Patents
Literature
36 results about "Strain energy release rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The energy release rate G is the rate at which energy is lost as a material undergoes fracture, which is an energy-per-unit-area. The energy release rate is mathematically understood as the decrement in total potential energy scaled by the increment in fracture surface area. Various energy balances can be constructed relating the energy released during fracture to the energy of the resulting new surface, as well as other dissipative processes such as plasticity and heat generation.
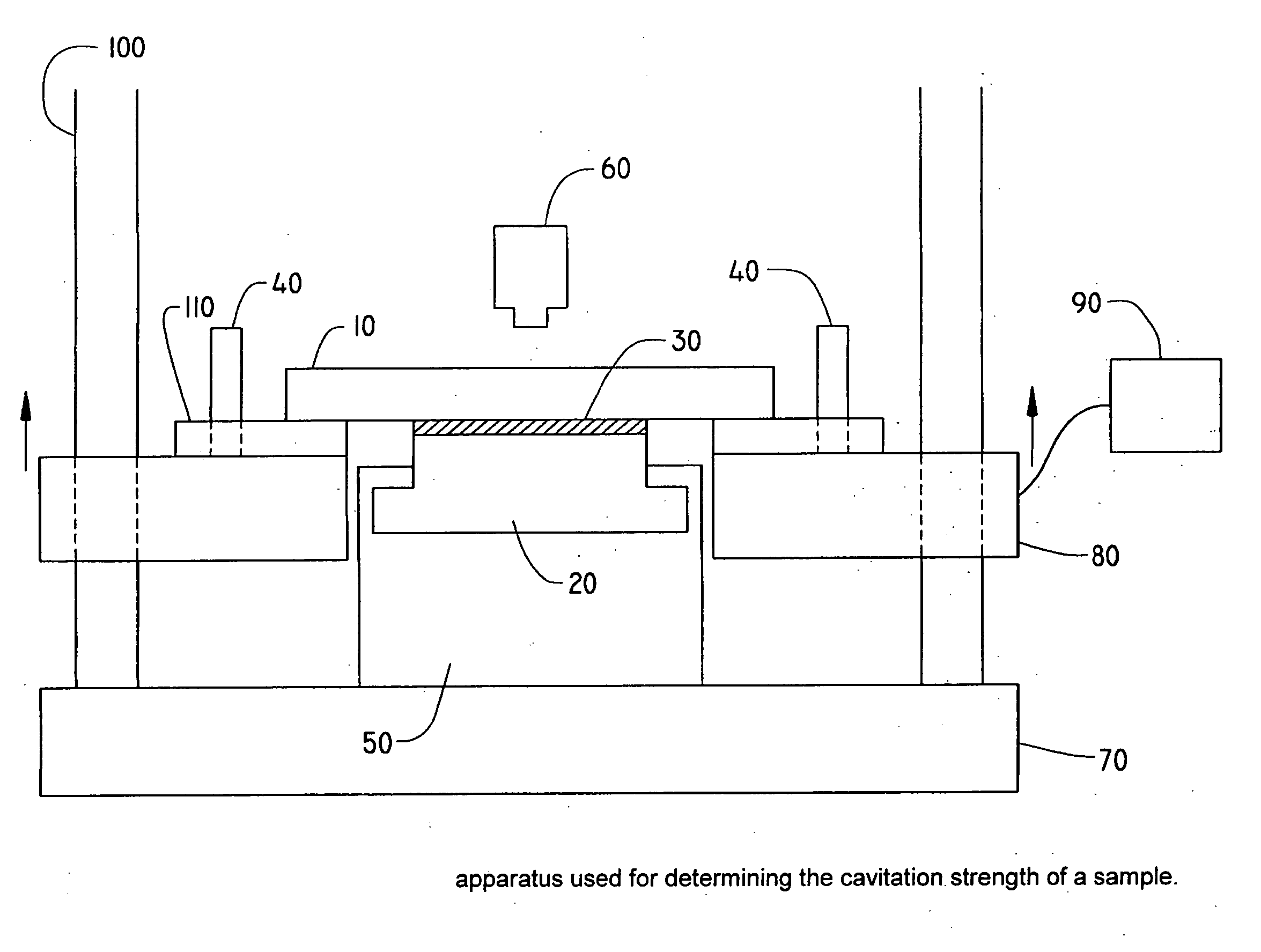
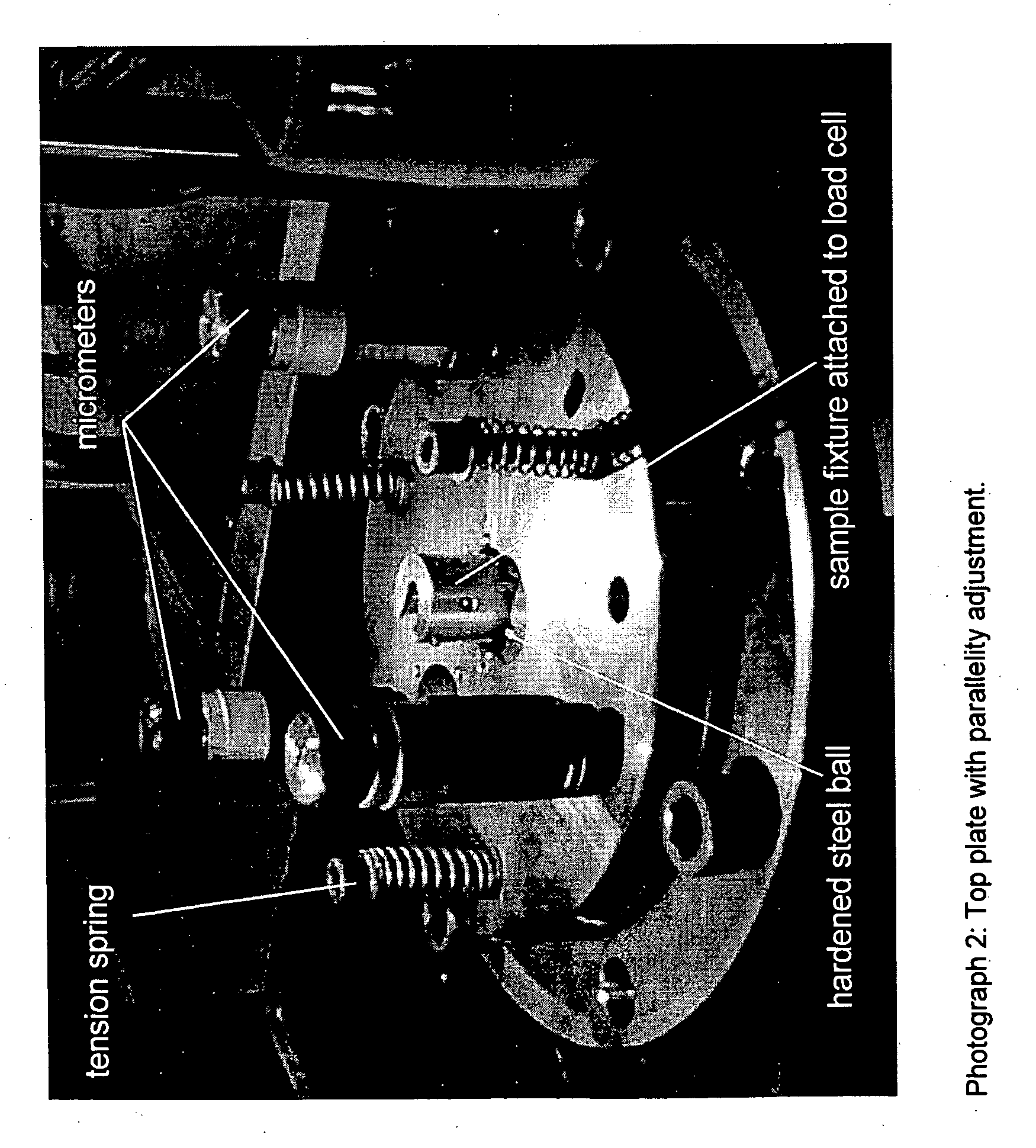
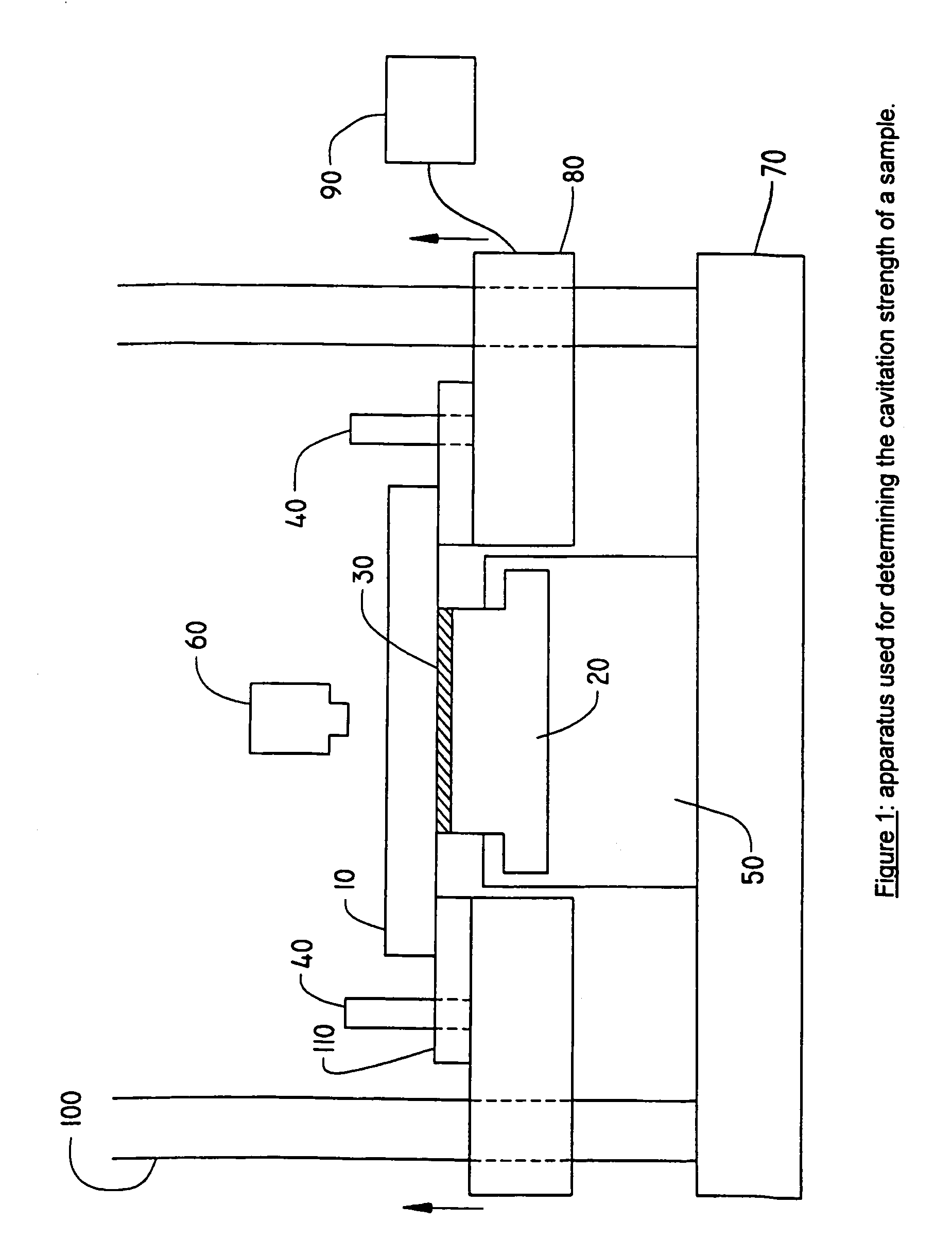
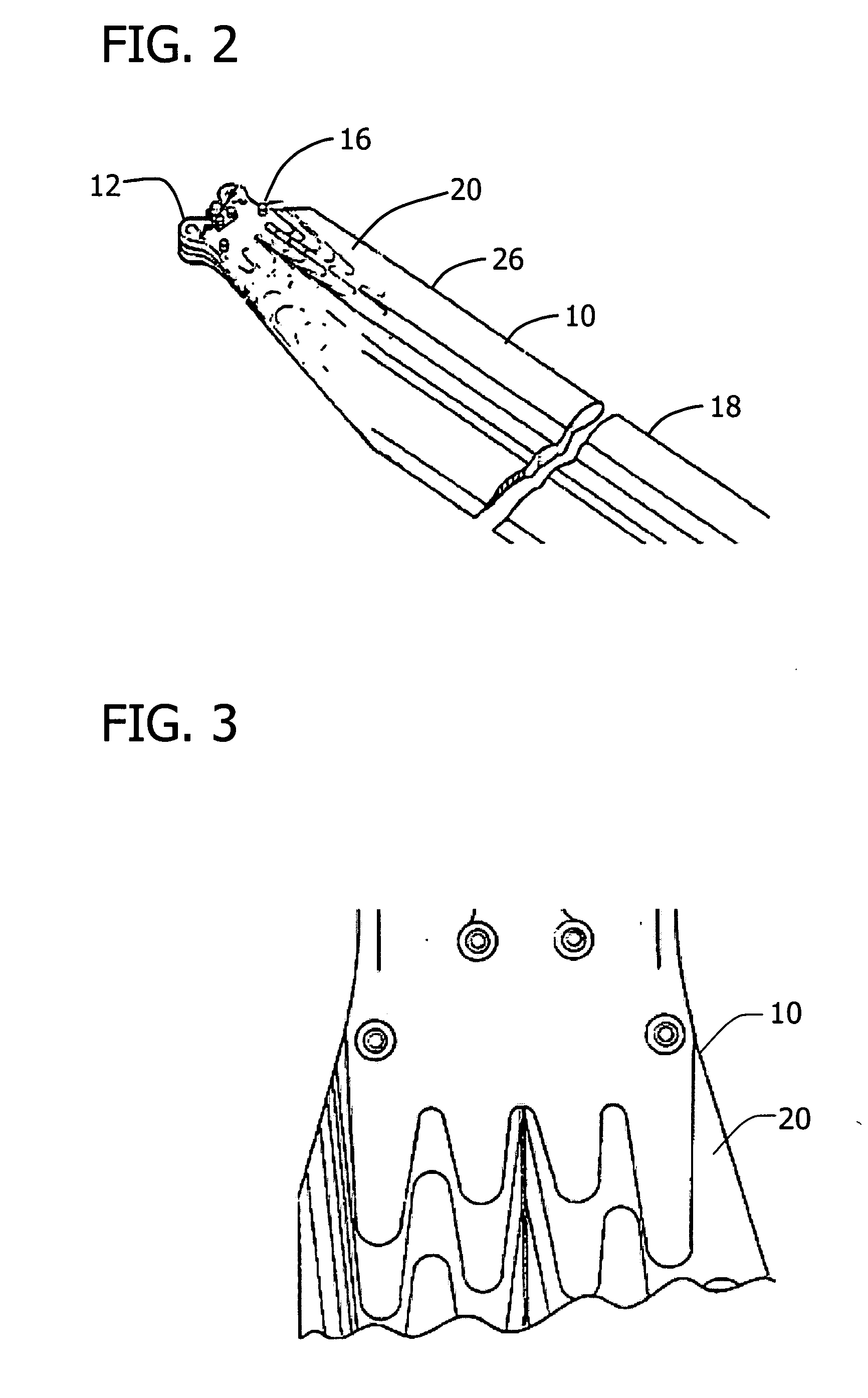
Coated optical fibers
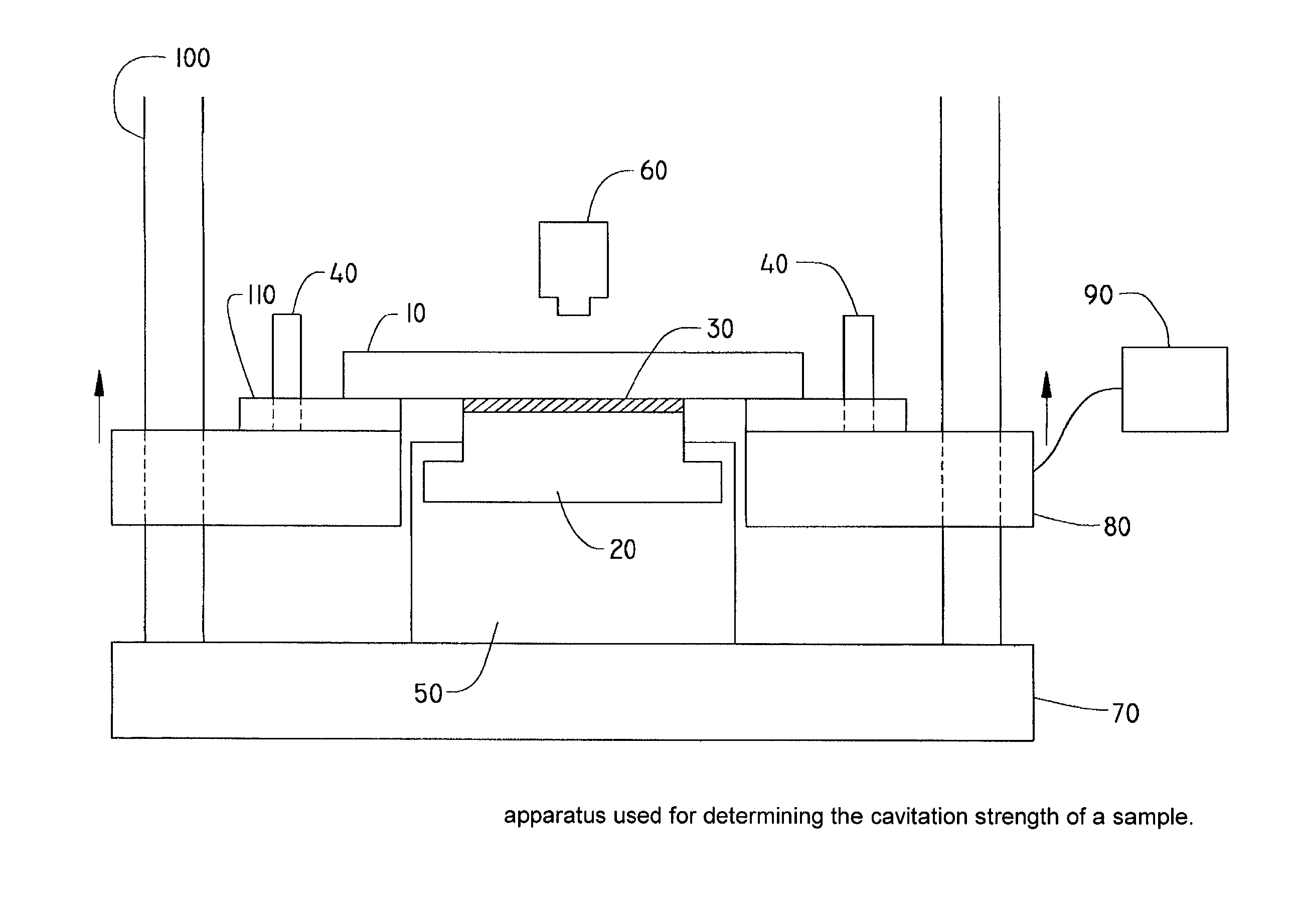
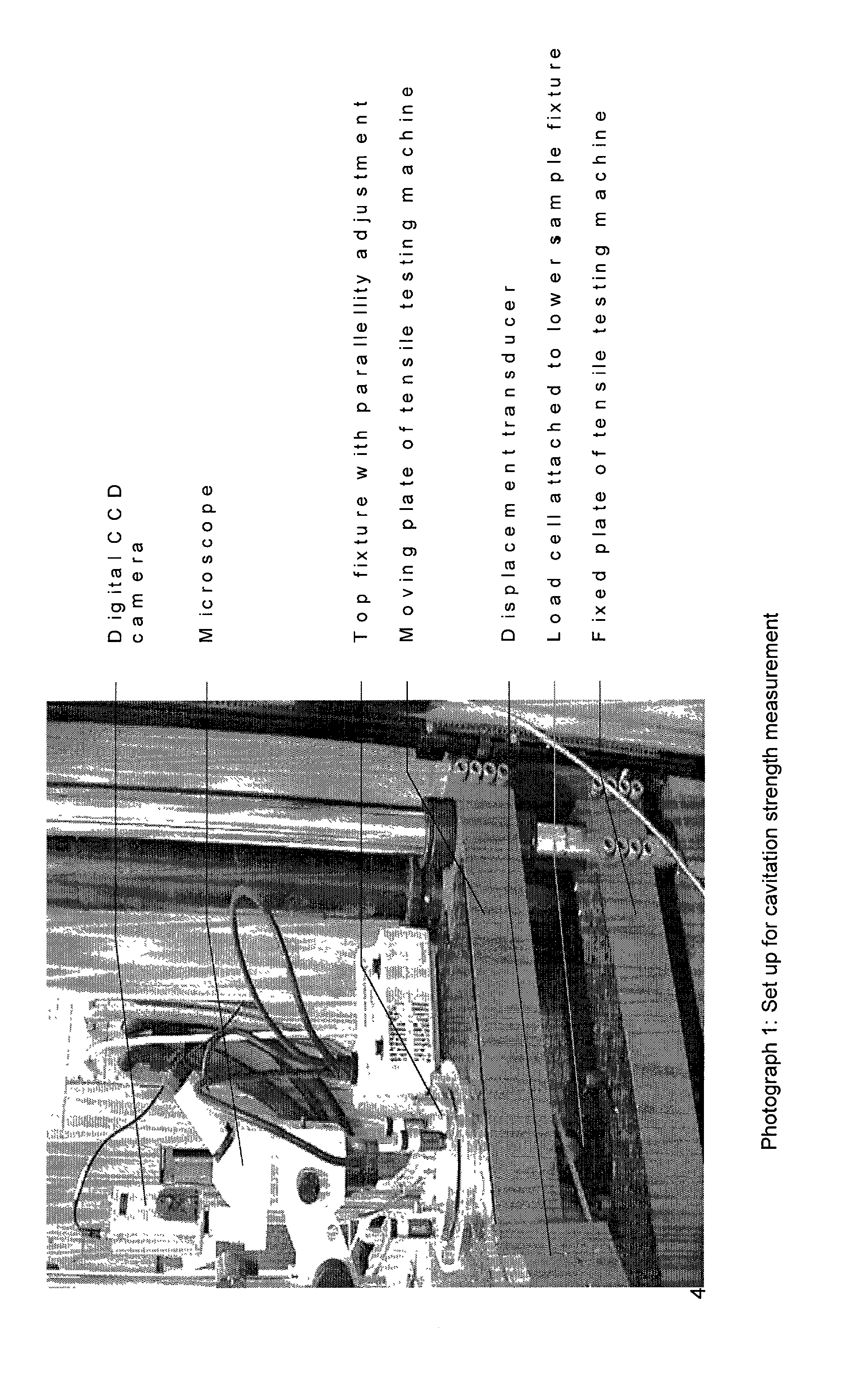
InactiveUS20020146225A1Sufficient high cavitation strengthLow modulusGlass optical fibreSynthetic resin layered productsHigh resistanceCavitation
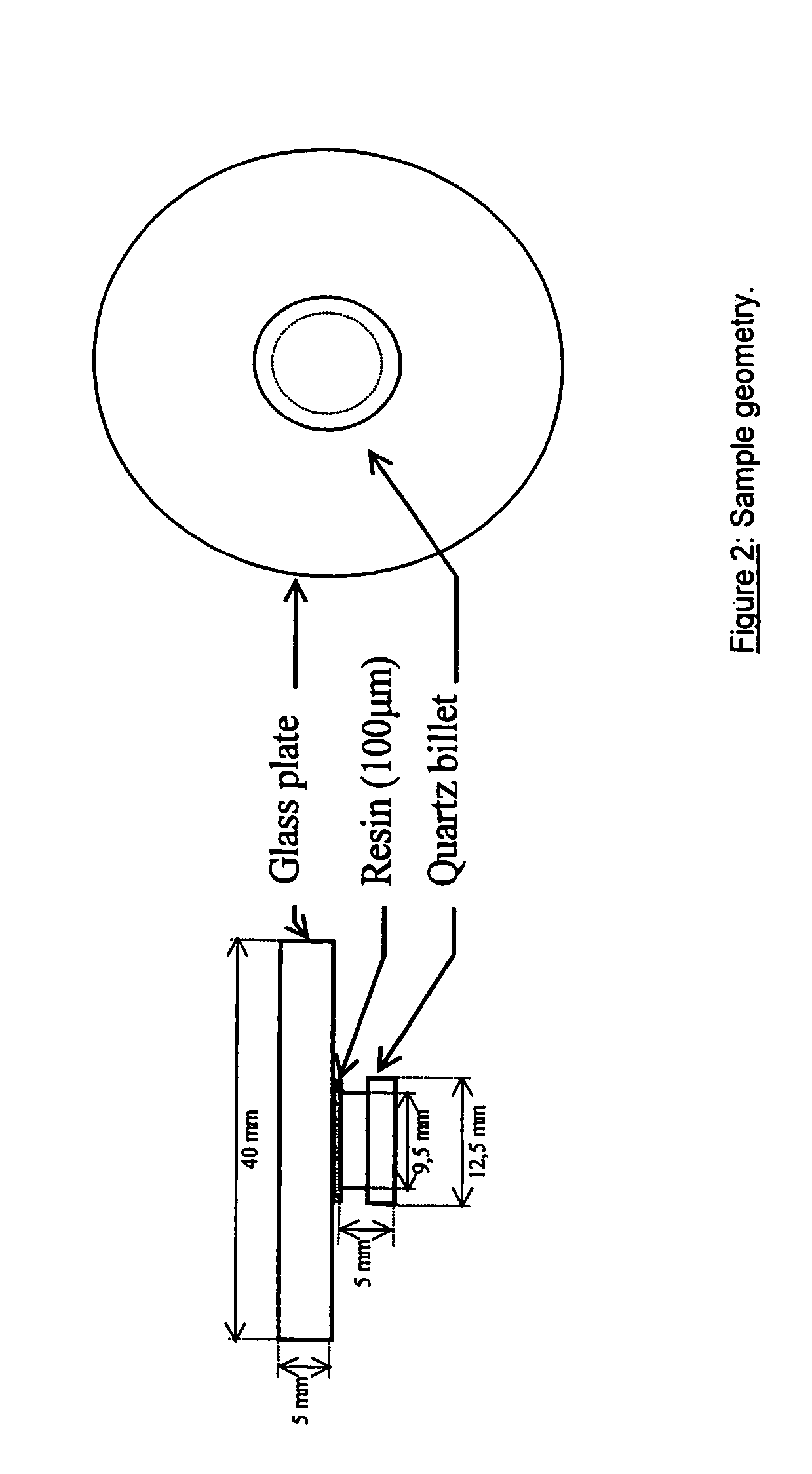
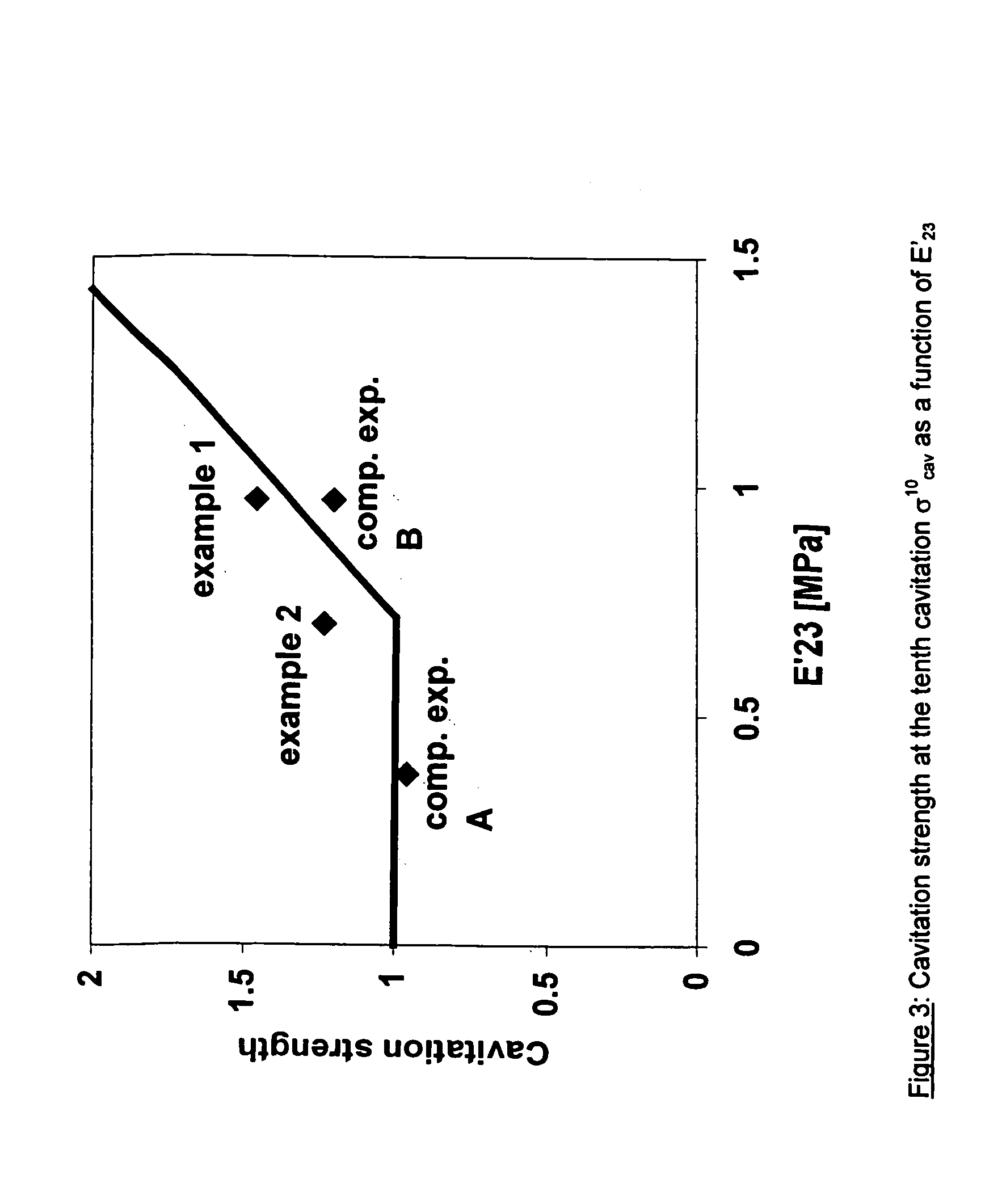
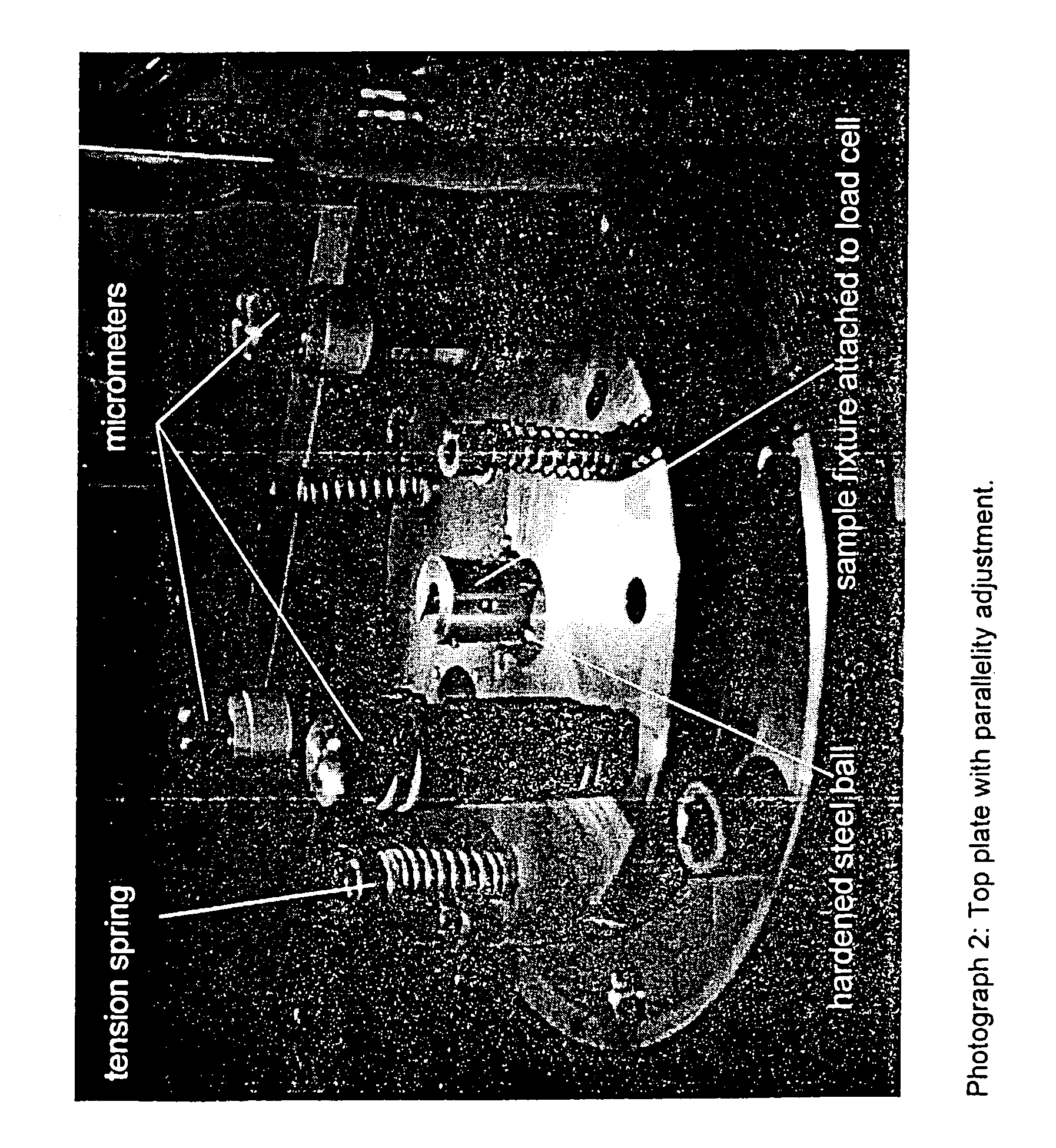
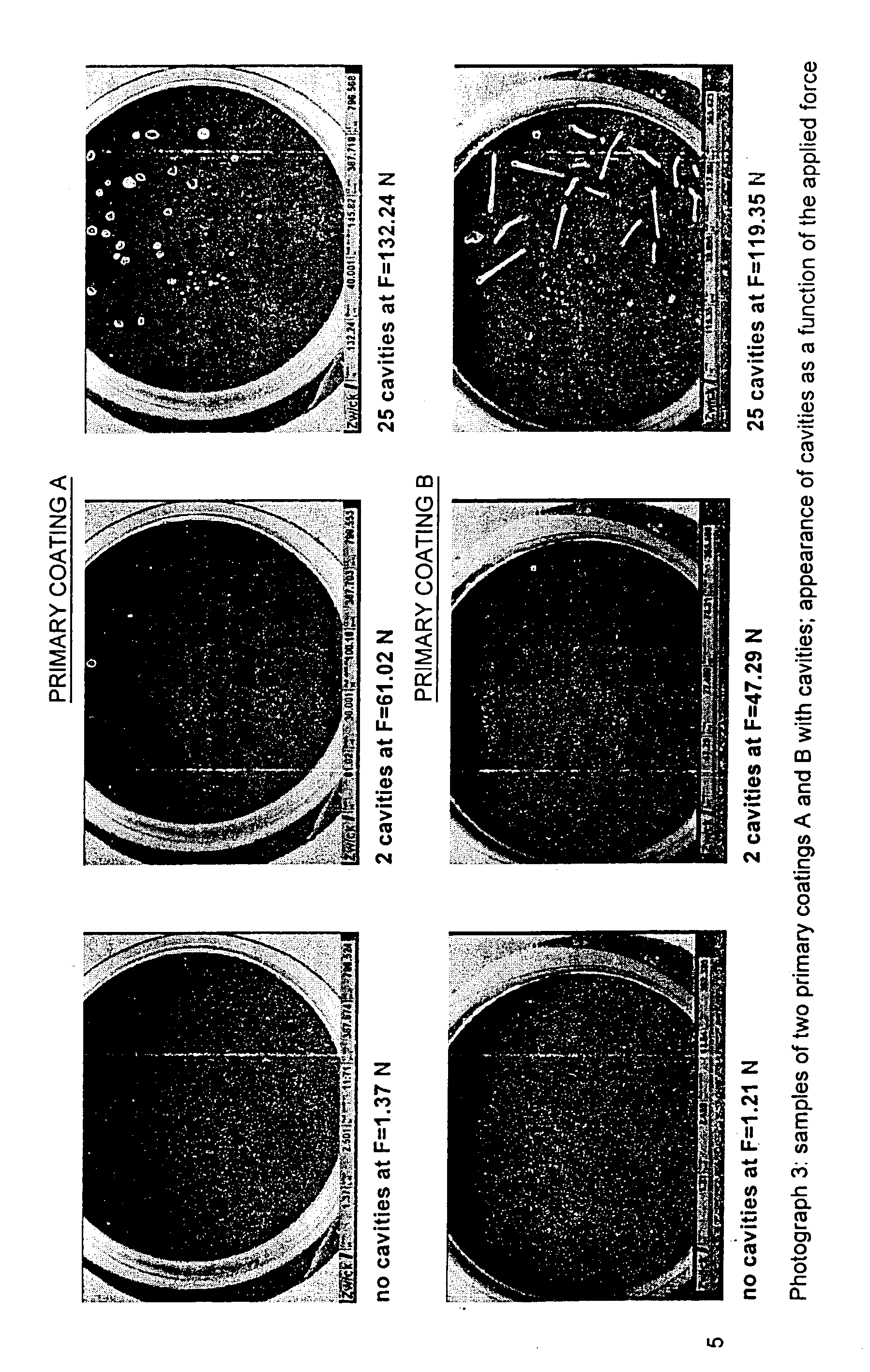
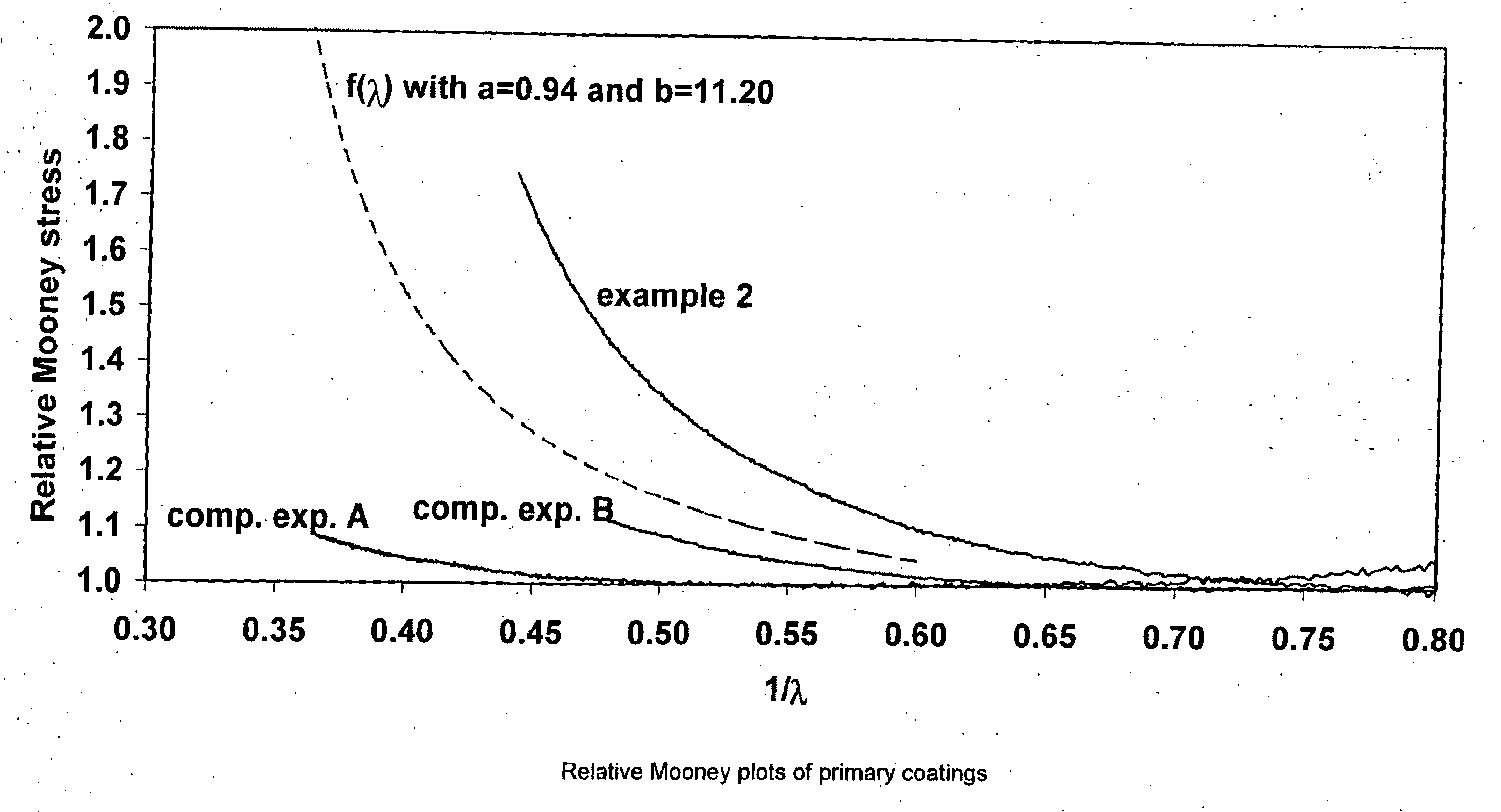
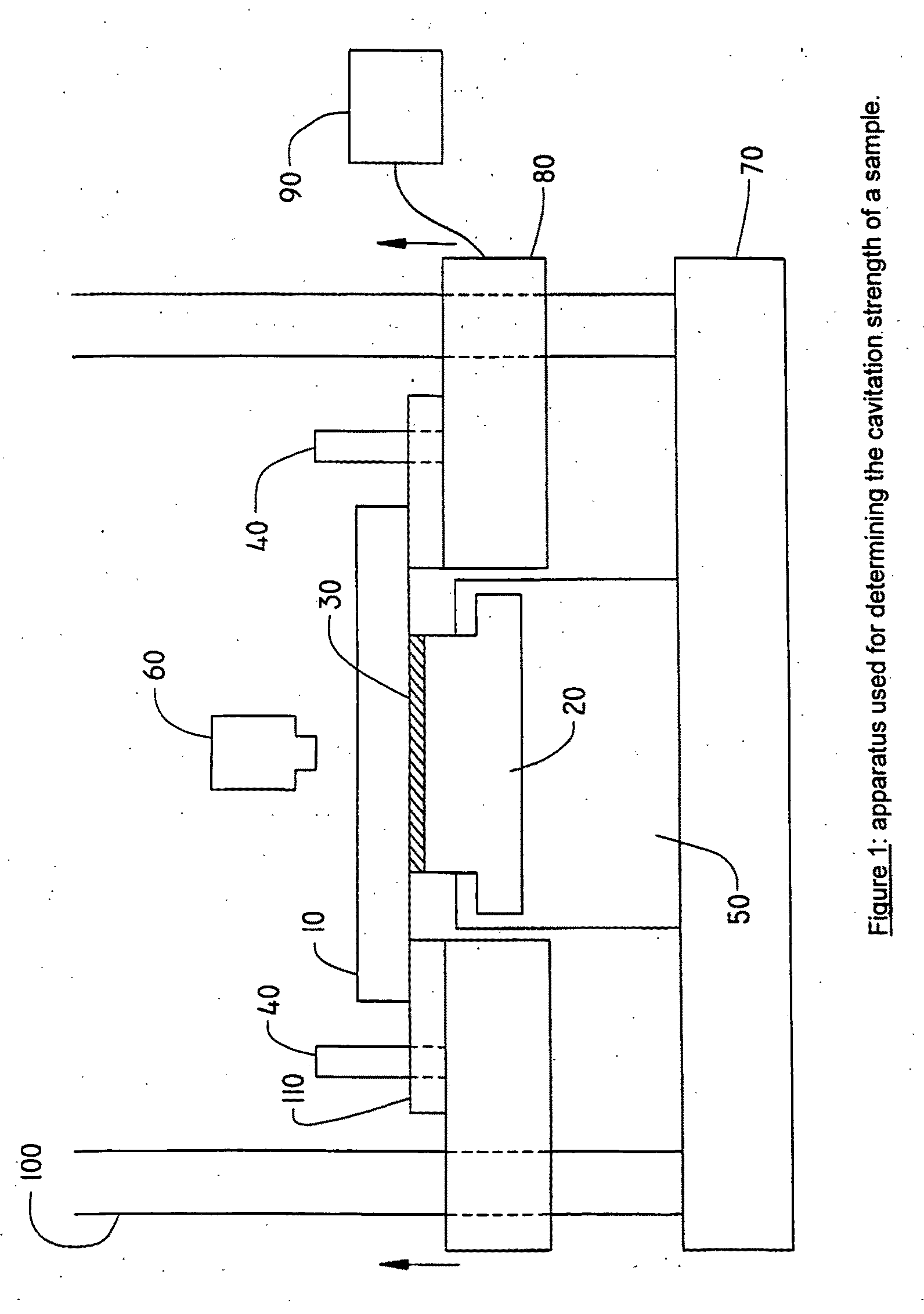
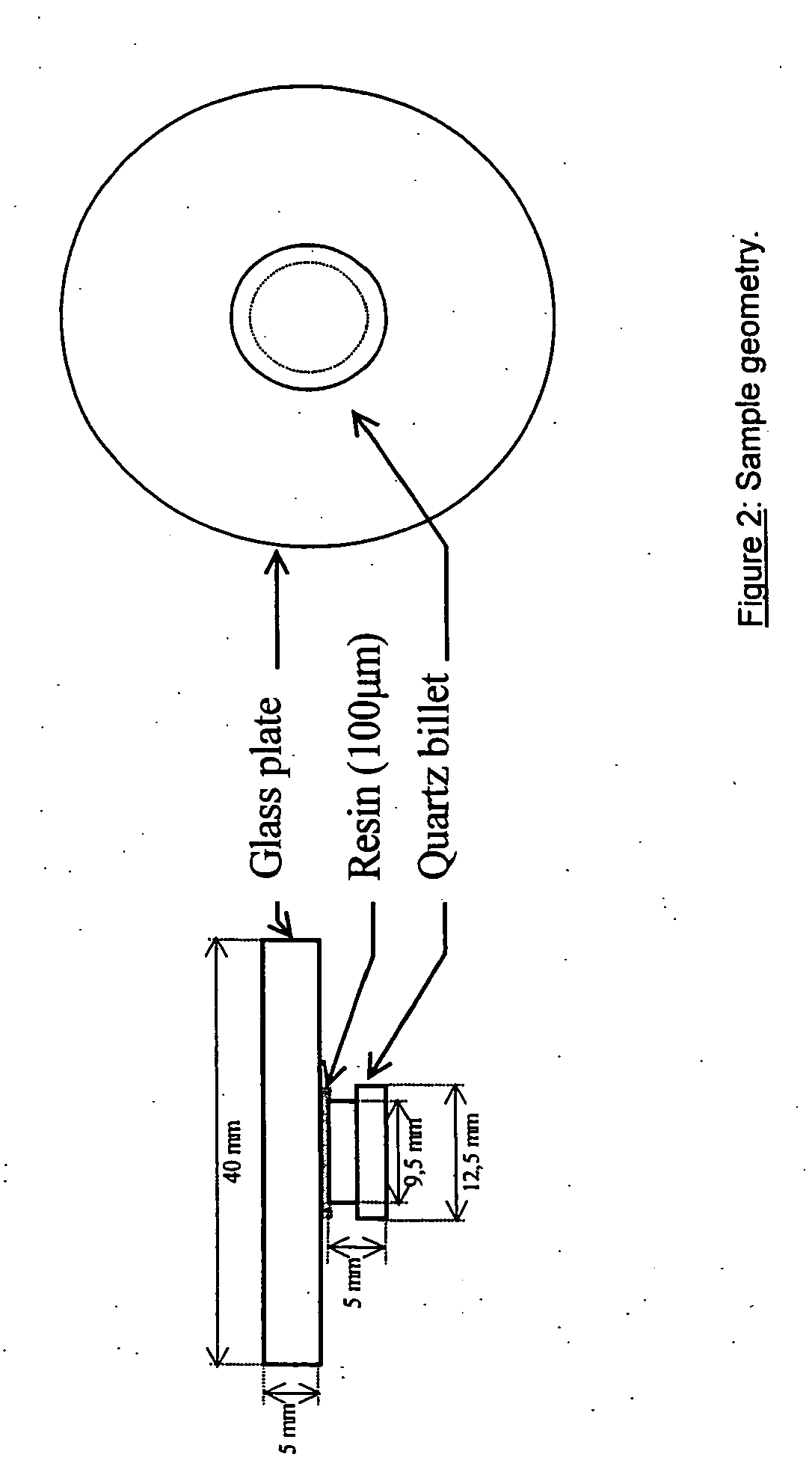
The invention relates to coated optical fibers comprising soft primary coatings and to such primary coatings for protecting glass optical fibers having a sufficient high resistance against cavitation. In particular, the primary coatings have a cavitation strength at which a tenth cavitation appears (sigma10cav) of at least about 1.0 MPa as measured at a deformation rate of 0.20% min-1 and of at least about 1.4 times their storage modulus at 23° C. The coating preferably shows strain hardening in a relative Mooney plot, preferably has a strain energy release rate Go of about 20 J / m2 or more, and preferably has a low volumetric thermal expansion coefficient. The invention furthermore provides a method and apparatus for measuring the cavitation strength of a primary coating.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
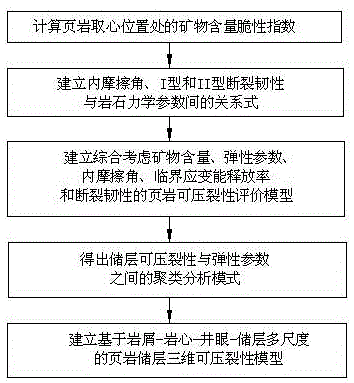
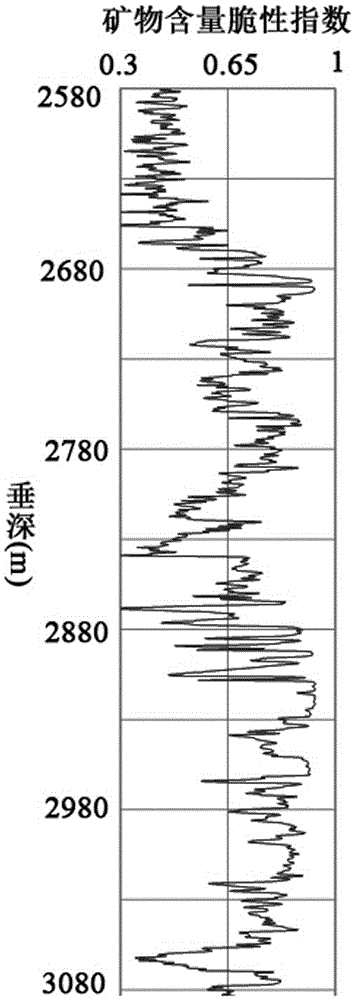
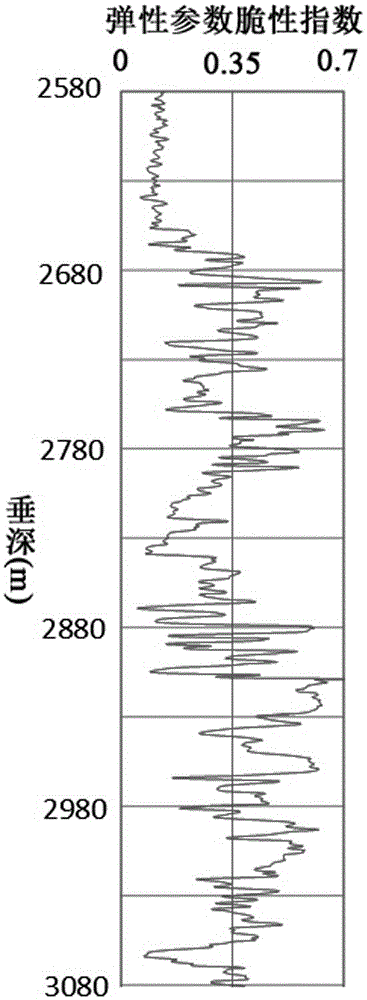
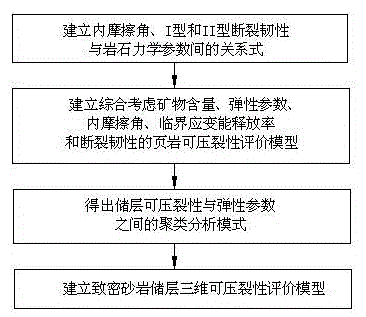
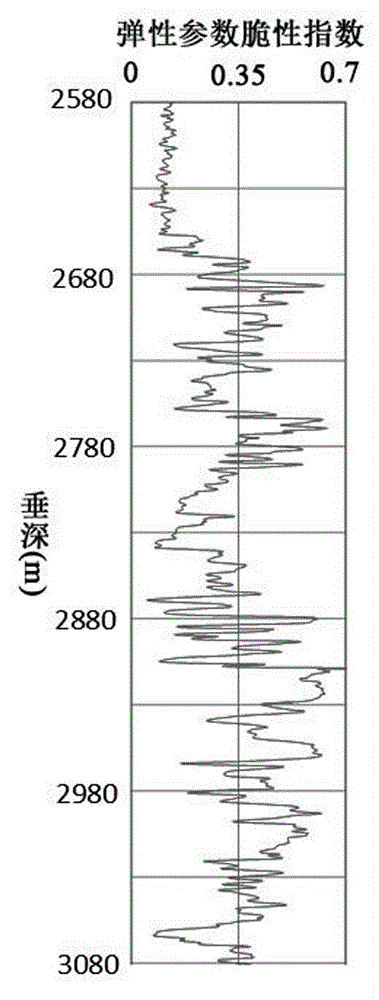
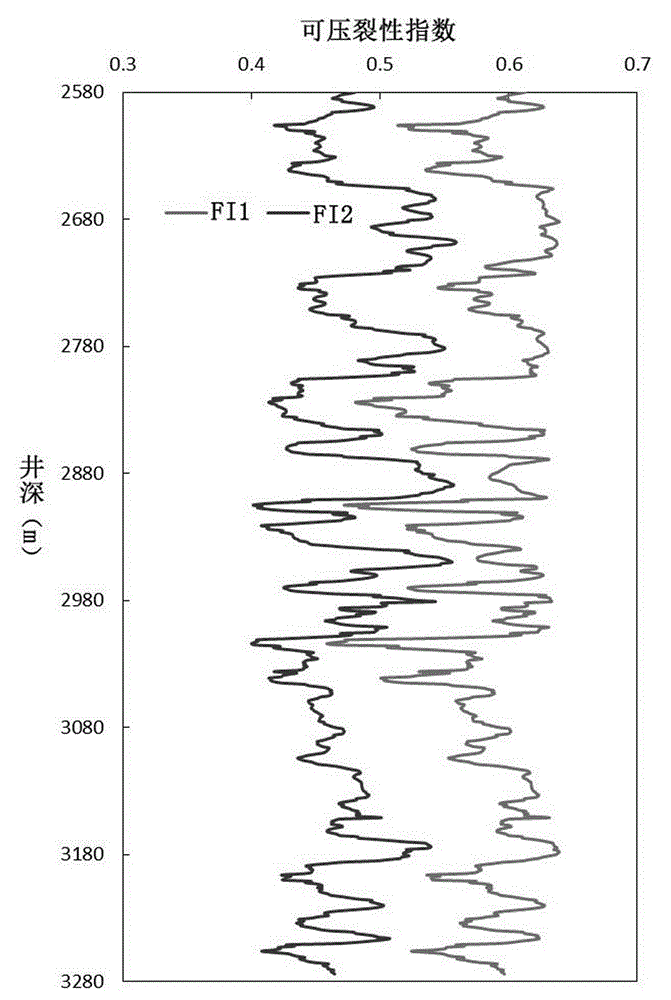
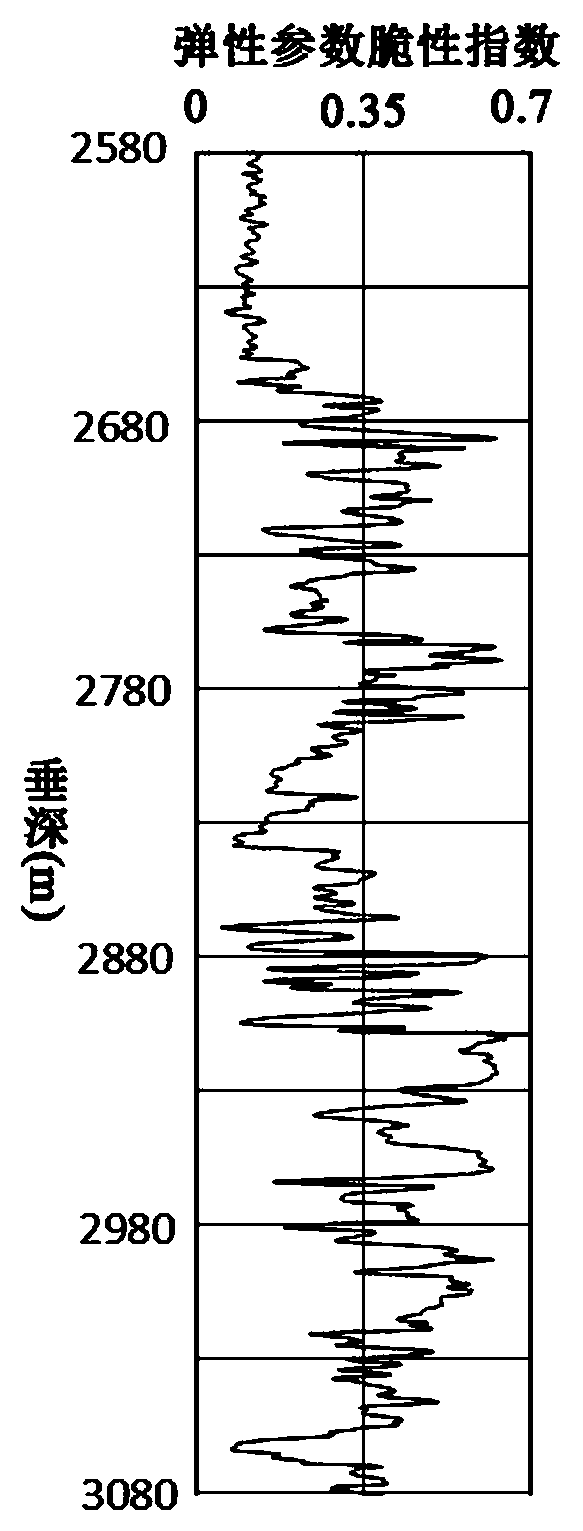
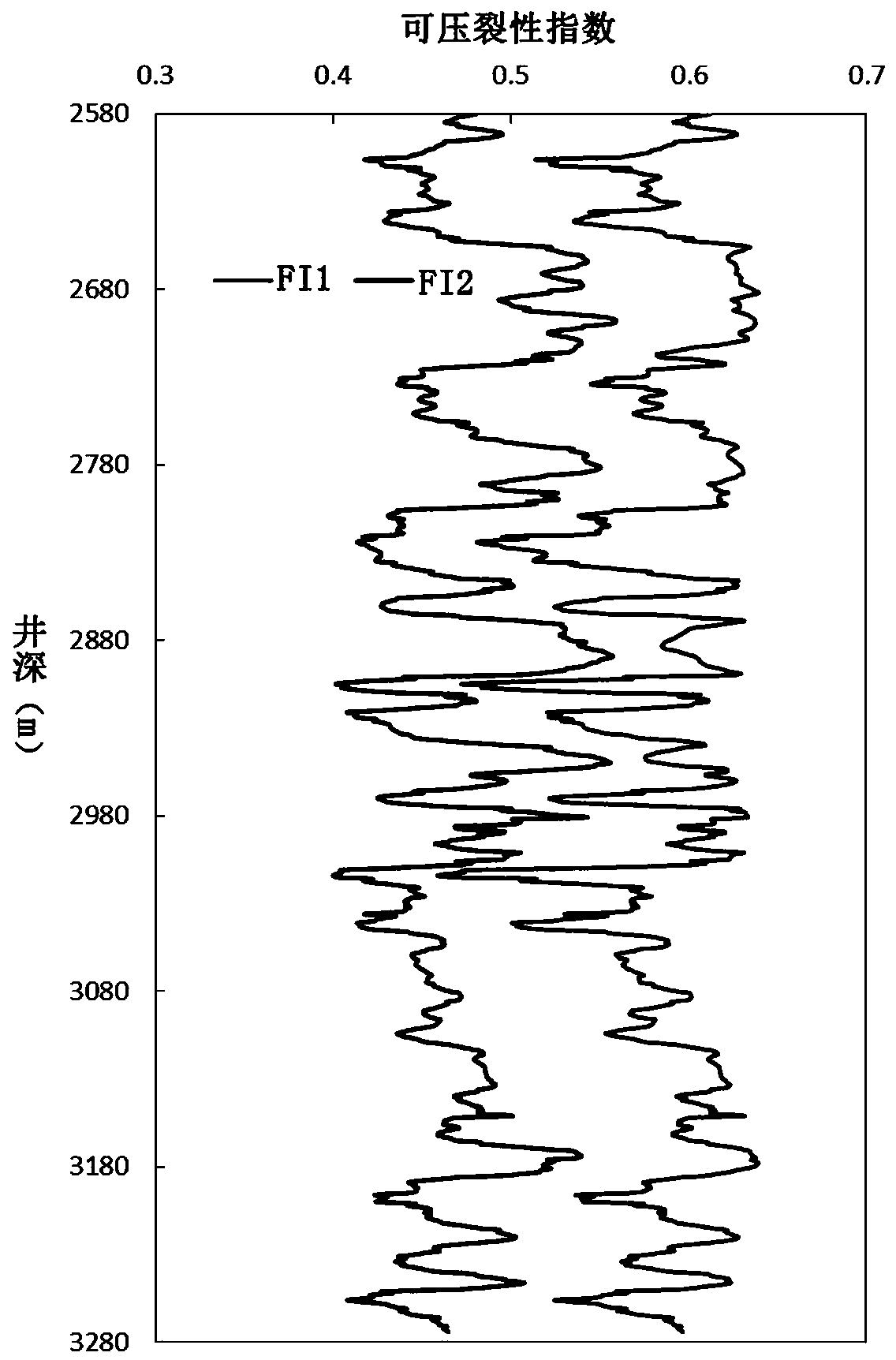
Debris-core-borehole-reservoir multiscale shale reservoir three-dimensional fracturing evaluation method
ActiveCN105156103ALarge capacityQuantification of fracabilityBorehole/well accessoriesType fractureWell placement
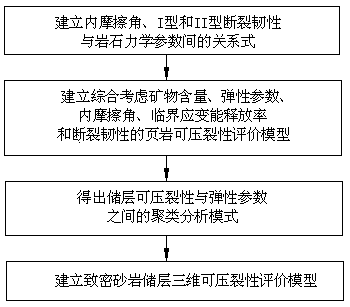
The invention relates to a debris-core-borehole-reservoir multiscale shale reservoir three-dimensional fracturing evaluation method. The method comprises the steps of: (S1) calculating mineral content brittleness indexes in a shale coring position; (S2) building relations among an internal friction angle, I type and II type fracture toughness and rock mechanical parameters; (S3) building shale fracturing evaluation models comprehensively considering a mineral content, elastic parameters, the internal friction angle, a critical strain energy release rate and the rapture toughness; (S4) applying a support vector machine algorithm to obtain a cluster analysis mode between a reservoir fracturing performance and the elastic parameters; and (S5) applying the cluster analysis mode and a reservoir three-dimensional elastic parameter data body to obtain a debris-core-borehole-reservoir multiscale shale reservoir three-dimensional fracturing model. The method can be applied to obtain the fracturing performance of any space position in a shale reservoir, so that the well position selection blindness is prevented, and the fracturing modification effect and the after-pressing yield are improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV +1
Modeling method for compact sandstone reservoir three-dimensional fracability model
ActiveCN105134156AImproving the effectiveness of volumetric fracturingShorter payback timeFluid removalSpecial data processing applicationsModel methodWell placement
The invention relates to a modeling method for a compact sandstone reservoir three-dimensional fracability model. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a relation formula among an internal friction angle, I type and II type crack fracture toughness and the parameter of sandstone mechanical characteristics; S2, establishing a shale fracability evaluation model which comprehensively considers an elastic parameter, the internal friction angle, the critical strain energy release rate and fracture toughness; S3, adopting a support vector machine algorithm to obtain a cluster analysis mode between the reservoir fracability and the elastic parameter; S4, adopting the cluster analysis mode to obtain a reservoir three-dimensional elastic parameter data body, and establishing the multi-scale compact sandstone reservoir three-dimensional fracability evaluation model based on the core, the borehole and the reservoir of multiple scales. According to the method, the fracability of an arbitrary space position in the compact sandstone reservoir can be obtained, a sweet spot with high fracability can always be drilled when drilling a compact sandstone gas well, blindness of well location selection is avoided, and the fracture modification effect and the yield after fracture are improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Coated optical fibers
InactiveUS20060062539A1Low stress levelGlass optical fibreNatural mineral layered productsHigh resistanceCavitation
The invention relates to coated optical fibers comprising soft primary coatings and to such primary coatings for protecting glass optical fibers having a sufficient high resistance against cavitation. In particular, the primary coatings have a cavitation strength at which a tenth cavitation appears (σ10cav) of at least about 1.0 MPa as measured at a deformation rate of 0.20% min−1 and of at least about 1.4 times their storage modulus at 23° C. The coating preferably shows strain hardening in a relative Mooney plot, preferably has a strain energy release rate Go of about 20 J / m2 or more, and preferably has a low volumetric thermal expansion coefficient. The invention furthermore provides a method and apparatus for measuring the cavitation strength of a primary coating.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Coated optical fibers
The invention relates to coated optical fibers comprising soft primary coatings and to such primary coatings for protecting glass optical fibers having a sufficient high resistance against cavitation. In particular, the primary coatings have a cavitation strength at which a tenth cavitation appears (σ10cav) of at least about 1.0 MPa as measured at a deformation rate of 0.20% min−1 and of at least about 1.4 times their storage modulus at 23° C. The coating preferably shows strain hardening in a relative Mooney plot, preferably has a strain energy release rate Go of about 20 J / m2 or more, and preferably has a low volumetric thermal expansion coefficient. The invention furthermore provides a method and apparatus for measuring the cavitation strength of a primary coating.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Strike-slip fault structure evolution analytical method
InactiveCN108680952AReduce spendingEasy to operateSeismic signal processingTectonic stressKinematics
The invention belongs to the oil and gas field exploration and development and mineral evaluation and prediction field and relates to a strike-slip fault structure evolution analytical method. According to the strike-slip fault structure evolution analytical method, the fault paleo fall of different positions of a strike-slip fault is calculated, so that the periodic rhythm change of the paleo fall of the fault along a strike-slip direction is analyzed; restored graben-horst structures at two sides of the strike-slip fault in different periods are used to determine basin prototypes at the twosides of the strike-slip fault before the deposition of different strata, and identify the damping sections of the strike-slip fault; the unit movement intensity of the fault is calculated to characterize the strike-slip amount of the strike-slip fault; the calculated strain energy release rate of the strike-slip fault is used to analyze the dynamic mechanisms of different portions of the strike-slip fault; and the numerical simulation of a tectonic stress field is used to explain the fault from the aspect of dynamics and verify the formation mechanism of the strike-slip fault. The method foranalyzing the formation mechanism and evolution process of the strike-slip fault is systematically provided from a time and space four-dimensional perspective in the aspects of geometry, kinematics and dynamics.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Disbond resistant composite joint and method of forming
A disbond resistant multi-laminate composite product is provided having, a first member; a second member of composite material bonded to the first member; a third member of composite material bonded to at least the second member and being so positioned and arranged such that when the second and third members are stressed at least a portion of the third member will have higher stress than the adjacent second member. The third member preferably has a terminal portion adjacent the second member in which terminal portion the strain energy release rate is higher than in the adjacent second member when the second and third members are stressed. The second and third members are preferably so positioned and arranged such that the third member initiates delamination from the second member before the second member initiates delamination from the first member when the first, second and third members are under stress. A stress level indicator is preferably associated with the third member to measure the stress levels in the third member.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Disbond resistant composite joint and method of forming
ActiveUS20060204364A1Simple arrangementSimple structurePropellersPump componentsStress levelEngineering
A disbond resistant multi-laminate composite product is provided having, a first member; a second member of composite material bonded to the first member; a third member of composite material bonded to at least the second member and being so positioned and arranged such that when the second and third members are stressed at least a portion of the third member will have higher stress than the adjacent second member. The third member preferably has a terminal portion adjacent the second member in which terminal portion the strain energy release rate is higher than in the adjacent second member when the second and third members are stressed. The second and third members are preferably so positioned and arranged such that the third member initiates delamination from the second member before the second member initiates delamination from the first member when the first, second and third members are under stress. A stress level indicator is preferably associated with the third member to measure the stress levels in the third member.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
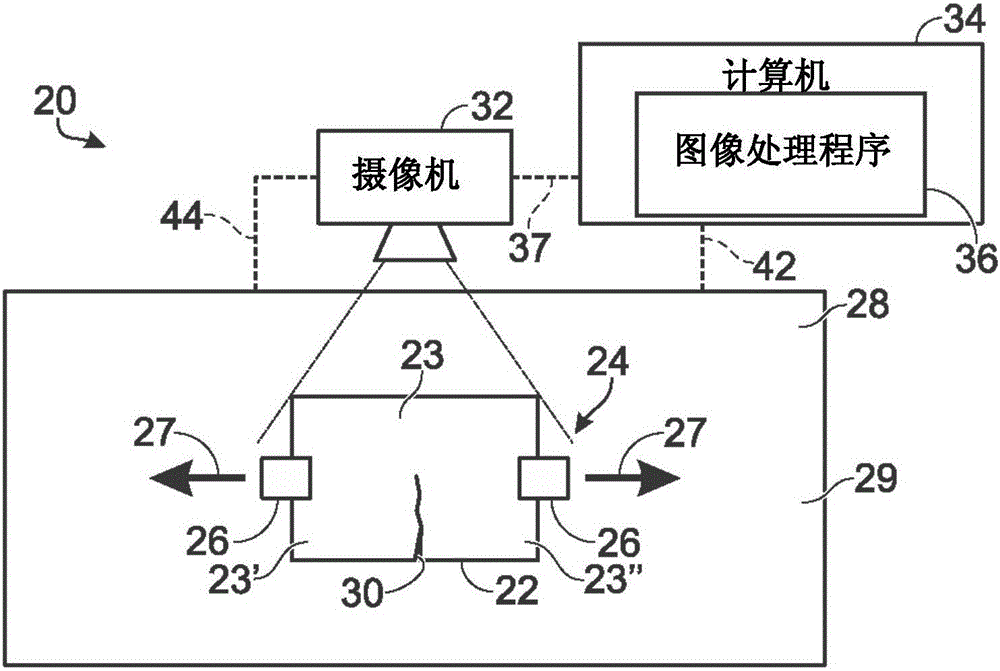
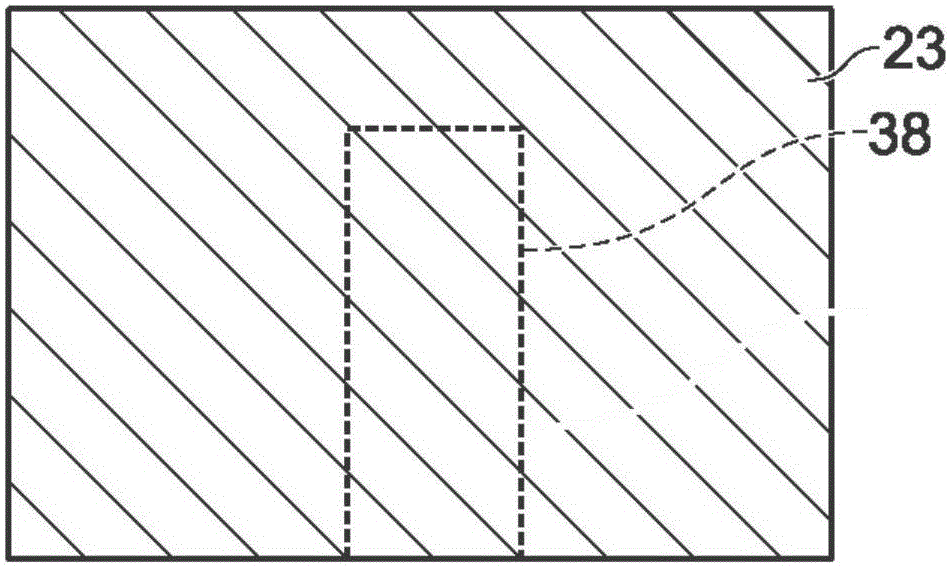
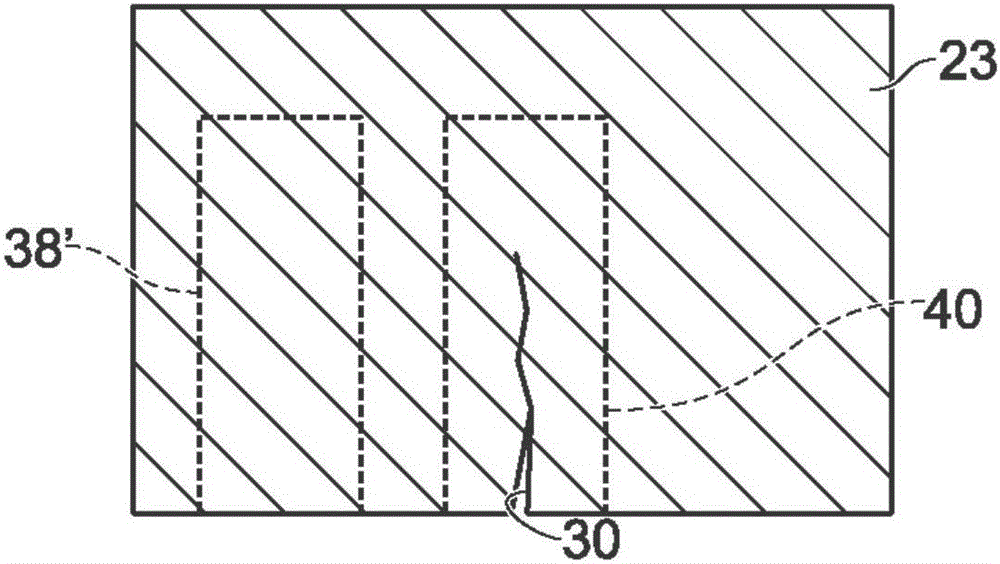
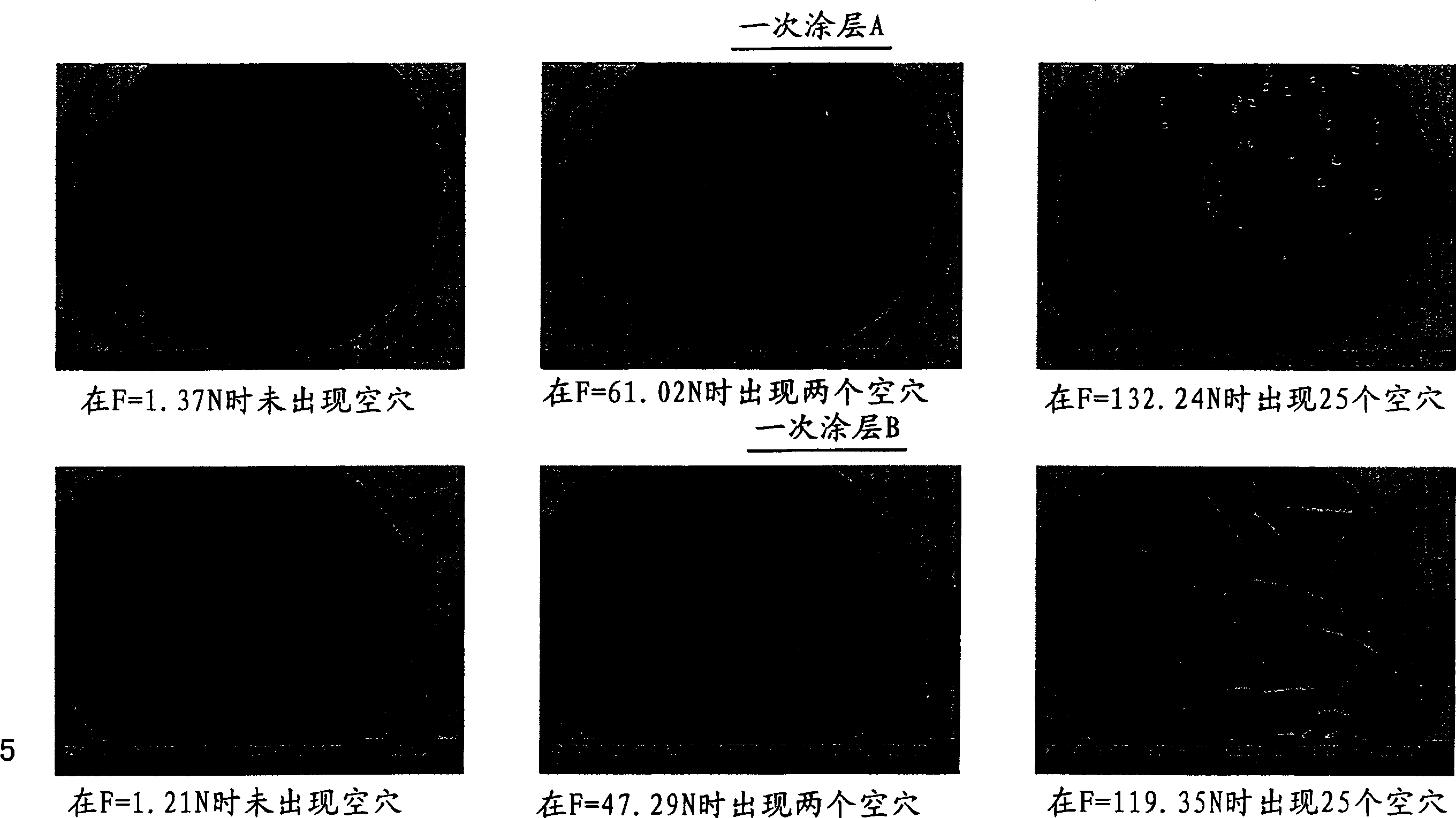
Systems and methods for detecting crack growth
ActiveCN105387809AOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansComputer scienceColor contrast
A system and method for detecting crack propagation in a material test specimen may include color contrasting a surface of a test specimen, acquiring a plurality of photographic images of the specimen during application of a stress load, processing the plurality of images to detect characteristics of pixels that are outside a baseline range of pixel characteristics indicative of a contrast between a crack in the test specimen and the color contrasted surface of the test specimen, and generating an output of a strain energy release rate based on changes in detected crack length over time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Coated optical fibers
InactiveUS20030215196A1Low stress levelRelieve pressureGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresHigh resistanceCavitation
The invention relates to coated optical fibers comprising soft primary coatings and to such primary coatings for protecting glass optical fibers having a sufficient high resistance against cavitation. In particular, the primary coatings have a cavitation strength at which a tenth cavitation appears (sigma<10>cav) of at least about 1.0 MPa as measured at a deformation rate of 0.20% min<-1 >and of at least about 1.4 times their dynamic modulus at 23° C. The coating preferably shows strain hardening in a relative Mooney plot, preferably has a strain energy release rate Go of about 20 J / m<2 >or more, and preferably has a low volumetric thermal expansion coefficient. The invention furthermore provides a method and apparatus for measuring the cavitation strength of a primary coating.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Anti-impact ferrous rare earth permanent magnet and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN101154489AImprove impact resistanceAvoid damageInorganic material magnetismChemical compositionRare earth
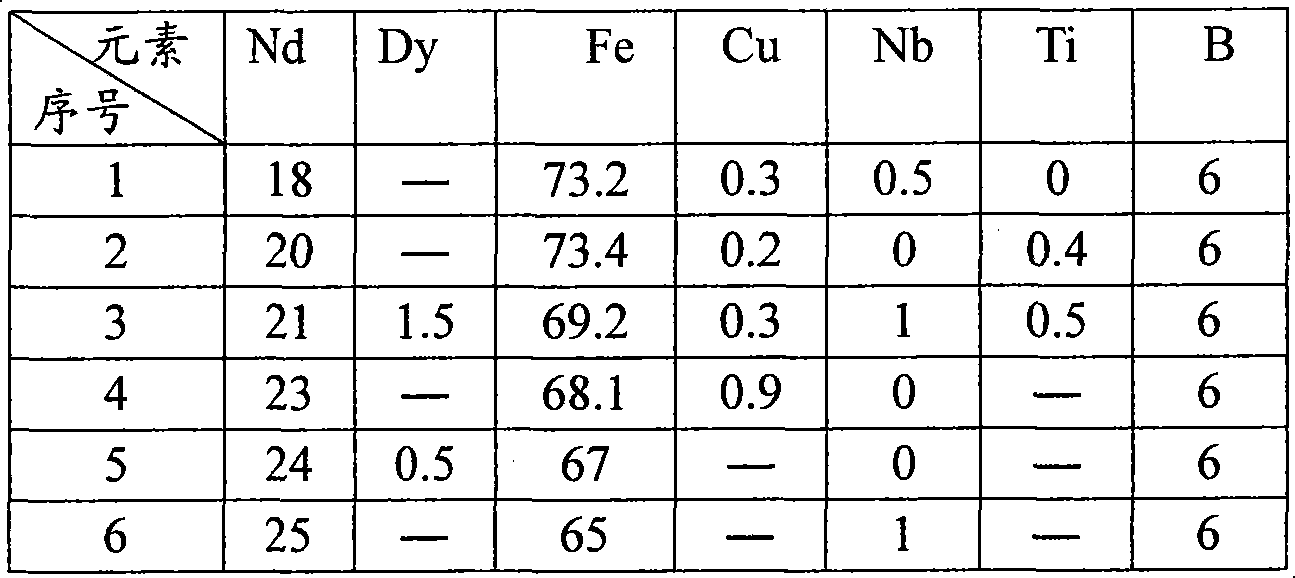
The invention provides a shock resistance iron base rare-earth permanent-magnet material and a preparation method of the same. The chemical composition are that Nd18-25, Re0.5-1.5, TM65-73, M0.1-1 and B5-6, wherein, Re is the lanthanon chosen from Dy and Tb, TM is the transition element chosen from Fe and Co, and M is the microadd element chosen from Nb, Cu and Ti. The preparation method is to increase the proportion of Nd with low hardness and high plasticity in the magnet to improve the ultimate strain energy rate so as to improve the obdurability and shock resistance of magnet. Relative to the machinable magnet of FeCrCo, the invention prepares the magnet with stronger magnetism and machinable property as well as shock resistance, thereby lowering the processing cost of magnet.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
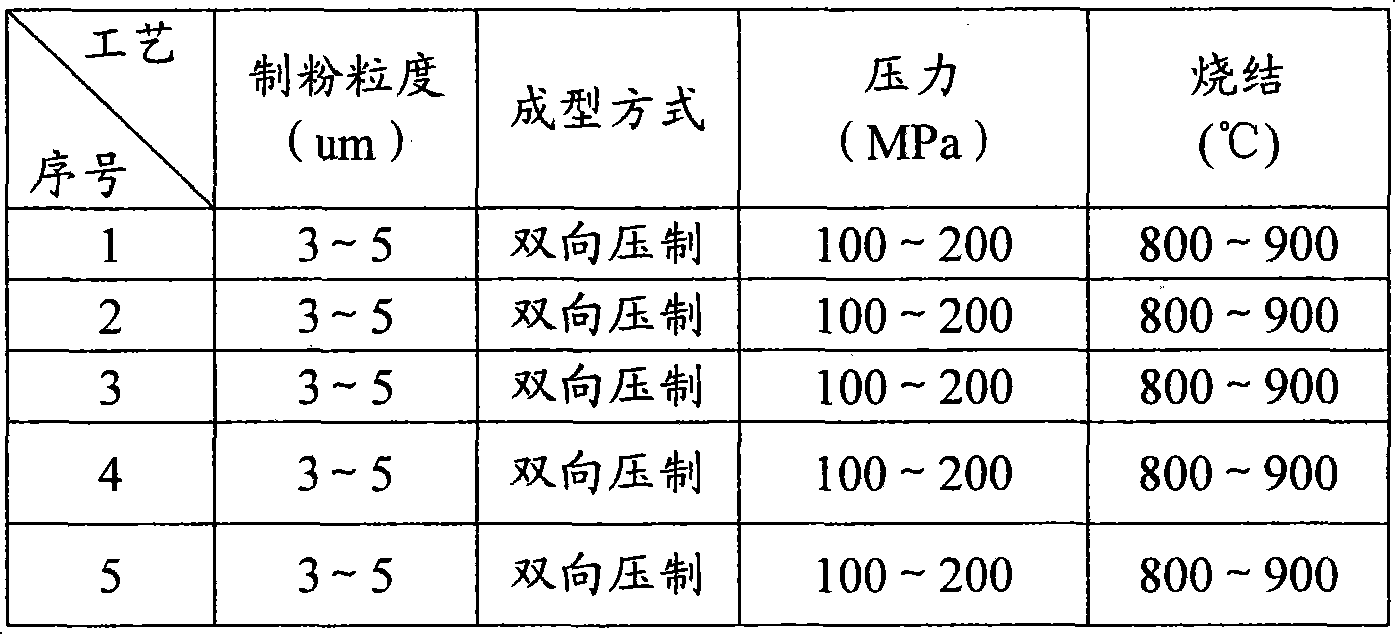
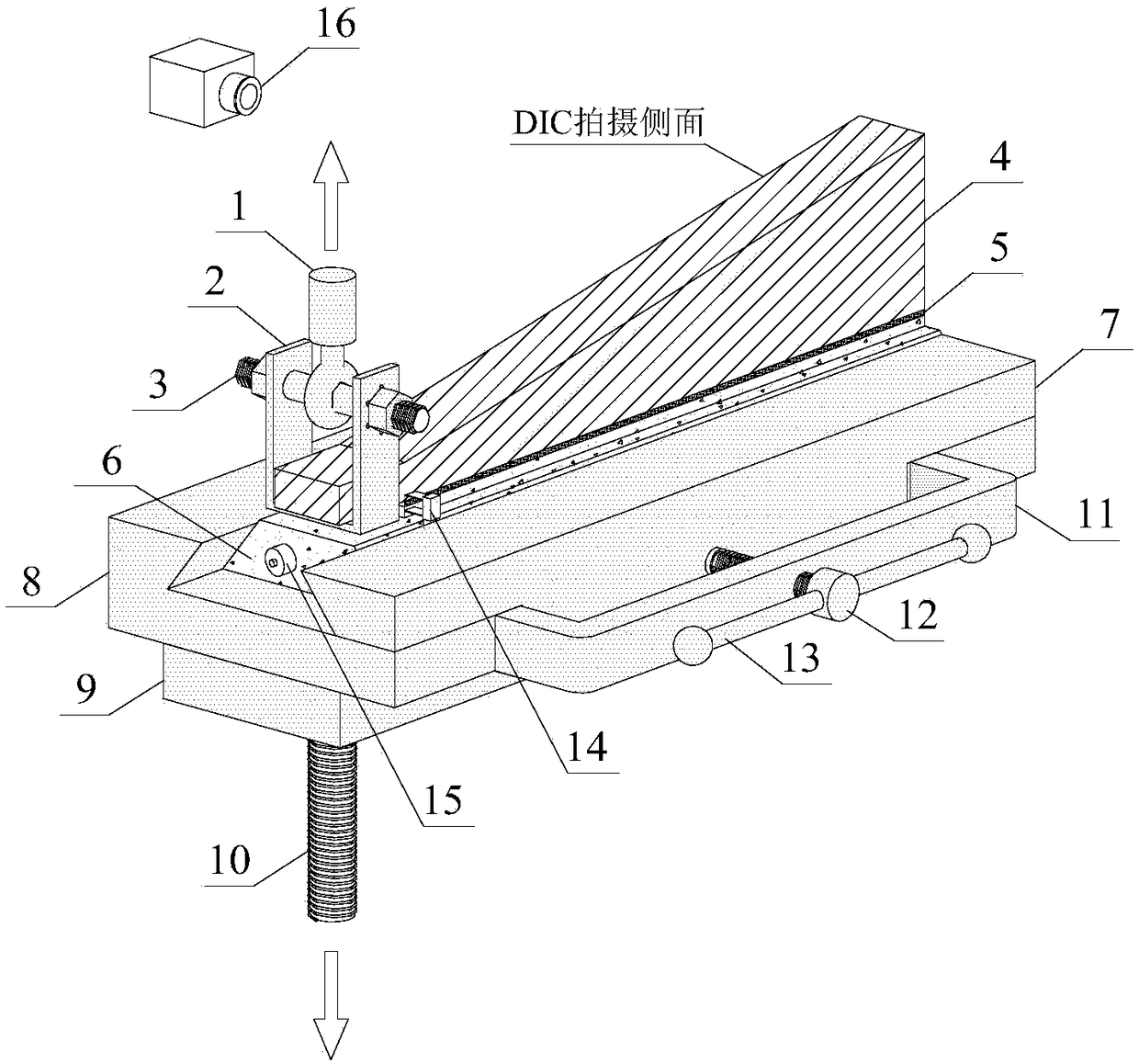
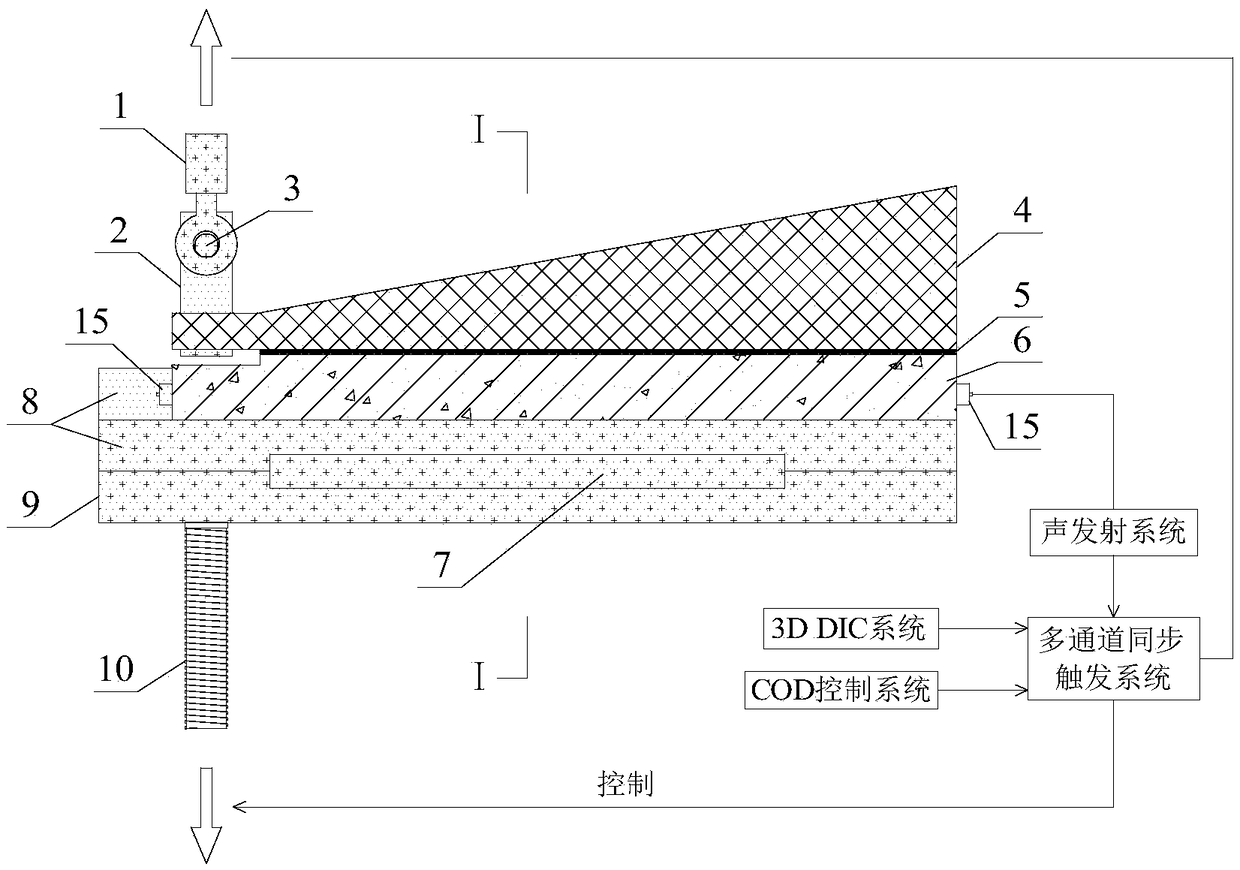
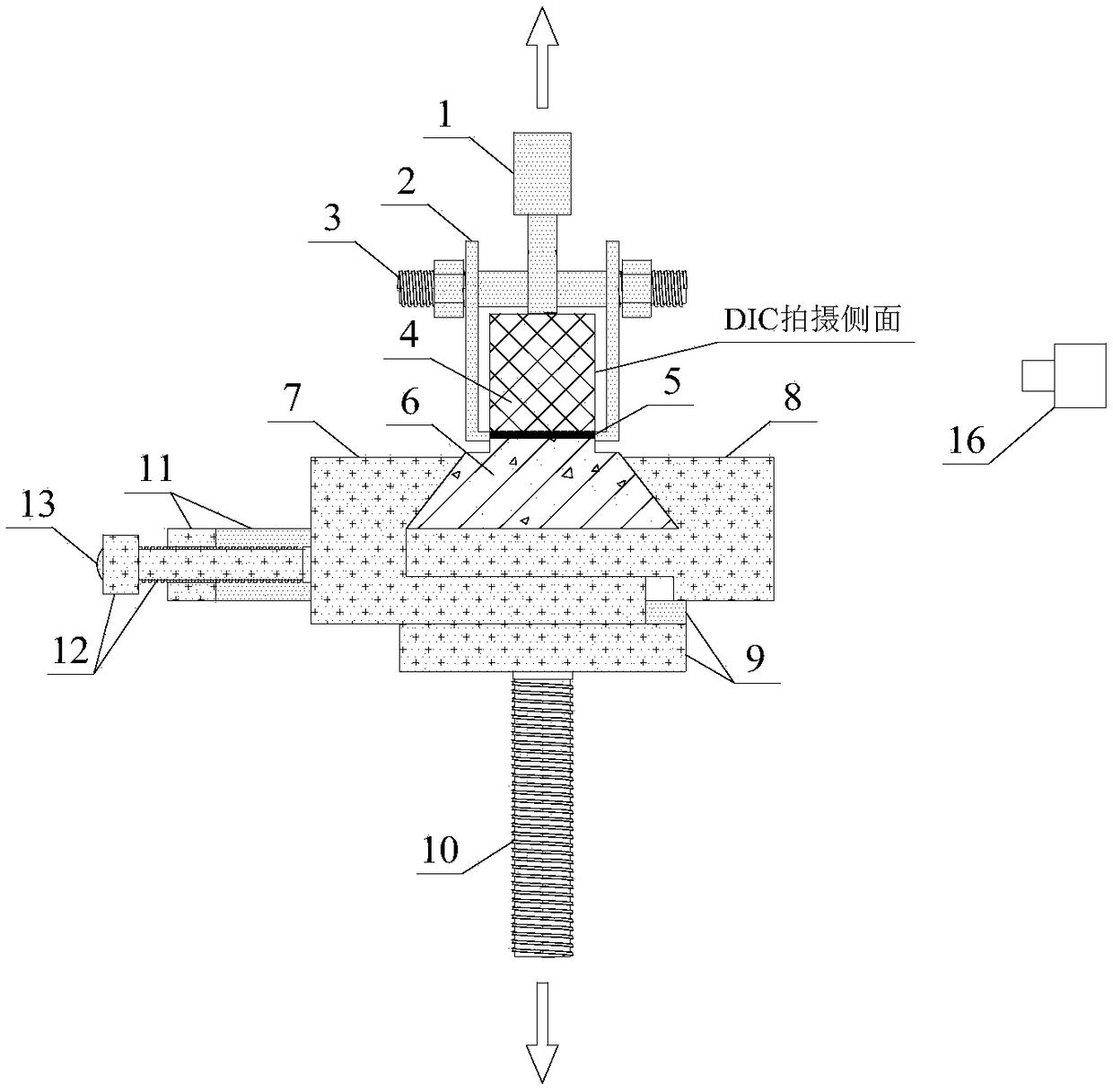
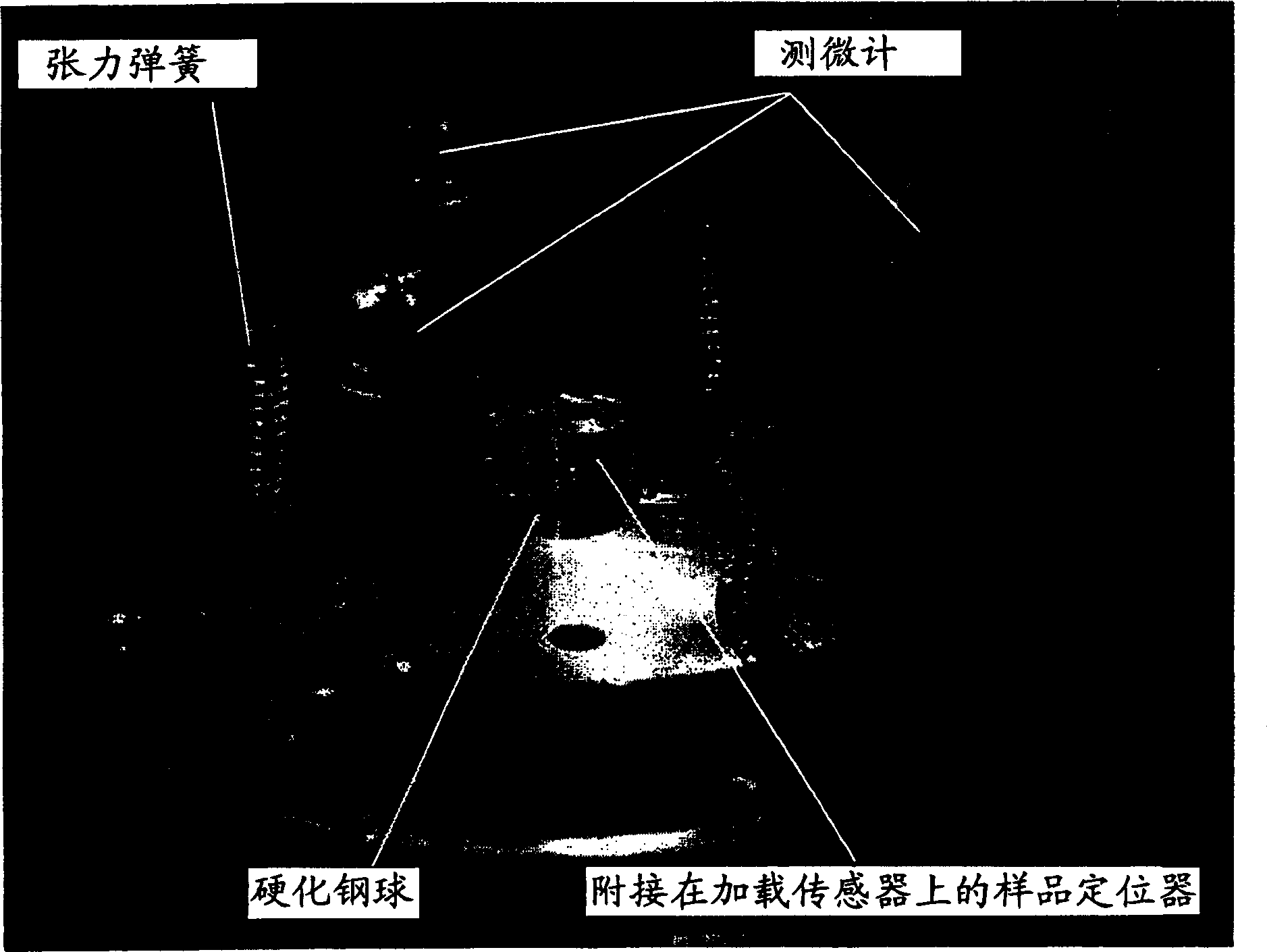
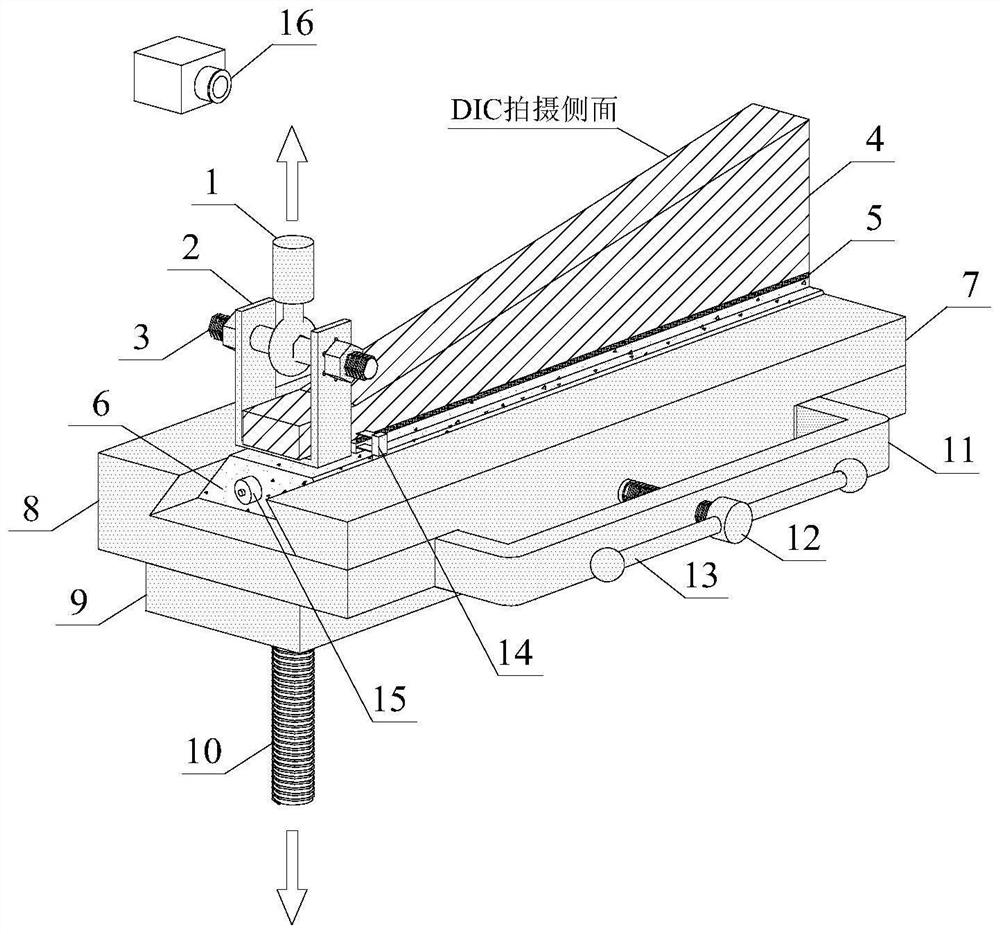
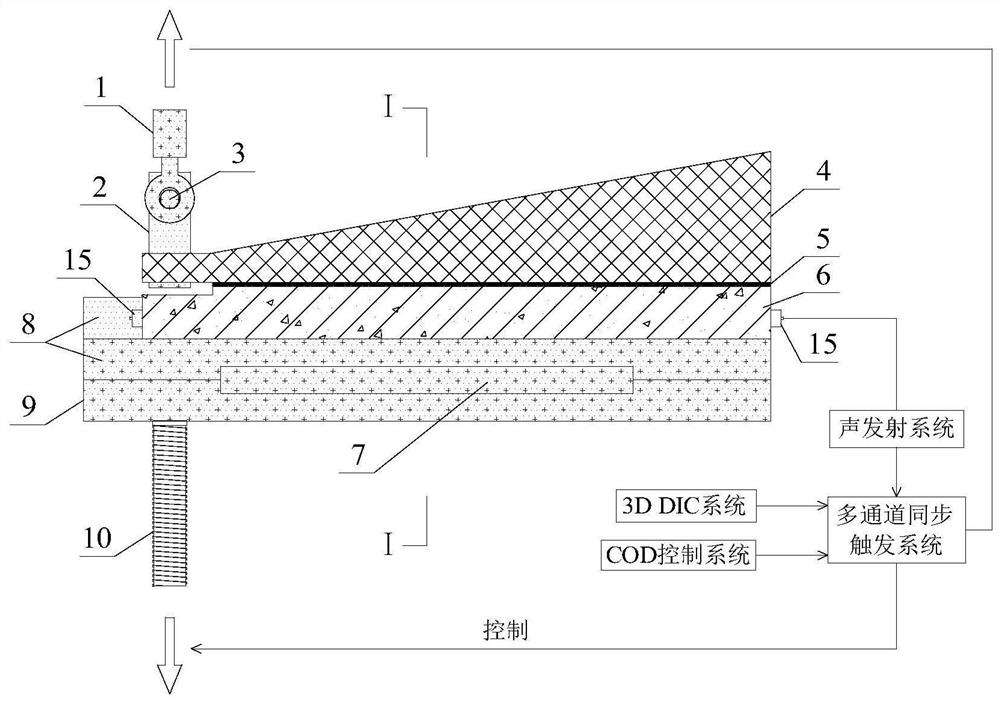
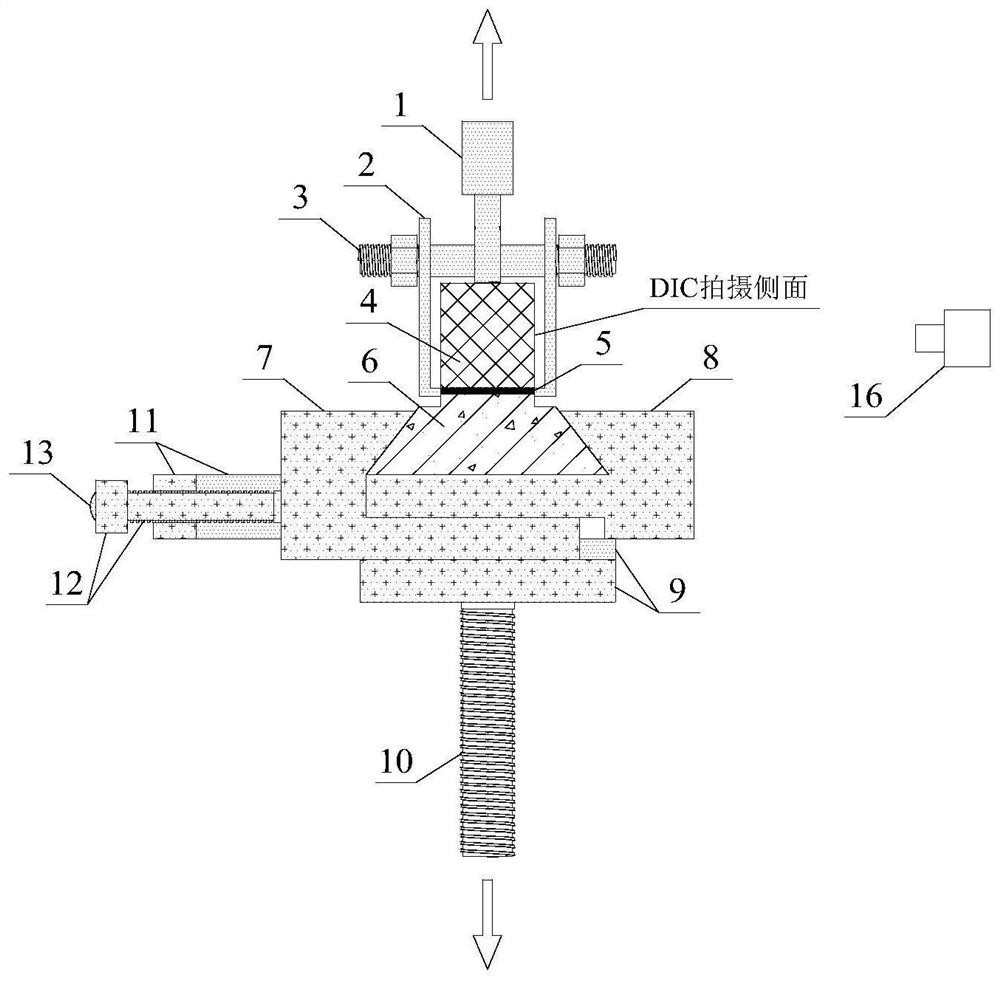
Measuring device and method for describing fracture toughness of FRP-concrete bond surface
ActiveCN109357937ASimple calculationAvoid influenceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCantilevered beamTip position
The invention discloses a measuring device and method for describing the fracture toughness of an FRP-concrete bond surface, comprising a fixing fixture, a test piece frame and a cantilever beam. In the invention, the FRP-concrete bond surface does not need preserved cracks, thereby avoiding the need for the measurement of the crack tip position in the test and the effects of the length of the preserved cracks and the tip shape on the test results. The height of the cantilever beam is along the axis of the cantilever beam, and linearly increases from the cantilever end to the trailing end. Thecross sections of the cantilever end and the trailing end are rectangular. The height of a single cantilever beam used in the invention increases linearly along the beam axis direction. During the fracture process, the flexibility of the single cantilever beam increases with the cracks, and the gradient change of the length is constant, which simplifies the calculation of the critical strain energy release rate of a type I fracture of the FRP-reinforced concrete.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
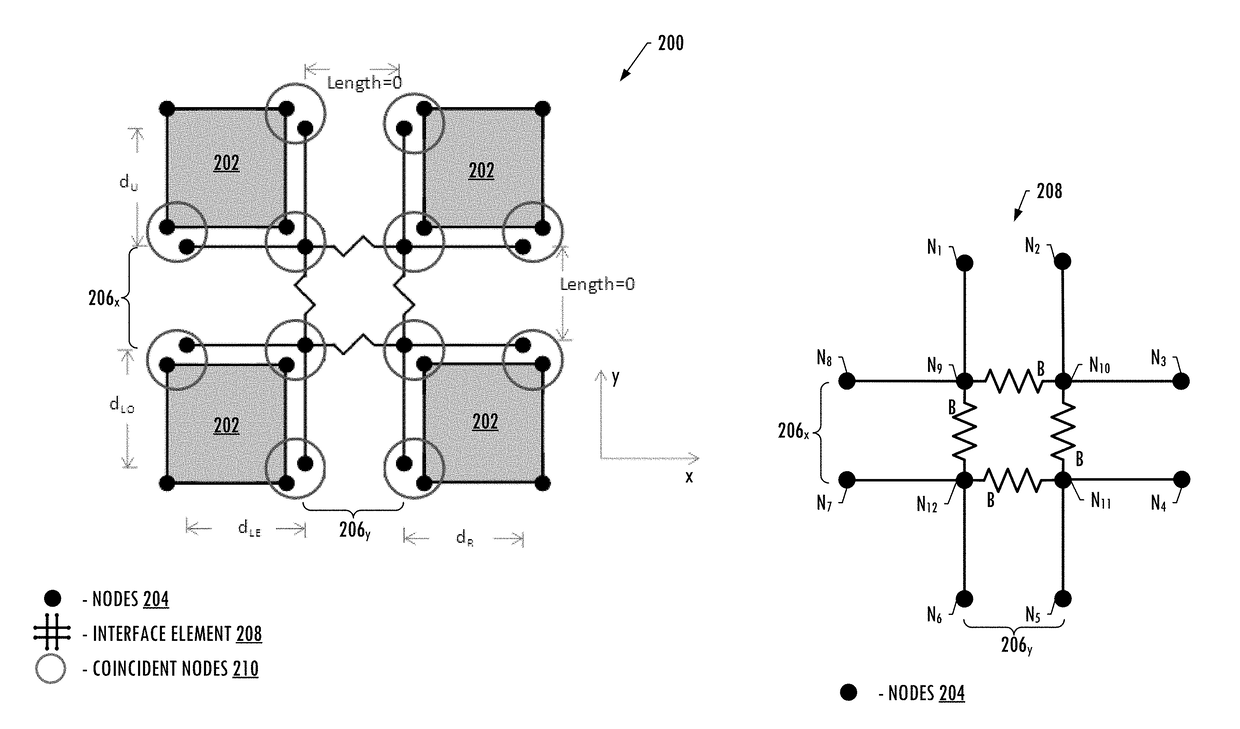
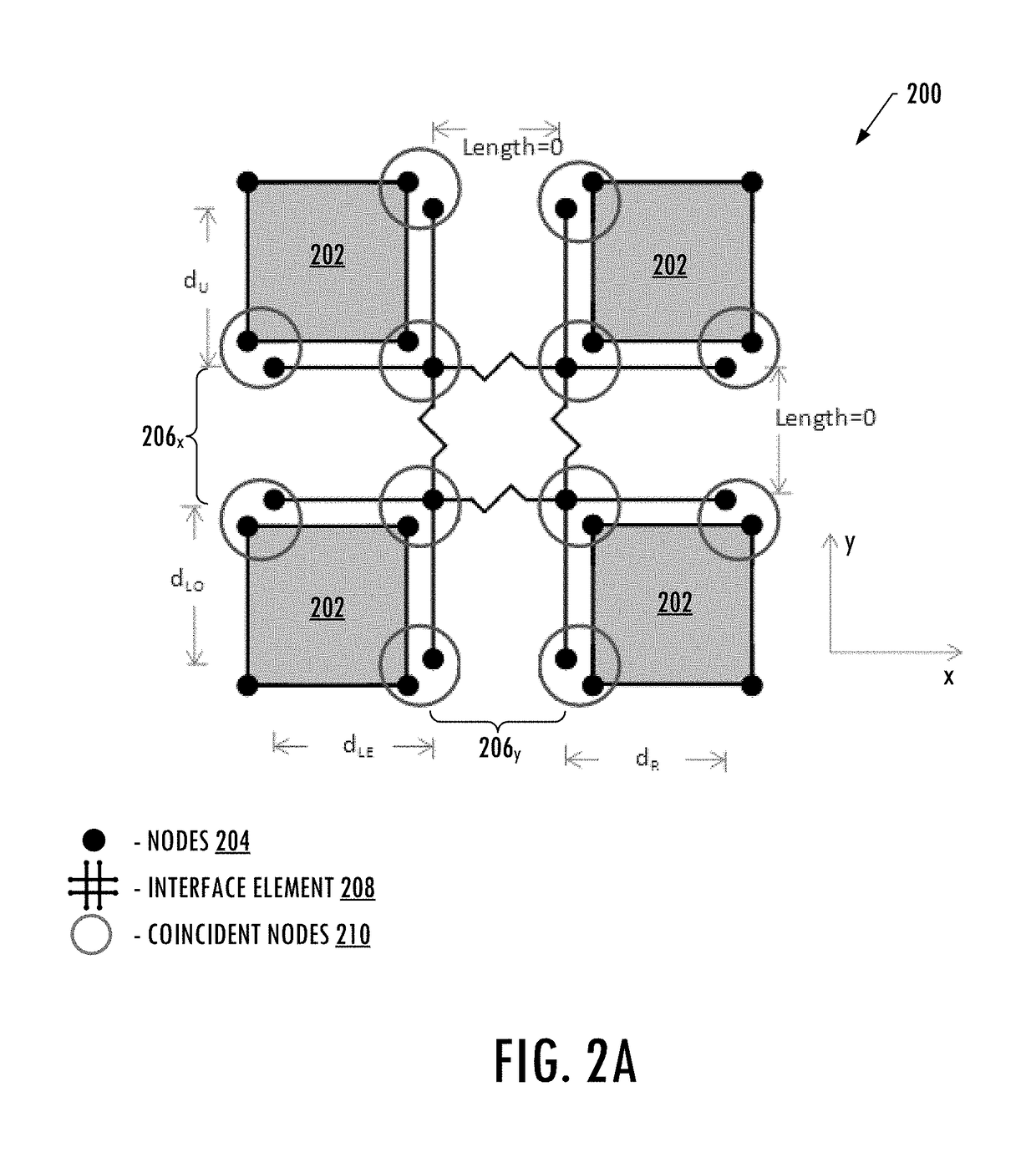
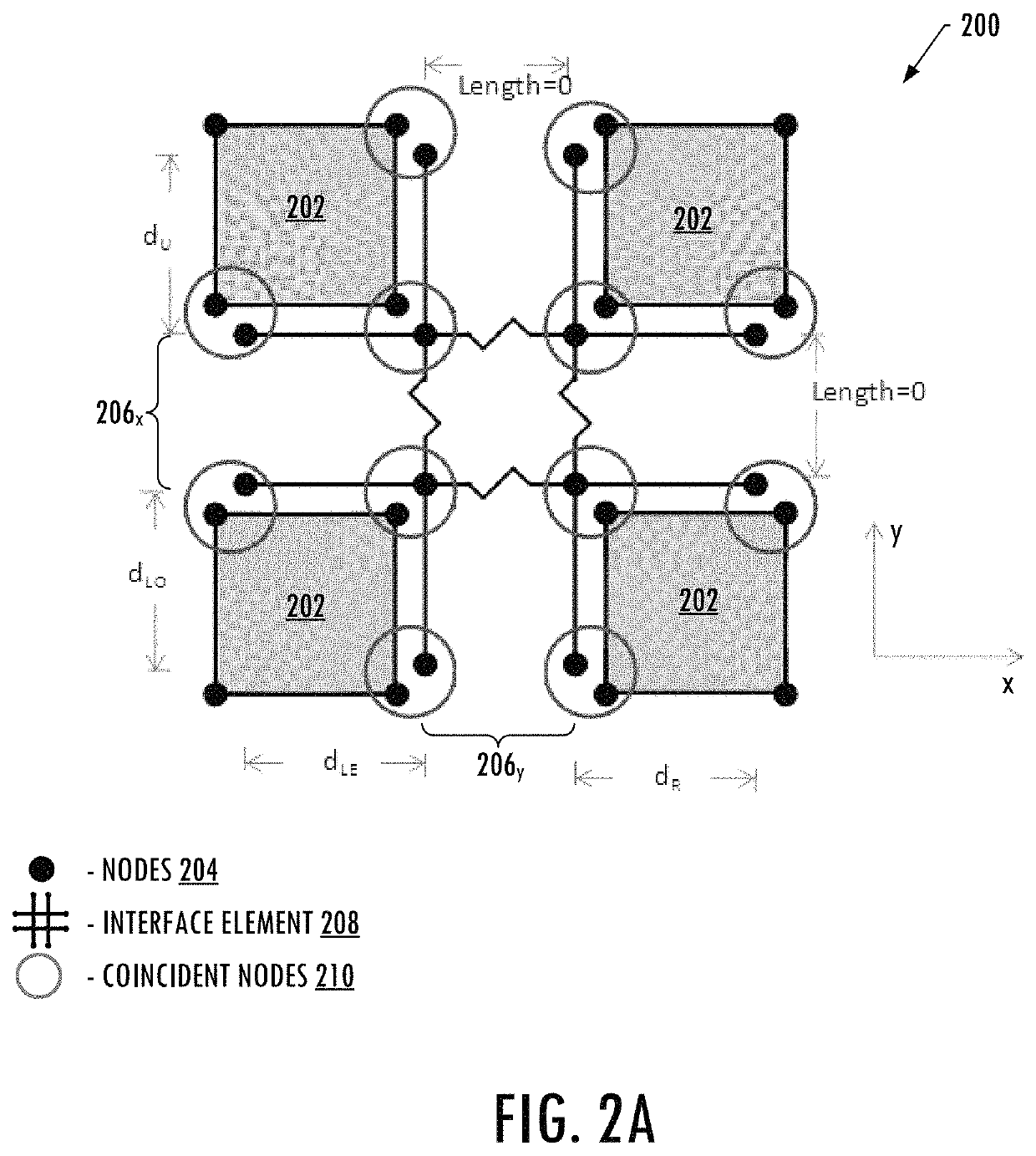
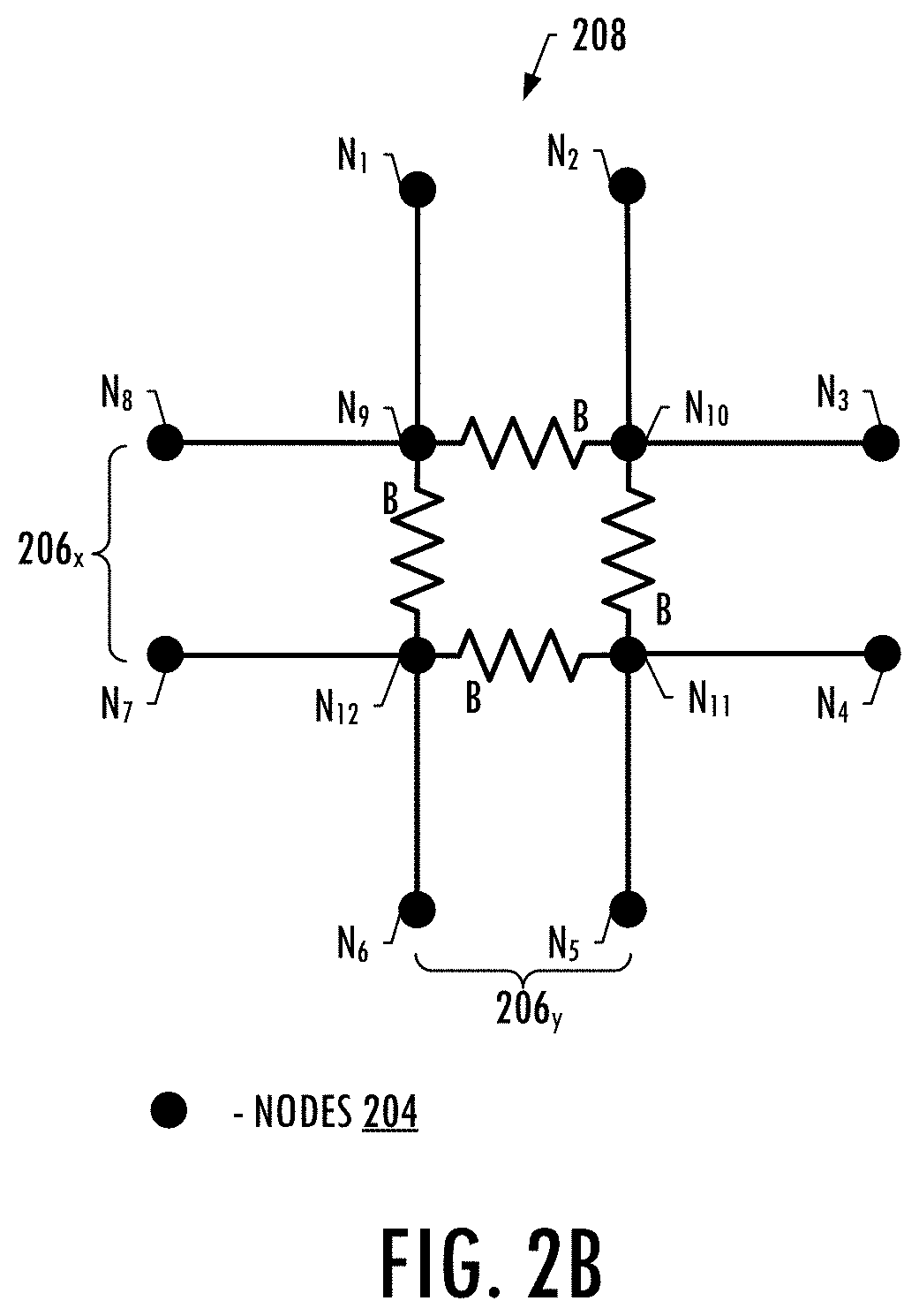
Finite element modeling and analysis of crack propagation in multiple planes of a structure
An apparatus is provided for predicting propagation of a crack in a structure. A finite element model is provided that represents the layers of the structure by meshes of elements having interfaces defined between adjacent elements in orthogonal potential crack planes. Overlapping interface elements are defined at the interfaces and include a plurality of node pairs spaced apart along multiple interfaces and having a node cluster therebetween that includes bound node pairs. The nodes of each node pair are coincident with respective nodes of the adjacent elements on opposite sides of the interface. An analysis of the finite element model under an external load is performed in which a crack tip is established at a node cluster. A strain energy release rate between the nodes of the bound node pairs of the node cluster is calculated and based thereon propagation of the crack is identified.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
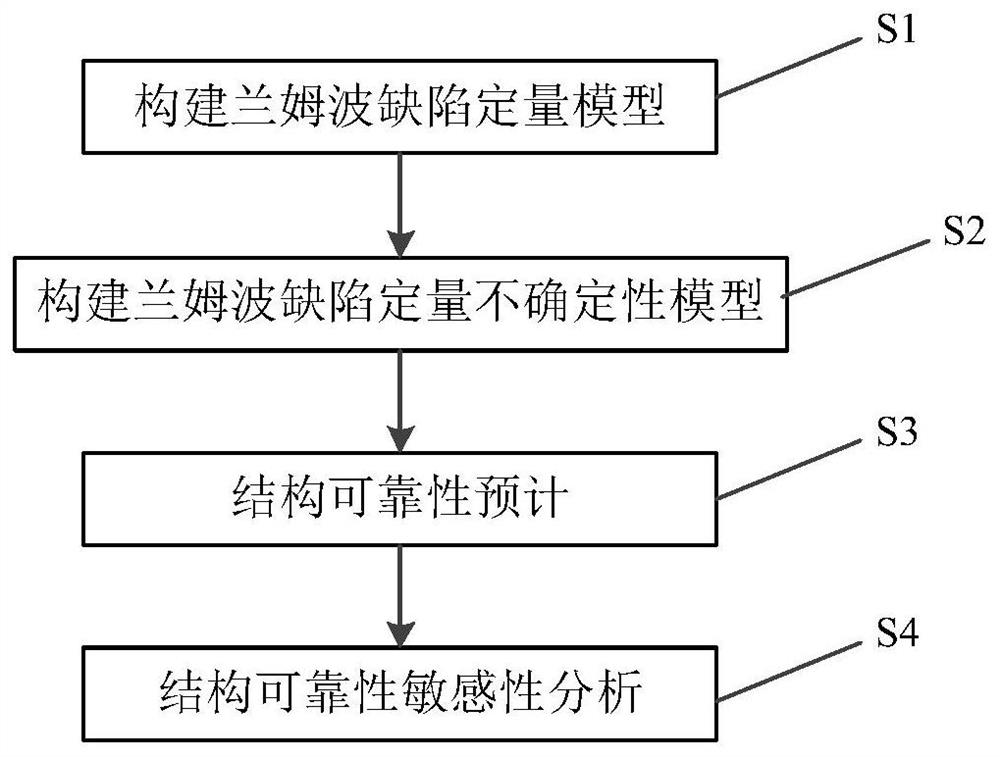
Structural reliability sensitivity analysis method based on Lamb wave defect quantification
ActiveCN112182935ATimely formulation of maintenance support strategiesPracticalSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationStructural reliabilitySensitive analysis
The invention provides a structural reliability sensitivity analysis method based on Lamb wave defect quantification, and the method comprises the steps: building a Lamb wave defect quantification model through a Lamb wave damage detection signal, and building a Lamb wave defect quantification uncertainty model through a maximum likelihood method, constructing a unit defect size performance parameter model by means of a strain energy release rate theory, constructing a unit fatigue crack propagation model by means of a Paris formula, constructing a structural overall dynamics model containinglocal defects by combining a finite element theory, and performing structural reliability prediction; and quantifying the influence of the quantitative uncertainty of the local unit defects in the structure on the structure reliability by adopting a sensitivity analysis method. The influence of uncertainty distribution parameters of all parameters in the Lamb wave defect quantitative model and thefatigue crack propagation model on the overall reliability of the structure is quantified, the uncertainty of reliability evaluation and life prediction results can be reduced conveniently, and the method has high practicability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Coated optical fibers
InactiveCN1841102ASmall expansion coefficientGlass optical fibreCarbon compoundsFiberHigh resistance
The invention relates to coated optical fibers comprising soft primary coatings and to such primary coatings for protecting glass optical fibers having a sufficient high resistance against cavitation. In particular, the primary coatings have a cavitation strength at which a tenth cavitation appears ( sigma <10>cav) of at least about 1.0 MPa as measured at a deformation rate of 0.20% min<-1> and of at least about 1.4 times their dynamic modulus at 23 DEG C. The coating preferably shows strain hardening in a relative Mooney plot, preferably has a strain energy release rate Go of about 20 J / m<2> or more, and preferably has a low volumetric thermal expansion coefficient. The invention furthermore provides a method and apparatus for measuring the cavitation strength of a primary coating.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Testing method for measuring interfacial strength of copper filling TSV
InactiveCN103196828ASolve the problem of difficult interface strength testingAccurate Critical Strain Energy Release RateUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisCopperElectronic packaging
The invention discloses a testing method for measuring interfacial strength of a copper filling TSV (Through Silicon Via), and belongs to the field of three-dimensional electronic packaging testing. The method comprises the steps that a TSV electrocoppering pillar is extruded from a TSV through hole by a nanoindentor to obtain load on a pressure head / a displacement curve in the extrusion process; unloading and reloading are carried out in different stages of extrusion to obtain an unloading curve and a loading curve; and the distance between a copper pillar top end after unloading to the upper surface of a TSV adapter board is obtained by using an atomic force microscope (AMF). The energy consumed by interface destroy, namely interface cracking power can be obtained through analysis, and a critical strain energy release rate of an interface can be obtained through dividing an area of the destroyed interface with the interface cracking power. With the adoption of the method, the interfacial strength of the TSV generated by different electroplating technologies in the practical production process can be obtained, and the reliability of the TSV in the service process can be improved through comparing and selecting the optimal electroplating technology.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Coated optical fibers
InactiveUS20100058877A1Glass optical fibreForce measurement by measuring optical property variationHigh resistanceCavitation
The invention relates to coated optical fibers comprising soft primary coatings and to such primary coatings for protecting glass optical fibers having a sufficient high resistance against cavitation. In particular, the primary coatings have a cavitation strength at which a tenth cavitation appears (σ10cav) of at least about 1.0 MPa as measured at a deformation rate of 0.20% min−1 and of at least about 1.4 times their storage modulus at 23° C. The coating preferably shows strain hardening in a relative Mooney plot, preferably has a strain energy release rate Go of about 20 J / m2 or more, and preferably has a low volumetric thermal expansion coefficient. The invention furthermore provides a method and apparatus for measuring the cavitation strength of a primary coating.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Coated optical fibers
InactiveCN1419470ASmall expansion coefficientGlass optical fibreCarbon compoundsHigh resistanceFiber
The invention relates to coated optical fibers comprising soft primary coatings and to such primary coatings for protecting glass optical fibers having a sufficient high resistance against cavitation. In particular, the primary coatings have a cavitation strength at which a tenth cavitation appears ( sigma <10>cav) of at least about 1.0 MPa as measured at a deformation rate of 0.20% min<-1> and of at least about 1.4 times their dynamic modulus at 23 DEG C. The coating preferably shows strain hardening in a relative Mooney plot, preferably has a strain energy release rate Go of about 20 J / m<2> or more, and preferably has a low volumetric thermal expansion coefficient. The invention furthermore provides a method and apparatus for measuring the cavitation strength of a primary coating.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Adhesive member
Owner:CANON KK
Synergistic toughening of epoxy modified by graphene and block copolymer
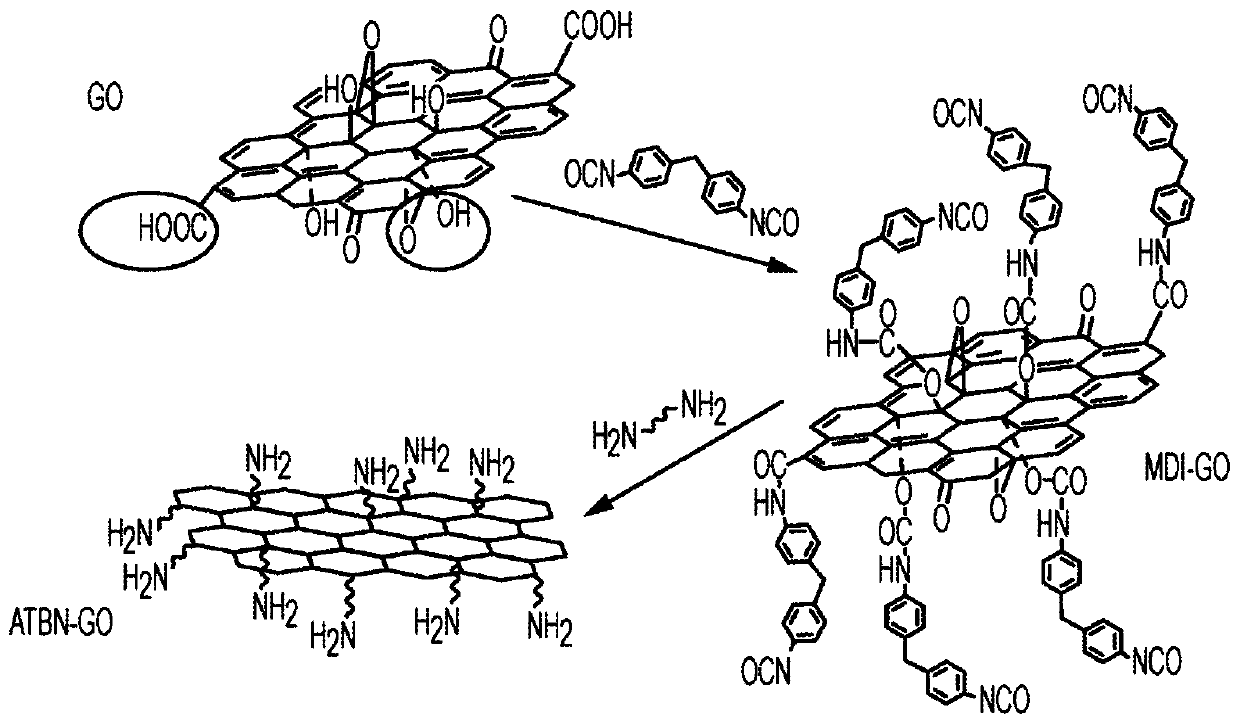
InactiveCN109983077AIncreased critical strain energy release rateCarbon compoundsEpoxyPolymer science
Embodiments are directed to compositions comprising (i) amphiphilic block copolymer; (ii) resin material; and amine modified graphene oxide; where the composition shows a synergic effect in critical strain energy release rate (Glc) value versus predicted value calculated by adding (i) the Glc value for neat resin material, plus (ii) the difference in Glc found when adding the amphiphilic block copolymer to the resin material versus the neat resin material, plus (iii) the difference in Glc found when adding the amine modified graphene oxide to the resin material versus the neat resin material.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
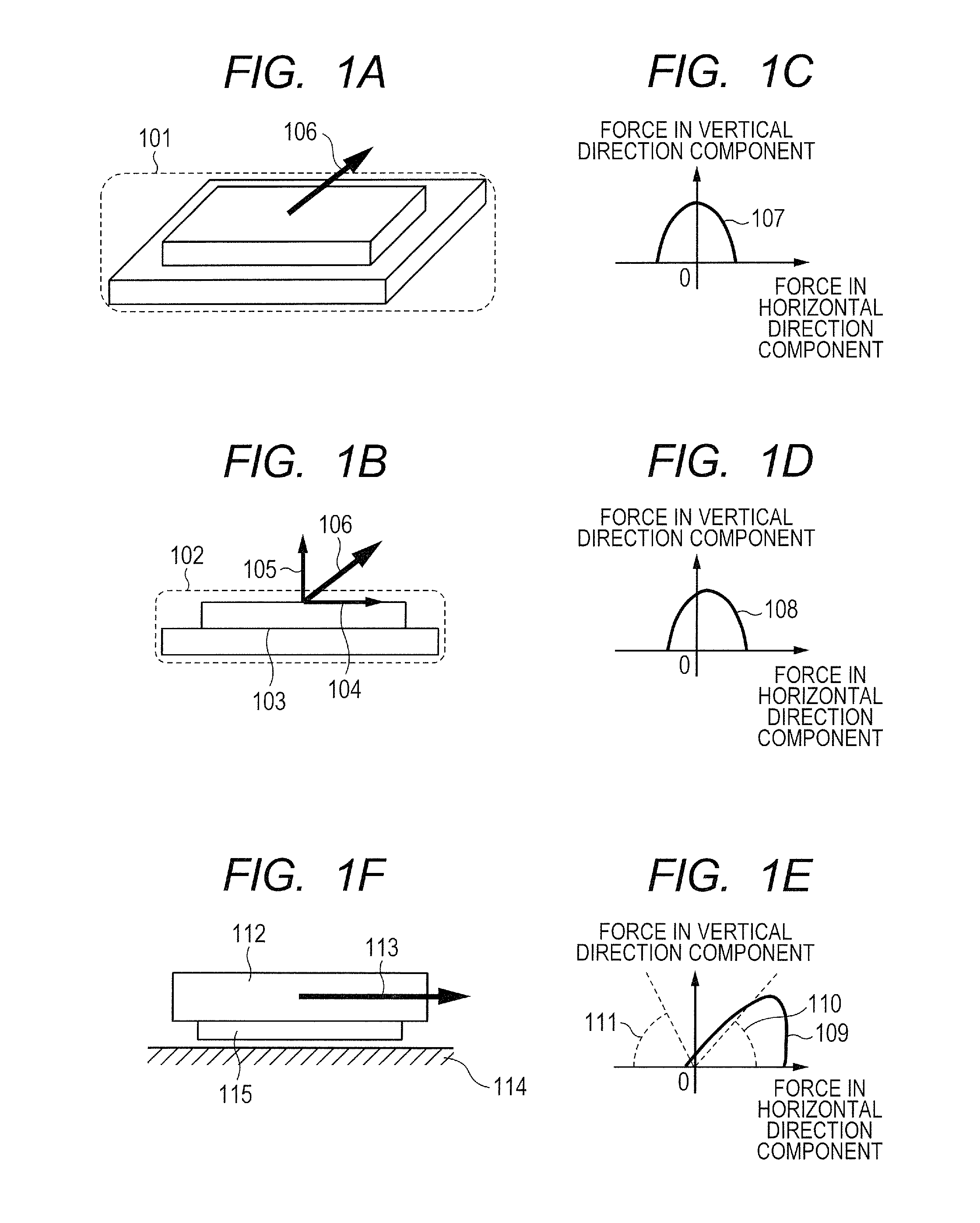
Adhesive member
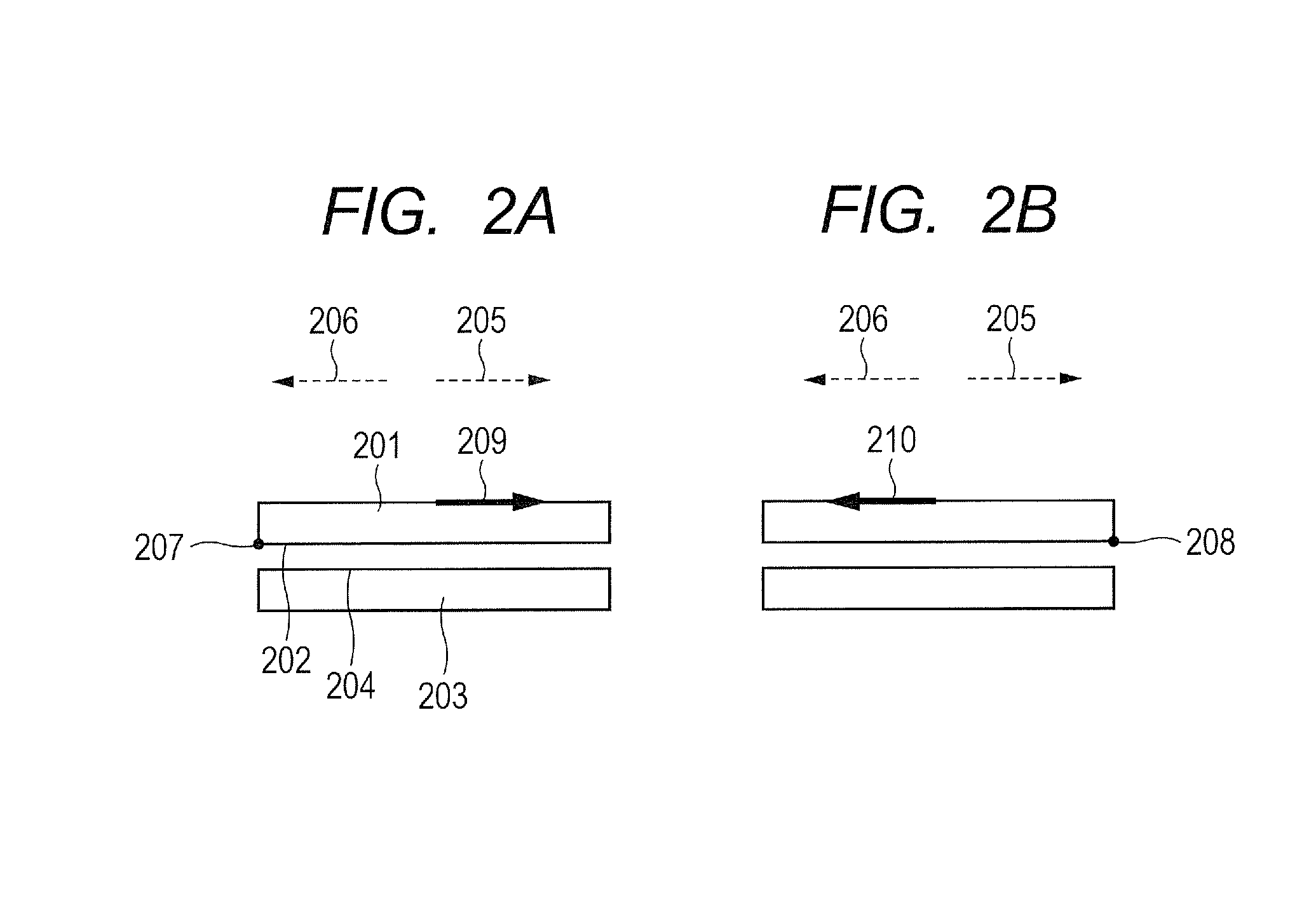
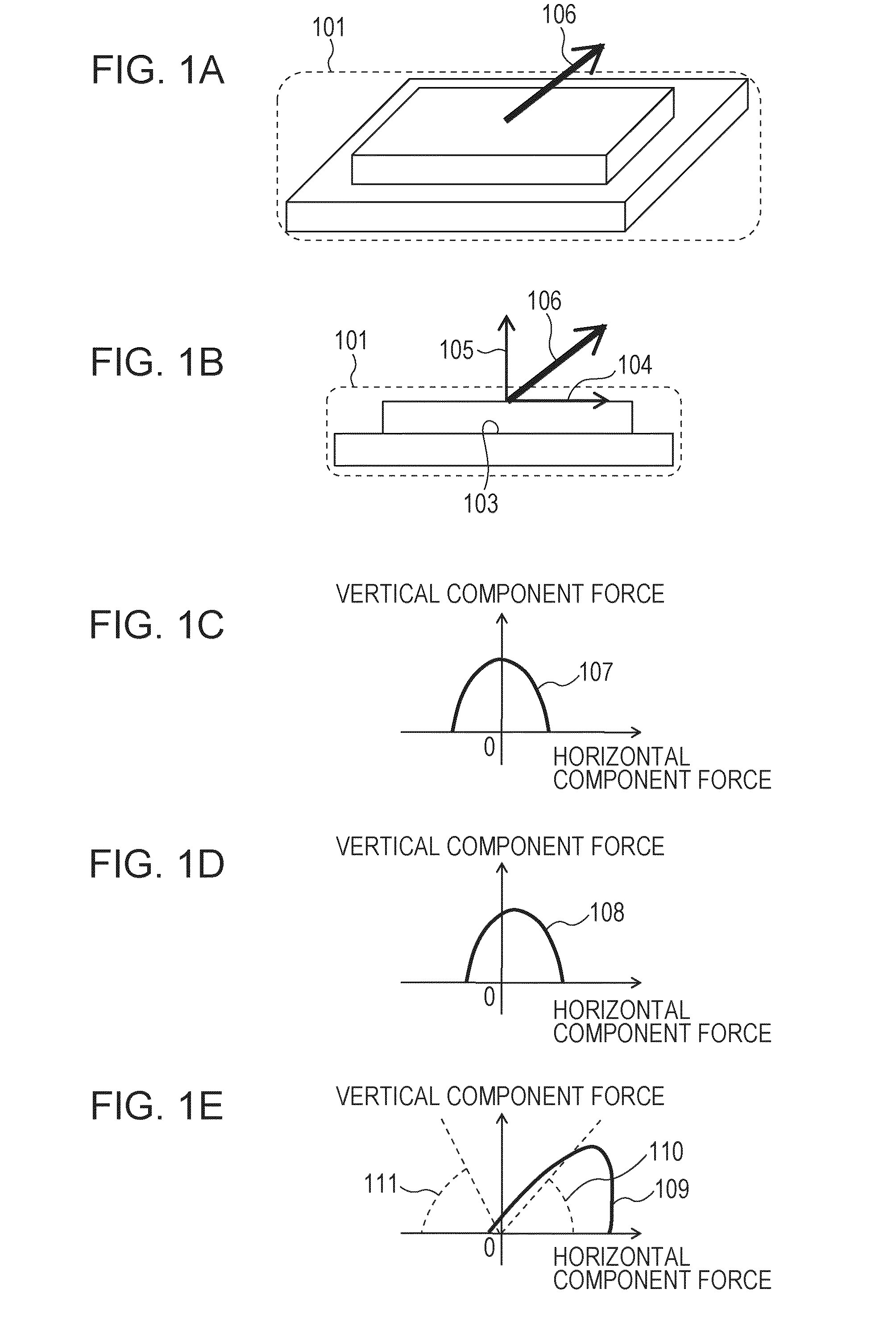
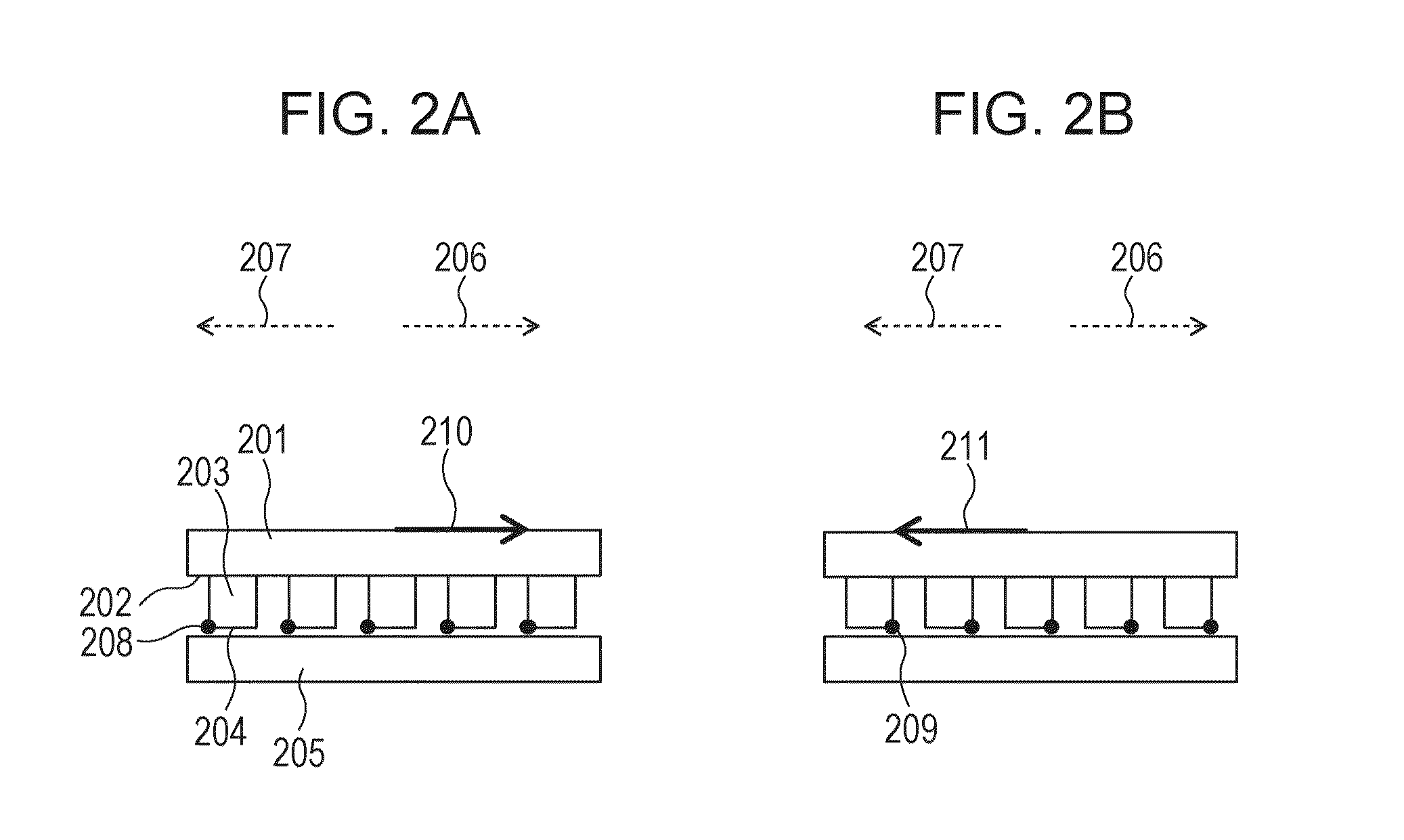
InactiveUS20160312071A1Strong directional dependencyFilm/foil adhesivesChemistryStrain energy release rate
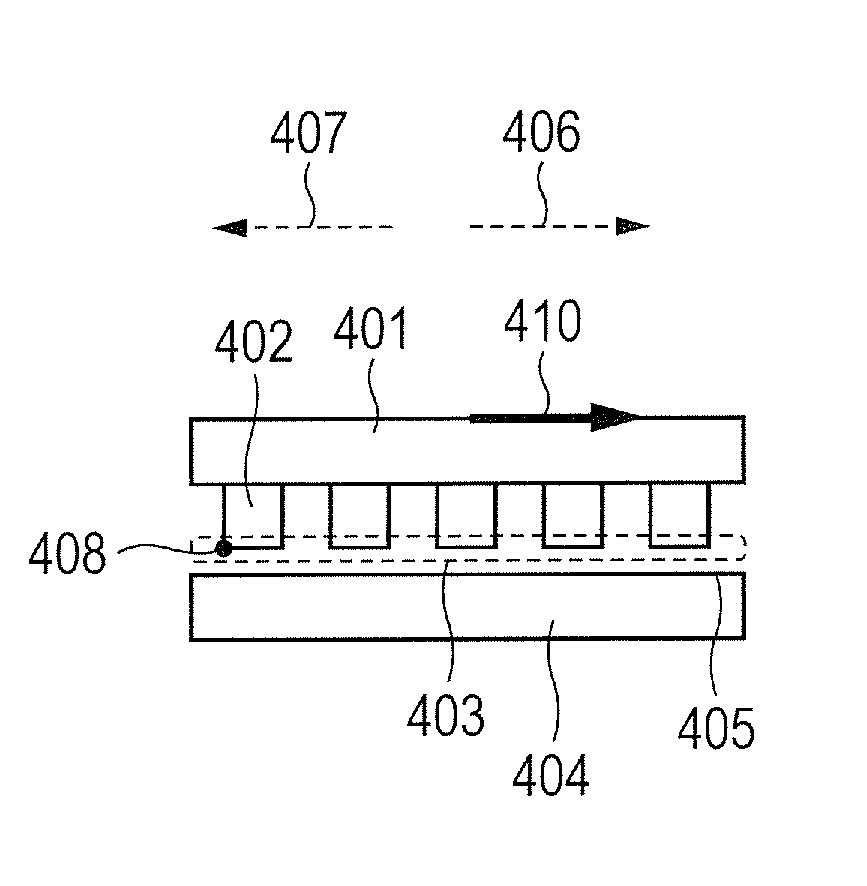
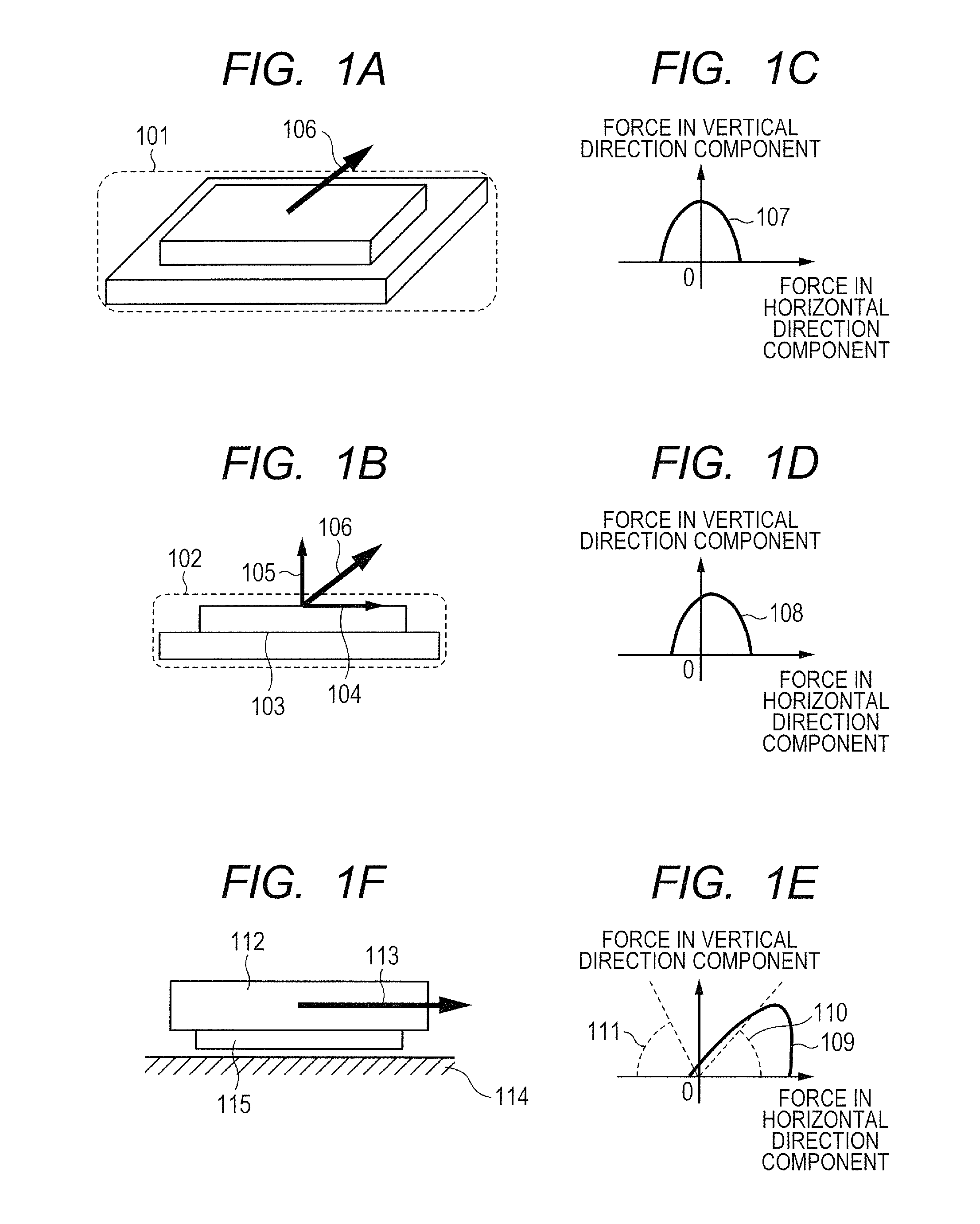
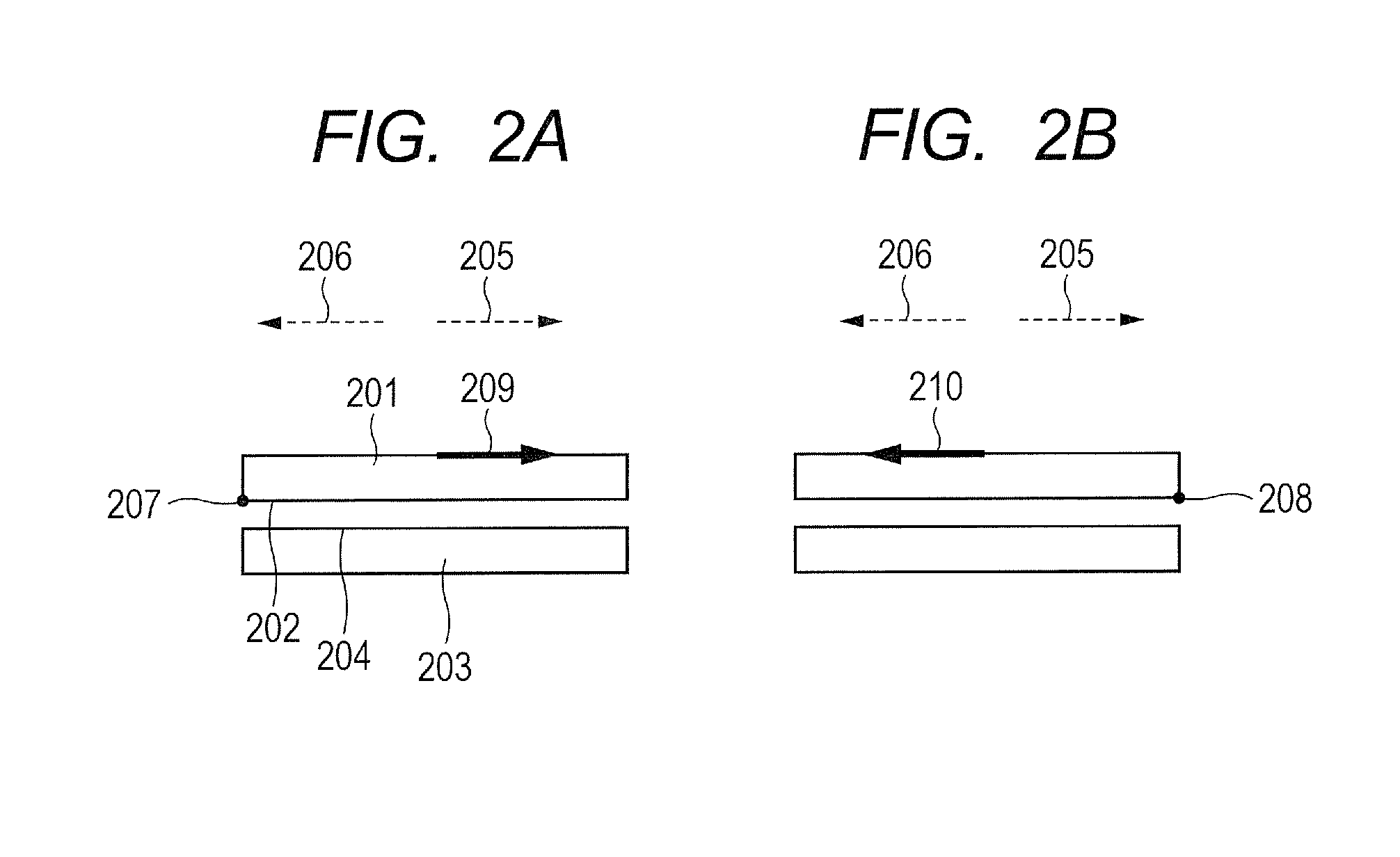
Provided is an adhesive member whose adhesive force has relatively strong directional dependency. Specifically, provided is an adhesive member, which is configured to adhere to an adherend through an intersurface force, wherein when a strain energy release rate is defined as G1b and G2b and an adhesive energy is defined as Δγ1b and Δγ2b respectively, a horizontal section obtained by cutting the adhesive member parallel to an adhesive surface has an asymmetrized shape so that G1b / Δγ1b≠G2b / Δγ2b is satisfied.
Owner:CANON KK
A Modeling Method for 3D Fractability Model of Tight Sandstone Reservoir
ActiveCN105134156BImproving the effectiveness of volumetric fracturingShorter payback timeFluid removalSpecial data processing applicationsFeature parameterArenite
The invention relates to a modeling method for a compact sandstone reservoir three-dimensional fracability model. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a relation formula among an internal friction angle, I type and II type crack fracture toughness and the parameter of sandstone mechanical characteristics; S2, establishing a shale fracability evaluation model which comprehensively considers an elastic parameter, the internal friction angle, the critical strain energy release rate and fracture toughness; S3, adopting a support vector machine algorithm to obtain a cluster analysis mode between the reservoir fracability and the elastic parameter; S4, adopting the cluster analysis mode to obtain a reservoir three-dimensional elastic parameter data body, and establishing the multi-scale compact sandstone reservoir three-dimensional fracability evaluation model based on the core, the borehole and the reservoir of multiple scales. According to the method, the fracability of an arbitrary space position in the compact sandstone reservoir can be obtained, a sweet spot with high fracability can always be drilled when drilling a compact sandstone gas well, blindness of well location selection is avoided, and the fracture modification effect and the yield after fracture are improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Fracture mechanics based method for composite damage tolerance criteria
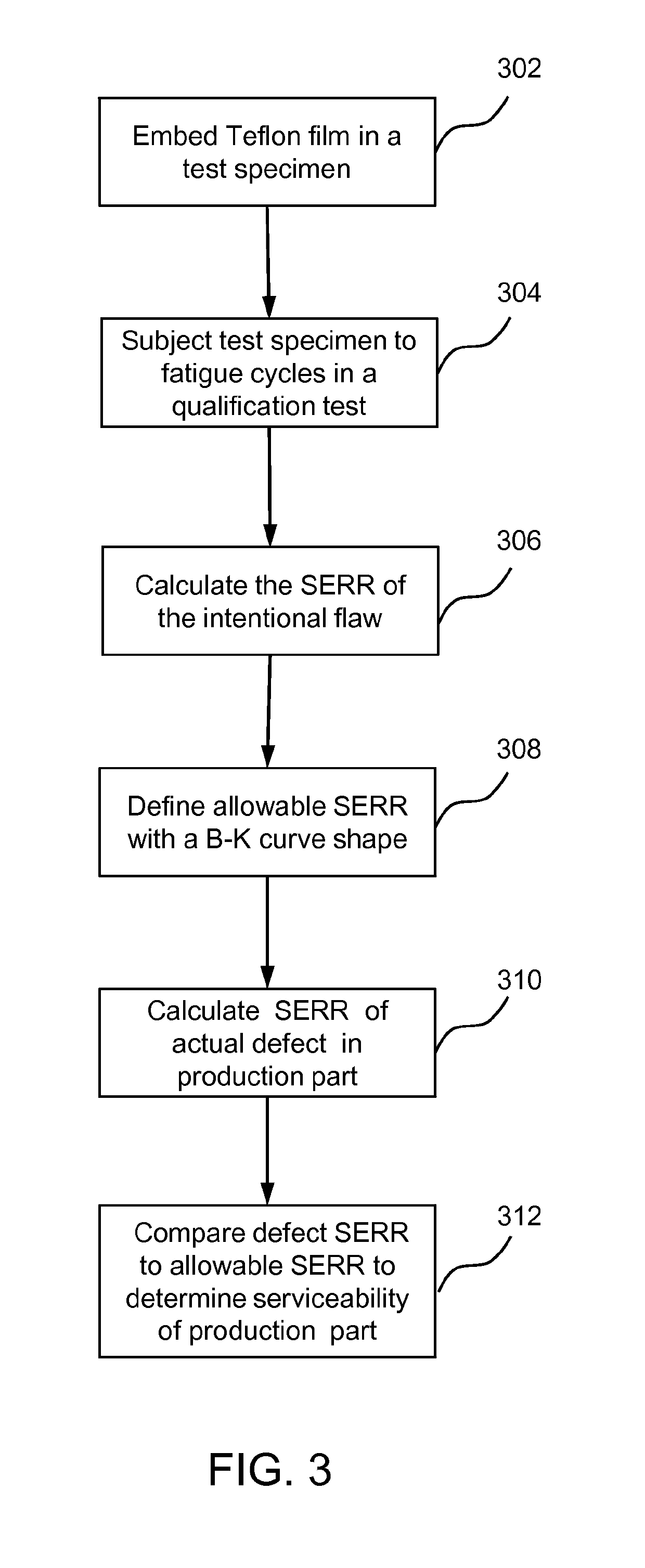
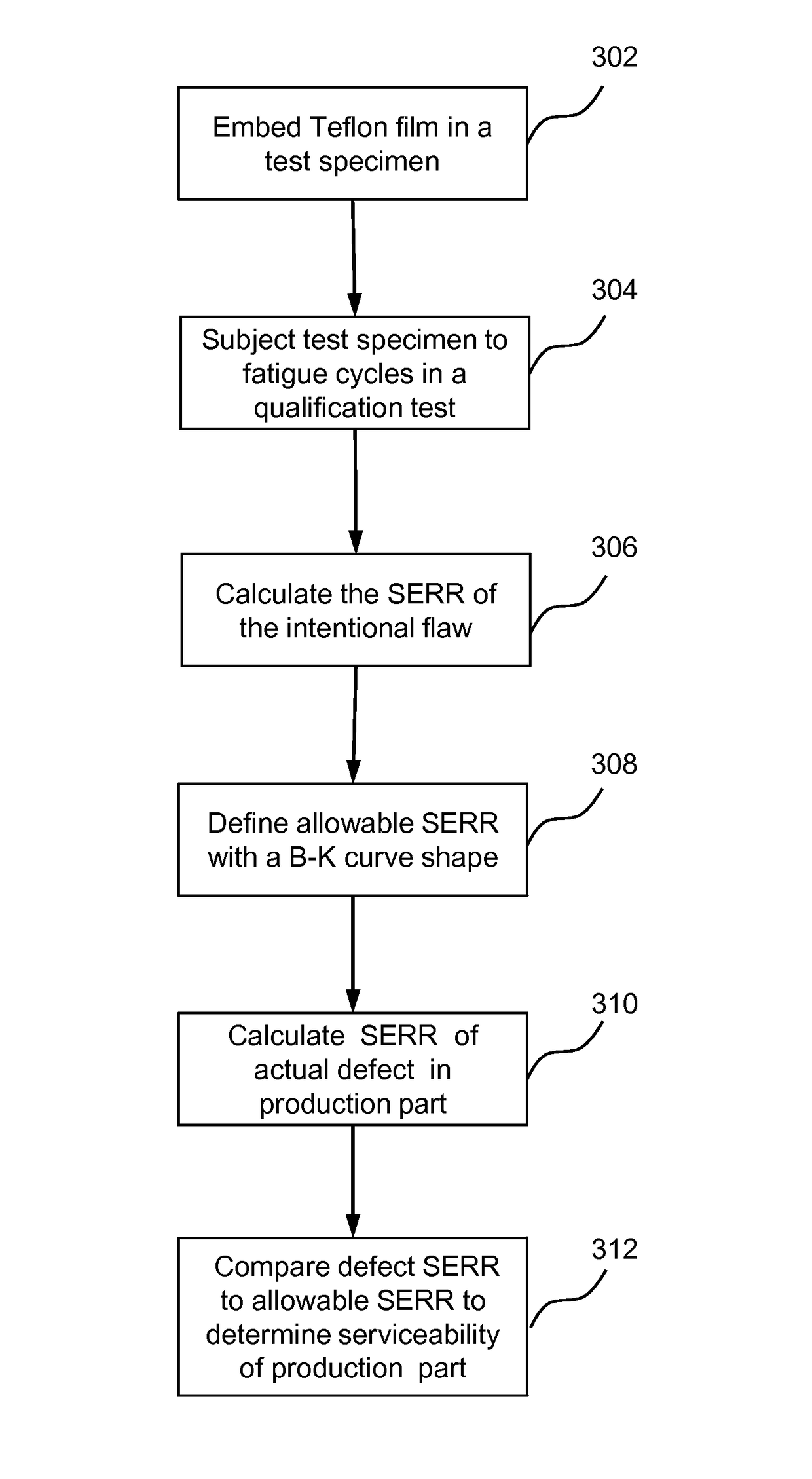
InactiveUS10330563B2Saves unnecessary scrapReduce wasteDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCurve shapeStrain energy
A system and method to substantiate safe-life criteria of a structure with an anomaly includes a flaw in a critical loaded region of a test structure; a processor; and memory having instructions stored thereon that, when executed by the processor, cause the system to receive first signals indicative of strain energy release rates (SERR) for the flaw at the critical loaded region of a test structure; fit the first signals for the flaw SERR to a Benzeggah-Kenane (B-K) mixed mode curve shape; determine values indicative of B-K criteria of the test structure in response to the fitting of the first signals; receive second signals indicative of SERR for the production structure; and compare the second signals with the B-K criteria of the test structure to substantiate the safe-life criteria.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Adhesive member
InactiveUS20160312072A1Strong directional dependencyFilm/foil adhesivesElastic modulusPoisson's ratio
Provided is an adhesive member whose adhesive force has relatively strong directional dependency. Specifically, provided is an adhesive member, which is configured to adhere to an adherend through an intersurface force, wherein when a strain energy release rate is defined as G1a and G2a and an adhesive energy is defined as Δγ1a and Δγ2a respectively, at least one of an elastic modulus or a Poisson's ratio of the adhesive member is nonuniformized so that G1a / Δγ1a≠G2a / Δγ2a is satisfied.
Owner:CANON KK
Fracture mechanics based method for composite damage tolerance criteria
InactiveUS20170108402A1Saves unnecessary scrapReduce wasteDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCurve shapeStrain energy
A system and method to substantiate safe-life criteria of a structure with an anomaly includes a flaw in a critical loaded region of a test structure; a processor; and memory having instructions stored thereon that, when executed by the processor, cause the system to receive first signals indicative of strain energy release rates (SERR) for the flaw at the critical loaded region of a test structure; fit the first signals for the flaw SERR to a Benzeggah-Kenane (B-K) mixed mode curve shape; determine values indicative of B-K criteria of the test structure in response to the fitting of the first signals; receive second signals indicative of SERR for the production structure; and compare the second signals with the B-K criteria of the test structure to substantiate the safe-life criteria.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Finite element modeling and analysis of crack propagation in multiple planes of a structure
An apparatus is provided for predicting propagation of a crack in a structure. A finite element model is provided that represents the layers of the structure by meshes of elements having interfaces defined between adjacent elements in orthogonal potential crack planes. Overlapping interface elements are defined at the interfaces and include a plurality of node pairs spaced apart along multiple interfaces and having a node cluster therebetween that includes bound node pairs. The nodes of each node pair are coincident with respective nodes of the adjacent elements on opposite sides of the interface. An analysis of the finite element model under an external load is performed in which a crack tip is established at a node cluster. A strain energy release rate between the nodes of the bound node pairs of the node cluster is calculated and based thereon propagation of the crack is identified.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Coated optical fibers
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Seam-following cave-finding acid fracturing numerical simulation method and simulation system
PendingCN114547923ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelKarst
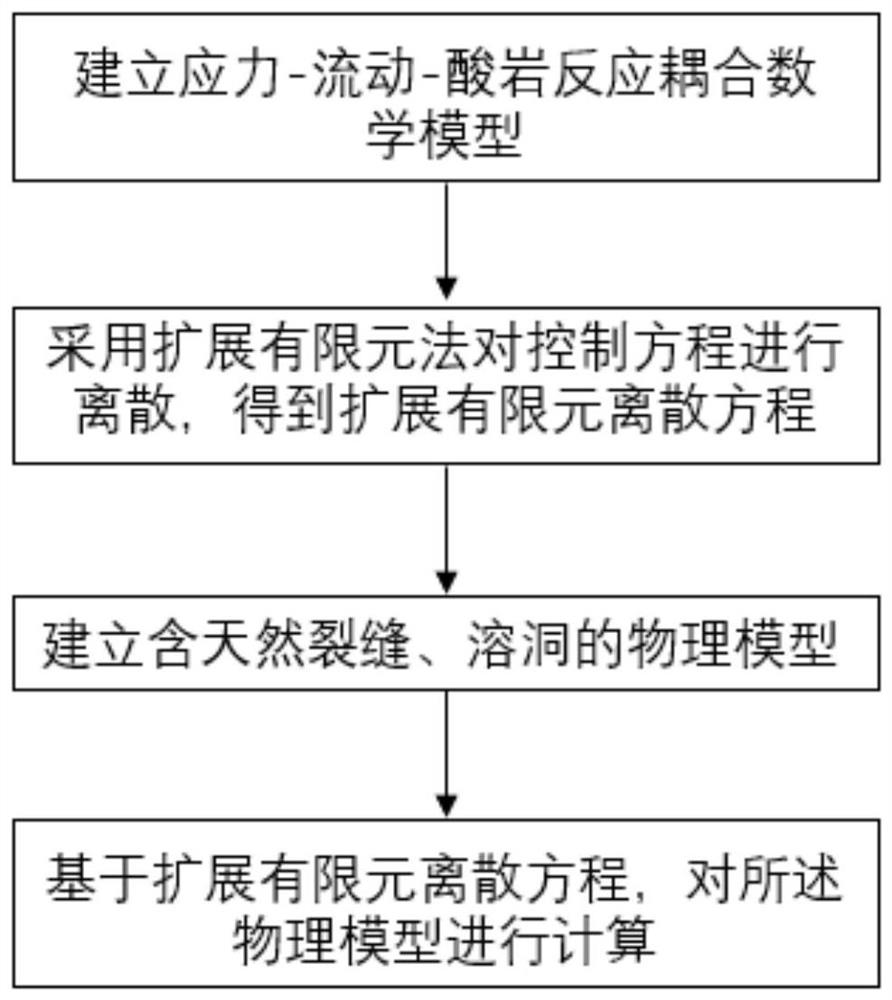
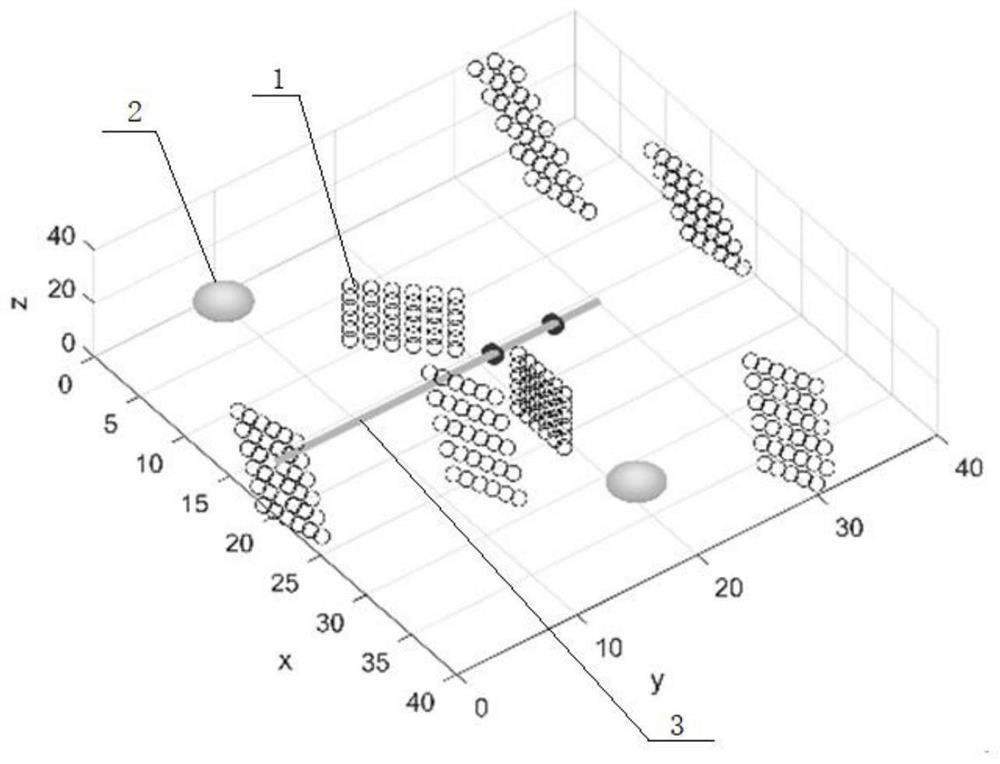
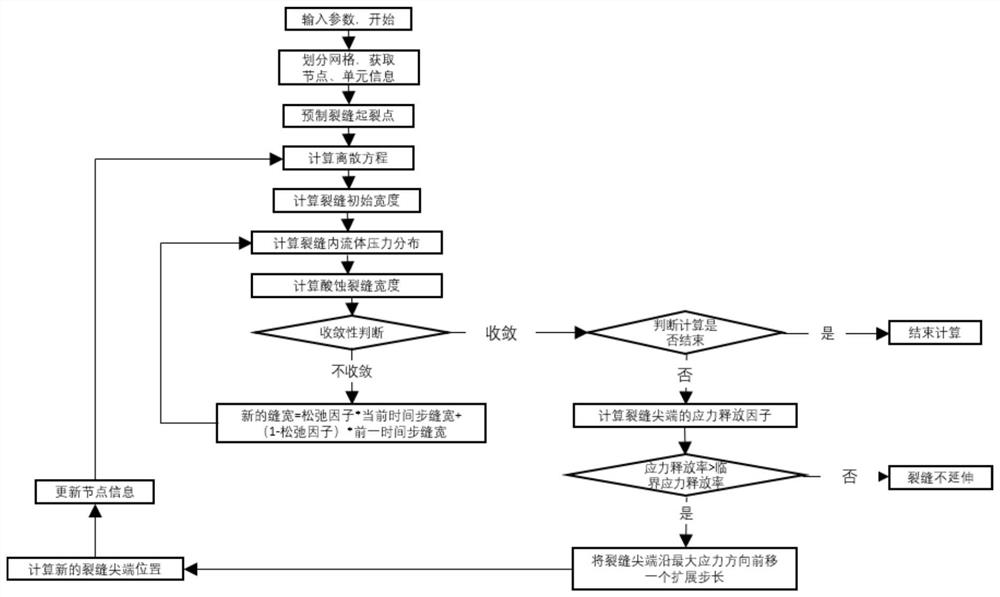
The invention discloses a fracture-following cavern-finding acid fracturing numerical simulation method, which comprises the following steps: establishing a stress-flow-acid rock reaction coupling mathematical model: establishing a stress-flow-acid rock reaction coupling control equation, and setting initial conditions and boundary conditions; adopting a maximum strain energy release rate criterion to judge crack propagation; combining the control equation and the boundary condition by adopting a weighted margin method to obtain an equivalent integral weak form of the control equation; discretizing the control equation by adopting an extended finite element method to obtain an extended finite element discrete equation; establishing a physical model containing natural fractures and karst caves; and calculating the physical model based on the extended finite element discrete equation. According to the method, a set of crack hole type carbonate reservoir acid etching crack propagation model comprising a stress module, a flow module and an acid rock reaction module is established, a control equation is discretized by adopting an expansion finite element method, crack propagation is judged by utilizing a maximum strain energy release rate criterion, and an acid etching crack propagation path is researched.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A measuring device and method for describing fracture toughness of frp-concrete bonding surface
ActiveCN109357937BSimple calculationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCantilevered beamReinforced concrete
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
Bonding member
A bonding member includes a base and a protrusion that protrudes from a surface of the base and that has an end face adhering to a substrate with a surface force between the end face and the substrate. Δγ1c and Δγ2c differ from each other so as to satisfy G1c / Δγ1c≠G2c / Δγ2c, where G1c denotes a strain-energy-release rate at a first release portion of the protrusion when a force is exerted in a first direction parallel to the surface, Δγ1c denotes an adhesive energy at the first release portion, G2c denotes a strain-energy-release rate at a second release portion of the protrusion when a force having the same magnitude as the force exerted in the first direction is exerted in a second direction opposite to the first direction, and Δγ2c denotes an adhesive energy at the second release portion.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com