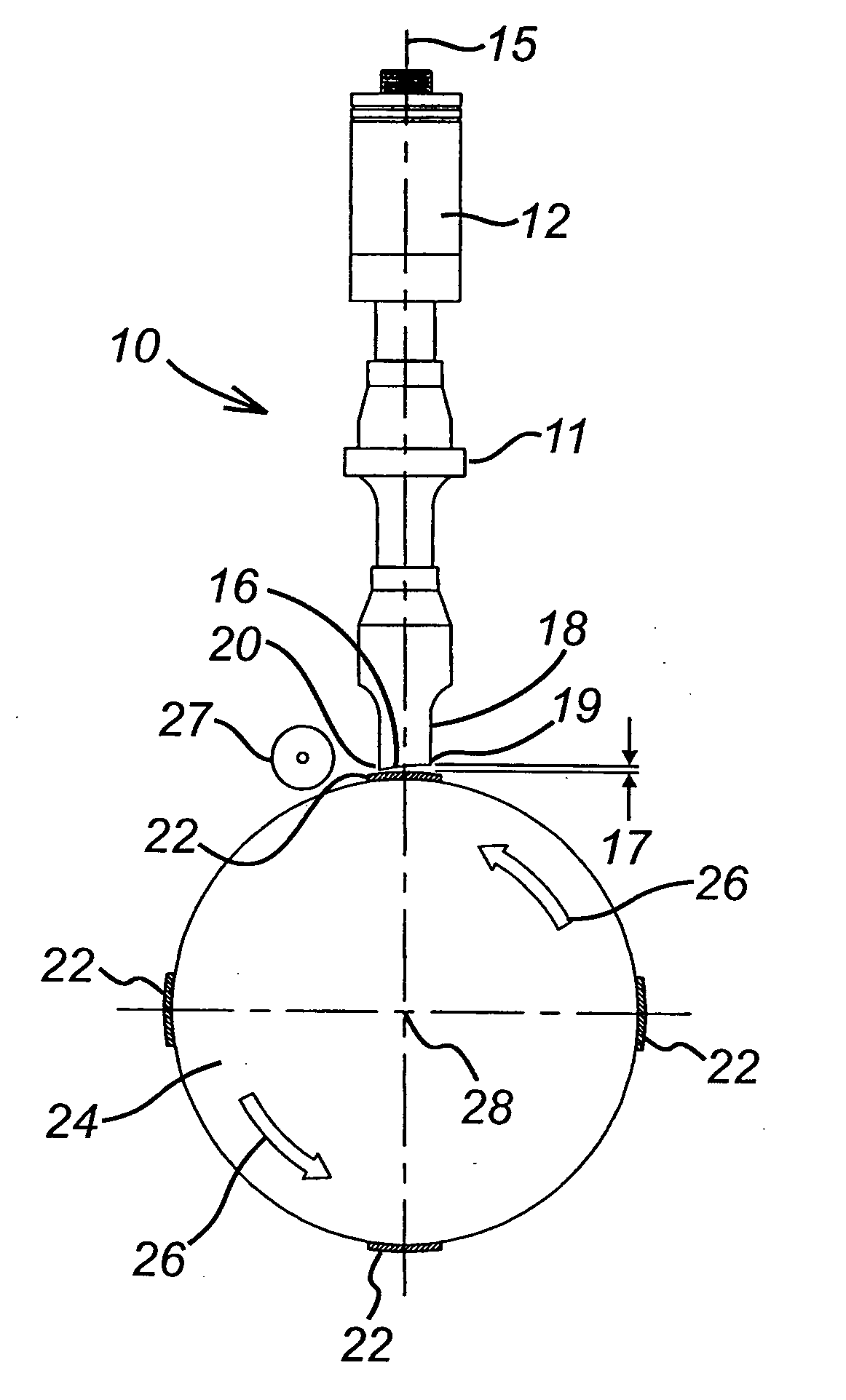
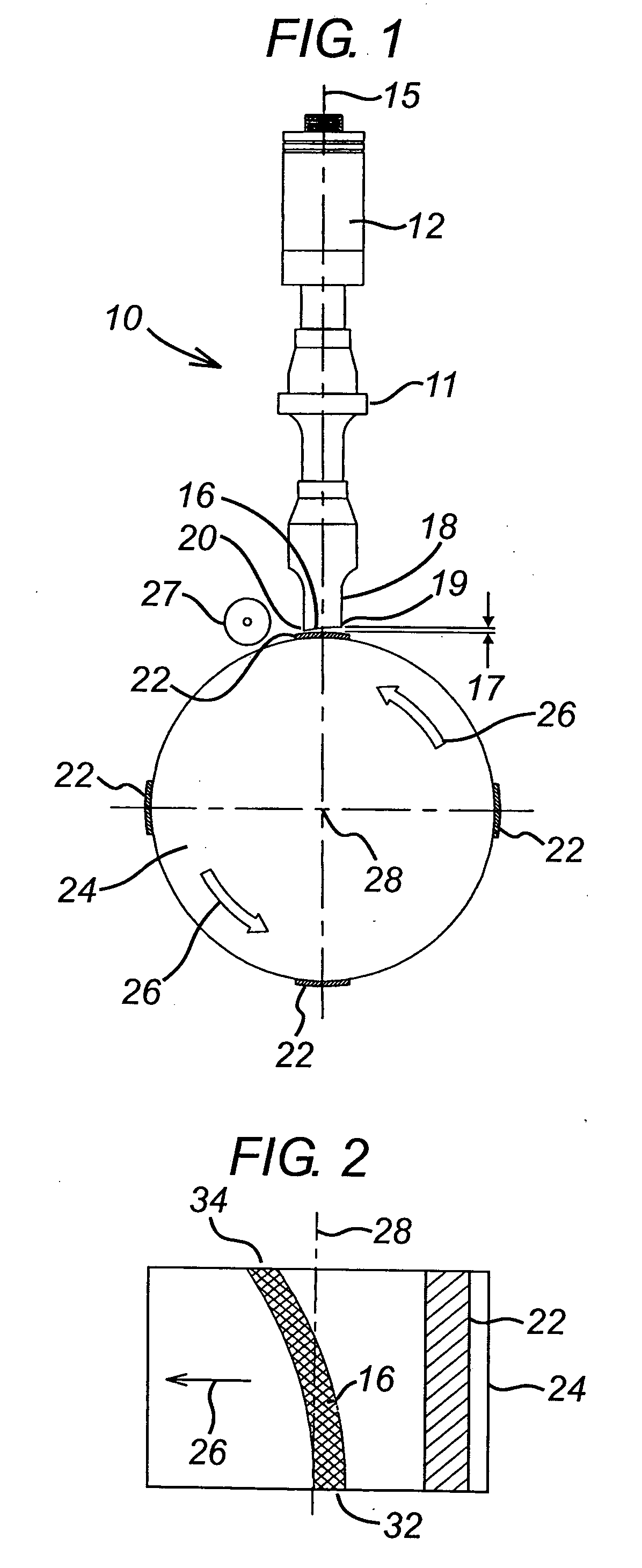
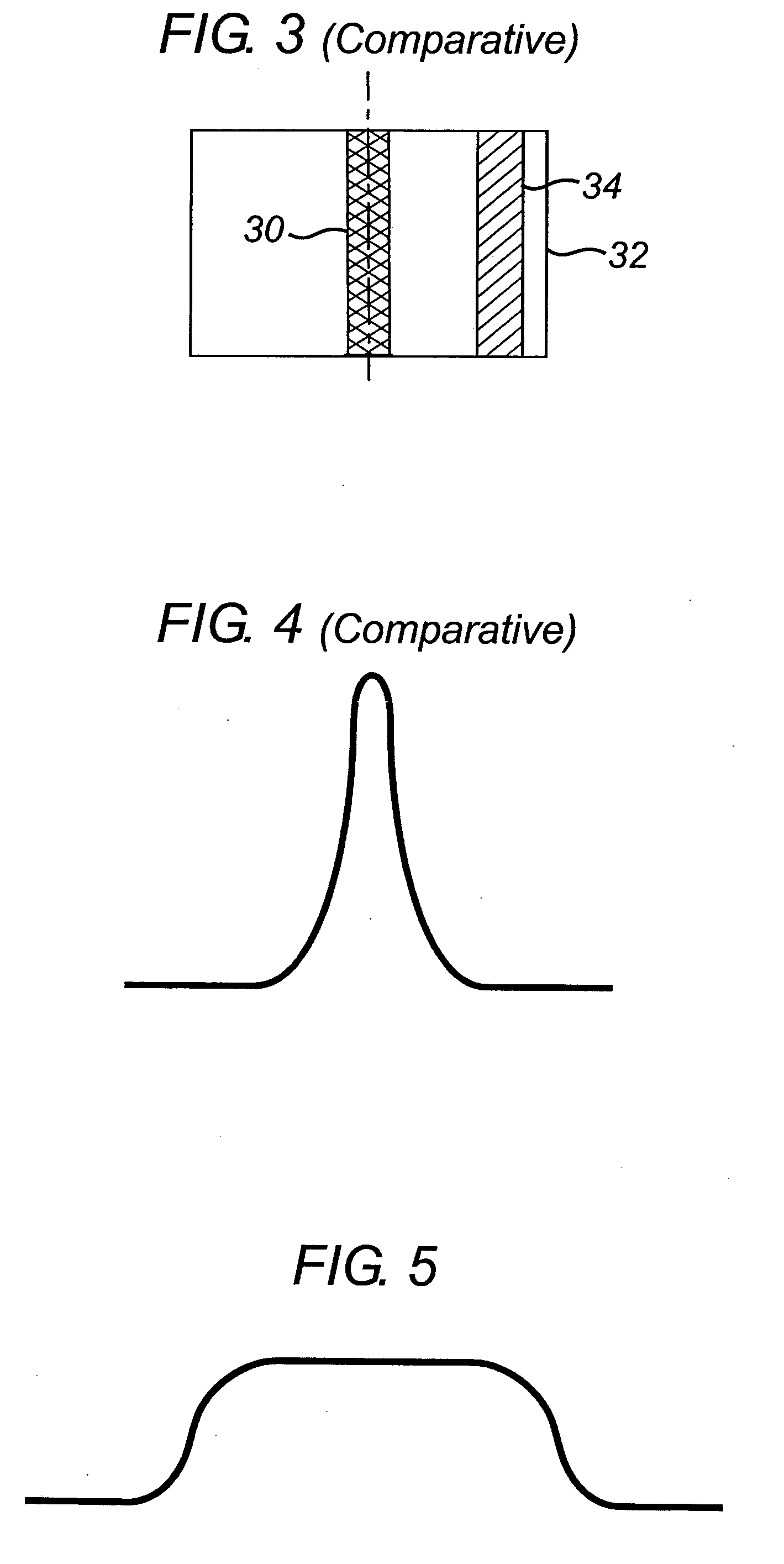
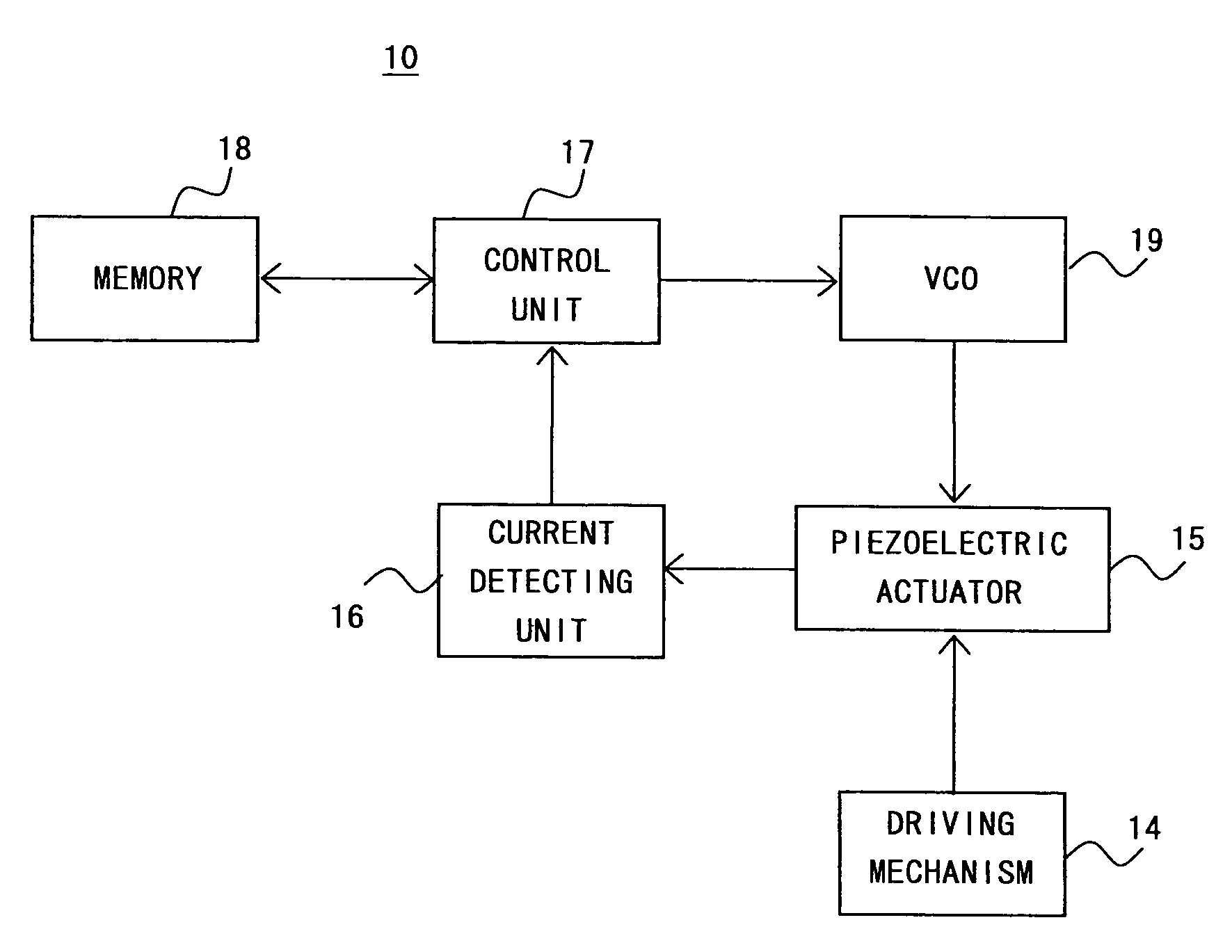
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Ultrasonic actuator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
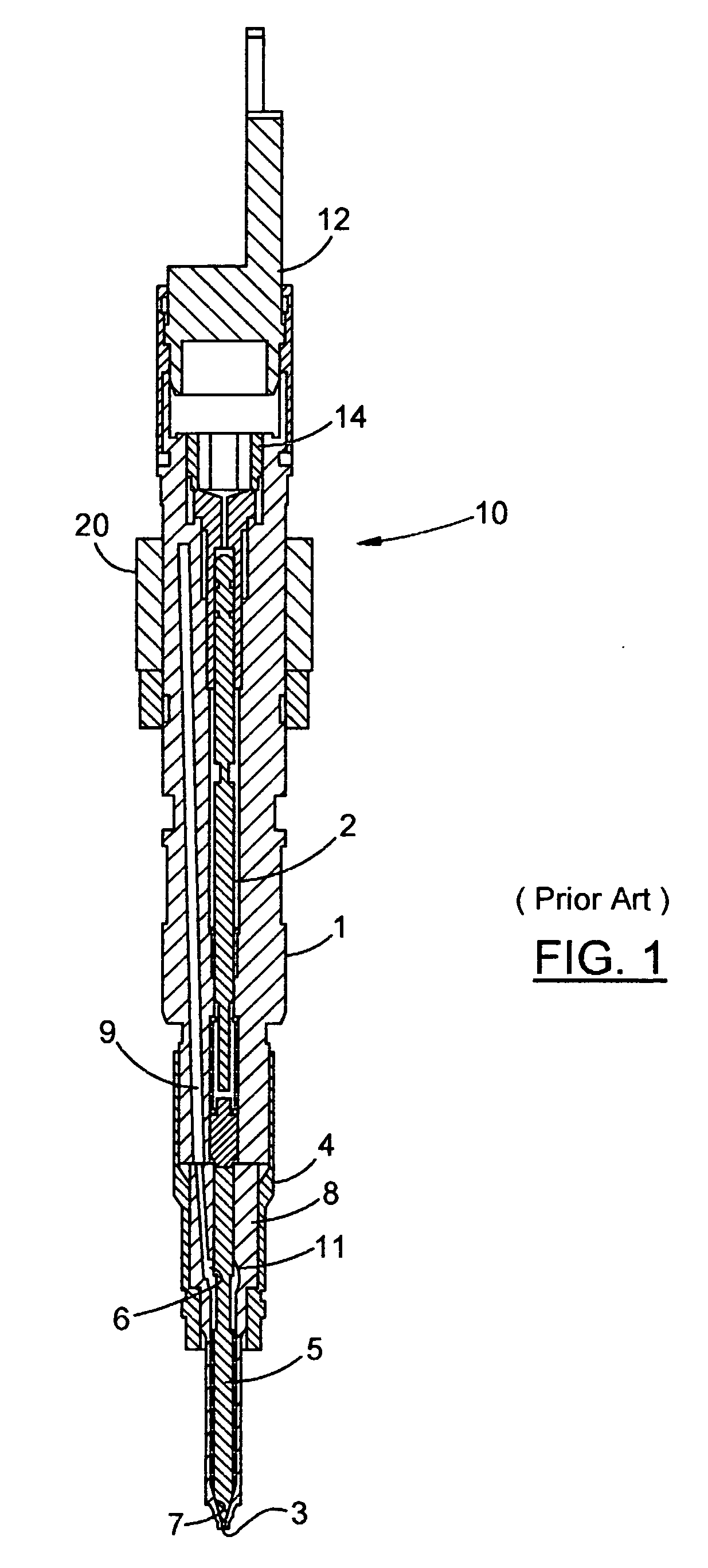
Method and apparatus for the ultrasonic actuation of the cantilever of a probe-based instrument
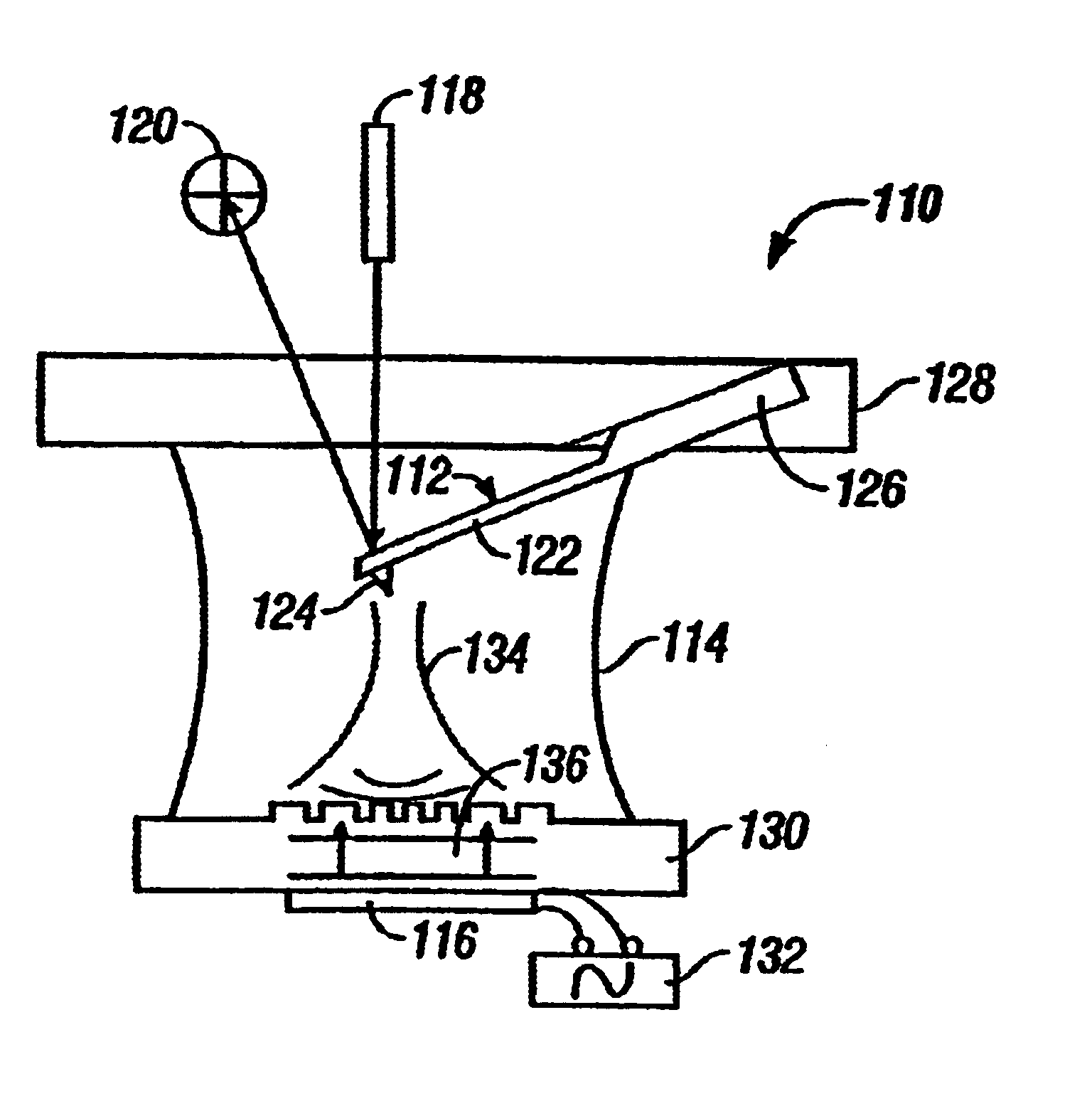
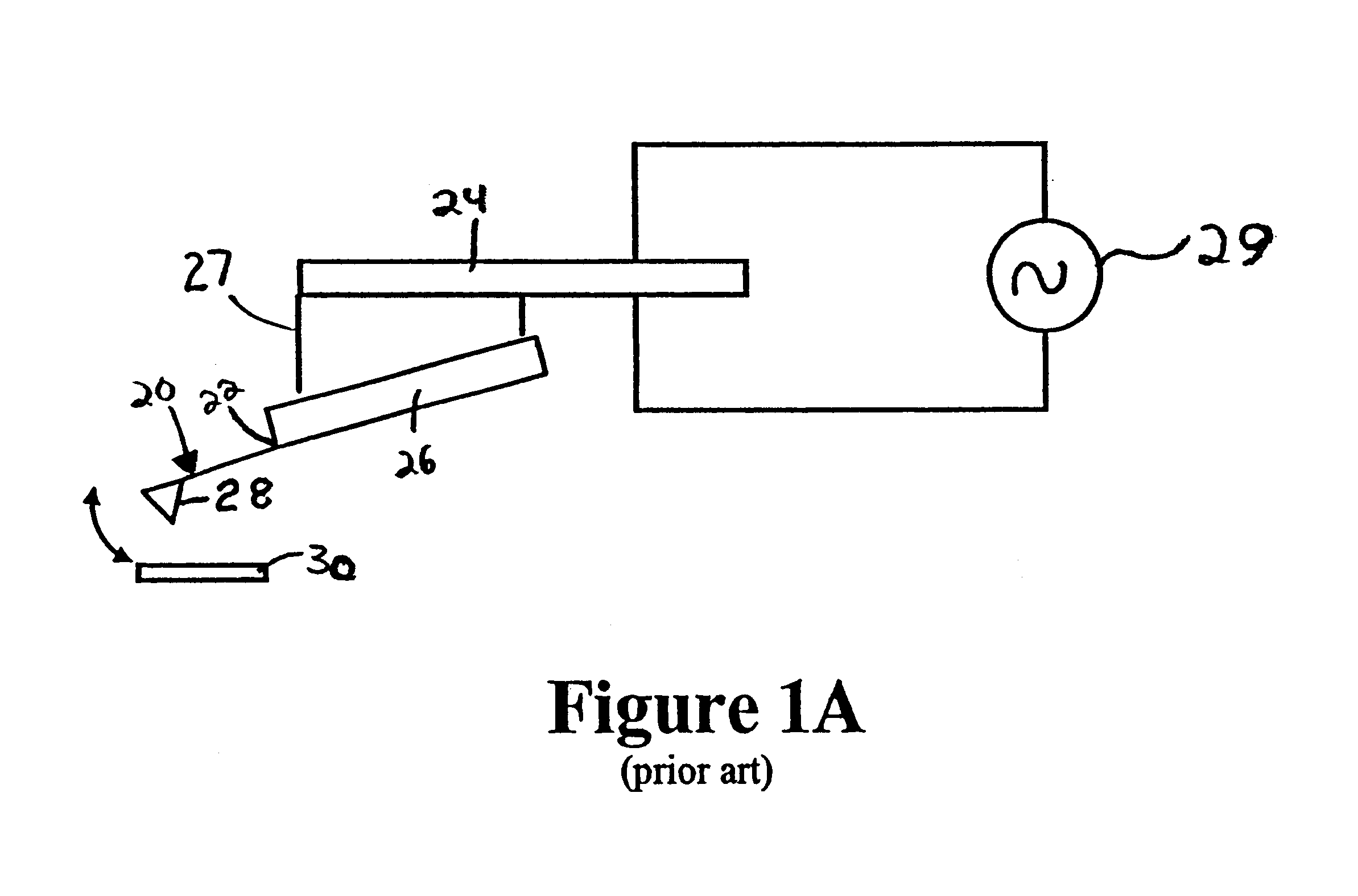
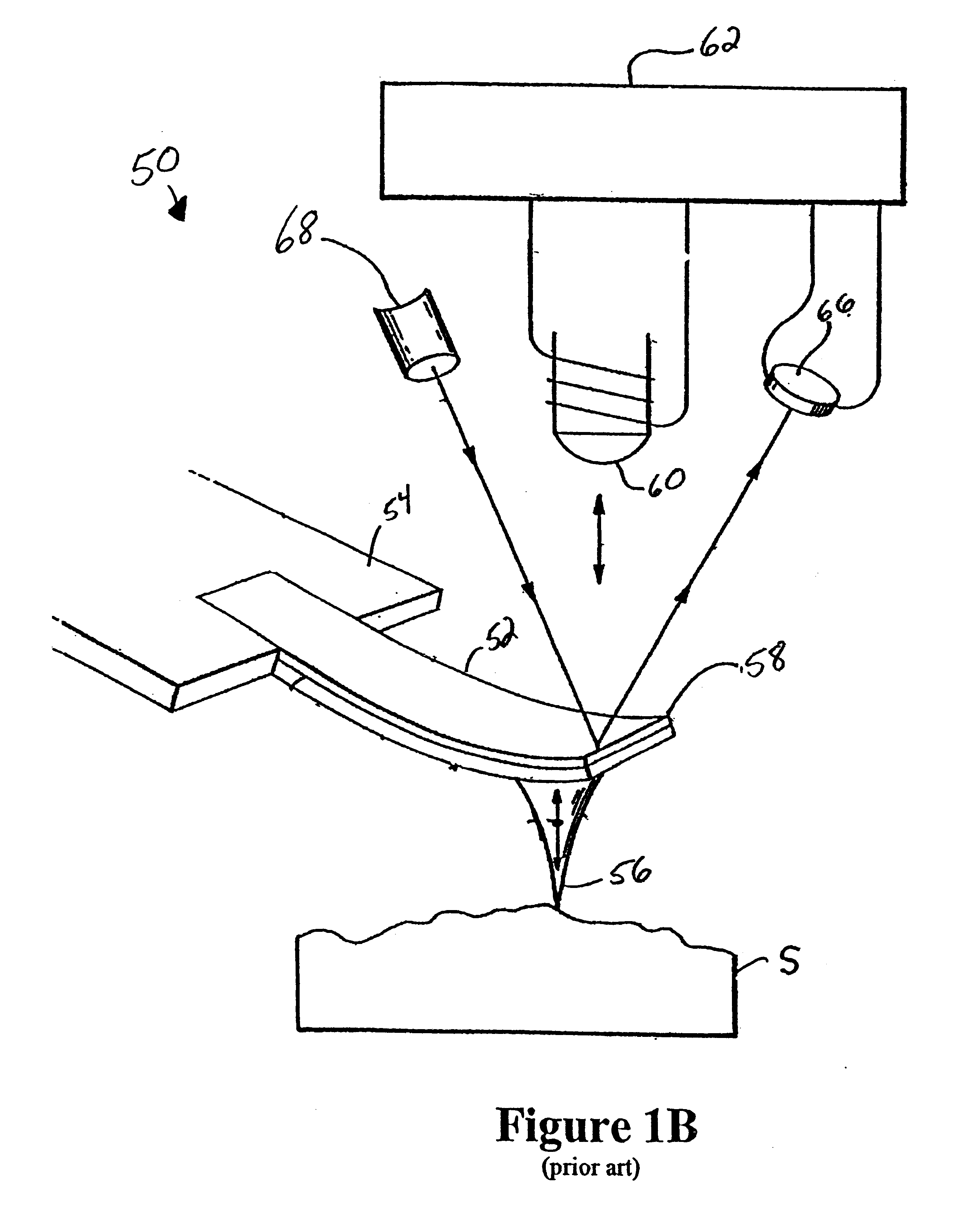
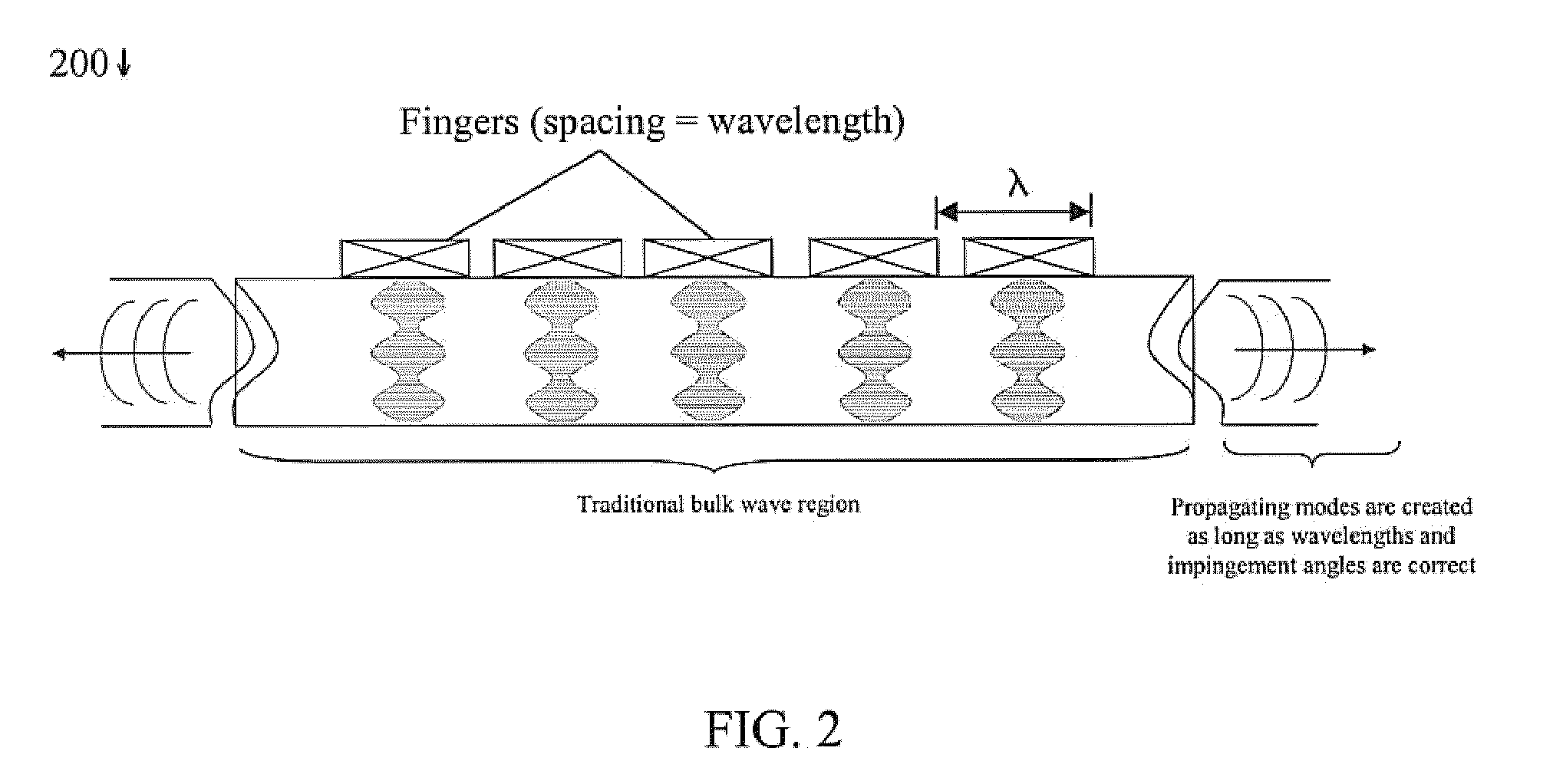
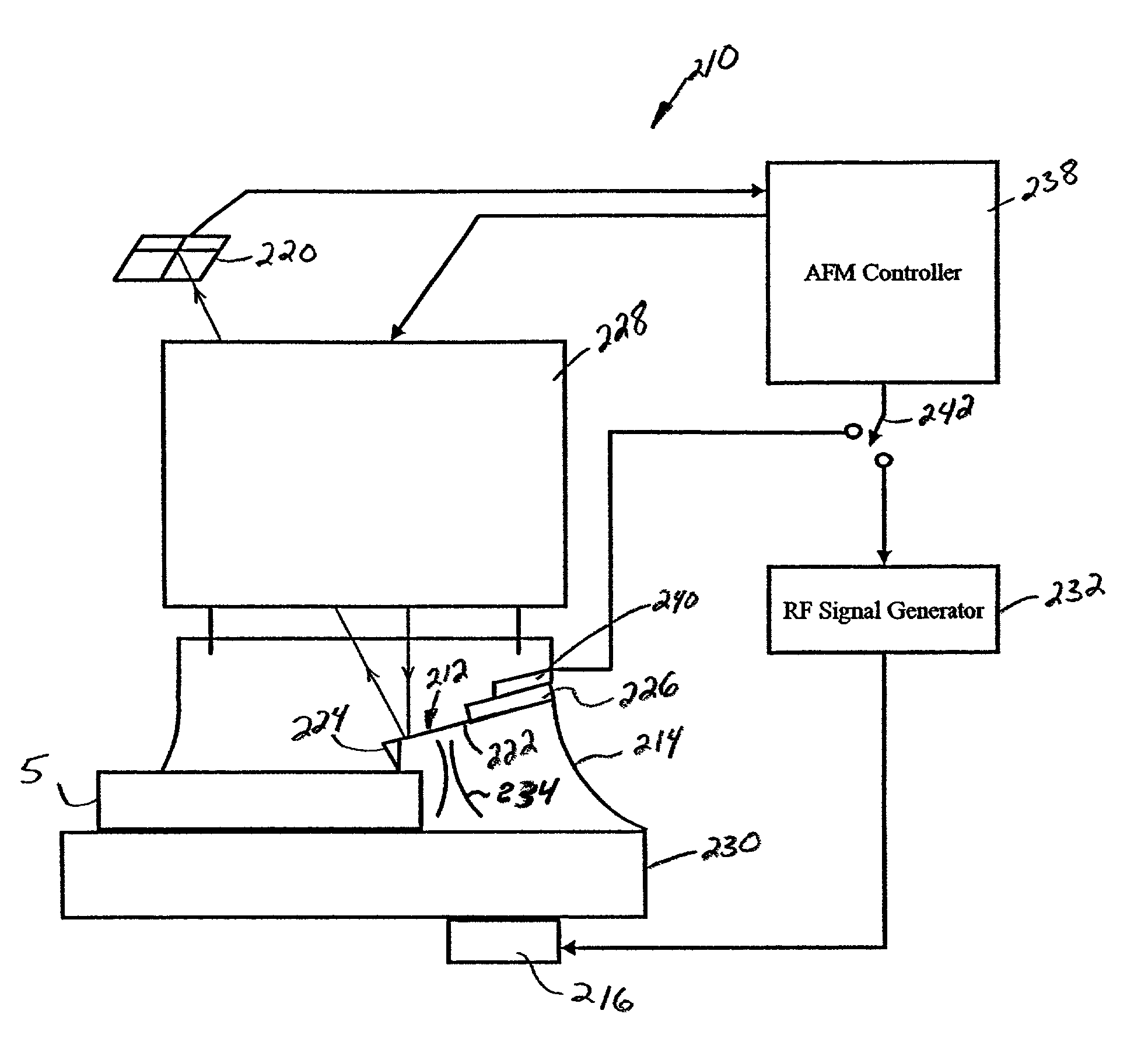
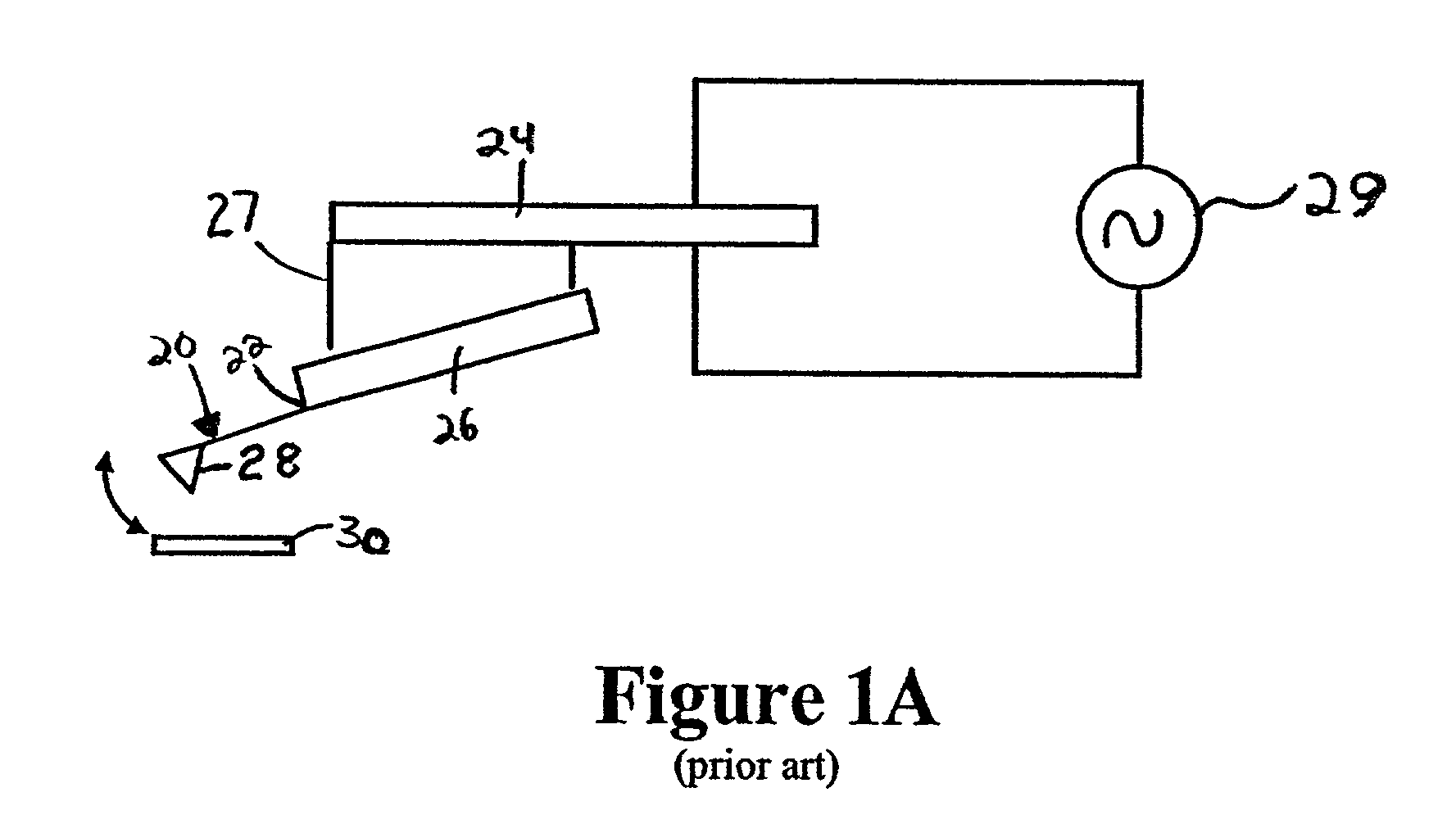
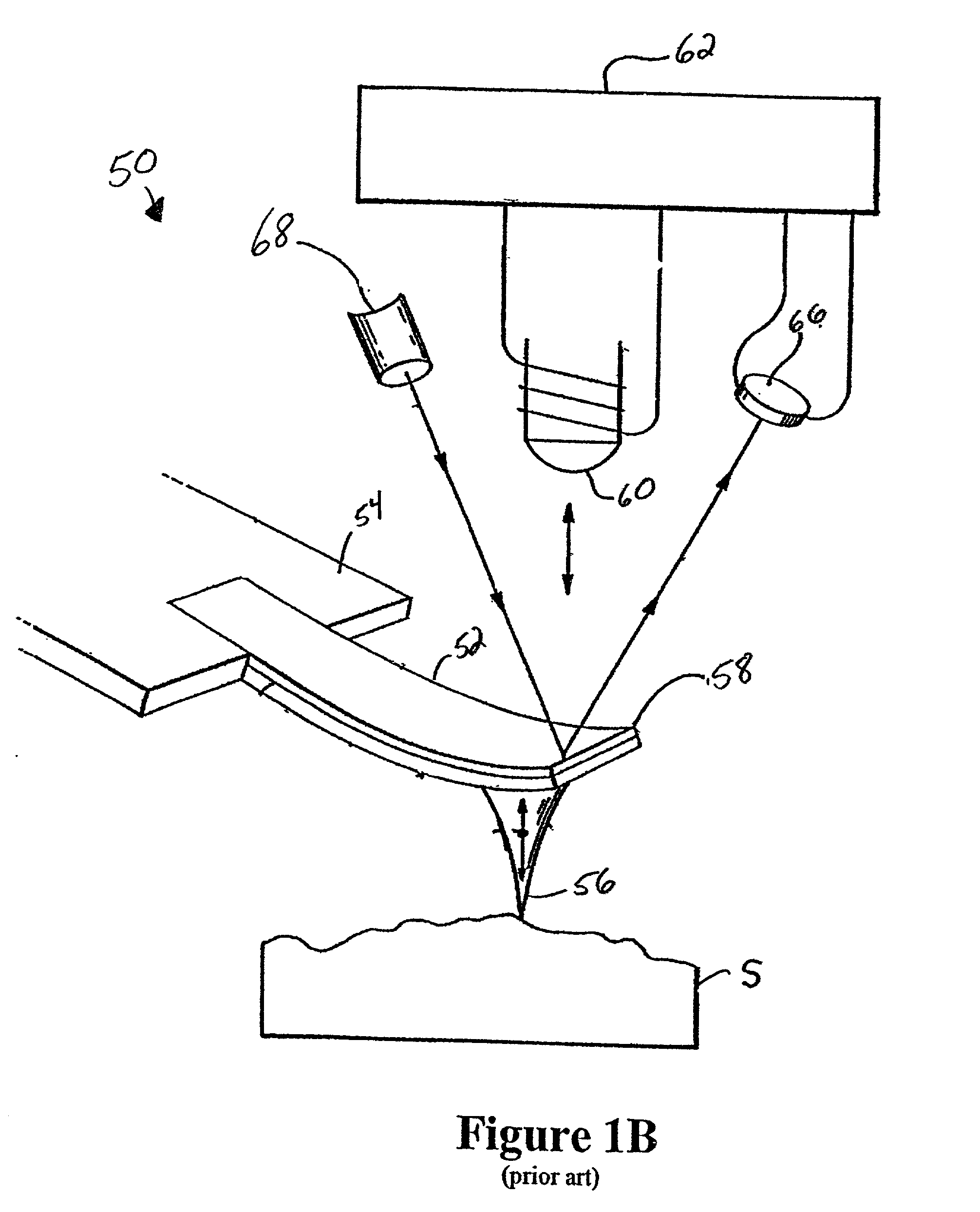
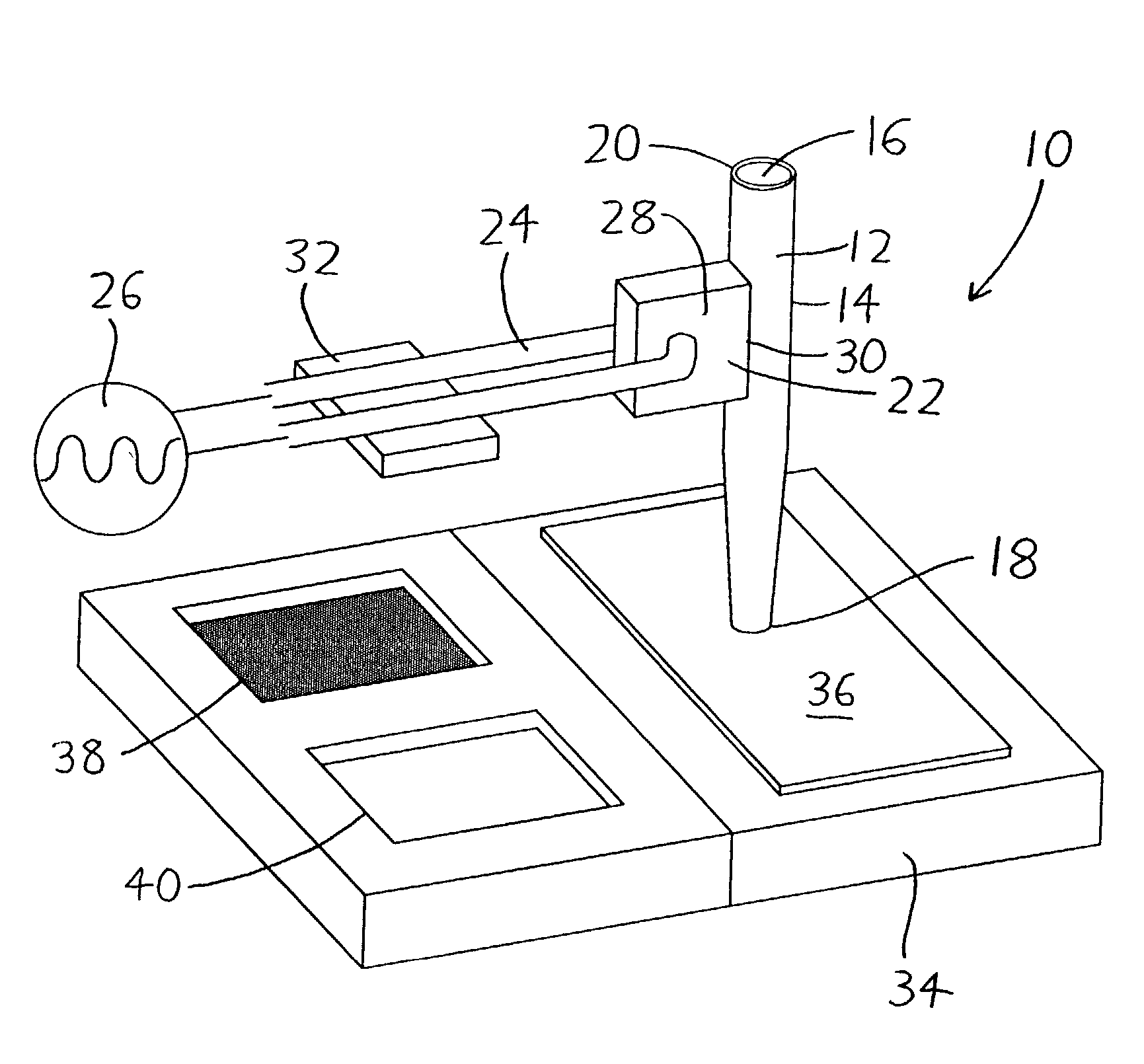
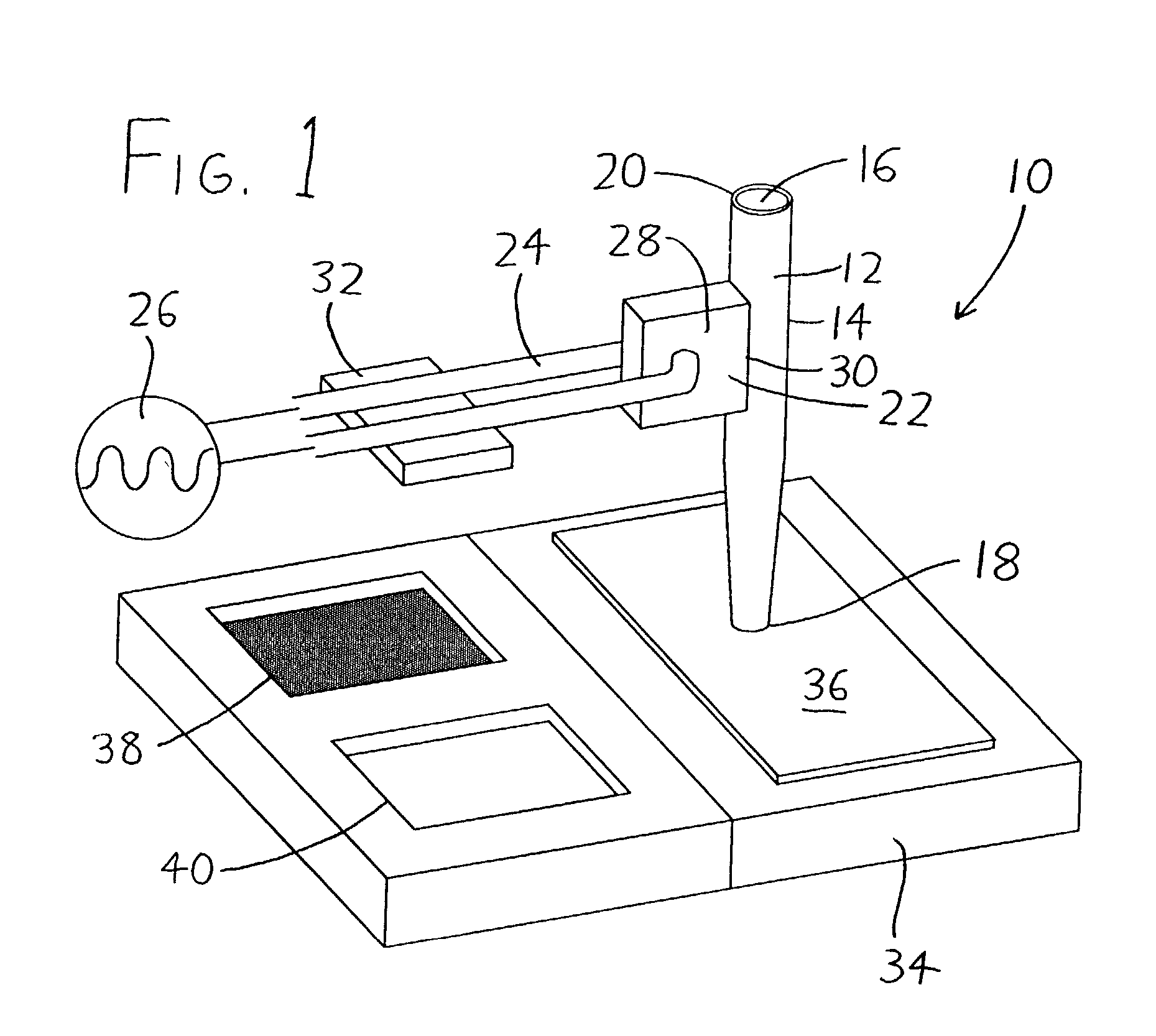
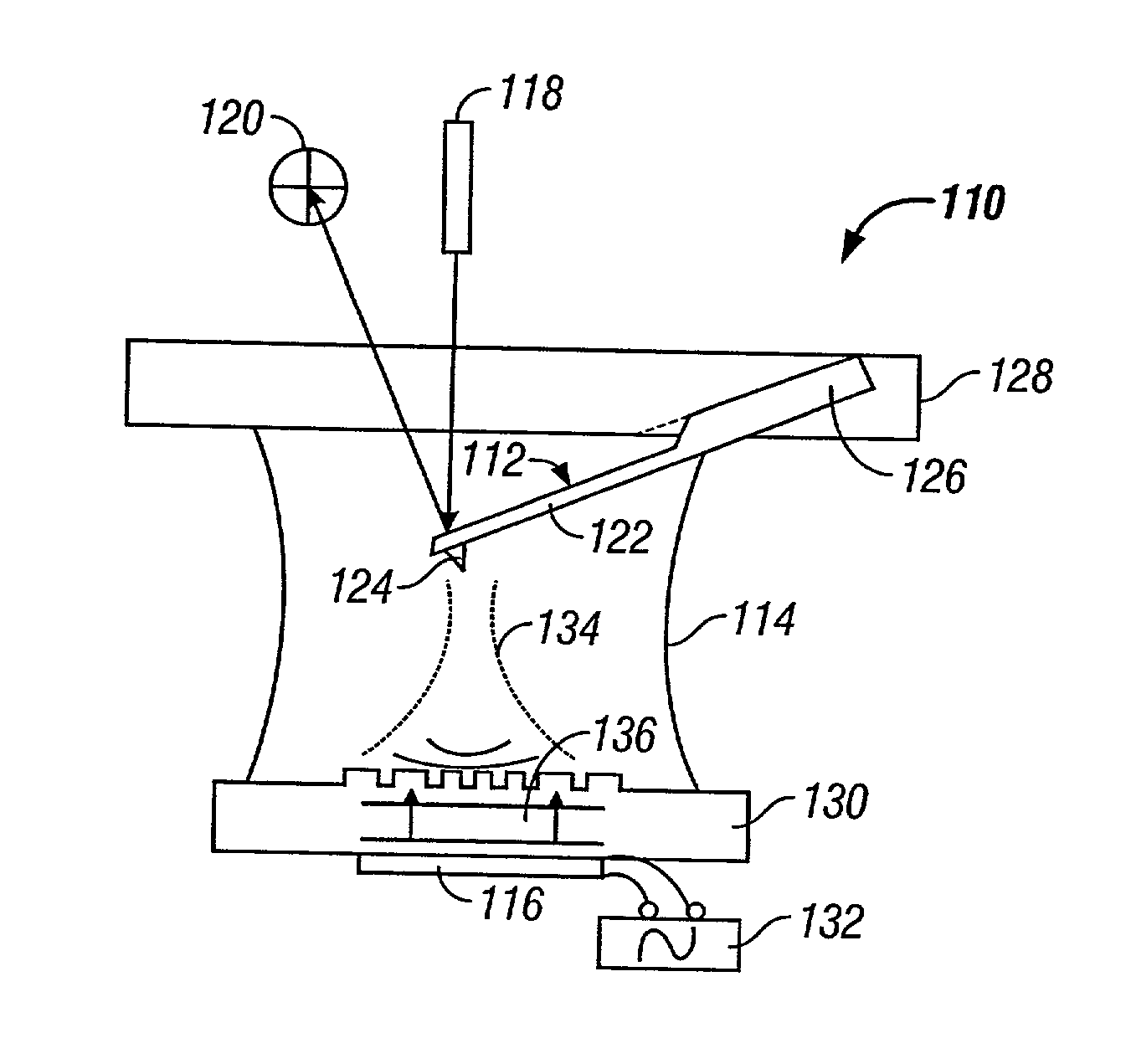
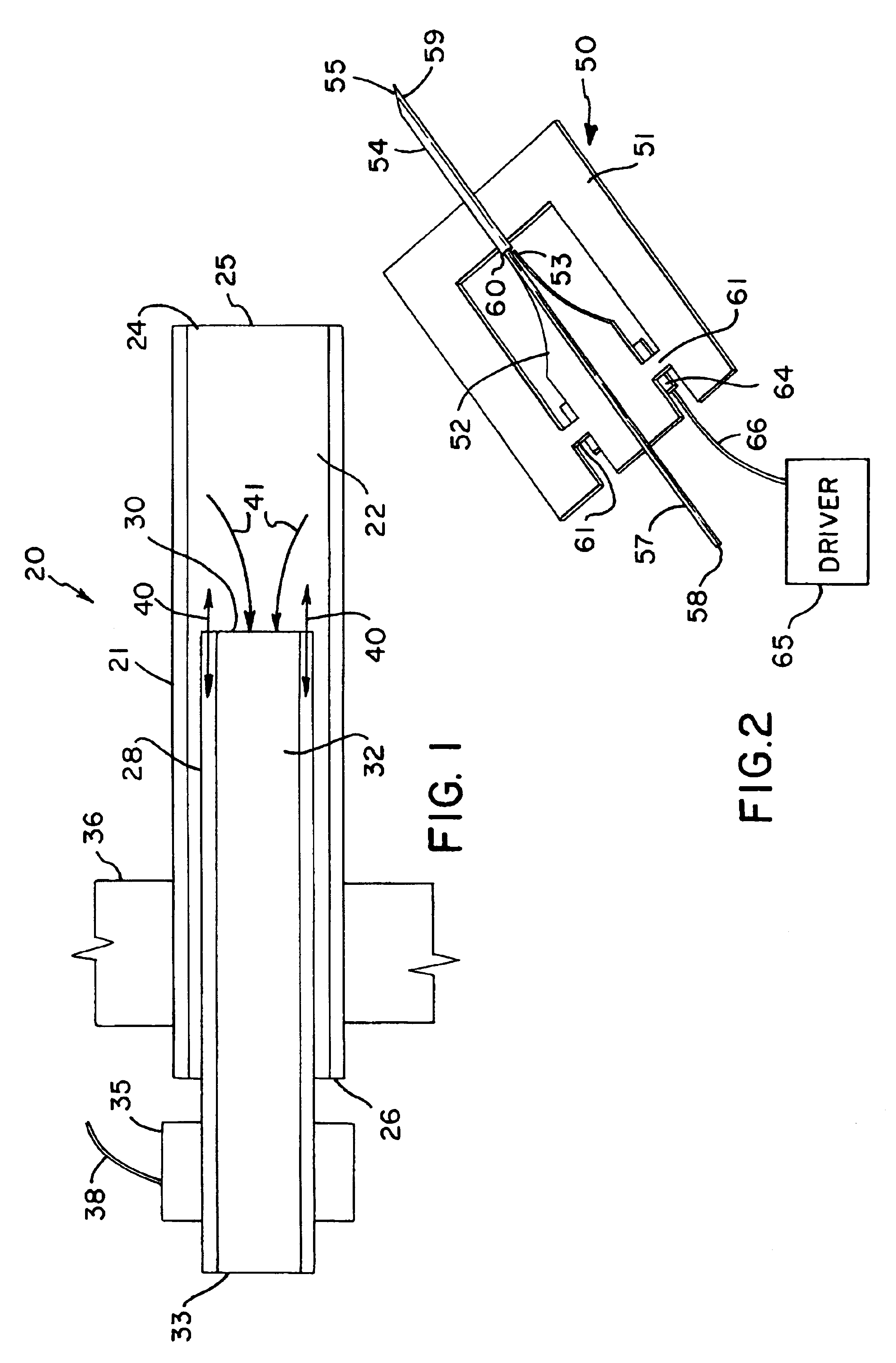
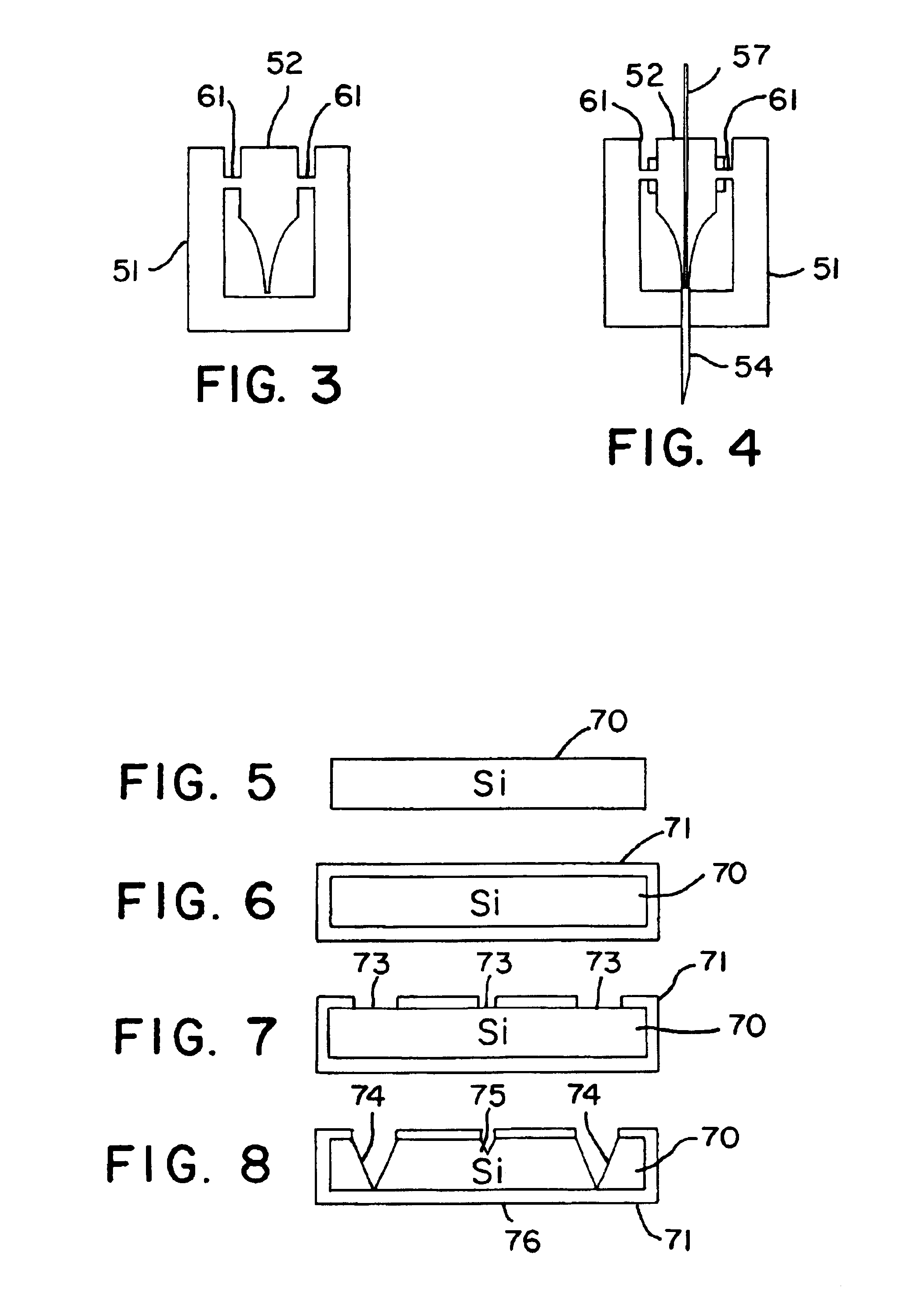
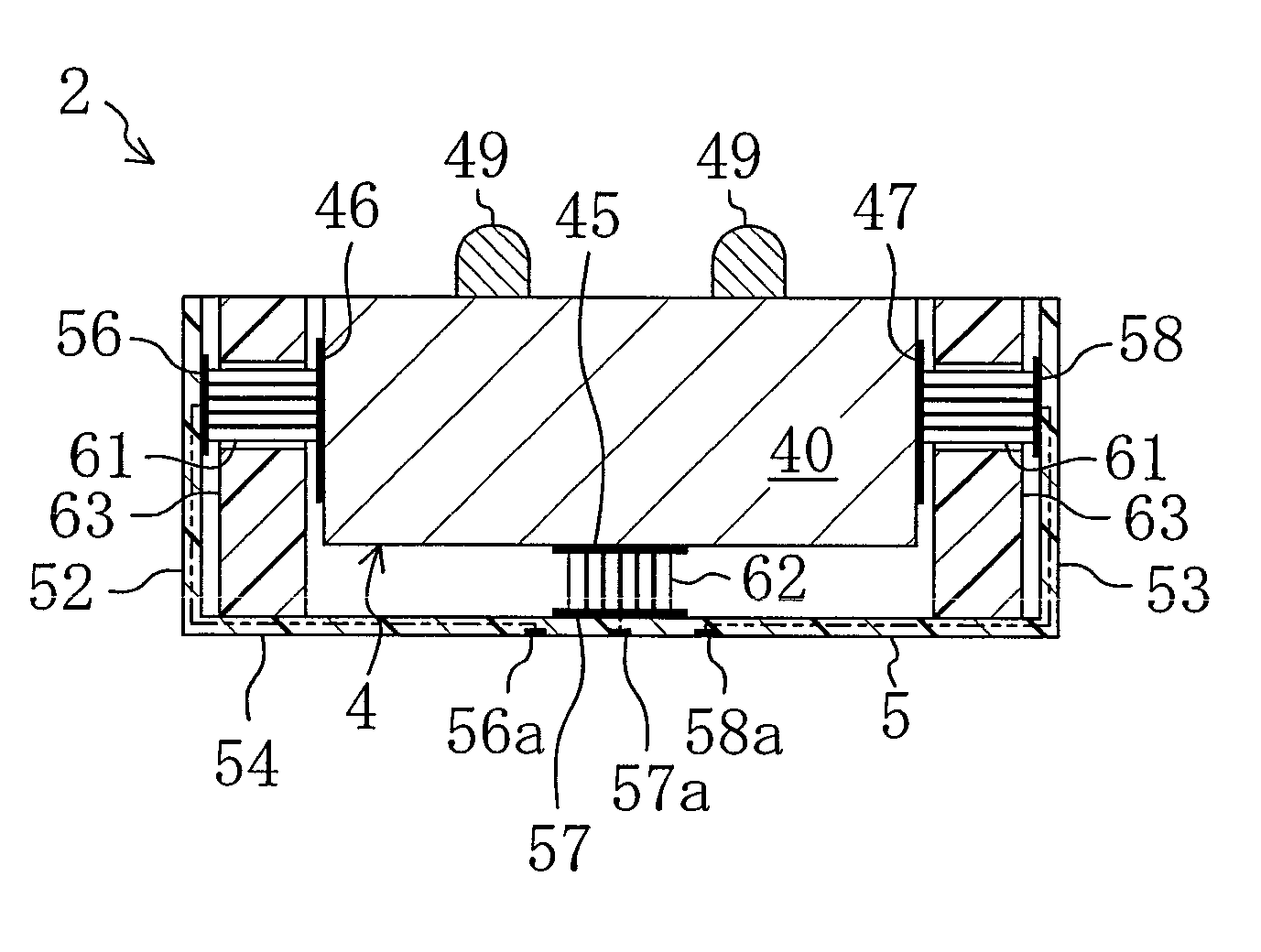
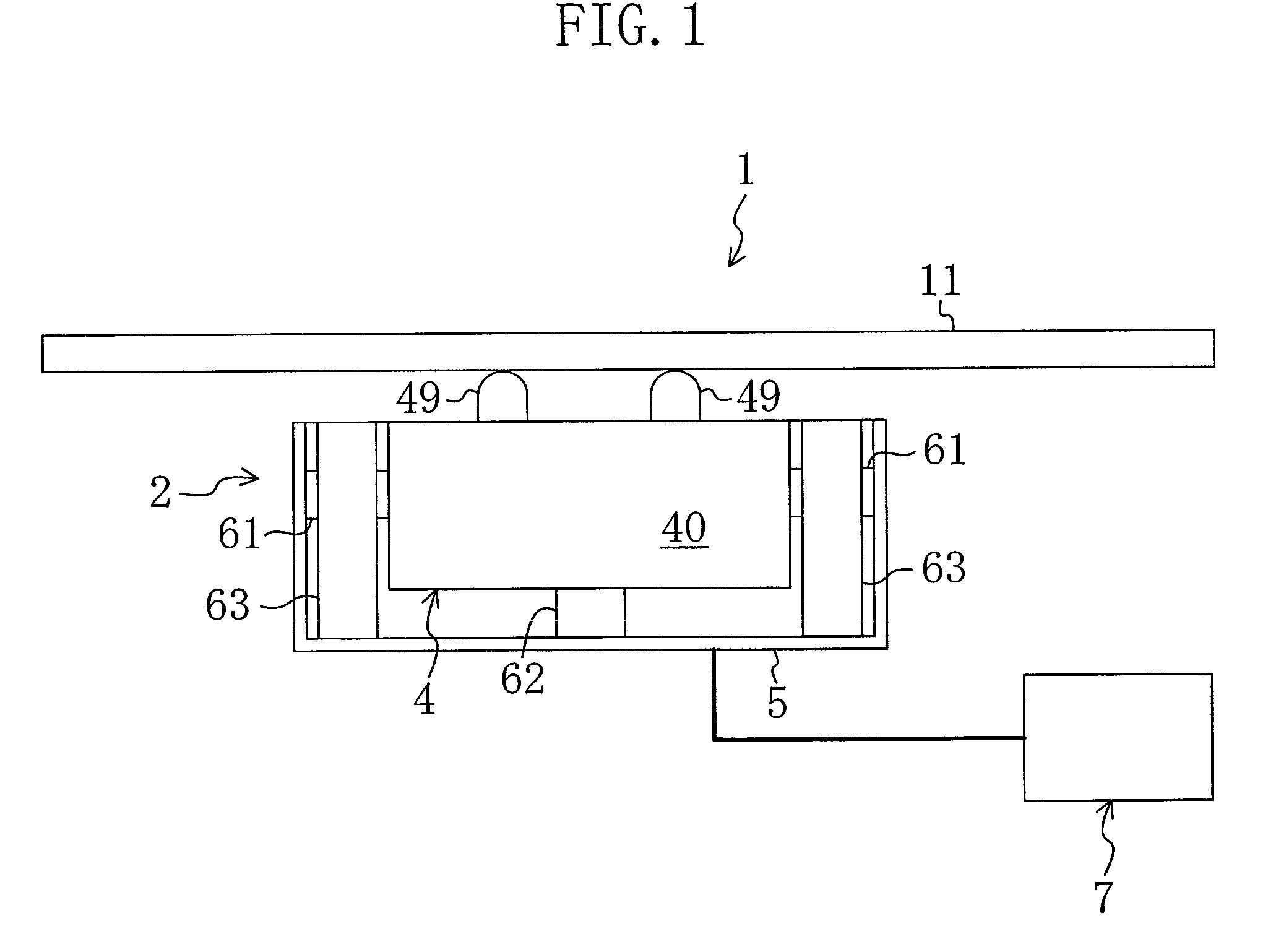
The cantilever of a probe-based metrology instrument such as an AFM is deflected by directing a beam of ultrasonic energy at the cantilever to apply ultrasonically generated acoustic radiation pressure to the cantilever. The energy is generated by an ultrasonic actuator such as a ZnO transducer driven by a power source such an RF signal generator. The transmitted beam preferably is shaped by focusing, collimation, or the like so that it impinges at least primarily on a region of interest of the cantilever such as the free end. The ultrasonic actuator produces a much better controlled force on the cantilever than can be achieved through the use of a traditional piezoelectric actuator and, accordingly, produces a response free of spurious effects (at least when the cantilever is operating in liquid). It also has a frequency bandwidth in the MHz range.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
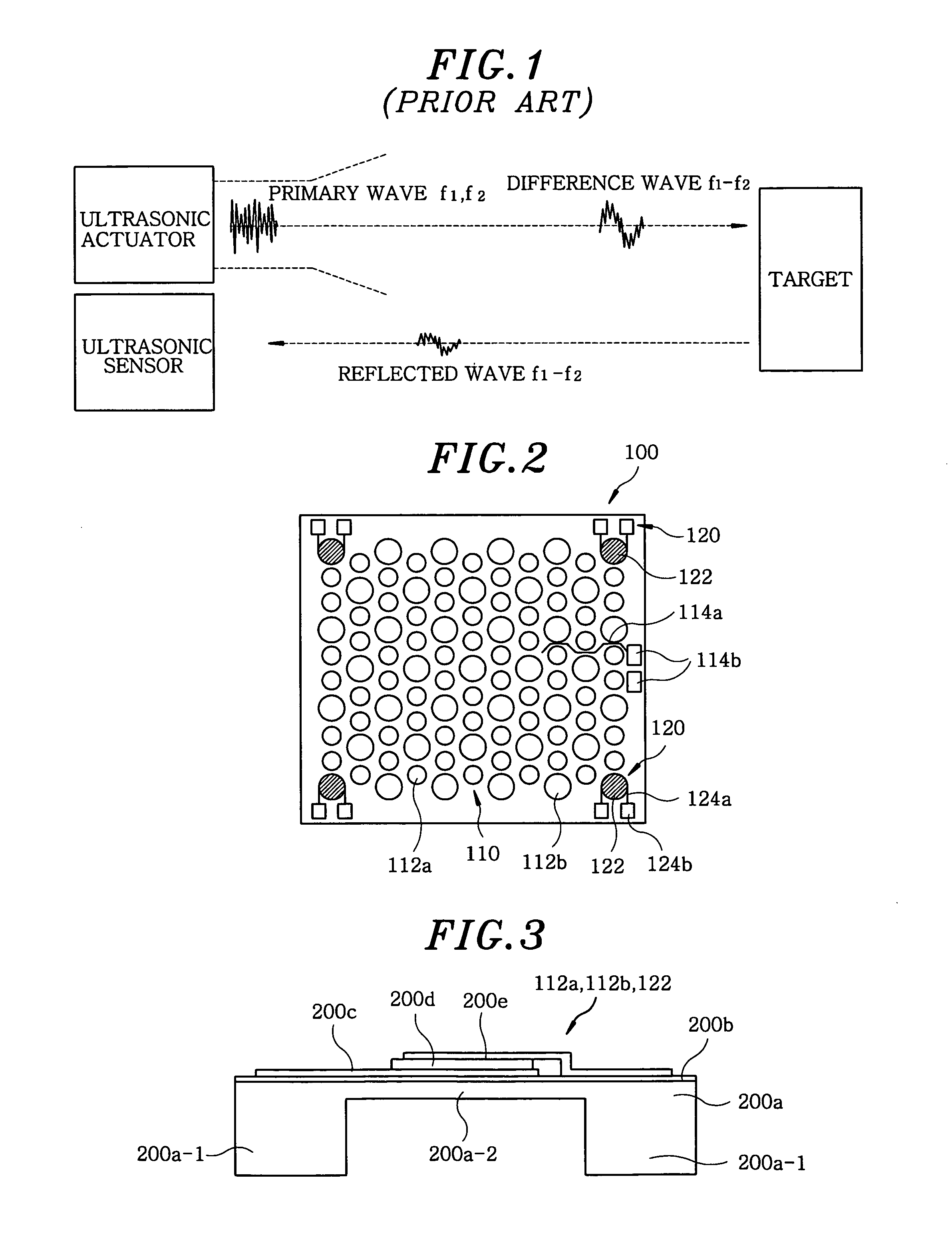
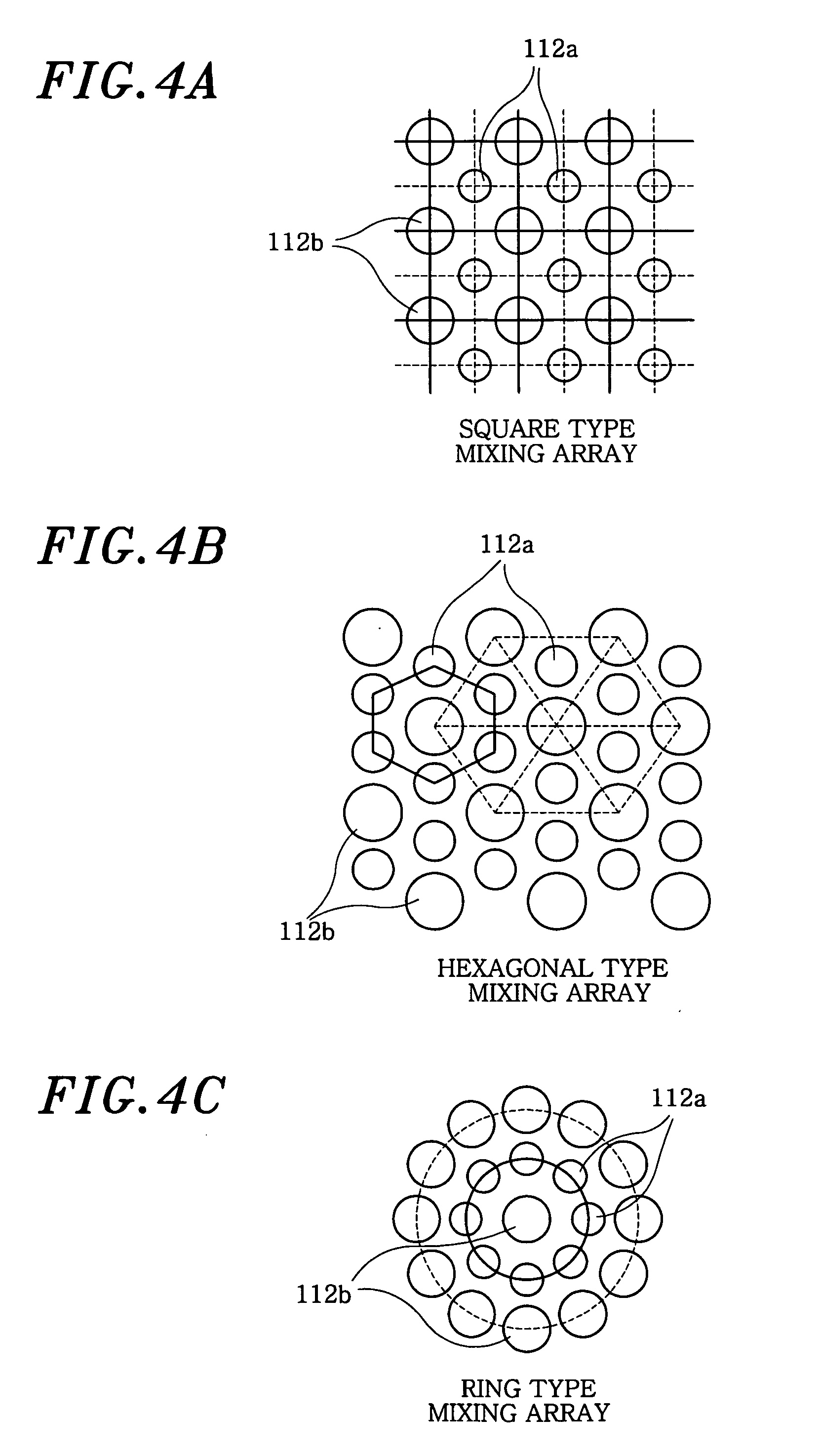
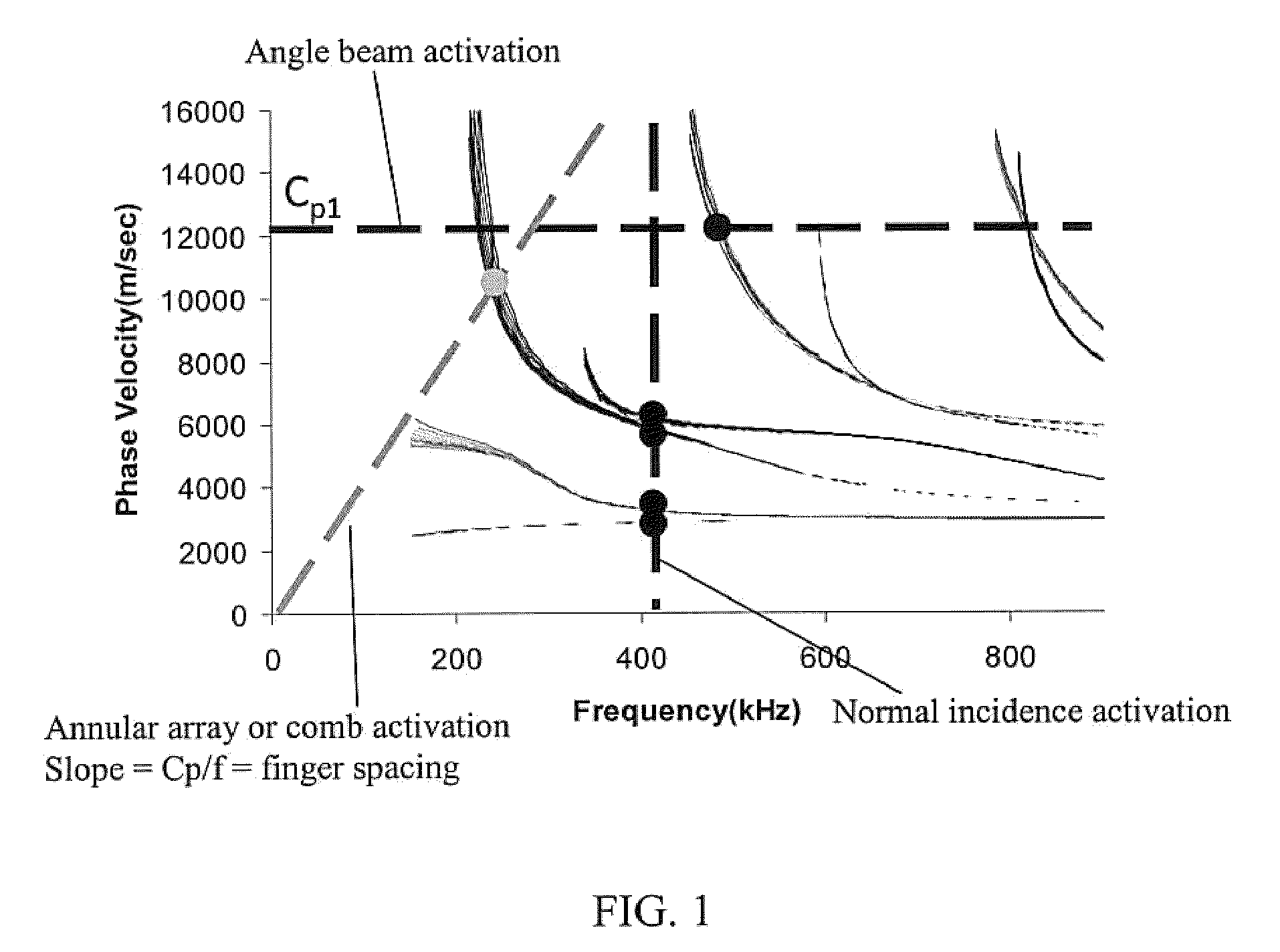
Ultrasonic transducer for ranging measurement with high directionality using parametric transmitting array in air and a method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20080013405A1Improve directionalityMechanical vibrations separationAcoustic wave reradiationSonificationFrequency wave
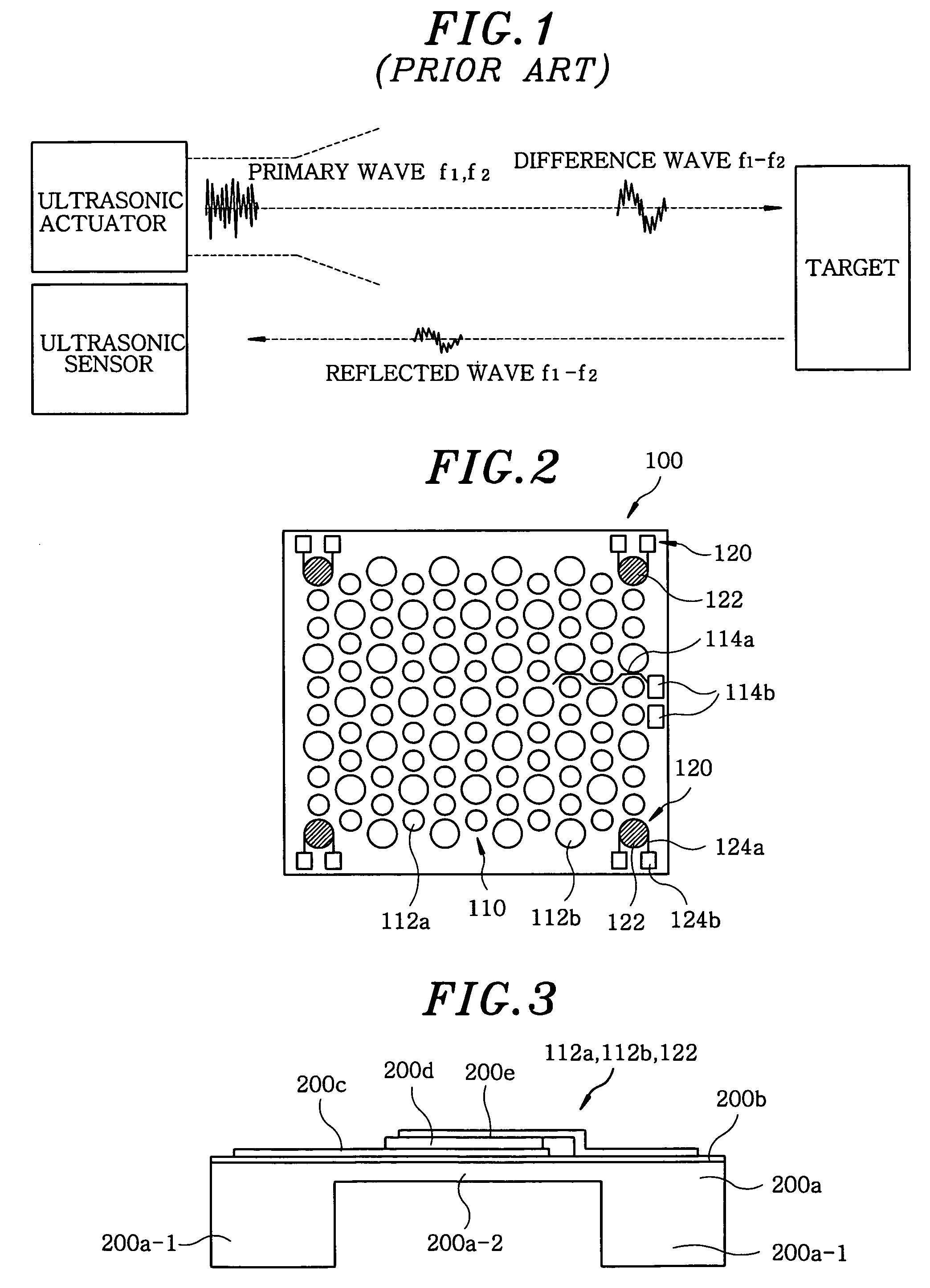
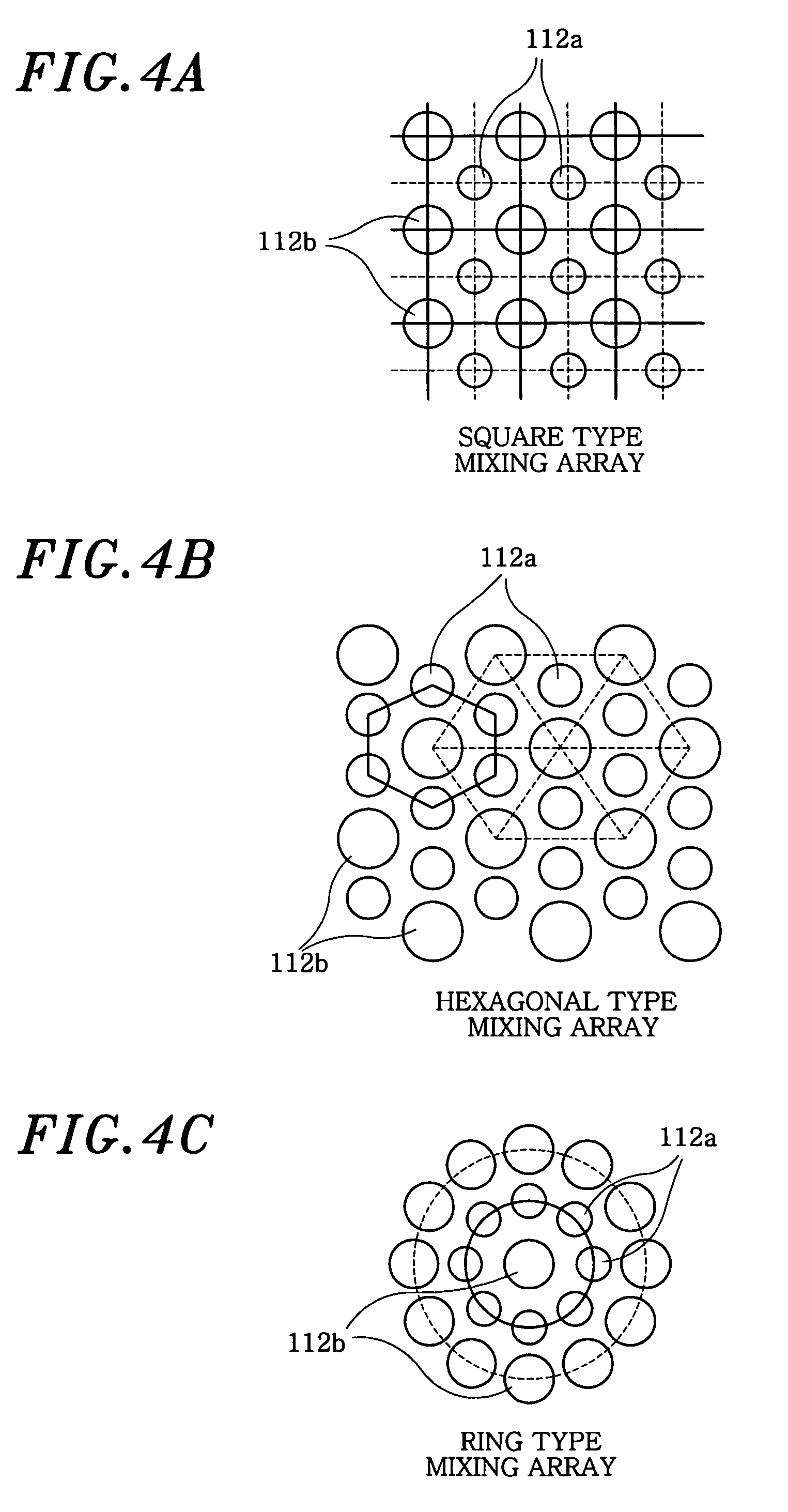
A multiple resonances type ultrasonic transducer for a ranging measurement with high directionality using a parametric transmitting array in air, includes an ultrasonic actuator unit formed with a regularly mixing array of first unit actuators having a resonance frequency of f1 and second unit actuators having a resonance frequency of f2. The ultrasonic actuator unit generates a difference frequency wave (fd=f1−f2) with high directionality by forming a parametric transmitting array in air through generating two ultrasonic waves with high pressure in air. Further, the transducer includes an ultrasonic sensor unit formed with one or more unit sensors having a resonance frequency of the difference frequency (fd=f1−f2), for sensing a reflected ultrasonic pulse'signal from a target.
Owner:MOON WONKYU
Ultrasonic vibration system and method for removing/avoiding unwanted build-up on structures
InactiveUS20100031972A1Avoid overall overheatingIncrease coveragePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDe-icing equipmentsStructural health monitoringEngineering
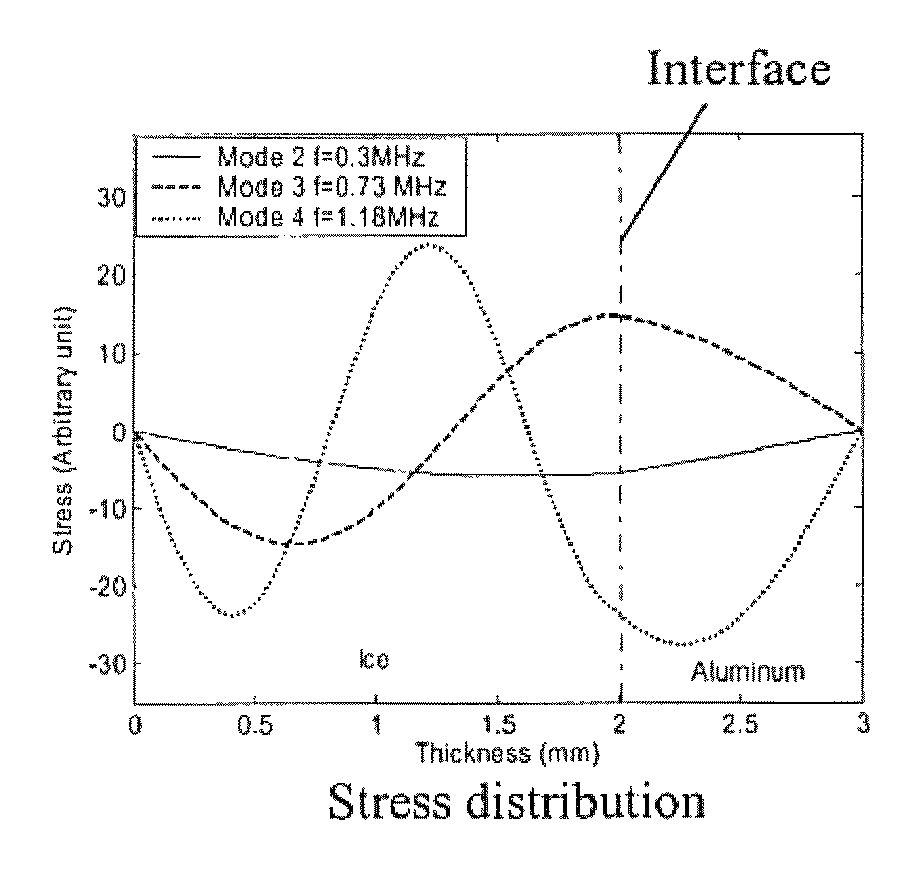
An ultrasonic method for removing and / or avoiding unwanted build-up on structures is provided, wherein the term build-up refers to, but is not limited to, ice, dirt, mud, or other wanted debris or contamination. Deicing or anti-icing structures of interest can include, but are not limited to, helicopter rotor blades, other helicopter blade components, fixed wing aircraft components, windshields in aircraft, automobiles, and other vehicles, ship hulls or other ship components, heat exchangers and other tubing where frost or ice could form, air-conditioning components, head lamp and other light coverings, bridge structures and components, and any structure where anti-icing or deicing would be beneficial. One or more ultrasonic actuators permanently embedded or coupled to the structure may be used accomplish the removal. The technique presented herein could also be utilized for non-destructive evaluation and structural health monitoring applications.
Owner:FUKUOKA BROADCASTING CORPORATION
Methods and apparata for precisely dispensing microvolumes of fluids
InactiveUS6874699B2Reduce vibrationUniform sizeTesting/calibration apparatusMachines/enginesMicrometerEngineering
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Ultrasonic transducer for ranging measurement with high directionality using parametric transmitting array in air and a method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS7460439B2Mechanical vibrations separationAcoustic wave reradiationFrequency waveSonification
A multiple resonances type ultrasonic transducer for a ranging measurement with high directionality using a parametric transmitting array in air, includes an ultrasonic actuator unit formed with a regularly mixing array of first unit actuators having a resonance frequency of f1 and second unit actuators having a resonance frequency of f2. The ultrasonic actuator unit generates a difference frequency wave (fd=f1−f2) with high directionality by forming a parametric transmitting array in air through generating two ultrasonic waves with high pressure in air. Further, the transducer includes an ultrasonic sensor unit formed with one or more unit sensors having a resonance frequency of the difference frequency (fd=f1−f2), for sensing a reflected ultrasonic pulse signal from a target.
Owner:MOON WONKYU
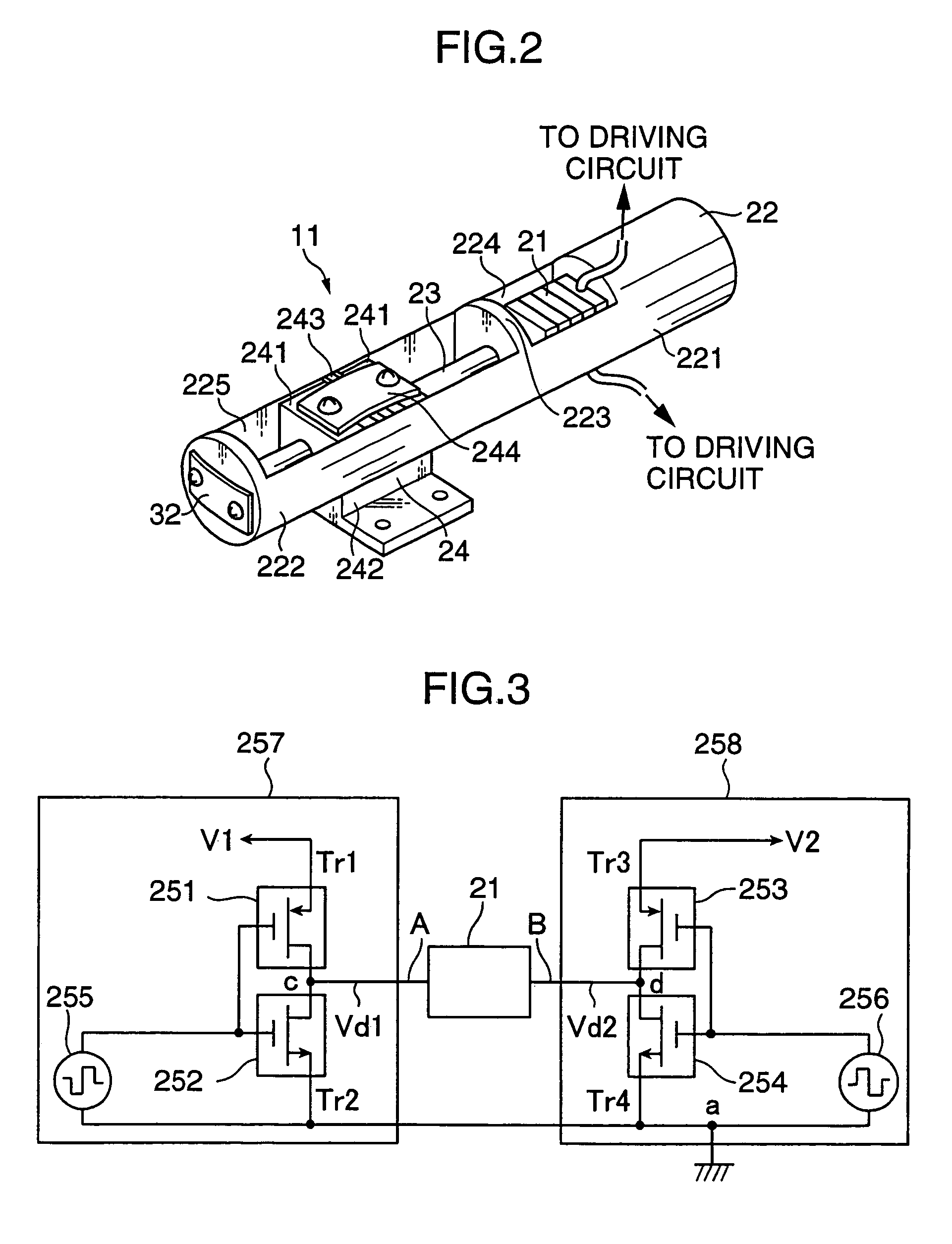
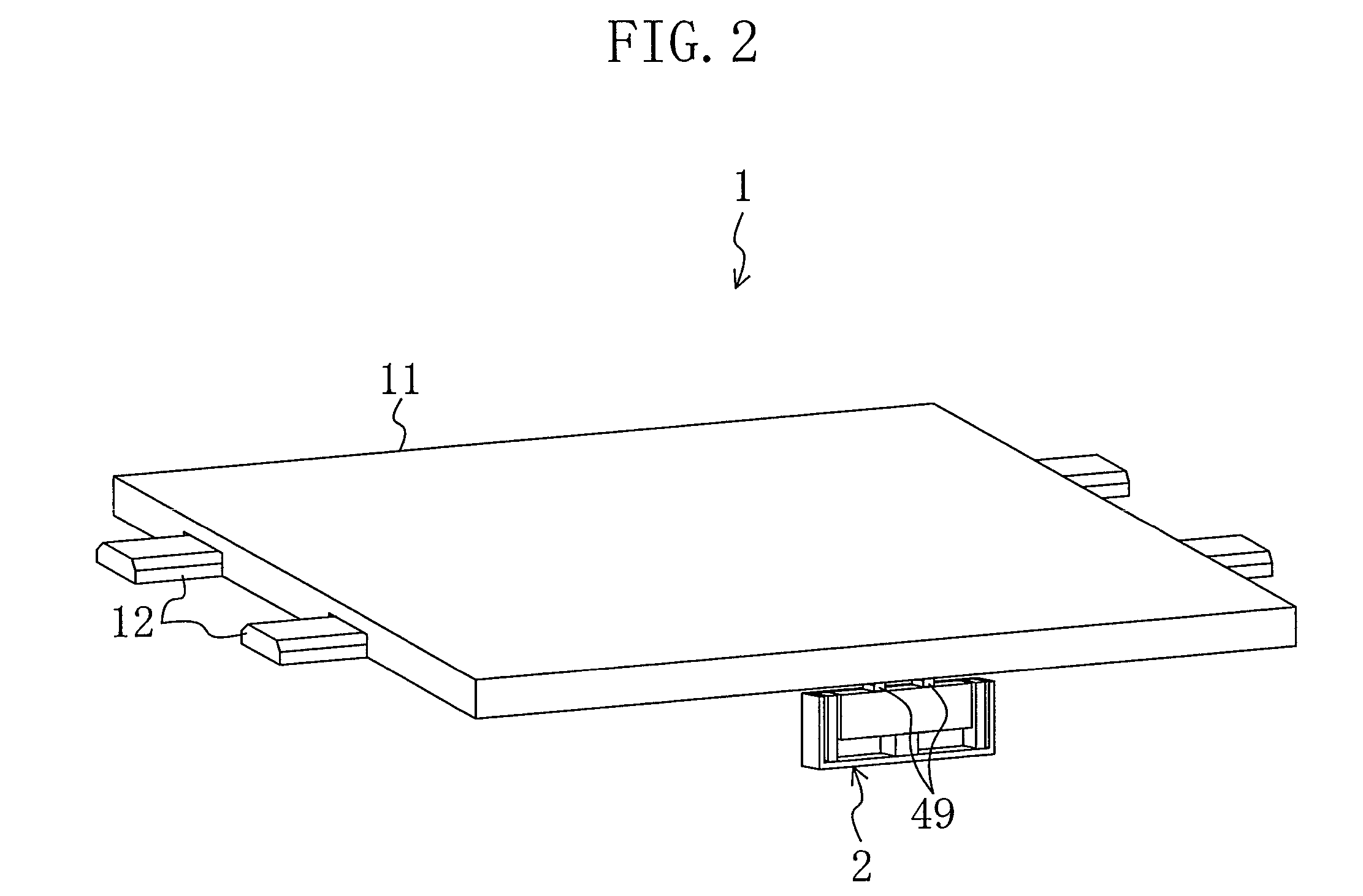
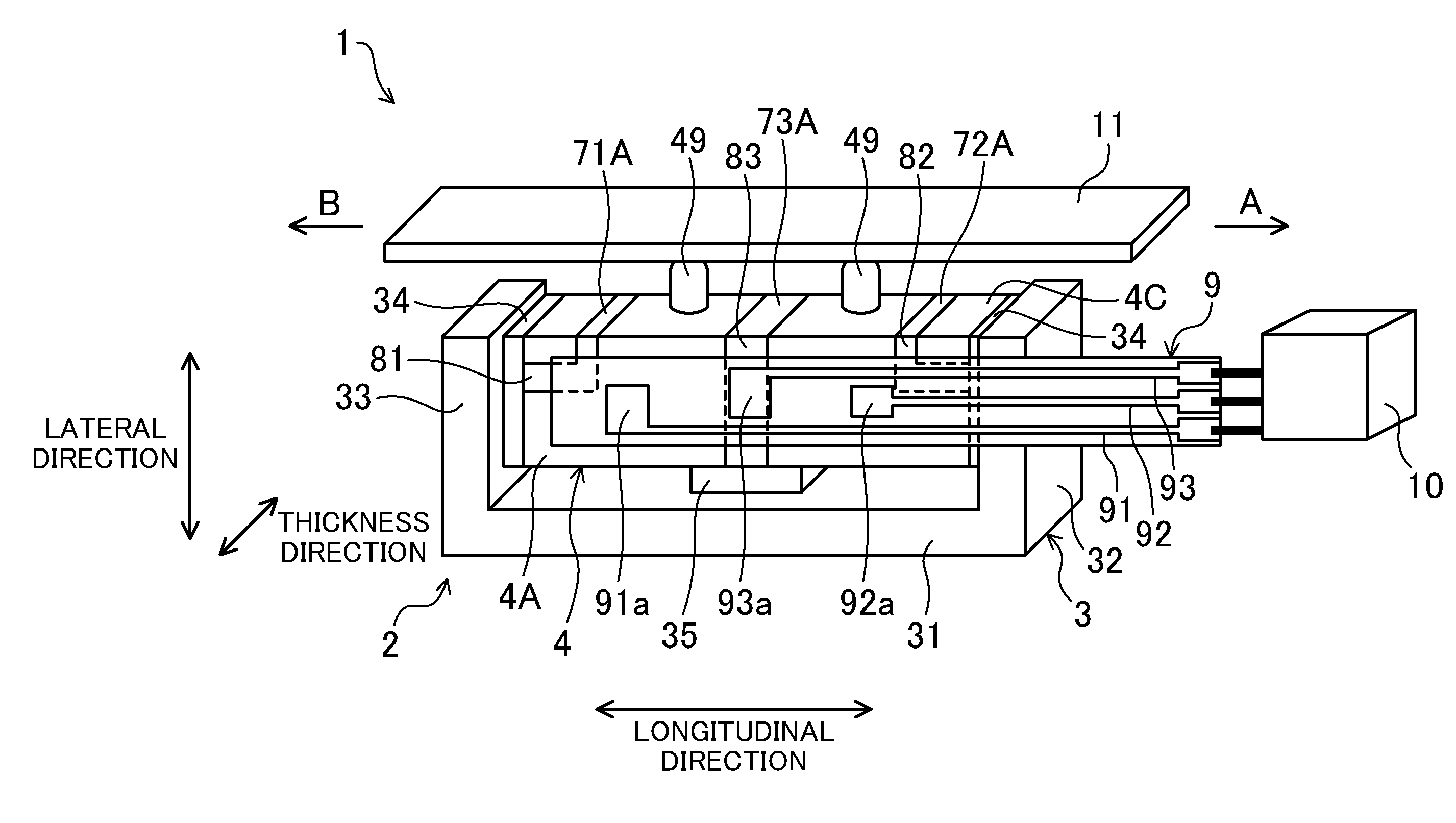
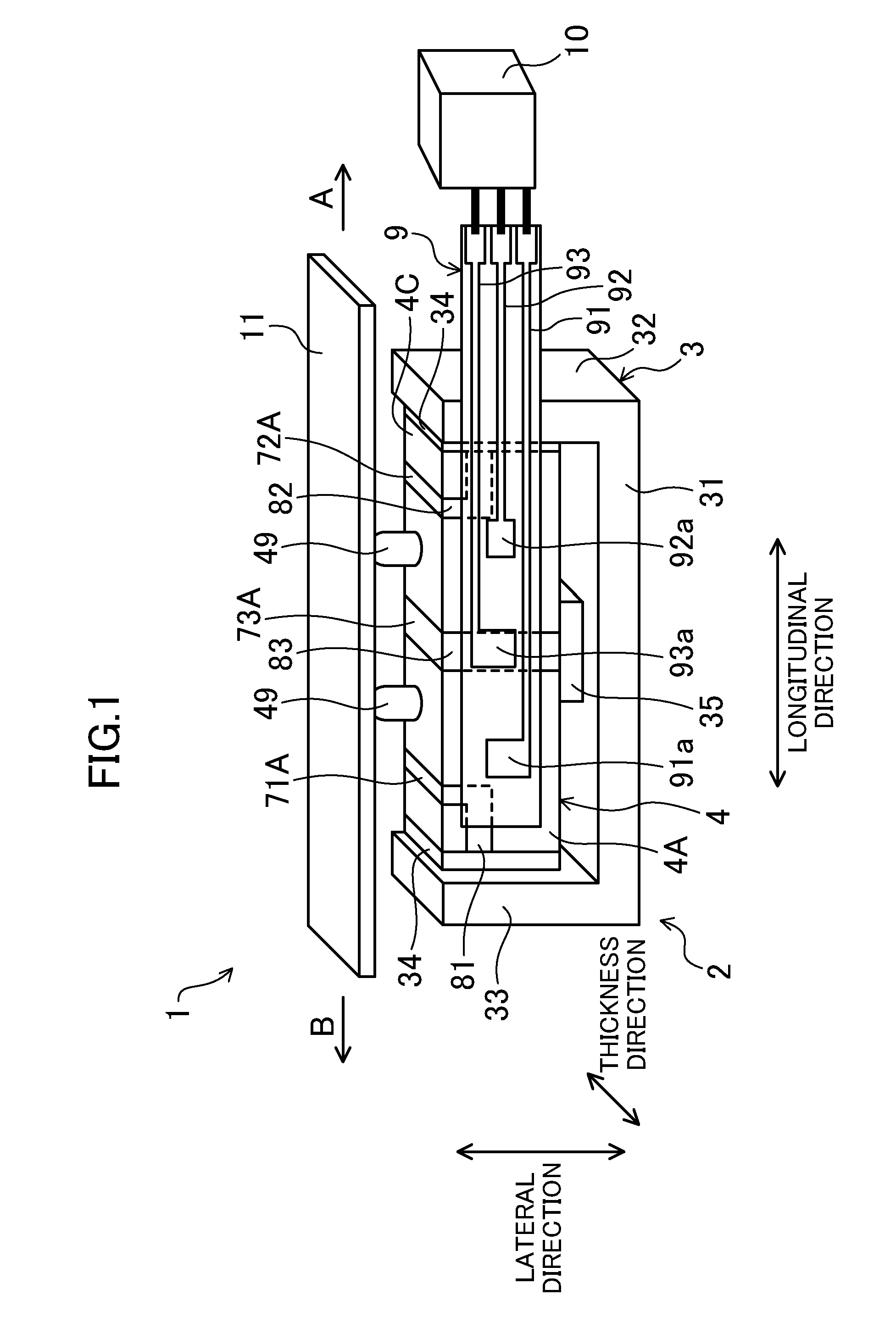
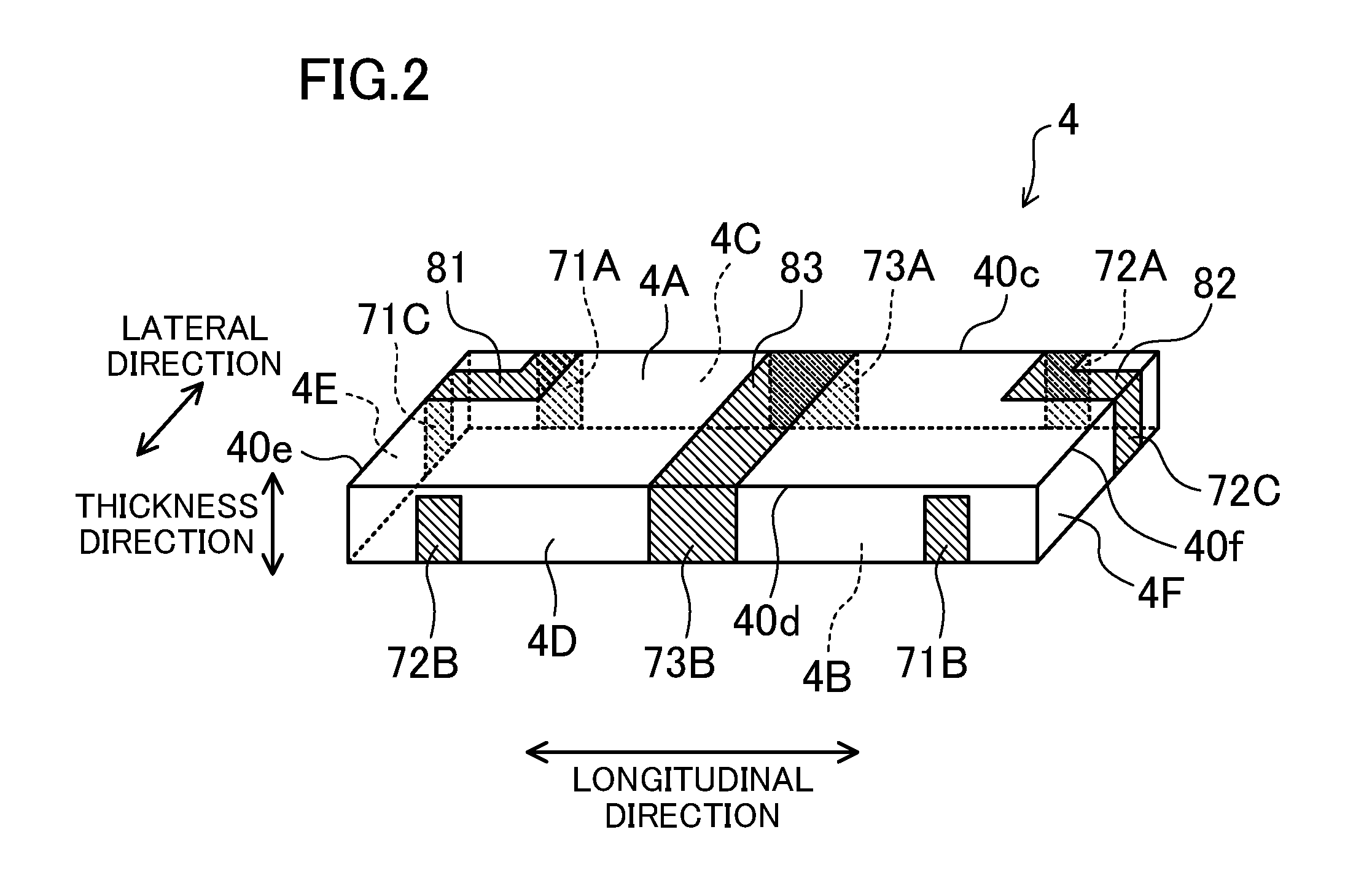
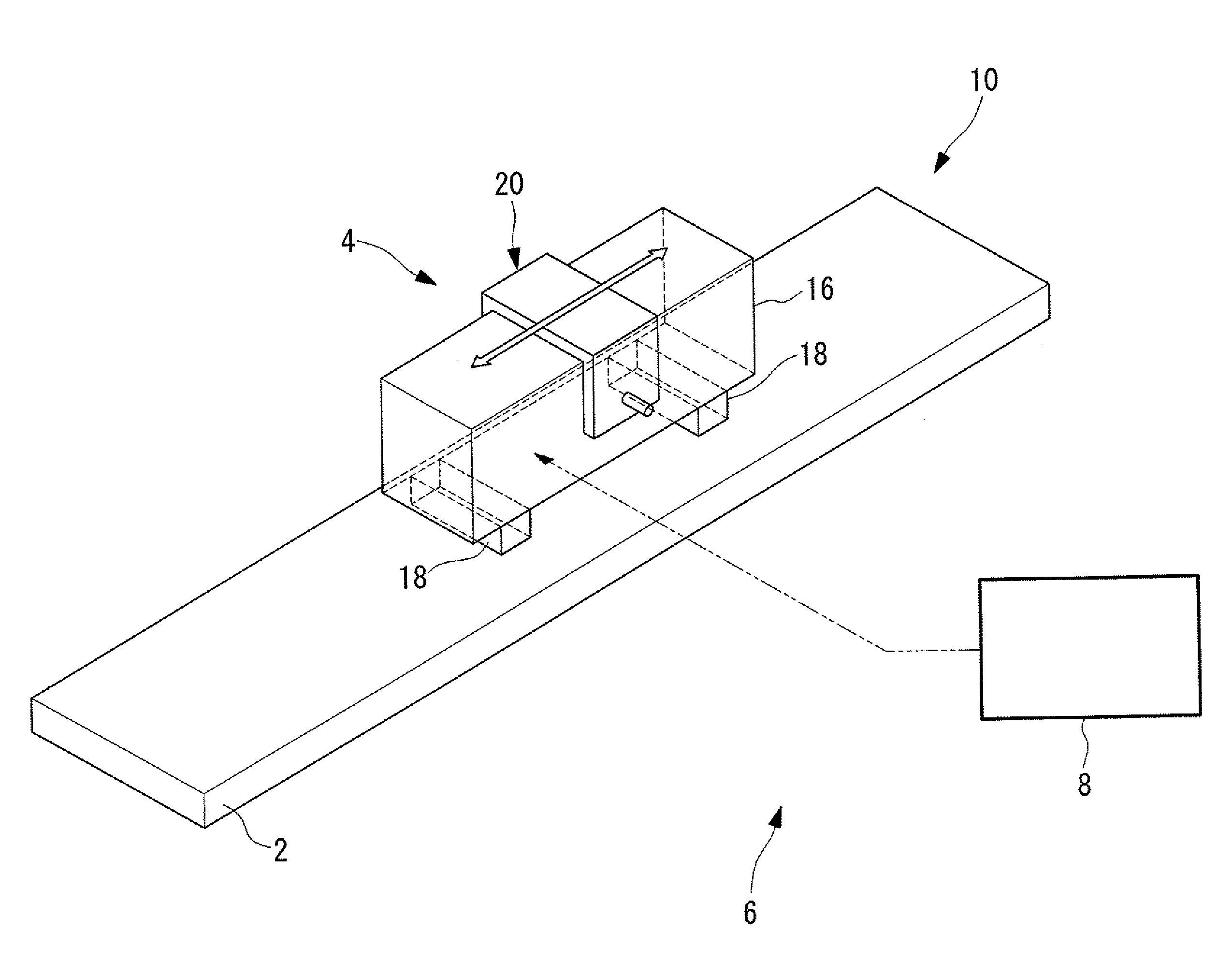
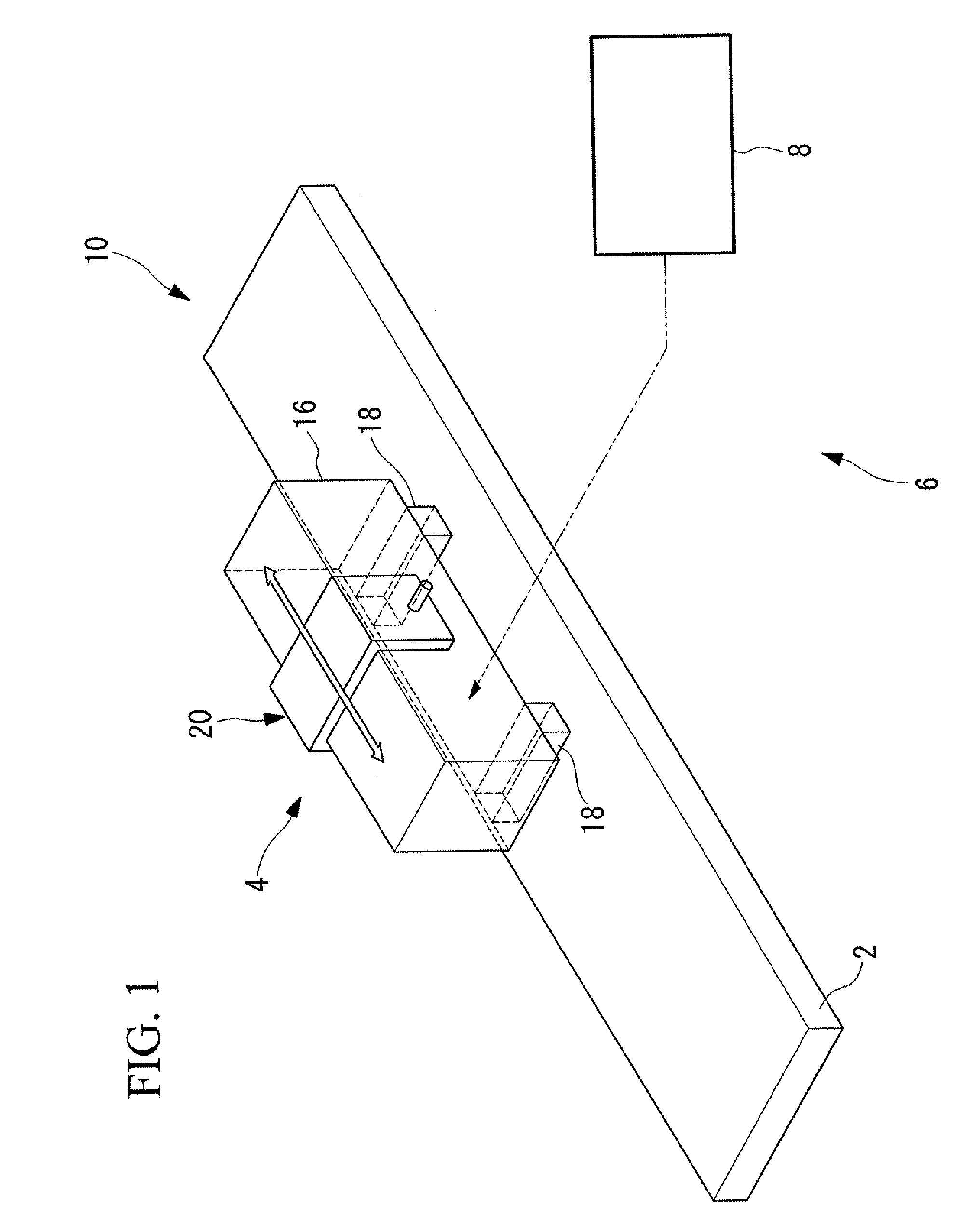
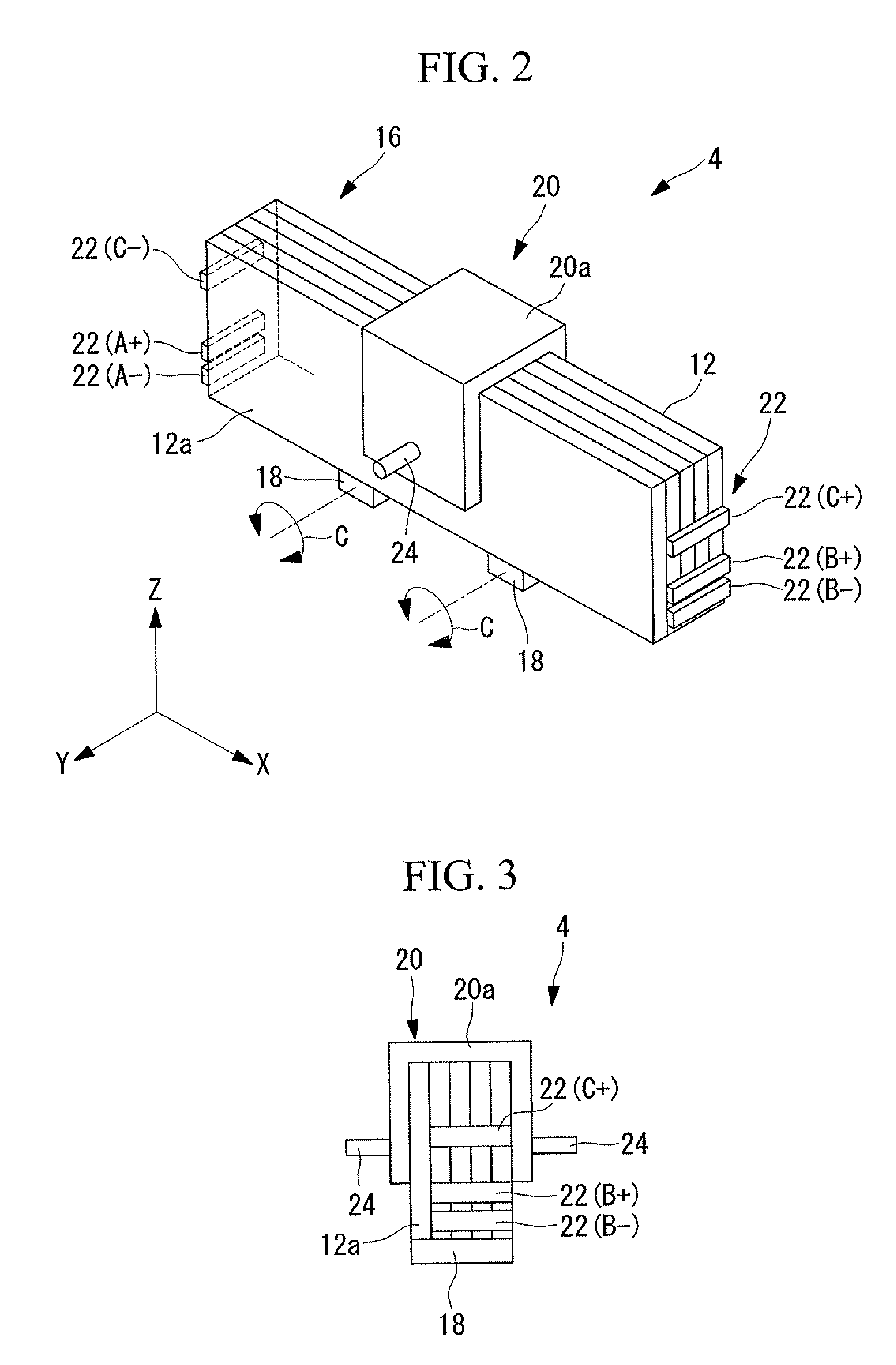
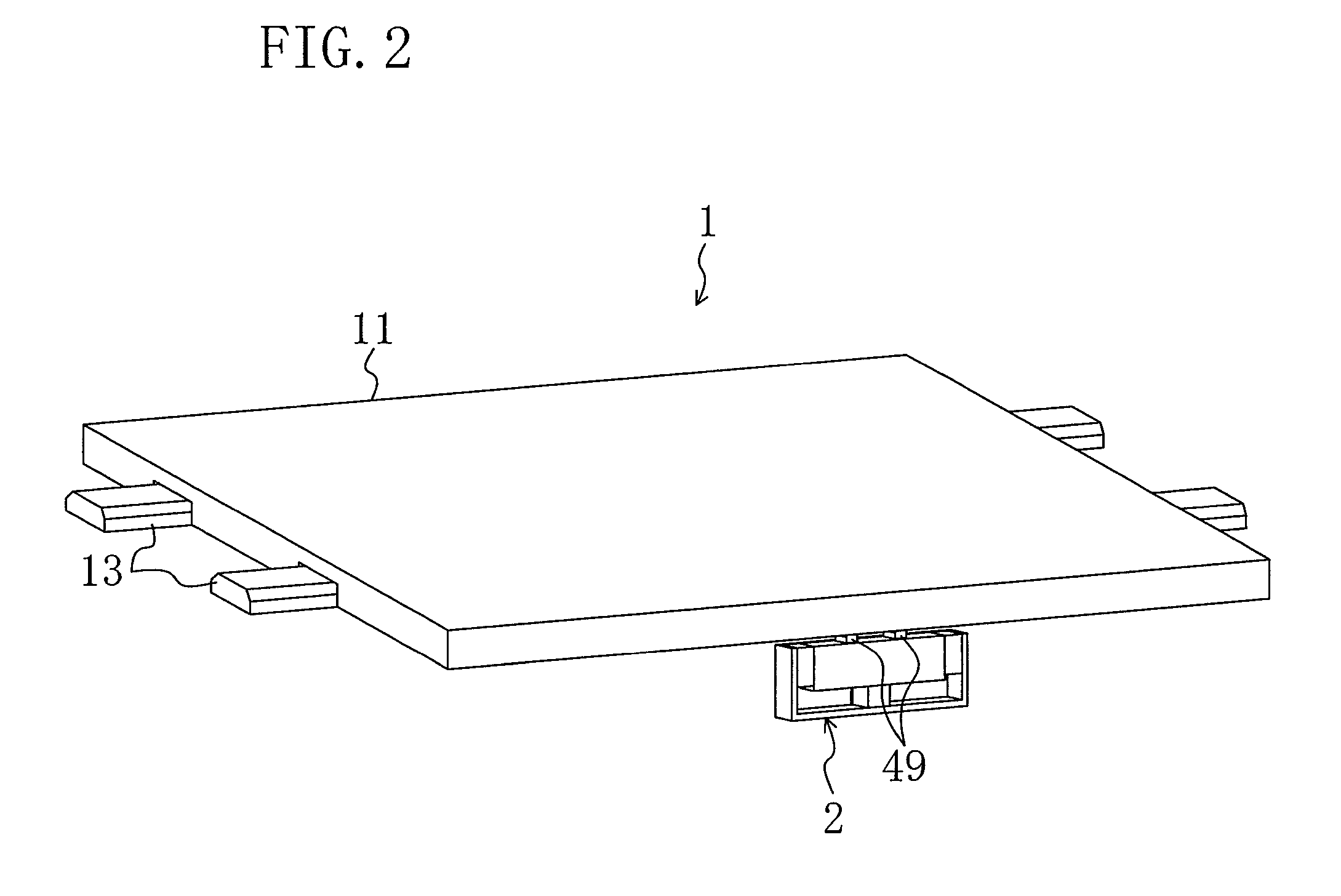
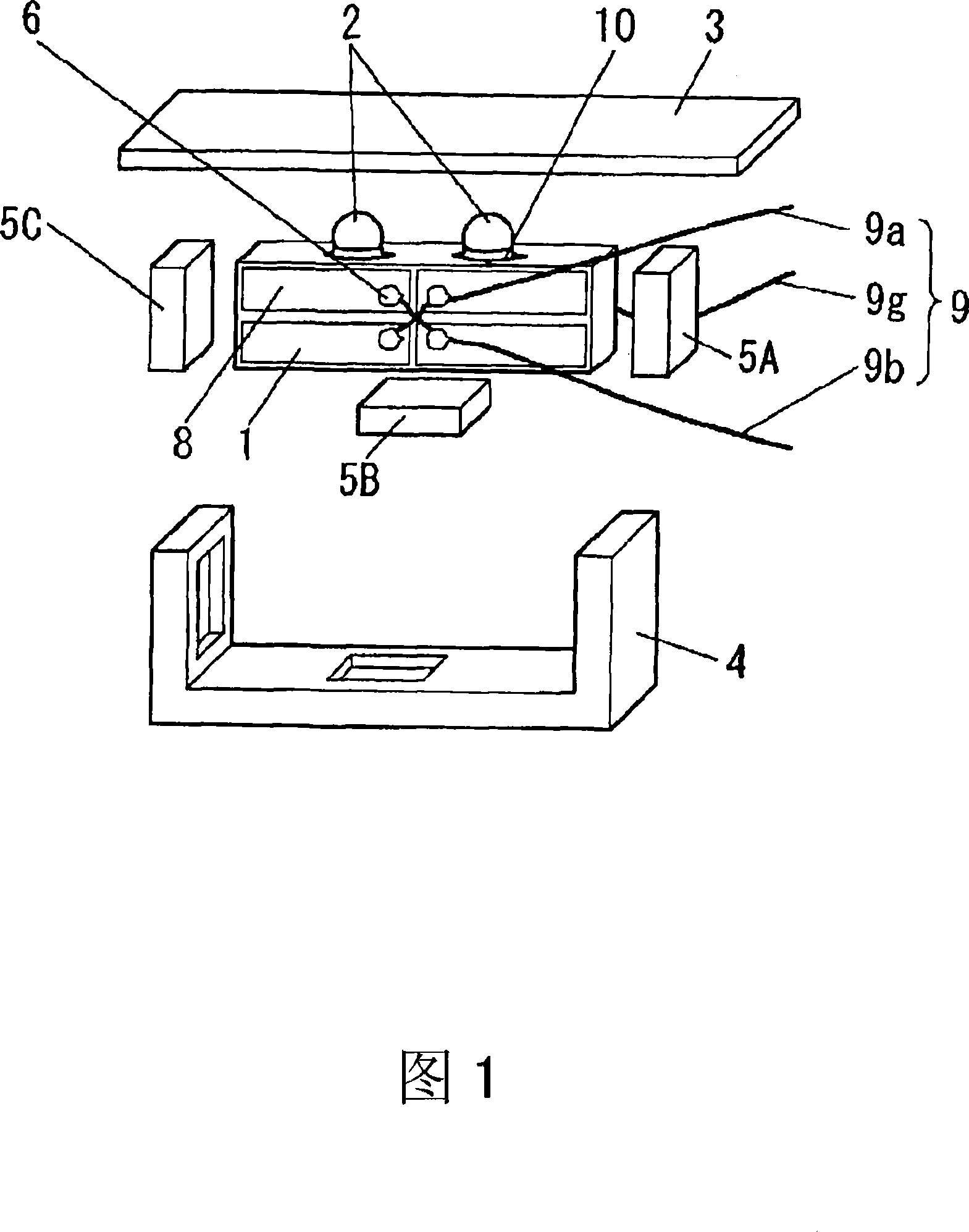
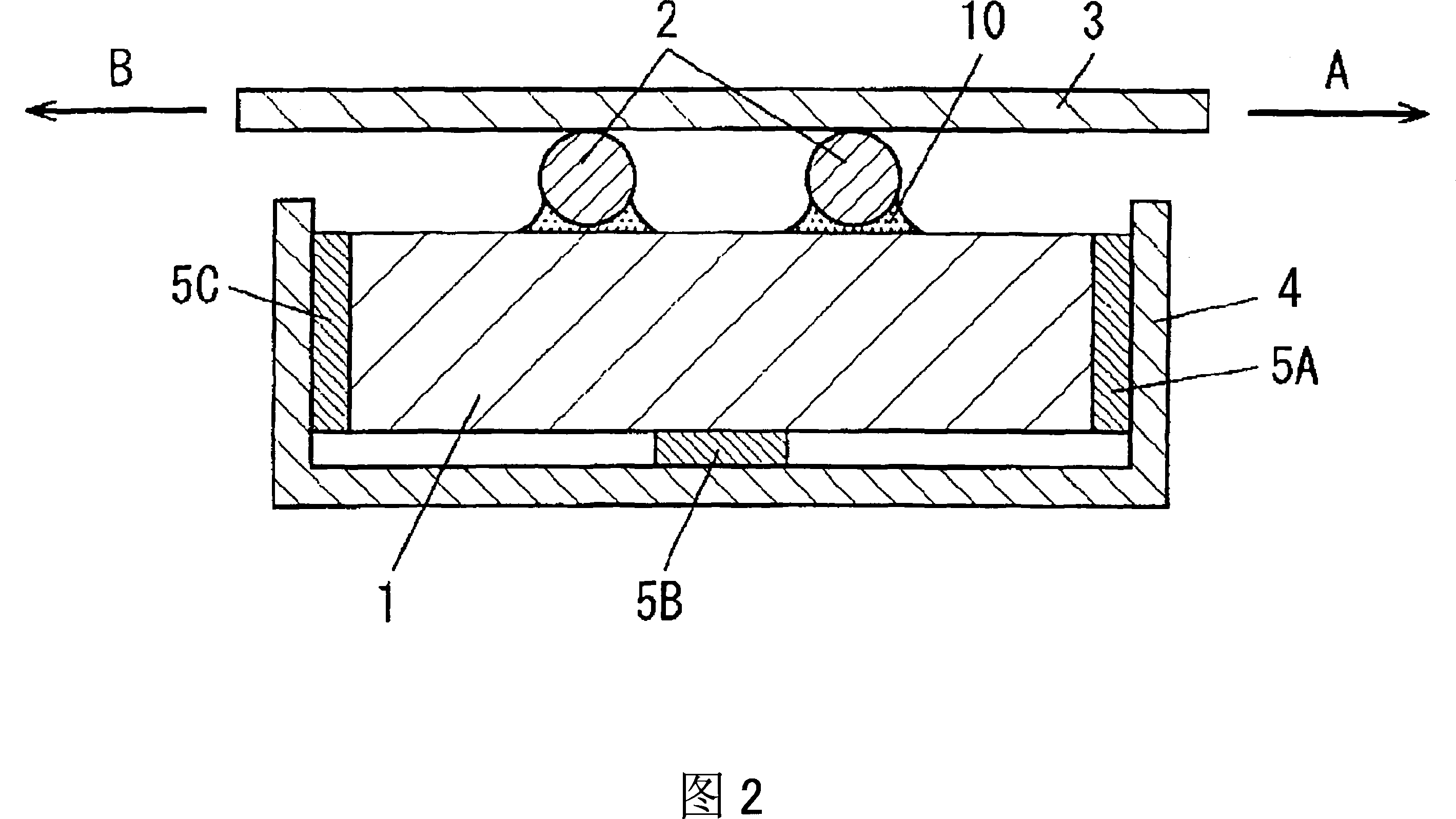
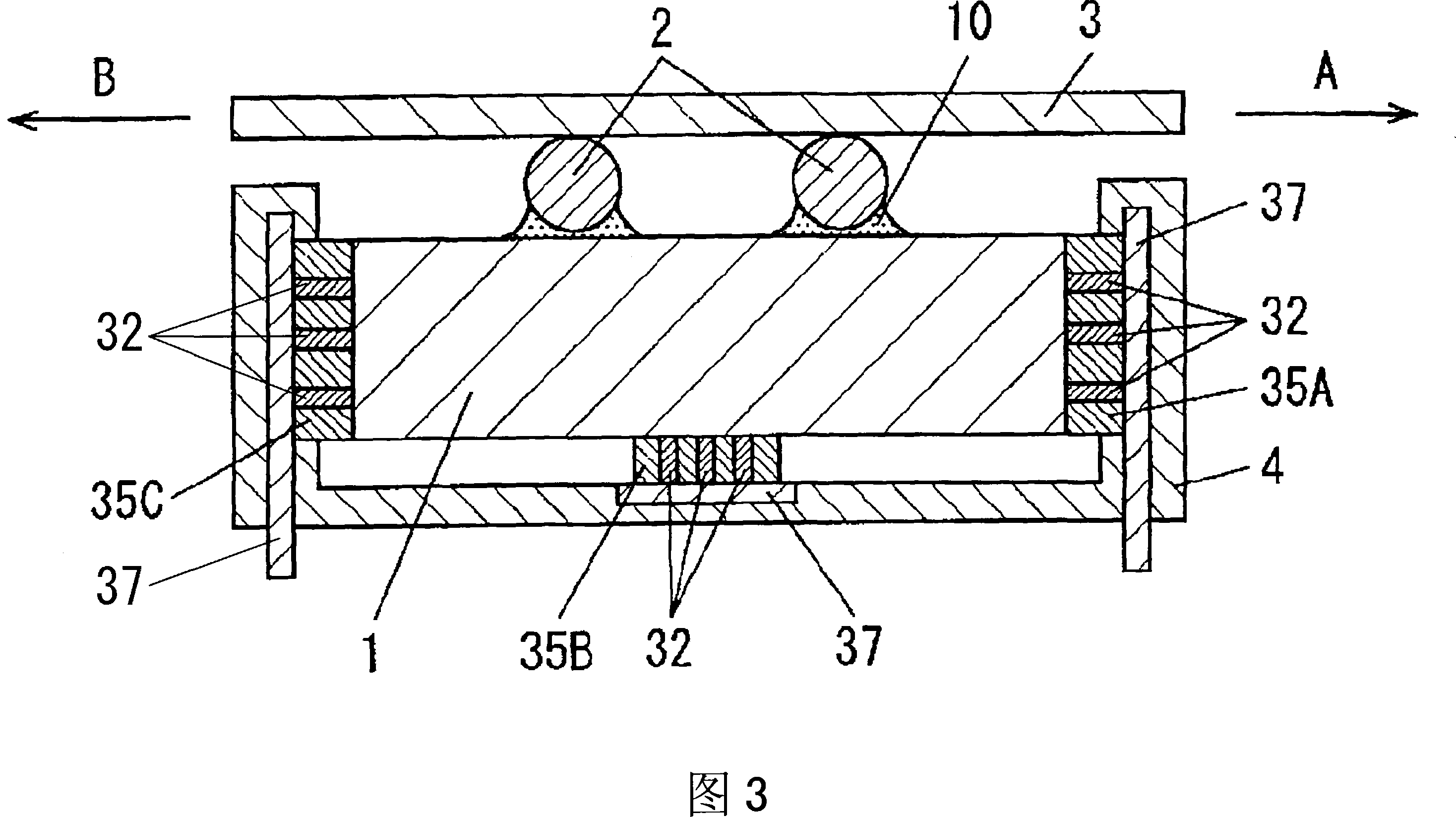
Driving device, position controller provided with driving device, and camera provided with position controller
InactiveUS7085484B2PrintersPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonic actuatorControl theory
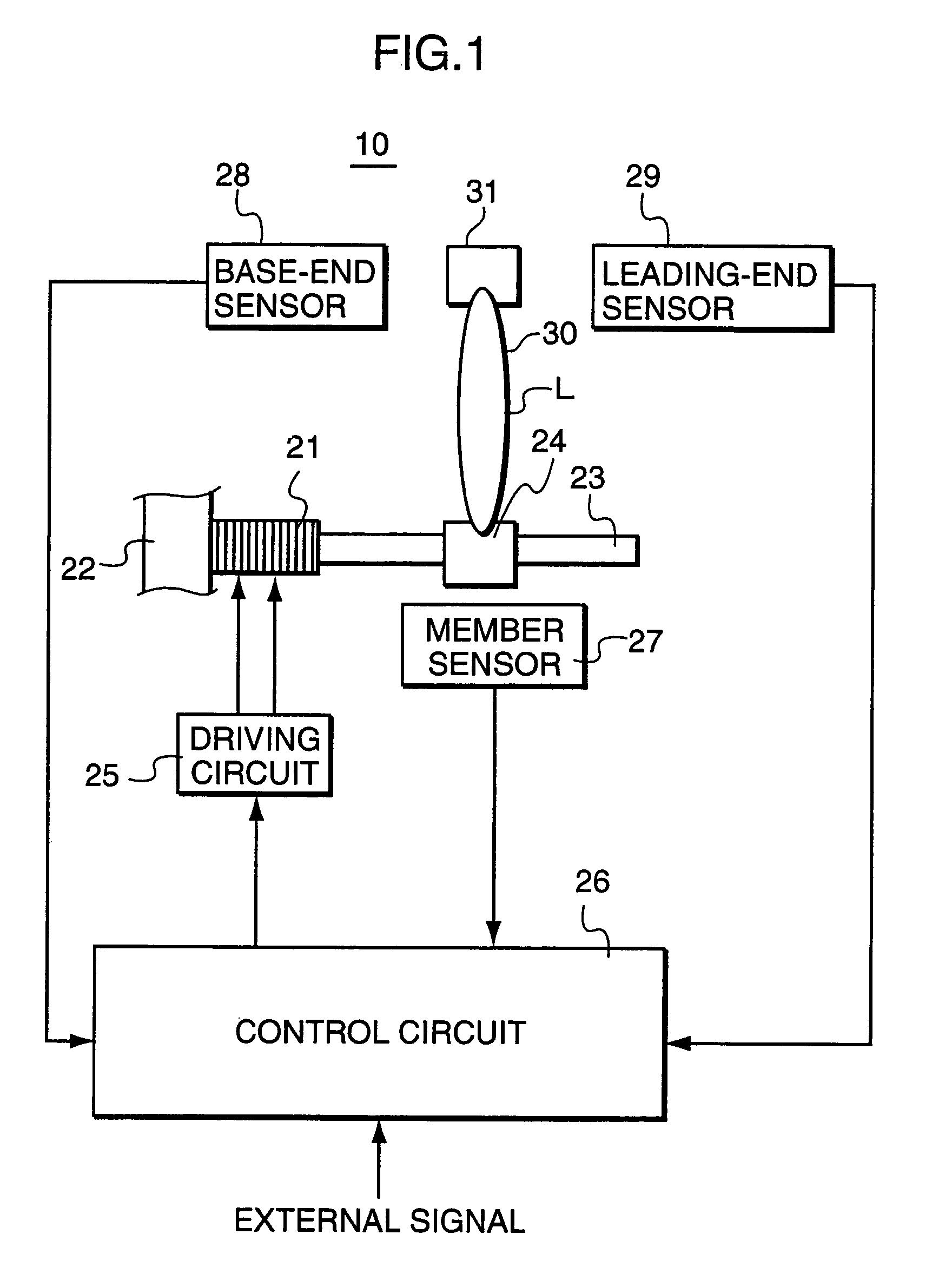
A driving device for an ultrasonic actuator for driving a movable member is provided with a member sensor for detecting a present position of the movable member, a calculator for calculating a control target position of the movable member, a driving circuit for generating such a drive voltage as to drive the ultrasonic actuator in a specified resonant state, and a control circuit for controlling an operative state of the movable member by adjusting at least one of physical quantities specifying the drive voltage as a maneuverable physical quantity in accordance with a difference between the present position and the control target position so that the movable member pursues the control target position. There can be provided a driving device capable of executing a position servo control while being driven in a specified resonant state, and a position controller and a camera provided with such a driving device.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Ultrasonic vibration system and method for removing/avoiding unwanted build-up on structures
InactiveUS8217554B2Reduce the amount requiredIncrease the areaPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDe-icing equipmentsStructural health monitoringEngineering
An ultrasonic method for removing and / or avoiding unwanted build-up on structures is provided, wherein the term build-up refers to, but is not limited to, ice, dirt, mud, or other wanted debris or contamination. Deicing or anti-icing structures of interest can include, but are not limited to, helicopter rotor blades, other helicopter blade components, fixed wing aircraft components, windshields in aircraft, automobiles, and other vehicles, ship hulls or other ship components, heat exchangers and other tubing where frost or ice could form, air-conditioning components, head lamp and other light coverings, bridge structures and components, and any structure where anti-icing or deicing would be beneficial. One or more ultrasonic actuators permanently embedded or coupled to the structure may be used accomplish the removal. The technique presented herein could also be utilized for non-destructive evaluation and structural health monitoring applications.
Owner:FBS INC
Method and apparatus for the ultrasonic actuation of the cantilever of a probe-based instrument
InactiveUS20030041669A1NanotechAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMetrologyUltrasonic actuator
The cantilever of a probe-based metrology instrument such as an AFM is deflected by directing a beam of ultrasonic energy at the cantilever to apply ultrasonically generated acoustic radiation pressure to the cantilever. The energy is generated by an ultrasonic actuator such as a ZnO transducer driven by a power source such an RF signal generator. The transmitted beam preferably is shaped by focusing, collimation, or the like so that it impinges at least primarily on a region of interest of the cantilever such as the free end. The ultrasonic actuator produces a much better controlled force on the cantilever than can be achieved through the use of a traditional piezoelectric actuator and, accordingly, produces a response free of spurious effects (at least when the cantilever is operating in liquid). It also has a frequency bandwidth in the MHz range.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
Nebulizer systems and methods
A nebulizer assembly configured for removable attachment to an ultrasonic actuator includes a base plate portion, a porous mesh member, and a cover member. The base plate portion includes an opening extending therethrough, and is substantially rigid such that ultrasonic vibrations from the ultrasonic actuator may be transmitted through the base plate portion to the porous mesh member to vibrate the porous mesh member. The porous mesh member is configured for passage therethrough of a nebulized fluid, and is disposed in the opening of the base plate portion proximate a fluid emission side of the nebulizer assembly. The cover member is disposed on a second side of the nebulizer assembly opposite the fluid emission side. The cover member covers the opening and defines a cavity between the cover member and the porous mesh member. The cavity is configured to retain a fluid to be nebulized.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Drive unit, lens barrel, and camera
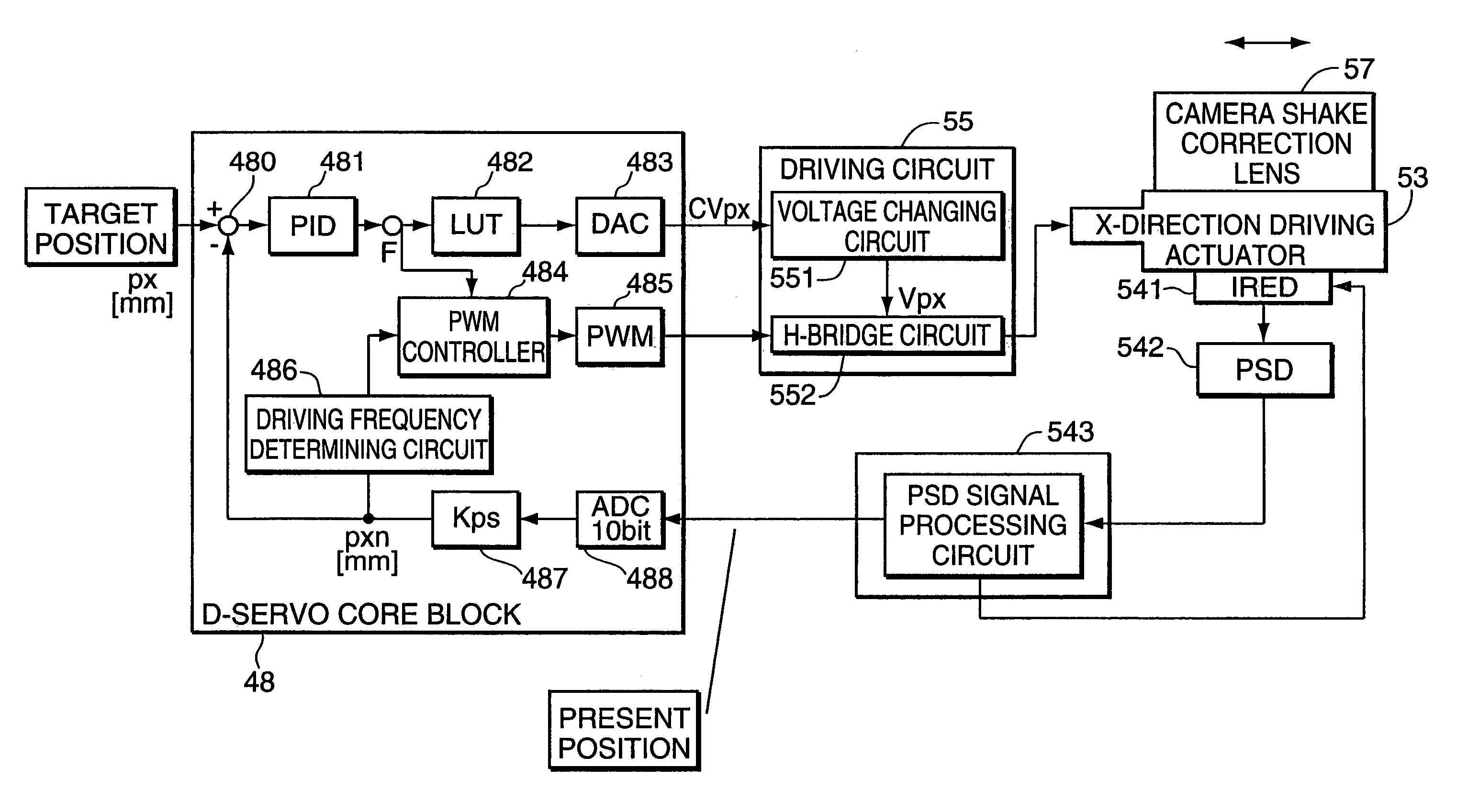
ActiveUS20100226637A1Reduce power consumptionAvoid high forcePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesProjector focusing arrangementElectricityPhase difference
A drive unit includes an ultrasonic actuator, which has an actuator body formed using a piezoelectric element and outputs a driving force by vibration of the actuator body, and a control section which induces vibration in the actuator body by supplying a plurality of AC voltages to the piezoelectric element. The control section provides, in combination, phase control, which controls the driving force by adjusting a phase difference between a first and a second AC voltages, and wave-number control, which controls the driving force by adjusting the wave number included in a predetermined burst period in each AC voltage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
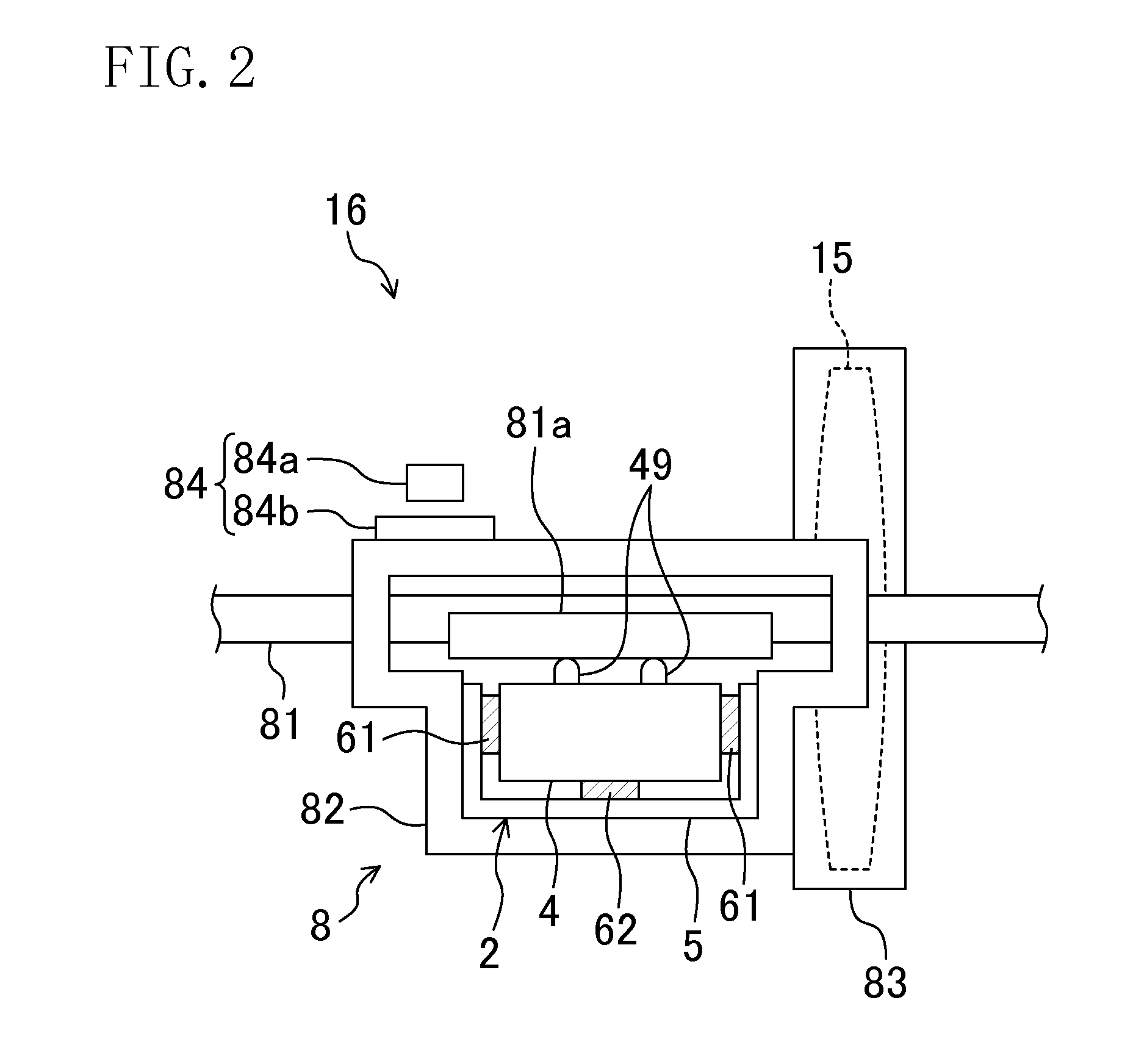
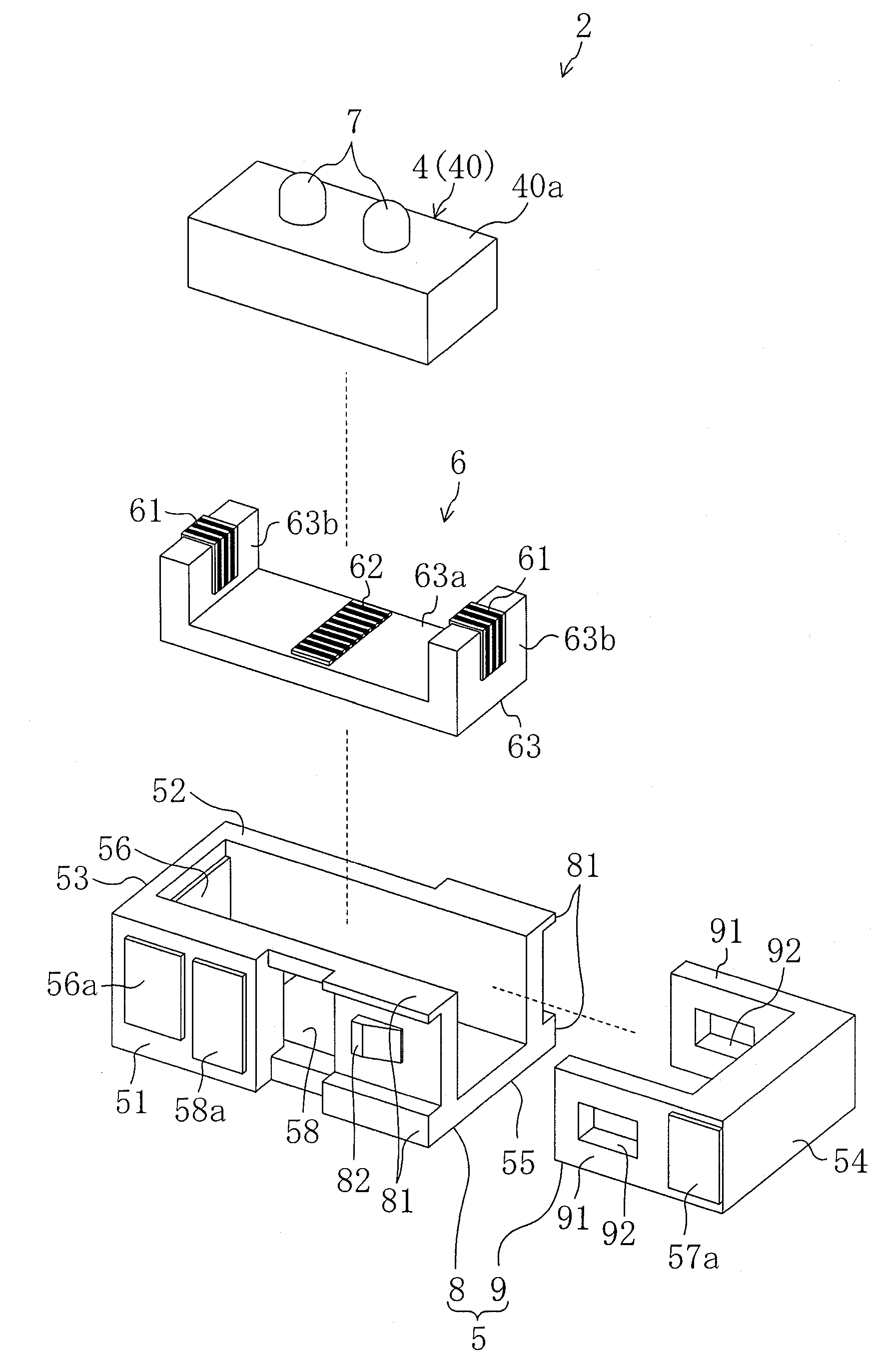
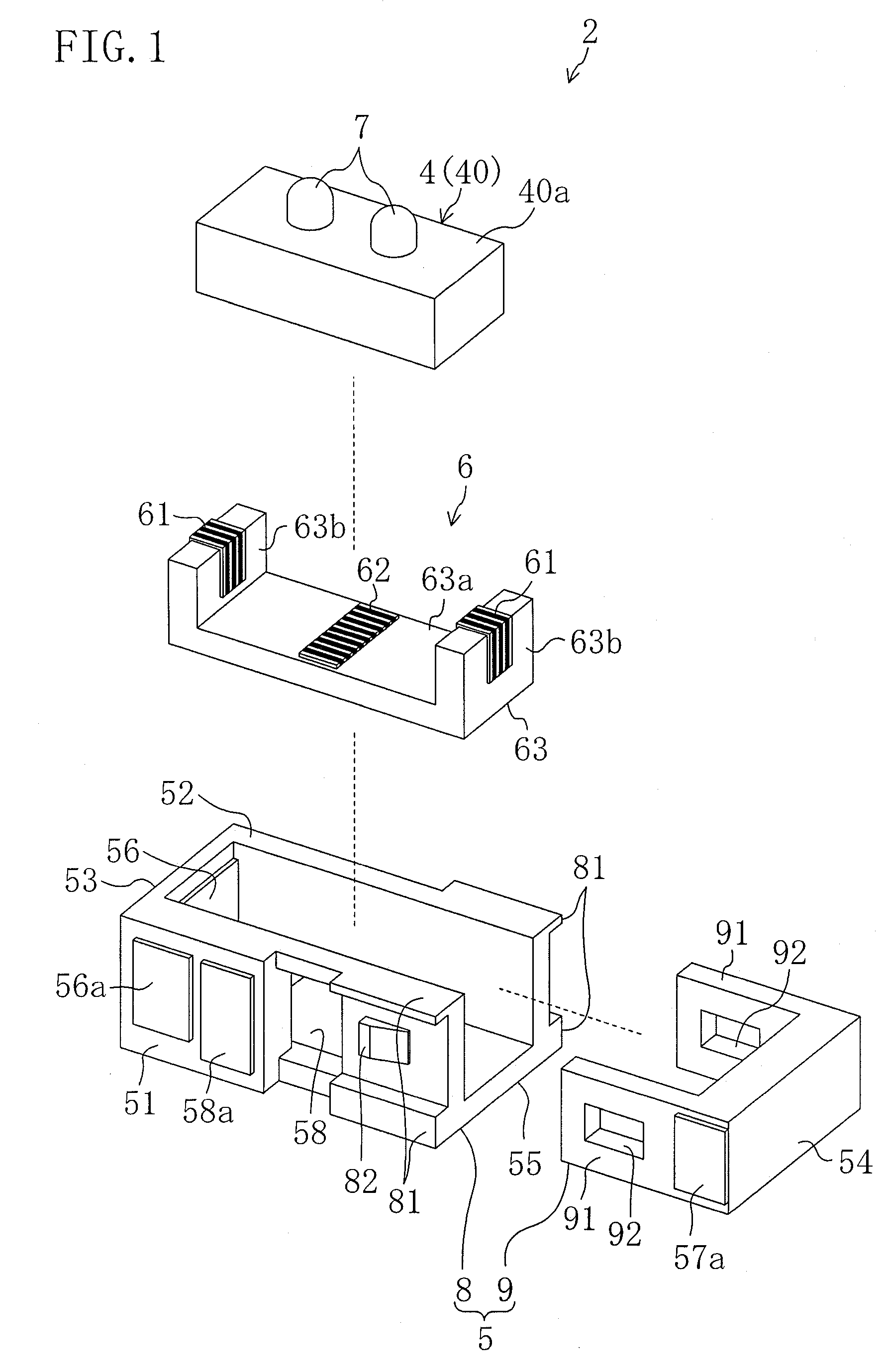
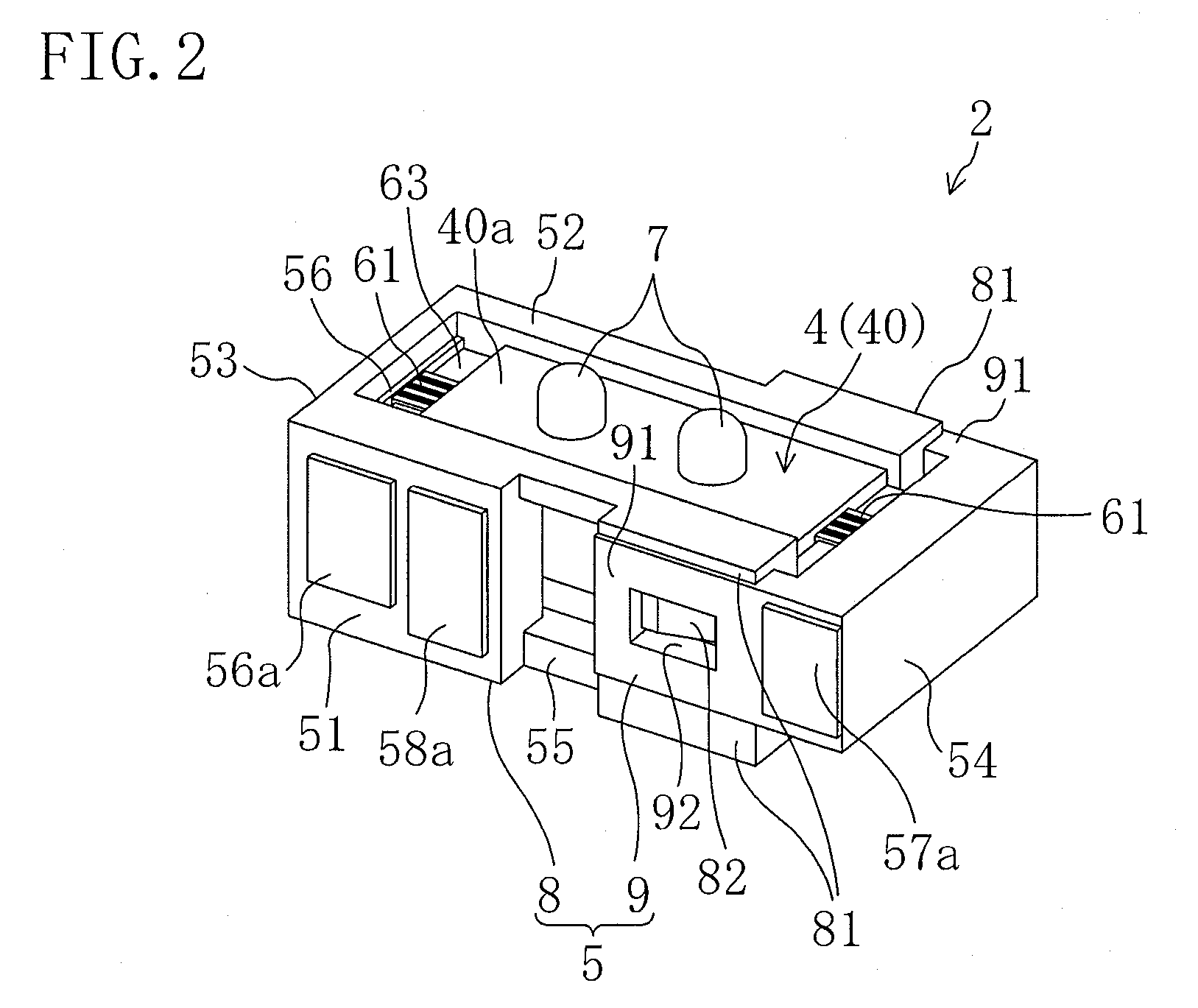
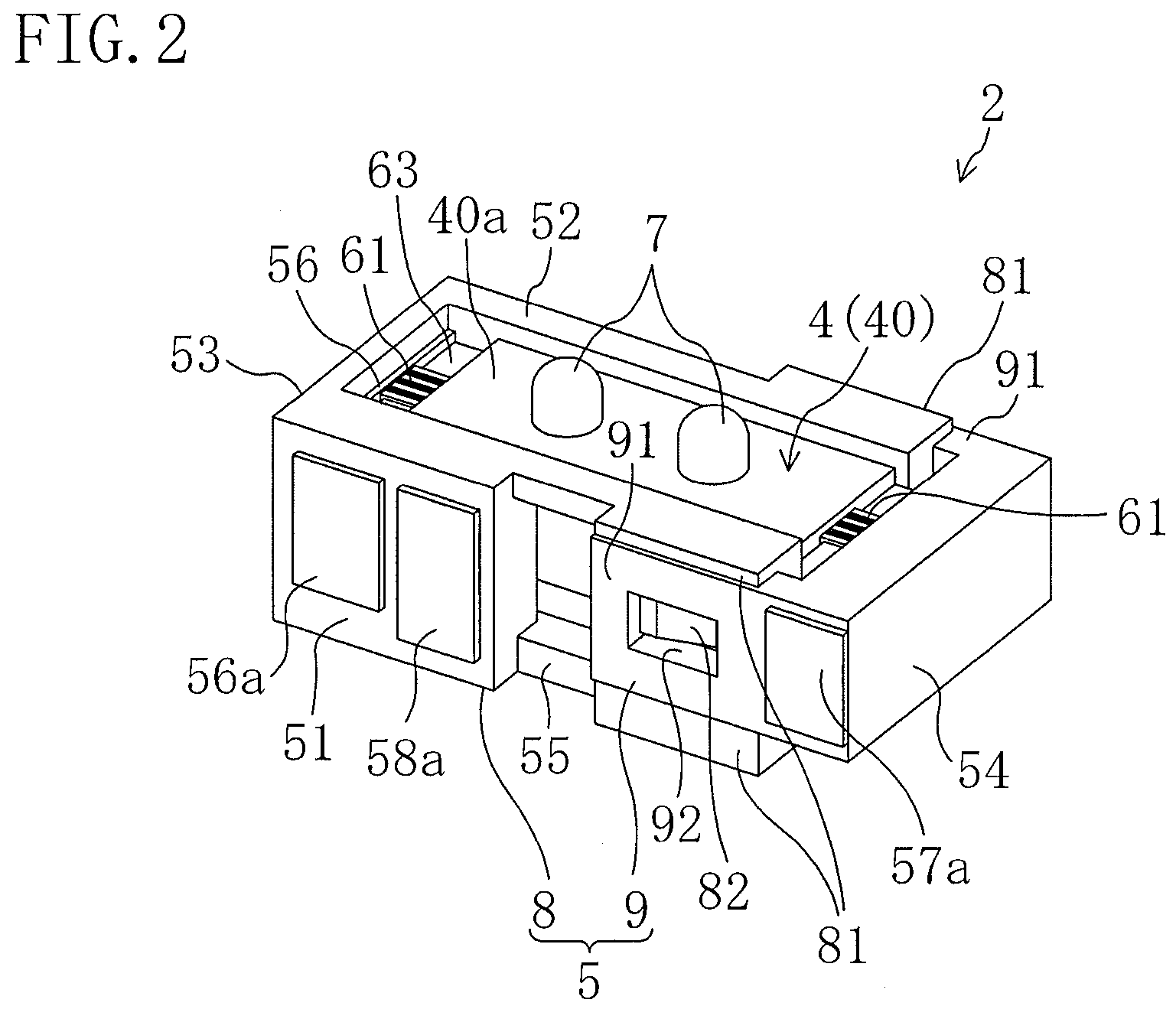
Vibration actuator and drive unit including the same
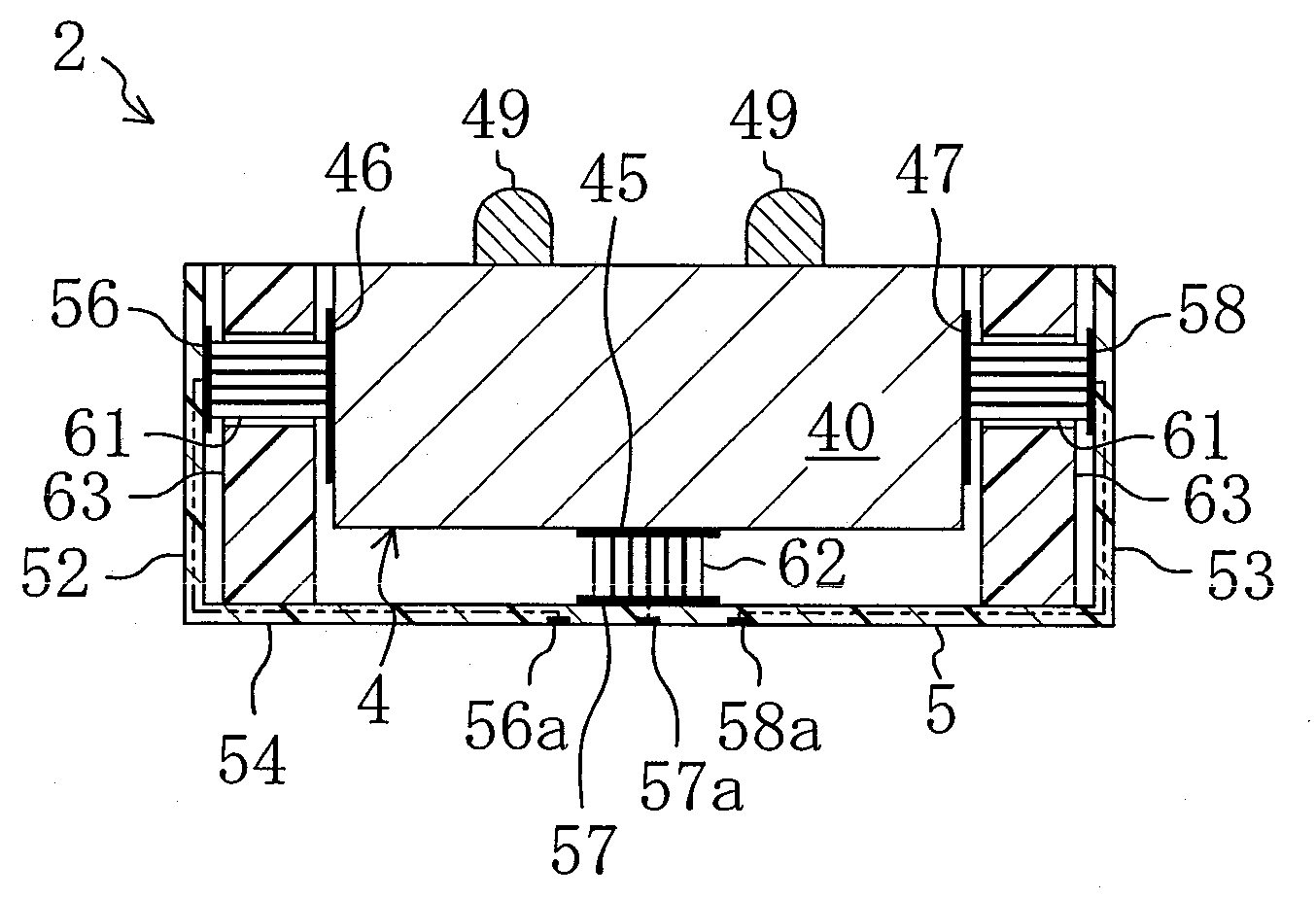
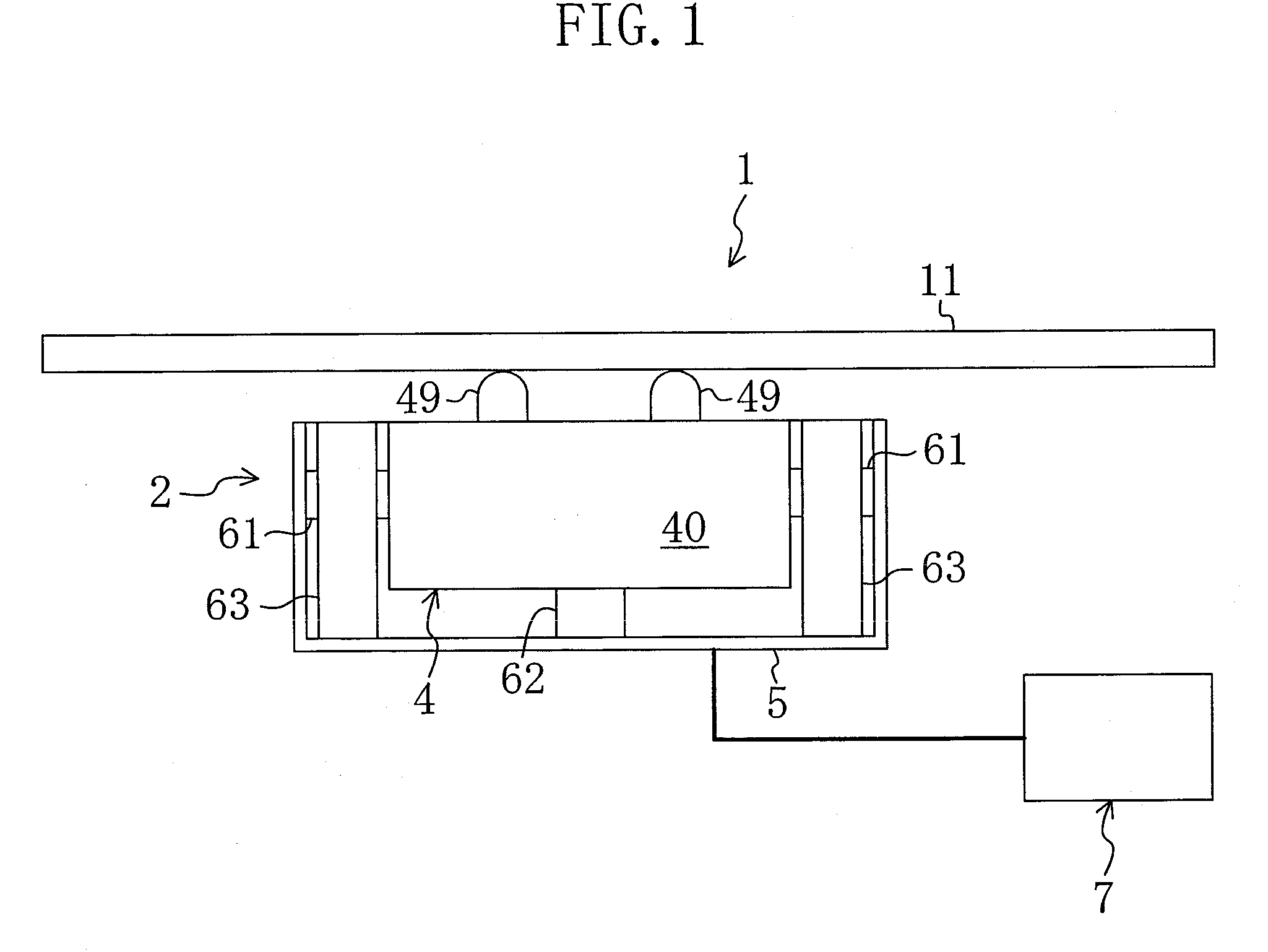
InactiveUS20090015099A1Avoid partialAvoid breakingPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesLongitudinal vibrationUltrasonic actuator
An ultrasonic actuator includes an actuator body, a case and a support rubber. The support rubber is made of conductive rubber having alternately stacked insulating layers and conductive layers and arranged between the case and the actuator body such that an external electrode and an electrode is brought into conduction and applies in advance a compressive force in the direction of longitudinal vibration to the actuator body at a non-node part of the vibration of the actuator body. The support rubber is arranged such that the stacking direction of the conductive rubber intersects with a plane including the direction of longitudinal vibration and the direction of bending vibration of the actuator body.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and apparata for precisely dispensing microvolumes of fluids
InactiveUS20040071601A1Reduce vibrationUniform sizeTesting/calibration apparatusMachines/enginesHemt circuitsEngineering
Devices and methods for depositing fluids on substrates in patterns of spots, lines, or other features use a nozzle, which is preferably configured similarly to a micropipette, having a piezoelectric crystal or other ultrasonic actuator coupled to one of its sides. The nozzle may be charged via capillary action by dipping it into a well containing the fluid to be deposited, and may then be positioned over a desired area of a substrate, at which point activation of the ultrasonic actuator at ultrasonic frequencies will eject the fluid onto the substrate. The needle may subsequently be dipped into a well of rinsing fluid for cleaning. Spots or lines on the order of 5 micrometers width may be generated, making the invention particularly suitable for use in biological applications such as microarray production and in microelectronics applications such as the printing of organic circuitry.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Vibration actuator
InactiveUS20080278035A1Efficiency of vibration be reducedAvoid vibrationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringUltrasonic actuator
An ultrasonic actuator includes: an actuator body using a piezoelectric element and generating a plurality of vibrations of different vibration directions; a driver element provided in the actuator body and operated in accordance with the vibration of the actuator body to output a driving force in a predetermined driving direction; a case containing the actuator body; at least one support rubber provided between the actuator body and the case to elastically support the actuator body along the driving direction with respect to the case; and at least one stopper provided between the actuator body and the case which comes into contact with at least one of the actuator body and the case when the actuator body is displaced in a direction opposite the driving direction such that the displacement of the actuator body in the direction opposite the driving direction is limited.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
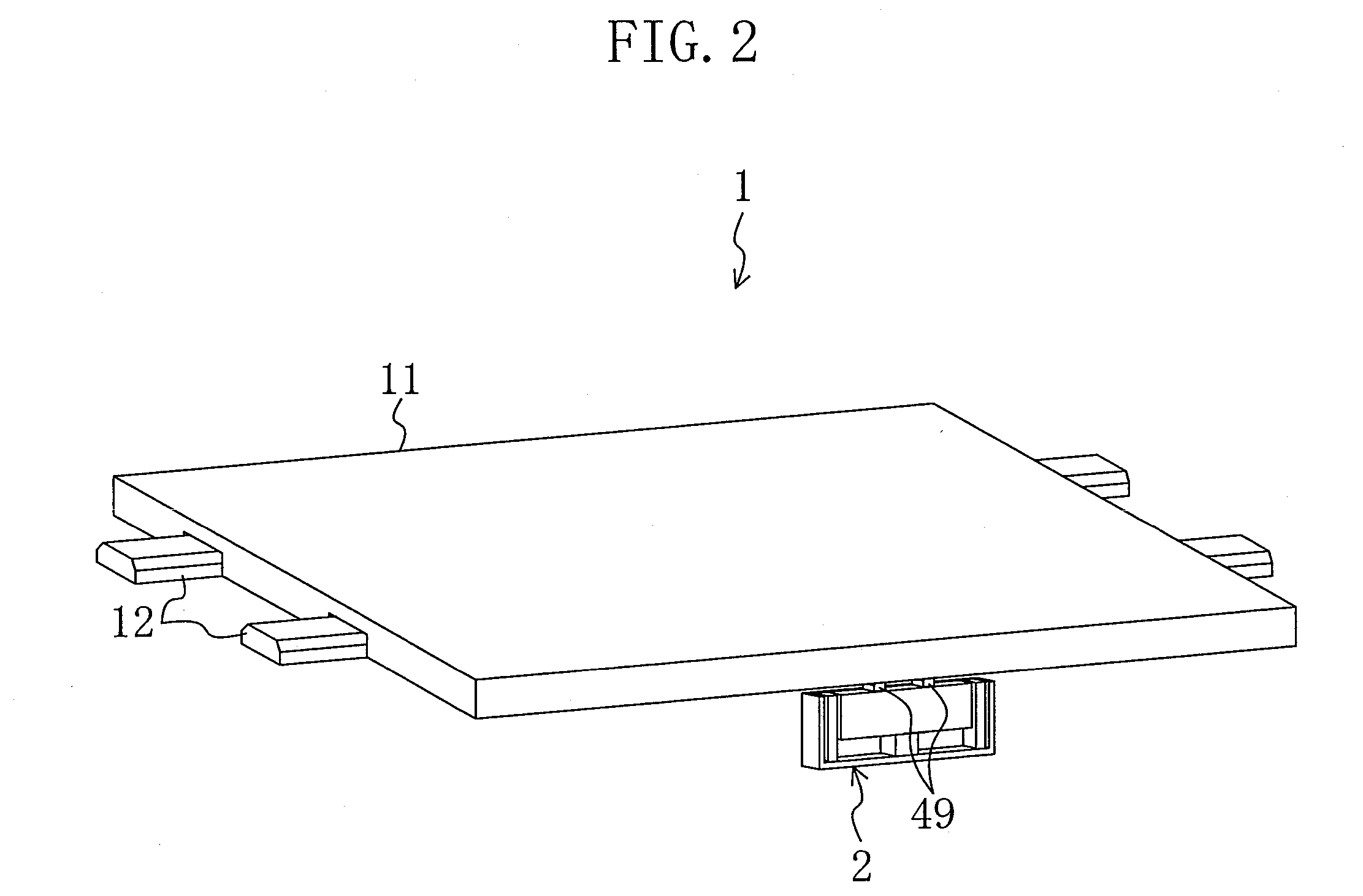
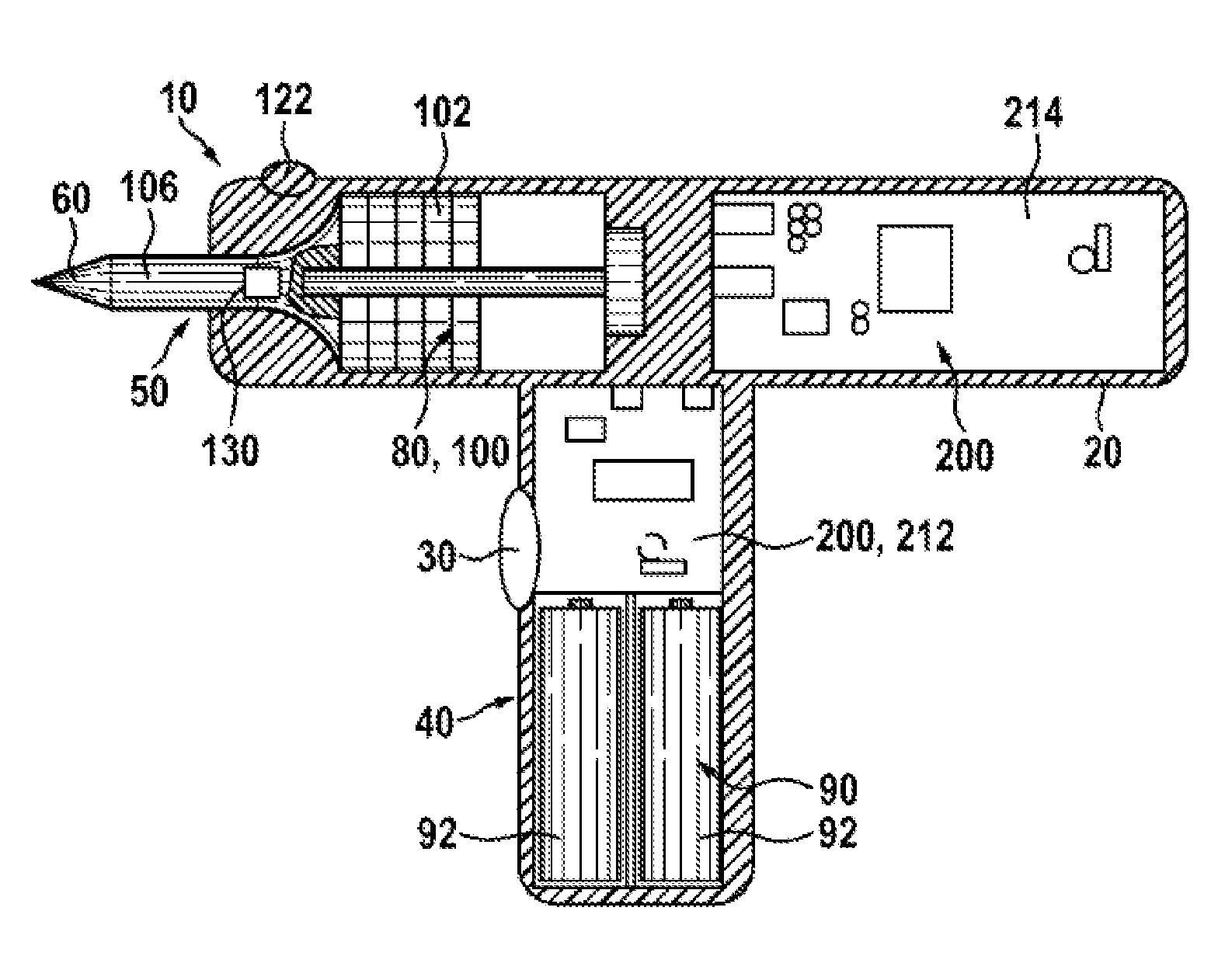
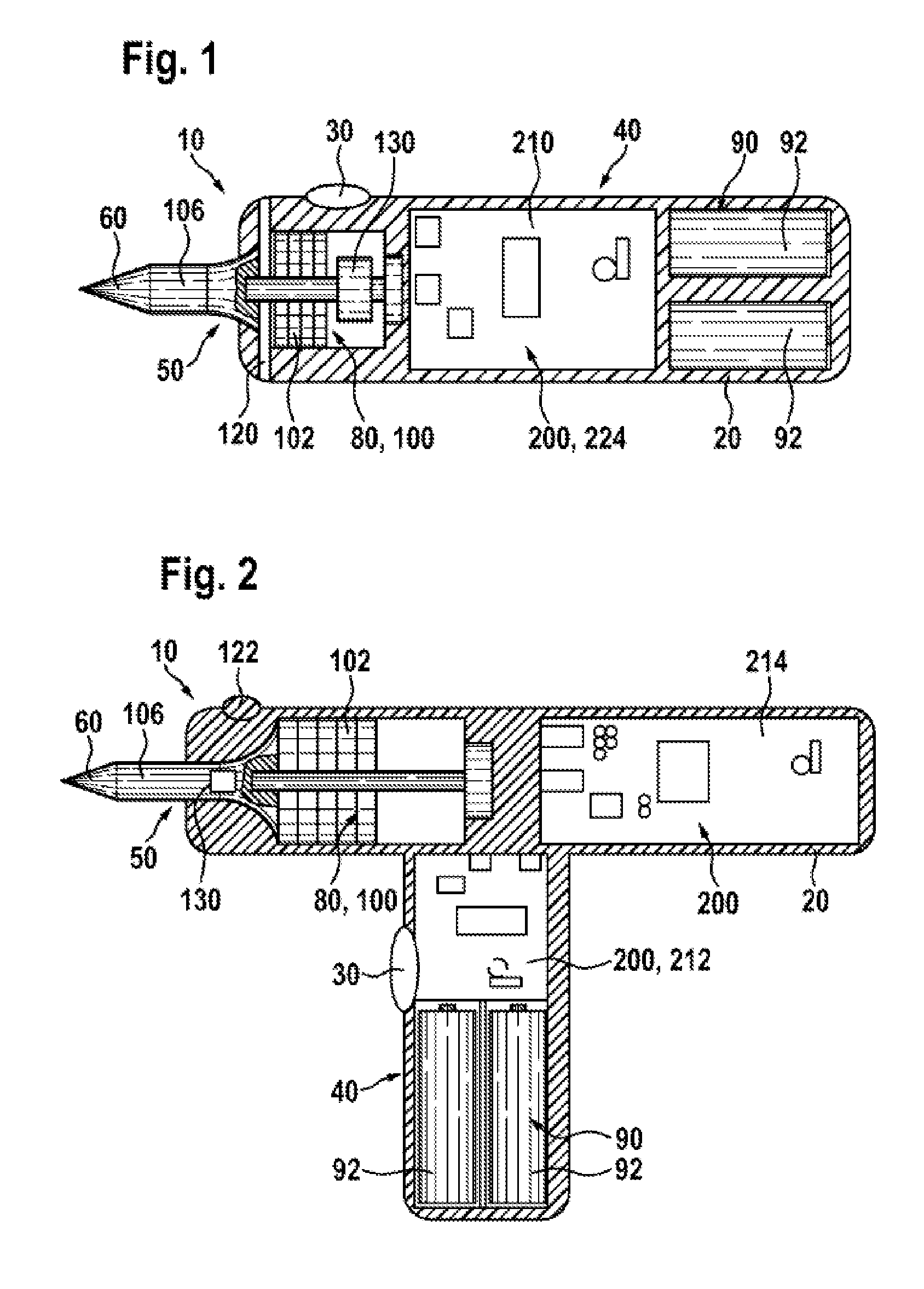
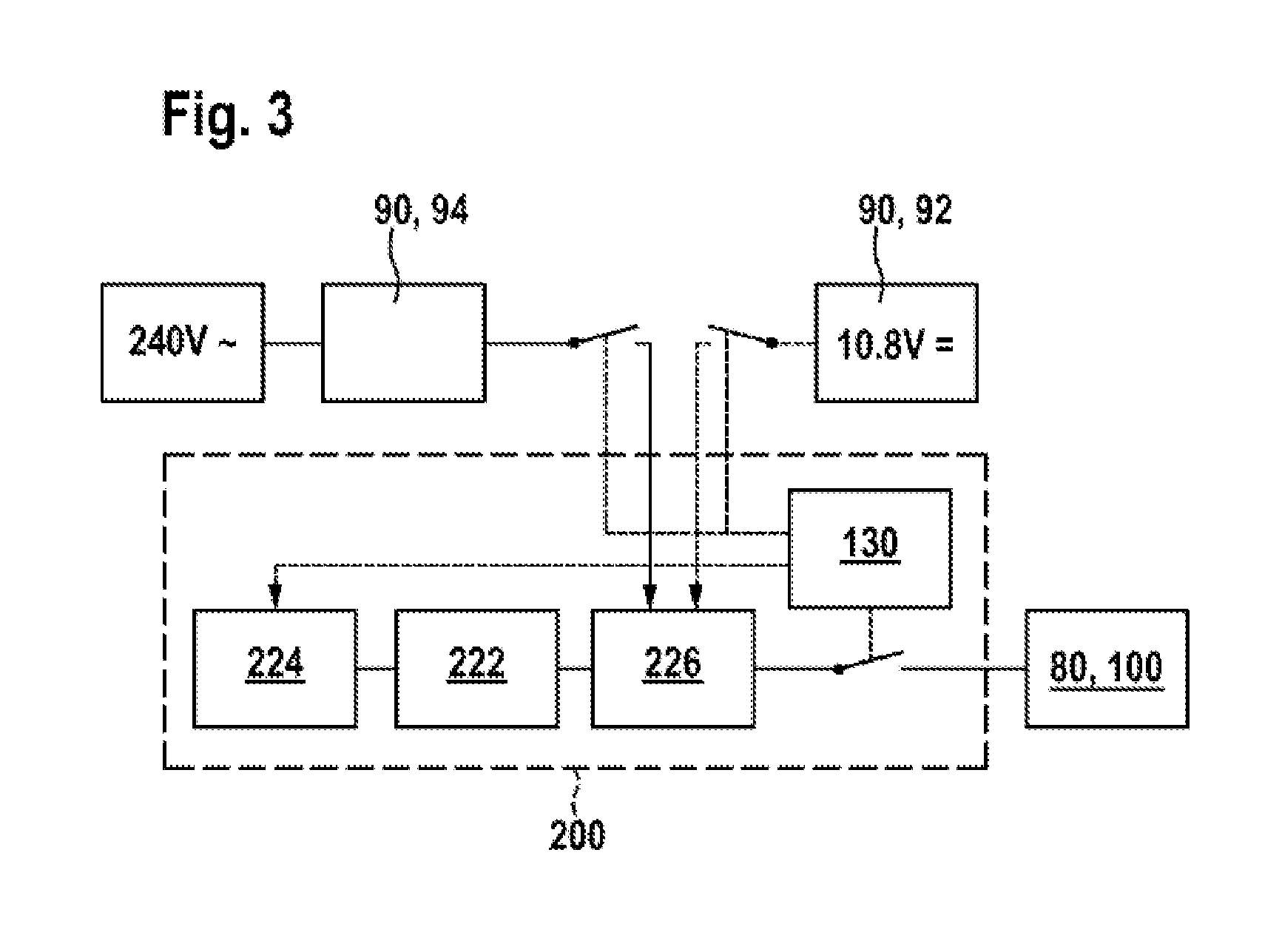
Hand-Held Power Tool
InactiveUS20120279742A1Reduce loadDefect can be causedPortable power-driven toolsMetal working apparatusLoop controlHand held
The disclosure relates to a hand-held power tool including a housing having a handle portion, a tool portion for a tool that can be driven to move linearly and / or oscillate, an operator part on the housing side for the activation of the tool and / or the power tool on the user side, a drive unit for producing a working movement of the tool, an electronic unit for supplying the drive unit at least with open-loop control and / or closed-loop control signals, and an operating voltage unit for making an electrical DC voltage available. The drive unit includes at least one excitation actuator, especially an ultrasonic actuator, having a volume of an excitation-active material. The actuator is supplied with power by the operating voltage unit, when operated, and is controlled in an open or closed loop control by the electronic unit.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method and apparatus for the ultrasonic actuation of the cantilever of a probe-based instrument
InactiveUS20030041657A1NanotechAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMetrologyUltrasonic actuator
The cantilever of a probe-based metrology instrument such as an AFM is deflected by directing a beam of ultrasonic energy at the cantilever to apply ultrasonically generated acoustic radiation pressure to the cantilever. The energy is generated by an ultrasonic actuator such as a ZnO transducer driven by a power source such an RF signal generator. The transmitted beam preferably is shaped by focusing, collimation, or the like so that it impinges at least primarily on a region of interest of the cantilever such as the free end. The ultrasonic actuator produces a much better controlled force on the cantilever than can be achieved through the use of a traditional piezoelectric actuator and, accordingly, produces a response free of spurious effects (at least when the cantilever is operating in liquid). It also has a frequency bandwidth in the MHz range.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Ultrasonically actuated needle pump system
InactiveUS6923790B2Efficient pumpingMinimal disruptionInfusion syringesSurgeryEngineeringUltrasonic actuator
An ultrasonically driven pump, which may be used for sampling body fluids or atomizing liquids, has a stationary outer needle and an inner needle mounted within the bore of the outer needle. The distal end of the inner needle is positioned adjacent to the distal end of the outer needle. The inner needle is ultrasonically vibrated by an ultrasonic actuator without vibrating the outer needle, with resulting draw of liquid through the distal end of the outer needle into the bore of the inner needle for discharge through the proximal end of the inner needle. The outer needle can be formed to have a penetrating tip suited for penetrating the skin of a subject to allow sampling of body fluids including interstitial fluids. The pump can also be used for atomizing liquid, by drawing liquid from a supply that is pumped from the distal end to an open proximal end of the inner needle where the liquid is discharged by atomization into the atmosphere.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Vibration actuator
InactiveUS7834523B2Low efficiencyAvoid vibrationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringUltrasonic actuator
An ultrasonic actuator includes: an actuator body using a piezoelectric element and generating a plurality of vibrations of different vibration directions; a driver element provided in the actuator body and operated in accordance with the vibration of the actuator body to output a driving force in a predetermined driving direction; a case containing the actuator body; at least one support rubber provided between the actuator body and the case to elastically support the actuator body along the driving direction with respect to the case; and at least one stopper provided between the actuator body and the case which comes into contact with at least one of the actuator body and the case when the actuator body is displaced in a direction opposite the driving direction such that the displacement of the actuator body in the direction opposite the driving direction is limited.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Vibratory actuator
InactiveUS20110156536A1Improve reliabilityReduce and prevent degradationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesUltrasonic actuatorPhysics
In an ultrasonic actuator, piezoelectric layers and internal electrode layers are stacked. External electrodes are formed on a principal surface exposed to an outside of the outermost piezoelectric layer. Side electrodes connected to the internal electrode layers and the external electrodes are formed on side surfaces of a body including the piezoelectric layers and the internal electrode layers. A first divided electrode and a first external electrode are connected together by a plurality of side electrodes. A second divided electrode and a second external electrode are connected together by a plurality of side electrodes. A minus electrode layer and a third external electrode are connected together by a plurality of side electrodes.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Driving method and driving device for standing-wave-type ultrasonic actuator
InactiveUS20080164783A1Frictional forceStatic frictionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesEngineeringLongitudinal vibration
The invention provides a driving method and driving device for a standing-wave-type ultrasonic actuator which can prevent falling of and eliminate unstable motion of a driven body during activation, and which can shorten the time for the driven body to stop moving when driving is to be stopped. In the driving method for a standing-wave-type ultrasonic actuator, by generating a longitudinal vibration and a flexural vibration in an ultrasonic vibrator, a substantially elliptical vibration is produced at a friction-contact member of the ultrasonic vibrator, and with a frictional force of the elliptical vibration serving as a propulsive force, the ultrasonic vibrator and a driven body in contact with the ultrasonic vibrator are made to move relative to each other. The longitudinal vibration is excited at activation time, and the flexural vibration is excited thereafter.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
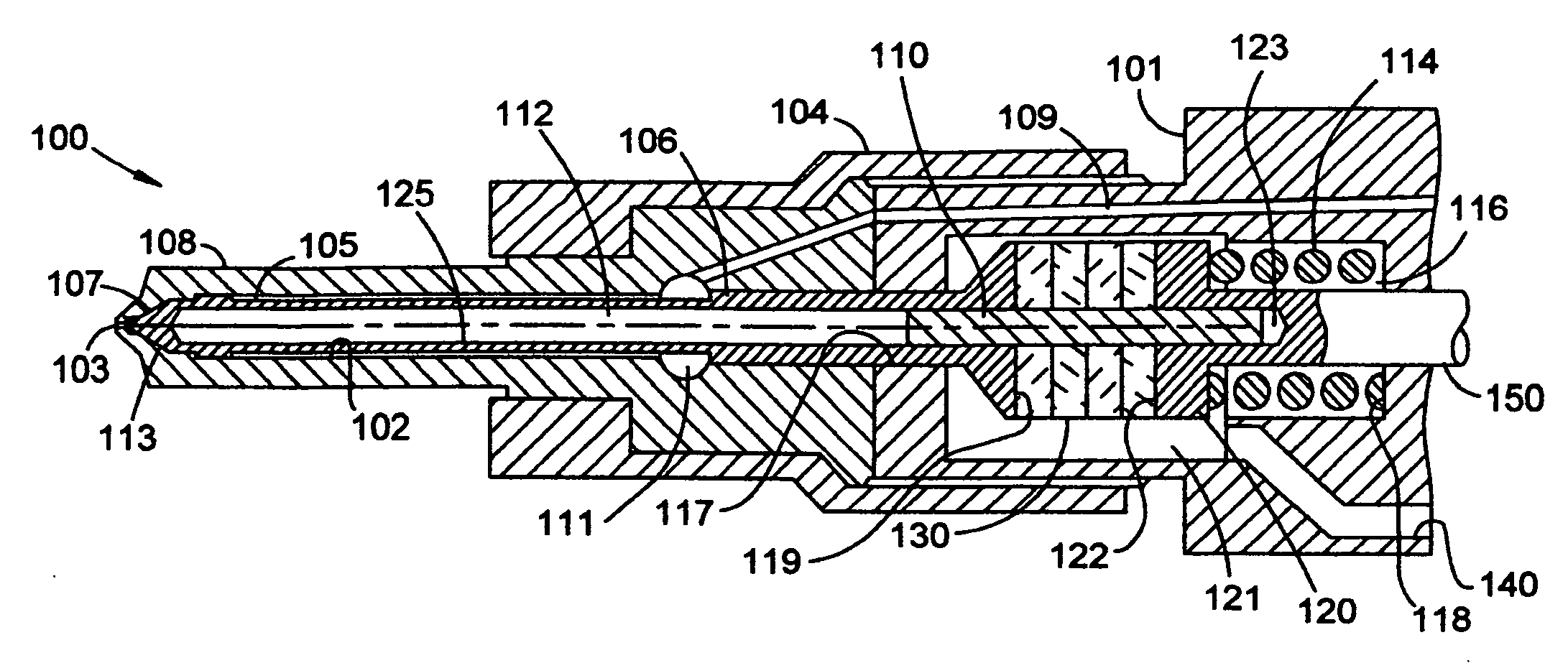
Ultrasonically activated fuel injector needle
InactiveUS20090057438A1Increase heightSmall sizeMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesInjector nozzleEngineering
A fuel injector intended for use on an internal combustion engine contains an injector needle that is longitudinally driven by an ultrasonic actuator during the time the injector valve is open to provide an atomized fuel spray output of sub-micron droplet sizes. A piezoelectric disk stack is mounted within the injector housing to surround a portion of the injector needle component and is used to provide the mechanical ultrasonic stimulation to the injector valve at the end of the injector needle and set up a corresponding wave-front at the injector valve to atomize the fuel as it leaves the injector nozzle.
Owner:ADVANCED PROPULSION TECH
Drive unit
InactiveUS7679265B2Simple configurationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectric/magnetic position measurementsContact pressureUltrasonic actuator
A drive unit includes a guide, a stage which is movable relative to the guide, an ultrasonic actuator for moving the movable body and a control unit for controlling the ultrasonic actuator. The ultrasonic actuator includes a driver element in contact with the stage and is fixed to the guide. A surface of the stage in contact with the driver element is an undulating surface. The control unit detects the position of the stage based on a change in contact pressure on the driver element due to the undulating surface.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Ultrasonic actuator
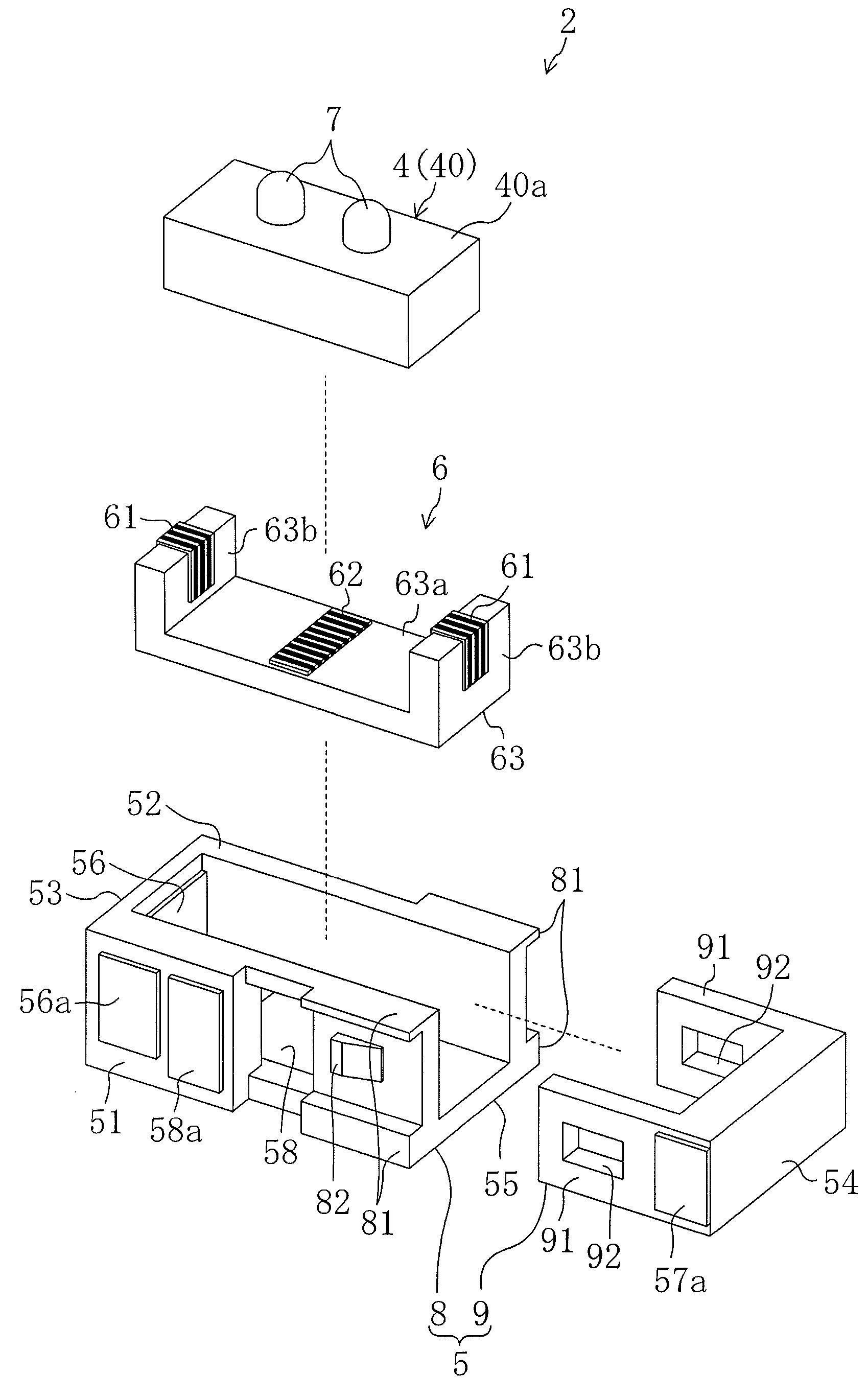
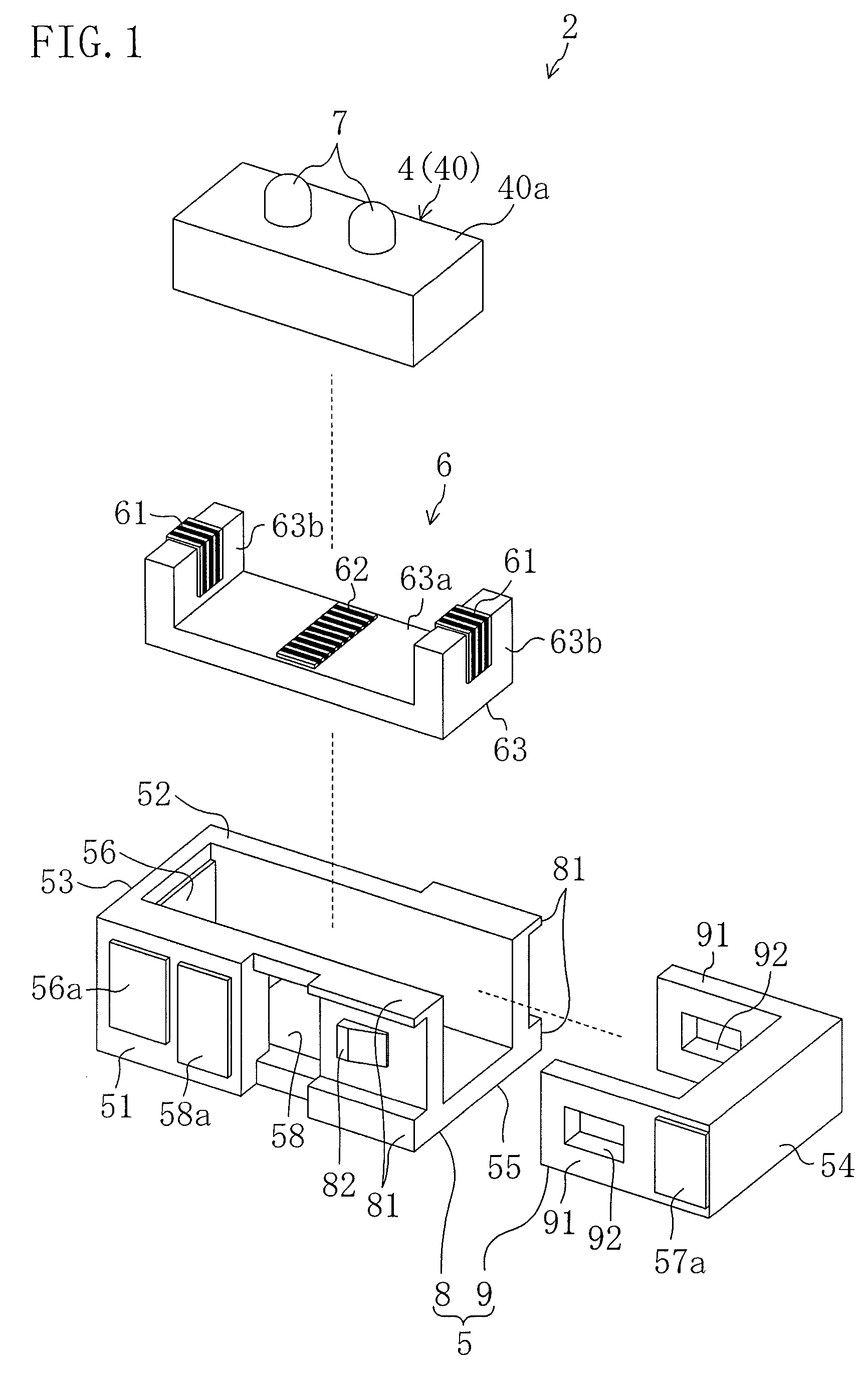
InactiveCN101160710AReduce exposureReduce contact portionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringUltrasonic actuator
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Rotary ultrasonic sealing
InactiveUS20100243172A1Improving weld homogeneityHigh strengthLaminationLamination apparatusUltrasonic actuatorMechanical engineering
The invention is an apparatus for forming an ultrasonic weld that includes a sonotrode having an ultrasonic actuator coupled to an elongate sealing end face for delivering ultrasonic energy to the webs in the sealing gap and a rotating cylindrical anvil having at least one raised portion extending longitudinally along an outer surface thereof. The raised portion has a radially outer surface, whereby the sealing gap is defined intermittently between the end face of the sonotrode and the radially outer surface of the raised portion of the anvil as the raised portion rotates past the end face of the sonotrode. The elongate sealing end face of the sonotrode has a substantially helical surface, whereby the sealing gap travels helically along the surface as the raised portion of the anvil cylinder rotates past the end face of the sonotrode.
Owner:LAVAZZA PROFESSIONAL NORTH AMERICA LLC
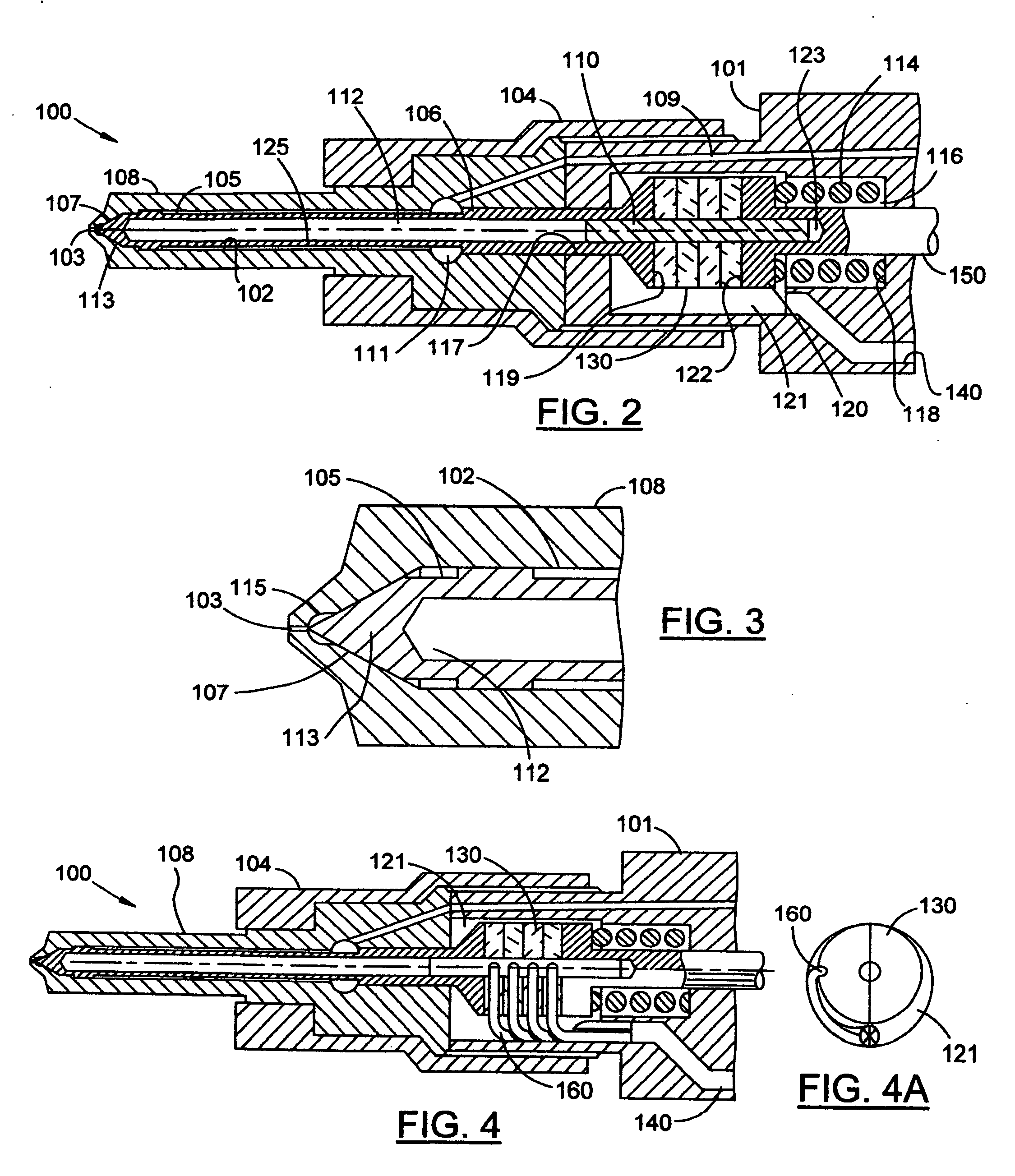
Ultrasonic actuator, driving method of the ultrasonic actuator, lens driver, and portable device
InactiveUS7671510B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesProjector focusing arrangementEngineeringUltrasonic actuator
An ultrasonic actuator according to an embodiment of the present invention includes: a stator generating a rotational driving force in accordance with a driving signal having a train pulse, which is used, for example, an AF mechanism; and a rotor converting the rotational driving force into actual movement. In the thus-structured ultrasonic actuator of the present invention, the driving signal is obtained by removing a predetermined number of pulses from the pulse train upon deceleration, and the remaining number of consecutive pulses is set to at least 2 or 4 or more.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Ultrasonically actuated needle pump system
InactiveUS6869420B2Efficient pumpingMinimal disruptionSurgeryMedical devicesEngineeringUltrasonic actuator
An ultrasonically driven pump, which may be used for sampling body fluids or atomizing liquids, has a stationary outer needle and an inner needle mounted within the bore of the outer needle. The distal end of the inner needle is positioned adjacent to the distal end of the outer needle. The inner needle is ultrasonically vibrated by an ultrasonic actuator without vibrating the outer needle, with resulting draw of liquid through the distal end of the outer needle into the bore of the inner needle for discharge through the proximal end of the inner needle. The outer needle can be formed to have a penetrating tip suited for penetrating the skin of a subject to allow sampling of body fluids including interstitial fluids. The pump can also be used for atomizing liquid, by drawing liquid from a supply that is pumped from the distal end to an open proximal end of the inner needle where the liquid is discharged by atomization into the atmosphere.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
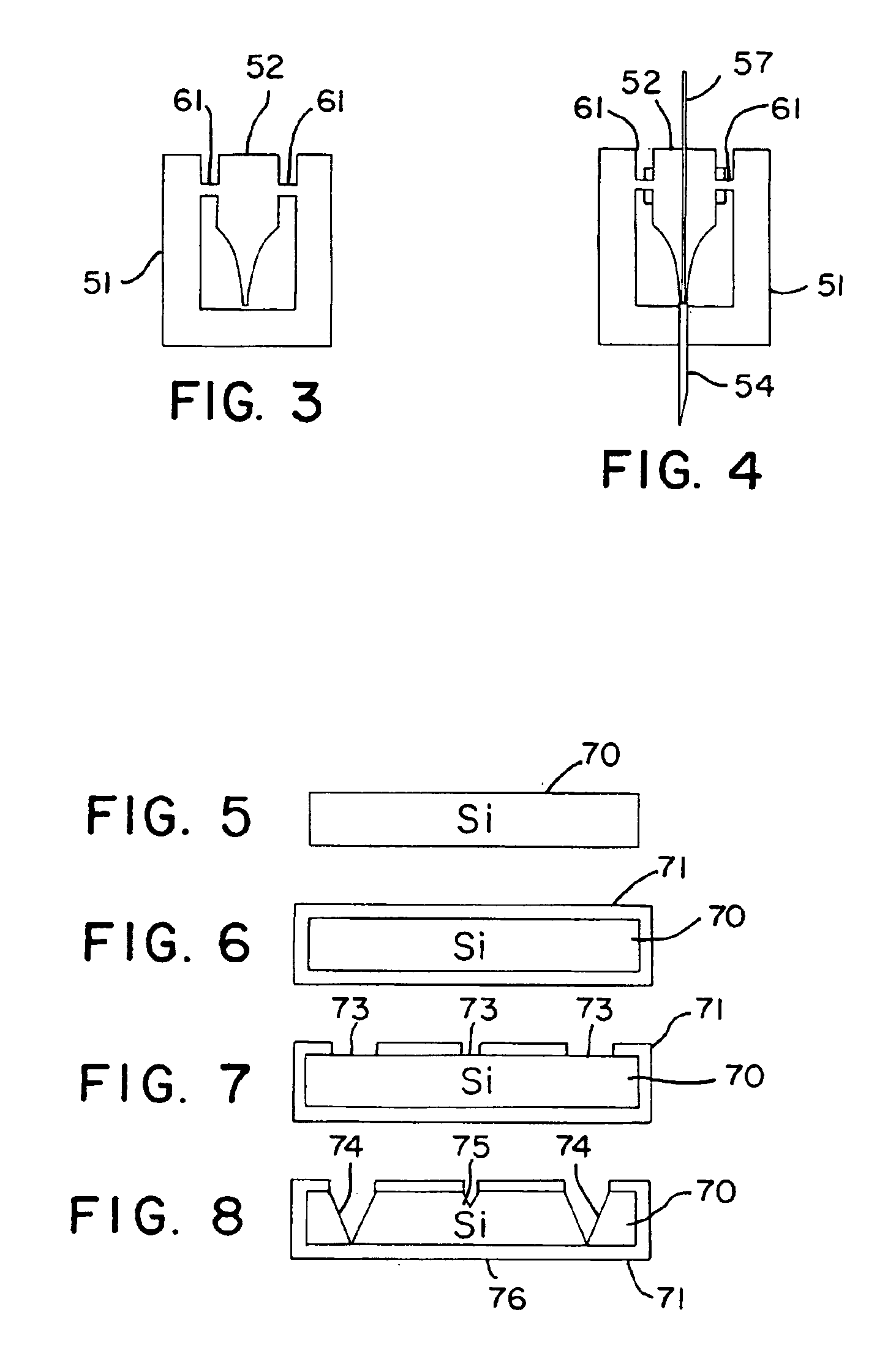
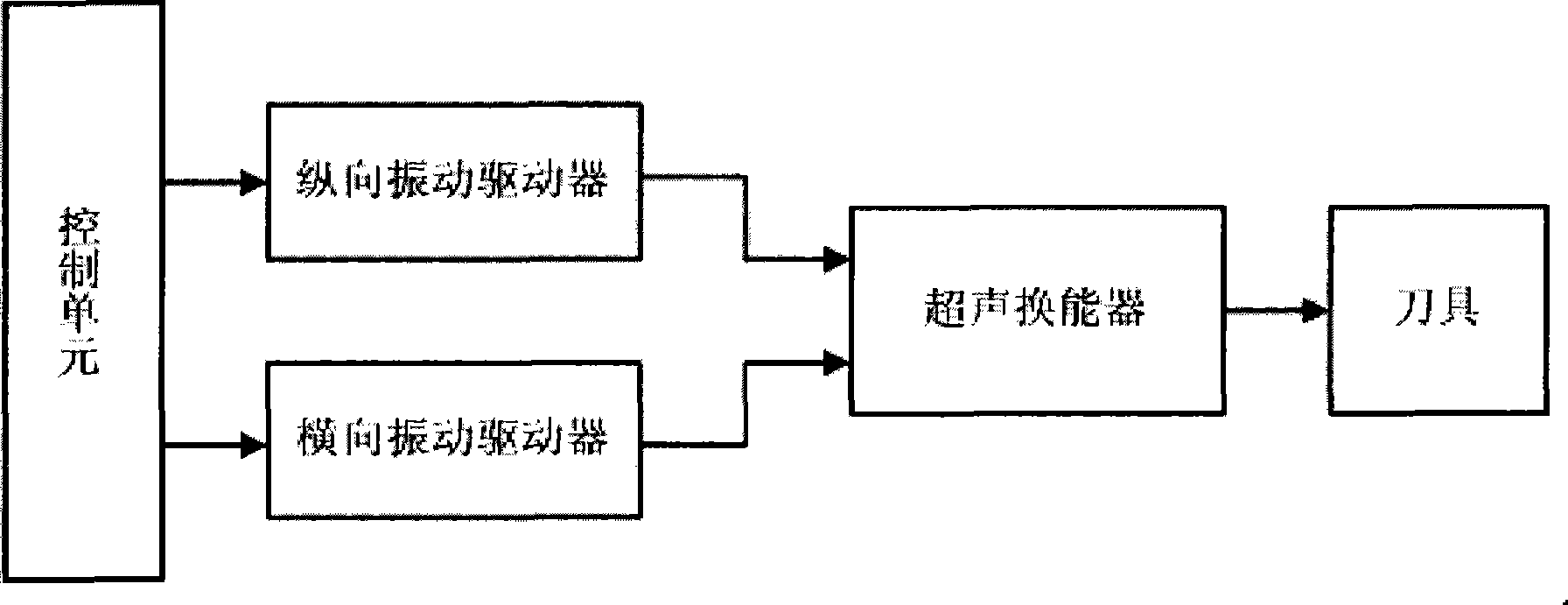
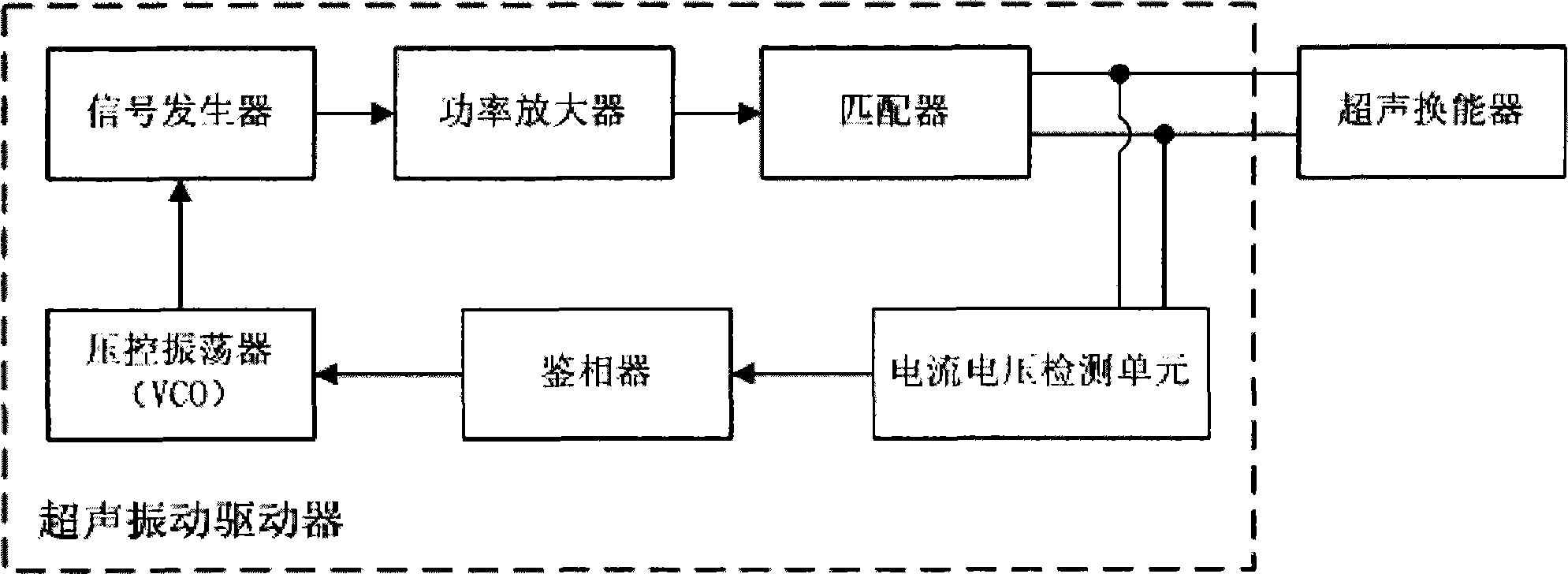
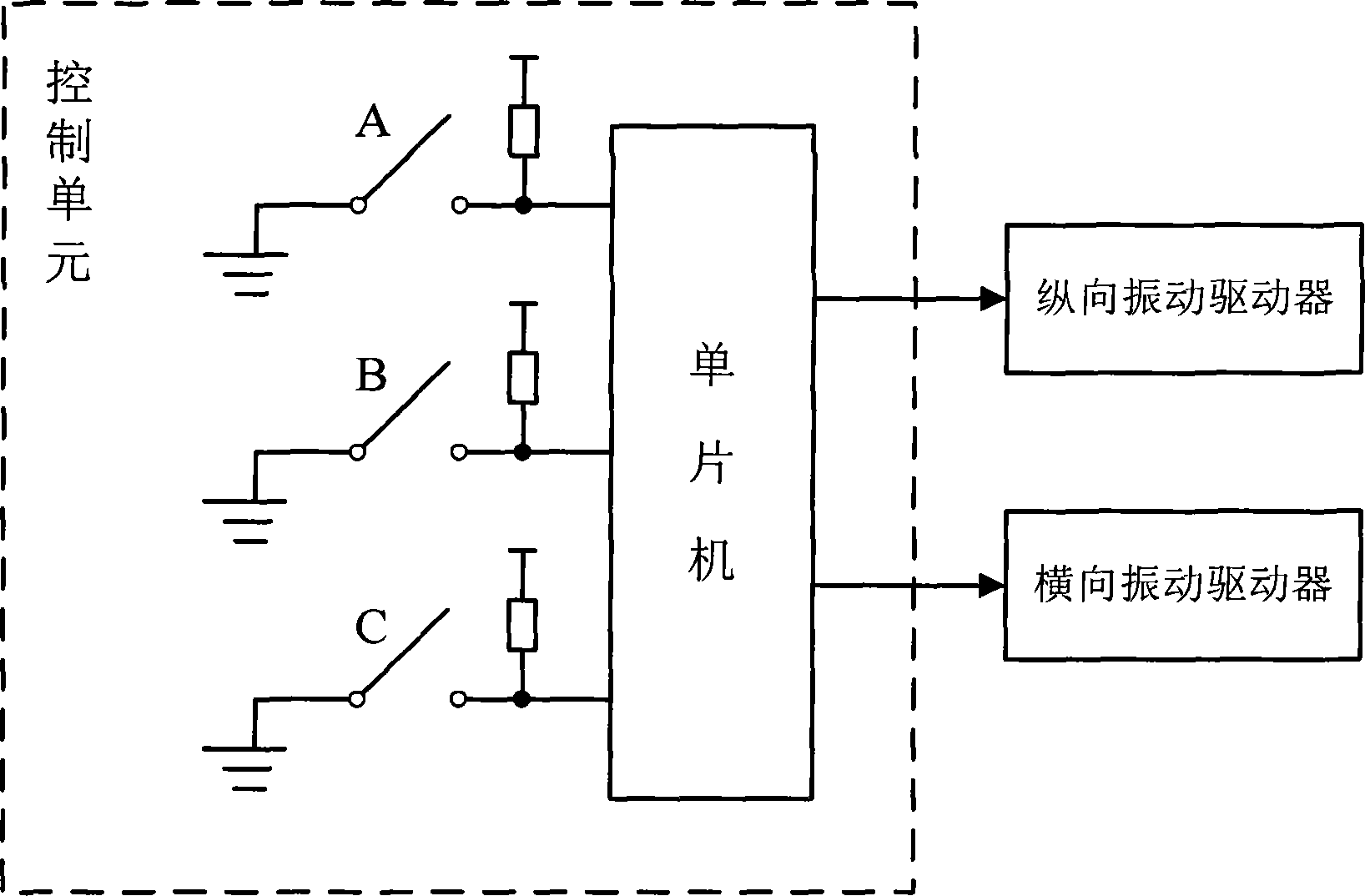
Ultrasonic cutter device used for bone operations
ActiveCN104207824AImprove the efficiency of bone cuttingImprove reliabilityIncision instrumentsEngineeringUltrasonic actuator
The invention relates to an ultrasonic cutter device used for bone operations. The ultrasonic cutter device comprises a control unit, a longitudinal ultrasonic actuator, a transverse ultrasonic actuator, an ultrasonic transducer and a cutter. The cutter is connected with the ultrasonic transducer, the longitudinal ultrasonic actuator and the transverse ultrasonic actuator drive the ultrasonic transducer to conduct longitudinal compound vibration and transverse compound vibration under the control of the control unit and transfer generated ultrasonic wave energy to the cutter. According to the ultrasonic cutter device, by using the longitudinal compound vibration and the transverse compound vibration of the ultrasonic transducer, the bone cutting efficiency of the ultrasonic bone cutter is improved; the longitudinal compound vibration and the transverse compound vibration of the ultrasonic transducer are achieved through driving of the corresponding actuators respectively, the structure of the part, held by the hand of an operator, of an instrument is simplified, the size is reduced, and the reliability is greatly improved.
Owner:厚凯(天津)医疗科技有限公司
Ultrasonic actuator device and applications thereof
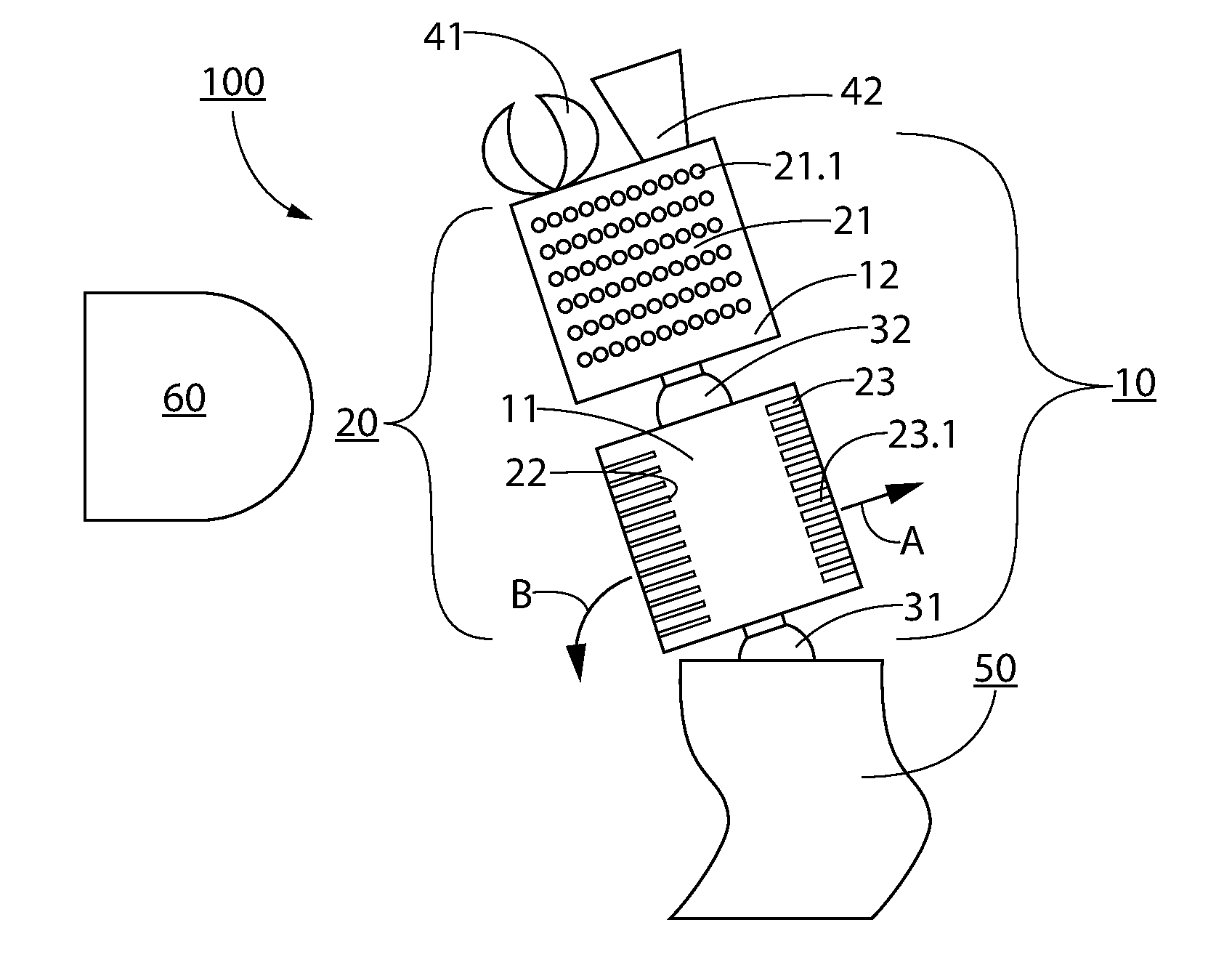
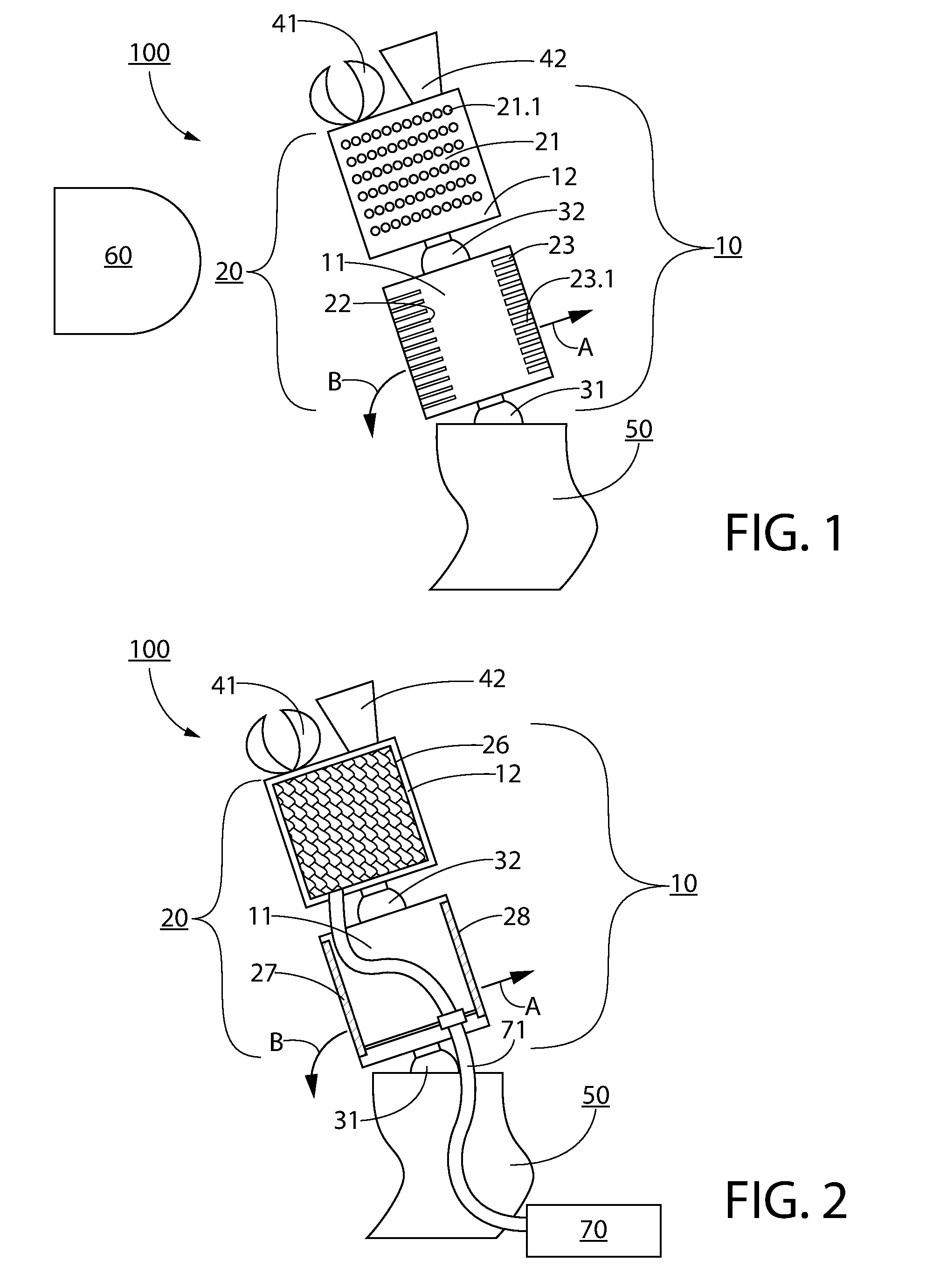
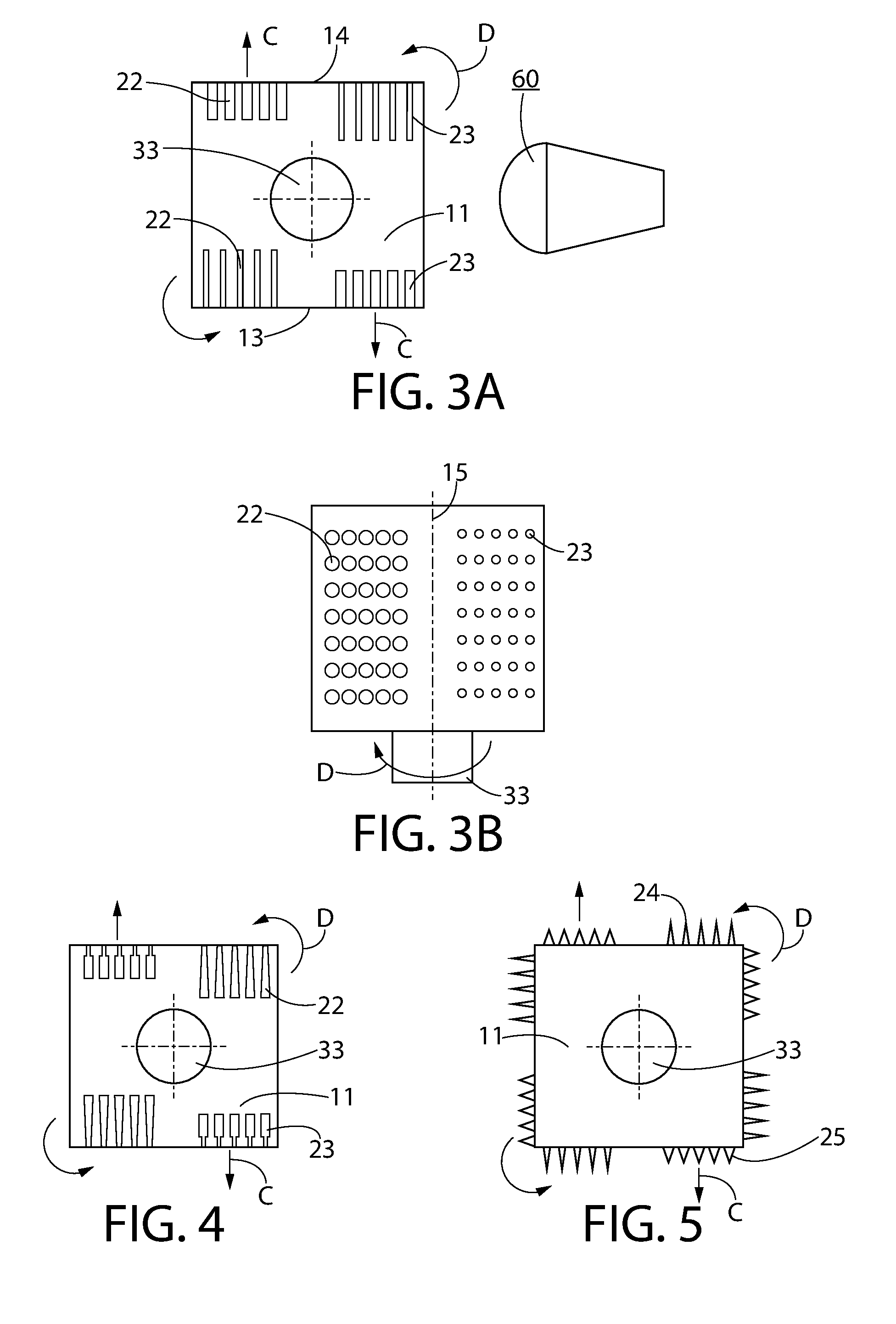
ActiveUS20160181951A1Minimize impactSimplified structure and controlPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEndoscopesEngineeringUltrasonic actuator
Ultrasonic actuator device (100) includes actuator arm arrangement (10) including first and second actuator sections (11,12), wherein the first section is arranged for coupling with support structure (50) and the second section is movable relative to the first section, and ultrasonic driver device (20) including at least one ultrasonic driver unit (21-28) coupled with at least one of first and second sections for driving actuator arm arrangement (10) and for providing movement of the second section relative to the first section, and wherein actuator arm arrangement (10) is movable with at least two degrees of freedom and the at least one ultrasonic driver unit includes an array of oscillating elements being arranged for creating an acoustic stream in an adjacent medium in response to application of ultrasound. Furthermore, an operational instrument including at least one ultrasonic actuator device (100) and a method of using the device are described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Ultrasonic-actuator driving apparatus and ultrasonic-actuator driving method
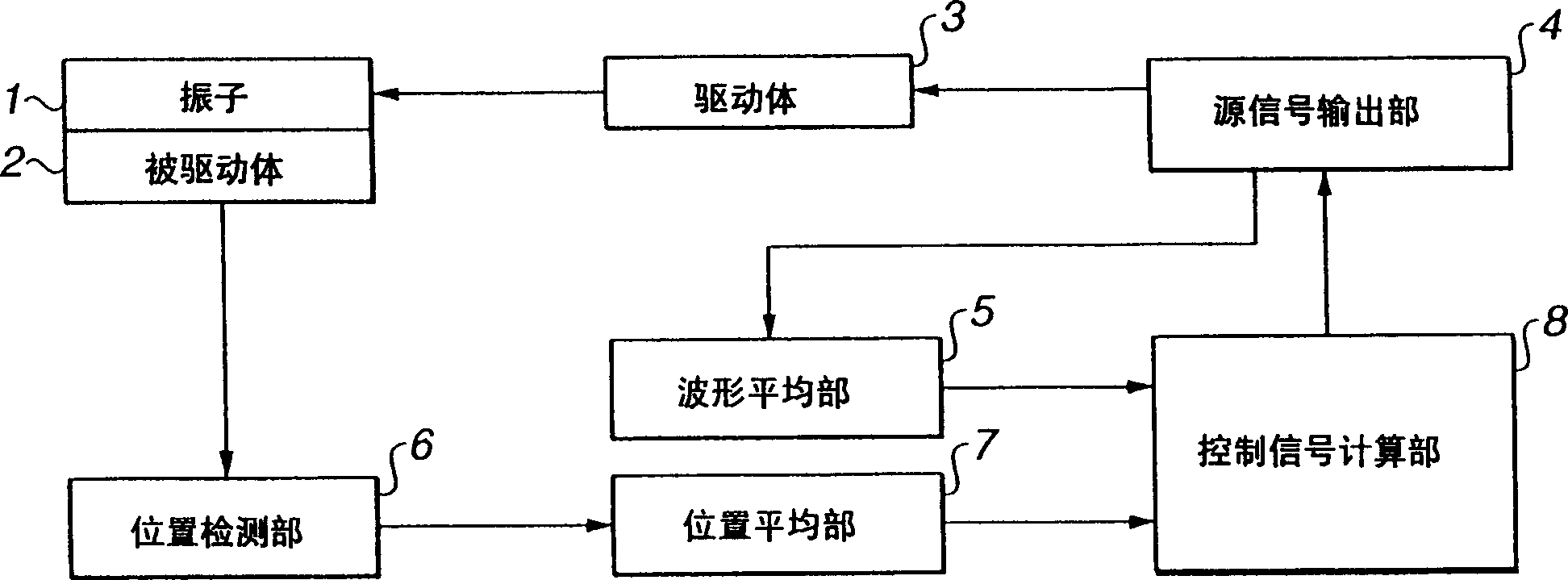
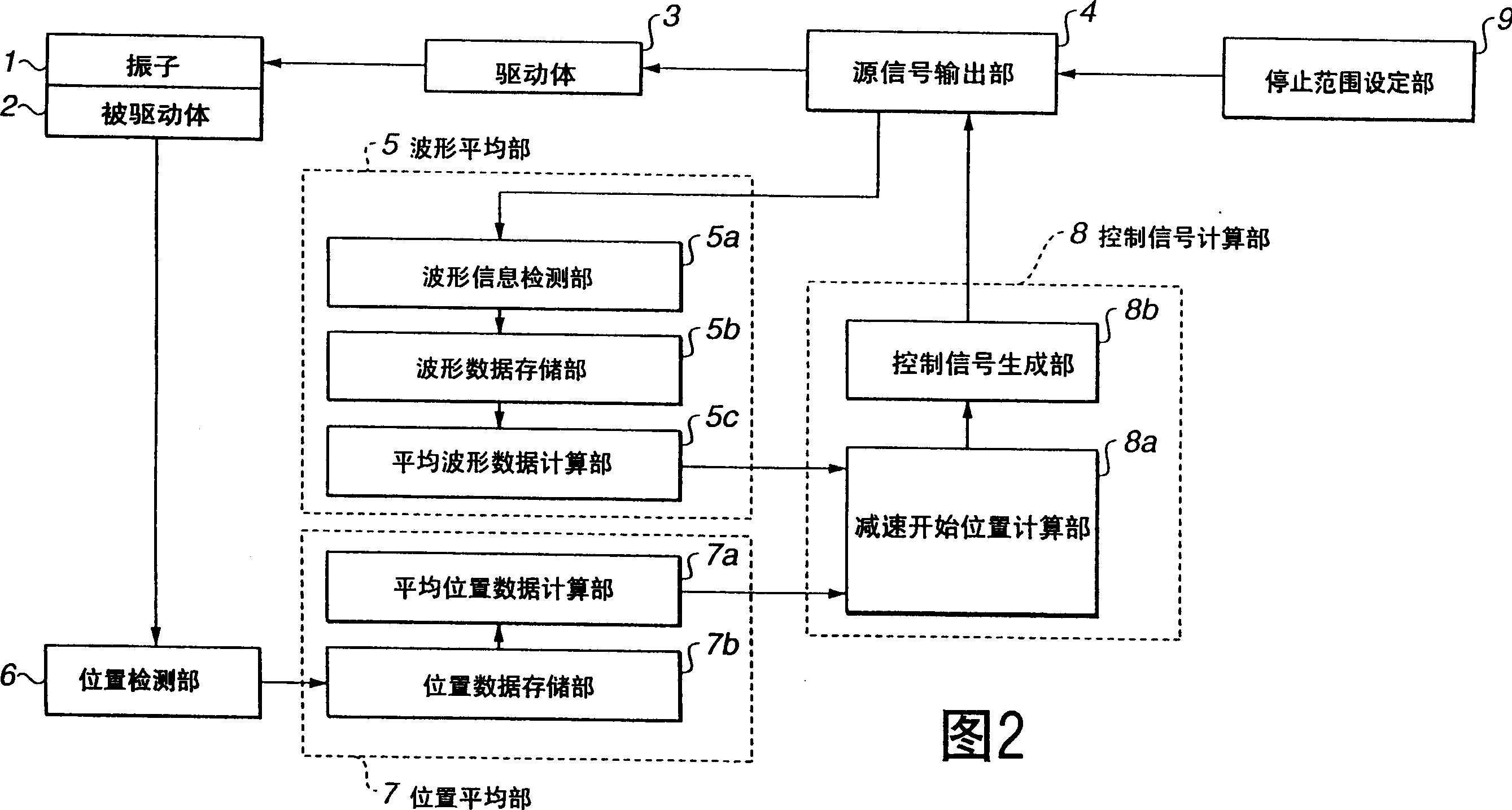
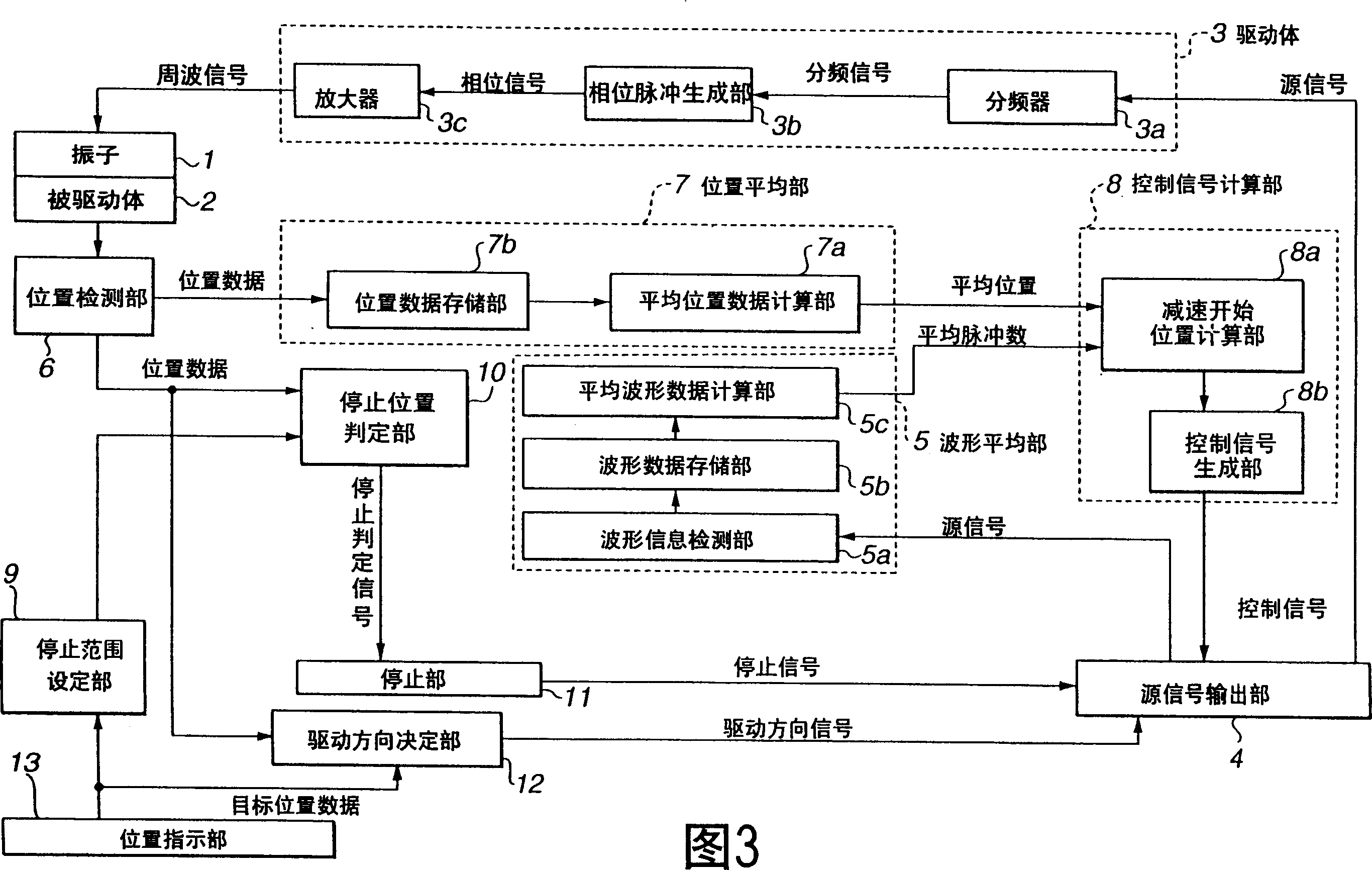
InactiveCN1551479APrecise positioningPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsLocation detectionControl signal
An ultrasonic-actuator driving apparatus includes an ultrasonic actuator including a transducer and a driven body that is in contact with the transducer, the transducer to which a frequency signal is applied friction-driving the driven body; an original-signal outputting unit for outputting an original signal; a waveform averaging unit for averaging the original signals during a predetermined period to calculate average-waveform data; a position detecting unit for detecting an absolute position of the driven body with respect to the transducer; a position averaging unit for averaging the absolute positions during a predetermined period to calculate average-position data; a control-signal calculating unit that generates a control signal for controlling the frequency of the original signal based on the average-waveform data and the average-position data and supplies the control signal to the original-signal outputting unit; and a driving unit for generating the frequency signal based on the original signal and applying the frequency signal to the transducer.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Vibration actuator and drive unit including the same
InactiveUS7642696B2Reduce stepsAvoid partialPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesLongitudinal vibrationEngineering
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
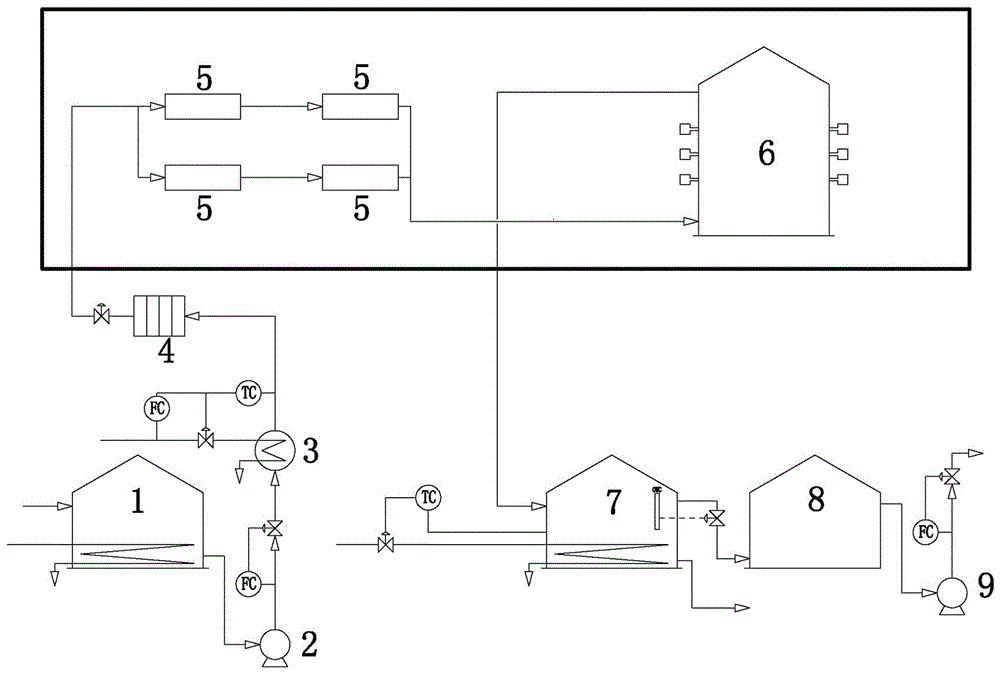
Super-high power ultrasonic sump oil emulsion breaking dehydration method
InactiveCN105776704AAchieve dehydrationAchieve recyclingFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsUltrasound - actionOil emulsion
The invention discloses a super-high power ultrasonic sump oil emulsion breaking dehydration method.The method comprises the steps that water-containing sump oil in a sump oil stock tank (1) is preheated and pressurized through a water-containing sump oil pump (2) and fed into a sump oil heater (3) to be heated to 50-85 DEG C; the heated water-containing sump oil is fed into an ultrasonic actuator (5) for continuous ultrasonic initial emulsion breaking; the sump oil obtained after initial emulsion breaking is fed into a pulse type ultrasonic emulsion breaking tank (6) through a pipeline for secondary emulsion breaking; the water-containing sump oil obtained after secondary emulsion breaking flows into a settlement separation dehydration tank (7) to be heated to 40-80 DEG C for settlement and layering to obtain sump oil, sewage and solid flocculent impurities; the sump oil located at the upper portion of the settlement separation dehydration tank (7) automatically flows into a finished sump oil tank (8); sewage and impurities enter a settling pond from the bottom of the settlement separation dehydration tank (7) through a sewage disposal well.According to the two-time ultrasonic emulsion breaking, sump oil dehydration is achieved, the sump oil dehydration rate is larger than 90%, and the sewage oil content is smaller than 500 mg / L.
Owner:JIANGSU DAXUAN PETROCHEM EQUIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com