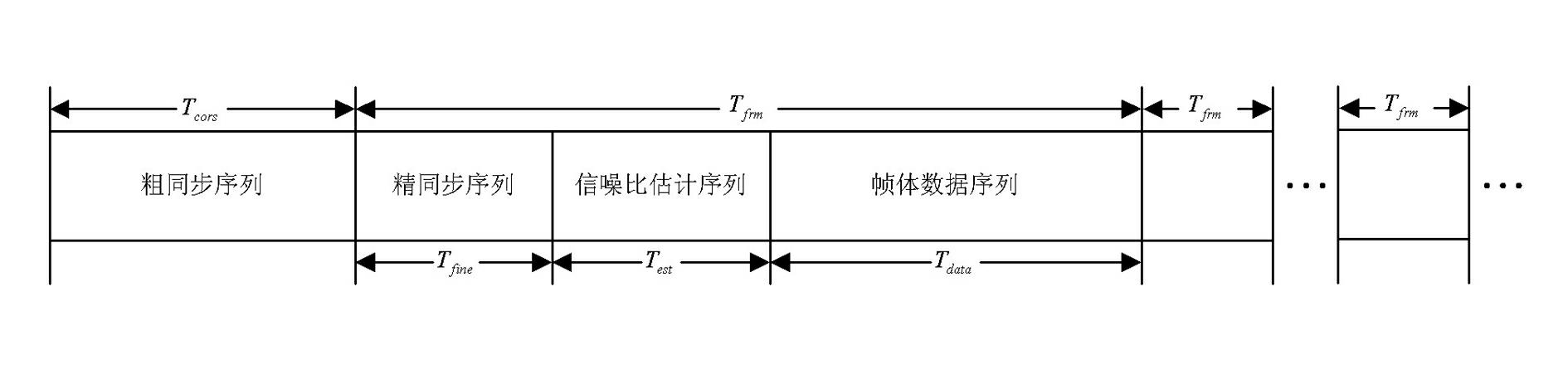
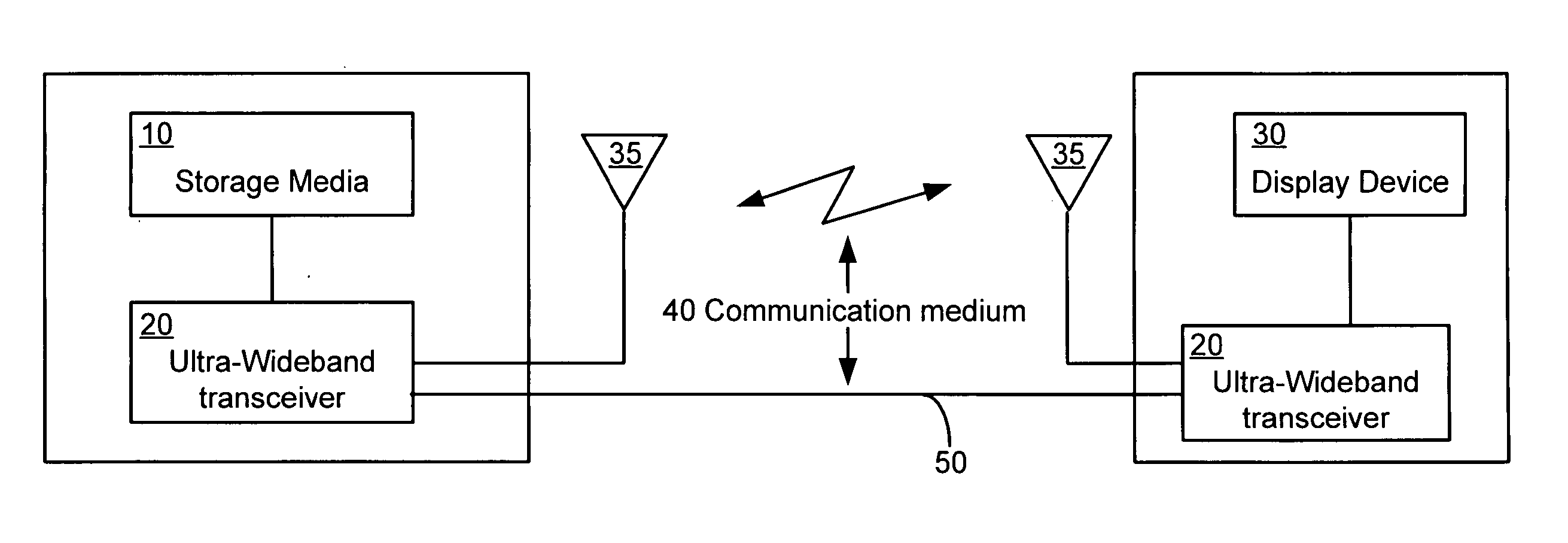
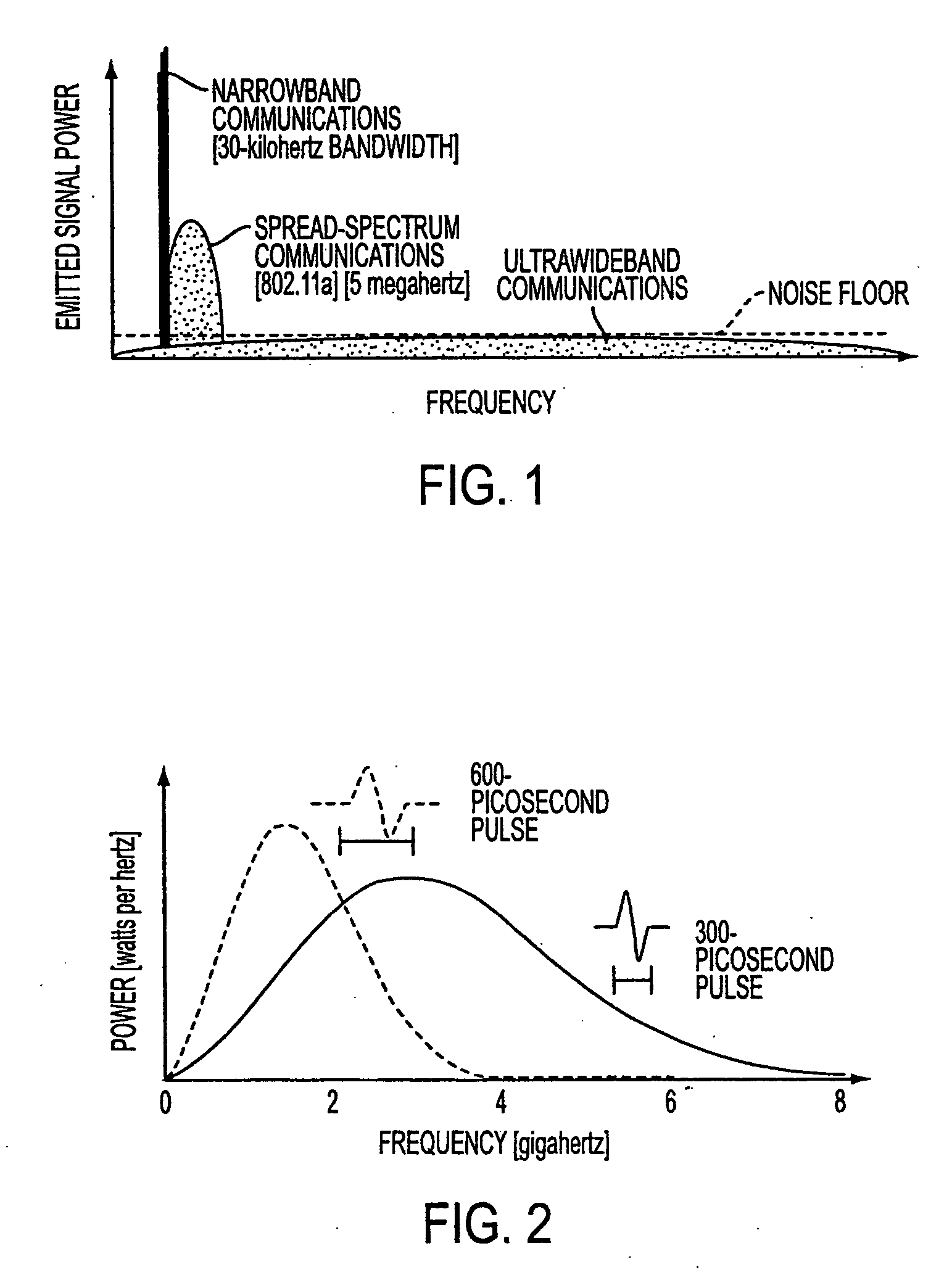
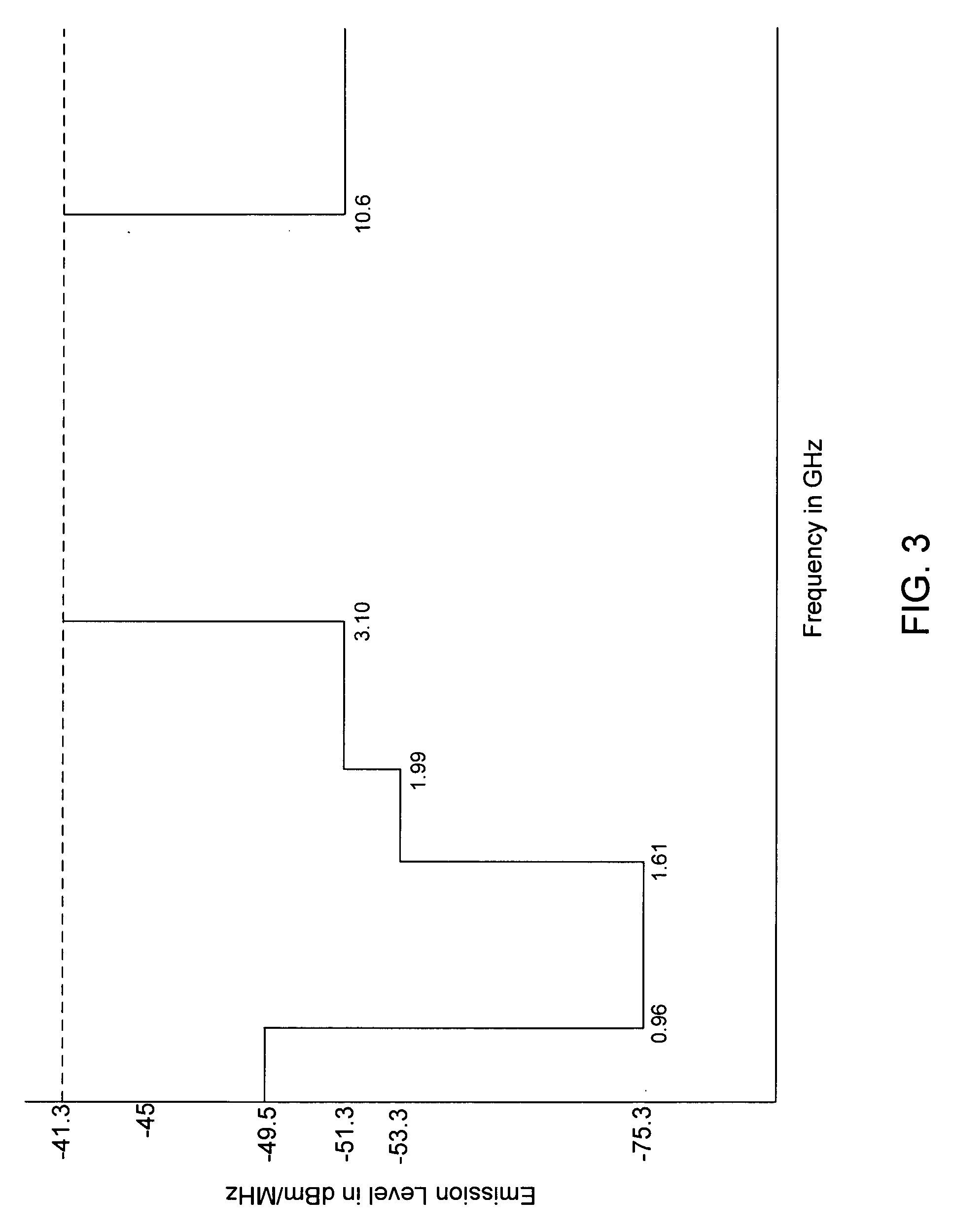
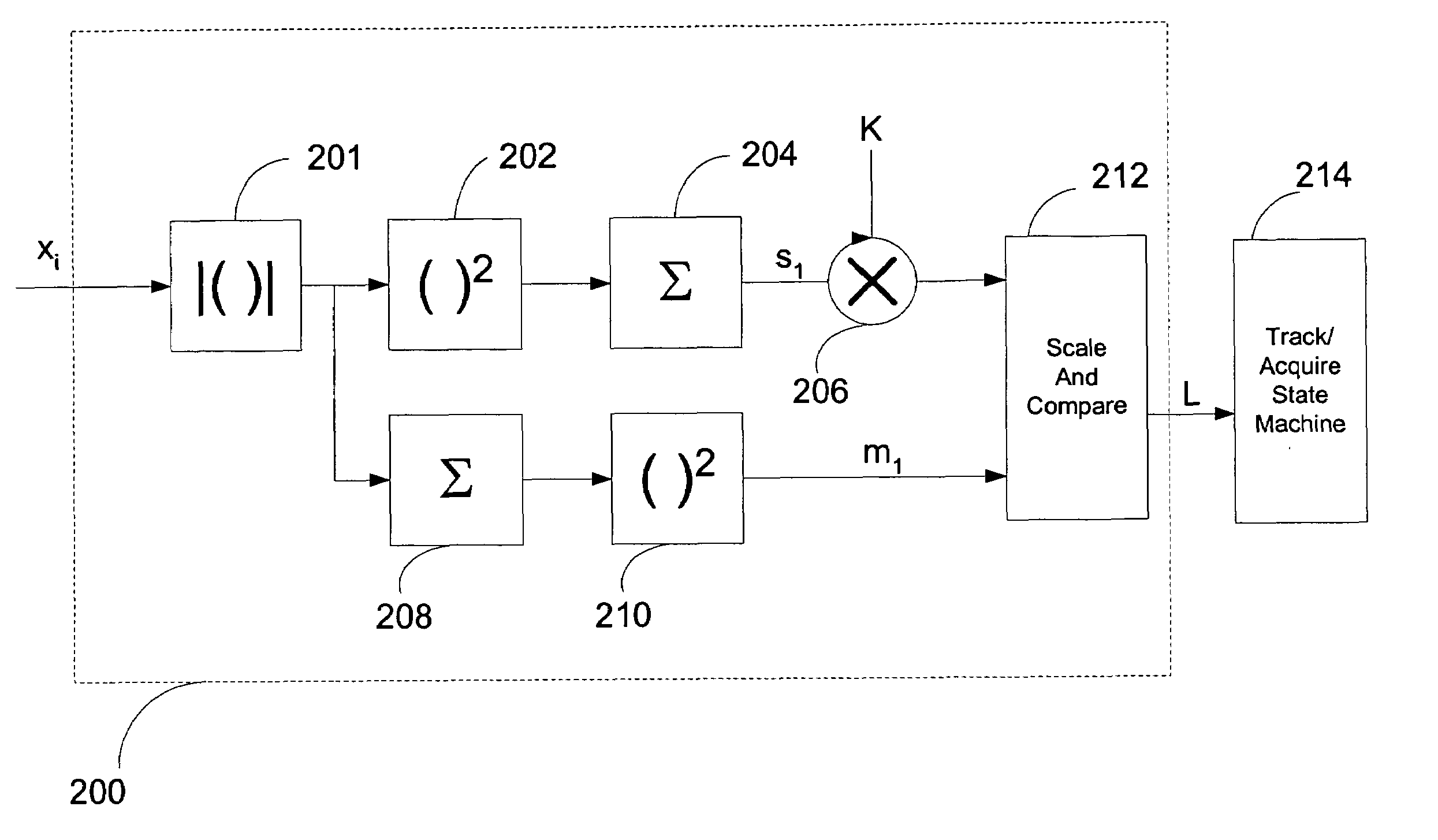Patents
Literature
225 results about "Ultra wideband communication systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
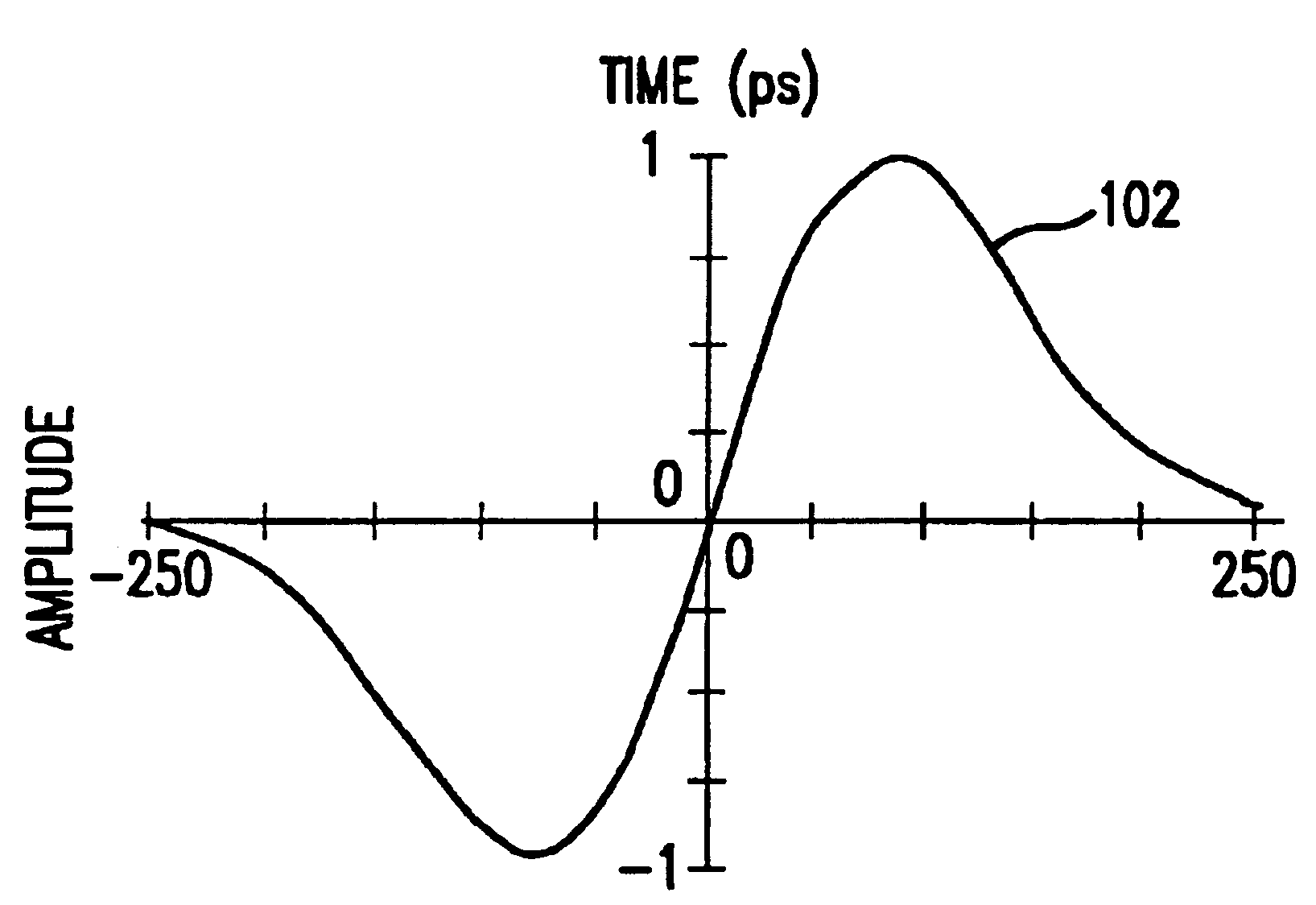
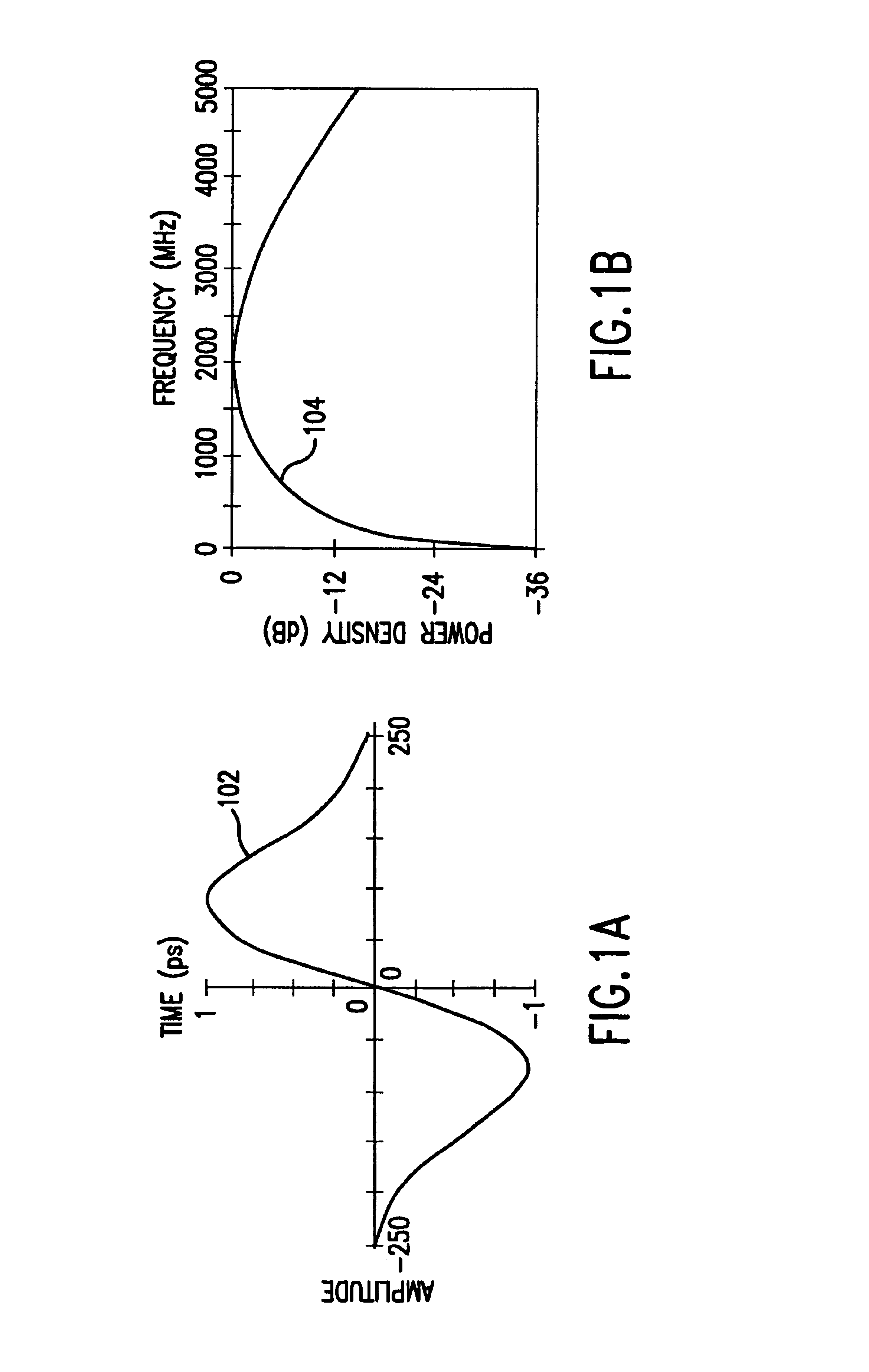
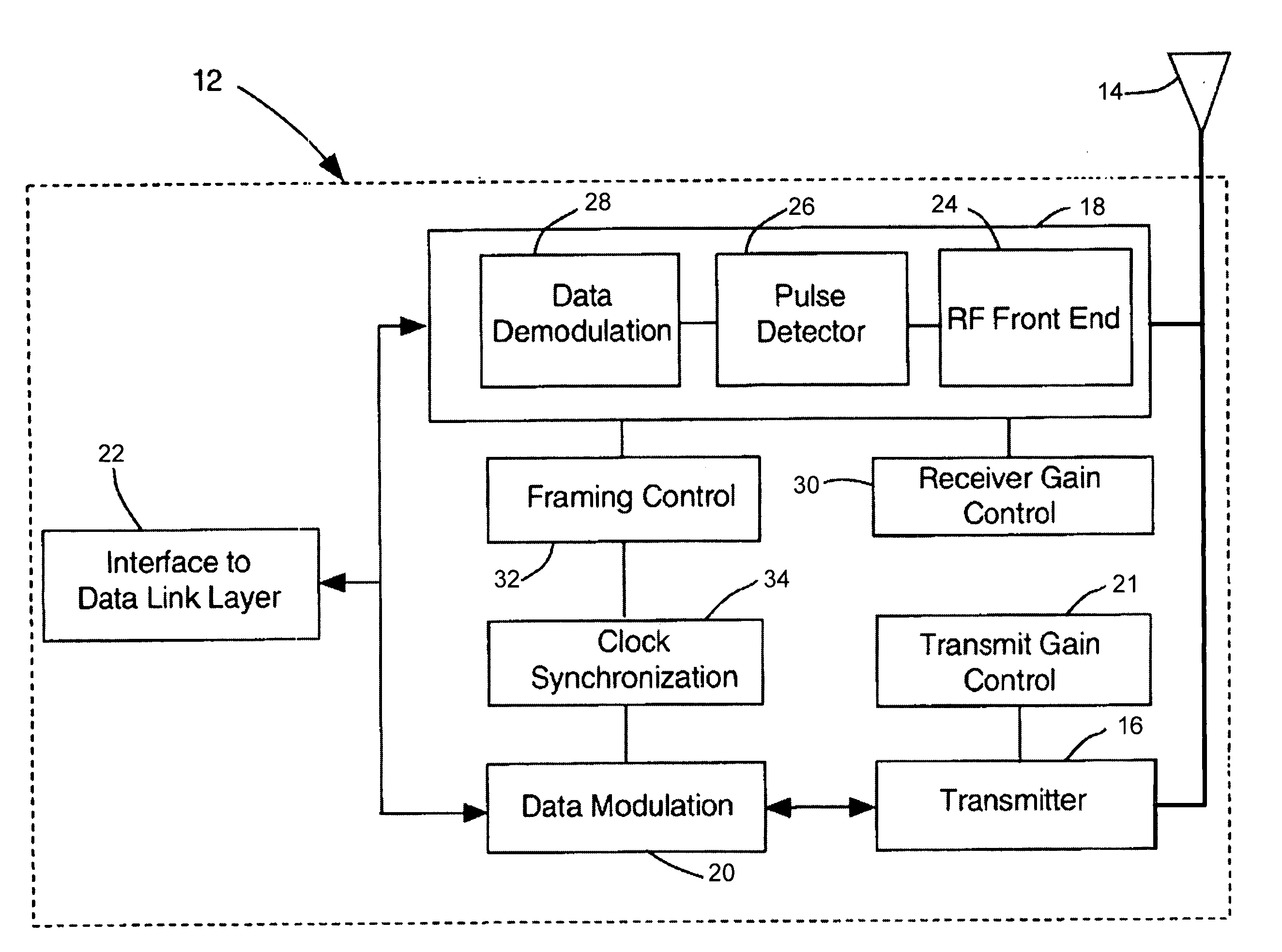
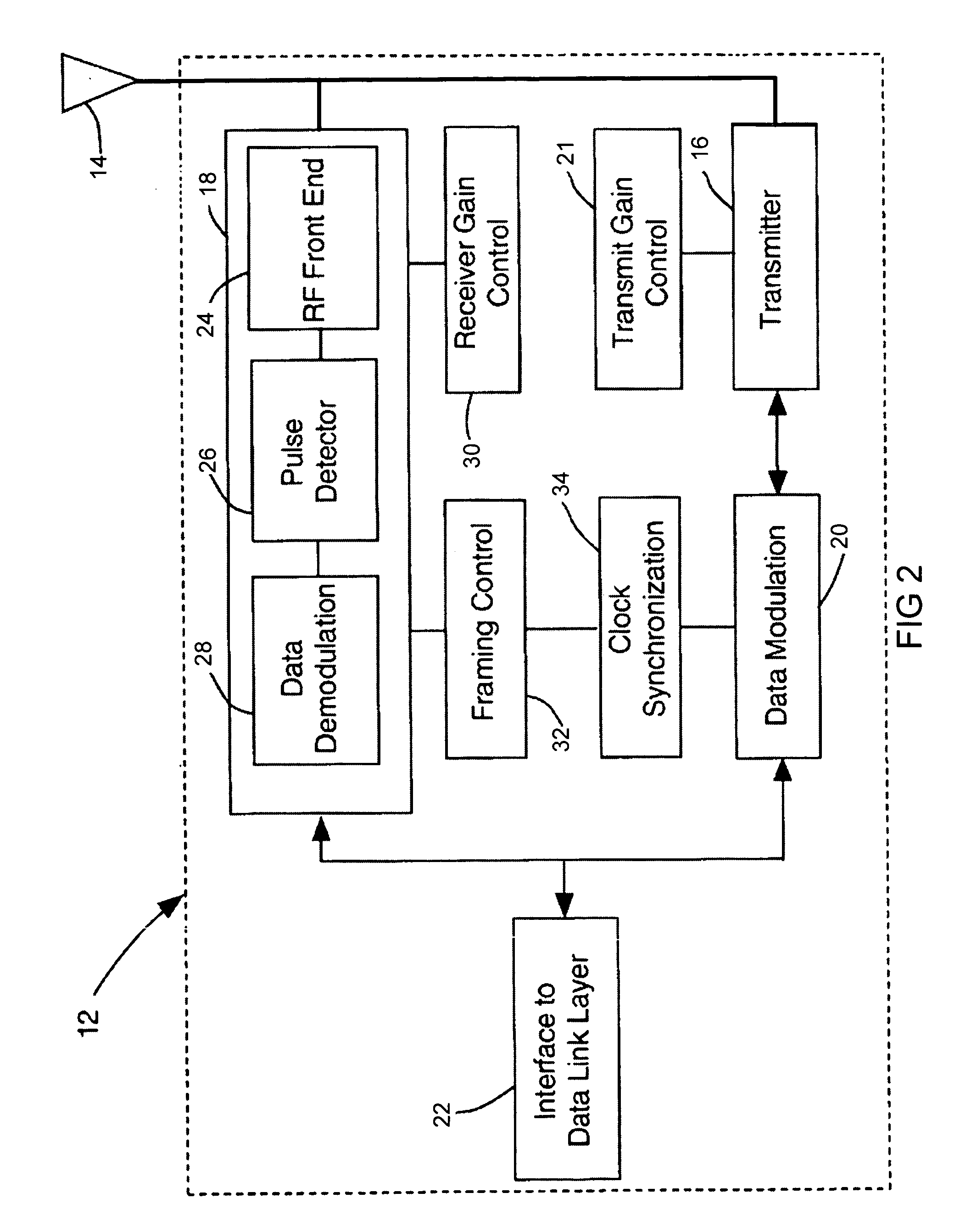
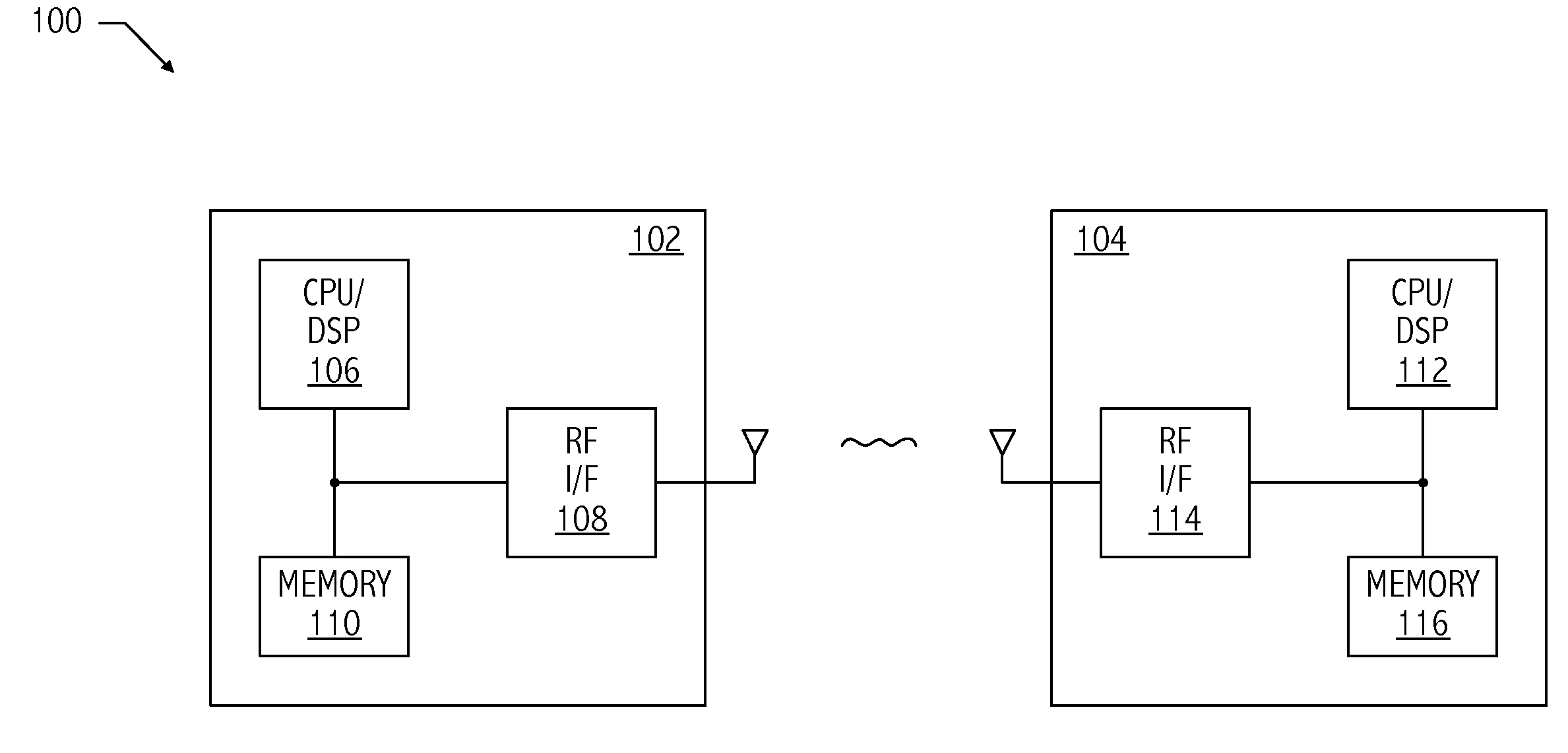
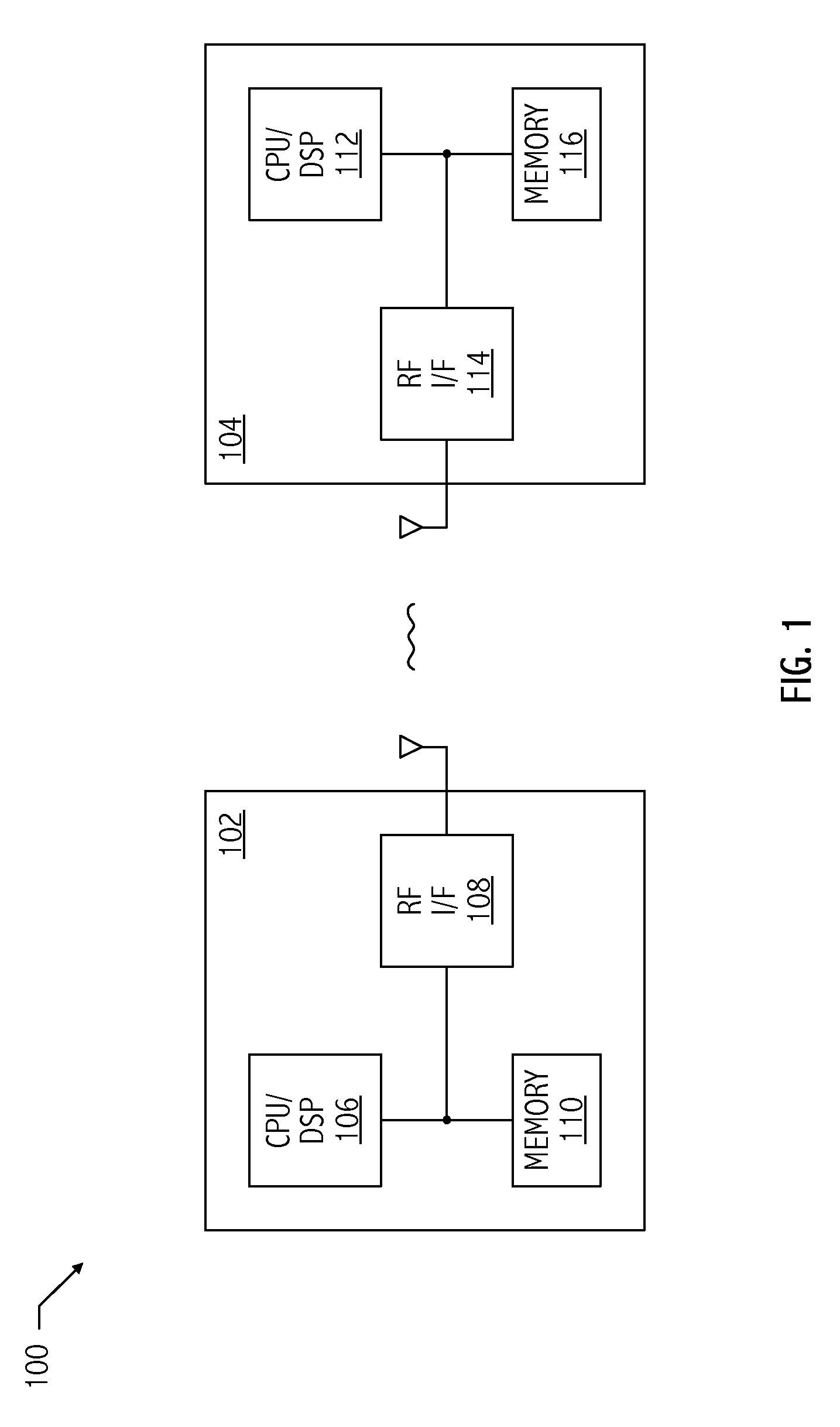
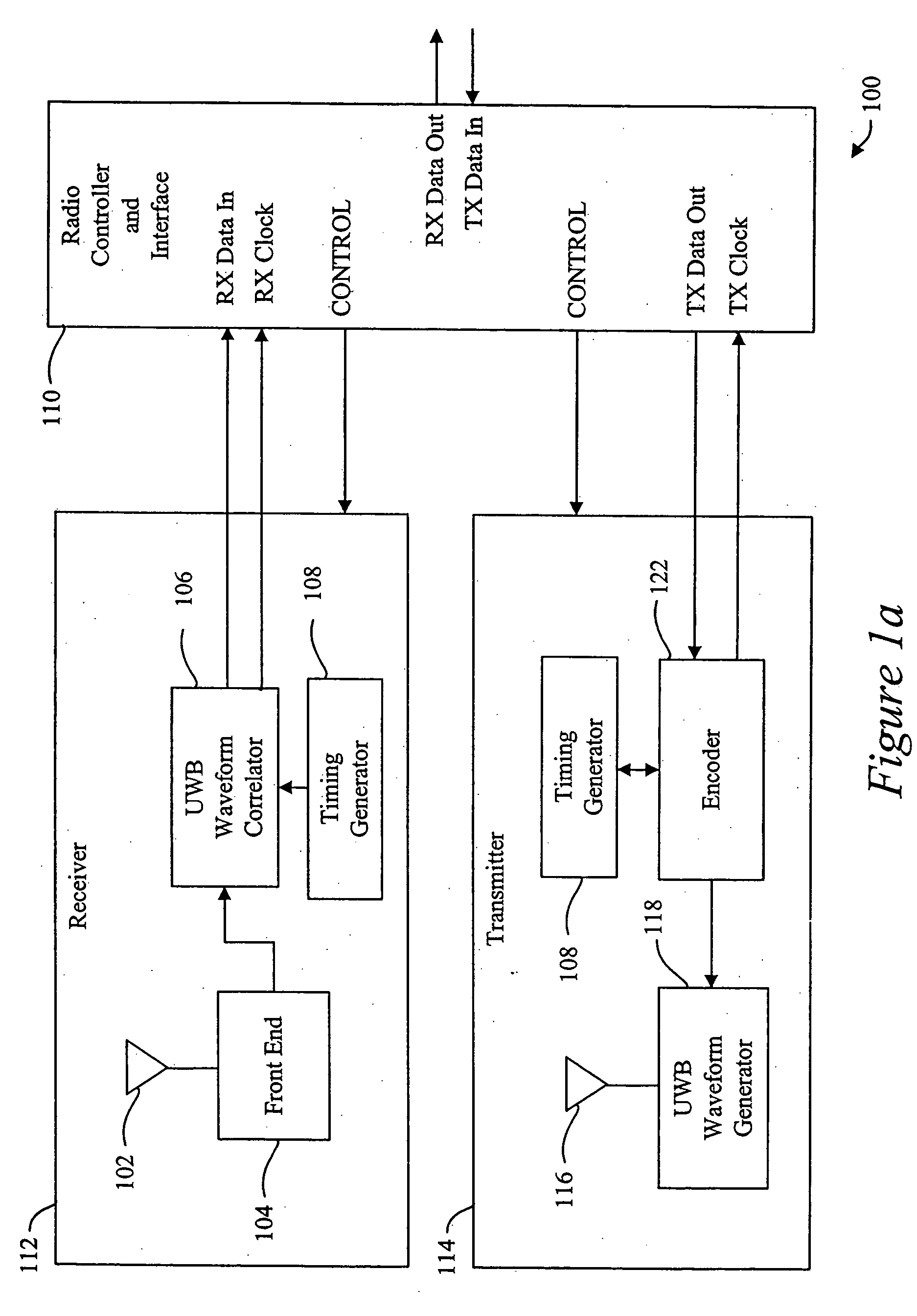
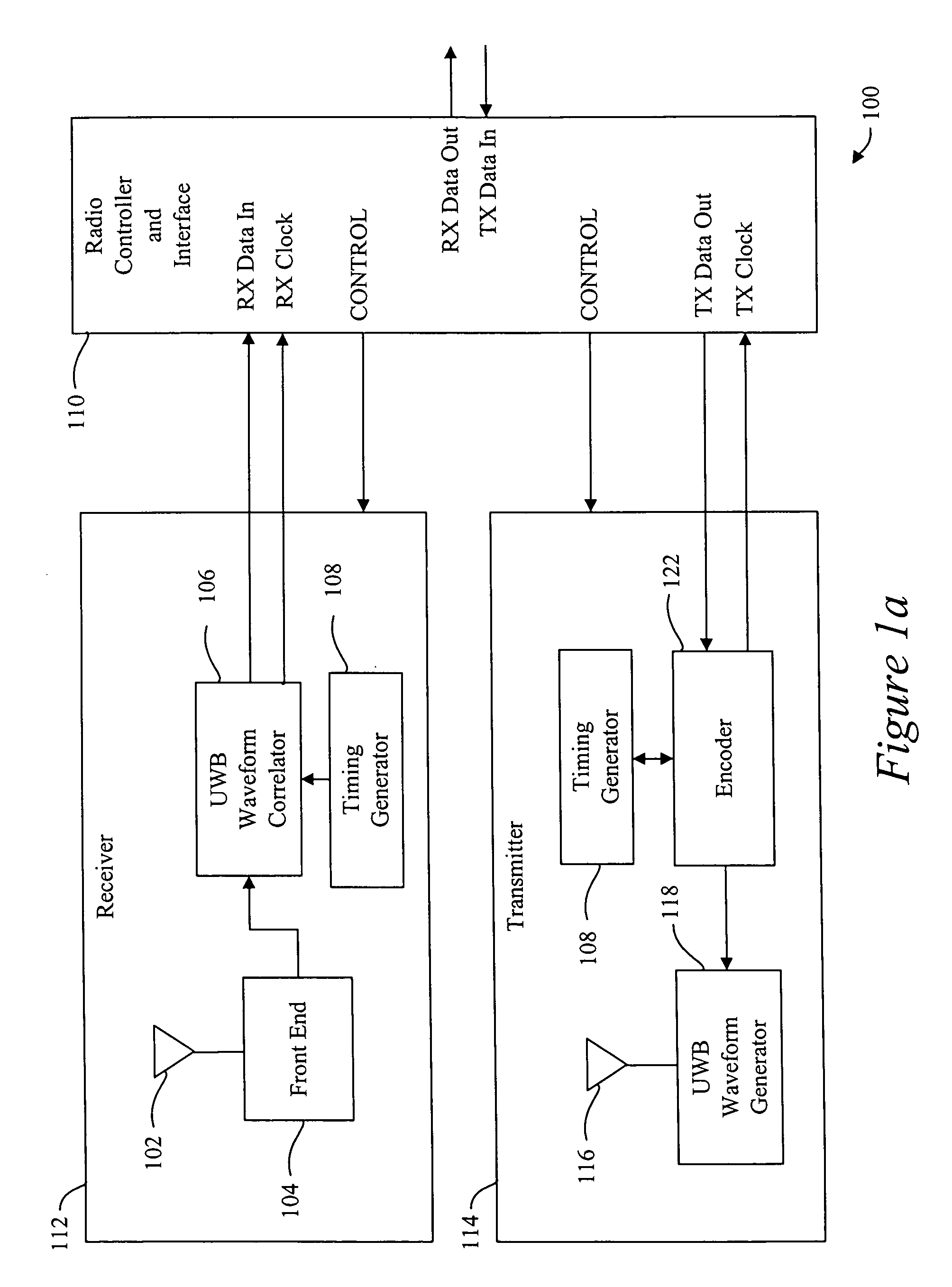
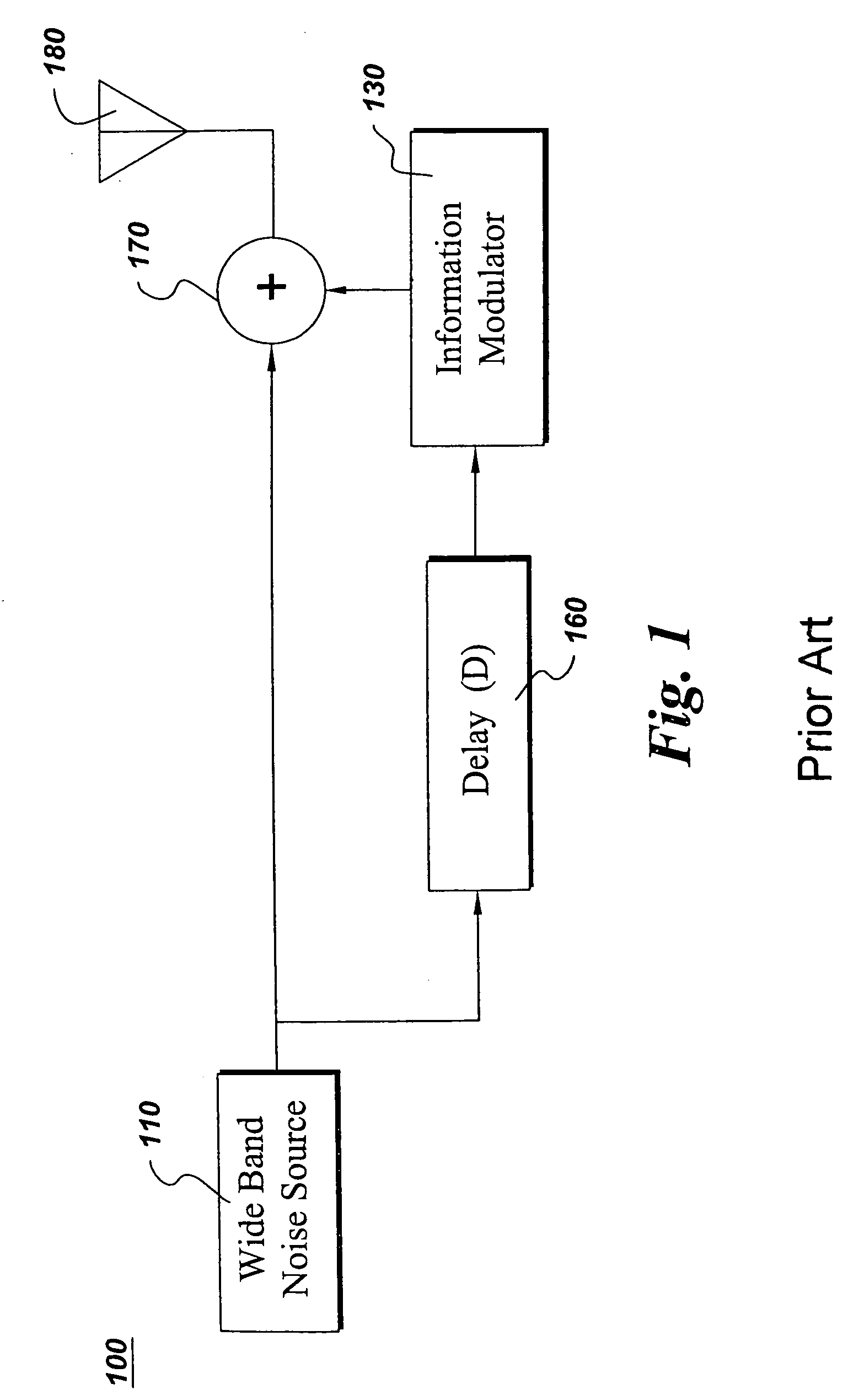
Ultrawide-band communication system and method
InactiveUS6847675B2Remove distortionUndesirable modulationAngle modulationCode division multiplexTime delaysRadio receiver
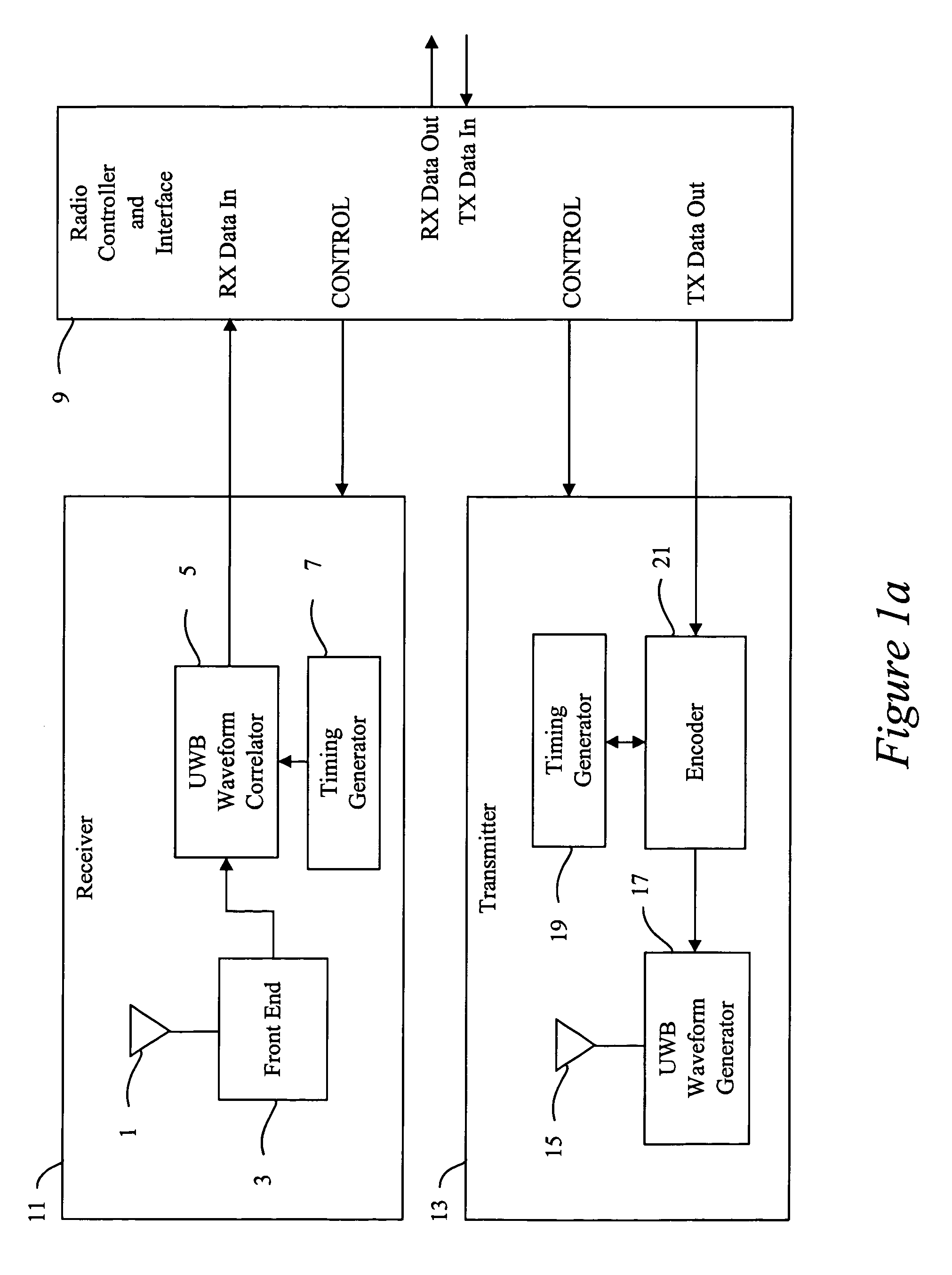
An impulse radio communications system using one or more subcarriers to communicate information from an impulse radio transmitter to an impulse radio receiver. The impulse radio communication system is an ultrawide-band time domain system. The use of subcarriers provides impulse radio transmissions added channelization, smoothing and fidelity. Subcarriers of different frequencies or waveforms can be used to add channelization of impulse radio signals. Thus, an impulse radio link can communicate many independent channels simultaneously by employing different subcarriers for each channel. The impulse radio uses modulated subcarrier(s) for time positioning a periodic timing signal or a coded timing signal. Alternatively, the coded timing signal can be summed or mixed with the modulated subcarrier(s) and the resultant signal is used to time modulate the periodic timing signal. Direct digital modulation of data is another form of subcarrier modulation for impulse radio signals. Direct digital modulation can be used alone to time modulate the periodic timing signal or the direct digitally modulated the periodic timing signal can be further modulated with one or more modulated subcarrier signals. Linearization of a time modulator permits the impulse radio transmitter and receiver to generate time delays having the necessary accuracy for impulse radio communications.
Owner:TDC ACQUISITION HLDG
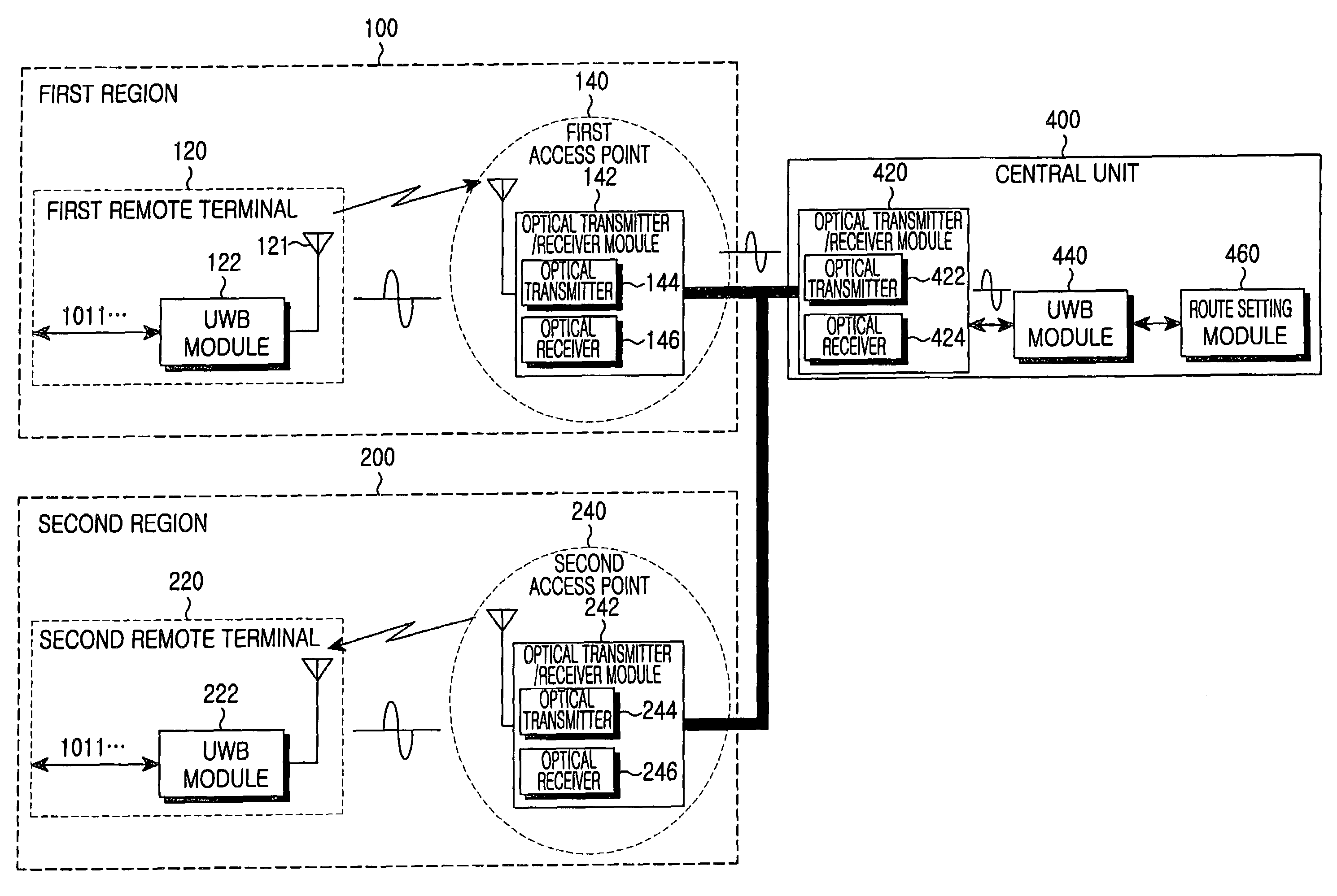
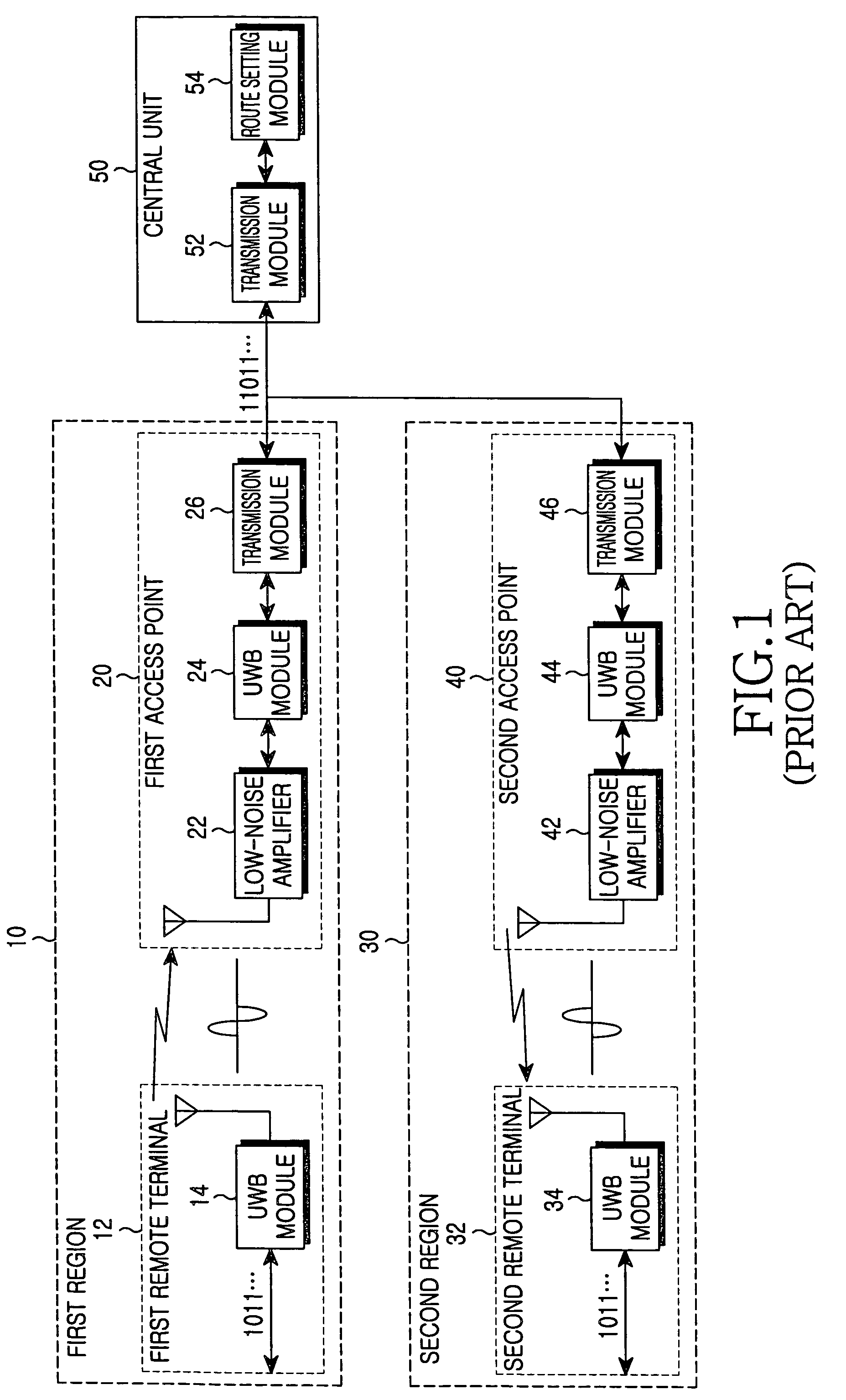
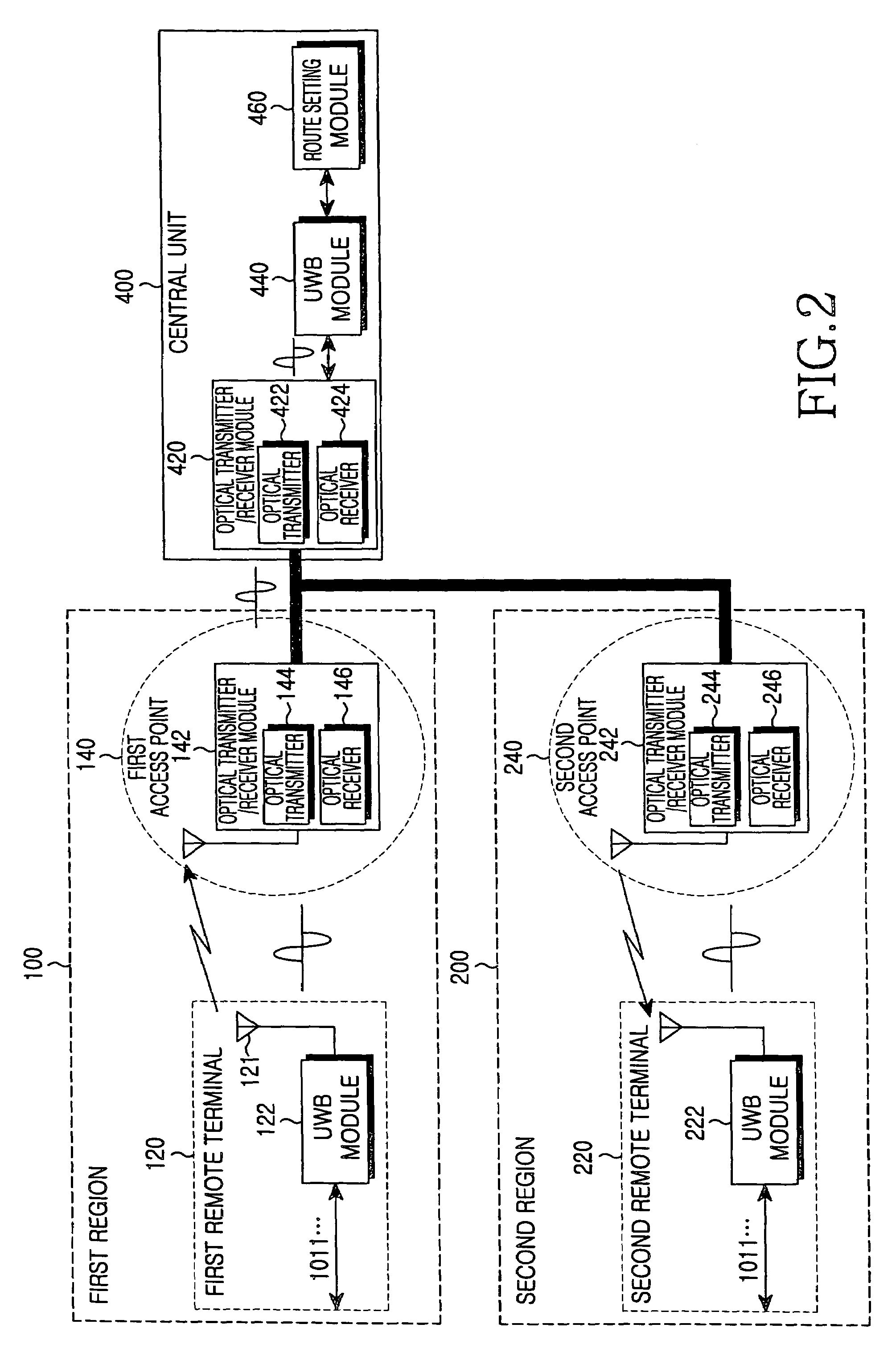
Indoor local area network system using ultra wide-band communication system
InactiveUS7366150B2Increase profitLow costNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDigital dataBroadband
An indoor local area network (LAN) system using an ultra wide-band (UWB) communication system is provided. The indoor LAN system includes at least one remote terminal including a UWB module for converting input digital data to be transmitted into an analog signal of an ultra wide-bandwidth and wirelessly transmitting the converted analog signal via an antenna of the remote terminal. The UWB module receives an analog signal of the ultra wide-bandwidth via the antenna and converts the received analog signal into a digital signal. The indoor LAN system further includes at least one access point for performing USB-based wireless communication with the remote terminal in a corresponding area. The access point is adapted to receive the analog signal of the ultra wide-bandwidth transmitted from the remote terminal and convert the received analog signal into an optical signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
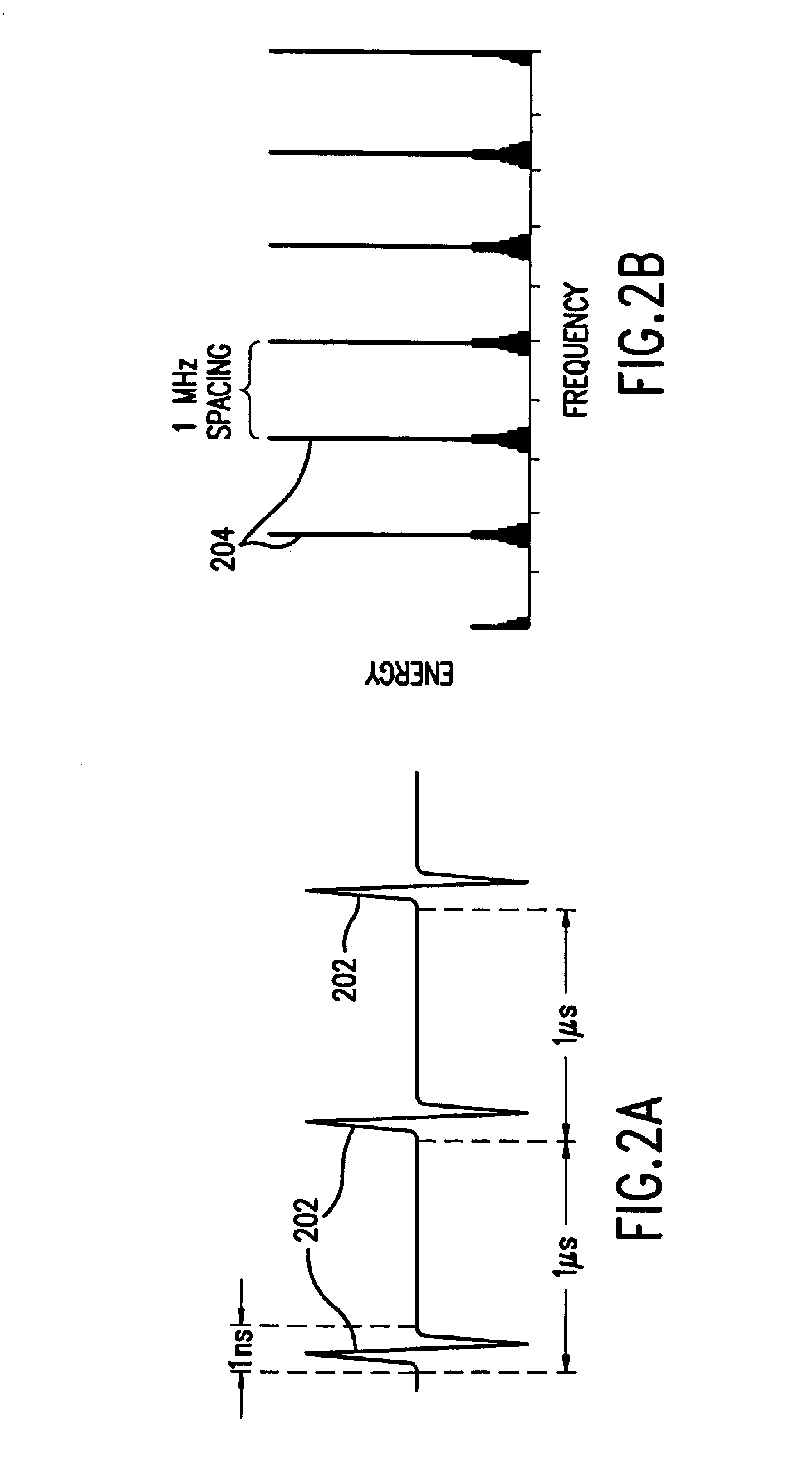
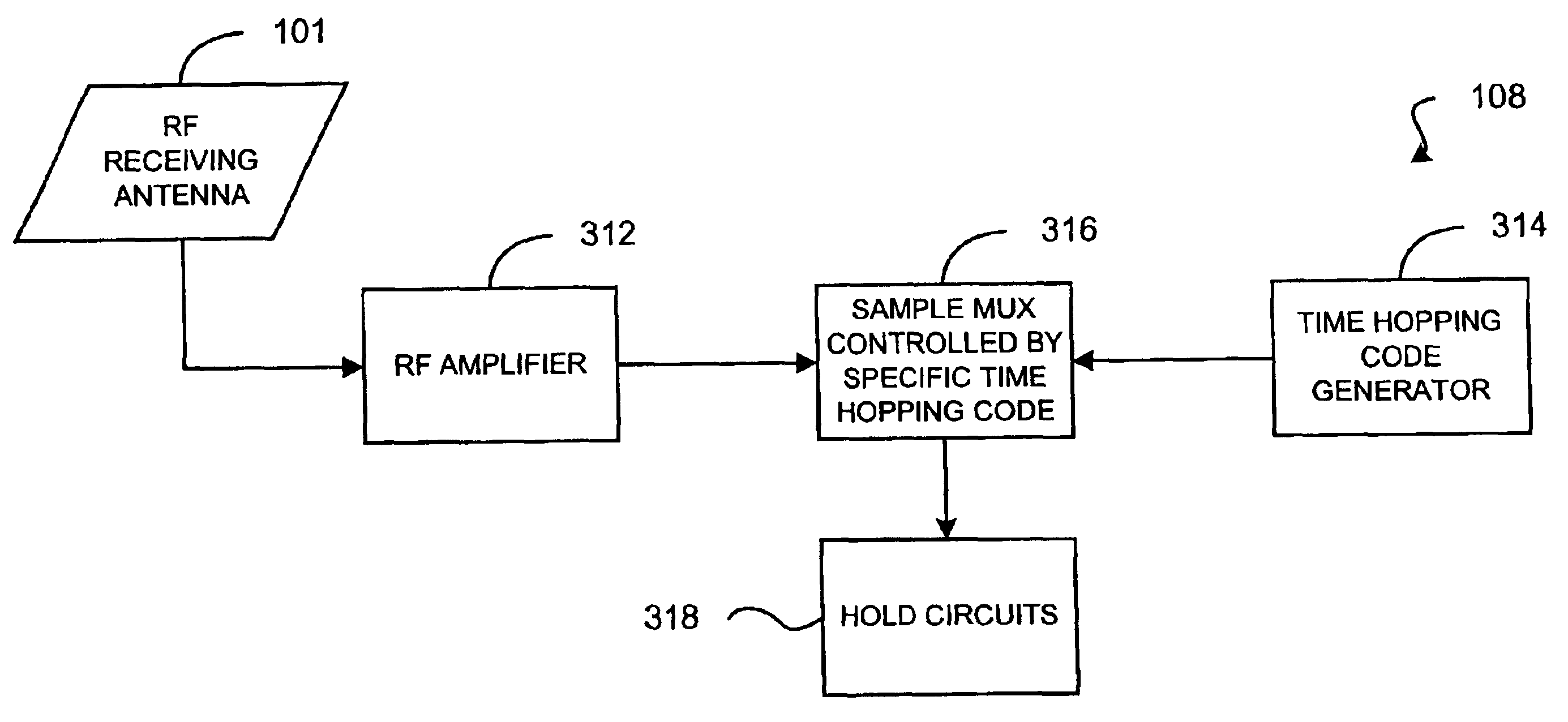
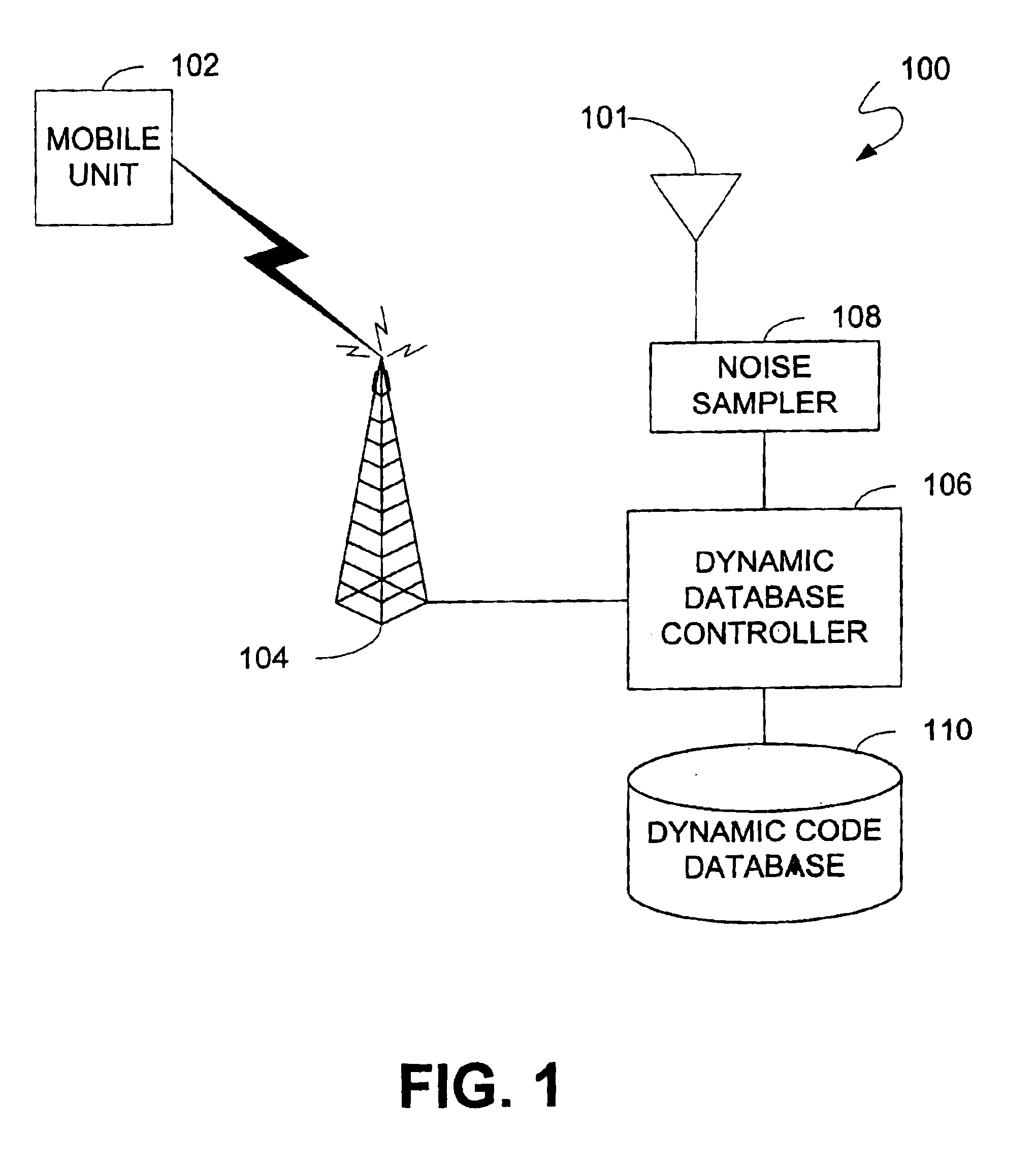
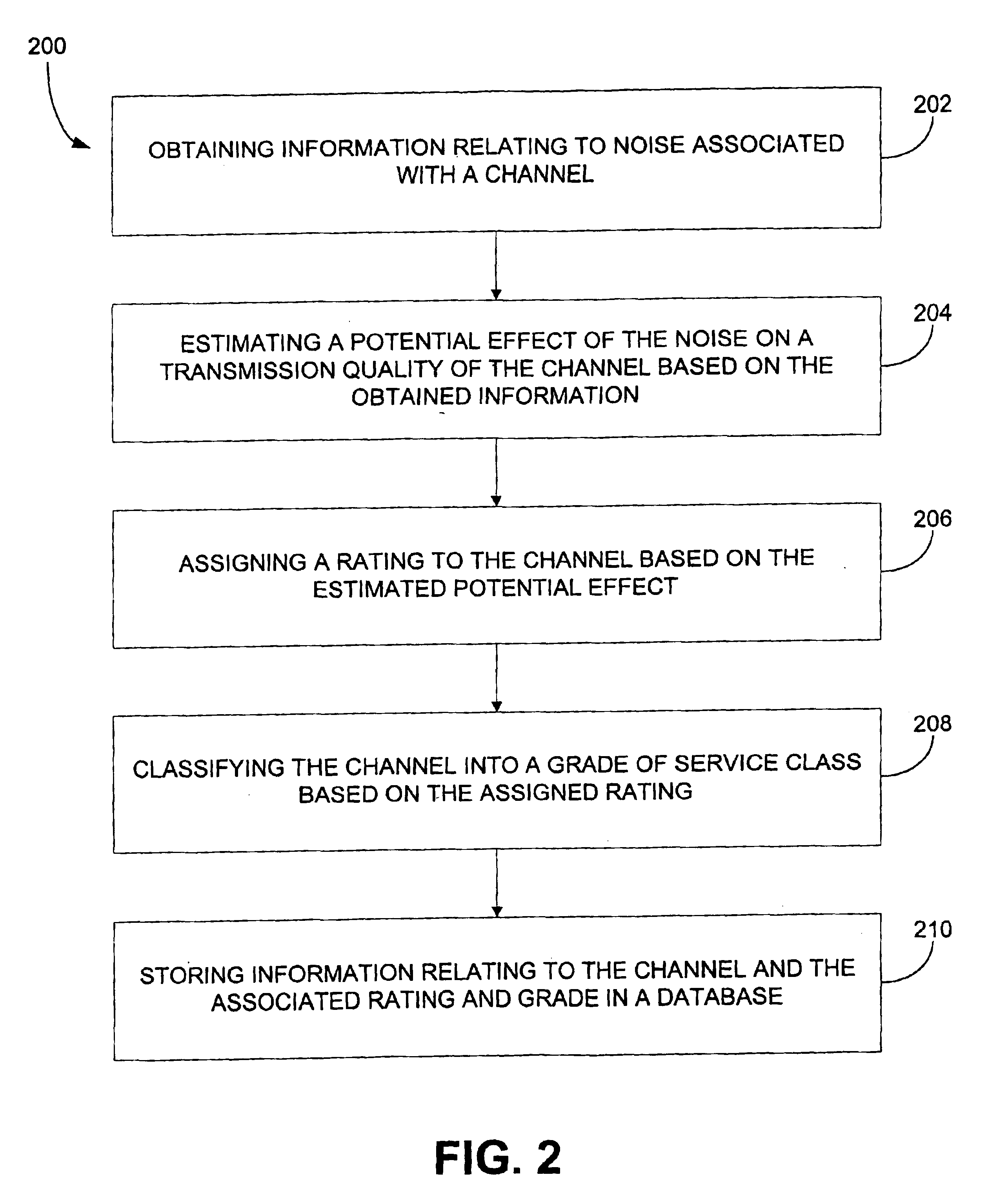
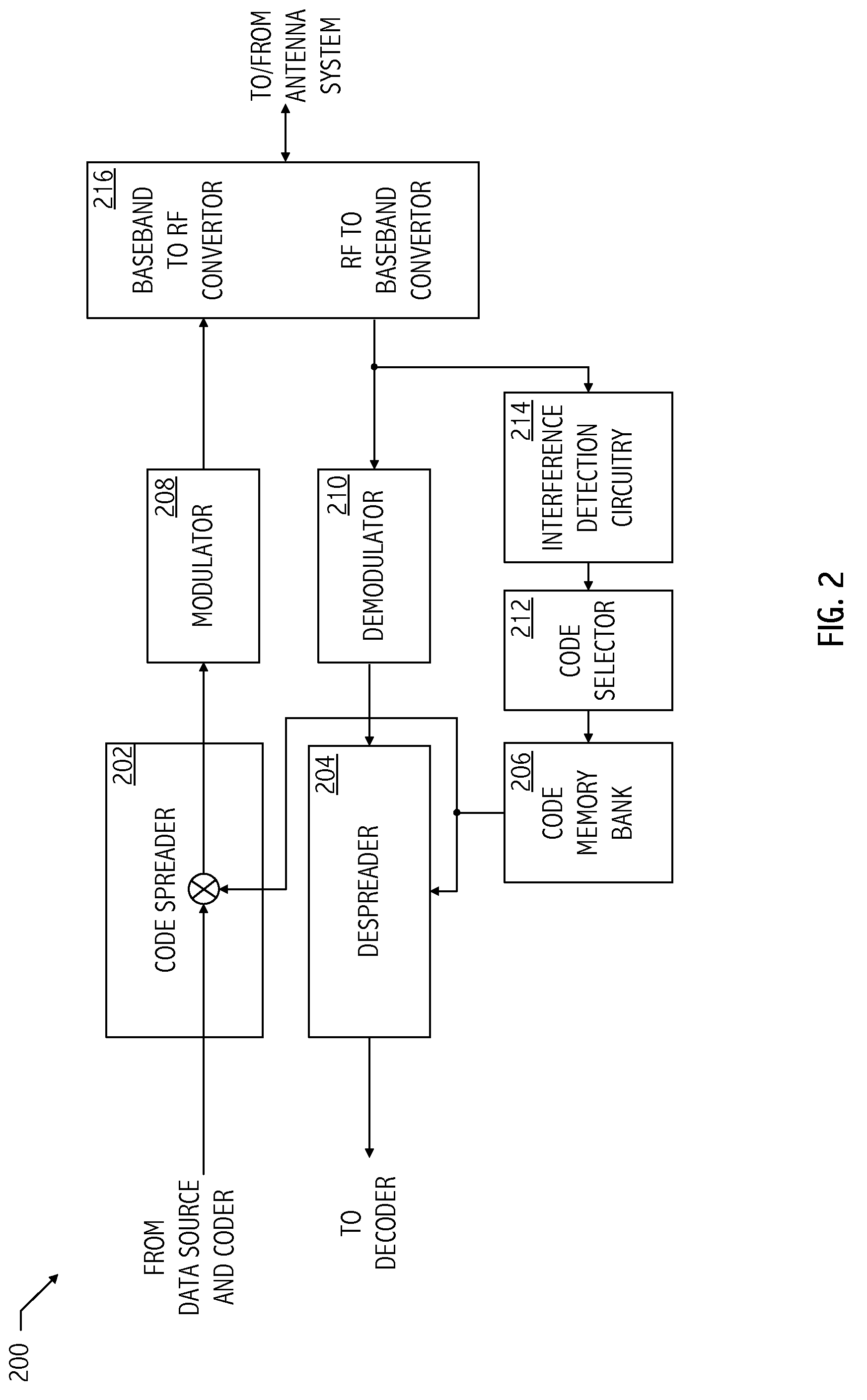
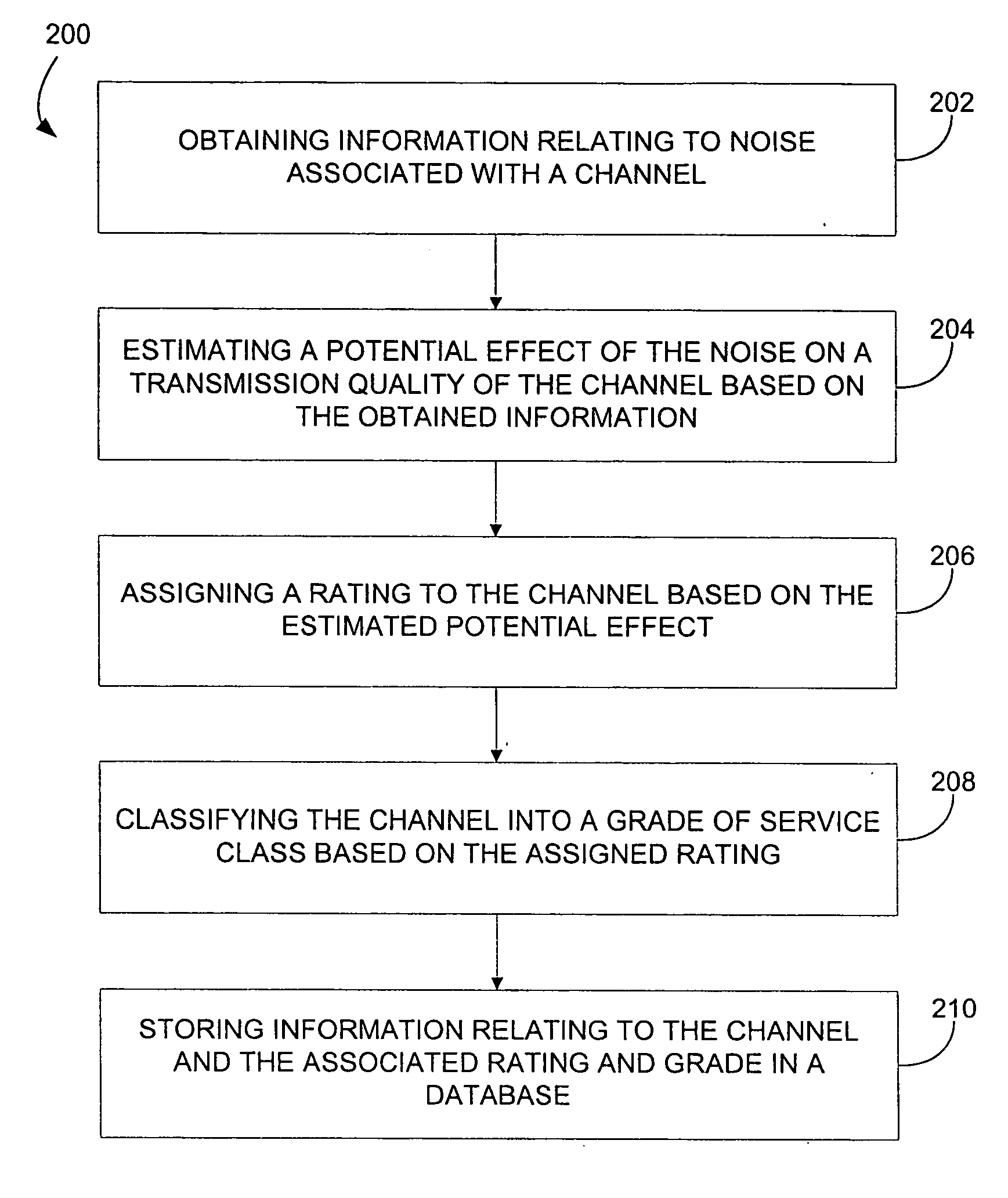
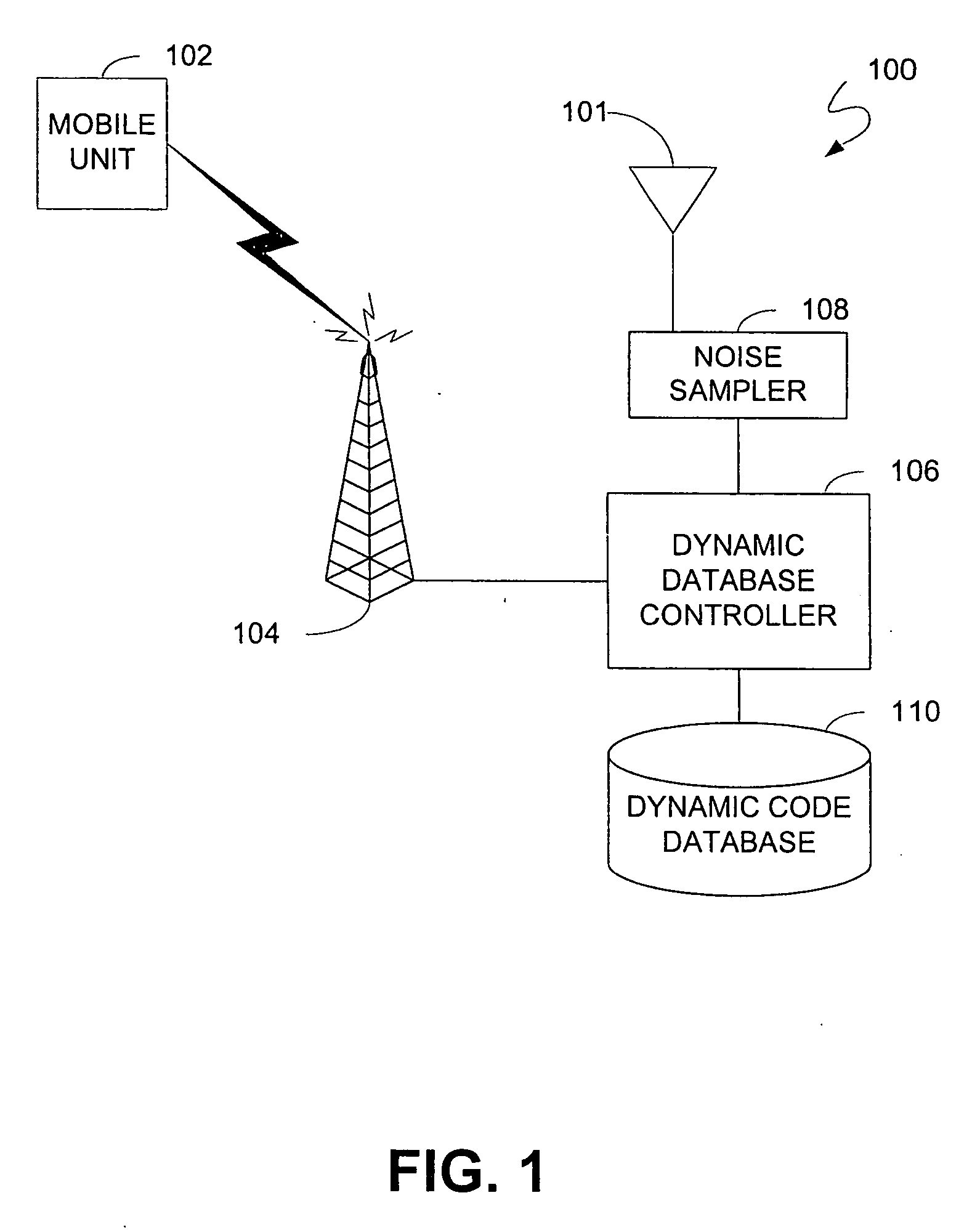
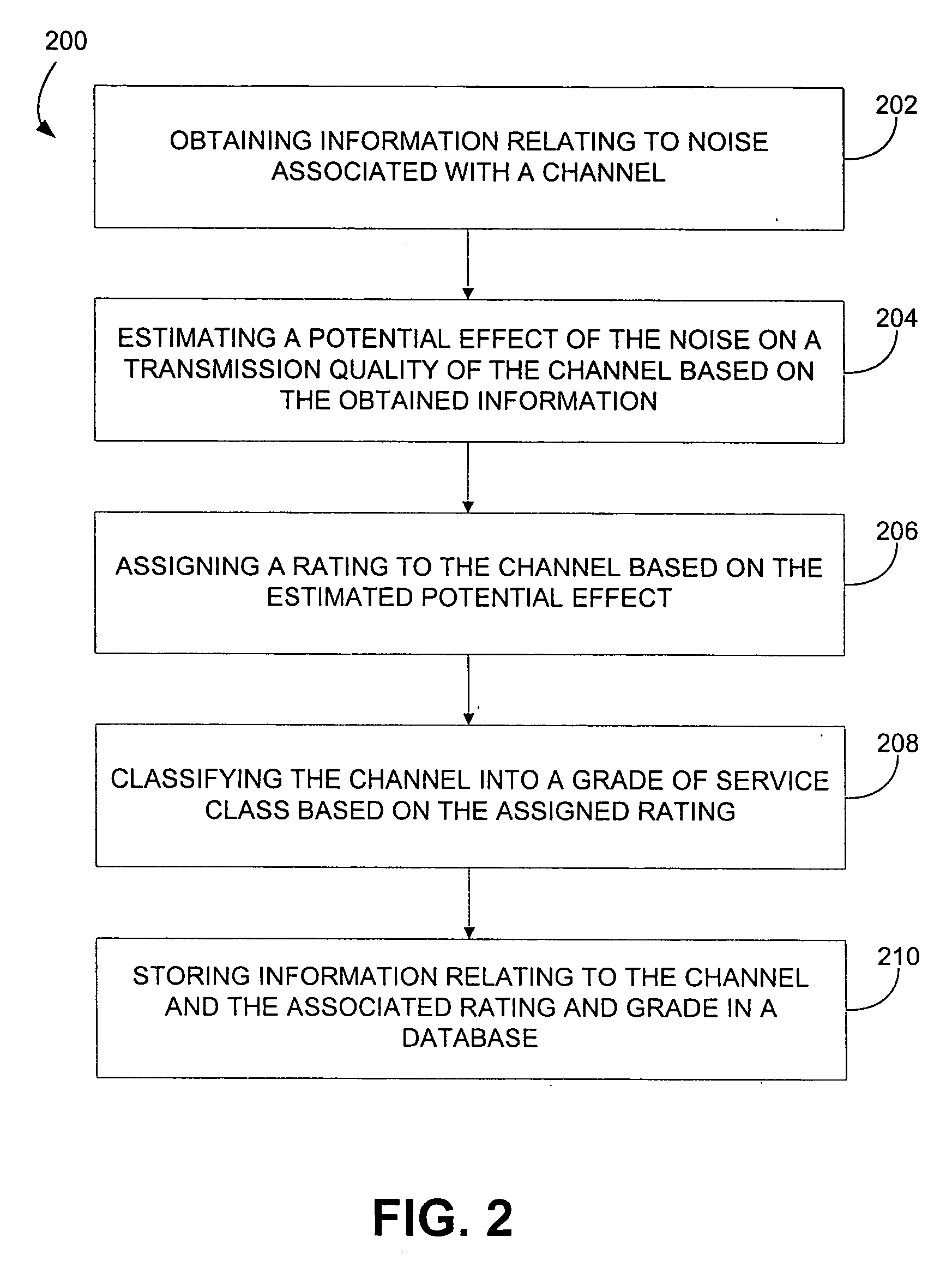
Mapping radio-frequency noise in an ultra-wideband communication system
InactiveUS6937674B2Quality improvementImprove reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTime segmentEngineering
A system and method for mapping radio-frequency (RF) noise, and estimating channel quality in a multi-channel ultra-wideband communication system is provided. One method includes placing a plurality of time bins within a plurality of time frames and assigning a plurality of UWB communication channels comprising selected time bins. RF noise amplitude data is then sampled from selected time bins. The sampled RF noise amplitude data from the time bins is then averaged, thereby obtaining an average RF noise amplitude in each of the plurality of channels. The RF noise amplitude indicates the amount of RF noise present in a channel. The channels may then be ranked based on the characteristics of the RF noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Impulse ultra-wideband radio communication system
ActiveUS20090258669A1Reduce complexityImprove performanceModulated-carrier systemsSubstation equipmentRound complexityCarrier signal
A method and apparatus are provided for implementing an impulse ultra-wideband communications system which combines the technique of transmitted reference (TR) with a code-sifted reference scheme that separates the reference and the data pulses with a sequence of codes such as a subset of Walsh codes. The combination of the two techniques in ultra-wideband (UWB) radio systems removes the wideband delay elements required by conventional TR UWB systems. The invention provides a system with no analog carriers and lower complexities than other UWB systems, and which has better performances, higher tolerance to nonlinearity, and larger capacities
Owner:CHENGDU SPROUTING TECH CO LTD
Ultra wideband communication system, method, and device with low noise reception
InactiveUS6859506B1Avoid problemsAvoid self-interferenceModulated carrier system with waveletsError preventionLow noiseSignal on
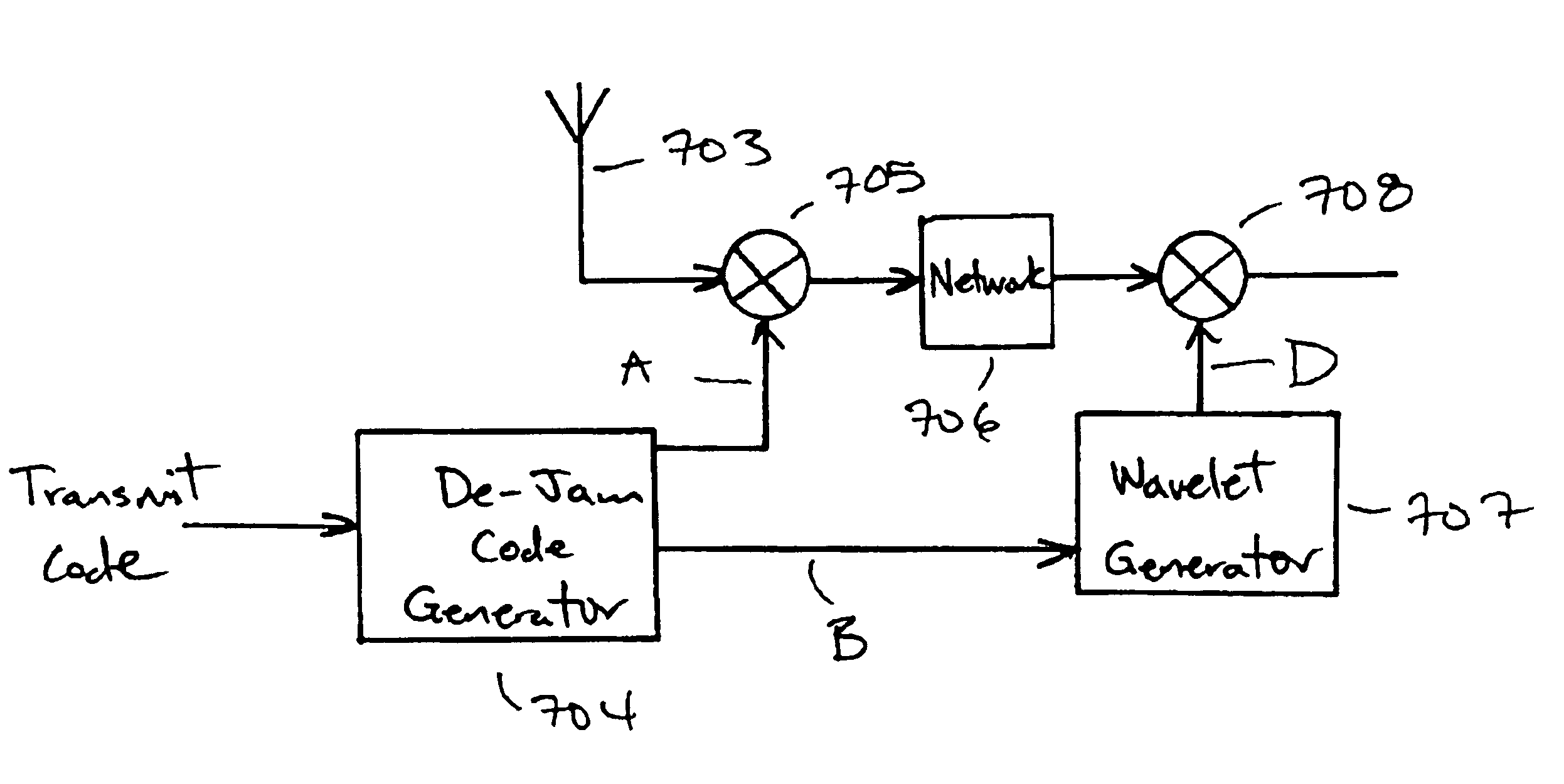
An ultra-wide band (UWB) waveform receiver with noise cancellation for use in a UWB digital communication system. The UWB receiver uses a two-stage mixing approach to cancel noise and bias in the receiver. Self-jamming is prevented by inverting a portion of the received signal in the first mixer and then coherently detecting the partially and synchronously inverted signal in the second mixer. Since the drive signals on both mixers are not matched to the desired signal, leakage of either drive signal does not jam the desired signal preventing the receiver from detecting and decoding a weak signal.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
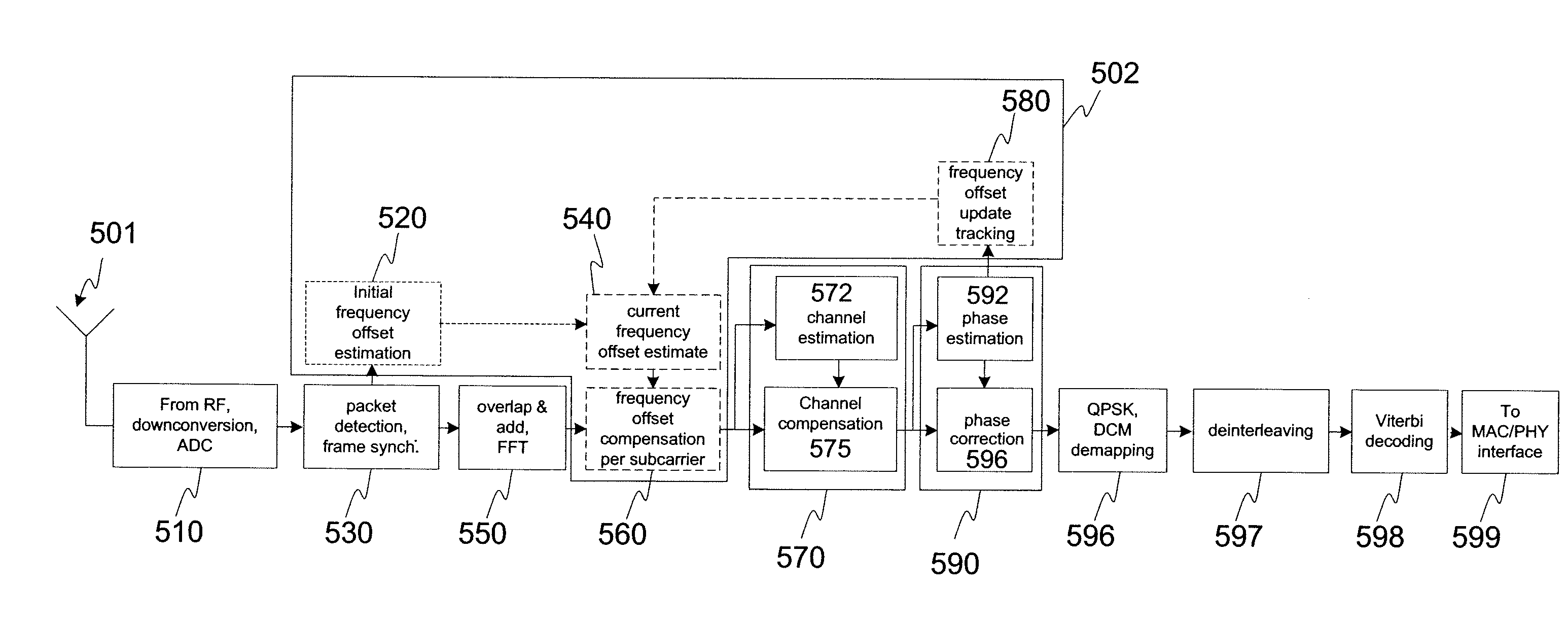
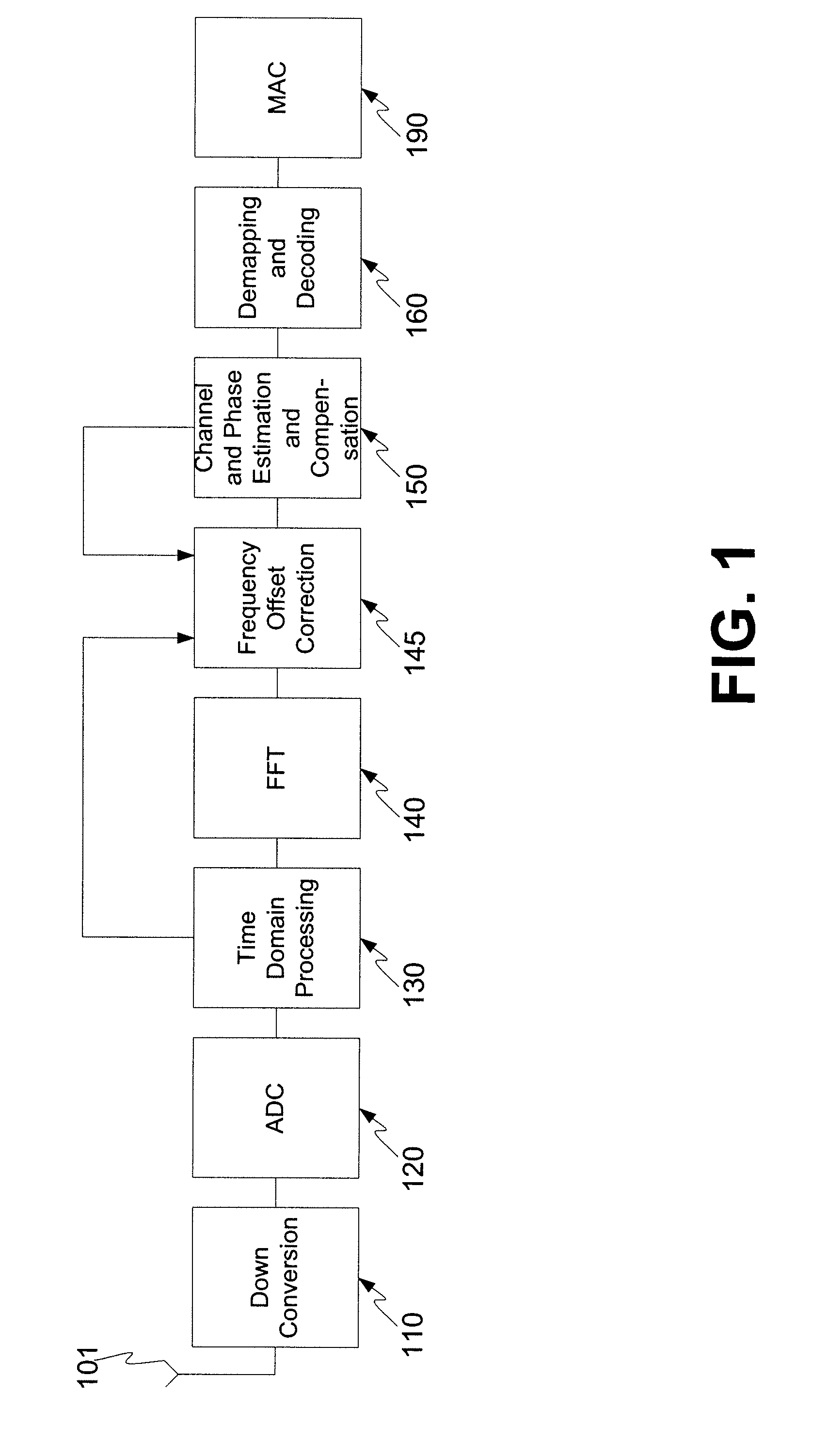
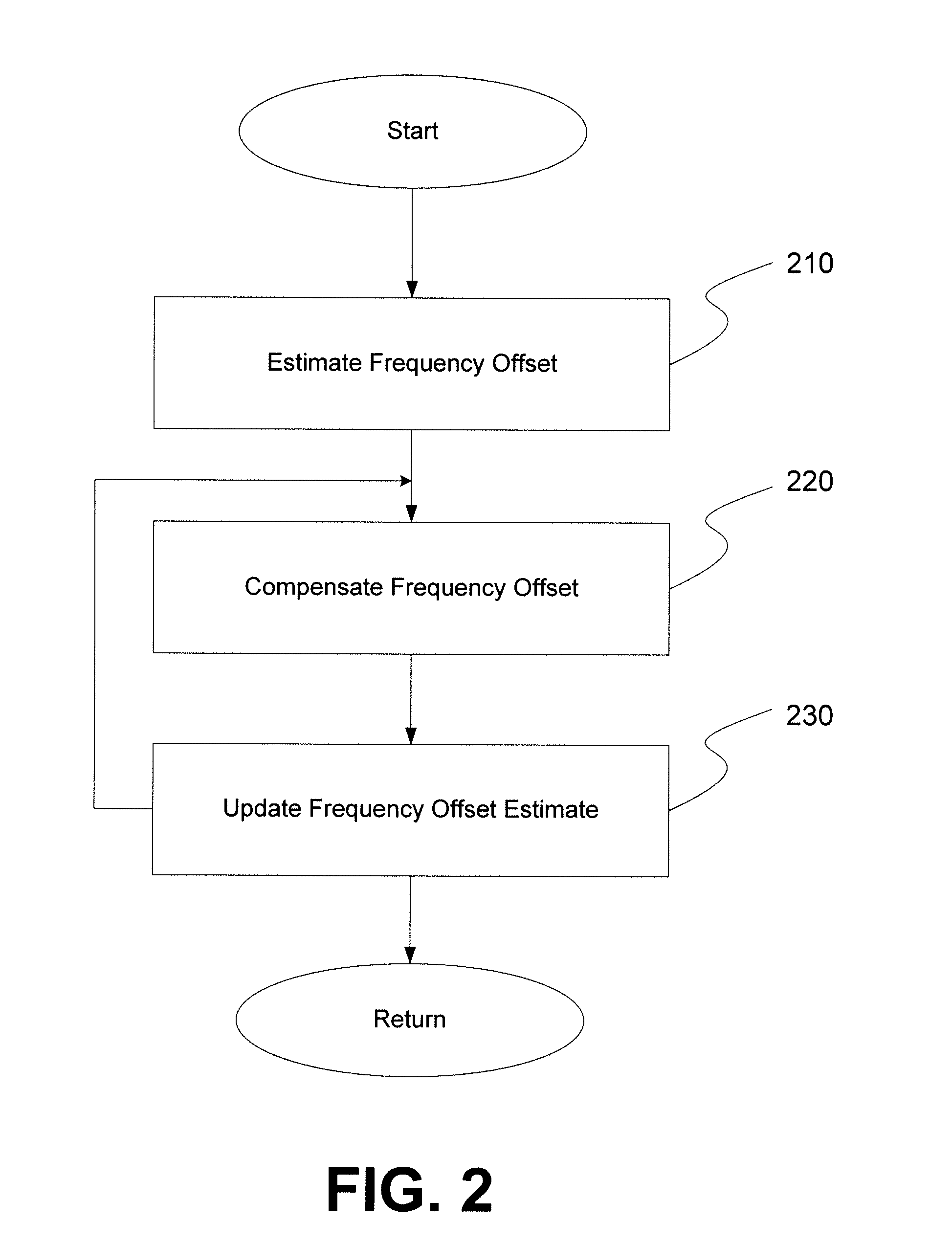
Frequency offset correction for an ultrawideband communication system
ActiveUS20070268976A1Improves initial frequency offset estimateIncrease frequencyAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationTime domainEngineering
A method and a receiver system for subcarrier-specific frequency offset correction including frequency offset estimation, updating and compensation. The method includes initial frequency offset estimation in time domain using packet preamble, frequency offset compensation during channel estimation symbols using the initial frequency offset estimate, and frequency offset update tracking during header and data part both being performed in the frequency domain. The initial frequency offset estimation includes using a sum over a number of time lagged autocorrelation results, corresponding to a number of the last consecutive symbols of the preamble part of the packet with the autocorrelations being the result of a sum over a window of cross-correlations between the incoming signal and the respective packet synchronization sequence. The receiver includes receiver blocks for initial frequency offset estimation, frequency offset compensation, frequency offset update tracking and obtaining a current frequency offset estimate.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
Systems, apparatus and methods for variable rate ultra-wideband communications
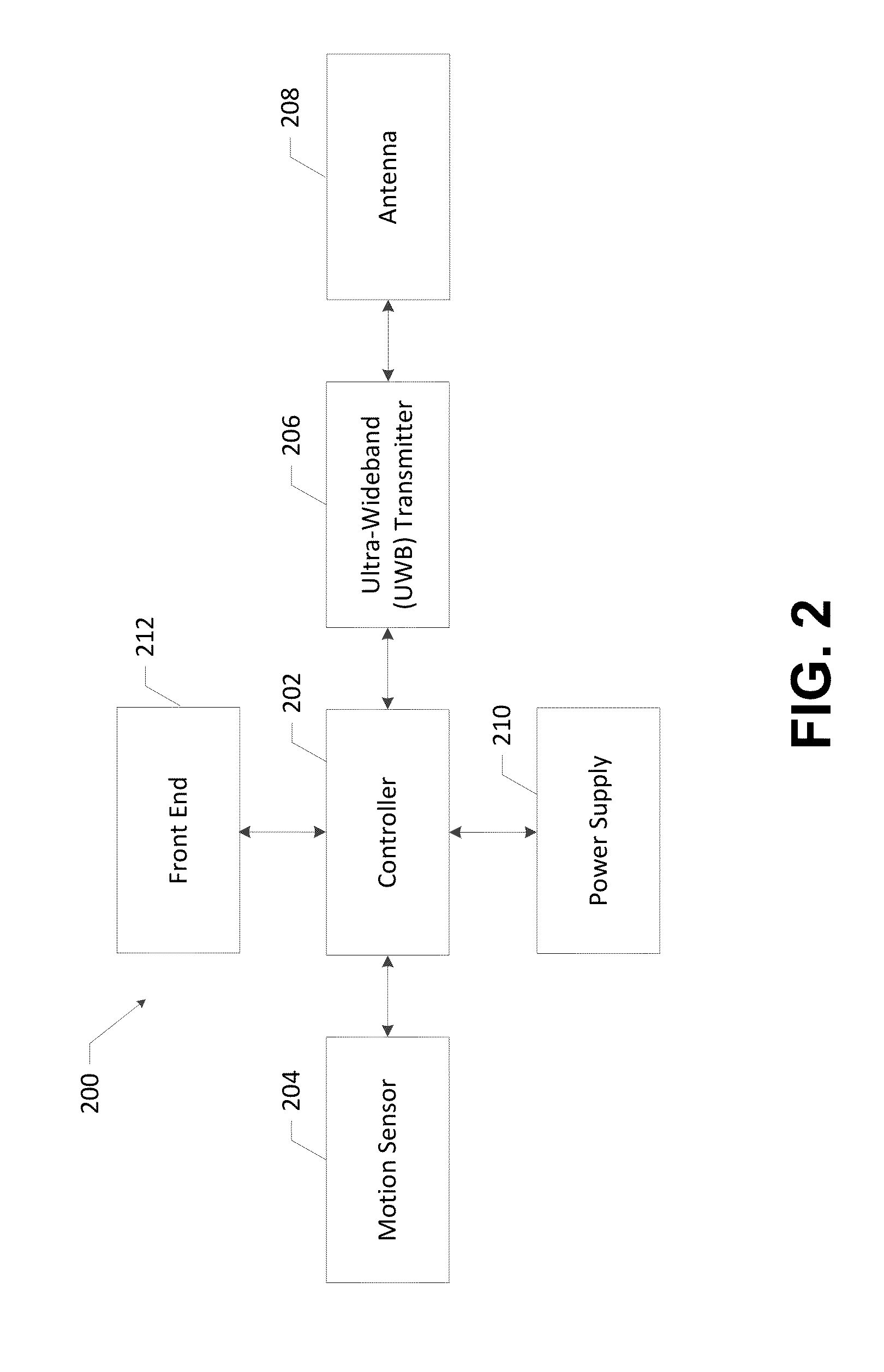
ActiveUS20150356332A1Position fixationSubscribers indirect connectionUltra wideband communication systemsRadio frequency
Systems, methods, apparatuses, and computer readable media are disclosed for providing variable blink rate ultra-wideband (UWB) communications. Some embodiments may provide for a radio frequency (RF) tag including a motion sensor, processing circuitry, and a UWB transmitter. The motion sensor may be configured to generate one or more motion data values indicating motion of the RF tag. The UWB transmitter may be configured to transmit blink data at variable blink rates. The processing circuitry may be configured to receive the one or more motion data values from the motion sensor, determine a blink rate for the UWB transmitter based on the one or more motion data values, and control the UWB transmitter to wirelessly transmit the blink data at the blink rate. In some embodiments, the RF tag may include a UWB receiver and the blink rate may be controlled remotely by a system.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Ultra wide band communication systems and methods
InactiveUS20050018762A1Easy to makeLow costEnergy efficient ICTMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTransceiverTime division multiple access
Ultra wide band communication systems and methods are provided. In one embodiment, an ultra wide band communication system includes a first and a second communication device. A lowest common ultra wide band pulse repetition frequency is determined, and data is transmitted between the communication devices using the lowest common ultra wide band pulse repetition frequency. In another embodiment, a first and second slave transceiver communicate with a master transceiver using a time division multiple access frame, with the master transceiver providing transmission synchronization. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Narrowband interference rejection for ultra-wideband systems
InactiveUS20100304681A1Reduced signal powerReduce distractionsTransmission noise suppressionUltra wideband communication systemsWide band
A technique for reducing interference between a direct-sequence ultra-wideband communications system and a narrowband communications system uses interference-rejecting spreading codes to reduce signal power in a frequency band associated with the narrowband communications system. A method of operating an ultra-wideband communications system includes applying an interference-rejecting spreading code to a signal for transmission. The interference-rejecting spreading code is configured to reduce power in a particular frequency band of a transmit or receive power spectral density associated with the ultra-wideband signal without substantially reducing power outside that particular frequency band of the transmit or receive power spectral density associated with the ultra-wideband signal.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
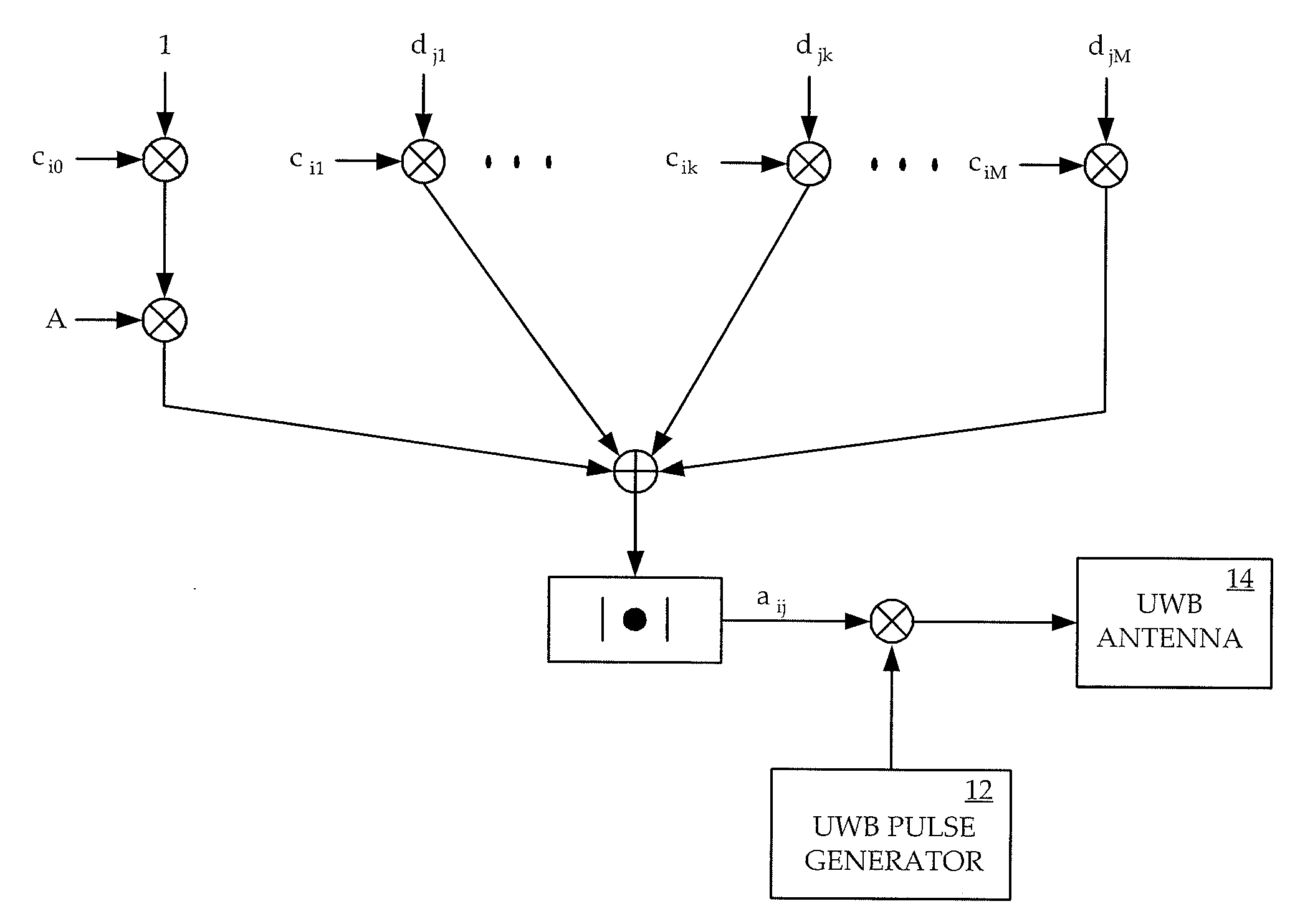
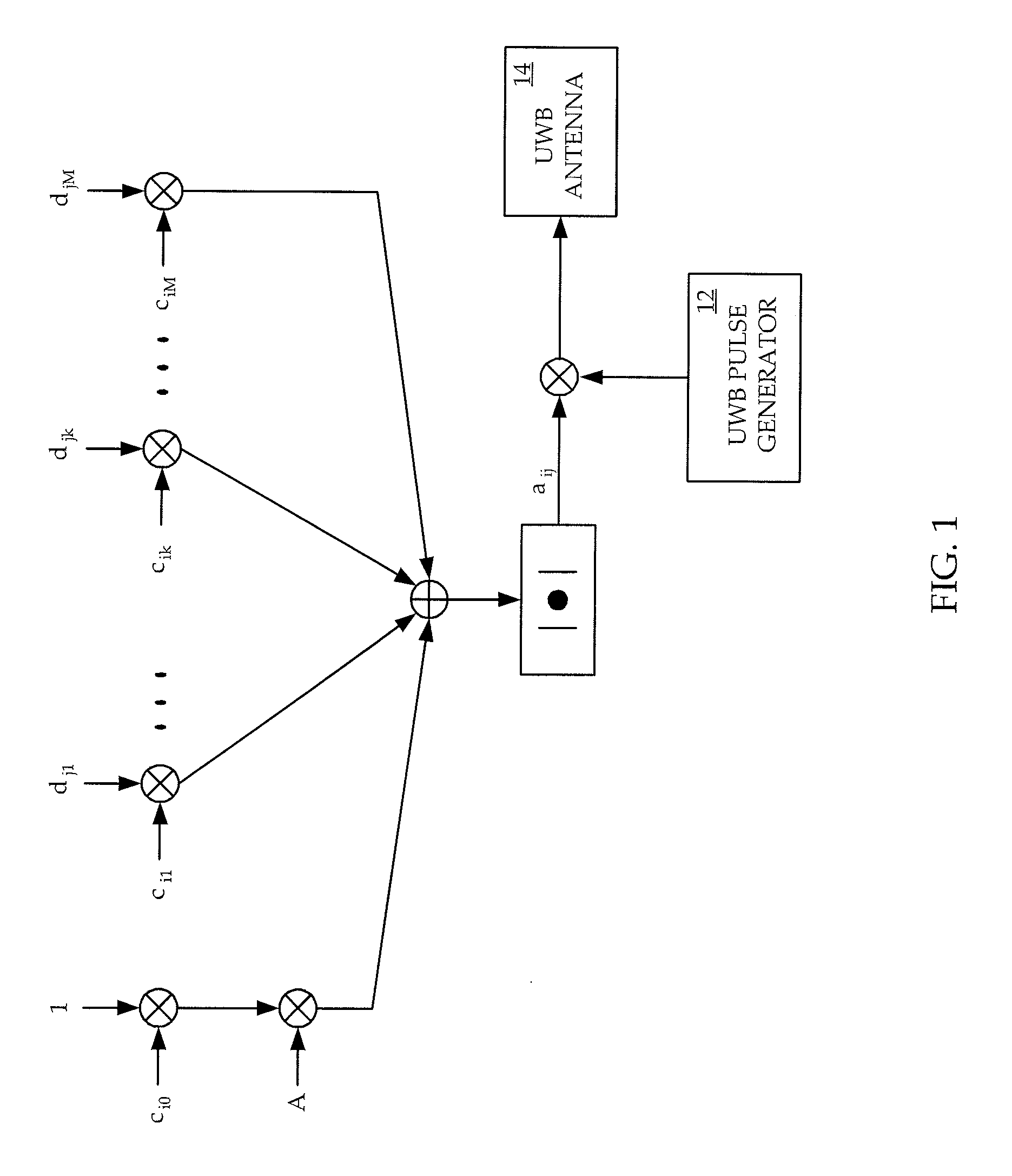
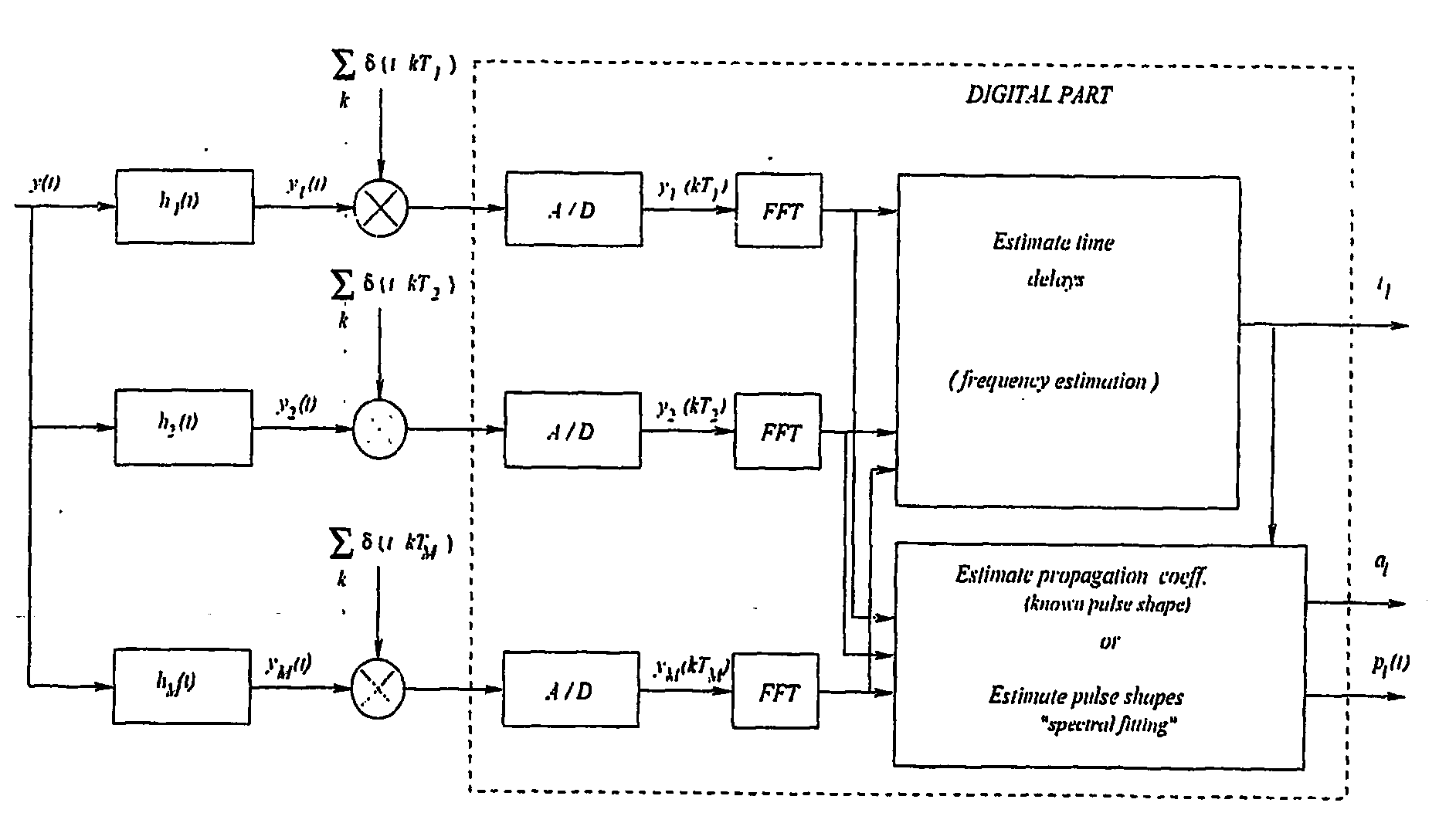
Synchronization And Channel Estimation With Sub-Nyquist Sampling In Ultra-Wideband Communication Systems
InactiveUS20060193371A1Reduce receiver complexityReduced sampling rate requirementsDigital technique networkBaseband system detailsBandpass filteringBroadband
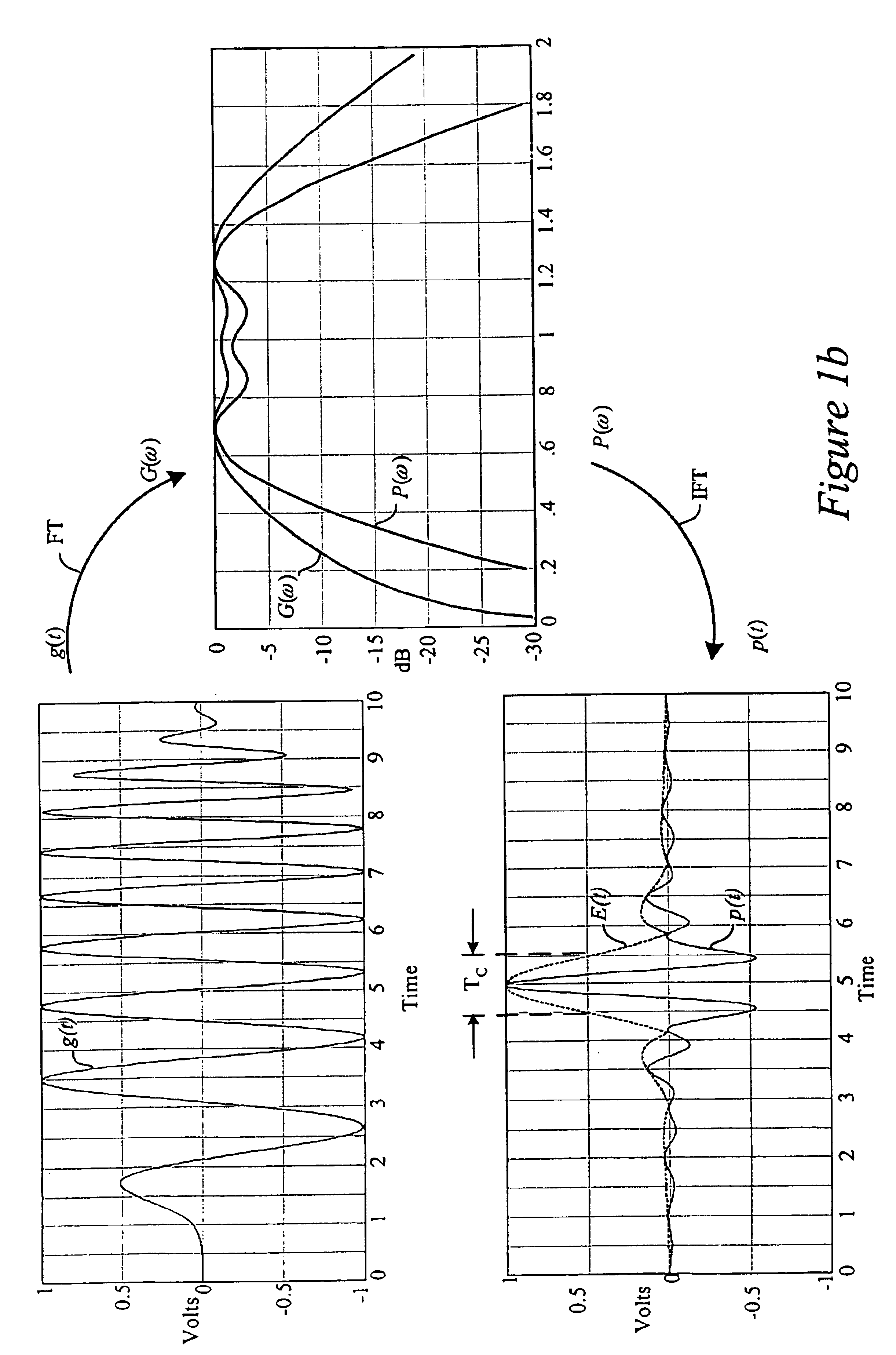
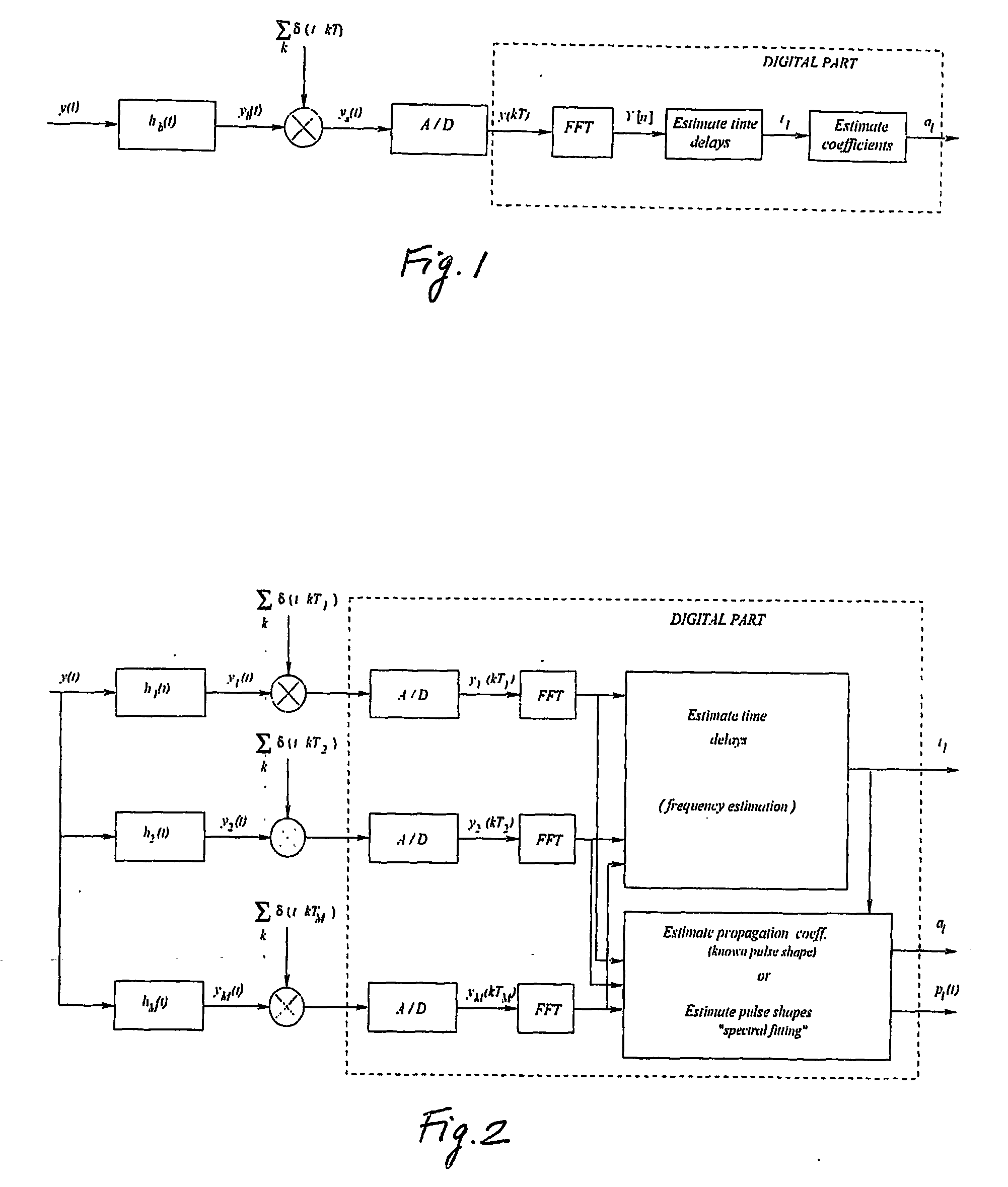
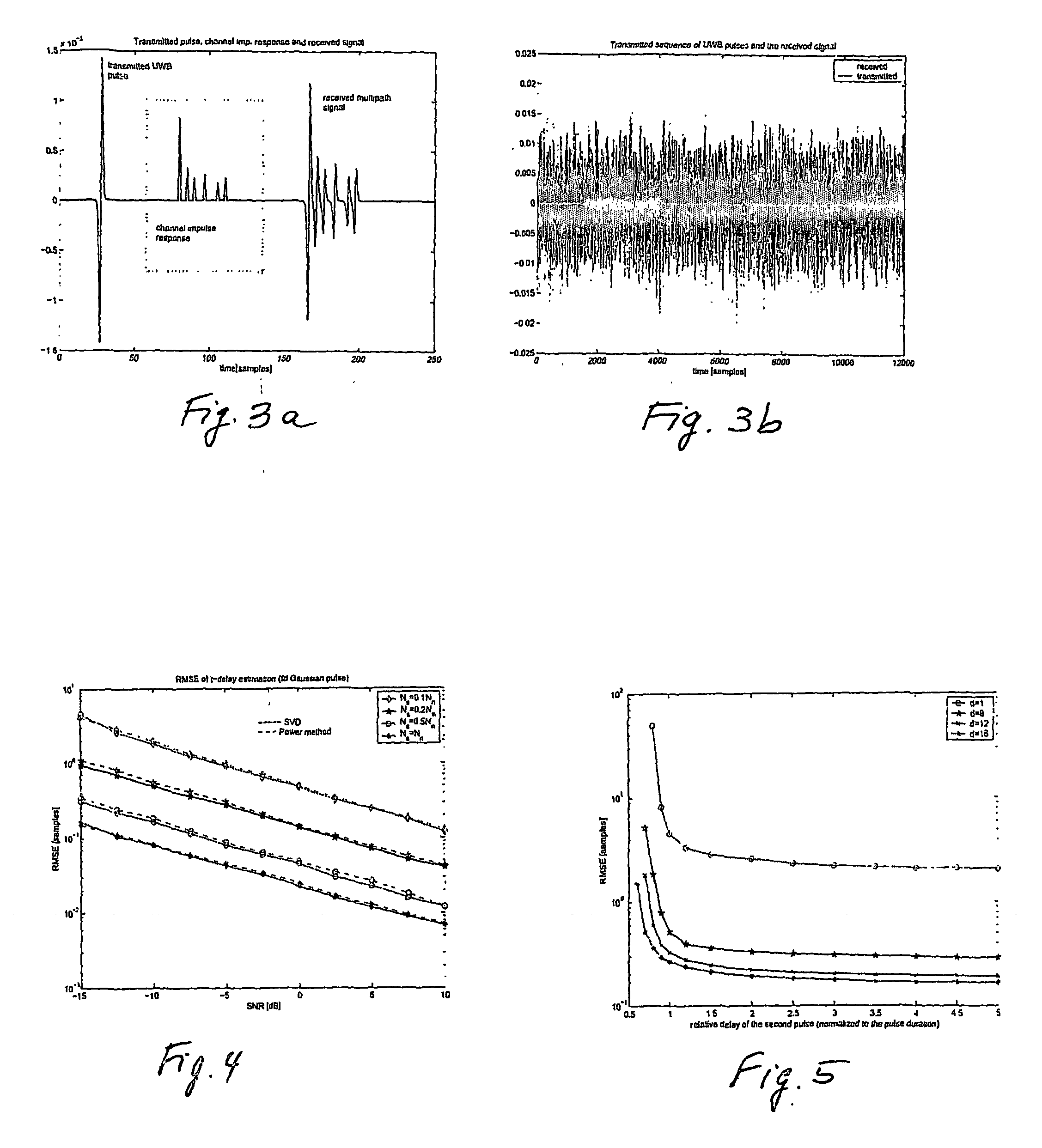
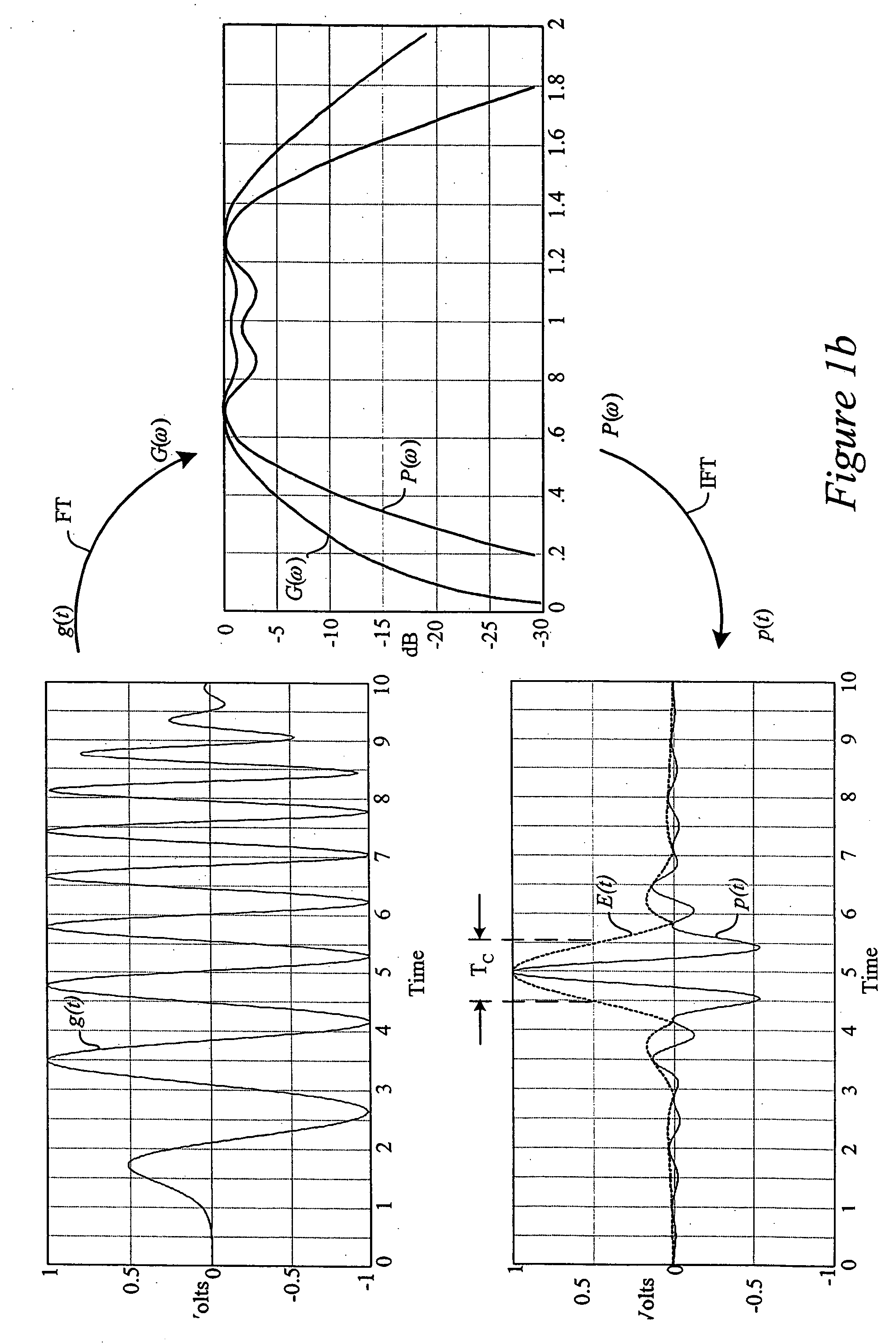
The system and method for estimating impulse response of a wideband communication channel represented as linear combination of L time-shifted pulsed P1(t) with propagation coefficients a1, comprising functionalities or steps for obtaining an ultrawideband signal (y(t) of FIG. 1) received over the channel, filtered (h(1) of FIG. 1) with low pass / bandpass filter and sampled uniformly at a sub-Nyquist rate; a functionality for determining discrete-Fourier-transform coefficients Yj and Sj (FFT of FIG. 1) from the sampled received signal and a transmitted ultra-wide-band pulse, respectively; a functionality for determining dominant singular vectors of a matrix having Yj+l4 / Sj+i4, as its i, j-elements; a functionality for estimating a plurality of powers of signal poles from the dominant singular vectors and determining the times shifts from the estimated powers; and a functionality for determining the propagation coefficients from a system of linear equalizations.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive ternary A/D converter for use in an ultra-wideband communication system
ActiveUS8436758B2Electric signal transmission systemsSynchronisation arrangementBuck converterĆuk converter
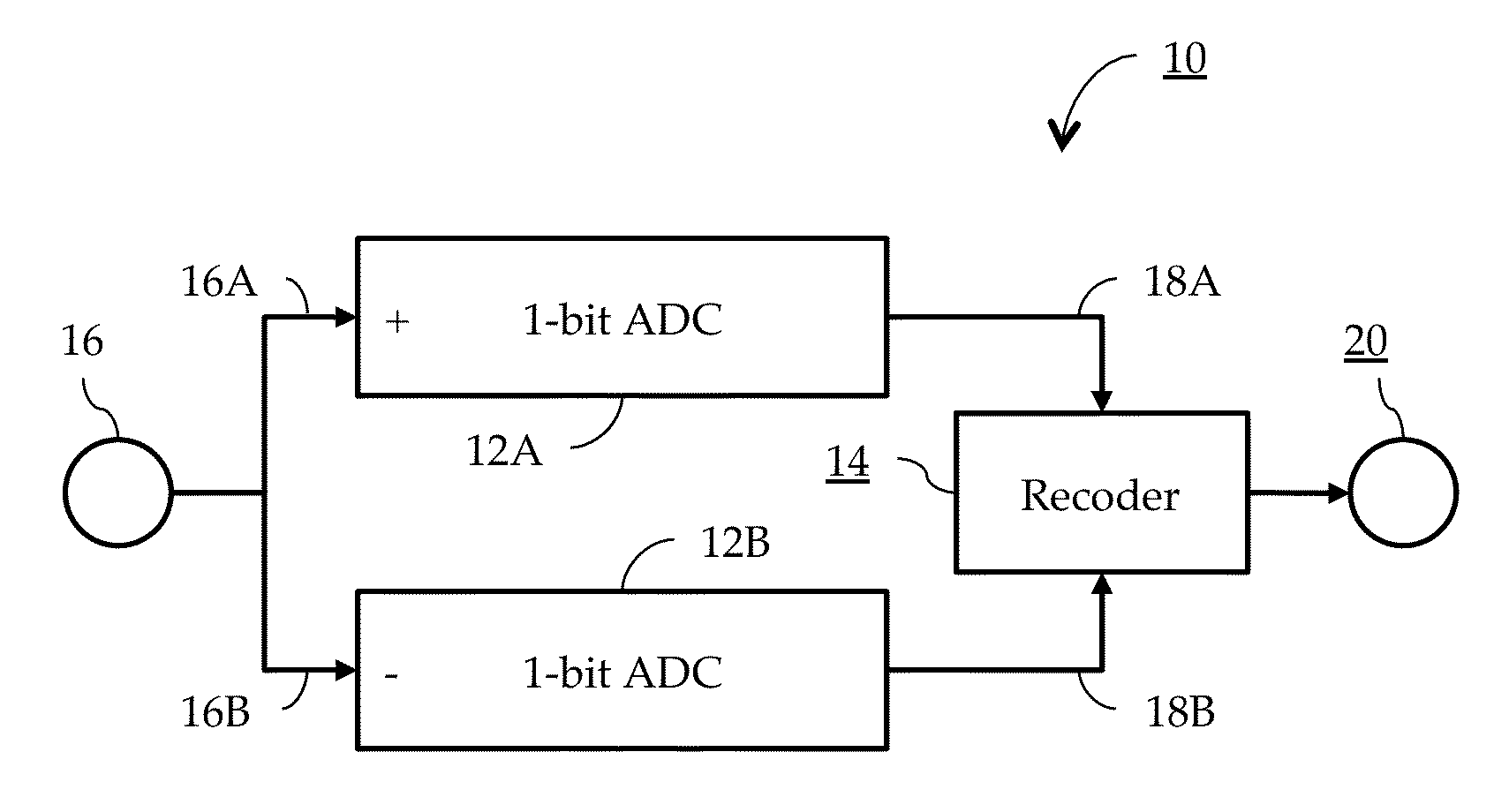
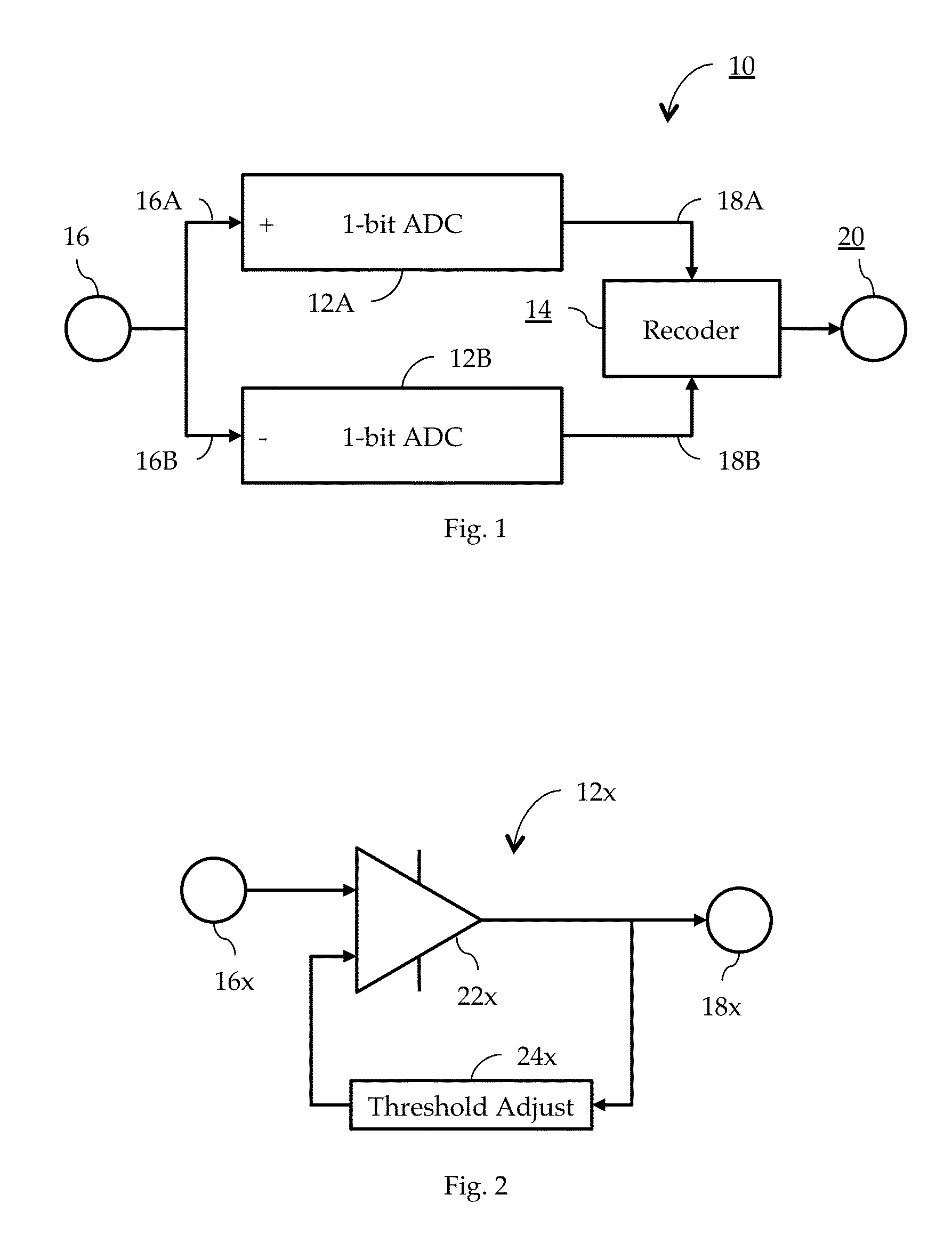
In an ultra-wideband communication system, a 1-trit ternary analog-to-digital converter (“ADC”) having dynamic threshold adaption and providing an output in ternary form [+1, 0, −1]. The ternary ADC includes a pair of 1-bit binary ADCs, one being configured in a non-inverting form, and one being configured in an inverting form. Each binary ADC includes an feedback network mechanism, thereby allowing for simultaneous and independent adaptation of the pair of thresholds, compensating for the effects of any DC offset that may be present. The use of a trit-based ternary encoding scheme improves system entropy.
Owner:DECAWAVE
Impulse radio-based ultra wideband (IR-UWB) system using 1-bit digital sampler and bit decision window
ActiveUS20080056419A1Low costReduce power consumptionSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsOn-off keyingEngineering
An impulse radio-based ultra wideband communication system, using an ultra wideband impulse and a 1-bit high-speed digital sampler, includes a transmitting RF module, a receiving RF module, a signal recovery unit, a transmitting signal processor, a receiving signal processor, and an ultra wideband antenna. The transmitting RF module includes an integrated impulse generator capable of implementing on-off-keying modulation and pulse position modulation, and an amplifier for amplifying output of the integrated impulse generator. The receiving RF module includes a two stage envelope detector for detecting a received signal and a comparator for converting the detected signal into a rectangular pulse. The signal recovery unit restores the signal from the receiving RF module to a digital signal using the 1-bit digital sampler. The signal processor includes a receiving signal processor for synchronizing the digital signal and decoding the detected signal. The ultra wideband antenna transmits and receives an ultra wideband signal.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
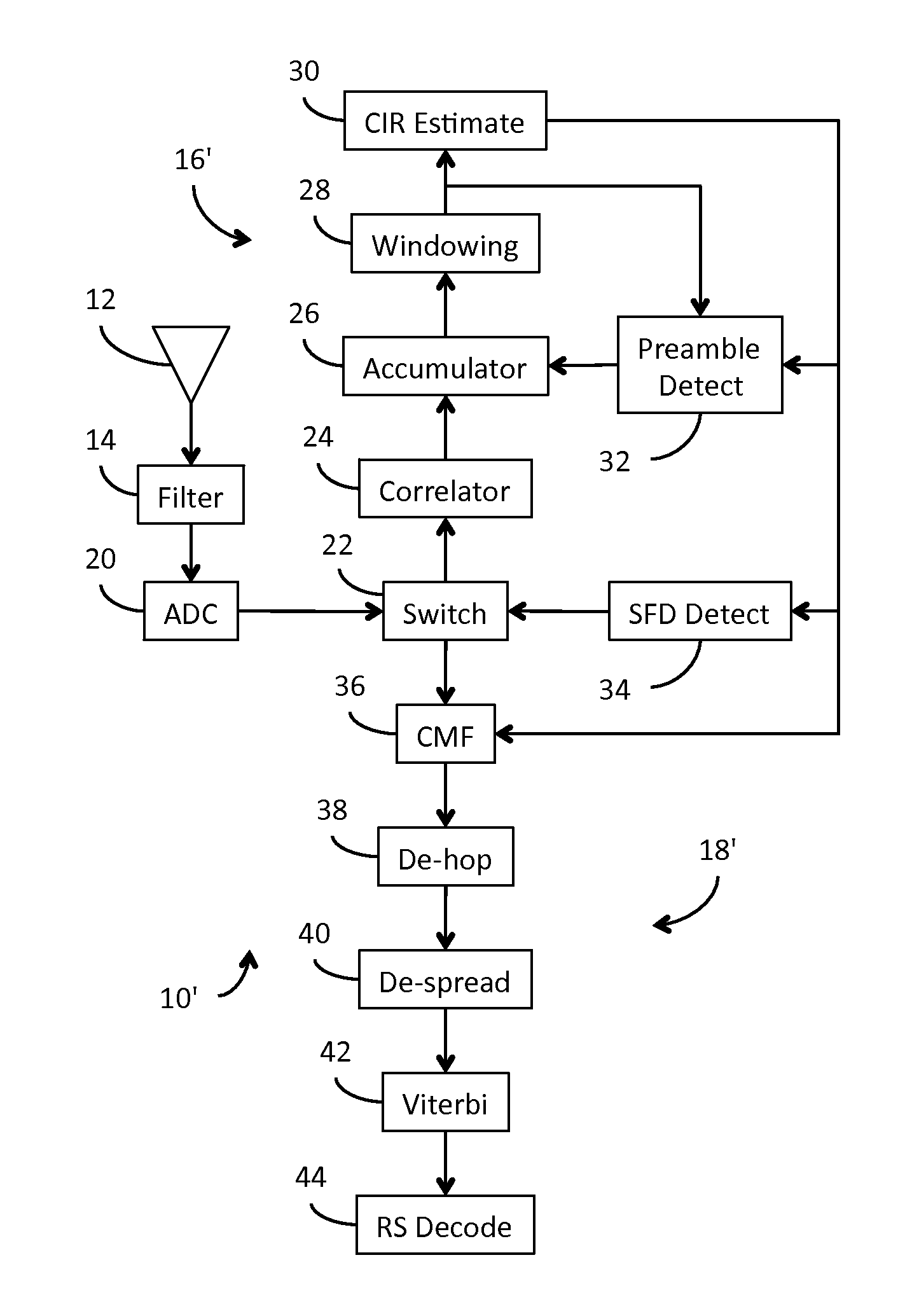
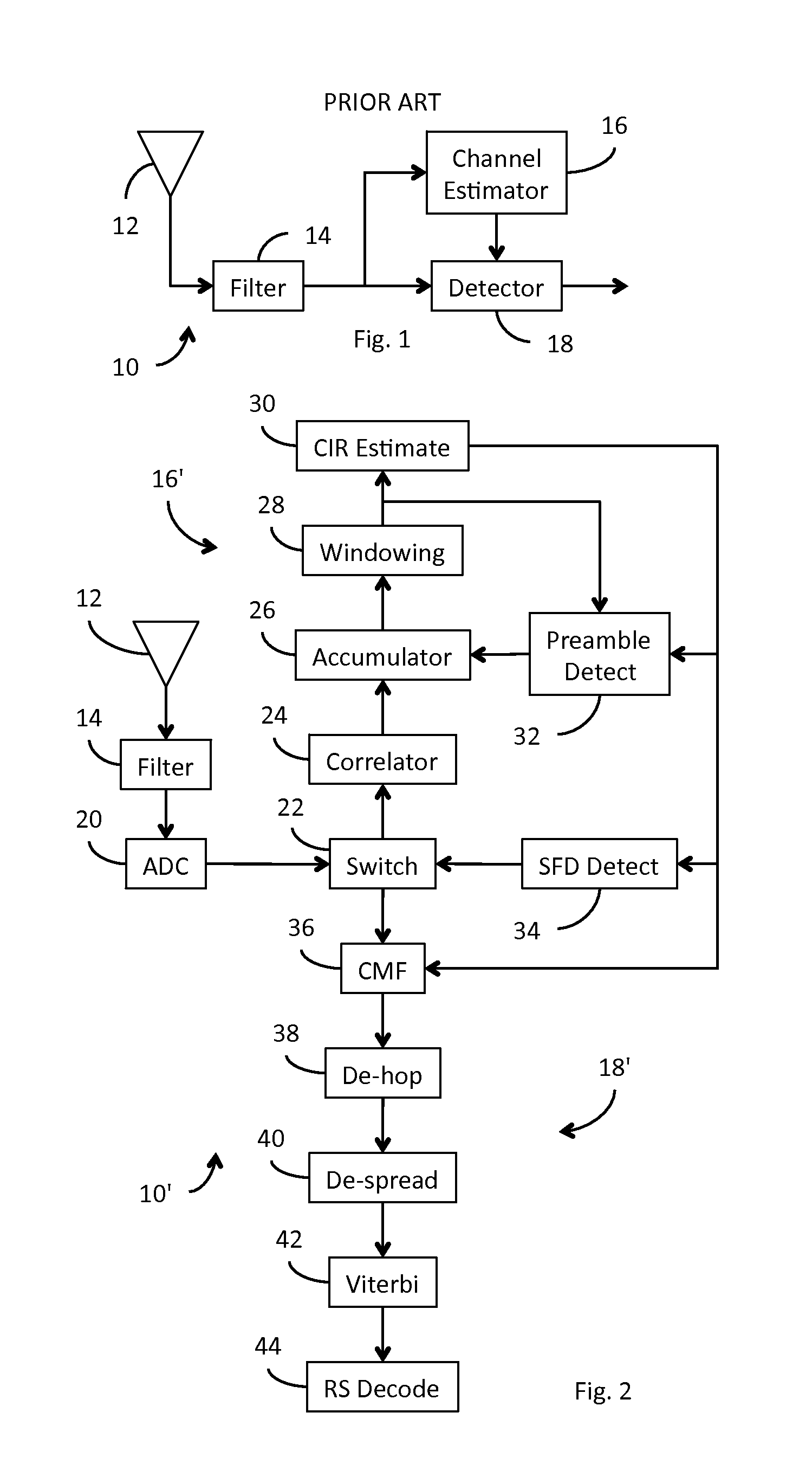
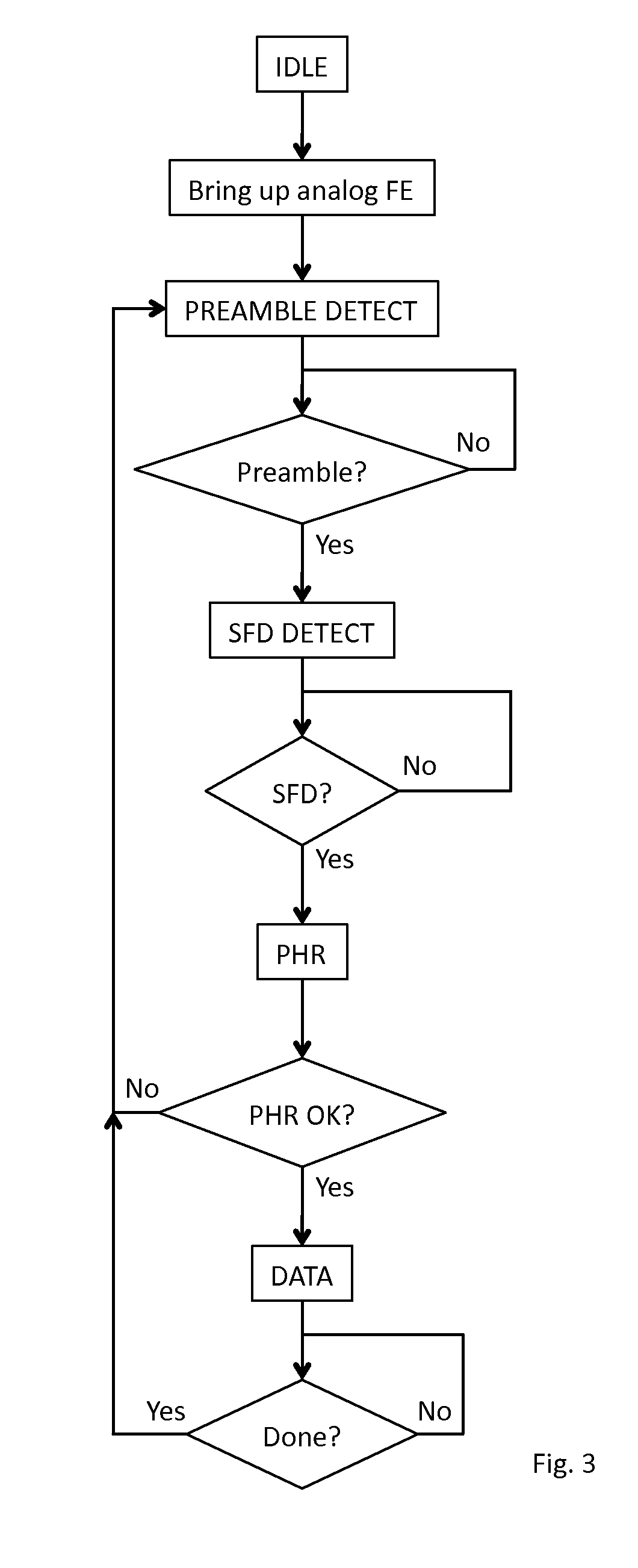
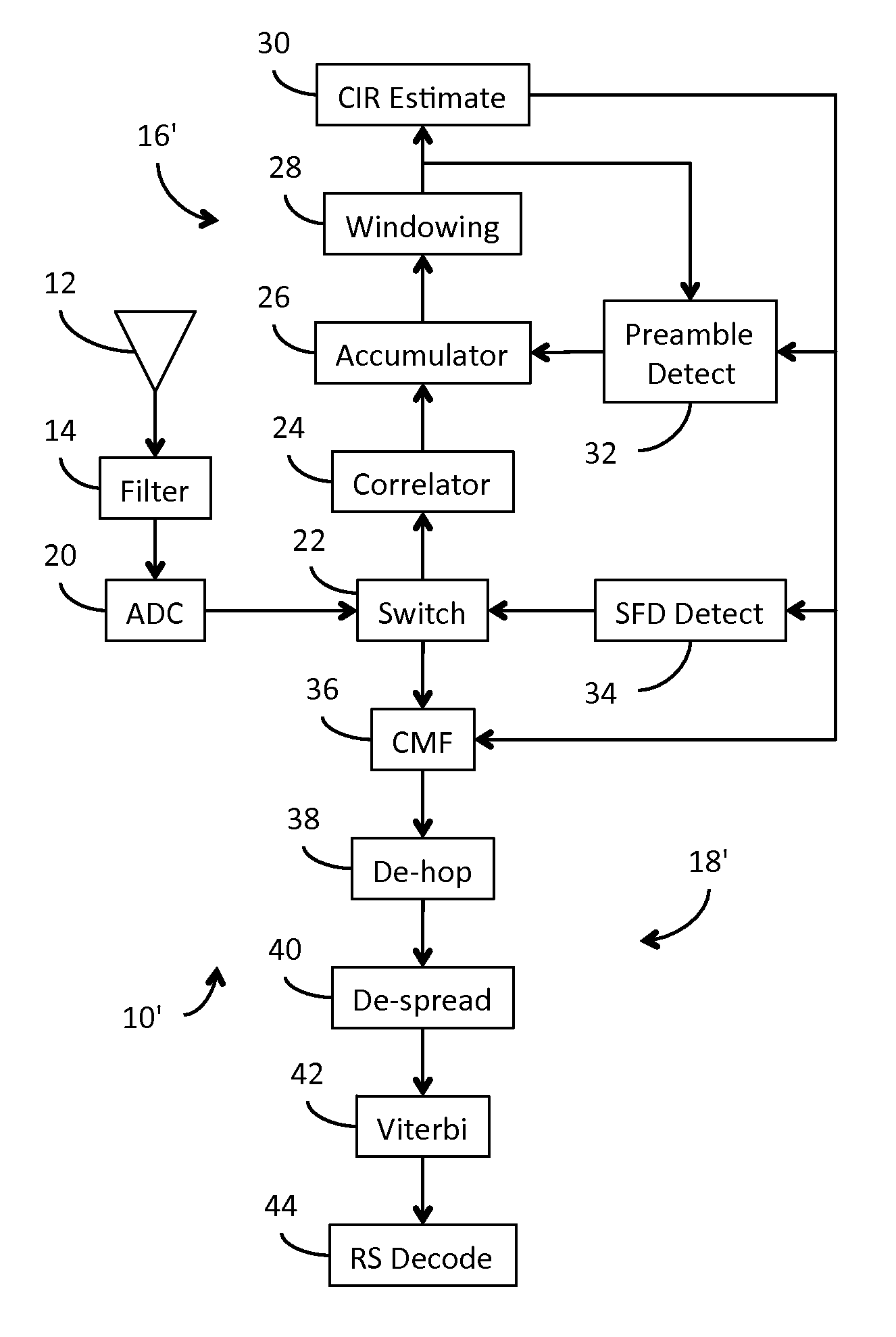
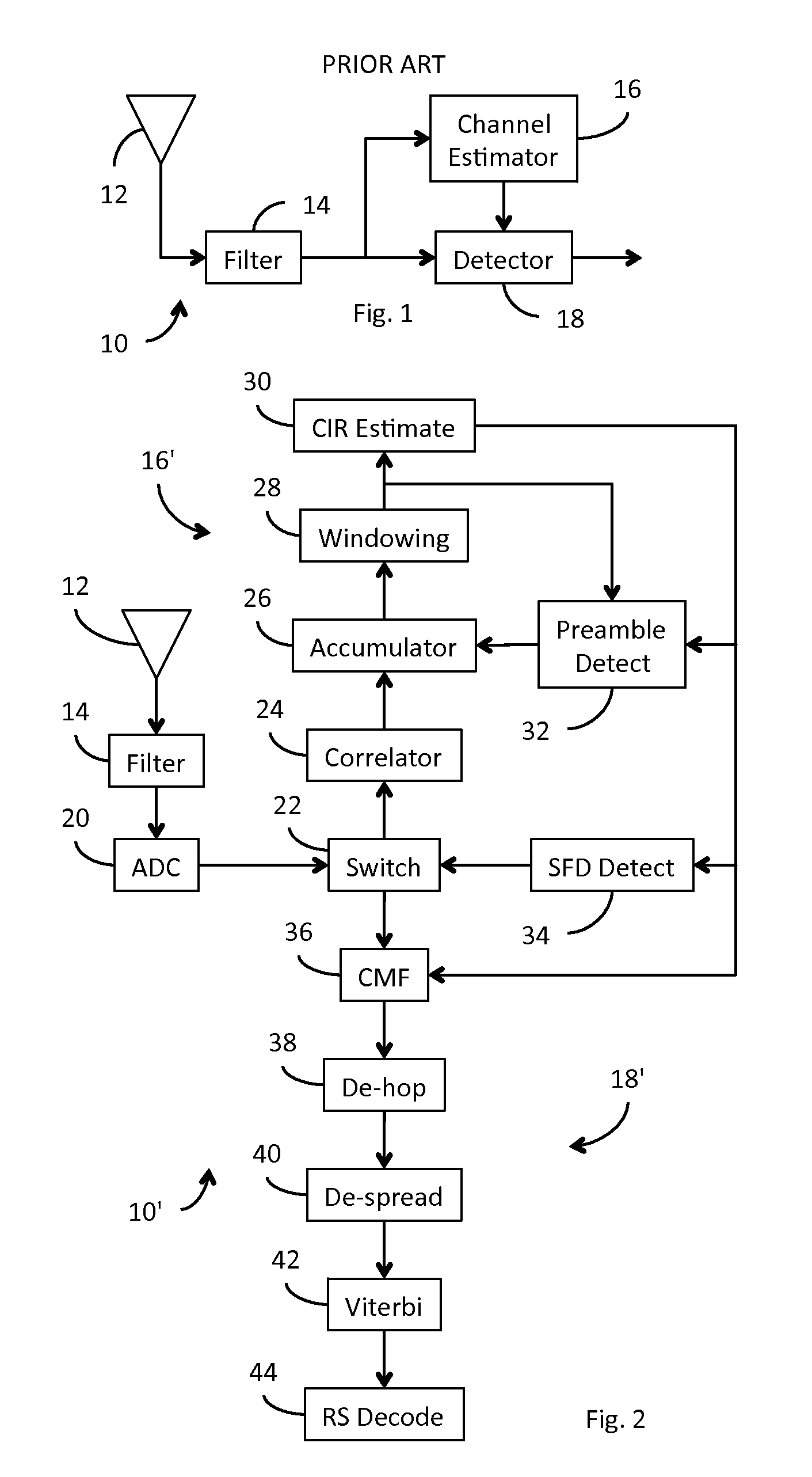
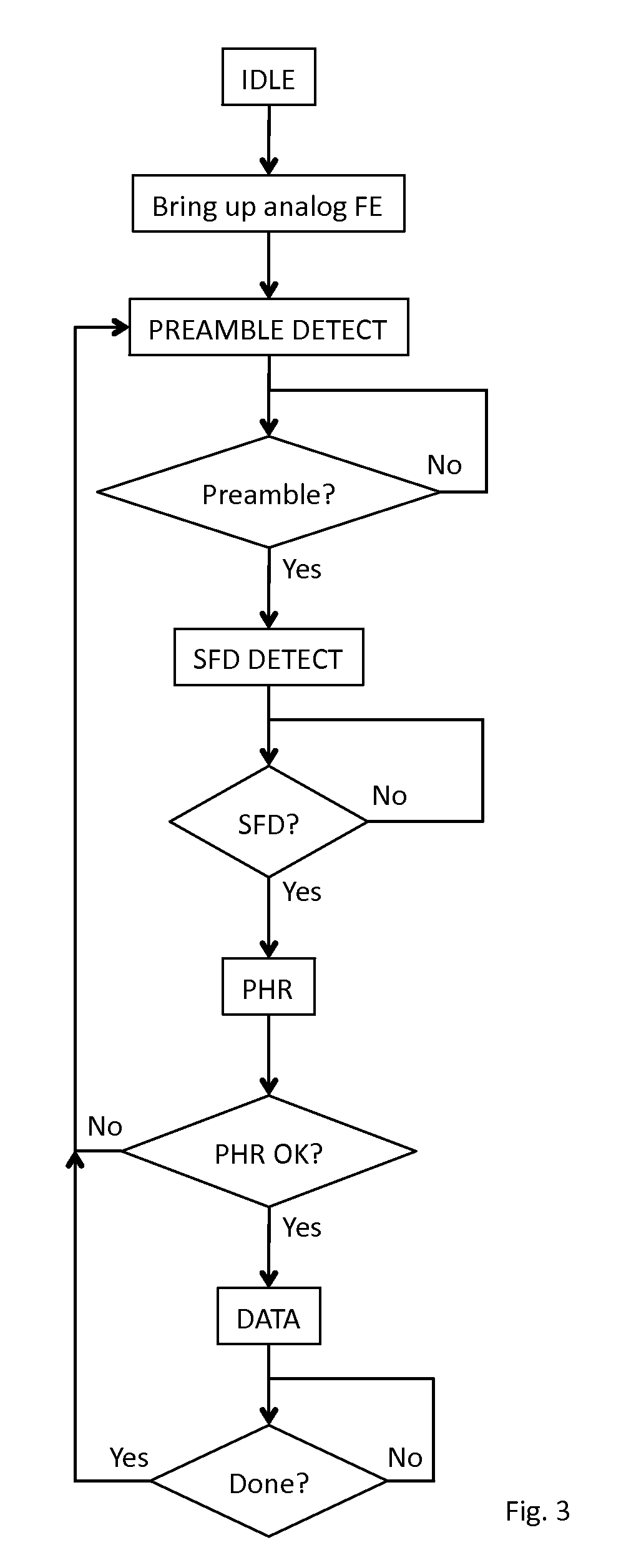
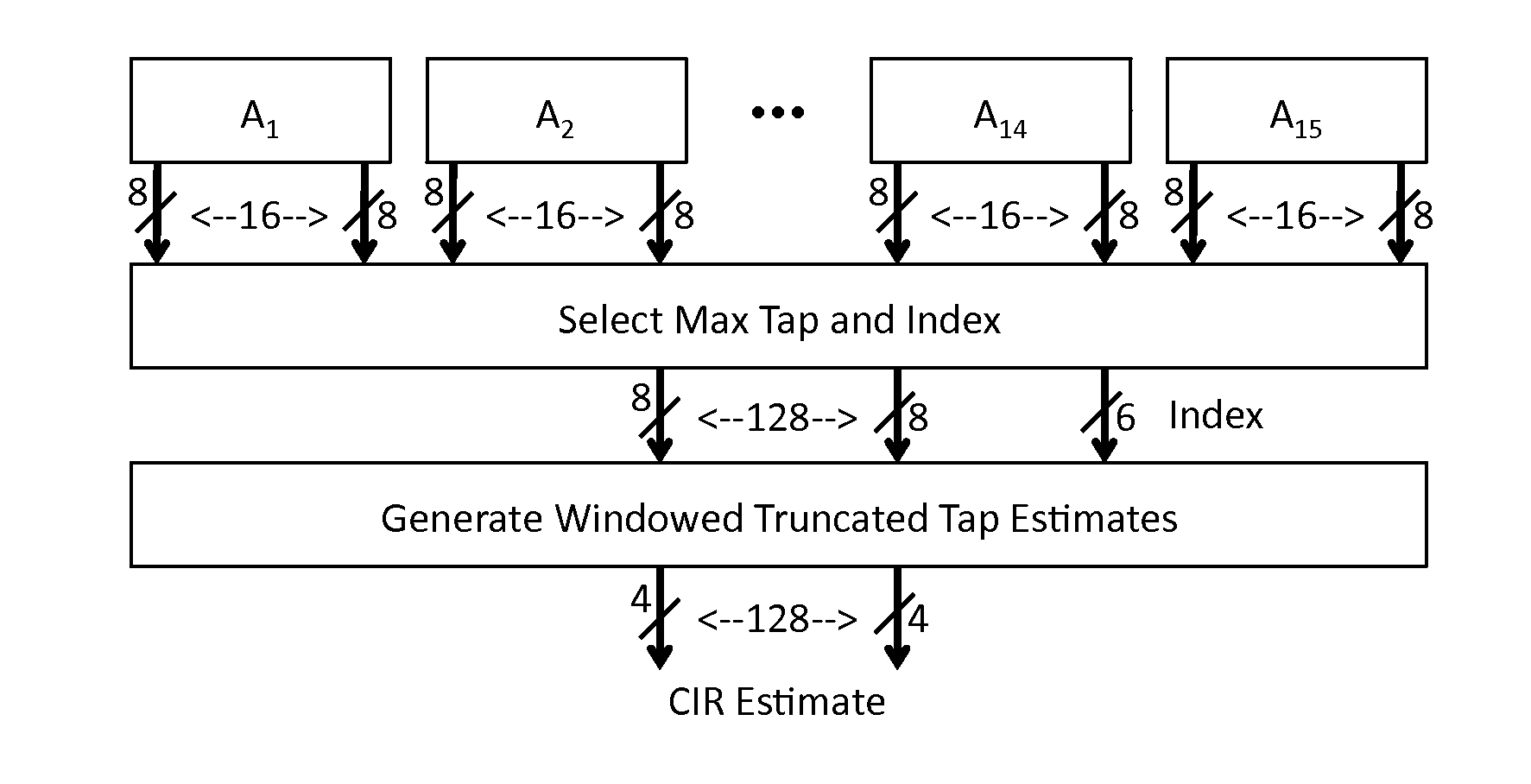
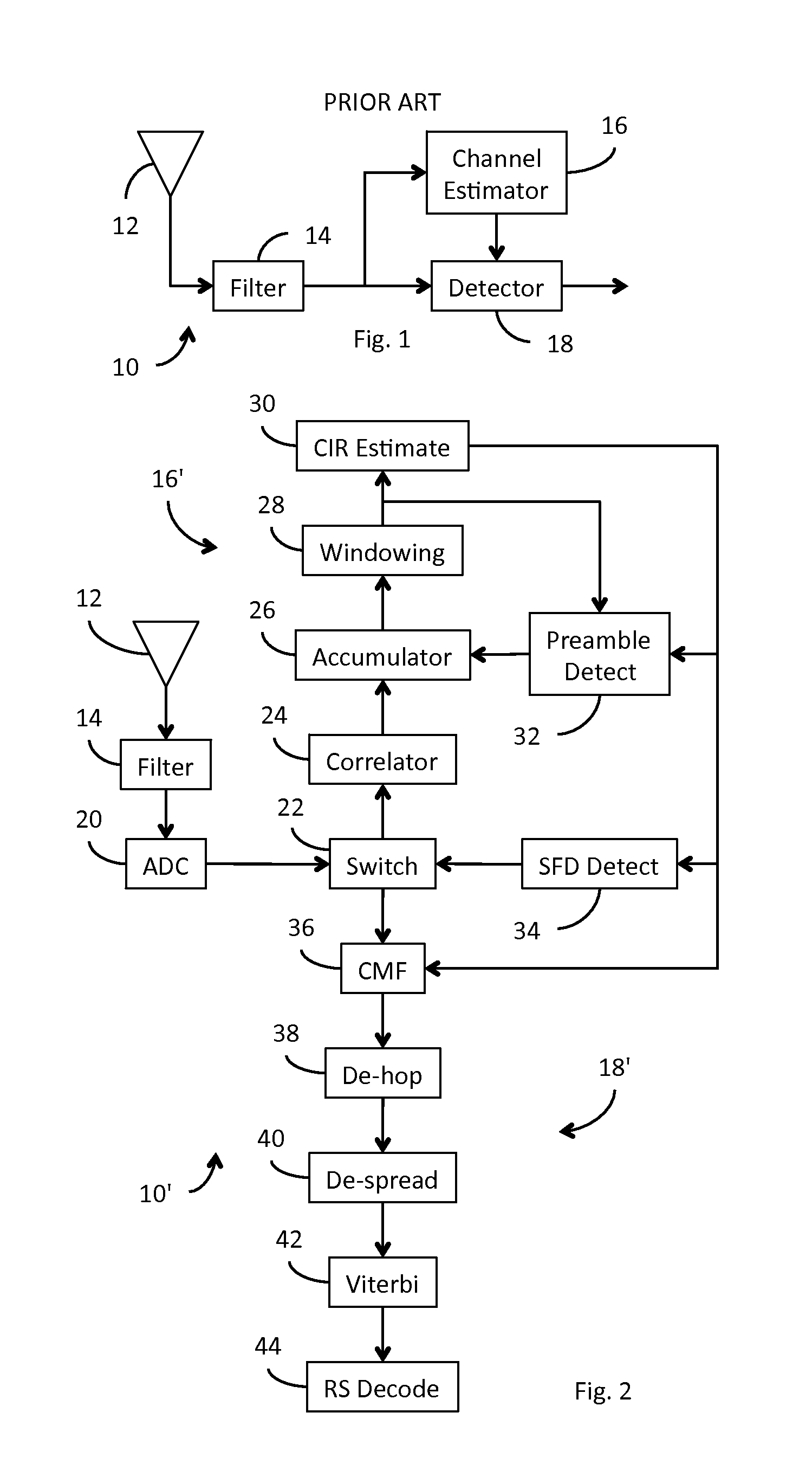
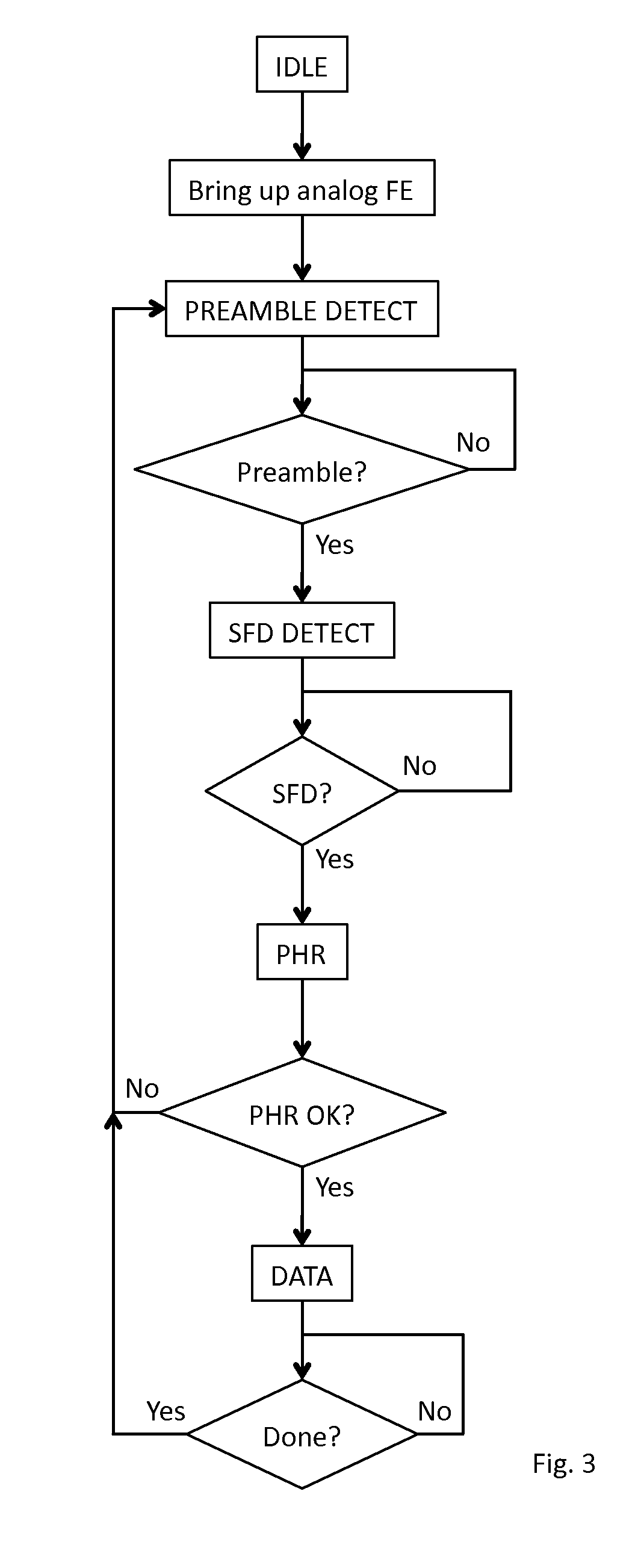
Receiver for use in an ultra-wideband communication system
ActiveUS8437432B2Less powerModulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexChannel impulse responseBroadband
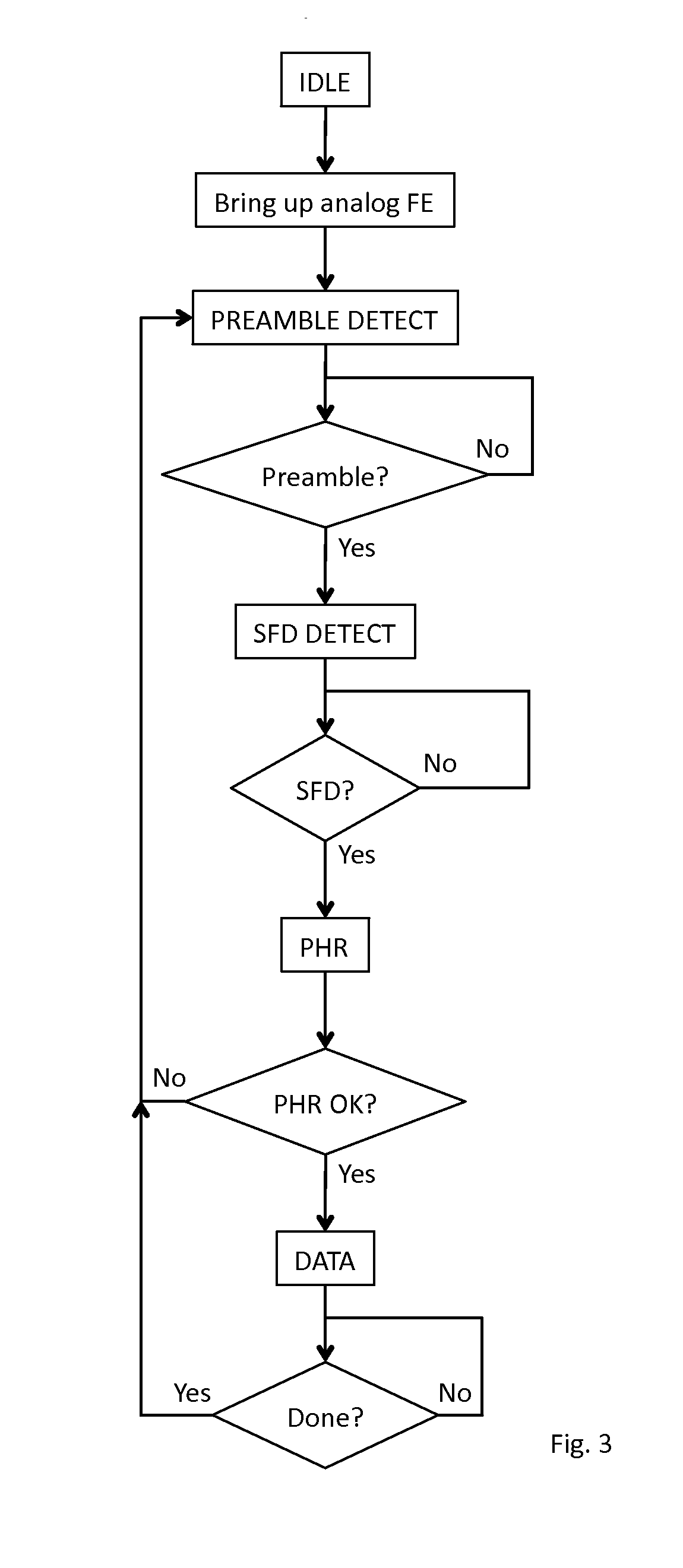
In an ultra-wideband (“UWB”) receiver, a received UWB signal is periodically digitized as a series of ternary samples. The samples are continuously correlated with a predetermined preamble sequence to develop a correlation value. When the value exceeds a predetermined threshold, indicating that the preamble sequence is being received, estimates of the channel impulse response (“CIR”) are developed. When a start-of-frame delimiter (“SFD”) is detected, the best CIR estimate is provided to a channel matched filter (“CMF”) substantially to filter channel-injected noise.
Owner:DECAWAVE
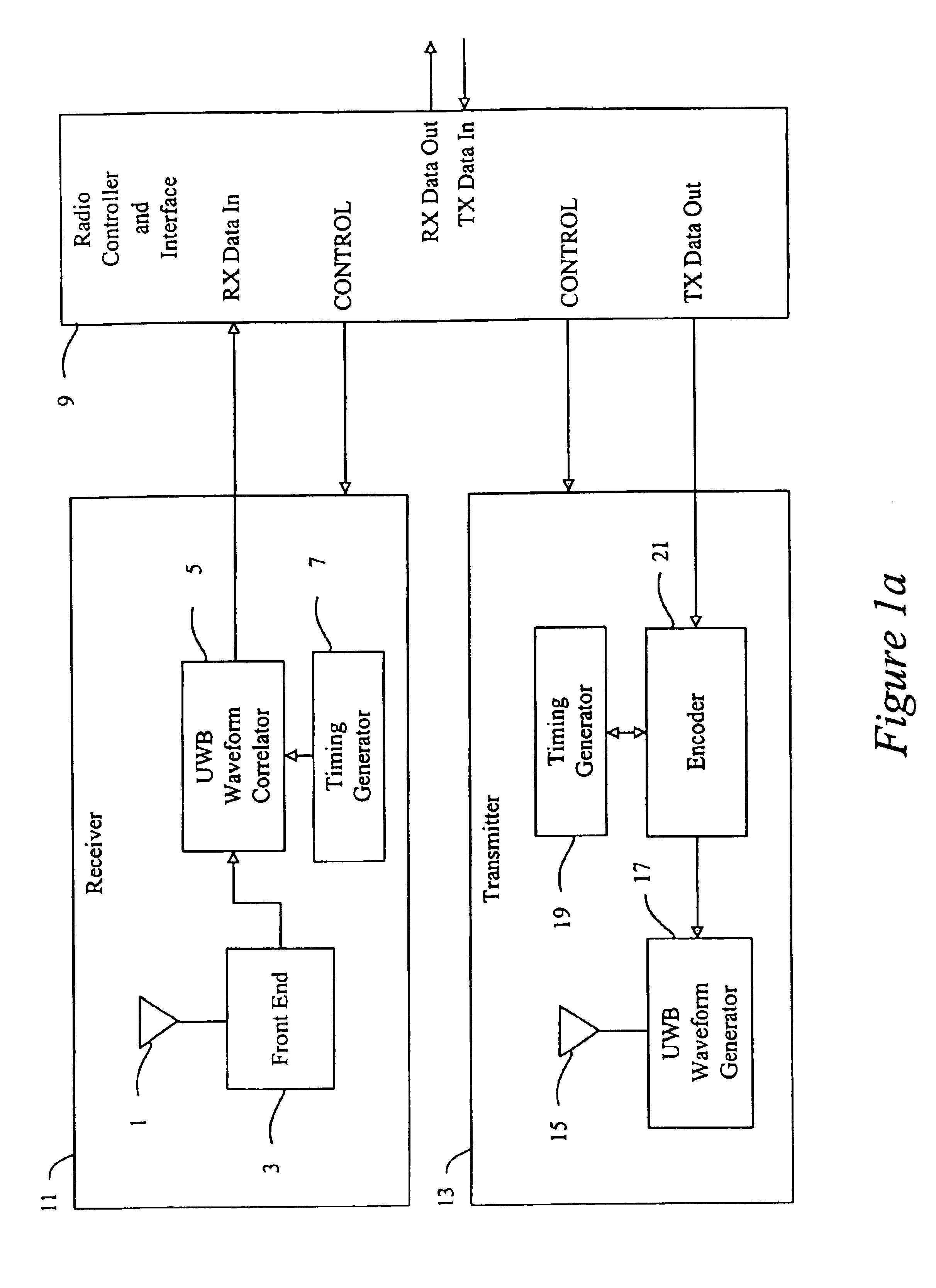
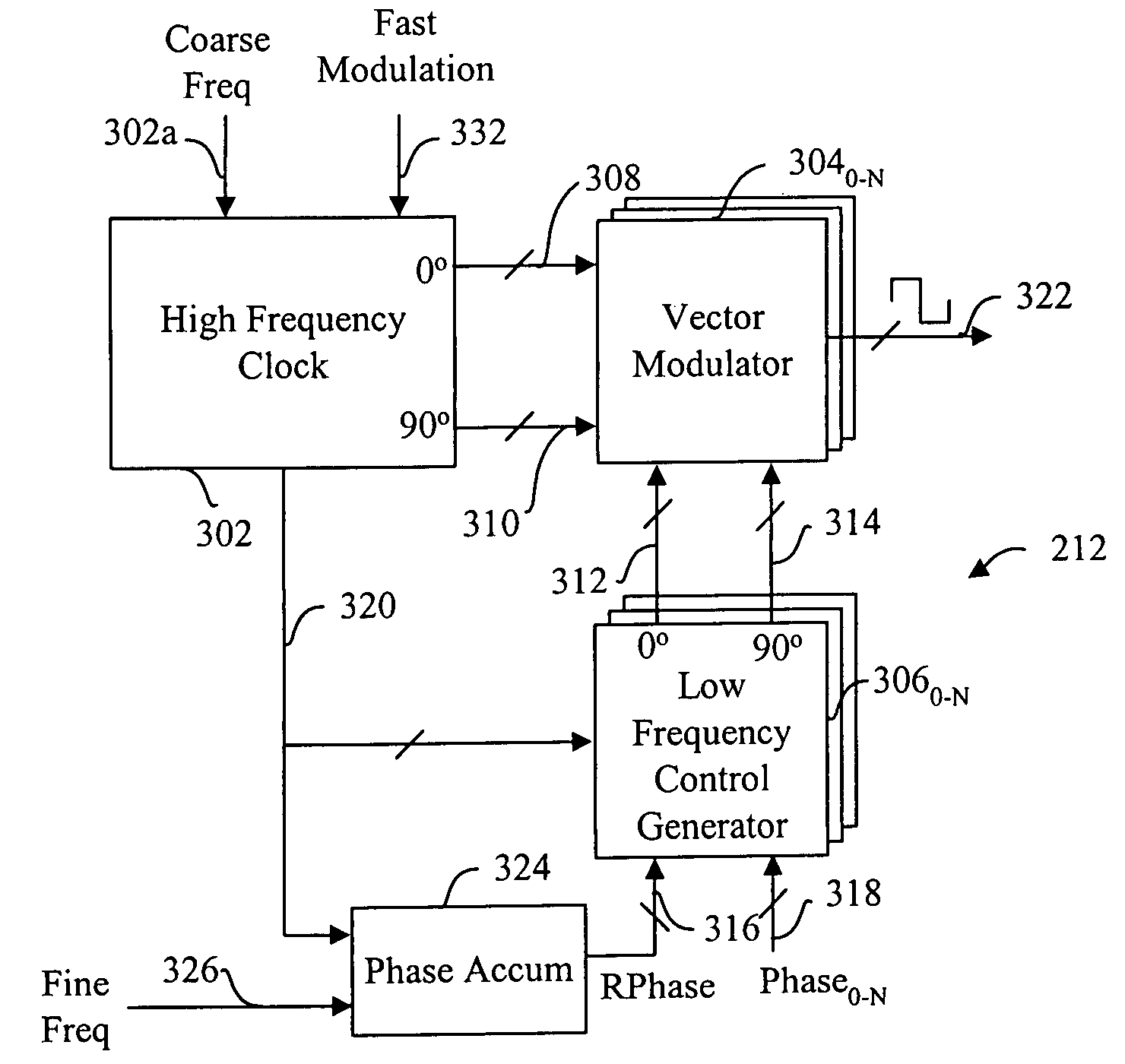
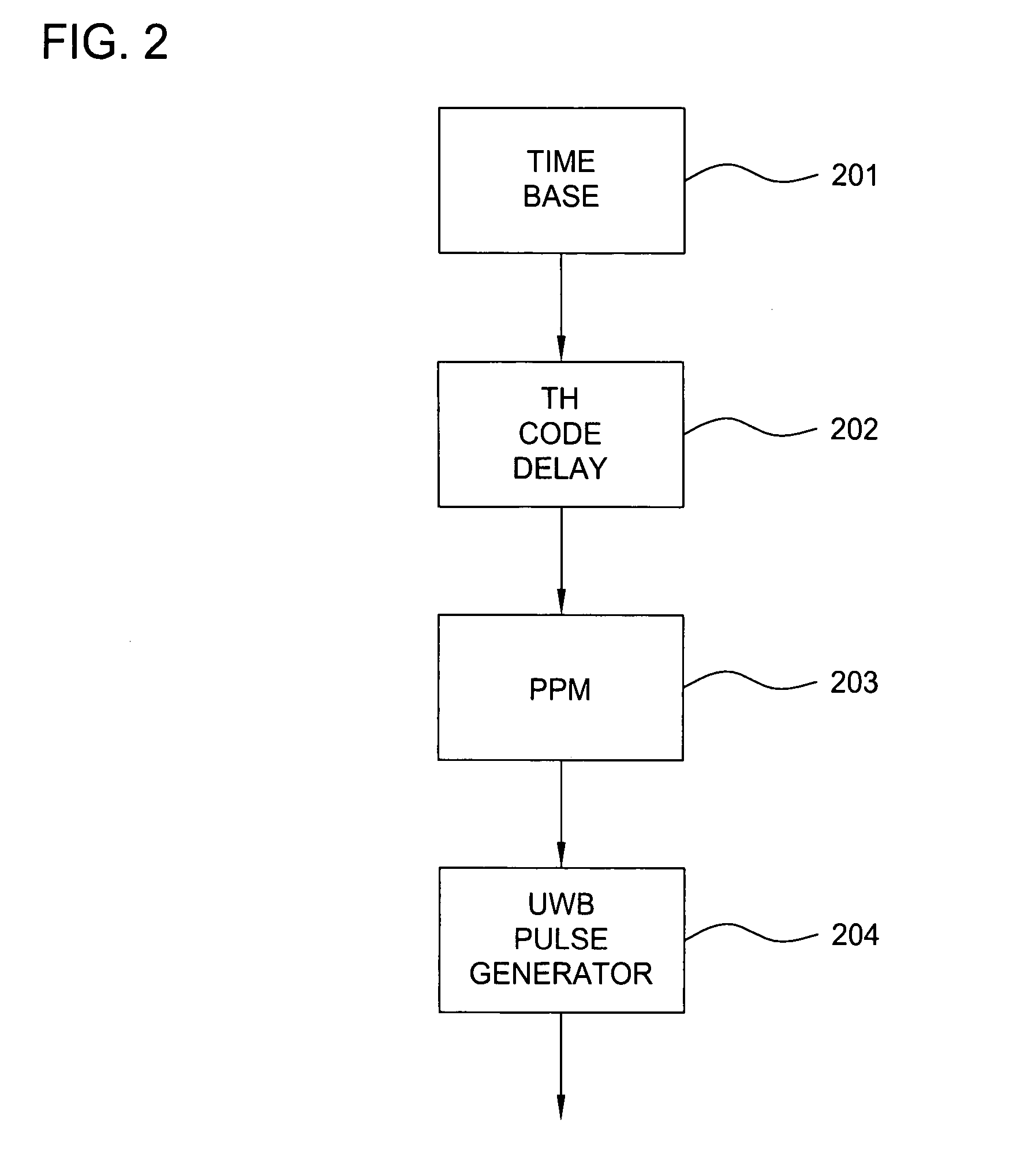
Low power, high resolution timing generator for ultra-wide bandwidth communication systems
InactiveUS20050265428A1Decreased power and part count and costImprove linearityModulated carrier system with waveletsAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase noiseControl signal
An ultra wide bandwidth communications system, method and computer program product including an ultra wide bandwidth timing generator. The timing generator includes a high frequency clock generation circuit having low phase noise; a low frequency control generation circuit; and a modulation circuit coupled between the high frequency clock generation circuit and the low frequency control generation circuit. The high frequency clock generation circuit generates a plurality of high frequency clock signals. The low frequency control generation circuit generates a plurality of low frequency control signals. The modulation circuit modulates the high frequency clock signals with the low frequency control signals to produce an agile timing signal at a predetermined frequency and phase. The agile timing signal is generated at the predetermined frequency and phase by adjustments to at least one of frequency of the low frequency control signals, phase of the low frequency control signals, frequency of the high frequency clock signals, and phase of the high frequency clock signals.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Low power, high resolution timing generator for ultra-wide bandwidth communication systems
An ultra wide bandwidth communications system, method and computer program product including an ultra wide bandwidth timing generator. The timing generator includes a high frequency clock generation circuit having low phase noise; a low frequency control generation circuit; and a modulation circuit coupled between the high frequency clock generation circuit and the low frequency control generation circuit. The high frequency clock generation circuit generates a plurality of high frequency clock signals. The low frequency control generation circuit generates a plurality of low frequency control signals. The modulation circuit modulates the high frequency clock signals with the low frequency control signals to produce an agile timing signal at a predetermined frequency and phase. The agile timing signal is generated at the predetermined frequency and phase by adjustments to at least one of frequency of the low frequency control signals, phase of the low frequency control signals, frequency of the high frequency clock signals, and phase of the high frequency clock signals.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
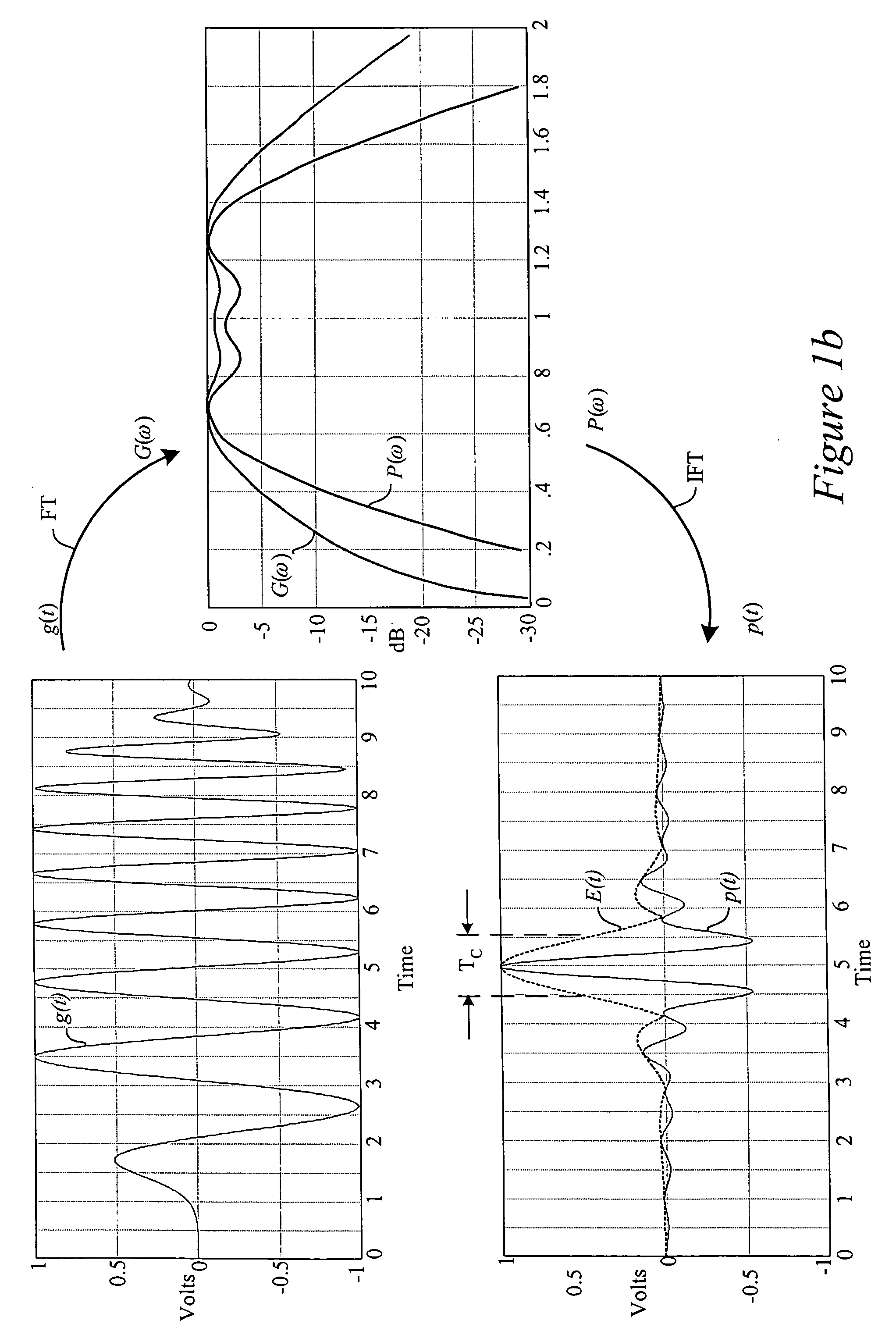
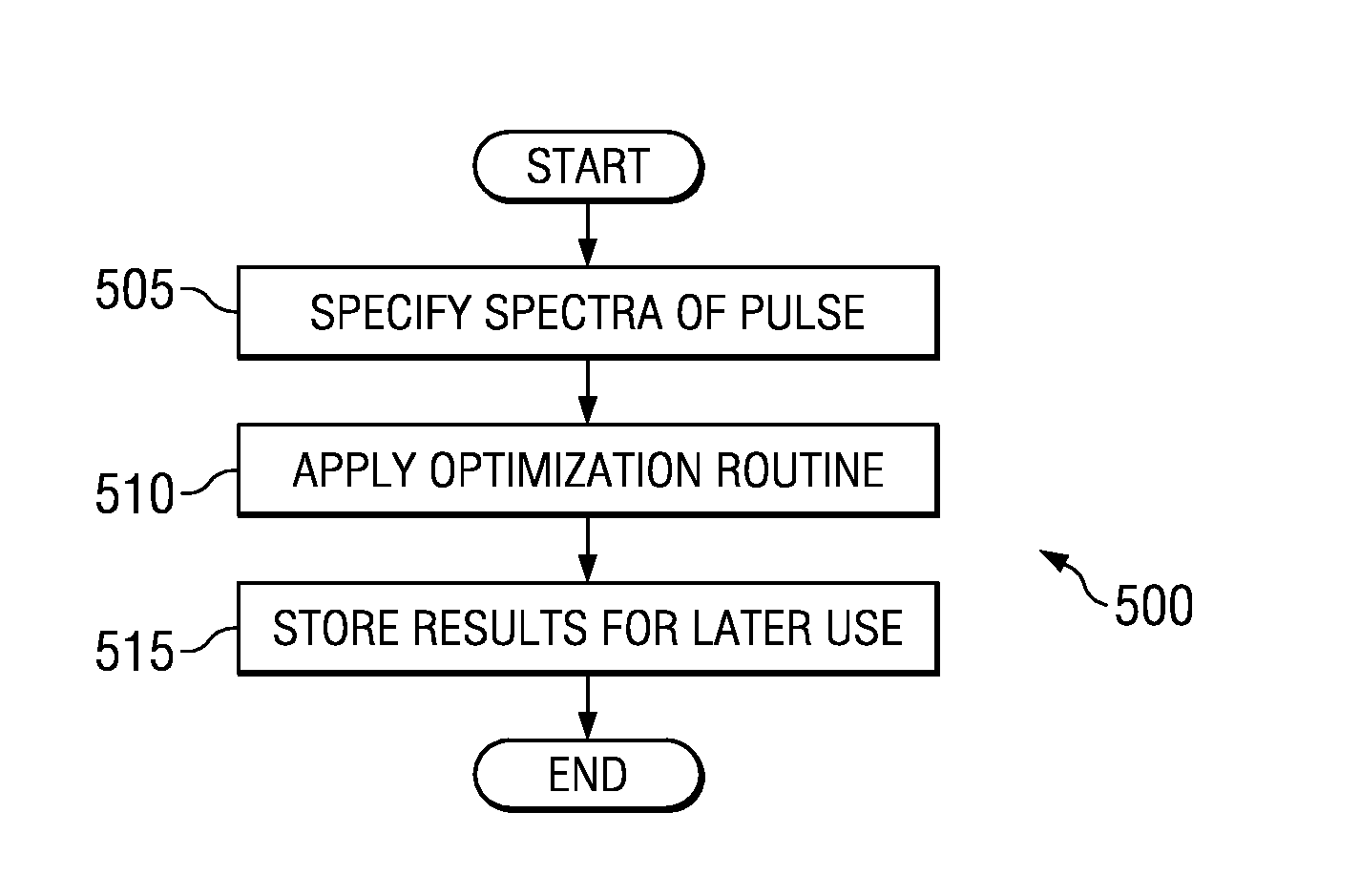
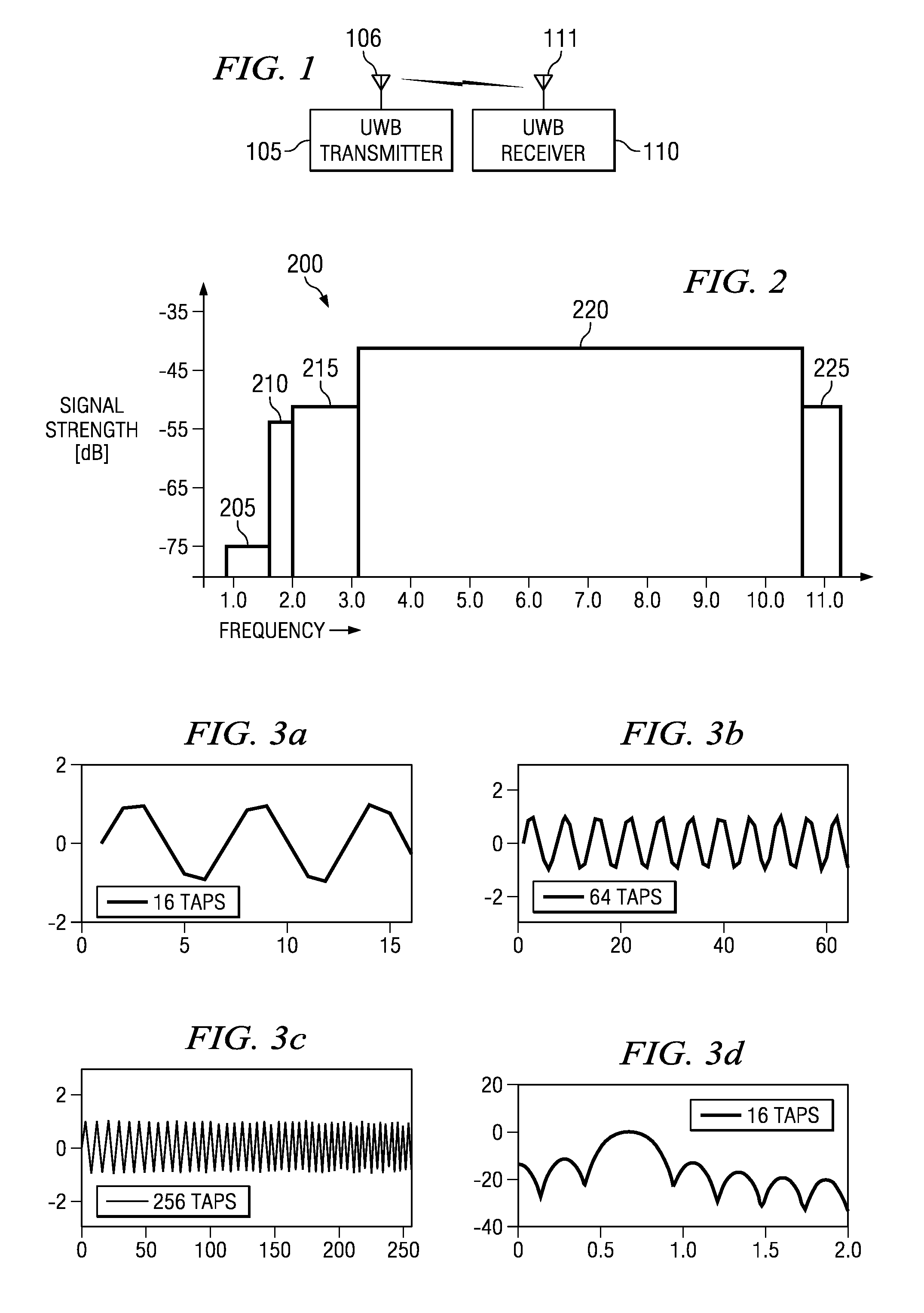
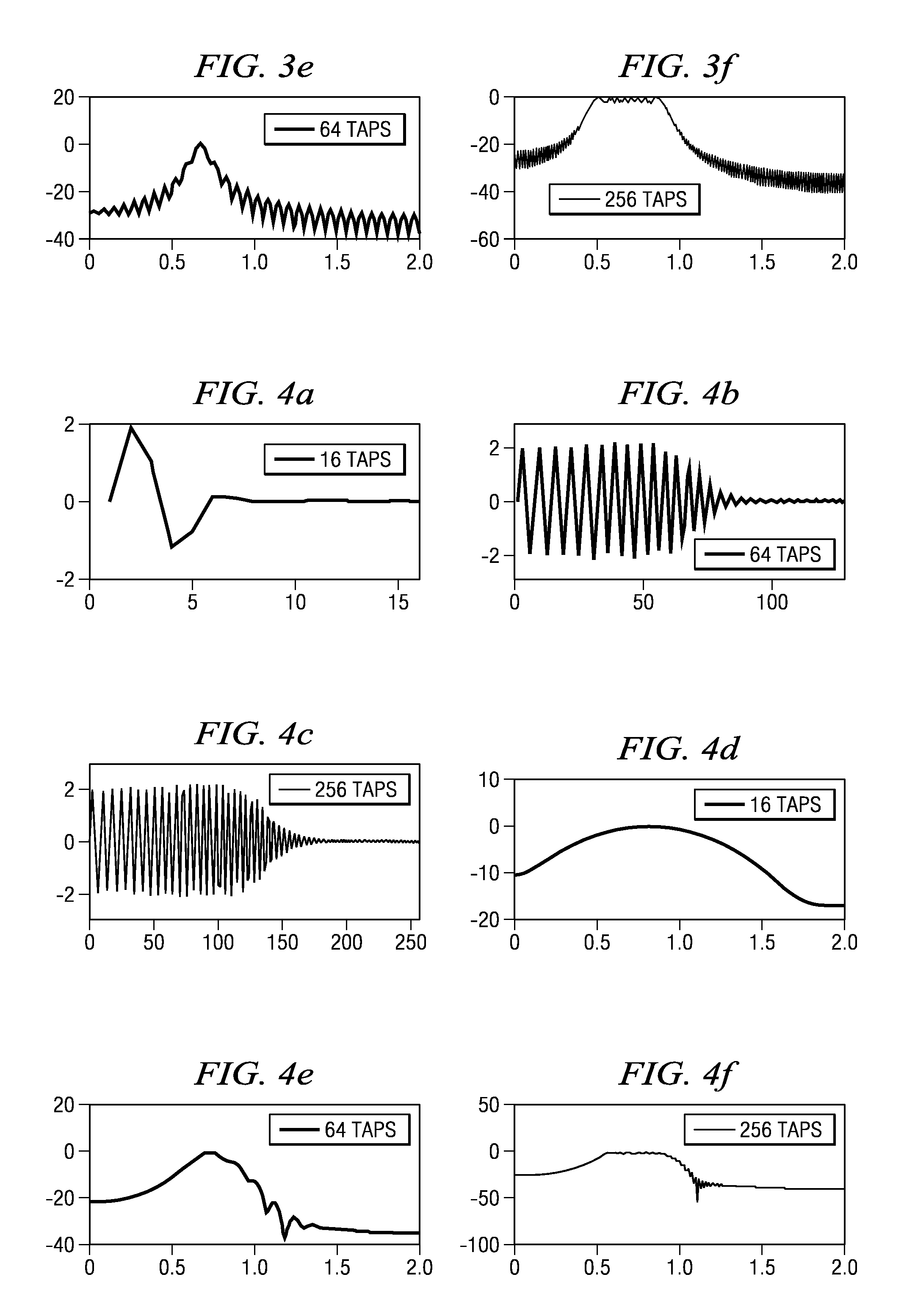
Method for transmit pulse design for ultra-wideband communications
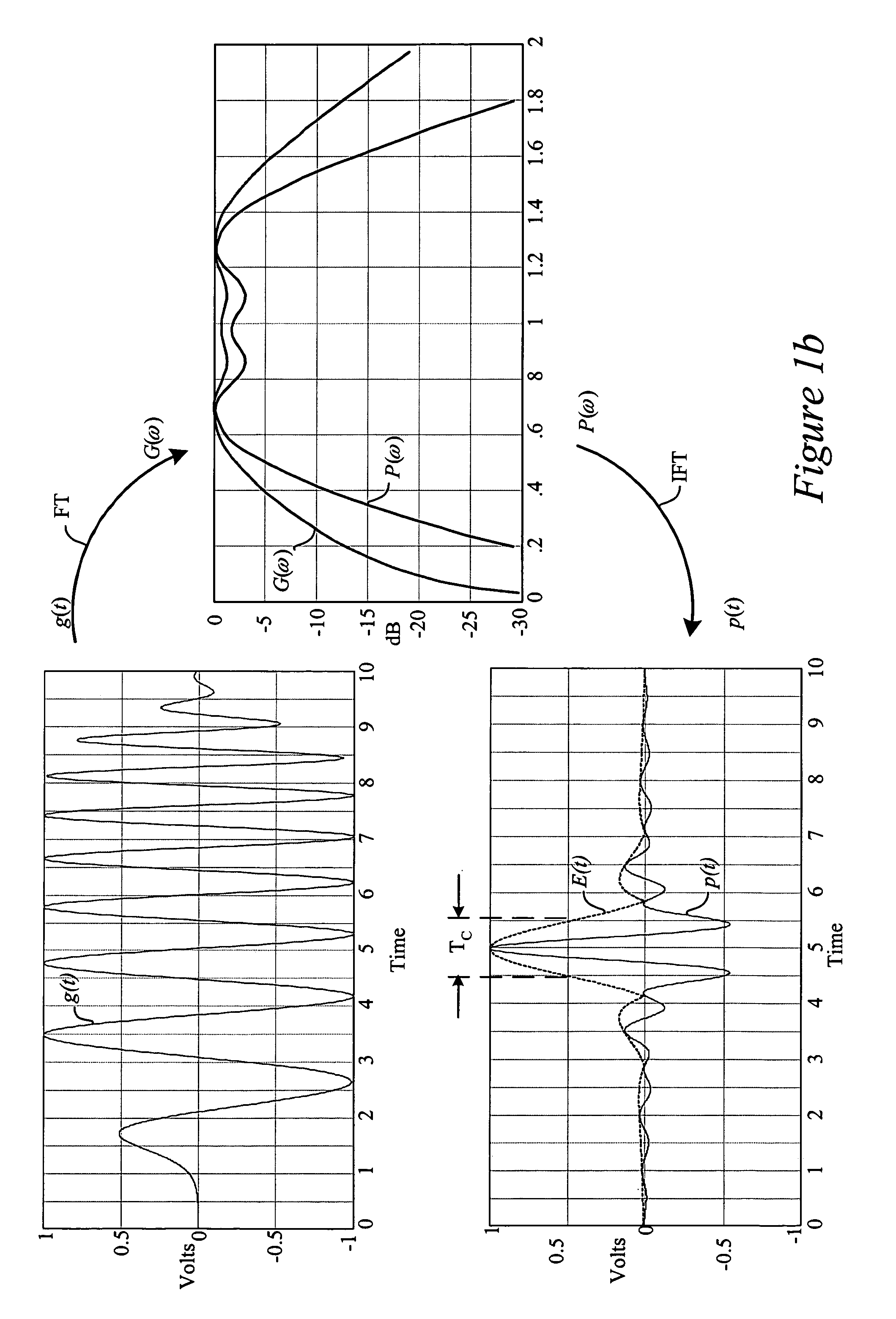
ActiveUS7489720B2Improve approximationSimple and inexpensive implementationTransmissionFrequency spectrumBroadband
Method for designing transmission pulses for ultra-wideband communications systems. A preferred embodiment comprises specifying a spectral description for the pulse. After a spectral description is created, then an approximation of the pulse can be created and well known optimization techniques, such as the least squares technique, can be used to minimize the difference between the approximation and the pulse. If the communications system is operating in the presence of interferers, then the spectral mask can be modified to ensure that the approximation carries no signal information in frequencies corresponding to the interferers.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
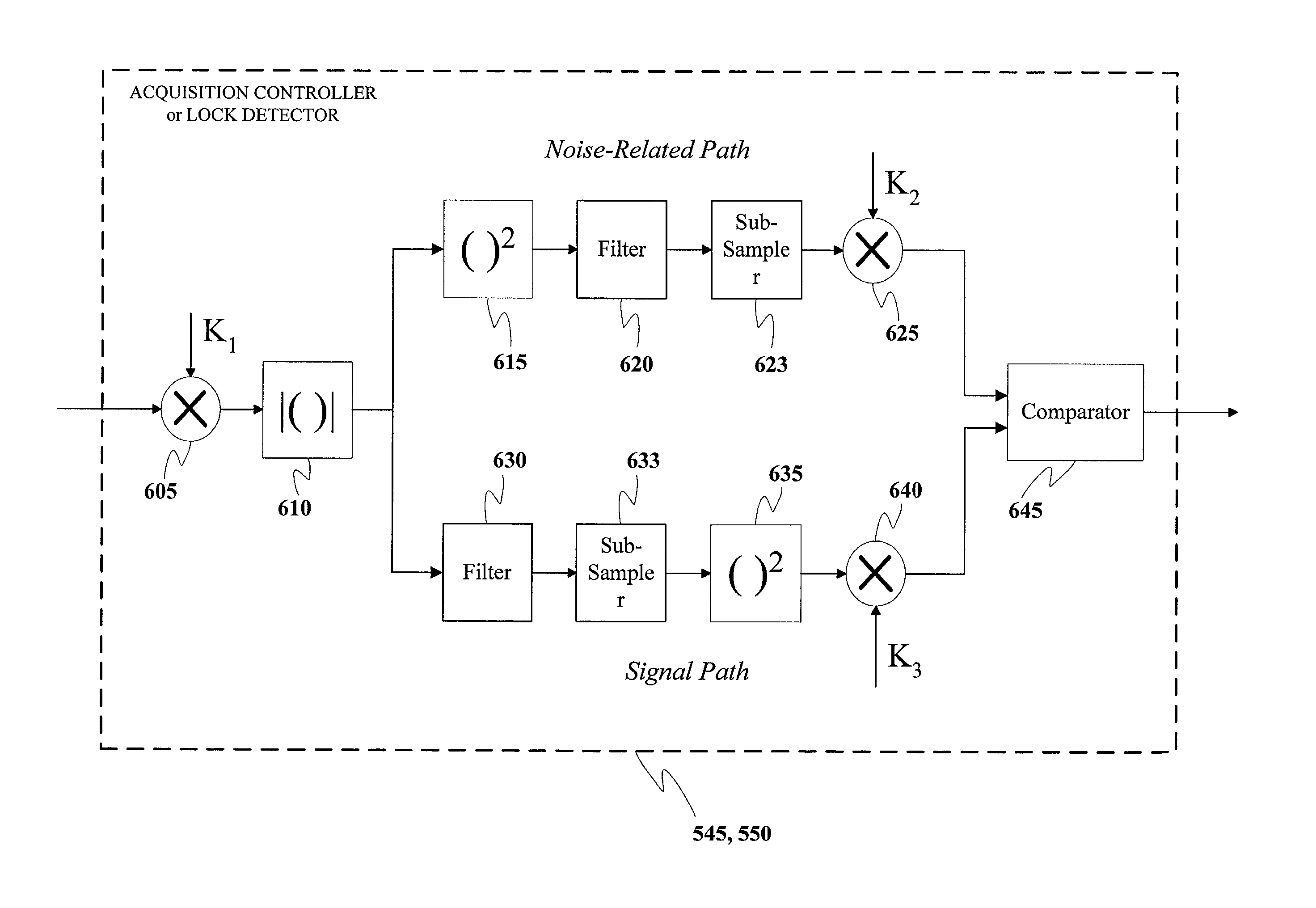
Mode controller for signal acquisition and tracking in an ultra wideband communication system
InactiveUS7110473B2Effective calculationModulated carrier system with waveletsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Finite-state machine
A system and method is provided for controlling the mode of operation in a UWB receiver. In one variation, the system and method determines the mode of operation by reading a set number of samples of the signal, estimating mode parameters, calculating a mode probability, and then transitioning in a finite state machine between a track and an acquisition state depending on the value of the mode probability. Exemplary versions of the mode controller include a signal to noise ratio calculator, a signal and noise power estimator, and an AGC initialization circuit.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Receiver For Use In An Ultra-Wideband Communication System
ActiveUS20130163638A1Preventing numberMultiple carrier systemsAngle demodulationChannel impulse responseBroadband
In an ultra-wideband (“UWB”) receiver, a received UWB signal is periodically digitized as a series of ternary samples. The samples are continuously correlated with a predetermined preamble sequence to develop a correlation value. When the value exceeds a predetermined threshold, indicating that the preamble sequence is being received, estimates of the channel impulse response (“CIR”) are developed. When a start-of-frame delimiter (“SFD”) is detected, the best CIR estimate is provided to a channel matched filter (“CMF”) substantially to filter channel-injected noise.
Owner:DECAWAVE
Mode Controller for signal acquisition and tracking in an ultra wideband communication system
InactiveUS6965630B1Effective calculationModulated carrier system with waveletsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Mode control
A system and method for controlling the mode of operation in a UWB receiver. In one variation, the system and method determines the mode of operation by reading a set number of samples of the signal, estimating mode parameters, calculating a mode probability, and then transitioning in a finite state machine from either a tracking to an acquisition state or vice versa depending on the value of the mode probability. Exemplary versions of the mode controller include a signal to noise ratio calculator, a signal and noise power estimator, and an AGC initialization circuit.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Receiver for use in an ultra-wideband communication system
ActiveUS20120069868A1Less powerModulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexChannel impulse responseEngineering
In an ultra-wideband (“UWB”) receiver, a received UWB signal is periodically digitized as a series of ternary samples. The samples are continuously correlated with a predetermined preamble sequence to develop a correlation value. When the value exceeds a predetermined threshold, indicating that the preamble sequence is being received, estimates of the channel impulse response (“CIR”) are developed. When a start-of-frame delimiter (“SFD”) is detected, the best CIR estimate is provided to a channel matched filter (“CMF”) substantially to filter channel-injected noise.
Owner:DECAWAVE
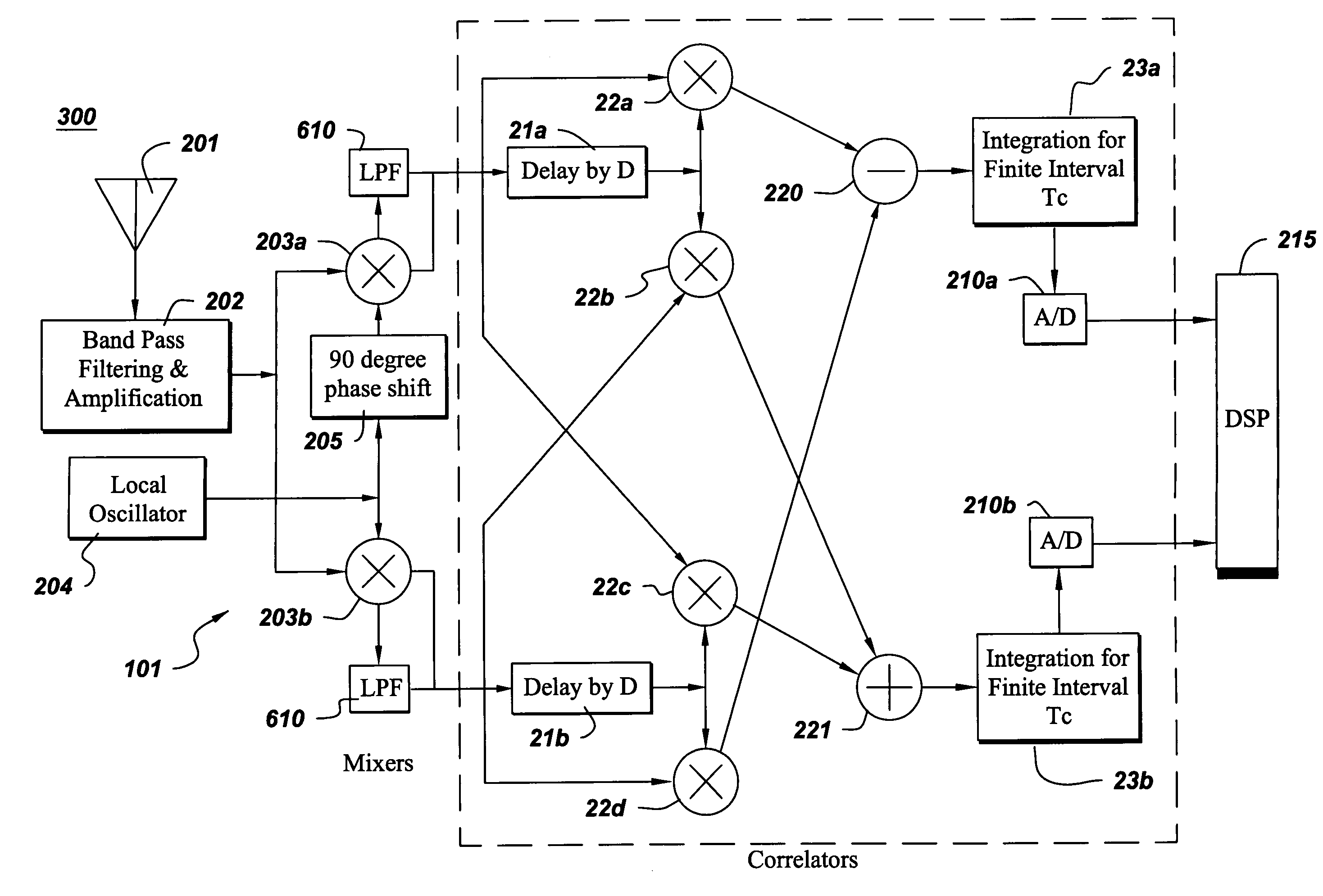
Leakage nulling receiver correlator structure and method for ultra wide bandwidth communication system
InactiveUS6937646B1Component can be removedCancel noiseModulated carrier system with waveletsMultiplex communicationBandpass filteringUltra wideband communication systems
A receiver correlator structure for an ultra wide bandwidth communication system includes an antenna, a mixer, a bandpass filter, and a convertor. The receiver receives, via the antenna, an ultra wide bandwidth signal comprising a sequence of wavelets of particular shapes and positions, and transmits the received ultra wide bandwidth signal to the mixer. The mixer also receives and mixes with the received ultra wide bandwidth signal a local ultra wide bandwidth signal comprising a sequence of wavelets of particular shapes and positions correlated to the received ultra wide bandwidth signal. The bandpass filter removes the DC components from the mixed signal, and provides the resultant signal to the convertor. The receiver structure eliminates the local ultra wide bandwidth signal AC bias and DC bias terms and 1 / f noise, yet detects long sequences of logical 1's and 0's, and allows operation with reduced bandwidth convertors.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Dynamic differentiated link adaptation for ultra-wideband communication system
InactiveUS20050201446A1Lower levelFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationEngineeringMobile station
Optimum usage of time diversity and significantly higher data rates are achieved by utilizing an adaptive Ultra-wideband impulse radio (UWB IR) transmission scheme based upon information about the channel state at a particular time instant. Through the use of channel state information, the transmission scheme is adjusted for the particular channel state. In particular, the system is adapted dynamically for each user by varying the number of pulses transmitted per bit in response to the channel state. The channel state is a dynamic parameter of the transmission system that is typically measured or estimated by the receiver. An adaptation element responds to the channel state information to determine a desired number of pulses per bit to be utilized in a transmission channel for subsequent UWB IR communication. This desired number of pulses per bit is then supplied to and used by an adaptive transmitter for subsequent transmission by a particular mobile station.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Mapping radio-frequency noise in an ultra-wideband communication system
InactiveUS20060285577A1Improve quality and reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTime segmentEngineering
A system and method for mapping. radio-frequency (RF) noise, and estimating channel quality in a multi-channel ultra-wideband communication system is provided. One method includes placing a plurality of time bins within a plurality of time frames and assigning a plurality of UWB communication channels comprising selected time bins. RF noise amplitude data is then sampled from selected time bins. The sampled RF noise amplitude data from the time bins is then averaged, thereby obtaining an average RF noise amplitude in each of the plurality of channels. The RF noise amplitude indicates the amount of RF noise present in a channel. The channels may then be ranked based on the characteristics of the RF noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Method for reconstructing signals
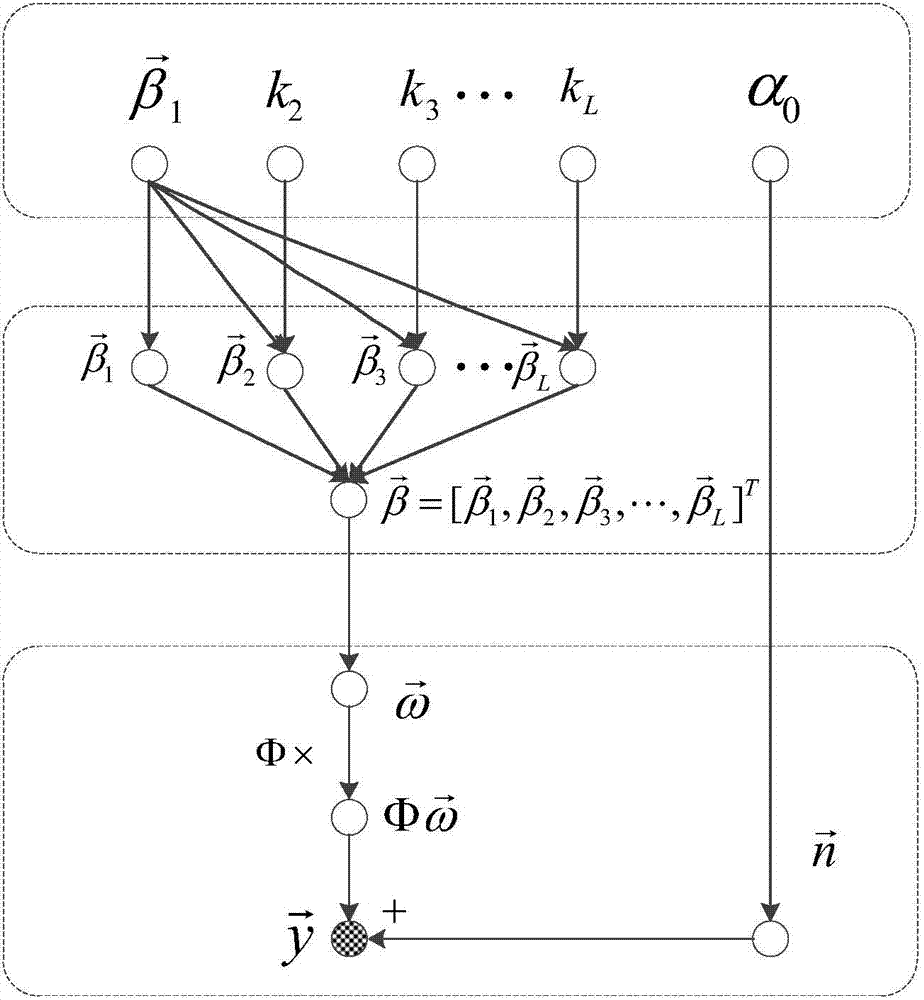
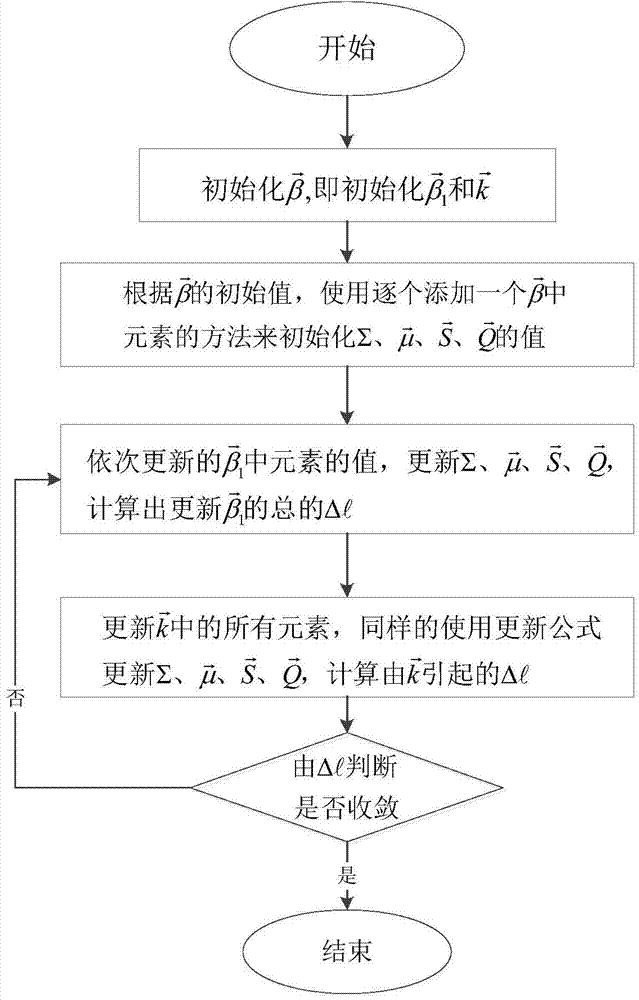
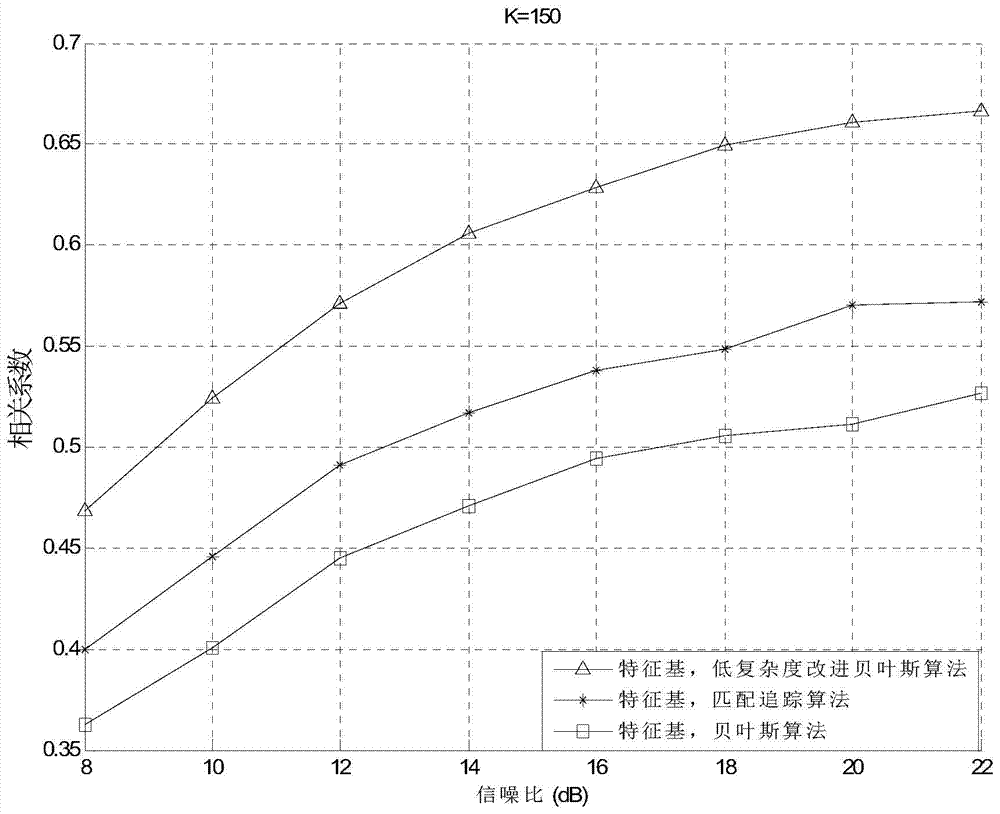
InactiveCN103888145AReduce the complexity of recovery operationsImprove recovery effectCode conversionBayesian compressive sensingWide band
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communications, and particularly relates to a method for reconstructing signals in an ultra-wide-band communication system by the adoption of a low-complexity improved Bayes compressed sensing algorithm. The method comprises the steps that firstly, sectioning and filtering are conducted on received signals, then a measuring matrix is used for conducting linear combination on the filtered signals again, after a series of relatively simple iterative operations, the expansion coefficient of original signals under the characteristic base can be measured, and therefore reconstruction of the original signals is realized. According to the method for reconstructing the signals, on one hand, the Bayes compressed sensing algorithm is improved by fully utilizing the characteristics of the characteristic base, the restorability is improved, more importantly, the complex matrix inversion process in the Bayes compressed sensing algorithm is avoided, and particularly, when the length of the signals is large and the order of the matrix is large, the signal restoration operation complexity can be effectively lowered.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
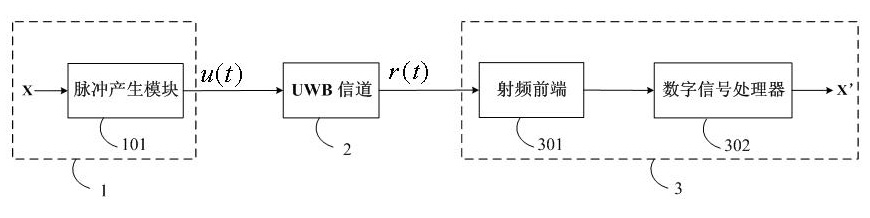
Pulse UWB (Ultra Wide Band) communication system based on CS (Compressed Sensing) theory
InactiveCN102104396AOvercoming the problem of high implementation complexitySolve the sparse problemTransmitter/receiver shaping networksPrecodingLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a pulse UWB (Ultra Wide Band) communication system based on a CS (Compressed Sensing) theory. A digital signal (X) transmitted by a transmitting terminal is effectively observed by introducing signal detection in the CS theory through a sparse algorithm in a digital signal processor, combining a random precoding module added at the transmitting terminal and matching with apulse generating module, a UWB channel and a low-speed sampler, and a common recovery reconfiguration algorithm in the CS theory is utilized to recover and reconstruct the digital signal (X) and realize communication. In the communication system provided by the invention, a plurality of parallel correlators and low-speed samplers needed in a first parallel scheme are not needed at a receiving terminal so that the problem of high hardware implementation complexity in the parallel scheme is solved; meanwhile, the low-speed sampler is directly used at the receiving terminal for sampling, and an analogue information converter is not used, so that the influence of the causality of a low-pass filter in the analogue information converter on observation is avoided and the problem of sparse observation matrix caused by the causality in a serial scheme is solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
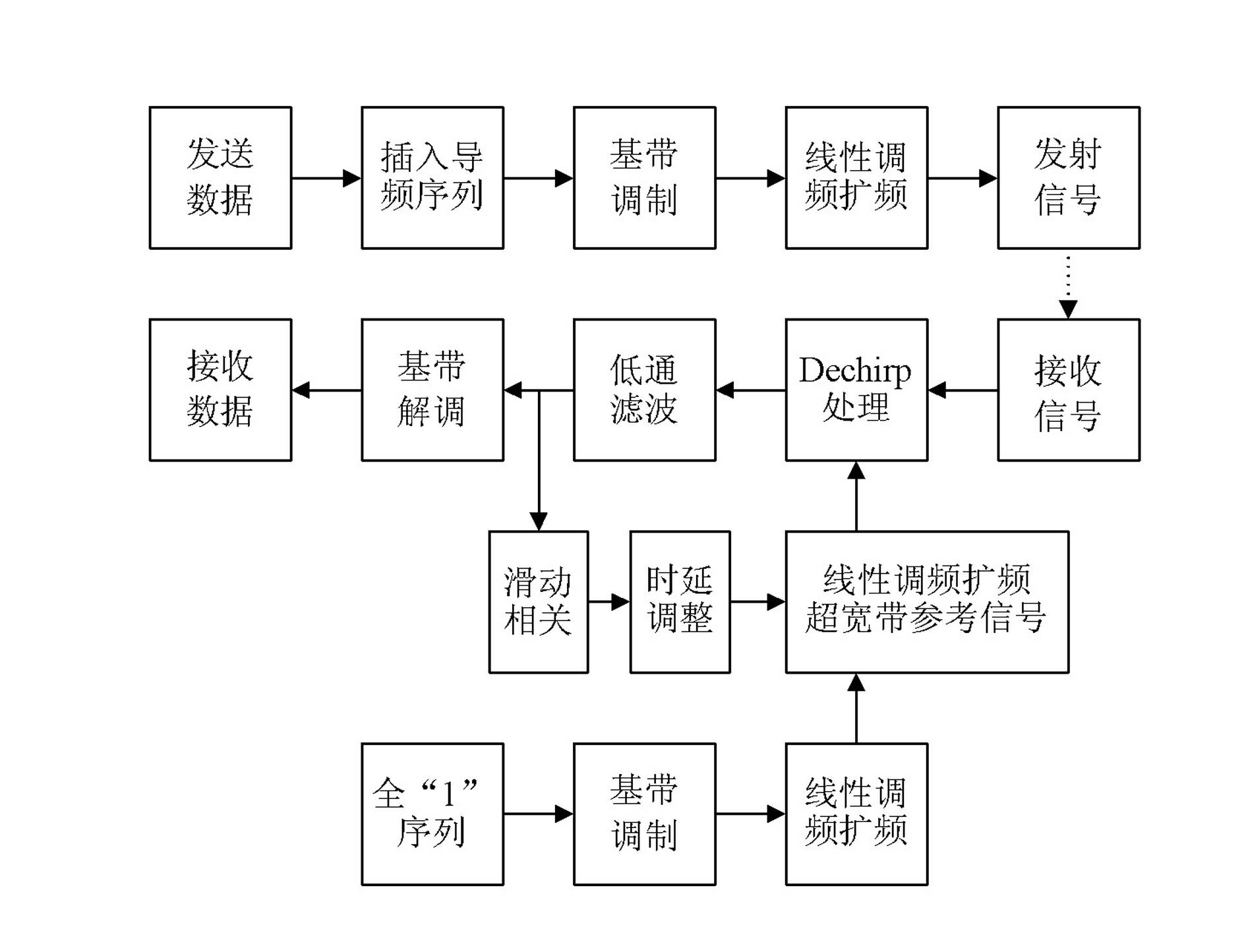
Ultra-wideband communication method based on time-frequency conversion and slippage correlation
ActiveCN102255631ASimple designImprove electromagnetic compatibilityTransmissionPhase correlationLow speed
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband communication method based on Dechirp and slippage correlation, comprising the following steps of: at a transmitting terminal of an ultra-wideband communication system, inserting a pilot sequence in sent data firstly; then, performing base-band modulation and linear frequency modulation and spread spectrum; outputting an ultra-wideband transmission signalat the linear frequency modulation and spread spectrum of an available radio frequency band; at a receiving terminal of the ultra-wideband communication system, firstly by using a slippage correlation method, completing synchronization of a received signal through adjusting the time delay of an ultra-wideband reference signal of the linear frequency modulation and spread spectrum; then, mixing the ultra-wideband reference signal of the linear frequency modulation and spread spectrum with the received signal, namely, performing Dechirp process; and finally, after filtering in low pass, demodulating the base band of the received signal. According to the ultra-wideband communication method, the sampling rate and the signal processing scale of the receiving terminal can be reduced; the synchronization precision requirements are not high; the complexity is very low; and the method is especially applicable for ultra-wideband expand distance low-speed communication with high spread spectrum gain.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
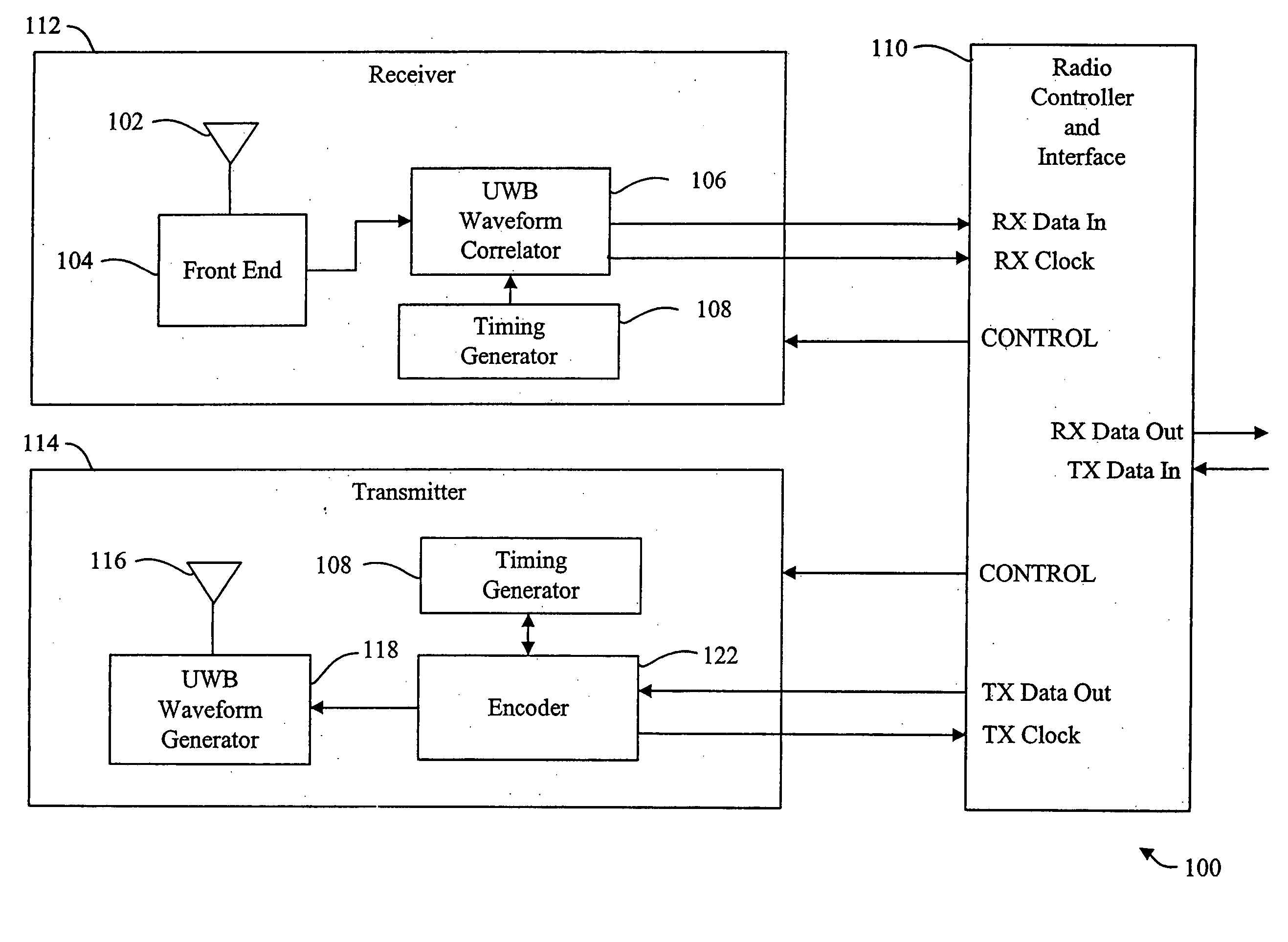
Ultra-wideband communications system and method
InactiveUS20070014369A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoTransceiver
An ultra-wideband communications network and methods for communication are provided. In one embodiment, an ultra-wideband transceiver transmits digital video data that is in a lossy or lossless compression format. The lossy or lossless format may be a wavelet-based format. The transmitted ultra-wideband signal may be transmitted in a single or in multiple frequency bands. The network may further include a second ultra-wideband transceiver and a video display device. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
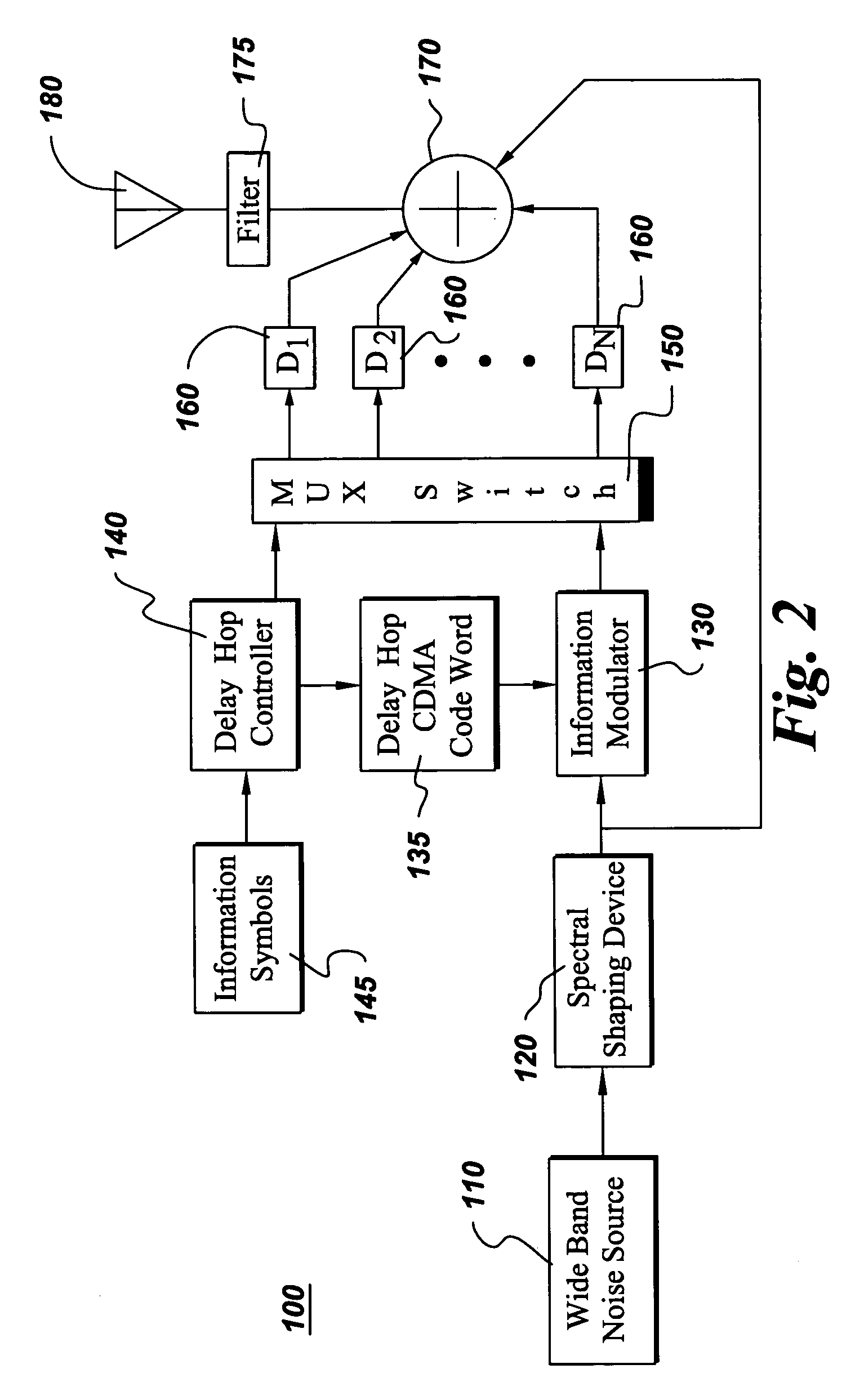
Ultra-wideband communications system and method using a delay hopped, continuous noise transmitted reference
ActiveUS7068715B2Synchronization is simpleUsable levelFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationBroadbandUltra wideband communication systems
An ultra-wideband (UWB) communications system combines the techniques of a transmitted reference (TR) and a multiple access scheme called delay hopping (DH). Combining these two techniques using UWB signaling using a continuous noise transmitted waveform avoids the synchronization difficulties associated with conventional approaches. This TR technique is combined with the DH multiple access technique to create a UWB communications scheme that has a greater multiple access capacity than does the UWB TR technique by itself.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ultra broadband antenna of integrated filter
InactiveCN102110899AHigh bandwidthReduce complexityAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringUltra wideband communication systems
The invention provides an ultra broadband antenna of an integrated filter, which comprises a medium substrate, a microstrip feeder structure of a radiating unit arranged on one side of the medium substrate, the other side of the medium substrate is partially grounded, the radiating unit is provided with a split-ring resonator (SRR), and a microstrip line is directly connected to the radiating unit. The antenna relates to the invention has excellent broadband property and good omnidirectional radiation property, and the antenna is integrated with a filter with a complementary split-ring resonator (CSRR), so that the influence between the communication of local area network and ultra broadband communication system of the antenna can be prevented. The antenna provided by the invention has the advantages that the design is simple and compact, the volume is small, the process is convenient and the cost is low. The antenna can be applied to electronic reconnaissance device and electronic countermeasure device and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com