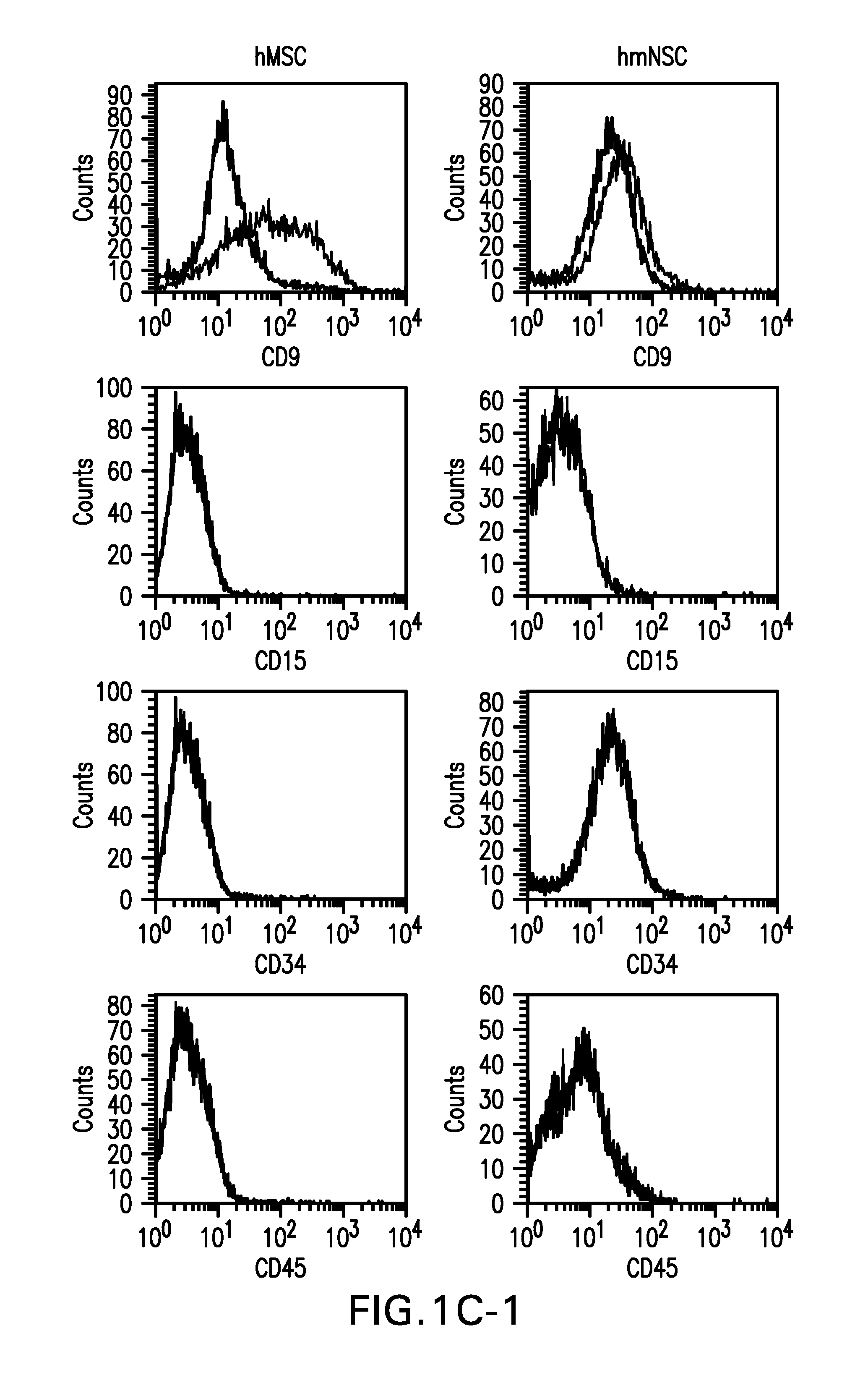
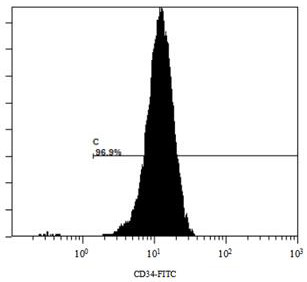
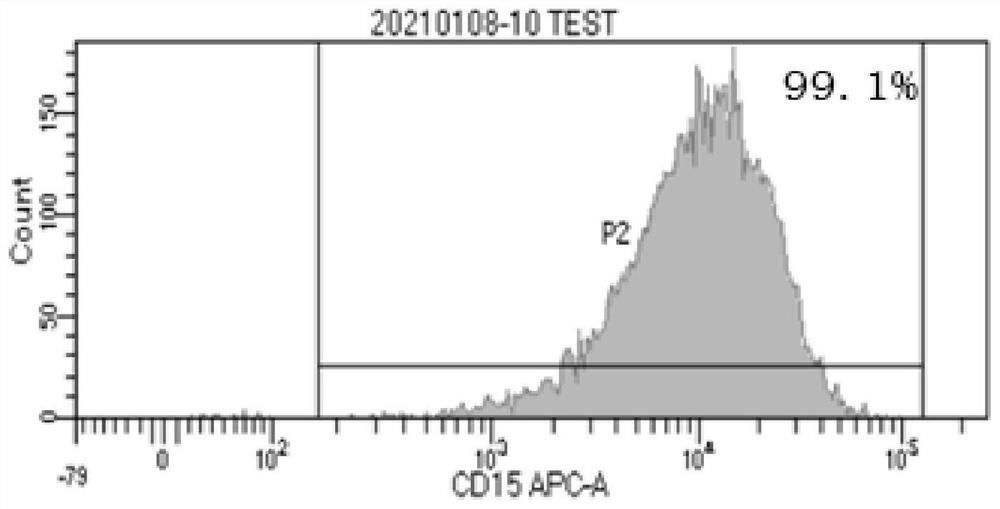
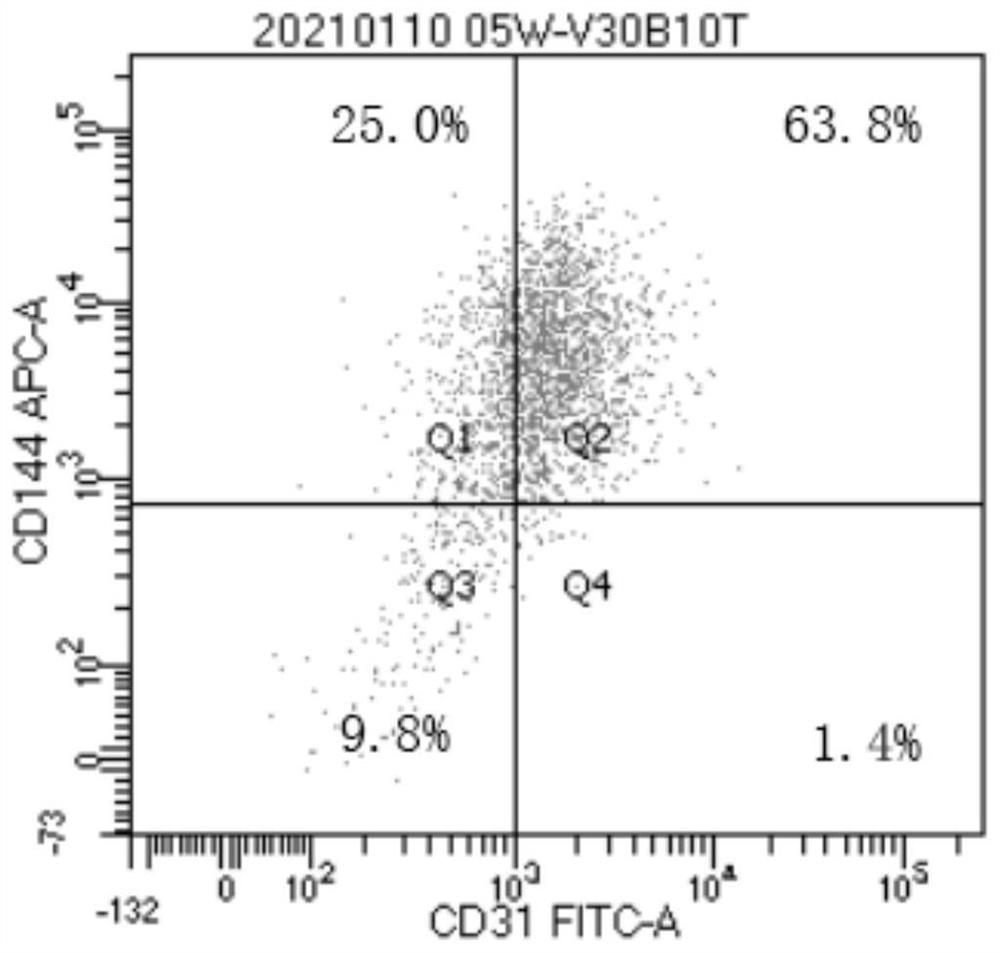
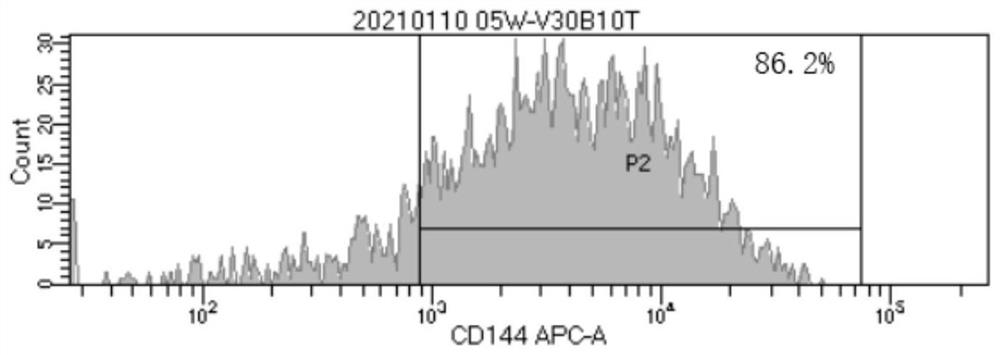
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Mesodermal cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
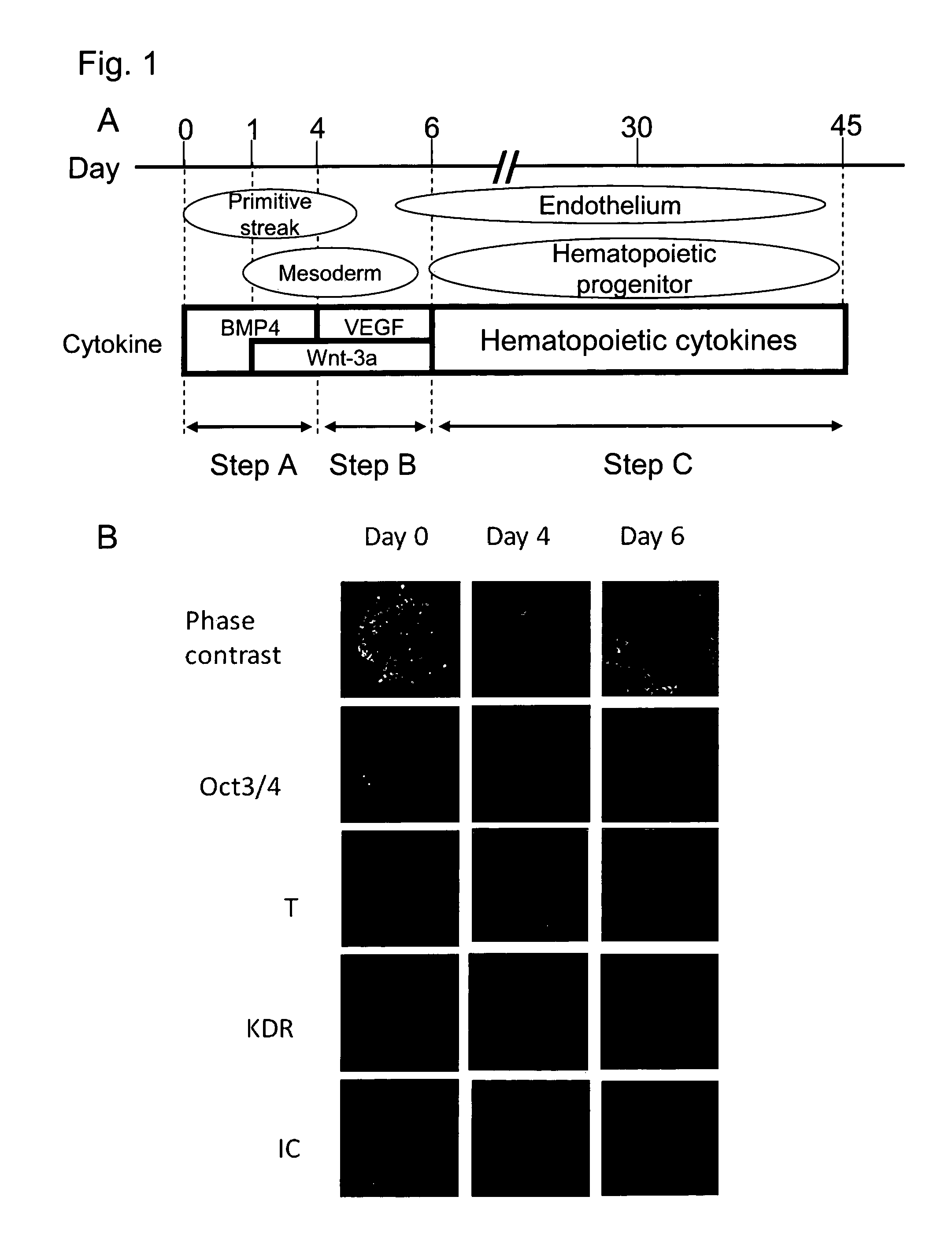
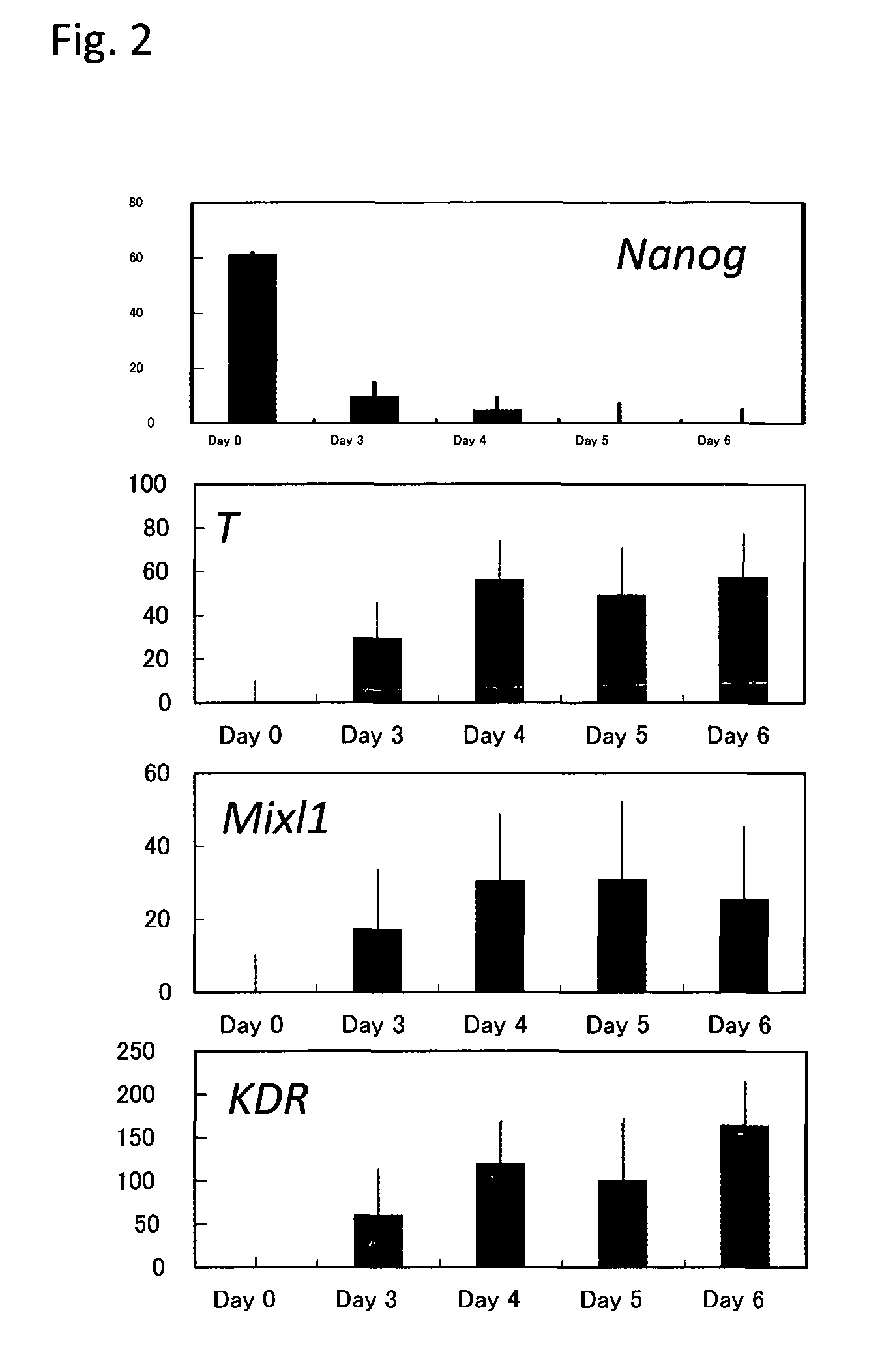
The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium, non-epithelial blood cells and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes).
Compositions And Methods For Self-Renewal And Differentiation In Human Embryonic Stem Cells
ActiveUS20070281355A1Efficient productionEffectively lead to differentiationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderGerm layerFeeder Layer
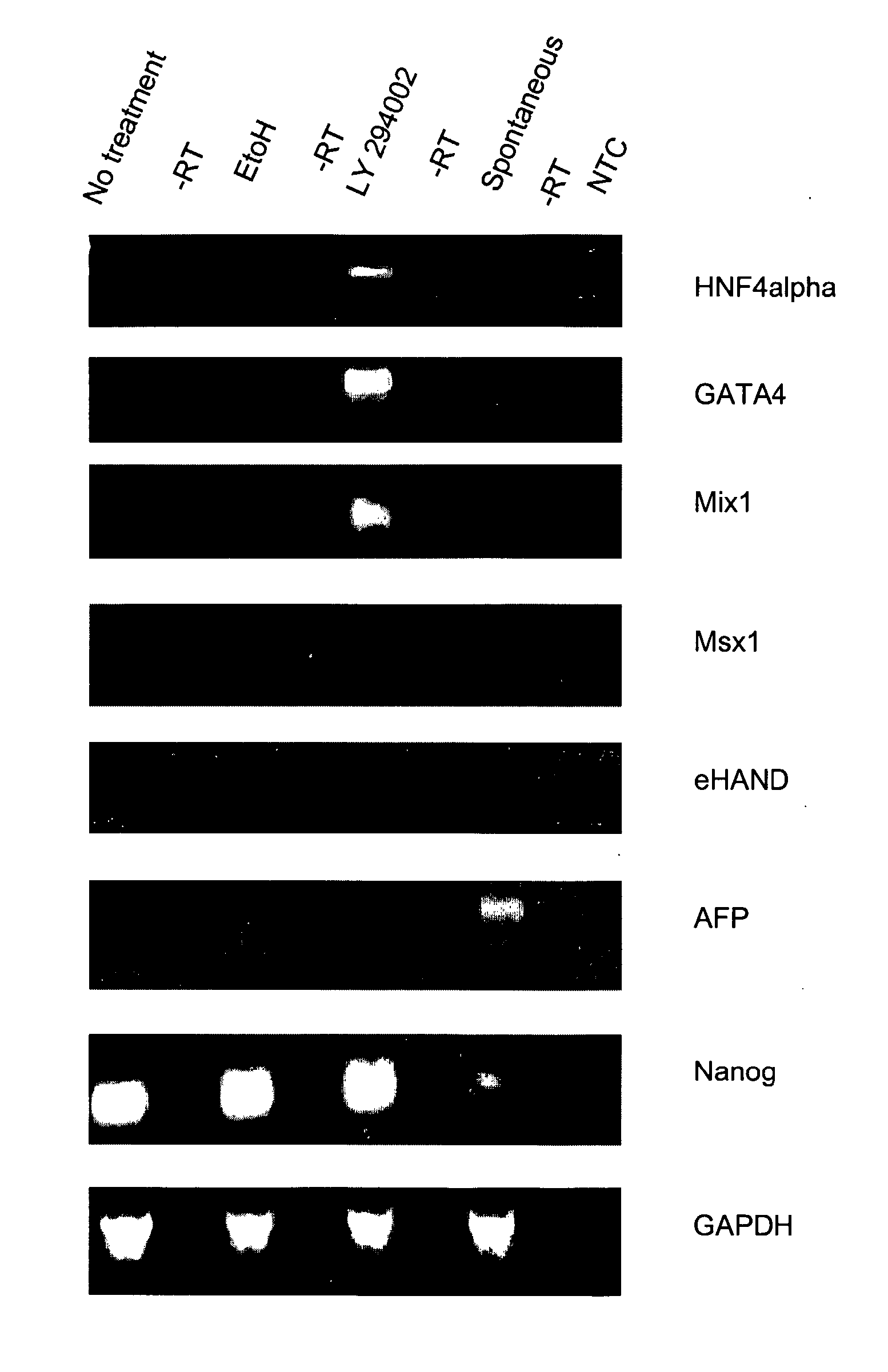
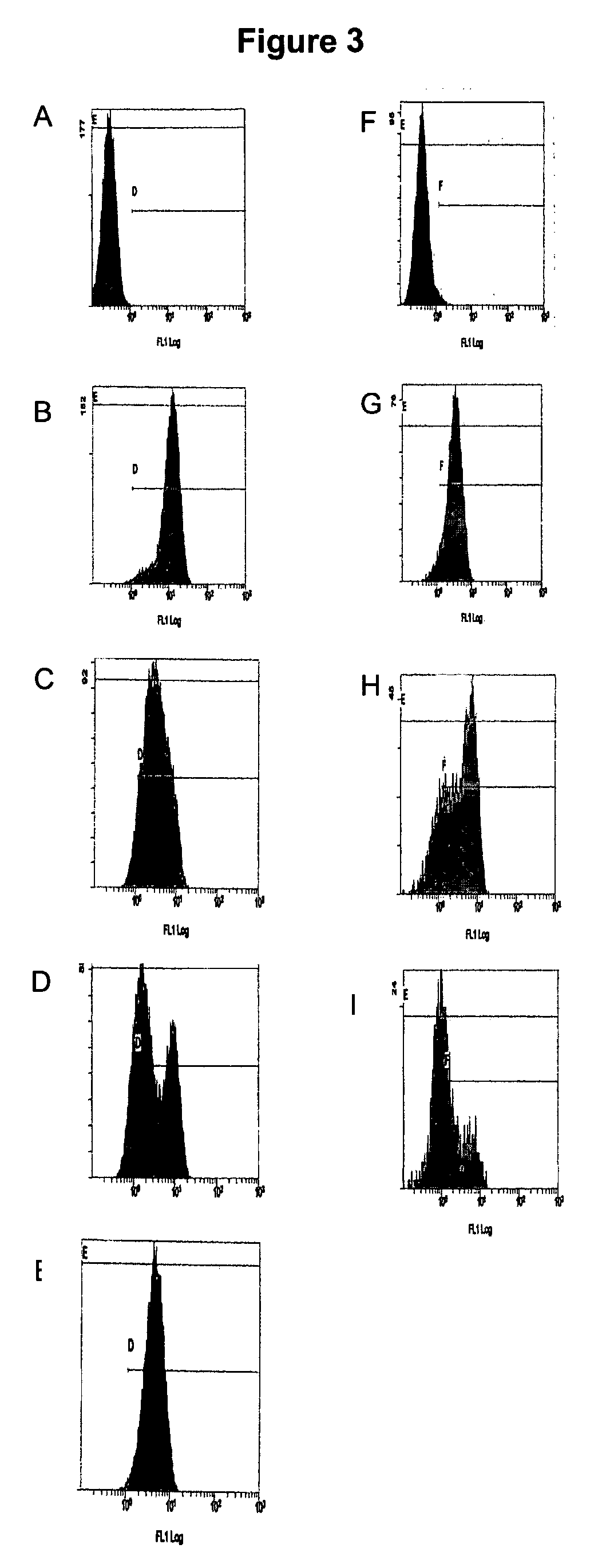
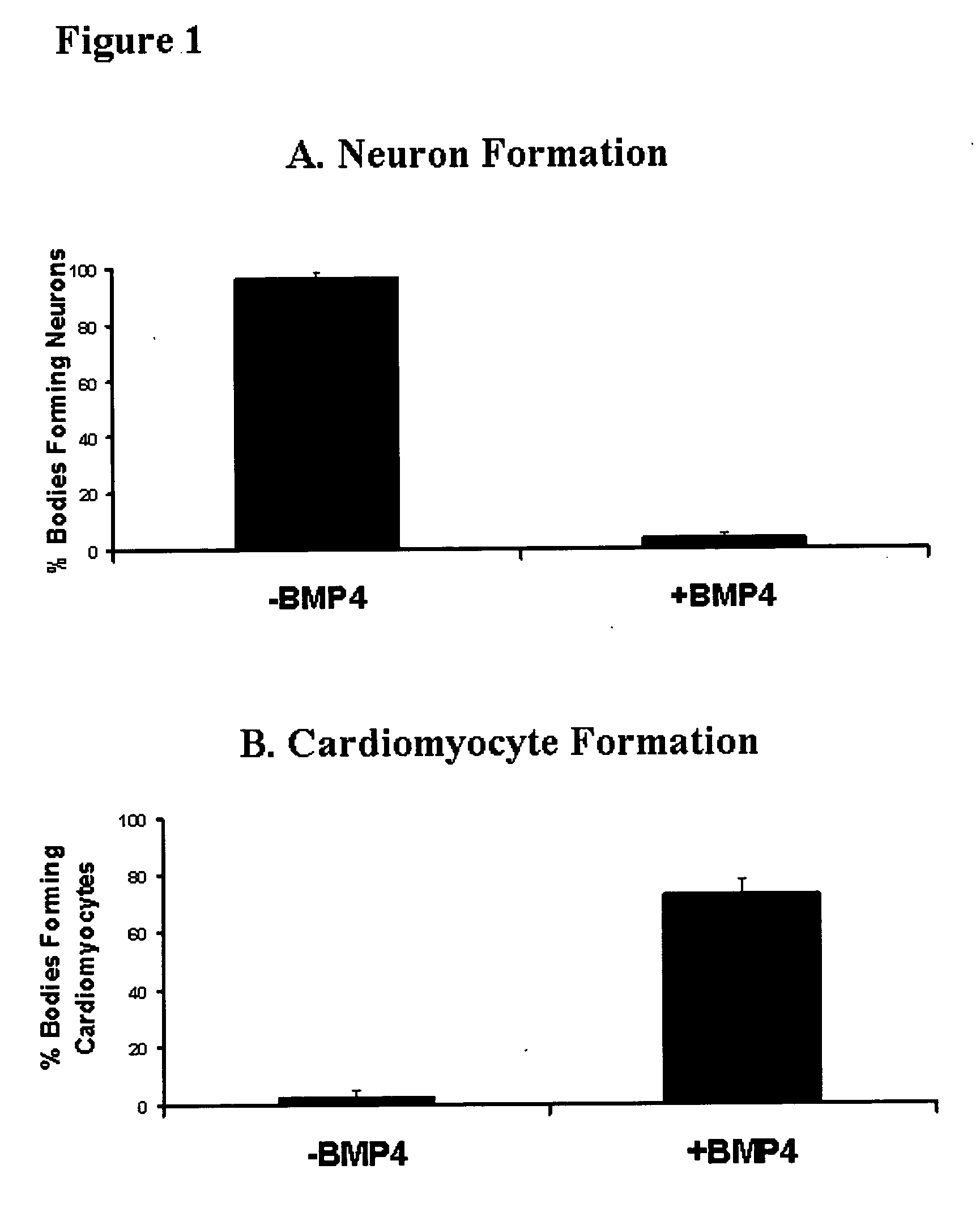
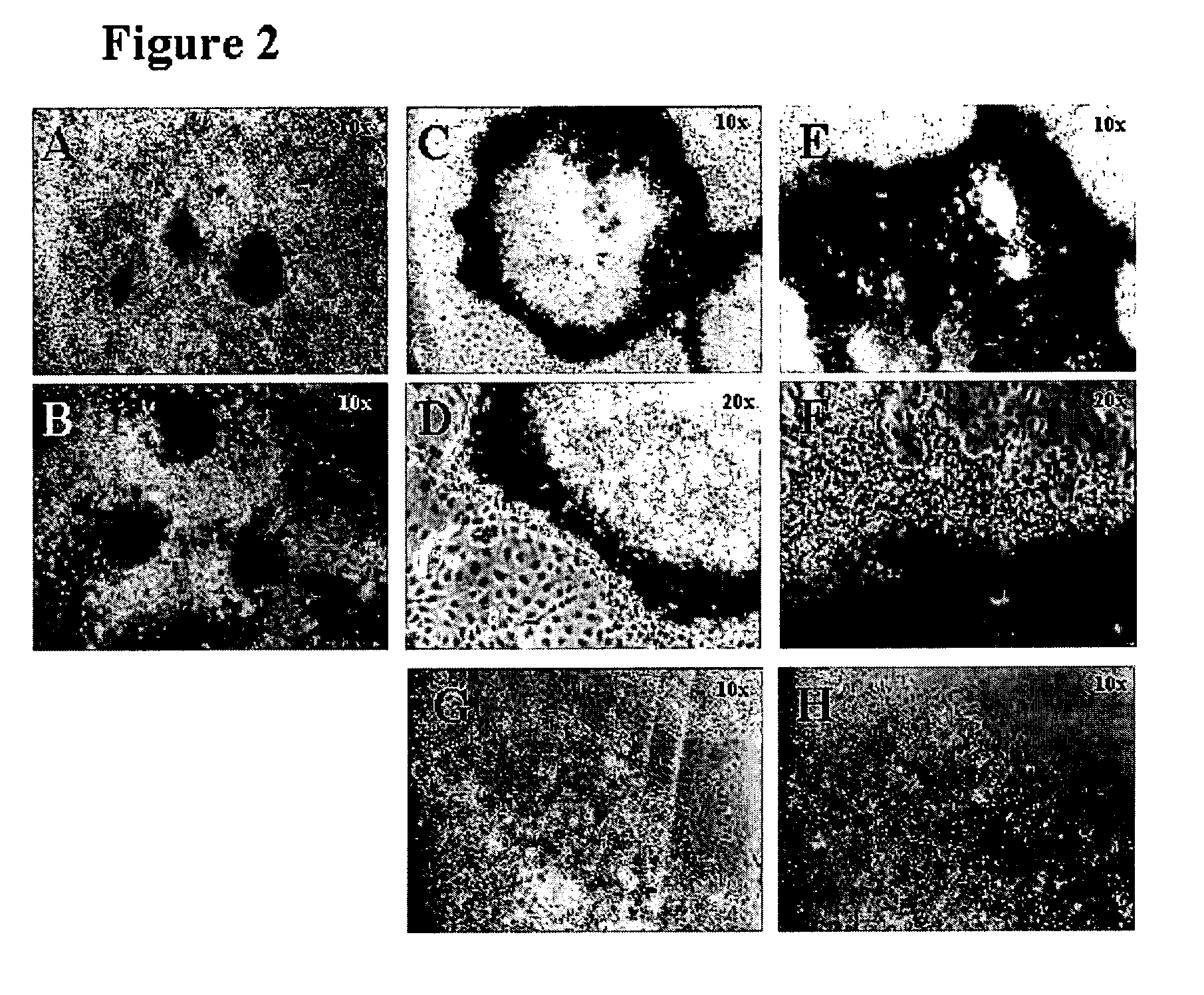
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the production of differentiated mammalian cells. More particularly, the present invention provides cellular differentiation methods employing culturing the cells on a feeder layer or under feeder-free conditions in cell culture and further contacting the cells with an inhibitor of the PI3-kinase pathway for the generation of differentiated mammalian cells from pluripotent mammalian stem cells. Preferably, the differentiated cell is selected from the group consisting of a mesendodermal cell, a mesodermal cell, and an endodermal cell.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC +1
Methods for increasing definitive endoderm differentiation of pluripotent human embryonic stem cells with PI-3 kinase inhibitors
ActiveUS8187878B2Efficient productionEffectively lead to differentiationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderGerm layerFeeder Layer
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC +1
Method for the preparation of cells of mesodermal lineage
The present invention relates generally to the generation of cells of mesodermal lineage. More particularly, the present invention contemplates a method for the preparation of differentiated or partially differentiated mesodermal cells and their use in tissue repair, regeneration and / or augmentation therapy. The identification and generation of the mesodermal cells further provides a source of transcriptome or proteome data to assess the expression profile of genes associated with the maintenance of mesodermal cells as well as their differentiation, proliferation, expansion and / or renewal potential.
Owner:ADELAIDE RES & INNOVATION PTY LTD
Multipotent stem cells derived from placenta tissue and cellular therapeutic agents comprising the same
InactiveUS20070243172A1Negative immunological responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsGerm layerDisease
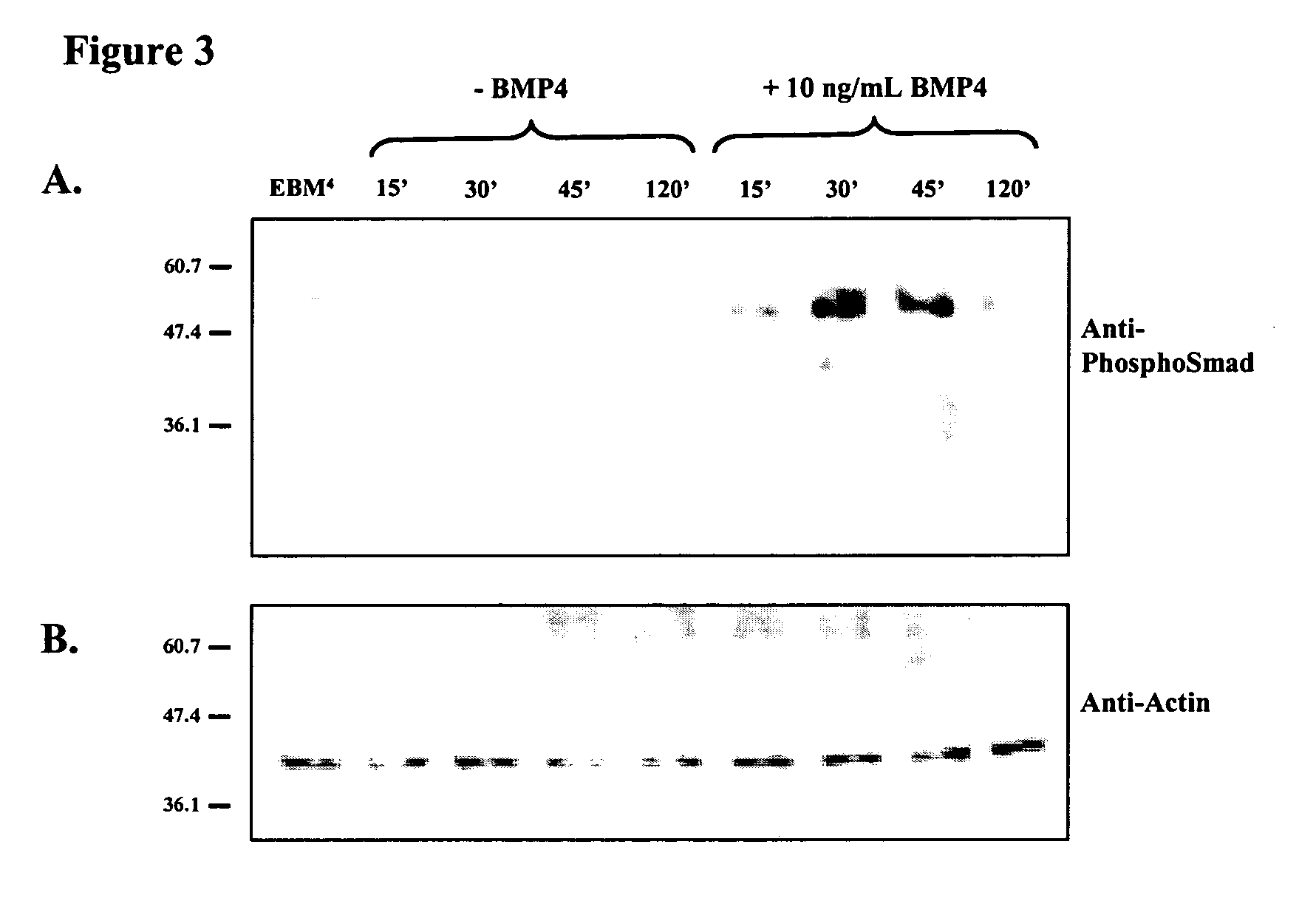
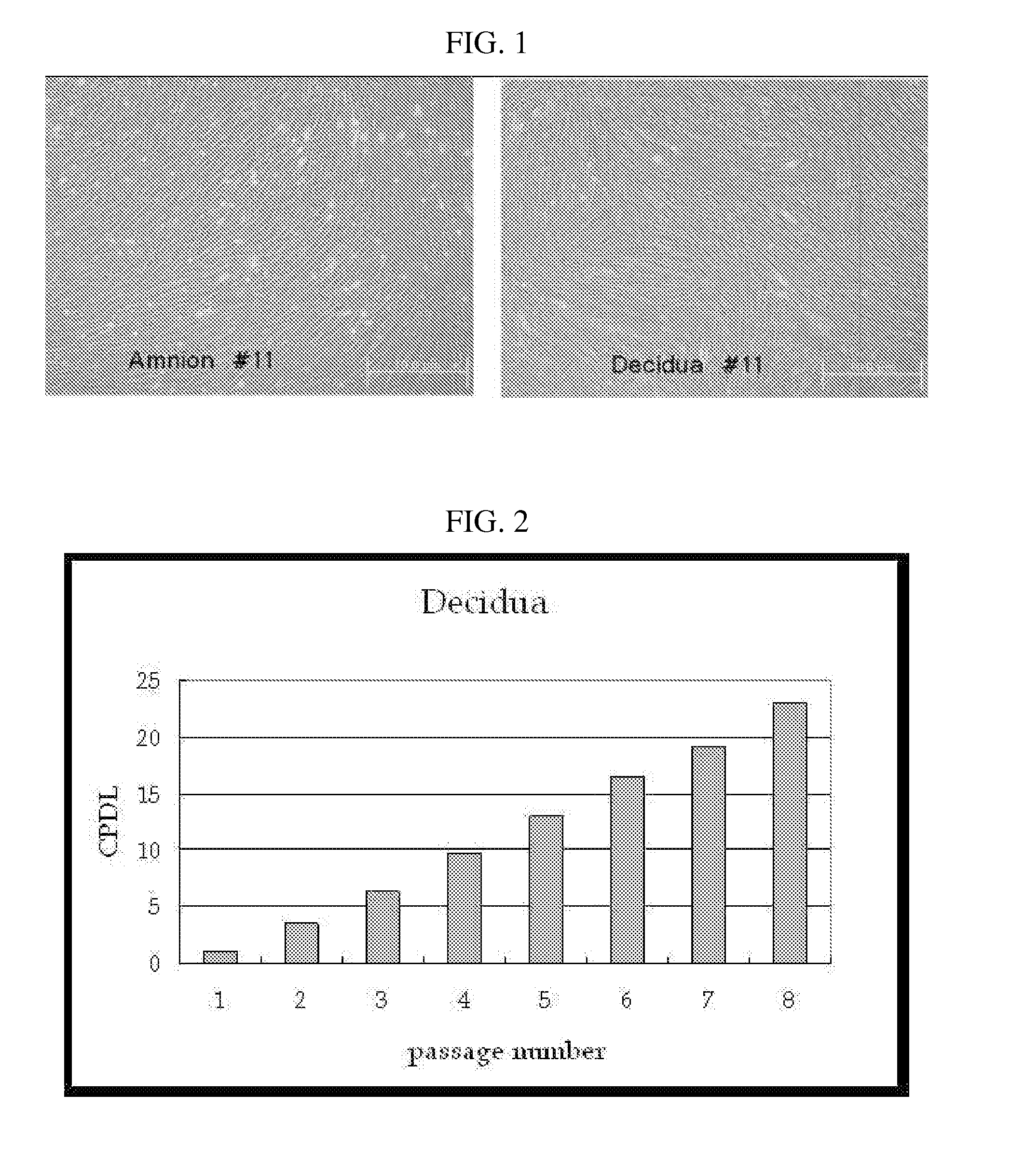
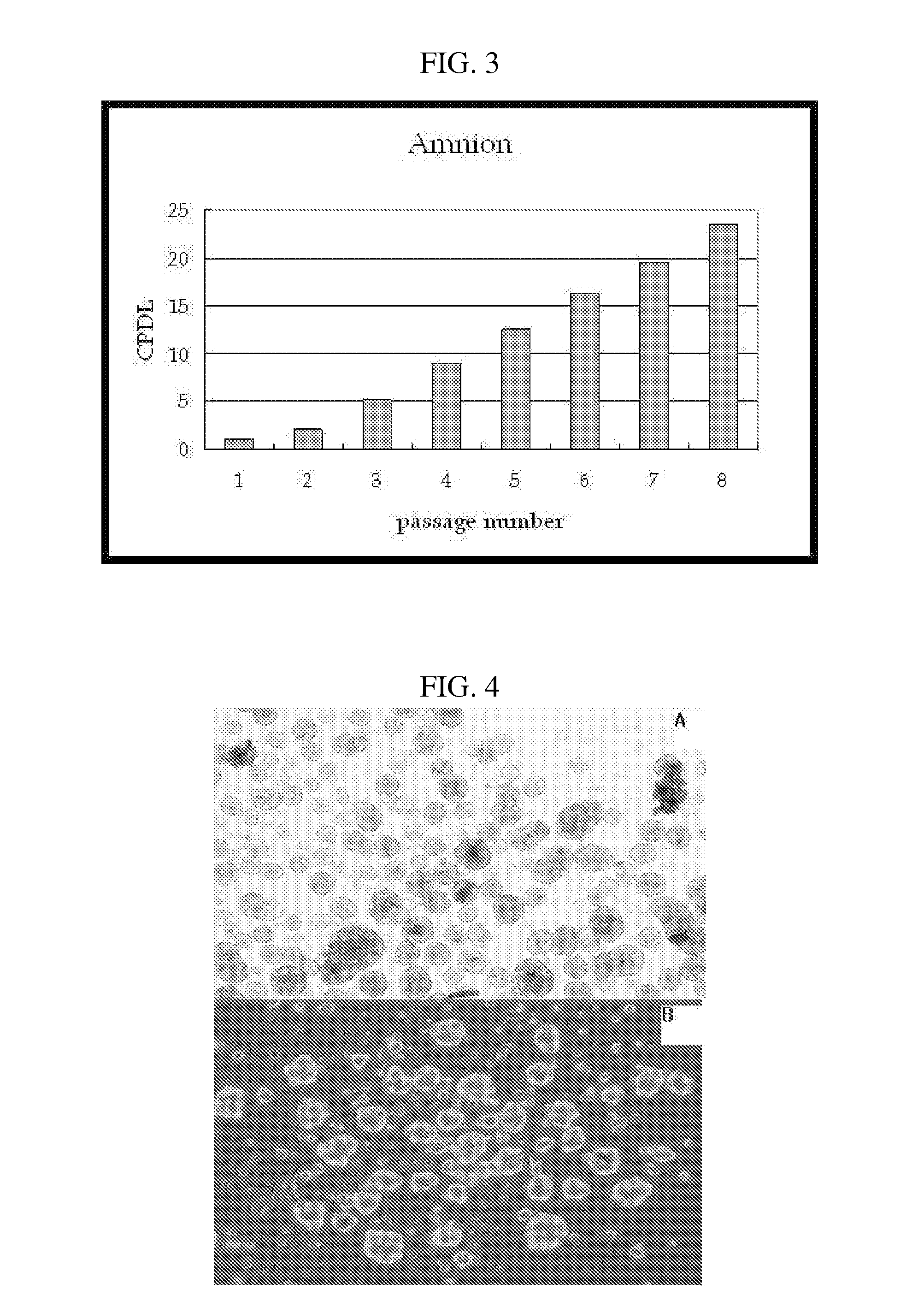
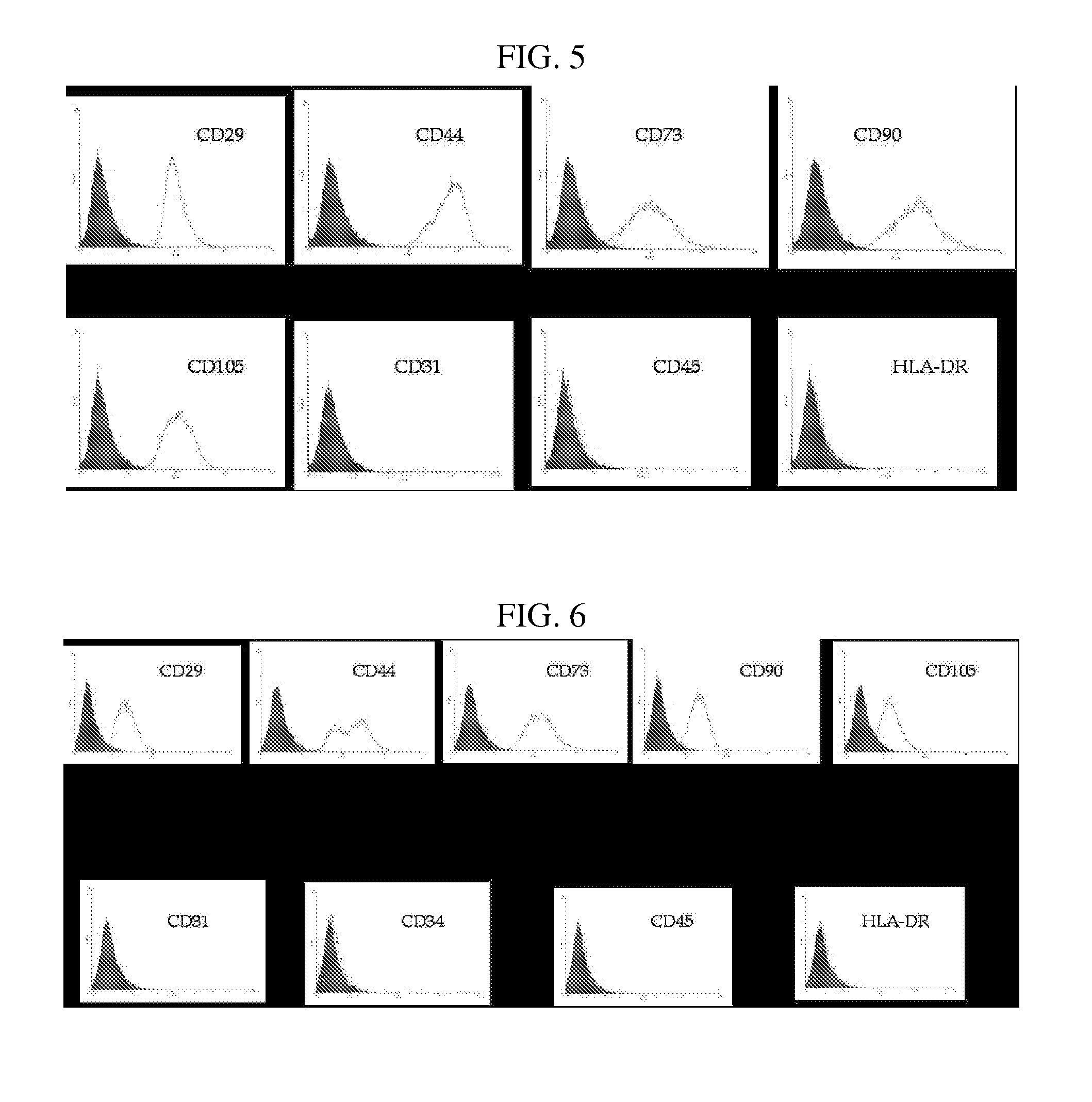
The present invention relates to placenta tissue-derived multipotent stem cells and cell therapeutic agents containing the same. More specifically, to a method for producing placenta stem cells having the following characteristics, the method comprising culturing amnion, chorion, decidua or placenta tissue in a medium containing collagenase and bFGF and collecting the cultured cells: (a) showing a positive immunological response to CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105, and showing a negative immunological response to CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-DR; (b) showing a positive immunological response to Oct4 and SSEA4; (c) growing attached to plastic, showing a round-shaped or spindle-shaped morphology, and forming spheres in an SFM medium so as to be able to be maintained in an undifferentiated state for a long period of time; and (d) having the ability to differentiate into mesoderm-, endoderm- and ectoderm-derived cells. Also the present invention relates to placenta stem cells obtained using the production method. The inventive multipotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, osteogenic cells, nerve cells, satellite cells, fat cells, cartilage-forming cells, osteogenic cells, or insuline-secreting pancreatic β-cells, and thus are effective for the treatment of muscular diseases, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, nervous diseases, diabetes and the like, and are useful for the formation of breast tissue.
Owner:RNL BIO
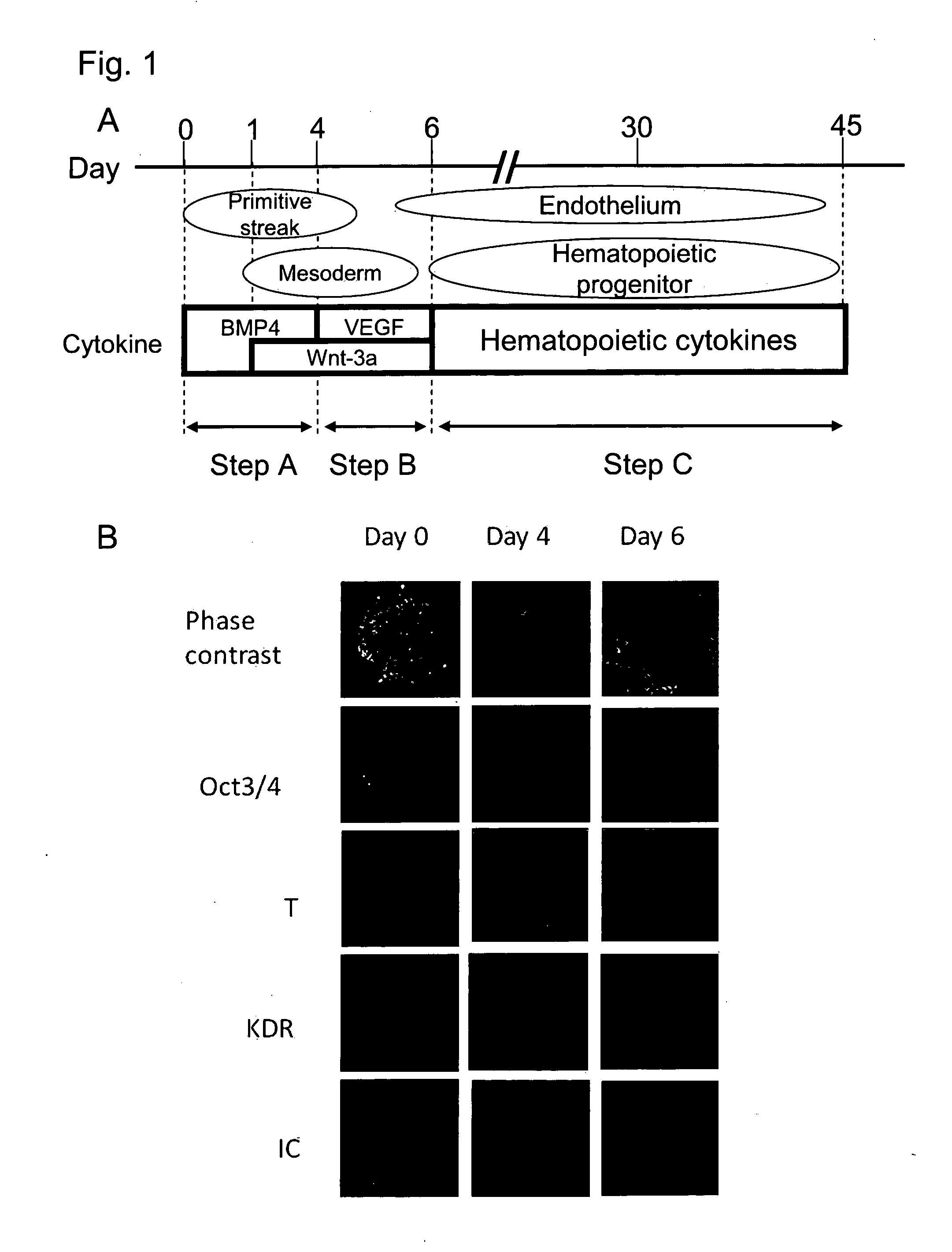
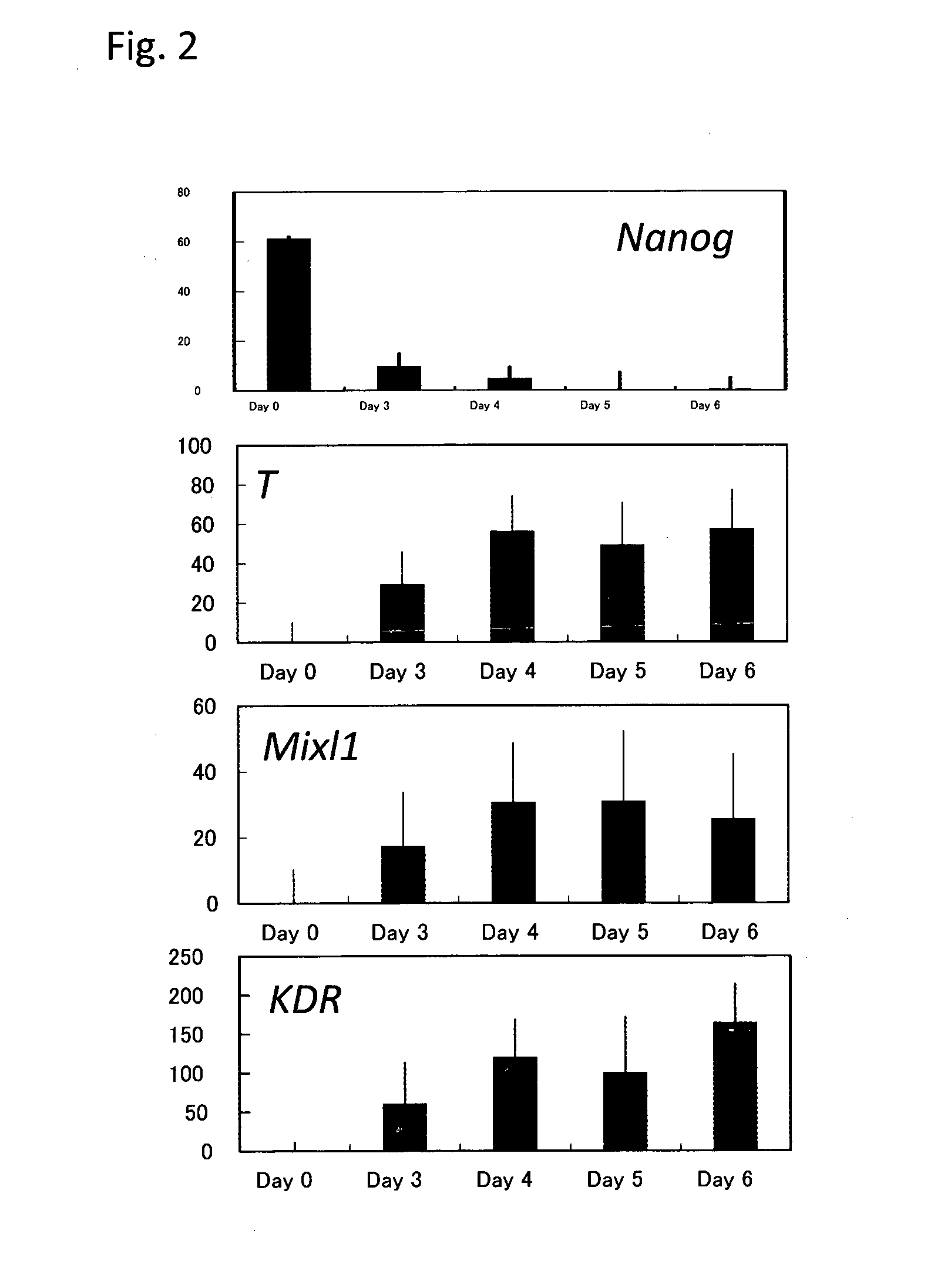
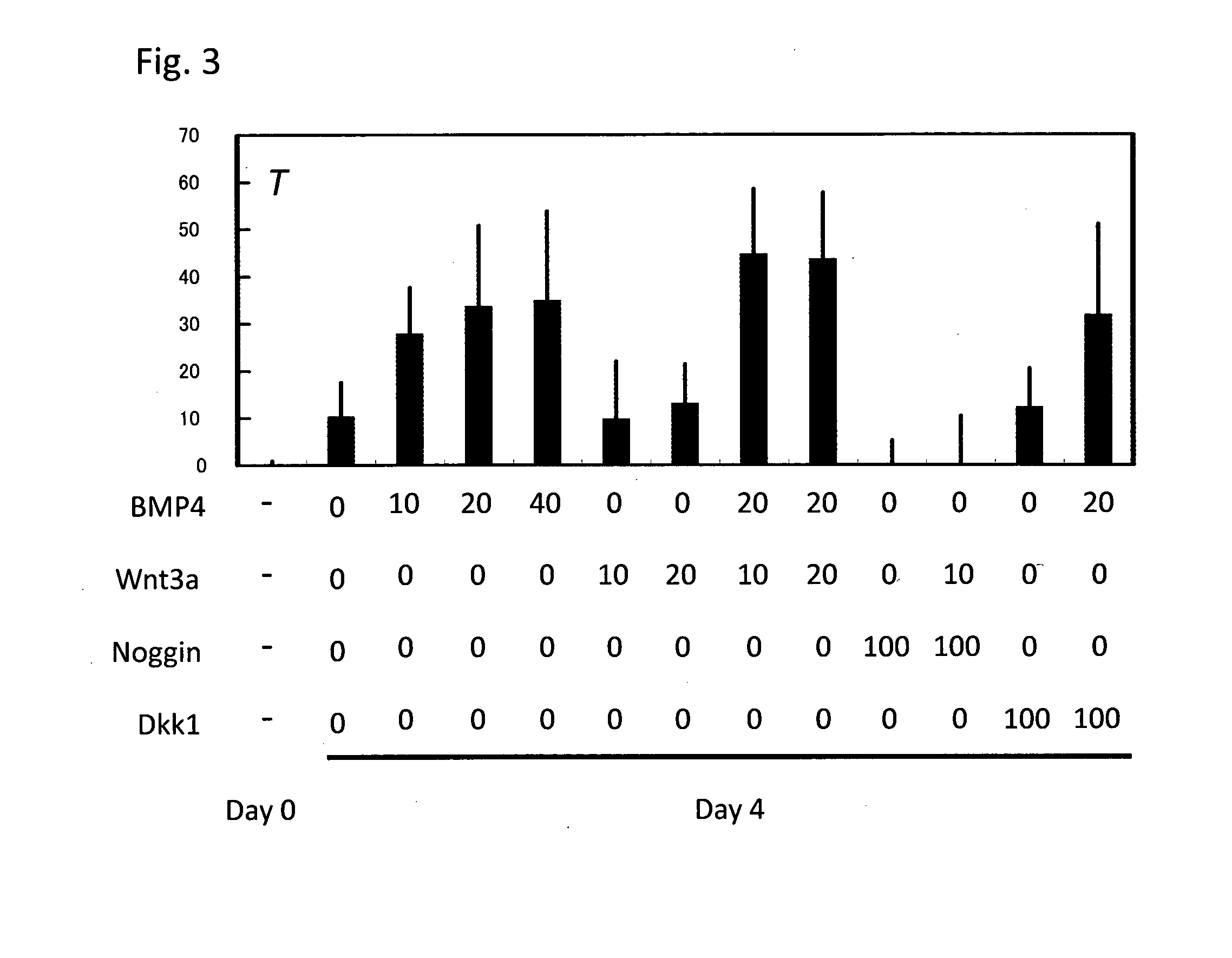
Method for producing mesodermal cells by culturing under adherent conditions and without co-culture with cells from a different species in a serum-free medium
InactiveUS8652845B2Efficient productionBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsGerm layerSerum free media
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method of inducing differentiation from pluripotent stem cells to skeletal muscle progenitor cells
InactiveUS20120164731A1Stable supplyEfficiently obtainedCulture processMuscular disorderProgenitorDisease
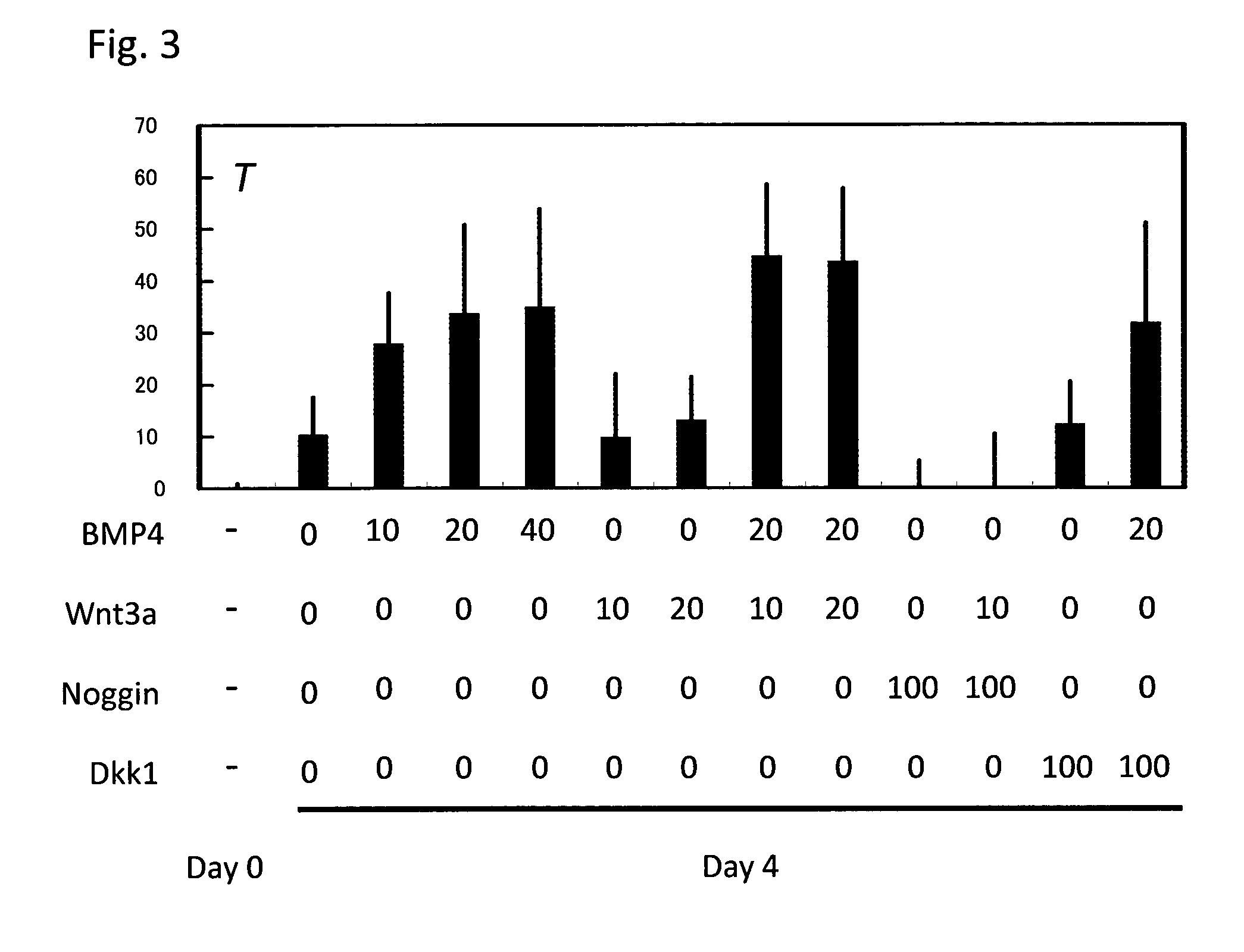
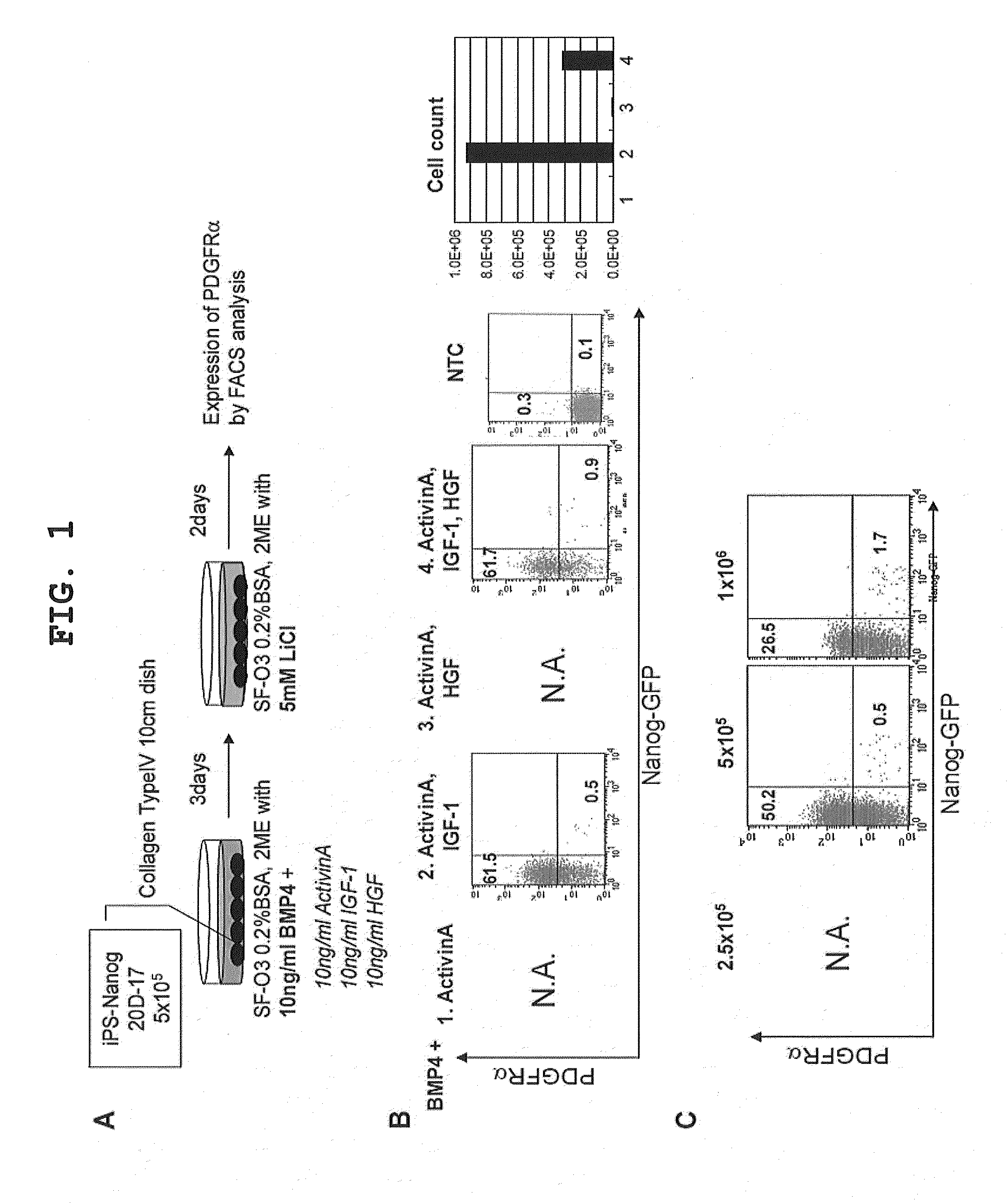
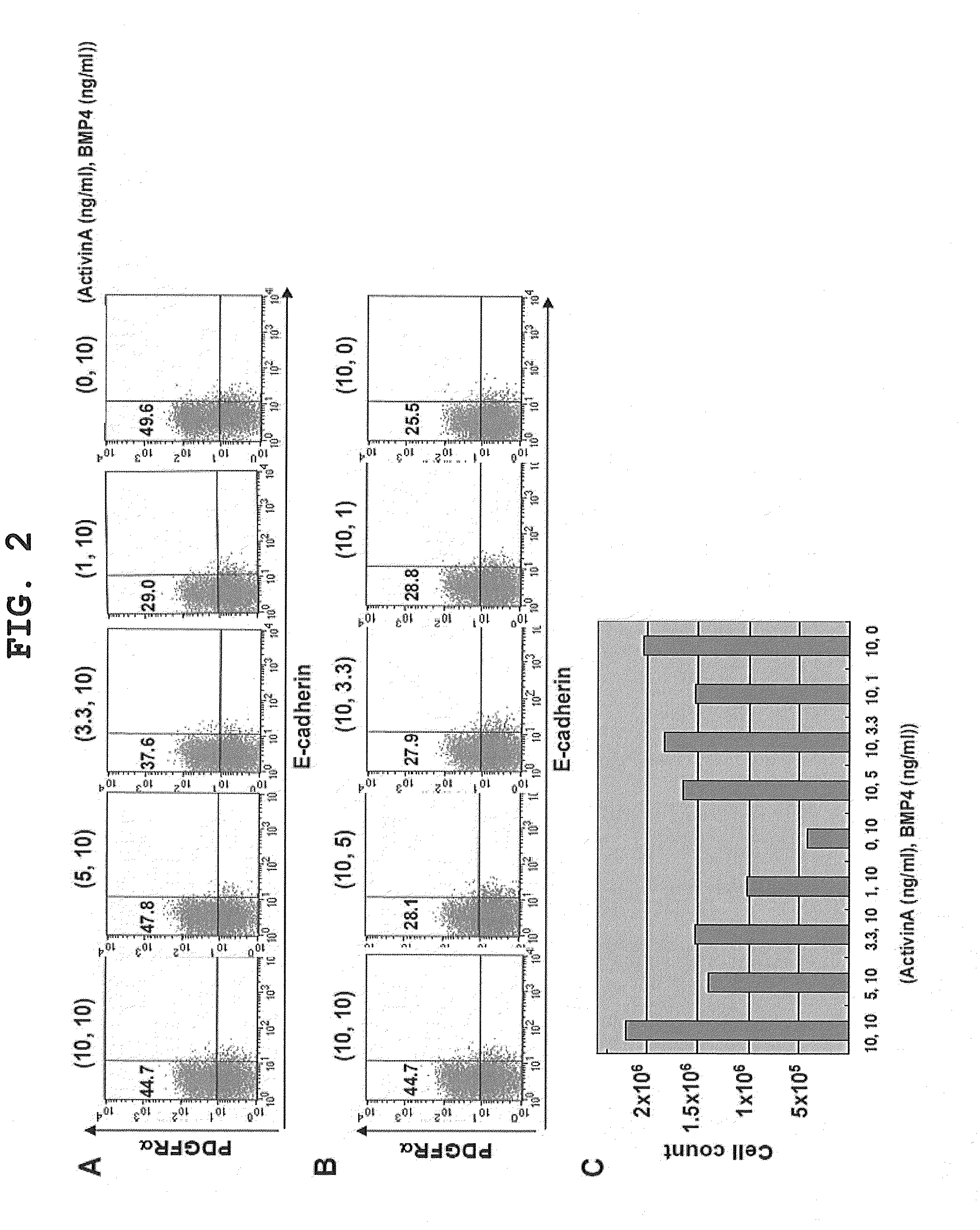
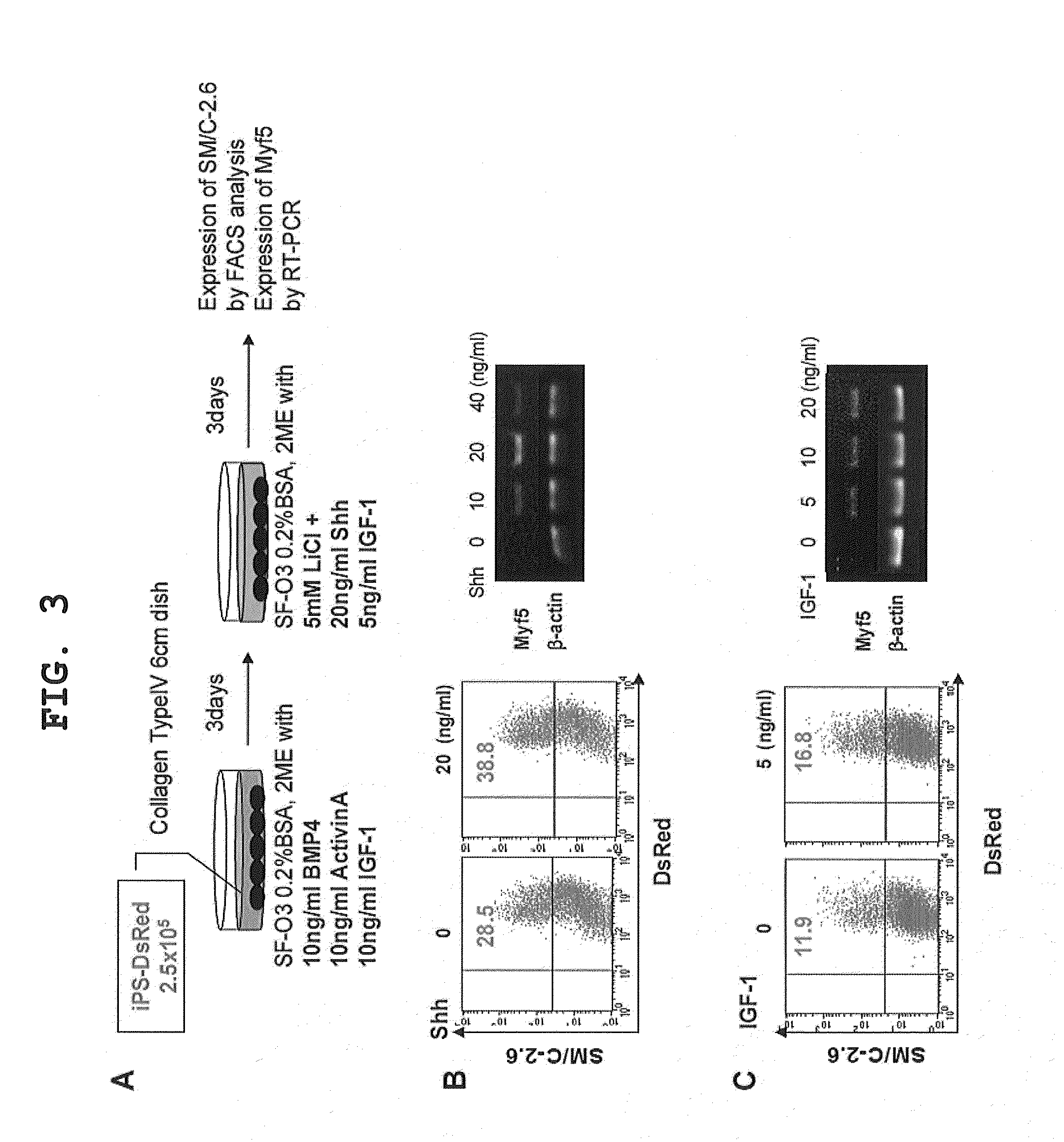
Provided is a method of producing a skeletal muscle progenitor cell using a pluripotent stem cell, particularly an iPS cell, the method comprising the step 1) of culturing a pluripotent stem cell under serum-free conditions, and in the presence of Activin A, to allow the cell to differentiate into a PDGFRα-positive mesodermal cell, and the step 2) of culturing the mesodermal cell under serum-free conditions, and in the presence of a Wnt signal inducer, to allow the cell to differentiate into a skeletal muscle progenitor cell. Also provided are a cell population containing a skeletal muscle progenitor cell as obtained by the method, and a skeletal muscle regeneration promoting agent and therapeutic agent for muscular diseases such as muscular dystrophy, the promoting agent or agent comprising the skeletal muscle progenitor cell as an active ingredient.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Preparation method of epicardial cells from stem cells
InactiveCN106635969ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsGerm layerAdventitial cell
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Tissue structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20160122722A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsGerm layerMesenchymal stem cell
A tissue structure for enabling comprehensive understanding of gene patterns of mature cells and a method of preparing the tissue structure are provided. A tissue structure is obtained by co-culturing an endodermal, ectodermal, or mesodermal cell derived from a stem cell and at least one cell and / or factor selected from the group consisting of a vascular cell, a mesenchymal cell, a factor secreted by a vascular cell, a factor secreted by a mesenchymal cell, and a factor secreted when both a vascular cell and a mesenchymal cell exist. A value obtained by assay of a plurality of functions using a Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient is closer to a value of a cell or biological tissue sampled from an adult than a value of a cell or biological tissue sampled from a fetus.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA CITY UNIV +1
Method for inducing differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into mesodermal cells
InactiveUS20130011924A1Efficient productionArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
The present invention provides a method for inducing differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into mesodermal cells, comprising the step of culturing pluripotent stem cells in a serum-free medium without forming an embryoid body and without coculturing with cells from a different species.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
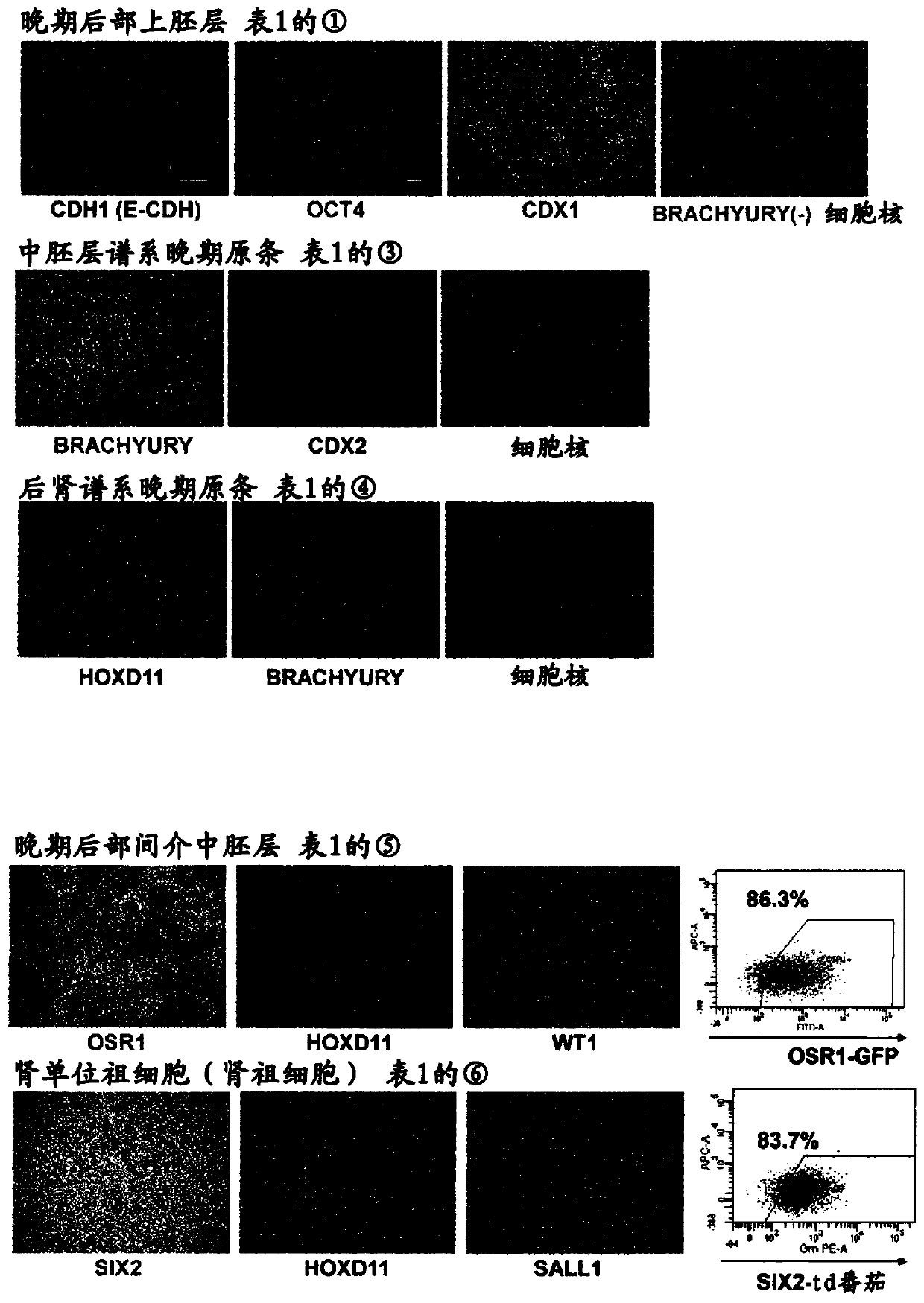
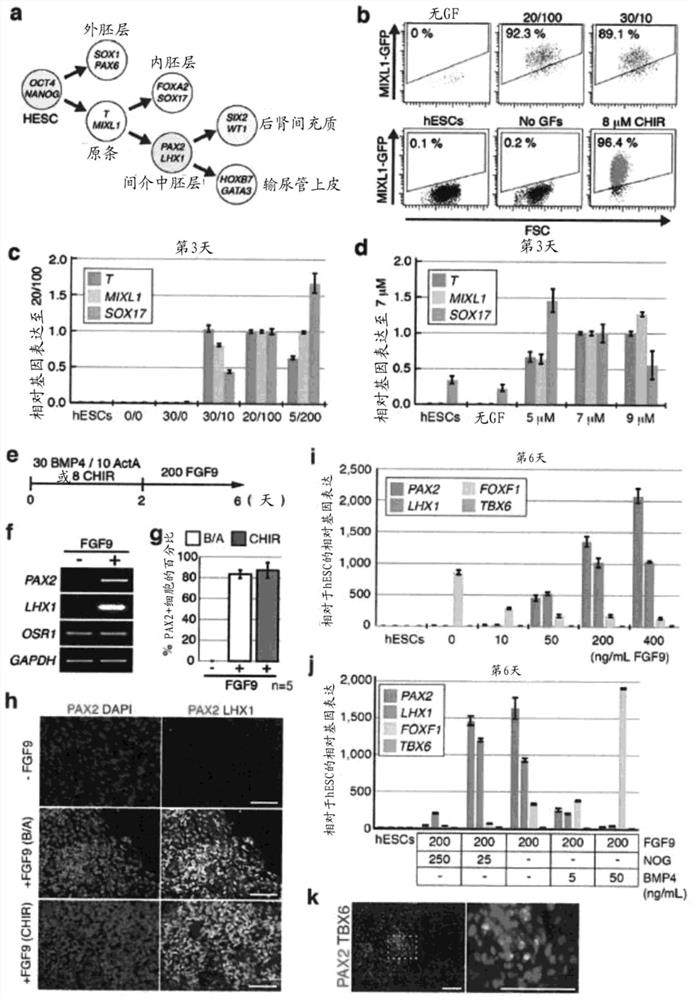
Method for inducing differentiation of intermediate mesodermal cell to renal progenitor cell, and method for inducing differentiation of pluripotent stem cell to renal progenitor cell
A method for producing renal progenitor cells from pluripotent stem cells, comprising steps (i) to (vi): (i) culturing the pluripotent stem cells in a culture medium containing FGF2, BMP4, a GSK-3[beta] inhibitor and retinoic acid or a derivative thereof; (ii) culturing cells produced in step (i) in a culture medium containing FGF2, a GSK-3[beta] inhibitor and BMP7; (iii) culturing cells producedin step (ii) in a culture medium containing FGF2, a GSK-3[beta] inhibitor, BMP7 and a TGF[beta] inhibitor; (iv) culturing cells produced in step (iii) in a culture medium containing FGF2, a GSK-3[beta] inhibitor, BMP7, activin and a ROCK (Rho-kinase) inhibitor; (v) culturing cells produced in step (iv) in a culture medium containing retinoic acid or a derivative thereof and FGF9; and (vi) culturing cells produced in step (v) in a culture medium containing a GSK-3[beta] inhibitor and FGF9 to induce renal progenitor cells from intermediate mesodermal cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method of using stem cells to prepare epicardial cells
The invention provides a method of using multipotent stem cells to prepare epicardial cells, comprising: 1) inducing multipotent stem cells to differentiate into mesodermal cells by activating a WNT signal pathway; 2) converting the mesodermal cells in step 1) into myocardial precursor cells by inhibiting the WNT signal pathway; 3) converting the myocardial precursor cells in step 2) into preliminary epicardial cells by activating a fibroblast growth factor signal pathway and the WNT signal pathway; preparing pericardial cells with the preliminary epicardial cells of step 3). The invention also relates to: a method of using multipotent stem cells to prepare vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac fibroblasts; epicardial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac fibroblasts all of which are prepared through the above method; and their application.
Owner:重庆斯德姆生物技术有限公司
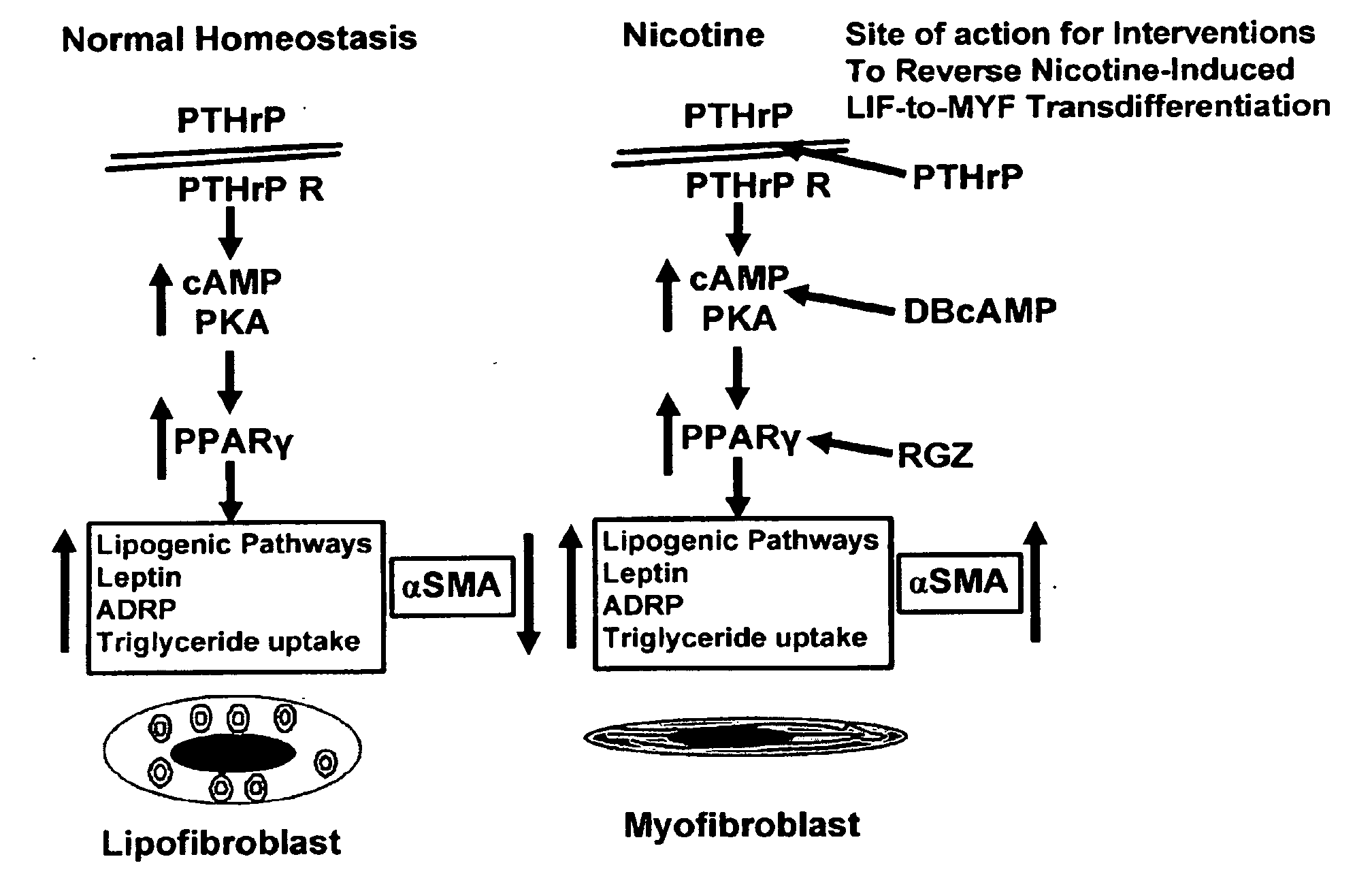
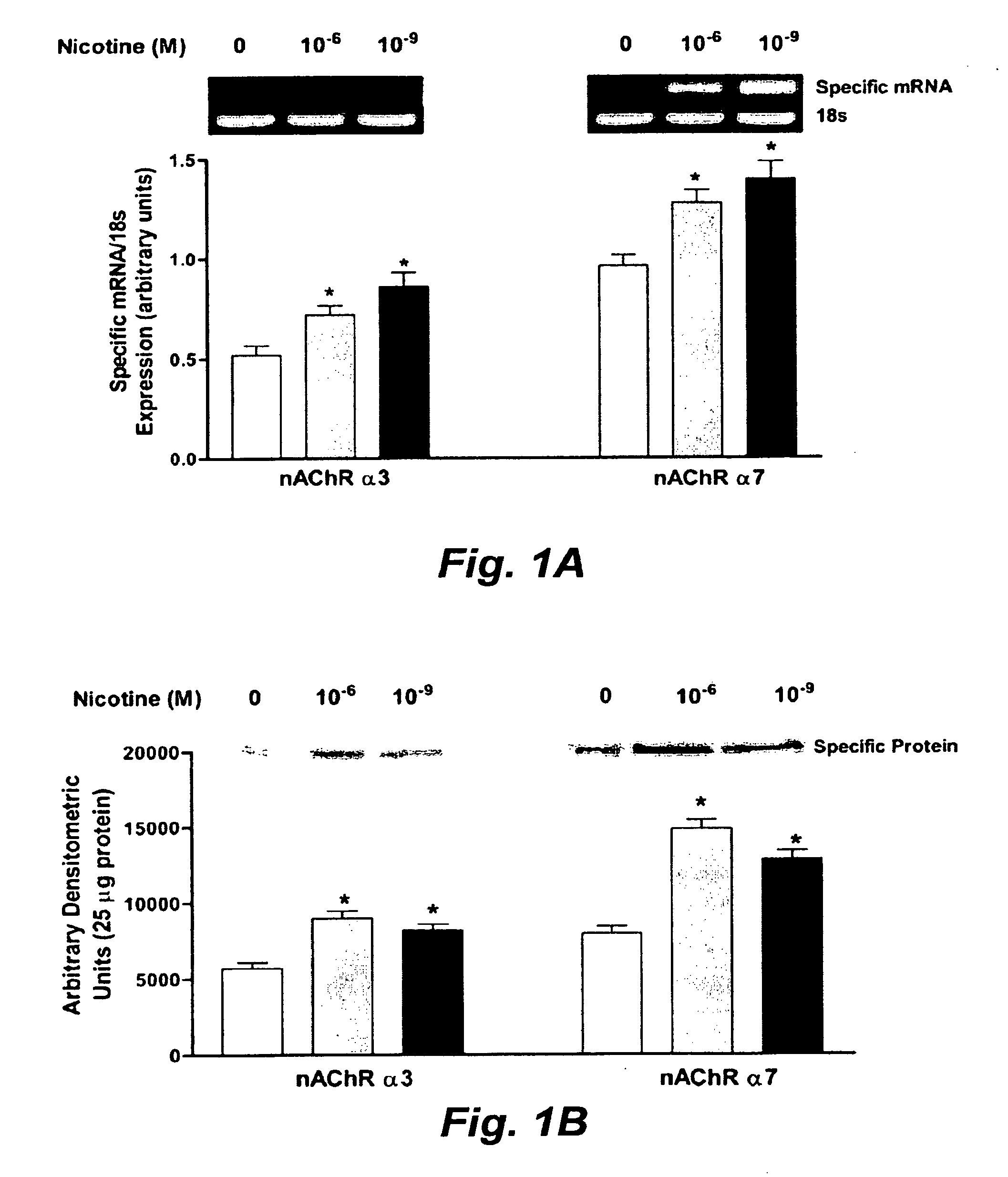
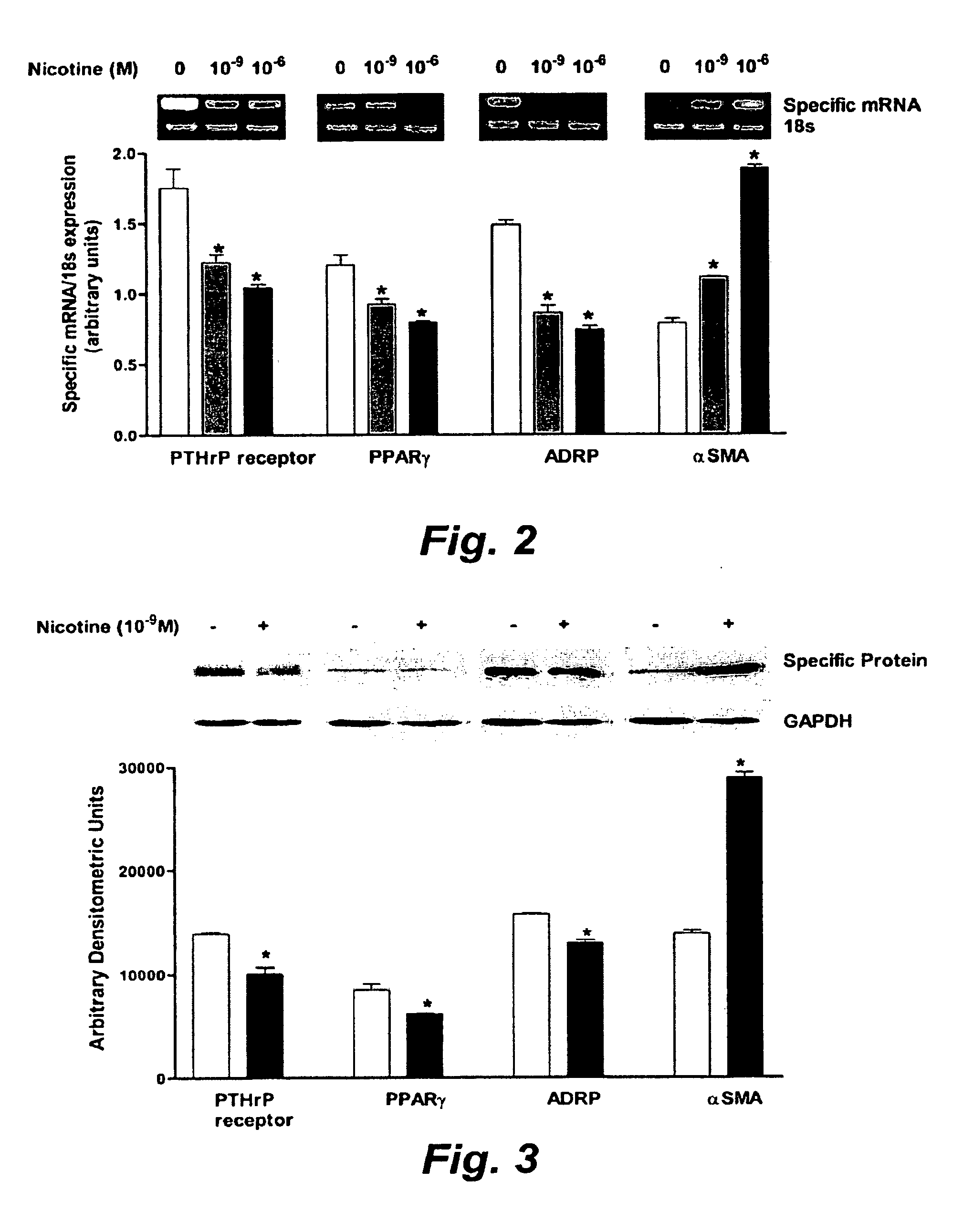
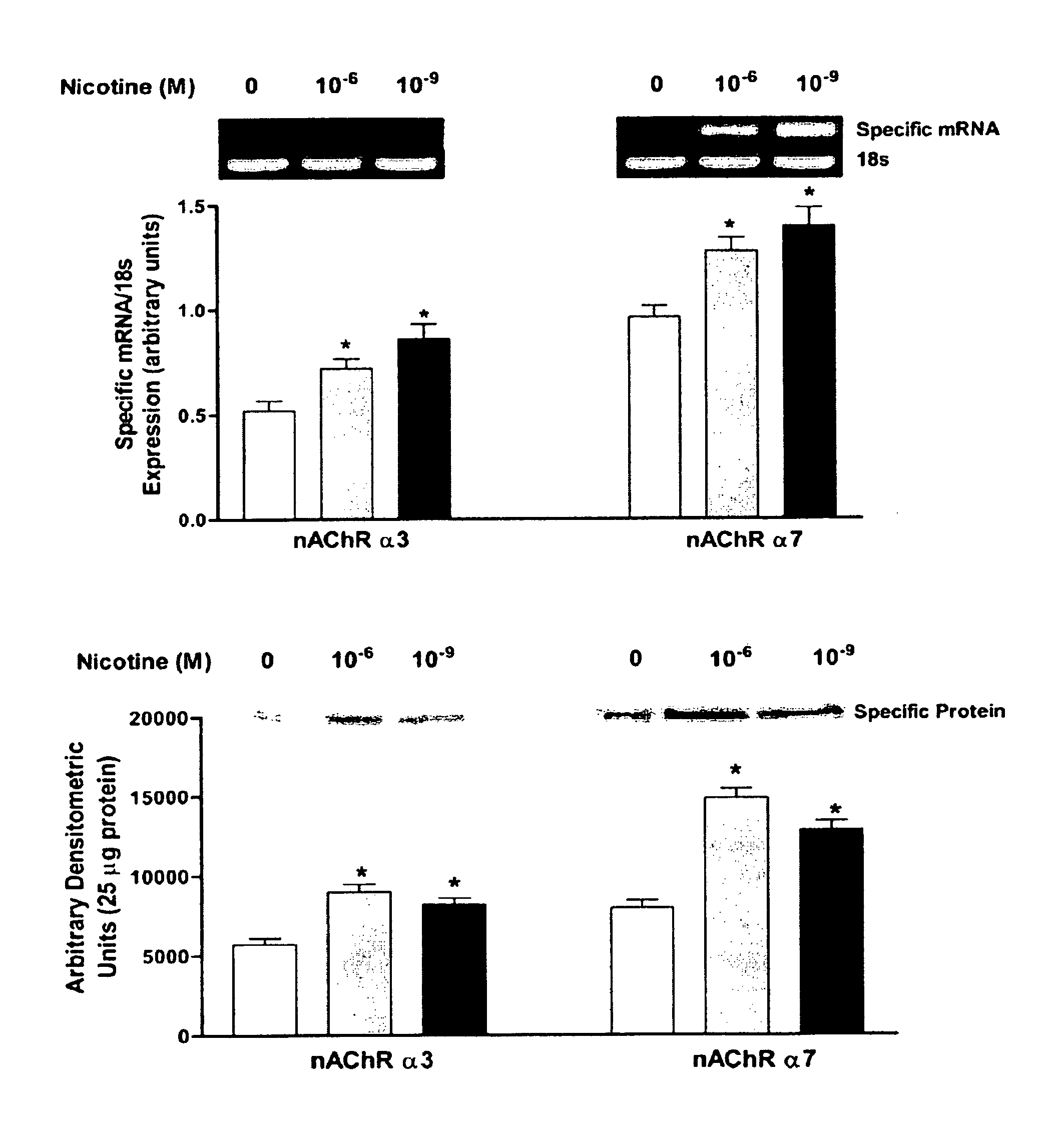
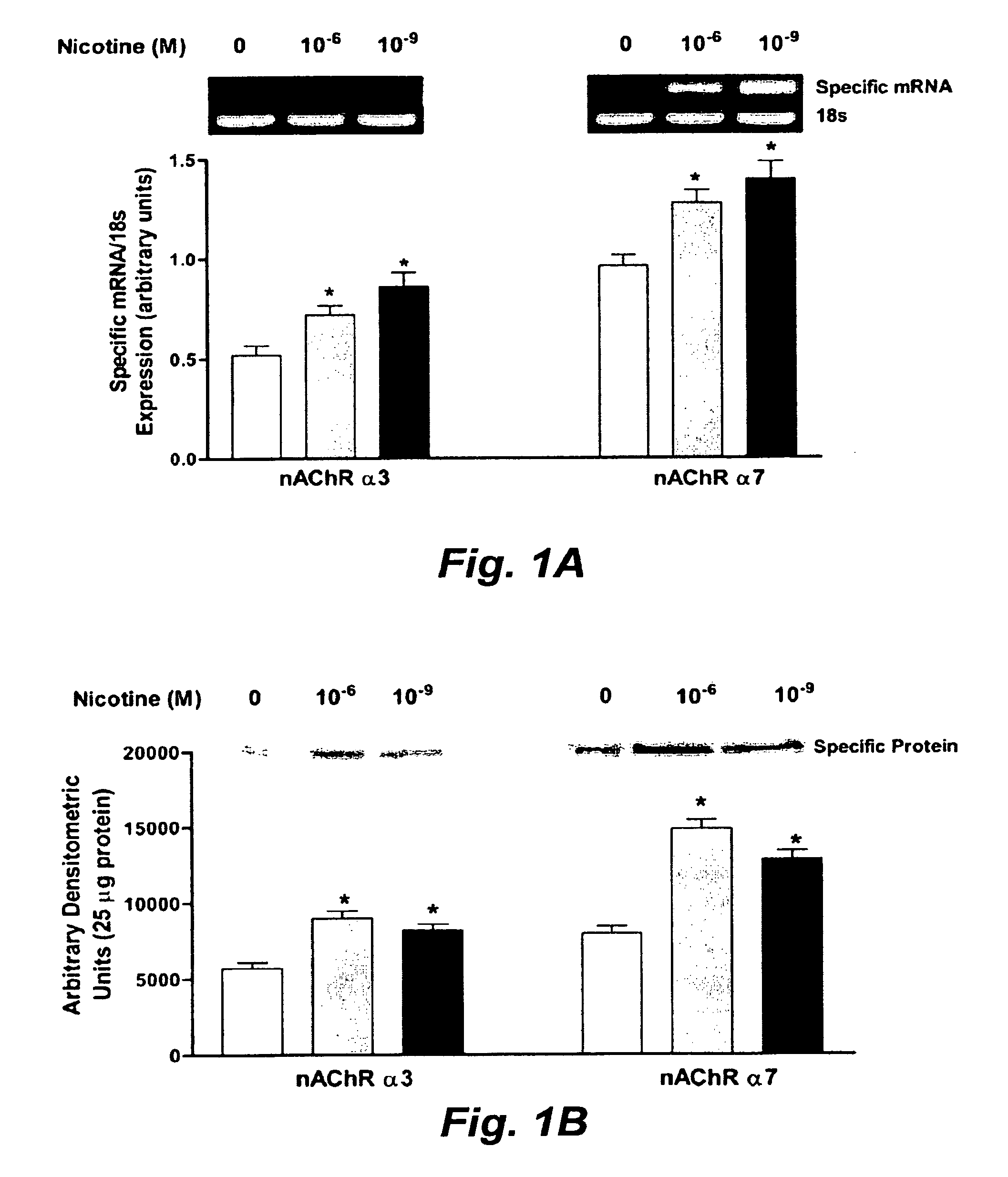
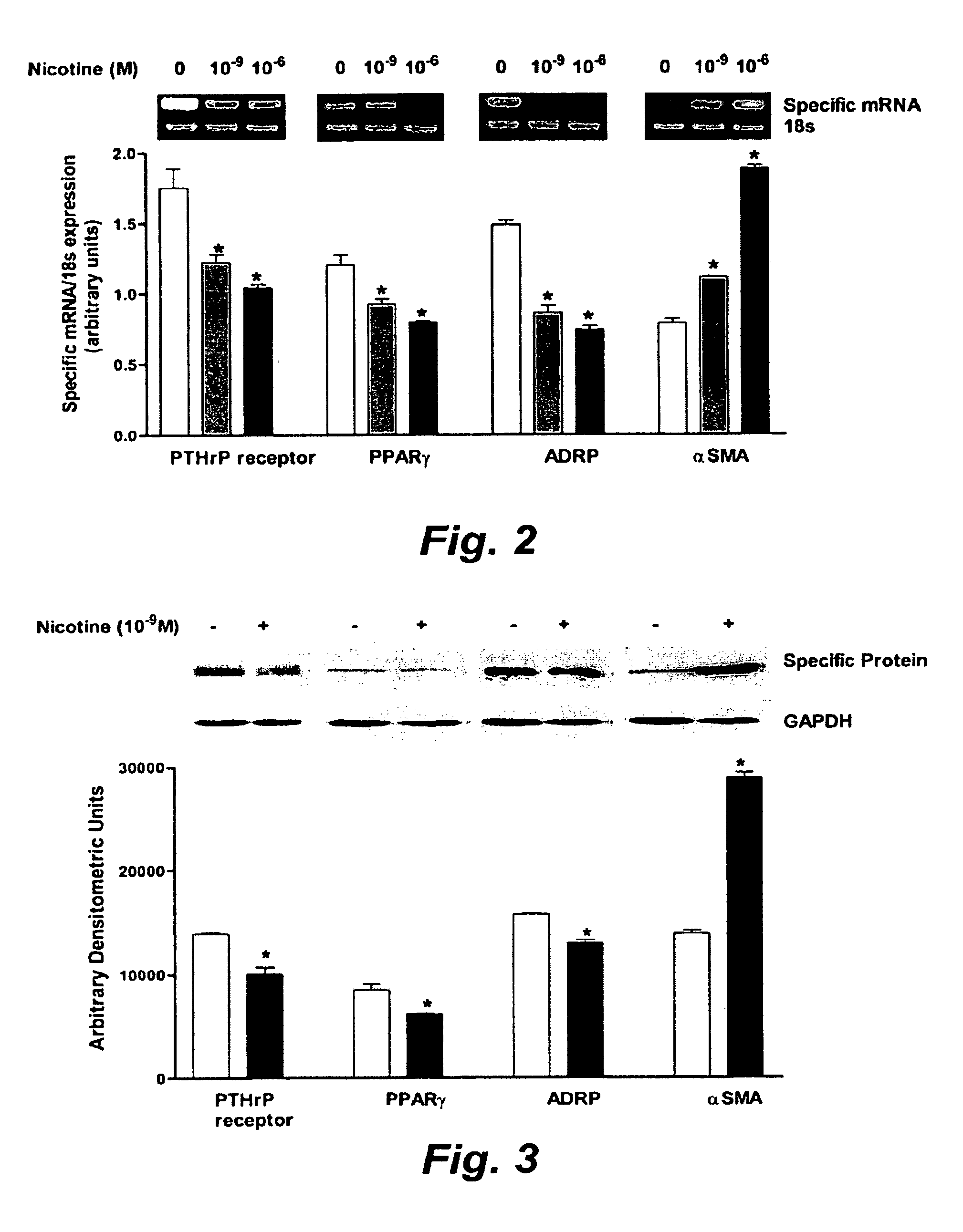
Treatment for nicotine-induced lung disease using peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists
ActiveUS20100010056A1Inhibiting and repairing deleterious effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGerm layerInjury cause
This invention provides pertains to the discovery that that nicotine interrupts molecular signaling between endodermal and mesodermal cells of the lung alveolus. Treatment of the lung with specific molecular agents (e.g., PPAR gamma agonists) can prevent and / or reverse the injury caused by nicotine.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Culture method and cell cluster
Owner:PUBLIC UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA CITY UNIV +1
A method for in vitro differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into ventricular myocytes
ActiveCN104508121BHigh purityDrug screeningArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellInduced pluripotent stem cell
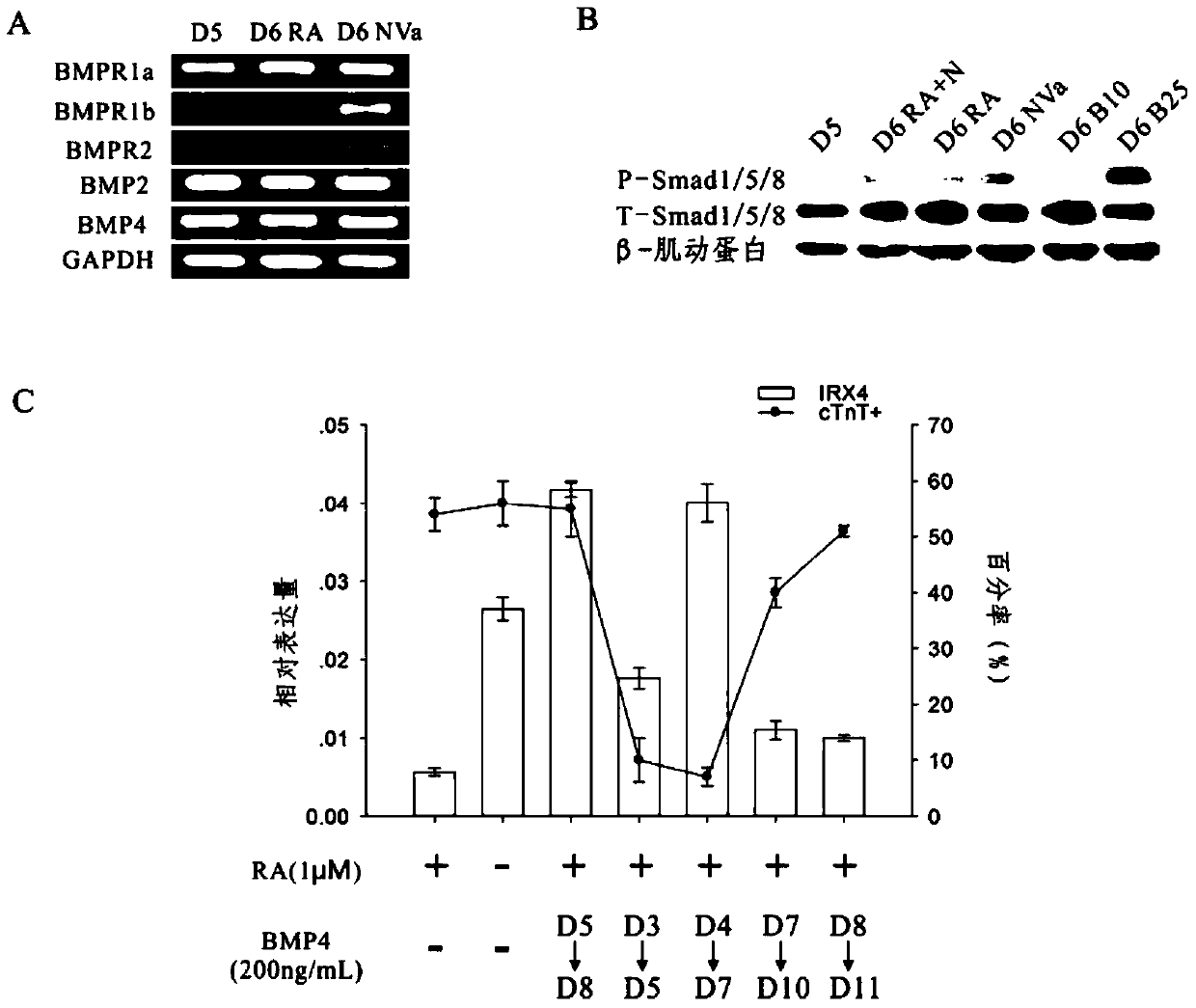
The present invention provides a method for inducing pluripotent stem cells to differentiate into ventricular myocytes in vitro, which is to maintain, amplify, and cultivate pluripotent stem cells in vitro, and in the middle stage of myocardial differentiation of pluripotent stem cells, the mesoderm cells or myocardial precursor cells develop into In the period of cardiomyocyte differentiation, substances that can directly or indirectly activate the Smad1 / 5 / 8 signaling pathway are added to the medium to make the stem cells differentiate into ventricular myocytes. Utilizing the method of the present invention, ventricular myocytes with biological activity and function have been successfully obtained, which not only reveals the regulatory mechanism in the differentiation process of myocardial precursor cells into ventricular myocytes, but also differentiates human ventricular myocytes to cell transplantation for the treatment of myocardium. Infarction and cardiac toxicology analysis and the development of cardiac-related drugs have a wide range of applications.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
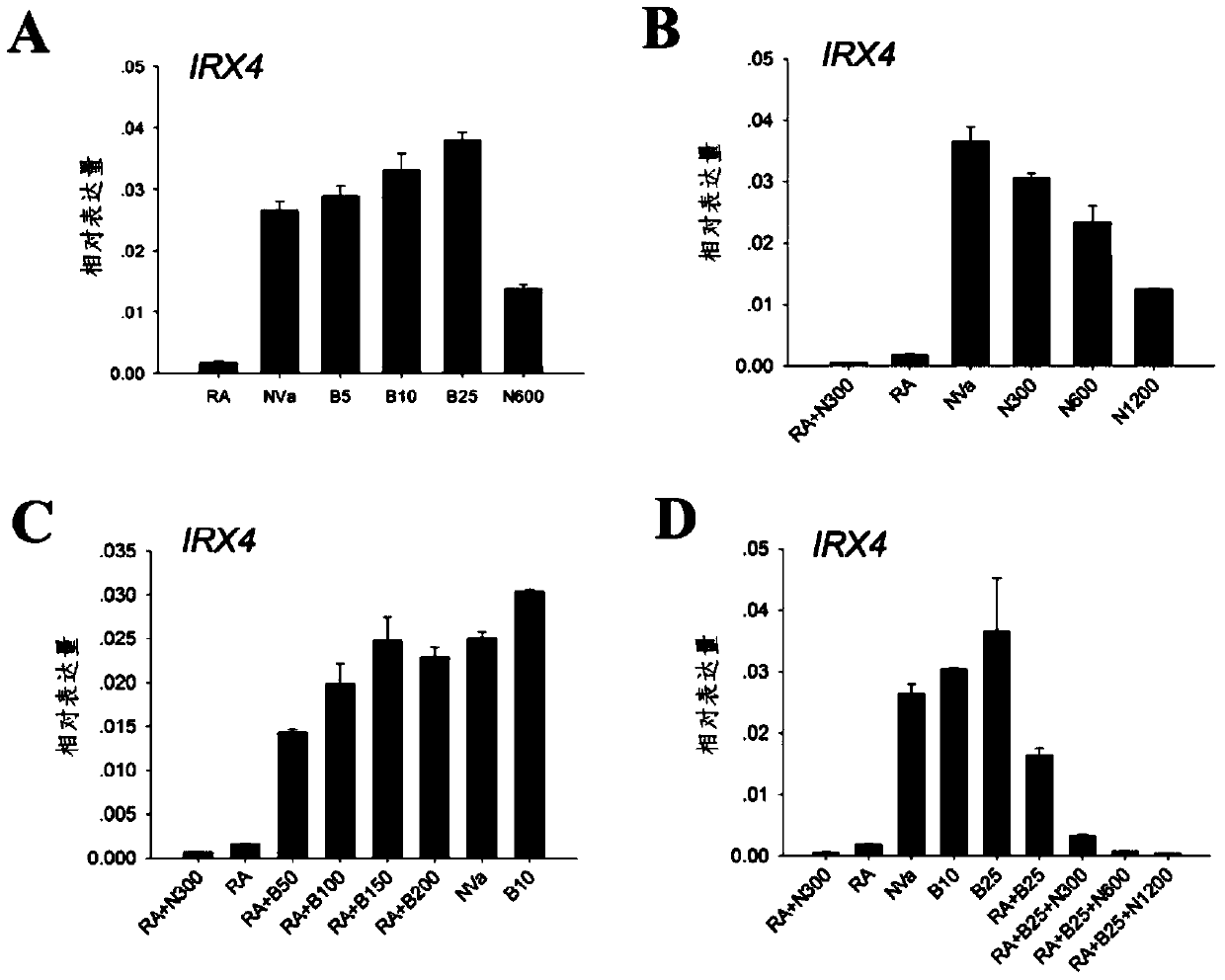
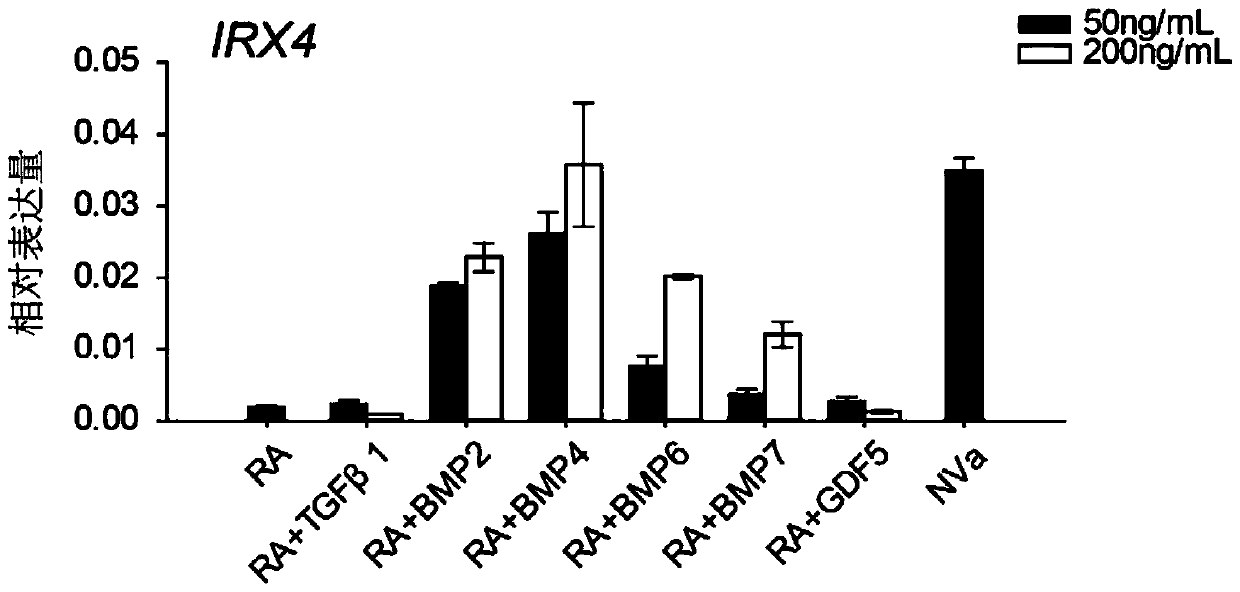
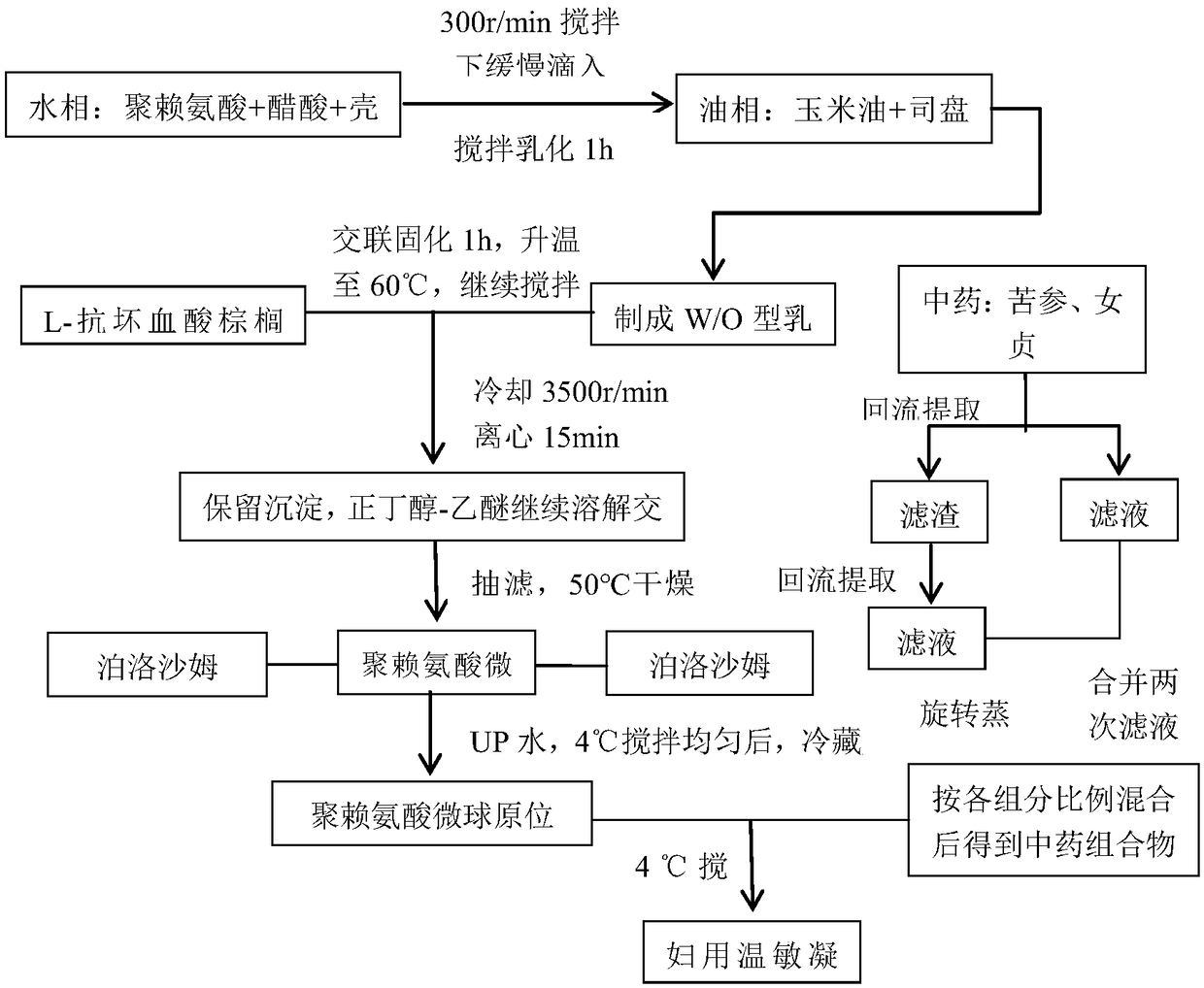
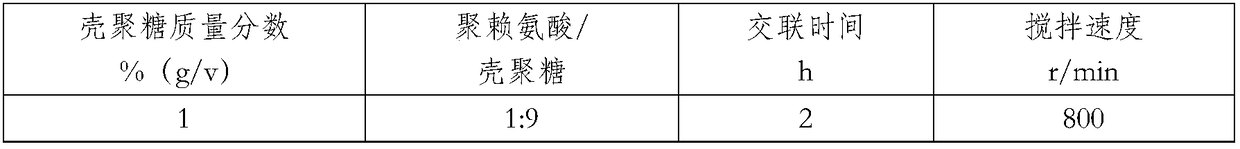
Pharmaceutical composition for treating female reproductive track infection and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108159123APromote regenerationPromote circulationOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryWound healingMicrosphere
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition for treating female reproductive track infection and a preparation method thereof. The pharmaceutical composition comprises polylysine microspheres, fructus ligustri lucidi, radix sophorae flavescentis, fructus cnidii, Chinese usnea, poloxamer F127 and poloxamer F68, wherein the content of the polylysine microspheres is 0.01-0.05% by mass percent; the total content of fructus ligustri lucidi, radix sophorae flavescentis, fructus cnidii and Chinese usnea is 1-7%; the ratio of fructus ligustri lucidi to radix sophorae flavescentis to fructus cnidii to Chinese usnea is 1:1:2:1; the content of poloxamer F12 is 17-30%; the content of F68 is 0-20%; and the rest is water. After the polylysine microspheres and the traditional Chinese medicine composition are compounded, vaginal wound healing is effectively promoted. The pharmaceutical composition has a repair and regeneration promotion function on cells of a mesoderm and an ectoderm, and canpromote regeneration of blood capillaries, improve the local blood circulation and quicken wound healing. Polylysine becomes amino acid after being decomposed and can serve as a nutrient substance tobe absorbed.
Owner:成都山信药业有限公司
Antagonists of BMP and TGF beta signalling pathway
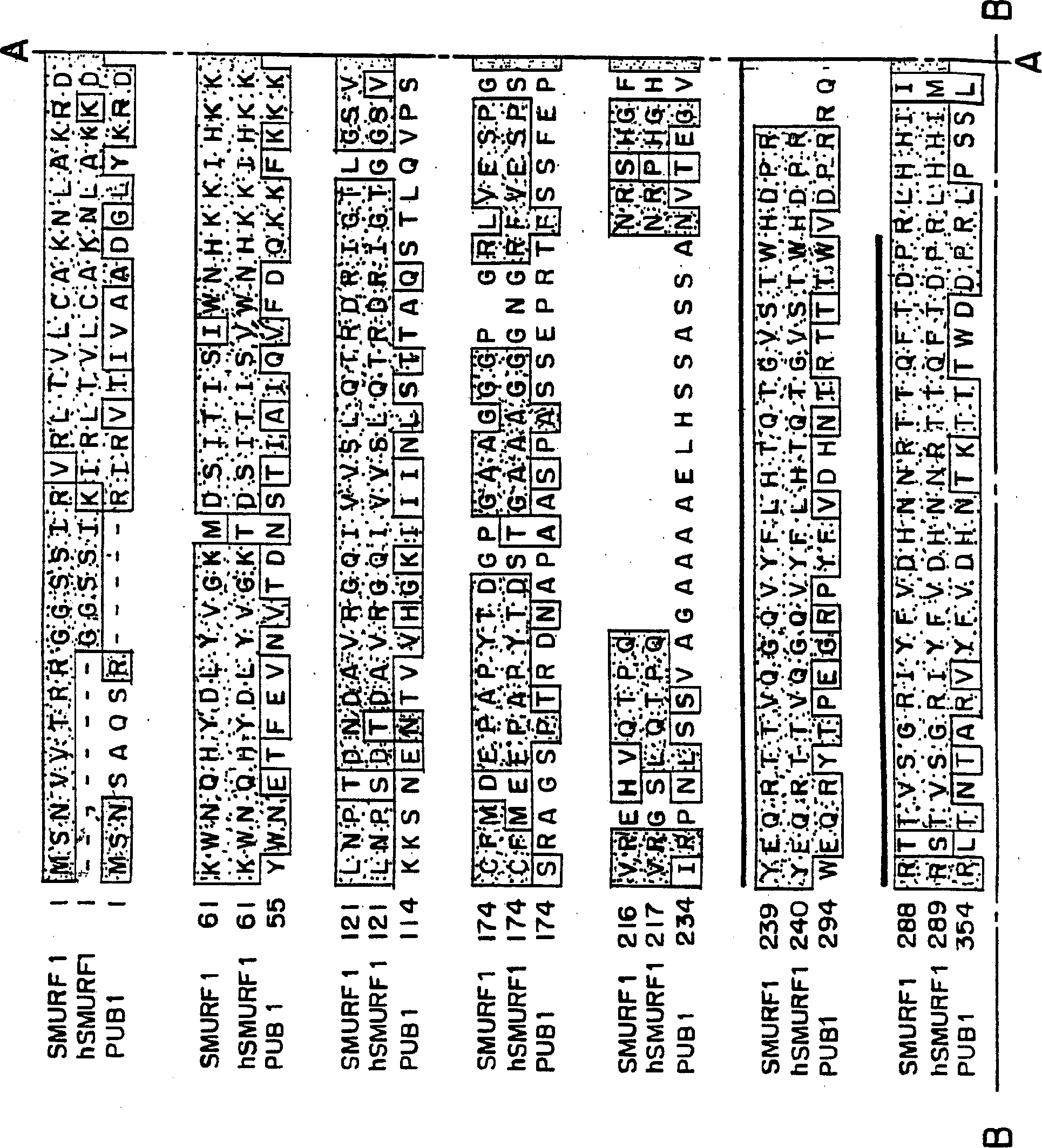
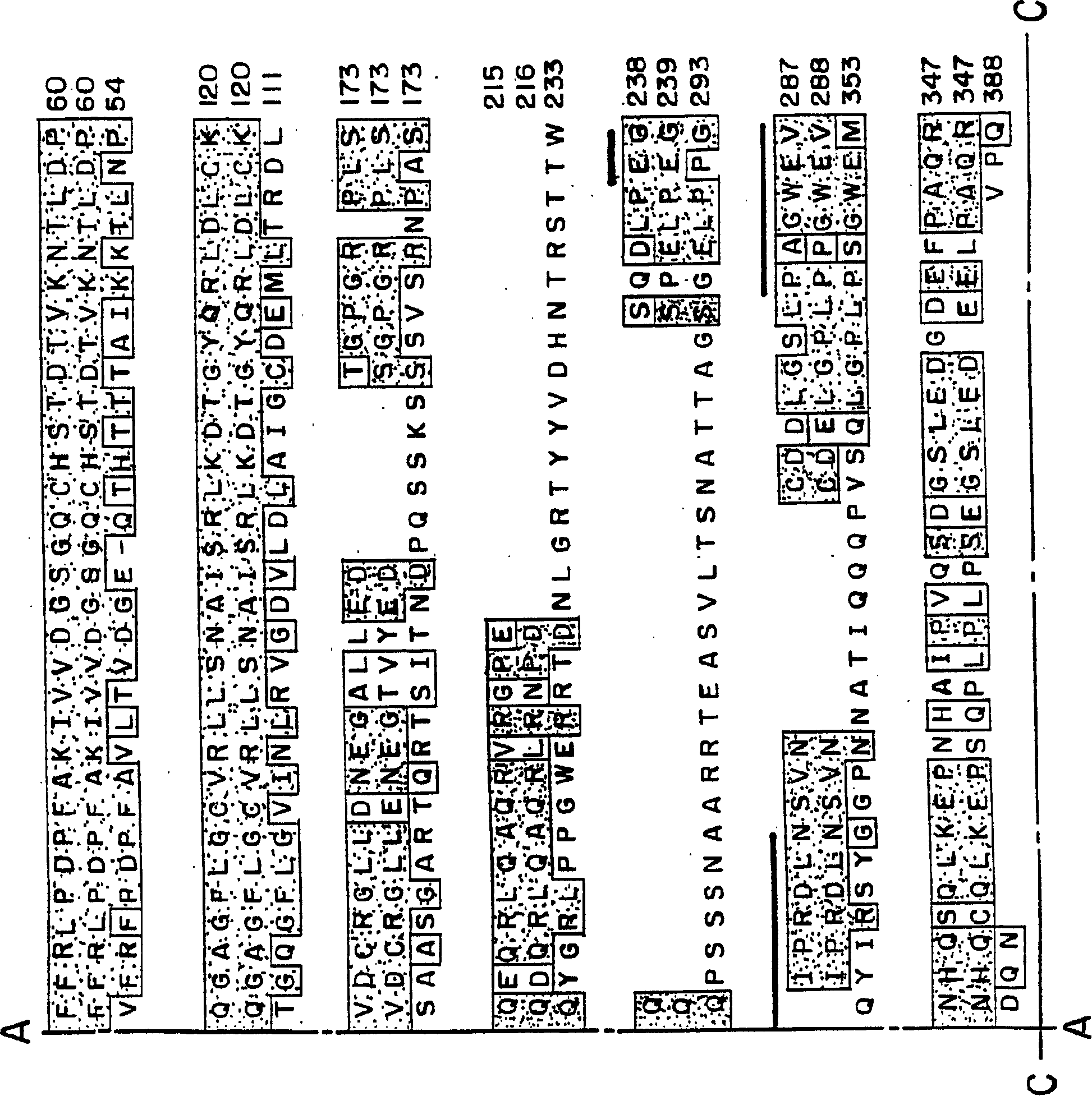
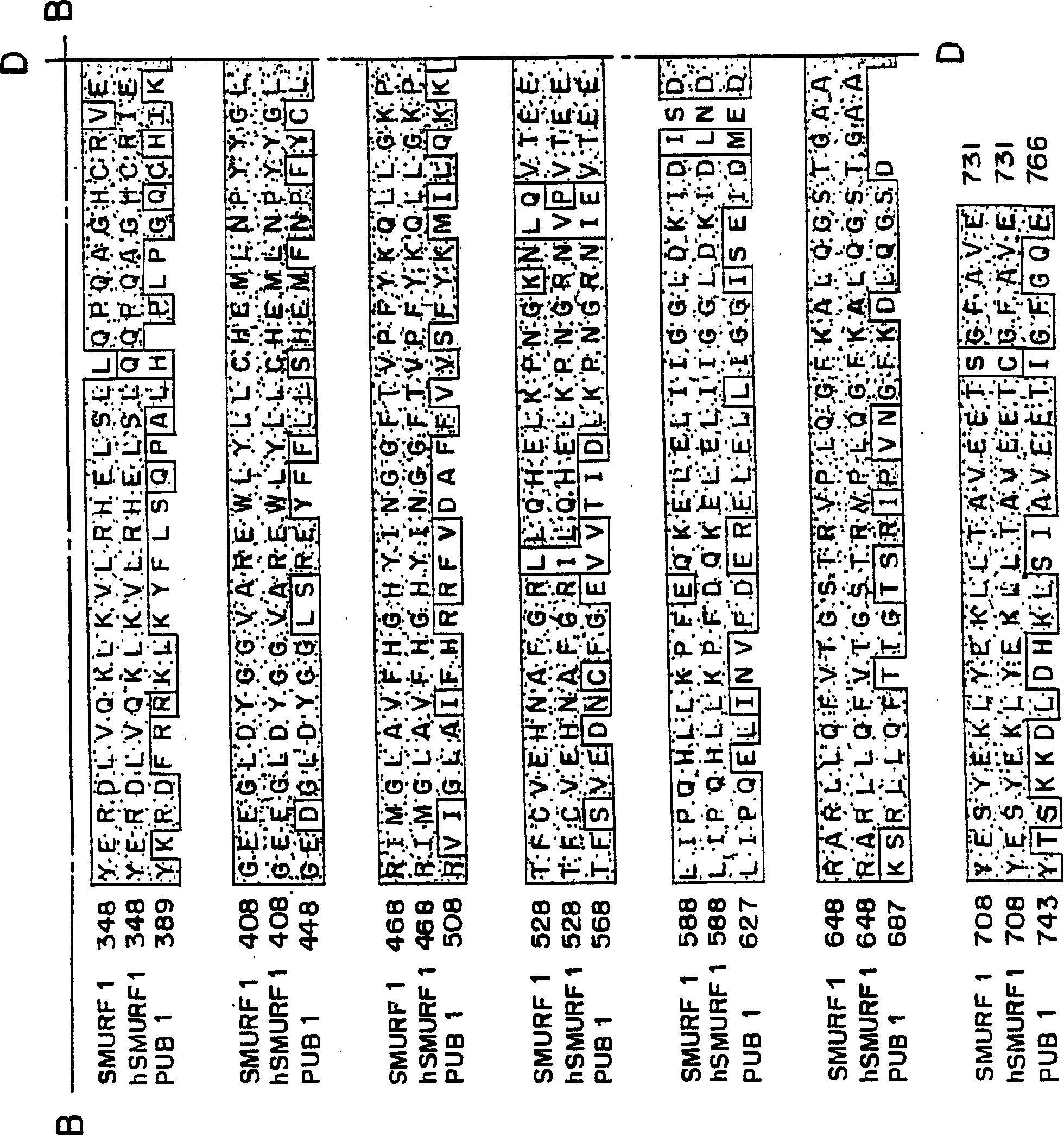
This invention provides unique members of the Hect family of ubiquitin ligases that specifically target BMP and TGF beta / activin pathway-specific Smads. The novel ligases have been named Smurf1 and Smurf2. They directly interact with Smads1 and 5 and Smad7, respectively, and regulate the ubiquitination, turnover and activity of Smads and other proteins of these pathways. Smurf1 interferes with biological responses to BMP, but not activin signalling. In amphibian embryos Smurf1 inhibits endogenous BMP signals, resulting in altered pattern formation and cell fate specification in the mesoderm and ectoderm. The present invention provides a unique regulatory link between the ubiquitination pathway and the control of cell fate determination by the TGF beta superfamily during embryonic development. Thus, Smurf1 is a negative regulator of Smad1 signal transduction, by targeting Smad1, Smurf1 blocks BMP signalling. In mammalian cells, Smurf2 suppresses TGF beta signalling, and in Xenopus, blocks formation of dorsal mesoderm and causes anterior truncation of the embryos. Smurf2 forms a stable complex with Smad7, which induces degradation and downregulation of TGF beta / activin signalling.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
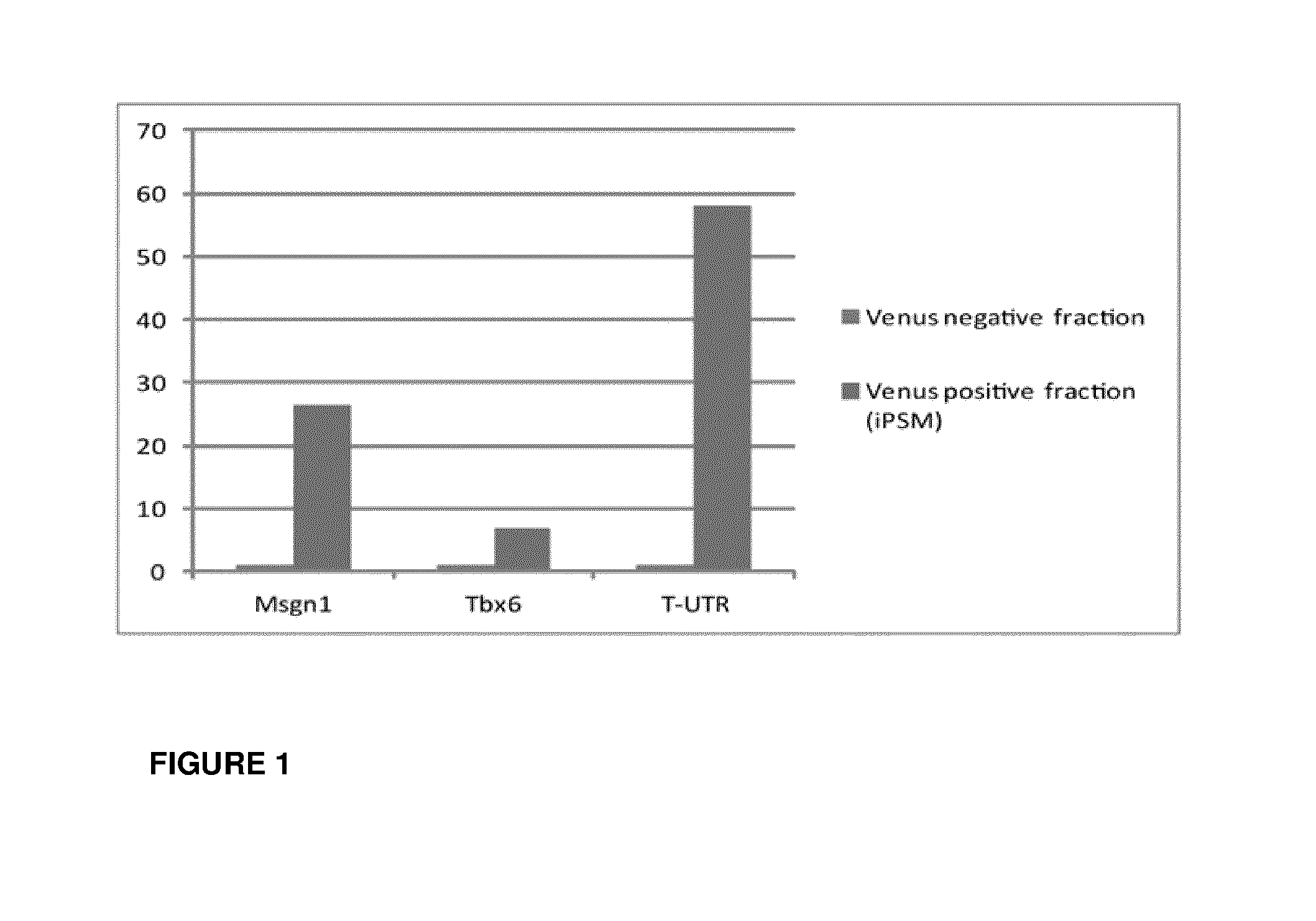
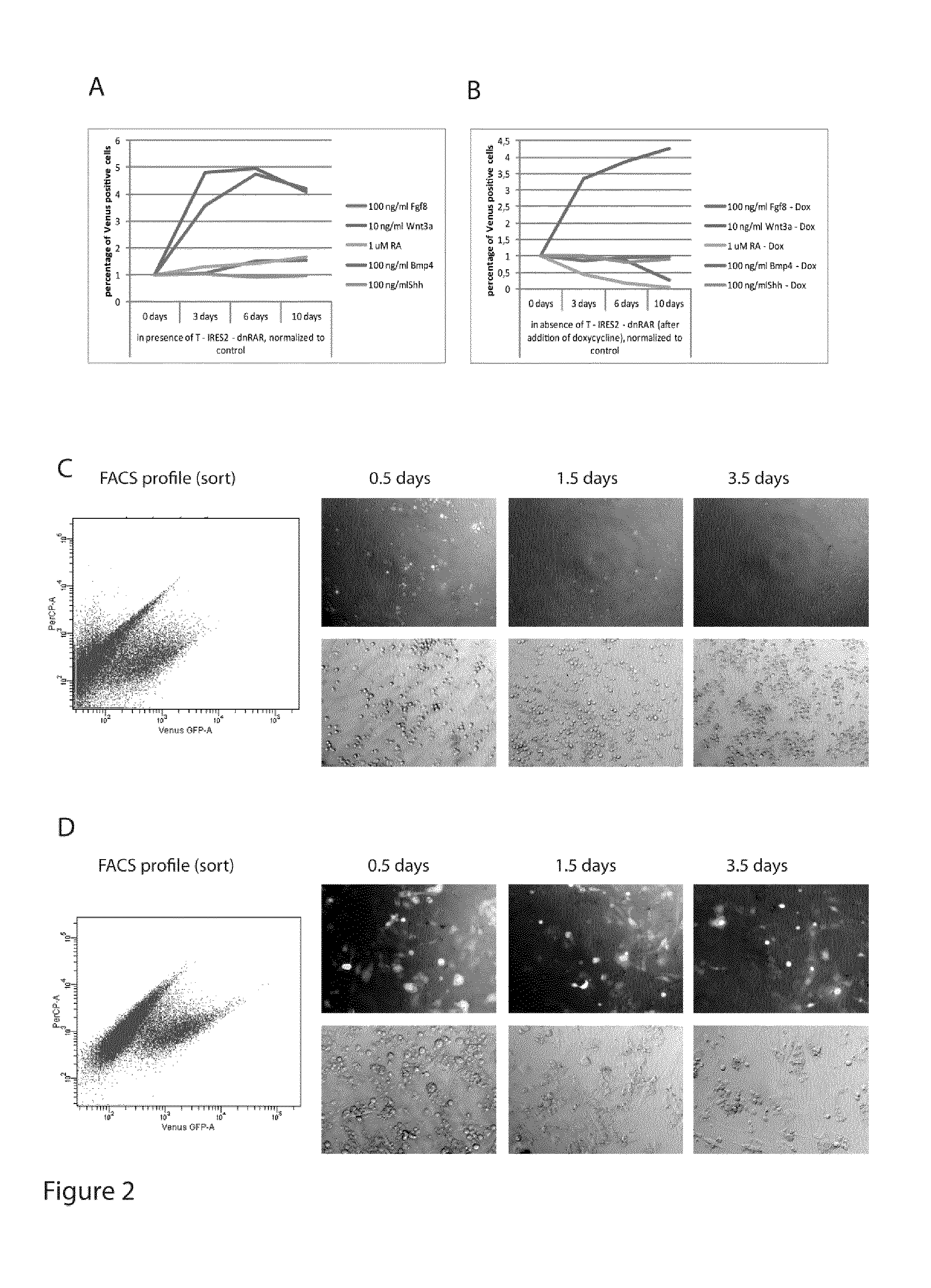
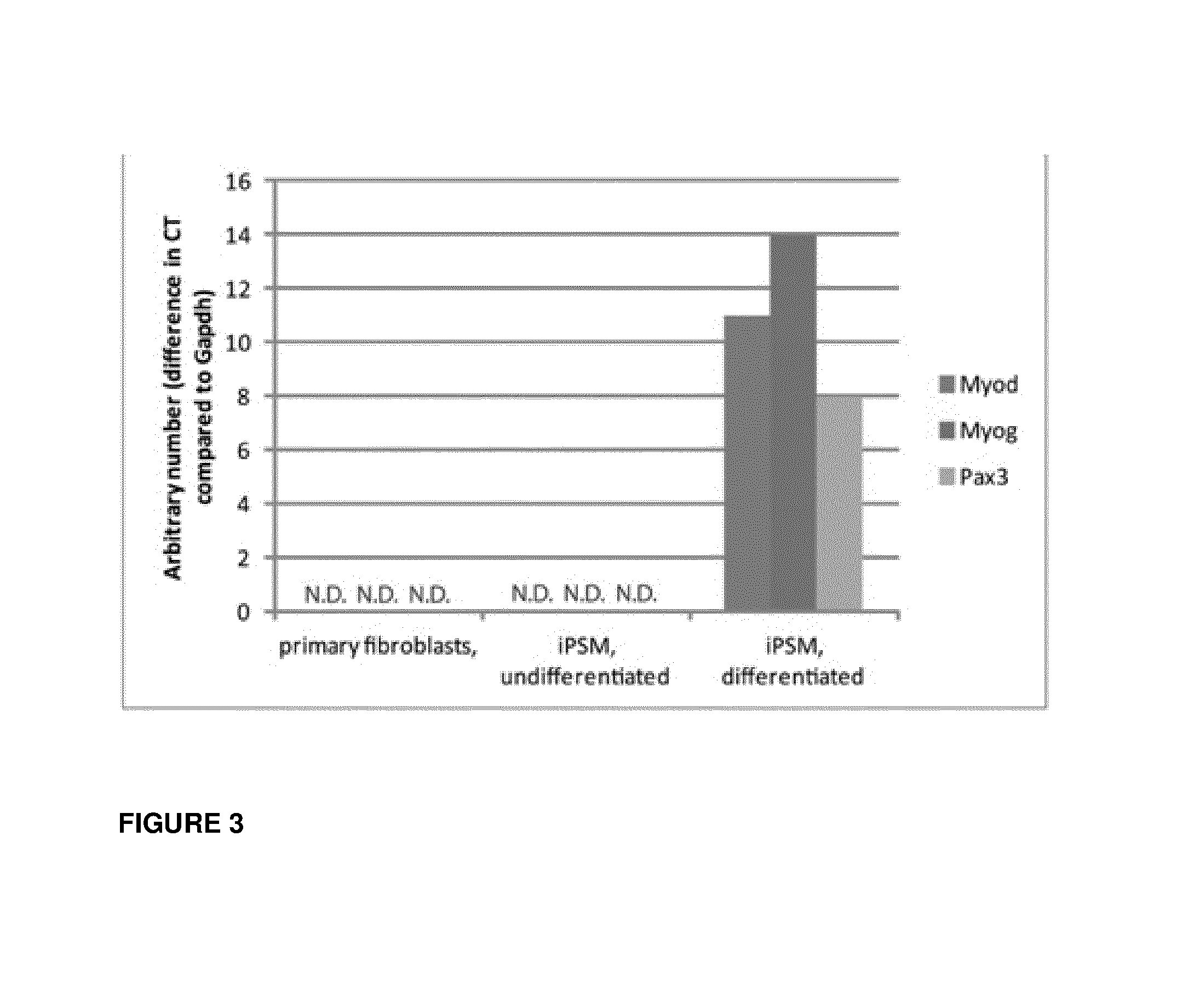
Induced presomitic mesoderm (IPSM) cells and their use
The invention relates to a method for reprogramming target cells to multipotent progenitor cells capable of differentiating into muscular, skeletal or dermal cell lines. In particular, the invention relates to an ex vivo method for preparing induced presomitic mesoderm (iPSM) cells, said method comprising the steps of: a) providing target cells to be reprogrammed, and, b) culturing said target cells under appropriate conditions for reprogramming said target cells into iPSM cells, wherein said appropriate conditions comprises increasing expression of at least one T-Box transcription factor in said target cells. The invention further relates to the use of said iPSM cells, for example, for regenerating skeletal, muscle, dermal and cartilage tissues.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +3
Induction of pluripotent stem cells into mesodermal lineages
InactiveUS20110306131A1Promotes commitment and survivalGenetic material ingredientsArtificial cell constructsGerm layerProgenitor
Owner:RUDY REIL DIANE ELIZABETH
Method of generating neural stem cells
The present invention relates to a method of generating neural stem cells from mesodermal cells. The invention further provides a cell population which has neural stem cell-like characteristics. The neural stem cells prepared according to the invention are useful in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Owner:NEUROPROGEN LEIPZIG
A method for inducing differentiation into NK cells from human embryonic stem cells
The invention relates to a method for inducing differentiation into NK cells from human embryonic stem cells, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering; the method includes the recovery and passage of human embryonic stem cells, inducing mesodermal cells, and inducing CD34 cells + Hematopoietic stem cells, isolation and purification of CD34 + Hematopoietic stem cells, induced to obtain NK cells, expanded and cultured; the human embryonic stem cells are human embryonic stem cell line H9; the recovery and passage of the human embryonic stem cells, the human embryonic stem cells are revived and passaged, passed to the second generation, and the cells are confluent When the ratio is more than 80%, it is used to induce mesodermal cells; the present invention uses human embryonic stem cells to induce differentiation to obtain NK cells, and when the effect-target ratio is 20:1, the killing rate of HELA tumor cell line The killing rate of the LOVO tumor cell line was 91.24%.
Owner:SHANDONG XINRUI BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for inducing directional endothelial differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells
ActiveCN112980770AHigh endothelial induction efficiencyArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsEndothelial differentiationFGF8
The invention relates to a method for inducing directional endothelial differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. The method specifically comprises the following steps: 1, when the human pluripotent stem cells reach 80% fusion or above, induced differentiation is performed on digested stem cells by using a differential medium containing 10-50ng / ml of WNT3a; 2, induced differentiation is further performed on the cells by using a differentiation medium containing 10-50ng / ml of WNT3a and 10-30ng / ml of BMP2; 3, induced differentiation is further performed on the induced differentiated cells in the step 2 by using a differential medium containing 10-30ng / ml of BMP2 into mesodermal cells; and 4, induced differentiation is further performed on the cells by using a culture medium containing 10-15ng / ml of FGF8 into endothelial cells. According to the invention, by improving the mediums and related cell factors, the experimental scheme can have higher endothelial induction efficiency.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Tissue structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS11060065B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGerm layerBlood vessel
A tissue structure for enabling comprehensive understanding of gene patterns of mature cells and a method of preparing the tissue structure are provided. A tissue structure is obtained by co-culturing an endodermal, ectodermal, or mesodermal cell derived from a stem cell and at least one cell and / or factor selected from the group consisting of a vascular cell, a mesenchymal cell, a factor secreted by a vascular cell, a factor secreted by a mesenchymal cell, and a factor secreted when both a vascular cell and a mesenchymal cell exist. A value obtained by assay of a plurality of functions using a Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient is closer to a value of a cell or biological tissue sampled from an adult than a value of a cell or biological tissue sampled from a fetus.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA CITY UNIV +1
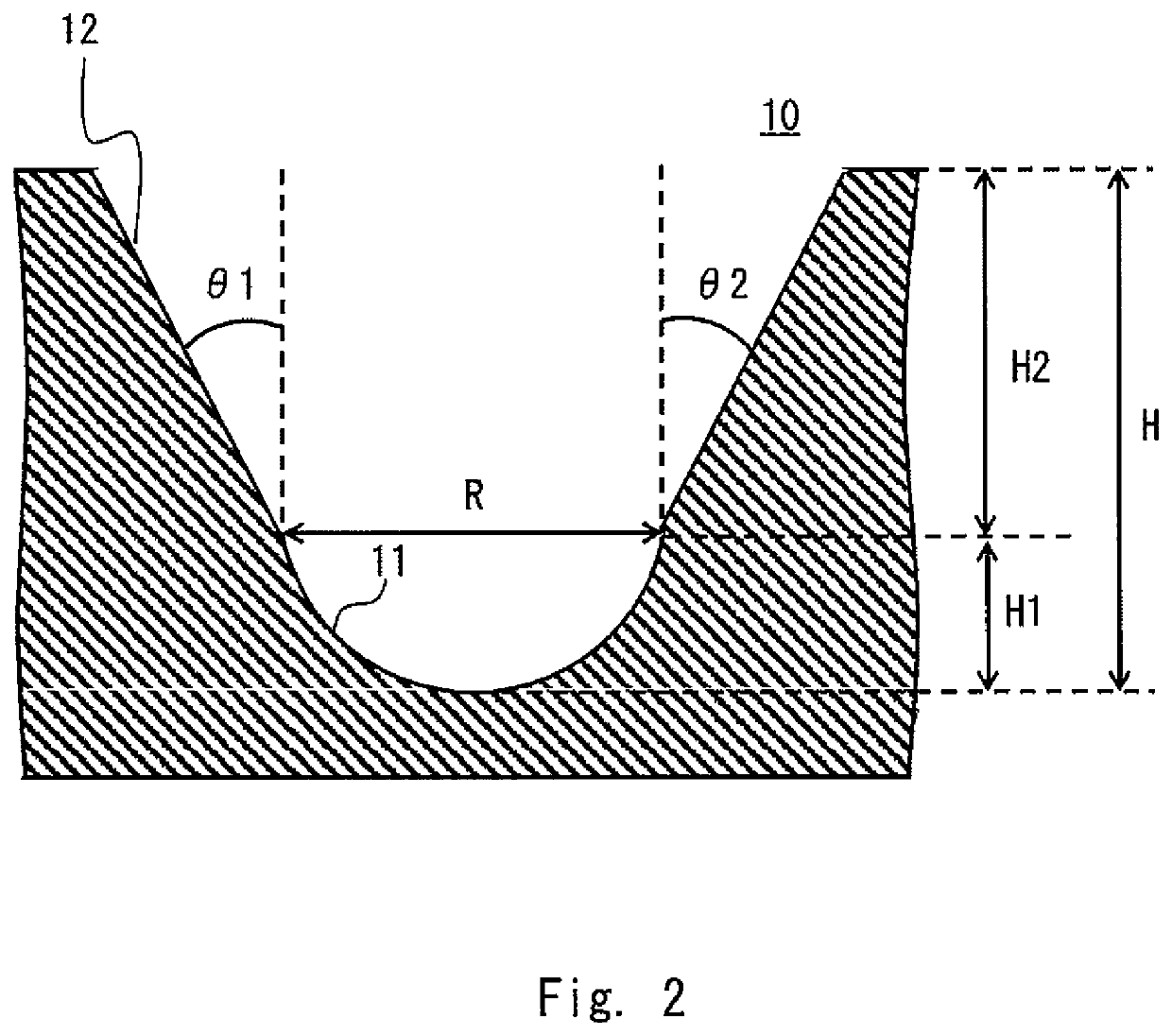
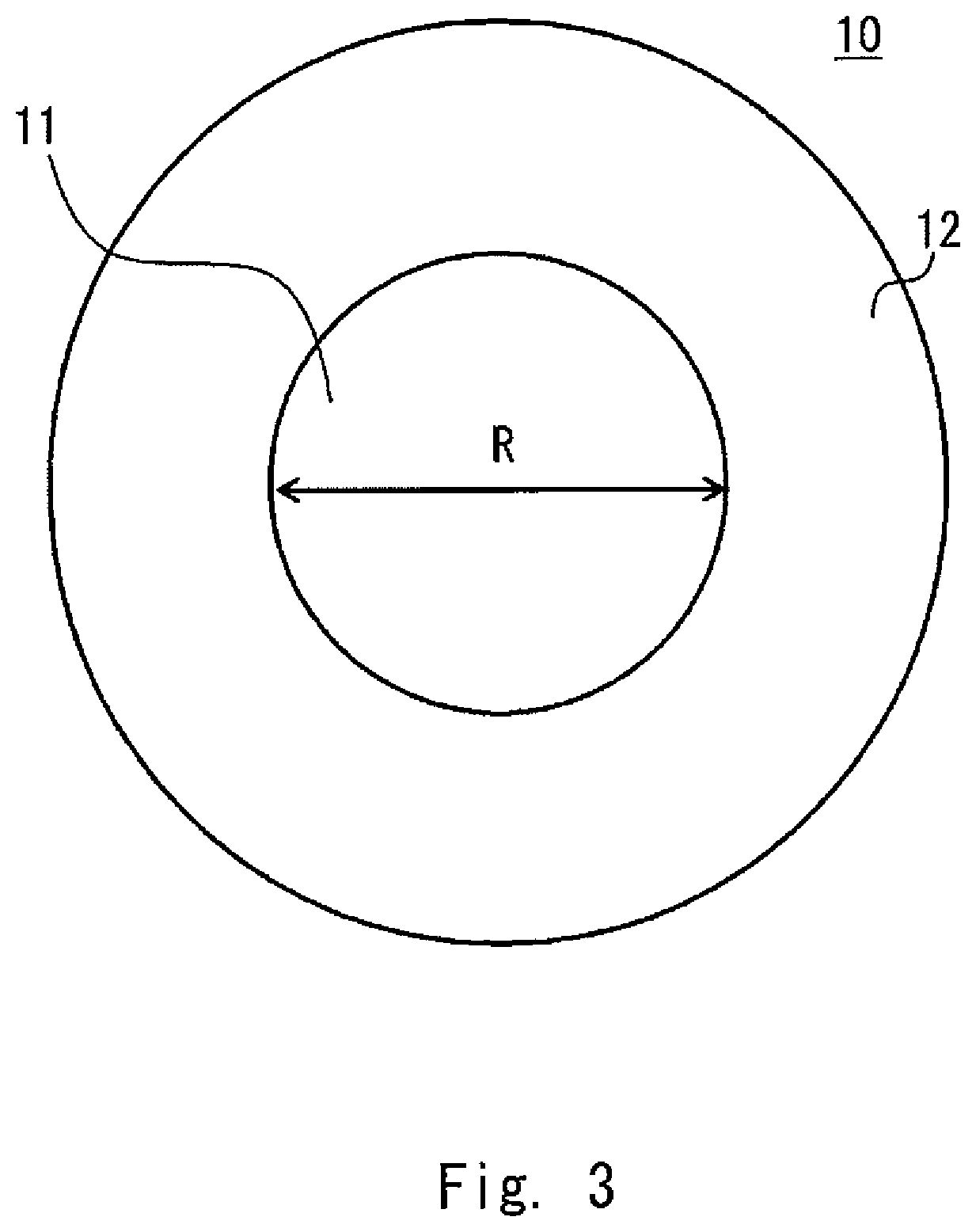
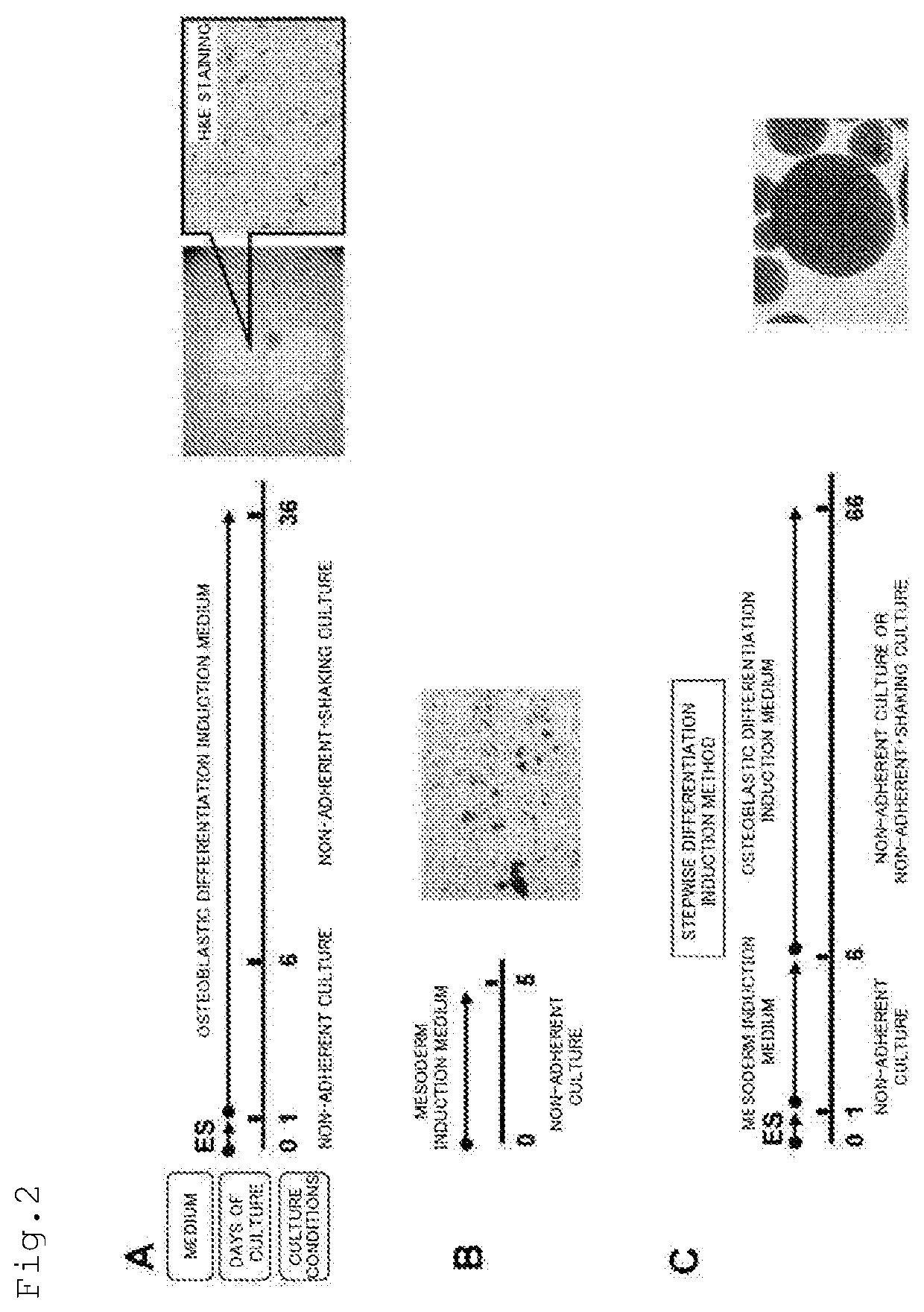
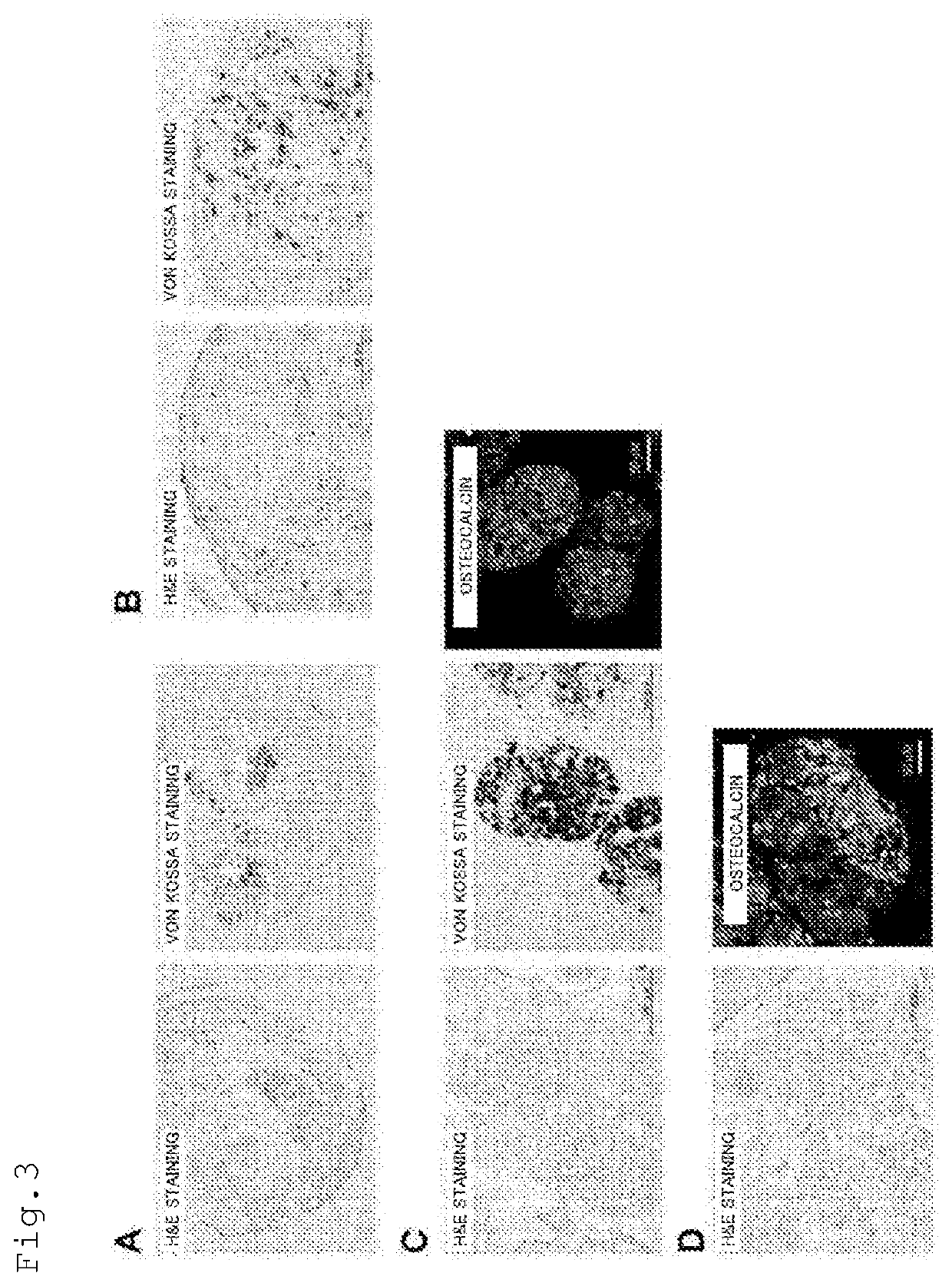
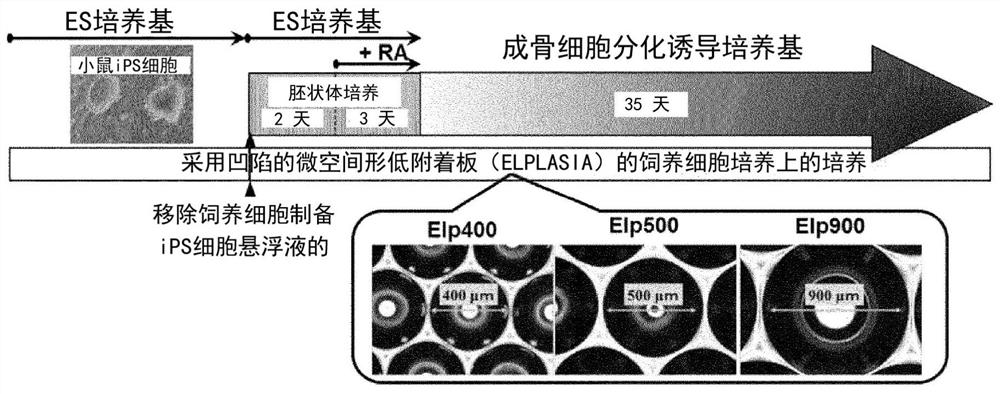
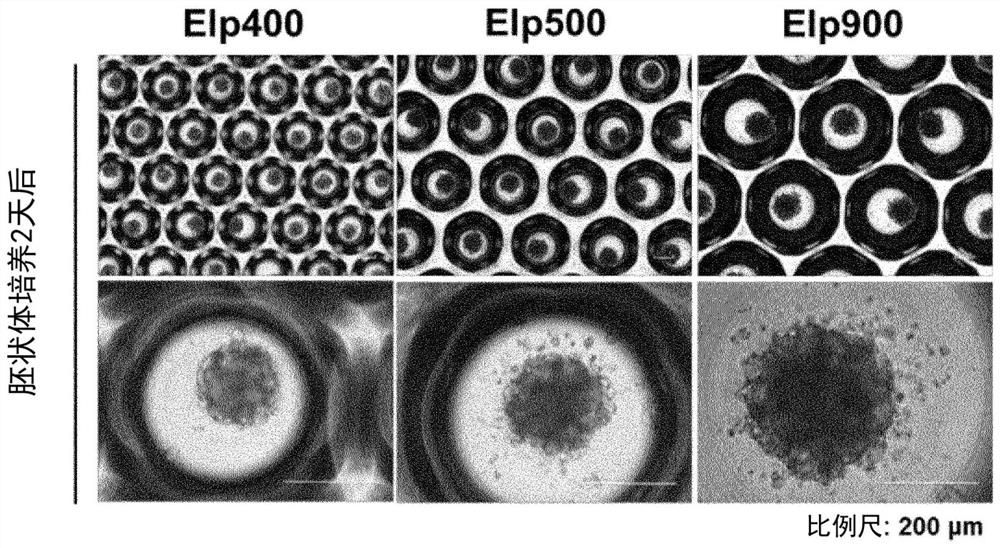
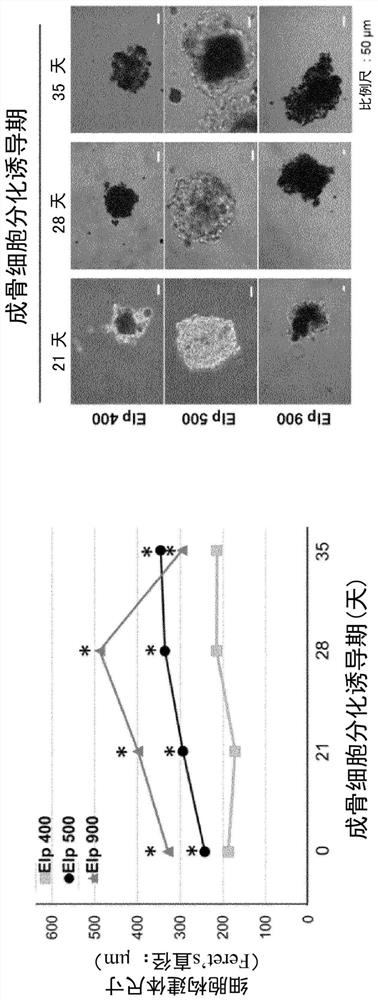
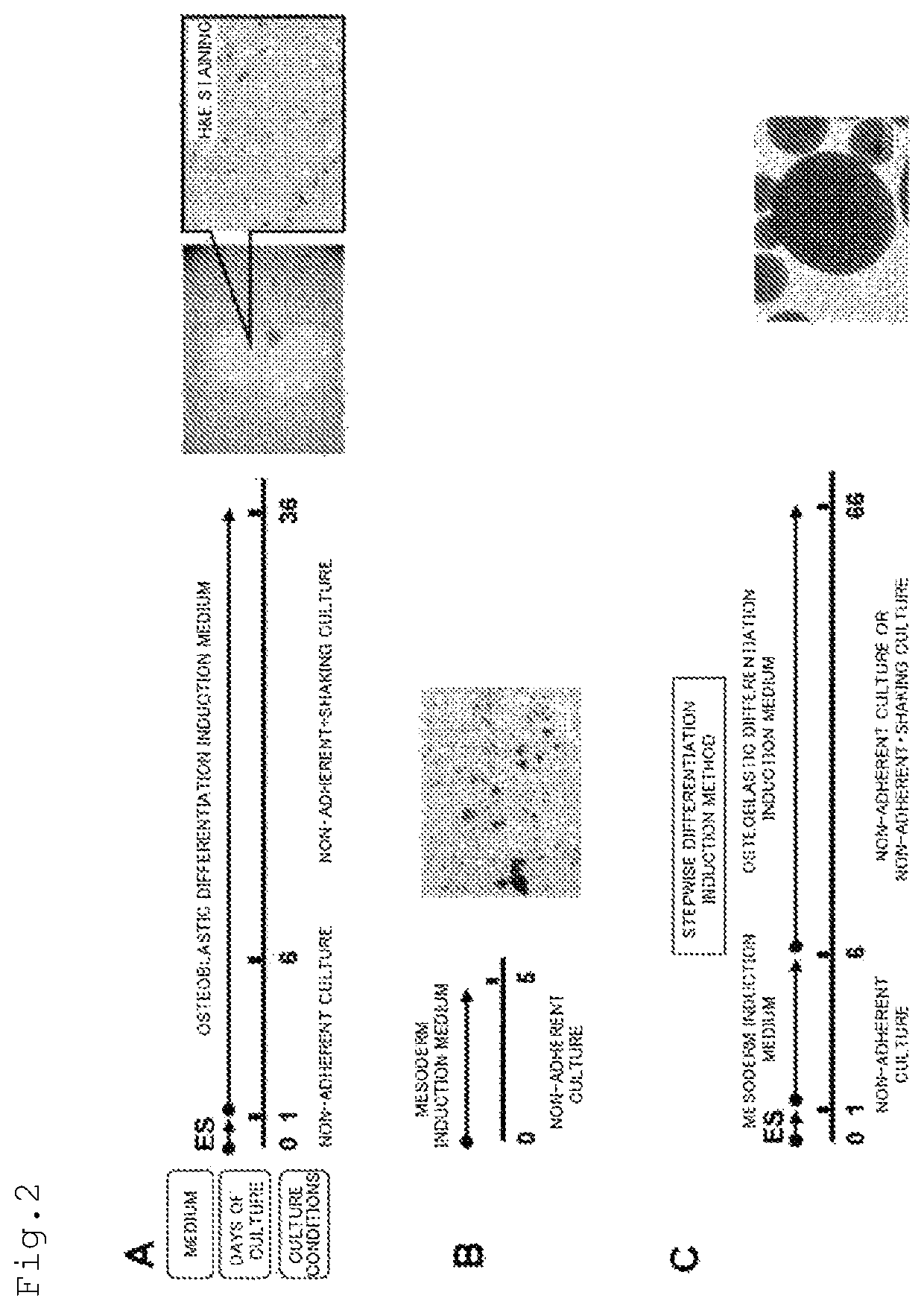
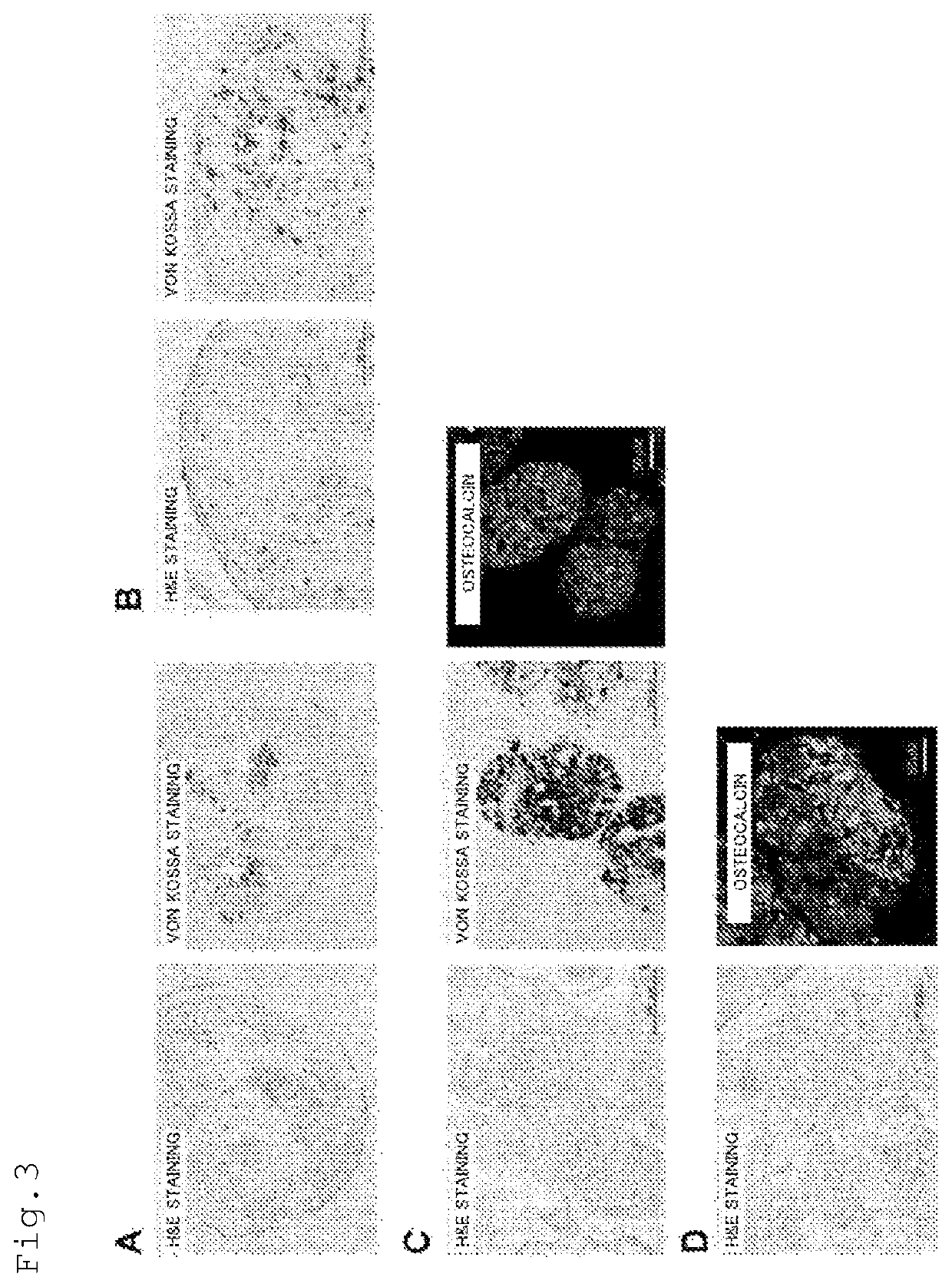
METHOD FOR PRODUCING OSTEOBLAST CLUSTER USING HUMAN iPS CELLS
The present invention provides a method of producing an osteoblast construct from human iPS cells, the method including the steps of: (1) inducing formation of an embryoid body by subjecting undifferentiated human iPS cells to non-adherent culture; (2) inducing differentiation of the human iPS cells into mesodermal cells by subjecting the embryoid body of the human iPS cells obtained in the step (1) to non-adherent culture; and (3) inducing differentiation into osteoblasts by subjecting the mesodermal cells of the human iPS cells obtained in the step (2) to non-adherent culture.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Treatment for nicotine-induced lung disease using peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists
This invention provides pertains to the discovery that that nicotine interrupts molecular signaling between endodermal and mesodermal cells of the lung alveolus. Treatment of the lung with specific molecular agents (e.g., PPAR gamma agonists) can prevent and / or reverse the injury caused by nicotine.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Method for producing osteoblast cluster using ips cells
PendingCN113728093AHigh bone regeneration capacityCulture processCell culture supports/coatingInducer CellsBiochemistry
The invention provides a method for producing an osteoblast cluster from iPS cells, said method comprising: (1) a step for inducing the formation of embryoid bodies by non-adhesively culturing undifferentiated iPS cells; (2) a step for inducing the differentiation of the iPS cells into mesodermal cells by non-adhesively culturing the embryoid bodies of the iPS cells obtained in step (1); and (3) a step for inducing the differentiation into osteoblasts by non-adhesively culturing the mesodermal cells of the iPS cells obtained in step (2), wherein the aforesaid steps (1) and (2) are carried out using a culture container which is provided with a bottom face and a circular side wall standing from the bottom face and in which a plurality of concave portions are formed in the bottom face in such a manner as to be independent from each other.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Method for producing osteoblast cluster using human iPS cells
ActiveUS11459547B2Culture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOsteoblast cell differentiationOsteoblast cell
The present invention provides a method of producing an osteoblast construct from human iPS cells, the method including the steps of: (1) inducing formation of an embryoid body by subjecting undifferentiated human iPS cells to non-adherent culture; (2) inducing differentiation of the human iPS cells into mesodermal cells by subjecting the embryoid body of the human iPS cells obtained in the step (1) to non-adherent culture; and (3) inducing differentiation into osteoblasts by subjecting the mesodermal cells of the human iPS cells obtained in the step (2) to non-adherent culture.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
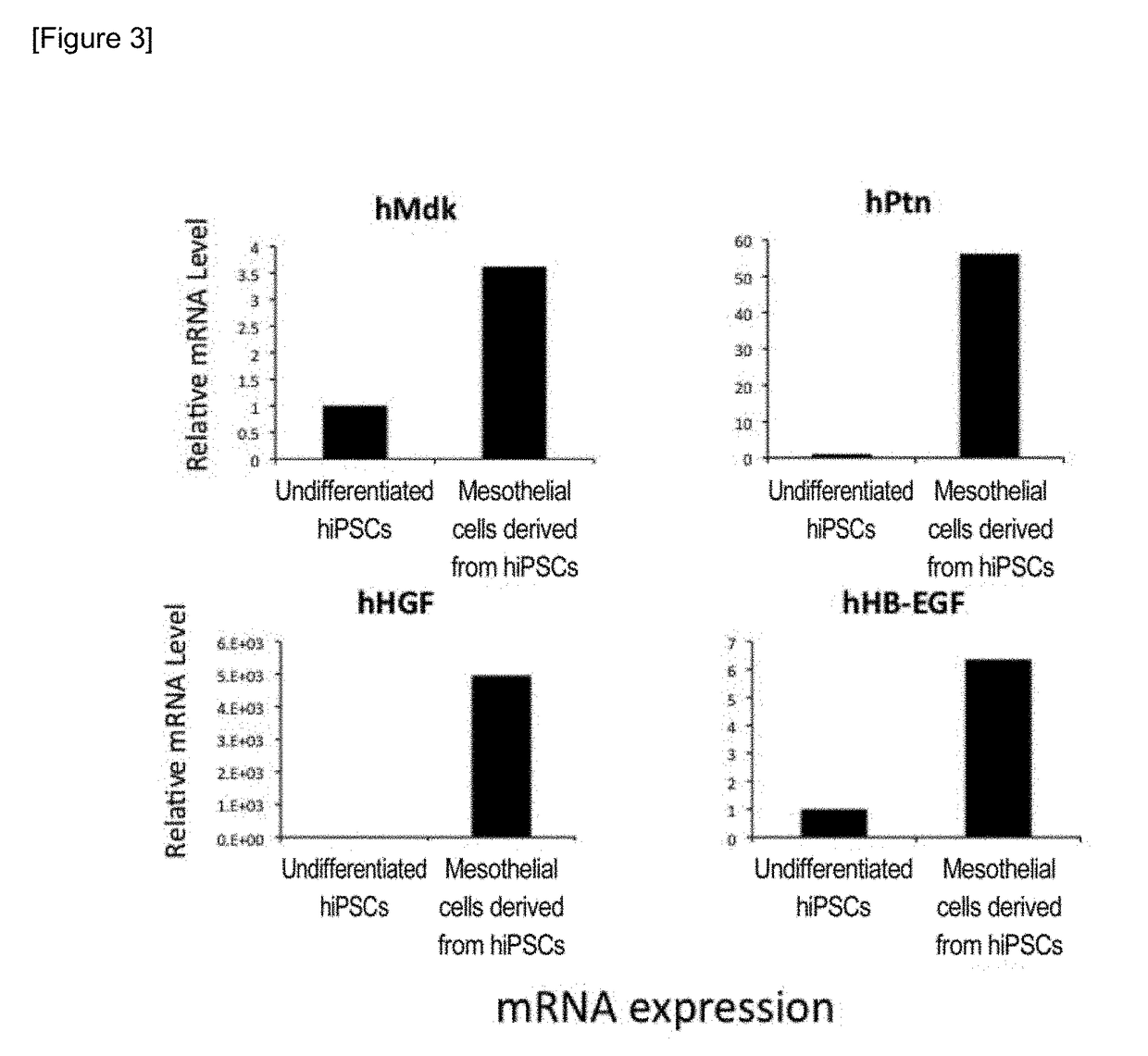
Method for producing mesothelial cells and a cell sheet for preventing adhesion
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for differentiating mesodermal cells into mesothelium cells. The present invention provides a method for producing mesothelial cells, including a first culturing step of culturing mesodermal cells in a medium containing basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and oncostatin M.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Induction of pluripotent stem cells into mesodermal lineages
InactiveUS20110306130A1Promotes commitment and survivalGenetic material ingredientsArtificial cell constructsProgenitorGerm layer
The present invention provides a method of inducing mesoderm derived cells from pluripotent stem cells. In contrast to methods known in the art that are often designed to replicate in vivo events of mesoderm induction, the present invention provides a unique, yet simple, method whereby pluripotent stem cells are mesodermally primed in the presence of factors that concomitantly inhibit the spontaneous differentiation of endoderm and ectoderm during expansion and suspension steps. Exposure and / or adherence of primed aggregates to a extracellular matrix that promotes the commitment and survival of induced mesoderm progenitors, followed by exposure to various mesoderm associated factors, allows for the subsequent induction of such cells into terminally differentiated lineages, such as cardiomyocytes. End products of this induction system will ultimately provide an unlimited source of mesoderm-derived cell types for therapeutic and pharmacological purposes.
Owner:RUDY REIL DIANE ELIZABETH
renal progenitor cells
ActiveCN105473706BMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellNephron
There is provided a method for the simultaneous production of nephron progenitor cells and ureteric epithelial progenitor cells, comprising the step of contacting intermediate mesoderm cells with fibroblast growth factor 9 and / or fibroblast growth factor 20 , and optionally one or more selected from: bone morphogenetic protein 7; heparin; Wnt agonists; retinoic acid; The concentrations of Wnt agonist, retinoic acid and / or RA antagonist can be manipulated to favor the relative production of nephron progenitor cells and ureteric epithelial progenitor cells. The intermediate mesoderm cells are ultimately derived from human pluripotent stem cells via the posterior primitive streak stage. The nephron progenitor cells and ureteric epithelial progenitor cells may have end uses such as for kidney repair and regeneration, bioprinting of kidneys, and screening of compounds for nephrotoxicity.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Method for determining undifferentiated state of pluripotent stem cell, method for subculturing pluripotent stem cell, and device for use in said methods
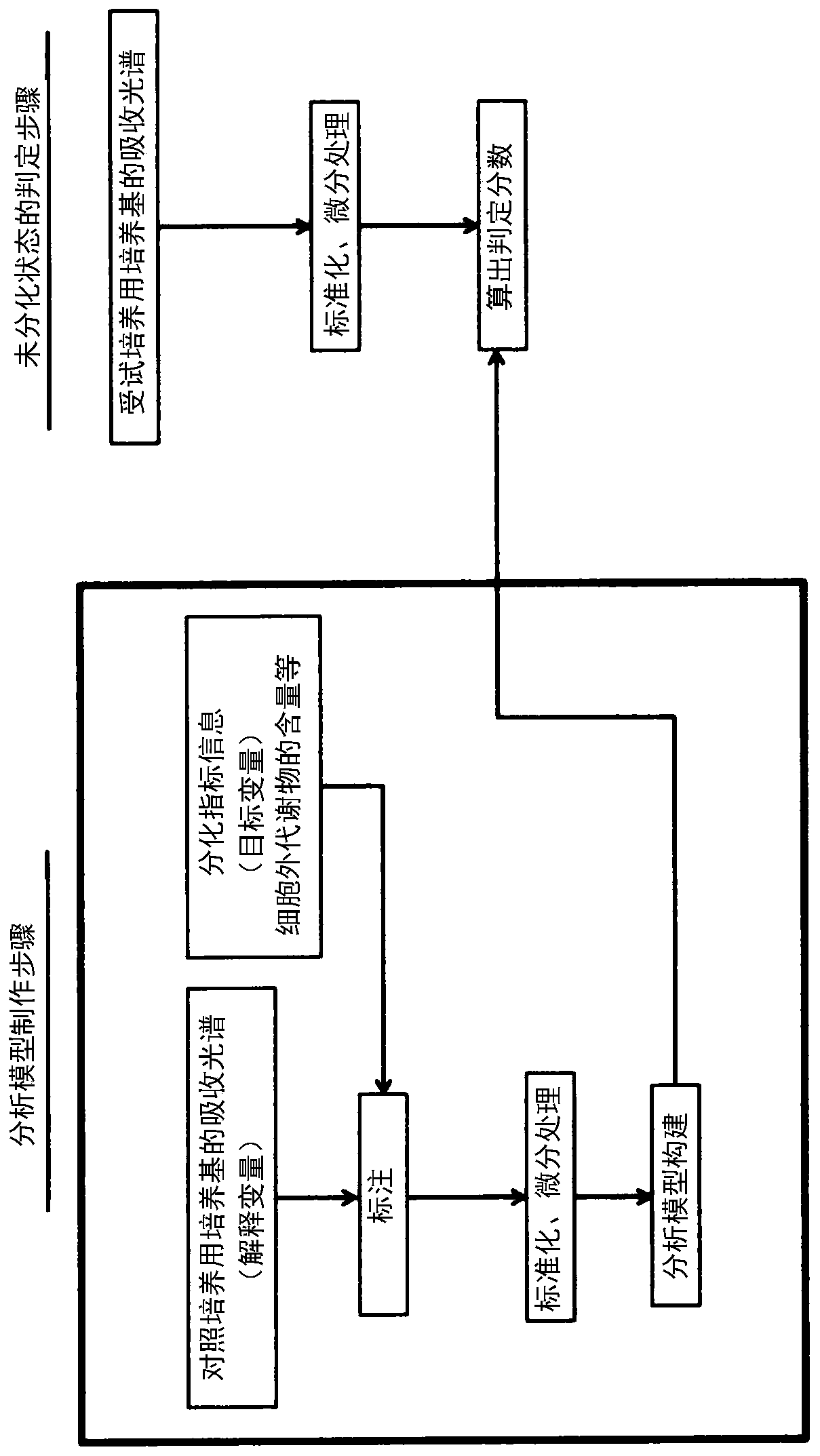
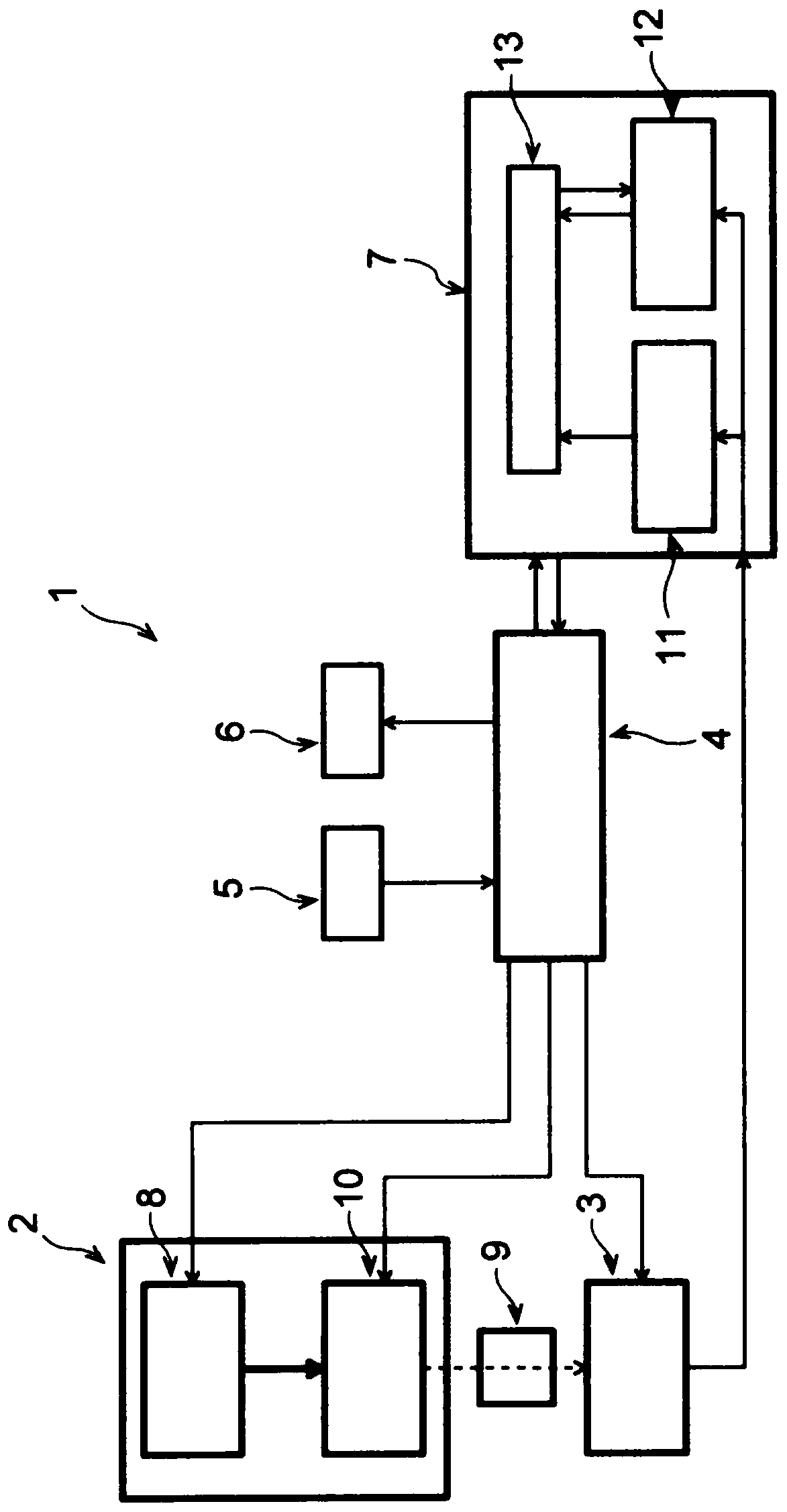
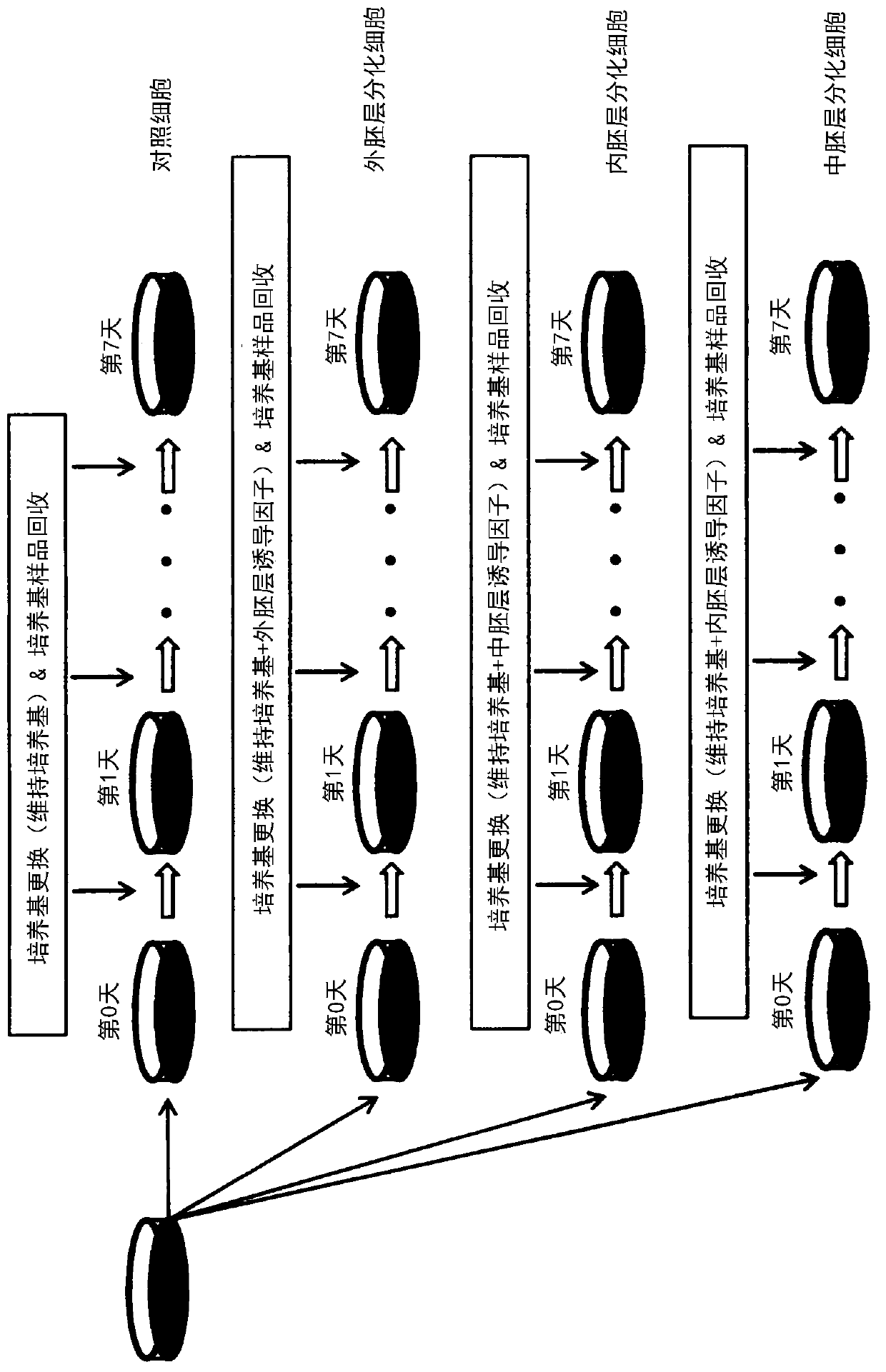
ActiveCN110997928AEasy to judgeQuick and high-precision judgmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGerm layerAbsorbance
The present disclosure provides a method for determining the undifferentiated state of a pluripotent stem cell, the method comprising irradiating a culture medium being tested in which the pluripotentstem cell is cultured, with light having wavelengths in all or a part of the range of 190-2500 nm, detecting reflected light, transmitted light, or transmitted and reflected light thereof to obtain absorbance spectral data, and analyzing the absorbances in all or in a partial range of the measured wavelengths of the absorbance spectral data, on the basis of an analysis model which is previously created using a plurality of types of control culture media used in culturing the pluripotent stem cell, to determine the undifferentiated state of the pluripotent stem cell, wherein the plurality of types of control culture media include one or more differentiation-inducing media selected from a medium used in maintaining the undifferentiated state of the pluripotent stem cell, a medium for inducing differentiation to an ectodermal cell, a medium for inducing differentiation to a mesodermal cell, and a medium for inducing differentiation to an endodermal cell.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com