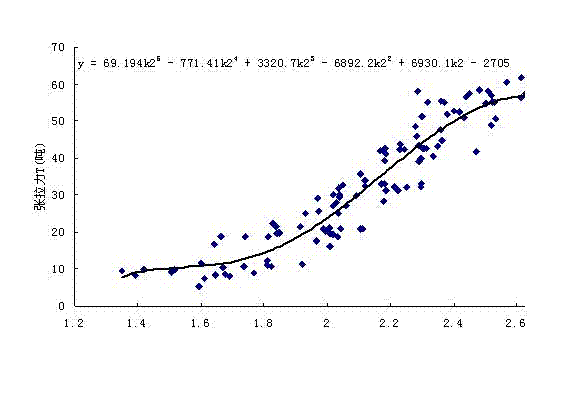Patents
Literature
31 results about "Force dynamics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Force dynamics is a semantic category that describes the way in which entities interact with reference to force. Force Dynamics gained a good deal of attention in cognitive linguistics due to its claims of psychological plausibility and the elegance with which it generalizes ideas not usually considered in the same context. The semantic category of force dynamics pervades language on several levels. Not only does it apply to expressions in the physical domain like leaning on or dragging, but it also plays an important role in expressions involving psychological forces (e.g. wanting or being urged). Furthermore, the concept of force dynamics can be extended to discourse. For example, the situation in which speakers A and B argue, after which speaker A gives in to speaker B, exhibits a force dynamic pattern.
Dynamic controller for controlling a system
InactiveUS7050866B2Minimize error valueOutput errorAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsComputation using non-denominational number representationNarrow rangeDynamic models
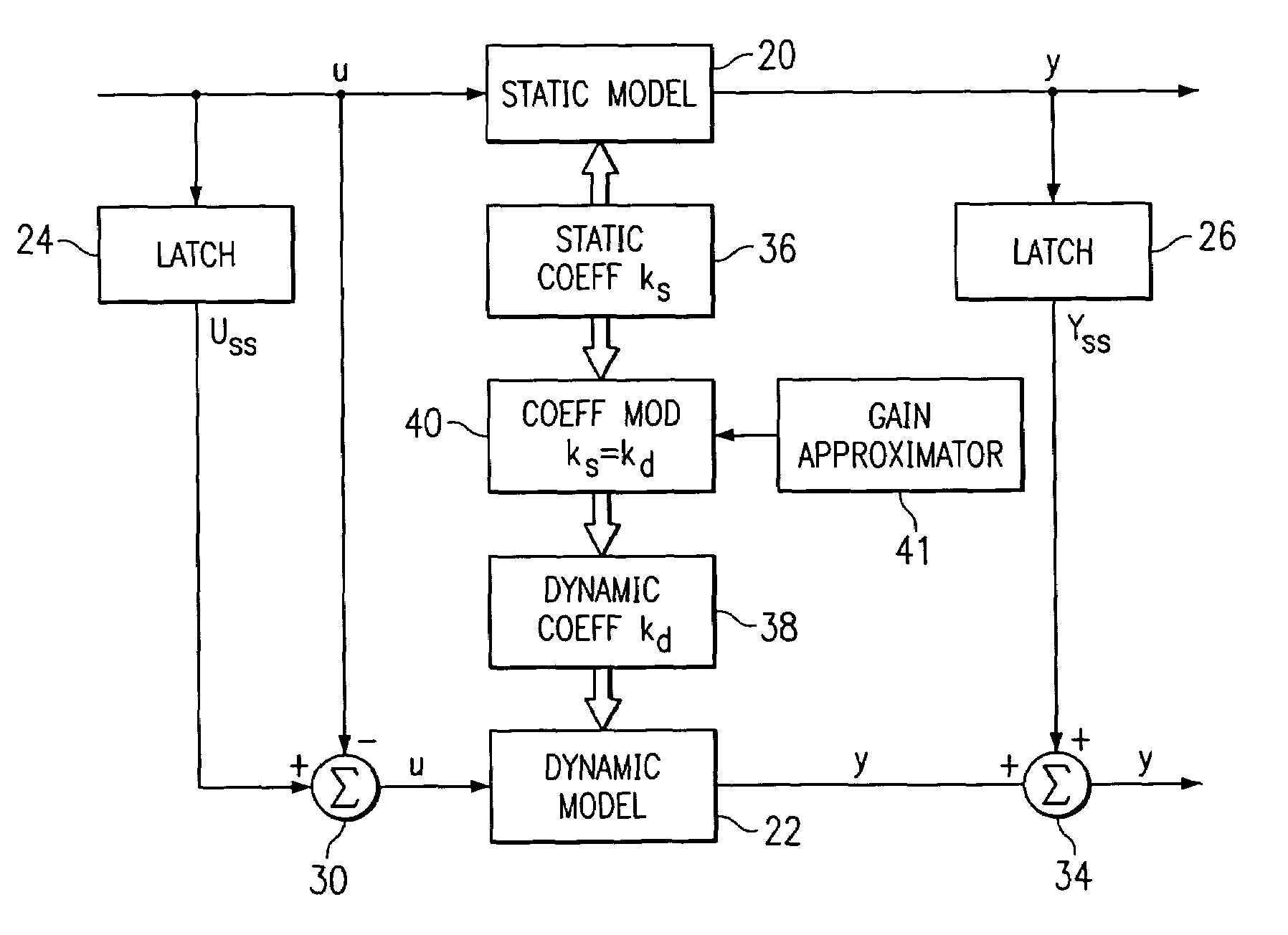
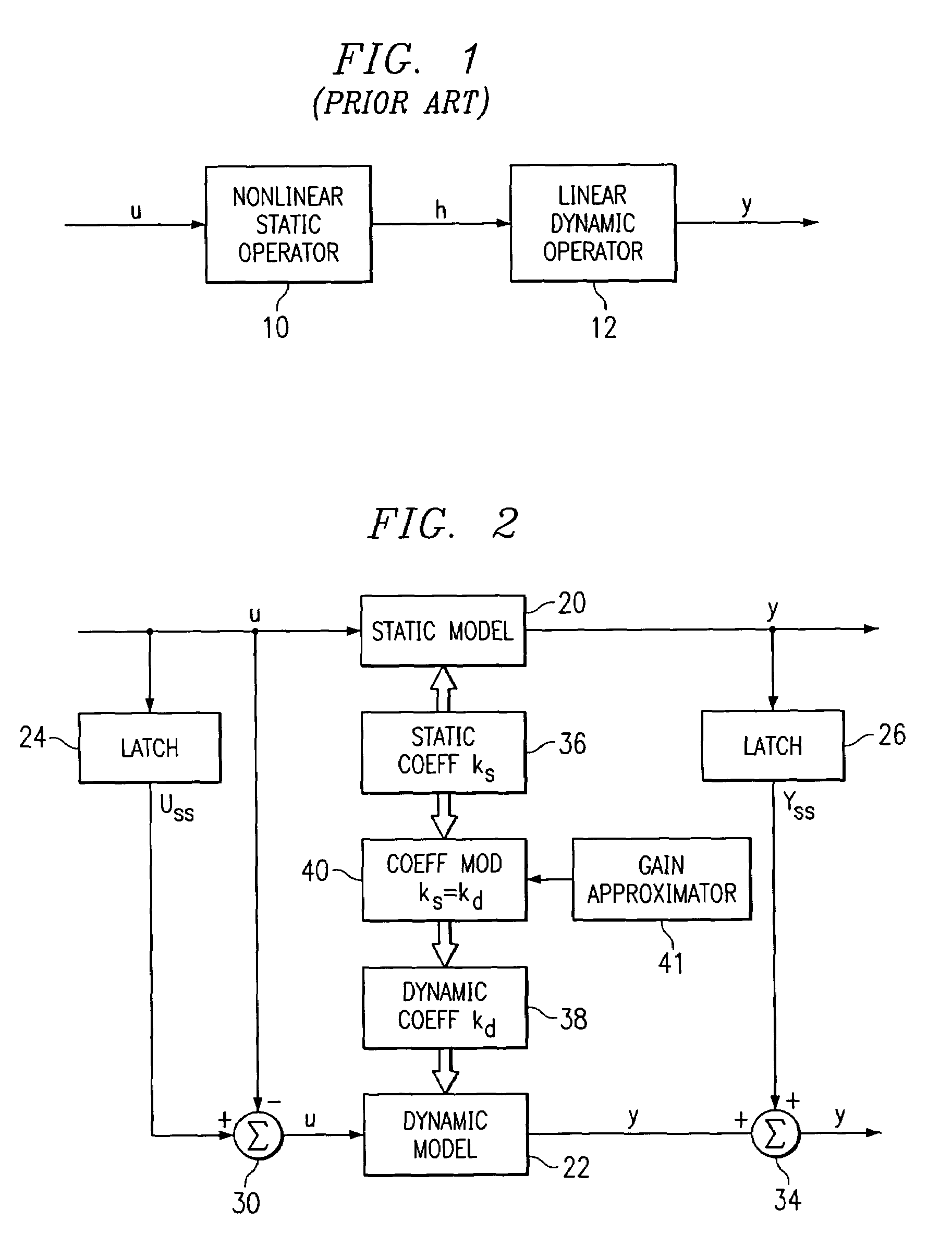
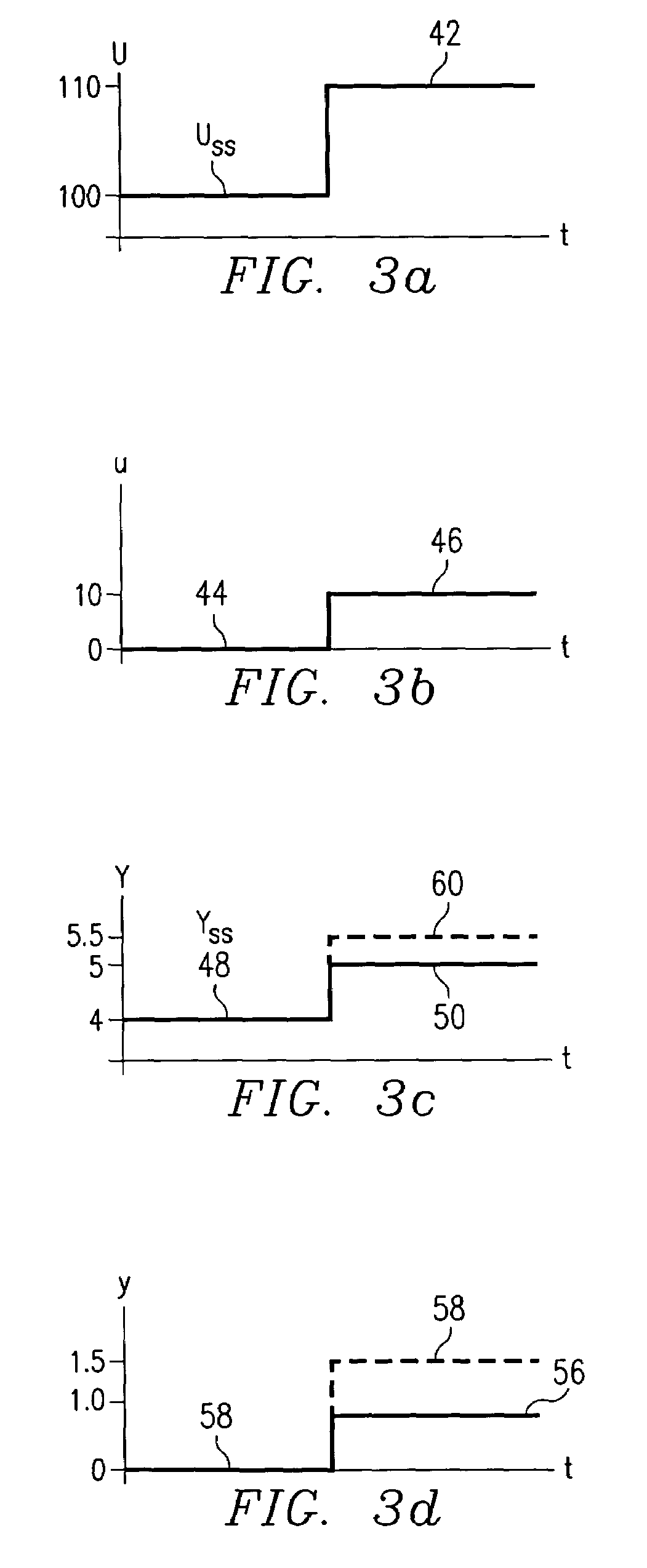
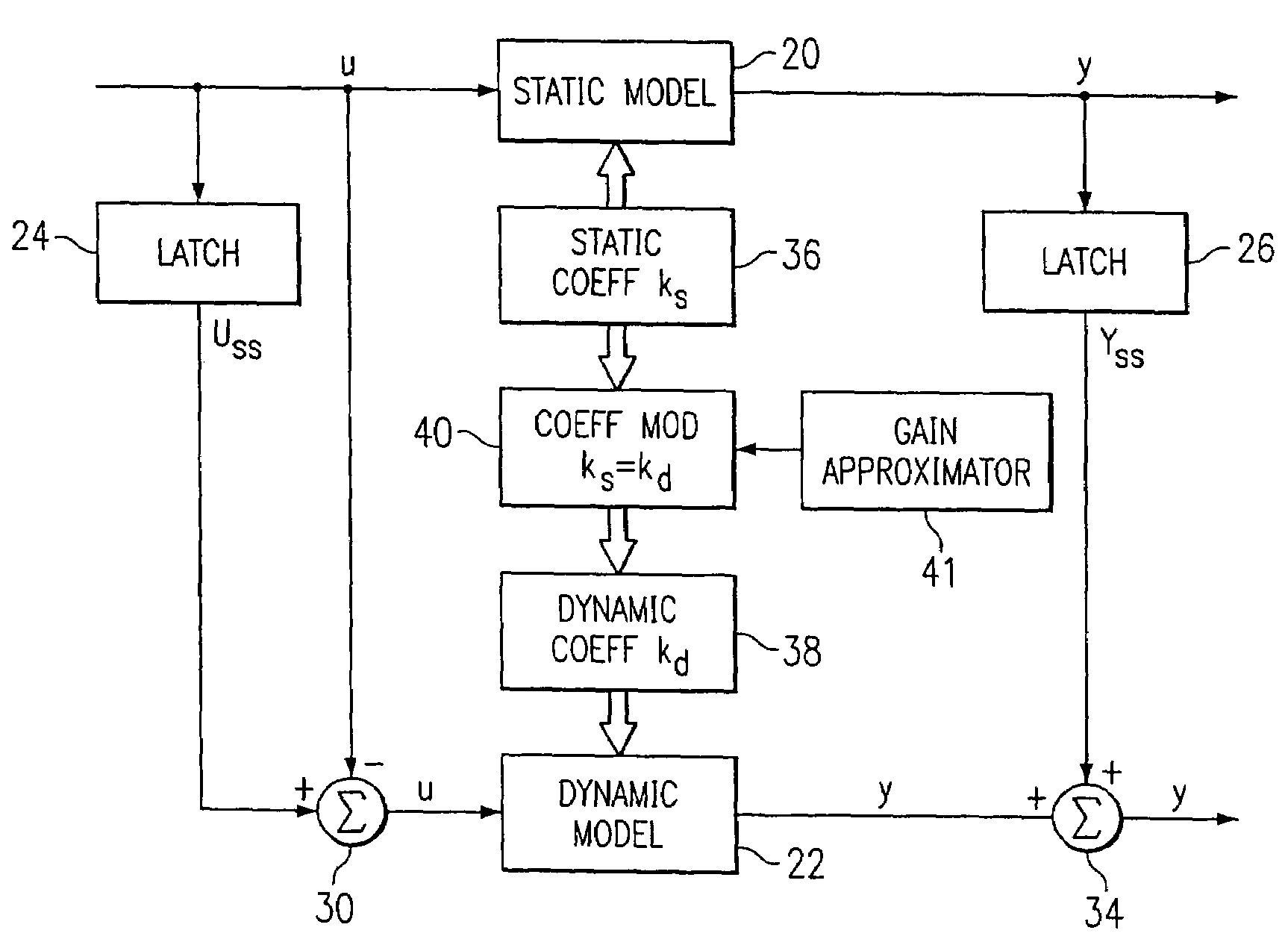
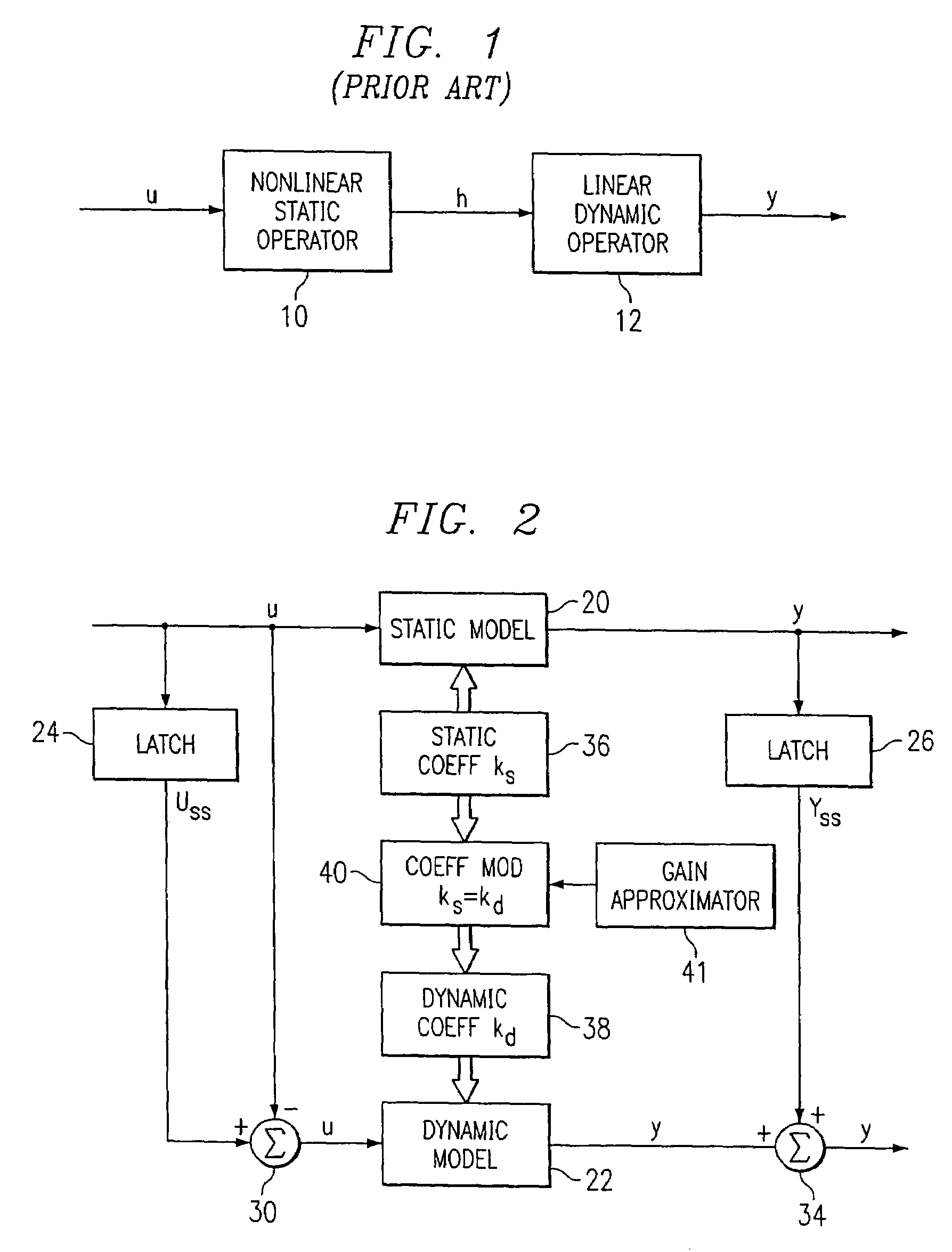
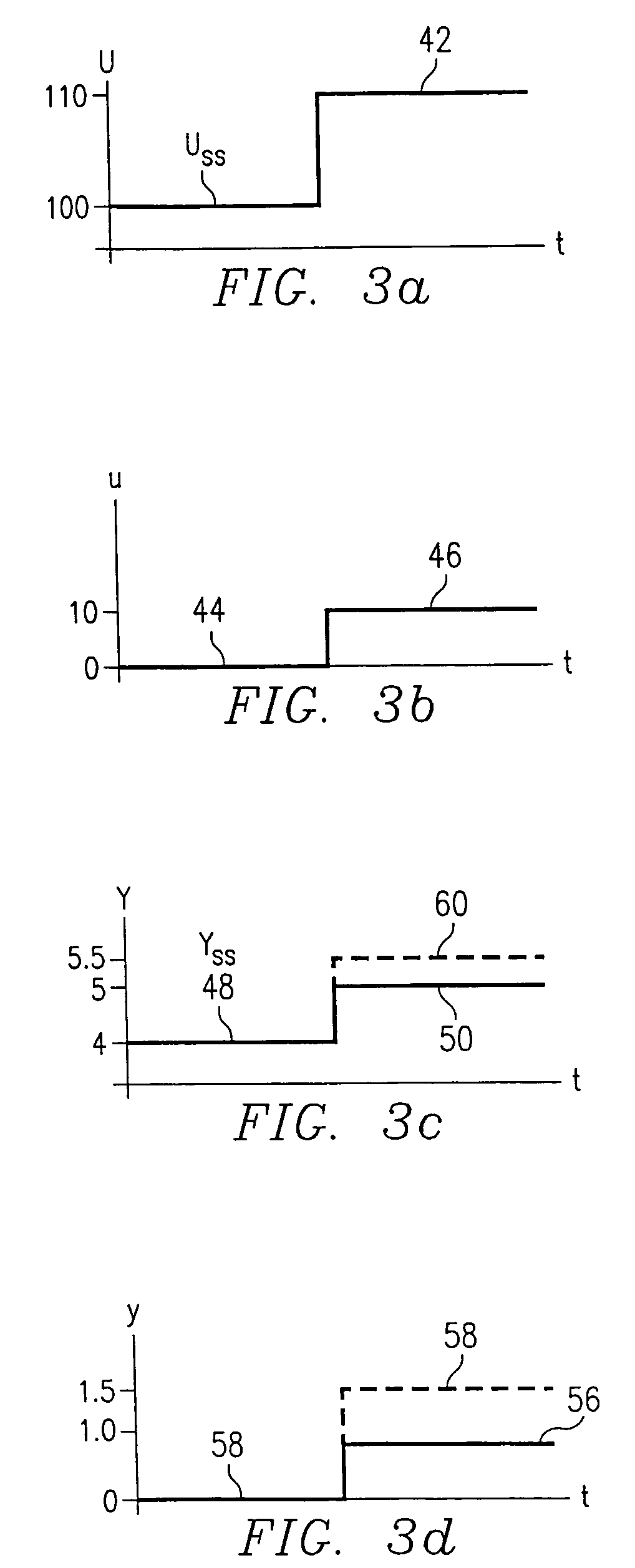
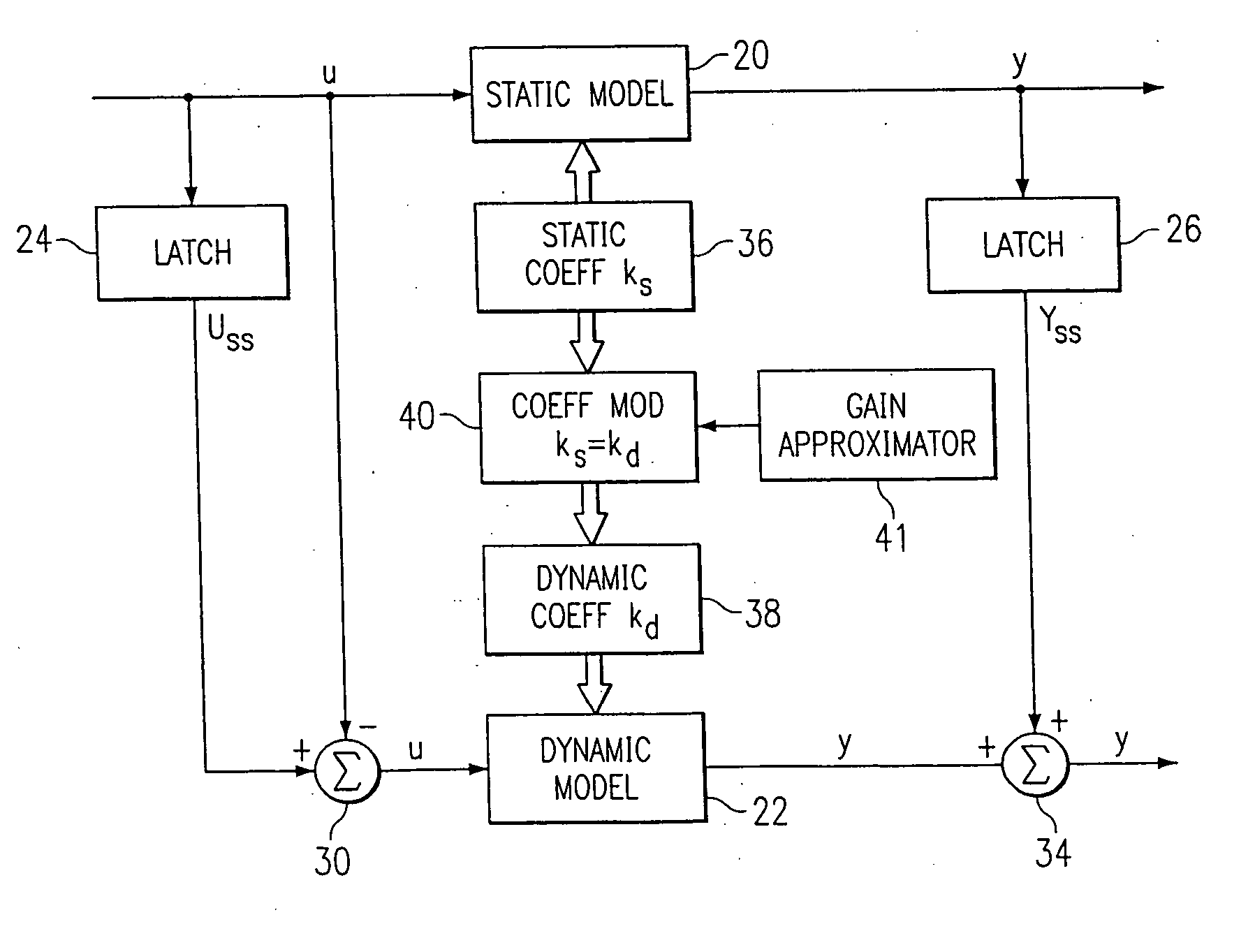
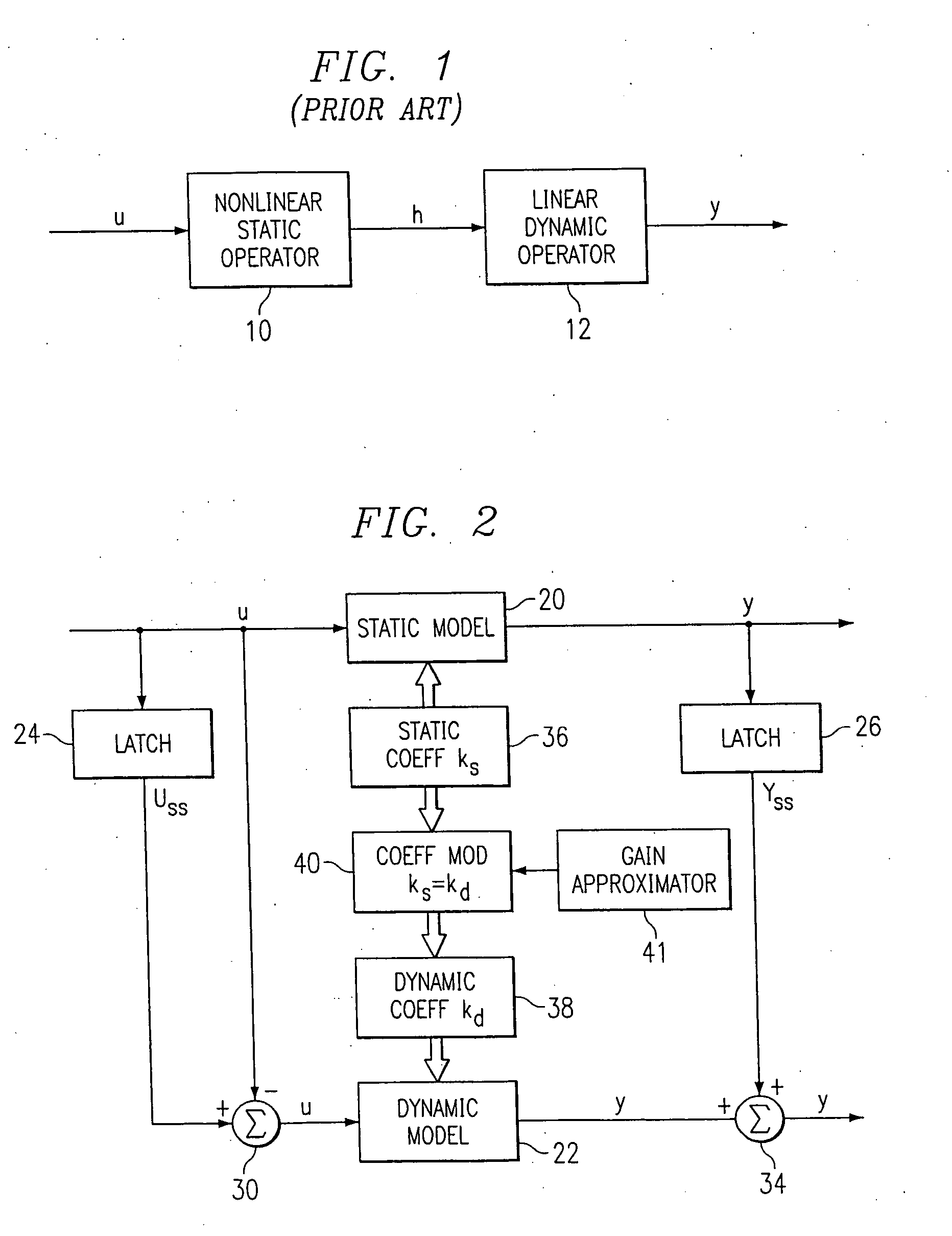
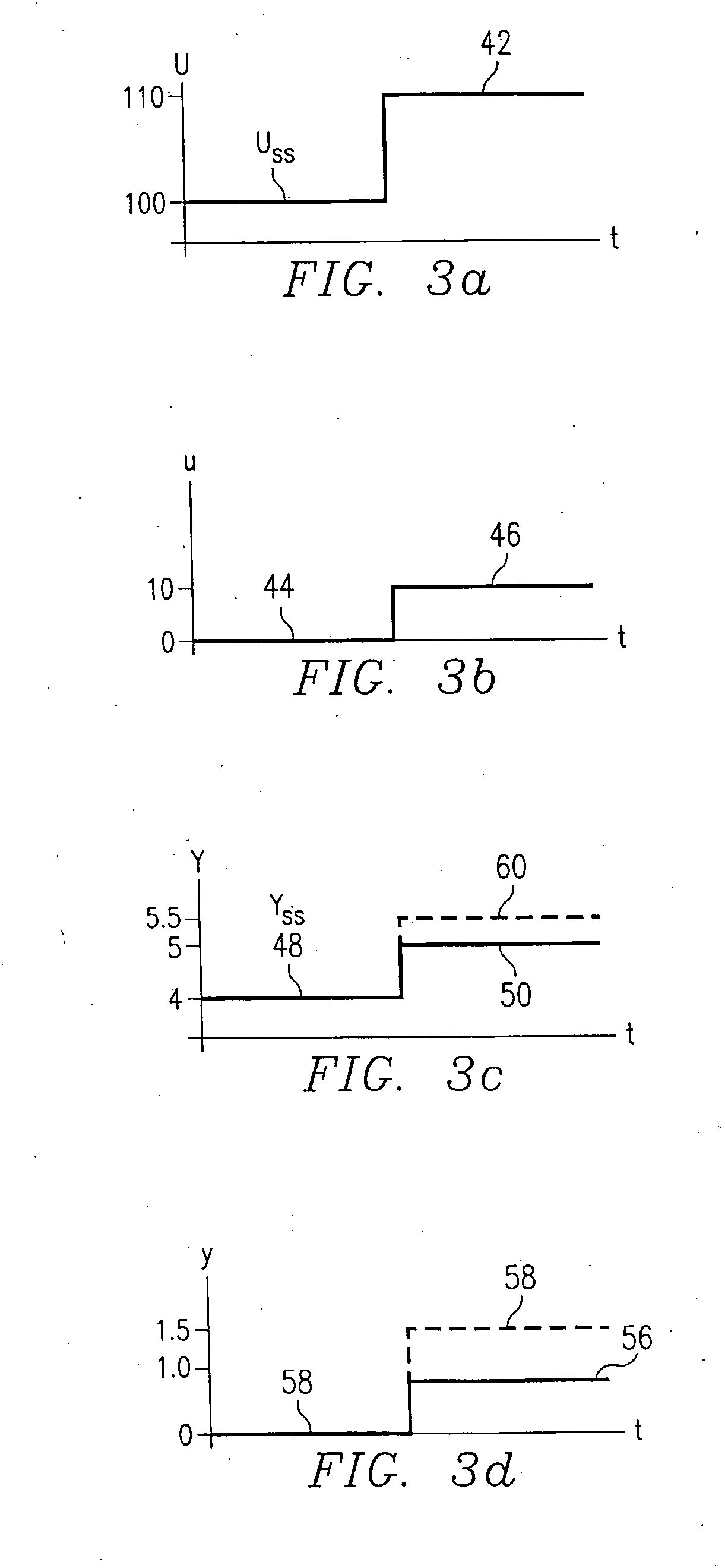
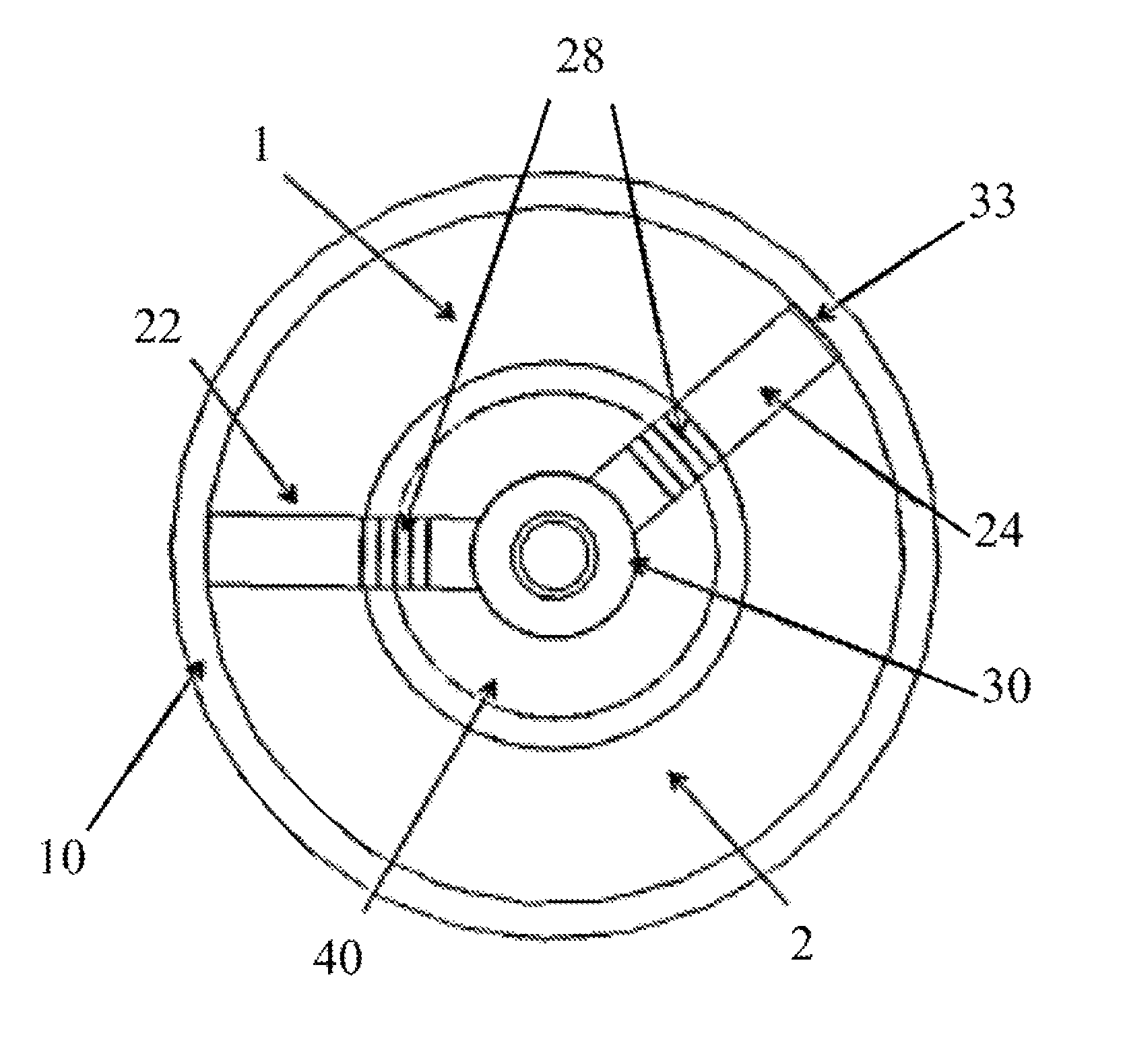
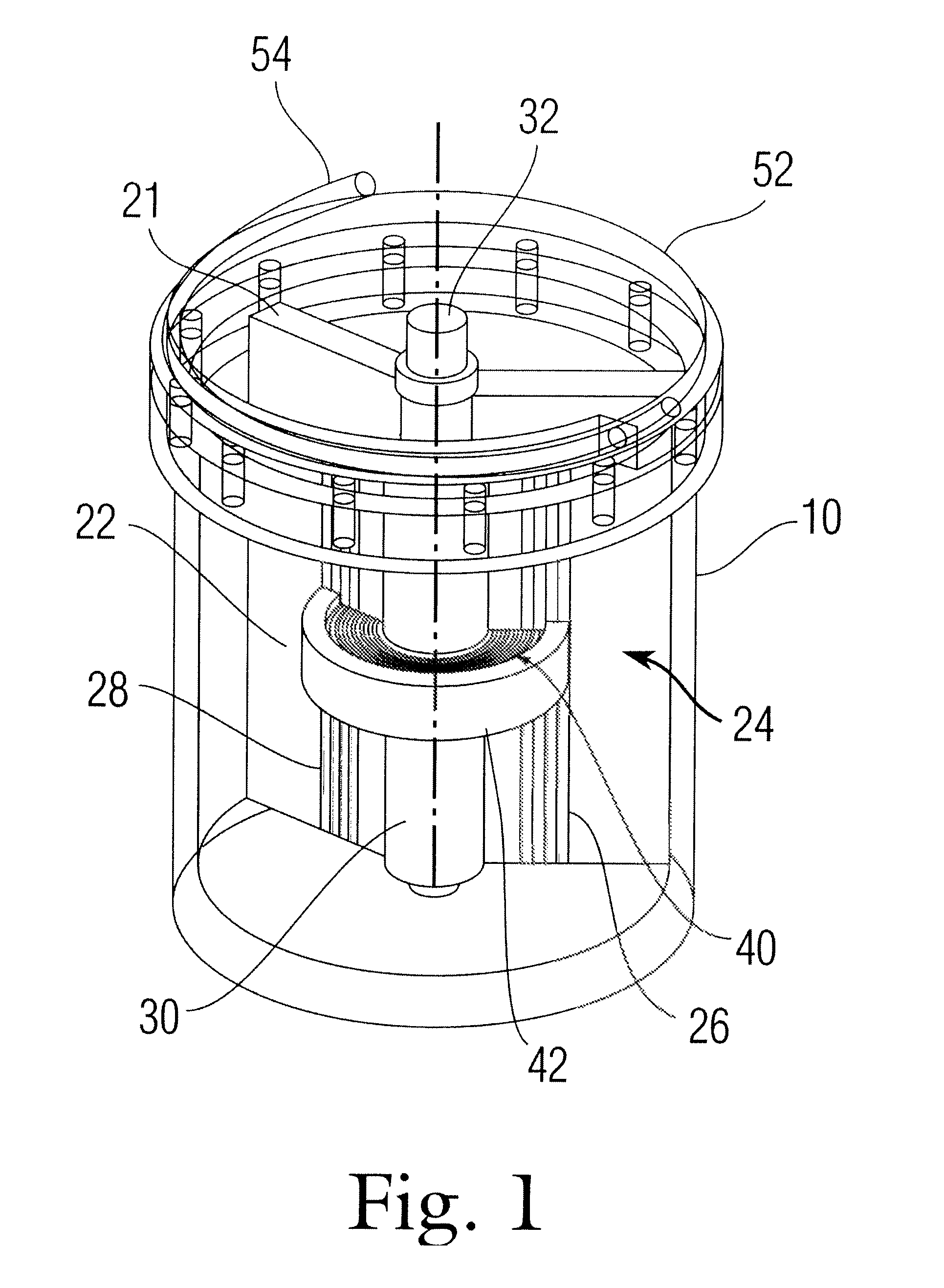
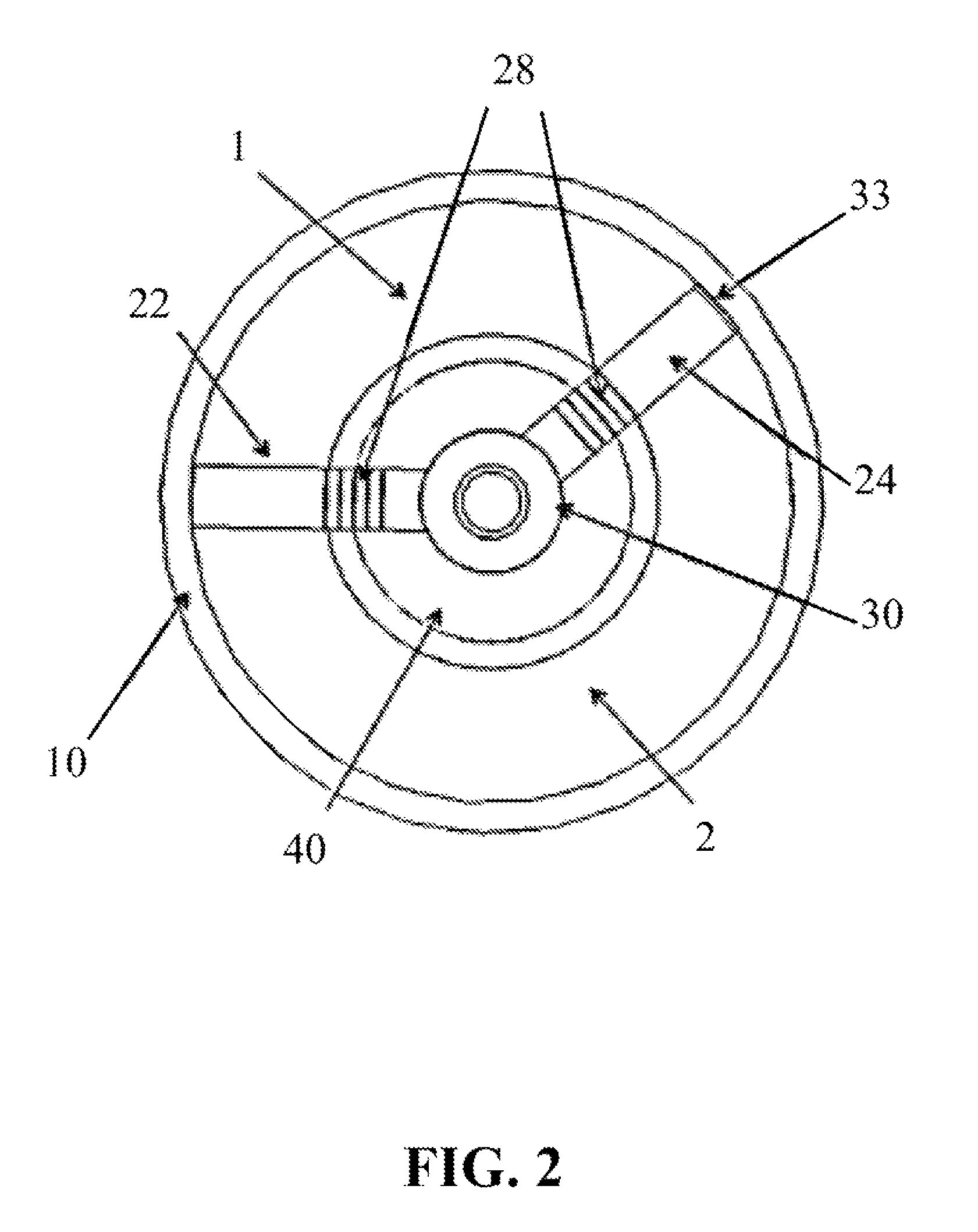
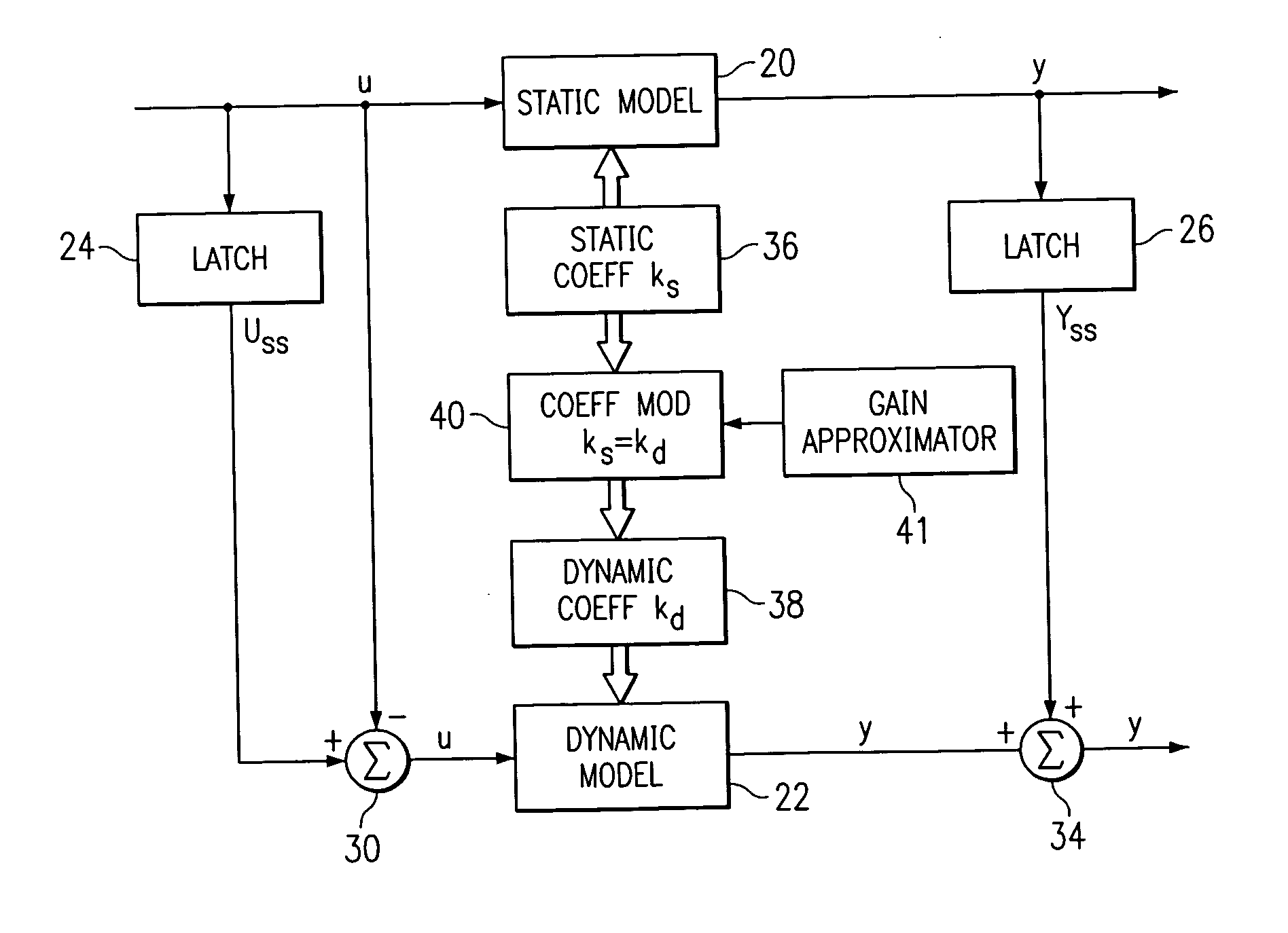
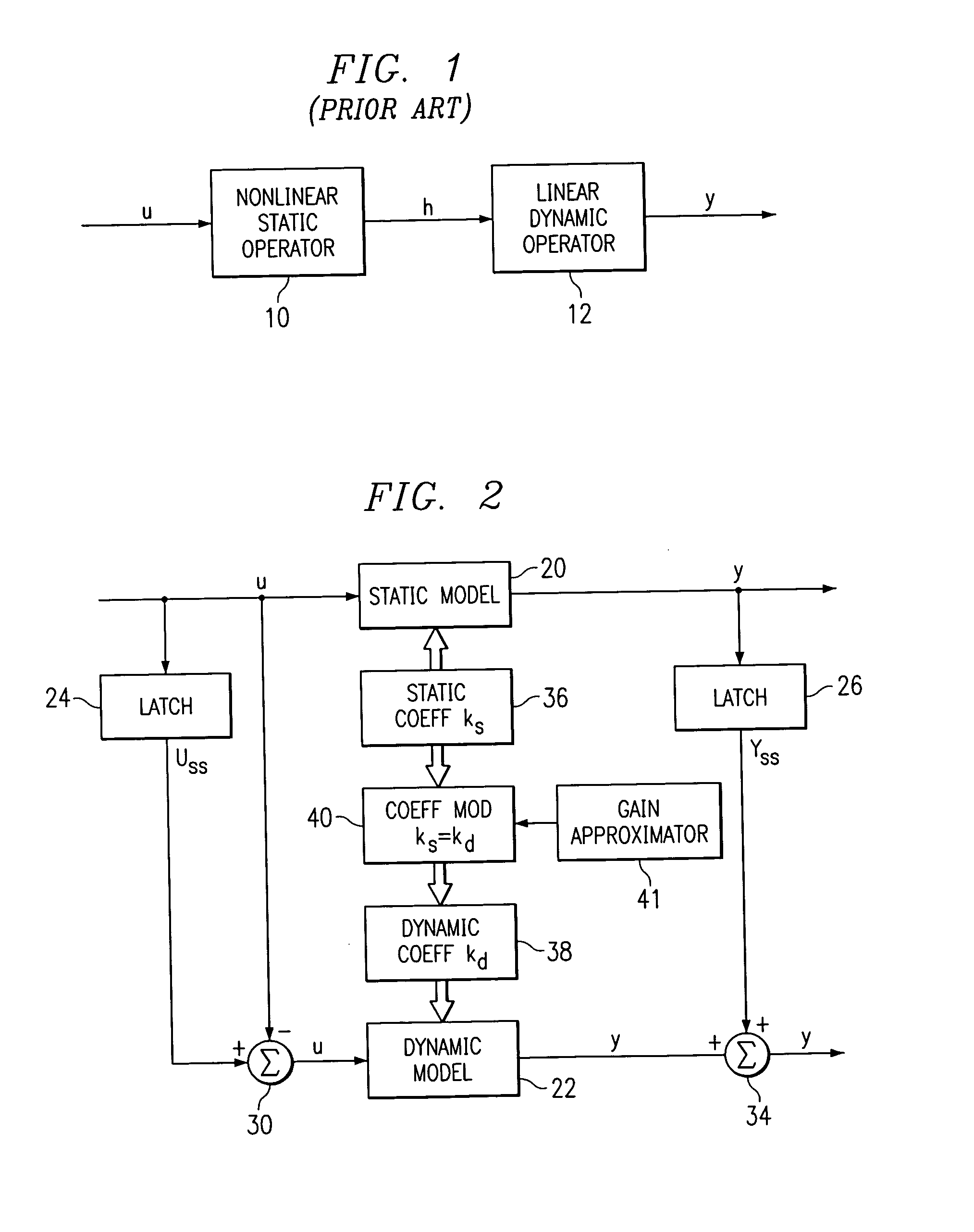
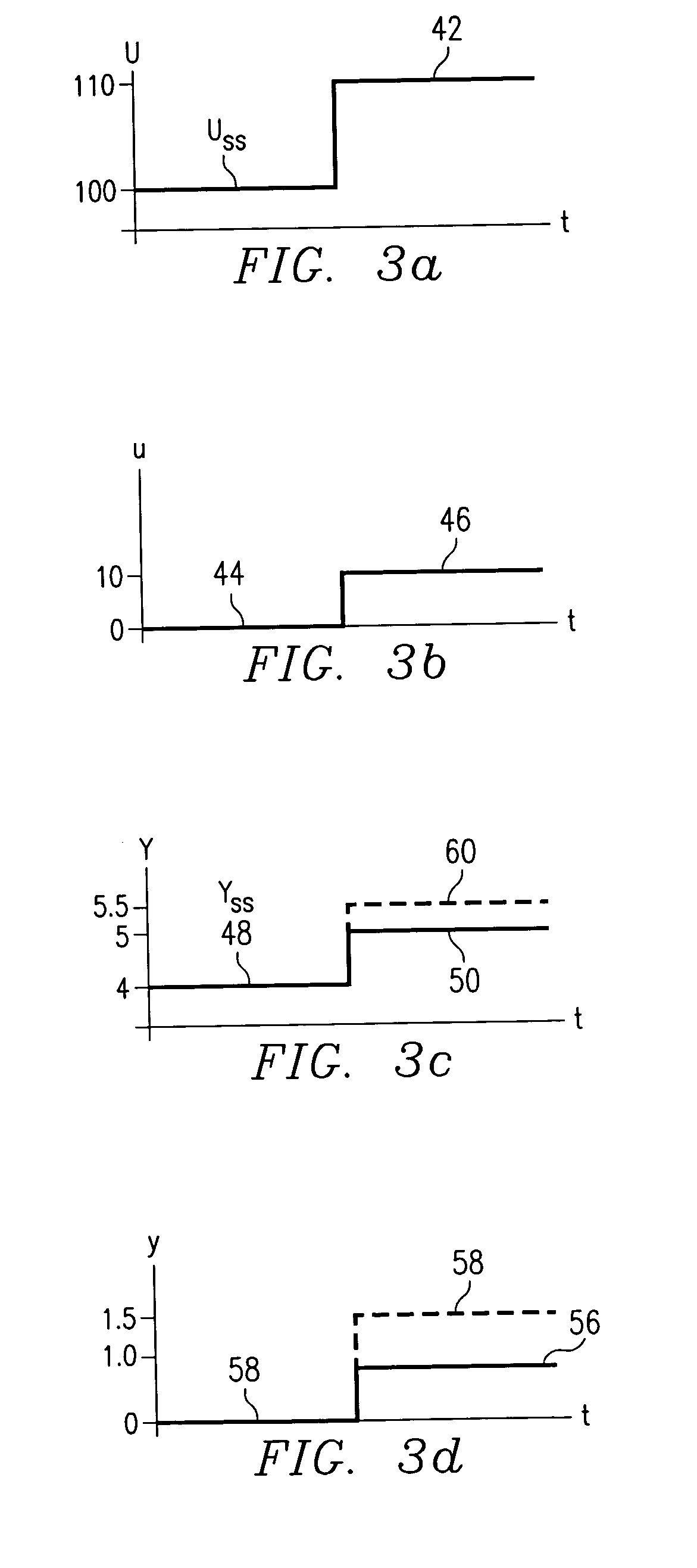
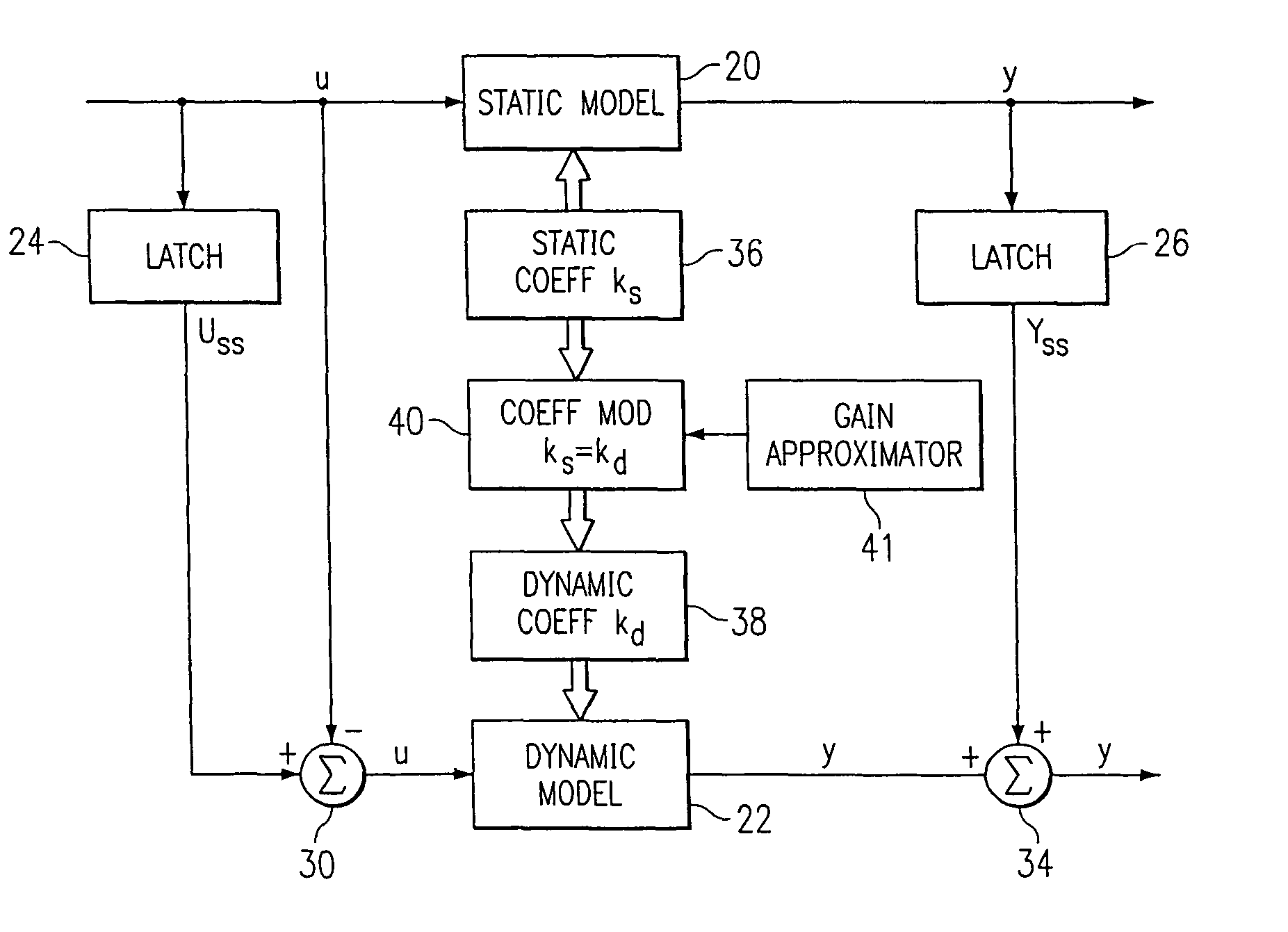
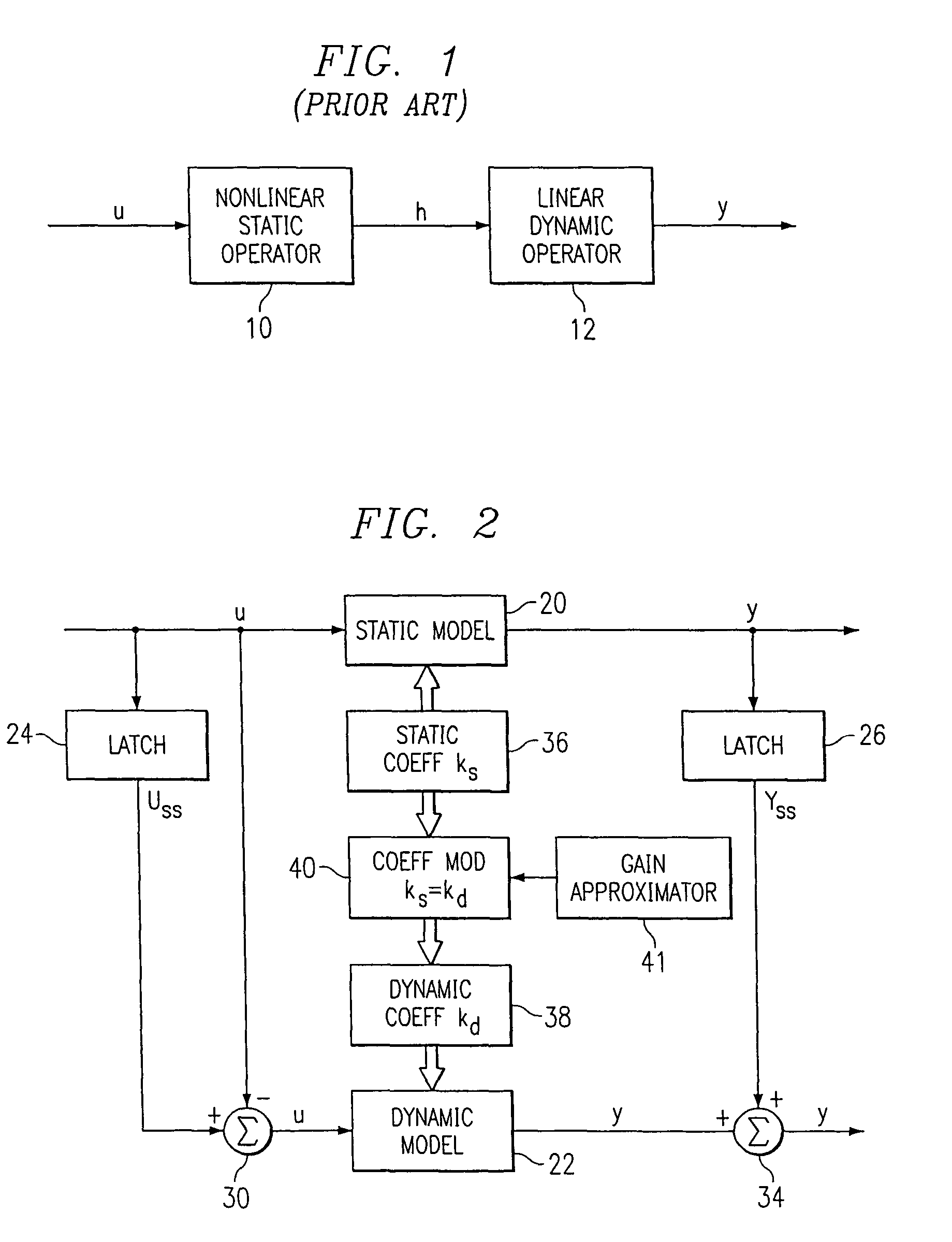
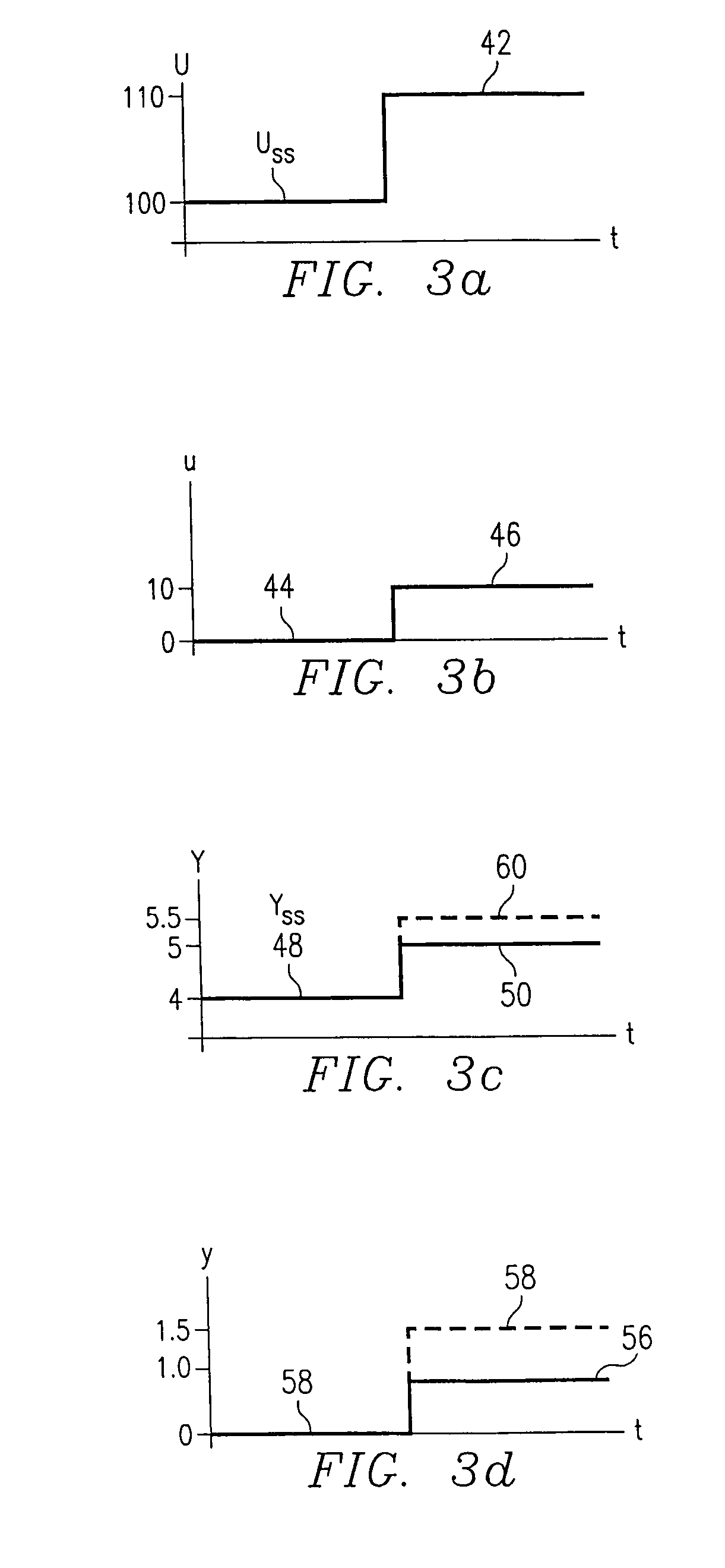
A method for providing independent static and dynamic models in a prediction, control and optimization environment utilizes an independent static model (20) and an independent dynamic model (22). The static model (20) is a rigorous predictive model that is trained over a wide range of data, whereas the dynamic model (22) is trained over a narrow range of data. The gain K of the static model (20) is utilized to scale the gain k of the dynamic model (22). The forced dynamic portion of the model (22) referred to as the bi variables are scaled by the ratio of the gains K and k. The bi have a direct effect on the gain of a dynamic model (22). This is facilitated by a coefficient modification block (40). Thereafter, the difference between the new value input to the static model (20) and the prior steady-state value is utilized as an input to the dynamic model (22). The predicted dynamic output is then summed with the previous steady-state value to provide a predicted value Y. Additionally, the path that is traversed between steady-state value changes.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Method and apparatus for attenuating error in dynamic and steady-state processes for prediction, control, and optimization
InactiveUS7610108B2Minimize error valueOutput errorProgramme-controlled manipulatorTemperatue controlNarrow rangeDynamic models
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Master-slave mode two-in-parallel twelve degree of freedom generalized force adjustment loading mechanism
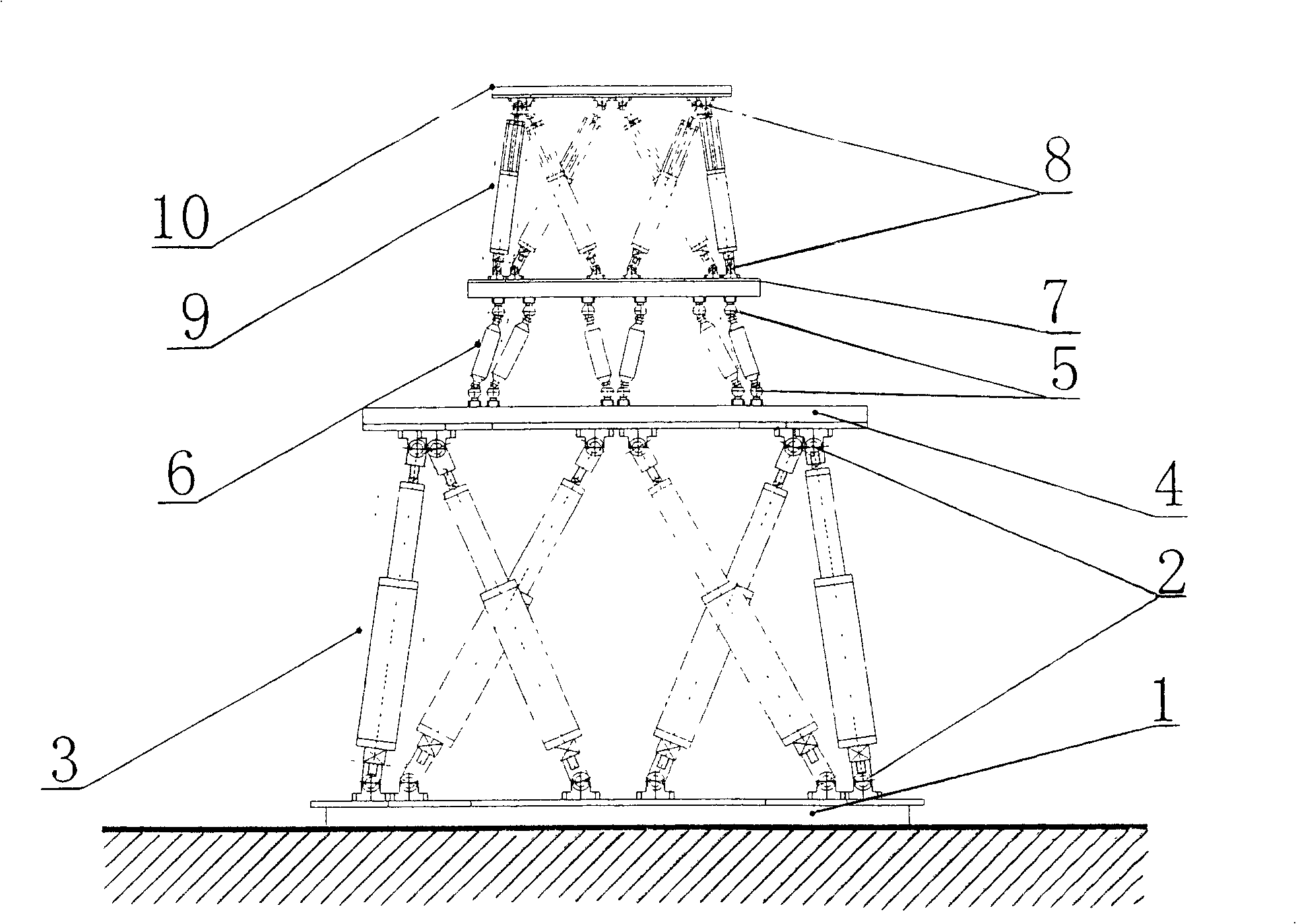
InactiveCN101016971AImprove linearityRealize compound vibration dampingUsing mechanical meansStands/trestlesAviationEngineering
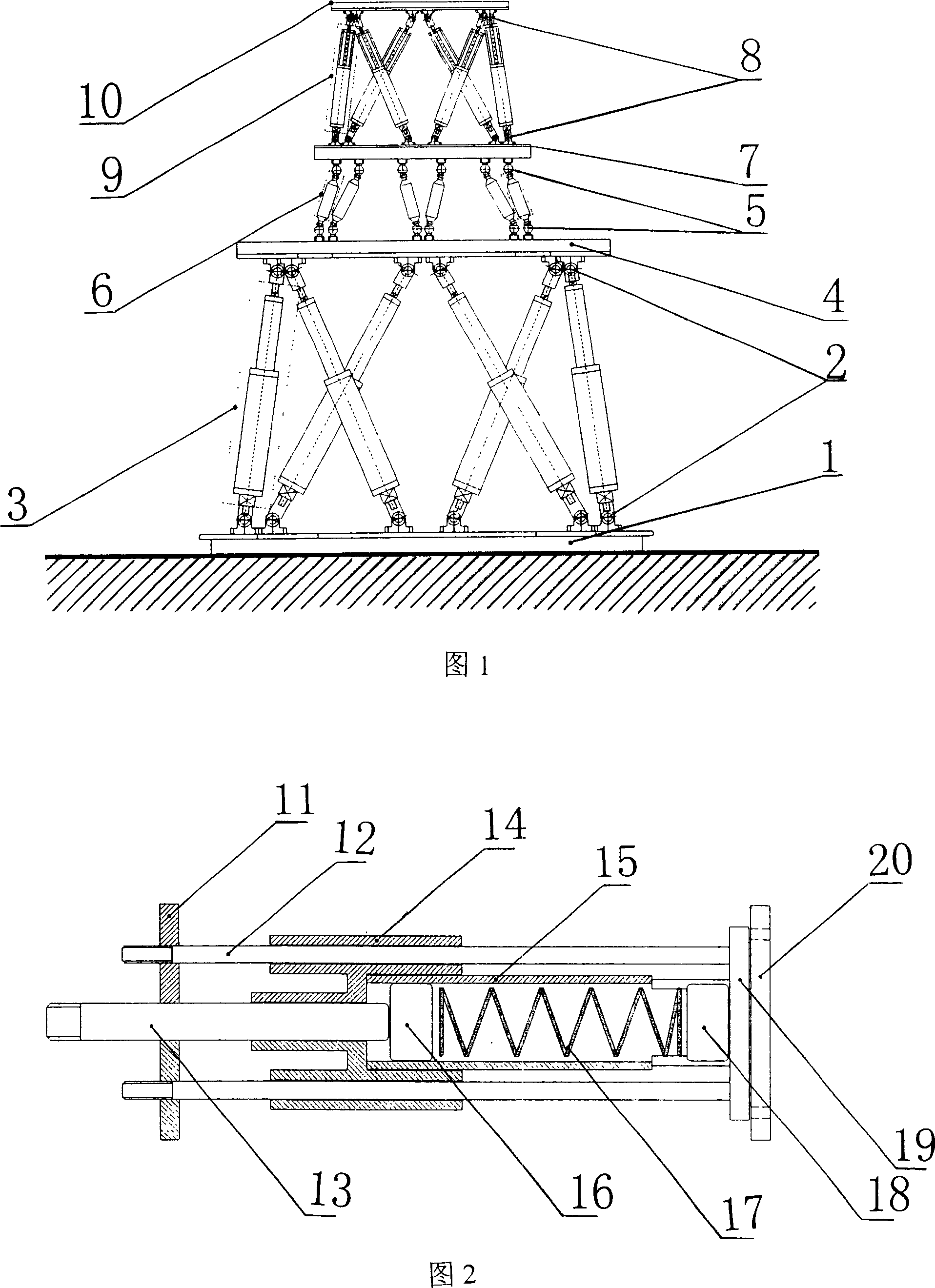
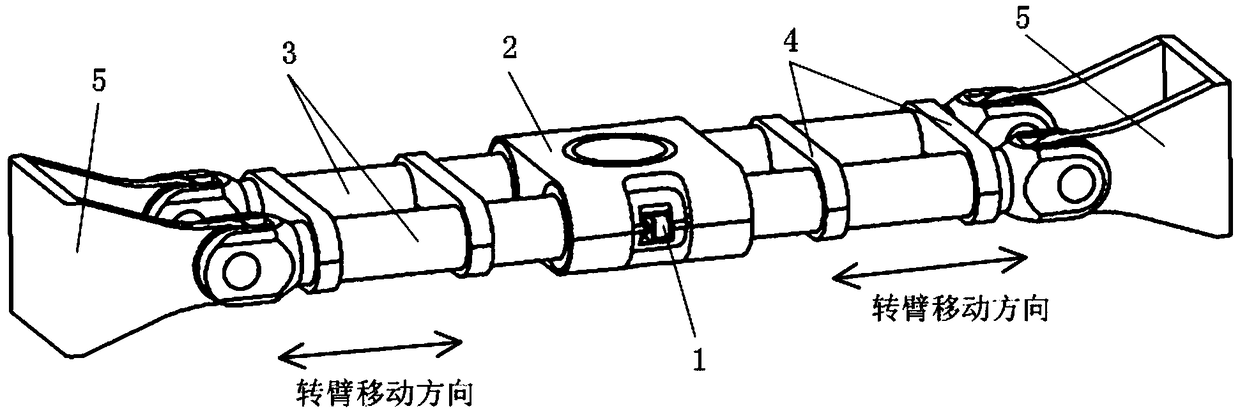
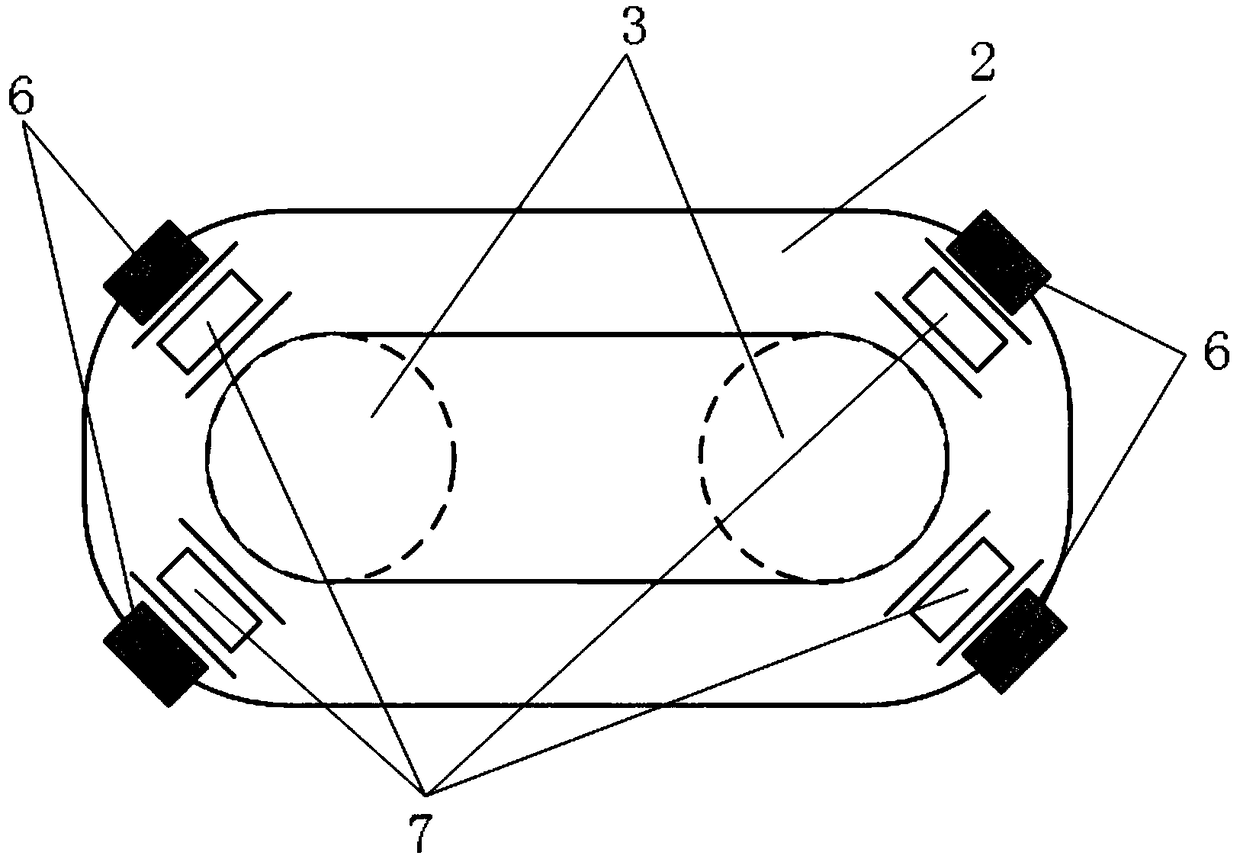
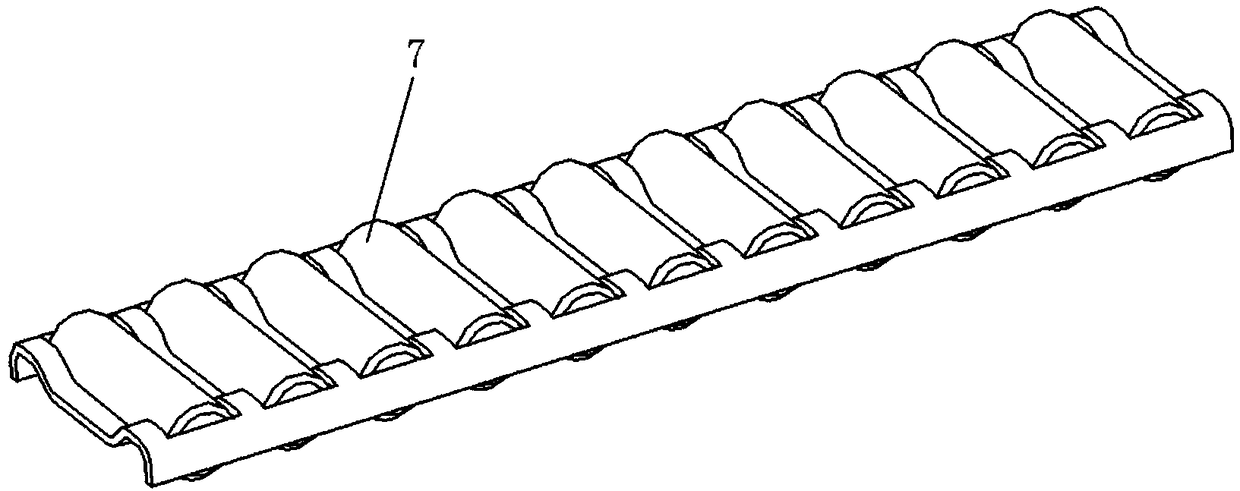
The invention discloses a parallel twelve-freedom loading device, used in spatial loading test and fatigue test on aviation material, comprising a Stewart active parallel six-freedom loading device, a SPS six-dimension force / torque sensor and a SPS inactive parallel six-freedom adjuster, wherein the Stewart active parallel six-freedom loading device simulates the spatial motion, the active and inactive platforms of inactive parallel six-freedom adjuster follows to operate and draw or compress the bidirectional isomorphism spring device, to test wide force dynamical load, to supply high accuracy and better reliability to the six-freedom wide force dynamic synchronous loading system, to be used in spatial-ground semi-physical simulation test or the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
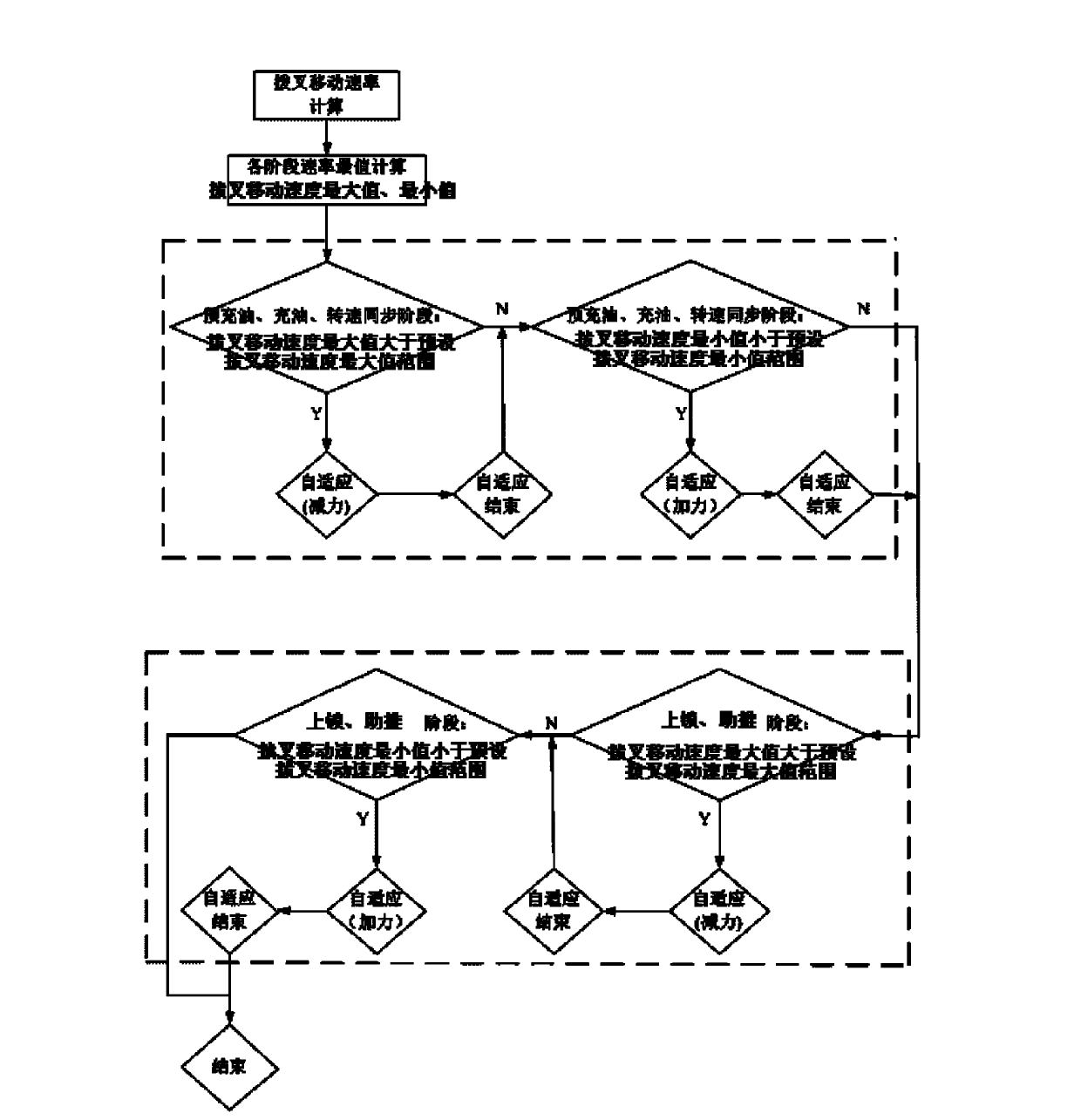
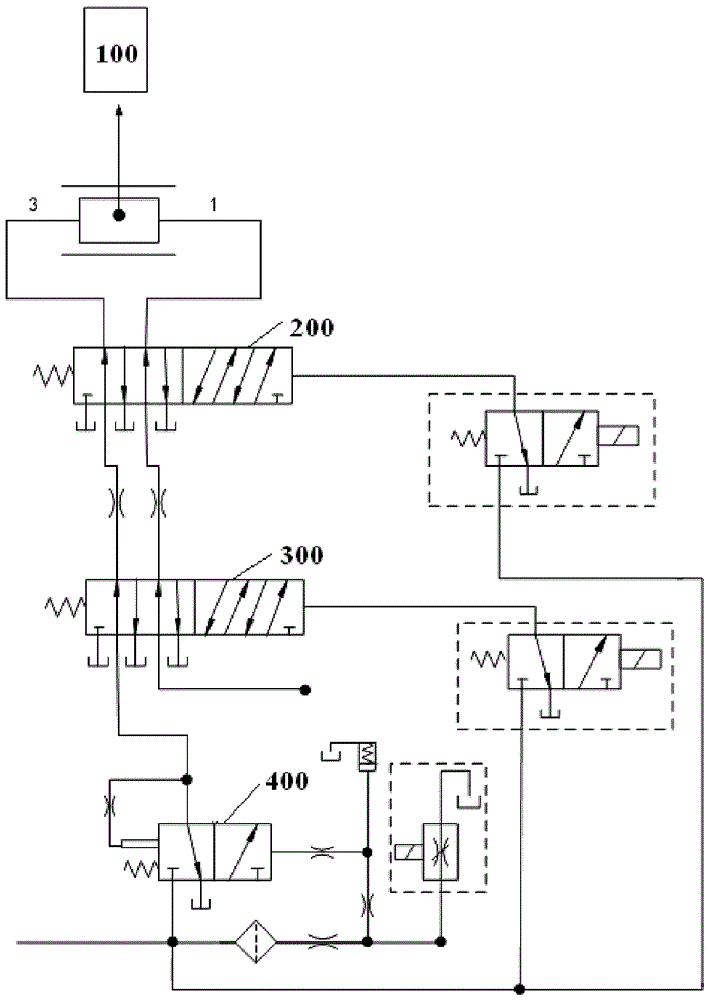
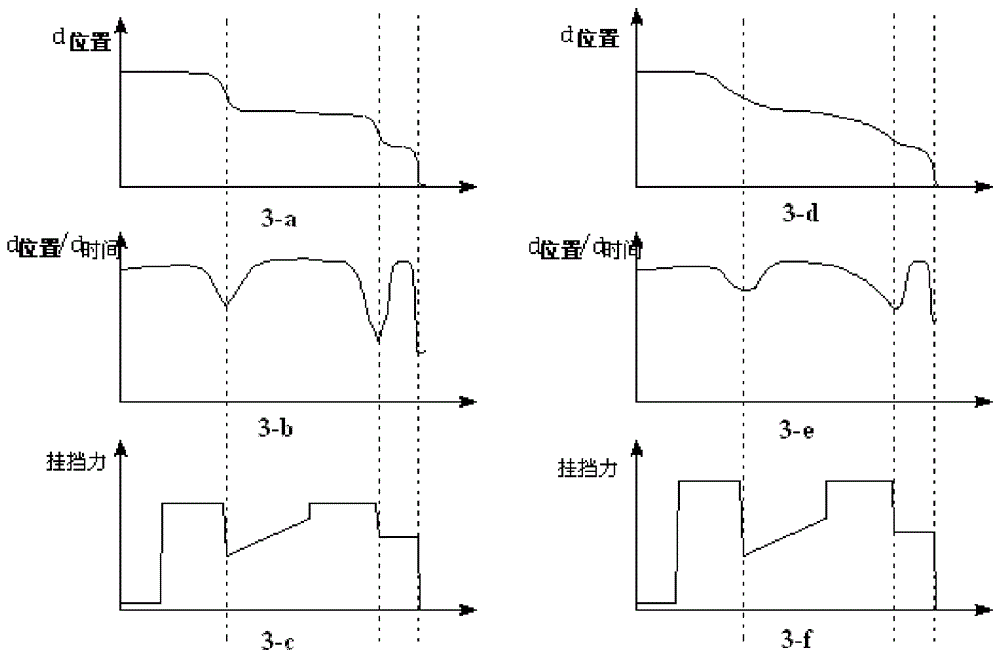
Double-clutch type automatic transmission fork shifting gear engaging force dynamic self-adapting method
ActiveCN103867702AReduce calibration workloadGood fork controlGearing controlAutomatic transmissionNoise optimization
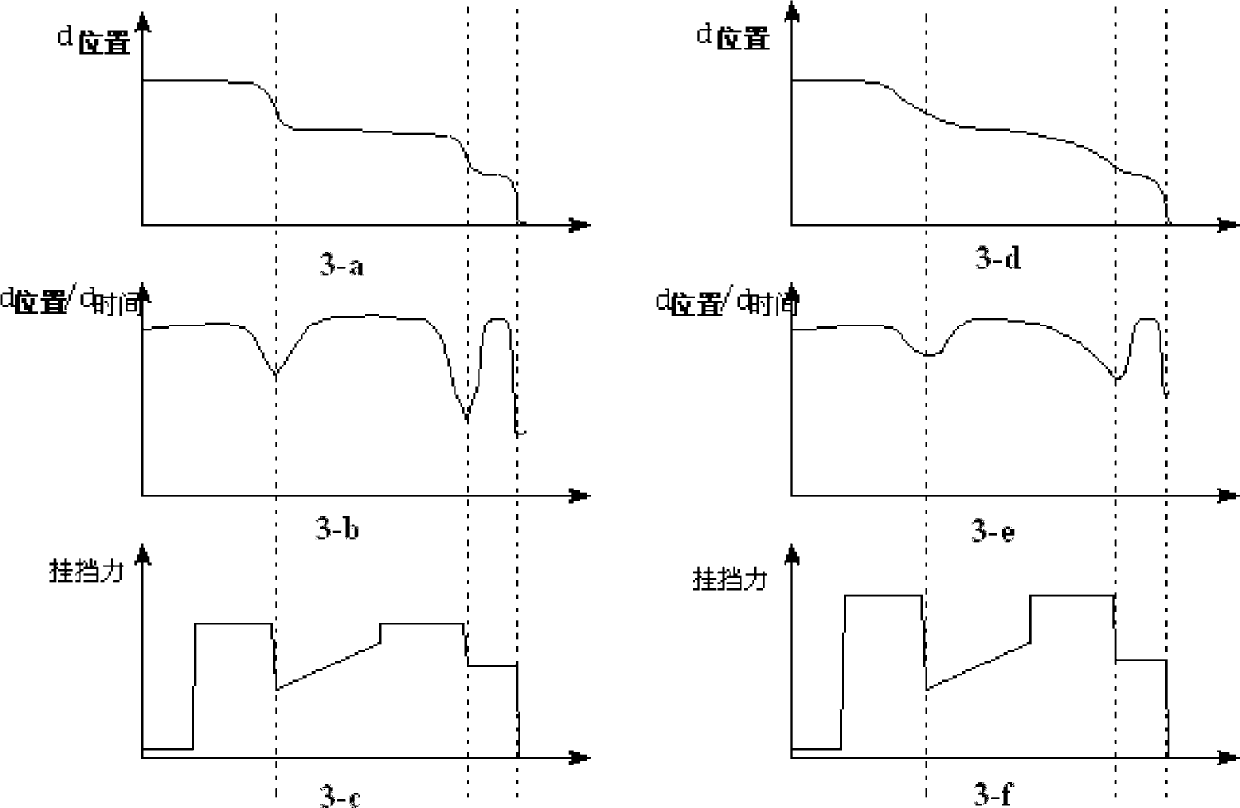
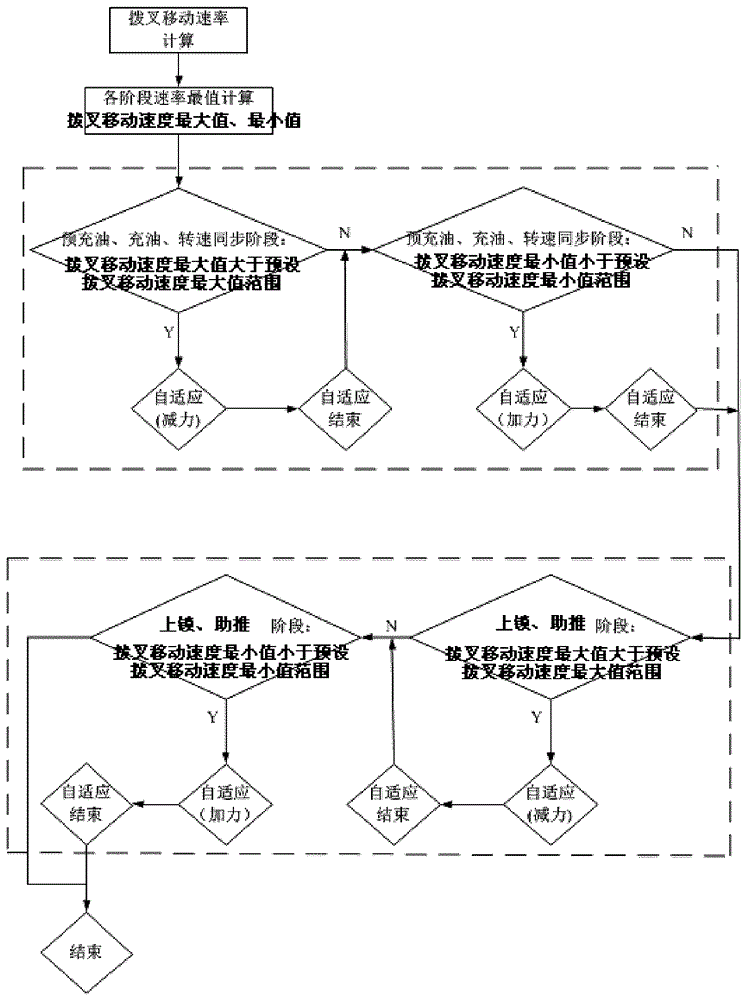
The invention discloses a double-clutch type automatic transmission fork shifting gear engaging force dynamic self-adapting method. The fork shifting is divided into a plurality of stages during the gear shifting process. The double-clutch type automatic transmission fork shifting gear engaging force dynamic self-adapting method comprises the following steps of (1) obtaining ranges of a maximum value and a minimum value of a preset shifting fork movement speed at different stages during fork shifting gear engaging; (2) computing a shifting fork real-time movement speed and confirming a maximum value and a minimum value of the shifting fork movement speed at the different stages during the fork shifting gear engaging; (3) comparing the maximum value and the minimum value of the shifting fork movement speed with the range of the maximum value and the minimum value of the preset shifting fork movement speed at the same stage, obtaining the fork shifting gear engaging force to be adjusted and the stage and recording and adjusting the fork shifting gear engaging force when the shifting fork gear shifting achieves a corresponding stage. The double-clutch type automatic transmission fork shifting gear engaging force dynamic self-adapting method is applied to control of a double-clutch automatic transmission and achieves vehicle gear shifting noise optimization.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
Method and apparatus for minimizing error in dynamic and steady-state processes for prediction, control, and optimization
InactiveUS20060259197A1Minimize error valueOutput errorComputer controlSimulator controlNarrow rangeDirect effects
A method for providing independent static and dynamic models in a prediction, control and optimization environment utilizes an independent static model (20) and an independent dynamic model (22). The static model (20) is a rigorous predictive model that is trained over a wide range of data, whereas the dynamic model (22) is trained over a narrow range of data. The gain K of the static model (20) is utilized to scale the gain k of the dynamic model (22). The forced dynamic portion of the model (22) referred to as the bi variables are scaled by the ratio of the gains K and k. The bi have a direct effect on the gain of a dynamic model (22). This is facilitated by a coefficient modification block (40). Thereafter, the difference between the new value input to the static model (20) and the prior steady-state value is utilized as an input to the dynamic model (22). The predicted dynamic output is then summed with the previous steady-state value to provide a predicted value Y. Additionally, the path that is traversed between steady-state value changes.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
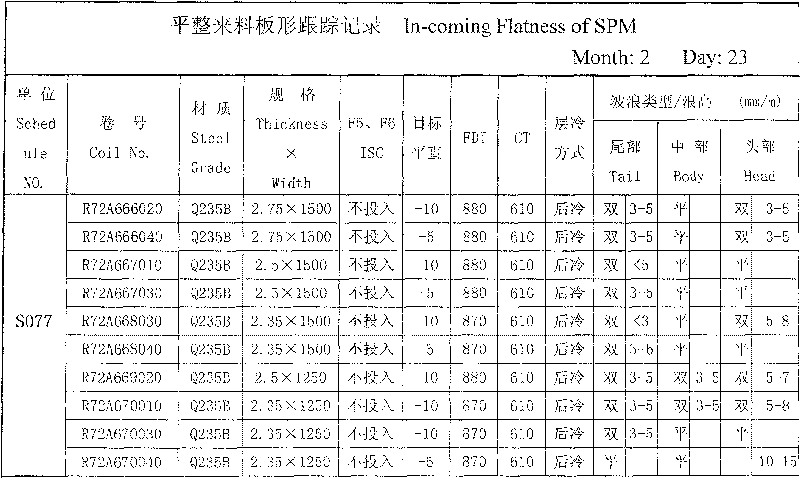
Diversified cross-connection control method for plate shape of hot rolling band steel
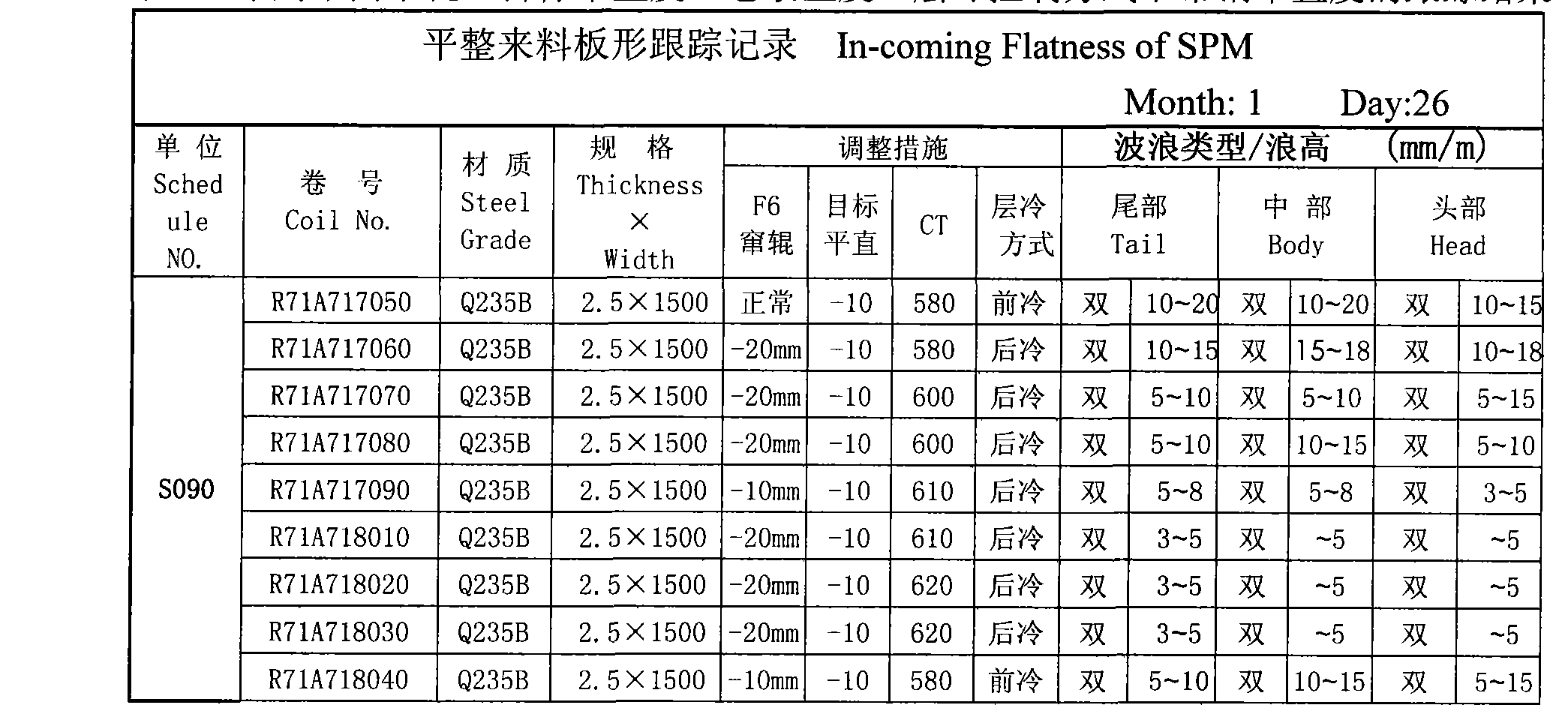
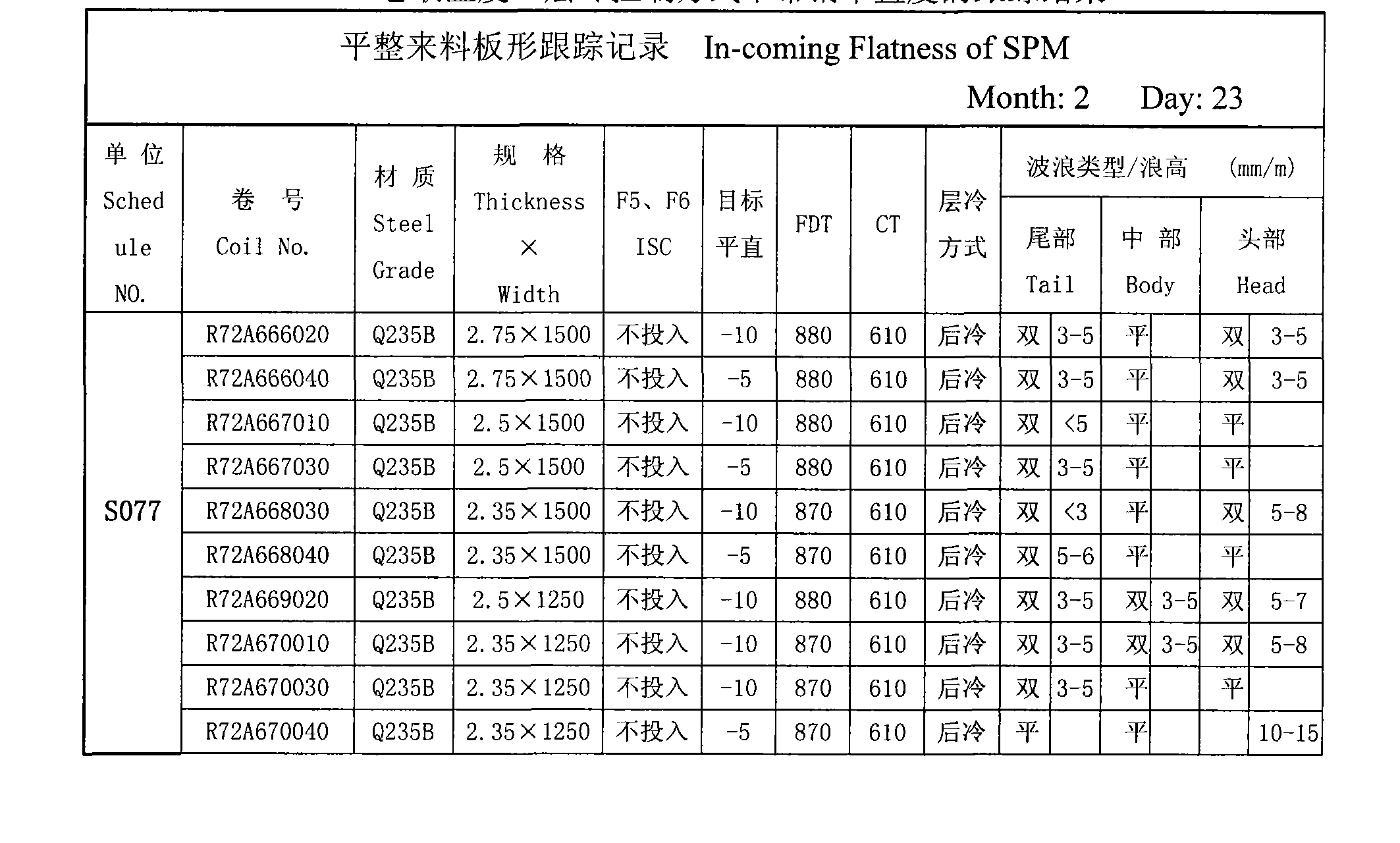
InactiveCN101372018AEasy to controlMeet the standard requirementsProfile control deviceProduction lineThermal state
A hot rolling bandprofil pluralism intersect control method is suitable for controlling the shape of strip in the hot rolling band steel production line. The purpose is to improve the potential shape of the hot rolling band steel and increase the product quality; the method aims at the hot rolling band steel production line of a fining mill set which is provided with seven rolling mills (F1-F7), firstly, the rolling loading and the bowed roll force dynamic control are adjusted; the thermal state target alignment controlling value is modified; micro-waves are used for rolling; the alignment target reference value is 0 I-unit; the target alignment -5 I-unit- -10 I-unit is taken; laminated cooling CTC adopts aftercooling mode; the heat stress of the band steel generated in a run out table ROT is reduced; the reeling target temperature CT is mended within 600 DEG C-650 DEG C; the working roll of the sixth rolling mill (F6) of the fining mill set shifts rolls for compensation; the use of cooling water among the rolling mills is optimized.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
A turbine pump inducer cavitation flow numerical prediction method based on low-temperature fluid
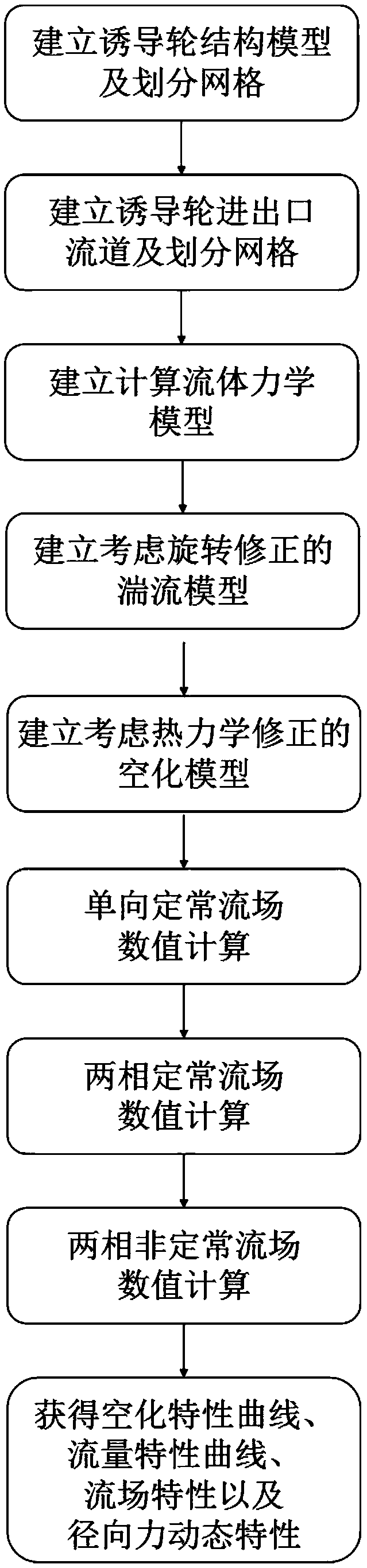
ActiveCN109684767AIncrease credibilityAccurate performance assessmentGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationImpellerEngineering
The invention discloses a turbine pump inducer cavitation flow numerical prediction method based on low-temperature fluid, and belongs to the technical field of impeller machinery. The implementationmethod comprises the following steps: establishing an inducer model and an inlet and outlet runner model according to actual working conditions, and dividing grids; Establishing a computational fluidmechanics model, carrying out rotation correction on the turbulence model, and carrying out thermodynamic correction on the cavitation model; Setting and calculating boundary conditions of the single-phase steady flow to obtain a single-phase result; Calculating two-phase steady flow by taking a single-phase result as an initial value, and then changing inlet pressure and outlet mass flow to obtain calculation results of different working conditions; Calculating unsteady flow of the two phases by taking the two-phase steady result as an initial value to obtain an unsteady calculation result; By analyzing a calculation result, accurate flow field characteristic distribution, inducer performance and radial force dynamic characteristics of the inducer under the action of a flow field are obtained, the inducer is assisted to be designed and optimized, and the experiment cost and time are saved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
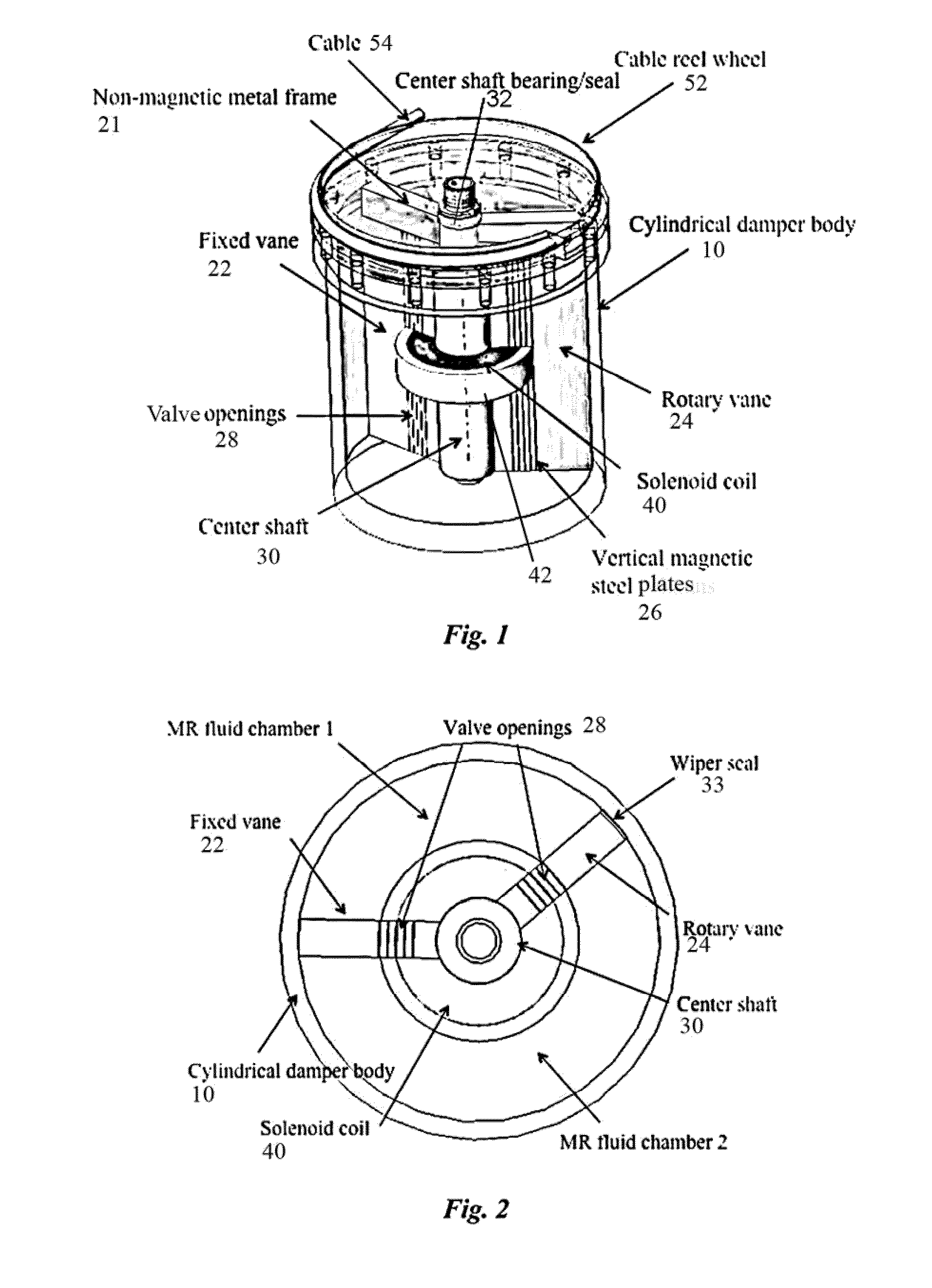
Rotary vane magnetorheological (MR) energy absorber
ActiveUS20100300819A1Increase damper strokeCompact profileLiquid resistance brakesSpringsLinear motionMagnetorheological fluid
A rotary vane magnetorheological energy absorber, which enables a longer stroke capability in a more compact configuration than conventional magnetorheological devices, is disclosed. This novel device design is attractive for applications where long stroking capability, high force dynamic range, device size, and device weight are important. The improved magnetorheological energy absorber comprises an internal or external flow valve and a hollow body enclosing fixed and rotary vanes as well as magnetorheological fluid. Fluid flow in the valve is restricted as a solenoid is activated, thus adjusting the capability of the device to react torque. Various flow valve configurations are disclosed, as well as various motion translation mechanisms for translating linear motion to rotary motion for use of the rotary vane magnetorheological energy absorber. The improved design minimizes the amount of magnetorheological fluid required as compared to conventional linear stroke energy absorbers, thus minimizing device weight.
Owner:INNOVITAL LLC +1
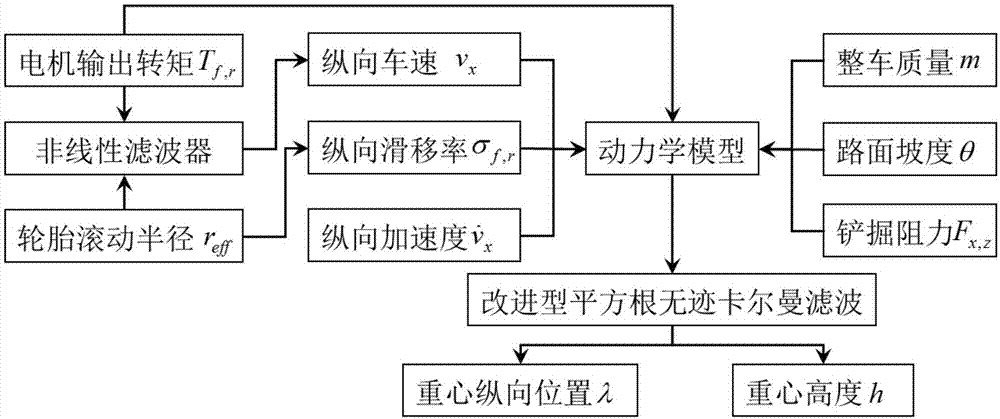
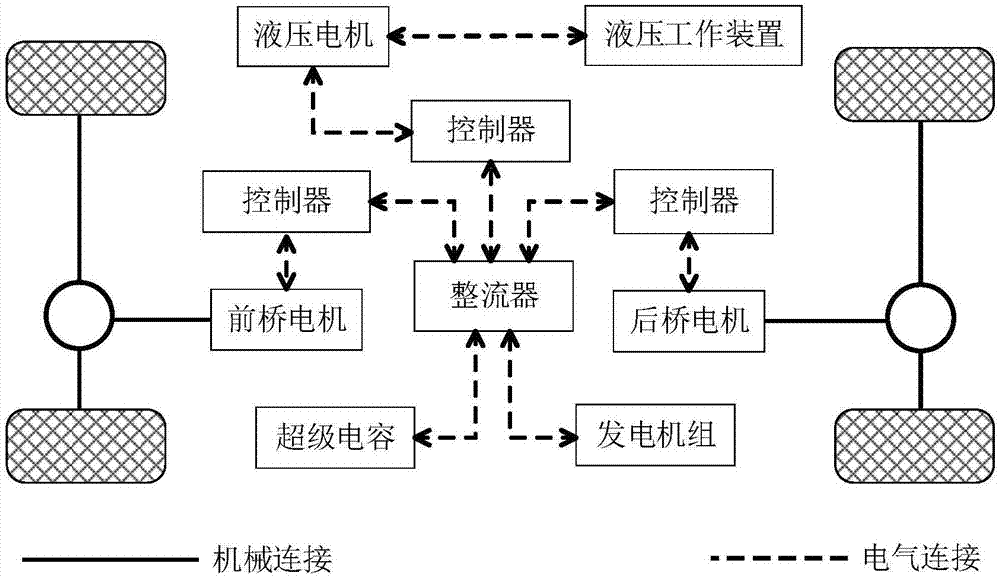
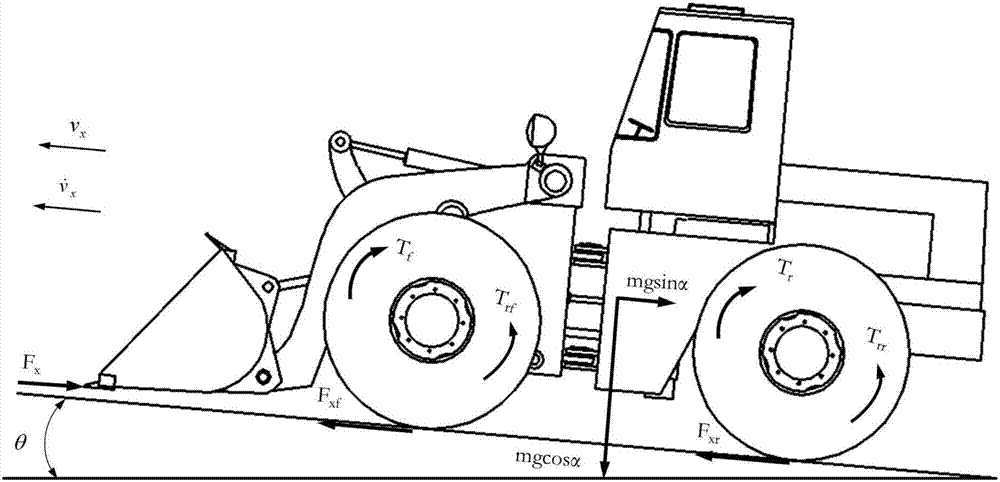
Wheel type loading machine tire longitudinal force dynamic estimation method
The invention provides a wheel type loading machine tire longitudinal force dynamic estimation method. The method comprises the steps of firstly, based on motor output torque capable of being known inreal time of a front motor and a rear motor of a wheel type loading machine independently electrically driven by a front axle and a rear axle and the measured tire rolling radius, and through estimation of a nonlinear filter, obtaining the longitudinal speed; then, constructing a state equation and a measurement equation according to the longitudinal acceleration and slope obtained through measurement of a sensor and the estimated longitudinal speed and through the calculated front tire and rear tire slip rate and the whole vehicle mass and the spading resistance obtained by looking up a table or conducting calculation; finally, estimating dynamic front wheel longitudinal force and rear wheel longitudinal force through extended Kalman filter. By means of the method, accurate tire longitudinal force dynamic parameters are provided for wheel type loading machine intellectualized dynamics control independently electrically driven by the front axle and the rear axle, and the whole-vehiclecontrol precision and performance are improved. The method is applicable to wheel type loading machine of longitudinal motion in all working conditions, less sensors are utilized, and the price is low.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Rotary vane magnetorheological (MR) energy absorber
ActiveUS8424656B2Suppress energyCompact profileLiquid resistance brakesSpringsLinear motionMagnetorheological fluid
Owner:INNOVITAL LLC +1
Method and apparatus for modeling dynamic and steady-state processes for prediction, control and optimization
InactiveUS20050075737A1Minimize error valueOutput errorComputation using non-denominational number representationAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsNarrow rangeModel dynamics
A method for providing independent static and dynamic models in a prediction, control and optimization environment utilizes an independent static model (20) and an independent dynamic model (22). The static model (20) is a rigorous predictive model that is trained over a wide range of data, whereas the dynamic model (22) is trained over a narrow range of data. The gain K of the static model (20) is utilized to scale the gain k of the dynamic model (22). The forced dynamic portion of the model (22) referred to as the bi variables are scaled by the ratio of the gains K and k. The bi have a direct effect on the gain of a dynamic model (22). This is facilitated by a coefficient modification block (40). Thereafter, the difference between the new value input to the static model (20) and the prior steady-state value is utilized as an input to the dynamic model (22). The predicted dynamic output is then summed with the previous steady-state value to provide a predicted value Y. Additionally, the path that is traversed between steady-state value changes.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
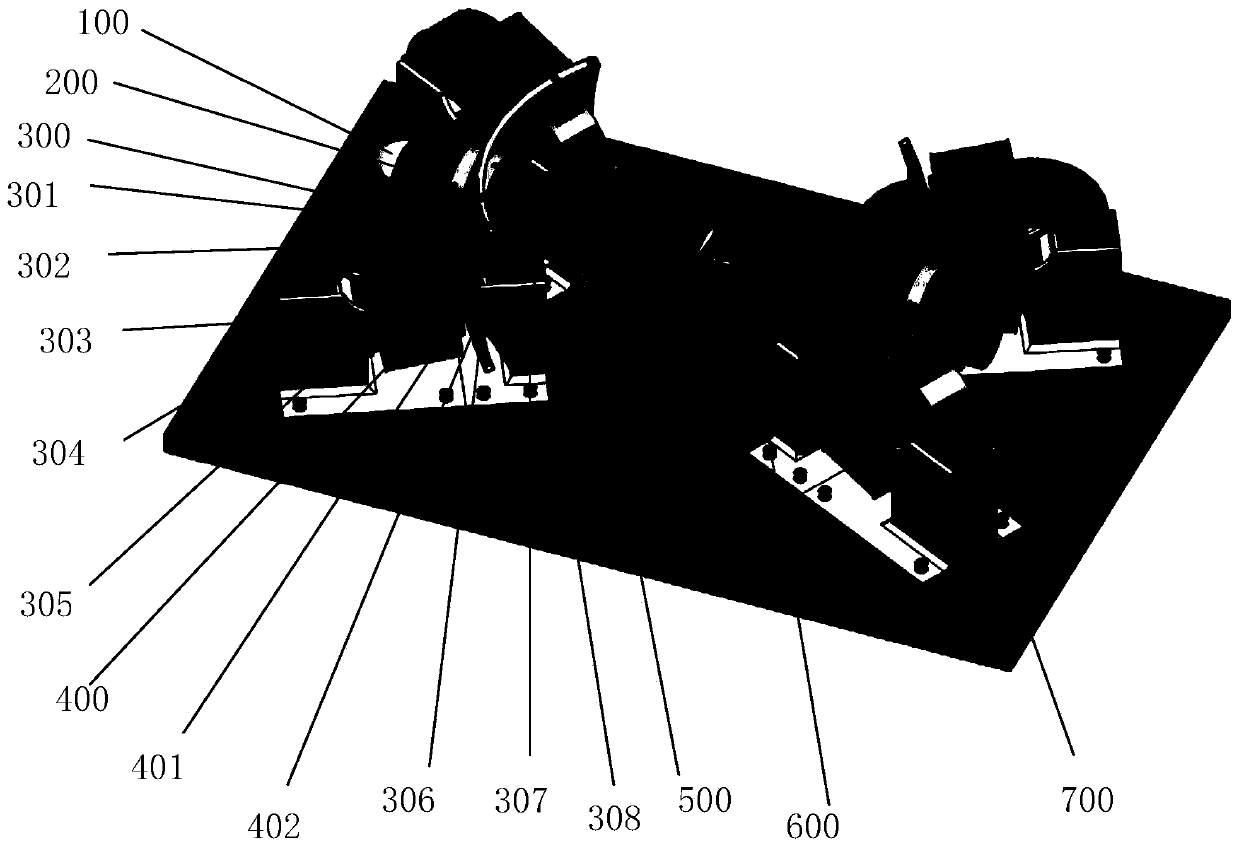
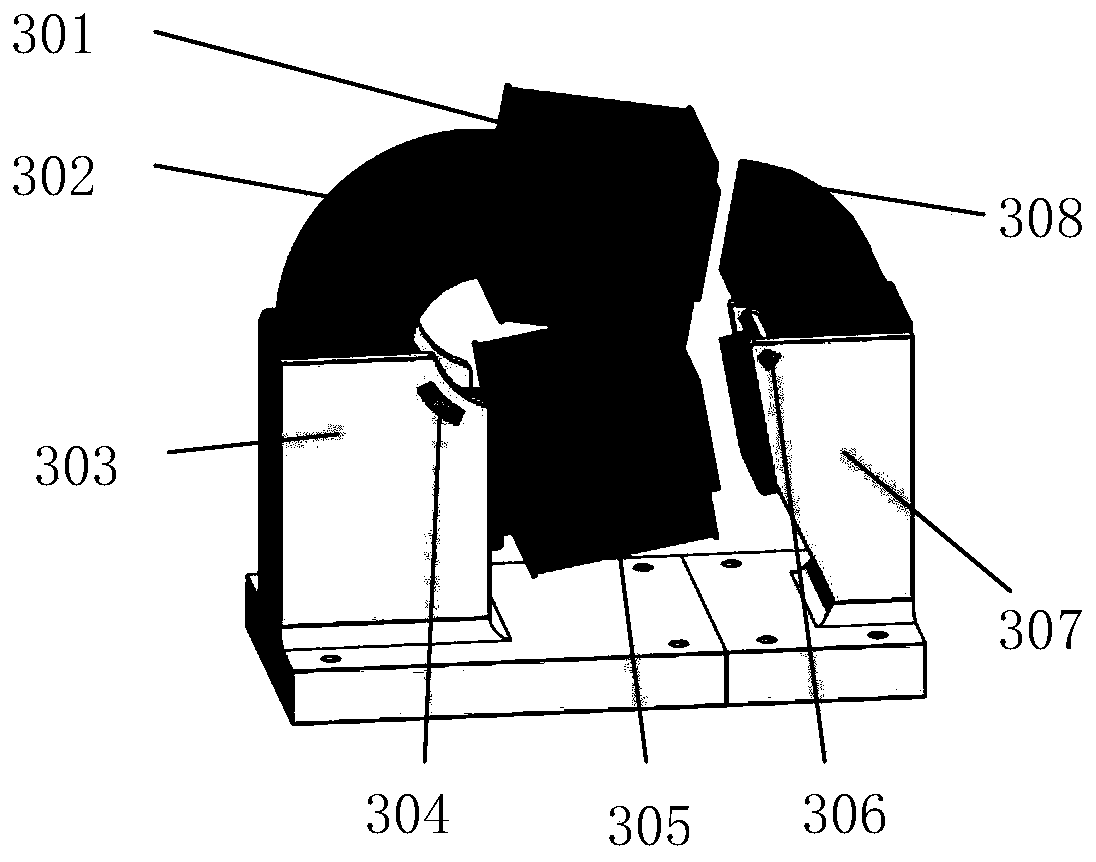
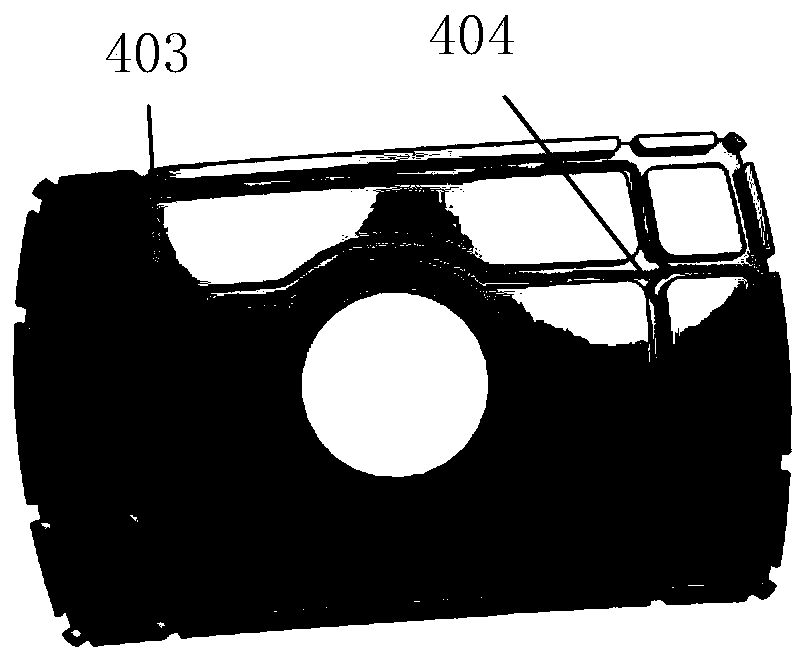
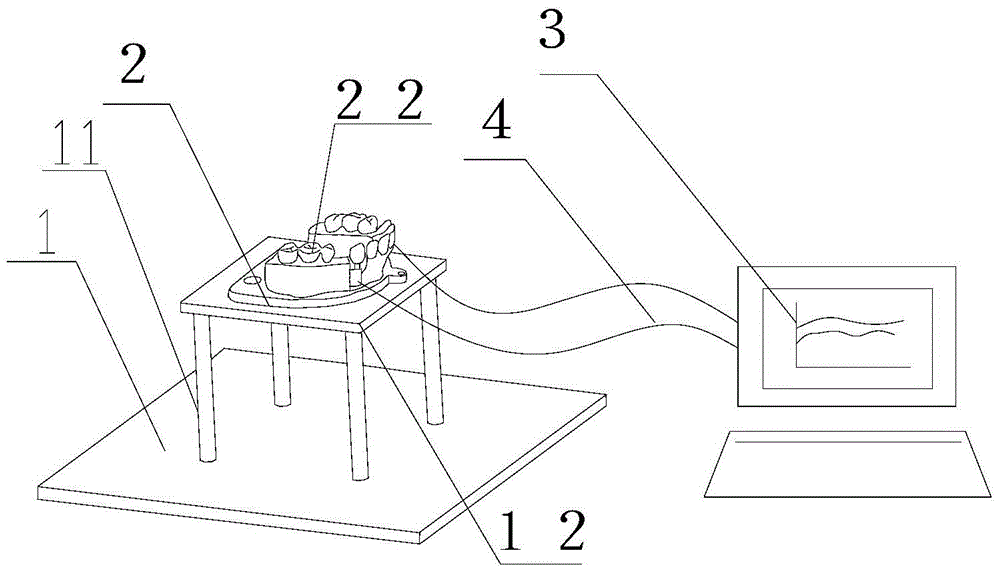
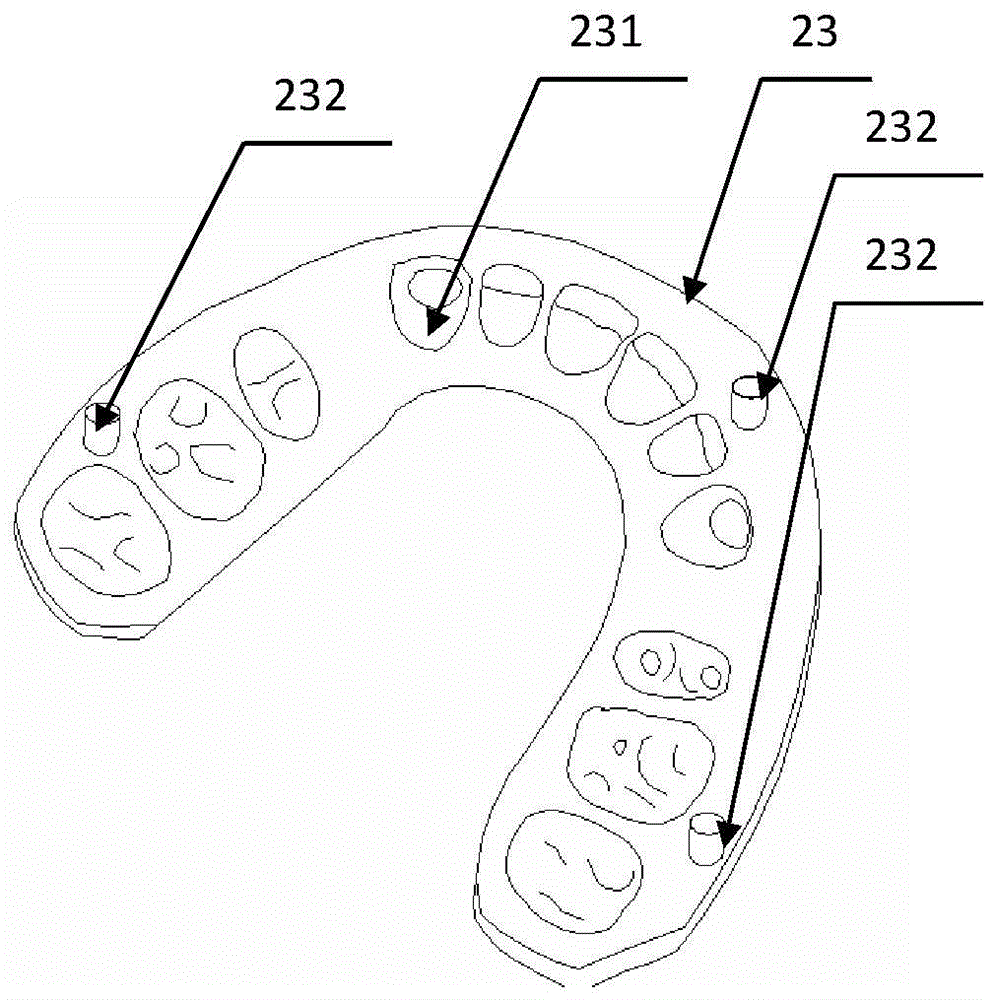
Three-dimensional orthodontic force dynamic measurement method and apparatus capable of simulating movement of teeth
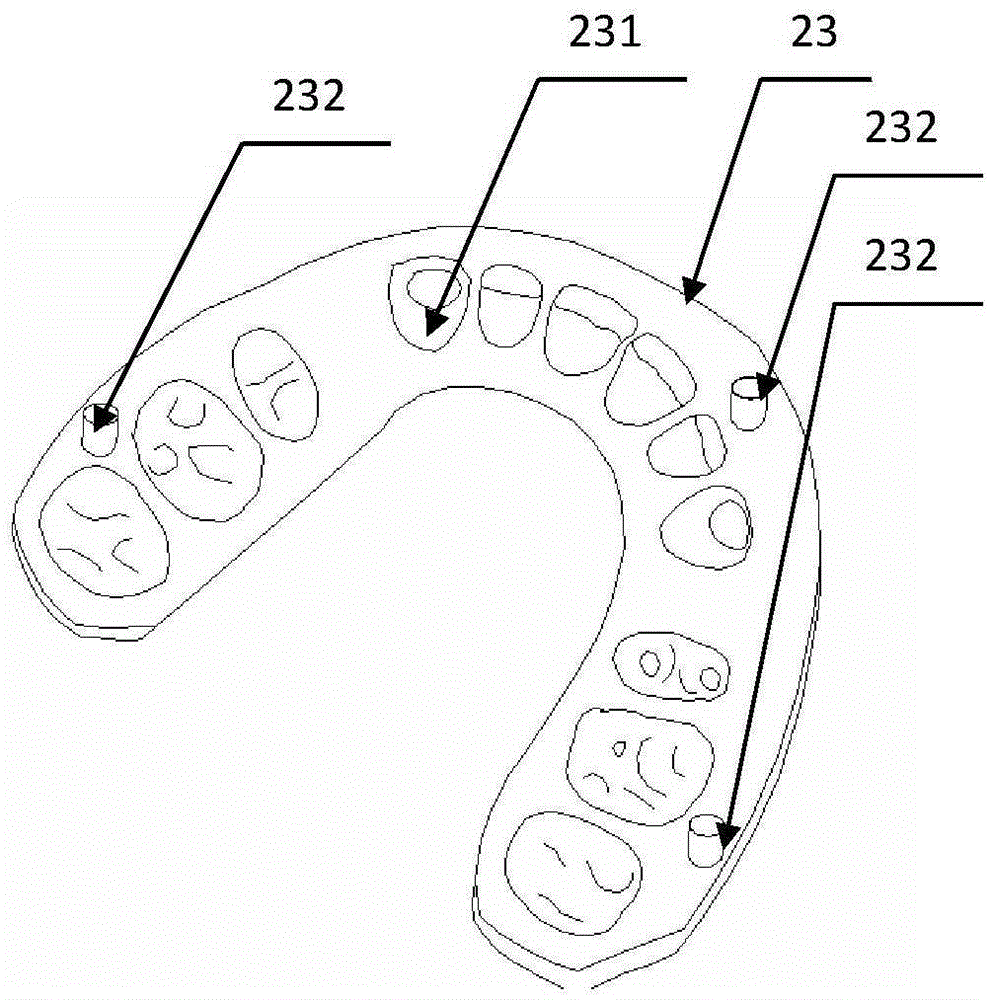
The invention provides a three-dimensional orthodontic force dynamic measurement method and apparatus capable of simulating movement of teeth. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out CT scanning so as to obtain data of the oral cavity of a patient, then reconstructing a complete tooth model and segmenting a tooth whose orthodontic force is to be measured into two parts, i.e., a tooth crown and a tooth root; making whole dentition and a positioning guide plate; and installing a tooth mechanical measurement assembly between the tooth crown and the tooth root of the to-be-measured tooth, then pressing the dentition into paraffin and simulating tooth movement in orthodontic treatment. The apparatus constructed according to the dynamic measurement method provided by the invention comprises a measurement base, a test tooth occlusion model and a processor, wherein the a plurality of columns are mounted on the measurement base, the tops of the columns are fixedly connected with a support plate, the test tooth occlusion model is arranged on the support plate, the tooth mechanical measurement assembly of the test tooth occlusion model is connected with the processor, and the the test tooth occlusion model is placed in a temperature-controlled box. The invention has the following beneficial effects: the dynamic measurement method and apparatus can realize real-time dynamic simulation and measurement of orthodontic force of arch wires on the to-be-measured tooth in orthodontic treatment.
Owner:盛源(河北)医疗产业有限公司
Integrated centrifugal machine dynamic balancing device and balancing method
The invention discloses an integrated centrifugal machine dynamic balancing device and balancing method. According to the integrated centrifugal machine dynamic balancing device and the integrated centrifugal machine dynamic balancing method, balancing capacity is only related to self weight of a rocker arm system and axial translation displacement of rocker arms, and is not limited by aspects like capacity of a centrifugal machine, mass of movable clump weights and moving distance; the speed of a centrifugal field is only dozens of times that of gravitational acceleration due to mounting positions, the requirement on G value tolerance capacity of the entire balancing device is not high, and the device can reliably operate under a large-G value working condition; the entire dynamic balancing adjusting process of the centrifugal machine rocker arms is a double-closed loop control process and comprises a position closed loop feedback control inner ring between rocker arm practical offsettranslation and motion control of a hydraulic servo system and a force feedback closed loop control outer ring composed of rocker arm unbalanced force monitoring and unbalanced force control; and safe, reliable and accurate operation of an unbalanced force dynamic balancing system can be effectively guaranteed through a double-closed loop control method, and real-time updating, on-line monitoringand dynamic balancing can be carried out on unbalanced force under operation of the centrifugal machine.
Owner:GENERAL ENG RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Methods for Establishing Simulated Force Dynamics Between Two or More Digital Assets Displayed in an Electronic Interface
InactiveUS20140096026A1Still image data indexingNatural language data processingForce dynamicsData store
A system includes a server connected to a network, the server having access to a processor and a data repository and software running from a non-transitory physical medium, the software providing for establishing a client-server connection between the server and at least one user-operated computing appliance connected to the network, maintaining an active data session between one or more users involved in working with the image and / or text-based projects through a graphics user interface (GUI), detecting interactive boundaries between items in a collection of items placed on an editable canvas, detecting, upon movement of at least one of the items, the intersection of one or more of the interactive boundaries, and implementing physics assigned to the items upon confirmation of intersection of the interactive boundaries.
Owner:INTERACTIVE MEMORIES
Magneto-rheological damper with mixed flow type fluid flowing channel
ActiveCN104963986AIncrease the lengthIncrease the areaSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionCircular discMixed flow
The invention discloses a magneto-rheological damper with a mixed flow type fluid flowing channel. The magneto-rheological damper is mainly composed of a piston rod, a damper end cover, a sleeve, a piston end cover, a valve bush, a valve element, a floating piston, a magnet exciting coil, a positioning disc, magnetic conductive discs, a lifting lug and the like. A fluid flowing channel among the left magnetic conductive disc, the valve bush and the valve element forms a first section of effective damping gap and a second section of effective damping gap. A fluid flowing channel between the right magnetic conductive disc and the valve element forms a third section of effective damping gap and a fourth section of effective damping gap. When electric conduction is carried out on the magnet exciting coil, the four sections of effective damping gaps generate a magnetic field with a certain size, the viscosity of magneto-rheological fluid flowing through the four sections of effective damping gaps is increased, the yield stress is improved, and therefore pressure difference is formed between a first cavity and a second cavity of the damper. The damping force can be effectively controlled by controlling the magnitude of applied current. The magneto-rheological damper is wide in damping force dynamic adjustment range, simple in structure, small in size and particularly applicable to vibration damping systems of railways, automobiles, bridges and the other structures.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
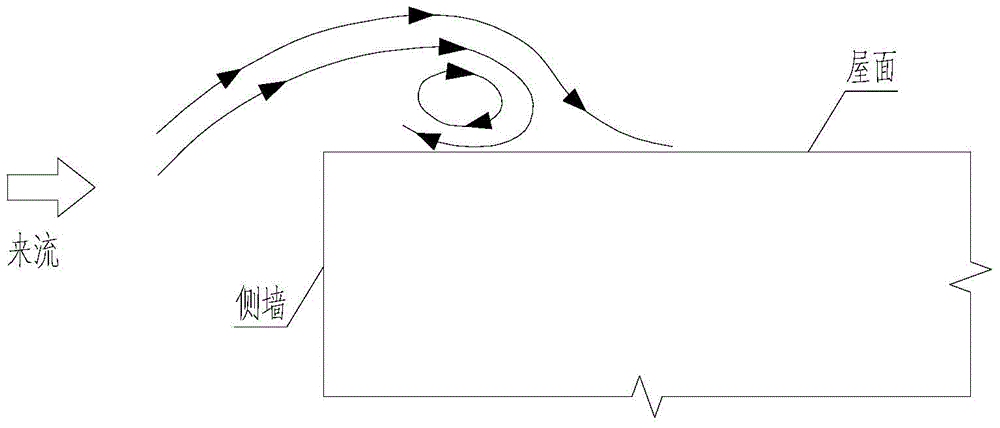
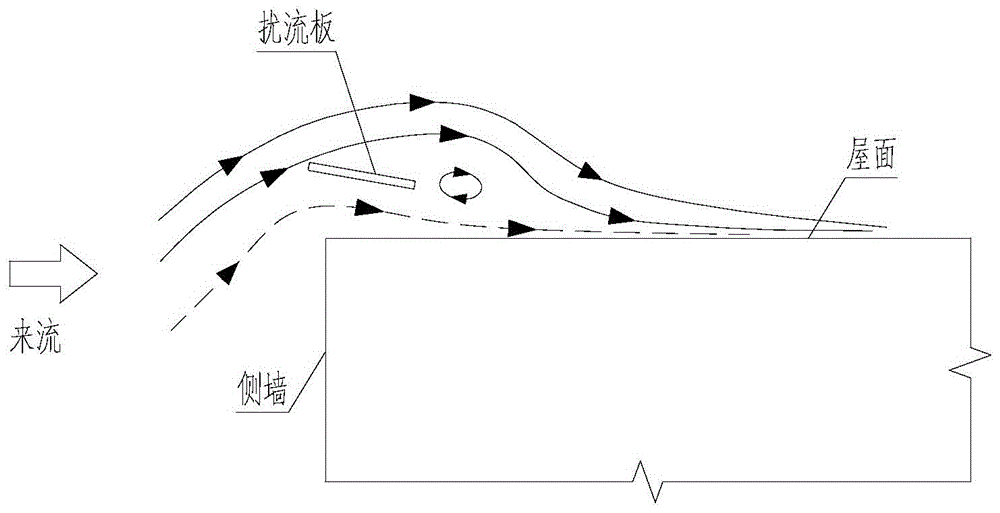
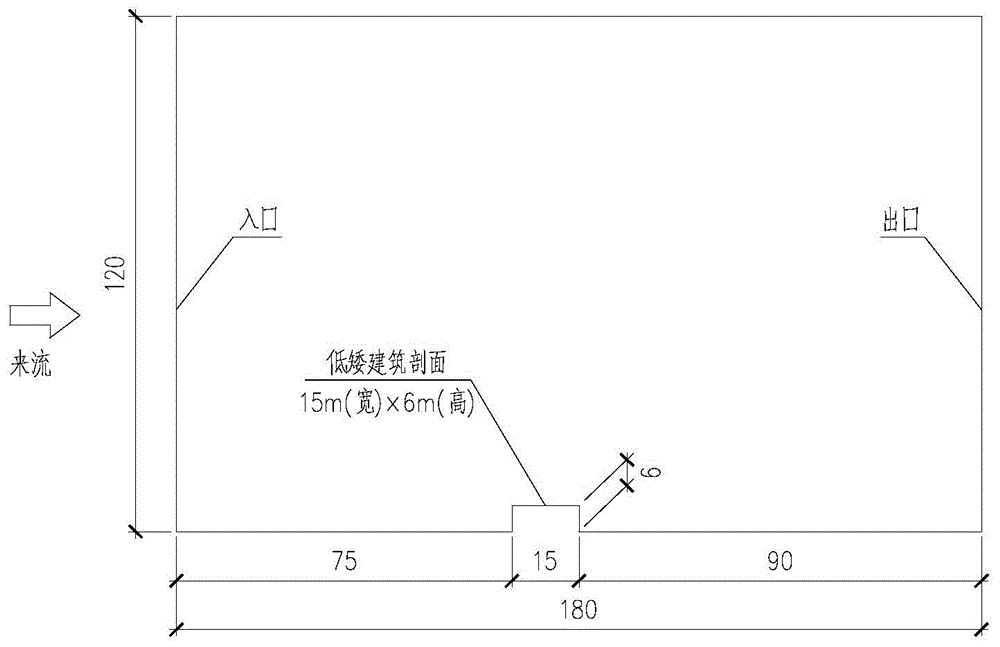
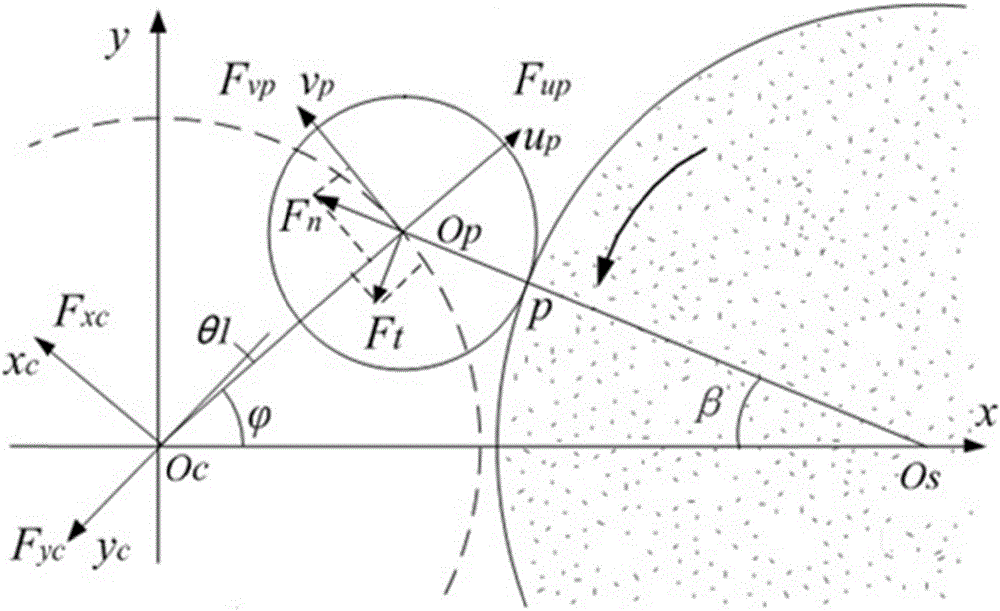
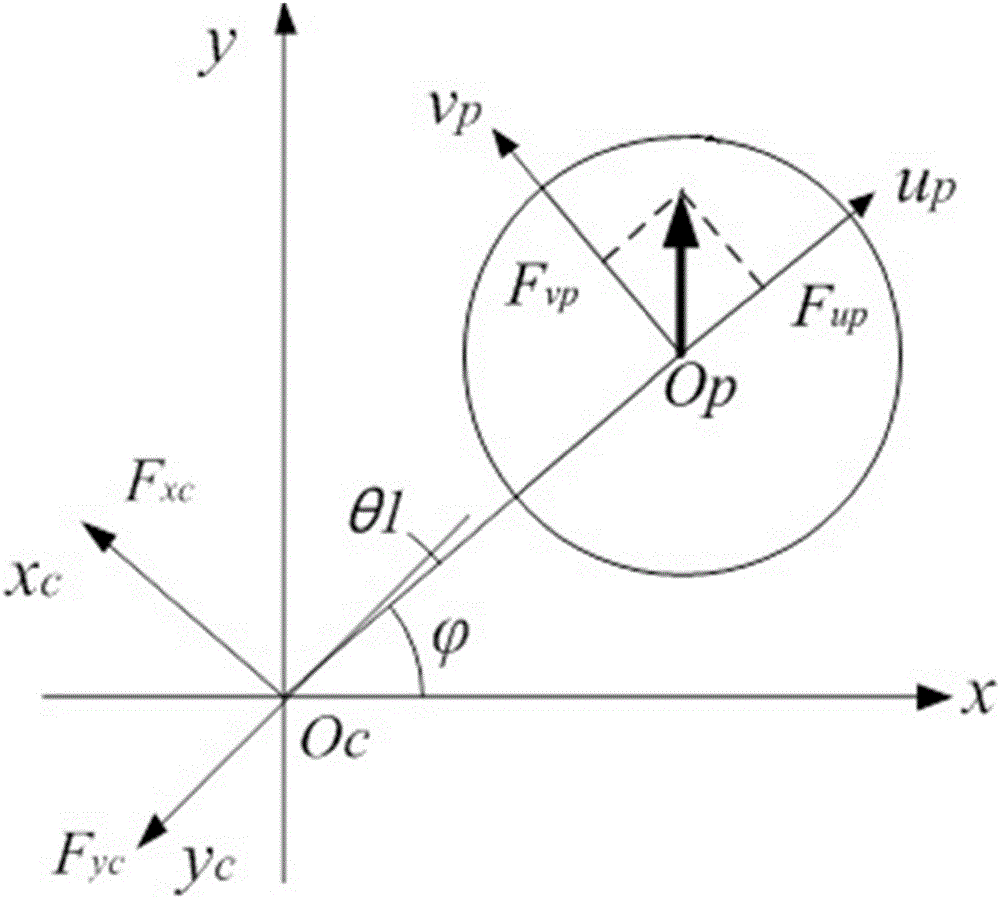
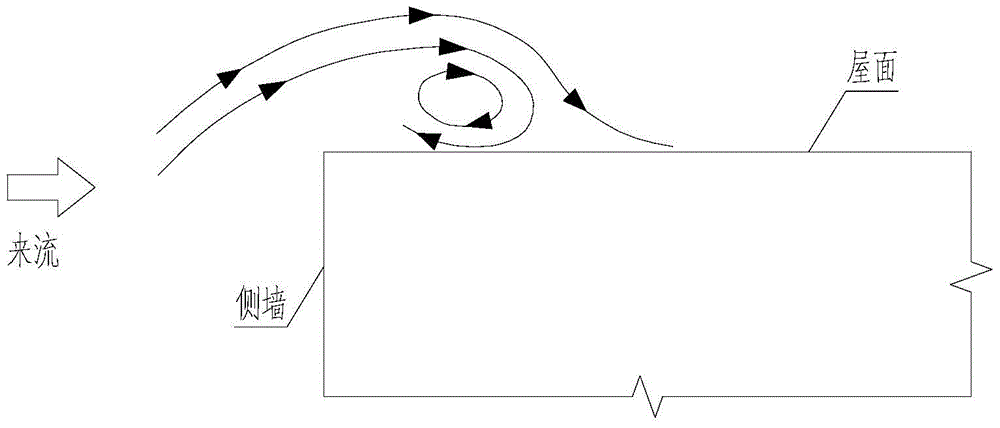
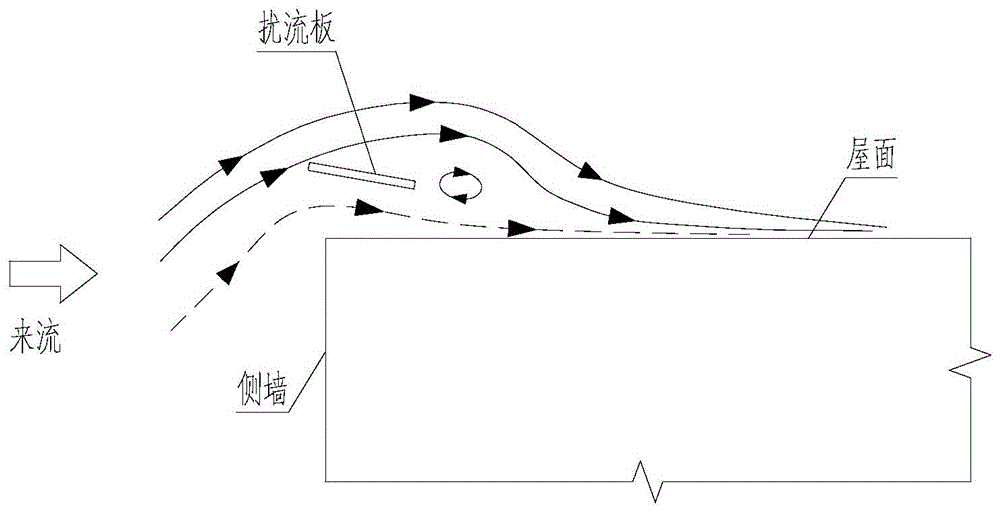
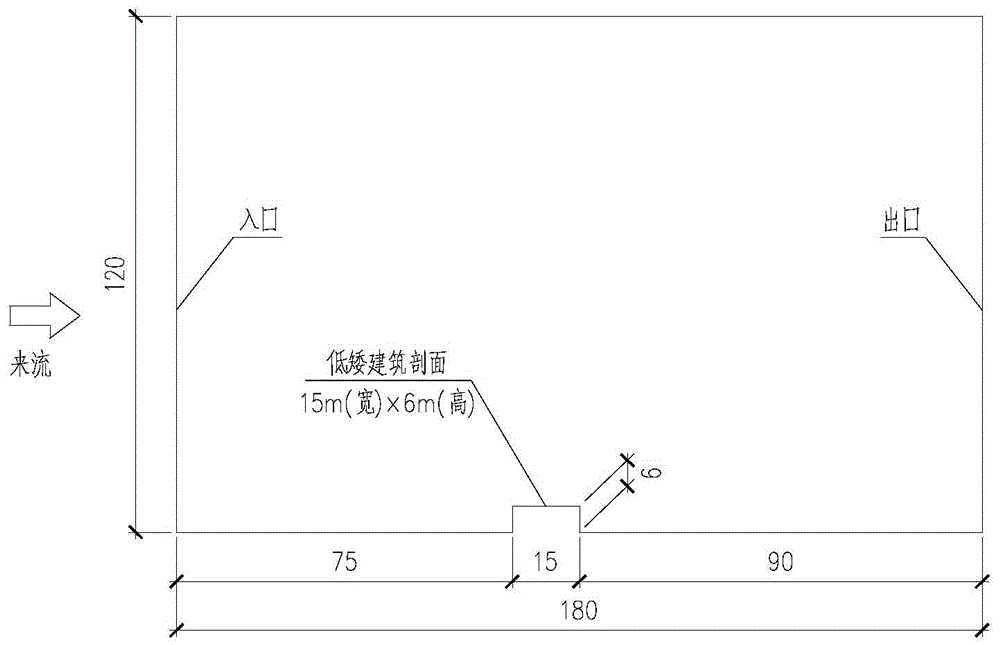
Strong wind attraction force dynamic inhibition device of roof of short building
The invention relates to a strong wind attraction force dynamic inhibition device of a roof of a short building. The inhibition device is used for reducing strong wind load induced by vortex of the roof of a short building. The inhibition device comprises a streamline type spoiler plate assembly, a wind speed device, a servo controller, a driving motor and an external power supply. The streamline type spoiler assembly is fixedly connected with the roof via a spoiler plate support and is in transmission connection with the spoiler plate support. The wind speed device is used for measuring wind speed in real time. The servo controller is connected with the wind speed device and used for sending out control instructions according to real-time wind speed. The driving motor is connected with the servo controller and the spoiler plate support and changes the included angle between streamline type spoiler plate assembly and the horizontal plane according to the control instructions, thereby achieving strong wind attraction force dynamic inhibition. The external power supply is connected with the wind speed device and the driving the motor so as to provide electricity. Compared with the prior art, the inhibition device is advantaged by effective reduction of strong wind load induced by vortex of the roof of a short building, simple structure, remarkable effects, stable performance and reduction of construction cost.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN INST GRP CO LTD
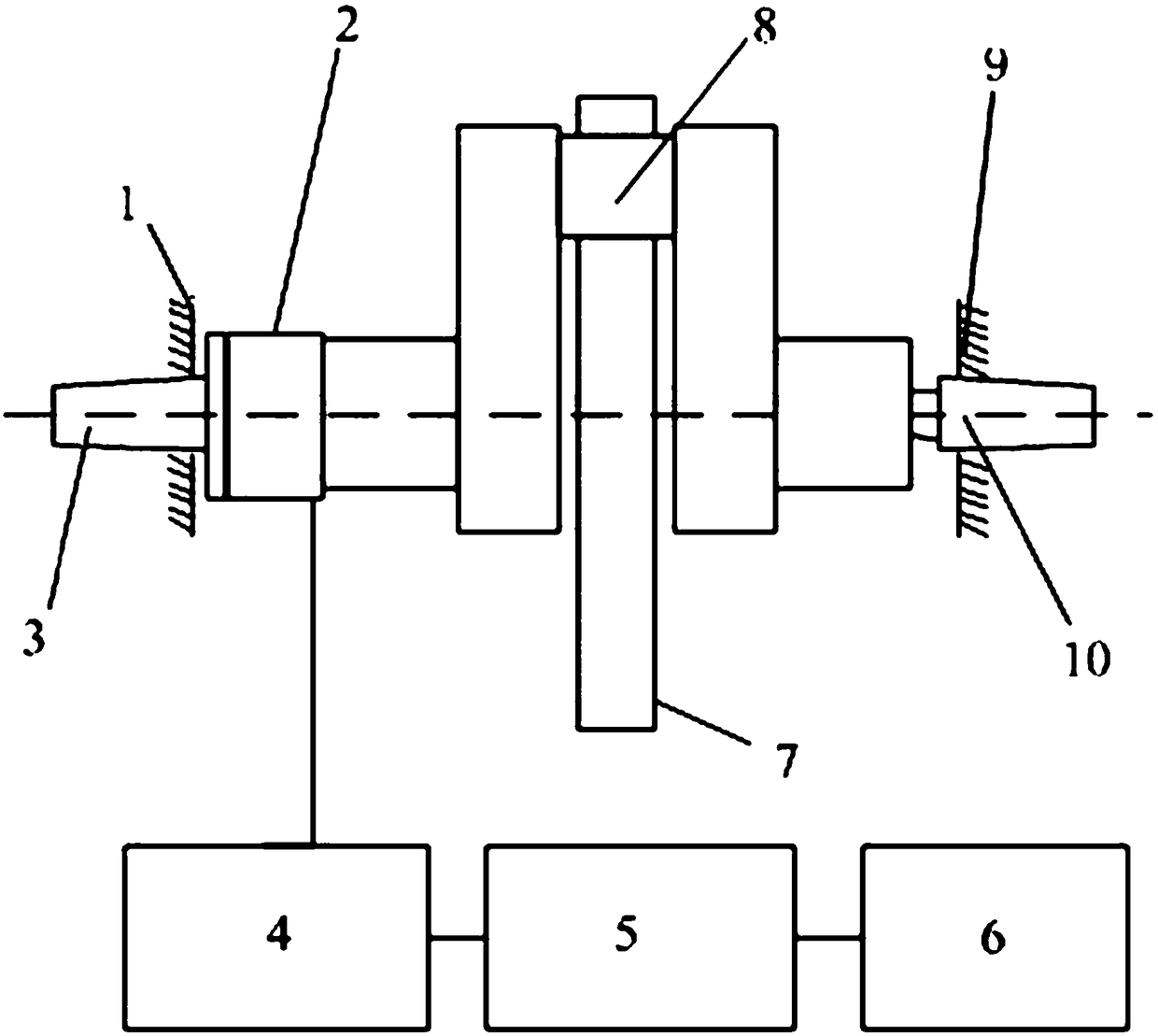
Crankshaft connecting rod neck follow-up grinding force dynamic measurement method and device
ActiveCN105922133ASolving Dynamic Measurement ProblemsRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding feed controlMeasurement deviceMathematical model
The invention provides a crankshaft connecting rod neck follow-up grinding force dynamic measurement method and device. The crankshaft connecting rod neck follow-up grinding force dynamic measurement device comprises a crankshaft, a sand wheel, a rotary measuring cell and a measuring unit, wherein a main shaft neck of one end of the crankshaft is connected with a sand wheel head frame, and a main shaft neck of the other end of the crankshaft is connected with a sand wheel tail frame; the sand wheel makes contact with a crankshaft connecting rod neck of the crankshaft; the rotary measuring cell is arranged on one of the main shaft necks of the crankshaft; and the measuring unit is connected with the rotary measuring cell. The crankshaft connecting rod neck follow-up grinding force dynamic measurement method and device have the following beneficial effects that the dynamic change of grinding force in the crankshaft connecting rod neck planetary motion process is converted into grinding force applied to the main shaft necks by building a mathematical model of grinding force in the crankshaft connecting rod neck follow-up grinding process, the grinding force is collected through a series of measuring equipment, and finally the crankshaft follow-up grinding force dynamic measurement method is formed; spatial position dynamic, continuous and precise measuring can be conducted on normal and tangential components of the grinding force at a grinding point of the connecting rod neck; and the method is suitable for engineering practice and solving the dynamic measuring problem of the crankshaft follow-up grinding force.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for minimizing error in dynamic and steady-state processes for prediction, control, and optimization
InactiveUS8311673B2Minimize error valueOutput errorComputer controlSimulator controlNarrow rangeDynamic models
A method for providing independent static and dynamic models in a prediction, control and optimization environment utilizes an independent static model (20) and an independent dynamic model (22). The static model (20) is a rigorous predictive model that is trained over a wide range of data, whereas the dynamic model (22) is trained over a narrow range of data. The gain K of the static model (20) is utilized to scale the gain k of the dynamic model (22). The forced dynamic portion of the model (22) referred to as the bi variables are scaled by the ratio of the gains K and k. Thereafter, the difference between the new value input to the static model (20) and the prior steady-state value is utilized as an input to the dynamic model (22). The predicted dynamic output is then summed with the previous steady-state value to provide a predicted value Y.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Diversified cross-connection control method for plate shape of hot rolling band steel
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
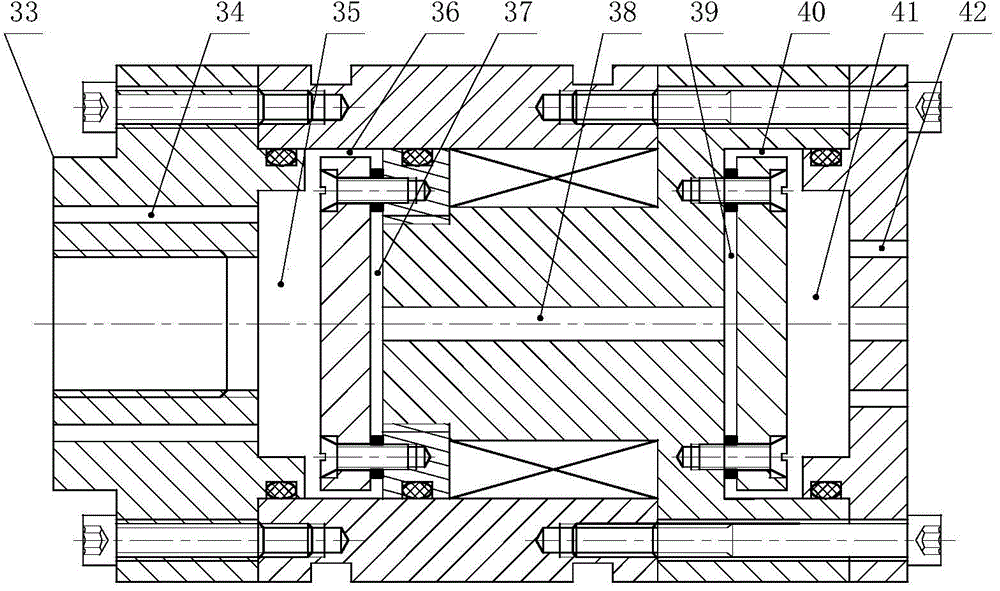
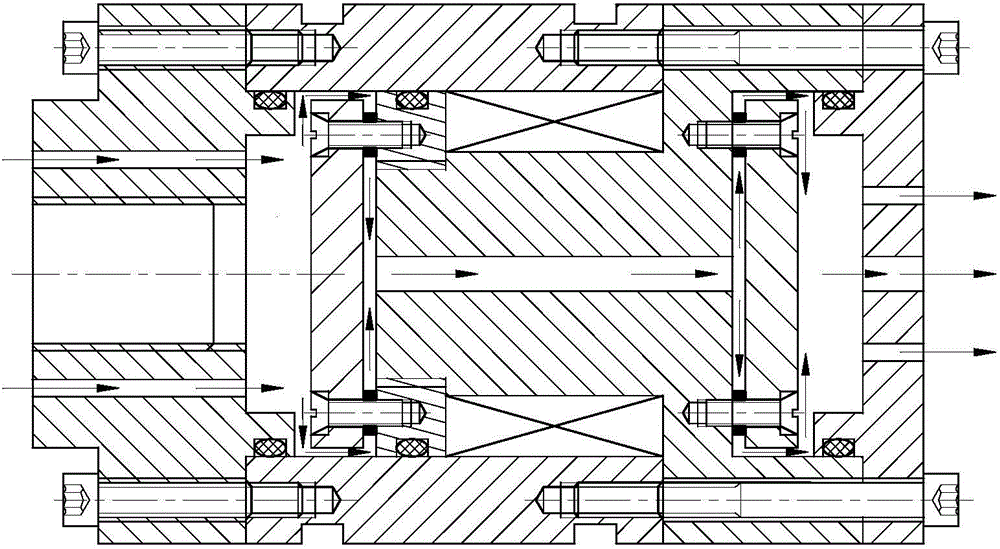
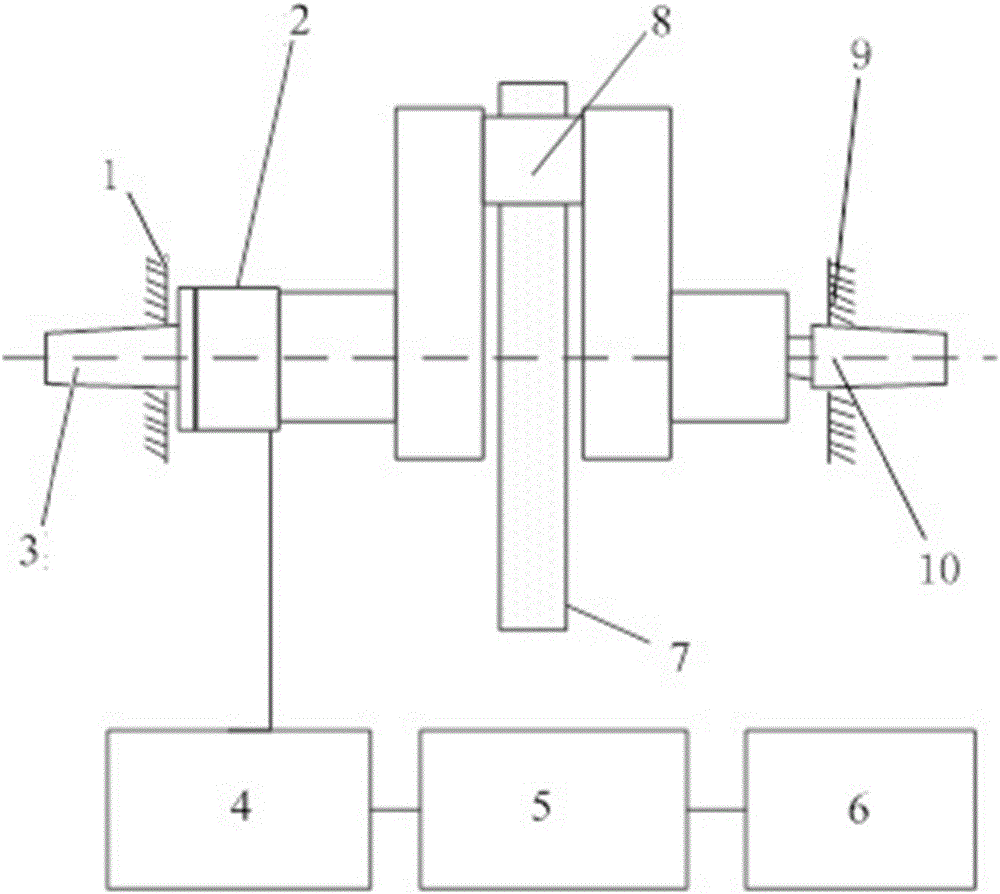
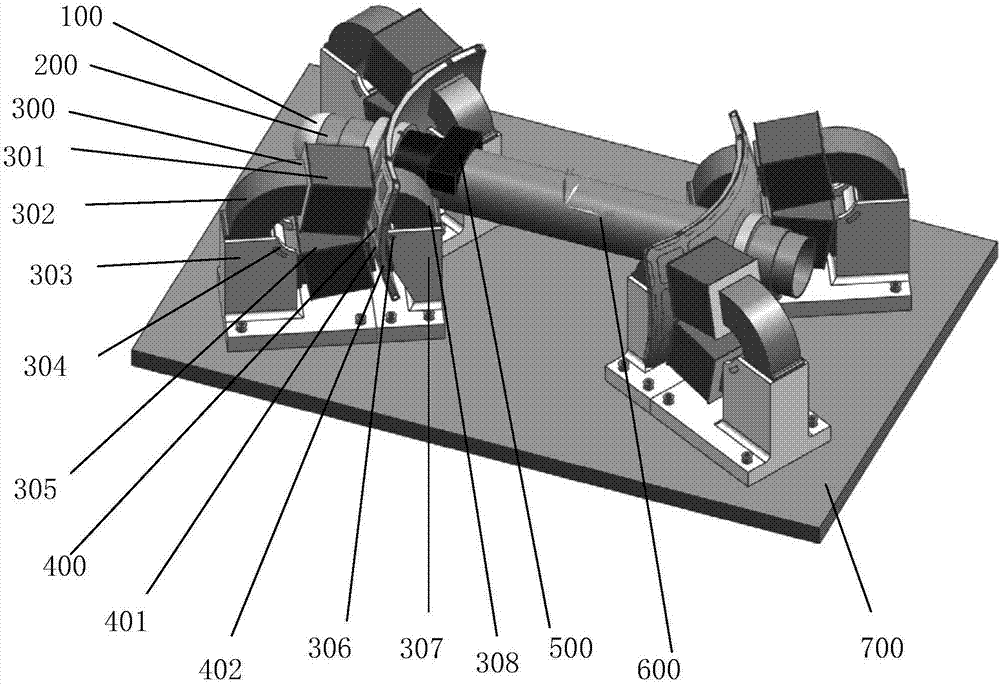
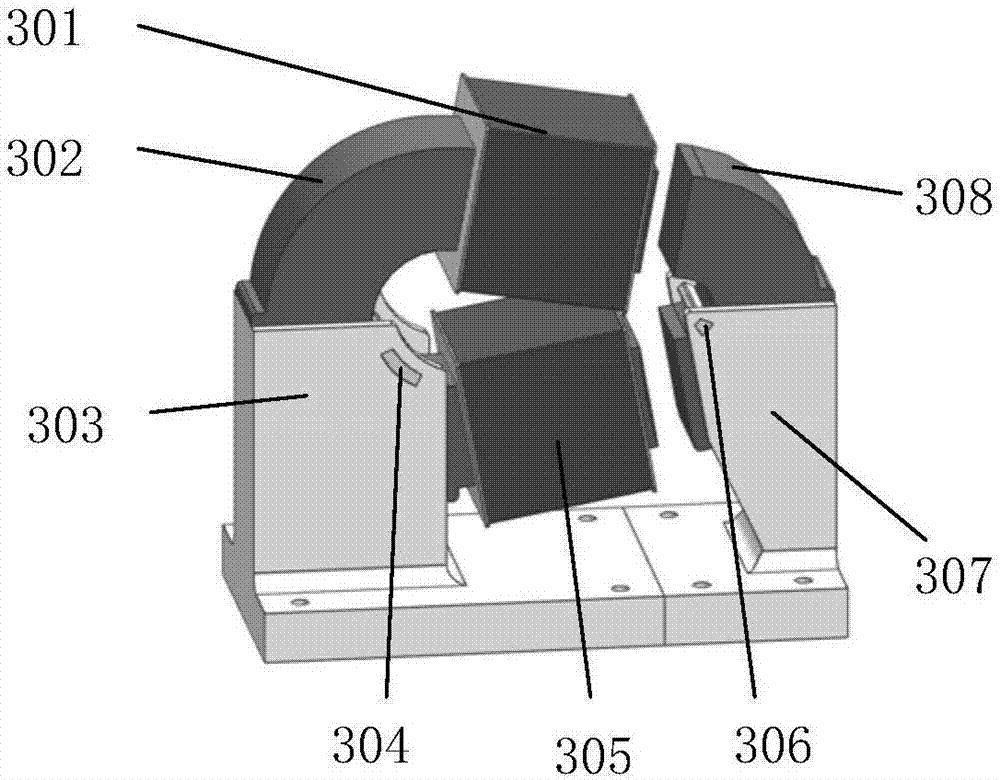
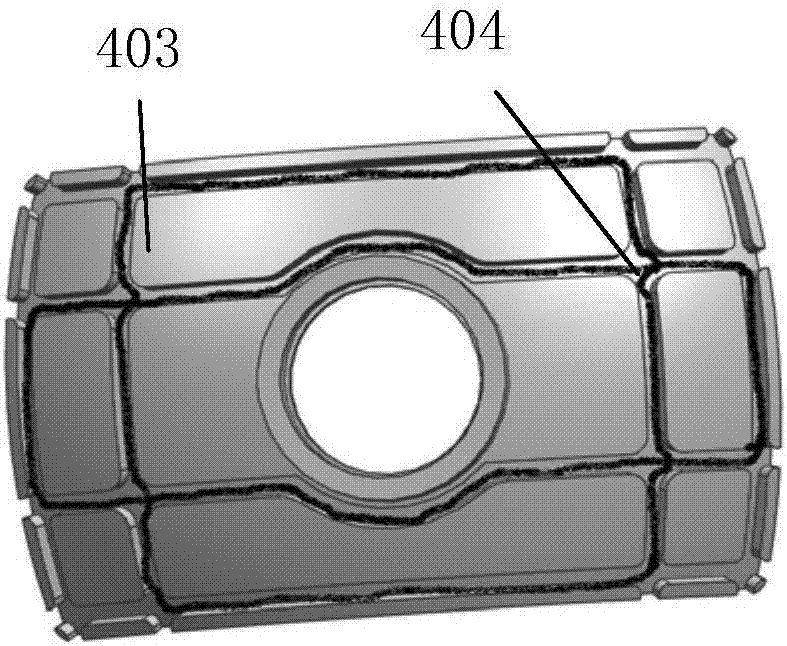
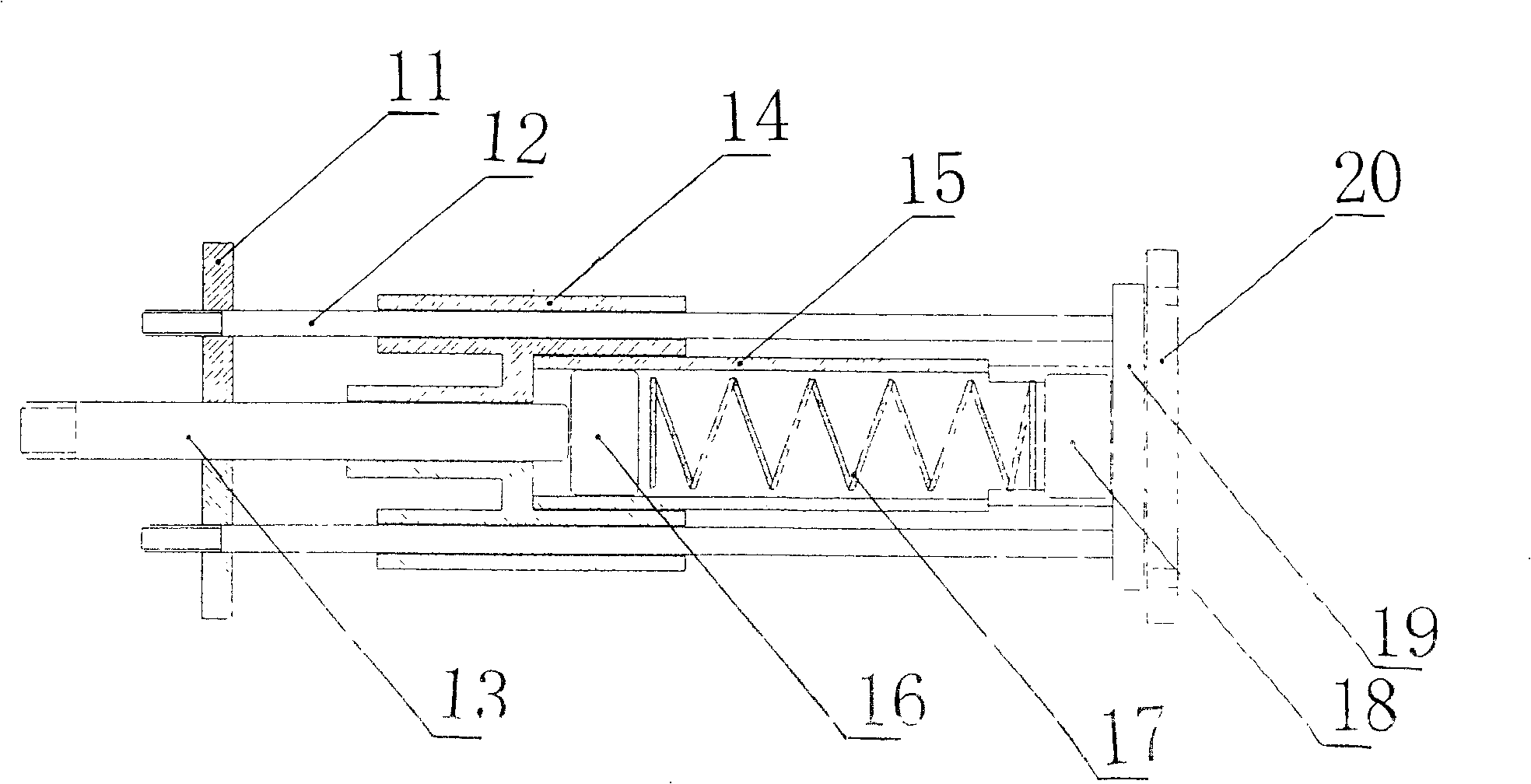
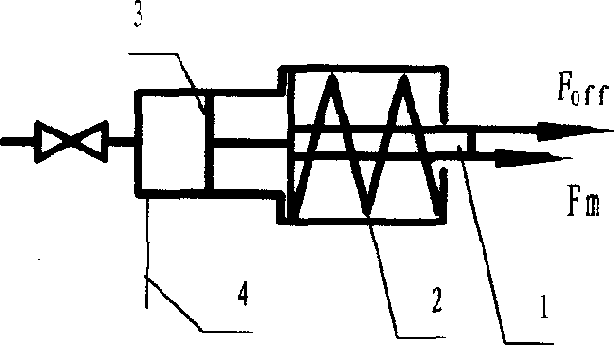
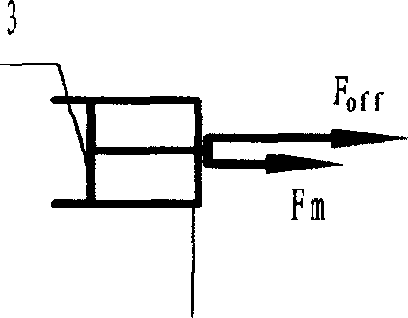
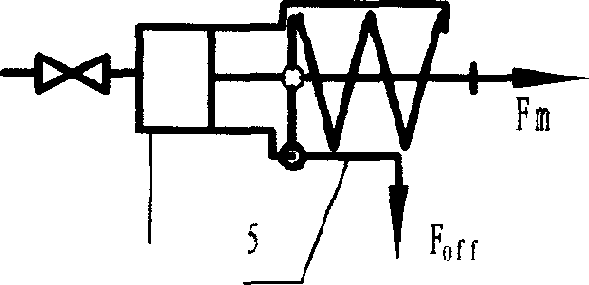
Forced dynamic derivative balance dynamic corrector
The invention provides a forced dynamic derivative balance dynamic corrector comprising a pedestal; two arc coils; an installing sleeve and an installing platform, wherein the two ends of the installing sleeve are installed on the two arc coils through the installing platform; and multiple magnetic field generators which are arranged on the pedestal, wherein the arc coils are arranged in the Lorentz force effect channel formed by the magnetic field generators in a floating way. In working of the dynamic corrector, the arc coils are electrified and then move in the strong magnetic field formedby the magnetic field generators to generate the Lorentz force, and the force changes along with the change of the moving speed and direction of the movement calibration frame so as to form alternating dynamic load and thus dynamic calibration of the balance can be realized.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Dynamic self-adaptive method of shift fork force in dual-clutch automatic transmission
ActiveCN103867702BReduce calibration workloadGood fork controlGearing controlAutomatic transmissionNoise optimization
The invention discloses a double-clutch type automatic transmission fork shifting gear engaging force dynamic self-adapting method. The fork shifting is divided into a plurality of stages during the gear shifting process. The double-clutch type automatic transmission fork shifting gear engaging force dynamic self-adapting method comprises the following steps of (1) obtaining ranges of a maximum value and a minimum value of a preset shifting fork movement speed at different stages during fork shifting gear engaging; (2) computing a shifting fork real-time movement speed and confirming a maximum value and a minimum value of the shifting fork movement speed at the different stages during the fork shifting gear engaging; (3) comparing the maximum value and the minimum value of the shifting fork movement speed with the range of the maximum value and the minimum value of the preset shifting fork movement speed at the same stage, obtaining the fork shifting gear engaging force to be adjusted and the stage and recording and adjusting the fork shifting gear engaging force when the shifting fork gear shifting achieves a corresponding stage. The double-clutch type automatic transmission fork shifting gear engaging force dynamic self-adapting method is applied to control of a double-clutch automatic transmission and achieves vehicle gear shifting noise optimization.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
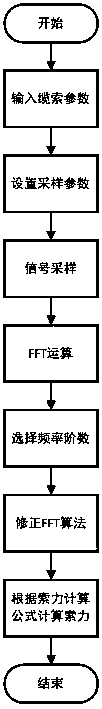
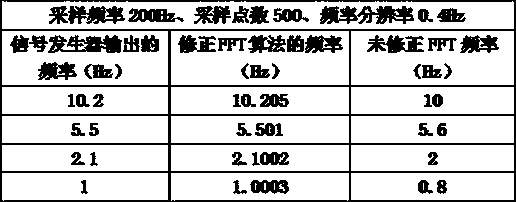
Cable force dynamic tester based on modified FFT algorithm and algorithm thereof
The invention relates to a cable force dynamic tester based on a modified FFT algorithm and an algorithm thereof, belonging to the technical field of civil engineering. The cable force dynamic tester and the algorithm are applied to the structure safety and health monitoring industry. The cable force dynamic tester comprises a vibration sensor, an anti-aliasing filter, an ADC converter, an embedded processor, a keyboard, an RTC real-time clock, a power supply management module, an LCD display and a DSP processor. The vibration sensor is connected to the anti-aliasing filter which is connected to the ADC converter, and the ADC converter is connected to the embedded processor. The keyboard, the RTC real-time clock, the LCD display and the DSP processor are connected to the embedded processor. According to the cable force dynamic tester and the algorithm, a modified FFT method is used, a precise actual frequency value is obtained, thus the frequency value precision of force value measurement is within 5 / 10000 through the modified FFT method, the frequency precision after conventional FFT calculation only reaches 2%, and the lower a frequency is, the larger an error is.
Owner:JIANGXI FASHION TECH
Dynamic Measurement Method of Follow-up Grinding Force of Crankshaft Connecting Rod Neck
ActiveCN105922133BSolving Dynamic Measurement ProblemsRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding feed controlMeasurement deviceMathematical model
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
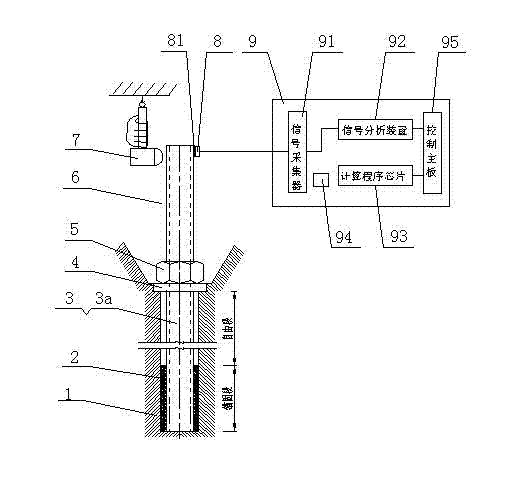
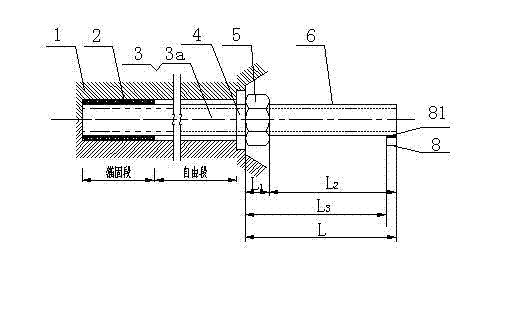
Pre-tightening force dynamic monitoring system for pre-stressed anchor bar strengthening project
ActiveCN101865739BSolve the problem of failureAvoid failureForce measurement by measuring frquency variationsPre stressTransducer
The invention discloses a pre-tightening force dynamic monitoring system for a pre-stressed anchor bar strengthening project. The system comprises a deformed steel bar, a retainer plate and nuts, wherein one end of the deformed steel bar is provided with an anchorage; the anchorage is combined with soil mass to anchor the deformed steel bar in the soil mass and stretch the deformed steel bar intoa pre-stressed deformed steel bar anchor bar; the outer end of the pre-stressed deformed steel bar anchor bar is provided with an exposed section; the top end of the exposed section is provided with an acceleration transducer and a vibrator; the acceleration transducer is connected with a tensile force detector of the pre-stressed deformed steel bar anchor bar; and a signal acquisition device, a signal analyzing device, a calculating procedure chip, a rechargeable battery and a control main board are built in the detector; the technical scheme overcomes the defects of high use cost, inconvenient operation and maintenance, low testing accuracy, narrow application range, failure of the anchor bar and the like existing in a conventional detection method; and the pre-tightening force dynamic monitoring system is suitable for instantaneous detection and whole-process monitoring of the tensile force of the pres-stressed deformed steel bar anchor bar in the large-area projects of instable soil mass slope, retaining wall, deep foundation pit and the like strengthened by the pres-stressed deformed steel bar anchor bar.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Security force dynamic deployment method for social surface
InactiveCN110019602AIncrease profitPrecise with policeData processing applicationsGeographical information databasesMultiple formsEngineering
The invention discloses a security force dynamic deployment method for a social surface. The security force dynamic deployment method comprises the following steps: classifying public security sticking points built in a city according to the principles of road levels, whether smart sticking points exist or not and whether supports exist or not; arranging defense lines at intercity entrances and exits of cities to form compound clamping points which are mutually connected and mutually planned; according to a set standard, achieving scientific and reasonable measurement, calculation and deployment of the social security strength by combining various factors of the social security situation. Various forms of display of the urban security force deployment situation are achieved, on one hand, the number of police personnel at each clamping point or post is displayed in a table form, and on the other hand, the security force and configuration conditions of the city from the defense line to the clamping points and the posts are visually displayed in combination with a GIS map.
Owner:CHINA CHANGFENG SCI TECH IND GROUPCORP
Master-slave mode two-in-parallel twelve degree of freedom generalized force adjustment loading mechanism
InactiveCN100449196CImprove linearityRealize compound vibration dampingUsing mechanical meansStands/trestlesAviationEngineering
The invention discloses a parallel twelve-freedom loading device, used in spatial loading test and fatigue test on aviation material, comprising a Stewart active parallel six-freedom loading device, a SPS six-dimension force / torque sensor and a SPS inactive parallel six-freedom adjuster, wherein the Stewart active parallel six-freedom loading device simulates the spatial motion, the active and inactive platforms of inactive parallel six-freedom adjuster follows to operate and draw or compress the bidirectional isomorphism spring device, to test wide force dynamical load, to supply high accuracy and better reliability to the six-freedom wide force dynamic synchronous loading system, to be used in spatial-ground semi-physical simulation test or the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Digital antilock braking system
InactiveCN1603181AImprove securityModulation is easy to implementBraking element arrangementsEngineeringForce dynamics
The invention relates to a brake system used in automobile and motorcycle. It is adjusted the braking force in the form of pulse-width modulation. The bias force device is adopted to realize modulated in bigger range with smaller braking force. This make the modulation be easy to realize. The difficulty of controlling the controlling force is reduced by adopting the method of force adding-position-force changing. The active digital braking and the passive digital are connected tightly with each other by adopting the technique of bias force reversing, assistant braking oil cylinder, oil-way switching, so that the control and the adjust of the braking force are changed at his pressure. Compared with the simulation ABS system, the invention can simplify the structure of the brake, reduce the precision of the machining, and save the cost. As well as, it can adopt more advanced intelligent control method to improve the braking performance. Based on this, it can be more conveniently to realize the high-level control, such as ASR, front-back braking force dynamic distribution, left-right braking force balance control, and so on, and make the safety of the braking be improved to a new level.
Owner:朱筱杰
A dynamic suppression device for strong wind suction on the roof of a low building
Owner:TONGJI UNIV ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN INST GRP CO LTD
A Dynamic Calibrator of Forced Dynamic Derivative Balance
The invention provides a forced dynamic derivative balance dynamic corrector comprising a pedestal; two arc coils; an installing sleeve and an installing platform, wherein the two ends of the installing sleeve are installed on the two arc coils through the installing platform; and multiple magnetic field generators which are arranged on the pedestal, wherein the arc coils are arranged in the Lorentz force effect channel formed by the magnetic field generators in a floating way. In working of the dynamic corrector, the arc coils are electrified and then move in the strong magnetic field formedby the magnetic field generators to generate the Lorentz force, and the force changes along with the change of the moving speed and direction of the movement calibration frame so as to form alternating dynamic load and thus dynamic calibration of the balance can be realized.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Three-dimensional orthodontic force dynamic measurement method and device capable of simulating tooth movement
The invention provides a three-dimensional orthodontic force dynamic measurement method and apparatus capable of simulating movement of teeth. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out CT scanning so as to obtain data of the oral cavity of a patient, then reconstructing a complete tooth model and segmenting a tooth whose orthodontic force is to be measured into two parts, i.e., a tooth crown and a tooth root; making whole dentition and a positioning guide plate; and installing a tooth mechanical measurement assembly between the tooth crown and the tooth root of the to-be-measured tooth, then pressing the dentition into paraffin and simulating tooth movement in orthodontic treatment. The apparatus constructed according to the dynamic measurement method provided by the invention comprises a measurement base, a test tooth occlusion model and a processor, wherein the a plurality of columns are mounted on the measurement base, the tops of the columns are fixedly connected with a support plate, the test tooth occlusion model is arranged on the support plate, the tooth mechanical measurement assembly of the test tooth occlusion model is connected with the processor, and the the test tooth occlusion model is placed in a temperature-controlled box. The invention has the following beneficial effects: the dynamic measurement method and apparatus can realize real-time dynamic simulation and measurement of orthodontic force of arch wires on the to-be-measured tooth in orthodontic treatment.
Owner:盛源(河北)医疗产业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com