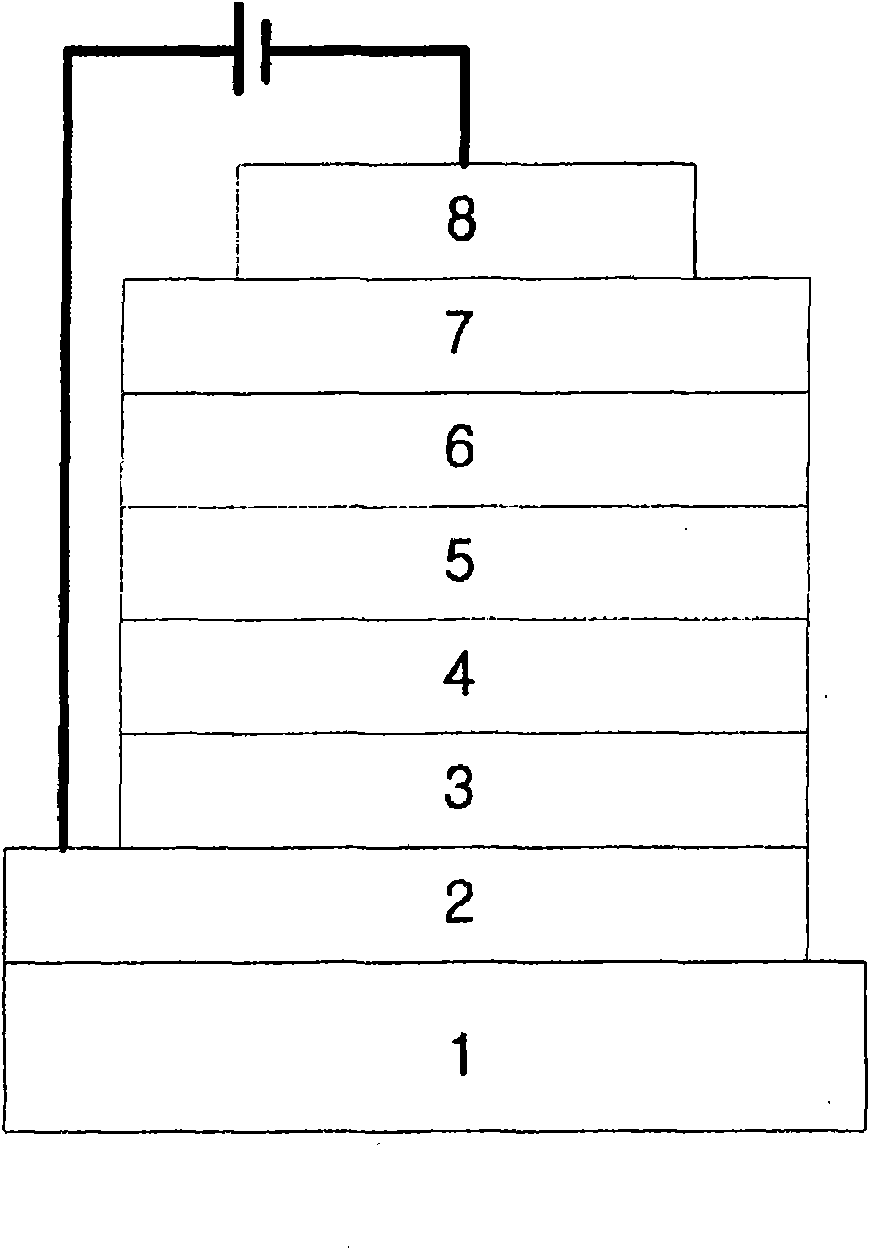
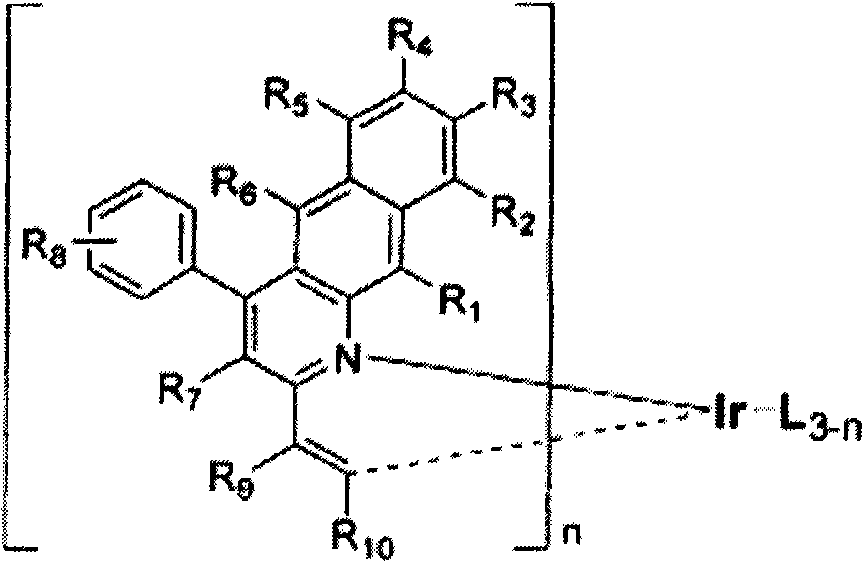
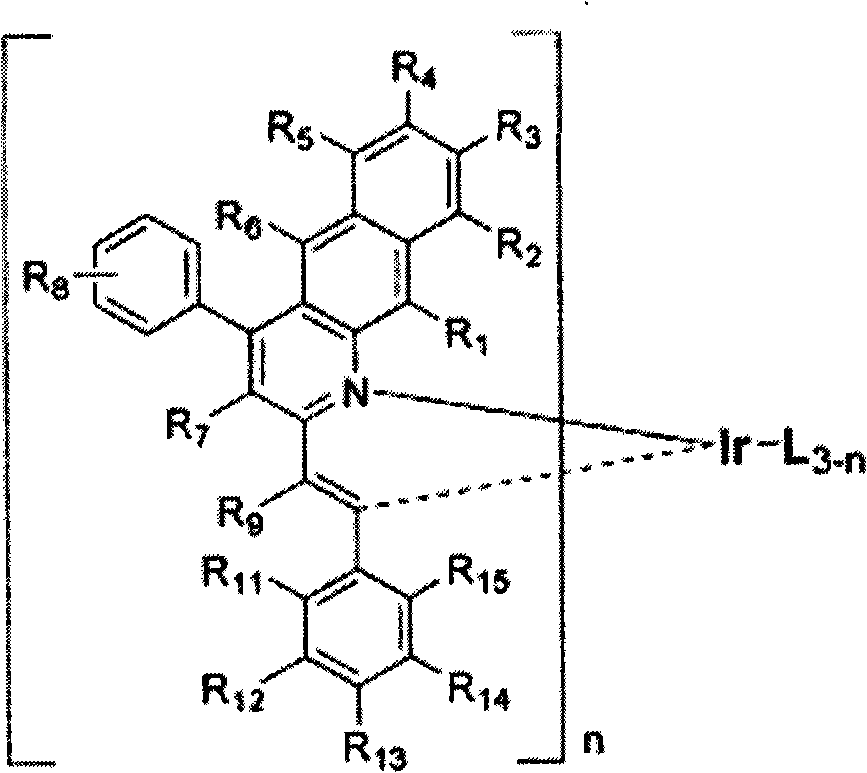
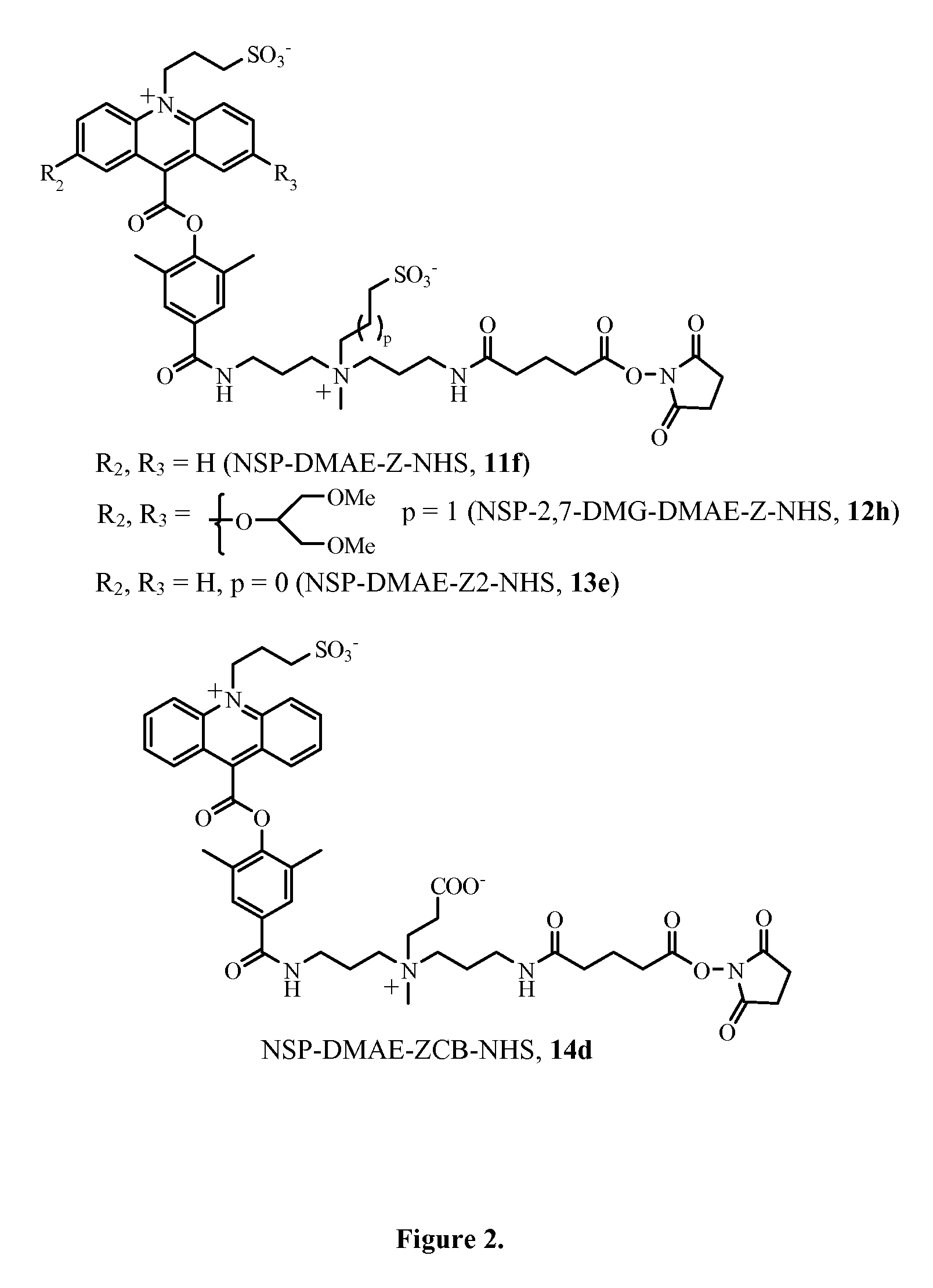
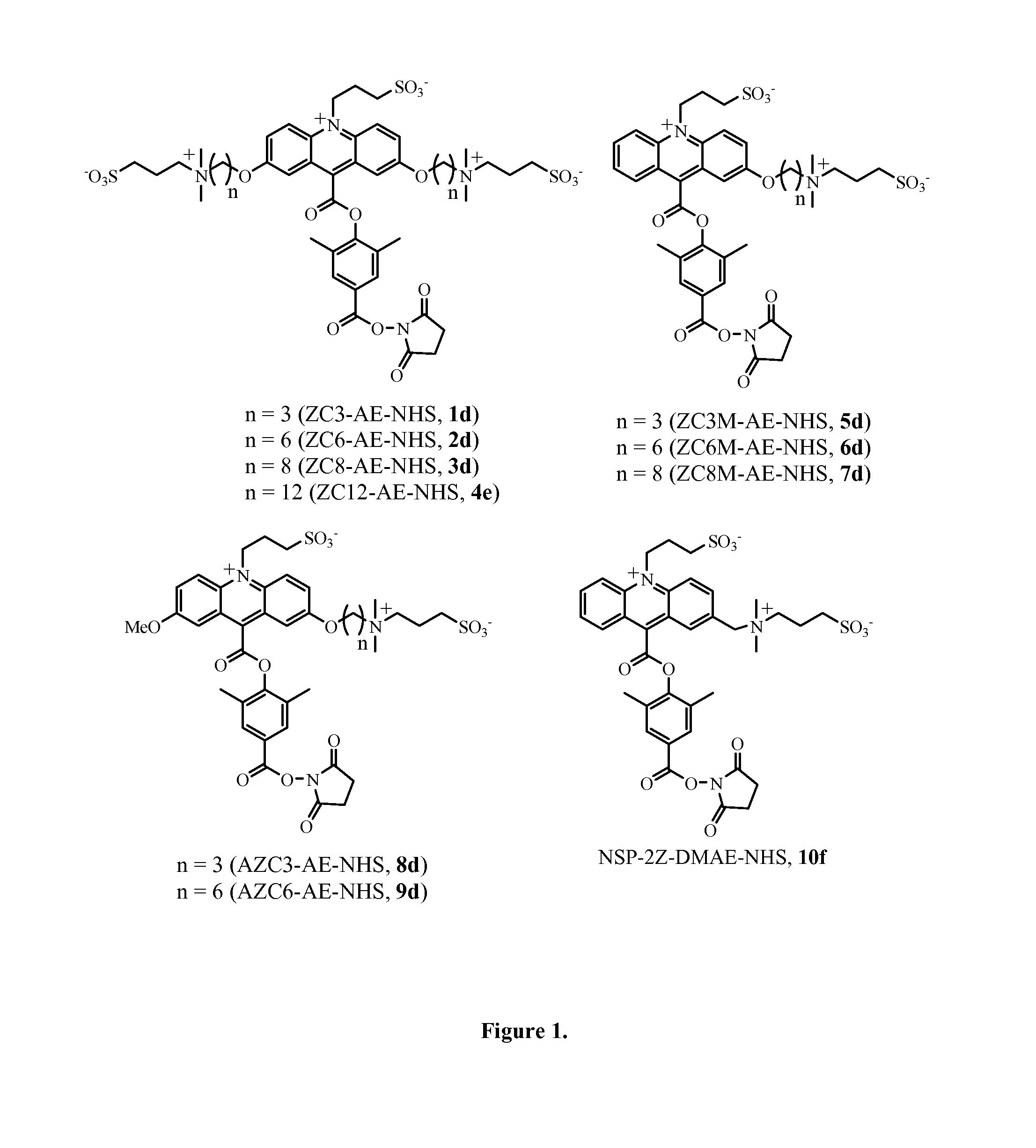
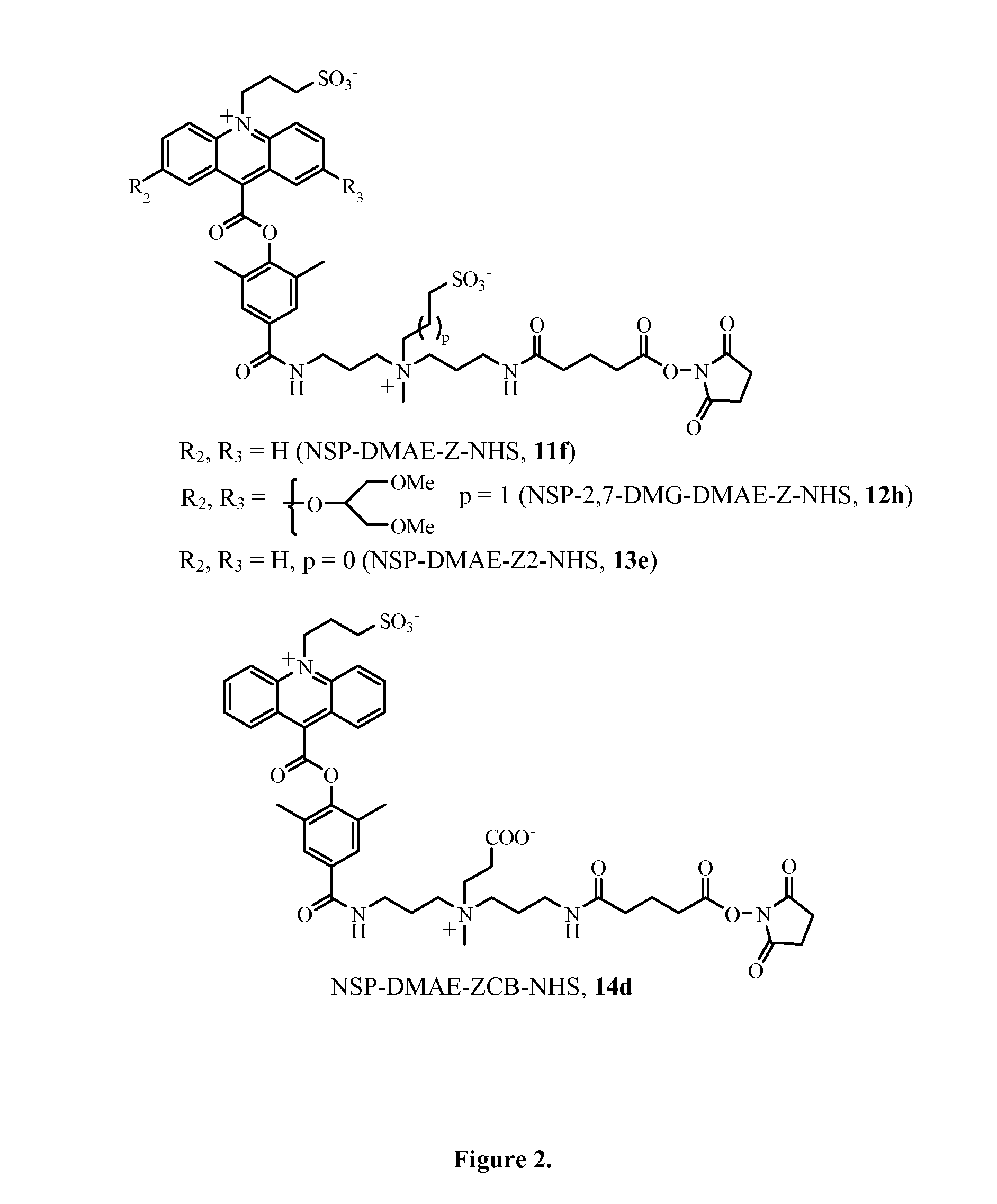
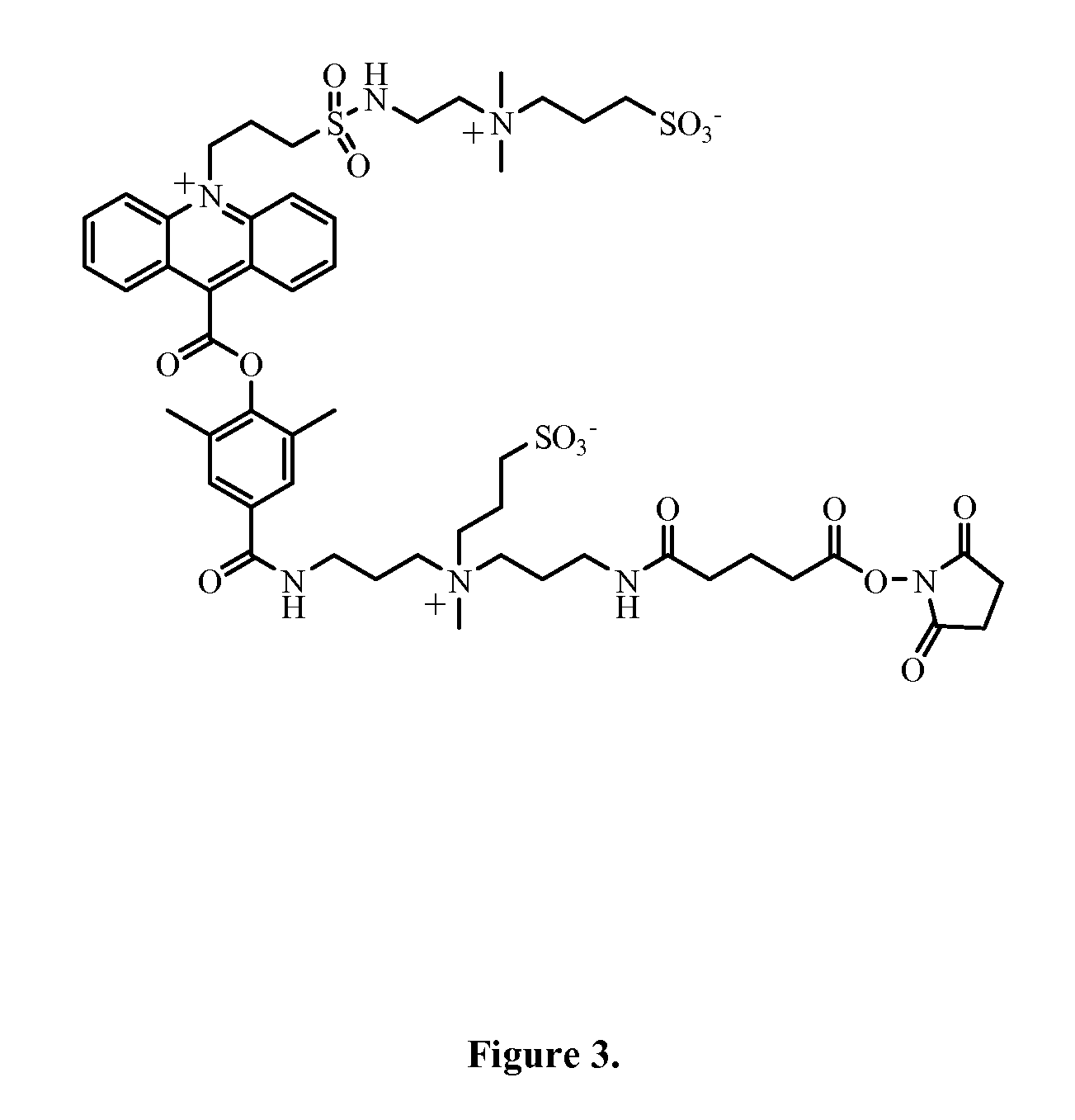
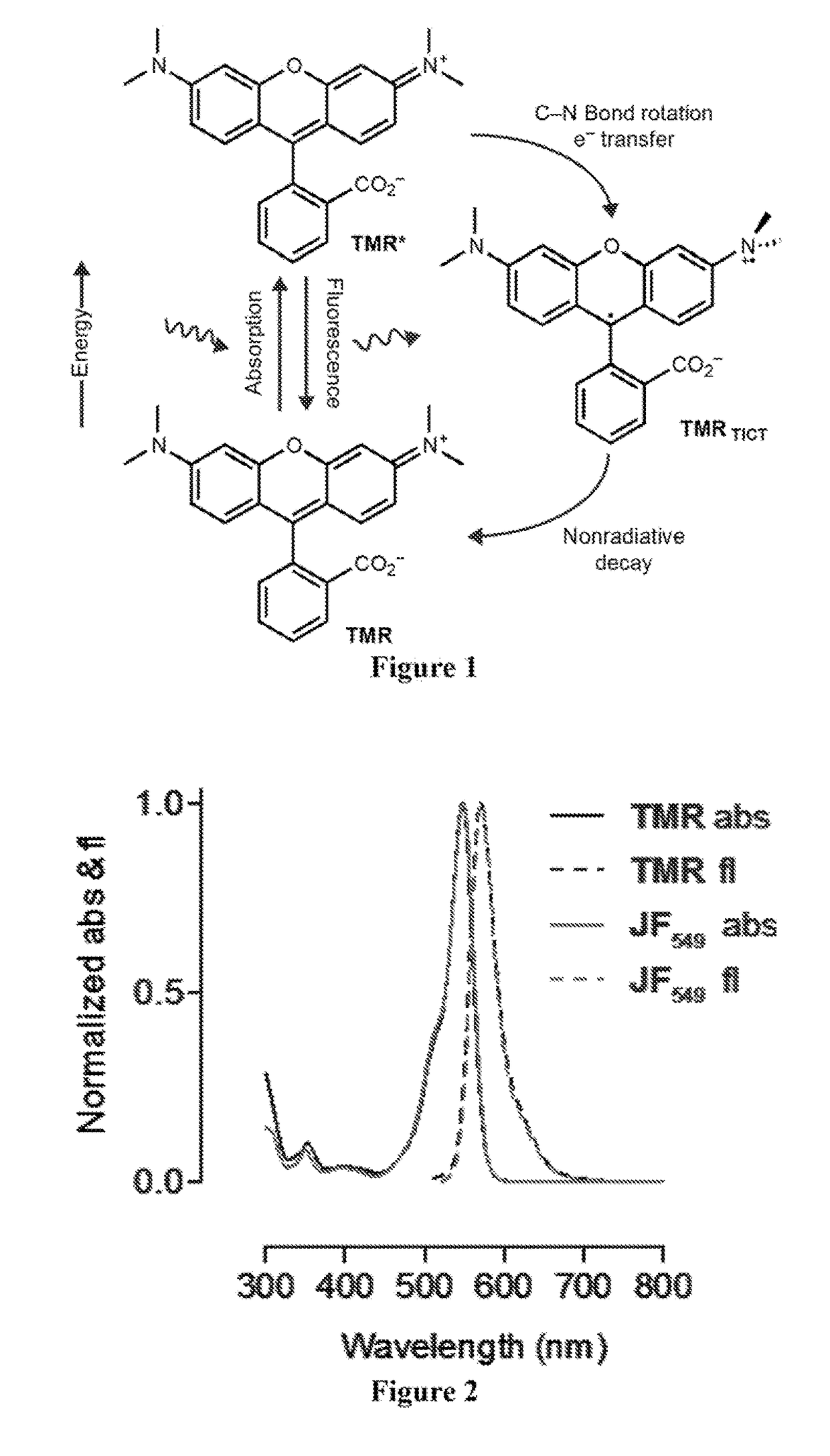
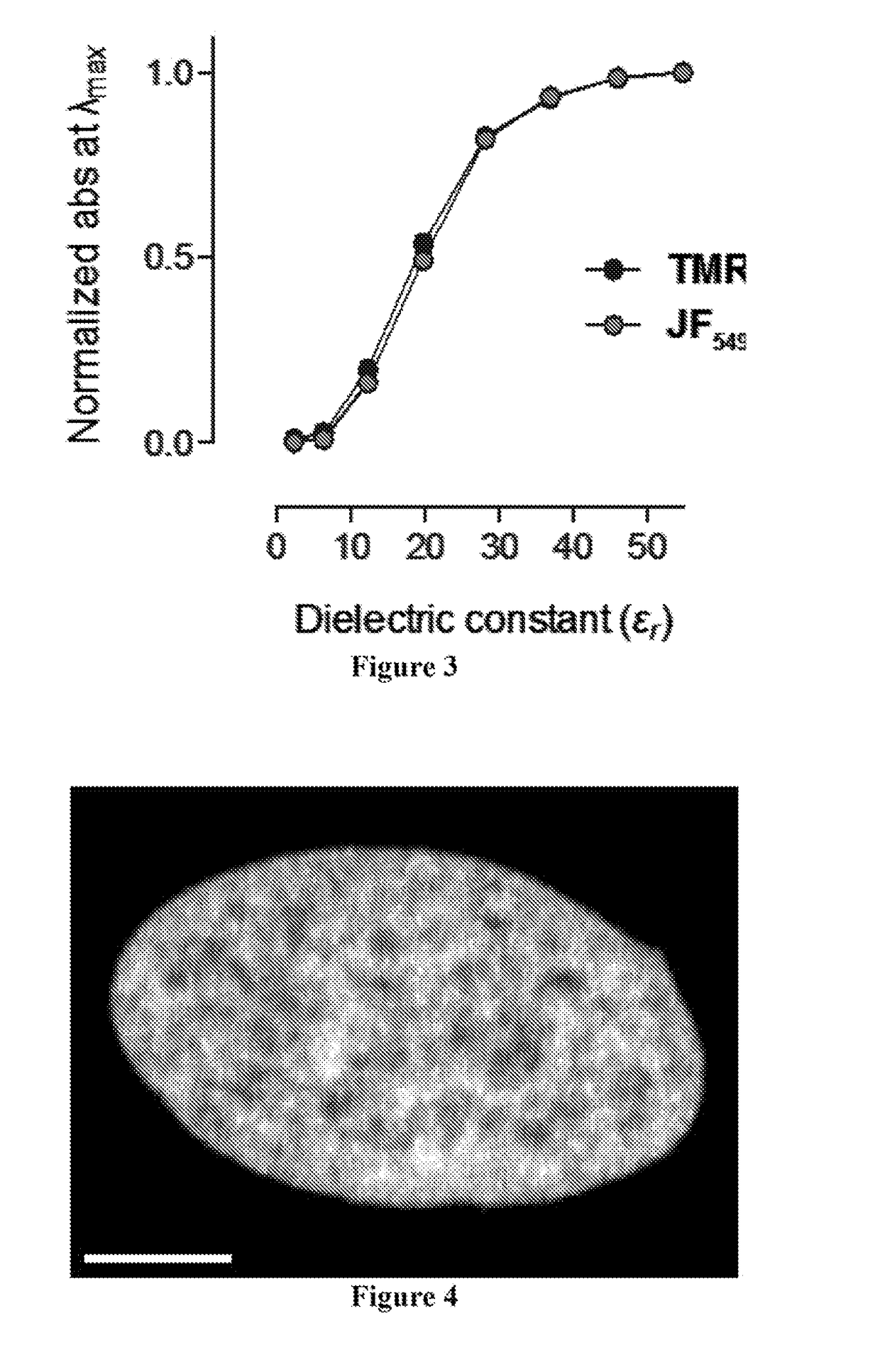
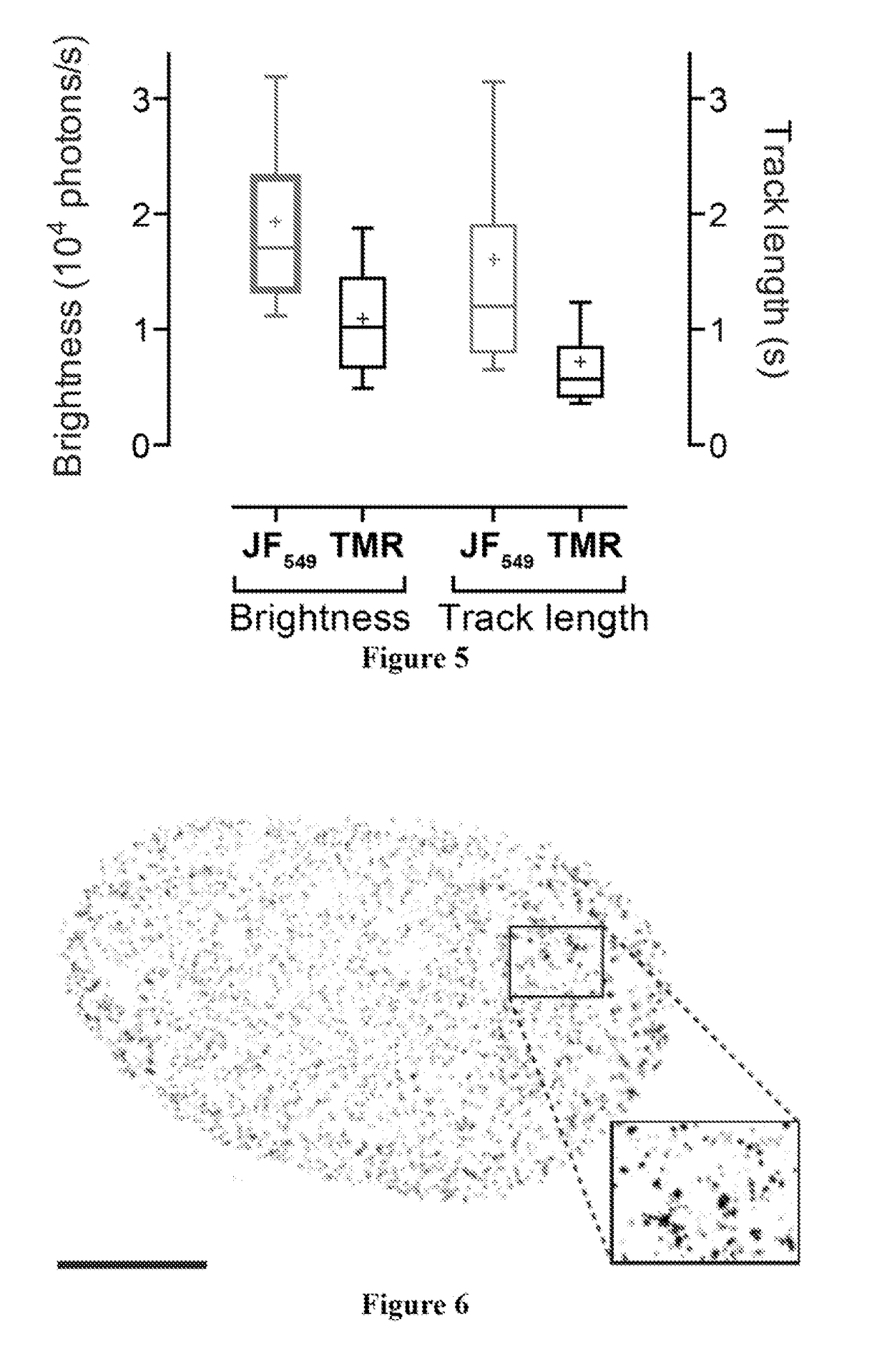
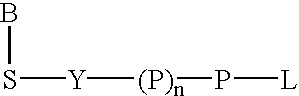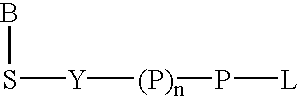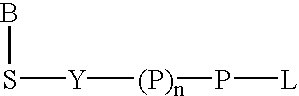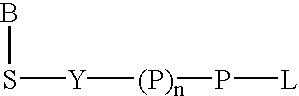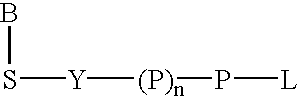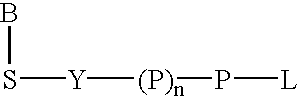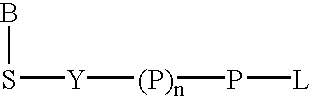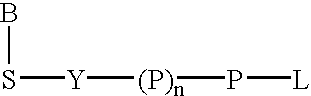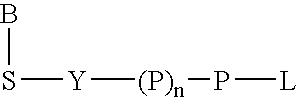Patents
Literature
99results about "Acridine dyes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS7041812B2Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
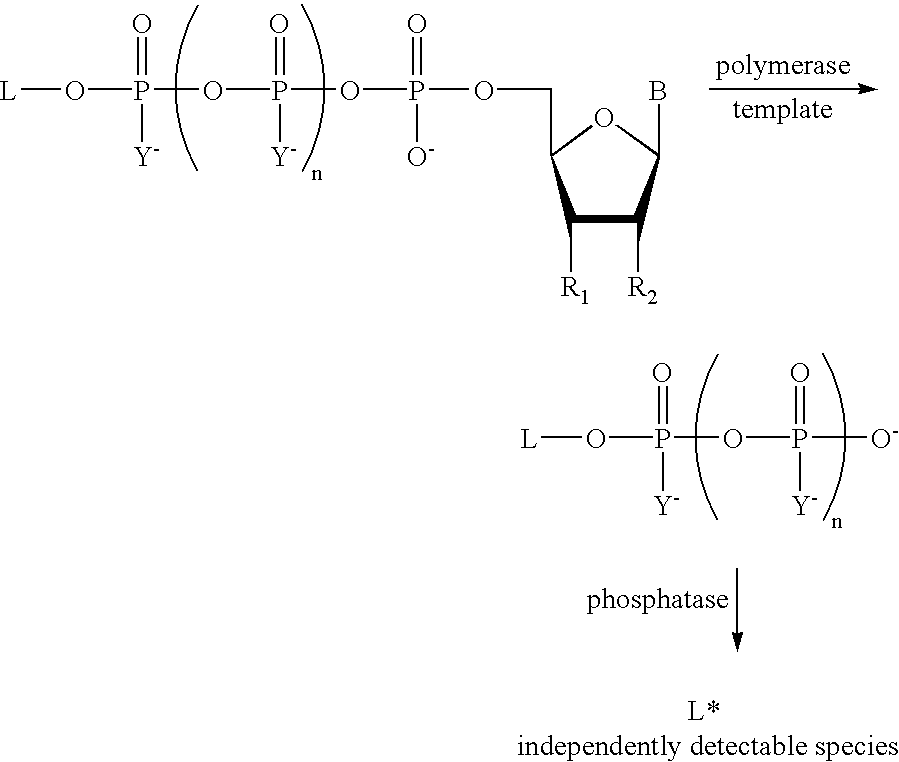
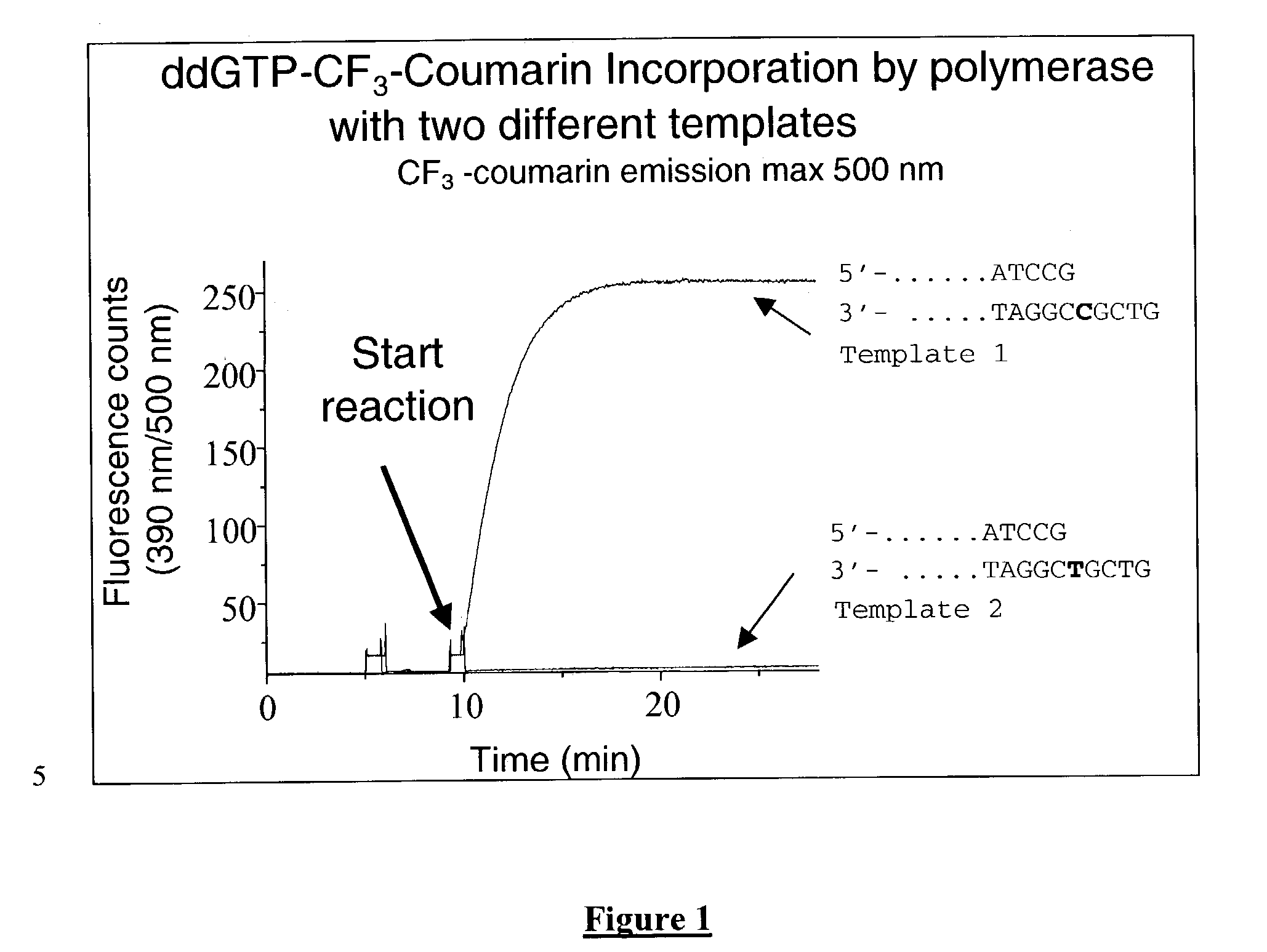
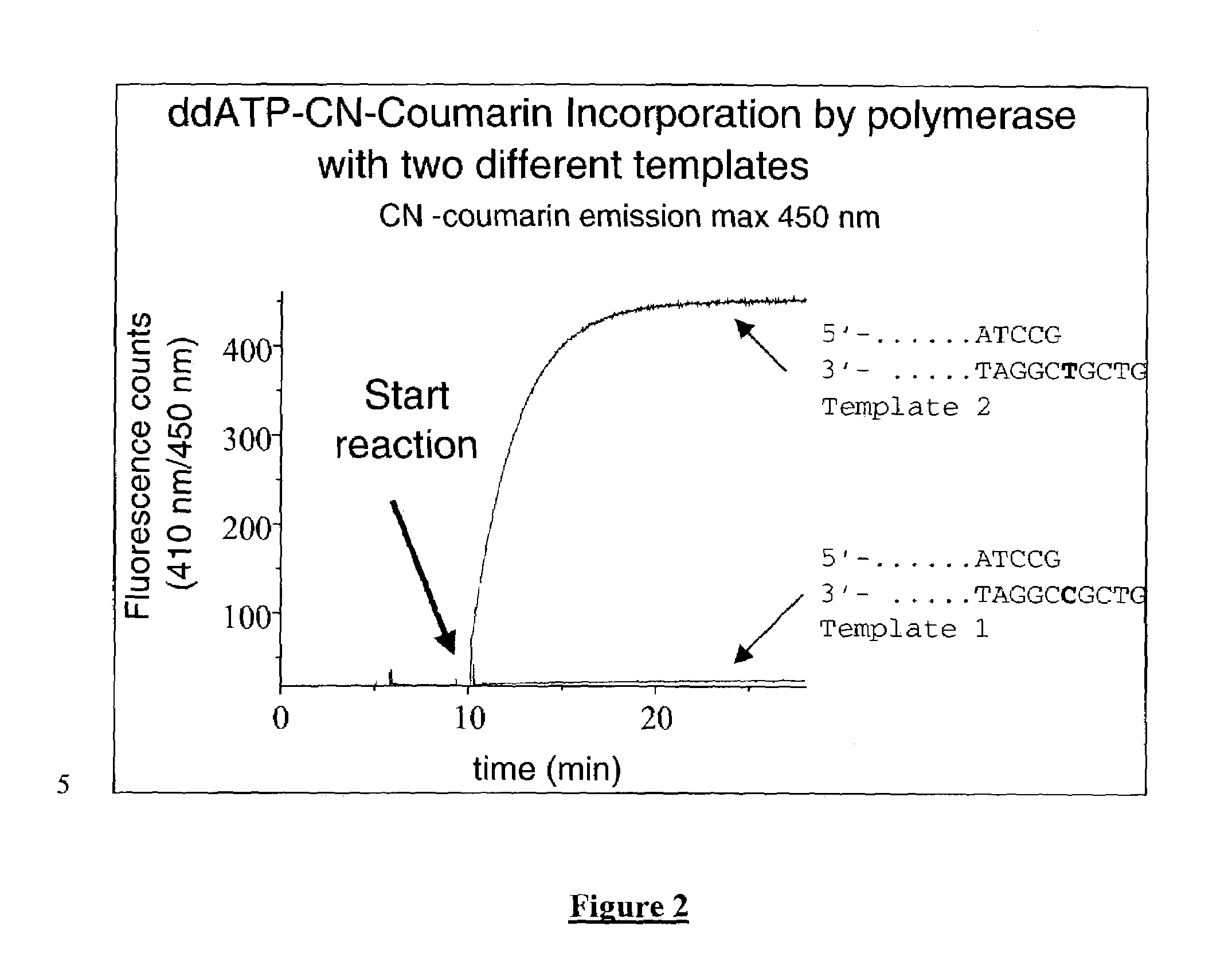
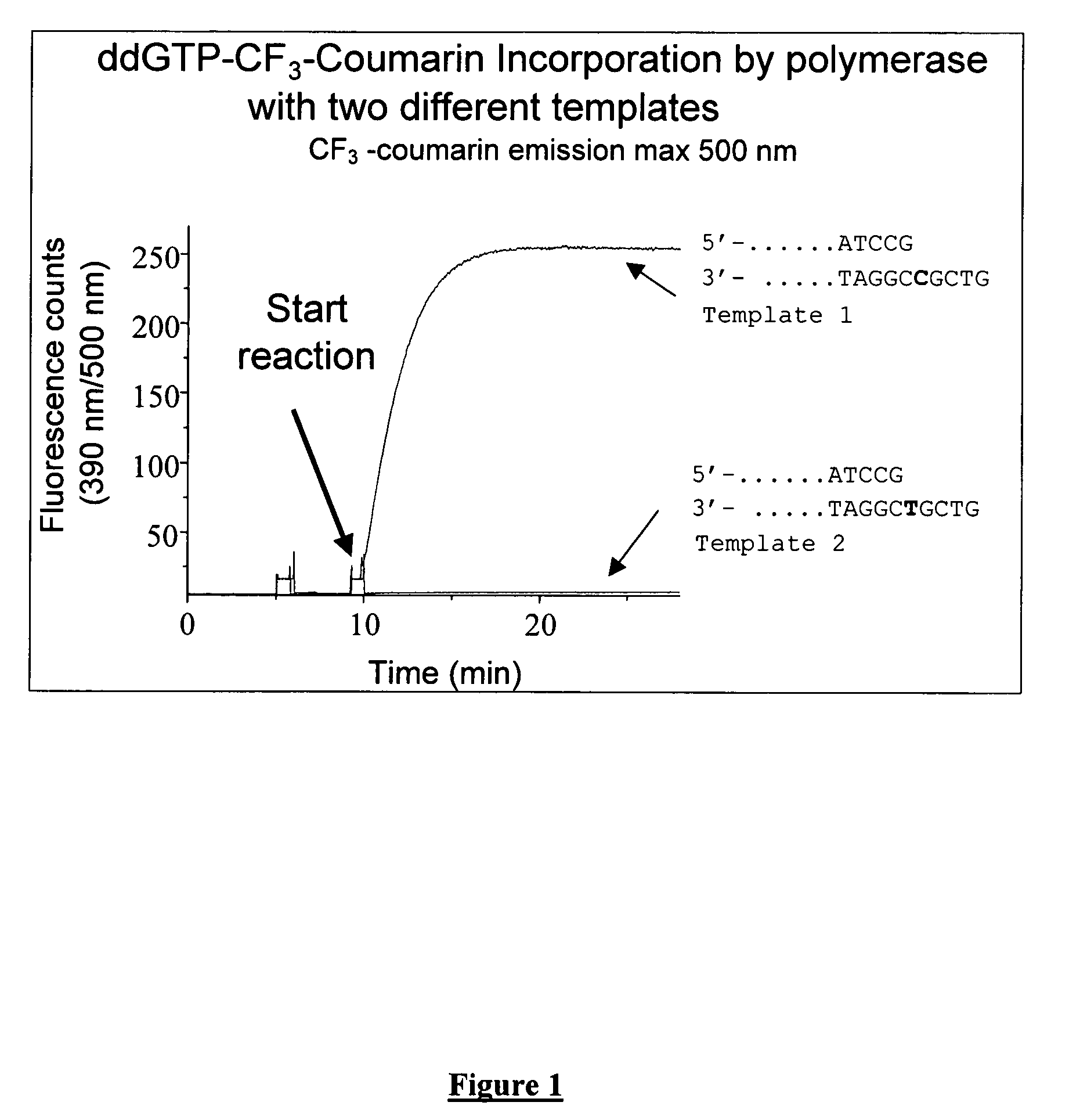
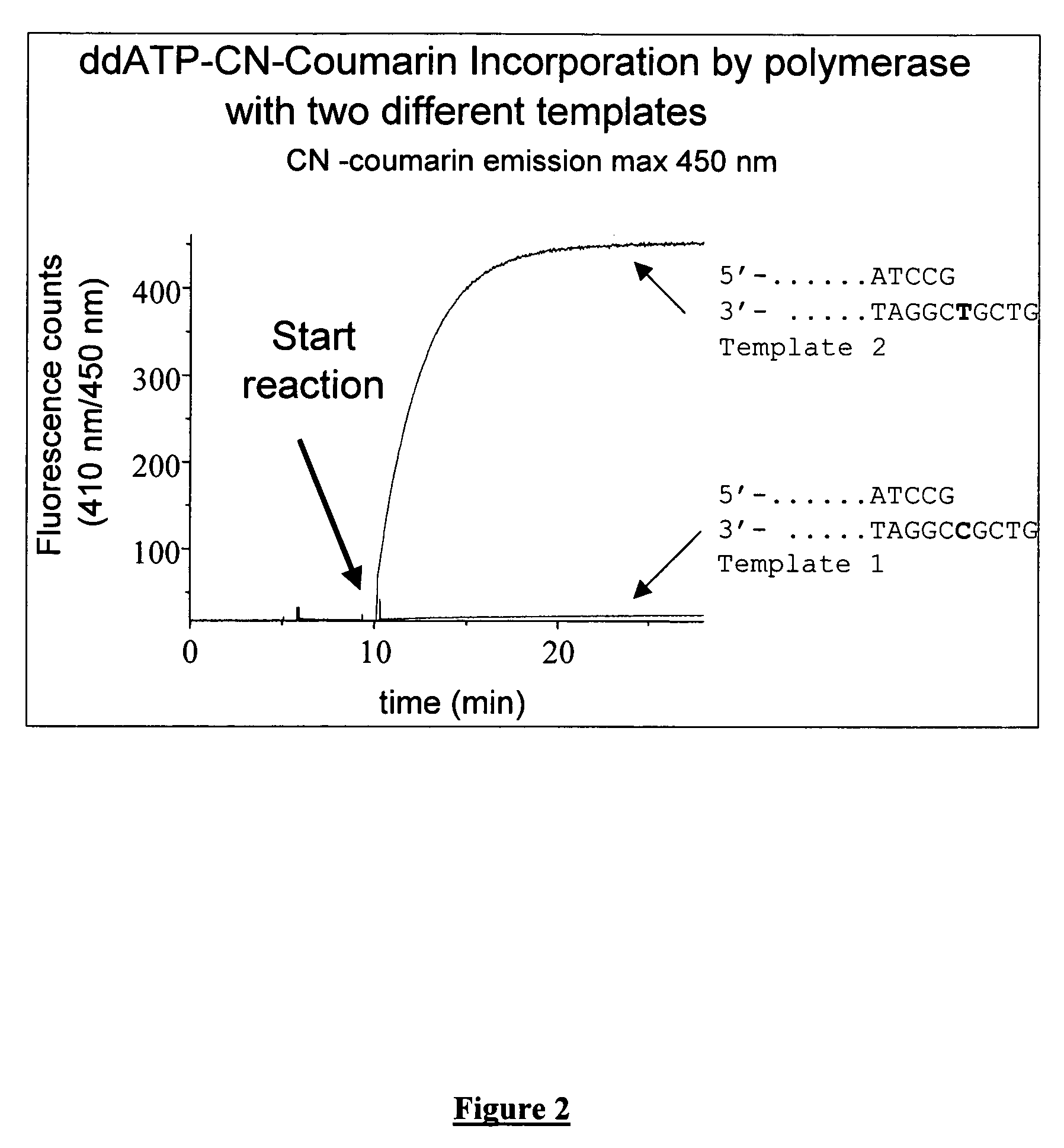
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, characterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have colorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Removal of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphate or polyphosphate transferring enzyme leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS20030124576A1Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, charcterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have calorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
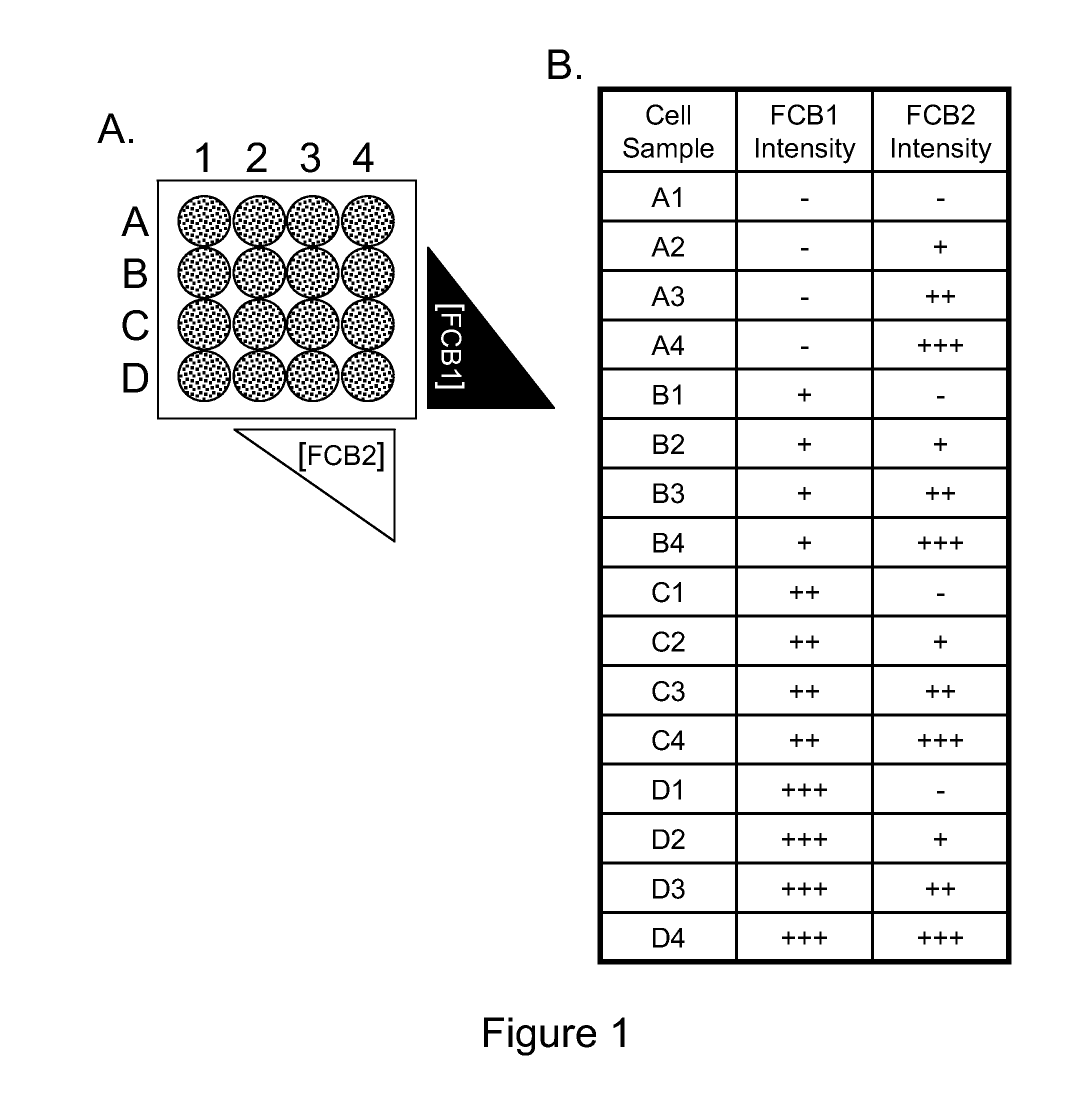
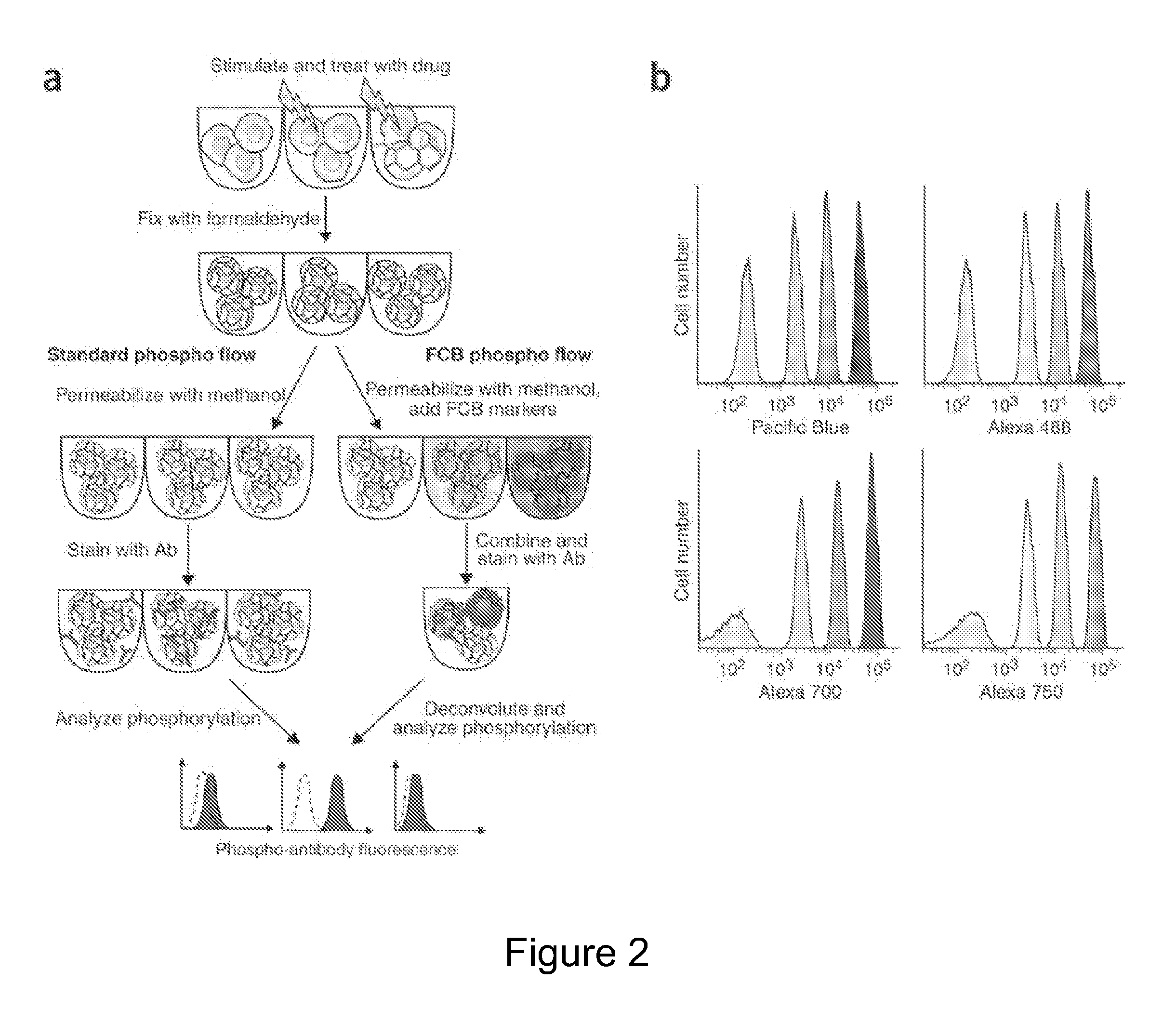
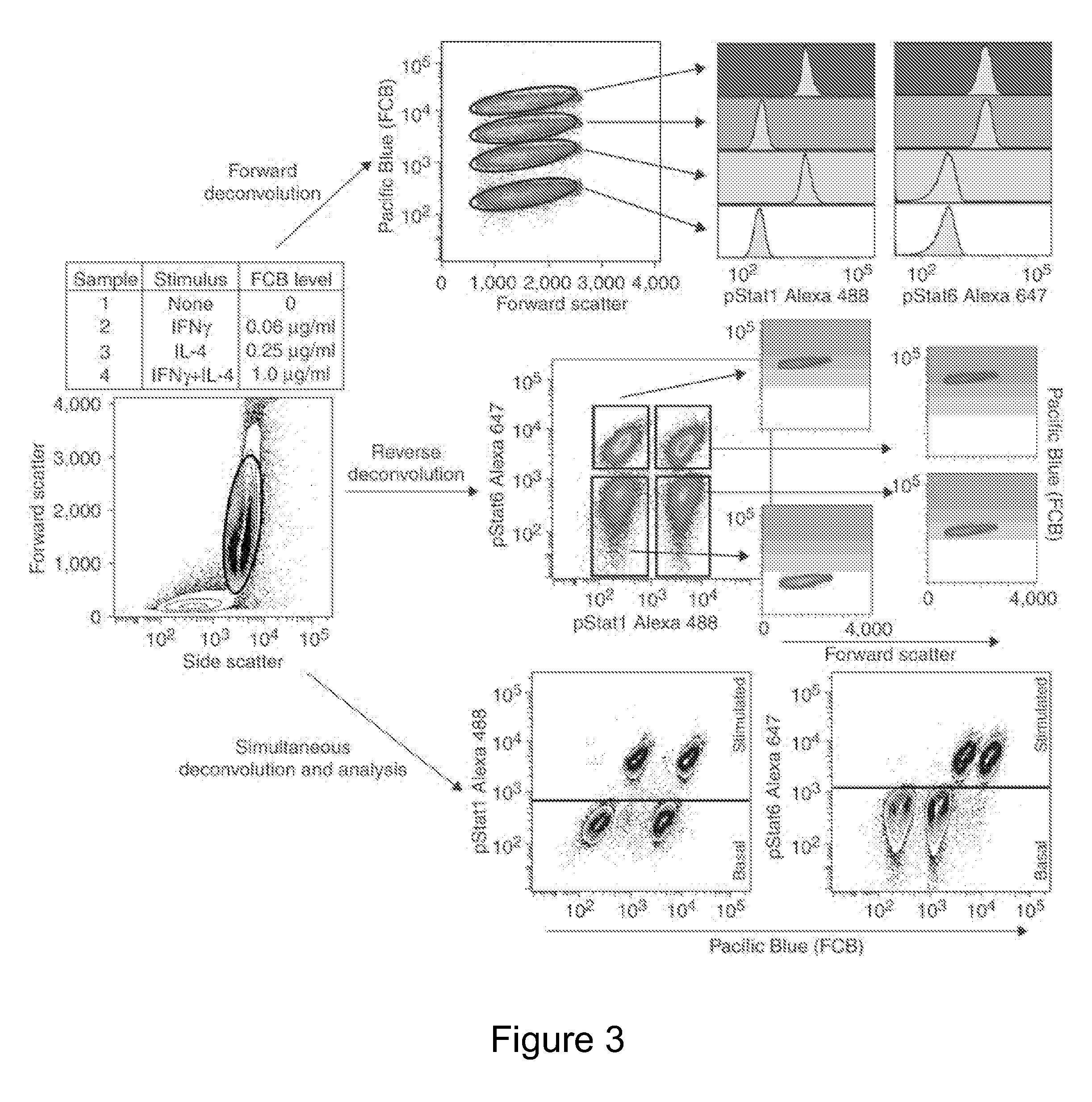
Multiplex Cellular Assays Using Detectable Cell Barcodes
InactiveUS20110263457A1Improve throughputReduce consumptionOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexingAnalyte
We describe herein a cell-based multiplexing technique called detectable cell barcoding (DCB). In DCB, each individual sample is labeled with a different DCB signature that distinguishes each sample by one or both of detected intensity or type of detection characteristic. The samples are then combined and analyzed for a detectable characteristic of interest (e.g., presence of an analyte). By employing multiple distinct DCB labels at varying concentrations, one can perform multiplex analyses on up to hundreds or thousands (or more) of cell samples in a single reaction tube. DCB reduces reagent consumption by factors of 100-fold or more, significantly reduces data acquisition times and allows for stringent control sample analysis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention relates to improved methods of detecting a target using a labeled substrate or substrate analog. The methods comprise reacting the substrate or substrate analog in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which produces a labeled moiety with independently detectable signal only when such substrate or substrate analog reacts. The present invention, in particular, describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
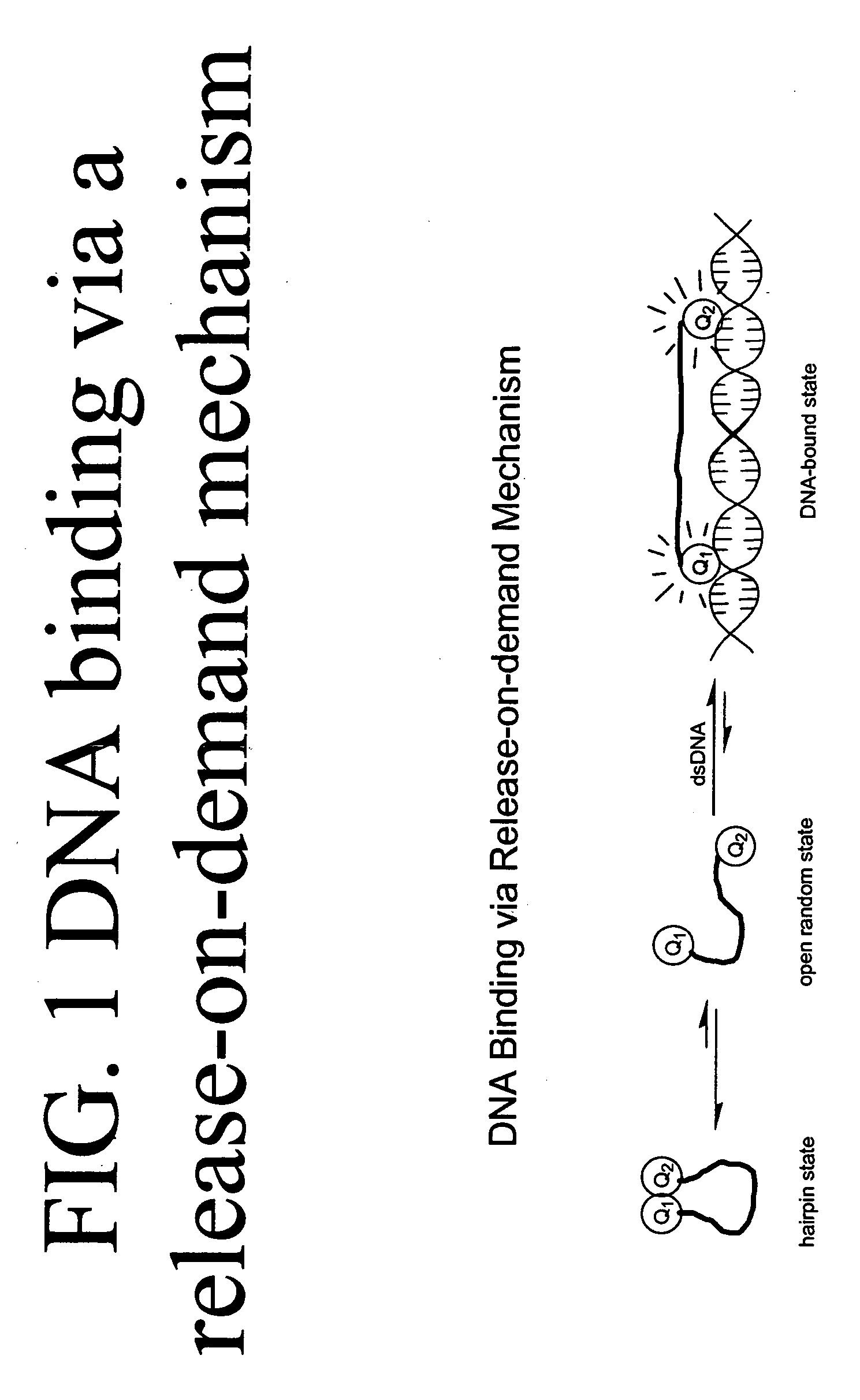
Methods of using dyes in association with nucleic acid staining or detection and associated technology
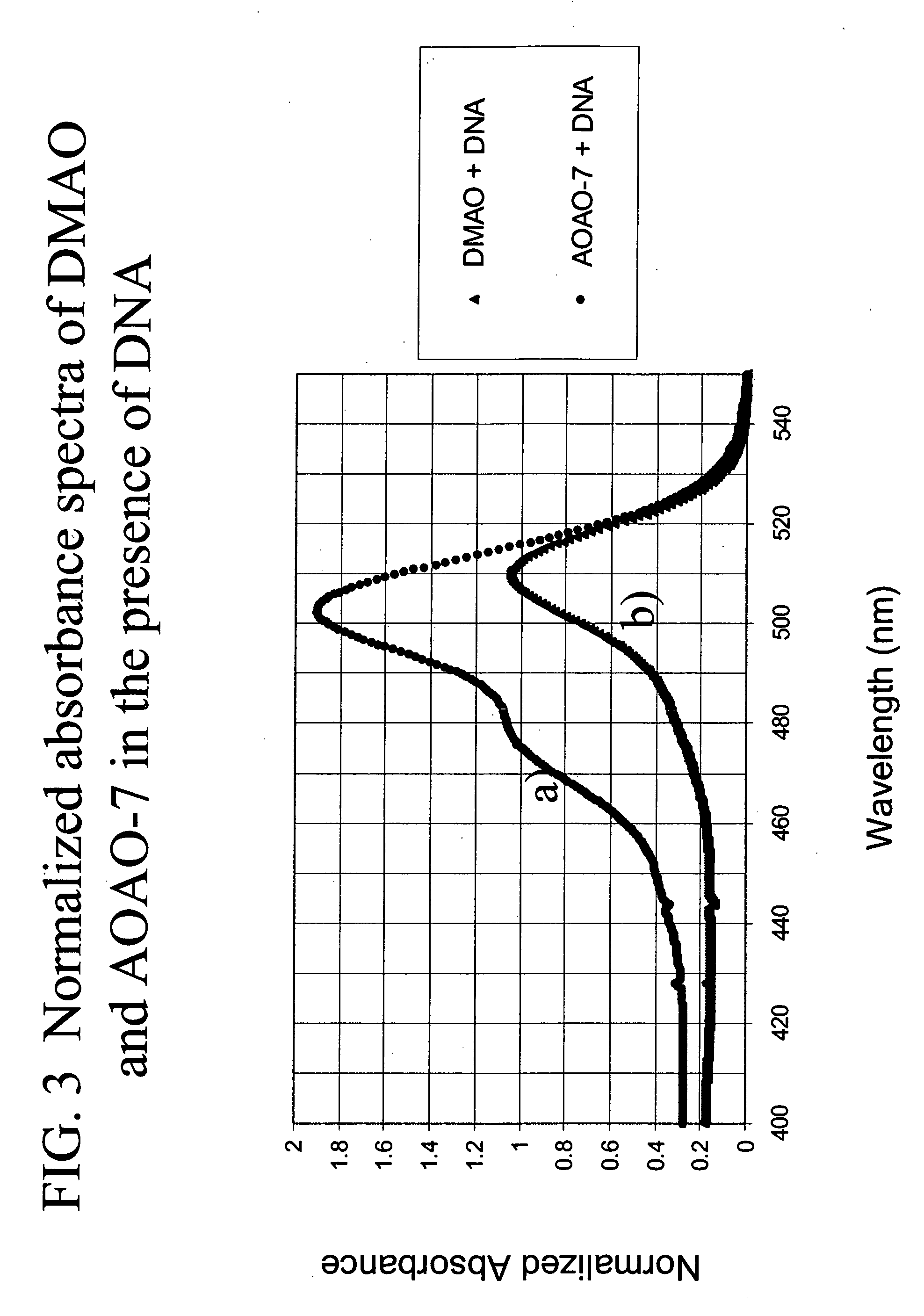
ActiveUS7601498B2Low toxicityIncrease signal strengthMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesNucleic acid detectionStaining
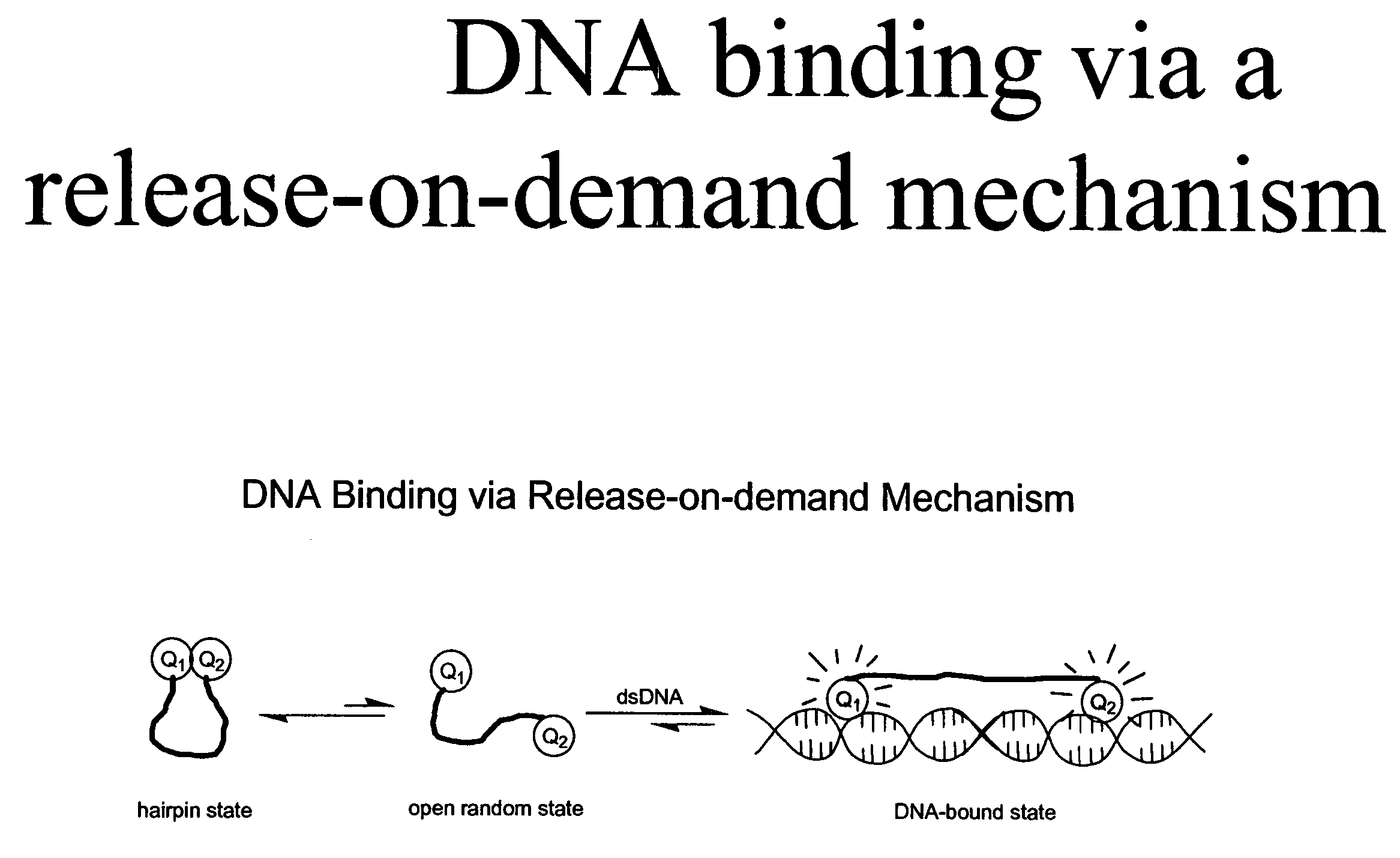
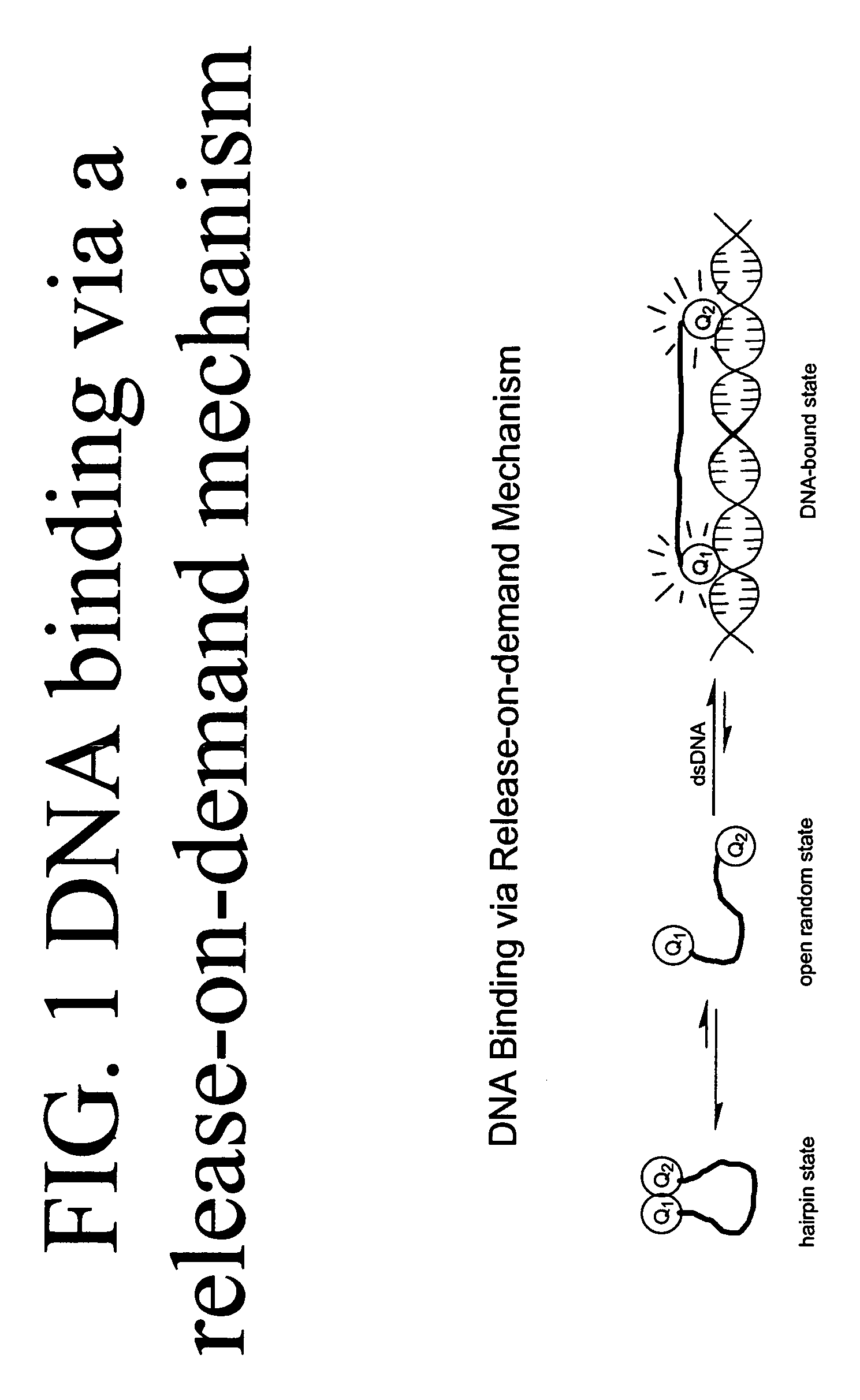
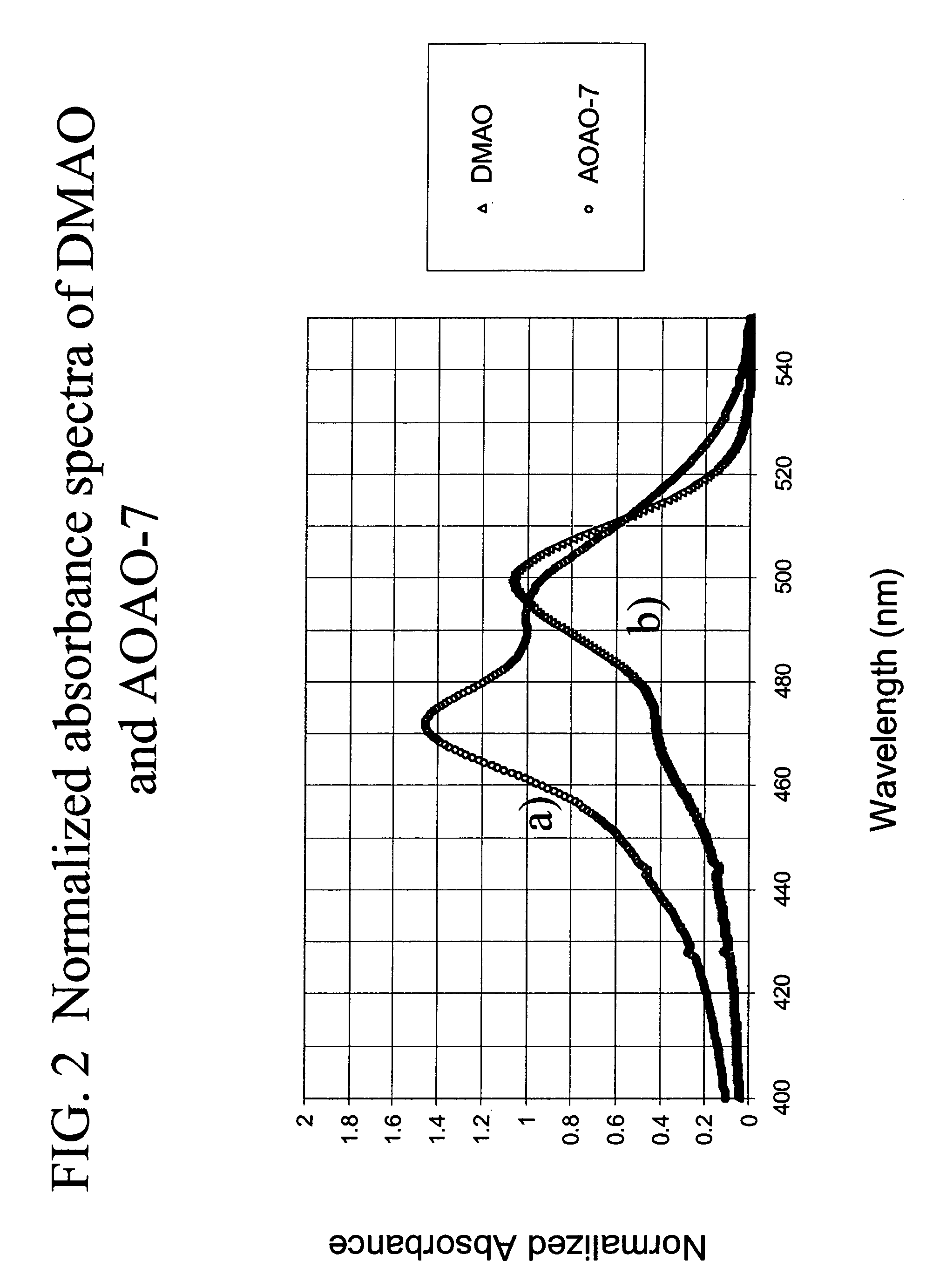
Methods of using dyes and associated technology are provided. A dye, such as a monomeric dye or a dimeric dye, may be used in a nucleic acid gel staining application and / or a nucleic acid detection application. Such a dye and a salt that comprises an anion that is associated with a strong acid and a cation that is associated with a strong base may be used in such an application. A dimeric dye, such as a dimeric dye capable of forming a hairpin-like structure, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids via a release-on-demand mechanism. A dimeric dye having low background fluorescence in the absence of nucleic acids and high fluorescence in the presence of nucleic acids, upon binding therewith, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides with new linkers
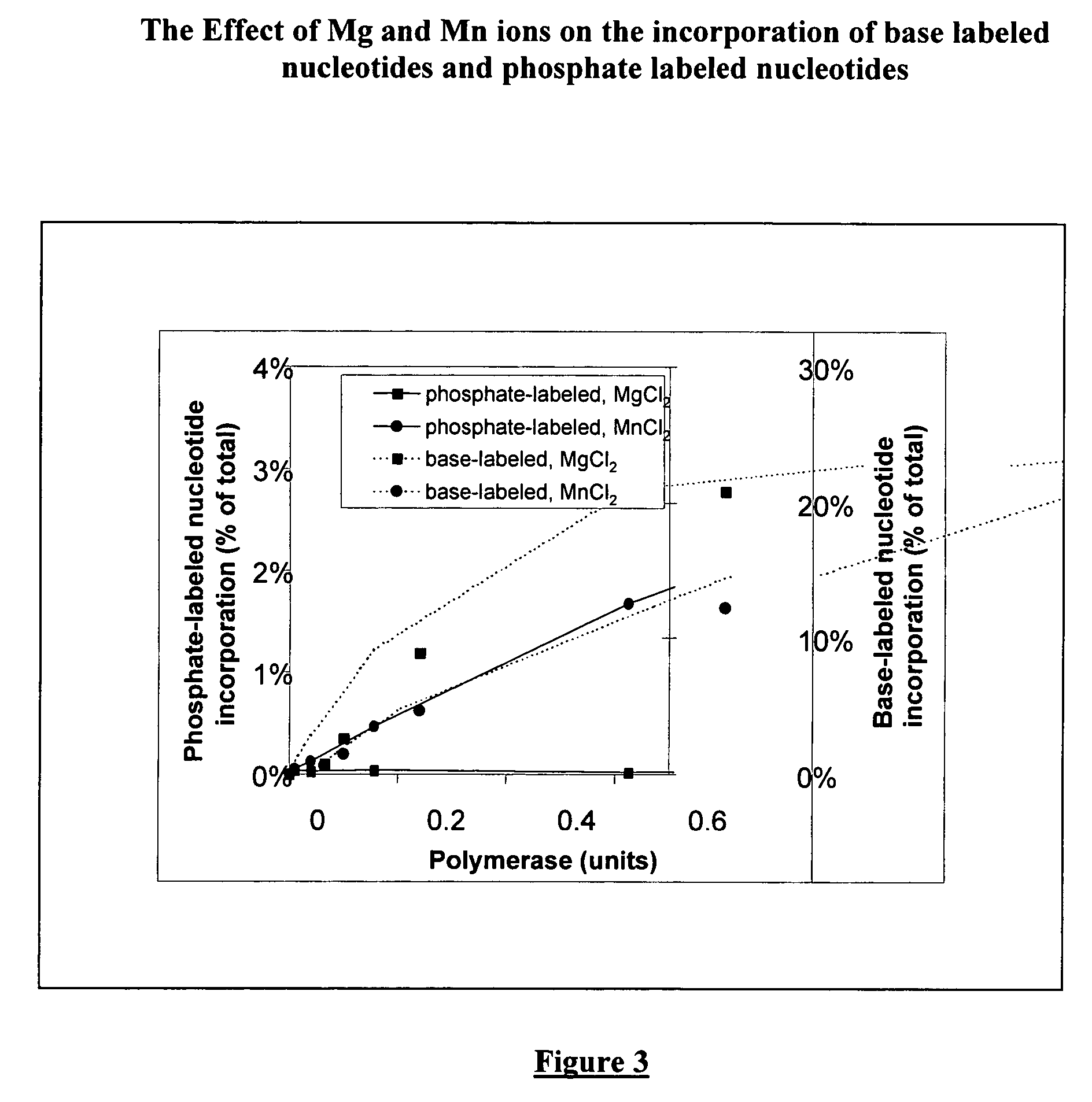
The present invention describes methods of using terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides in the presence of a manganese salt to enhance their substrate properties towards various enzymes. Particularly described are methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases, in the presence of a manganese salt. Further provided are manganese complexes of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as well as terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides with new linkers with enhanced substrate properties.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
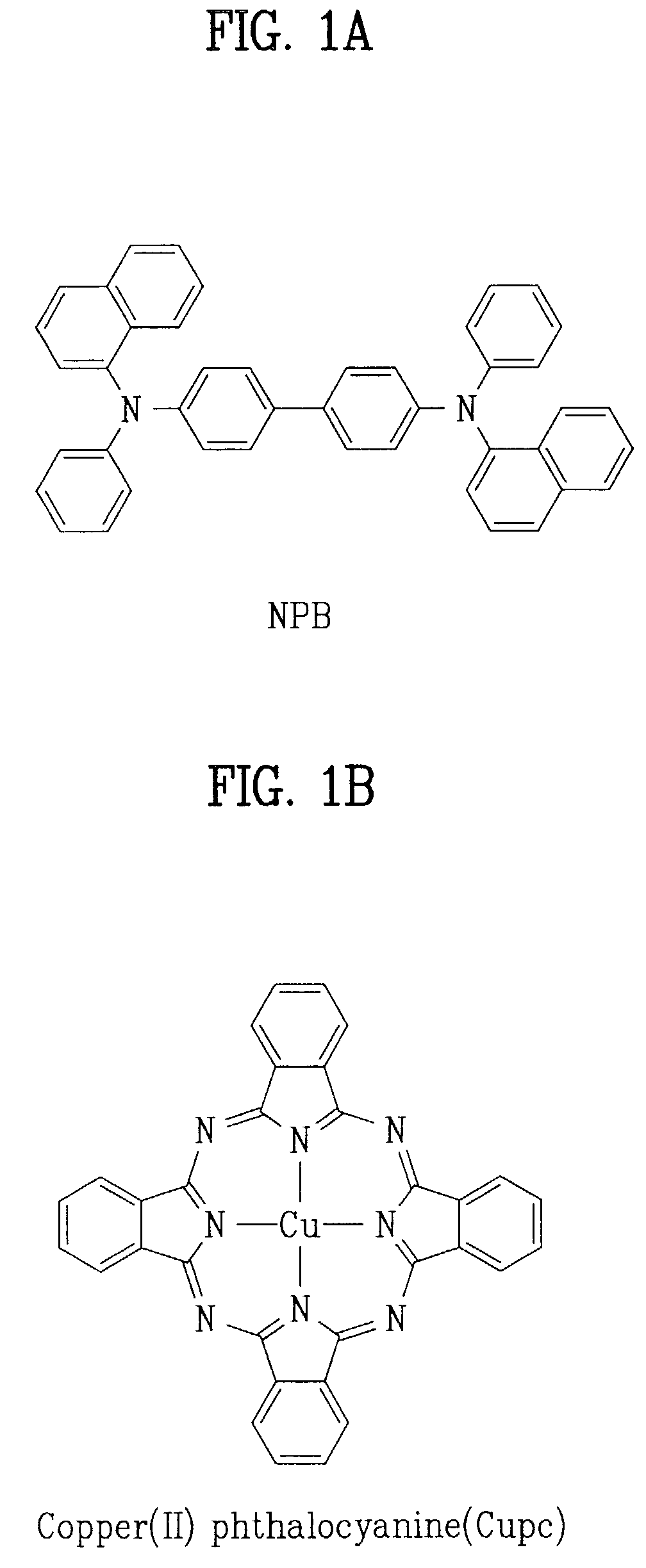
Thermal activation delayed fluorescent material and organic electroluminescent device
ActiveCN105503766AShort lifeImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryBenzene azine dyesAcridineTriplet state
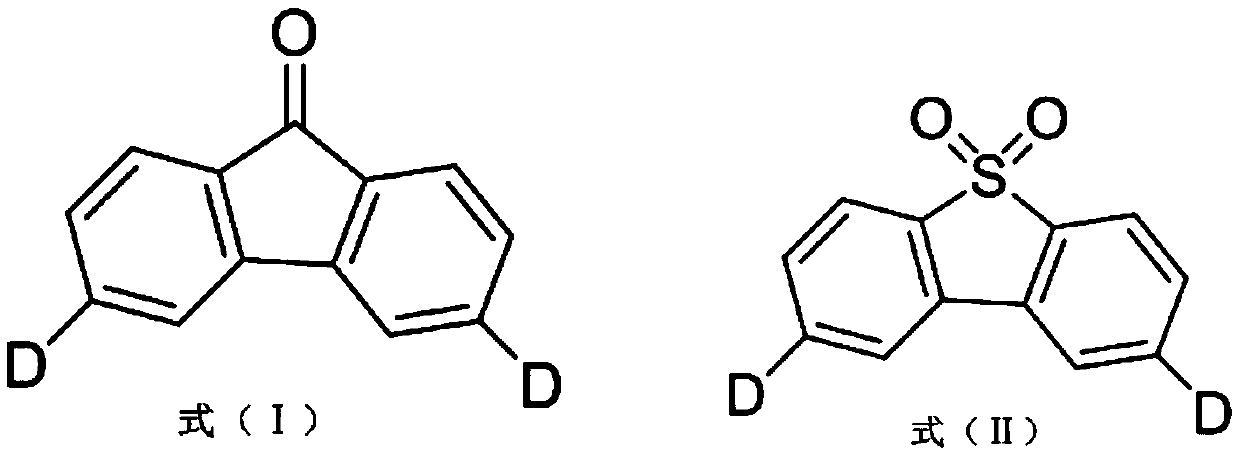
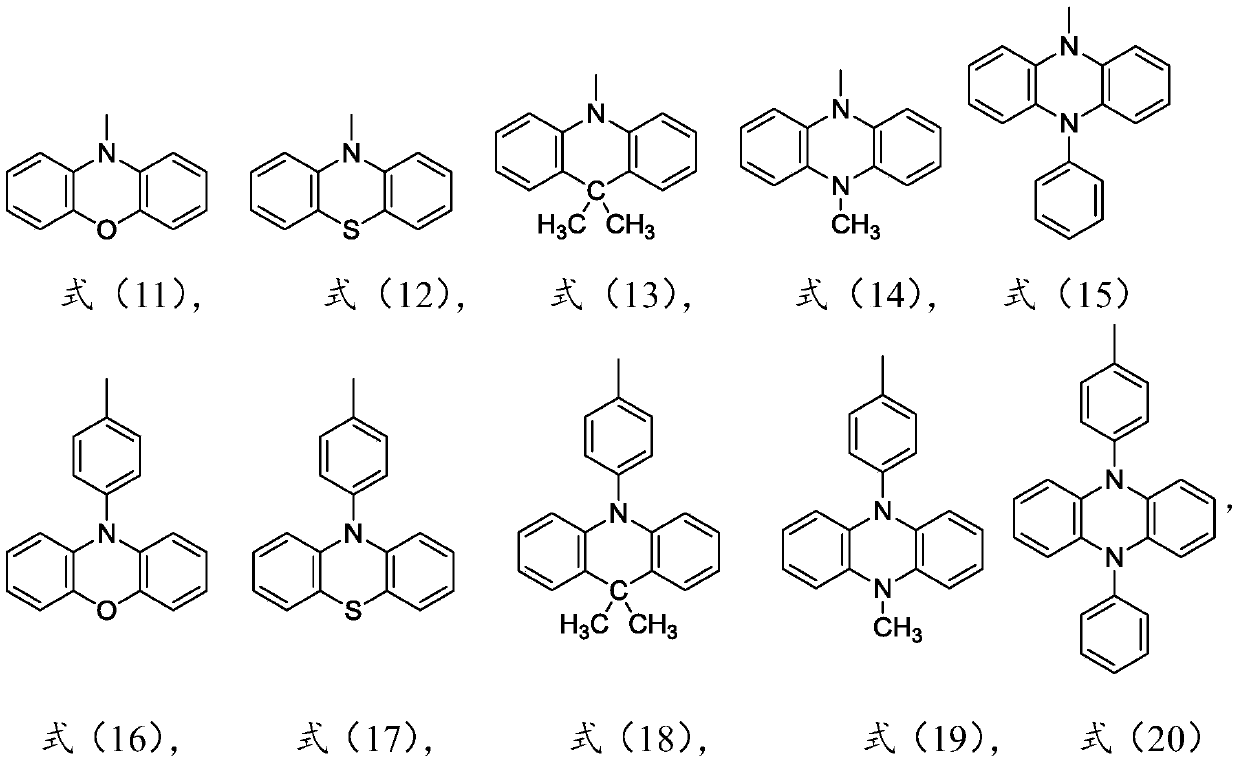
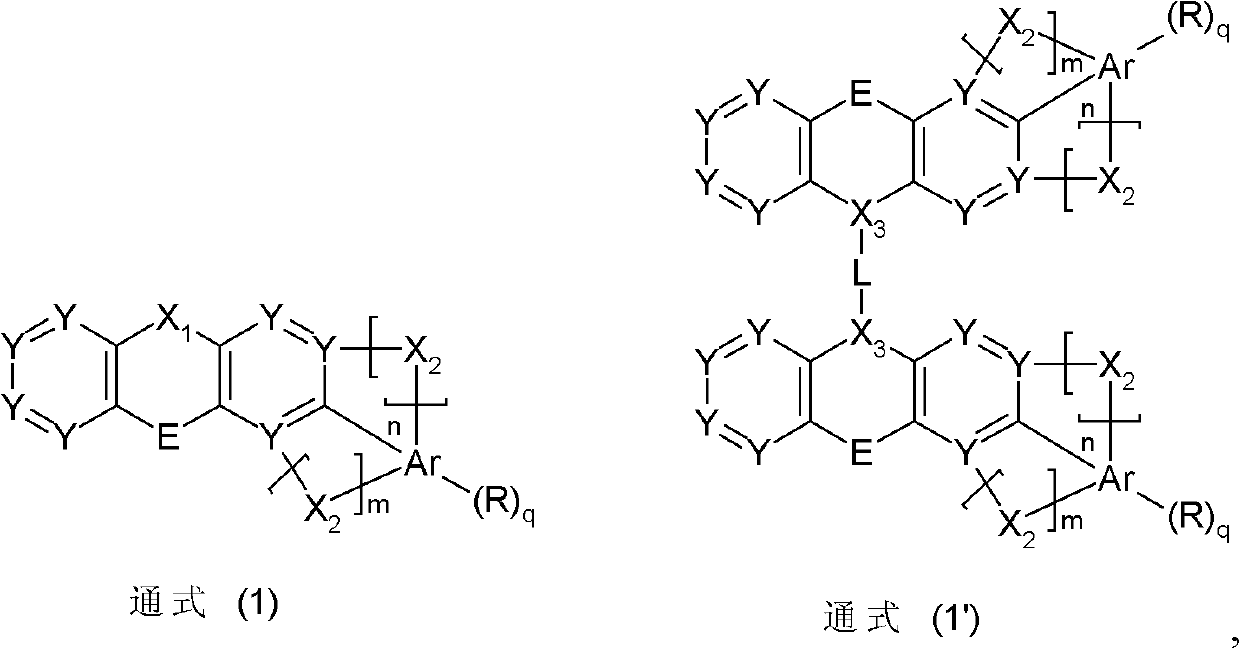
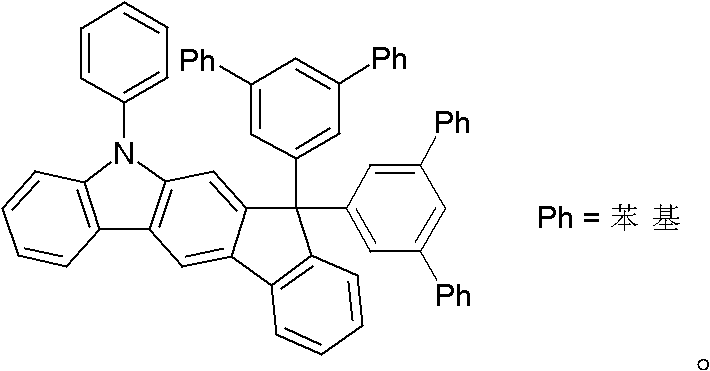
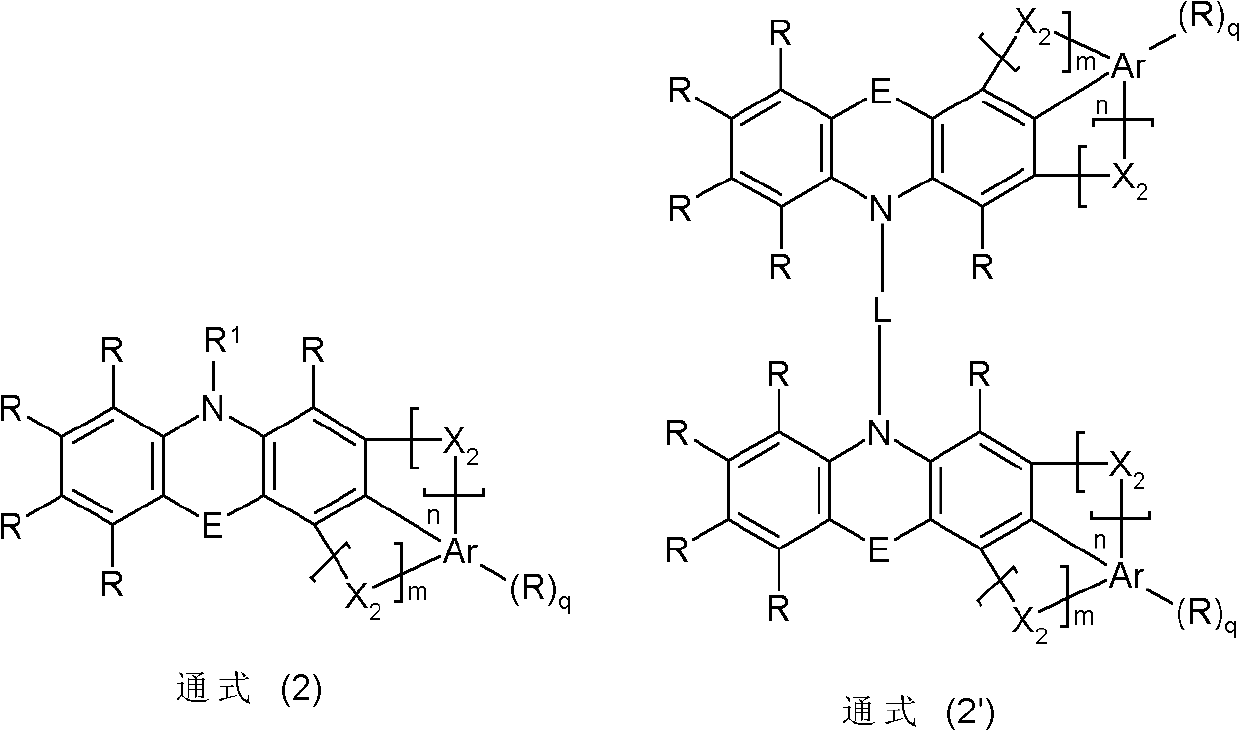
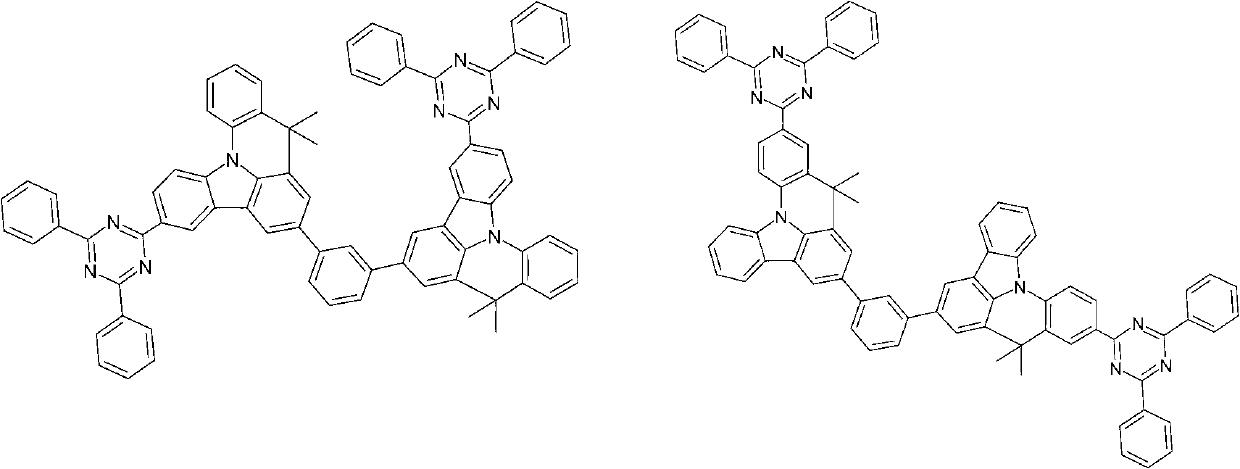
The invention relates to a thermal activation delayed fluorescent material with a general formula of the structure shown as the formula (I) or the formula (II). D is one of phenoxazinyl, phenothizainyl, 9,9-dimethyl acridine, 9-methyl phenazinyl, 9-phenyl phenazinyl, 4-phenoxazinyl-1-phenyl, 4-phenothizainyl-1-phenyl, 4-(9,9-dimethyl)acridinyl-1-phenyl, 4-(9-methyl)-phenazinyl-1-phenyl, 4-(9-phenyl)phenazinyl-1-phenyl and 3,5-bis-carbazolyl-1-phenyl. The invention further relates to an organic electroluminescent device which comprises a light-emitting layer, and luminescent dye of the light-emitting layer is the thermal activation delayed fluorescent material. The singlet state-triplet state energy gap (delta EST) of the thermal activation delayed fluorescent material is very small, triplet state excitors can be converted into singlet state excitors through inverse intersystem crossing (RIST) to emit light, and the efficiency and stability of an OLED device can be improved. The formula is shown in the description.
Owner:KUNSHAN GO VISIONOX OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Materials for organic electroluminescent devices
ActiveCN102448946AImprove power efficiencyImprove stabilityIndium organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsElectricityTransport layer
The present invention describes indenocarbazole derivatives having electron and hole transport properties, especially for use in the emission layer and / or charge transport layer of electroluminescent devices or as matrix material. The invention further provides a process for preparing the compounds of the invention, and electronic devices comprising them.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS7507485B2Improve luminous efficiencyMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesHost materialOrganic electroluminescence
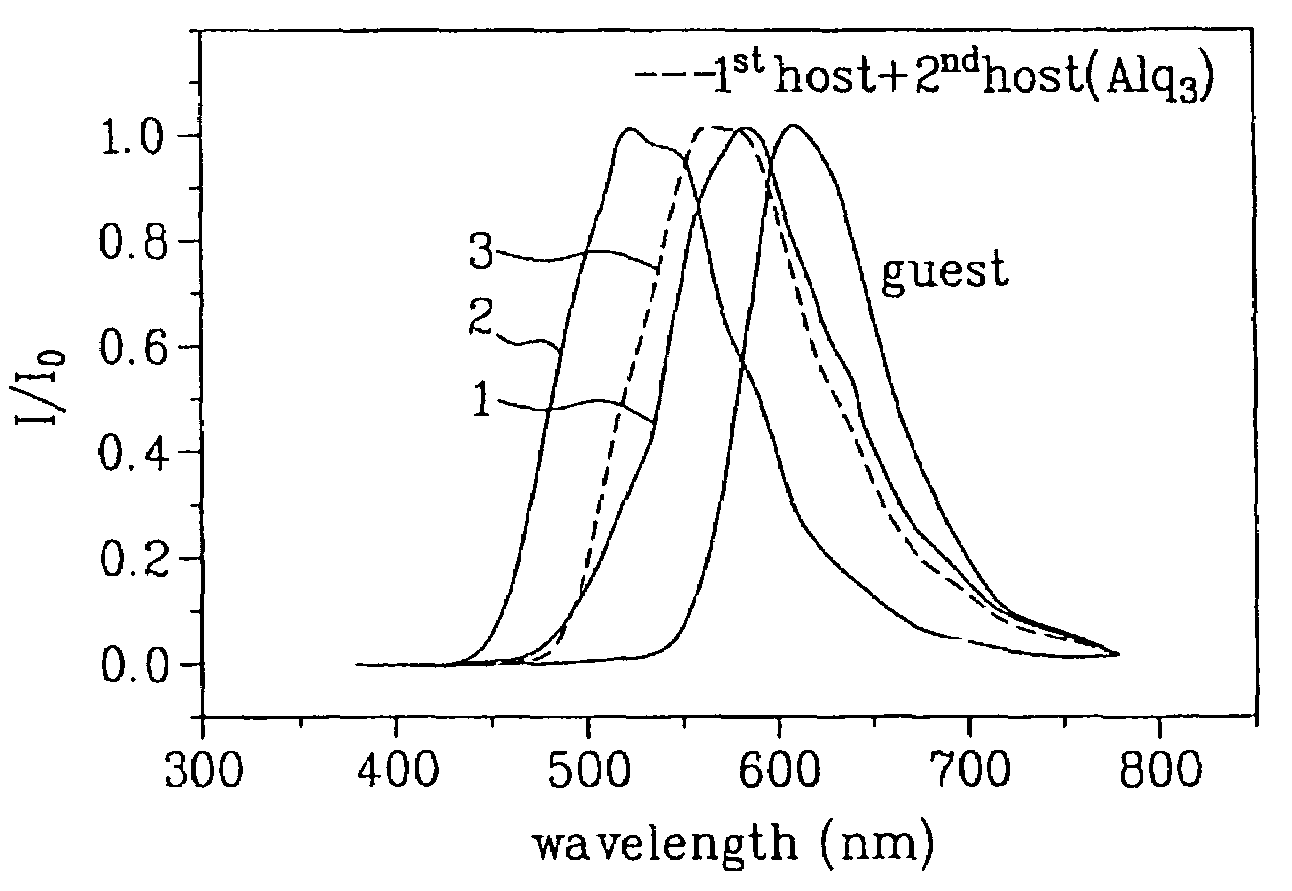
Disclosed is an organic electroluminescent device including a first electrode, a second electrode, and a light-emitting layer having a guest material of a red luminescent material and at least two host materials so as to be formed between the first and second electrodes. One of the host materials is a composite including the following structural formula:Moreover, one of the host materials can be a substituted or non-substituted quinoline derivative.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Methods of using dyes in association with nucleic acid staining or detection and associated technology
ActiveUS20060211029A1Increase DNA detection sensitivity“effective dye concentrationMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesStainingStrong acids
Methods of using dyes and associated technology are provided. A dye, such as a monomeric dye or a dimeric dye, may be used in a nucleic acid gel staining application and / or a nucleic acid detection application. Such a dye and a salt that comprises an anion that is associated with a strong acid and a cation that is associated with a strong base may be used in such an application. A dimeric dye, such as a dimeric dye capable of forming a hairpin-like structure, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids via a release-on-demand mechanism. A dimeric dye having low background fluorescence in the absence of nucleic acids and high fluorescence in the presence of nucleic acids, upon binding therewith, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
Spiro compound and organic luminescence device using the same
InactiveUS20060134425A1Improve efficiencyIncrease brightnessMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesArylHydrogen atom
Provided are a novel spiro compound, and an organic luminescence device using the spiro compound and having an optical output with an extremely high efficiency and a high luminance, and an extremely high durability. The Spiro compound is represented by the following general formula [I]: (wherein R1, R2, R3, and R4 represent a hydrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aralkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group, a substituted amino group, a cyano group, or a halogen atom, and R1, R2, R3, and R4 may be identical or different from each other; and Ar1 and Ar2 represent a substituted or unsubstituted condensed polycyclic aromatic group or a substituted or unsubstituted condensed polycyclic heterocyclic group, which may be identical or different from each other.)
Owner:CANON KK
Phosphonylated fluorescent dyes and conjugates
Reagents are provided for the introduction of phosphonate groups into fluorescent dyes. Methods are also provided for preparing dye conjugates.
Owner:ELITECHGROUP MDX LLC
Display
ActiveUS20140332790A1Long life-timeLow working voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingArylHalogen
Display comprising at least one organic light emitting diode, wherein the at least one organic light emitting diode comprises an anode, a cathode, a light emitting layer between the anode and the cathode, and at least one layer comprising a compound according to formula (I) between the cathode and the light emitting layer:wherein A1 and A2 are independently selected from halogen, CN, substituted or unsubstituted C1-C20-alkyl or heteroalkyl, C6-C20-aryl or C5-C20-heteroaryl, C1-C20-alkoxy or C6-C20-aryloxy,A3 is selected from substituted or unsubstituted C6-C40-aryl or C5-C40-heteroaryl,m=0, 1 or 2,n=0, 1 or 2.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Compound and photoelectric device, image sensor and electronic device including the same
ActiveUS20170352811A1Light absorption efficiency can be improvedImprove efficiencySilicon organic compoundsIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsPhysical chemistryMaterials science
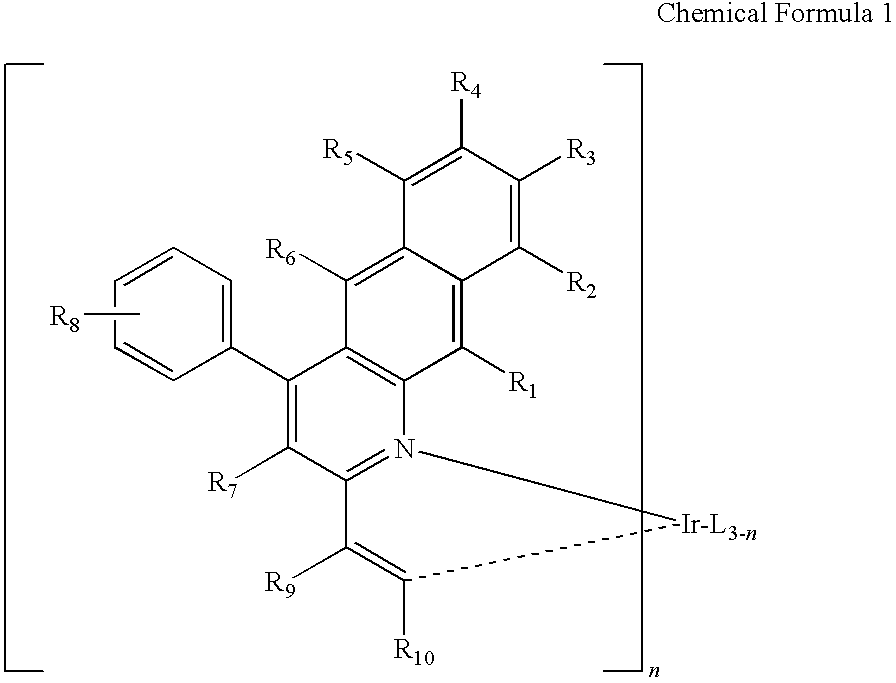
A compound represented by Chemical Formula 1, and a photoelectric device, an image sensor, and an electronic device including the same are disclosed.In Chemical Formula 1, each substituent is the same as defined in the detailed description.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and kit for assessing viable cells
ActiveUS20110312012A1Fast resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh concentrationThiol
The present invention provides simple, rapid methods and procedures for analyzing cells, hereunder quantitative and qualitative assessment of cells, such as viability. The present invention relates to the use of various optionally substituted reporter compounds particularly detectable upon their reaction with thiol-containing species present in higher concentrations in intact (e.g., living) cells than in non-intact (e.g., dead, stressed and apoptotic) cells. The present invention also relates to the use of various optionally substituted reporter compounds particularly detectable upon their reaction with species present in intact and / or non-intact cells. Moreover, the present invention relates to the use of measuring techniques and / or instruments coupled with the use of various optionally substituted reporter compounds. The invention further relates to compositions used in methods for analyzing cells, such as a composition comprising N-(7-dimethylamino-4-methyl-3-coumarinyl)-maleimide (DACM).
Owner:CHEMOMETEC AS
Materials for Organic Electroluminescent Devices
ActiveCN102282130AImprove power efficiencyImprove stabilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityTransport layer
The present invention describes indenofluorene derivatives of the general formula I, II, III or IV having emitting and hole-transporting properties, in particular for use in the emission and / or charge-transport layer of electro-luminescent devices. The invention furthermore relates to a process for the preparation of the compounds according to the invention and to electronic devices comprising same.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
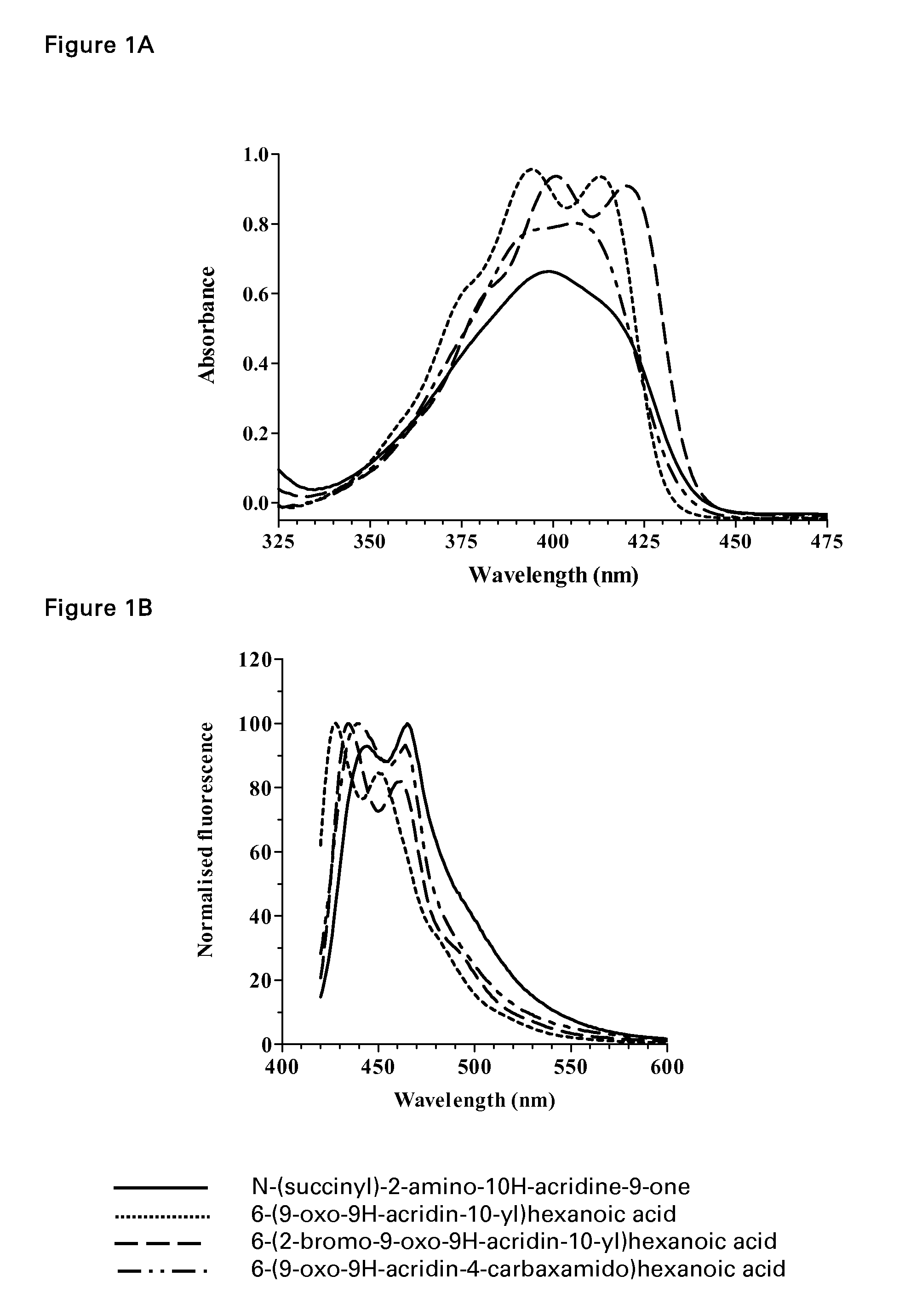
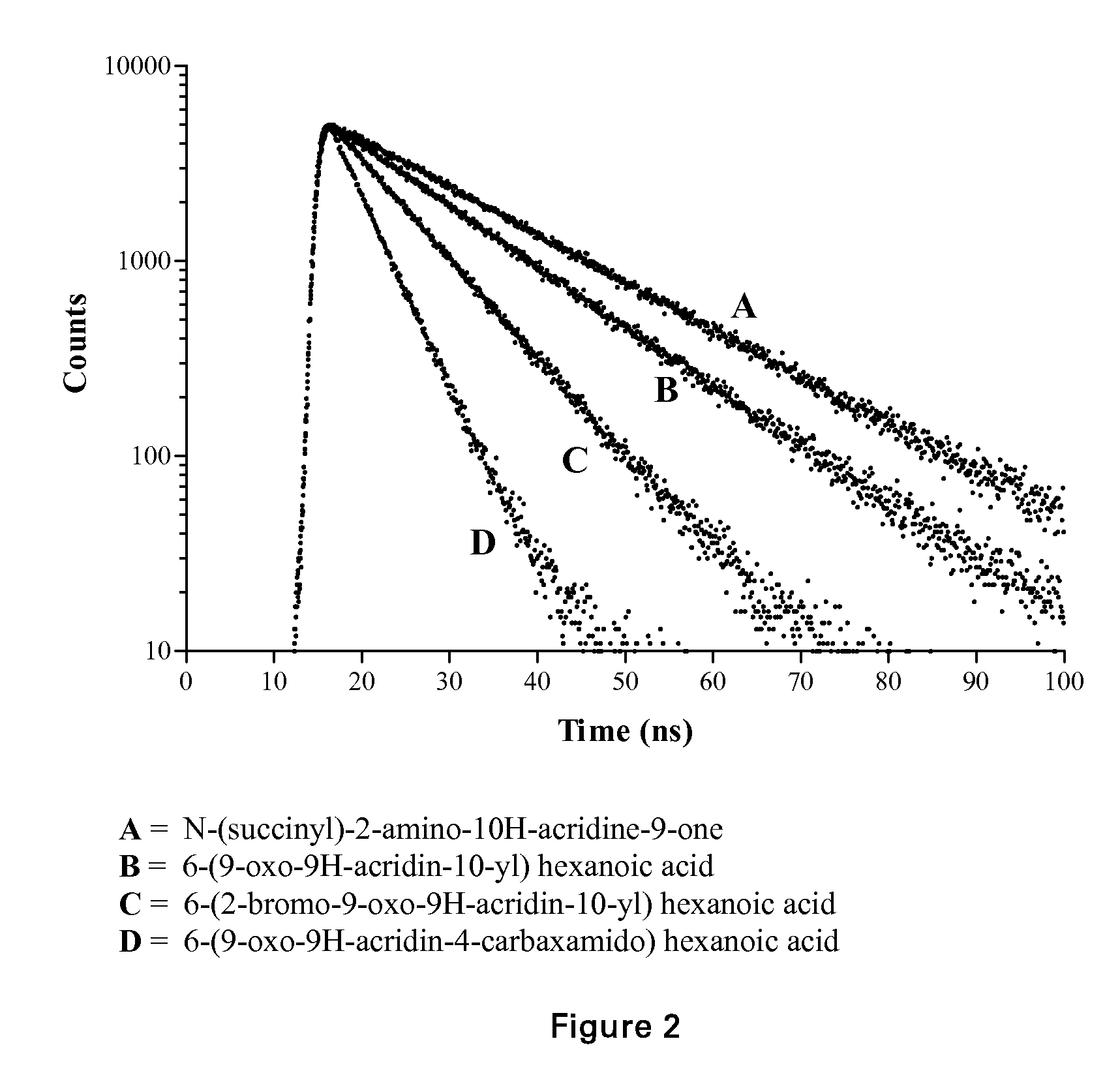
Acridone derivatives as labels for fluorescence detection of target materials
InactiveUS8034558B2Simple requirementsEasy to analyze and useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhosphateBiological materials
Owner:TTP LABTECH
Compounds for electronic devices
ActiveCN102725268AHigh hole mobilityImprove power efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic chemistryChemistry
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Novel Organic Dye And Preparation Method Thereof
InactiveCN102803394AImprove efficiencyHigh molar absorptivityMonoazo dyesMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic dyePhotoelectric conversion
The present invention relates to a novel organic dye for a dye-sensitized photoelectric conversion device, and a preparation method thereof. The organic dye according to the present invention is used as a dye-sensitized photoelectric conversion device in a dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) and provides improved molar absorptivity, Jsc (short circuit photocurrent density) and photoelectric conversion efficiency when compared with known dyes, thereby being capable of remarkably improving the efficiency of the solar cell.
Owner:DONGJIN SEMICHEM CO LTD
Novel organic electroluminescent compounds and organic electroluminescent device using the same
InactiveCN101550167AImprove luminous efficiencyImprove overall lifespanIndium organic compoundsMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic electroluminescenceOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates to novel organic electroluminescent compounds, and organic electroluminescent devices comprising the same. Specifically, the novel organic electroluminescent compounds according to the invention are characterized in that they are represented by Chemical Formula (1).
Owner:GRACEL DISPLAY INC
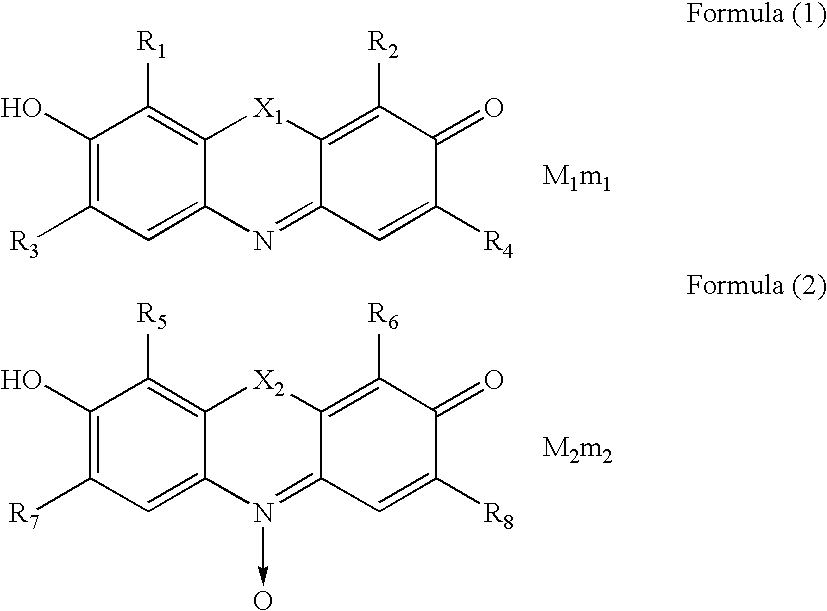
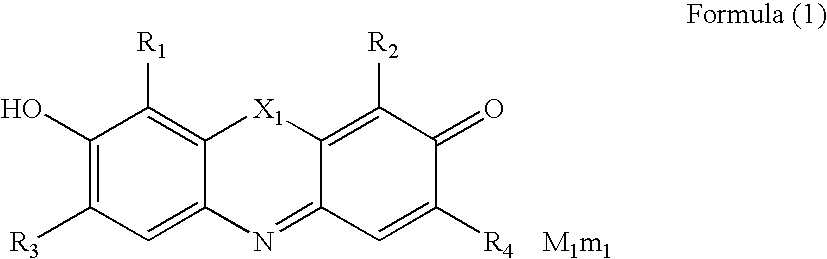
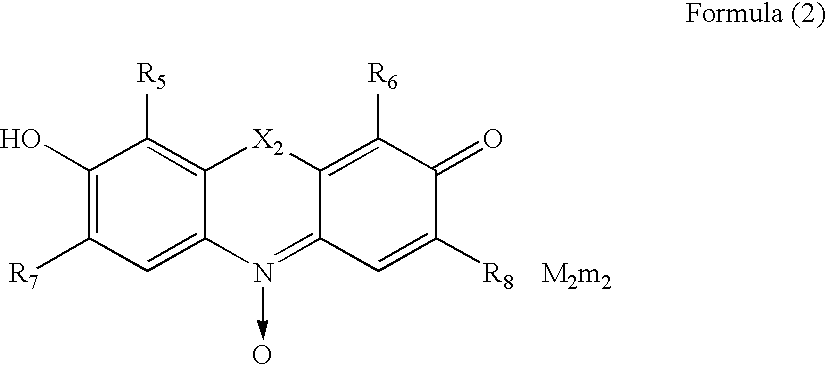
Hair-dyeing agent
A hair-dyeing agent, which contains at least one compound represented by formula (1) or (2) as a dye: wherein X1 and X2 each are an oxygen atom, nitrogen atom, sulfur atom, or dialkylmethylene group; R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, and R8 each independently are a hydrogen atom or substituent; M1 and M2 each are a counter ion to balance the charge of the molecule; and m1 and m2 each are a number of 0 or more necessary to neutralize the charge of the molecule.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Zwitterion-containing acridinium compounds
ActiveUS8778624B2Reduce non-specific bindingImprove hydrophilicityOrganic chemistryChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAssay sensitivityOnium
Hydrophilic, chemiluminescent acridinium compounds containing zwitterions are disclosed. These acridinium compounds, when used as chemiluminescent labels in immunochemistry assays and the like, exhibit decreased non-specific binding to solid phases and provide increased assay sensitivity.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Zwitterion-containing acridinium compounds
ActiveUS20120225497A1Improve hydrophilicityReduce non-specific bindingOrganic chemistryAcridine dyesAcridineImmunochemistry assay
Hydrophilic, chemiluminescent acridinium compounds containing zwitterions are disclosed. These acridinium compounds, when used as chemiluminescent labels in immunochemistry assays and the like, exhibit decreased non-specific binding to solid phases and provide increased assay sensitivity.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Light emitting material, delayed fluorescent emitter, organic light emitting device, and compound
ActiveUS9685615B2Organic chemistryPyronine/xanthon/thioxanthon/selenoxanthan/telluroxanthan dyesCompound aHydrogen atom
A compound represented by the following general formula is useful as a light emitting material. X represents an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom. R1 to R8 represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent, provided that at least one of R1 to R8 is a carbazolyl group, etc.
Owner:KYULUX INC
Novel organic electroluminescent compounds and organic electroluminescent device using the same
InactiveUS20100102710A1Improve luminous efficiencyExtended service lifeIndium organic compoundsMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic electroluminescencePhotochemistry
The present invention relates to novel organic electroluminescent compounds, and organic electroluminescent devices comprising the same. Specifically, the novel organic electroluminescent compounds according to the invention are characterized in that they are represented by Chemical Formula (1):
Owner:GRACEL DISPLAY INC
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention relates to improved methods of detecting a target using a labeled substrate or substrate analog. The methods comprise reacting the substrate or substrate analog in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which produces a labeled moiety with independently detectable signal only when such substrate or substrate analog reacts. The present invention, in particular, describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrate for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Azetidine-substituted fluorescent compounds
ActiveUS9933417B2Silicon organic compoundsPyronine/xanthon/thioxanthon/selenoxanthan/telluroxanthan dyesFluorescenceSubject matter
The presently-disclosed subject matter includes azetidine-substituted fluorescent compounds, where the compounds may be used as probes, dyes, tags, and the like. The presently-disclosed subject matter also includes kits comprising the same as well as methods for using the same to detect a target substance.
Owner:HOWARD HUGHES MEDICAL INST
Light emitting material, delayed fluorescent emitter, organic light emitting device, and compound
ActiveUS20160141516A1Excellent luminous propertiesOrganic chemistryPyronine/xanthon/thioxanthon/selenoxanthan/telluroxanthan dyesCompound aCarbazole
A compound represented by the following general formula is useful as a light emitting material. X represents an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom. R1 to R8 represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent, provided that at least one of R1 to R8 is a carbazolyl group, etc.
Owner:KYULUX INC
Nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic derivative and organic electroluminescence device using the same
InactiveCN102812004AImprove luminous efficiencyLow voltage driveOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesArylSulfur
A nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic derivative represented by the following formula, wherein X1 to X3 are a single bond, CRaRb, NRc, an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, and when all of X1 to X3 is a single bond, at least one of Ara, Arb and Arc is an aryl group having 6 to 20 ring carbon atoms substituted with a heteroaryl group, an aryloxy group or a heteroaryloxy group, or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 5 to 20 ring atoms.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com