Patents
Literature
33 results about "Muscle belly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
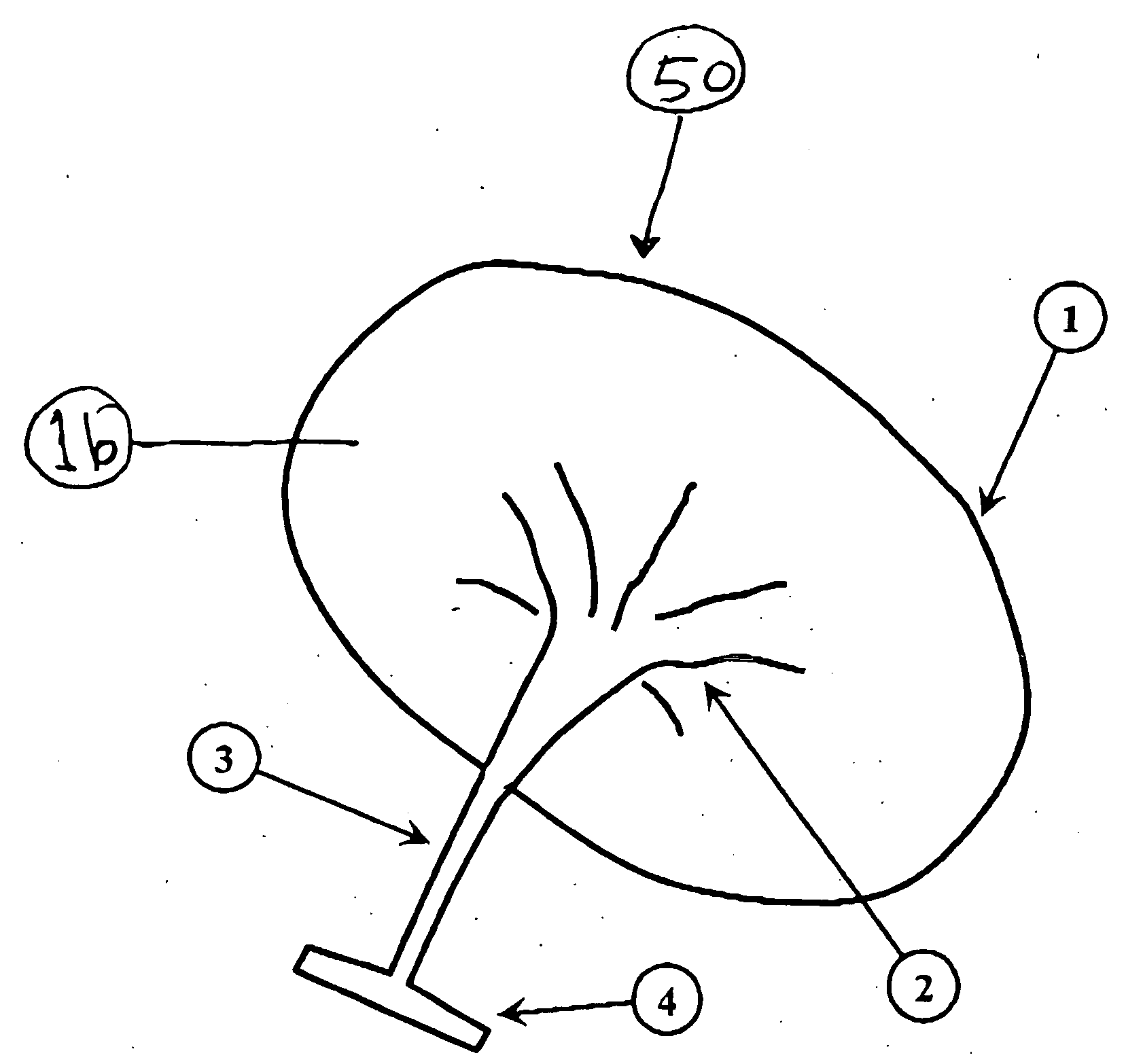
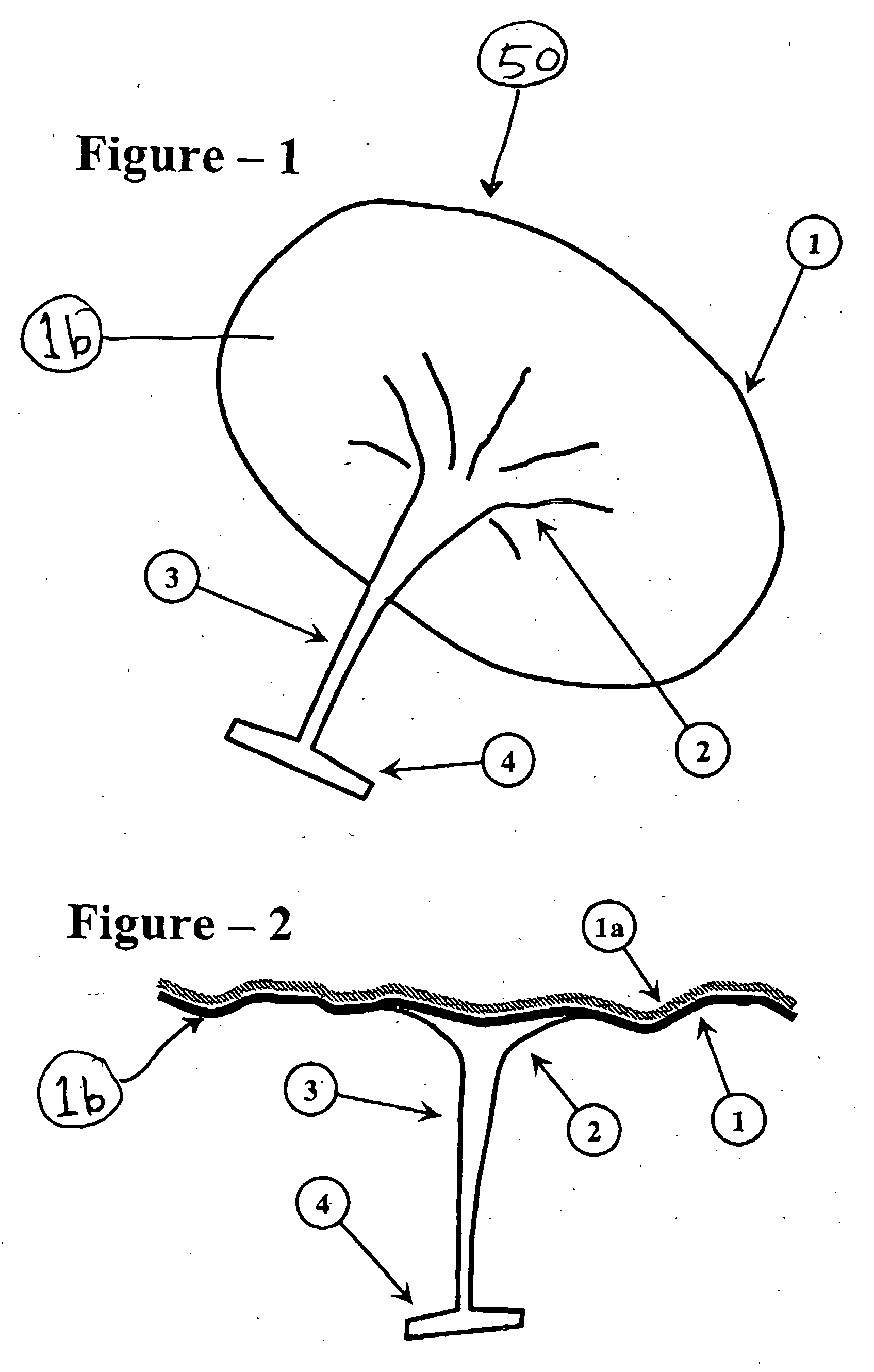
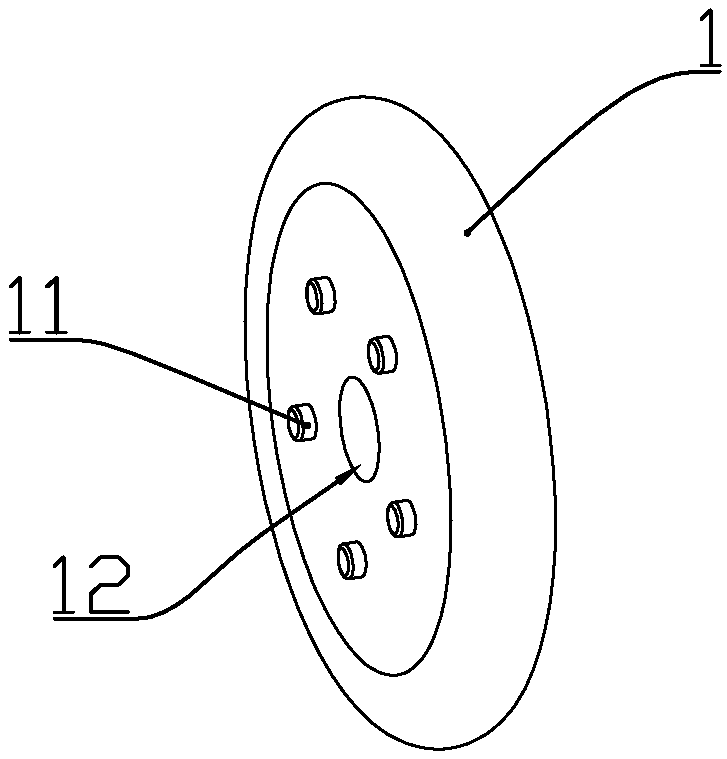
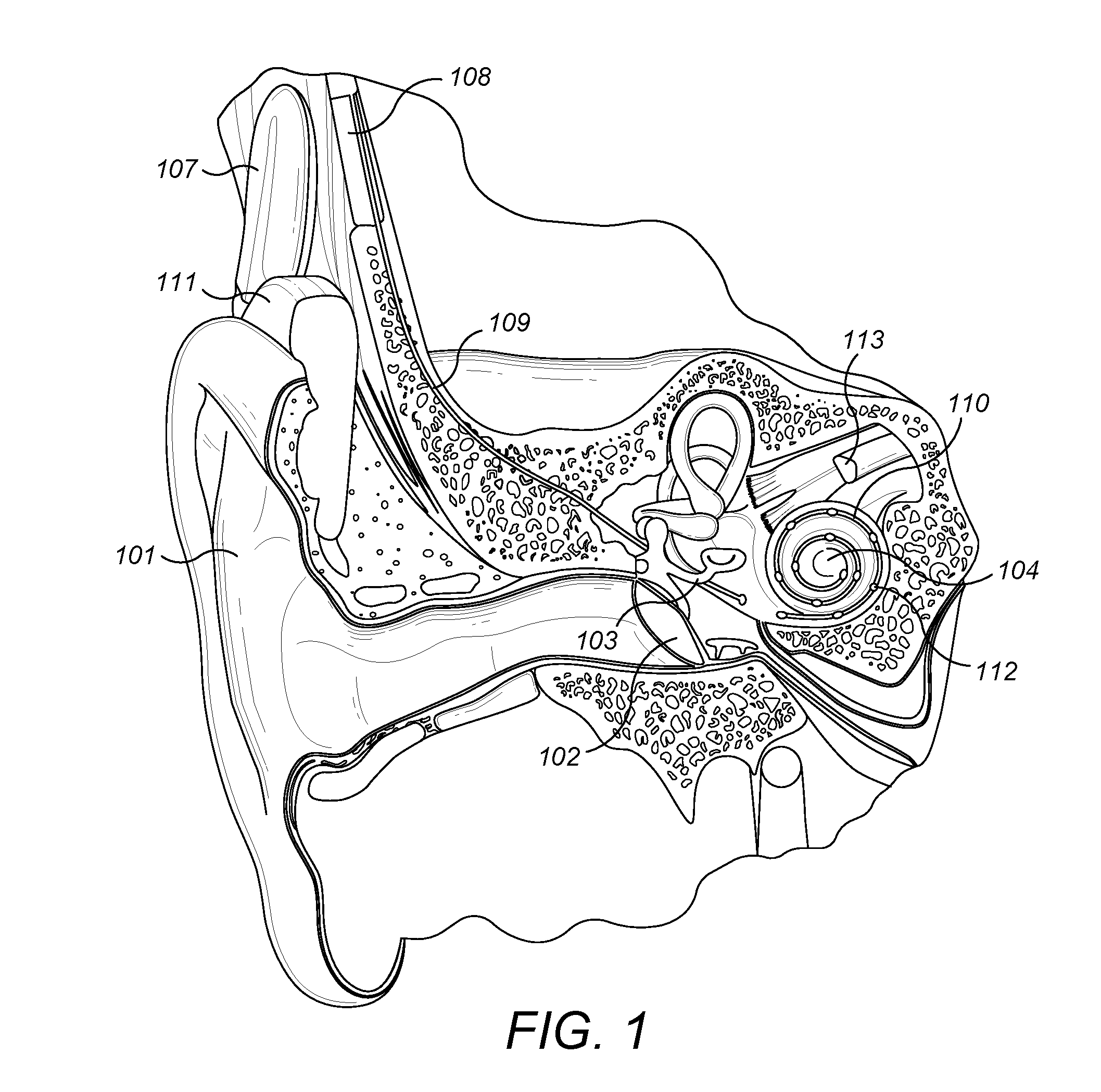
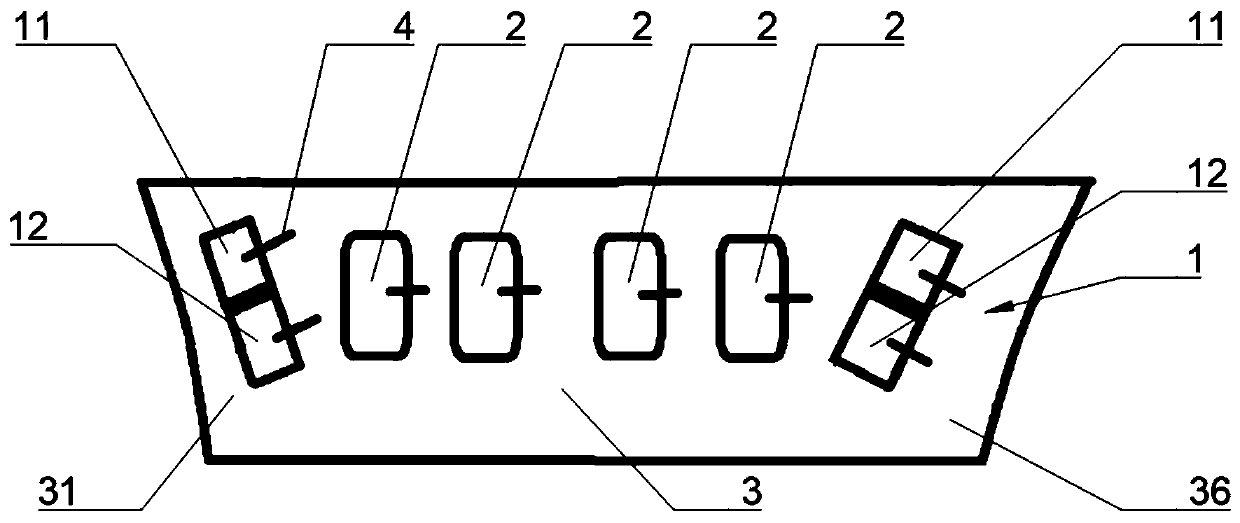
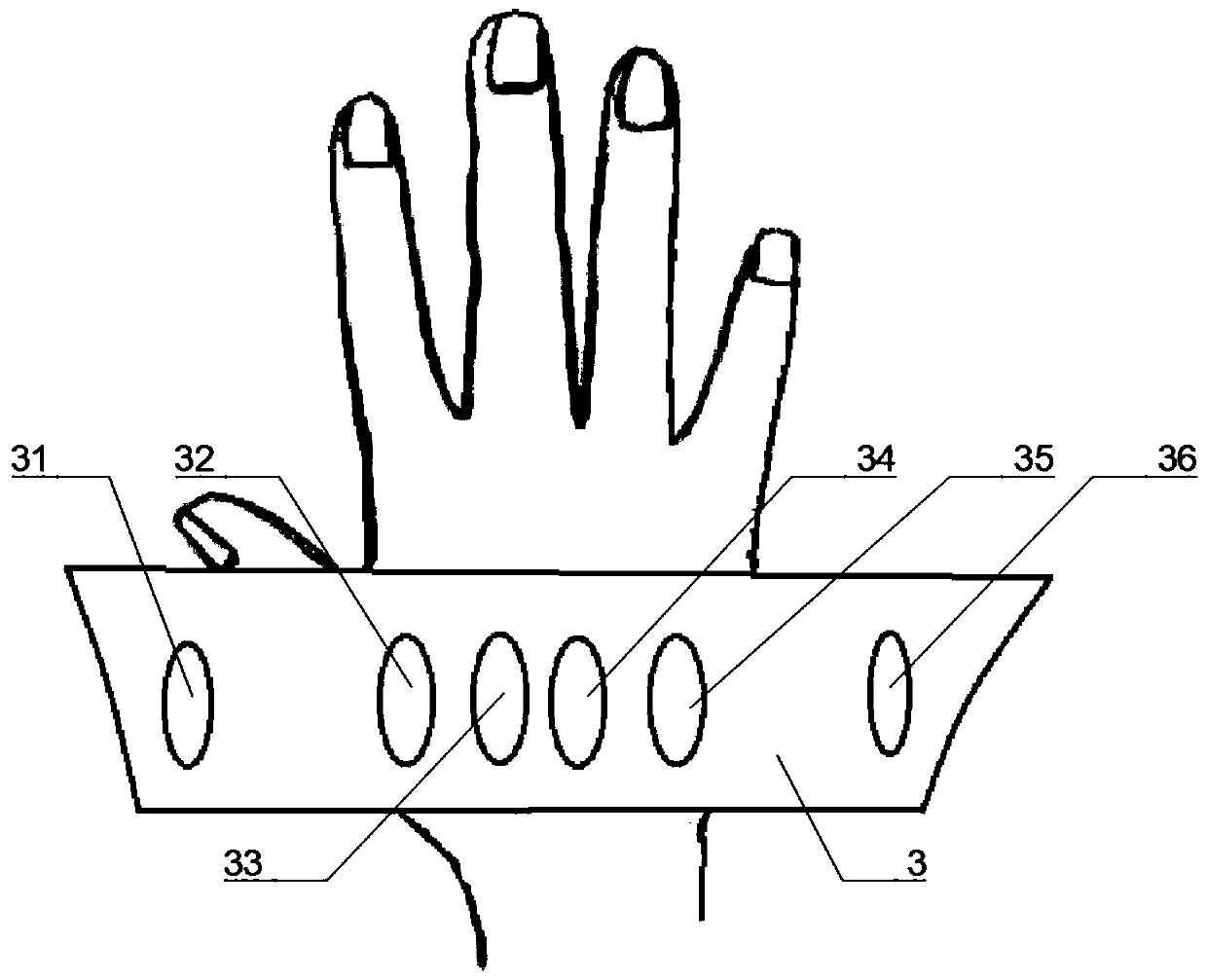
Region of organ component of muscle betwen the head of muscle and distal part of muscle.
Method and apparatus for stimulating the lower back and abdominal muscles
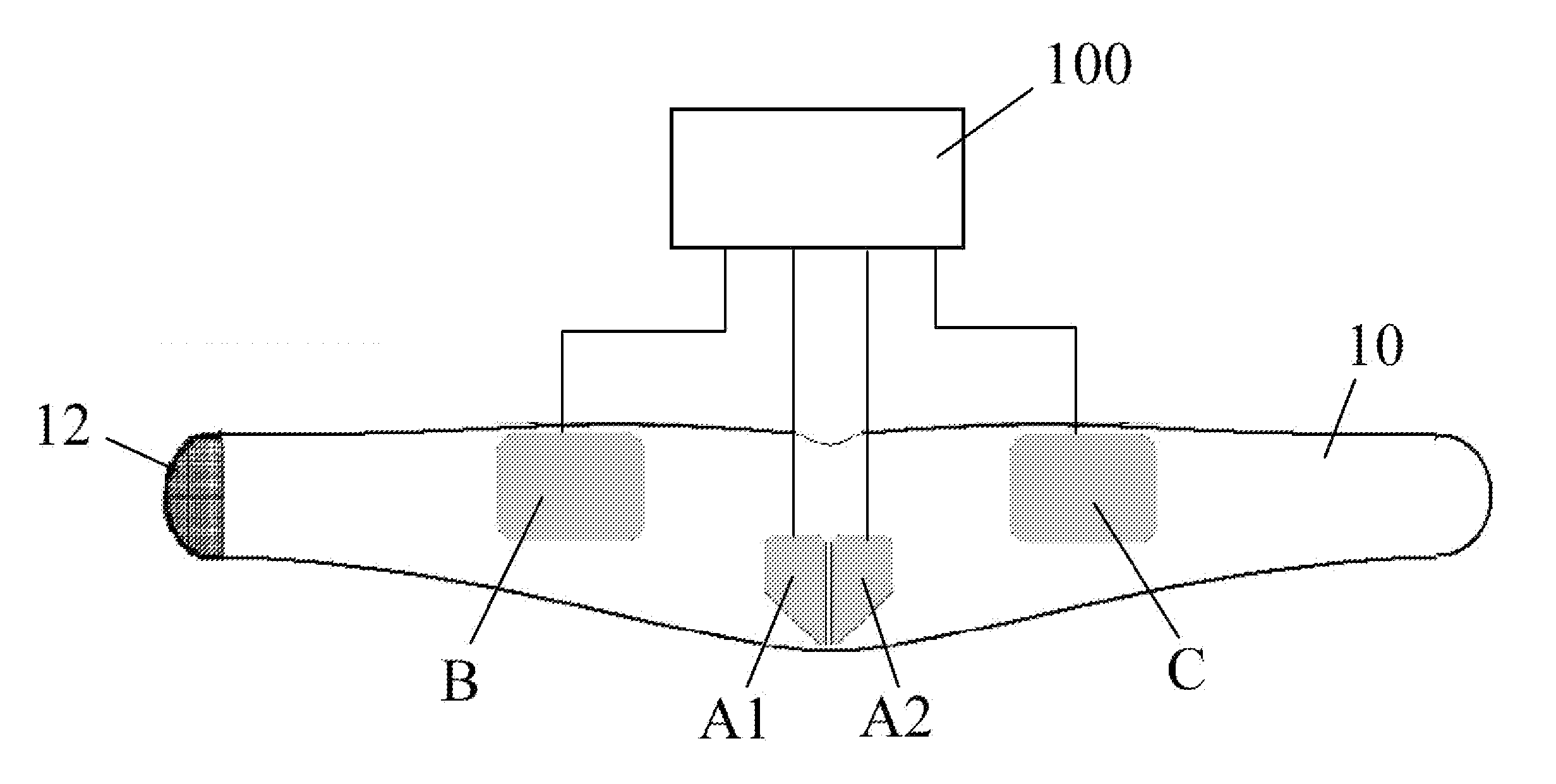
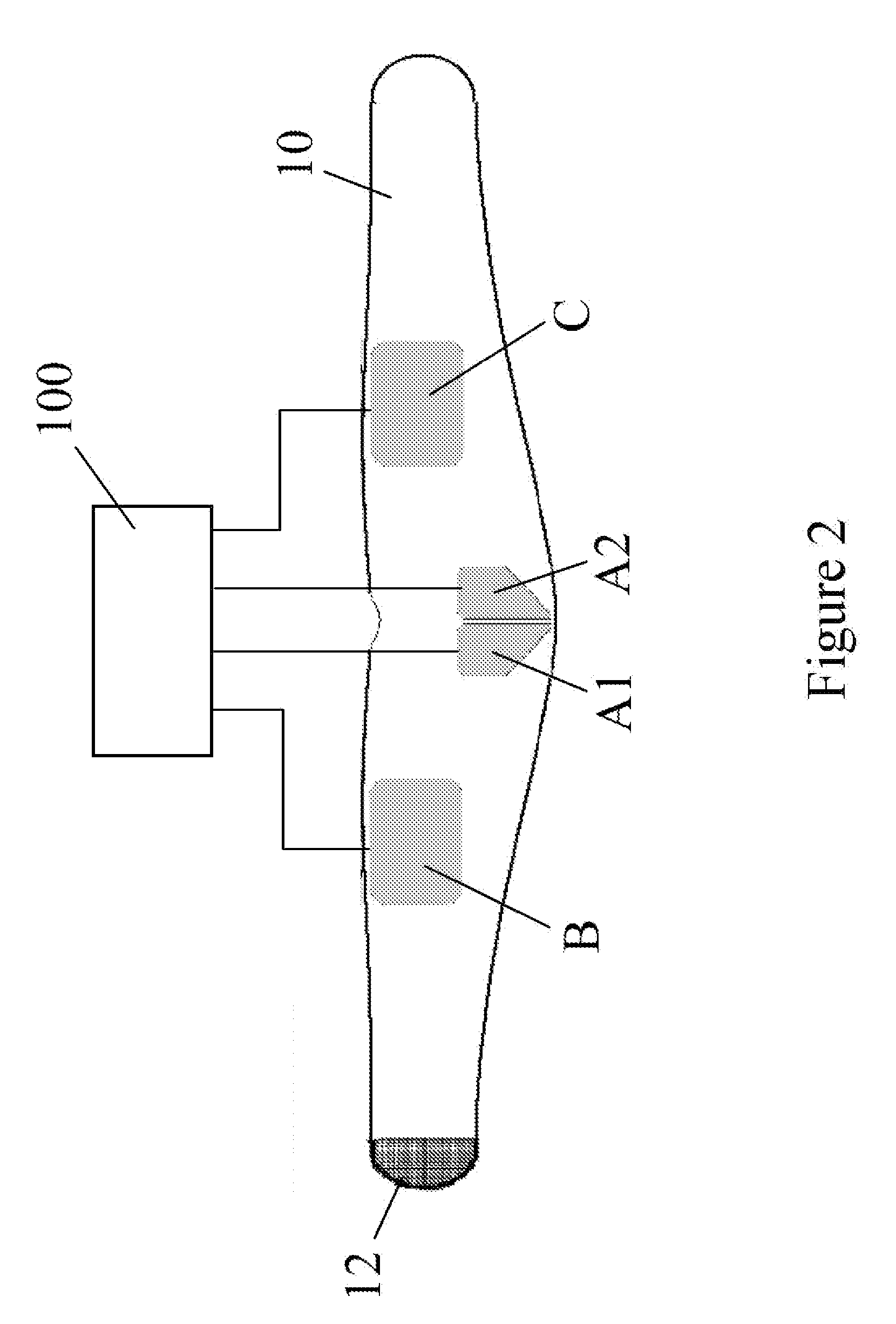
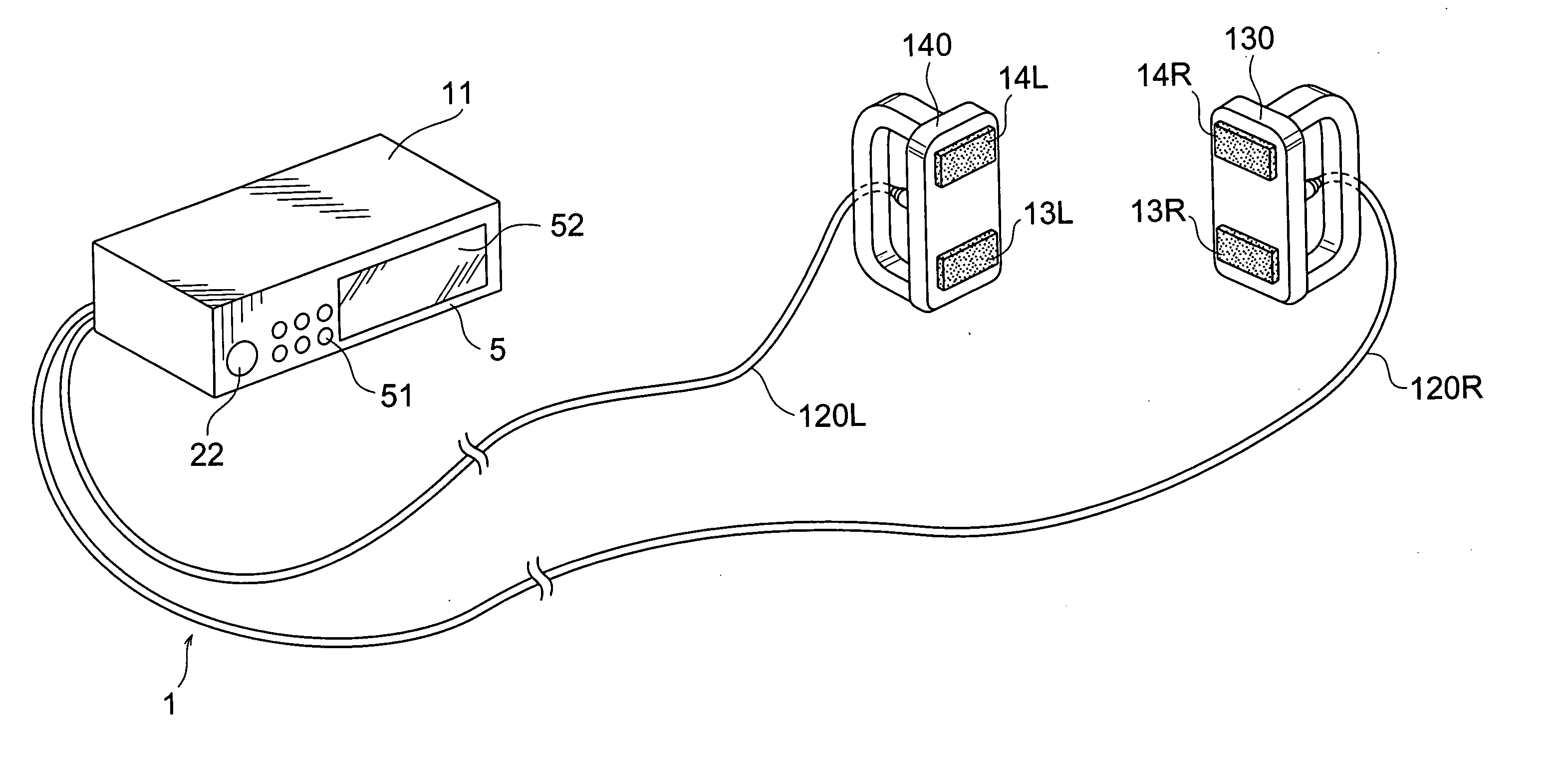
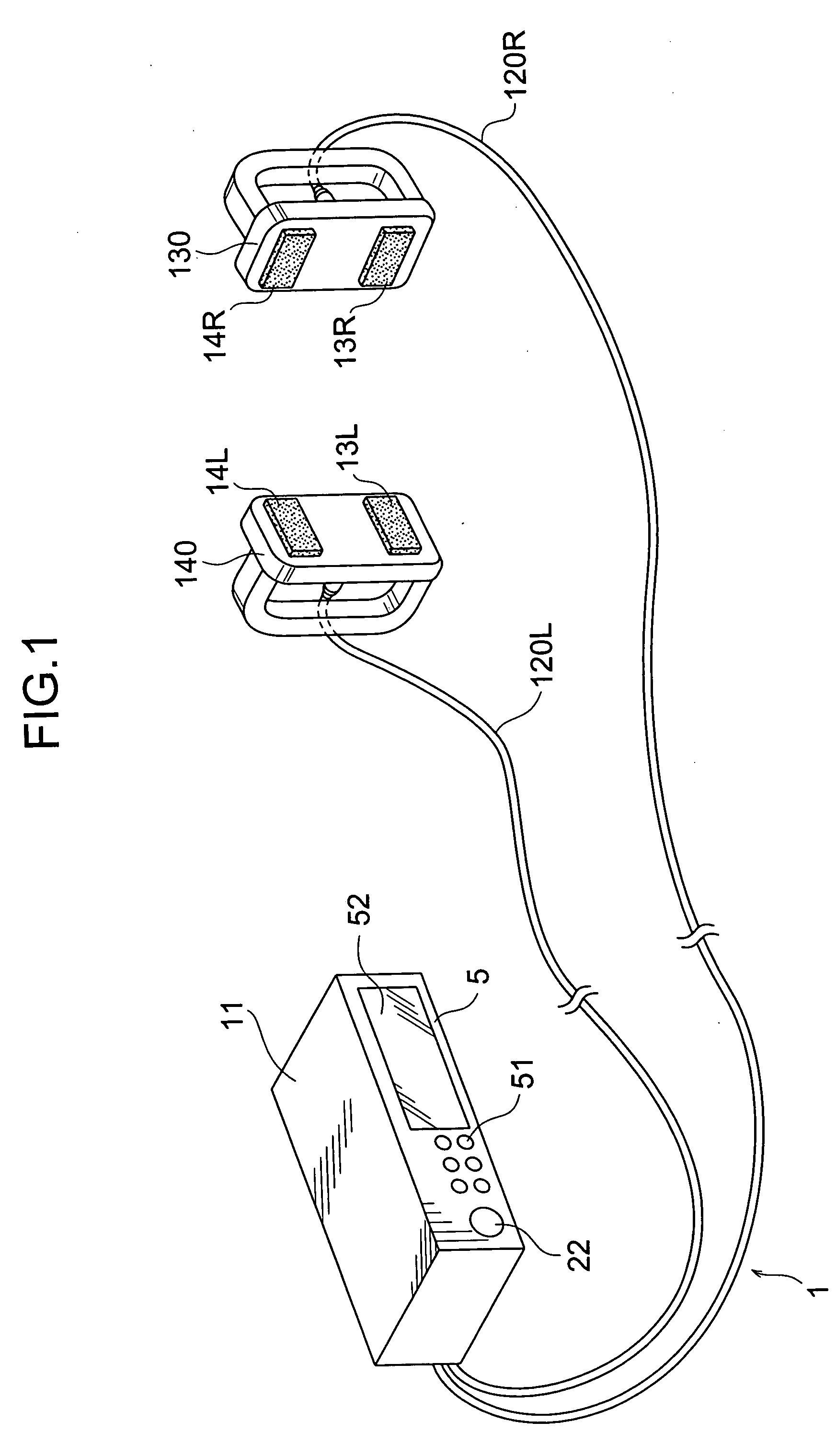
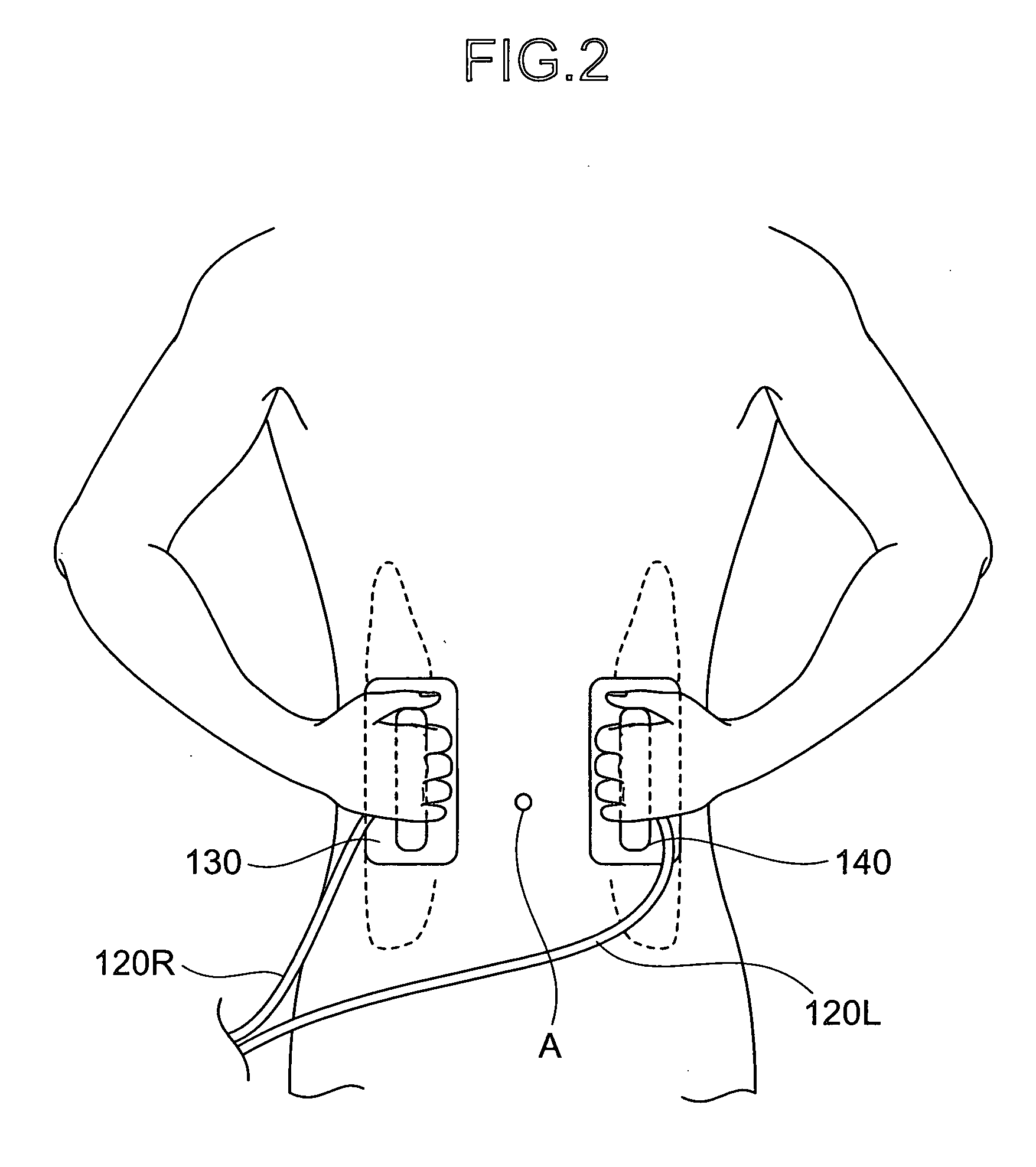
A method and apparatus for stimulating the lower back and abdominal muscles in a patient comprising applying a first electrode A1 / A2 substantially centrally to the lower lumbar region of the patient's body, and applying second and third electrodes B, C respectively to opposite side flanks of the patient's body. The electrodes are energised to apply a first group of muscular stimulation current pulses which flow between the second and third electrodes and a second group of muscular stimulation current pulses which flow between the first electrode and the second and third electrodes alternately.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE DUBLIN NAT UNIV OF IRELAND DUBLIN +1
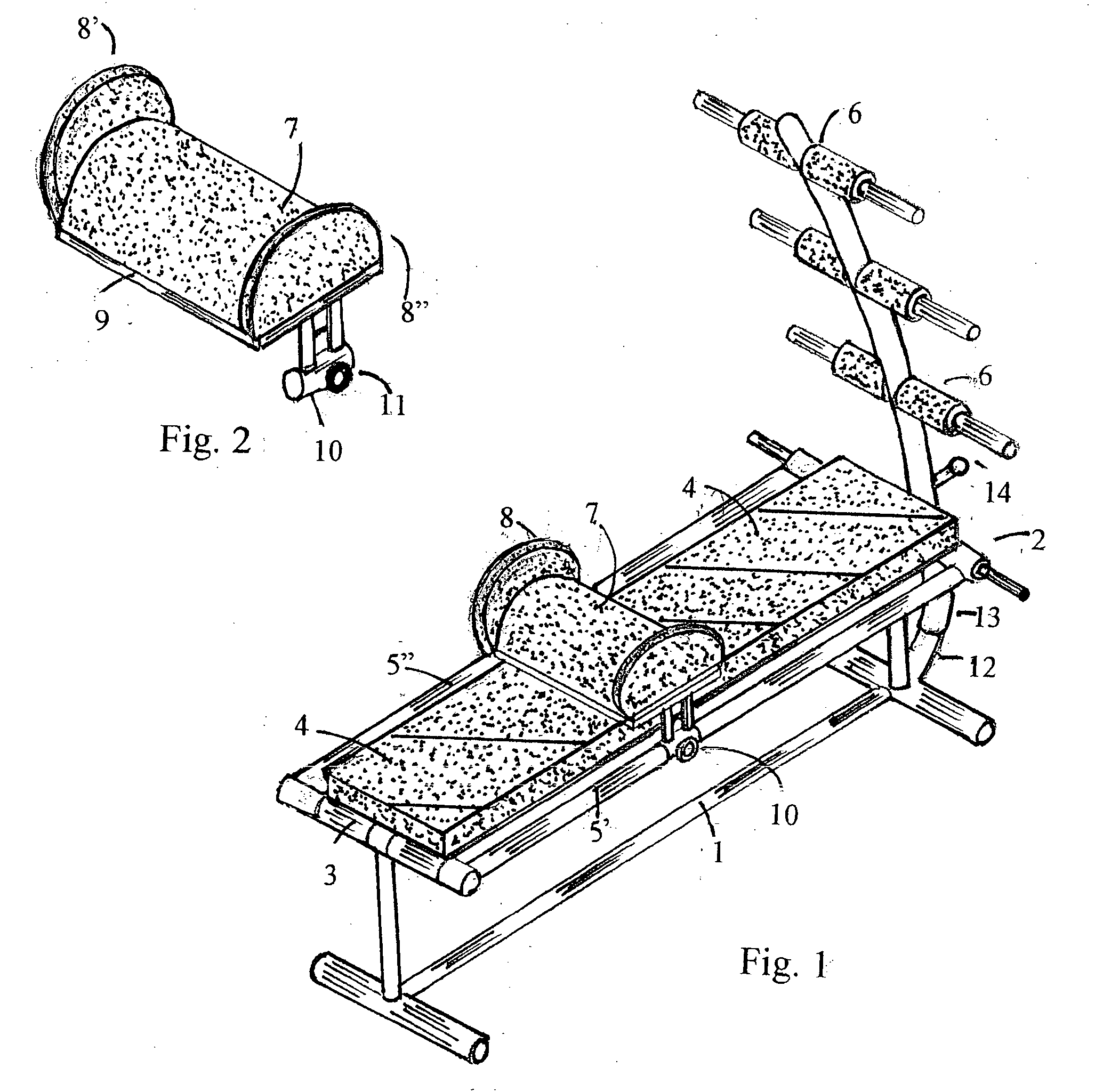
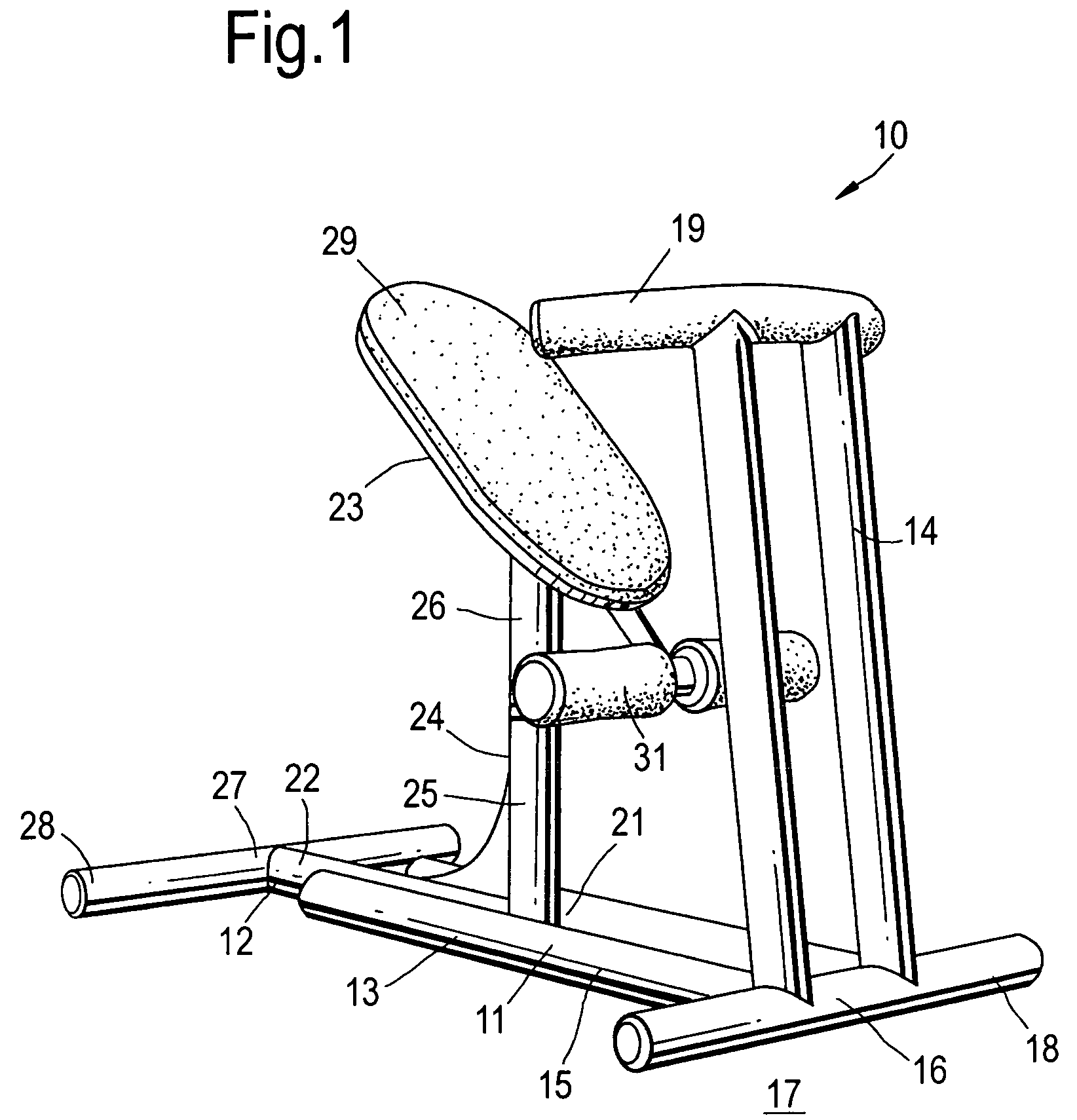
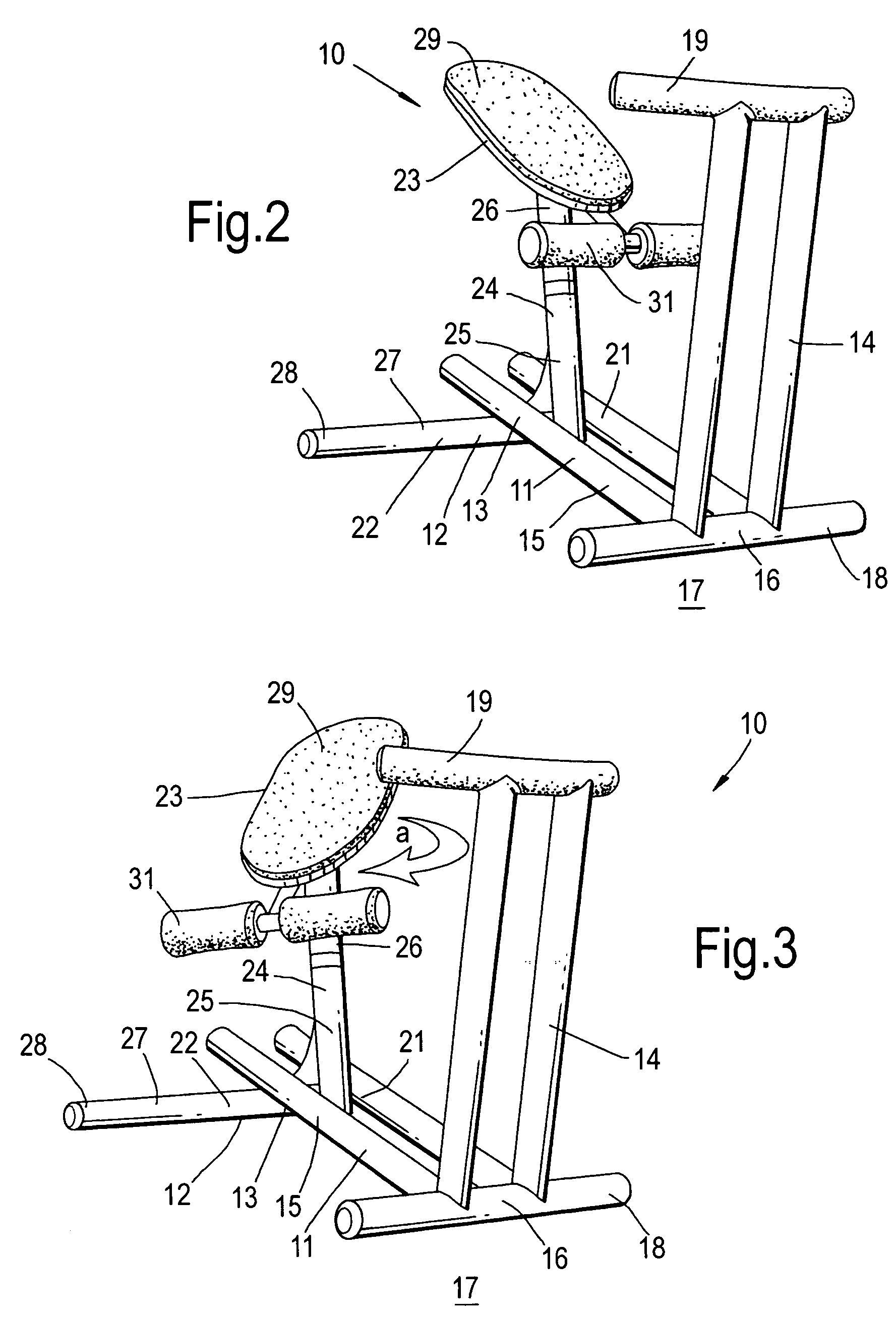
Biodynamic apparatus for performing correct SIT-UP and LEGS-UP exercises and methods
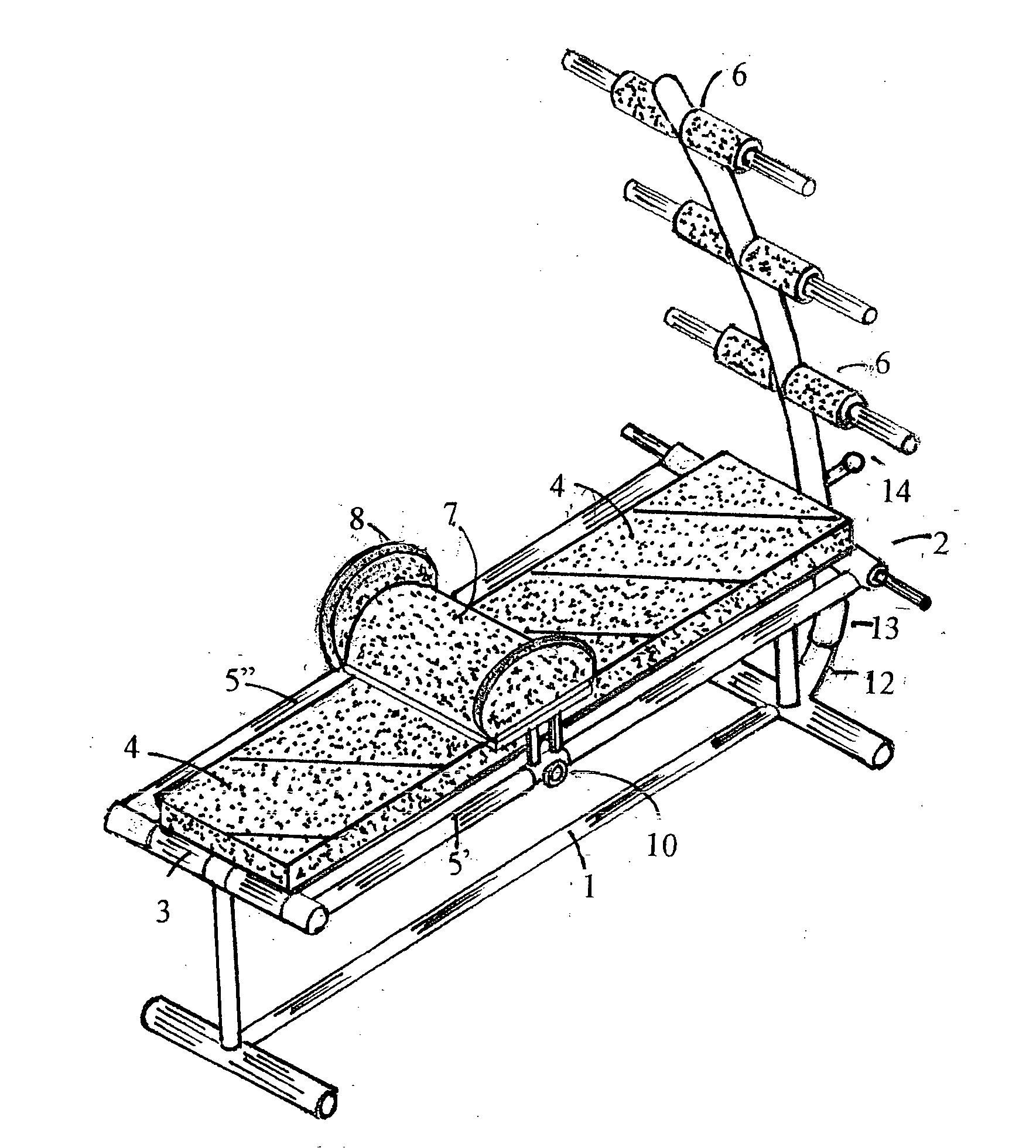
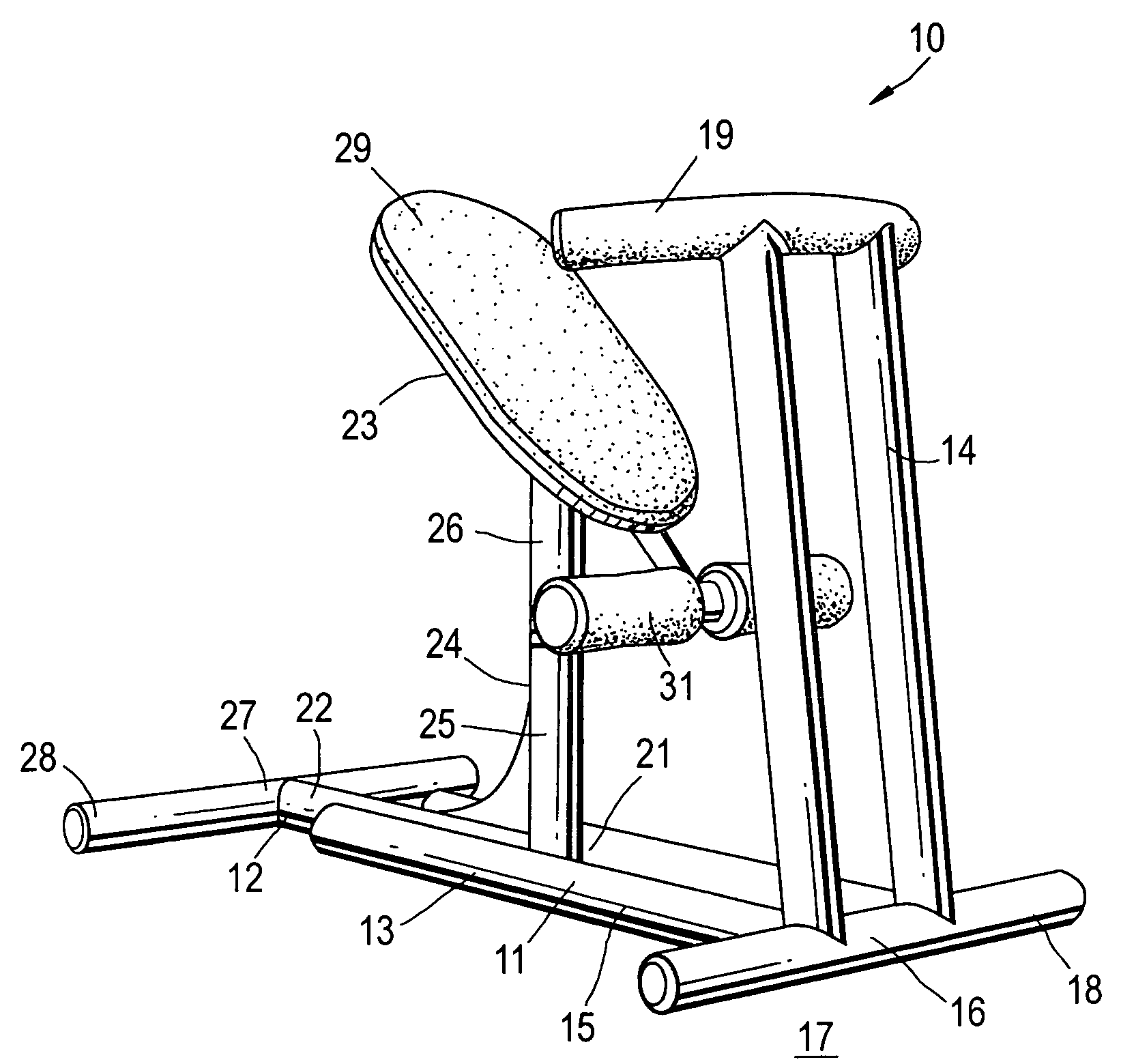
A biodynamic apparatus to perform correct, safe and effective SIT-UP and LEGS-UP exercises and simultaneously perform spinal arching, spinal decompression, and flexibility exercises, comprising of two part frame hinged at one end and a set of parallel bars that elevate and anchor the legs of the user concentrating the exercise in the abdominal area of the body. The main feature of the apparatus is provided by a device the inventor calls “flexor”. The flexor is not an ordinary lumbar support. Its function is to meet the natural fulcrum of the human torso, which is below the sacrum, to safely and efficiently articulate. Most exerciser bend the spine during the exercise, rather than the pelvis putting a tremendous negative stress on the vertebra and on the intervertebral discs. With the help of the “Flexor” the torso can move from horizontal to at least 90 degrees angle as one straight piece, free from the gravitational stress produced on the spine, especially on the cervical vertebra, by the weight of the head during the initiation of the exercises. It is a fact that ordinary SIT-UP and LEGS-UP exercises the work is performed for the most part by the neck, back and lumbar muscles during the first part of the movement placing a dangerous negative stress on the spine, and especially on the spinal cord. With the use of this apparatus, the reverse can be observed. The user by lying on the “flexor” places in traction the entire set of abdominal, pectoral and neck muscles creating a direct line of force between the abdomen and the head. The spine is arched and decompressed, the abdominal muscles are in traction and the lumbar muscles are neutralized since there are bent beyond their working point. This position of the body allows to safely concentrate 100% the force on the abdominal muscles to initiate the primary work constituted by the lifting of head of the user, instead of the neck, and on the lumbar muscles of the user, as well as to protect the spine and the weak abdominal muscles from negative stress and subsequent short and long term injuries. Decompression, arching, and flexibility of the spine, being achieved during this new method of performing SIT-UP and LEGS-UP exercises, simultaneously, make this apparatus bio-dynamically correct, as far as distribution, compensation and equalization of stresses; meet the scientific principles of muscle dynamics of traction and contraction; protect the spine from negative stress, especially the weak cervical and lumbar areas; maintain and enhance the spine's integrity and flexibility; and obtain maximum abdominal muscle developments, which are the major benefits of this invention. The flexor is mounted on two external parallel railing as to adjust to the length of all users. It also has an internal adjustable mechanism that allows its two padded flanges to adjust in width to accommodate all waist sizes of users for additional support and prevention of lateral stress to the lower spine.
Owner:PANDOZY RAFFAELE MARTINI
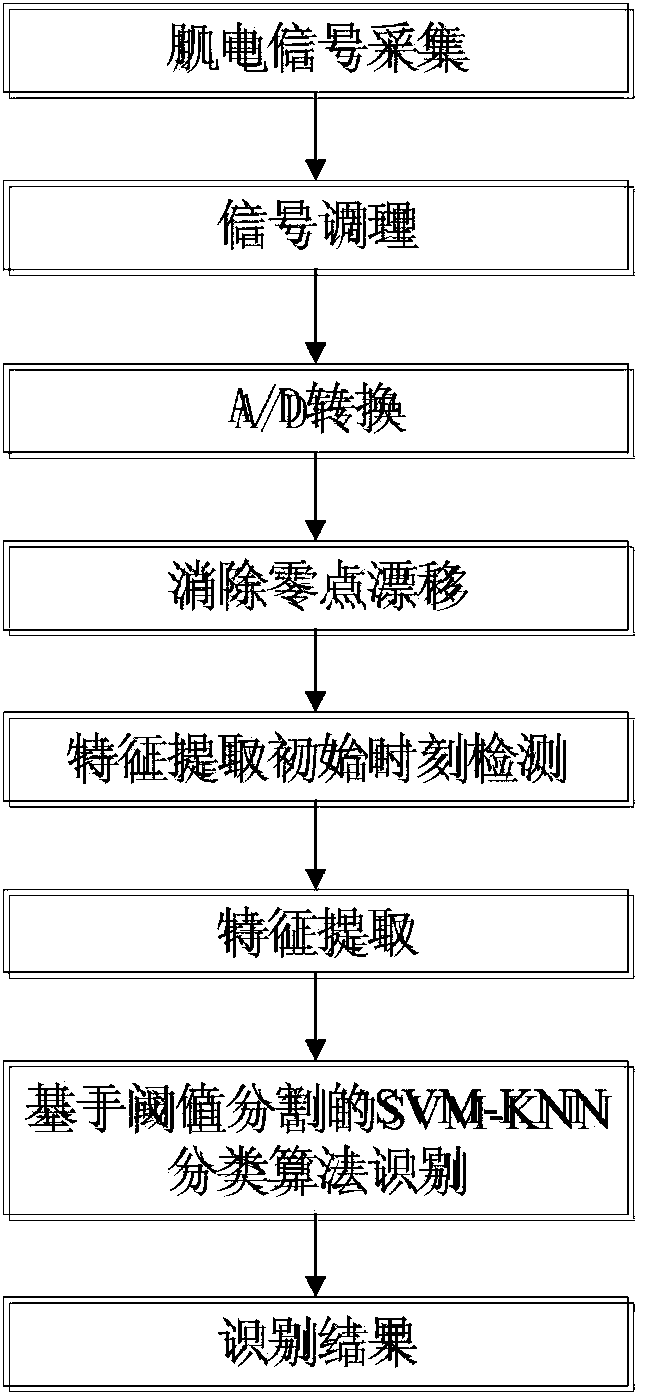
Exoskeleton walking mode identification method based on electromyographic signals
ActiveCN103984962AReduce usageGuaranteed real-timeCharacter and pattern recognitionMicrocomputerFiber
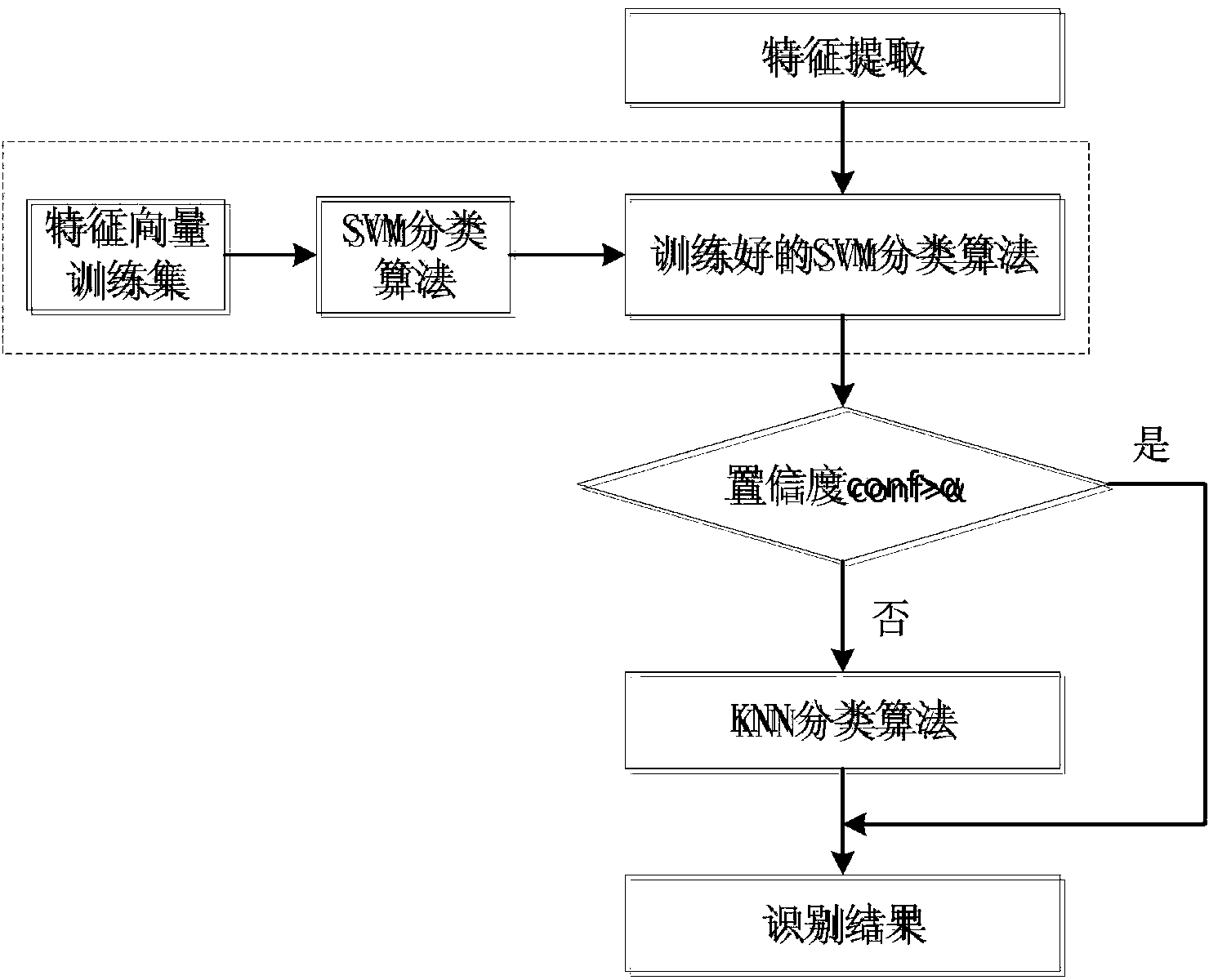
The invention relates to an exoskeleton walking mode identification method based on electromyographic signals. The exoskeleton walking mode identification method based on the electromyographic signal comprises the steps of (1) electromyographic signal collection, wherein an electromyographic electrode is attached to the muscle belly along the selected muscle group muscle fibers, an electromyographic signal sensor is connected with the electromyographic electrode through an electrode buckle, and a single-chip microcomputer fixed to the exoskeleton is connected with the electromyographic signal sensor through a wire and used for collecting the electromyographic signals; (2) electromyographic signal conditioning, wherein after the step (1), surface electromyographic signals collected by the electromyographic electrode are input to the electromyographic signal sensor for signal conditioning; (3) exoskeleton walking mode identification through an SVM-KNN classification algorithm based on threshold segmentation, wherein the surface electromyographic signals processed in the step (2) are input to the single-chip microcomputer for A / D conversion, preprocessing for elimination of zero drift, detection feature extraction initial time, feature extraction and classification through the SVM-KNN classification algorithm based on threshold segmentation, and finally the exoskeleton walking mode is identified.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
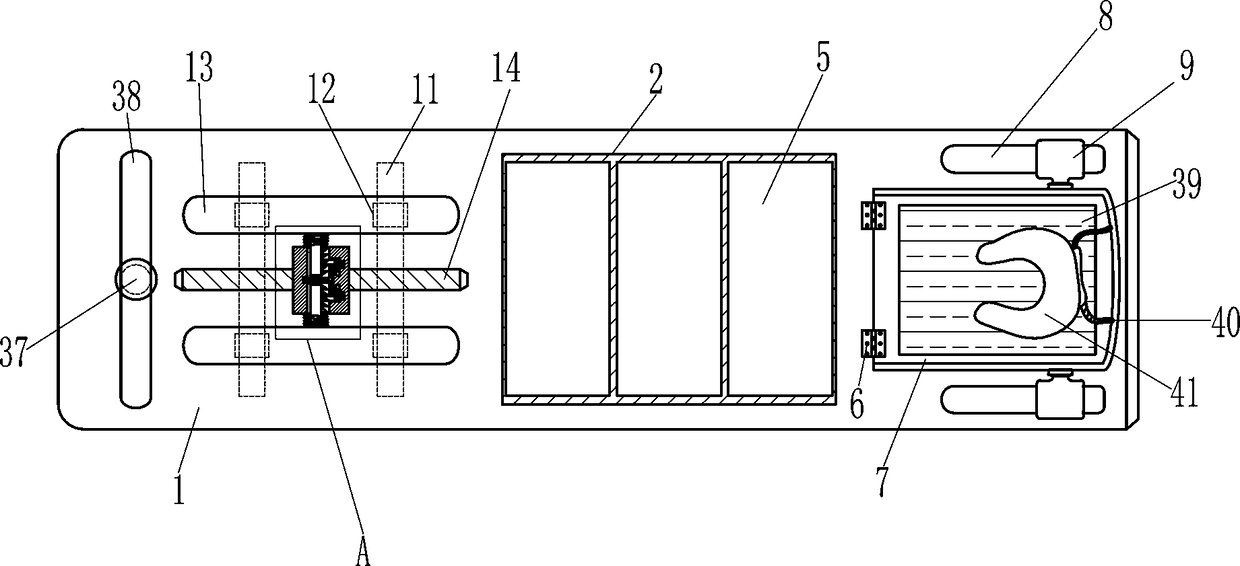
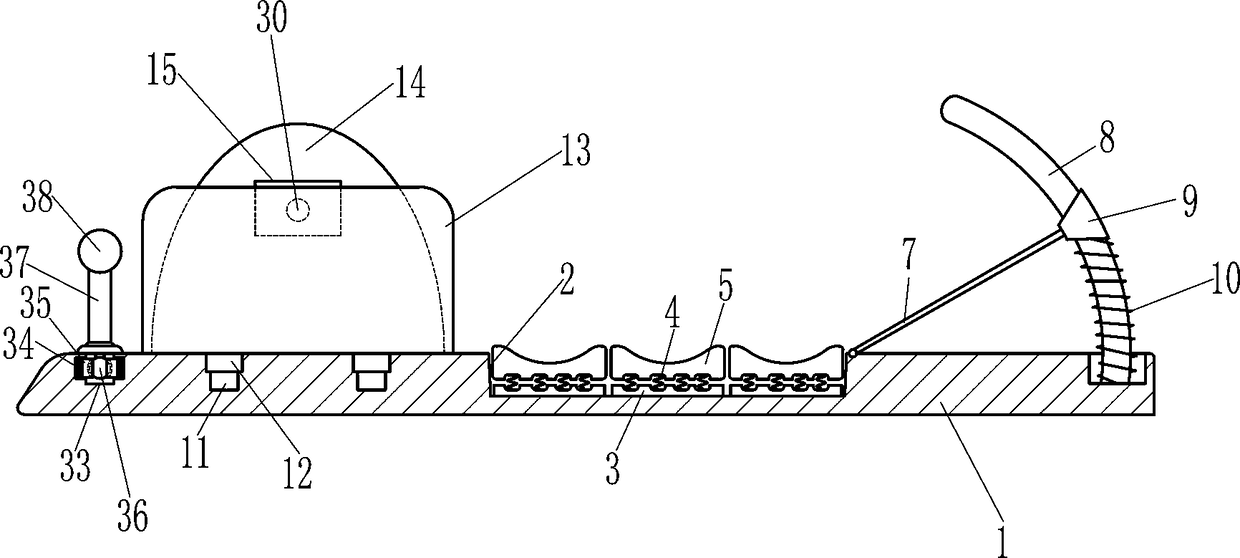
Apparatus and methods for abdominal muscle and gluteal muscle exercise
InactiveUS7137933B2Easy portabilityEasy to storeResilient force resistorsStiltsEngineeringFixed position
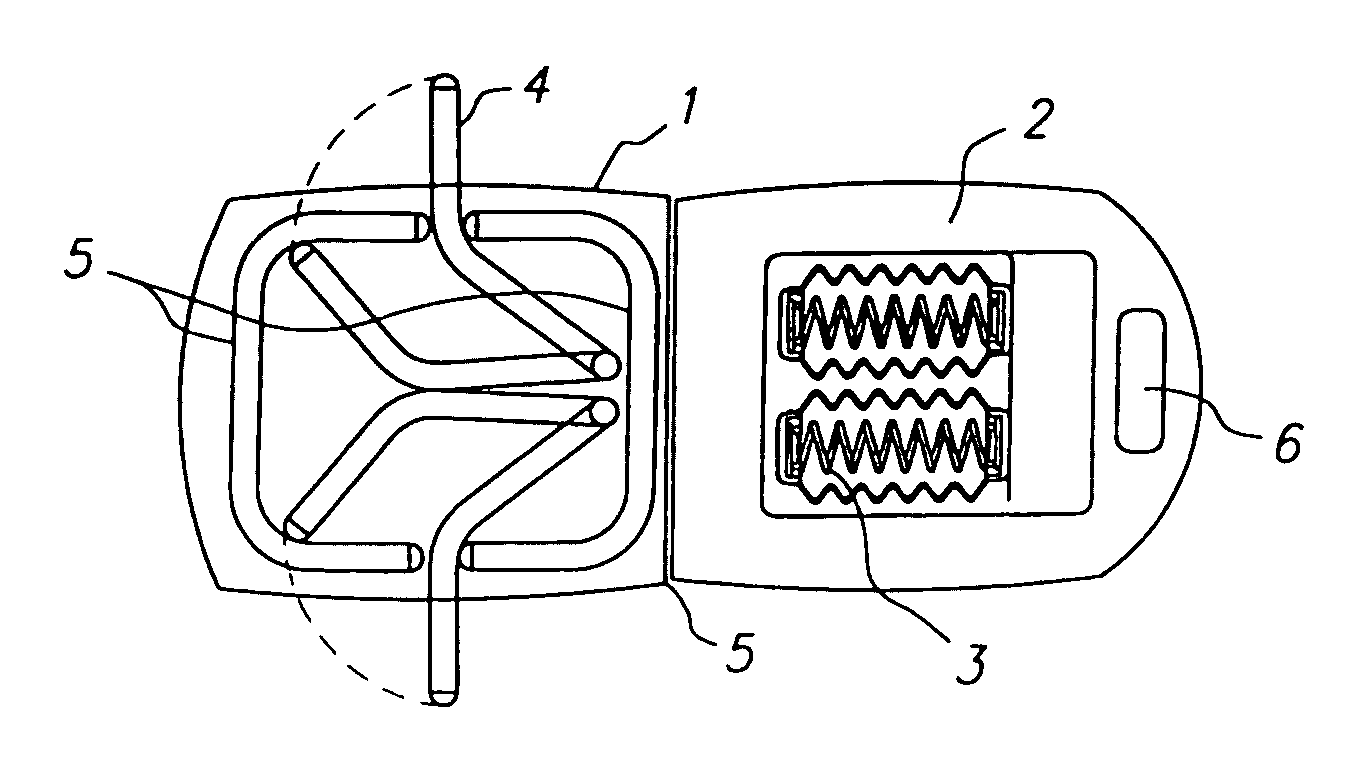
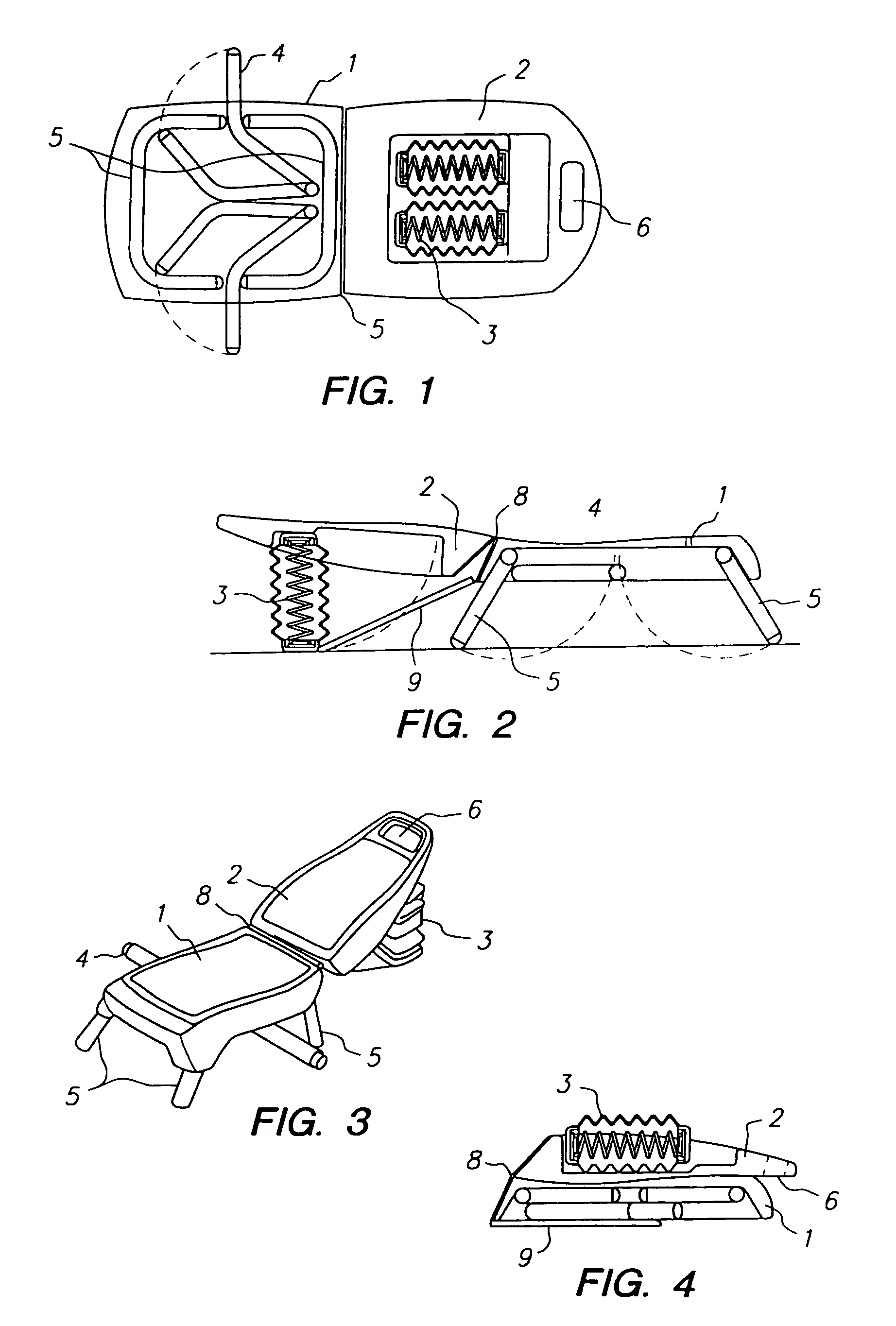
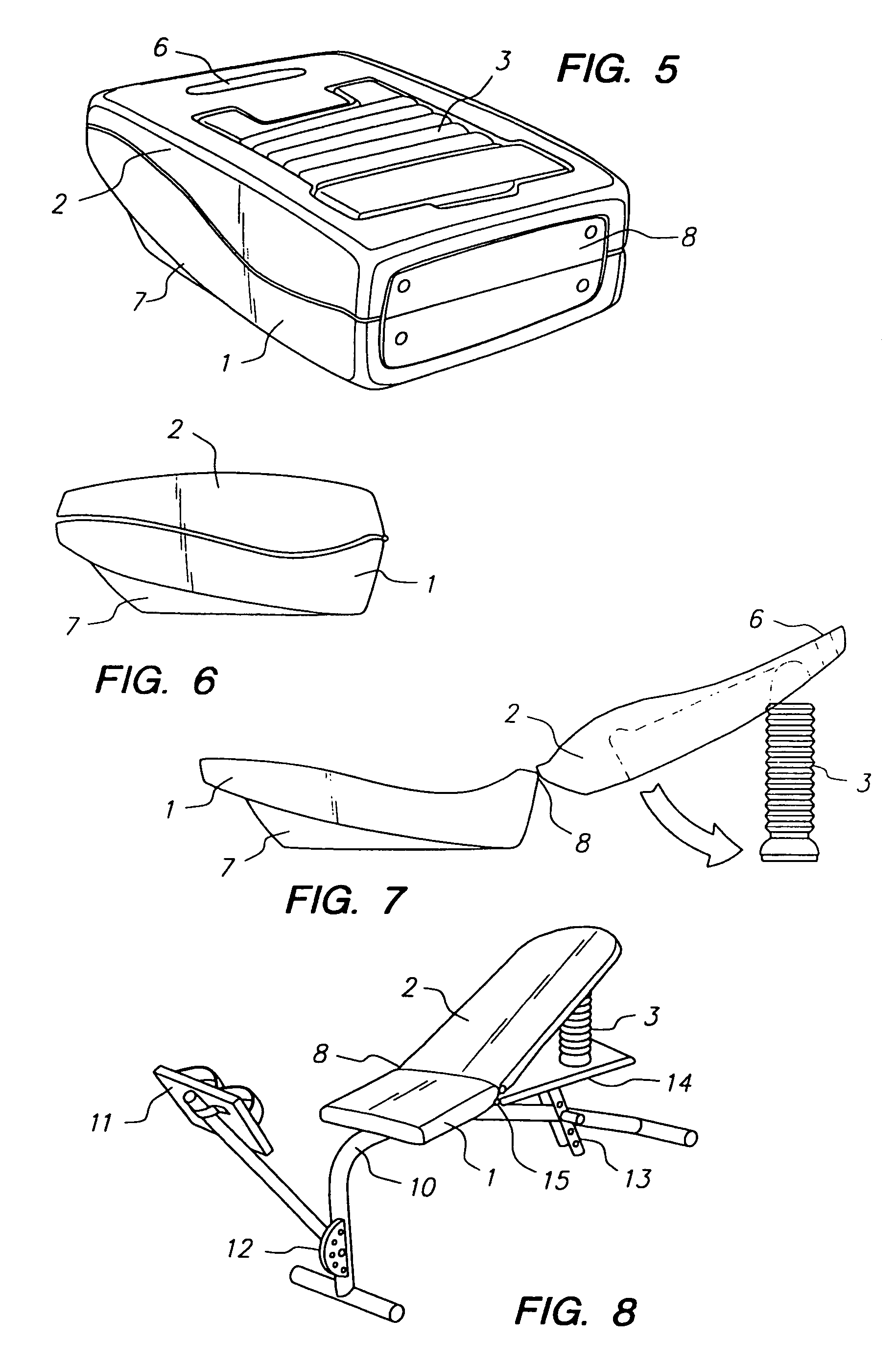
Device and methods for strengthening and toning the abdominal and gluteal muscles. A seat is mounted in a fixed position on a base, and a back is pivotally mounted for movement about an axis toward the rear of the seat, with springs or elastic cords yieldably urging the backrest to pivot in an upward direction toward a raised position. To strengthen and condition the upper, lateral and oblique abdominal muscles and gluteal muscles, an exerciser rests upon the seat, with his back against the backrest, and the elastic cords or springs assist him in raising his back and also allow him to extend to the full range of backward motion while absorbing the impact of that motion. To exercise the lower abdominal muscles and gluteal muscles, the exerciser reclines on the seat, with his legs on the backrest and the elastic cords or springs assisting him in raising his legs and absorbing the impact of lowering them.
Owner:2014 SHIFFERAW FAMILY REVOCABLE TRUST
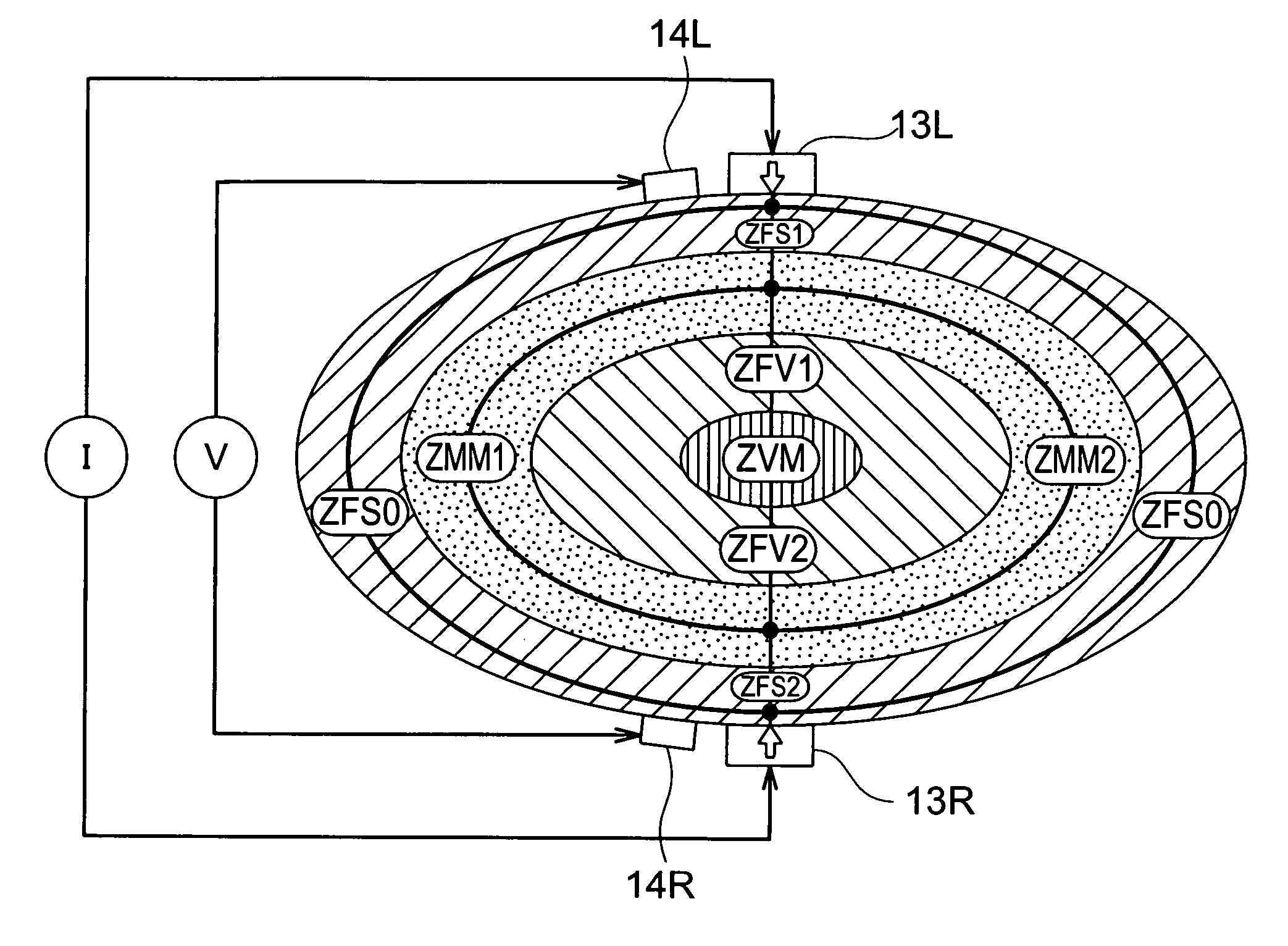
Trunk visceral fat measuring method and apparatus, trunk skeletal muscle amount measuring apparatus, trunk subcutaneous fat measuring method and apparatus, and trunk visceral and subcutaneous fat measuring method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060235327A1Improve measurement repeatabilityImprove reliabilityPerson identificationSensorsPotential differenceVisceral fat
A method and apparatus capable of measuring visceral fat tissues accumulated in the trunk with high accuracy apply a current to a body part where a subcutaneous fat tissue layer is thin or a body part where a skeletal muscle tissue layer has no or a thin muscle belly portion from a pair of current applying electrodes, measure a potential difference which has occurred in the tissue through which the current has passed by a pair of voltage measuring electrodes, and determine the visceral fat tissue volume of the trunk by use of the impedance of the trunk which has been obtained by use of the measured potential difference.
Owner:TANITA CORP
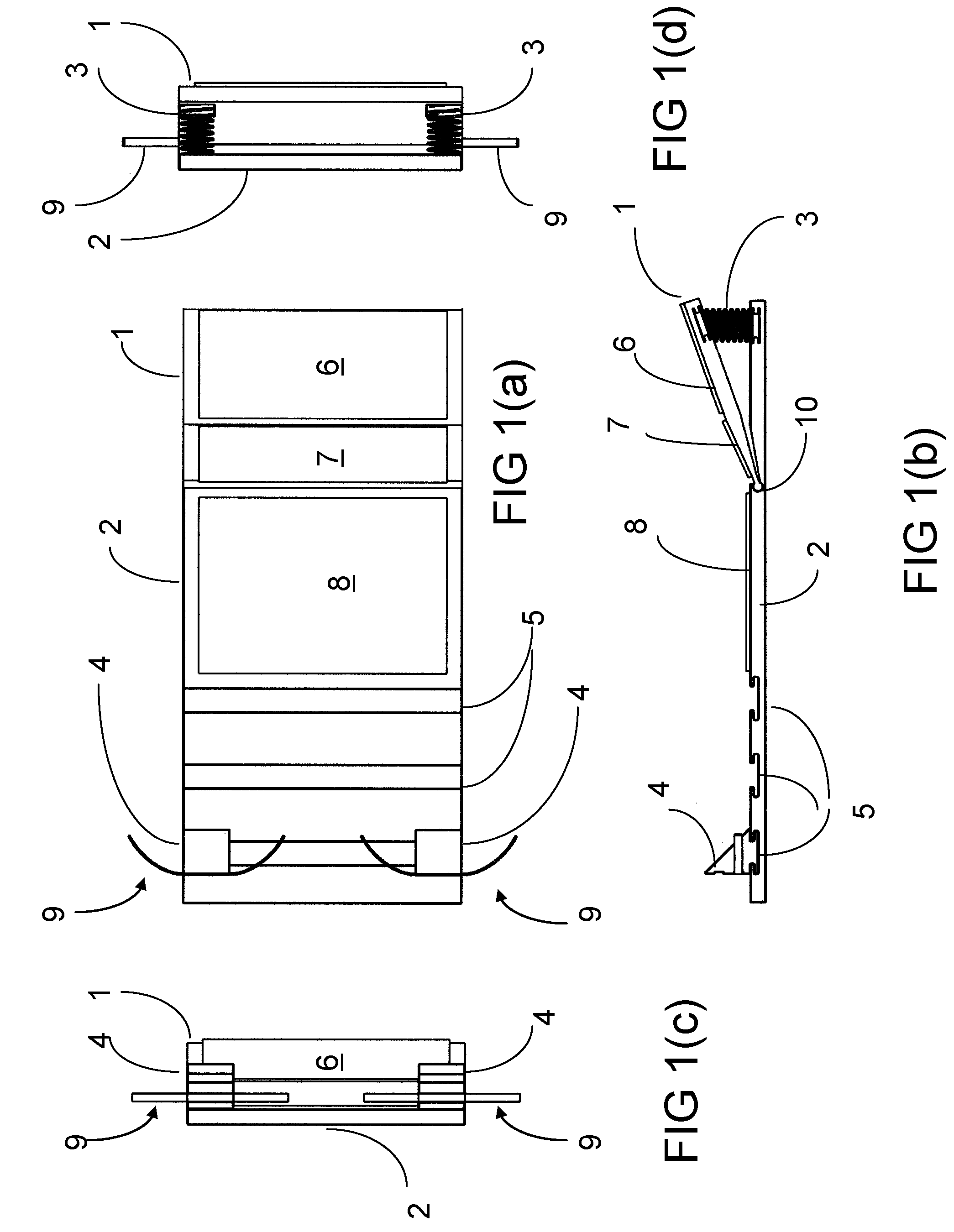
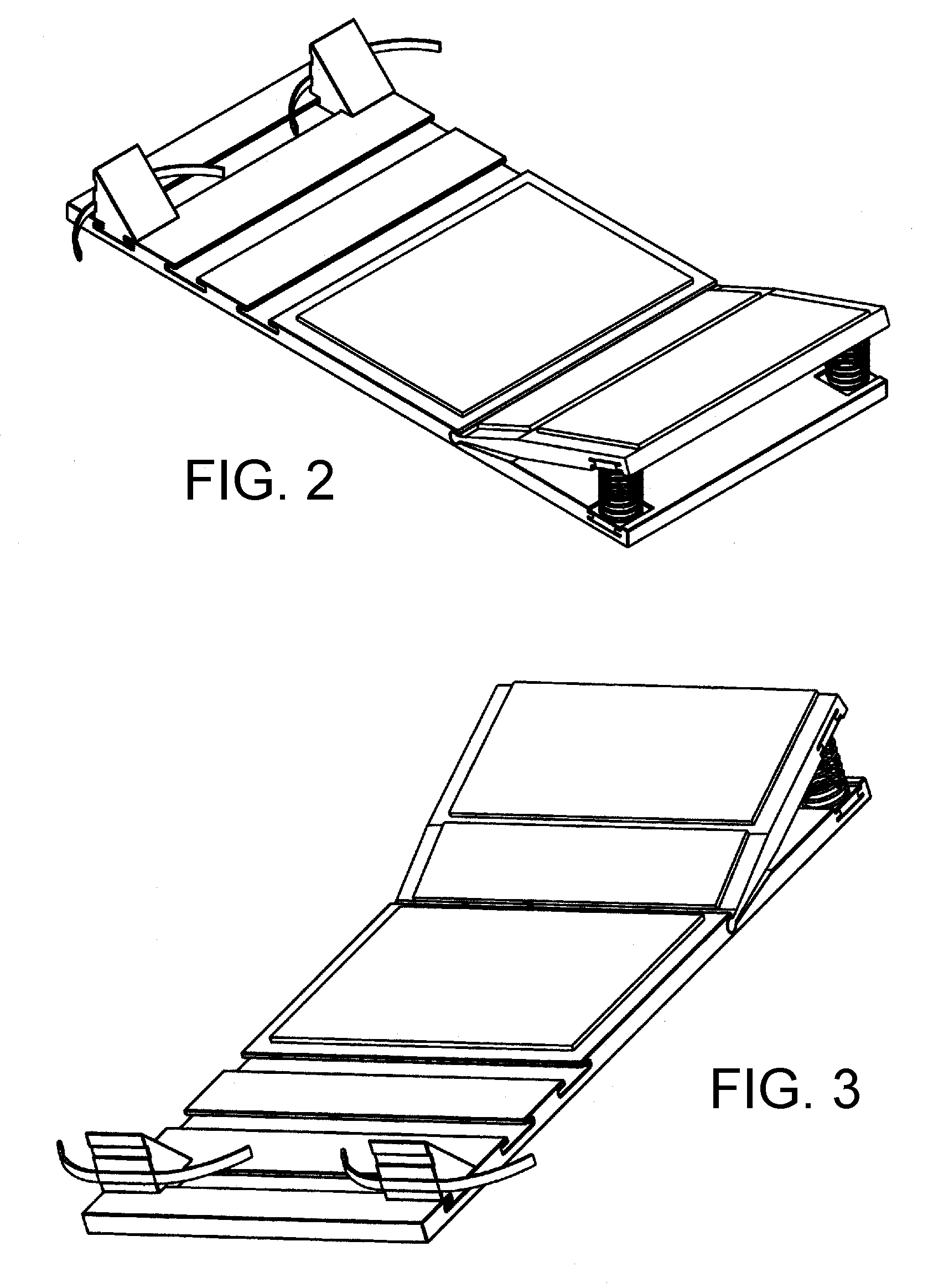
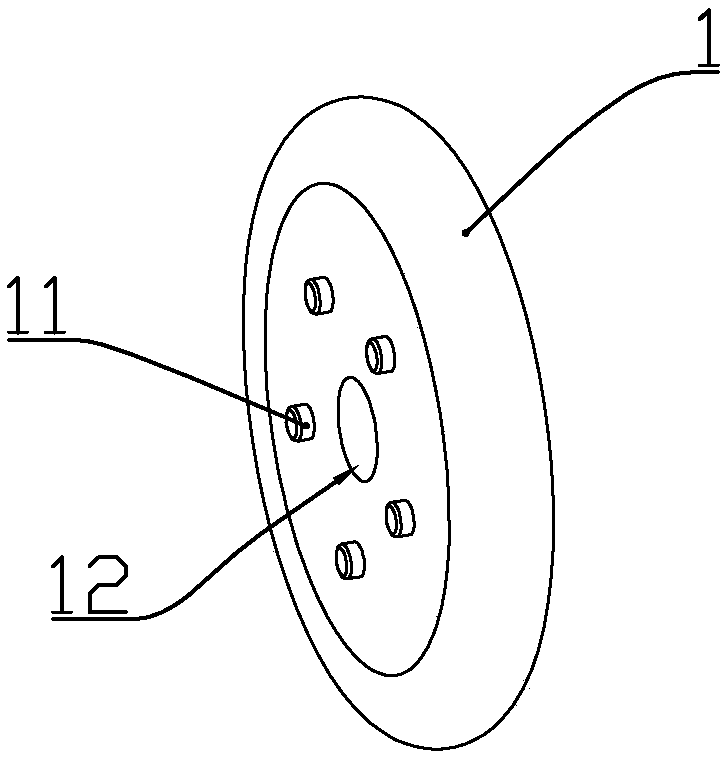
Abdominal muscle training apparatus
InactiveUS7488281B2Improve stabilityImprove performanceStoolsSpace saving gamesEngineeringMuscle belly
Exercise apparatus (10) for training a user's abdominal muscles comprises a lever frame (11) linked to a support frame (12) at a pivot (13). The lever frame (11) has first and second arms (14,15) joined at a junction (16) also forming a fulcrum for the lever frame (11). The support frame (12) consists of a base member (22) having a seat portion (23) associated with, and laterally rotatable relative to, the base member (22). The apparatus (10) may be used to perform either simple or compound abdominal muscles training exercises. In a simple exercise, the user∝s abdominal muscles are exercised by pushing the first arm (14) away from the user's body to rotate the lever frame (11) about its fulcrum (16), causing the seat portion (23) associated with the base member (22) to lift and tilt. In a compound exercise, the user's obliques and transversus abdominal muscles are exercised by performing an abdominal twisting motion to cause the seat portion (23) to rotate relative to the base member (22).
Owner:PROGRESSIVE SPORTS TECH
Belly loose muscle exercising and training device
InactiveCN109938993AAvoid strainPromote recoveryGymnastic exercisingVibration massageMuscle strainsFoot supports
The invention relates to a belly loose muscle exercising and training device which comprises a base plate, a fixing support, a foot support, an exercising device and an auxiliary device. The fixing support is installed in the middle of the upper end of the base plate. An annular groove is formed in the middle of the fixing support, a yoga ball is arranged inside the annular groove, the foot support is installed between the base plate and the left end of the fixing support, the exercising device is installed at the upper end of the fixing support, and the auxiliary device is installed between the base plate and the right end of the fixing support. The problems that when an existing belly exercising instrument is in use, the belly exercising effect is poor, vibration massage cannot be performed on the belly initiatively, loose muscles cannot be protected, and belly muscles of the user are likely to be strained can be solved, and the device has the advantages that the using effect is good, the requirement for training of different strengths can be met, vibration massage can be performed on the belly, meanwhile, the loose muscles can be protected, and belly muscle strains are avoided.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Polypeptide and microbial preparation for improving ox myotendinous development and its production
InactiveCN101074420AGuaranteed retentionGuaranteed special effectsFungiBacteriaHigh concentrationDigestion
A polypeptide and microbial feed additive for improving beef muscle belly connective tissue synthetic function is safe and non-toxic. The process is carried out selecting natto rod, lichenized bacillus, plant lactobacillin, cheese lactobacillin and beer yeast, independent or composite culturing to obtain composite bacterium, naturalizing while expansion culturing, solid fermenting with culture medium and aseptic water, fast low-temperature drying by drier, adding into special carrier, crushing and screening to obtain final product. It obtains high-concentration enteric beneficial microbial pool and mixtures of health-care soybean peptide, oligo-peptide and short peptide containing natto-kinase. It's practical and economical, and it tastes good and can improve digestion-absorbing function of beef for protein in feed.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUANGBO ECOLOGICAL ENG
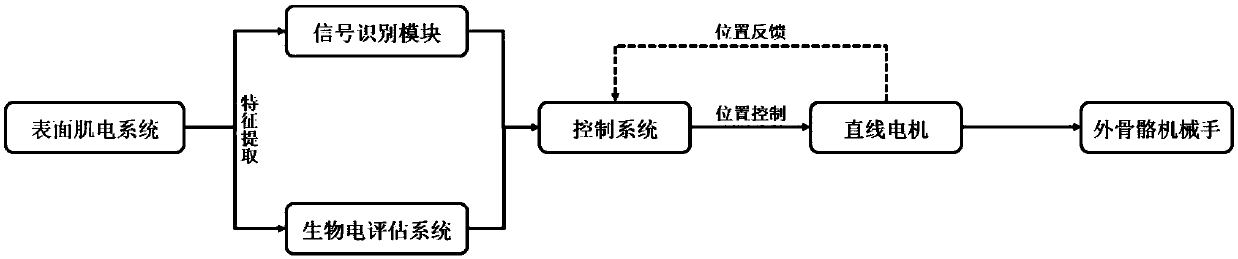
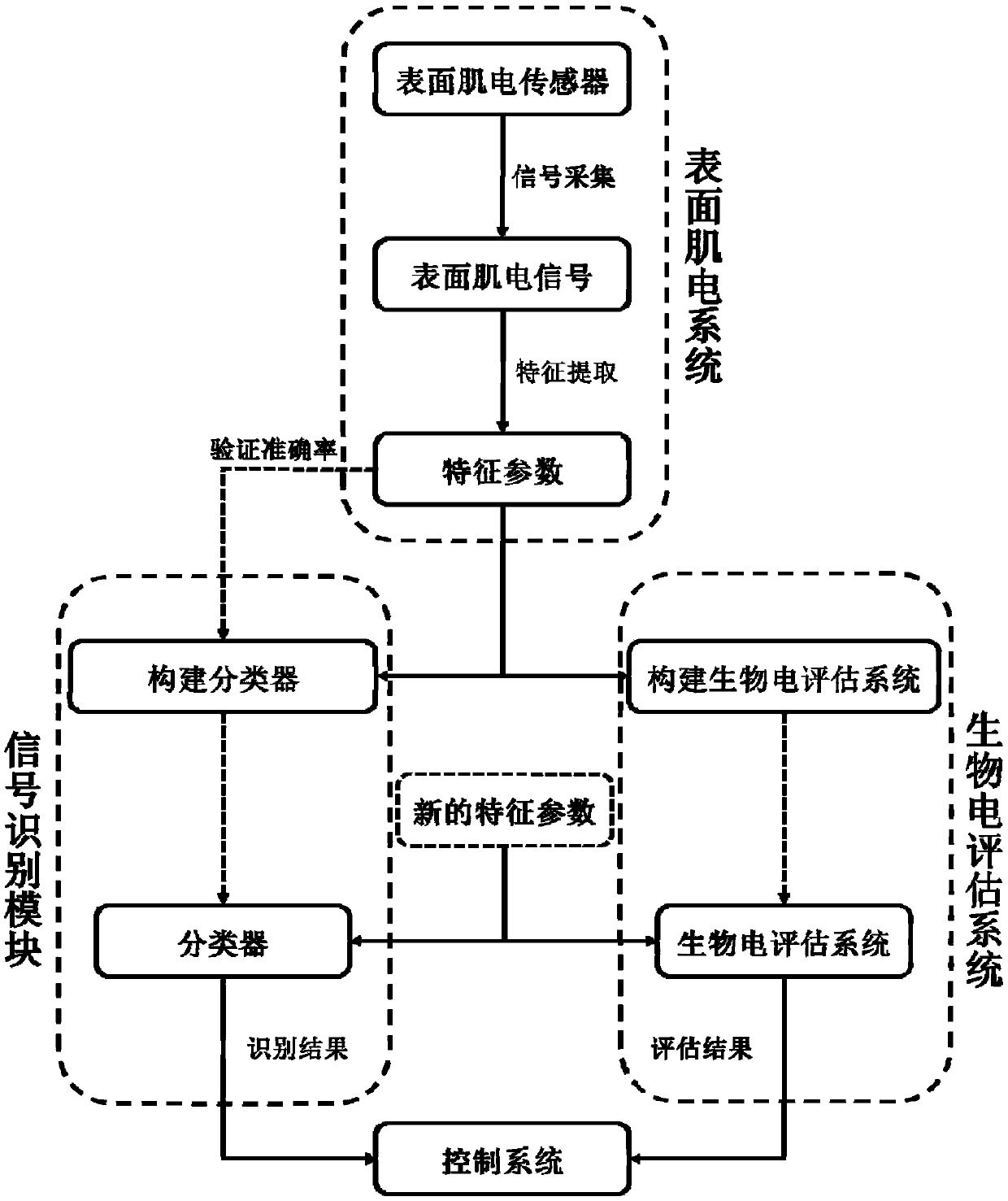
Intelligent exoskeleton rehabilitation mechanical arm based on normal side biological electrical control and method
ActiveCN108743223AImprove human-computer interactionGood treatment effectDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesFeature extractionControl system
The invention discloses an intelligent exoskeleton rehabilitation mechanical arm based on normal side biological electrical control and a method. A driving mechanism is arranged on a dorsal metacarpaplatform, and separately drives movement of each mechanical unit of an exoskeleton mechanical arm body, and the control system receives a position signal fed back by the driving mechanism, and controls movement and / or stop of the driving mechanism; surface myoelectricity sensors of a surface myoelectricity system are arranged on muscle bellies of hand and forearm related muscles of normal side upper limbs, surface myoelectricity signals of the corresponding muscles are collected, feature extraction is conducted, a signal identification module receives surface myoelectricity feature parameters,the feature parameters are sent to a trained classifier, different action types are identified, a bioelectric assessment system receives the surface myoelectricity feature parameters, assessment is conducted on personal features and a real-time state of a patient, and the assessment result is obtained; the identification result and the assessment result are sent to the control system to control movement of the driving mechanism, and then the hand on the affected side is driven to move.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
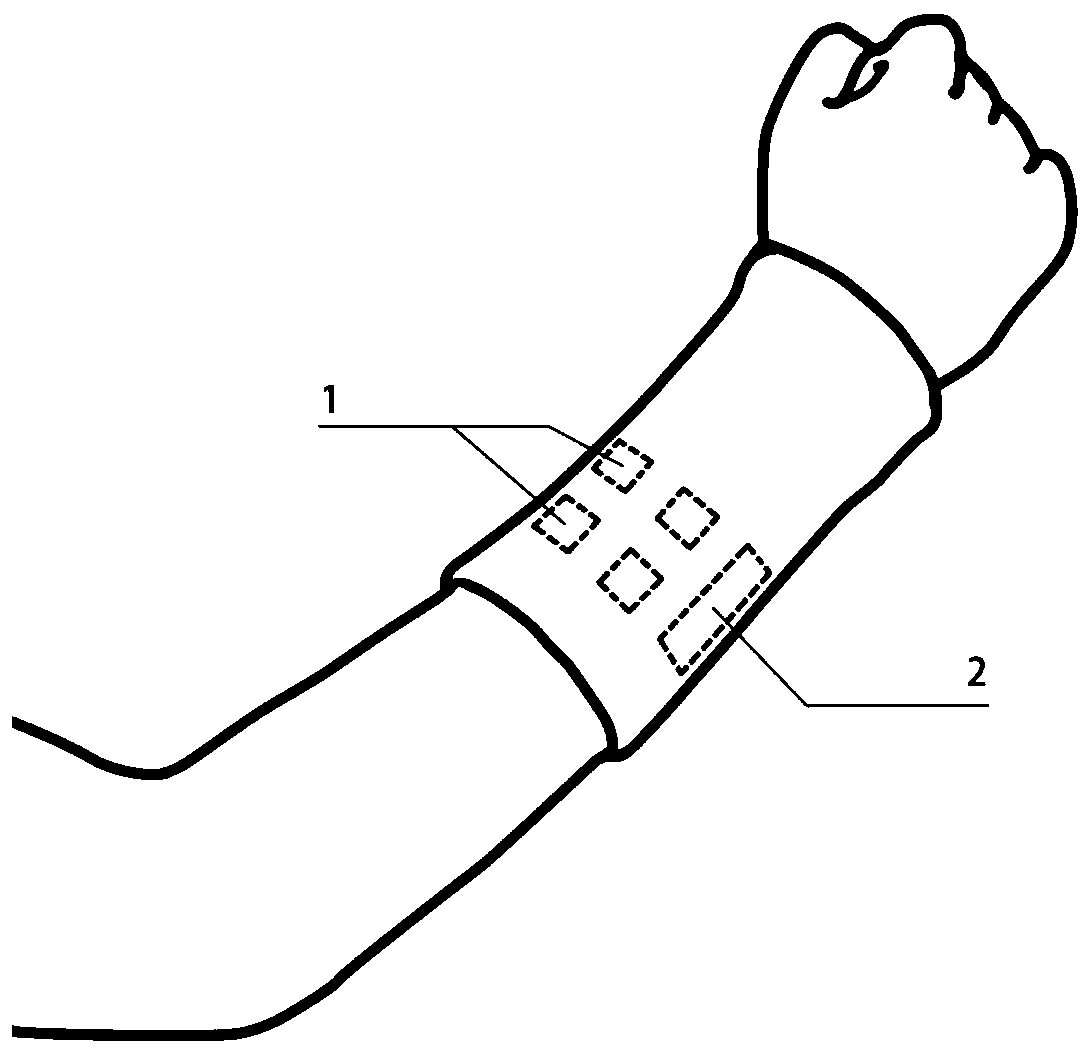
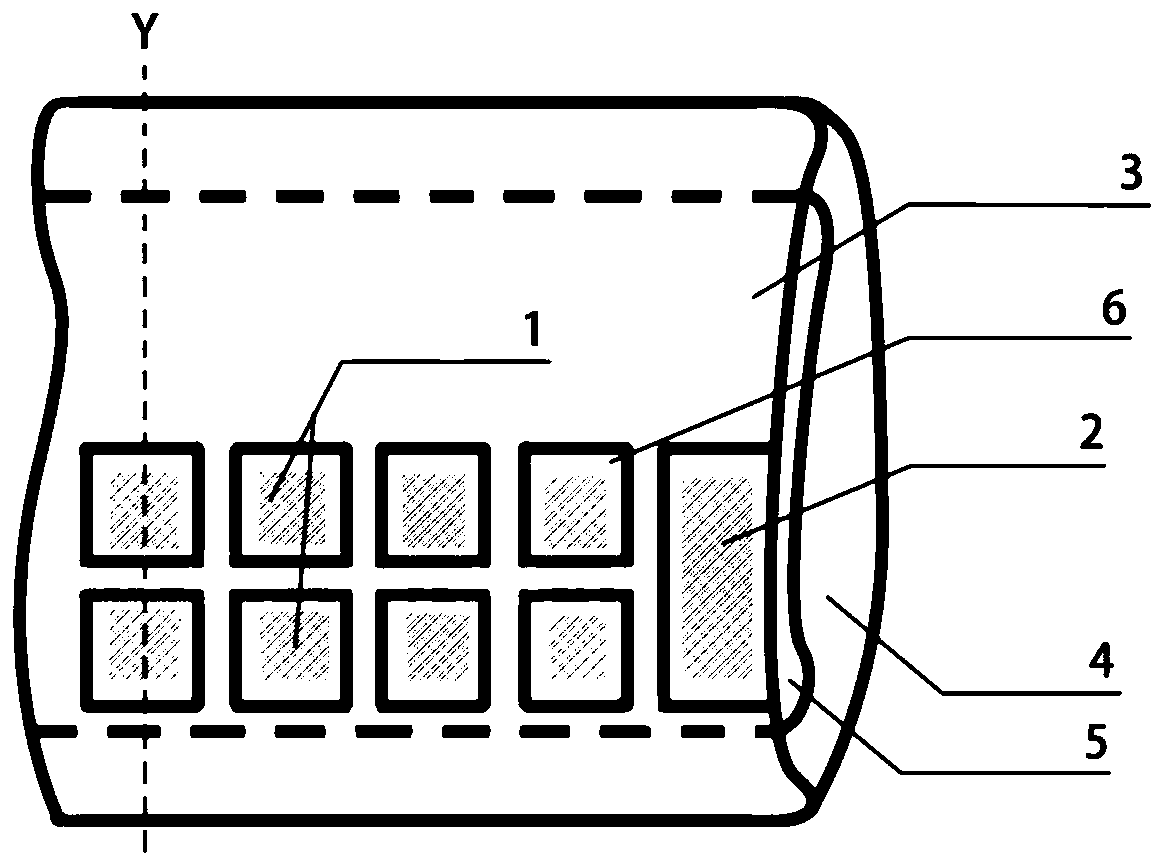
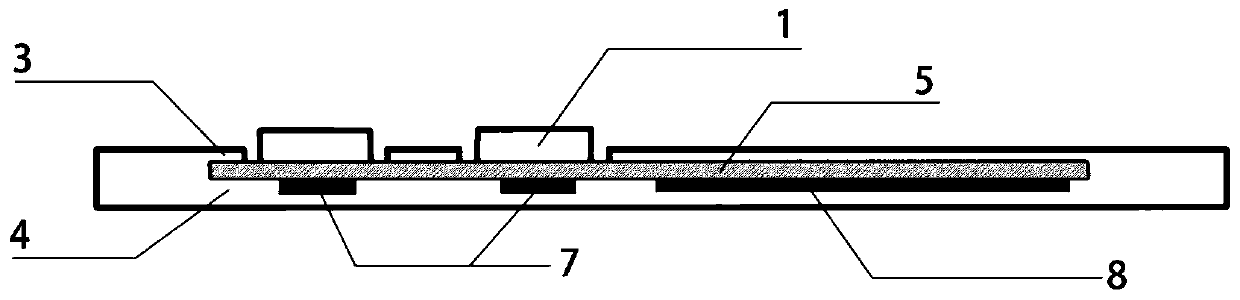
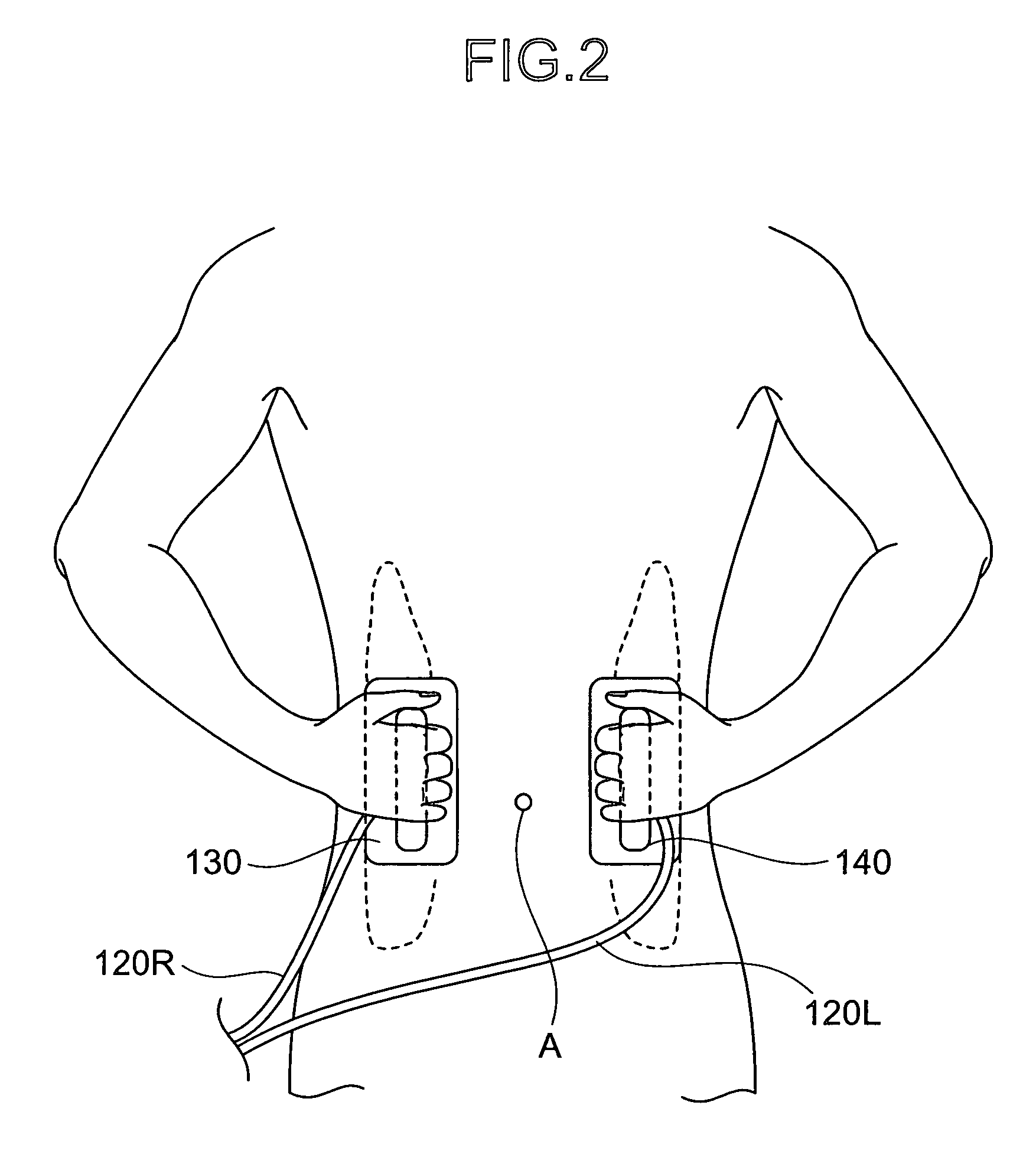
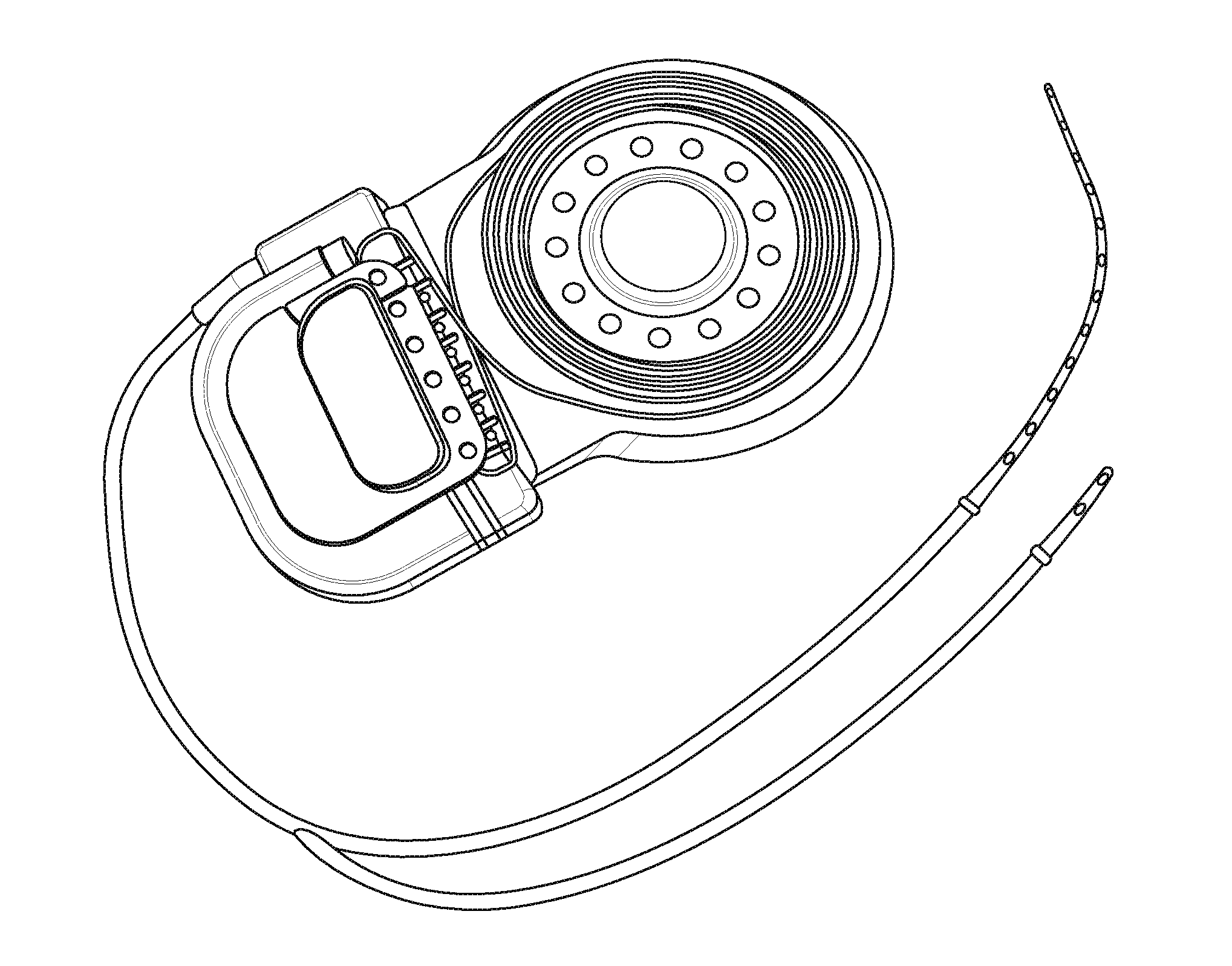
Multi-channel hand myoelectric acquisition wrist strap based on fabric electrode
InactiveCN109998542AImprove signal-to-noise ratioEasy to useDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHand movementsEngineering
The invention relates to a multi-channel hand myoelectric acquisition wrist strap based on a fabric electrode. Differential electrodes and a reference electrode are uniformly arranged on the wrist strap; the differential electrodes and the reference electrode are located on the portions, slightly close to the wrist, in the middle of the forearm. If the differential electrodes and the reference electrode are too close to the wrist, the electrodes are away from the muscle belly, and the signal intensity is low. If the differential electrodes and the reference electrode are too away from the wrist, the resolving power of the electrodes on finger movements is not strong. The center distance between every two differential electrodes is not larger than 30 mm, and if the distance is selected to be too large, too many effective frequency components of myoelectric signals are lost. The differential electrodes are distributed in pairs, the number of the pairs is n, and the differential electrodes correspond to four muscle groups related to hand movements. The rectangular reference electrode is arranged in a non-muscle activity area as much as possible, and the reference electrode is used forproviding null voltage reference, so that the signals are stable as soon as possible. The wrist strap is light, convenient to use and comfortable to wear; due to the characteristics of the fabric electrode, skin does not need to be pretreated or coated with conductive paste for collection, and the wrist strap is suitable for long-term collection.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Exercise apparatus for strengthening abdominal muscles
An exercise apparatus that lies flat on the floor having a back rest rises up when supported by two springs. The lower part of the back and buttocks lie horizontal while the upper part of the back is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. When not in use, the upper back rest folds down flat so that the device can be stored under a bed. The two springs provide back support when the individual is in the reclining position. However, as a person goes from a sitting position to a reclining position, when his or her shoulders contact the back rest, the springs compress and then expand to assist the individual in rising up. The device has two specially designed positionable foot rests with straps to provide a place for the individual to place his or her feet.
Owner:ARAUJO WILLIAM
Trunk visceral fat measuring method and apparatus, trunk skeletal muscle amount measuring apparatus, trunk subcutaneous fat measuring method and apparatus, and trunk visceral and subcutaneous fat measuring method and apparatus
InactiveUS7925340B2Improve measurement repeatabilityImprove reliabilityPerson identificationSensorsFat MeasurementPotential difference
A method and apparatus capable of measuring visceral fat tissues accumulated in the trunk with high accuracy apply a current to a body part where a subcutaneous fat tissue layer is thin or a body part where a skeletal muscle tissue layer has no or a thin muscle belly portion from a pair of current applying electrodes, measure a potential difference which has occurred in the tissue through which the current has passed by a pair of voltage measuring electrodes, and determine the visceral fat tissue volume of the trunk by use of the impedance of the trunk which has been obtained by use of the measured potential difference.
Owner:TANITA CORP
Exercise device for strengthening of abdominal muscles
InactiveUS20070149371A1Eliminates onset muscle sorenessEliminates unhealthy stressPhysical therapyStiltsMedicineMuscle belly
An exercise device for strengthening of abdominal muscles employing a resistance mechanism is disclosed.
Owner:GEJDOS MARIAN
Stapedius muscle electrode
ActiveUS8280480B2Easy to fixSimple structureHead electrodesElectromyographyElectrode arrayBiomedical engineering
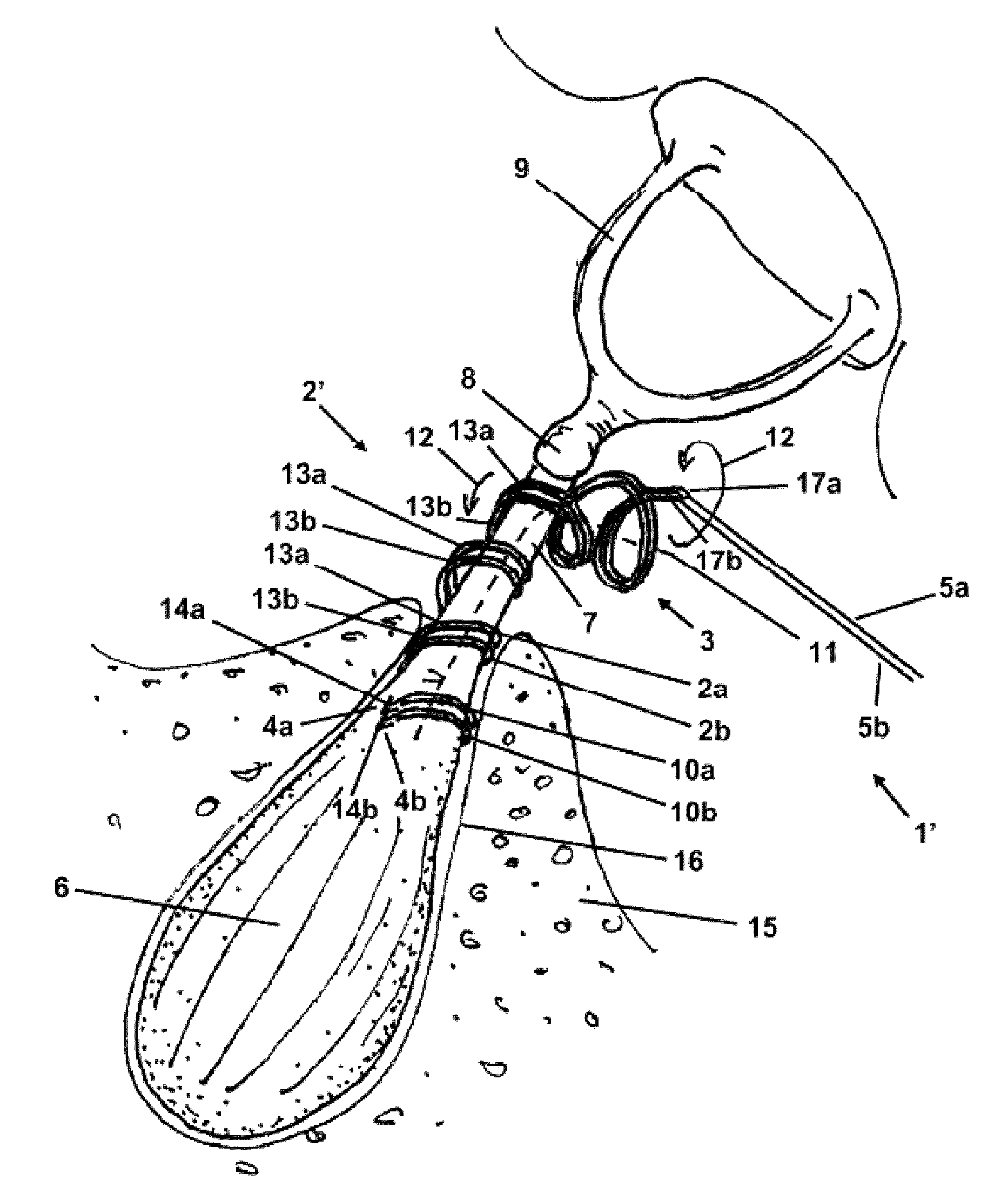
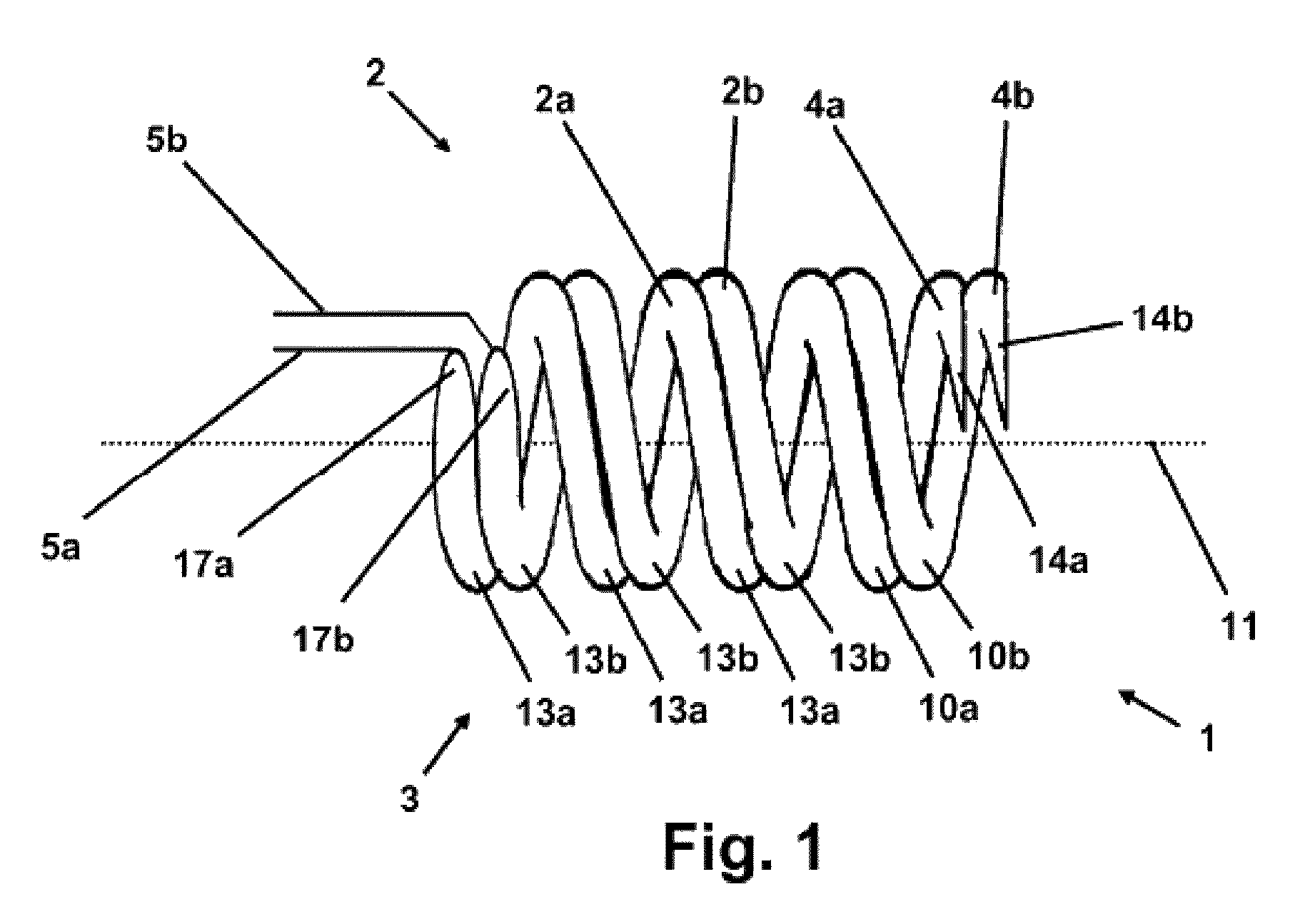
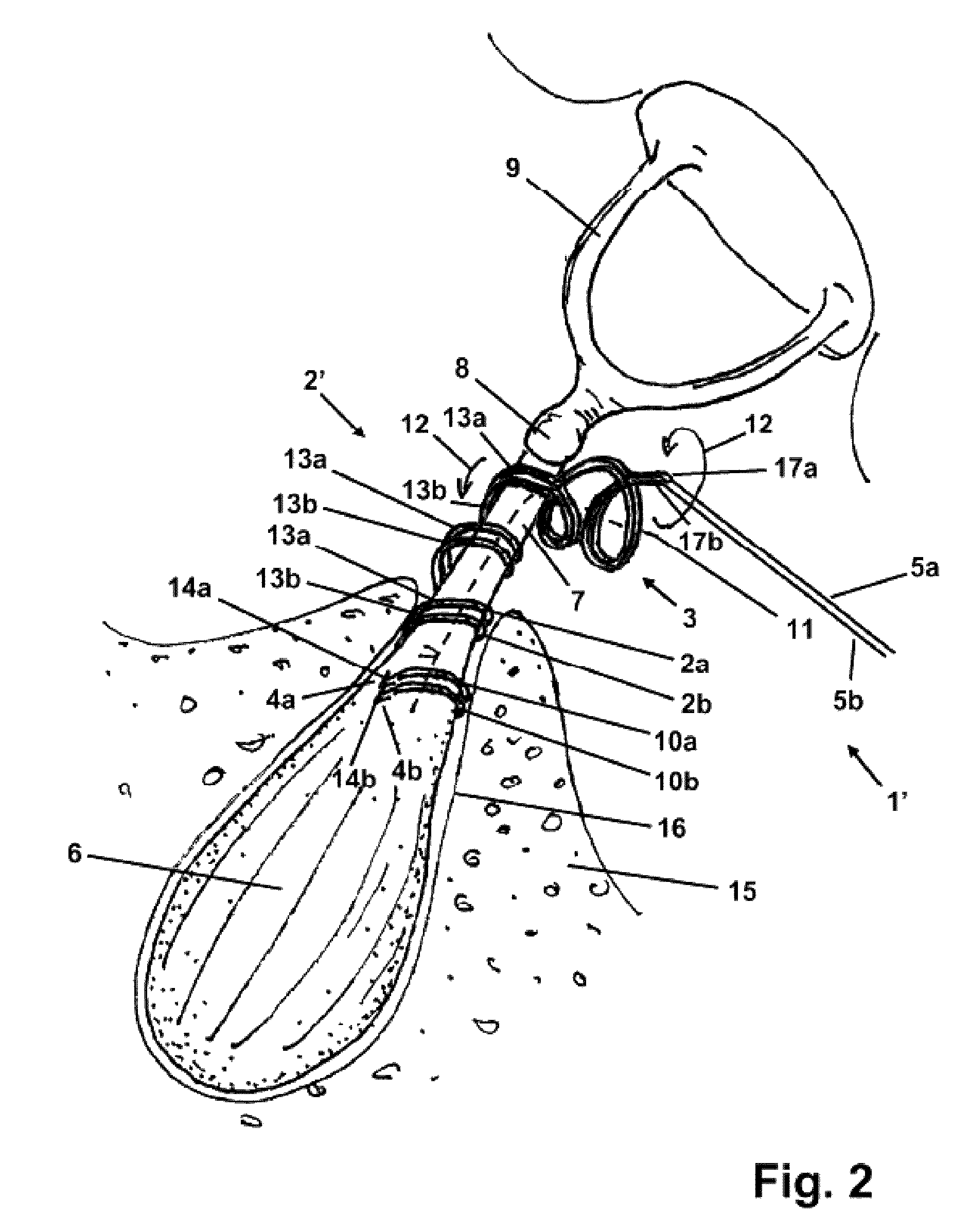
The invention relates to a stapedius muscle electrode array for detecting the action elements generated when a human stapedius muscle is contracted. Said array comprises an electrode (2, 2′, 2″) that is adapted for bipolar discharge and is to be attached to a human stapedius muscle. The electrode has two flexible, elastic, electrically conducting elongate elements (2a, 2b), each of which has a distal (4a, 4b) and a proximal end (17a, 17b) and is helically preshaped along at least some of the length thereof to the distal end (4a, 4b) thereof in such a way that the distal end (4a, 4b) and a section of the respective elongate element (2a, 2b) which adjoins the distal end (4a, 4b) can be placed at least in part around the tendon (7) extending between the stapedius muscle and the stapes while the helical part can be guided along the tendon (7), can be moved in the direction of the stapedius muscle, and can be at least partly twisted into and / or slid onto the region of the muscle belly (6) adjoining the tendon (7). The two elongate elements (2a, 2b) are electrically insulated from one another, and the helical parts (3) thereof are intertwined in such a way as to run around a common centerline (11), allowing the helical parts (3) to be jointly placed around the tendon (7), be guided along the tendon (7), and be brought in contact with the stapedius muscle.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Sports equipment used for abdominal muscle exercise
ActiveCN109331412APrevent affecting fitness effectImprove fitness effectMuscle exercising devicesAssisted exerciseSports equipment
The invention relates to a sports equipment, in particular to sports equipment for abdominal muscle exercise. The object of the invention is to provide the sports equipment for abdominal muscle exercise, wherein the equipment can assist exercise and massage the back. According to the technical scheme, the sports equipment for abdominal muscle exercise includes an installation plate, a first concave plate, a first spring, a second concave plate, a hinge, a lying board, an arc slide rod, a first slide block, a second spring, a slide rail and the like. The middle of the installation plate is provided with a groove, the bottom in the groove is uniformly provided with three first concave plates, and the tops of the three first concave plates are connected with the four first springs. People place the legs between a fixation plate and a baffle and do abdominal exercise under the auxiliary effects of the arc slide rod and the first slider, people with weaker physique can also easily completesit-ups, and thus people can persist in exercise; by placing the feet on the left side of a cross bar, the feet can be fixed, and the situation is avoided that people disorderly move the feet while exercising the abdominal muscle and the fitness effect is thus affected.
Owner:杨松平
Abdominal muscle exercise apparatus
Apparatus for exercising the abdominal muscles includes a flexible substrate that substantially conforms to a user's abdomen, with a tacky pressure-sensitive adhesive disposed on one side of the flat or contoured surface, for adhering the exercise apparatus to the user's abdomen, and a system for attaching additional weight to the apparatus for providing increased resistance. The pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) allows the exercise apparatus to adhere to the user's abdomen, and enables releasable attachment, such that the apparatus can be attached and detached from the abdomen repeatedly, and can be reused. Optional weights are attached to the apparatus to increase resistance, as desired. While on his / her hands and knees, the user contracts the stomach muscles and pulls his / her abdomen with the attached apparatus inward toward the spine, thus exercising the abdominal muscles.
Owner:PEARSON JON D
Abdominal muscle exercise equipment
ActiveCN106267711AEven by forceTurn for easy controlMovement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesPortable powerEngineering
The invention discloses abdominal muscle exercise equipment. The abdominal muscle exercise equipment comprises a supporting pipe, two rollers arranged on the supporting pipe and a speed change mechanism installed between the two rollers. Motors are fixedly installed at the two ends in the supporting pipe respectively, a circuit board and a storage battery are fixedly installed at the positions, at the outer ends of the two motors, in the supporting pipe respectively, portable power sources are installed at the two ends in the supporting pipe, and a reverse rotation button is fixedly connected to the position, close to one roller, of the outer wall of the supporting pipe. The speed change mechanism comprises a transmission base, a positioning frame and an annular gear. According to the abdominal muscle exercise equipment, rotation of the rollers can be conveniently controlled, and the situation that as the rollers roll out of control, strain of a user is caused can be prevented; the abdominal muscle exercise equipment can serve as a common abdominal exercise roller by taking out the speed change mechanism; the portable power sources in the supporting pipe can be taken out as needed to serve as a portable charger.
Owner:NANTONG TENGTAI SPORTING FITNESS CO LTD
Gesture sensor
ActiveCN108108016AReduce weightReduce power consumptionInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingInteraction systemsSignal conditioning
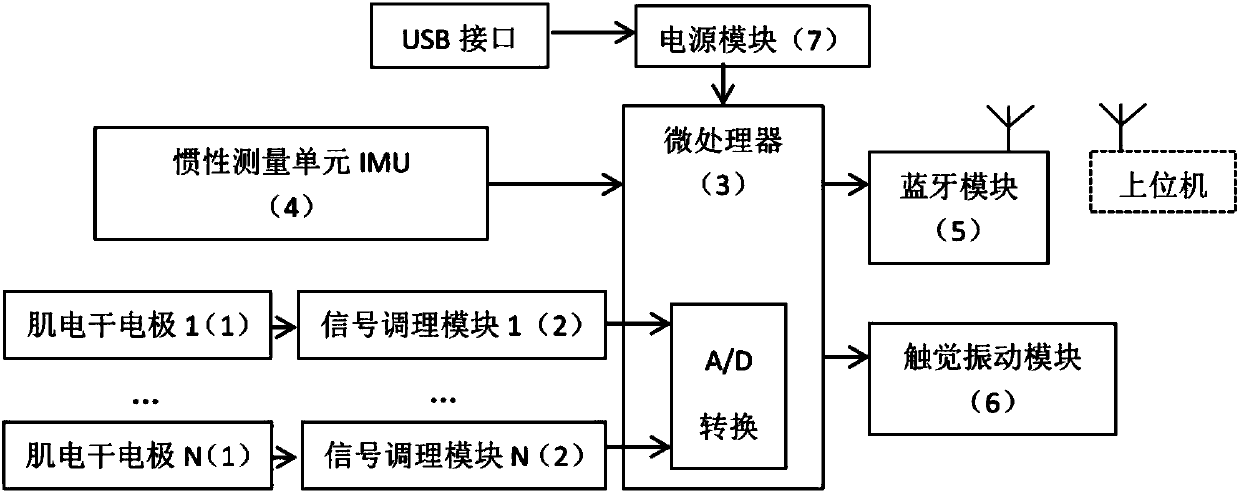
The invention discloses a gesture sensor, which comprises a myoelectricity dry electrode, a myoelectricity signal conditioning module, a microprocessor, an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), a touch vibration module, a power supply module and a Bluetooth module, wherein the gesture sensor can be worn on the muscle belly part of the front arm of the left hand or the right hand of an operator; throughthe myoelectricity dry electrode, the myoelectricity signal of the front arm is collected and is sent to the myoelectricity signal conditioning module; through the IMU, the motion data of the front arm is collected, is converted into a digital signal through A / D and is subjected to filtering preprocessing; the digital signal is sent to an upper computer or other intelligent terminals through a Bluetooth module; and the myoelectricity signal and the IMU data are subjected to fusion processing to judge the gesture made by the operator at present. The gesture sensor can be applied to a human-computer interaction system of gesture sensing and control, is convenient in operation and is high in experience feeling.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
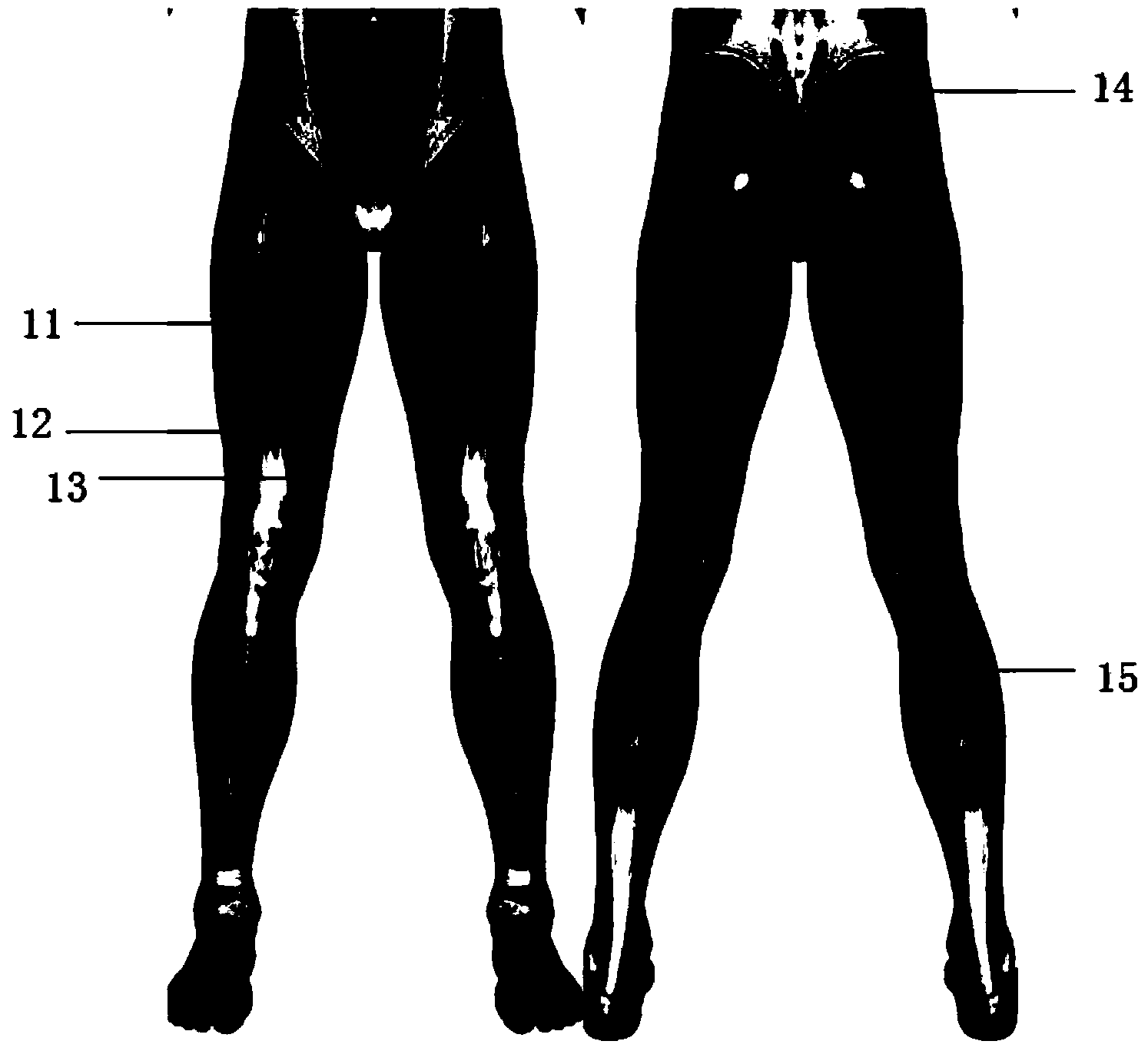
Leg figure correction pants
InactiveCN104274263ACorrect bad postureIn line with the laws of mechanicsMedical scienceHuman bodyEngineering
The invention provides a pair of leg figure correction pants. The pair of leg figure correction pants is in tight fit with the lower limbs of the human body and comprises two pants legs. The pair of leg figure correction pants further comprises elastic spiral structures located on the inner surface of the pants legs. Each elastic spiral structure comprises a force exerting part and an anchoring part, wherein the force exerting part is located on a muscle tendon part of the corresponding lower limb and the anchoring part is located on the muscle belly part of the corresponding lower limb. Each force exerting part and the corresponding anchoring part are both fixed to the inner surface of the corresponding pants leg and connected through an elastic band. The width L1, in the direction perpendicular to the stretching direction of the corresponding elastic band, of each force exerting part is smaller than the width L2, in the direction perpendicular to the stretching direction of the anchoring part, of the corresponding elastic band. According to the leg figure correction pants, after the elastic bands in the elastic spiral structures are stretched, due to the fact that the force exerting parts perceive rotating force obviously, the incorrect postures of the legs are corrected effectively, the purpose of enabling people to autonomously maintain a correct leg posture is achieved, and the pair of leg figure correction pants accords with the mechanical laws of the leg movement of the human body.
Owner:许夏杰
Abdominal muscle exercising apparatus
ActiveCN107802988AAvoid strainIncrease resistanceBatteries circuit arrangementsFrom muscle energyMuscle strainsEngineering
The invention discloses an abdominal muscle exercising apparatus. The abdominal muscle exercising apparatus comprises a supporting pipe made of aluminum alloy, a speed change mechanism and idler wheels which are arranged in pair, and the idler wheels which are arranged in pair are installed on the supporting pipe; the speed change mechanism in installed at the inner side of one idler wheel. When abeginner uses a power roller, the speed change mechanism generates resistance in a forward pushing process, and the direction of holding the power roller can be adjusted; when the power of the handsor the abdomen reaches the limit and cannot provide enough support, a reversing button can be pressed, a motor in the supporting pipe rotates, a driven rotor rotates, a magnet b on the driven rotor drives a magnet a on an annular gear to rotate, the annular gear rotates, a gear b is driven, a gear a drives a gear d, a gear c drives an inner gear on a drive base to rotate, the drive base makes theidler wheels reduce speed, backward force is generated to make the idler wheels reciprocate, thus the rotation of the idler wheels is conveniently controlled, and the situation that a user suffers from muscle strains when the idler wheels are out of control during rolling is prevented.
Owner:福建省德鲁士润滑油有限公司
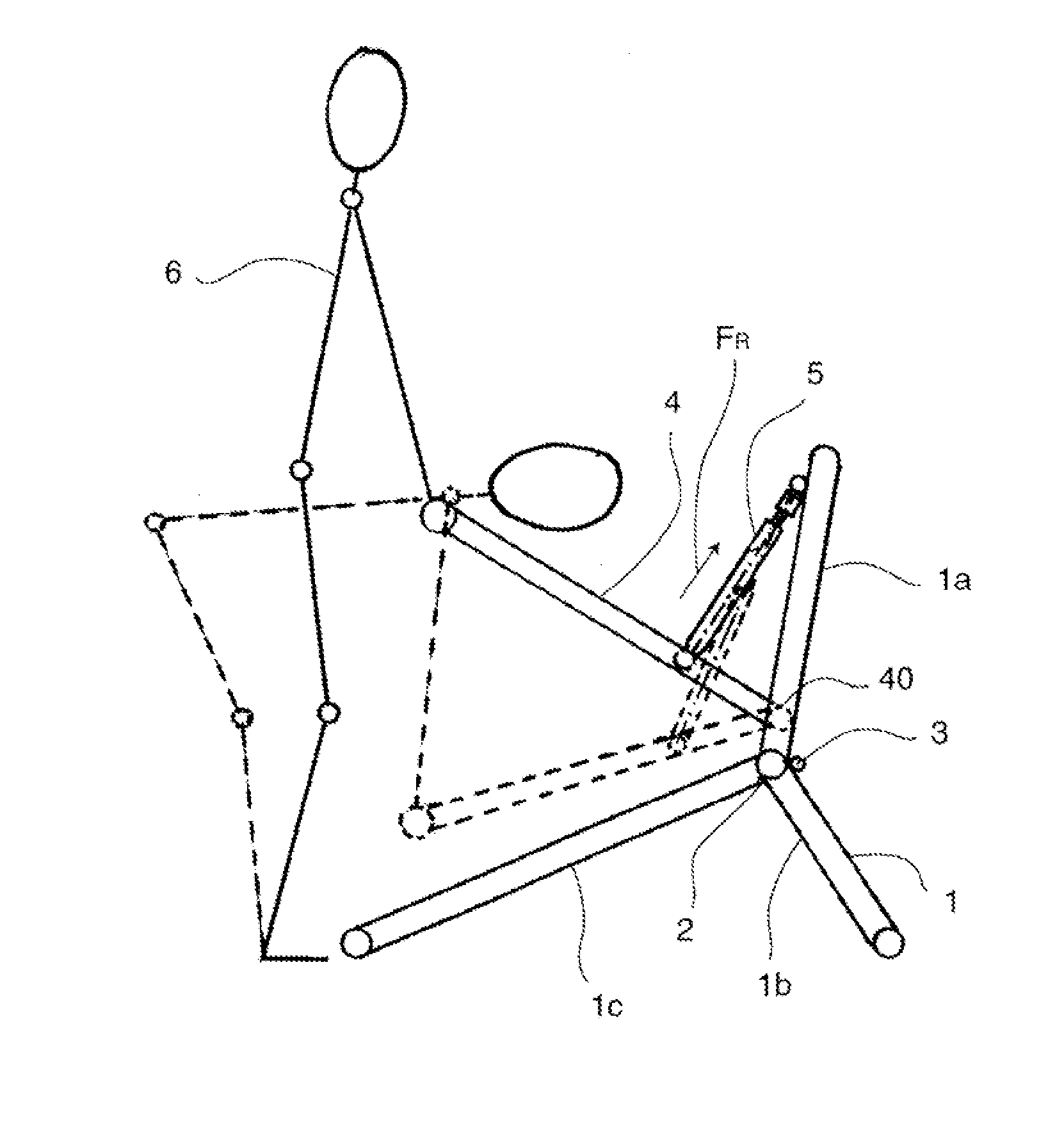
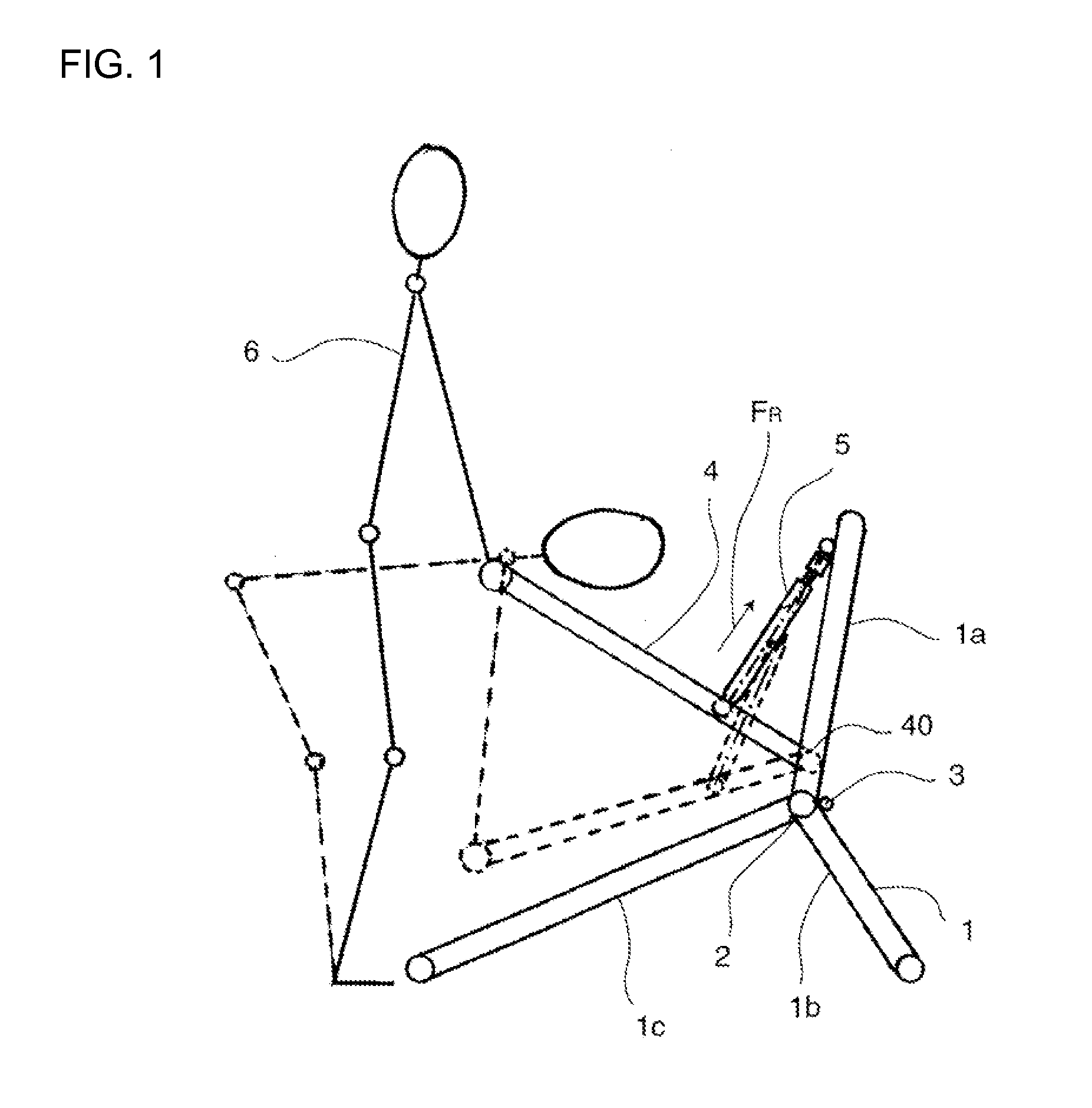
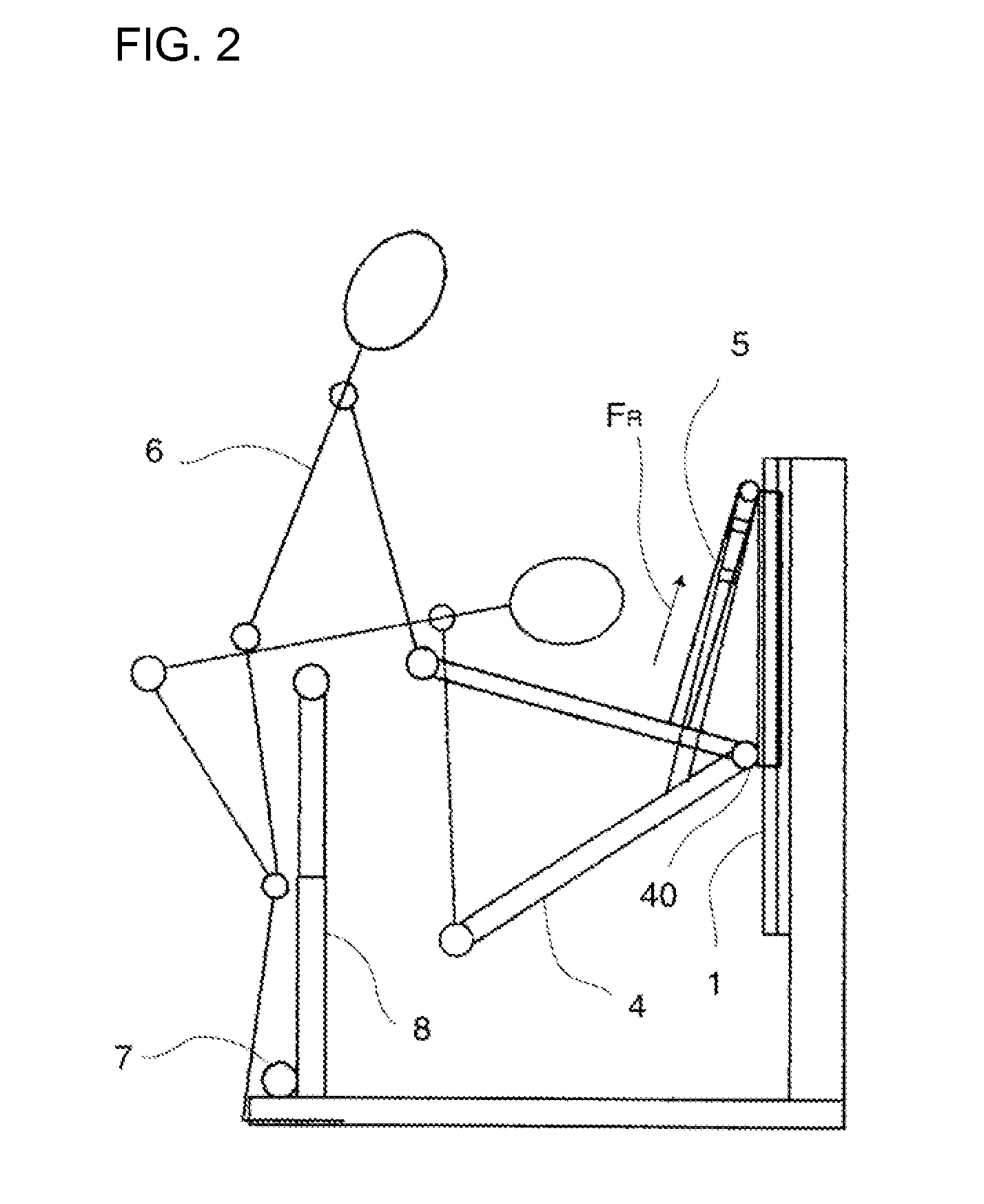
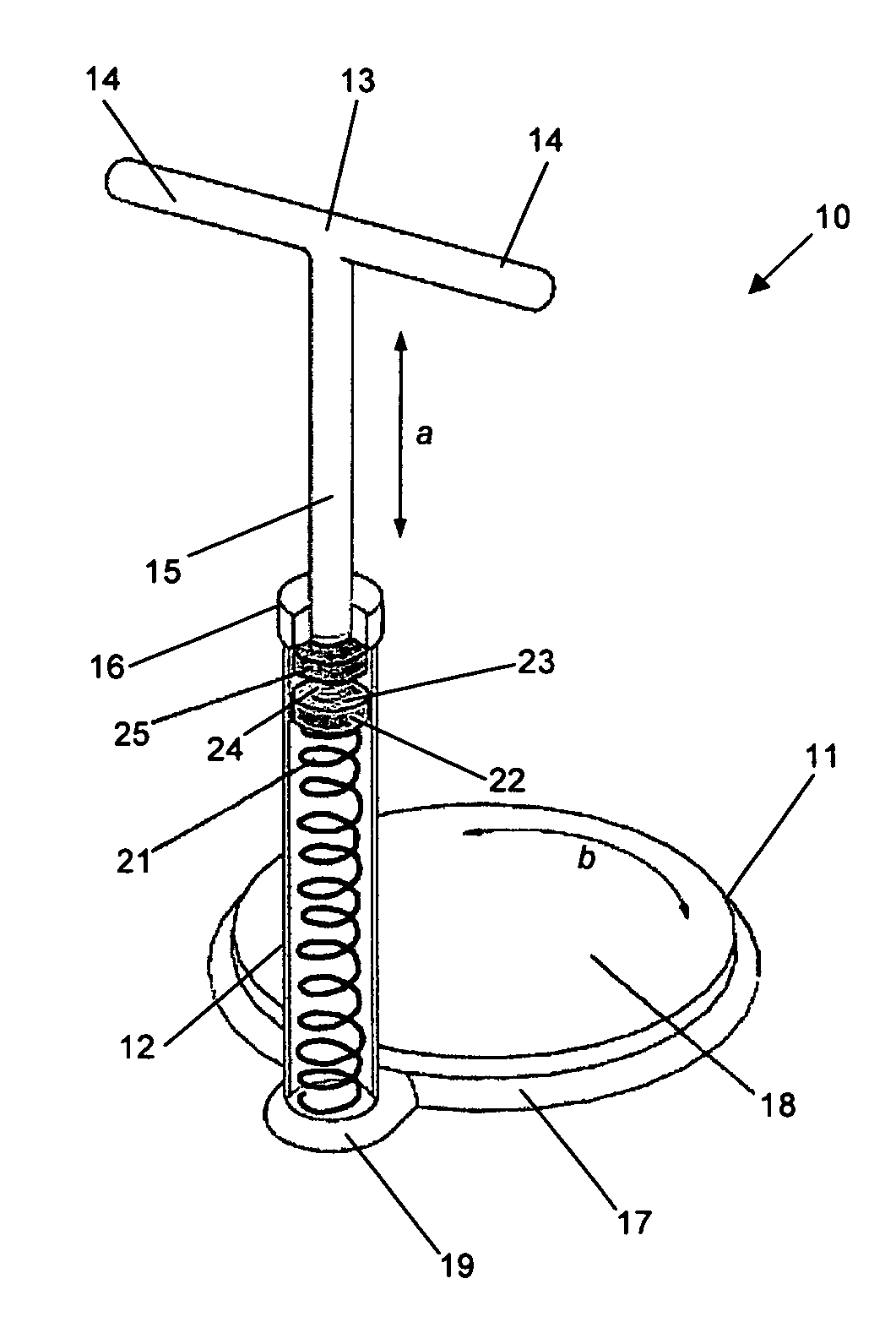
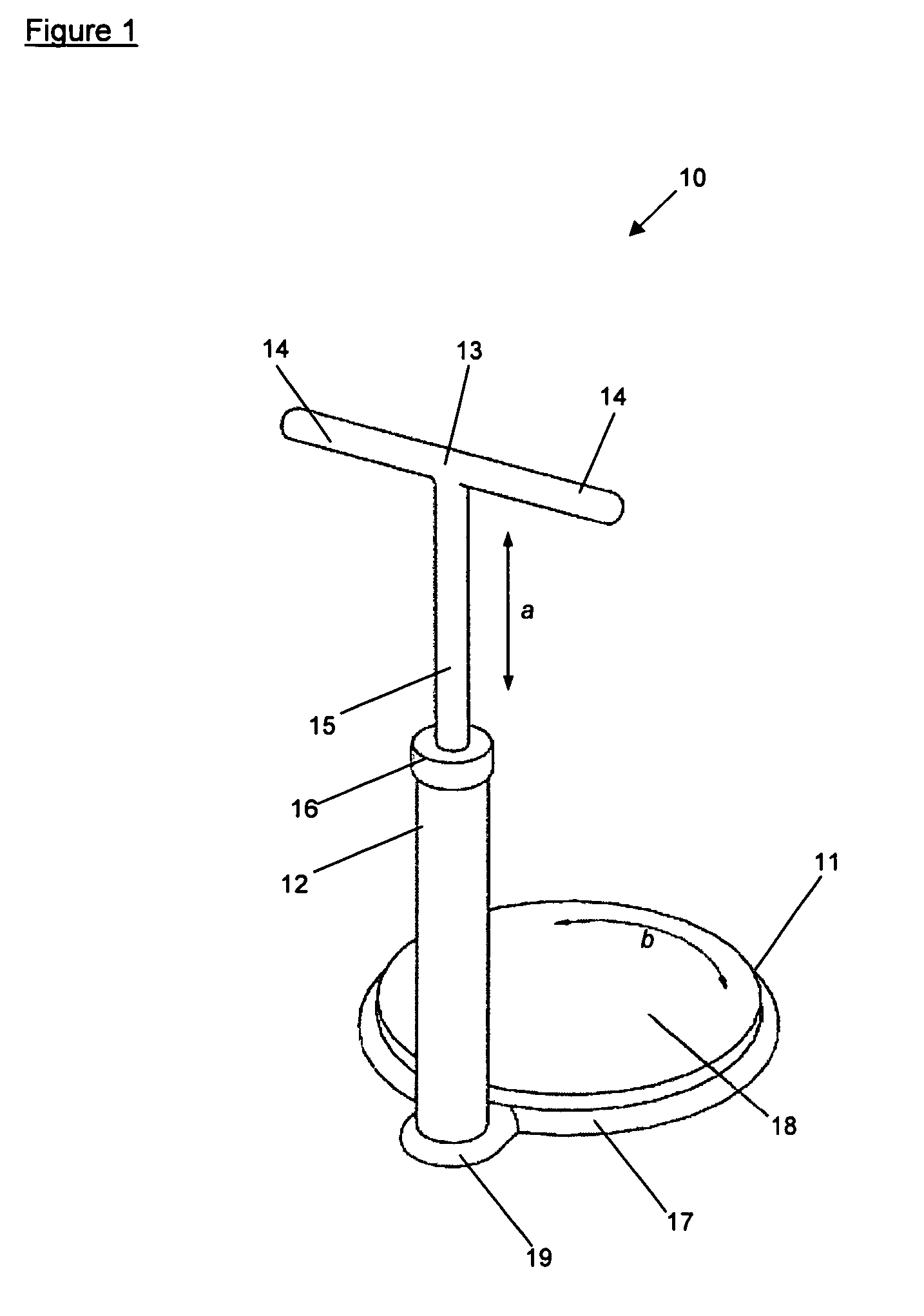
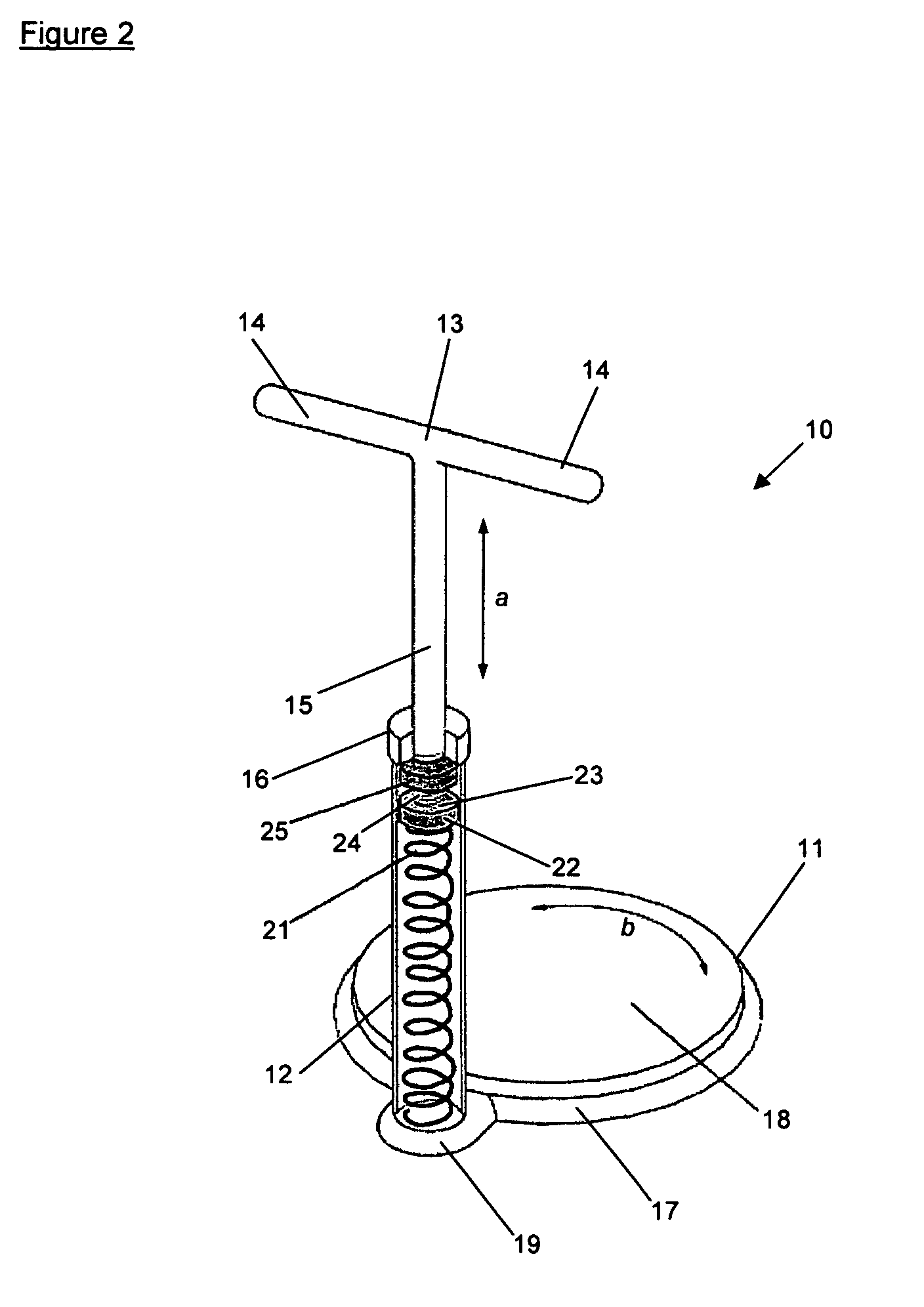
Abdominal muscle training device
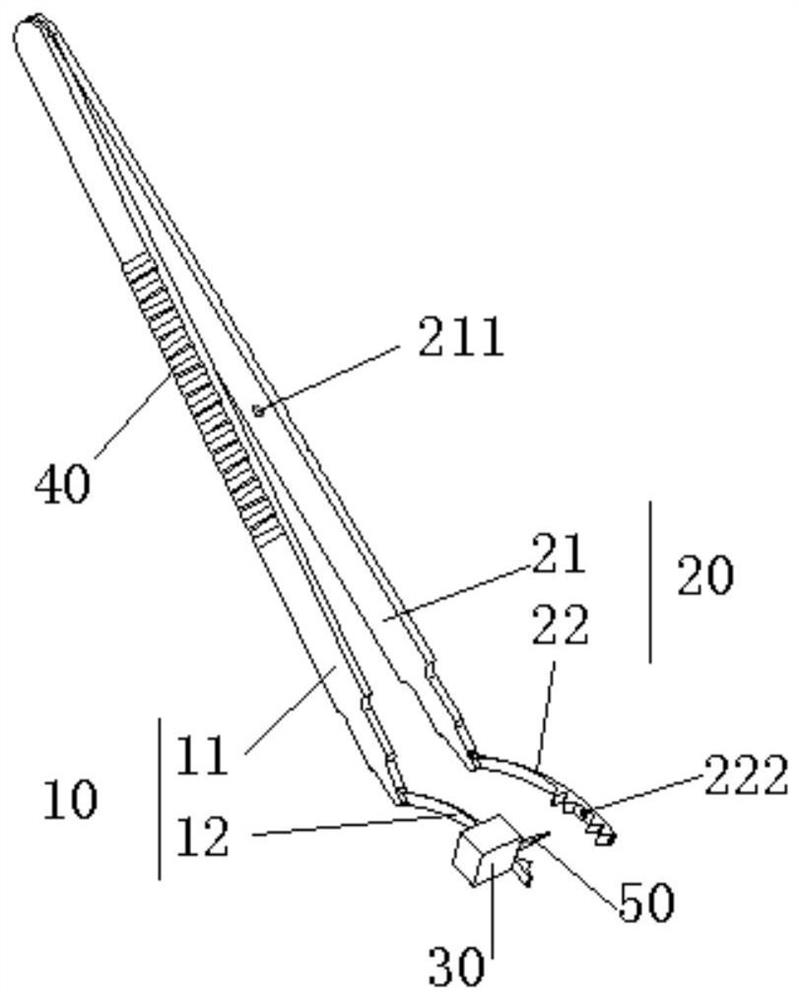
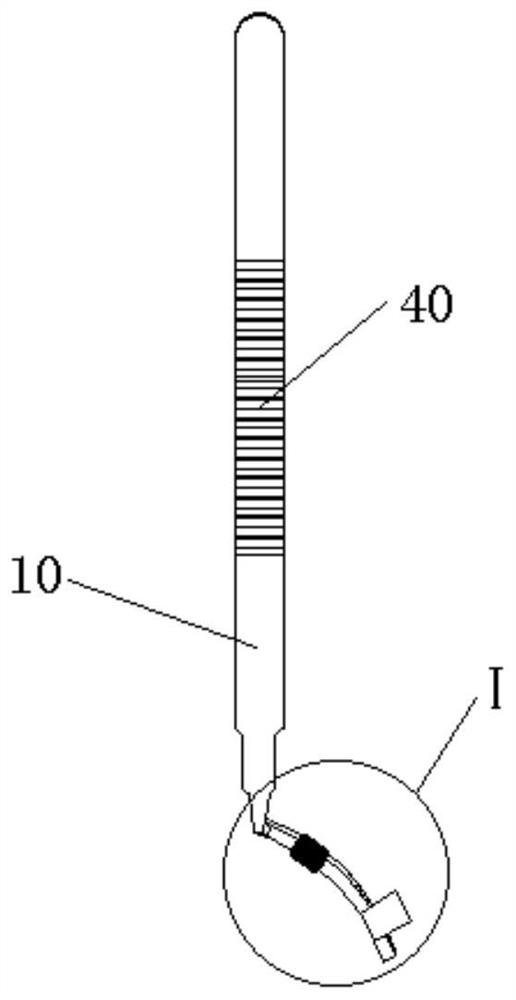
InactiveUS7874969B2Improve efficiency and specificityPrevent removalResilient force resistorsFreely-suspended gymnasticsEngineeringPlunger
A training device (10) for exercising the abdominal muscles (40) of a user (30), comprises a base portion (11), an upstanding resistance member (21) contained within a housing (12) and a plunger (13). The resistance member (21) is operably connected to the plunger (13) and is biased normally to urge the plunger (13) upwardly out of the housing (12). By standing on the base portion (11) and exerting a downward force (c) on the plunger (13) whilst keeping his arms (41, 42) and legs (43, 44) straight, the user (30) causes his abdominal muscles (40) to work to overcome the resistance to the downward motion of the plunger (13) provided by the resistance member (21), thus driving the plunger (13) downwards into the housing (12).
Owner:PROGRESSIVE SPORTS TECH
Abdominal muscle exercise device
InactiveCN107823849AEven by forceTurn for easy controlMovement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesPortable powerEngineering
The invention discloses an abdominal muscle exercise device. The abdominal muscle exercise device comprises a supporting tube, two rolling wheels arranged on the supporting tube, and a speed change mechanism arranged between the two rolling wheels, wherein motors are fixedly mounted at two ends of the inside of the supporting tube; a circuit board and a storage battery are fixedly mounted at the positions, at the outer ends of each motor, in the supporting tube; portable power supplies are mounted at two ends of the inside of the supporting tube; a reversing button is fixedly connected to theposition, close to the rolling wheels, of the outer wall of the supporting tube; the speed change mechanism comprises a transmission base, a positioning frame and an annular gear. For the abdominal muscle exercise device, the rotation of the rolling wheels can be conveniently controlled, so that the strain caused to a user due to the fact that the rolling wheels are out of control during rolling is avoided; after the speed change mechanism is taken out, the abdominal muscle exercise device can be used as a common abdomen building wheel; the portable power supplies in the supporting tube can betaken out according to requirements and used as charge pals.
Owner:杨慧
Cervicothoracic spine restorator
ActiveUS11147704B2Preventing and correcting the straight neck or military neckEasy to relaxChiropractic devicesVibration massagePectoralis minor muscleCervicothoracic spine
A cervicothoracic spine restorator is disclosed. In the cervicothoracic spine restorator, a fixing structure is further included, such that relaxation of muscles such as pectoralis major muscle, pectoralis minor muscle, rectus abdominis muscle, and trapezius muscle or latissimus dorsi muscle can be easily performed. Further, the blood vessel may be expanded and the blood may be supplied smoothly to the head. This may help recovery and correction during a short correction period. There is an advantage that a separate correction mechanism, which is used for spine correction such as a abdomen band, is unnecessary.
Owner:YOO WON SEOK +1
Abdominal muscle exercise device
InactiveCN107823848AEven by forceTurn for easy controlMovement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesPortable powerEngineering
The invention discloses an abdominal muscle exercise device. The abdominal muscle exercise device comprises a supporting tube, two rolling wheels arranged on the supporting tube, and a speed change mechanism arranged between the two rolling wheels, wherein motors are fixedly mounted at two ends of the inside of the supporting tube; a circuit board and a storage battery are fixedly mounted at the positions, at the outer ends of each motor, in the supporting tube; portable power supplies are mounted at two ends of the inside of the supporting tube; a reversing button is fixedly connected to theposition, close to the rolling wheels, of the outer wall of the supporting tube; the speed change mechanism comprises a transmission base, a positioning frame and an annular gear. For the abdominal muscle exercise device, the rotation of the rolling wheels can be conveniently controlled, so that the strain caused to a user due to the fact that the rolling wheels are out of control during rolling is avoided; after the speed change mechanism is taken out, the abdominal muscle exercise device can be used as a common abdomen building wheel; the portable power supplies in the supporting tube can betaken out according to requirements and used as charge pals.
Owner:杨慧
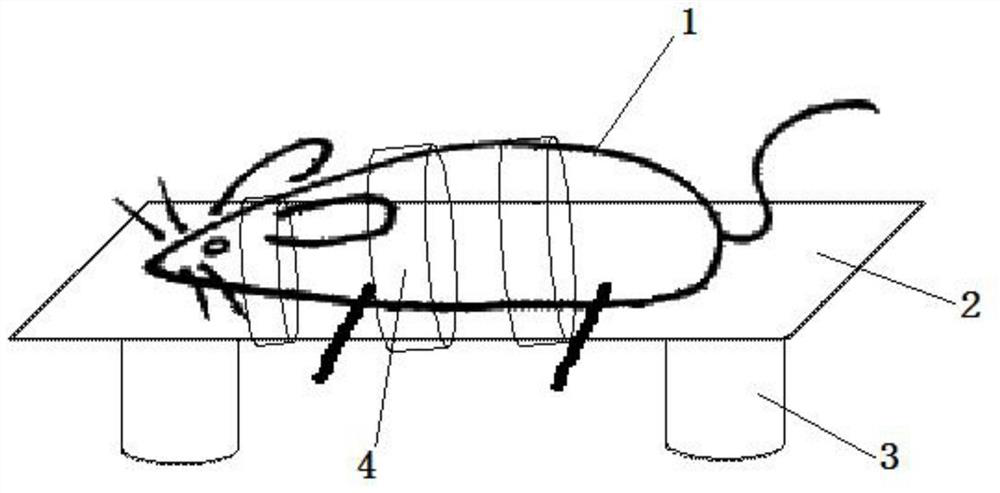
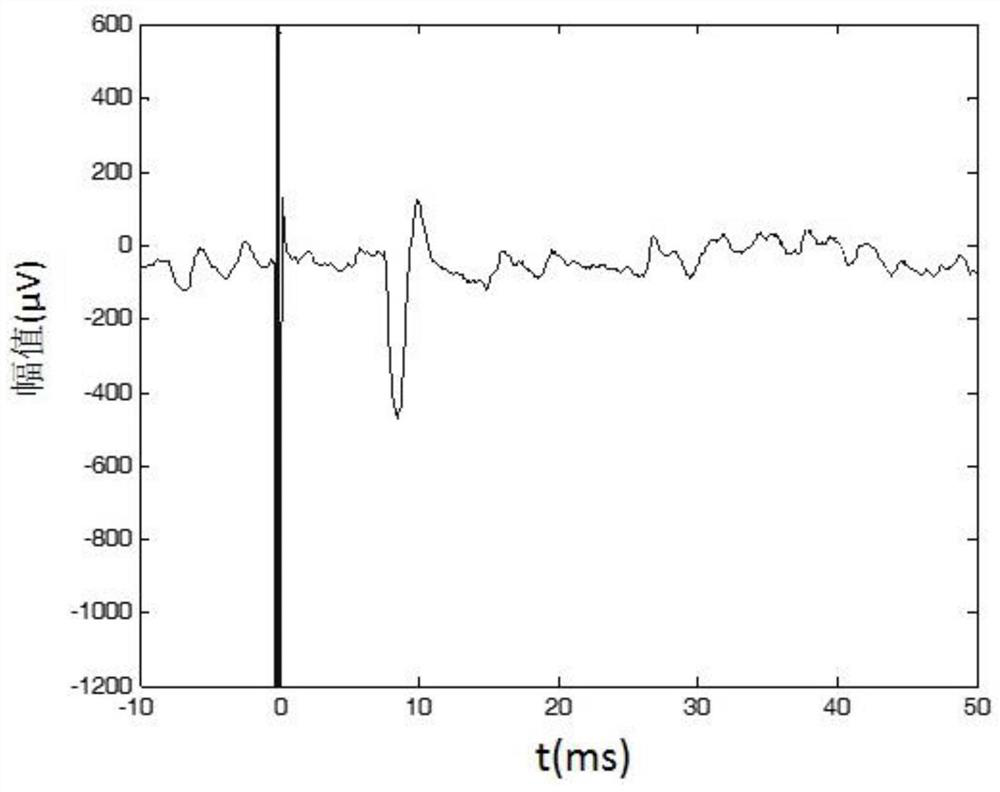
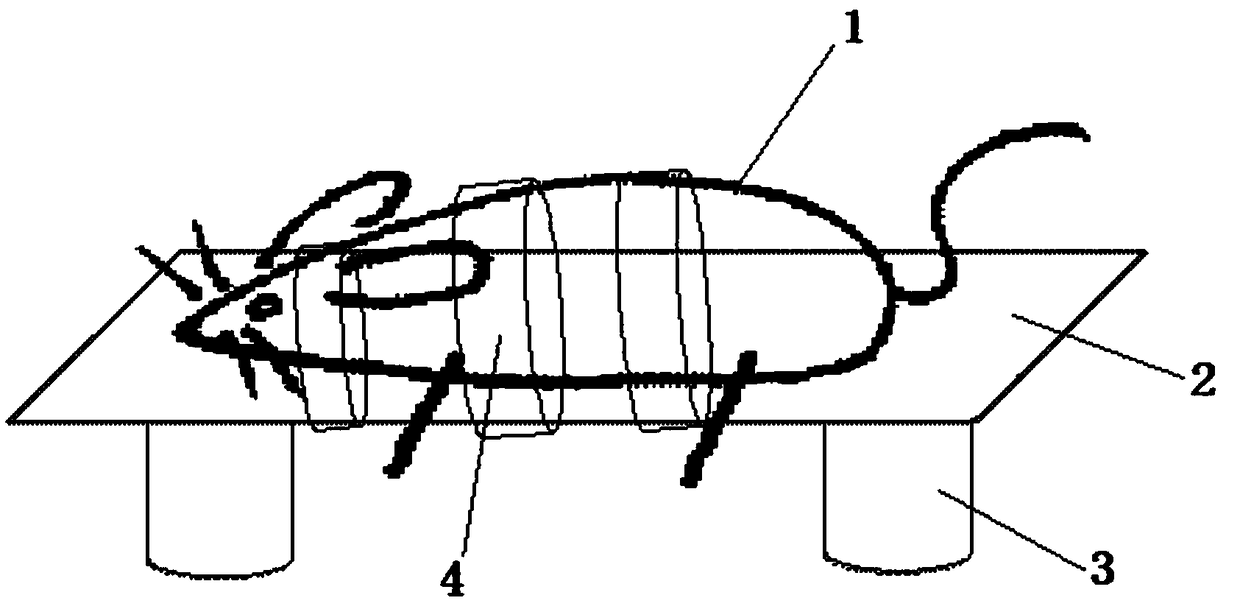
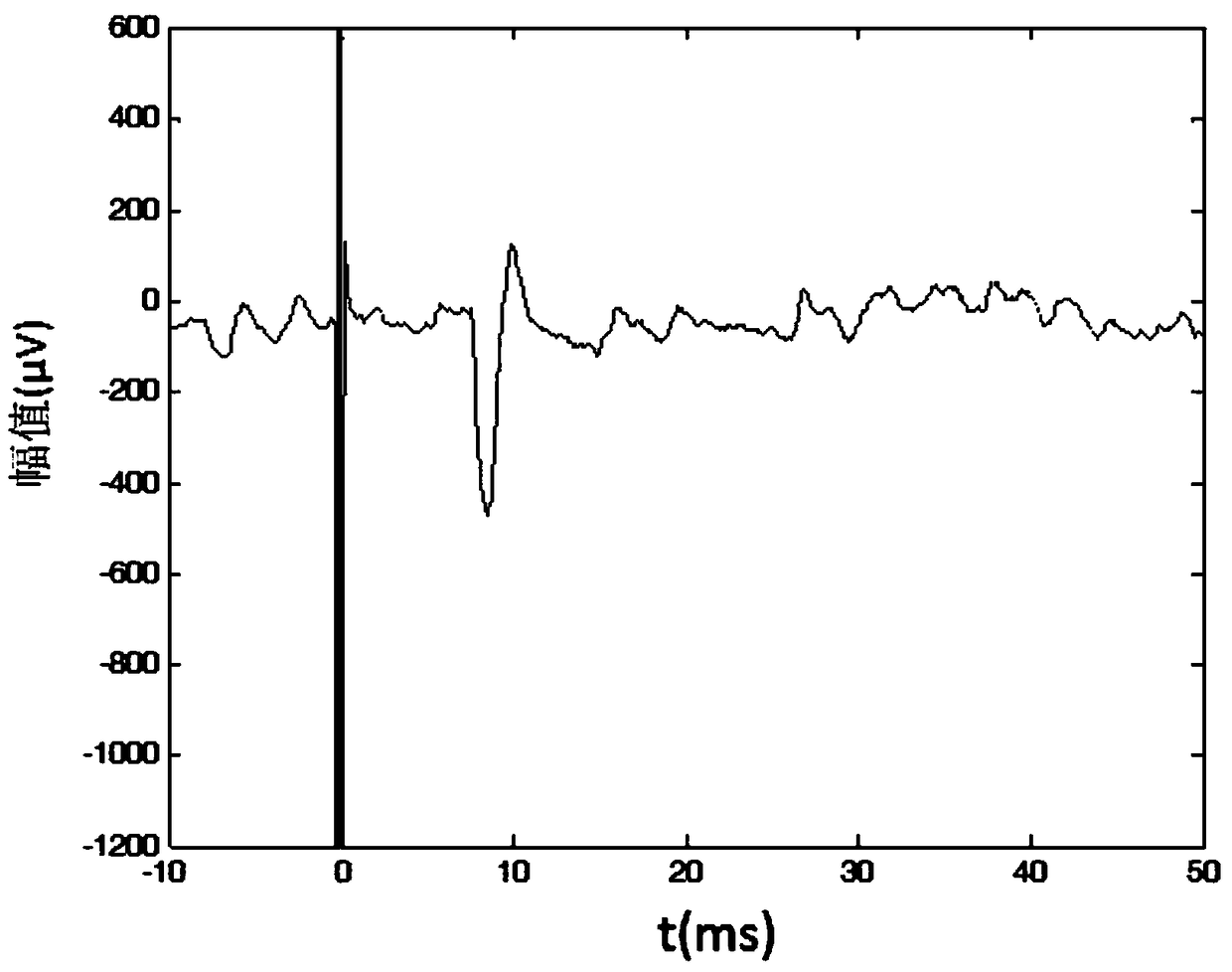
A method for measuring tms motor threshold in awake rats
A method for measuring the TMS motor threshold in rats in an awake state, comprising: anesthetizing the rats for 2-3 minutes by means of inhalation gas anesthesia; The restraint is fixed on the bracket, the height of the bracket is greater than the length of the front and rear limbs of the rat, so that the rat limbs are suspended in the air and kept in a relaxed state; the hair around the target muscles of the rat limbs is shaved to expose the belly and tendon of the target muscles, and the surface EMG is pasted. Measuring electrodes and grounding electrodes; TMS pulses are applied to the motor cortex of rats in an awake state, and TMS in an awake state of rats is completed by observing the twitching of the rat limbs or by analyzing the motor-evoked potentials in the surface electromyographic signals of the target muscles Measurement of motor threshold. The invention can measure the TMS movement threshold of the rat in the awake state. Compared with the TMS motor threshold under anesthesia, the TMS motor threshold in the awake state is more helpful to accurately set the TMS stimulation intensity in the rat TMS experiment.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Novel Recording Approach of Stapedius Muscle Activity
InactiveUS20160325095A1Head electrodesElectromyographyPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFacial nerve
A method of placing a stapedius activity sensor in a stapedius muscle of a patient is described. The stapedius muscle has a tendon end connecting to the stapes bone, and an opposing muscle belly end where the facial nerve innervates the stapedius muscle. A mastoidectomy is performed to create an opening through mastoid bone of the patient. A lead groove is drilled in temporal bone of the patient following a route along the facial nerve to the muscle belly end of the stapedius muscle. The stapedius activity sensor is then introduced along the lead groove to insert a distal end of the stapedius activity sensor into the muscle belly end of the stapedius muscle.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Method for measuring TMS movement threshold in mouse waking state
ActiveCN108903939AEasy to restrain and fixAccurate settingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMotor evoked potentials monitoring
The invention discloses a method for measuring a TMS movement threshold in a mouse waking state. The method comprises the following steps: performing 2-3 minutes of anesthesia on a mouse by using a suction-type gaseous anesthesia mode; placing the anesthetic mouse on a bracket, and constraining and fixing the mouse on the bracket through a self-adhering bandage, wherein a height of the bracket isgreater than a length of front and rear limbs of the mouse, enabling the limbs of the mouse to be suspended and keeping a relaxing state; barbering around a target muscle of the limbs of the mouse, exposing a muscle belly and a muscle tendon of the target muscle, and pasting a surface myoelectricity measuring electrode and a grounding electrode; in the waking state of the mouse, enabling a TMS pulse to act on a mouse movement cortex, through observing mouse limb movement or through analyzing a movement evoked potential in a surface electromyogram signal at the target muscle, completing measurement of the TMS movement threshold in the mouse waking state. The method is capable of measuring the TMS movement threshold in the mouse waking state. The TMS movement threshold in the waking state ismore helpful to accurately set TMS stimulus intensity in a mouse TMS experiment compared with the TMS movement threshold in an anesthetic state.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Rehabilitation therapeutic apparatus for intelligently activating intrinsic muscles of hand
PendingCN109821150AFlexible adjustmentAdjust the site of electrical stimulationVibration massageArtificial respirationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationHand muscle
The invention discloses a rehabilitation therapeutic apparatus for intelligently activating intrinsic muscles of the hand. The rehabilitation therapeutic apparatus comprises a controller, two electrode slice assemblies, multiple first electrode slices and a first elastic layer for wrapping the hand. The electrode slice assemblies and the first electrode slices are all arranged on the first elasticlayer, the two electrode slice assemblies are located at the ends of the first elastic layer respectively, the first electrode slices are located between the two electrode slice assemblies and sequentially arranged in the length direction of the first elastic layer, and the electrode slice assemblies and the first electrode slices correspond to the positons, opposite to muscle bellies of the handmuscles, of the first elastic layer. The first electrode slices and the two electrode slice assemblies are electrically connected with a controller and electrically connected with a surface myoelectricity detecting device and a vibration device, and the vibration device and the surface myoelectricity device are connected with the controller. Thus, the arrangement of the electrode slices on the hand can be adjusted by stretching the first elastic layer, and the hand muscles can be targetedly treated through the electrode slices and the vibration device.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
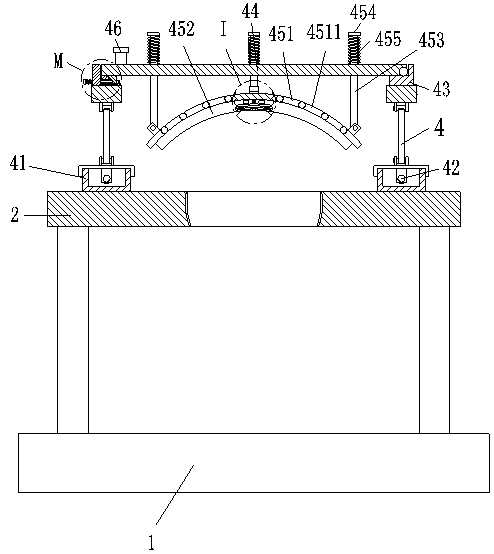
Auxiliary device for exercising abdominal muscles
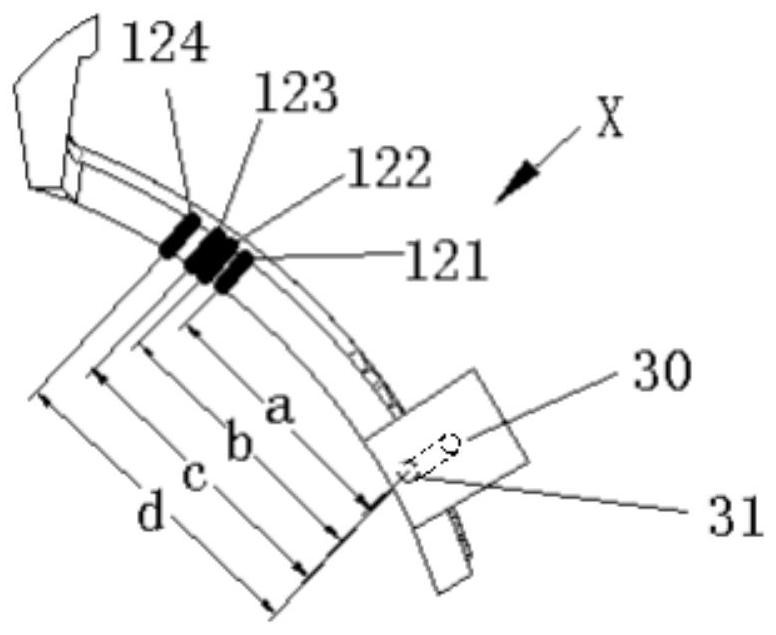
InactiveCN104159643APostural stabilityReduce volumeMuscle exercising devicesRight lesser trochanterShortest distance
Owner:朴刚茂
Needle holding forceps
The invention provides a pair of needle holding forceps, which relates to the technical field of medical instruments and comprises a first forceps arm and a second forceps arm, one end of the first forceps arm is fixedly connected with one end of the second forceps arm, and the other end of the first forceps arm and the other end of the second forceps arm can be close to each other or far away from each other. A needle holding structure used for clamping a suture needle is arranged at the other end of the first forceps arm, and a through hole corresponding to the needle holding structure is formed in the second forceps arm. When the front end of the first forceps arm and the front end of the second forceps arm are used for clamping, the needle tip part of the suture needle clamped by the needle holding structure can penetrate through the muscle belly bottom behind the muscle stopping end of the rectus ocularis and the through hole, the needle tip is pulled out, the suture is tightened, and the vessel forceps are fixed to an operation towel. Compared with the prior art, the pair of needle holding forceps provided by the invention can realize needle passing while clamping, avoids secondary injury caused by repeated attempts in a mode of firstly clamping the muscle stopping end of the rectus eye muscle by using a pair of toothed forceps and then passing the needle, and meanwhile, can prevent sclera from being punctured and reduce the surgical risk.
Owner:GUANGDONG NO 2 PROVINCIAL PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com