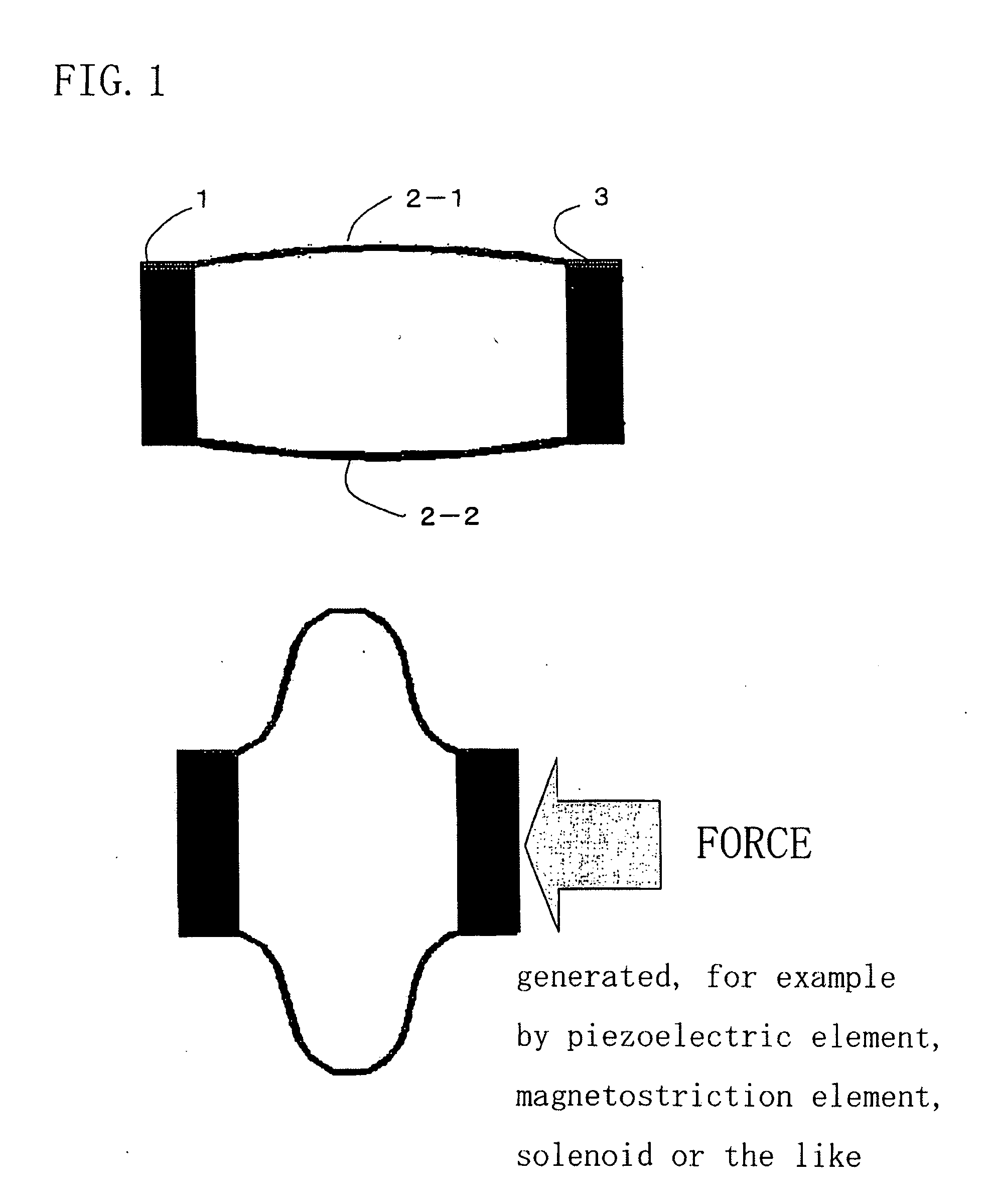
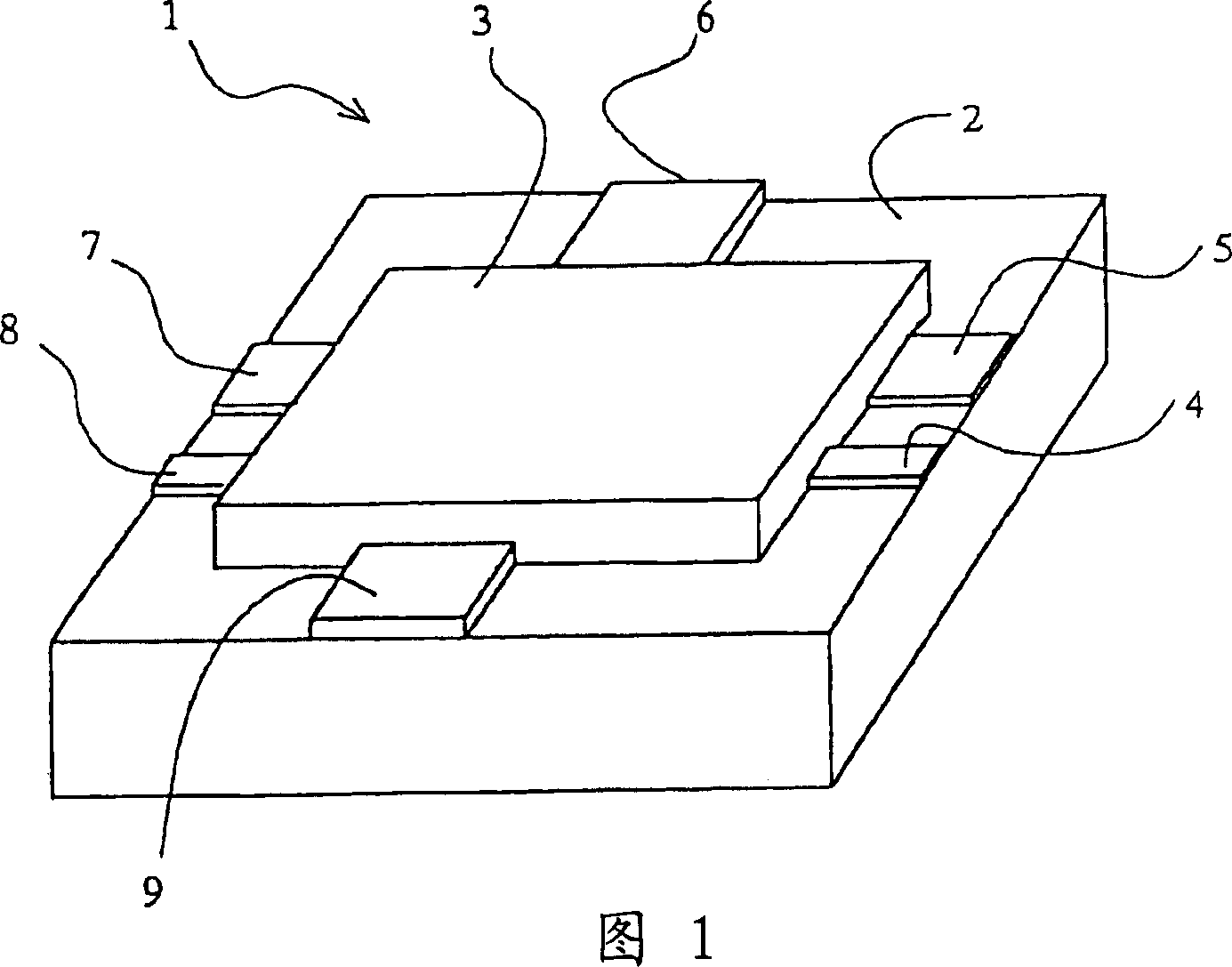
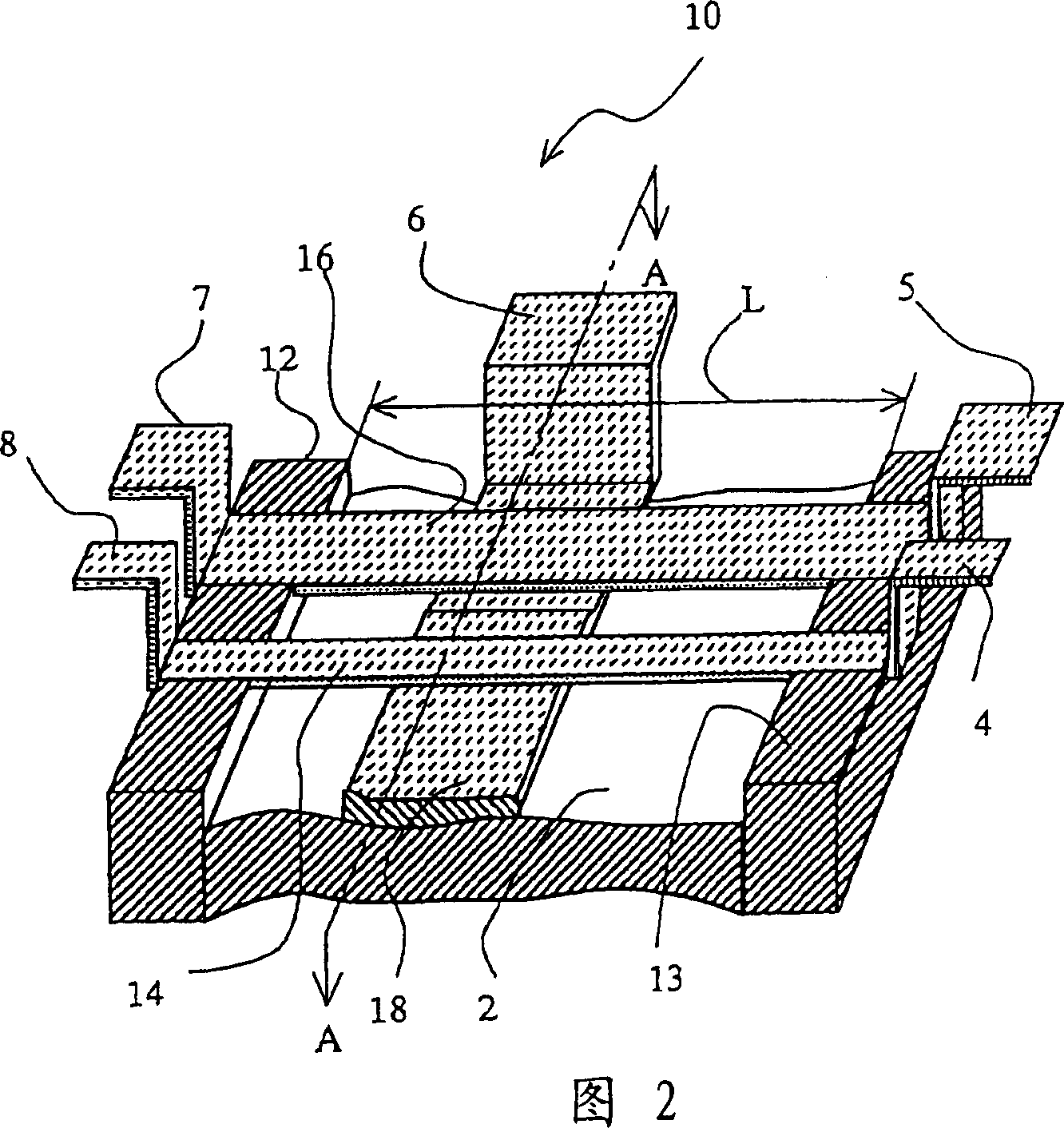
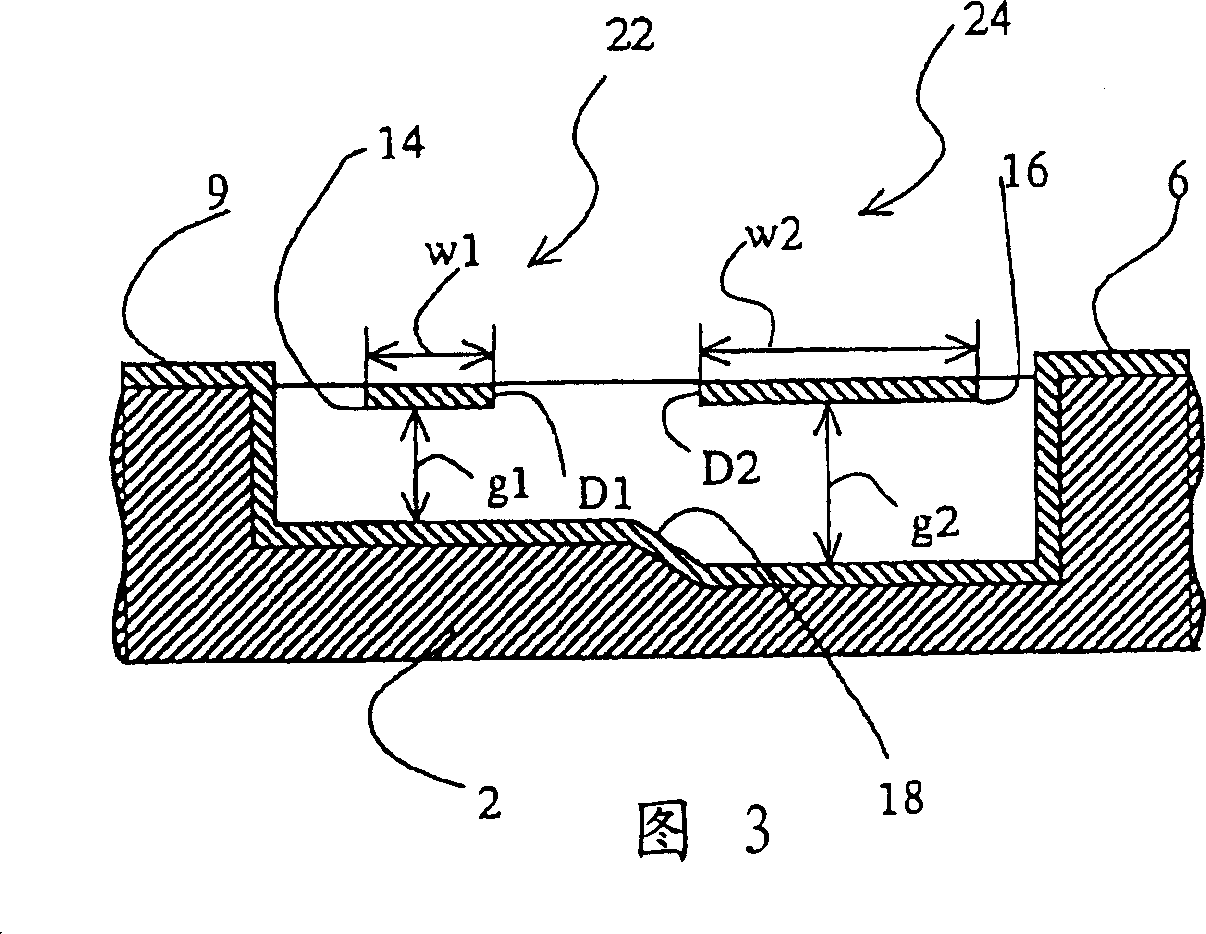
Patents
Literature
58results about "Magnetostrictive relays" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
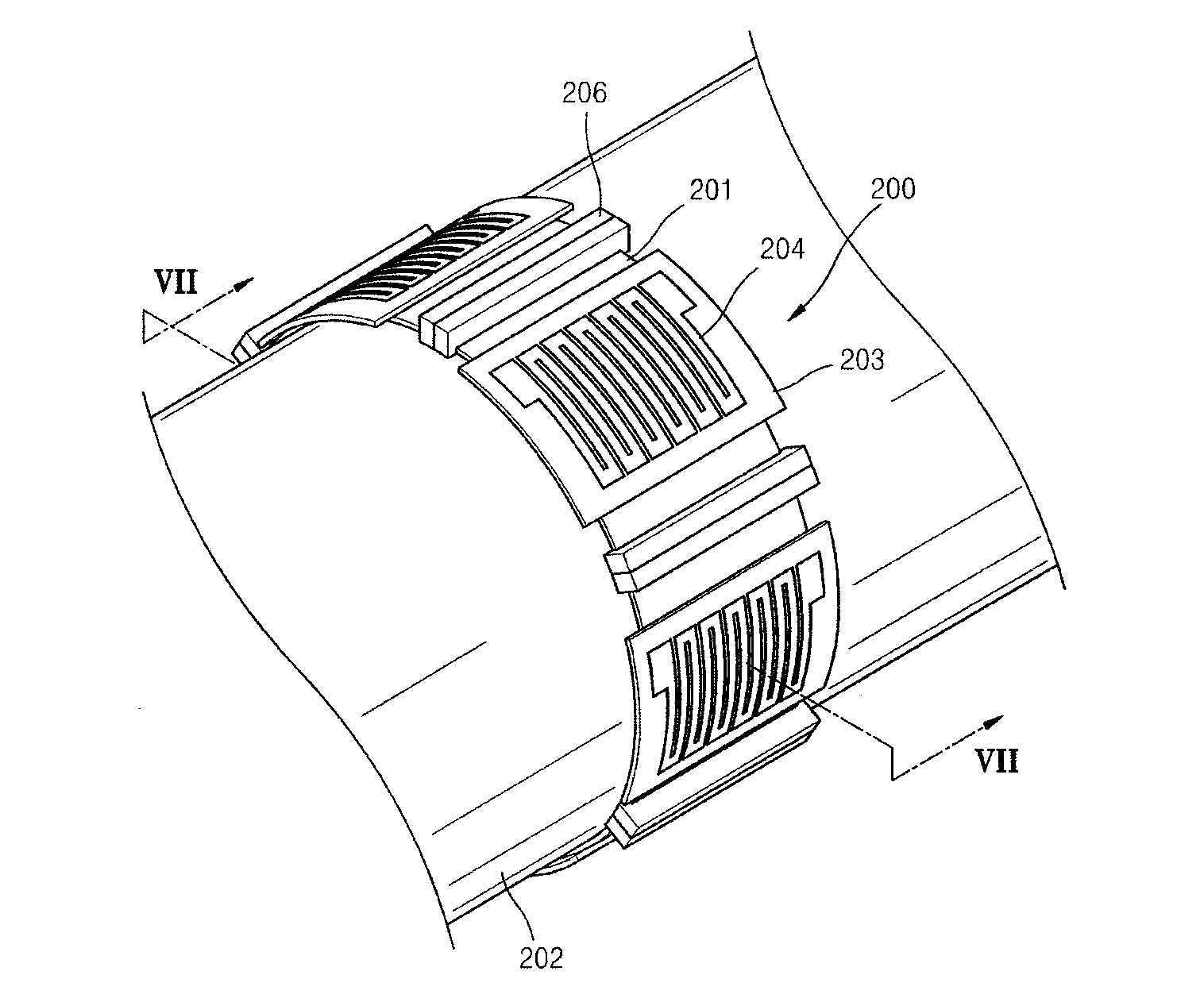
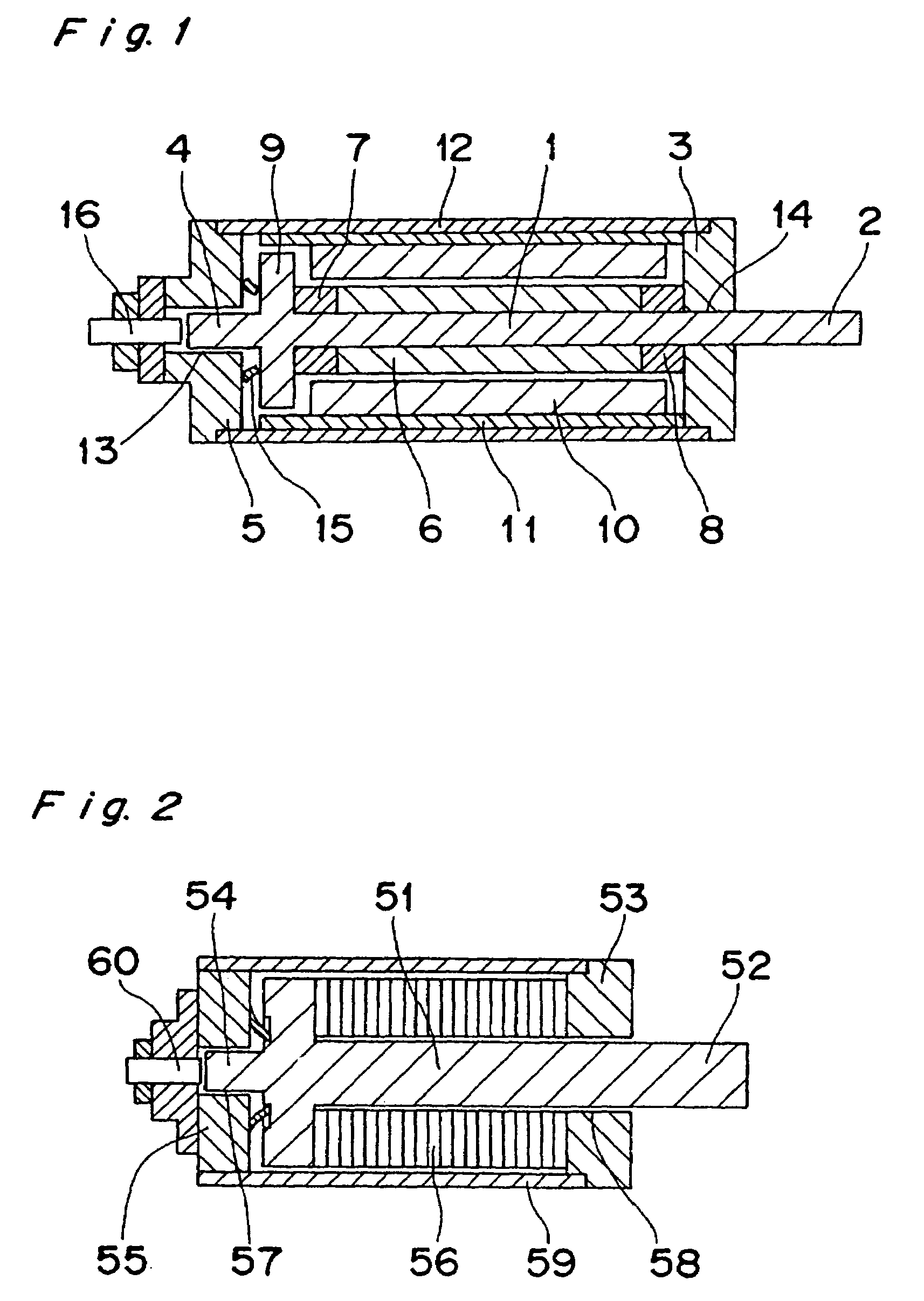
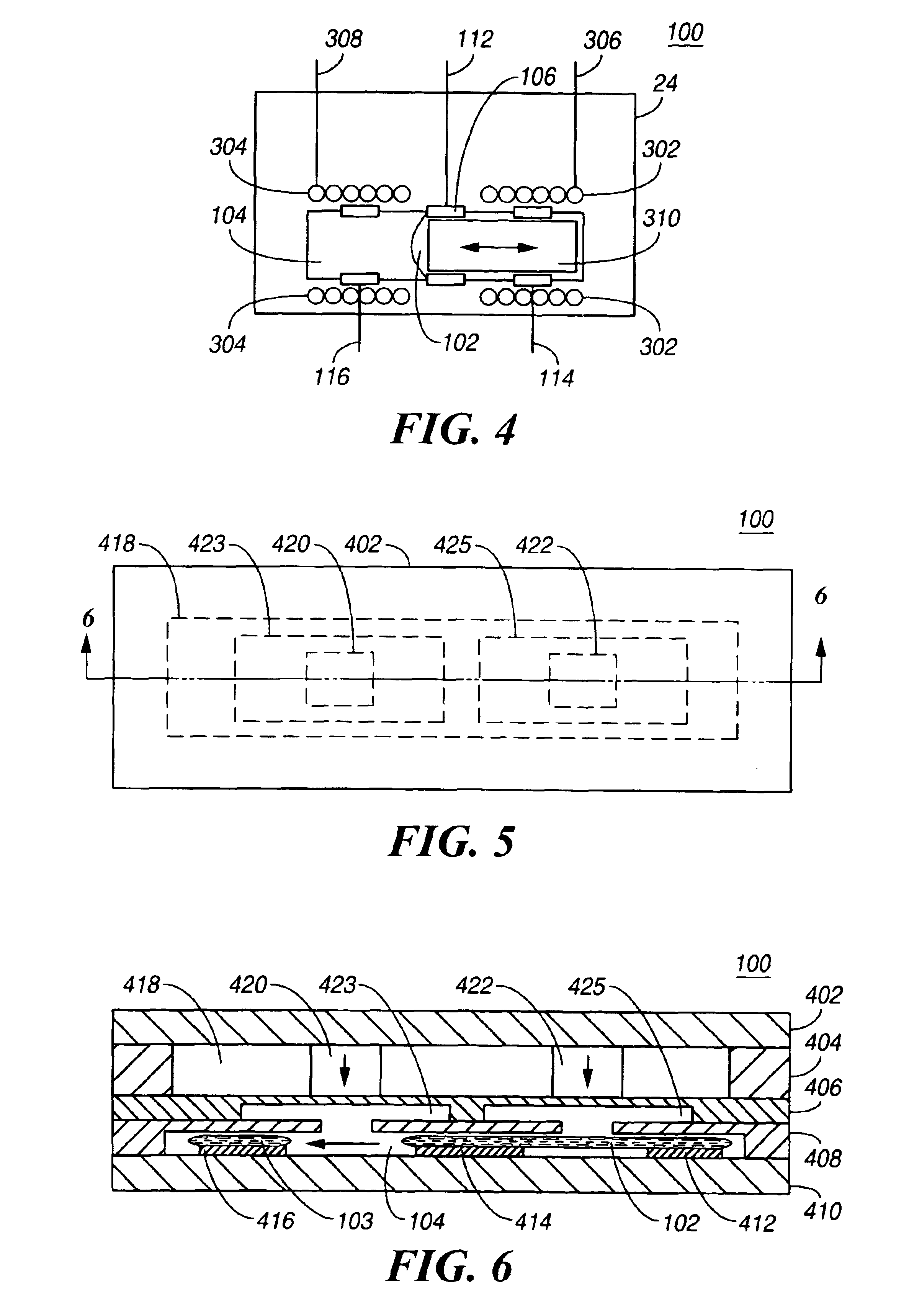
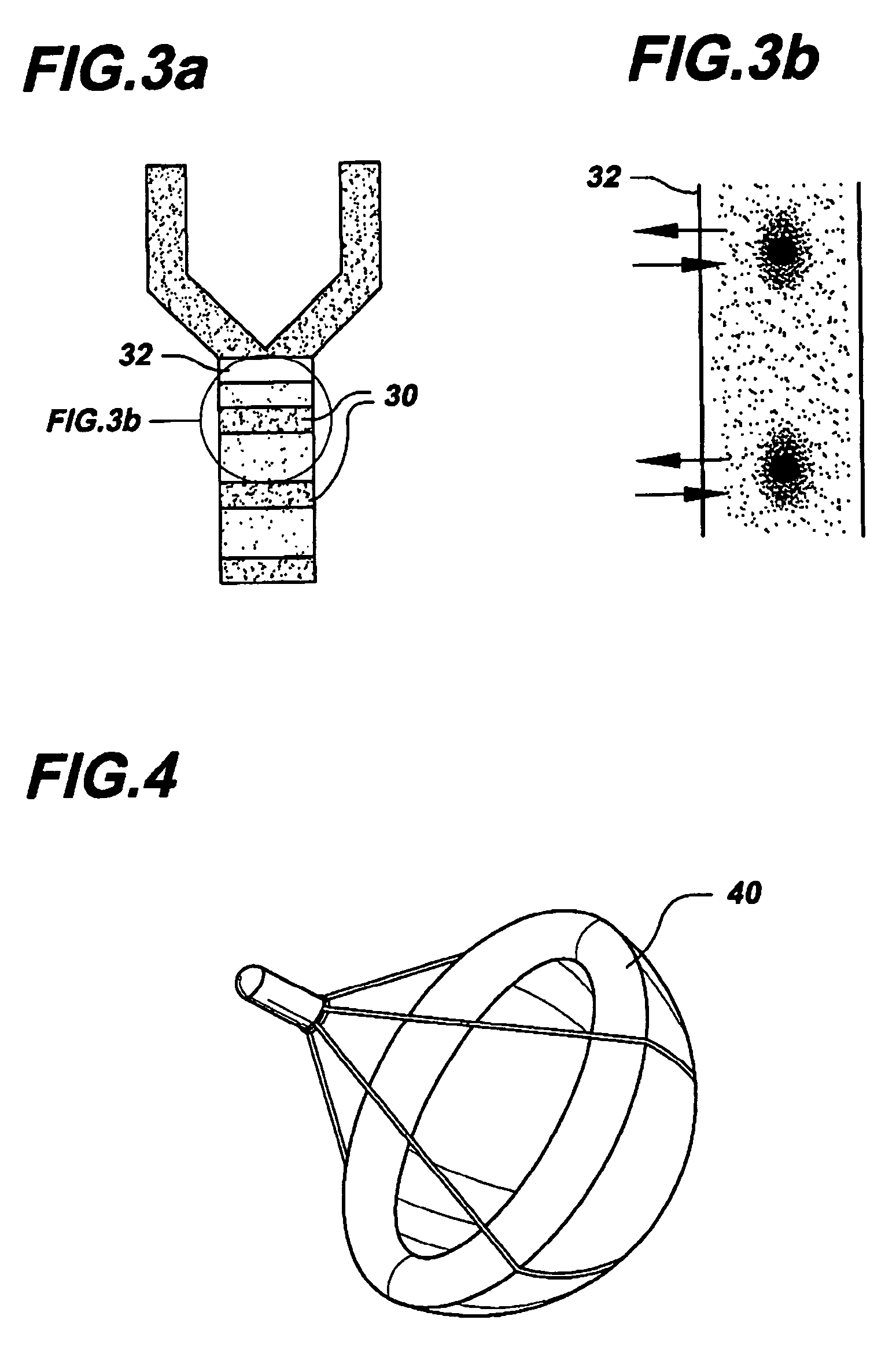
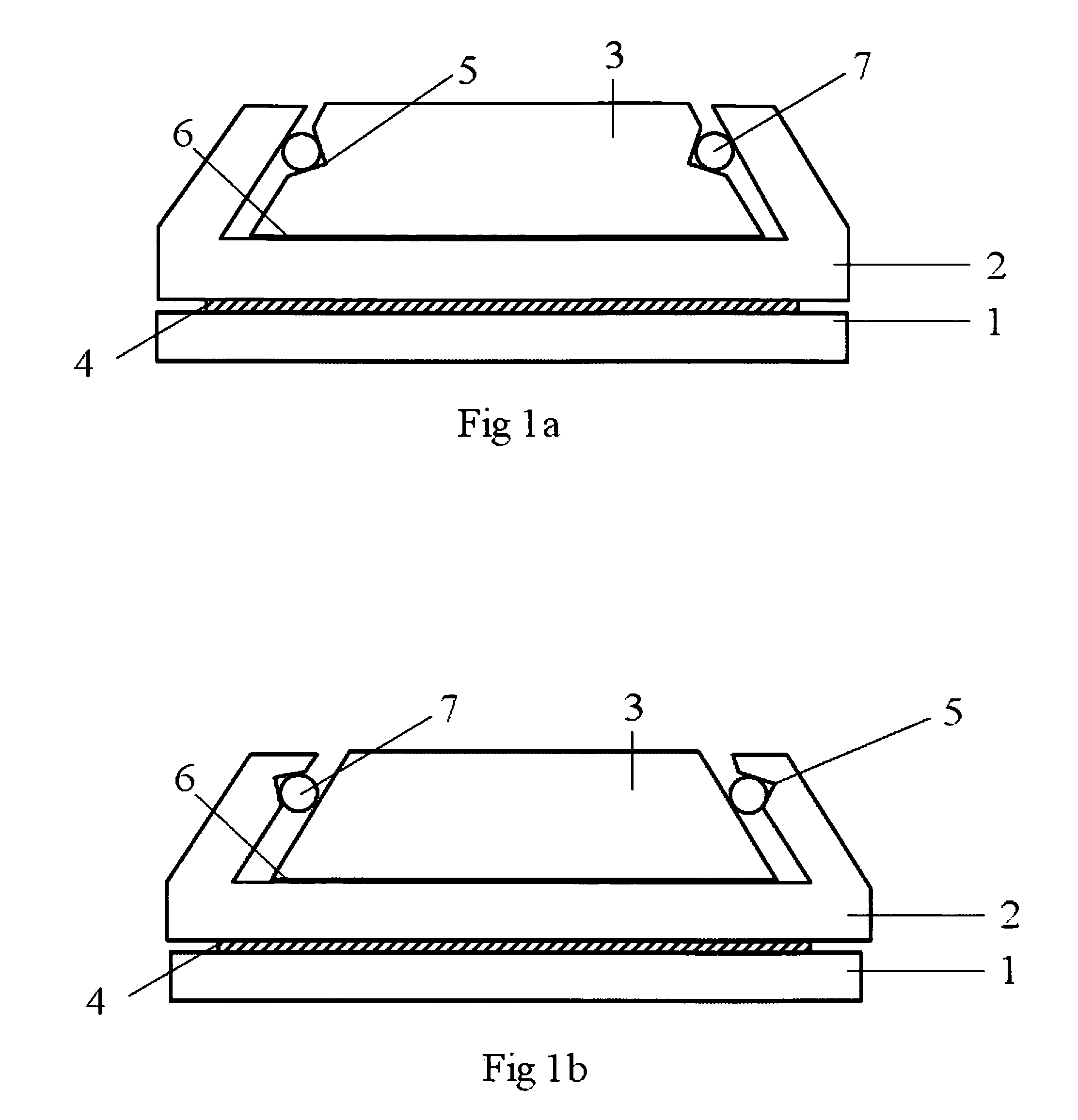
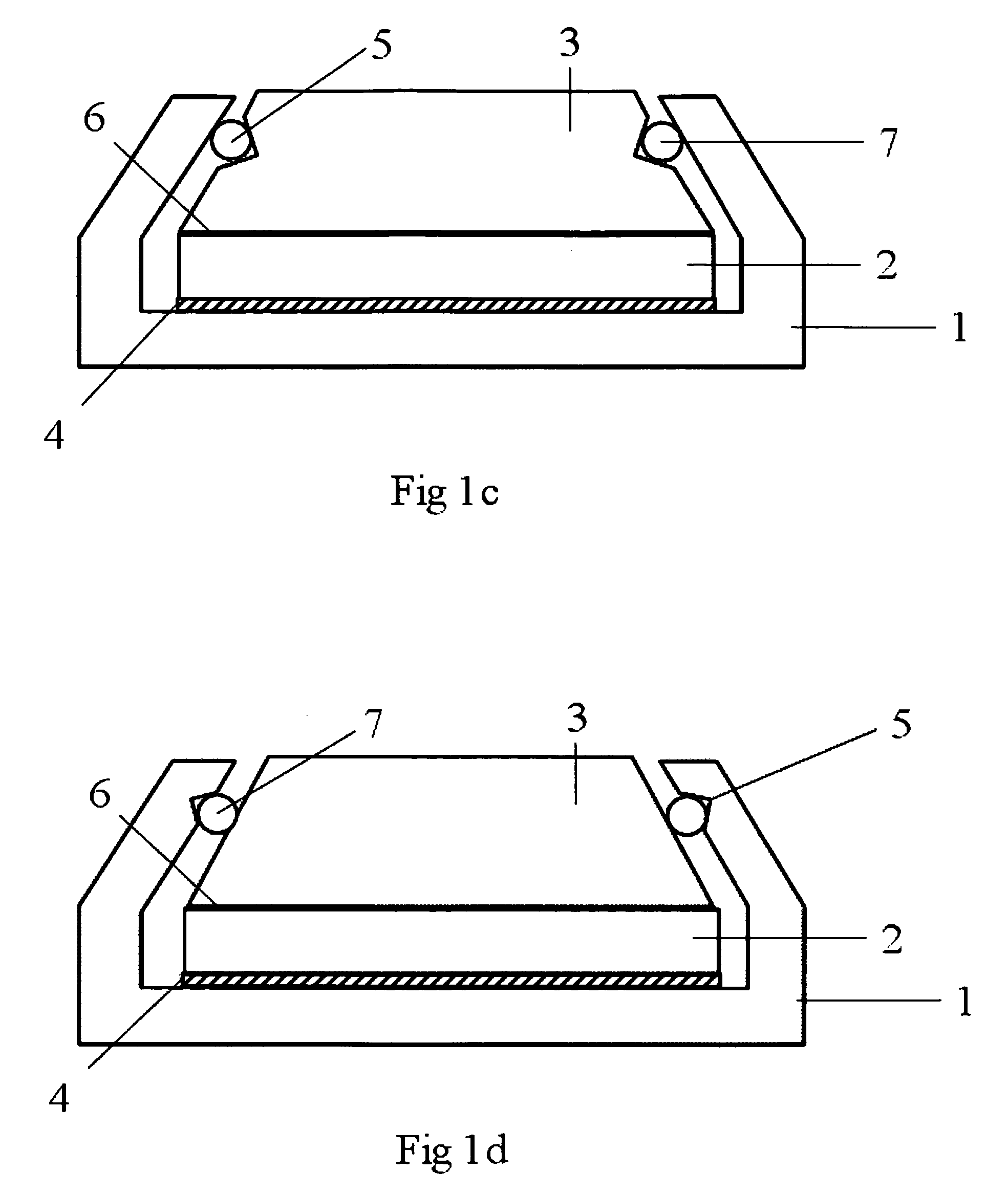
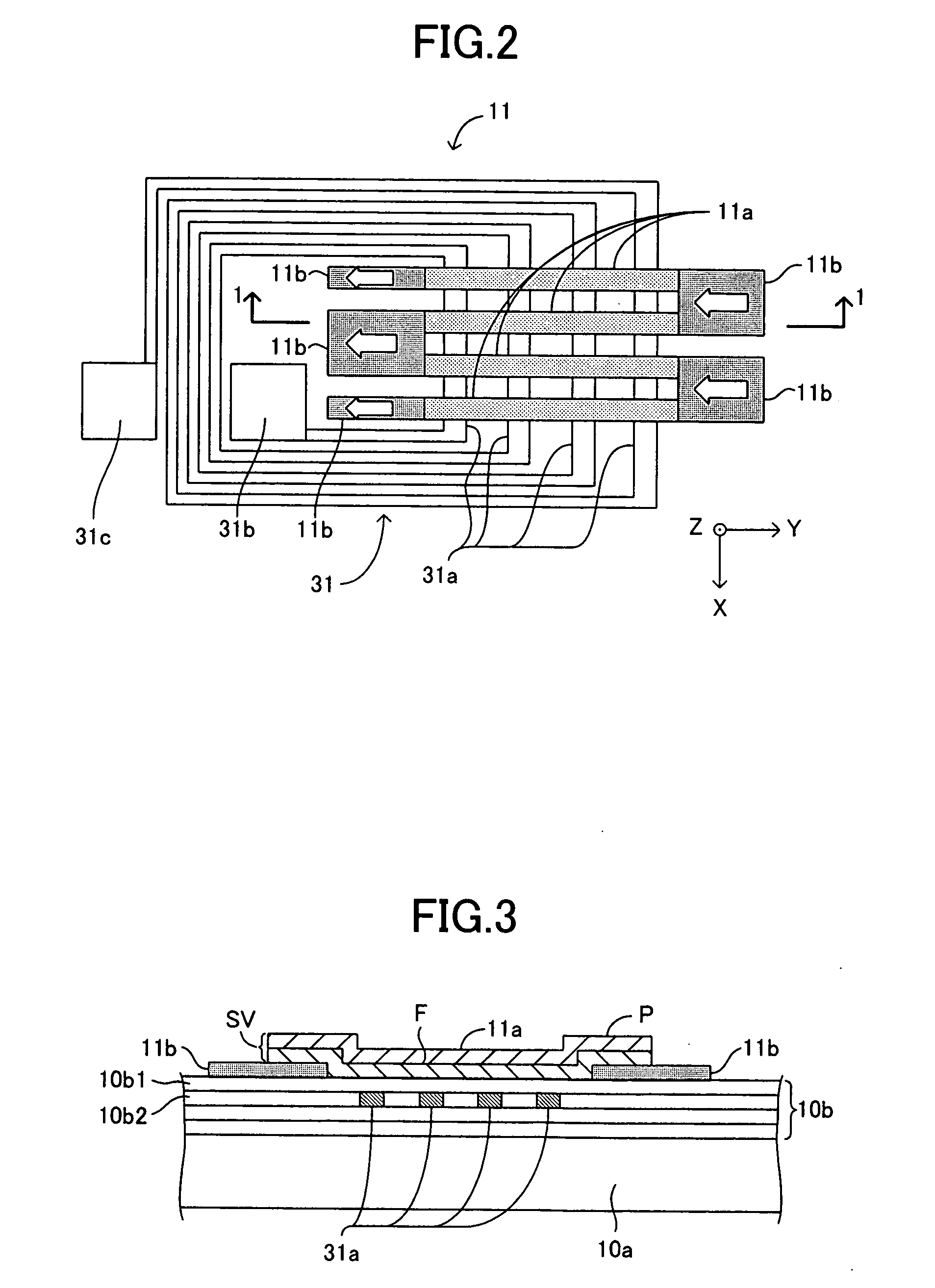
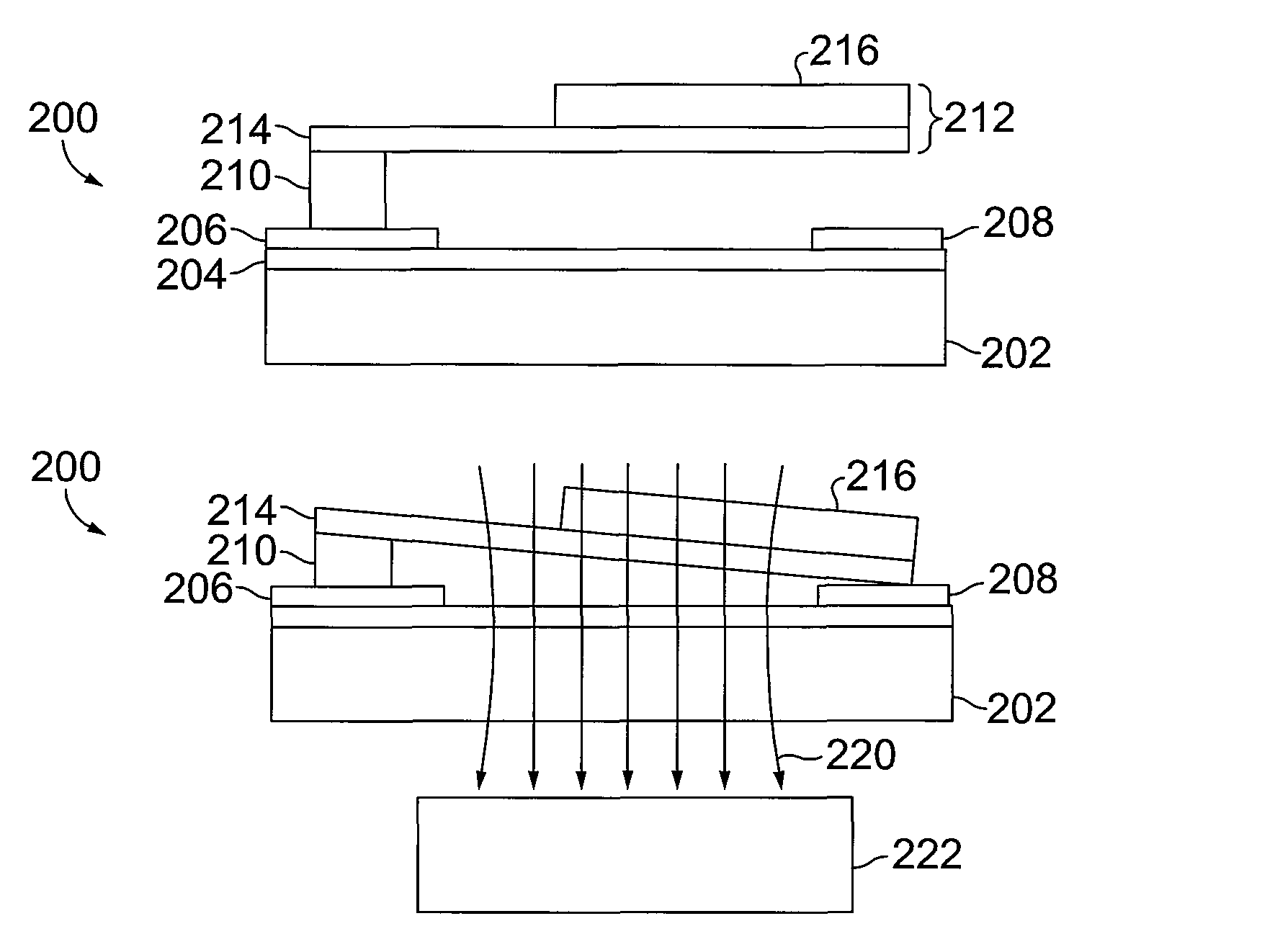
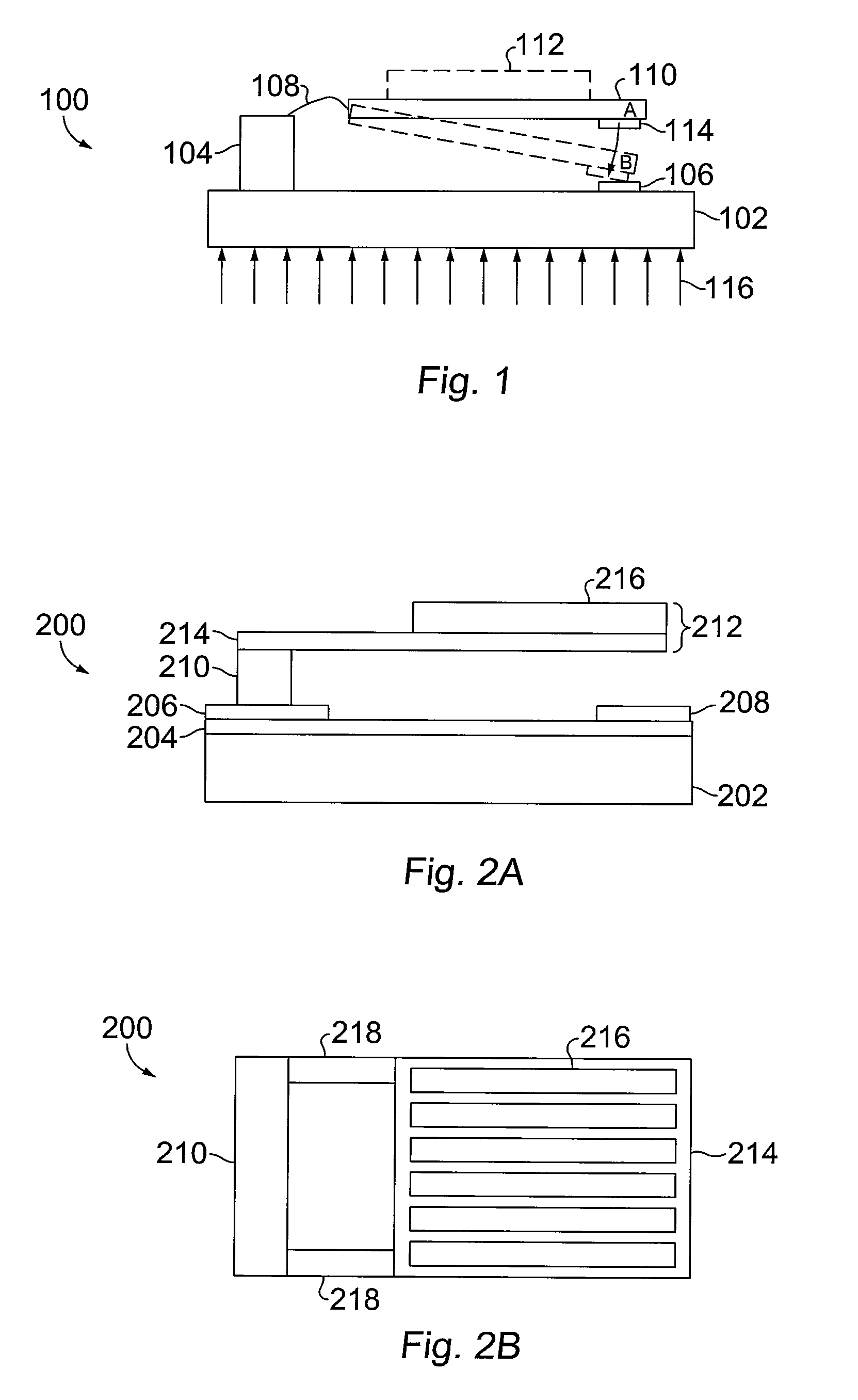
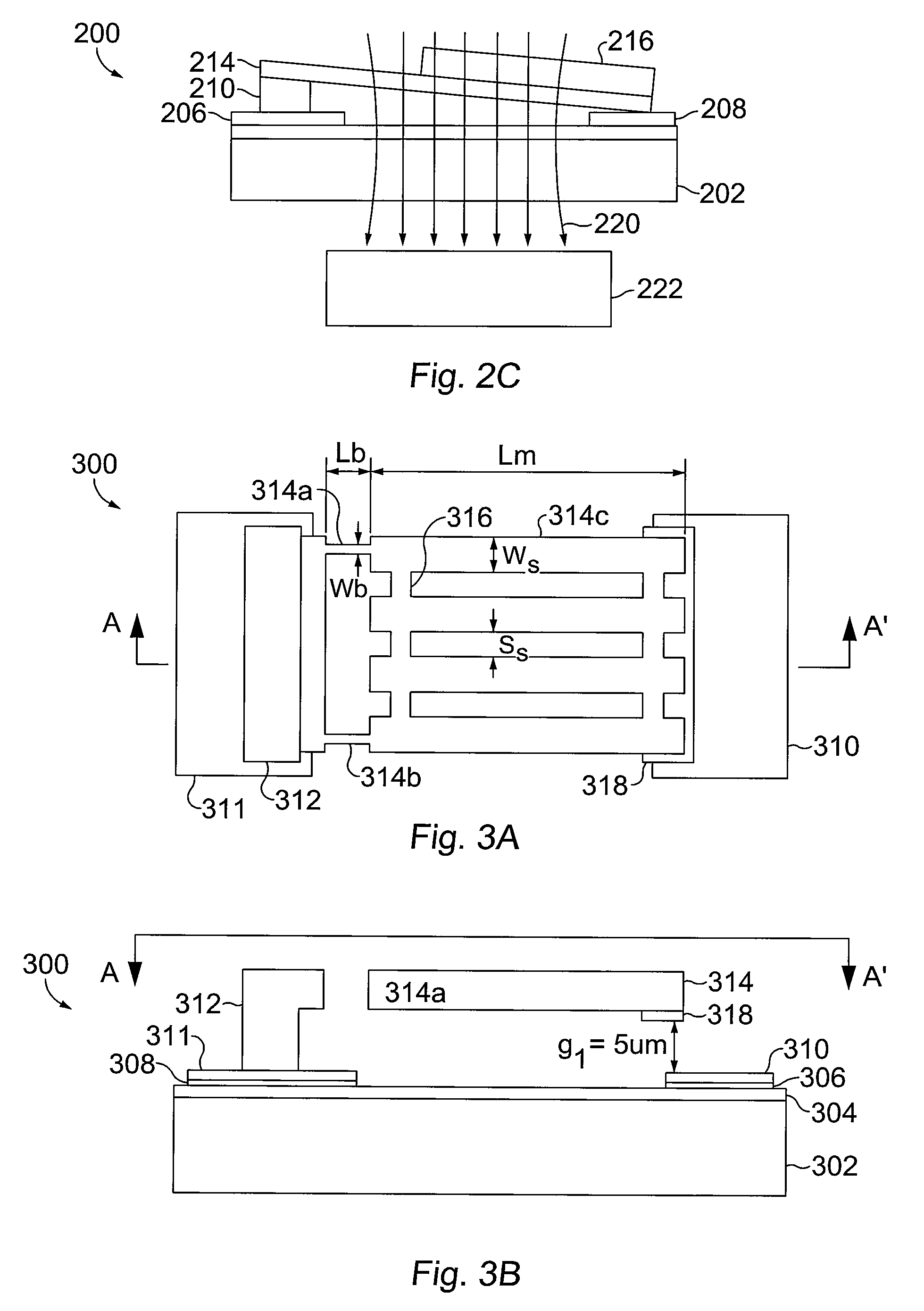
Segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer, apparatus for diagnosing structural fault by using the same, and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20100259252A1Accurate detectionDirection is limitedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetsPatch arrayMeander
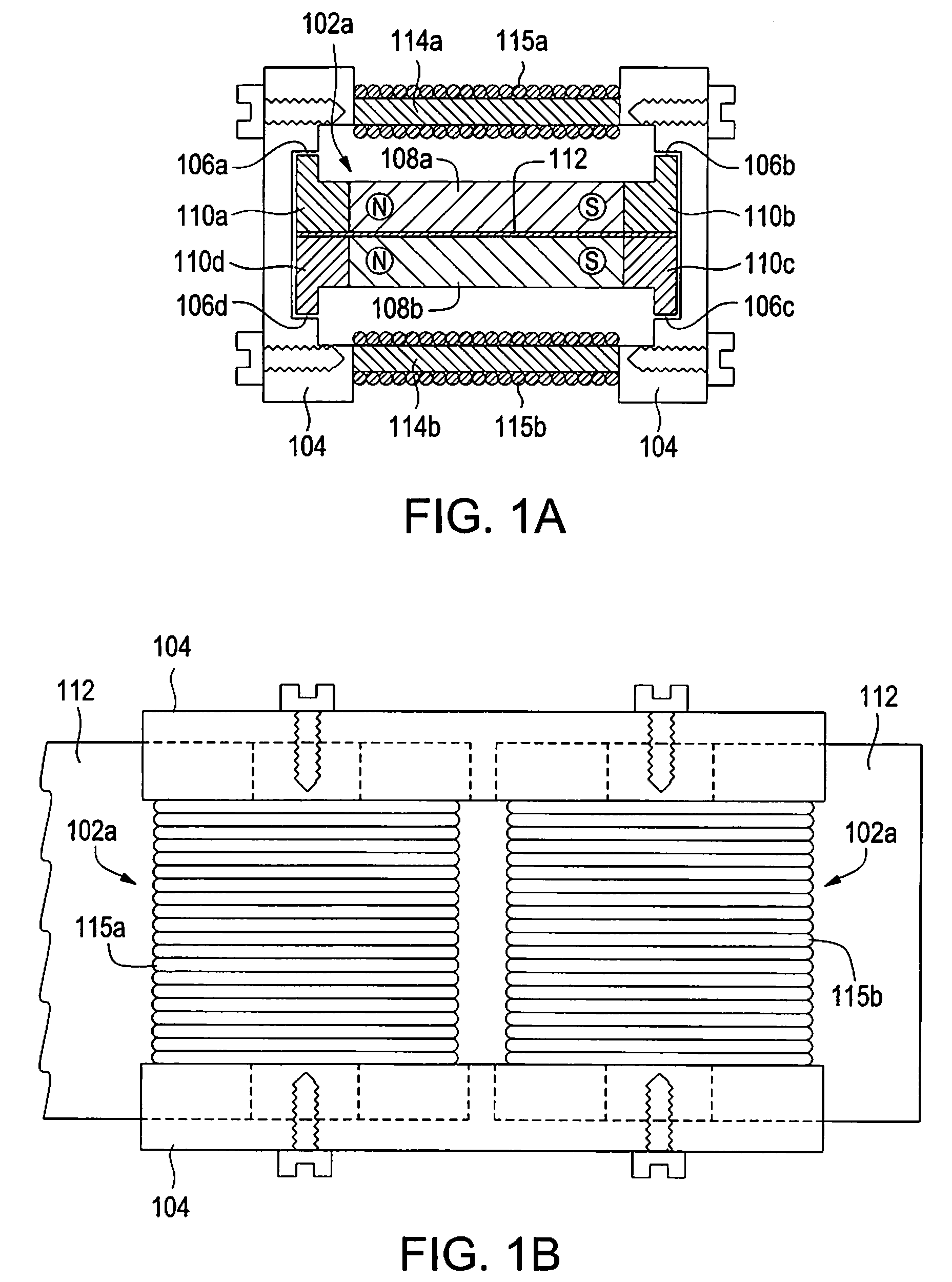
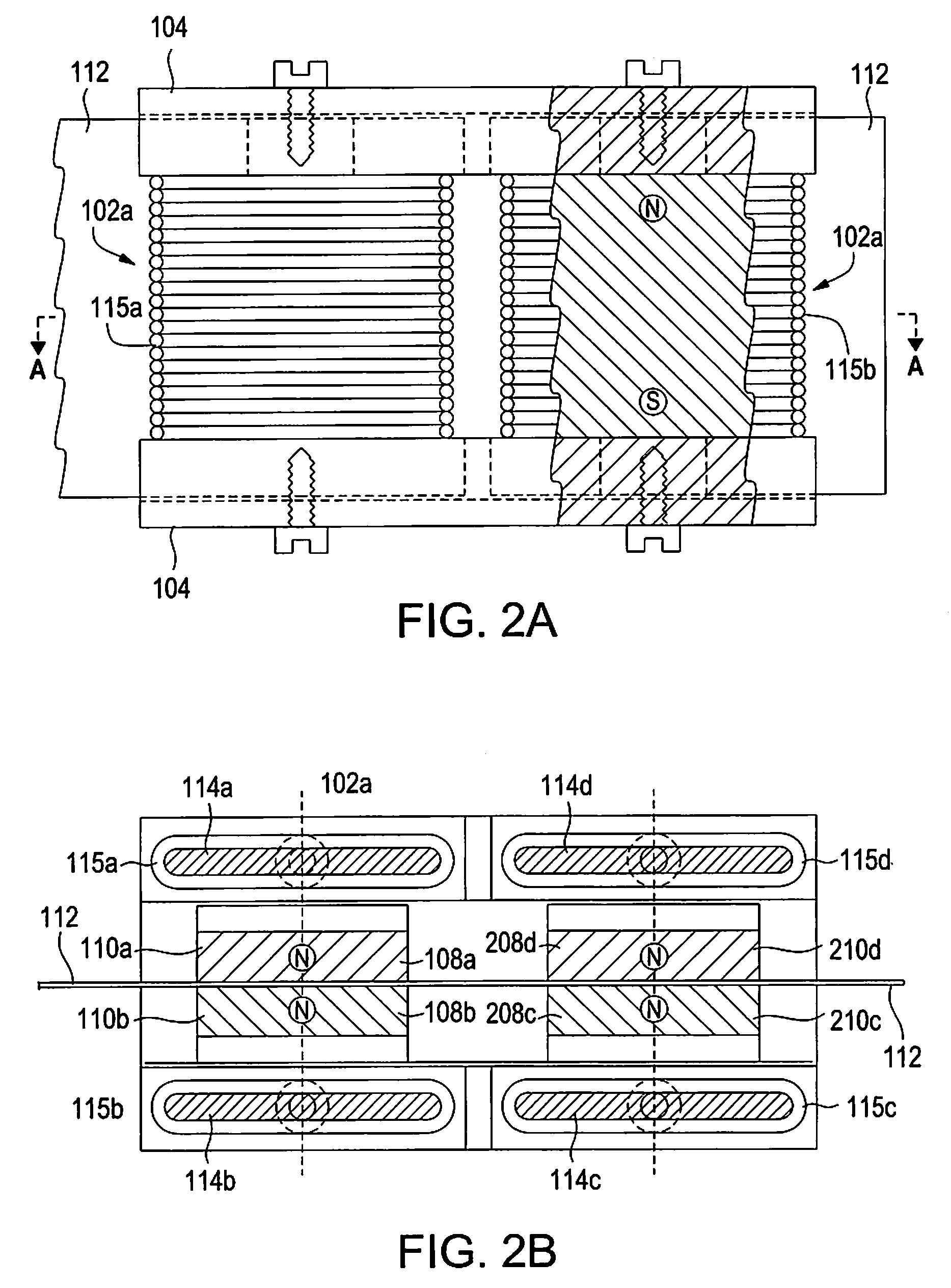
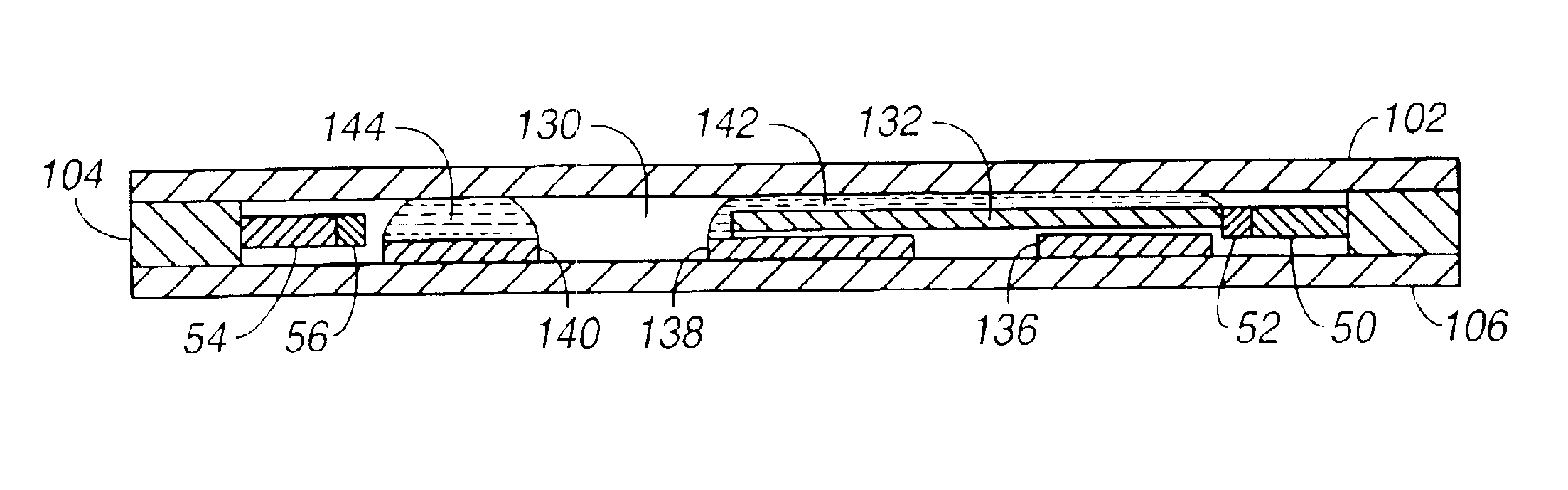
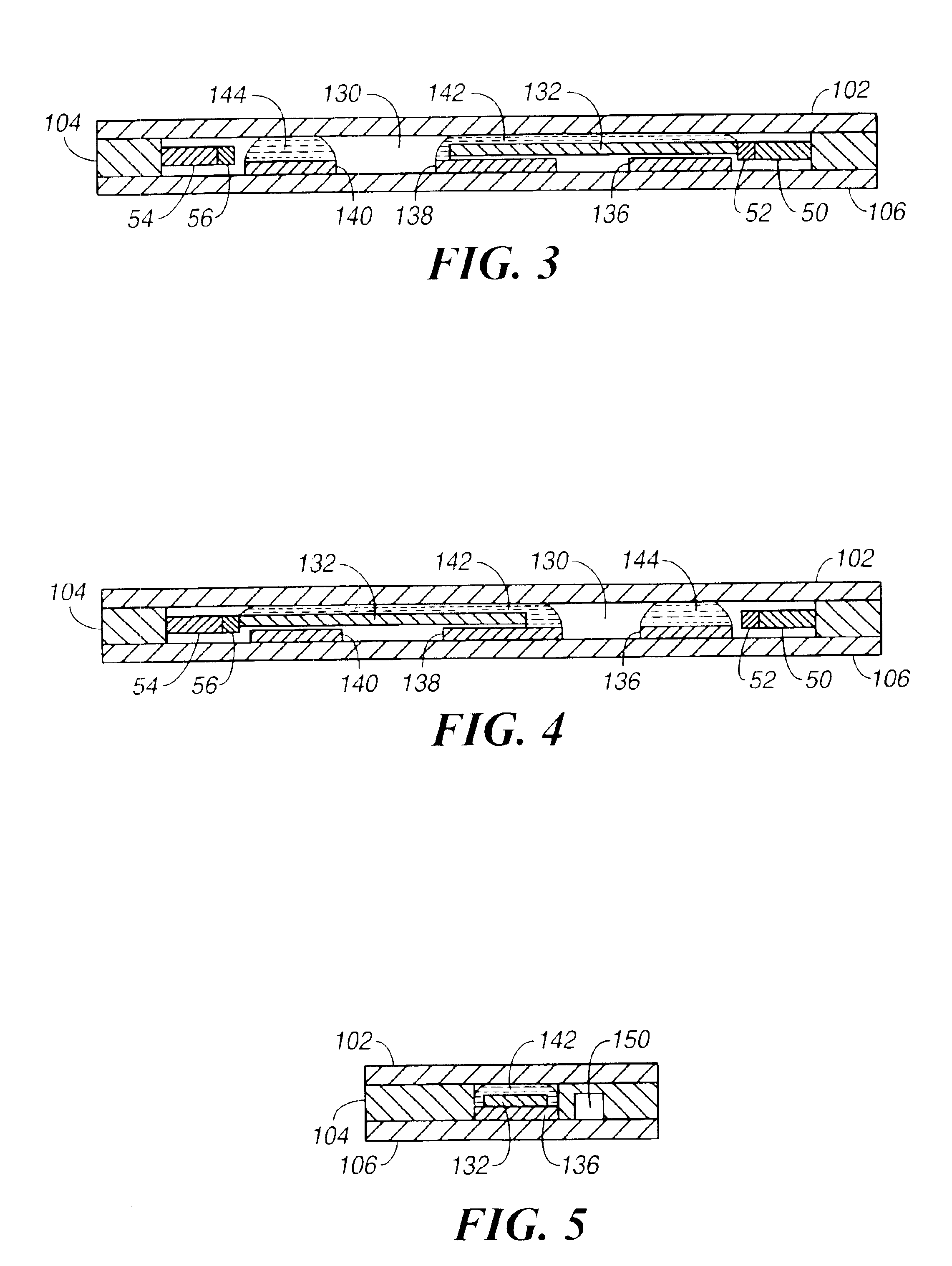
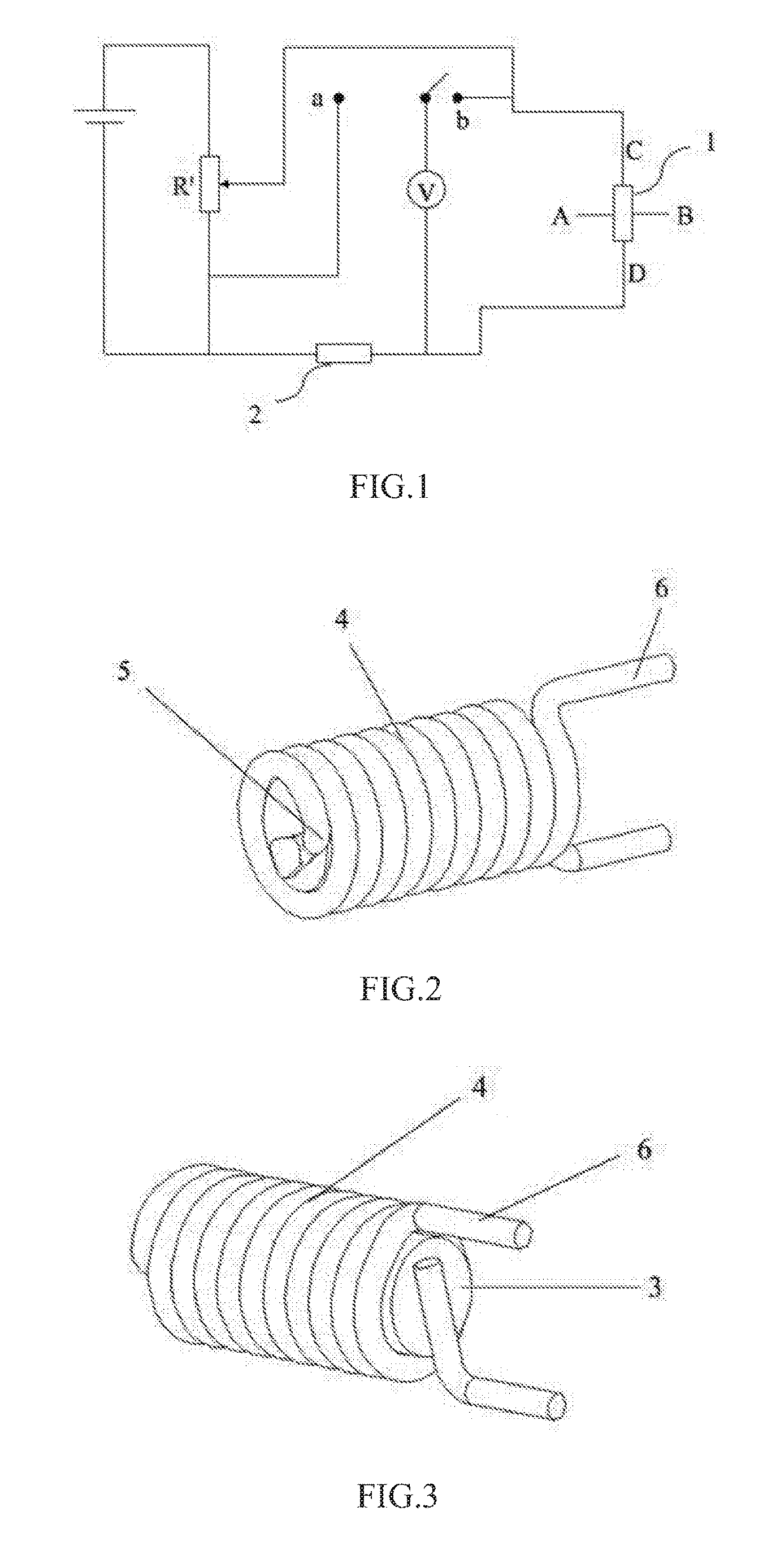
A segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer capable of generating a high frequency shear wave in a structure such as a rod or a pipe, a structural fault diagnosing apparatus including the segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer, and a method of operating the segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer are shown. The segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer includes a plurality of magnetostrictive patches attached along a circumference of a rod member; a plurality of insulators that are disposed on the magnetostrictive patches; a plurality of meander coils, each of the meander coils comprising a plurality of coil lines extending along the circumference direction of the rod member on each of the insulators, wherein a current flows through adjacent coil lines in opposite directions to one another; and a plurality of magnets that respectively form a magnetic field along the circumferential direction of the rod member on the magnetostrictive patches.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Electromagnetostrictive actuator
InactiveUS7323960B2Increase freedomLiquid surface applicatorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringActuator
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetostrictive thin film actuator
InactiveUS7250839B2Well mixedValve arrangementsCosmonautic vehiclesMagnetostrictive actuatorEngineering
Owner:ENERGEN
Magnetoresistive smart switch
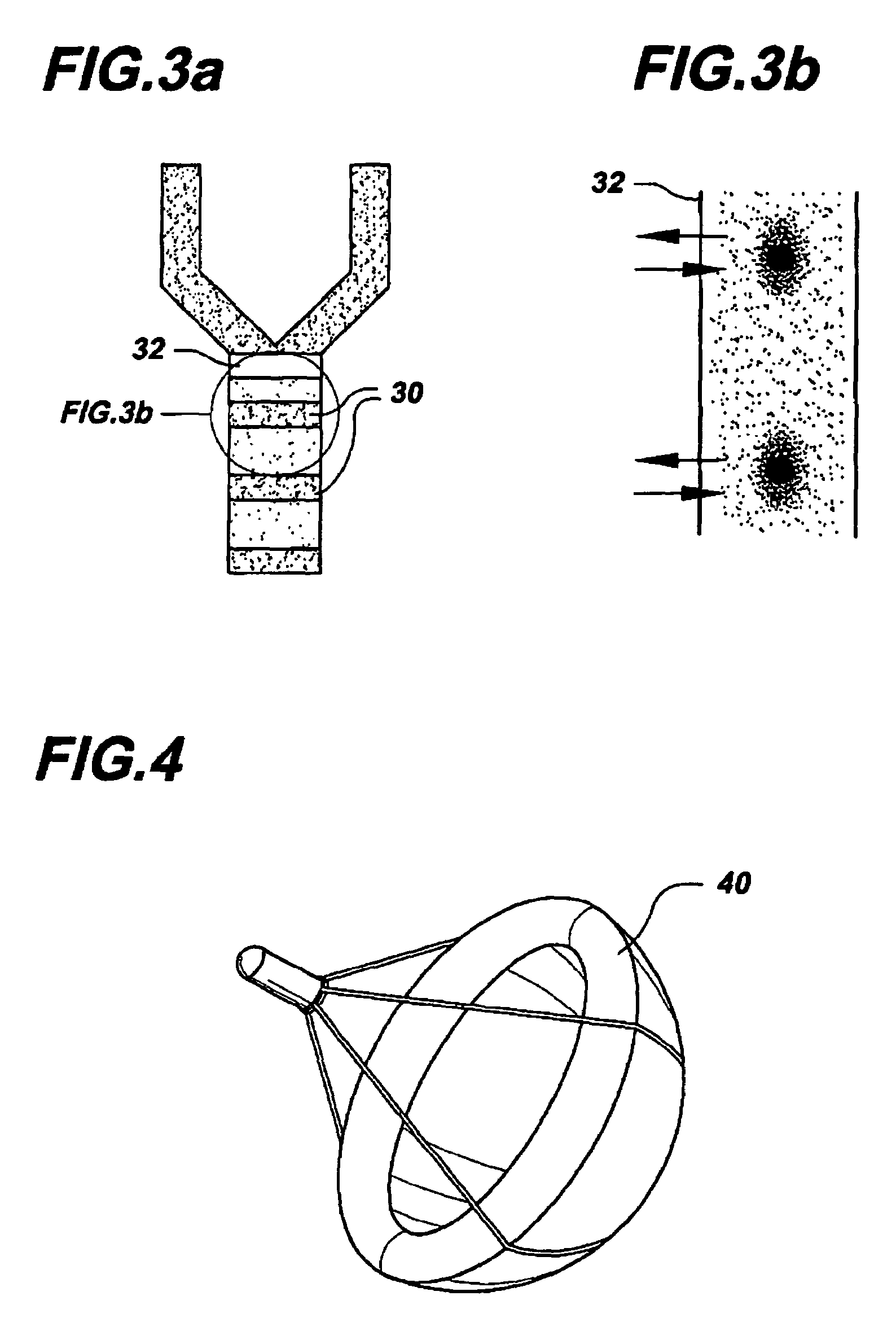
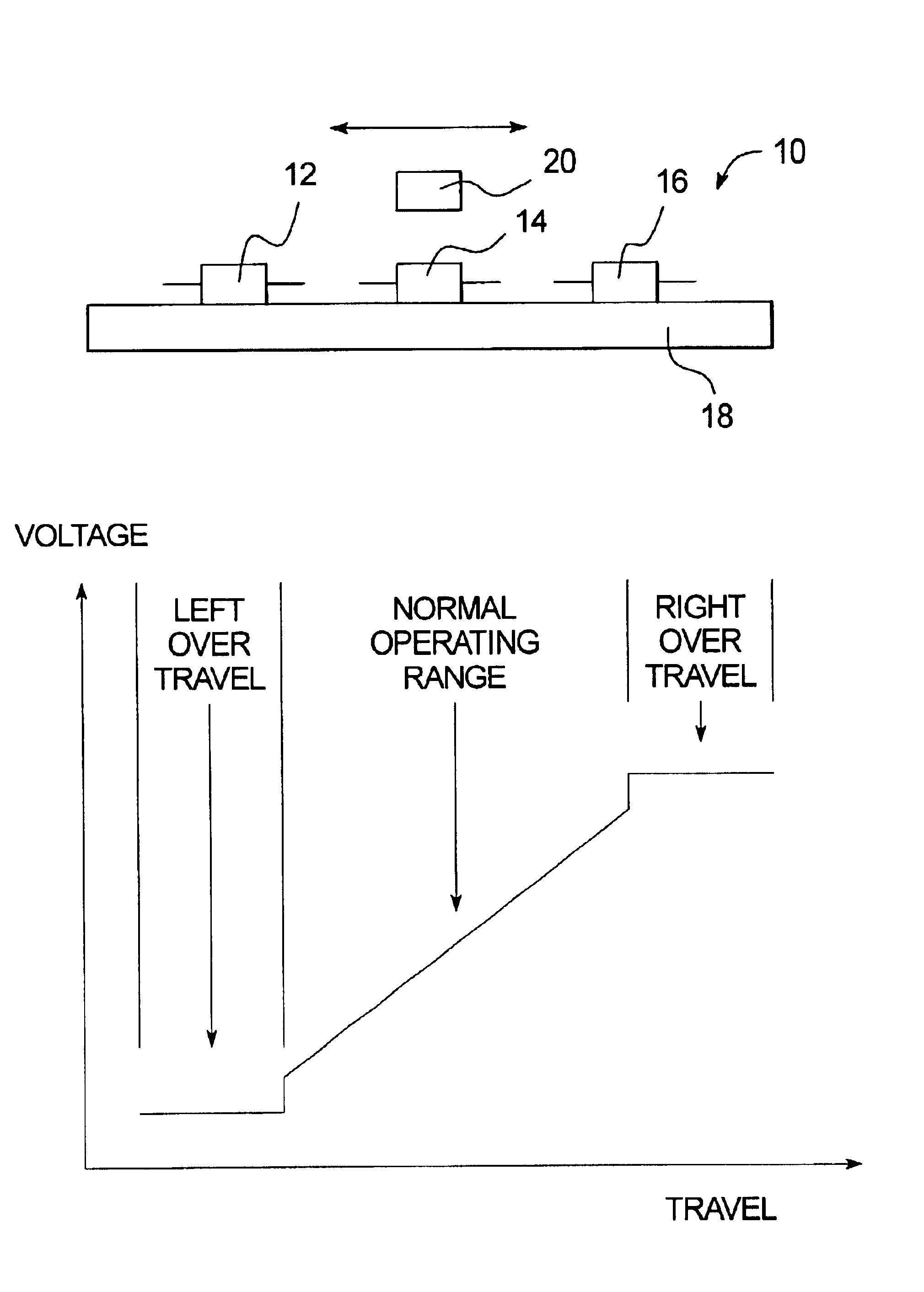
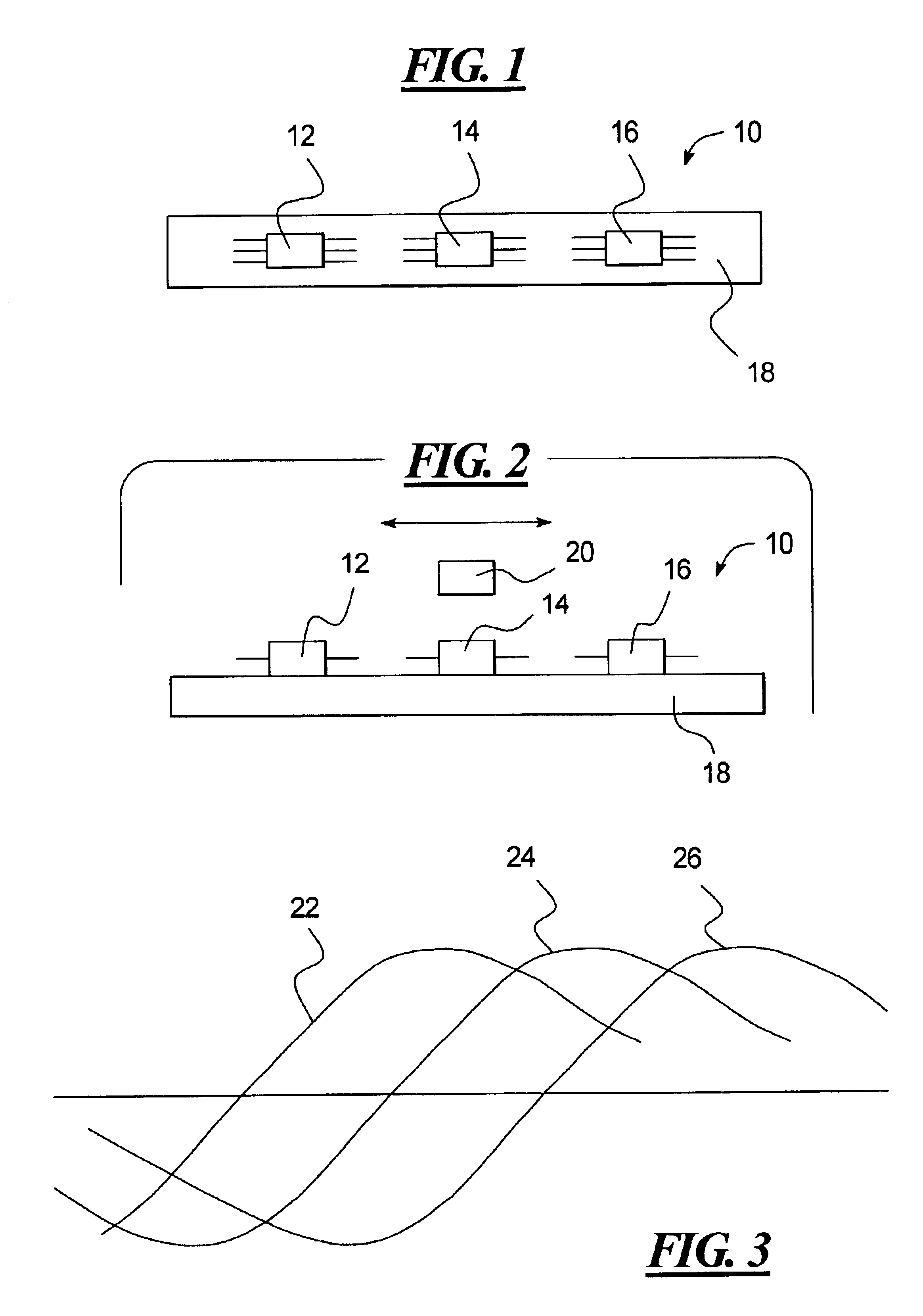
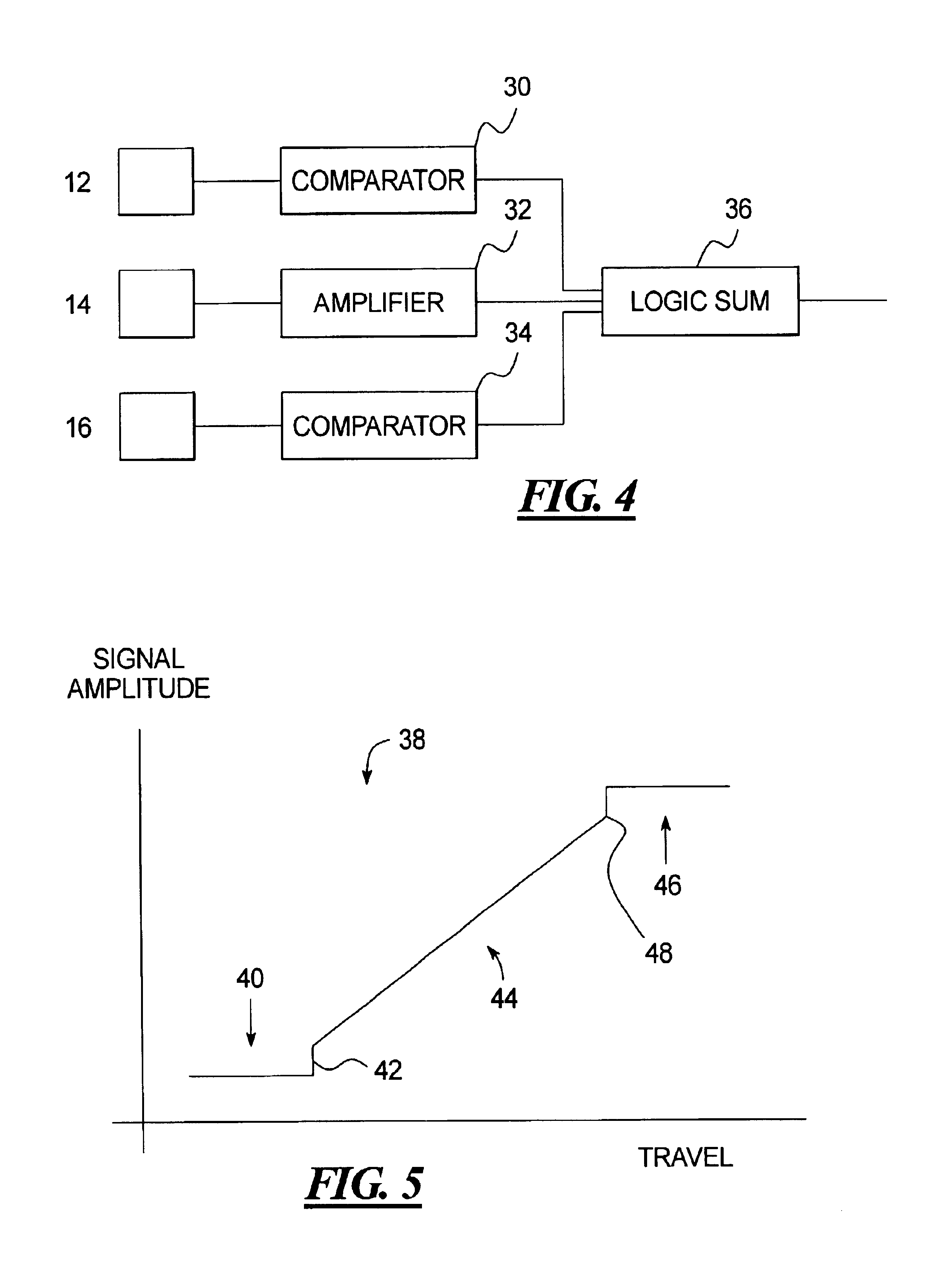
A smart switch has a magnetic operator, at least one magnetic sensor located to sense movement of the magnetic operator, and a processor that processes an output of the magnetic sensor so as to detect right and left over travel ranges and a normal operating range of the magnetic operator. The magnetic sensor may be a magnetoresistive sensor.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Device Having a Shape Memory Element
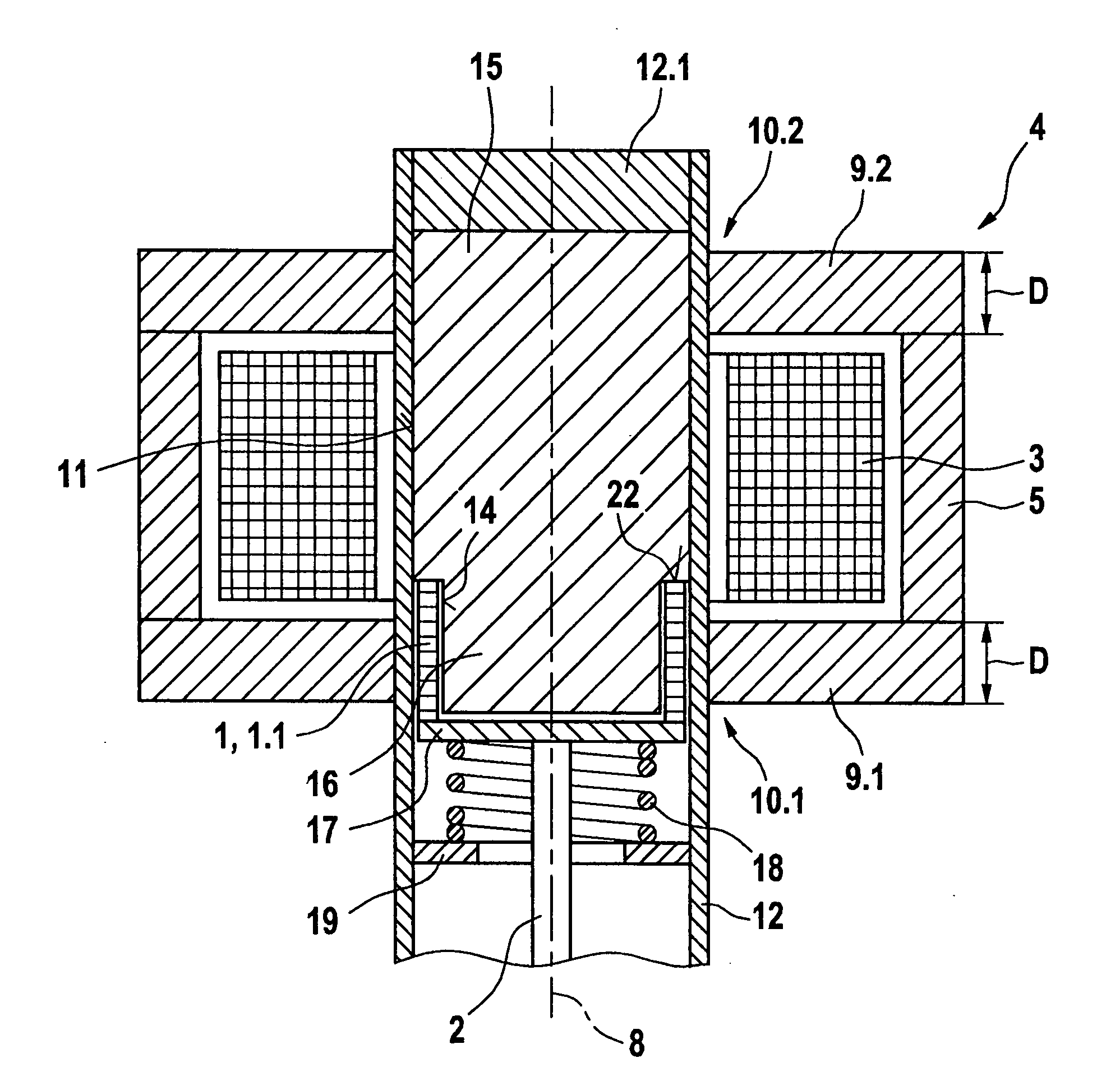
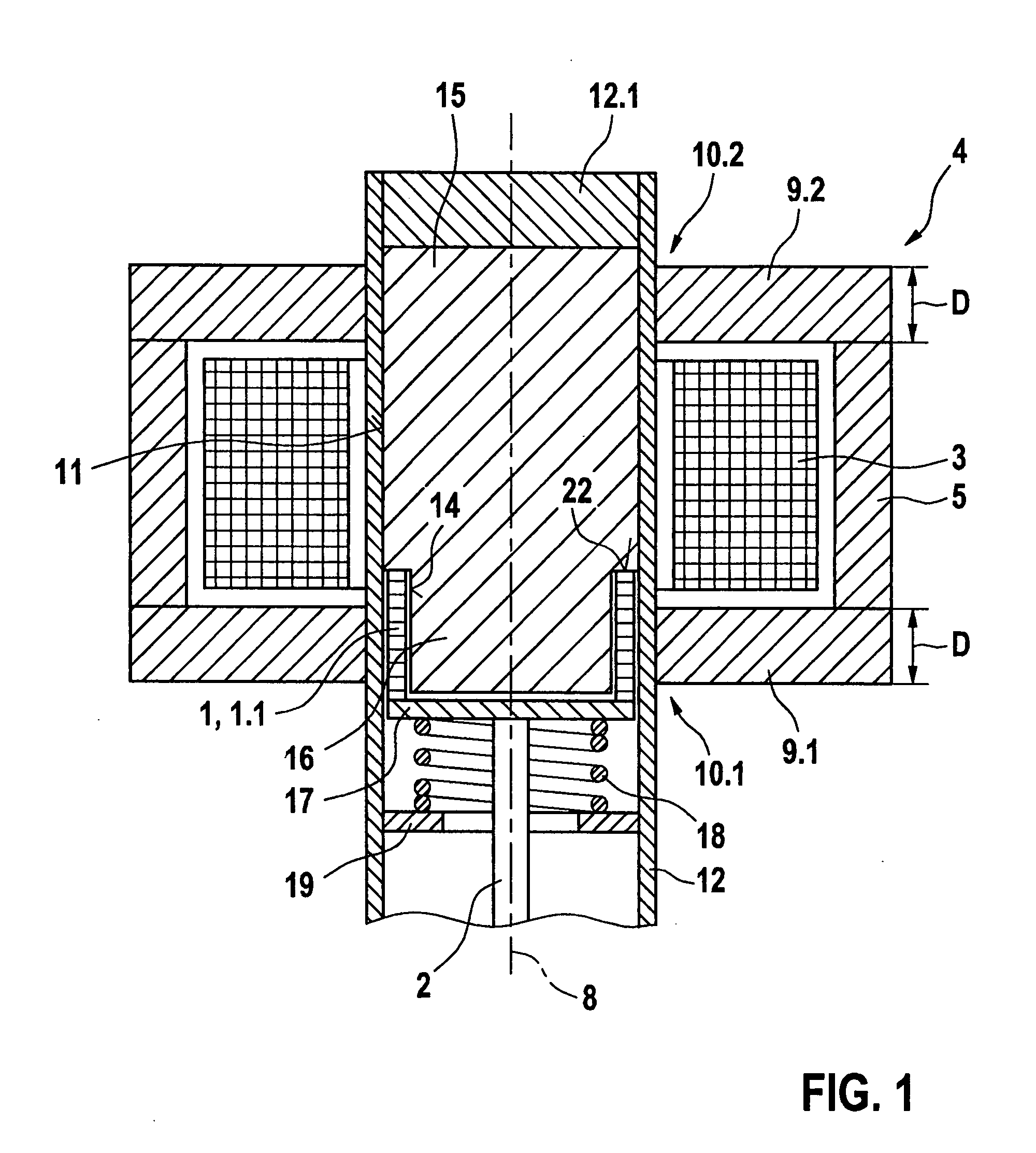
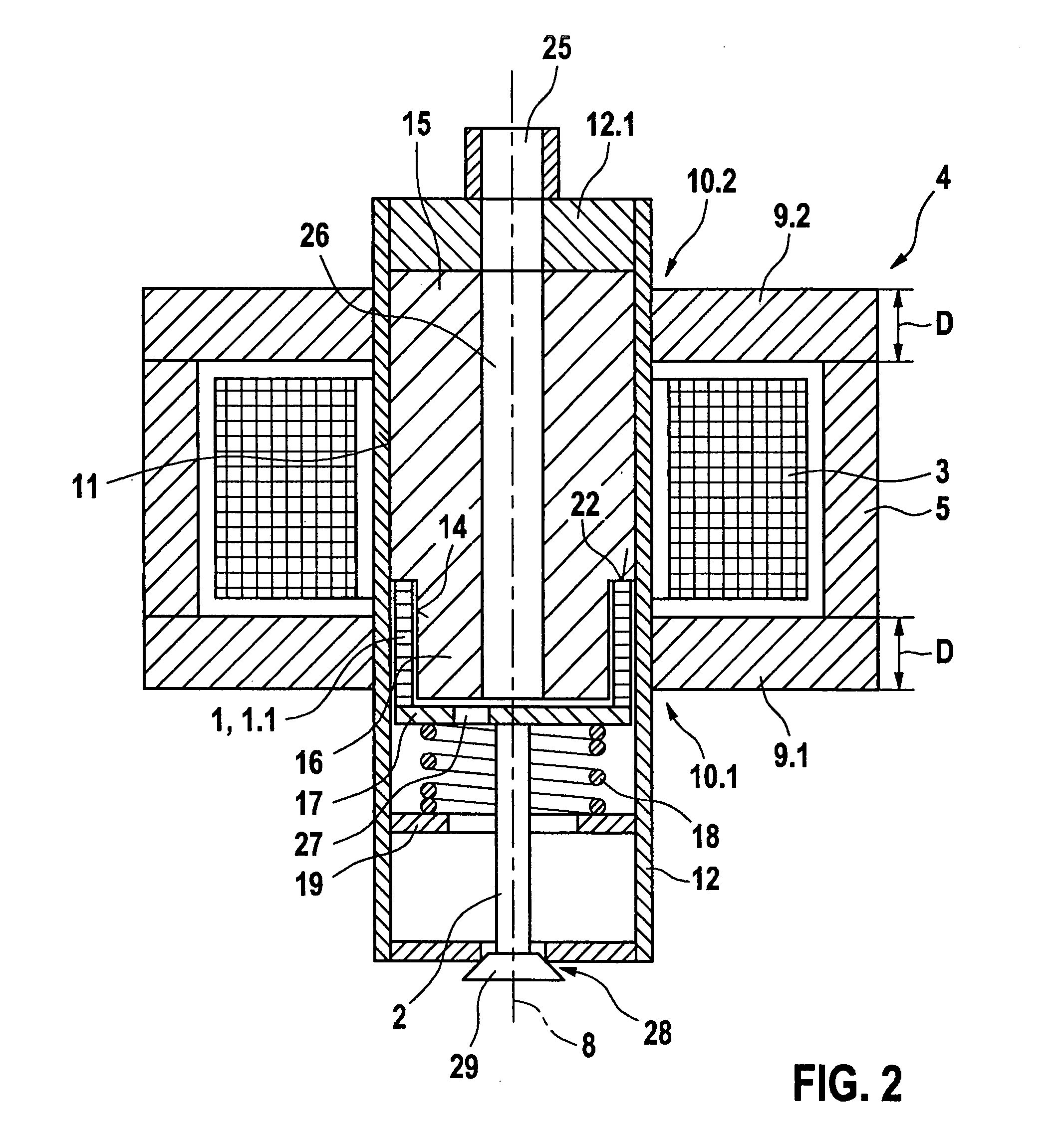
InactiveUS20090033448A1Different thermal expansionTravel can be limitedPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMagnetsEngineeringActuator
Conventional devices have a valve needle and a shape memory element which, by the application of a controllable magnetic field, executes a control stroke travel that operates the actuator, and having a coil that excites the magnetic field which is situated in a magnet housing which, at its end face, is bordered with respect to an actuating axis by a front wall in each case, the front walls having a through opening radially within the coil. It is a disadvantage that the magnetic field excited around the coil is conducted unfavorably, so that at most a slight magnetic field develops in the shape memory element. The shape memory element has a magnetic field flowing through it, in the direction of its longitudinal extension, if at all. Since the shape memory element has a high magnetic resistance and is developed to be very long in the axial direction, only a very weak magnetic field can be induced in the shape memory element. In response to the magnetic field that is weak at most, the shape memory element can generate only a very slight lift of the valve needle. In the device according to the present invention, a strong magnetic field is conducted through the shape memory elements, and in this way, a large control stroke travel is achieved. The shape memory element(s) is / are positioned generally only in the through opening(s).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Stepping flexures
InactiveUS7504921B2Easy constructionMore forceElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetic circuitEngineeringActuator
An actuator for moving a load has a frame forming a race between two surfaces thereof, at least two elements joined together by at least one flexible member, the elements and the at least one flexible member being disposed between the two surfaces of the frame that forms a race, one of the elements further joined to the load by a portion of the at least one flexible member, wherein when an element comes into contact with a surface of the frame it will stick thereto absent a repelling force, and moving means disposed to selectively attract or repel a corresponding element towards or away from one or the other of the two surfaces of the frame that forms the race. The actuator effects movement of the load in a direction towards or away from the elements, by changing a position of at least one of the elements on a surface of the frame that forms the race.
Owner:NASA
Method and apparatus for maintaining a liquid metal switch in a ready-to-switch condition
InactiveUS6946776B2Reduce the required powerContact surface shape/structurePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesVibratory signalLiquid state
A method and apparatus for maintaining a liquid metal switch in a state of readiness for switching. The liquid metal switch has a liquid metal volume contained in a cavity of a switch body. A signal path though the cavity is made or broken by energizing an actuator to move the liquid metal volume within the cavity in response to a switching signal. To maintain readiness, a signal generator supplies a vibratory signal to the actuator. The resulting vibrations in the liquid metal volume allow the liquid metal volume to be subsequently moved with reduced power.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Magnetically biased magnetopropant and pump
InactiveUS7893801B2Increase capacityEnhance magnetostrictive behaviorPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSpace environmentShape change
Provided is a system and method for enabling pressure or acoustic waves to induce magnetostrictive volume or shape change, providing greater control over magnetopropants. A coating material and the spacing between a magnetopropant and a magnetic particle are selected such that a certain pressure causes change in the relative distance of magnetopropant and magnetic particle, thereby changing the amount of magnetostriction. The coating material, magnetopropant, and magnetic particle are assembled to form a pressure sensitive magnetopropant. Given this structure, changes in pressure will cause a fluctuation of the amount of magnetostriction. In a pore space environment, this causes a change in pore space with resulting change in permeability and, hence, changes in fluid flow.
Owner:KNOBLOCH CHARLES SARON
Actuator
InactiveUS6803846B2Large displacementImprove responsePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMagnetsEngineeringActuator
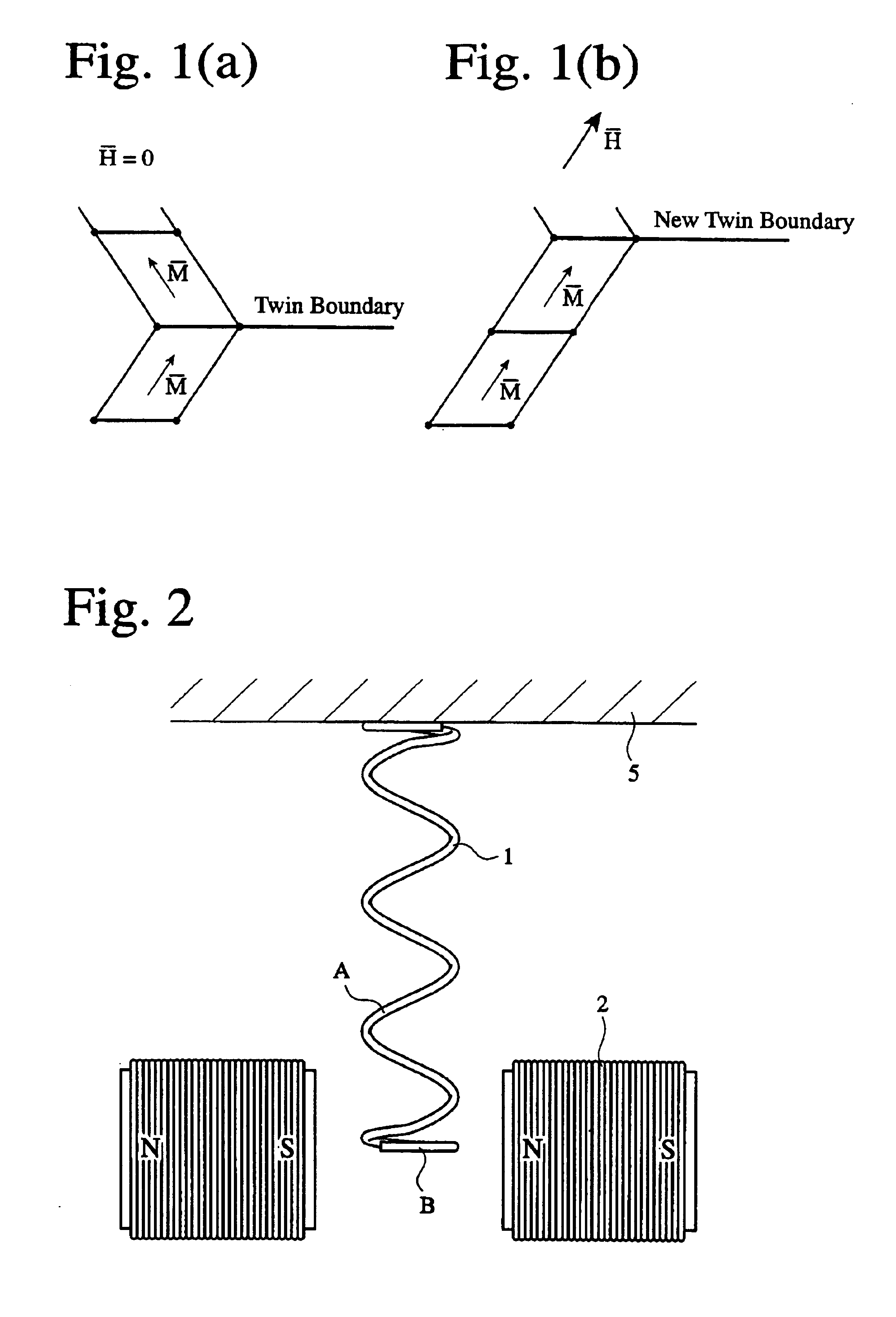
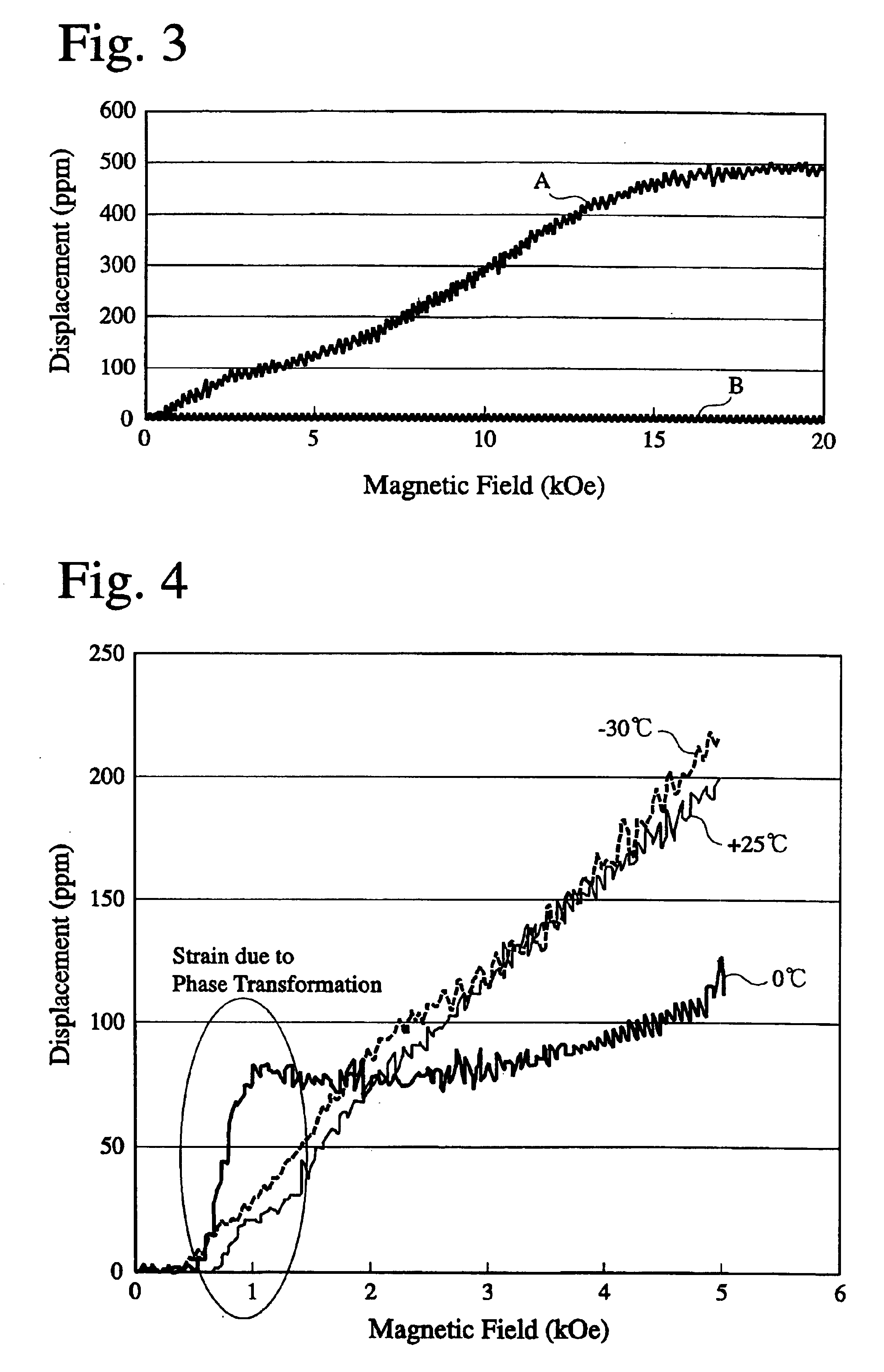
An actuator comprising a magnetic, resilient, shape memory member formed by a substance having a twin structure, and a magnetic field generator, at least part of the magnetic, resilient, shape memory member being disposed in a gradient magnetic field generated from the magnetic field generator such that the twin structure is reoriented by the magnetic field, whereby the shape memory resilient member is driven.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Magnetostrictive thin film actuator
InactiveUS20060028309A1Well mixedValve arrangementsCosmonautic vehiclesMagnetostrictive actuatorEngineering
Magnetostrictive actuator. The actuator includes a flexible substrate and a magnetostrictive film on the substrate. The shape of the flexible substrate is altered in the presence of a magnetic field.
Owner:ENERGEN
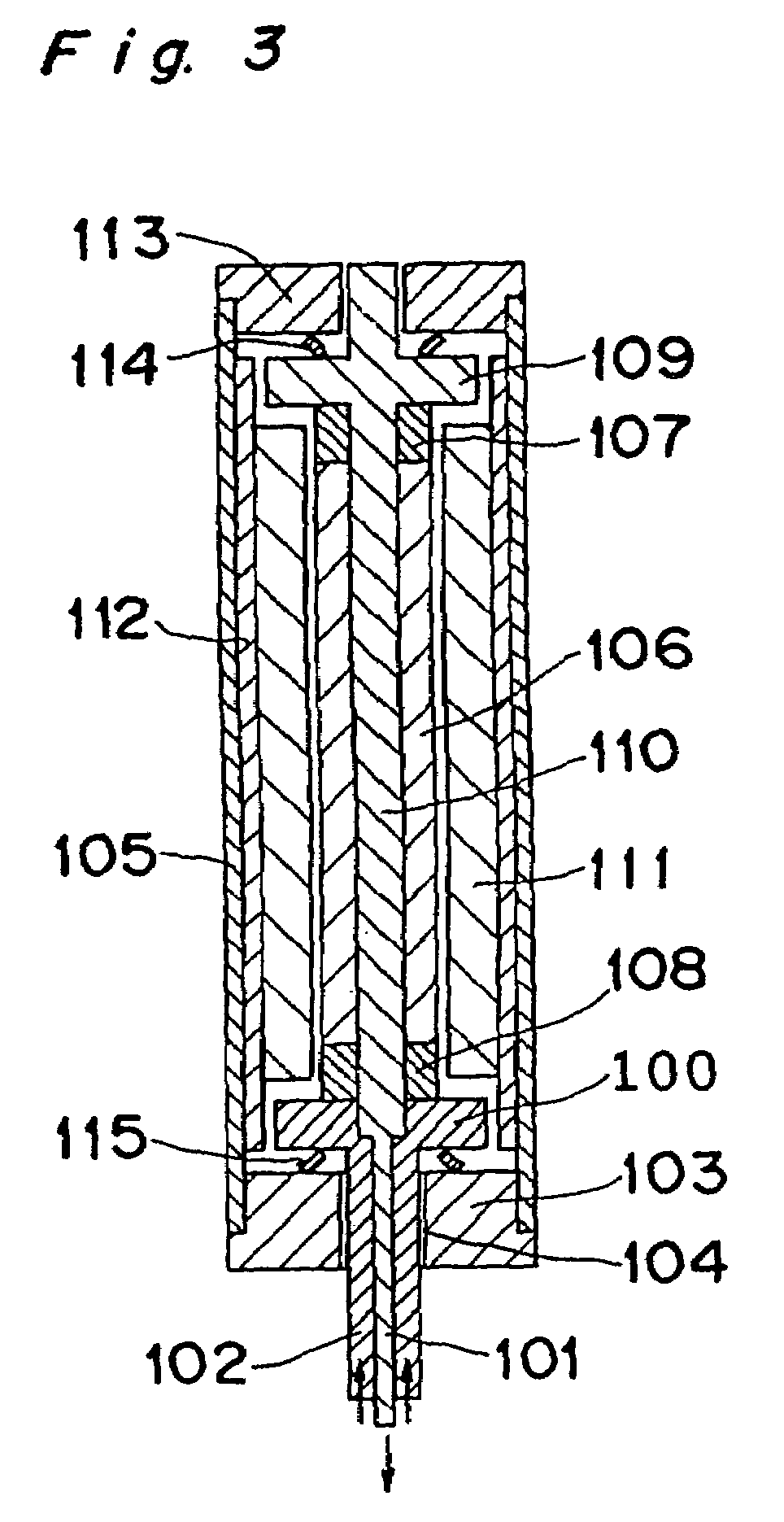
Segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer, apparatus for diagnosing structural fault by using the same, and method of operating the same
ActiveUS8354842B2Accurate detectionDirection is limitedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetsPower flowPatch array
A segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer capable of generating a high frequency shear wave in a structure such as a rod or a pipe, a structural fault diagnosing apparatus including the segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer, and a method of operating the segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer are shown. The segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer includes a plurality of magnetostrictive patches attached along a circumference of a rod member; a plurality of insulators that are disposed on the magnetostrictive patches; a plurality of meander coils, each of the meander coils comprising a plurality of coil lines extending along the circumference direction of the rod member on each of the insulators, wherein a current flows through adjacent coil lines in opposite directions to one another; and a plurality of magnets that respectively form a magnetic field along the circumferential direction of the rod member on the magnetostrictive patches.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
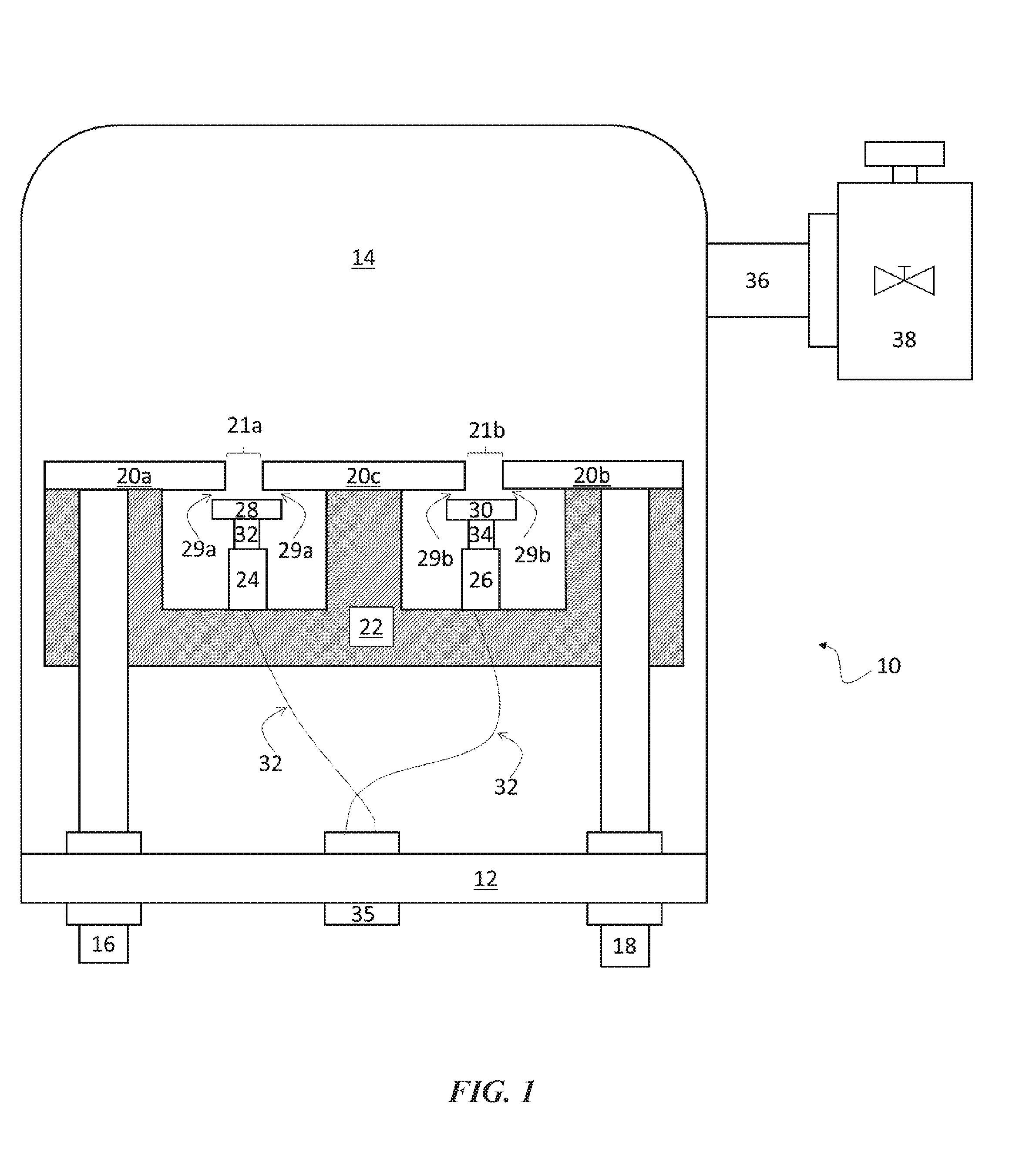
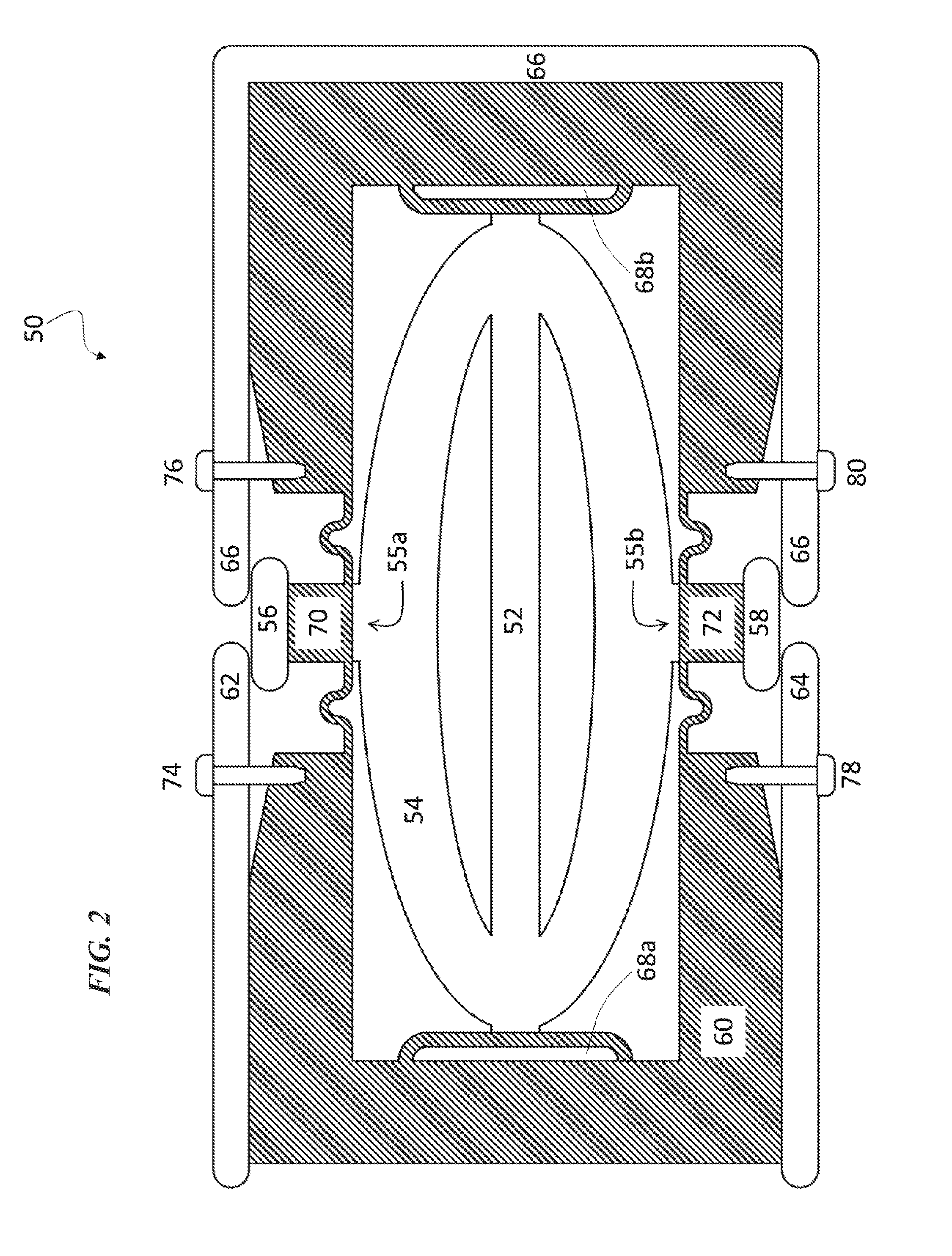
Damped longitudinal mode latching relay
InactiveUS6876130B2Avoid damageContact surface shape/structurePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesContact padPiezoelectric actuators
A piezoelectric relay is disclosed in which a solid slug moves within a switching channel formed in relay housing. An electrical circuit passing between fixed contact pads in the switching channel is completed or broken by motion of the solid slug. Motion of the solid slug is controlled by at least two piezoelectric actuators within the switching channel. Motion of the solid slug is resisted by an electrically conductive liquid, such as a liquid metal, that wets between the solid slug and the contact pad in the switching channel. The surface tension of the, liquid provides a latching mechanism for the relay.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Inertial positioner and an optical instrument for precise positioning
InactiveUS8063383B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer moduleHot swapping
We disclose a precision positioner based on an inertial actuator, an optical instrument for accurate positional readout and control, and an electrostatically clamped assembly for holding any instrument or device. All aspects of the present invention present a significant improvement over the prior art: a positioner is robust and compact; an optical instrument for positional control is a profoundly simple and compact module; a clamping assembly is self-aligning and suitable for robotic hot-swapping of objects being positioned.
Owner:PRYADKIN DR SERGIY
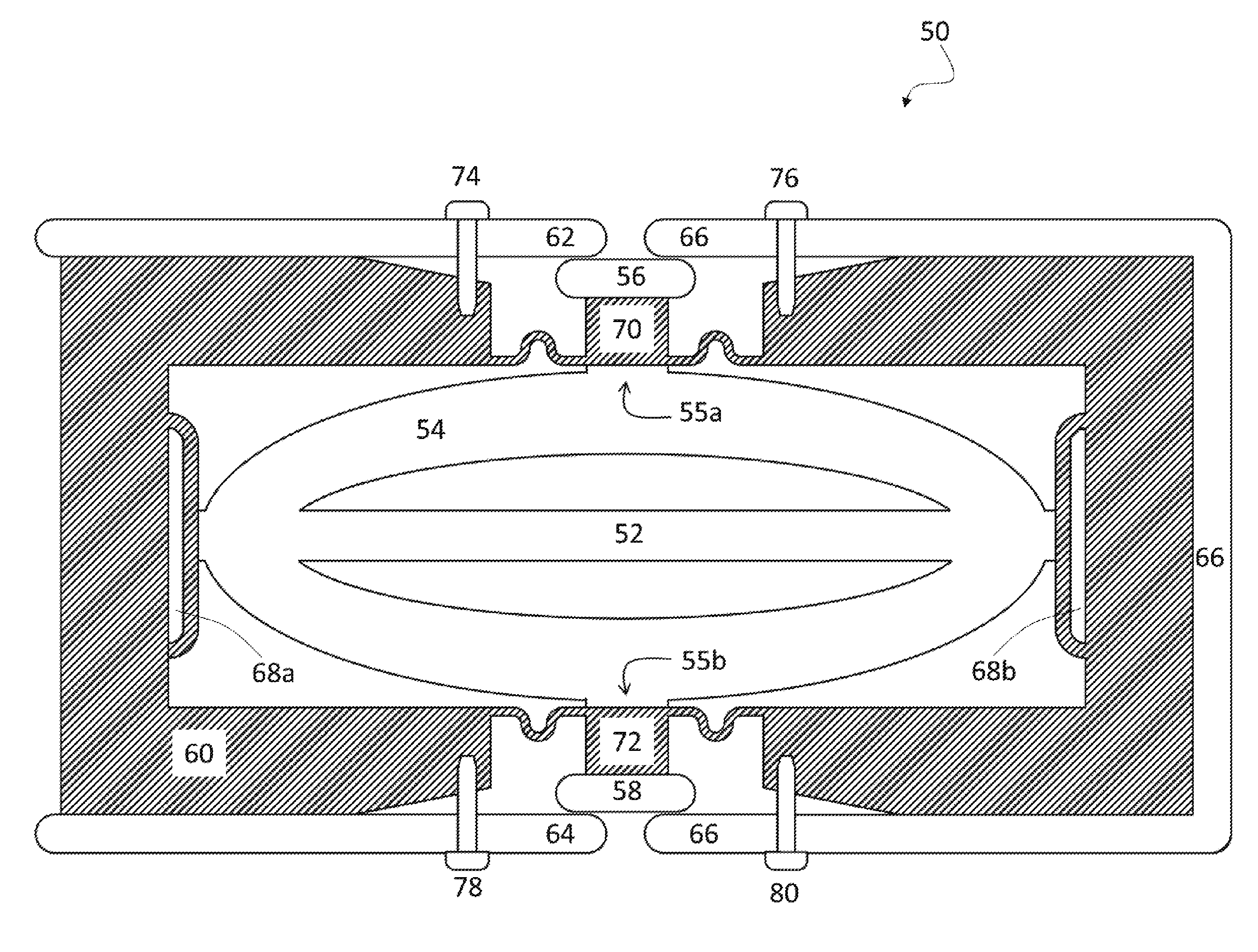
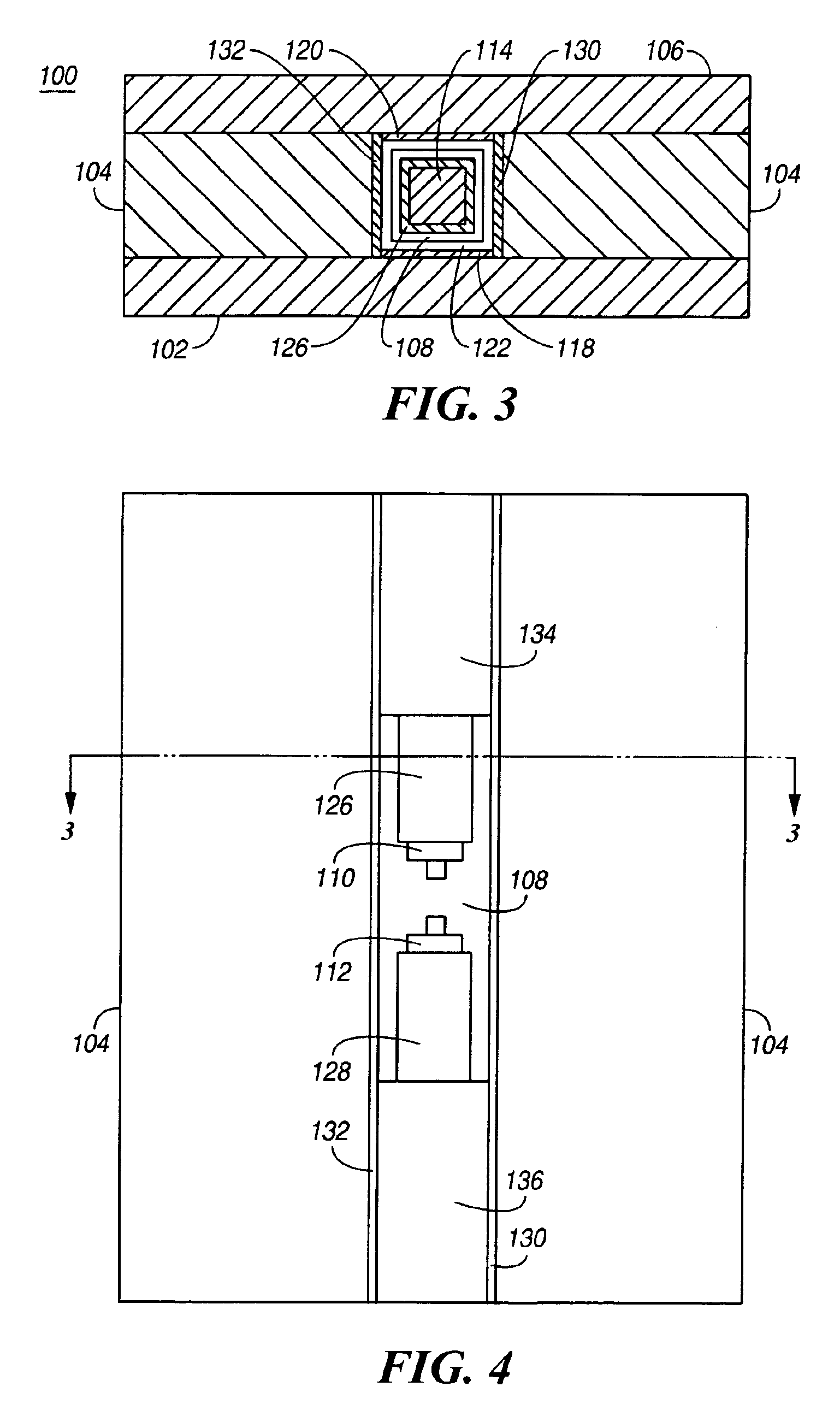
Magnetostrictive electrical switching device
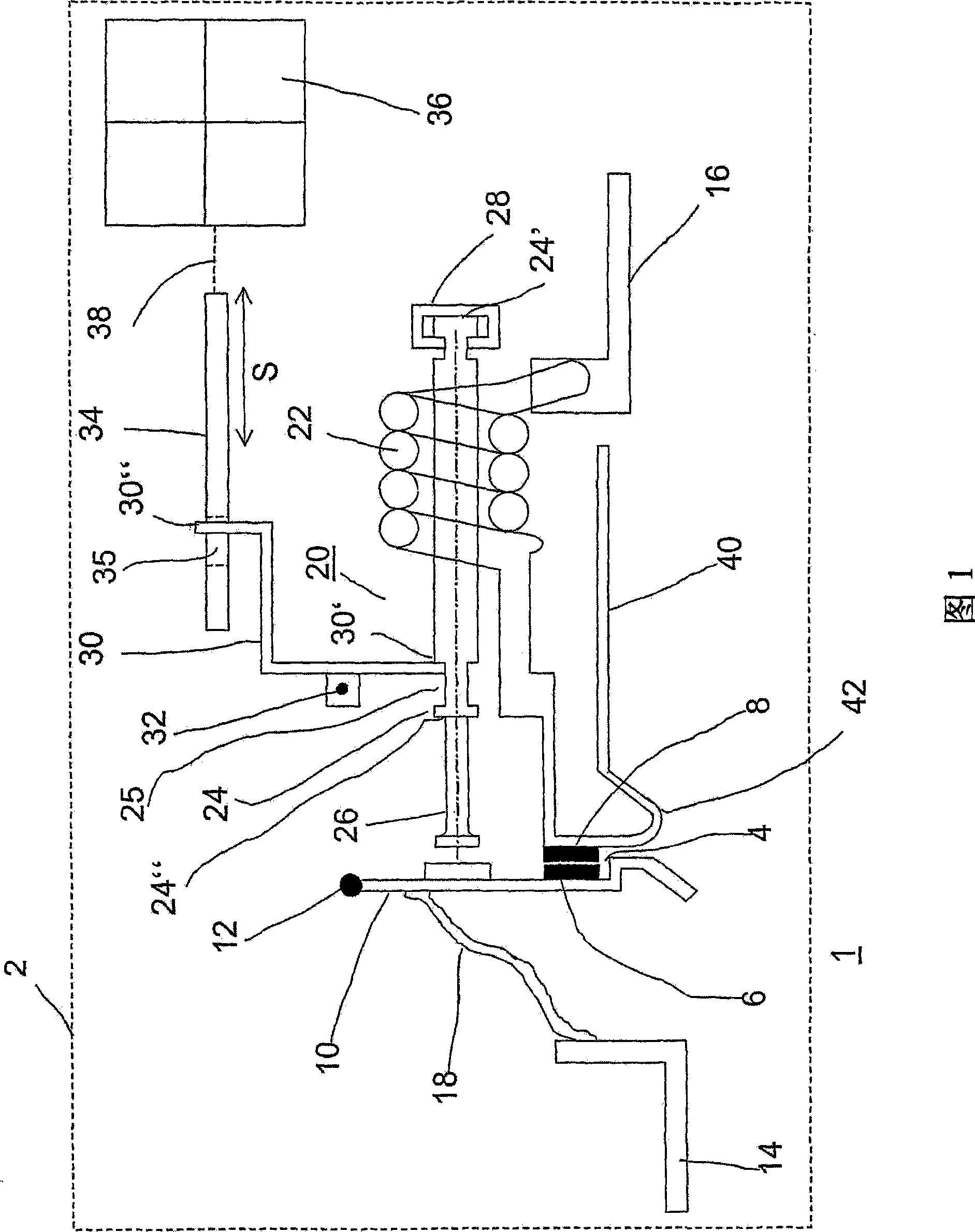
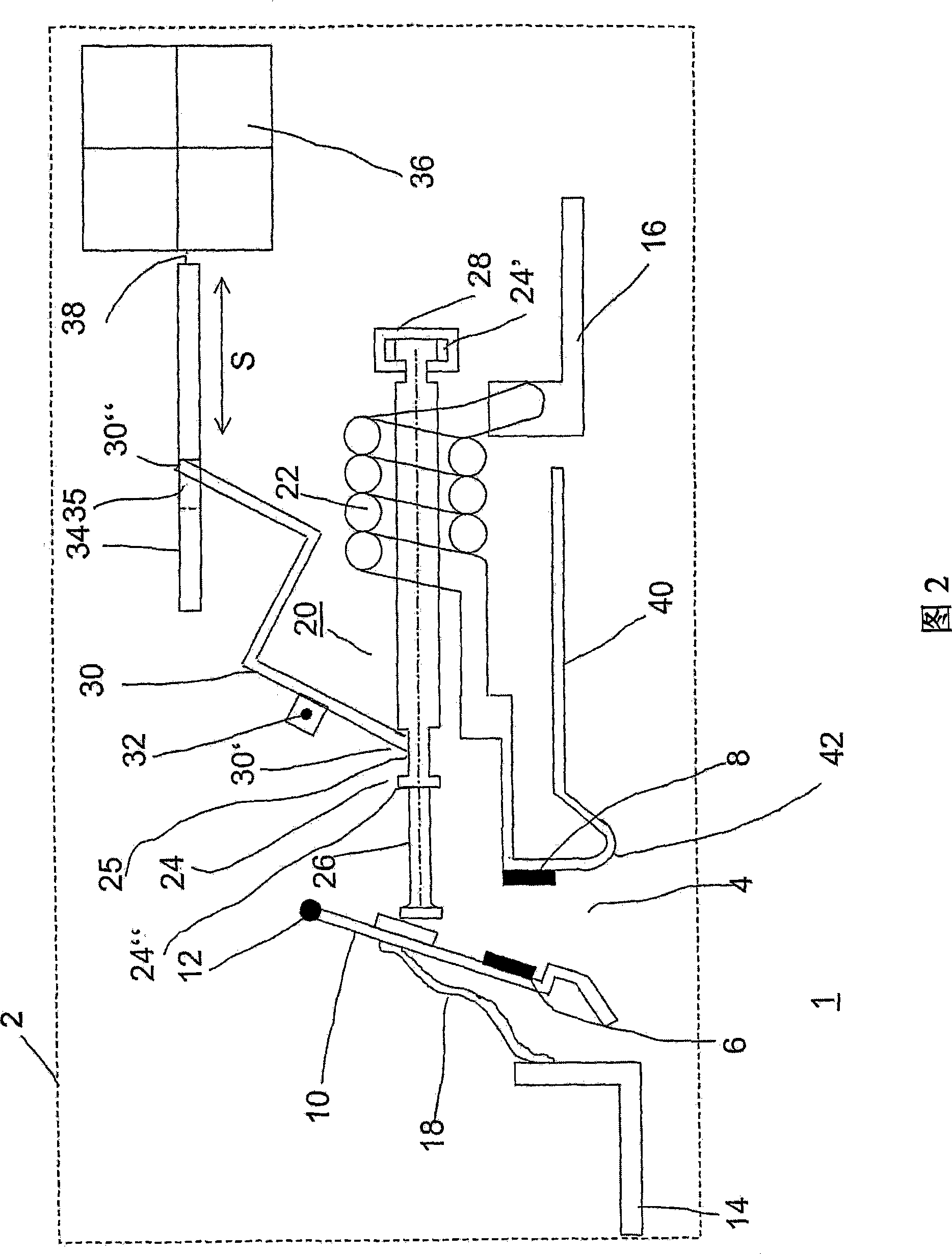
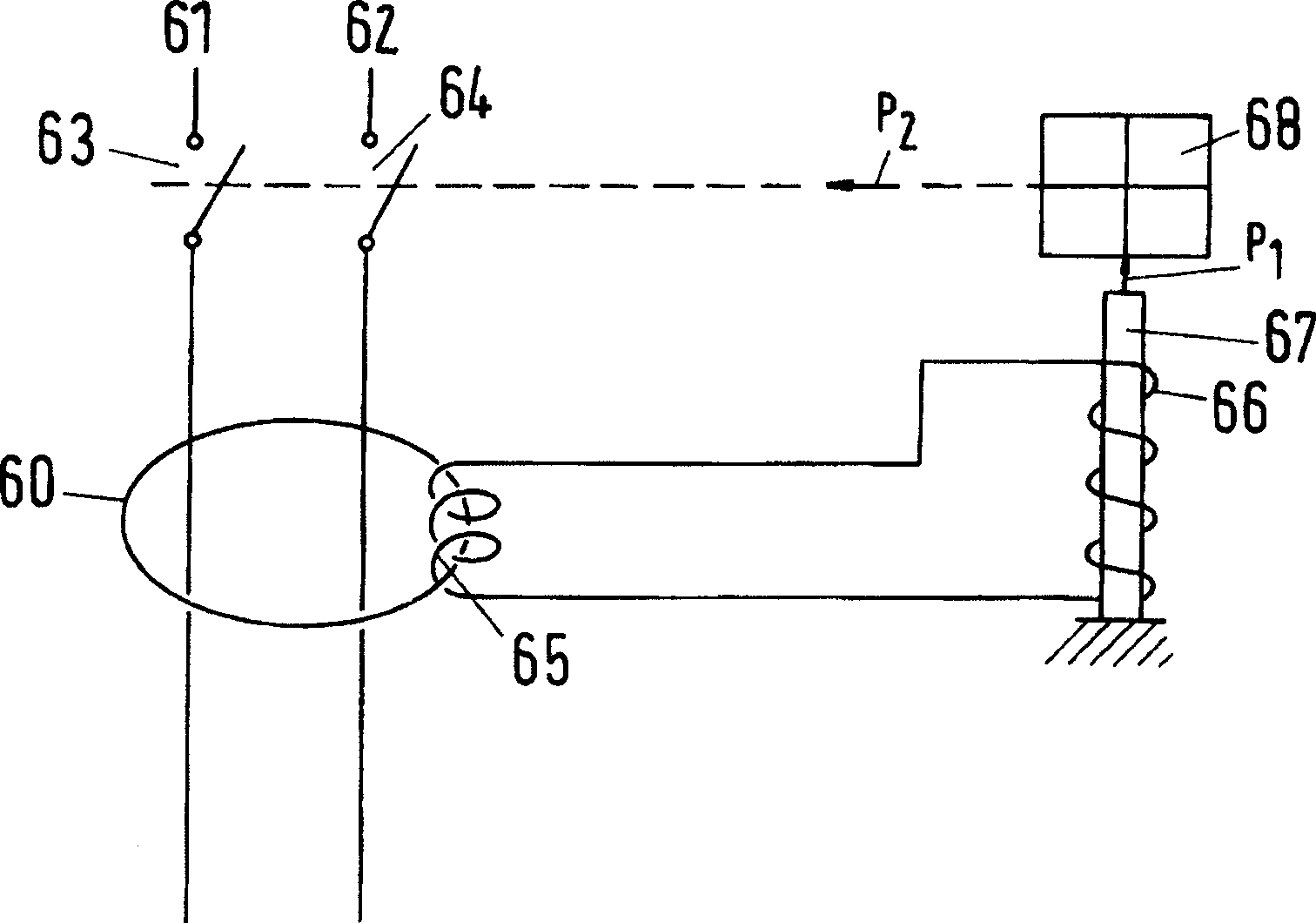
InactiveUS20080284547A1Protective switch detailsMagnetostrictive relaysShape-memory alloyElectrical switching
The disclosure proposes an electrical switching device having at least one contact point having at least one drive, which opens the contact point directly and / or via a switching mechanism with a latching point and which drive has an element having a predetermined shape, which element consists of a shape memory alloy, which changes its shape under the influence of an electromagnetic field and, in the process, opens or closes a contact point or double contact point or unlatches a switching mechanism.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Integrated, lighted ultrasonic inserts
InactiveUS8496475B2Easy to chargeMinimal fluctuationBatteries circuit arrangementsMagnetsElectricityLight equipment
Owner:HU FRIEDY MFG
Magnetoresistive smart switch
InactiveUS20050156591A1Burglar alarm by openingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSmart switchEngineering
A smart switch has a magnetic operator, at least one magnetic sensor located to sense movement of the magnetic operator, and a processor that processes an output of the magnetic sensor so as to detect right and left over travel ranges and a normal operating range of the magnetic operator. The magnetic sensor may be a magnetoresistive sensor.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
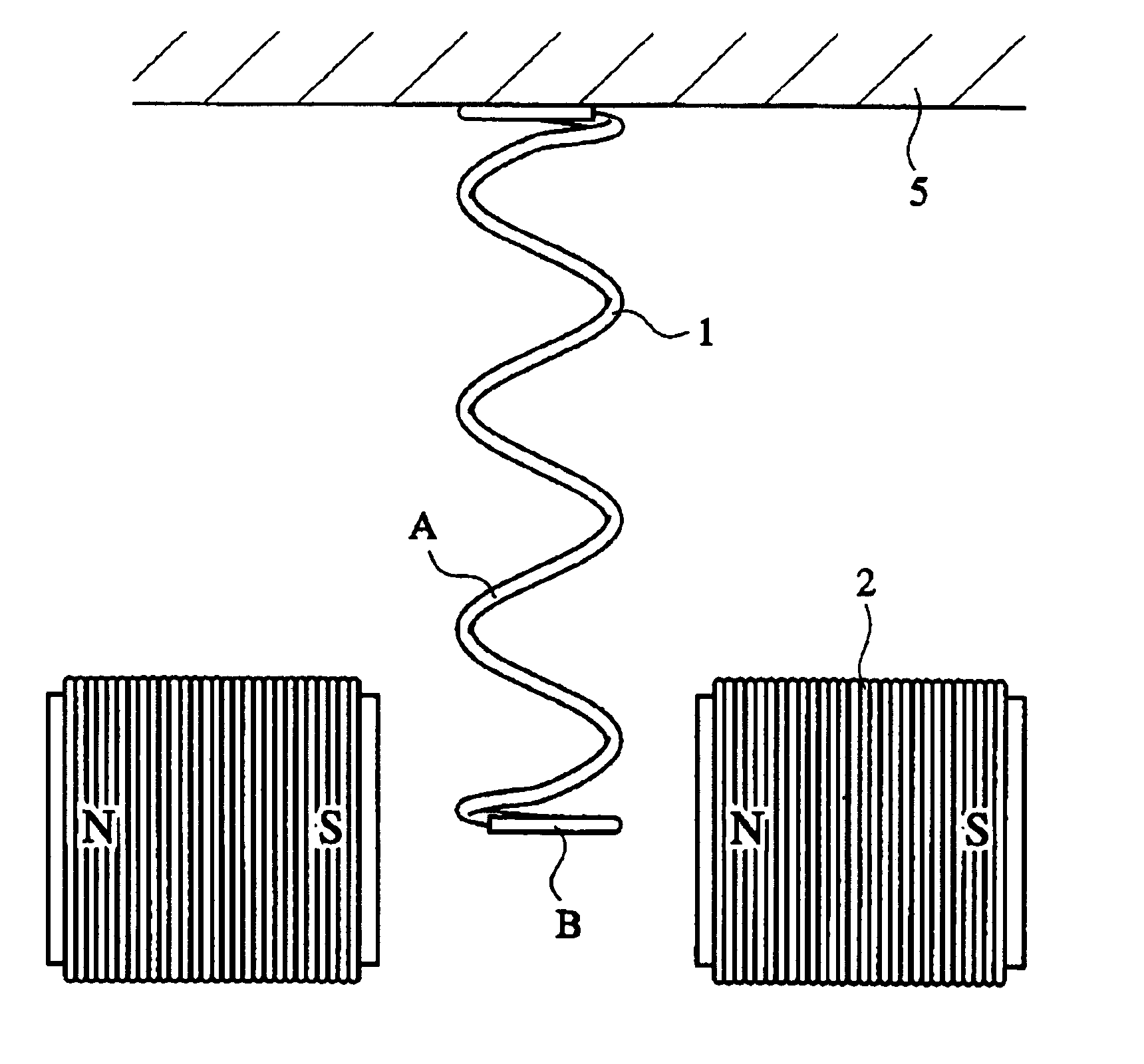
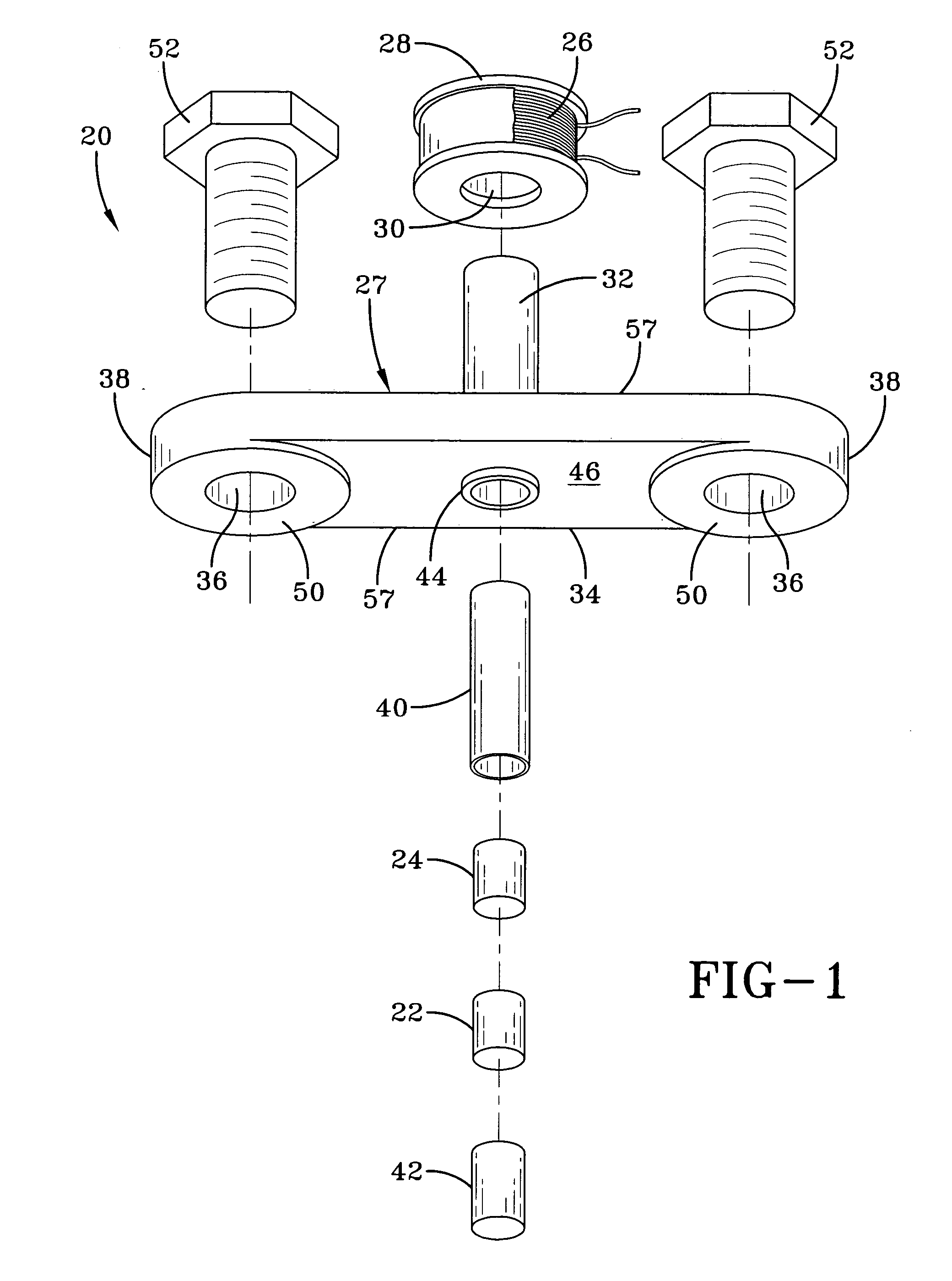
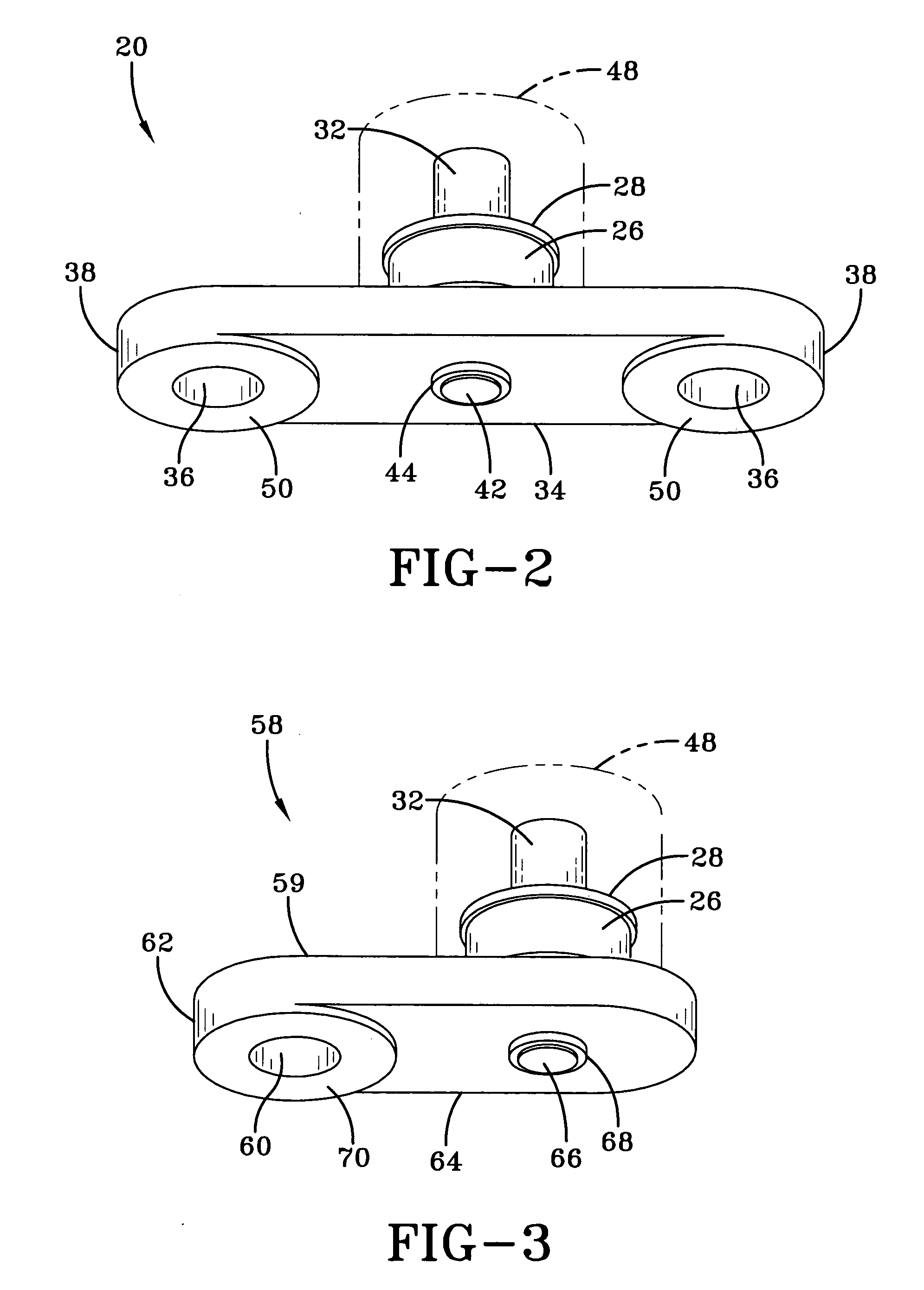
Magnetostrictive stress wave sensor
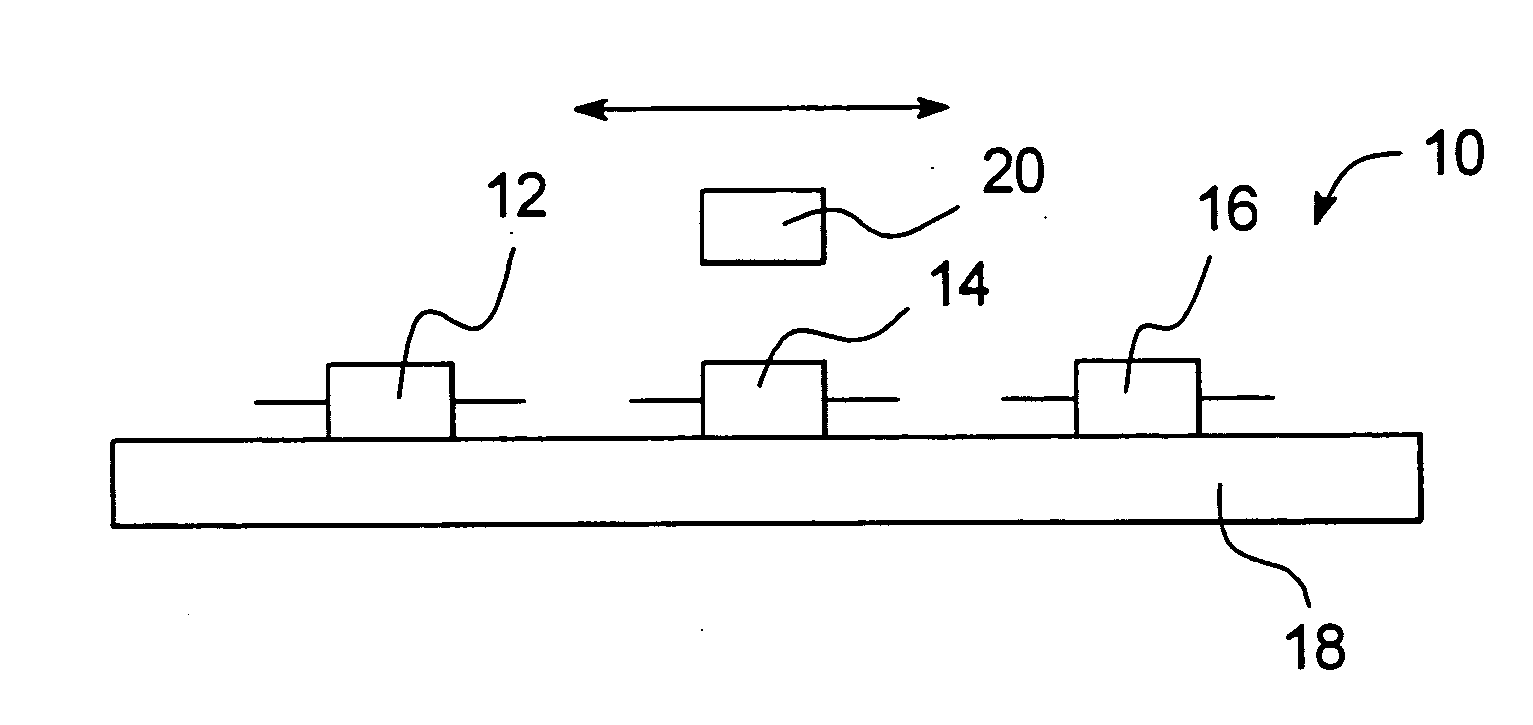
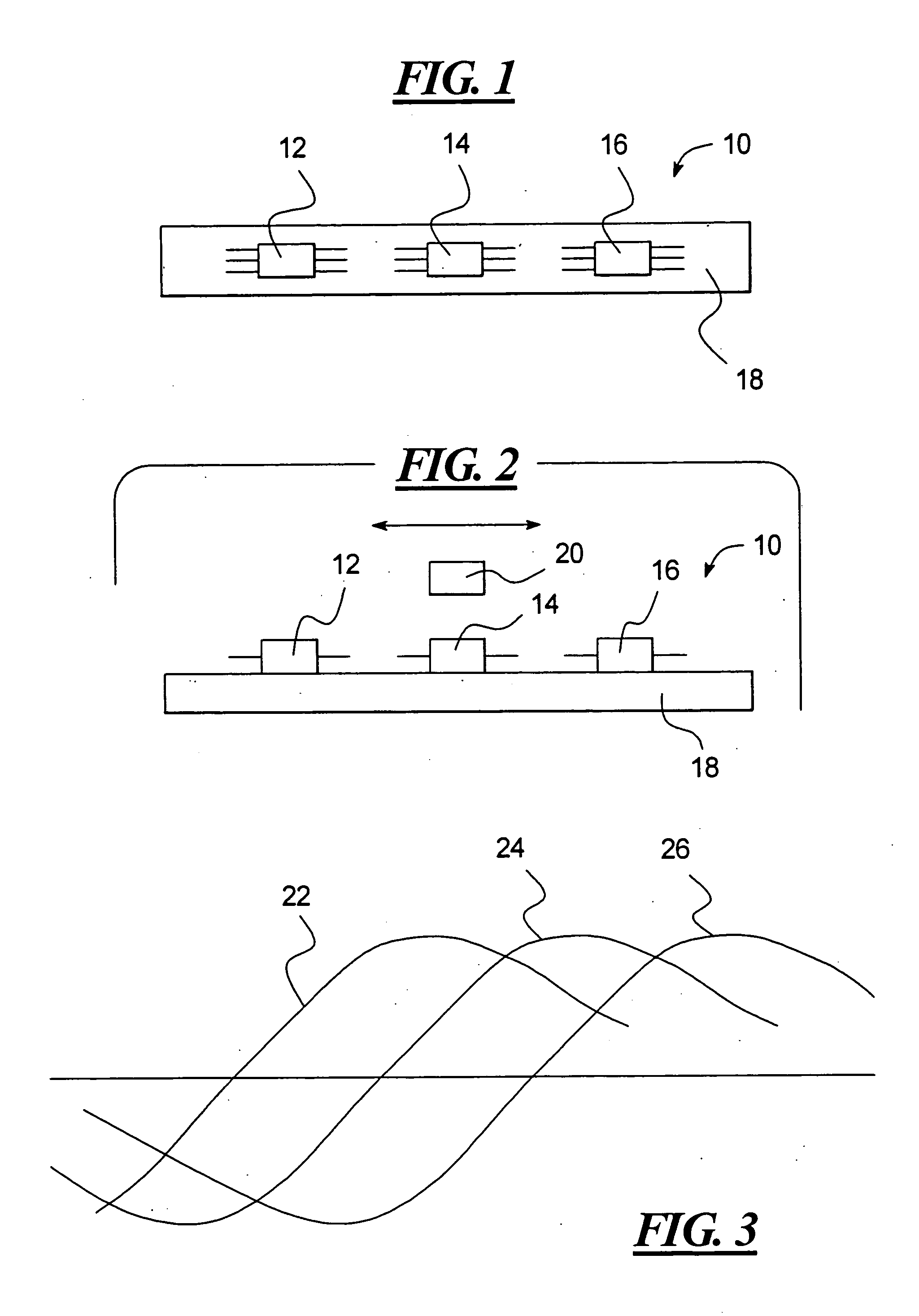
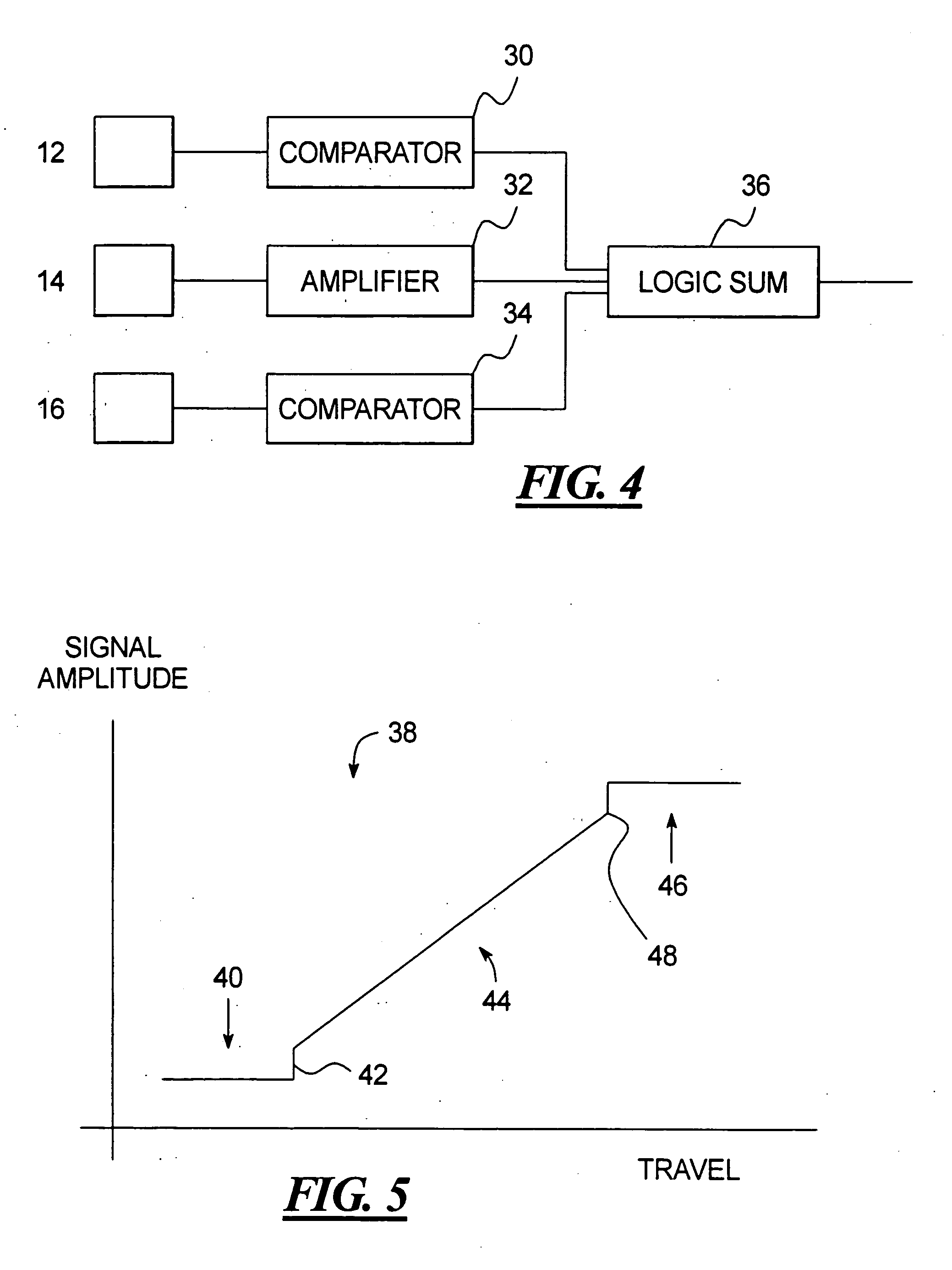
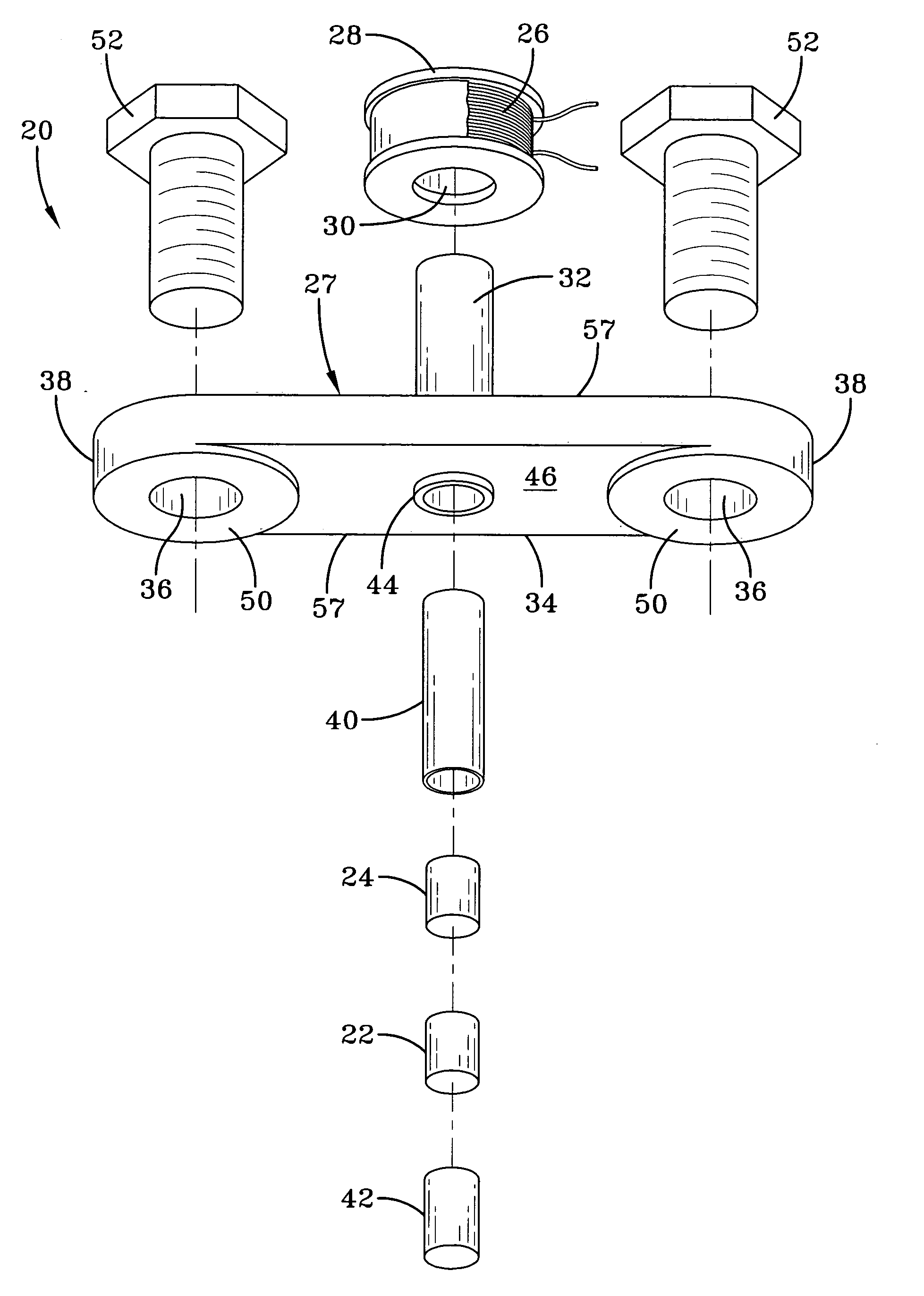
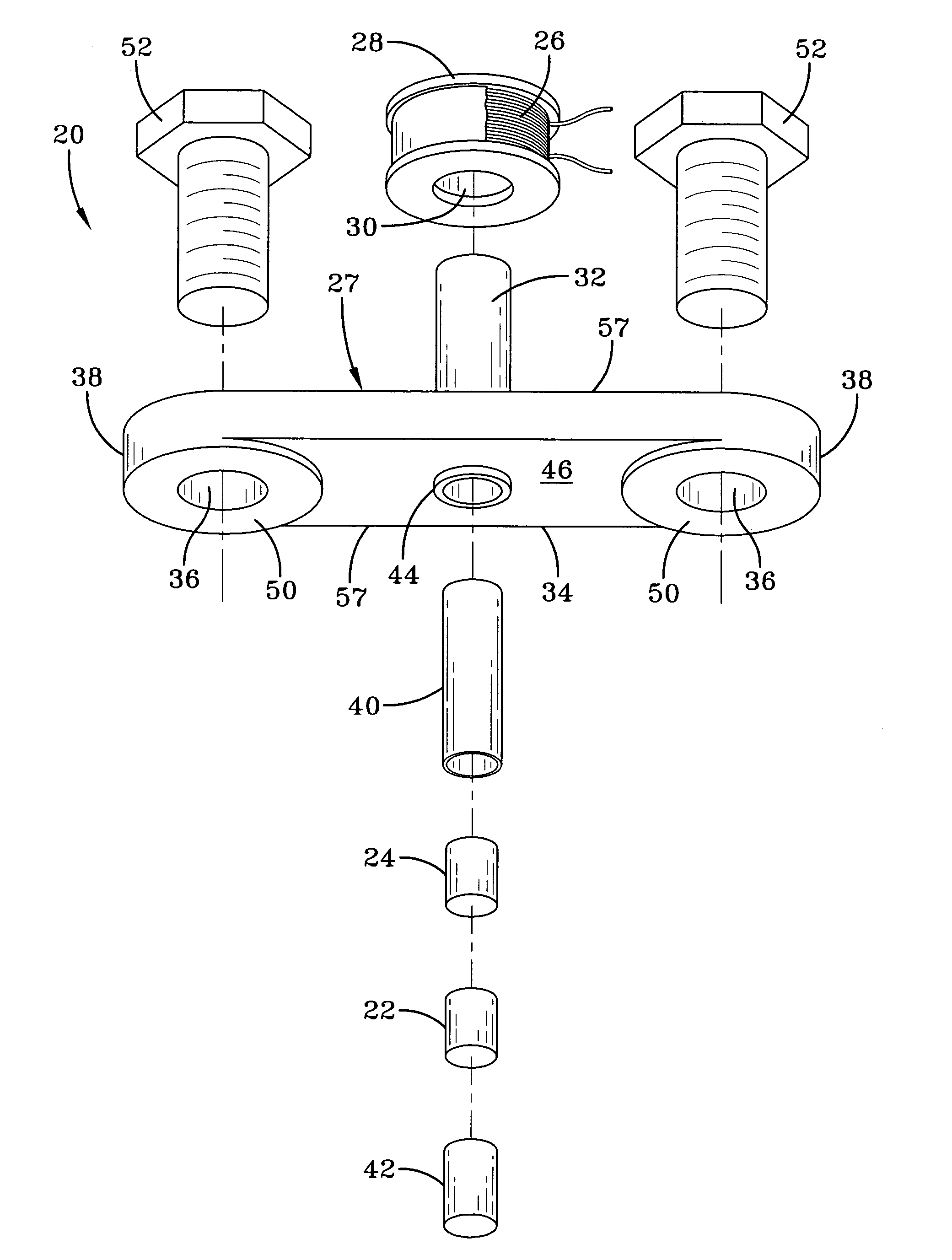
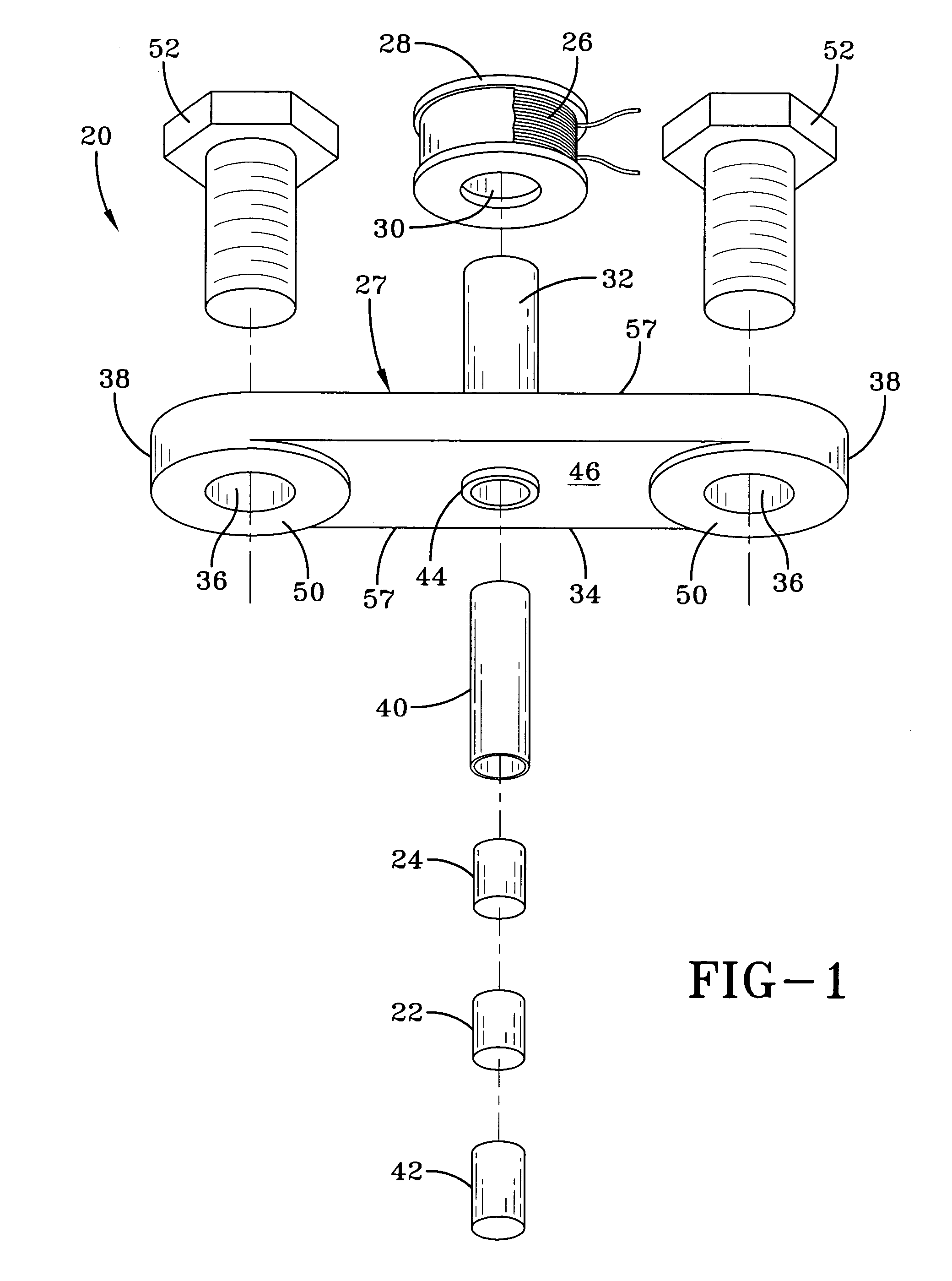
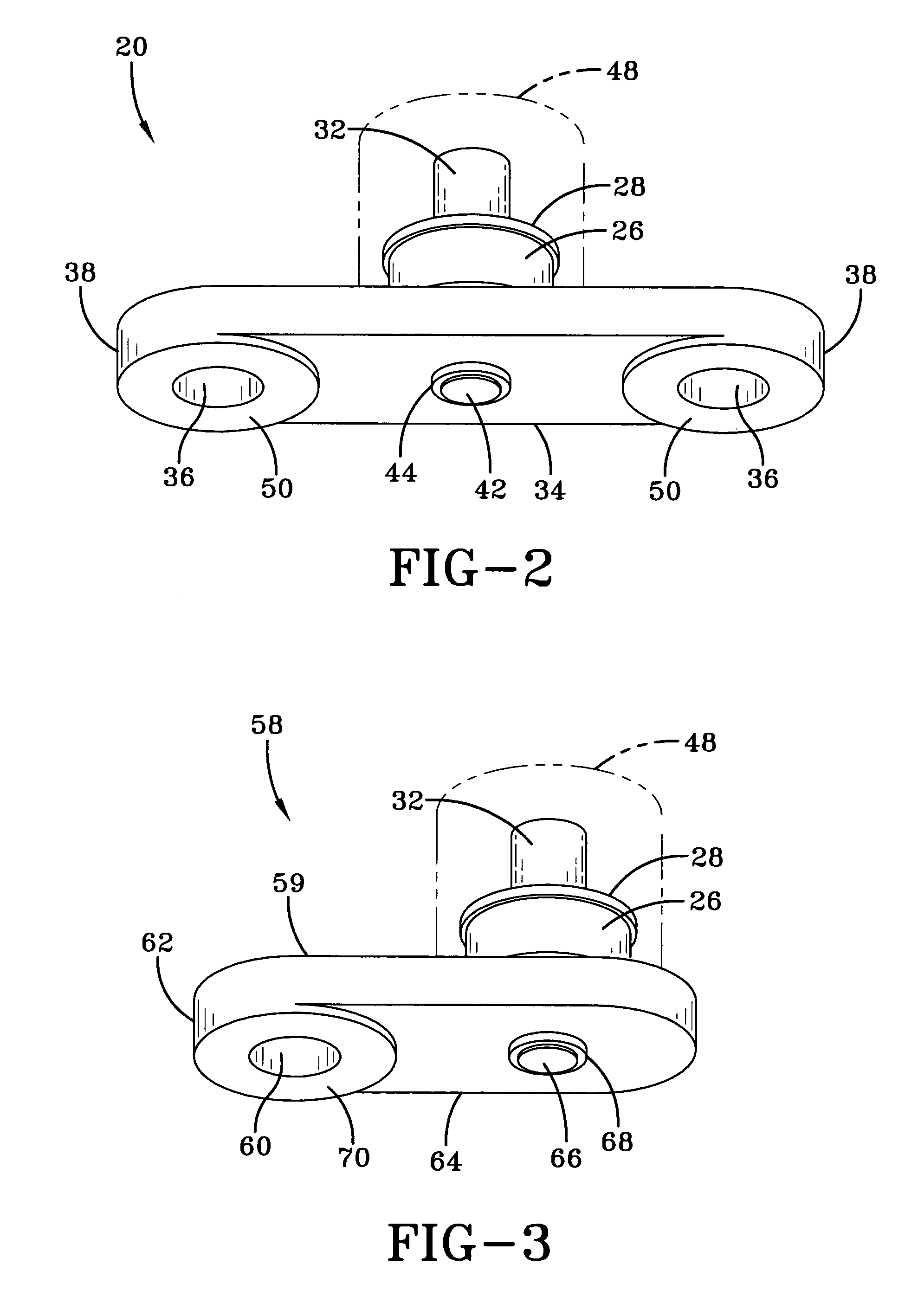
ActiveUS20050194240A1Easy to detectEasy to digitizeVibration measurement in solidsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDc currentElectrical current
A shock sensor has a housing with a Terfenol-D type sensing element positioned inside a sensing coil. A permanent biasing magnet is positioned in engagement with the Terfenol-D sensing element, and a spacer engages the Terfenol-D sensing element and extends from the housing. The housing has a beam with one or two mounting holes through which fasteners extend to mount the shock sensor to a structural member. The housing places the spacer in compression against the structural member. In an alternative embodiment a DC current can be supplied to the sensing coil to provide the biasing magnetic field. A high frequency filter separates the shock sensing signal from the applied DC biasing current.
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
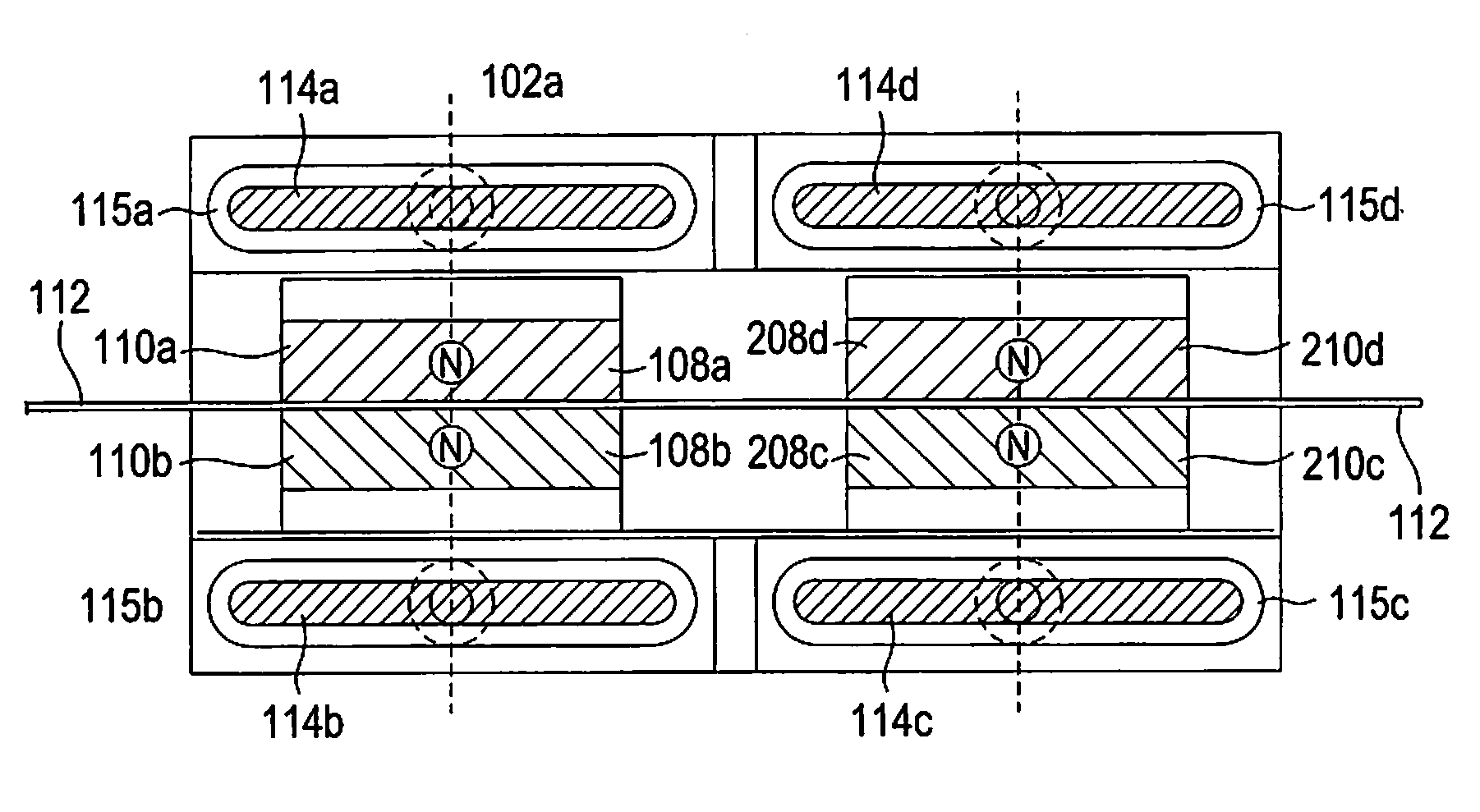
Magnetic sensor, production process of the magnetic sensor and magnetic array suitable for the production process
InactiveUS20050212632A1Efficient magnetizationMaintain detection accuracyNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismElectrical polarityMagnetic orientation
The present invention aims to provide a magnetic sensor provided with a magnetoresistive effect element capable of stably maintaining a direction of magnetization in a magnetic domain of a free layer. The magnetic sensor includes a magnetoresistive effect element provided with narrow zonal portions 11a . . . 11a including a pinned layer and a free layer. Disposed below both ends of the free layer are bias magnet films 11b . . . 11b composed of a permanent magnet that applies to the free layer a bias magnetic field in a predetermined direction and an initializing coil 31 that is disposed in the vicinity of the free layer and applies to the free layer a magnetic field having the direction same as that of the bias magnetic field by being energized under a predetermined condition. Further, magnetizing the bias magnet films and fixing the direction of magnetization of the pinned layer are performed by a magnetic field formed by a magnet array configured such that plural permanent magnets are arranged on a lattice point of a tetragonal lattice and a polarity of a magnet pole of each permanent magnet is different from a polarity of the other adjacent magnet pole spaced by the shortest route.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Stepping flexures
InactiveUS20080079520A1Improve aerodynamic performanceEasy constructionElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetic circuitEngineeringActuator
An actuator for moving a load has a frame forming a race between two surfaces thereof, at least two elements joined together by at least one flexible member, the elements and the at least one flexible member being disposed between the two surfaces of the frame that forms a race, one of the elements further joined to the load by a portion of the at least one flexible member, wherein when an element comes into contact with a surface of the frame it will stick thereto absent a repelling force, and moving means disposed to selectively attract or repel a corresponding element towards or away from one or the other of the two surfaces of the frame that forms the race. The actuator effects movement of the load in a direction towards or away from the elements, by changing a position of at least one of the elements on a surface of the frame that forms the race.
Owner:NASA
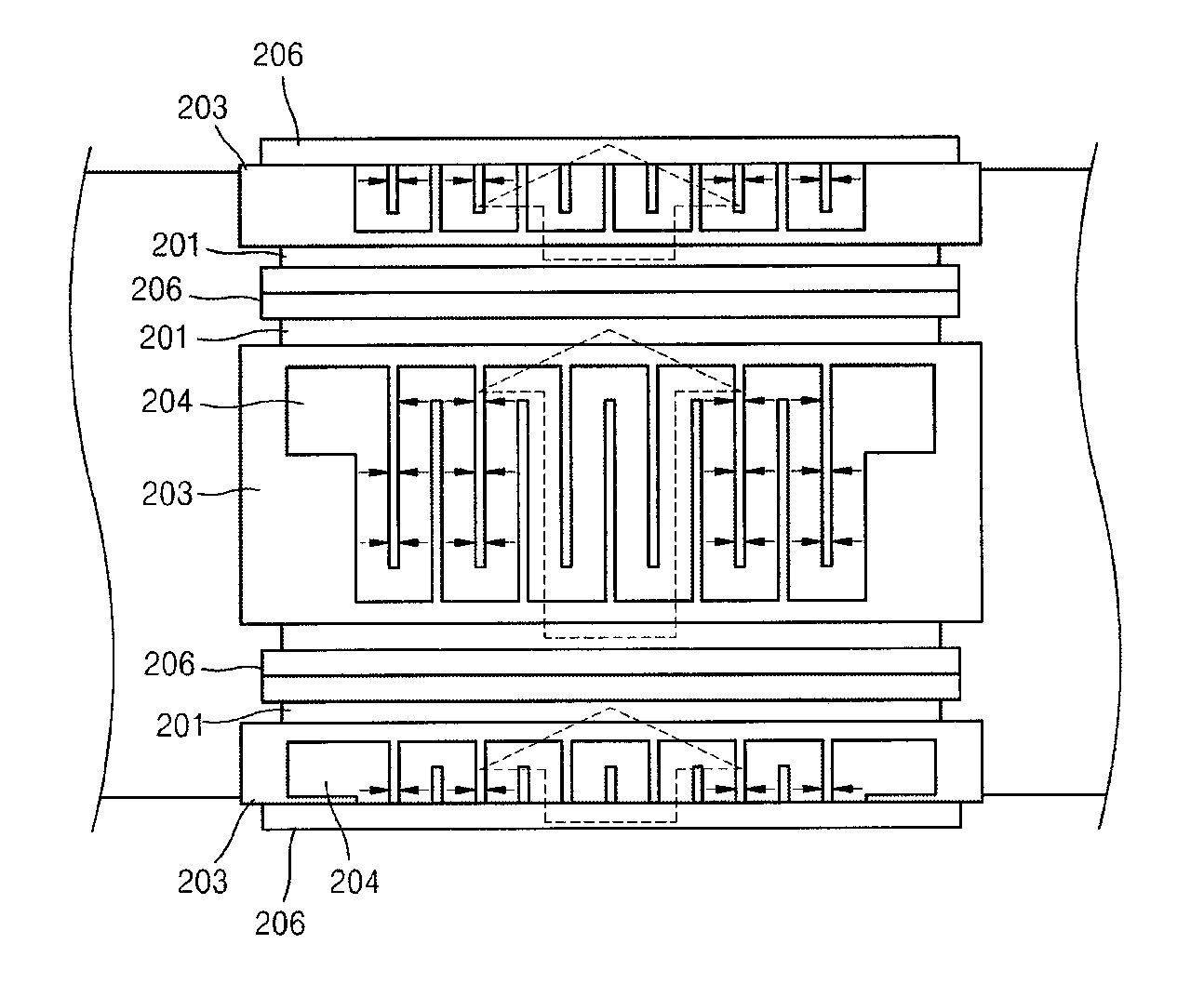
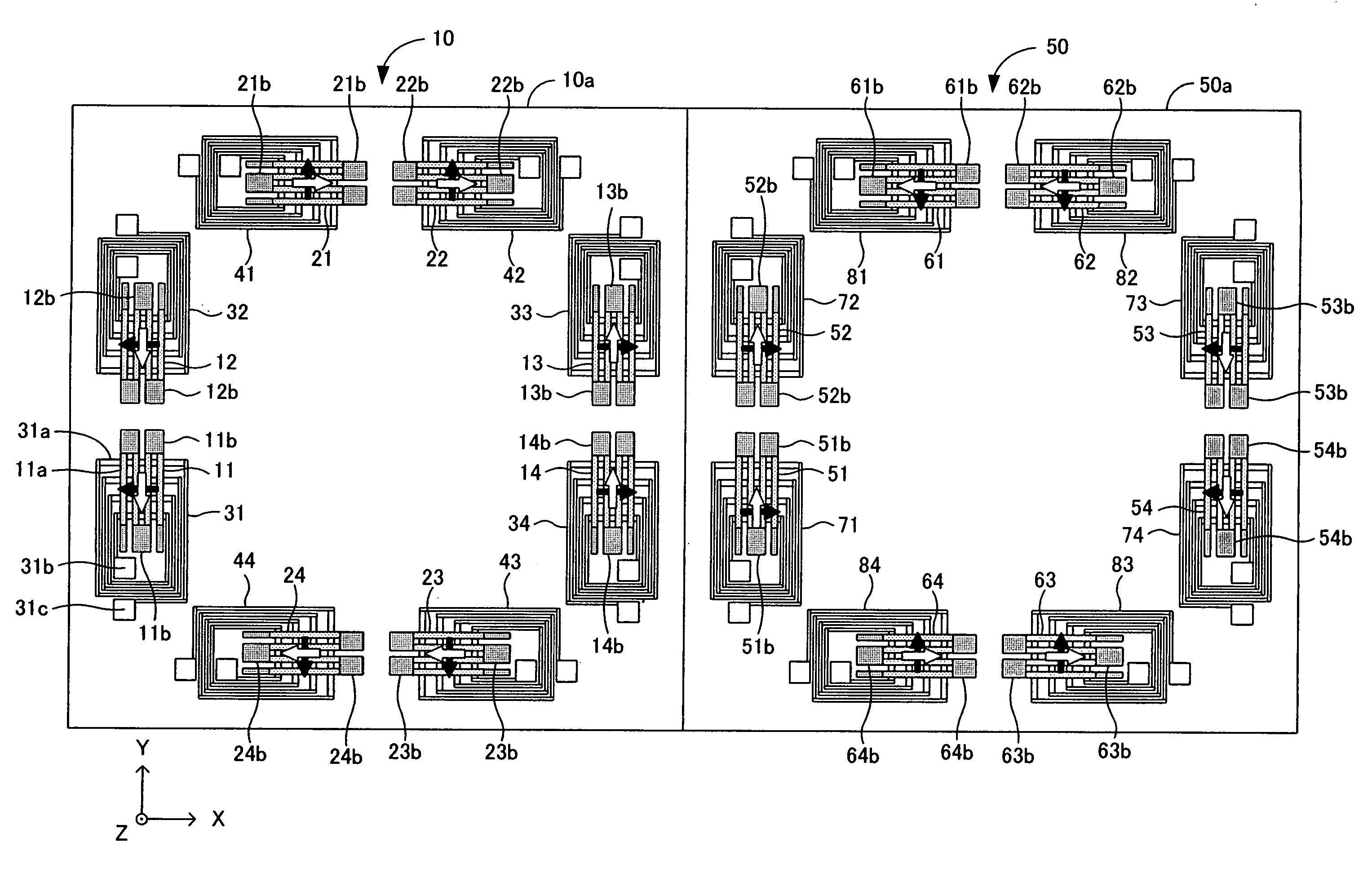
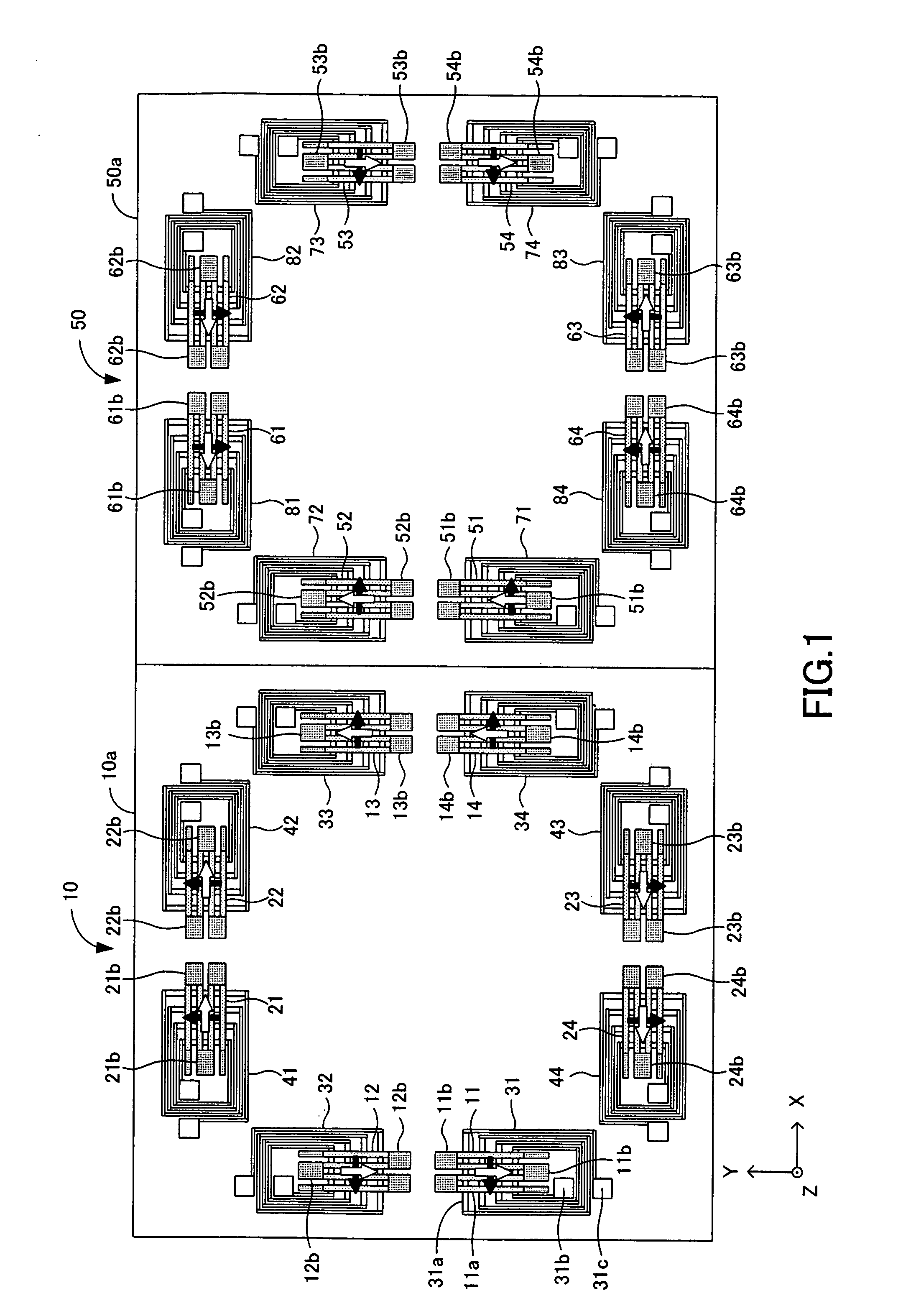
Microelectromechanical system
ActiveUS8174342B2Accurate and reliable operationElectromagnetic relay detailsMagnetostrictive relaysMagnetic actuationMicroelectromechanical systems
The invention relates to microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), and more particularly, to MEMS switches using magnetic actuation. The MEMS switch may be actuated with no internal power consumption. The switch is formed in an integrated solid state MEMS technology. The MEMS switch is micron and / or nanoscale, very reliable and accurate. The MEMS switch can be designed into various architectures, e.g., a cantilever architecture and torsion architecture. The torsion architecture is more efficient than a cantilever architecture.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Resonator Capable of Varying Its Resonance Frequency and Method for Varying Its Resonance Frequency
InactiveUS20090115289A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMagnetsResonanceActuator
The present invention provides a resonator capable of varying its resonance frequency of good performance with a low dispersion at a high manufacturing yield and a low cost. The resonator comprises a fixed electrode 1; a movable electrode 3 arranged with a predetermined distance apart from and parallel to the fixed electrode; a plurality of conductive leaf springs 2 with conductive property, all of which are bent outward or inward beforehand, arranged parallel apart from each other wherein, one end of each leaf spring is integrated into the fixed electrode and the other end of each leaf spring is integrated into the movable electrode; and an actuator 6 attached to the movable electrode for deforming the leaf springs by pushing or pulling the movable electrode.
Owner:MICROPRECISION
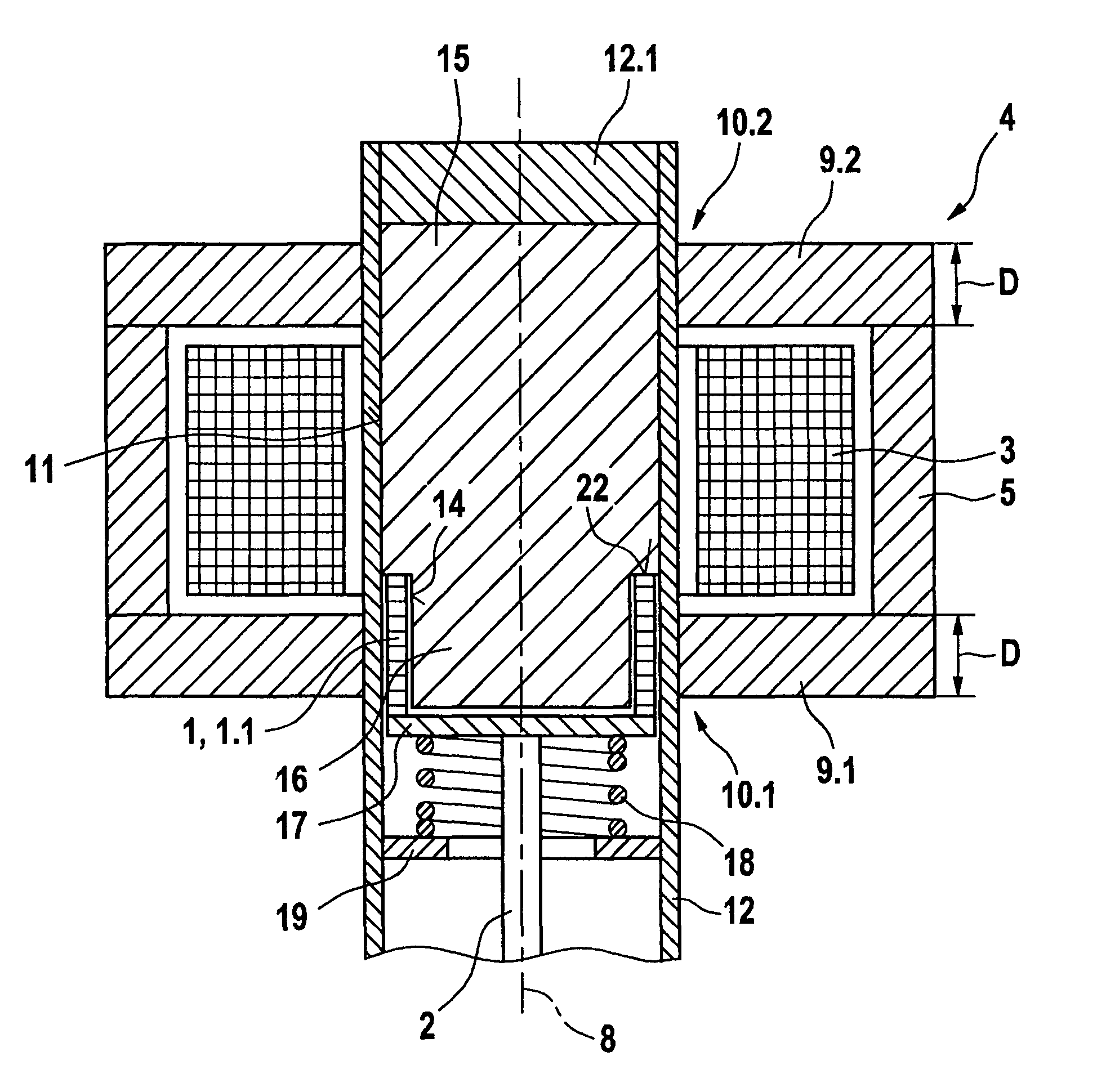
Electromechanical switch
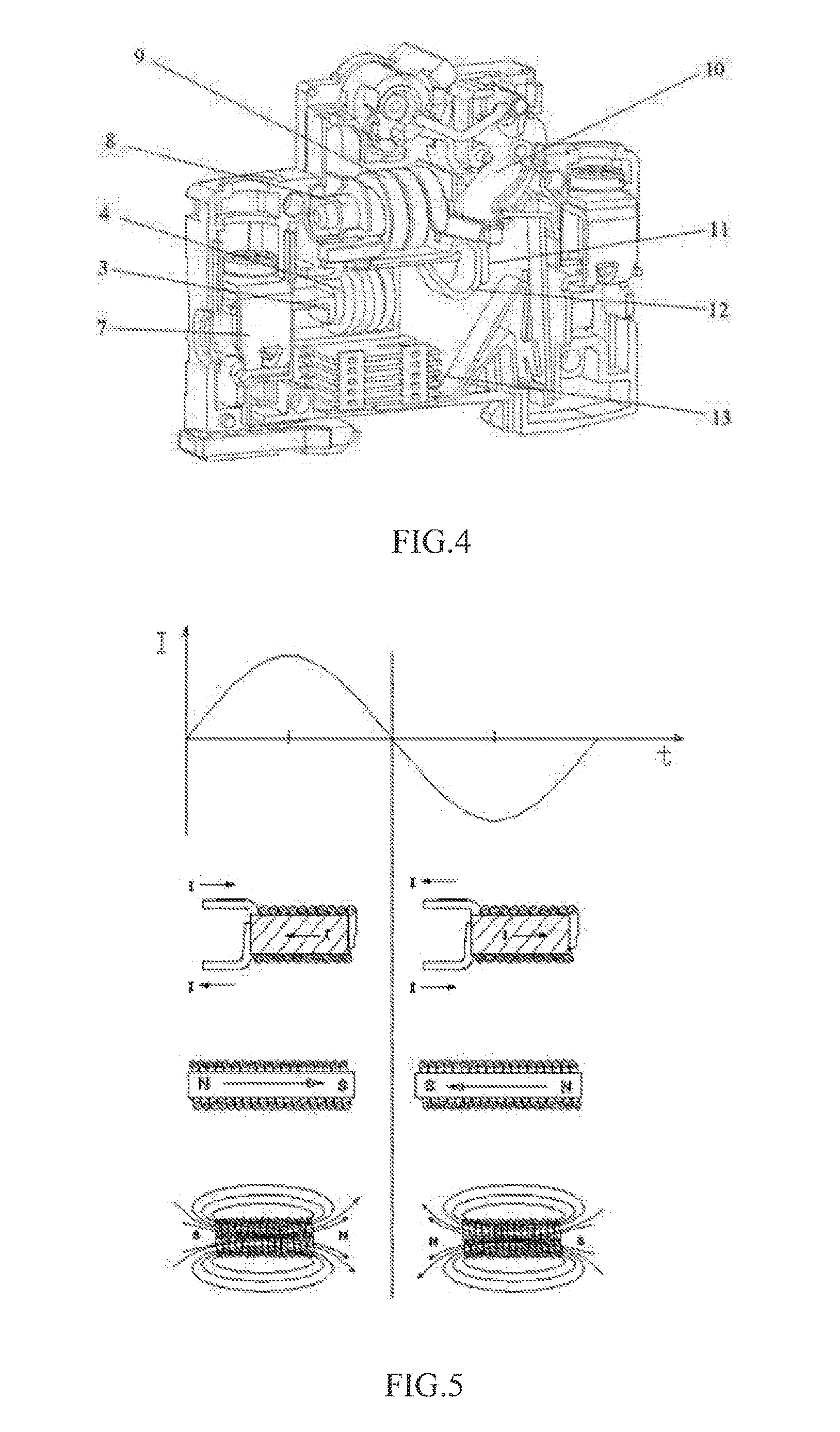
There is provided an electro-mechanical switch capable of performing high-speed switching response with a low drive voltage. An electro-mechanical switch main body (10) which is a MEMS switch includes a first movable electrode (14) and a second movable electrode (16) having both ends fixed and bridged by a first anchor (12) and a second anchor (13) formed on a silicon substrate (2) and a fixed electrode (18) opposing to these movable electrodes. The first movable electrode (14) having a relatively weak spring force and the fixed electrode (18) constitute a first electro-mechanical switch (22) which can be driven with a low voltage. The second movable electrode (16) having a relatively strong spring force and the fixed electrode (18) constitute a second electro-mechanical switch (24) which can be driven and latched with a low voltage. The first movable electrode (14) is rapidly displaced by a low drive voltage to rapidly turn on the first electro-mechanical switch and the second movable electrode (16) rapidly performs natural oscillation by the restoration force to rapidly turn off the second electro-mechanical switch. The returning second movable electrode (16) is latched with low drive voltage and the second electro-mechanical switch is turned on.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
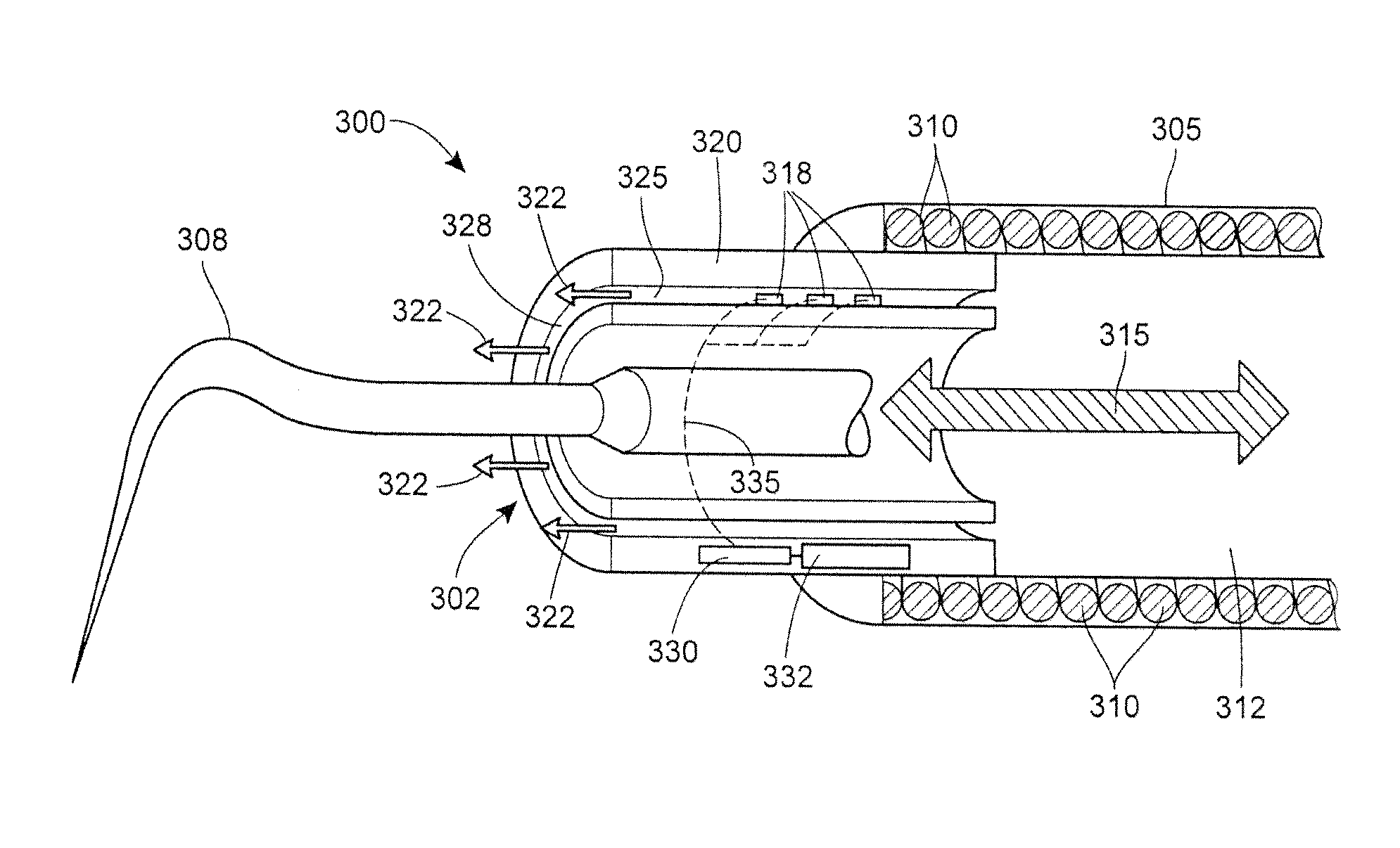
Ultrafast electromechanical disconnect switch
ActiveUS20160329182A1Ultrafast voltage withstand capabilityHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesMagnetostrictive relaysElectricityElectrical conductor
An ultrafast electrical (e.g., transfer, disconnect, etc.) switch that is simple, compact, does not require high energy to operate, ultralow loss, clean, and capable of being automatically reset. The invention includes a fast electromechanical switch having a drive mechanism integrated into the switching chamber. The integration of the drive mechanism into the switching chamber provides faster contact travel and therefore a faster switching operation. Additionally, the switching chamber is a self-contained environment that may consist of a high-pressure gas or a vacuum. The invention further includes an ultrafast disconnect switch. The invention generally is an integrated piezoelectric-actuator-based mechanical switching mechanism. The mechanism has a central piezoelectric actuator that extends to pull contacts inwards in order to obtain two disconnects within a millisecond or less. Surrounding the piezoelectric actuator is a polymer insulating shell and beyond the shell is the metallic conductor.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
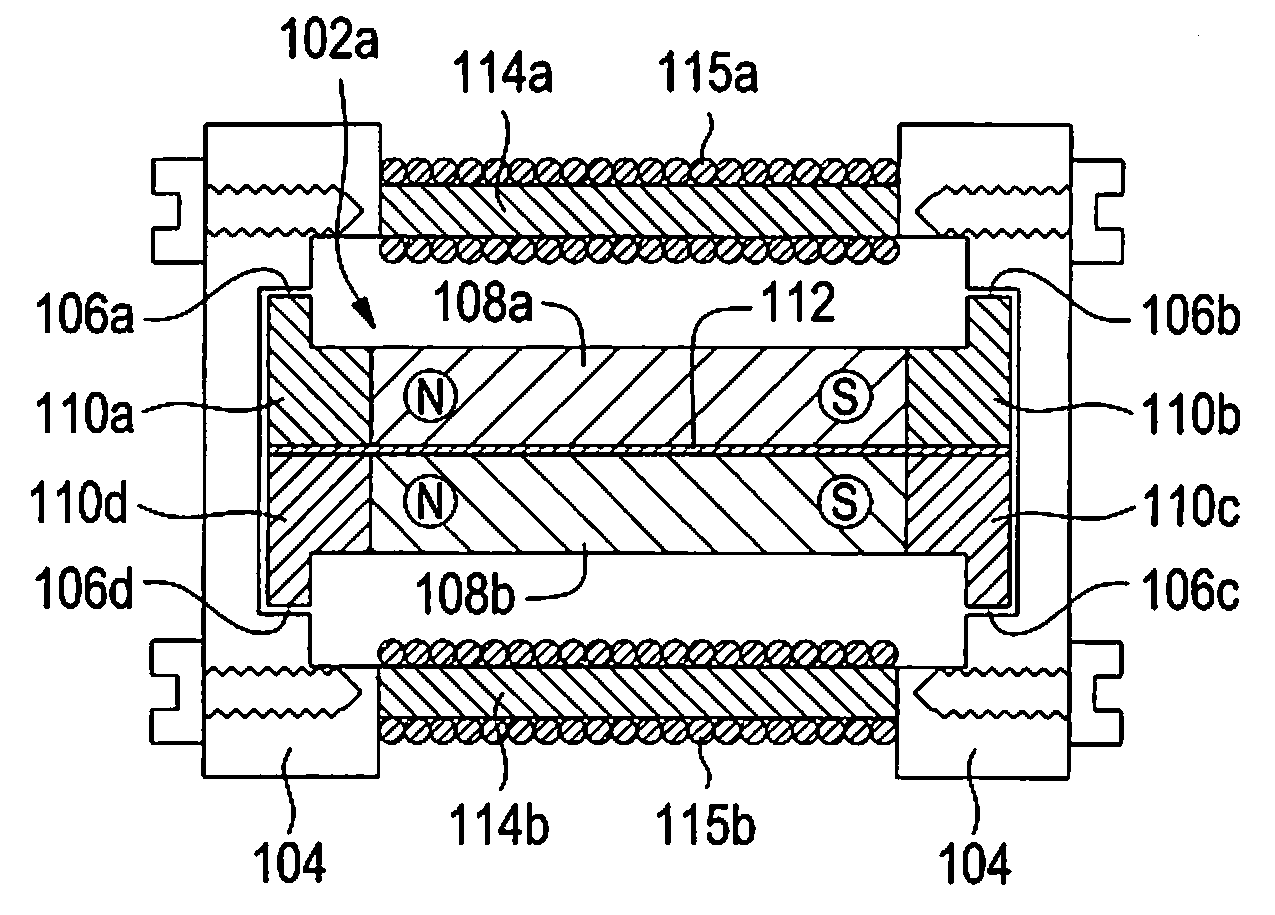
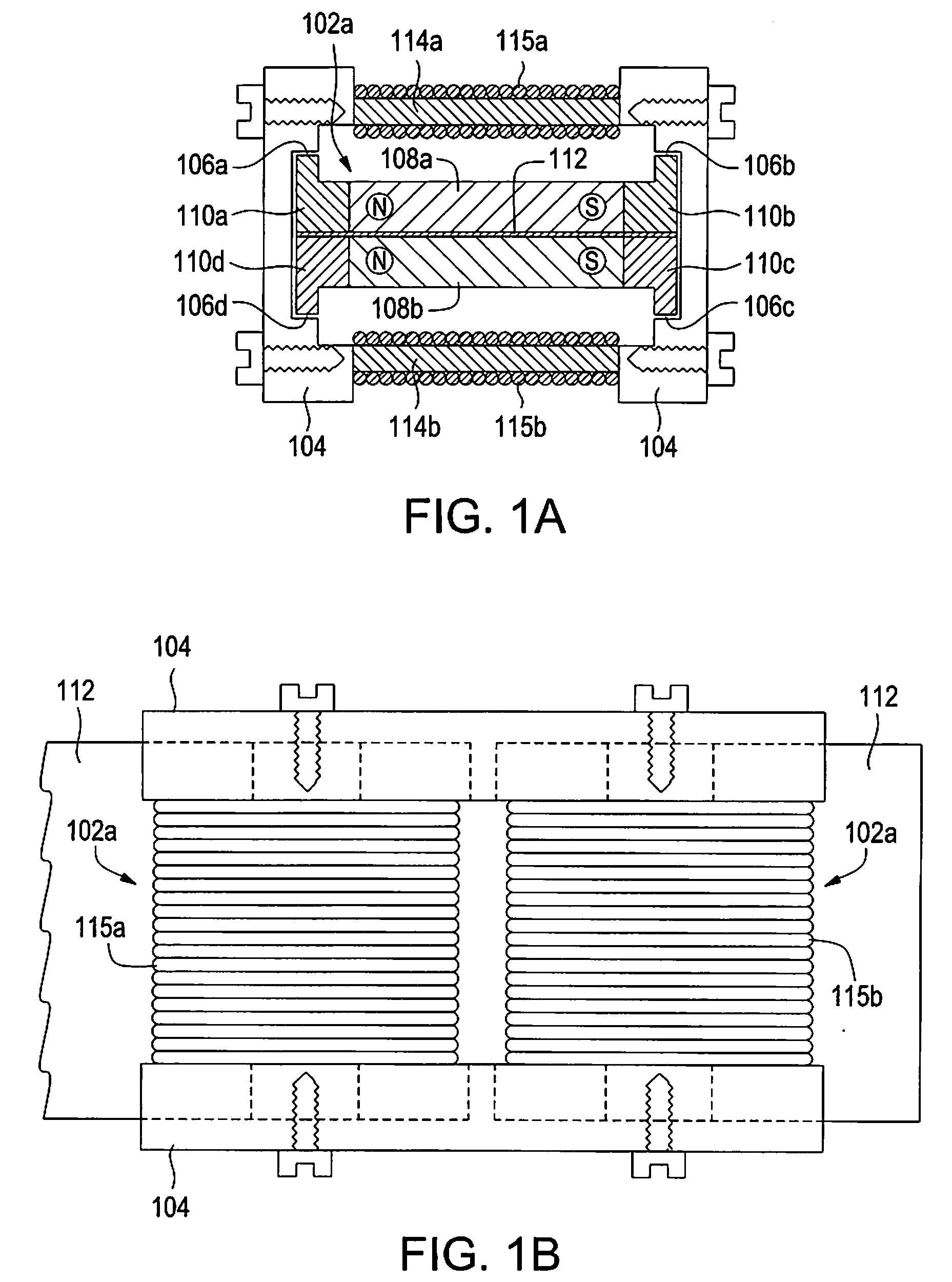
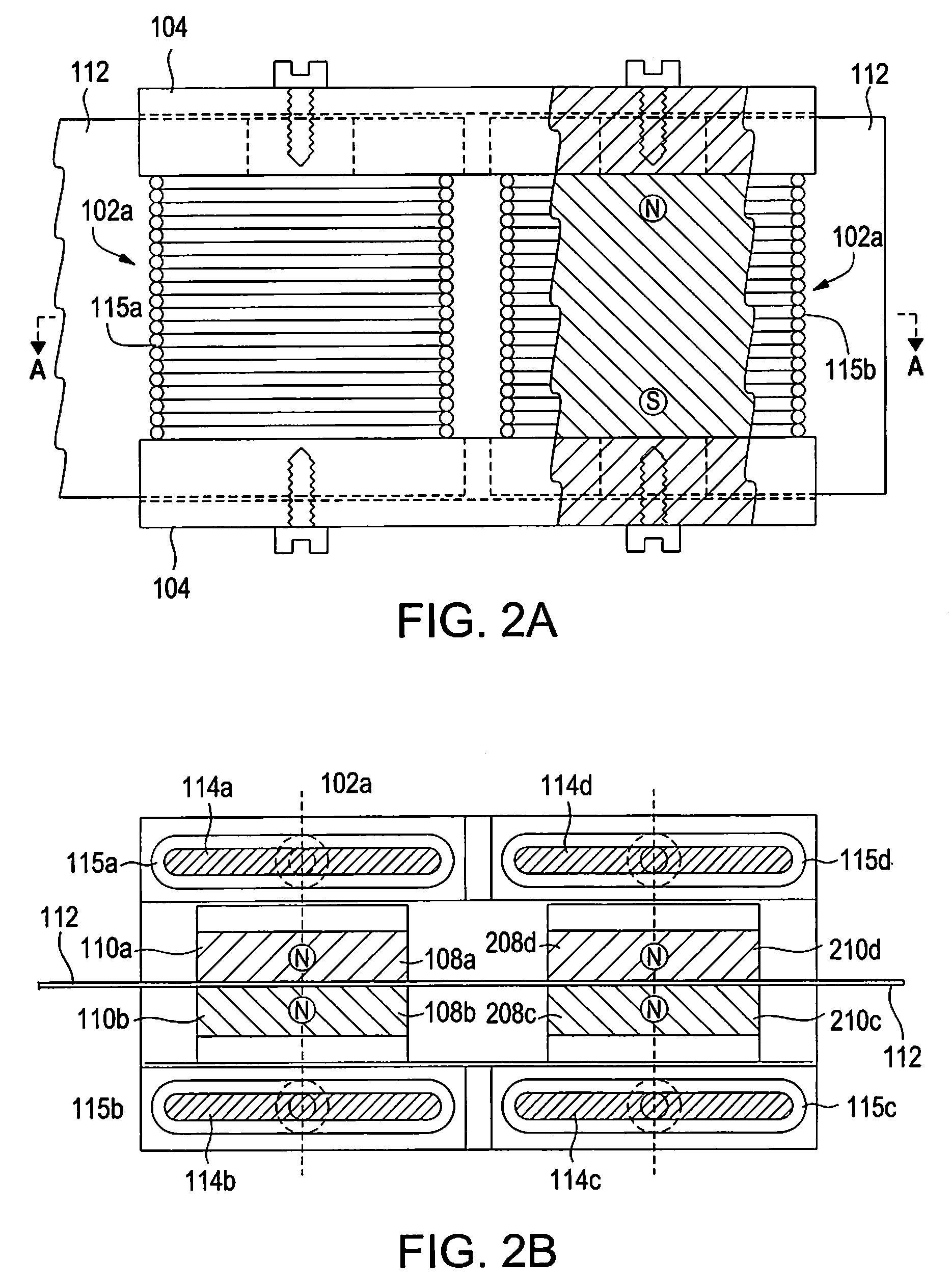
Device having a shape memory element
InactiveUS8237525B2Travel can be limitedDifferent thermal expansionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesEngineeringRisk stroke
Conventional devices have a valve needle and a shape memory element which, by the application of a controllable magnetic field, executes a control stroke travel that operates the actuator, and having a coil that excites the magnetic field which is situated in a magnet housing which, at its end face, is bordered with respect to an actuating axis by a front wall in each case, the front walls having a through opening radially within the coil. It is a disadvantage that the magnetic field excited around the coil is conducted unfavorably, so that at most a slight magnetic field develops in the shape memory element. The shape memory element has a magnetic field flowing through it, in the direction of its longitudinal extension, if at all. Since the shape memory element has a high magnetic resistance and is developed to be very long in the axial direction, only a very weak magnetic field can be induced in the shape memory element. In response to the magnetic field that is weak at most, the shape memory element can generate only a very slight lift of the valve needle. In the device according to the present invention, a strong magnetic field is conducted through the shape memory elements, and in this way, a large control stroke travel is achieved. The shape memory element(s) is / are positioned generally only in the through opening(s).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
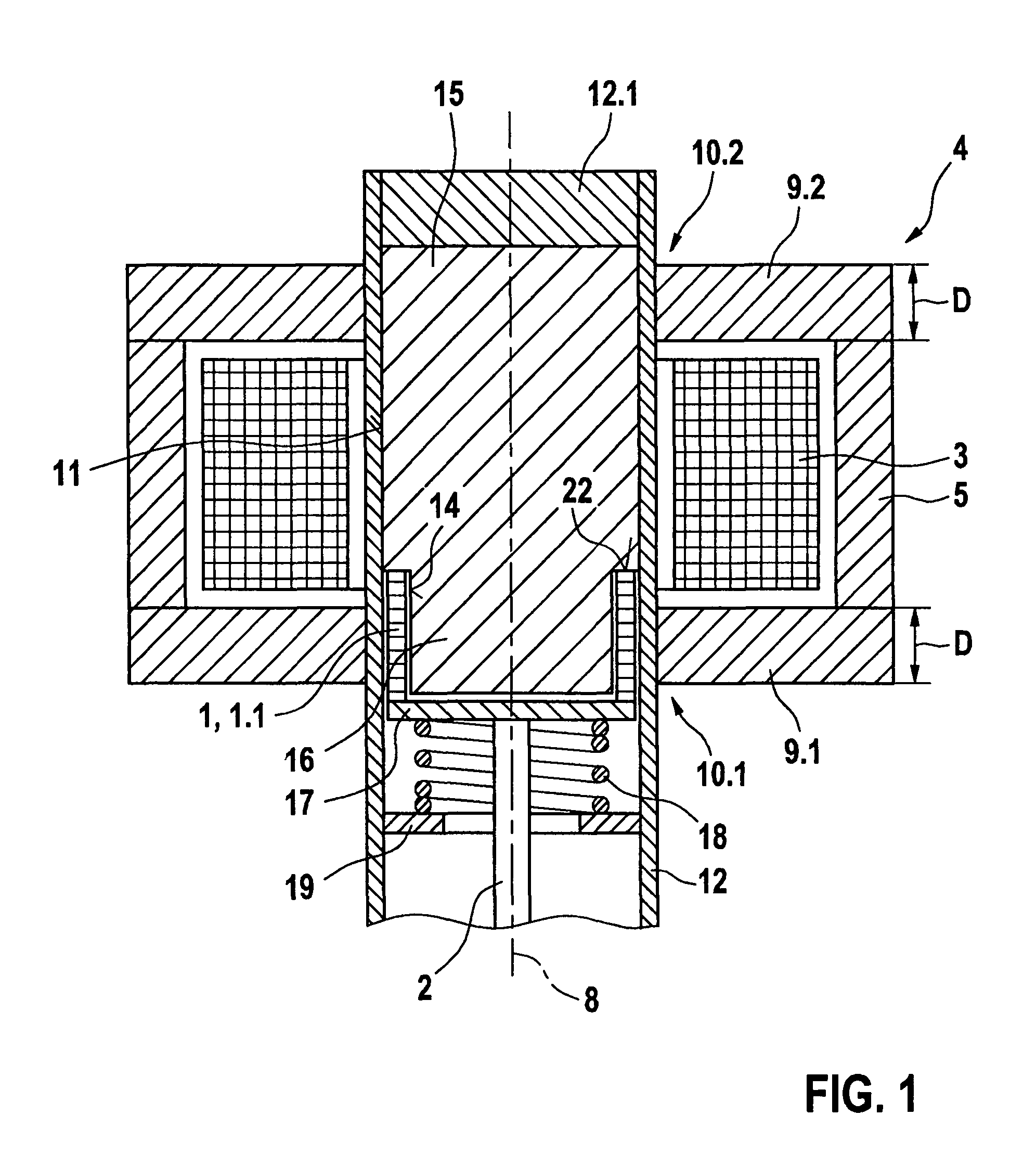
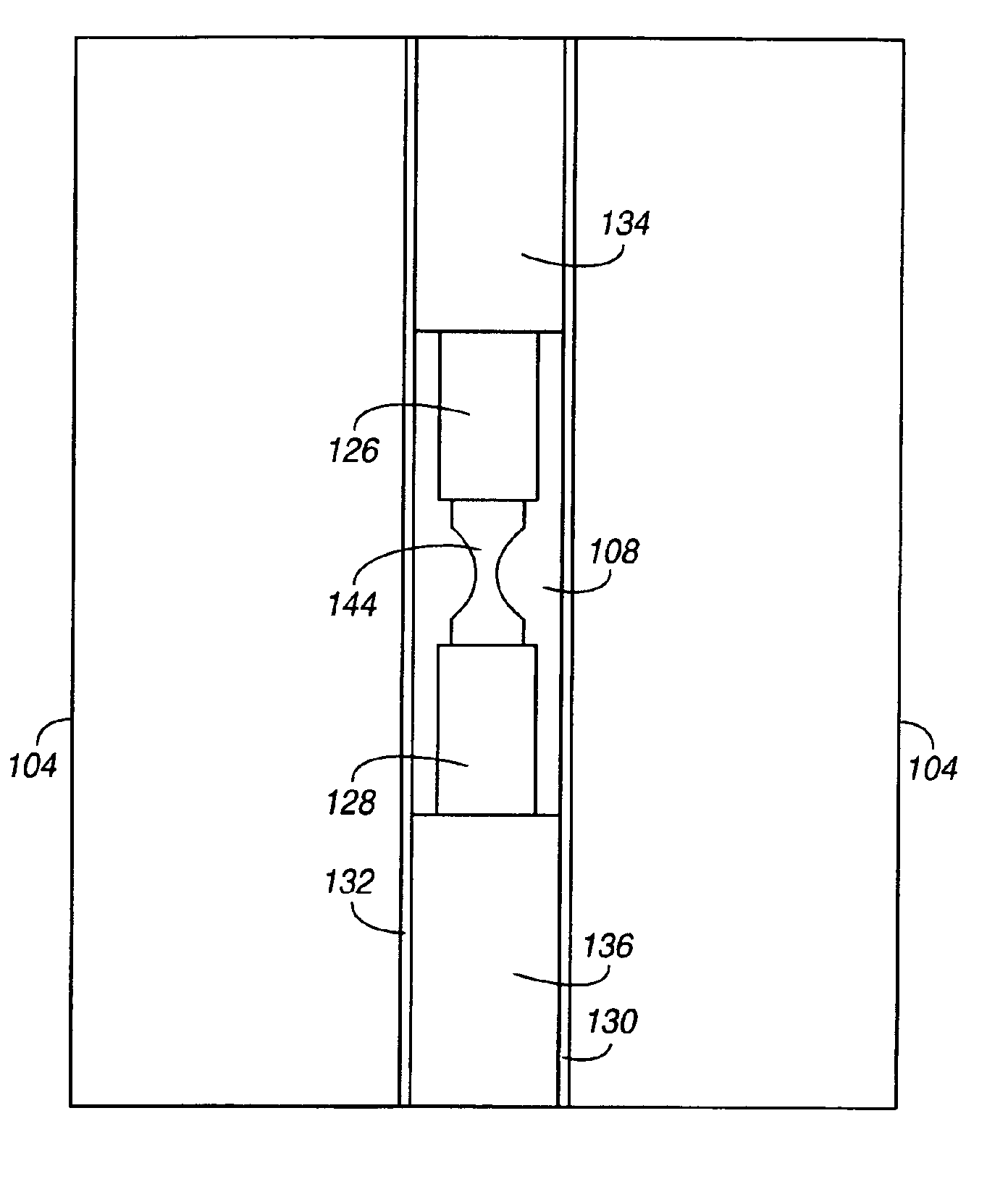
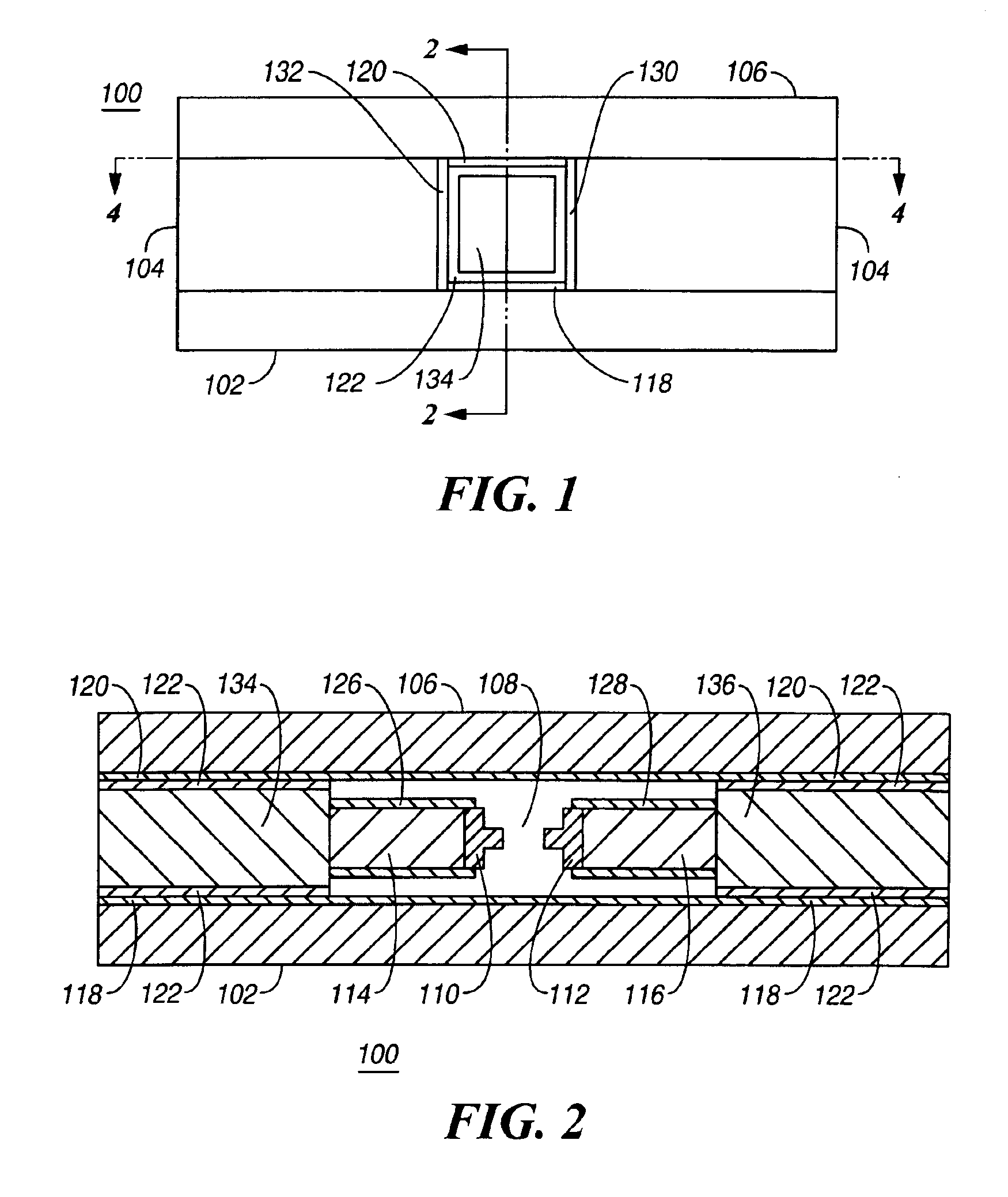
High-frequency, liquid metal, latching relay with face contact
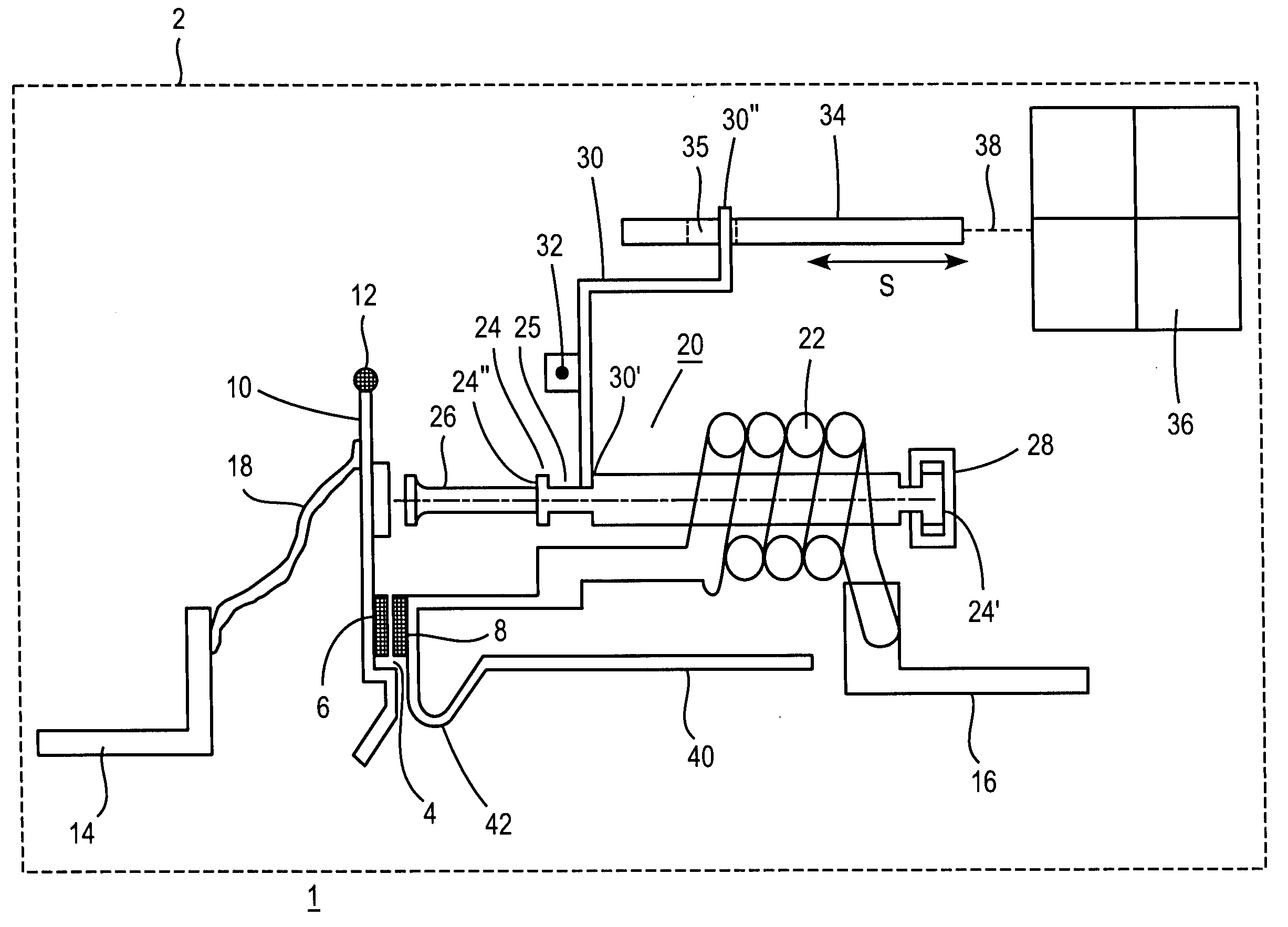
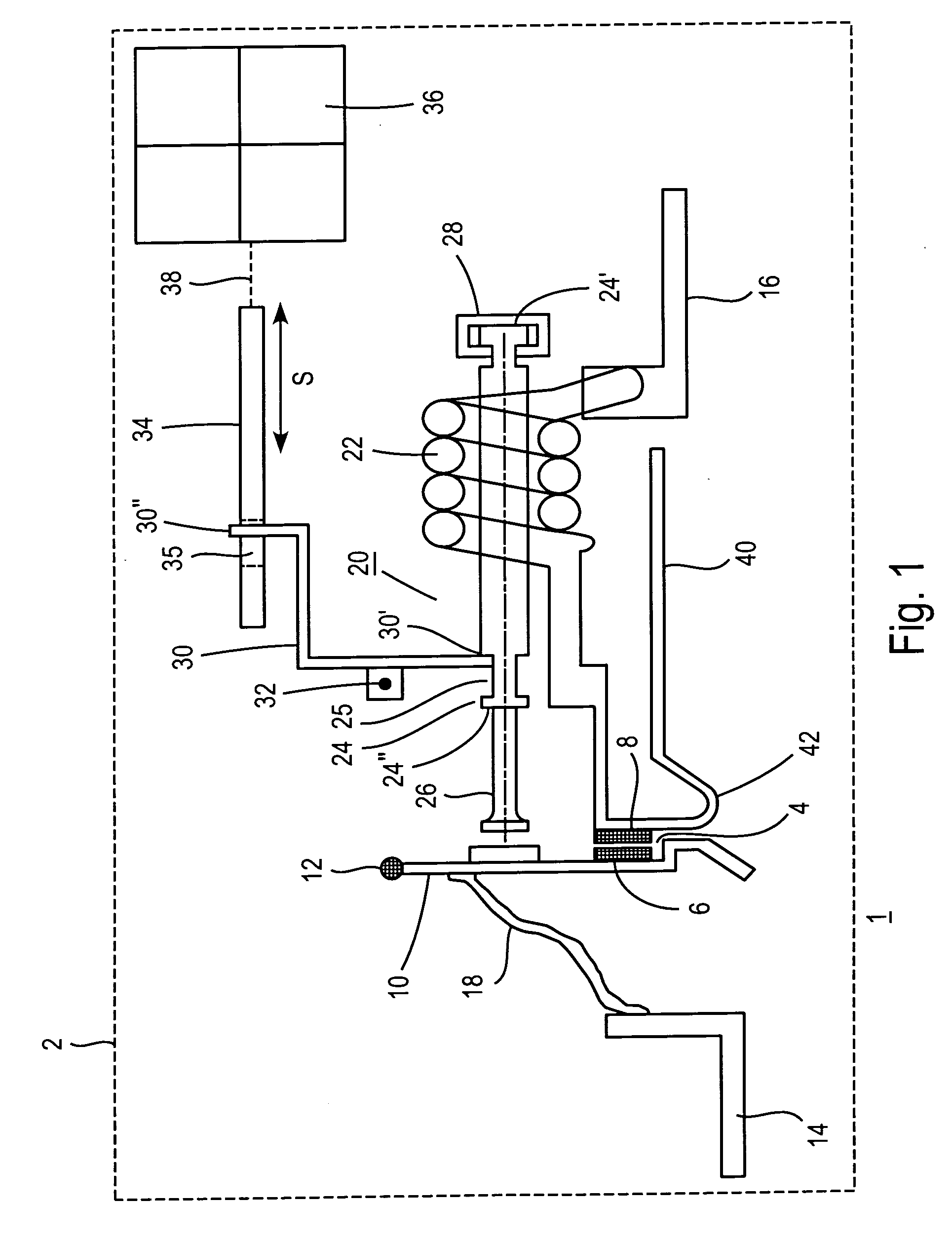
InactiveUS6876131B2Increase the gapHigh-frequency switchingContact surface shape/structurePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric actuatorsHemt circuits
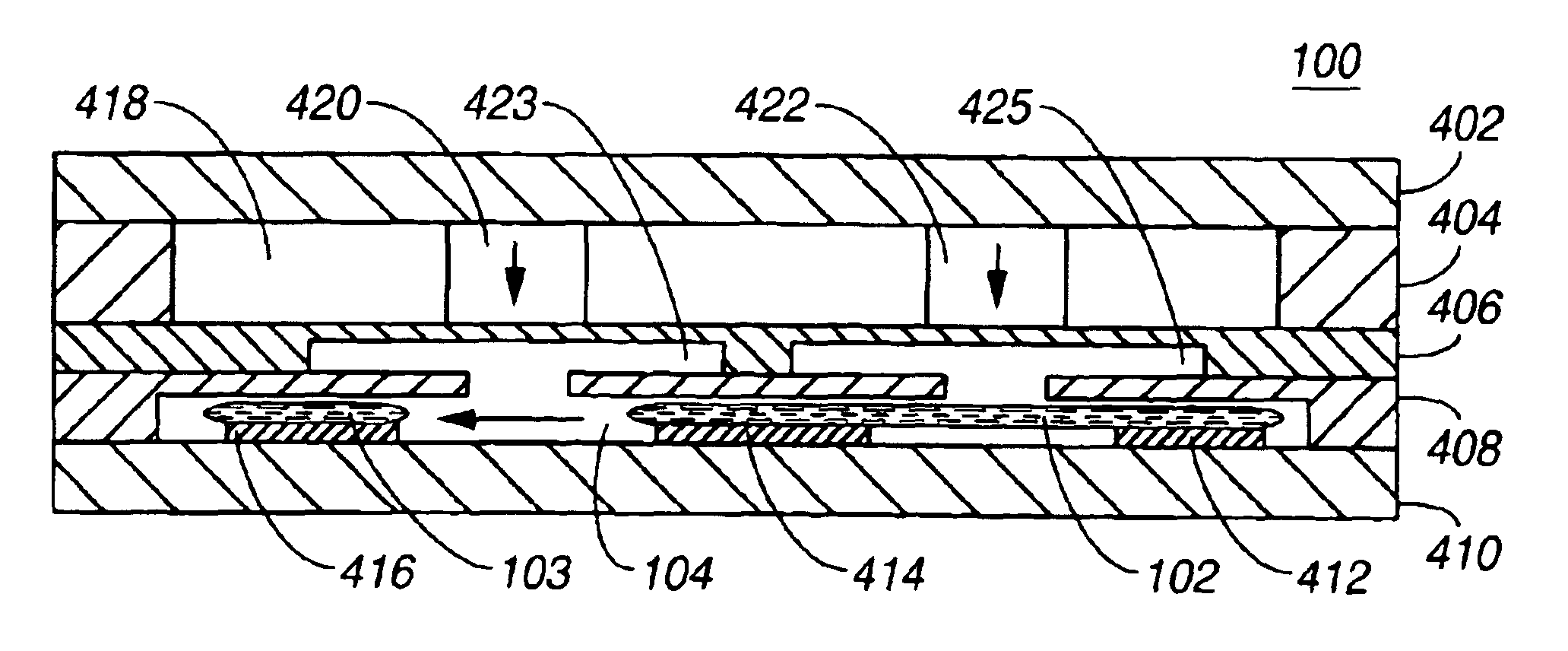
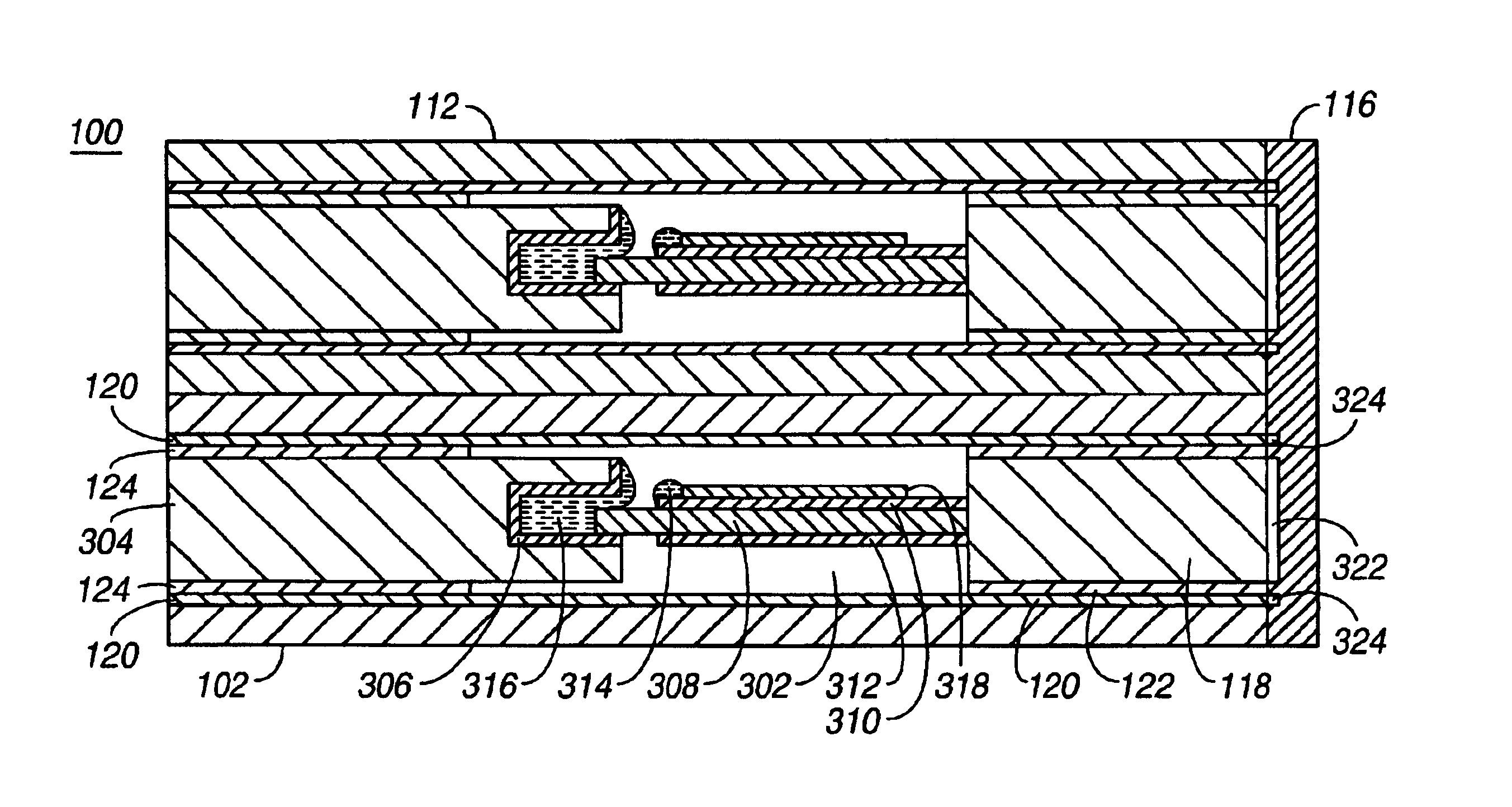
An electrical relay using conducting liquid in the switching mechanism. The relay is amenable to manufacture by micro-machining techniques. In the relay, two electrical contacts are held a small distance apart. The facing surfaces of the contacts each support a droplet of a conducting liquid, such as a liquid metal. An actuator is energized to reduce the gap between the electrical contacts, causing the two liquid metal droplets to coalesce and form an electrical circuit. The actuator is then de-energized and the electrical contacts return to their starting positions. The liquid metal droplets remain coalesced because of surface tension. The electrical circuit is broken by energizing an actuator to increase the gap between the electrical contacts and break the surface tension bond between the liquid metal droplets. The droplets remain separated when the piezoelectric actuator is de-energized because there is insufficient liquid metal to bridge the gap between the contacts. Additional conductors are included in the assembly to provide a coaxial structure and allow for high frequency switching.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Integrated, Lighted Ultrasonic Inserts
InactiveUS20110140815A1Minimal fluctuationEasy to chargeBatteries circuit arrangementsMagnetsElectricityLight equipment
Embodiments of a magnetostrictive device, a dental lighting system, a method of illuminating a lighting apparatus and a lighting apparatus are disclosed. The embodiments may include a lighting apparatus with a light source, an electrical power storage device and a switch. When the switch detects a magnetic field, the switch may complete an electrical connection between the electrical power storage device and the switch, thus illuminating the light source. The magnetic field may be magnetostrictively or non-magnetostrictively generated, and maybe be produced by a receptacle, a hand-piece or the lighting apparatus itself. A user may switch the light source on and off. In a magnetostrictive device, the light may be illuminated even when a tip is not activated, and the electrical power storage device may be inductively re-charged. The lighting apparatus may be included in an insert of a magnetostrictive device, such as a magnetostrictive ultrasonic hand-held dental device.
Owner:HU FRIEDY MFG
Magnetostrictive electrical switching device
InactiveCN101390180AMagnetostrictive relaysProtective switch operating/release mechanismsShape-memory alloyElectrical switching
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Circuit Breaker for hierarchically controlling short-circuit current and trips
ActiveUS20170047183A1Reduced power rangeAvoiding large-area power failure accidentHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesAir-break switchesElectrical resistance and conductanceCurrent limiting
The invention discloses a short circuit current hierarchical control tripping parameter circuit breaker. According to the invention, resistance of an alloy magnetic resistance body is changed through circuit current, and contract control can be carried out on short-circuit current. The control range of the circuit breaker can achieve that no magnetic resistance will be generated when current is no more than 8 times of rated operational current, and current limiting may be realized by the magnetic resistance when current is 8 times more than rated value. In this way, hierarchical control on short-circuit current of different levels of circuits can be carried out, and short-circuit current can be limited in a predetermined range, thereby restricting the short-circuit current in a predetermined range, solving a problem of power supply flickering, and avoiding large-area power failure accidents caused by override trip existing in an electrical control switch.
Owner:XIAMEN TAIHANG TECH
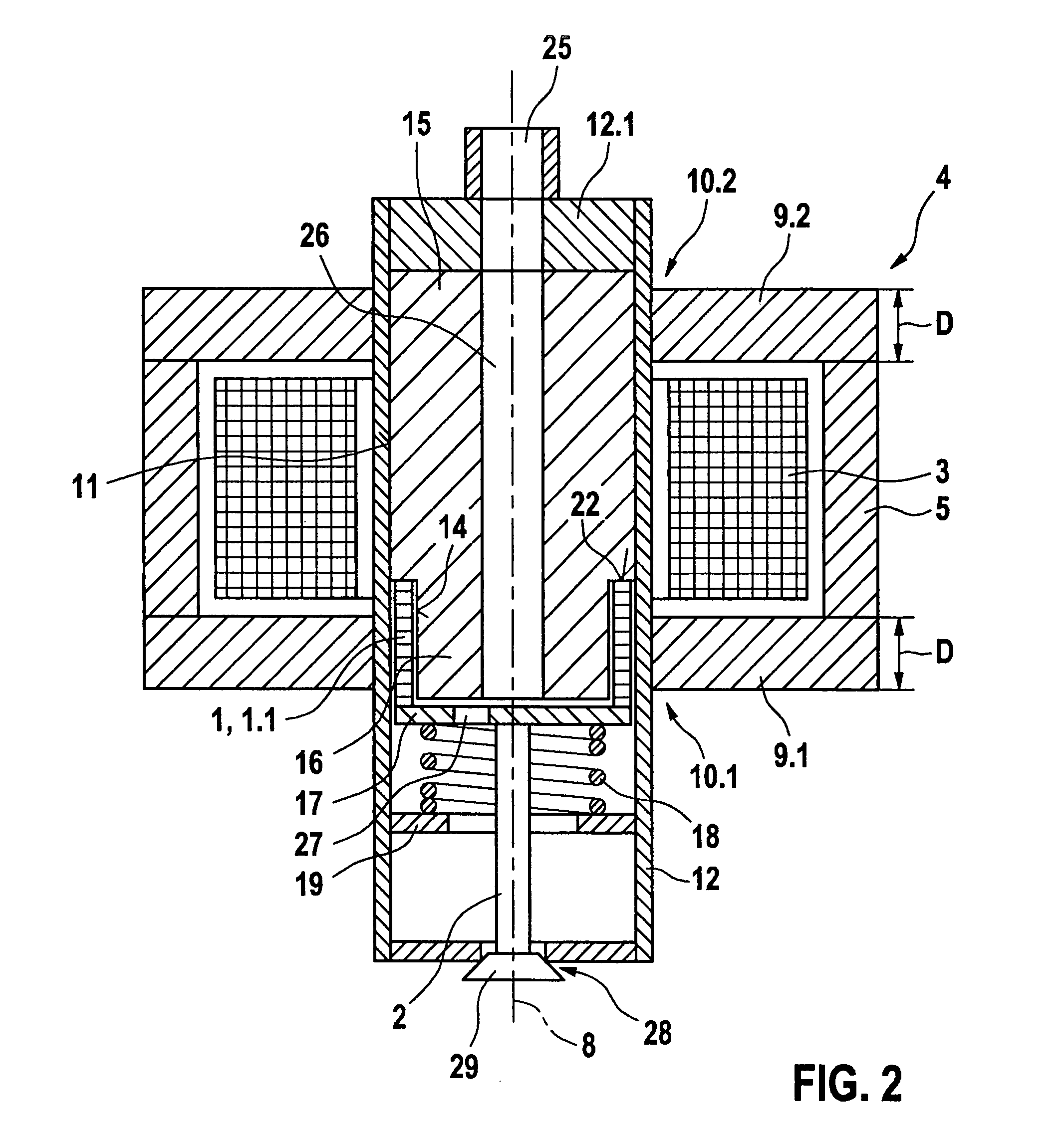
Insertion-type liquid metal latching relay array
InactiveUS6879088B2High-frequency capabilityAmenable to manufactureContact surface shape/structurePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesContact padRest position
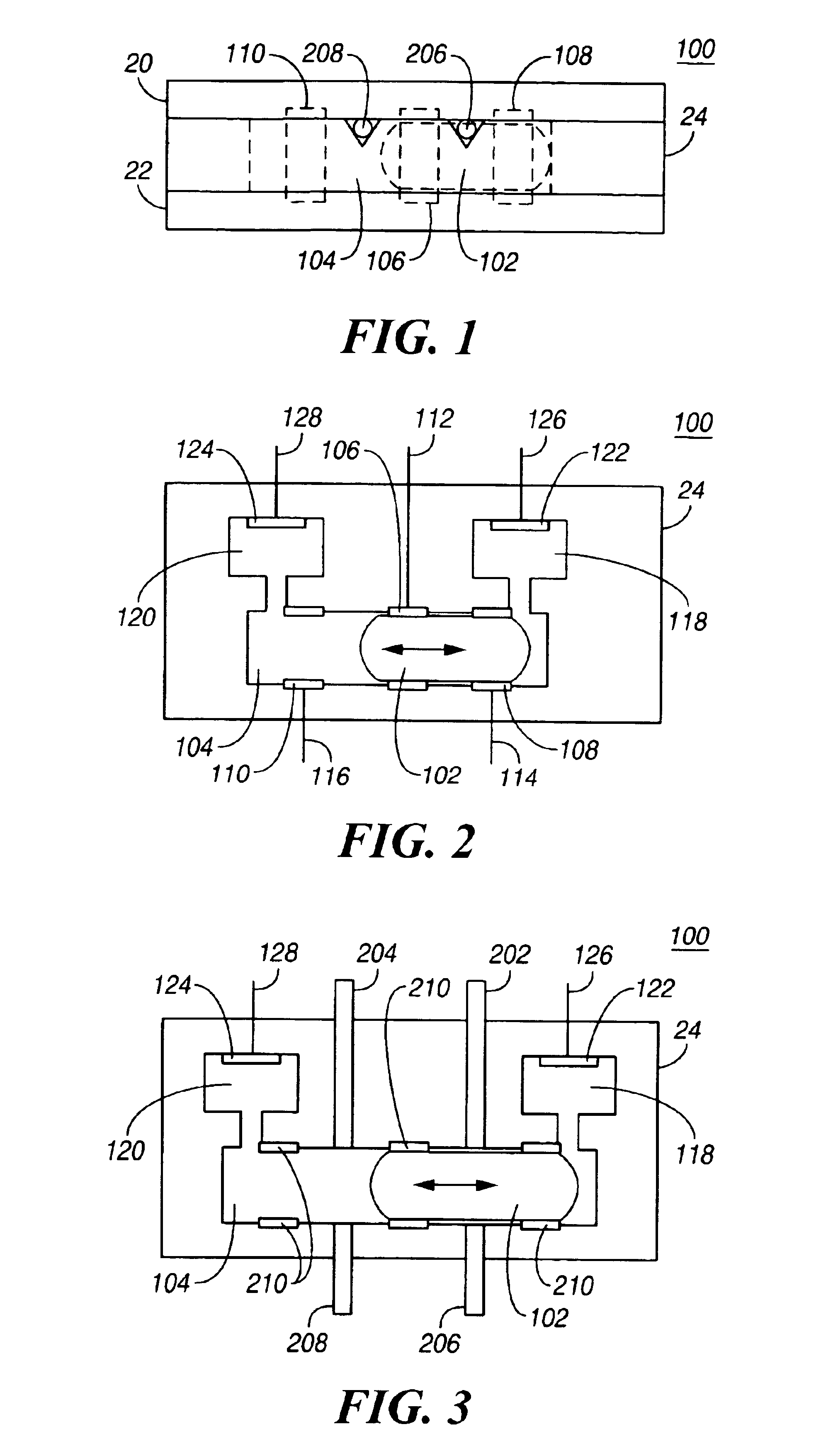
An electrical relay array using conducting liquid in the switching mechanism. The relay array is amenable to manufacture by micro-machining techniques. Each element of the relay array uses an actuator, such as a piezoelectric element, to cause a switch actuator to insert into a cavity in a static switch contact structure. The cavity has sides and a pad on its end that are wettable by the conducting liquid. The cavity is filled with the conducting liquid, which may be liquid metal. Insertion of the switch actuator into the cavity causes the conducting liquid to be displaced outward and come in contact with the contact pad on the switch actuator. The volume of conducting liquid is chosen so that when the actuator returns to its rest position, the electrical contact is maintained by surface tension and by wetting of the contact pads on both the static switch contact structure and the actuator. When the switch actuator retracts away from the static switch contact structure, the available volume for conducting liquid inside the fixed switch contact structure increases and the combination of the movement of the conducting liquid into the cavity and the contact pad on the switch actuator moving away from the bulk of the conducting liquid causes the conducting liquid connection between the fixed and moving contact pads to be broken. When the switch actuator returns to its rest position, the contact remains electrically open because there is not enough conducting liquid to bridge the gap without being disturbed. The high frequency capability is provided by the additional conductors in the assembly, which act to make the switch a coaxial structure.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Magnetostrictive stress wave sensor
ActiveUS7081801B2Easily detected and digitizedLarge outputVibration measurement in solidsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDc currentEngineering
A shock sensor has a housing with a Terfenol-D type sensing element positioned inside a sensing coil. A permanent biasing magnet is positioned in engagement with the Terfenol-D sensing element, and a spacer engages the Terfenol-D sensing element and extends from the housing. The housing has a beam with one or two mounting holes through which fasteners extend to mount the shock sensor to a structural member. The housing places the spacer in compression against the structural member. In an alternative embodiment a DC current can be supplied to the sensing coil to provide the biasing magnetic field. A high frequency filter separates the shock sensing signal from the applied DC biasing current.
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
Popular searches
Using electrical means Mechanical vibrations separation Magnetostrictive property measurements Electrical/magnetic solid deformation measurement Material analysis by using resonance Measurements using magnetic resonance Material magnetic variables Specific gravity measurement Coatings Piezoelectric/electrostrictive devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com