Patents
Literature
70 results about "Robots actuators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
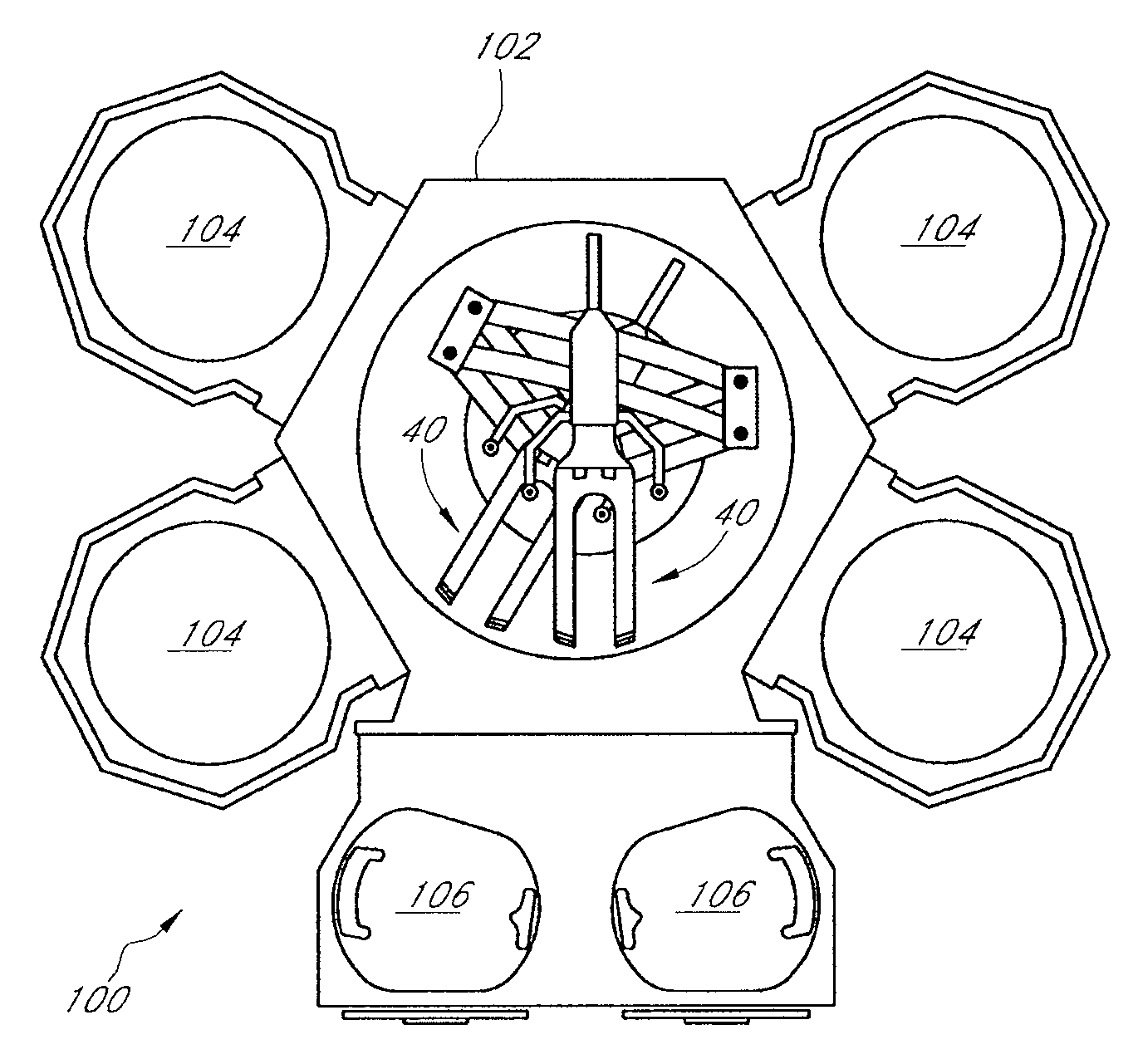
Position sensor system for substrate transfer robot
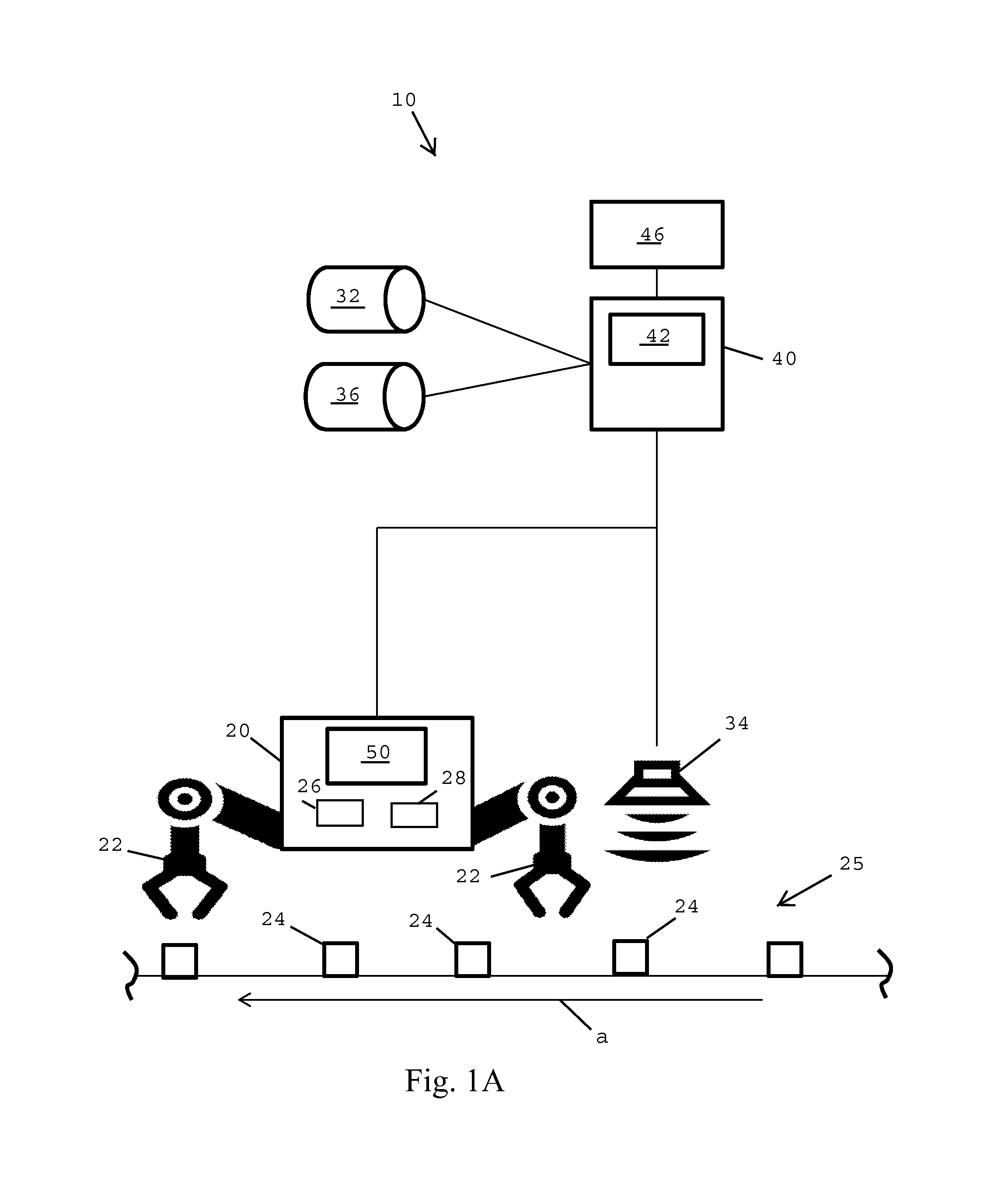
A substrate processing apparatus comprises a substrate handling chamber, a pair of position sensors, and a substrate transfer robot. Each of the sensors comprises an emitter configured to emit a beam of light, and a receiver configured to receive the light beam. The substrate transfer robot comprises an end effector and a robot actuator. The end effector is configured to hold a substrate such that the substrate has a same expected position with respect to the end effector every time the substrate is held. The robot actuator is configured to move the end effector within the handling chamber to transfer substrates among a plurality of substrate stations. An edge of a substrate held in the expected position by the end effector can partially block a light beam of one of the position sensors, while another end of the end effector partially blocks a light beam of the other position sensor.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
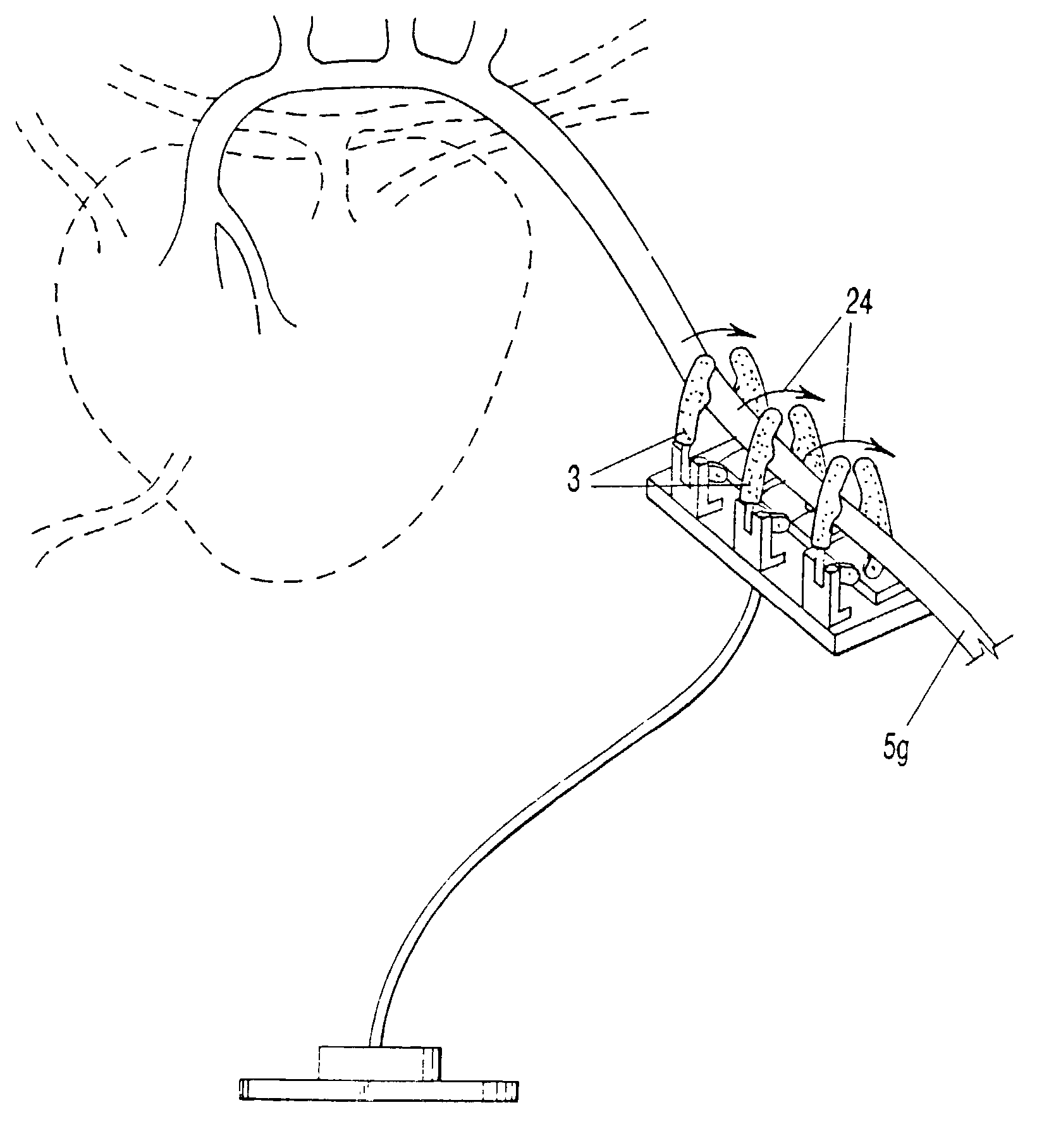
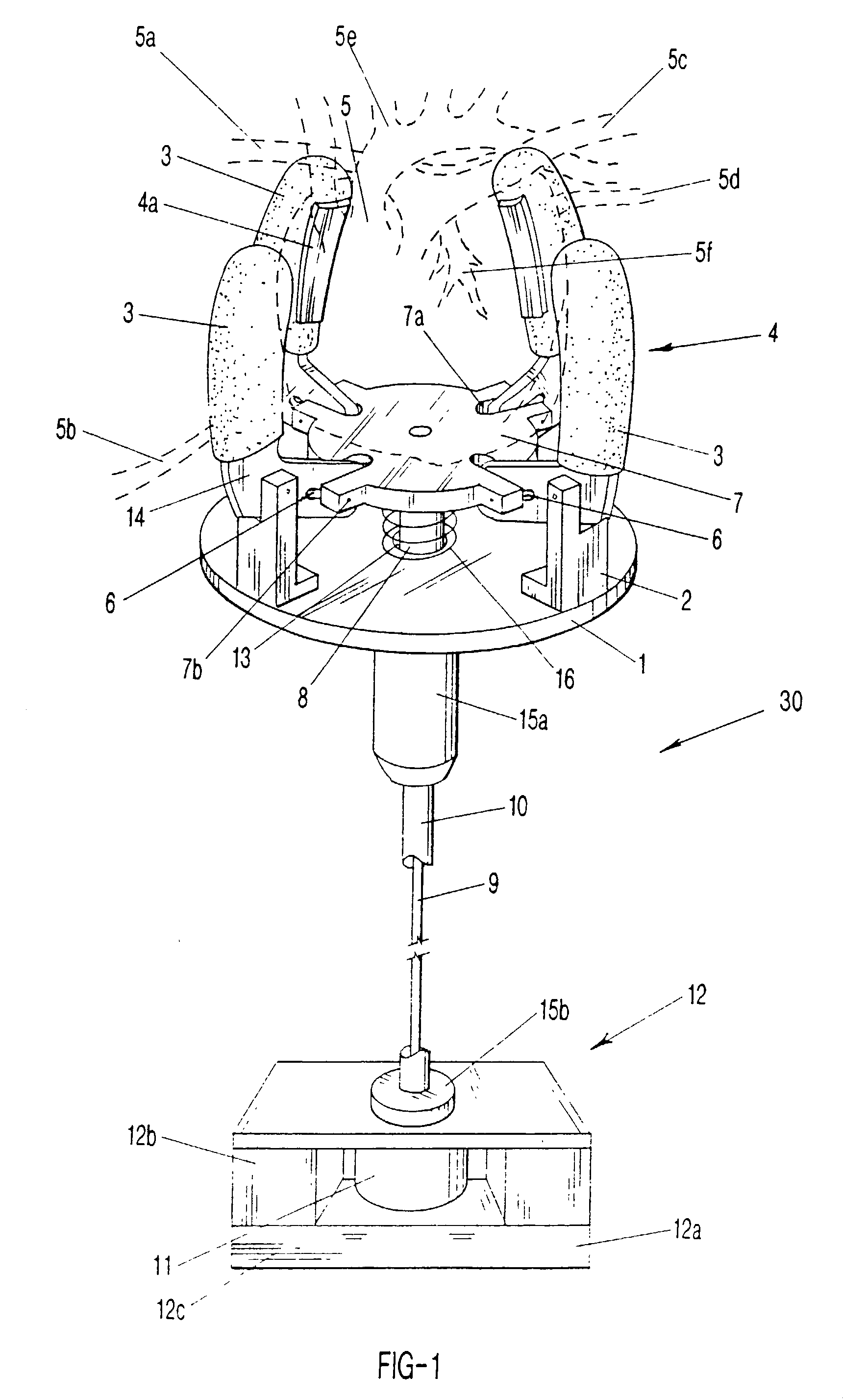
Electrically-controllable multi-fingered resilient heart compression devices
InactiveUS20030032855A1Different selectionControl devicesIntravenous devicesPump bloodRobots actuators
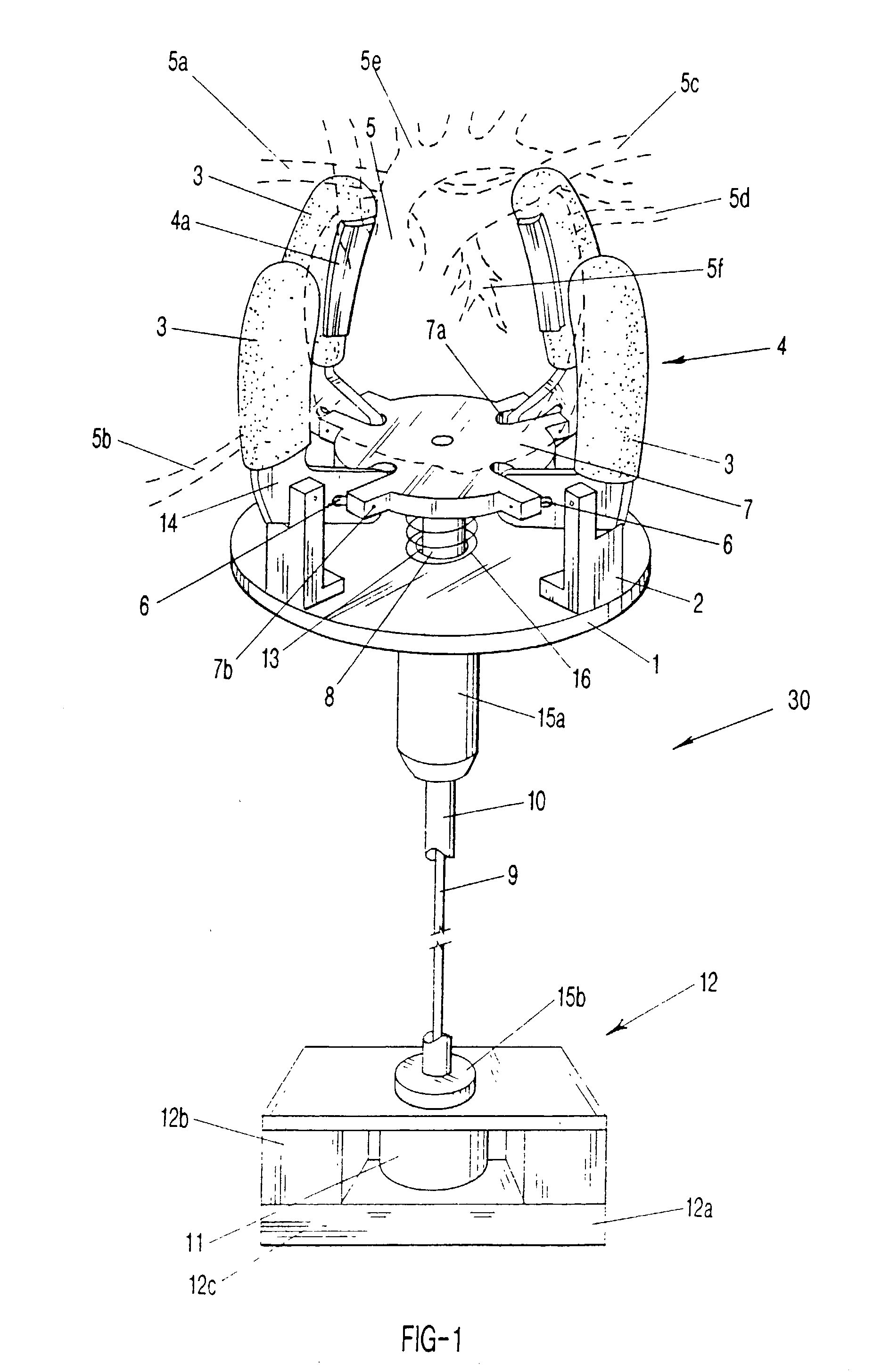
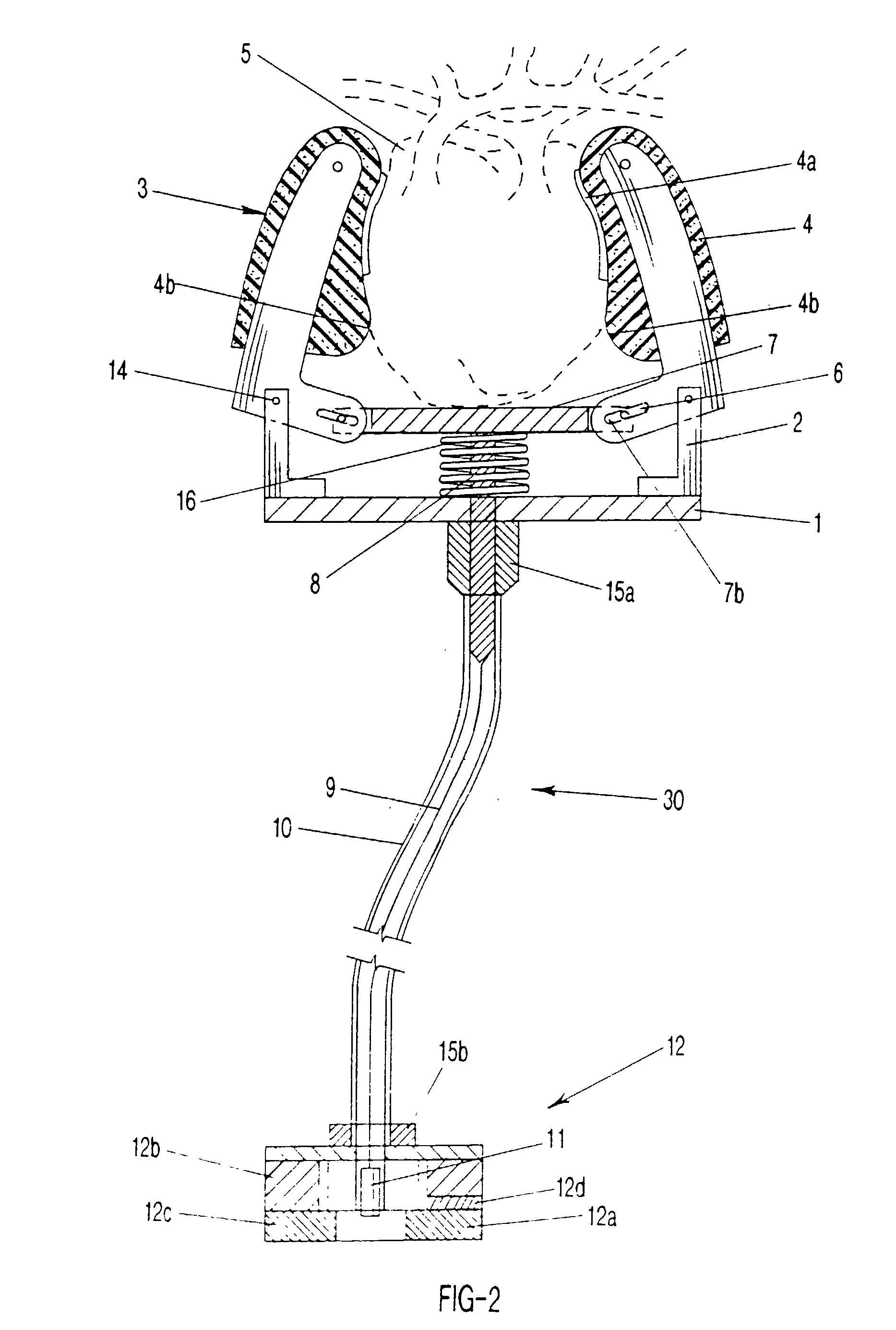
Soft, multi-fingered resilient robotic fingers for selectively assisting heart ventricles or other organ to produce internal pressure and to pump blood, in synchrony with the systolic contraction of the ventricle or organ, as well as providing arrhythmia control of a beating heart. The apparatus is electrically-controlled and implantable. The plurality of soft fingers monitor and gently squeeze the heart (systole) or organ to enhance blood circulation and assist the heart or organ. The soft fingers work in harmony, by means of a micro-processor controlled solenoid or other linear robotic actuators such as metal-hydride actuators or polymeric artificial muscles, and a resilient body or a spring, to close once the solenoid is powered to retract away from the heart or organ when the solenoid is not powered. Monitoring electrodes can be affixed to the soft fingers. The power supply for the implanted device can be transcutaneously rechargeable batteries.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
Control device for robot
ActiveUS20110160907A1Increase flexibilityProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringRepresentative element
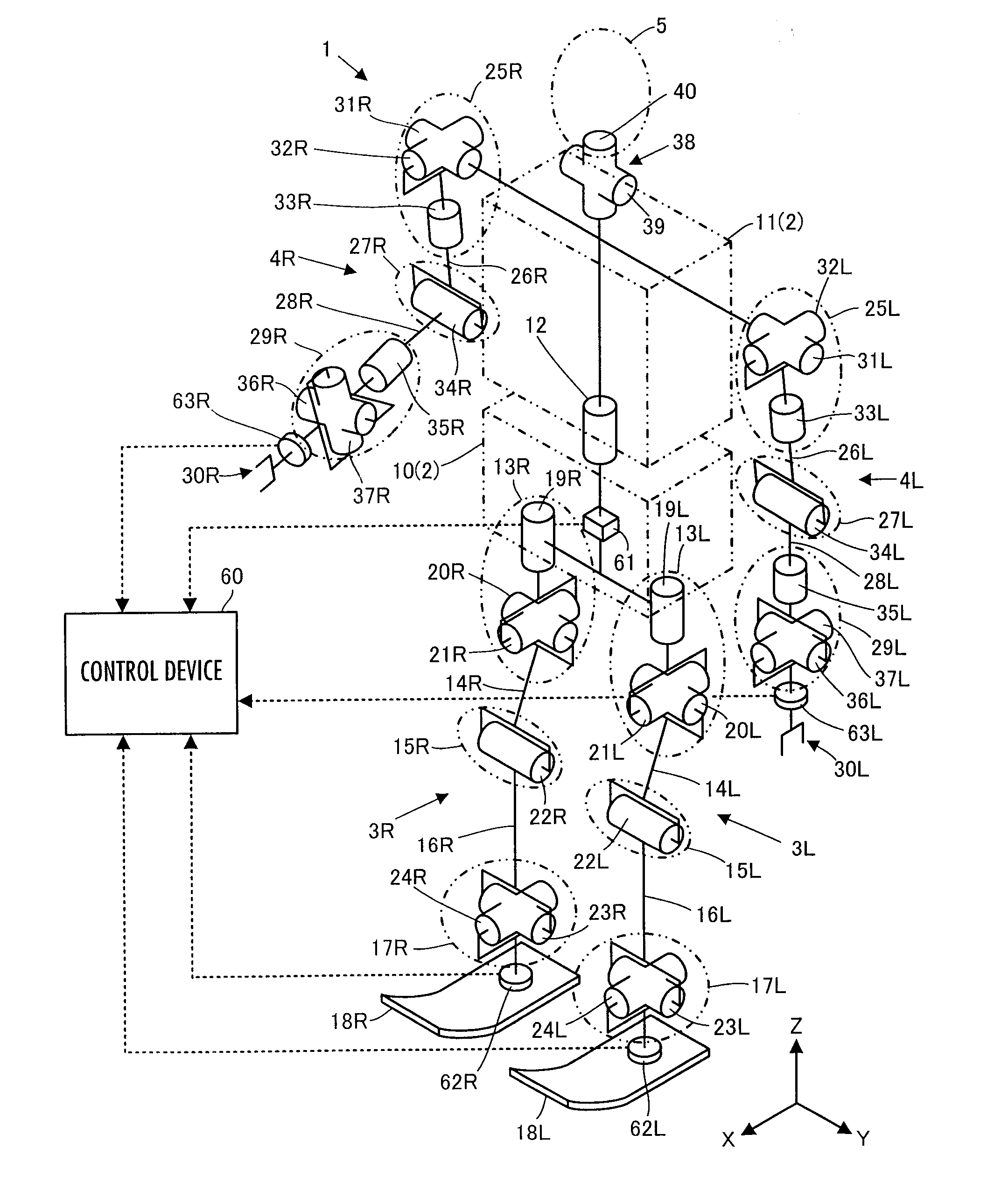
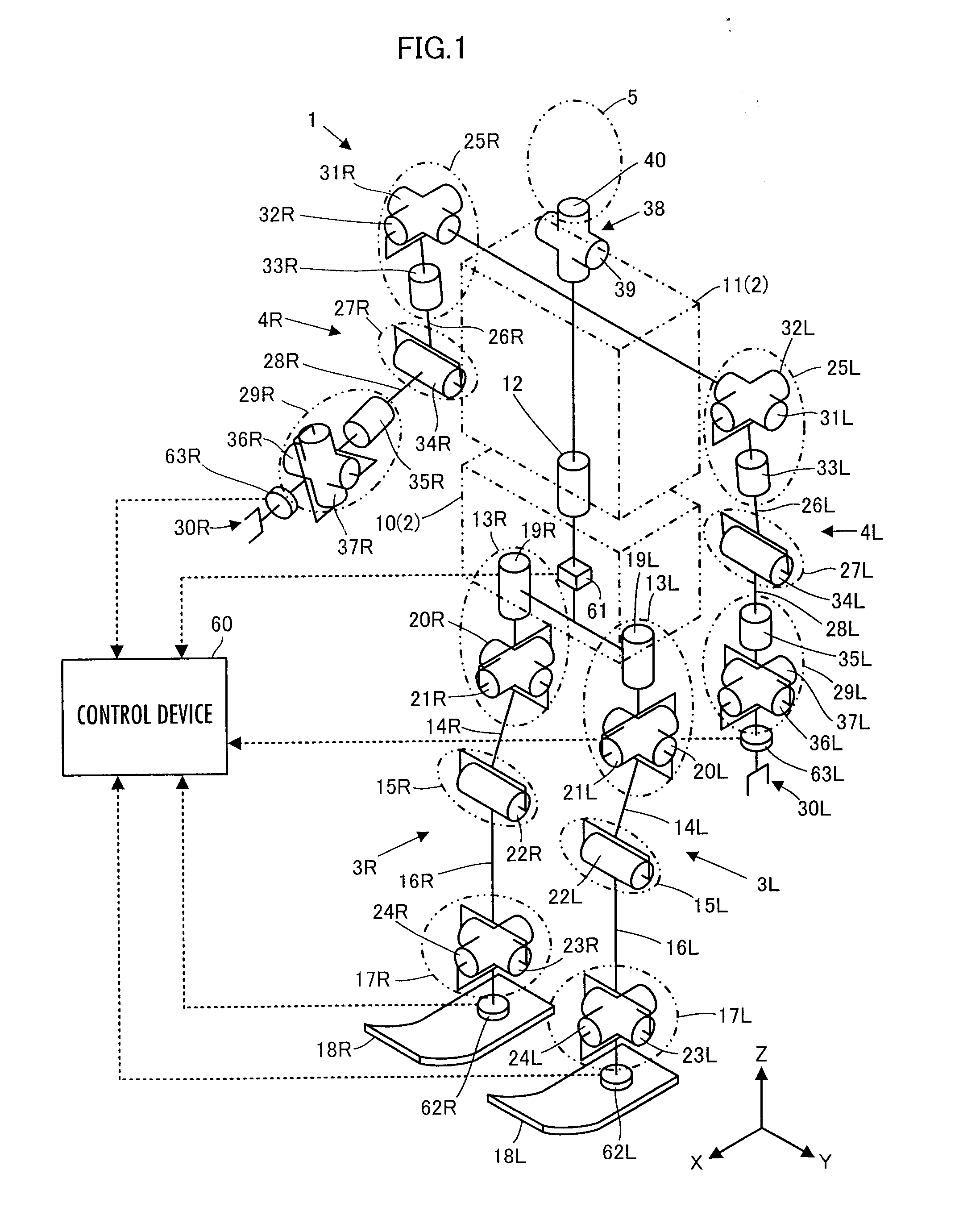
A control device for a robot determines, as a desired driving force to be imparted to a joint, a component value corresponding to the displacement amount of each joint out of a desired generalized force vector τcmd that satisfies the relationship indicated by expression 01 given below by using basic parameter group of M, N, and Jacobian matrixes Jc and Js, a desired value ↑C of the motion acceleration of a contact portion representative element representing a motion of a contact portion of a robot 1, generalized variable observation information, and a desired value ↑S′ of a first-order differential value of a predetermine type of state amount, and then controls the operation of an actuator of the robot 1 on the basis of the determined desired driving force.S′+(Js*M−1*Tc−Js′)*q′=(Js*M−1*Pc)*(τcmd−τcmpn) Expression 01
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
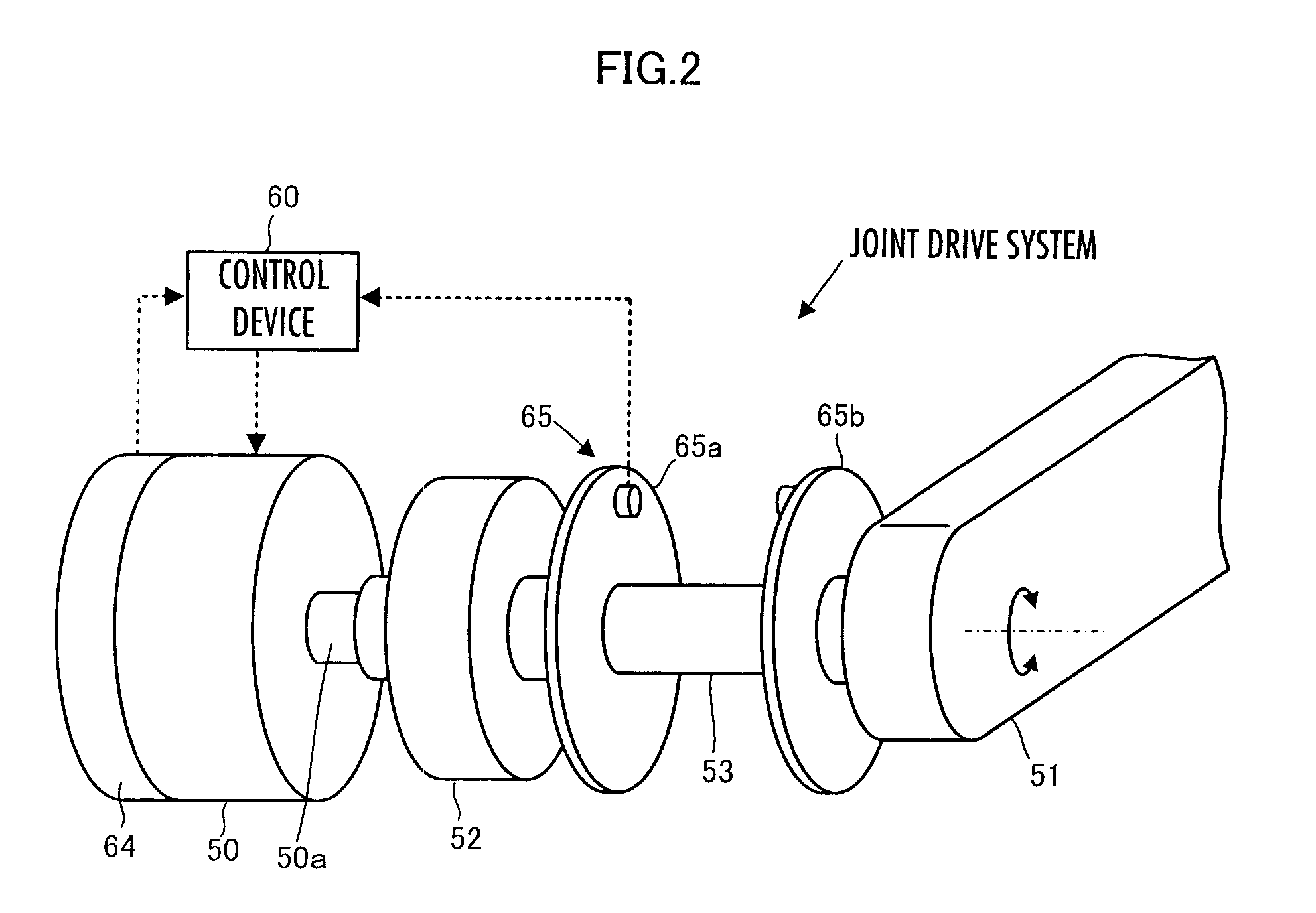
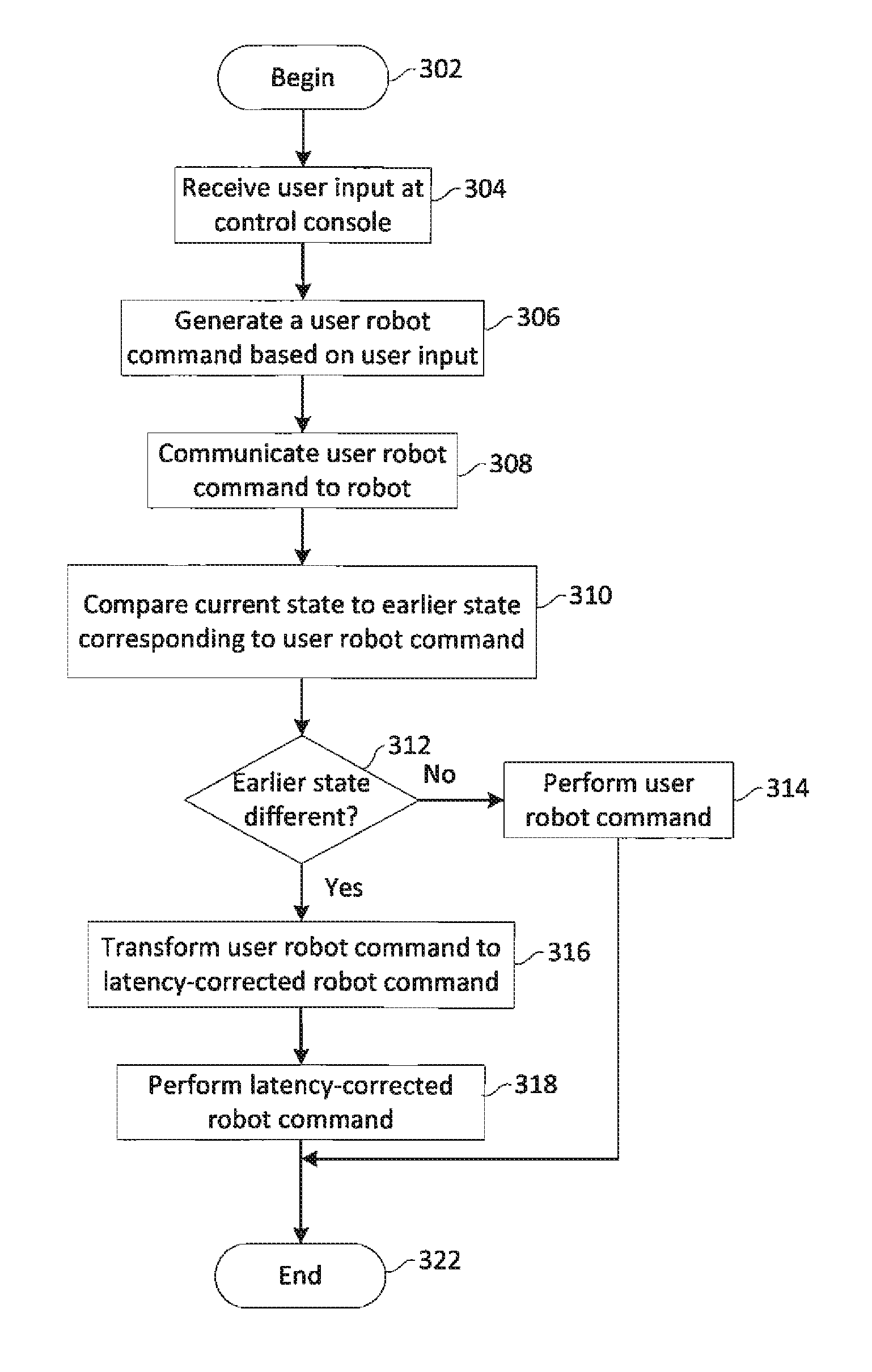
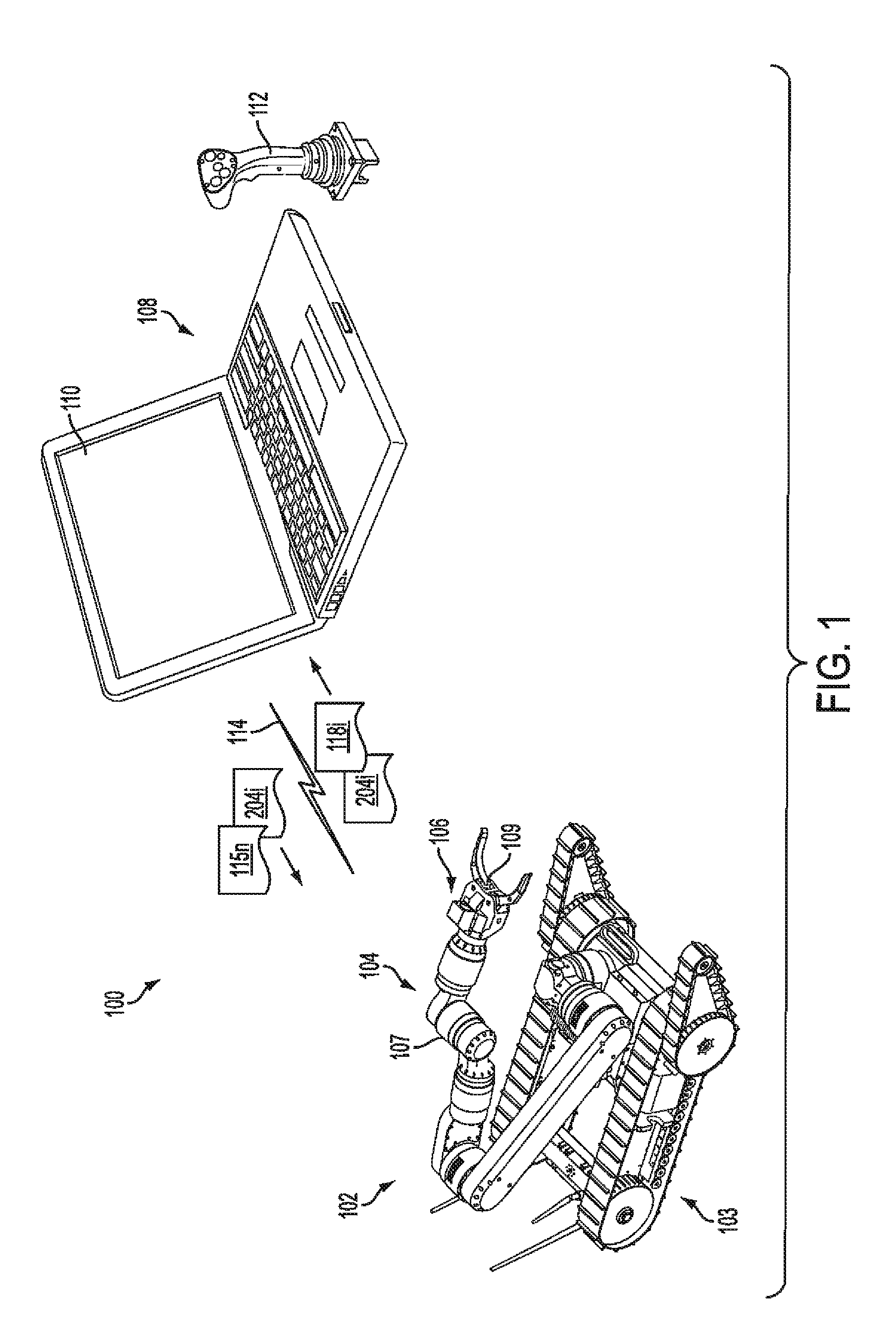
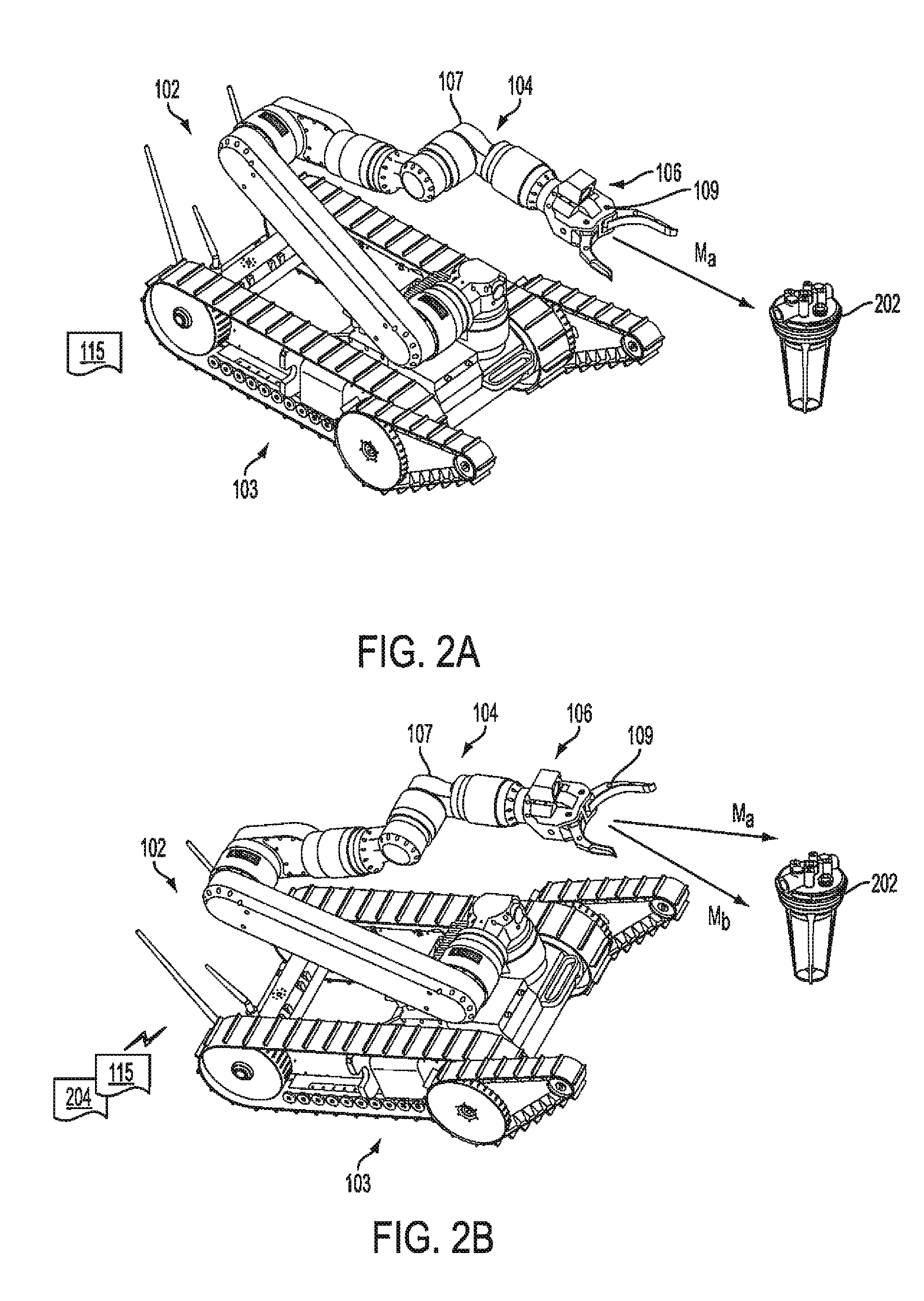
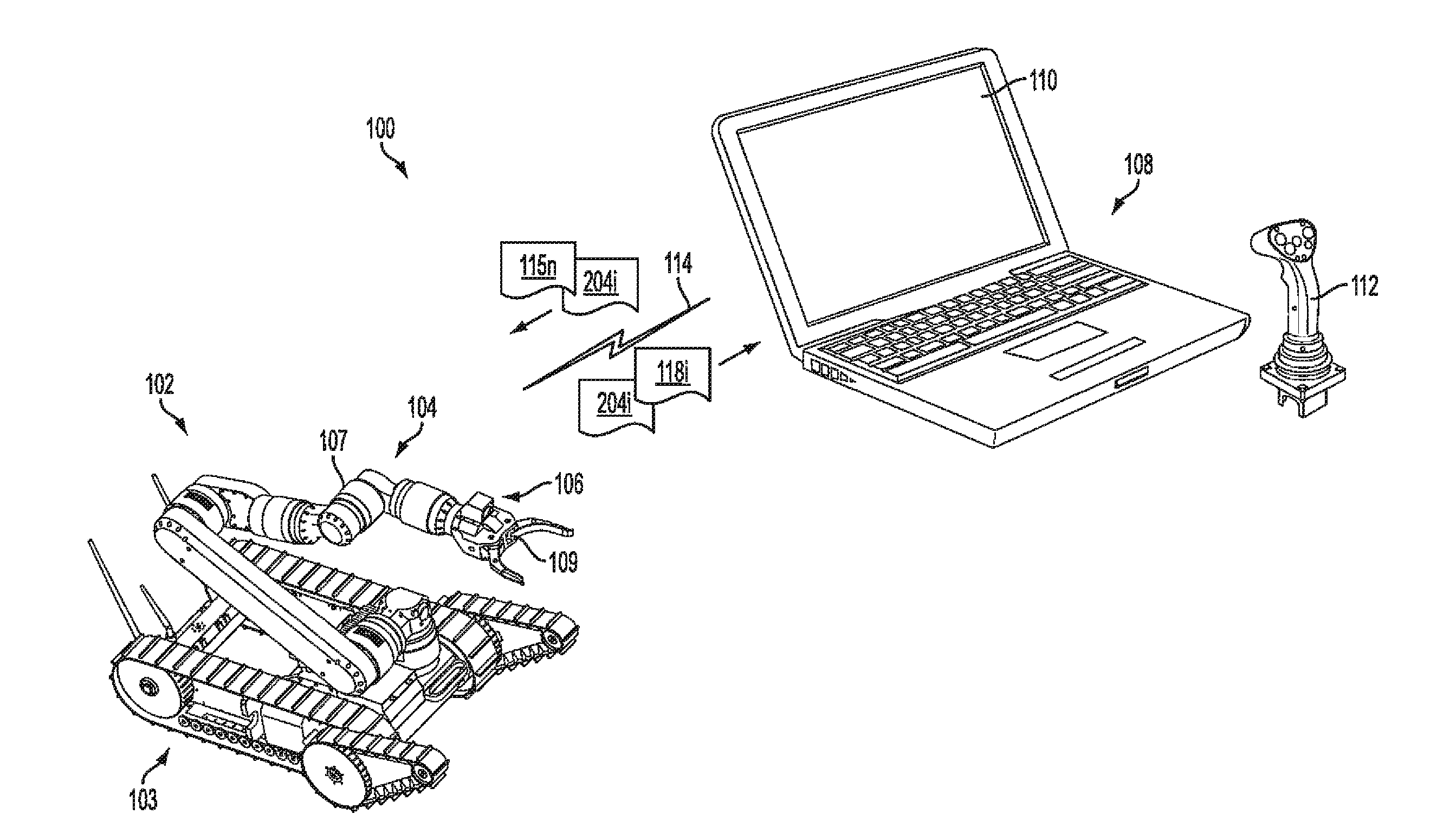
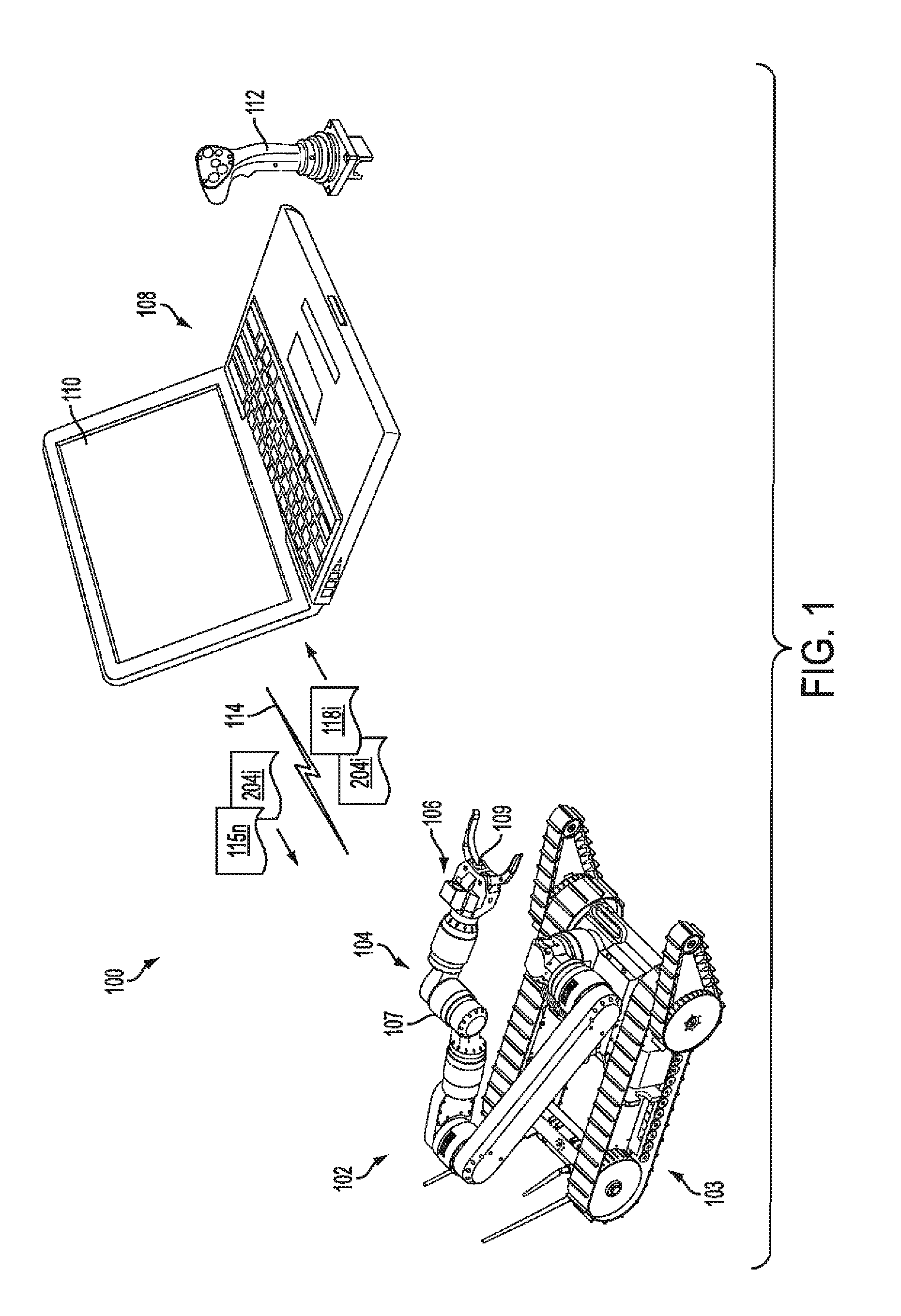
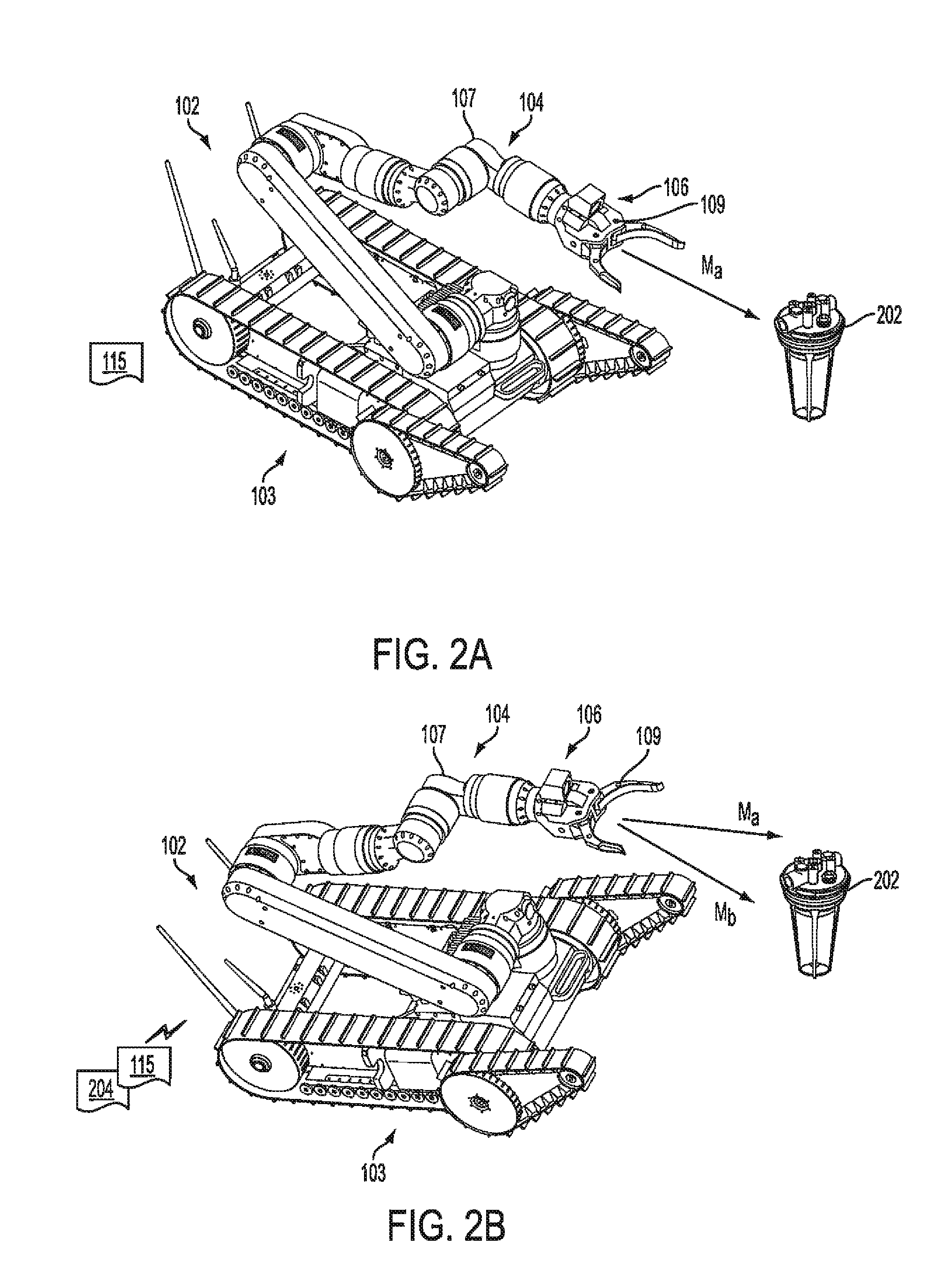
Control synchronization for high-latency teleoperation
Robotic system (100) includes a processing device (512) and a plurality of robot actuators (501) to cause a specified motion of the robot (102). The processing device (512) responds to one or more user robot commands (115) initiated by a control operator input at a remote control console (108). A user robot command will specify a first movement of the robot from a first position to a second position. The processing device will compare a current pose of the robot to an earlier pose of the robot to determine a difference between the current pose and the earlier pose. Based on this comparing, the processing device will selectively transform the user robot command to a latency-corrected robot command which specifies a second movement for the robot which is different from the first movement.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Position sensor system for substrate transfer robot
A substrate processing apparatus comprises a substrate handling chamber, a pair of position sensors, and a substrate transfer robot. Each of the sensors comprises an emitter configured to emit a beam of light, and a receiver configured to receive the light beam. The substrate transfer robot comprises an end effector and a robot actuator. The end effector is configured to hold a substrate such that the substrate has a same expected position with respect to the end effector every time the substrate is held. The robot actuator is configured to move the end effector within the handling chamber to transfer substrates among a plurality of substrate stations. An edge of a substrate held in the expected position by the end effector can partially block a light beam of one of the position sensors, while another end of the end effector partially blocks a light beam of the other position sensor.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
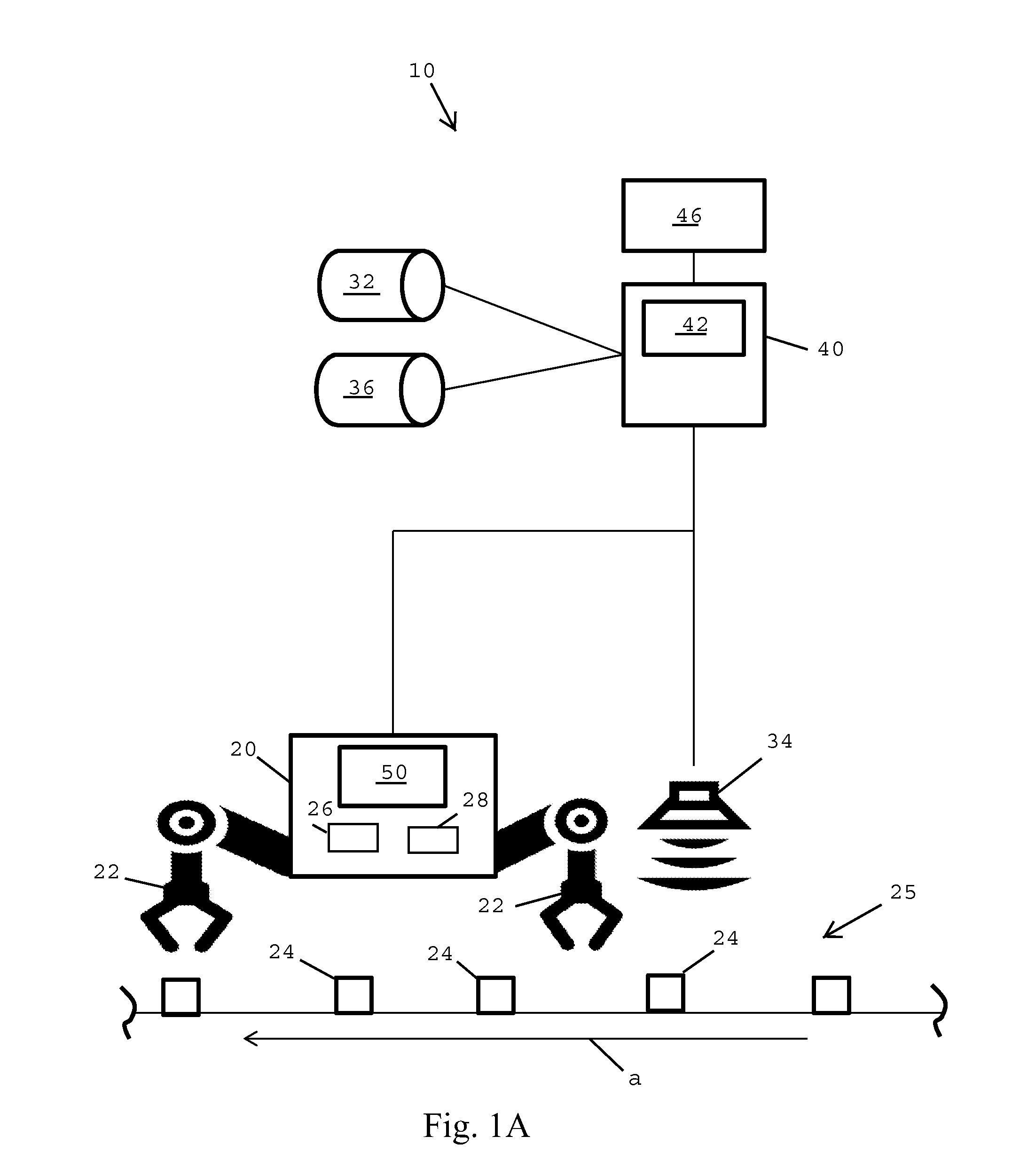
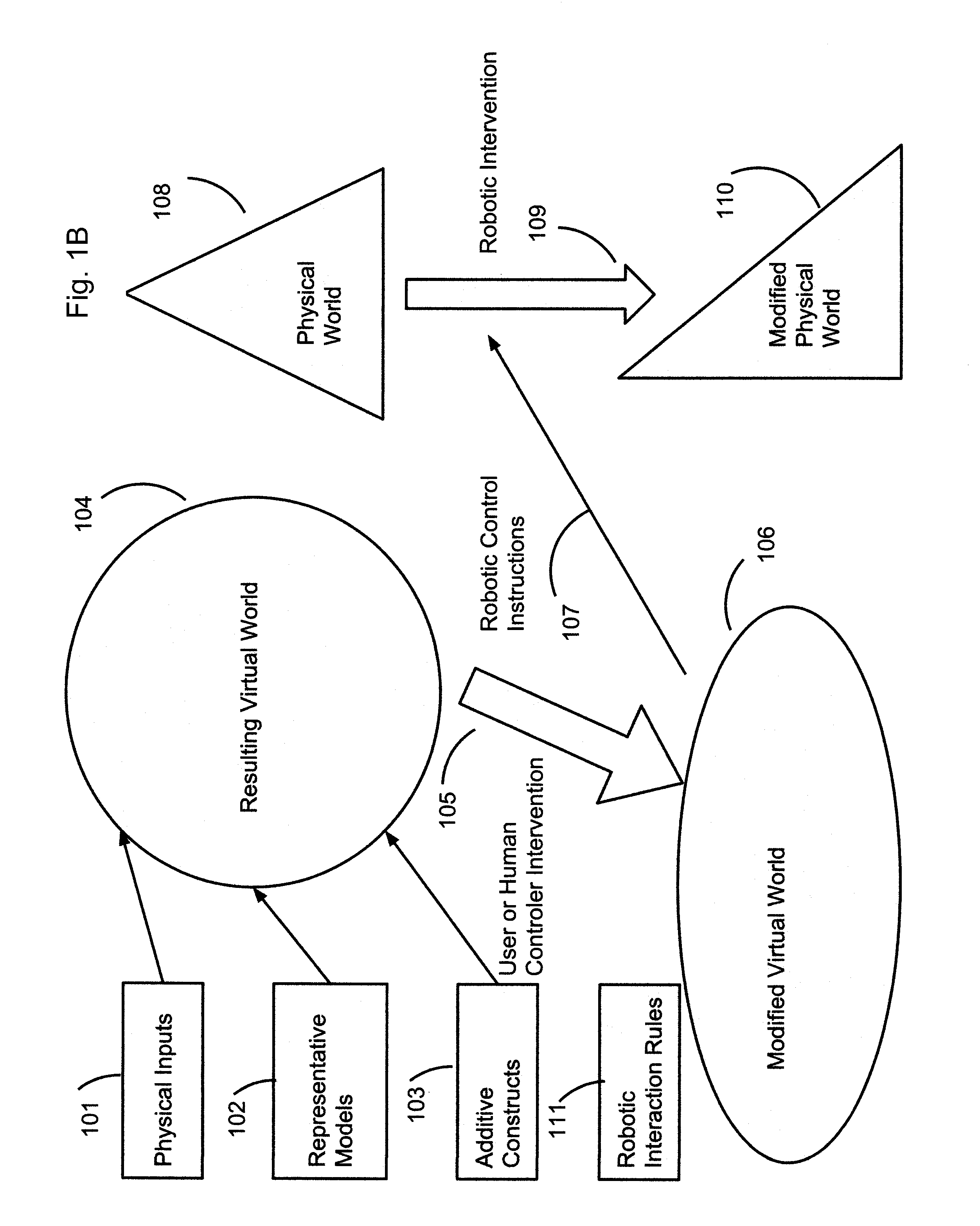
Robotic Control System Using Virtual Reality Input
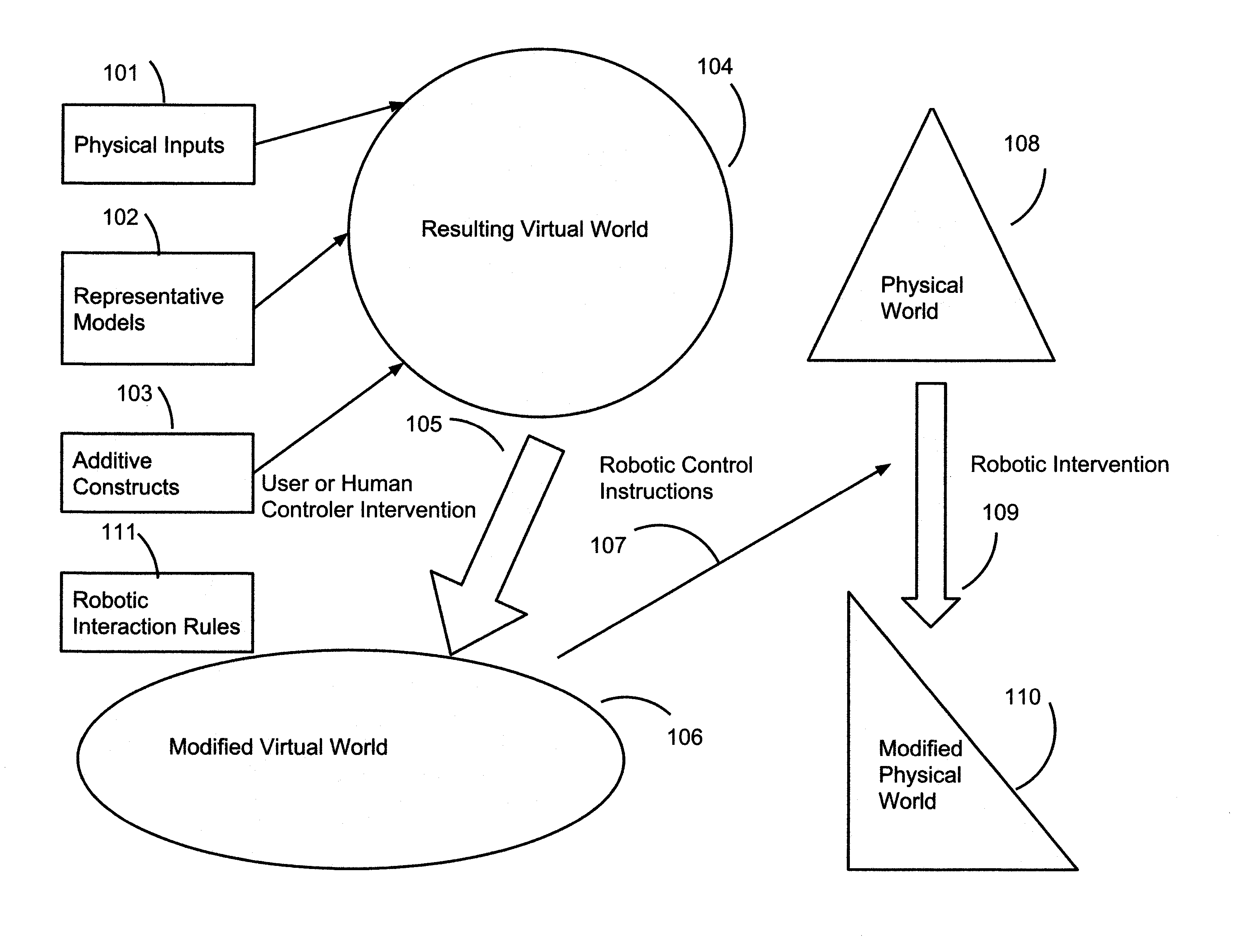
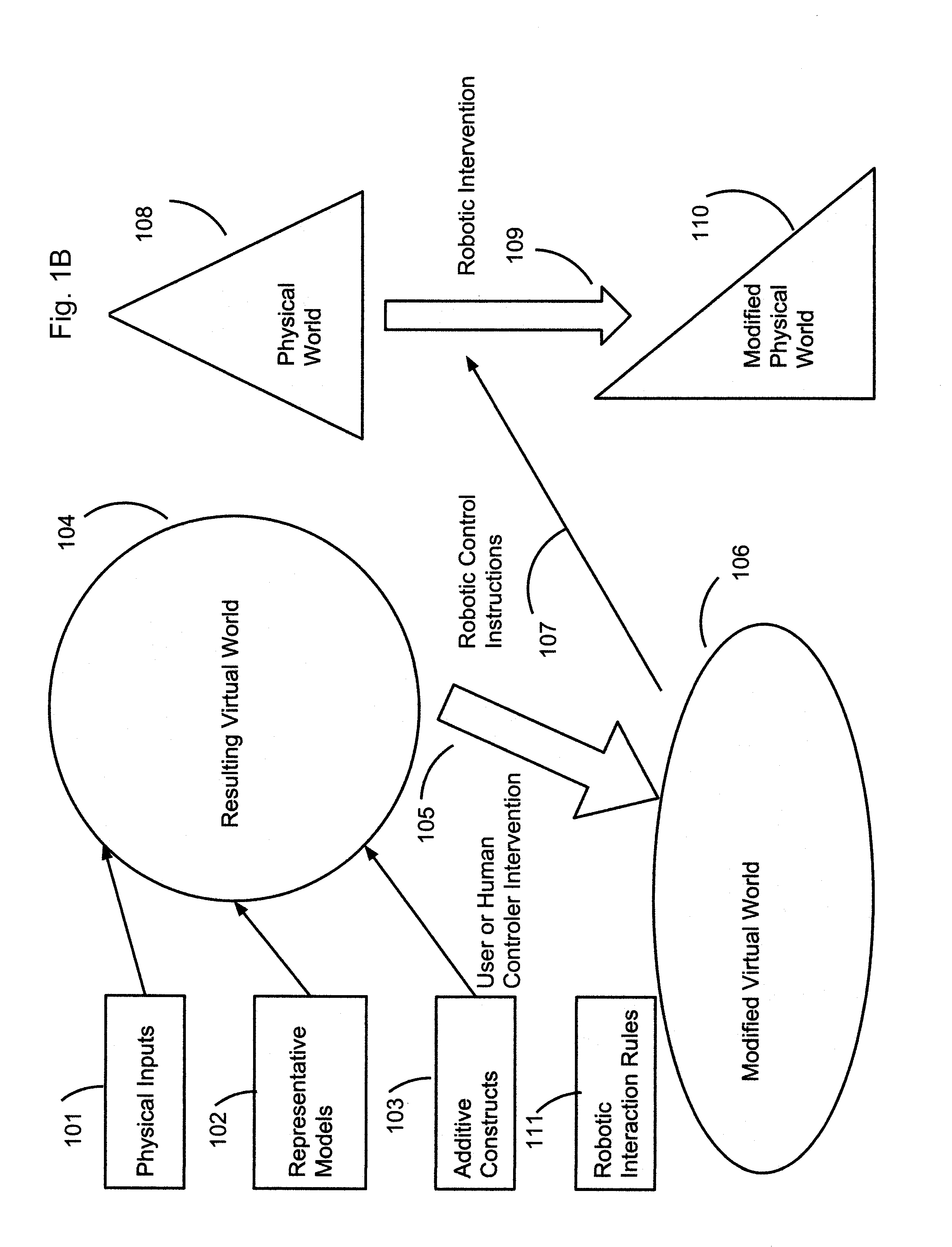
A robotic system and method performs tasks autonomously on real-world objects (RWOs) upon receipt of inputs from a virtual reality environment. A robotic actuator has tools to manipulate the RWOs, and a set of robot-specific instructions for actuating the tools. A first set of rules governs the RWOs, and sensors detect the presence of the RWOs. A virtual reality (VR) computer uses sensor data to generate a virtual world (VW) including virtual world objects (VWOs) representative of RWOs. A second set of rules governs the VWOs. A user manipulates the VWOs to generate a modified virtual world (MVW). A transformation engine captures differences between the VW and MVW, transforms the differences into inputs for the robotic actuator. An autonomous instruction engine receives the inputs to identify RWOs and combines the inputs with the first set of rules to generate combined instructions usable by the robotic actuator to manipulate RWOs autonomously.
Owner:PARKER COLEMAN P
Robot sand core lock core, core setting method and system
ActiveCN101249548AQuality improvementImprove quality reliabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorFoundry mouldsProduction rateControl room
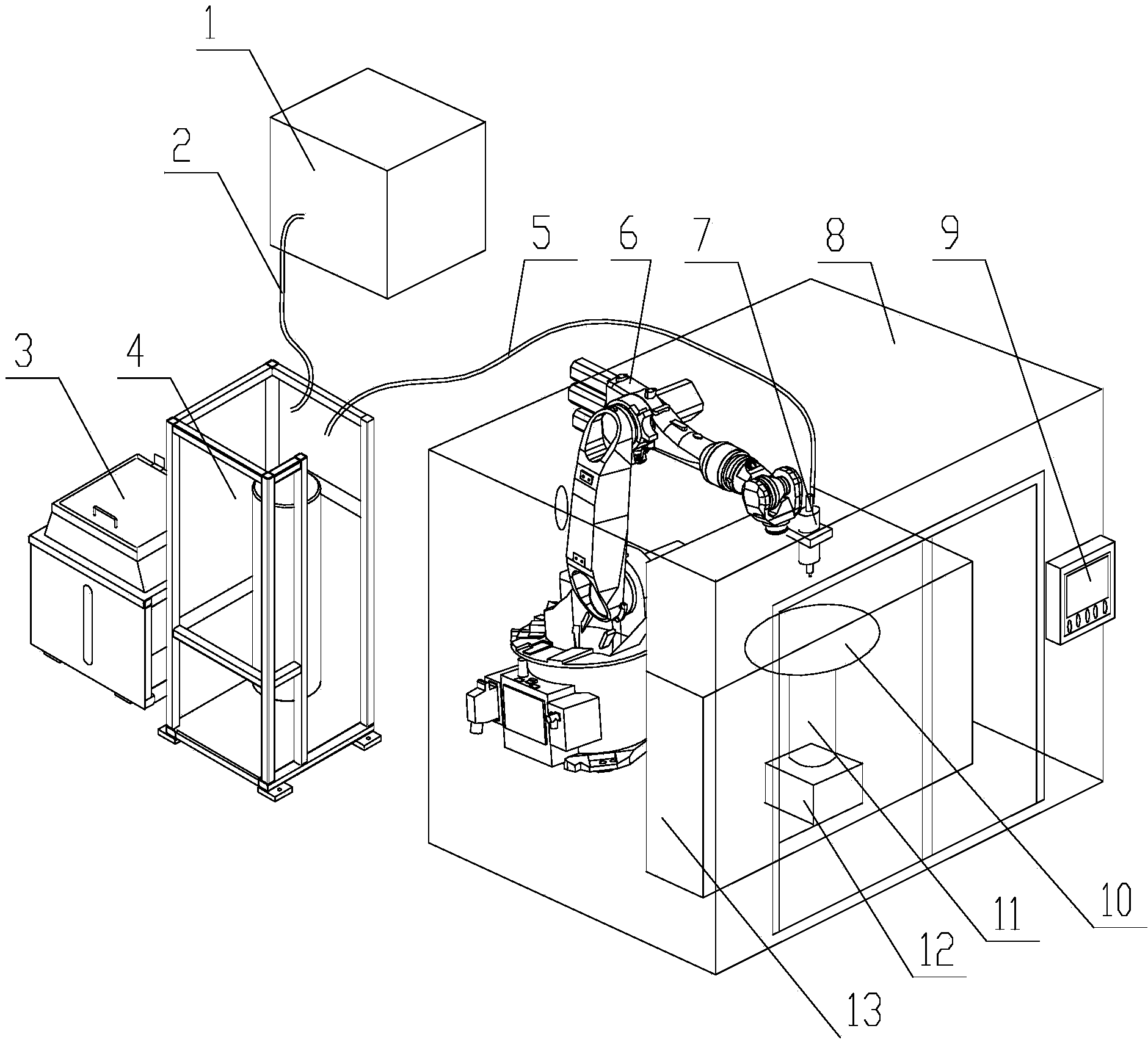
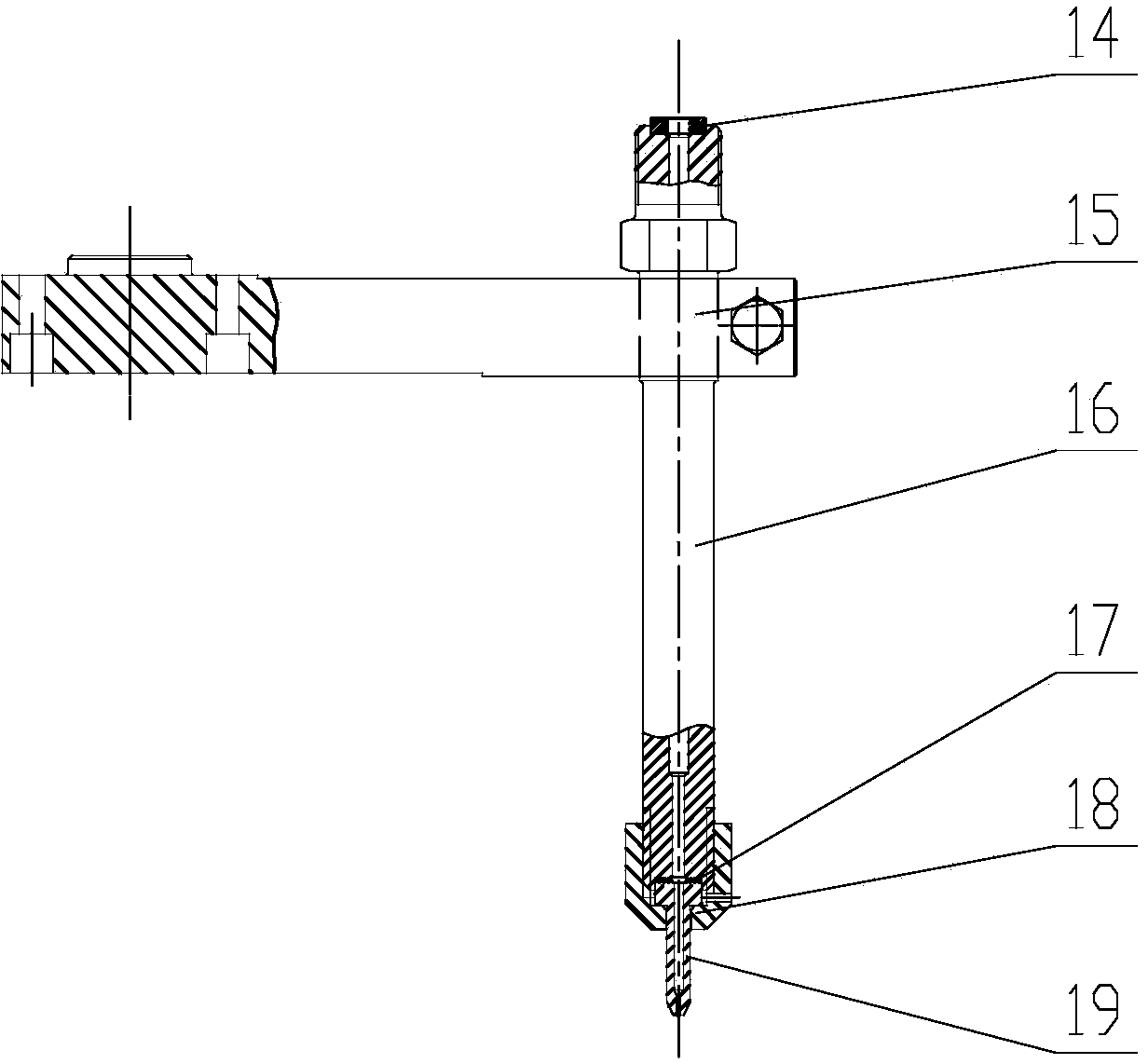
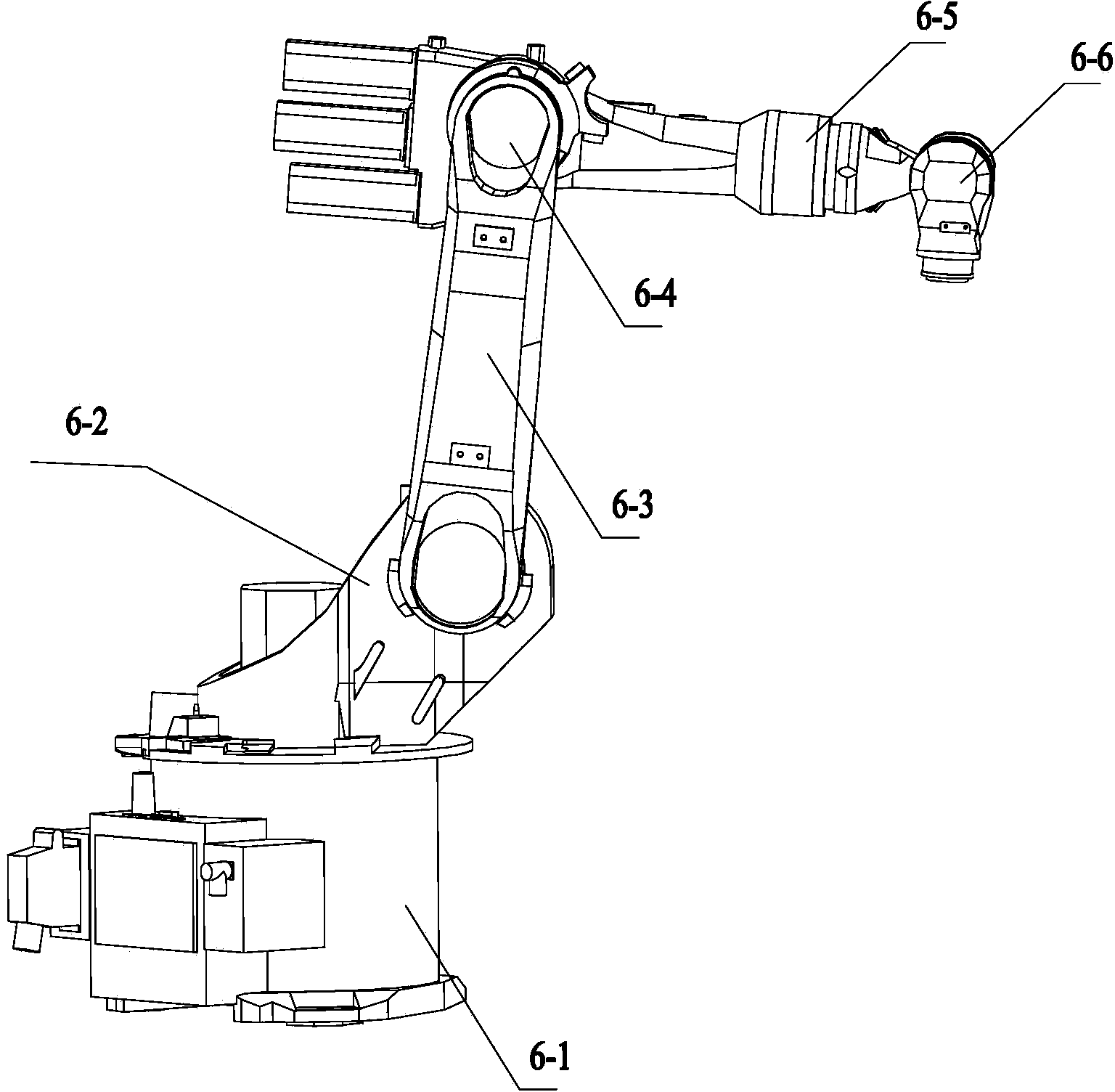
The invention relates to a method and a system for locking and setting a sand core by a robot, which is characterized in that the system comprises the multi-degree-of-freedom industrial robot, a core locking platform and a central control room, wherein the robot actuator is connected with a 3D scanner and a flexible fixture at the tail end; the core locking platform is arranged on one side of the robot; and the central control room is arranged on the other side of the robot and comprises a computer as well as an auxiliary control unit for controlling and monitoring the robot, the core locking platform and the 3D scanner. The system can achieve automatic accurate gripping, conveying, locking and setting processes of the sand core, greatly improve labor production rate, lower labor intensity while ensuring high-accuracy core locking and setting processes and improving the quality of a final product.
Owner:廊坊智通机器人系统有限公司 +1
Robot actuator and humanoid robot having the same
ActiveUS20110067518A1Effective reflectionAccurate and efficient assemblyProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsHumanoid robot naoBall screw
Disclosed herein are a robot actuator and a humanoid robot having the same. The robot actuator includes a rotation driving source, a ball screw member including a ball screw part connected to the rotation driving source and a nut part connected to the ball screw part, a guide member separated in parallel from the ball screw part, a slider member movably supported by the guide member, and a connection member connecting the slider member and the nut part to move the slider member in connection with movement of the nut part, and the connection member is relatively movably connected to at least one of the nut part and the slider member. Therefore, efficiency in force reflection and back-drivability of the actuator is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
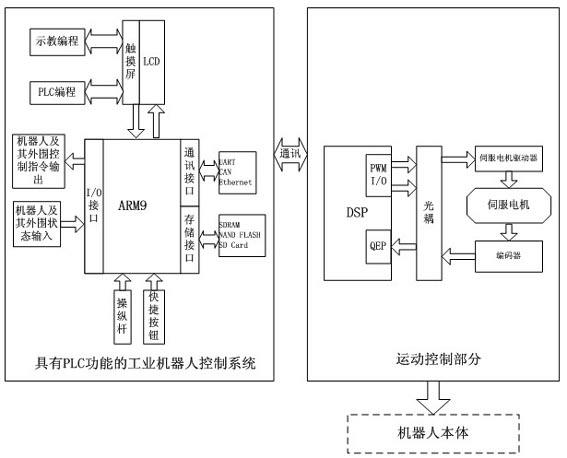
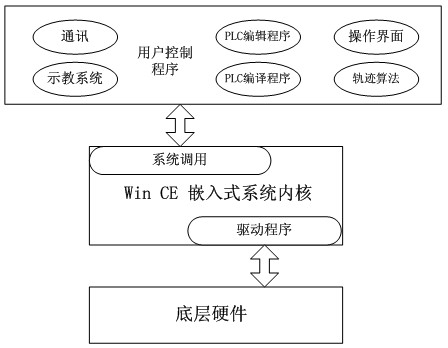
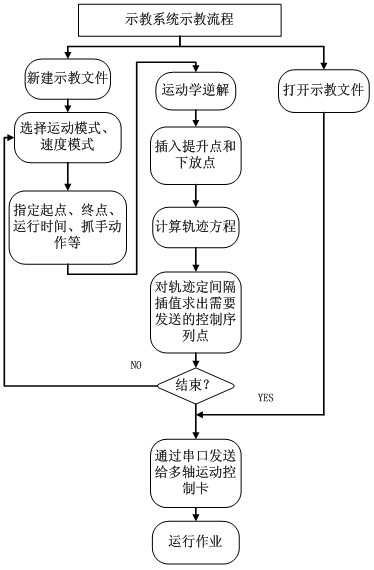
Six-axis industrial robot control system with PLC (programmable logic control) function
InactiveCN102658549AEasy to controlRealize automatic controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutomatic controlLiquid-crystal display
The invention relates to a six-axis industrial robot control system with a PLC (programmable logic control) function. Teaching control and PLC control can input a command to an ARM (advanced RISC (reduced instruction set computer) machine) micro-processor through an LCD (liquid crystal display) and a touch screen display module, an operating lever module and a fast button can directly input the command to the ARM micro-processor, an I / O (input / output) interface module is connected with the input and output signal end of a robot actuator, the ARM micro-processor is used for performing data storage and calling with a memory module, and after the ARM micro-processor is used for processing data and calculating a trajectory, a communication module can send a control signal to an execution control unit of a robot. A PLC system and a robot teaching control system are integrated into a whole, and various algorithms can be applied for improving the control performances of a motor. The operation is more convenient and simpler, and the automatic control of the robot can be realized. Different programs can be called and controlled against the robot under different conditions through the PLC, so that the same robot can complete the flexible control of different works. The system is novel in integral structure, small and exquisite in design, convenient and fast to use.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Control synchronization for high-latency teleoperation
Robotic system (100) includes a processing device (512) and a plurality of robot actuators (501) to cause a specified motion of the robot (102). The processing device (512) responds to one or more user robot commands (115) initiated by a control operator input at a remote control console (108). A user robot command will specify a first movement of the robot from a first position to a second position. The processing device will compare a current pose of the robot to an earlier pose of the robot to determine a difference between the current pose and the earlier pose. Based on this comparing, the processing device will selectively transform the user robot command to a latency-corrected robot command which specifies a second movement for the robot which is different from the first movement.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Articulated robot actuator
ActiveUS20180133894A1Complex actuationReduce mechanical frictionProgramme-controlled manipulatorActuatorControl theory
The present invention relates to an articulated robot actuator capable of minimizing the volume and weight thereof, securing flexibility to avoid mechanical friction, and complexly actuating a plurality of joints of an articulated robot having a multi-joint muscle structure to enable a natural movement.
Owner:ANGEL ROBOTICS CO LTD
Machining center
InactiveUS20080271302A1Eliminate the problemThread cutting machinesAssembly machinesTransport systemEngineering
A machining center is provided enabling a high degree of machining automation. The machining center includes a master machining head including multiple spindles mounted fixedly to the machining base. A workpiece transport system transports workpieces between machining stations and also moves it toward and away from the machining stations which are preferable fixedly mounted. Registration pins mounted to the master machine head register with a receiving socket carried by the workpiece platform or associated workpiece fixture. A robot actuator is provided which loads and unloads workpieces with the machining center 10 and can also potentially provide other functions such as tool inspection tool changing, workpiece repositioning.
Owner:ANN ARBOR MACHINE
Suspension abrasive water jet cutting equipment
InactiveCN104175230AIncrease flexibilityLong conveying distanceAbrasive machine appurtenancesAbrasive blasting machinesEngineeringHigh pressure water
The invention relates to suspension abrasive water jet 3D cutting equipment adopting a seven-shaft intelligent robot, in particular to suspension abrasive water jet cutting equipment which comprises a high-pressure pump station used for providing cutting power, an abrasive filling device and a suspension abrasive generating device used for producing abrasive, wherein a discharge hole of the abrasive filling device is connected with a feed hole of a high-pressure container arranged in the suspension abrasive generating device through a feed pipe, a water inlet of the abrasive filling device is connected with a water outlet of the high-pressure container arranged in the suspension abrasive generating device through a water inlet pipe; high-pressure water generated by the high-pressure pump station is connected with a tee joint arranged in the suspension abrasive generating device through a high-pressure pipe. The product provided by the invention adopts a pre-mixing suspension abrasive cutting technology, the cutting pressure is low, and the efficiency is high; the equipment adopts a high-pressure hose as a suspension abrasive conveying pipeline, the conveying distance is long, and the equipment ensures that a nozzle device can realize high-precision motion of any track and any angle in space under the drive of a robot actuator.
Owner:西安远诚机电科技有限公司
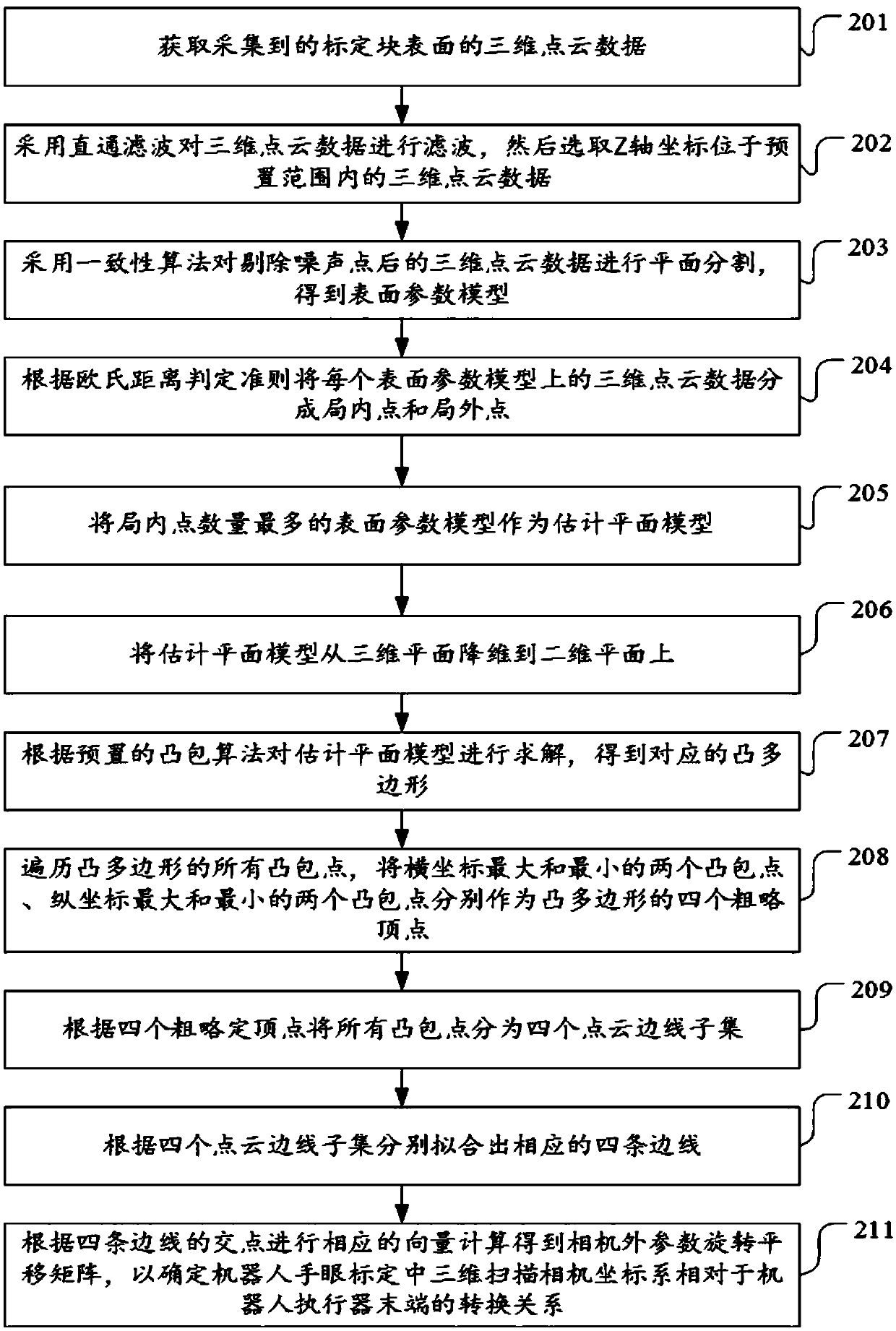
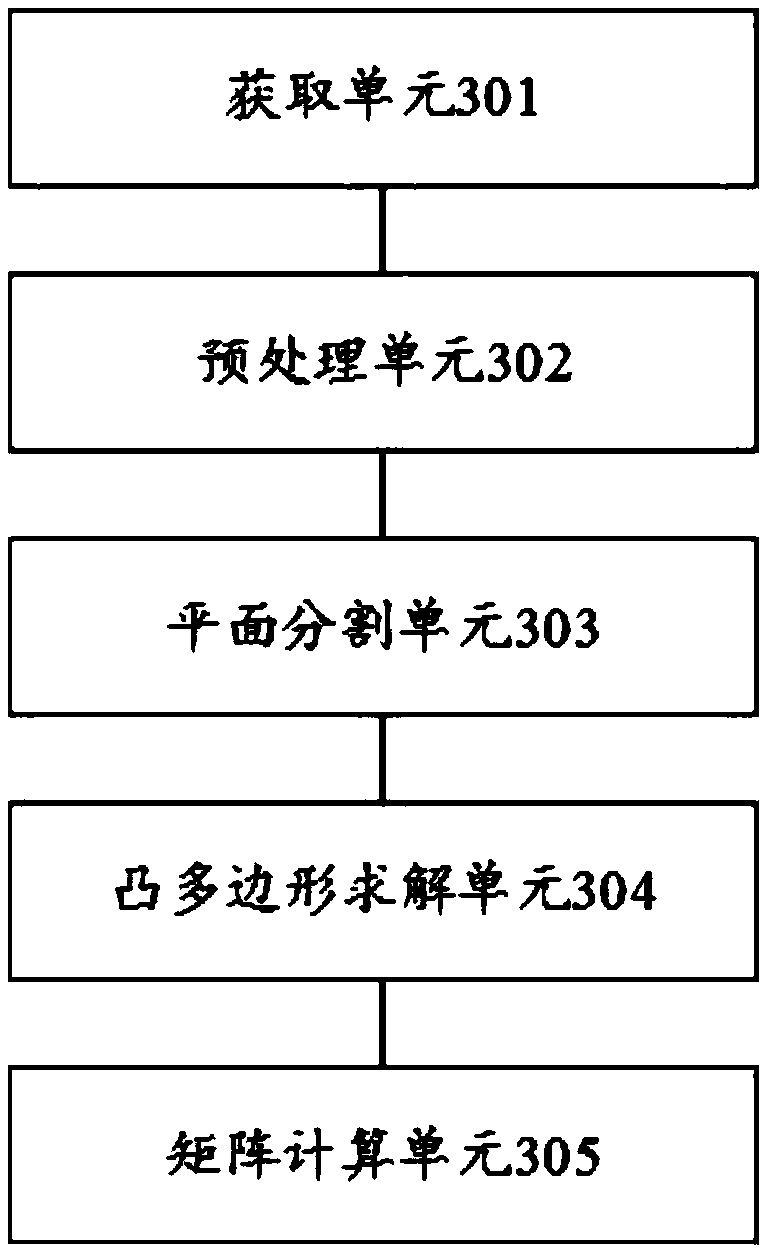
Calibration method and device for hand-eye relation of polishing operation arm
ActiveCN108994844ASolve the technical problem that does not apply to the rapid automatic identification of grinding system requirementsGrinding speed is fastProgramme-controlled manipulatorPlane segmentationRobot hand
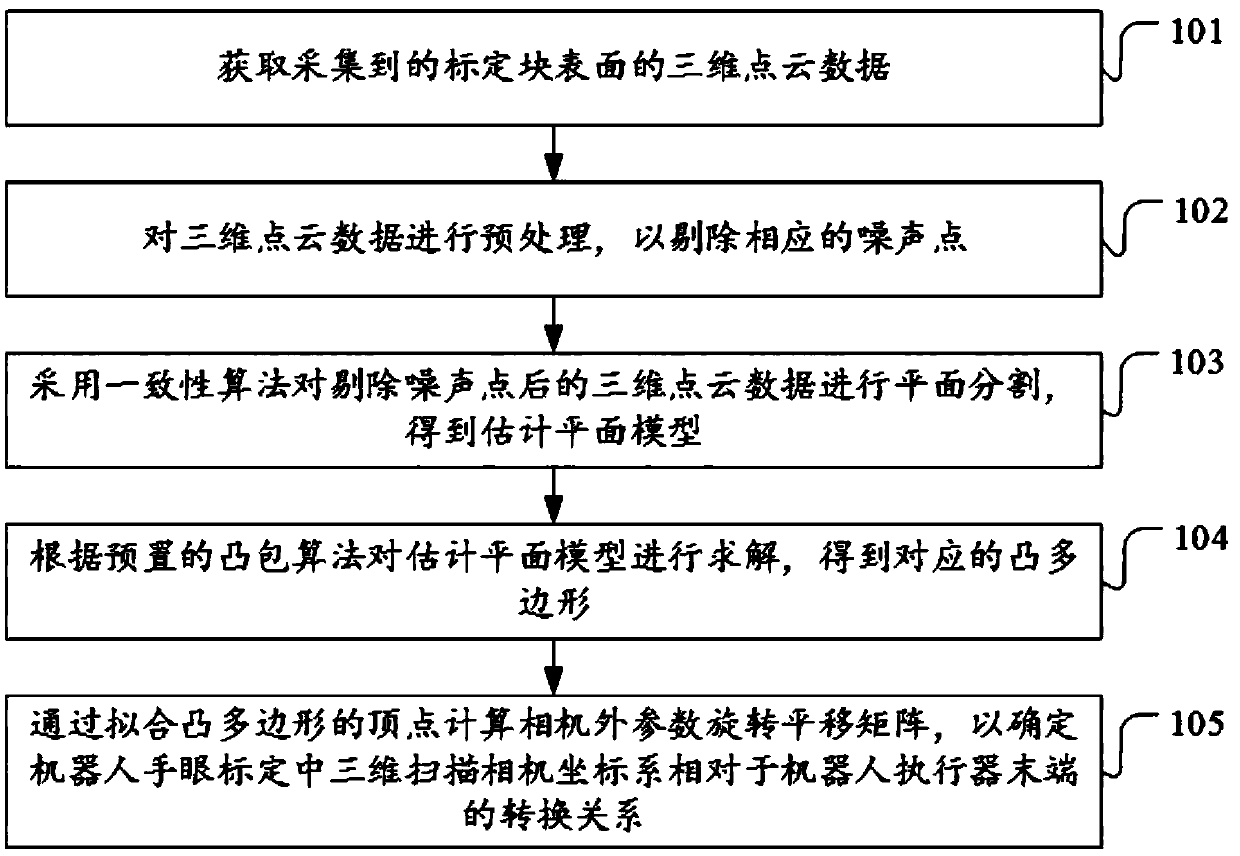
The invention discloses a calibration method and device for a hand-eye relation of a polishing operation arm. The calibration method comprises the steps that collected three-dimensional point cloud data of the surface of a calibration block is acquired; preprocessing is carried out on the three-dimensional point cloud data to remove corresponding noise points; a consistency algorithm is adopted tocarry out plane segmentation on the three-dimensional point cloud data with the noise points being removed, and an estimation planar model is obtained; according to a preset convex hull algorithm, the estimation planar model is solved, and a corresponding convex polygon is obtained; and by fitting vertexes of the convex polygon, an outer parameter rotation translation matrix RW(Cam) of a camera is calculated so that a transformational relation MCam(Tool) of a three-dimensional scanning camera coordinate system relative to the robot actuator tail end in robot hand-eye calibration can be determined. The technical problems that traditional visual sensor 3D calibration is not suitable for rapid automatic identification required by a polishing system is solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Electrically-controllable multi-fingered resilient heart compression devices
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
External intervening full-coverage intelligent robot fire-fighting and rescue system for high-rise building fire protection
ActiveCN106178356AWith demonstration learning functionImprove performanceFire rescueFire protectionEngineering
The invention discloses an external intervening full-coverage intelligent robot fire-fighting and rescue system for high-rise building fire protection. The external intervening full-coverage intelligent robot fire-fighting and rescue system mainly solves the problem that when a high-rise or super high-rise building catches a fire, due to the height of a floor catching the fire is too large, and a fire extinguishing facility in the building loses efficacy or an external wall fire hazard occurs or an external wall fire hazard vertically spreads, external intervening fire-fighting and rescue cannot be carried out. By means of the external intervening full-coverage intelligent robot fire-fighting and rescue system, two fire protection water columns sprayed out from two adjacent unit robots reach any ignition point at appropriate visual portions of an external wall, a place in a room and an indoor place of the building. By means of the external intervening full-coverage intelligent robot fire-fighting and rescue system, arms of the adjacent unit robots are connected, an upwards-arching transverse beam can be formed through the connected arms, a stretchable type rescue rigging arranged on the arms of the robot can automatically droop and extend out while the upwards-arching transverse beam is formed, trapped persons at any floor can be rescued through the rescue rigging, firemen can be conveyed to any floor, intervening deep into the building for fire-fighting and rescue through a fireplug arranged on a robot actuator is achieved.
Owner:郭宝安
Software robot actuator with rigidity independently controllable
InactiveCN109048856AChange the stiffnessIncrease stiffnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsExpansion chamberActuator
The invention provides a software robot actuator with rigidity independently controllable. The software robot actuator with rigidity independently controllable comprises a gas actuation portion and arigidity adjustment portion. The rigidity adjustment portion comprises a rigidity adjustment chamber and a granular medium yarn bag. The rigidity adjustment chamber is located at the bottom of the gasactuation portion. The granular medium yarn bag is tiled inside the rigidity adjustment chamber. The rigidity of the actuator is changed by changing the gas pressure in the rigidity adjustment chamber. The upper surface of the gas actuation portion is zigzag. The rigidity adjustment chamber is adhered to the lower surface of the gas actuation portion. The gas actuation portion comprises a plurality of gas actuation expansion chambers. Each gas actuation expansion chamber is arranged inside one single saw tooth, and every two adjacent gas actuation expansion chambers communicate with each other through an internal channel. According to the software robot actuator with rigidity independently controllable, the rigidity of the gas actuator can be changed on the premise that the motion flexibility is not affected, and the controllability is higher.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Vertical travelling mechanism for wind tower maintenance robot
The invention discloses a vertical travelling mechanism for a wind tower maintenance robot. The vertical travelling mechanism comprises a robot operation platform, an operation platform traction mechanism and a surface operation platform. The robot operation platform comprises a support, a robot actuator, the vertical travelling mechanism and a platform suction device; the operation platform traction mechanism comprises a fixing hanger, a telescopic cantilever and a servo lifting mechanism; the surface operation platform is disposed on a bearing platform of a wind generator or the ground near a wind tower, the surface operation platform comprises a robot control device and a working material conveying system, and the robot control device is in signal connection respectively with the robot actuator, a reel motor, a touch sensor, the platform suction device and a positioning suction device; the working material conveying system is connected with the robot actuator through a flexible conveying line. The vertical travelling mechanism has the advantages such as light weight, ease of implementation, low cost and no special requirement on operation sites and climbing faces.
Owner:内蒙古中科凌胜科技有限公司
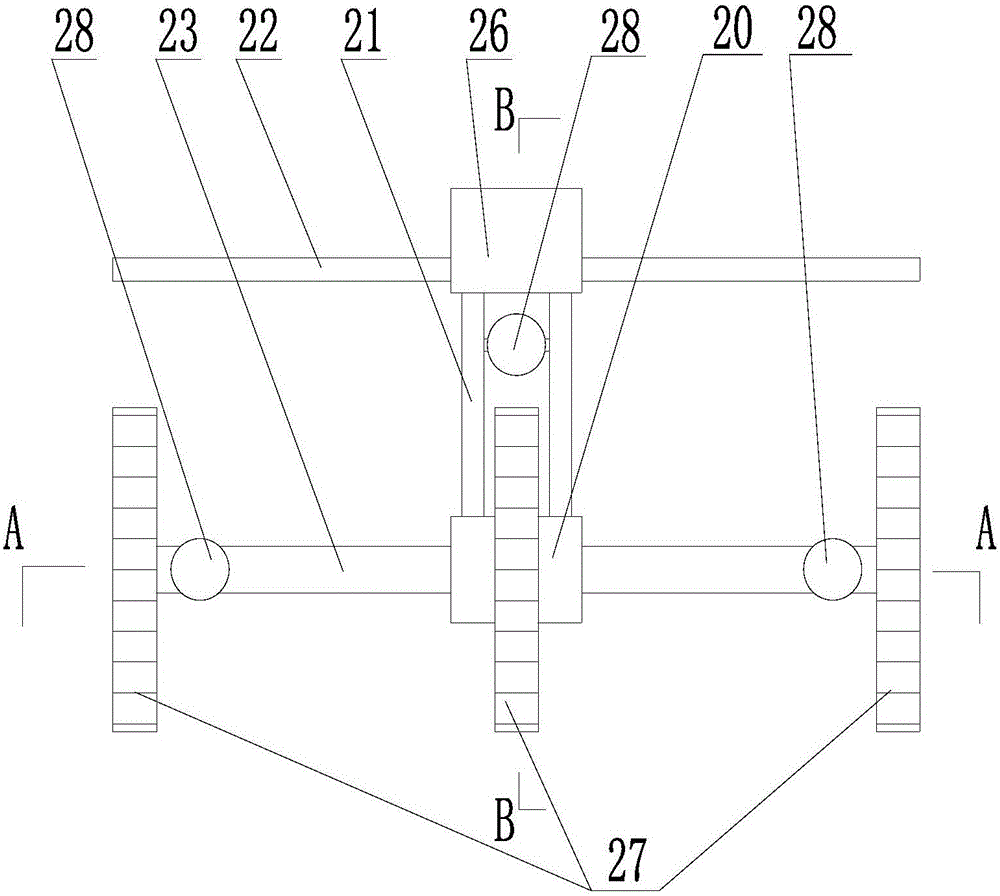
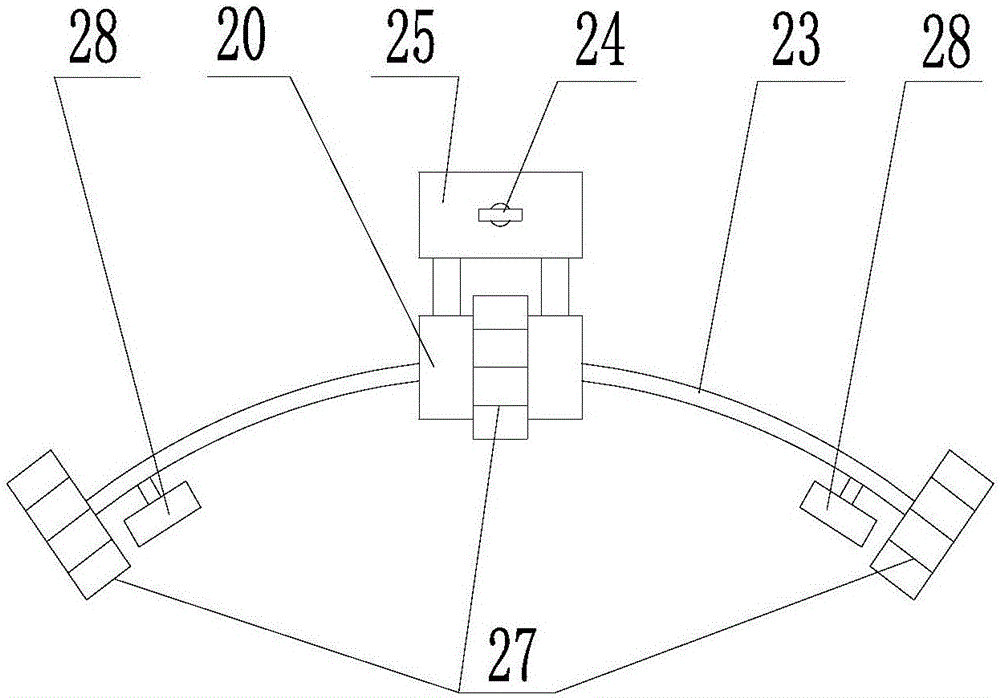
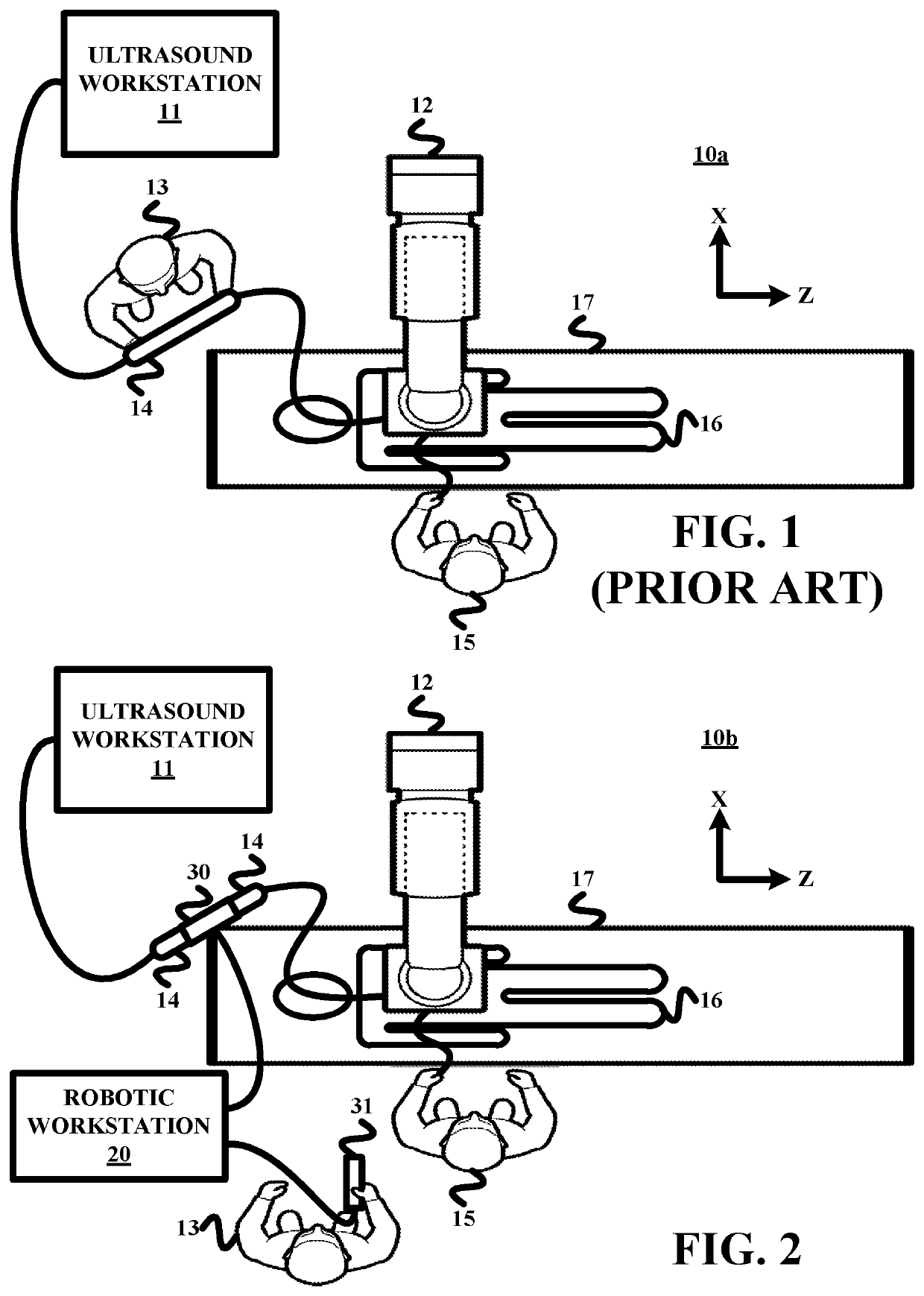
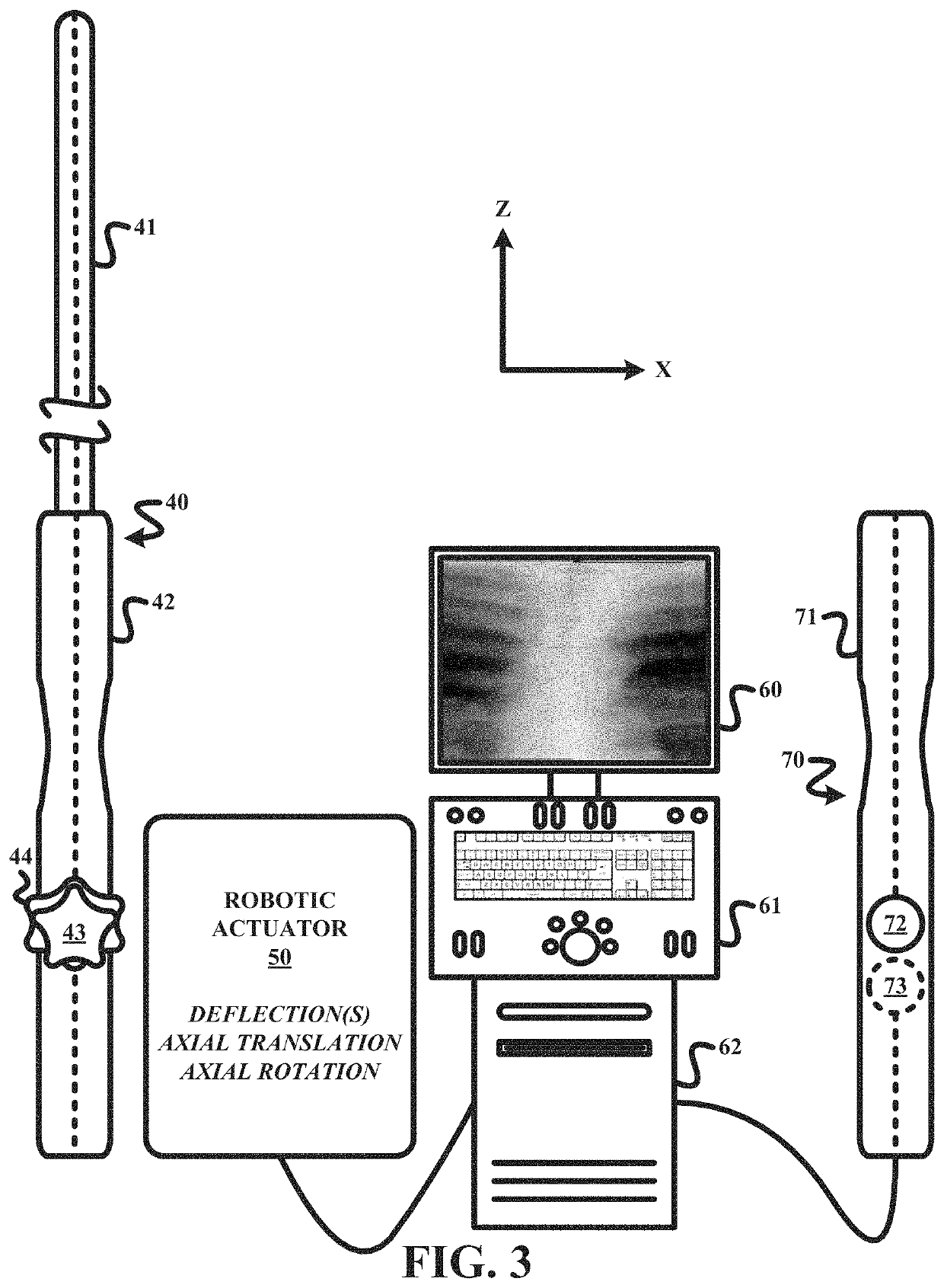
Remote robotic actuation of a transesophageal echocardiography probe
ActiveUS10813708B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterAccelerometerPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A replica control tool (70) for remotely controlling a control handle (42) of an interventional tool (e.g., a probe, a catheter and a flexible scope) is robotically controlled by a robotic actuator (50). The replica control tool (70) employs a replica control handle (71) is substantially a replica of a structural configuration of the control handle (42) of the interventional tool. A control input device (72) (e.g., a joystick or a trackball) is movable relative to the replica control handle (71). The replica control tool (70) further employs a robotic actuator controller (75) for remotely controlling the robotic actuator (50) in response to any movement of the control input device (72) relative to the replica control handle. The replica control tool (70) may further employ an electromechanical device (73) (e.g., an accelerometer) co-rotatable with the replica control handle (71) whereby the controller (75) remotely controls the robotic actuator (50) in response to a rotation of the electromechanical device (73).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Robot actuator and humanoid robot having the same
ActiveUS8579343B2Effective reflectionAccurate and efficient assemblyProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsHumanoid robot naoBall screw
Disclosed herein are a robot actuator and a humanoid robot having the same. The robot actuator includes a rotation driving source, a ball screw member including a ball screw part connected to the rotation driving source and a nut part connected to the ball screw part, a guide member separated in parallel from the ball screw part, a slider member movably supported by the guide member, and a connection member connecting the slider member and the nut part to move the slider member in connection with movement of the nut part, and the connection member is relatively movably connected to at least one of the nut part and the slider member. Therefore, efficiency in force reflection and back-drivability of the actuator is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Robotic control system using virtual reality input
A robotic system and method performs tasks autonomously on real-world objects (RWOs) upon receipt of inputs from a virtual reality environment. A robotic actuator has tools to manipulate the RWOs, and a set of robot-specific instructions for actuating the tools. A first set of rules governs the RWOs, and sensors detect the presence of the RWOs. A virtual reality (VR) computer uses sensor data to generate a virtual world (VW) including virtual world objects (VWOs) representative of RWOs. A second set of rules governs the VWOs. A user manipulates the VWOs to generate a modified virtual world (MVW). A transformation engine captures differences between the VW and MVW, transforms the differences into inputs for the robotic actuator. An autonomous instruction engine receives the inputs to identify RWOs and combines the inputs with the first set of rules to generate combined instructions usable by the robotic actuator to manipulate RWOs autonomously.
Owner:PARKER COLEMAN P
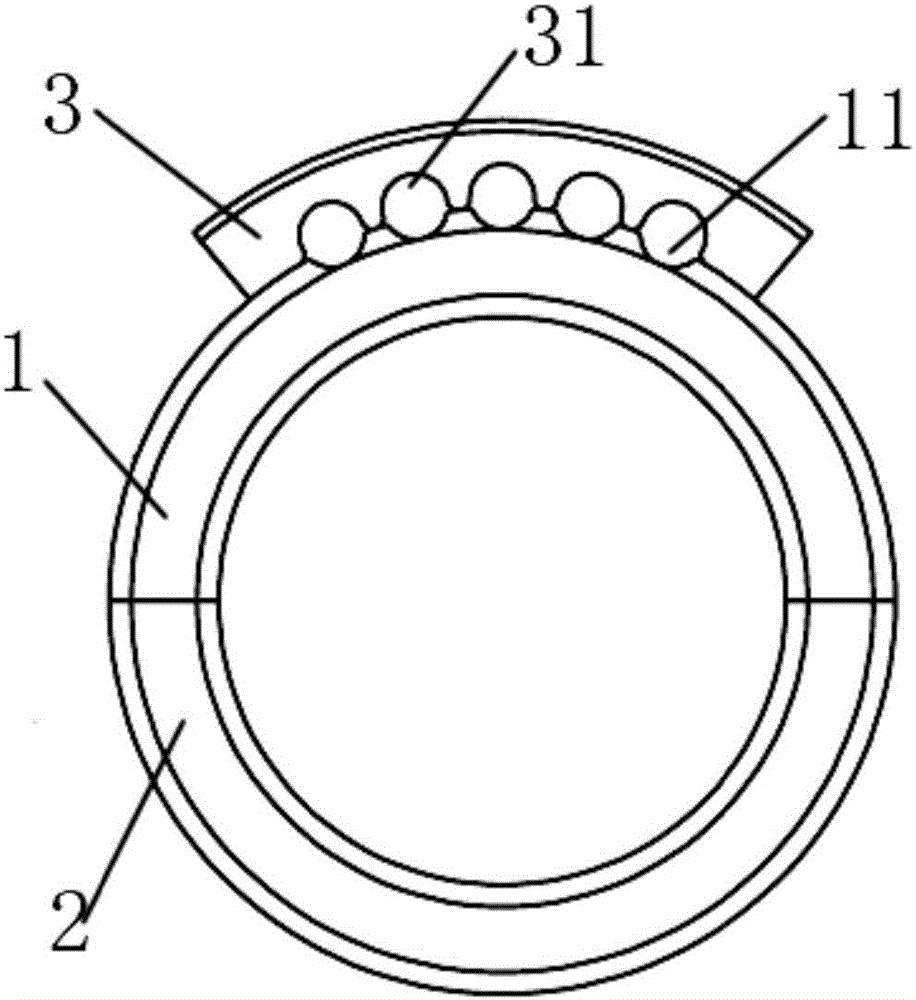
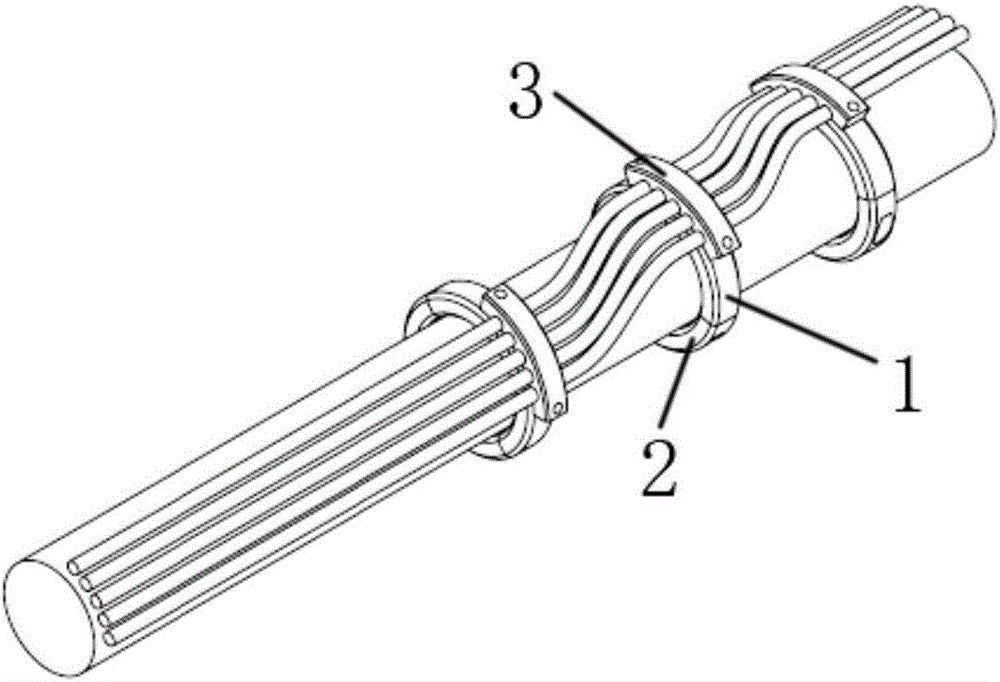
Cable restraining device suitable for robot executer
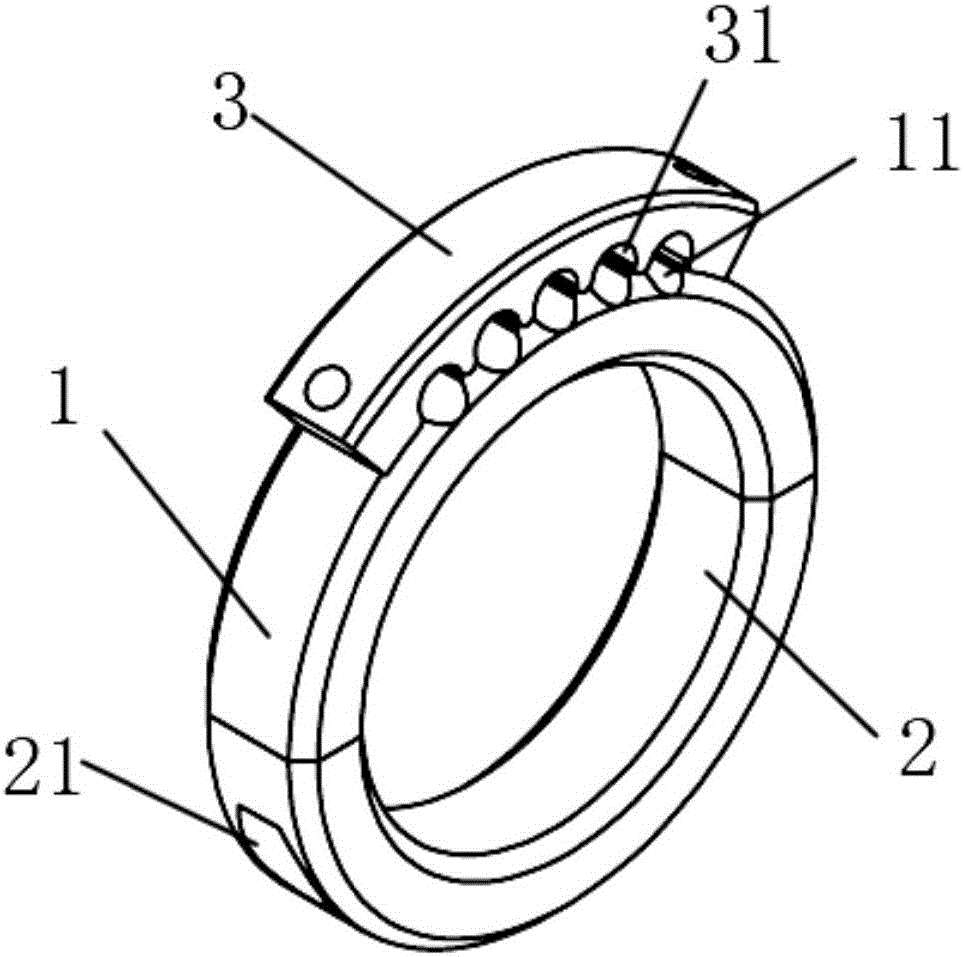
PendingCN106737866AAvoid problems such as interferenceCreate simple structuresManipulatorShortest distanceEngineering
The invention provides a cable restraining device suitable for a robot executer. The cable restraining device comprises an upper half ring, a lower half ring and a cable fixing base. The upper half ring and the lower half ring are the same in radius and are spliced to form an integral circular ring, and the two ends of the lower half ring and the two ends of the upper half ring are fixedly connected. The cable fixing base is of an arc structure, and a plurality of axially-formed arc fixing base grooves are formed in the inner wall of the cable fixing base. A plurality of upper half ring grooves corresponding to the fixing base grooves are formed in the outer wall of the upper half ring. The fixing base grooves and the upper half ring grooves are spliced into cable holes used for fixing a cable. The cable fixing base is fixedly connected with the upper half ring. According to the cable restraining device, the cable is kept close to a robot with the short distance, and meanwhile the problems such as interference caused by cable postures in the using process are solved.
Owner:清研同创机器人(天津)有限公司
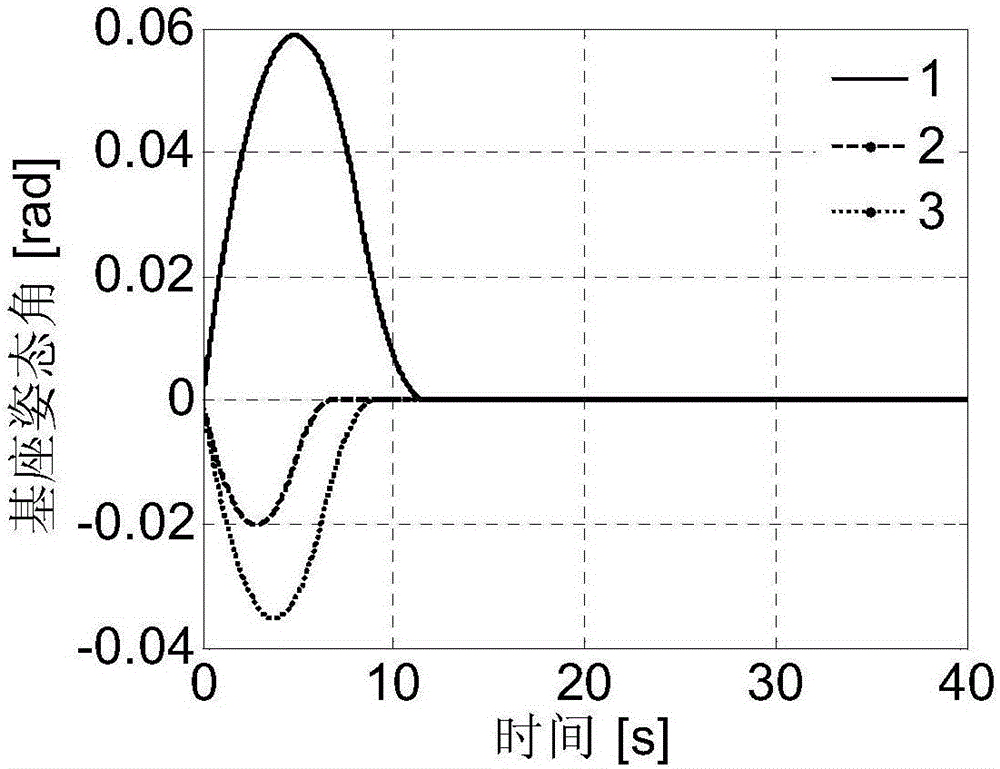
Rapid attitude stabilization method suitable for space robot actuator failure
ActiveCN106708078AReduce consumptionThe base posture is fast and stableCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsStabilization controlInverse dynamics
The invention discloses a rapid attitude stabilization method suitable for space robot actuator failure. An inverse dynamic model is acquired on the basis of establishing a system dynamic model, and the relationship between the control moment and mechanical arm joint movement under the given base attitude movement condition is acquired by aiming at the characteristics. The balance attitude required by stabilization of the system is determined by considering the problems of failure of an actuating mechanism and the limited amplitude and direction of the output moment so that the control moment is enabled to balance the angular momentum of the system under the attitude. The attitude angle change of the base in the whole stabilization process is acquired by considering the initial movement state and the balance attitude of the base through combination of the constraint and inputted to a control model so as to acquire the corresponding working state of the actuating mechanism and the rotating rule of all the joints of the mechanical arm. Compared with the conventional control method considering the actuator failure, base stabilization control under the condition of providing single shaft moment only is realized by the method for the first time, and the time consumed in the whole stabilization process is greatly reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
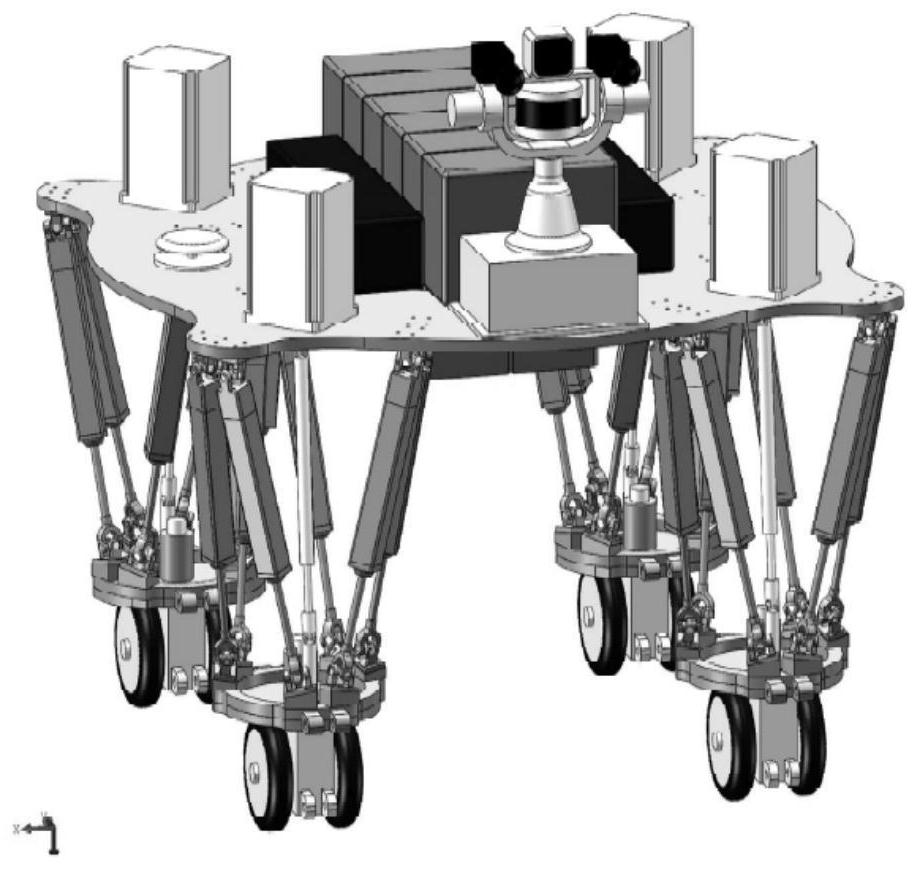
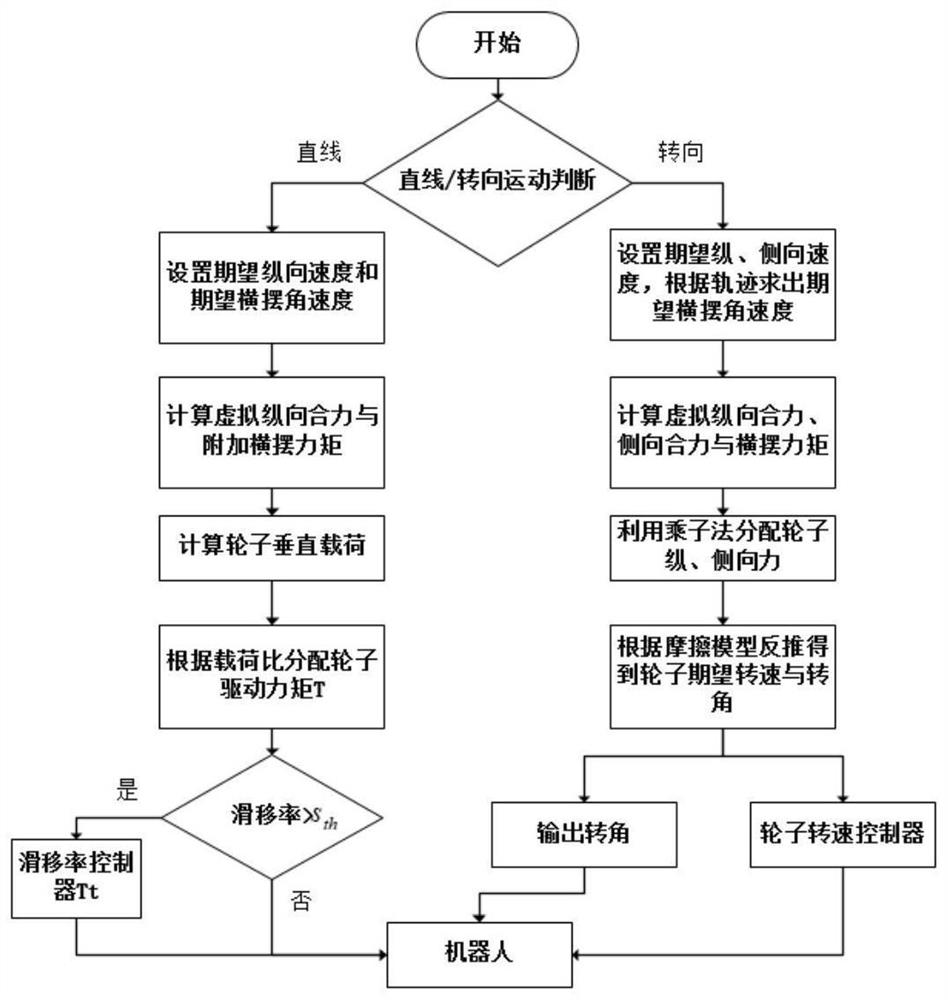
Four-wheel cooperative control method for wheeled robot
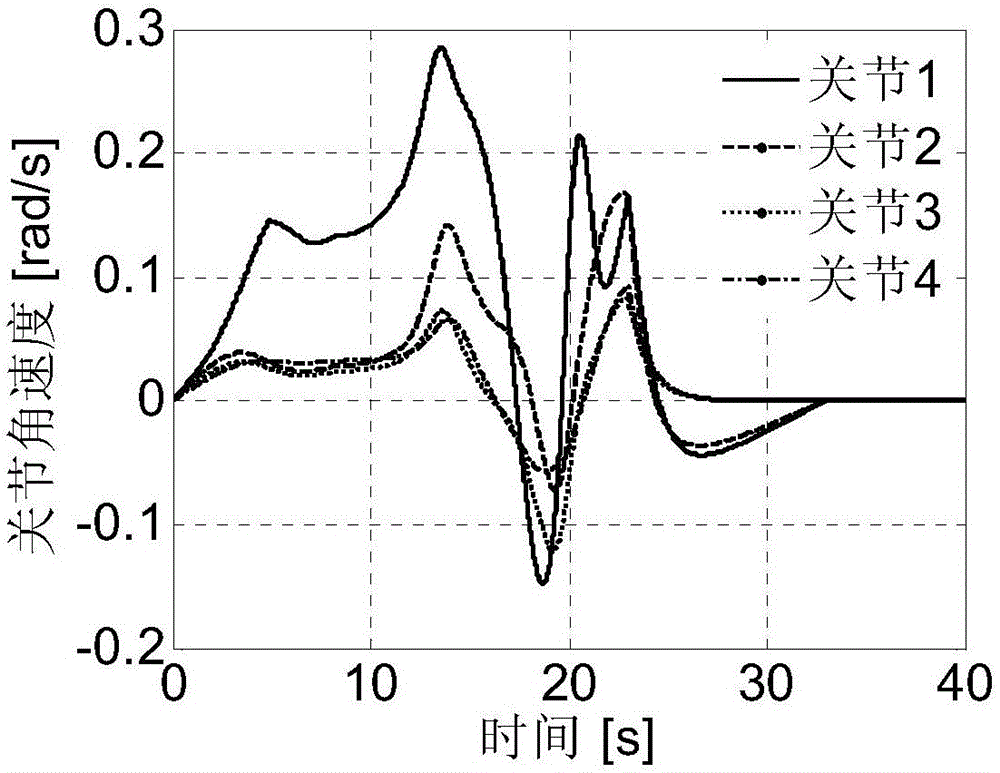
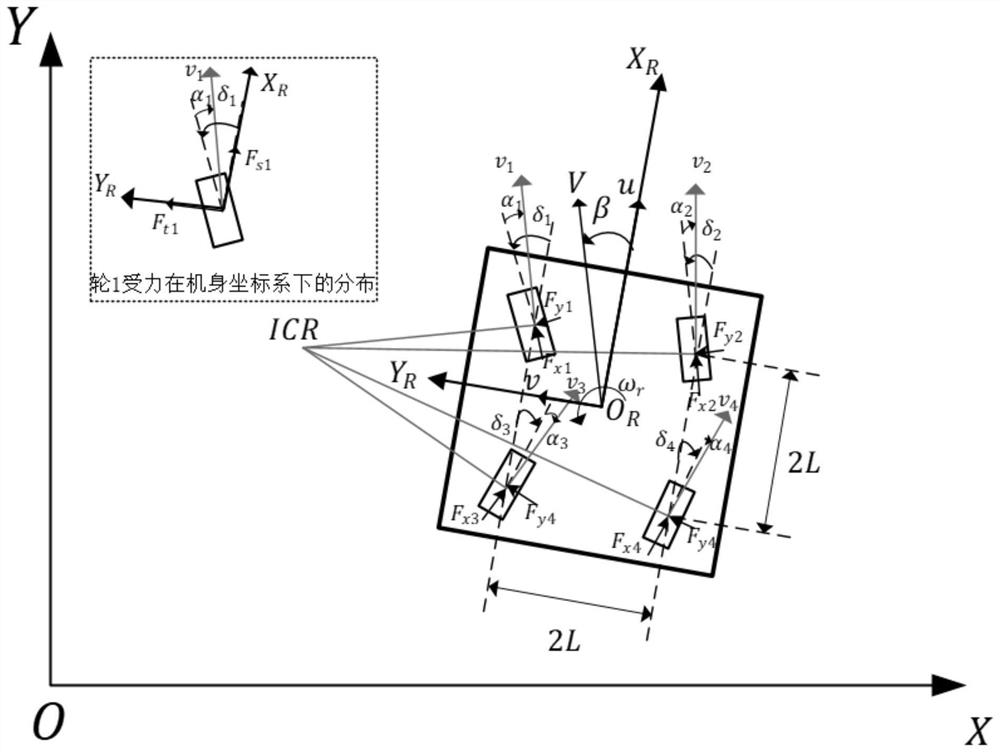
ActiveCN111752150ACollaborative fastGuaranteed stabilityControllers with particular characteristicsSimultaneous control of multiple variablesLinear motionSimulation
The invention discloses a four-wheel cooperative control method for a wheeled robot. The stability of movement of a wheeled robot can be kept. The method comprises the steps of under linear motion, determining virtual longitudinal resultant force added with virtual yawing moment required by the wheeled robot to track the expected longitudinal speed, distributing the virtual longitudinal resultantforce to each wheel, and further calculating driving moment of each wheel; judging whether the wheels slip or not, and controlling a non-slipping wheel by adopting the driving torque; for the slippingwheel, using a robust self-adaptive controller for controlling the rotating speed of the wheel, so that the slipping rate of the slipping wheel tracks a slipping rate threshold value; under the steering motion, calculating various forces by using a steering fuselage speed controller, optimally distributing the longitudinal force and the lateral force of each wheel by taking the minimum adhesion margin as a target, and converting the longitudinal force and the lateral force into expected rotating speeds and rotating angles of the wheels; inputting the expected rotating angle into a wheeled robot actuator to be controlled, and inputting the expected rotating speed into a robust self-adaptive rotating speed controller to obtain the driving torque of the wheels.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Servo-controlled 3D drawing robot
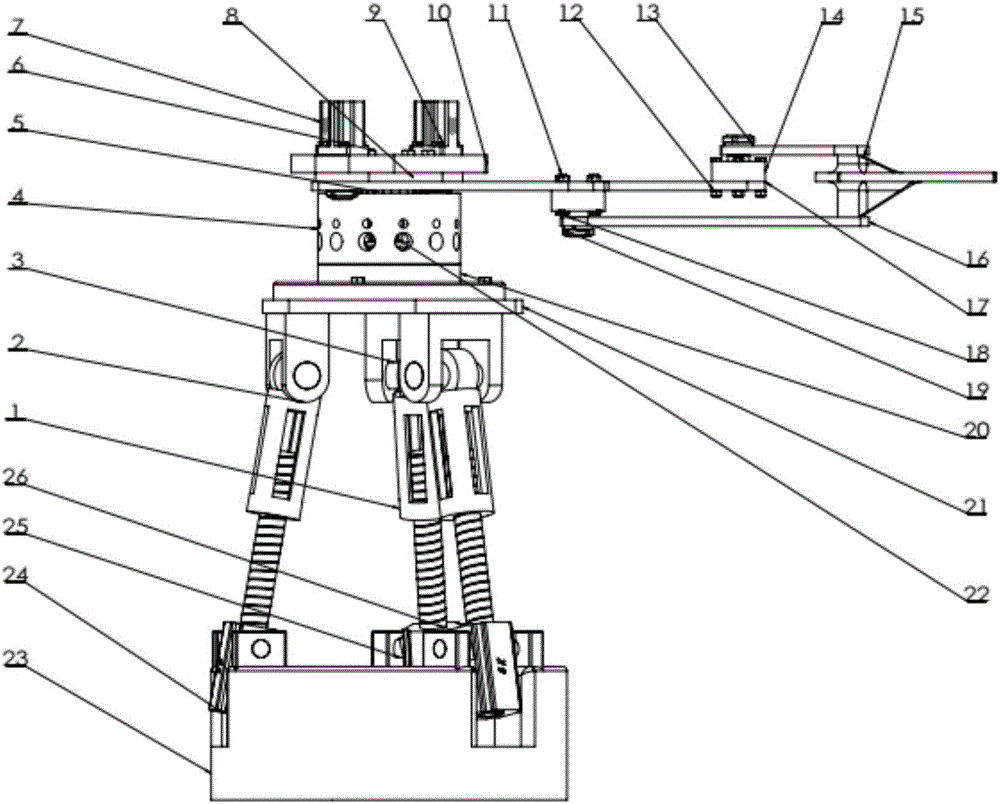
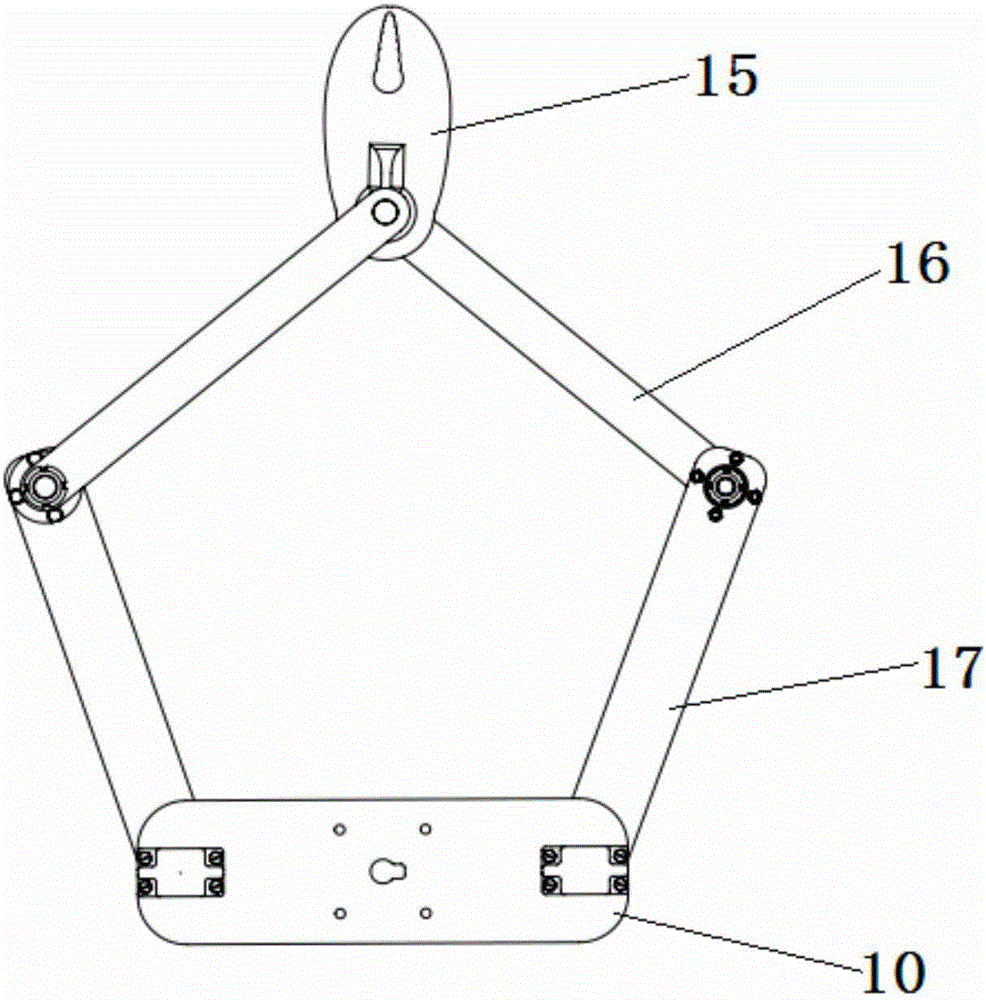
InactiveCN106346461AReduce cumulative errorLarge working spaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorInterference fitHuman body
The invention relates to a servo-controlled 3D drawing robot composed of a 3-DOF parallel base, a waist auxiliary device and a five-rod robot actuator. The servo-controlled 3D drawing robot can realize plane and space drawing operation with a small driving moment during actual work. The five-rod robot actuator realizes drawing of a two-dimensional plane complex curve through a five-rod structure, and proper interference fit is utilized in the five-rod structure to lower the transmission error, so that the drawing process is convenient to control precisely and stably; an embedded structure is adopted in the waist auxiliary device, and a servo motor is utilized for enlarging working space for actuation; the 3-DOF parallel base imitating movement of the shoulder of a human body enables the drawing robot to realize space drawing operation at three degrees of freedom. The product has the advantages of being flexible in structure, small in occupied space, good in compatibility and stability, low in weight and cost, good in locating precision and the like.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Movement speed control method for cable-driven camera robot
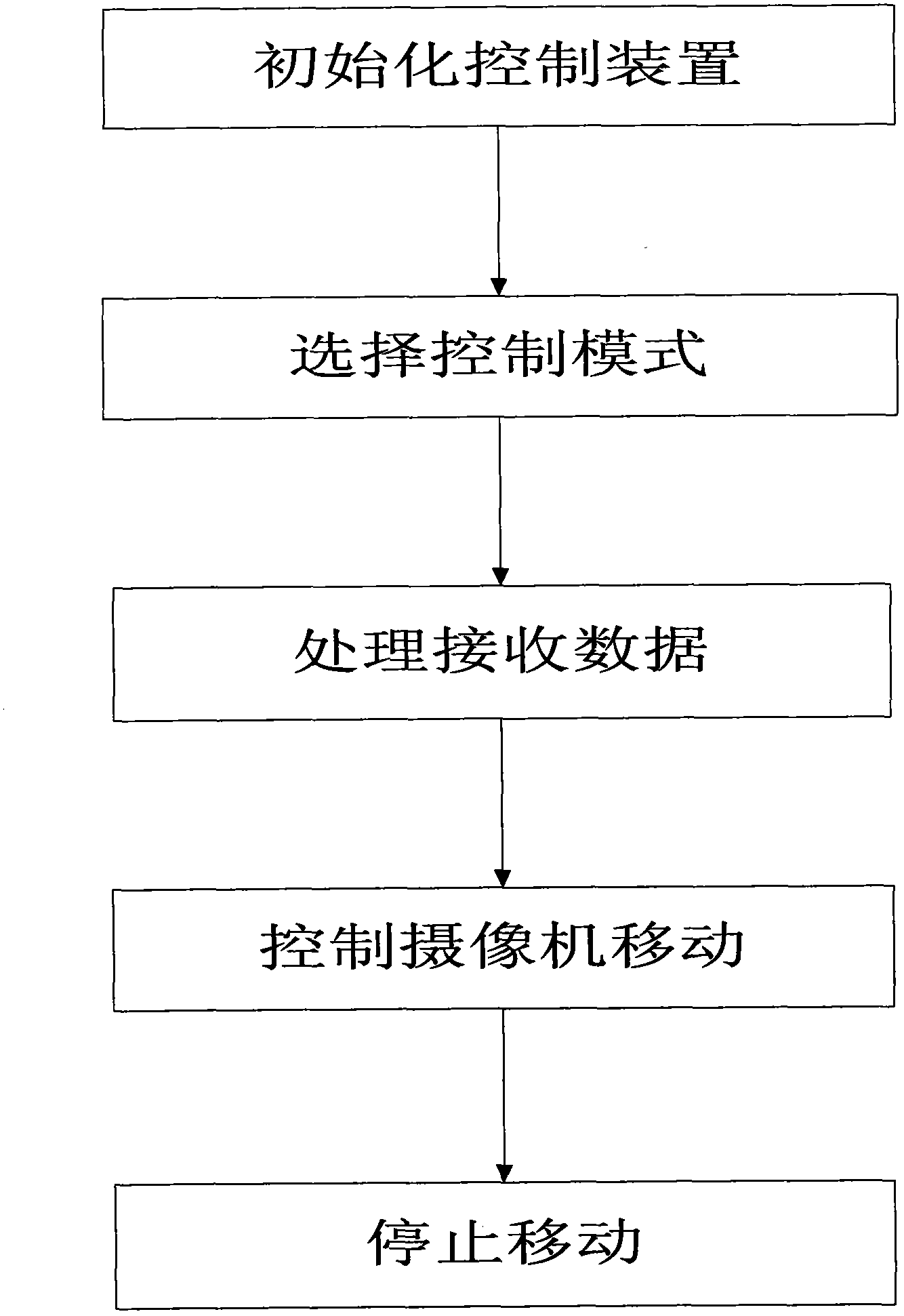
InactiveCN103286783AOvercome the shortcoming of sudden change in speed and unstable movementSmooth and controllable movement speedTelevision system detailsProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer scienceThree dimensional motion
The invention discloses a movement speed control method for a cable-driven camera robot. The method includes the steps of initializing a control device, selecting a control mode, processing received data, controlling a camera to move, stopping movement of the camera and the like. Movement speed of the camera robot is controlled in a point-motion control mode and a handle control mode; in the point-motion control mode, the movement speed of the camera robot is increased from zero to a constant speed to keep the camera robot moving at the constant speed by controlling a point-motion knob; in the handle control mode, the movement speed of the camera robot changes with change of rocking angle of a handle by controlling the handle, a control program of a camera robot actuator controls telescoping speed and length of four cables of the camera robot according to a transmitted speed vector, and the camera robot is controlled to be in stable three-dimensional motion in the specified space according to the specified speed vector.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Pipeline flexible robot and control method thereof during moving in pipeline
The invention discloses a pipeline flexible robot and a control method thereof during moving in a pipeline. The pipeline flexible robot comprises a driving control device and a flexible transmission assembly, wherein the driving control device comprises a driving mechanism, a pipeline detection sensor and a controller; the driving mechanism and the pipeline detection sensor are electrically connected with the controller; the flexible transmission assembly comprises n transmission units and n-1 plate springs; every two adjacent transmission units are connected through one plate spring; a robotexecution device can be installed at the front end of the first transmission unit; the rear end of the nth transmission unit is connected with the driving mechanism; and the pipeline detection sensorsends the detected pipeline bending condition to the controller, the controller controls the driving mechanism to drive the flexible transmission assembly to bend and swing in the pipeline according to the pipeline bending condition, and then the movement of the pipeline flexible robot in the pipeline is realized.
Owner:中铁长江交通设计集团有限公司
Edible Pneumatic Soft Robotic Actuators
The present invention relates to a biocompatible, digestible and edible material for use in soft edible robots. The present invention provides a pneumatic actuator for edible robotics, and a toy set including at least one pneumatic actuator and an inflating device. Further, the biocompatible, digestible and edible material can be used for making bubble gum products.
Owner:THE HAVERFORD SCHOOL
Controllable soft valve achieving single input multiple output through magnetic control and optical control and control method of controllable soft valve
ActiveCN111536273ASimple structureLow costOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesThin membraneEngineering
The invention discloses a controllable soft valve achieving single input multiple output through magnetic control and optical control and a control method of the controllable soft valve, and relates to the field of soft robot actuators. The controllable soft valve comprises a silica gel pipe and multiple same soft valve bodies. The multiple soft valve bodies are arranged side by side and jointly connected to the silica gel pipe, and valve pieces of the soft valve bodies are magnetic SMP films. The magnetic SMP films are controlled through a magnetic field and an optical field, so that the magnetic SMP films deform, on-off states of the different soft valve bodies are switched, and therefore the function of single input multiple output is achieved. The controllable soft valve is simple in structure, the valve pieces of the soft valve bodies are arranged into the magnetic SMP films, and therefore the controllable soft valve further has the beneficial effects of being small in size, resistant to water logging, simple in structure, high in reliability, low in cost and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
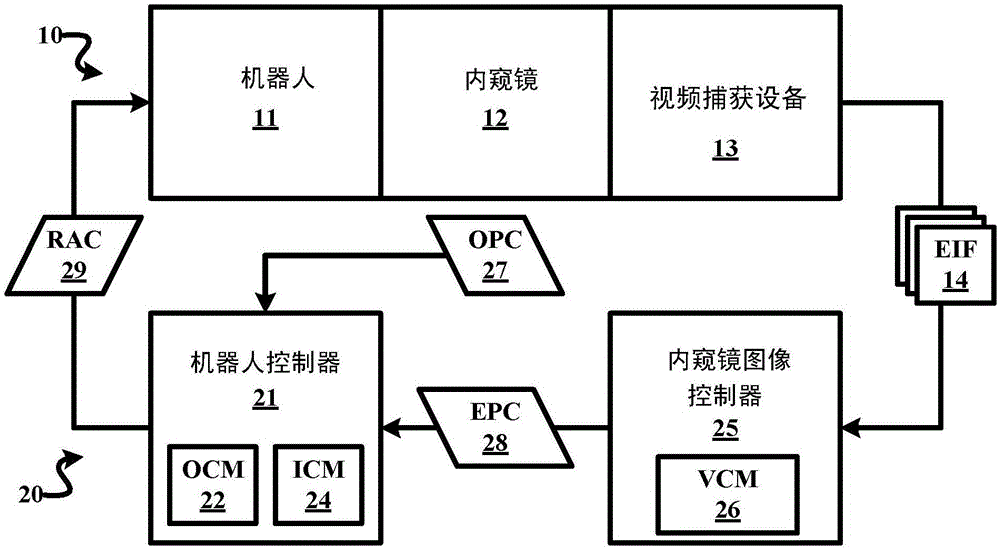
Robotic control of surgical instrument visibility
A robot guiding system employs a robot unit (10) including an endoscope (12) and a robot (11), and a control unit (20) including an endoscopic image controller (22) and a robot controller (21). In operation, the endoscope (12) generates an endoscopic image of an anatomical region as the robot (11) move the endoscope (12) within the anatomical region in response to robot actuator commands. The endoscopic image controller (22) controls a display of the endoscopic image(14) of the anatomical region and generates endoscope pose commands to maintain a visibility of two or more interventional instruments within the display of the endoscopic image(14) relative to a center of the endoscopic image (14). The robot controller (21) generates the robotic actuator commands responsive to the endoscope pose commands.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com