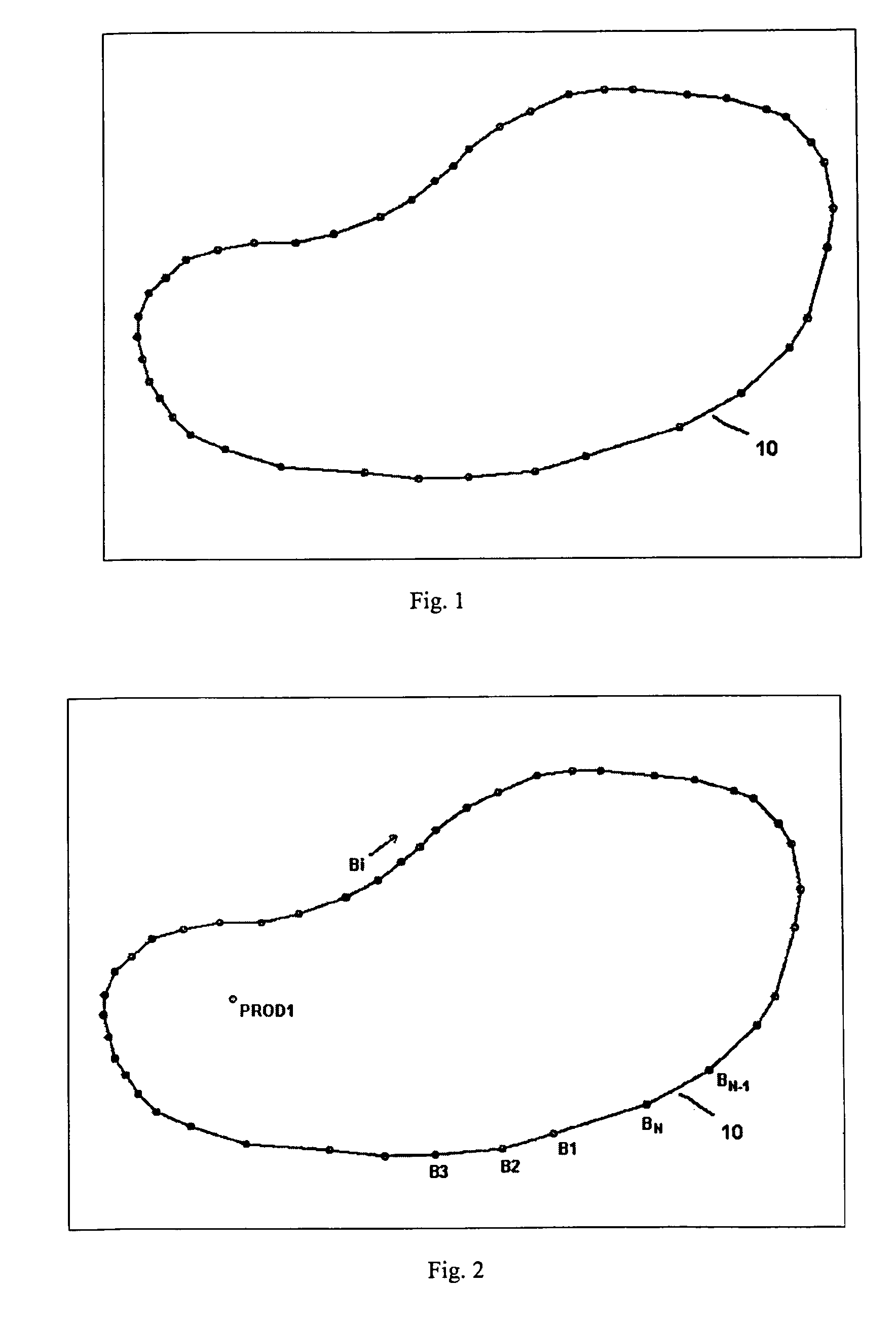
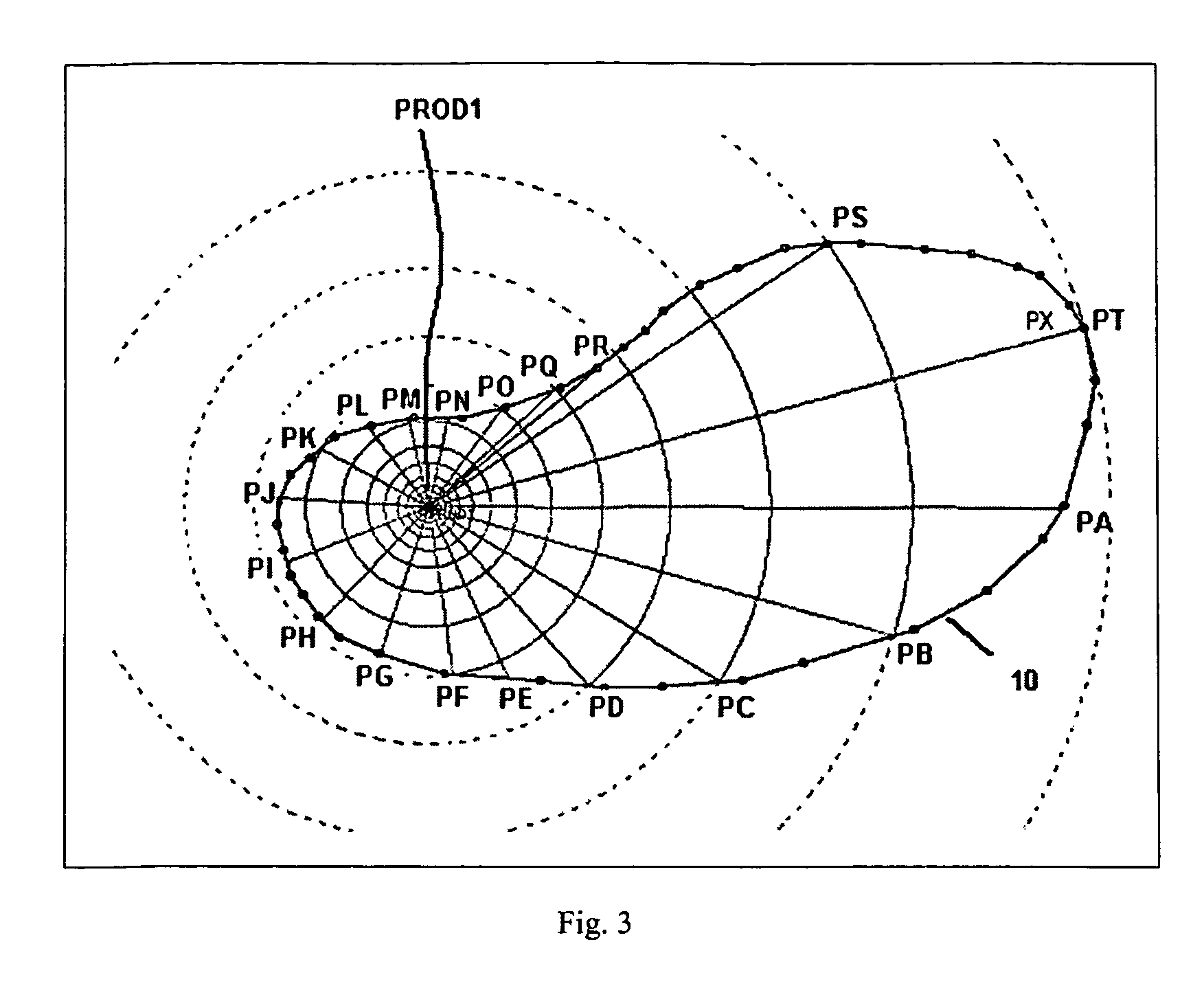
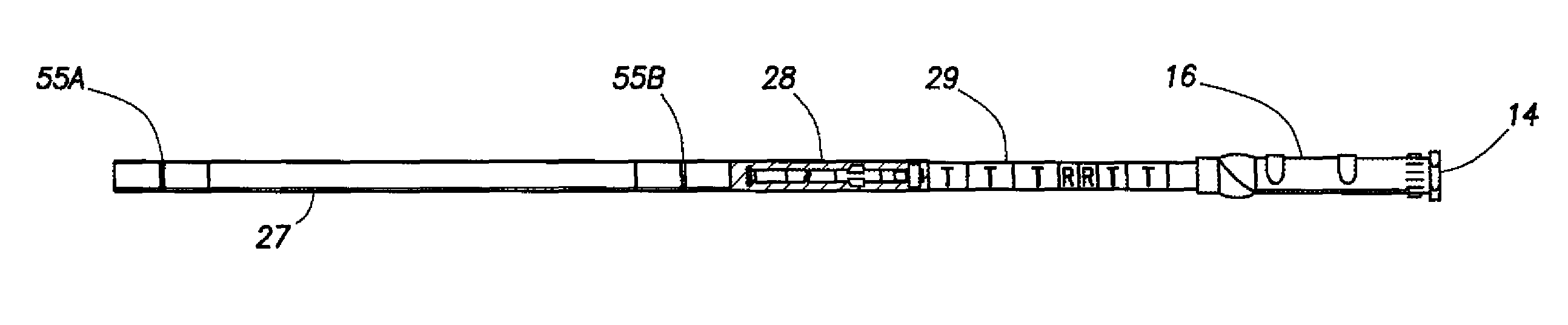
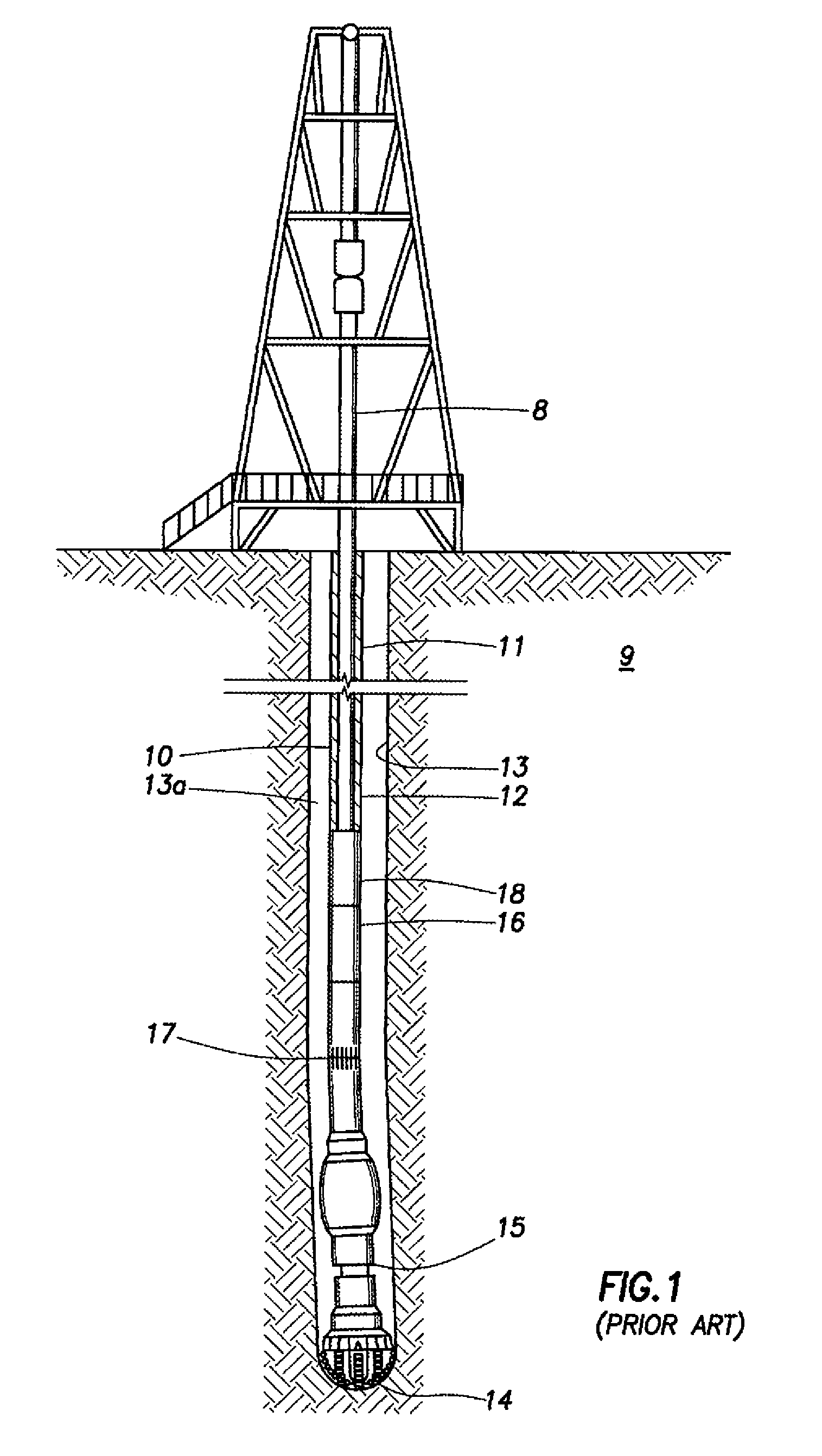
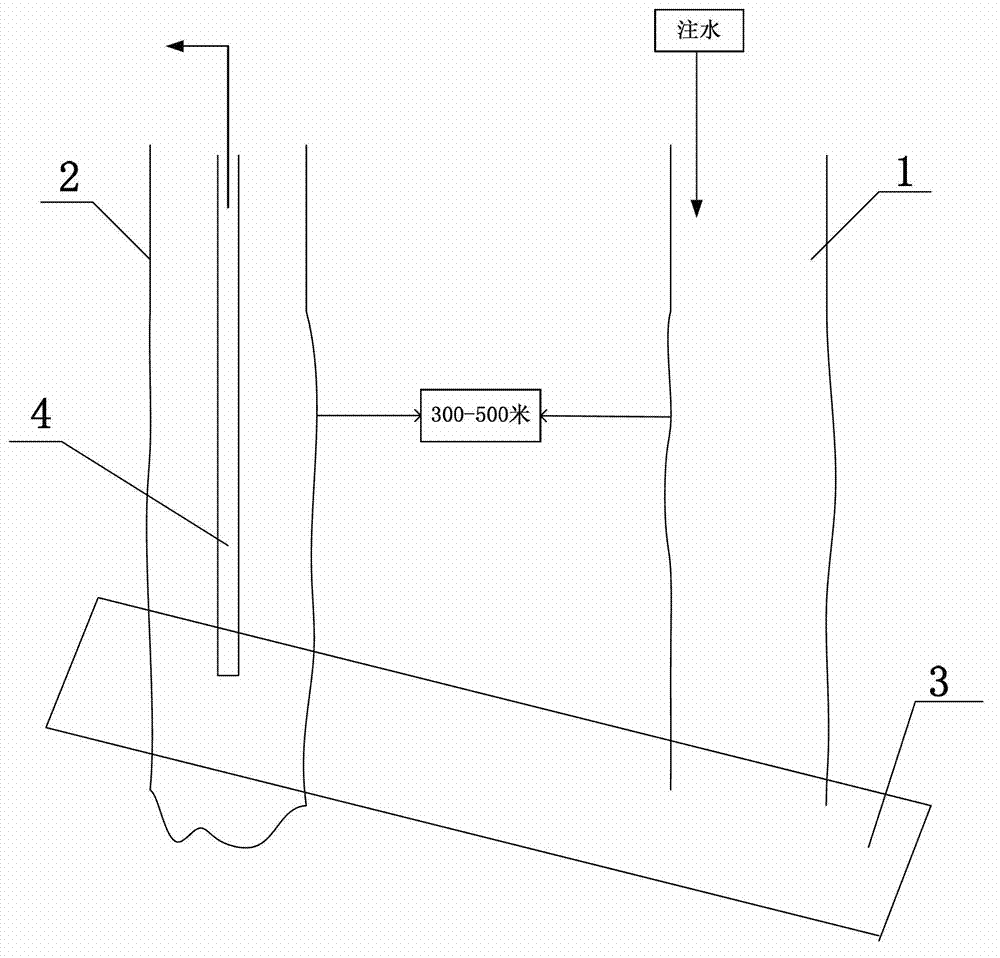
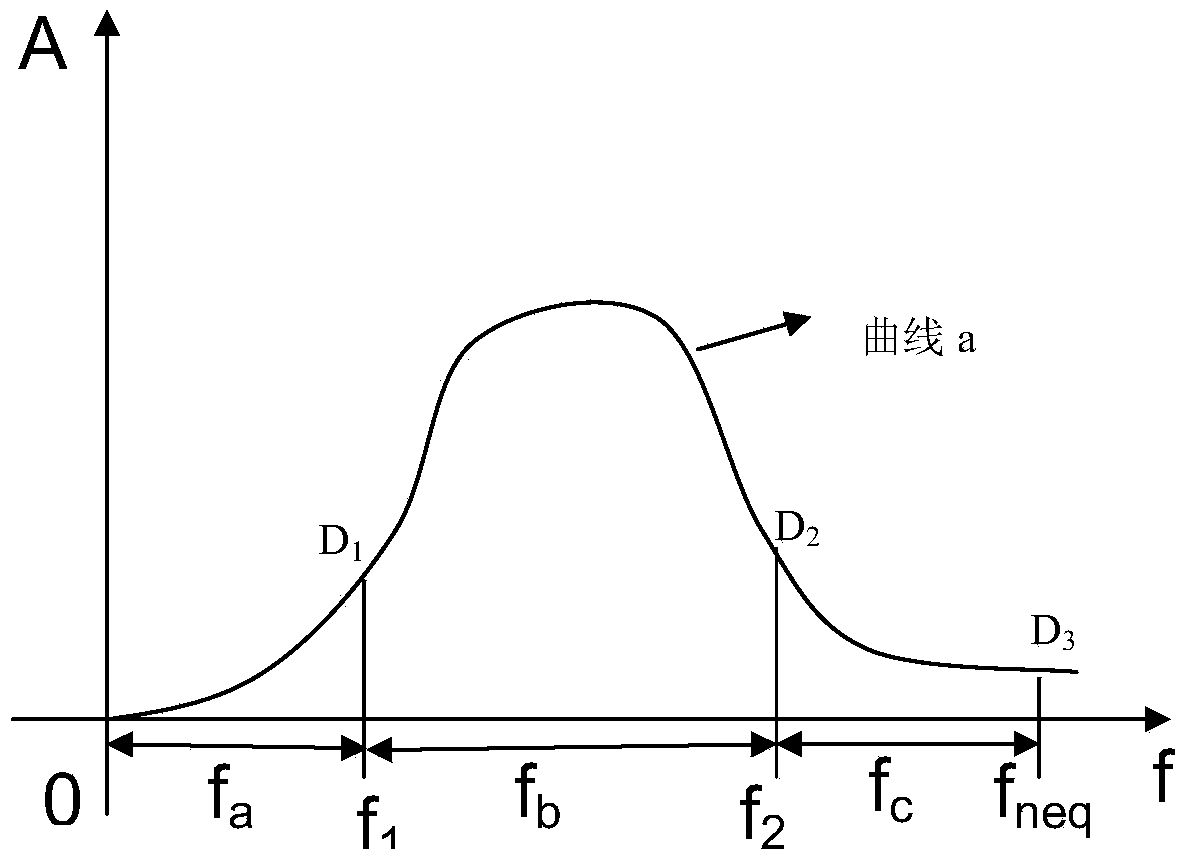
Patents
Literature
333 results about "Well placement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Well Placement Fundamentals. Well Placement Fundamentals provides a reference for petrotechnical experts involved in the real-time positioning of wellbores using LWD data and geological criteria. Chapters on geology, drilling, MWD, and LWD provide the fundamental cross-domain knowledge required for successful well placement operations.
Method and Apparatus for Orchestration of Fracture Placement From a Centralized Well Fluid Treatment Center
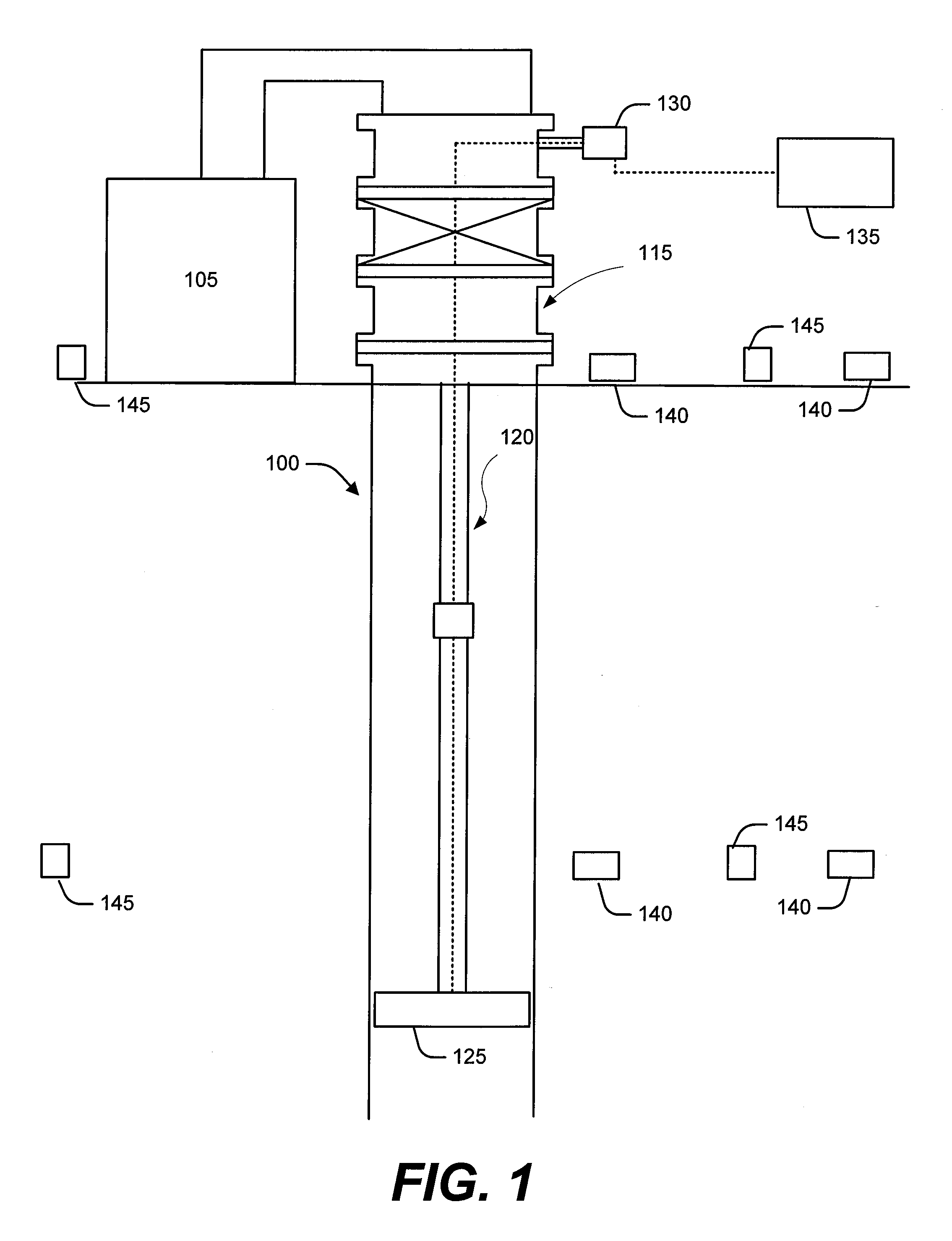
A method and apparatus for orchestrating multiple fractures at multiple well locations in a region by flowing well treatment fluid from a centralized well treatment fluid center is disclosed that includes the steps of configuring a well treatment fluid center for fracturing multiple wells, inducing a fracture at a first well location, measuring effects of stress fields from the first fracture, determining a time delay based in part upon the measured stress effects, inducing a second fracture after the time delay at a second location based upon the measured effects, and measuring the stress effects of stress fields from the second fracture. Sensors disposed about the region are adapted to output effects of the stress fields. Location and orientation of subsequent fractures is based on the combined stress effects of the stress fields as a result of the prior fractures which provides for optimal region development.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
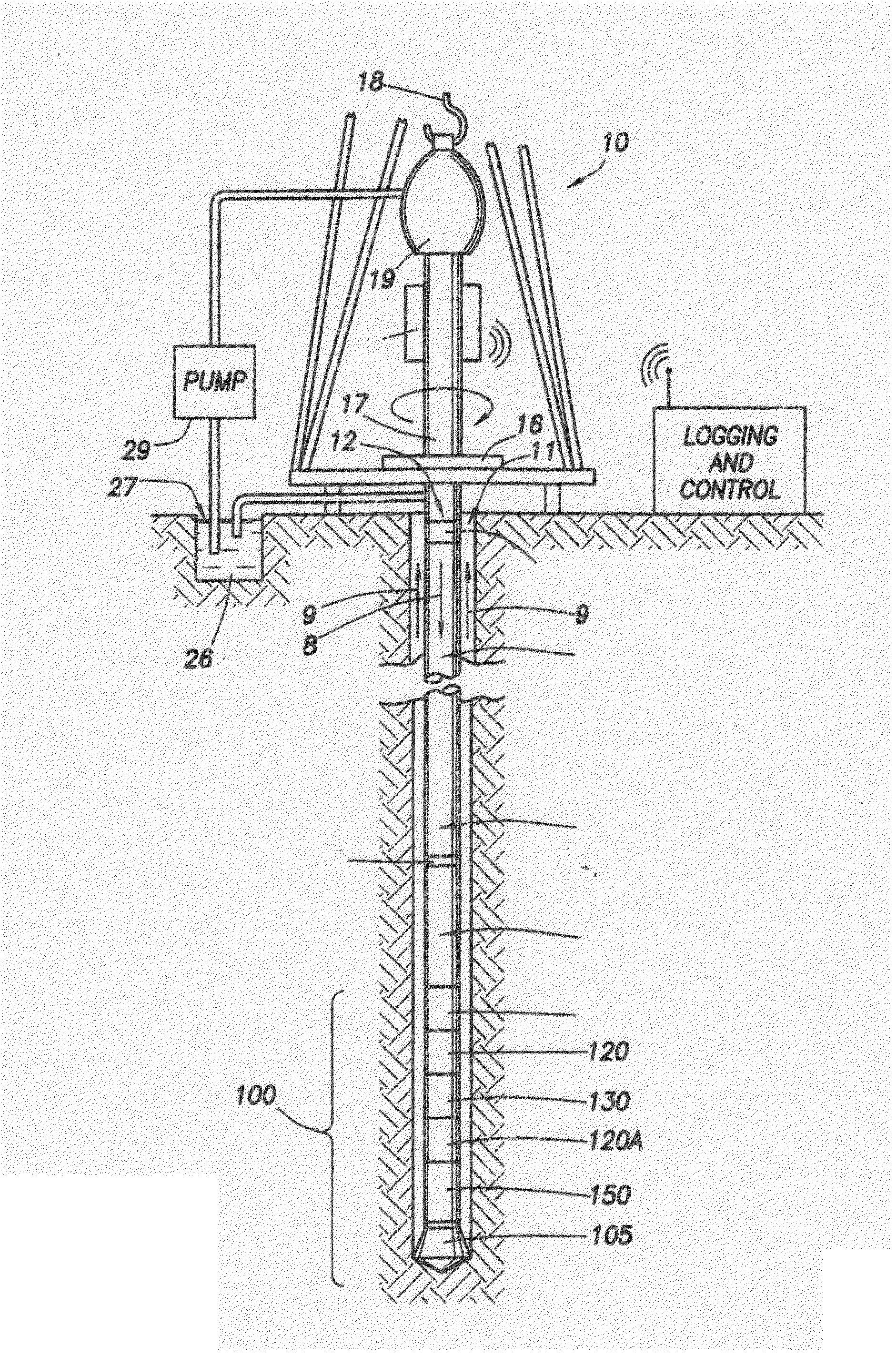
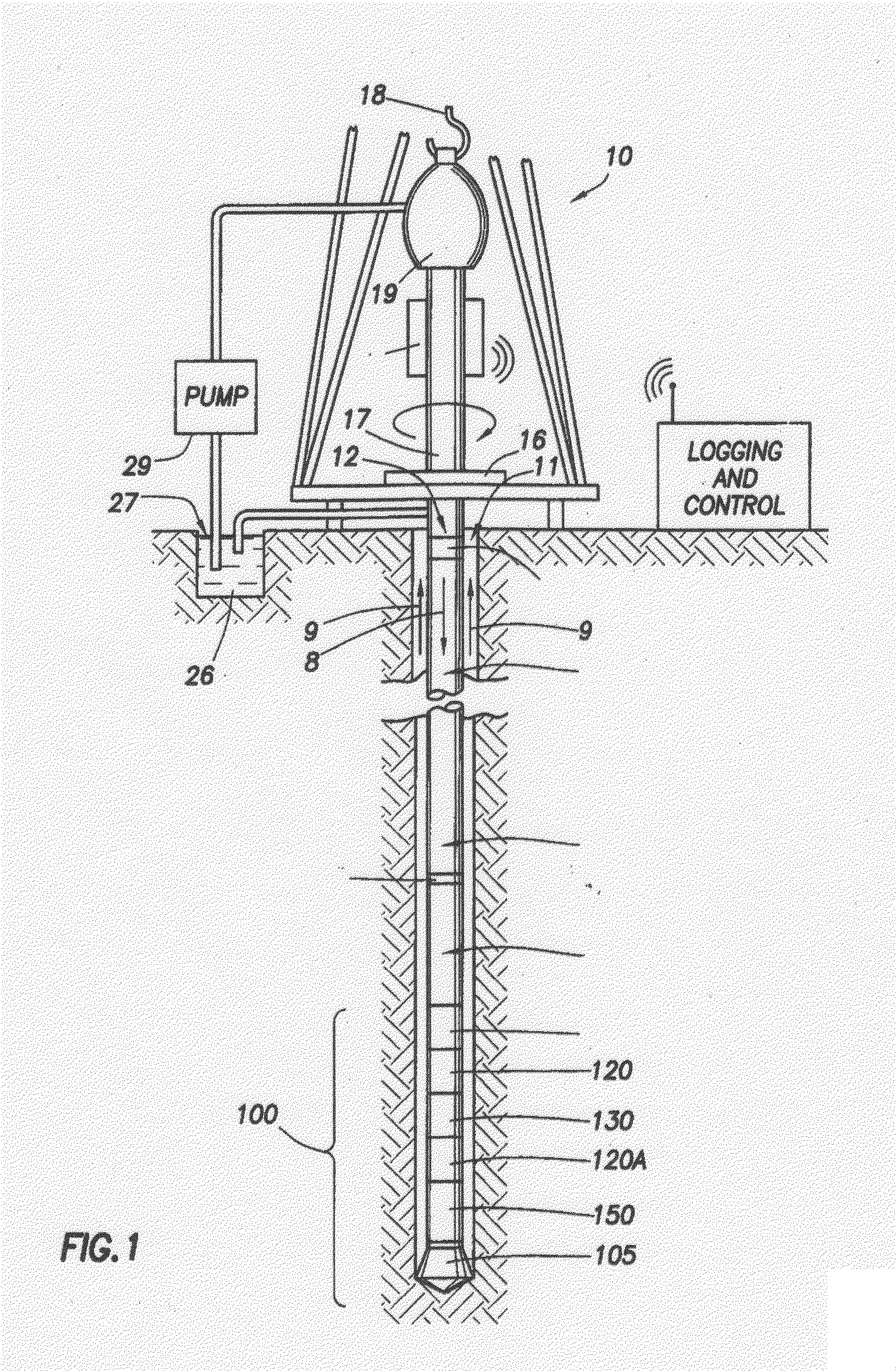
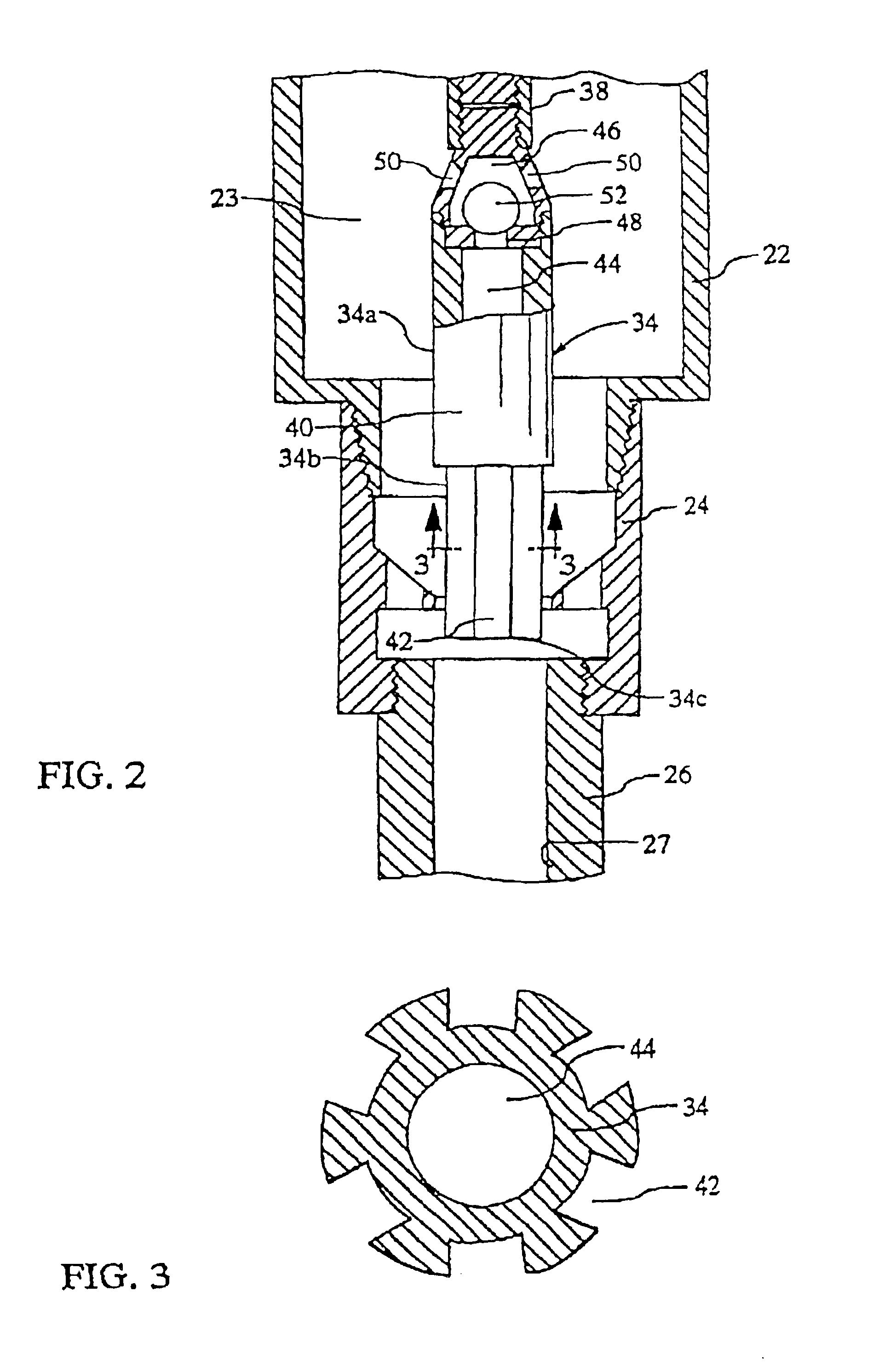
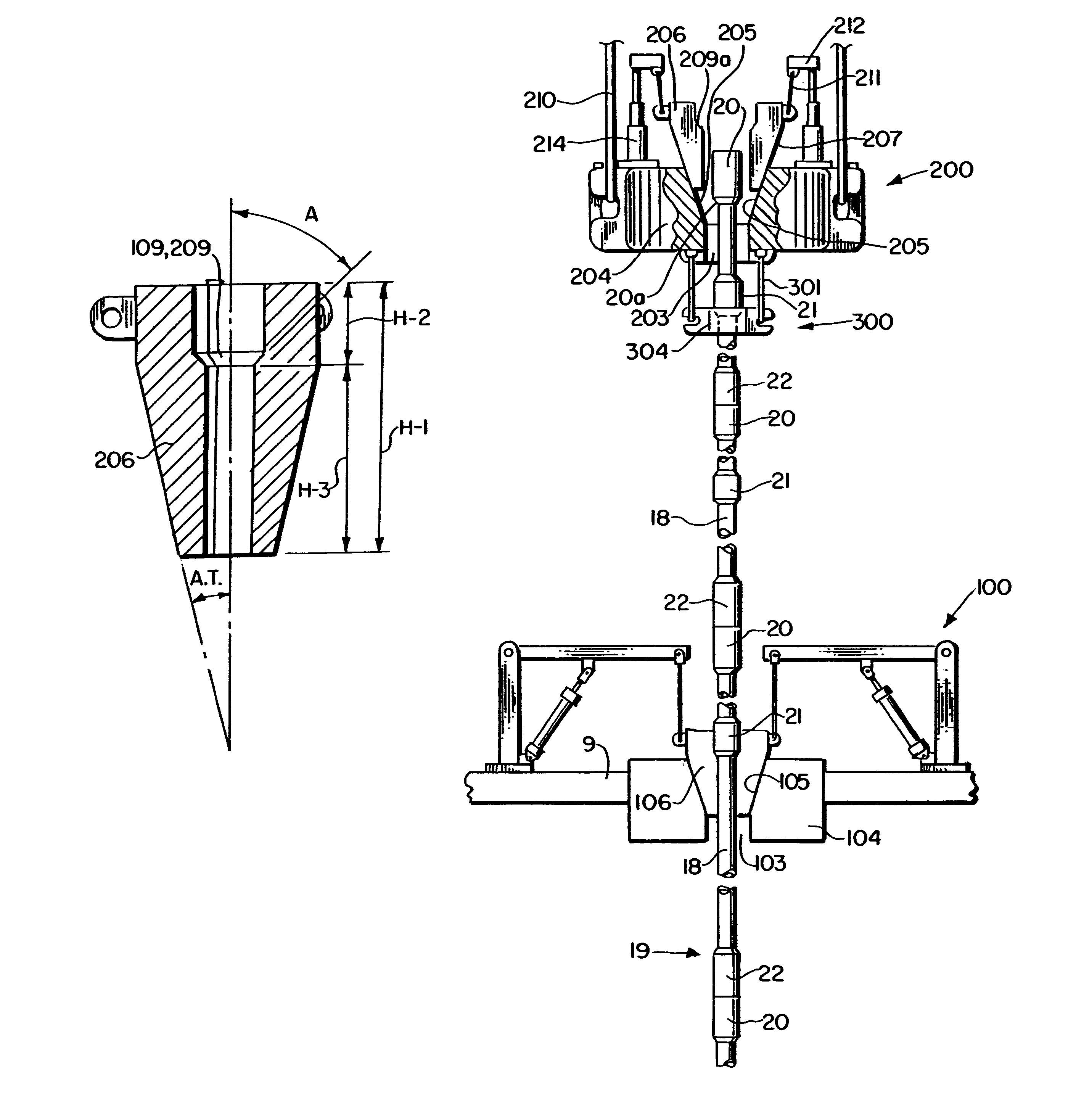
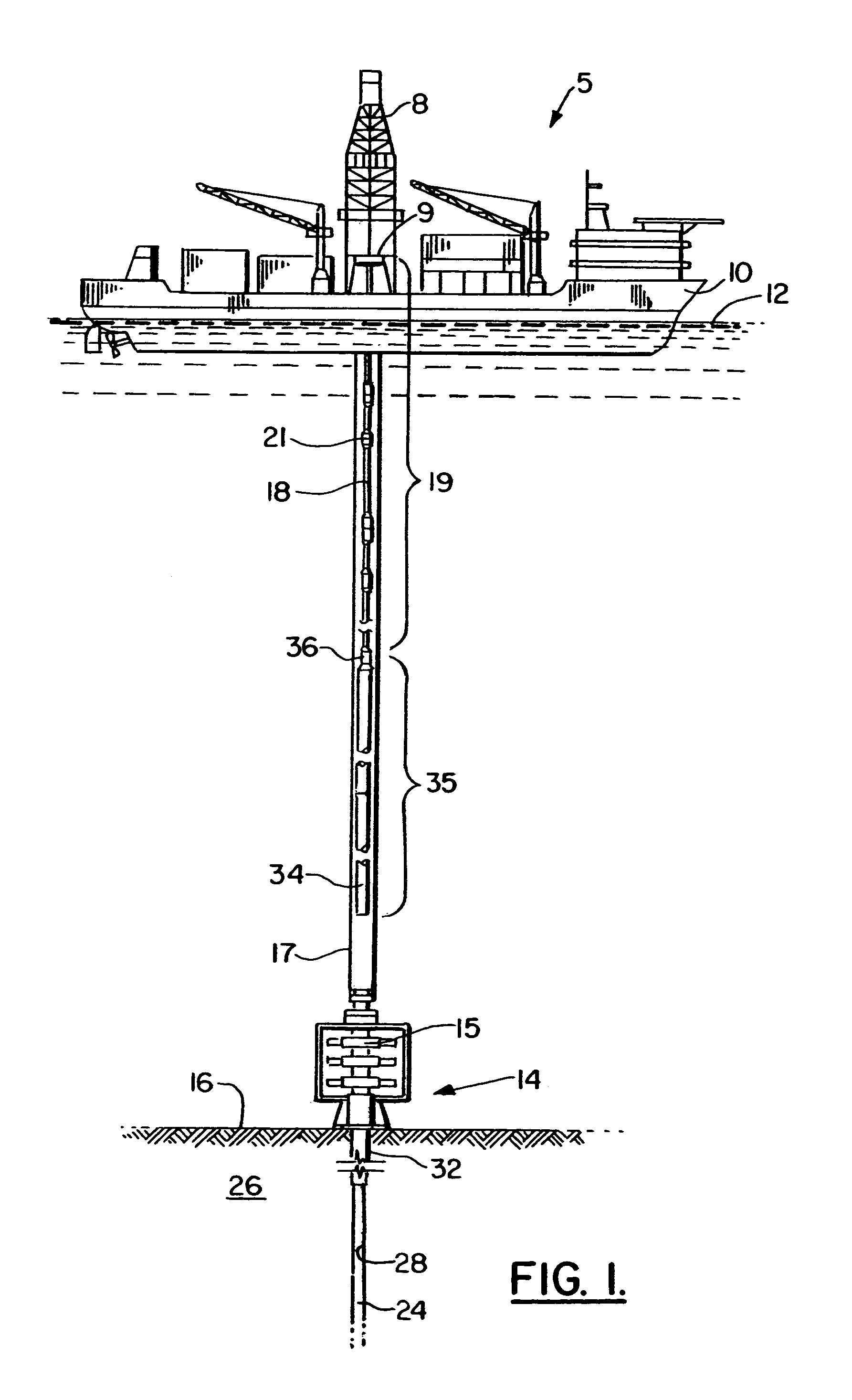
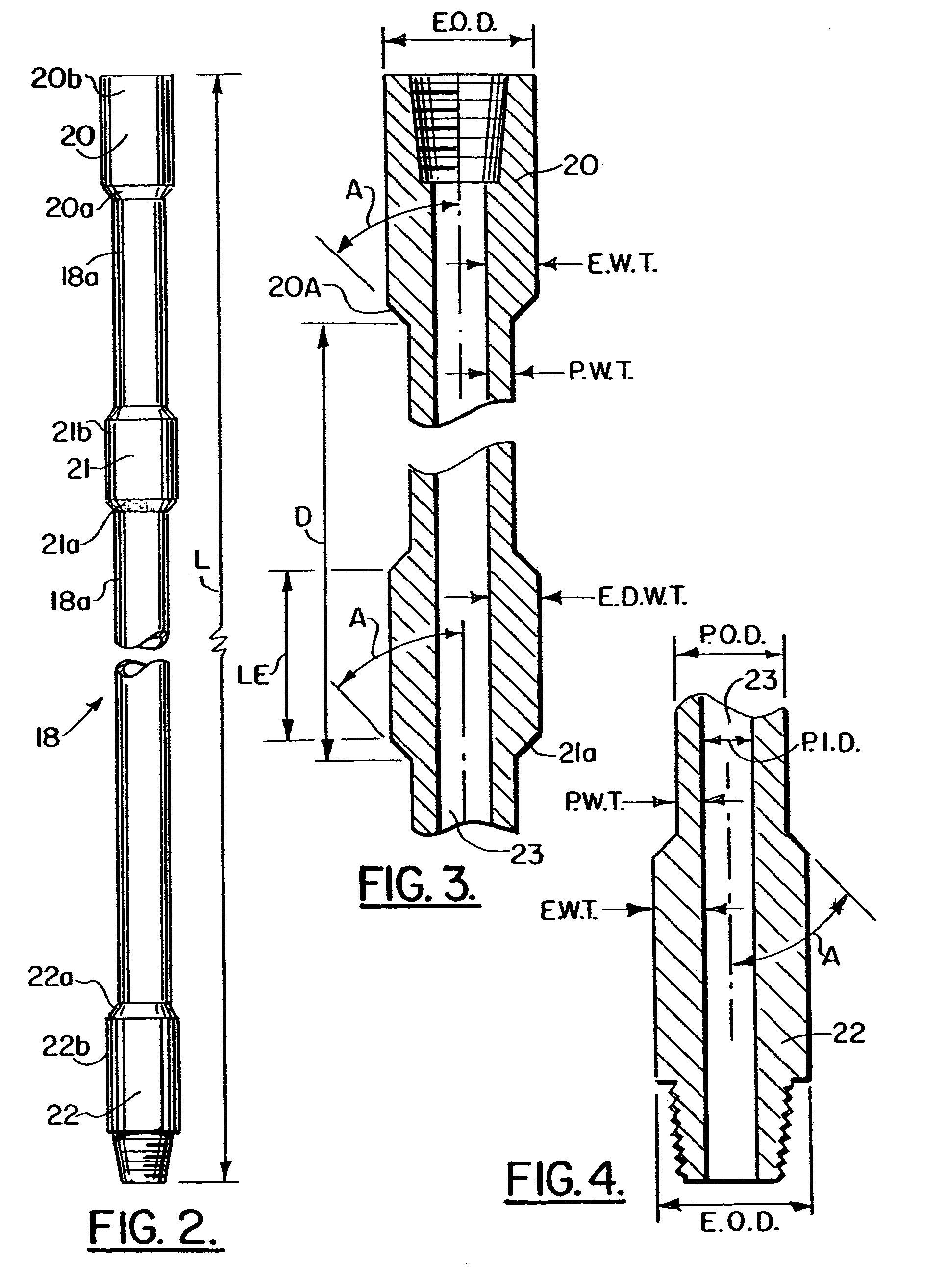
Apparatus and system for well placement and reservoir characterization
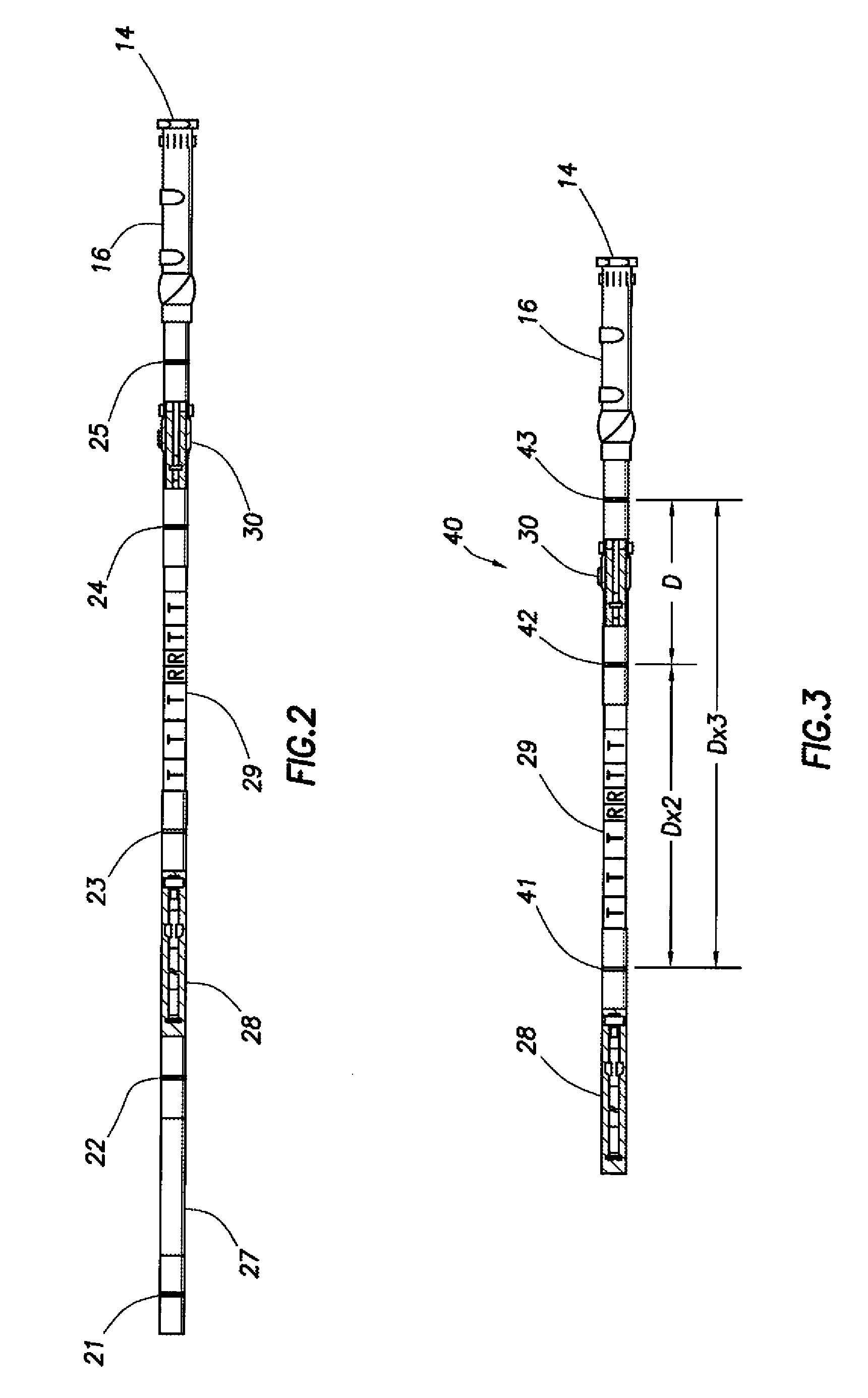
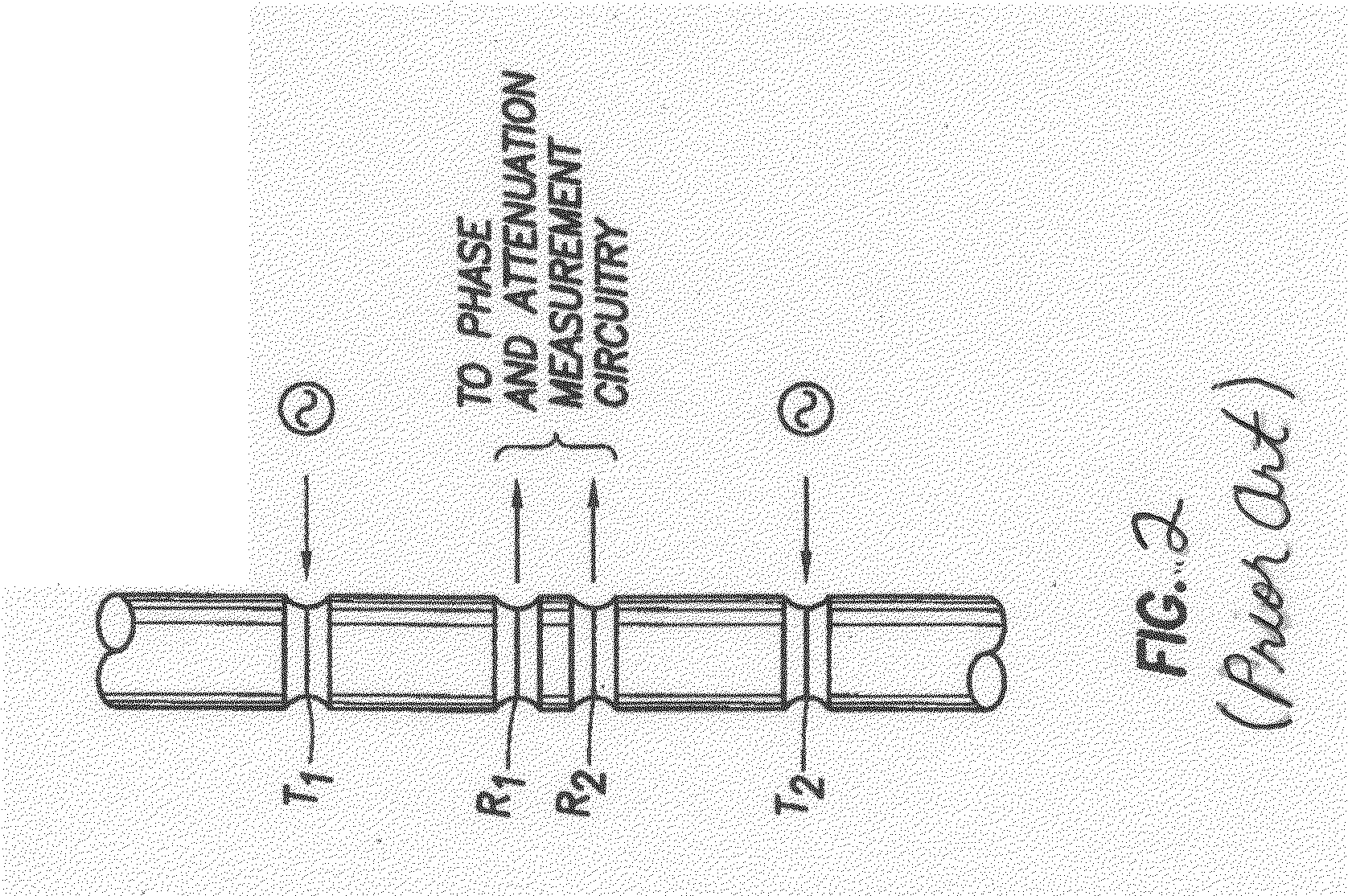
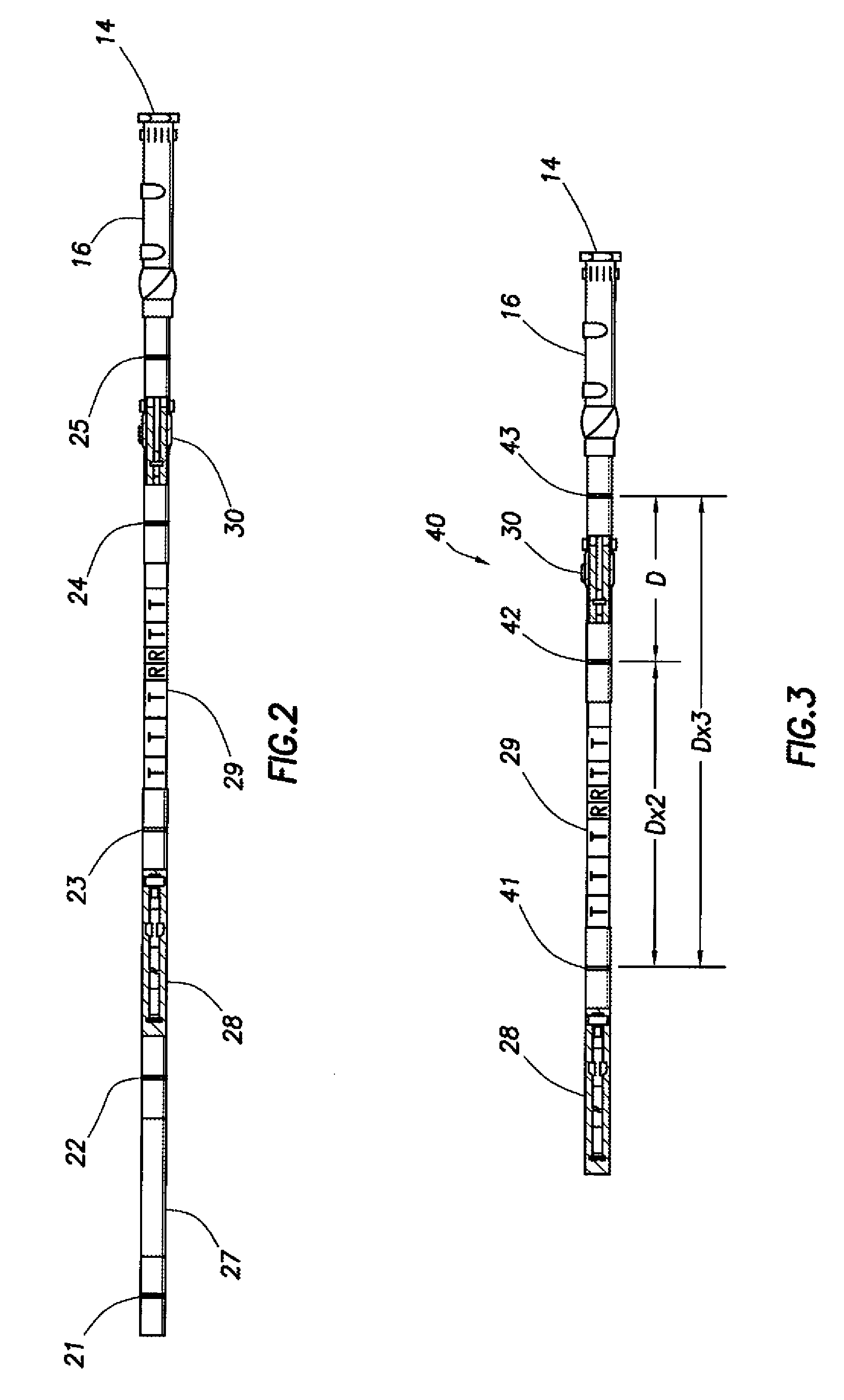
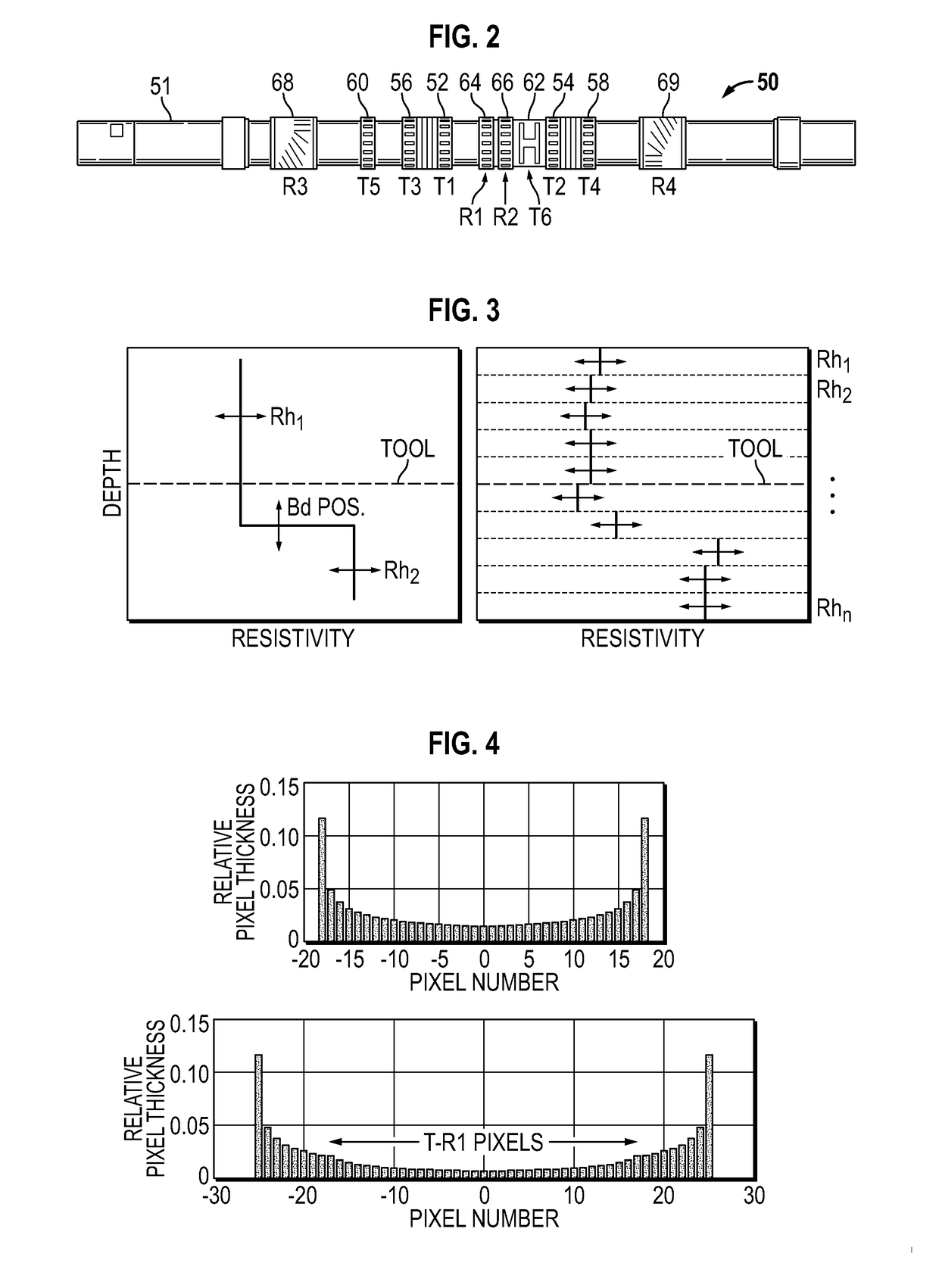
ActiveUS20060011385A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsModular designEngineering
A resistivity array having a modular design includes a transmitter module with at least one antenna, wherein the transmitter module has connectors on both ends adapted to connect with other downhole tools; and a receiver module with at least one antenna, wherein the transmitter module has connectors on both ends adapted to connect with other downhole tools; and wherein the transmitter module and the receiver module are spaced apart on a drill string and separated by at least one downhole tool. Each transmitter and receiver module may comprise at least one antenna coil with a magnetic moment orientation not limited to the tool longitudinal direction. A spacing between the transmitter and receiver module may be selected based on expected reservoir thickness.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus and system for well placement and reservoir characterization
ActiveUS20080136419A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsComputer moduleEngineering
A modular downhole apparatus to determine a formation property, the apparatus being incorporated into a drill string comprising one or more downhole tools and drill pipe, the drill pipe being of the same or various lengths, the modular downhole apparatus comprising a first module having one or more antennas, wherein the first module has connectors on both ends adapted to connect with the drill string; and a second module having one or more antennas, wherein the second module has connectors on both ends adapted to connect with the drill string; wherein the first module and the second module are spaced apart on the drill string; and wherein one or more of the one or more antennas of one or both of the modules has a dipole moment that is tilted or transverse.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
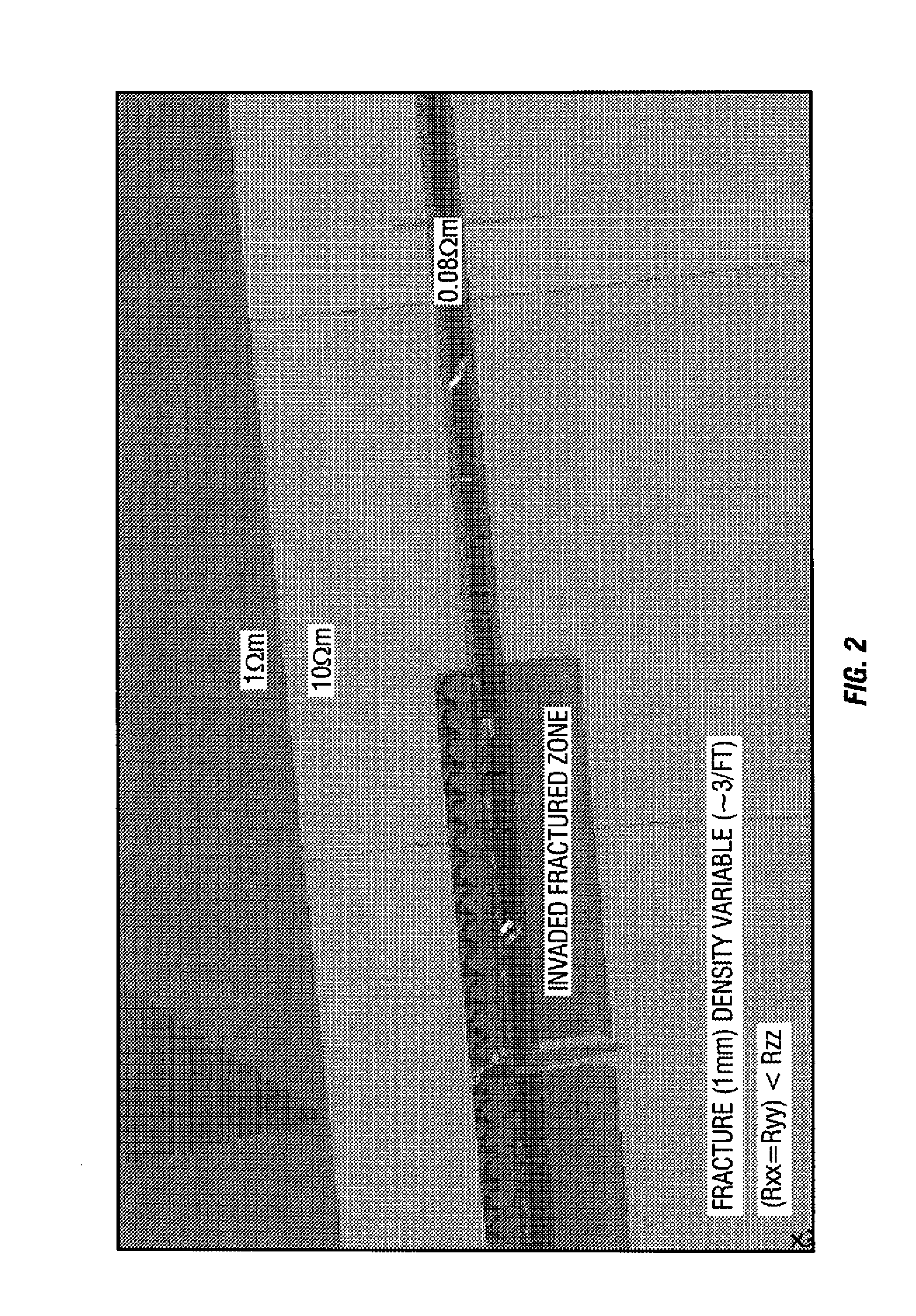
Directional resistivity measurement for well placement and formation evaluation
ActiveUS20110238312A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingHarmonicWell placement
The present disclosure relates to a method to determine a formation property of a subsurface formation. A downhole logging tool having two or more antennas, at least two of the antennas having a transversely-sensitive element and an axially-sensitive element is provided. Azimuthally-sensitive measurements are obtained using the antennas of the downhole logging tool. The measurements are fitted to a Fourier series having Fourier coefficients that include channel gains, if any. A DC component, a first harmonic component, and a second harmonic component are determined from the Fourier series, a measurement type is determined using the DC component, the first harmonic component, and / or the second harmonic component, and the formation property of the subsurface formation is determined using the determined measurement type.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
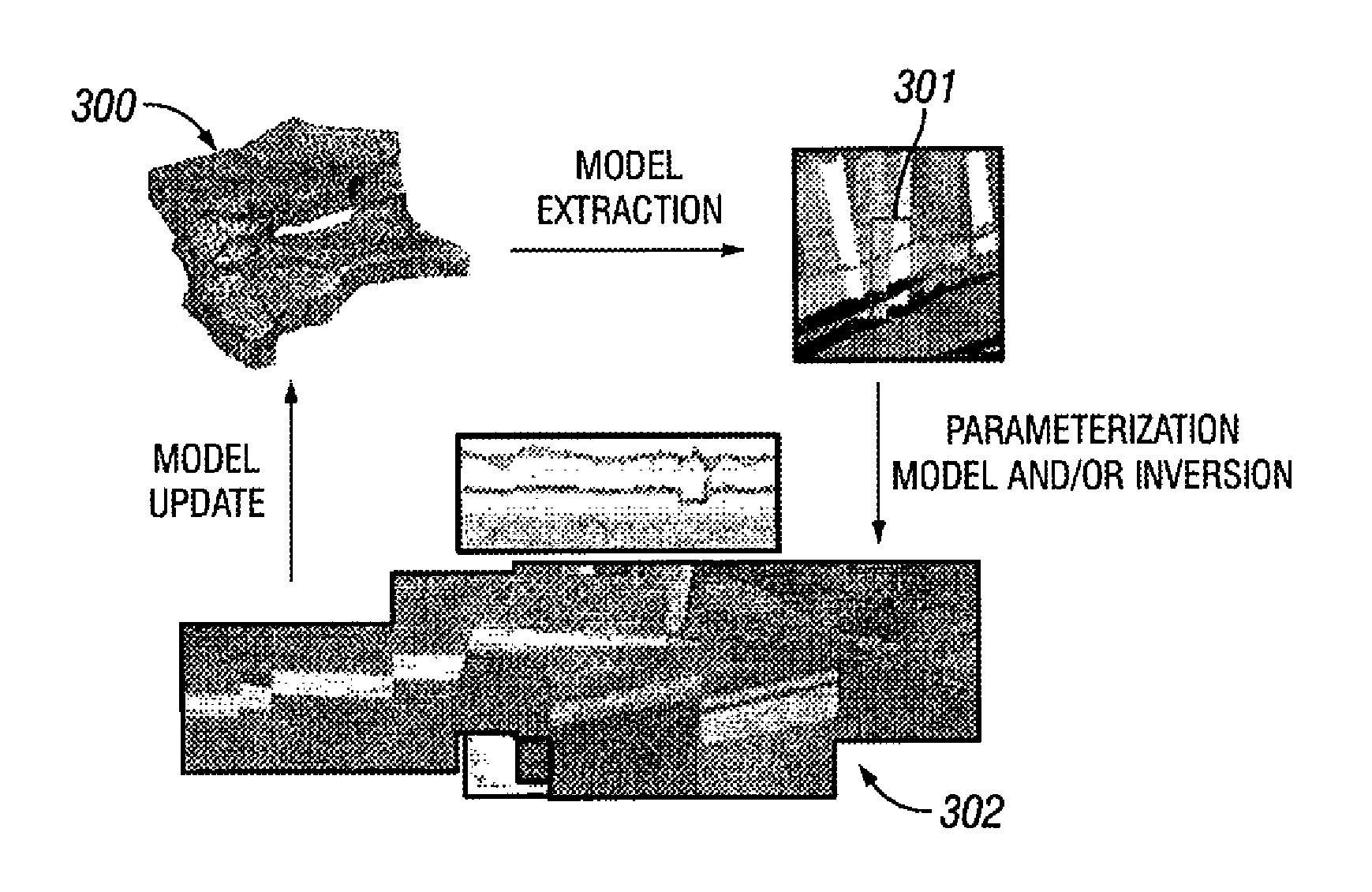
Formation modeling while drilling for enhanced high angle for horizontal well placement
ActiveUS20110106514A1Easy to useGeological measurementsAnalogue processes for specific applicationsPhysics basedWell placement
Methods for three-dimensionally characterizing a reservoir while drilling a high angle or horizontal wellbore through the reservoir are disclosed. An initial reservoir model for the reservoir is selected and a section is extracted for a planned trajectory of the wellbore. A secondary model is generated by performing secondary modeling for at least part of the planned trajectory. An area of interest is identified within the secondary model where statistical uncertainty is high. Possible causes of the statistical uncertainty are identified for the area of interest within the secondary model that are not present or accounted for in the initial reservoir model. A set of parameters for the area of interest are defined at that are based on the possible causes of statistical uncertainty. The area of interest is logged with at least one logging while drilling LWD tool. Sensitivities of the LWD tool response to the subset of parameters are evaluated by performing at least one tertiary model for a range of the subset of parameters. The most sensitive parameters from the subset of parameters and corresponding measurements are identified. One or more real-time LWD measurements to be used for proactive well placement along the planned trajectory are identified and are based on the most sensitive parameters. The initial reservoir model is updated while drilling with information from the tertiary model. The model update is based on physics-based modeling or on inversion and on running multiple models and selection of a best candidate model based on correlations between the tool measurements and modeled results for each geologic model.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
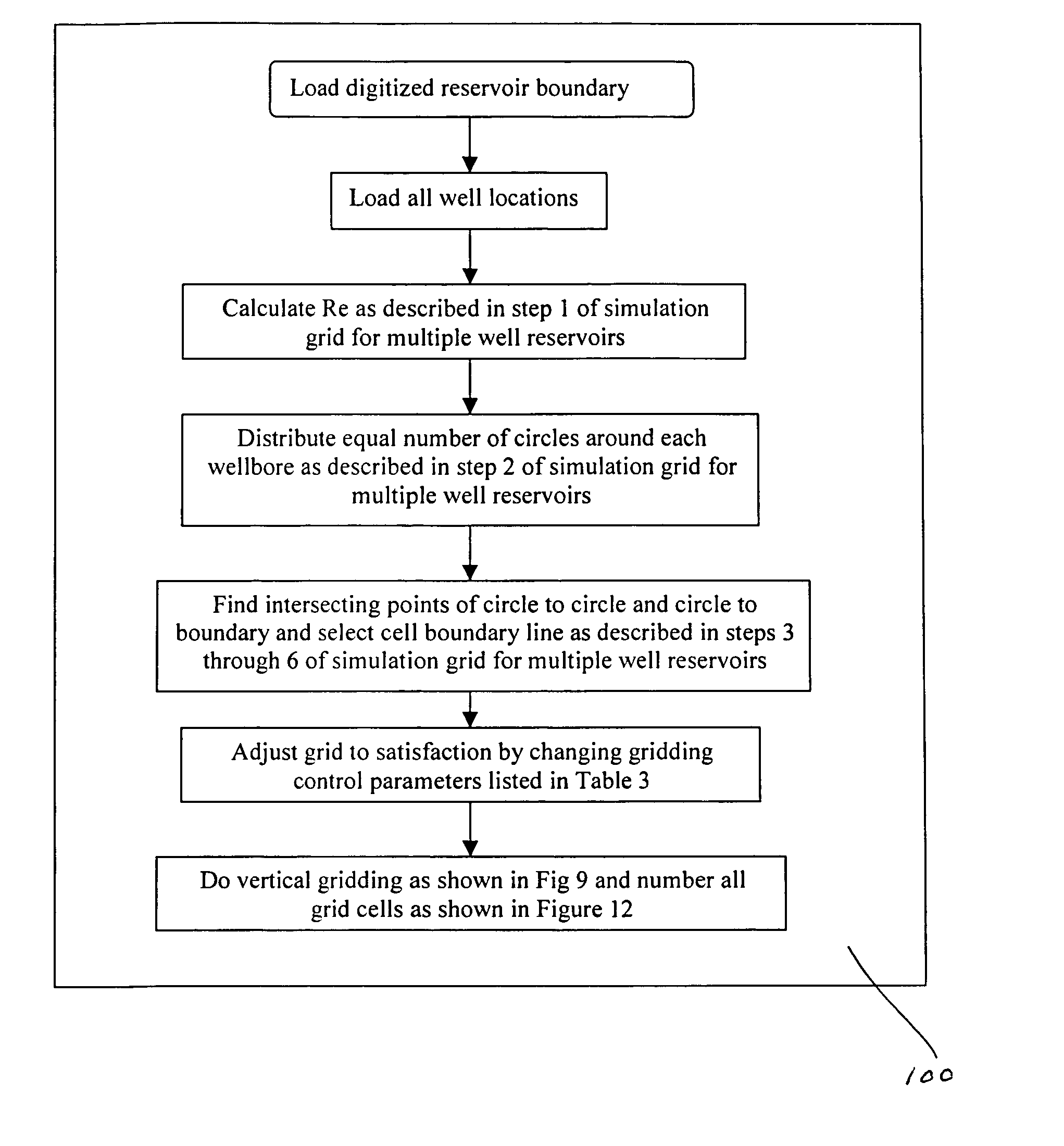
Method for producing full field radial grid for hydrocarbon reservoir simulation
InactiveUS7096122B2Speed up the flowLittle involvementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingGeomodellingClassical mechanicsEngineering
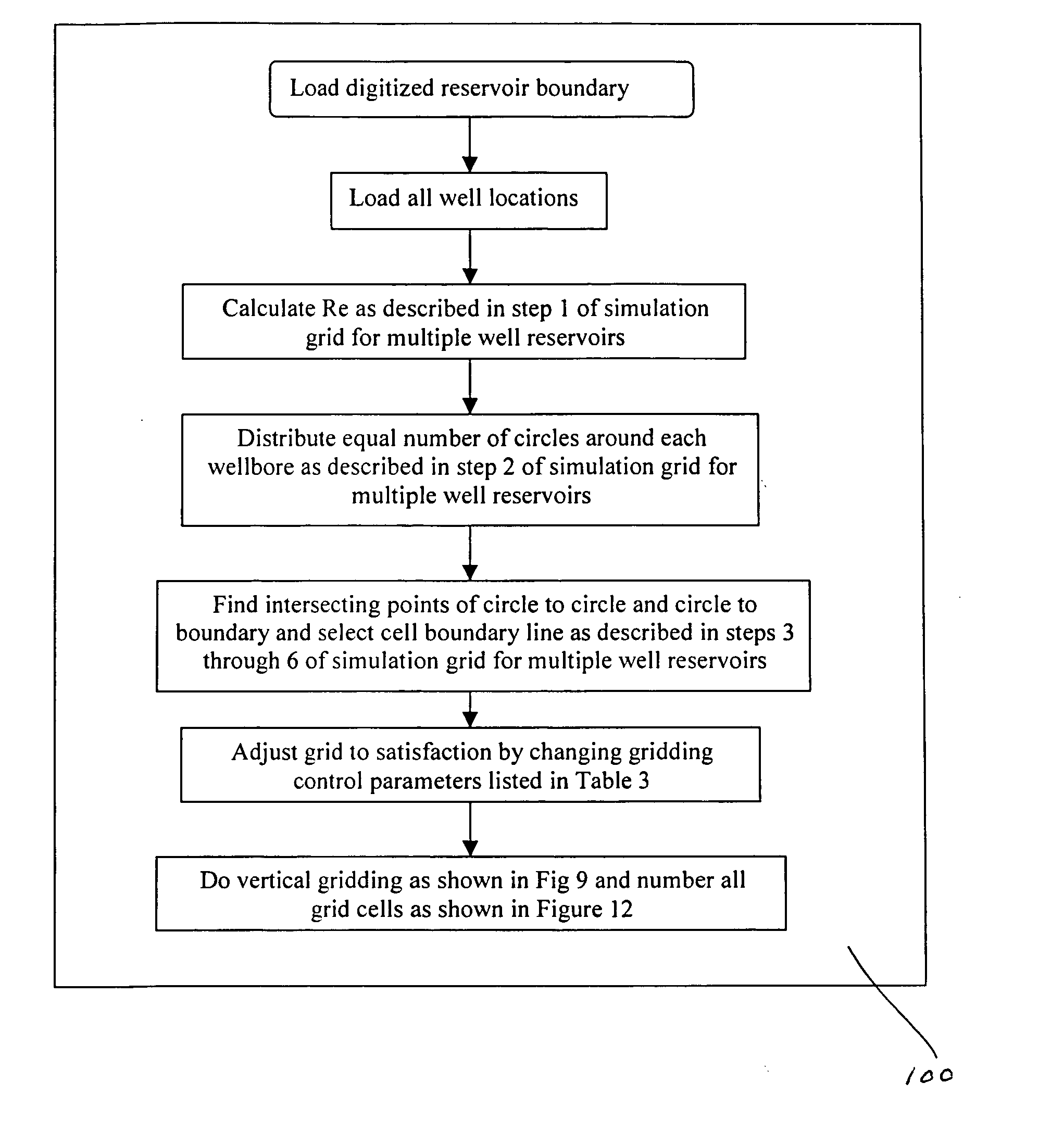
A method producing full field radial grid includes both aerial and vertical gridding to divide a reservoir structure into simulation grid cells. The aerial gridding is performed by 1) specifying a reservoir boundary (including faults) and well locations; 2) distributing a set of concentric circles around each well location; 3) determining the circle-circle and circle-boundary intersection locations of these circles; 4) forming the aerial grid by selecting circles, arc segments of intersecting circles and radial lines which connect the ends of these arc segments to the corresponding well center; 5) and forming additional grid lines by selecting the connecting lines of two wells if their circles intersect, adding additional radial lines to certain wells, and connecting end points of certain selected arc segments. The vertical gridding is performed by casting the aerial grid vertically downwardly through all the layers defined in the reservoir structure.
Owner:HAN DIANLI
Apparatus and system for well placement and reservoir characterization
ActiveUS7755361B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsComputer moduleWell placement
A modular downhole apparatus to determine a formation property, the apparatus being incorporated into a drill string comprising one or more downhole tools and drill pipe, the drill pipe being of the same or various lengths, the modular downhole apparatus comprising a first module having one or more antennas, wherein the first module has connectors on both ends adapted to connect with the drill string; and a second module having one or more antennas, wherein the second module has connectors on both ends adapted to connect with the drill string; wherein the first module and the second module are spaced apart on the drill string; and wherein one or more of the one or more antennas of one or both of the modules has a dipole moment that is tilted or transverse.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Formation modeling while drilling for enhanced high angle for horizontal well placement
ActiveUS8489375B2Easy to useGeological measurementsAnalogue processes for specific applicationsWell placementWellbore
LWD measurements to be used for proactive well placement while drilling a high angle or horizontal wellbore in a reservoir are defined. An initial reservoir model is provided and a section is extracted for a planned wellbore trajectory. A secondary model is generated for the planned trajectory. An area of interest is identified where statistical uncertainty is high. Possible causes of the statistical uncertainty are identified that are not present in the initial reservoir model. A set of parameters are defined based on the possible causes of statistical uncertainty. The area of interest is logged with LWD tool. Sensitivities of the LWD tool response to a subset of parameters are evaluated by performing tertiary model for a range of the subset of parameters. The most sensitive parameters from the subset of parameters and corresponding measurements are identified. LWD measurements are defined based on the most sensitive parameters.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
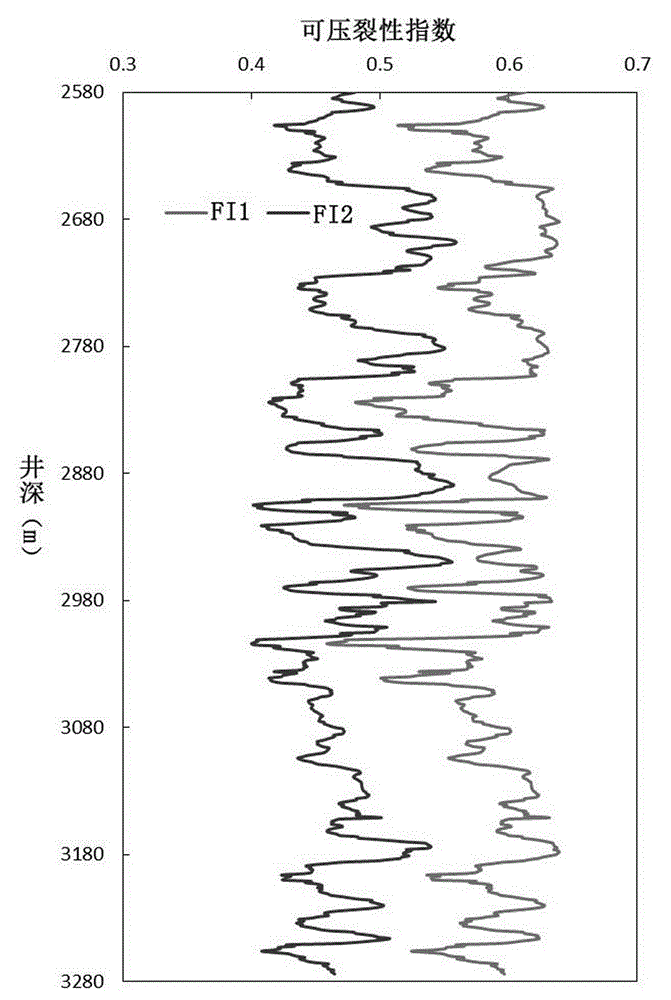
Debris-core-borehole-reservoir multiscale shale reservoir three-dimensional fracturing evaluation method
ActiveCN105156103ALarge capacityQuantification of fracabilityBorehole/well accessoriesType fractureWell placement
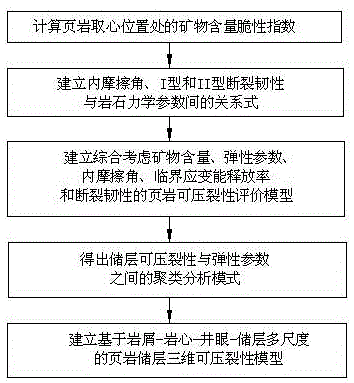
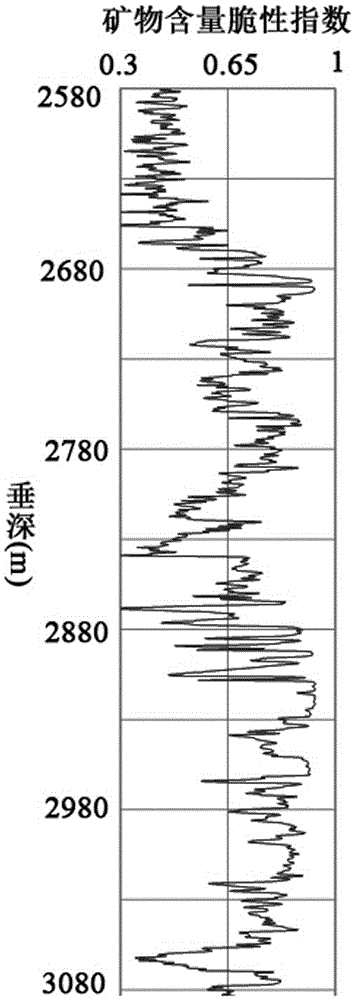
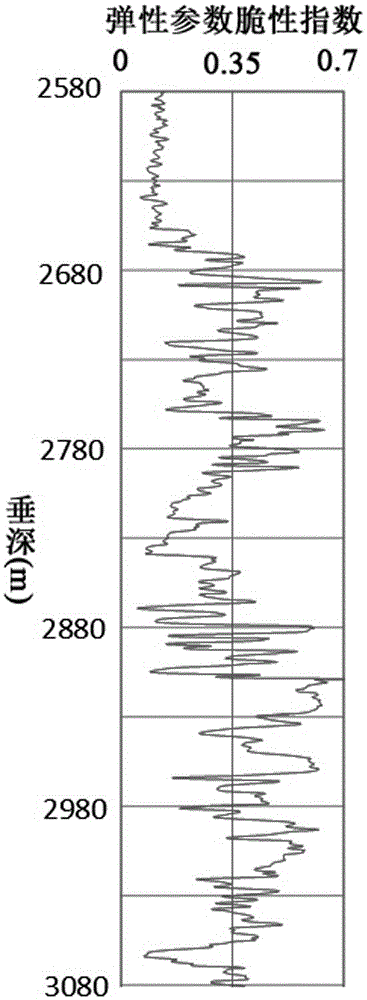
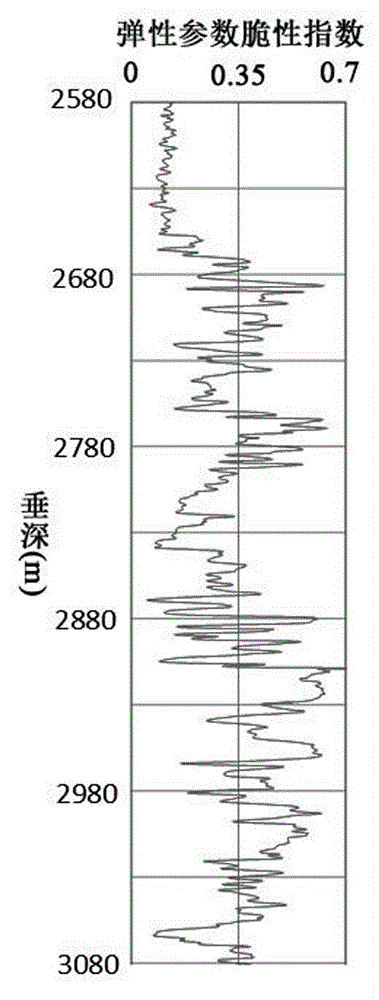
The invention relates to a debris-core-borehole-reservoir multiscale shale reservoir three-dimensional fracturing evaluation method. The method comprises the steps of: (S1) calculating mineral content brittleness indexes in a shale coring position; (S2) building relations among an internal friction angle, I type and II type fracture toughness and rock mechanical parameters; (S3) building shale fracturing evaluation models comprehensively considering a mineral content, elastic parameters, the internal friction angle, a critical strain energy release rate and the rapture toughness; (S4) applying a support vector machine algorithm to obtain a cluster analysis mode between a reservoir fracturing performance and the elastic parameters; and (S5) applying the cluster analysis mode and a reservoir three-dimensional elastic parameter data body to obtain a debris-core-borehole-reservoir multiscale shale reservoir three-dimensional fracturing model. The method can be applied to obtain the fracturing performance of any space position in a shale reservoir, so that the well position selection blindness is prevented, and the fracturing modification effect and the after-pressing yield are improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV +1
Method for producing full field radial grid for hydrocarbon reservoir simulation
InactiveUS20050021234A1Work flow easyLittle involvementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingGeomodellingFull fieldWork flow
A method producing full field radial grid (called here Radial-X Grid) for more accurate and efficient reservoir simulation and improving simulation work flow. The Radial-X Grid method produces both aerial and vertical gridding to divide a reservoir structure into simulation grid cells. The aerial gridding is performed by 1) specifying a reservoir boundary (including faults) and well locations; 2) distributing a set of concentric circles around each well location; 3) determining the circle-circle and circle-boundary intersection locations of these circles; 4) forming the aerial grid by selecting circles, arc segments of intersecting circles and radial lines which connect the ends of these arc segments to the corresponding well center; 5) and forming additional grid lines by selecting the connecting lines of two wells if their circles intersect, adding additional radial lines to certain wells, and connecting end points of certain selected arc segments. Thus, the aerial boundary of each individual grid cell is formed from elements selected from the group of arc segment, well radial line, reservoir boundary, connection line of well to well, arc segment end to arc segment end. The vertical gridding is performed by casting the aerial grid vertically downwardly through all the layers defined in the reservoir structure. The Radial-X Grid method is advantageous for petroleum reservoir simulation applications because it is easy to use, runs fast, produces no grid orientation effect, provides efficient use of grid cells, provides precision modeling and provides better reservoir boundary and fault conformance.
Owner:HAN DIANLI
Modeling method for compact sandstone reservoir three-dimensional fracability model
ActiveCN105134156AImproving the effectiveness of volumetric fracturingShorter payback timeFluid removalSpecial data processing applicationsModel methodWell placement
The invention relates to a modeling method for a compact sandstone reservoir three-dimensional fracability model. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a relation formula among an internal friction angle, I type and II type crack fracture toughness and the parameter of sandstone mechanical characteristics; S2, establishing a shale fracability evaluation model which comprehensively considers an elastic parameter, the internal friction angle, the critical strain energy release rate and fracture toughness; S3, adopting a support vector machine algorithm to obtain a cluster analysis mode between the reservoir fracability and the elastic parameter; S4, adopting the cluster analysis mode to obtain a reservoir three-dimensional elastic parameter data body, and establishing the multi-scale compact sandstone reservoir three-dimensional fracability evaluation model based on the core, the borehole and the reservoir of multiple scales. According to the method, the fracability of an arbitrary space position in the compact sandstone reservoir can be obtained, a sweet spot with high fracability can always be drilled when drilling a compact sandstone gas well, blindness of well location selection is avoided, and the fracture modification effect and the yield after fracture are improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
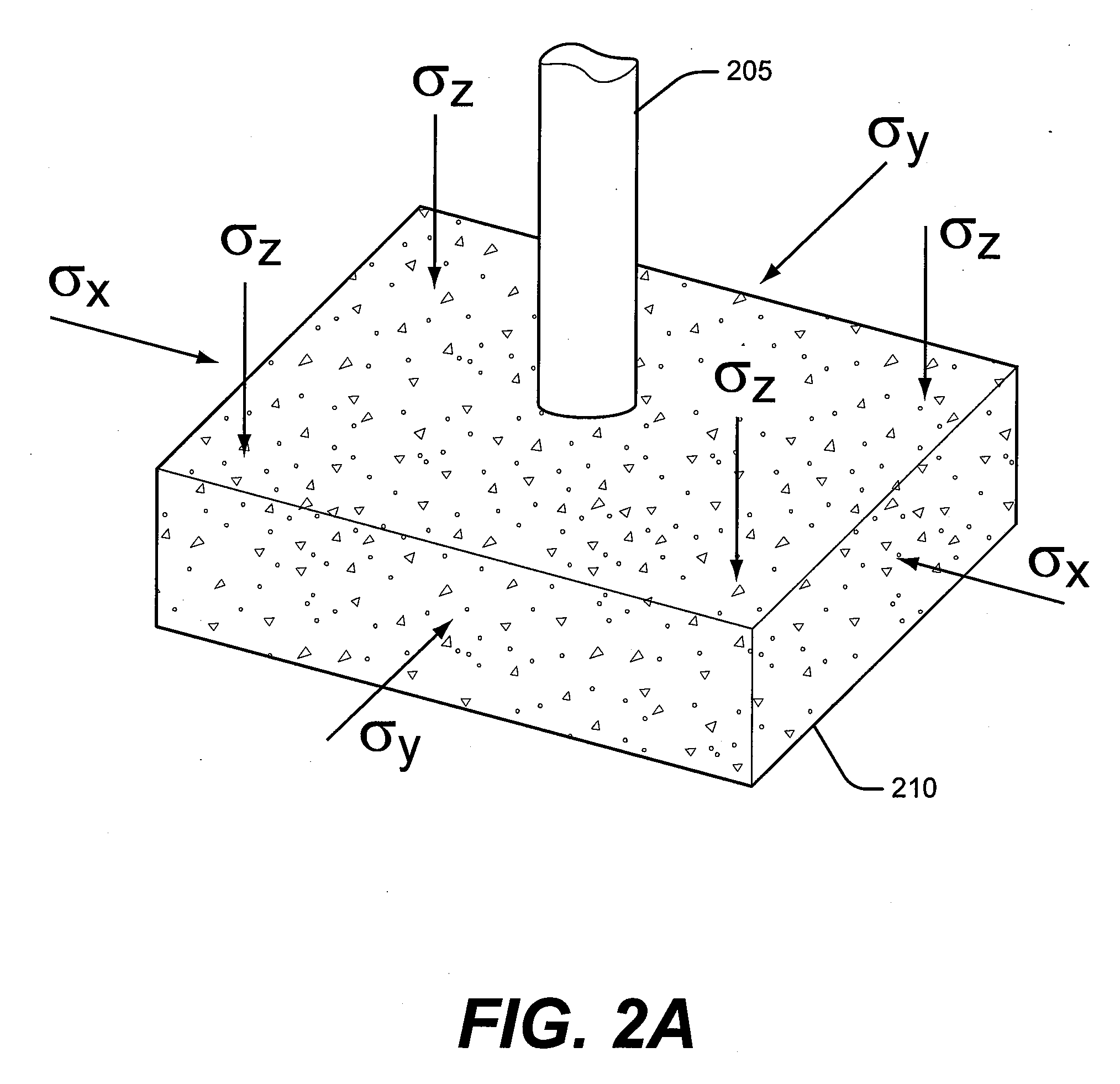
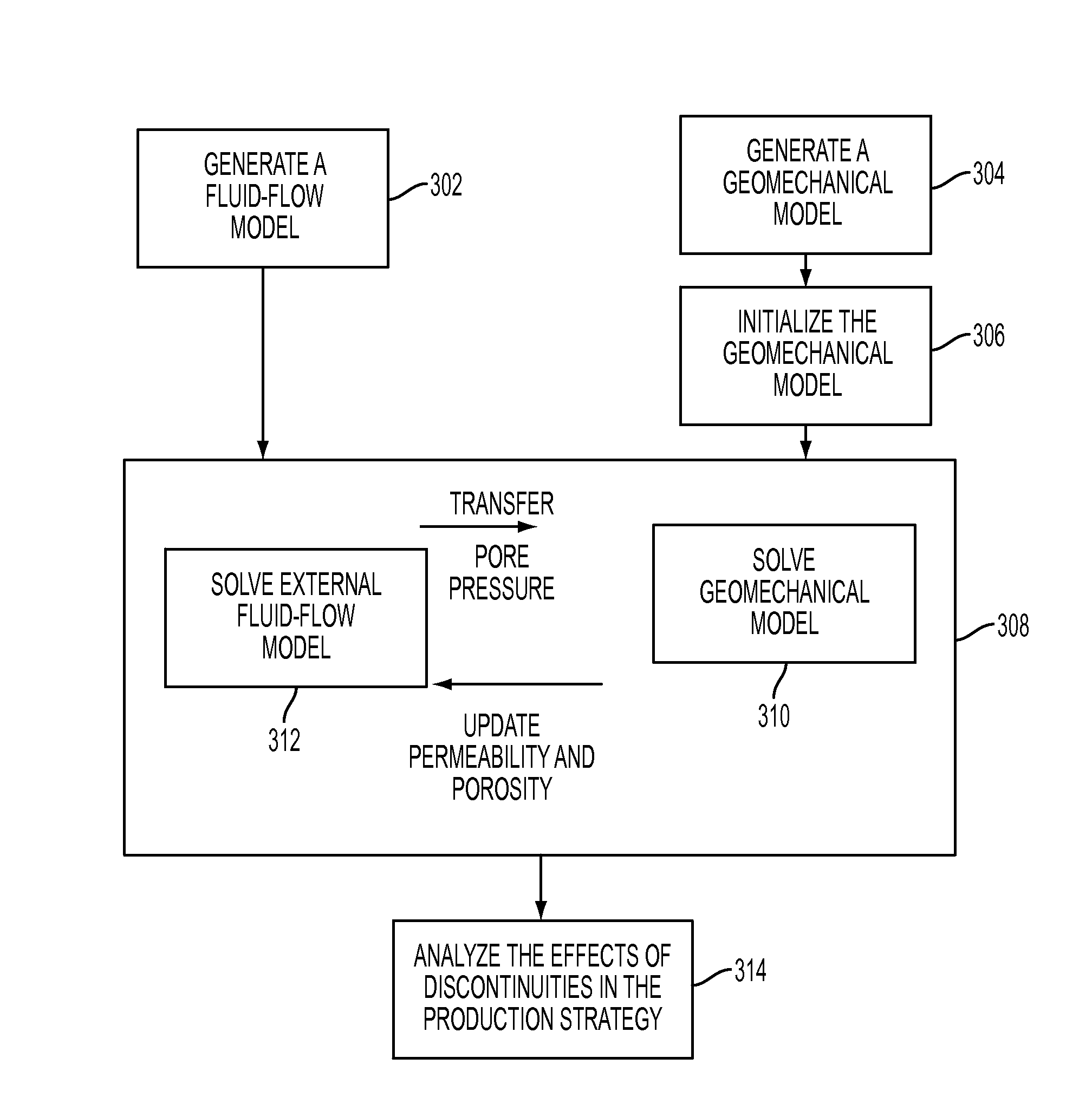
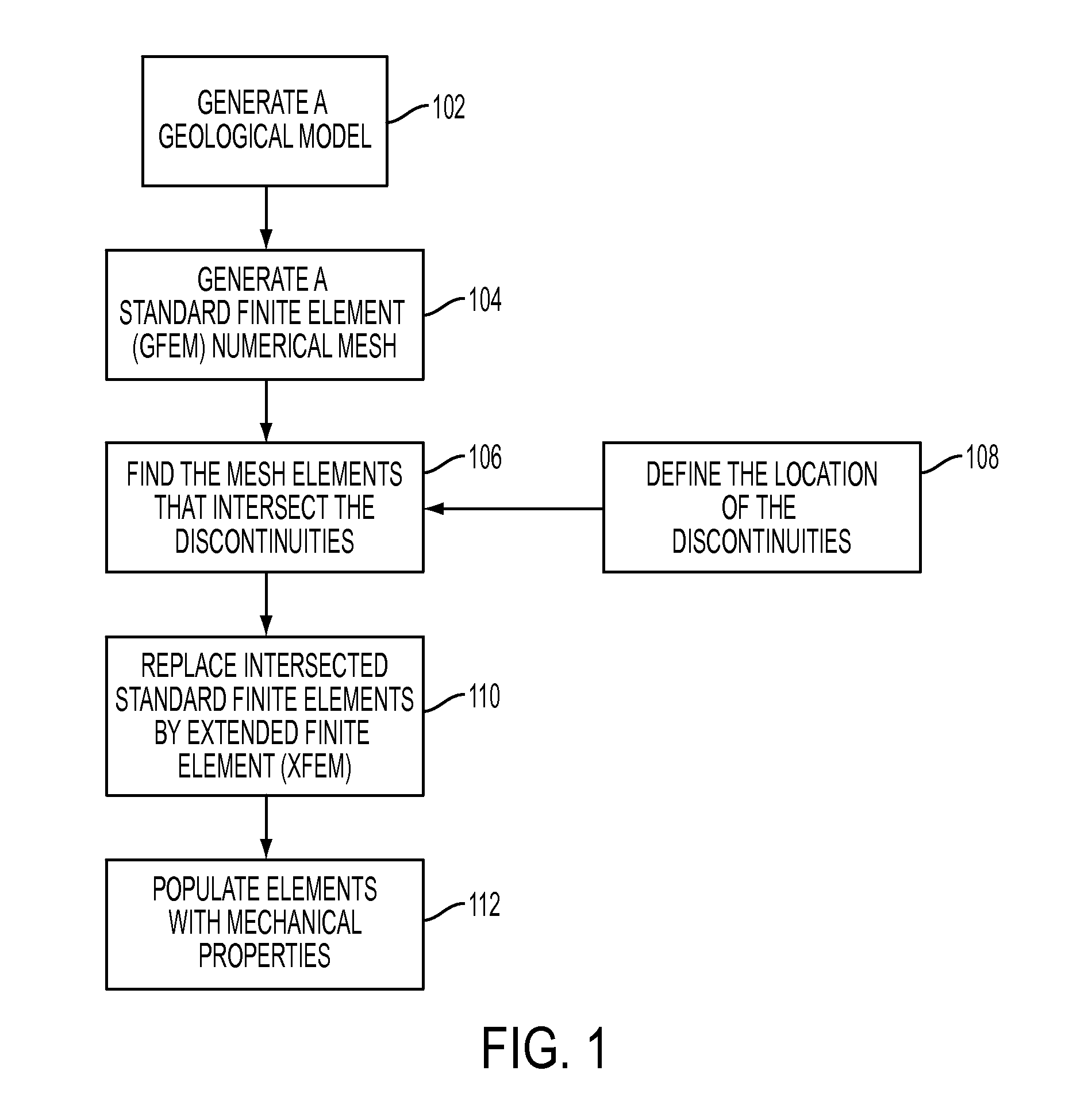
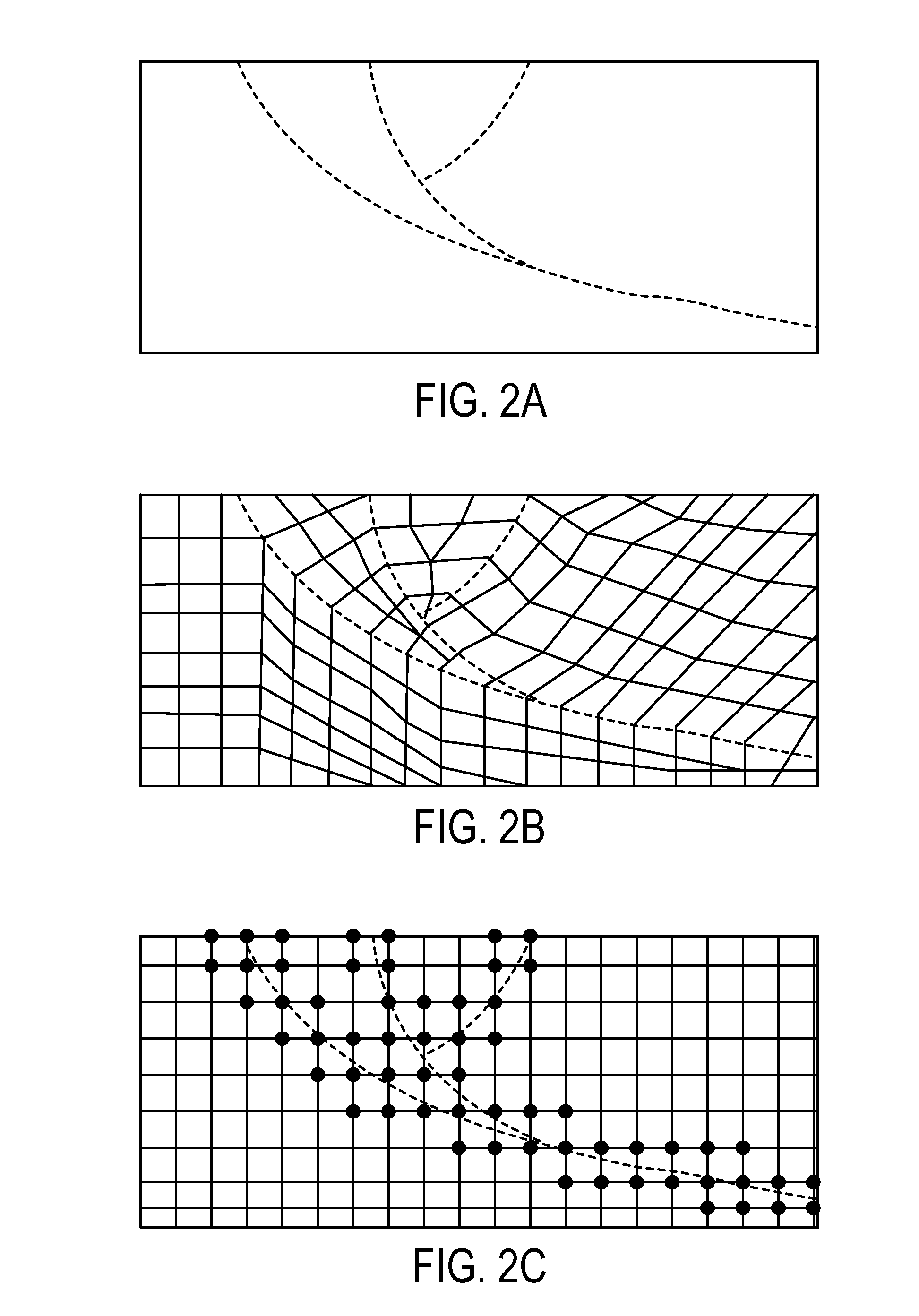
Method to assess the impact of existing fractures and faults for reservoir management
Assessing the impact of existing fractures and faults for reservoir management, in one aspect, may comprise employing a numerical mesh to generate a geomechanical model, the numerical mesh representing a geological reservoir and its surrounding regions, the numerical mesh comprising delimitation associated with regions and layering of geology without constraining the numerical mesh to explicitly represent a fault or fracture, initializing the geomechanical model to define initial stress-strain compatible with measured stress in well locations associated with the geological reservoir, generating a fluid-flow model employing the numerical mesh, solving for a coupled solution of the fluid-flow model and the geomechanical model, and employing the solved fluid-flow model and the geomechanical model to assess the impact.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
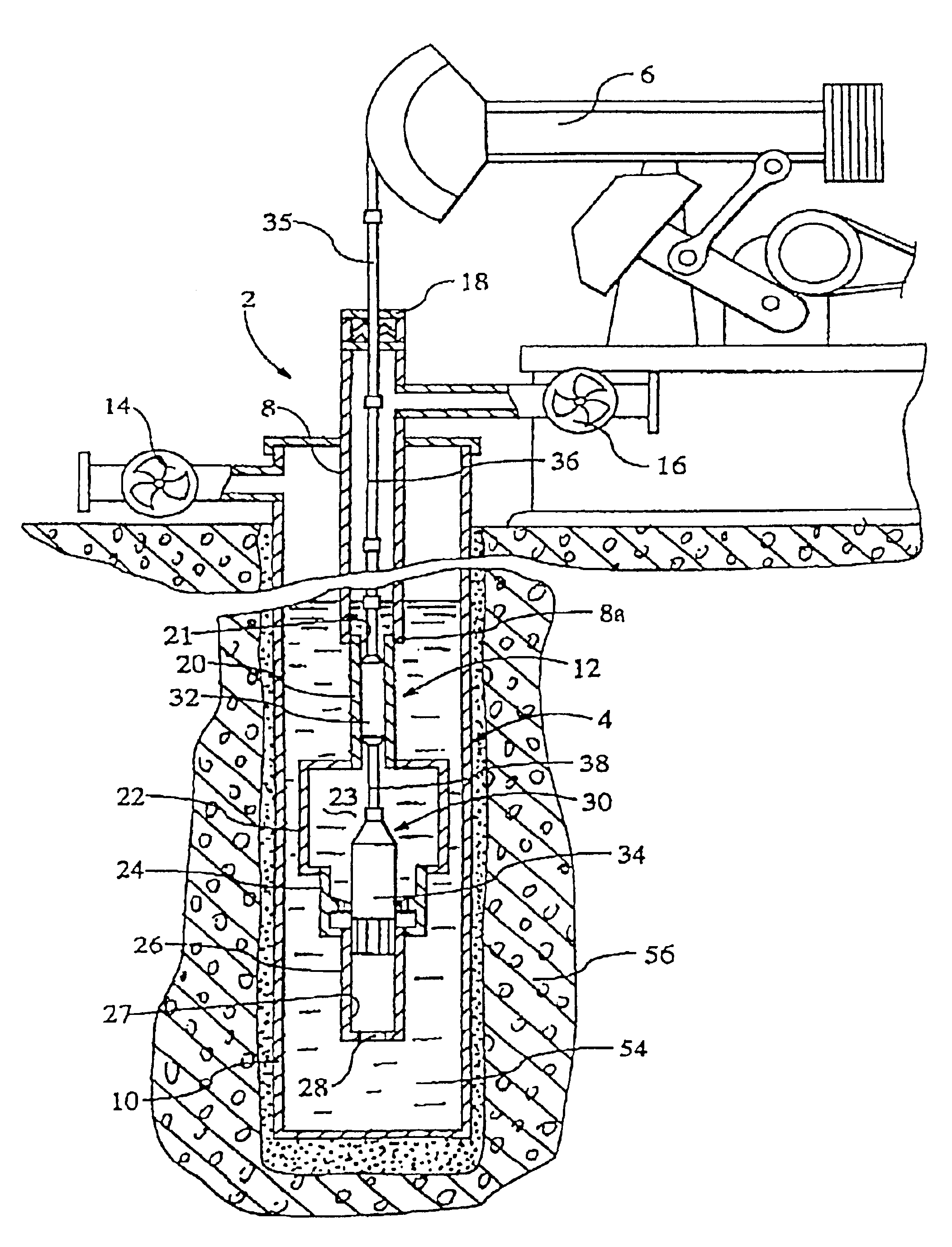
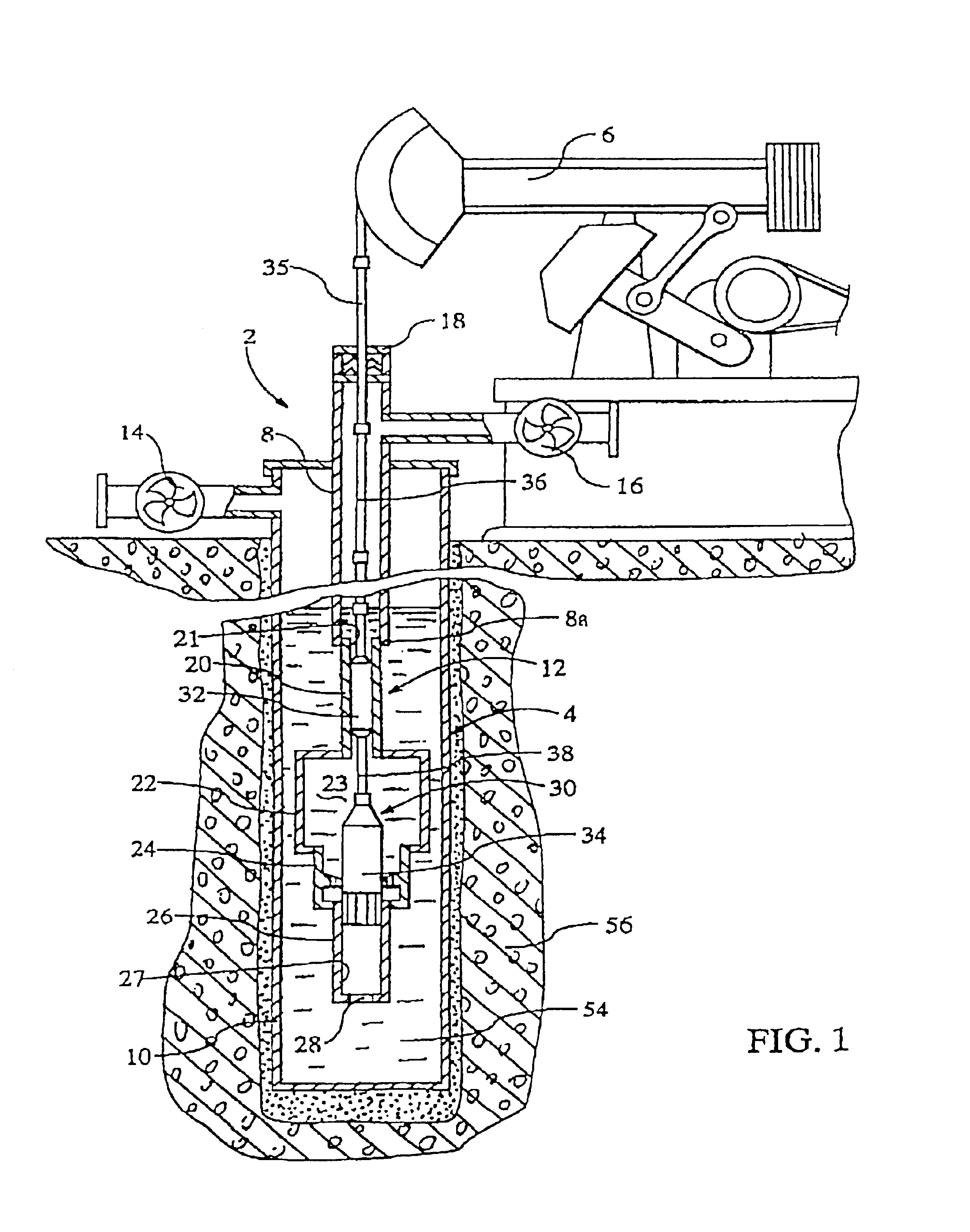
Method and apparatus for seismic stimulation of fluid-bearing formations
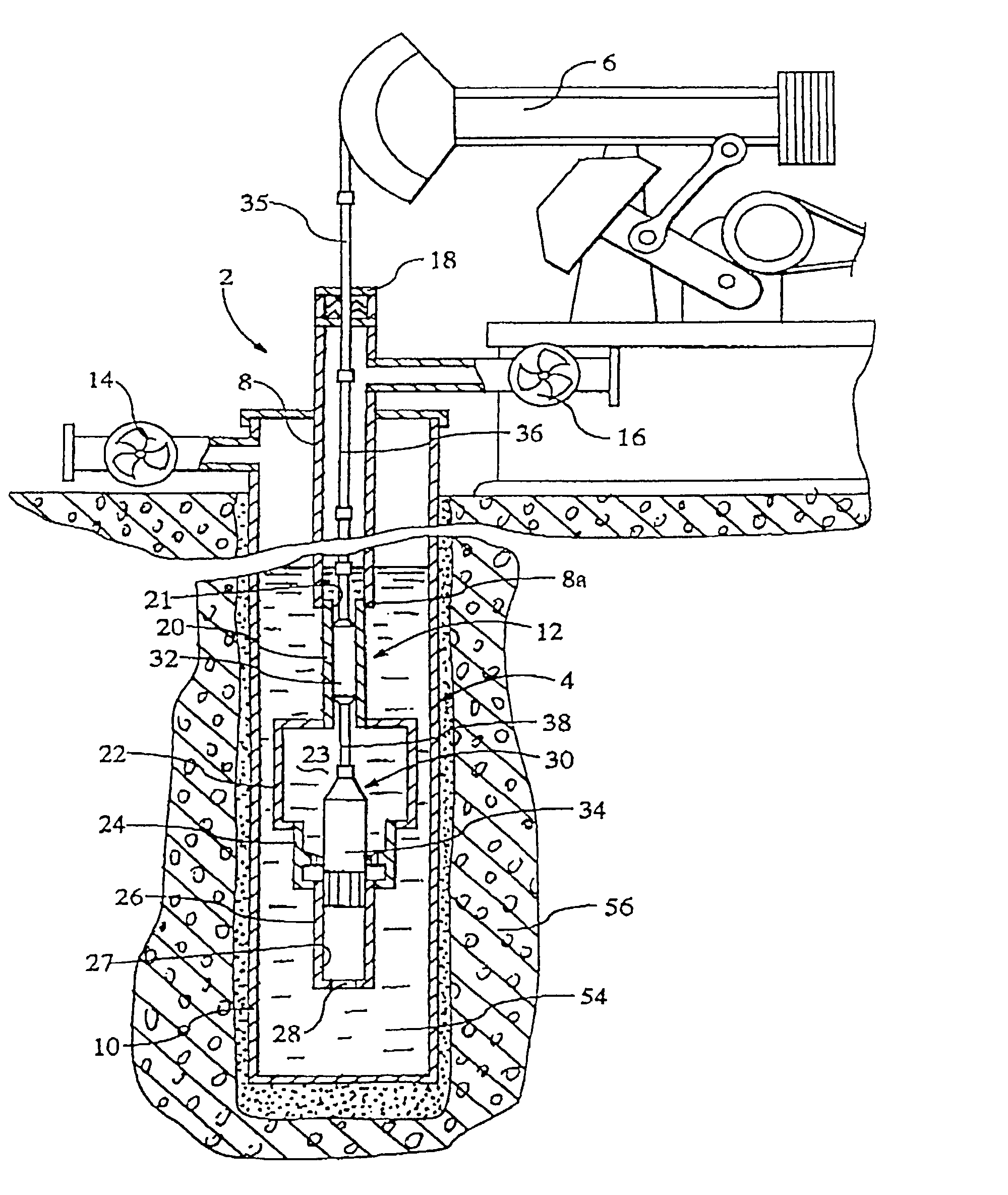
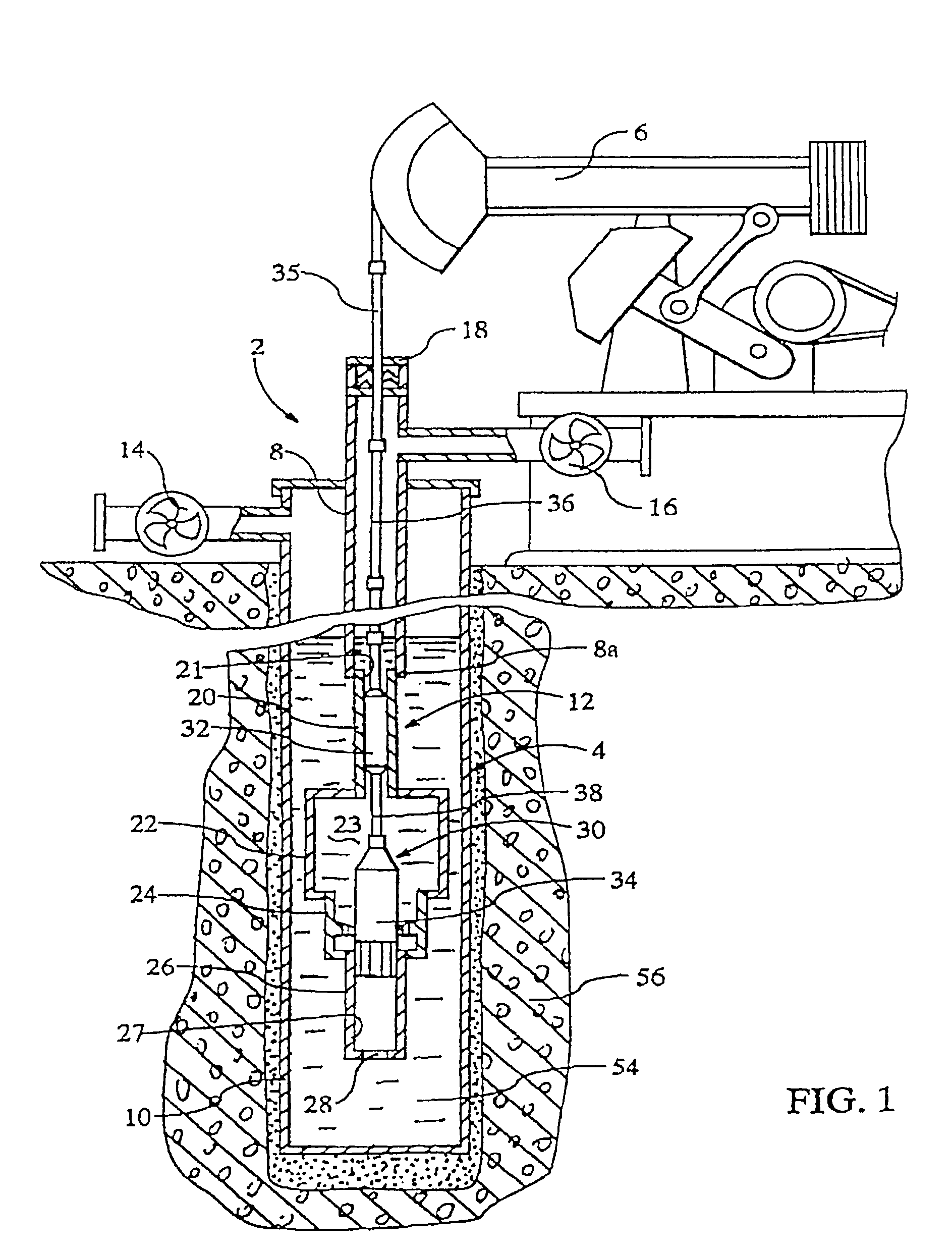
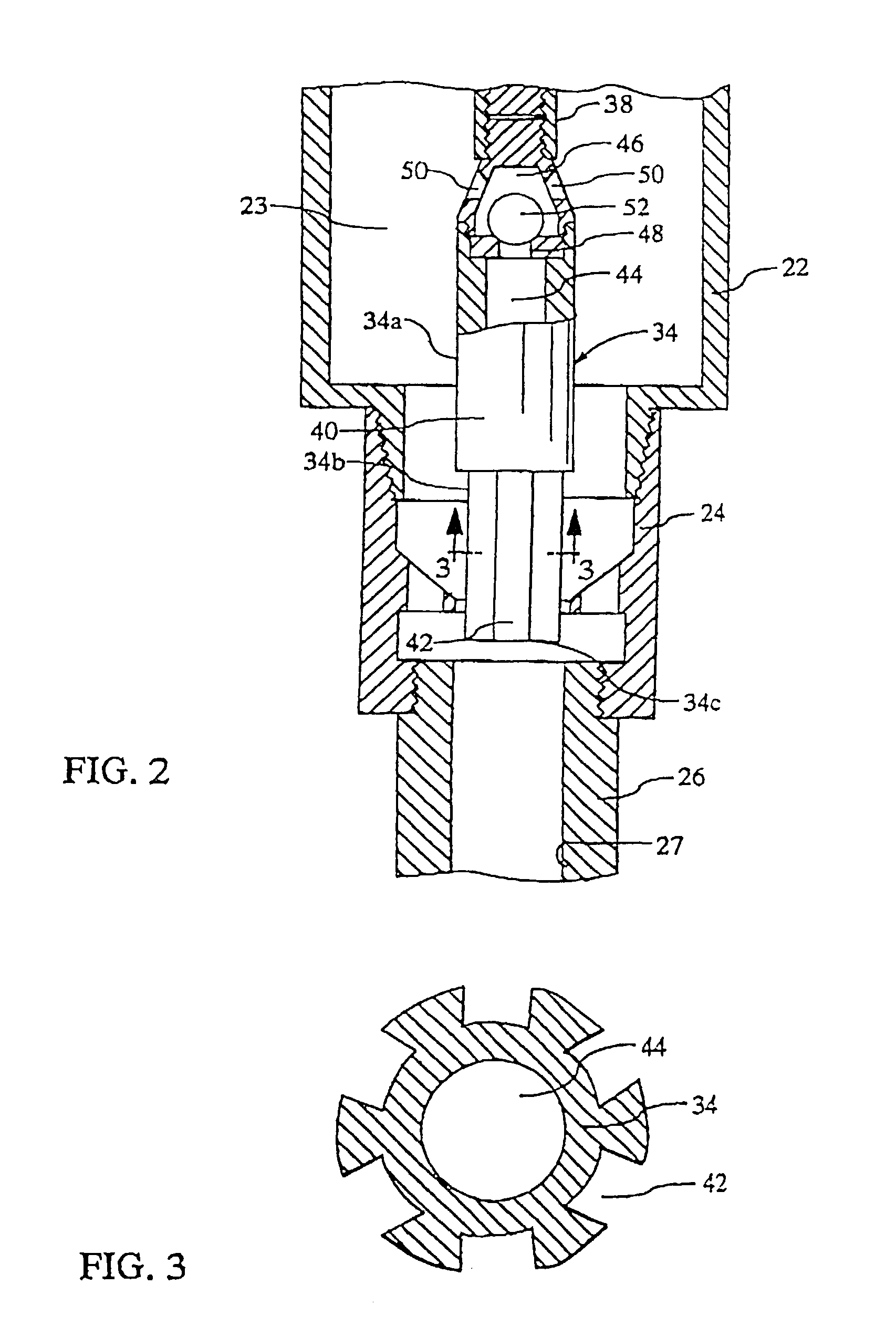
InactiveUS20030201101A1Volume of compression is reducedLarge caliberConstructionsFluid removalShock waveEngineering
An apparatus and seismic method for producing an shock wave in an oil well borehole, with a pumping unit arranged at the wellhead, a tubing string extending downward into the production casing of the well, a hollow cylinder assembly connected with the bottom of the tube string, and pair of plungers arranged within the cylinder assembly and connected with the pumping unit with sucker rods and a polish rod for compressing liquid contained within the cylinder assembly and discharging the compressed liquid into the production casing, thereby generating a shock wave. The cylinder assembly includes an upper cylinder, a lower cylinder below the upper cylinder, a crossover cylinder below the upper and lower cylinders, and a compression chamber cylinder containing a compression chamber arranged between the crossover cylinder and the upper cylinder. The lower cylinder is adapted to receive the lower plunger, and the upper cylinder is adapted to receive the upper plunger. The lower plunger has a larger diameter than the upper plunger, and the plunger movement effects the volume of the compression chamber by reduction, the liquid contained therein becomes compressed and is discharged on the down stroke into the well. In addition, remote seismic data is collected and processed from remote well locations.
Owner:APPLIED SEISMIC RES CORP
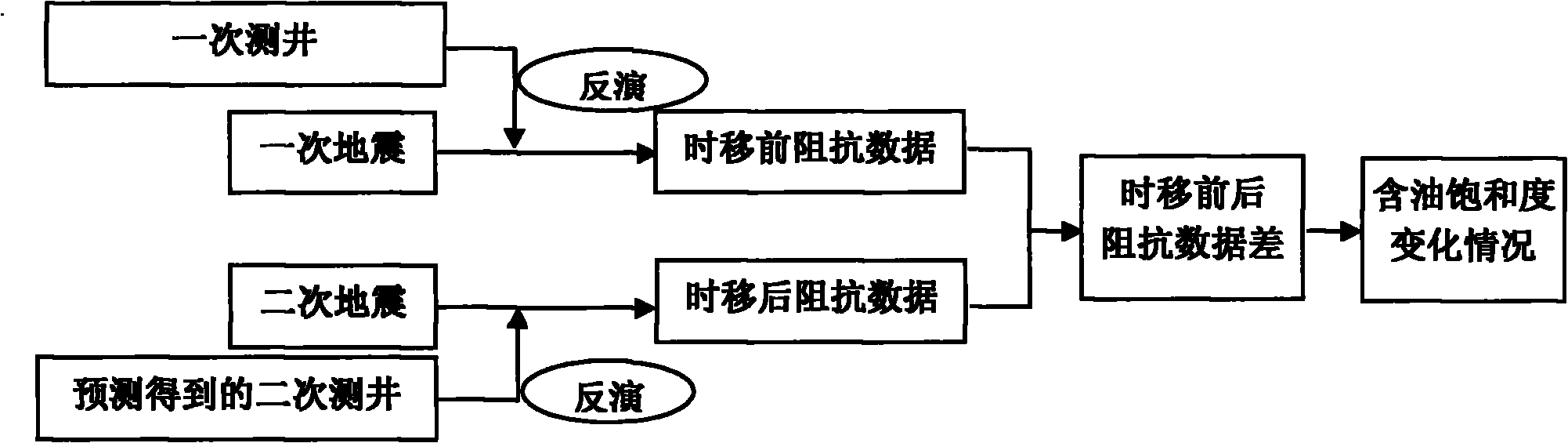
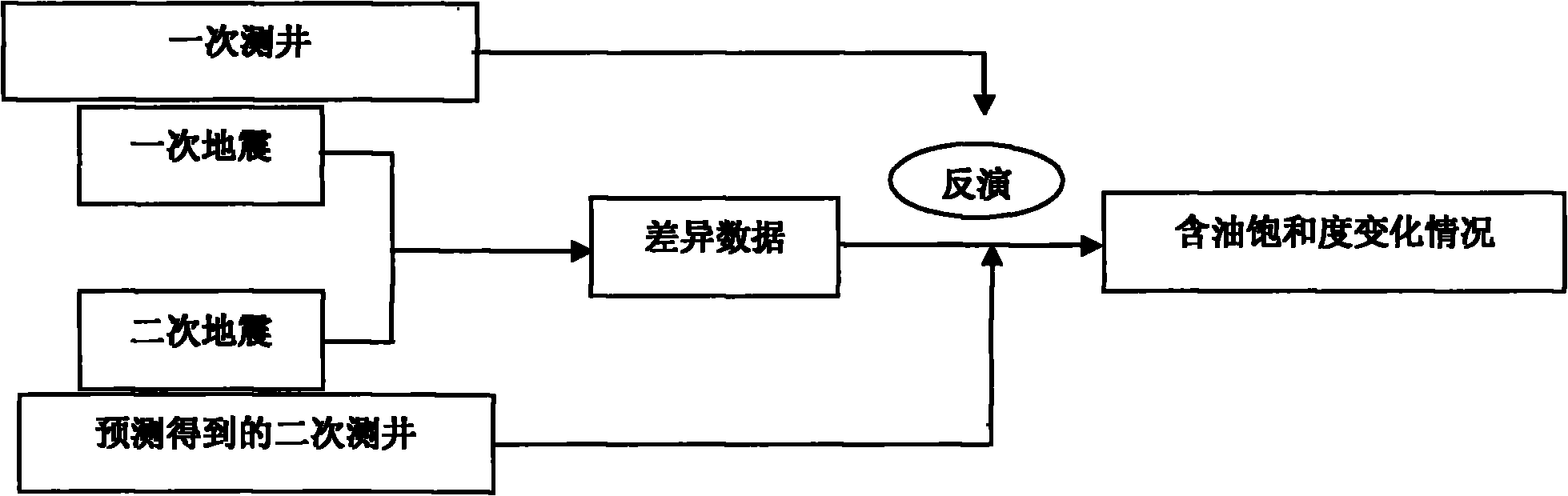
Method for carrying out well design by using time-lapse seismic
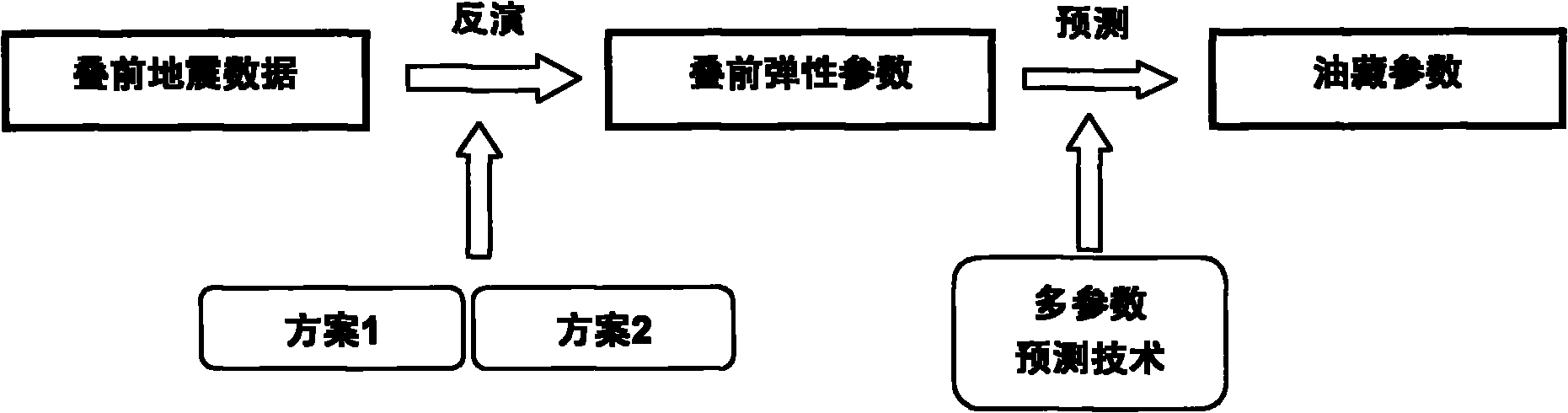
ActiveCN101872024ASmall amount of calculationHigh precisionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingLongitudinal waveChange prediction
The invention discloses a method for carrying out well design by using time-lapse seismic, which comprises the following steps: 1) respectively obtaining seismic data of two different time points according to methods of the step a and the step b: a. detecting the stratum basic parameters of a region to be detected, manufacturing an oil deposit profile of the region to be detected, establishing a stratum profile module according to the oil deposit profile, and obtaining three data bodies: the longitudinal wave speed, the transverse wave speed and the density according to the stratum basic parameters and the stratum profile module; and b. carrying out AVO forward modeling to obtain the overlapped seismic data of each incidence angle; 2) processing the seismic data in the two times to obtain seismic data difference; 3) carrying out reversion on the seismic data difference to obtain longitudinal wave difference, transverse wave difference, density difference and longitudinal and transverse wave speed ratio difference; 4) predicting the oil deposit parameter change; and 5) carrying out well design. The invention forms the difference reversion based on the time-lapse seismic for realizing the oil deposit parameter change prediction process and determining the well design, and the goal can not be realized by using conventional methods.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Method and apparatus for seismic stimulation of fluid-bearing formations
InactiveUS6899175B2Reduce volumeLarge caliberConstructionsFluid removalEngineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus and seismic method for producing an shock wave in an oil well borehole, with a pumping unit arranged at the wellhead, a tubing string extending downward into the production casing of the well, a hollow cylinder assembly connected with the bottom of the tube string, and pair of plungers arranged within the cylinder assembly and connected with the pumping unit with sucker rods and a polish rod for compressing liquid contained within the cylinder assembly and discharging the compressed liquid into the production casing, thereby generating a shock wave. The cylinder assembly includes an upper cylinder, a lower cylinder below the upper cylinder, a crossover cylinder below the upper and lower cylinders, and a compression chamber cylinder containing a compression chamber arranged between the crossover cylinder and the upper cylinder. The lower cylinder is adapted to receive the lower plunger, and the upper cylinder is adapted to receive the upper plunger. The lower plunger has a larger diameter than the upper plunger, and the plunger movement effects the volume of the compression chamber by reduction, the liquid contained therein becomes compressed and is discharged on the down stroke into the well. In addition, remote seismic data is collected and processed from remote well locations.
Owner:APPLIED SEISMIC RES CORP
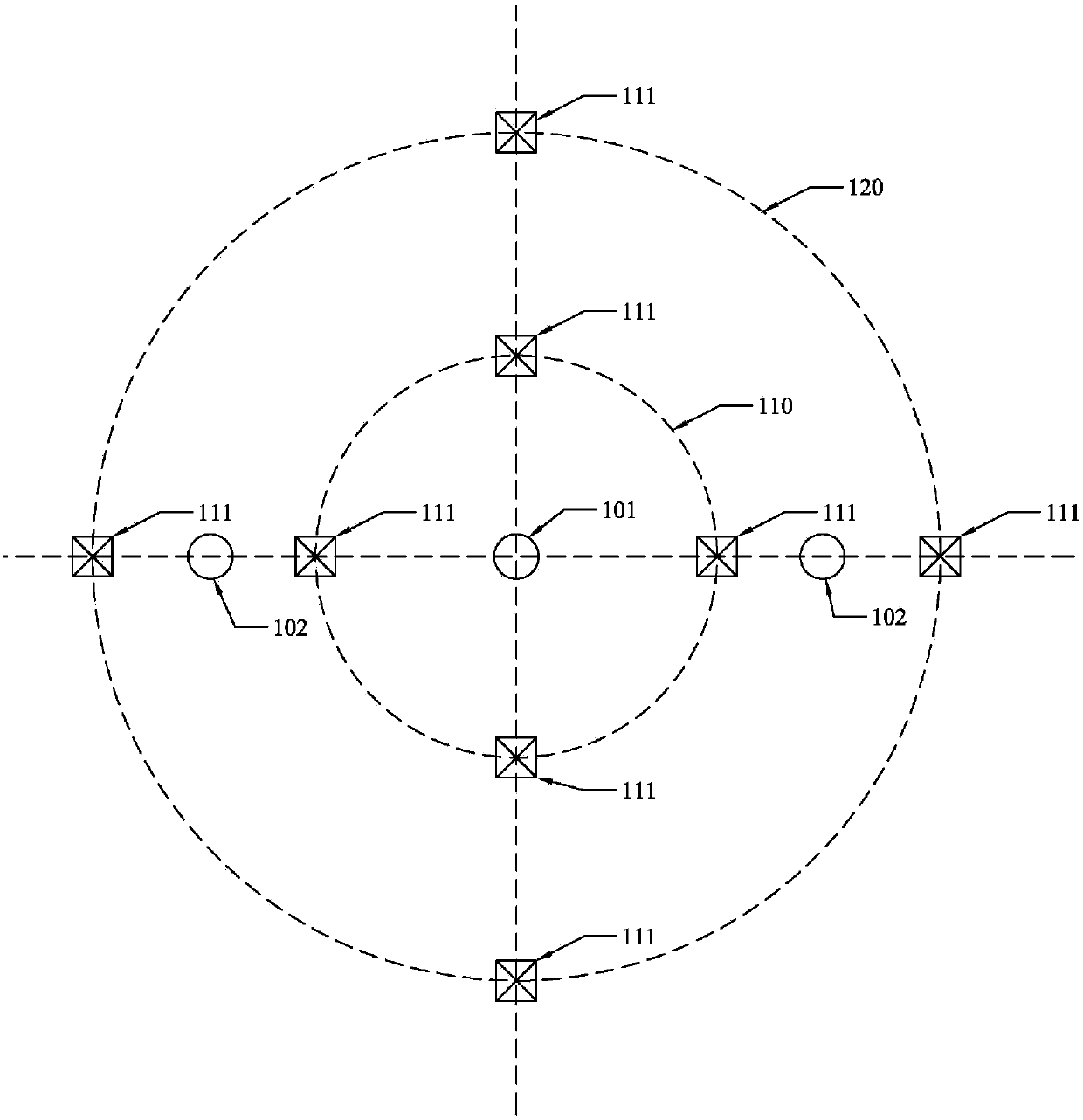
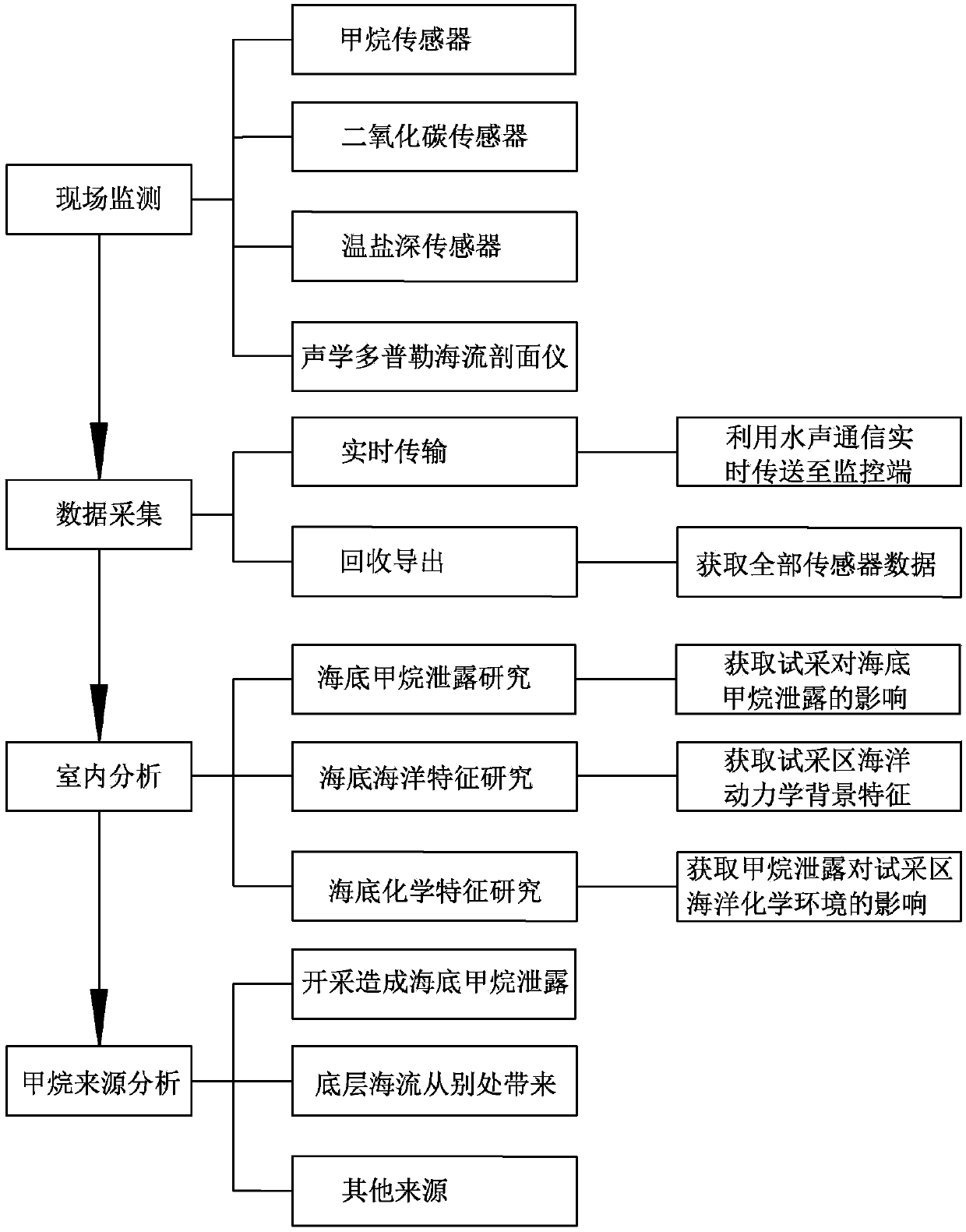
Sea-region natural gas hydrate seabed methane monitoring system and method
ActiveCN107678055AReal-time leak monitoringAvoid measurement errorsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSeismologyObservational errorBuoy
The invention discloses a sea-region natural gas hydrate seabed methane monitoring system and a method. A mining well position is taken as a center and pilot production well positions are arranged inan equidistance mode. The mining well position is taken as the center and a first monitoring circle and a second monitoring circle are arranged. The first monitoring circle and the second monitoring circle are provided with multiple groups of seabed subsurface buoys used for monitoring a seabed methane concentration so as to form a seabed methane data matrix. The system and the method have advantages that bottom-supported seabed subsurface buoys are used to make up disadvantages in the prior art; through a underwater control technology, physical and chemical sensors capable of measuring a plurality of parameters are integrated together; long-period in-situ observation is performed on a seabed environment of a seabed boundary of a seabed natural gas hydrate reservoir forming area so that ameasurement error which may be caused by an existing method is avoided; and through a underwater acoustic communication technology, a seabed environment parameter is transmitted to a sea surface monitoring platform, real-time seabed methane leakage monitoring is provided for hydrate mining and an important meaning is possessed.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN TECH MARINE SYST CO LTD
Apparatus and system for well placement and reservoir characterization
ActiveUS7612565B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsComputer moduleModular design
A resistivity array having a modular design includes a transmitter module with at least one antenna, wherein the transmitter module has connectors on both ends adapted to connect with other downhole tools; and a receiver module with at least one antenna, wherein the transmitter module has connectors on both ends adapted to connect with other downhole tools; and wherein the transmitter module and the receiver module are spaced apart on a drill string and separated by at least one downhole tool. Each transmitter and receiver module may comprise at least one antenna coil with a magnetic moment orientation not limited to the tool longitudinal direction. A spacing between the transmitter and receiver module may be selected based on expected reservoir thickness.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
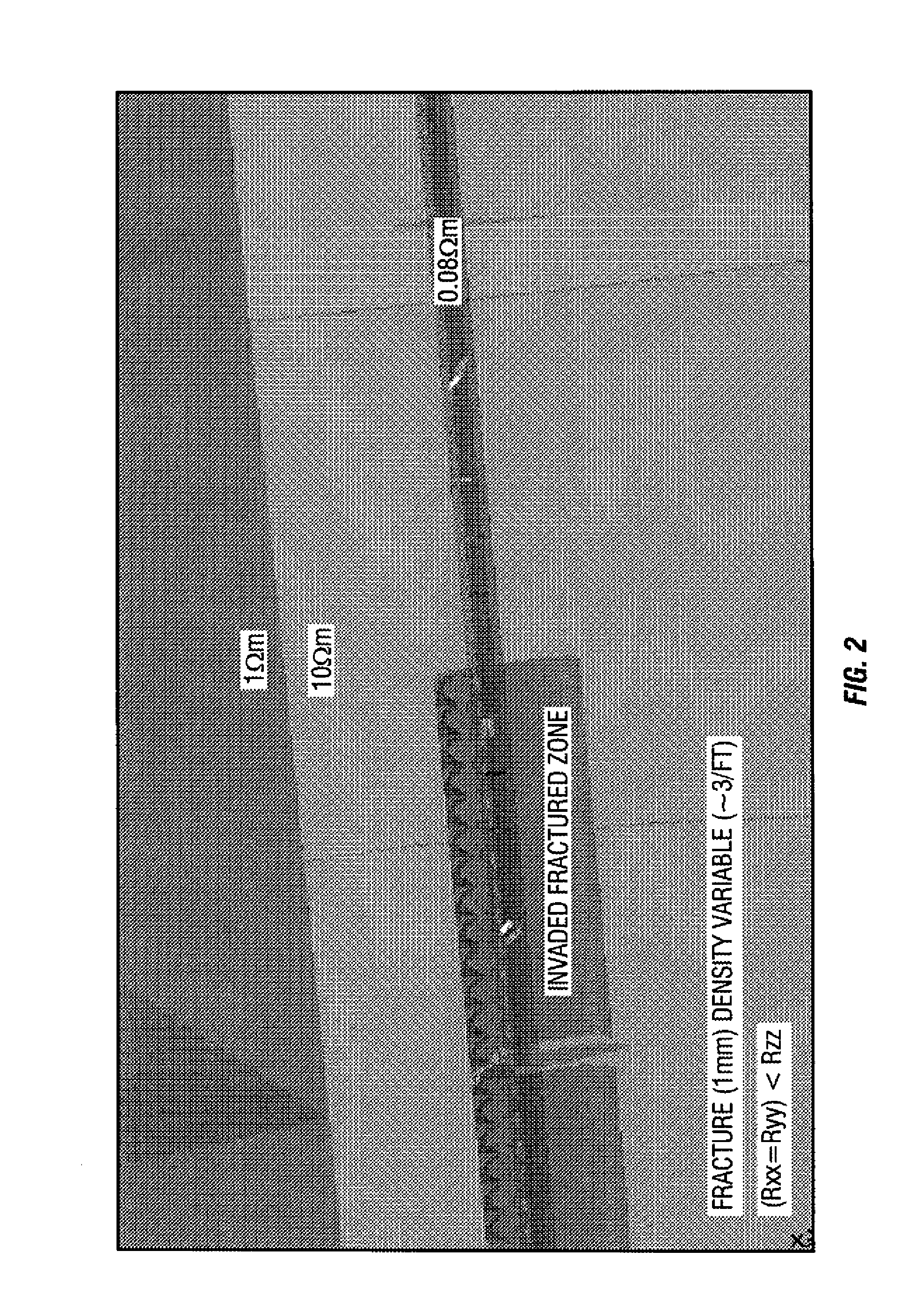
Inversion Techniques For Real-Time Well Placement And Reservoir Characterization
ActiveUS20170075021A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsWell placementPixel based
A method is disclosed herein. The method includes disposing an electromagnetic logging tool in a borehole penetrating a formation, the electromagnetic logging tool being part of a drill string in the formation, the drill string having a drill bit. The method includes acquiring measurements using the electromagnetic logging tool. Further, the method includes using a processor, applying a pixel-based inversion to the acquired measurements to determine at least one formation property, wherein applying the pixel-based inversion includes using adaptive regularization.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Seismic facies control-based sedimentary microfacies recognition method
ActiveCN107121699AHigh resolutionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingHorizonImage resolution
The present invention relates to a seismic facies control-based sedimentary microfacies recognition method. The method includes the following steps that: 1) logging information is normalized; 2) fine horizon calibration is performed; 3) a model framework is determined; 4) a low frequency model is established; 5) a seismic data impedance value and a formation reflection coefficient are obtained, if synthetic trace data are in optimal matching with an actual seismic data trace, and drilling impedance is in optimal matching with seismic data impedance, and the method shifts to step 6), otherwise, the method shifts to the step 3); 6) well seismic constraint inversion is performed, a wave impedance inversion data body is obtained; 7) the top and bottom of a reservoir are traced and explained, with the top reflection layer and bottom reflection layer of the reservoir adopted as control surfaces, interlayer attributes are extracted from the inversion data body; and 8) seismic attributes are utilized to constrain the boundaries of sedimentary microfacies, and the spread of the sedimentary microfacies is described. According to the method, the logging information is adopted to constrain seismic inversion, and therefore, the resolution of an inversion result can be improved, the sedimentary microfacies of a target interval can be well depicted, the planar distribution of a thin sand layer can be predicted, and a basis can be provided for well location deployment.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Apparatus for, and method of, landing items at a well location
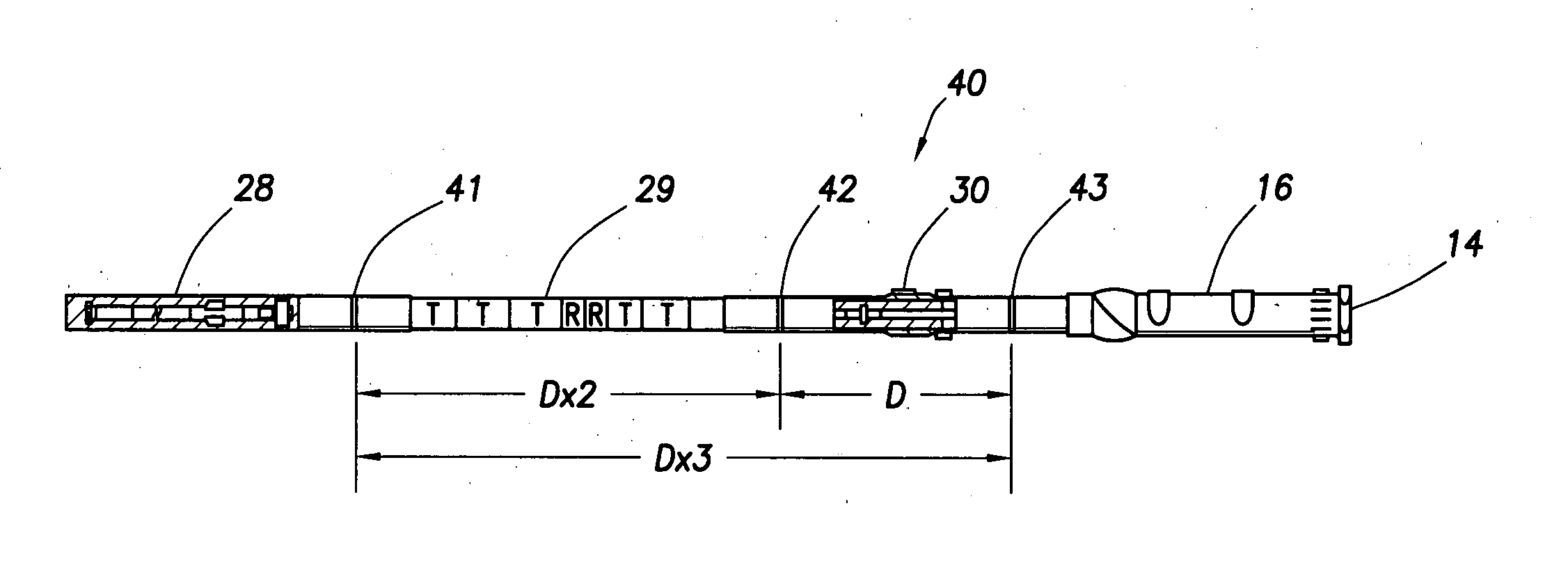
An apparatus for, and method of, lowering items from a drilling rig to a well located below it. One embodiment includes the use of a landing string comprised of drill pipe having an enlarged diameter section with a shoulder along with upper and lower holders having wedge members also with shoulders that engage and support the drill pipe at the shoulder of the enlarged diameter section. In this embodiment the drill pipe and wedge members can be rotatable with respect to each other.
Owner:IRONGATE RENTAL SERVICES LLC
Method of using flexible spinal needle assemblies
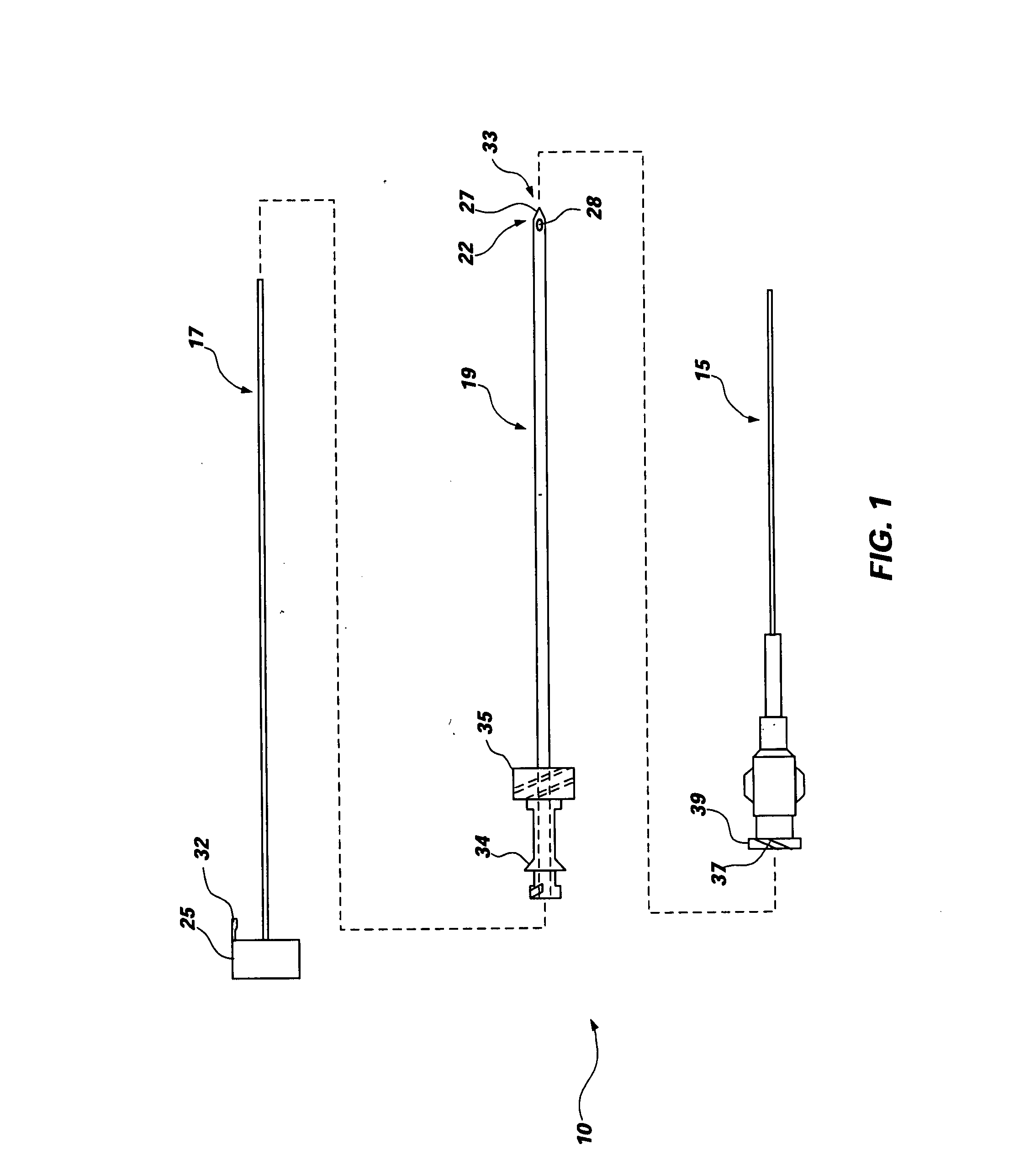
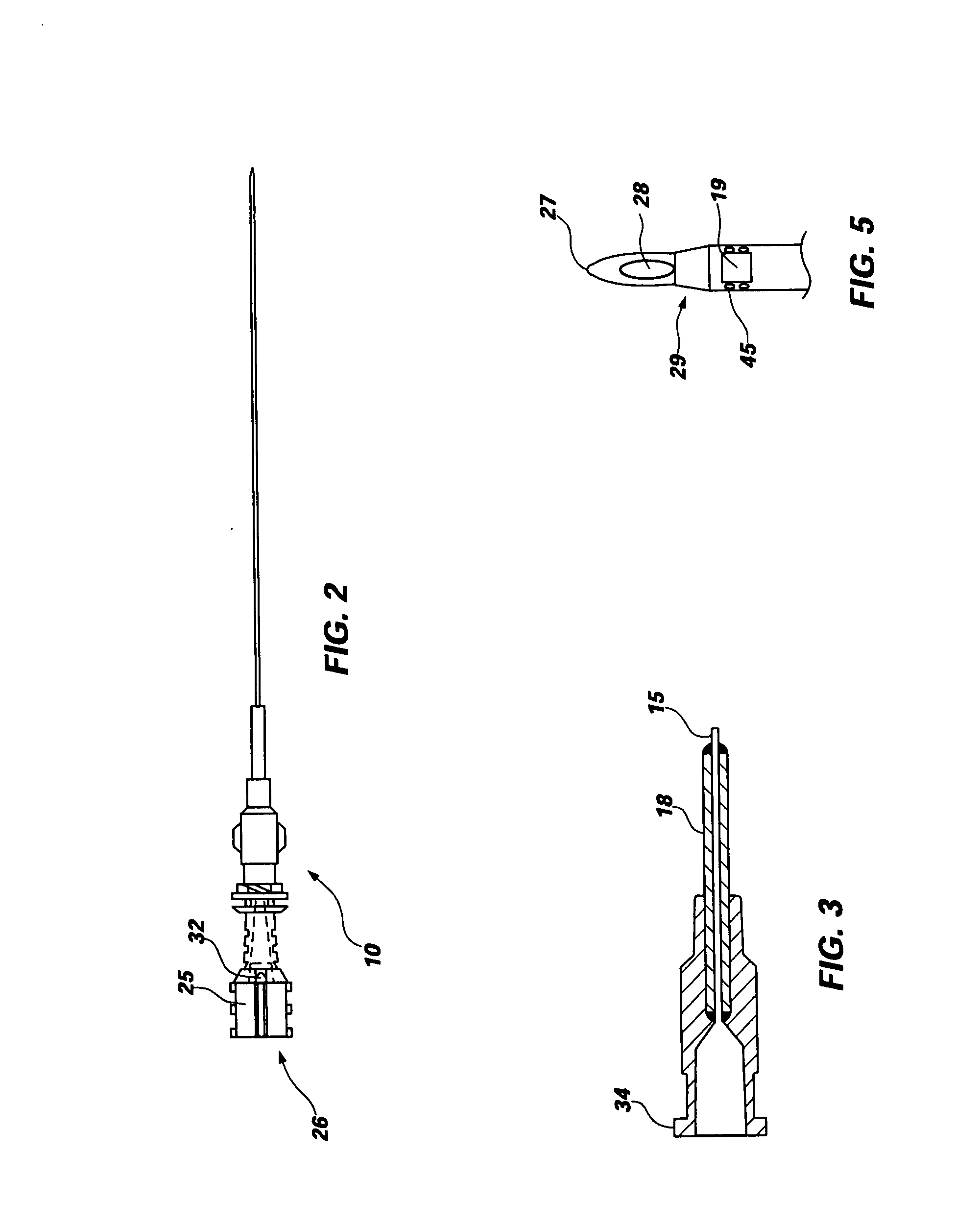
InactiveUS20080065017A1Easy and faster flowSimple and straightforward insertionGuide needlesInfusion syringesSpinal needlesWell placement
A method of using an assembly to insert a flexible spinal needle and minimize incidence of post dural puncture headache is provided. The assembly typically includes a support needle with a non-cutting piercing tip and an exteriorly mounted flexible needle. The flexible needle gauge may be reduced, while ease of use is increased by the exterior mounting. The flexible needle provides increased flexibility allowing for movement of a patient's torso after insertion. A central stylet may be included to prevent entry of matter into the support needle opening during insertion. In other embodiments, methods for allowing single stick insertion procedures to provide better placement by allowing placement to be determined and adjusted based on physical feedback obtained during the single stick insertion.
Owner:RACZ N SANDOR +1
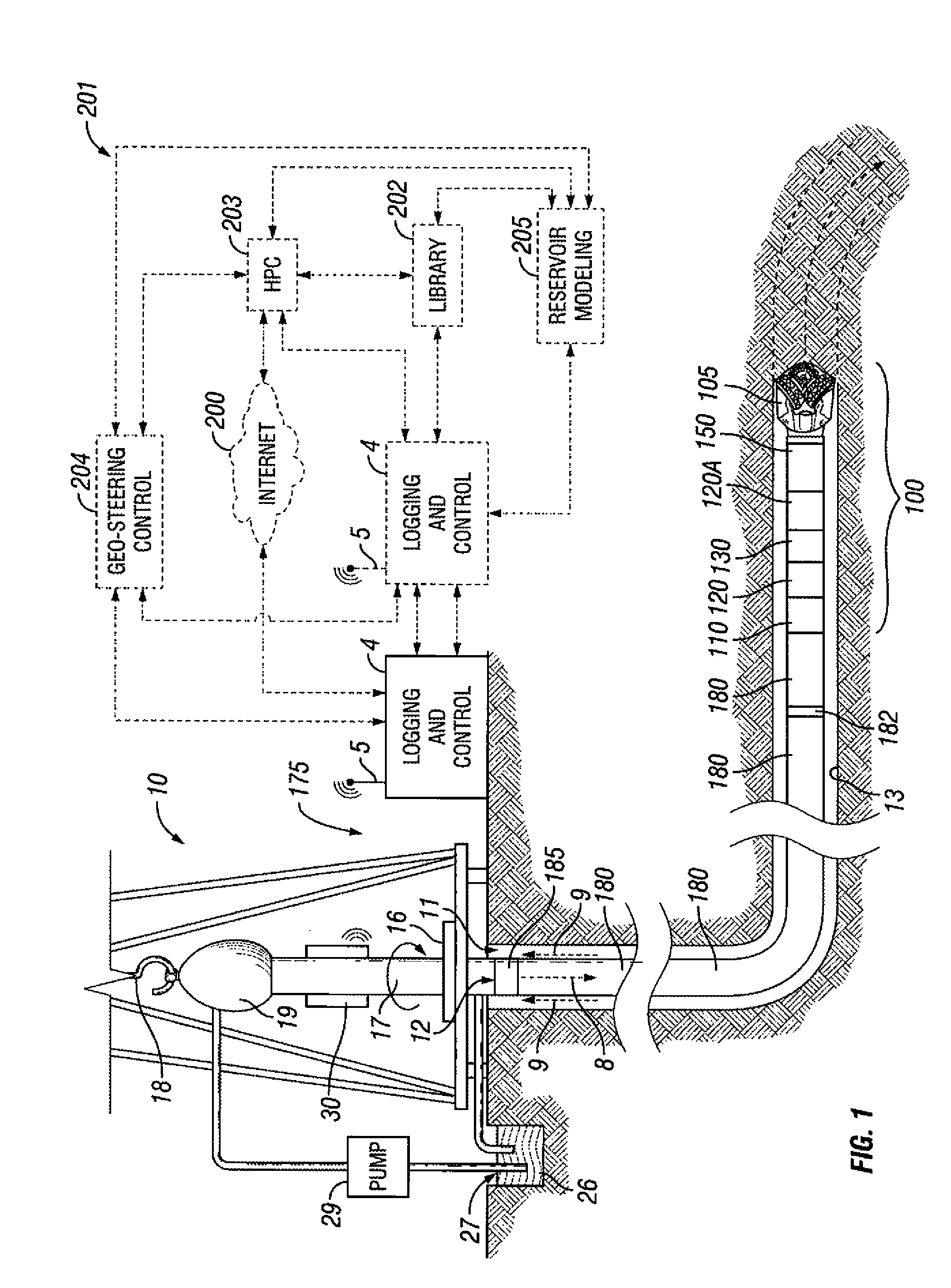
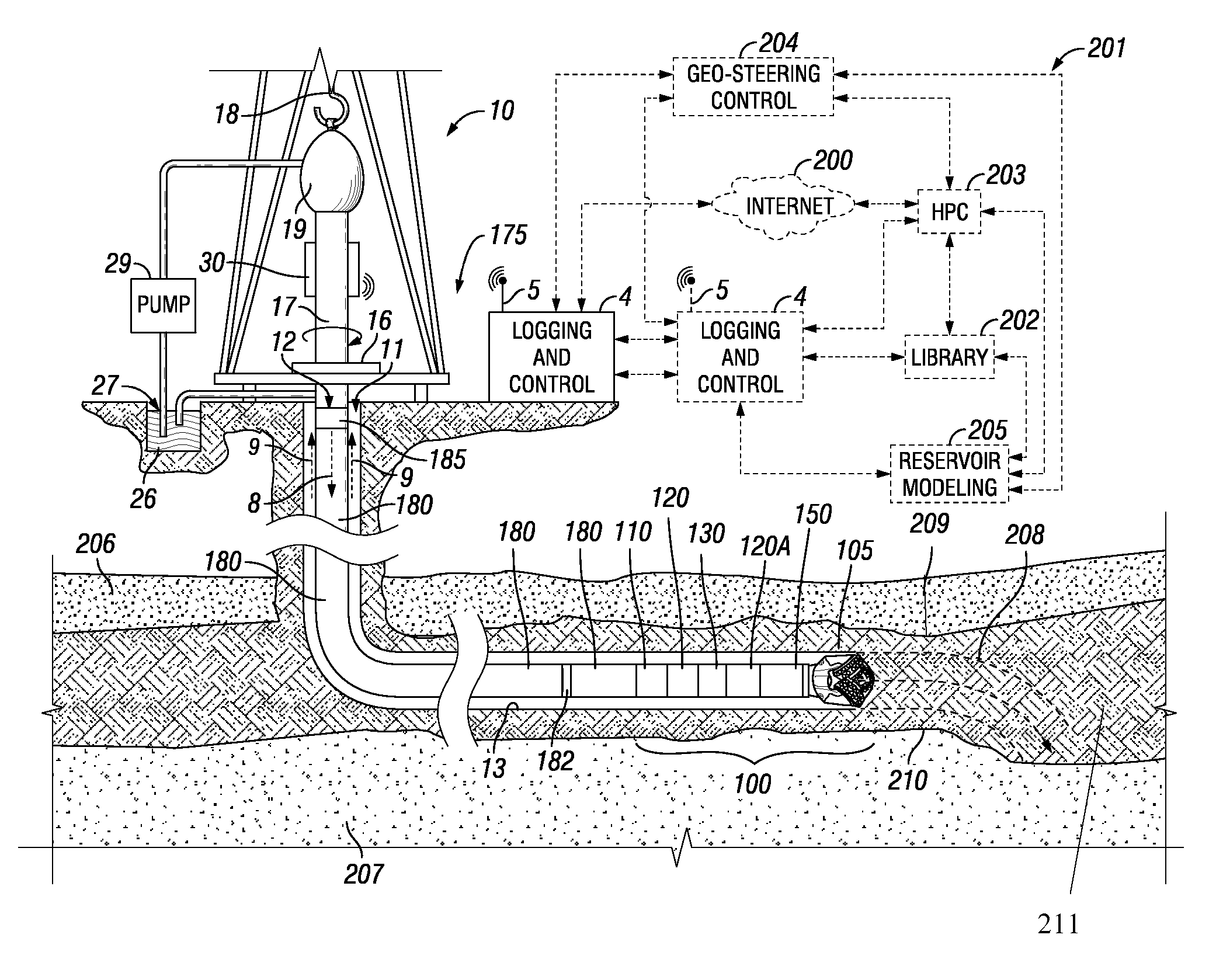
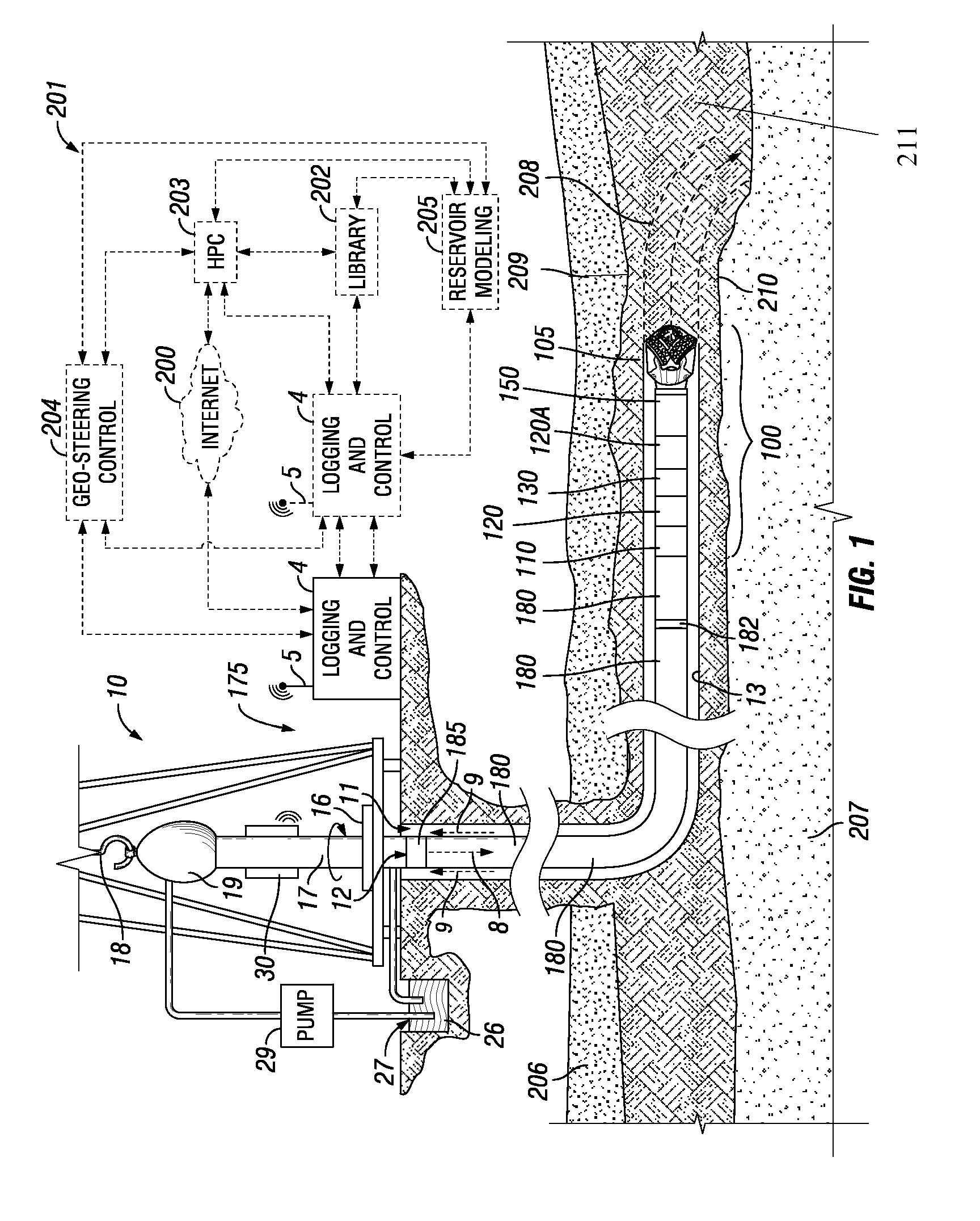
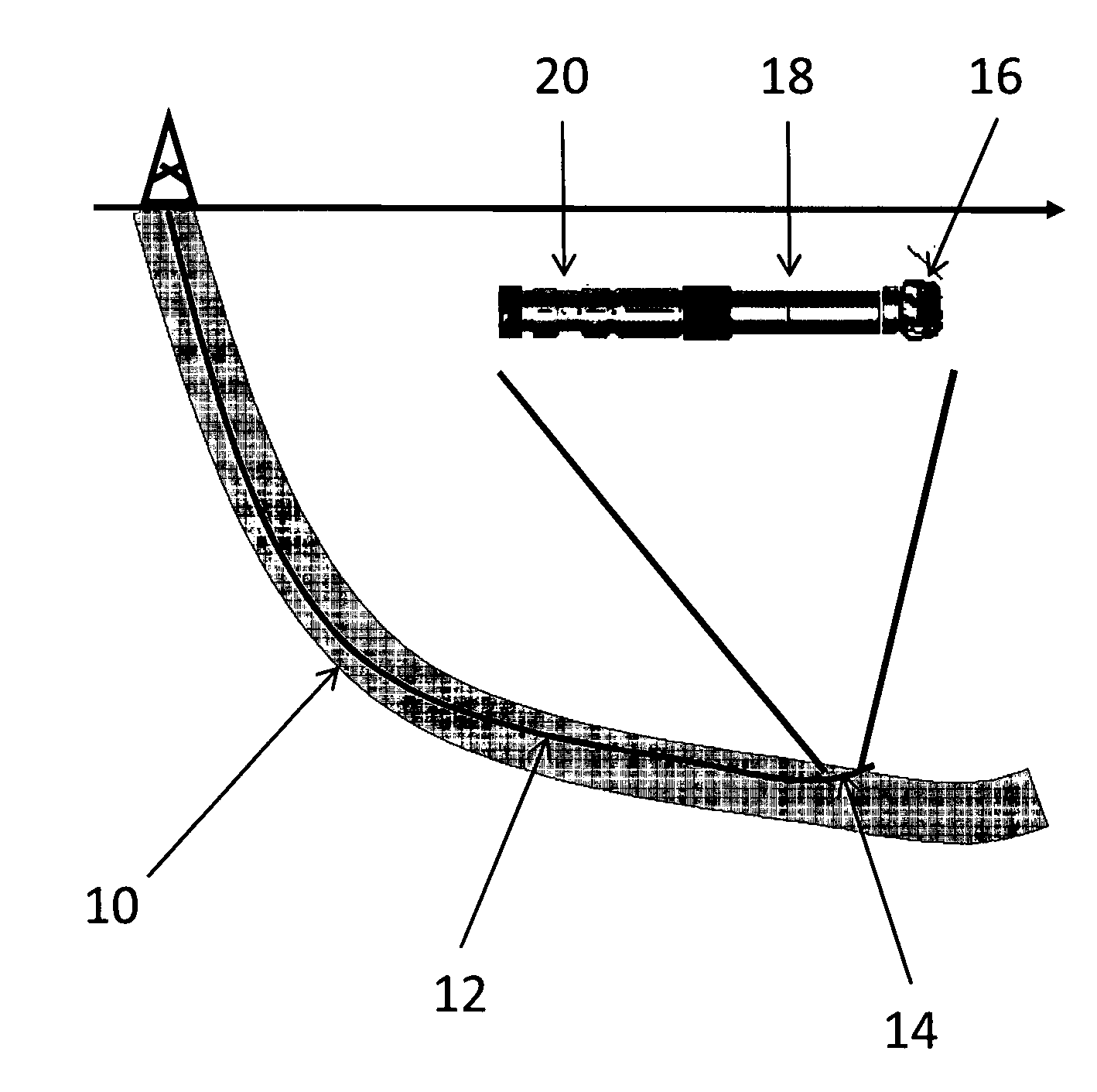
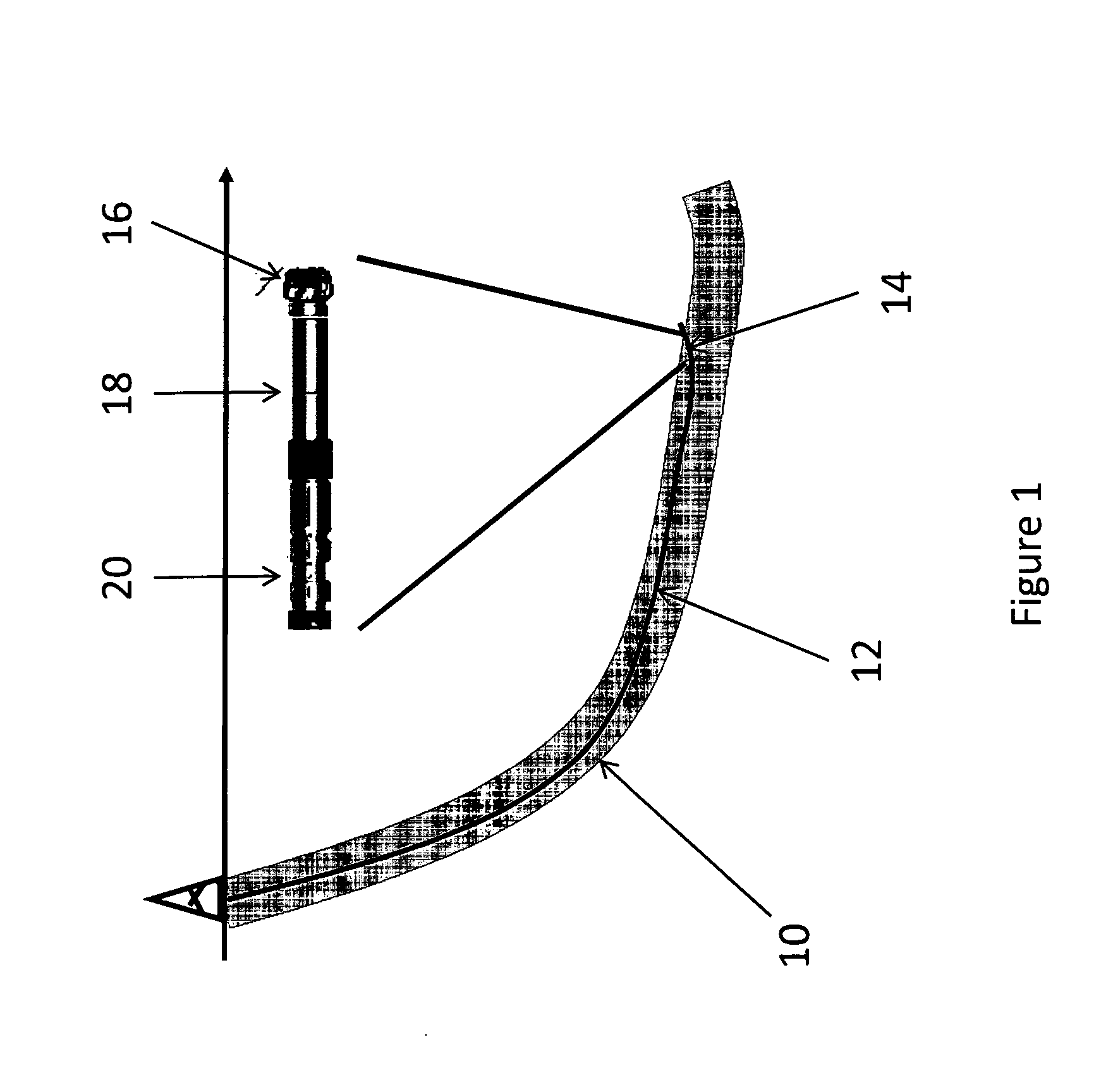
Well Placement 3d Advisor- Method and System To Monitor And Assist A Well Placement Operation
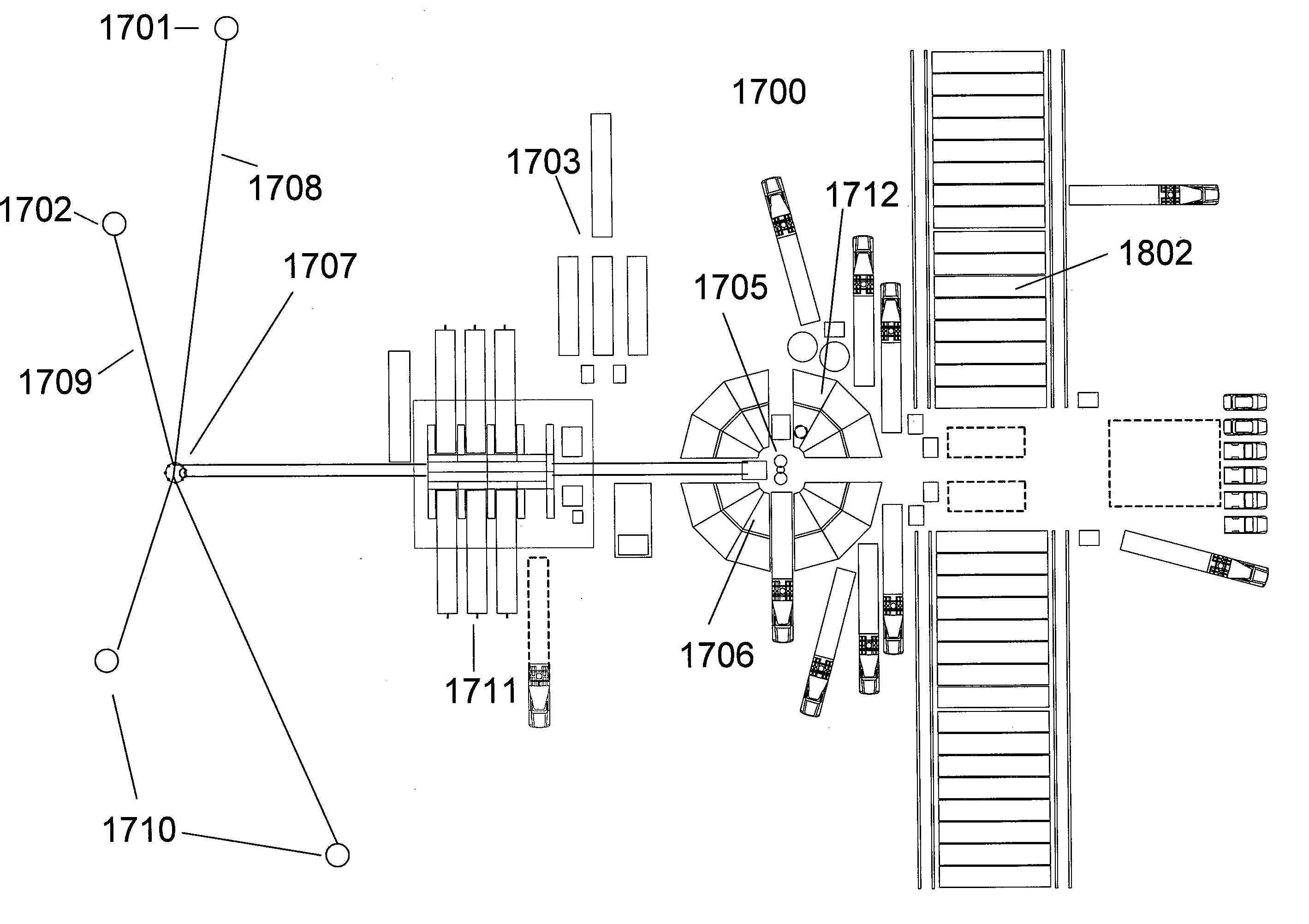
A method of displaying information relating to a well drilling operation, comprising generating a sub-surface model of the underground formation through which the well is being drilled; generating a representation of the well being drilled, of the drilling equipment being used to drill the well, including parameters relating to the use of the drilling equipment; generating a 3D image of the formation, the well and the drilling equipment; and generating an image within the 3D image comprising volumes representing virtual objects, such as a cone of possible well placement if drilling proceeds under the current conditions, or the envelope of investigation of a given sensor.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method of circular mining geothermal resources
ActiveCN103090571ASolve the problem of drilling wellsOther heat production devicesGeothermal energy generationSoil scienceWell drilling
The invention relates to a method of circular mining geothermal resources. The method comprises following steps: (1) an area with a relatively-high geothermal gradient is confirmed; (2) a reservoir stratum in the area with the relatively-high geothermal gradient is confirmed; (3) well positions of two wells are confirmed along a main extending direction of the reservoir stratum, well drilling is conducted, one well is arranged on a relatively-low position of the reservoir stratum and is a water inlet well, and the other well is arranged on a relatively-high position of the reservoir stratum and is a water outlet well; (4) the water inlet well and the water outlet well are all drilled on the reservoir stratum, then perforation is conducted on the same reservoir stratum segment, a reservoir stratum channel is obtained, and the water inlet well is communicated with the water outlet well through the reservoir stratum; (5) on the ground, ground surface fresh water is injected from the water inlet well, the ground surface fresh water passes through the reservoir stratum channel, then hot water after heated is obtained, hot water after heated flows into the water outlet well, and then the hot water is sent to the water outlet well.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Seismic signal frequency division processing method
InactiveCN104216014AMeeting the needs of integrated studiesSeismic signal processingOctaveGeological structure
A seismic signal frequency division processing method comprises the steps of (i) utilizing an earthquake acquisition device to obtain a seismic signal; (ii) performing format conversion on seismic data acquired in a field and meeting the format requirement of data processing; (iii) performing observing system definition and trace header setting on the seismic data meeting the format requirement; (iv) performing frequency analysis and octave scanning and quantitatively analyzing the influence of each frequency component on underground geological structure; (v) dividing the seismic signal into different frequency bodies; (vi) respectively performing exquisite seismic data processing on the frequency bodies D1, D2 and D3, including spherical diffusion compensation, earth's surface consistency residual amplitude compensation, earth's surface consistency deconvolution, predictive deconvolution, statics correction, horizontal stacking and migration imaging; (vii) reconstructing the processed frequency bodies into a final result data body according to the geological structure; (viii) performing final effective filtering and reasonable gain processing on reconstructed data body and then using the data body on the aspects of seismic exploration comprehensive research, underground geological structure explanation, inversion and fracture prediction and the like so as to help geological workers to find favorable oil and gas construction and lithologic trap and improve the well drilling accuracy.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
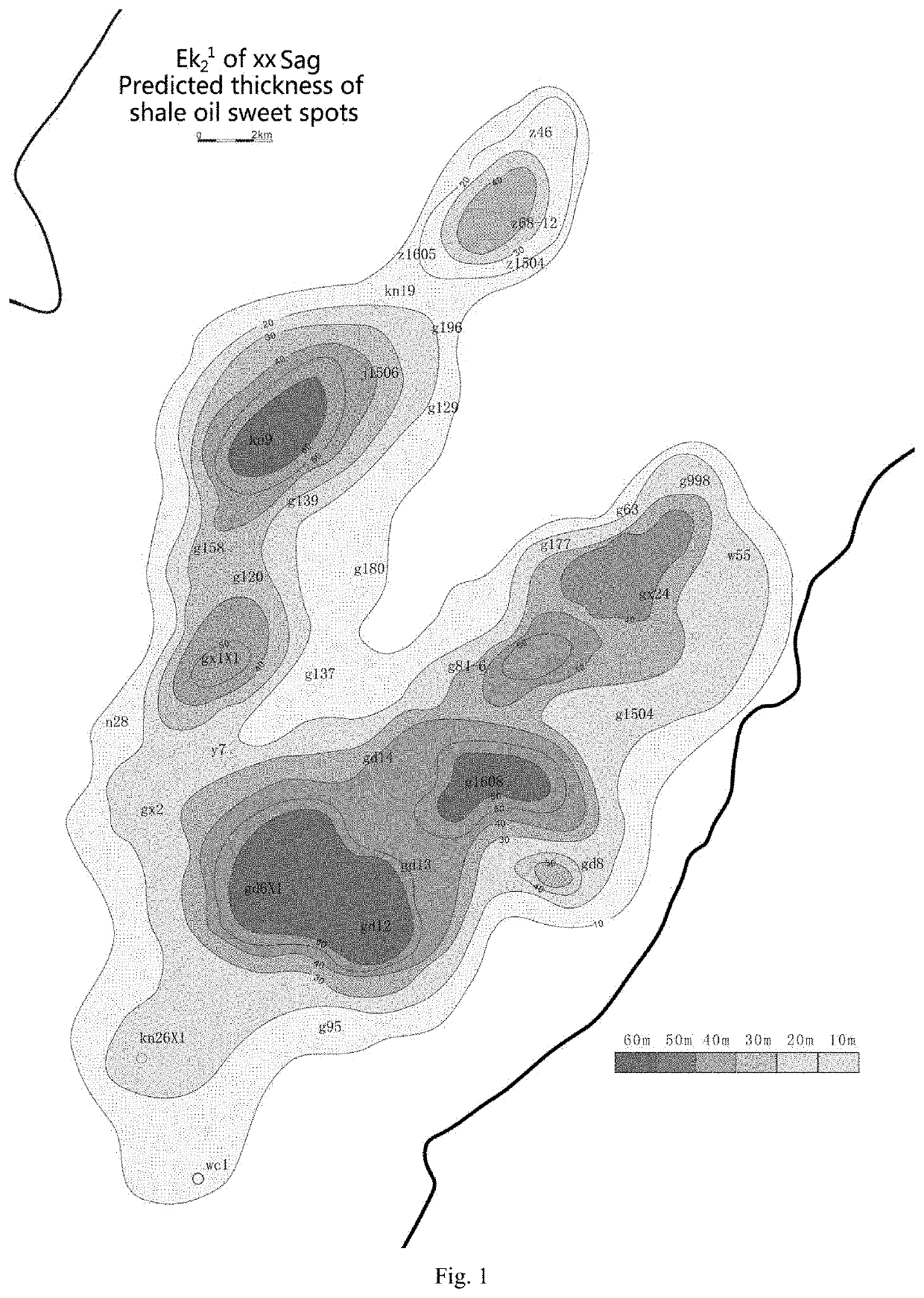
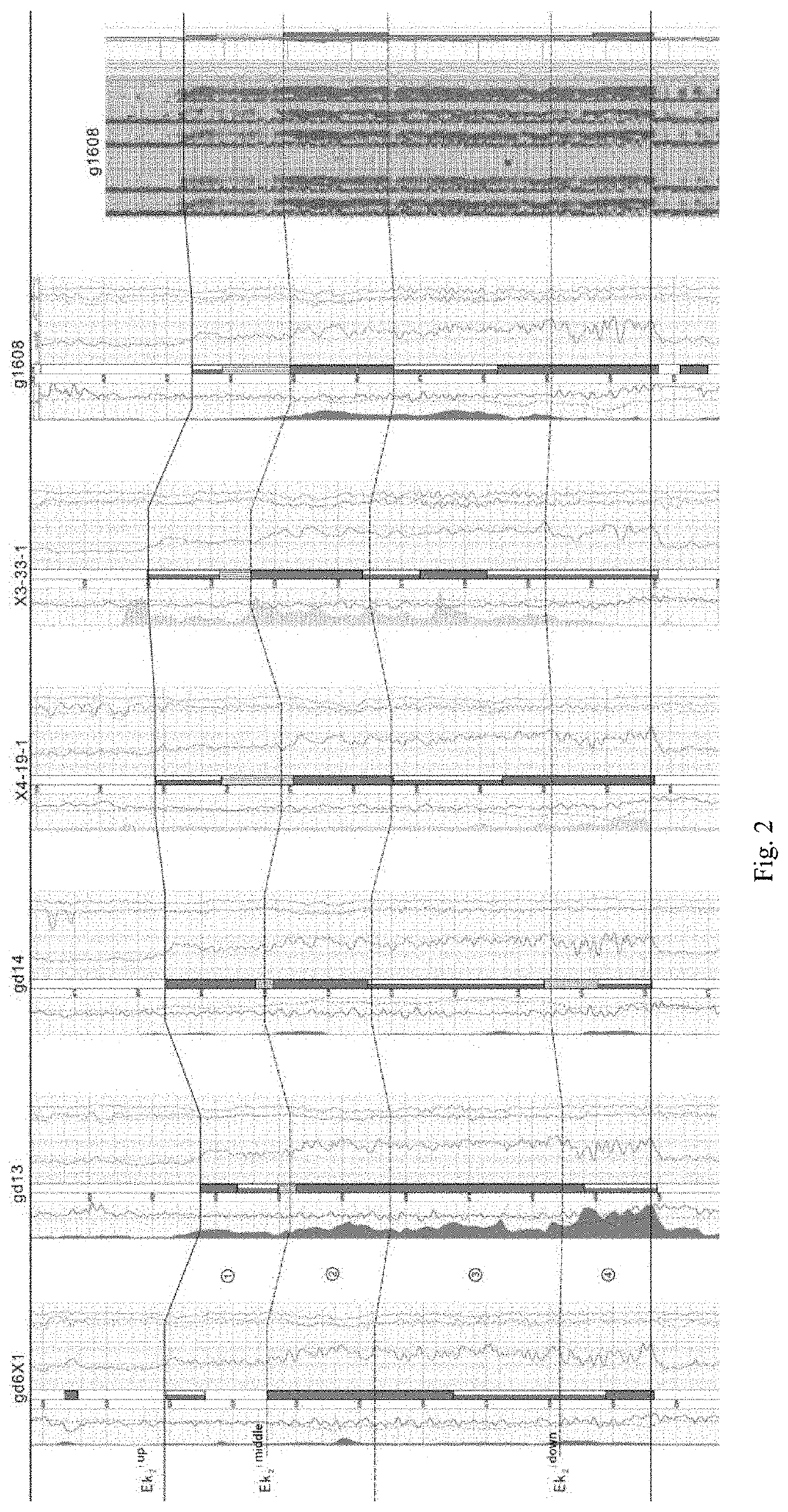
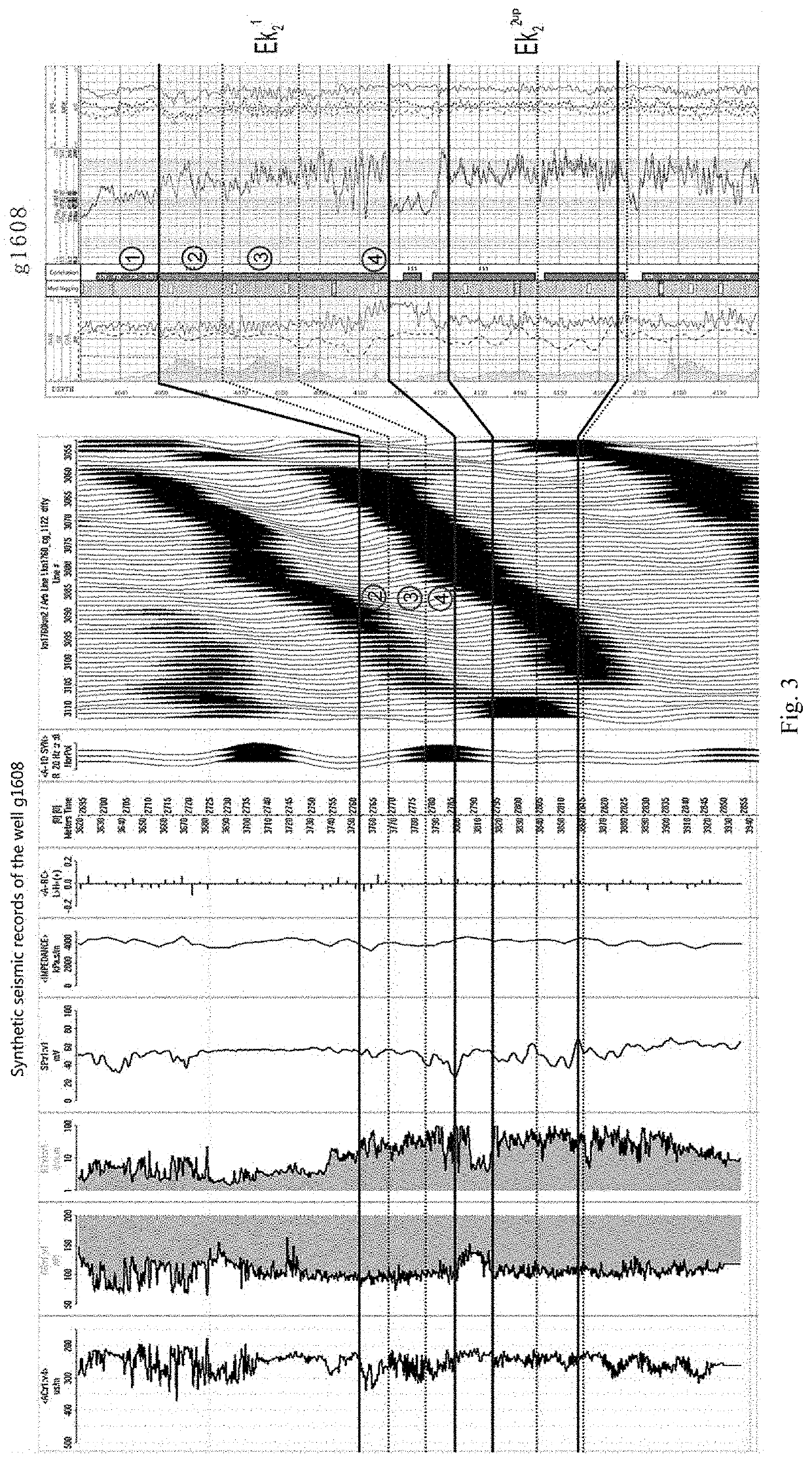
Research method of trajectory design and on-site tracking and adjustment of shale oil horizontal well
ActiveUS10689954B1Trajectory rationalizationLayer is smallSurveyFluid removalThermodynamicsWell drilling
The present invention discloses a research method of trajectory design and on-site tracking and adjustment of a shale oil horizontal well, including identification and evaluation of shale oil sweet spots, optimal selection and trajectory design of the horizontal well, and on-site tracking and adjustment of the shale oil horizontal well. The “four-optimal and two-fine” practice in the research method of trajectory design and on-site tracking and adjustment of the shale oil horizontal well of the present invention lays a foundation for high and stable production of shale oil in closed lake basins and the integration of production and reserves increase. It provides a set of technical methods for the design and research of optimal selection of horizontal well locations and dynamic tracking analysis of drilling in shale oil development areas, and has great significance for reference and popularization.
Owner:DAGANG OIL FIELD OF CNPC
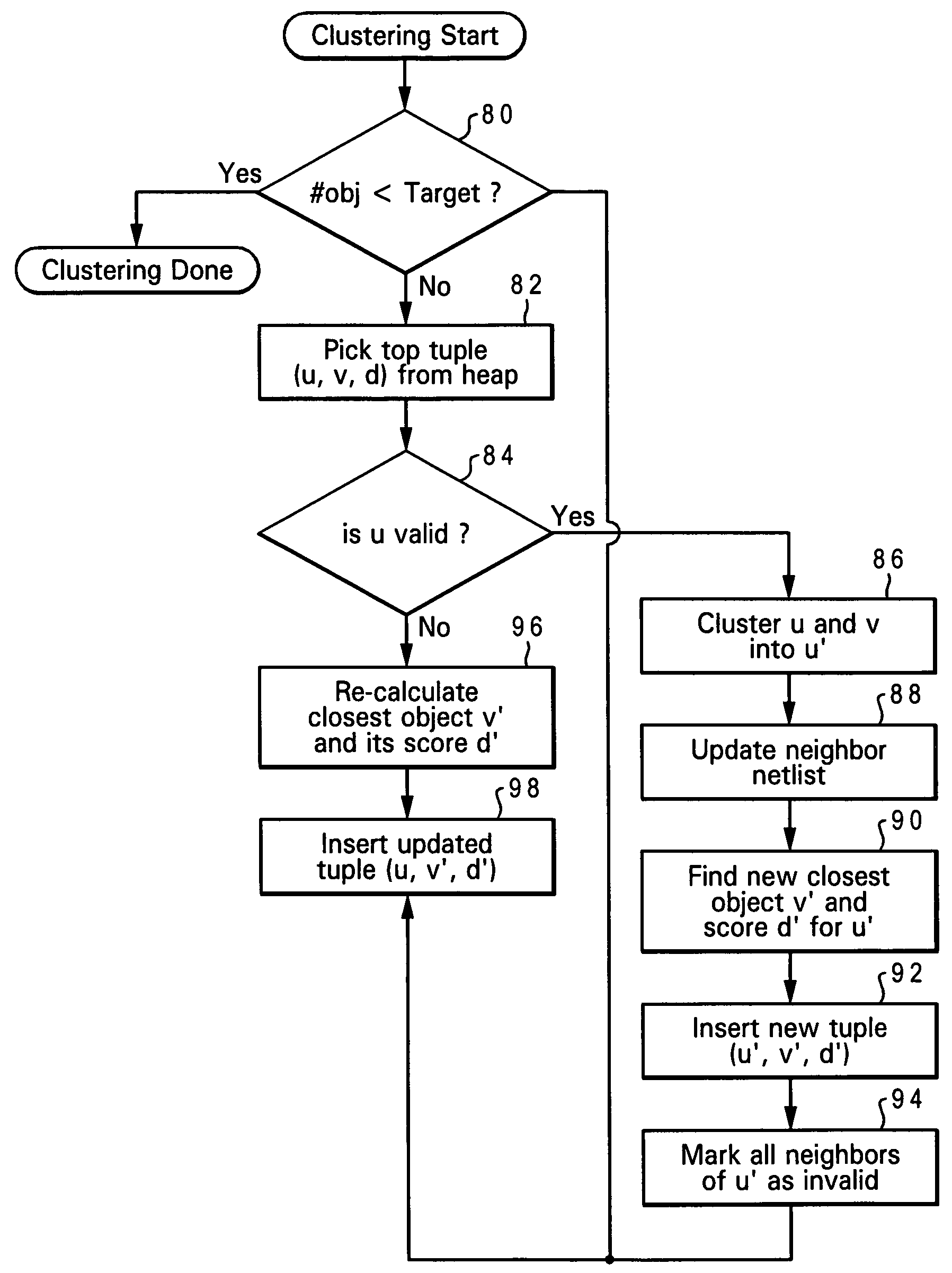
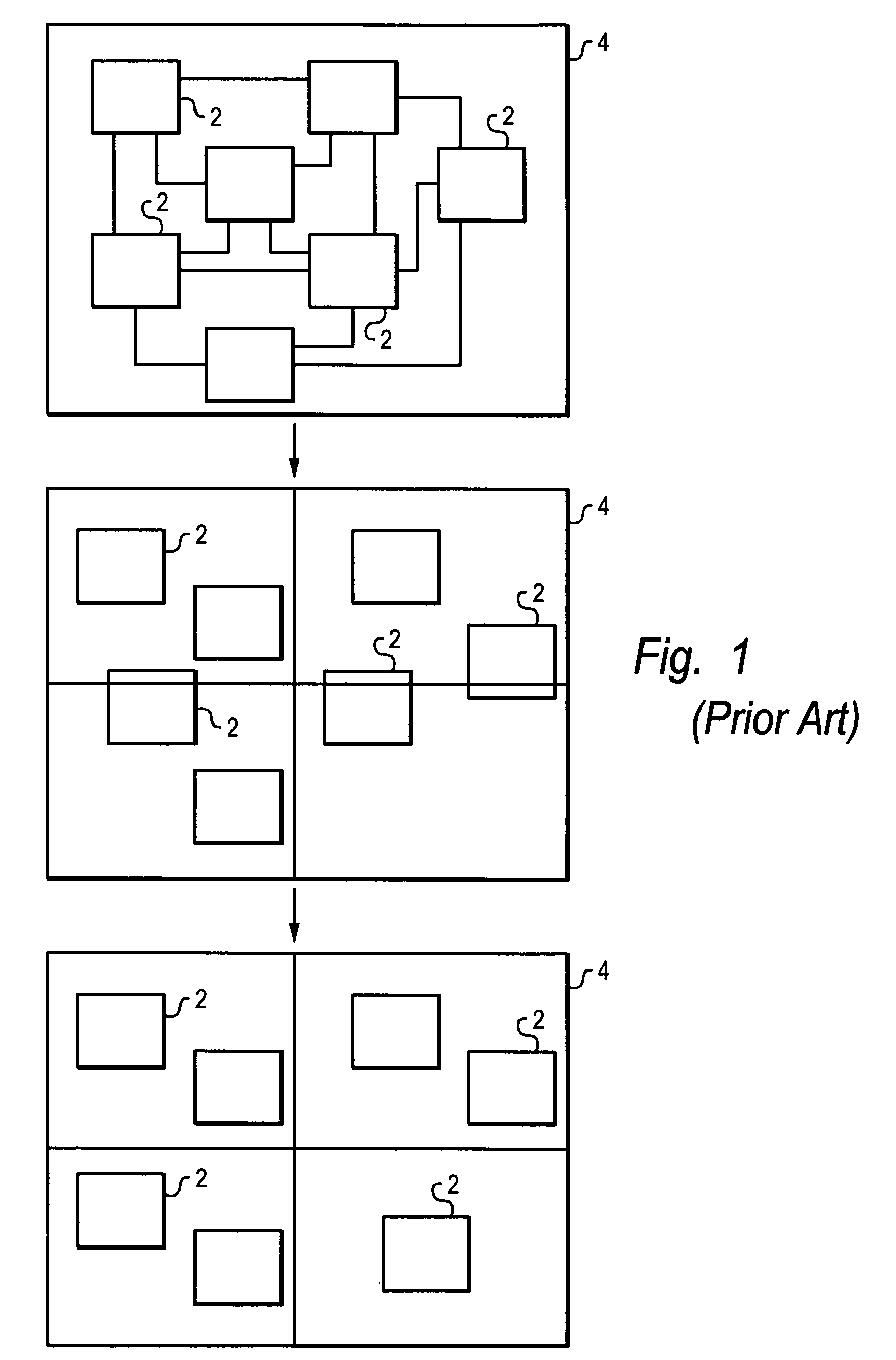
Clustering techniques for faster and better placement of VLSI circuits
InactiveUS7296252B2Improve scalabilityReduce in quantityComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationWell placementCluster based
A placement technique for designing a layout of an integrated circuit by calculating clustering scores for different pairs of objects in the layout based on connections of two objects in a given pair and the sizes of the two objects, then grouping at least one of the pairs of objects into a cluster based on the clustering scores, partitioning the objects as clustered and ungrouping the cluster after partitioning. The pair of objects having the highest clustering score are grouped into the cluster, and the clustering score is directly proportional to the total weight of connections between the two objects in the respective pair. The clustering scores are preferably inserted in a binary heap to identify the highest clustering score. After grouping, the clustering score for any neighboring object of a clustered object is marked to indicate that the clustering score is invalid and must be recalculated. The calculating and grouping are then repeated iteratively based on the previous clustered layout. Cluster growth can be controlled indirectly, or controlled directly by imposing an upper bound on cluster size.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
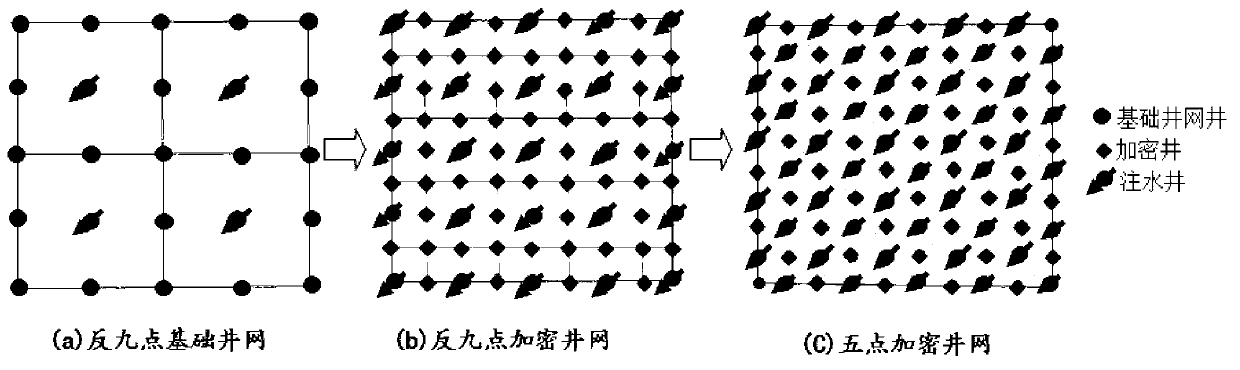
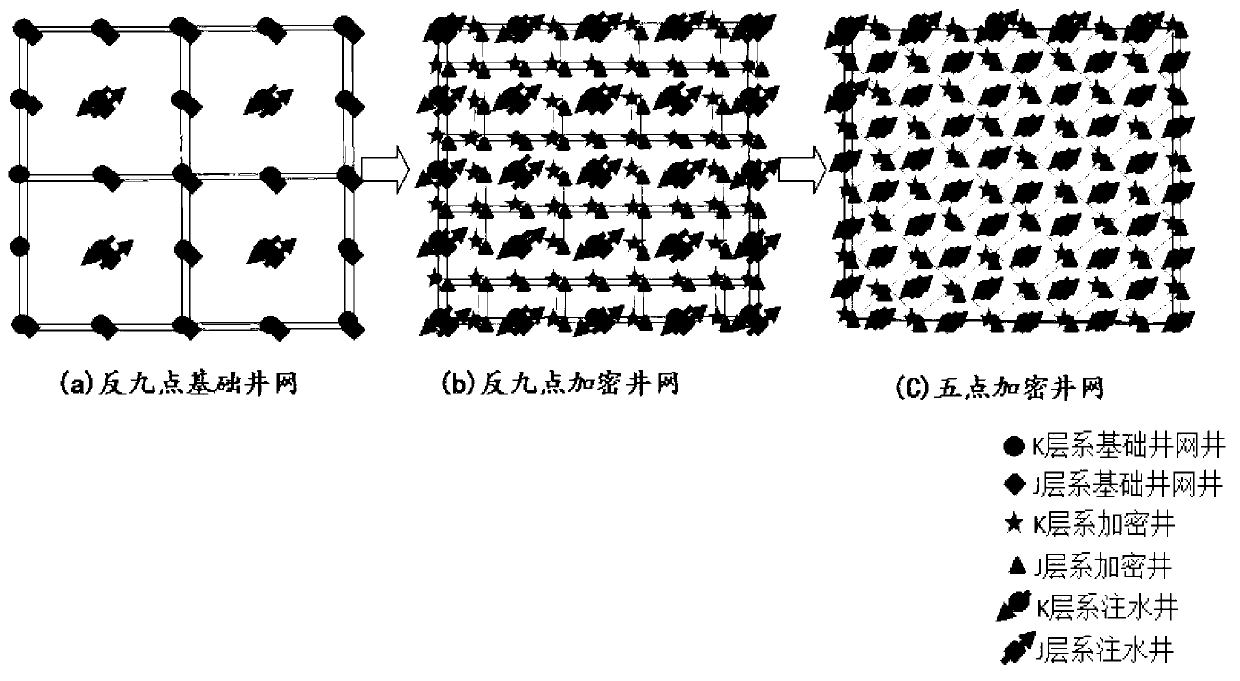
Longitudinally superposed developing three-strata oil reservoir well pattern and deployment method thereof
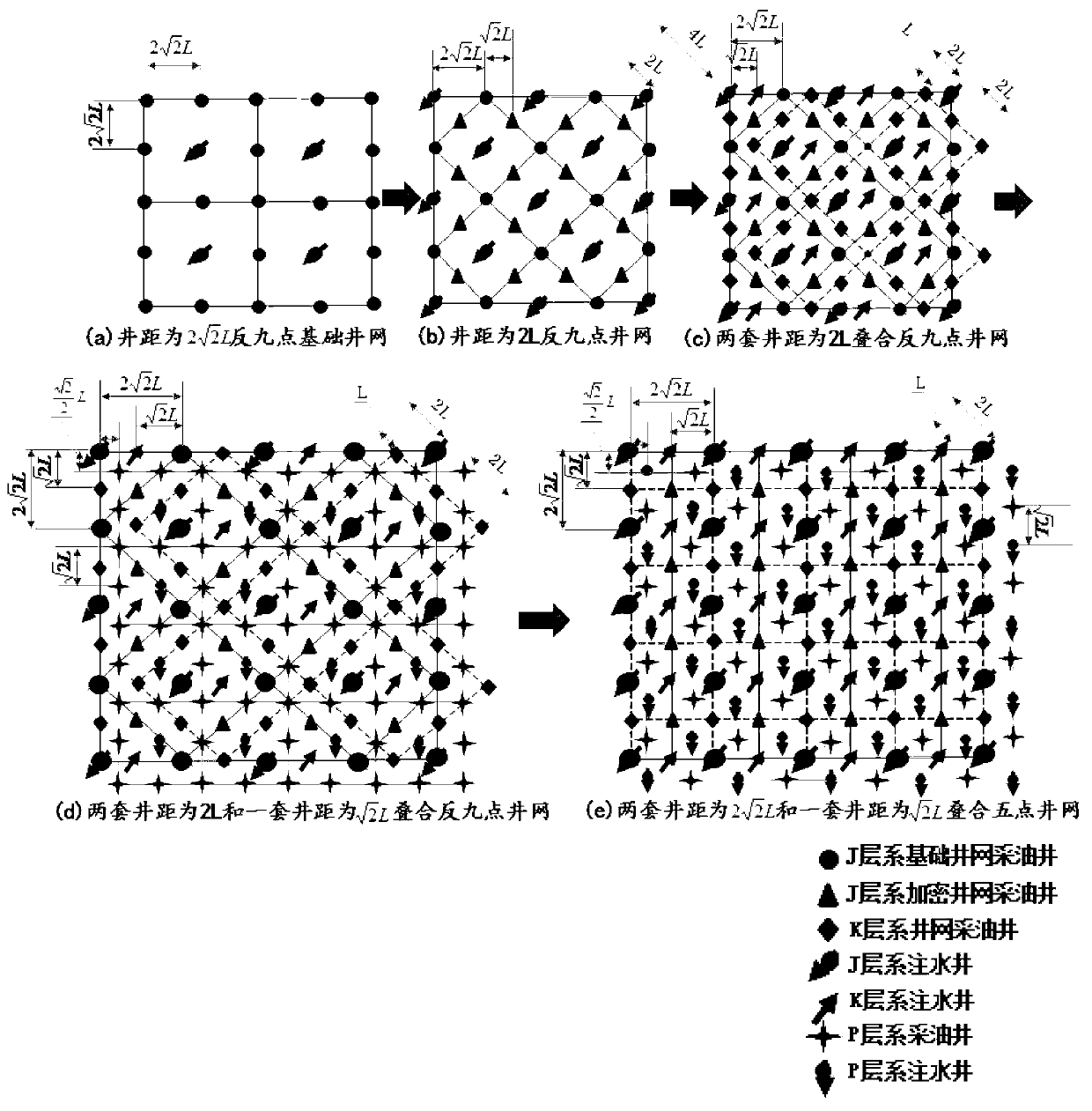
The embodiment of the invention discloses a longitudinally superposed developing three-strata oil reservoir well pattern and a deployment method of the longitudinally superposed developing three-strata oil reservoir well pattern. To the longitudinally superposed developing three-strata oil reservoir, the well spacing of a basic well pattern is 2*(square root of 2)*L; after being encrypted once, the well spacing of a middle transitional well pattern is 2L; after being encrypted twice, two superposed inverted nine-spot well patterns with well spacing of 2L are formed; after being encrypted for three times, two superposed inverted nine-spot well patterns with well spacing of 2L and one superposed inverted nine-spot well pattern with well spacing of (square root of 2)*L are formed; and after pairwise alternatively development, the well spacing of the plane well pattern of each strata has a rational well spacing of L; the evolution process of the well spacing is as follows: 2*(square root of 2)* L to 2L to (square root of 2)*L to L; the middle process of well patterns conversion with a well spacing of 2L and (square root of 2)*L is added; at the same drilling speed, well placement uniformity coefficient and reserve control speed are increased; the well spacing is encrypted in the alternation of well patterns; each well pattern can realize order development to each longitudinal strata; the utilization ratio of the well patterns is improved; meanwhile, the oil reservoir is uniformly used, so that the method is in favor of increasing accumulated oil production of an oil field and improving the recovery ratio; and interlayer interference generated by commingled extracting oil in multiple oil layers of longitudinal series of strata is avoided.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Clustering techniques for faster and better placement of VLSI circuits
InactiveUS20060031804A1Improve scalabilityReduce in quantityComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationWell placementIntegrated circuit layout
A placement technique for designing a layout of an integrated circuit by calculating clustering scores for different pairs of objects in the layout based on connections of two objects in a given pair and the sizes of the two objects, then grouping at least one of the pairs of objects into a cluster based on the clustering scores, partitioning the objects as clustered and ungrouping the cluster after partitioning. The pair of objects having the highest clustering score are grouped into the cluster, and the clustering score is directly proportional to the total weight of connections between the two objects in the respective pair. The clustering scores are preferably inserted in a binary heap to identify the highest clustering score. After grouping, the clustering score for any neighboring object of a clustered object is marked to indicate that the clustering score is invalid and must be recalculated. The calculating and grouping are then repeated iteratively based on the previous clustered layout. Cluster growth can be controlled indirectly, or controlled directly by imposing an upper bound on cluster size.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Evaluation method for describing compressibility of shale reservoir
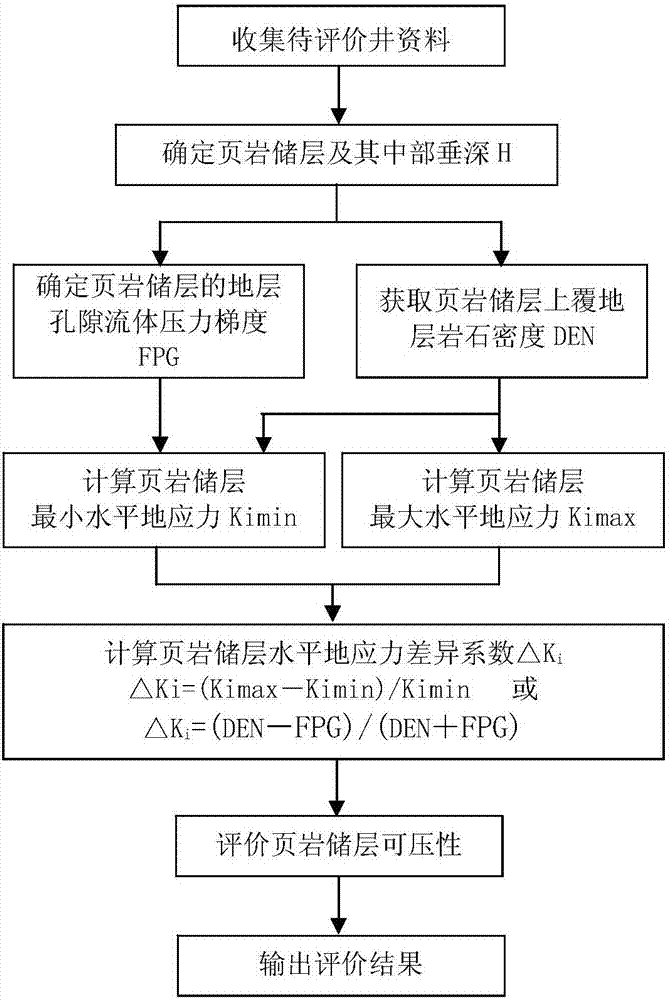
The invention relates to an evaluation method for describing the compressibility of a shale reservoir. The evaluation method comprises the following steps that material contents including a well-site design report of a well to be evaluated, well-logging materials and well-measuring materials of the well to be evaluated are collected; according to the collected materials, the shale reservoir and the vertical depth H of the middle of the shale reservoir are determined, the fluid pressure gradient (FPG) of a stratum pore of the shale reservoir is determined, and the density (DEN) of stratum rock overlaying the shale reservoir is obtained; according to the FPG and DEN, the largest horizontal crustal stress Kimax and the smallest horizontal crustal stress Kimin of the shale reservoir are calculated; and the diversity factor delta Ki of the horizontal crustal stress of the shale reservoir is calculated, the compressibility of the shale reservoir is evaluated, and an evaluation result is output. The diversity factor delta Ki of the horizontal crustal stress of the shale reservoir is calculated through parameters of the FPG, the DEN and the like, and the compressibility of the shale reservoir is evaluated according to the delta Ki. The evaluation method is applied in more than 300 wells among shale gas wells in areas such as the middle Yangtze area, the Jiannan gas-field and the like, and the verification coincidence rate of the staged fracturing effect is 97.1%.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +3
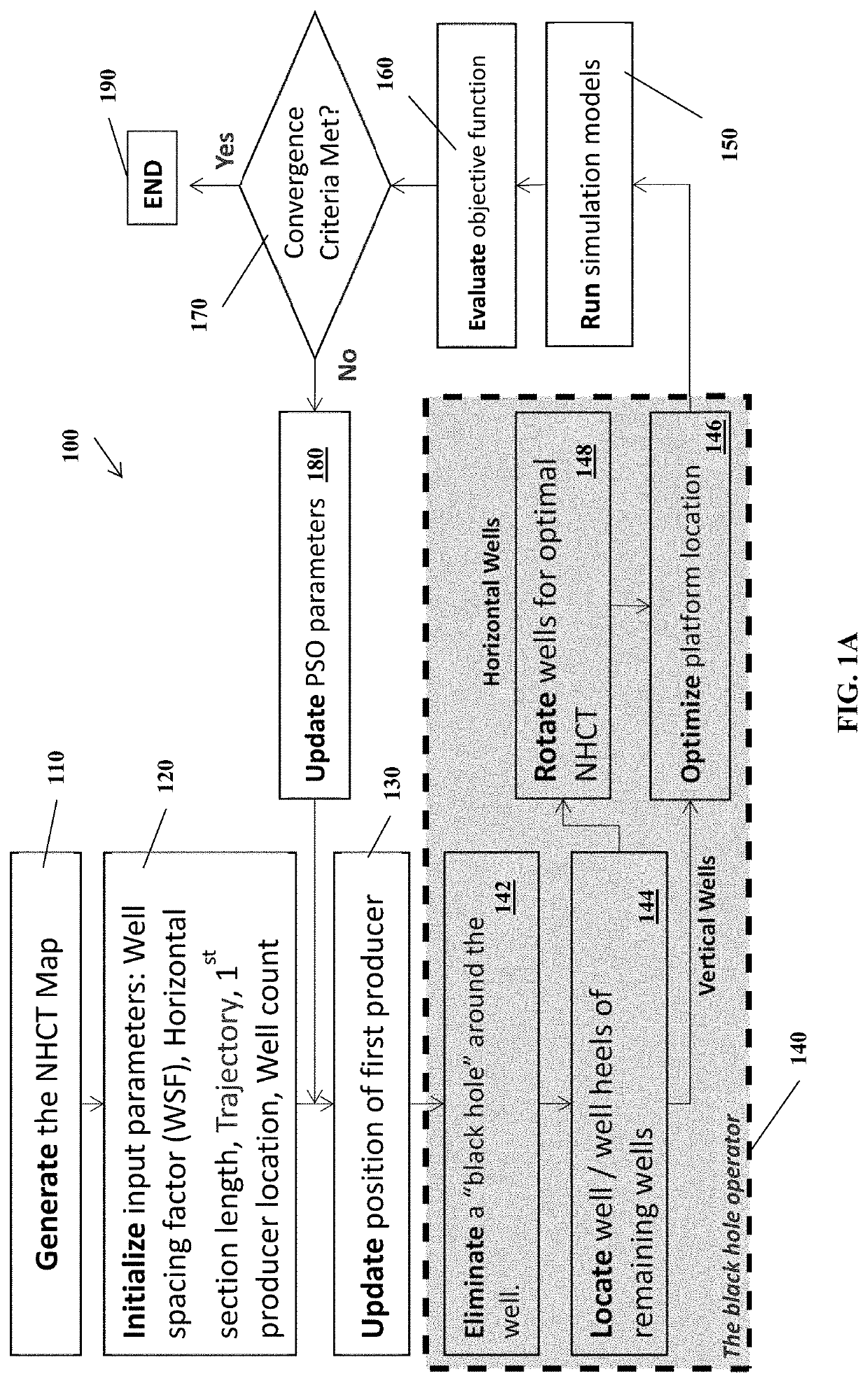
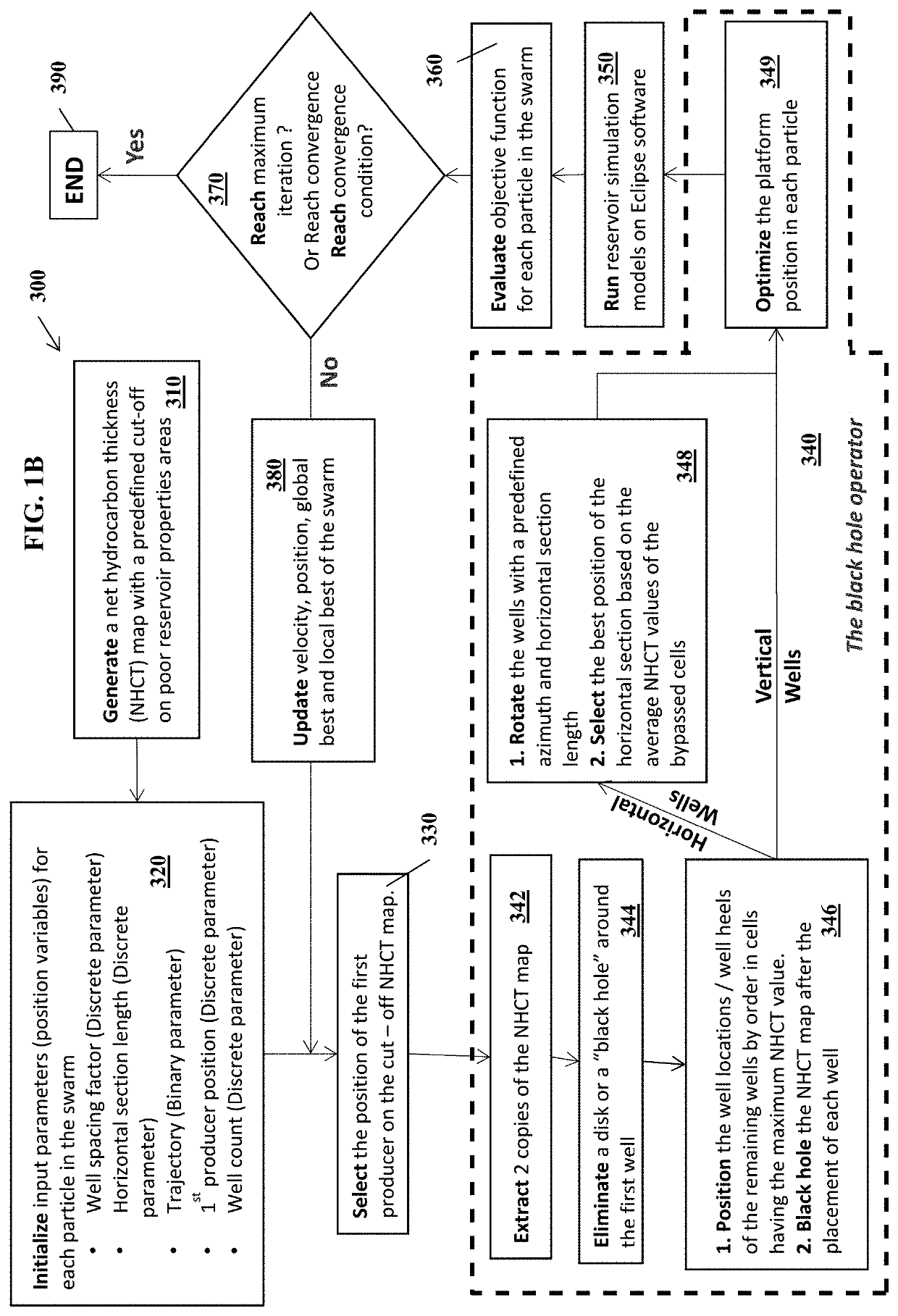
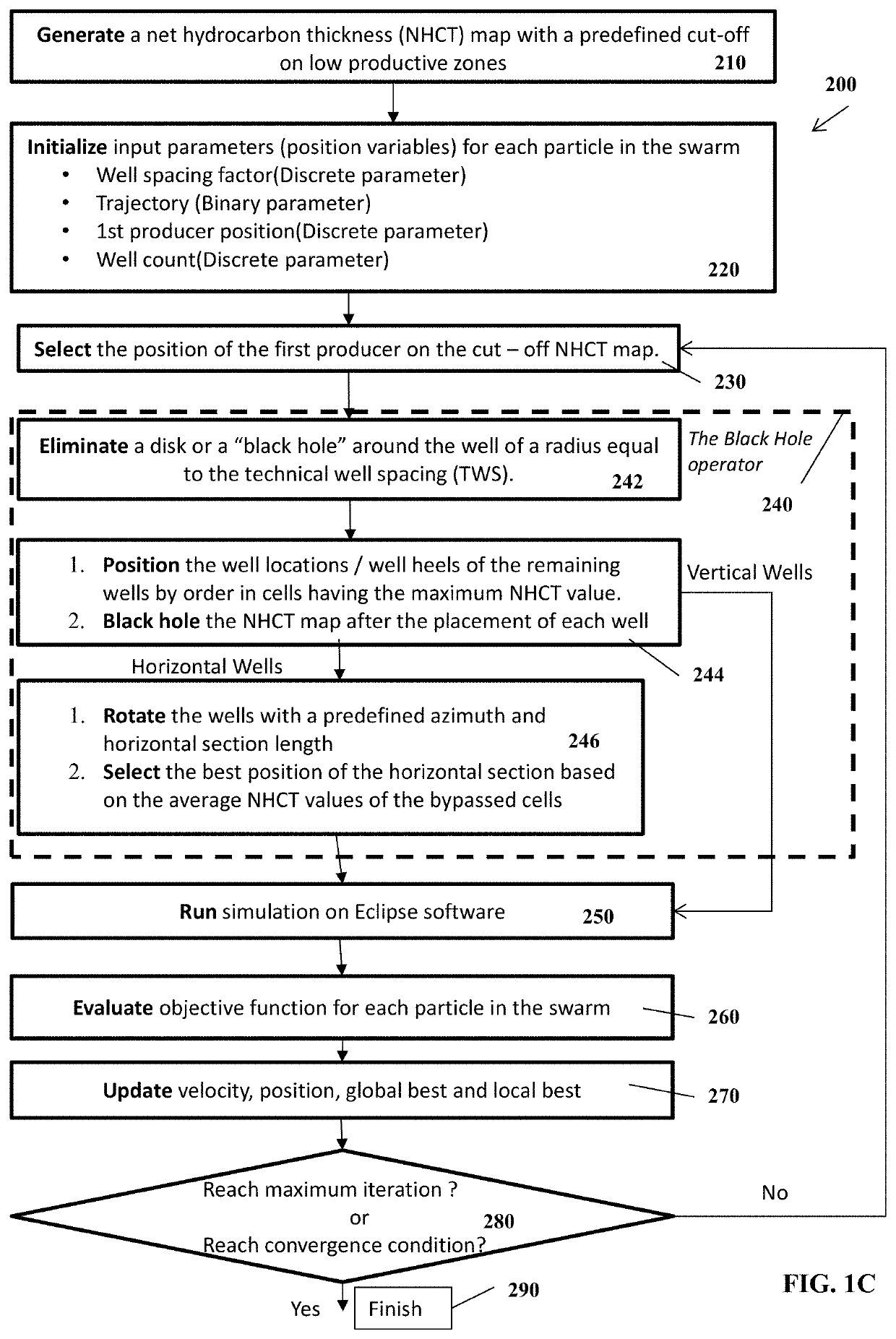
Black hole particle swarm optimization for optimal well placement in field development planning and methods of use
Provided herein are systems, methods and apparatuses for a Black Hole Particle Swarm Optimization for Optimal Well Placement in Field Development Planning.
Owner:AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF BEIRUT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com