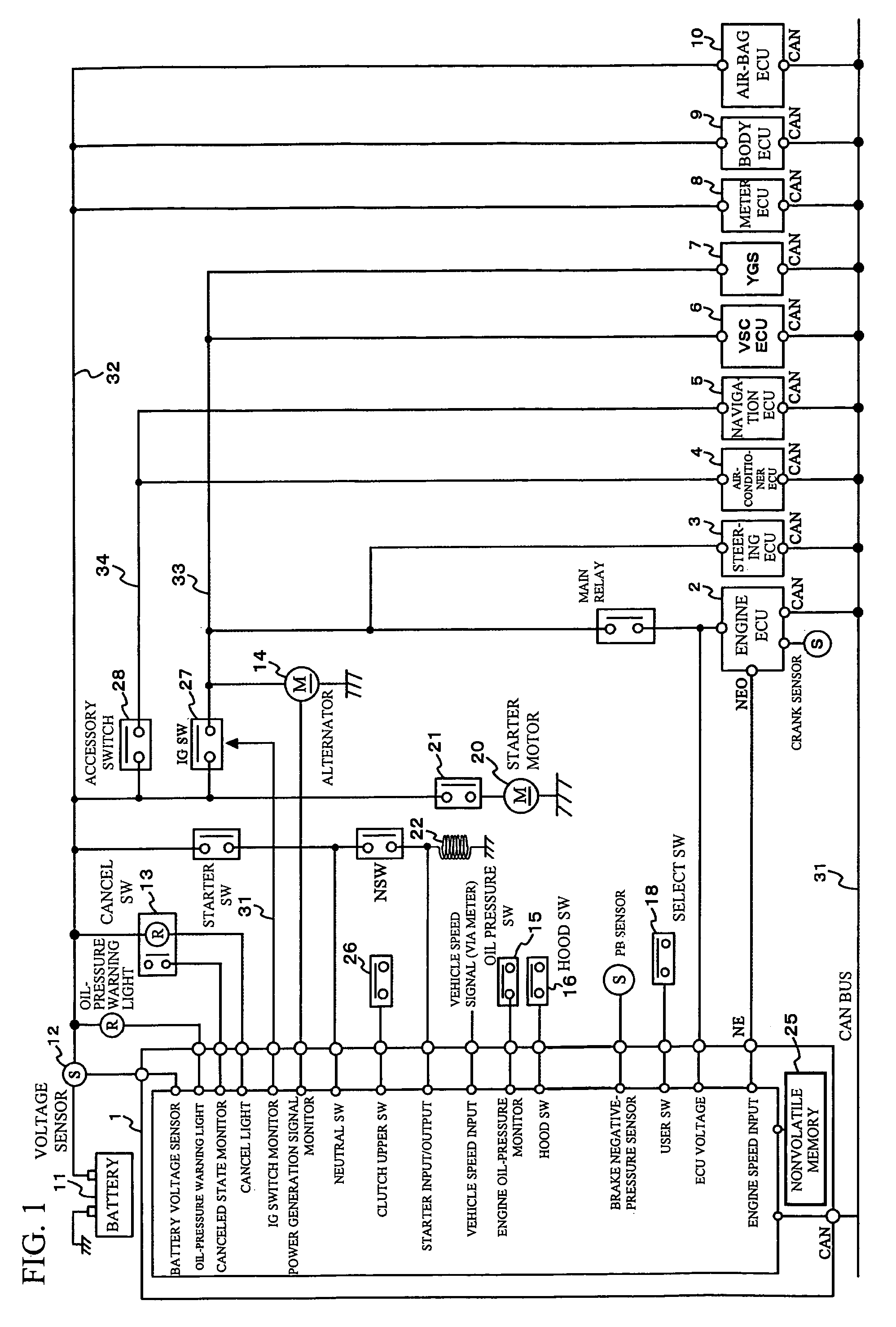
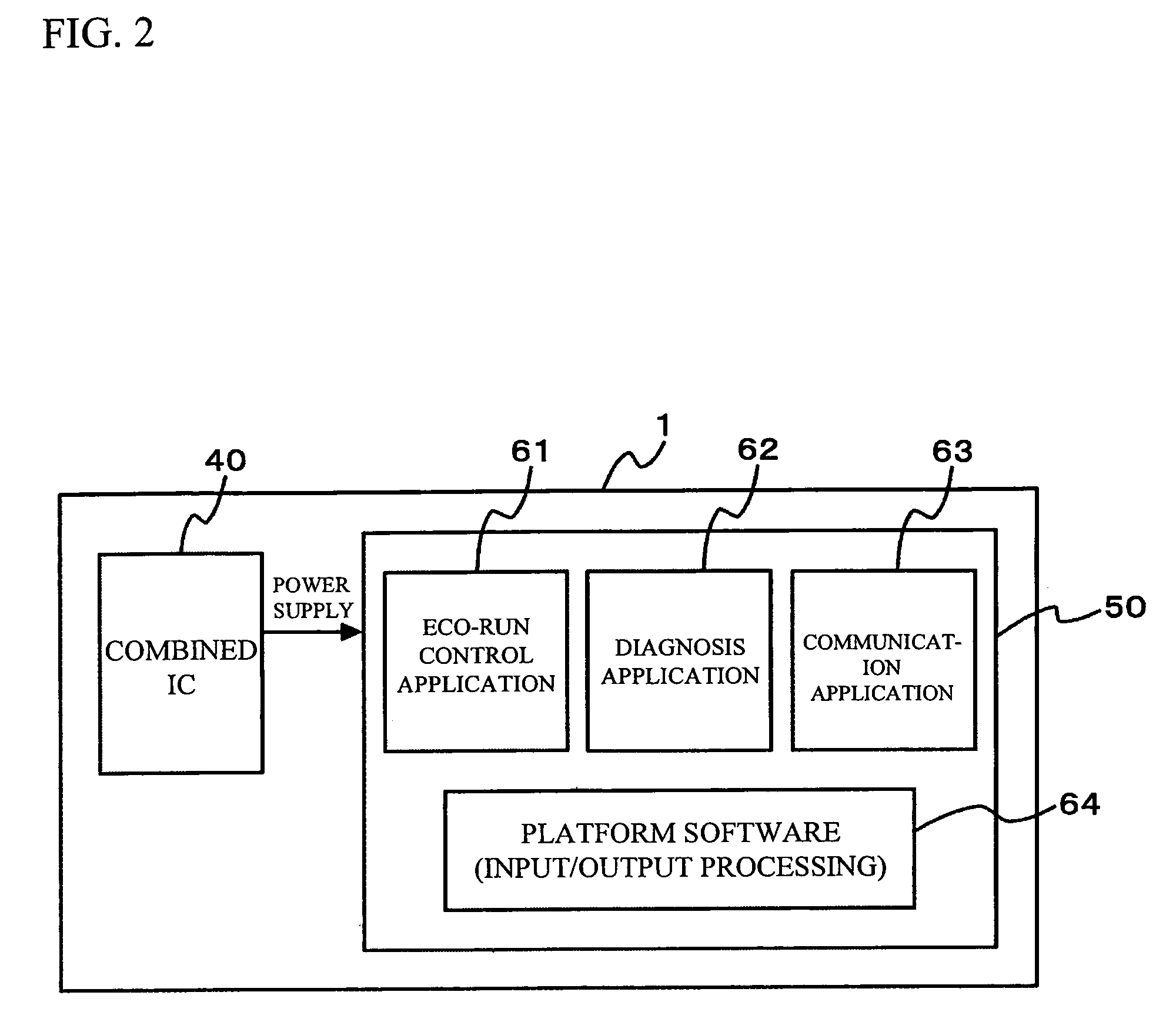
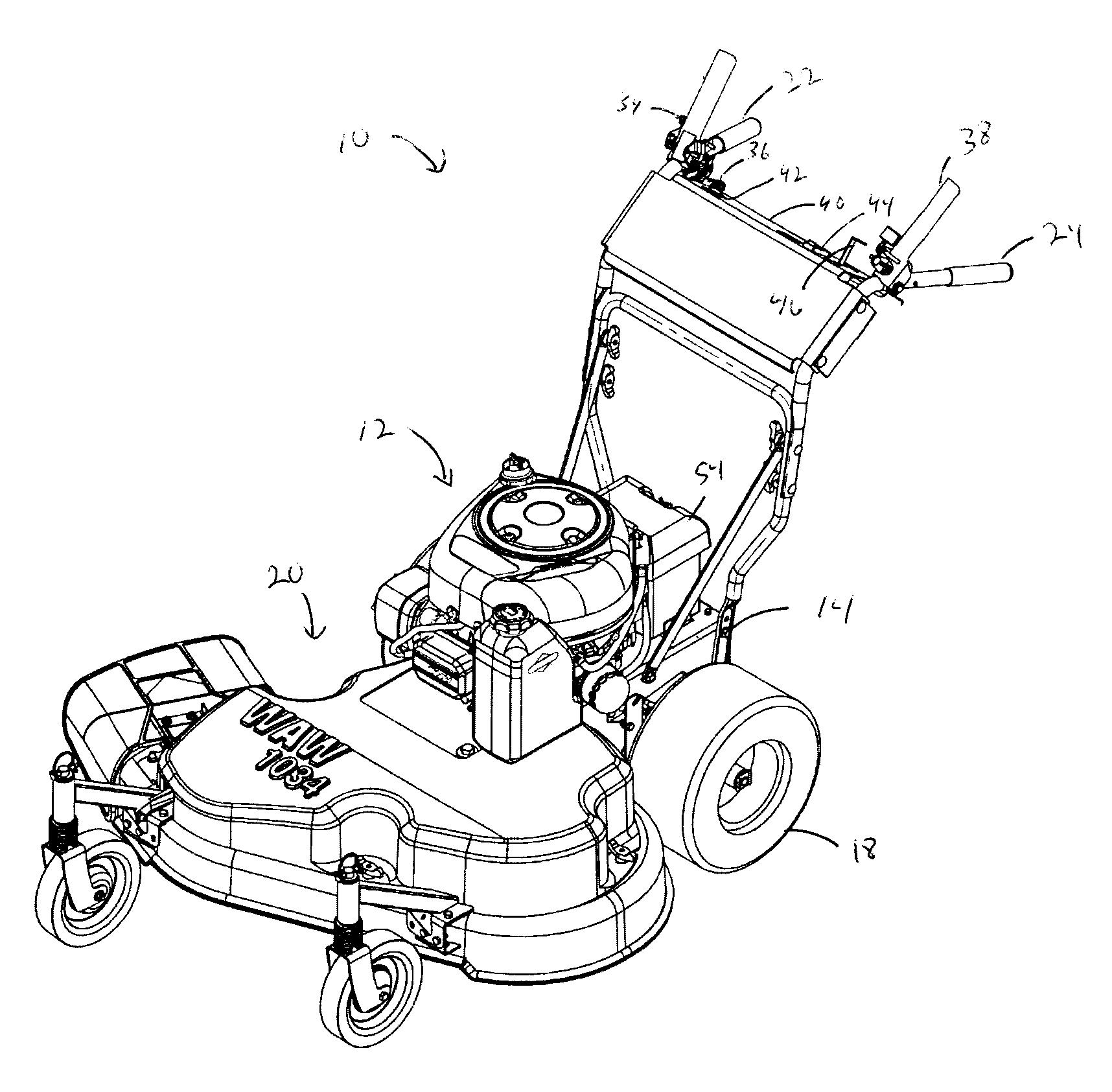
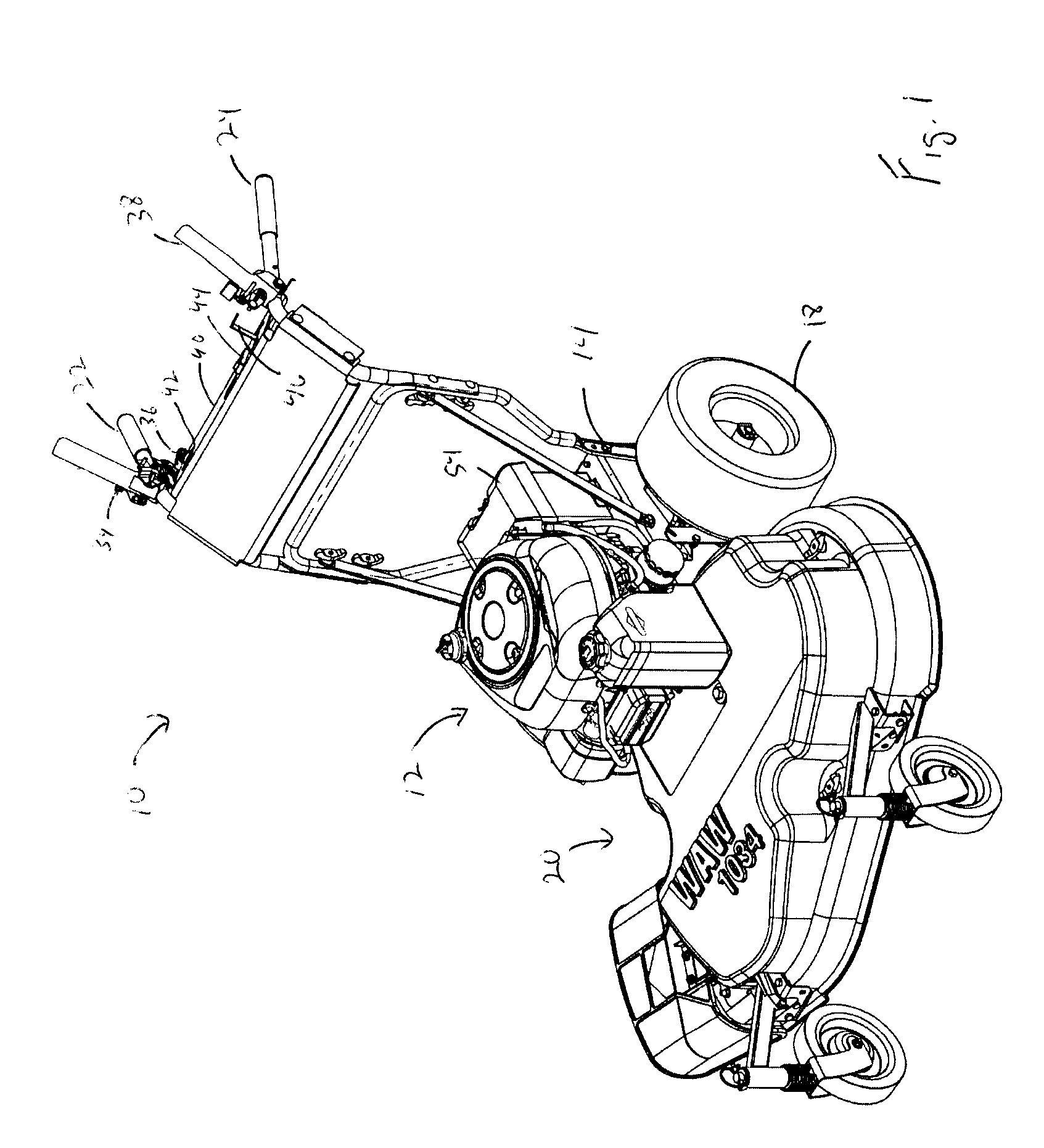
Patents
Literature
513results about "Ignition safety means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
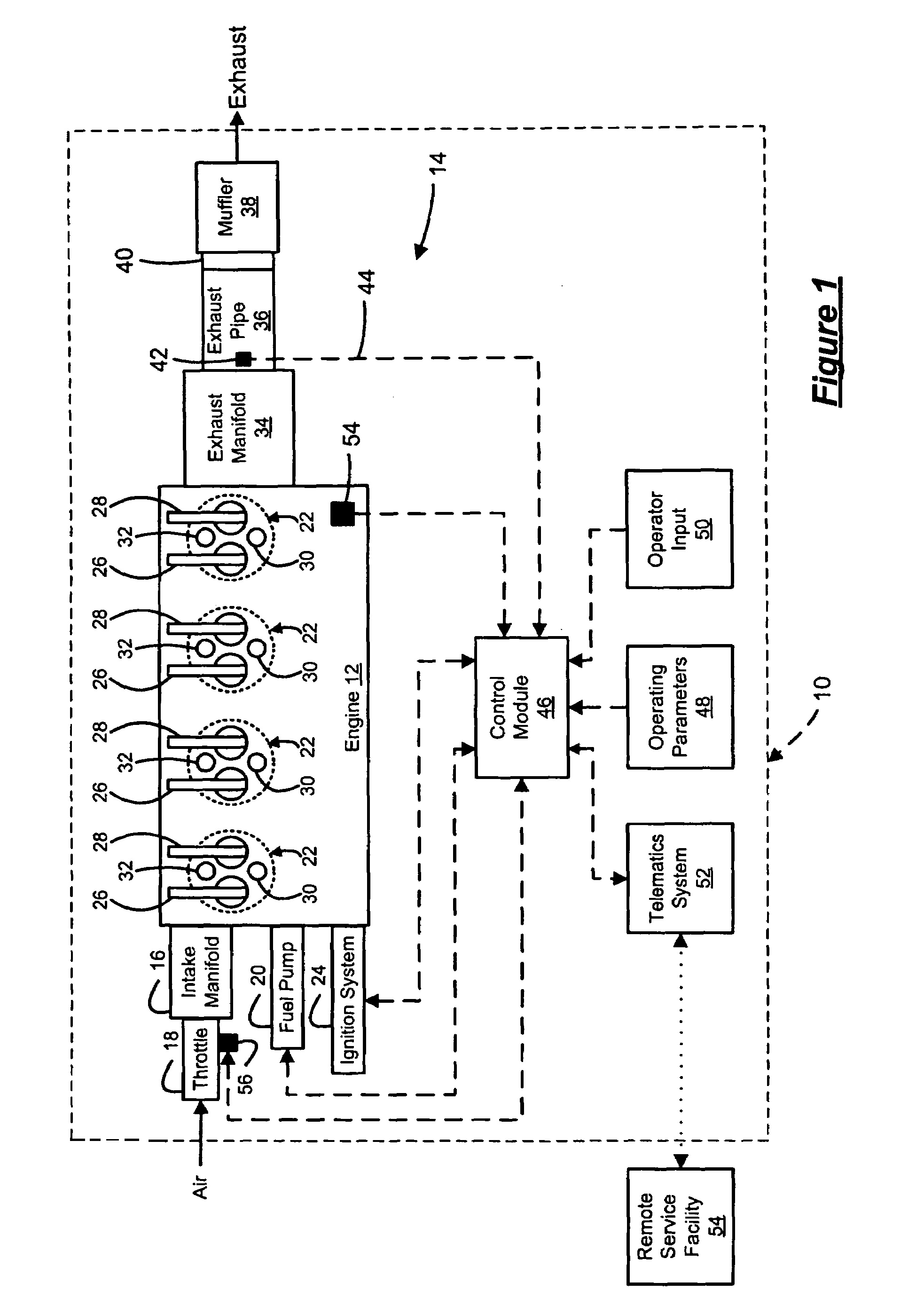
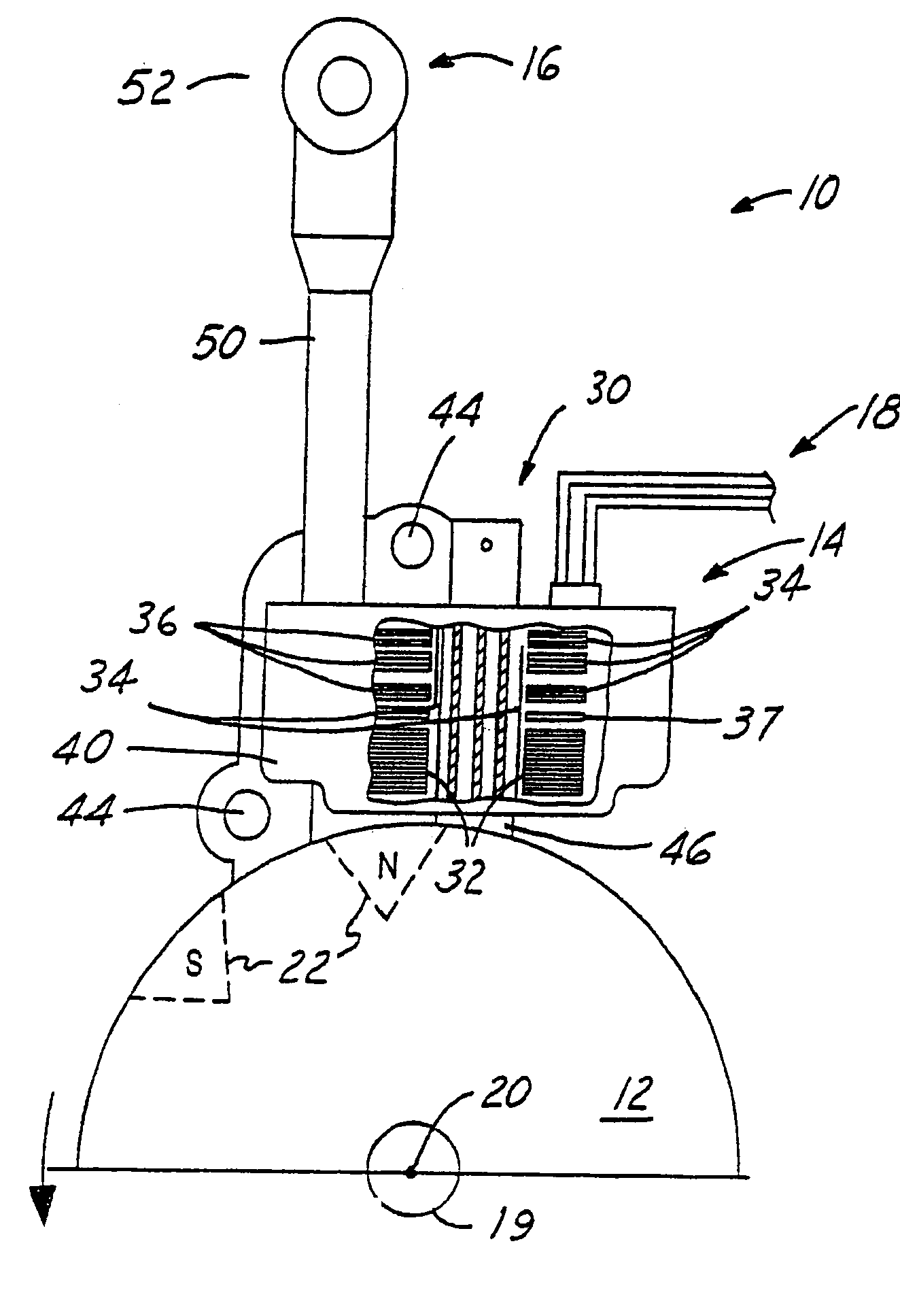
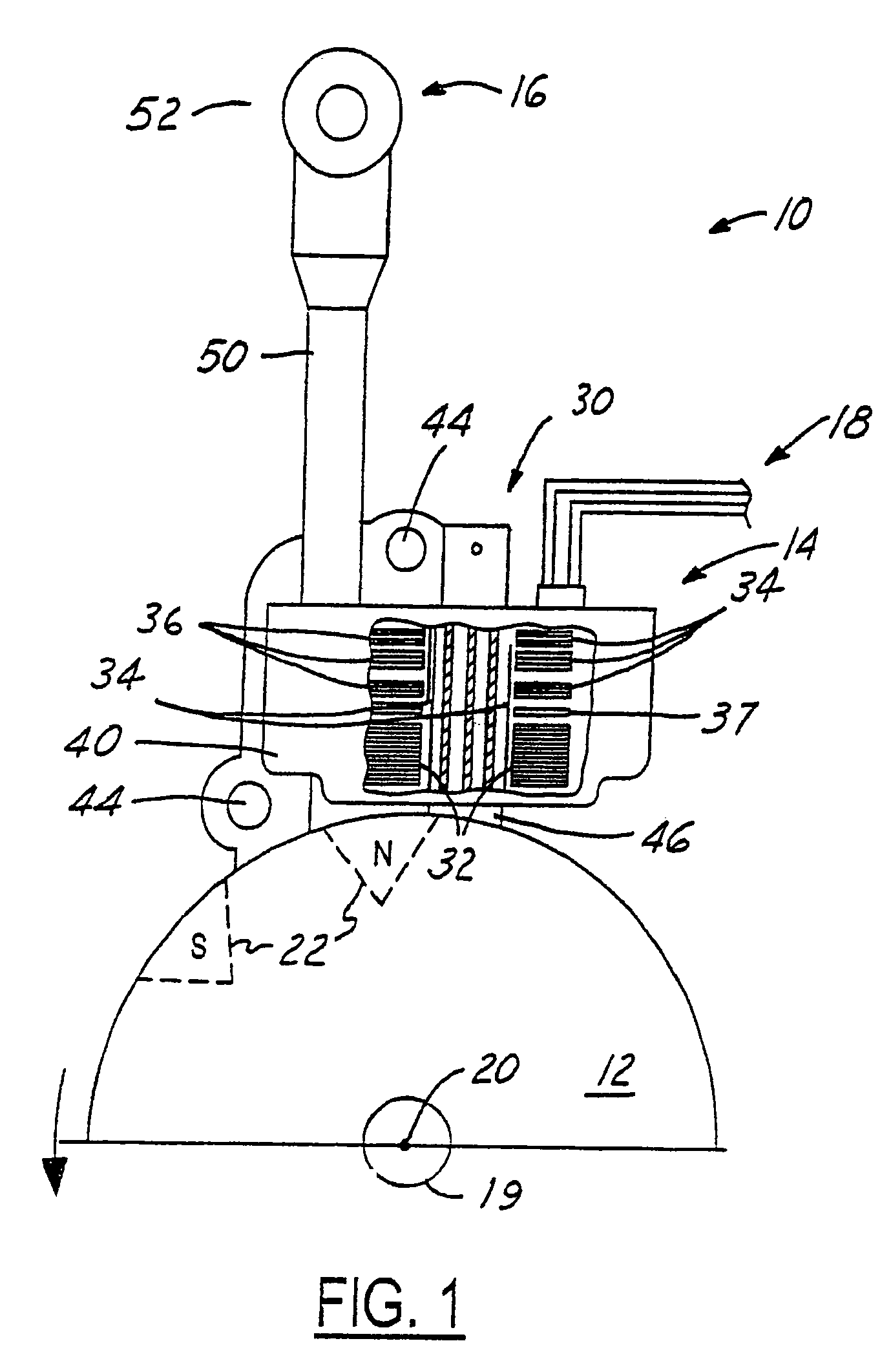
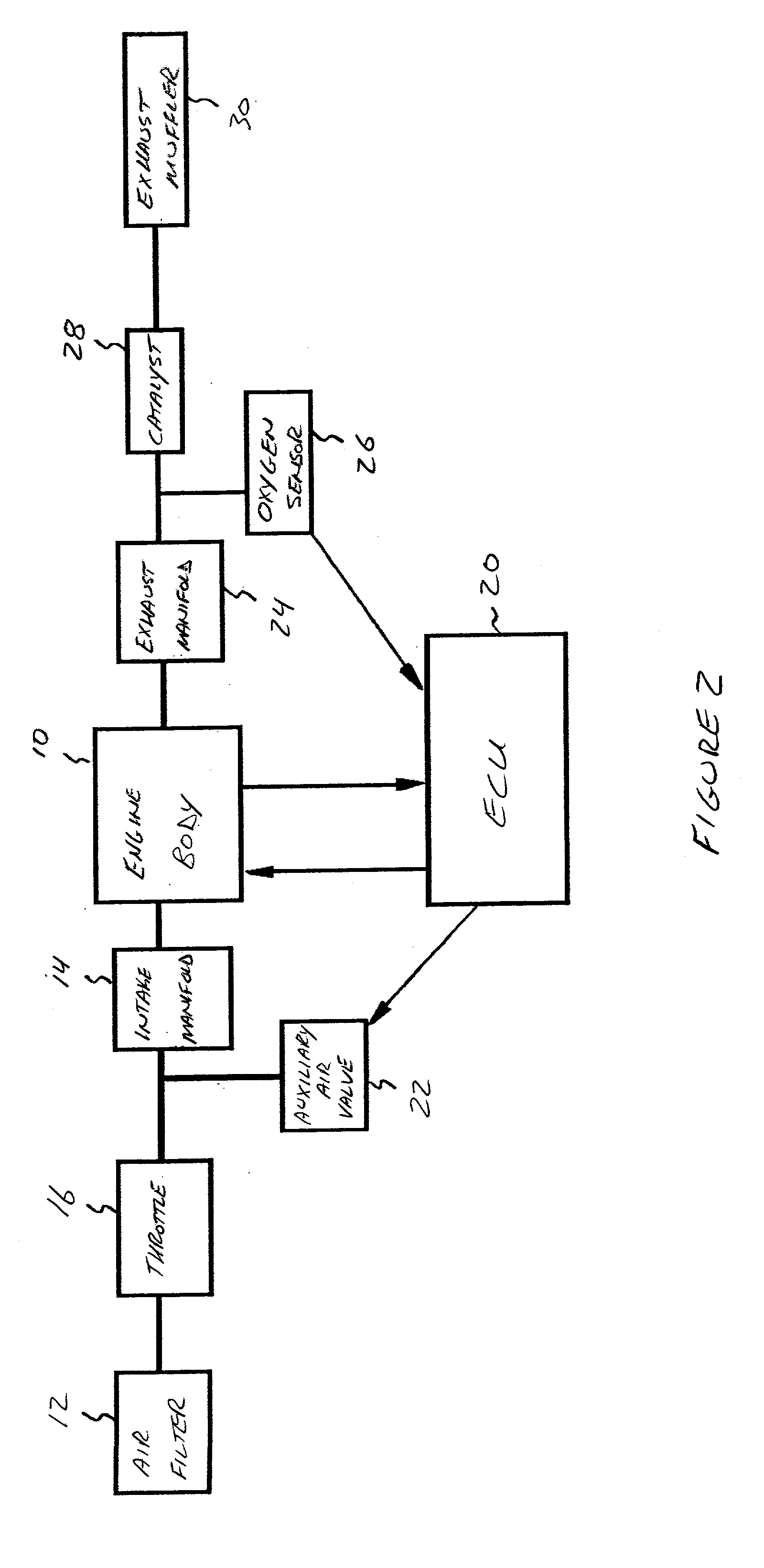
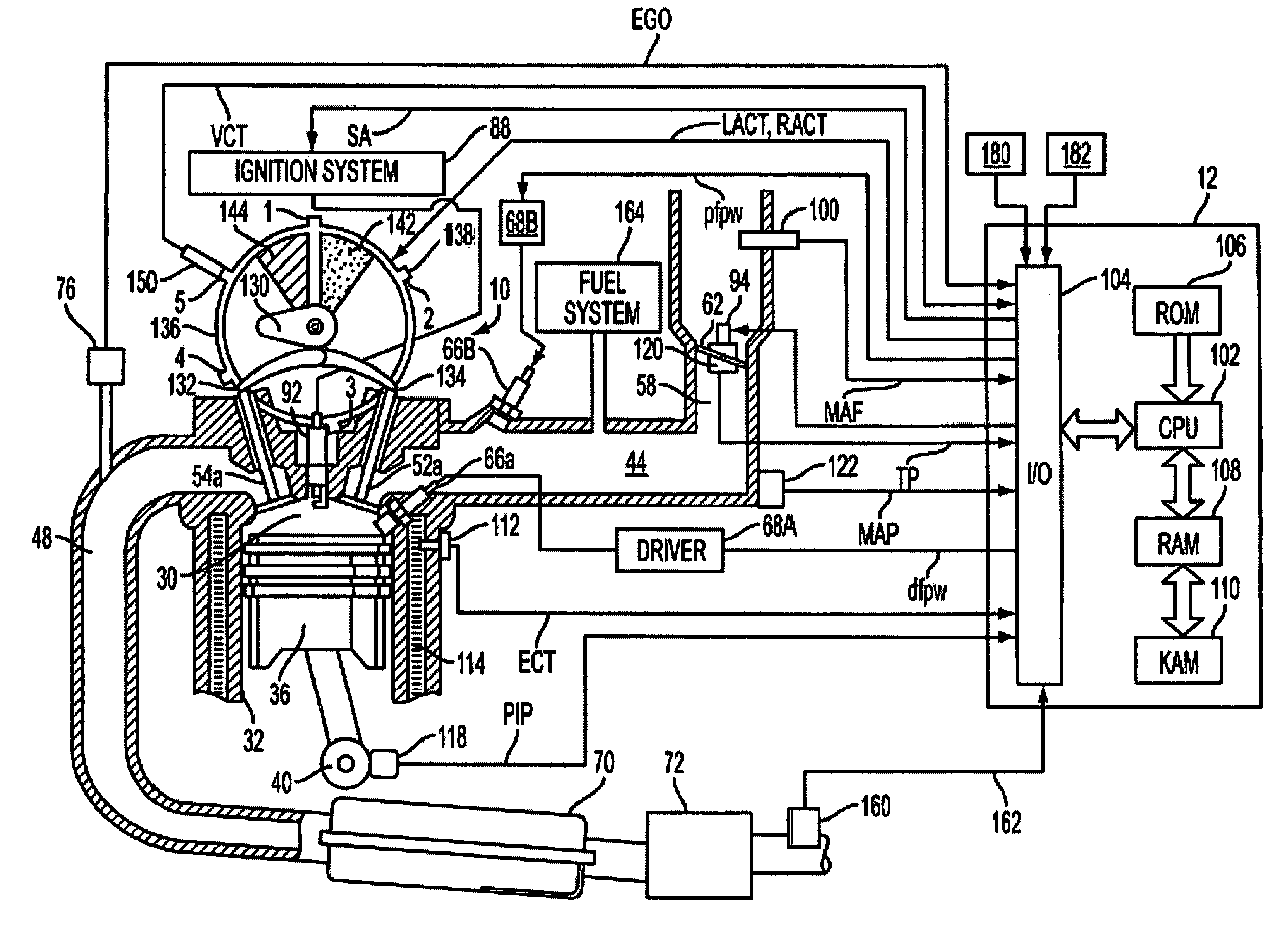
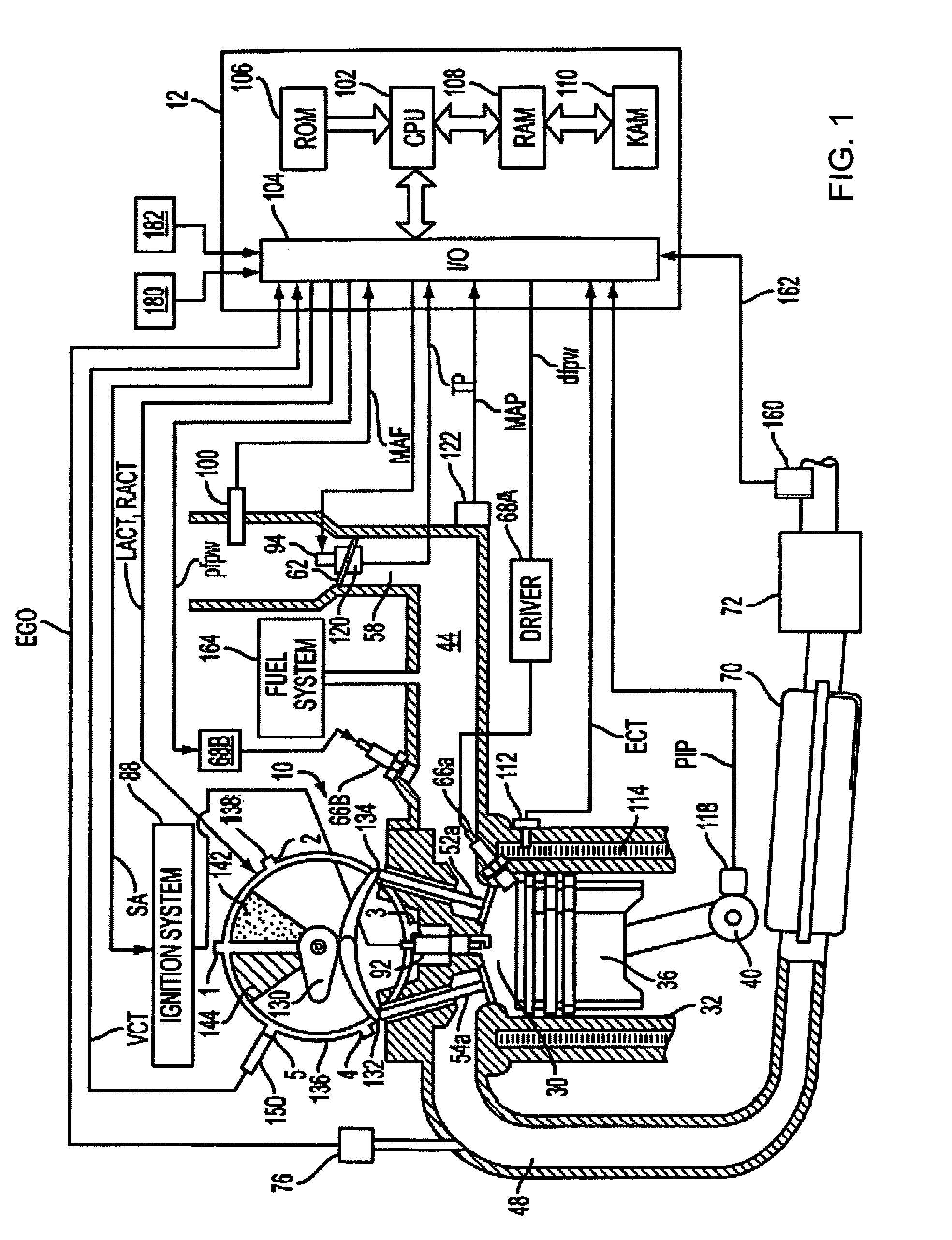
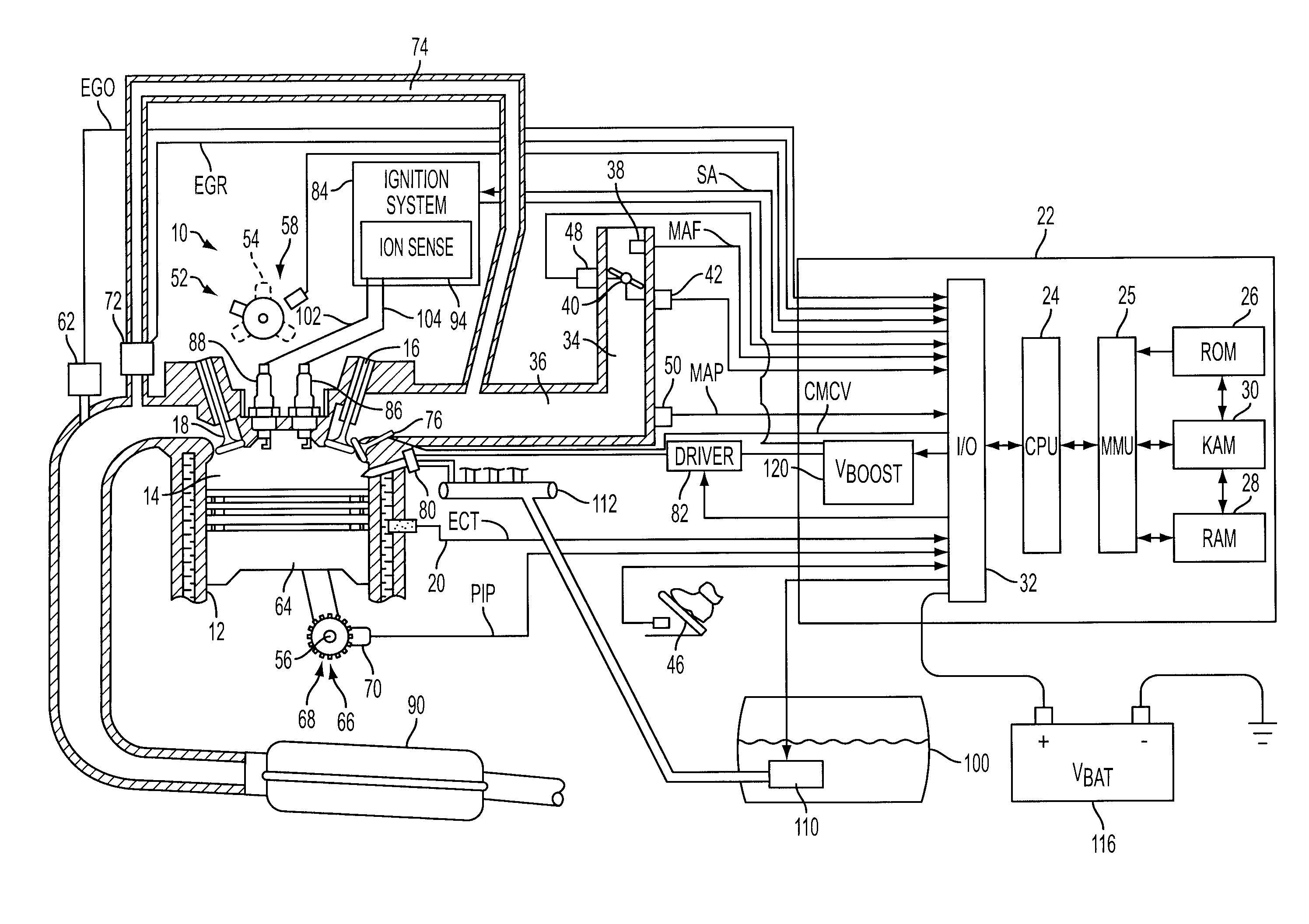
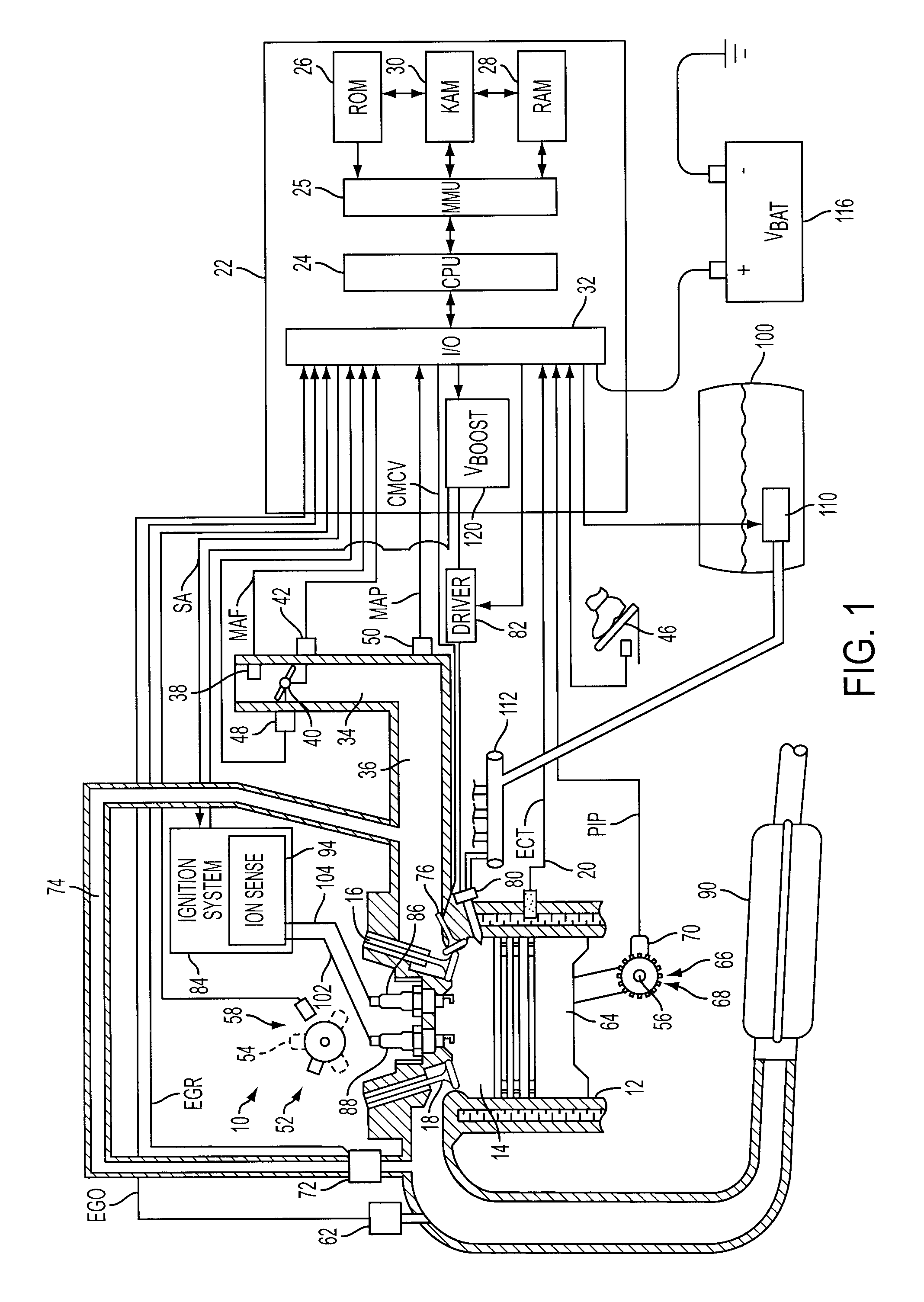
Spark control for improved engine operation
InactiveUS20070215130A1Low costImprove charge cooling effectElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberControl system
A system for an engine of a vehicle, comprising of at least one combustion chamber located in the engine, a delivery system configured to deliver a fuel and a substance to the combustion chamber, an ignition system including a spark plug configured to ignite the fuel within the combustion chamber, and a control system configured to vary a number of sparks performed by the spark plug in relation to a combustion event of the combustion chamber responsive to a condition of the ignition system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
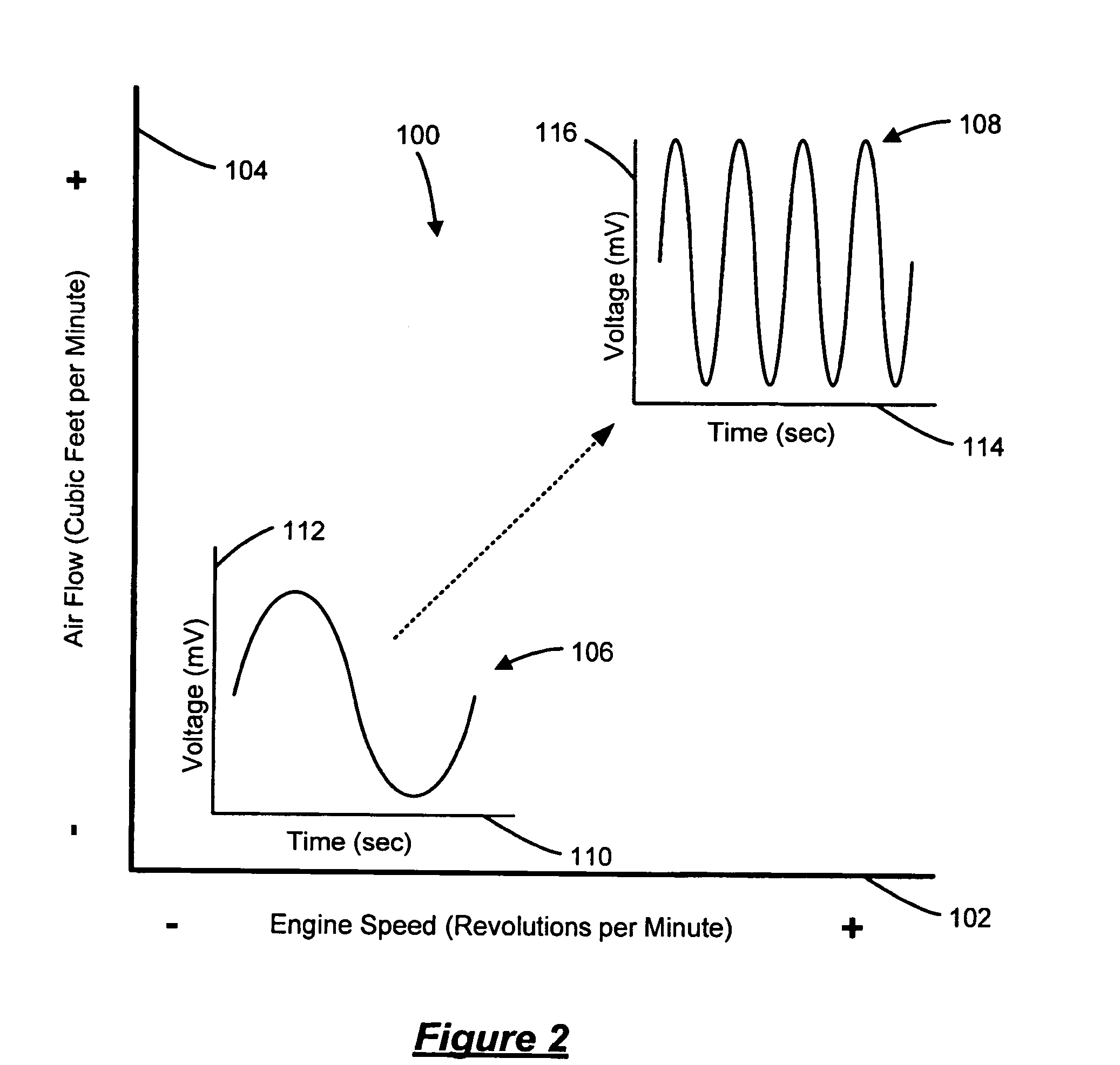
Air/fuel imbalance detection system and method
A method for detecting emissions from an internal combustion engine generally including determining a reference air / fuel mixture signal based on an engine speed and an airflow into the engine. The method includes determining an actual air / fuel mixture signal from an air / fuel mixture sensor and comparing the reference air / fuel mixture signal to the actual air / fuel mixture signal. The method also includes determining whether an air / fuel imbalance condition occurs based on the comparison and setting a service indicator based on the determination of whether the air / fuel imbalance condition occurred.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
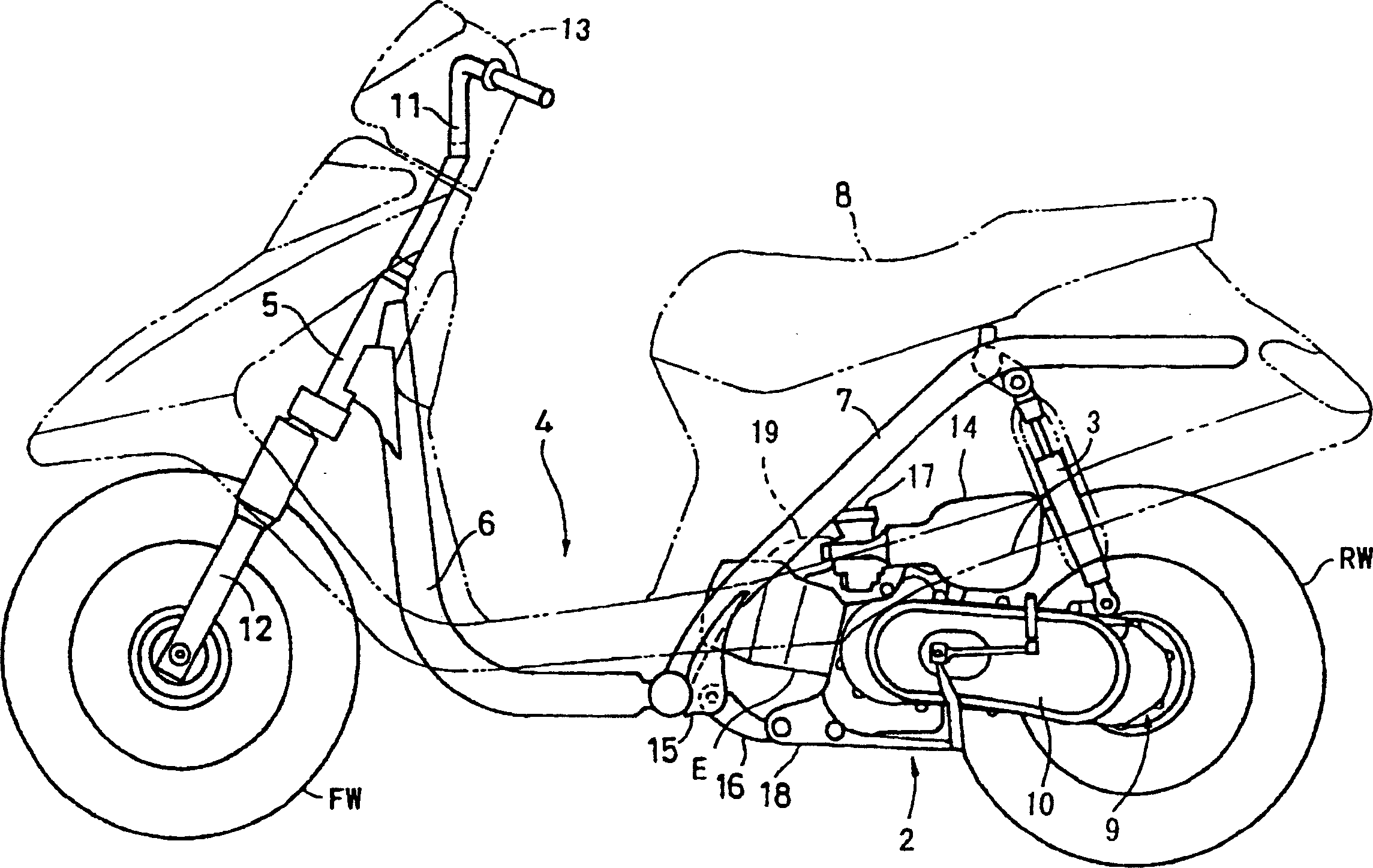
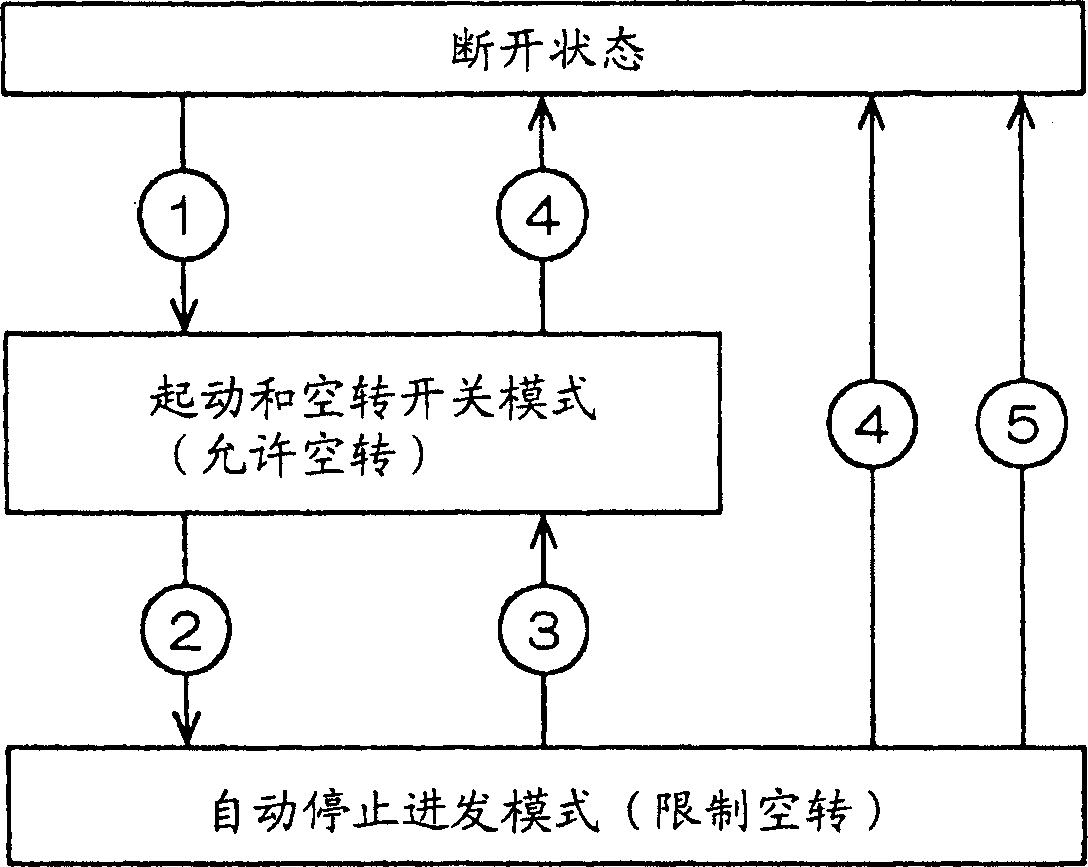
Automatic internal combustion engine stop device, internal combustion engine provided with the same and automatic internal combustion engine stop method
ActiveUS20070199533A1Short timeGrowth inhibitionPower operated startersElectrical controlStops deviceEngineering
In an automatic stop device that automatically stops the operation of an internal combustion engine after a predetermined automatic stop condition is satisfied, a load acting on the engine is removed when the automatic stop condition is satisfied. When the automatic stop condition is satisfied, the between the magnitude of the load on the internal combustion engine before and after of the automatic stop condition is satisfied is determined, and an ignition timing retard amount of an ignition plug is decided such that the retard amount is increased as the difference becomes greater. The ignition timing is retarded by the retard amount substantially at the same moment as the load removing operation before the automatic stop control is initiated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
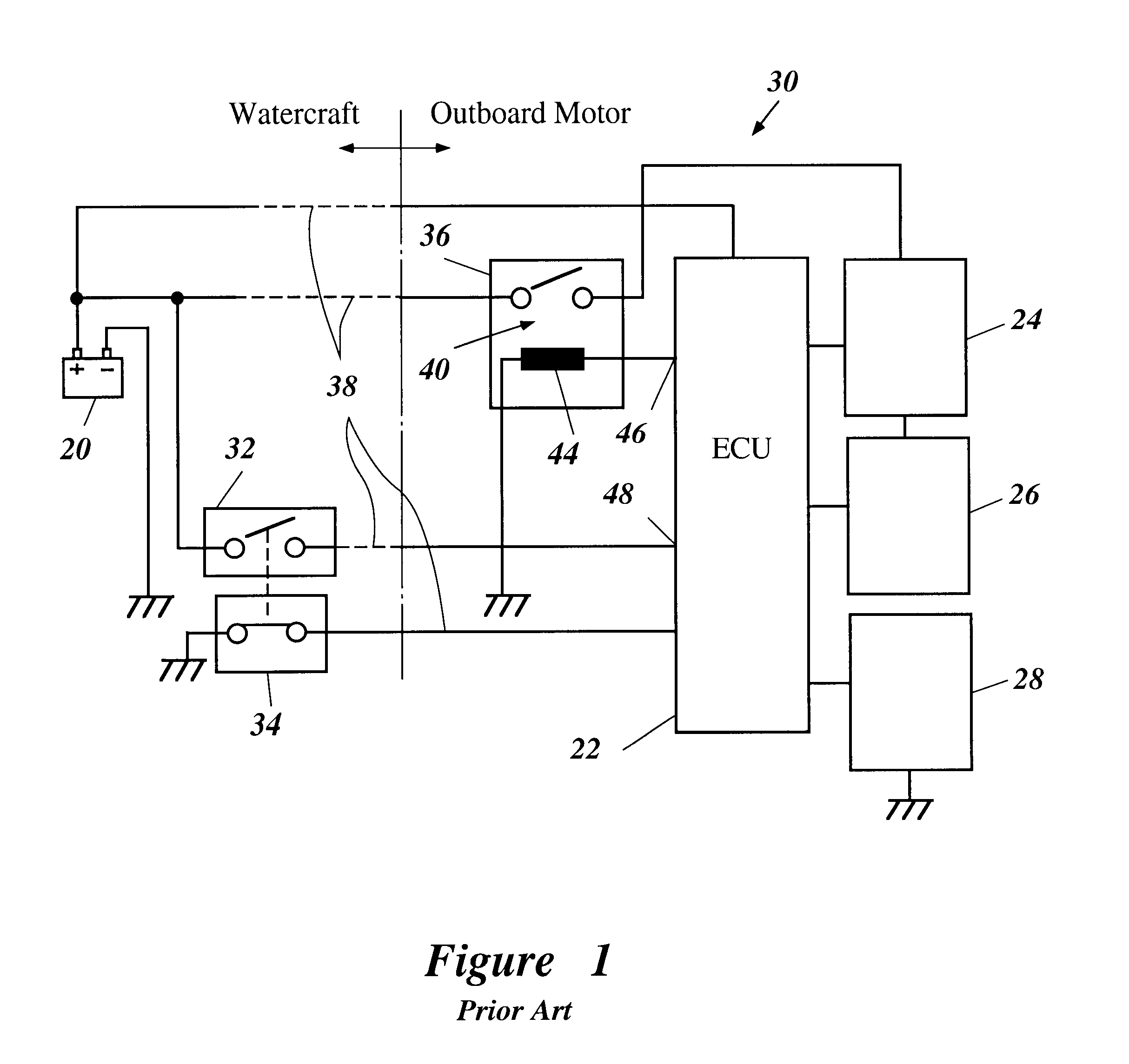
Start safety ignition system
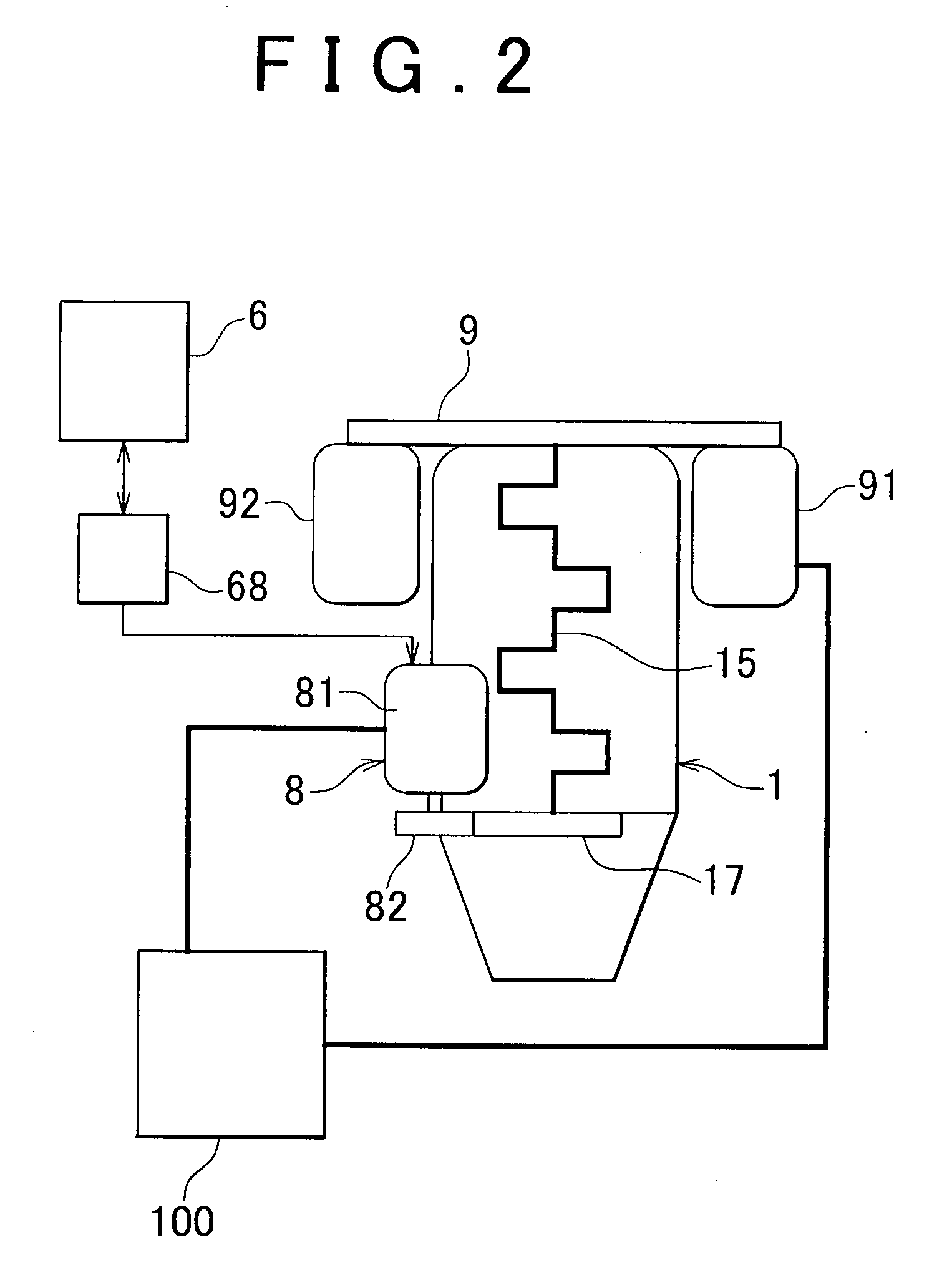
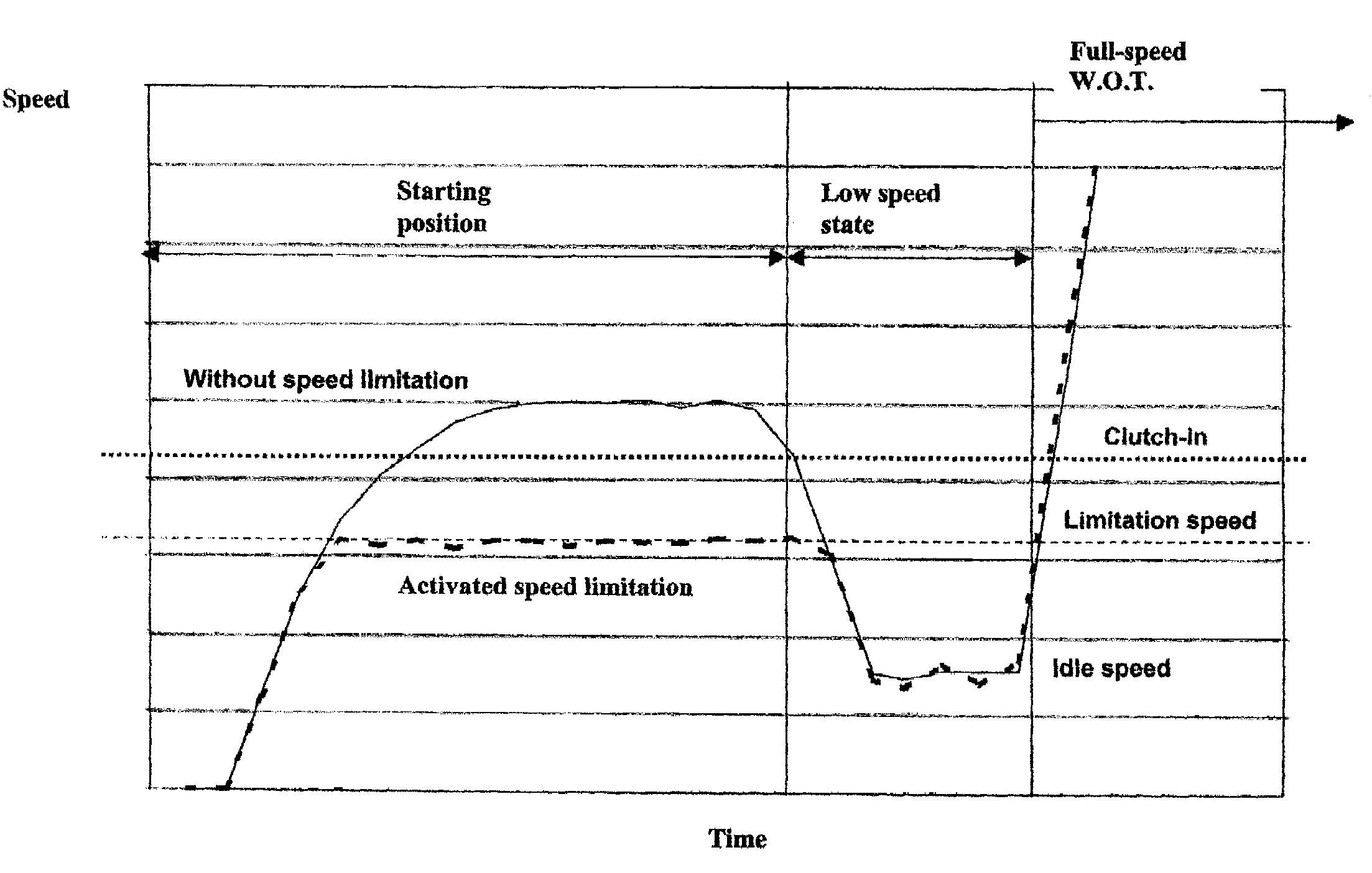
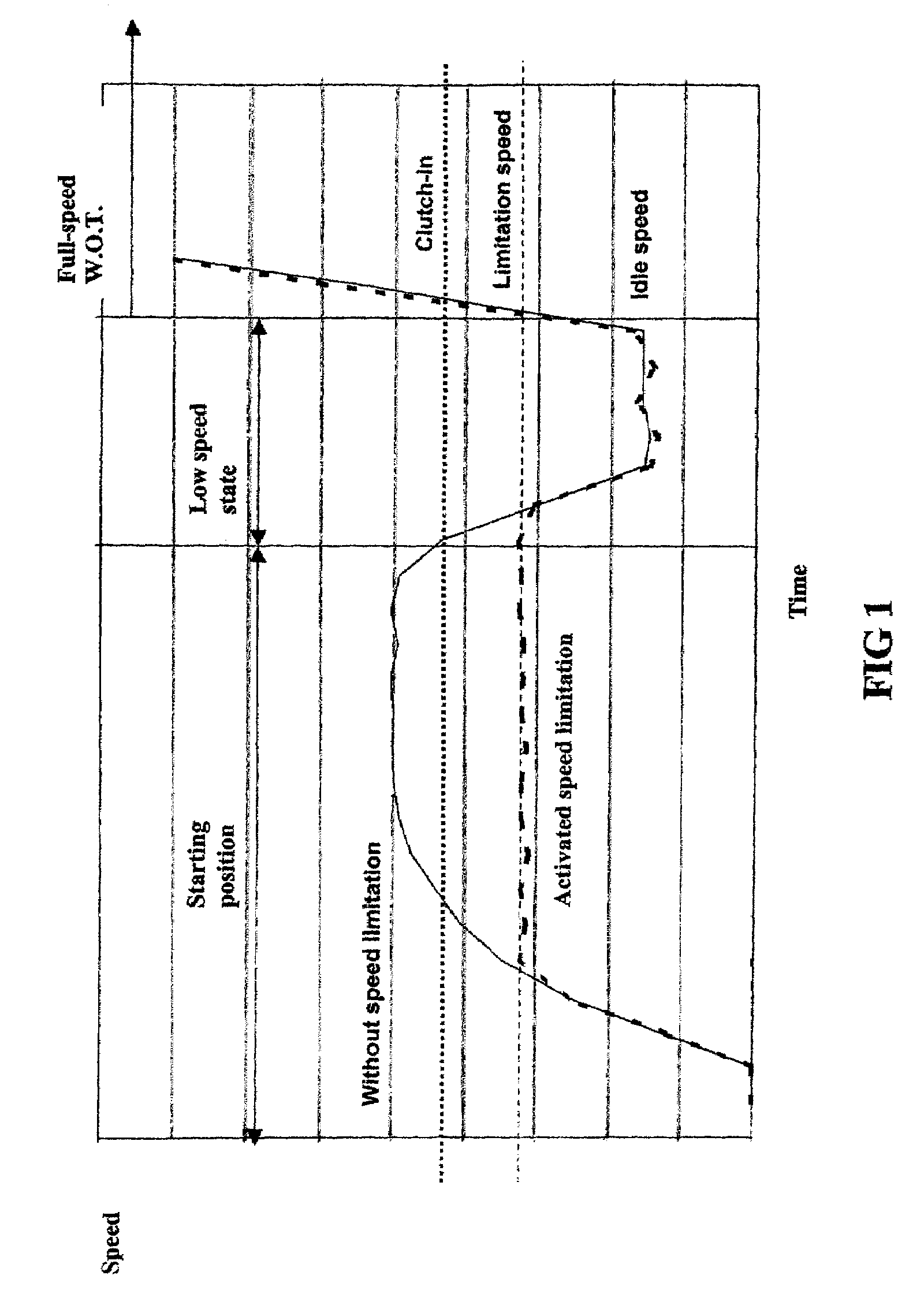
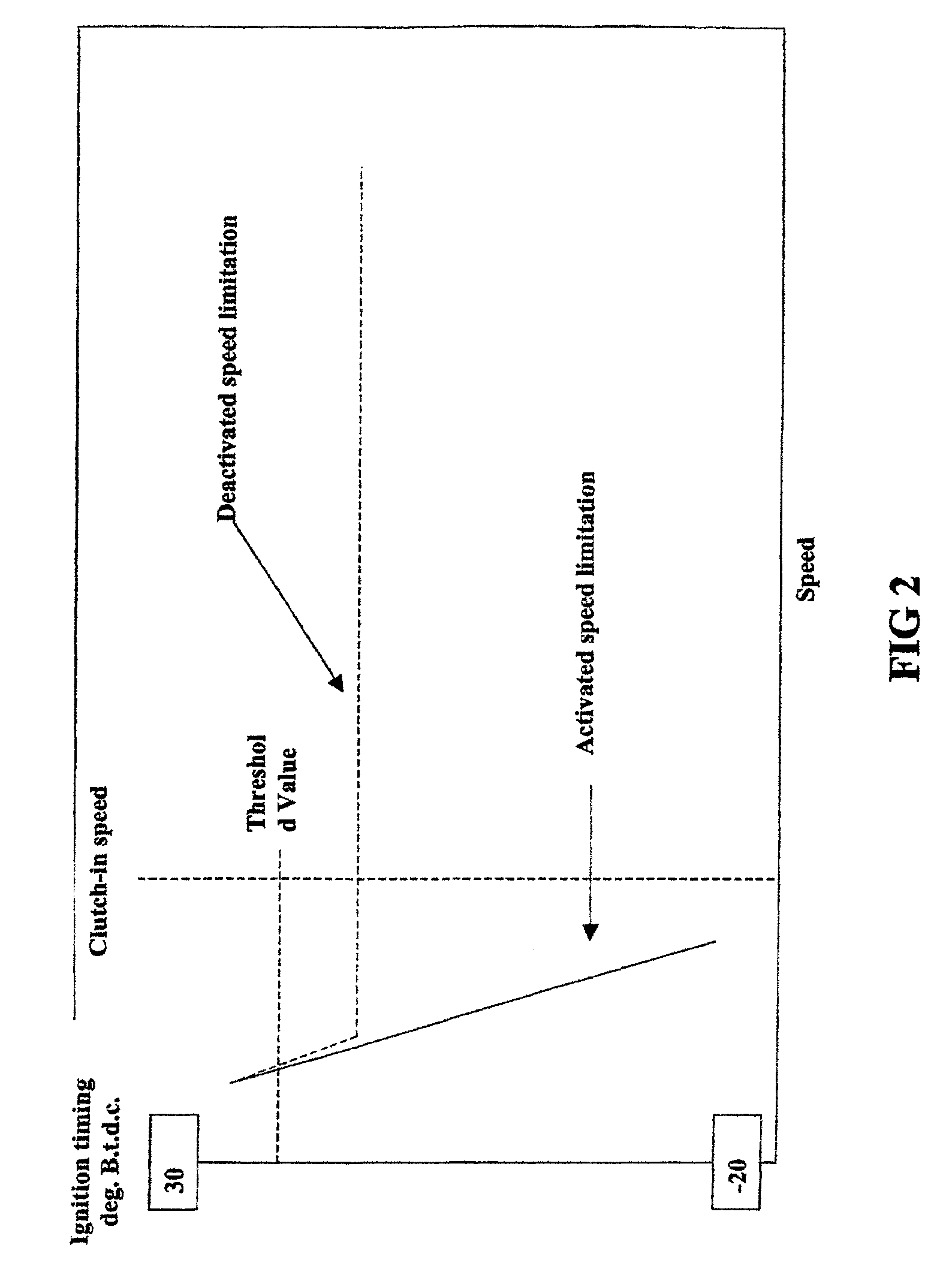
A method for controlling an ignition system of an internal combustion engine having a primary firing pulse generator for charging a capacitor. An electronic switch is included for discharging the capacitor via an ignition coil to generate an ignition voltage. A microcomputer operates the switch to control the ignition timing of the generator. The microcomputer is in communication with a speed sensor that detects the rotational speed of the engine and a speed limitation control that limits the engine speed to a limitation speed below the clutch-in speed of an included centrifugal clutch. The speed limitation control is active or activated when one of either starting the engine or an operating problem of the power tool is detected. The speed limitation control is deactivated when a low speed state of the engine is detected.
Owner:HUSQVARNA AB
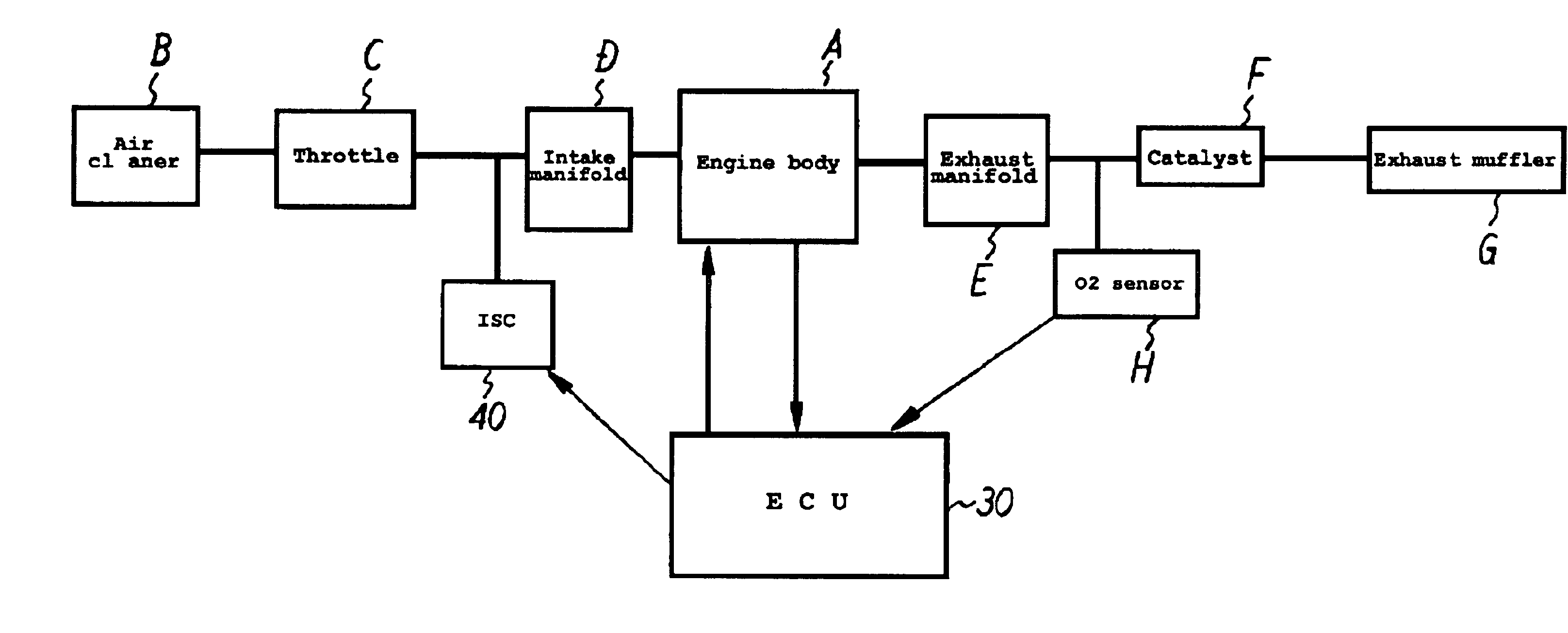
Ignition timing control system for light duty combustion engines
InactiveUS7000595B2Guaranteed uptimeAccelerate emissionsAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl systemNormal mode
A control system for a low cost, light duty combustion engine, where the control system generally utilizes engine speed and / or temperature input signals and independent operating sequences to determine a desired ignition timing and air-to-fuel ratio for a combustible mixture. There are several independent operating sequences, each one of which is designed to optimally control the engine under certain conditions. These operating sequences include a Cranking sequence that commences after the engine is initially turned on, a Warm Up sequence which follows the Cranking sequence, a Normal Mode sequence for typical operating conditions, an Acceleration sequence for certain increases in engine speed, a Come Down sequence for when a sufficient engine speed is followed by a certain decrease in speed, and a Recovery Bump sequence for when the engine speed dips below a predetermined level.
Owner:WALBRO LLC
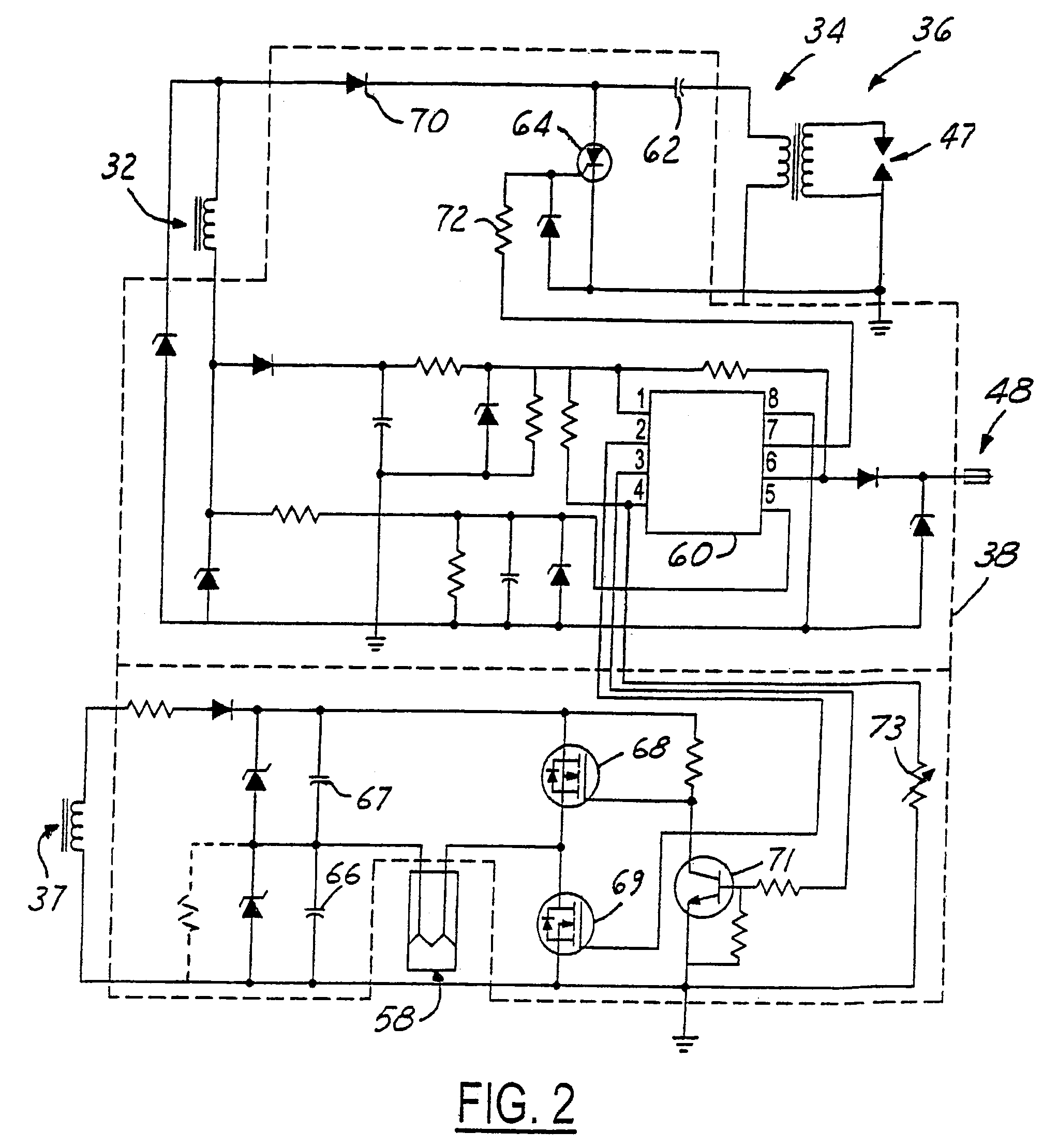
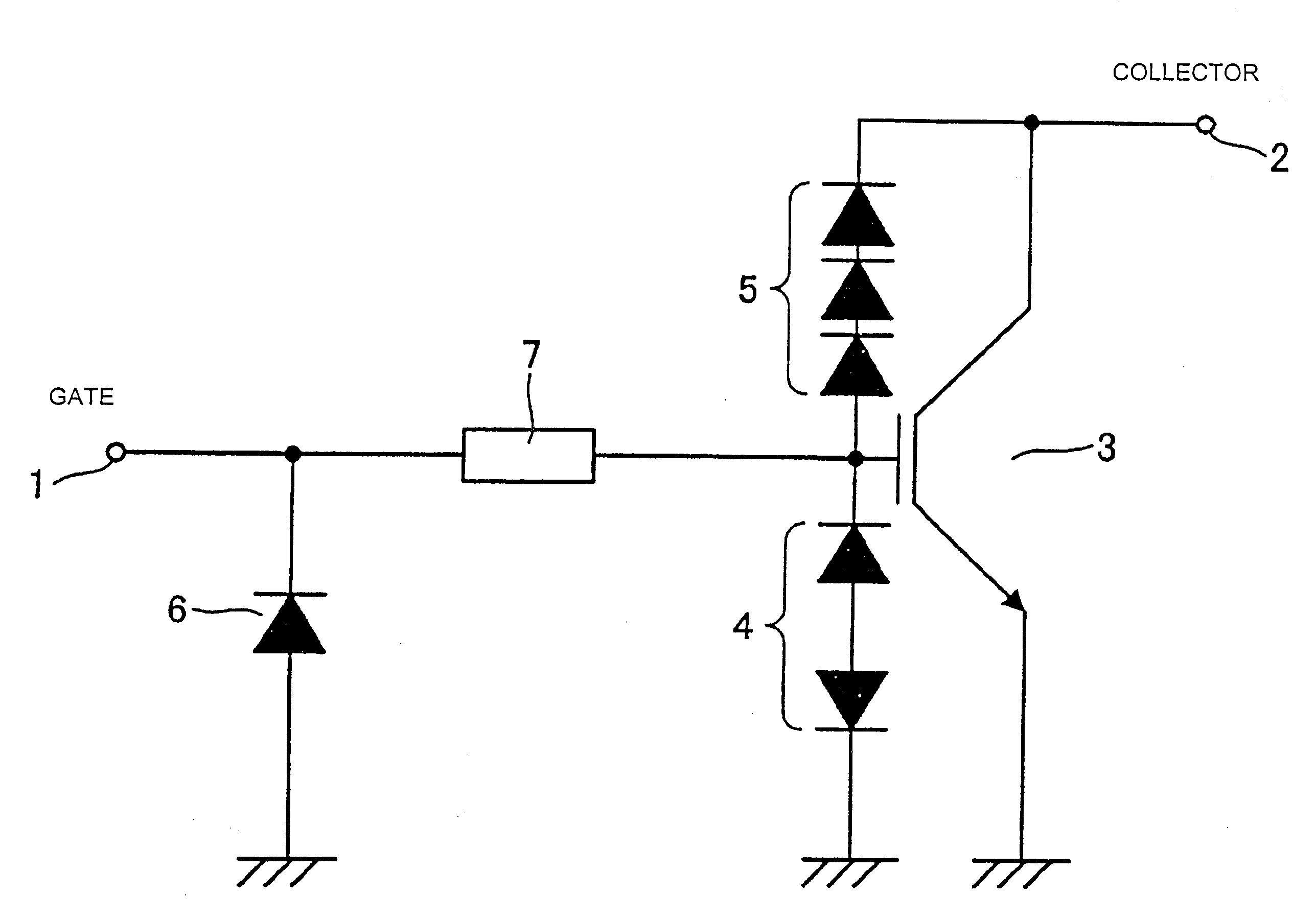
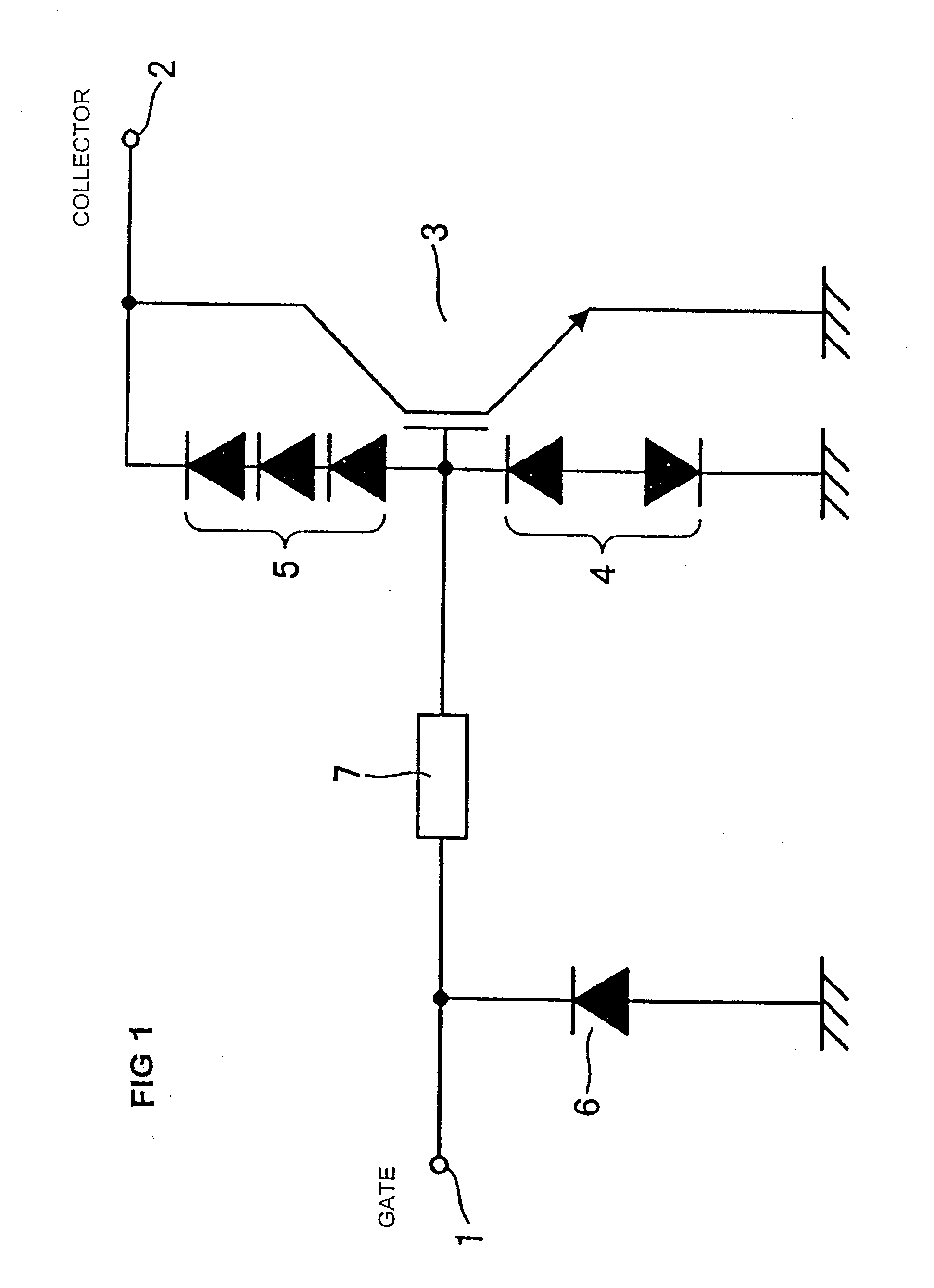
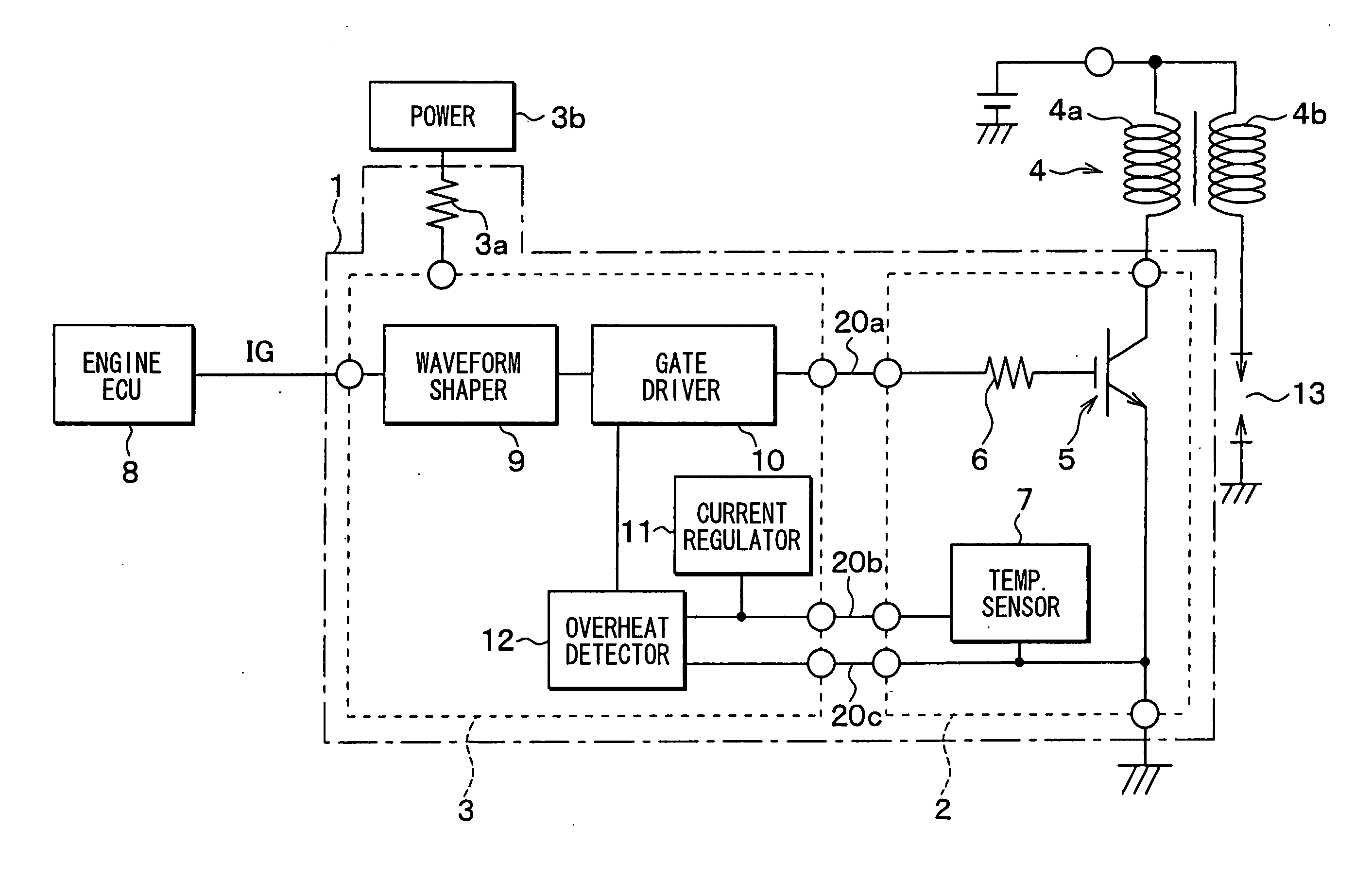
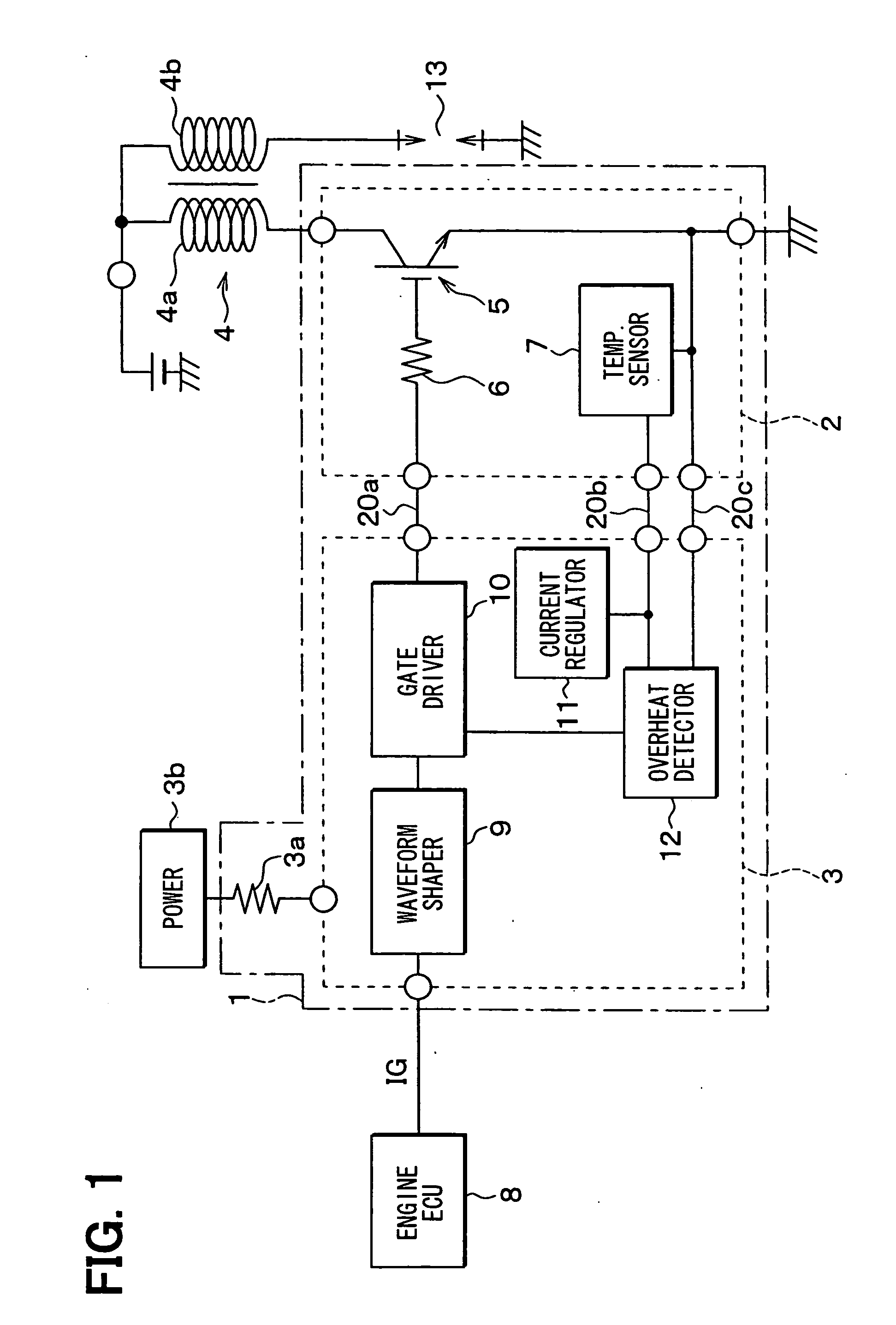
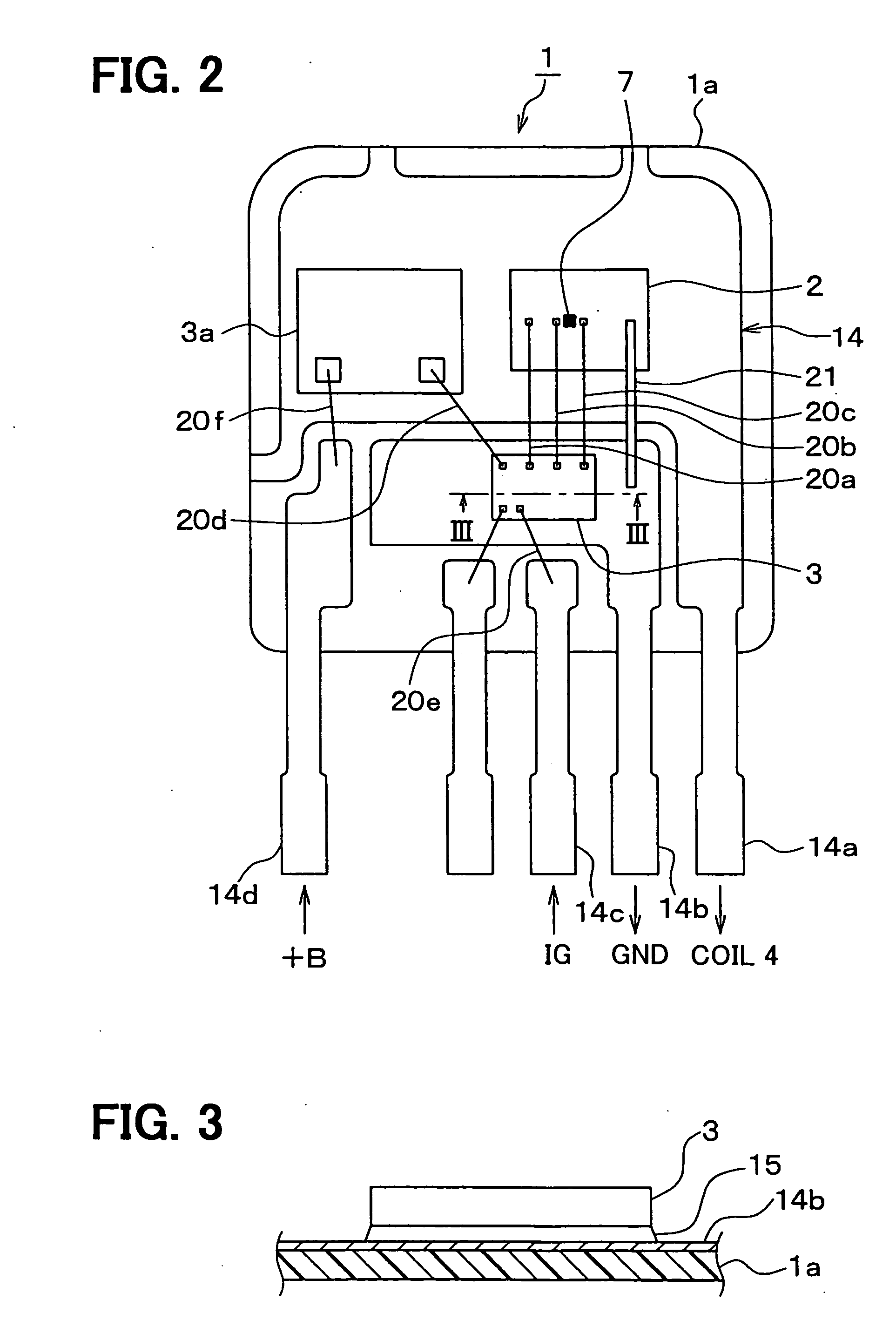
Semiconductor device and internal combustion engine ignition device
InactiveUS20100059028A1Feedback loop can be eliminatedConstantTransistorSolid-state devicesLow voltageDevice material
A semiconductor device includes an IGBT, a constant voltage circuit, and protection Zener diodes. The IGBT makes / breaks a low-voltage current flowing in a primary coil. The constant voltage circuit and the protection Zener diodes are provided between an external gate terminal and an external collector terminal. The constant voltage circuit supplies a constant gate voltage to the IGBT to thereby set a saturation current value of the IGBT to a predetermined limiting current value. The IGBT has the saturation current value in a limiting current value range of the semiconductor device.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Control system for engine
InactiveUS20020189592A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemHigh torque
An electronically controlled engine management system for a multi-cylinder engine unnoticeably disables and enables various cylinder groups to preserve fuel economy. The engine management system enables the operator to enjoy high torque represented from a multi-cylinder engine and to maintain good fuel economy.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
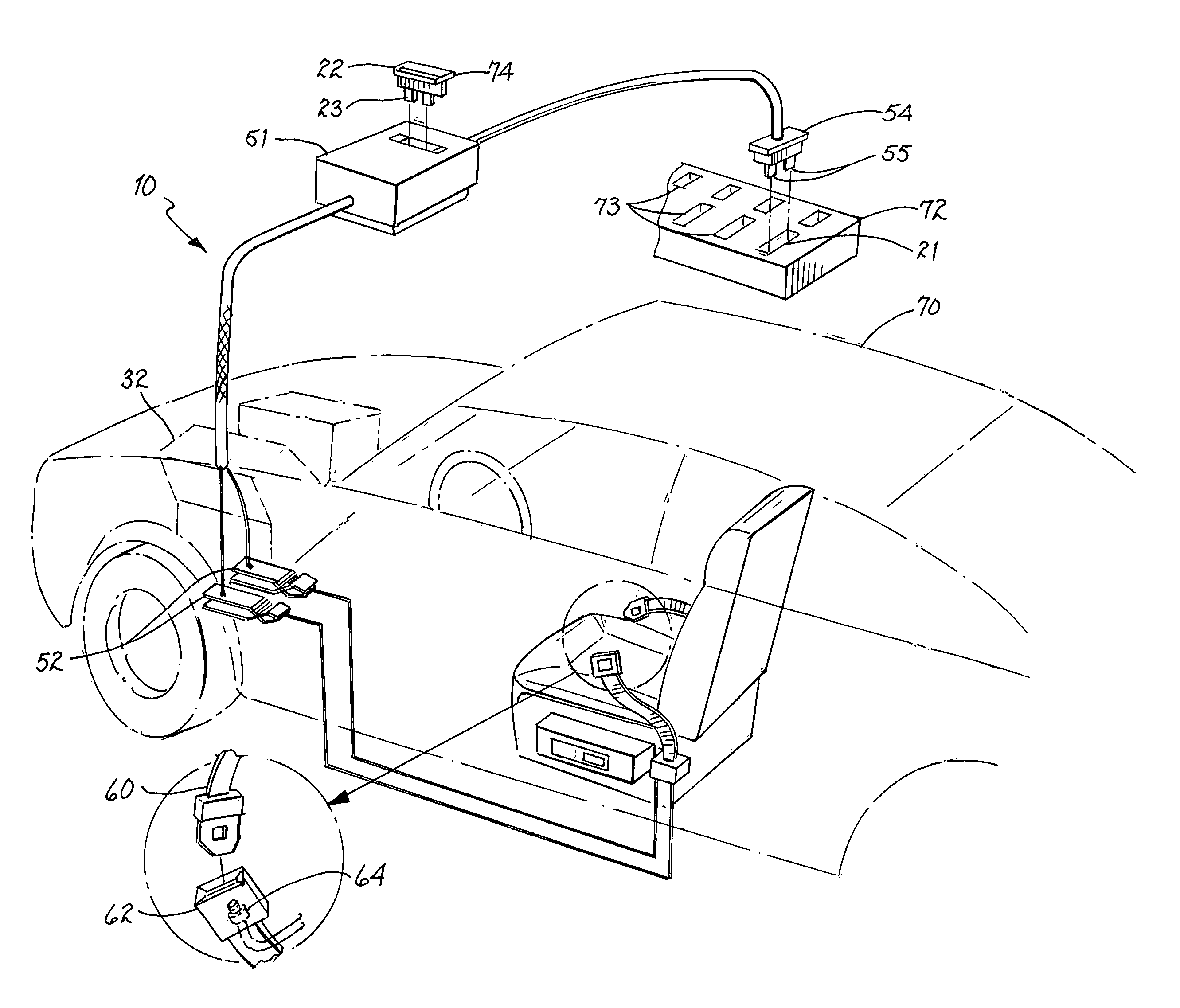
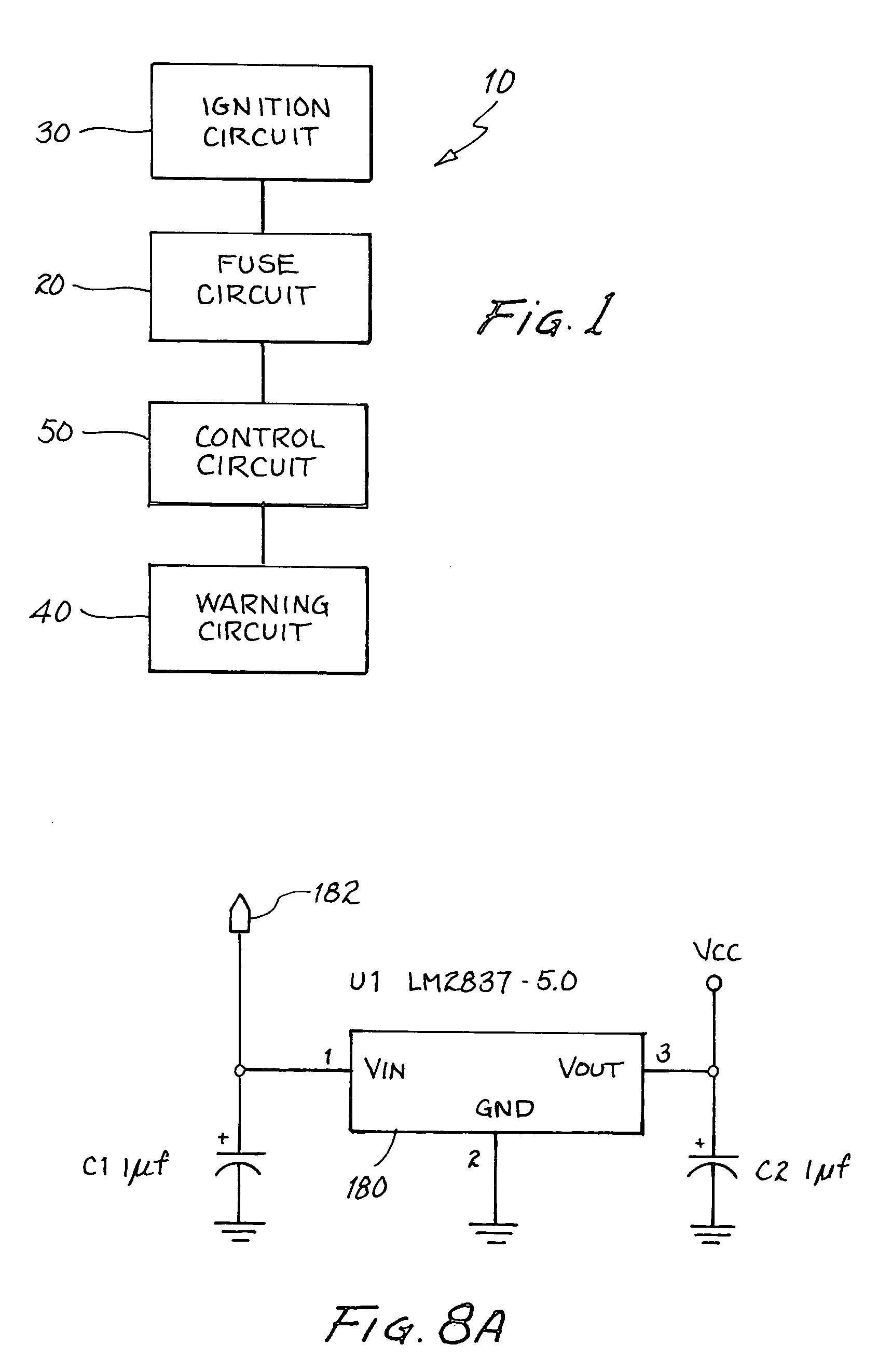
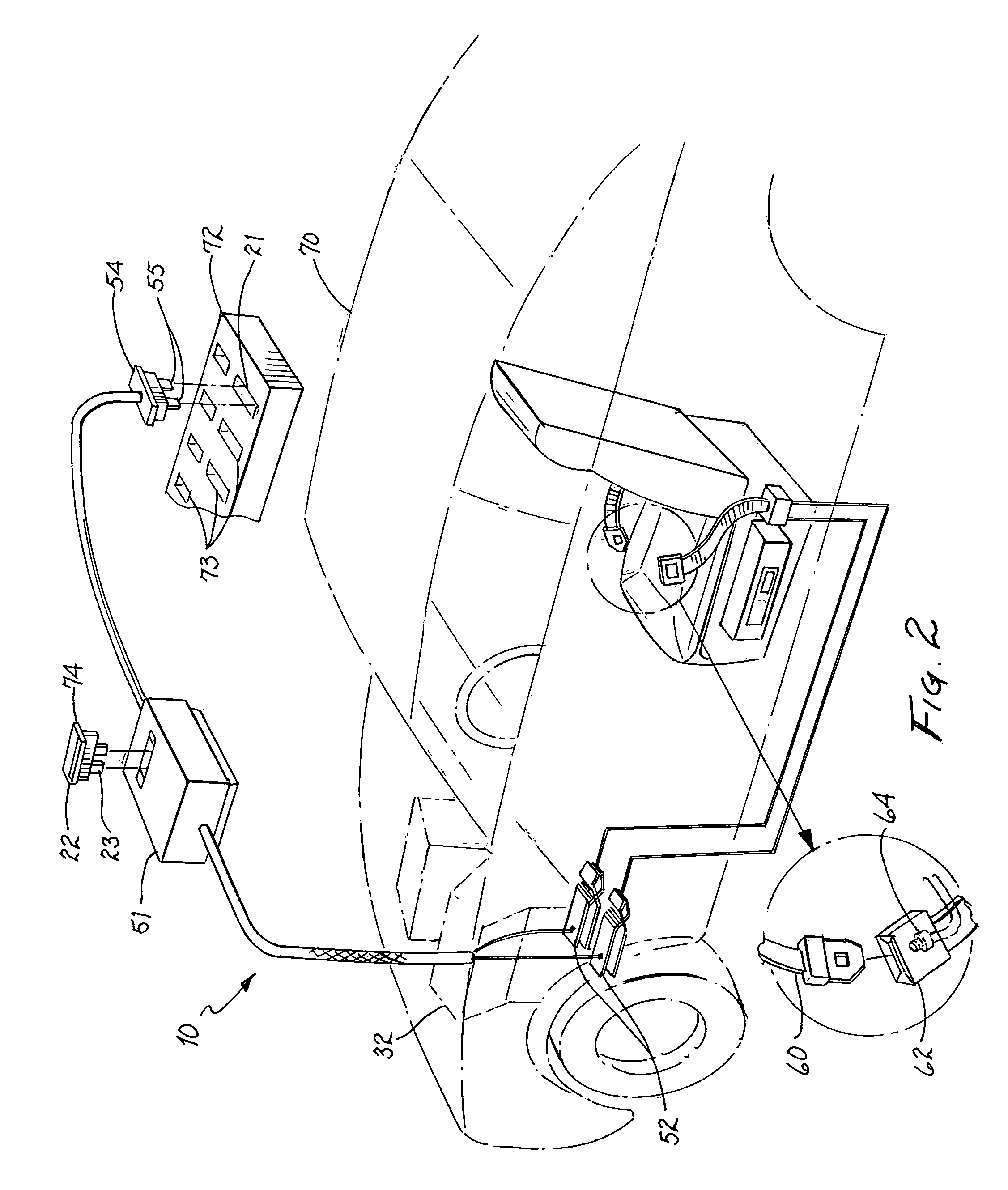
Ignition safety device and method therefor
An ignition safety system and method. A control circuit is coupled to a warning circuit indicating a safety condition. The control circuit is further coupled to a fuse circuit to control an operation of a motor ignition circuit in response to the safety condition.
Owner:ALLISON III ROBERT D
Method for starting an engine
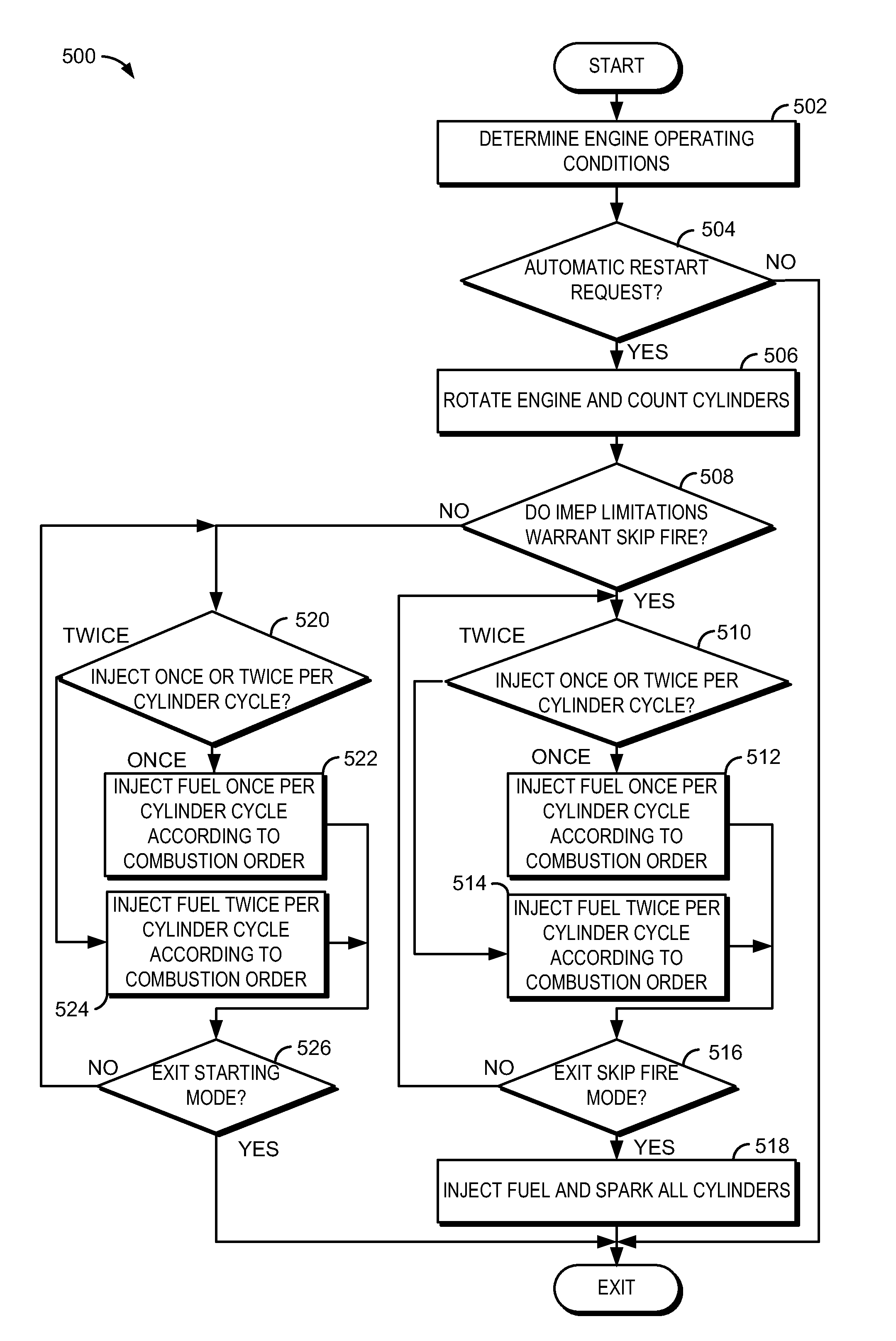
InactiveUS7931002B1Improve fuel economyMore outputElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionAutomotive engineering
A method for improving starting of an engine that may be repeatedly stopped and started is presented. In one embodiment, the method skips combustion in at least one cylinder, according to the engine combustion order, to control engine speed when an engine is automatically restarted. The skipped combustion event may be related to a level of IMEP when combustion in a cylinder occurs under an operating condition.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Eco-run control device and method for resetting the same
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Implement With Two Hand Interlock
InactiveUS20090223475A1Simpler andEasy to useMowersElectric motor startersExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
An implement includes an electric starter operatively connected to an internal combustion engine to start the internal combustion engine. An ignition circuit actuates the electric starter. A first normally open switch forming part of the ignition circuit is mounted on the implement at a first position and must be held closed by an operator for the ignition circuit to actuate the electric starter. A second normally open switch forming part of the ignition circuit is mounted on the implement at a second position and must be held closed by an operator for the ignition circuit to actuate the electric starter. The first position is spaced from the second position a sufficient distance to prevent an operator from closing both the first normally open switch and the second normally open switch with a single hand.
Owner:ARIENS
Control system for engine
InactiveUS6928988B2Increase torqueImprove fuel economyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemHigh torque
An electronically controlled engine management system for a multi-cylinder engine unnoticeably disables and enables various cylinder groups to preserve fuel economy. The engine management system enables the operator to enjoy high torque represented from a multi-cylinder engine and to maintain good fuel economy.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
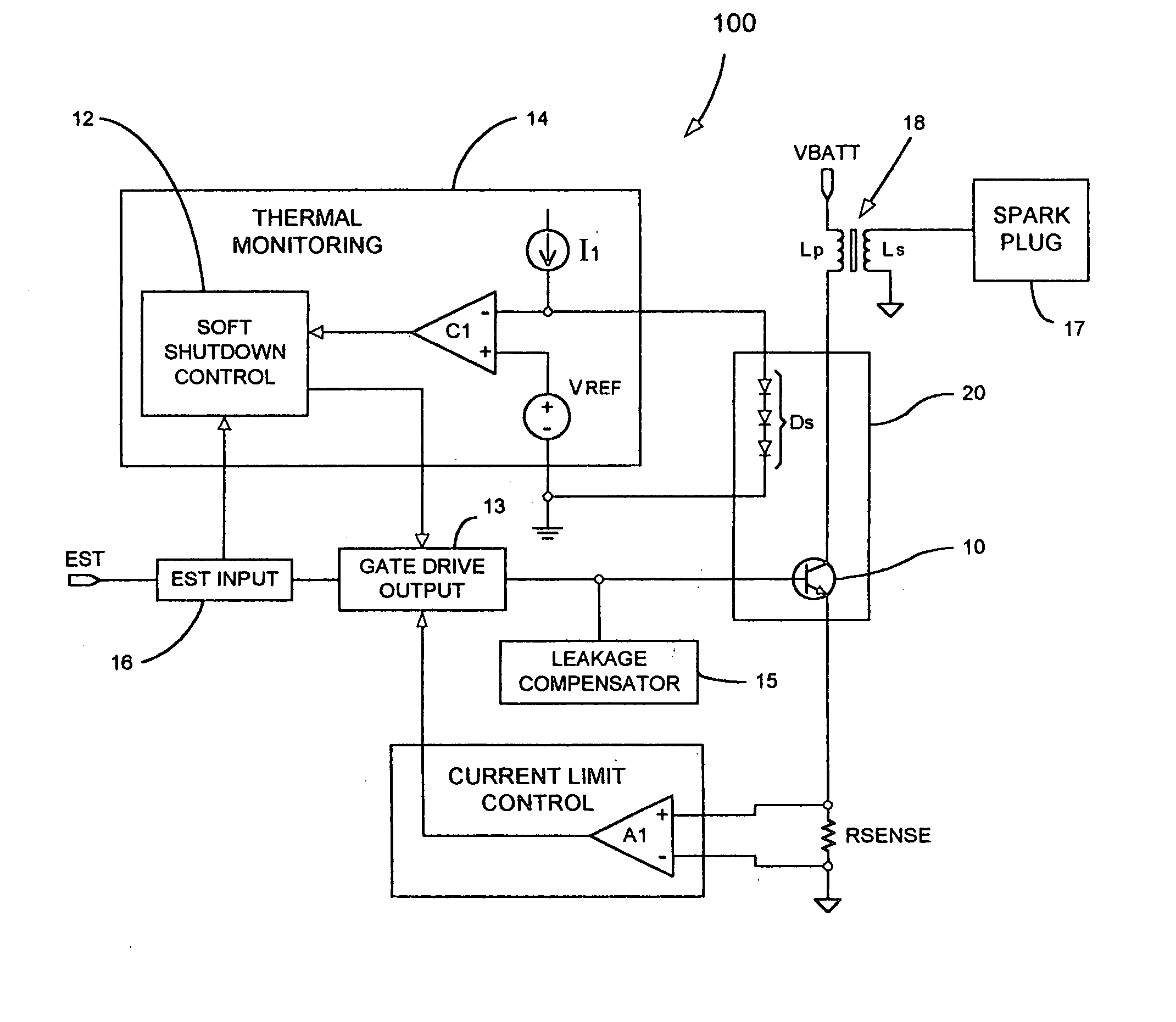
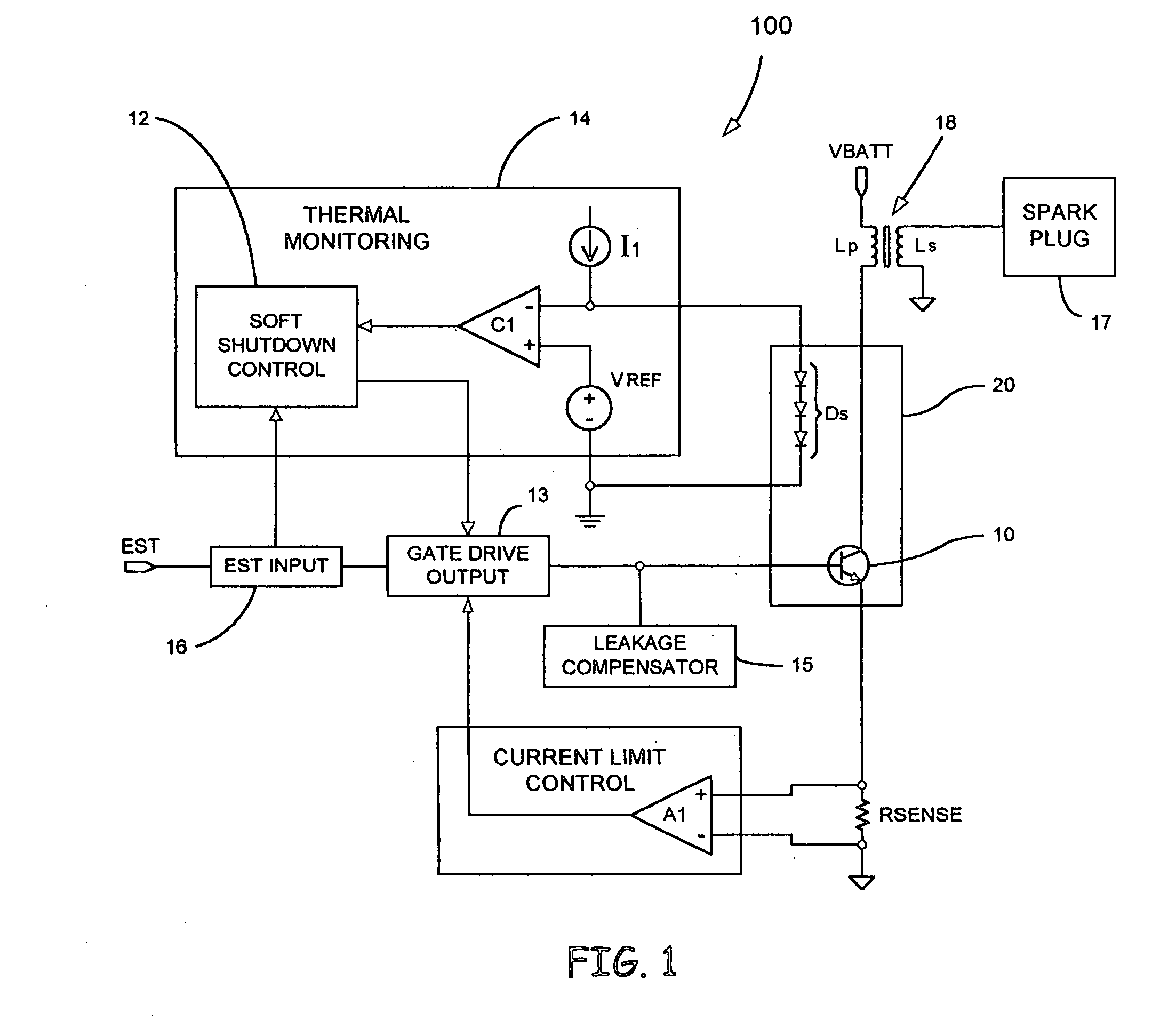
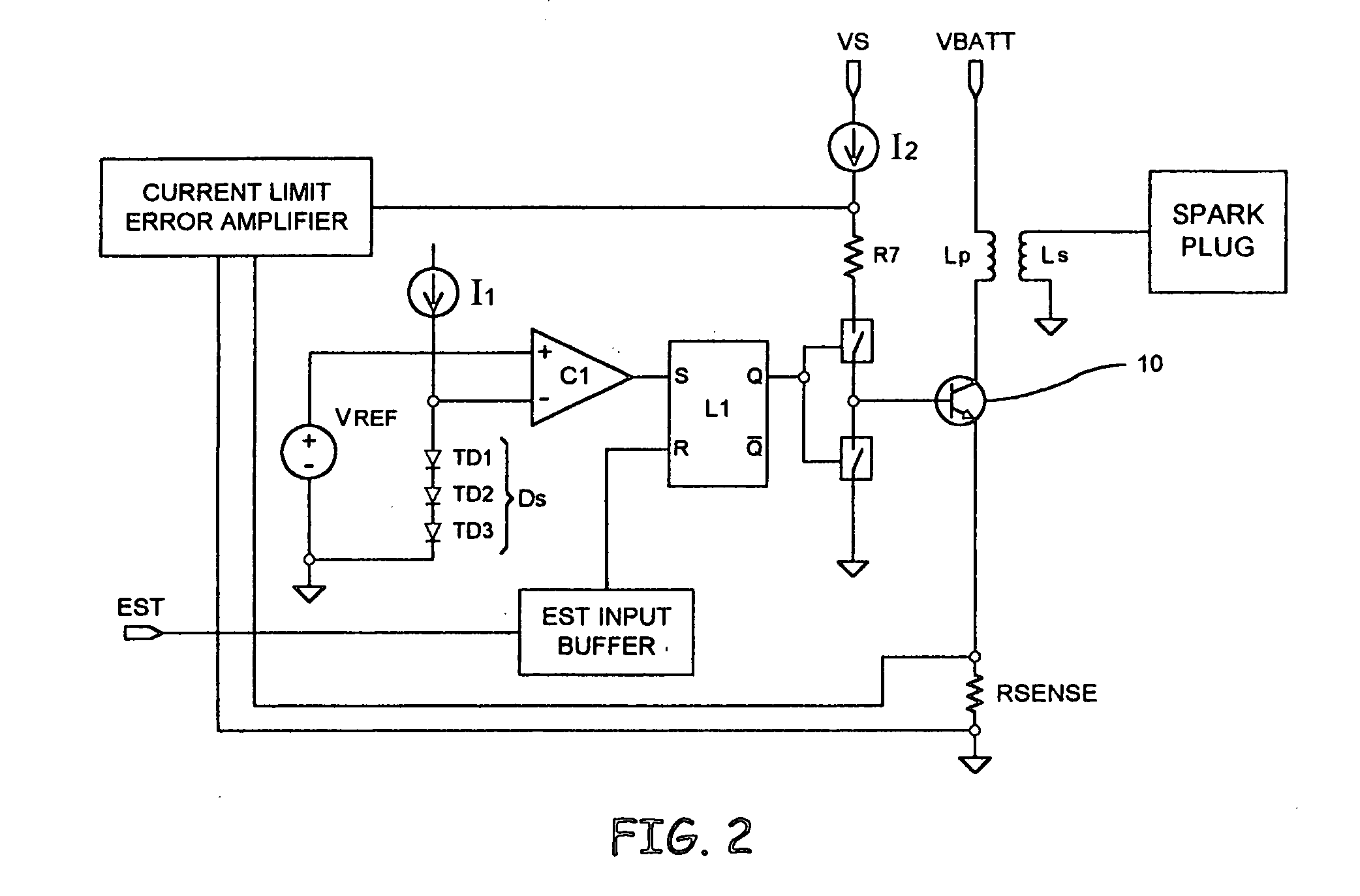
Automotive ignition system with sparkless thermal overload protection
ActiveUS20050178372A1Electrical controlThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsThermal monitoringDriving current
An interface for providing thermal overload protection includes a switching device, a temperature indicating device, a drive circuit and a thermal monitoring circuit. The thermal monitoring circuit is coupled across the temperature indicating device and provides a shutdown signal to the drive circuit when the temperature of the switching device is above a predetermined temperature level as indicated by a temperature signal provided by the temperature indicating device. The drive circuit responds to the shutdown signal by removing current sources and current sinks from a control terminal of the switching device at which point leakage currents cause the switching device to reduce a drive current to an inductive load.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
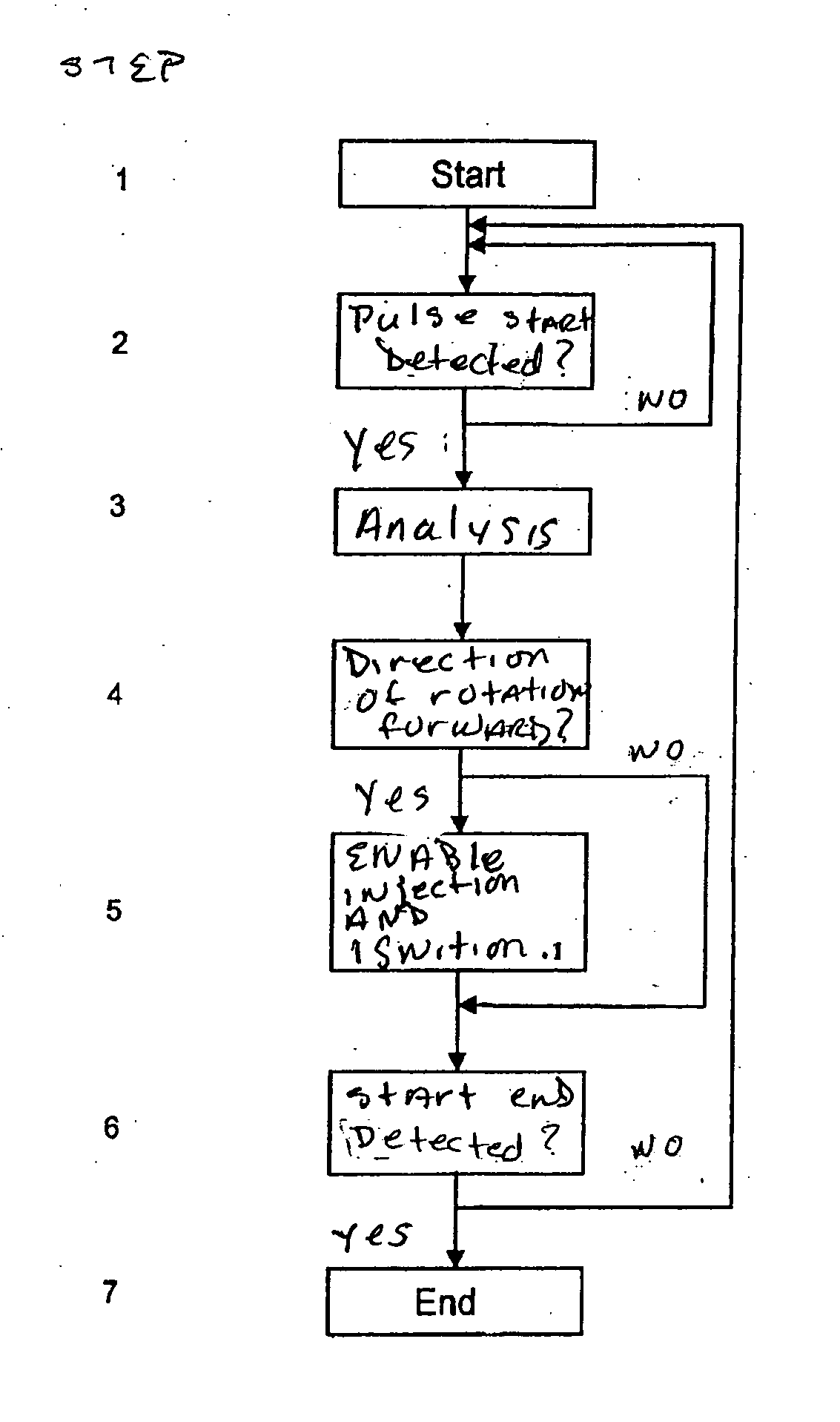
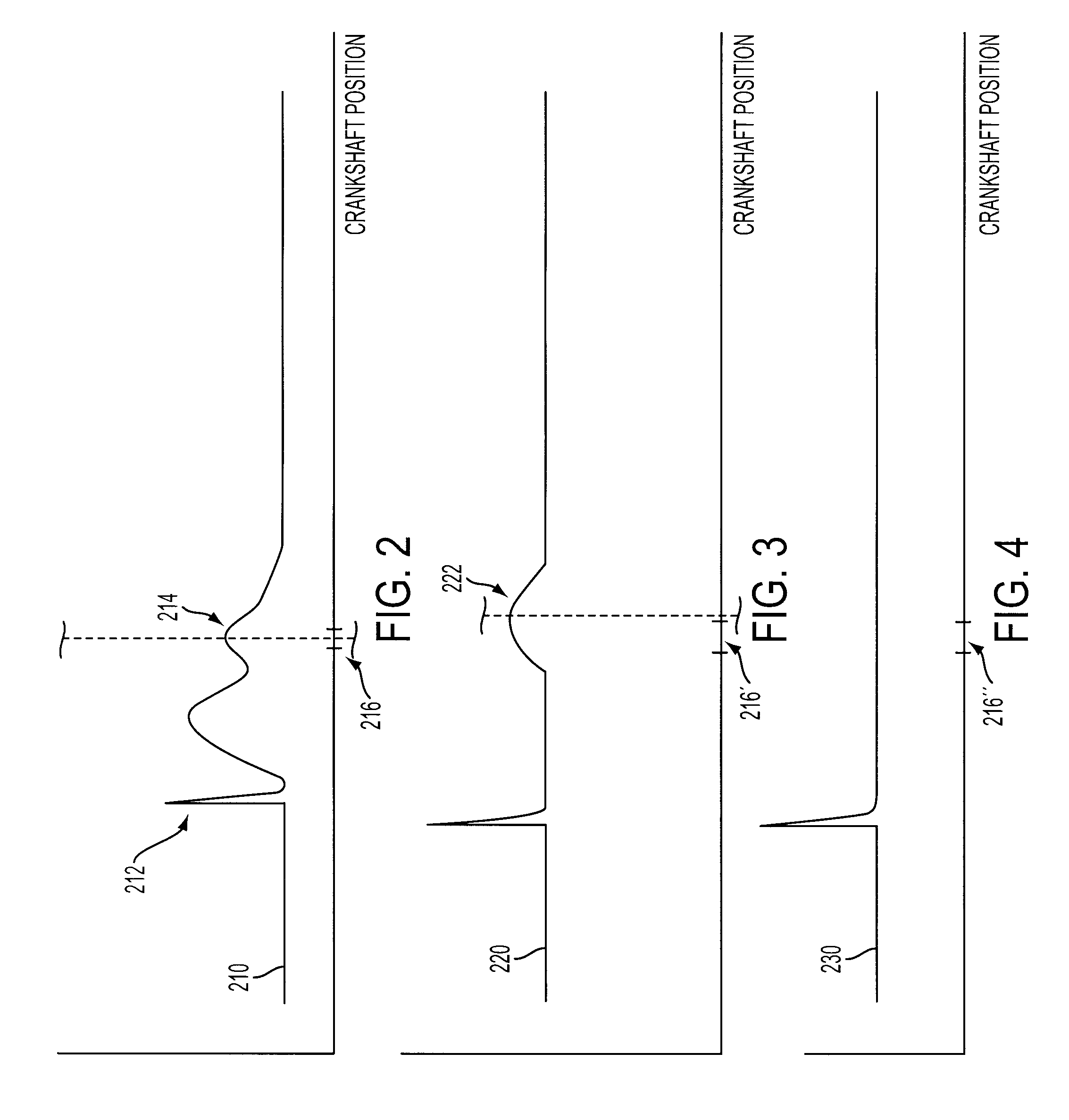
Method for detecting reverse rotation for internal combustion engines
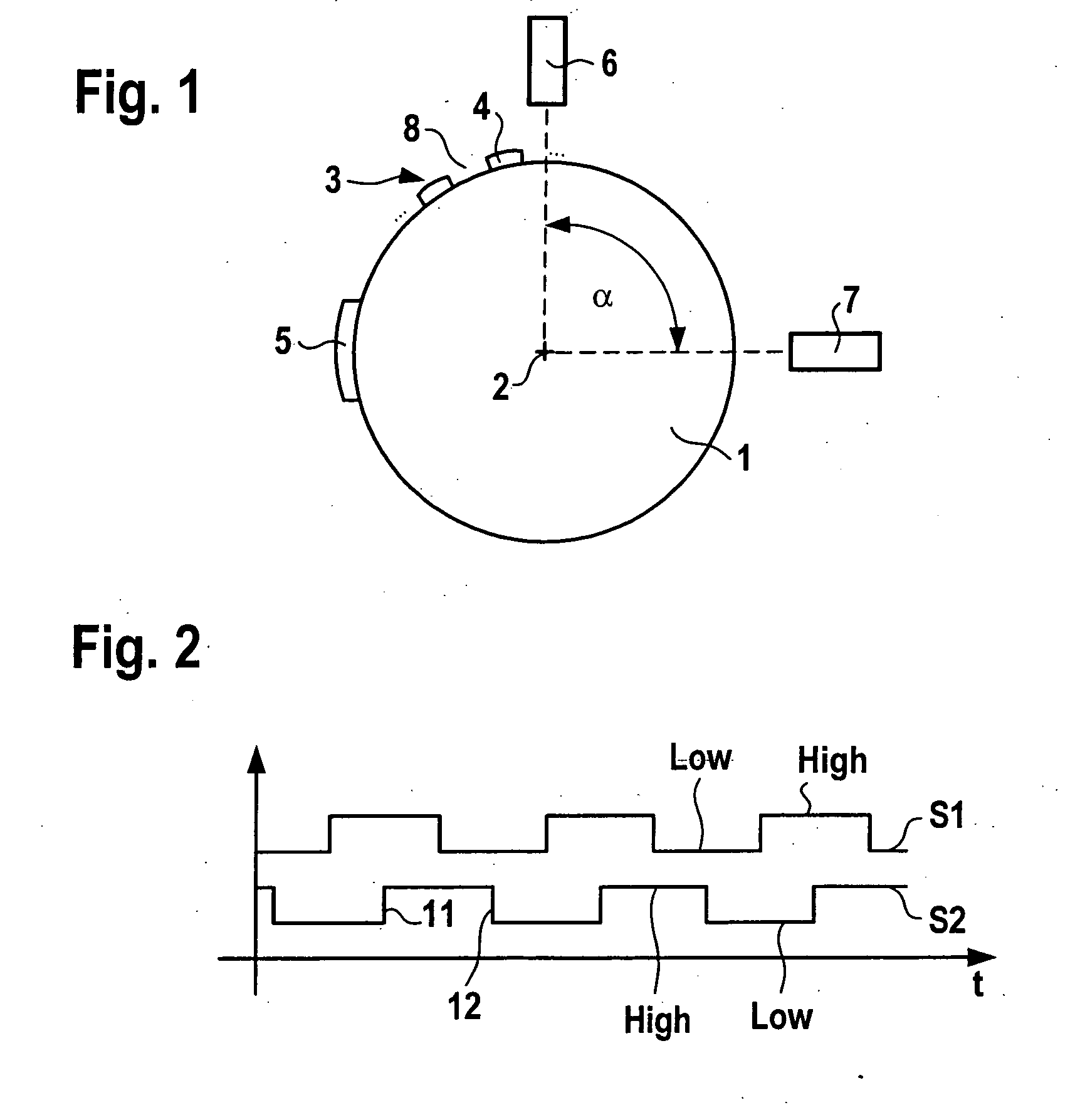
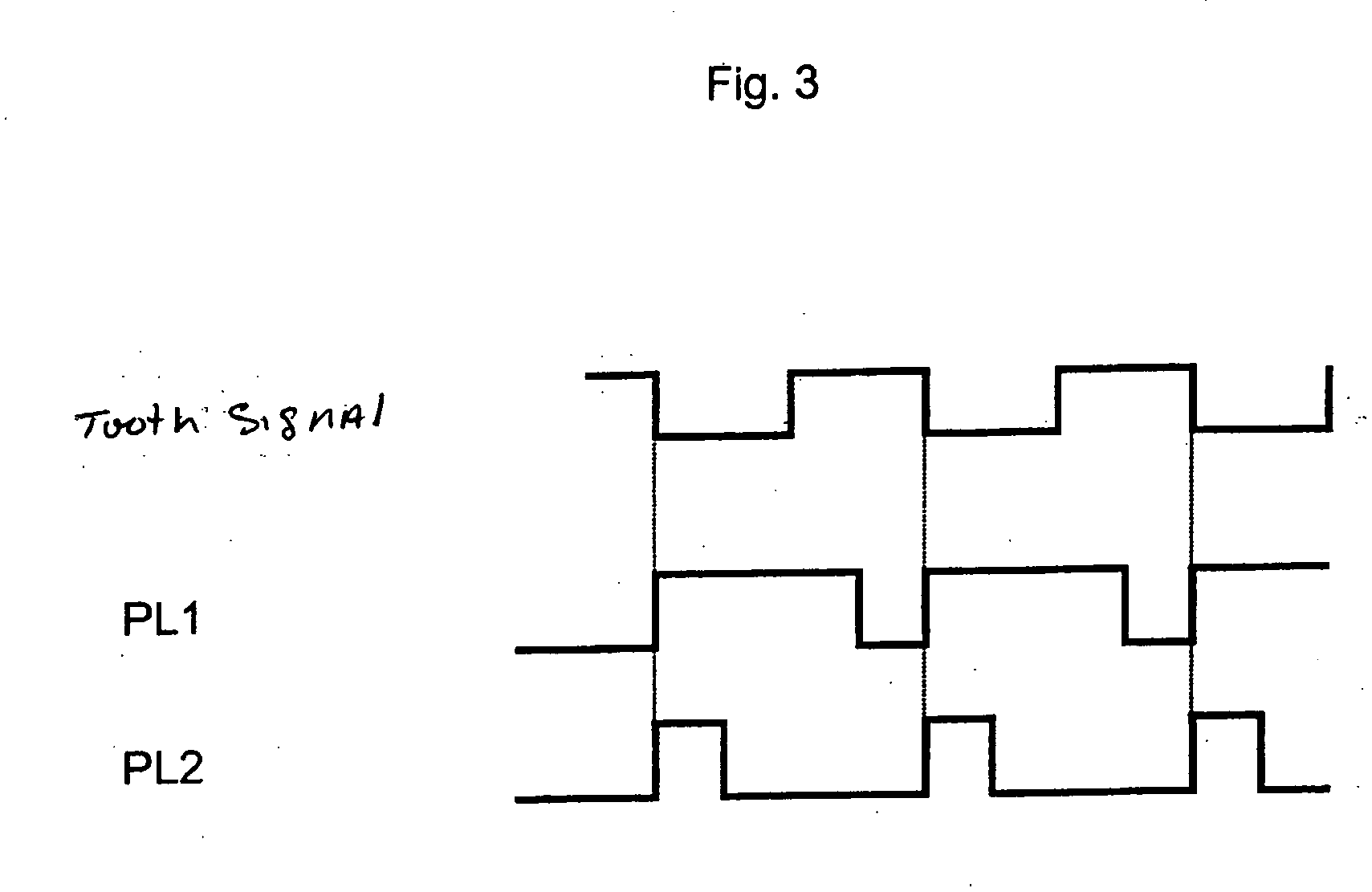
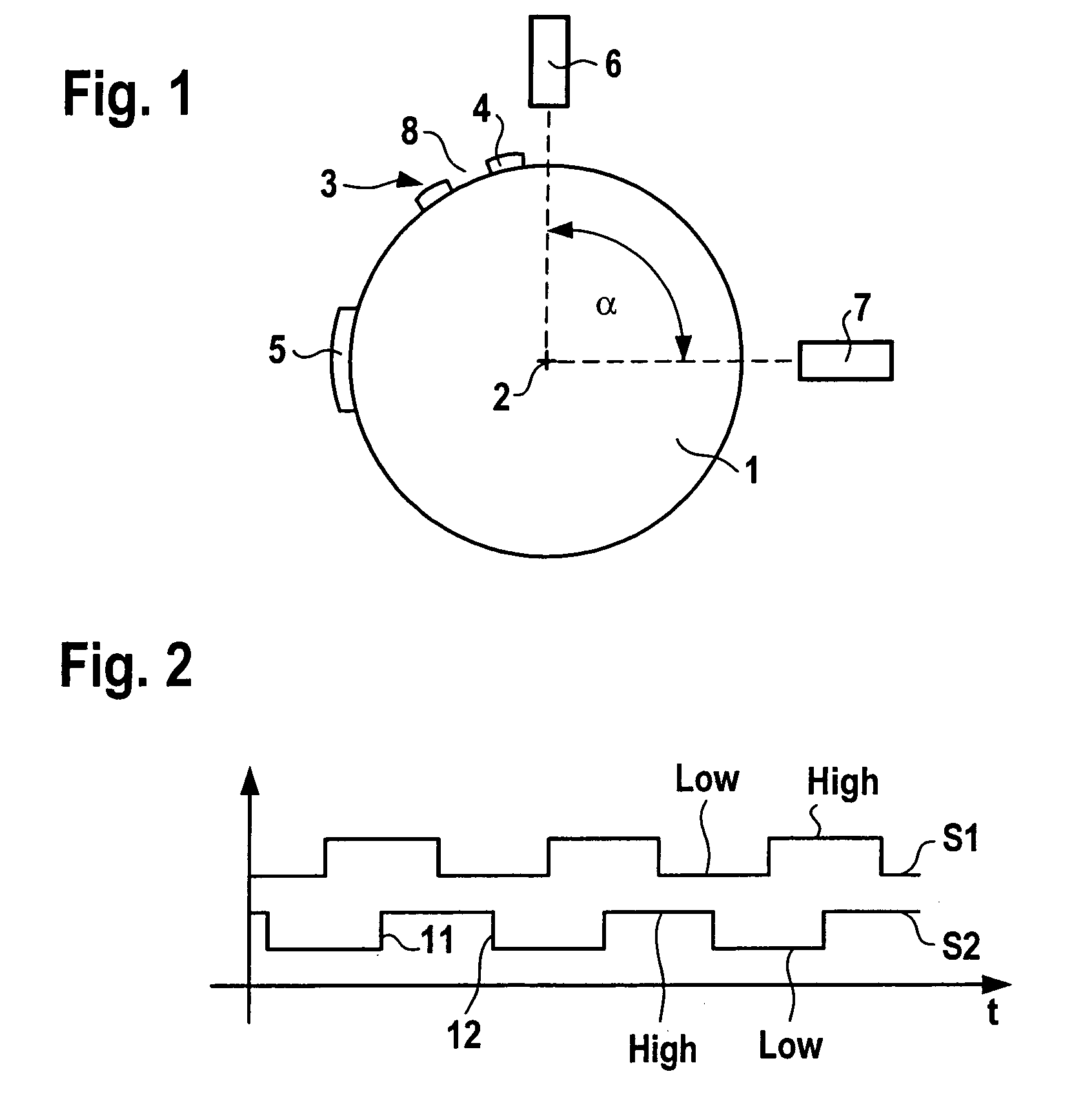
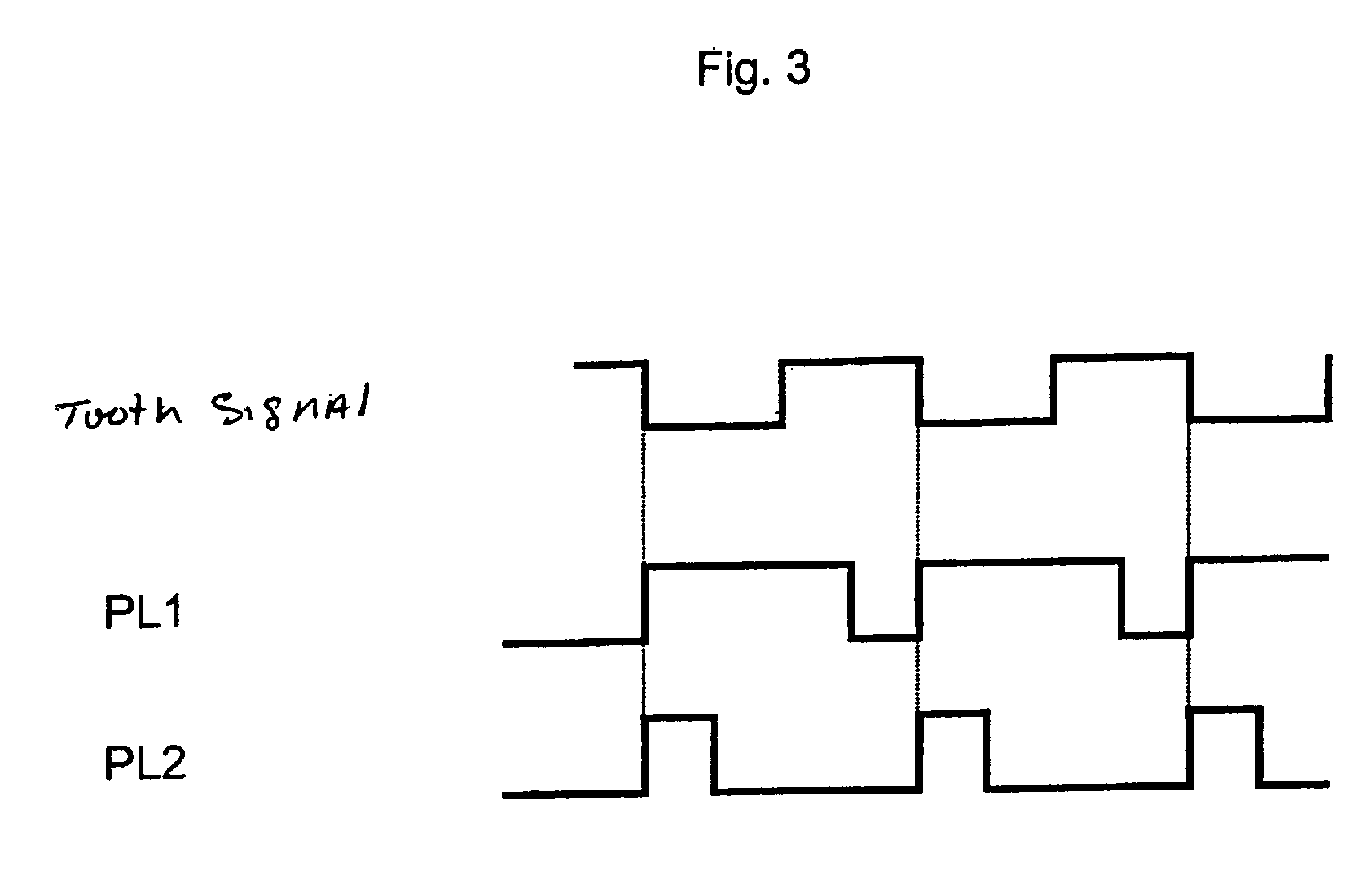
In a method for detecting reverse rotation when starting an internal combustion engine having a sensor disk which is coupled to a crankshaft of the engine, the sensor disk having a marking via an alternating arrangement of teeth and tooth spaces, and a first sensor and a second sensor each capable of generating an electric signal which may assume at least two signal levels, being associated with the sensor disk, one of the signal levels being associated with a tooth and the other signal level with a tooth space, a rising or falling signal edge of the one signal and the signal level of the other signal being used for determining the direction of rotation and increment of the angle of rotation of the crankshaft, the start characteristics are improved by determining the direction of rotation during the start of the engine as early as at the first signal edge.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
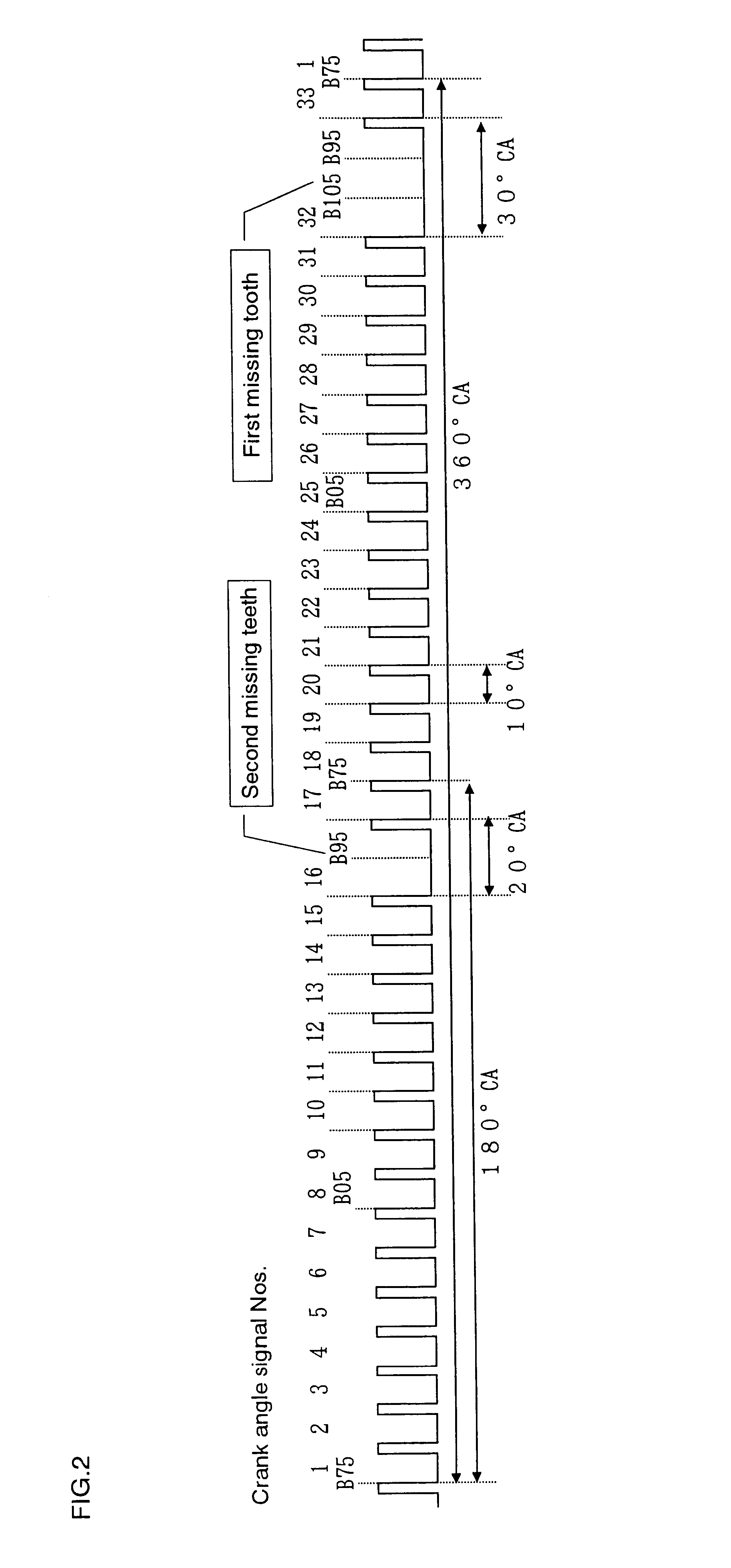
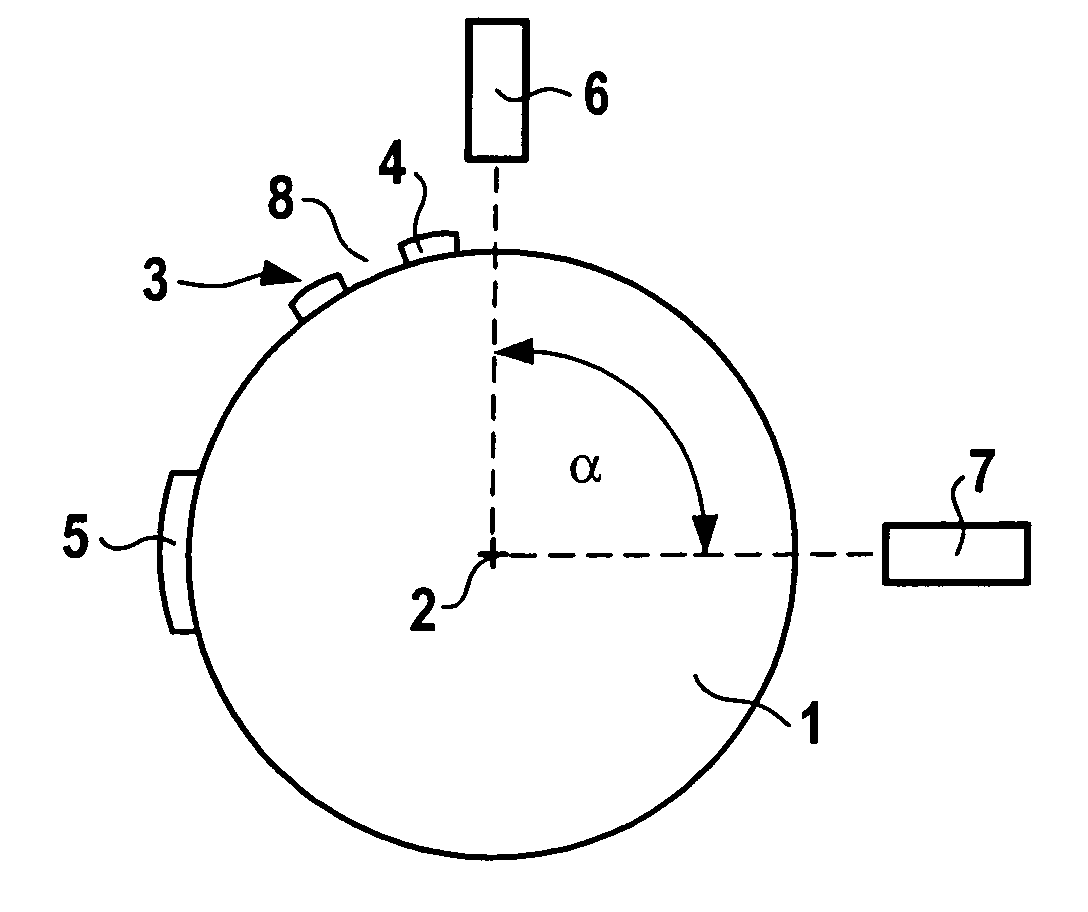
Crank angle detection apparatus
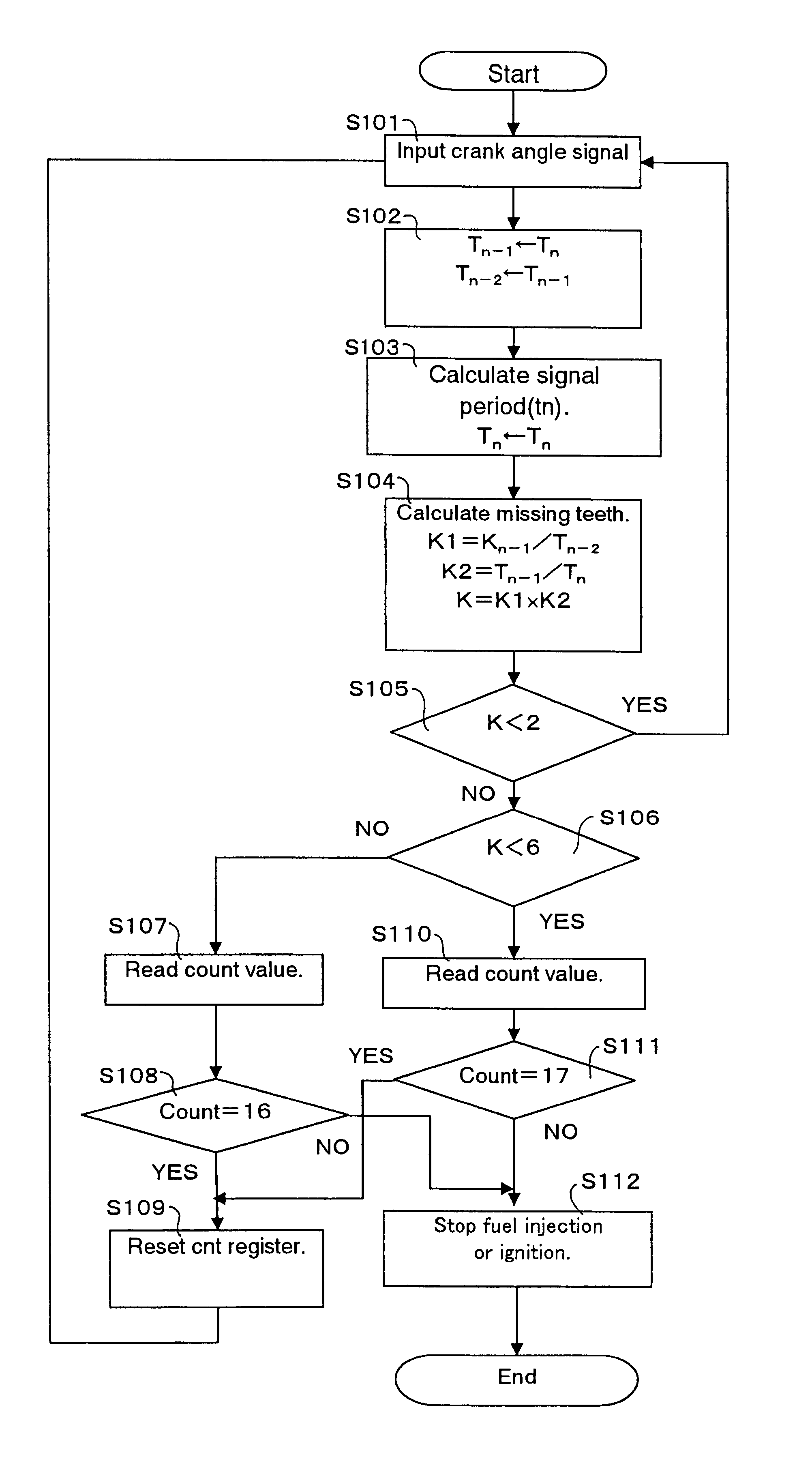
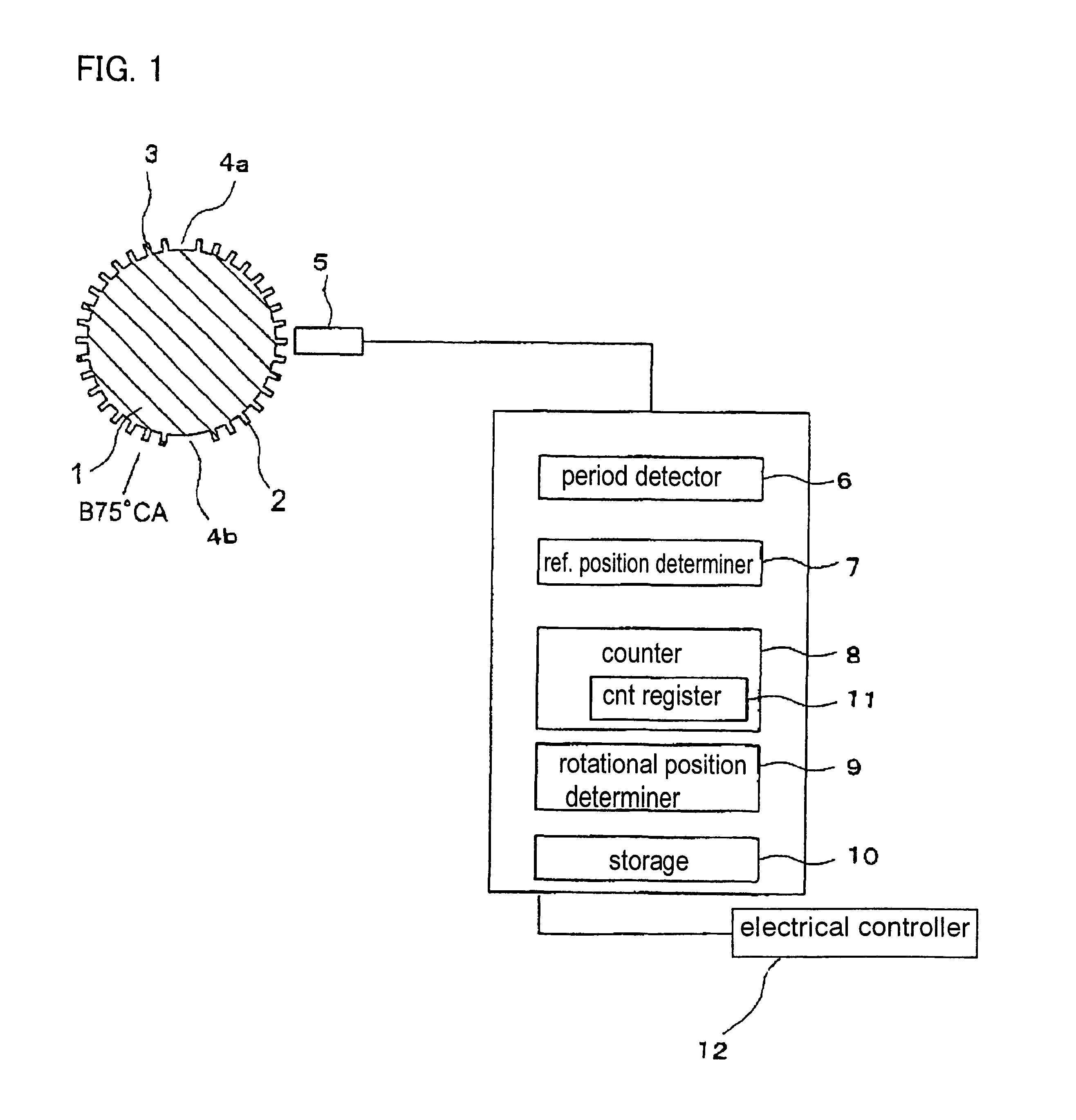
Even if the engine is started from any crank angle position, it is possible to correctly determine the rotational direction of a crankshaft, so that fuel injection or ignition can be stopped when the crankshaft is rotating in the reverse direction. A measurement member has a plurality of angular position detection portions arranged at equal intervals in a circumferential direction of the crankshaft and a plurality of reference position detection portions at which a part of the angular position detection portions is missing. A crank angle sensor is arranged near the measurement member for generating a crank angle signal representative of the rotational position of the crankshaft. A period detector detects periods of pulses of the crank angle signal. A reference position determiner determines a plurality of reference positions based on the signal periods. A counter counts the pulses of the crank angle signal. A rotational direction determiner detects the rotational direction of the crankshaft from the number of pulses counted between a plurality of reference positions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
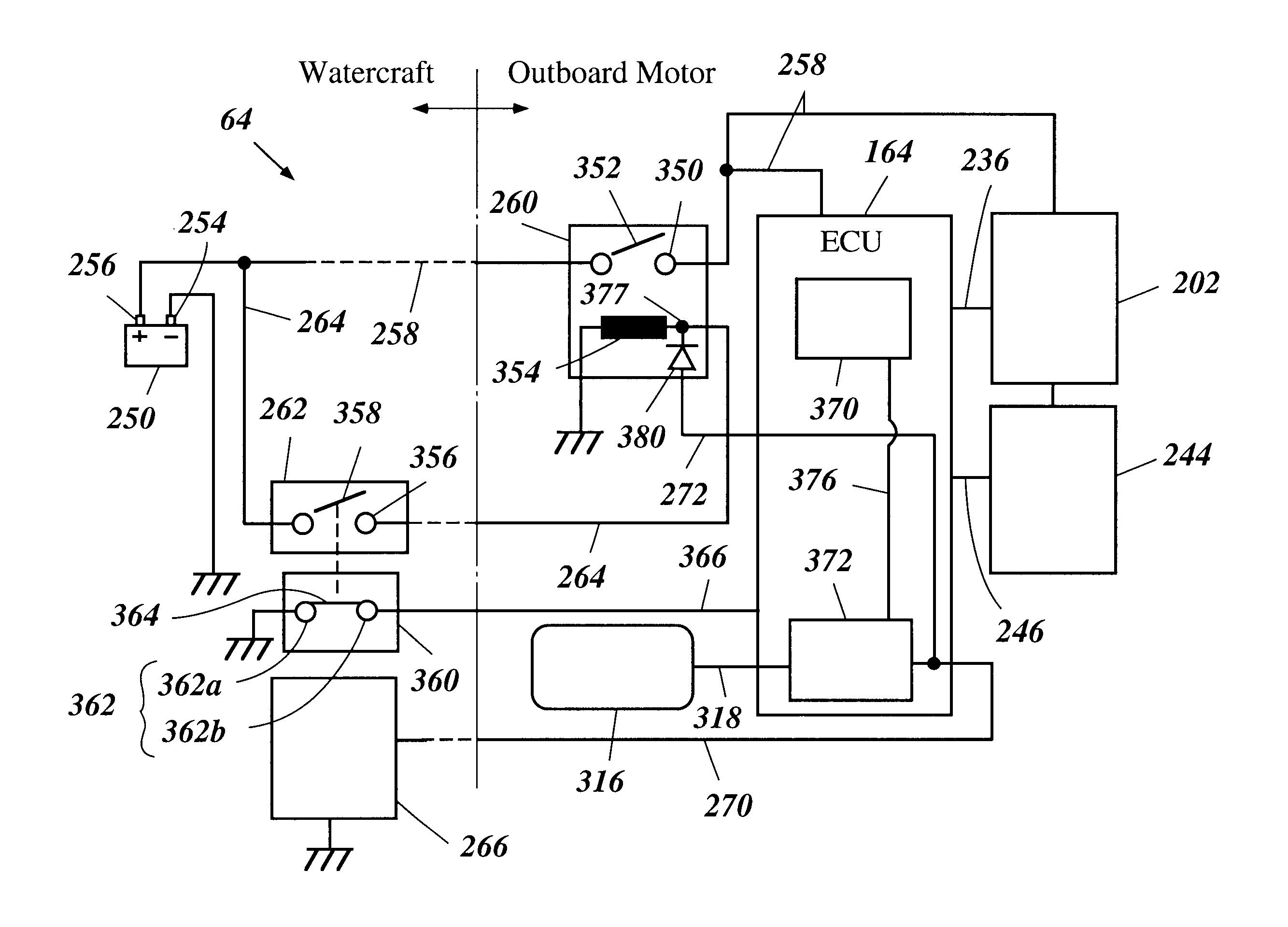
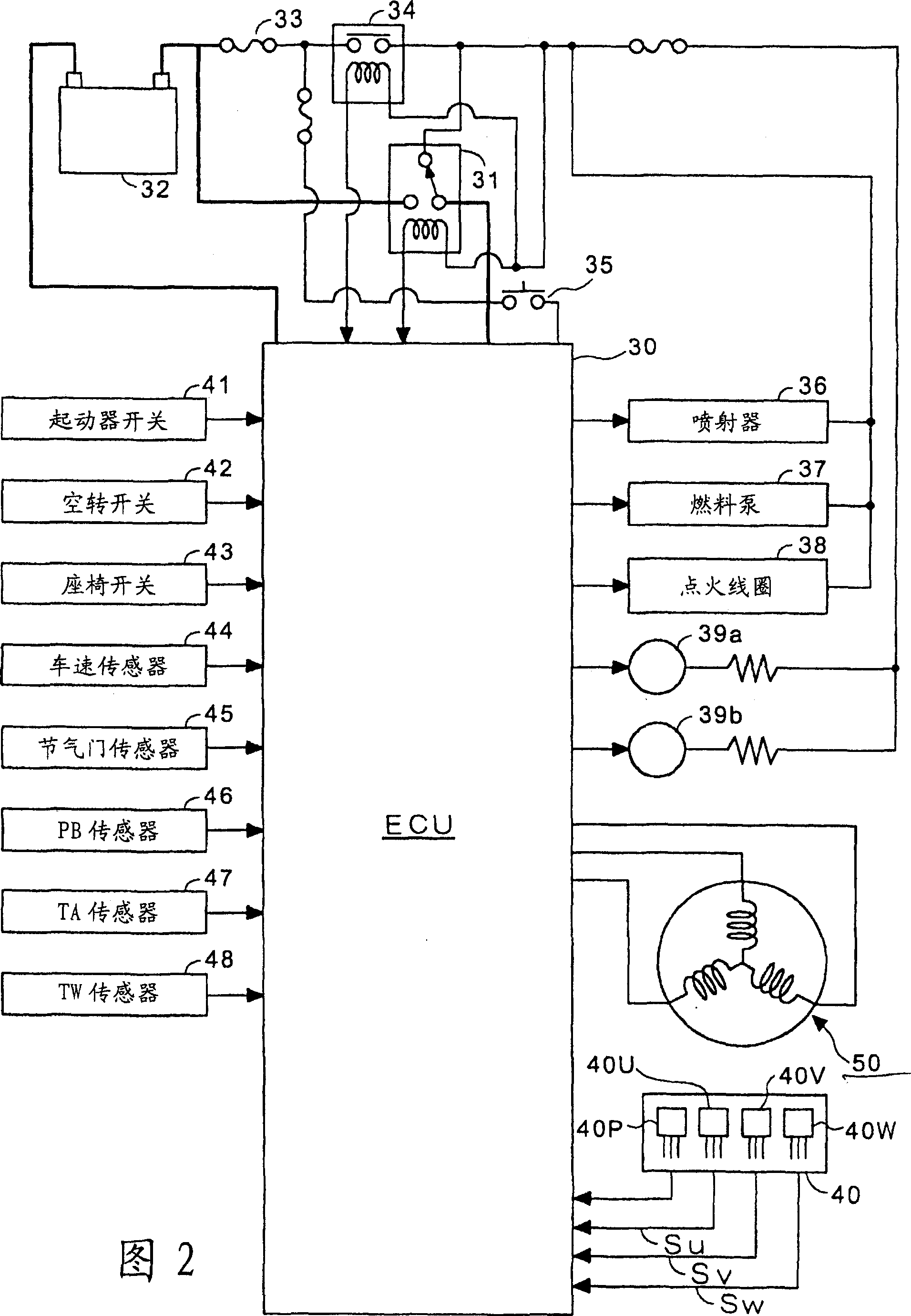
Electrical control for engine
An electrical control system for an engine includes a power supply system that supplies electric power to an engine control unit. The system has a power source connected to the engine control unit via a locking relay. The relay includes an exciting coil that is energized by electrical power when a main switch is closed. The control unit comprises a tacho-pulse shaping circuit or a fuel pump drive circuit that outputs a signal that prolongs the energized state of the coil after the main switch is opened. The signal prolongs the energized state of the coil for a preset time.
Owner:YAMAHA MARINE KK
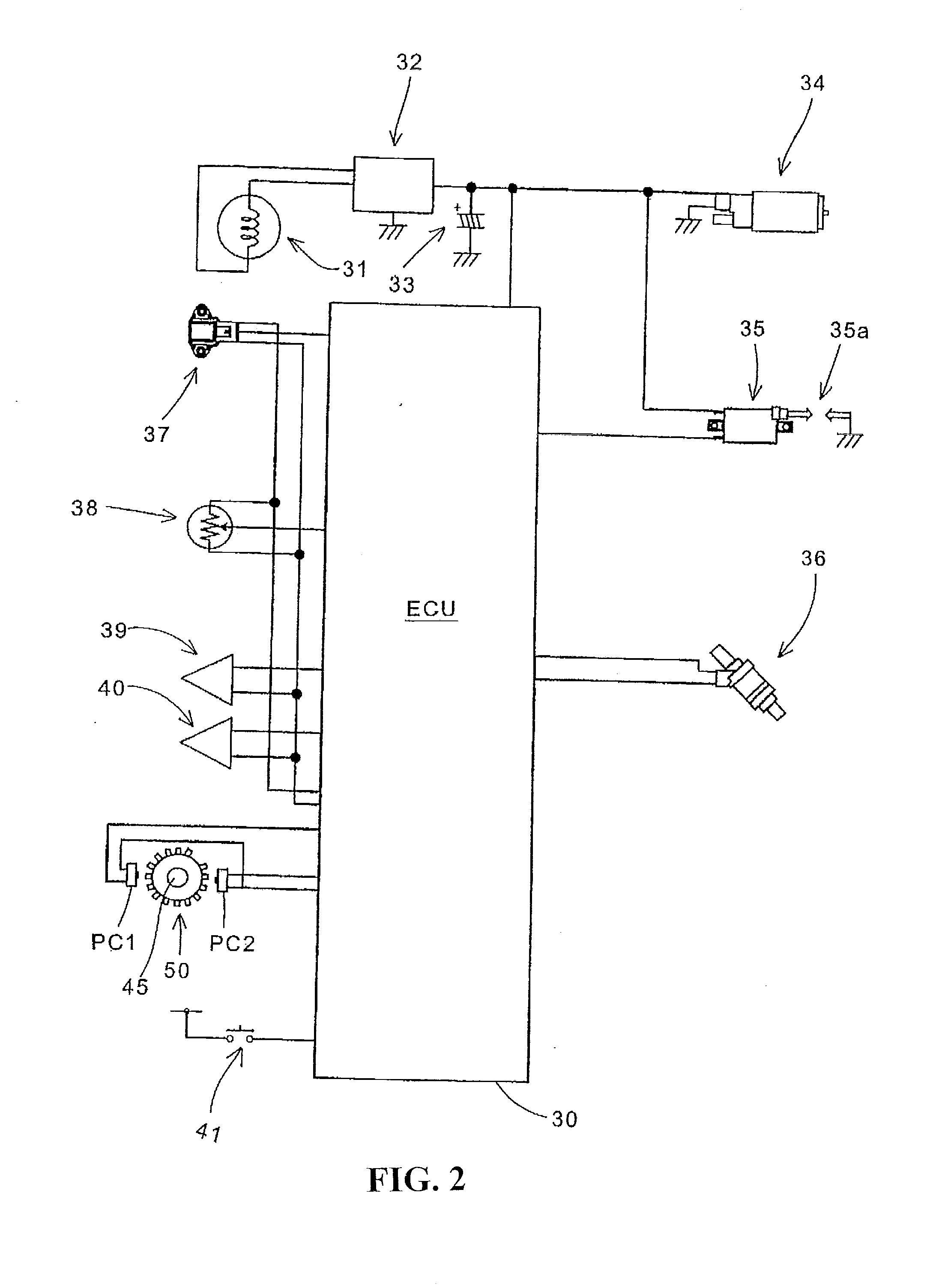
Spark control for improved engine operation
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
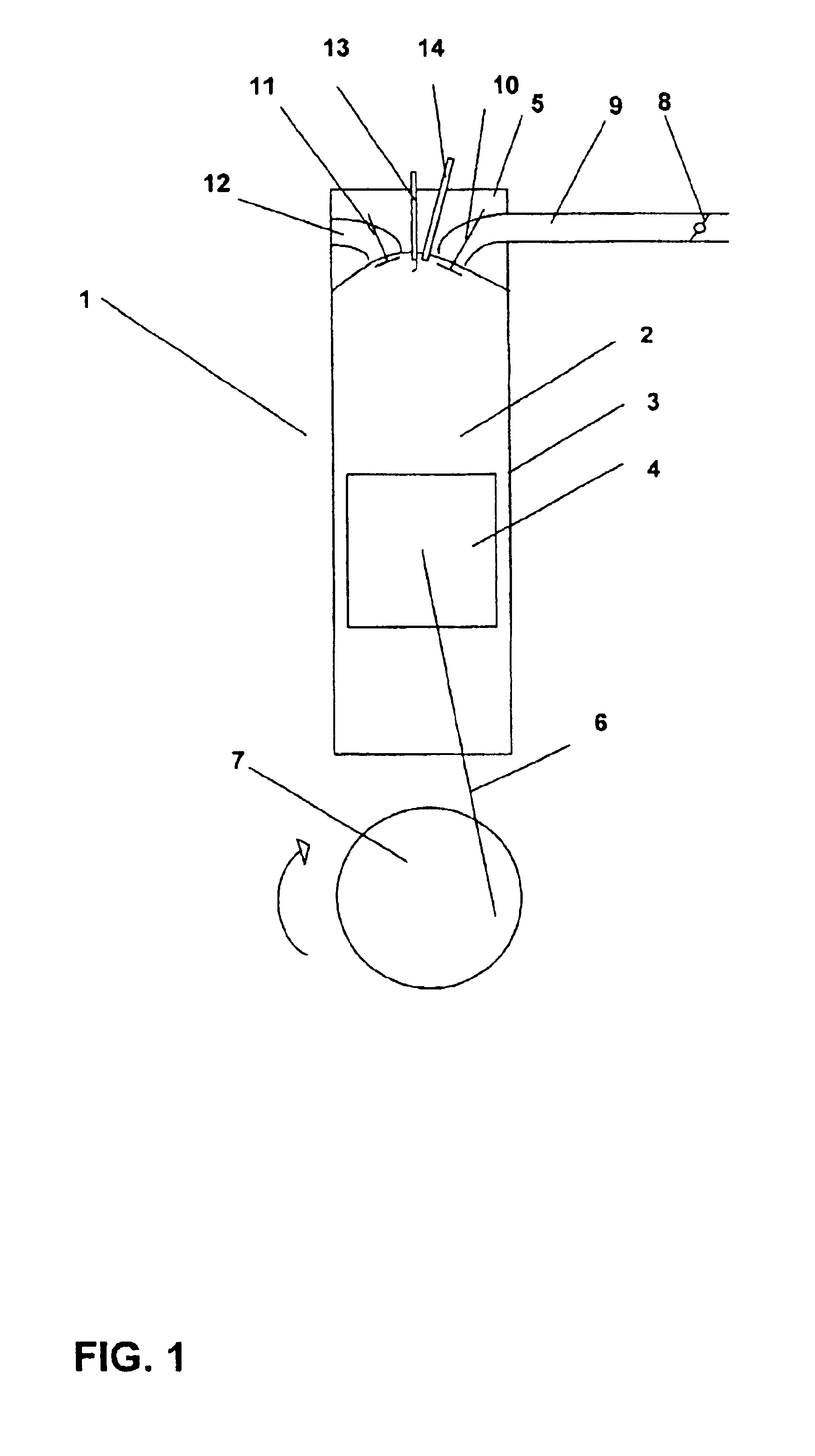
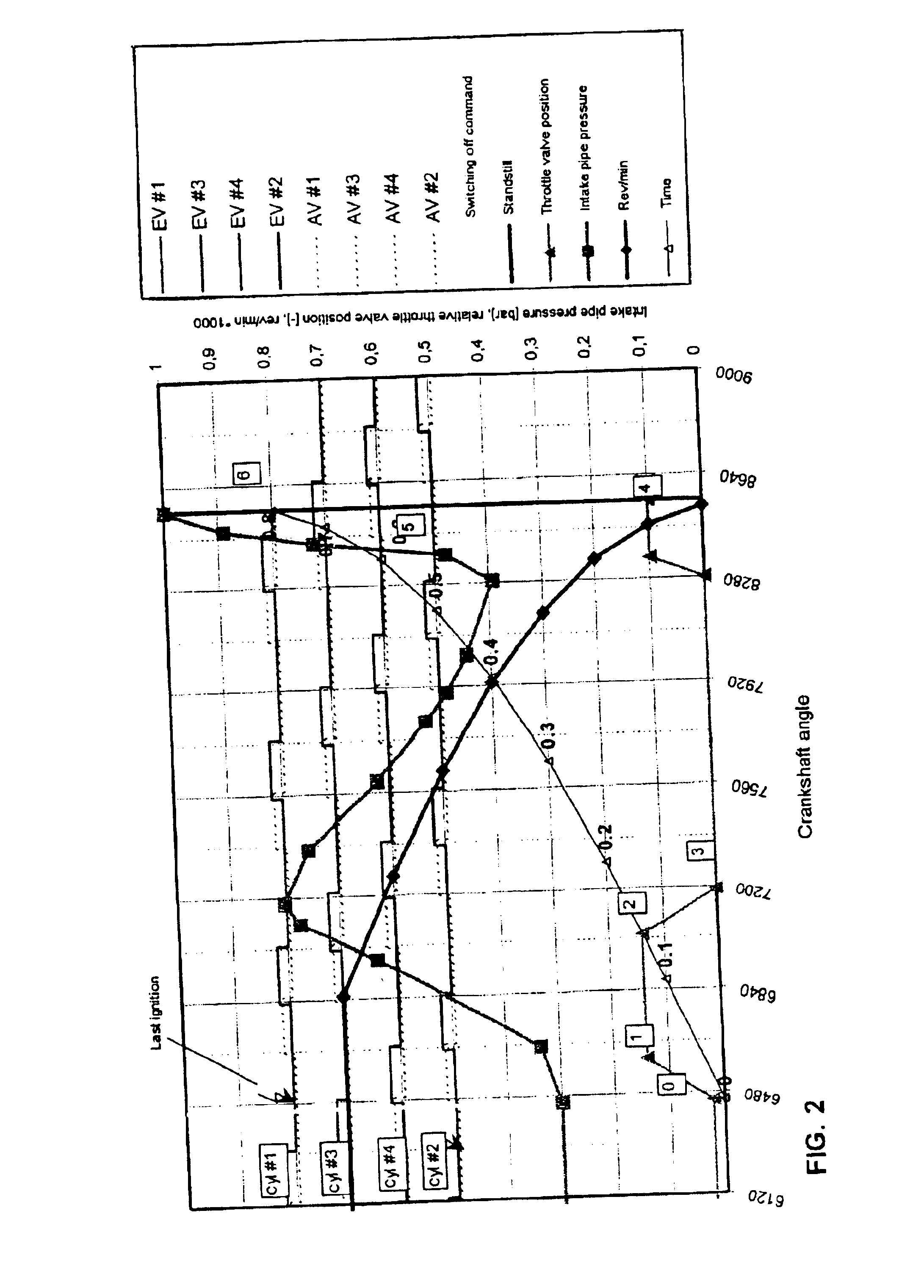
Method and system for switching off an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS6910457B2High strengthRaise the ratioElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl mannerExternal combustion engine
The invention relates to a method for switching off an internal combustion engine and to an internal combustion engine suitable for carrying out said method. Here, after a switching off command for an internal combustion engine, the throttle valve in the air intake system is again opened to enable a relatively large amount of fresh air to be sucked into the combustion chambers of the internal combustion engine. This considerably increases the gas forces in the combustion chambers while the engine slows to a standstill, so that the internal combustion engine can be switched off in a controlled manner. At the same time, products of combustion, which may possibly still be present, are removed from the combustion chambers of the internal combustion engine. As a result, the preconditions for directly starting the internal combustion engine without a starter are created.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method for monitoring an ignition system
ActiveUS20130206106A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease volumeEngine controllersElectric motor startersElectricitySoot
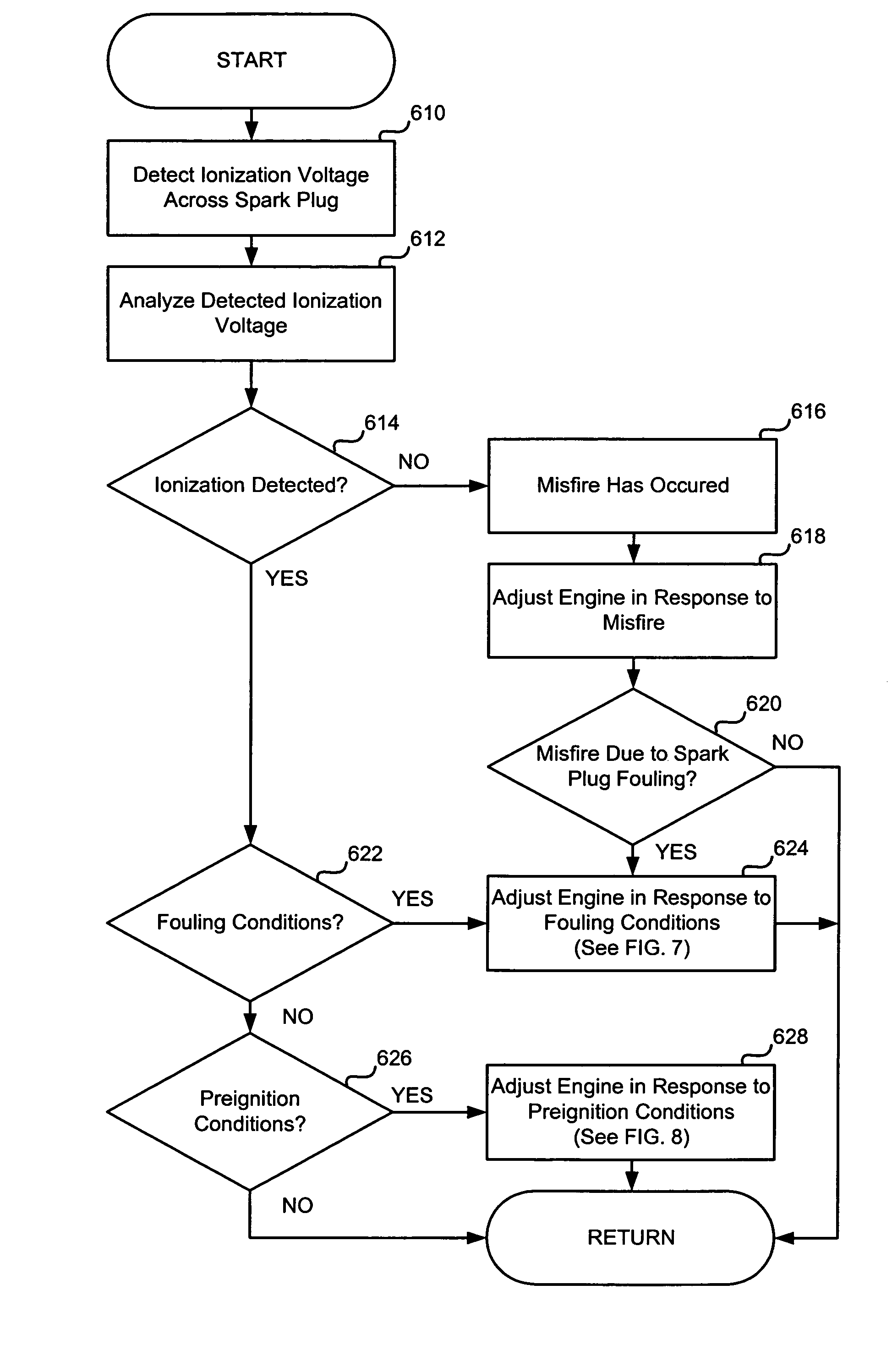
A system for monitoring and cleaning a spark plug is disclosed. In one example, an amount of carbonaceous soot at the center electrode ceramic of the spark plug is determined in response to a voltage of a sense resistor that is in electrical communication with the spark plug. The system may institute spark plug cleaning after carbonaceous soot is detected so that the possibility of engine misfire may be reduced.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Power switching control device for electric systems
ActiveUS20060244496A1Increase heightElectric spark ignitersSolid-state devicesCombustionPower switching
A power switching control device for electric systems such as an ignition device for internal combustion engines has a control circuit IC and a switching IC. A temperature sensor is provided in the switching IC. The control circuit IC is joined to a grounding terminal through a conductive layer provided therebetween. Thus, the substrate potential of the control circuit IC is stabilized to the ground potential so that the temperature sensor is prohibited to operate erroneously due to electromagnetic noise.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Combustion Control Using Ion Sense Feedback And Multi-Strike Spark To Manage High Dilution And Lean AFR
ActiveUS20100206267A1Improve combustion qualityEasy to controlAnalogue computers for vehiclesInternal-combustion engine testingCombustionInternal combustion engine
A system and method for operating a multiple cylinder internal combustion engine having at least one actuator for controlling charge dilution of at least one cylinder and at least one spark plug per cylinder include attempting to improve combustion quality by modifying ignition energy of the at least one spark plug before modifying charge dilution of the cylinder, and modifying both ignition energy and charge dilution substantially simultaneously to establish combustion if an ionization sense signal associated with the cylinder indicates a misfire.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
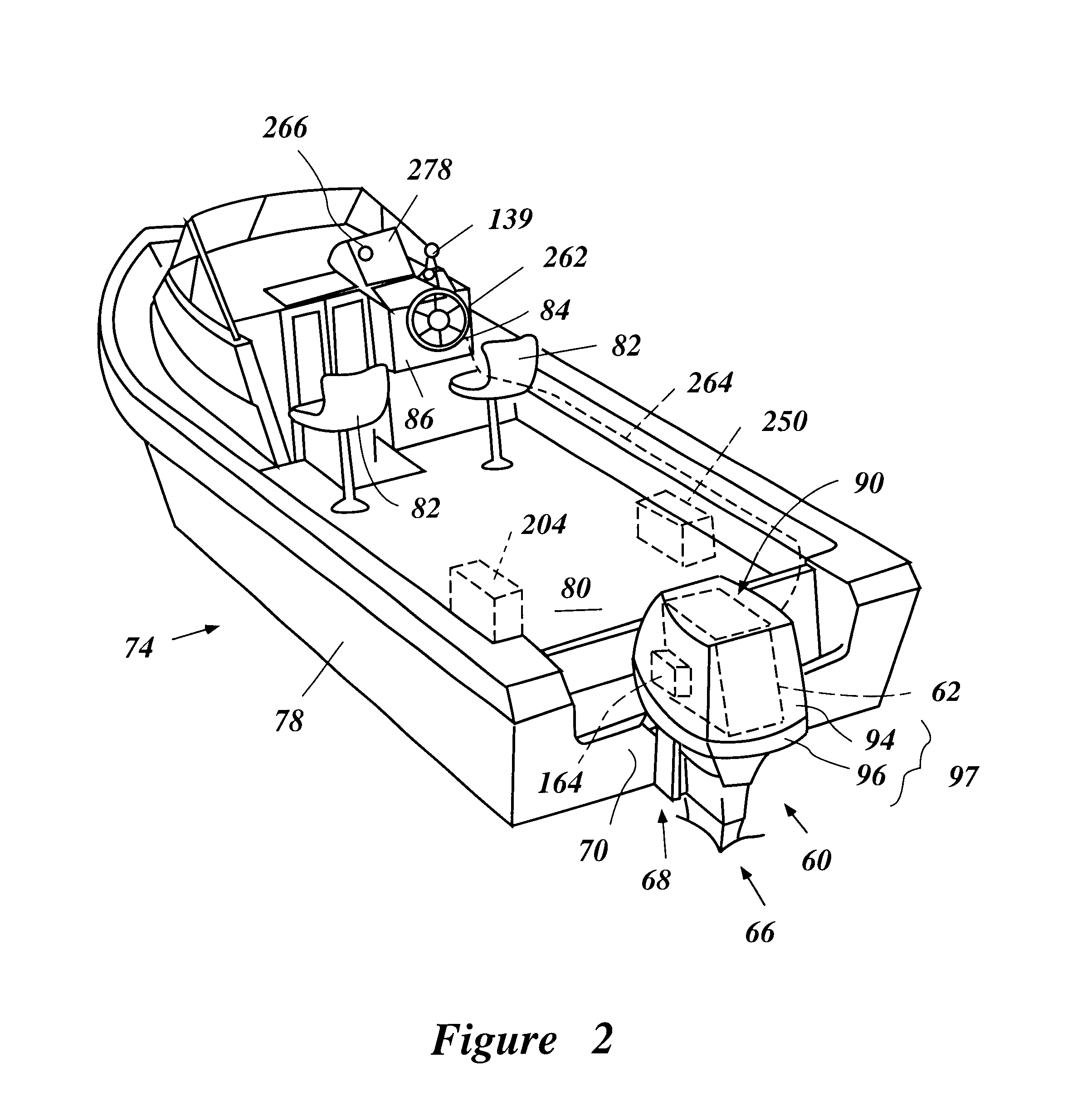
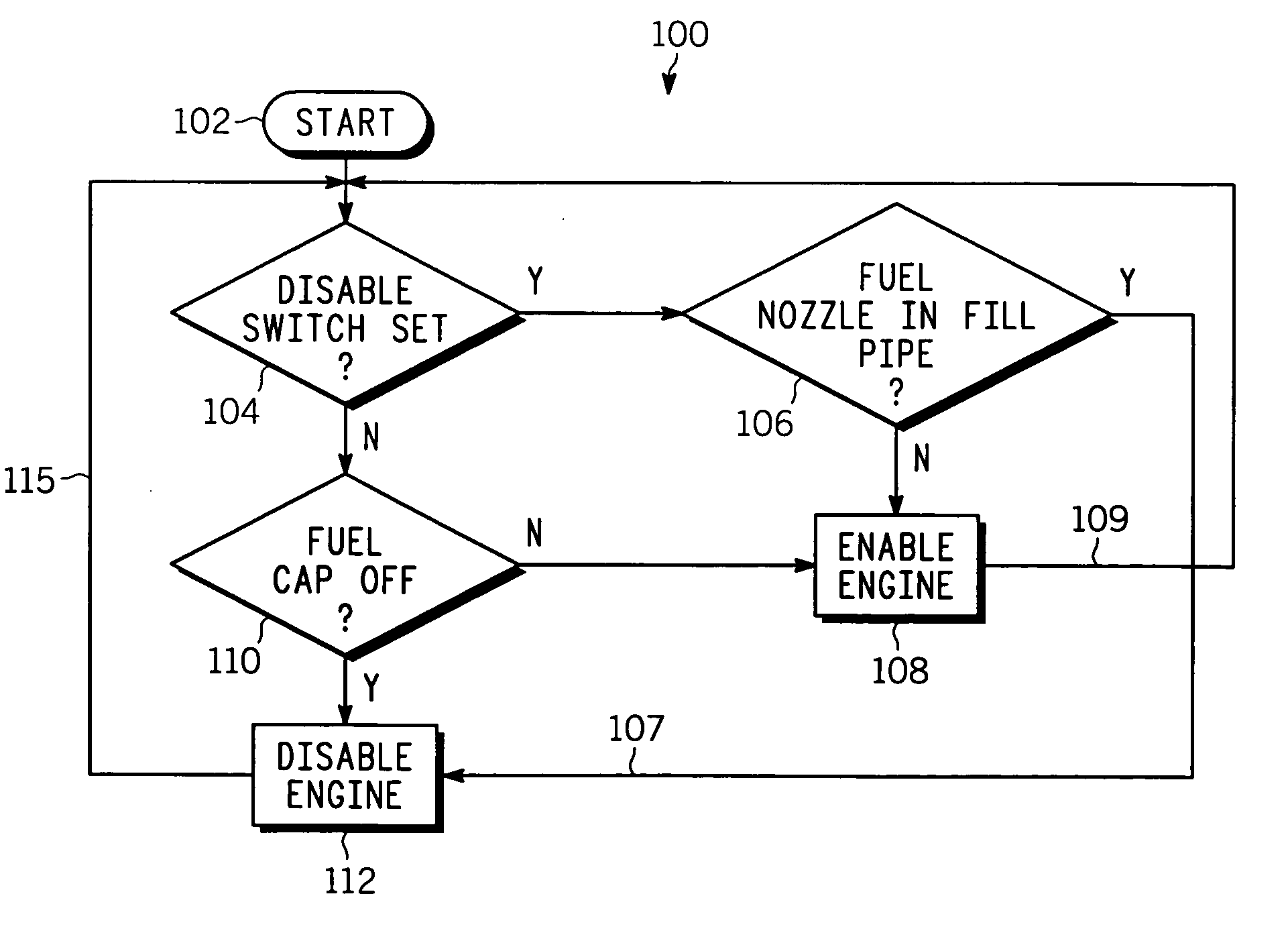
Vehicle fueling arrangement
Methods and apparatus are provided for limiting engine operation during fueling. The apparatus comprises, an engine control for enabling or disabling operation of the engine, one or more sensors for detecting whether (i) a cap is on the vehicle fuel fill-pipe, and (ii) a fueling nozzle is in the fuel fill-pipe, a processor coupled to the engine control and the one or more sensors receiving information therefrom and directing the engine control to enable or disable the vehicle engine depending upon the sensor outputs, thereby, disabling the engine when the cap is not on the fill-pipe and / or a fueling nozzle is in the fill-pipe, and enabling the engine when not true. In a further embodiment, a fuel level sensor coupled to the processor is used to detect whether a fuel level change rate R(t)≧Rc where Rc is a predetermined value, and if so, disabling the engine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method of detecting an ionization current
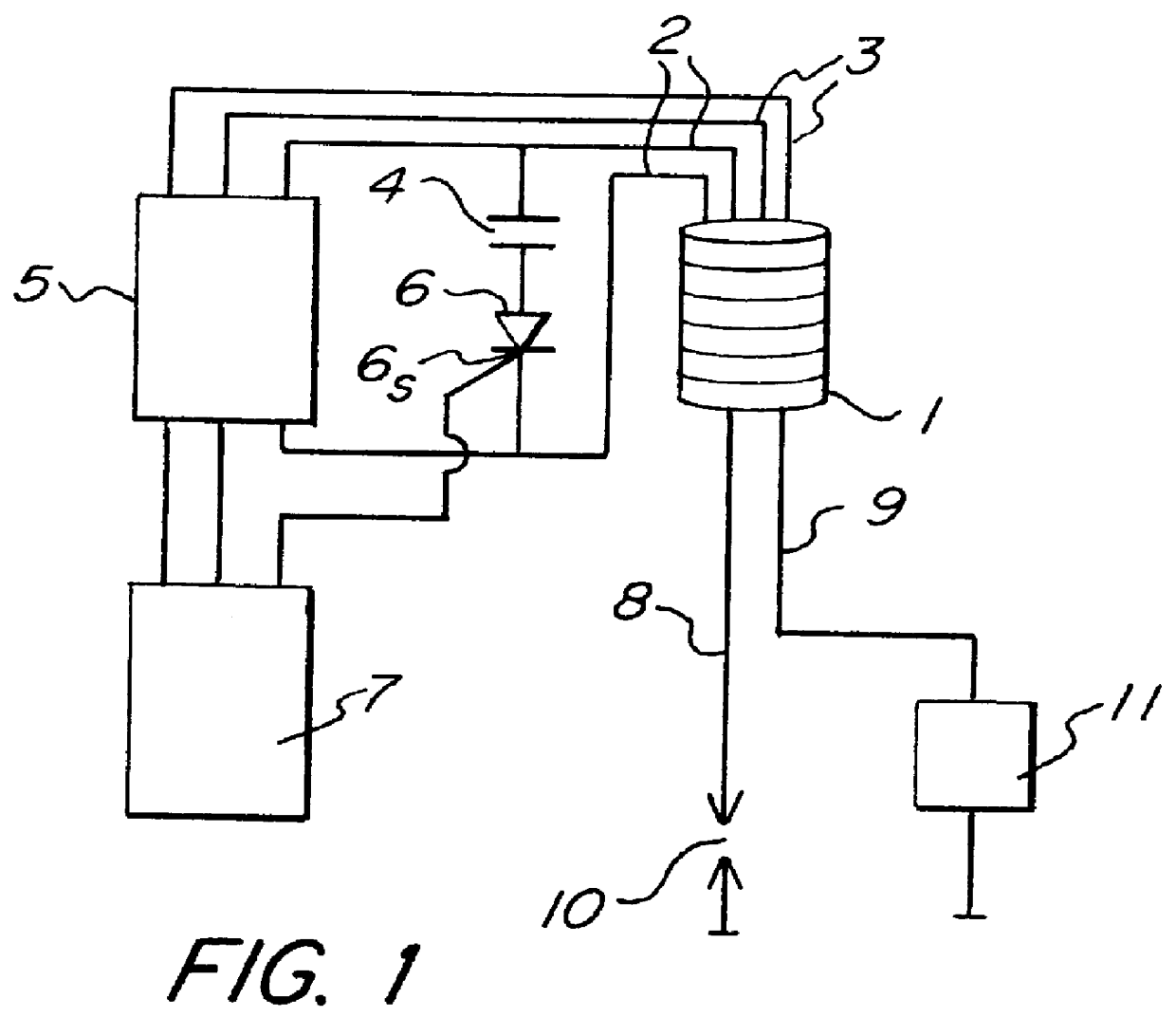
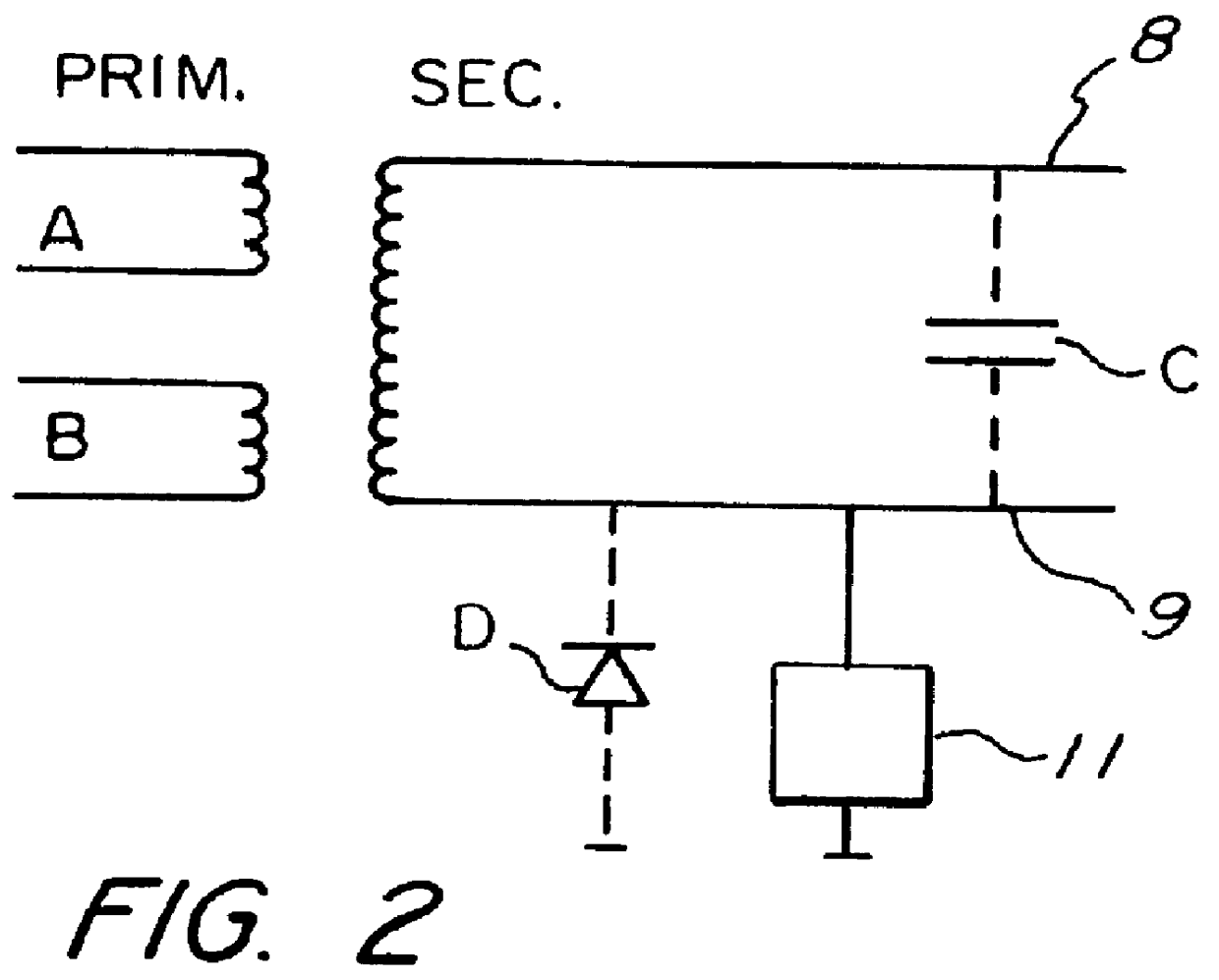
PCT No. PCT / SE97 / 01022 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 10, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 10, 1998 PCT Filed Jun. 11, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 47875 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 18, 1997A method for generation of a low test voltage is used for the purpose of detecting an ionization current in the spark gap of an internal combustion engine. The voltage is generated by a controllable ignition magneto (5) arranged in order to charge (2) an ignition capacitor (4). The voltage is applied (3) to the primary side of the ignition device after generation of a spark and after the decay of the spark, after which the ionization current is detected (11) on the secondary side of the ignition device.
Owner:SEM AB
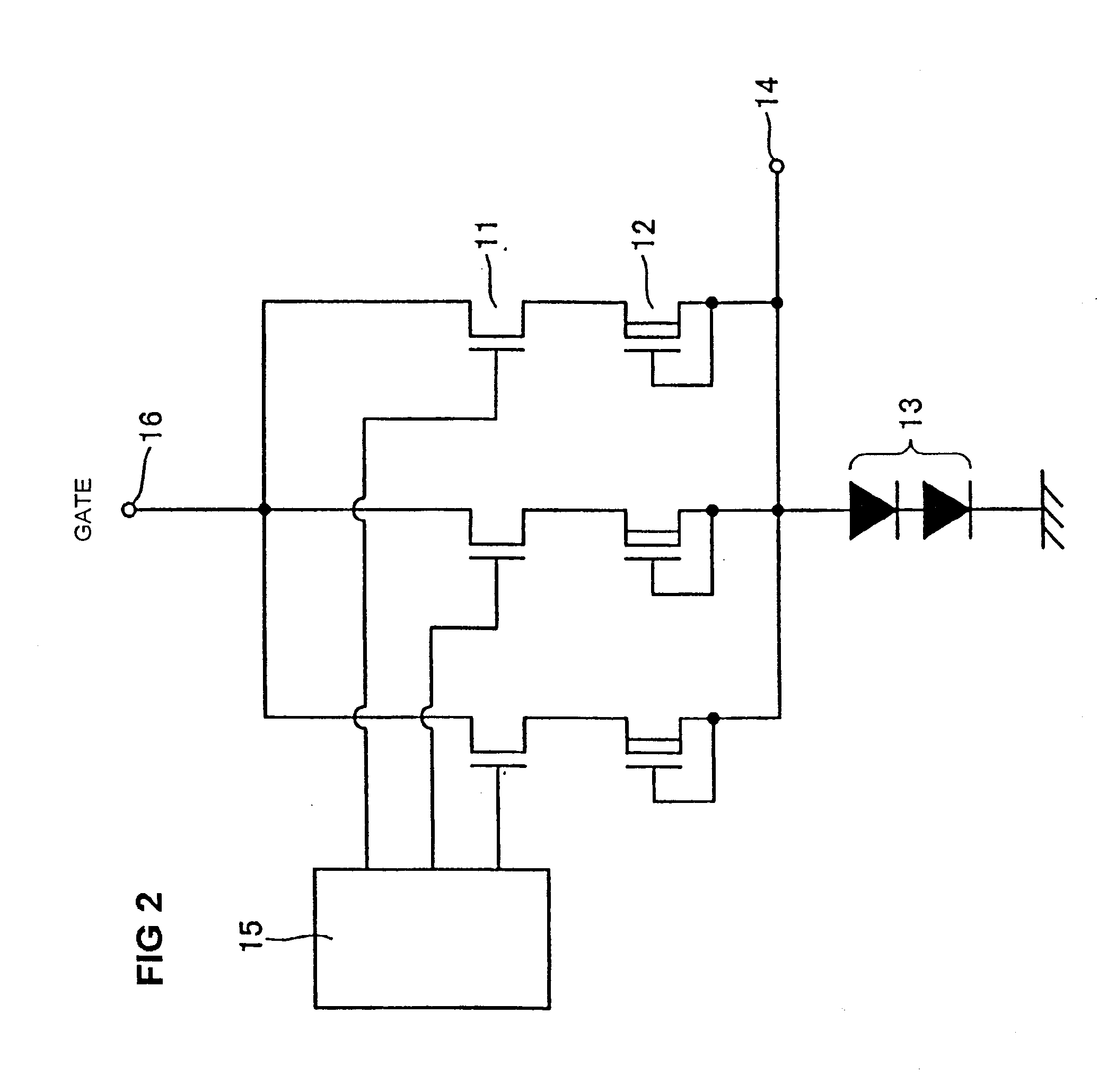
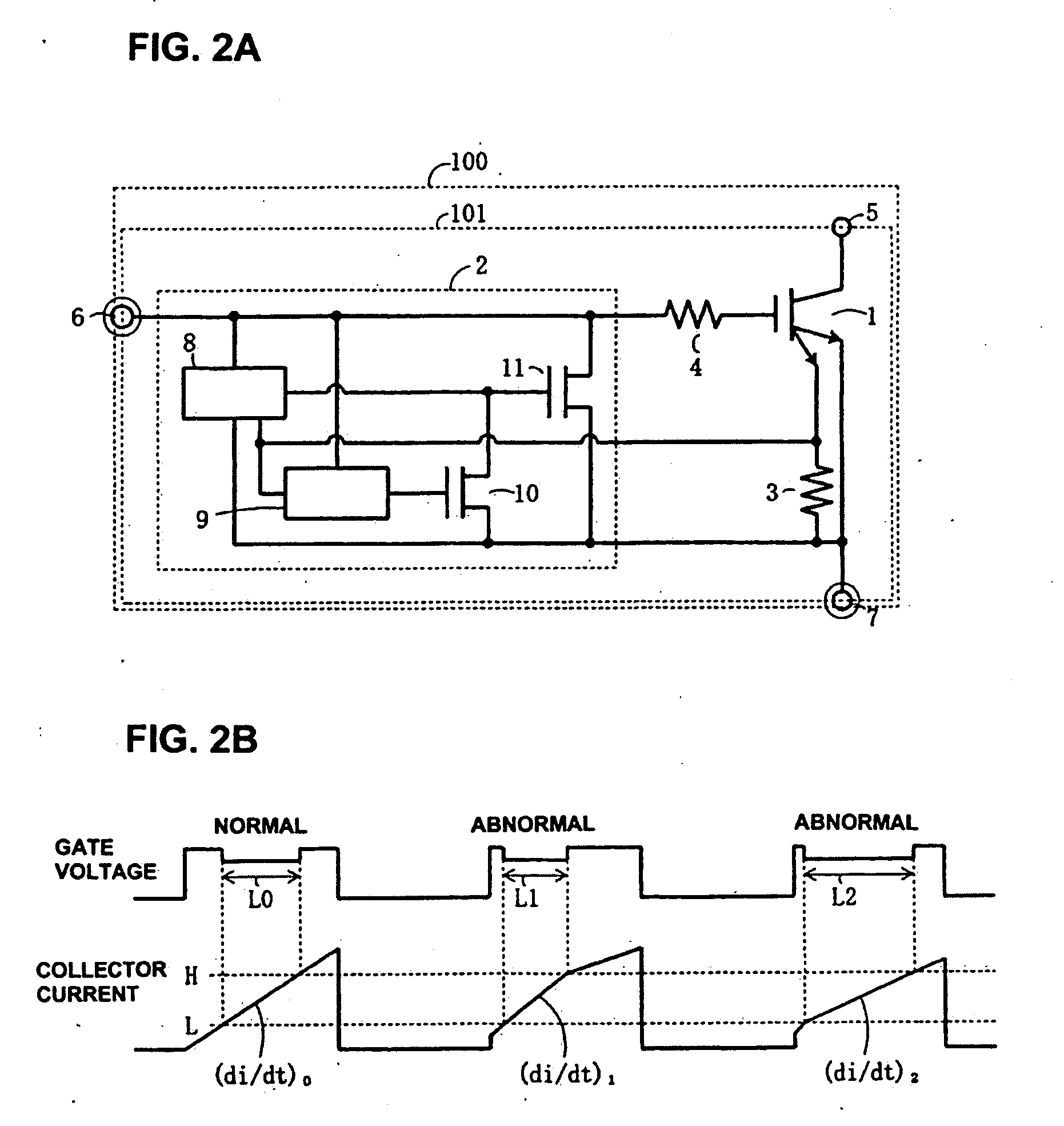
Igniter system
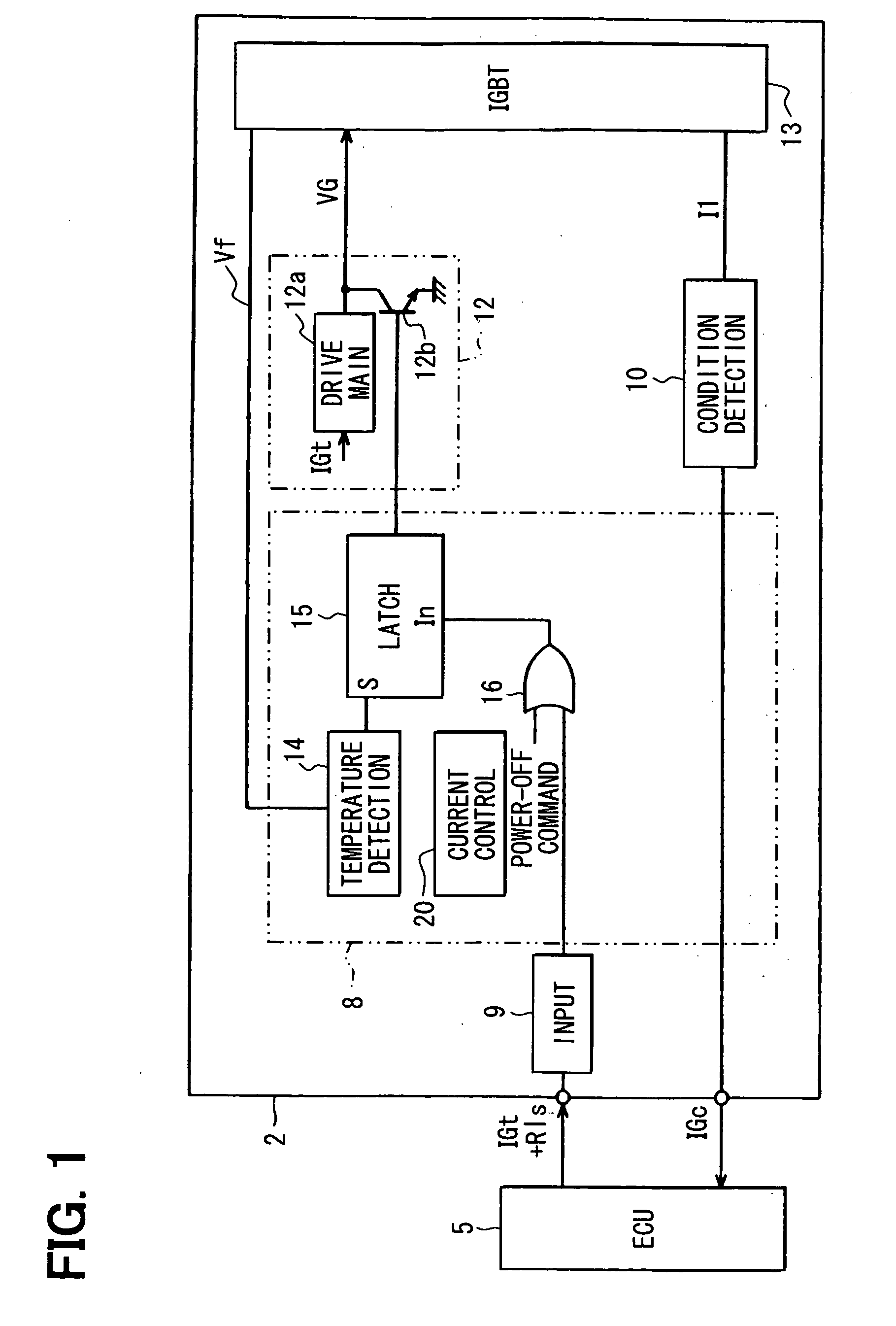
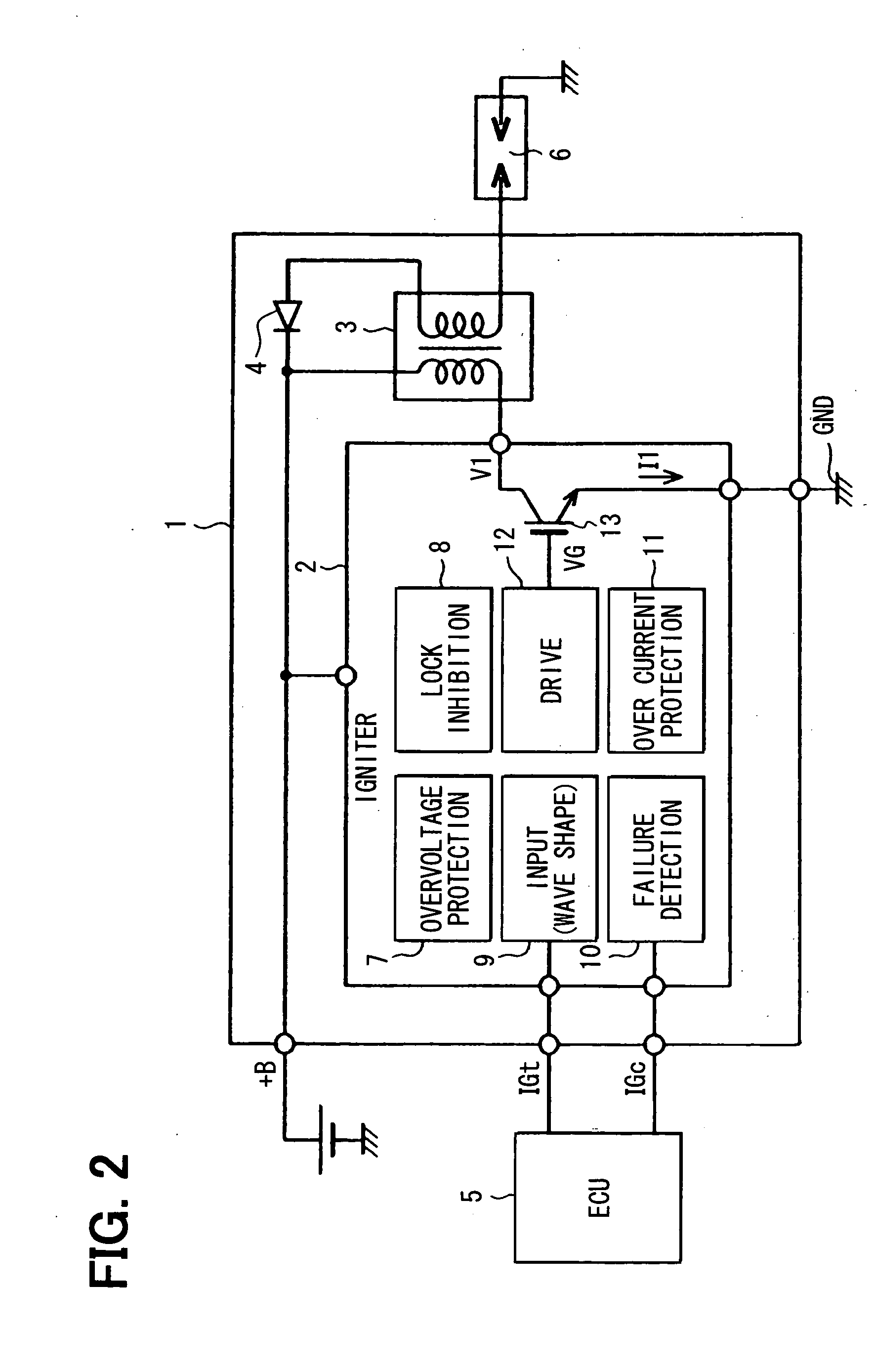
InactiveUS20090139505A1Improve reliabilityPreventing misfires and melting or deteriorationMachines/enginesInstallations with induction energy storageCombustion chamberEngineering
A coil failure detection circuit detects a rise of a collector current of an IGBT and a timer circuit measures the length of a rise period. If the rise is not a normal one, an electronic control unit judges that a coil failure has occurred. The electronic control unit turns off the IGBT to prevent misfires and stops a flow of fuel gas to a combustion chamber to prevent melting or deterioration of a catalyst.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
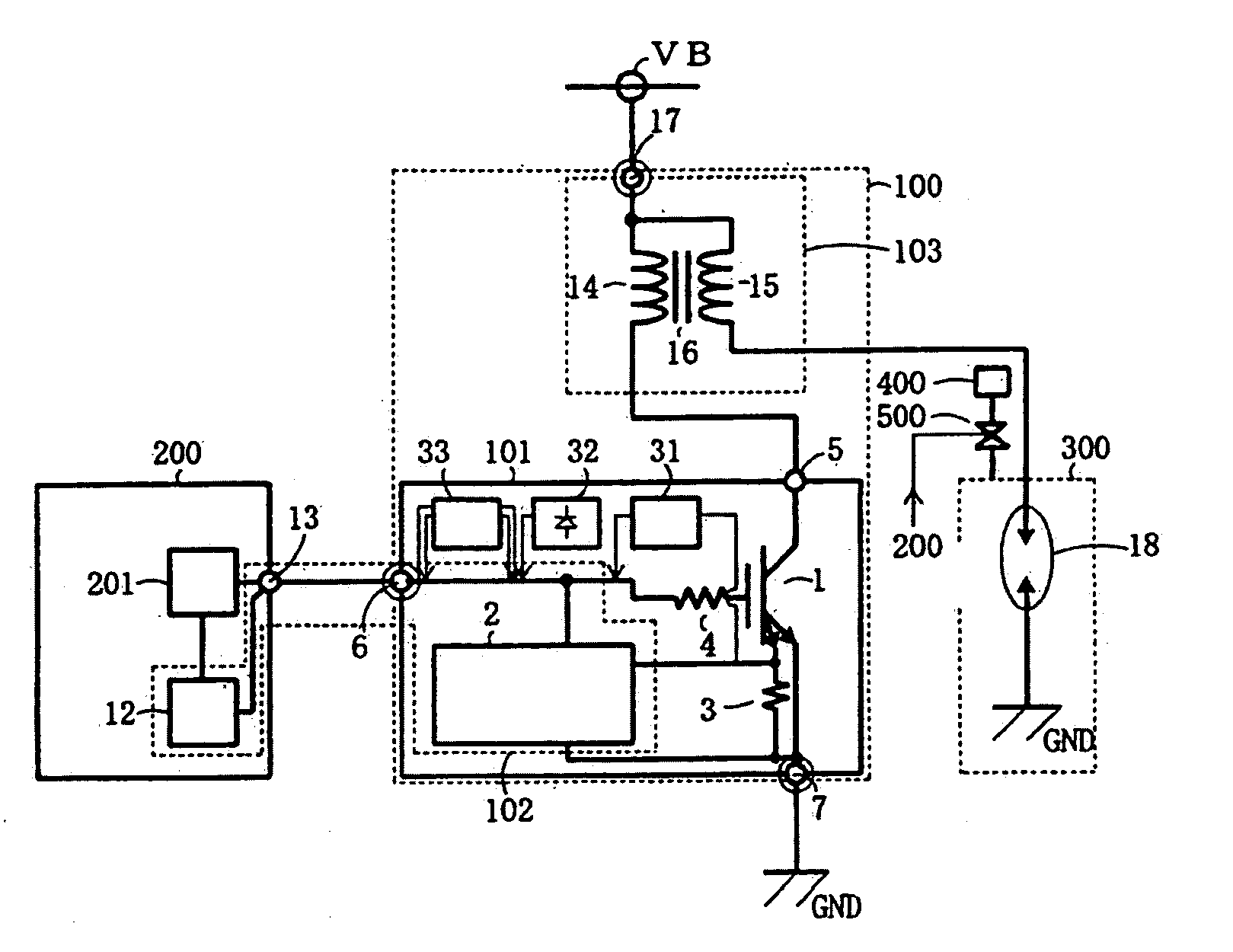
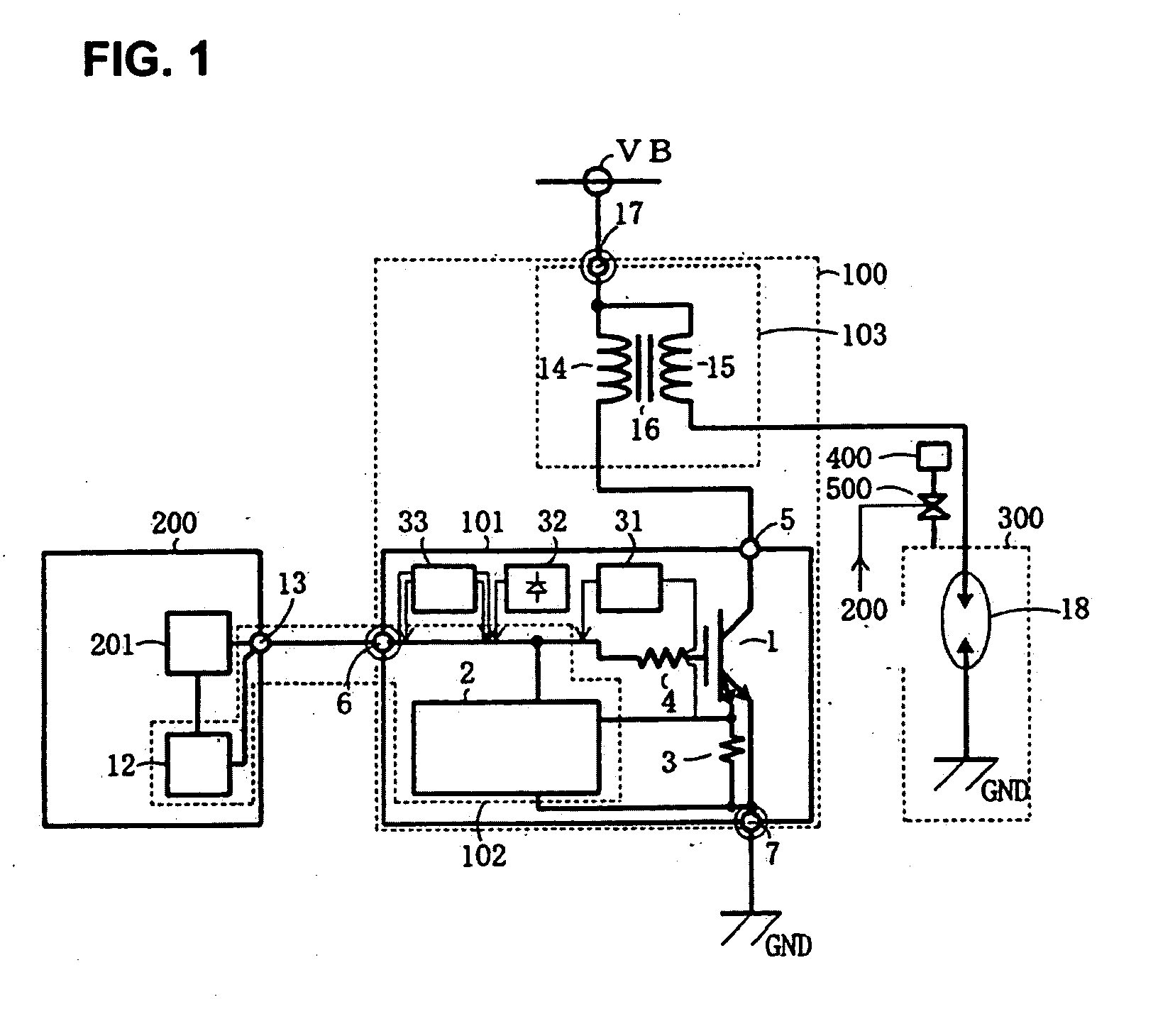
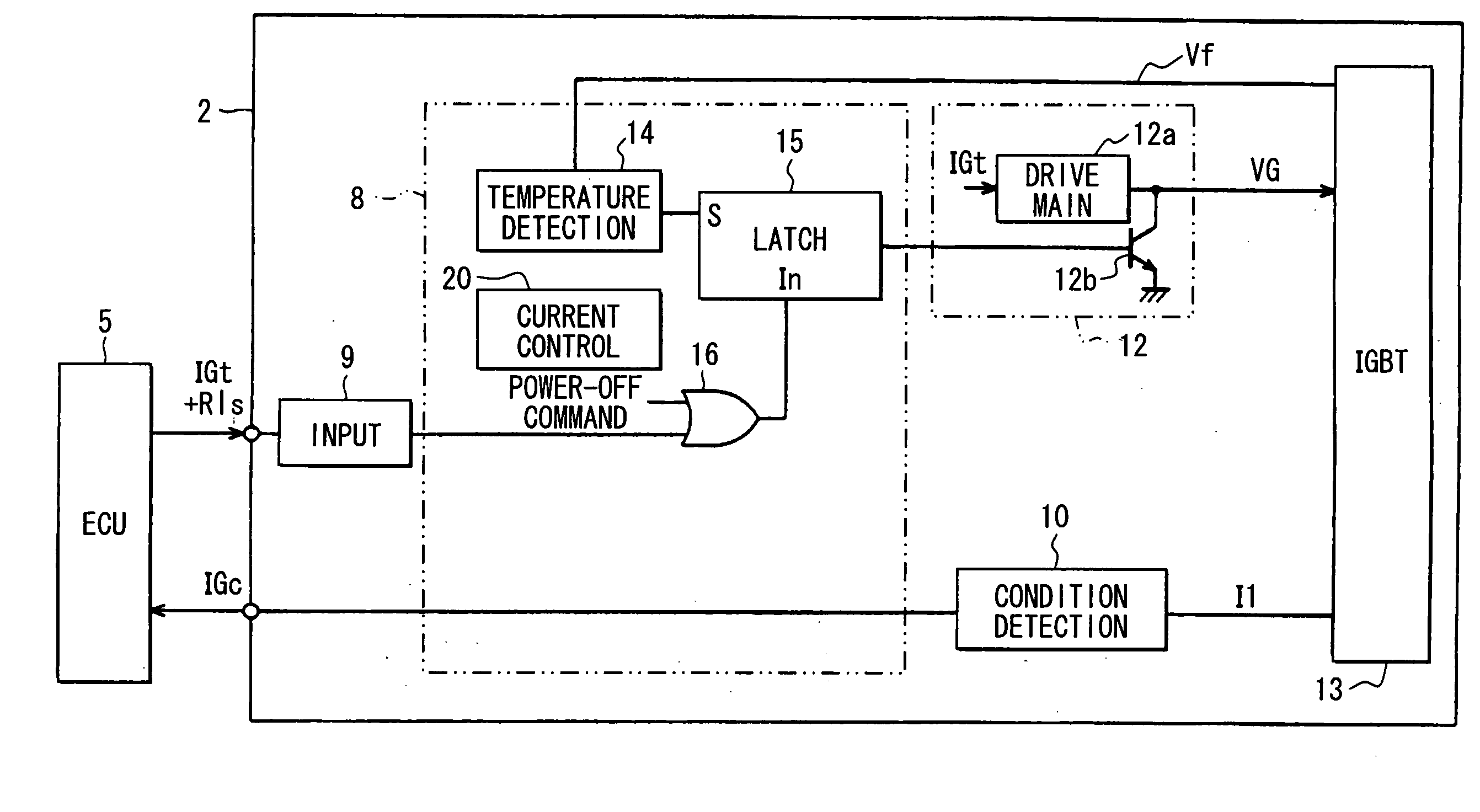
Ignition device for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20100263644A1Facilitated releaseOther installationsMachines/enginesPower flowInternal combustion engine
When an ECU applies to an igniter a plurality of pulse signals, the duty ratio of which is lower than a predetermined duty ratio, as a lock release signal, a latch circuit of a lock inhibition circuit stops applying a shut-off signal to a shut-off circuit thereby to release a lock condition of an IGBT. A drive main circuit thus restarts current supply to the IGBT. A condition detection circuit outputs to the ECU a condition signal corresponding to the current supplied while the IGBT is turned on.
Owner:DENSO CORP
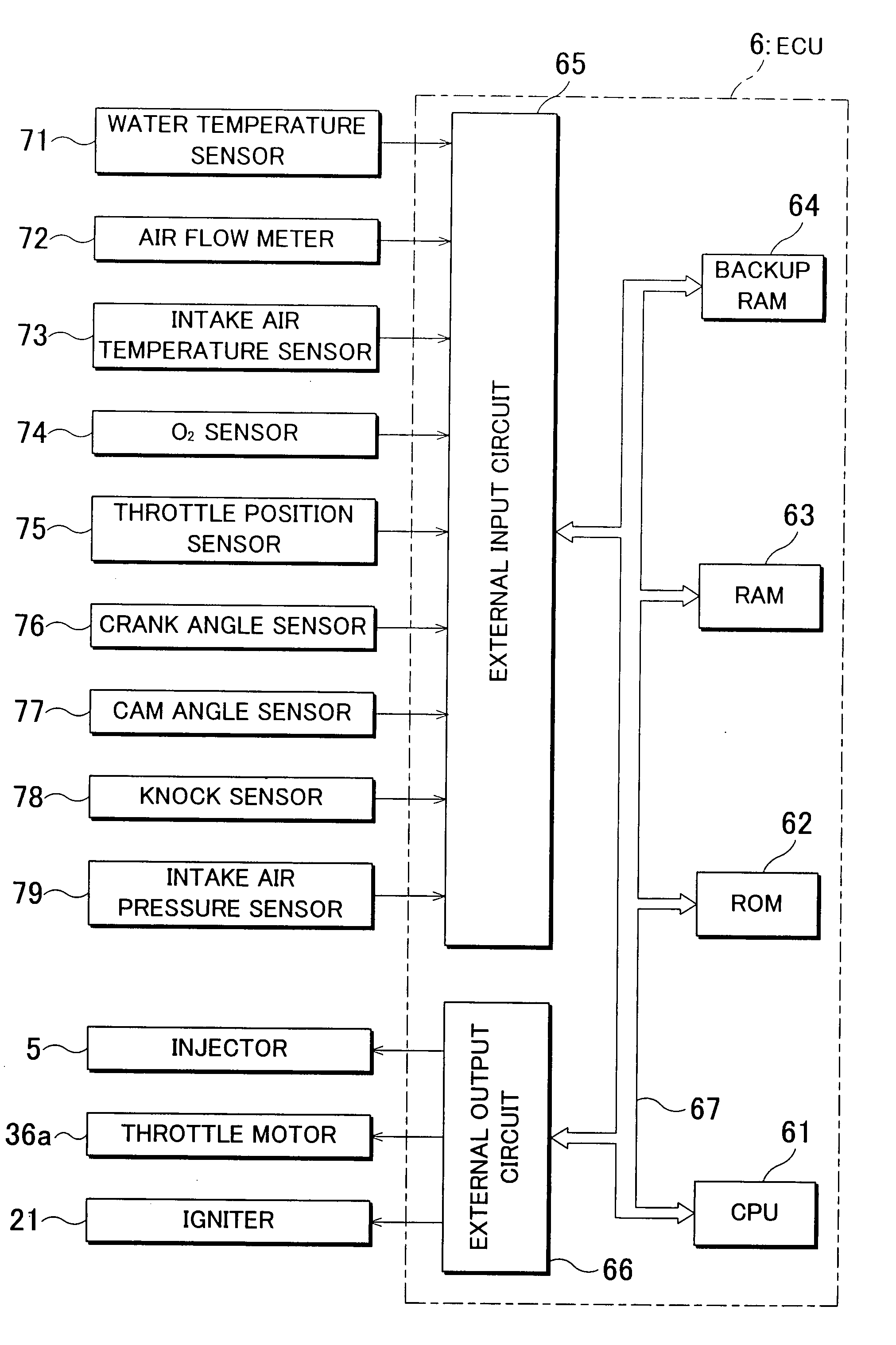
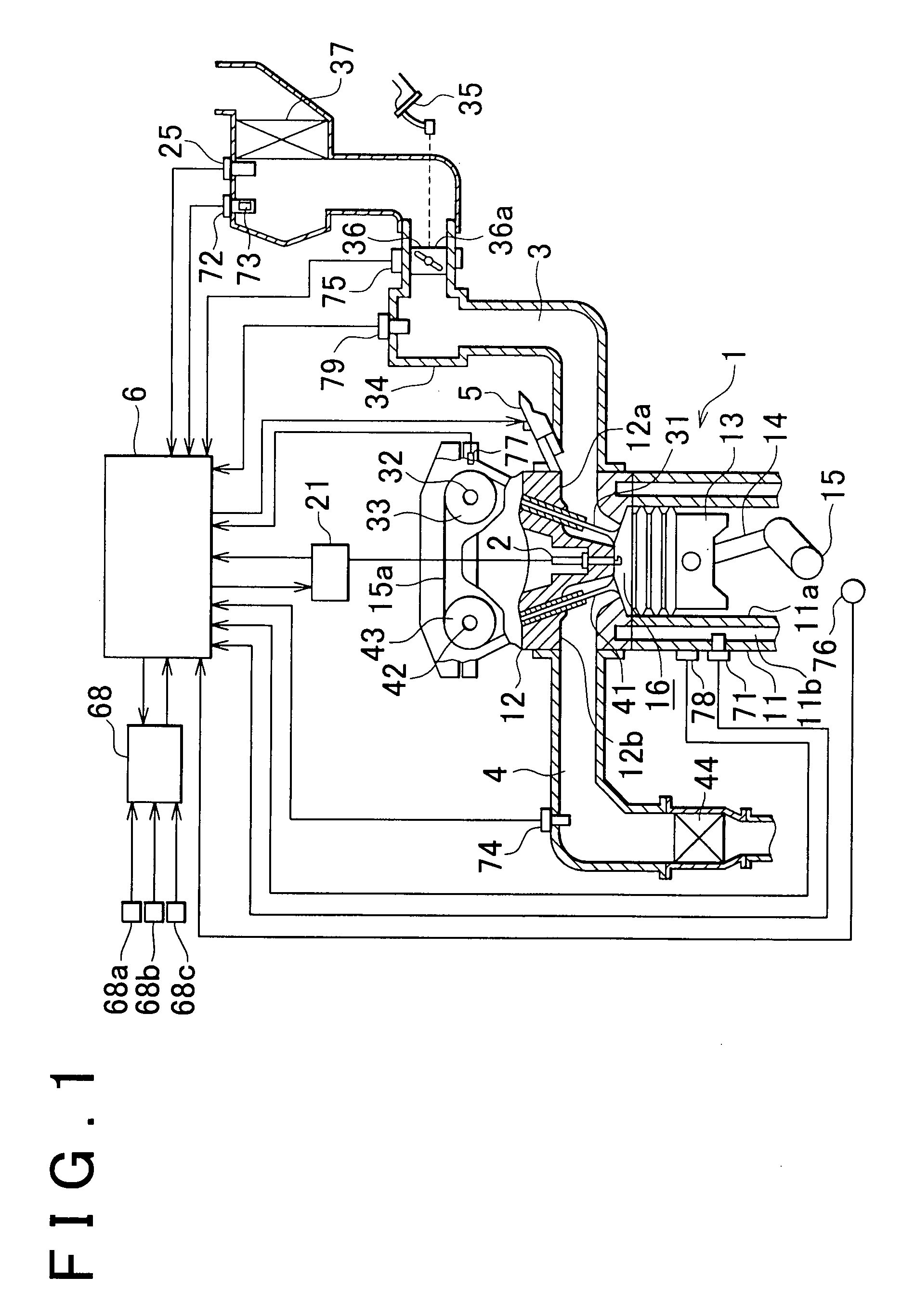
Control apparatus for internal combustion engine
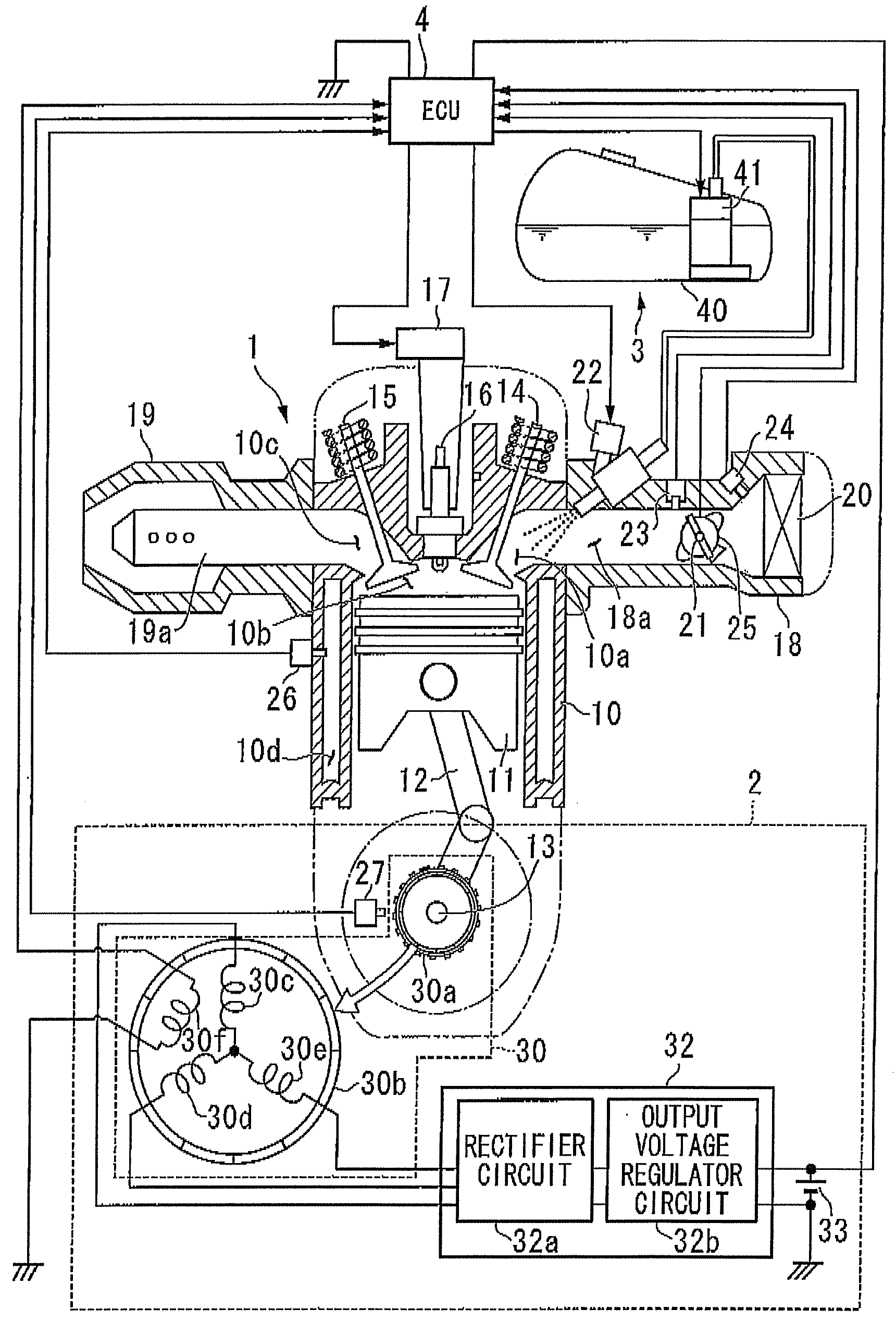
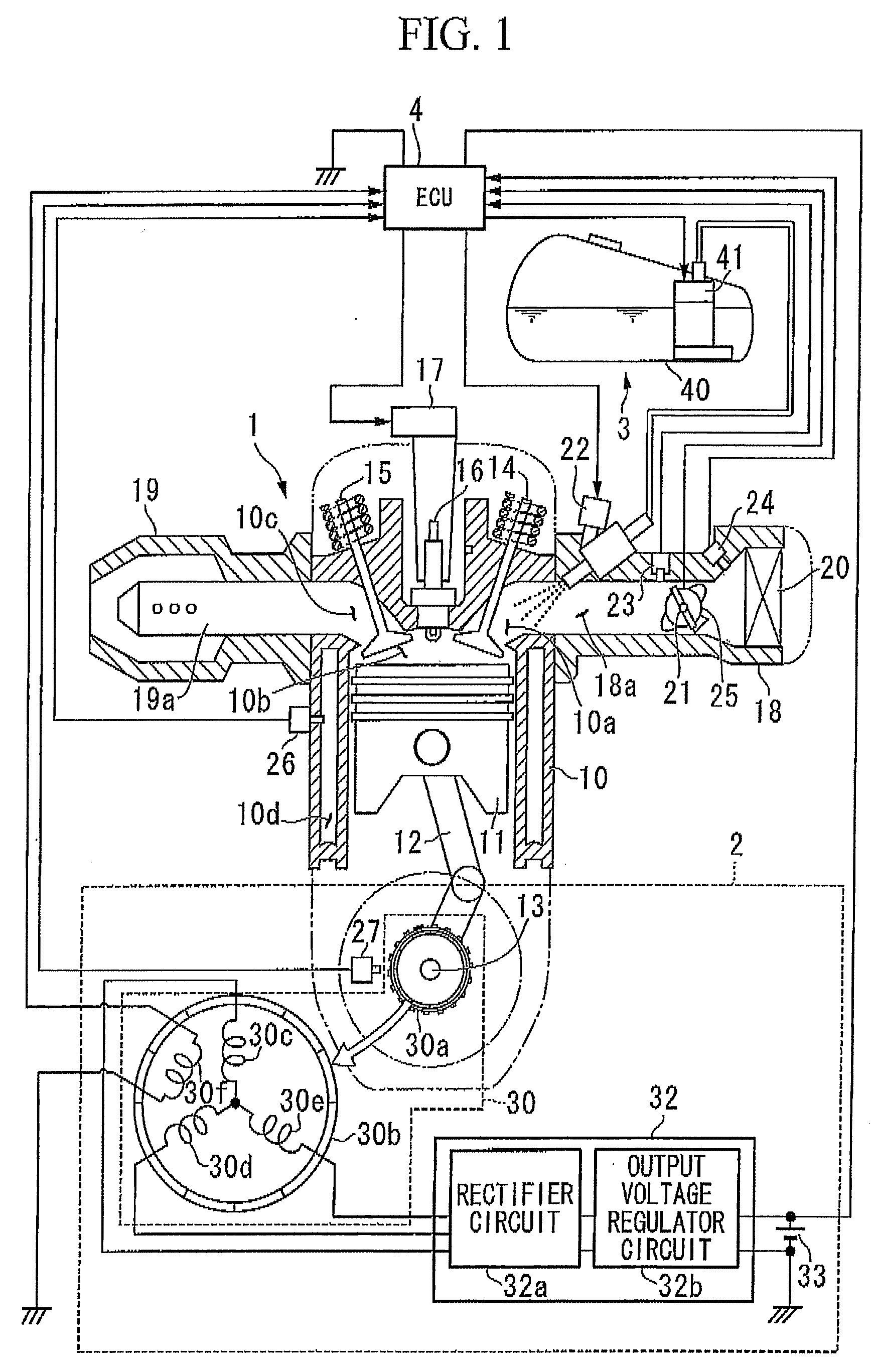
InactiveUS20090063008A1Improve detection accuracyPrevent rebounding of kick pedal more reliablyAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlIgnition coilElectrical polarity
A control apparatus for an internal combustion engine, includes: a crankshaft; a crank angle detection unit; a generator; and a control unit to which alternating voltage signals are input, that ascertains ignition timings based on crank signals, performs ignition control so as to spark the internal combustion engine at the ignition timings, performs polarity determination processing in which the control unit determines a polarity of the alternating voltage signal each predetermined cycle and determines a current polarity determination result, and performs reverse rotation detection processing in which the control unit obtains the current polarity determination result each time the crank signal is detected so that the control unit ascertains a polarity cycle of the alternating voltage signals and in which the control unit determines that the crankshaft is in reverse rotation and stops the ignition control.
Owner:KEIHIN CORP
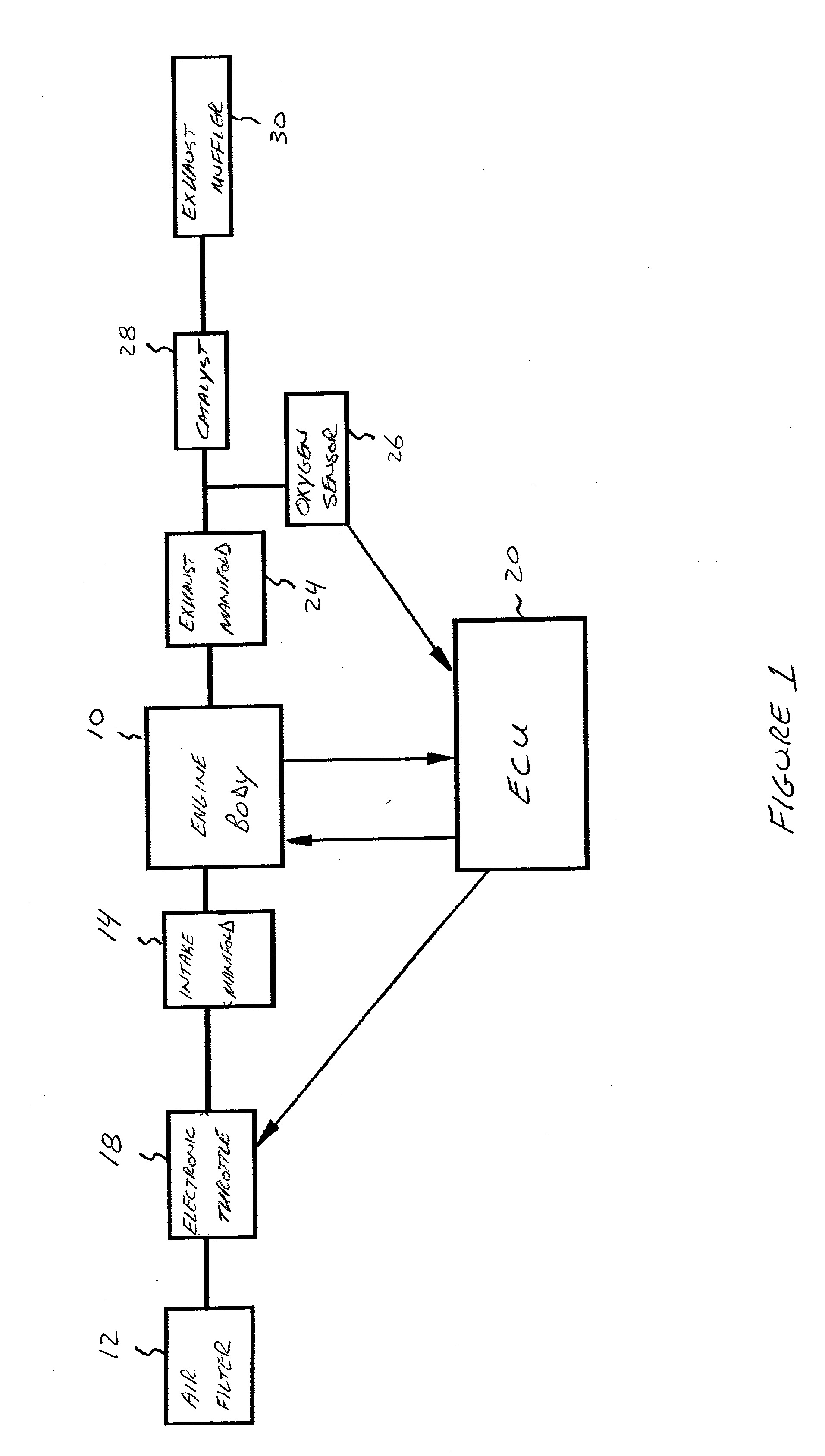
Engine control device
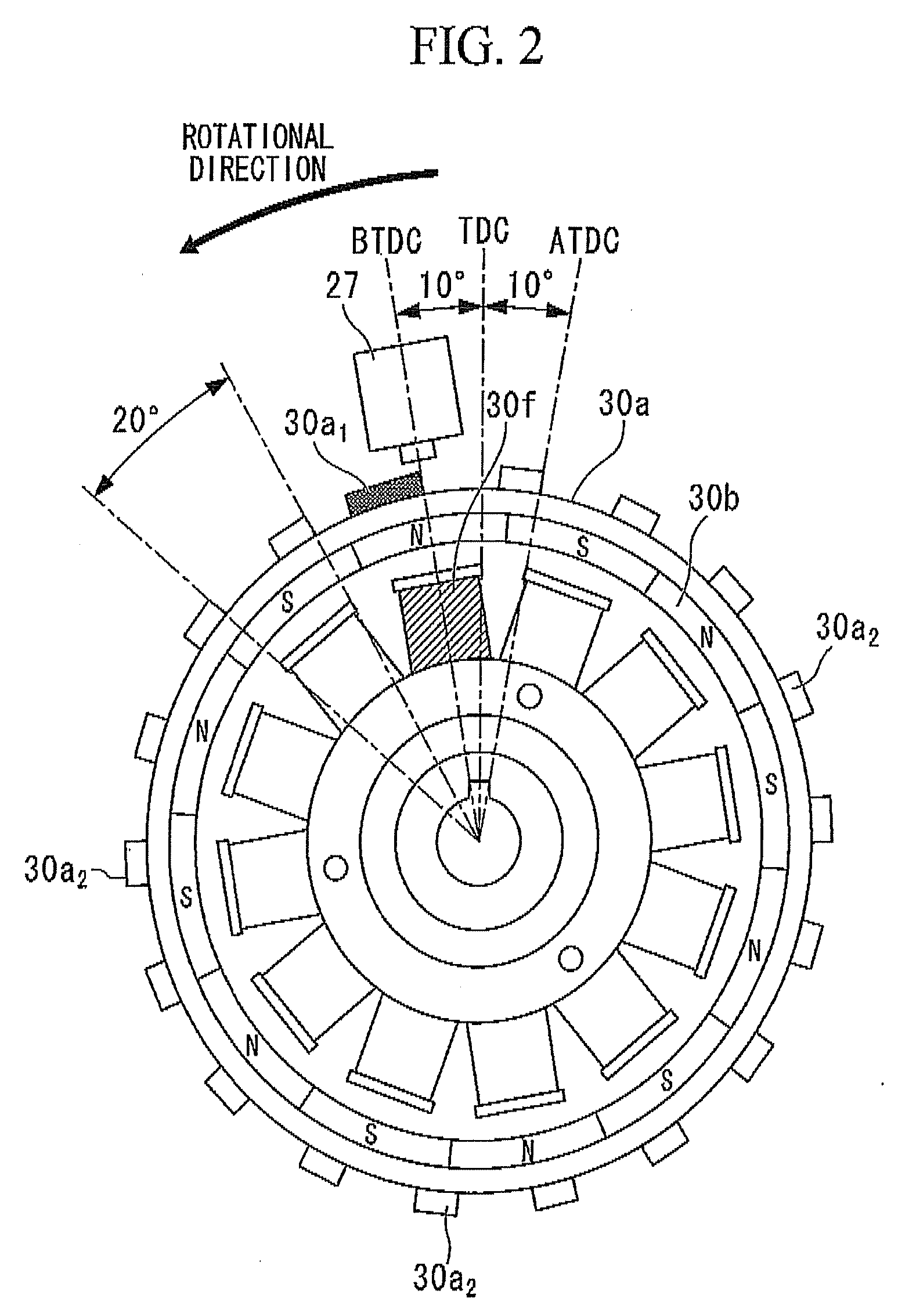
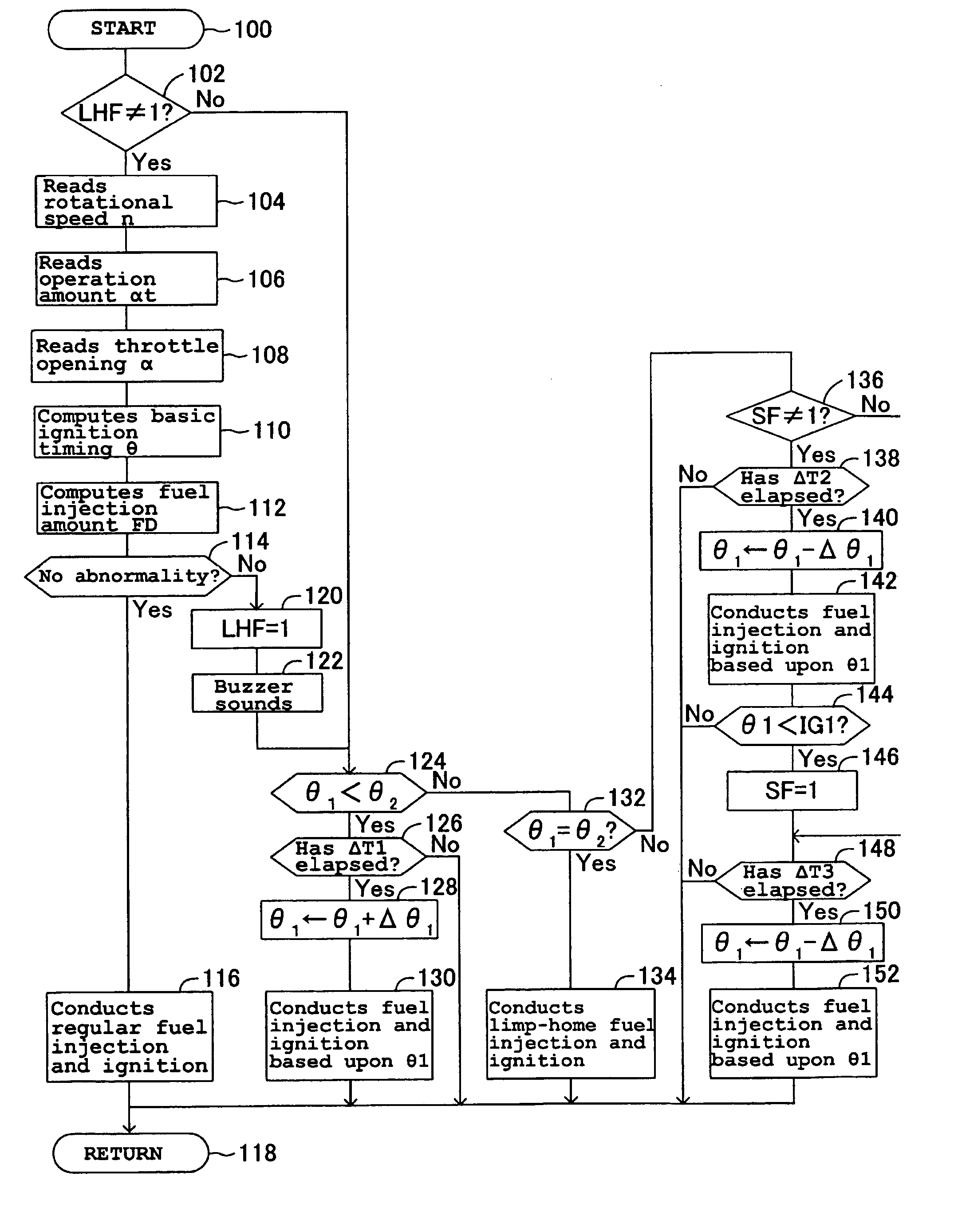
An engine control device can include a throttle valve for adjusting an amount of air supplied to an engine, operation amount detecting sensors for detecting an operation amount of a throttle lever, a motor for driving the throttle valve between open and closed positions according to detection values of the operation amount detecting sensor 21a or the like, and throttle opening detecting sensors for detecting an opening of the throttle valve is provided with a limp-home mechanism for keeping the throttle valve in a mechanically neutral position when an abnormality occurs. When the throttle valve is in the mechanically neutral position, an ignition timing control can be switched in a stepwise manner over a predetermined time period from a regular ignition timing control to a limp-home ignition timing control.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
Engine start control system
ActiveCN1667253AAvoid power consumptionFavorable designValve arrangementsPower operated startersControl systemCrankshaft
The purpose of this invention is to detect reverse rotation of an engine based on output signals of a rotor sensor, and prohibit fuel injection or engine ignition when the engine is rotated reversely. In this engine start control device, a crankshaft is reversely rotated up to a prescribed position after engine stop to be ready for next engine start. It is provided with an injector to inject fuel as the crankshaft reaches a prescribed angle, an ignition device to ignite the engine at a prescribed timing after fuel injection, an ACG starter to function as a starter motor and a generator, the rotor sensor to output phase signals for multiple phases by detecting the rotor position of the ACG starter, a means to determine the rotation direction of the engine based on the output signal of the rotor sensor, and a means to prohibit fuel injection when the engine is reversely rotated.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method for detecting reverse rotation for internal combustion engines
In a method for detecting reverse rotation when starting an internal combustion engine having a sensor disk which is coupled to a crankshaft of the engine, the sensor disk having a marking via an alternating arrangement of teeth and tooth spaces, and a first sensor and a second sensor each capable of generating an electric signal which may assume at least two signal levels, being associated with the sensor disk, one of the signal levels being associated with a tooth and the other signal level with a tooth space, a rising or falling signal edge of the one signal and the signal level of the other signal being used for determining the direction of rotation and increment of the angle of rotation of the crankshaft, the start characteristics are improved by determining the direction of rotation during the start of the engine as early as at the first signal edge.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Reverse rotation preventive device for engine of motorcycle
ActiveUS20100319666A1Guaranteed uptimeMuscle operated startersEngine controllersCounter rotationCrankshaft
A reverse rotation preventive device wherein an engine can be restarted without once stopping the vehicle even in the case where a reverse rotation preventive function is operated in response to momentary locking of a rear wheel. A plurality of reluctors are arranged at regular intervals, exclusive of a toothless part at one location with a crank pulse rotor rotated synchronously with a crankshaft of the engine, and a first and second pulse generators each of which outputs a pulse signal corresponding to the interval of the reluctors. Reverse rotation preventive means inhibits ignition of a spark plug by operating the reverse rotation preventive function when the interpulse time of the pulse signal exceeds a predetermined time and cancels the inhibition of the ignition when it is detected that a crankshaft is in normal rotation after the ignition is inhibited by the operation of the reverse rotation preventive function.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com