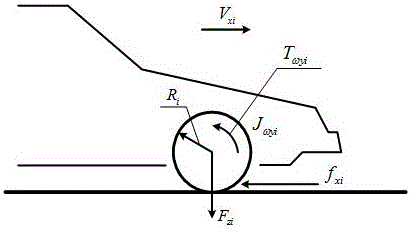
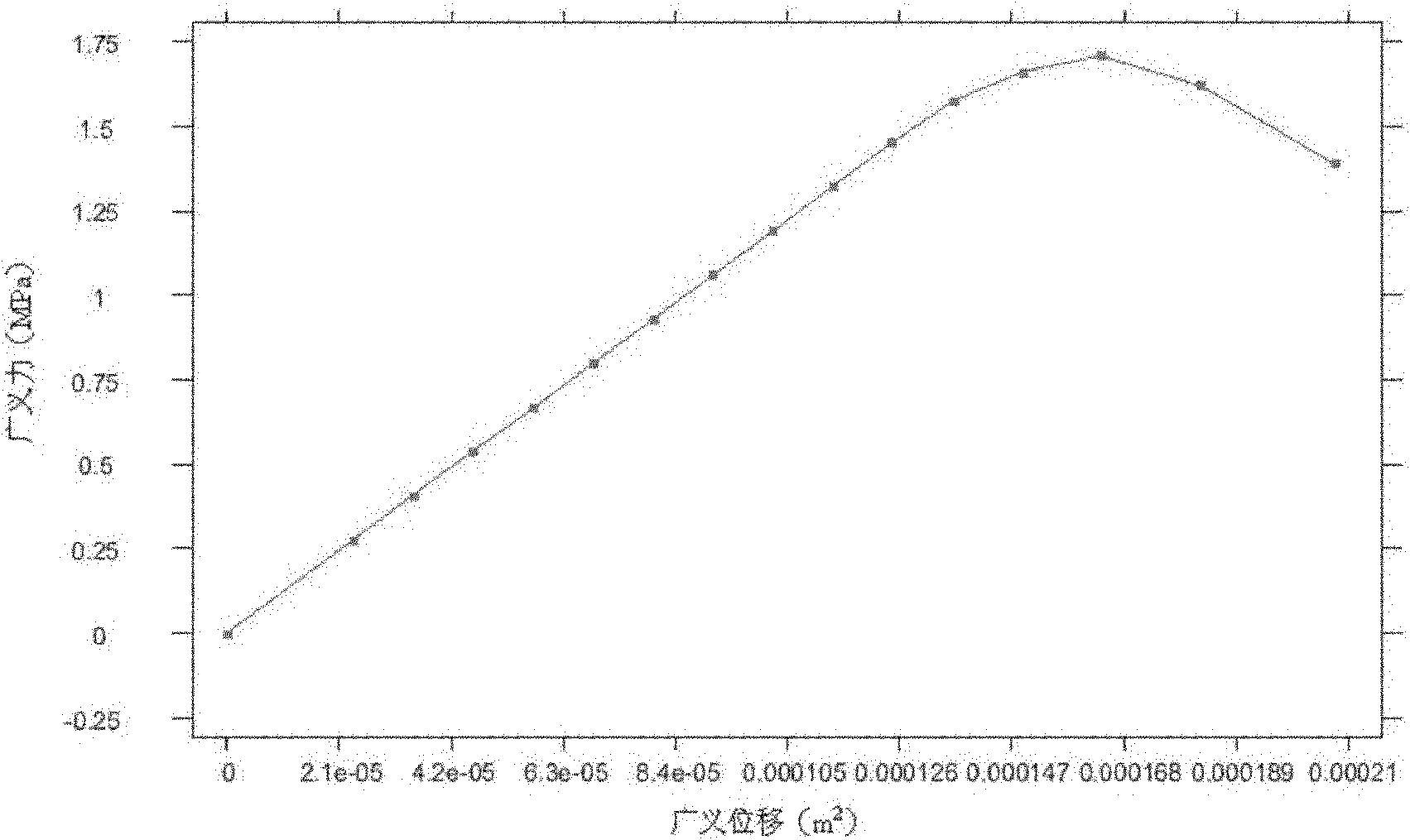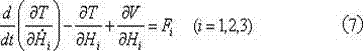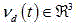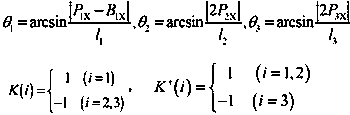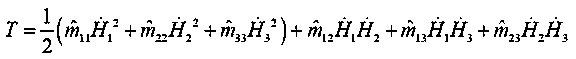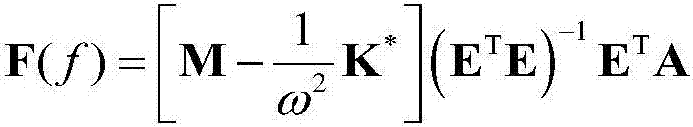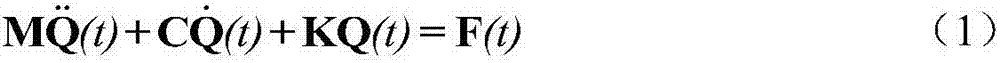Patents
Literature
65 results about "Generalized forces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Generalized forces find use in Lagrangian mechanics, where they play a role conjugate to generalized coordinates. They are obtained from the applied forces, Fᵢ, i=1,..., n, acting on a system that has its configuration defined in terms of generalized coordinates. In the formulation of virtual work, each generalized force is the coefficient of the variation of a generalized coordinate.
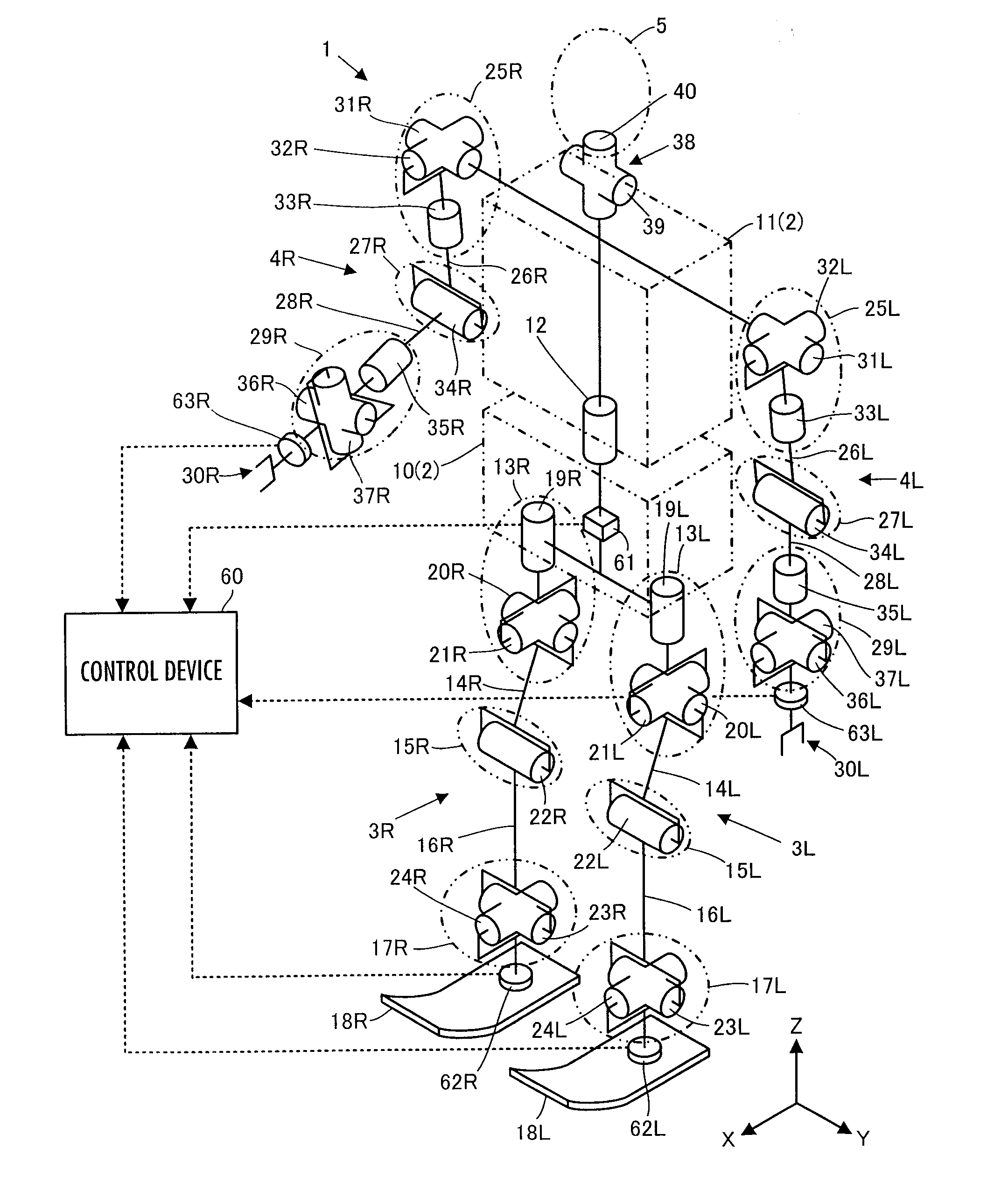
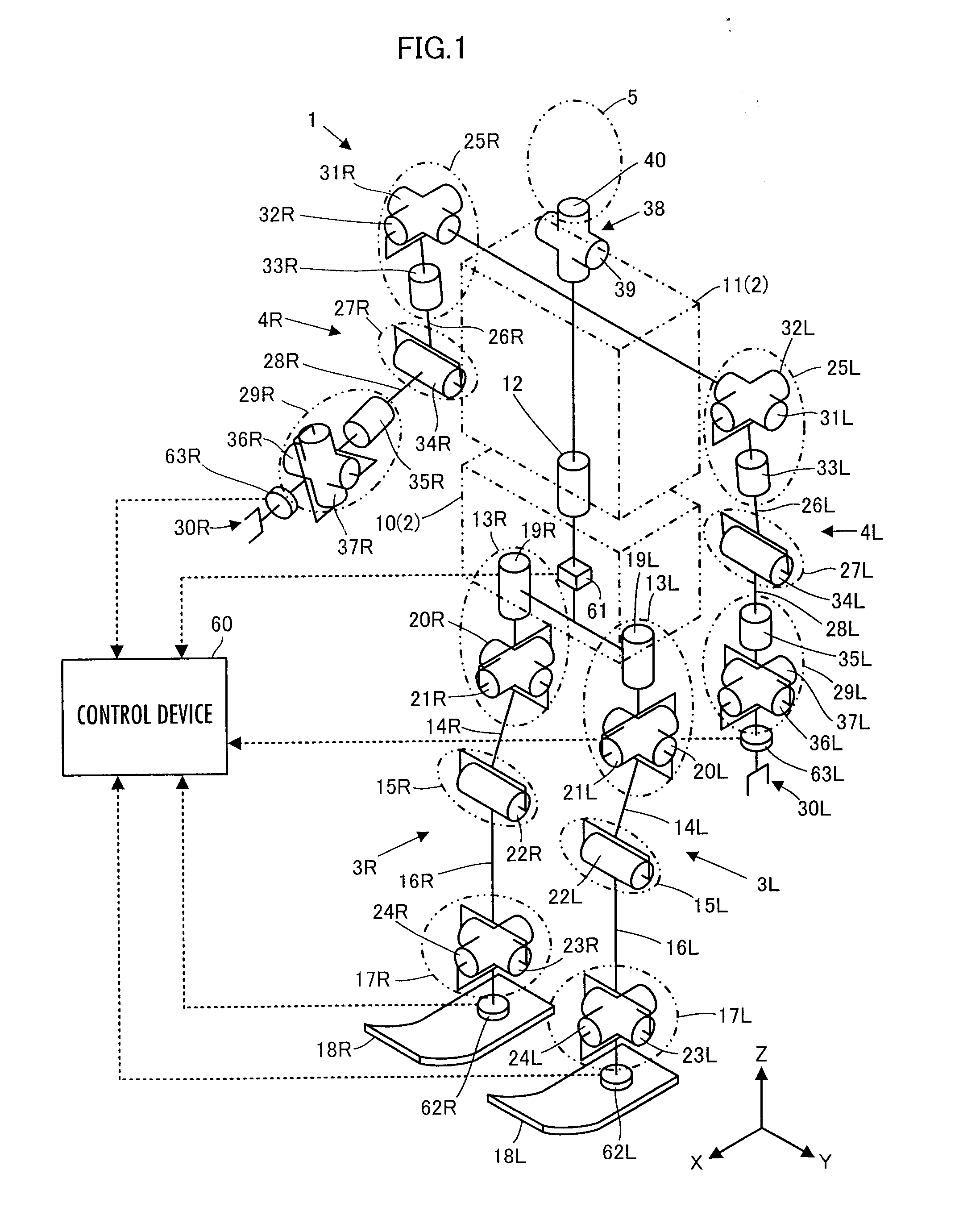
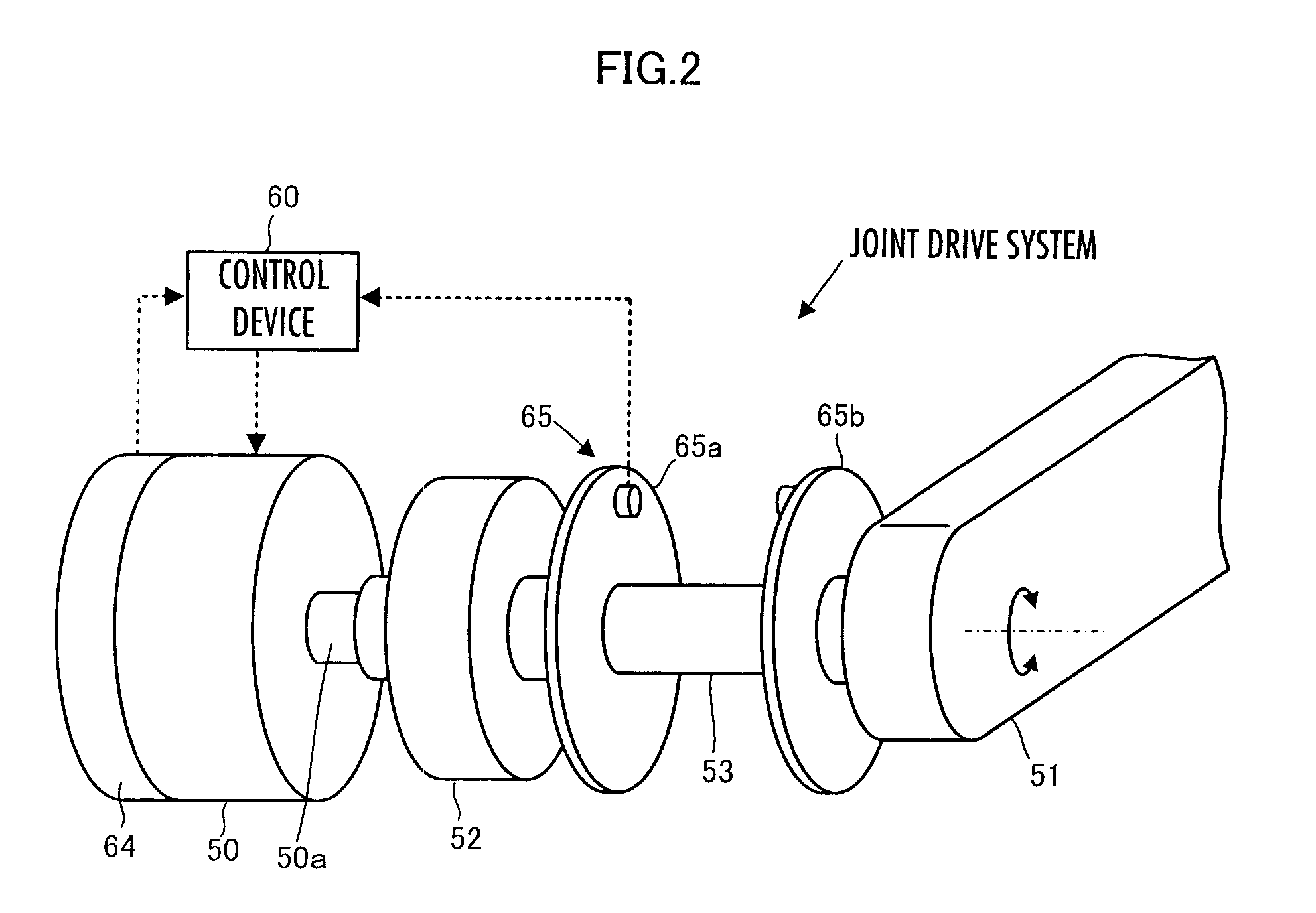
Control device for robot
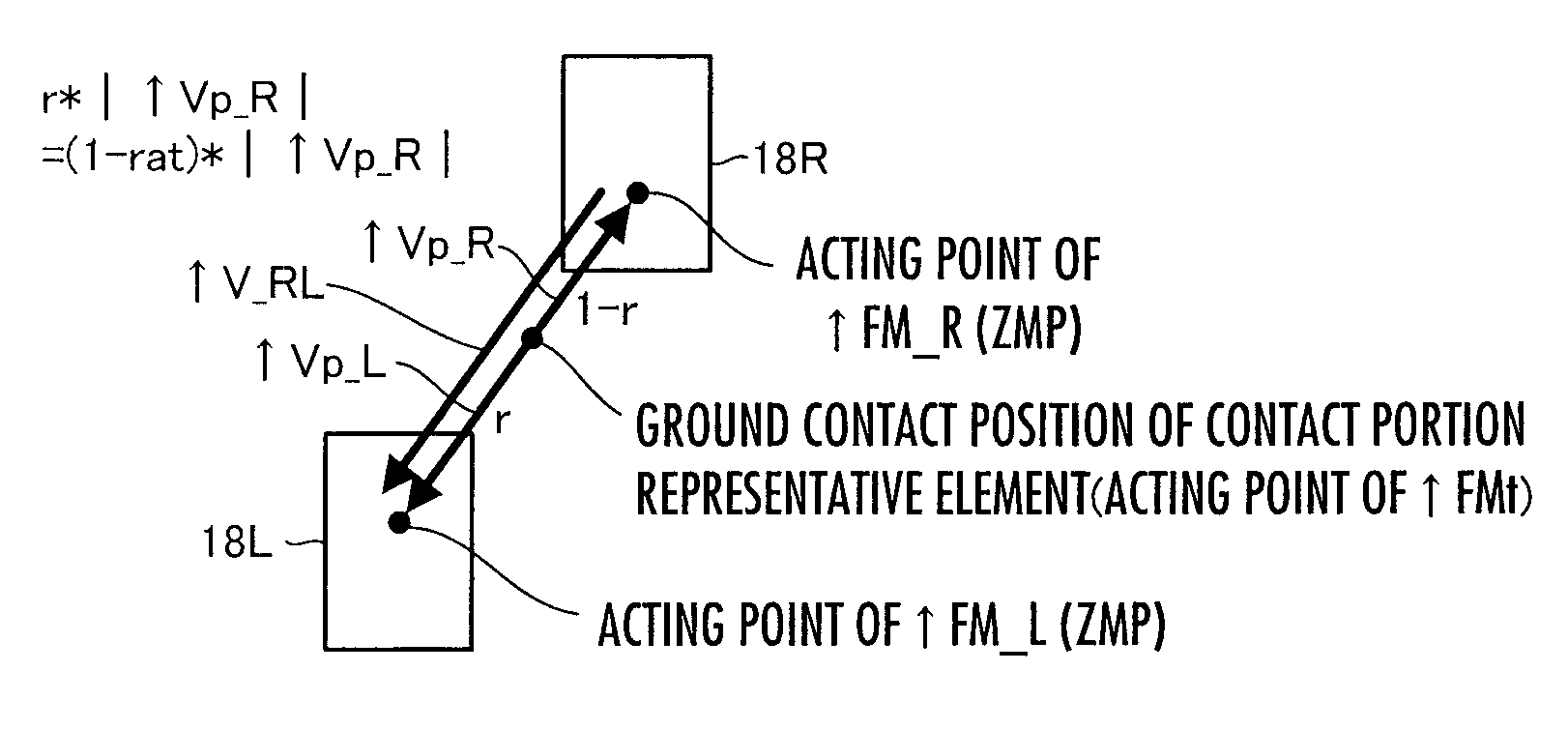
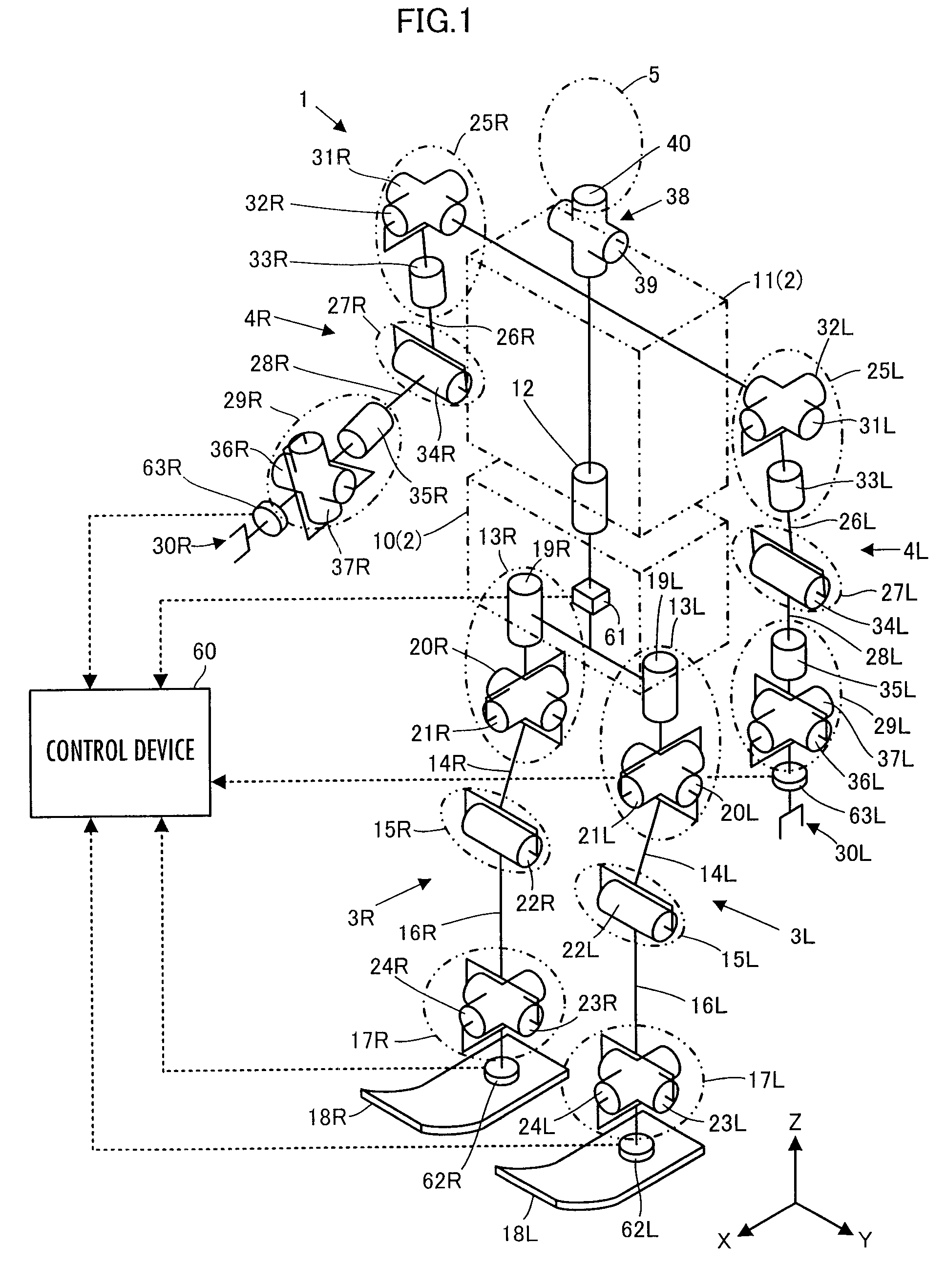
ActiveUS20110160907A1Increase flexibilityProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringRepresentative element
A control device for a robot determines, as a desired driving force to be imparted to a joint, a component value corresponding to the displacement amount of each joint out of a desired generalized force vector τcmd that satisfies the relationship indicated by expression 01 given below by using basic parameter group of M, N, and Jacobian matrixes Jc and Js, a desired value ↑C of the motion acceleration of a contact portion representative element representing a motion of a contact portion of a robot 1, generalized variable observation information, and a desired value ↑S′ of a first-order differential value of a predetermine type of state amount, and then controls the operation of an actuator of the robot 1 on the basis of the determined desired driving force.S′+(Js*M−1*Tc−Js′)*q′=(Js*M−1*Pc)*(τcmd−τcmpn) Expression 01
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
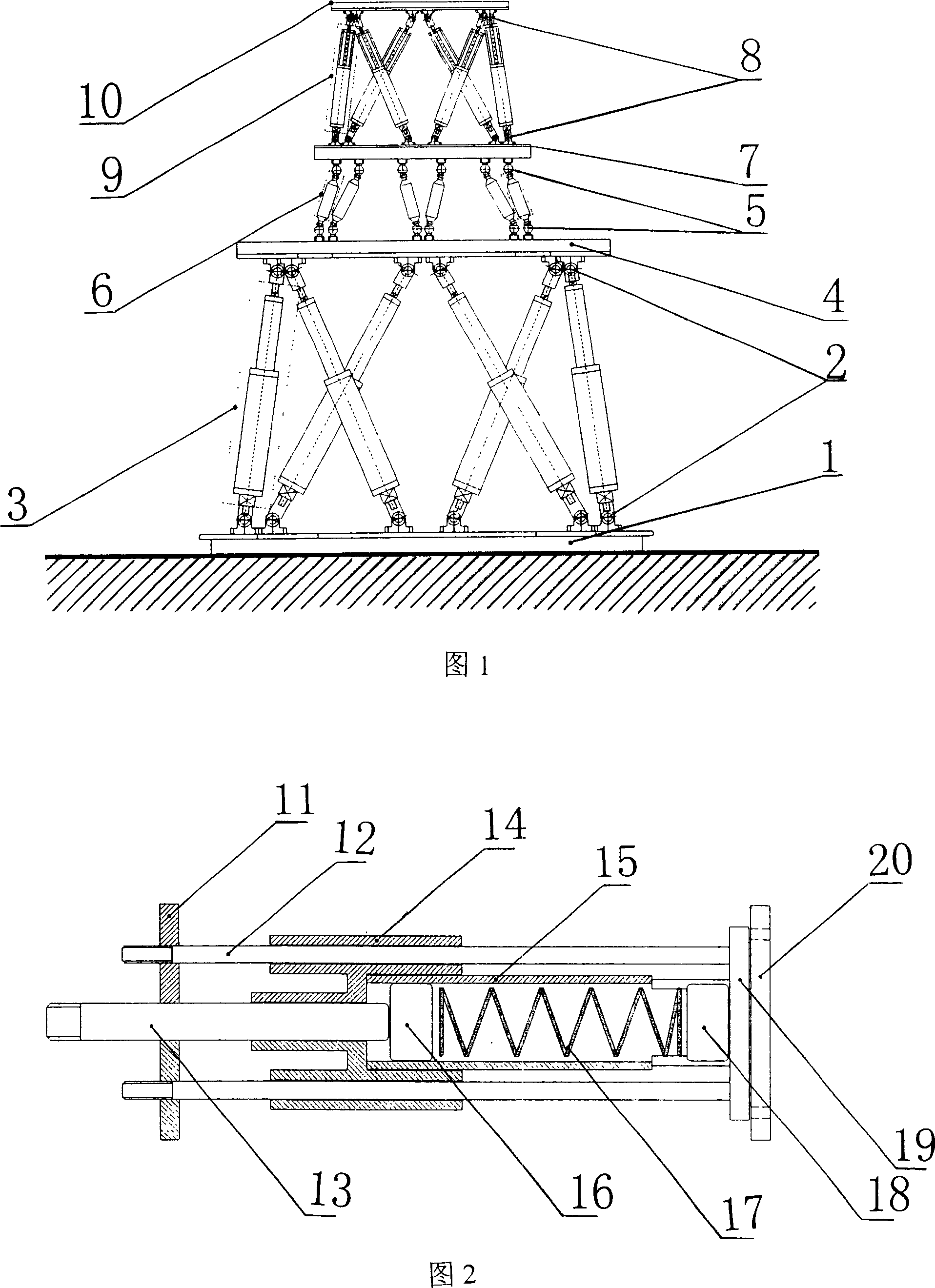
Master-slave mode two-in-parallel twelve degree of freedom generalized force adjustment loading mechanism
InactiveCN101016971AImprove linearityRealize compound vibration dampingUsing mechanical meansStands/trestlesAviationEngineering
The invention discloses a parallel twelve-freedom loading device, used in spatial loading test and fatigue test on aviation material, comprising a Stewart active parallel six-freedom loading device, a SPS six-dimension force / torque sensor and a SPS inactive parallel six-freedom adjuster, wherein the Stewart active parallel six-freedom loading device simulates the spatial motion, the active and inactive platforms of inactive parallel six-freedom adjuster follows to operate and draw or compress the bidirectional isomorphism spring device, to test wide force dynamical load, to supply high accuracy and better reliability to the six-freedom wide force dynamic synchronous loading system, to be used in spatial-ground semi-physical simulation test or the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Control device for robot
ActiveUS8532824B2Increase flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlRepresentative elementEngineering
A control device for a robot determines, as a desired driving force to be imparted to a joint, a component value corresponding to the displacement amount of each joint out of a desired generalized force vector τcmd that satisfies the relationship indicated by expression 01 given below by using basic parameter group of M, N, and G, Jacobian matrixes Jc and Js, a desired value ↑C of the motion acceleration of a contact portion representative element representing a motion of a contact portion of a robot 1, generalized variable observation information, and a desired value ↑S′ of a first-order differential value of a predetermine type of state amount, and then controls the operation of an actuator of the robot 1 on the basis of the determined desired driving force.S′+(Js*M−1*Tc−Js′)*q′=(Js*M−1*Pc)*(τcmd−τcmpn) Expression 01
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
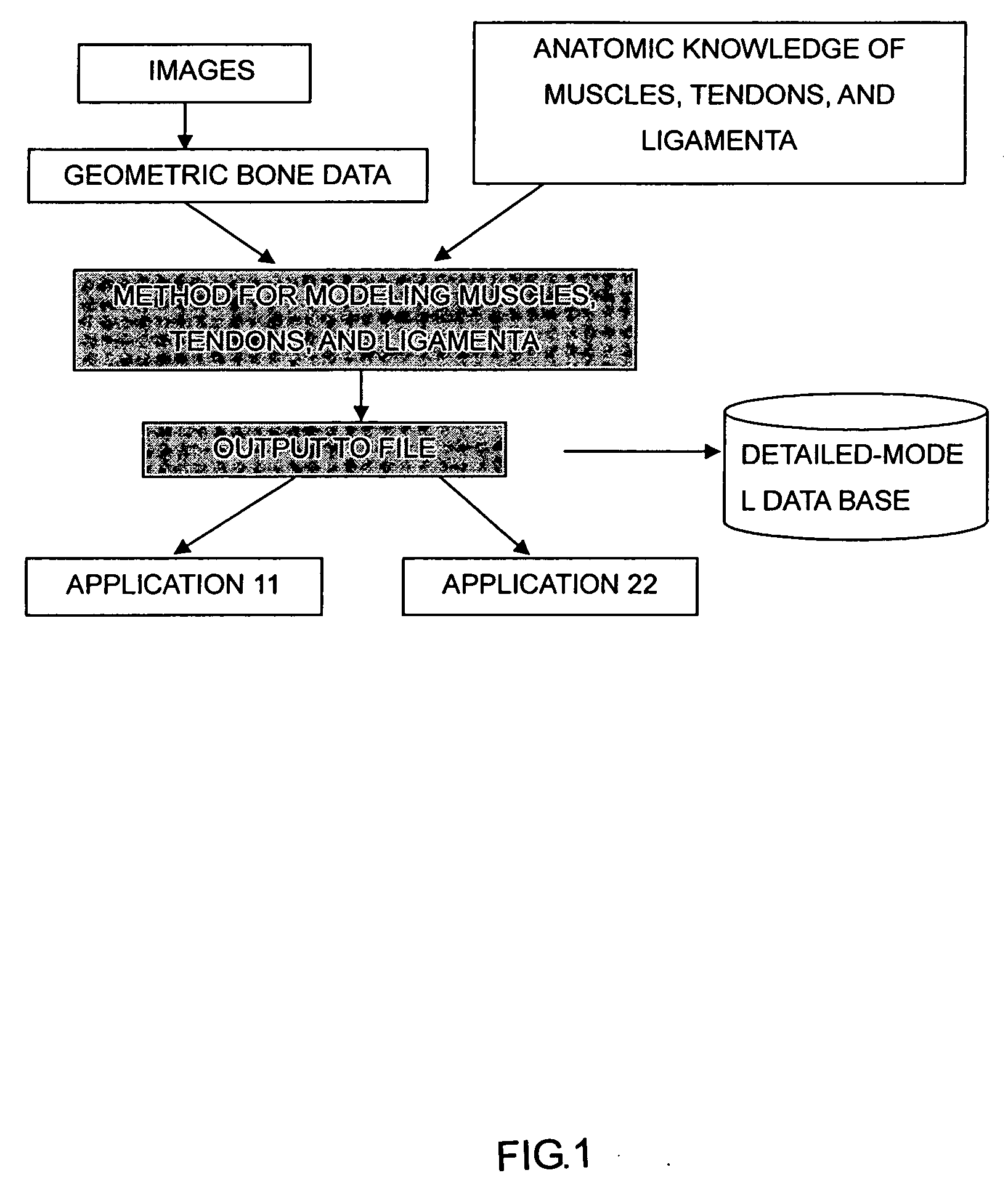
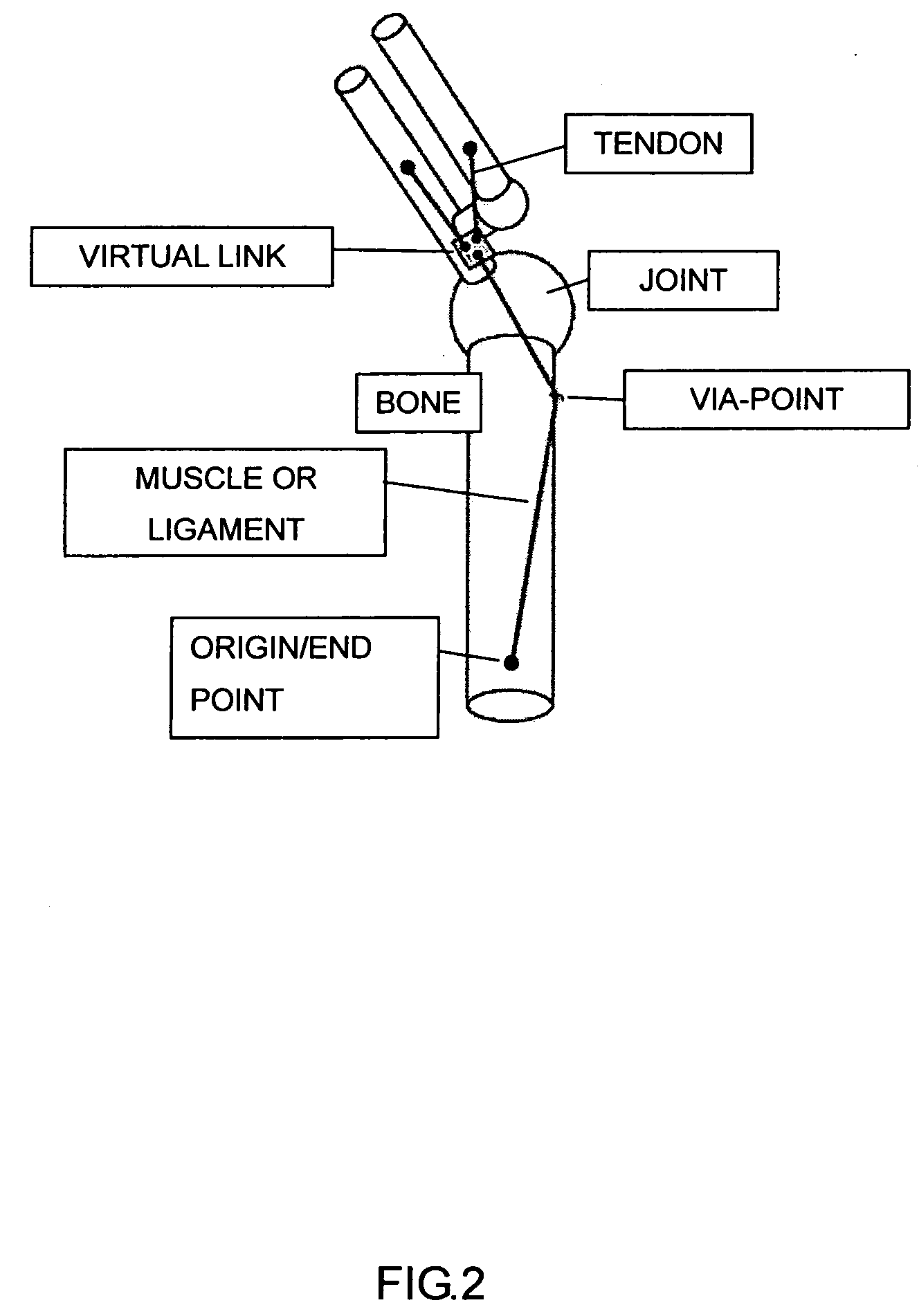
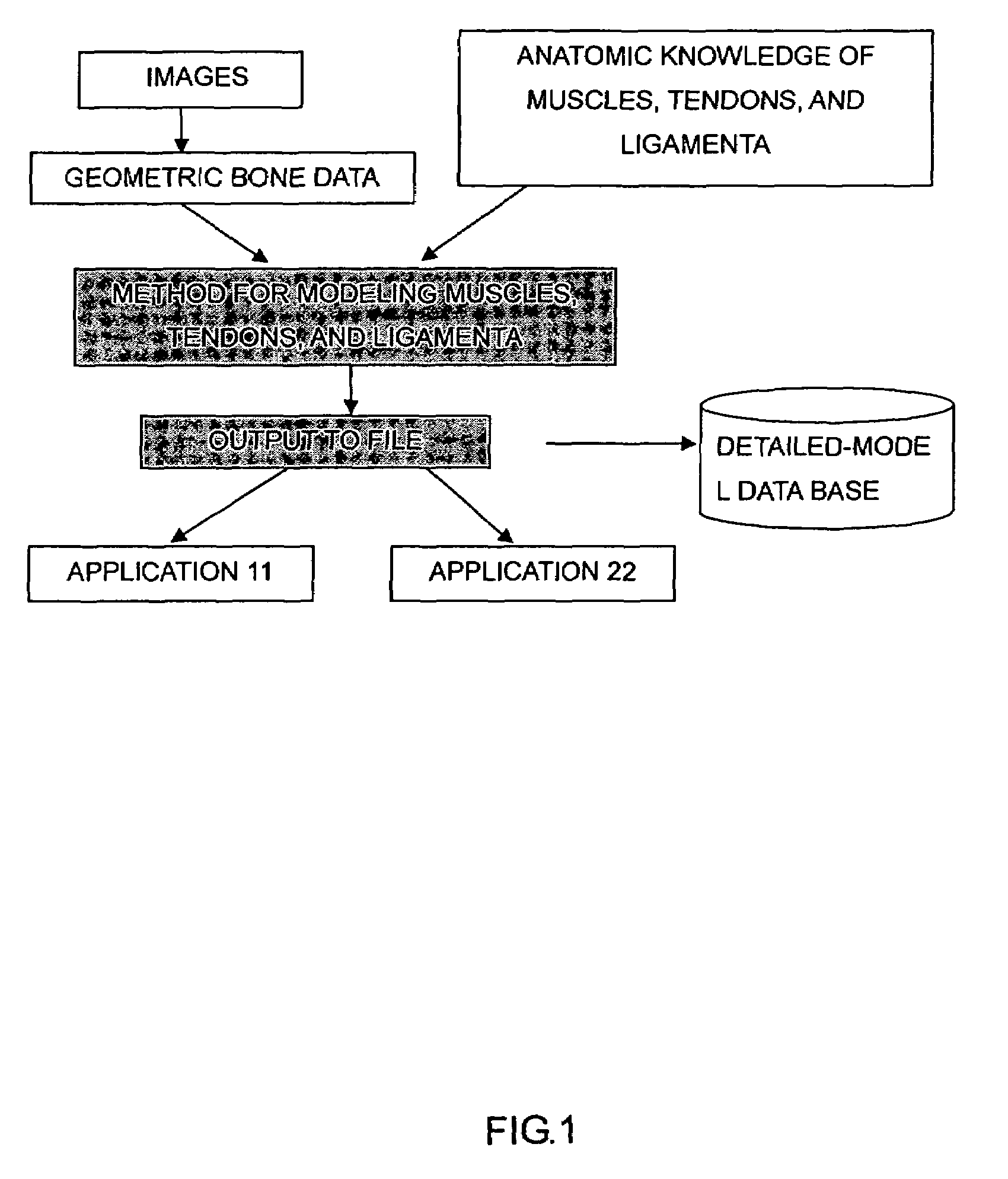
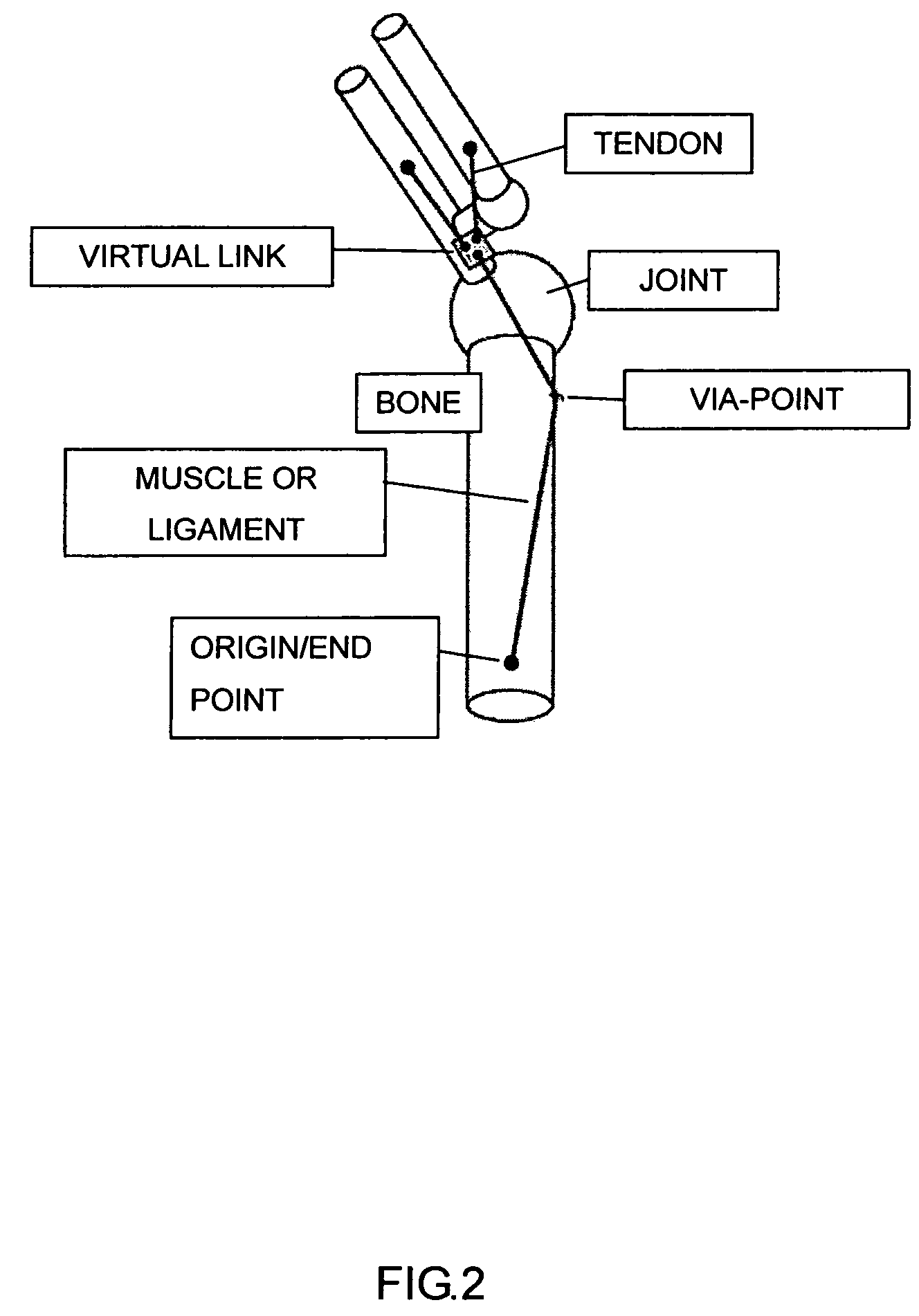
Body mechnics calculating method, body mechanics model, its model data, and body model producing method
InactiveUS20060100818A1Promote generationForce measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyBody mechanics
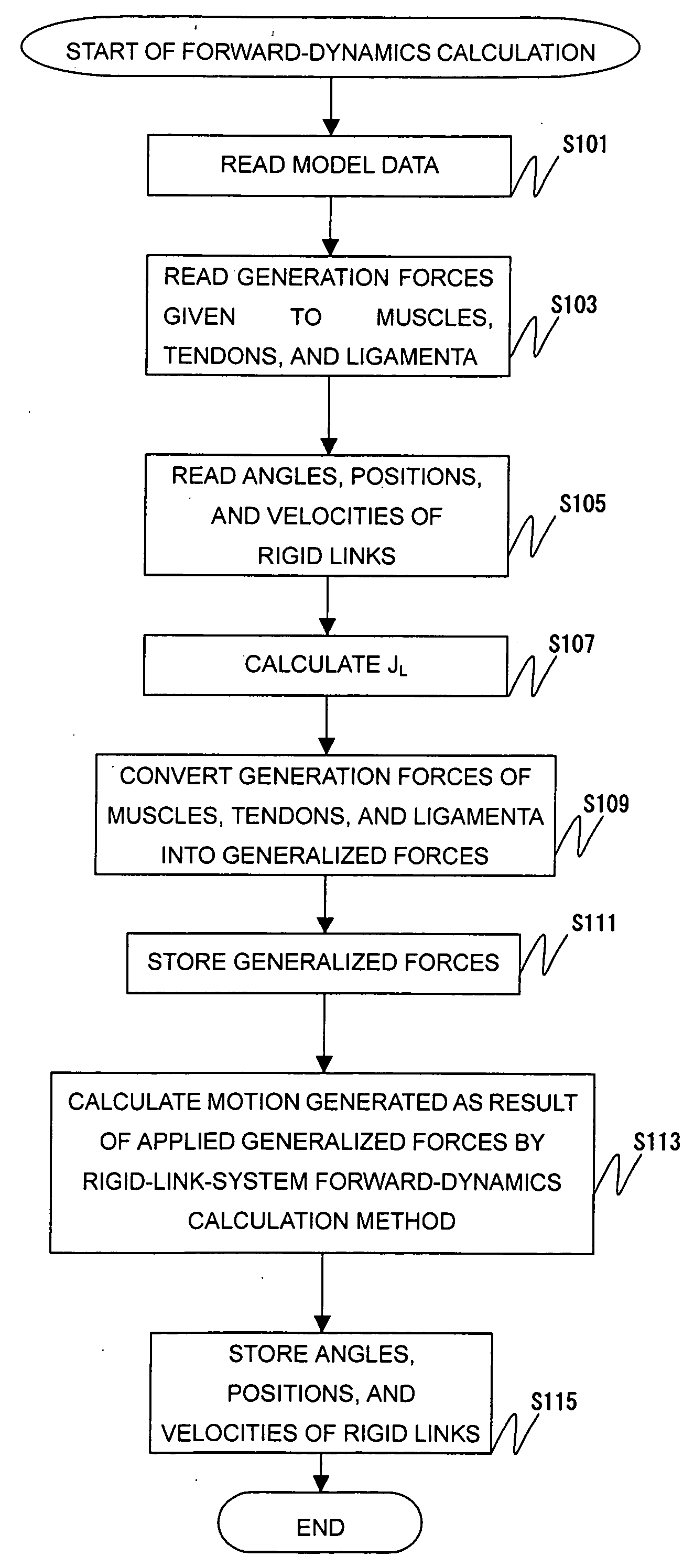
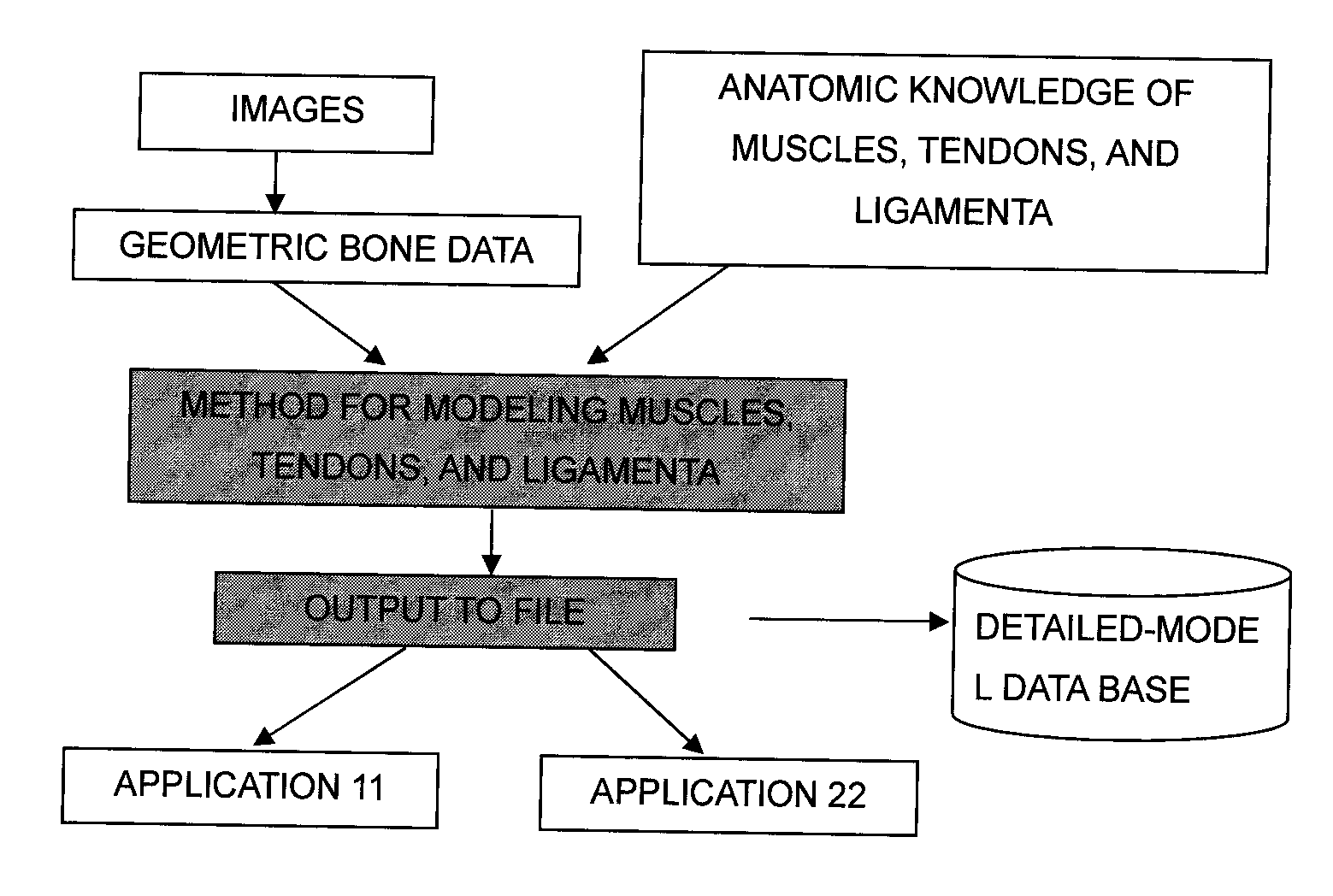
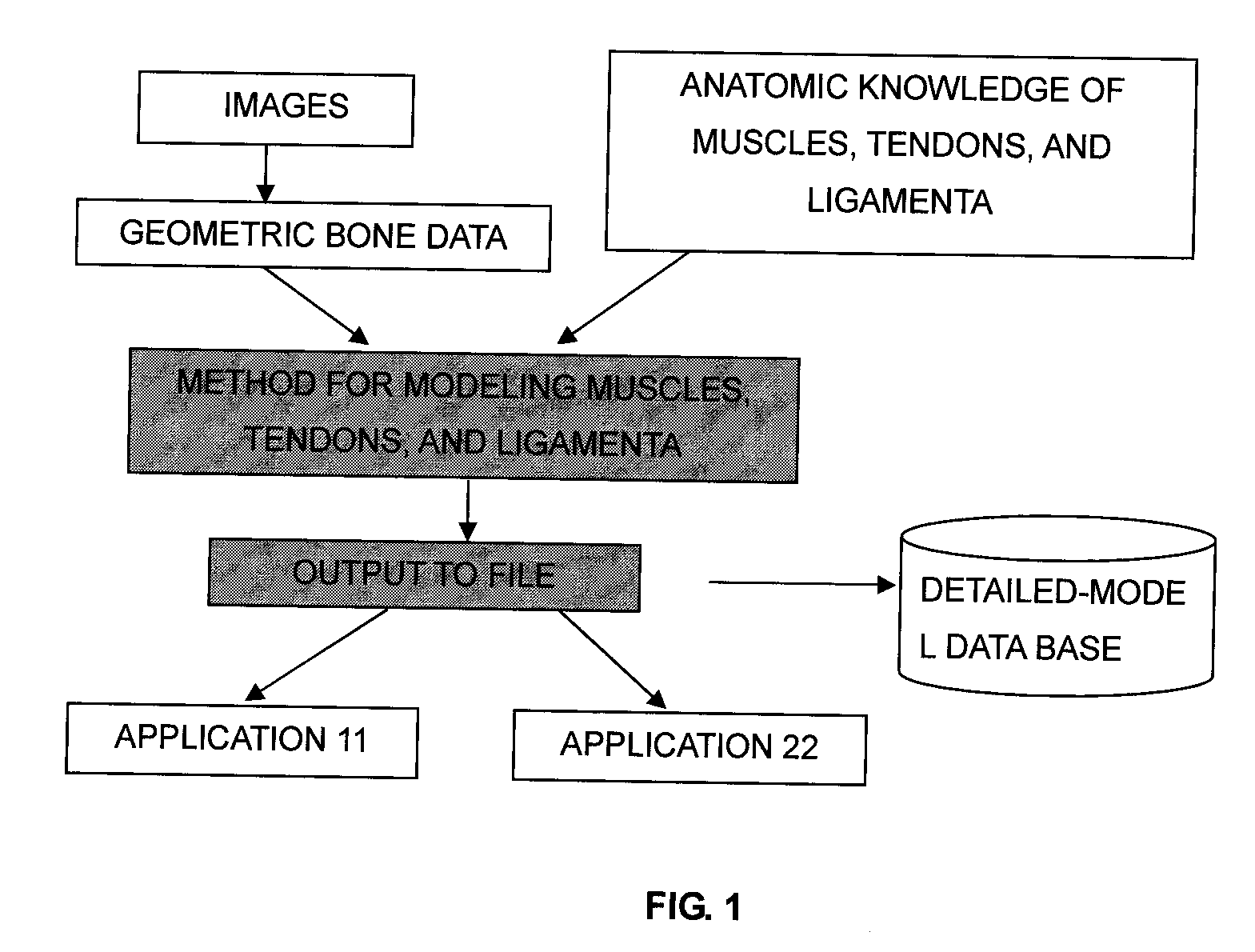
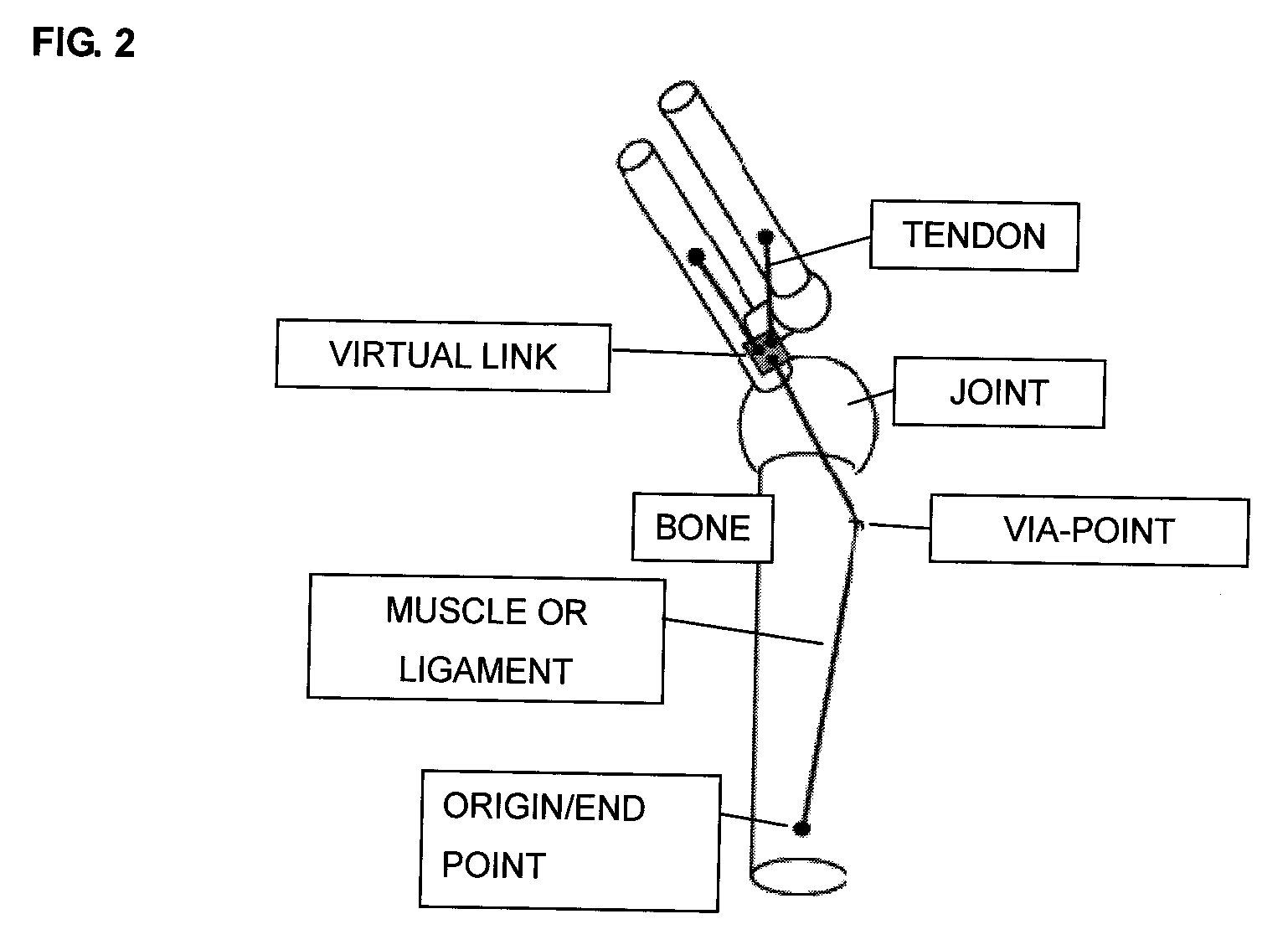
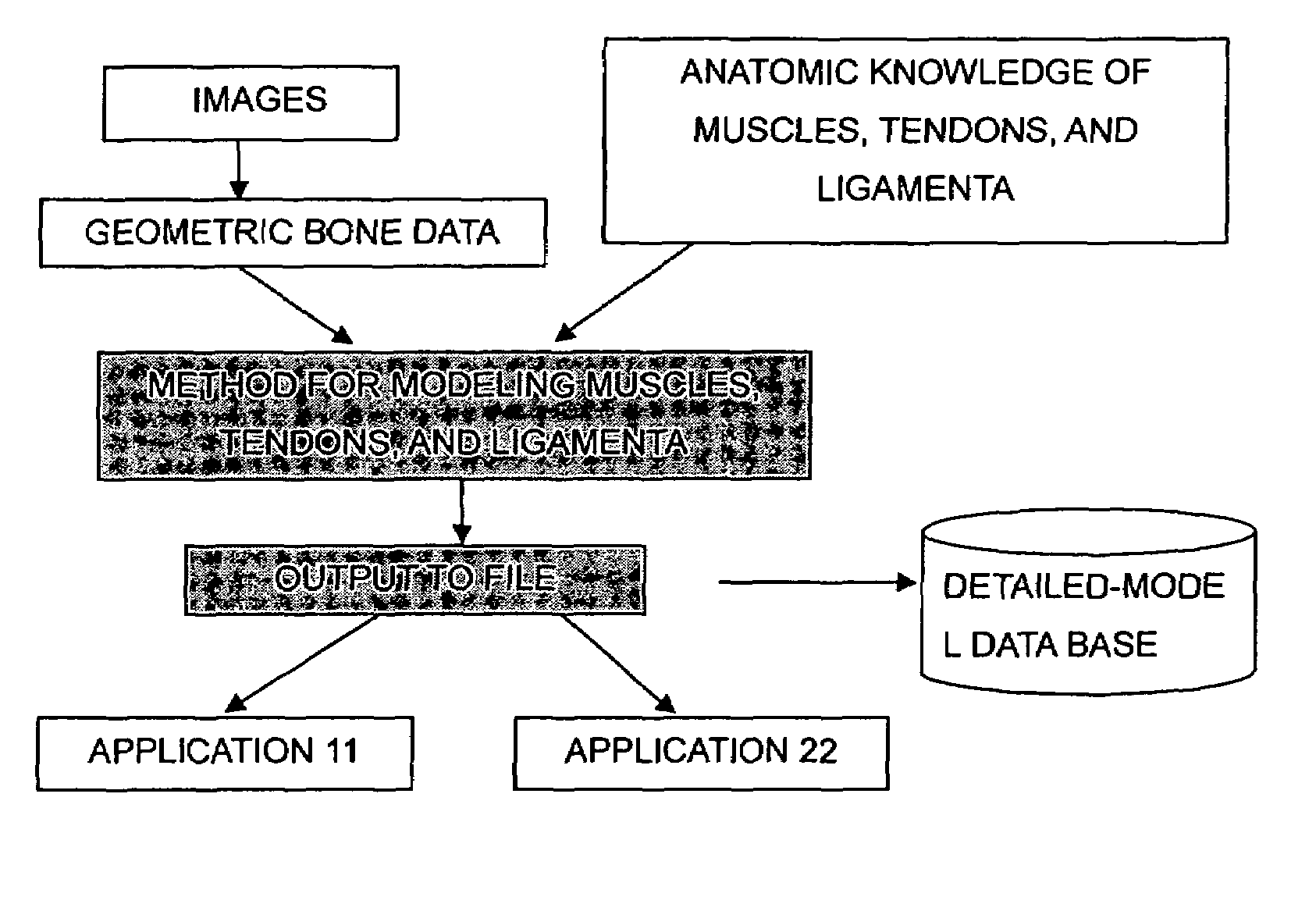
A forward / reverse mechanics calculation of an accurate model of a human body having bone geometrical data and muscle / cord / band data is carried out at high speed. When a new skeleton geometrical model is given, a mapping between the new skeleton geometrical model and a pre-defined normal body model representing a normal body is defined to automatically produce a new body model. A processing unit reads model data to be subjected to mechanics calculation, reads a produced force f of a wire / virtual link exerted on the body model, reads the angle, position and velocity of the current rigid body link, calculates the Jacobian JL of the length of each wire concerning the joint angle, converts the read produced force f of the muscle / cord / band into a generalized force τG according to the defined Jacobian JL, stores the generalized force, determines the acceleration of the whole body of a motion produced when the generalized force τG is exerted on the body and calculates the velocity and position of each rigid body link, and stores them.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
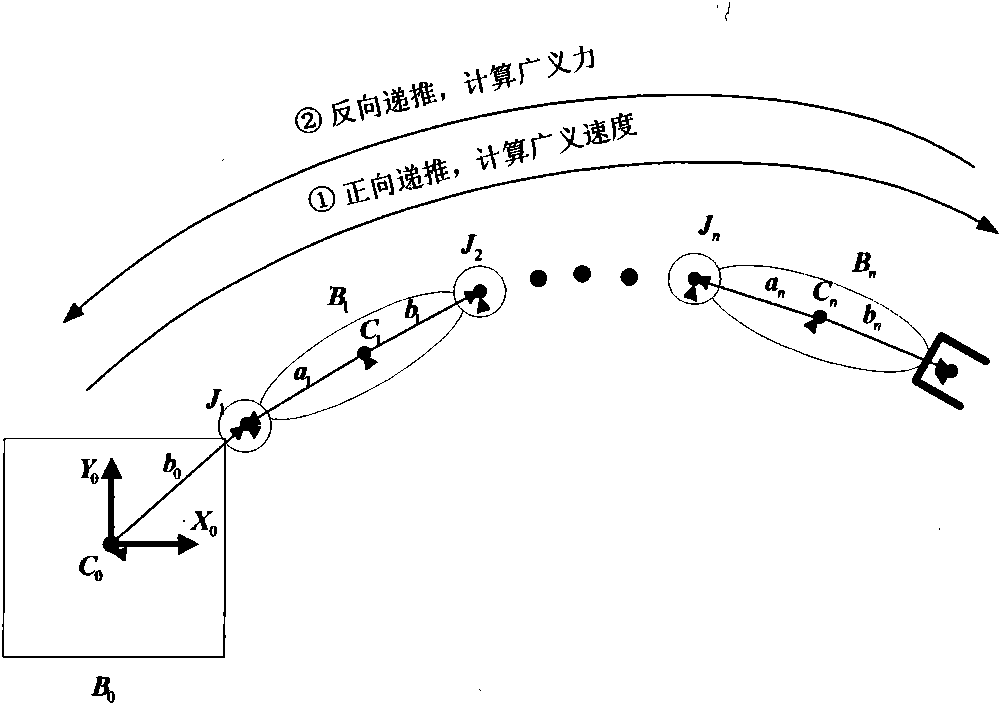
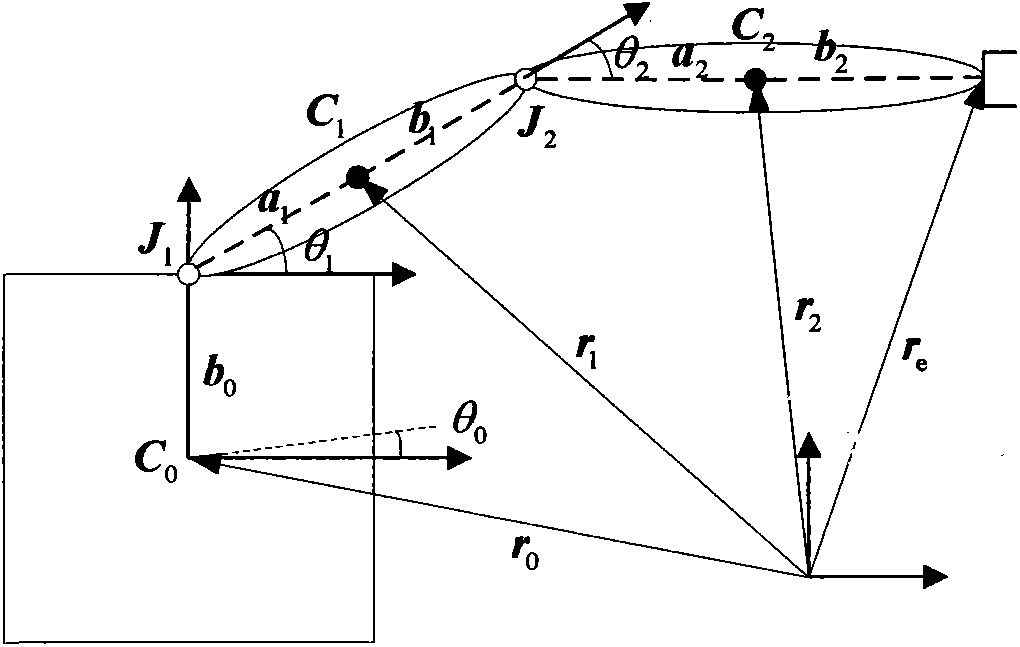
Space manipulator modeling method based on differential geometry
ActiveCN103399986AImprove design accuracyImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringForward recursion
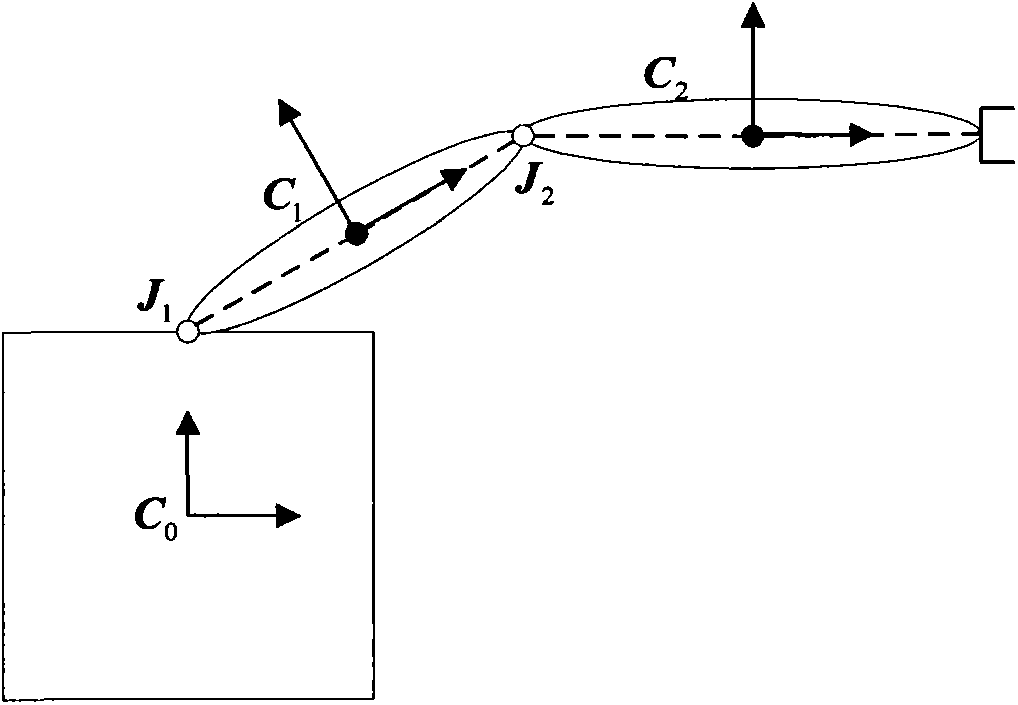
The invention discloses a space manipulator modeling method based on different geometry. On the foundation that each level rigid body zero position of a space manipulator system is selected, initializing conditions such as a zero position joint vector, a centroid joint vector and an initial vector are calculated and given, and a matrix related to initial parameters and a coordinate position matrix are calculated. The generalized velocity of each connecting rod is calculated through forward recursion, and the generalized force of each connecting rod is calculated through reverse recursion. Each quantity is substituted into the matrixes, and a kinetic equation compact in form is written down. The model has the advantages of being uniform in modeling form and small in operating amount, improving calculation efficiency and accuracy of the space manipulator modeling, and improving the designing accuracy of the space manipulator. The space manipulator modeling method based on differential geometry can be applied to modeling of other space multi-rigid-body systems.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Borehole wall sloughing analysis method
InactiveCN102182453AImprove stabilityPlay a protective effectBorehole/well accessoriesAnalysis methodGeneralized forces
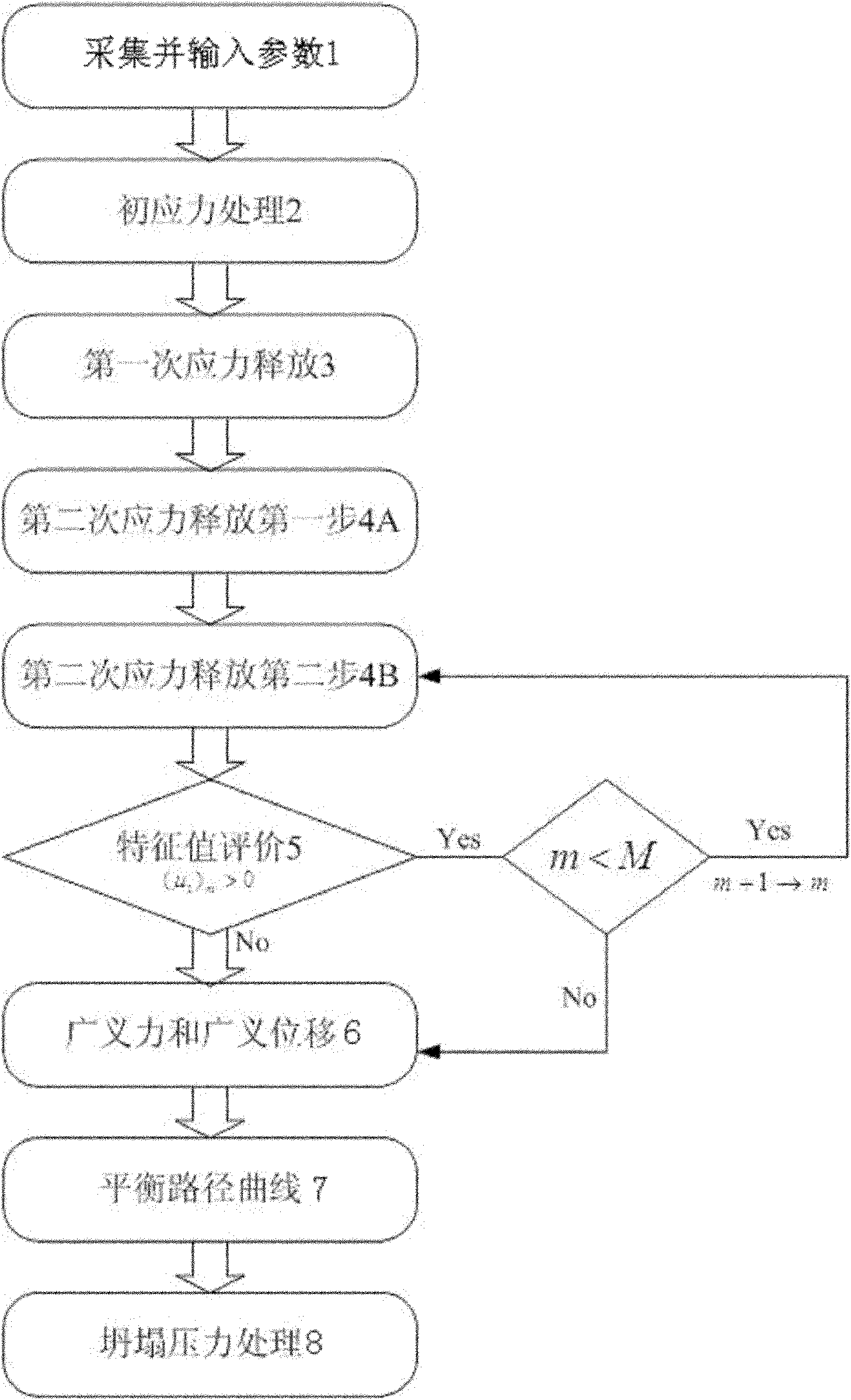
The invention relates to a borehole wall sloughing analysis method which comprises the steps of parameter collection and input (1), initial stress processing (2), first time of stress release (3), first step of second time of stress release (4A), second step of second time of stress release (4B), characteristic value evaluation (5), generalized force and generalized displacement (6), path curve balancing (7), and collapse pressure processing (8). Evaluation is conducted according to a minimum obtained characteristic value (Mu1) m, and when the minimum obtained characteristic value (Mu1) m is more than 0, if m is less than M, m plus 1 arrows m, thus entering the second step of the second time of the stress release (4B); otherwise, a total field is obtained; when the minimum characteristic value (Mu1) m is less than 0, a disturbance field is calculated according to an interpolation method; and the collapse pressure qcr and a plastic area distribution area corresponding to the qcr are calculated, so as to determine the density of collapse prevention drilling fluid. The borehole wall sloughing analysis method has the effect of being capable of analyzing the borehole wall stability of a strain softening plastic stratum under the condition of non-uniform ground stress; and the density of the collapse prevention drilling fluid is designed, thus playing the role of protecting a reservoir stratum during on-site drilling.
Owner:CNPC DRILLING RES INST +1
Lagrange dynamic model of space tether system and controller
ActiveCN107145071ASolve the target pose modeling problemEasy to controlAdaptive controlSpace tetherTarget capture
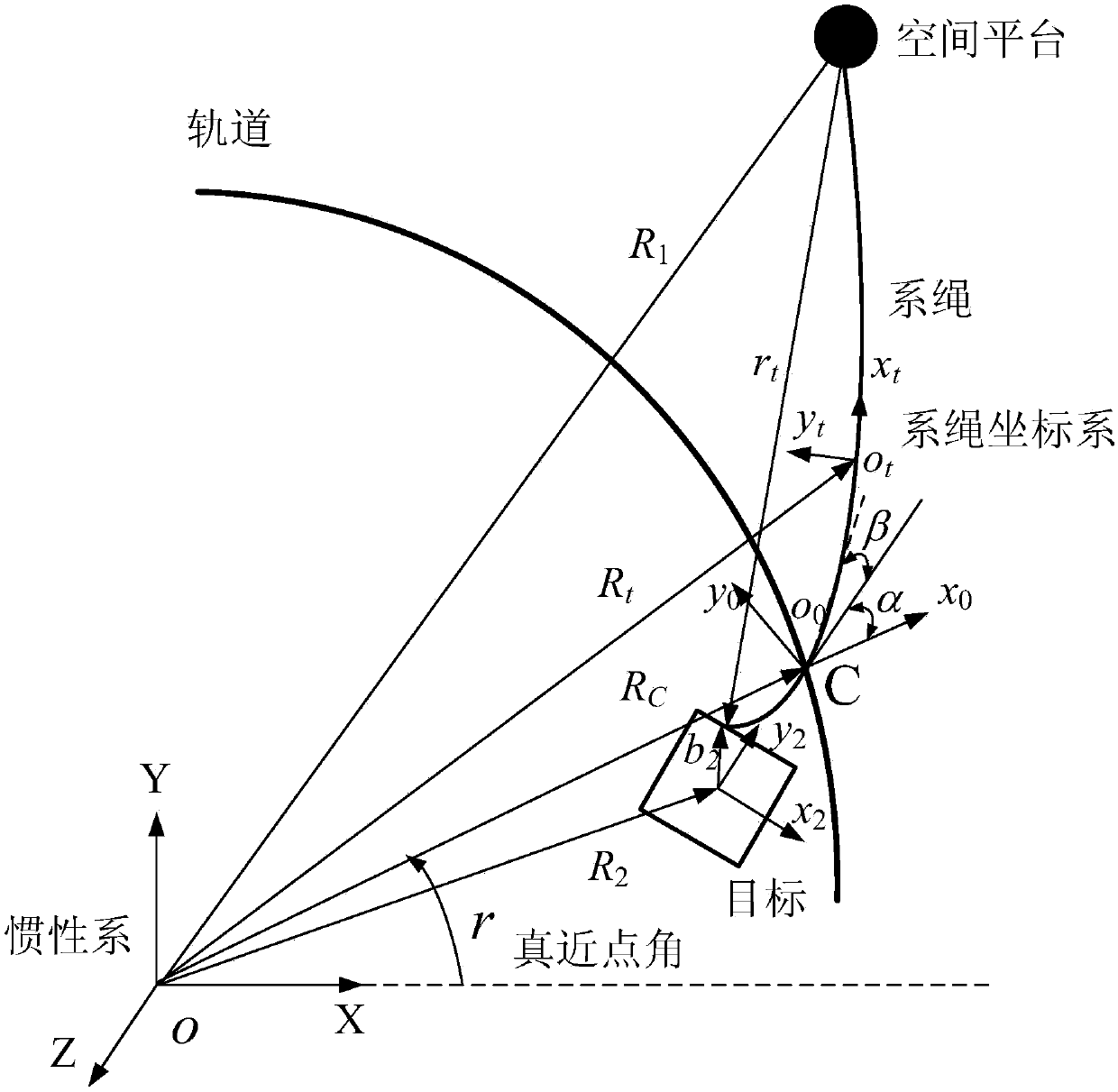
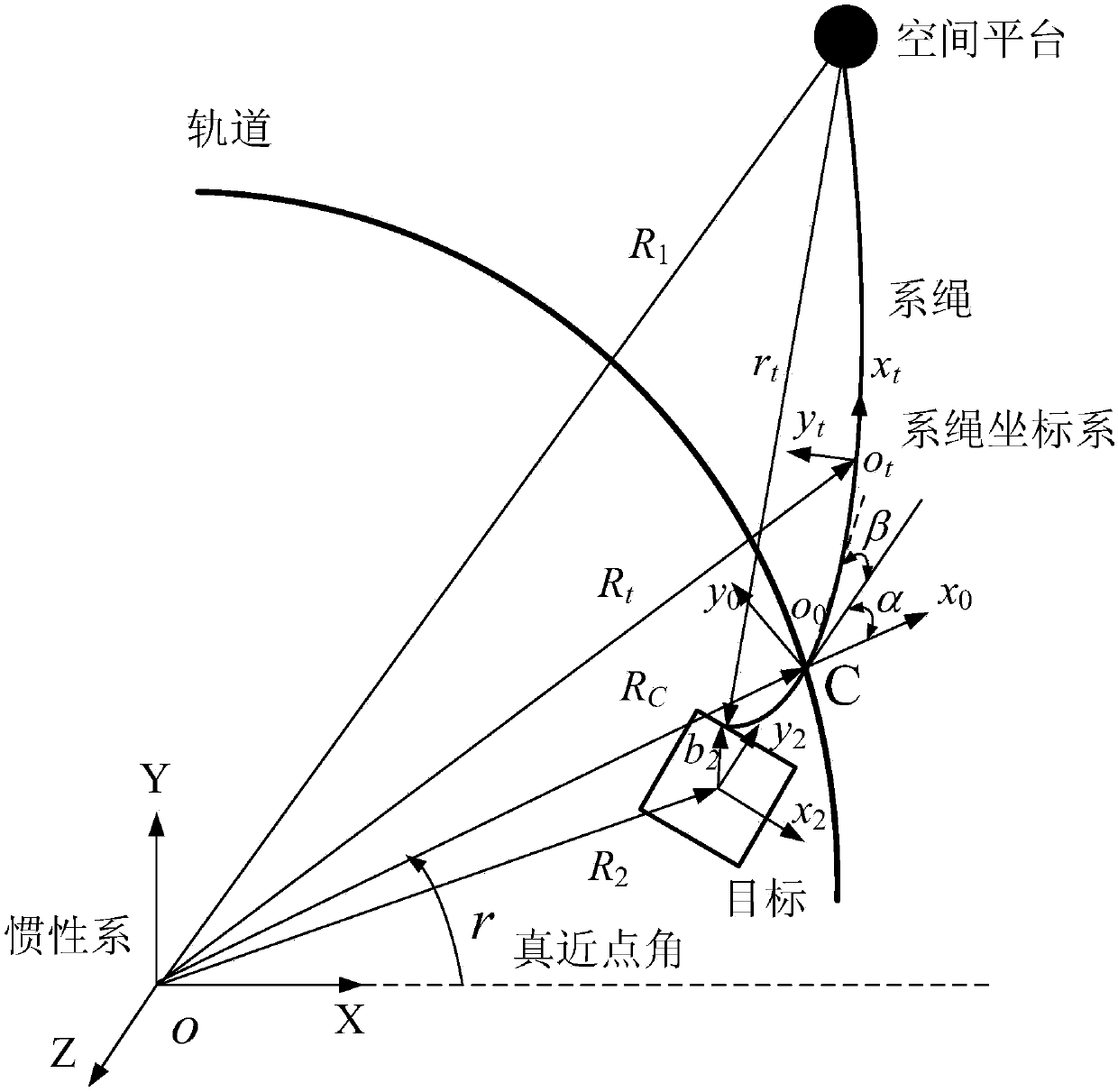
The present invention relates to a Lagrange dynamic model of a space tether system and a controller. Aiming at the modeling problem of the space tether system, six parameters consisting of three attitude angles, a tether surface internal angle, a tether surface external angle, the tether length and the like are considered, the Lagrangian method is employed to detailedly deduce the generalized force model of the tether, and a generalized state stability controller is designed. The Lagrange dynamic model of space tether system and the controller can solve the tether system target attitude modeling problem when a platform is equivalent to the target quality; and the designed controller can realize the control of the tether system generalization state variables after target capture.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Generalized force application magnet and conductor rail magnetic suspension vehicle or train using the same
InactiveCN101083447ASave on construction costsLow costField or armature current controlPropulsion systemsBogieVehicle frame
The invention relates to a generalized force magnet, which forms the magnetic flux change of using the rise and drop change of the voltage or the current pulse in the coil, thus has the induced electromotive force, the induced current and the reverse induction field in the conductor. Through regulating the time ratio, pulse waveform and so on of impulse in the electric current rise and drop to realize the repelling force, the attraction or the vibration power which is exerted on all conductors, and enables this magnet to maintain separates or mutual attraction relatively static or back and forth vibrates with each kind of conductor. One kind magnetic suspension vehicles or the train which used the above magnet, provides the separation aerosol magnet, the guidance magnet, the actuation magnet, the brake / back-draft magnet in the bogie or the frame of the locomotive and lower part vehicles (and essential degaussing magnet); the kind of vehicles no need to rebuild the existing railroad to realize high speed or / heavy load travel on the conductor track specially on the existing railroad.
Owner:田景华
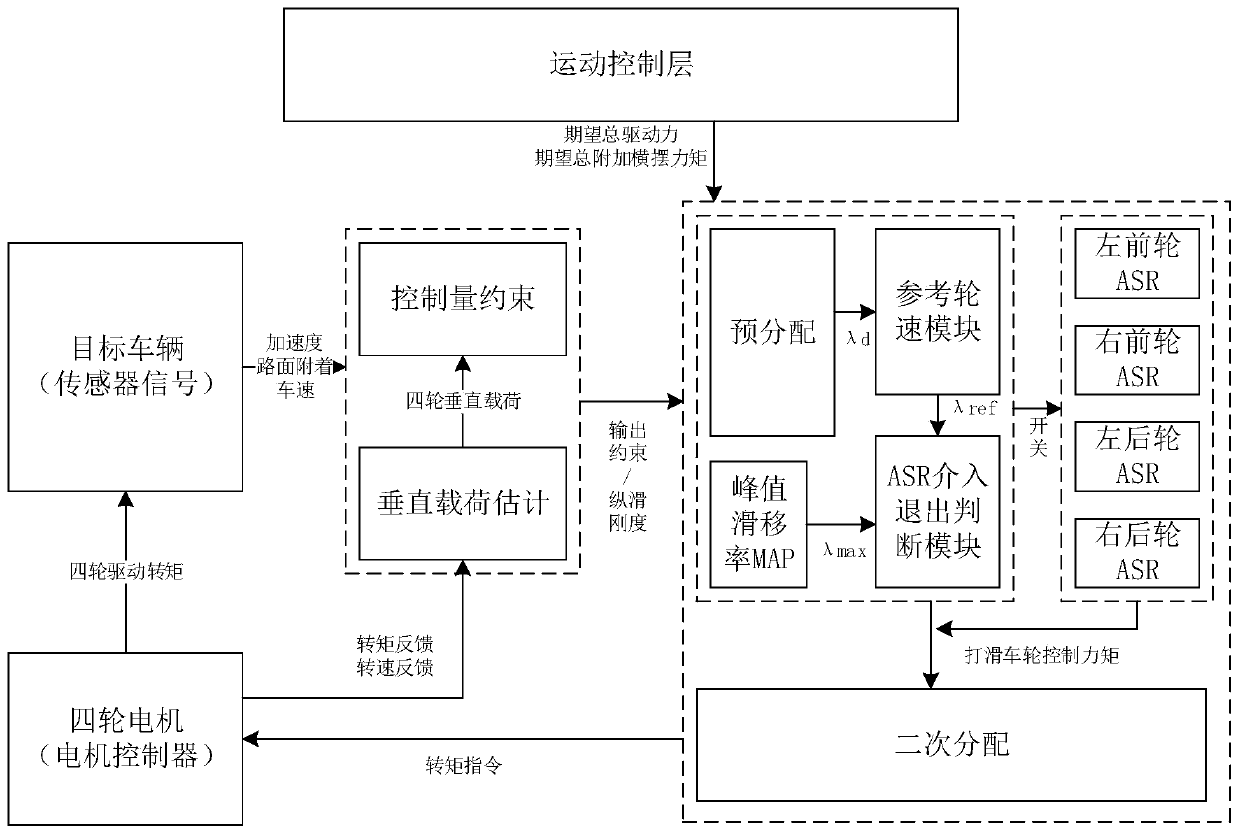
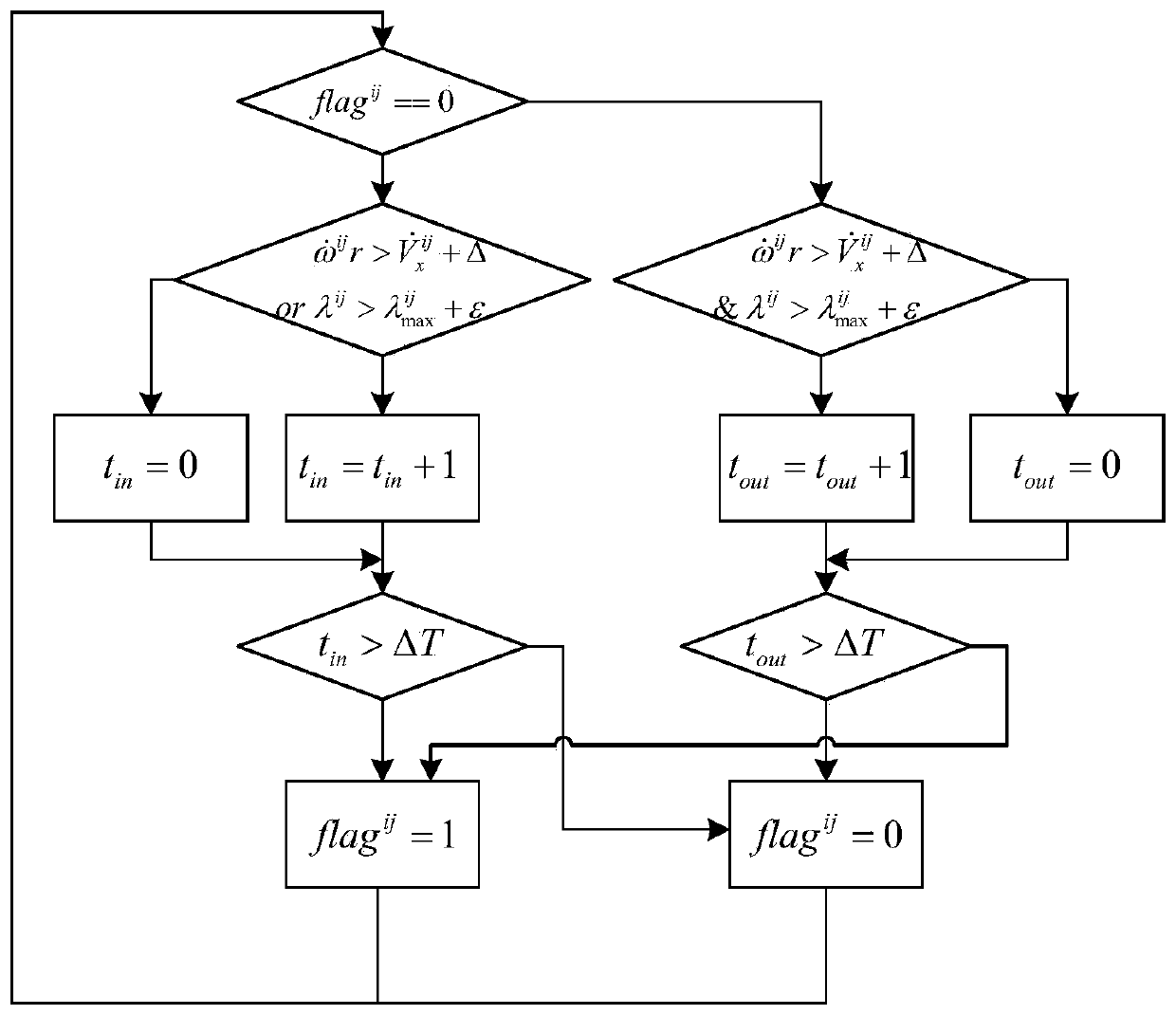
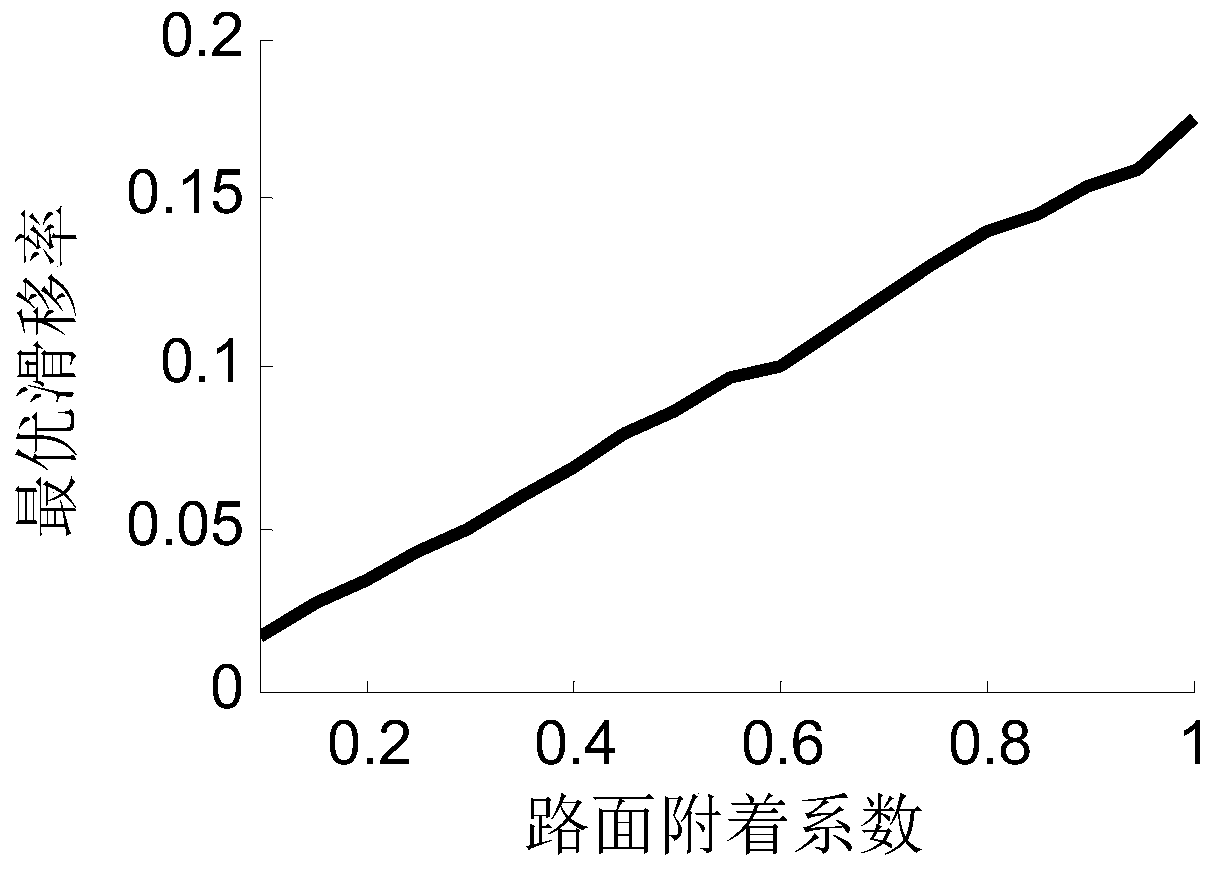
Torque distribution control system for considering coordination of maneuverability and wheel stability, and method
ActiveCN110103963AHigh control precisionEffective anti-slipSpeed controllerElectric energy managementDistribution controlRoad surface
The invention relates to a torque distribution control system for considering coordination of maneuverability and wheel stability, and a method. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the range constraint of wheel output torque is obtained; (2) generalized force demands for a motion control layer are pre-distributed; (3) the peak slip rate corresponding to a road surface adhesion coefficient and the reference wheel speed of each wheel are obtained, and the working mode of each wheel is determined; (4) an anti-saturation integral slip-mode variable-structure controller is built, anda difference value between the actual wheel speed and the reference wheel speed serves as input to obtain control torque; (5) the non-slip wheels serve as a control variable of secondary distribution,the weighted sum of the minimum generalized force tracking error and the minimum adhesion utilization rate serves as a target function, and optimization solution is conducted; and (6) finally, a torque instruction of a driving anti-slip control unit and a torque instruction of a four-wheel torque distribution control unit are combined to be output to a motor controller. Compared with the prior art, the torque distribution control system for considering coordination of maneuverability and wheel stability, and the method have the advantages of secondary distribution, effective slip preventing,comprehensive consideration, precise control and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
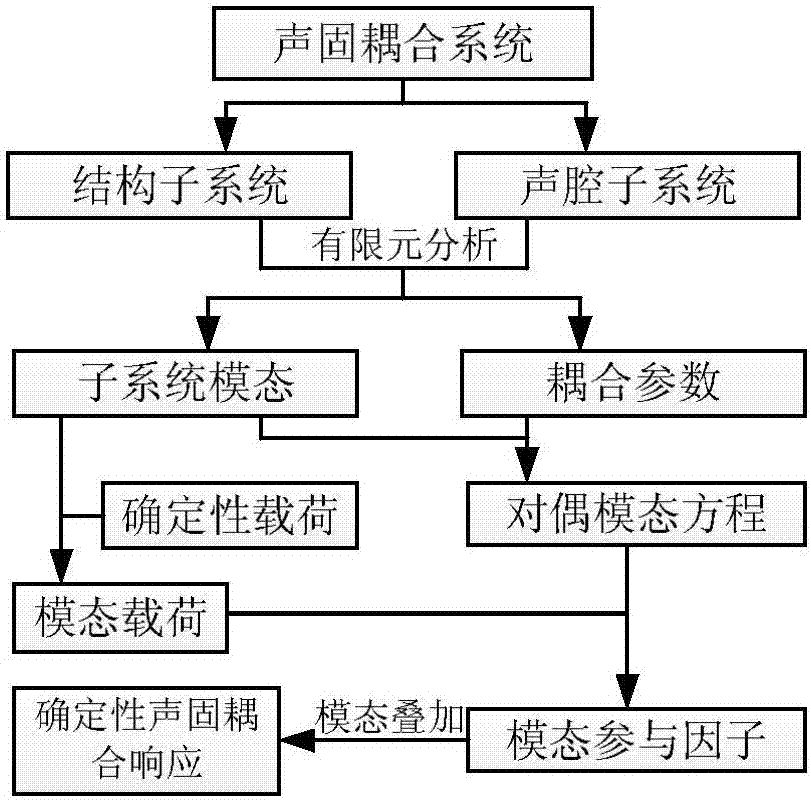
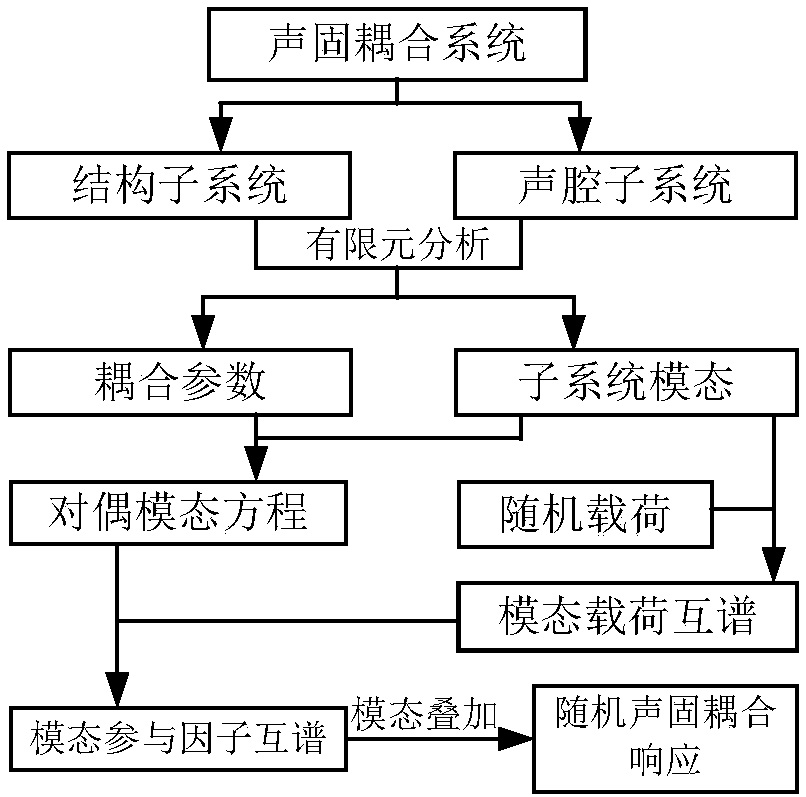
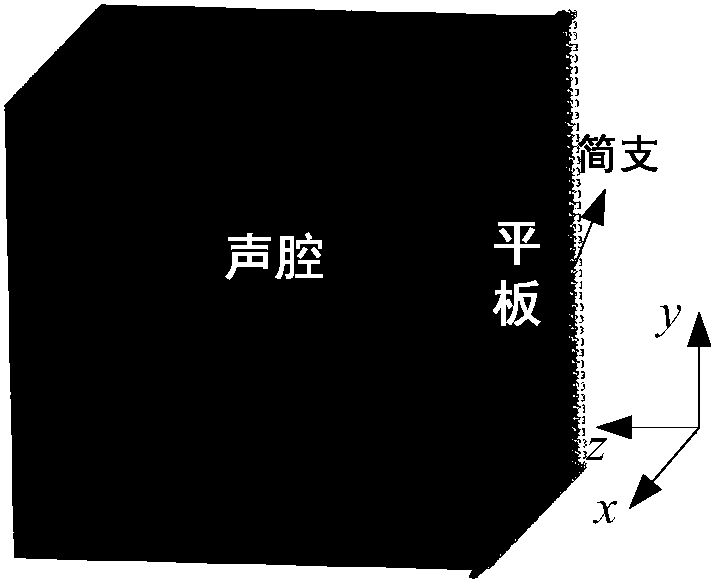
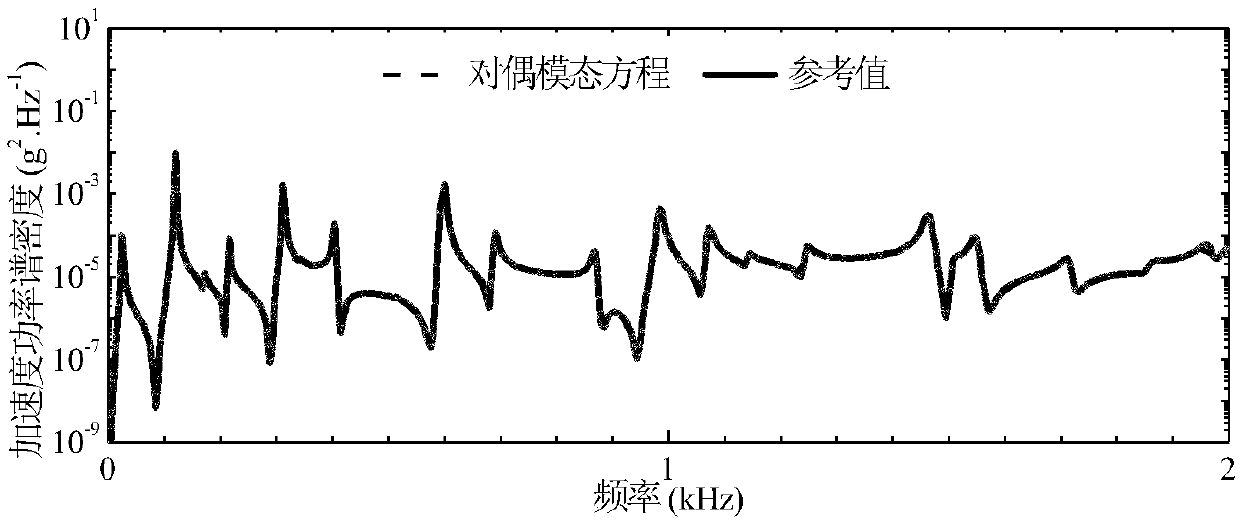
Certainty acoustic-structure coupling response prediction method based on dual-modality equation
ActiveCN107133422AImproving the prediction efficiency of acoustic-solid coupling responseShorten the design cycleGeometric CADSustainable transportationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFinite element method
The invention discloses a certainty acoustic-structure coupling response prediction method based on dual-modality equations. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dividing structures and acoustic cavities in an acoustic-structure coupling system into different subsystems; (2) calculating modalities of structure subsystems and acoustic cavity subsystems; (3) calculating coupling parameters of modalities of adjacent subsystems; (4) establishing dual-modality equations of a coupling system; (5) performing preprocessing so as to obtain generalized force loads to subsystem modalities under the action of certainty loads; (6) calculating the dual-modality equations so as to obtain participation factors of all modalities; and (7) through modality overlapping, calculating certainty acoustic-structure coupling response. According to the certainty acoustic-structure coupling response prediction method disclosed by the invention, the system is divided into continuously coupled subsystems, certainty vibration of the system is described through subsystems inside limited frequency bands, and the analysis efficiency of the method is higher than that of conventional finite element methods.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A three-dimensional steel bridge tower vortex-induced vibration calculation method
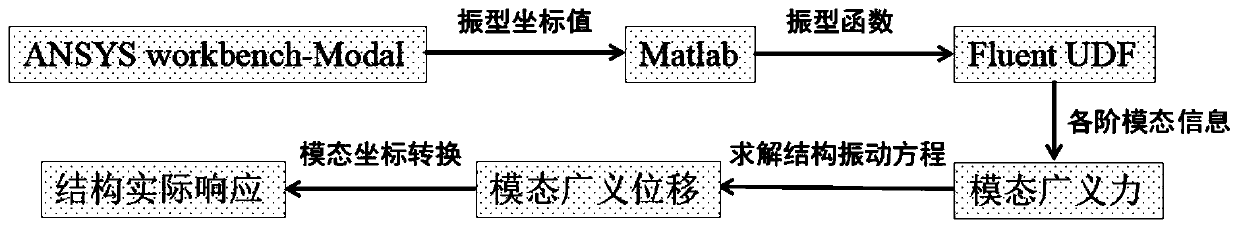
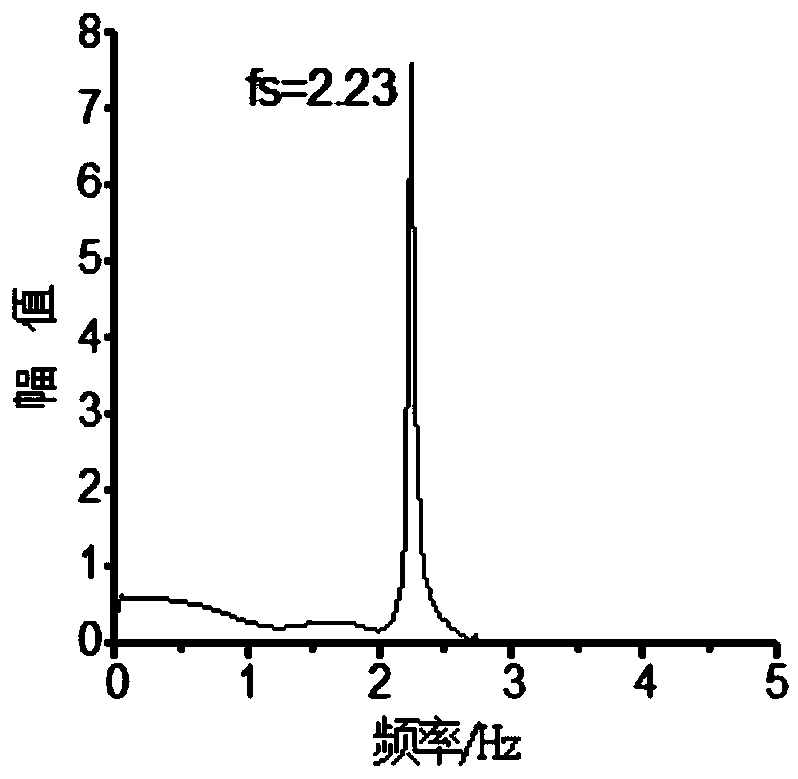
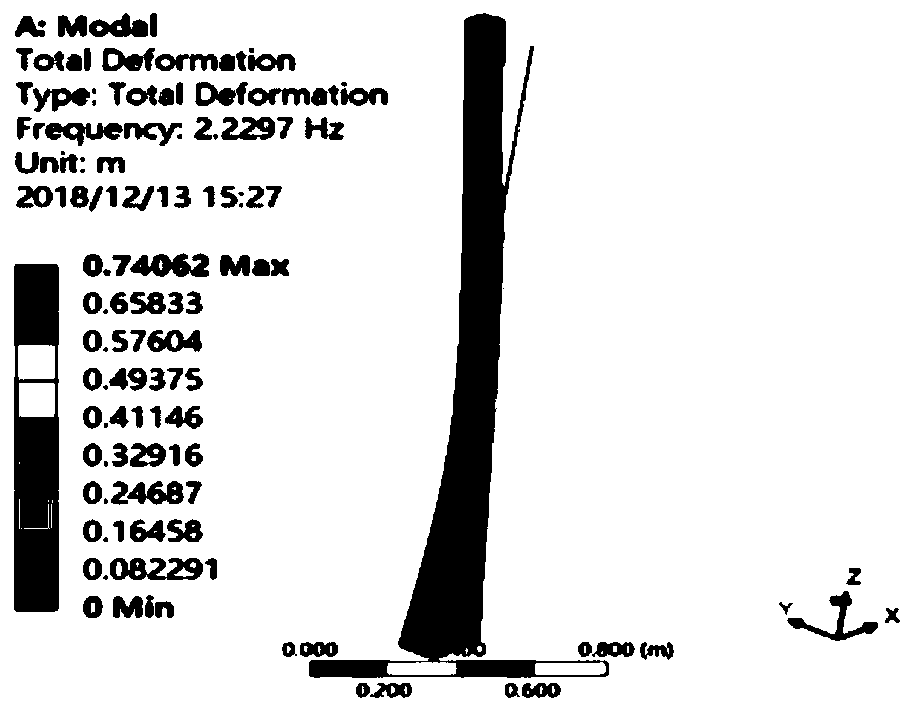
ActiveCN109885864ASolve the problem of distortion and negative volumeSustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic methodEngineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional steel bridge tower vortex-induced vibration calculation method, which achieves the three-dimensional steel bridge tower fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation through the dynamic mesh technology. The method comprises the steps of extracting the bending vibration mode coordinate values in the bridge direction and the transverse bridge direction througha Modal module of ANSYS workbench; performing function fitting by utilizing Matlab software to obtain a corresponding vibration mode function; inputting the vibration mode function into a user-defined program code UDF of the Fluent; analyzing the fluid to obtain a velocity field and a pressure field, obtaining generalized force by the user-defined program code UDF embedded into the Fluent, and substituting the generalized force into a structural vibration equation to solve to obtain generalized displacement; and obtaining an actual response of the structure through modal coordinate conversion, finally utilizing a dynamic mesh macro command to specify mesh movement so as to update the mesh position, and performing calculation of the next time step until convergence. According to the method, a computational fluid dynamics method is applied, and the business software Fluent is subjected to secondary development by compiling the user-defined program code UDF, so that the three-dimensionalsteel bridge tower fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation is achieved, the UDF can achieve parallel computing of the Fluent, and efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
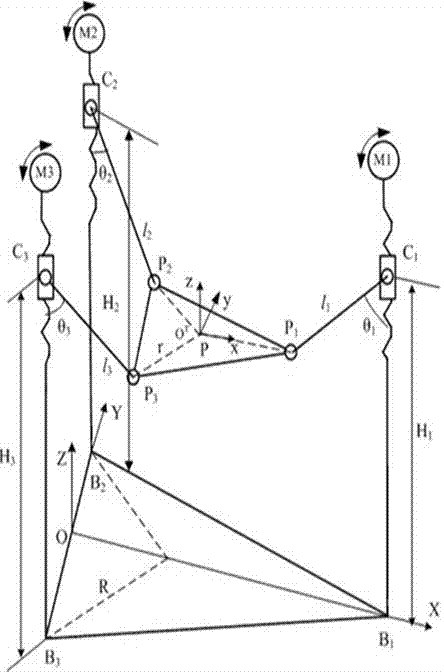
Equivalent mass determination method of 3-PRS series-parallel mechanism
ActiveCN107009350ASimple structureSimple control systemProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringGeneralized forces
The invention discloses an equivalent mass determination method of a 3-PRS series-parallel mechanism. Servo motors are set to work in a torque mode; the known torques of the servo motors are converted to axial forces of ball screws and acting forces of slide blocks on stand columns; system generalized force of the whole 3-PRS series-parallel mechanism is obtained by solving through a geometric method; then, a fixed coordinate system and a local coordinate system are respectively built on a static platform and a movable platform to calculate kinetic energy and potential energy of each system component to build a lagrange equation of the whole mechanism; and such multiple parameters as generalized velocity and acceleration in the equation are calculated through distance measurement grating rulers of the mechanism to obtain equivalent mass of the 3-PRS series-parallel mechanism. The method provides technical guidance for robot structure design and optimization, path planning and control system optimization.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Dual-modal equation-based dynamic response analysis method for random noise environment
ActiveCN107748815AImprove dynamic response prediction efficiencyShorten the design cycleGeometric CADSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementRandom noiseStructural coupling
The invention provides a dual-modal equation-based dynamic response analysis method for a random noise environment. The method comprises the following steps of (1) dividing a structure and a vocal cavity in an acoustic-structural coupling system into different subsystems; (2) calculating modes of the structure subsystem and the vocal cavity subsystem; (3) calculating coupling parameters between the modes in the adjacent subsystems; (4) establishing a dual-modal equation of the coupling system; (5) through preprocessing, obtaining a cross-power spectrum of generalized force loads on the modes of the subsystems under the action of random loads; (6) calculating the dual-modal equation to obtain a cross-power spectrum of participation factors of all the modes; and (7) through modal superposition, calculating a random acoustic-structural coupling response of the system. The random dynamic response analysis method provided by the invention is the dual-modal equation-based dynamic response analysis method for the random noise environment. According to the method, the system is divided into the continuous coupling subsystems, and random vibration of the system is described by using the modes of the subsystem in a limited frequency band; and the analysis efficiency of the method is higher than that of a conventional finite element method.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Stress calculation method for steel-concrete composite beam
InactiveCN110032829AEfficient analysis of stress variation problemsAdapt to boundary conditionsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationHysteresisEngineering
The invention provides a stress calculation method for a steel-concrete composite beam, and relates to the field of bridge construction. The method comprises the following steps: dividing a compositebeam into a plurality of beam section units, each beam section unit comprising at least two nodes; obtaining all generalized forces including an axial force and node forces of the two shear hysteresisunits on each node on the beam section unit, and forming a node force matrix; constructing a node displacement matrix corresponding to the node force matrix; obtaining a balance equation comprising the node force matrix and the node displacement matrix based on the node force matrix and the node displacement matrix; obtaining a node displacement matrix with known node displacement based on the balance equation; and calculating the stress of the beam section unit based on the node displacement matrix. The method solves the problem that a stress calculation method in the prior art cannot effectively analyze the stress change of the main beam of the composite beam cable-stayed bridge caused by the sudden change of the shear hysteresis displacement boundary condition, the continuous change ofthe load and the shear hysteresis displacement boundary condition and other factors in the construction process.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Redundant drive vehicle dynamics control distribution method
The invention discloses a redundant drive vehicle dynamics control distribution method, and aims at solving the problem on the control distribution of constrained redundant drive vehicle dynamics. According to the redundant drive vehicle dynamics control distribution method disclosed by the invention, an expected generalized force / torque of a vehicle is determined based on a sliding mode variable structure control, an optimal distribution relationship between the expected generalized force / torque decided by an upper controller and a wheel slip ratio as well as a sideslip angle is established based on an improved fixed-point square control distribution method, priority levels of control tasks are designed based on driving and operating conditions of a vehicle, and a wheel slip ratio and side slip angle joint tracking controller is designed based on an integral sliding mode control, to coordinate and control a steering / driving / braking system of the automobile and ensure each wheel to move according to an expected slip ratio and slip angle. The invention mainly combines a control distribution method and a redundant drive vehicle dynamics system, a nonlinear coupling constraint to tire side longitudinal side force is taken into consideration, stability domain of a vehicle system is expanded, and system safety and reliability are improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Speed optimization method of 3-PRS parallel mechanism
ActiveCN104772755AHigh speedImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsRobot kinematicsGeneralized forces
Aiming at the technical problem that power source driving force of existing trapezoidal acceleration and S-shaped acceleration methods cannot be fully used, the invention provides a speed optimization method of a 3-PRS parallel mechanism, which belongs to the field of robot kinematics. The method comprises the steps of calculating the height, which corresponds to a tail end required pose curve, of sliding blocks first, then calculating the speed and acceleration which correspond to the heights of the sliding blocks, then determining an optimized coefficient, and setting the movement law of the sliding blocks according to the optimized coefficient and controlling the movement of the parallel mechanism at last. The time-varying optimized coefficient is obtained by using a constraint condition that the sum of three branch equivalent loads and instantaneous generalized force is not larger than the driving force, so that the movement law of the three sliding blocks is controlled by using the optimized coefficient. According to the optimization method provided by the invention, the power source driving force is fully used by the 3-PRS parallel mechanism at different working states, and the tail end running speed and the working efficiency are increased.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
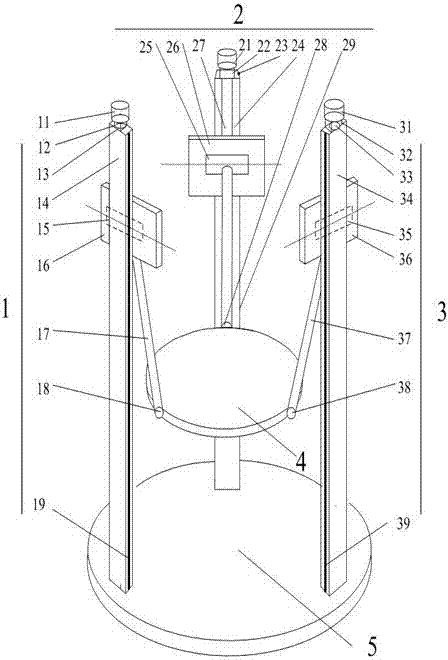
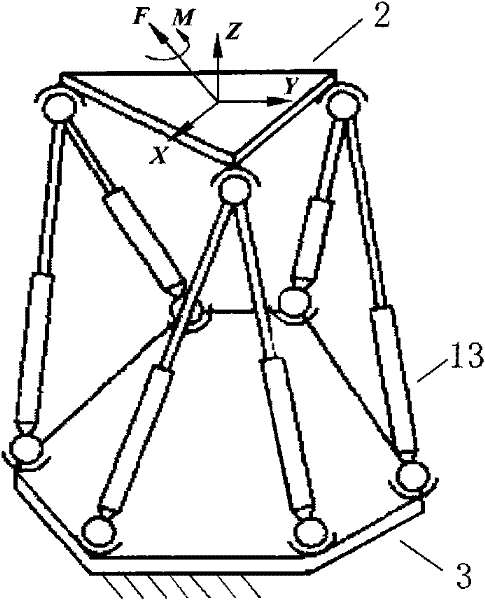
Spring structure type multiple free degree parallel mechanism generalized force and force moment testing device
InactiveCN101038219AIncrease stiffnessStable structureForce measurement by elastic gauge deformationMoment measureRelative motion
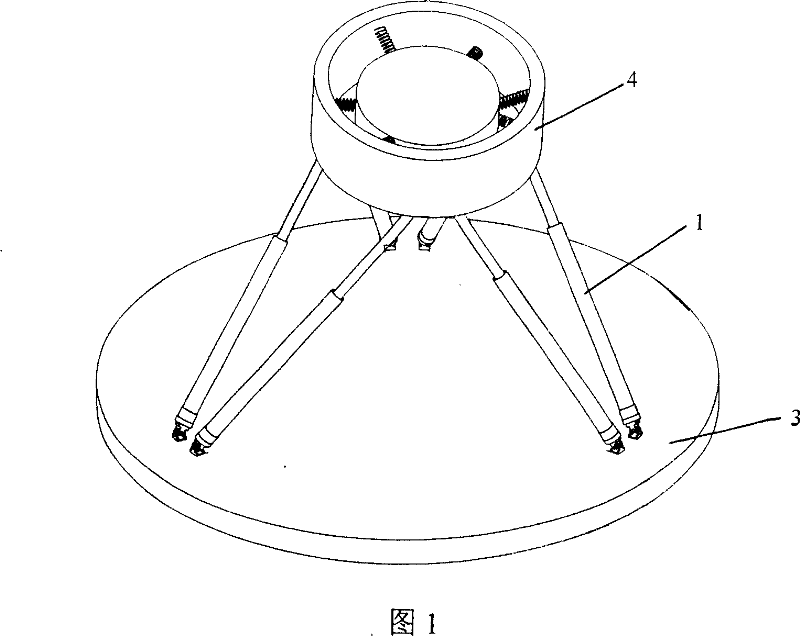
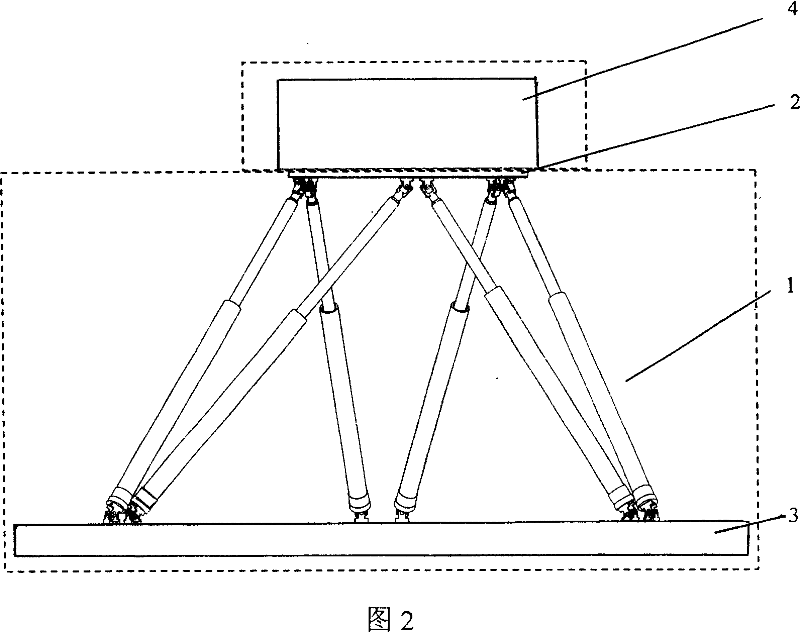
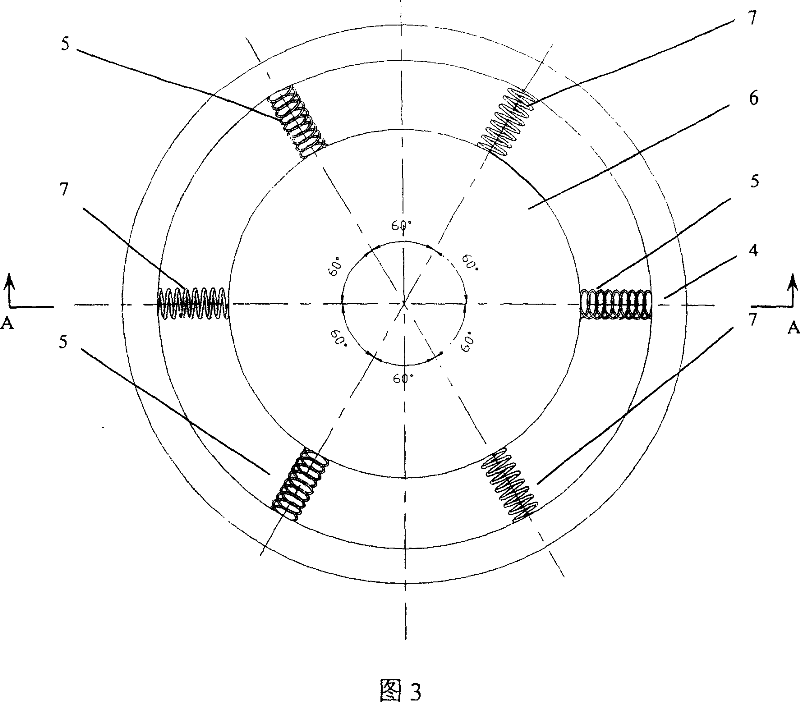
The present invention discloses a generalized force and force moment measuring device of the multiple-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism in a spring structure format. The measuring device includes a multiple-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism, a transverse spring, a diagonal drawn spring, a fixed external frame and a connection mechanism; the fixed external frame does not move relatively to the base of the parallel mechanism, and the connection mechanism is connected to the moveable platform of the multiple-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism in a rigid and moveable mode and is connected to the fixed external frame through a plurality of springs. The present invention provides a compact, ideal and succinct measuring device of force and force moment, and the device can be used for measuring the generalized force and force moment of all kinds of multiple-degree-of-freedom platforms and for loading.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Generalized force-loading multidimensional fore-measuring bench calibration device and calibration method
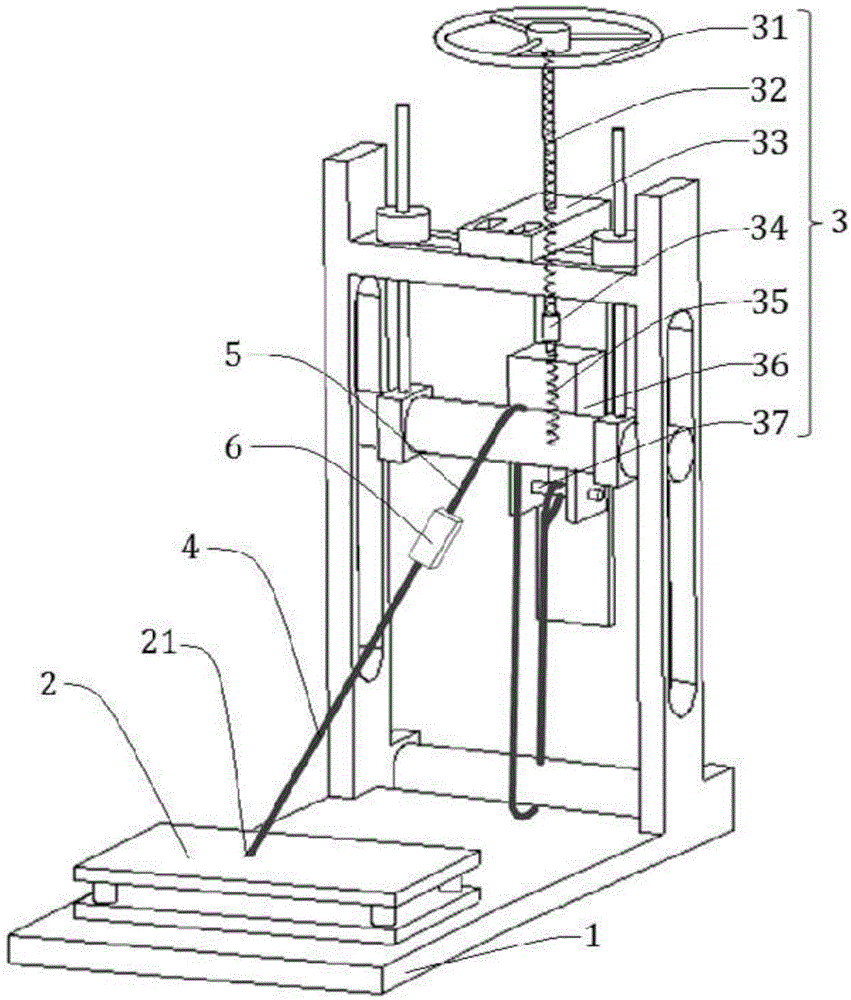
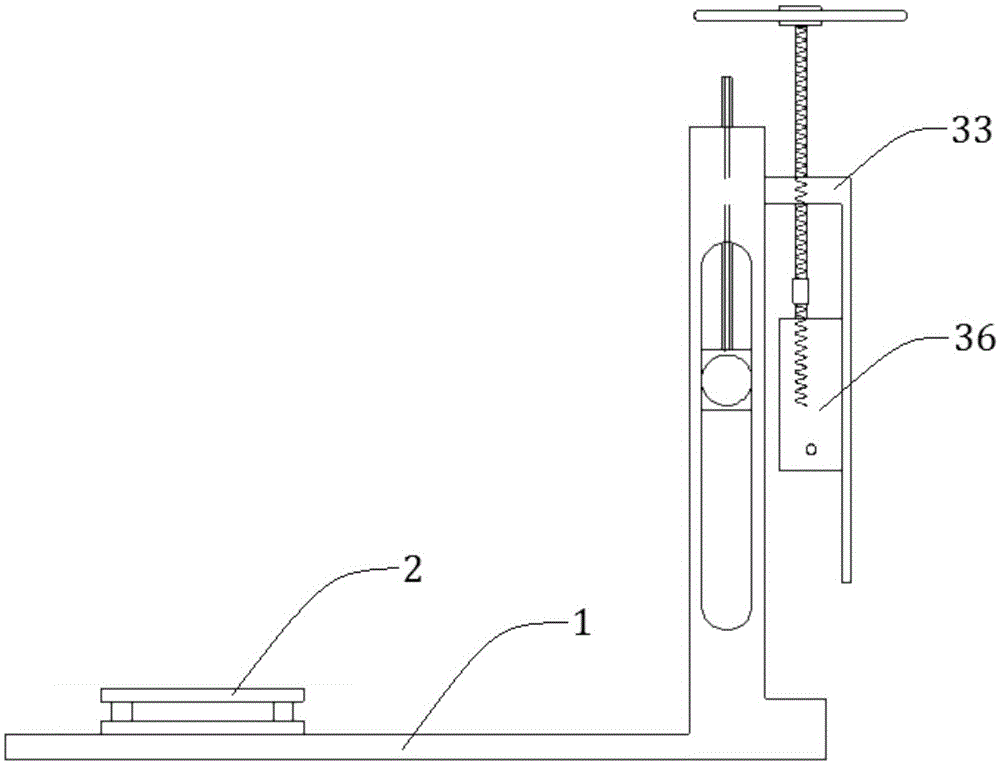
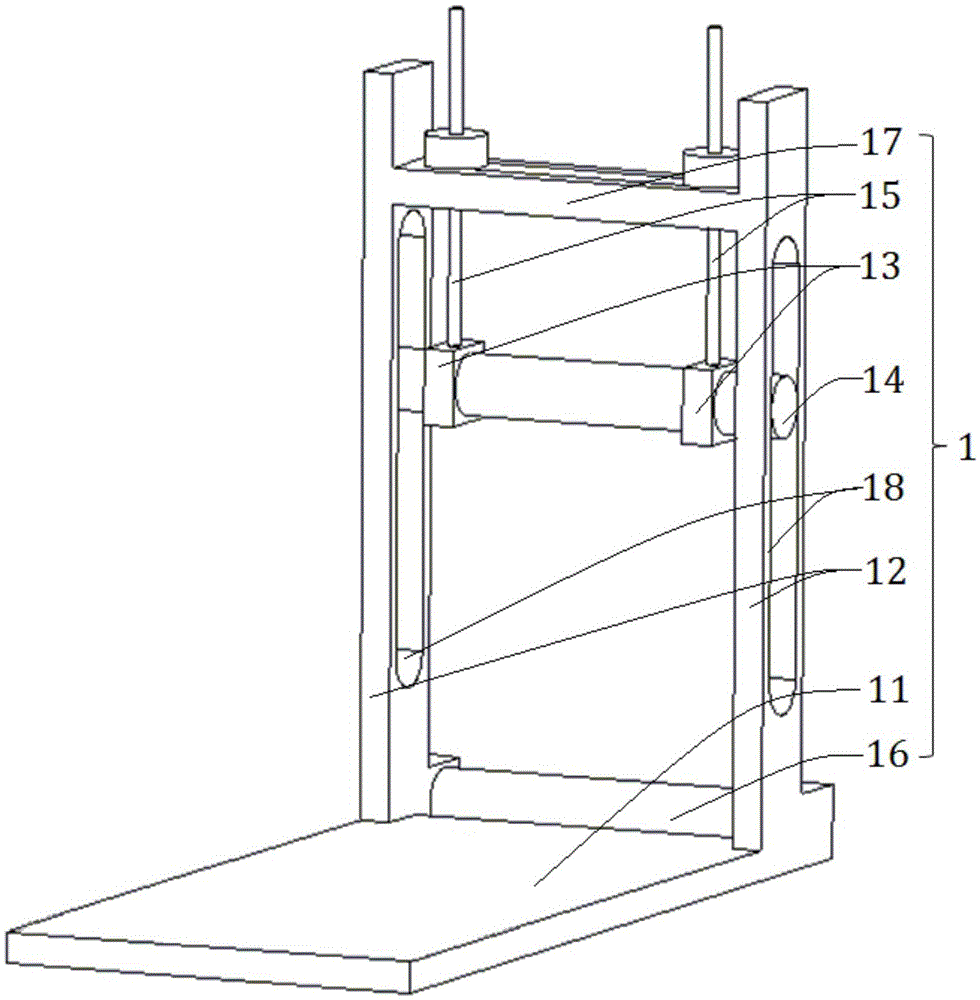
ActiveCN105675206AContinuous Vector Force LoadingReduce mistakesForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingEngineeringMulti dimensional
The invention relates to a generalized force-loading multidimensional fore-measuring bench calibration device and calibration method. The calibration device comprises a main calibration bench frame, a multi-dimensional force-measuring bench, a force applying mechanism, a first steel cable, a second steel cable and a sensing device. The main calibration bench frame is in an L shape; the multi-dimensional force-measuring bench is fixed at one side of the main calibration bench frame and a loading point is arranged; and the loading point, the first steel cable, the sensing device, the second steel cable and the force applying mechanism are connected successively. The force applying mechanism fixedly connected with the other side of the main calibration bench frame consists of a brake valve hand wheel, a first bidirectional screw rod, a connecting sleeve, a second bidirectional screw rod and a traction box, wherein the brake valve hand wheel, the first bidirectional screw rod, the connecting sleeve, the second bidirectional screw rod and the traction box are connected successively from top to bottom. The first bidirectional screw rod is provided with a fixed plate; and one end, in an inverted L shape of the fixed plate is connected with the main calibration bench frame fixedly and the other end is arranged by corresponding to the traction box. And a groove is formed in the bottom of the traction box and a traction sliding rod is arranged. According to the invention, forces and moments at multiple directions can be applied; and continuous vector force loading also can be realized, so that the error can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
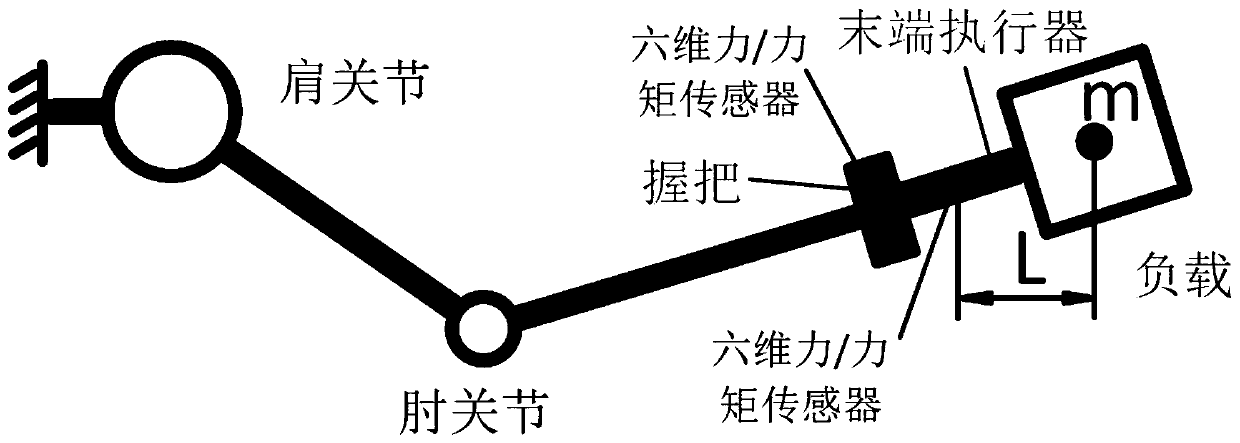
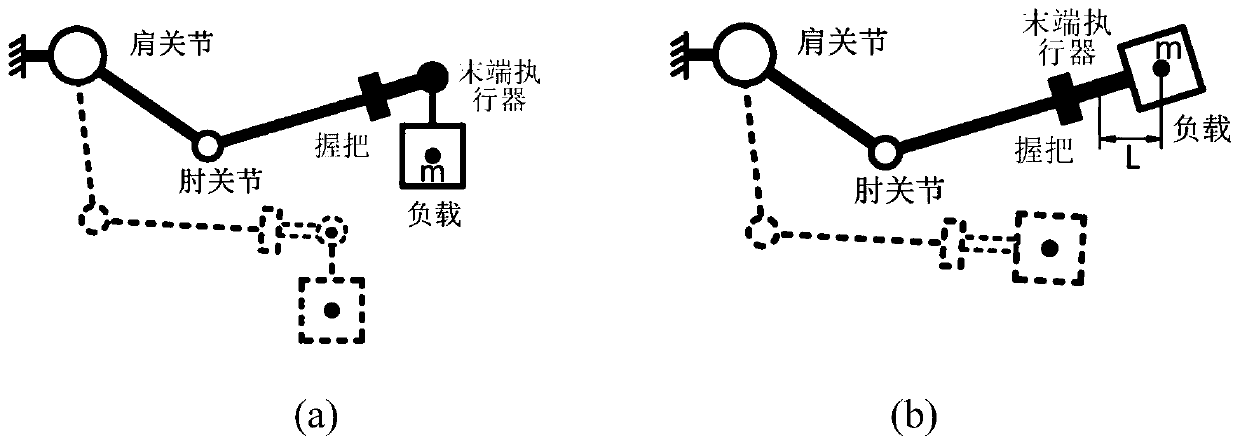
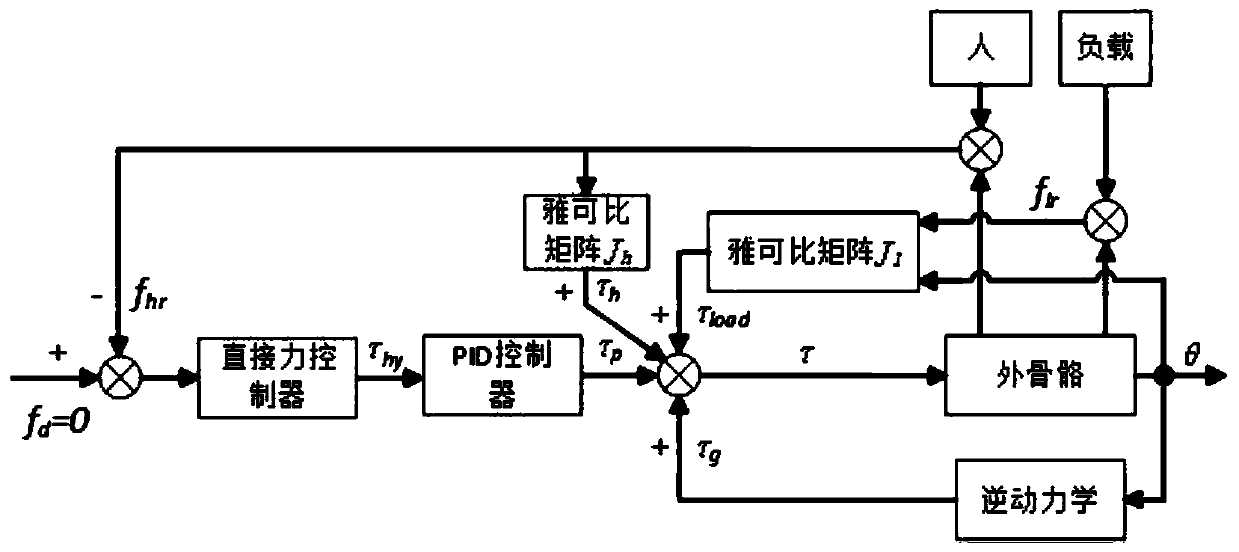
Cooperative control method of upper limb exoskeleton with dynamic load compensation
InactiveCN109746902AMinimizeTo achieve the goal of coordinated controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorInverse dynamicsUpper limb
The invention discloses a cooperative control method of upper limb exoskeleton with dynamic load compensation, which utilizes the generalized force of the load on the upper limb exoskeleton and the corresponding jacoby matrix to obtain a joint torque Tload required for compensating the load influence; the joint torque Tg caused by the dead weight of the upper limb exoskeleton is obtained through inverse dynamics, the torque Th of the human-machine interaction force mapped to the joint space is obtained by using the interaction force between the human and the upper limb exoskeleton and the corresponding jacoby matrix, and each joint of the upper limb exoskeleton is controlled by using the final joint torque T, wherein T = T g+T load+T h, and then the interaction force fhr between the humanand the exoskeleton is measured; when fhr is not 0, the human-machine interaction force caused by the load can be compensated in real time through feedback compensation of the direct force controllerand PID controller.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
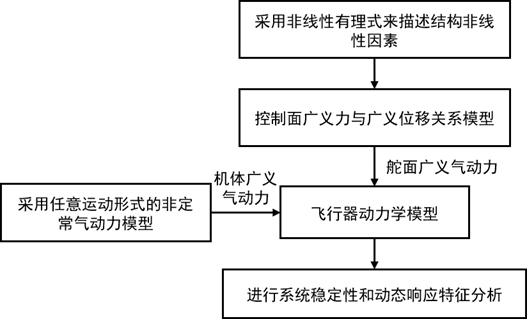
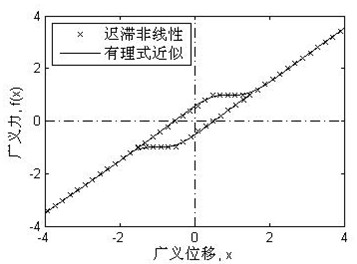
Flexible flight dynamics modeling method considering structural nonlinearity
ActiveCN113806871AShort modeling cycleImproving Simulation Calculation EfficiencyGeometric CADSustainable transportationKinetics equationStructural engineering
The invention discloses a flexible flight dynamics modeling method considering structural nonlinearity. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an aircraft flight dynamics equation containing nonlinear aeroelastic wings by using an unsteady aerodynamic force; fitting the relationship between the hysteresis nonlinear generalized force and the displacement by adopting a rational formula, so as to establish an aircraft flight kinetic equation containing nonlinear rigidity and nonlinear damping at the same time; and finally, solving response characteristics and stability of the nonlinear flight dynamics model by using a numerical method or a harmonic balance method. The unified expression form for describing the nonlinearity of the structure established by the invention can solve the problems of aircraft gap nonlinear dynamic modeling and subsequent dynamic analysis under the conditions of installation gaps between control surface hinges and connecting pieces, aging and loosening of parts and the like, so that a guiding idea is provided for related controller design; and the method has a certain engineering application value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Engine misfire fault diagnosis method based on mass center generalized force recognition
InactiveCN109269810AIncreased sensitivityInternal-combustion engine testingDynamic stiffnessFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to an engine misfire fault judgment method based on mass center generalized force recognition. The method comprises the following steps of (1), obtaining the coordinates of a suspension system of an engine, the inertia parameters of the engine, the dynamic stiffness of the main shafts of the suspension system, and the included angles between the main shafts and the axes of afixed coordinate system; (2), testing a vibration acceleration response signal under a steady-state working condition of the engine; (3), extracting the amplitudes, phases and frequencies of the harmonic components of the vibration acceleration response signal of the suspension system by means of a ratio correction method of a discrete spectrum correction technology added with a Hanning window; and (4), recognizing the mass center generalized force of the engine according to the following formula as shown in the description by utilizing the results in the steps (1) and (3), analyzing the characteristics of a vibration signal of the mass center generalized force of the engine, and distinguishing engine misfire faults. According to the method, the sensitivity of misfire fault judgment is high.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
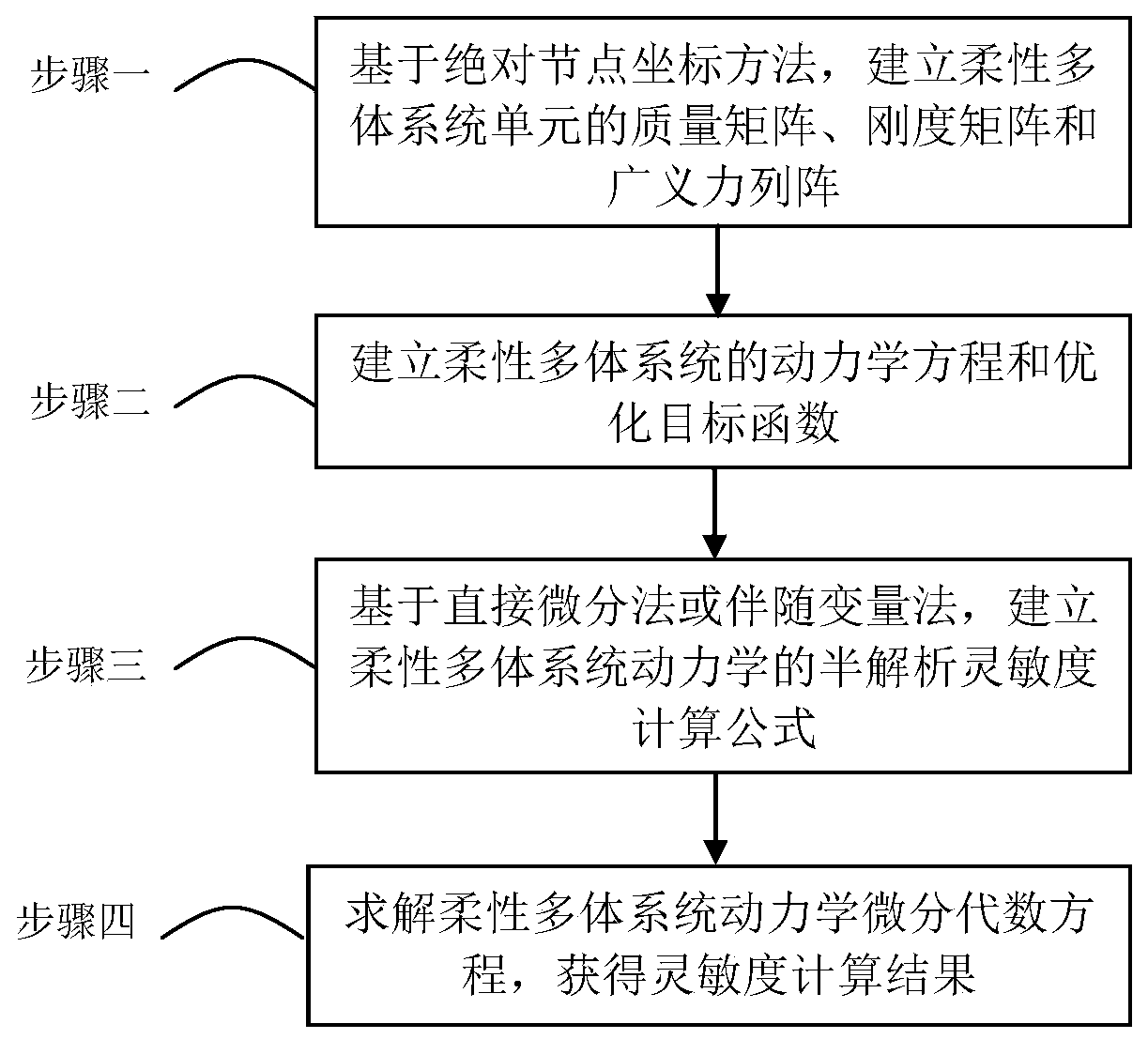
Flexible multi-body system dynamics semi-analytical sensitivity analysis method based on absolute node coordinate description
ActiveCN111159636AImprove computing efficiencyImprove calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmAlgebraic equation
The invention relates to the technical field of dynamics system optimization, and provides a flexible multi-body system dynamics semi-analytical sensitivity analysis method based on absolute node coordinate description. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a mass matrix, a rigidity matrix and a generalized force array of the flexible multi-body system based on an absolute node coordinate method; secondly, establishing a kinetic equation and an optimization objective function of the flexible multi-body system; thirdly, based on a direct differential method or an adjoint variable method, establishing a semi-analytical sensitivity calculation formula of the flexible multi-body system dynamics; and finally, solving the dynamic differential algebraic equation of the flexible multi-body system to obtain a sensitivity calculation result. The method is based on an absolute node coordinate method and a multi-body system dynamics theory. A semi-analytical sensitivity calculation formula of the flexible multi-body system is established to solve the sensitivity analysis problem of dynamics of the flexible multi-body system, a set of new strategy for sensitivity analysis of the flexible multi-body system is provided, and convenience is provided for sensitivity calculation of the large-scale complex flexible multi-body system.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
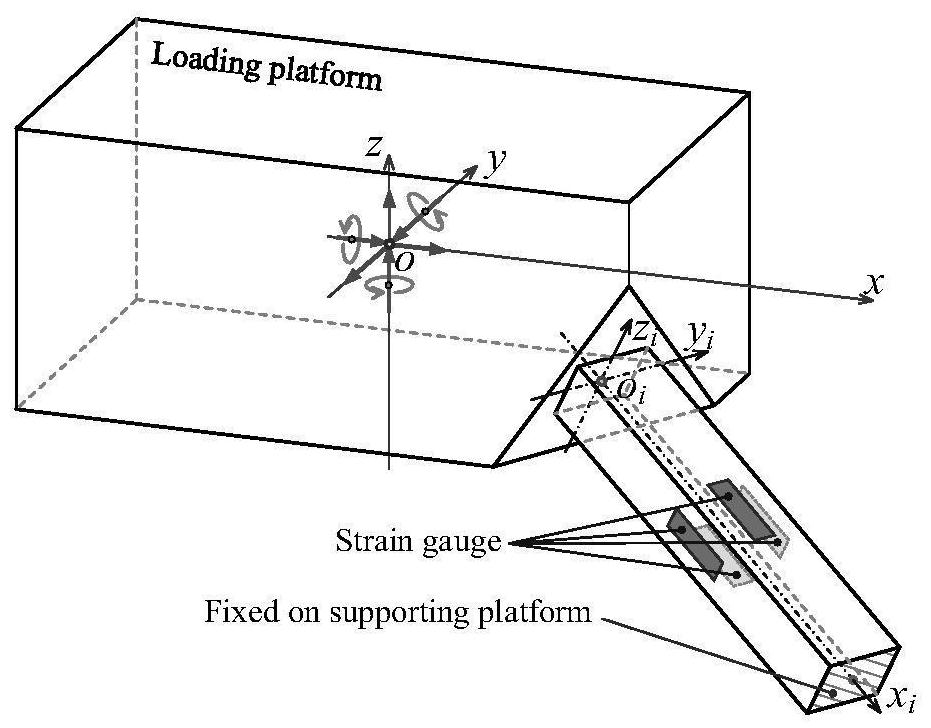
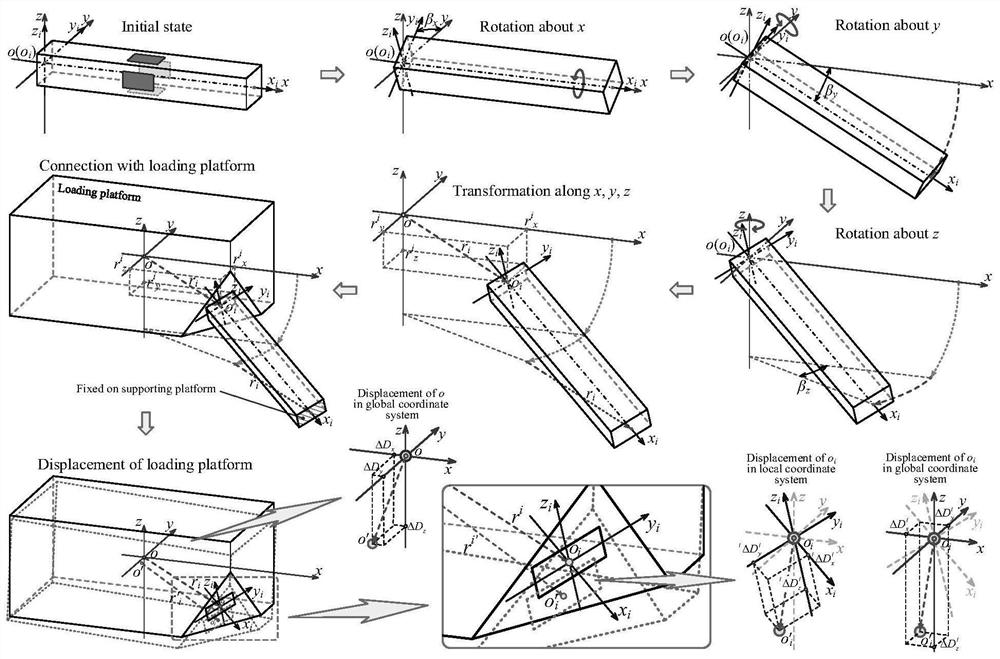
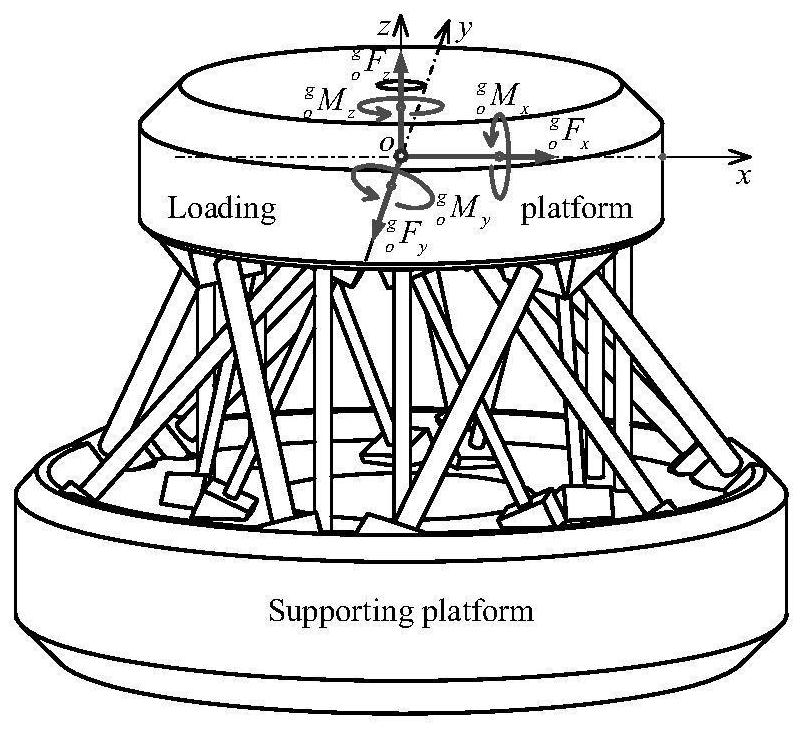
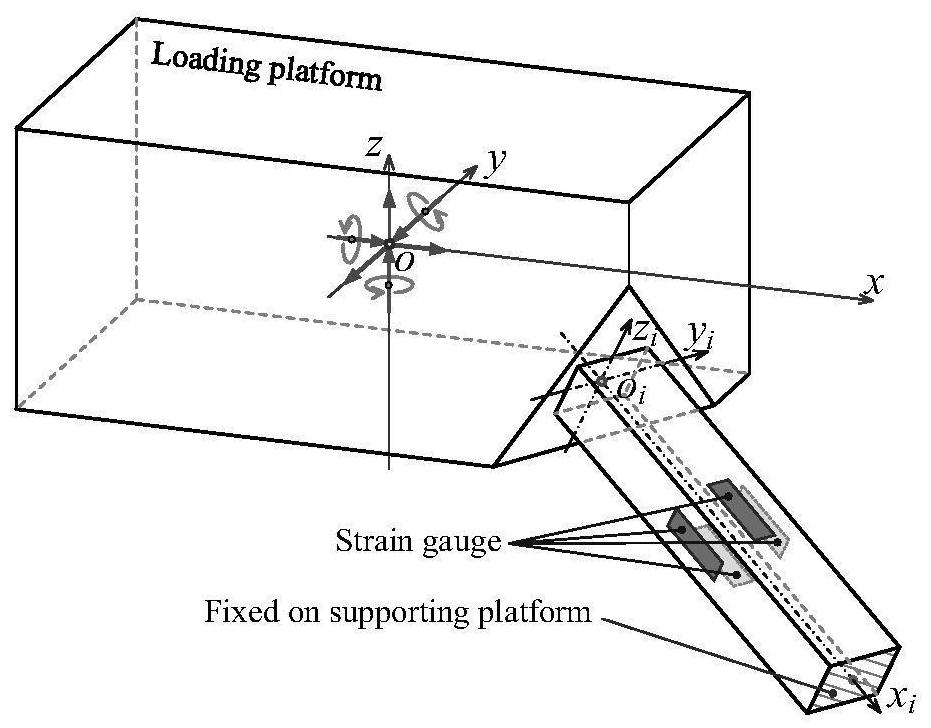
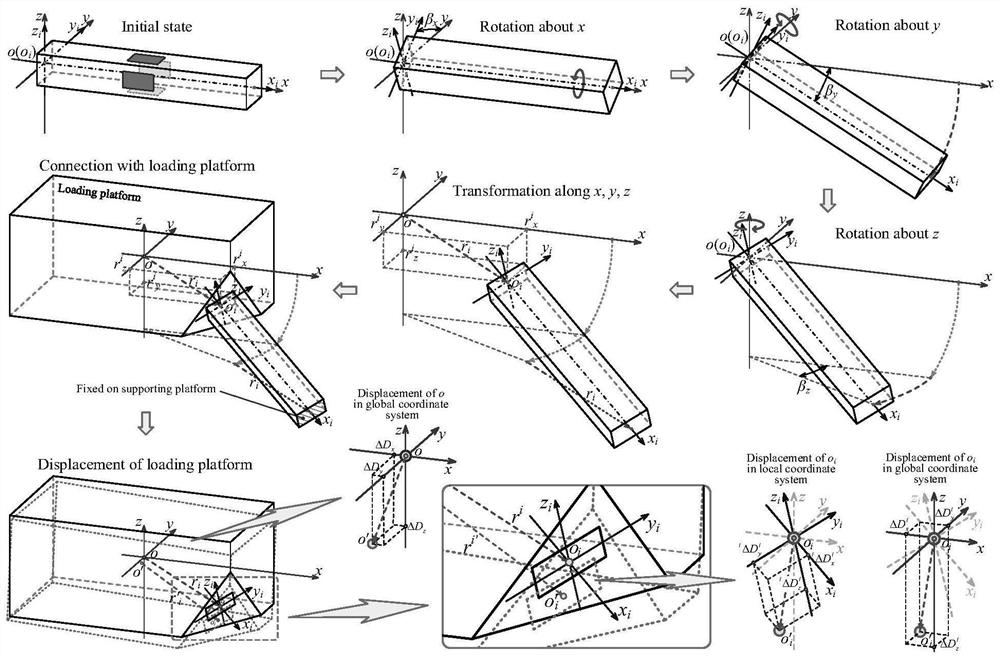
Multi-dimensional force acquisition method based on parallel rod system multi-dimensional force sensor
ActiveCN112611498AHigh measurement accuracyImprove structural rigidityForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesMeasurement of force componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a multi-dimensional force acquisition method based on a parallel rod system multi-dimensional force sensor, belongs to the technical field of sensor measurement, and aims to solve the problems that multi-dimensional force obtained by an existing multi-dimensional force sensor is large in inter-dimensional coupling, low in precision, small in structural rigidity of the sensor and the like. According to the method, a vector transformation relation matrix between a local coordinate system and a global coordinate system is established, considerable measurement is obtained according to local deformation displacement of an origin of a load platform coordinate system along / around a measurement axis under a local coordinate system, and deformation displacement of a load platform under the global coordinate system is calculated; all local deformation displacements of the corresponding local coordinate origin of each strain beam under the local coordinate system are calculated according to the deformation displacement of the load platform under the global coordinate system, and the local generalized force of each strain beam under the local coordinate system is calculated according to the local deformation displacement of each strain beam under the local coordinate system; and the linear equation set is solved to obtain the multi-dimensional force of the multi-dimensional force sensor. The method is mainly used for multi-dimensional force acquisition of the multi-dimensional force sensor.
Owner:马洪文 +1
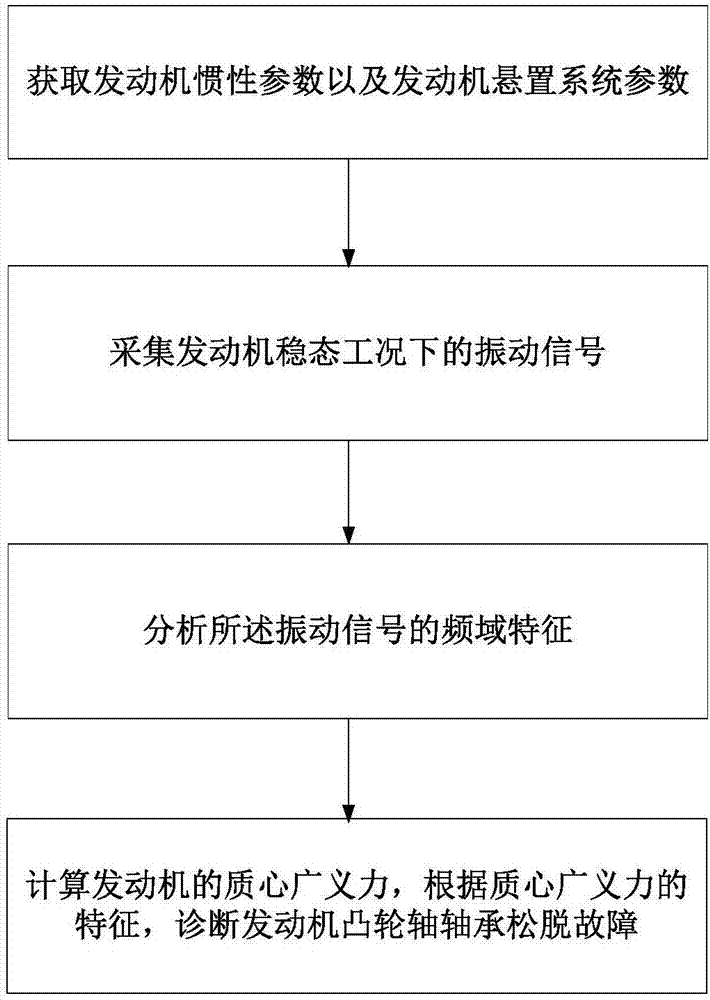
Engine camshaft bearing loose failure diagnosis method and system
InactiveCN107505134AIncreased sensitivityReduce the impactMachine bearings testingGeneralized forcesSystem parameters
The invention relates to an engine camshaft bearing loose failure diagnosis method and an engine camshaft bearing loose failure diagnosis system. The engine camshaft bearing loose failure diagnosis method comprises the steps of: acquiring an engine inertia parameter and an engine suspension system parameter; acquiring a vibration signal of an engine in a steady-state condition; analyzing frequency domain characteristics of the vibration signal; and calculating a center-of-mass generalized force of the engine according to the engine inertia parameter, the engine suspension system parameter and the frequency domain characteristics of the vibration signal, and diagnosing a engine camshaft bearing loose failure according to characteristics of the center-of-mass generalized force.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
Trajectory tracking control method for space five-degree-of-freedom free flight mechanical arm
ActiveCN110641738AHigh precisionHigh speedCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusFree flightGeneralized forces
The invention discloses a trajectory tracking control method for a space five-degree-of-freedom free flight mechanical arm. The trajectory tracking control method can solve the accurate problem that aspace object is captured and manipulated by the five-degree-of-freedom space free-flight mechanical arm installed on a spacecraft. The trajectory tracking control method mainly comprises the following four points that 1), a D-H method is applied to establish a forward kinematic model of the mechanical arm; 2) a Lagrange equation is applied to establish a dynamical model of the mechanical arm; 3),a Jacobi transpose matrix and a PD controller are combined to introduce a generalized force vector; and 4), Simulink software is used for constructing a simulation model according to a dynamical differential equation. According to the method, the kinematic and dynamical models of the mechanical arm are constructed at the same time, and the method of the Jacobi transpose matrix in combination withthe PD controller is applied, so that the problem that a kinematic control method applied widely at present cannot well track and control the space high-speed high-precision mechanical arm is effectively solved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Body dynamics calculation method, body dynamics model and model data thereof, and body-model generation method
A forward / reverse mechanics calculation of an accurate model of a human body having bone geometrical data and muscle / cord / band data is carried out at high speed. When a new skeleton geometrical model is given, a mapping between the new skeleton geometrical model and a pre-defined normal body model representing a normal body is defined to automatically produce a new body model. A processing unit reads model data to be subjected to mechanics calculation, reads a produced force f of a wire / virtual link exerted on the body model, reads the angle, position and velocity of the current rigid body link, calculates the Jacobian JL of the length of each wire concerning the joint angle, converts the read produced force f of the muscle / cord / band into a generalized force τG according to the defined Jacobian JL, stores the generalized force, determines the acceleration of the whole body of a motion produced when the generalized force τG is exerted on the body and calculates the velocity and position of each rigid body link, and stores them.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Body dynamics calculation method, body dynamics model and model data thereof, and body-model generation method
InactiveUS7490012B2Promote generationForce measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyWhole body
A forward / reverse mechanics calculation of an accurate model of a human body having bone geometrical data and muscle / cord / band data is carried out at high speed. When a new skeleton geometrical model is given, a mapping between the new skeleton geometrical model and a pre-defined normal body model representing a normal body is defined to automatically produce a new body model. A processing unit reads model data to be subjected to mechanics calculation, reads a produced force f of a wire / virtual link exerted on the body model, reads the angle, position and velocity of the current rigid body link, calculates the Jacobian JL of the length of each wire concerning the joint angle, converts the read produced force f of the muscle / cord / band into a generalized force τG according to the defined Jacobian JL, stores the generalized force, determines the acceleration of the whole body of a motion produced when the generalized force τG is exerted on the body and calculates the velocity and position of each rigid body link, and stores them.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
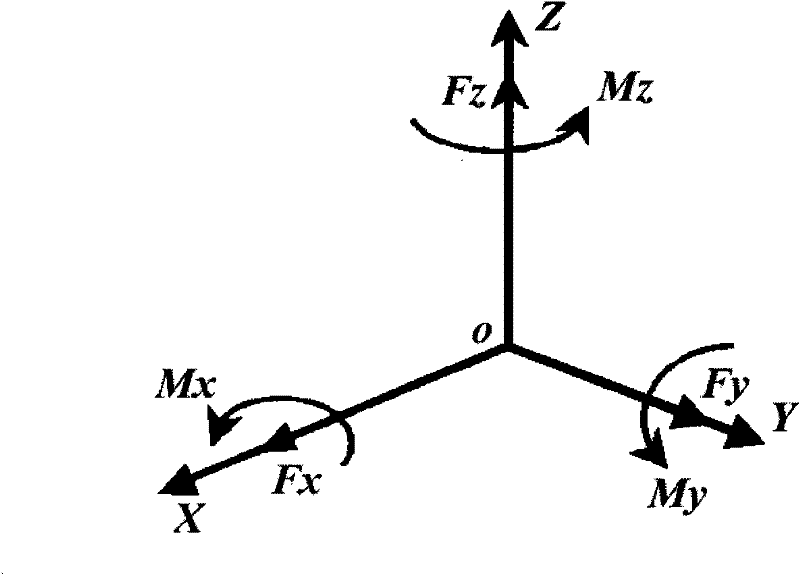
Six-component force sensor
InactiveCN102445290AOvercome isotropy that cannot be achieved simultaneouslyOvercome the defect of isotropy of momentForce measurementCouplingSingle type
The invention relates to mechanics parameter sensing device and particularly relates to a sensor used for a robot actuating mechanism or engineering detection device which needs to simultaneously detect and sense six orthogonal components of a spatial generalized force. The six-component force sensor comprises a main platform and an auxiliary platform, wherein a shell is arranged between the main platform and the auxiliary platform; three ball pivots are uniformly arranged at intervals along the circumference of the main platform, a support bar in a horizontal direction and a support bar in a vertical direction are connected to each ball pivot, and the ball pivots and the support bars are arranged in the shell; and the tail end of the support bar in the horizontal direction is connected with the shell, and the support bar in the vertical direction are connected with the auxiliary platform. The six-component force sensor has the advantages of symmetrical and compact structure, simple process and the like, and can be used for realizing single-type or combined-type six-component force sensors; and compared with a six-component force sensor based on a classic Stewart six-bar platform, the six-component force sensor provided by the invention has the advantages of small coupling degree and easiness for realization of isotropic property.
Owner:杨锦堂
Multi-dimensional Force Acquisition Method Based on Parallel Link Multi-dimensional Force Sensor
ActiveCN112611498BHigh measurement accuracyImprove structural rigidityForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesMeasurement of force componentsMechanical engineeringGlobal coordinate system
The invention relates to a multi-dimensional force acquisition method based on a parallel bar system multi-dimensional force sensor, which belongs to the technical field of sensor measurement. In order to solve the problems of large coupling between multi-dimensional forces obtained by existing multi-dimensional force sensors, low precision, and small structural stiffness of sensors. The invention establishes the vector transformation relation matrix between the local coordinate system and the global coordinate system, obtains the observable quantity according to the local deformation displacement of the origin of the coordinate system of the load platform along / around the measurement axis in the local coordinate system, and calculates the load platform under the global coordinate system According to the deformation displacement of the load platform in the global coordinate system, calculate all the local deformation displacements of the corresponding local coordinate origin of each strain beam in the local coordinate system, and calculate the local deformation displacement of each strain beam in the local coordinate system Calculate the local generalized force of each strain beam in the local coordinate system; obtain the multidimensional force of the multidimensional force sensor by solving the linear equation system. It is mainly used for multi-dimensional force acquisition of multi-dimensional force sensors.
Owner:马洪文 +1
Control method for robot
ActiveCN107650121ASmall amount of calculationGuaranteed stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoint coordinatesEngineering
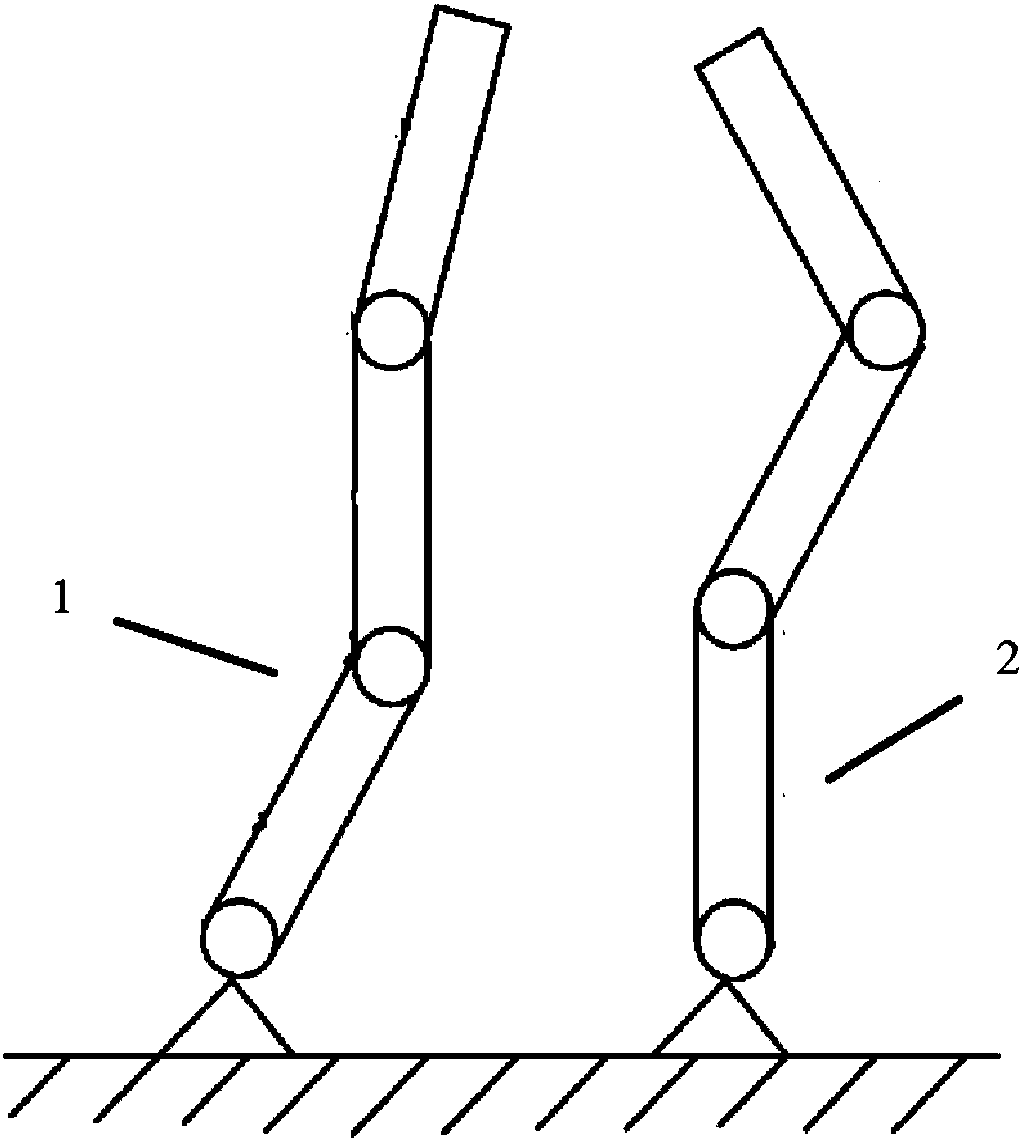
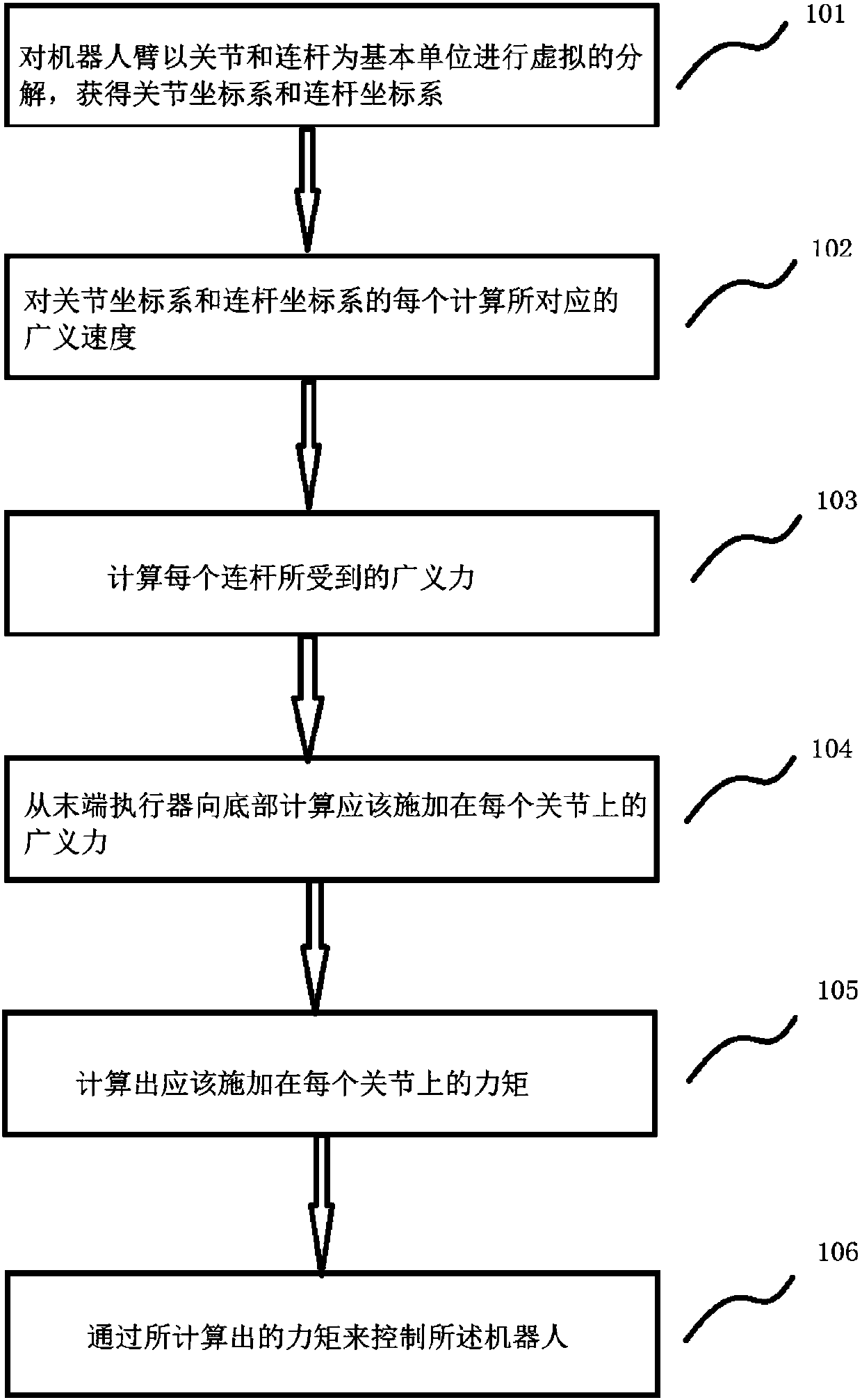
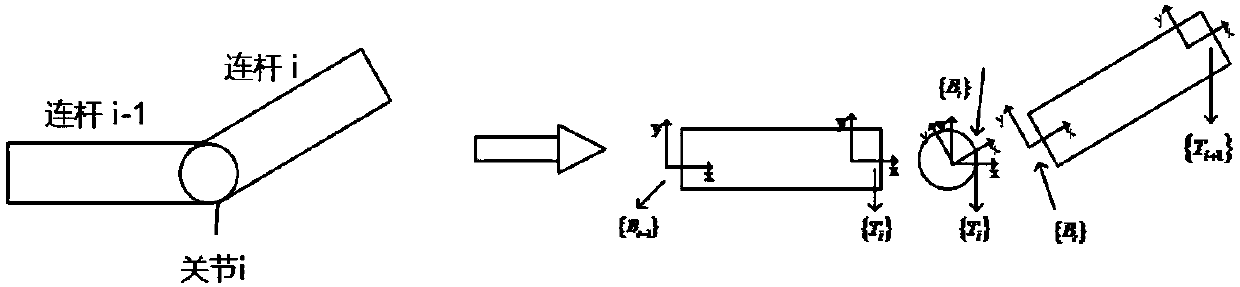
The invention discloses a control method for a robot. The robot comprises at least one arm. Each arm comprises a bottom, joints, connection rods and an end executor. The control method comprises the steps that the arms are decomposed with the joints and the connection rods as basic units so that joint coordinate systems and connection rod coordinate systems can be obtained; corresponding generalized velocities of each joint coordinate system and each connection rod coordinate system are calculated; the generalized force subjected by each connection rod is calculated; according to the calculated generalized force borne by each connection rod, the generalized force needing to be applied to each joint is calculated from the corresponding end executer to the corresponding bottom; the moment offorce to be applied to each joint is worked out; and the robot is controlled through the calculated moment of force. By adopting the control method, the calculated amount in real-time control can beeffectively reduced, and the real-time control purpose is achieved.
Owner:深圳力合精密装备科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com