Patents
Literature
41results about "Monocomponent polypeptides artificial filament" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
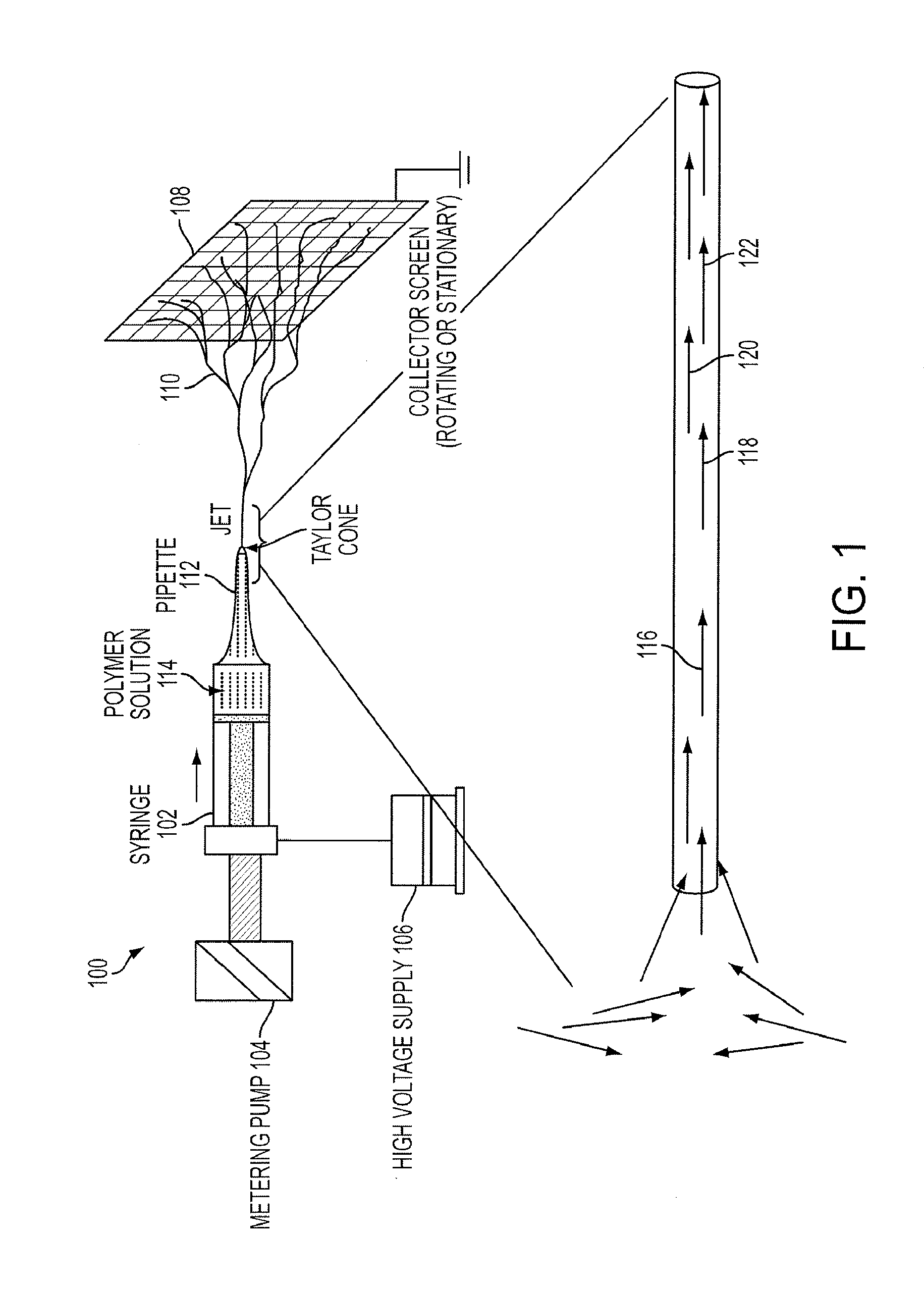
Artificial polypeptide fiber and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20140058066A1High stressImprove toughnessPeptide/protein ingredientsMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentFiberSpider Proteins
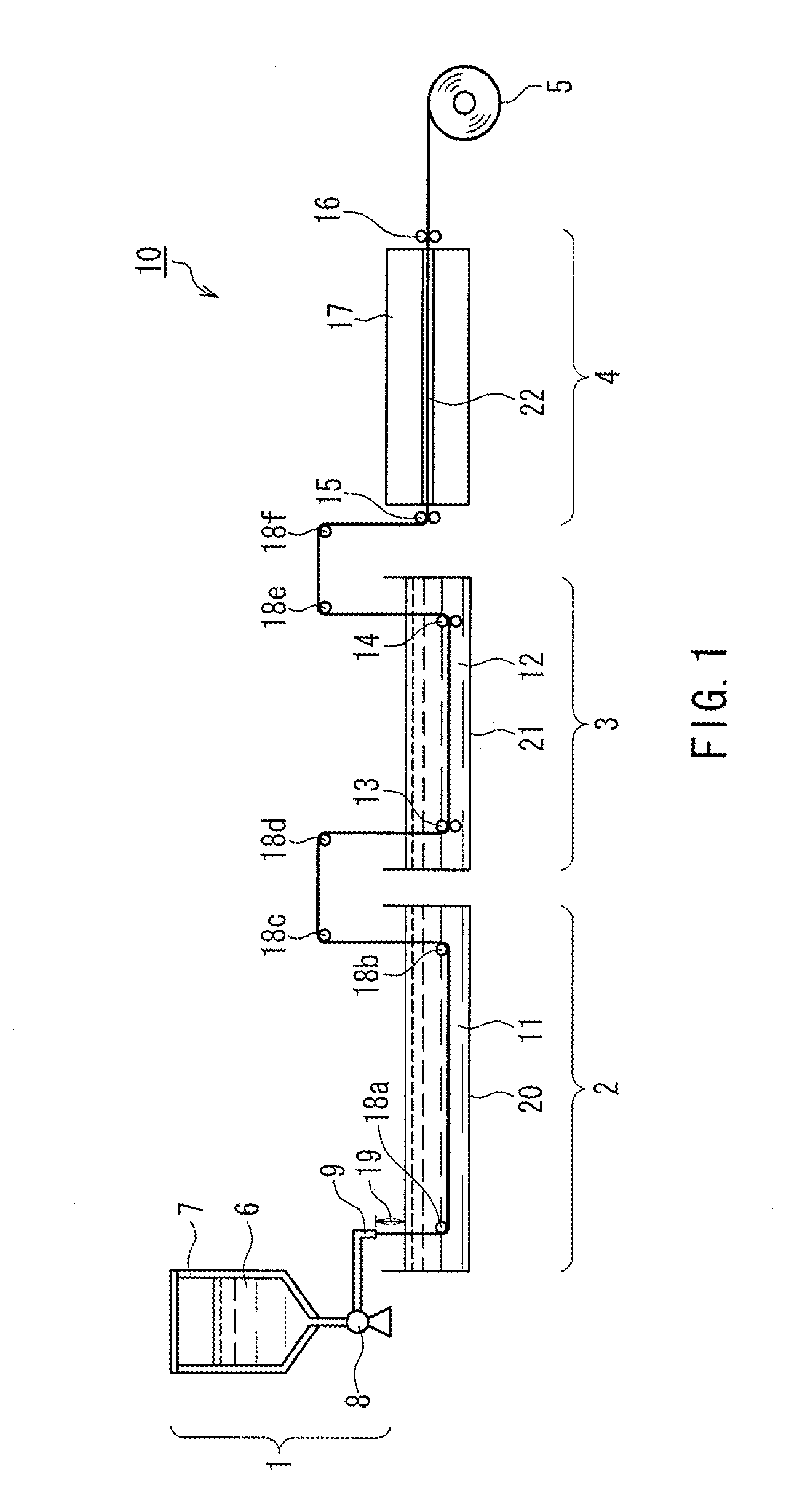
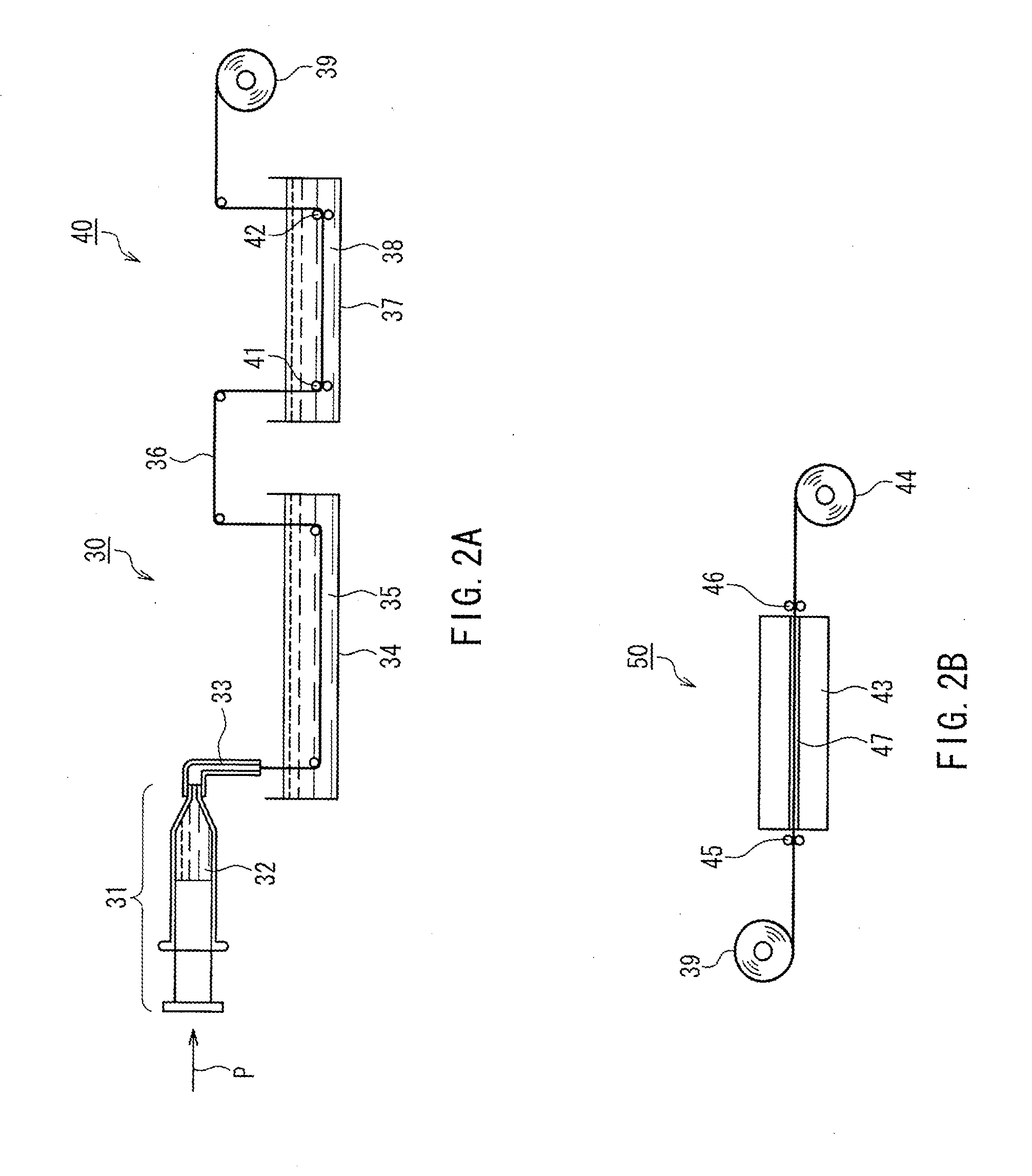
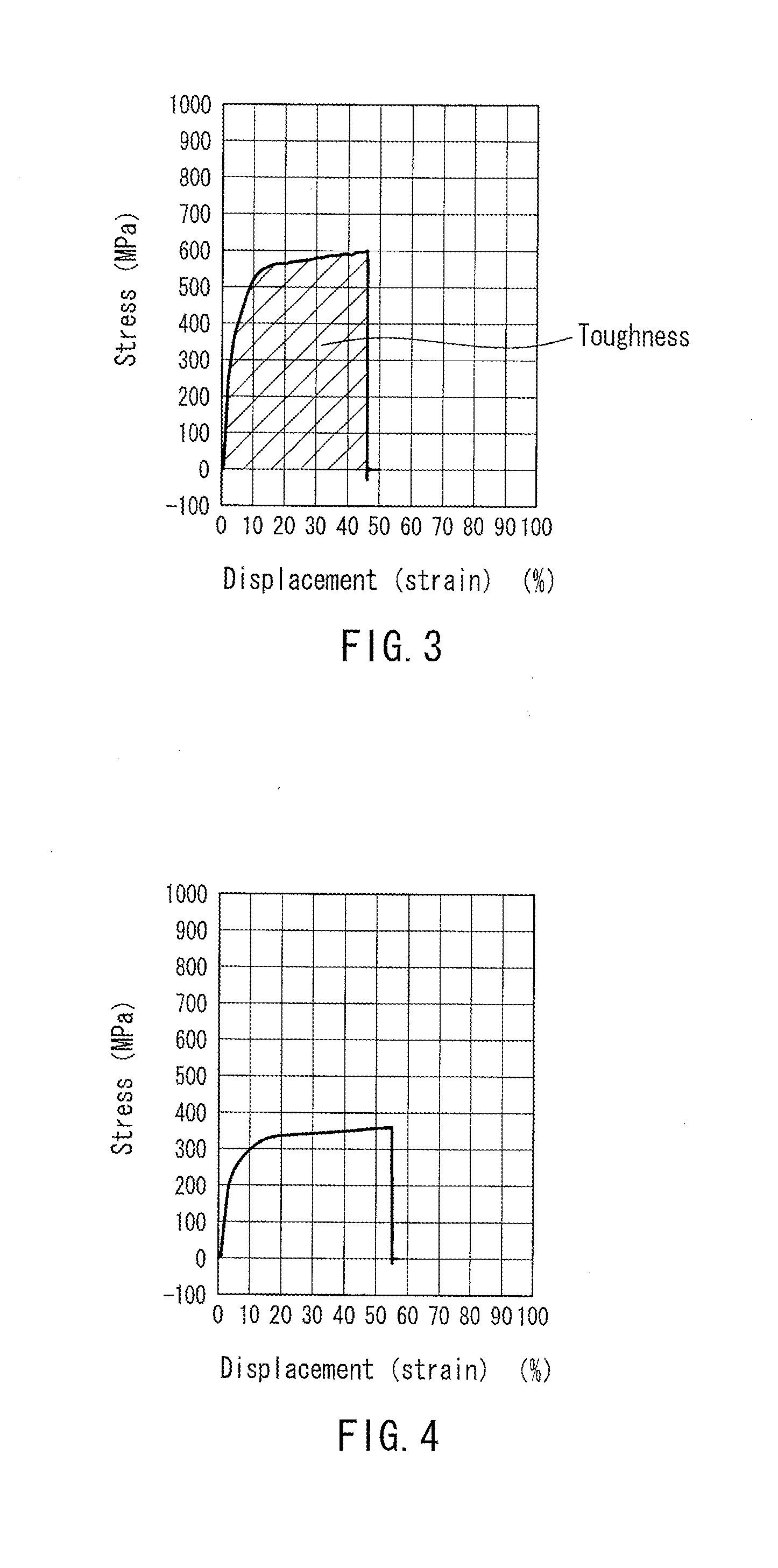
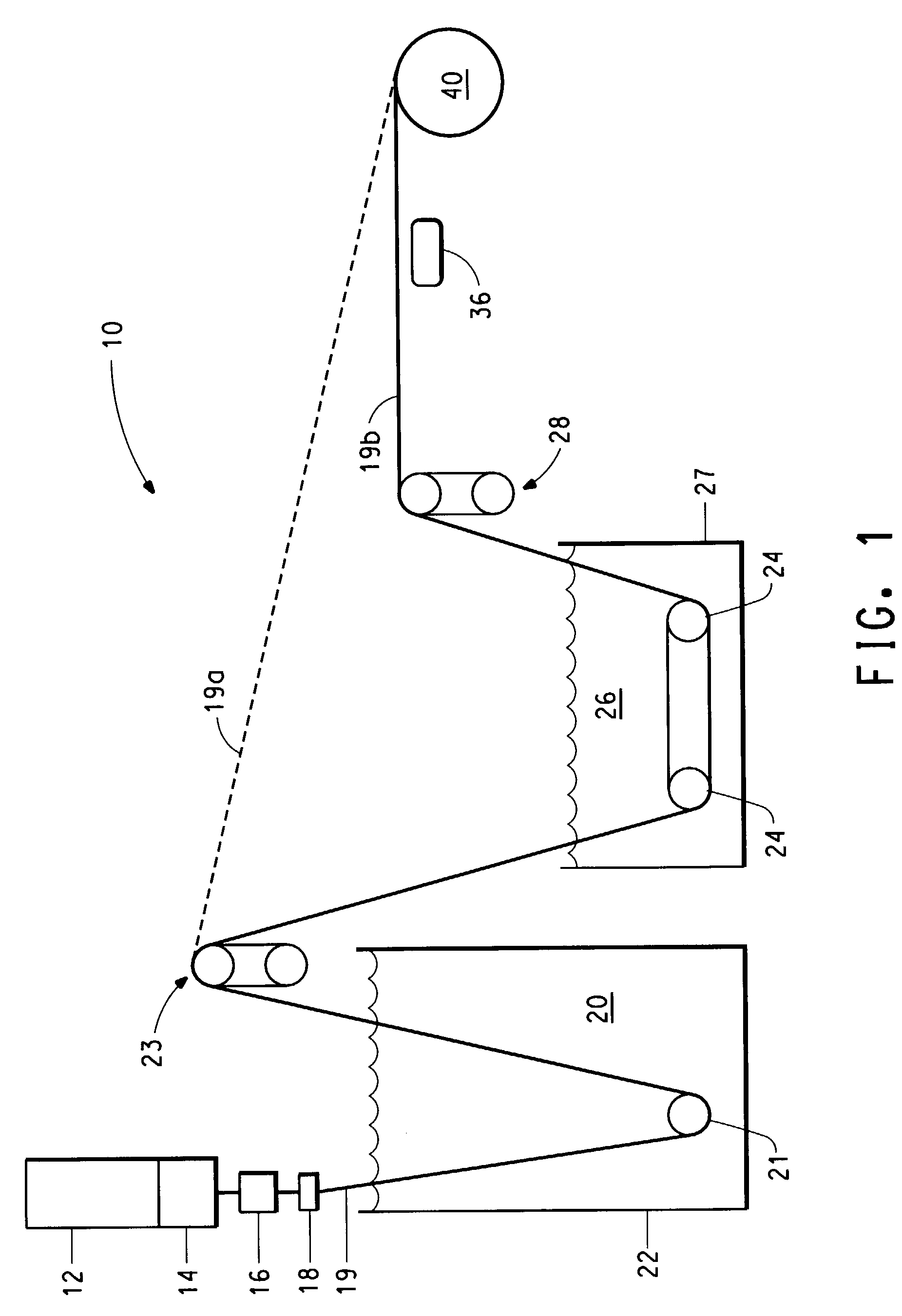
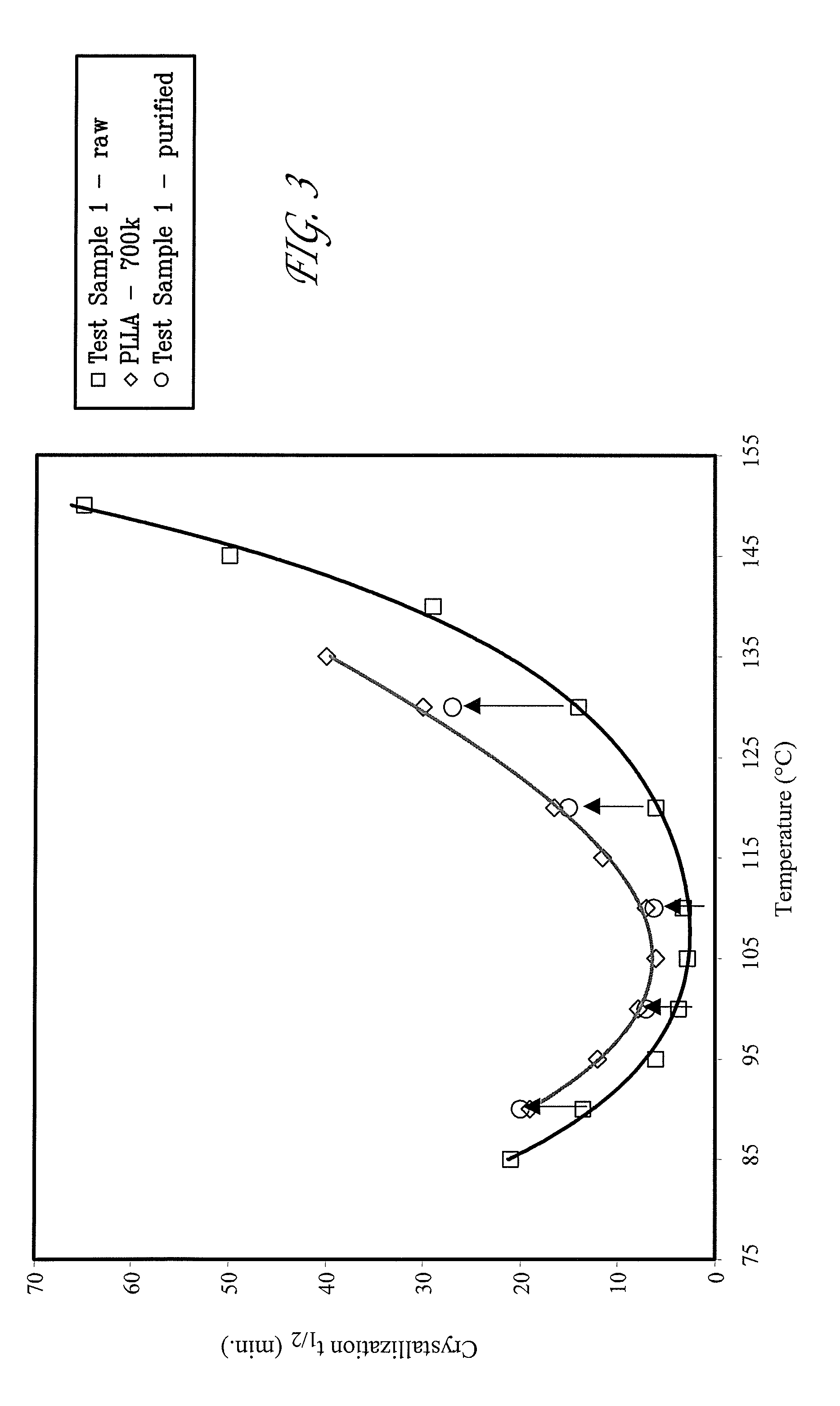
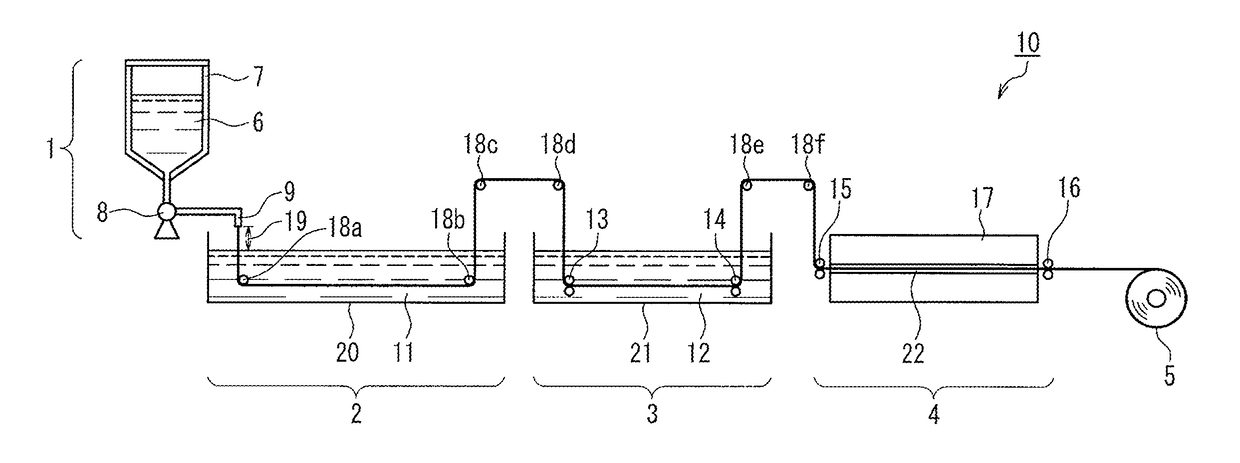
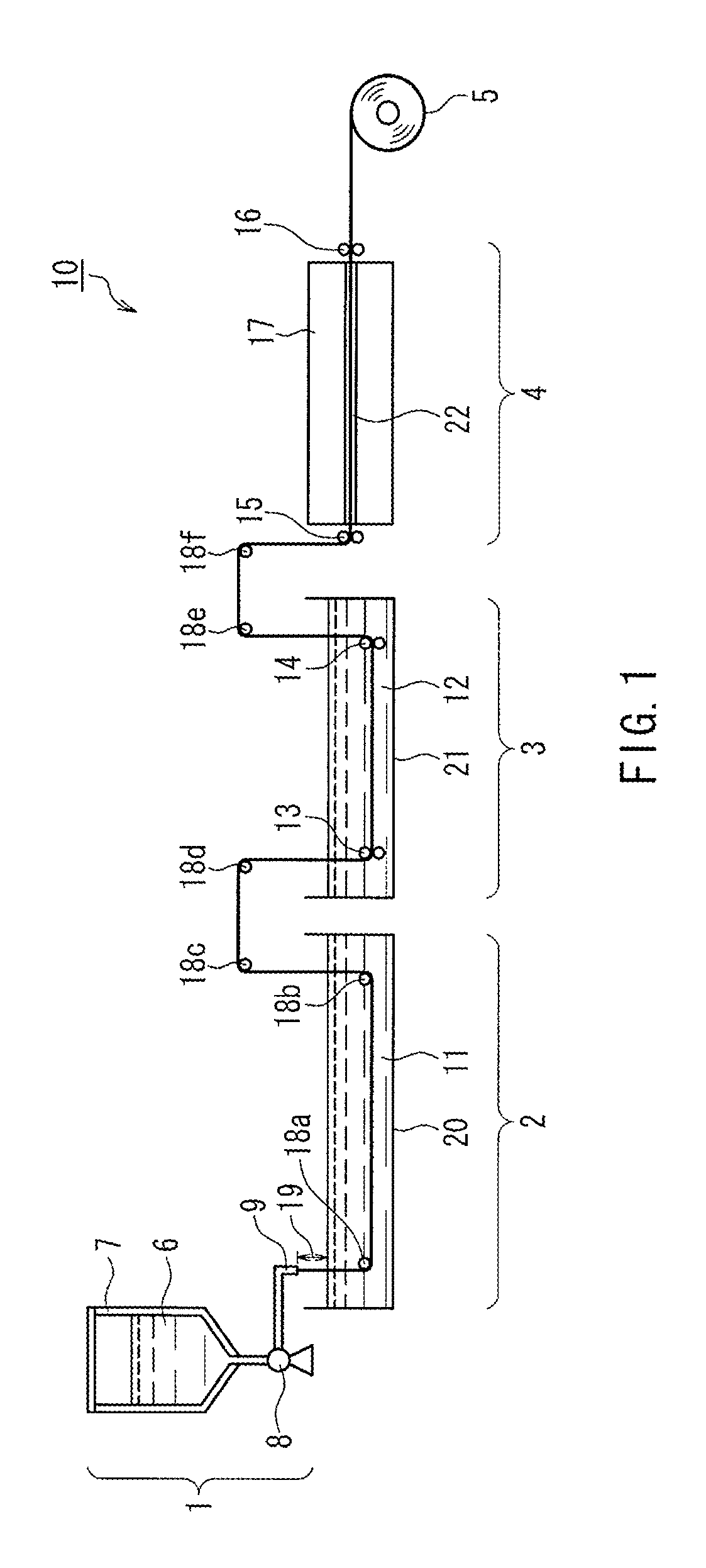
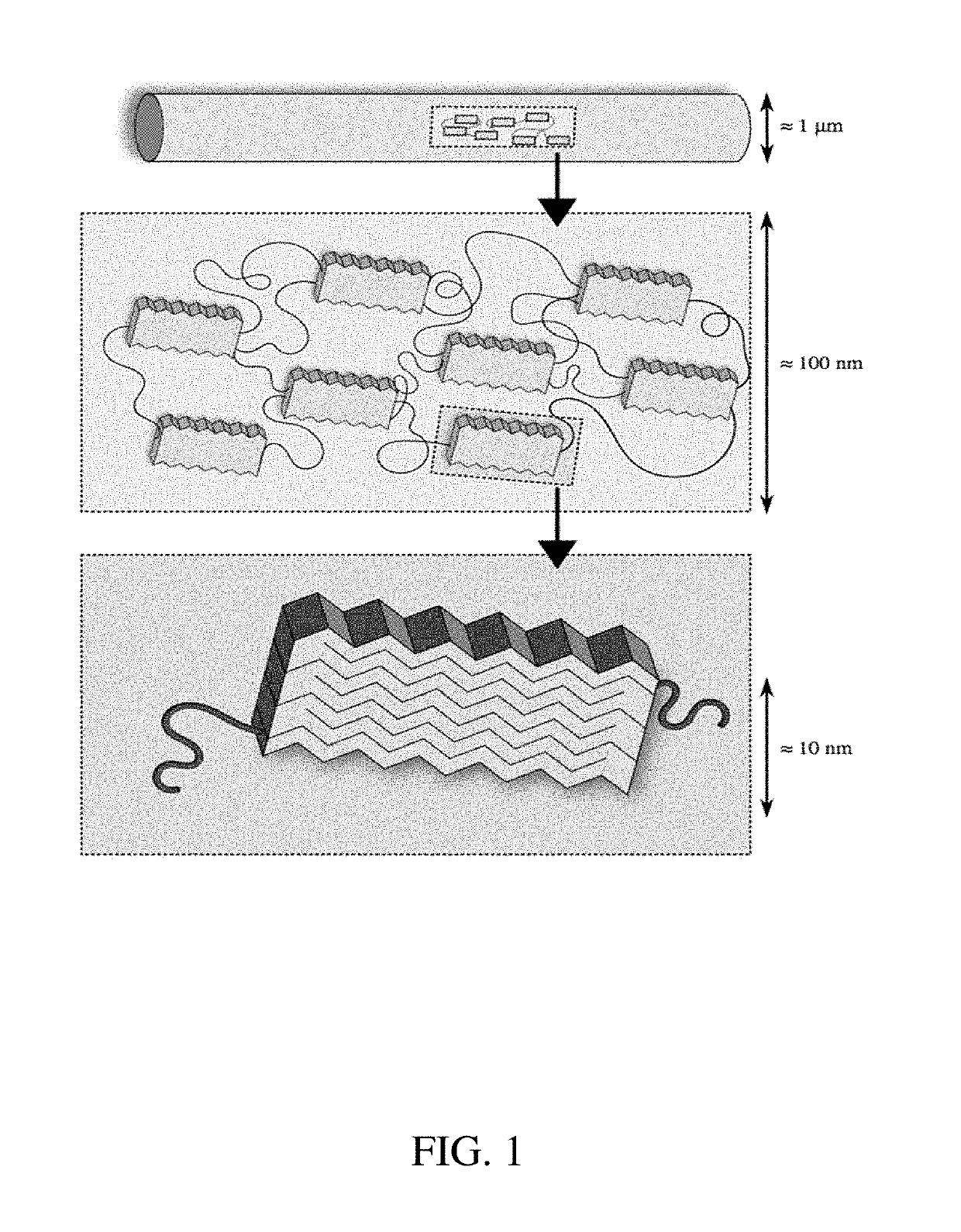
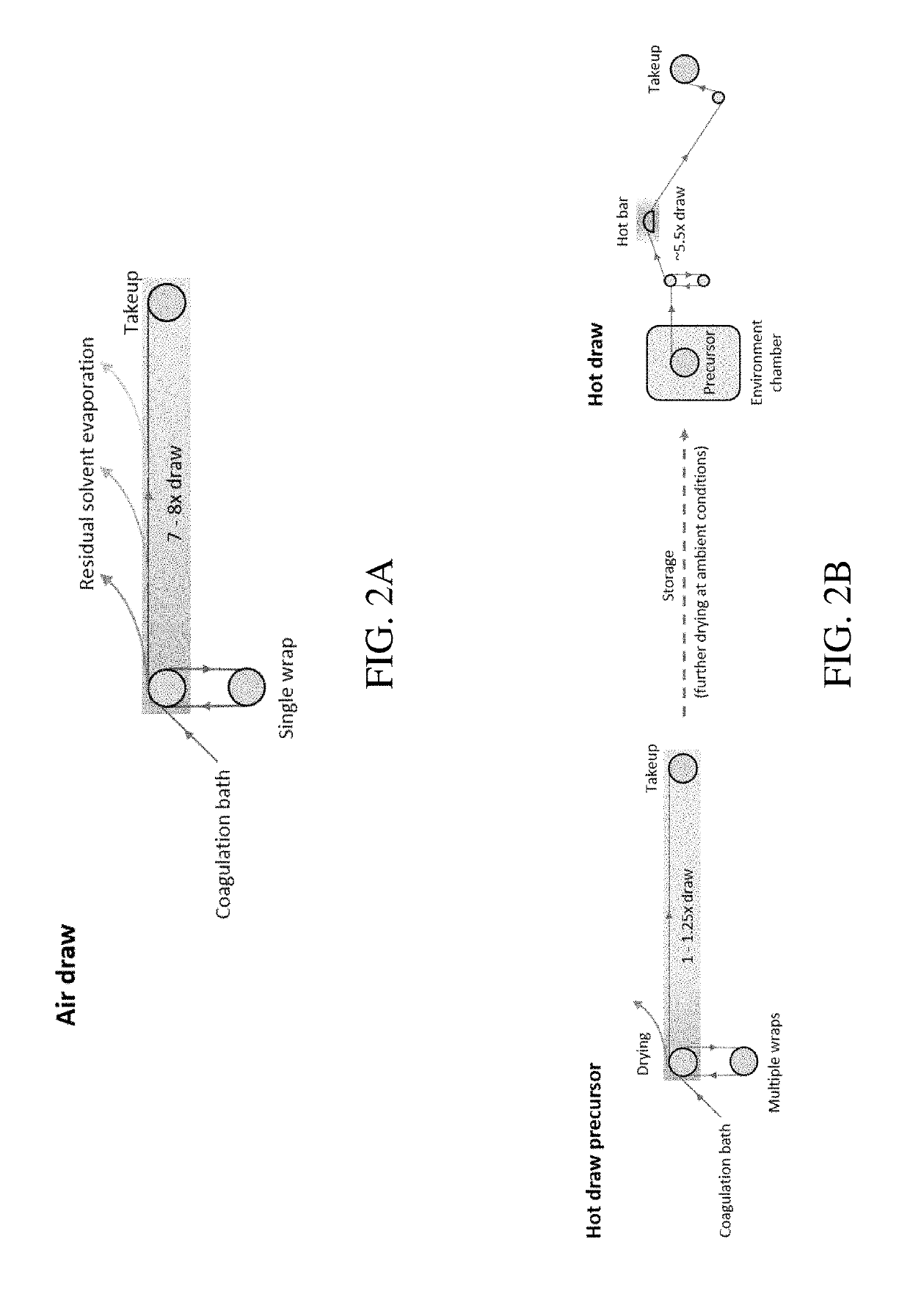
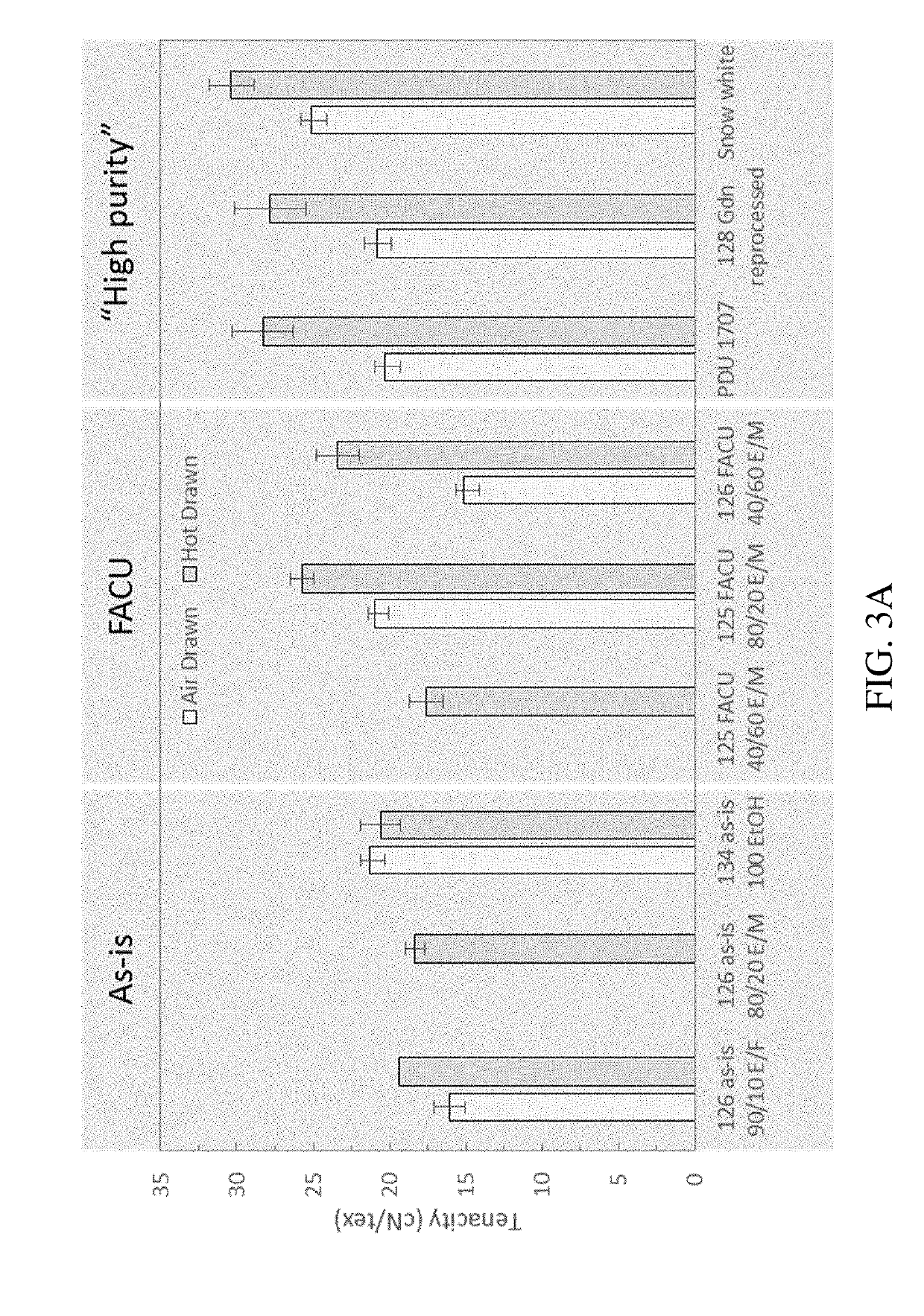
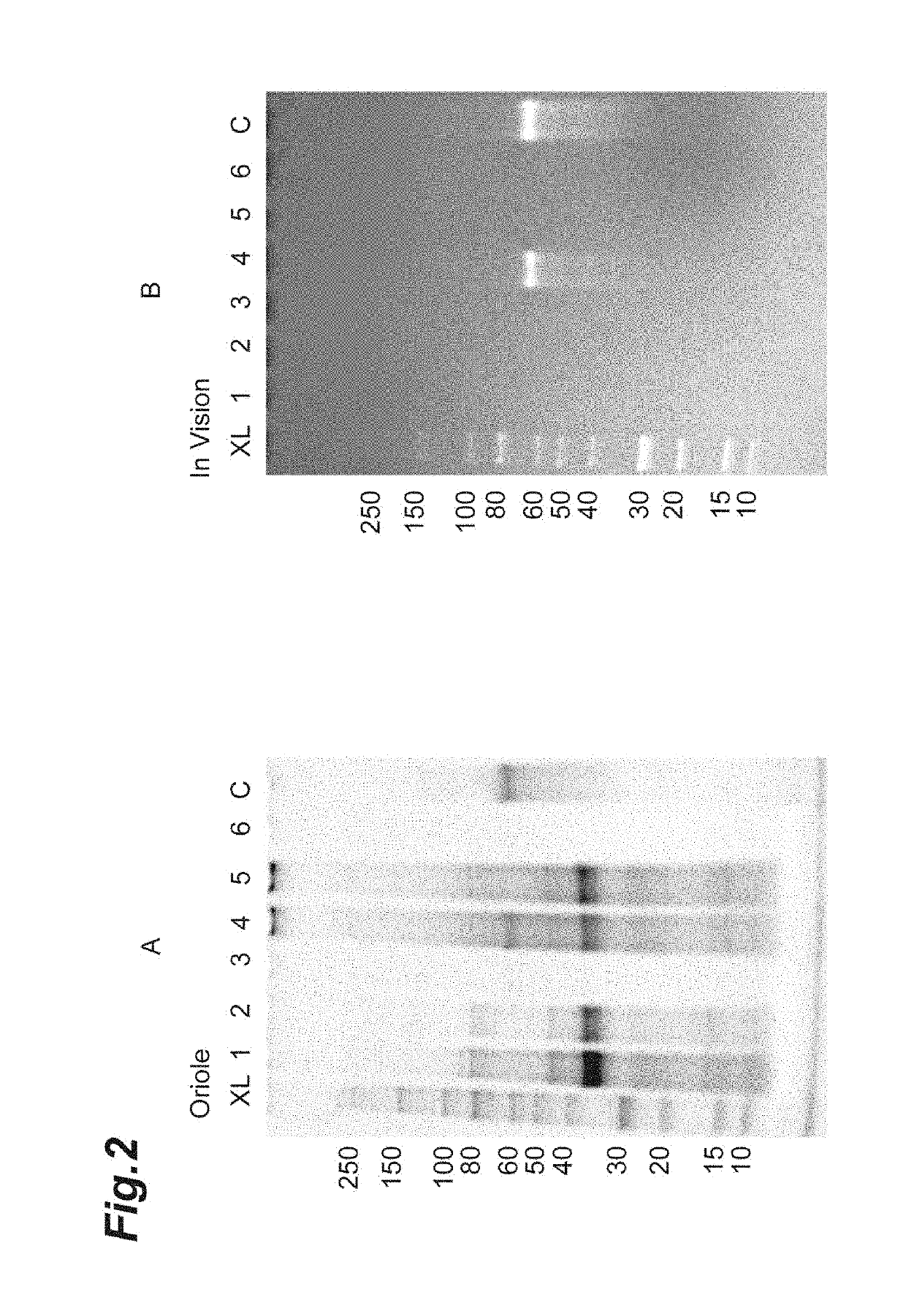
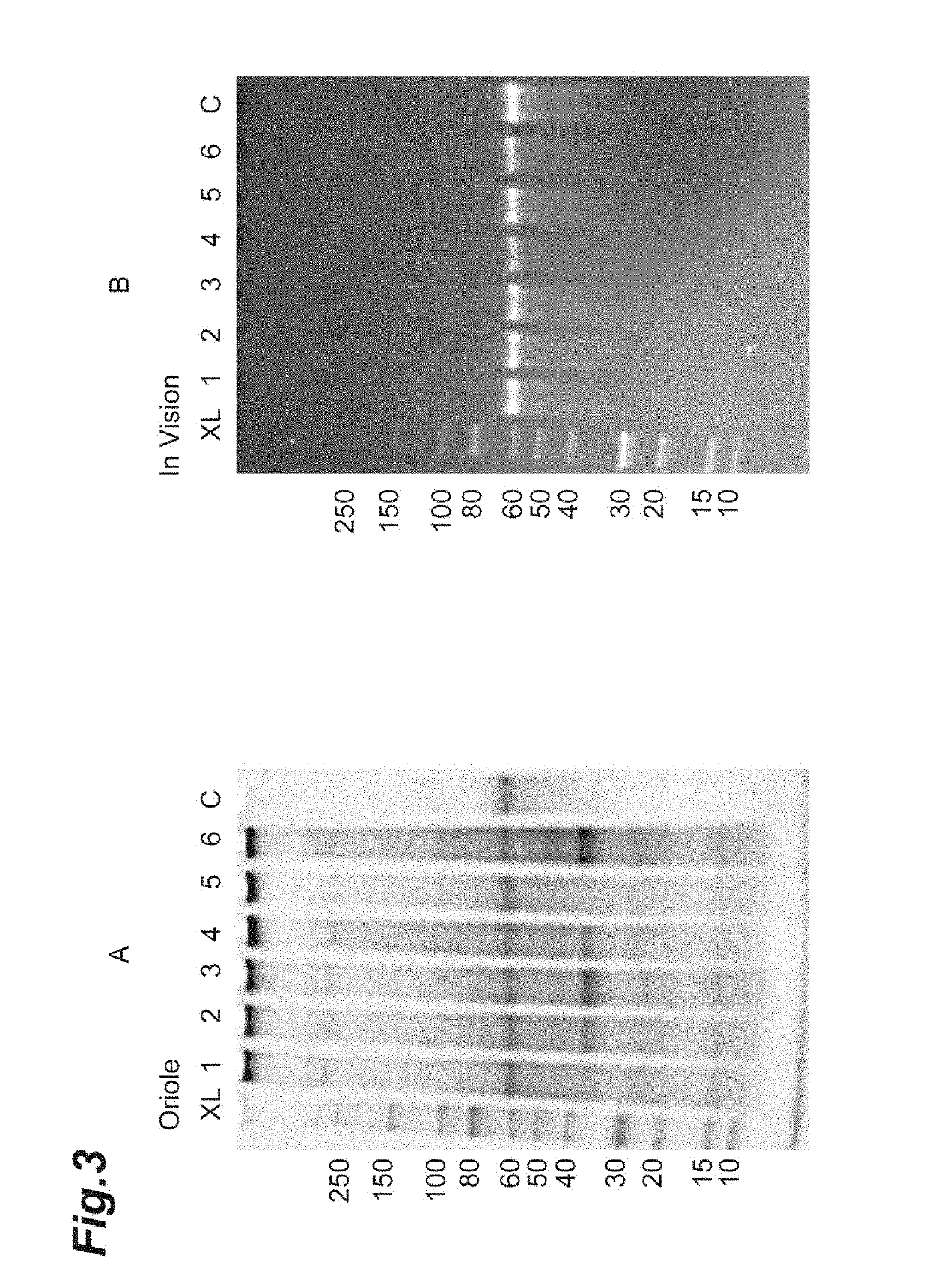
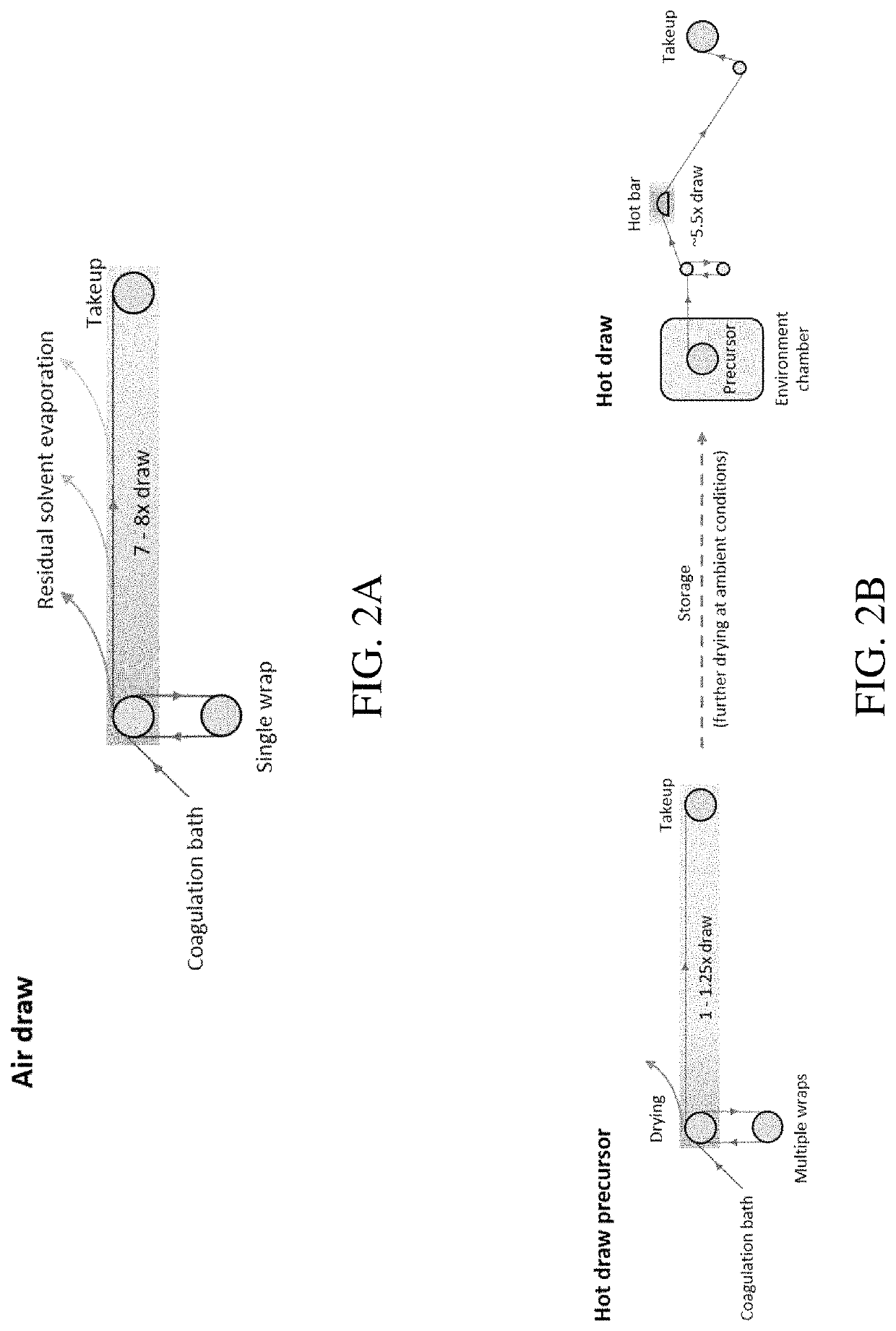
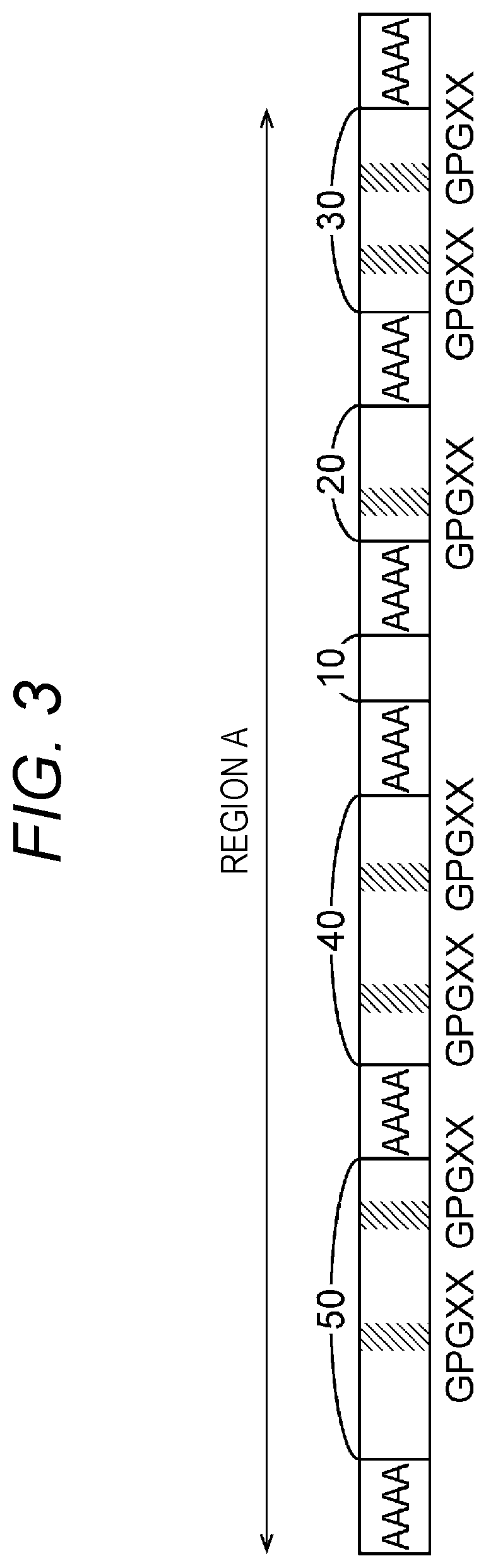
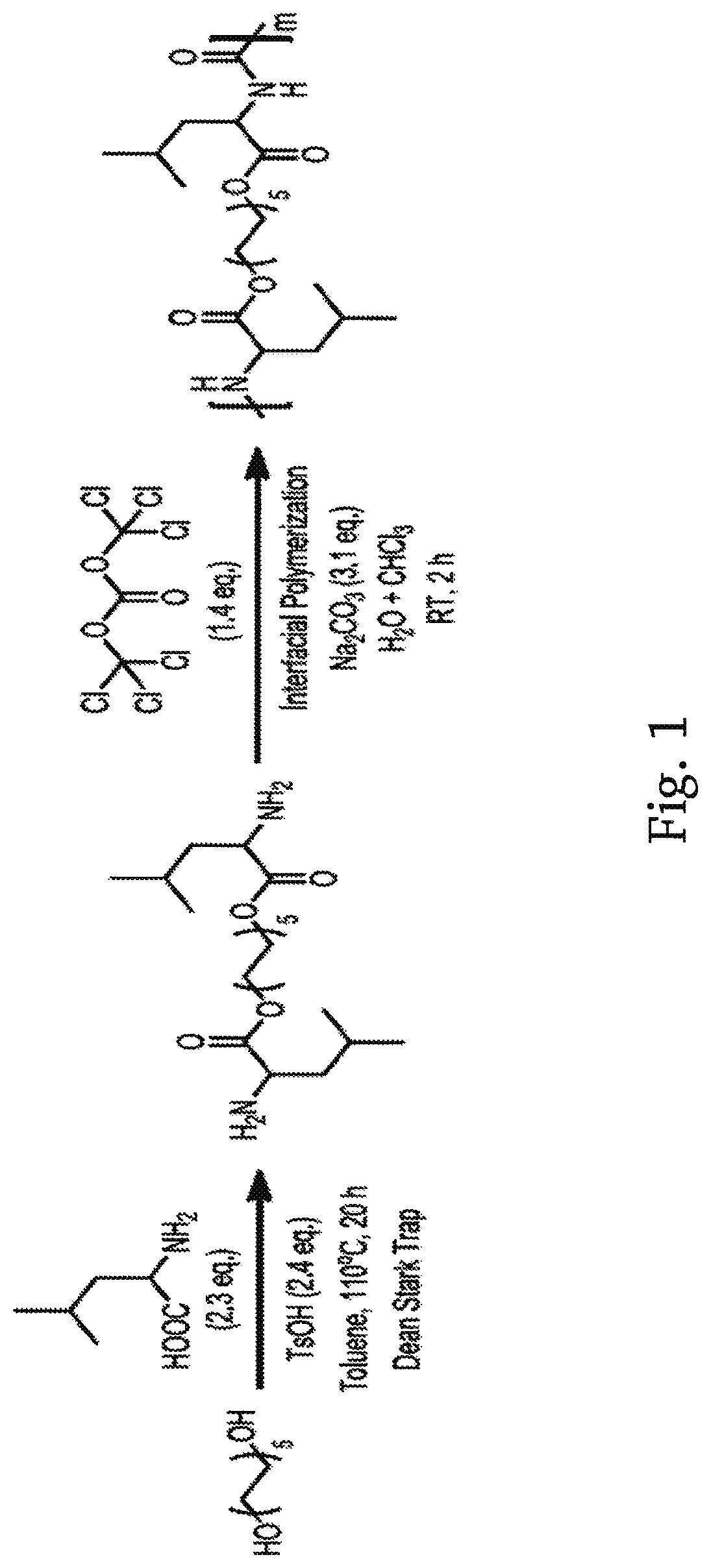
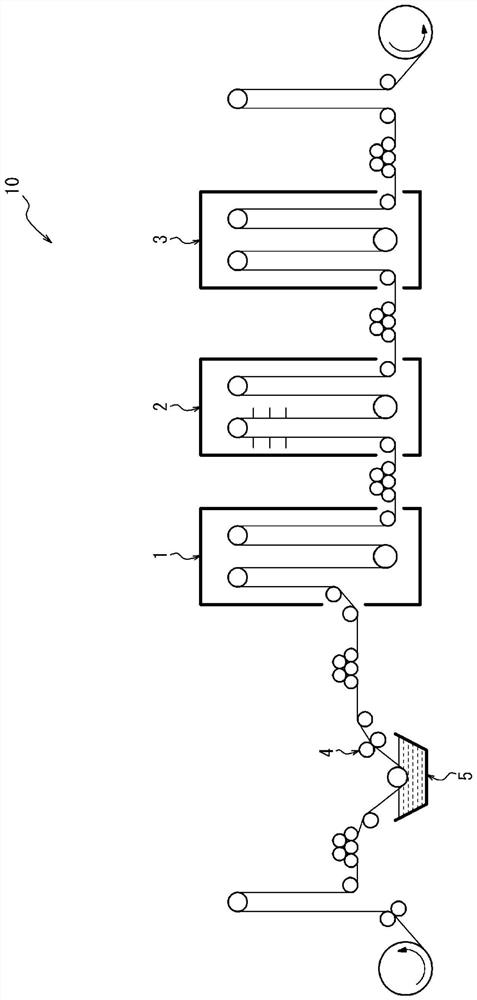
An artificial polypeptide fiber of the present invention is an artificial fiber containing a polypeptide as a main component, and has a stress of 350 MPa or more and a toughness of 138 MJ / m3 or more. A method for producing an artificial polypeptide fiber of the present invention is a method for producing the artificial polypeptide fiber obtained by spinning a spinning solution (6) containing a polypeptide derived from natural spider silk proteins and performing drawing of at least two stages. The drawing of at least two stages includes a first-stage drawing (3) in wet heat and a second-stage drawing (4) in dry heat. Thereby, the present invention provides high-toughness artificial polypeptide fibers having favorable stress and rupture elongation, and a method for producing the same.
Owner:SPIBER INC
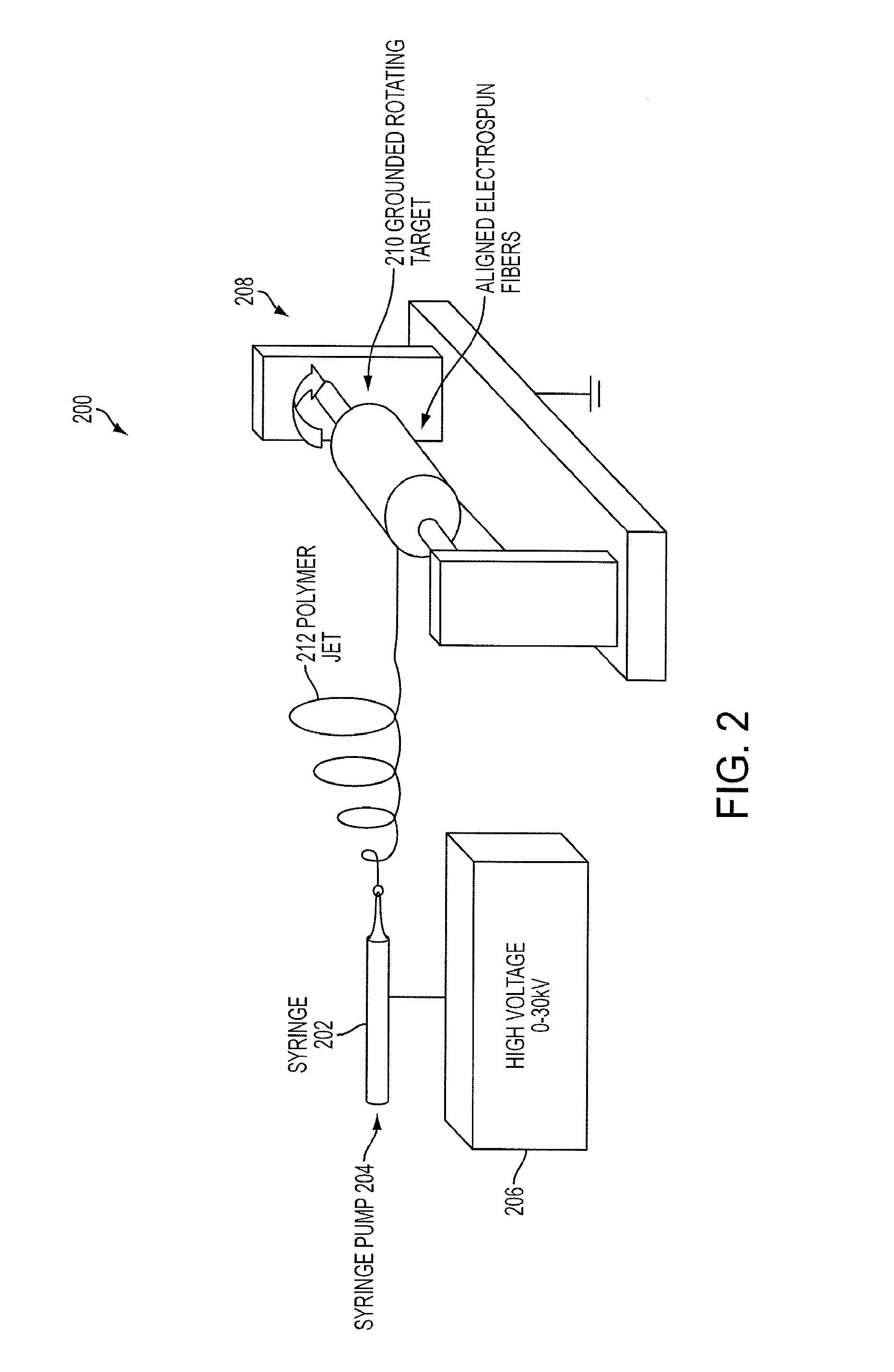
Polypeptide electrospun nanofibrils of defined composition
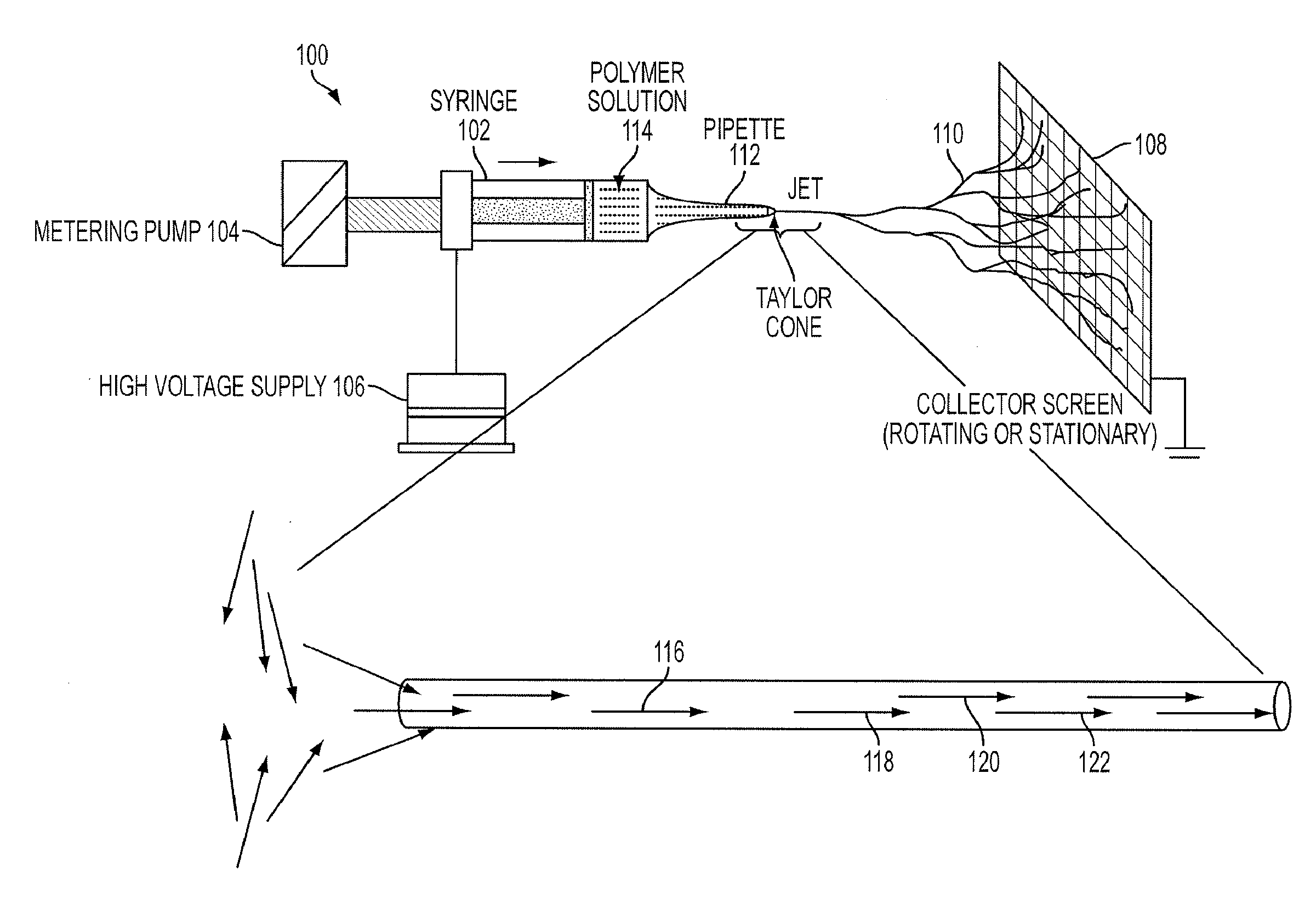
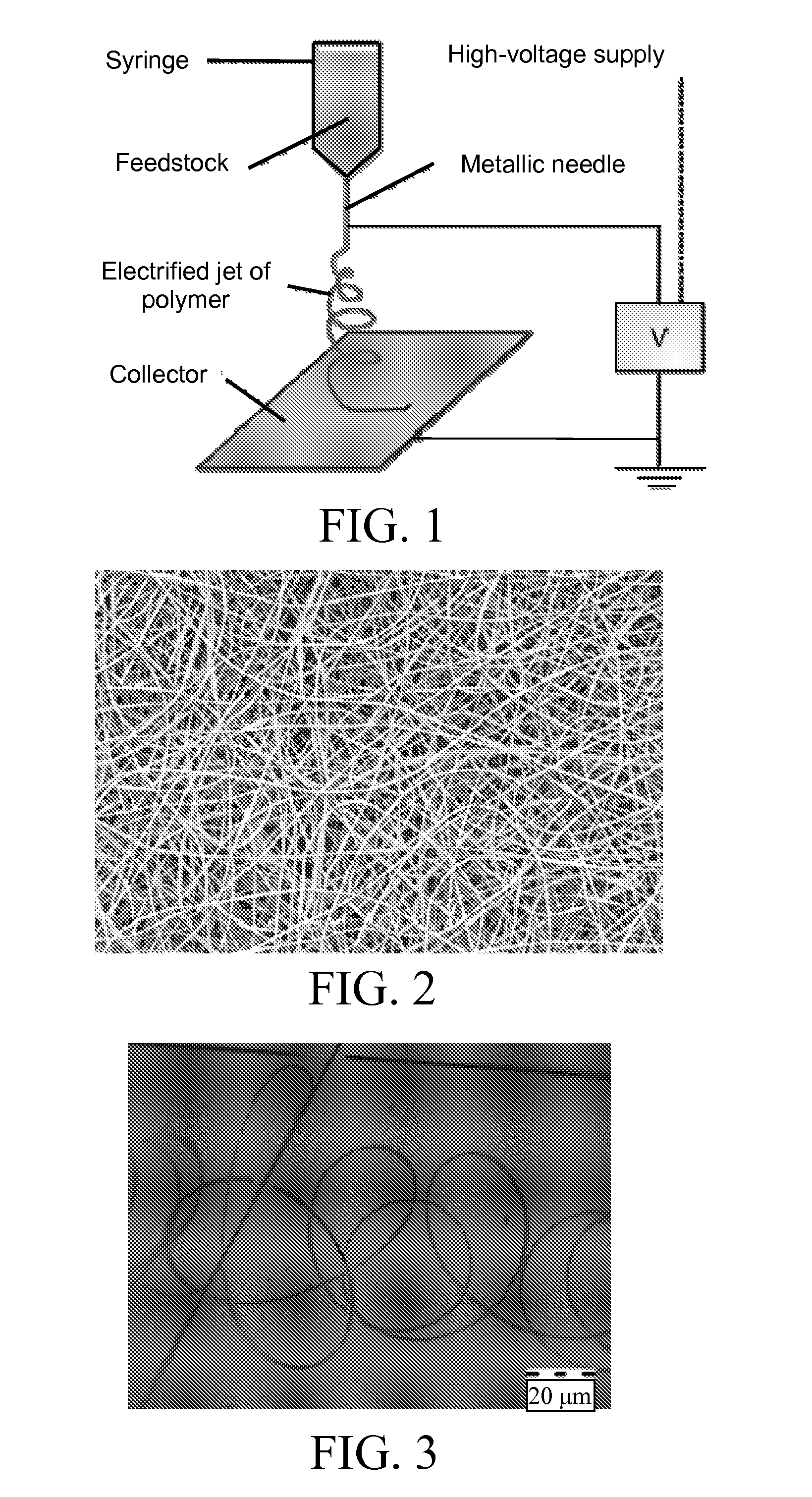
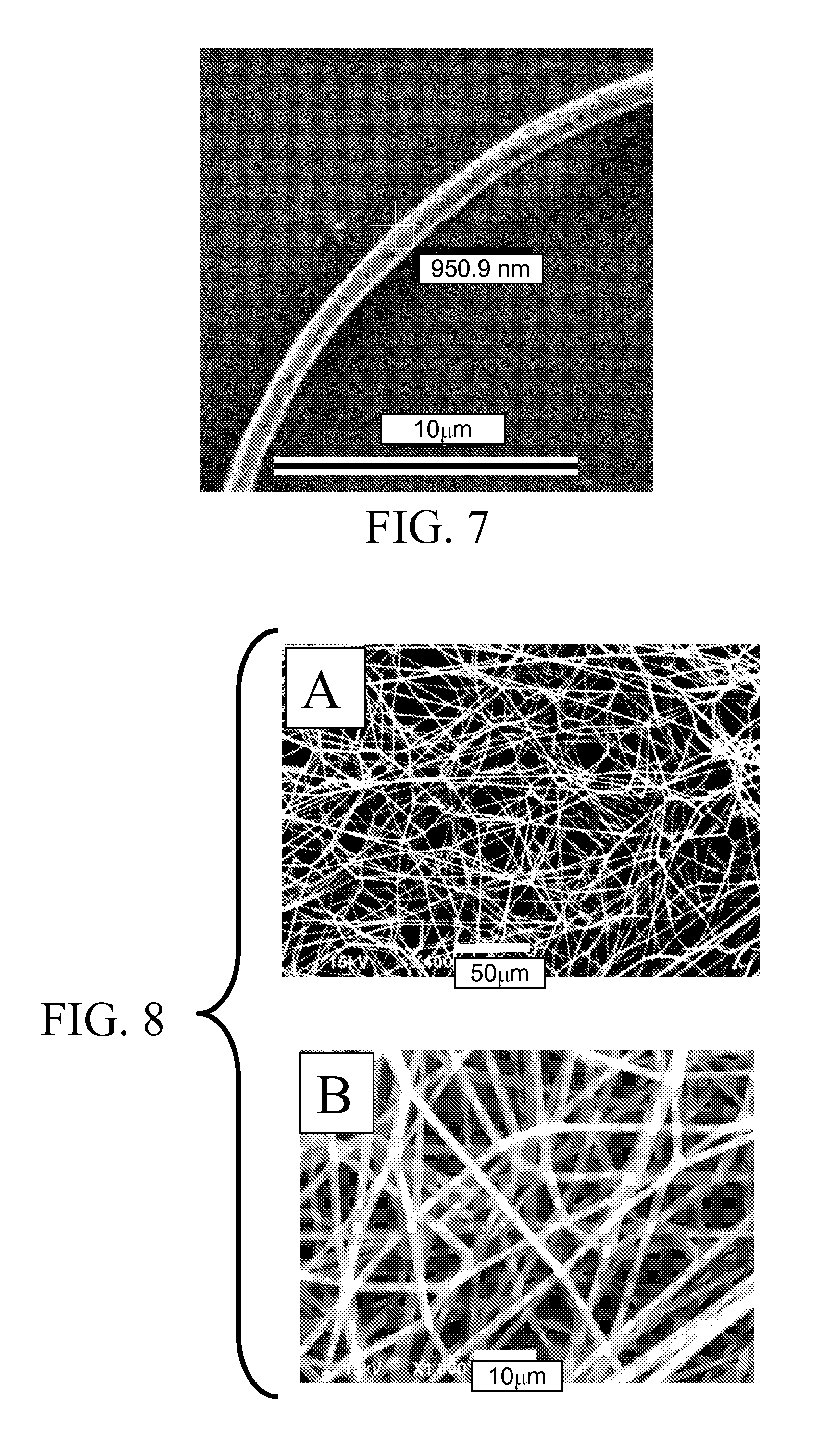
ActiveUS20130115457A1Electric discharge heatingMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentElectrospinningChemistry
Electrospun nanofibrils and methods of preparing the same are provided. The electrospun nanofibrils comprise at least one polypeptide. A polypeptide can be dissolved in a solution, and the solution can be electrospun into a nanofibril. The solution can be added to a syringe or syringe pump, and an electric field can be applied to electrospin the at least one polypeptide.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
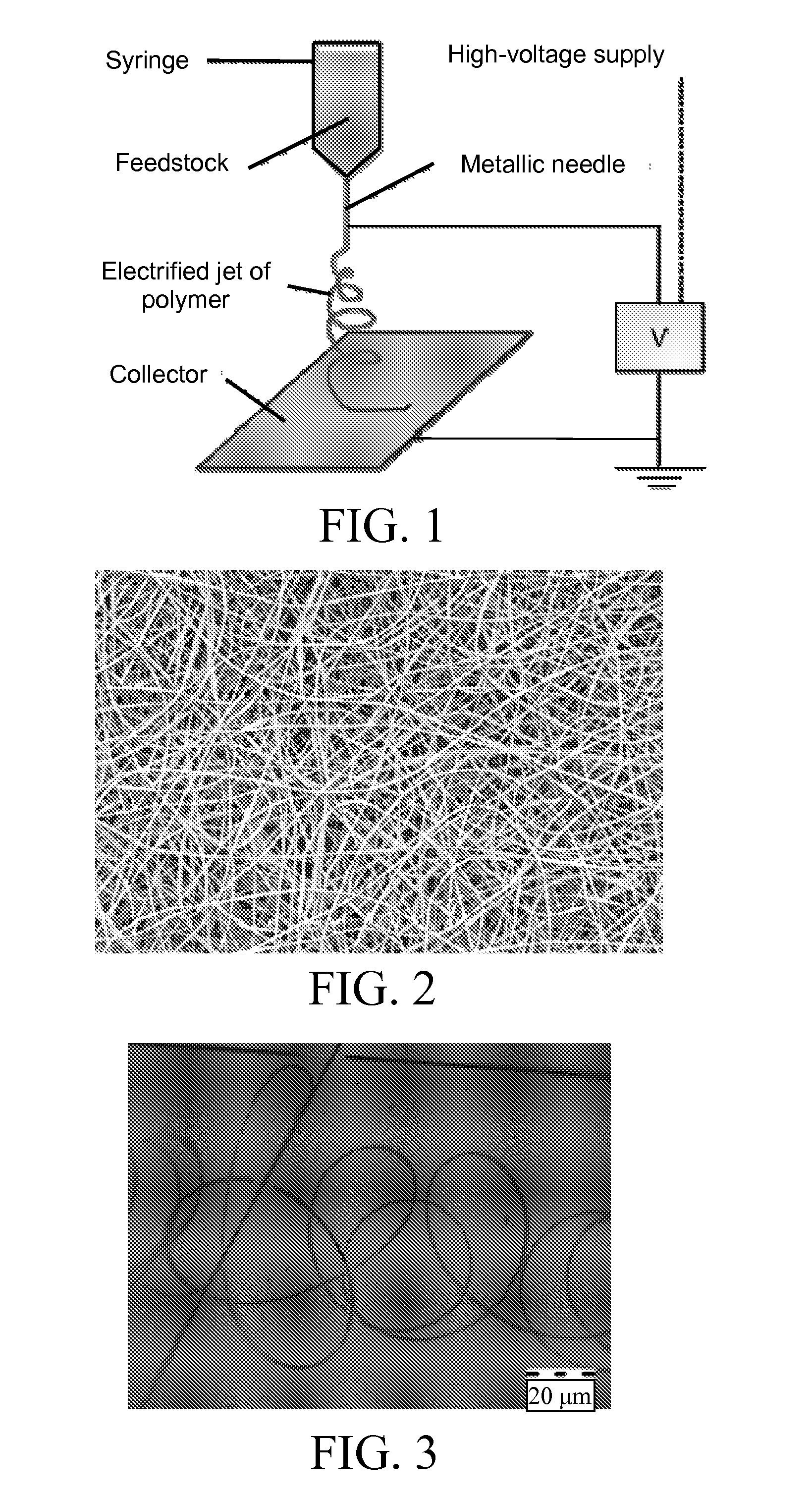
Articles of peptide nanostructures and method of forming the same
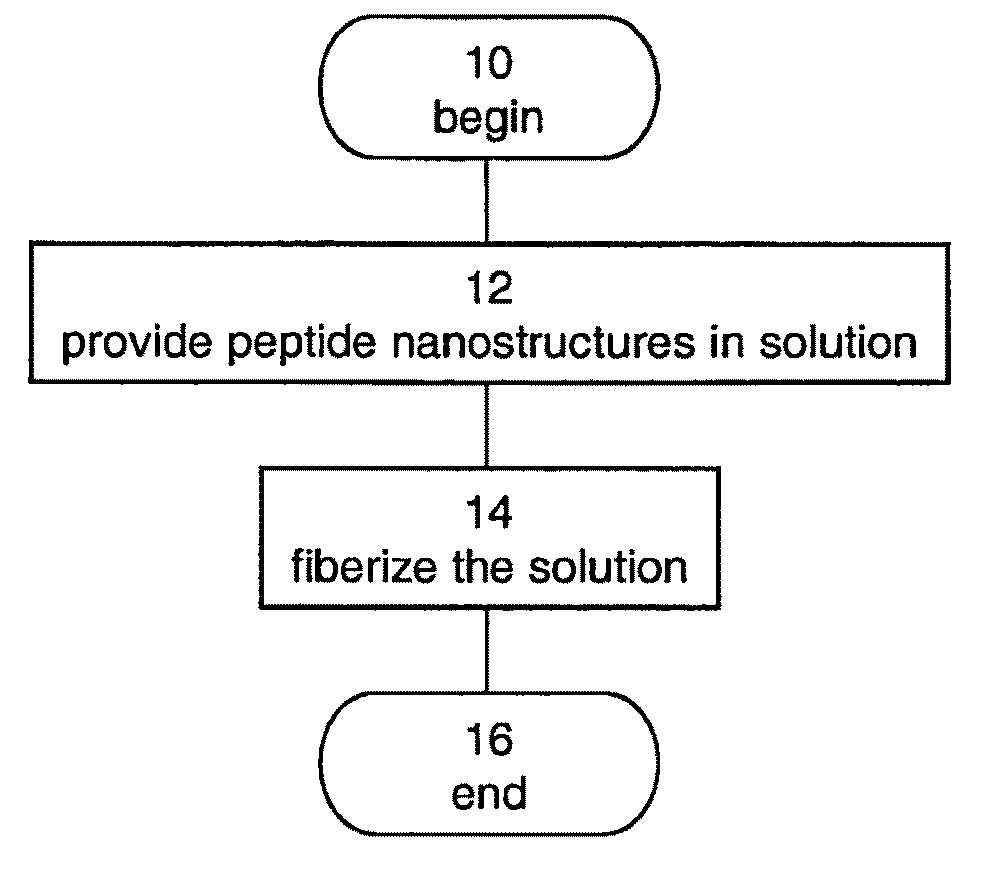
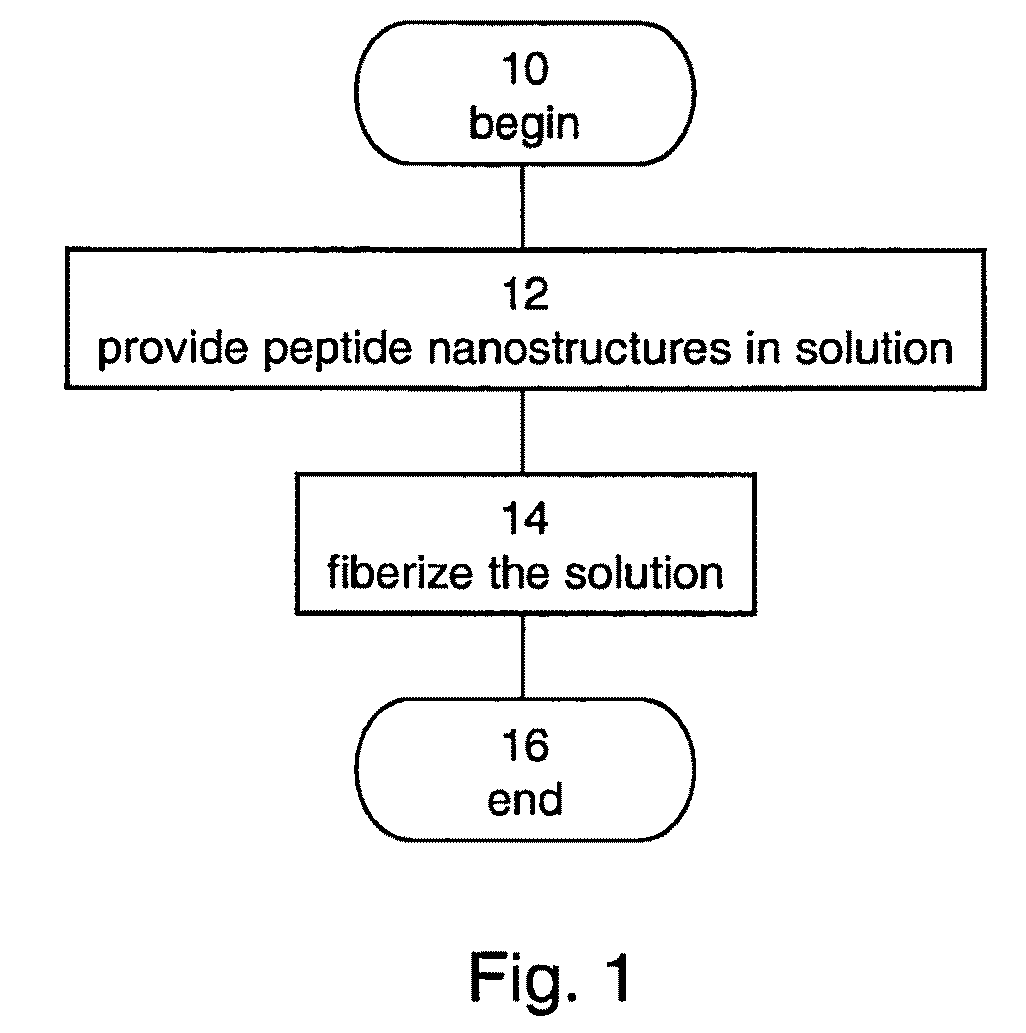
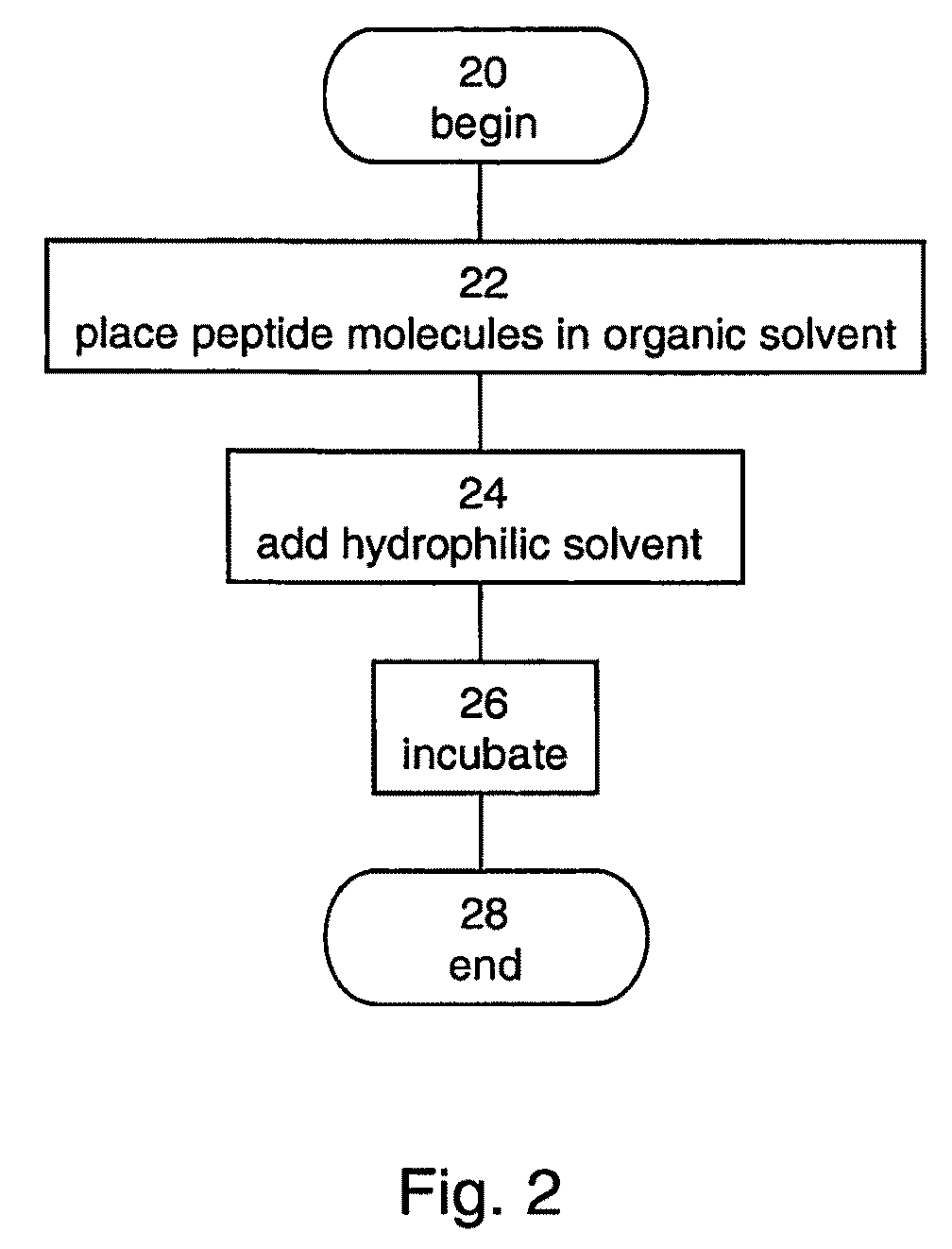
InactiveUS20090061190A1Monocomponent protein artificial filamentElectric discharge heatingFiberNanostructure
A method of forming a fiber made of peptide nanostructures is disclosed. The method comprises: providing peptide nanostructures in solution, and fiberizing the solution thereby forming at least one fiber of the peptide nanostructures. Also disclosed are methods of forming films and other articles using the peptide nanostructures.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method of forming a fiber made of peptide nanostructures
InactiveUS8568637B2Monocomponent protein artificial filamentElectric discharge heatingFiberNanostructure
A method of forming a fiber made of peptide nanostructures is disclosed. The method comprises: providing peptide nanostructures in solution, and fiberizing the solution thereby forming at least one fiber of the peptide nanostructures. Also disclosed are methods of forming films and other articles using the peptide nanostructures.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Process of making polypeptide fibers
InactiveUS7014807B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentFiberDivalent metal ions
Process of making polypeptide fibers including the steps of contacting a polypeptide with a solution of formic acid a divalent metal ion salt, or contacting a decrystallized polypeptide with formic acid having a water content less than 3 wt % and concentrating the resulting solution to a polypeptide concentration greater than 10 wt %.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
A kind of preparation method of water-stable γ-polyglutamic acid nanofiber
InactiveCN102277659AGood biocompatibilityEasy to operateMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentFilament/thread formingFiberBiocompatibility Testing
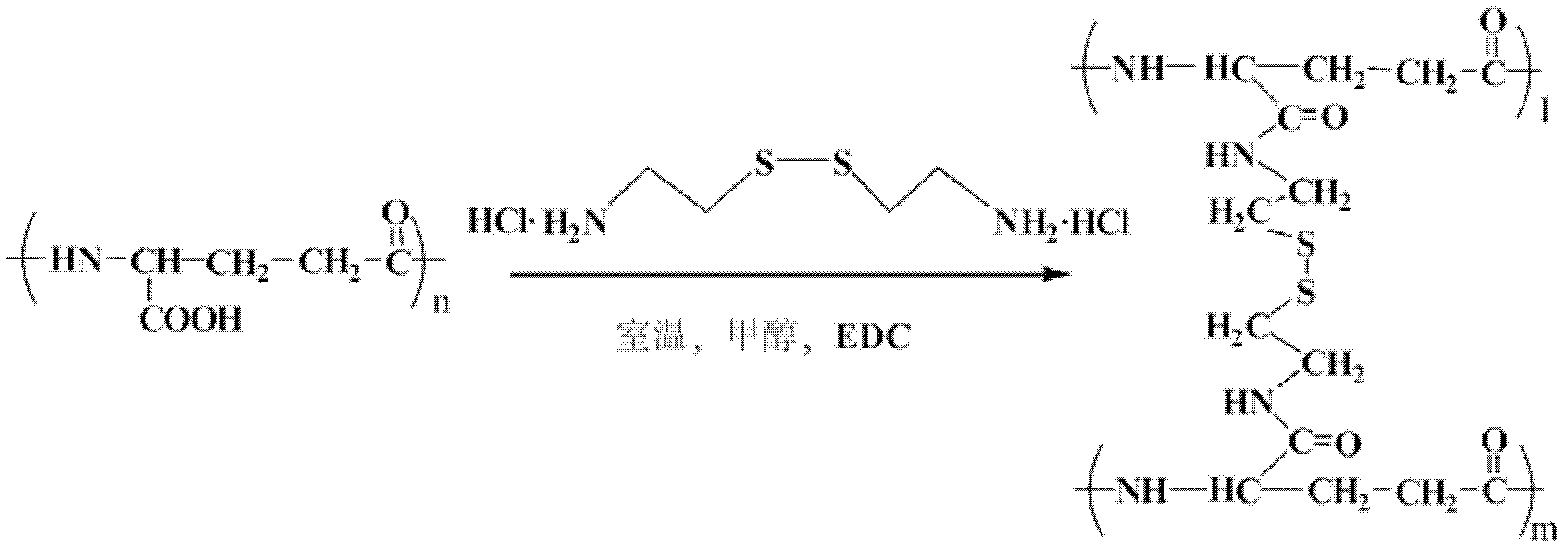
The invention relates to a preparation method of water stability gamma-polyglutamic acid nanometer fibers. The preparation method comprises the steps of: (1) preparing trifluoroacetic acid water solution of which the mass percentage concentration is 5%-10%, dissolving gamma-polyglutamic acid in the trifluoroacetic acid solution and stirring the solution for 6-8 hours to obtain gamma-polyglutamic acid solution; (2) spinning the gamma-polyglutamic acid solution via static spinning to obtain gamma-polyglutamic acid nanometer fibers; and (3) dissolving the gamma-polyglutamic acid nanometer fibersand EDC (ethylene dichloride) in methanol to have a reaction at room temperature for 3-5 hours, adding cystamine dihydrochlorid to have a reaction for 48-72 hours after the reaction is ended, rinsing, freezing and drying the products after the reaction of cystamine dihydrochlorid is ended, thus obtaining gamma-polyglutamic acid nanometer fibers with good water stability. The preparation method ofthe water stability gamma-polyglutamic acid nanometer fibers is simple and convenient in operation and has moderate technique conditions; the raw materials are easy to obtain, and the prepared gamma-polyglutamic acid nanometer fibers have good biocompatibility so the gamma-polyglutamic acid nanometer fibers have latent application merits in the field of the histological engineering bracket.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for production of polymer containing fibres
InactiveUS20130172478A1Increase in elongational viscosityHigh viscosityMonocomponent protein artificial filamentMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
Owner:AMSILK
Piezoelectric polymer fibers
ActiveUS8946974B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFiberElectricity
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Modified fibroin
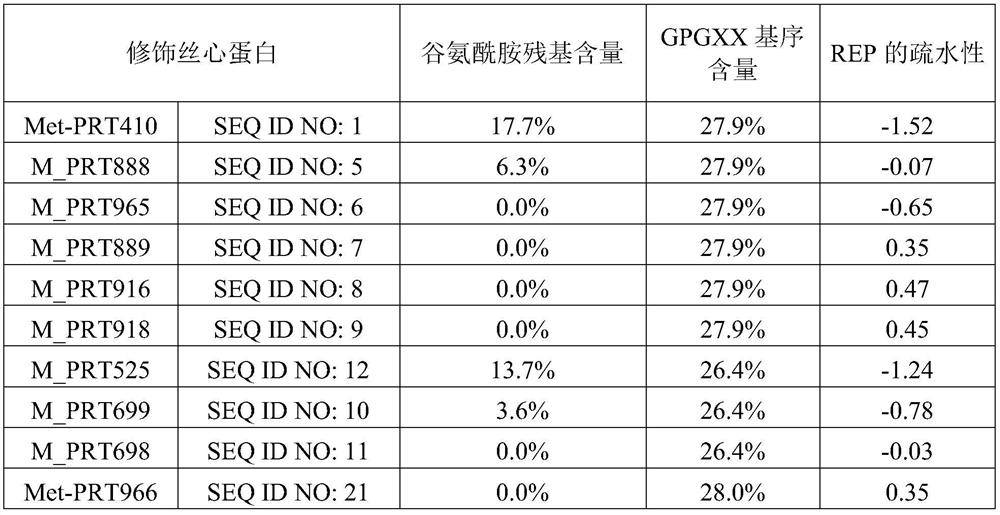
A modified fibroin includes a domain sequence indicated by formula 1: [(A)nmotif-REP]m. The domain sequence has an amino acid sequence having a reduced (A)nmotif content compared to naturally-derivedfibroin, said reduction being equivalent to the deletion of at least one (A)nmotif. [In formula 1, (A)nmotif indicates an amino acid sequence comprising 4-20 amino acid residues. The number of alanineresidues relative to the total number of amino acid residues in (A)nmotif is at least 83%. REP indicates an amino acid sequence comprising 10-200 amino acid residues. m indicates an integer between 8and 300. A plurality of (A)nmotif etc., may be the same amino acid sequence or different amino acid sequences.]
Owner:SPIBER INC
Micromachined spinneret
ActiveUS7291003B1Spinnerette packsMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentFiberMechanical engineering
A micromachined spinneret is disclosed which has one or more orifices through which a fiber-forming material can be extruded to form a fiber. Each orifice is surrounded by a concentric annular orifice which allows the fiber to be temporarily or permanently coated with a co-extrudable material. The micromachined spinneret can be formed by a combination of surface and bulk micromachining.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
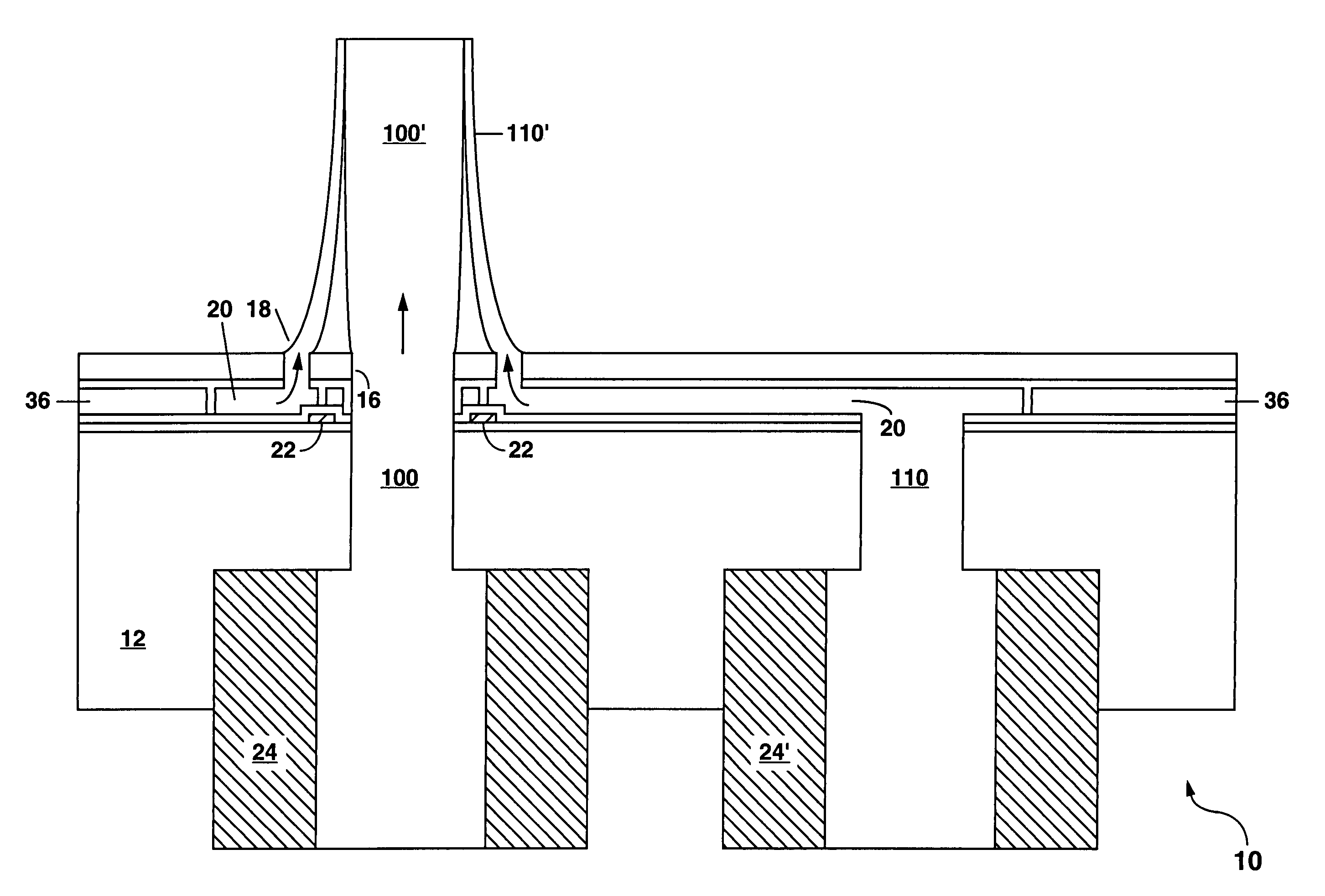
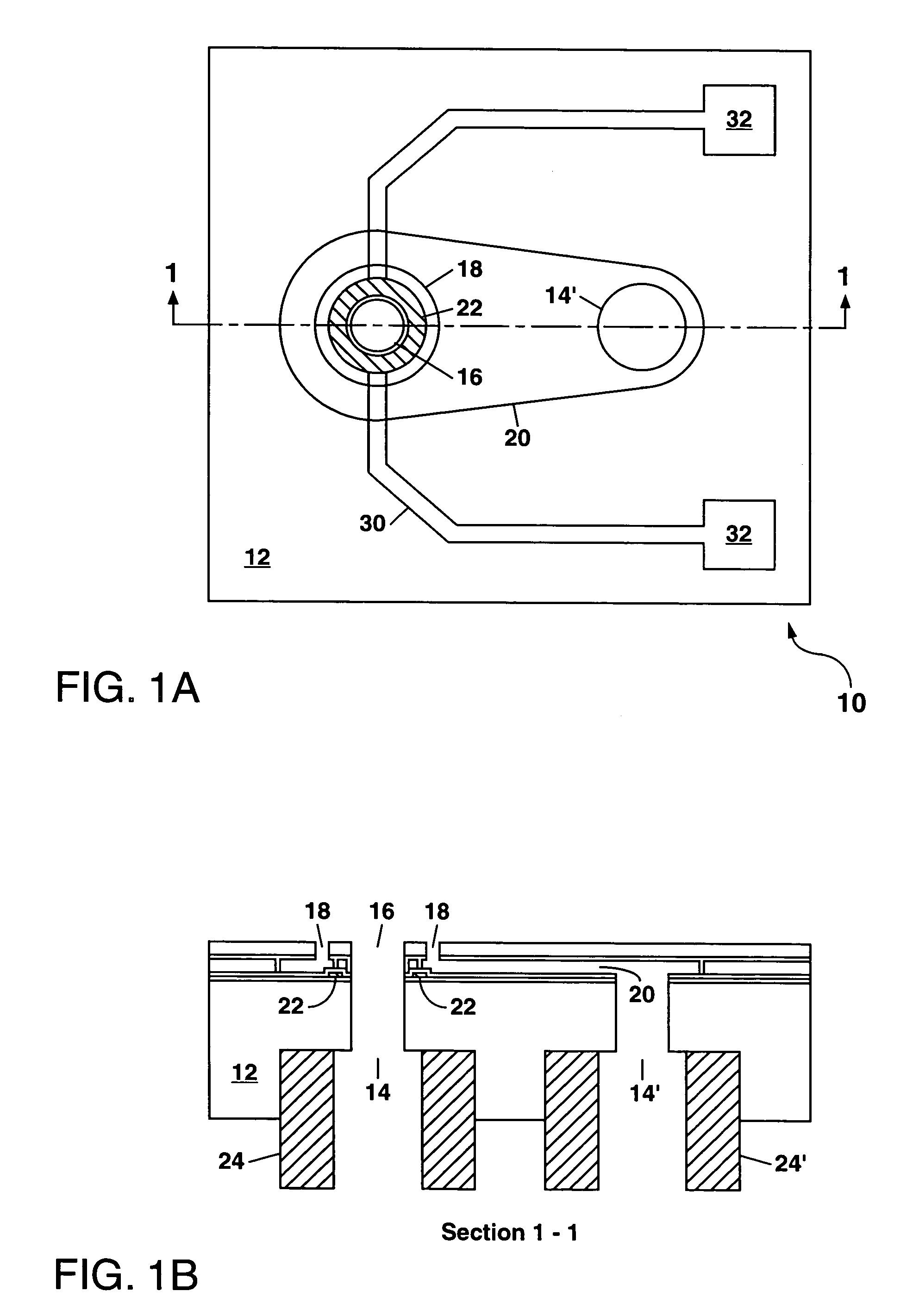
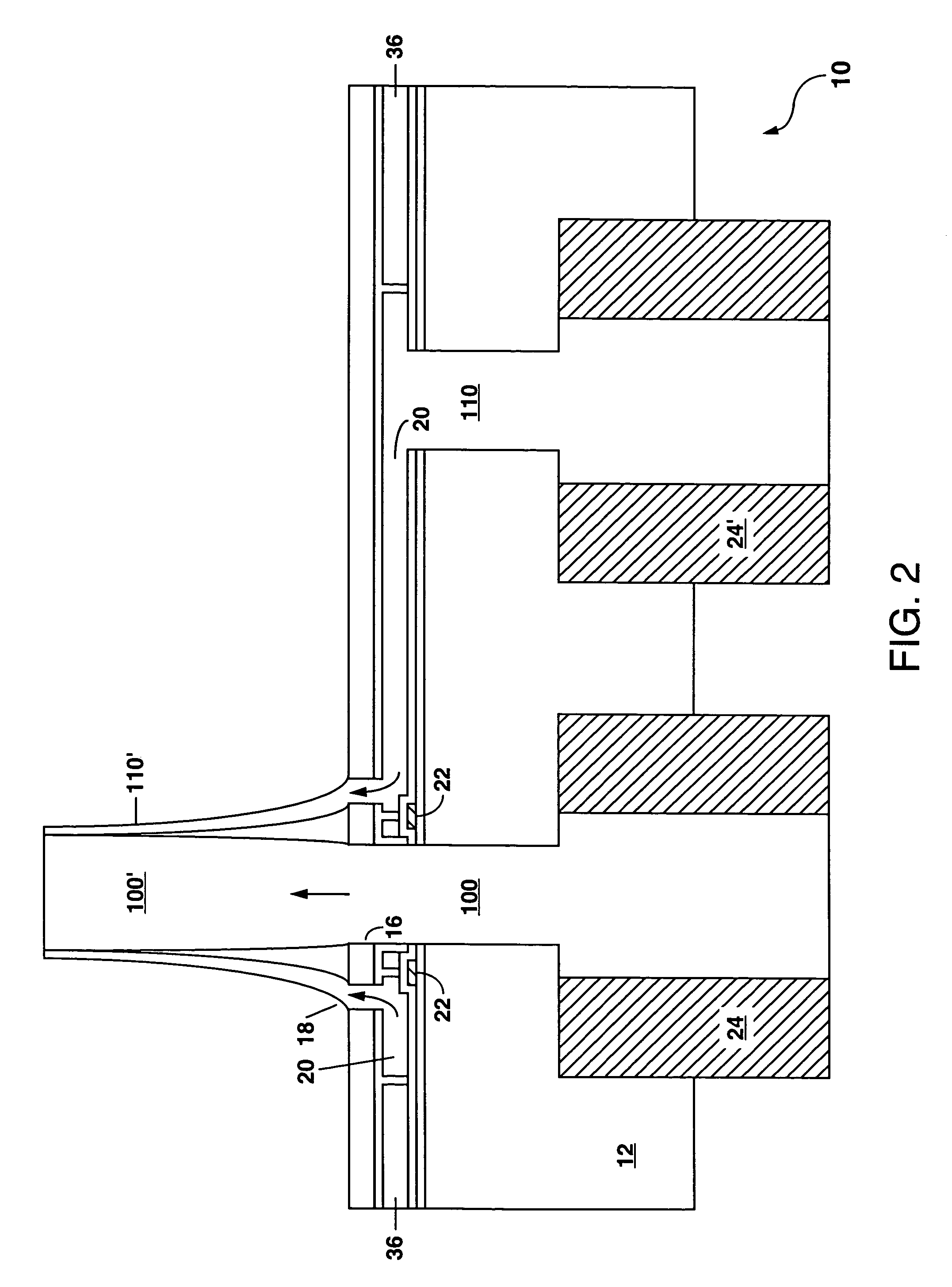
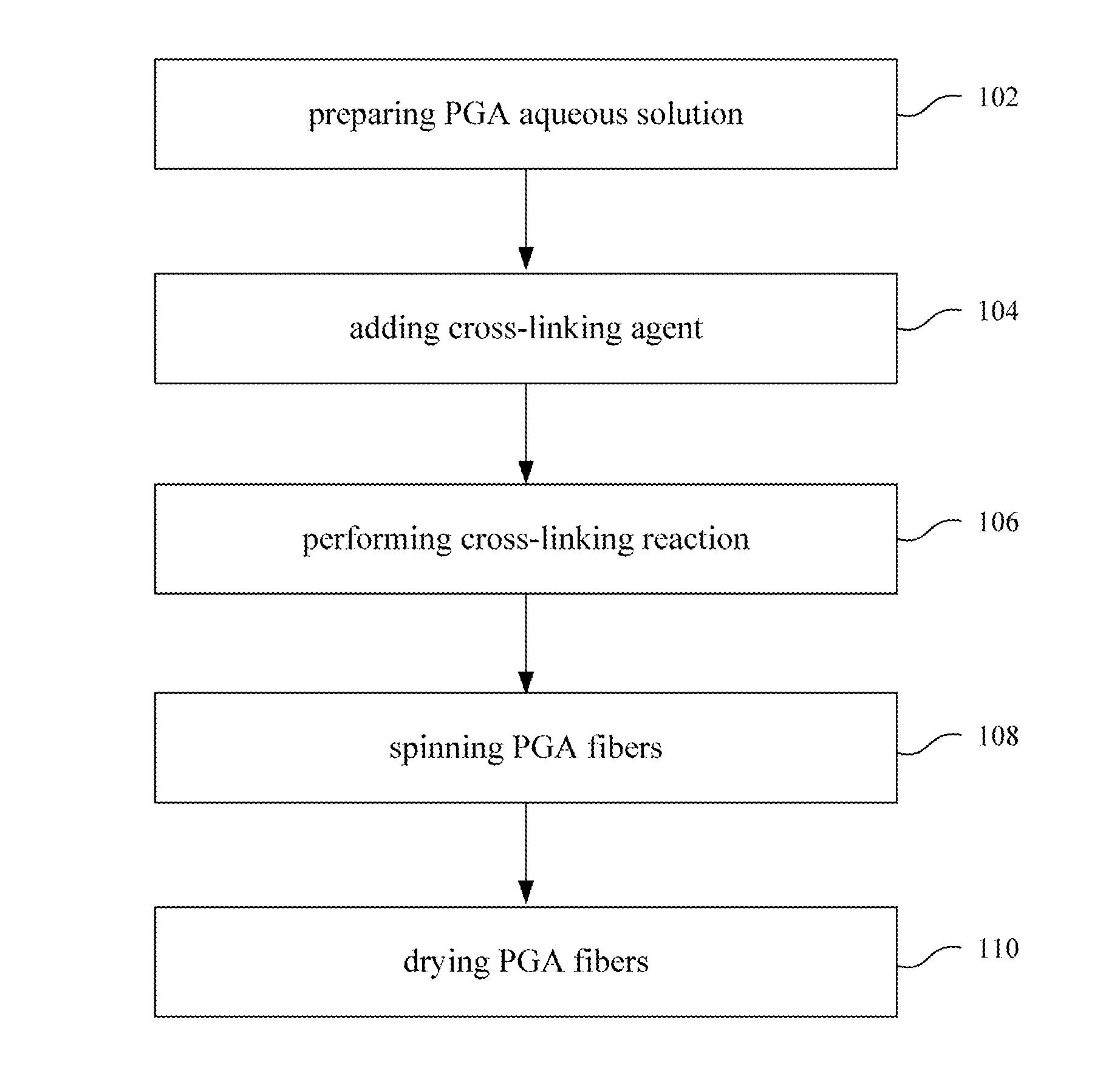
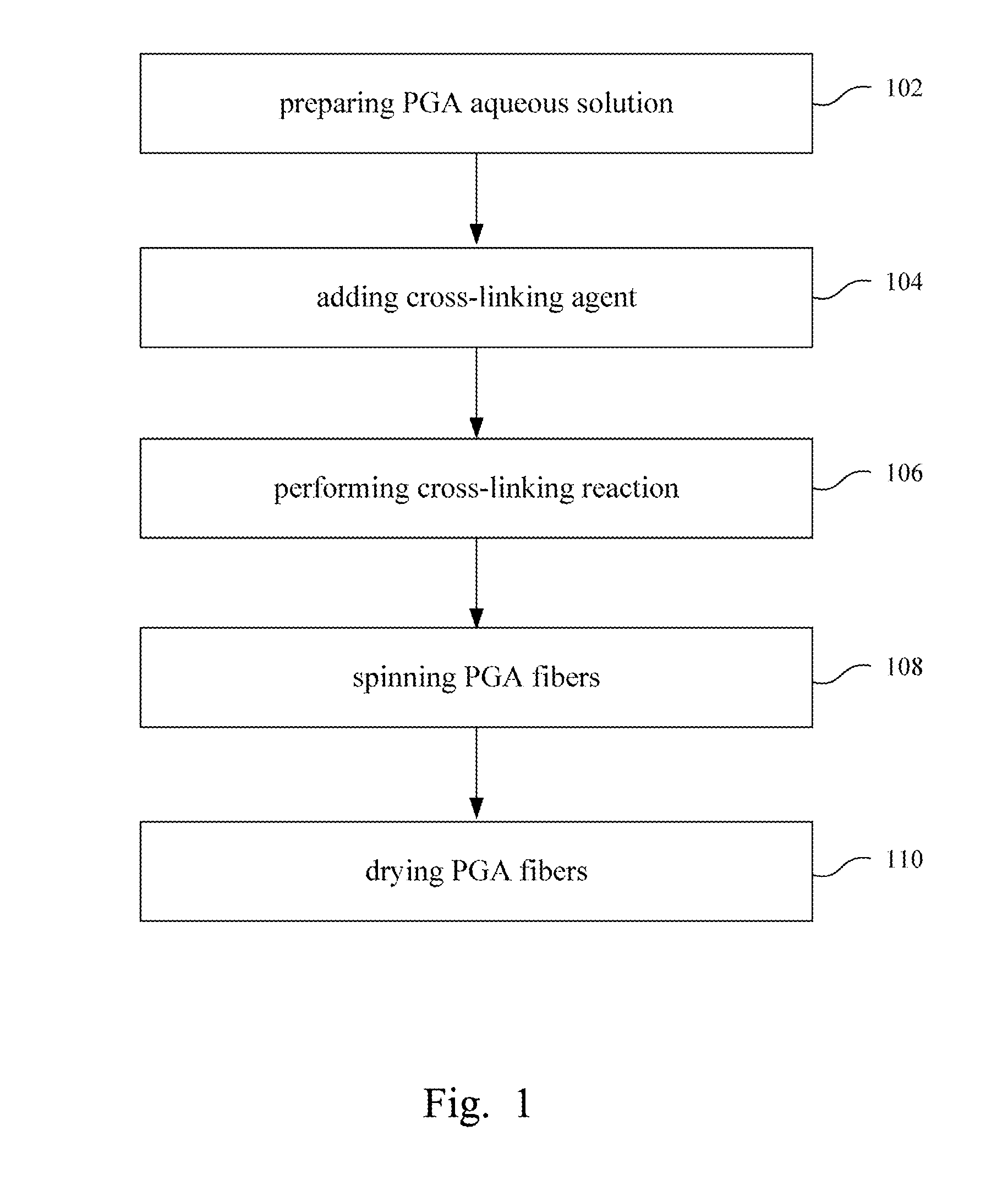
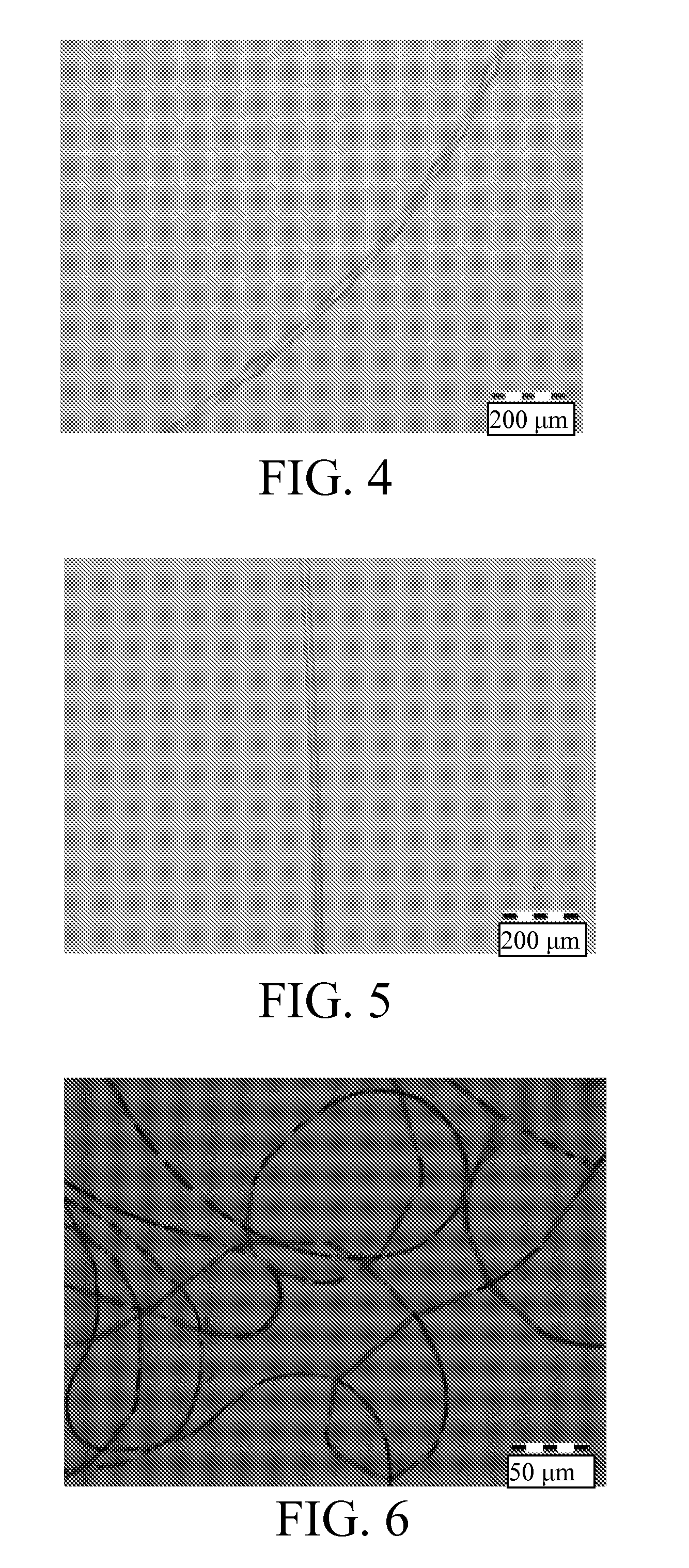
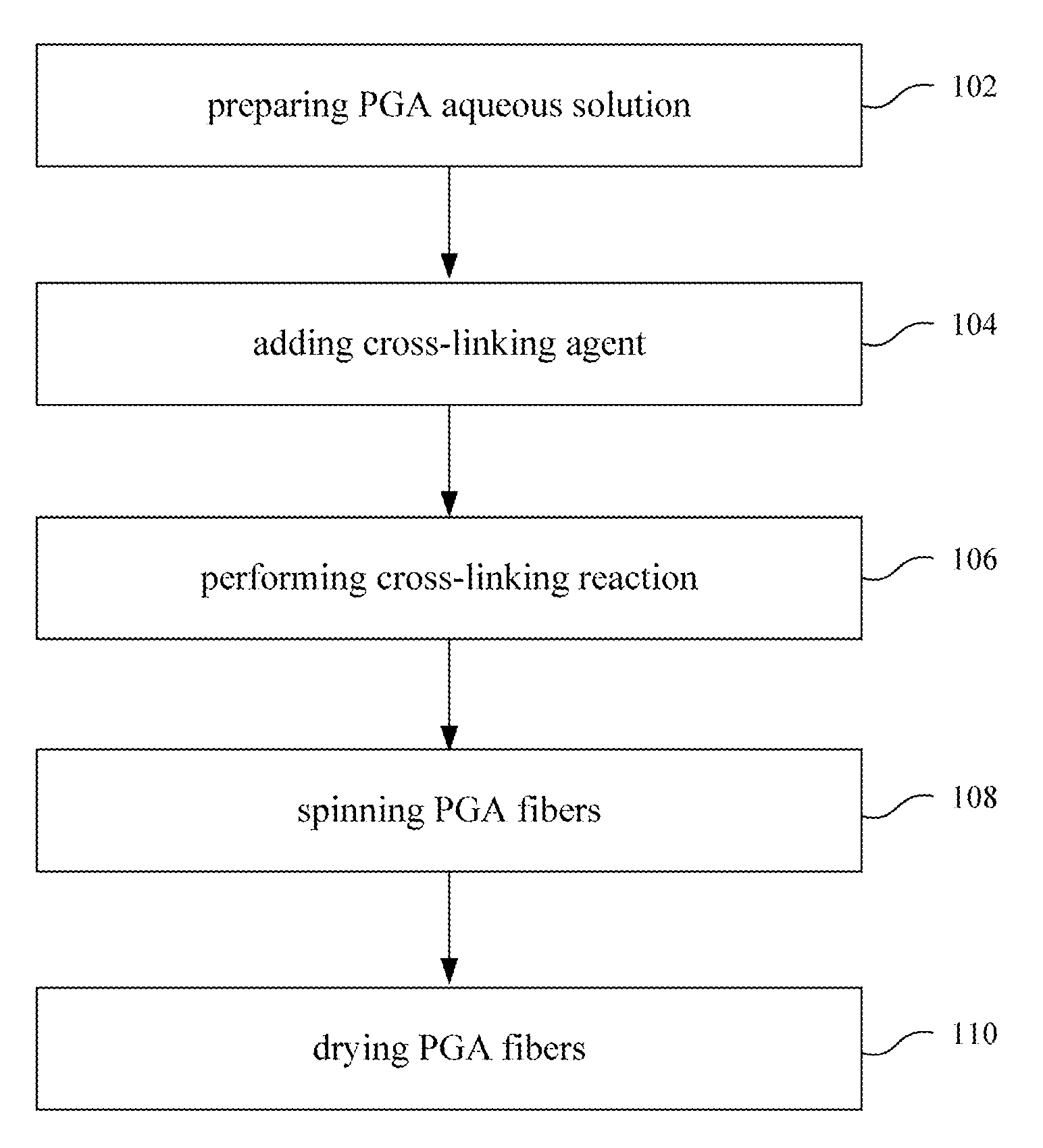
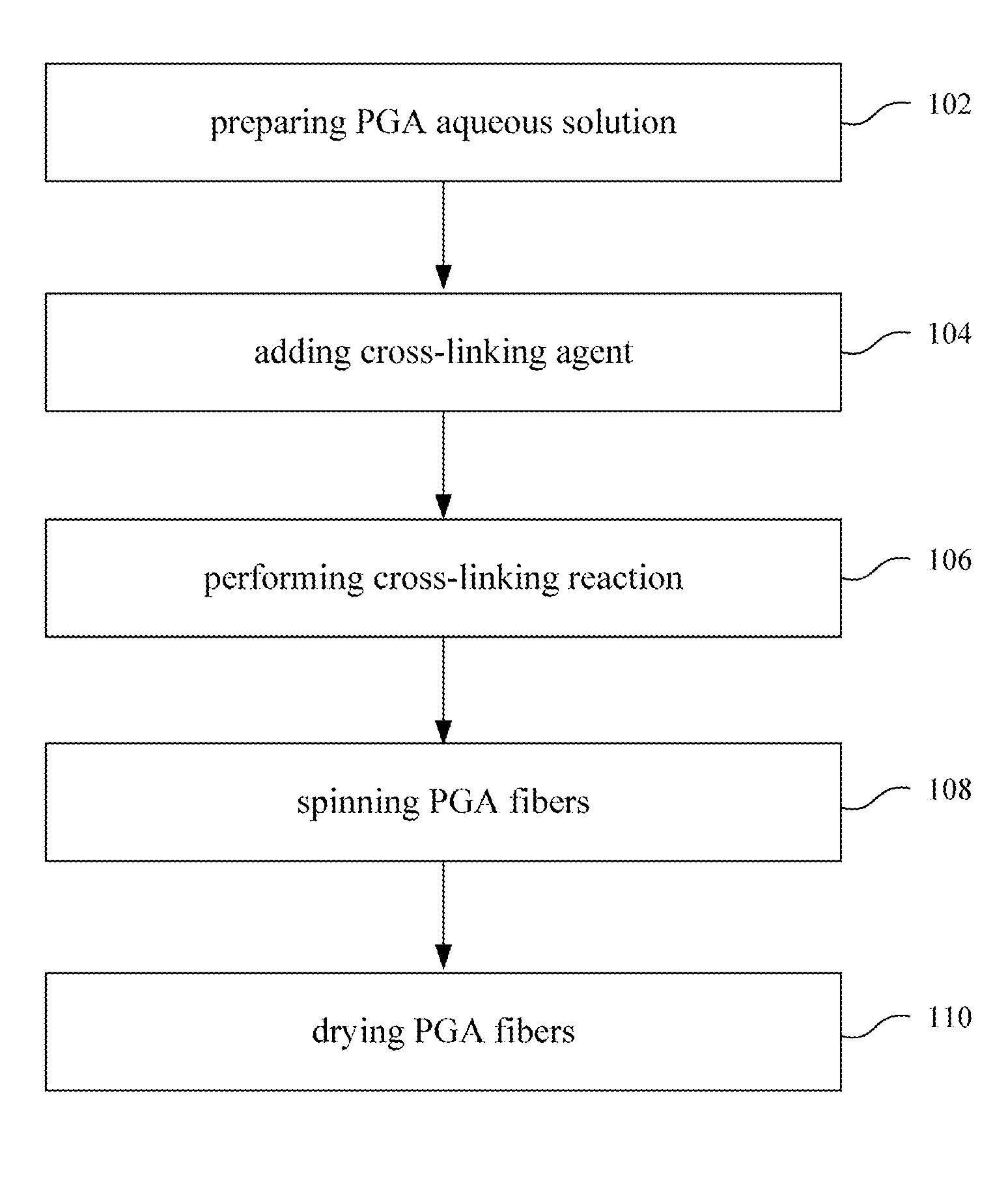
Water-Insoluble Polyglutamic Acid Fibers and Preparation Method Thereof
InactiveUS20100256326A1Monocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentFiberCross-link
A water-insoluble polyglutamic acid (PGA) fiber and a preparation method thereof are provided. In the preparation method, the PGA is cross-linked by a cross-linking agent and then passes through a spinning nozzle to form PGA fibers. Therefore, the highly water-absorbing PGA, which cannot be spun by conventional methods, can be spun to form PGA fibers and maintain the high water-absorption ability.
Owner:FAR EASTERN NEW CENTURY COPRRATION
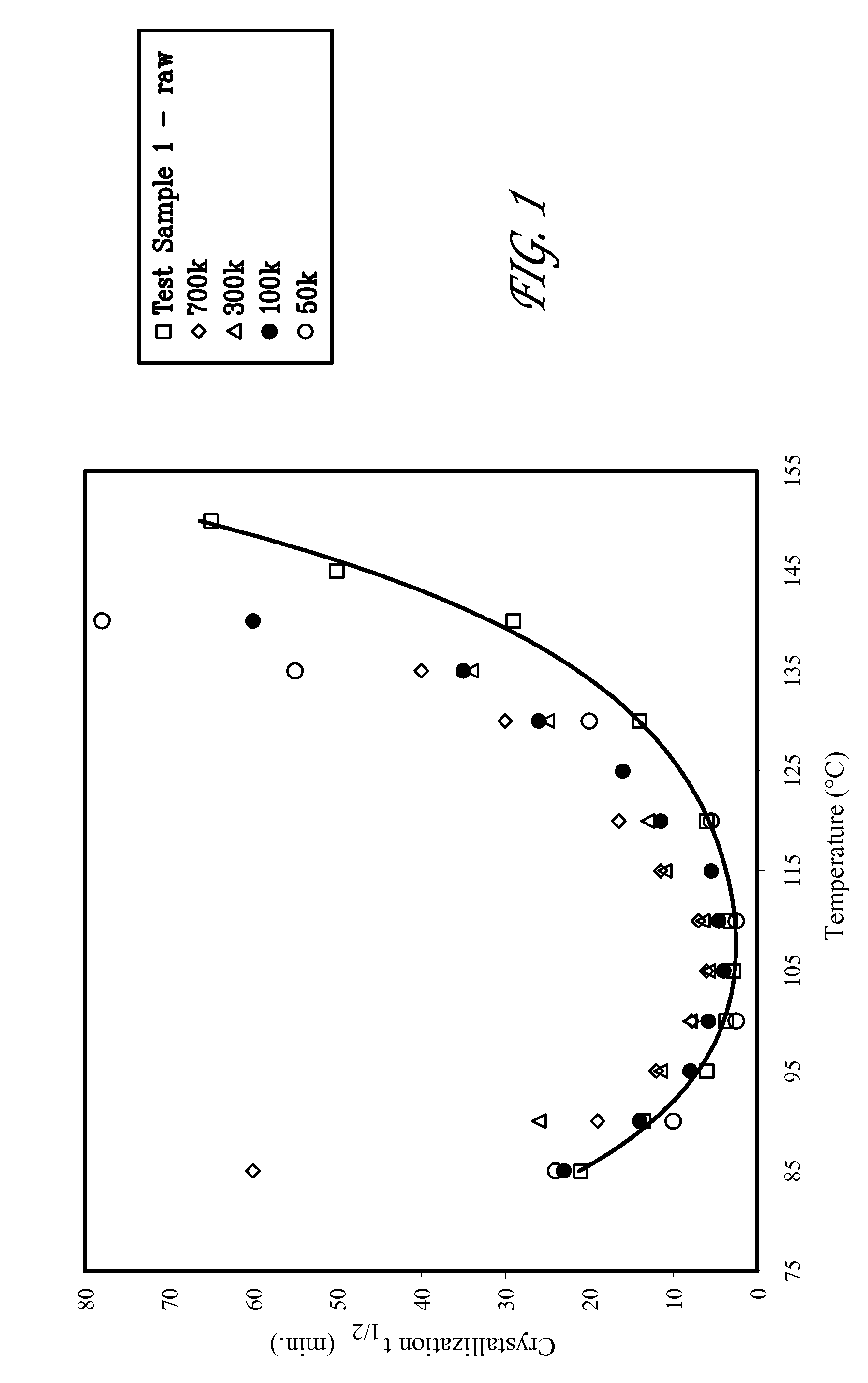
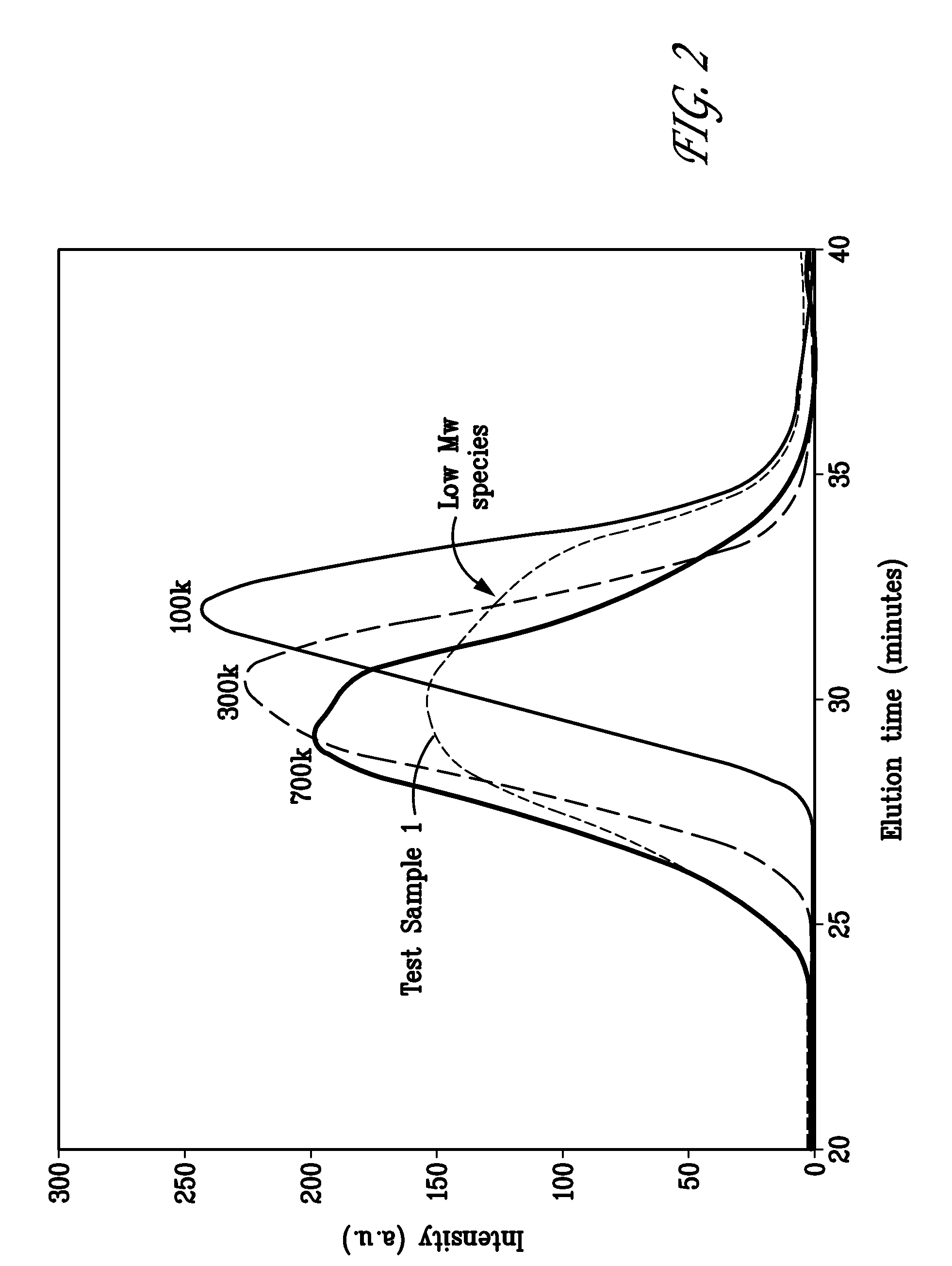
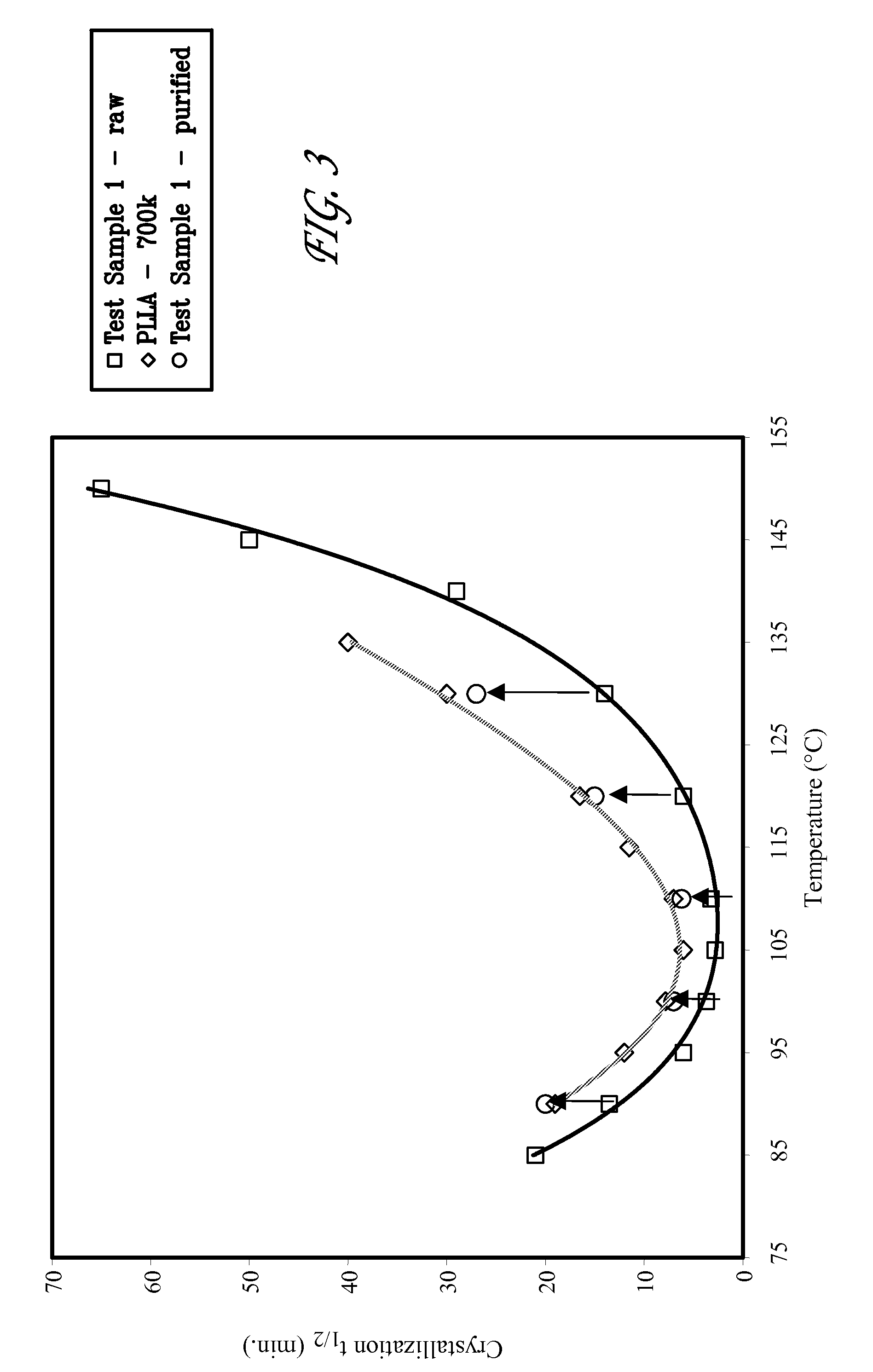
Bioabsorbable polymer compositions exhibiting enhanced crystallization and hydrolysis rates
Owner:ETHICON INC
Modified Fibroin
InactiveUS20190135880A1Improve productivityMaintain strengthPolypeptide with affinity tagMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentProtein CFibroin
Provided is a modified fibroin, including a domain sequence represented by Formula 1: [(A)n motif-REP]m, in which the domain sequence has an amino acid sequence having a reduced content of (A)n motif equivalent to an amino acid sequence in which, at least, one or a plurality of the (A)n motifs is deleted, as compared to naturally occurring fibroin.[In Formula 1, (A)n motif represents an amino acid sequence consisting of 4 to 20 amino acid residues and the number of alanine residues relative to the total number of amino acid residues in the (A)n motif is 83% or more, REP represents an amino acid sequence consisting of 10 to 200 amino acid residues, m represents an integer of 8 to 300, and a plurality of (A)n motifs or the like may be the same amino acid sequence or different amino acid sequences.]
Owner:SPIBER INC
Bioabsorbable polymer compositions exhibiting enhanced crystallization and hydrolysis rates
ActiveUS20120302528A1Improve crystallizationIncrease hydrolysis rateBiocideNervous disorderMelt blowingHydrolysis
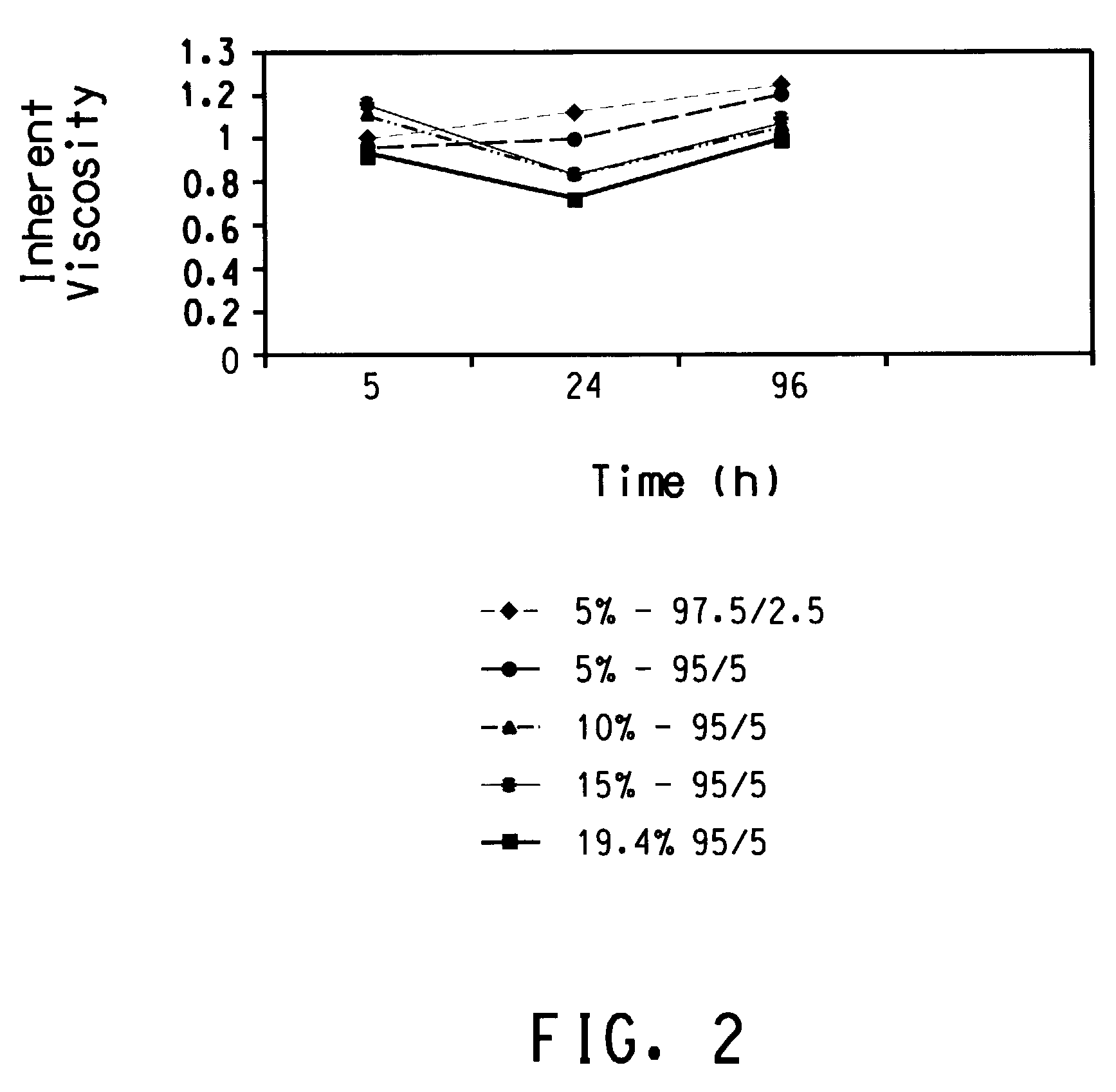
A bimodal bioabsorbable polymer composition. The composition includes a first amount of a bioabsorbable polymer polymerized so as to have a first molecular weight distribution; a second amount of said bioabsorbable polymer polymerized so as to have a second molecular weight distribution having a weight average molecular weight between about 10,000 to about 50,000 Daltons, the weight average molecular weight ratio of said first molecular weight distribution to said second molecular weight distribution is at least about two to one; wherein a substantially homogeneous blend of said first and second amounts of said bioabsorbable polymer is formed in a ratio of between about 50 / 50 to about 95 / 5 weight / weight percent. Also disclosed are a medical device, a method of making a medical device and a method of melt blowing a semi-crystalline polymer blend.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Artificial polypeptide fiber and method for producing the same
ActiveUS9617315B2High stressImprove toughnessMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentFiberSpider Proteins
An artificial polypeptide fiber of the present invention is an artificial fiber containing a polypeptide as a main component, and has a stress of 350 MPa or more and a toughness of 138 MJ / m3 or more. A method for producing an artificial polypeptide fiber of the present invention is a method for producing the artificial polypeptide fiber obtained by spinning a spinning solution (6) containing a polypeptide derived from natural spider silk proteins and performing drawing of at least two stages. The drawing of at least two stages includes a first-stage drawing (3) in wet heat and a second-stage drawing (4) in dry heat. Thereby, the present invention provides high-toughness artificial polypeptide fibers having favorable stress and rupture elongation, and a method for producing the same.
Owner:SPIBER INC
Polypeptide electrospun nanofibrils of defined composition
ActiveUS9428849B2Electric discharge heatingMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentElectrospinningChemistry
Electrospun nanofibrils and methods of preparing the same are provided. The electrospun nanofibrils comprise at least one polypeptide. A polypeptide can be dissolved in a solution, and the solution can be electrospun into a nanofibril. The solution can be added to a syringe or syringe pump, and an electric field can be applied to electrospin the at least one polypeptide.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
Method for Preparing High Water-Absorption and Anti-Bacterial Fibers
InactiveUS20120083179A1Simple processLow production costBiochemical fibre treatmentMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentFiberSodium hypochlorite solution
A method for preparing a polyglutamic acid (γ-PGA) fiber having antibacterial and water absorption properties is provided. The method includes providing a γ-PGA fiber and immersing it in a sodium hypochlorite solution. A relation exists between an immersing time T of the γ-PGA fiber and a concentration X of the sodium hypochlorite solution as shown in the formula below:10.2≦(T−64.55X2+50X)≦15.2,wherein X is 0.006-0.4 wt %.
Owner:FAR EASTERN NEW CENTURY COPRRATION
Process of making water-insoluble polyglutamic acid fibers
InactiveUS8273278B2Monocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentWet spinning methodsFiberCross-link
A water-insoluble polyglutamic acid (PGA) fiber and a preparation method thereof are provided. In the preparation method, the PGA is cross-linked by a cross-linking agent and then passes through a spinning nozzle to form PGA fibers. Therefore, the highly water-absorbing PGA, which cannot be spun by conventional methods, can be spun to form PGA fibers and maintain the high water-absorption ability.
Owner:FAR EASTERN NEW CENTURY COPRRATION
Method for purifying recombinant protein
InactiveCN109843905AHigh purityReduce the number of stepsMonocomponent protein artificial filamentConnective tissue peptidesChemistry
Disclosed is a method for purifying a recombinant protein from a recombinant cell in which a target recombinant protein is expressed within the cell as an insoluble body, said method characterized inthat said recombinant cell is treated under conditions in which a protein derived from a host cell would dissolve, but said recombinant protein would not dissolve, in a first aprotic polar solvent towhich an inorganic salt has been added or not added, a first soluble fraction is removed, and then an obtained first insoluble fraction is treated under conditions in which the recombinant protein would dissolve in a second aprotic polar solvent to which an inorganic salt has been added.
Owner:SPIBER INC
Method of Producing Polyamide Material with Peptides and Polyamide Material with Peptides
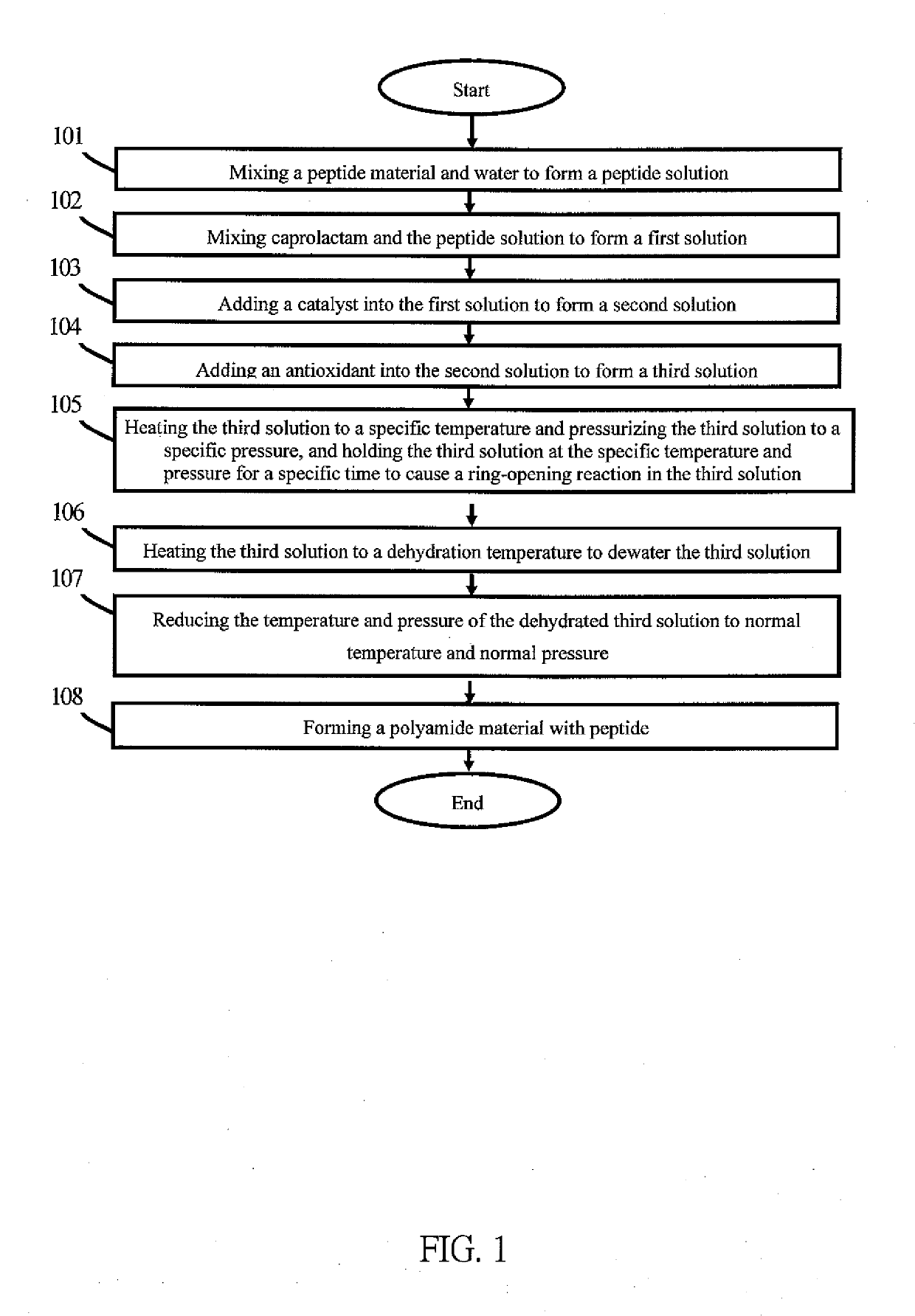
InactiveUS20190177881A1Suitable for productionReducing temperature and pressureMonocomponent protein artificial filamentMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentAntioxidantPolyamide
A method of producing polyamide material with peptides is disclosed. The method includes: mixing a peptide material and water to form a peptide solution; mixing caprolactam and the peptide solution to form a first solution; adding a catalyst into the first solution to form a second solution; adding an antioxidant into the second solution to form a third solution; causing a ring-opening reaction in the third solution; heating the third solution to a dehydration temperature to dewater the third solution; forming a polyamide material with peptides.
Owner:CAMANGI CORP
Peptide-based materials
The subject invention pertains to peptide-based materials comprising cross-linked peptides with random amino acid sequences that are soluble in water or ethanol before crosslinking but insoluble in water after crosslinking.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Methods of Generating Highly-Crystalline Recombinant Spider Silk Protein Fibers
ActiveUS20190093257A1Increased beta-sheet formationMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentSpider ProteinsMedicine
Provided herein are scalable methods of processing wet-spun fiber comprising recombinant spider silk polypeptides to generate a three-dimensional crystalline lattice of beta-sheet structures in the fiber.
Owner:BOLT THREADS
Method for Purifying Recombinant Protein
InactiveUS20190225646A1High puritySimple stepsMonocomponent protein artificial filamentConnective tissue peptidesInorganic saltsProtein insertion
Disclosed is a method for purifying a recombinant protein of interest from a recombinant cell expressing intracellularly the recombinant protein as an insoluble matter, comprising treating the recombinant cell under conditions where a protein derived from a host cell dissolves in a first aprotic polar solvent to which an inorganic salt is added or not but the recombinant protein does not dissolve, removing a first soluble fraction, and then treating the resulting first insoluble fraction under conditions where the recombinant protein dissolves in a second aprotic polar solvent to which an inorganic salt is added.
Owner:SPIBER INC
Peptide-Based Materials
The subject invention pertains to peptide-based materials comprising cross-linked peptides with random amino acid sequences that are soluble in water or ethanol before crosslinking but insoluble in water after crosslinking.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Metalloprotein compositions
ActiveUS20180119194A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementMetalloproteinAmino acid binding
The present invention relates to compositions comprising: a polypeptide, wherein at least a portion of the polypeptide has a coiled coil structure; and a chelate comprising a chelating agent and a metal ion; and wherein the chelate is bound to at least one amino acid of the polypeptide. In a preferred embodiment the polypeptide is a silk fibroin, wherein at least a portion of said silk fibroin has a coiled coil structure.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Composite molding composition including fibroin-like protein, and method for producing composite molding composition
ActiveUS20190186050A1Improve toughnessHigh strainSuture equipmentsMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentFiberComposite film
Provided are a composite molding composition such as a composite film and a composite fiber that have properties such as an improved tensile strength, strain and toughness as a result of blending a peptide or polyamino acid having a β-sheet structure with a natural or artificially modified fibroin-derived protein; a method for producing such composite molding composition; and a method for improving the physical properties of a composite molding composition containing a fibroin-derived protein.
Owner:RIKEN +1
Methods of generating highly-crystalline recombinant spider silk protein fibers
ActiveUS11208736B2Increased beta-sheet formationMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentPolymer scienceSpider Proteins
Provided herein are scalable methods of processing wet-spun fiber comprising recombinant spider silk polypeptides to generate a three-dimensional crystalline lattice of beta-sheet structures in the fiber.
Owner:BOLT THREADS
Modified Fibroin Fibers
PendingUS20220074077A1Reduce Shrinkage ProblemsMonocomponent polypeptides artificial filamentFilament manufacturePolymer scienceSpinning
Owner:SPIBER INC
Resorbable, amino acid-based poly(ester urea)s scaffold for vascular graft tissue engineering
Embodiments relate to amino acid-based poly(ester urea)s with amino acid residues selected L-leucine, L-isoleucine, L-valine or combinations thereof. The amino acid-based poly(ester urea)S may optionally include a second amino acid residue selected from proteinogenic amino acids and non-proteinogenic amino acids. The amino acid-based poly(ester urea)s are particular useful for the preparation of vascular grafts. Due to the biocompatibility of the amino acid-based poly(ester urea)s, vascular grafts prepared from amino acid-based poly(ester urea)s with small internal diameters (i.e. less than 5 mm) may be prepared and inserted into a patient or animal, and provide a substantial decrease in the risk of failure compared to conventional polymers used in vascular grafts.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Rubber-reinforcing fiber, rubber product, tire cord, and tire
PendingCN114829687AHigh strengthNatural rubber adhesivesFilm/foil adhesivesRubber materialPolymer science
Provided is a fiber for rubber reinforcement, which can be produced using a biologically derived raw material and is not susceptible to breakage even when compounded with a rubber material. The first rubber-reinforcing fiber according to the present invention is characterized by using a protein fiber containing a hydrophobic protein. The second rubber-reinforcing fiber according to the present invention is characterized by using a protein fiber having an initial tensile modulus of elasticity of 2.0 GPa or more when wet. The rubber-reinforcing fibers are preferably provided with a coating layer on the surface, and the coating layer is formed from an aqueous adhesive composition.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com