Patents
Literature
36 results about "X Ray Computerized Tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
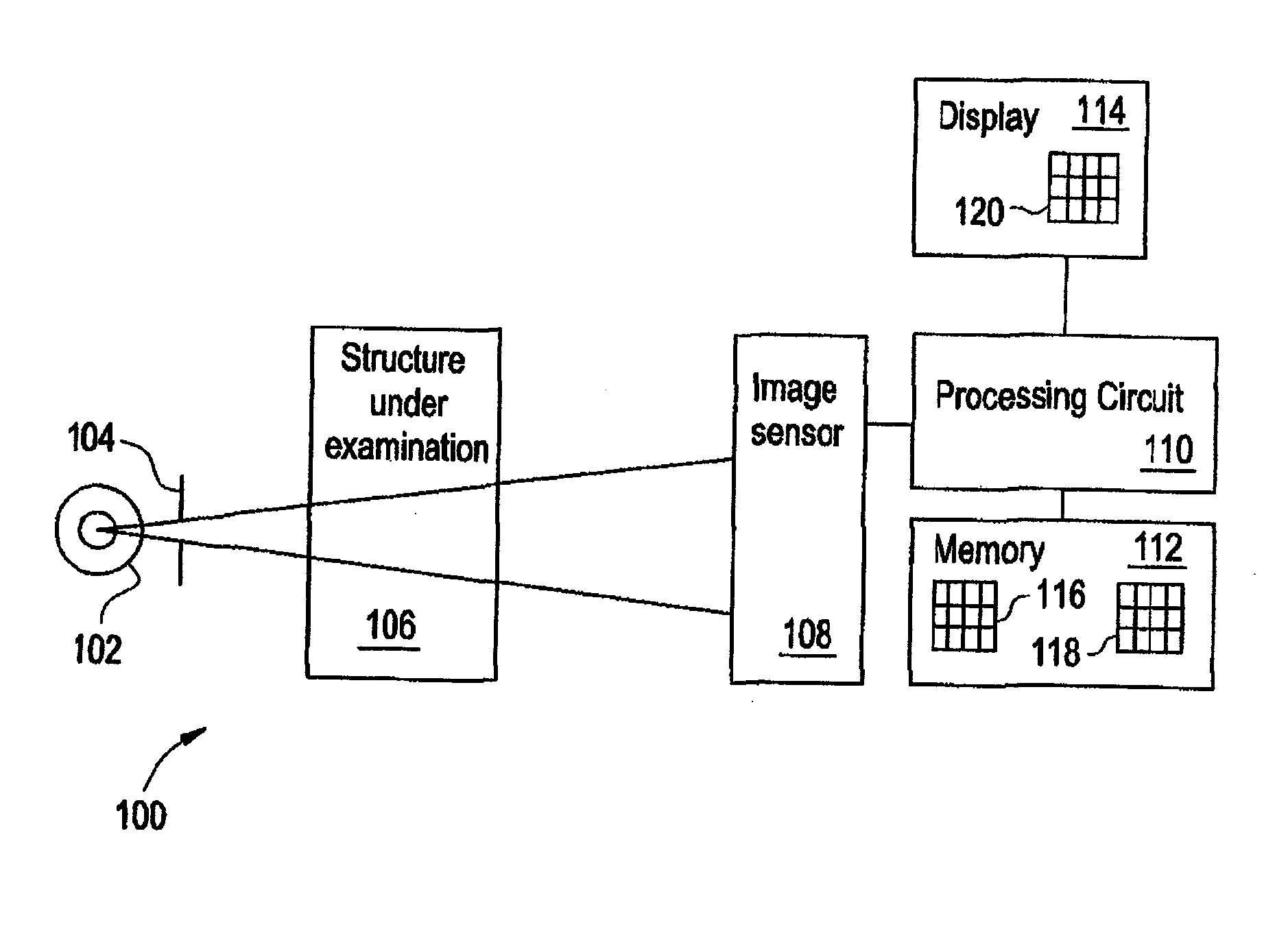
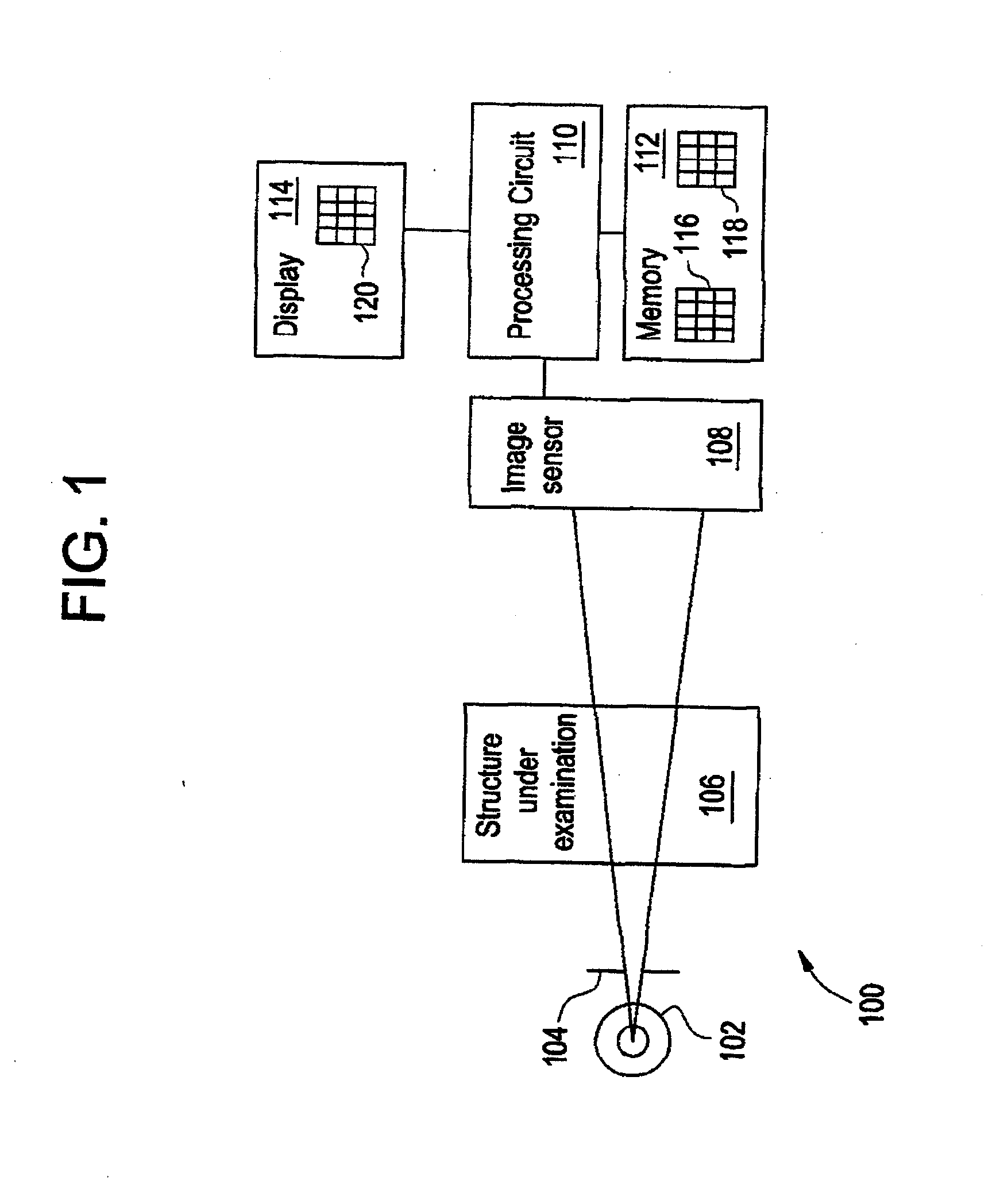
The schematic below shows the process of generating 3D, volumetric images using X-ray computed tomography (XCT). XCT is based on taking 2D ragiographs through a sample at many projections around the sample and computationally reconstructing a 3D image from the projections.
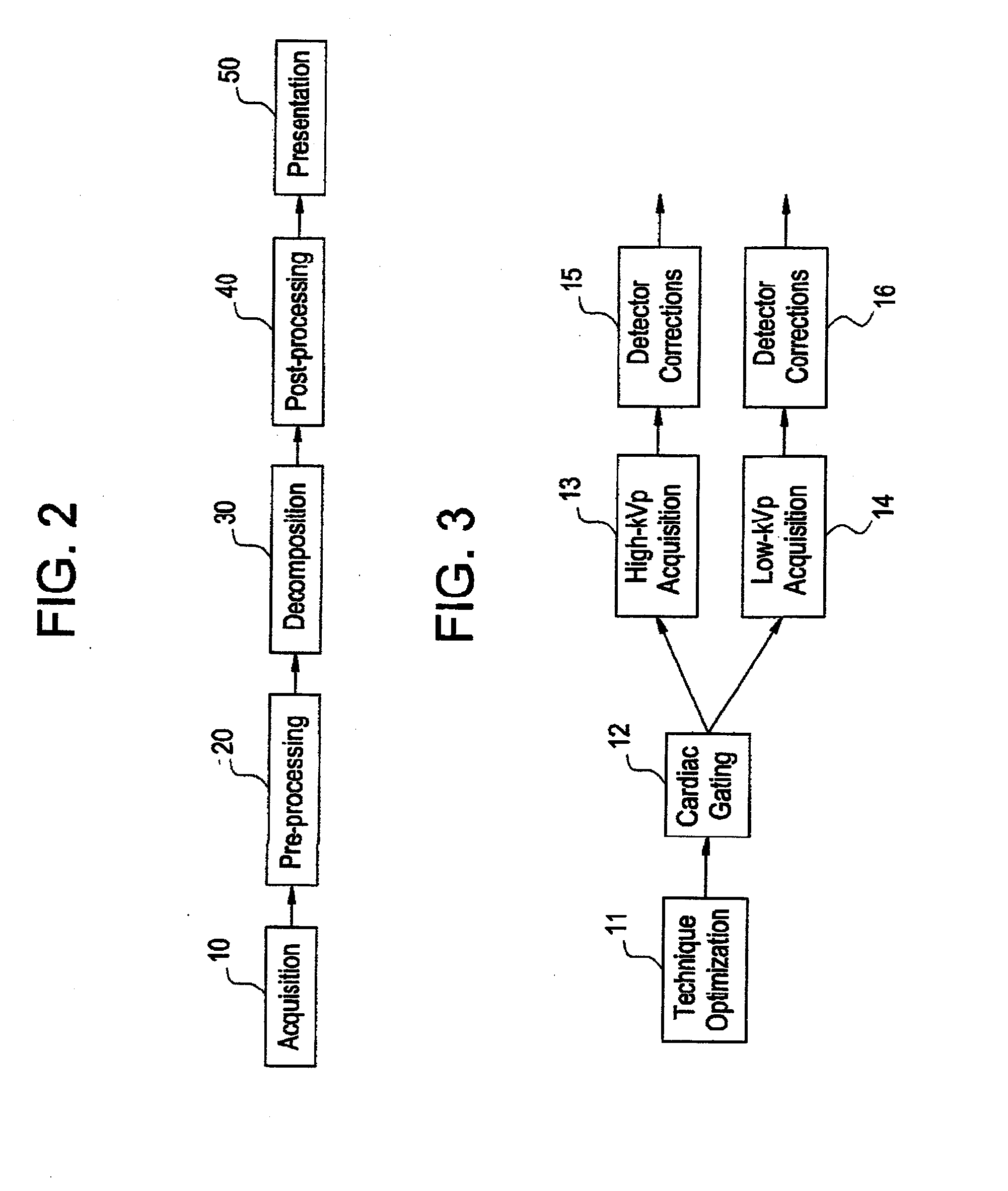
Computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction method, device and computerized tomography (CT) apparatus
ActiveCN103679642AGuaranteed Spatial ResolutionLow contrast capabilityImage enhancementComputerised tomographsMetal ArtifactImage resolution
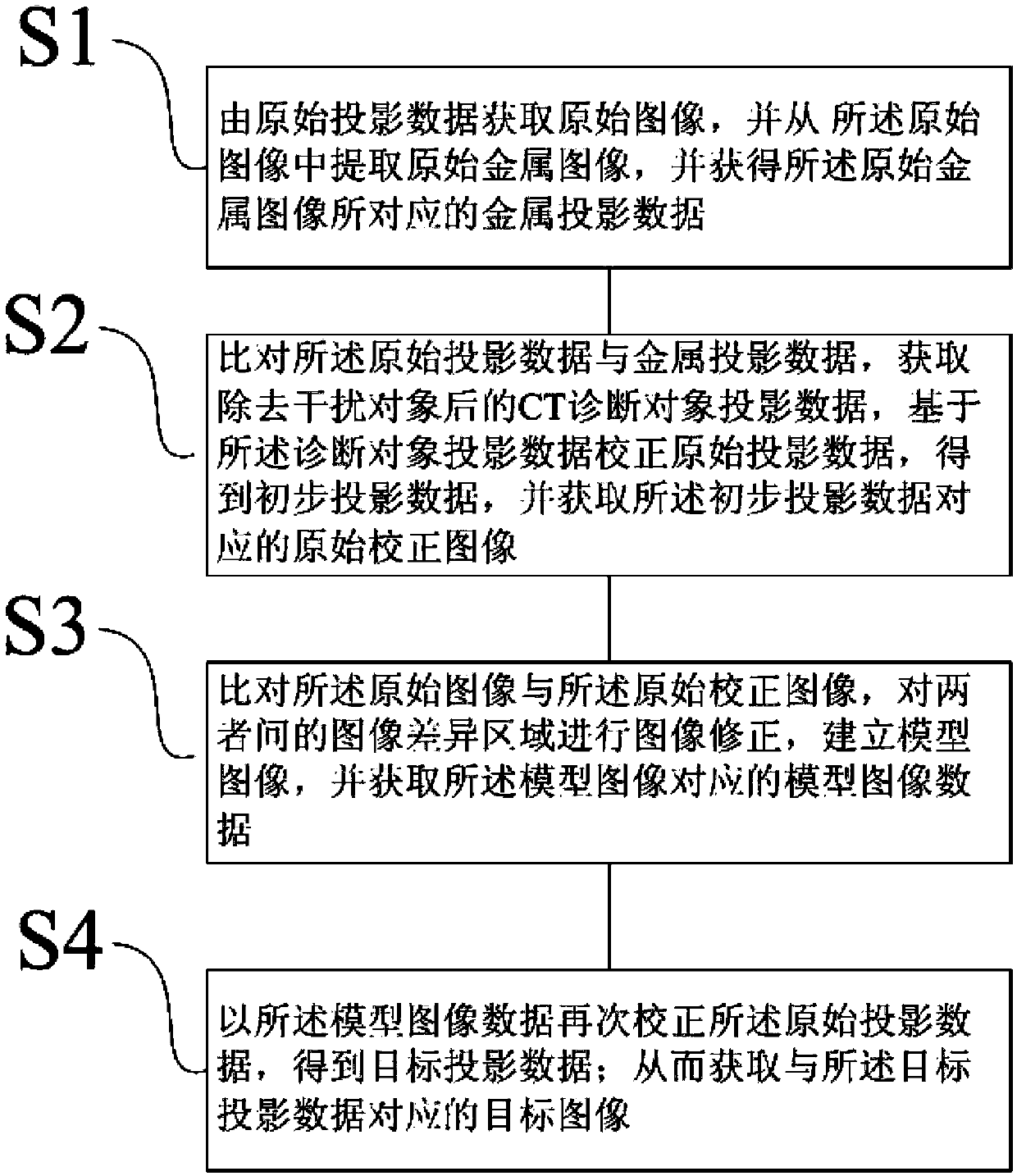
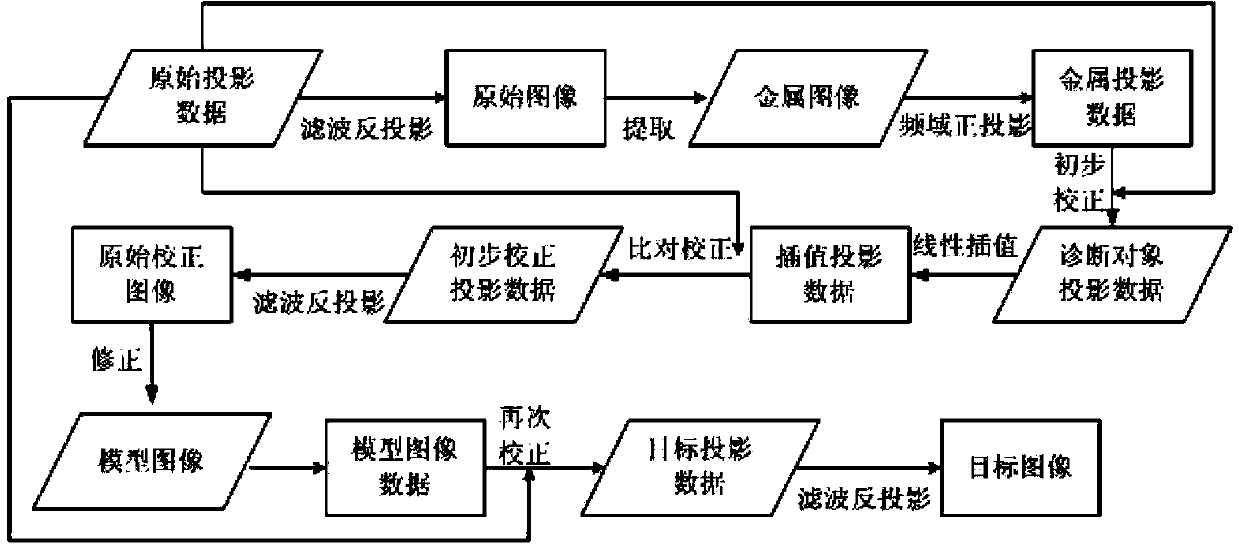
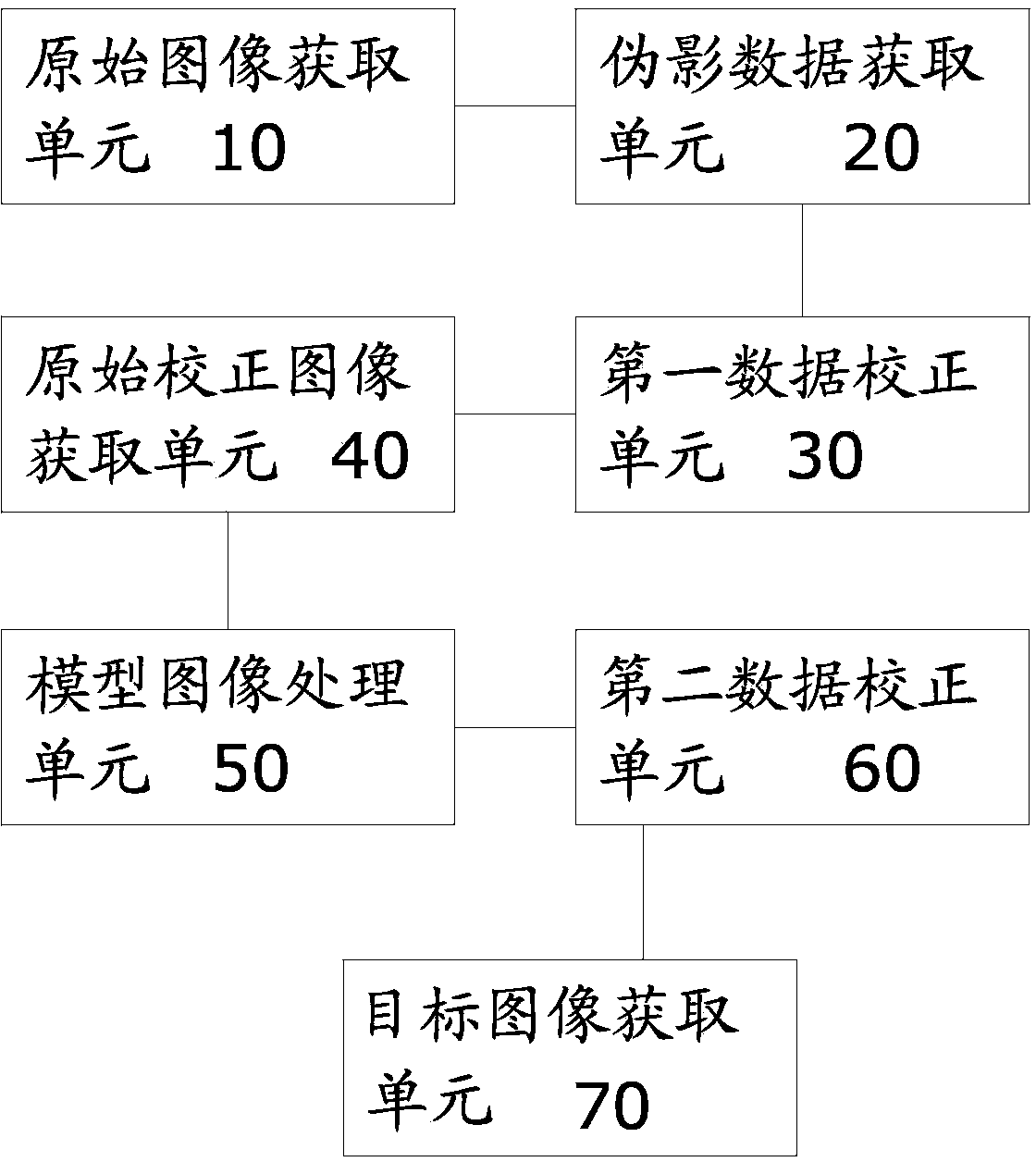
The invention provides a computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction method, a computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction device and a computerized tomography (CT) apparatus. The computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction method comprises the following steps that: a metal projection range caused by an interference object is determined according to an original image corresponding to original projection data; diagnosis object projection data after the removal of the interference object are obtained based on metal projection data in the metal projection range, and after that, the original projection data are corrected and a model image is constructed based on the diagnosis object projection data; and secondary correction is performed on the original projection data according to the projection data of the model image, and reconstruction is performed based on corrected target projection data and according to clinically-used scanning and image construction conditions so as to obtain a metal artifact-free target image, and therefore, the purpose of metal artifact correction can be achieved. According to the computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction method of the invention, the original projection data are adopted as a correction object, and therefore, the spatial resolution and low-contrast ability of a processed image can be ensured; and the original projection data completely contain all information of the interference object, and therefore, the introduction of a new artifact can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
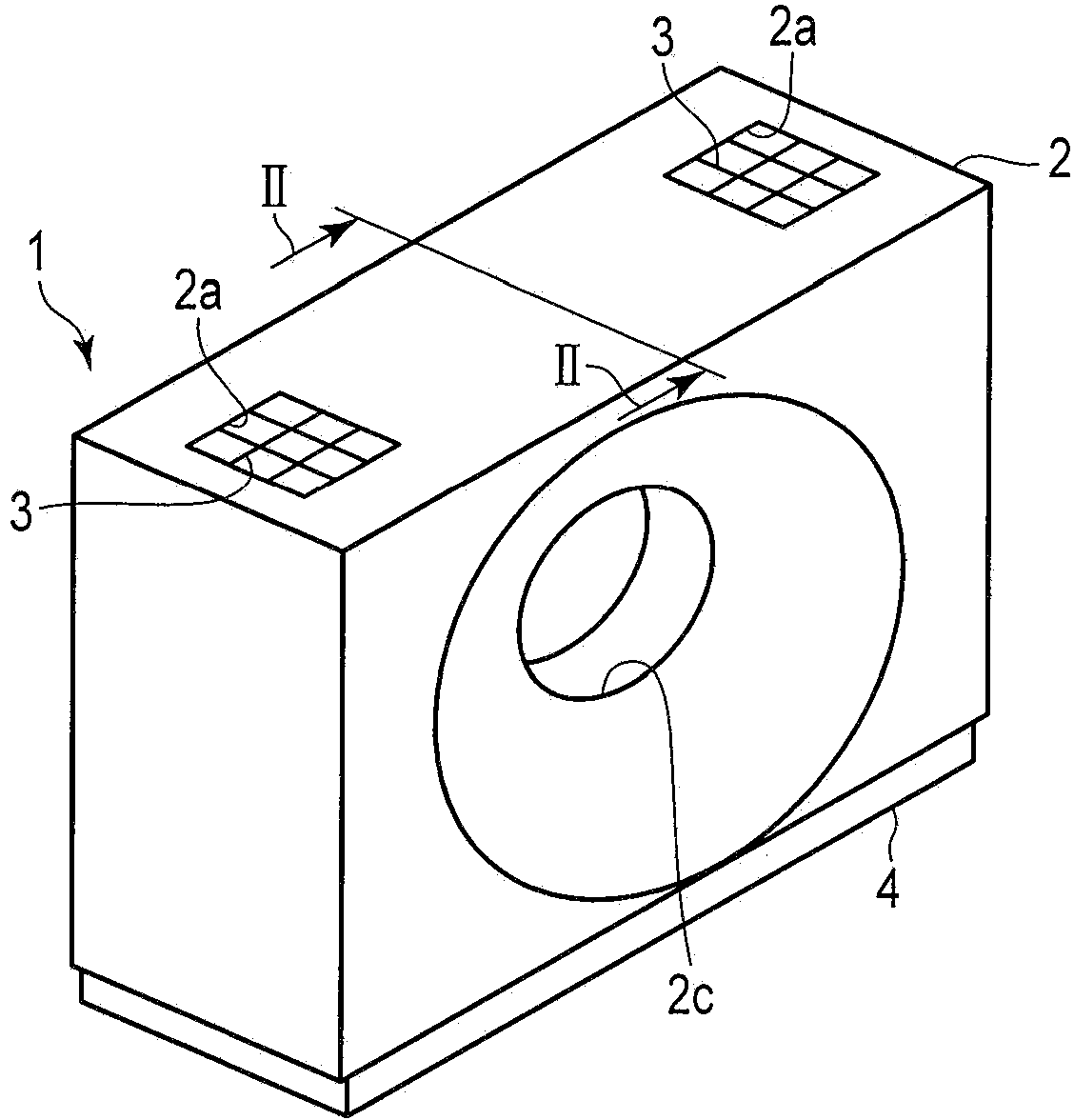
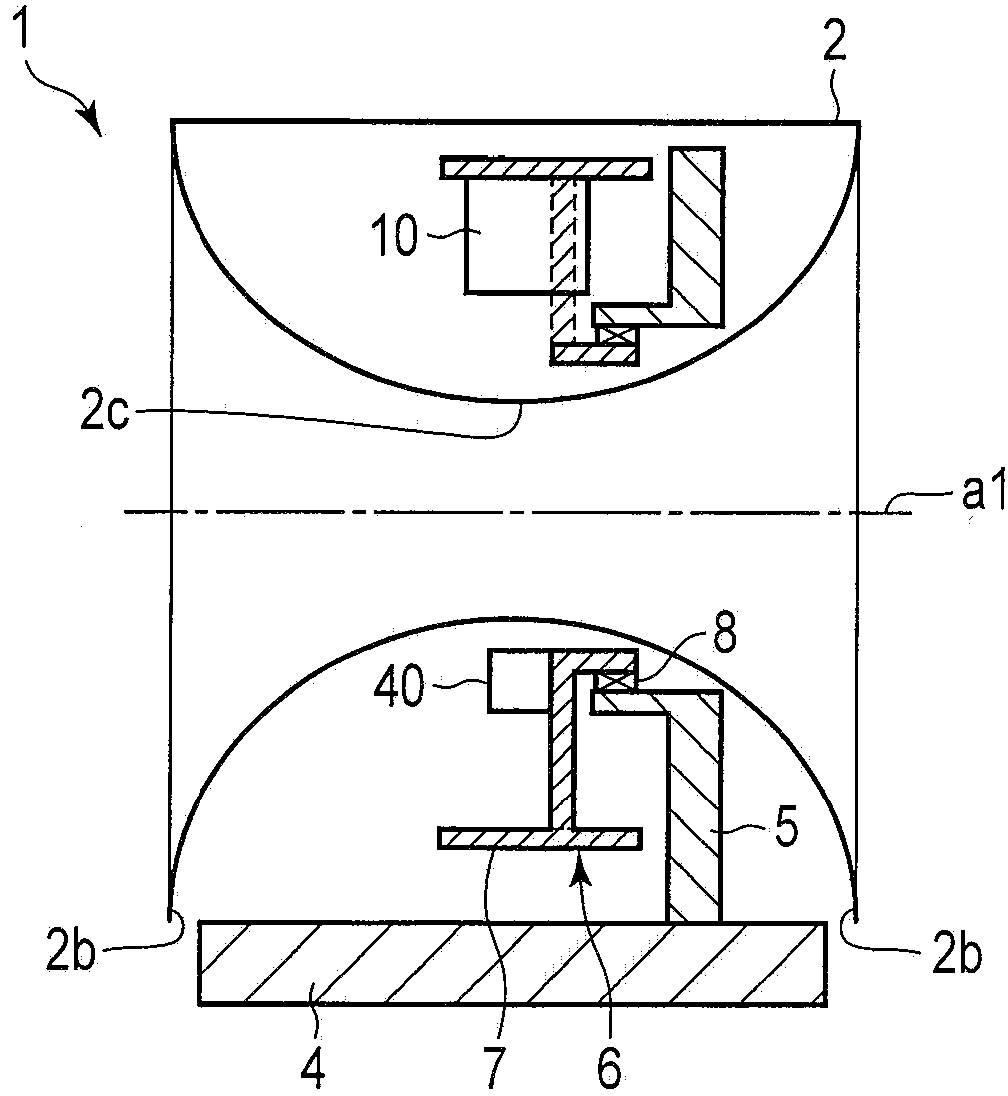
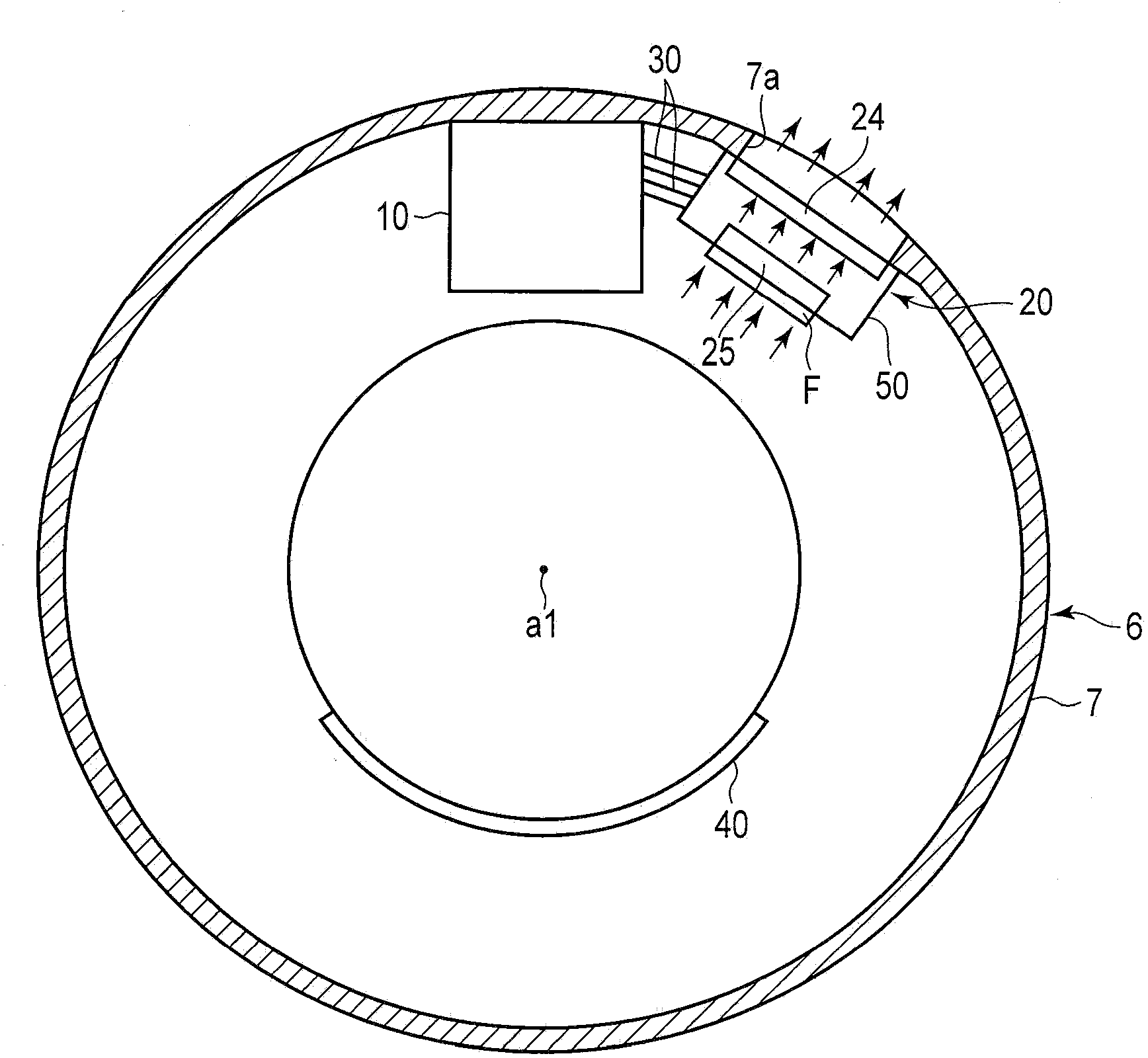
X-ray computerized tomography apparatus, breathing indication apparatus and medical imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20080089463A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic measurementsTemporal changeX-ray
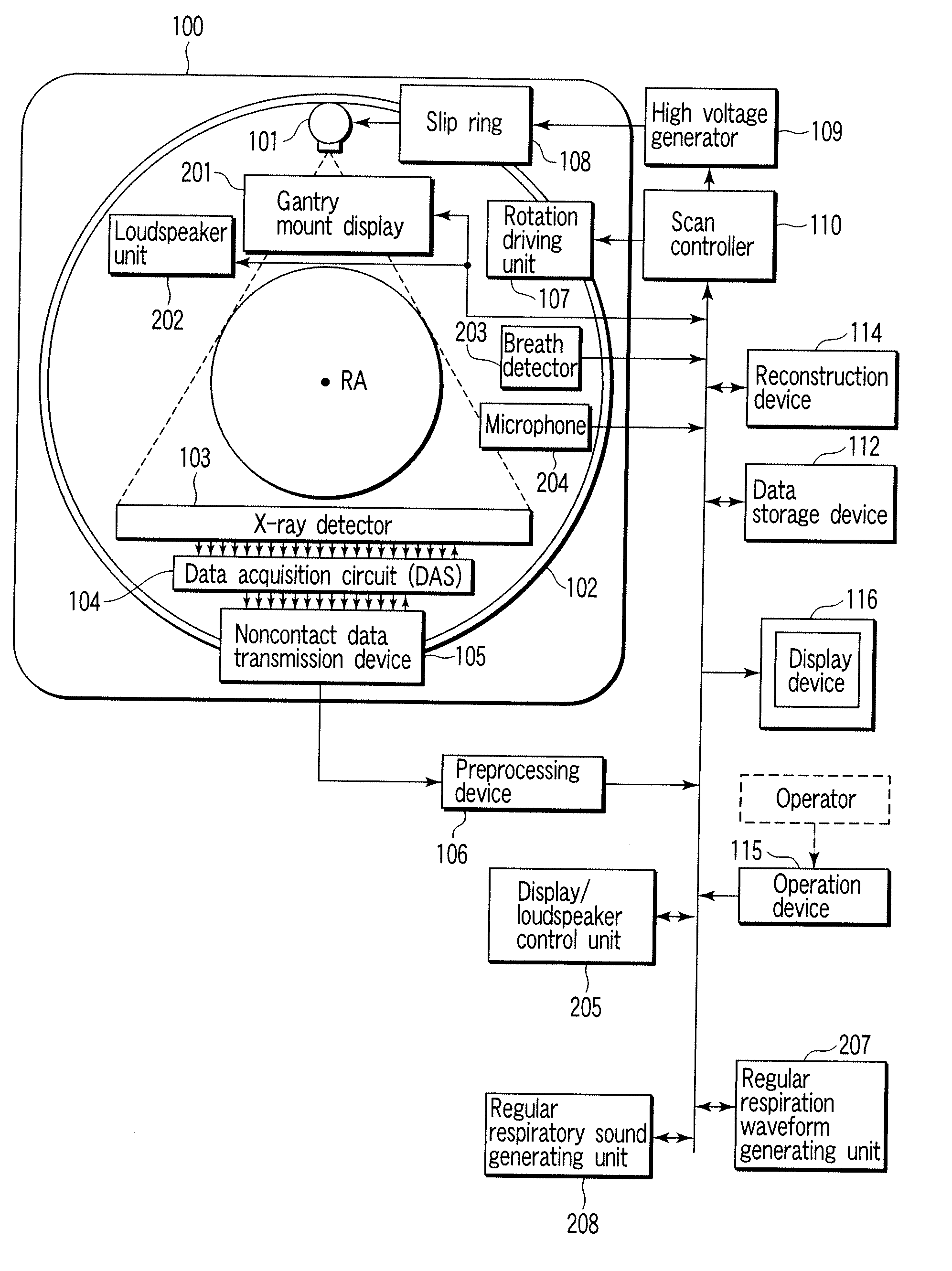
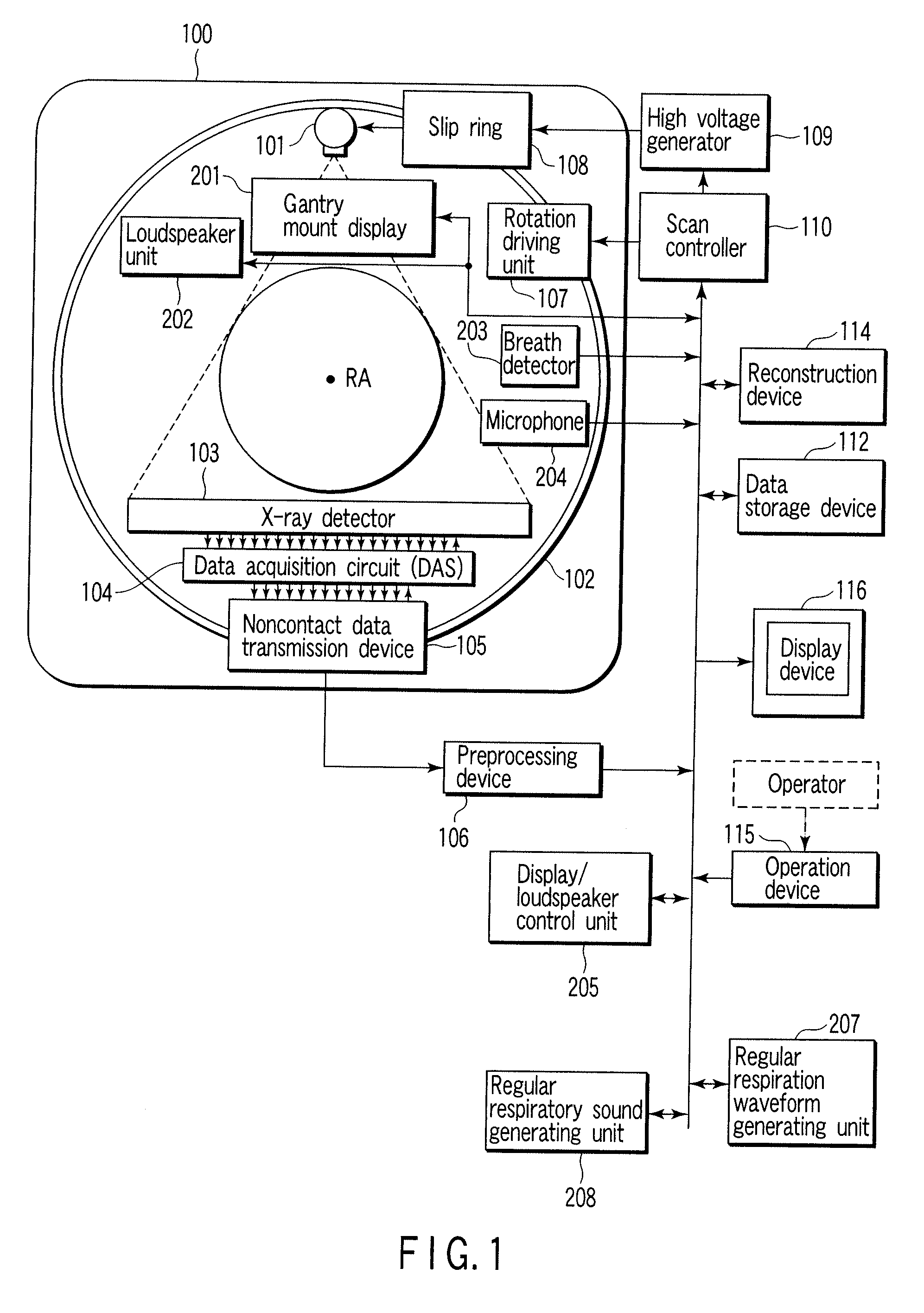
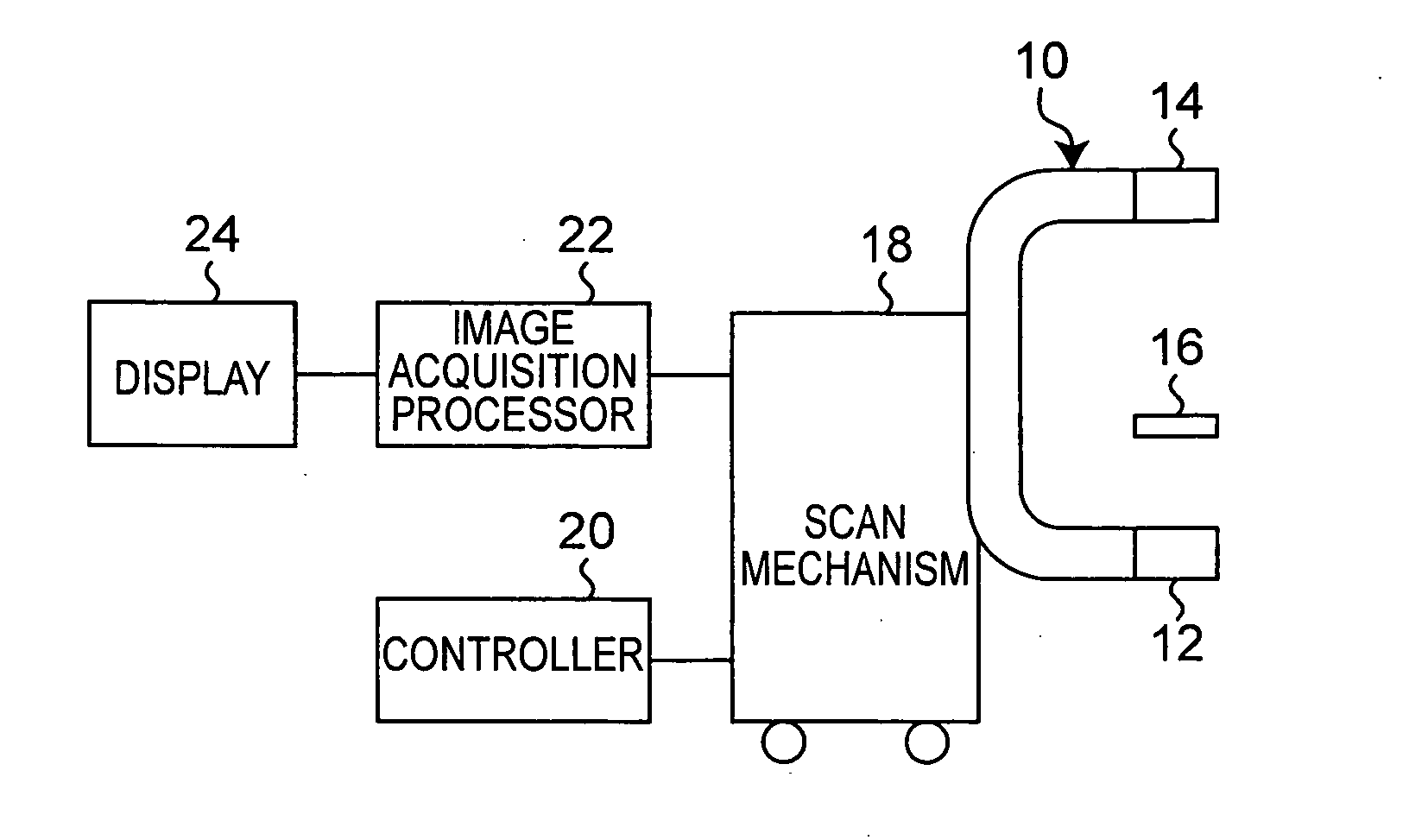
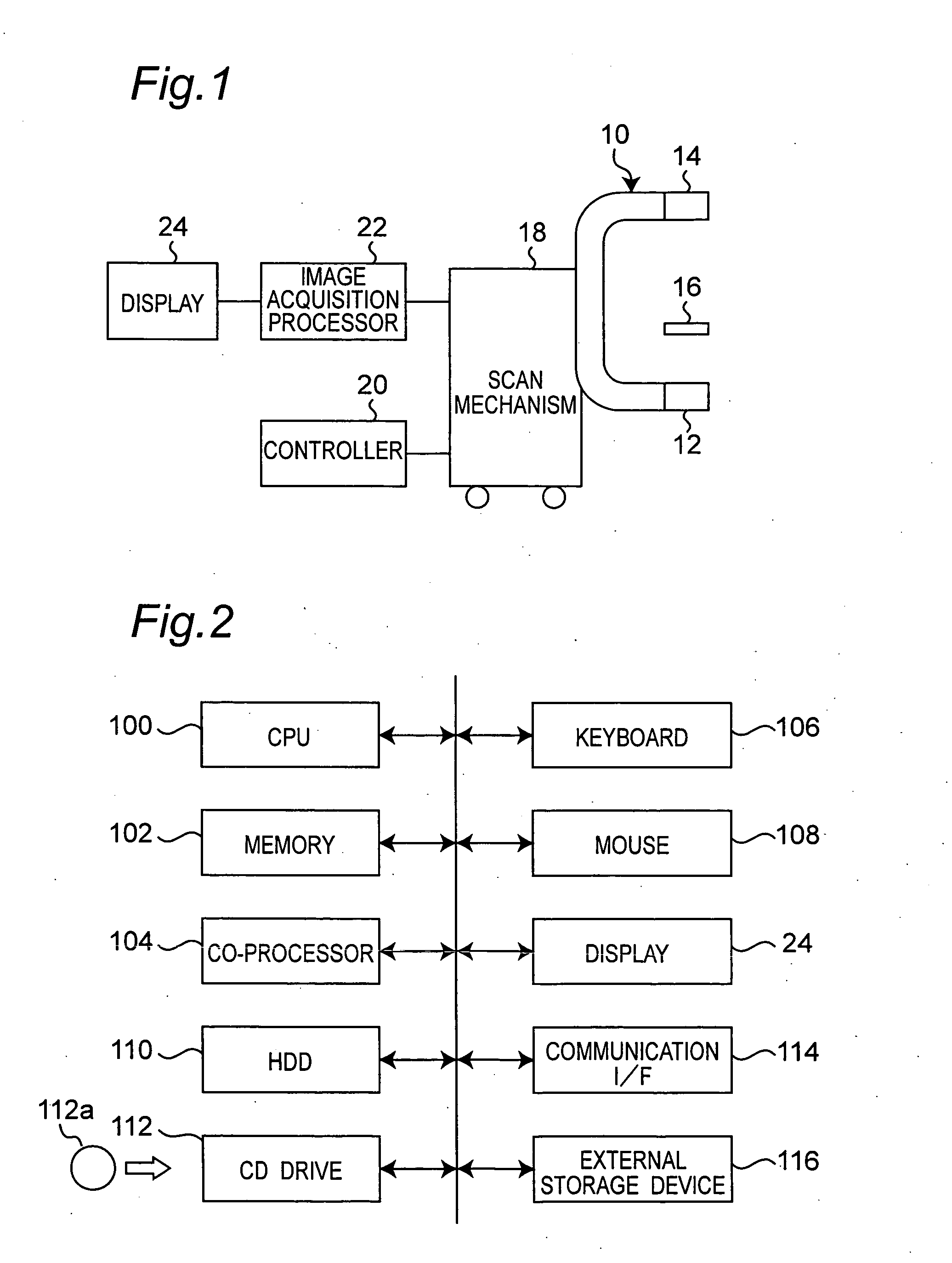
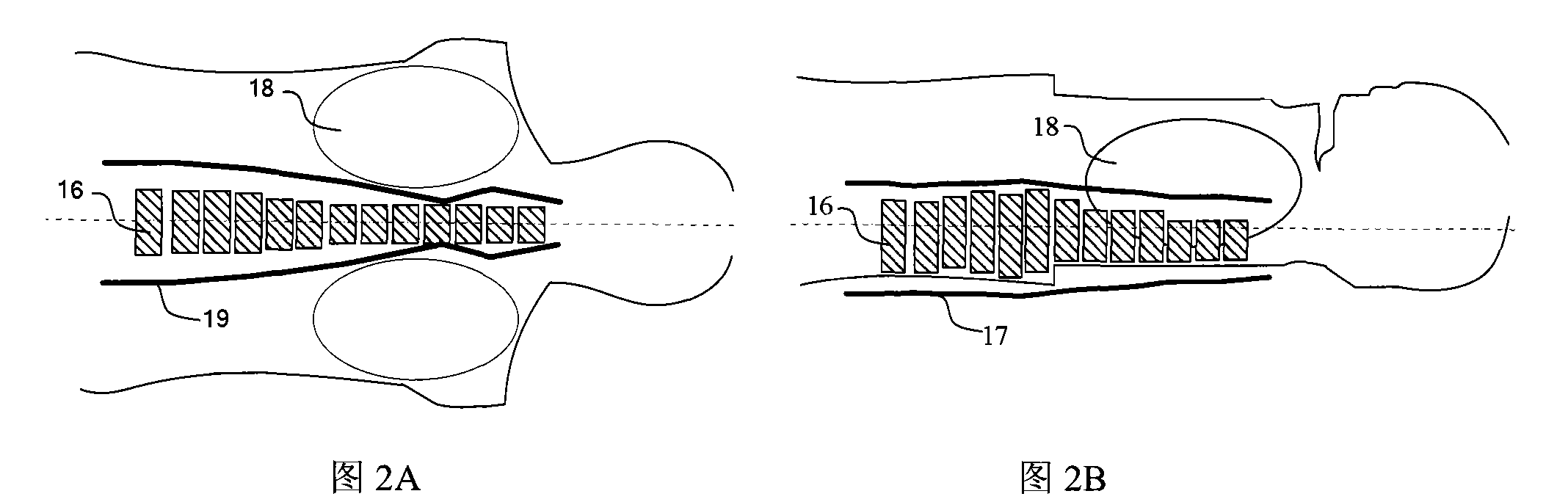
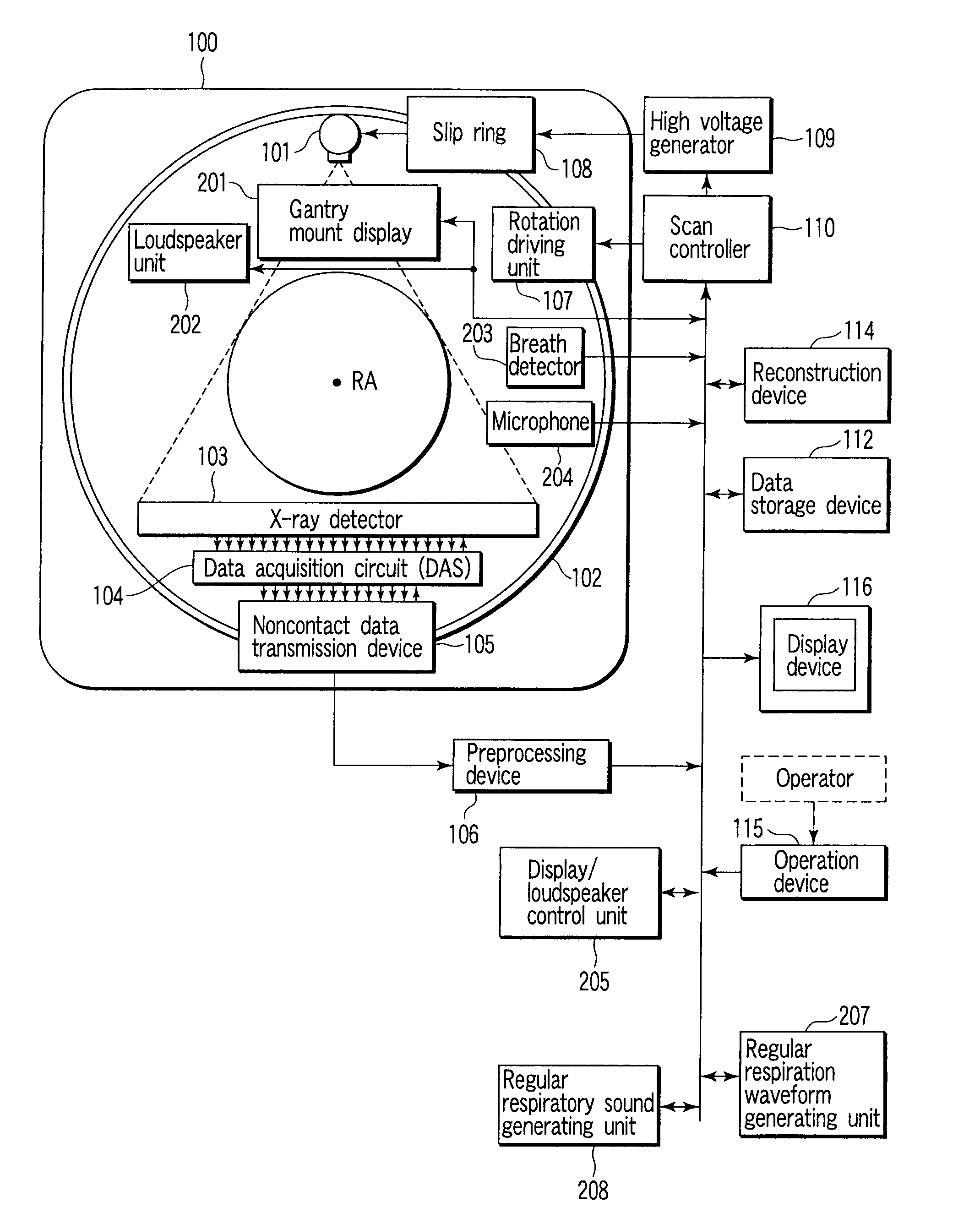
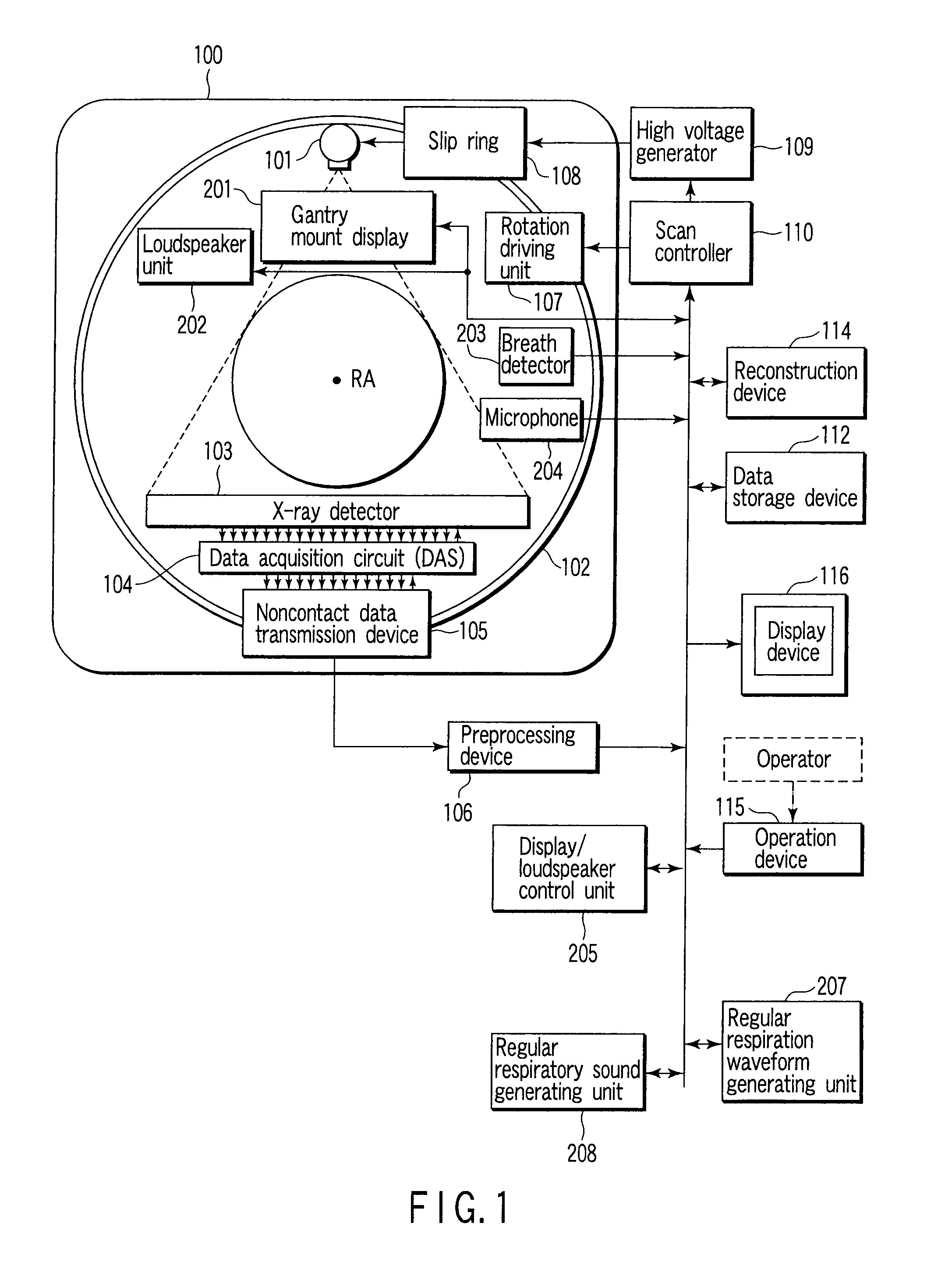
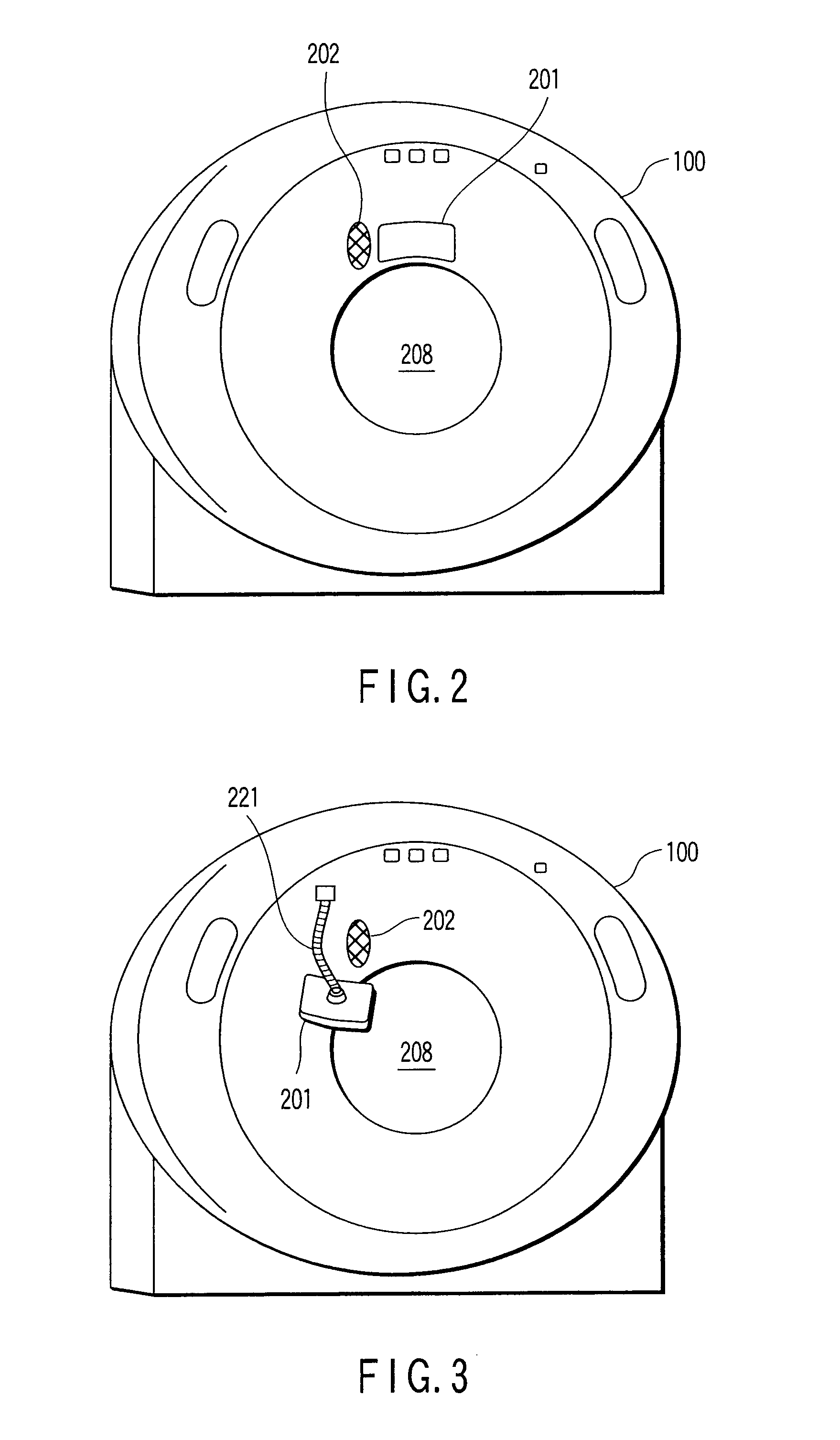
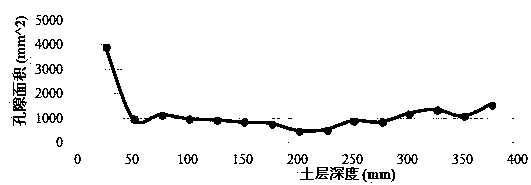
An X-ray computed tomographic apparatus includes a gantry 100 including an X-ray tube 101 which generates X-rays and an X-ray detector 103 which detects X-rays transmitted through a subject to be examined, a reconstruction device 114 which generates tomogram data on the basis of an output from the X-ray detector, a breath detector 203 which detects a respiration waveform representing a temporal change in respiration index value associated with the subject, a regular respiration waveform generating unit 207 which generates a respiration waveform with a regular respiration cycle which originates from the detected respiration waveform, and a gantry mount display 201 which displays the generated regular respiration waveform.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
System and method for computer aided detection and diagnosis from multiple energy images
A method, system, and storage medium for computer aided processing of an image set includes employing a data source, the data source including an image set acquired from X-ray projection imaging, x-ray computed tomography, or x-ray tomosynthesis, defining a region of interest within one or more images from the image set, extracting feature measures from the region of interest, and reporting at least one of the feature measures on the region of interest. The method may be employed for identifying bone fractures, disease, obstruction, or any other medical condition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
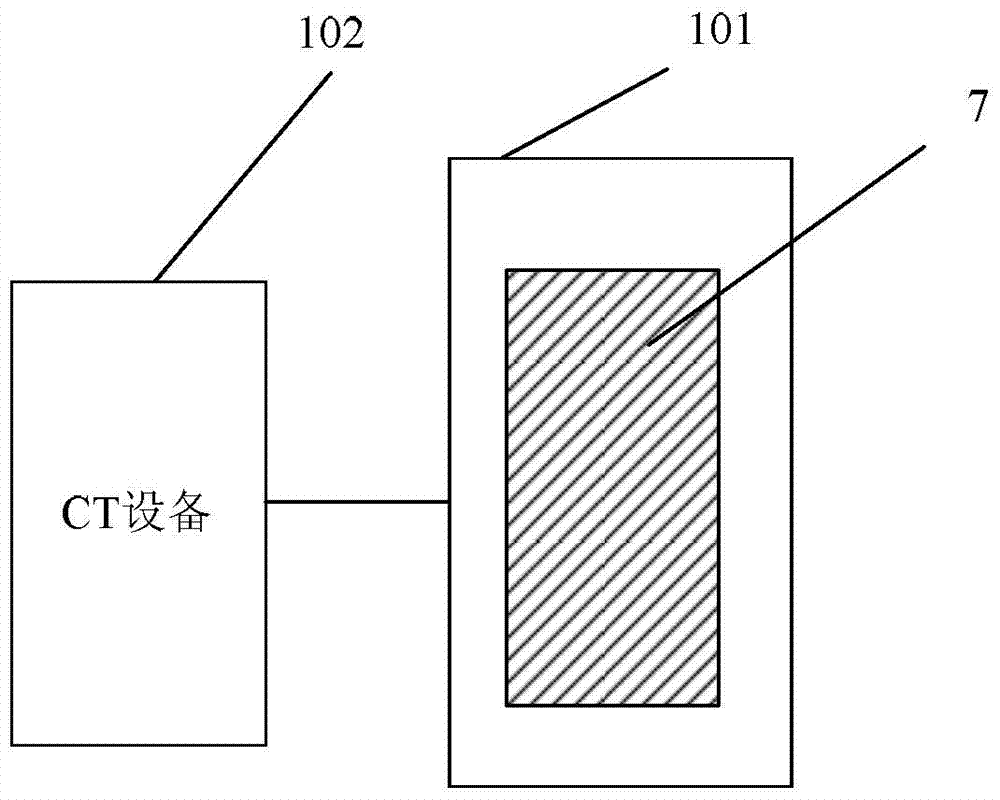
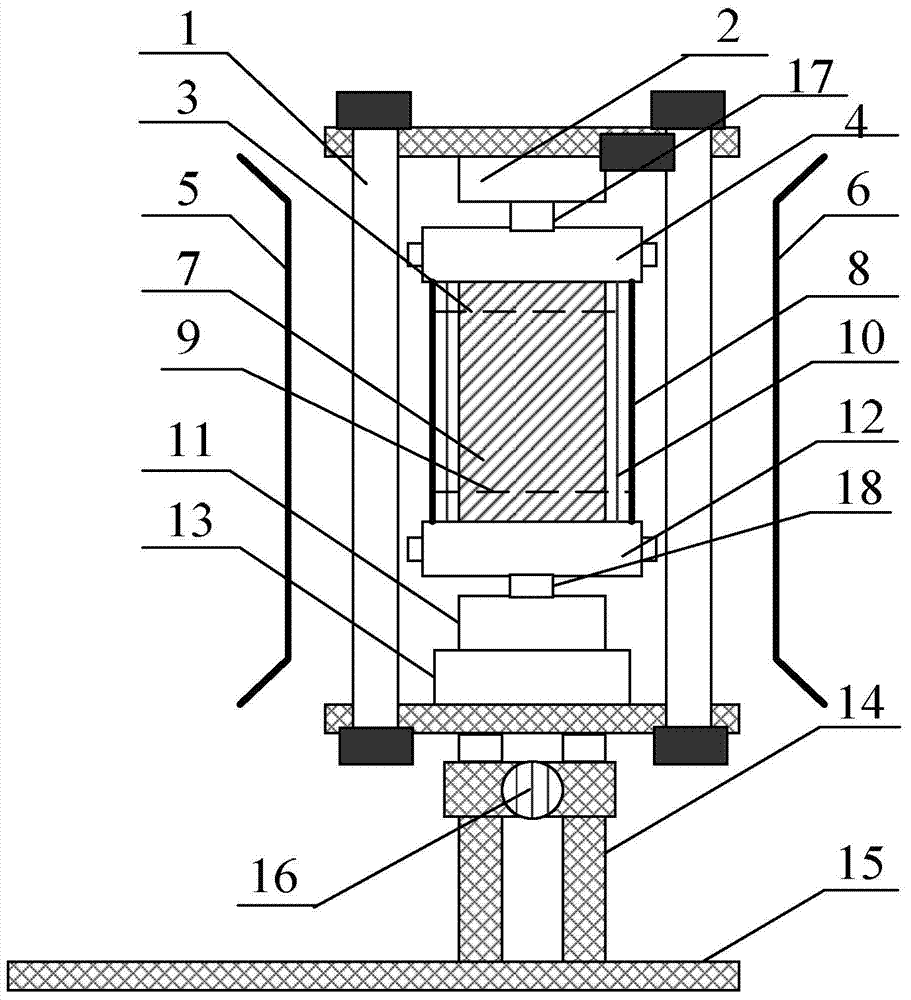
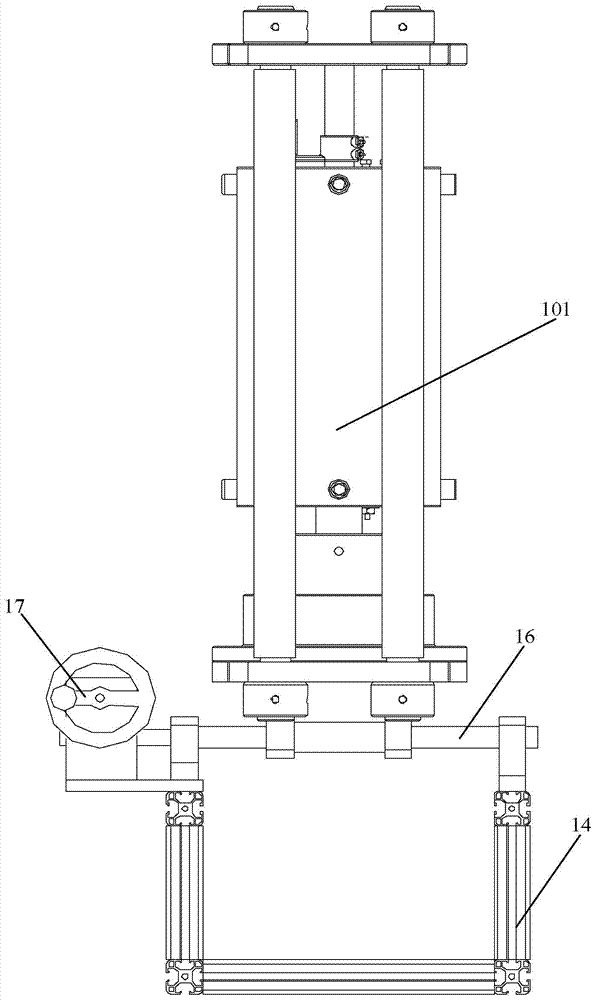
Rock performance evaluating device
ActiveCN103868801AEnables strain measurementSimple strain measurementMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesRock coreComputing tomography
The embodiment of the invention provides a rock performance evaluating device. The device comprises a pressure chamber and a CT (computed tomography) device, wherein the pressure chamber is a sealed cavity body, is positioned in the scanning range of an X-ray computerized tomography CT device, and is used for providing preset testing temperature and preset testing pressure for a rock core test specimen, wherein the preset testing temperature is higher than a first threshold, and the preset testing pressure is higher than a second threshold; the CT device is used for scanning the rock core test specimen to acquire image information of the internal structure of the rock core test specimen at different time, and analyzing according to the image information so as to obtain a strain curve of the rock core test specimen. The embodiment of the invention prevents the situation that the rock strain is measured by a sensor at high temperature, thereby measuring the rock strain simply and accurately at high temperature.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for performing non-destructive detection on evolution of three-dimensional carbonation depth of cement-based material through X-ray scanning
InactiveCN102590242AIntegrity guaranteedGuaranteed accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationPorosityObject based
The invention provides a method for performing non-destructive detection on evolution of the three-dimensional carbonation depth of a cement-based material through X-ray computerized tomography and relates to a novel detection method for the carbonation depth of a cement-based material. The main principle is that: an image is reconstructed by acquiring ray attenuation information of a rotary object based on an X-ray source; a carbonized region and a non-carbonized region of the cement-based material are distinguished according to difference of gray value; and the defects in the traditional pHmethod of phenolphthalein alcohol solution are overcome. Under the condition of not damaging a test piece, the evolution process of the three-dimensional carbonation depth of the cement-based material along with the time is detected. By the method, flaw space distribution in the carbonation process, the flaw volume, the flaw closing area, the evolution law of porosity and hole dimensional distribution and the topological properties, such as connectivity, sinuosity and the like, of the hole can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and system for eliminating geometrical artifacts in CT (Computerized Tomography) image
InactiveCN102652674APrecise removal of geometric artifactsEliminate geometric artifactsComputerised tomographsTomographyComputed tomographyGray level
The invention relates to a method and system for eliminating geometrical artifacts in a CT (Computerized Tomography) image. The method comprises the following steps of: performing CT scanning on a die body to obtain the projection coordinate of the mass center of the die body on a CT detector; defining geometrical parameters according to the projection coordinate of the mass center of the die body on the CT detector, and substituting the geometrical parameters in a reconstruction formula, wherein the geometrical parameters include: a distance h of a projection point of the turntable rotating center on the detector and a center of the detector, an included angle alpha between an ideal position of a straight line where the detector id and an actual position, and a distance SDD between the projection point of the turntable rotating center on the detector and an X ray source focus; performing CT scanning on an object to be imaged to obtain fan-beam projection parameters of the object to be imaged; and processing the fan-beam projection parameters of the object to be processed by the reconstruction formula to obtain CT image data of the object to be imaged and further obtain a CT image with the CT image data of the object to be imaged serving as a gray level. According to the technical scheme, the method and the system can be used for accurately obtaining the CT image without the geometrical artifacts.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Iterative reconstruction for x-ray computed tomography using prior-image induced nonlocal regularization
ActiveUS20160055658A1Improve current low-dose image qualityOptimize objective functionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionSuccessive over-relaxationImage estimation
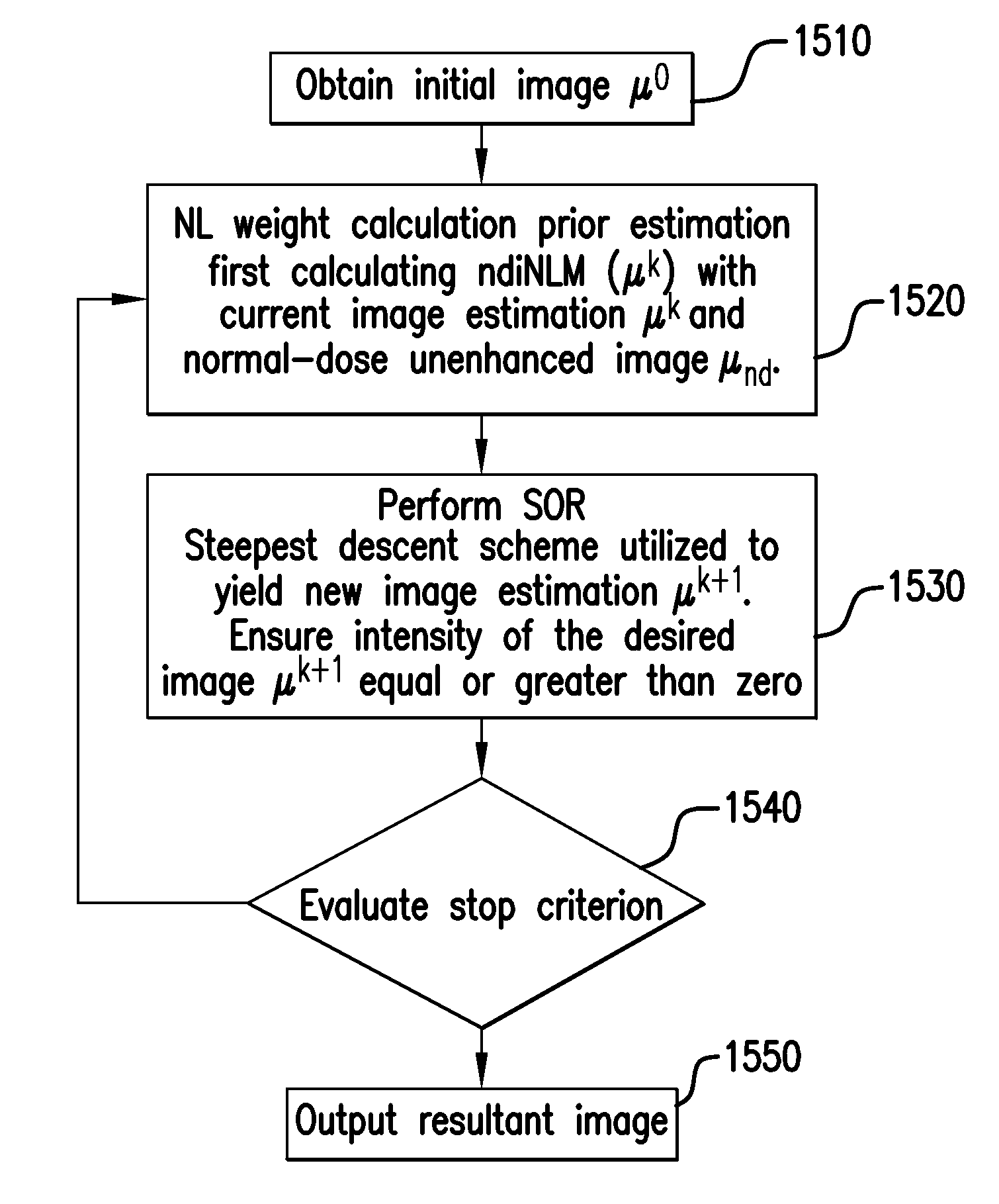
Disclosed is a method for performing X-ray Computed Tomography scanning, the method including acquiring a plurality of images of an object, obtaining an initial image from the plurality of images, calculating NonLocal weight of the initial image, utilizing a current image estimation and registered prior image, performing a successive over-relaxation optimization to yield a new image estimation with an intensity of the new image estimation equal or greater than zero, performing a cycle update, generating an image of the object utilizing the new image estimation obtained from the optimization, and outputting a resultant image.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
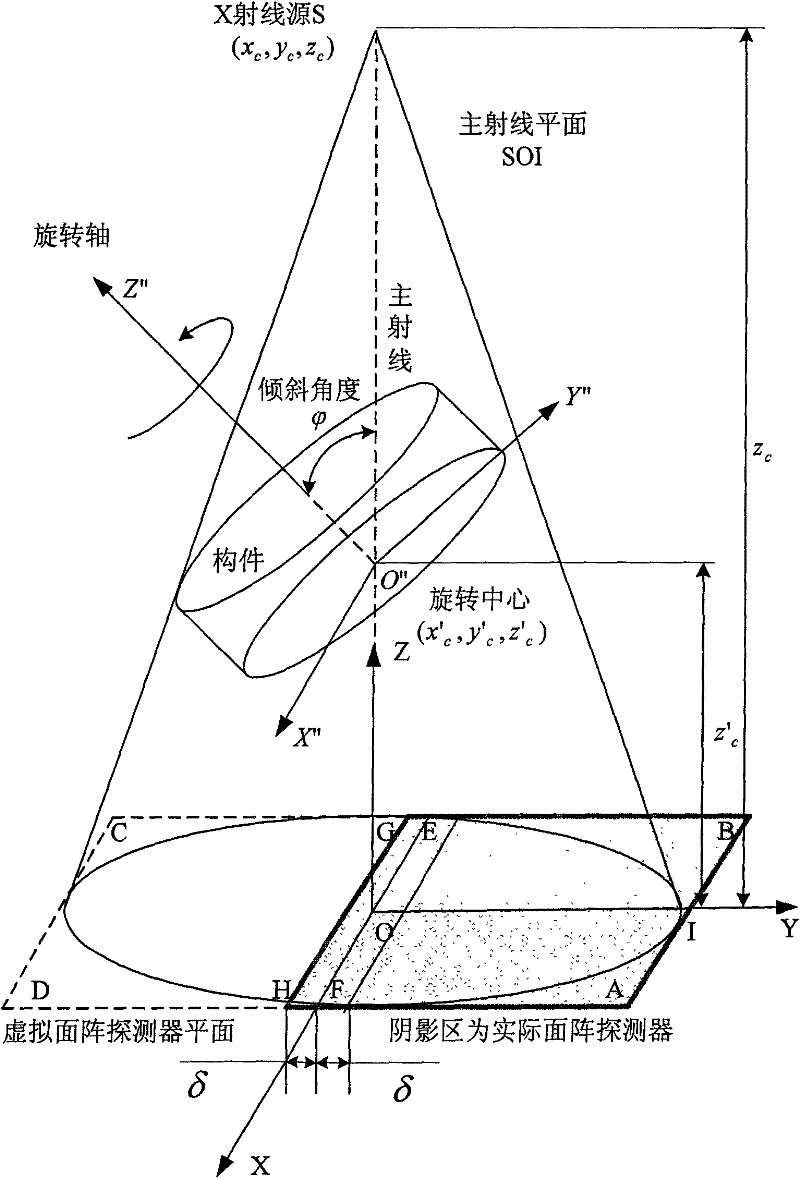
Three-dimensional digital imaging method of large view field cone-beam X-ray tilting scanning of biased detector
InactiveCN101634638AExpanded imaging field of viewImprove detection efficiencyComputerised tomographsTomographyDigital imagingPretreatment method
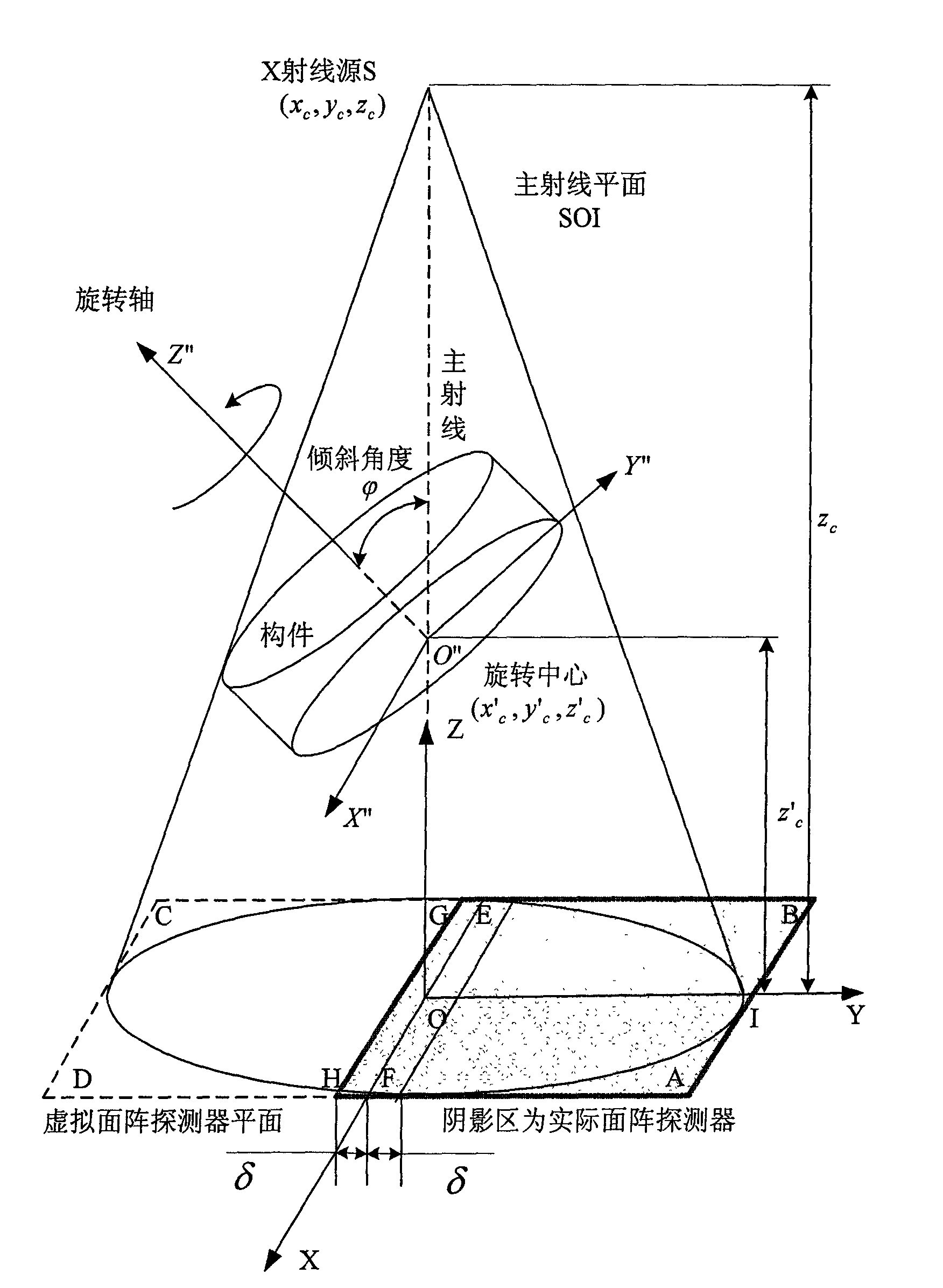
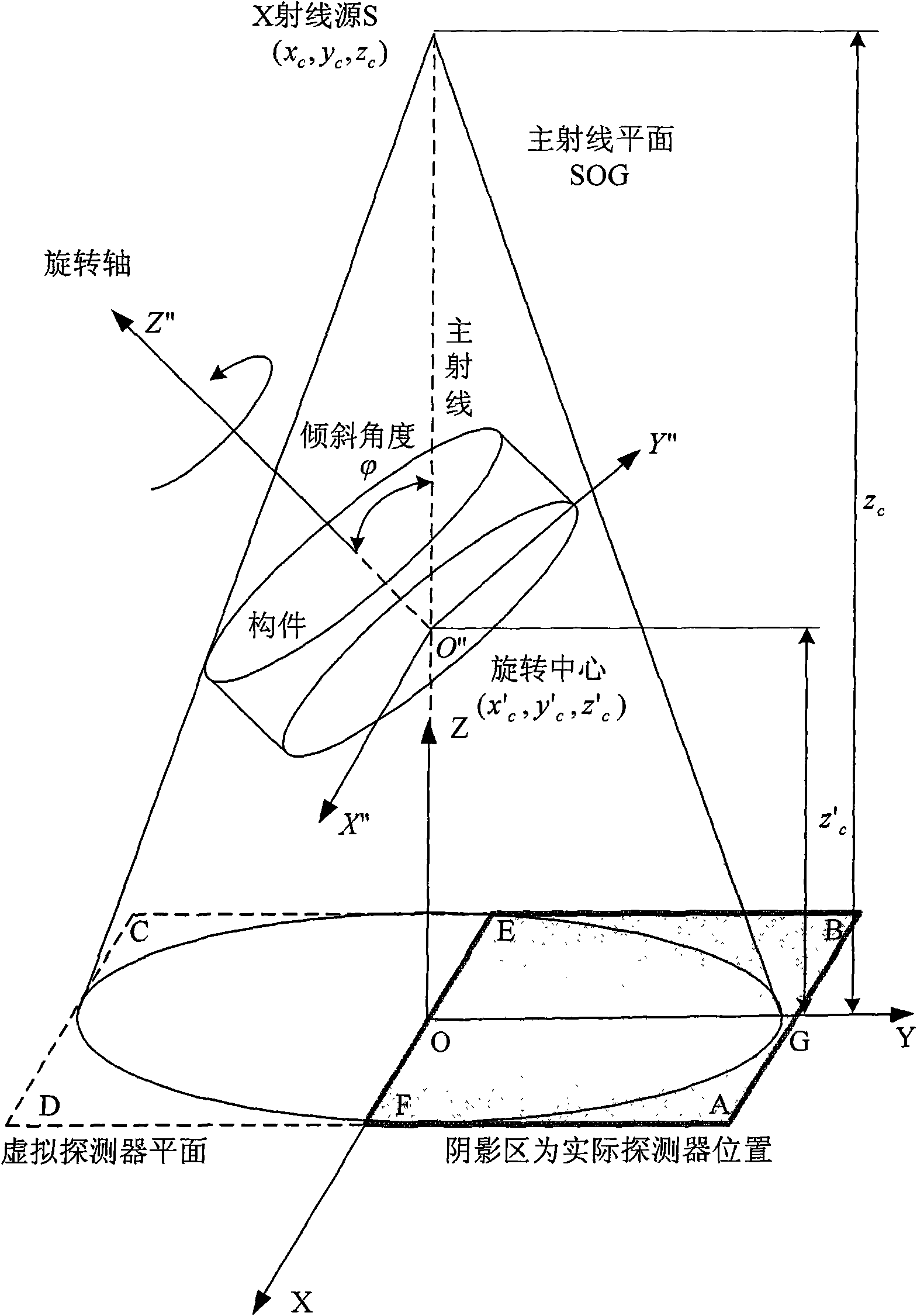
The invention relates to a three-dimensional digital imaging method of the large view field cone-beam X-ray tilting scanning of a biased detector, belonging to the technical field of X-ray computerized tomography (CT). In the three-dimensional digital imaging method, the area array detector is placed to be biased, and an X-ray source is used for generating cone-beam X-rays which irradiate a member imaging area with a certain angle in a penetrating and tilting way relative to the length and width surface of a member; in the scanning process, the X-ray source and the area array detector are static, the member rotates in an angle of 360 degrees in an equal angle and step length way surrounding a rotating shaft, and the area array detector acquires an X-ray signal modulated by the member under each rotation angle. A three-dimensional computerized tomography image of a scanning area can be reestablished and obtained by a data truncation smoothing preprocessing method and a filtering back projection reestablishing arithmetic according to data obtained by the area array detector under the scanning angle of 360 degrees. Compared with the traditional tilting scanning method, the three-dimensional digital imaging method can double the tilting scanning imaging view field without changing the system hardware and the scanning speed and has high reestablishment quality, simple process and high efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for X-ray image correction
ActiveUS20050047552A1Accurate collectionFast dataMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray image
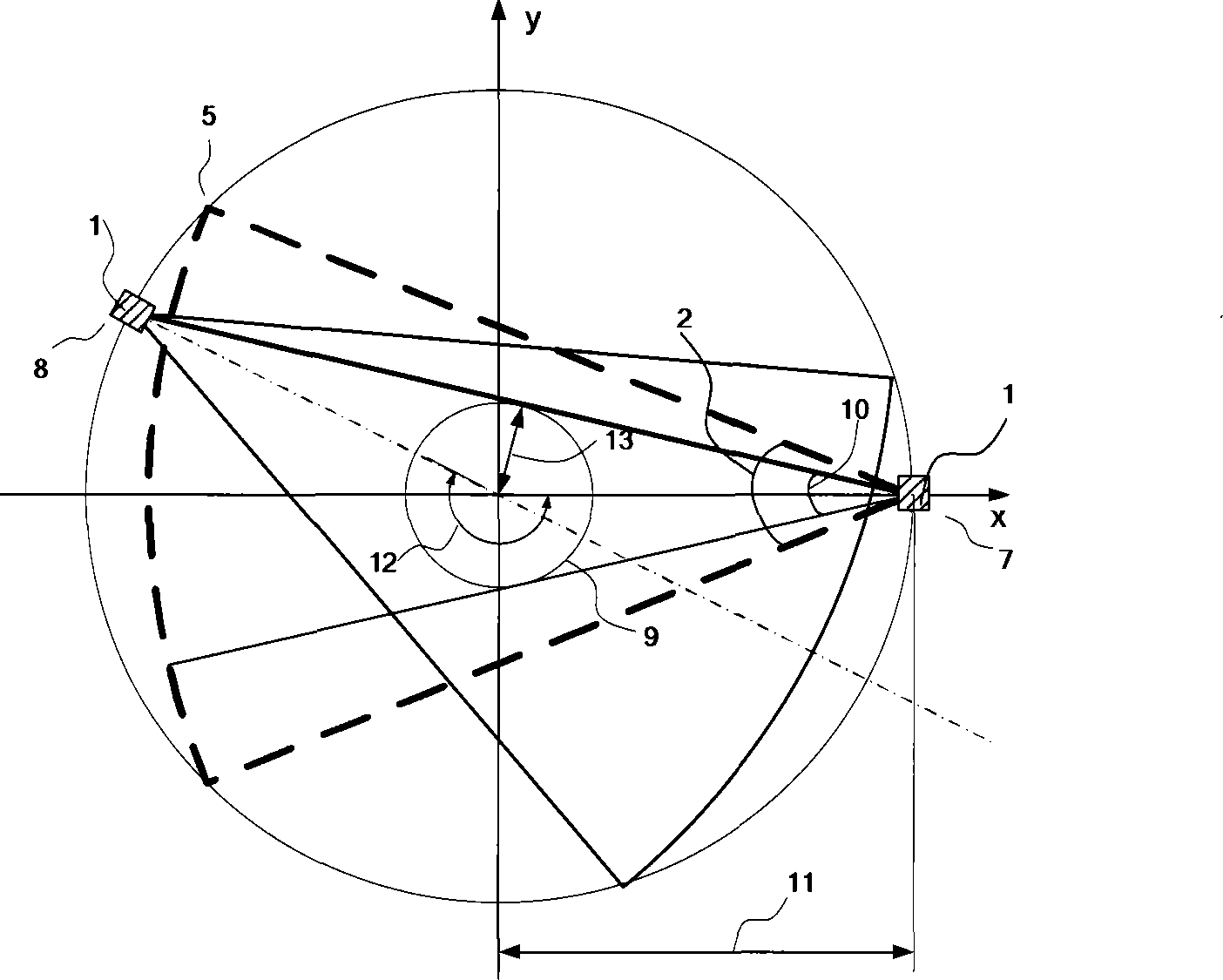
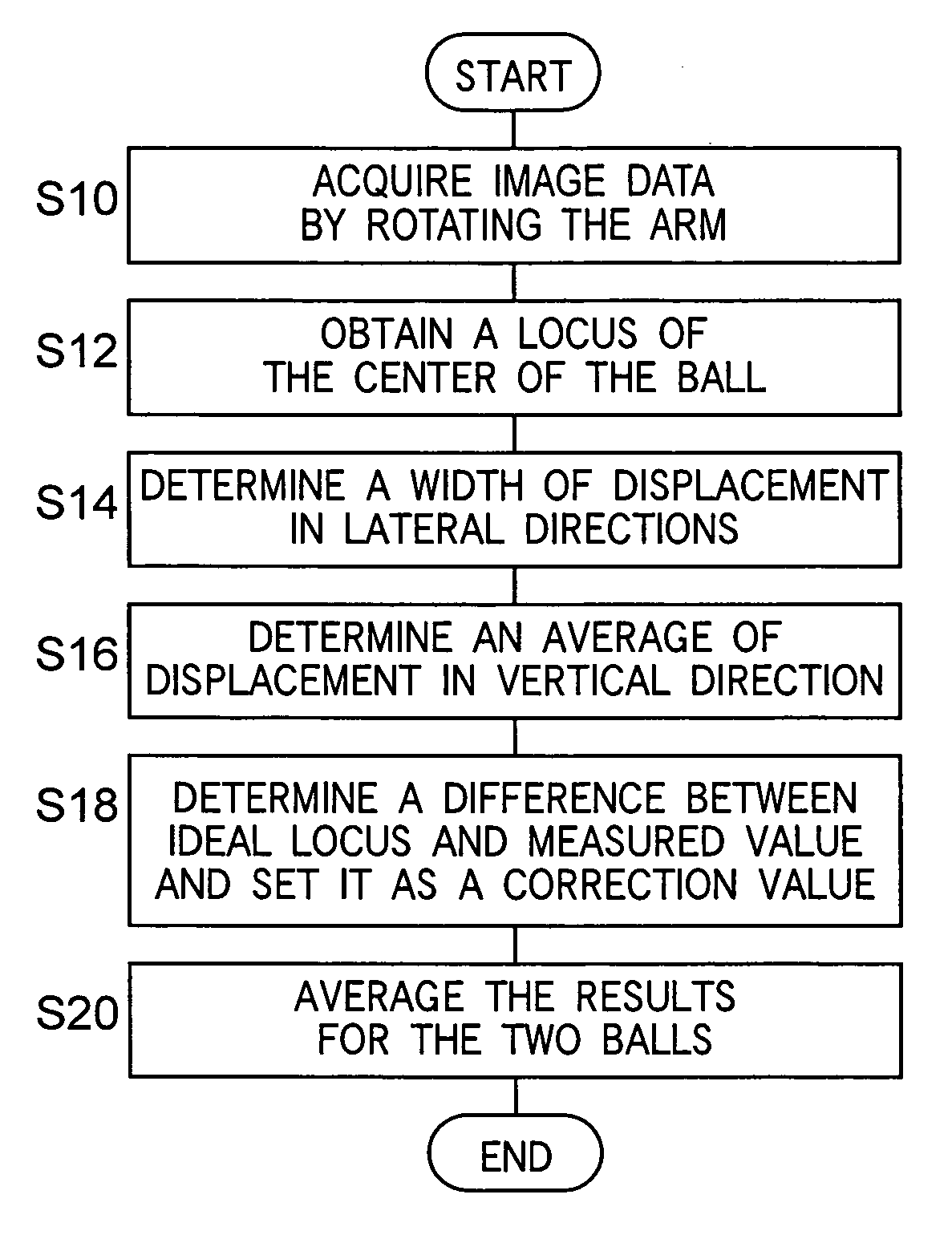
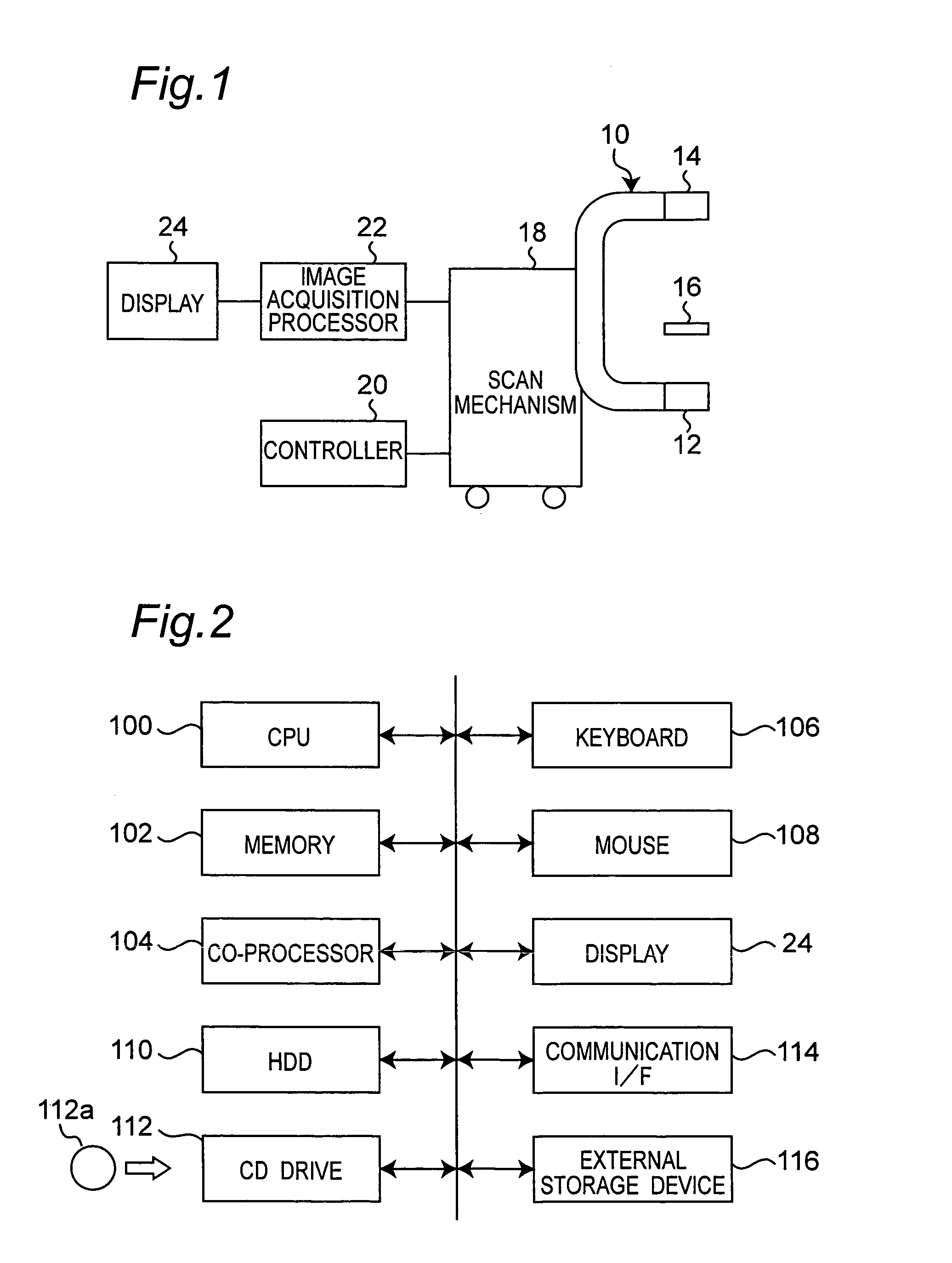
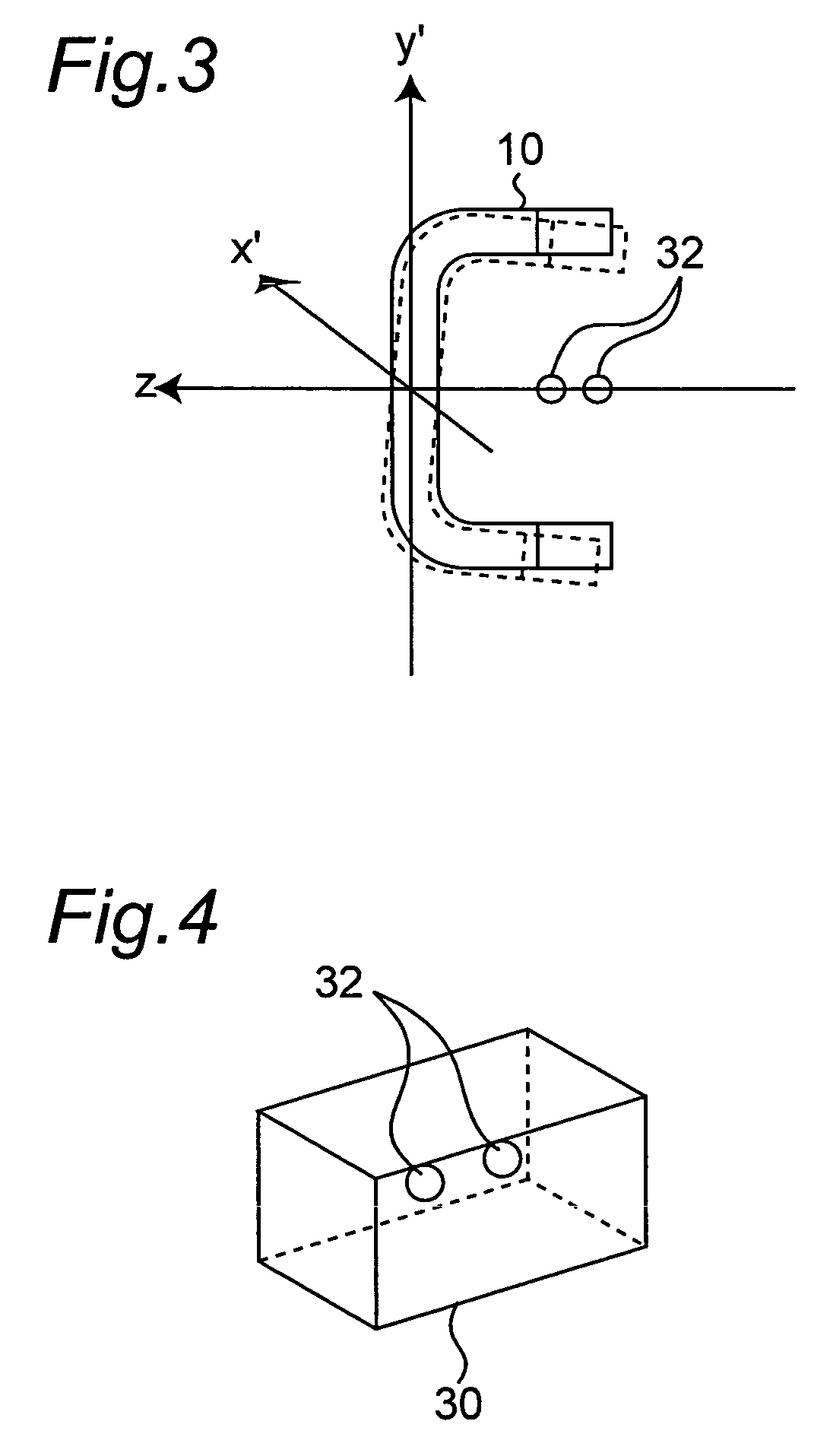
In an X-ray computerized tomography scanner, a correction phantom embedding an X-ray absorbing object is put on or around a non-vertical rotary axis between an X-ray source and a two-dimensional X-ray detector, and two dimensional imaging data of the phantom is acquired. Then a locus of the X-ray absorbing material is determined in the two-dimensional imaging data, and based on the locus an ideal locus is obtained in the direction of the rotary axis. Next, a difference between the calculated position of the ideal locus and a measured position is determined in the direction of the rotary axis. The difference is used to correct deviation in the direction of the rotary axis.
Owner:NIHON UNIVERSITY
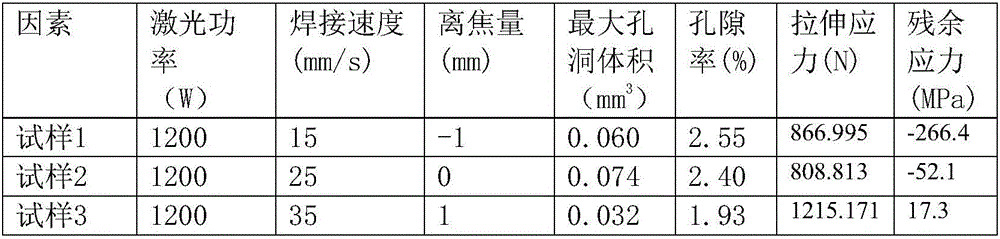
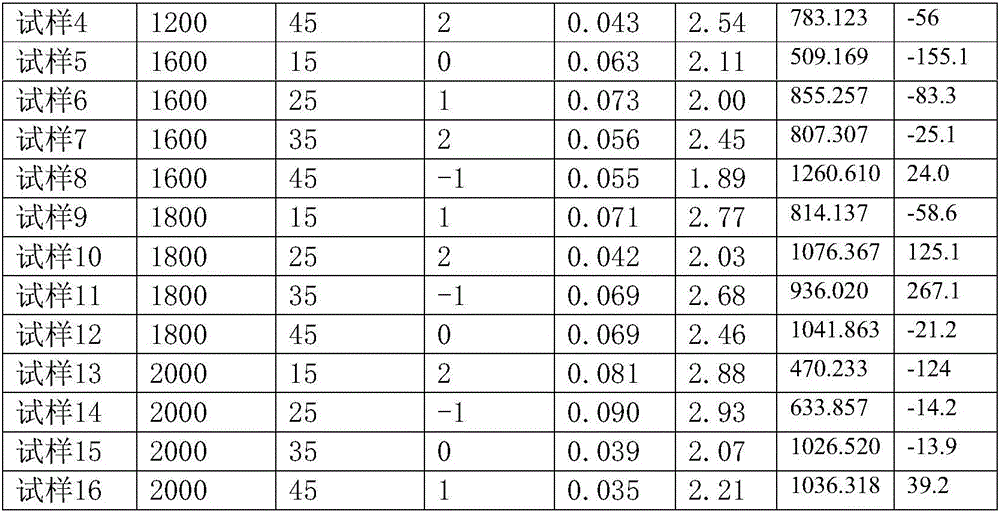
Nondestructive testing method of three-dimensional shape and stress characteristics of internal defects of metal welding seam
ActiveCN106770394AIntegrity guaranteedGuaranteed accuracyMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationPorosityElement analysis
The invention discloses a nondestructive testing method of a three-dimensional shape and stress characteristics of internal defects of a metal welding seam. According to the nondestructive testing method, with combination of an X-ray computed tomography scanning technology and a finite element analysis technology, the three-dimensional shape and the stress characteristics of the internal hole defects of the dissimilar metal welding seam can be tested under the condition without destroying a test piece. The method can also be used for obtaining space distribution, the hole size, the porosity, a pore-size distribution evolution law and the hole topological performance such as information including connectivity and tortuous degree of the internal hole defects of the dissimilar metal welding seam. The nondestructive testing method comprises the following steps: preparing a sample, scanning the test sample piece to acquire a scanned picture, recording a corresponding metal welding parameter, processing acquired scanned picture information, rebuilding a three-dimensional model, and testing and verifying the three-dimensional model by carrying out model mechanical analysis.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
X-ray computerized tomography system and method
ActiveCN102397078AReduce X-ray doseEasy to implementComputerised tomographsTomographySoft x rayImage resolution
The invention discloses an X-ray computerized tomography system, which is used for partially scanning an object to be detected. The system comprises a middle angle computing module, a rebuilding angle computing module and a scanner, wherein the middle angle computing module is used for computing a middle angle according to the size of the vision field cross section and the central coordinate of the object to be detected, and transmitting the middle angle to the rebuilding angle computing module; the rebuilding angle computing module is used for adding the middle angle to 180 degrees to obtain a rebuilding angle, and transmitting the rebuilding angle to the scanner; and the scanner is used for scanning a part of the object to be detected according to the rebuilding angle. The invention further discloses an X-ray computerized tomography method. Due to the adoption of the system and the method, the scanning time can be shortened, the time resolution can be increased, and the radiation dosage received by a patient can be reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS SHANGHAI MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
Wide visual field cone-beam X ray oblique scanning three-dimension digital imaging method based on algebraic reconstruction algorithm
InactiveCN101672806AImprove reconstructed image qualitySmall feature aliasing between layersMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSpecific gravity measurementSoft x rayVisual field loss
The invention belongs to the technical field of X ray computerized tomography (CT), and particularly relates to a wide visual field cone-beam X ray oblique scanning three-dimension digital imaging method based on an algebraic reconstruction algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring two-dimension projection data of a scanned component in detector biasing wide visual field cone-beam X ray oblique scanning way; and rebuilding an image by the algebraic reconstruction algorithm to obtain a three-dimension computerized tomography image in a scanning area. Compared with the widevisual field cone-beam X ray oblique scanning three-dimension digital imaging method based on a filter back projection algorithm, the method can effectively inhibit structure aliasing between layers and obviously improve the quality of the rebuilt picture in the condition that the system hardware, the scanning view field and the scanning speed are not changed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
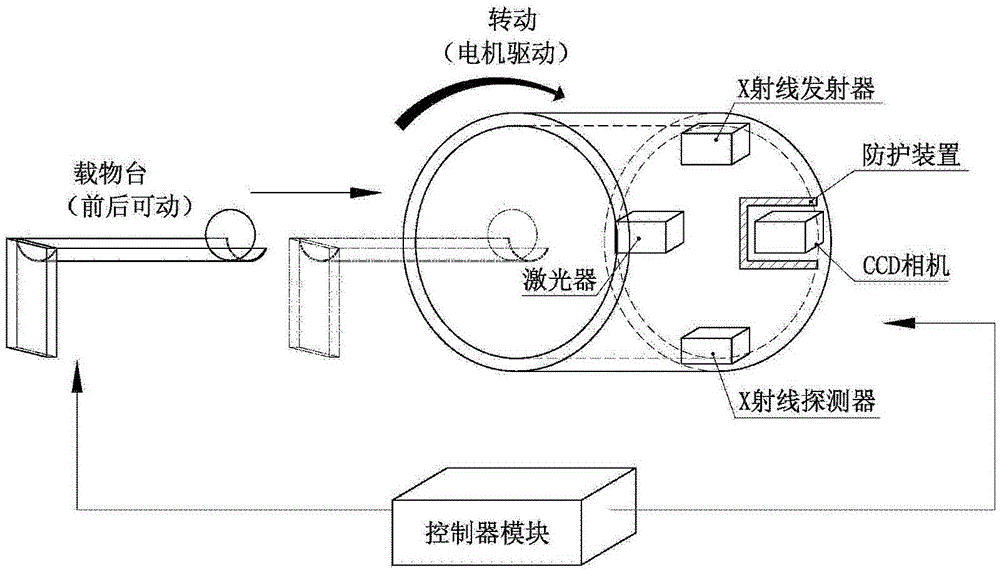
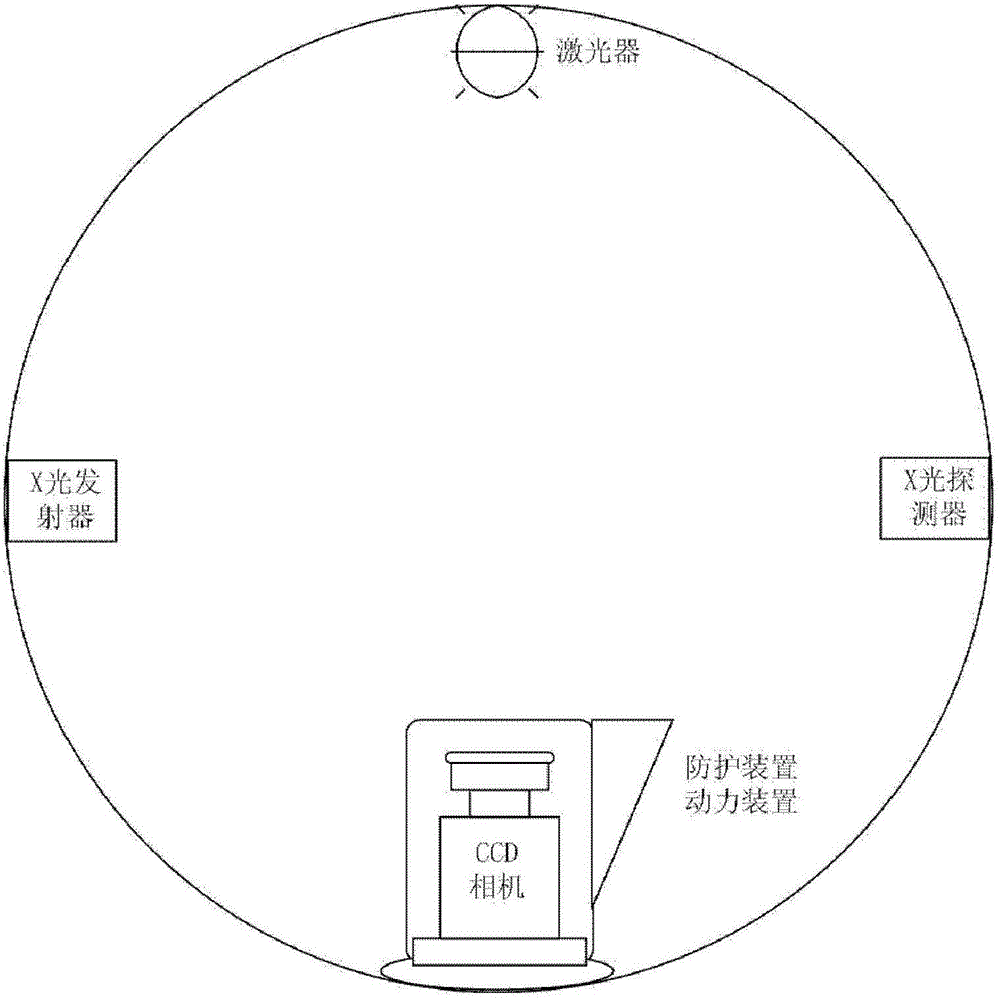
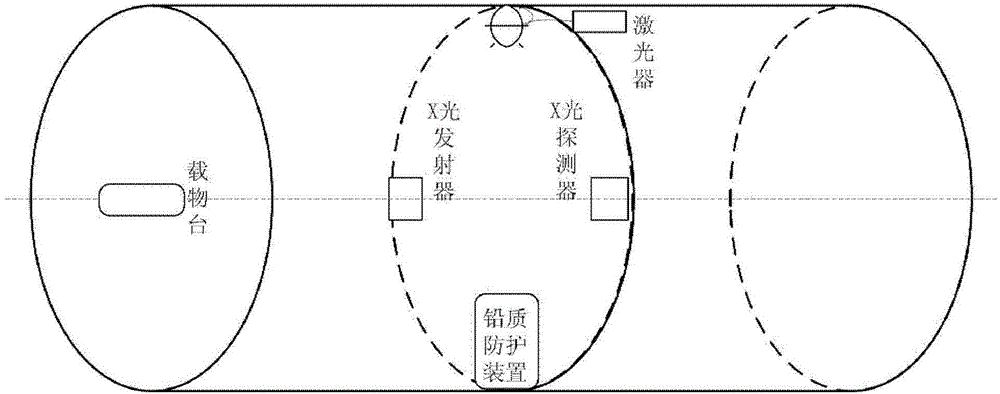
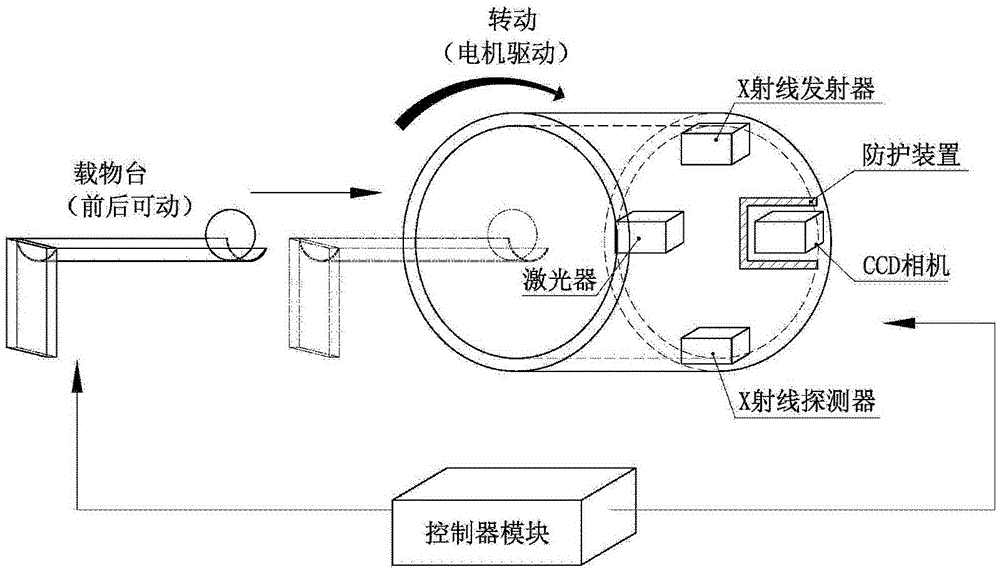
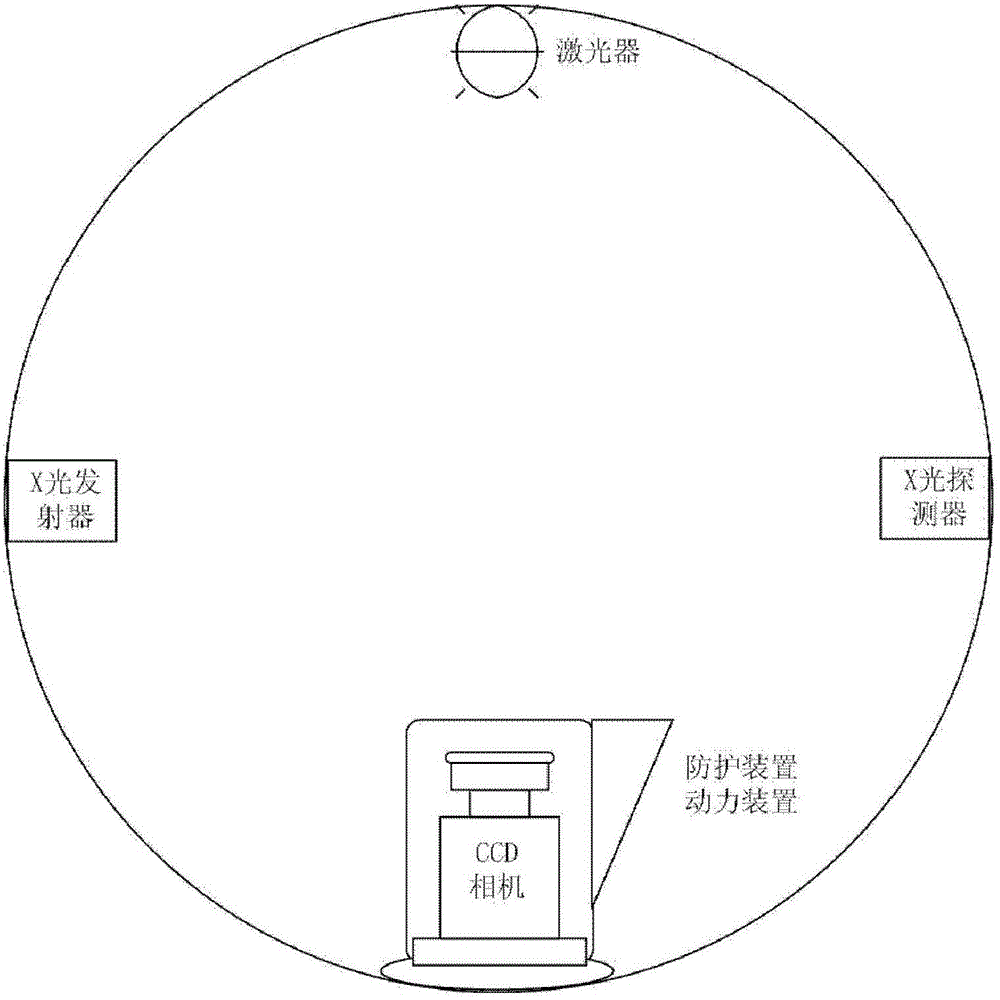
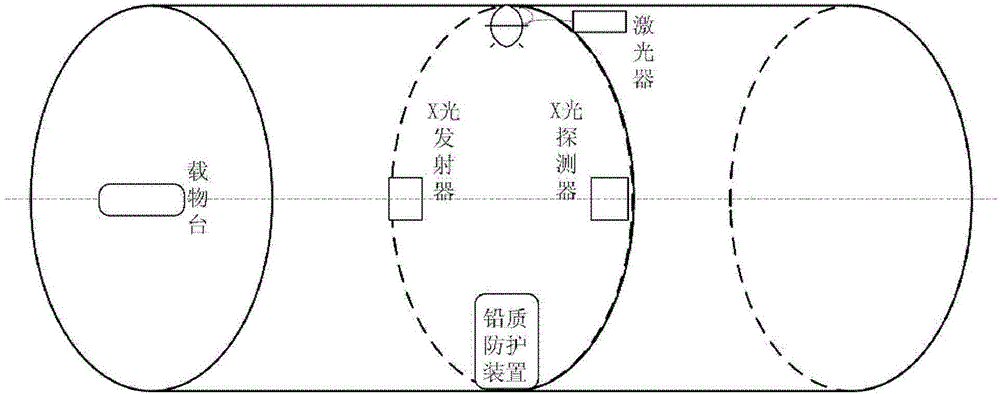
Automatically radiation-proof FMT-and-CT dual-mode imaging system
ActiveCN103330549AEffective protectionAvoid damageComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringRapid imagingTransport system
The invention discloses an automatically radiation-proof FMT-and-CT dual-mode imaging system. The automatically radiation-proof FMT-and-CT dual-mode imaging system comprises a signal collecting module, a controller module, a data transmission module, a power module and an automatically radiation-proof module, wherein the signal collecting module is used for collecting fluorescence excitation imaging data and X-ray computerized tomography data of an imaging sample, the controller module is used for controlling operation, parameter setting, data processing and data storage of other modules, the data transmission module is used for transmitting internal data of the system, the power module is used for providing electricity for the whole system, and the automatically radiation-proof module is used for protecting a CCD camera and reducing damage caused by X-rays to the CCD camera. The automatically radiation-proof FMT-and-CT dual-mode imaging system can achieve dual-mode rapid imaging of FMT and CT, and due to the fact that the automatically radiation-proof module is designed, when an X-ray power source is turned on, the CCD camera is effectively protected, and damage to an internal sensitization chip can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
X-ray tube assembly and x-ray computerized tomography scanner
InactiveCN104113976AReduce heat dissipationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesAir filterNonwoven fabric
According to one embodiment, an X-ray tube assembly includes a housing, an X-ray tube, a coolant to which at least a part of heat generated by the X-ray tube is transferred, a circulation channel through which the coolant is circulated, a circulation pump, a radiator, an air filter and a fan unit. The air filter is formed of a three-dimensional nonwoven fabric that is formed of irregularly tangled resin fibers and provides a three-dimensional structure having a spatial volume ratio of not less than 93%. The air filter permits air to pass therethrough to eliminate dust from the air.
Owner:TOSHIBA ELECTRON TUBE & DEVICES
X-ray computerized tomography system and method
ActiveCN102397080AReduce exposureAvoid overshadowingComputerised tomographsTomographySoft x rayX-ray
The invention discloses an X-ray computerized tomography system and an X-ray computerized tomography method. The system comprises an X-ray tube, a collimator, a detector, a computing assembly and an adjusting assembly, and is used for shooting a plurality of circular sections of an object to be detected in the scanning direction, wherein the detector comprises a plurality of detector channels; the X-ray tube, the collimator and the detector rotate synchronously around the object to be detected; the collimator is a collimator with an adjustable opening; the computing assembly is used for computing the opening width of the collimator needed for irradiating each circular section respectively, and transmitting the opening width to the adjusting assembly; and the adjusting assembly is used for adjusting the opening of the collimator according to the opening width. The invention further discloses the X-ray computerized tomography method. Due to the adoption of the system and the method, extra exposure of the surrounding area of the objected to be detected can be reduced, and the X-ray dosage received by a patient can be reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS SHANGHAI MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
X-ray computerized tomography apparatus, breathing indication apparatus and medical imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20100074394A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic measurementsSoft x rayTemporal change
An X-ray computed tomographic apparatus includes a gantry 100 including an X-ray tube 101 which generates X-rays and an X-ray detector 103 which detects X-rays transmitted through a subject to be examined, a reconstruction device 114 which generates tomogram data on the basis of an output from the X-ray detector, a breath detector 203 which detects a respiration waveform representing a temporal change in respiration index value associated with the subject, a regular respiration waveform generating unit 207 which generates a respiration waveform with a regular respiration cycle which originates from the detected respiration waveform, and a gantry mount display 201 which displays the generated regular respiration waveform.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method for determining and analyzing pore structure of saline-alkali soil
InactiveCN107941673ARapid determinationQuick calculationPermeability/surface area analysisAlkali soilSoil science
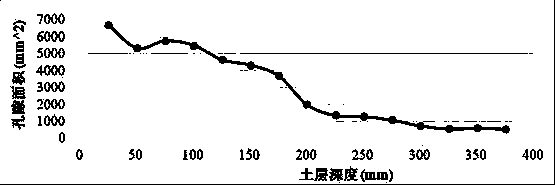
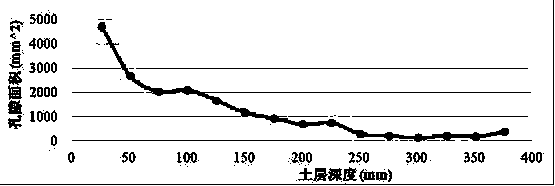
The invention relates to a method for determining and analyzing a pore structure of saline-alkali soil, and belongs to the field of soil structure determination and analysis method. The invention aimsto provide the method for determining the pore structure of the saline-alkali soil with no disturbance and no destruction and an application thereof, so as to solve the problem in the prior art thatsoil with macropore property cannot be measured under a condition without destroying soil. The method for determining and analyzing the pore structure of the saline-alkali soil includes the followingsteps: sample collection: selecting to-be-measured soil, knocking a sampling container into soil in a vertical direction, and collecting an original soil column; sample scanning: putting the originalsoil column into an X-ray computerized tomography scanner, and scanning; and image processing: inputting the scanned image of the cross section of the original soil column into a computer, and carrying out batch treatment on the image by the computer, to obtain the number and area of pores of the cross section of the original soil column. The spatial distribution of the macropore structure in thesoil column is more rapid, accurate and intuitive to determine and calculate.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Iterative reconstruction for X-ray computed tomography using prior-image induced nonlocal regularization
ActiveUS9558570B2Improve image qualityReconstruction from projectionImage generationSuccessive over-relaxationImage estimation
Disclosed is a method for performing X-ray Computed Tomography scanning, the method including acquiring a plurality of images of an object, obtaining an initial image from the plurality of images, calculating NonLocal weight of the initial image, utilizing a current image estimation and registered prior image, performing a successive over-relaxation optimization to yield a new image estimation with an intensity of the new image estimation equal or greater than zero, performing a cycle update, generating an image of the object utilizing the new image estimation obtained from the optimization, and outputting a resultant image.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Calibration method and device for hollow powder in metal powder
InactiveCN107831181AAccurately reflects hollow rateEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX Ray Computerized TomographyMetal powder
The invention relates to the field of 3D (three-dimensional) printing additive manufacturing and powder metallurgy, and provides a calibration method and device for hollow powder in metal powder. Themethod comprises the following steps of selecting and loading the same batch of quantitative metal powder into a container, obtaining a three-dimensional image of the metal powder loaded in the container by using an X-ray computerized tomography scan manner, analyzing holes in the three-dimensional image, judging spherical and near-spherical holes as the hollow powder of the metal powder, judgingother holes with irregular shapes as interspaces between powder, and obtaining a hollow rate of the metal powder according to the quantity of hollow metal powder and data of the three-dimensional image. By sampling and containing the quantitative metal powder through using the container, and then obtaining the three-dimensional image through X-ray computerized tomography scan, the hollow situationof all metal powder in a sample can be obtained, a detection result can be used for accurately embodying the hollow rate of the whole batch of metal powder, and the operation is simple and efficientin the whole detection process.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEINA ADDITIVE TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for X-ray image correction
ActiveUS7570734B2Accurate collectionFast dataMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
In an X-ray computerized tomography scanner, a correction phantom embedding an X-ray absorbing object is put on or around a non-vertical rotary axis between an X-ray source and a two-dimensional X-ray detector, and two dimensional imaging data of the phantom is acquired. Then a locus of the X-ray absorbing material is determined in the two-dimensional imaging data, and based on the locus an ideal locus is obtained in the direction of the rotary axis. Next, a difference between the calculated position of the ideal locus and a measured position is determined in the direction of the rotary axis. The difference is used to correct deviation in the direction of the rotary axis.
Owner:NIHON UNIVERSITY
Positron tomoscan and reconstruction methods
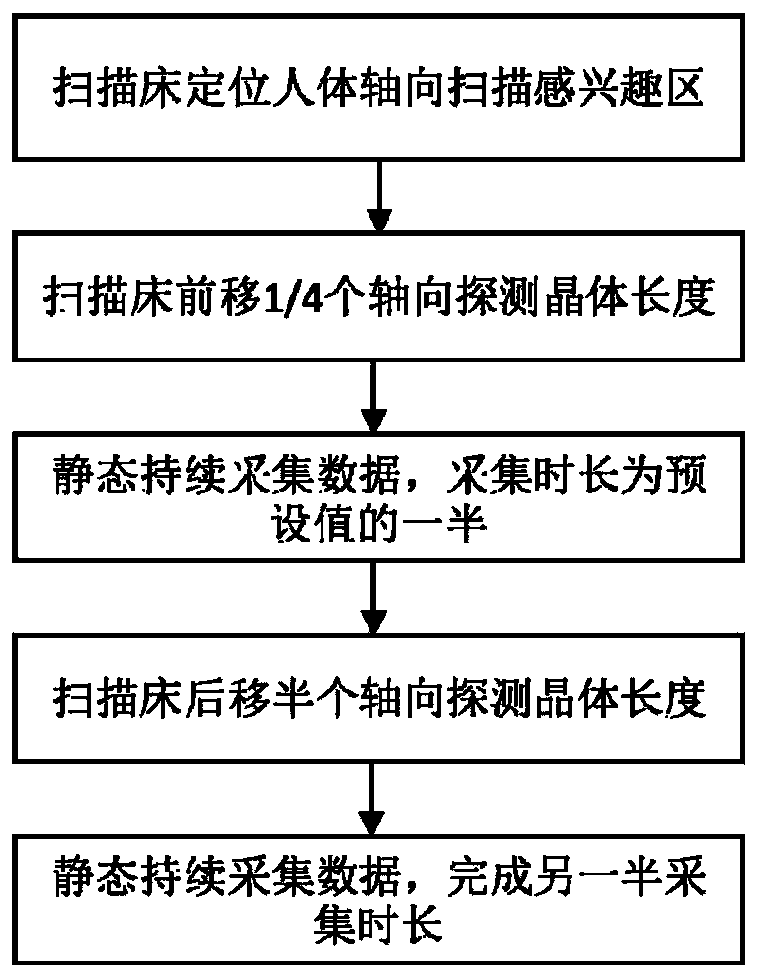
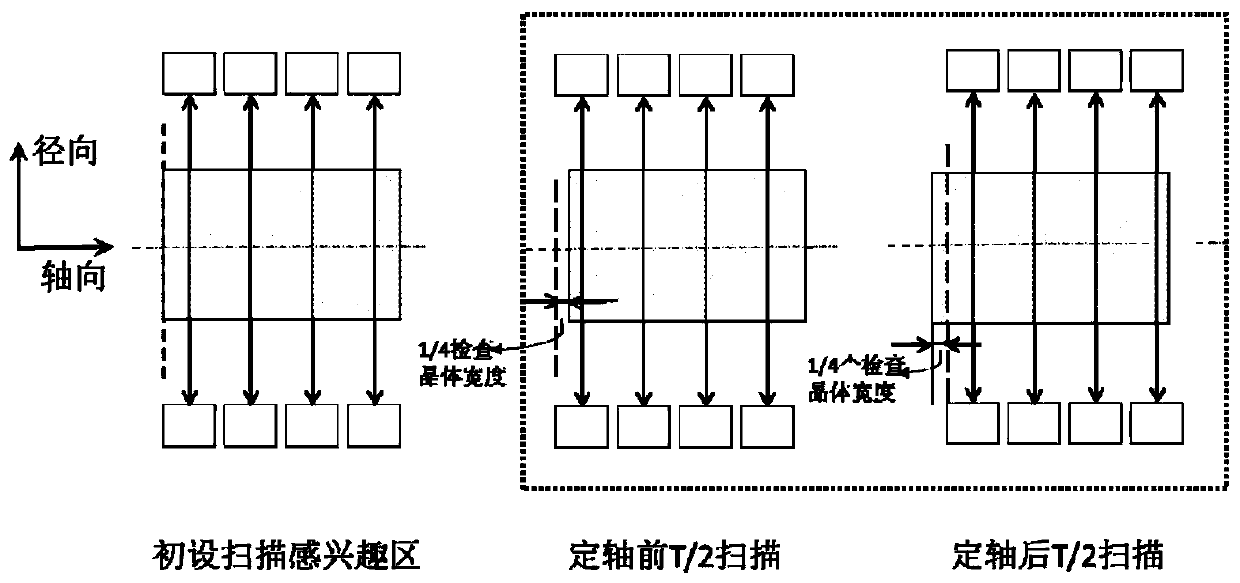
ActiveCN110559008ARich spatial informationIncrease spatial sampling rateComputerised tomographsTomographyReconstruction methodResolution rate
The invention provides a positron tomoscan method and a reconstruction method, and relates to the technical field of X-ray computed tomoscan imaging. The scanning method comprises the steps: a PET device is positioned to a predetermined axial region of interest; the axial region of interest is moved forward by 1 / 4 of the axial detector crystal width; the PET device starts to statically acquire data, and the continuous acquisition time is half of the preset single-bed scanning duration; the region of interest is moved backwards by half of the axial detector crystal width; and a static data acquisition task of remaining single-bed scanning time is completed. The reconstruction method comprises the step of combining two times of the scanning data on a coincidence event or on a sinogram. According to the scanning method, the positioning length of an original axial scanning region of interest is not changed; by controlling the small deviation of the scanning bed, two times of sub-scanning are carried out in the region of interest, the single scanning time is half of the original scanning time, and more fined spatial distribution information in the axial direction can be obtained, so that the axial imaging resolution rate of the PET system is improved.
Owner:FMI MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
X-ray low-dose computerized tomography (CT) image reconstruction method based on weighting alpha divergence constraint
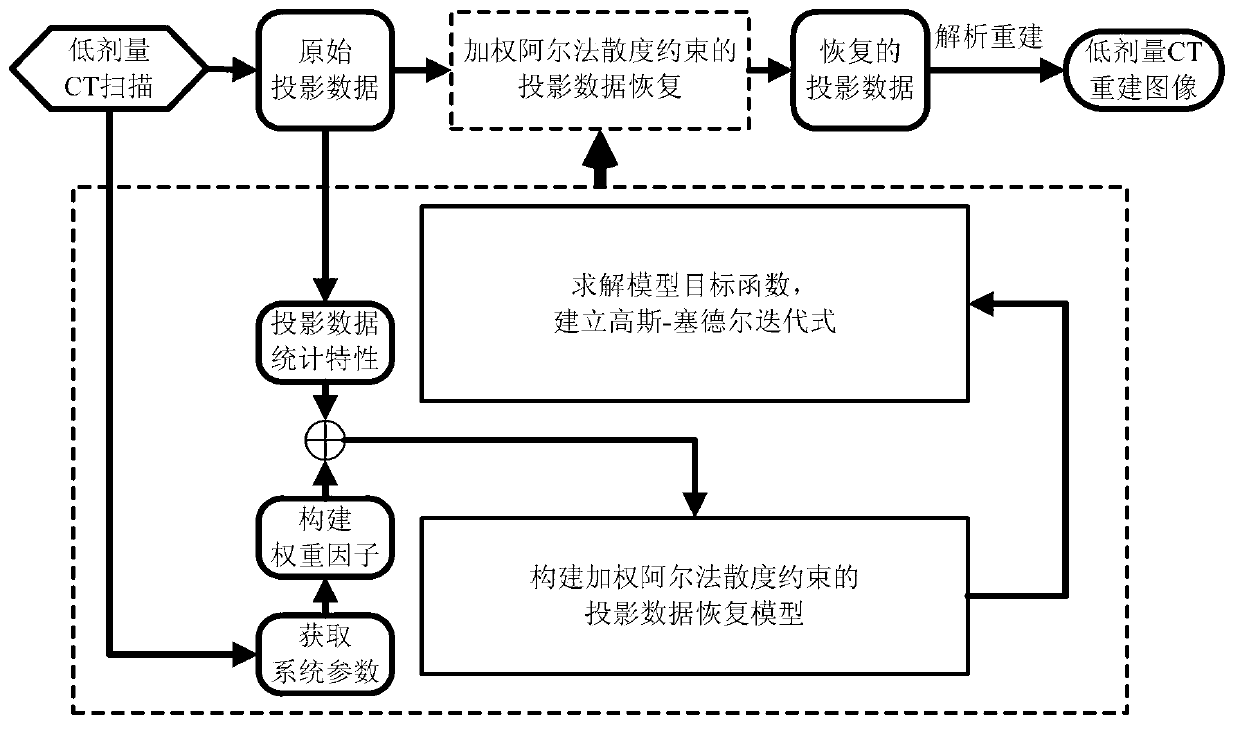
ActiveCN103136772AAchieving Quality RebuildsGuaranteed resolution2D-image generationX-rayReconstruction method
The invention discloses an X-ray low-dose computerized tomography (CT) image reconstruction method based on weighting alpha divergence constraint. The method comprises the steps of utilizing a CT imaging device to acquire low-dose CT projection data and an imaging system parameter; adopting alpha divergence measure as distance measure between original projection data with noise and projection data to be recovered, calculating the weight factor of the alpha divergence measure according to the acquired system parameter, and constructing a projection data recovering model based on the alpha divergence constraint; carrying out an objective function solution on the constructed projection data recovering model and establishing an iterative algorithm format; for the acquired low-dose CT projection data, carrying out an iteration solution on the projection data recovering model by means of the established iterative algorithm format; and carrying out image reconstruction on recovered projection data. The X-ray low-dose CT image reconstruction method based on the weighting alpha divergence constraint plays important roles in both noise suppression and edge preservation.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
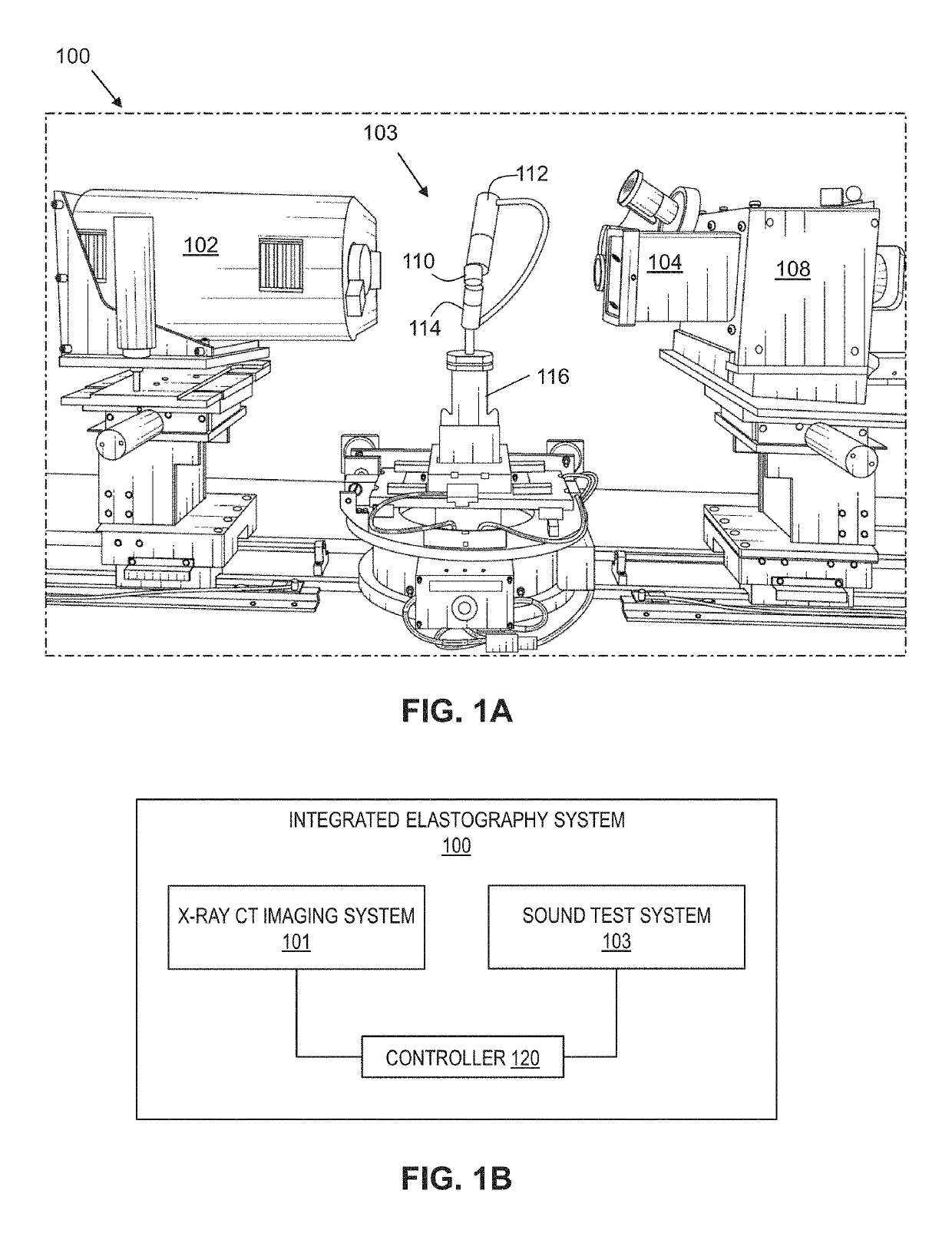
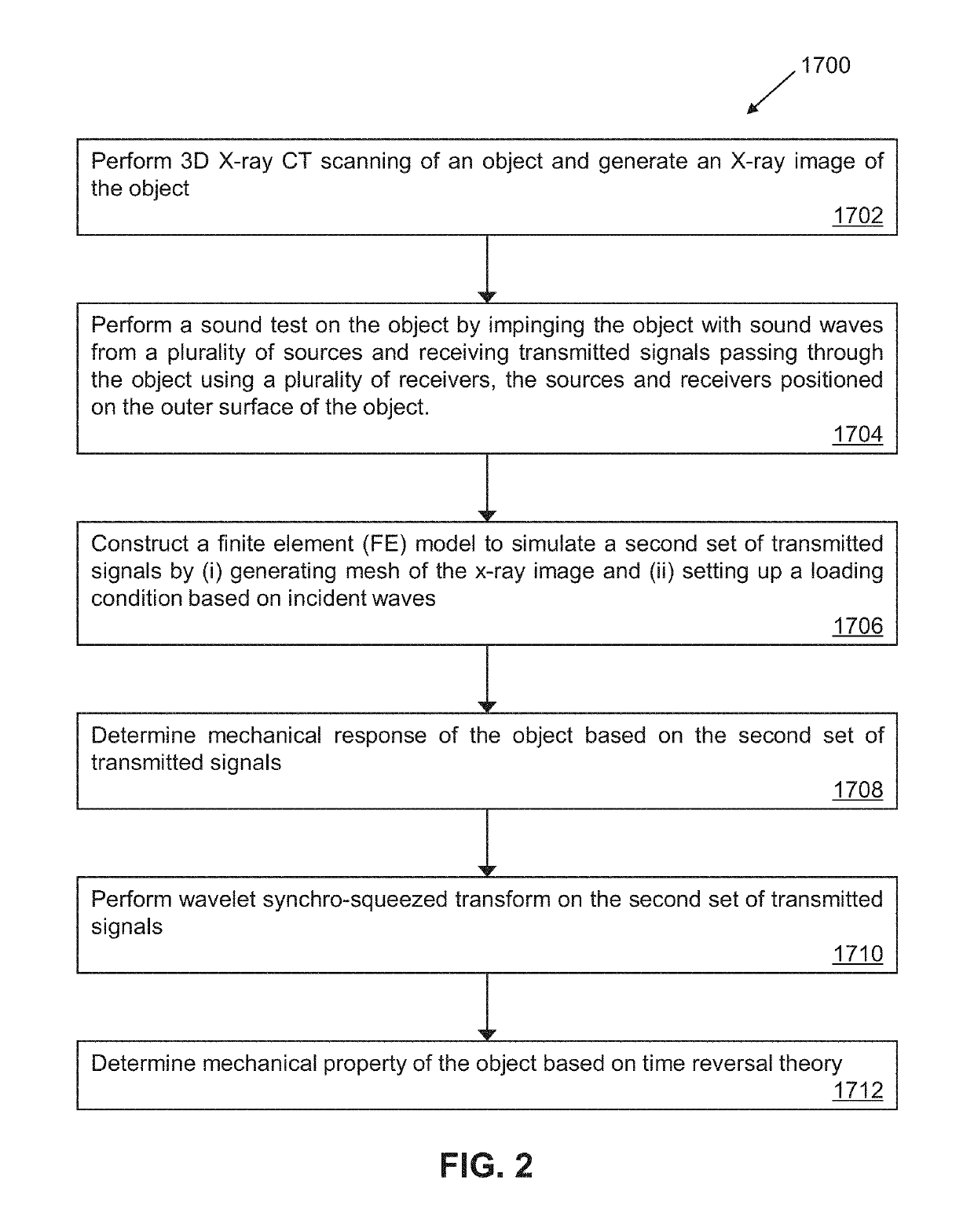
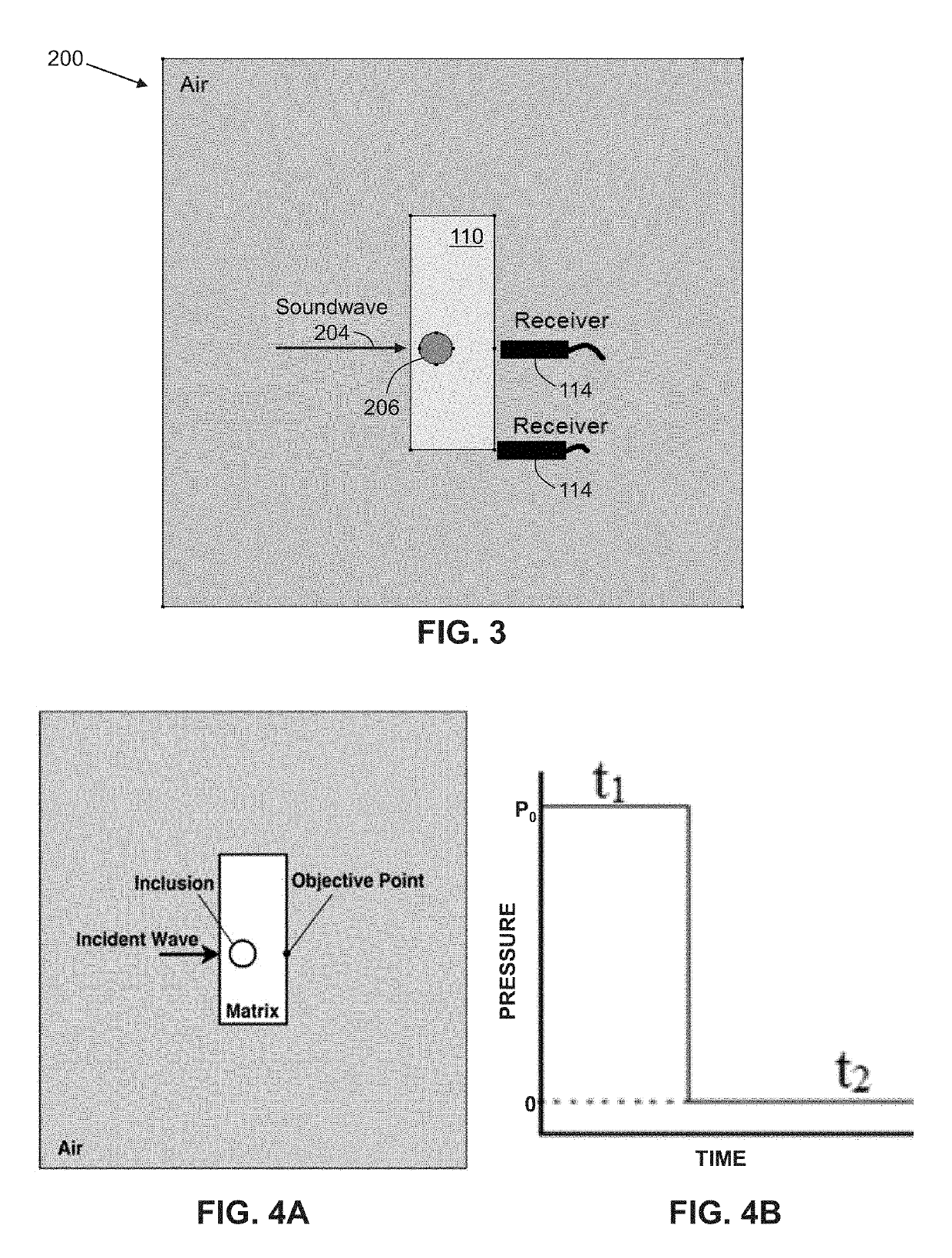
Elastography based on x-ray computed tomography and sound wave integration
ActiveUS20190313984A1Provide goodEliminate needImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAcoustic waveX Ray Computerized Tomography
Systems and methods for integrating a three-dimensional X-ray computed tomography system with an independent sound wave system to determine mechanical properties of tissue using signals from the sound wave system. Methods are disclosed that generate a numerical simulation and take the transmitted wave signals as the optimization objective to estimate modulus distribution of the tissue. Further, the mechanical properties of the tissue are reconstructed based on an inverse algorithm.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
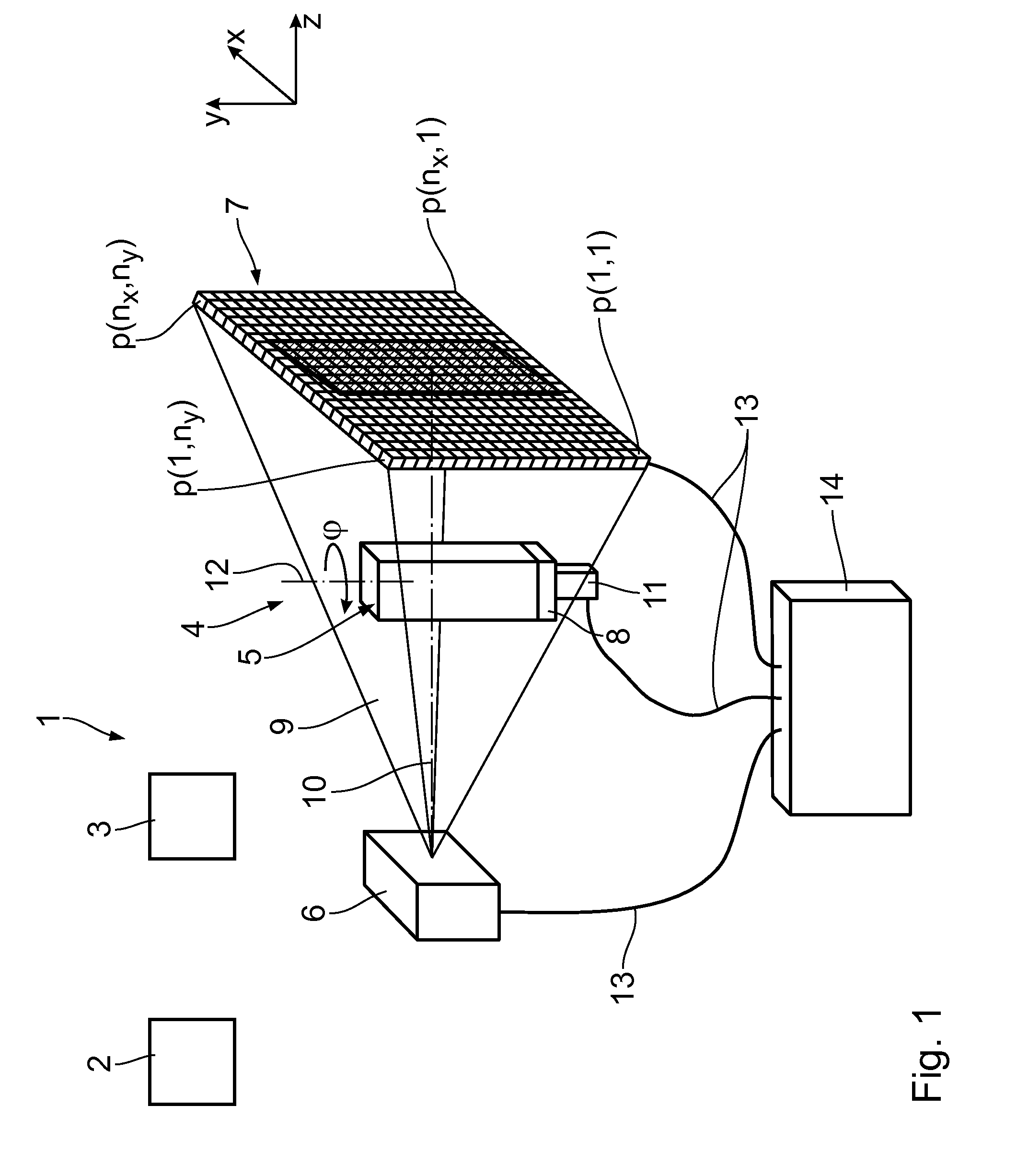
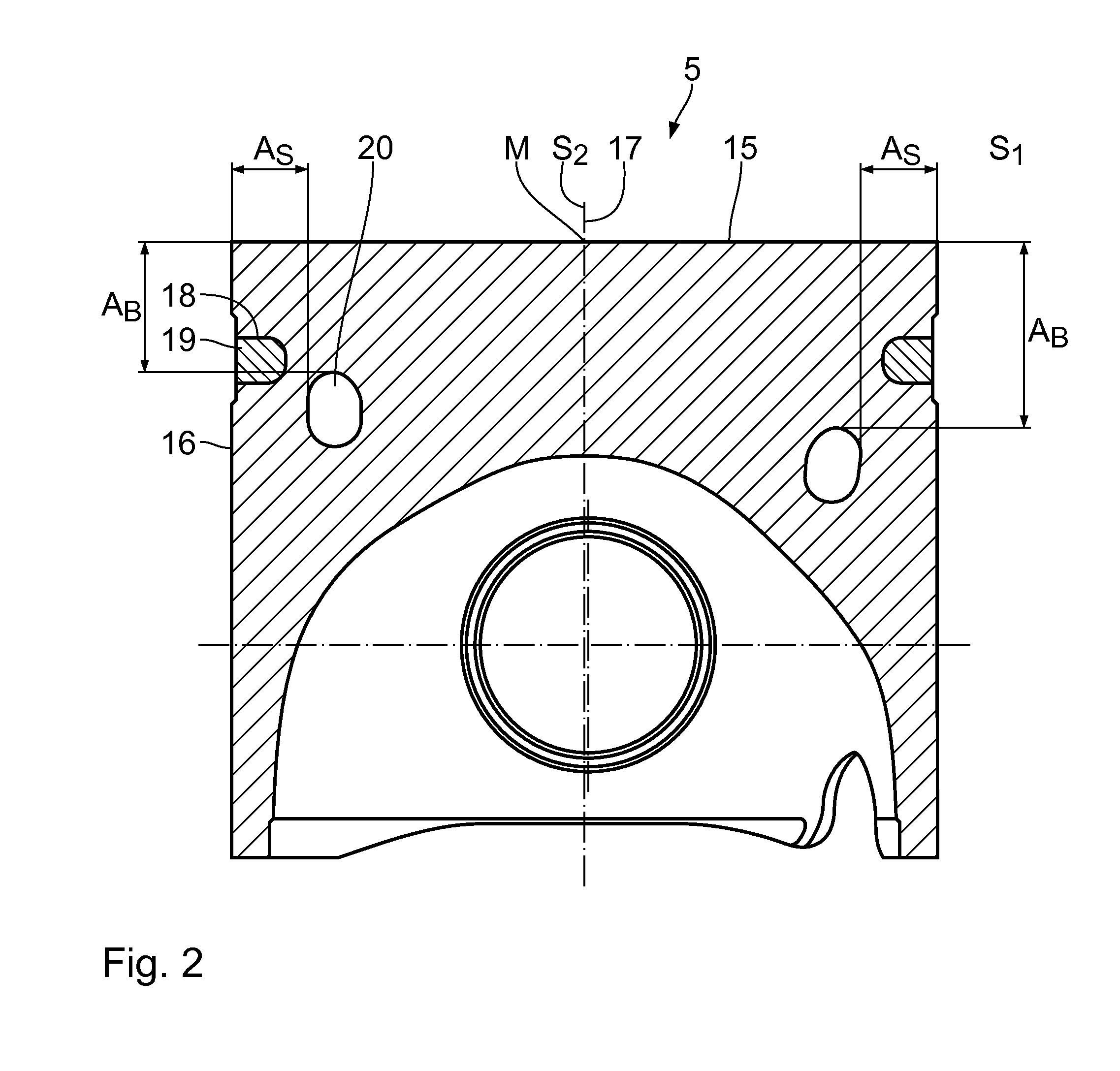
Method and evaluation device for determining the position of a structure located in an object to be examined by means of x-ray computer tomography
InactiveUS20130223722A1Simple and preciseSimple, precise and automaticImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelX-ray
In a method and an evaluation device for determining the position of a structure located in an object to be investigated by means of X-ray computer tomography, a cutting data record, which images the object in a cutting plane, is determined from a volume data record of the object. The cutting data record is binarized to form a binary data record, in which the structure voxels imaging the structure and the surface voxels imaging an object surface are determined. To determine the position, a distance data record is produced in such a way that a distance value, which characterizes the smallest distance of the respective distance voxel from the surface voxels, is assigned to each distance voxel of the distance data record. The distance voxels corresponding to the structure voxels are then determined and the associated distance values evaluated.
Owner:MAHLE INT GMBH
Three-dimensional digital imaging method of large view field cone-beam X-ray tilting scanning of biased detector
InactiveCN101634638BExpanded imaging field of viewImprove detection efficiencyComputerised tomographsTomographyPretreatment methodDigital imaging
The invention relates to a three-dimensional digital imaging method of the large view field cone-beam X-ray tilting scanning of a biased detector, belonging to the technical field of X-ray computerized tomography (CT). In the three-dimensional digital imaging method, the area array detector is placed to be biased, and an X-ray source is used for generating cone-beam X-rays which irradiate a member imaging area with a certain angle in a penetrating and tilting way relative to the length and width surface of a member; in the scanning process, the X-ray source and the area array detector are static, the member rotates in an angle of 360 degrees in an equal angle and step length way surrounding a rotating shaft, and the area array detector acquires an X-ray signal modulated by the member under each rotation angle. A three-dimensional computerized tomography image of a scanning area can be reestablished and obtained by a data truncation smoothing preprocessing method and a filtering back projection reestablishing arithmetic according to data obtained by the area array detector under the scanning angle of 360 degrees. Compared with the traditional tilting scanning method, the three-dimensional digital imaging method can double the tilting scanning imaging view field without changing the system hardware and the scanning speed and has high reestablishment quality, simple process and high efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Automatically radiation-proof FMT-and-CT dual-mode imaging system
ActiveCN103330549BEffective protectionAvoid damageComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringRapid imagingDual mode
The invention discloses an automatically radiation-proof FMT-and-CT dual-mode imaging system. The automatically radiation-proof FMT-and-CT dual-mode imaging system comprises a signal collecting module, a controller module, a data transmission module, a power module and an automatically radiation-proof module, wherein the signal collecting module is used for collecting fluorescence excitation imaging data and X-ray computerized tomography data of an imaging sample, the controller module is used for controlling operation, parameter setting, data processing and data storage of other modules, the data transmission module is used for transmitting internal data of the system, the power module is used for providing electricity for the whole system, and the automatically radiation-proof module is used for protecting a CCD camera and reducing damage caused by X-rays to the CCD camera. The automatically radiation-proof FMT-and-CT dual-mode imaging system can achieve dual-mode rapid imaging of FMT and CT, and due to the fact that the automatically radiation-proof module is designed, when an X-ray power source is turned on, the CCD camera is effectively protected, and damage to an internal sensitization chip can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
X-ray computerized tomography system and method
ActiveCN102397080BReduce exposureAvoid overshadowingComputerised tomographsTomographySoft x rayX-ray
The invention discloses an X-ray computerized tomography system and an X-ray computerized tomography method. The system comprises an X-ray tube, a collimator, a detector, a computing assembly and an adjusting assembly, and is used for shooting a plurality of circular sections of an object to be detected in the scanning direction, wherein the detector comprises a plurality of detector channels; the X-ray tube, the collimator and the detector rotate synchronously around the object to be detected; the collimator is a collimator with an adjustable opening; the computing assembly is used for computing the opening width of the collimator needed for irradiating each circular section respectively, and transmitting the opening width to the adjusting assembly; and the adjusting assembly is used for adjusting the opening of the collimator according to the opening width. The invention further discloses the X-ray computerized tomography method. Due to the adoption of the system and the method, extra exposure of the surrounding area of the objected to be detected can be reduced, and the X-ray dosage received by a patient can be reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS SHANGHAI MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
Rock performance evaluation device
ActiveCN103868801BEnables strain measurementSimple strain measurementMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesRock coreComputing tomography
The embodiment of the invention provides a rock performance evaluating device. The device comprises a pressure chamber and a CT (computed tomography) device, wherein the pressure chamber is a sealed cavity body, is positioned in the scanning range of an X-ray computerized tomography CT device, and is used for providing preset testing temperature and preset testing pressure for a rock core test specimen, wherein the preset testing temperature is higher than a first threshold, and the preset testing pressure is higher than a second threshold; the CT device is used for scanning the rock core test specimen to acquire image information of the internal structure of the rock core test specimen at different time, and analyzing according to the image information so as to obtain a strain curve of the rock core test specimen. The embodiment of the invention prevents the situation that the rock strain is measured by a sensor at high temperature, thereby measuring the rock strain simply and accurately at high temperature.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
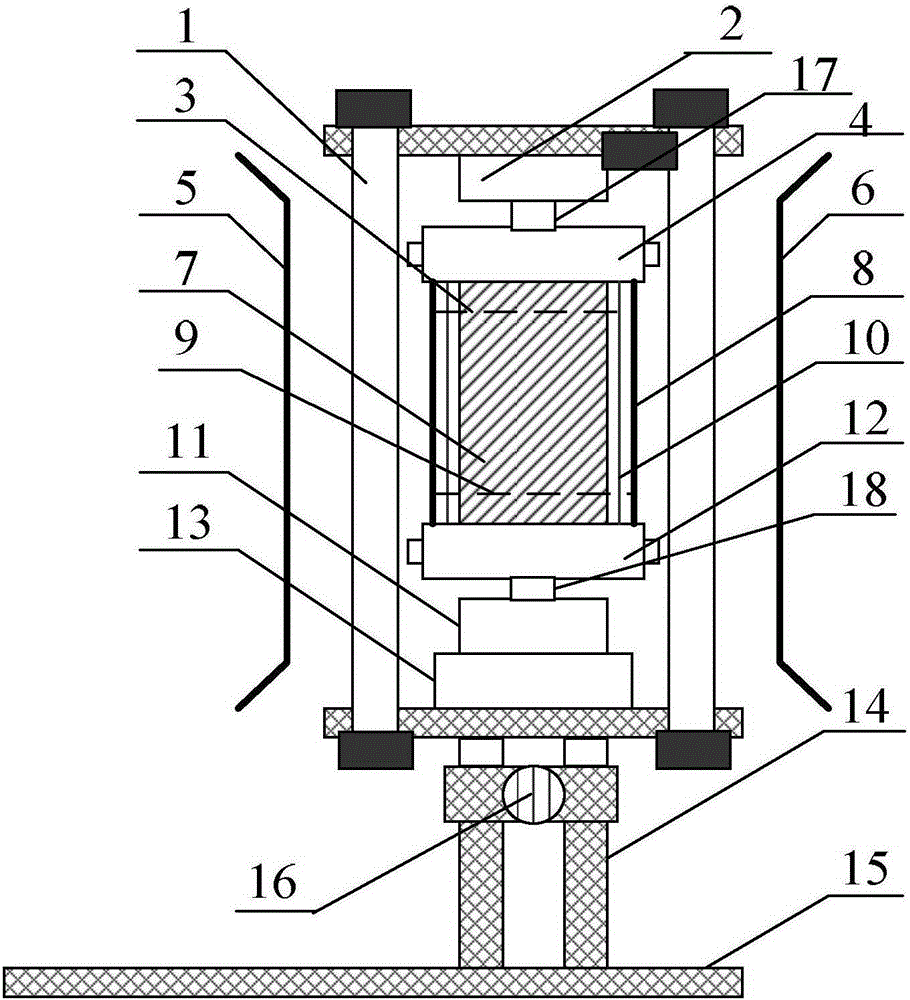
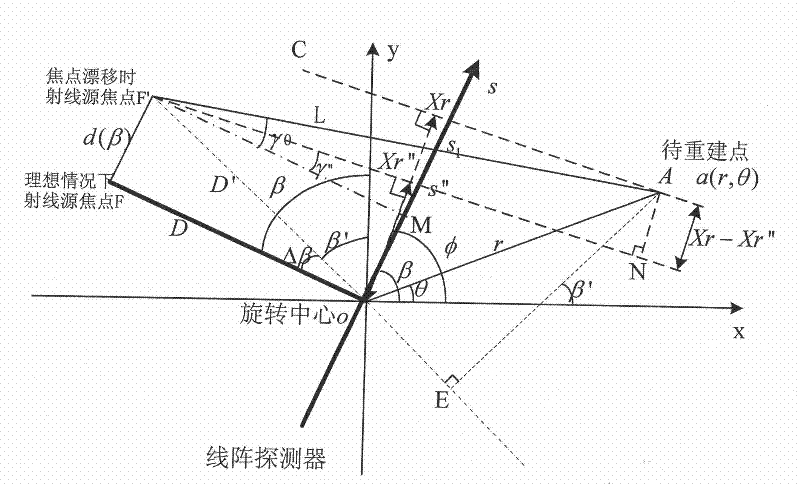
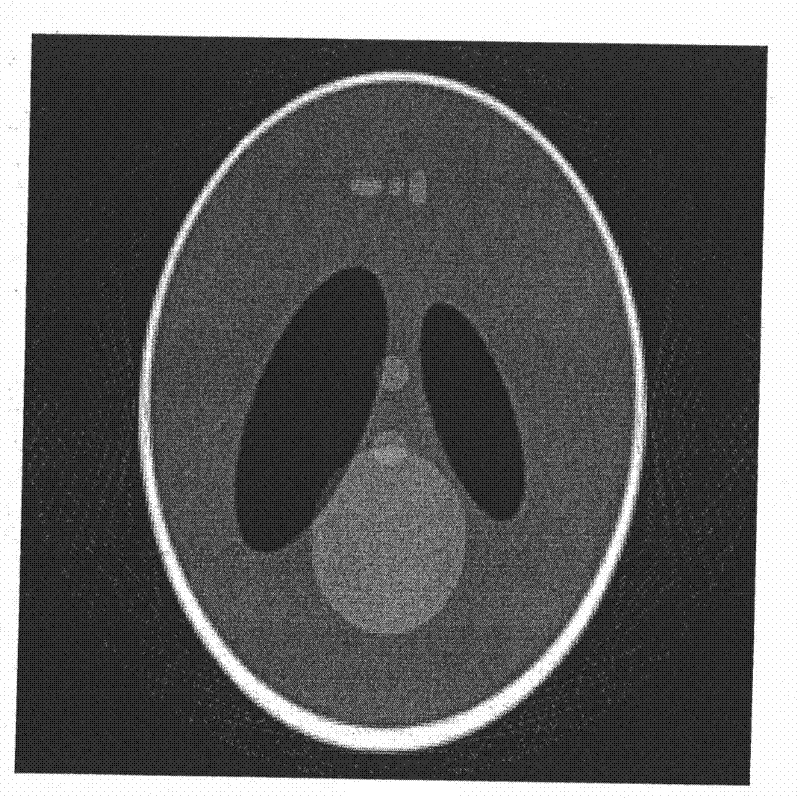
X ray source focus drifting CT reconstruction method
The invention belongs to the field of X ray computerized tomography (CT) technology, in particular to an X ray source focus drifting CT reconstruction method. The method is based on the filtered backprojection reconstruction theory, deduces weighting, filtering and backprojection calculation formulas of ST projection data according to the CT scanning geometric construction during the focus drifting of an X ray source, introduces a distance parameter of the focus drifting of the X ray source during reconstruction, thereby forming a novel reconstruction algorithm. Since the CT scanning geometric construction corresponding to the traditional reconstruction algorithm is different from the structure formed during the focus drifting of the X ray source, the traditional reconstruction algorithm can not be used to reconstruct the image of a two-dimension CT projection the X ray source focus of which drifts. The invention solves the problem of X ray CT reconstruction under the condition of thefocus drifting of the X ray source and has a simple and highly-efficient reconstruction process.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
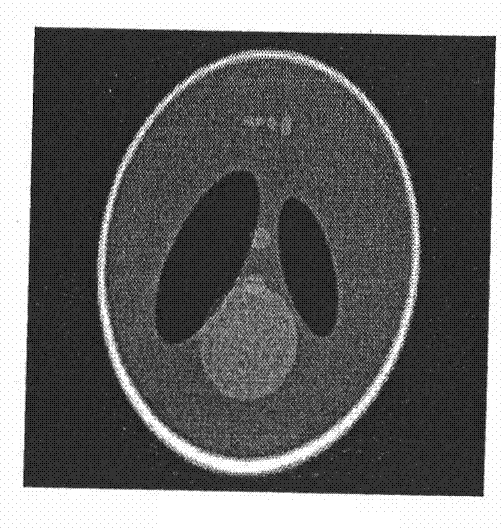
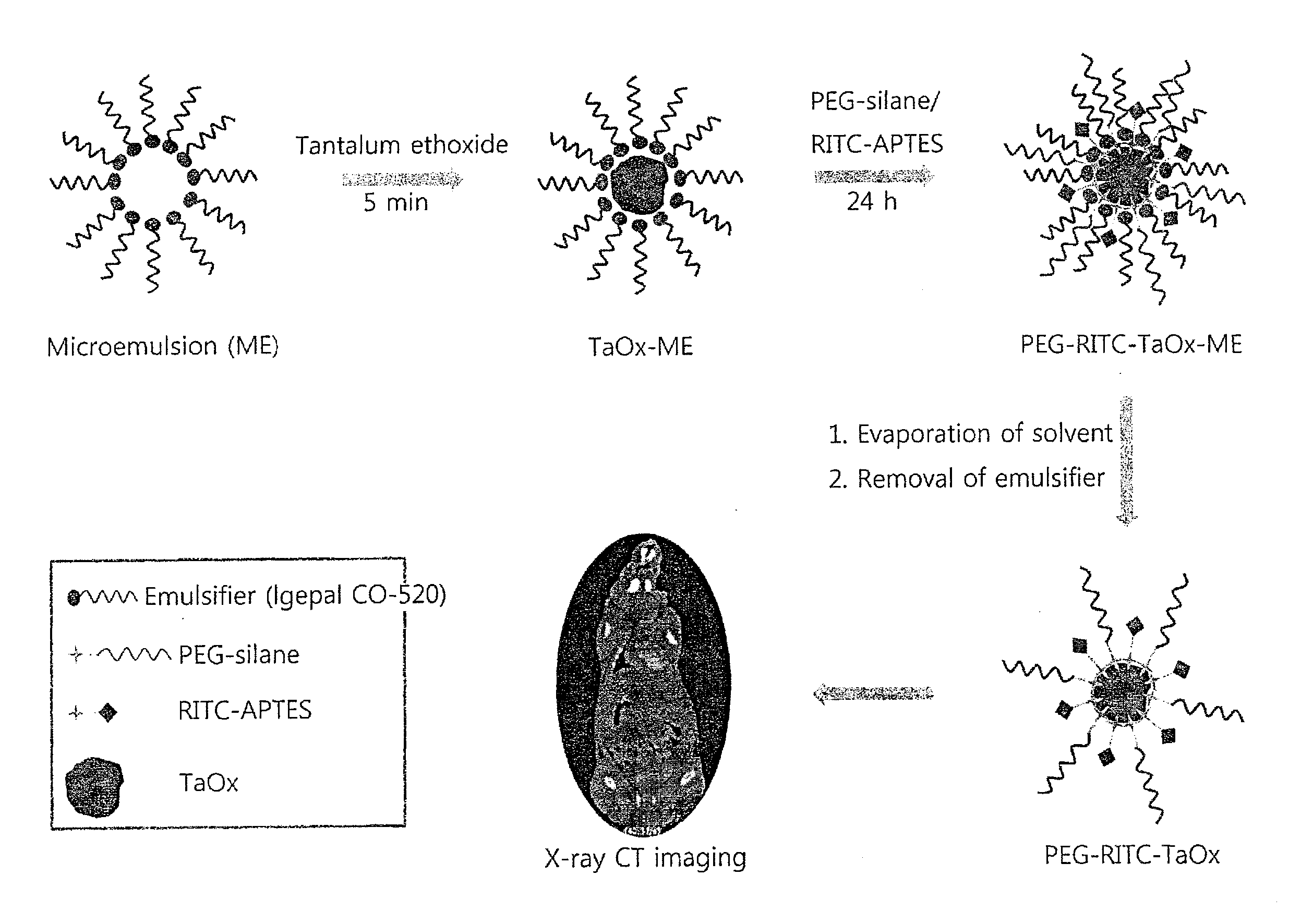
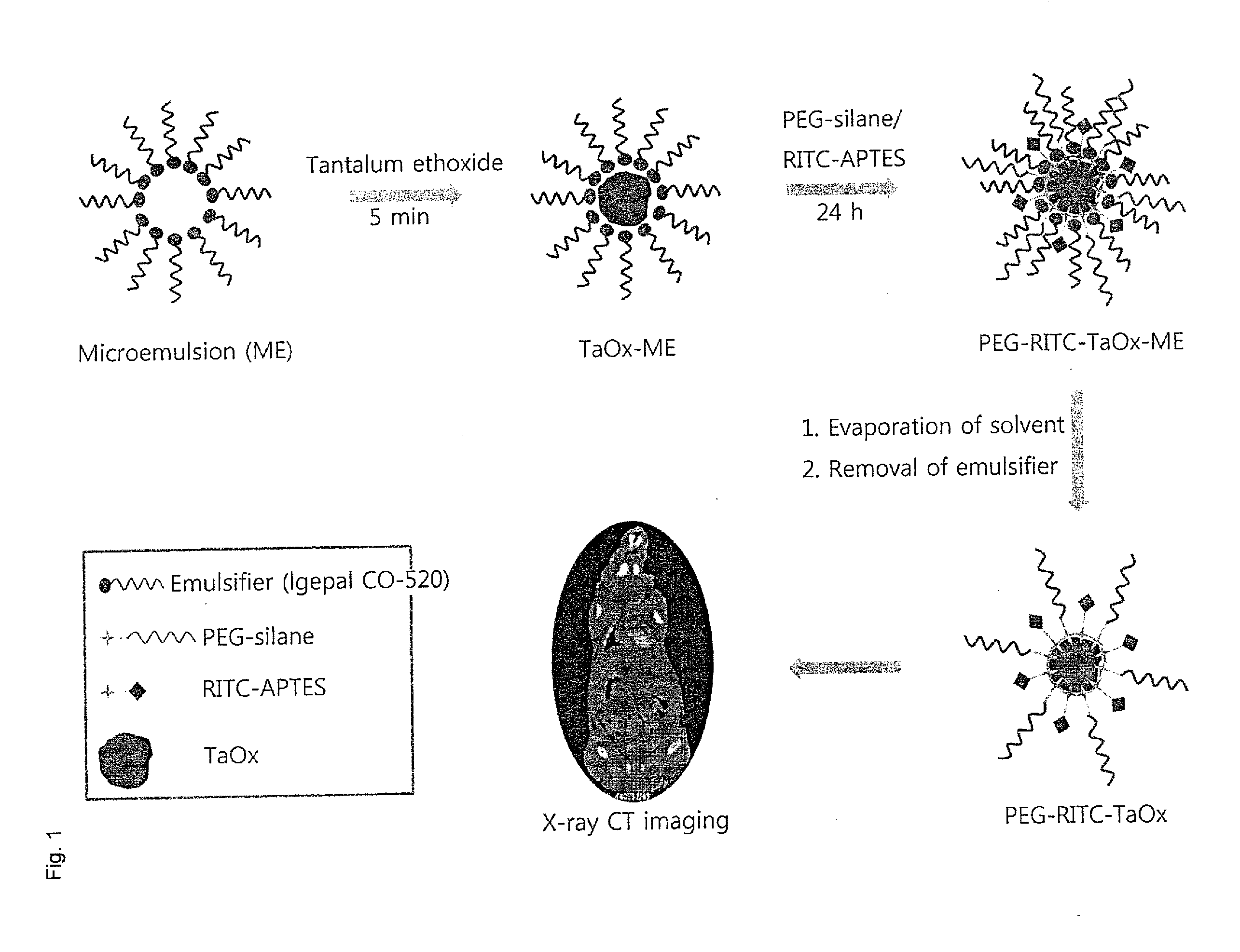
Surface-Modified Tantalum Oxide Nanoparticles, Preparation Method Thereof, and Contrast Medium for X-Ray Computed Tomography and Highly Dielectric Thin Film Using Same
ActiveUS20130065995A1Low costLarge scalePowder deliveryGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSilanesX-ray
The present invention relates to a surface-modified tantalum oxide nanoparticle, a method for preparation thereof, a contrast agent (medium) for X-ray computed tomography, and a highly dielectric (high-K) film using the same. In particular, the present invention is directed to a surface-modified tantalum oxide nanoparticle, a method for preparing surface-modified tantalum oxide nanoparticles, comprising: (i) adding an aqueous phase to an organic solvent which contains a surfactant, to prepare a water-in-oil microemulsion; (ii) introducing a tantalum precursor to said microemulsion; (iii) adding a surface-modifier having an organic silane group or phosphine group to a solution obtained at the step (ii); (iv) removing said organic solvent from a product obtained at the step (iii); and (v) separating surface-modified tantalum oxide nanoparticles from a mixture obtained at the step (iv), a contrast agent for X-ray computed tomography, and a highly dielectric (thin) film using the same.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com