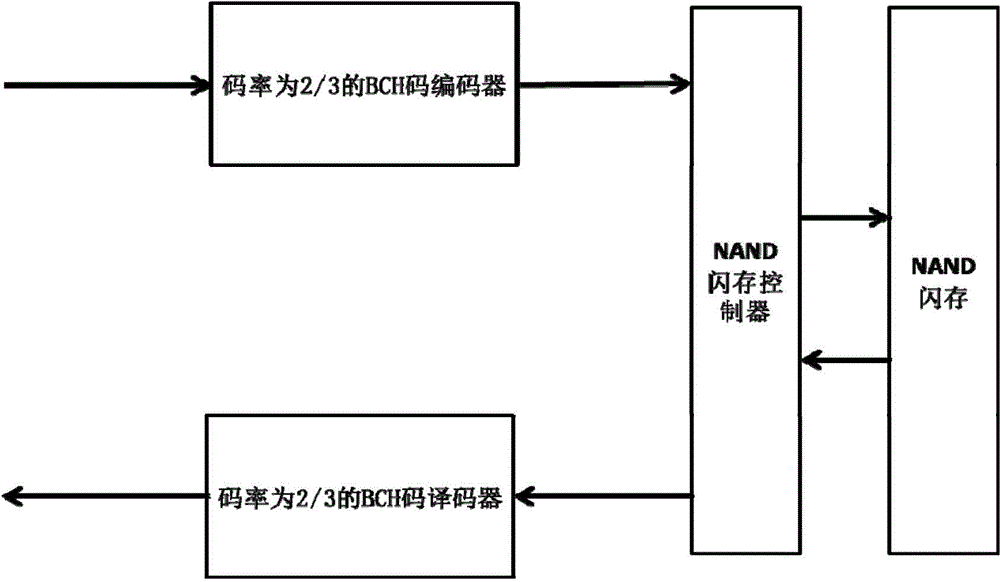
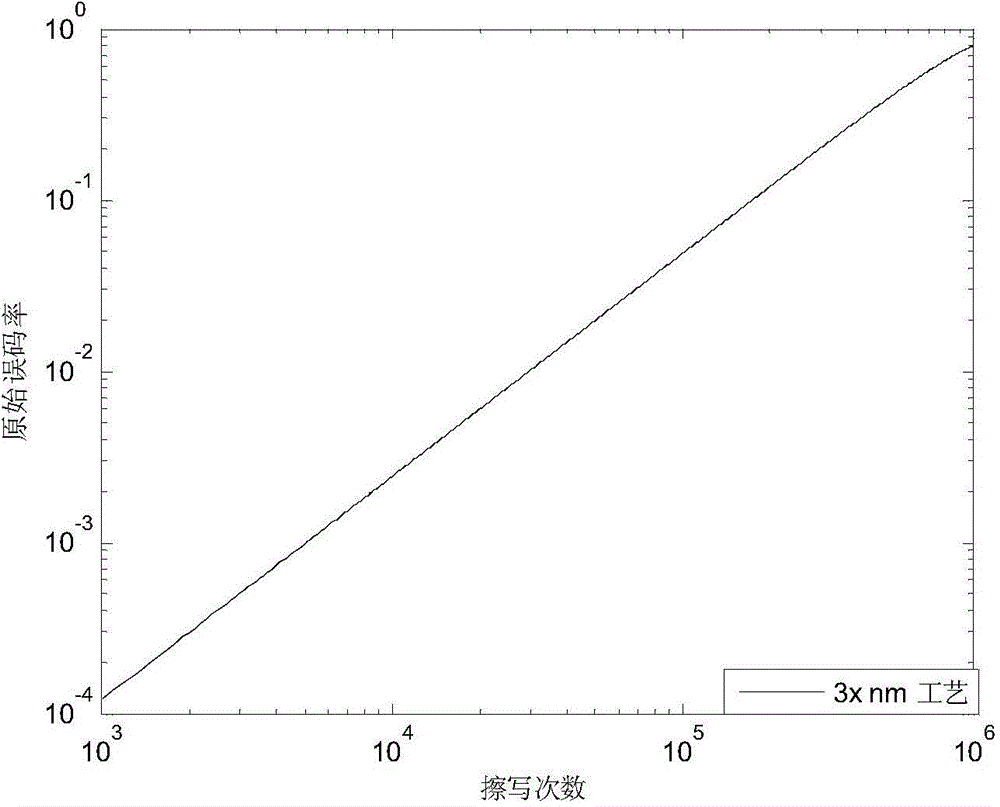
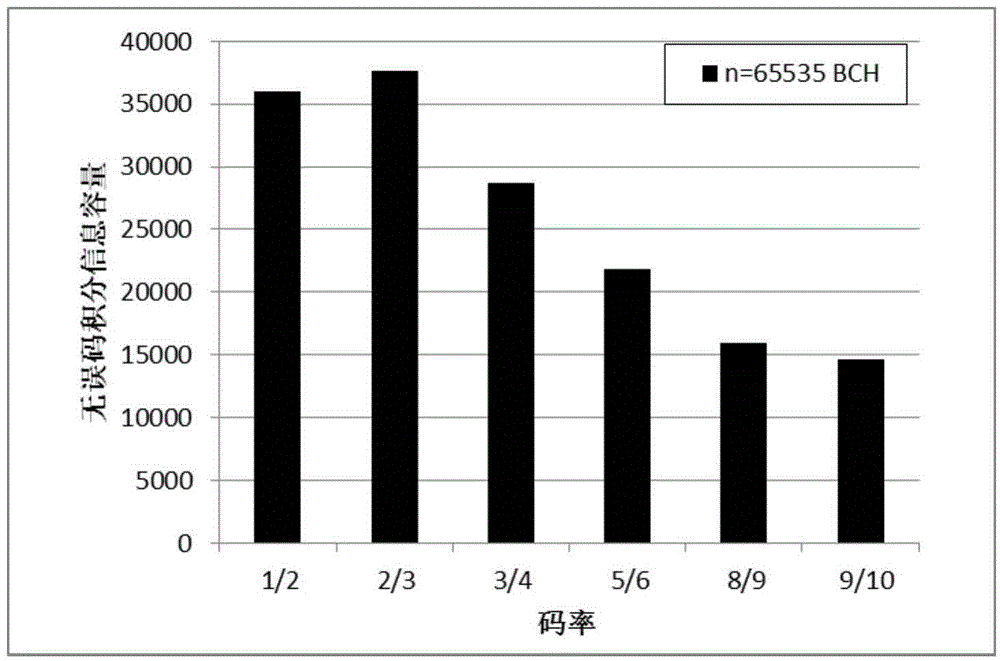
The present invention discloses an NAND flash memory error control code structure, comprising an ECC coder having a bit rate of 0.4 to 0.9, an ECC decoder having a bit rate of 0.4 to 0.9, and an NAND flash memory controller. The present invention further discloses an error code control method of the NAND flash memory error control code structure, comprising the following steps: 1. acquiring to NAND flash memories under different processes, acquiring a relationship between a raw bit error ratio (RBRR) and erasable times of the flash memory; 2. calculating an acceptable RBER when UBER is less than 10 to 15; 3. calculating the erasable times of the flash memory under different RRERs according to the previously acquired relationship between the erasable times and the RBER of the flash memory under different processes; 4. calculating a non-error bit integral information capacity of the flash memory; and 5. selecting a bit rate of the ECC. According to the present invention, the non-error bit integral information capacity can be ensured to the maximum and the long-term stability of the NAND flash memory can be ensured.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
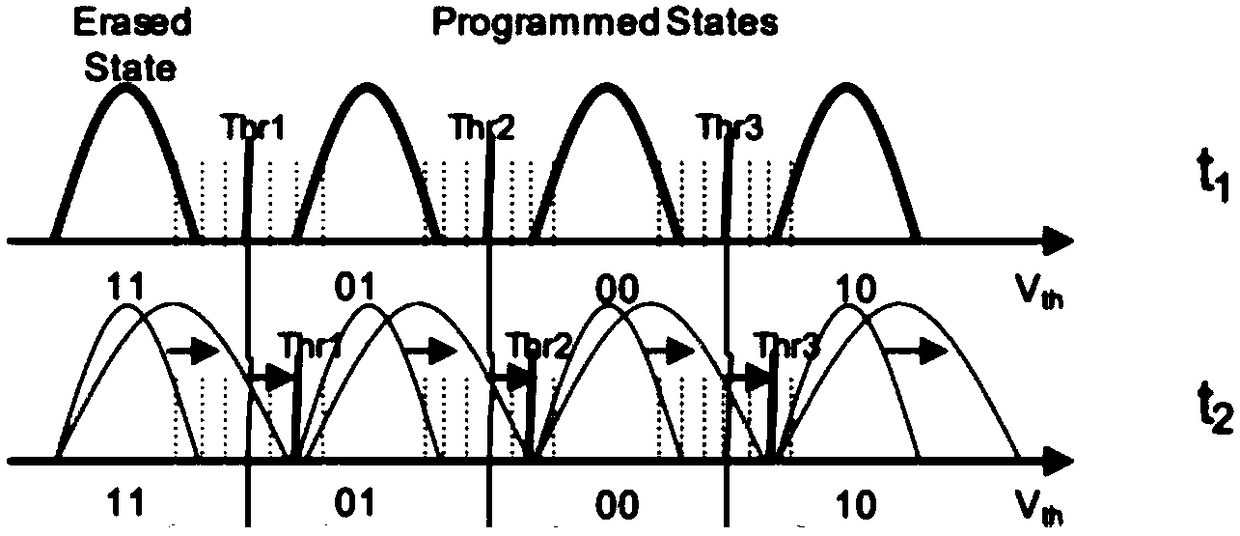
Determining a read apparent voltage infector page and infected page
Read Apparent Voltage (RAV) is an anomality in which an apparent threshold voltage of a storage cell transistor does not equal the actual threshold voltage of that same transistor by a large enough magnitude that the binary state of transistor is not read correctly. An infector page may cause the RAV anomality within a different infected page. To determine whether any page is an infector, each page is programmed, a page within each block is read, an acting infector page within an acting infector block is set, a possible infected page within a possible infected block is set, the acting infector page is read a predetermined plurality of instances, the possible infected page is read, a raw bit error rate (RBER) of the read of the possible infected page is determined, and the acting infector page is set as an actual infector page based upon the determined RBER.
Owner:IBM CORP
Equivalent residence time recovery method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment
ActiveCN114816835AImprove reading speedAccurate Compensation RestorationRead-only memoriesRedundant data error correctionData storeTemperature recording
The invention relates to the technical field of data storage, and provides an equivalent residence time recovery method and device, a storage medium and electronic device.The method comprises the steps that when a first storage breaks down, whether the fault category of the first storage belongs to a preset first fault category set or not is judged; if yes, periodically acquiring the temperature of the first memory, and recording time-temperature information of the first memory at each acquisition moment; when the first memory resumes working, calculating an equivalent residence time compensation value during the failure of the first memory according to the time-temperature information and sending the equivalent residence time compensation value to the first memory, or sending the time-temperature information to the first memory, and calculating the equivalent residence time compensation value by the first memory according to the time-temperature information; and recovering the equivalent residence time according to the compensation value. According to the invention, the equivalent residence time during the fault period of the memory can be accurately compensated and recovered, and the original bit error rate is reduced while the reading speed of the memory is improved.
Owner:DERA CO LTD
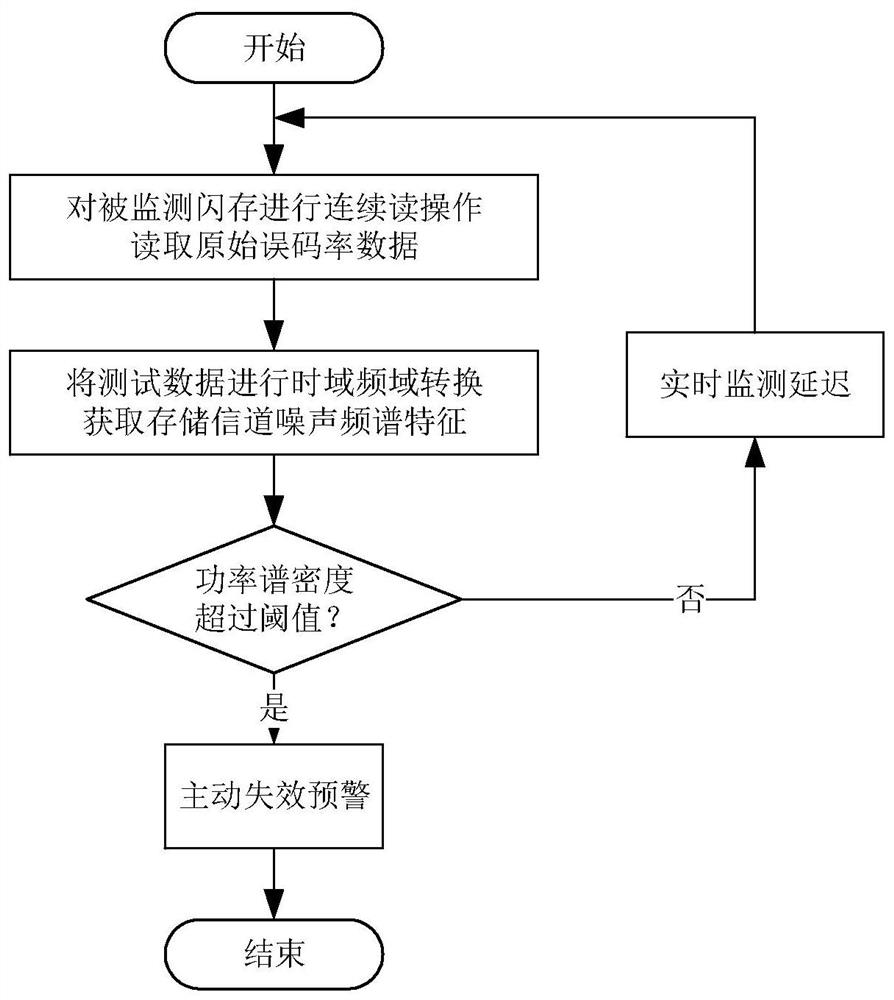
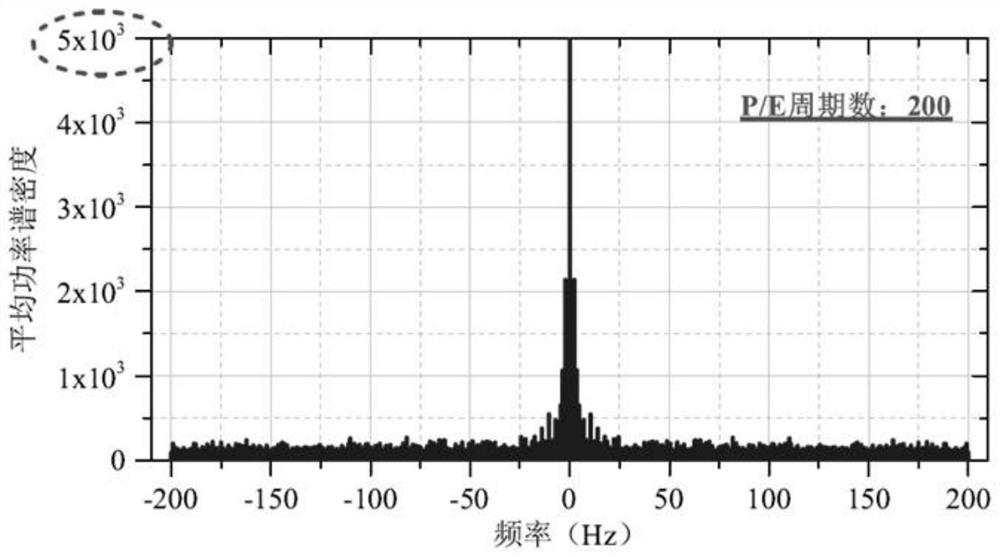
Flash memory reliability evaluation and failure early warning method based on storage channel noise spectrum characteristics
ActiveCN113314184ASimple means of data acquisitionFast data acquisitionStatic storageTime domainFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a flash memory reliability evaluation and failure early warning method based on storage channel noise spectrum characteristics. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the continuous reading operation of a monitored flash memory, and reading the original bit error rate data; performing time domain and frequency domain conversion on the test data to obtain flash memory channel noise spectrum features; and judging whether the power spectrum density of the flash memory channel noise spectrum feature exceeds a threshold value or not. According to the method, the noise data of the current storage channel can be quickly obtained, and the reliability of the current data of the flash memory can be evaluated and failure early warning can be performed by using noise spectrum features; and all-time internal data reliability monitoring and timely failure early warning can be realized on the premise of not influencing normal work of the flash memory, and the storage bit reliability of a threshold voltage overlapping region can be calculated by using a noise frequency entropy function to dynamically update a flash memory storage bit LLR table.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
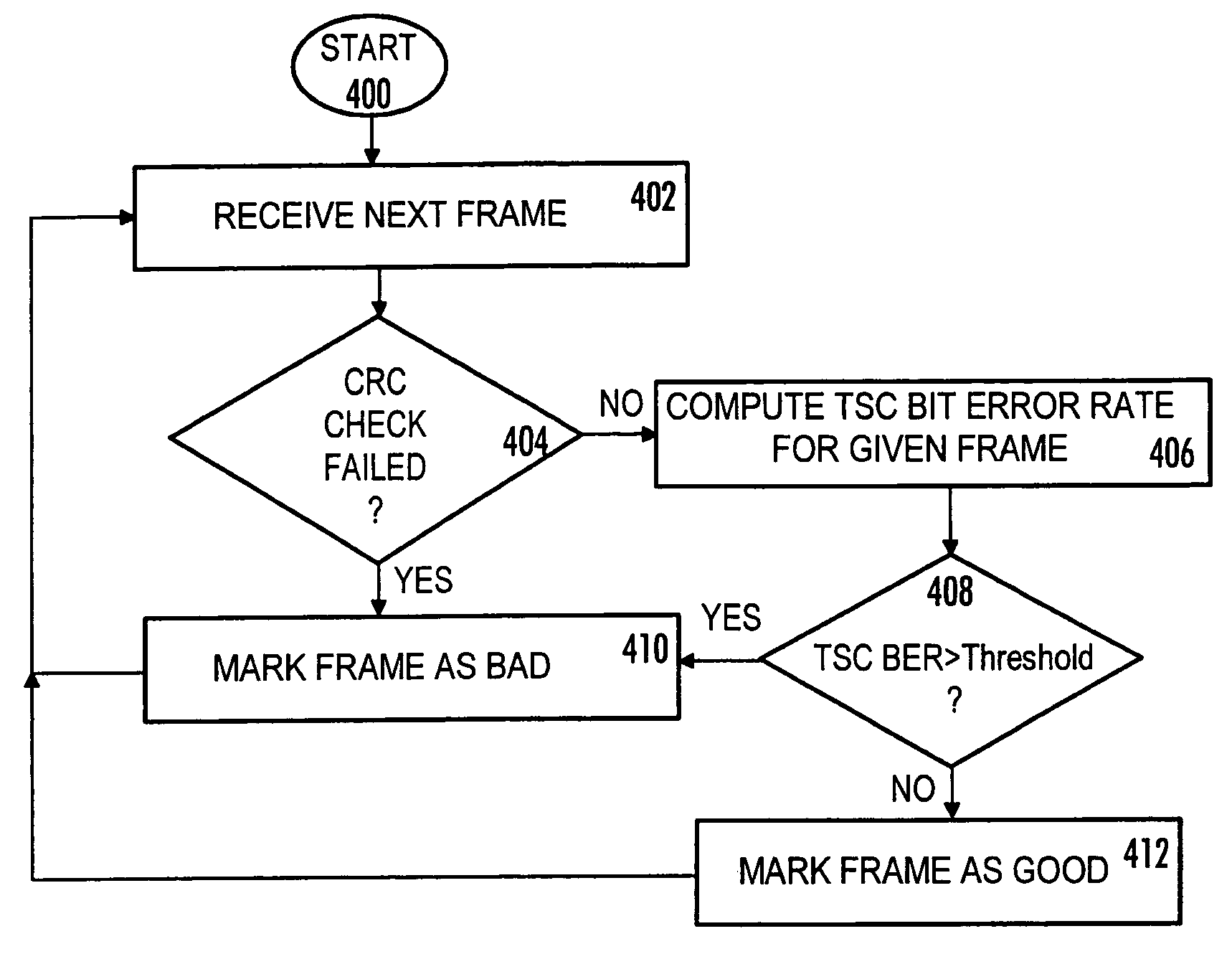
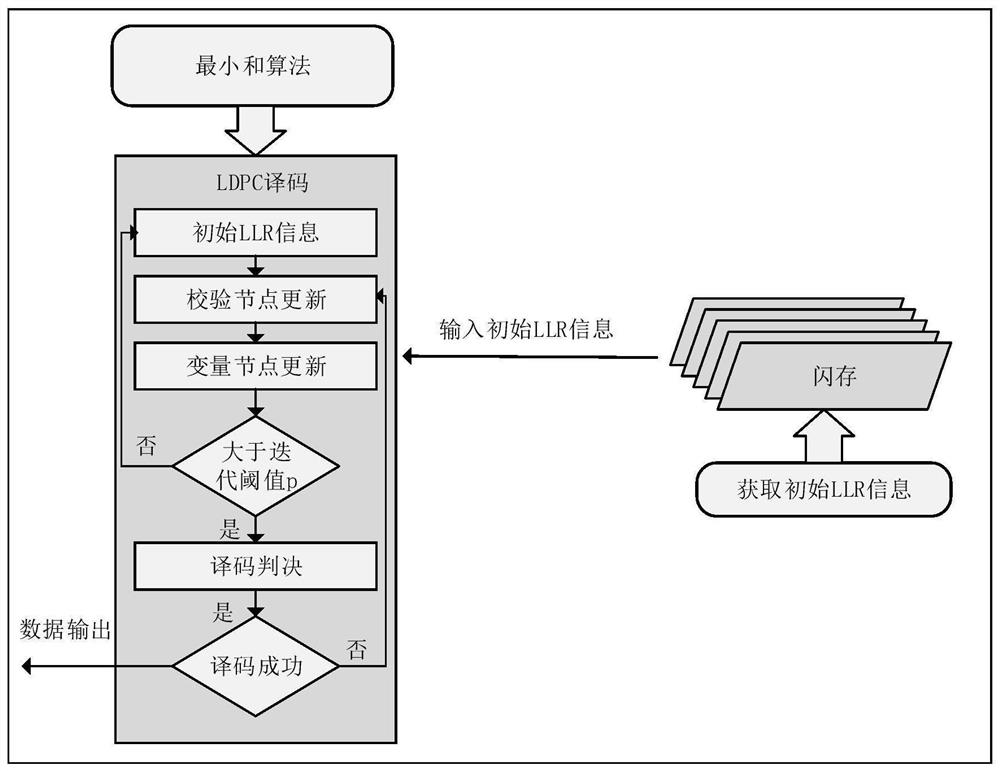
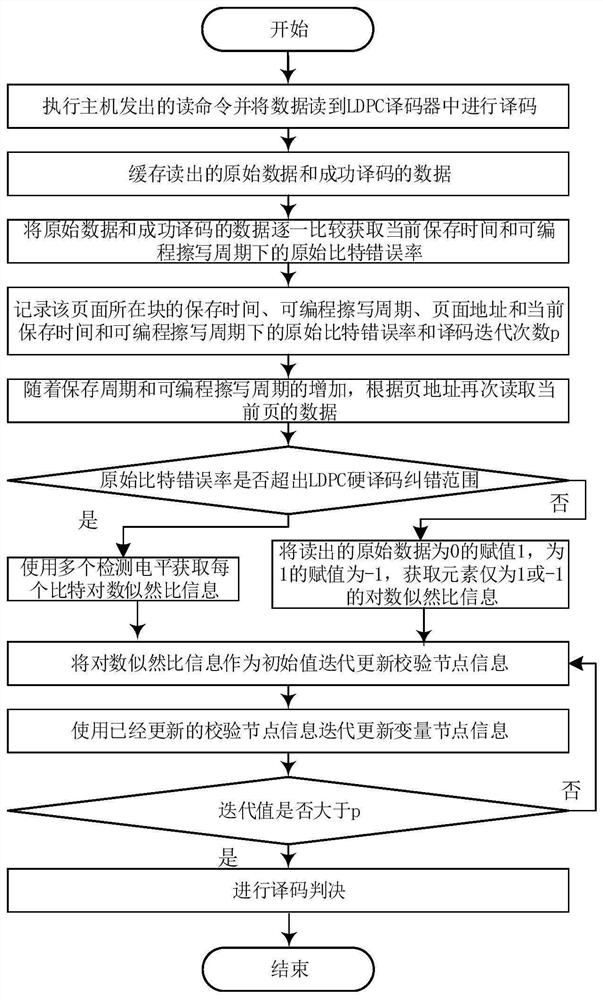
A raw bit error rate-aware decoding soft-decision delay reduction method
ActiveCN111294061BReduce Decoding LatencyError correction/detection using LDPC codesLogitLog likelihood
The invention discloses a decoding soft decision delay reduction method for sensing an original bit error rate. In order to ensure data storage reliability, the LDPC adopts a soft decision decoding algorithm based on log-likelihood ratio information, and has strong decoding error correction capability. However, in the decoding judgment process, the bit information is frequently judged, and high judgment delay is caused. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring change information of an original bit error rate according to a current LDPC decoding result; and according to thechange information of the bit error rate, directly iteratively updating the log-likelihood ratio information of the bit to a target value in the next decoding judgment process, and then executing judgment operation, so as to reduce the redundant judgment times and further reduce the soft-decision decoding judgment delay.
Owner:上海威固信息技术股份有限公司
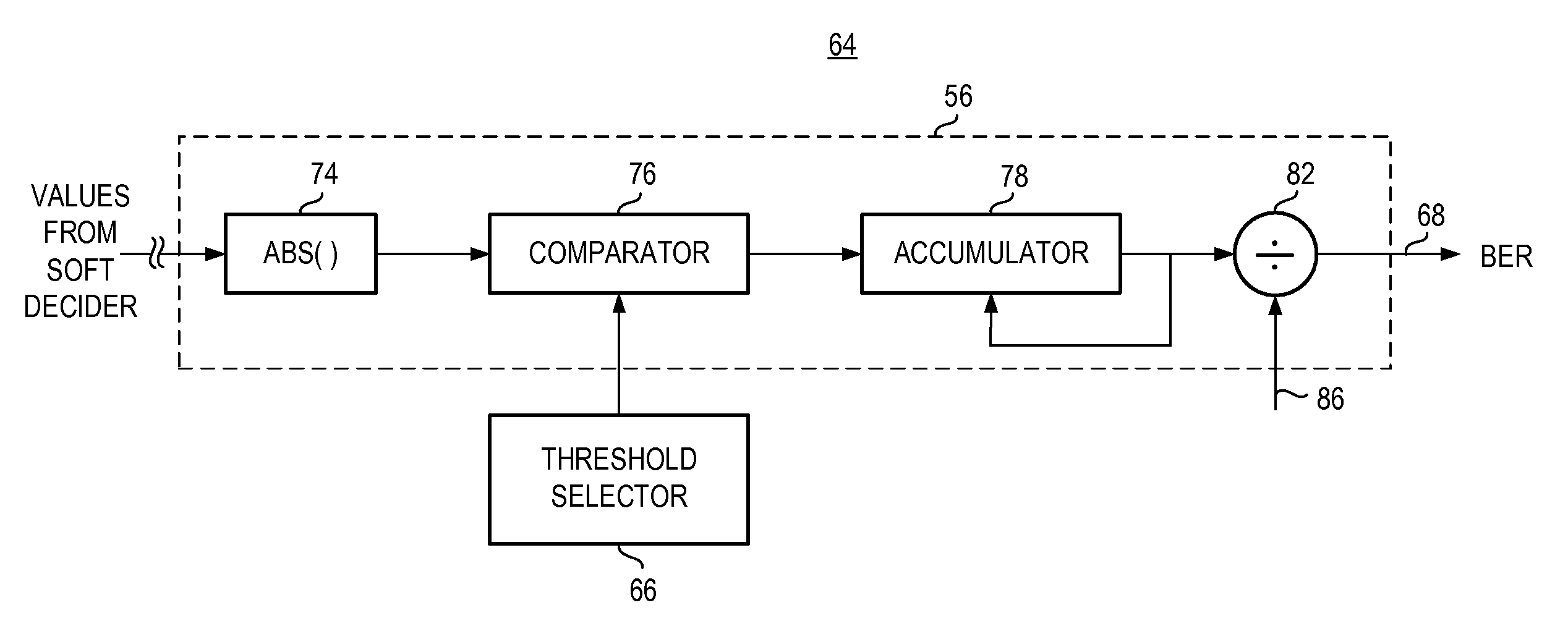
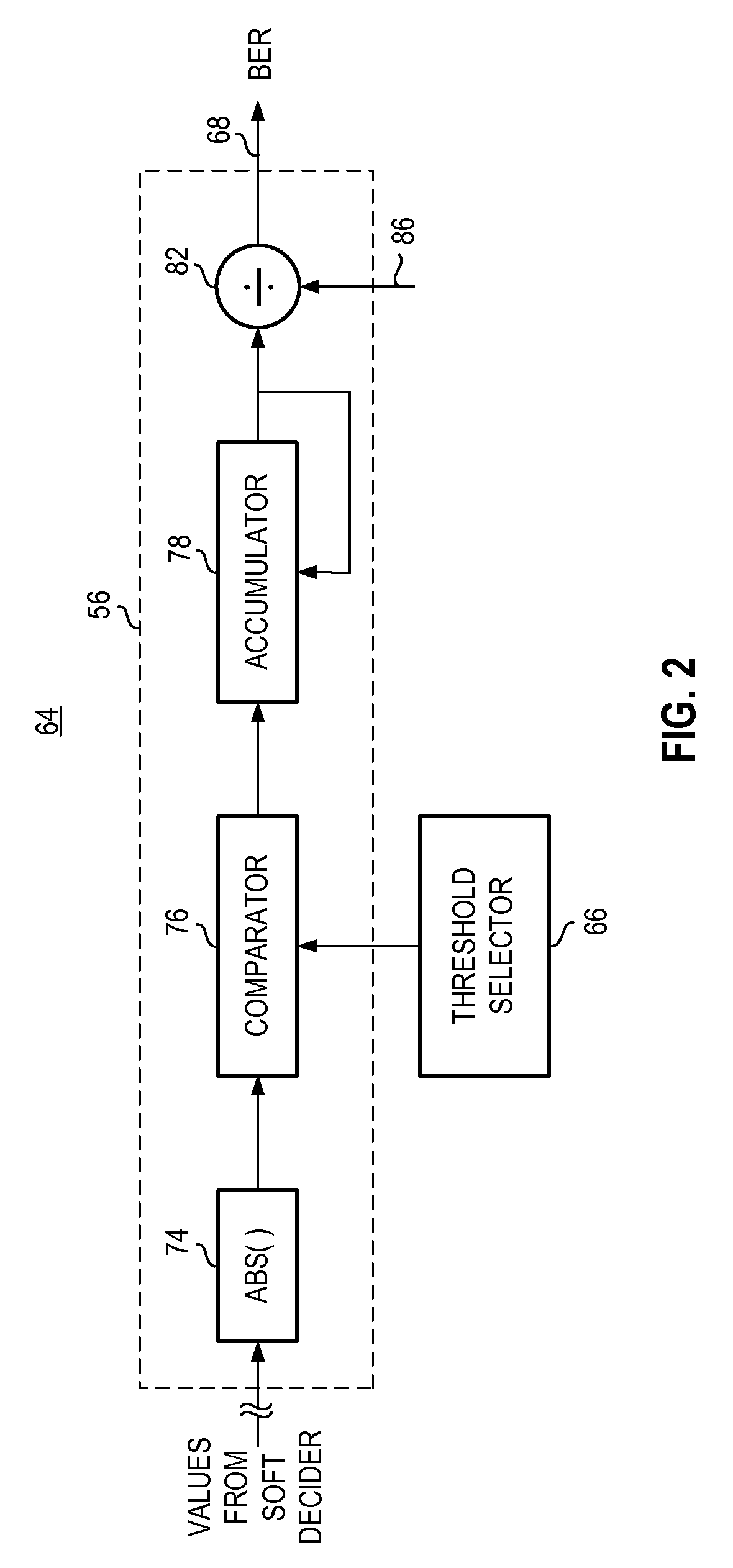
Apparatus, and associated method, for estimating a bit error rate of data communicated in a communication system
InactiveUS8166354B2Error preventionError detection/correctionCommunications systemCellular communication systems
Apparatus, and an associated method, for estimating a bit error rate of data communicated to a receiving station of a digital communications system, such as a GSM / EDGE cellular communication system. Soft decision values, indicative of confidence levels that decided values have been correctly decided are compared with threshold values by a comparator. A count is accumulated by a counter to whose counted value is representative of decided data values having associated therewith low levels of confidence that the decided values are correct. The count value is used in the formulation of the BER estimation.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Dummy error addition circuit
InactiveCN1149800CCorrect operation testingPhase-modulated carrier systemsShift registerQuadrature modulation
A dummy error addition circuit for adding a dummy error to an orthogonal modulation symbol data, wherein a value based on a specified bit error rate is loaded to count clock signals at a counter(11), a carrier of the counter(11)stores outputs from a PN data generator(21)in a shift register(22), outputs from a PN comparison circuit(3)when stored data agree with count values of the counter(11)are recognized as error pulses, a bit selector(40)randomly selects, on receiving error pulses and based on outputs from a PN data generator(41), bits to which to add errors in an orthogonal modulation data, e.g. a PSK modulation symbol data, at intervals based on a bit error rate, and bits selected from the orthogonal modulation data are inverted in a bit inversion circuit(5)for outputting to thereby add errors.
Owner:KENWOOD CORPORATION +1
RAID strip reconstruction method and solid state disk
ActiveCN107678694BImprove reliabilityExtend your lifeInput/output to record carriersRAIDReconstruction method
The invention discloses an RAID stripe reconstruction method applied to a solid state disk. The method is used for recombining physical block groups of an RAID memory array to form a new RAID stripe.The method comprises the steps of S1, detecting original error rates of physical blocks and updating and recording the original error rates in a block state table; S2, according to the original errorrates in the block state table, obtaining weak block information; S3, obtaining a weak block quantity through the block state table, and performing stripe organization for the physical blocks; and S4,performing block internal stripe organization in a staggered way for LSB pages and MSB pages of the physical blocks in a same RAID stripe. According to the RAID stripe reconstruction method, dynamicadjustment of the RAID stripe of the solid state disk is realized; data loss is avoided; storage space waste is avoided; the reliability of the solid state disk is improved; and the service life of the solid state disk is prolonged. Meanwhile, the invention furthermore discloses the solid state disk. The solid state disk comprises the RAID memory array and a controller used for performing adaptiveadjustment on the RAID memory array and managing data stored in the array.
Owner:SHENZHEN DAPU MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Determining a read apparent voltage infector page and infected page
ActiveUS20200117371A1Input/output to record carriersRead-only memoriesEngineeringBiomedical engineering
Read Apparent Voltage (RAV) is an anomality in which an apparent threshold voltage of a storage cell transistor does not equal the actual threshold voltage of that same transistor by a large enough magnitude that the binary state of transistor is not read correctly. An infector page may cause the RAV anomality within a different infected page. To determine whether any page is an infector, each page is programmed, a page within each block is read, an acting infector page within an acting infector block is set, a possible infected page within a possible infected block is set, the acting infector page is read a predetermined plurality of instances, the possible infected page is read, a raw bit error rate (RBER) of the read of the possible infected page is determined, and the acting infector page is set as an actual infector page based upon the determined RBER.
Owner:IBM CORP
A data recovery method and system for flash memory
ActiveCN108717385BReduce raw bit error rateRedundant data error correctionRedundant operation error correctionOriginal dataControl theory
The application discloses a data recovery method and system used for a flash memory. The method includes: reading original data on the basis of default reading voltage when the flash memory receives areading command; carrying out ECC (Error Correcting Code) checking on the original data, and judging whether a first error number is greater than maximum ECC error-correction capability; when the first error number is greater than the maximum ECC error-correction capability, determining rereading voltage by rereading error-correction, carrying out ECC checking on data read by the rereading voltage, and judging whether a second error number is greater than the maximum ECC error-correction capability; and when the second error number is greater than the maximum ECC error-correction capability,carrying out compensation on threshold voltage of a storage unit, and obtaining optimal reading voltage by rereading error-correction until a third error number after ECC checking on data read by theoptimum reading voltage is less than or equal to the maximum ECC error-correction capability. The method is capable of recovering flash memory data by combining data rereading and compensation, and effectively reduces an original bit error rate as compared with the prior art.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Interleaving and error-correcting method for reducing bit error rate of volume hologram storage system
ActiveCN102006088BEliminate the effects of uneven bit error rate distributionReduce bit error rateError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesOriginal dataThree dimensionality
The invention relates to an interleaving and error-correcting method for reducing bit error rate of a volume hologram storage system, comprising the following steps of: (1) firstly, carrying out error correction coding on data to be stored from three dimensionalities including a row direction, a line direction and among data pages; (2) after error correction coding, carrying out matching interleaving within data pages, and then carrying out block interleaving among the data pages to rearrange the sequence among the data pages; and (3) restoring the data obtained in the volume hologram storagesystem into original data by sequentially carrying out detection and postprocessing, demodulation and de-interleaving, and clearing error correction codes. In the invention, because the methods of matching interleaving among within pages and block interleaving among data pages are adopted and the Reed Solomon error correcting code is used for error correction from three dimensionalities, the influence of nonuniform distribution of bit error rate within pages and among data pages is eliminated, burst errors are overcome, random errors are corrected, and iteration decoding can be carried out inthree directions so that the bit error rate after correction is greatly reduced. The invention can be widely applied in various error modes of volume hologram storage channels.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com