Patents
Literature
60 results about "Space antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
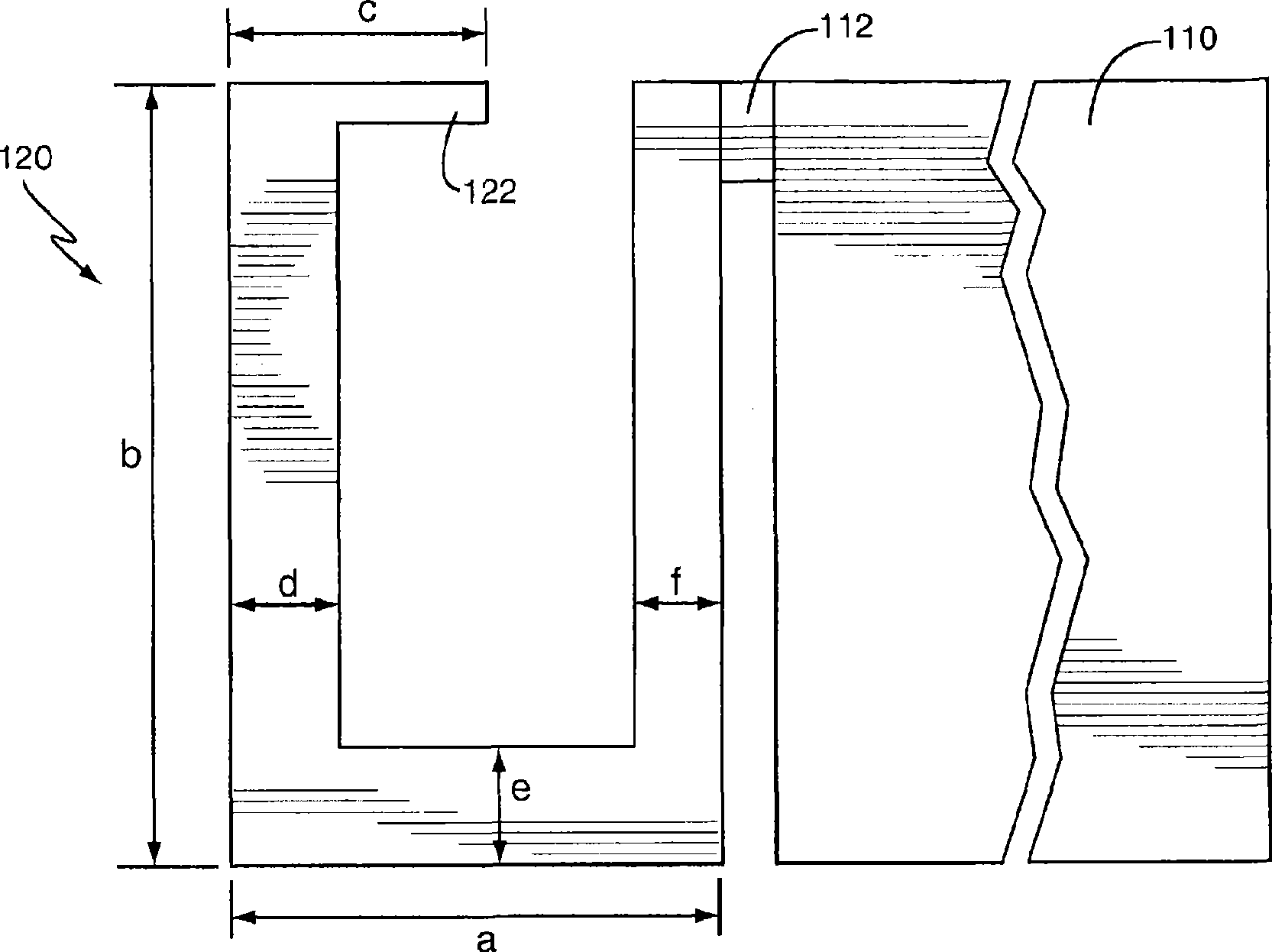
Antenna system and method
InactiveUS20050159187A1Maximize near-field to far field ratioMinimize peak far-field gainAntenna supports/mountingsPosition fixationPhase shiftedTransmitted power
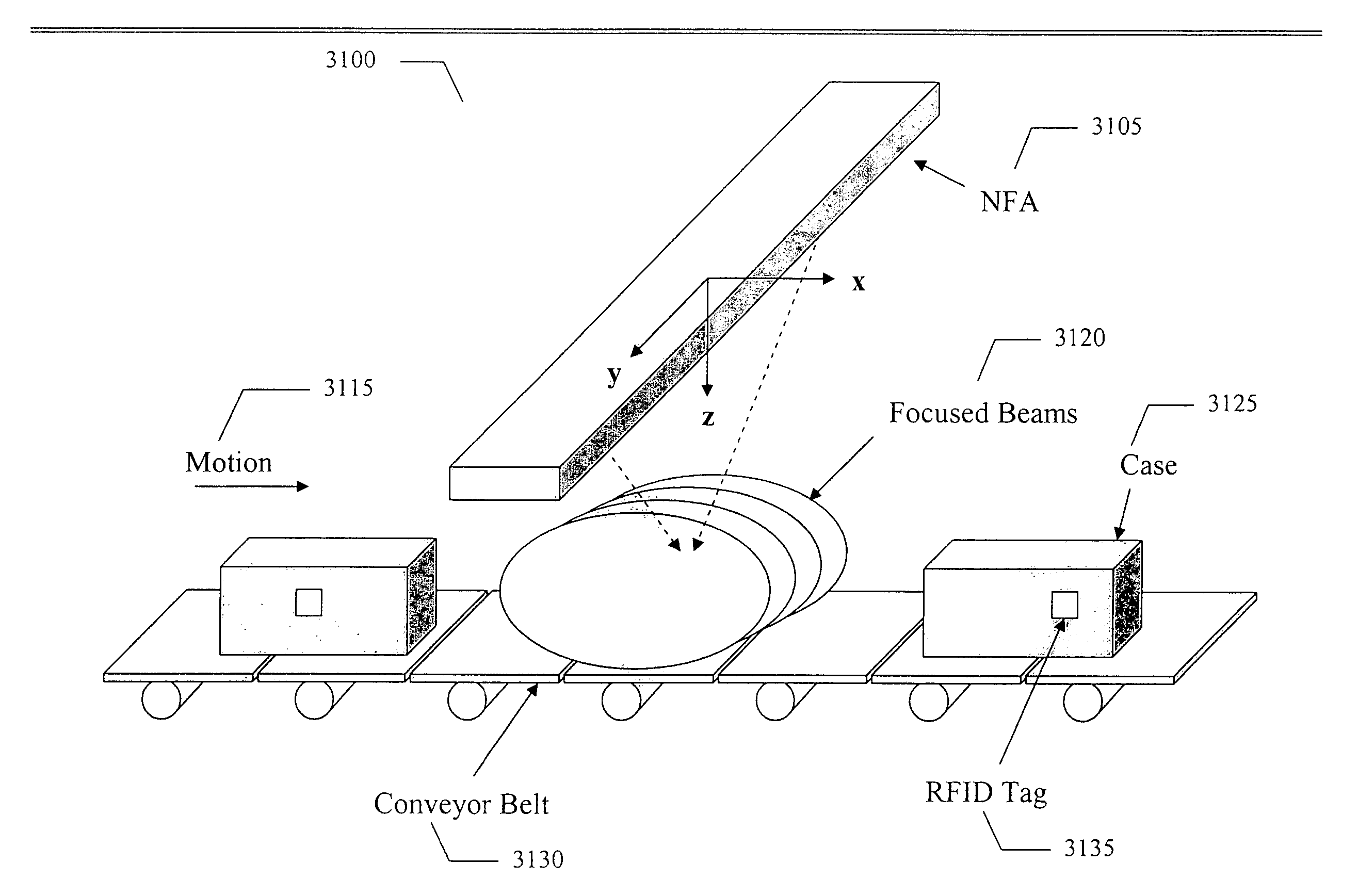
An embodiment of the present invention provides an antenna system, comprising a plurality of non-uniformly spaced antenna elements arranged substantially linearly, a power divider for dividing transmit power thereby coupling signals to the plurality of antenna elements, a phase shifter capable of phase shifting the signals between the power divider and the plurality of antenna elements such that radiated signals from each antenna element add coherently such that the radiated electromagnetic energy may be focused at a focal point in the near field region or in the Fresnel region of the antenna system. An embodiment of the present invention may also provide at least one additional receive antenna element capable of receiving signals backscattered from at least one RFID tag located in the near field of the focused array and the divider may create substantially equal power levels feeding each antenna element. The antenna elements may be similar or identical and each element may be oriented such that the individual element main beam may point in a unique direction.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Small wave-guide radiators for closely spaced feeds on multi-beam antennas
Owner:PRO BRAND INT
RFID tag reading system and method
ActiveUS20050110641A1Optimize dwell timeNear-field transmissionPosition fixationPhase shiftedTransmitted power
An embodiment of the present invention provides an RFID tag reading system, comprising an antenna system associated with a portal through which said RFID tag may pass, said antenna system comprising: a plurality of non-uniformly spaced antenna elements arranged substantially linearly; a power divider for dividing transmit power thereby coupling signals to said plurality of antenna elements; and a beamforming network capable of phase shifting the signals between the power divider and the plurality of antenna elements such that radiated signals from each antenna element add coherently such that the radiated electromagnetic energy is focused at a focal point in the near field region or in the Fresnel region of said antenna system.
Owner:NXP USA INC
MIMO wireless communication system
InactiveUS20020085643A1Spatial diversity is avoidedIncrease link capacitySpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPolarization diversityCommunications system
Previous MIMO systems have used spatially diverse antenna elements in order not to reduce the number of orthogonal channels that can be realised. The present invention recognises that this leads to large antenna sizes, as compared to multiple beam antenna systems which use closely spaced antenna elements. In order to provide a compact antenna unit, while still allowing a MIMO system to be exploited, the present invention recognizes that polarization diversity only can be used in a MIMO system without the need for spatially diverse antenna elements. Closely spaced antenna elements are used and this enables a compact MIMO antenna unit to be provided. In addition, such MIMO systems with polarization diversity but no spatial diversity can advantageously be used in line of sight situations and also combined with multi-beam antenna systems to further increase capacity.
Owner:APPLE INC
MIMO wireless communication system
InactiveUS6870515B2Avoid diversityIncrease link capacitySpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCommunications systemPolarization diversity
Previous MIMO systems have used spatially diverse antenna elements in order not to reduce the number of orthogonal channels that can be realized. The present invention recognizes that this leads to large antenna sizes, as compared to multiple beam antenna systems which use closely spaced antenna elements. In order to provide a compact antenna unit, while still allowing a MIMO system to be exploited, the present invention recognizes that polarization diversity only can be used in a MIMO system without the need for spatially diverse antenna elements. Closely spaced antenna elements are used and this enables a compact MIMO antenna unit to be provided. In addition, such MIMO systems with polarization diversity but no spatial diversity can advantageously be used in line of sight situations and also combined with multi-beam antenna systems to further increase capacity.
Owner:APPLE INC
RFID tag reading system and method
InactiveUS7187288B2Optimize dwell timeNear-field transmissionPosition fixationPhase shiftedTransmitted power
An embodiment of the present invention provides an RFID tag reading system, comprising an antenna system associated with a portal through which said RFID tag may pass, said antenna system comprising: a plurality of non-uniformly spaced antenna elements arranged substantially linearly; a power divider for dividing transmit power thereby coupling signals to said plurality of antenna elements; and a beamforming network capable of phase shifting the signals between the power divider and the plurality of antenna elements such that radiated signals from each antenna element add coherently such that the radiated electromagnetic energy is focused at a focal point in the near field region or in the Fresnel region of said antenna system.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method of performing antenna diversity in spread spectrum in wireless local area network
InactiveUS6563858B1Good diversity selection metricGood energySpatial transmit diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsHigh rate
A method of performing antenna diversity in a wireless spread spectrum communication system is disclosed. A spread spectrum phase shift keyed (PSK) packet signal having data symbols formed from high rate mode chips is received in each of two respective spaced antenna of a spread spectrum receiver. The bit sync peak sample is determined within the packet signal for each antenna. Predetermined bit sync samples are subtracted a predetermined number of chips on either side of the bit sync peak sample from the peak for each antenna. The antenna having the higher value obtained in the subtracting step accomplished for each antenna is selected.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC +1
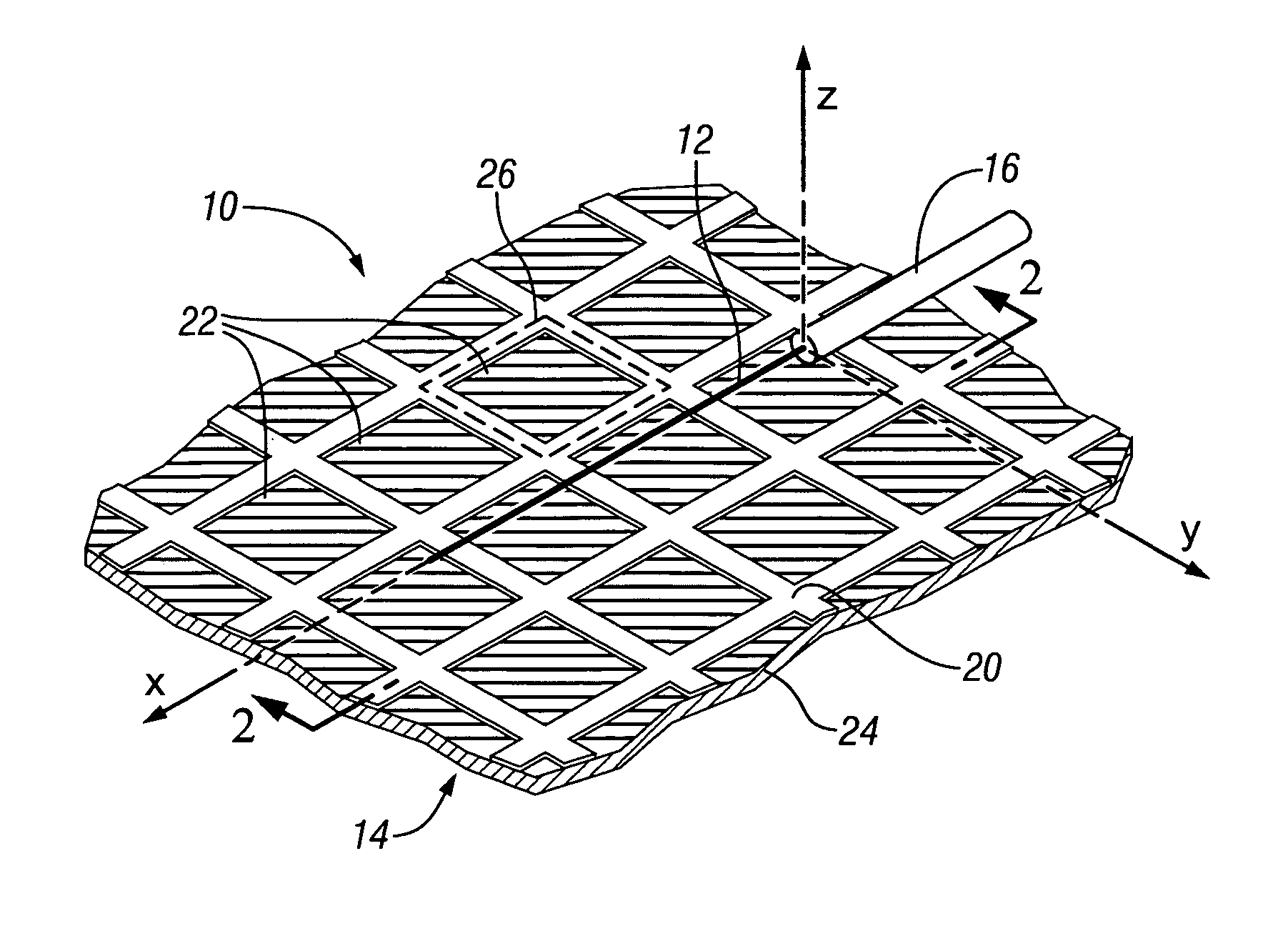
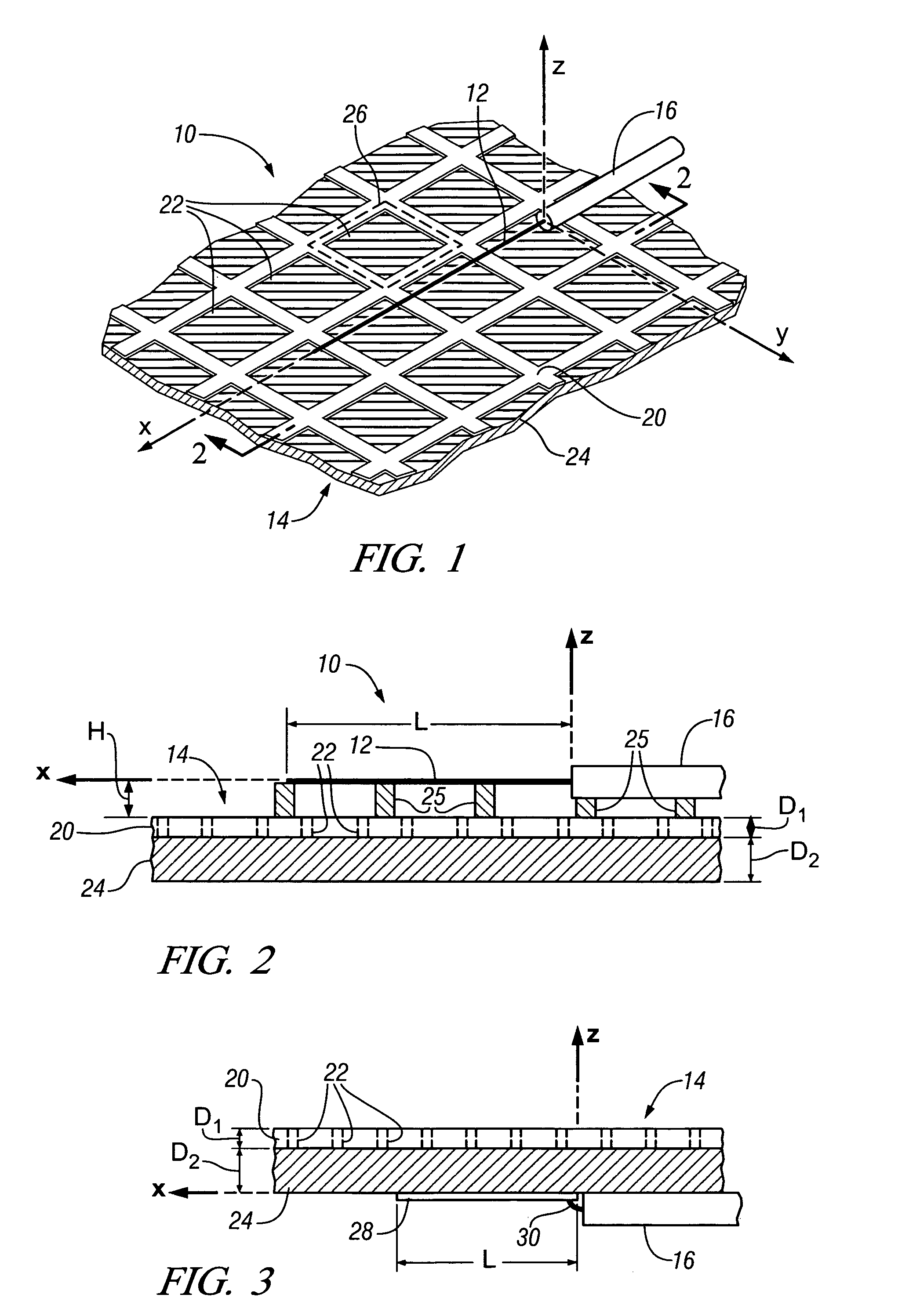
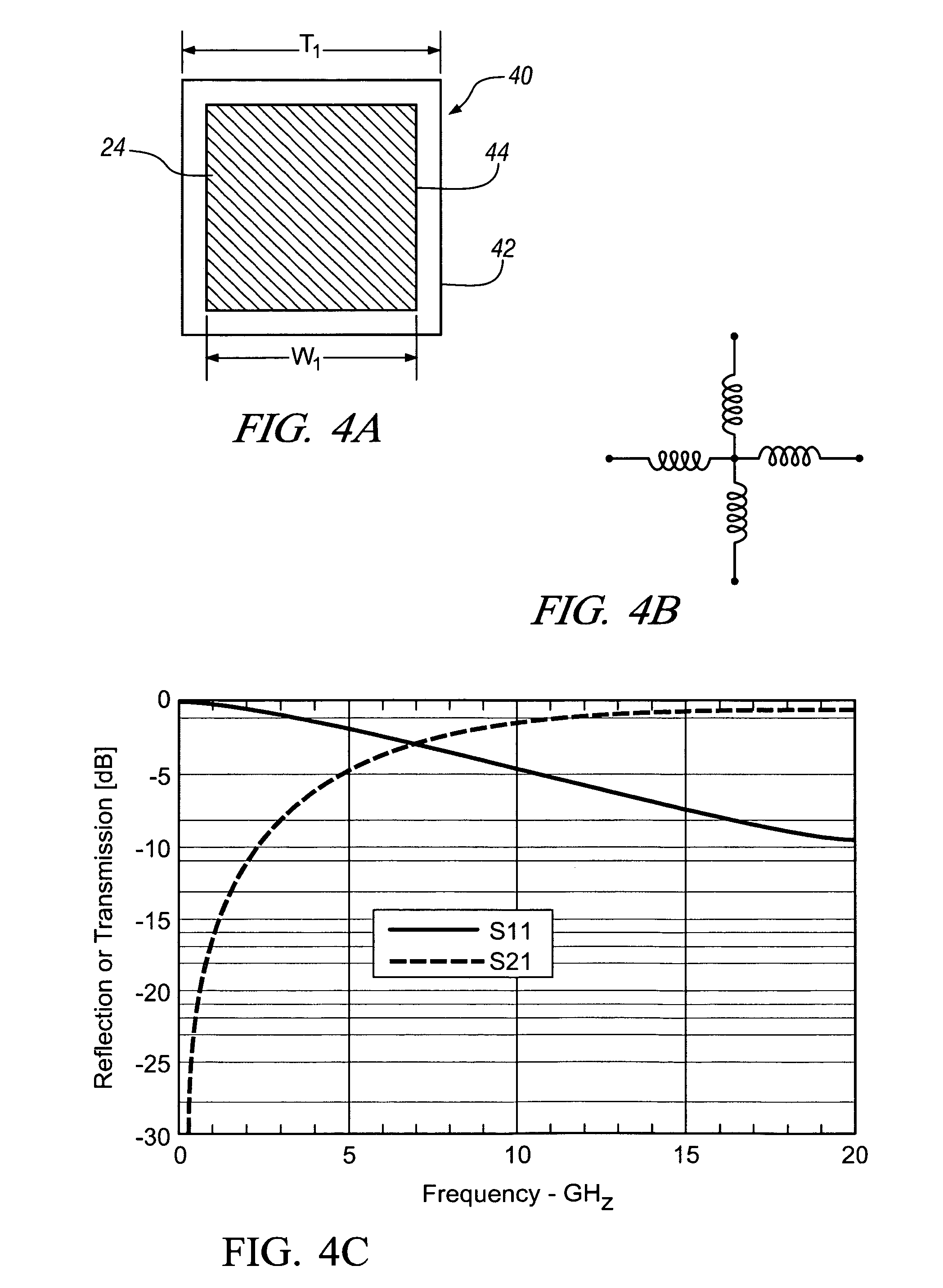
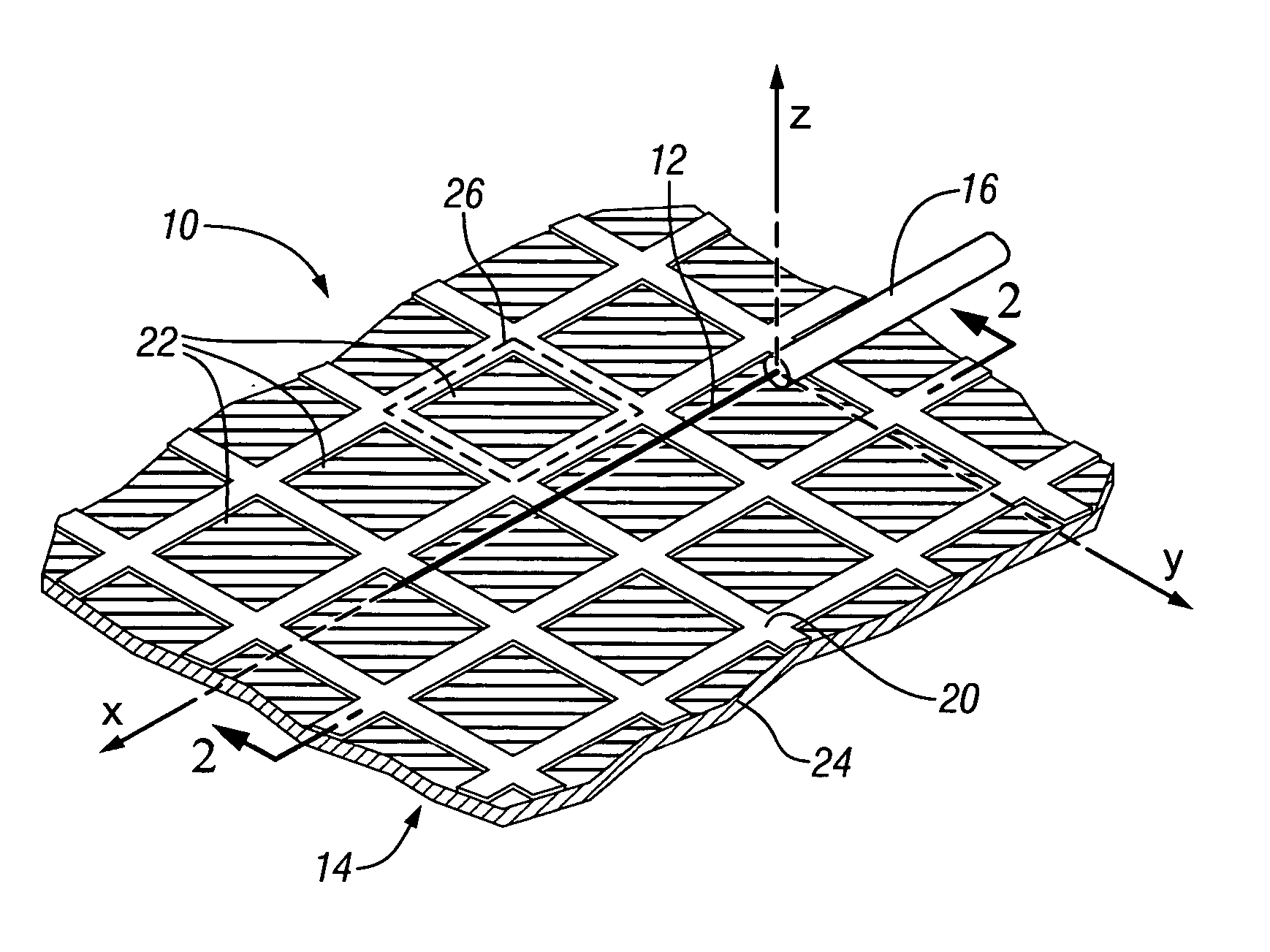
Method for fabricating antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics
InactiveUS20070159395A1Promote near field coupling of electromagnetic energyGreat fabricationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCombined useConductive materials
The radiation properties and wave guiding properties of frequency selective surfaces are used in conjunction with closely spaced antenna elements to fabricate antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics. The direction, magnitude, and polarization of radiation patterns for such antenna structures can be adjusted by varying the texture or patterning of layers of conducting material forming the frequency selective surfaces. The invention enables the fabrication of low profile antenna structures that can easily be conformed or integrated into complex surfaces without sacrificing antenna performance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for fabricating antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics
InactiveUS7429961B2Promote near field coupling of electromagnetic energyGreat fabricationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsConductive materialsAntenna element
The radiation properties and wave guiding properties of frequency selective surfaces are used in conjunction with closely spaced antenna elements to fabricate antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics. The direction, magnitude, and polarization of radiation patterns for such antenna structures can be adjusted by varying the texture or patterning of layers of conducting material forming the frequency selective surfaces. The invention enables the fabrication of low profile antenna structures that can easily be conformed or integrated into complex surfaces without sacrificing antenna performance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics
InactiveUS20070159396A1Promote near field coupling of electromagnetic energyGreat fabricationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsRadiation patternSelective surface
The radiation properties and wave guiding properties of frequency selective surfaces are used in conjunction with closely spaced antenna elements to fabricate antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics. The direction, magnitude, and polarization of radiation patterns for such antenna structures can be adjusted by varying the texture or patterning of layers of conducting material forming the frequency selective surfaces. The invention enables the fabrication of low profile antenna structures that can easily be conformed or integrated into complex surfaces without sacrificing antenna performance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics
ActiveUS20090002240A1Promote near field coupling of electromagnetic energyGreat fabricationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsRadiation patternSelective surface
The radiation properties and wave guiding properties of frequency selective surfaces are used in conjunction with closely spaced antenna elements to fabricate antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics. The direction, magnitude, and polarization of radiation patterns for such antenna structures can be adjusted by varying the texture or patterning of layers of conducting material forming the frequency selective surfaces. The invention enables the fabrication of low profile antenna structures that can easily be conformed or integrated into complex surfaces without sacrificing antenna performance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
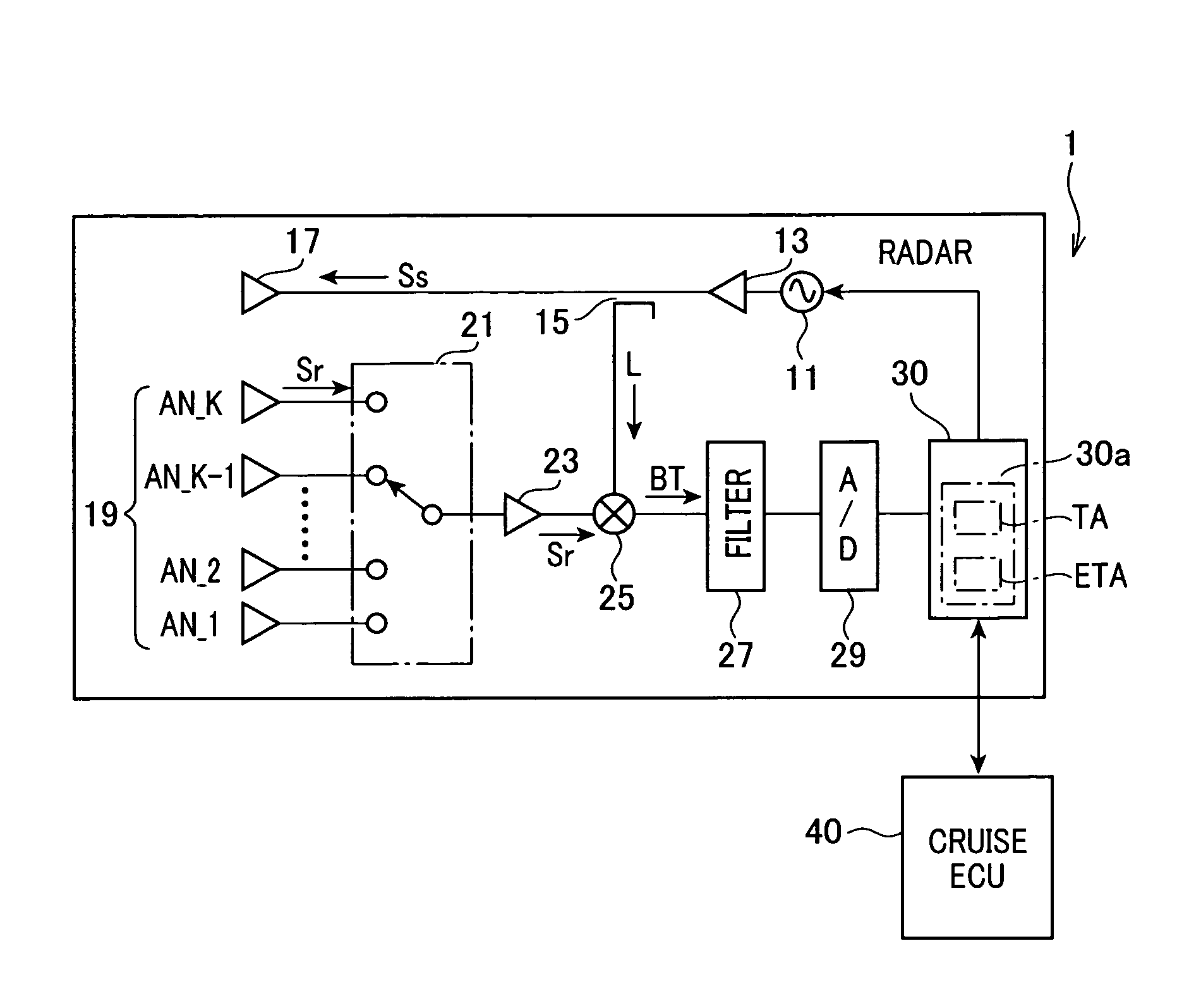
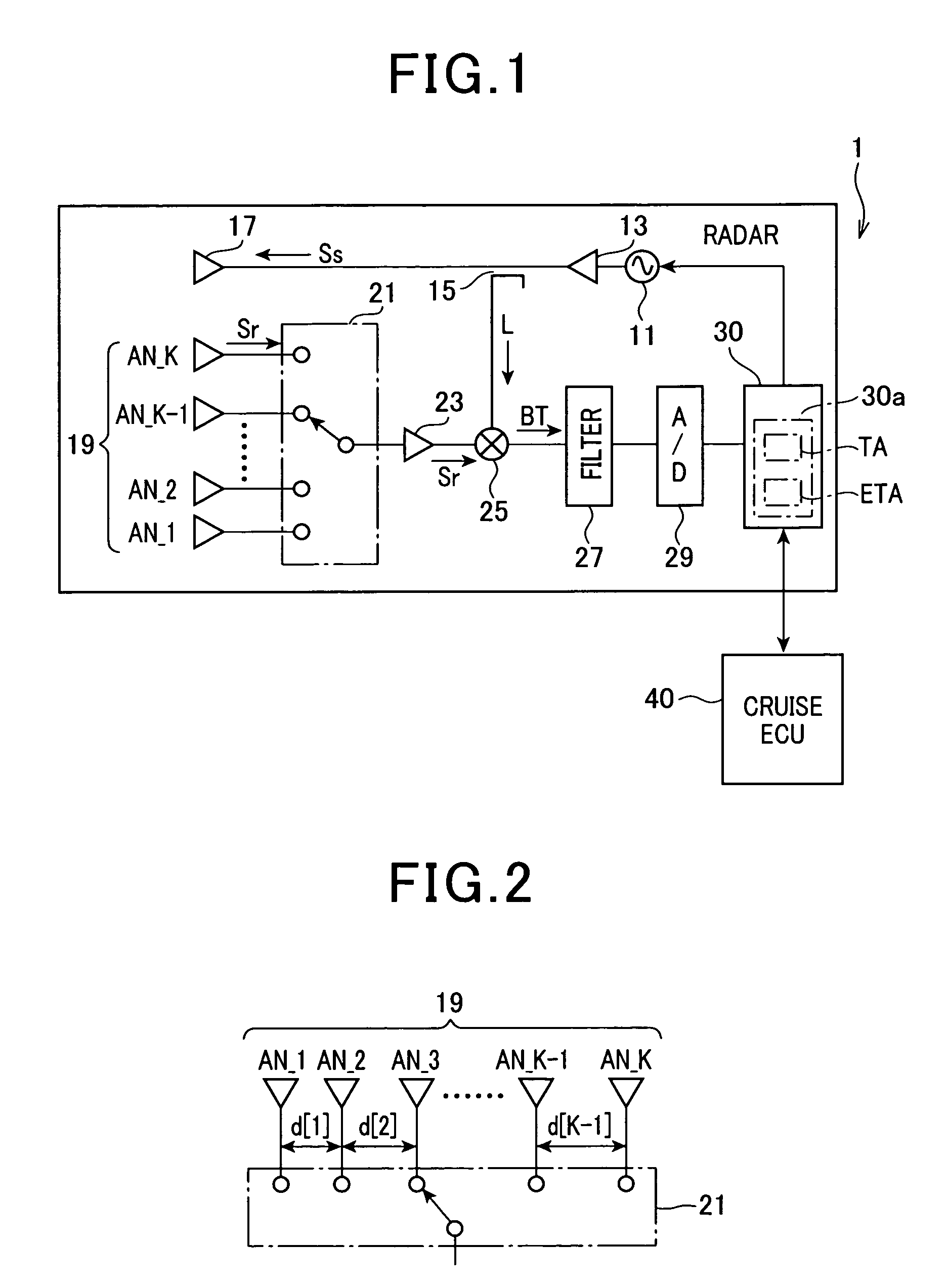
Radar with non-uniformly spaced antenna array
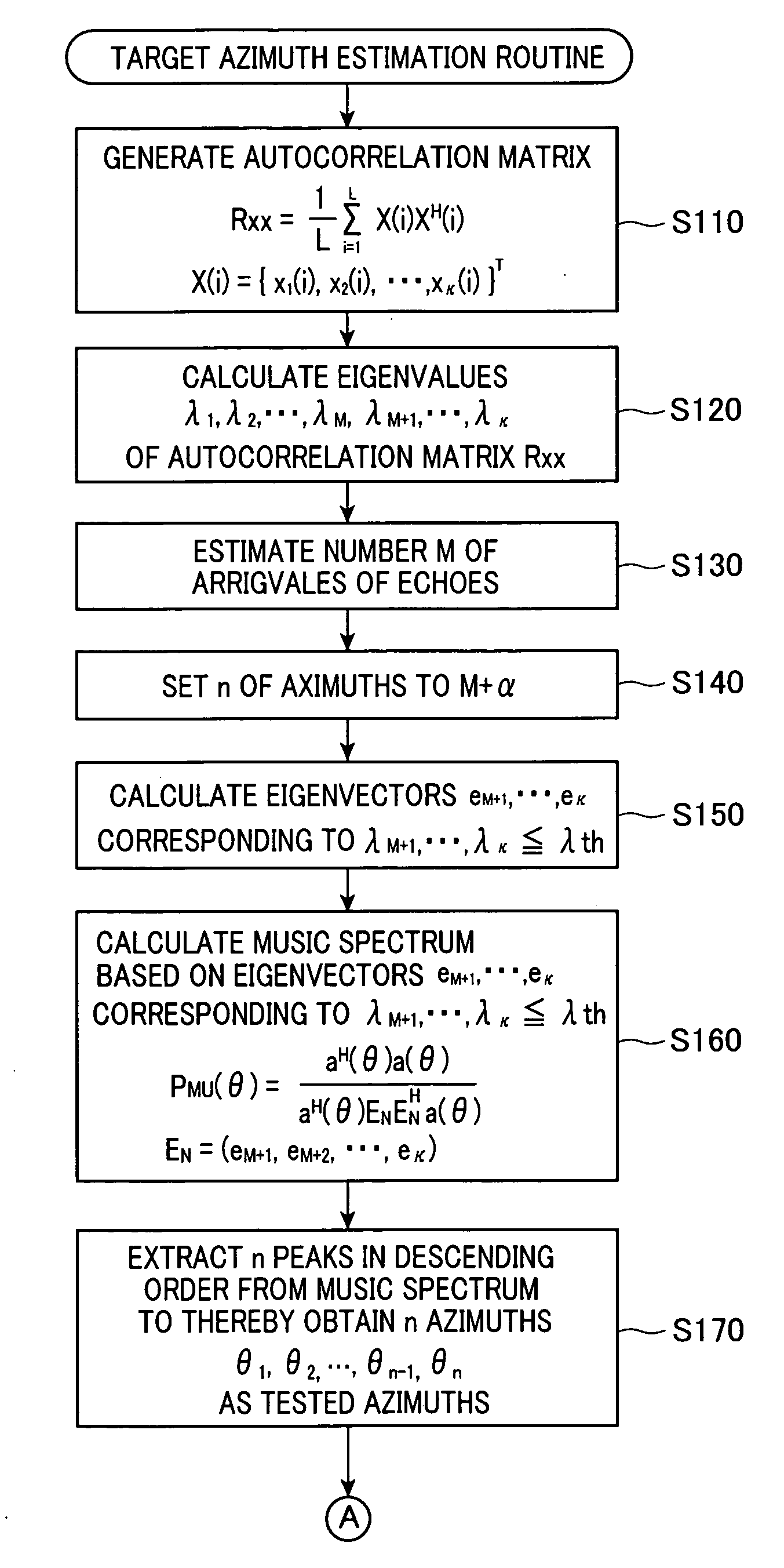
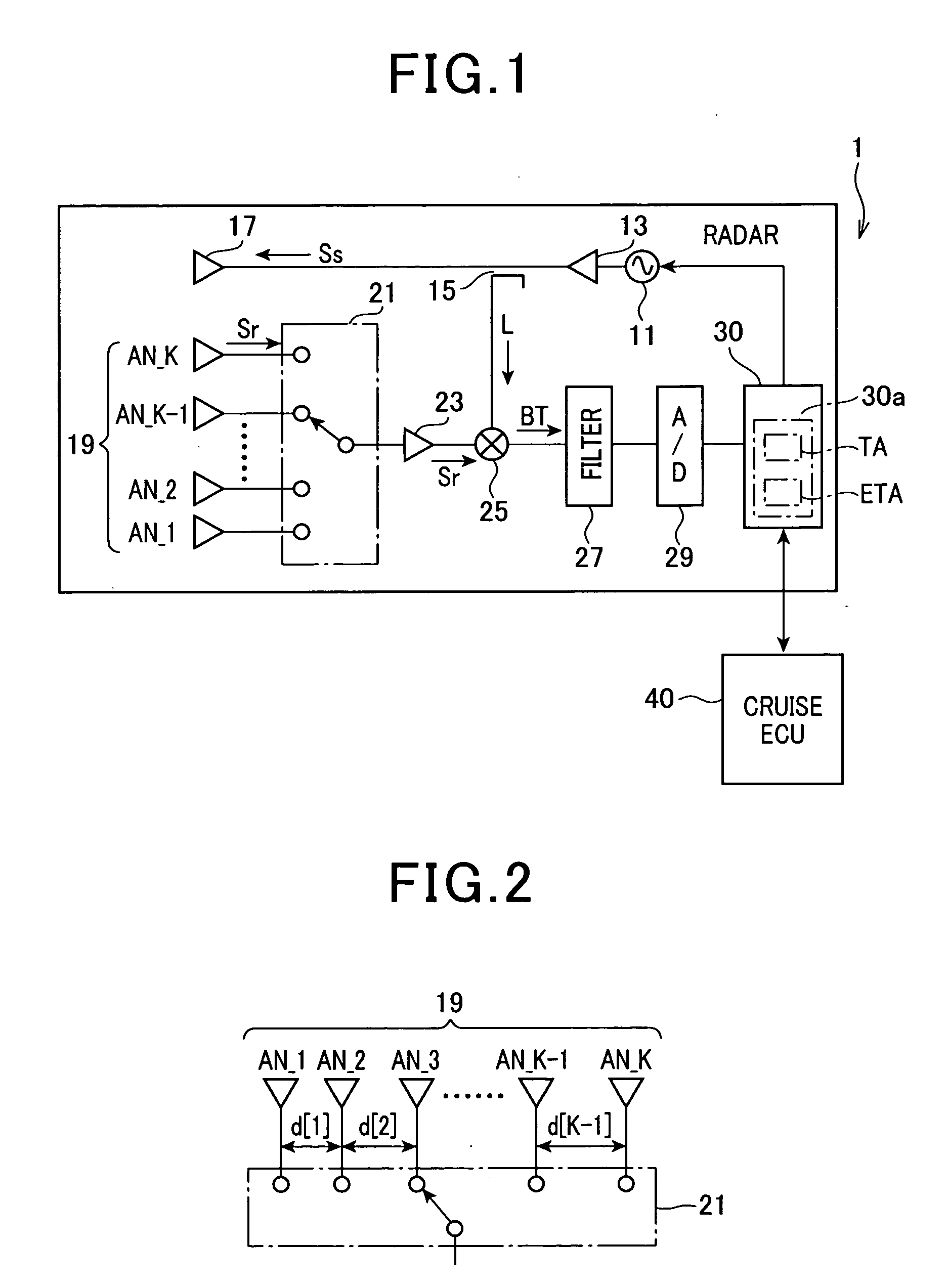
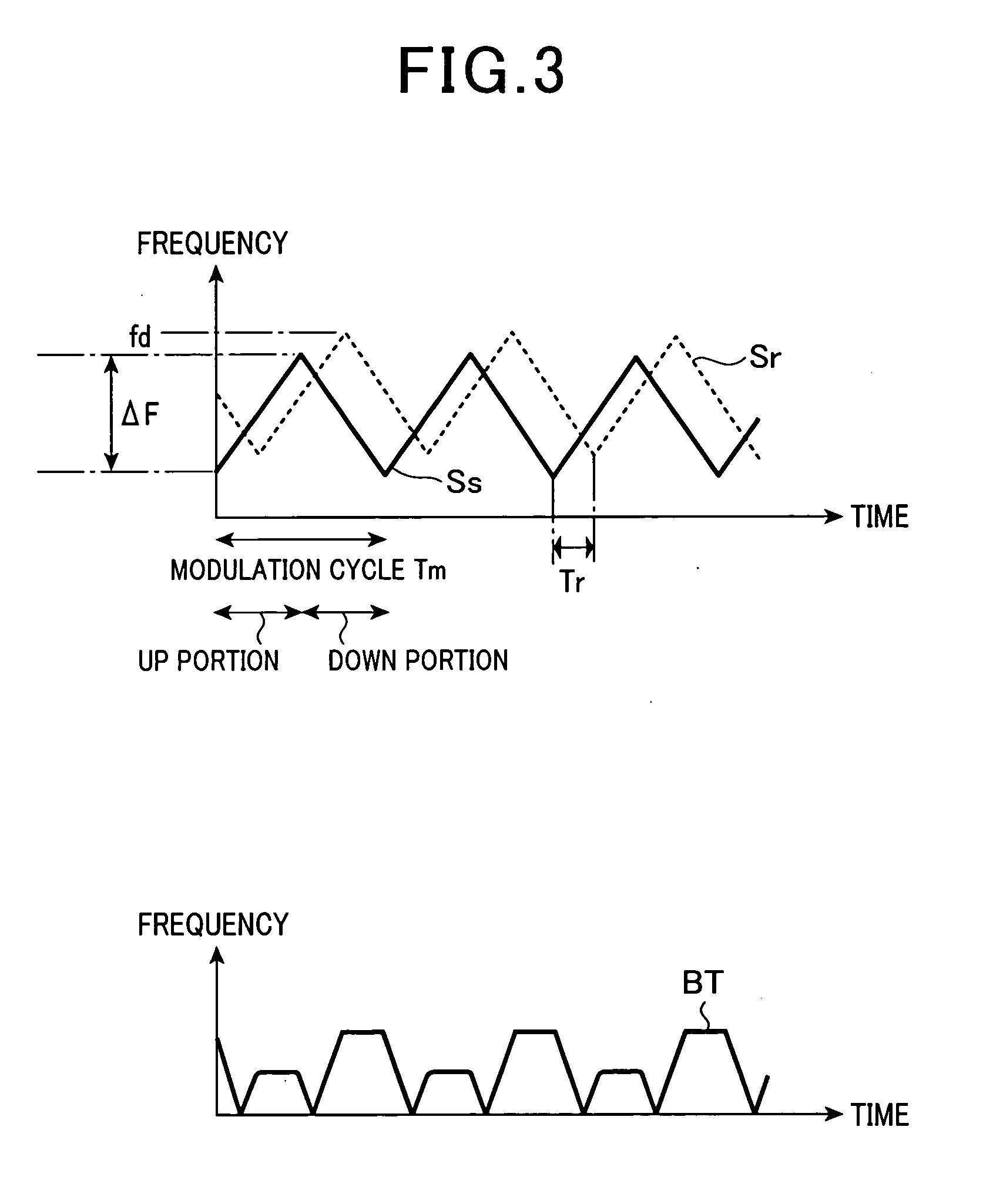
ActiveUS20100019954A1Raise the possibilityDeteriorating estimation accuracy of azimuthMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesIndividually energised antenna arraysSetterRadar
In a radar with a non-uniformly spaced antenna array, an extractor estimates a number of arrivals of echoes to the antenna array. A setter sets a number of azimuths corresponding to a number of extracted peaks as a number of tested azimuths greater than the number of arrivals of echoes by a preset number. A determiner determines a level of correlations among steering vectors respectively corresponding to the tested azimuths. A selector selects, from the tested azimuths, azimuths as power-estimation targets based on the determined level of the correlations among the steering vectors. A first estimator estimates a received power level from each power-estimation target. A second estimator estimates, from the power-estimation targets, an azimuth of the target based on the estimated received power level from each power-estimation target. The estimated received power level from the azimuth is equal to or greater than a preset threshold level.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Deformable antenna reflection surface
ActiveCN101872904ARealize on-orbit deformationHigh specific modulusAntennasStructural deformationVibration control
The invention discloses a deformable antenna reflection surface and relates to the antenna reflection surface. The invention aims at solving the problems that the existing reflector antenna can not meet the space environment which is complex and variable and can not carry out orbit thermal deformation control and on-orbit vibration control in space, thereby reducing the precision of the on-orbit reflector antenna and being incapable of meeting various space requirements because the existing space antenna can not have the structural deformation. A driver comprises an end cover, a driving shaft, a housing, a working coil or a conducting wire and a driving functional material body, wherein the end cover is arranged on the housing, the driving shaft is crisscross, one end of the driving shaftis connected with the end cover, the opposite end is connected with the driving functional material body, the other two ends are in contact with the side wall of the housing, the driving shaft can slide along the axial direction of the housing, and the working coil or the conducting wire is arranged between the driving shaft and the housing and positioned outside the driving functional material body. The antenna reflection surface is used for realizing the control of the orbit thermal deformation, the vibration control and the reflection surface deformation of a space-vehicle antenna.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
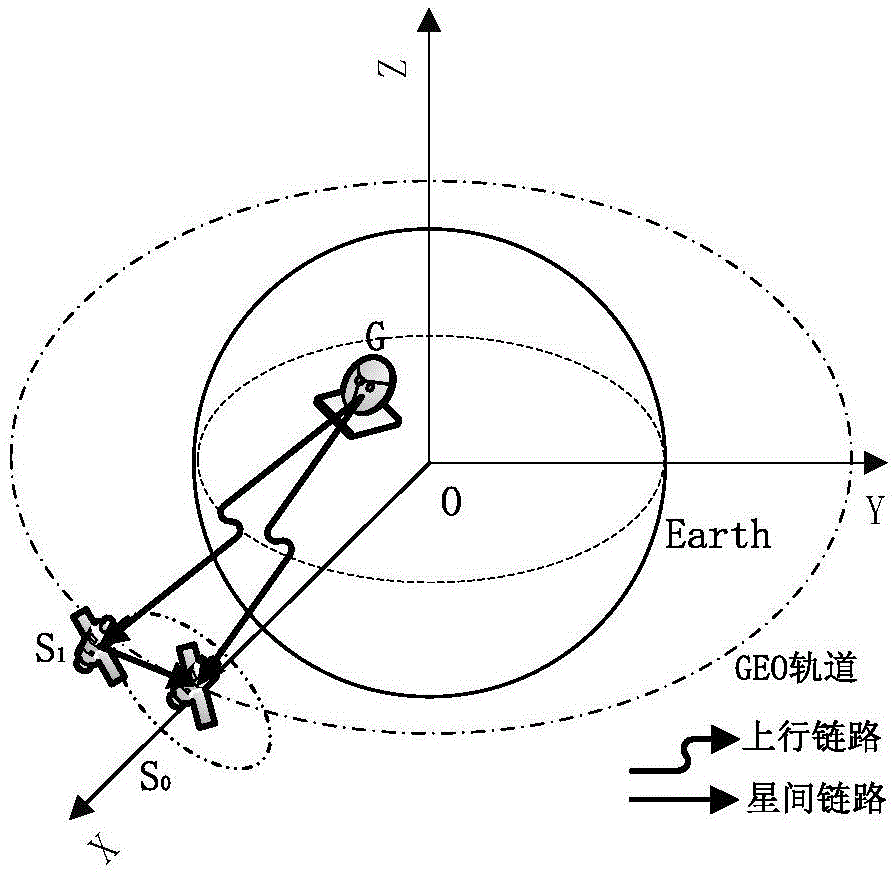
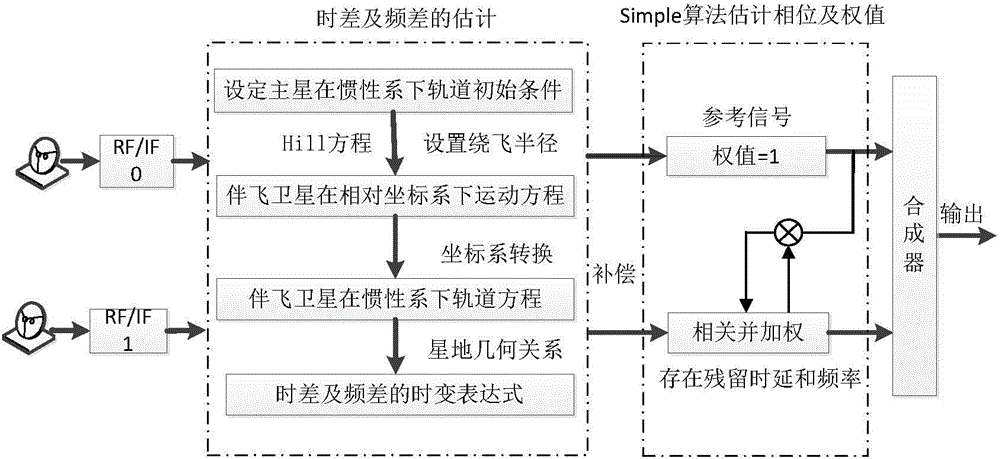
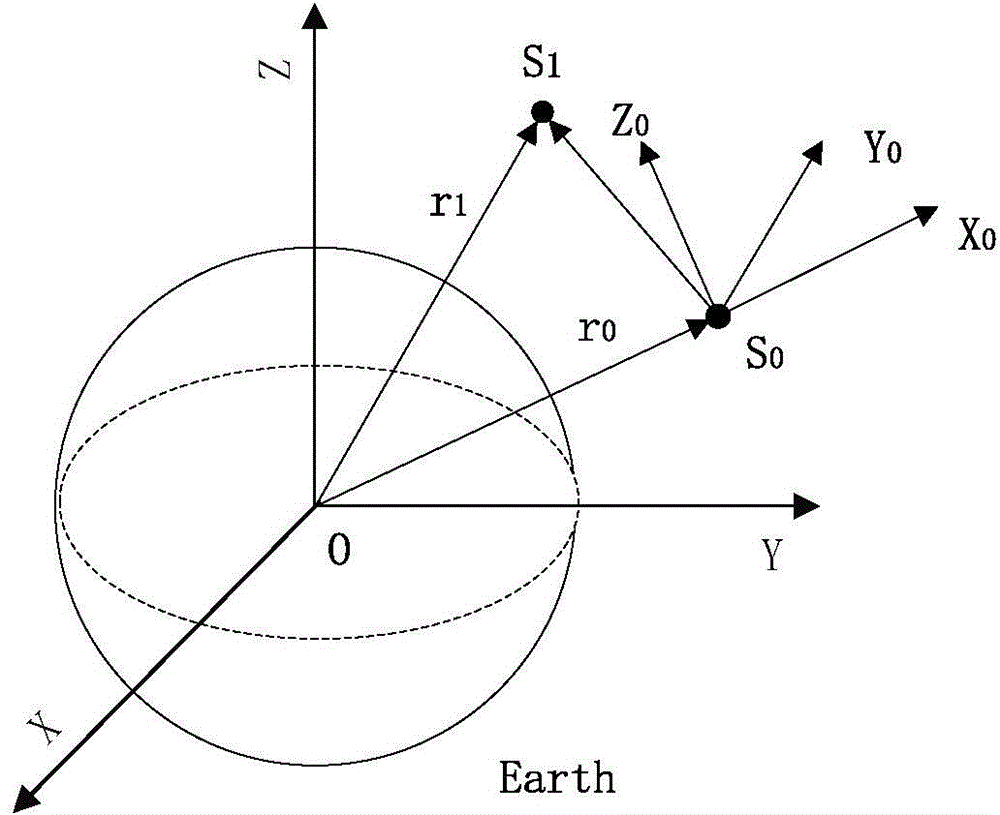
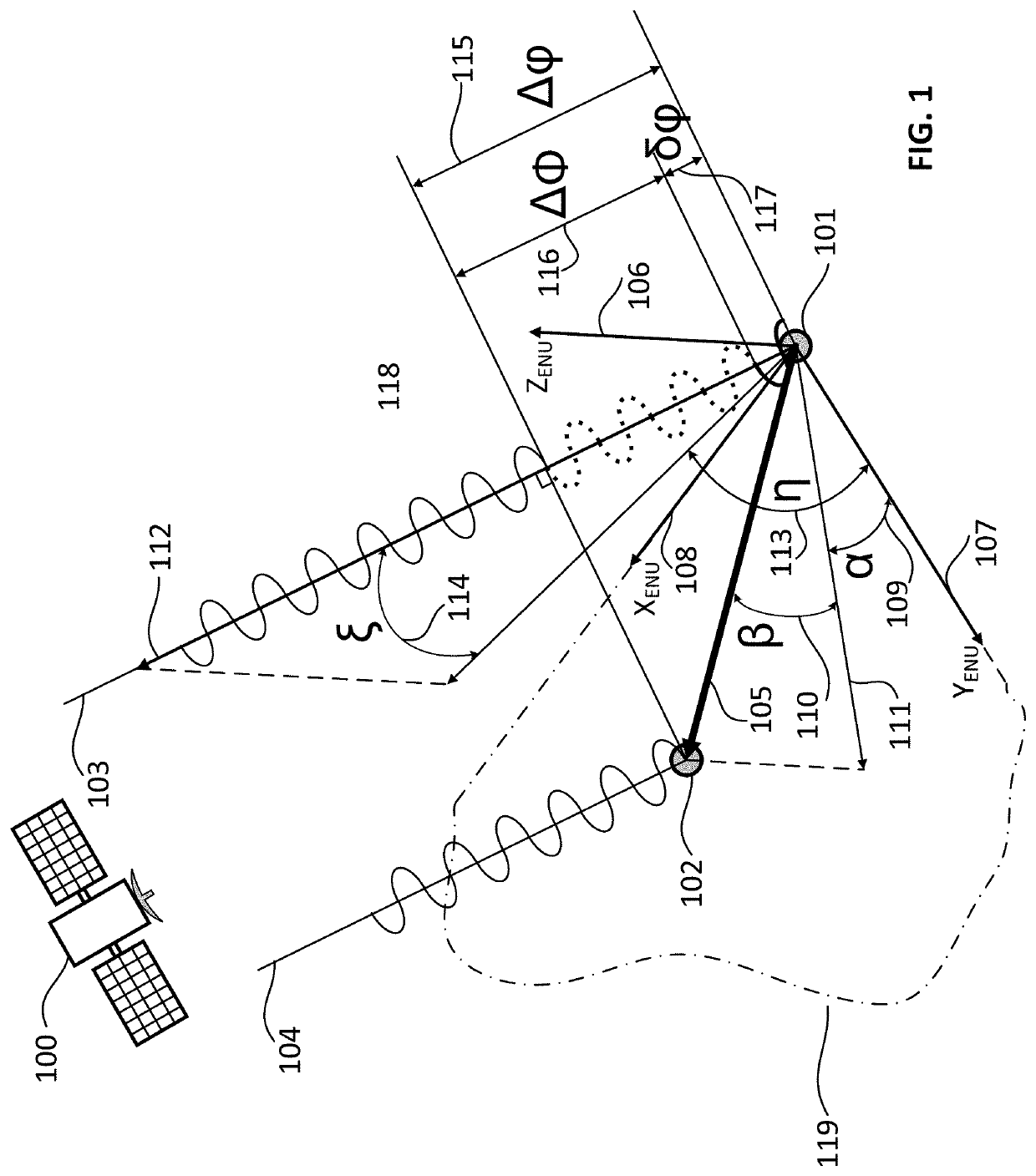
Space antenna array synthesis method based on satellite formation cooperation
ActiveCN104537202ASpecial data processing applicationsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Synthesis methods
The invention provides a space antenna array synthesis method based on satellite formation cooperation, which aims to solve the problem of low signal to noise ratio of single link reception in deep space communication. According to the method, a model which performs signal cooperative reception through formation of GEO satellite is established by a relative movement Hill equation; on the basis of fly-around of a circular formation by double satellites, an orbit is designed, expression formulas of delay difference and frequency difference of two links are offered, and the delay and frequency are compensated. On the basis, SIMPLE related algorithms are researched, two impact factors, residual difference and frequency difference, are added, impact of the two impact factors on phase estimated performance and signal synthesis performance is analyzed, and a reference for length selection of compensation data is provided. The method effectively improves the signal to noise ratio of the link, thereby improving the signal receiving performance of the deep space communication.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Radar with non-uniformly spaced antenna array
ActiveUS8144049B2Reduce impactImprove accuracyMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesIndividually energised antenna arraysRadarRemote sensing
In a radar with a non-uniformly spaced antenna array, an extractor estimates a number of arrivals of echoes to the antenna array. A setter sets a number of azimuths corresponding to a number of extracted peaks as a number of tested azimuths greater than the number of arrivals of echoes by a preset number. A determiner determines a level of correlations among steering vectors respectively corresponding to the tested azimuths. A selector selects, from the tested azimuths, azimuths as power-estimation targets based on the determined level of the correlations among the steering vectors. A first estimator estimates a received power level from each power-estimation target. A second estimator estimates, from the power-estimation targets, an azimuth of the target based on the estimated received power level from each power-estimation target. The estimated received power level from the azimuth is equal to or greater than a preset threshold level.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Positional information transmitter, communication terminal, and positioning system
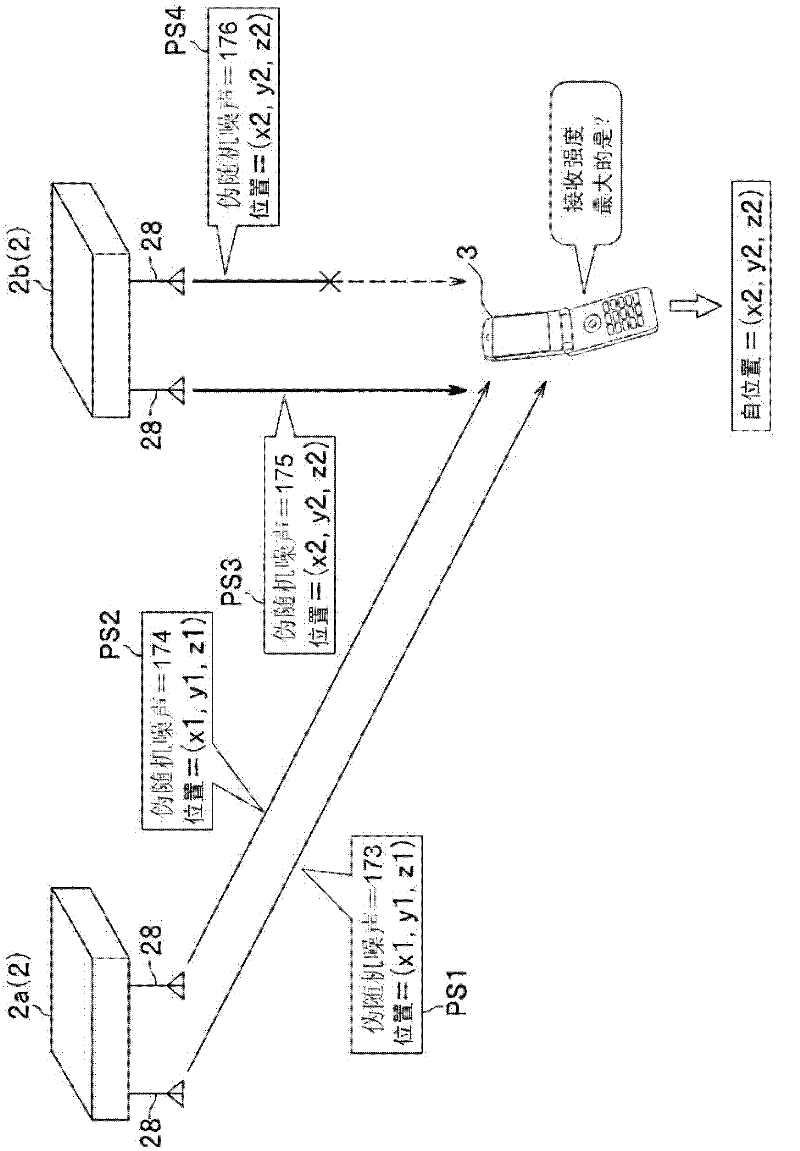
InactiveCN102472812APrevent the expansion of positioning errorsIncreased positioning timeBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationComputer terminalSatellite positioning
The invention provides a positional information transmitter, communication terminal, and positioning system. A positioning system for acquiring current positions outside and inside buildings, wherein the problems of the null points and / or signal interferences of a positional information transmitter located inside a building can be solved, thereby preventing the positioning errors from becoming large, while preventing the positioning time from increasing. A positional information transmitter (2) comprises a plurality of mutually spaced antennas (28) and a radio transmitting unit for repetitively transmitting, via the antennas, a positional information signal that is a radio signal having a compatibility with a satellite positioning signal transmitted from an artificial satellite and including a positional data indicating a particular position. The radio transmitting unit transmits the positional information signals, which include the same positional data, via the respective antennas (28) in parallel by use of mutually different channels or alternatively in a time division manner by use of any given channel.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
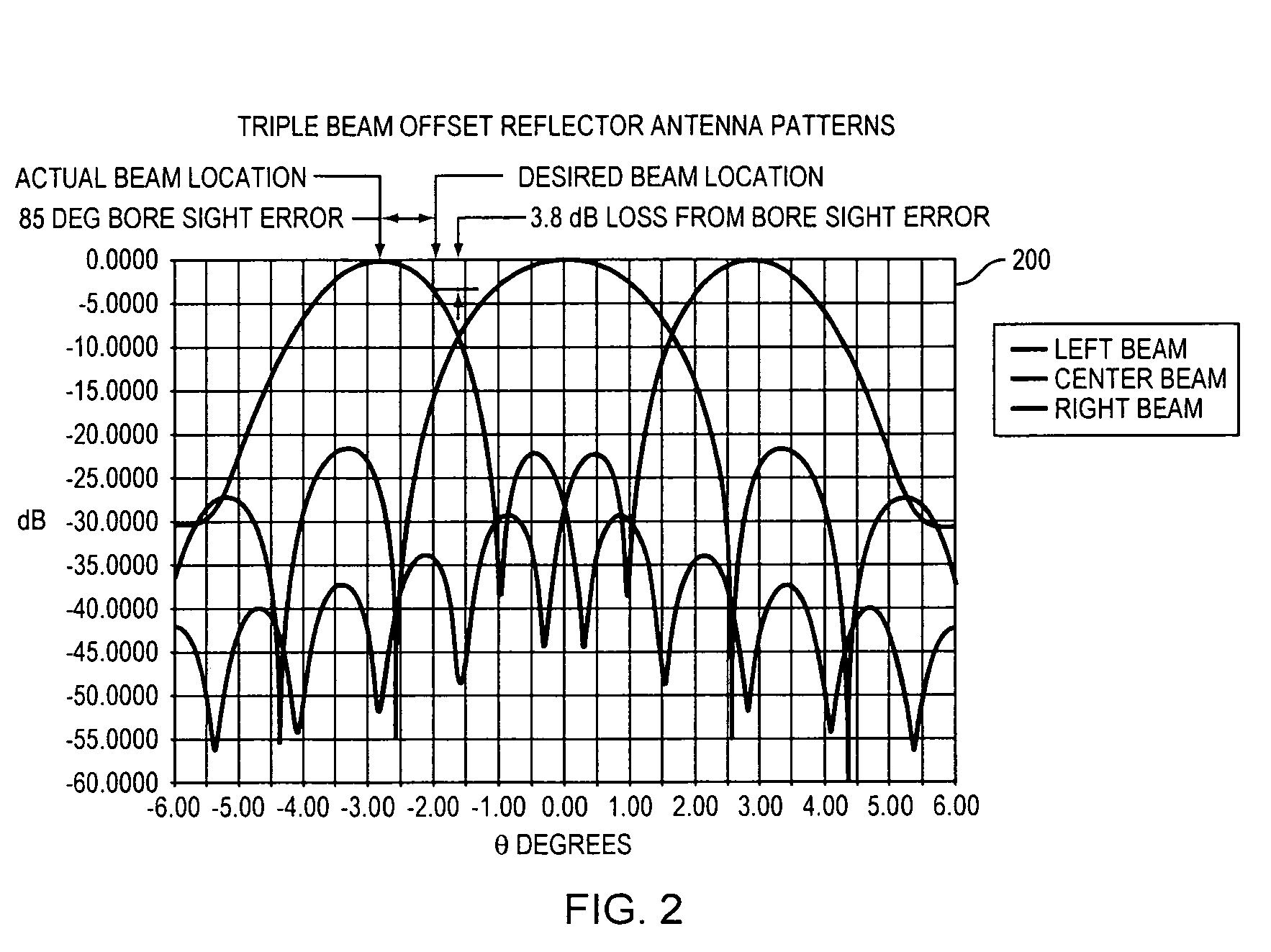
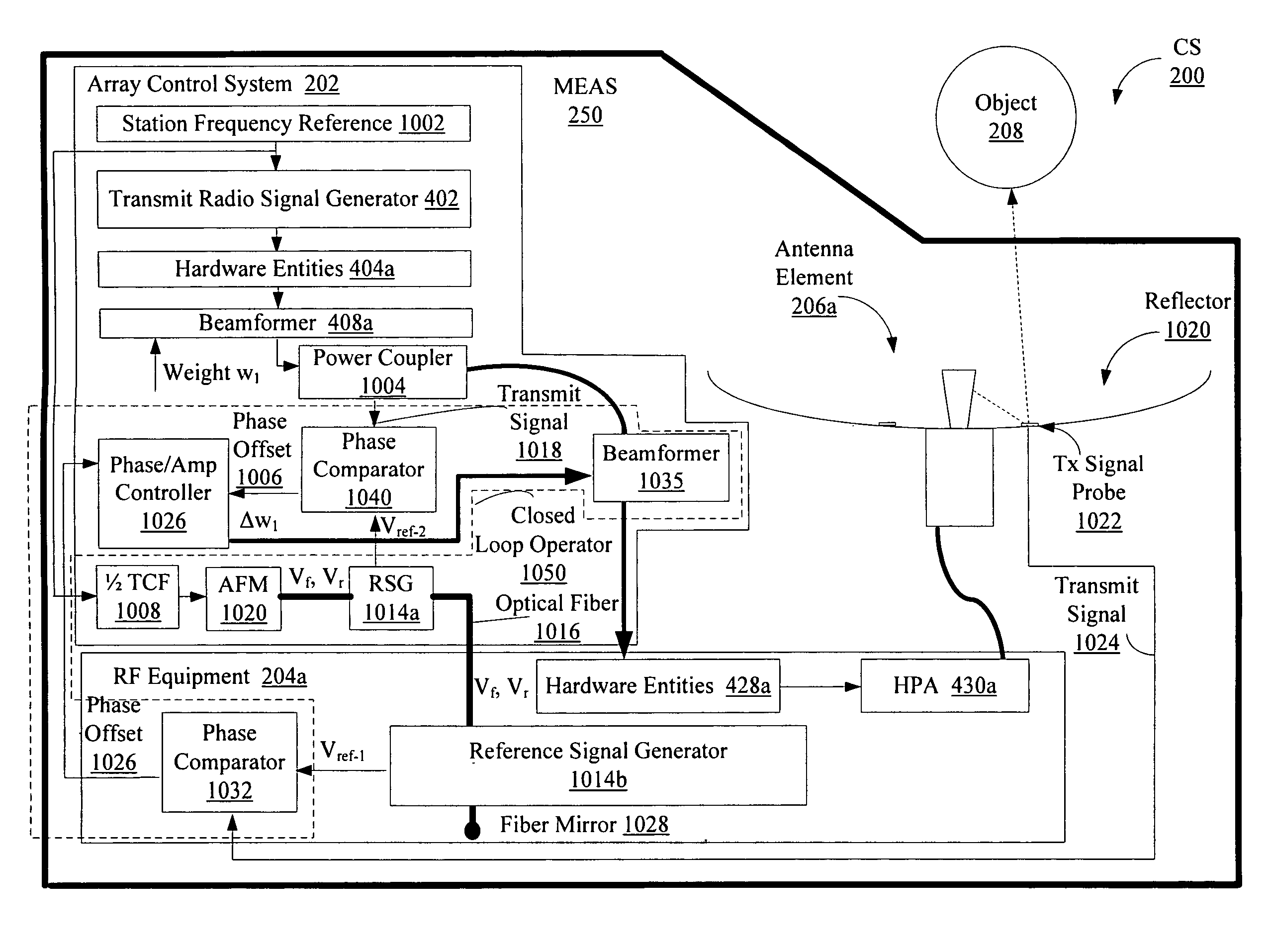
Compensation of beamforming errors in a communications system having widely spaced antenna elements
Systems and methods for operating a communications system. The methods involve computing one or more complex weights to be applied to transmit signals and receive signals by beamformers. The complex weights are based at least on configuration data for the communications system. The methods also involve applying a first plurality of weight corrections to the complex weights based on phasing errors occurring in a communication path inclusive of a control system and antenna elements. The methods further involve applying a second plurality of weight corrections to the complex weights based on phase differences at the antenna elements relative to a reference location for the receive signals.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Lever counter weight type gravity compensation device
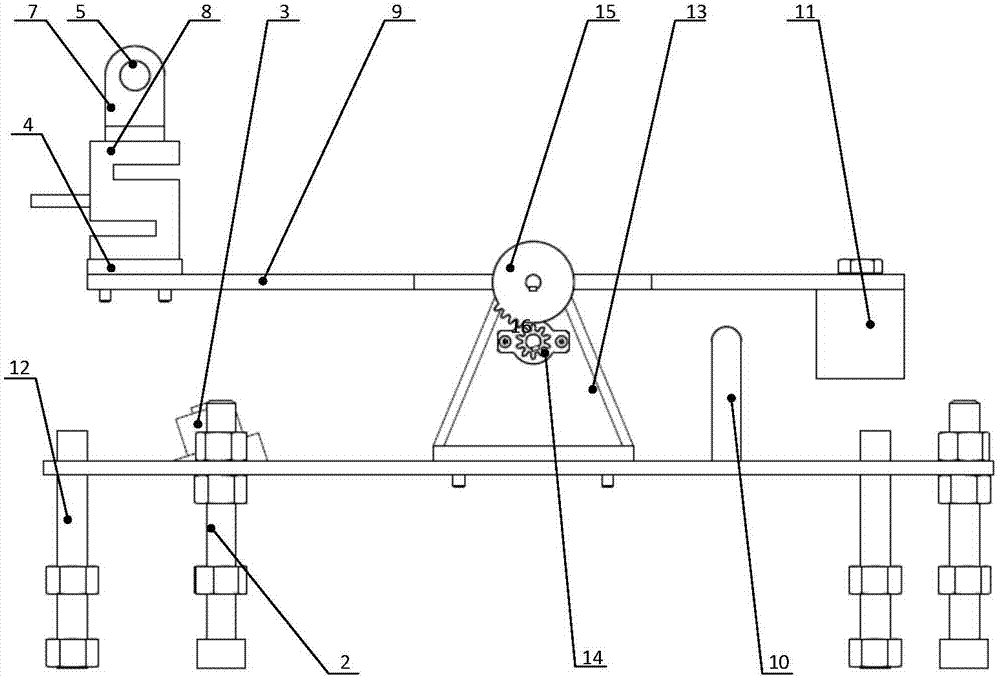
InactiveCN104709475AReal-time measurement of true compensation gravityAdjustable installation heightCosmonautic condition simulationsGear wheelGravitational force
The invention relates to a lever counter weight type gravity compensation device used for one-dimension deployed antenna ground deployment tests of spacecrafts such as satellites. The lever counter weight type gravity compensation device comprises a supporting assembly, a rotating plate assembly and a bottom plate assembly; the supporting assembly is composed of an adaptor, a rotating shaft, a plastic roller, a roller support, a pressure sensor and the like; the rotating plate assembly is composed of a rotating plate, a counter weight, rotating supports, a damper gear, an intermittent gear, bearings, a key and the like; the bottom plate assembly is composed of a bottom plate, bottom plate locking levers, sucked type electromagnets, a limiting pin, bottom plate guide rods and the like. When an antenna is deployed, the compensation device is in a sucked and combined state, and the sucked type electromagnets are powered on and sucked and combined with the rotating plate; after the antenna is deployed, the sucked type electromagnets are powered off, the rotating plate can rotate stably under the functions of the counter weight, the intermittent gear, the damper gear and the like, and finally the rotating plate supports the antenna to compensate the gravity. By means of the lever counter weight type gravity compensation device, the problem of gravity compensation of space antenna ground deployment tests is solved, the structure of the device is simple, the operation is convenient, the compensation force is adjustable, and no impact exists.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
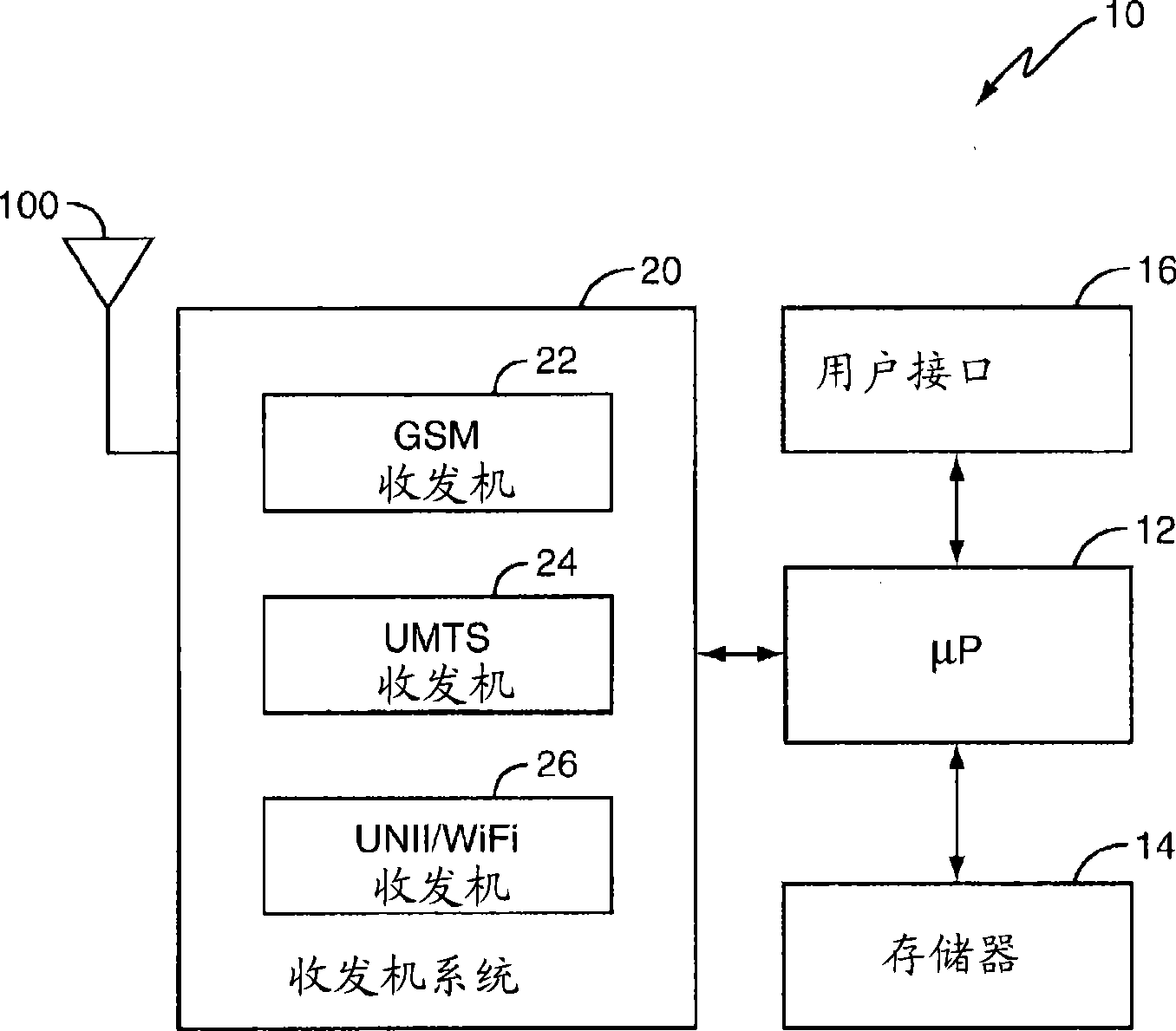
Multi-band antenna for GSM, UMTS, and WIFI applications
InactiveCN101443956ASimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandAntenna feeder
The multi-band antenna described herein includes multiple antenna elements that collectively resonate in multiple different frequency bands. One exemplary antenna includes first and second vertically spaced antenna elements that connect to a ground plane. A feed antenna element positioned between the first and second antenna elements connects to an antenna feed. The electromagnetic coupling produced by the arrangement of these antenna elements produces multiple resonant frequencies, and therefore, defines multiple operating frequency bands of the multi-band antenna.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Intelligent cell type inflation rigid body structure
InactiveCN106394854AChange shapeThe shape is adjusted by changing the air pressure inside the airbag 2Tents/canopiesRigid airshipsAviationSolar sail
The invention discloses an intelligent cell type inflation rigid body structure, in particular a method for forming a light-mass and pressure-resistance rigid body structure by arranging and combining multiple small airbags. A space inflation unfolding structure has such prominent advantages as small size, light weight, high reliability and low manufacturing cost; and along with appearance of such aviation equipment as large space antennas and solar sails with inflation pipes as force bearing frames in recent years, more and more attention is paid for the inflation unfolding structure. The novel inflation unfolding structure is designed by simulating a cell organization structure through a simulating mode; and a traditional inflation unfolding structure obtains more excellent mechanical properties by the finite element design.
Owner:郭鹏
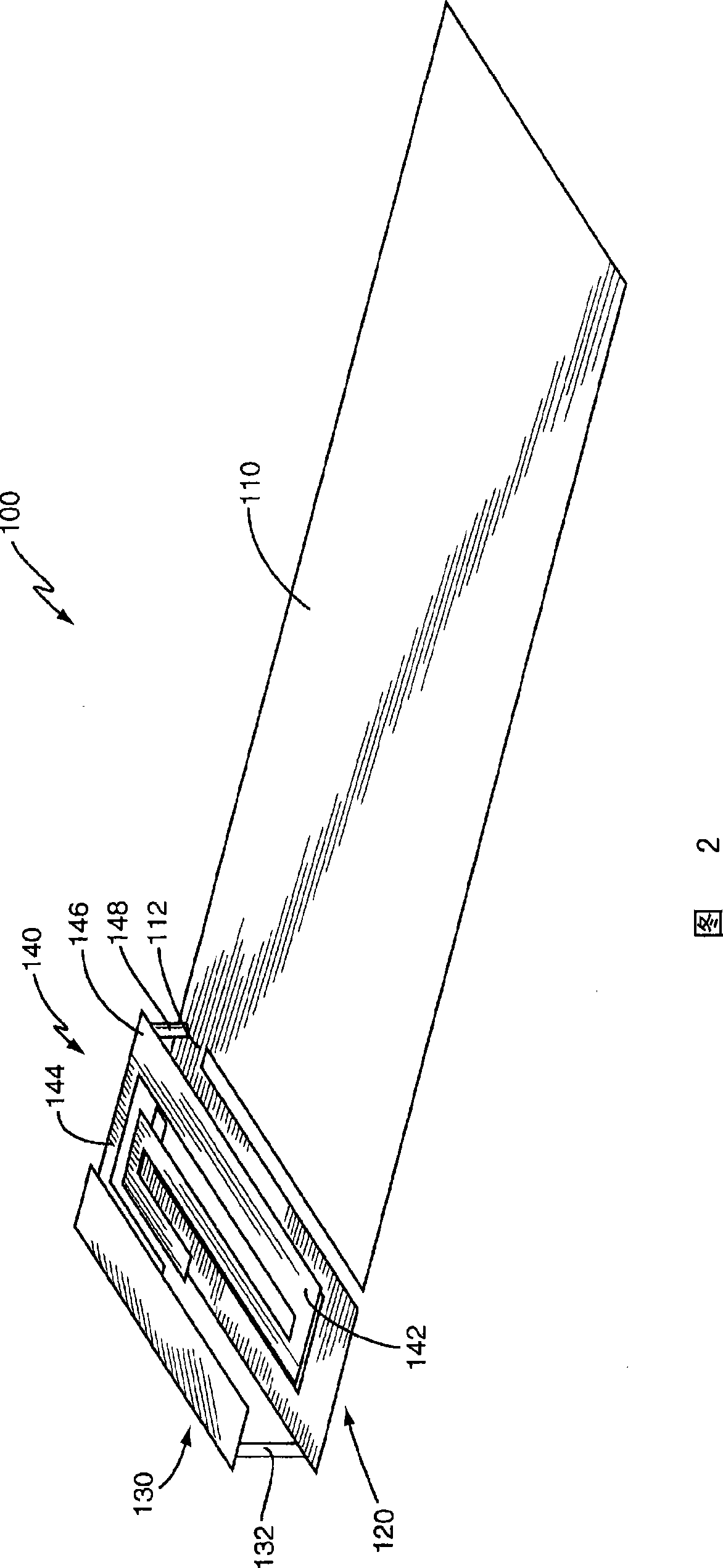
Small wave-guide radiators for closely spaced feeds on multi-beam antennas
A relatively low cost, easy to install and aesthetically pleasing digital video broadcast from satellite (DVBS) elliptical horn antenna designed to receive satellite television broadcast signals with circular polarity. This type antenna may be implemented as a multi-beam, multi-band antenna with closely spaced antenna feed horns operable for simultaneously receiving signals from multiple satellites that are closely spaced from the perspective of the antenna.
Owner:PRO BRAND INT
Deep space receiving antenna array correlated weighting method and system
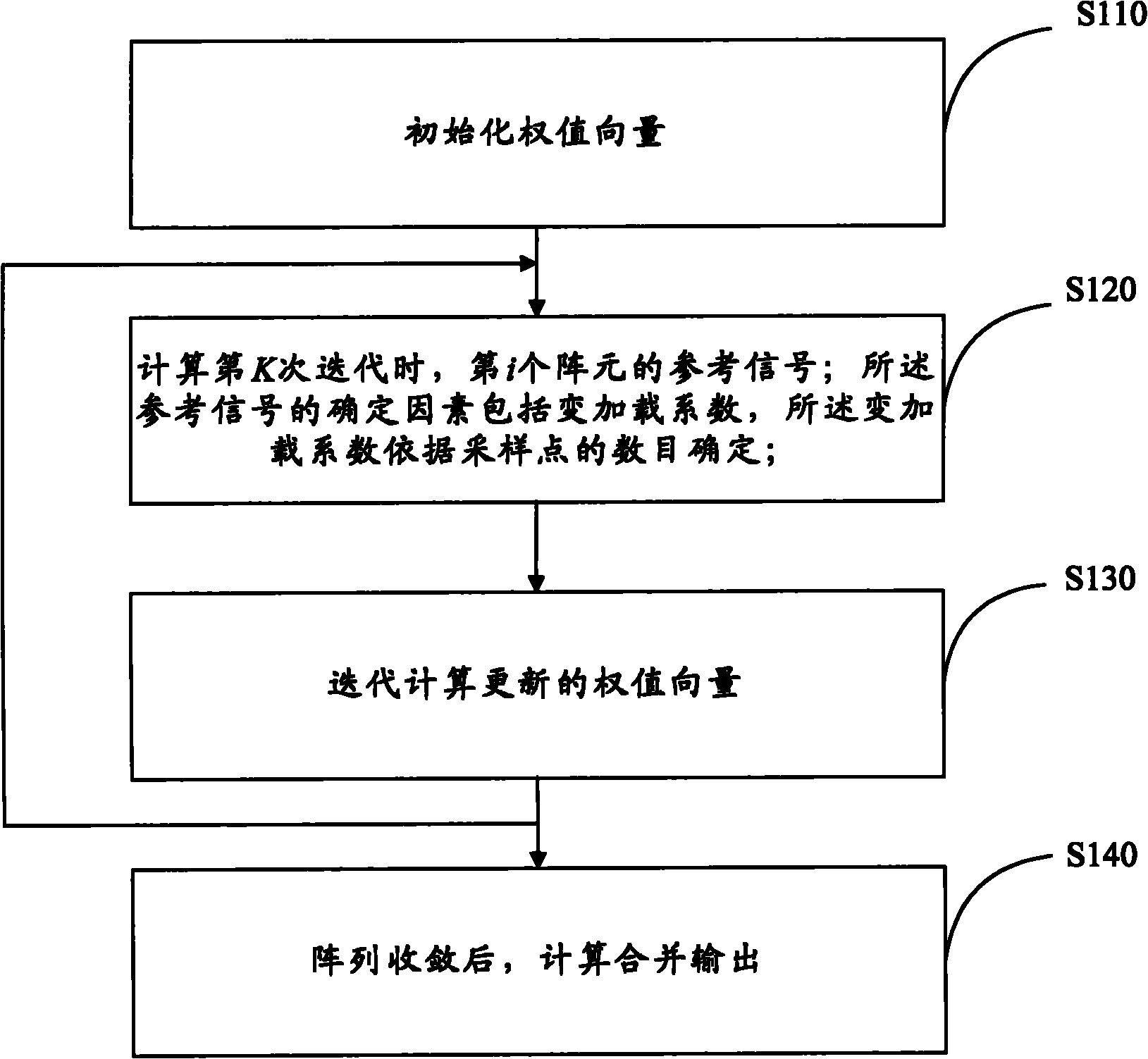
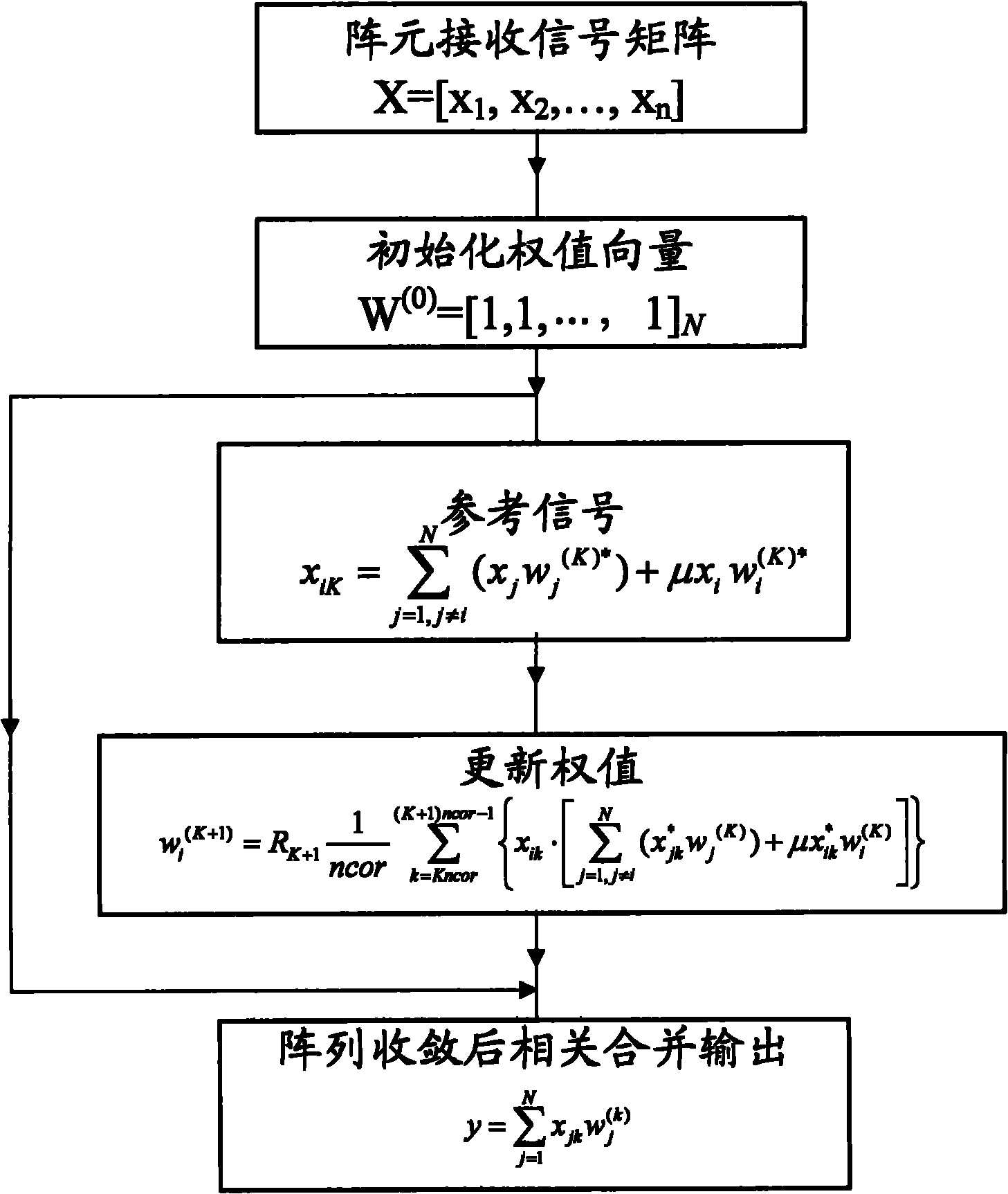
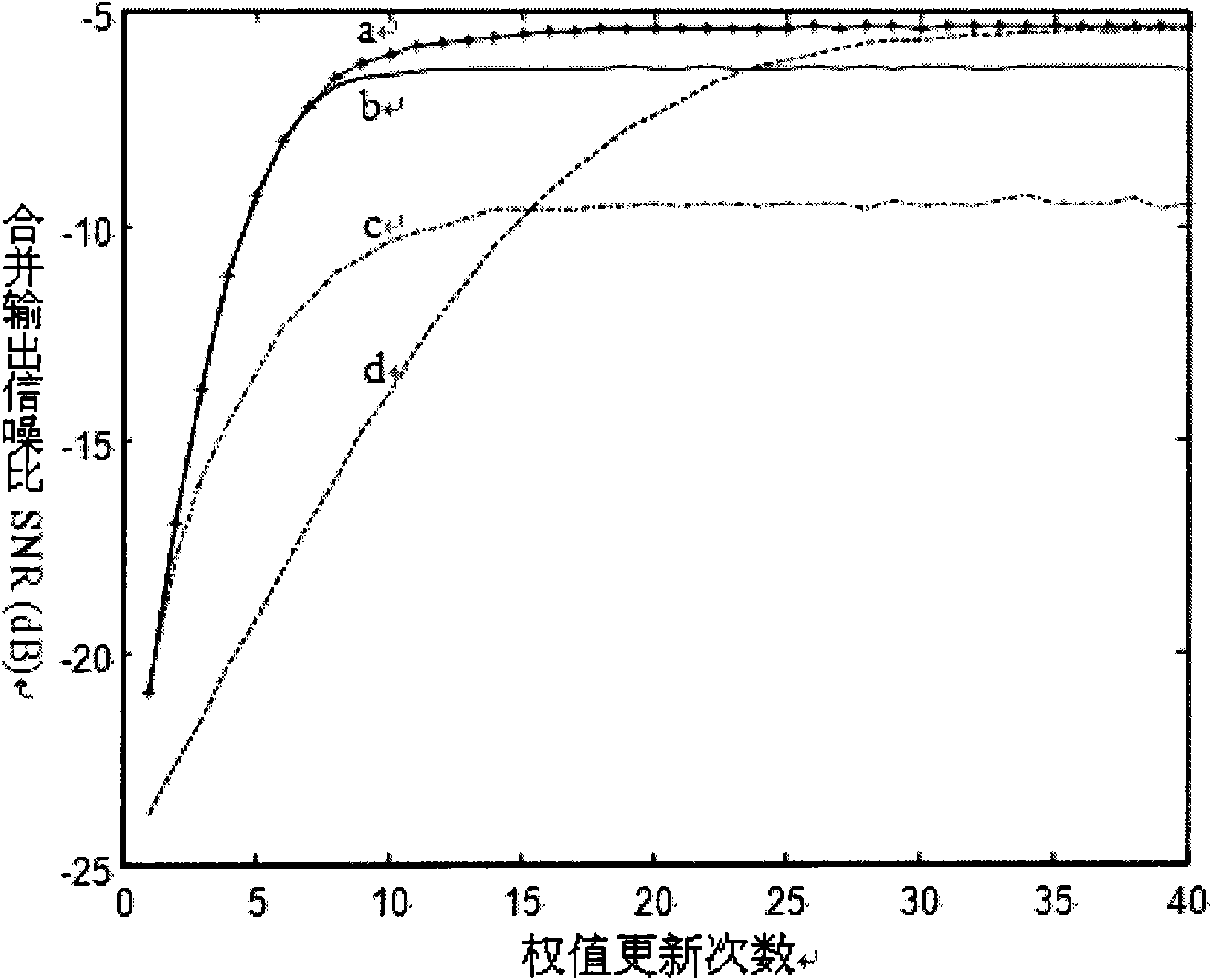
InactiveCN102006105AImprove convergence speedImprove computing powerDiversity/multi-antenna systemsArray elementRate of convergence
The invention discloses a deep space receiving antenna array correlated weighting method and a deep space receiving antenna array correlated weighting system. A deep space antenna array has N array elements, and a signal received by the ith array element from an aircraft is sampled as xi, wherein i is equal to 1, 2, ..., N. The method comprises the following steps of: initializing a weight vector; calculating a reference signal of the ith array element during the kth iteration from K=0, wherein a factor for determining the reference signal comprises a variable loading coefficient, and the variable loading coefficient is determined by the number of sampling points; performing iterative computation on the updated weight vector, and executing the calculation of the reference signal again; and after array convergence, calculating, combining and outputting. Due to the flexible selection of a load coefficient mu value, the method and the system can be applied to different application occasions; and the method and the system have excellent performance in the aspects of convergence rate and steady-state output performance, improve calculated performance, reduce calculated complexity and have important function for improving the performance of a wave beam forming method in the deep space antenna array.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
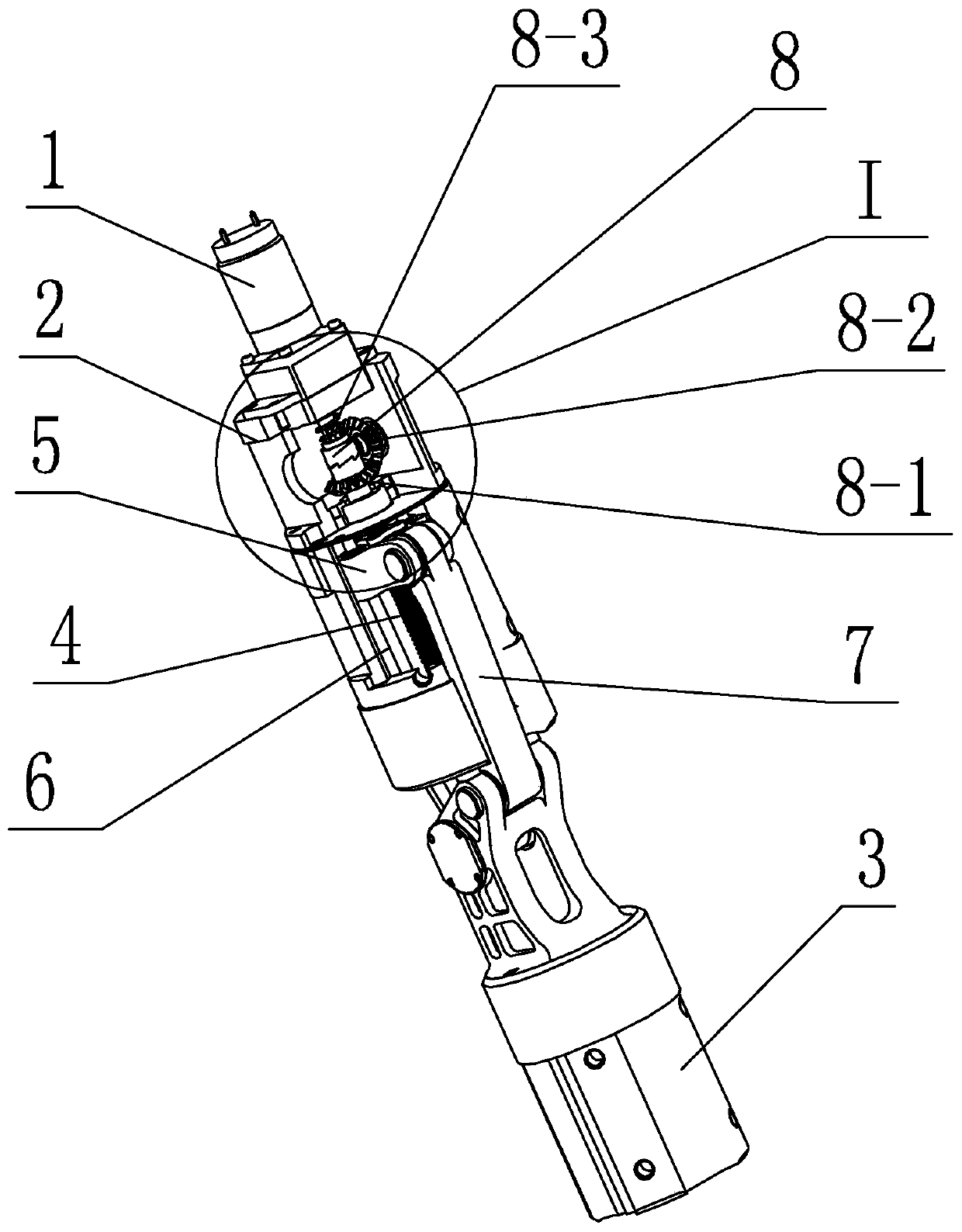
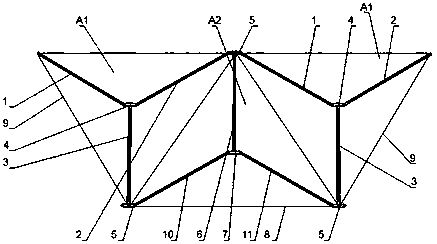
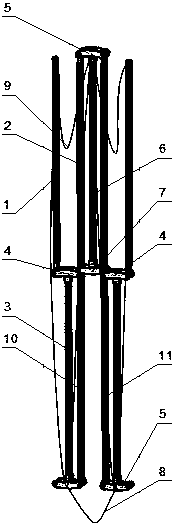
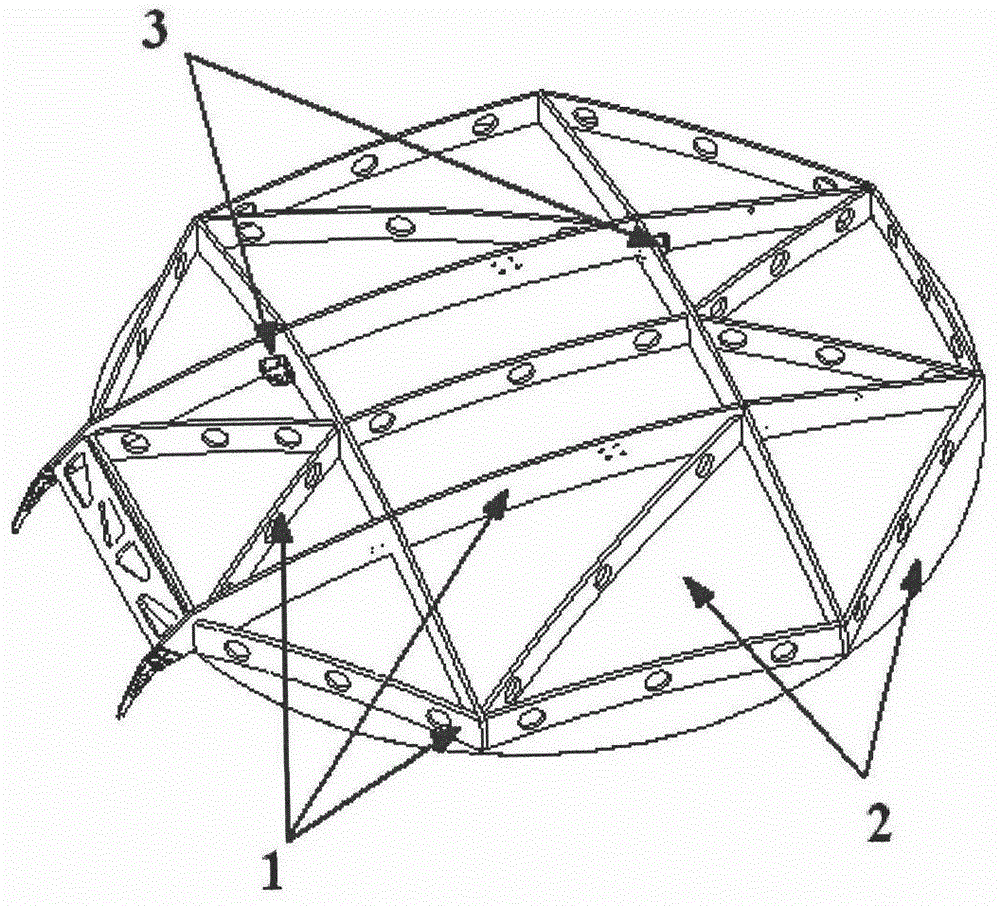
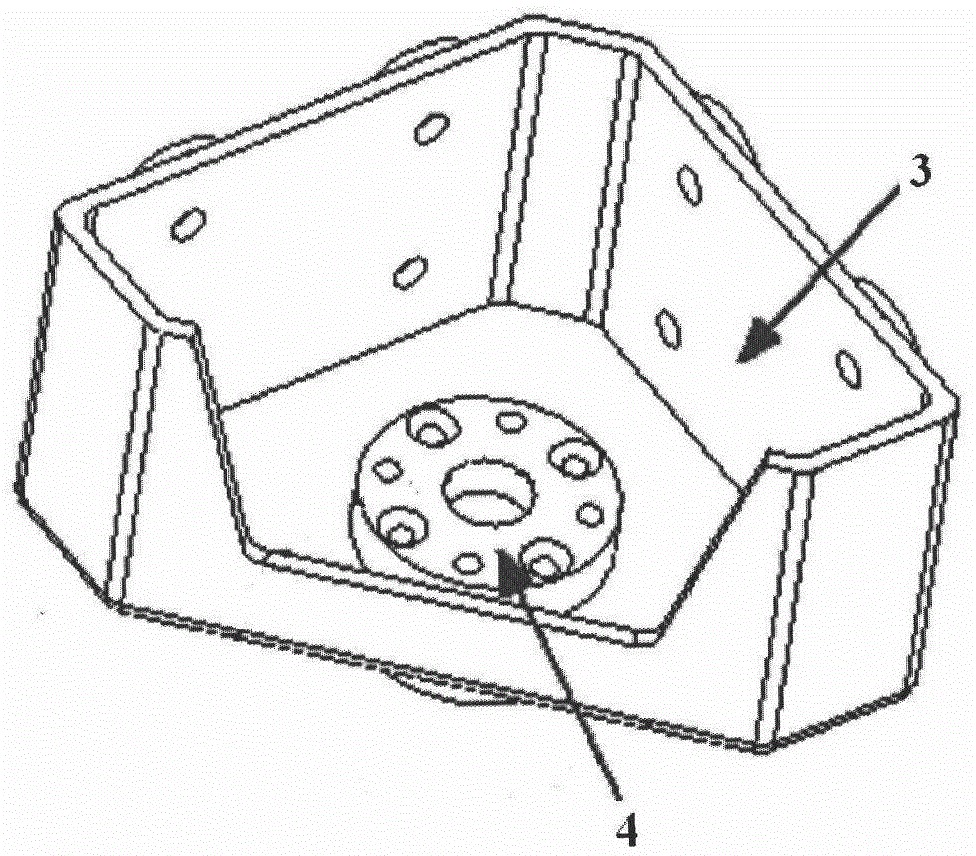
Passive butt joint mechanism used for on-orbit assembling of large space antennas
ActiveCN109356913AImprove reliabilityImprove carrying capacityFriction grip releasable fasteningsQuick-releasable antenna elementsButt jointComputer module
The invention discloses a passive butt joint mechanism used for on-orbit assembling of large space antennas. The passive butt joint mechanism is composed of a male head and a female head; the male head is connected with a movable antenna module; the female head is connected with a fixed antenna module; and the male head can slide into the female head and pushes a steel ball through a switching shaft, the steel ball abuts against the inner wall of the female head to achieve locking, and therefore the movable antenna module and the fixed antenna module are fixedly connected. When the male head bears the reversed unlocking force or vibration, self locking of the steel ball can be ensured, and thus locking reliability is ensured. When unlocking is needed, a male head bolt is manually dismounted, and the male head and the female head can be conveniently separated. Passive butt joint and locking between the two antenna modules can be achieved, in the butt joint process, angle and position errors can be eliminated through the convex-concave matching design of the male head and the female head, and self locking can be ensured in a locking state.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
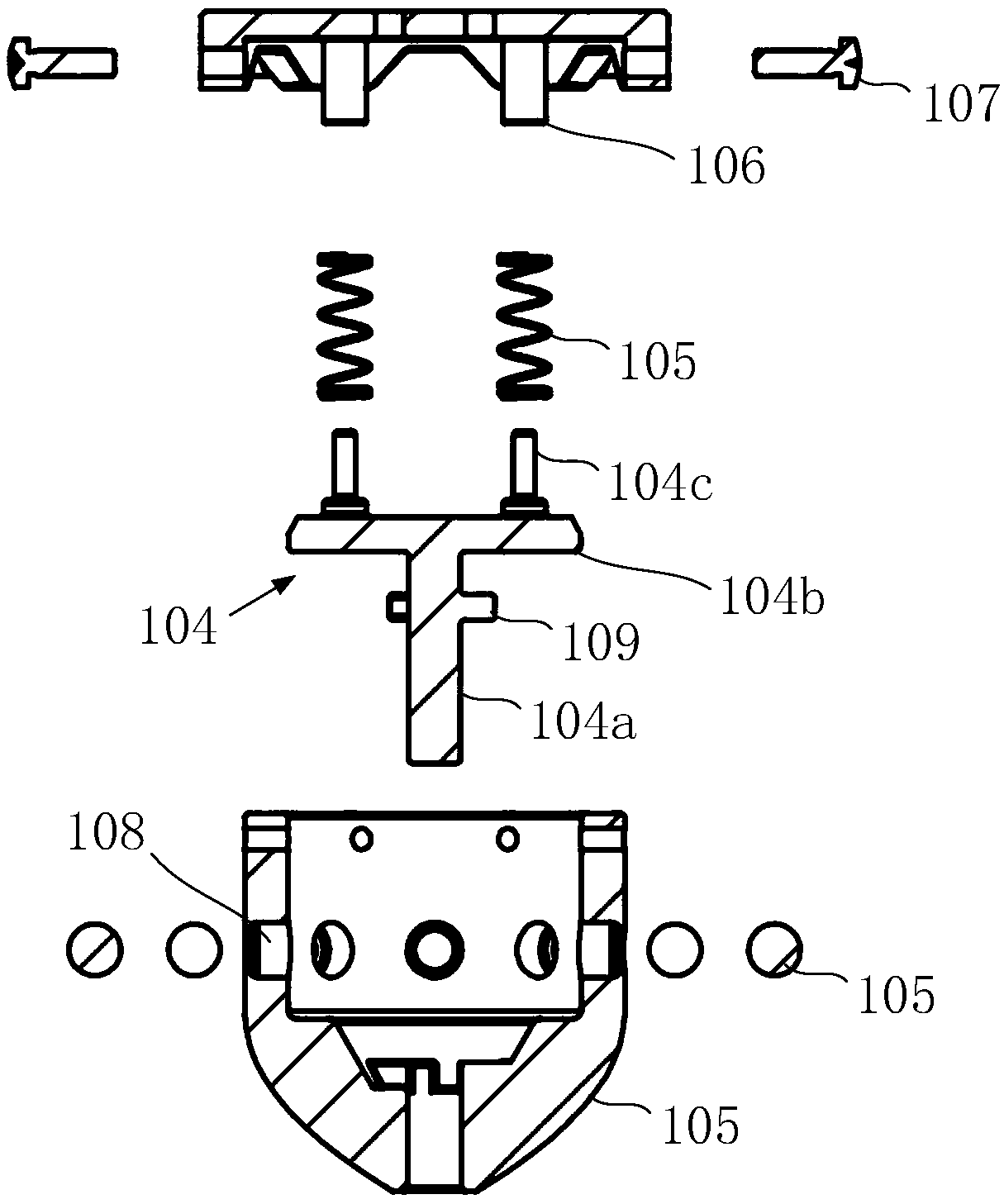
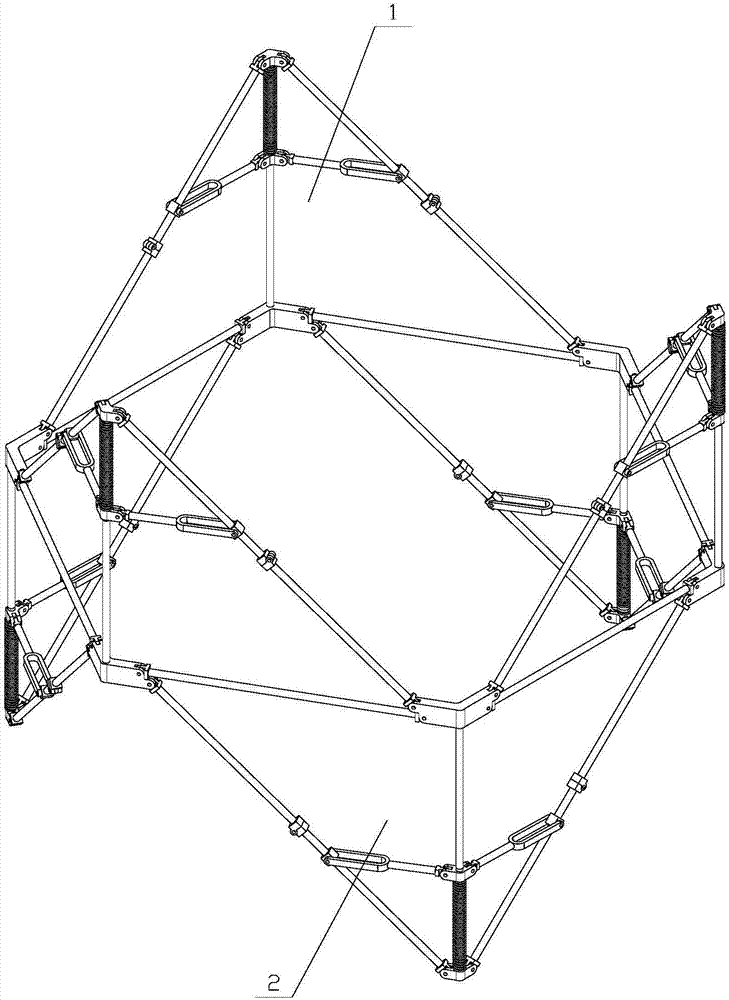
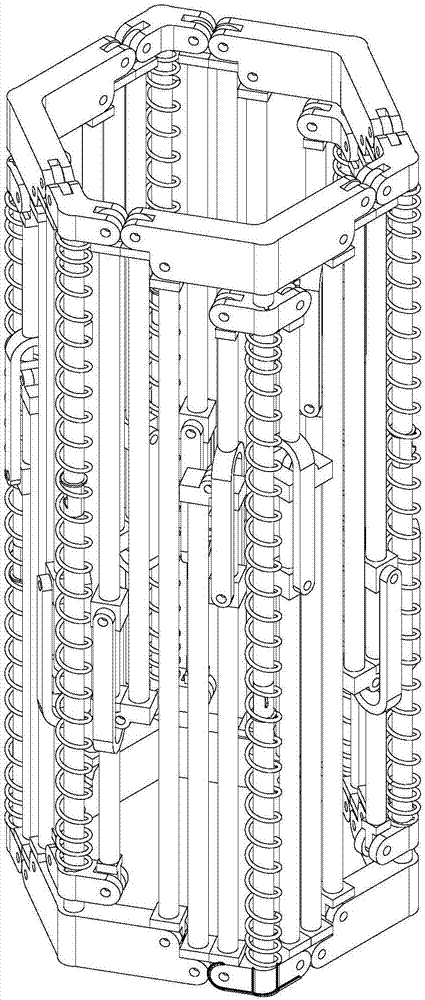
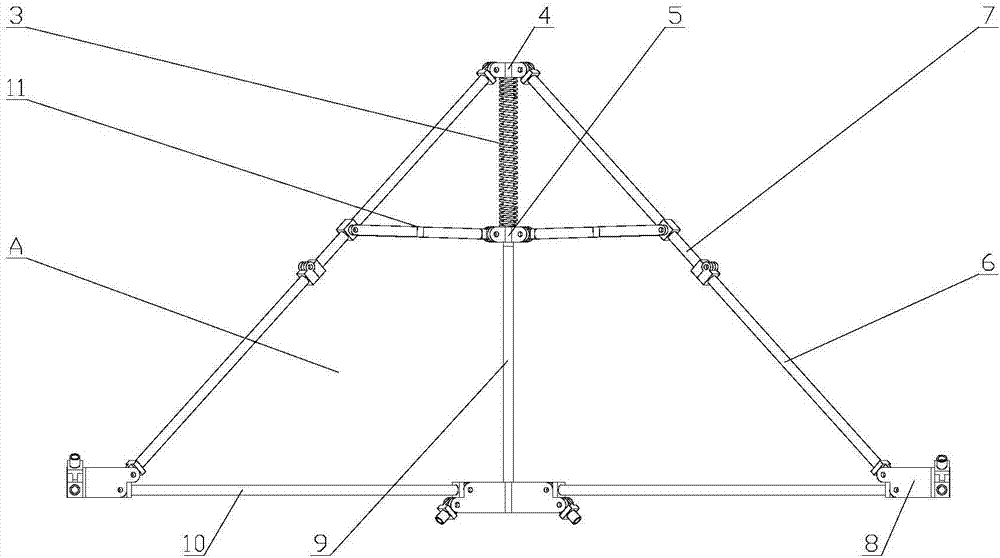
Spring-driven space deployable annular antenna device
ActiveCN107394407AMeet the use requirementsEnhanced geometric stabilityCollapsible/retractable loop antennasExtensibilityRight triangle
The invention discloses a spring-driven space deployable annular antenna device. The spring-driven space deployable annular antenna device comprises n sets of triangular deployable assemblies and an equilateral right triangle deployable unit A; the equilateral right triangle deployable unit A is composed of n sets of triangular deployable cooperative assemblies connected below the n sets of adjacent triangular deployable assemblies; n is greater than or equal to 2; the n sets of triangular deployable assemblies are connected end to end through four-head hinges; the n sets of triangular deployable cooperative assemblies and the n sets of triangular deployable assemblies share the same set of transverse rods connected through the four-head hinges; the n sets of triangular deployable assemblies and the n sets of triangular deployable cooperative assemblies are connected end to end; and, under the action of the elasticity of a spring, folding or unfolding is carried out, so that the deployable annular antenna device is formed. The device has relatively high geometric stability; a motion mechanism and a control system are simple; after being folded, the device is small in volume and high in accepting rate; an active driving device is unnecessary; the module extensibility is high; accessories are simple; and use requirements of large-aperture space antennas, such as communication satellites and space exploration, can be satisfied.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
GNSS-based attitude determination algorithm and triple-antenna GNSS receiver for its implementation
ActiveUS20210190971A1Improve accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingRF front endCarrier signal
An algorithm for determining of a vehicle orientation based on a coherent processing of GNSS signals received by three spaced antennas and a special GNSS receiver for implementing this algorithm are considered. The three antennas are logically combined into two pairs, with one of the antennas becoming common for both pairs. The GNSS receiver measures the first carrier phase difference between the signals received within each pair of antennas. The first differences of the full phases are represented as the sum of an integer number of periods of the carrier frequency and the fractional part of the period. Values of the fractional parts of the first differences are used to compute the orientation of the vector connecting the antennas phase centers within each pair. The use of the fractional parts of the first differences makes it possible to exclude the integer ambiguity resolution in carrier phase measurements. The attitude of the vehicle is calculated from the orientation of two non-collinear vectors with a common origin, measured by two pairs of antennas. In the special GNSS receiver for the vehicle's attitude measurements, each antenna is connected to its own RF front end. All RF front ends, heterodynes, digital navigation processors of this receiver are clocked from one common clock oscillator. In this case, all the carrier phase measurements of the GNSS signals received by the three spaced antennas are performed and processed coherently, i.e. in a common time scale.
Owner:TOPCON POSITIONING SYST INC
Foldable supporting arm hinged to automatic drive unit and driven by folding lead screw
ActiveCN109760853AIncrease the fold-to-expand ratioTake advantage ofCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsEngineeringSpaceflight
The invention discloses a foldable supporting arm hinged to an automatic drive unit and driven by a folding lead screw and belongs to the technical field of spaceflight, and solves the problems that the conventional foldable supporting arm is unfolded by virtue of drive of a hinge spring and a lead screw, is small in folding ratio and difficultly provides extending and supporting functions while serving as a large antenna and the like. The foldable supporting arm disclosed by the invention comprises a motor, a first connecting body, a second connecting body, a lead screw, a nut, a guide rod and a connecting rod, wherein the first connecting body is hinged to the second connecting body; the lead screw and the guide rod are arranged on the first connecting body; the axis of the lead screw and the axis of the guide rod are parallel to each other; the lead screw is driven by the motor; the nut is arranged on the lead screw; the nut is arranged on the guide rod in a sliding manner; one endof the connecting rod is hinged to the nut; the other end of the connecting rod is hinged to the second connecting body; and the hinged axis of the connecting rod and the second connecting body and the hinged axis of the first connecting body and the second connecting body are parallel to each other. The foldable supporting arm disclosed by the invention is applicable to support of space antennas.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Space thin film structure clamp shape optimization design method for restraining creases
ActiveCN108133097AIncrease the minimum principal stressIncrease working areaGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStress distributionSolar sail
The invention belongs to the field of aerospace thin film structural design, and provides a space thin film structure clamp shape optimization design method for restraining creases. The problem that aspace thin film structure is prone to creases under the tensile effect of a traditional clamp is solved. On the basis of nonlinear finite element analysis, the loading boundary conditions are changedby optimizing the shape of a clamp, the minimum main stress of units in a thin film area is maximized, the main stress distribution of the thin film is adjusted and controlled, the global optimum design is found through a global optimization algorithm, then a novel clamp with arcuate and inverted-T-shaped boundaries is obtained, and the aim of completely restraining the creases is achieved. The creases in the thin film are restrained, the thin film is not tailored, and it can be ensured that the thin film has sufficiently large working area; the method is suitable for designing the clamp fora space antenna, a solar sail and other space thin film structures, the thin film creases are easily restrained, the structure working performance is ensured, and no manufacturing, launching or running cost is added.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Large cable-strut truss type deployable antenna mechanism
ActiveCN111224210AExpand smoothlyIncrease stiffnessPivotable antennasAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesControl theoryTorsion spring
The invention belongs to the technical field of aerospace appliances and equipment, and particularly relates to a large cable-strut truss type deployable antenna mechanism. The cable-strut truss typedeployable antenna mechanism comprises a plurality of cable-strut truss type deployable units, wherein the plurality of deployable units are connected through connecting longitudinal rods to form thecable-strut truss type deployable antenna mechanism; each deployable unit comprises first deployable assemblies and a second deployable assembly arranged between the first deployable assemblies, the first deployable assemblies and the second deployable assemblies are triangular support bodies, and the first deployable assemblies and the second deployable assemblies are connected through third torsion spring connectors to form the deployable units. The large cable-strut truss type deployable antenna mechanism is good in reliability, compact in structure, good in rigidity after being completelyunfolded, capable of meeting the use requirement of a large space antenna and suitable for a satellite space folding and unfolding mechanism and the like.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Low-expansion mesh reflector using composite material connectors
The invention relates to a low-expansion mesh reflector using composite material connectors and belongs to the technical field of space antenna reflectors. The low-expansion mesh reflector comprises back ribs, reflecting surfaces and connectors. Each refecting surface is a quasi-isotropic TWF (true wave fiber) fabric reflecting surface, and each back rib is a composite material laminate back rib in a groined shape and having a symmetrical structure. Each connector is positioned at an included angle of two crossed back ribs in the back ribs, so that the connector and the two crossed back ribs are fixedly connected. A connector embedded part is positioned on a bottom face of the connector, and the reflector is fixed or mounted by the connector embedded part so as to be convenient for transportation or storage. The reflecting surface in the low-expansion mesh reflector uses the quasi-isotropic TWF fabric, has quite high light-transmittance and a lower thermal expansivity, influence of space light pressure to a molded surface of the reflecting surface can be effectively reduced, temperature gradient generated by the reflecting surface under a space thermal environment can be lowered, and since the temperature gradient is lowered, thermal deformation of the reflecting surface can be reduced.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
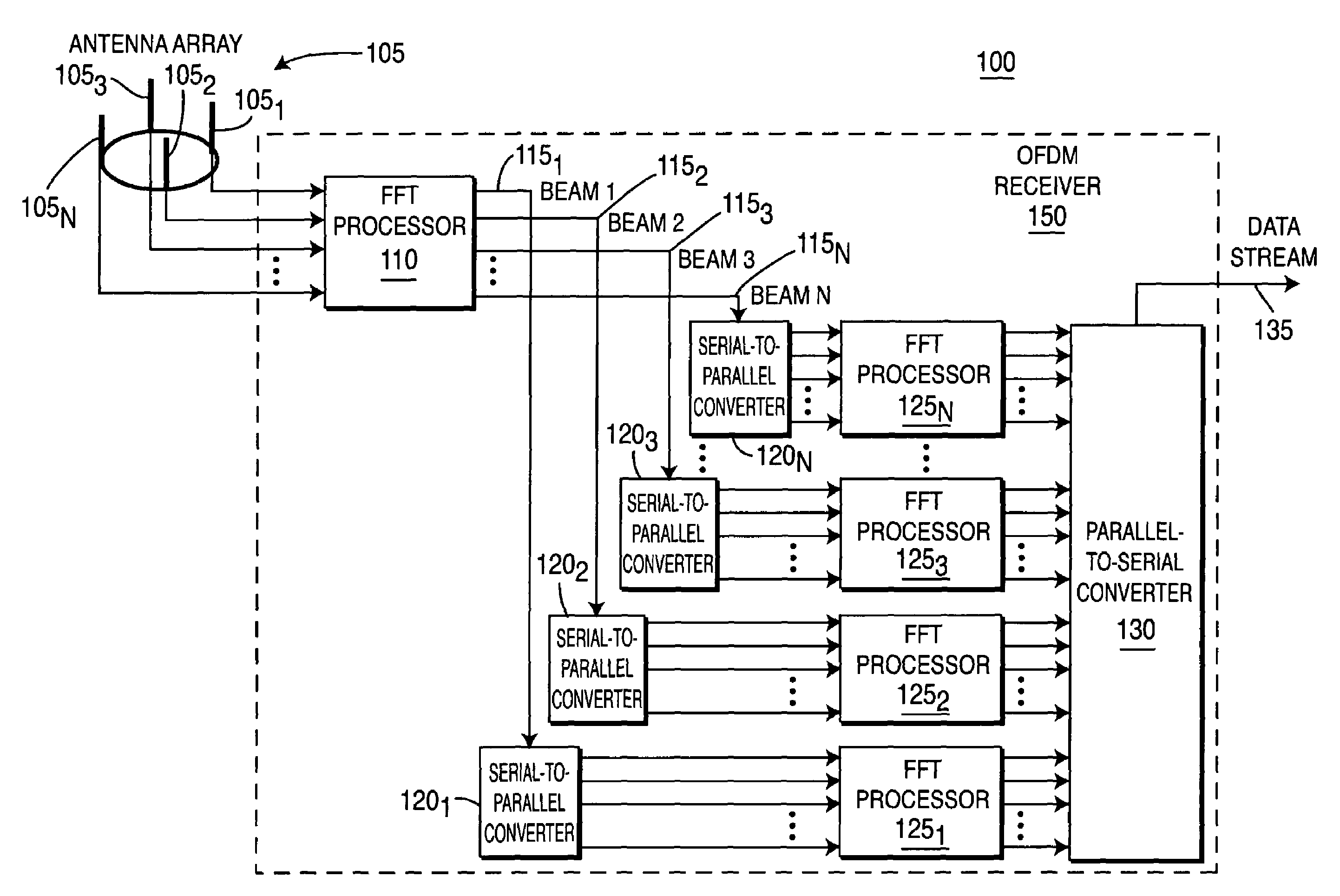
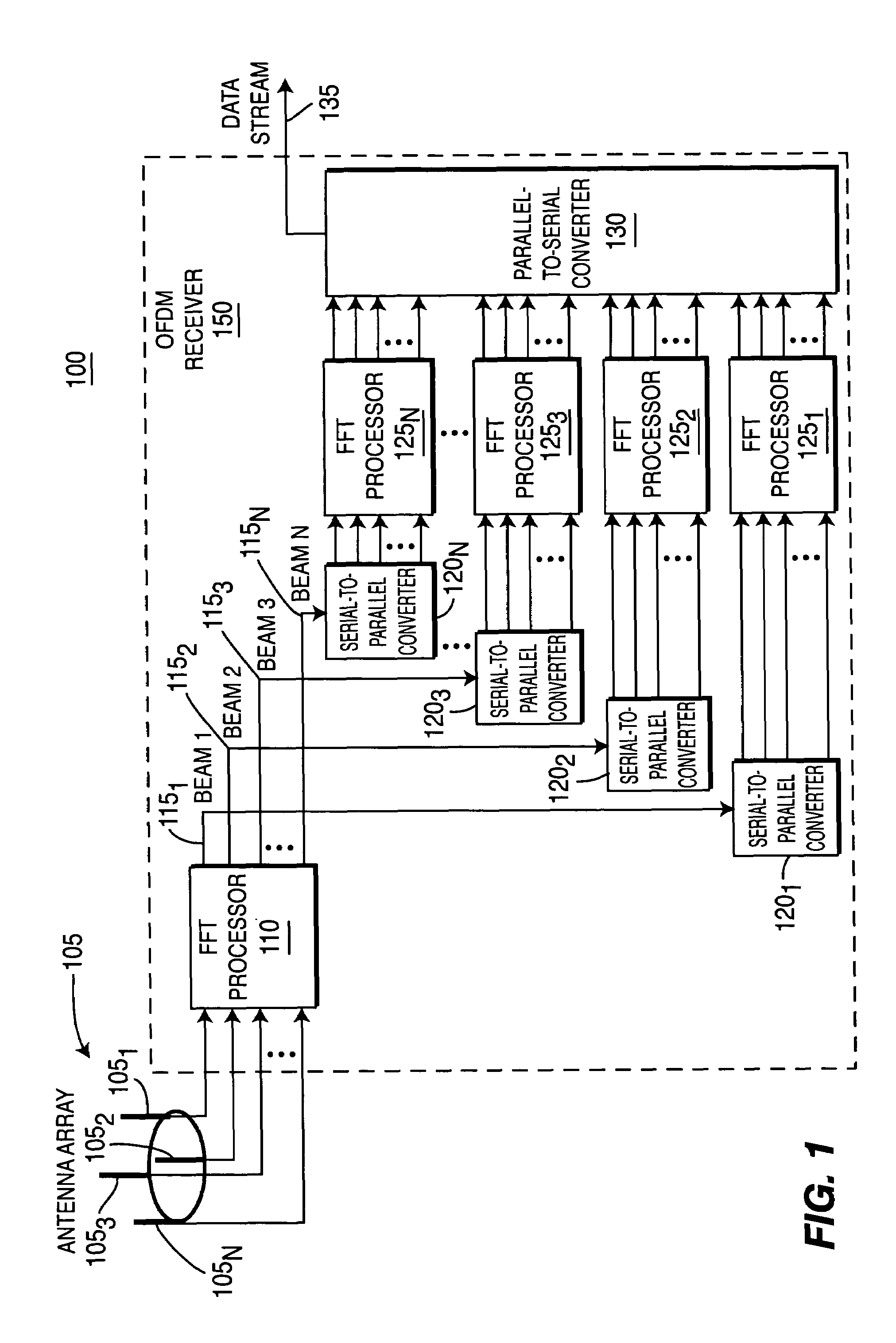
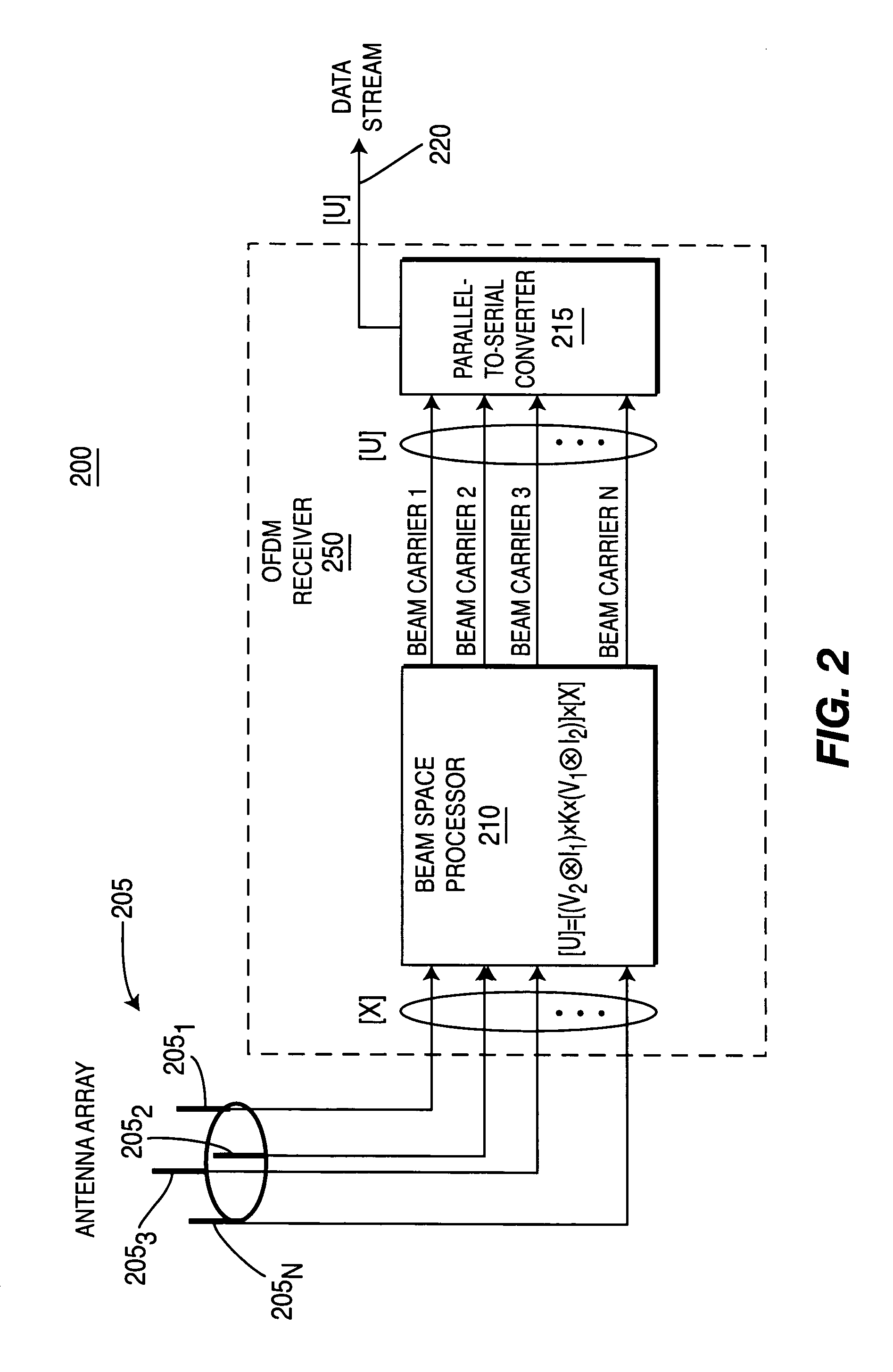
Wireless communication apparatus using fast fourier transforms to create, optimize and incorporate a beam space antenna array in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing receiver
InactiveUS7453964B2Polarisation/directional diversitySecret communicationFast Fourier transformOrder of operations
A wireless communication apparatus which uses fast Fourier transforms (FFTs) in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) receiver which incorporates a beam space antenna array. The beam space antenna array may be implemented with a Butler matrix array. The beam space antenna array may be a circular array, vertical array, or a combination of both circular and vertical arrays, for providing the desired angular antenna coverage. In one embodiment, the antenna array is optimized because the FFTs are linear invariant transform operators, whereby the order of operations in the OFDM receiver can be interchanged.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com