Patents
Literature
697 results about "Four-stroke engine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
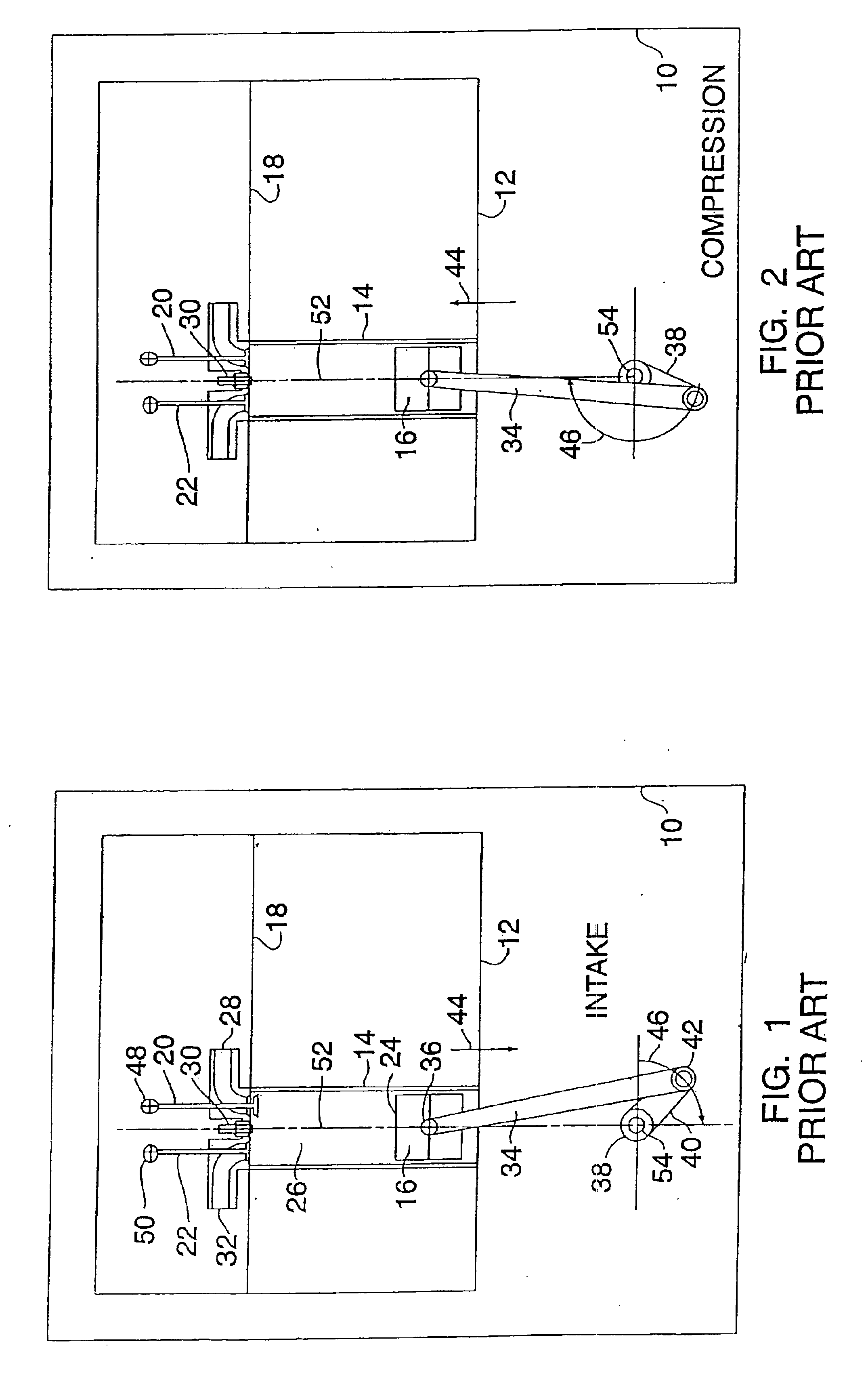
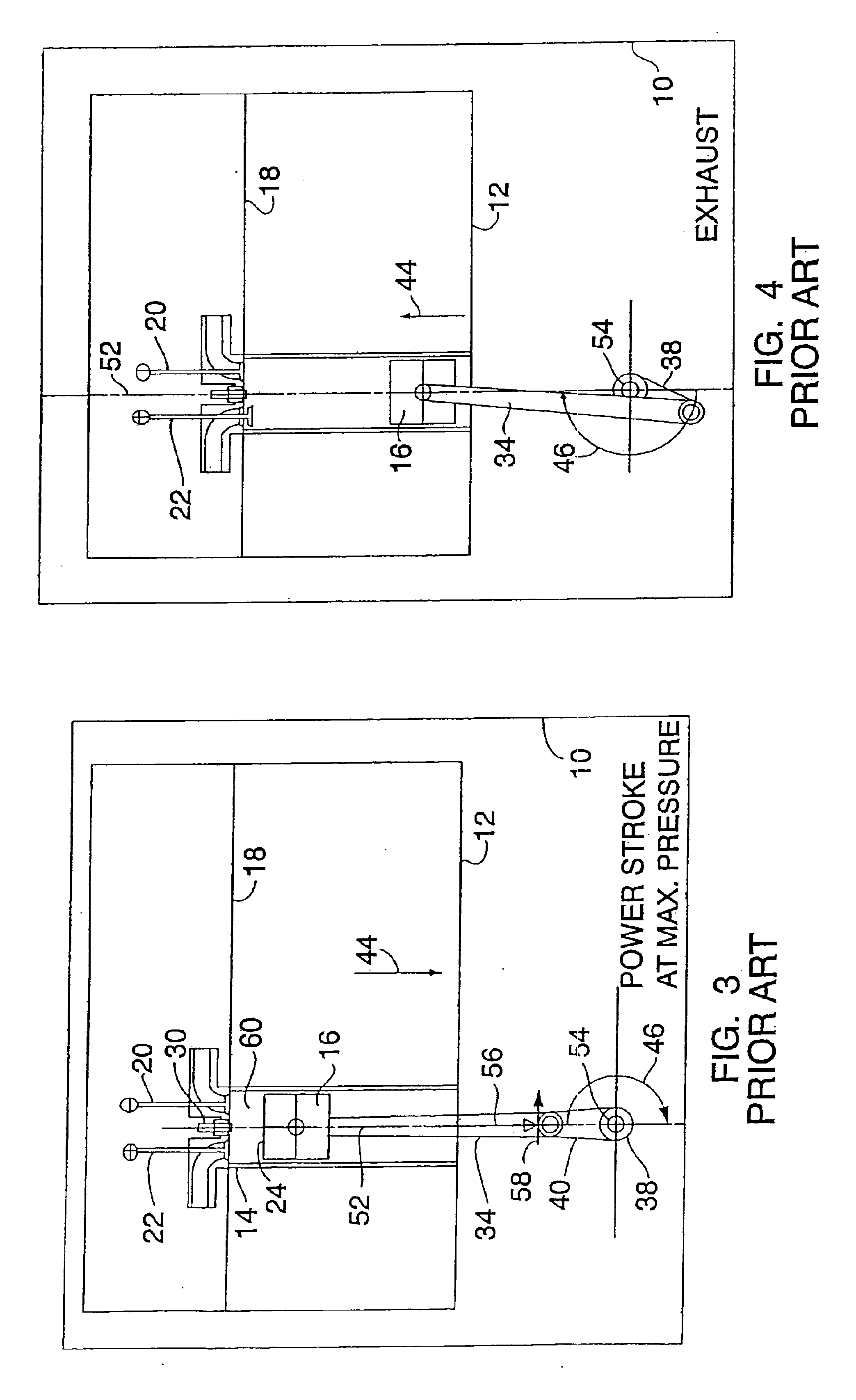
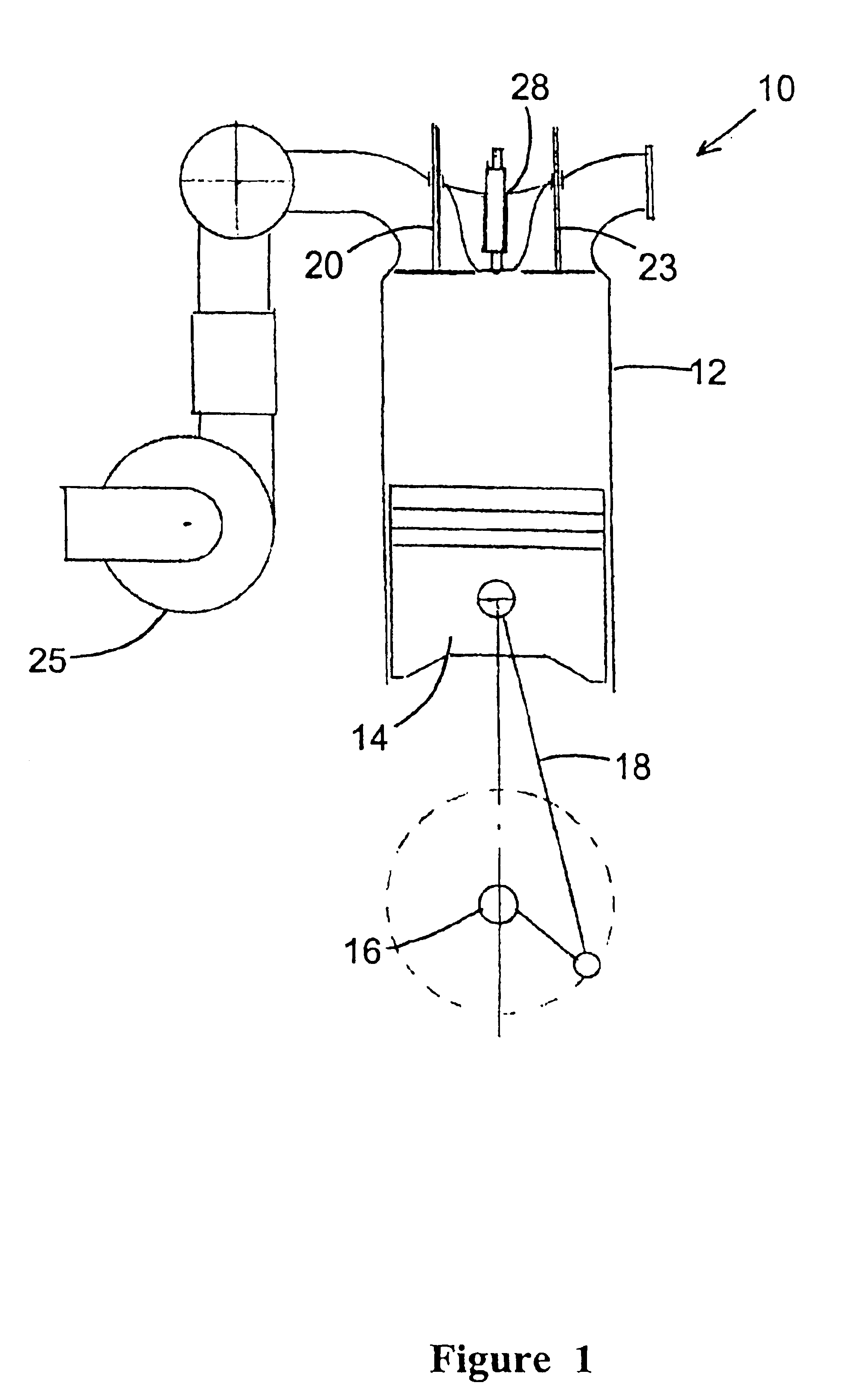
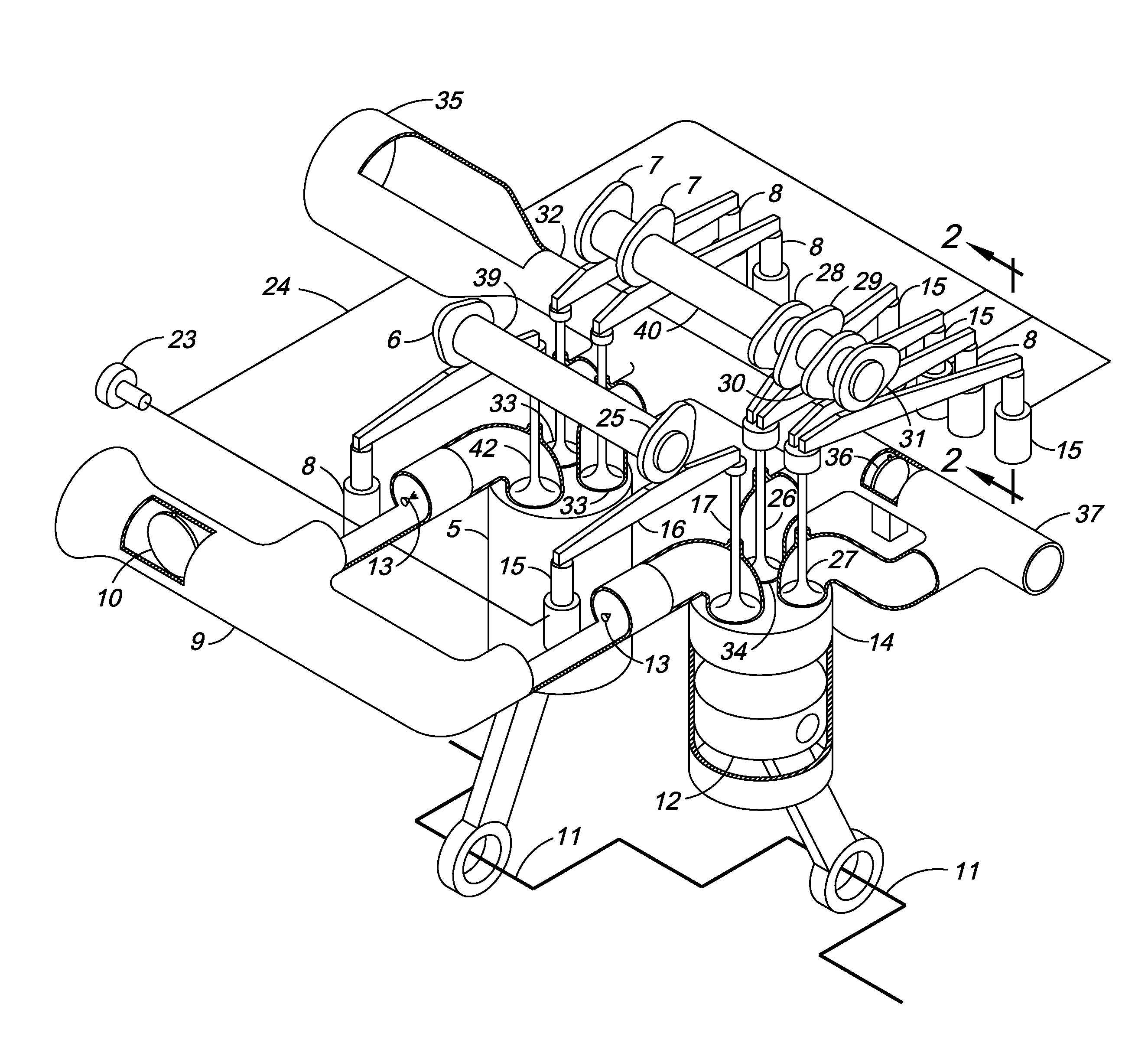
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction.
Split-cycle four-stroke engine
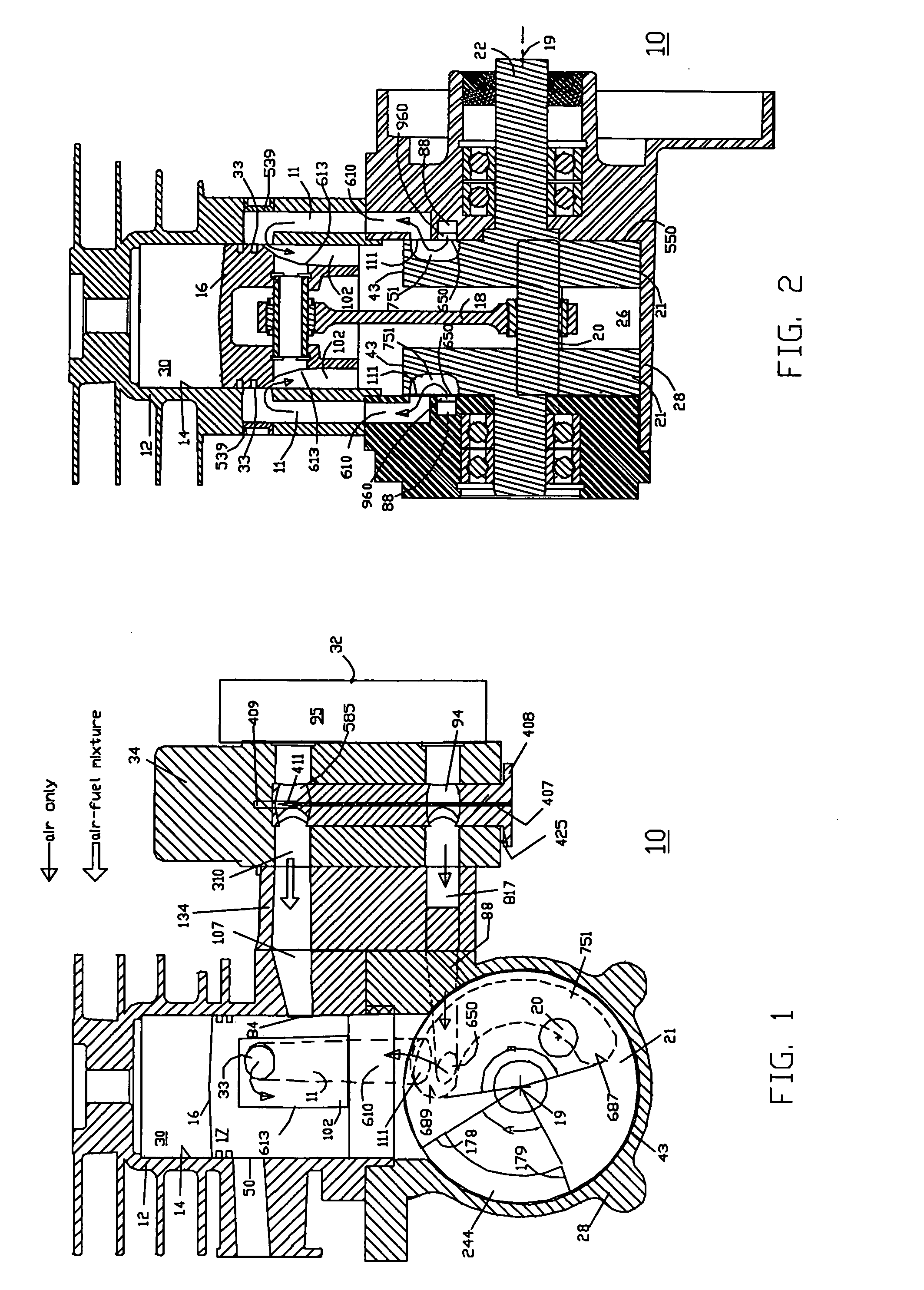
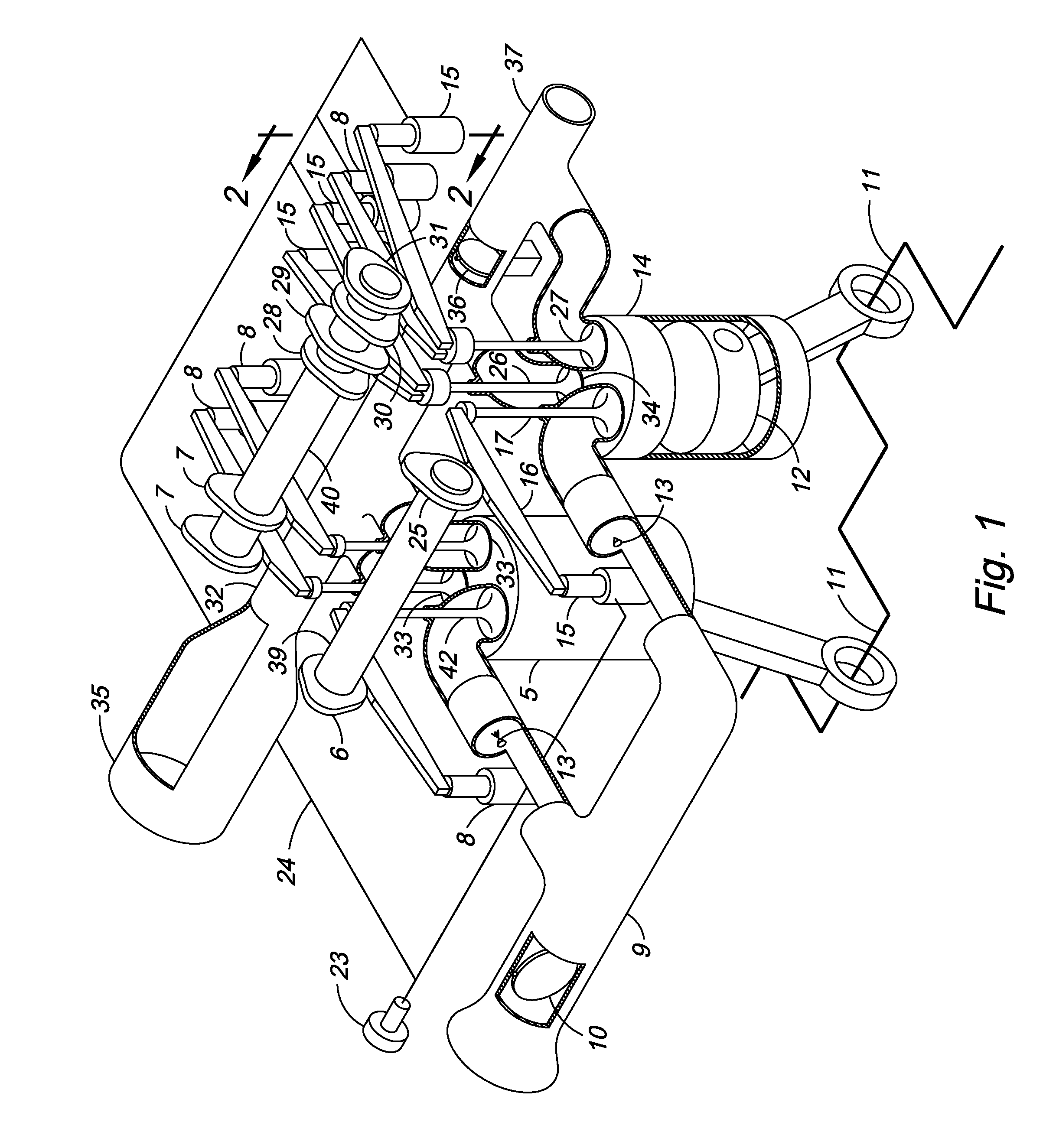
InactiveUS6952923B2Improve efficiencyImprove performanceInternal combustion piston enginesGas pressure propulsion mountingReciprocating motionFour-stroke engine
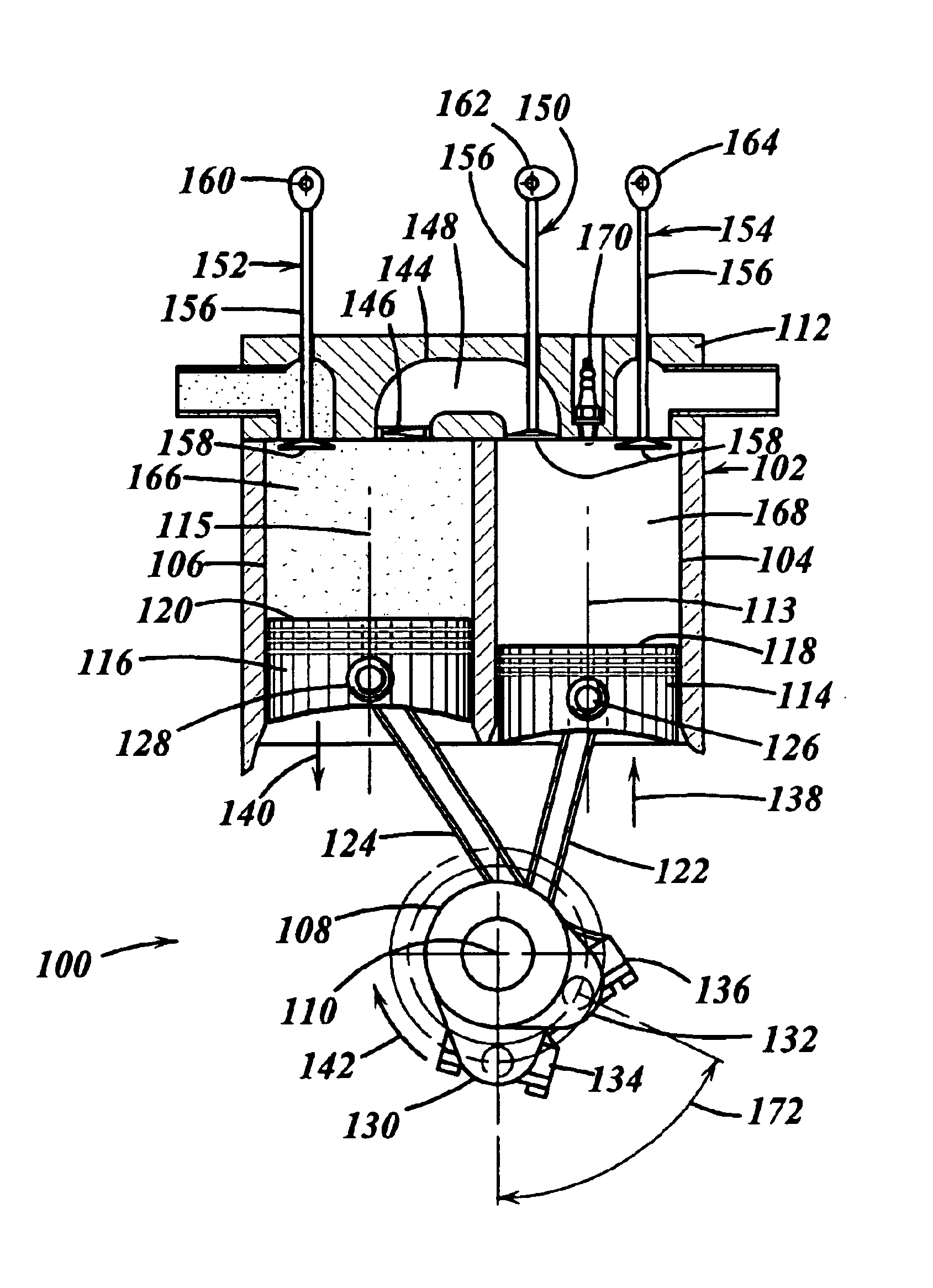
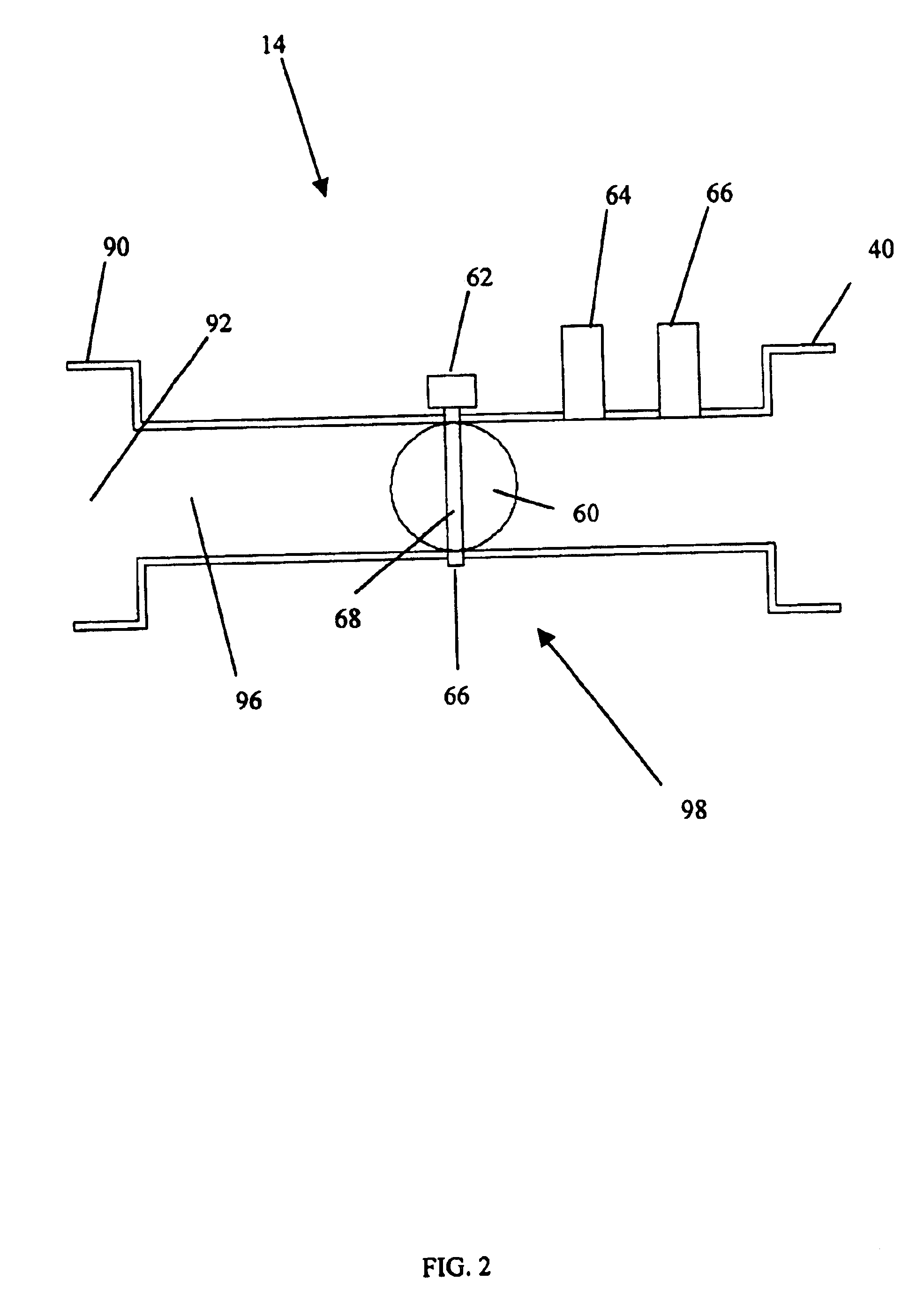
An engine has a crankshaft, rotating about a crankshaft axis of the engine. An expansion piston is slidably received within an expansion cylinder and operatively connected to the crankshaft such that the expansion piston reciprocates through an expansion stroke and an exhaust stroke of a four stroke cycle during a single rotation of the crankshaft. A compression piston is slidably received within a compression cylinder and operatively connected to the crankshaft such that the compression piston reciprocates through an intake stroke and a compression stroke of the same four stroke cycle during the same rotation of the crankshaft. A ratio of cylinder volumes from BDC to TDC for either one of the expansion cylinder and compression cylinder is substantially 20 to 1 or greater.
Owner:SKADERI GRUP LLC
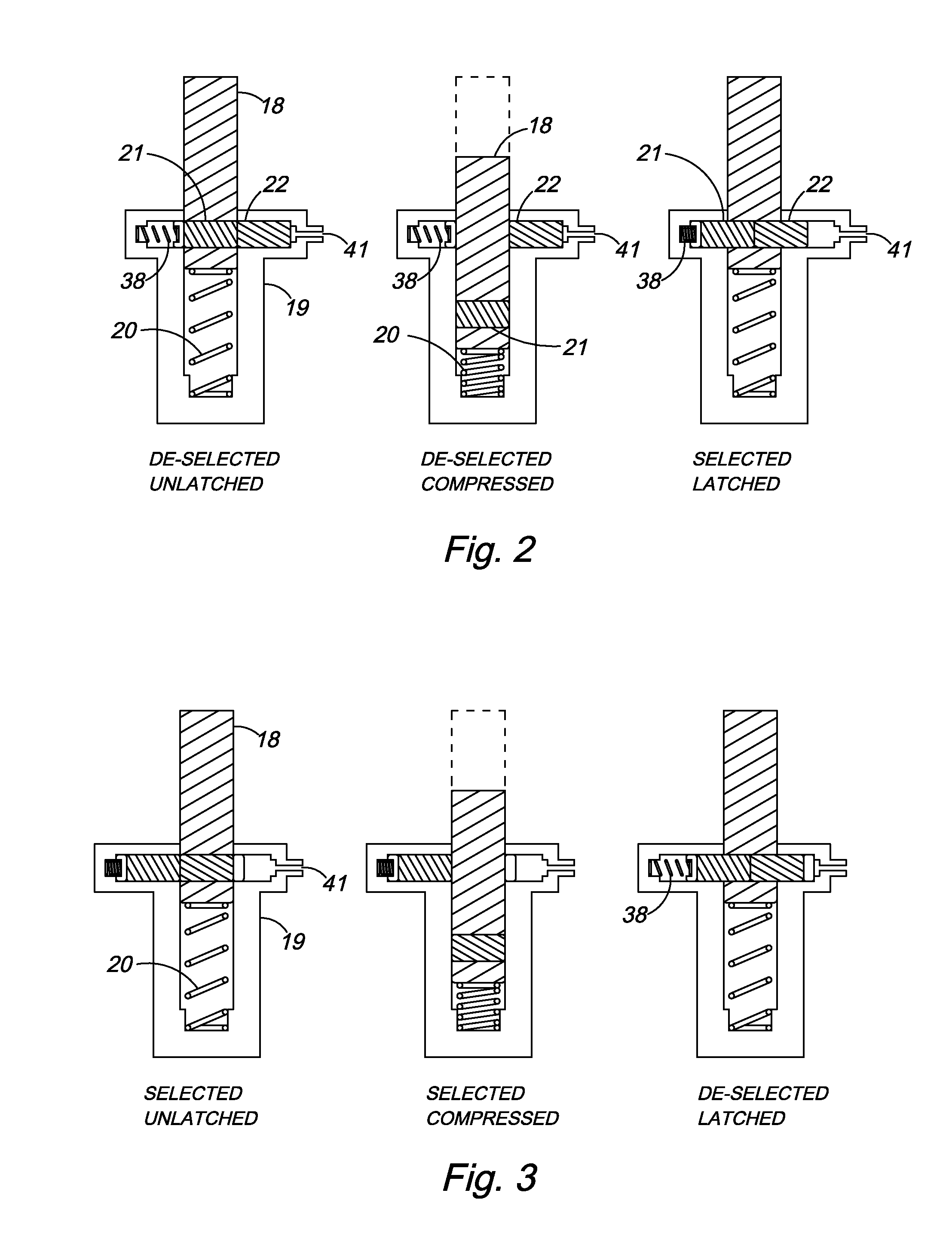
Starting an engine with electromechanical valves
ActiveUS6938598B1VariationLarge emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl mannerFour-stroke engine
A system and method to control engine valve timing to during the start of an internal combustion engine. Electromechanical valves are controlled in a manner to reduce engine vibration and hydrocarbon emissions during the start of an internal combustion engine. The method controls valves without an explicit four-stroke engine cycle during a start.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Engine timing control with intake air pressure sensor
InactiveUS6804997B1Reduce in quantityRobust implementationElectrical controlEngine testingExternal combustion engineInlet valve
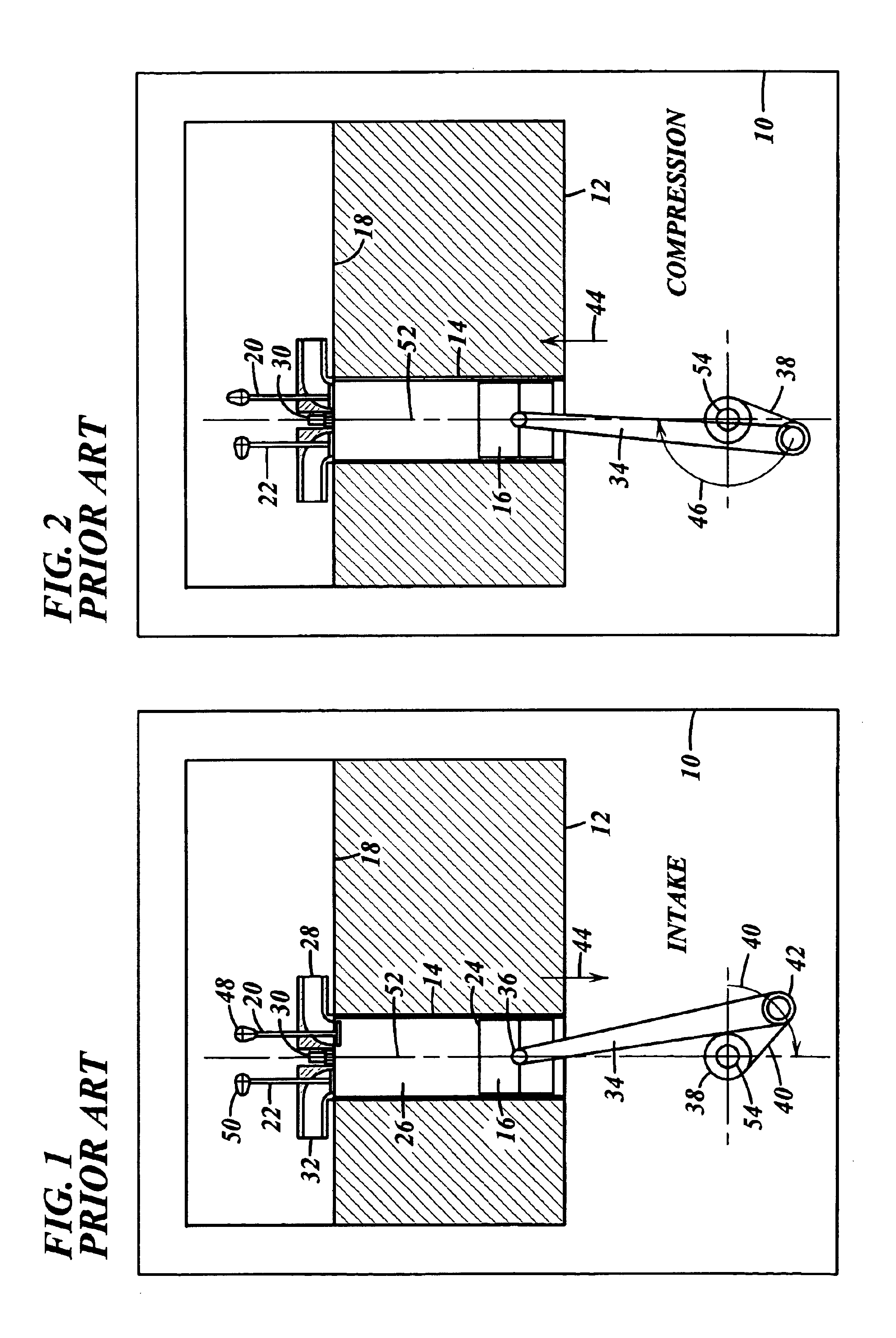
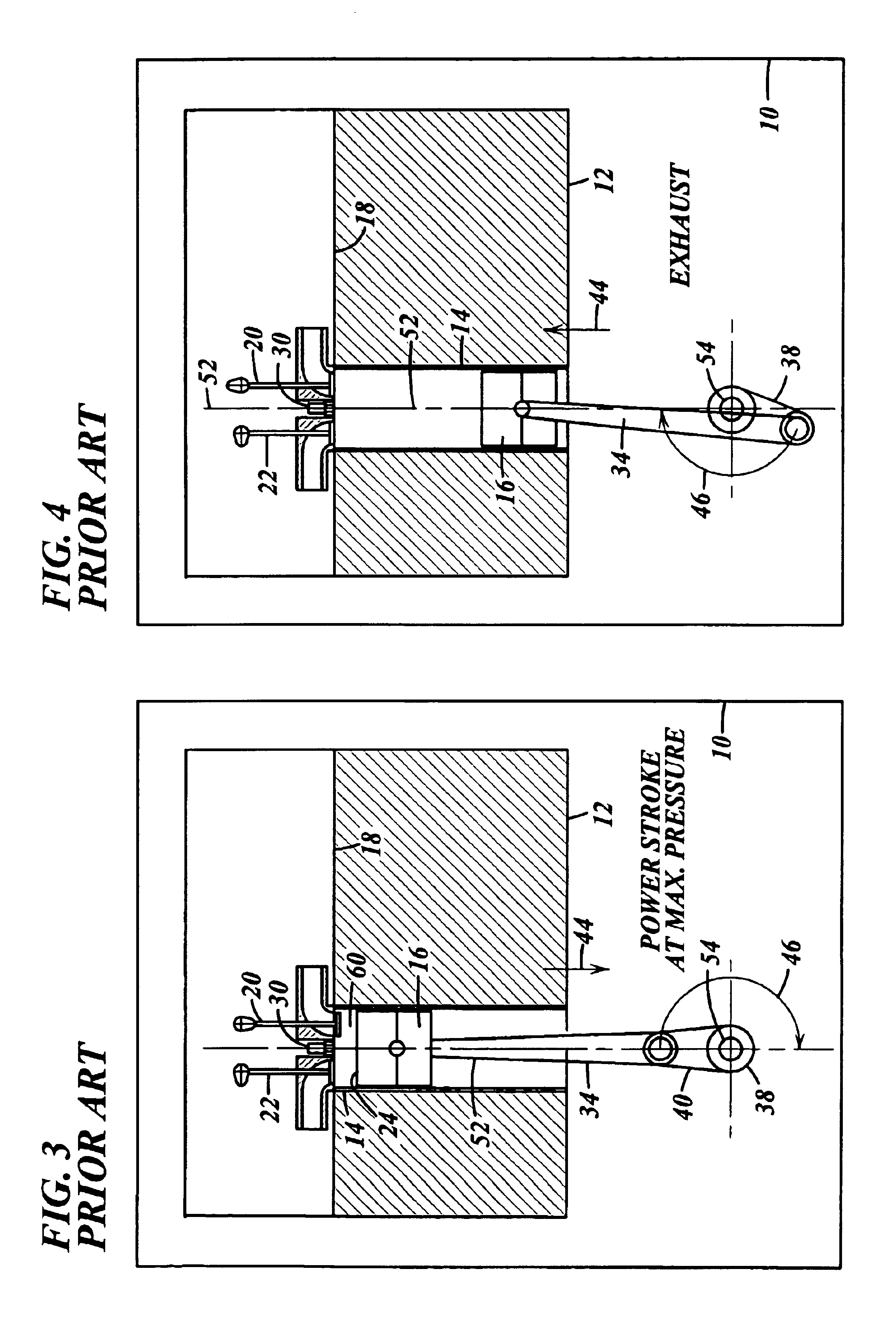
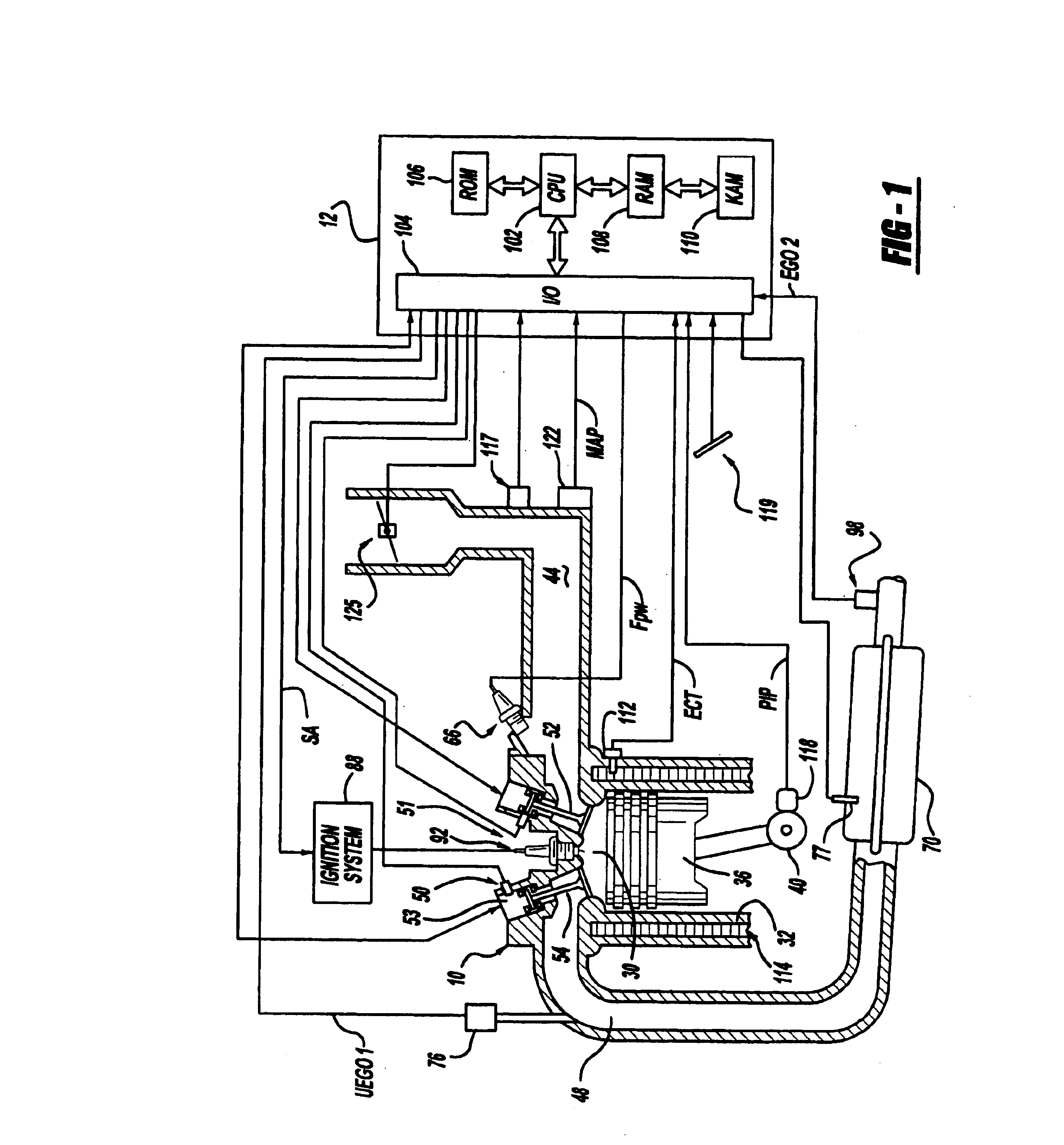
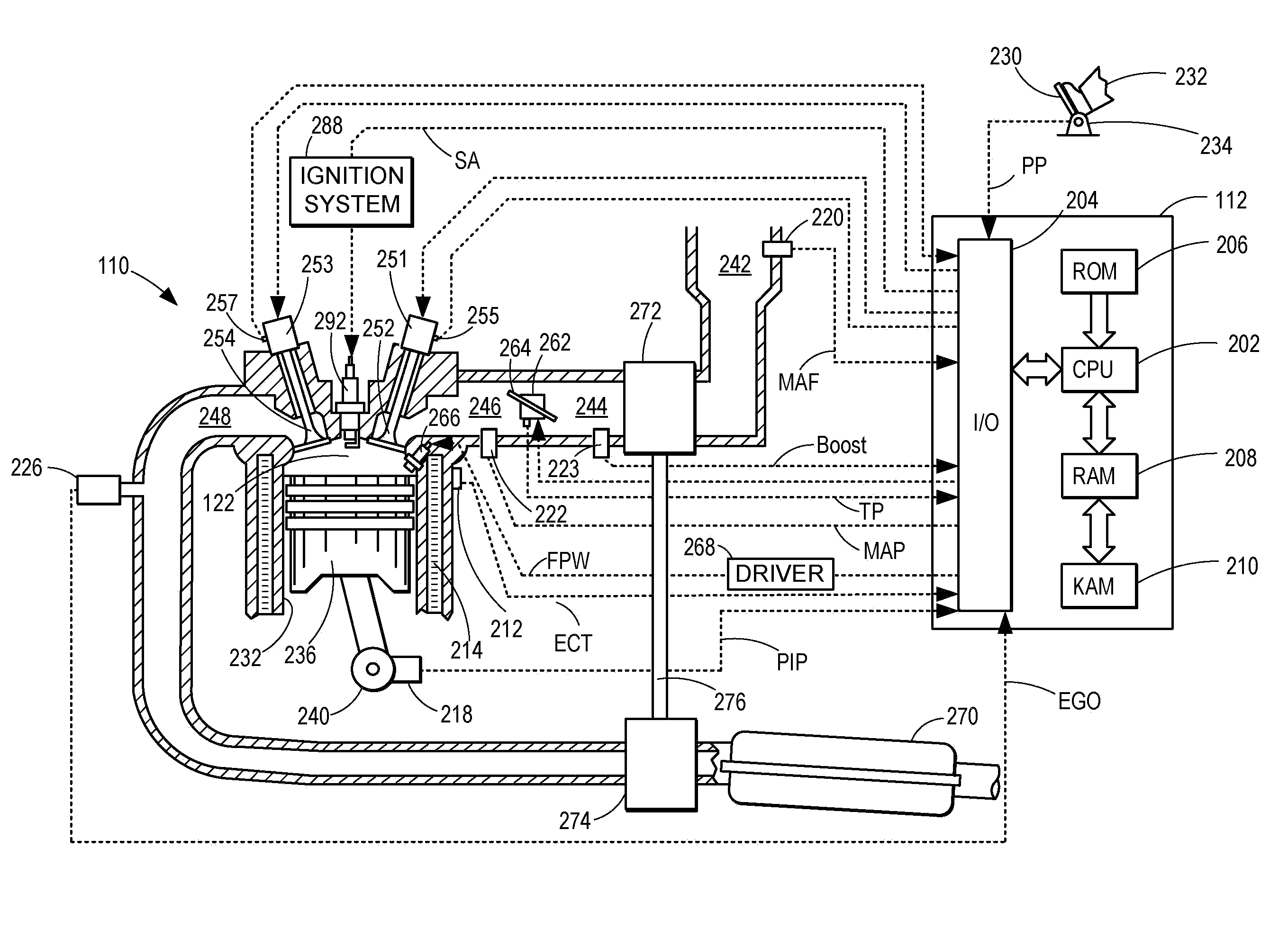
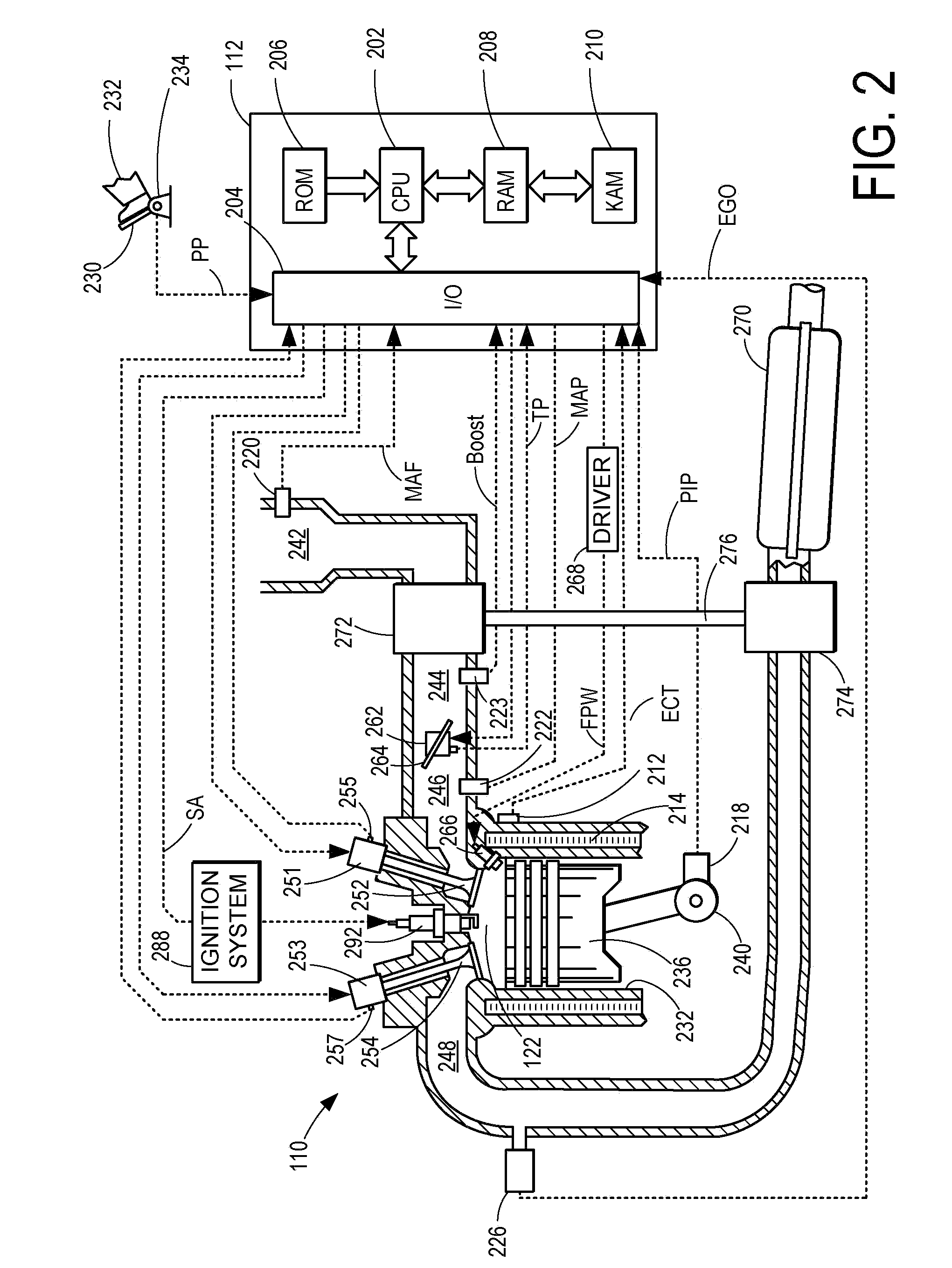
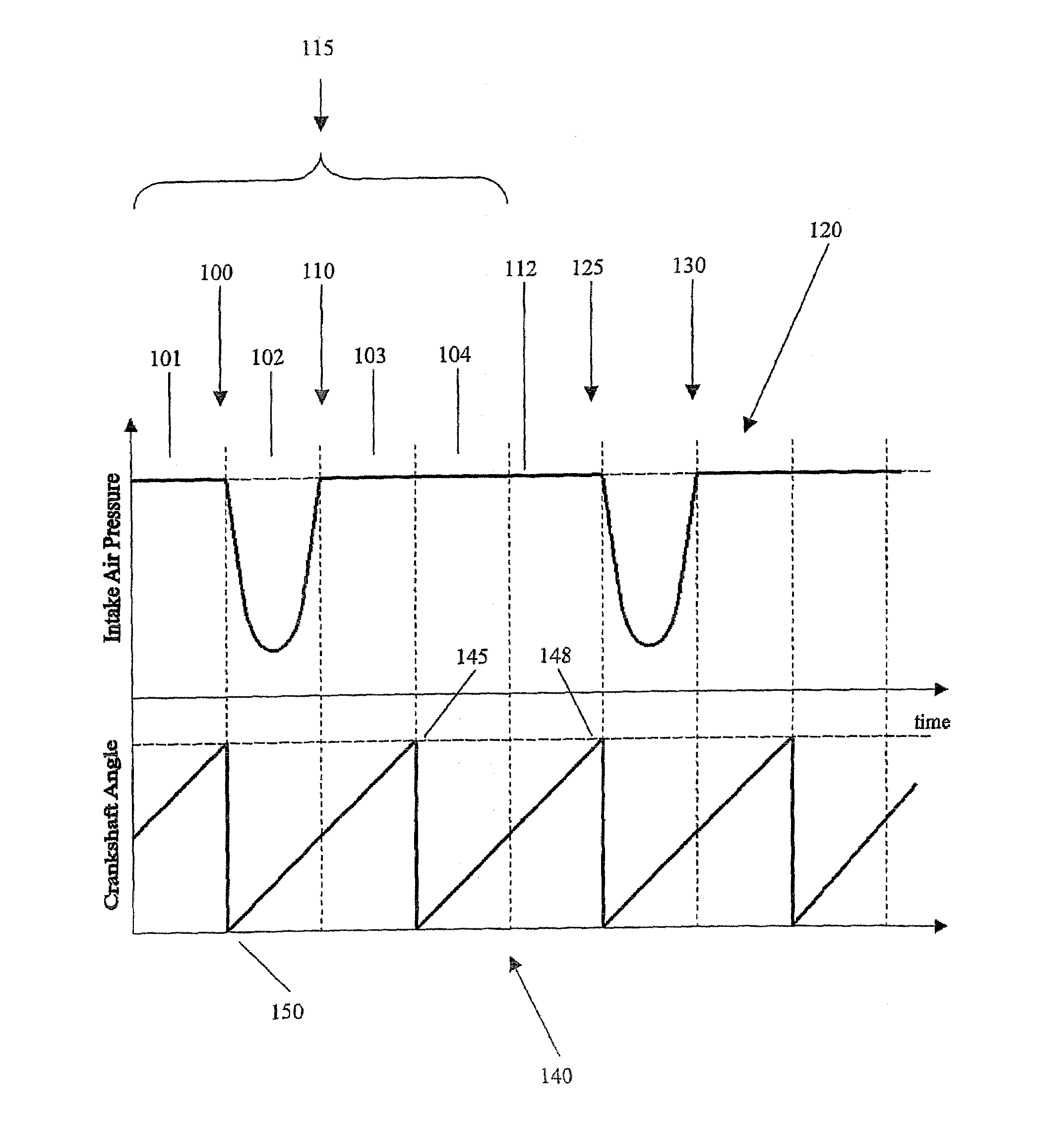
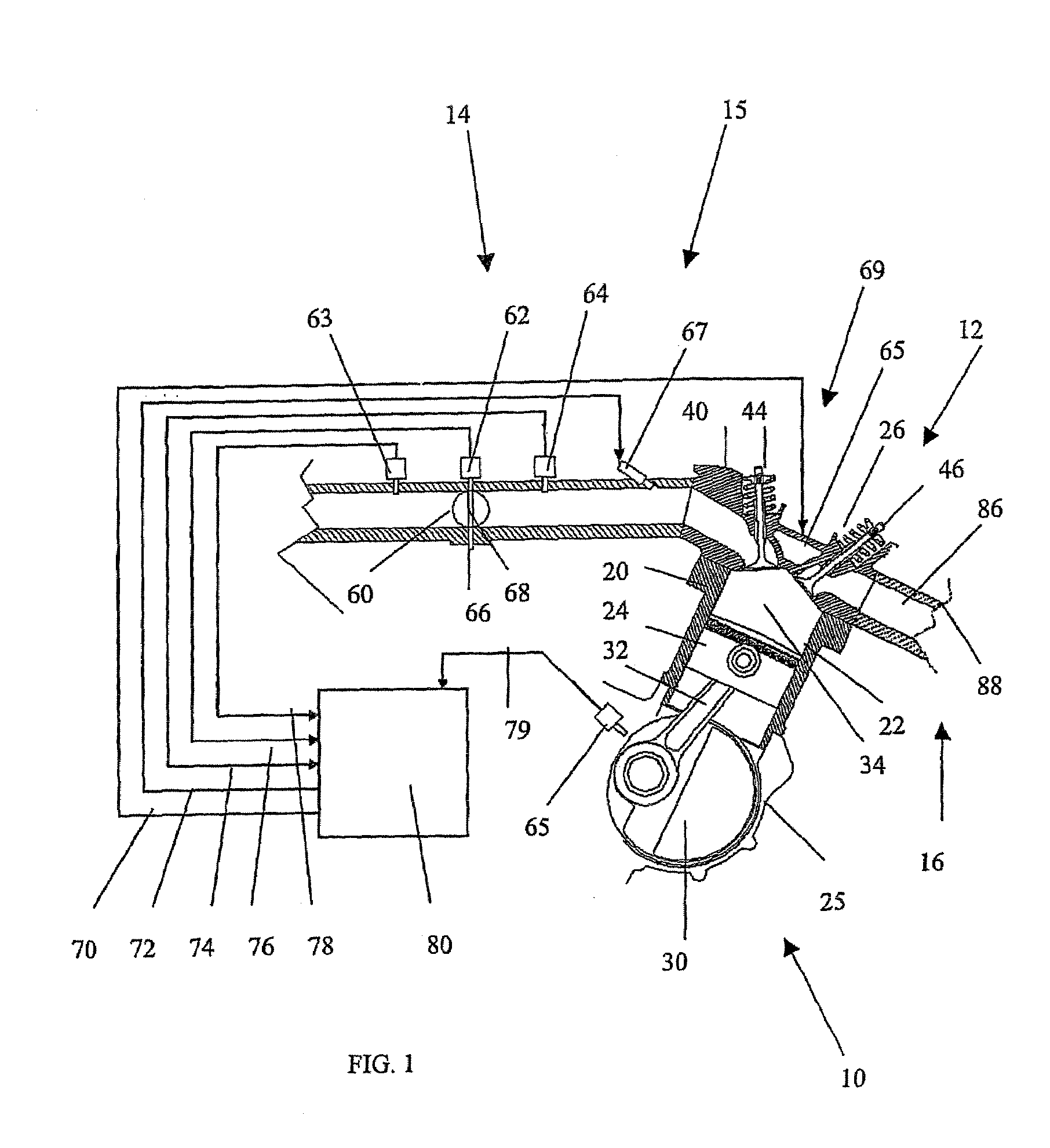
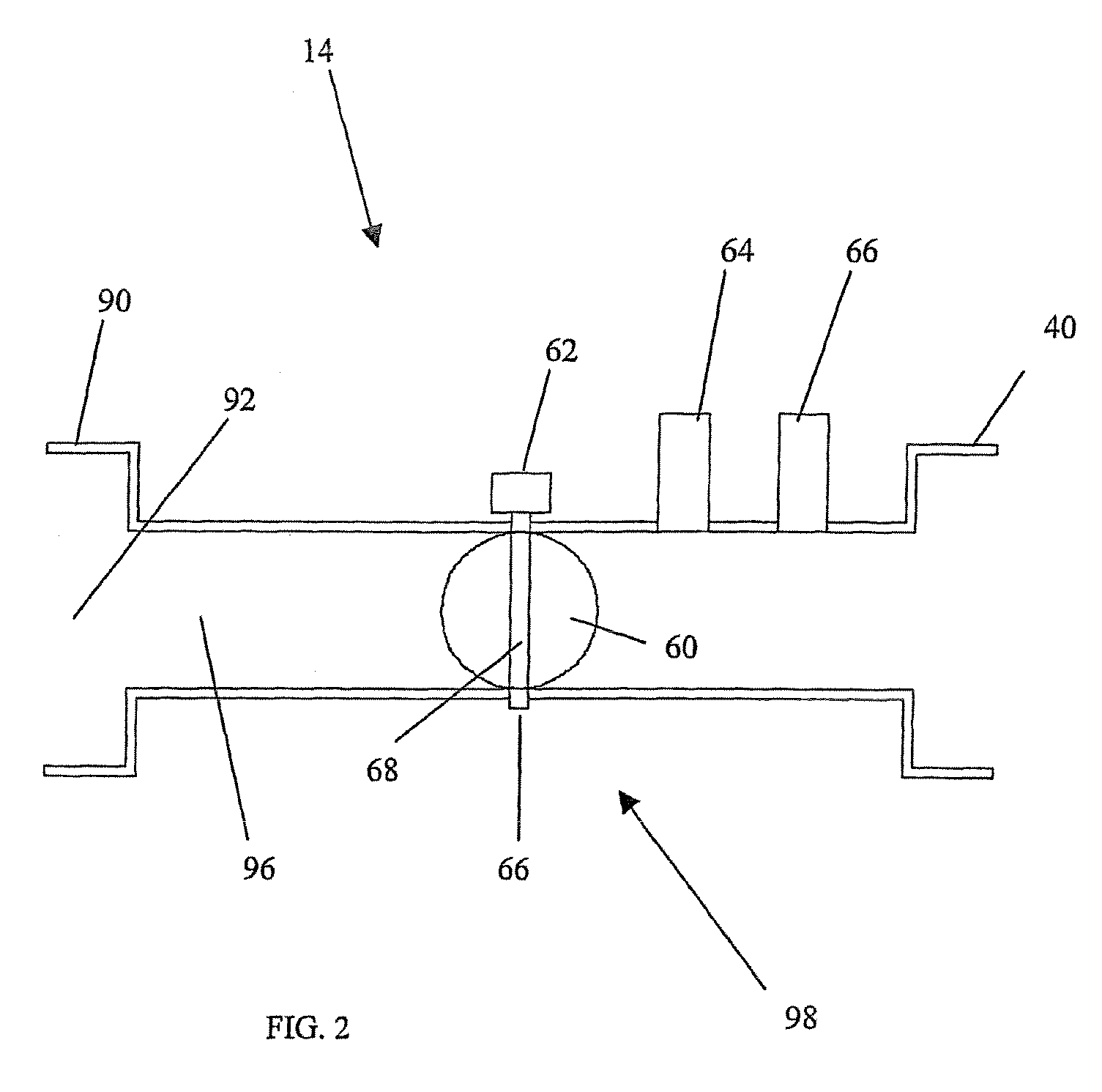
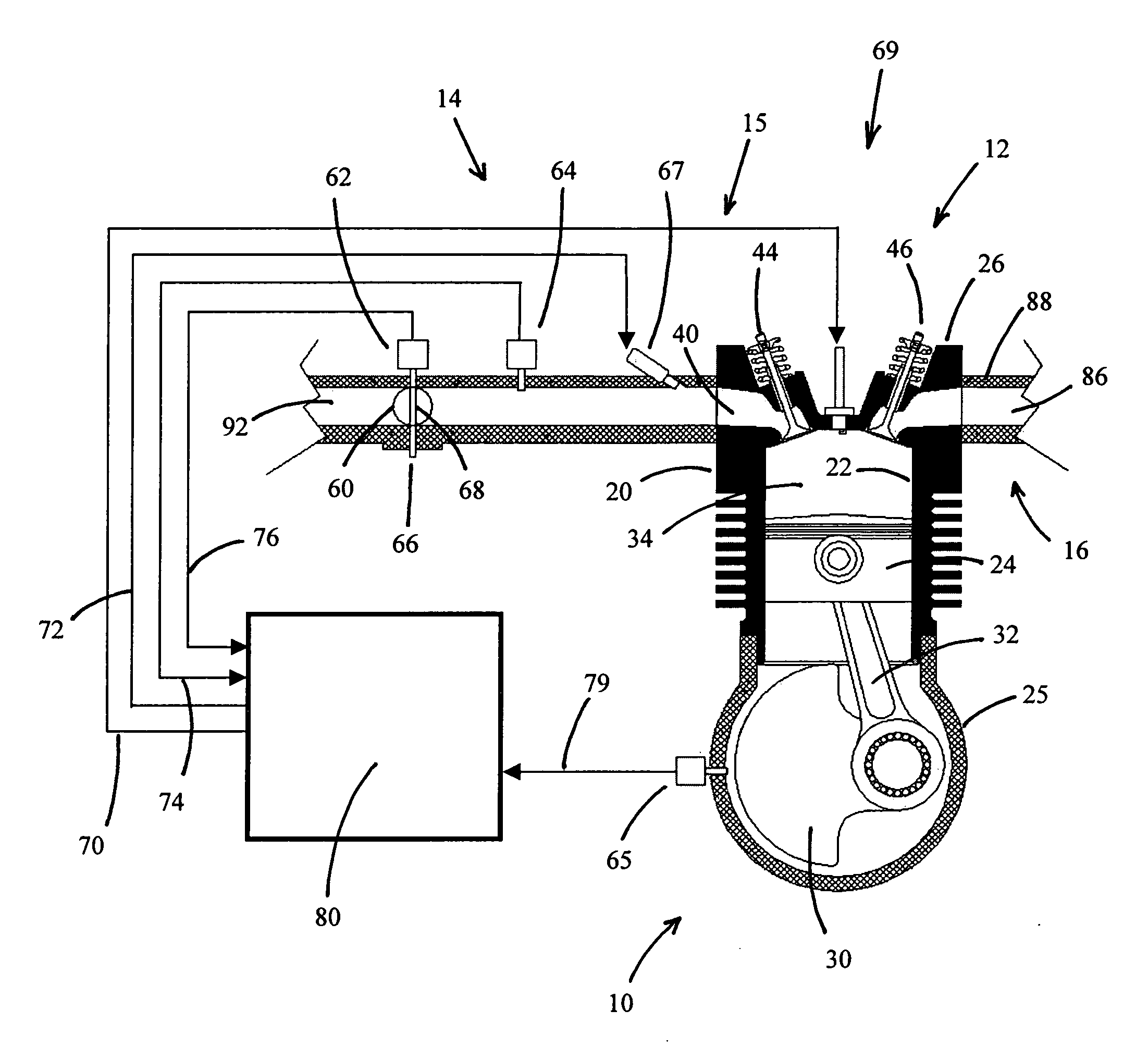
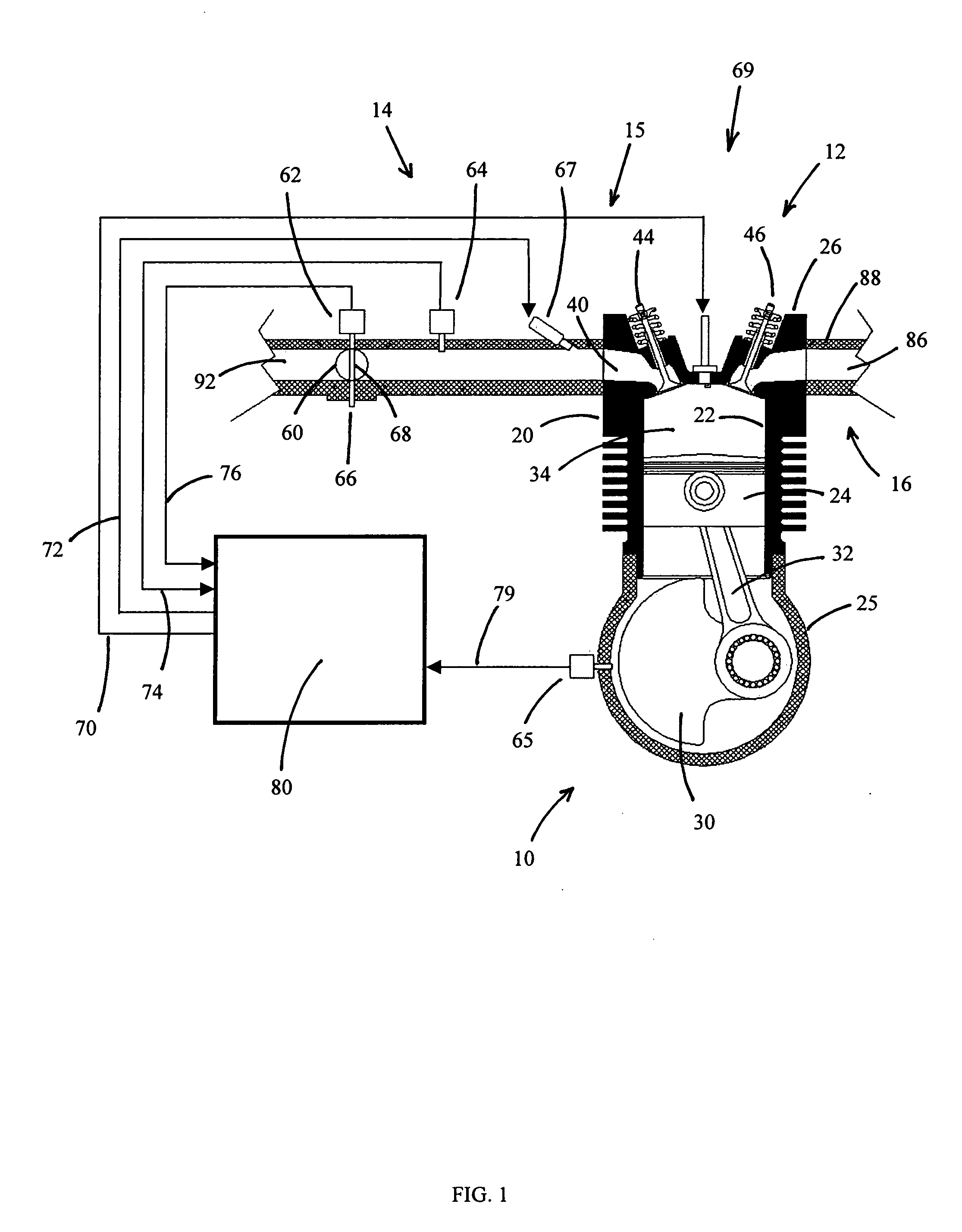
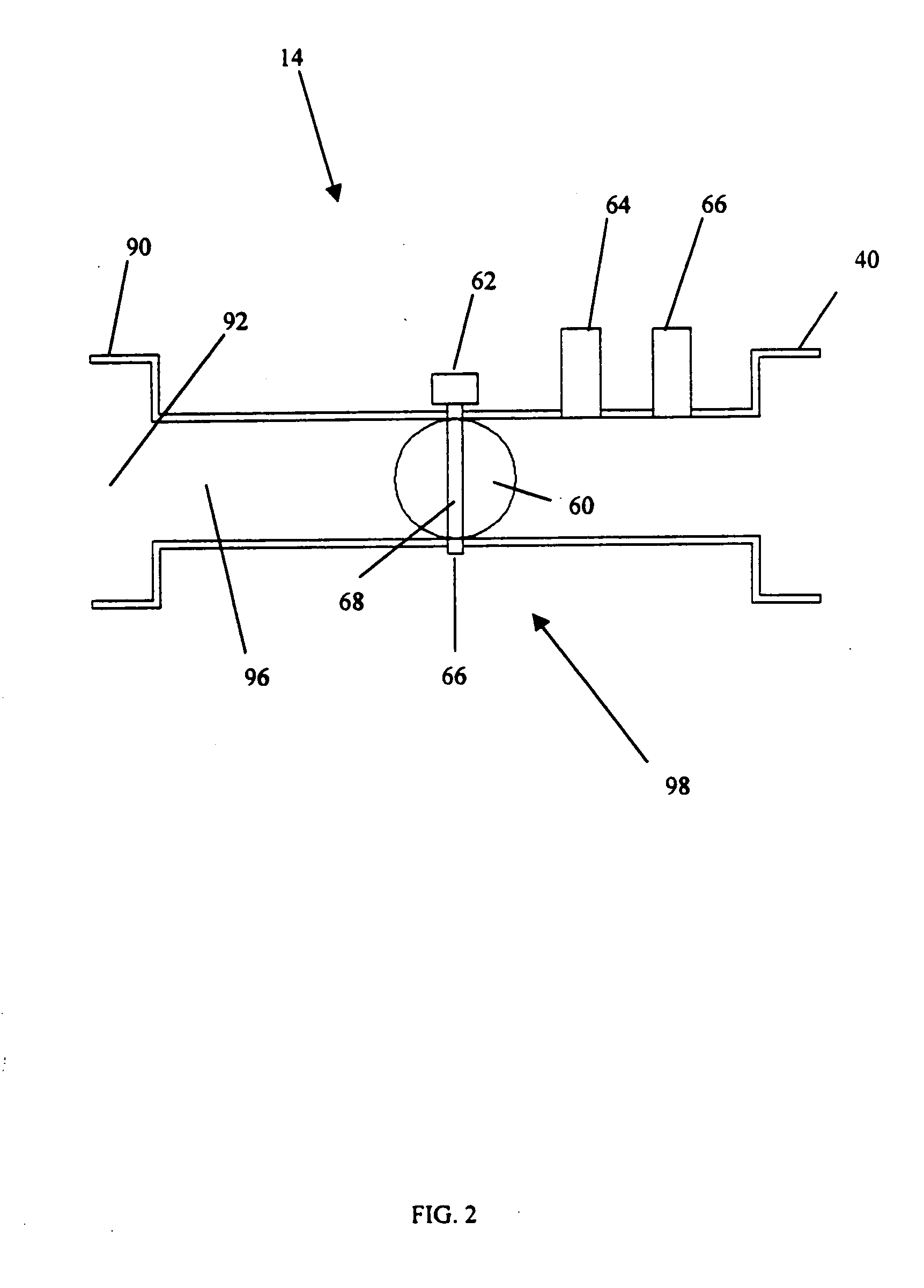
An engine control apparatus is disclosed for determining crankshaft position and engine phase of an internal combustion engine (10) through monitoring intake air pressure fluctuations (120). The opening of the intake valve (44) is mechanically linked to the crankshaft position of an engine. When the intake valve (44) opens it creates air pressure fluctuations in the air induction system (14) of the engine (10). The control apparatus is configured to determine intake air pressure fluctuations indicative of an intake air event (100 to 110) and thus a particular crankshaft position, and their corresponding period of the engine cycle. The controller then uses this information to determine crankshaft speed and position for the purpose of fuel injection and ignition timing of the internal combustion engine. Engine phase is also determined on four-stroke engines. The engine may also include a crankshaft position sensor in combination with monitoring intake air pressure fluctuations to increase resolution in determination of crankshaft position.
Owner:ELECTROJET TECH INC
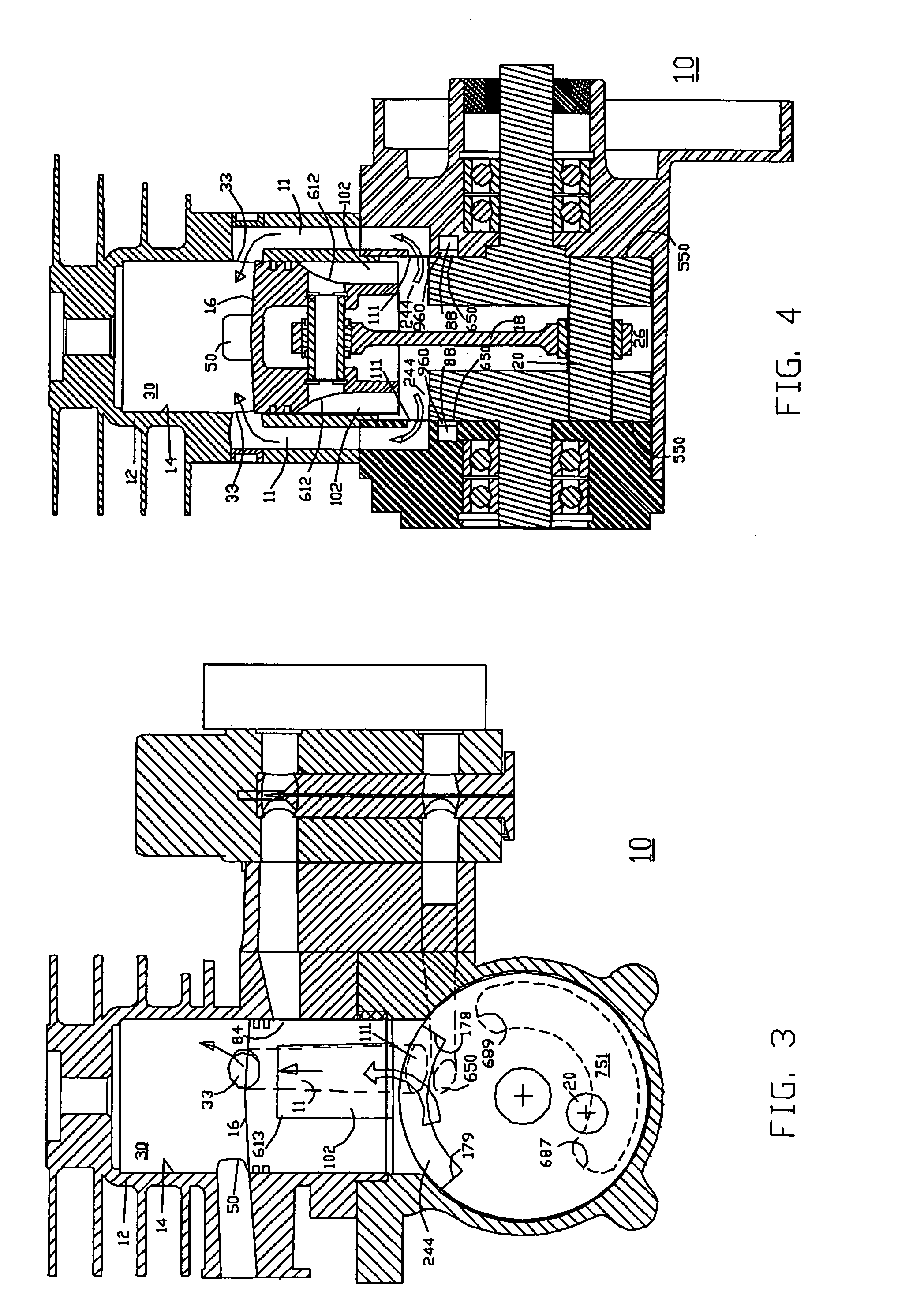
Split-cycle four-stroke engine
InactiveUS20050268609A1Improve efficiencyImprove performanceInternal combustion piston enginesGas pressure propulsion mountingReciprocating motionFour-stroke engine
An engine has a crankshaft, rotating about a crankshaft axis of the engine. An expansion piston is slidably received within an expansion cylinder and operatively connected to the crankshaft such that the expansion piston reciprocates through an expansion stroke and an exhaust stroke of a four stroke cycle during a single rotation of the crankshaft. A compression piston is slidably received within a compression cylinder and operatively connected to the crankshaft such that the compression piston reciprocates through an intake stroke and a compression stroke of the same four stroke cycle during the same rotation of the crankshaft. A ratio of cylinder volumes from BDC to TDC for either one of the expansion cylinder and compression cylinder is fixed at substantially 26 to 1 or greater.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST +1
Method and operation of an engine
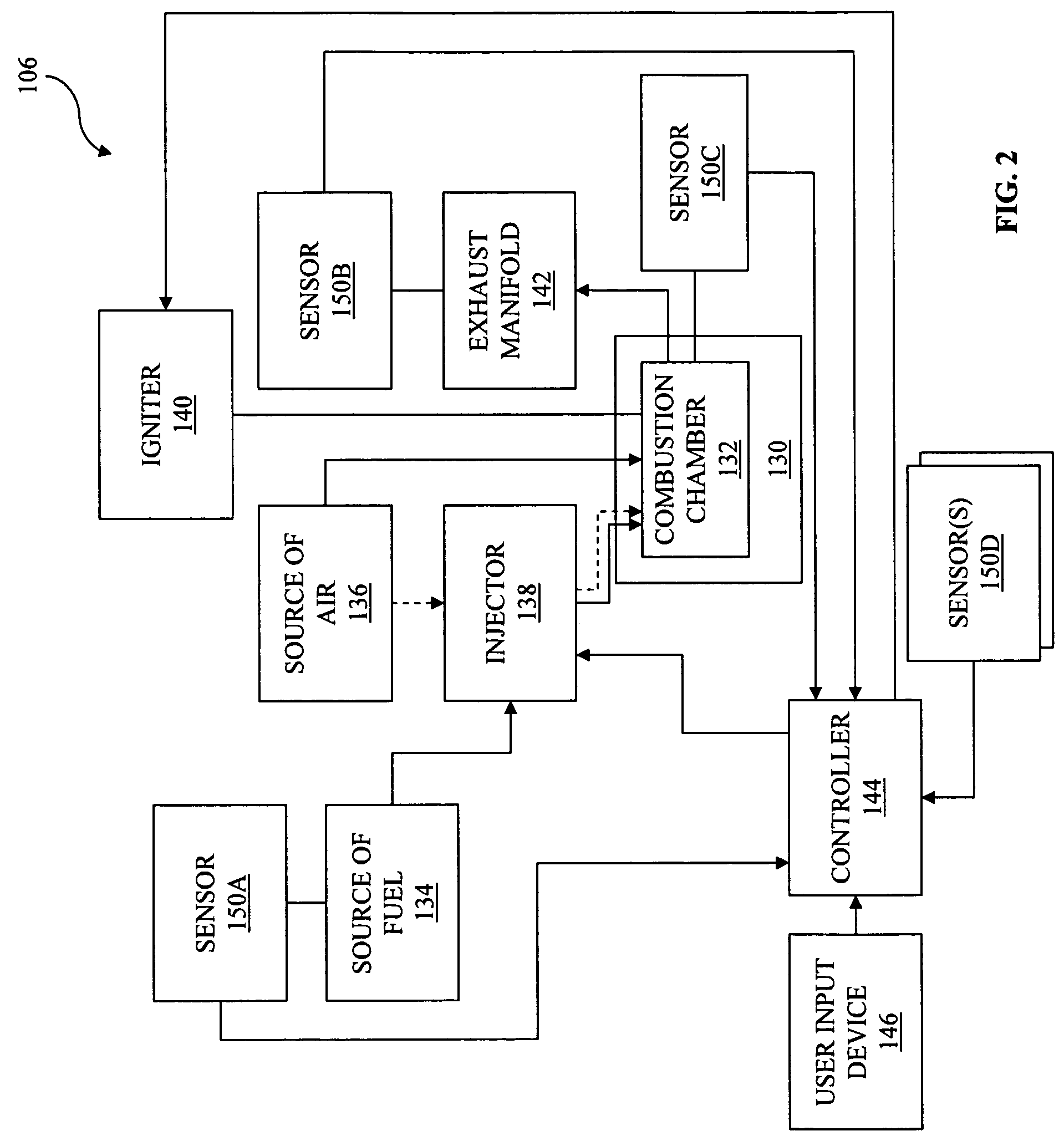
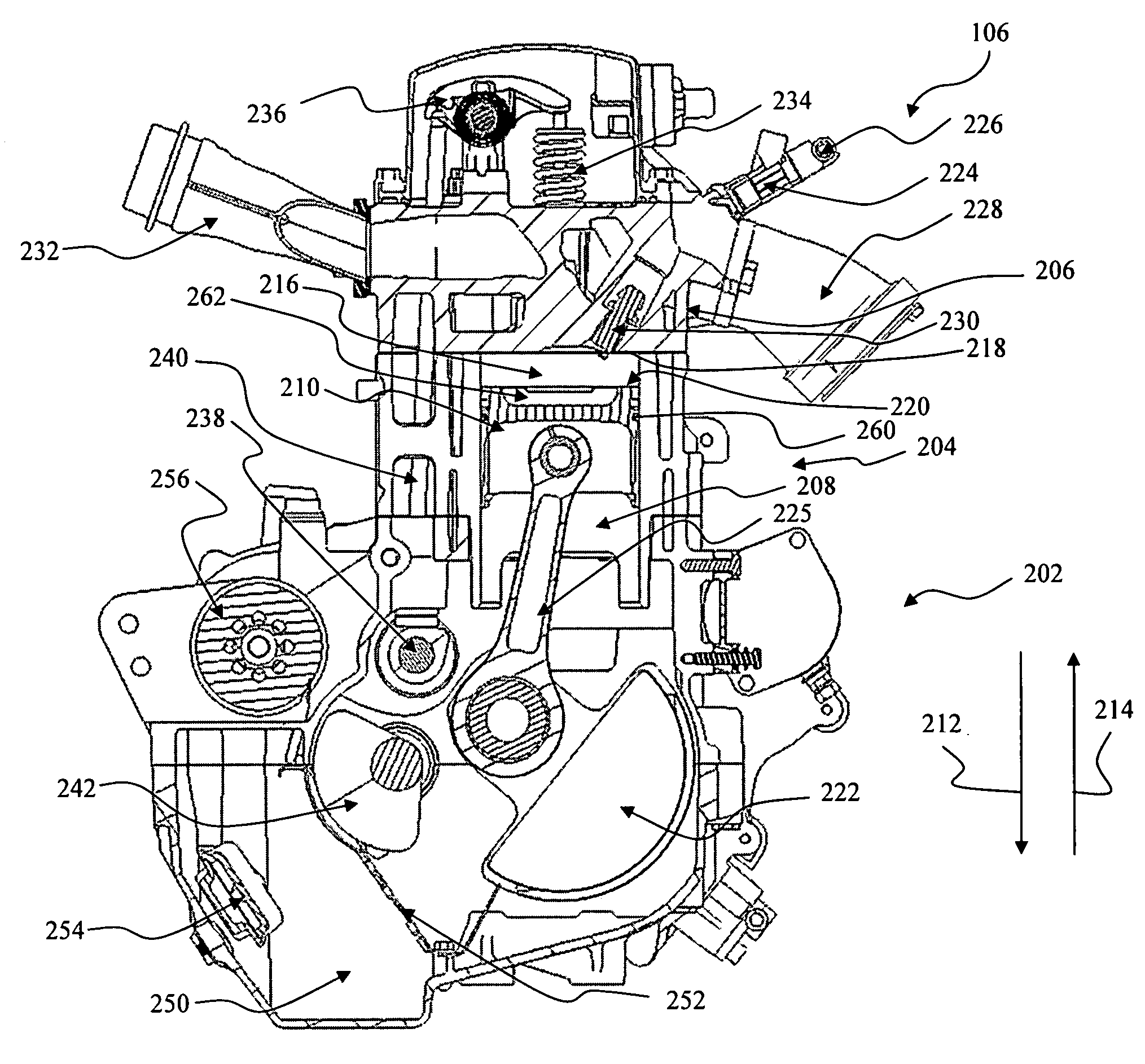
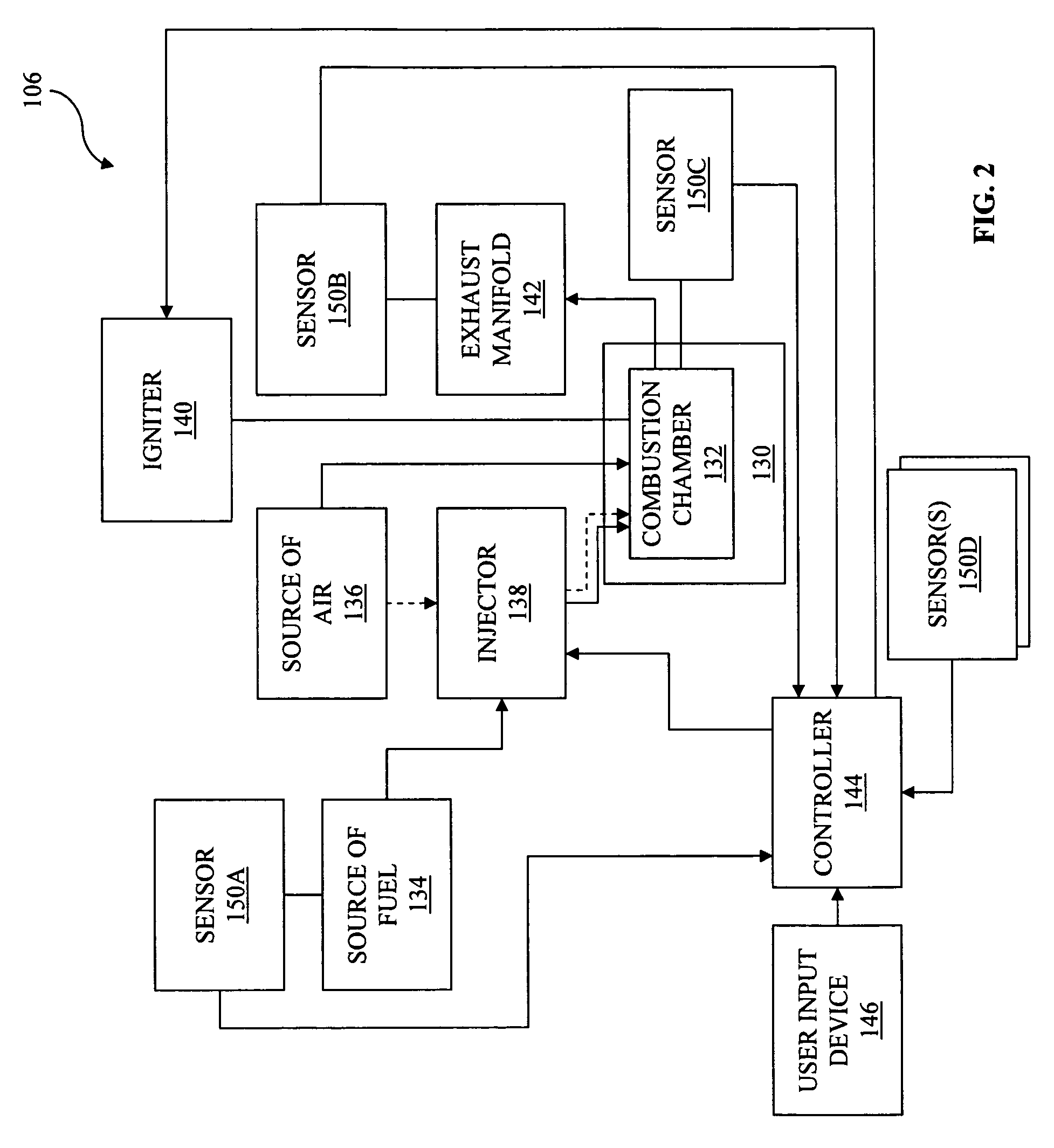
An engine is disclosed which may operate in a first operating state wherein a spark ignited fuel is ignited in a combustion chamber with an igniter and a second operating state wherein a compression ignited fuel is ignited in a combustion chamber with an igniter. A compression ratio in the combustion chamber being up to about eight to one. The engine may be a four-stroke engine. The engine may include a piston having a top portion with a recessed central portion.
Owner:POLARIS IND INC
Split four stroke engine
InactiveUS6880502B2Improve efficiencyIncrease the compression ratioCasingsInternal combustion piston enginesPhase shiftedReciprocating motion
An engine includes a crankshaft, rotating about a crankshaft axis of the engine. A power piston is slidably received within a first cylinder and is operatively connected to the crankshaft via first linkage system. The power piston reciprocates through a power stroke and an exhaust stroke of a four stroke cycle during a single rotation of the crankshaft. A compression piston is slidably received within a second cylinder and operatively connected to the crankshaft via second linkage system. The first and second linkage systems share no common mechanical link. The compression piston reciprocates through an intake stroke and a compression stroke of the same four stroke cycle during the same revolution of the crankshaft. The power piston leads the compression piston by a phase shift angle that is substantially equal to or greater than zero degrees and less than 30 degrees.
Owner:SKADERI GRUP LLC
Lubrication system for an engine
ActiveUS20090013959A1Fully lubricatedCombustion enginesPressure lubricationFour-stroke engineEngineering
A lubrication system for a small lightweight four-stroke engine is disclosed. The lubrication system, provided with a weight at one end of a flexible oil tube inserted into an oil reservoir, is capable of providing a sufficient lubrication to components of the engine which may operate in a horizontal posture, a vertical posture, or any posture therebetween.
Owner:LIN SZU LIANG
Control strategy for multi-stroke engine system
ActiveUS20090277434A1Improve engine efficiencyHigh outputElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFour-stroke enginePoppet valve
An engine system and a method of operation are described. As one example, the method may include: during a first operating condition, operating a cylinder of the engine in a two stroke cycle to combust a first mixture of air and fuel, and adjusting an opening overlap between an intake poppet valve and an exhaust poppet valve of the cylinder to vary a composition of exhaust gases exhausted by the cylinder via the exhaust poppet valve; and during a second operating condition, operating a cylinder of the engine in a four stroke cycle to combust a second mixture of air and fuel, and adjusting a relative amount of fuel contained in the second mixture of air and fuel to vary the composition of exhaust gases exhausted by the cylinder via the exhaust poppet valve.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and operation of an engine
ActiveUS20080041335A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFour-stroke engineCompression ratio
An engine is disclosed which may operate in a first operating state wherein a spark ignited fuel is ignited in a combustion chamber with an igniter and a second operating state wherein a compression ignited fuel is ignited in a combustion chamber with an igniter. A compression ratio in the combustion chamber being up to about eight to one. The engine may be a four-stroke engine. The engine may include a piston having a top portion with a recessed central portion.
Owner:POLARIS IND INC
Stratified scavenged two-stroke engine
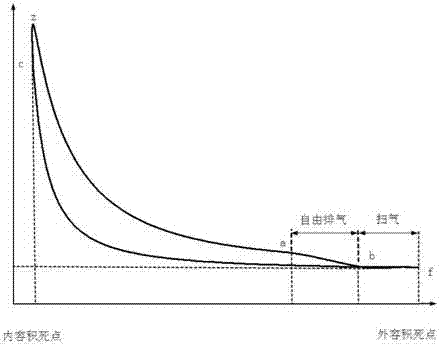
InactiveUS20050139179A1Increase volumeCombustion enginesEngine controllersCharge injectionFour-stroke engine
A two-stroke internal combustion engine includes at least one gaseous communication charge passage between a crankcase chamber and a combustion chamber of the engine and a piston to open and close the top end of the passage and a rotary valve to open and close the lower end of the transfer passage. The air inlet port to the transfer passage for stratified scavenging is opened and closed by the crank-web that has passages and cutouts. The rotary valve replaces the one-way reed valve used in stratified scavenged and charged two-stroke engines. The air passes from the lower end of transfer passage to the top end and into the crankcase through the piston passage, alternatively air may also pass through the adjacent transfer passage directly or through a passage in the piston into the crankcase. A two-stroke engine also consists of a charge injection system controlled by the crank web eliminating the one-way valve.
Owner:HOMELITE TECH
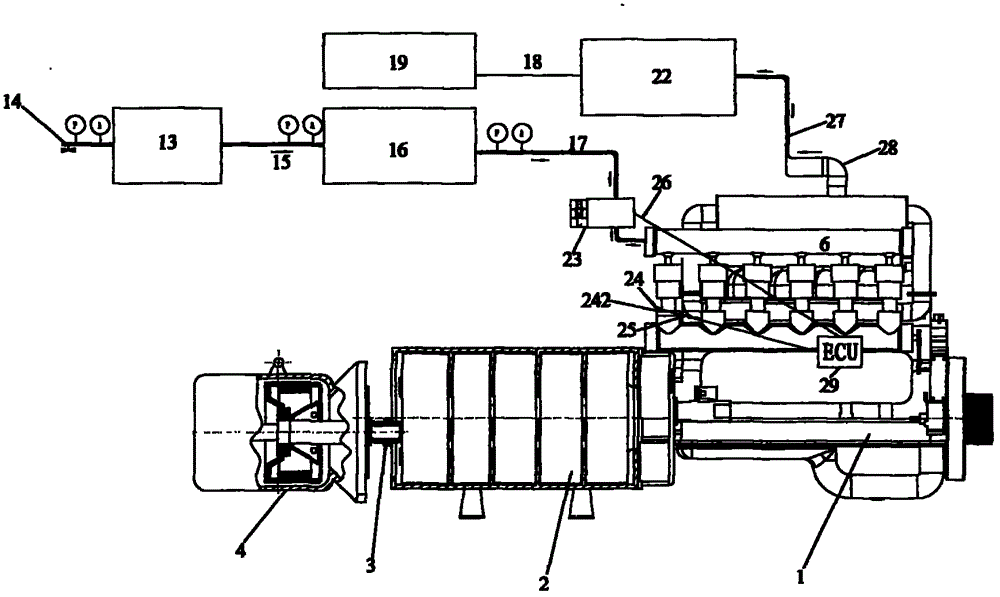
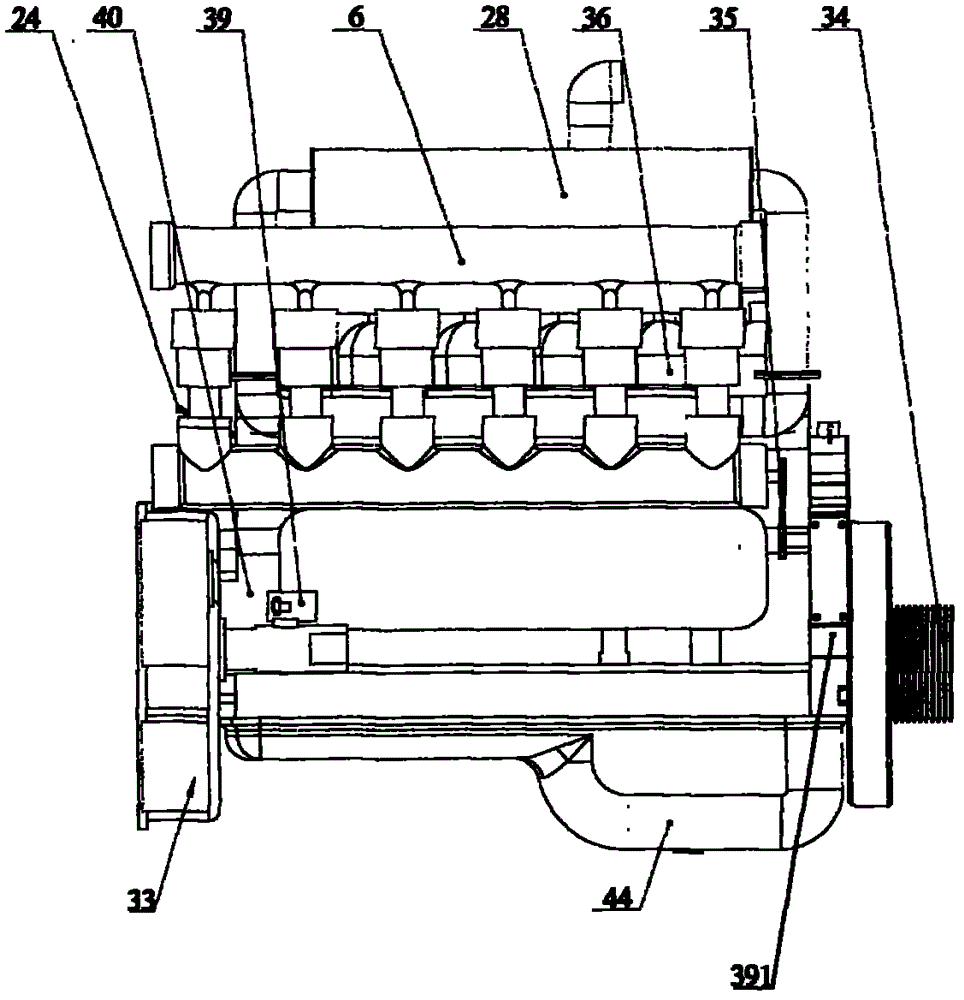
Two-stroke aerodynamic engine assembly
The invention relates to a two-stroke engine, in particular to a two-stroke aerodynamic engine assembly which takes compressed air as a power source. The two-stroke aerodynamic engine assembly comprises an engine body (1), a multicolumn power distributor (2), a power device (3), a controller system (6), an air inlet control compensated flow control valve (23), a high-pressure air tank set (13), a constant-pressure tank (16) and an electric control unit (ECU) (29).
Owner:周登荣 +1
Internal combustion engine machine incorporating significant improvements in power, efficiency and emissions control
InactiveUS7104227B2Increase powerImprove efficiencyValve arrangementsLubrication of auxillariesExternal combustion engineFour-stroke engine
A two stroke cycle internal combustion engine machine that does not require lubricating oil to be mixed with its fuel, producing greater efficiency, higher power to weight ratio, cooler operating temperatures, a wider speed range, greater simplicity, and lower toxic emissions, many of the improvements also transferable to four stroke engines.
Owner:WARREN III C MADISON
Engine timing control with intake air pressure sensor
InactiveUS7225793B2Reduce complexityLow costElectrical controlVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsExternal combustion engineInlet valve
An engine control apparatus is disclosed for determining crankshaft position and engine phase of an internal combustion engine through monitoring intake air pressure fluctuations. The opening of the intake valve is mechanically linked to the crankshaft position of an engine. When the intake valve opens it creates air pressure fluctuations in the air induction system of the engine. The control apparatus is configured to determine intake air pressure fluctuations indicative of an intake air event and thus a particular crankshaft position, and their corresponding period of the engine cycle. The controller then uses this information to determine crankshaft speed and position for the purpose of fuel injection and ignition timing of the internal combustion engine. Engine phase is also determined on four-stroke engines. The engine may also include a crankshaft position sensor in combination with monitoring intake air pressure fluctuations to increase resolution in determination of crankshaft position. A circuit is provided for simultaneously measuring intake temperature using a single bridge type pressure sensor in order to calculate air mass flow rate.
Owner:ELECTROJET TECH INC
Two-stroke internal combustion engine, method of operating two-stroke internal combustion engine and method of converting two-stroke engine
ActiveCN103748334AEmission reductionSimple structureInternal combustion piston enginesGaseous engine fuelsExhaust valveTop dead center
The invention relates a two-stroke internal combustion engine (10) comprising at least one cylinder (20) with a piston (24) arranged reciprocateably between its top dead center and bottom dead center, and a cylinder cover (26) defining a combustion chamber (22), oxygen containing gas inlet (18) in the lower part of the cylinder (20) to be open into the combustion chamber (22) at least while the piston is at its bottom dead center position, a gaseous fuel inlet (30) arranged in the cylinder between the oxygen containing gas inlet (18) and the cylinder cover(26), and an exhaust valve (28) arranged to the cylinder cover at a center axis of the cylinder. The cylinder cover(26) is provided with pilot ignition pre-chambers (36) opening into the combustion chamber (22) through pre-chamber ports (34).The preset invention relates also to method of operating the two-stroke engine (10).
Owner:WAERTSILAE SCHWEIZ AG
Four stroke engine auto-ignition combustion
ActiveUS7059281B2Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust valveGasoline direct injection
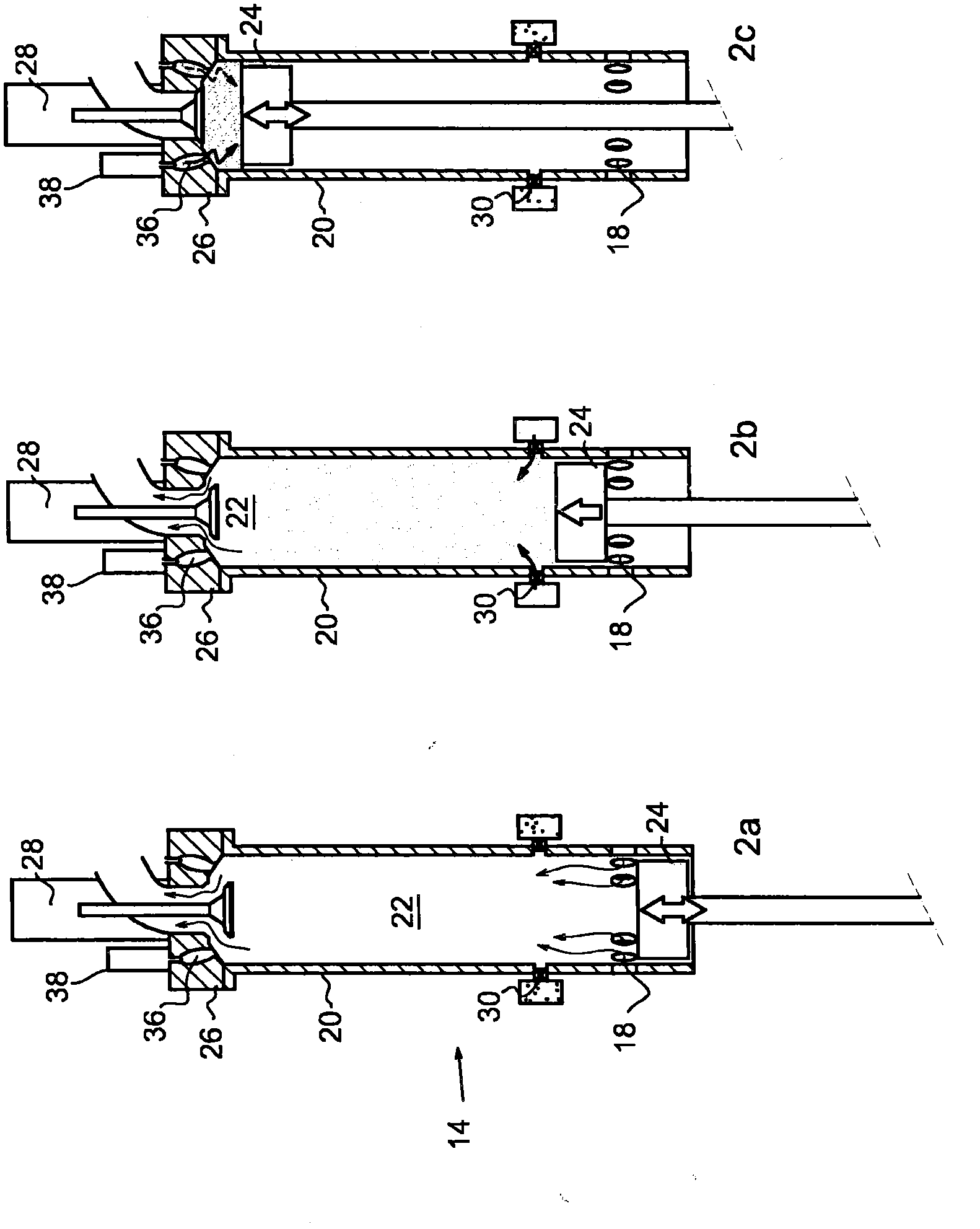
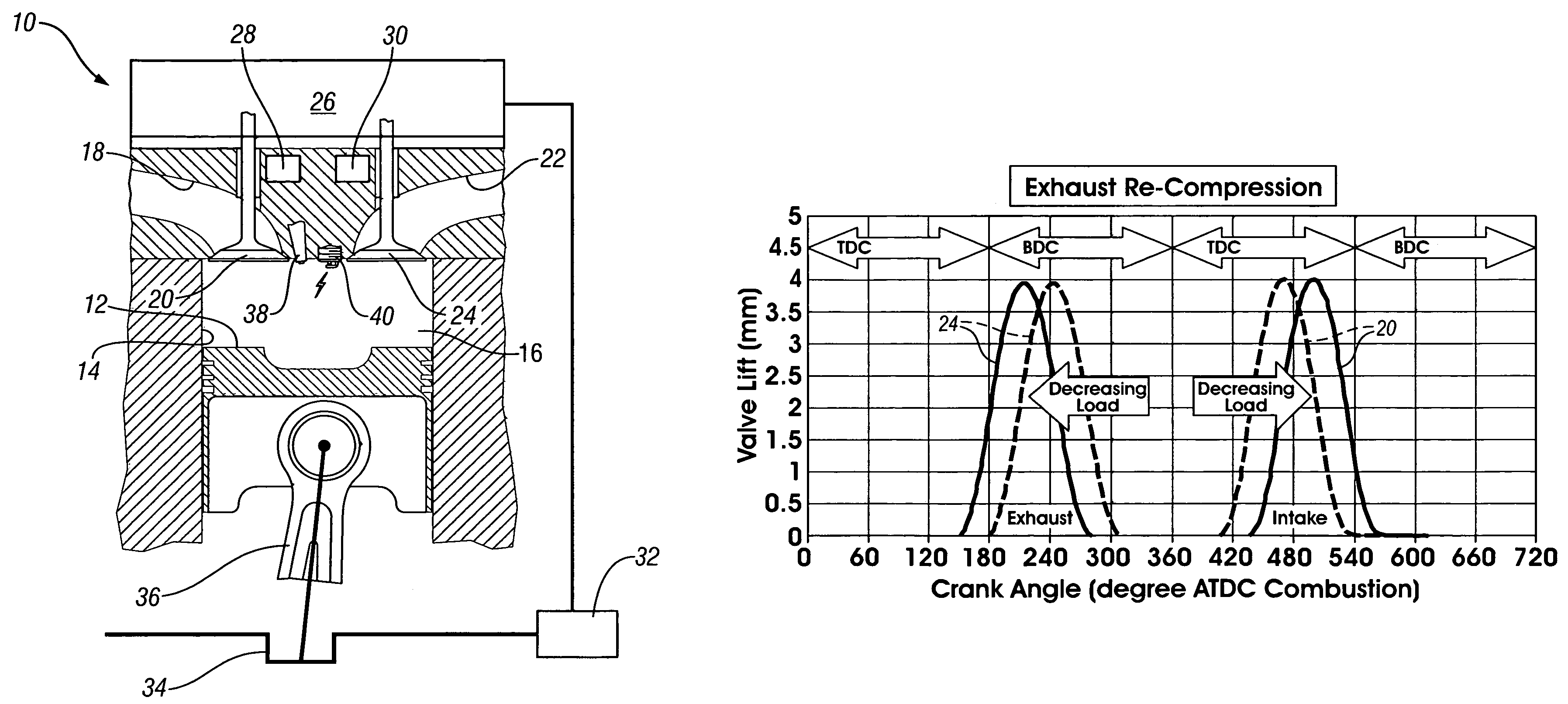
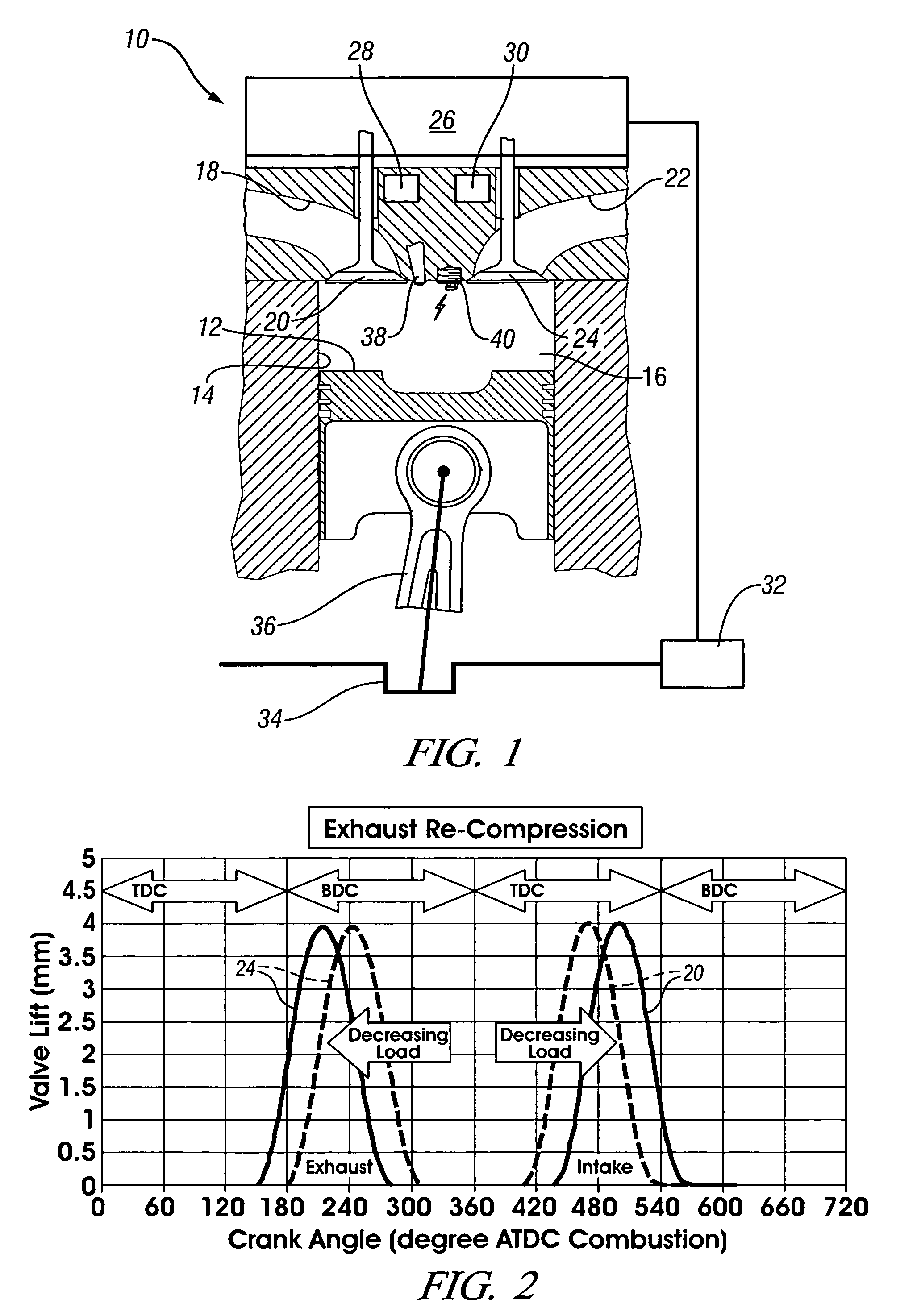
A method of operating a four-stroke gasoline direct-injection controlled auto-ignition combustion engine includes opening both the intake and exhaust valves during terminal portions of the expansion strokes and initial portions of the contraction strokes, injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber for mixing with retained gases and igniting the fuel near the ends of the contraction strokes. In the process, combustion gases are expanded to produce power during major portions of the expansion strokes, combusted gases are blown down into the exhaust outlet and the air inlet and are partially redrawn into the cylinder with fresh air during the terminal portions of the expansion strokes so the air charges are heated by the hot exhaust gases. Portions of the charges re-expelled and the remaining portions of the charges and injected fuel are compressed for ignition of the dilute fuel / air and exhaust gas mixture. Substantial reductions of NOx emissions result from the method.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Quick starting engine with electromechanical valves
ActiveUS7055483B2Improve trustReduce noiseElectrical controlOutput powerExhaust valveFour-stroke engine
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
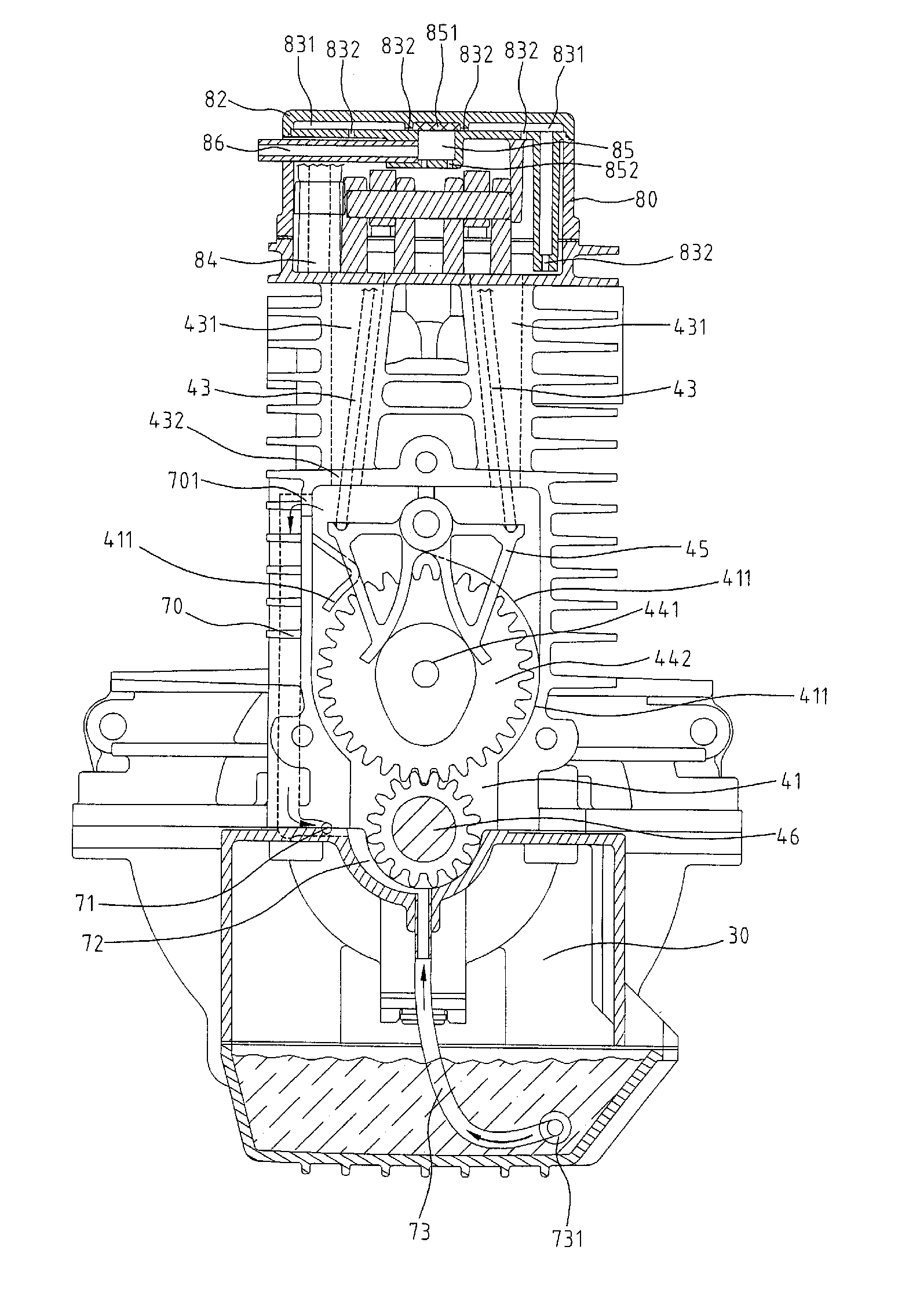
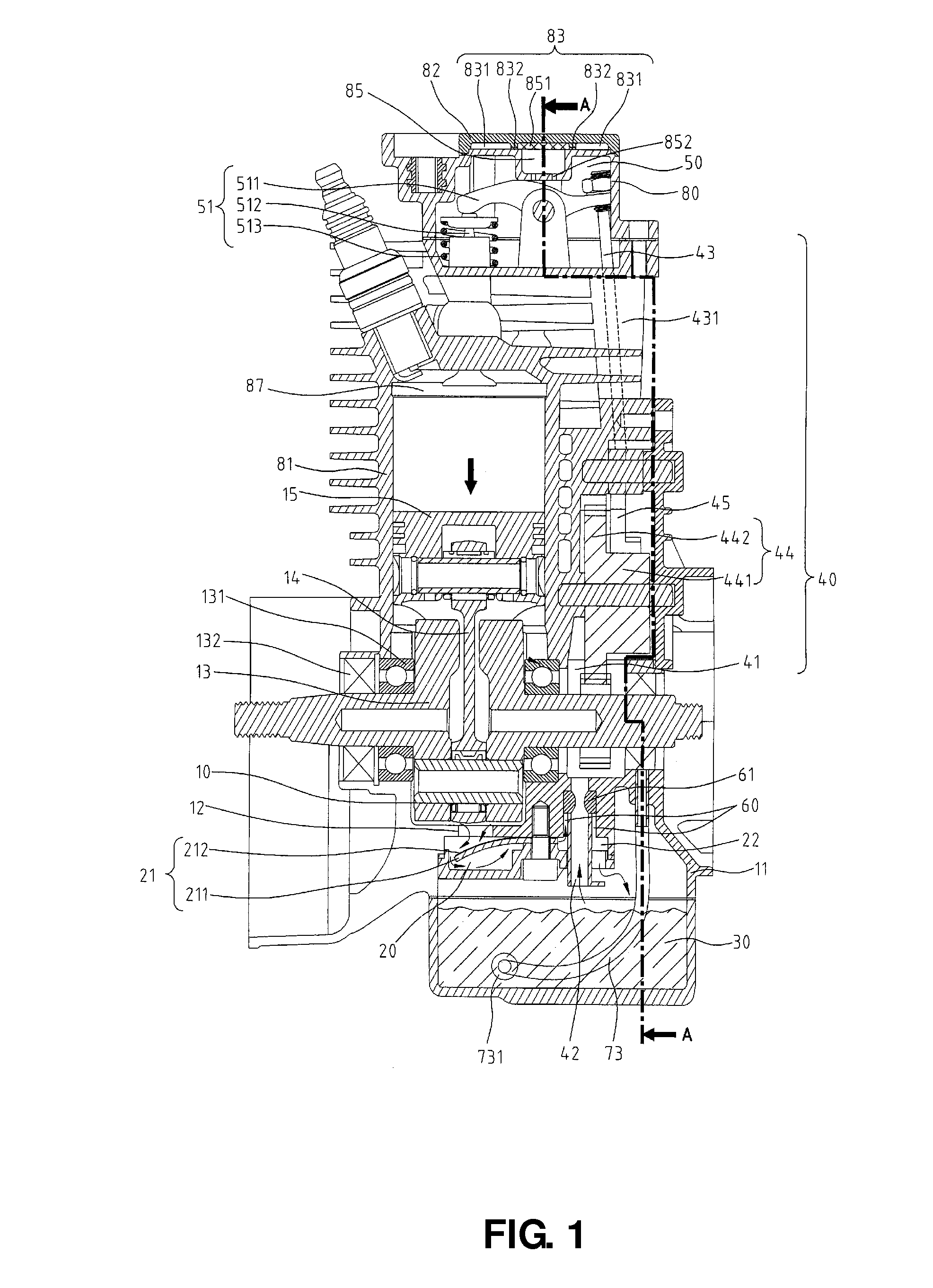
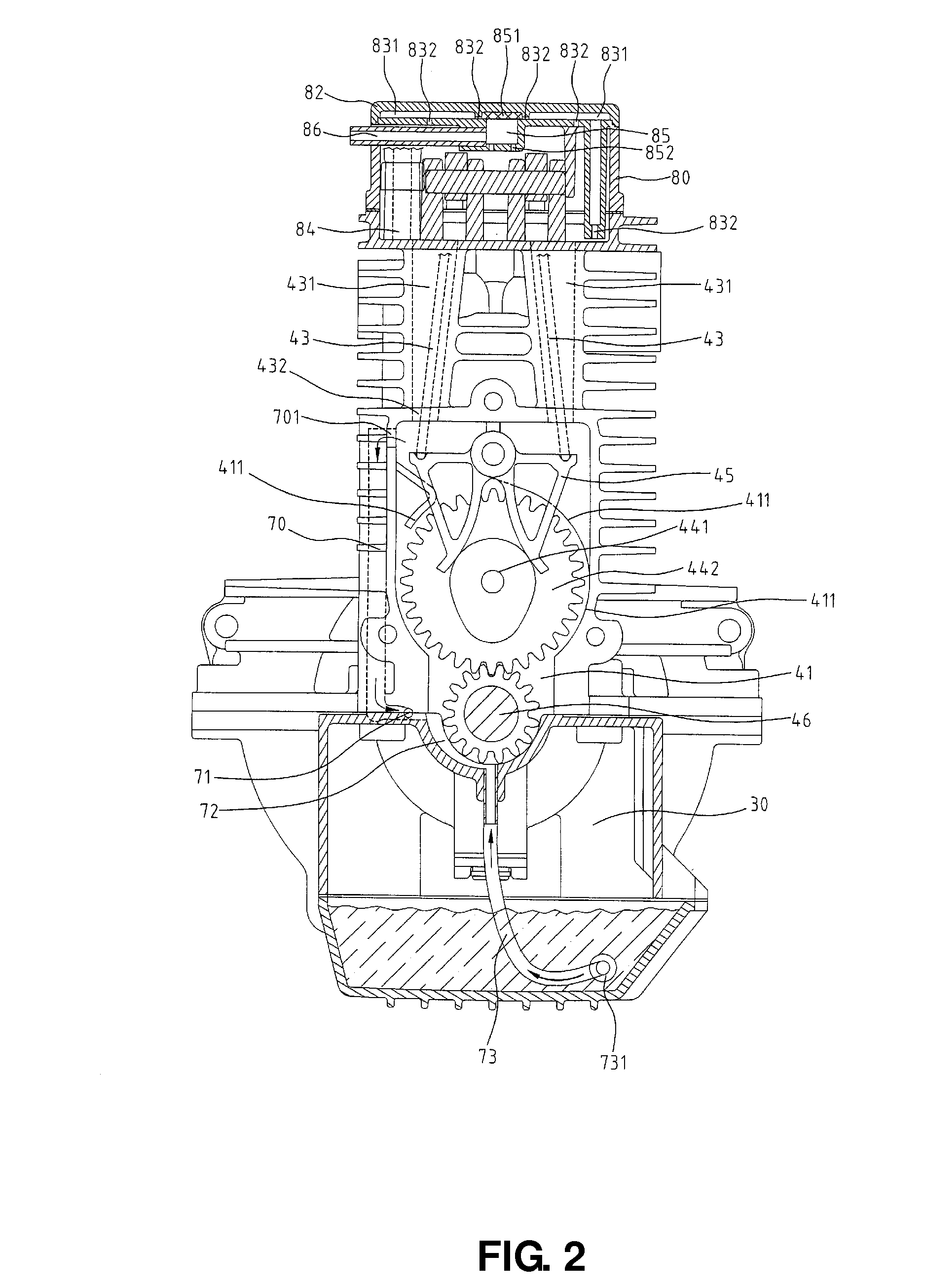
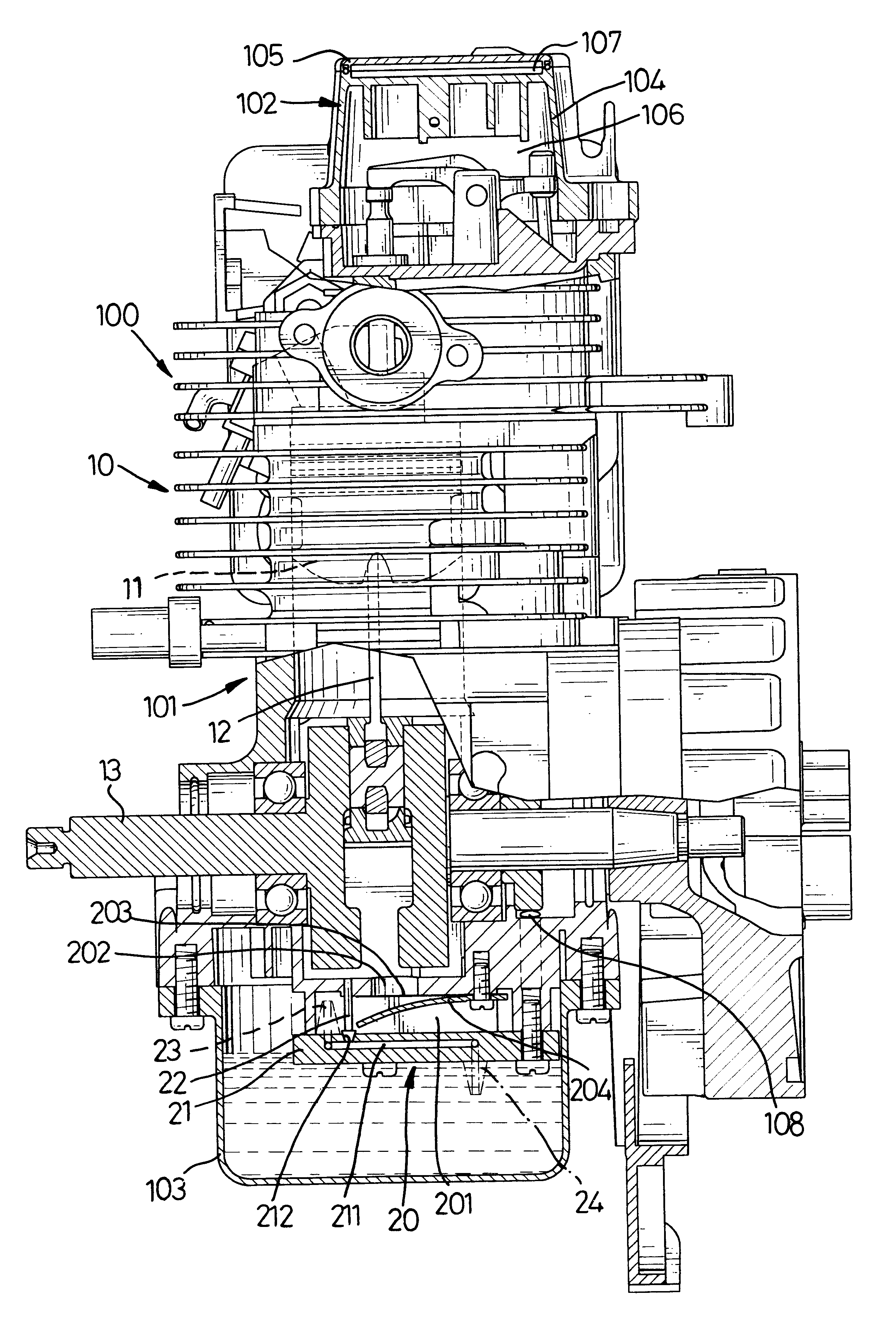
Dry-sump lubrication type four-stroke cycle engine
InactiveUS7040454B2Easy to usePrecision lubricationLubrication of auxillariesLubricant conduit arrangementsAir pumpFour-stroke engine
The interior of a crankcase is divided into a front crank chamber and a rear transmission chamber by a partition wall of a given height. A lower part of the transmission case is used as an oil reservoir chamber for reserving lubricating oil. Opposite ends of the crankcase are covered with covers to form a generator chamber and a clutch chamber. The crank chamber is connected to the generator chamber by a drain passage to drain oil collected in the crank chamber into the generator chamber. A scavenging pump placed in the clutch chamber sucks the oil collected in the generator chamber through an oil passage extending across the crankcase under the crank chamber and discharges the oil into an air space in the clutch chamber.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Engine timing control with intake air pressure sensor
InactiveUS20060118086A1Low costReduce complexityElectrical controlVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsBridge typeImage resolution
An engine control apparatus is disclosed for determining crankshaft position and engine phase of an internal combustion engine through monitoring intake air pressure fluctuations. The opening of the intake valve is mechanically linked to the crankshaft position of an engine. When the intake valve opens it creates air pressure fluctuations in the air induction system of the engine. The control apparatus is configured to determine intake air pressure fluctuations indicative of an intake air event and thus a particular crankshaft position, and their corresponding period of the engine cycle. The controller then uses this information to determine crankshaft speed and position for the purpose of fuel injection and ignition timing of the internal combustion engine. Engine phase is also determined on four-stroke engines. The engine may also include a crankshaft position sensor in combination with monitoring intake air pressure fluctuations to increase resolution in determination of crankshaft position. A circuit is provided for simultaneously measuring intake temperature using a single bridge type pressure sensor in order to calculate air mass flow rate.
Owner:ELECTROJET TECH INC
Four-cycle engine
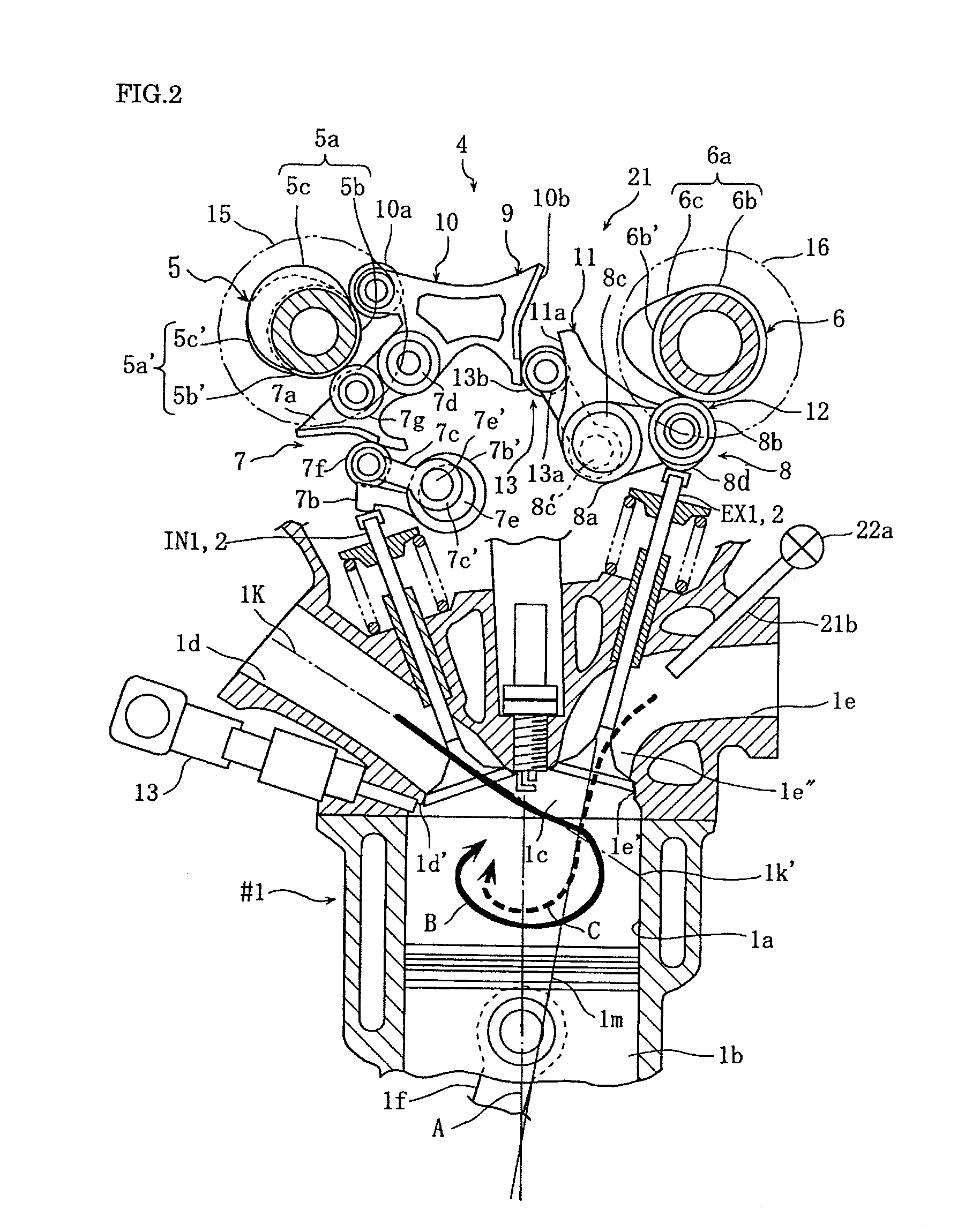
InactiveUS20100116255A1Expand the scope of operationIncreasing transient torqueElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal pressureExhaust valve
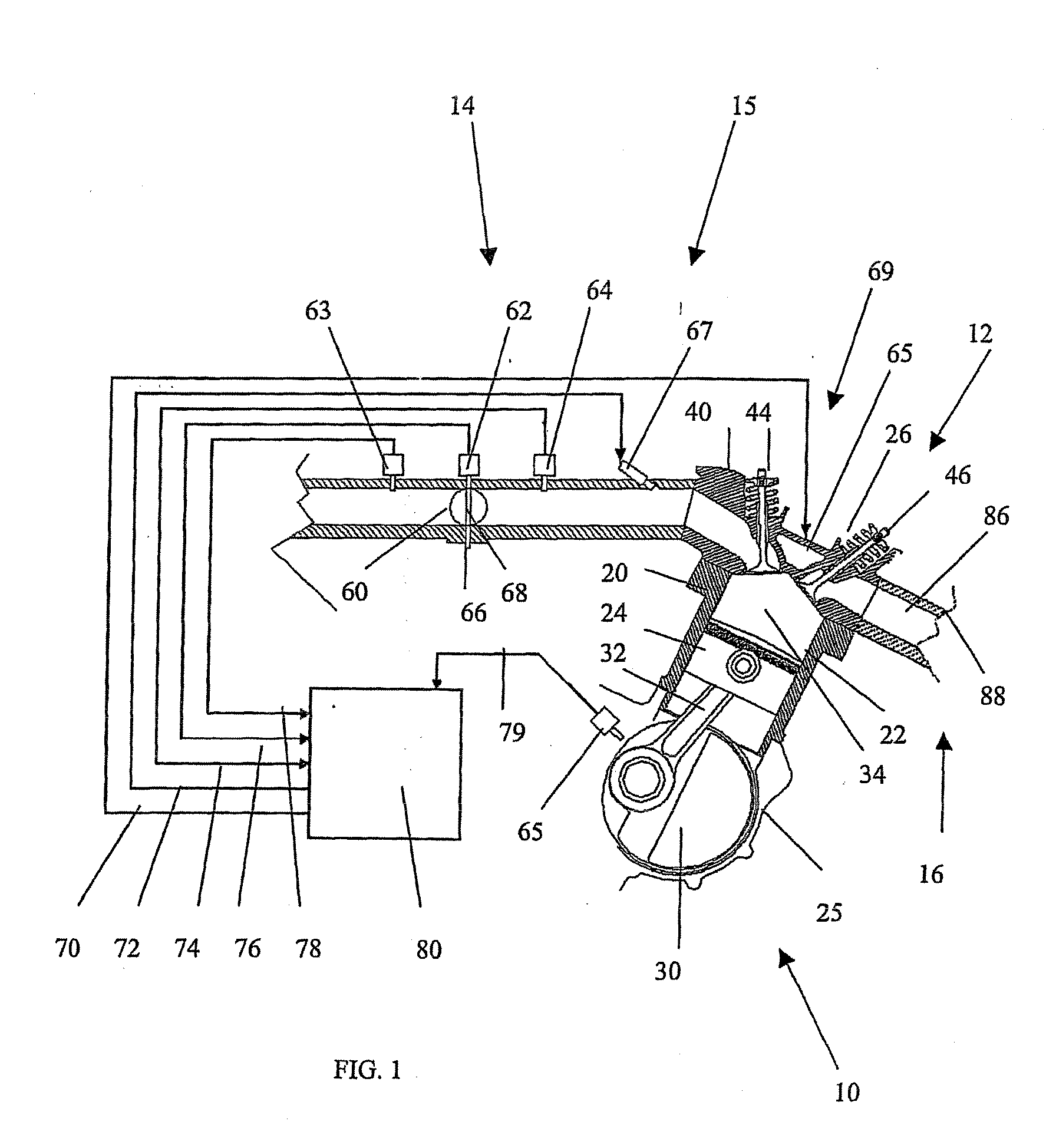
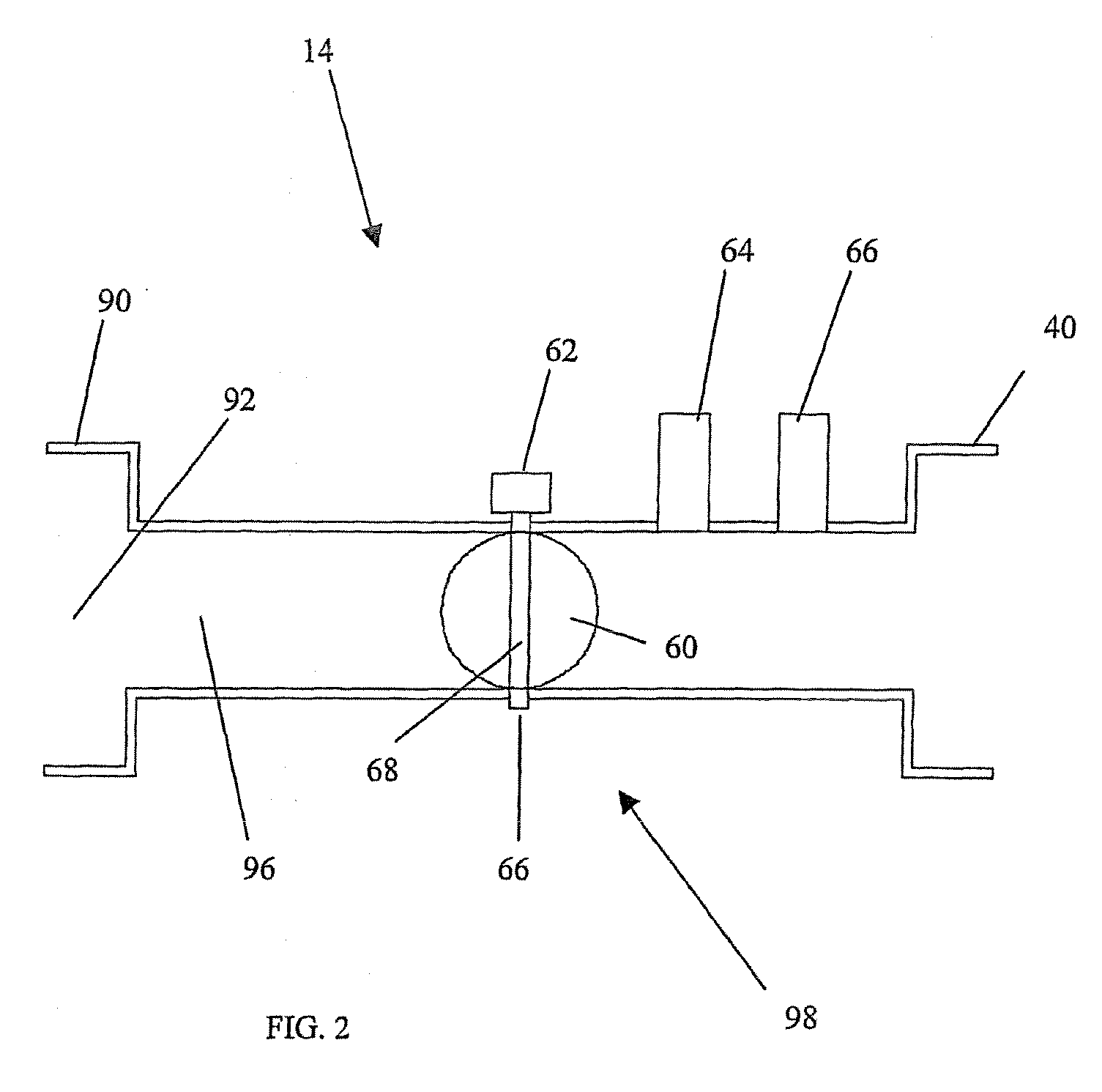
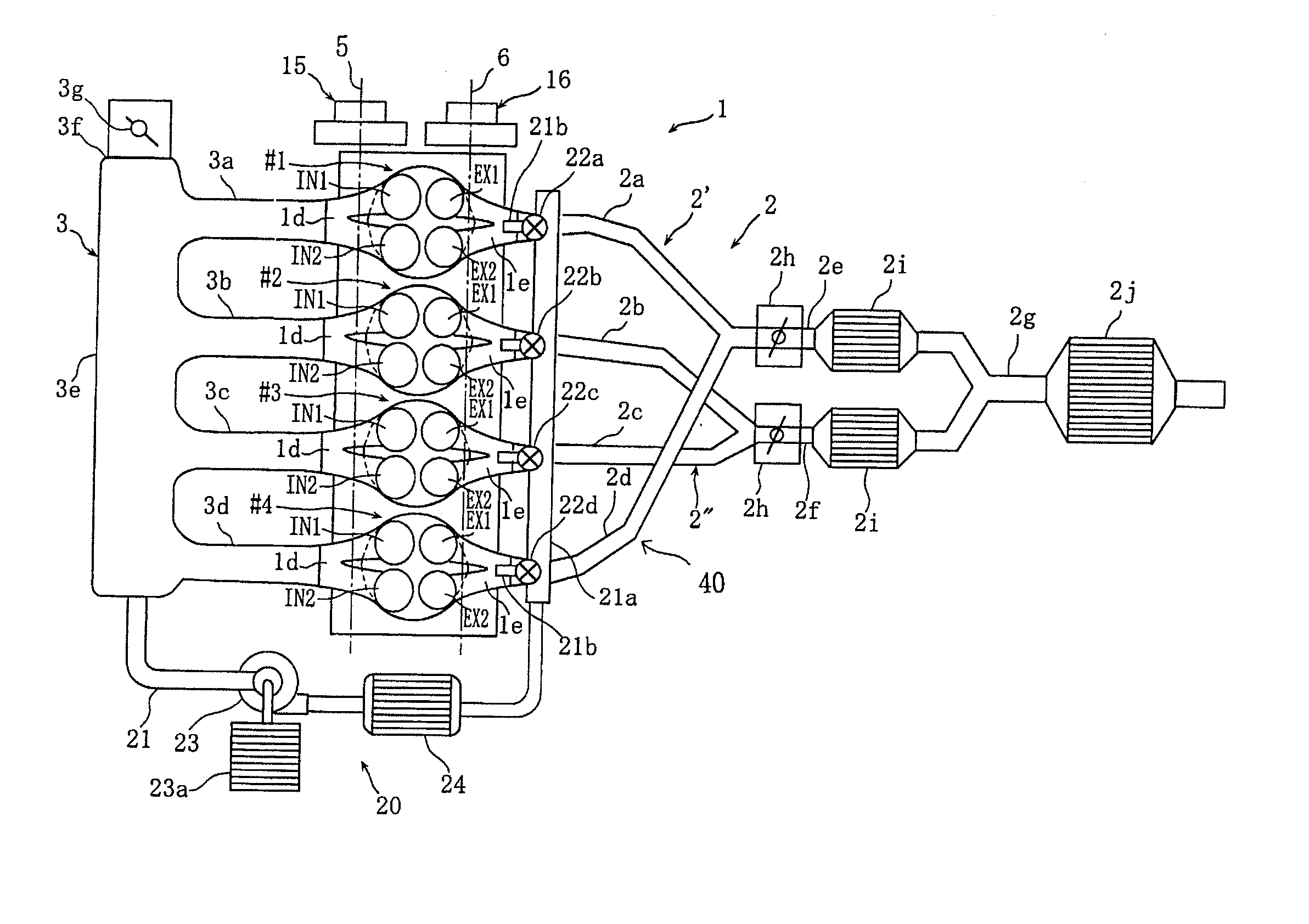
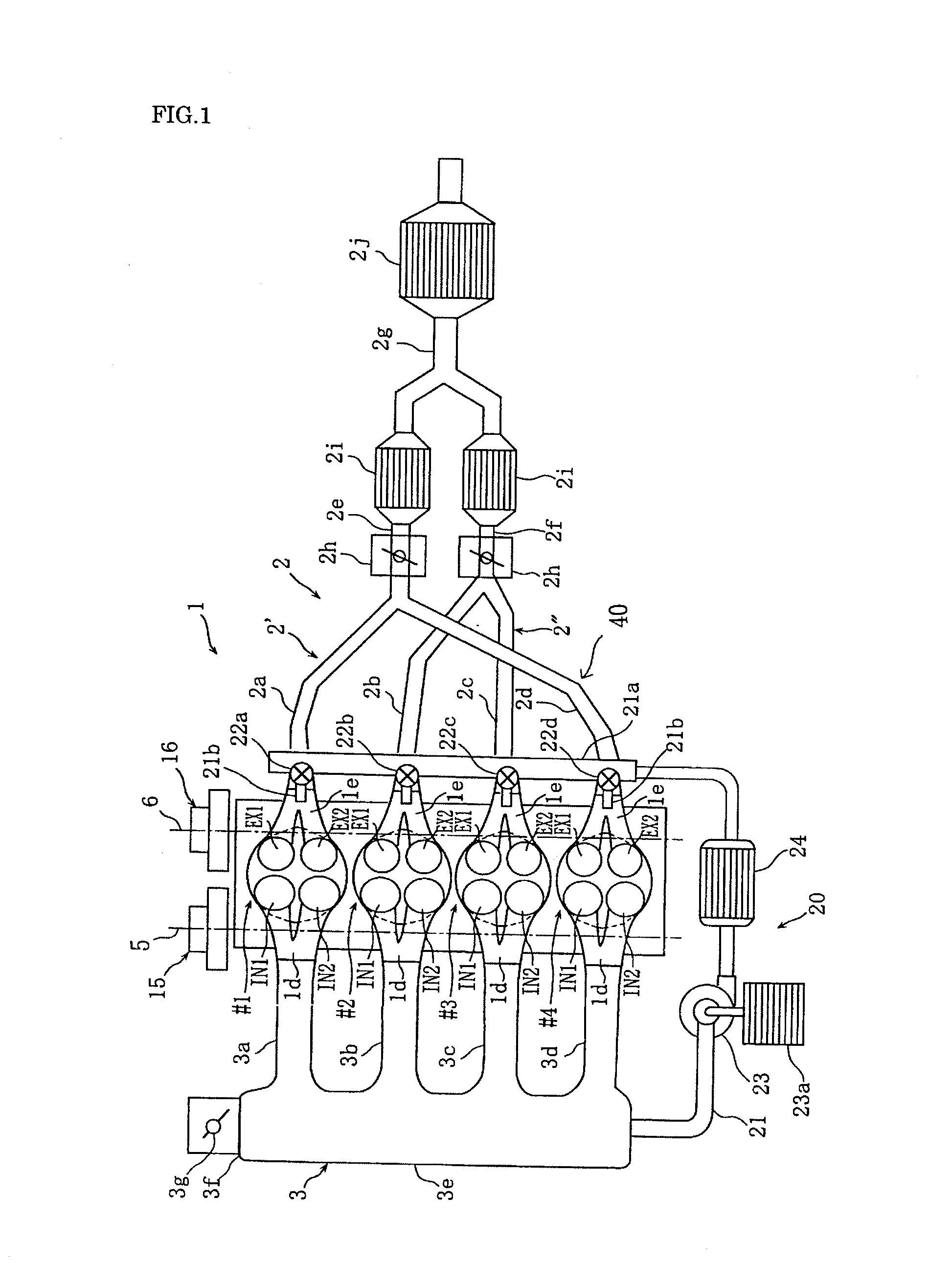
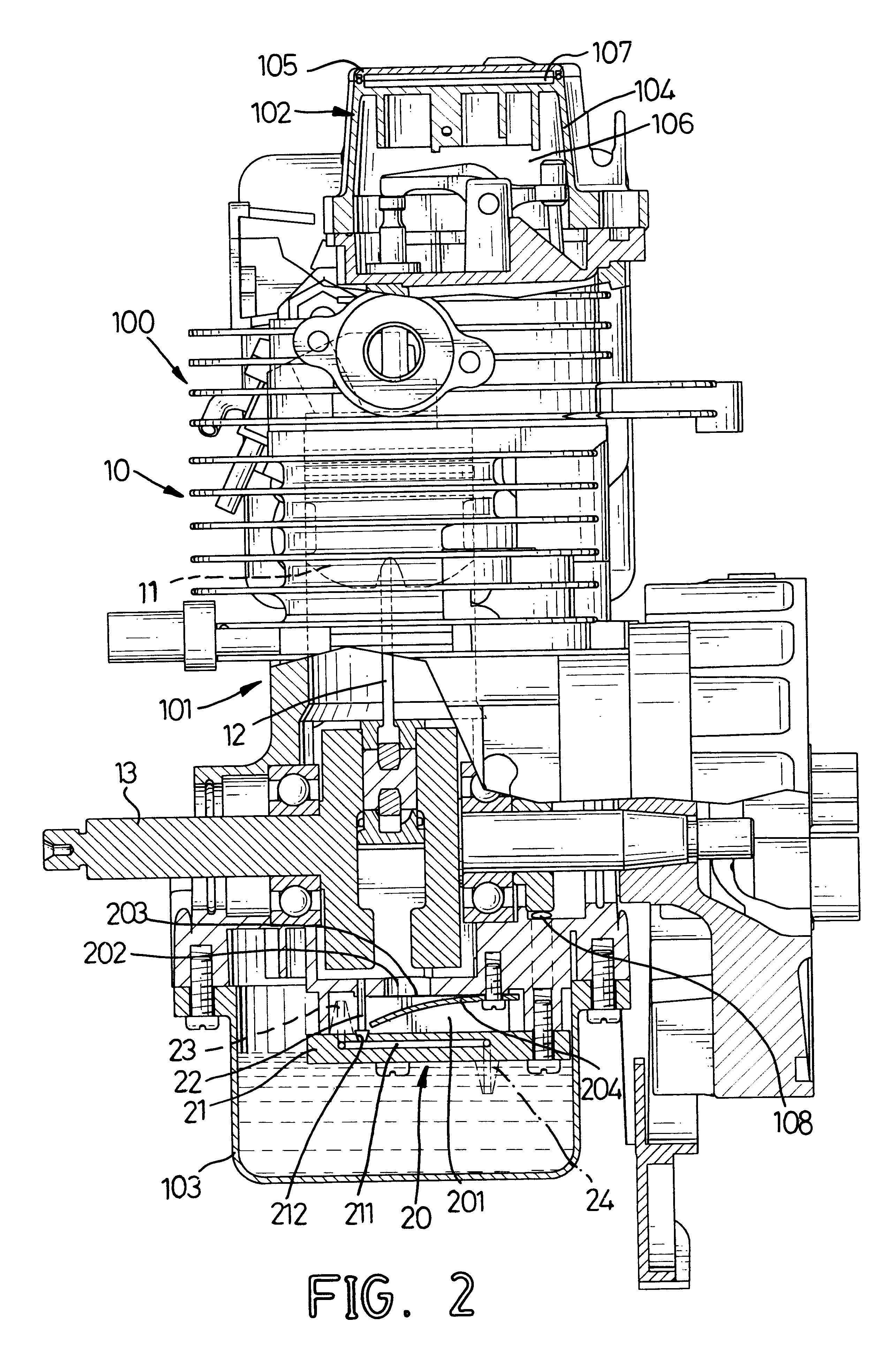
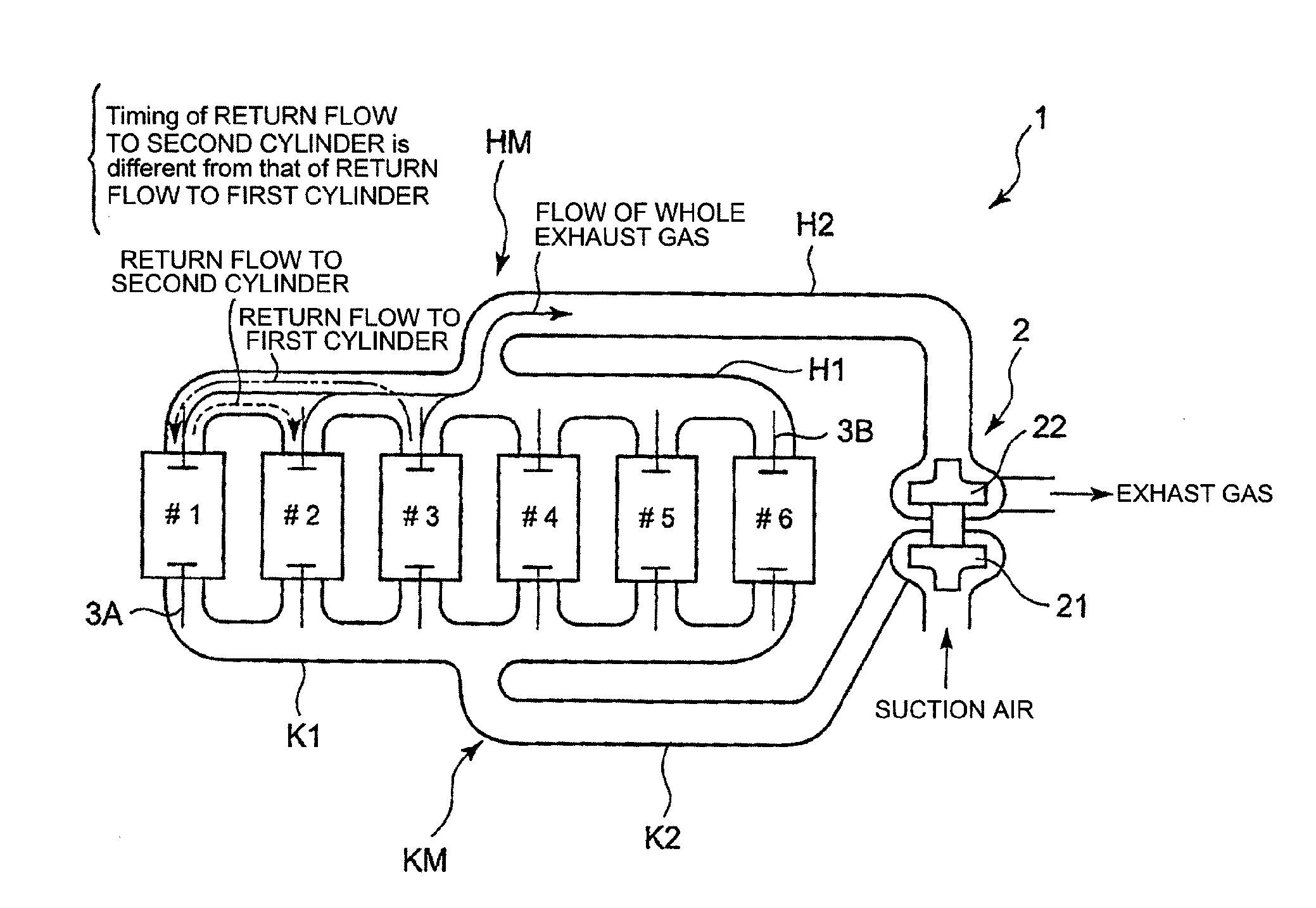
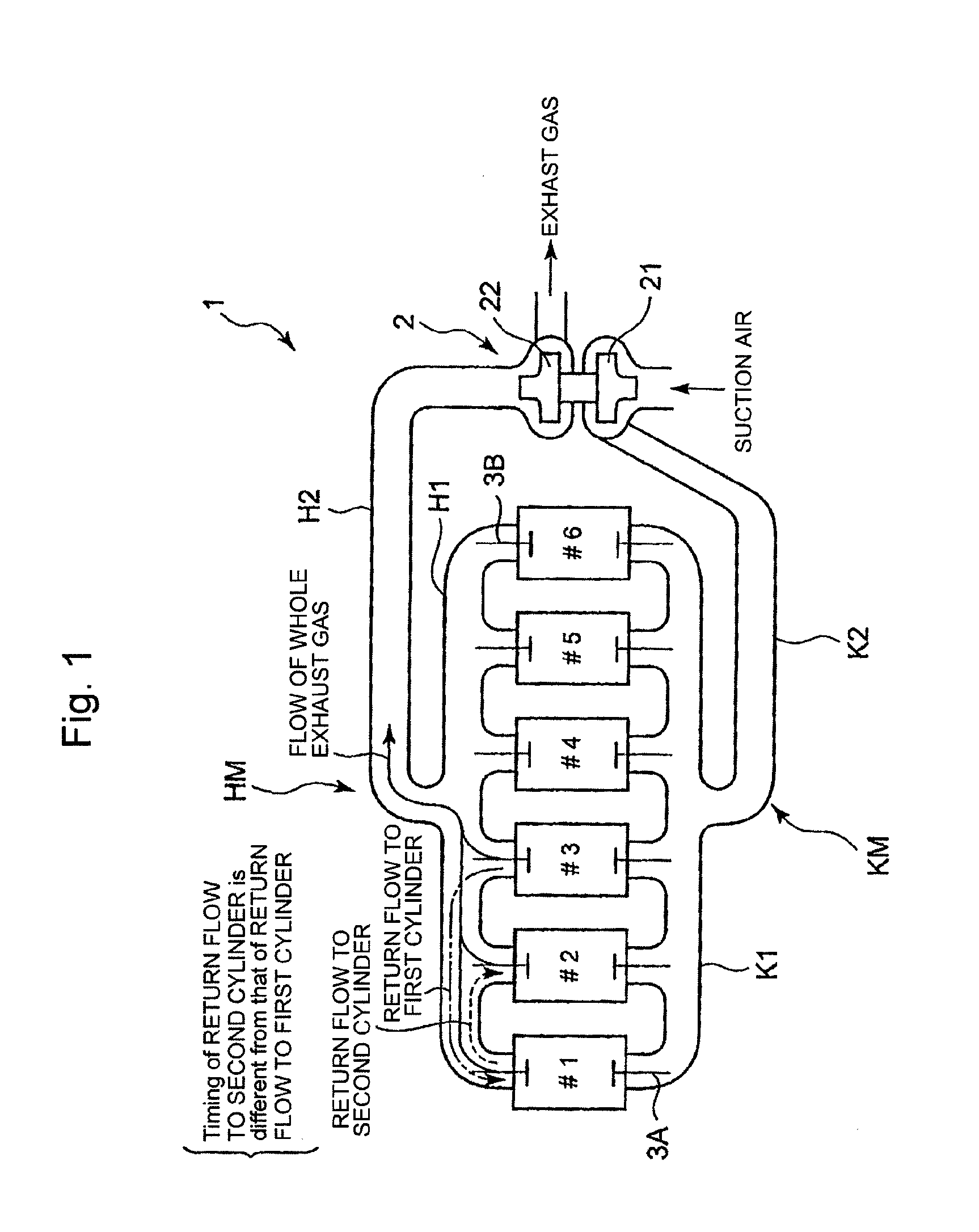
A four-stroke engine (1) structured to introduce fresh air and EGR gas into a cylinder (1a) includes a blowdown supercharging system (40) using a combustion chamber internal pressure when exhaust valves open in an expansion stroke of a first cylinder (hereinafter denoted as an exhaust blowdown pressure) for introducing EGR gas into a second cylinder from near a bottom dead center of an intake stroke to near a bottom dead center of a compression stroke of the second cylinder which is different from the first cylinder in combustion timing, and a secondary air supply system (20) supplying secondary air to an exhaust port (1e) of the second cylinder prior to arrival of the exhaust blowdown pressure at the second cylinder. The secondary air in the exhaust port and the EGR gas are supercharged into the second cylinder by the exhaust blowdown pressure from the first cylinder.
Owner:HATAMURA KOICHI
Electronic engine control with reduced sensor set
InactiveUS20050039526A1Low costReduce complexityElectrical controlEngine testingImage resolutionFour-stroke engine
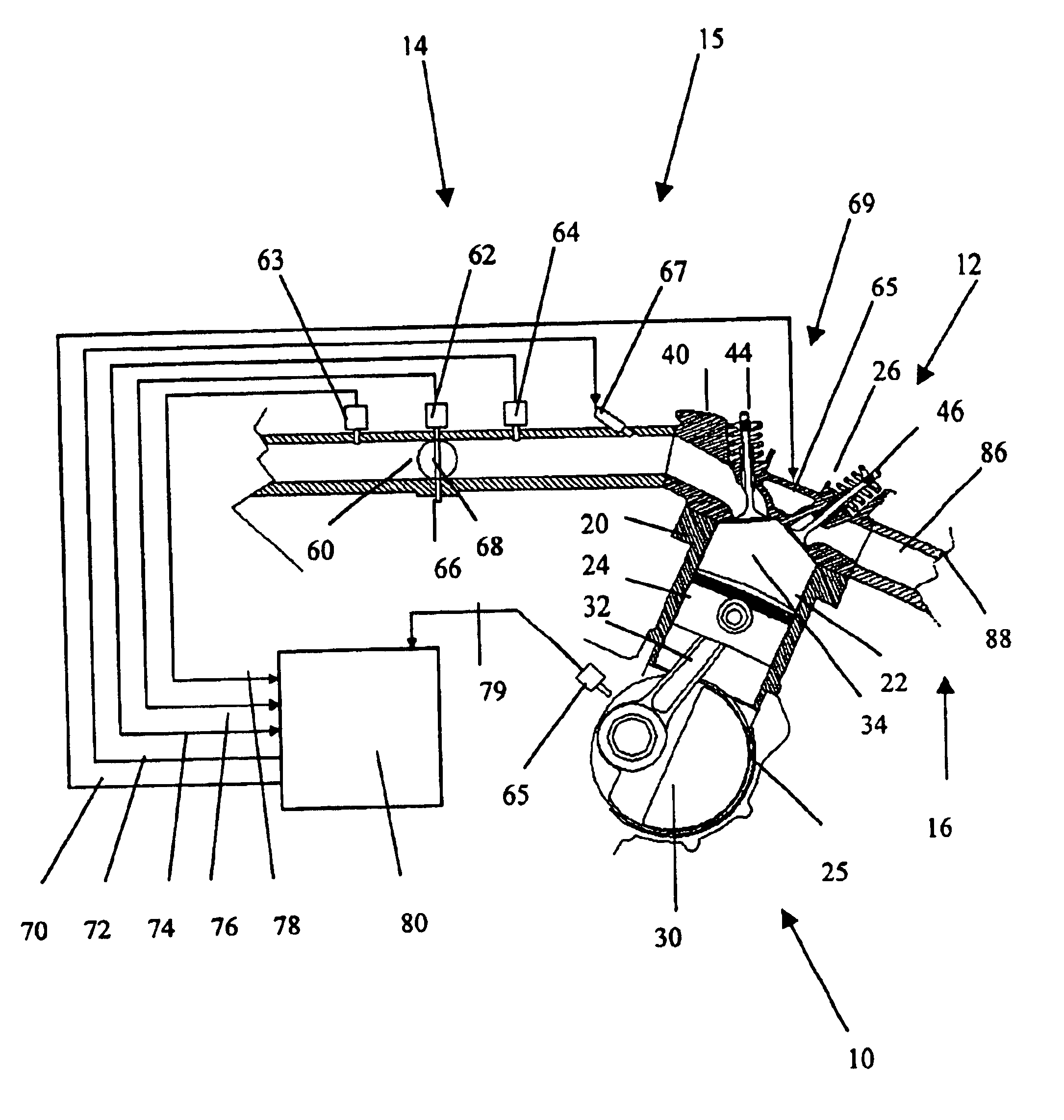
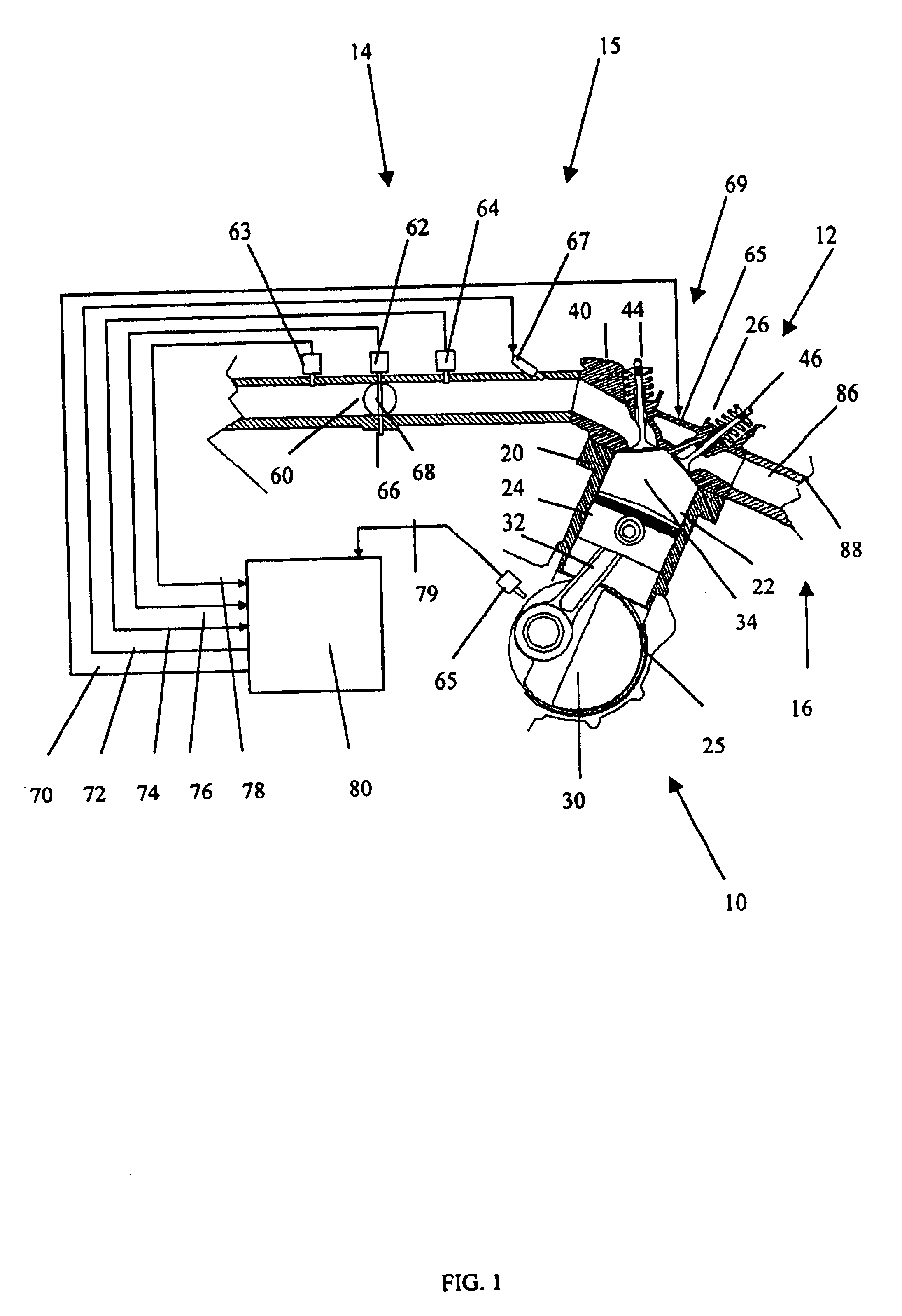
An engine control apparatus is disclosed for determining crankshaft position, engine phase, engine loading, and intake air mass of an internal combustion engine (10) through monitoring intake air pressure fluctuations (120). The opening of the intake valve (44) is mechanically linked to the crankshaft position of an engine. When the intake valve (44) opens it creates air pressure fluctuations in the air induction system (14) of the engine (10). The control apparatus is configured to determine intake air pressure fluctuations indicative of an intake air event (100 to 110) and thus a particular crankshaft position, and their corresponding period of the engine cycle. The controller then uses this information to determine crankshaft speed and position for the purpose of fuel injection and ignition timing of the internal combustion engine. Engine phase is also determined on four-stroke engines. Intake air pressure is used to determine intake air mass and loading of the engine. This combination results in a single sensor used in a system to determine intake air mass, engine loading, injected fuel mass, and to determine timing for fueling and ignition events. The engine may also include a crankshaft position sensor in combination with monitoring intake air pressure over time to increase resolution in the determination of crankshaft position.
Owner:ELECTROJET TECH INC
Contraposition two-stroke engine
InactiveCN102733947AInternal combustion piston enginesCylinder headsReciprocating motionFour-stroke engine
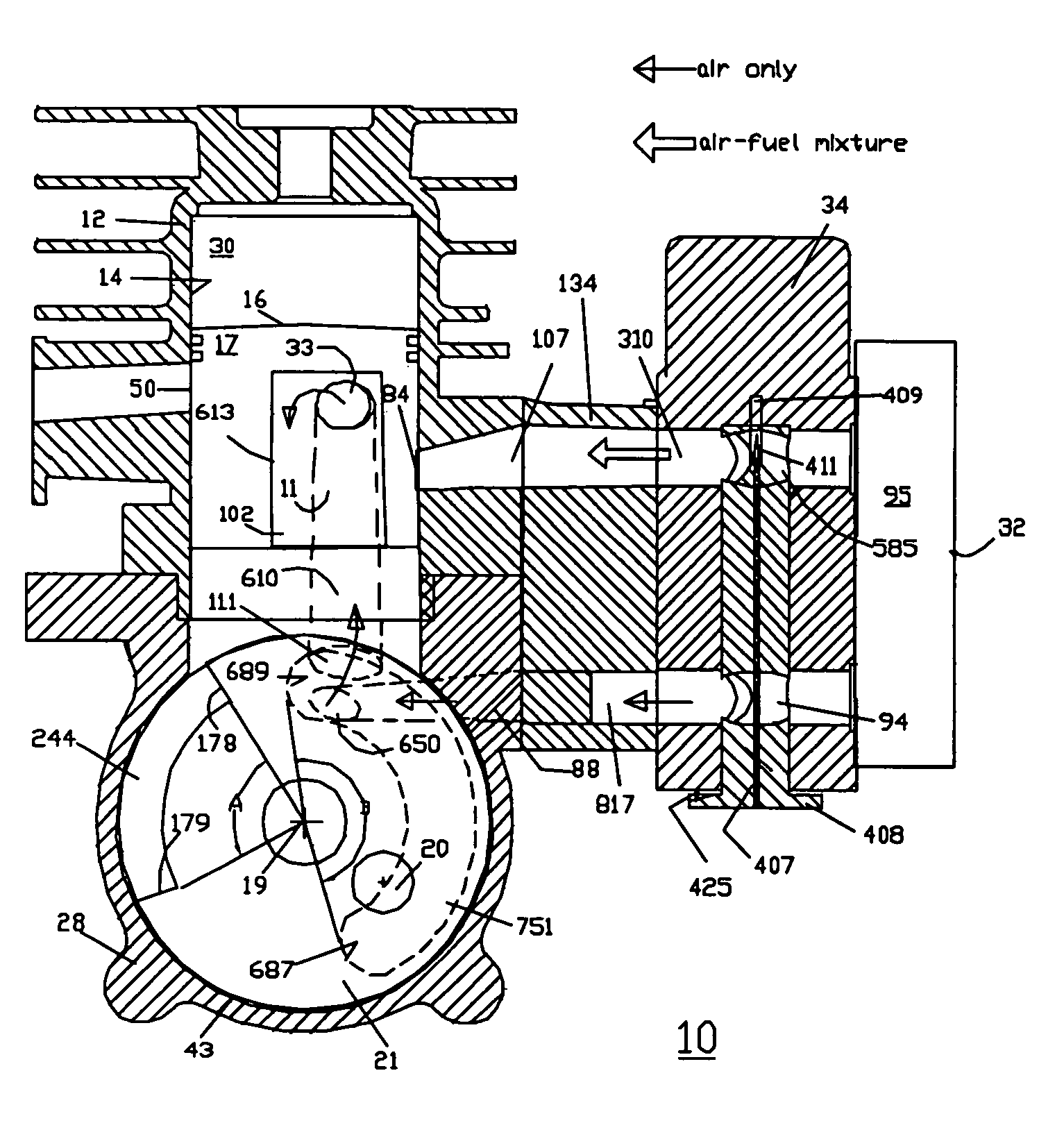
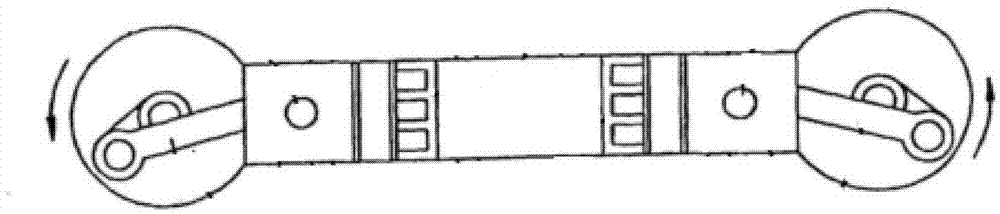
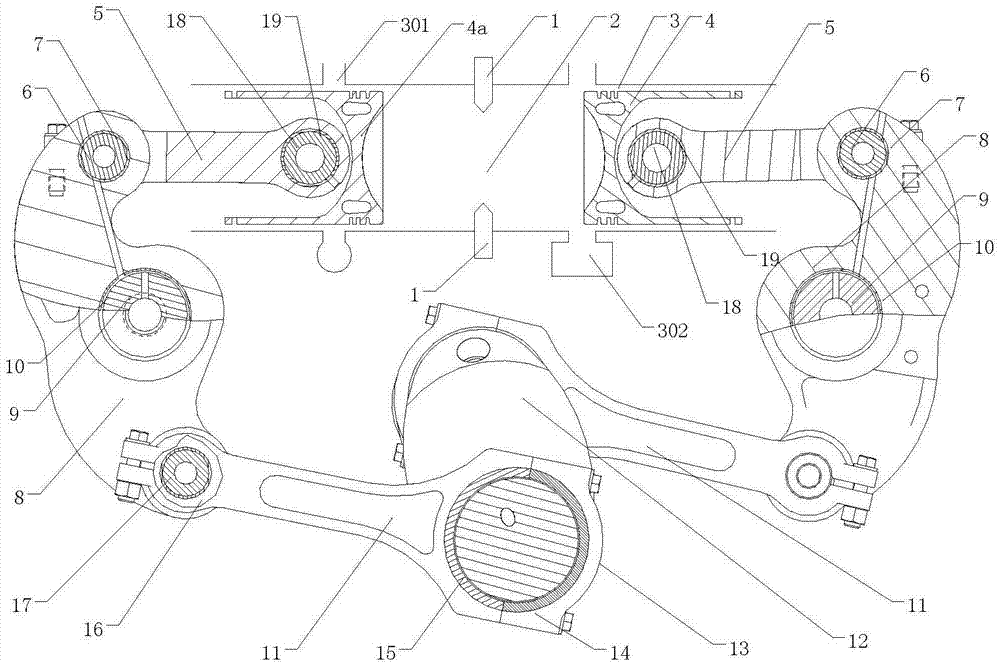
The invention discloses a contraposition two-stroke engine comprising a cylinder, a cylinder sleeve, an intake piston and an exhaust piston, upper connection rods, rocker arms, lower connection rods, and crankshafts, wherein the upper connection rods, the rocker arms and the lower connection rods are arranged on the same side as the intake piston and the exhaust piston; the cylinder sleeve and the top surfaces of the intake piston and the exhaust piston form a combustion chamber; the upper connection rods, the rocker arms and the lower connection rods on both sides are respectively arranged symmetrically; the rocker arms on both sides are respectively connected with the cylinder body by the respective rocker arm shafts; the intake piston is connected with the upper end of the rocker arm on the same side by the upper connection rod; the lower end of the rocker arm on the same side with the intake piston is connected with the crankshaft arranged right below the cylinder body by the lower connection rod on the same side with the intake piston; the connection relations between the exhaust piston and the upper connection rod, between the exhaust piston and the rocker arm, and between the exhaust piston and the lower connection rod on the same side are the same as those between the intake piston and the upper connection rod, between the intake piston and the rocker arm and the between the intake piston and the lower connection rod; the reciprocations of the intake piston and the exhaust piston drive the crankshafts by the rocker arms, the upper connection rods and the lower connection rods on the same sides. With the adoption of the engine, the shortages of the contraposition two-stroke engine are made up effectively.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Vibration measuring method of engine speed by applying four-point energy centrobaric correction method
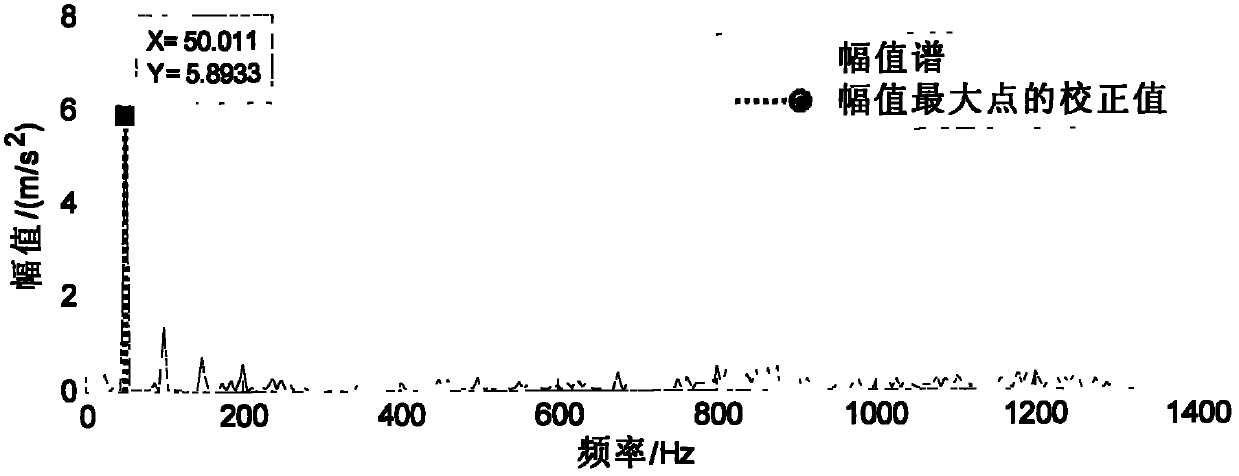
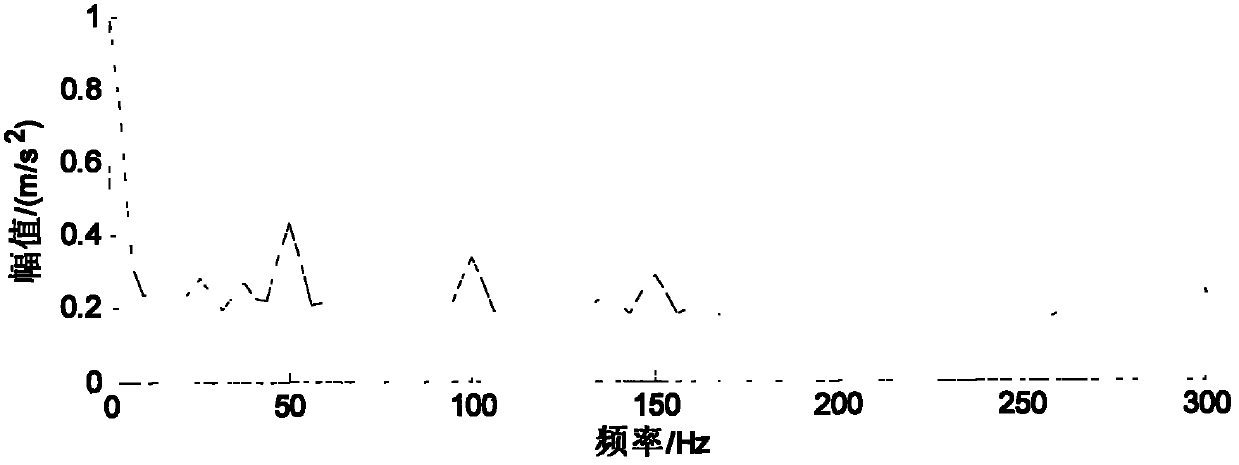
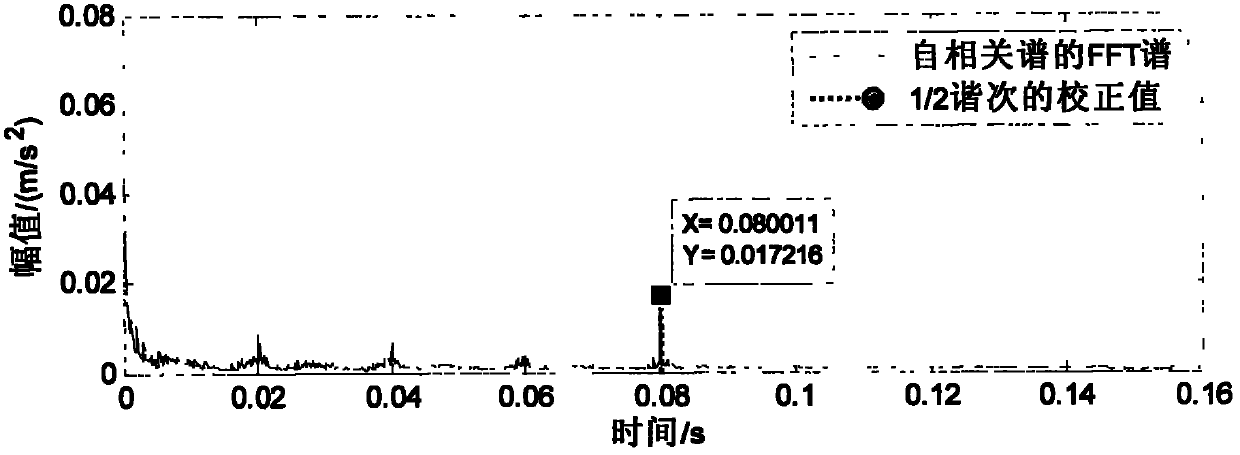
InactiveCN102095885ASolve the problem that the engine speed cannot be measuredImprove versatilityDevices characerised by mechanical meansVibration accelerationTime spectrum
The invention discloses a vibration measuring method of engine speed by applying a four-point energy centrobaric correction method, which comprises the steps of: discrete-sampling a vibration acceleration signal on the surface of an engine block to obtain a time series; obtaining a frequency domain signal X1(f) through fast Fourier transformation of Zn(t); correcting the peak frequency fi of X1(f) by adopting a four-point energy centrobaric correction method, and obtaining a corrected frequency; obtaining a time spectrum signal ZZn(t) through carrying out self-related transformation and fast Fourier transformation on the frequency domain signal X1(f); correcting the time ti corresponding to the peak of ZZn(t) by adopting the four-point energy centrobaric correction method again, and obtaining the corrected time; and finding the accurate 1 / 2 harmonic frequency value of the rotating speed w of the four stroke engine according to the corrected frequency and time, and calculating the rotating speed w of the engine through a relational expression. The vibration measuring method of engine speed can solve the problem that the rotating speed of the engine cannot be detected when the number of engine blocks cannot be determined; and the method has the advantages of better universality, high noise-proof performance and accurate and reliable result.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
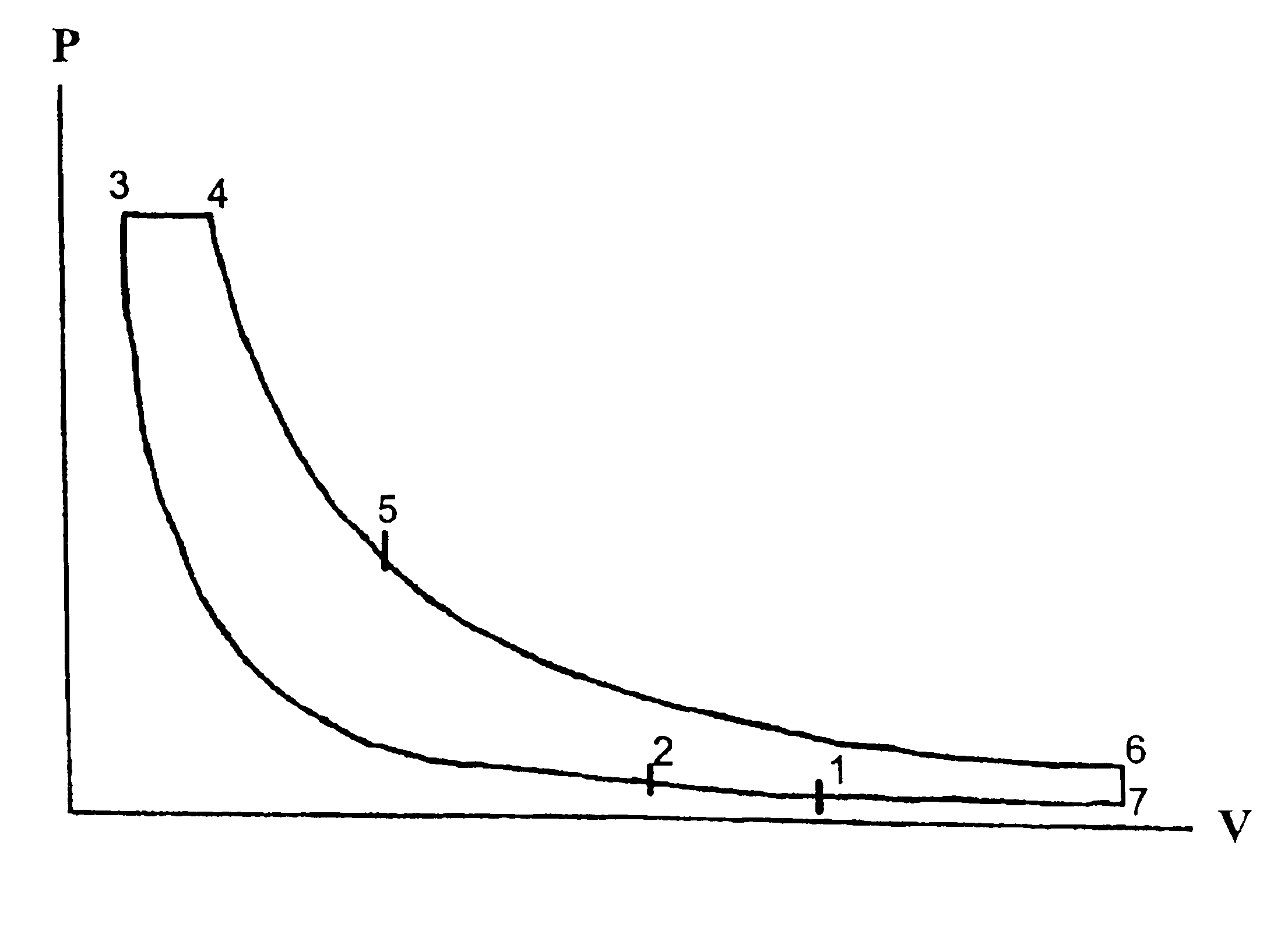
Over expanded limited-temperature cycle two-stroke engines
InactiveUS6848416B1Reduce NOx levelReducing post-combustion temperatureElectrical controlCombustion enginesPressure decreaseFour-stroke engine
A method for combusting fuel in an engine involving decreasing a first volume of gas to a second volume, in two stages, while increasing the pressure and temperature of that volume of gas (a compression process having a chosen compression ratio), then increasing the second volume to a third volume at constant pressure while adding heat until a predetermined temperature is obtained, increasing the third volume of gas to a fourth volume, in two stages while decreasing the pressure at the predetermined temperature (an expansion process having a chosen expansion ratio much greater than the compression ratio), decreasing the pressure to atmospheric pressure while removing heat under constant volume, and finally decreasing the volume of gas to the first volume while removing heat under constant pressure to complete an over expanded, limited-temperature cycle. Also disclosed is an engine employing said over expanded, limited-temperature cycle.
Owner:PIEN PAO C
Valve assembly for a two-stroke engine
ActiveUS7762220B2Reduce the possibilityDiscrepancies in valve position between the exhaust ports are reducedAnalogue computers for vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesValve actuatorFour-stroke engine
A two-stroke internal combustion engine is disclosed having first and second cylinders having respective exhaust ports. A valve assembly comprises at least one valve actuator. First and second valves are operatively connected to the at least one valve actuator. The first and second valves are each movable between a first position wherein the valve extends a first distance in the respective exhaust port and a second position wherein the valve extends a second distance in the respective exhaust port. A valve connecting member is rigidly connected to the first and second valves and movable therewith via a translational motion while maintaining a substantially constant angular orientation relative to the cylinder block. A position sensor has a first portion connected to the cylinder block and a second portion connected to the valve connecting member. An electronic control unit (ECU) electrically connected to the position sensor.
Owner:BRP ROTAX
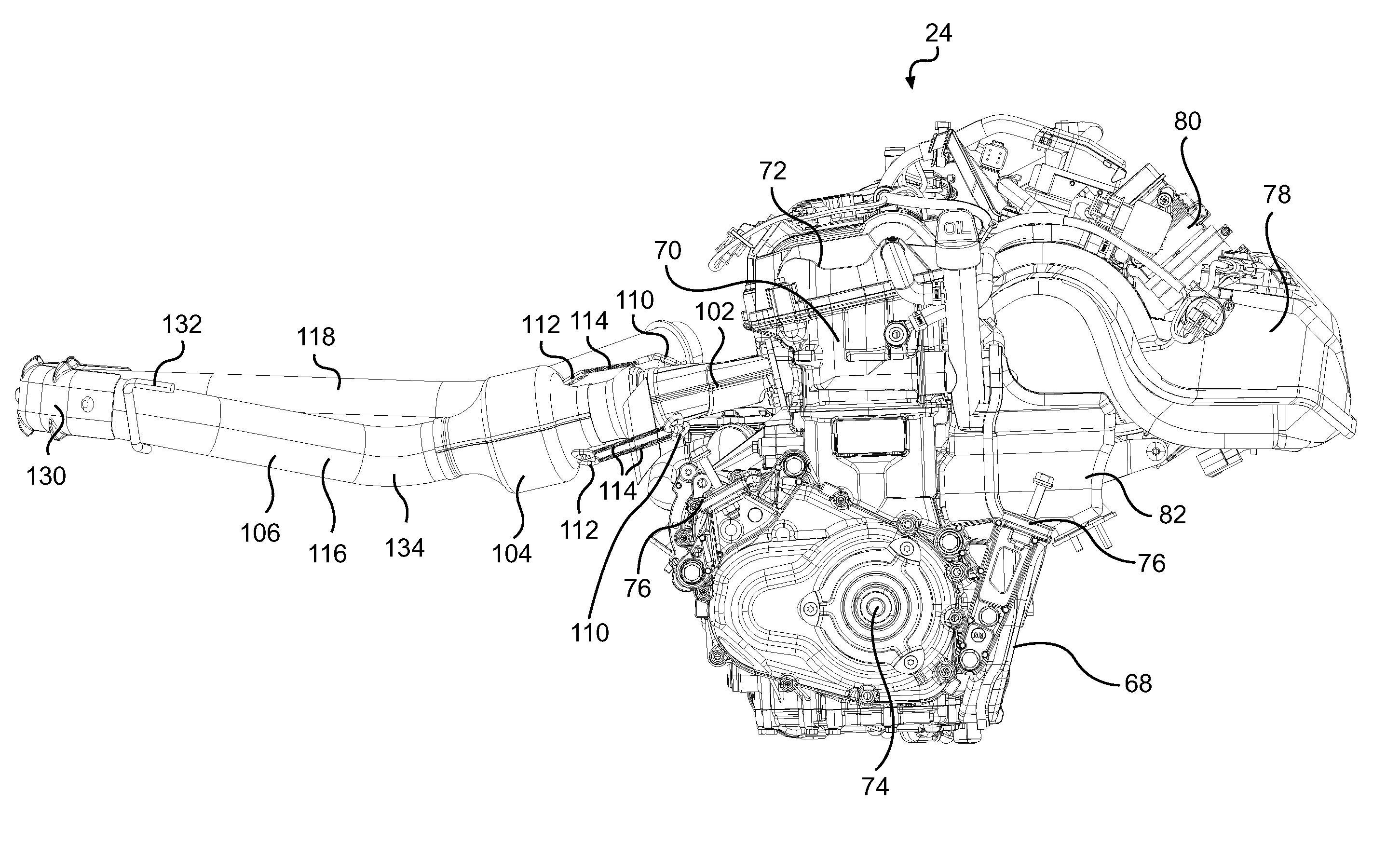
Snowmobile Exhaust System
ActiveUS20100108427A1Reduce engine noiseReduce the amount requiredSnowmobilesSledgesFour-stroke engineEngine mount
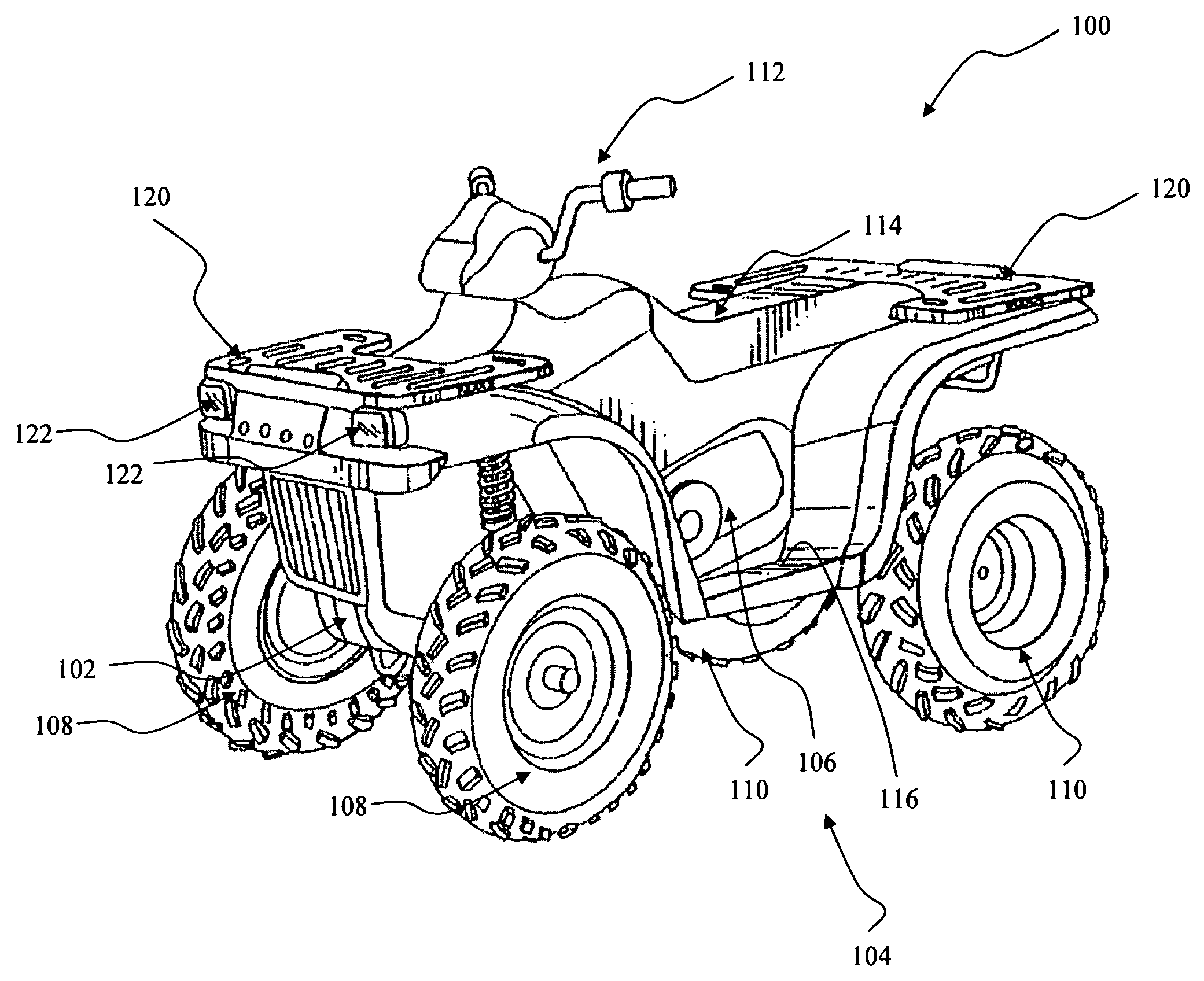
A snowmobile has a four-stroke engine mounted in an engine cradle and an exhaust system connected to the engine. The exhaust system includes a generally U-shaped exhaust pipe extending forwardly from the engine to a first point disposed forwardly of the engine cradle, and of suspension assemblies of the skis, and extending rearwardly from the first point to a second point disposed rearwardly of a front of the engine cradle.
Owner:BOMBARDIER RECREATIONAL PROD INC
Selective Compound Engine
InactiveUS20090301086A1Improve fuel efficiencyReduce cylinder compression ratioCombustion enginesHot gas positive displacement engine plantsExhaust valveFuel efficiency
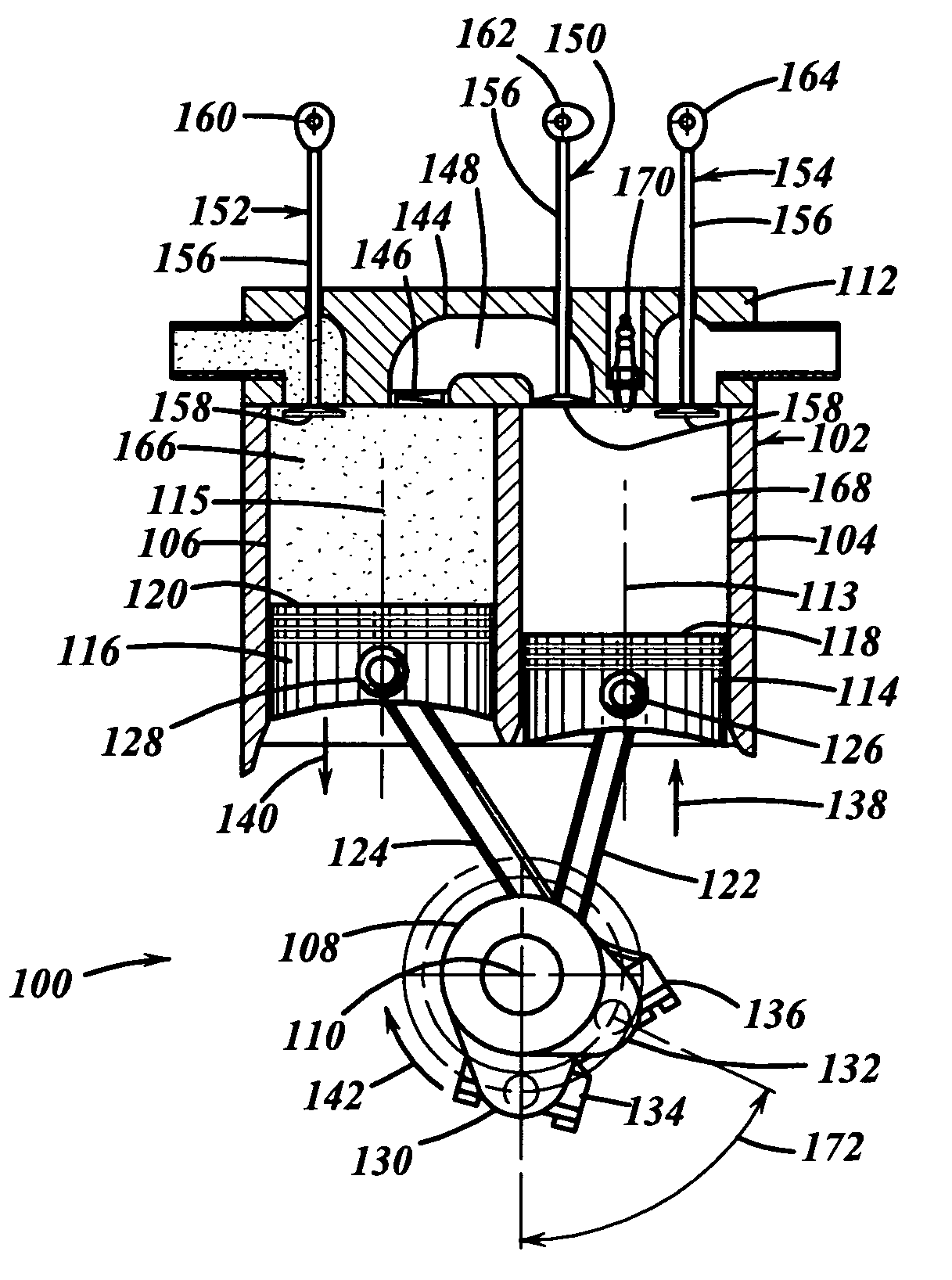
The fuel efficiency of an internal combustion reciprocating piston engine may be increased through selective secondary expansion of exhaust gas in the engine cylinders in order to recover exhaust gas energy which is otherwise wasted by cylinder blow-down at the end of the power stroke. Exhaust valve cam switching, intake valve deactivation, multiple exhaust valves, a specialized exhaust manifold arrangement and an exhaust gas diverter valve can be configured to enable a reciprocating engine to selectively operate in efficient eight stroke cycle compound mode when moderate engine power is demanded, then revert to conventional four stroke cycle non-compound mode operation when high engine power is demanded, without stopping the engine. For a road vehicle application, the benefit is substantially reduced highway cruising fuel consumption, while incurring minimal impact on engine weight, minimal impact on engine manufacturing cost, and no adverse impact on vehicle acceleration performance, hill climbing performance or trailer towing performance.
Owner:RALSTON MARK DIXON
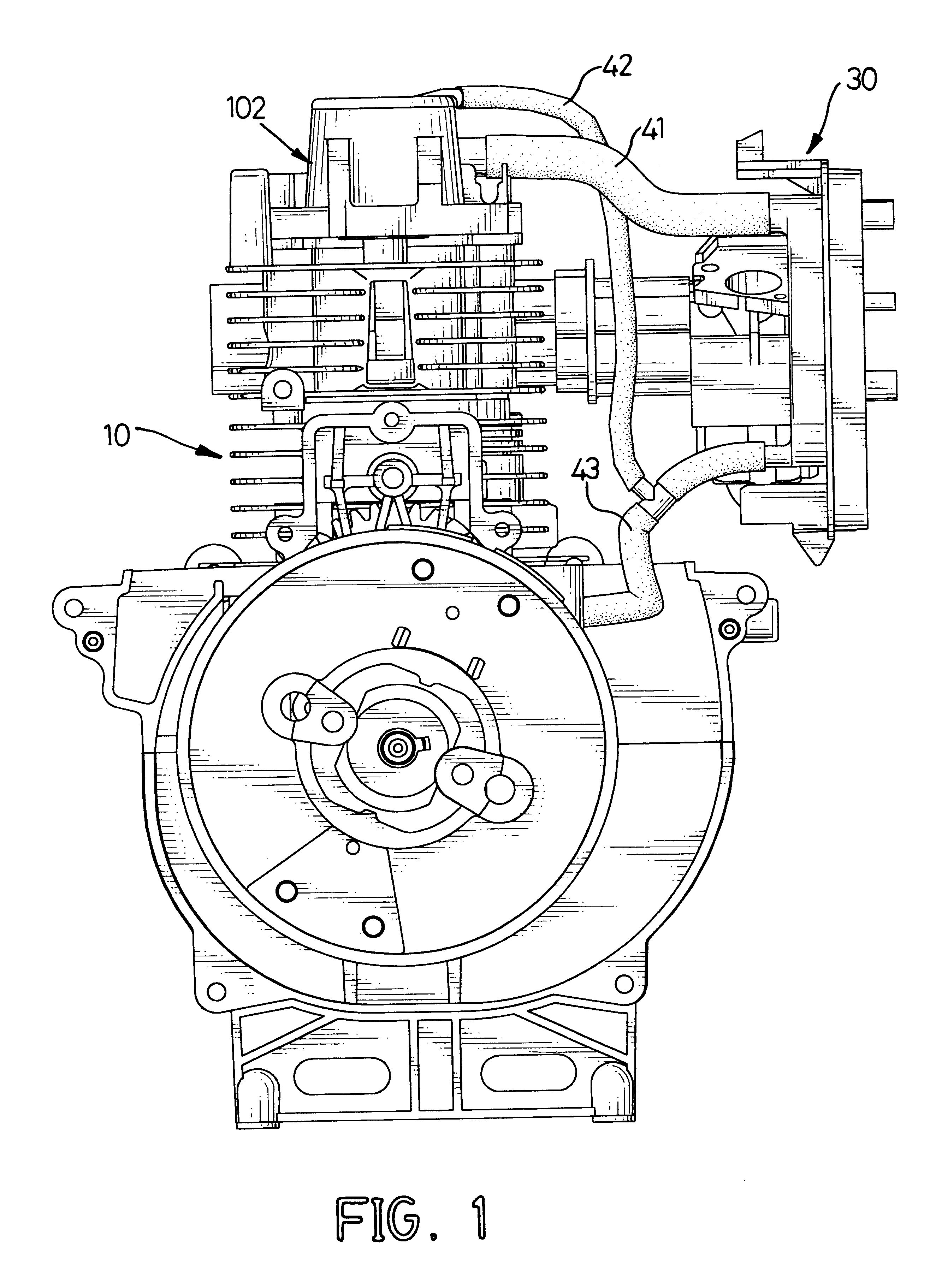
Four-stroke engine with an oil spray generating assembly for lubrication
InactiveUS6769391B1Lubrication of auxillariesLubricant conduit arrangementsFour-stroke engineEngineering
A four-stroke internal combustion engine includes a crankcase with a bottom, an oil pan and an oil spray generating assembly. The oil spray generating assembly having a closed sidewall, a valve, a bottom cap and nozzles is attached to the bottom of the crankcase and is enclosed by the oil pan. The closed sidewall is formed at the bottom of the crankcase to define a mist chamber enclosed by the bottom cap. The valve is mounted in the mist chamber with a valve port defined through the crankcase and a resilient valve flap corresponding to the valve port attached to the bottom of the crankcase. The nozzles are respectively mounted in the bottom cap out of the mist chamber inside the closed sidewall. The operation of the engine will produce an oil vapor for lubrication with the lubricating oil flowing out of the nozzles.
Owner:ECI ENGINE
Exhaust-valve lifting and lowering cam, turbocharged four stroke engine and valve timing control method
InactiveUS20120042649A1Simple structureAppropriate arrangementElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust valveFour-stroke engine
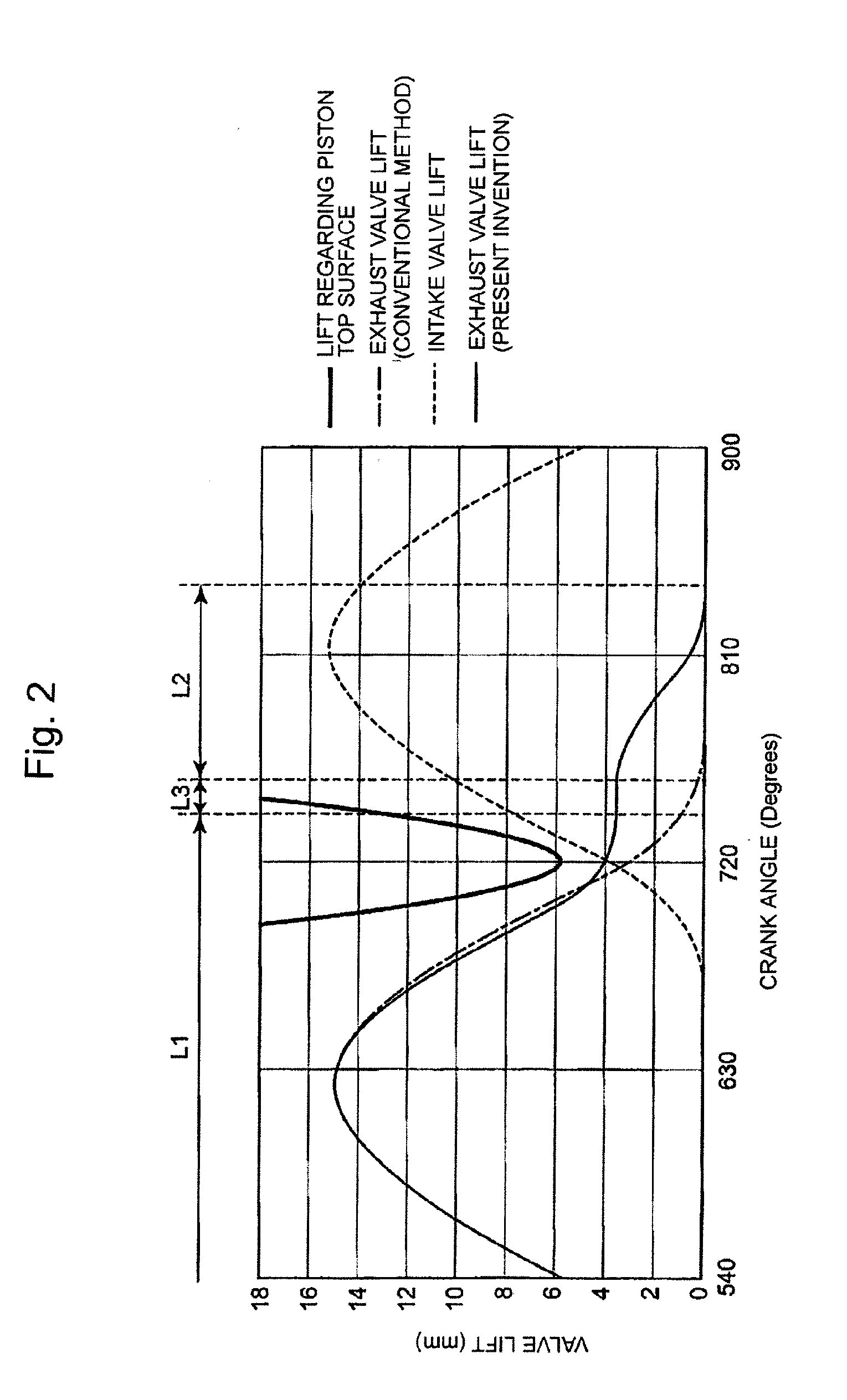
Providing a cam for lifting and lowering the exhaust valve so that the exhaust gas return-flow from one cylinder to another cylinder can be realized as greatly as possible, wherein the pistons and the exhaust valves do not come in contact with each other, and the valve control method does not depend on an electronic control approach. An exhaust cam for lifting and lowering the valve lift of the exhaust valve of one of the cylinders wherein the cam profile of the exhaust cam regarding the one of the cylinders including, but not limited to: a main exhaust lobe part for opening the exhaust valve so that the exhaust gas is discharged out of the cylinder; and, a gas return lobe part for opening the exhaust valve so that the quantity of the exhaust gas from the one of cylinders to the other cylinder is increased, the gas return lobe part being formed on the cam-follower descending part of the profile so as to delay the closing timing of the exhaust valve or maintain the valve lift-displacement regarding the exhaust valve larger, and wherein the cam profile is formed so that the interference between the exhaust valve and the piston is evaded and the overlap regarding the exhaust valve of the one cylinder and the exhaust valve of the other cylinder is increased by the manner that the main exhaust lobe part and the gas return lobe part rise outward from the base circle.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
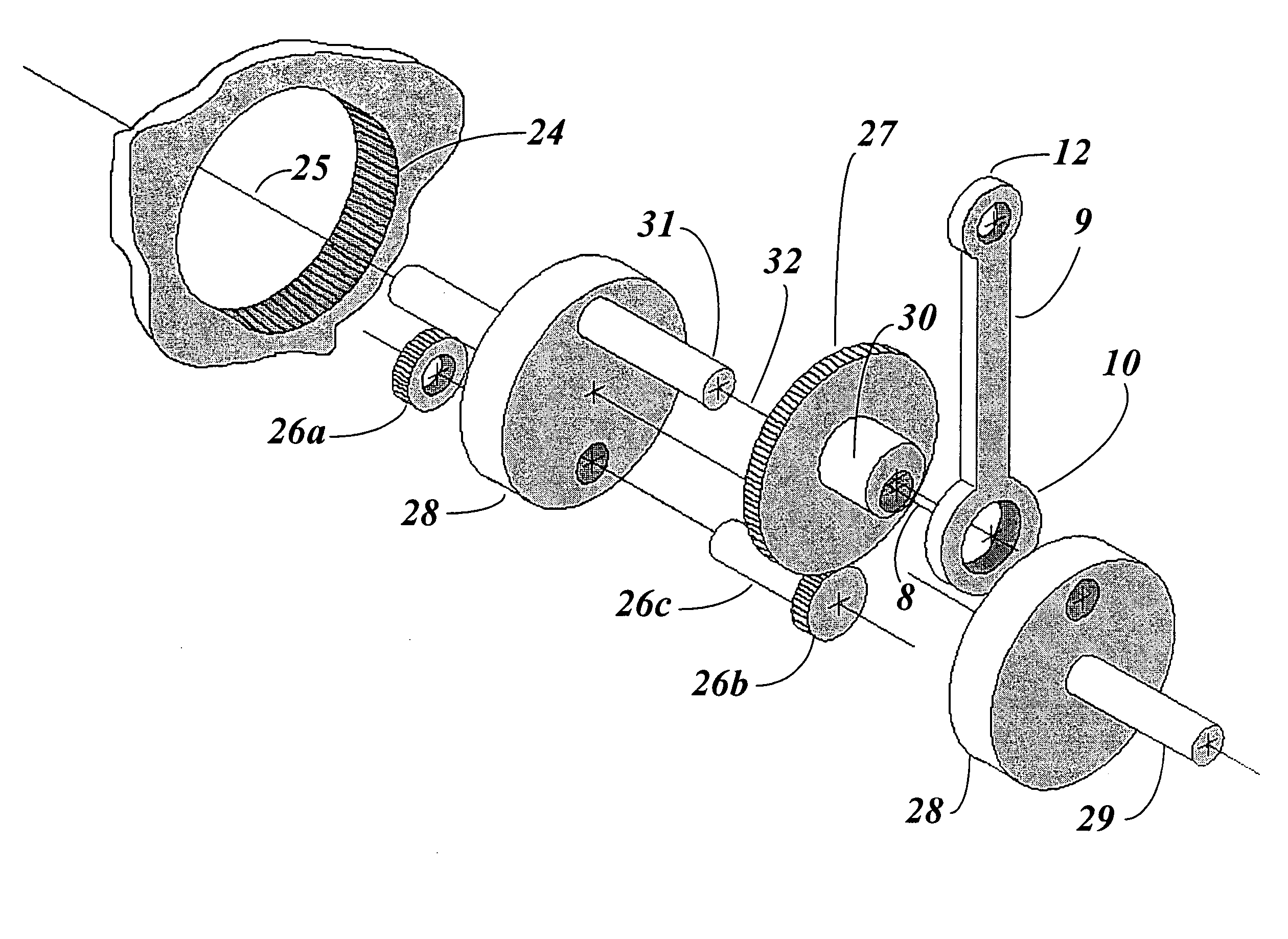
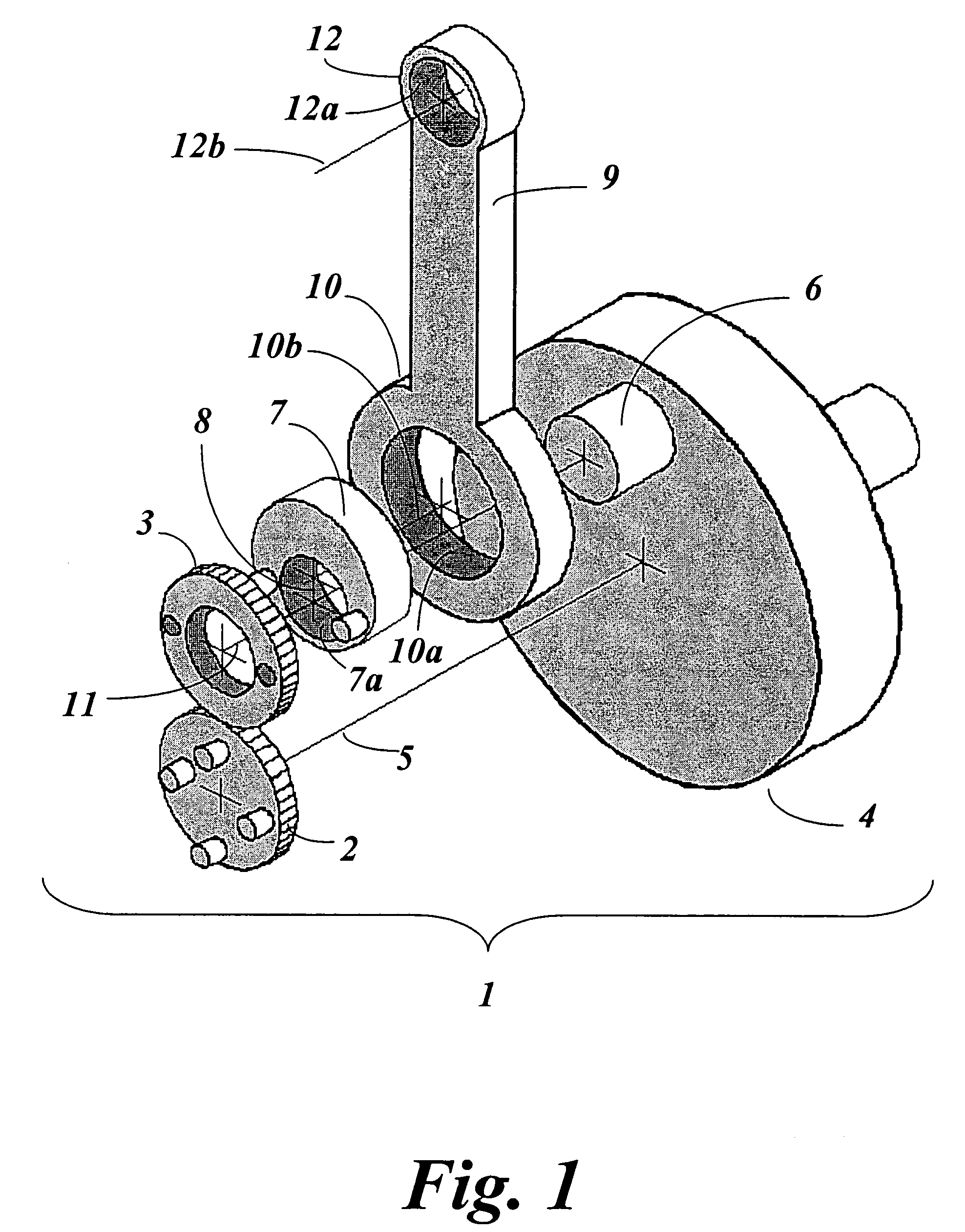
Epitrochoidal crankshaft mechanism and method
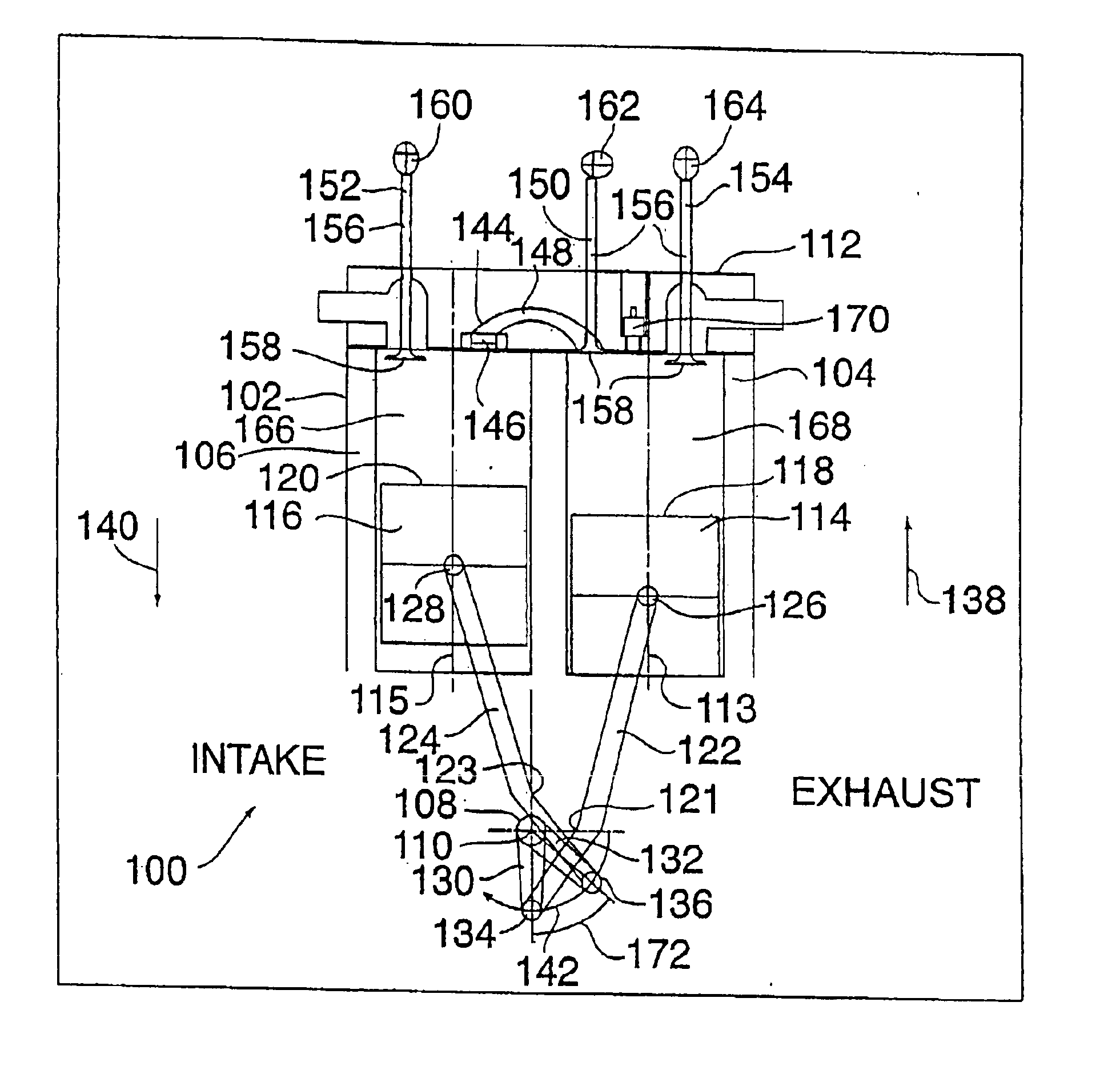
ActiveUS7185557B2High power outputImprove efficiencyRotary bearingsGearingFour-stroke engineInternal combustion engine
This invention relates to a mechanism and method for enhancing the performance of both two stroke and four stroke cycle reciprocating piston internal combustion engines, reciprocating piston pumps and compressors by generating an Epitrochoidal path of travel for the lower end of the connecting rod. The piston, attached to the upper end of the connecting rod, will be made to dwell at the lower part of its travel, enhancing the output of the engine, pump or compressor through better utilization of the available cylinder pressure.
Owner:MAROZZI
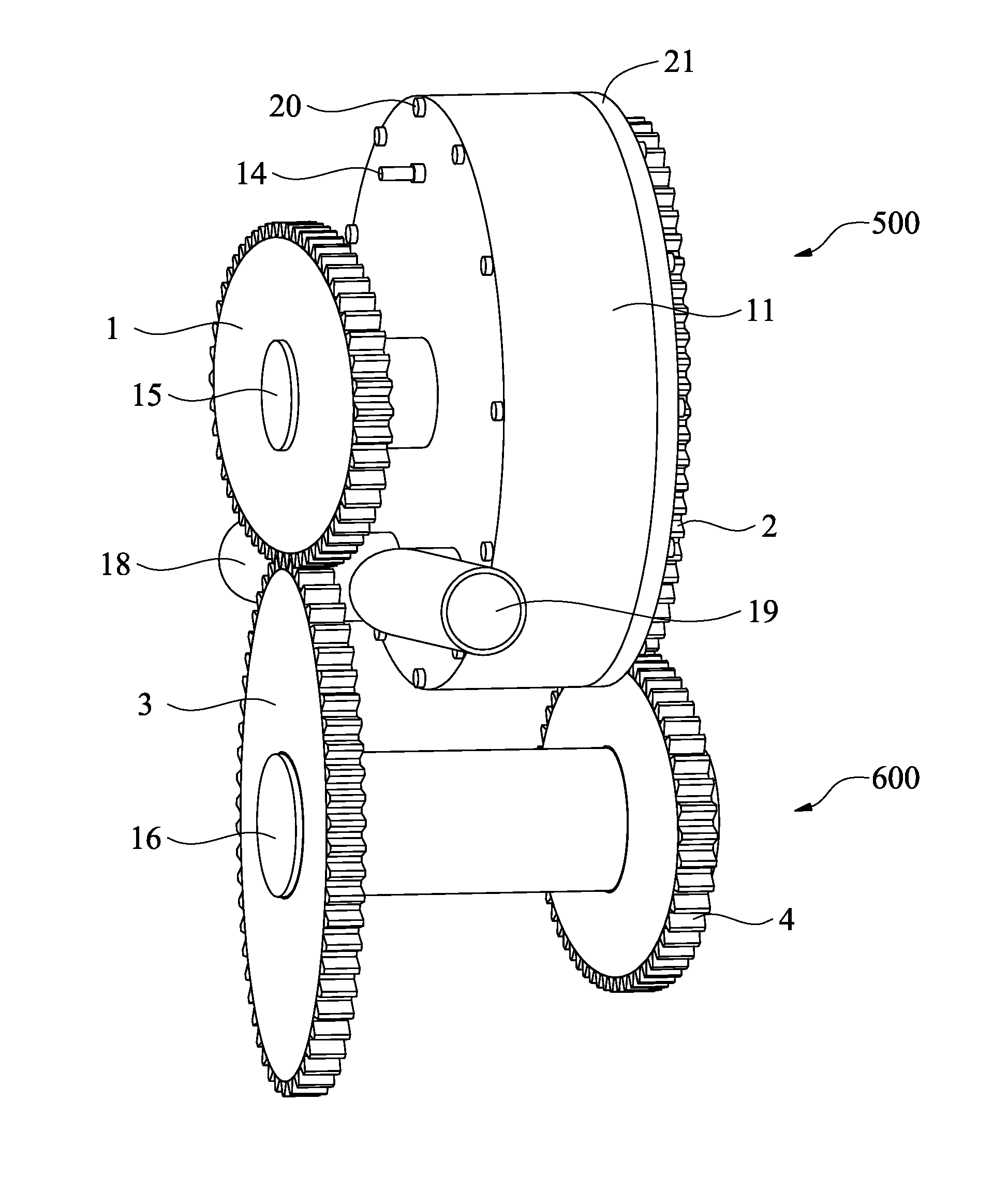
Rotary modulation engine
InactiveUS20120080006A1Reduce the number of partsReduce manufacturing costInternal combustion piston enginesEngine componentsRotation velocityFour-stroke engine
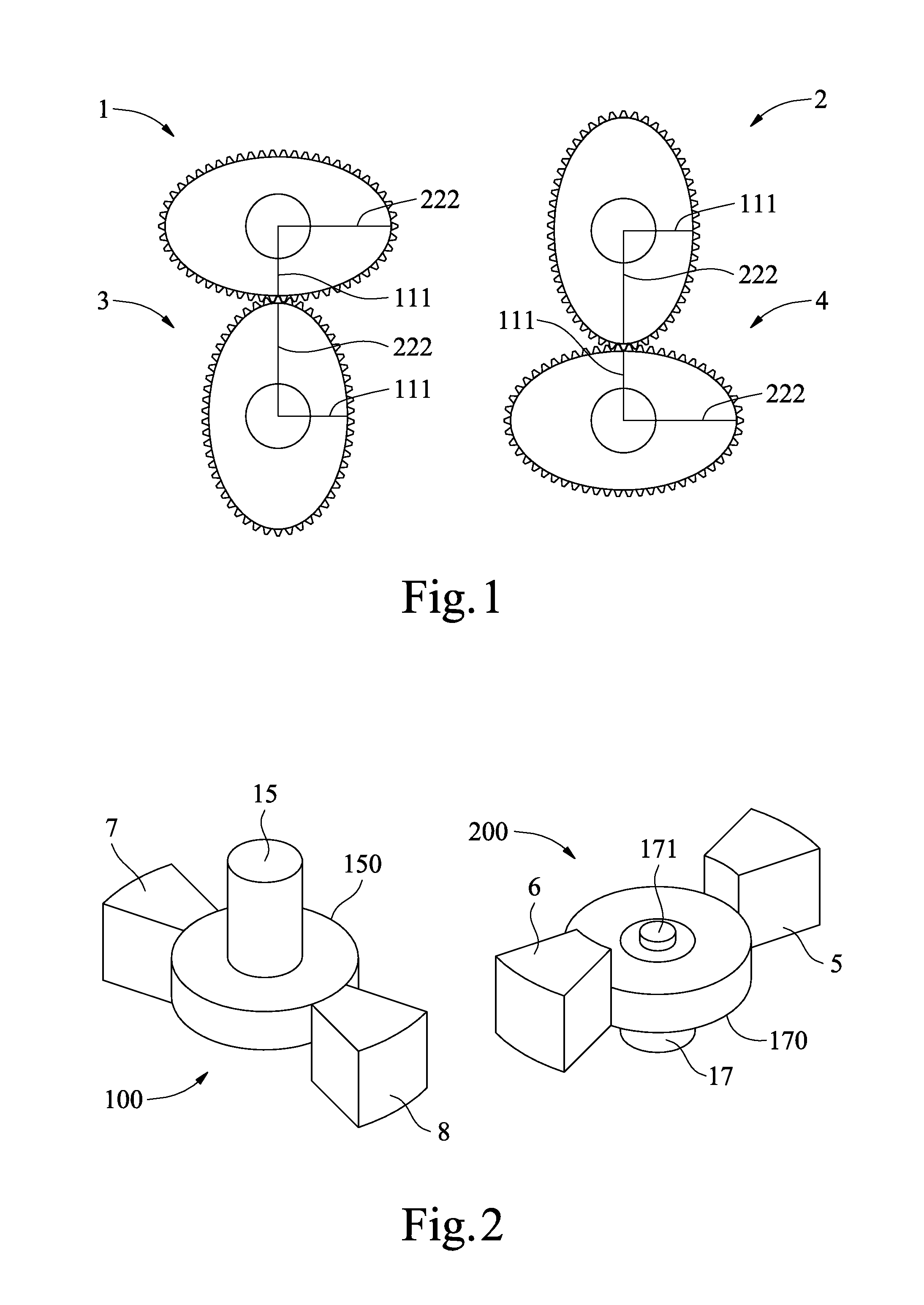
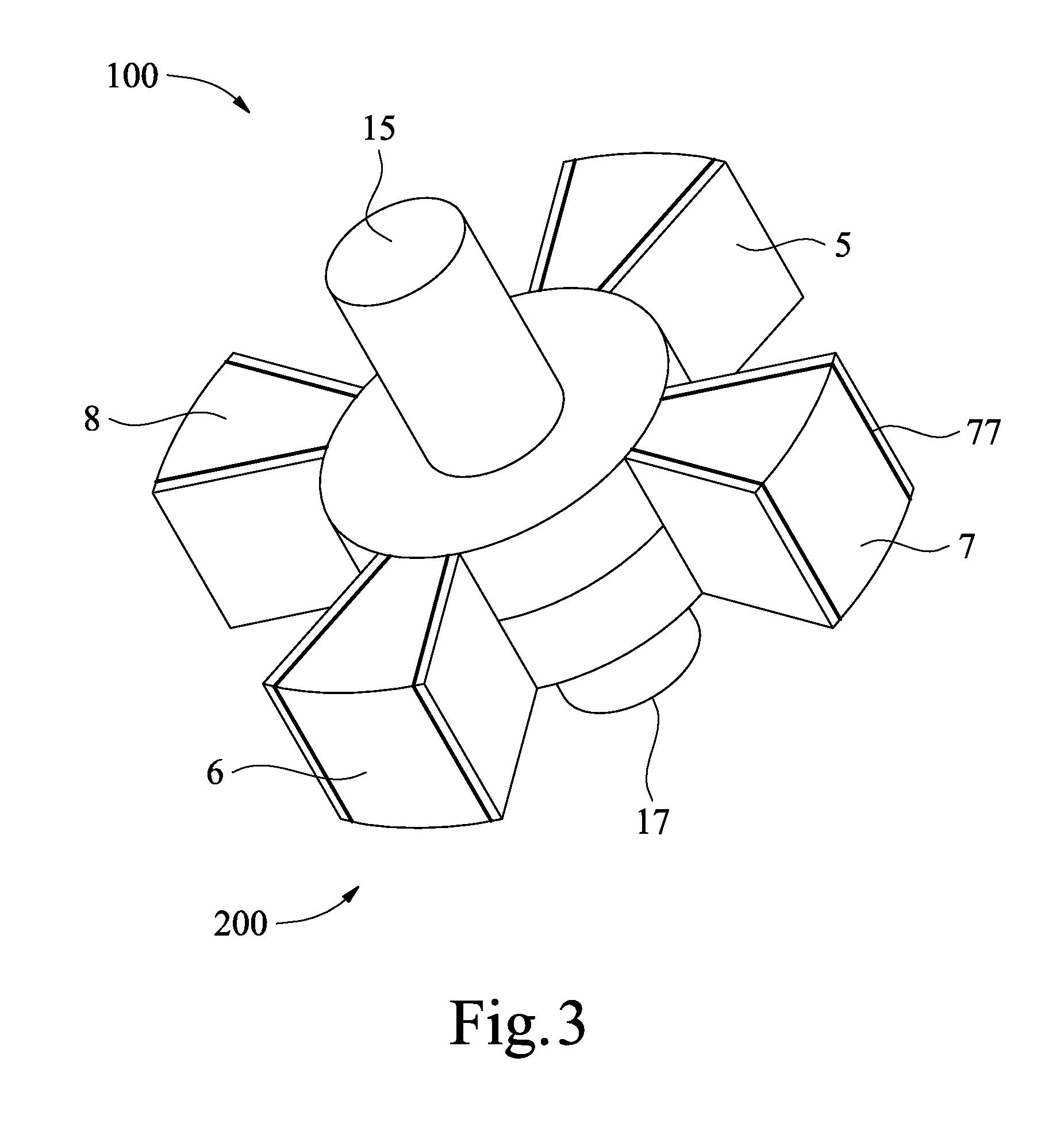
A rotary modulation engine enabling modulation of rotary pistons' rotational speeds is introduced. The rotary modulation engine utilizes four elliptical gears to drive two rotors that overlap each other with rotary pistons thereon alternating one another and rotating in the same direction. The elliptical gears also modulate the relative rotational speeds of these rotary pistons to thereby complete compression, power, exhaust and intake strokes four times in one revolution of a power output shaft of the engine. The rotary modulation engine with the above arrangements has smaller volume and improved efficiency as compared to the conventional four-stroke engine that requires two revolutions of the engine's crankshaft to complete four strokes. The rotary modulation engine can be applied to cars, ships, power generators and the like, and has reduced number of parts, volume and manufacturing cost while provides effectively upgraded operation efficiency.
Owner:YEH CHUN CHIANG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com