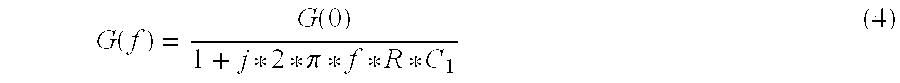Patents
Literature
75results about "Electroluminescent amplifiers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
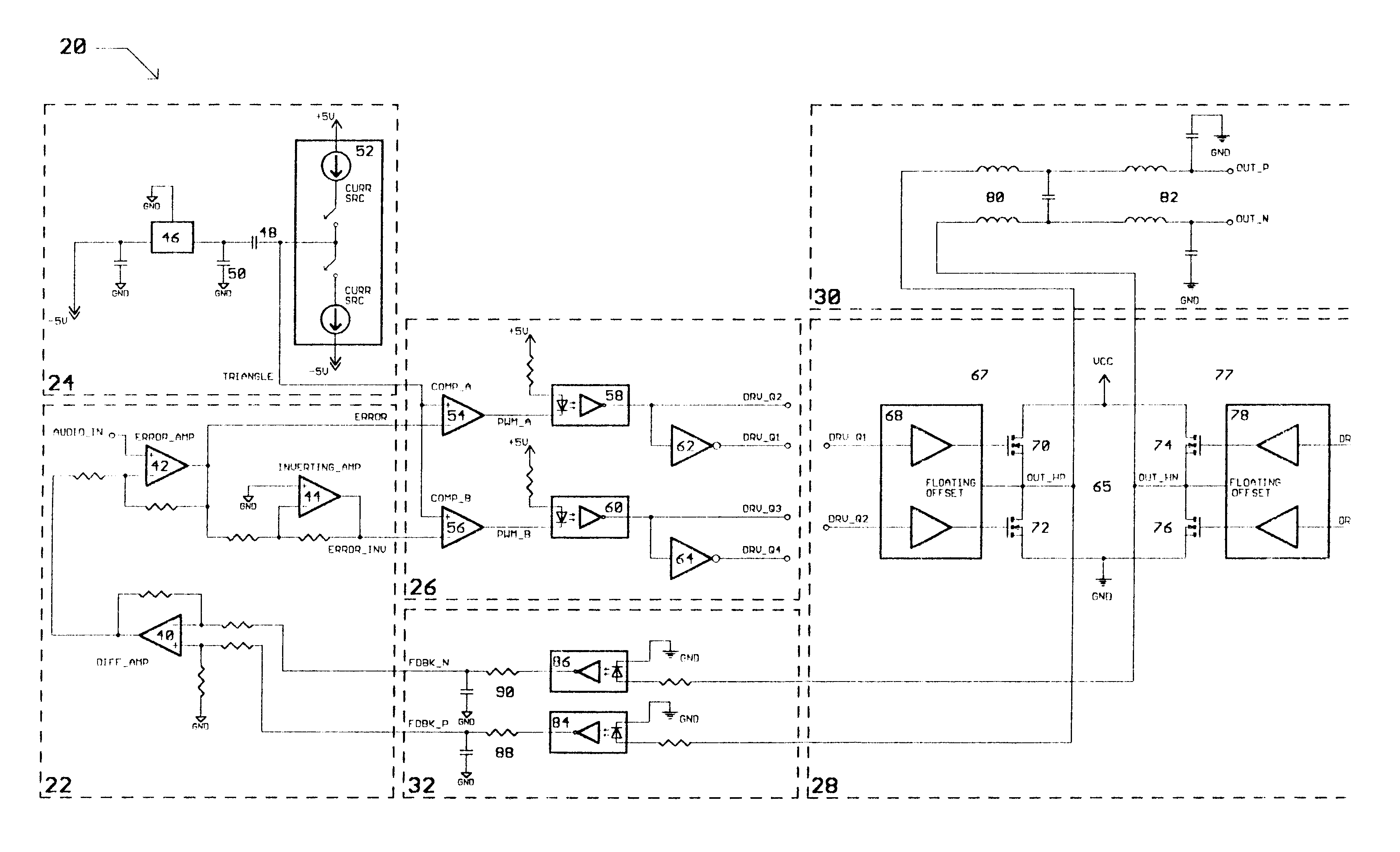
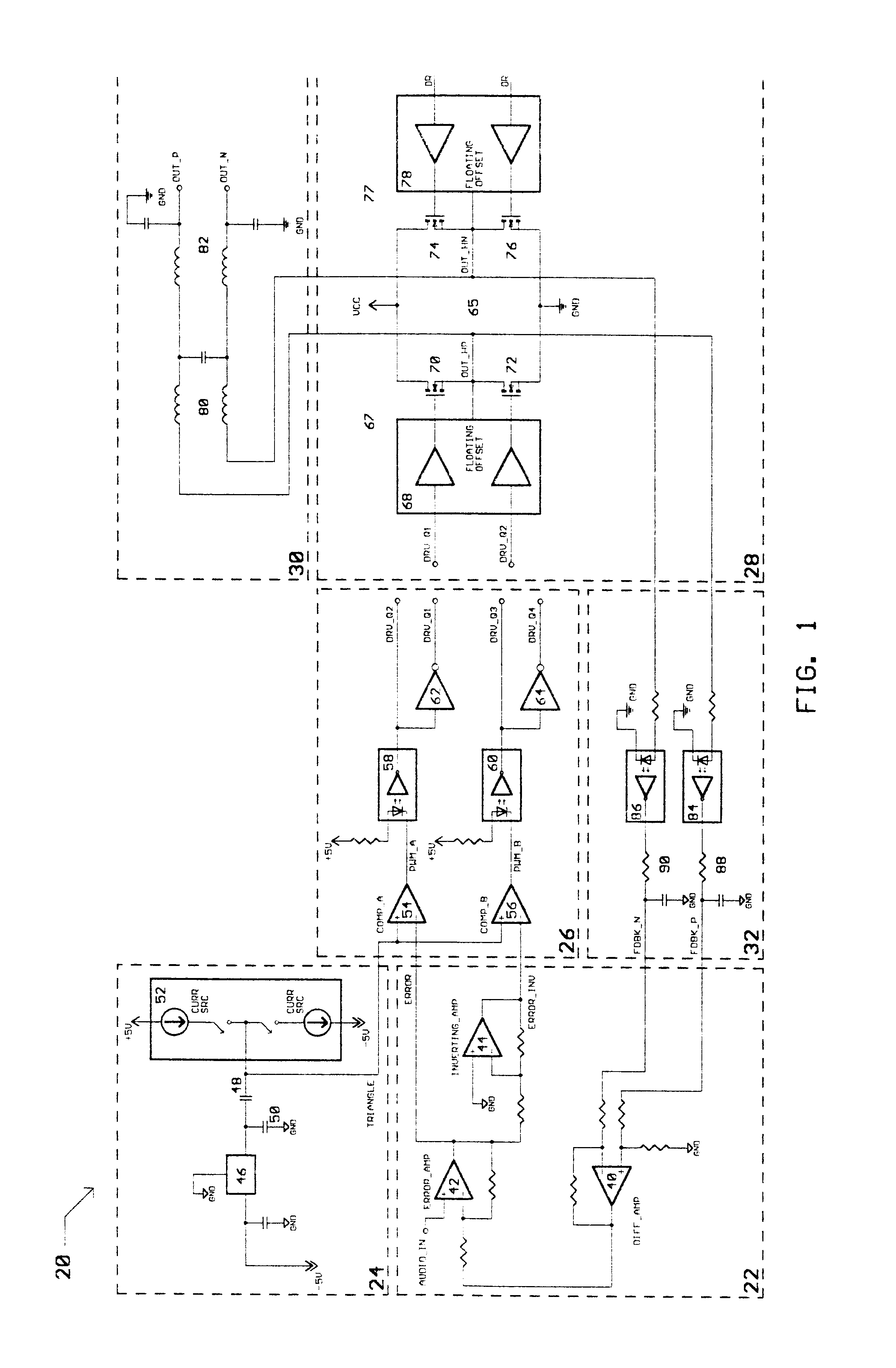
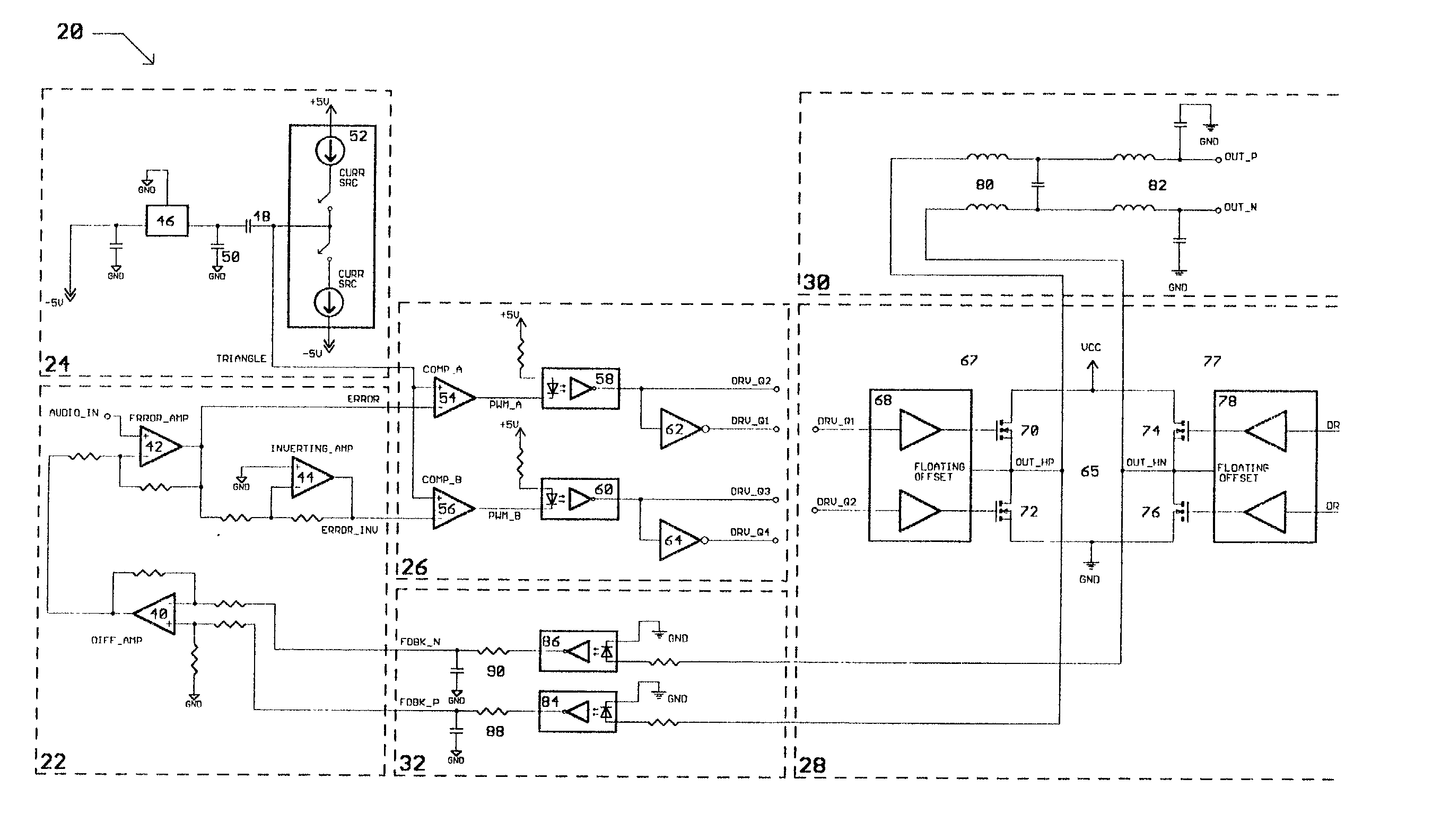
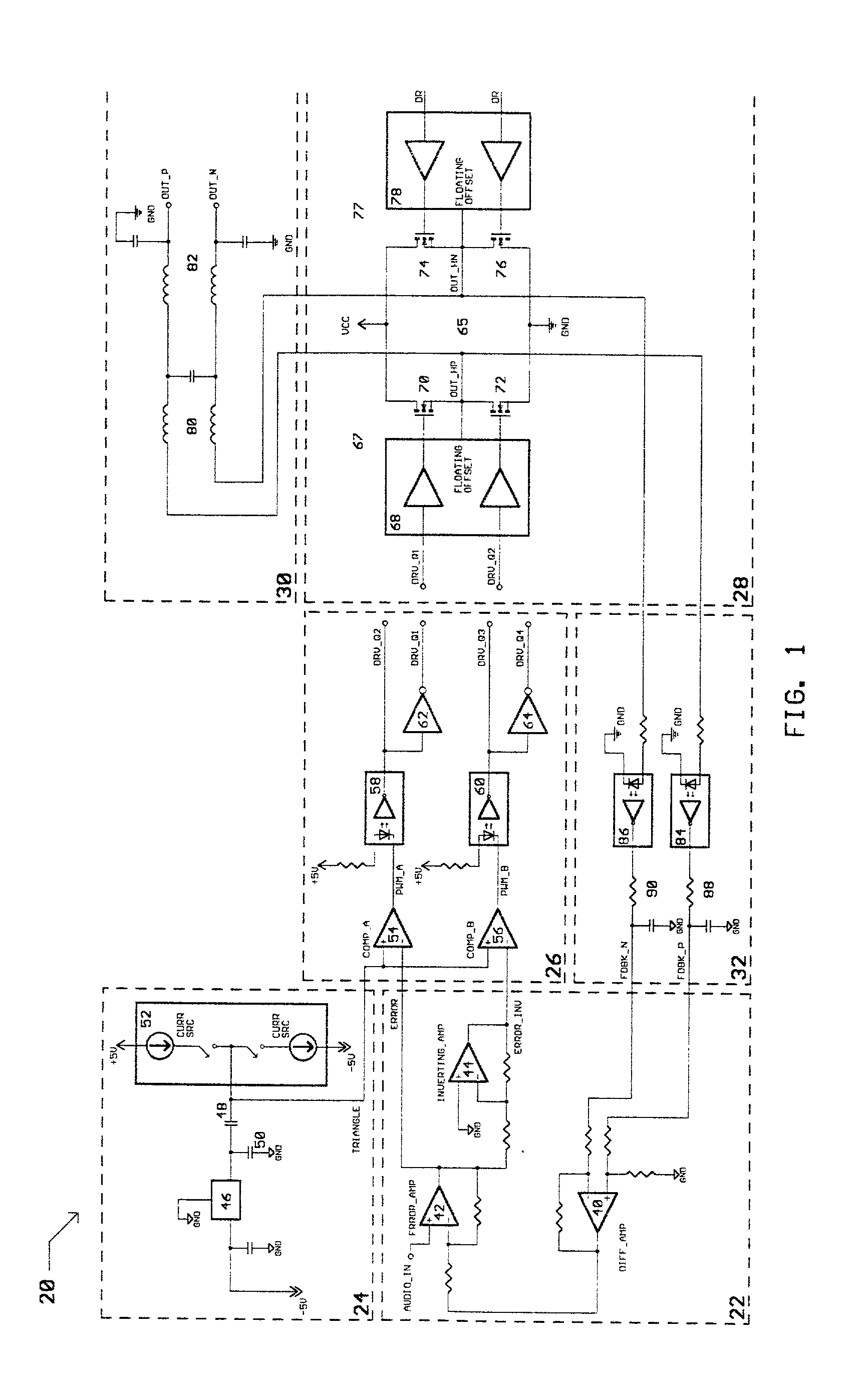
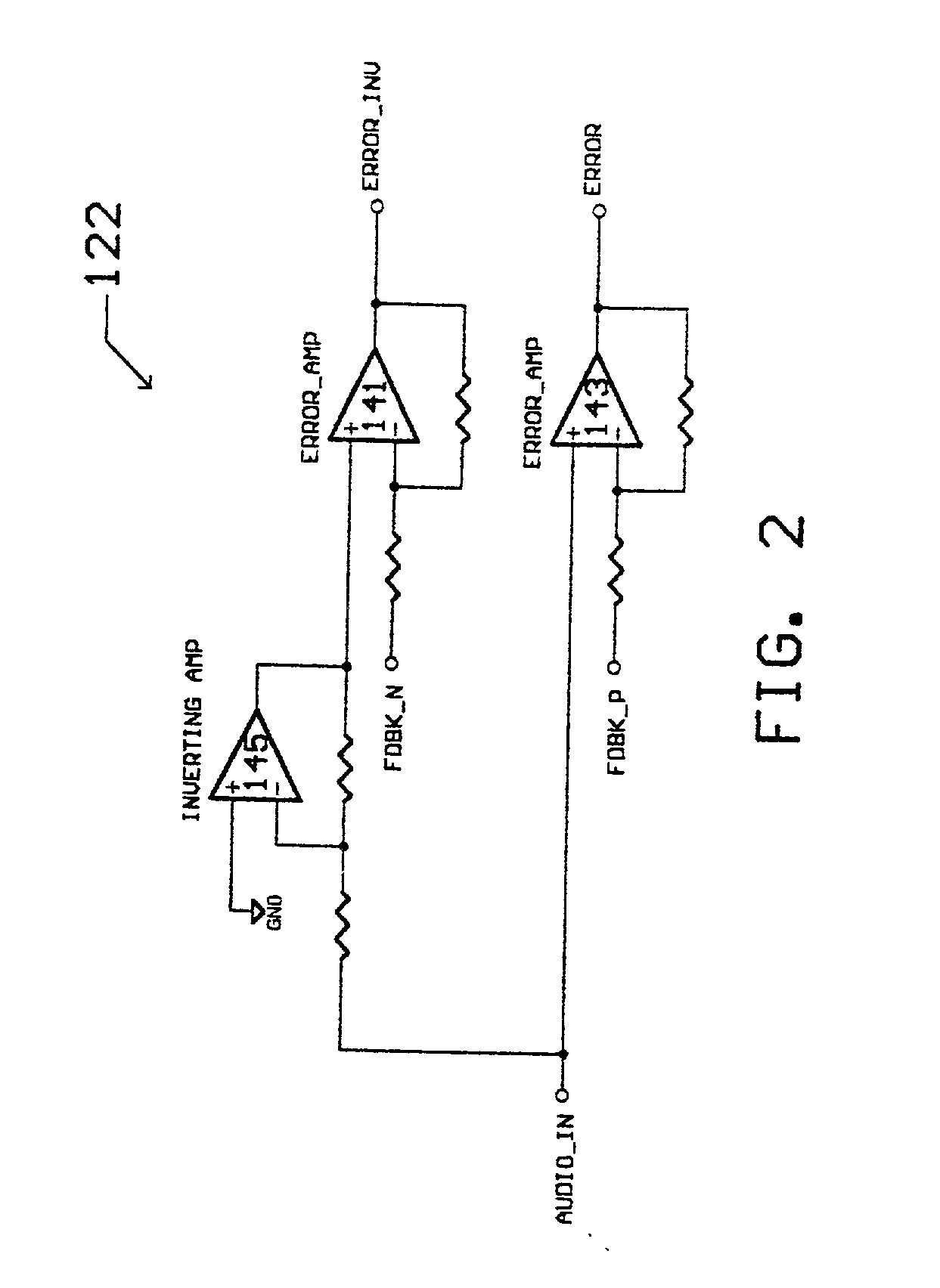
Class D switching audio amplifier
InactiveUS6563377B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierFiltration
A Class D switching audio amplifier incorporating four state modulation, input-to-output drive and feedback signal isolation, dual topology output filtration, and a low inductance board layout. The four state modulation results in a common mode voltage in the absence of audio. The input-to-output isolation of drive and feedback signals allows for elimination of large power transformers in applications without user-accessible outputs. Such isolation may make use of optical isolators. The output filter includes common mode and differential topology filter stages. The low inductance board layout treats the amplifier and power supply boards as modules, and utilizes both sides of the amplifier board in order to minimize trace length.
Owner:EVENSTAR MERGERSUB INC
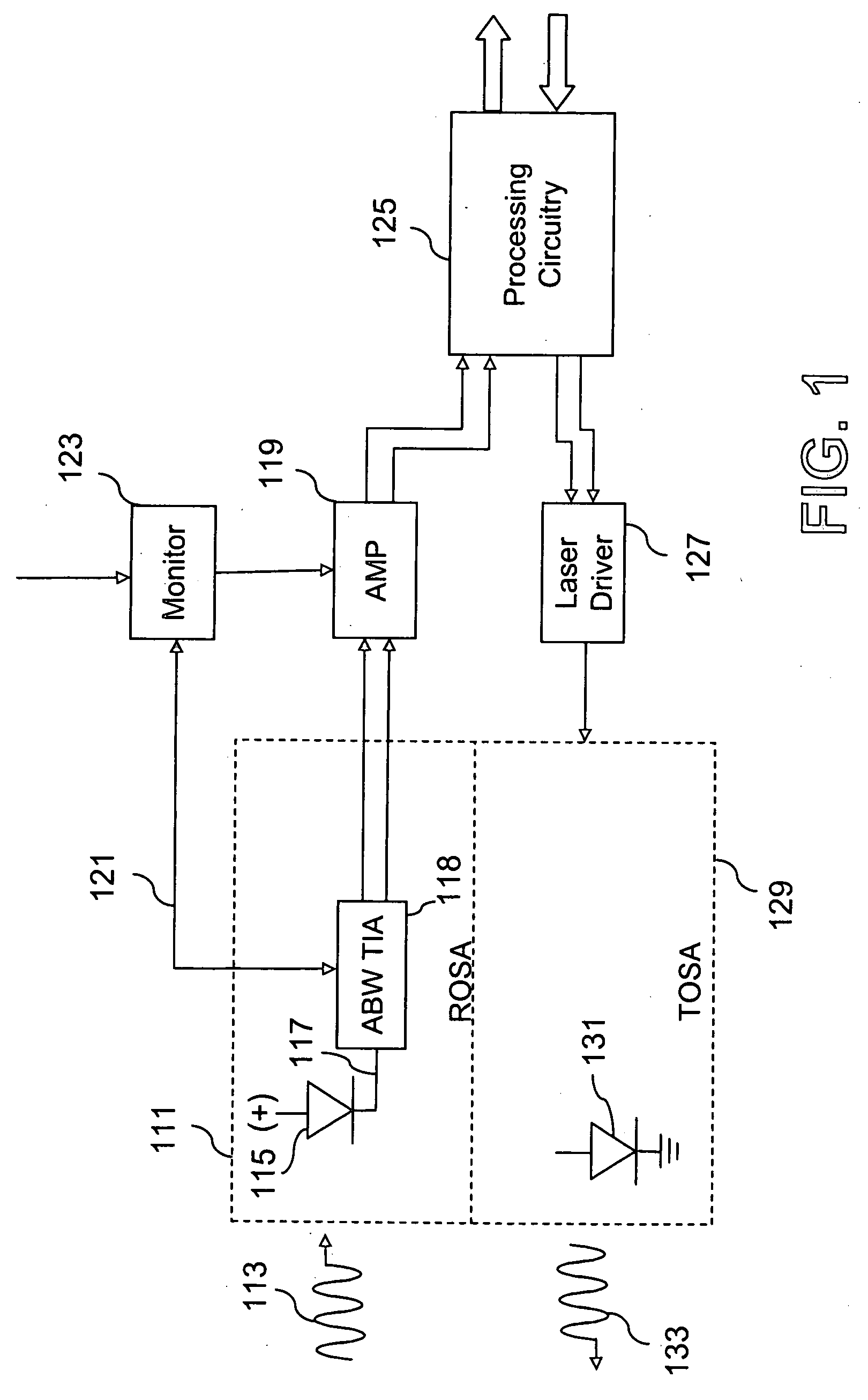
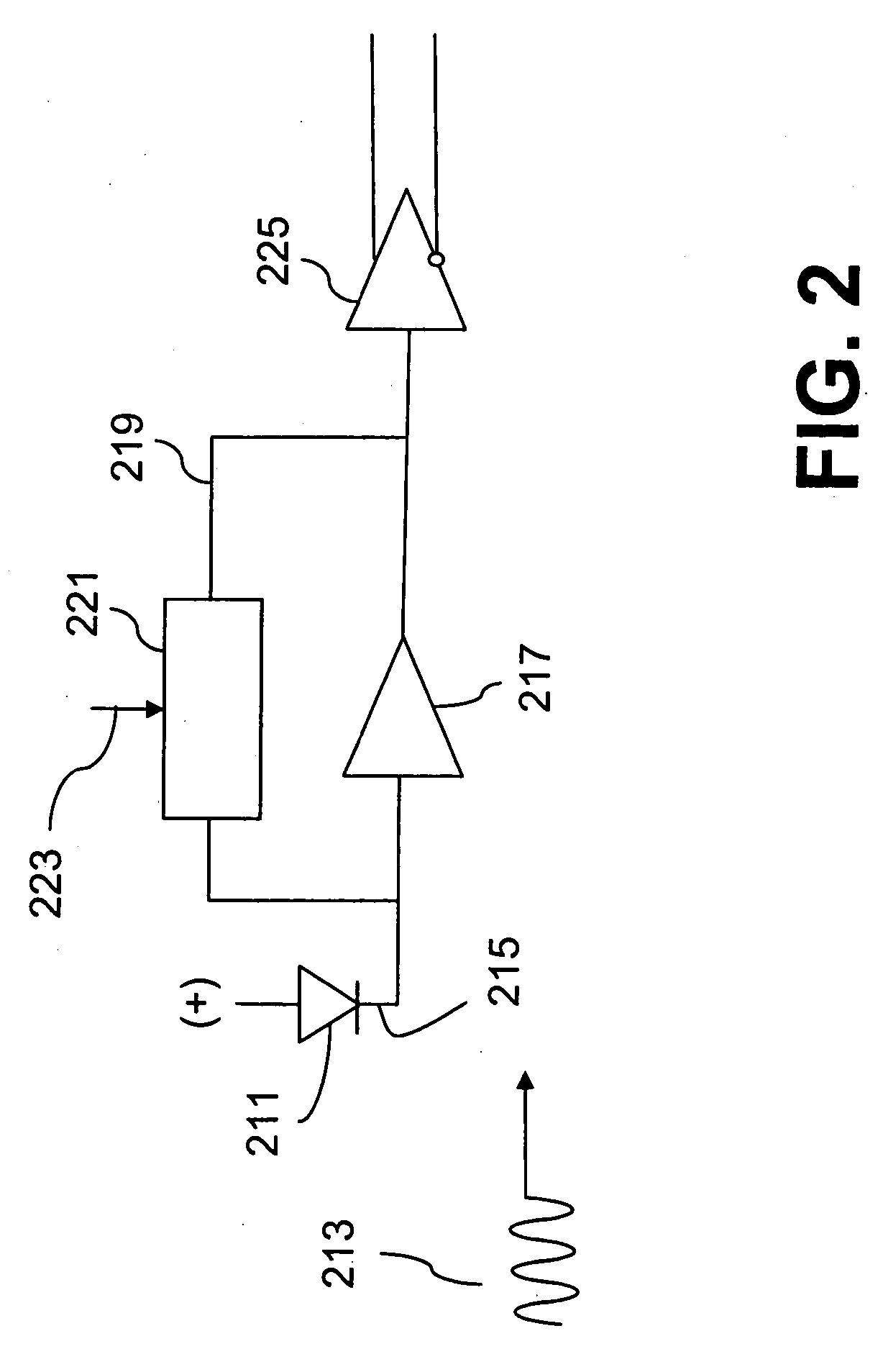
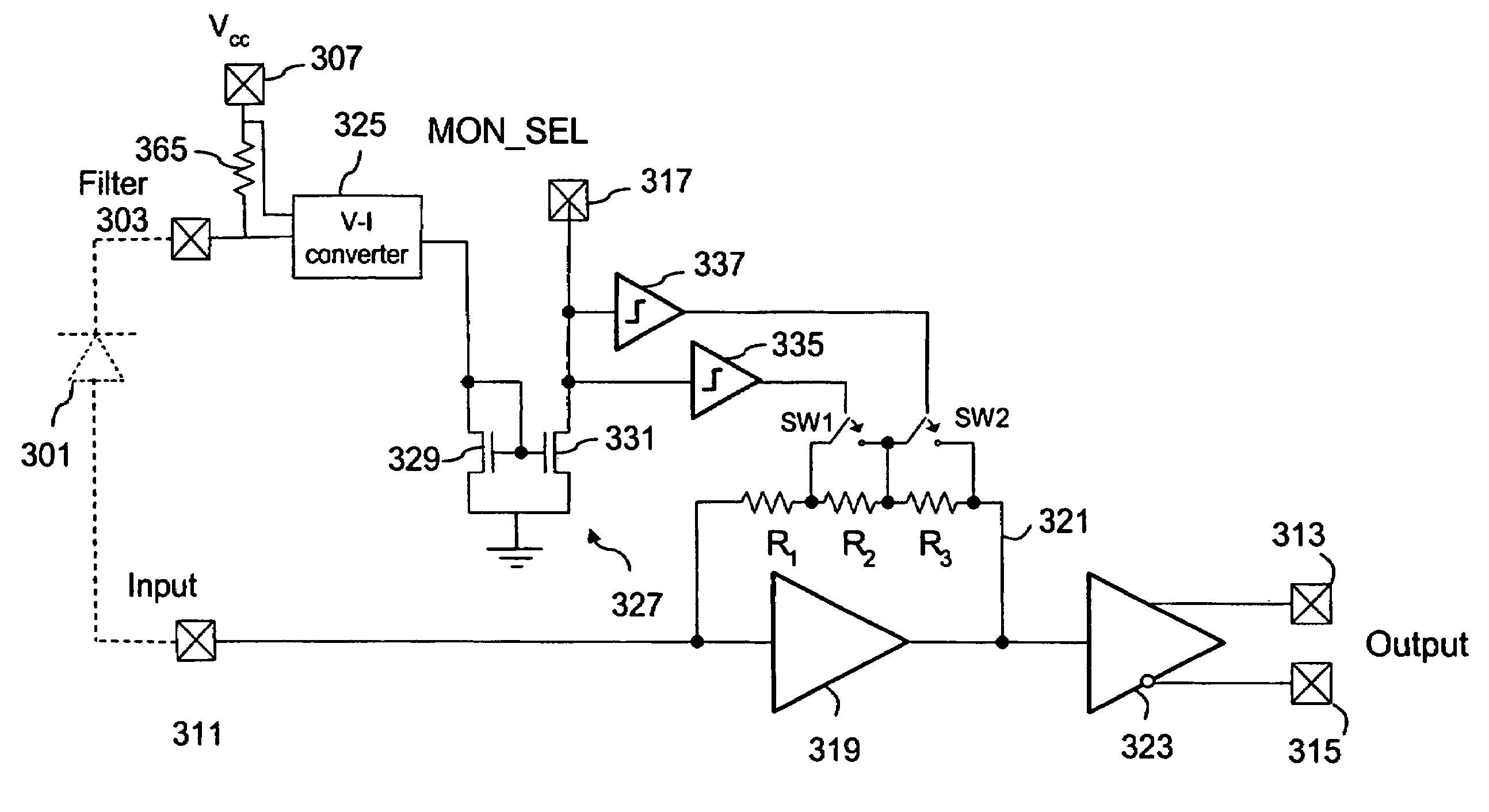
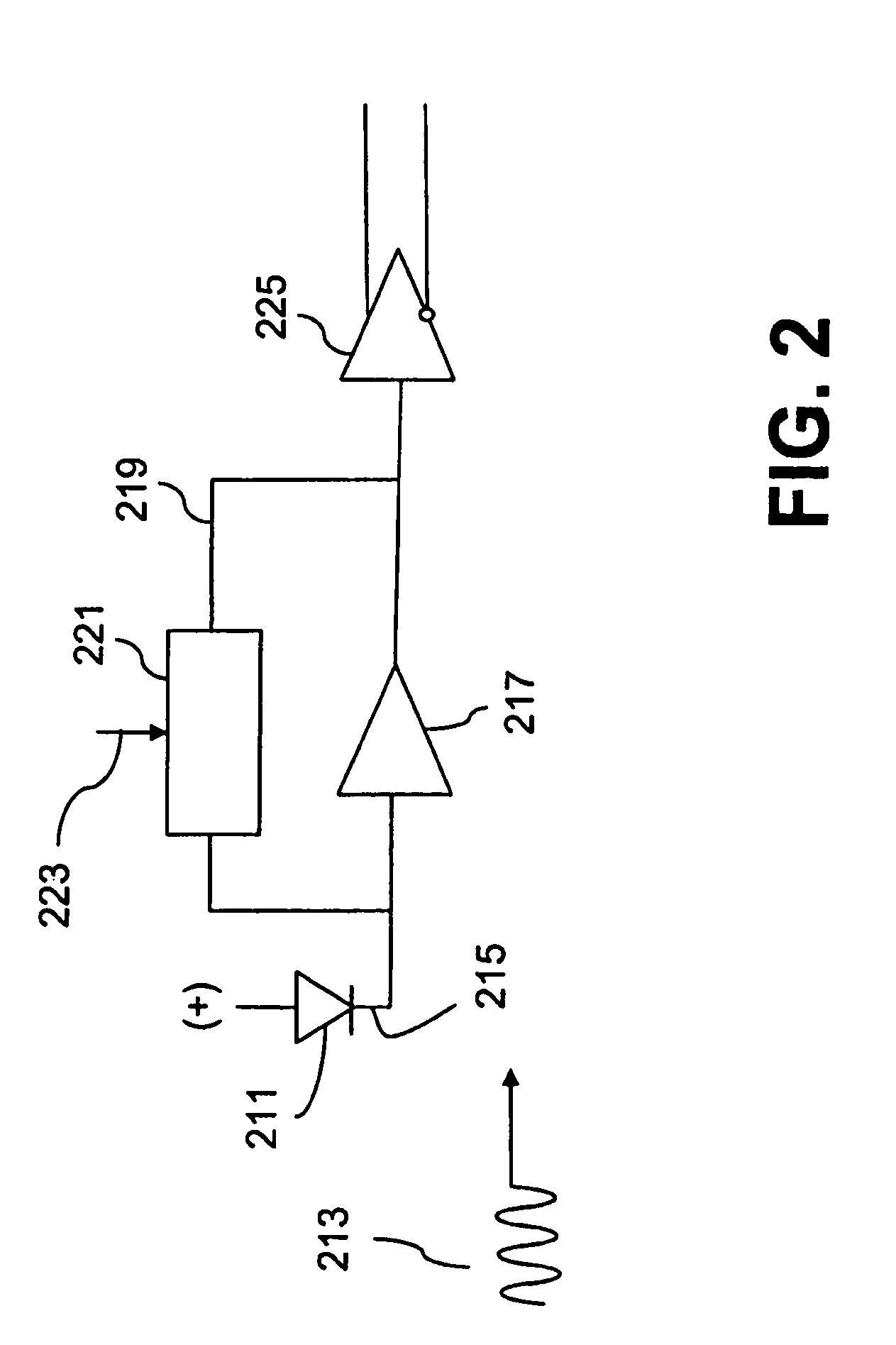
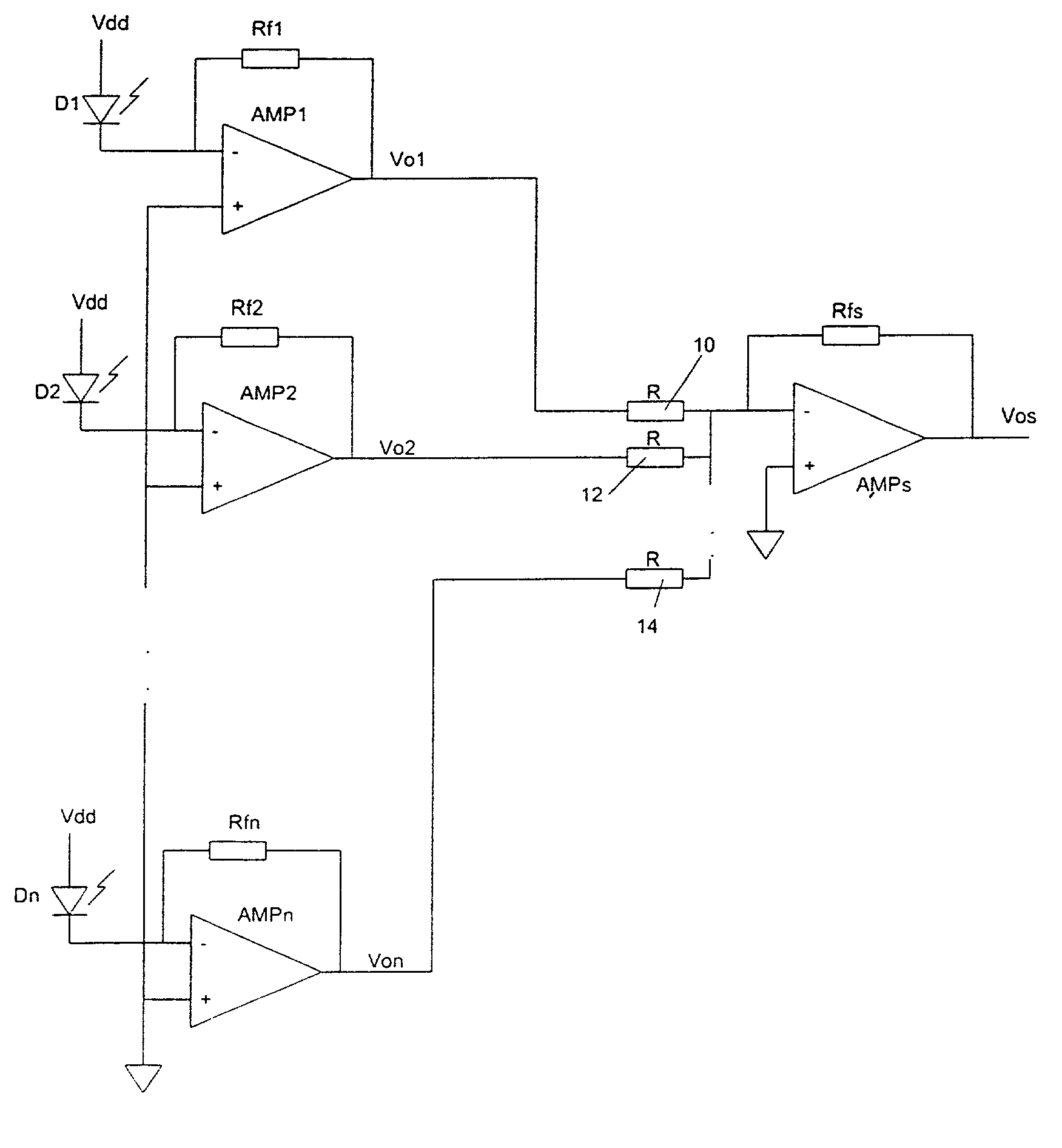
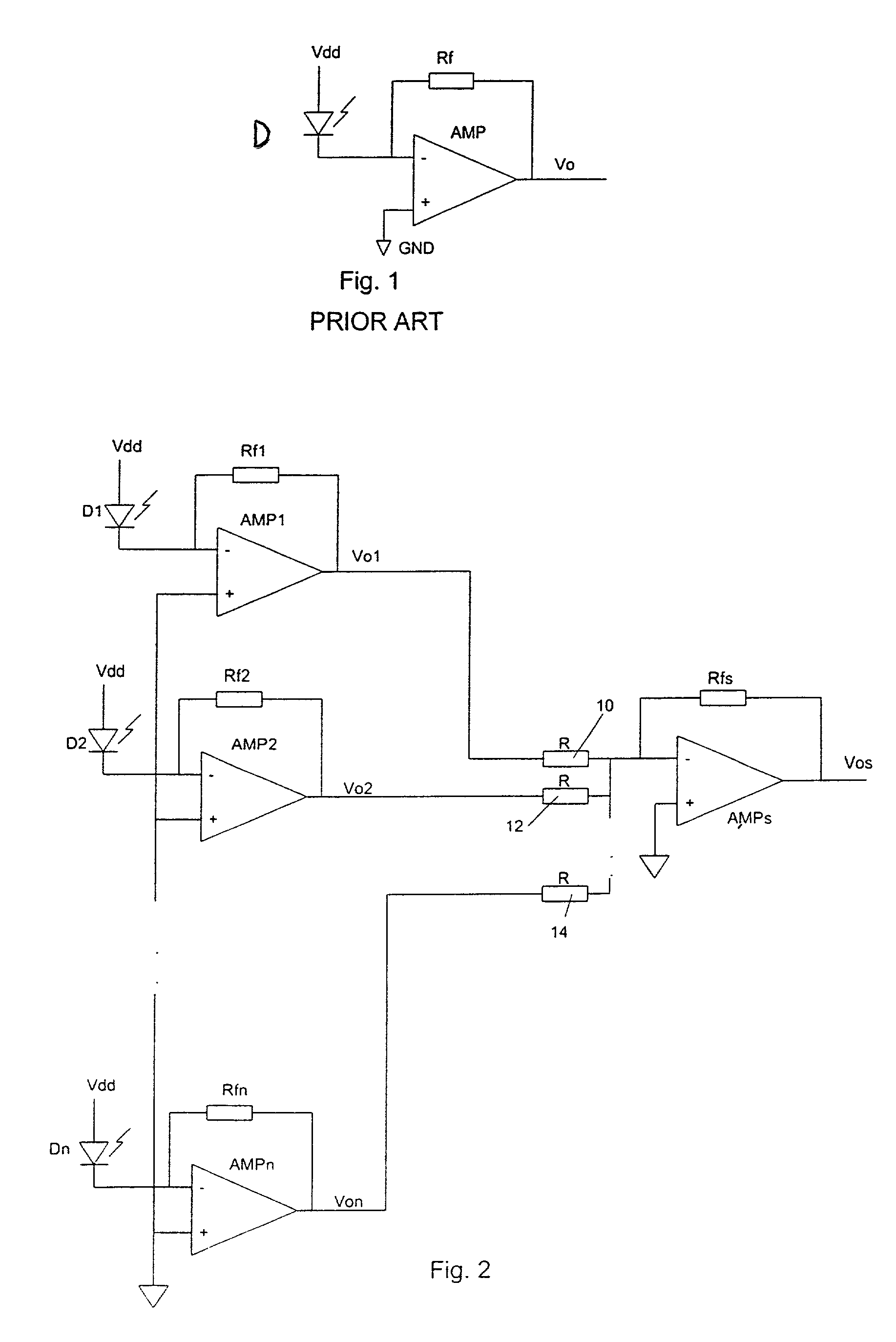
Variable bandwidth transimpedance amplifier with one-wire interface
InactiveUS20060045531A1Easy to understandNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifiers controlled by lightTransceiverAudio power amplifier
A bandwidth adjustable transimpedance amplifier. The bandwidth adjustable transimpedance amplifier includes a feedback path with a selectable resistance. The bandwidth adjustable transimpedance amplifier is preferably implemented with a photodiode in a five pin package for an optical transceiver system, with a single pin providing a monitor out function and a rate select input.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Class d switching audio amplifier
InactiveUS20030067348A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifiers with impedence circuitsAudio power amplifierTransformer
A Class D switching audio amplifier incorporating four state modulation, input-to-output drive and feedback signal isolation, dual topology output filtration, and a low inductance board layout. The four state modulation results in a common mode voltage in the absence of audio. The input-to-output isolation of drive and feedback signals allows for elimination of large power transformers in applications without user-accessible outputs. Such isolation may make use of optical isolators. The output filter includes common mode and differential topology filter stages. The low inductance board layout treats the amplifier and power supply boards as modules, and utilizes both sides of the amplifier board in order to minimize trace length.
Owner:EVENSTAR MERGERSUB INC
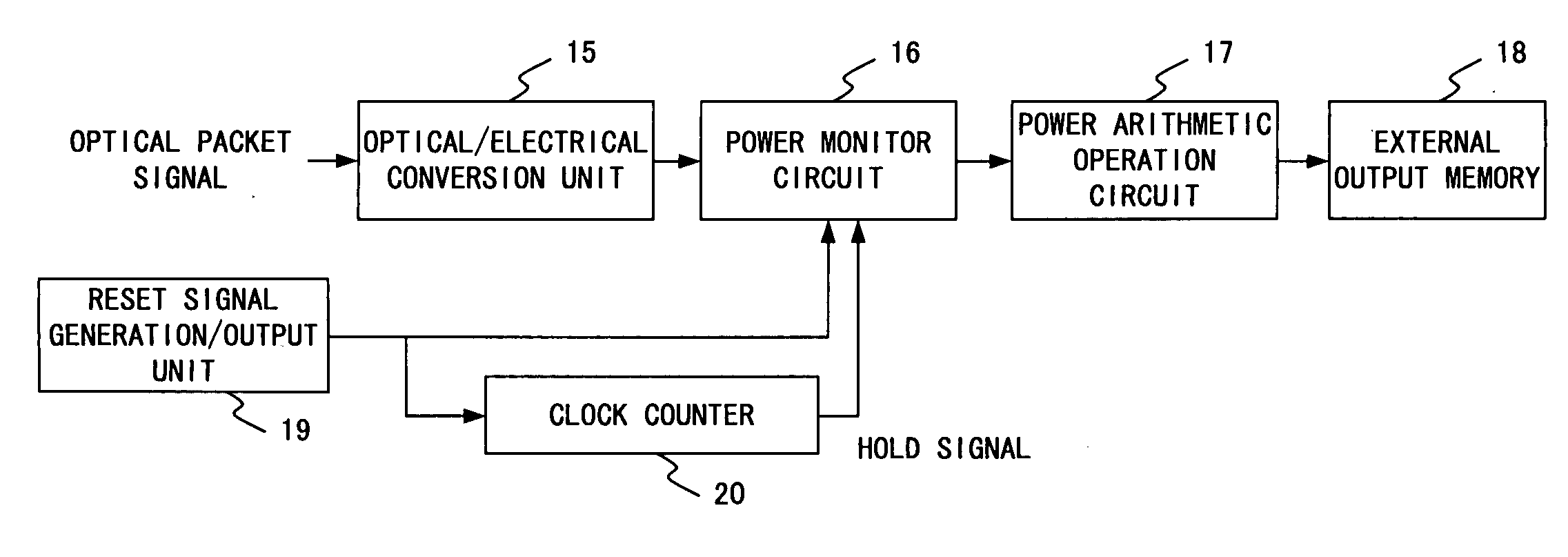
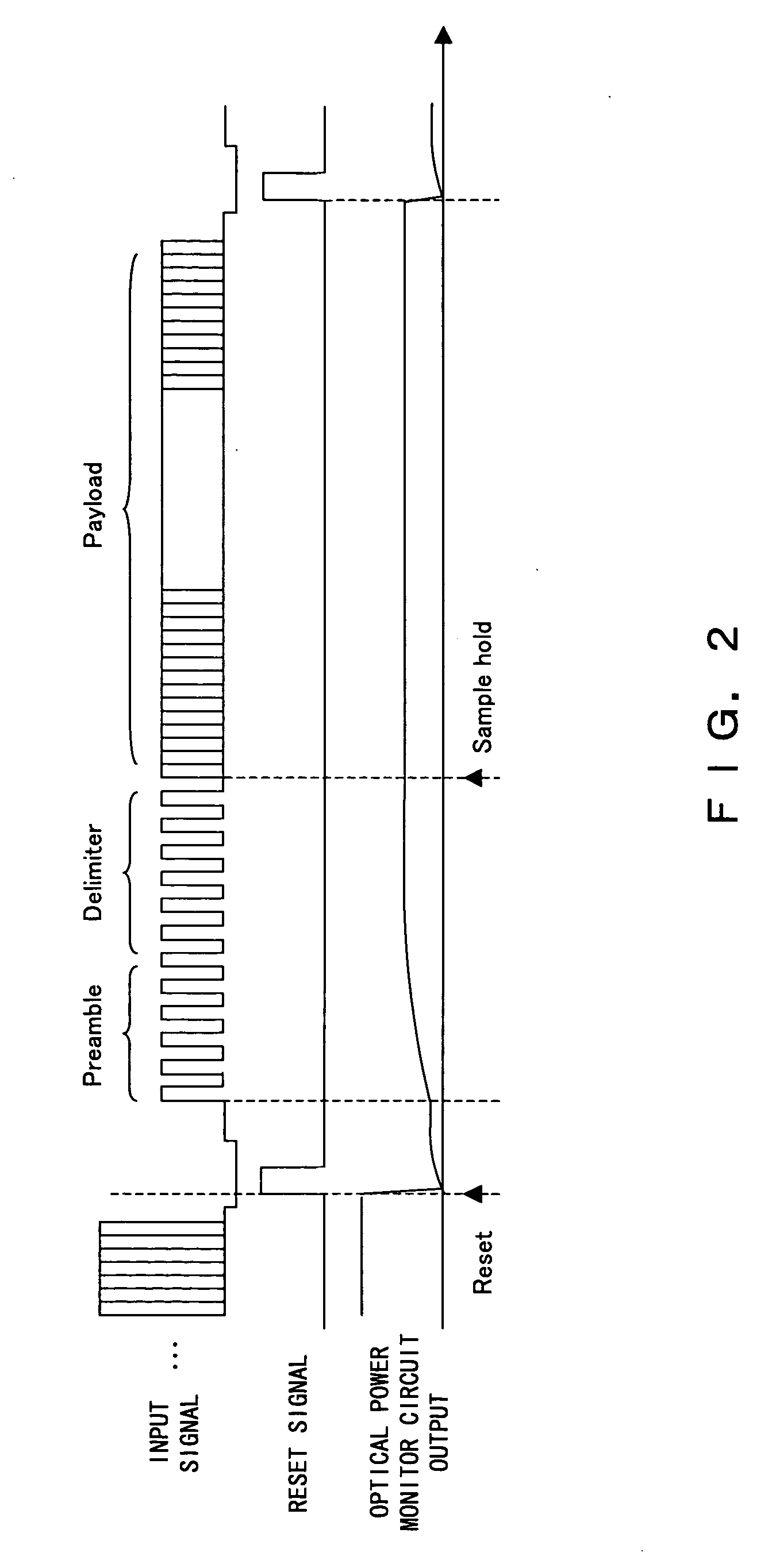
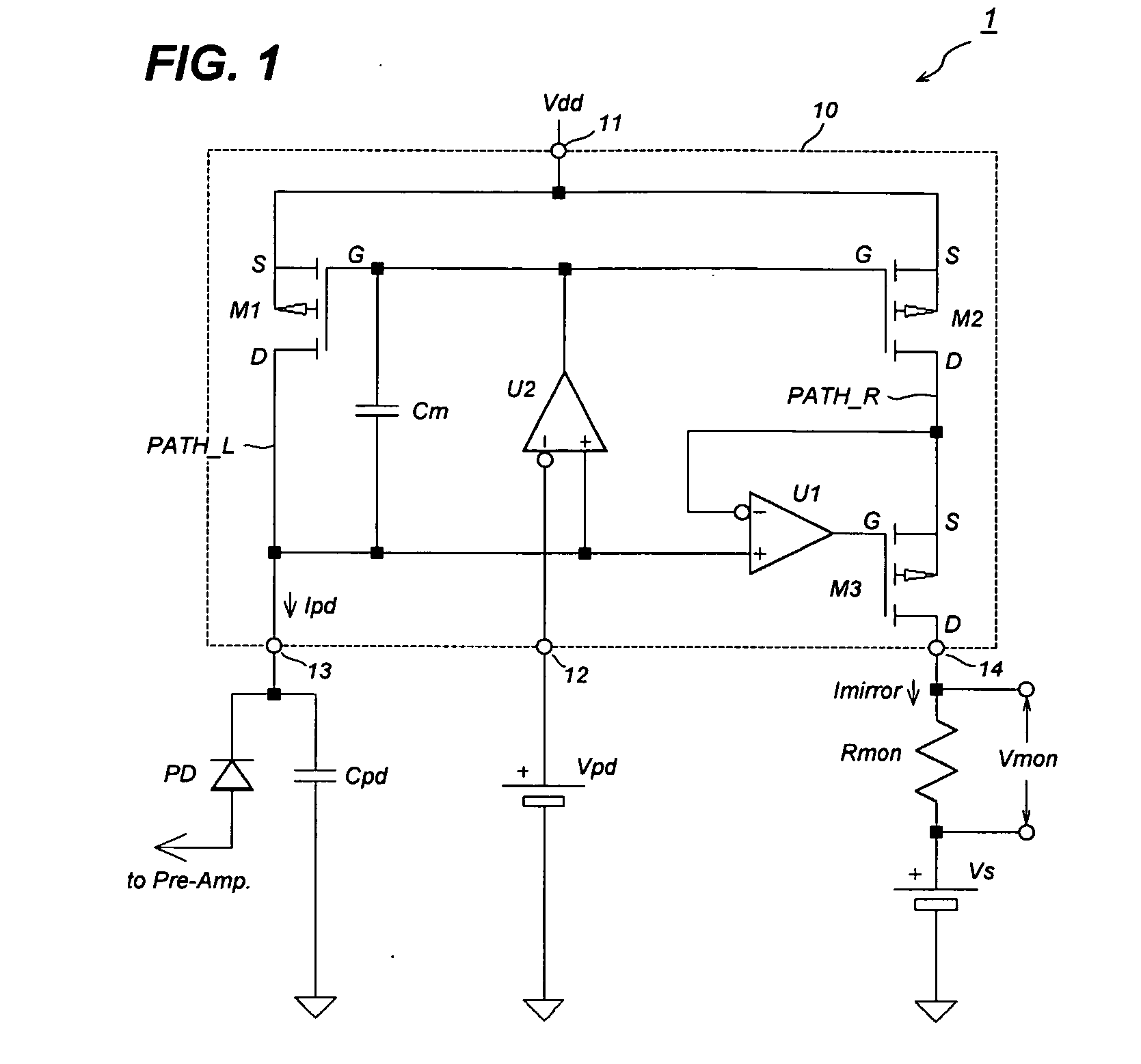
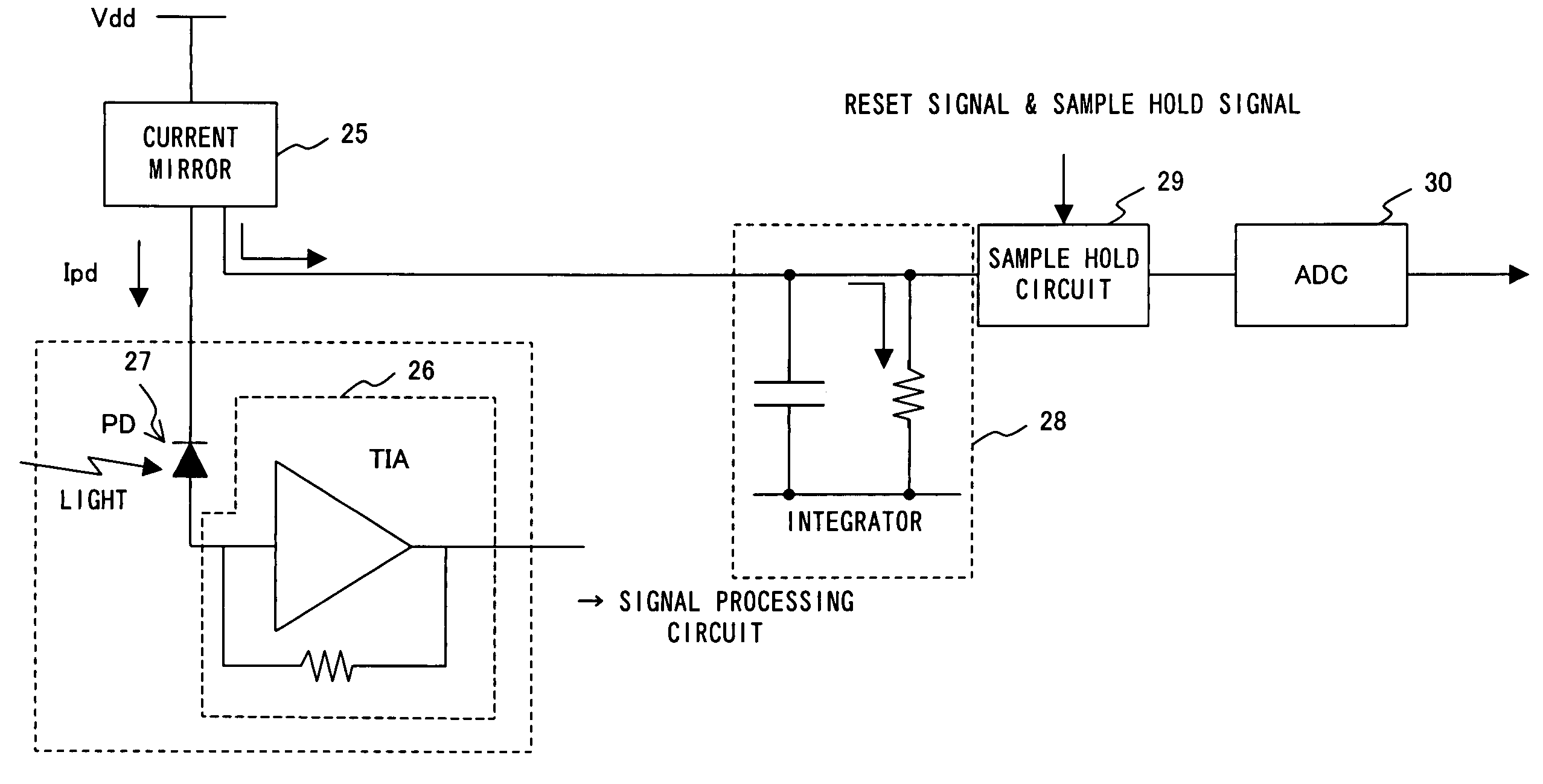
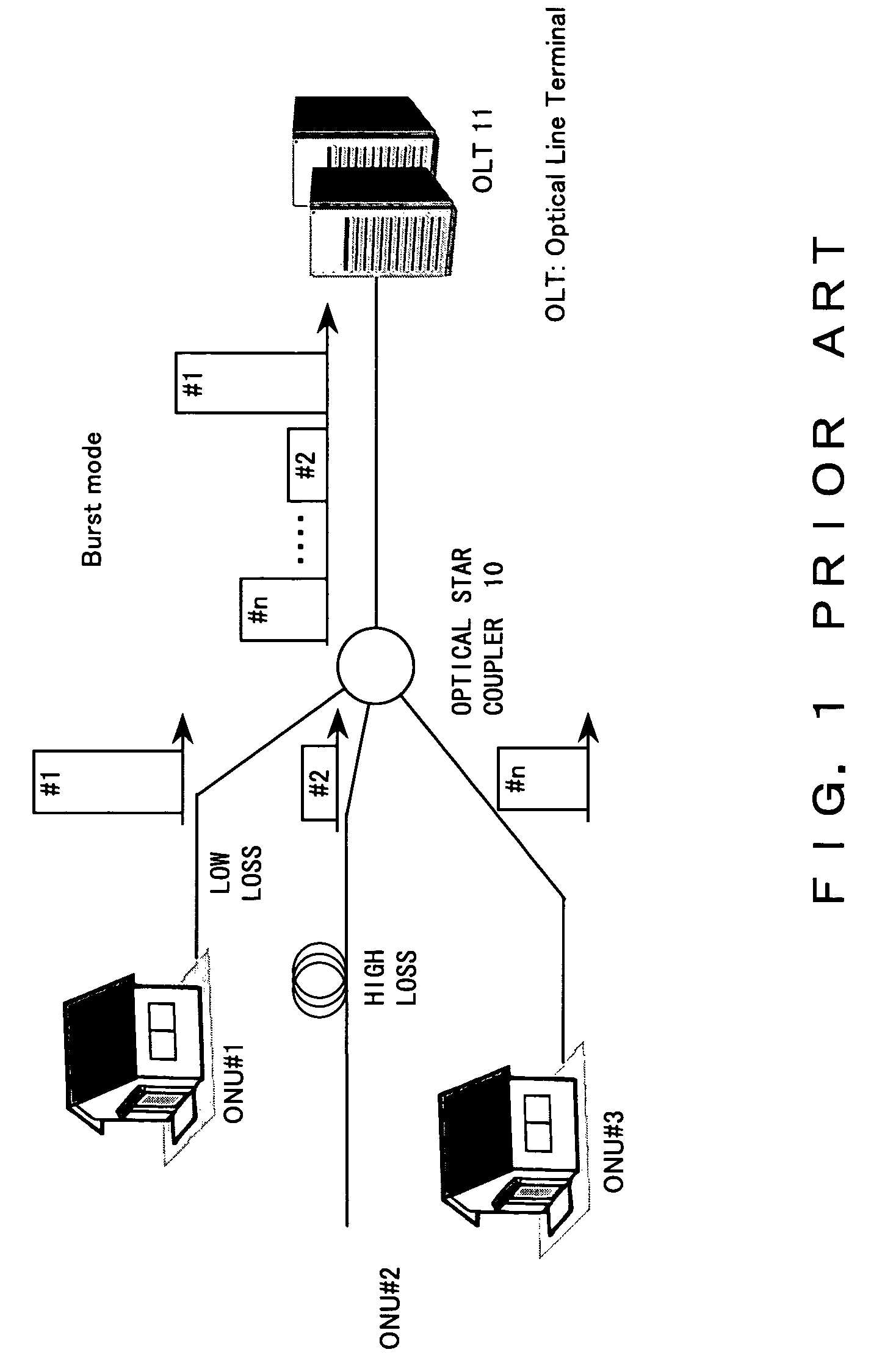
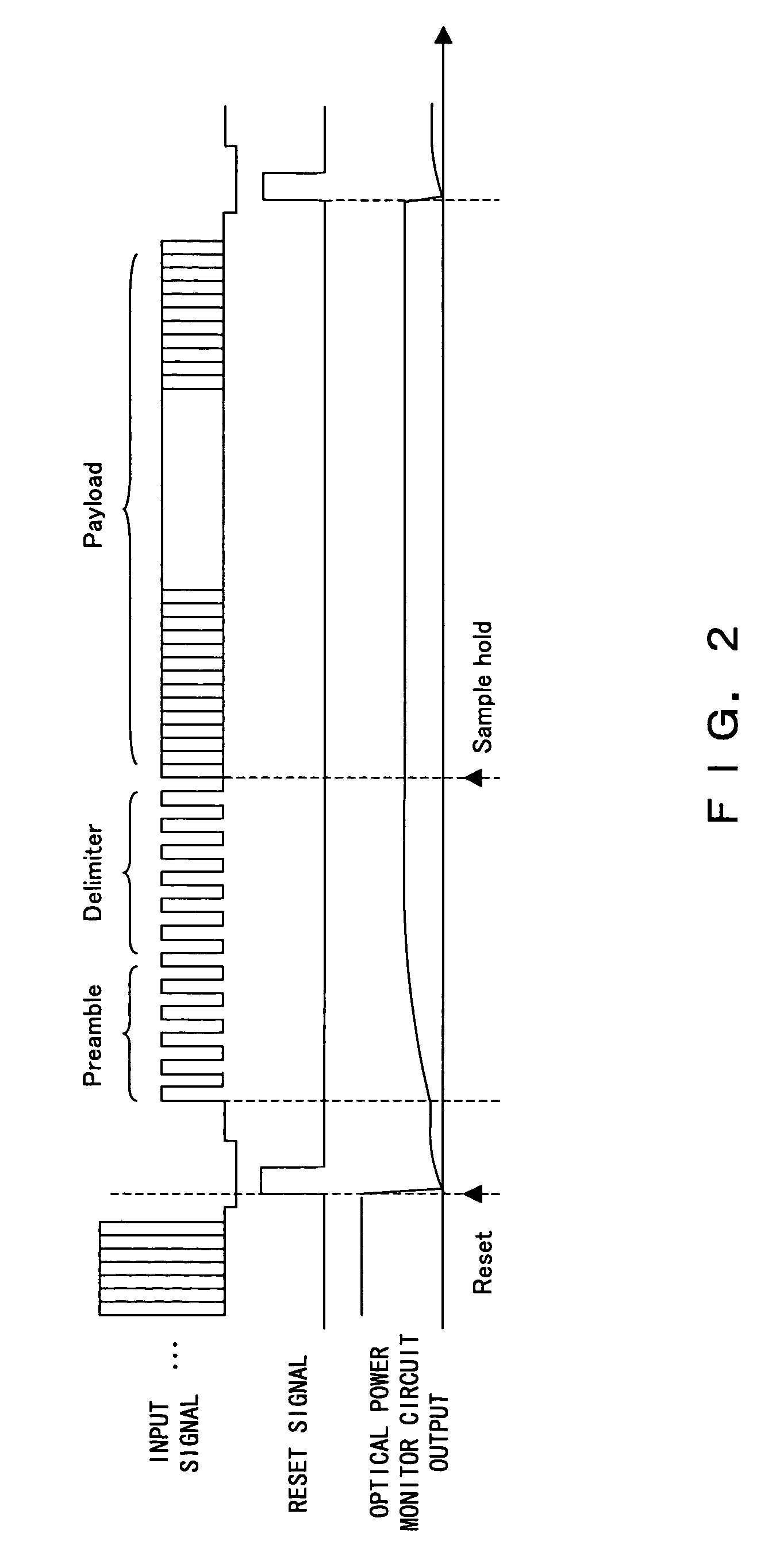
Optical power monitor for PON telecommunication
InactiveUS20080002973A1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationCommunications systemOptical power
In an optical telecommunication system in which an intensity of an arriving optical signal is different for each packet, detected is an optical intensity for each packet with little error. For this purpose, contrived is to detect an average optical intensity across header parts for each packet by focusing on the fact that the header part comprising the preamble and delimiter of a packet is in a bit pattern which includes approximately the same numbers of “0” and “1”.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optically isolated bias control circuit
InactiveUS20040257155A1Charge flow is minimalReduces flow of chargeTransistorAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationElectricityEngineering
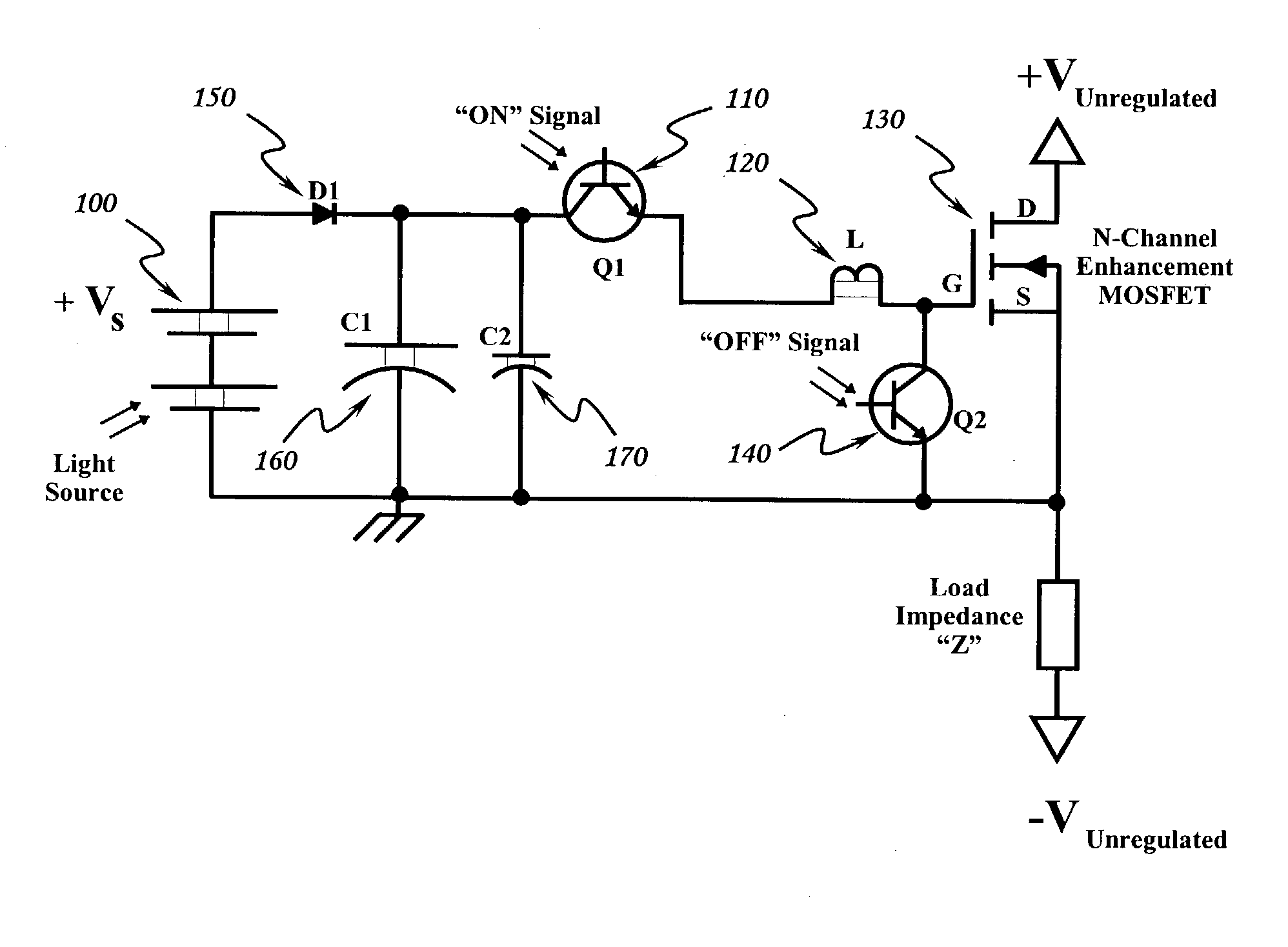
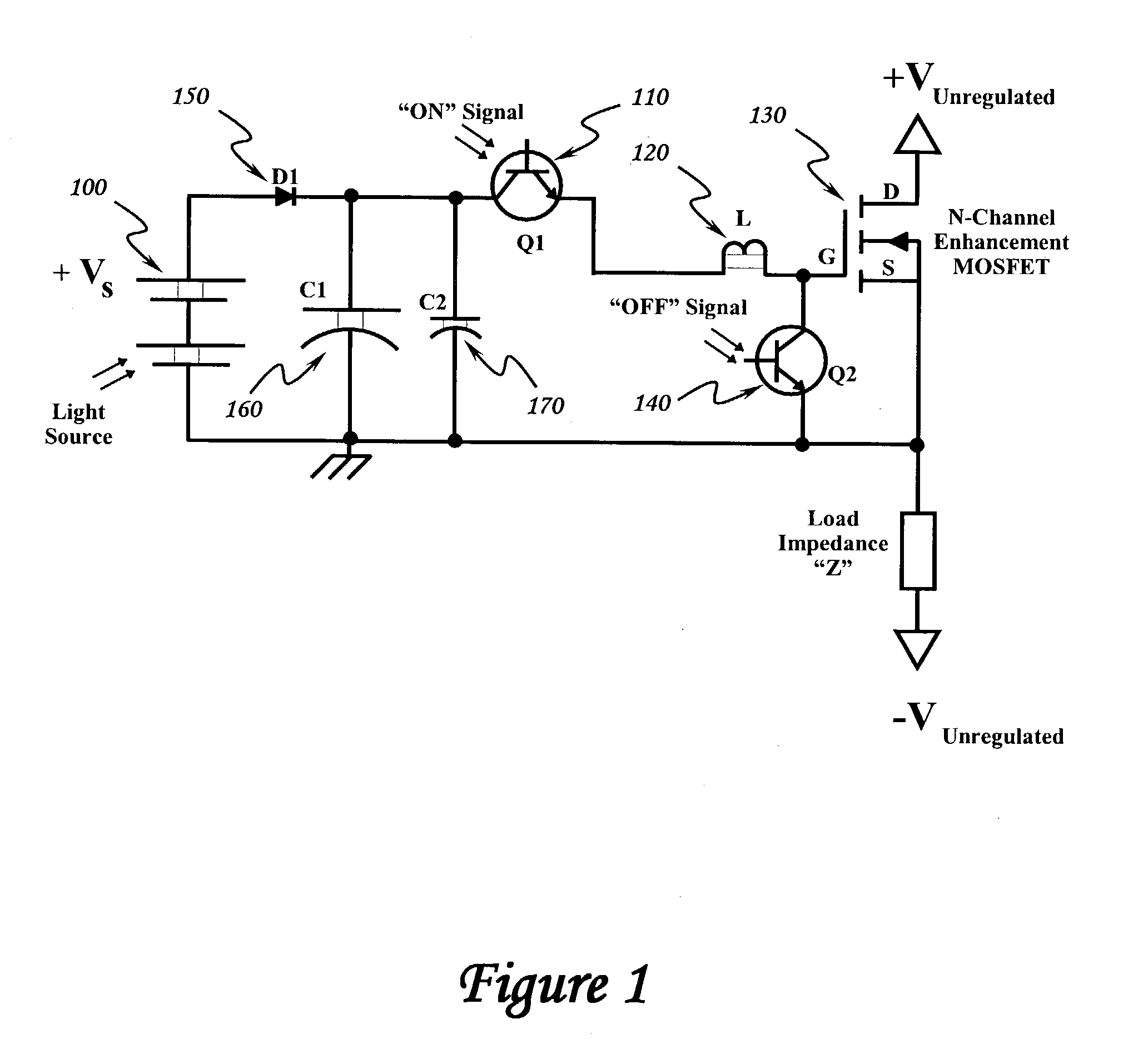
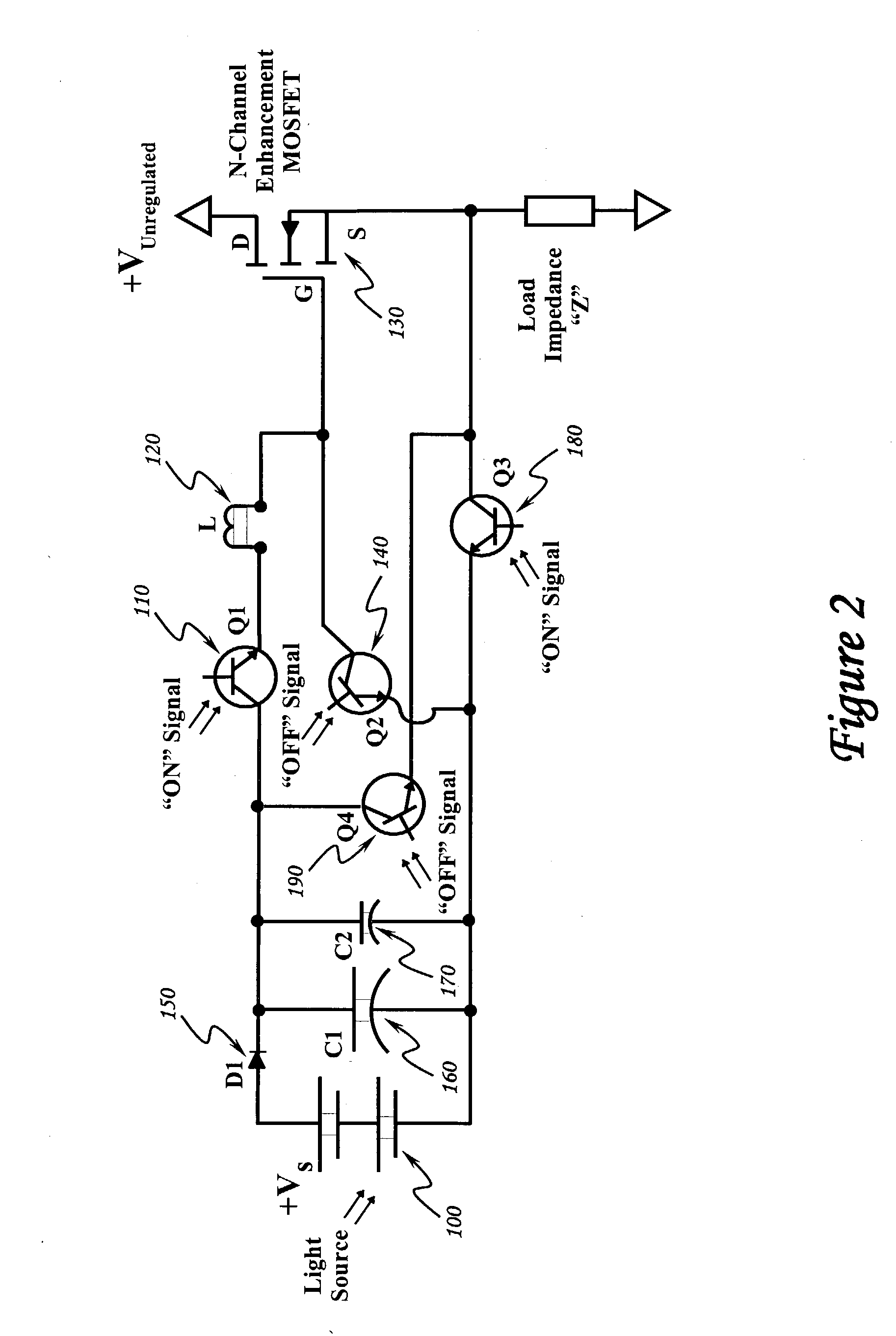
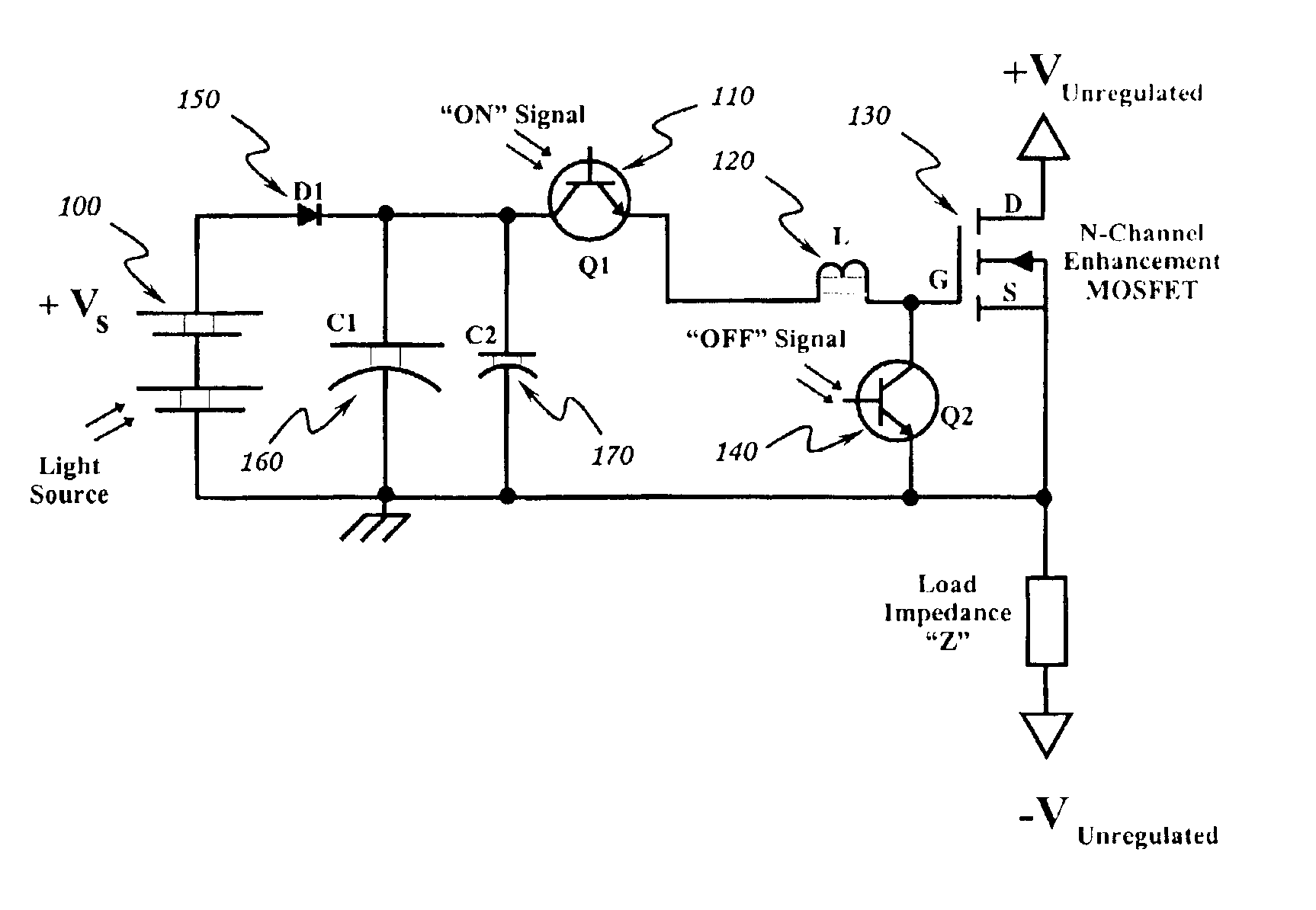
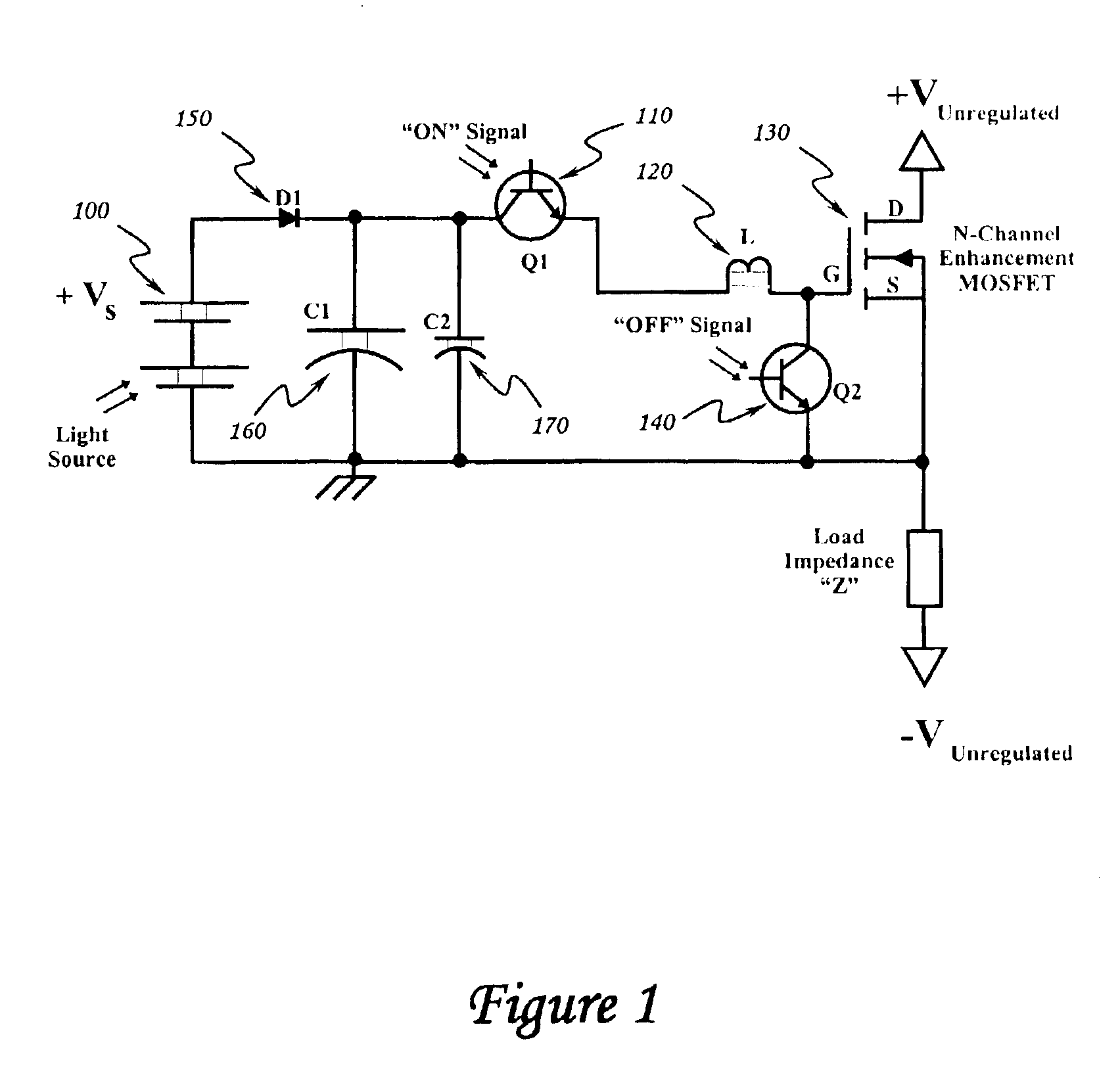
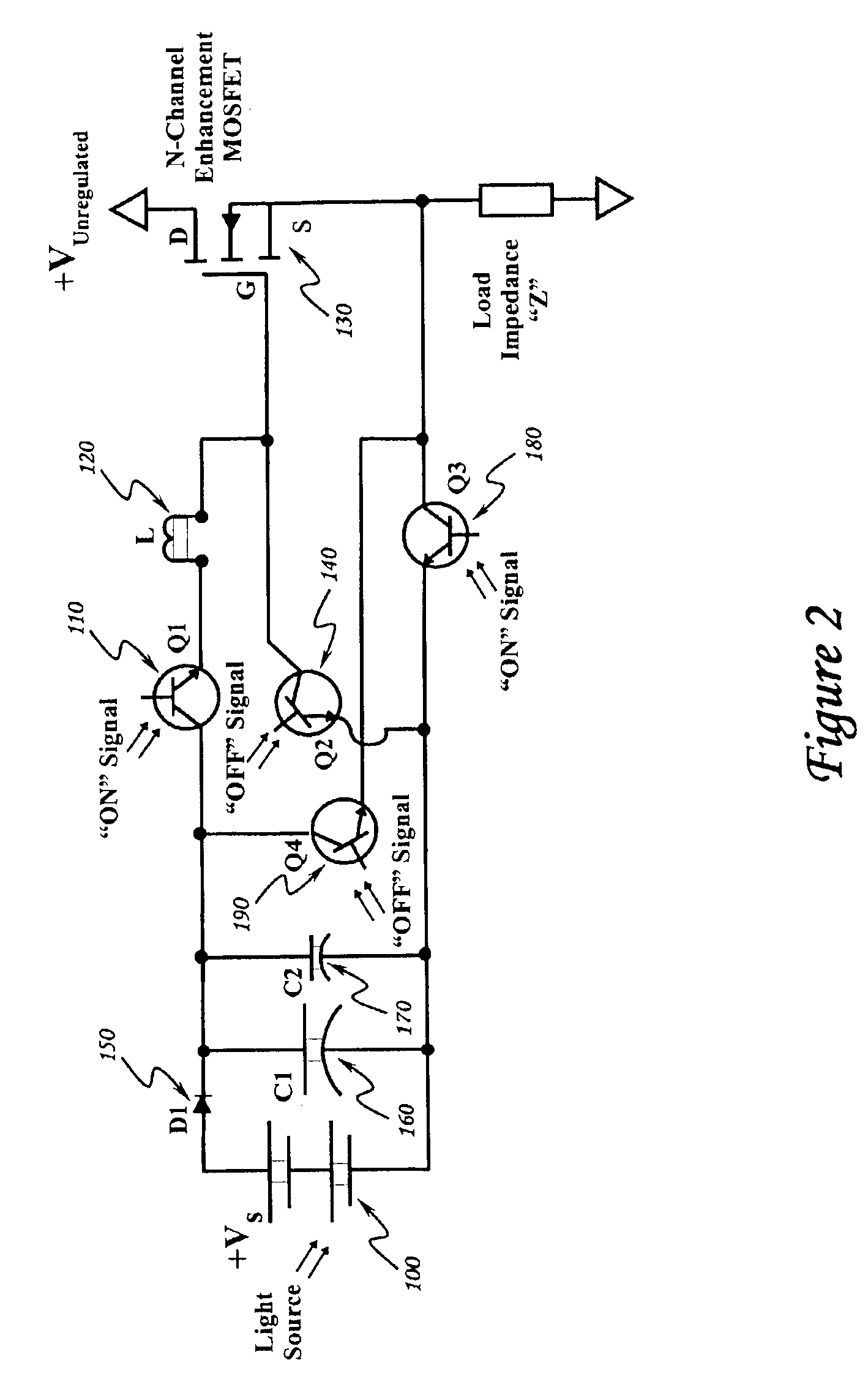
Optically isolated bias control circuit which provides bias current for switching circuits. Invention is amenable to high speed switching control with instantaneously variable pulse widths and duty cycles. Invention can be operated from DC upward in frequency, limited only by the characteristics of the implementing electrical components and electrical interconnections. Complementary embodiments of invention provide high speed operation with minimal electrical charge flow. Solar powered embodiments of invention may be used to control the switching of high power MOSFET-based switching circuits.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Parallel opto-electric structure for high sensitivity and wide bandwidth optical transceiver
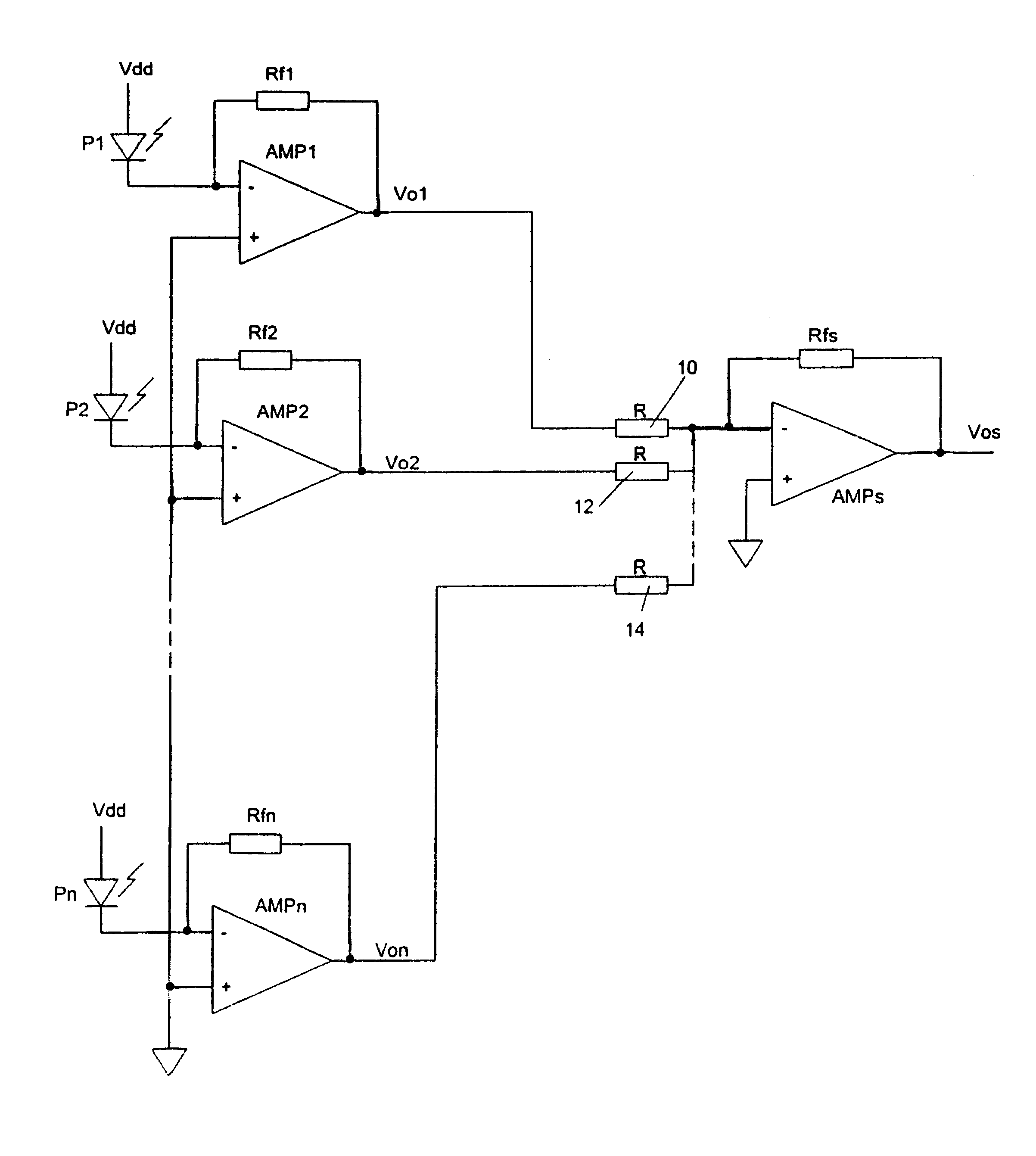
An optical receiver circuit including a plurality of PIN diodes, each associated with a dedicated element transimpedance amplifier, the outputs of the element transimpedance amplifiers being connected to a summing amplifier which sums the voltages output from the element transimpedance amplifiers. The optical receiver circuit provides the same output voltage value as a single large PIN diode having an active area comparable to the sum of the active areas of the smaller PIN diodes, and thus has the same high sensitivity as the single large PIN diode but a much wider bandwidth.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
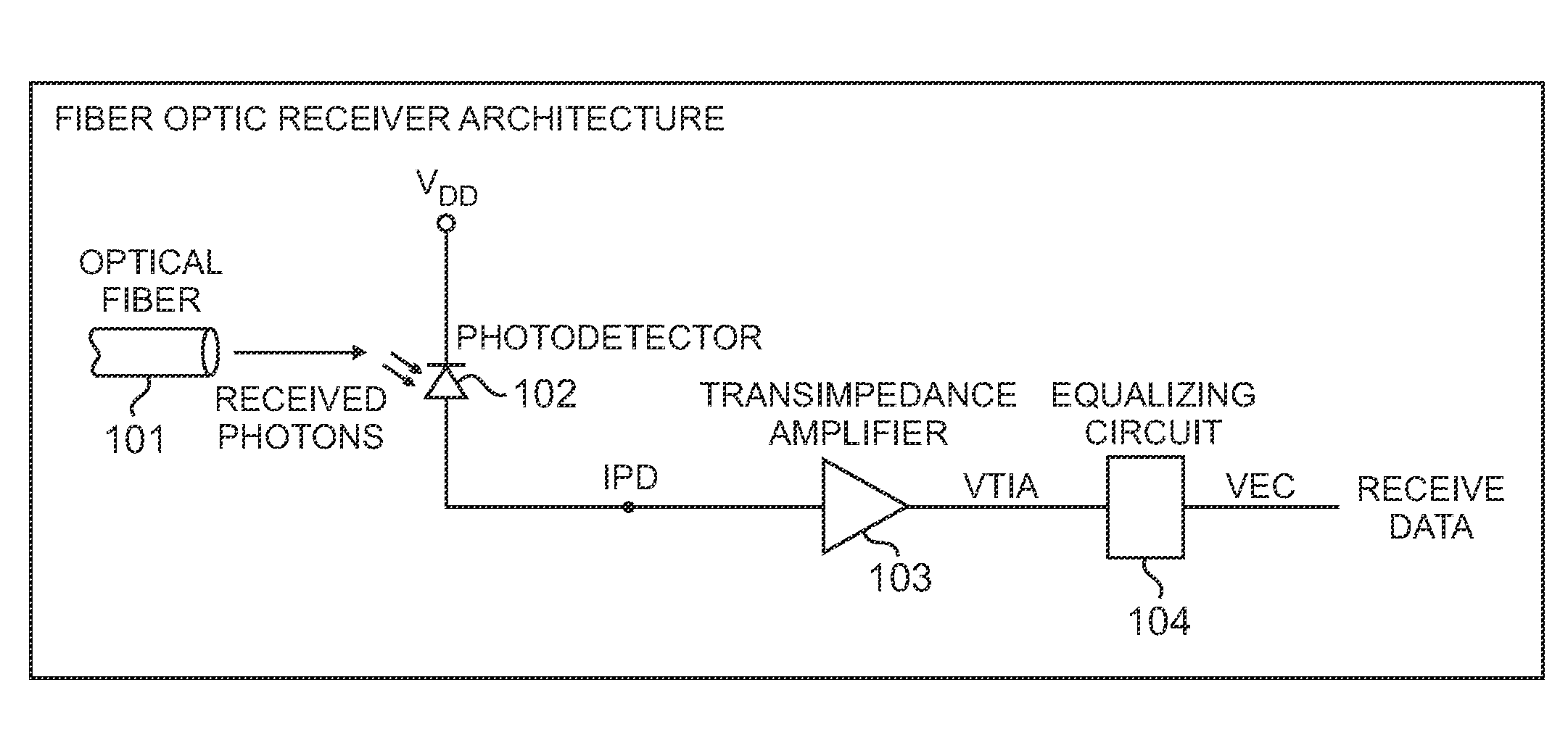
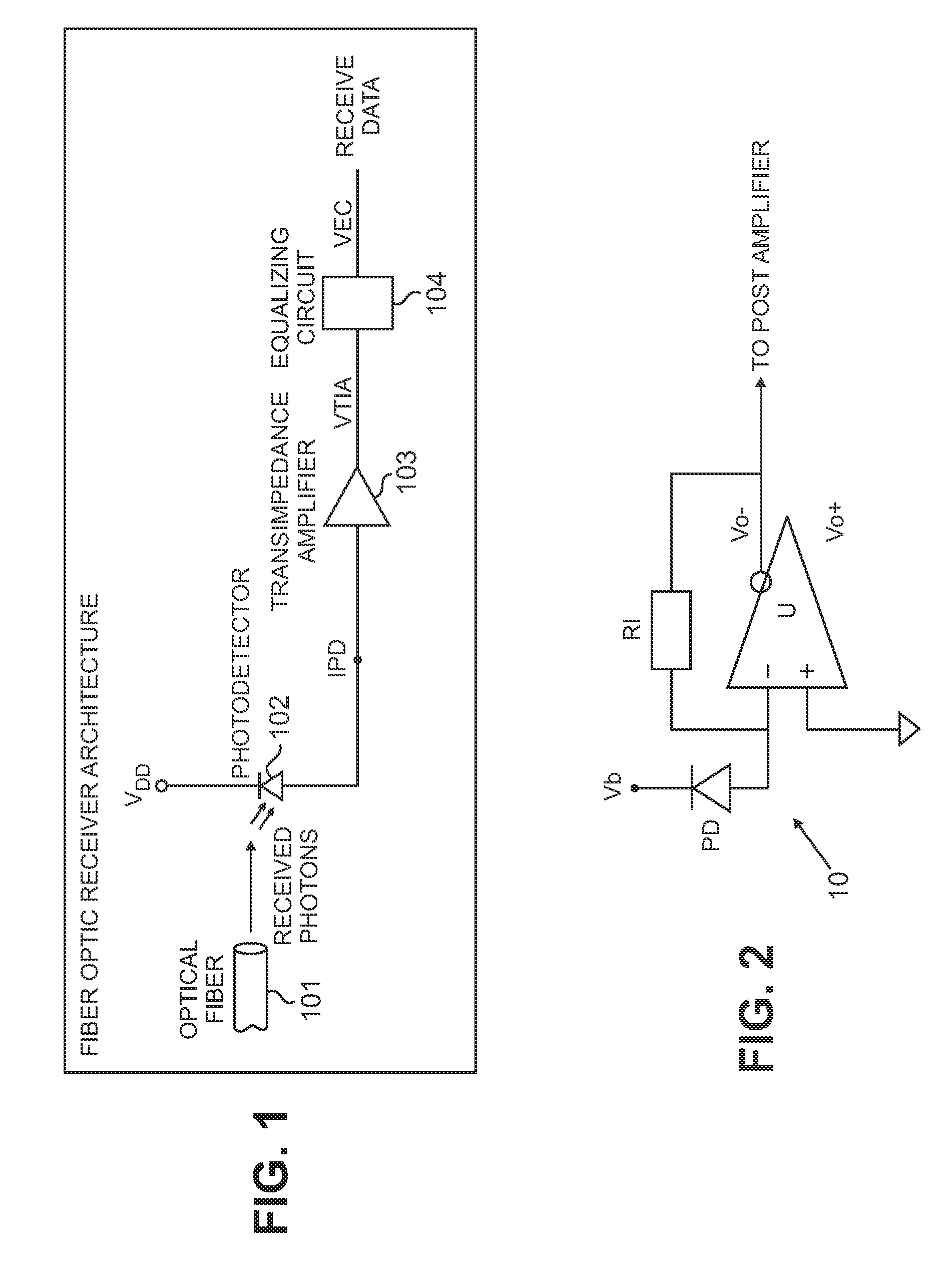
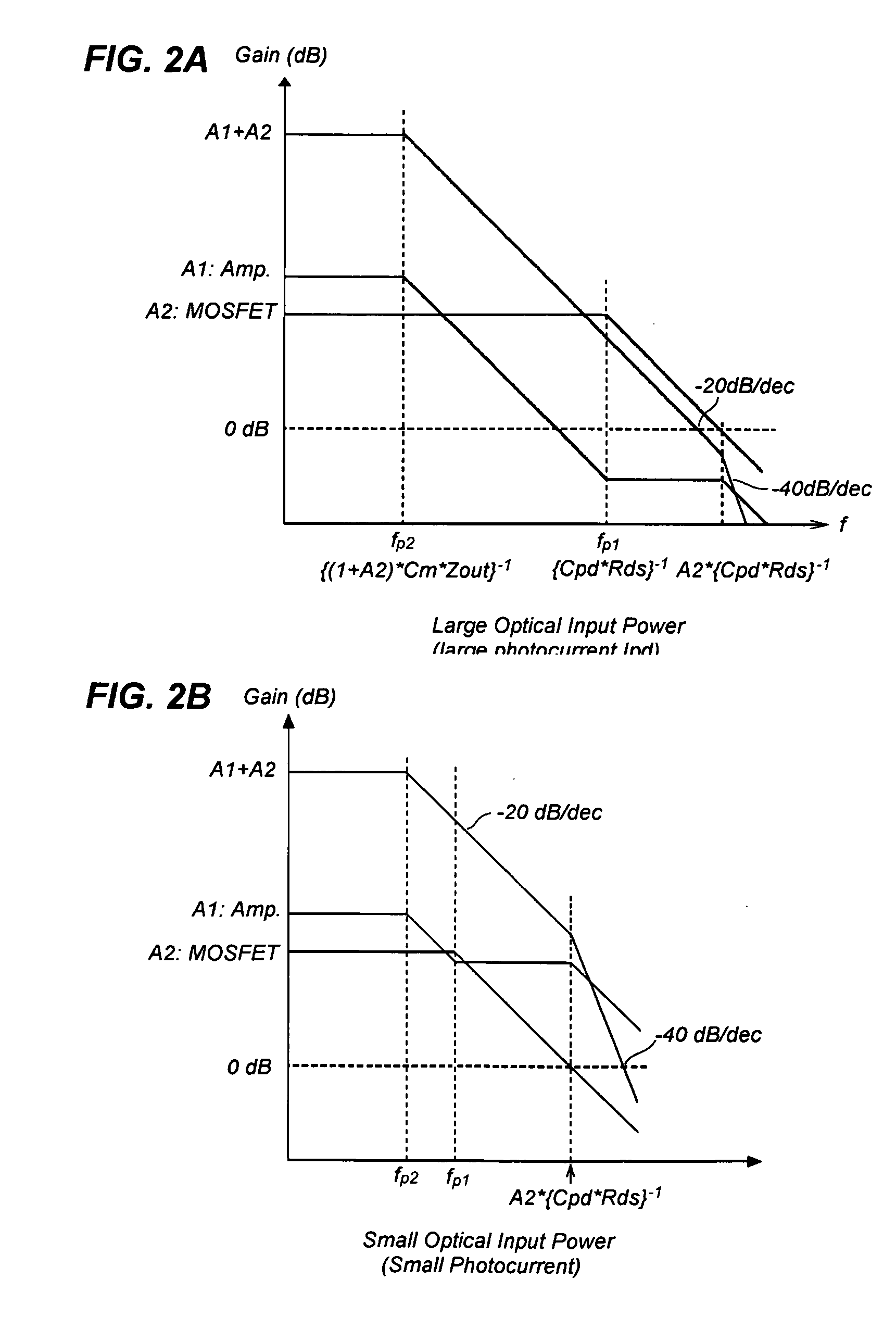
High Sensitivity Optical Receiver Employing a High Gain Amplifier and an Equalizing Circuit
ActiveUS20090315626A1Constant gainAmplifiers controlled by lightCoupling light guidesAudio power amplifierEngineering
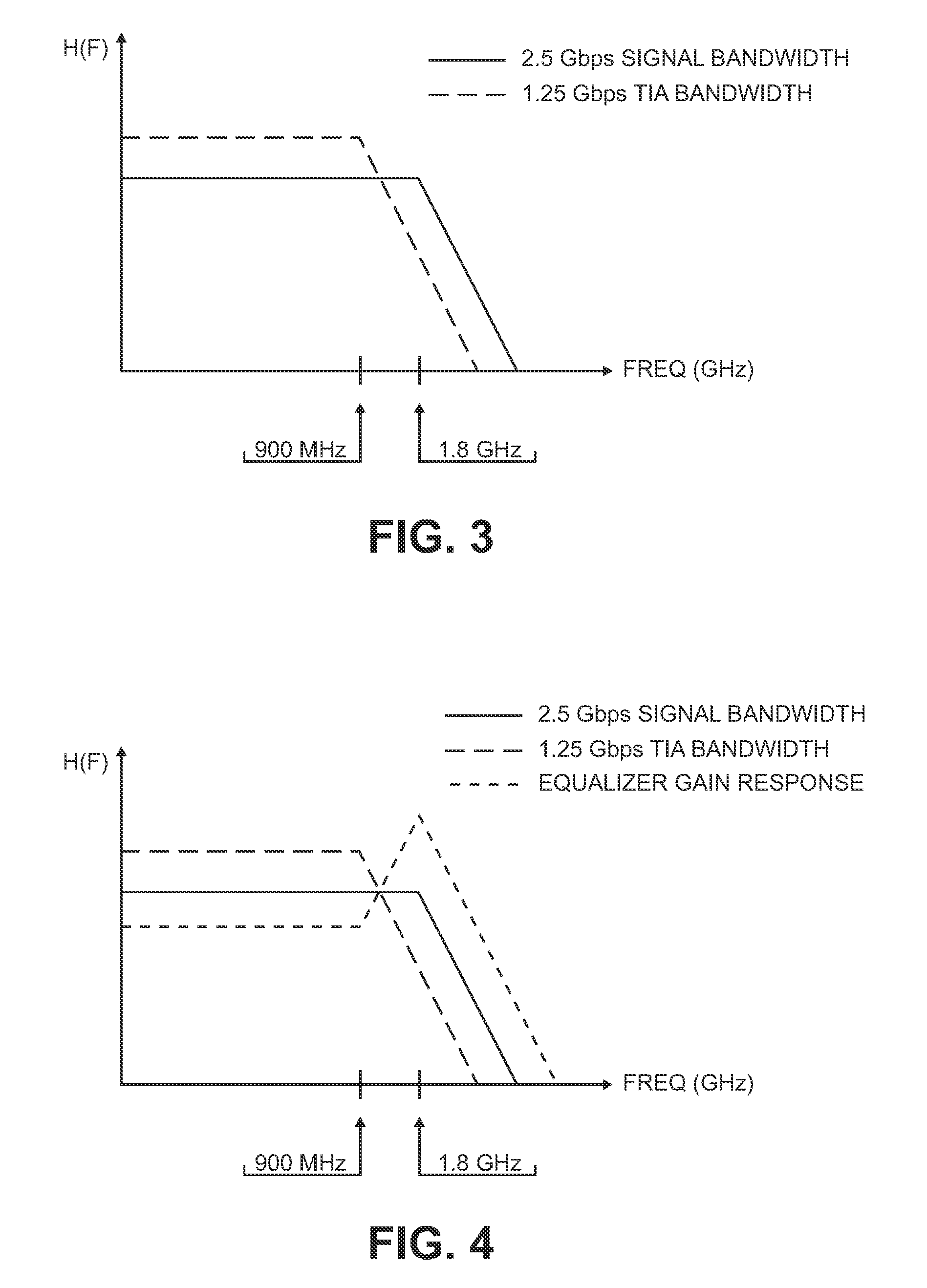
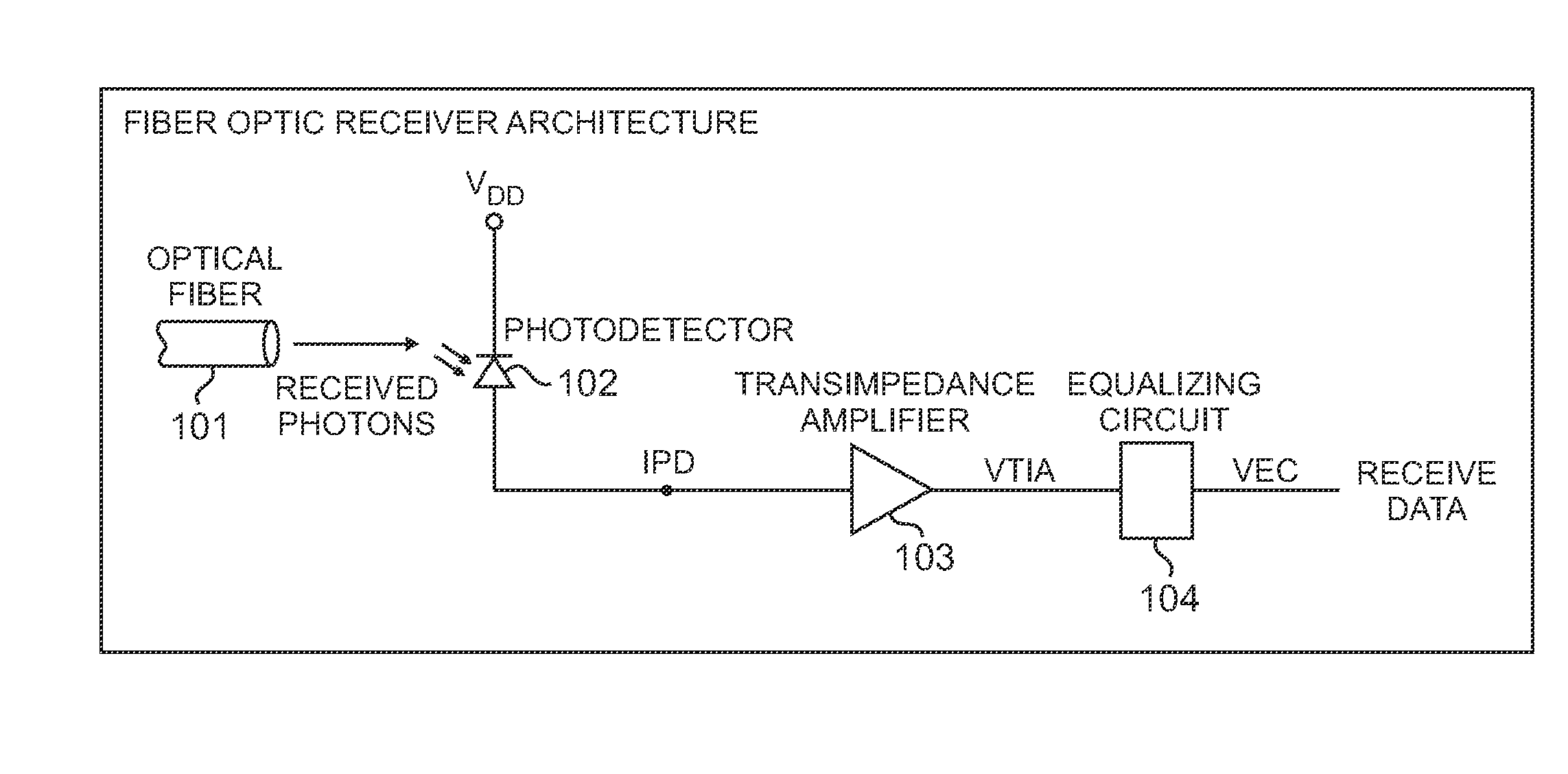
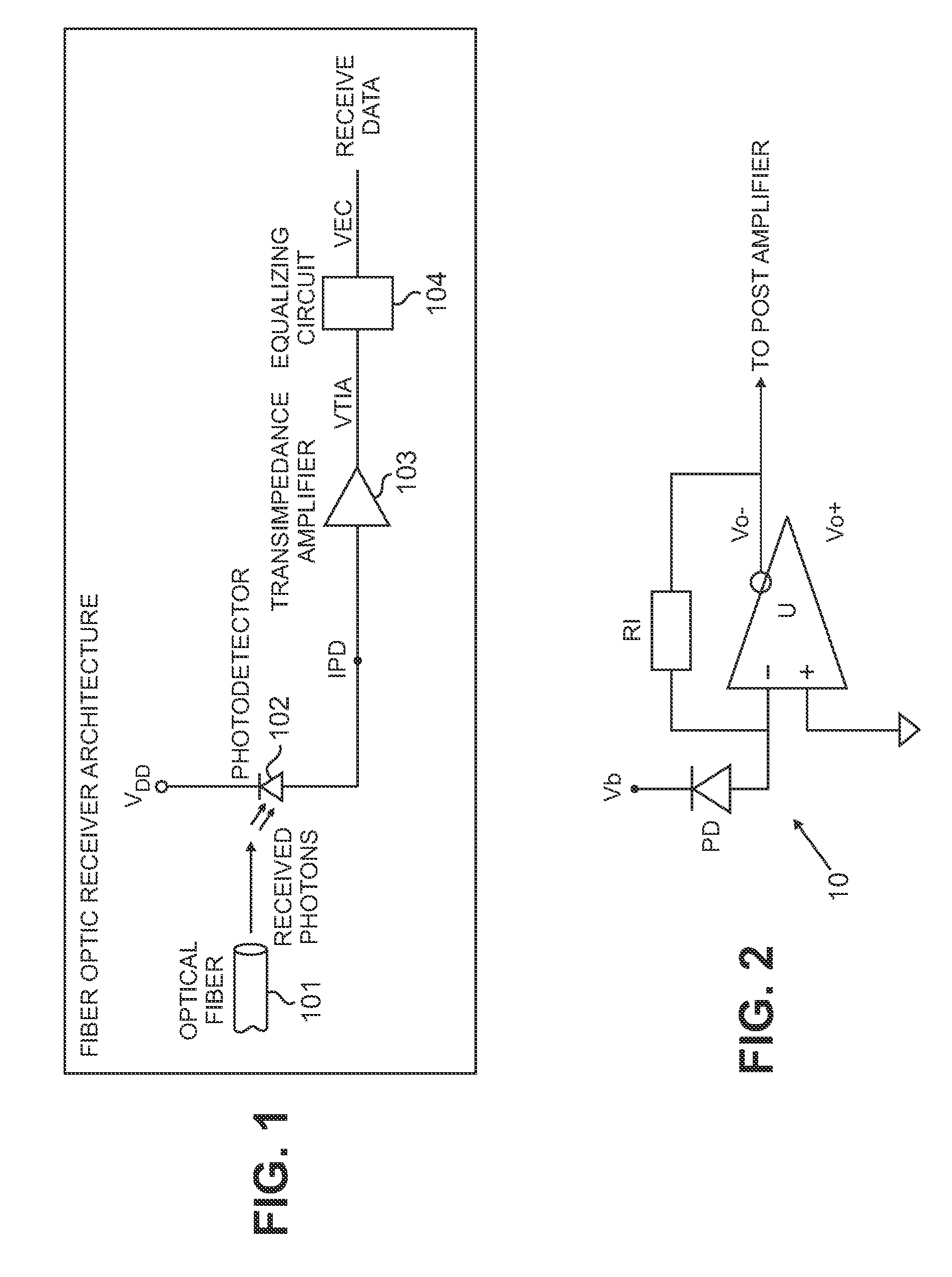
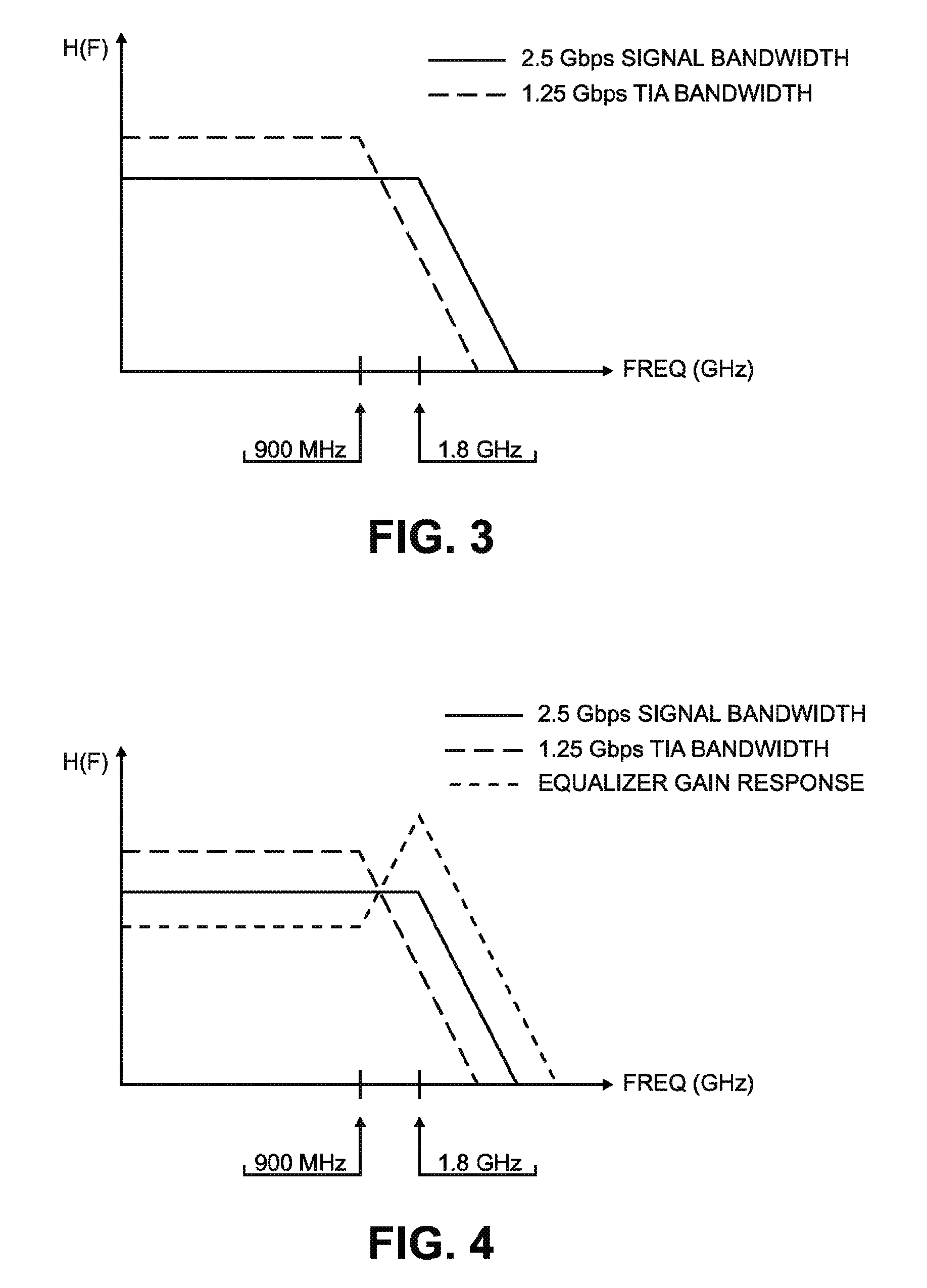
An optical receiver includes a light receiving element for converting an optical signal to an electrical signal having a first bandwidth and an amplifier for amplifying the electrical signal. The amplifier has a first gain response that yields a second bandwidth that is less than the first bandwidth. The optical receiver also includes an equalizing circuit operationally coupled to the amplifier. The equalizing circuit has a second gain response that compensates for the first gain response of the amplifier so that a substantially constant net gain is imparted by the amplifier and the equalizing circuit to the electrical signal over the first bandwidth.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
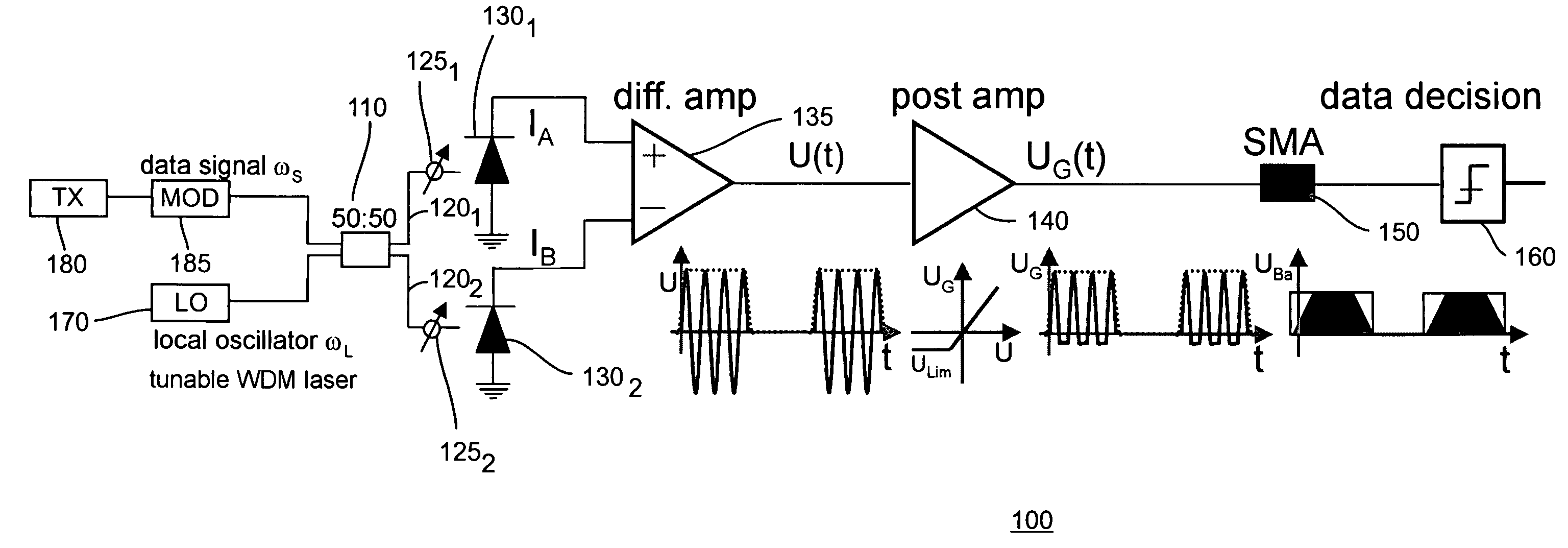
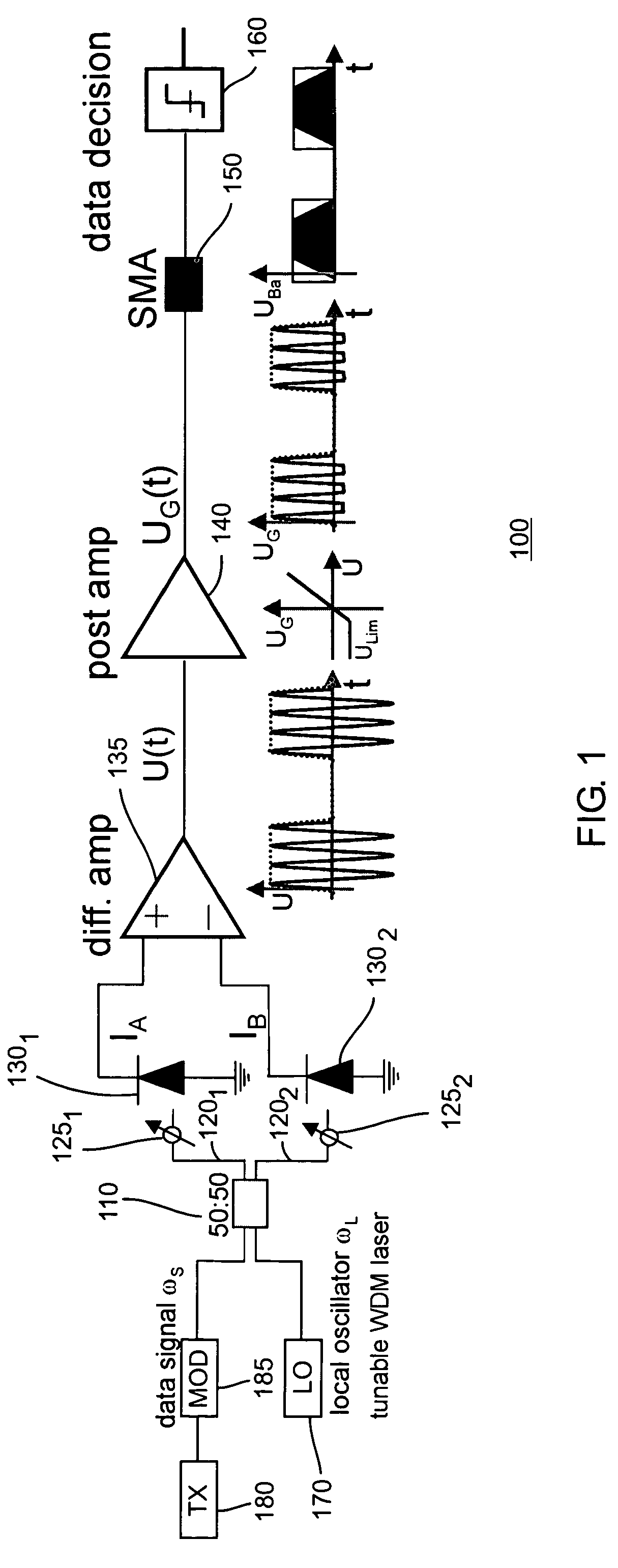
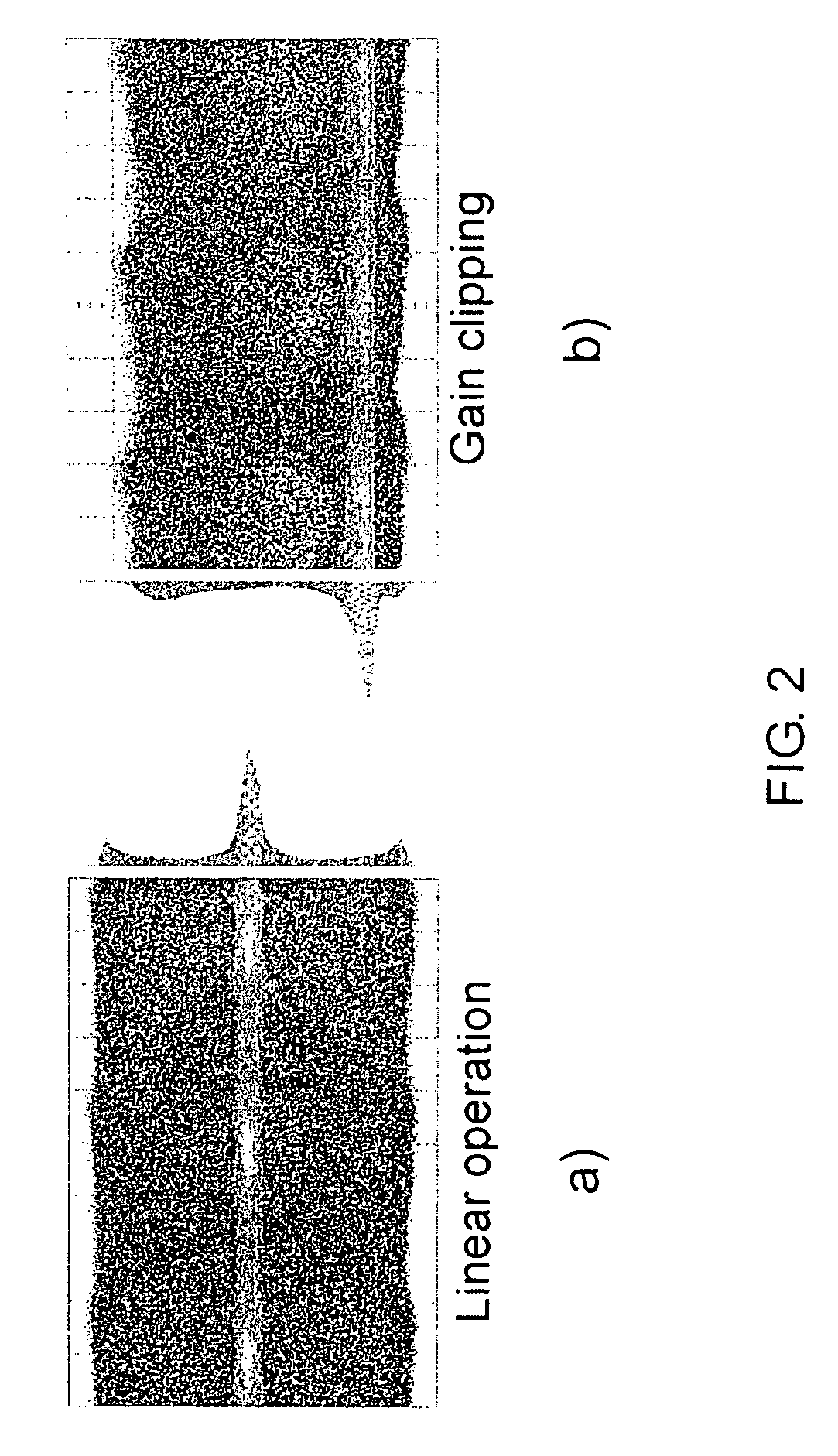
Multicasting optical switch fabric and method of detection based on novel heterodyne receiver
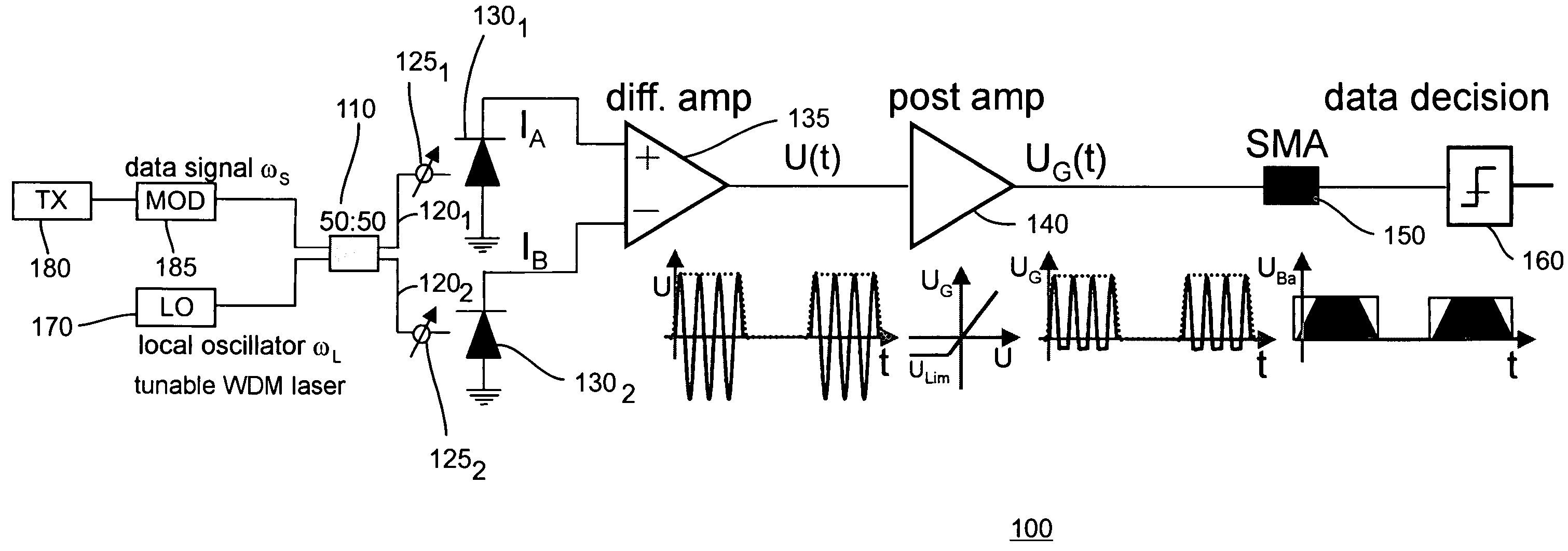
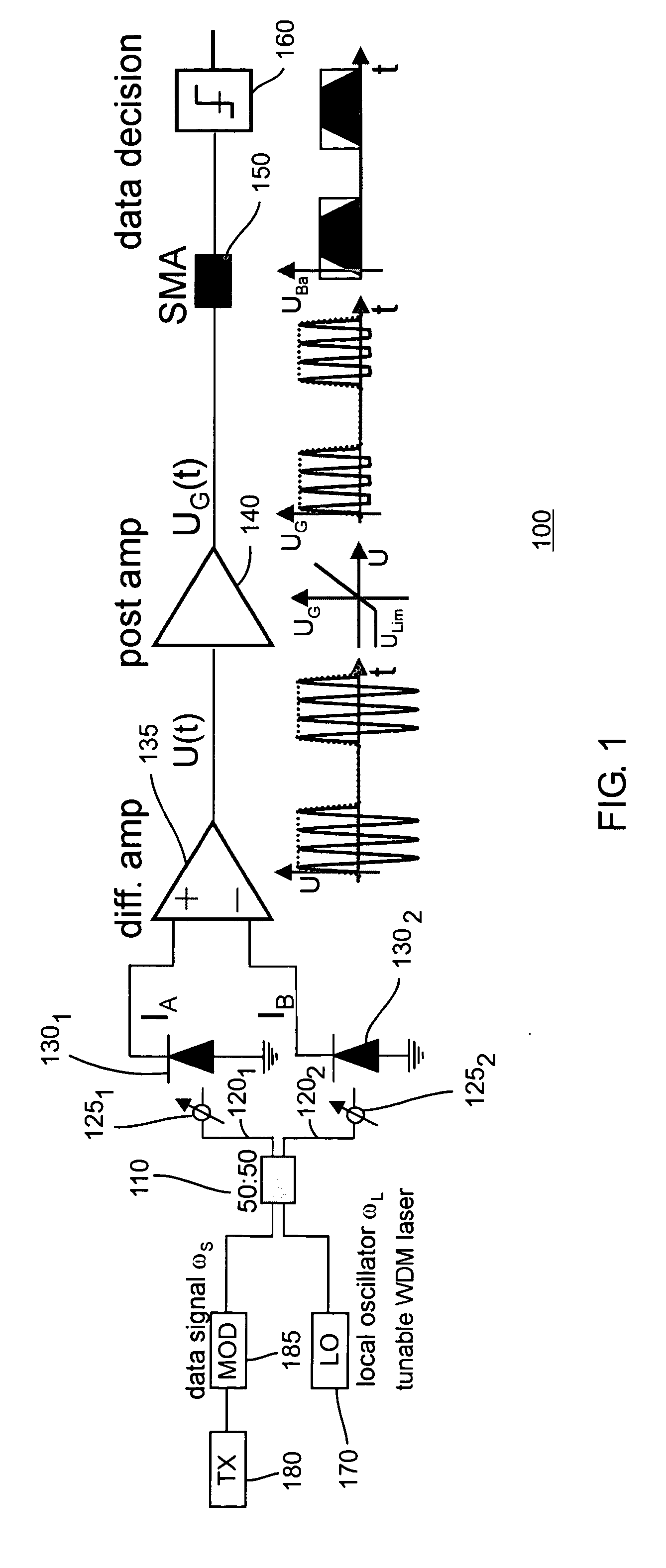
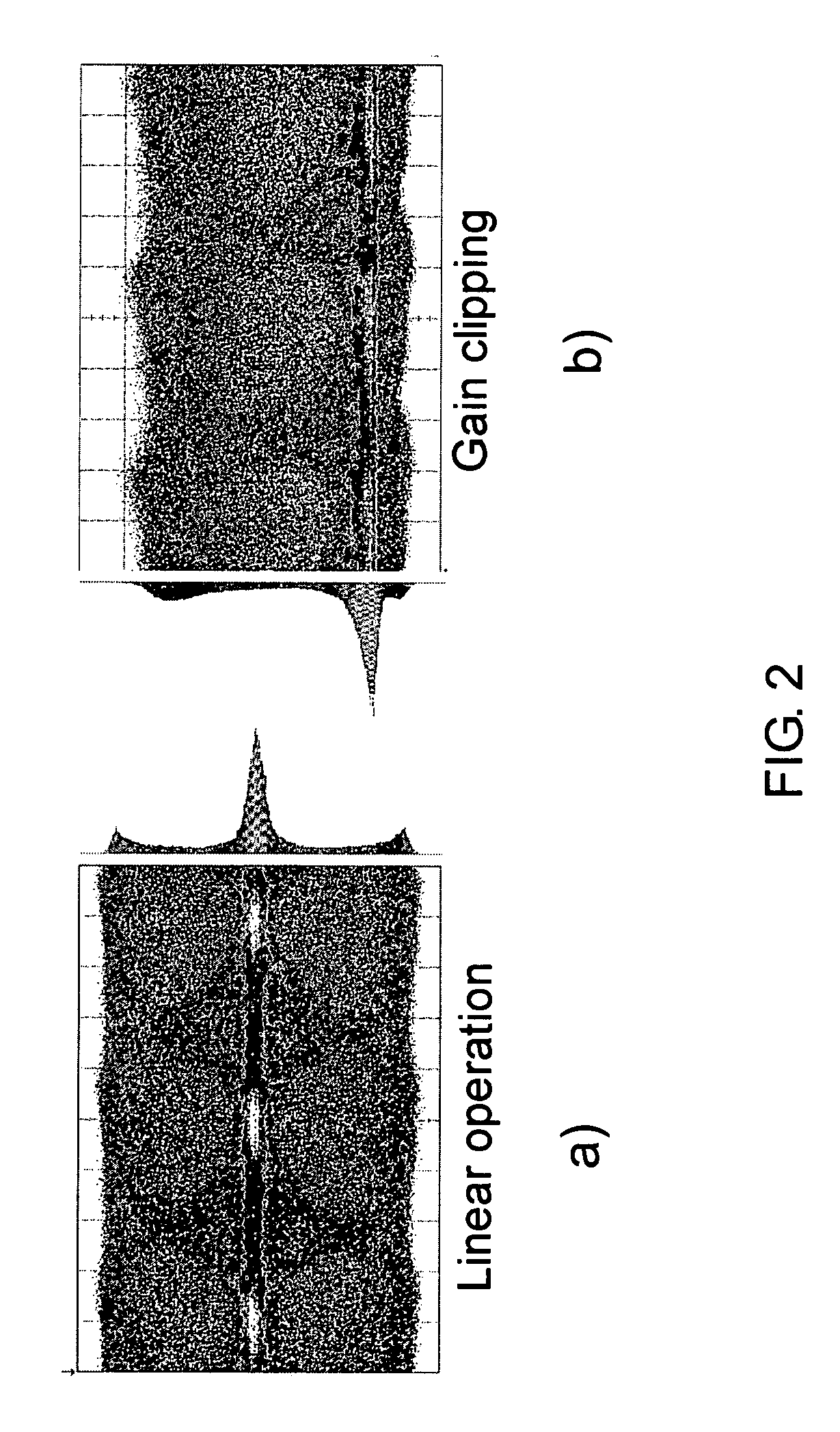
InactiveUS20050069333A1Time-consume wavelength fine tuningFast channel selectionAmplifiers controlled by lightTransmission monitoringLocal oscillatorEngineering
The inventors propose herein a switch fabric architecture that allows broadcasting and fast channel access in the ns-range. In various embodiments of the present invention, 10 Gb / s receiver modules are based on a novel heterodyne receiver and detection technique, which is tolerant to moderate wavelength drifts of a local oscillator. A gain clipped electrical amplifier is used in the novel receiver as a rectifier for bandpass signal recovery.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
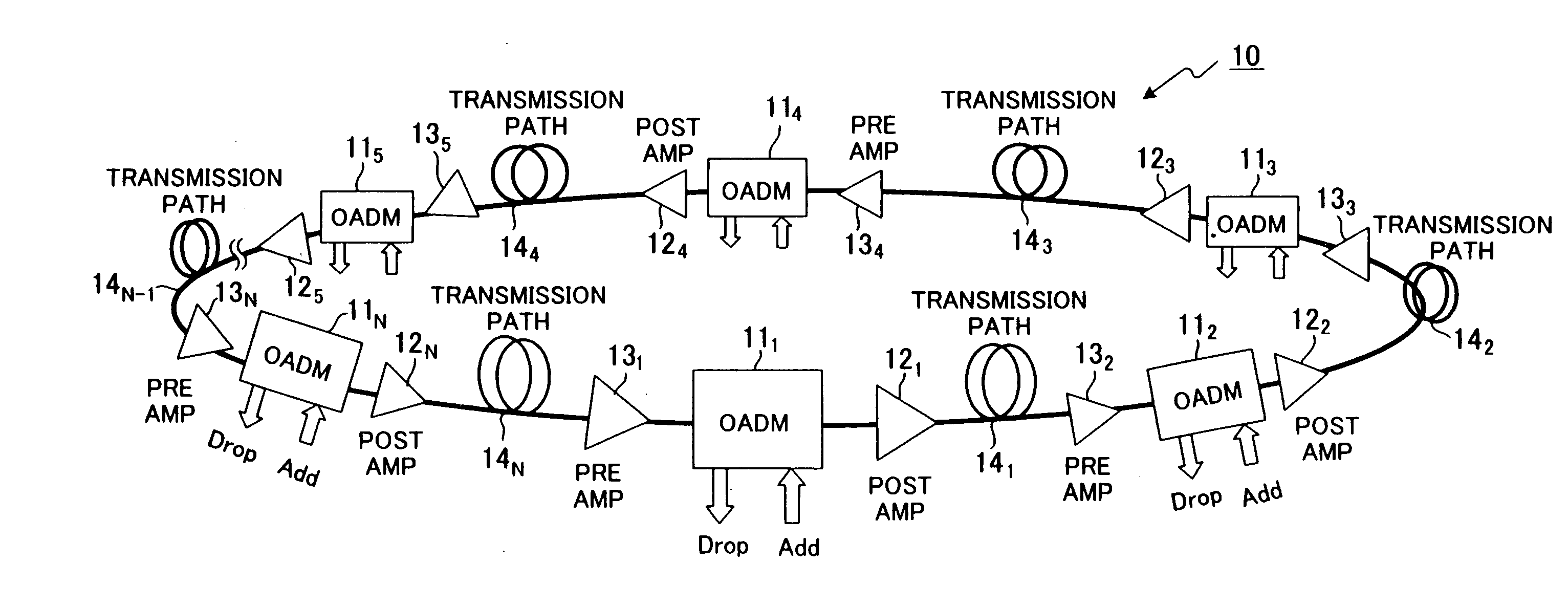
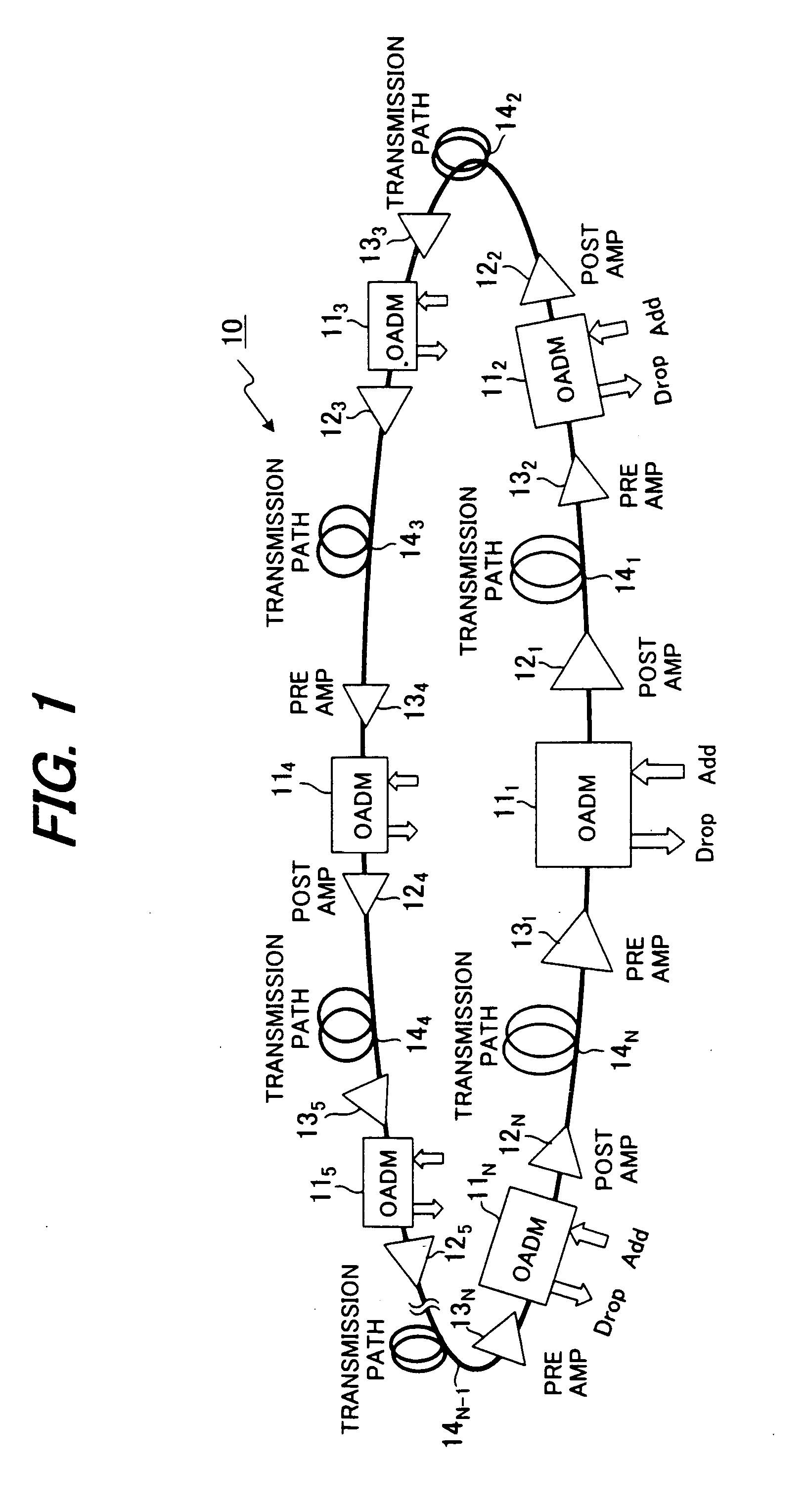
Wavelength-division-multiplexing optical transmission system and control method thereof
InactiveUS20070269215A1Keep the differenceFast transferLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingTransport system
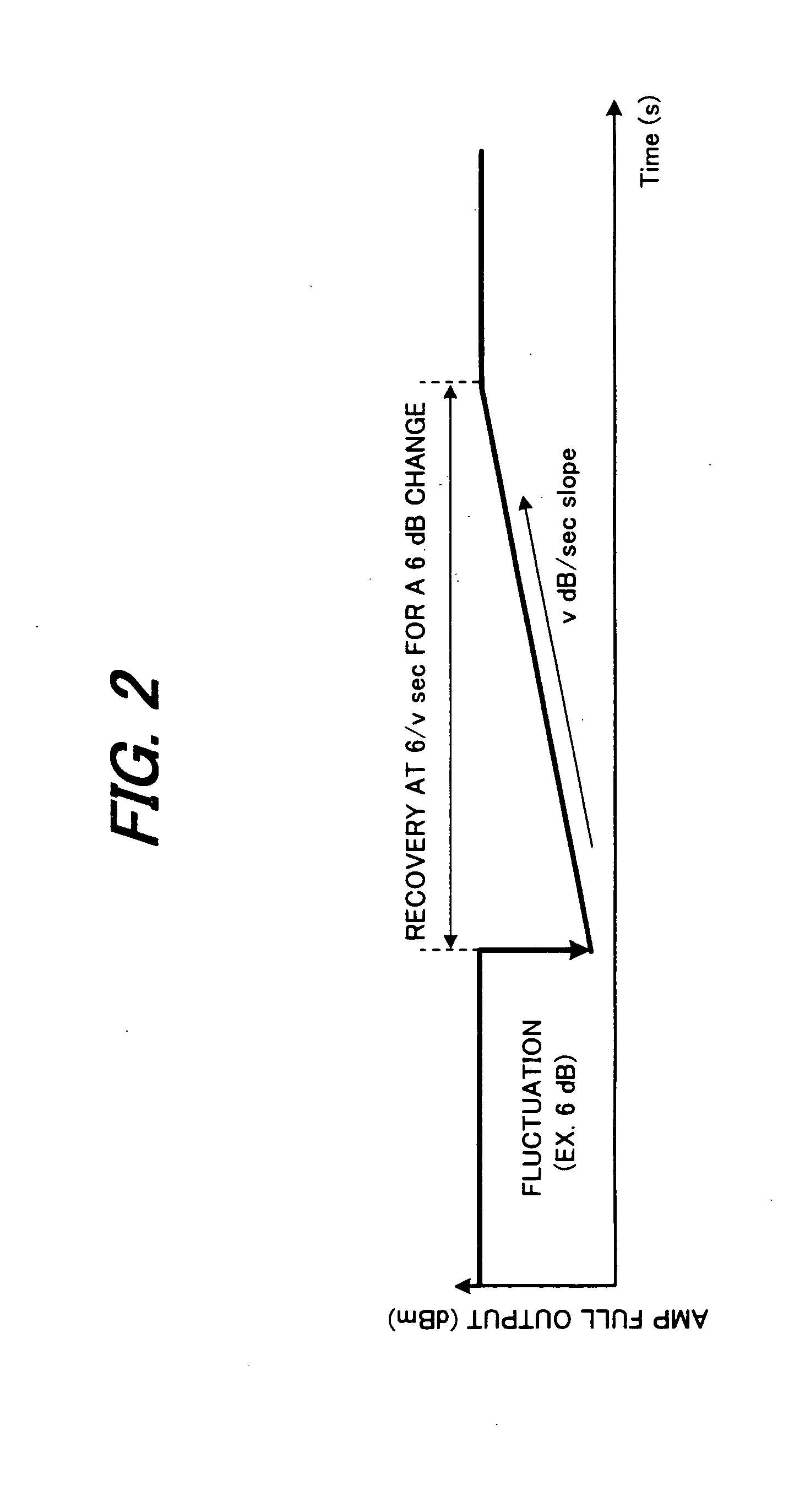
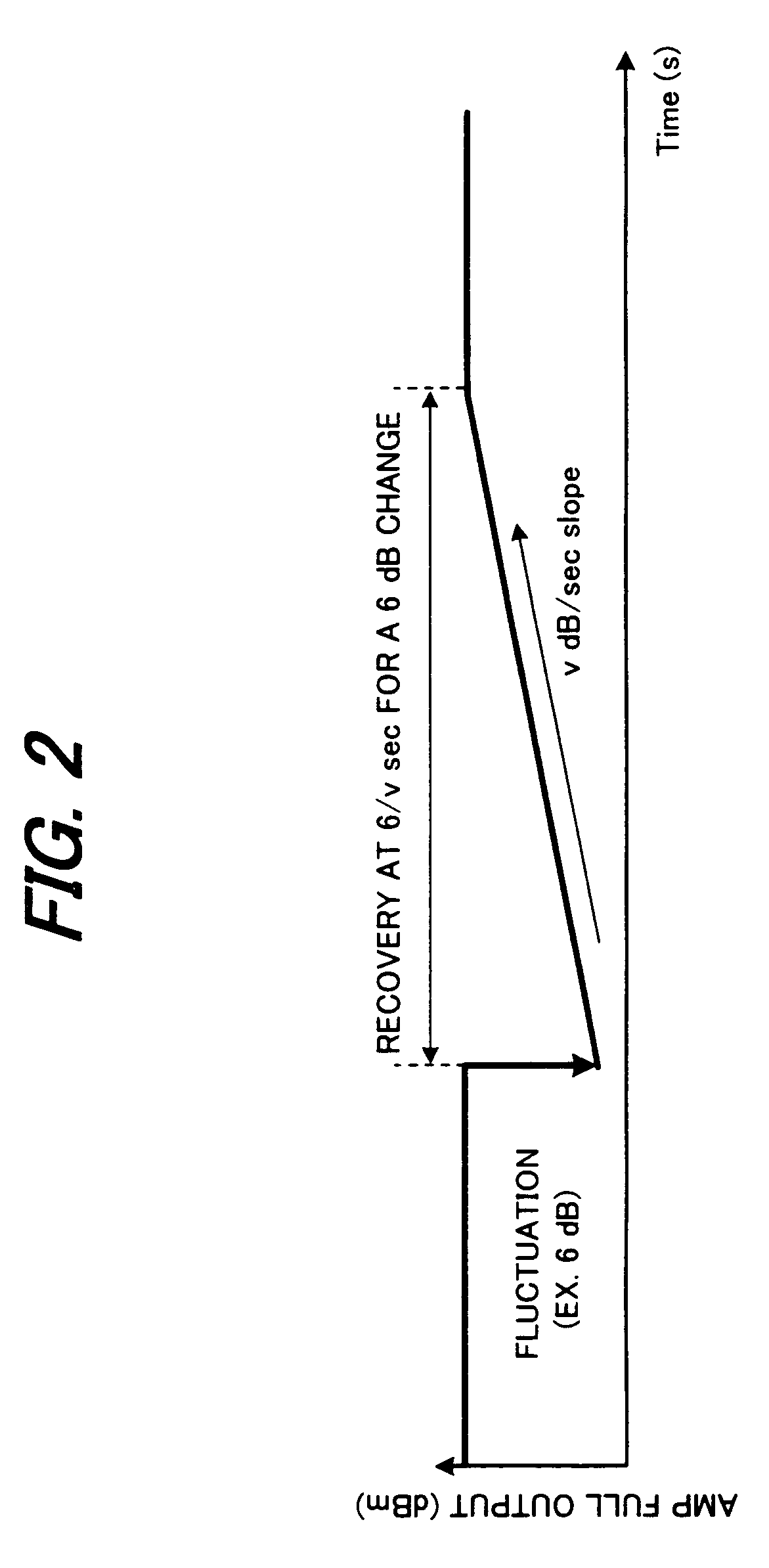
In a wavelength-division-multiplexing optical transmission system in which optical-node apparatuses that perform relay transmission of wavelength-division-multiplexed light are located at specified nodes in a main optical transmission path, an optical amplifier switches level control to constant-gain control when there is a notification of a change in the number of multiplexed wavelengths, and then after a specified amount of time restarts level control so that the level becomes a target level that corresponds to the actual number of wavelengths. When doing this, an optical-transmission-system-control unit controls the optical-transmission system so that the equationT<Y / (N·v)is satisfied, wherein T denotes a period from the time when a change in the number of multiplexed wavelengths occurs until said constant-gain control starts v denotes output-level-recovery speed of the optical amplifier, Y denotes fluctuation allowance of a receiving unit after wavelength-division-multiplexing transmission, and N is a maximum number of spans.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
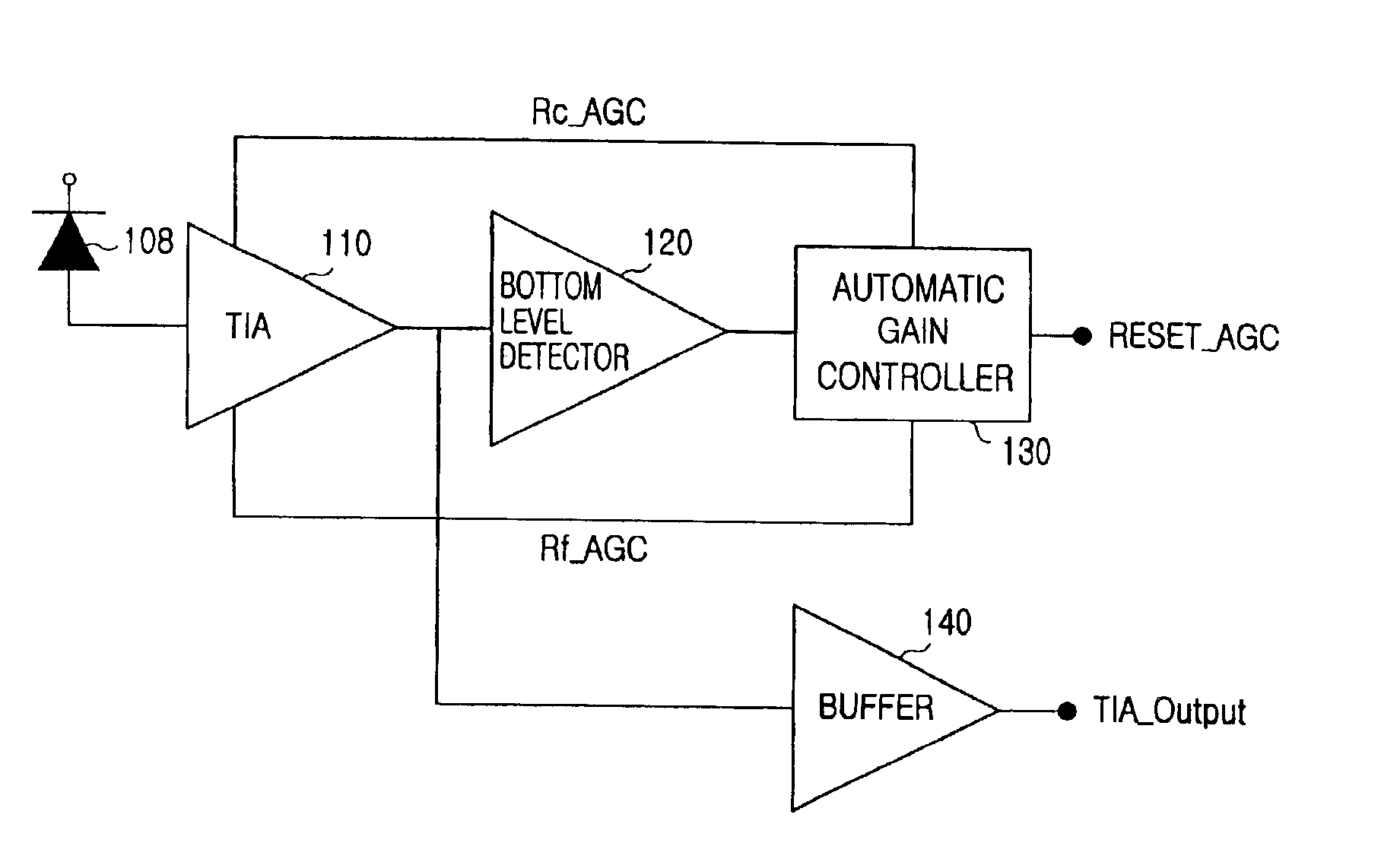
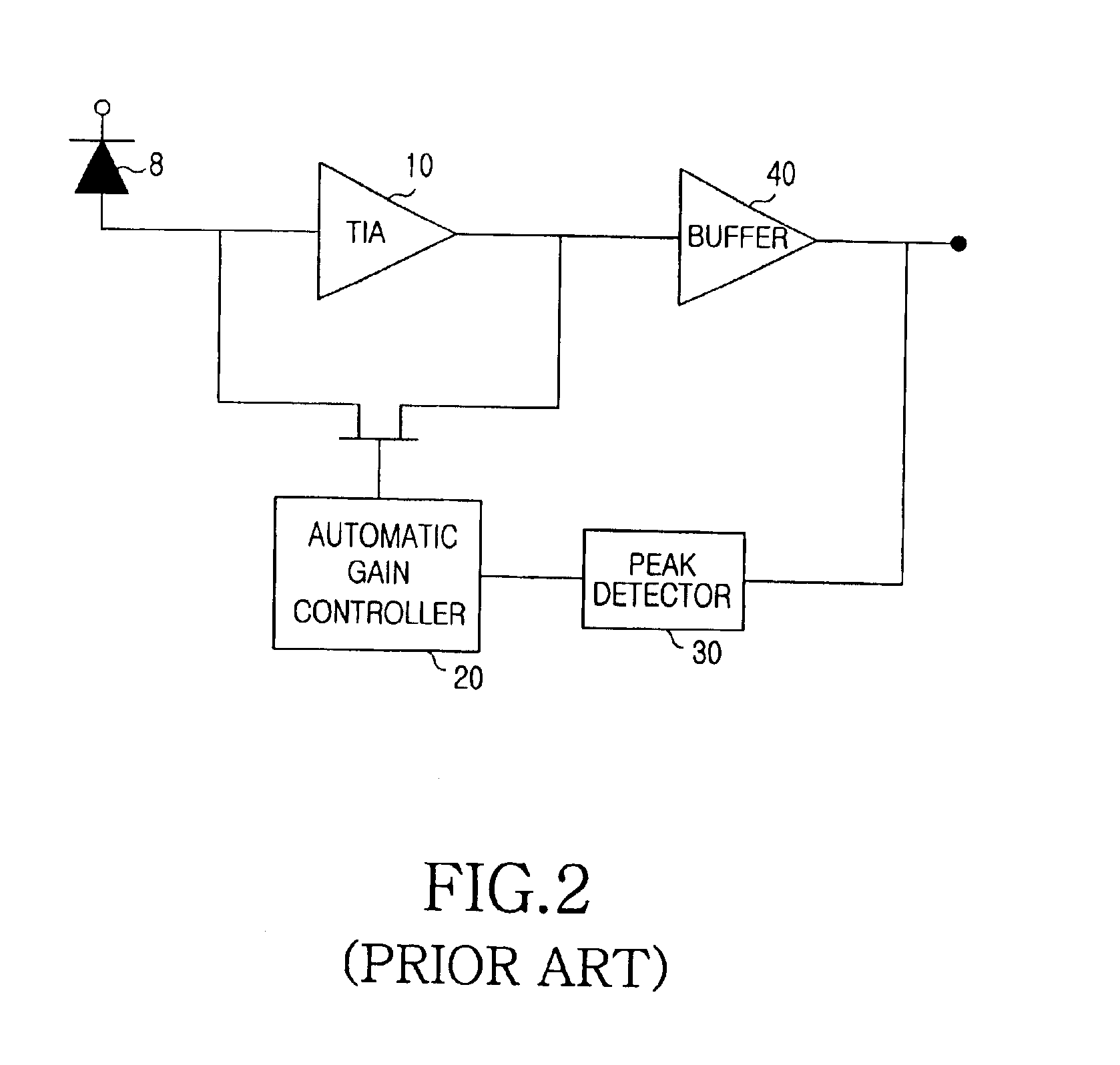
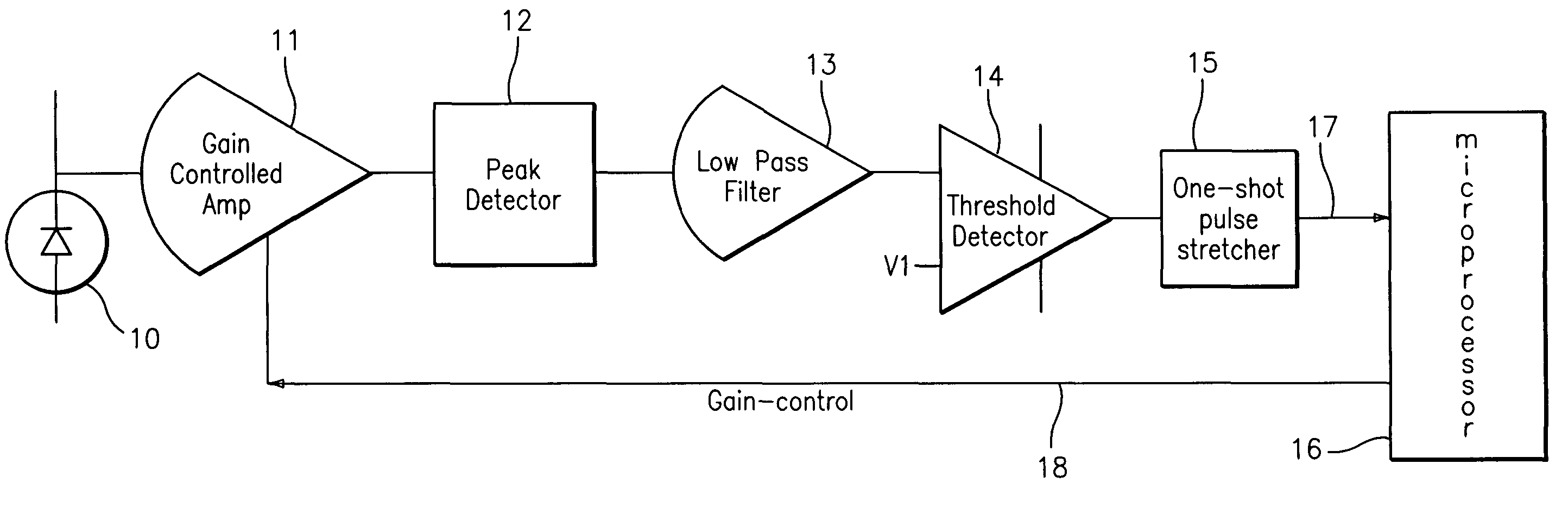
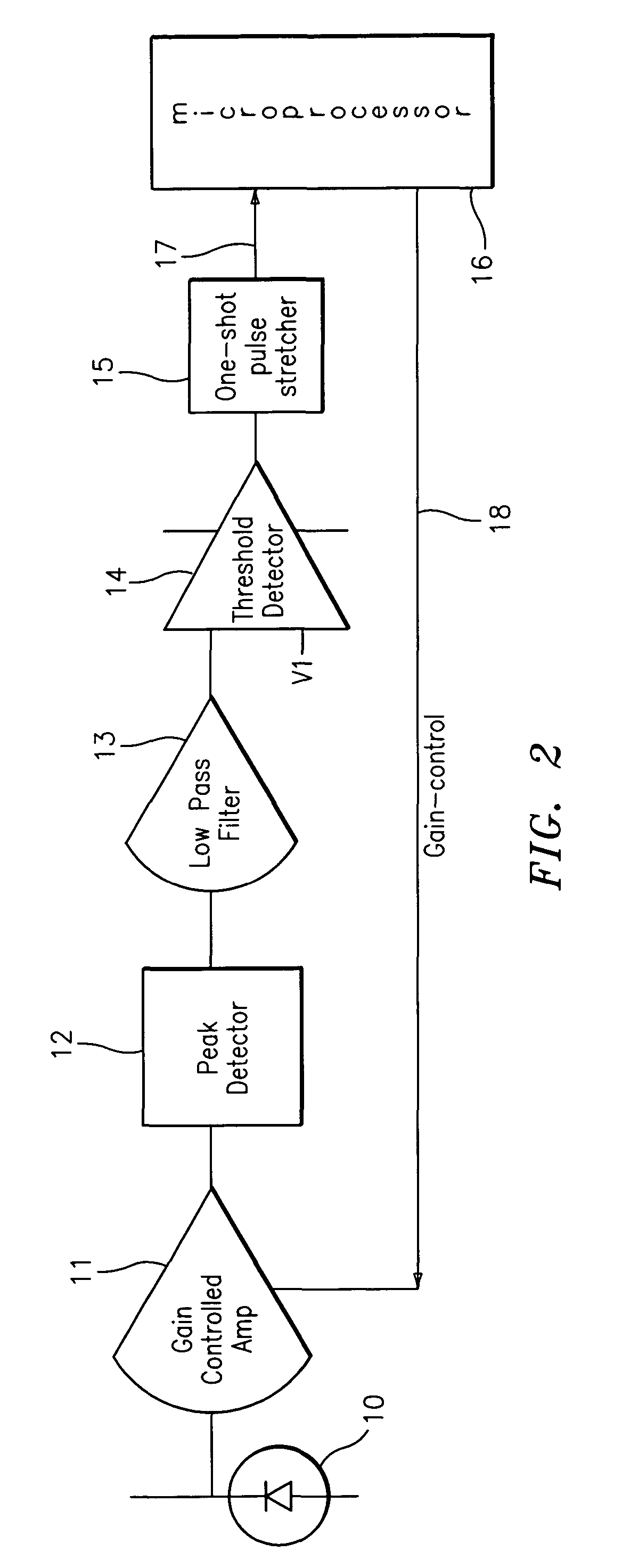
Automatic gain control device for a burst-mode optical receiver
InactiveUS6911644B2Shorten the timeQuick responseGain controlMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierAutomatic gain control
An automatic-gain-control device in an optical receiver is provided and includes a pre-amplifier for converting a current signal outputted from an optical detector to a voltage signal and a bottom level detector for detecting the bottom level from the output of the pre-amplifier, the automatic-gain-control device comprising a bottom signal-level-determining section for analyzing the bottom level from the bottom level detector and outputting a signal denoting the presence of a signal and a reset signal for initialization at intervals between packets; and an automatic-gain-control signal generating section for providing an automatic-gain-control signal by showing the presence of a signal, the automatic-gain-control-signal-generating section including a first transistor which turns on according to a signal from the bottom signal-level-determining section and a second transistor which is connected to a capacitor for charging or discharging a voltage applied by the first transistor, and the drain voltage of which becomes low when the capacitor is charged but becomes high when the capacitor is discharged.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Variable bandwidth transimpedance amplifier with one-wire interface
InactiveUS7657191B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlAudio power amplifierTransceiver
A bandwidth adjustable transimpedance amplifier. The bandwidth adjustable transimpedance amplifier includes a feedback path with a selectable resistance. The bandwidth adjustable transimpedance amplifier is preferably implemented with a photodiode in a five pin package for an optical transceiver system, with a single pin providing a monitor out function and a rate select input.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
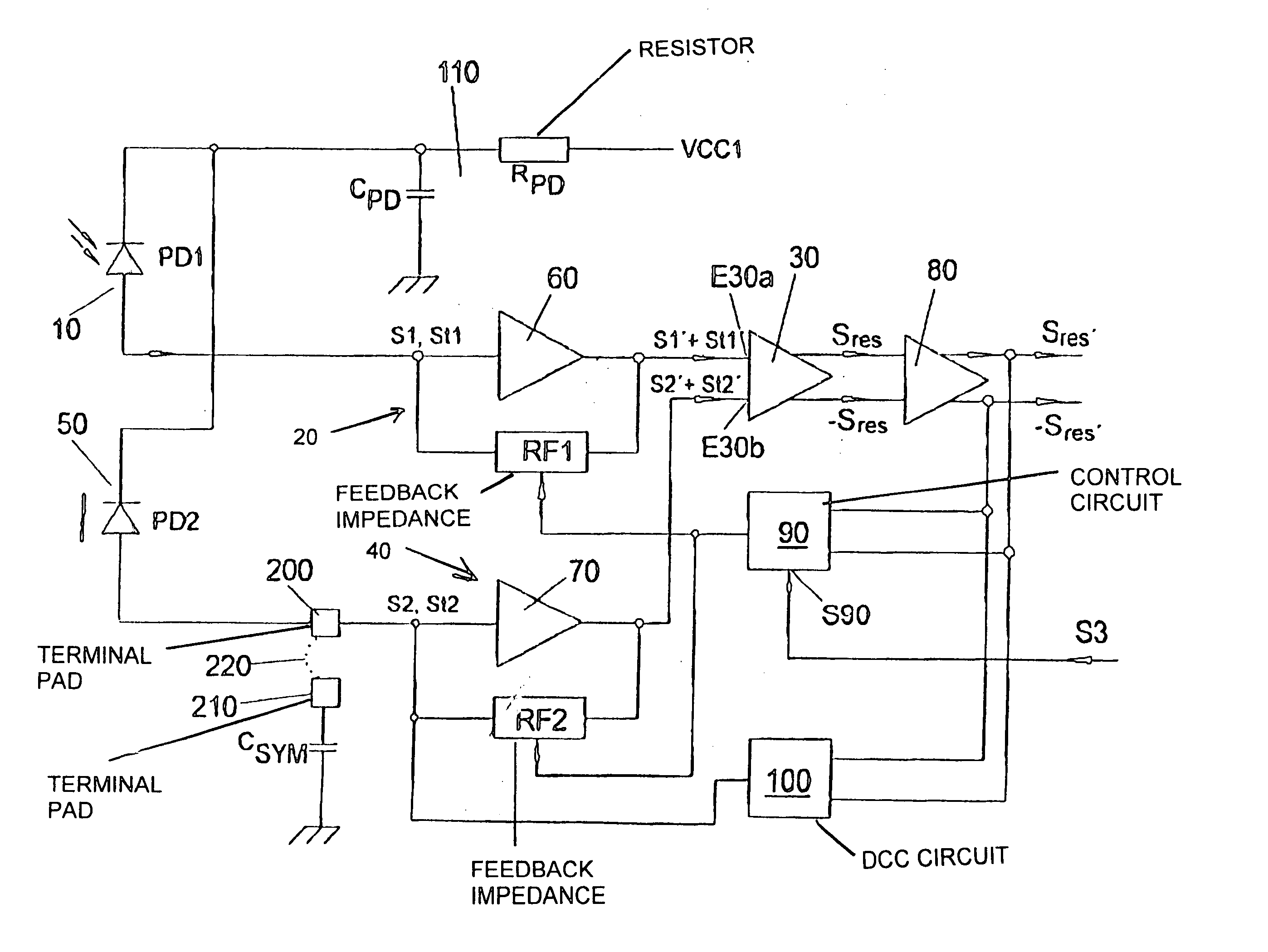
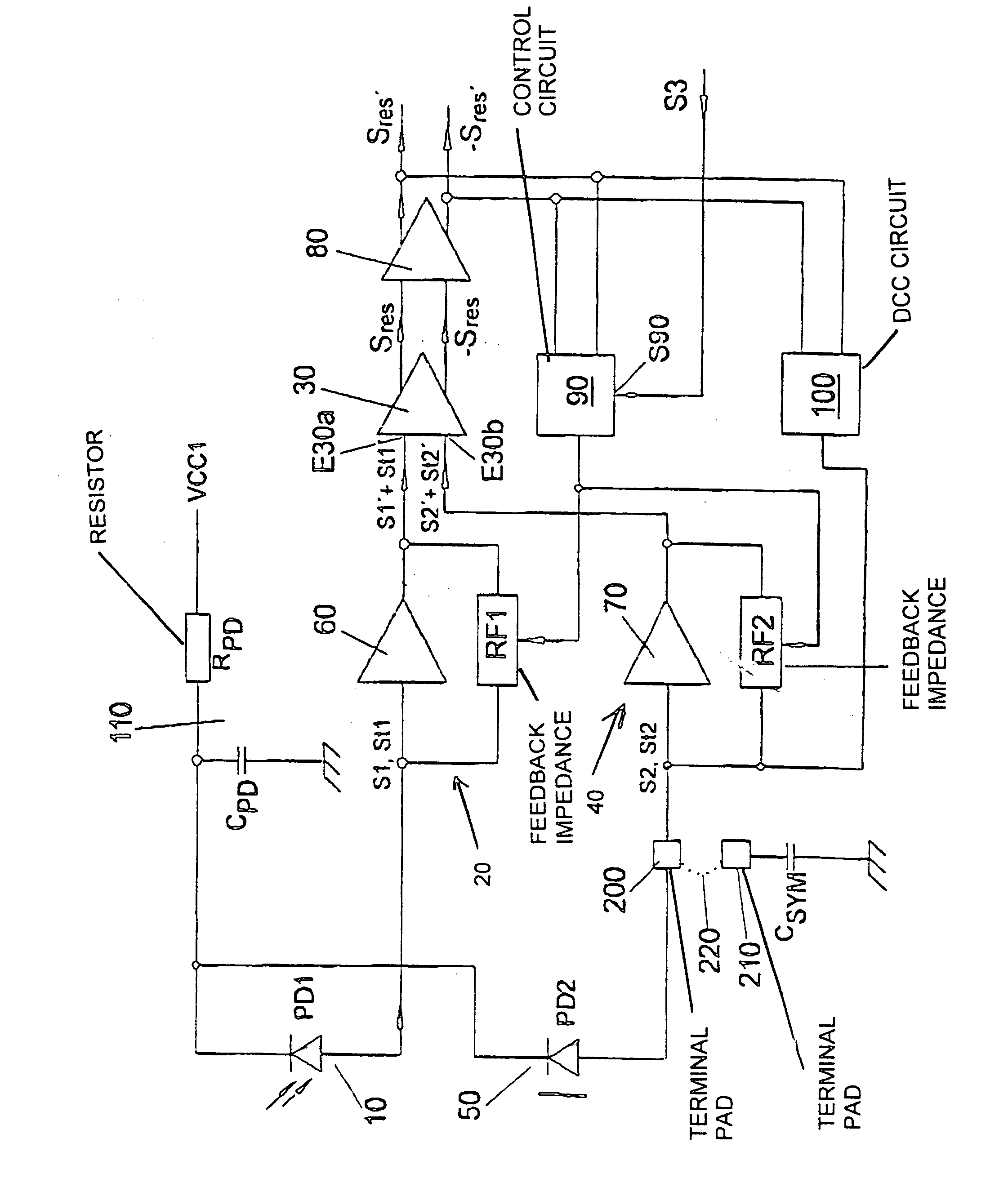
Optical receiver circuit
ActiveUS20050047801A1Suppress interferenceMaximum suppressionAmplifiers controlled by lightTransmission monitoringFree stateDifferential amplifier
An optical receiver circuit is constructed to be immune to interference from external interference signals. The optical receiver circuit includes a differential amplifier having an optical reception device connected to one input of the differential amplifier. The optical receiver circuit also includes an electrical element for simulating the electrical behavior of the reception device in the illumination-free state. The electrical element is connected to the other input of the differential amplifier.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multicasting optical switch fabric and method of detection based on novel heterodyne receiver
InactiveUS7373091B2Time-consume wavelength fine tuningQuick selectionGain controlMultiplier circuit arrangementsLocal oscillatorEngineering
The inventors propose herein a switch fabric architecture that allows broadcasting and fast channel access in the ns-range. In various embodiments of the present invention, 10 Gb / s receiver modules are based on a novel heterodyne receiver and detection technique, which is tolerant to moderate wavelength drifts of a local oscillator. A gain clipped electrical amplifier is used in the novel receiver as a rectifier for bandpass signal recovery.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
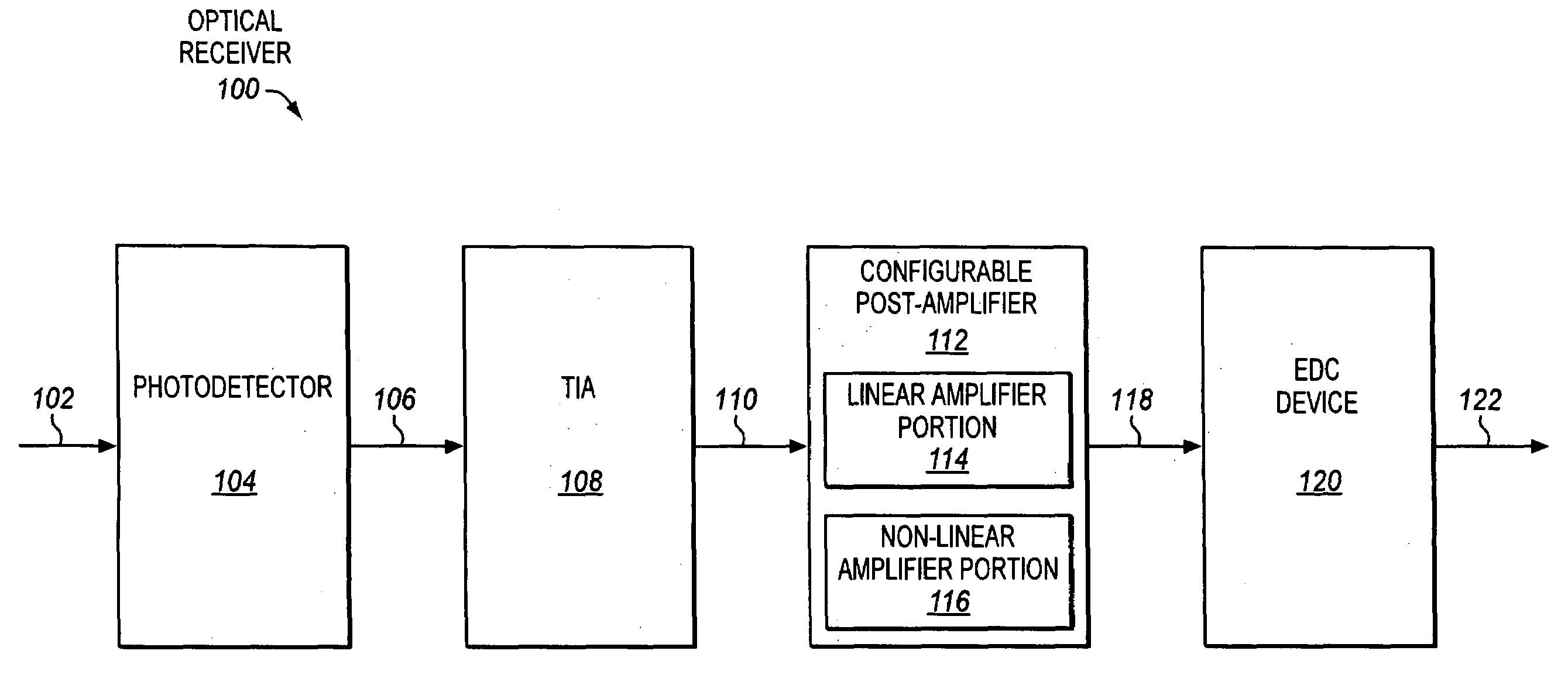
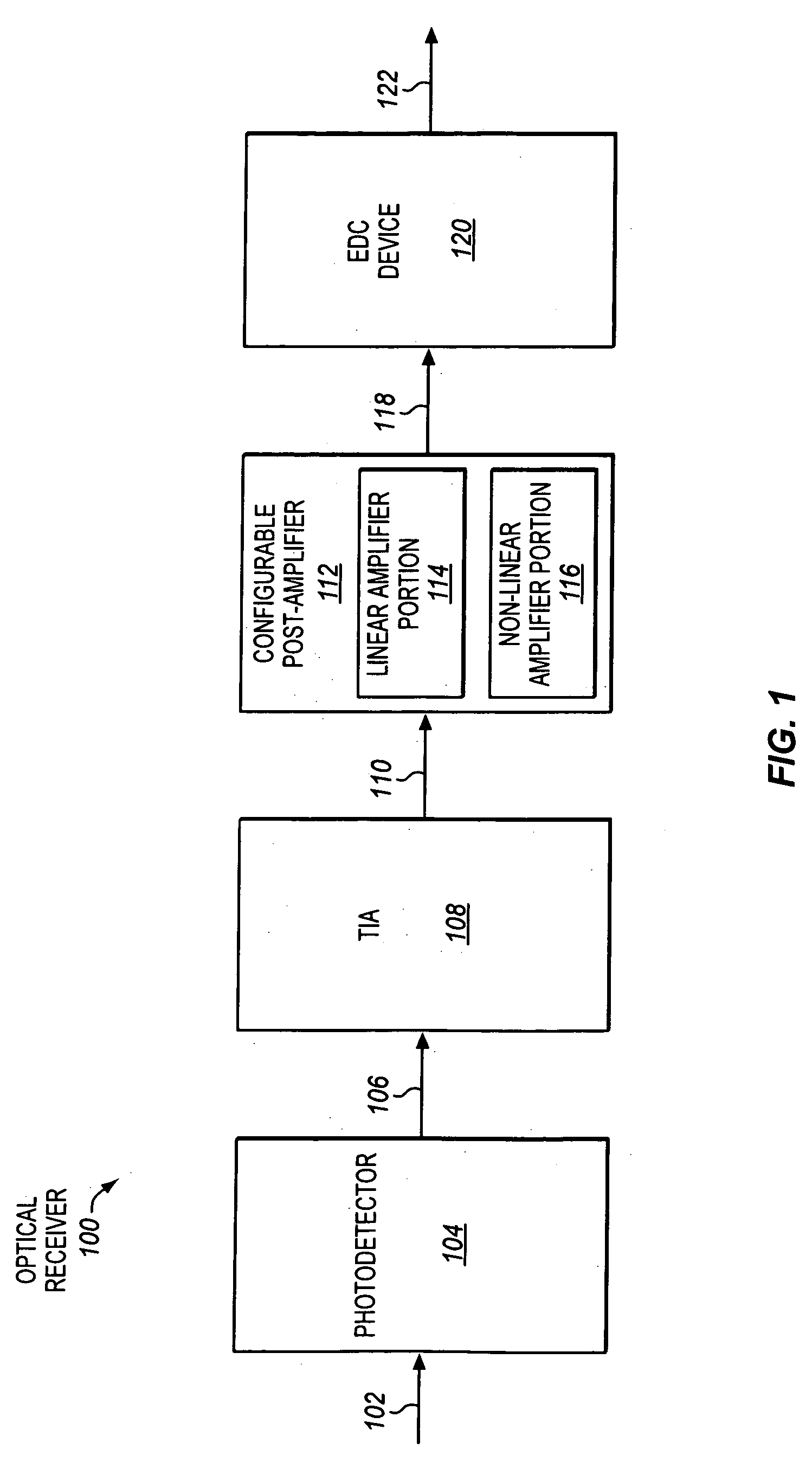
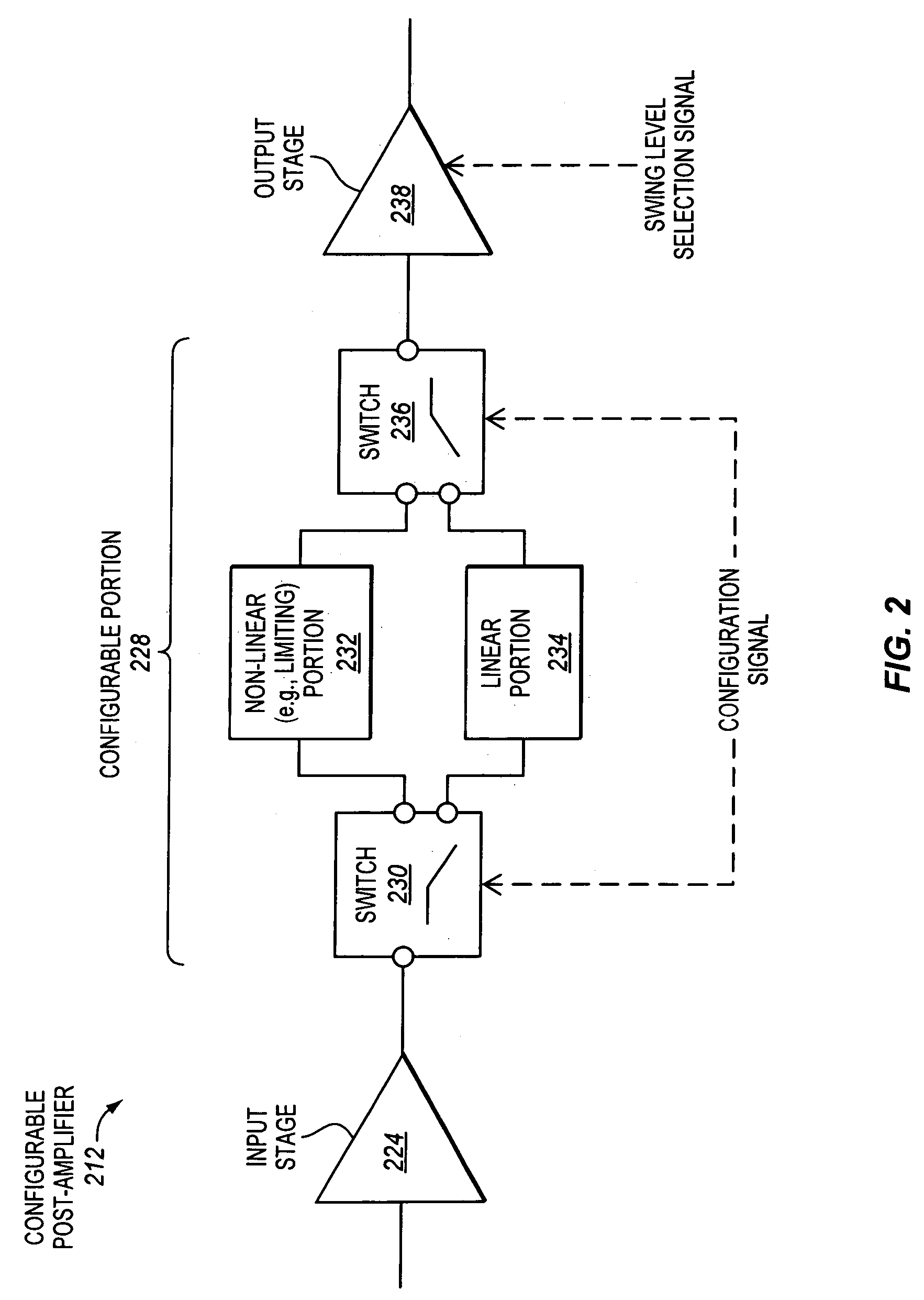
Configurable post-amplifiers that are capable of being configured to perform either substantially linear or limiting amplification for use in optical receivers
InactiveUS20080159756A1Amplifiers controlled by lightElectromagnetic receiversVoltage converterTransceiver
Configurable amplifiers for optical receivers and transceivers are disclosed. In one aspect, a configurable amplifier may be coupled with an output of a current-to-voltage converter to receive a voltage. The configurable amplifier may be capable of being configured to use either a substantially linear amplifier portion or a substantially non-linear amplifier portion to amplify the voltage.
Owner:INTEL CORP
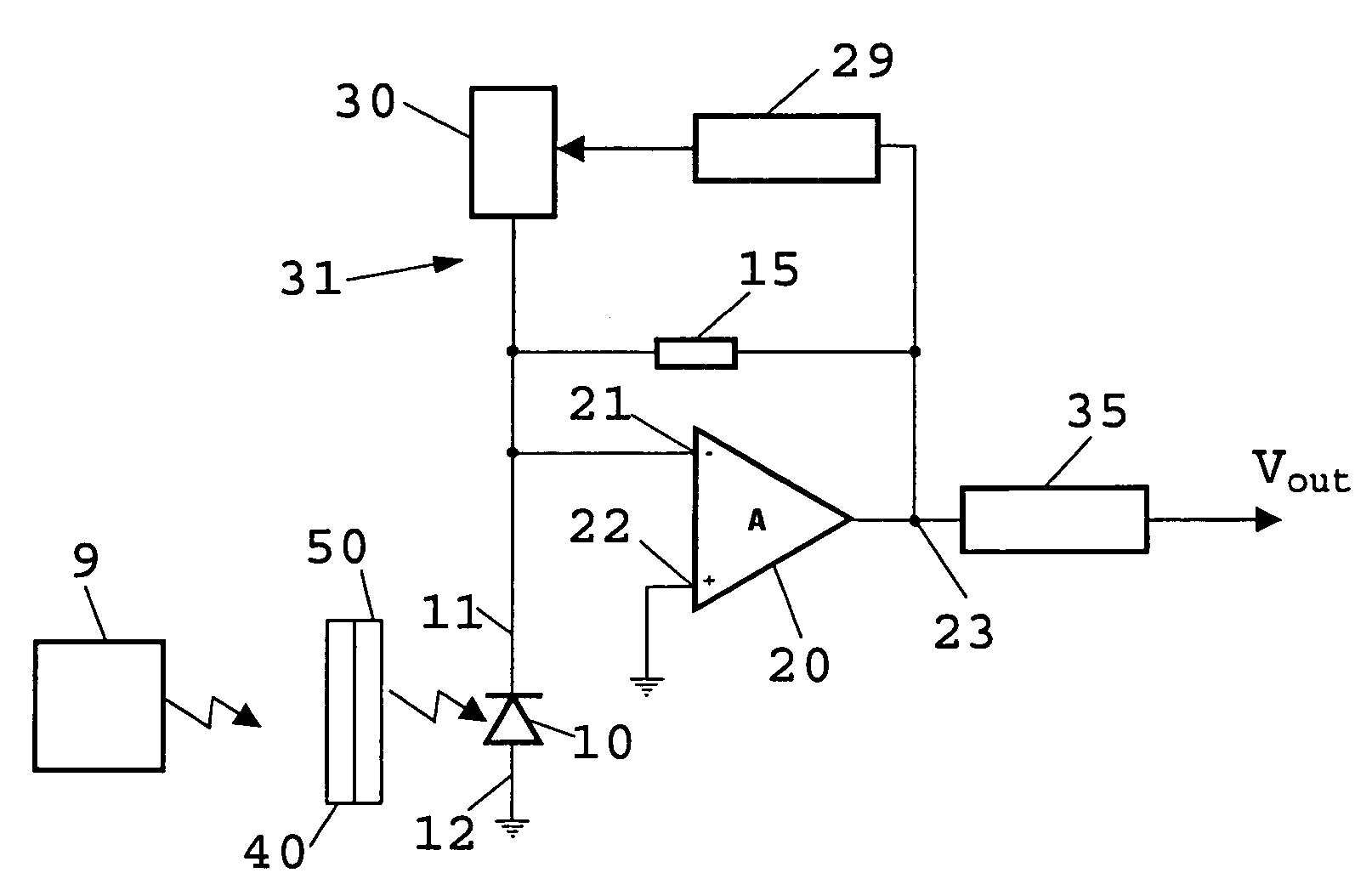
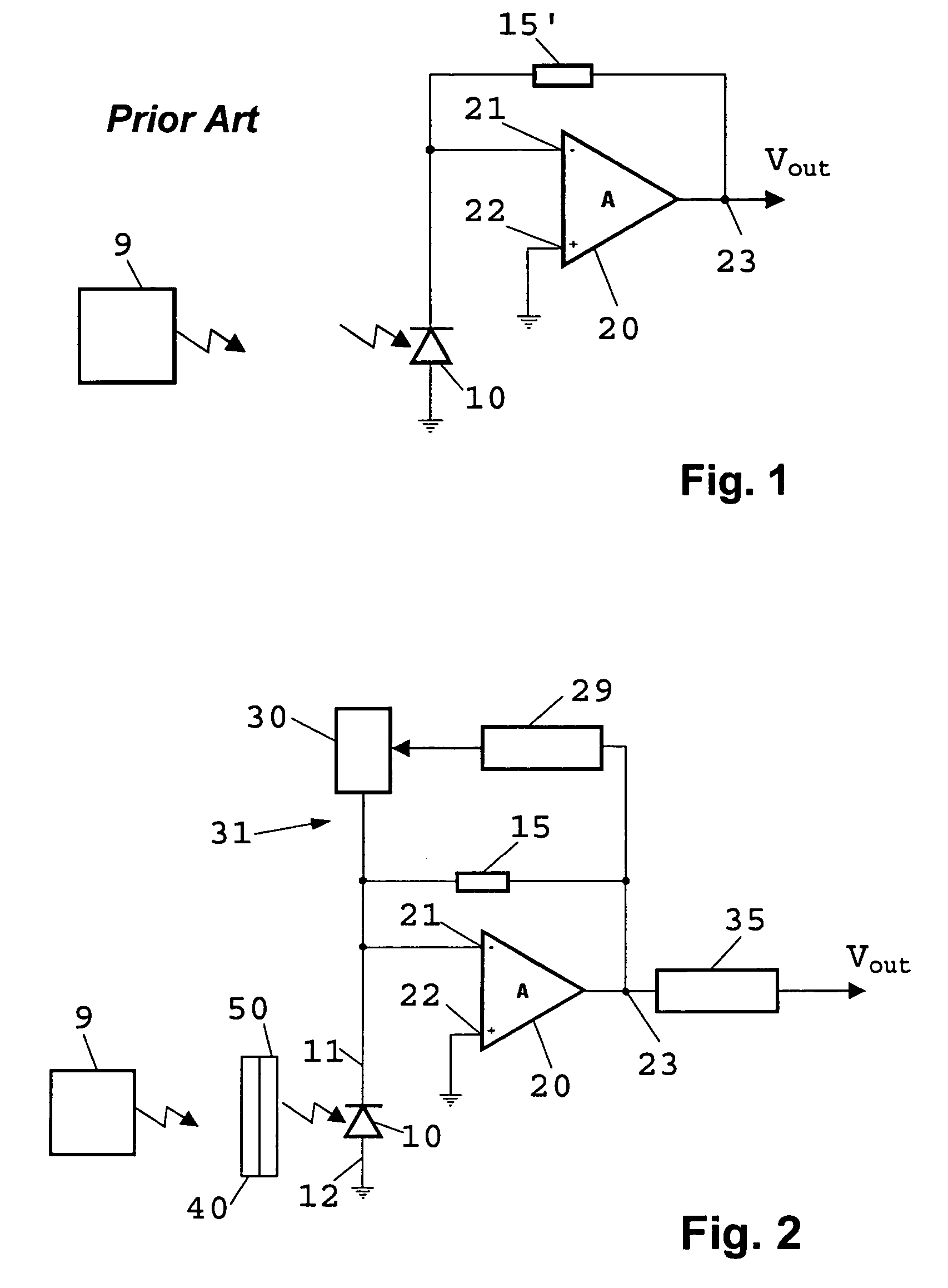
Low noise light receiver
InactiveUS7330668B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioEnhanced signalGain controlMaterial analysis by optical meansLow noiseLight source
The low noise light receiver comprises a light sensor for generating a sensor signal, the sensor signal comprising a wanted signal resulting from a light source and an interfering signal resulting from interfering light; an optical filter apparatus for reducing the interfering light; an electric filter apparatus connected to the light sensor for filtering out the interfering signal and for generating a correction signal that substantially compensates for the interfering signal; and a processing apparatus connected to the light sensor and the electric filter apparatus for processing the wanted signal in order to generate an output signal (Vout).
Owner:OPTOSYS SA
Optically isolated bias control circuit
InactiveUS6844779B2Improve immunityIncrease speedTransistorAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationInterconnectionPower MOSFET
Optically isolated bias control circuit which provides bias current for switching circuits. Invention is amenable to high speed switching control with instantaneously variable pulse widths and duty cycles. Invention can be operated from DC upward in frequency, limited only by the characteristics of the implementing electrical components and electrical interconnections. Complementary embodiments of invention provide high speed operation with minimal electrical charge flow. Solar powered embodiments of invention may be used to control the switching of high power MOSFET-based switching circuits.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
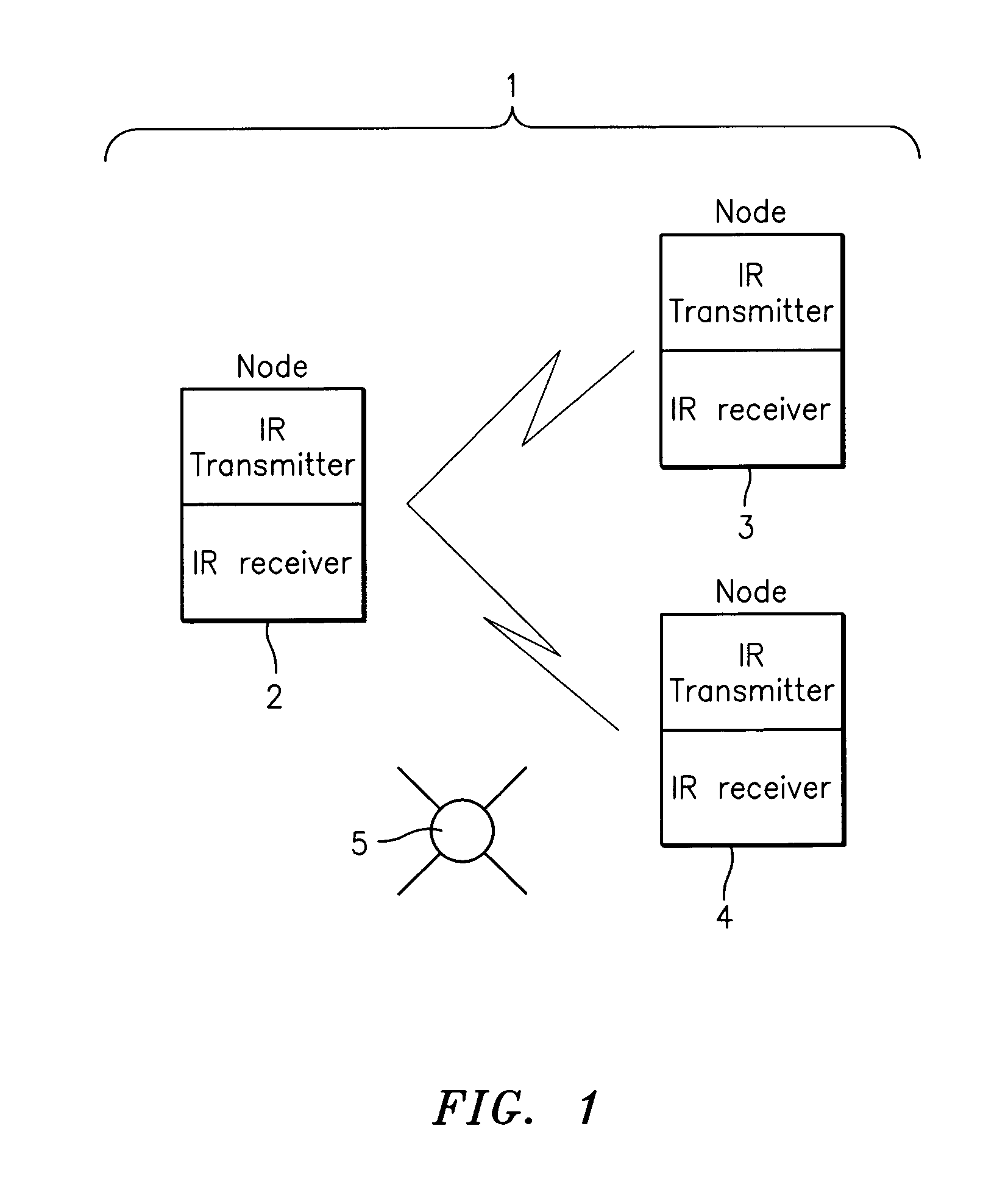
Digital iterative gain control
In an IR communication network, a method is described to optimize channel performance in the presence of strong and varying IR interference. The method controls of the channel gain based on quantitative measurement of the channel noise.
Owner:INNCOM INT INC
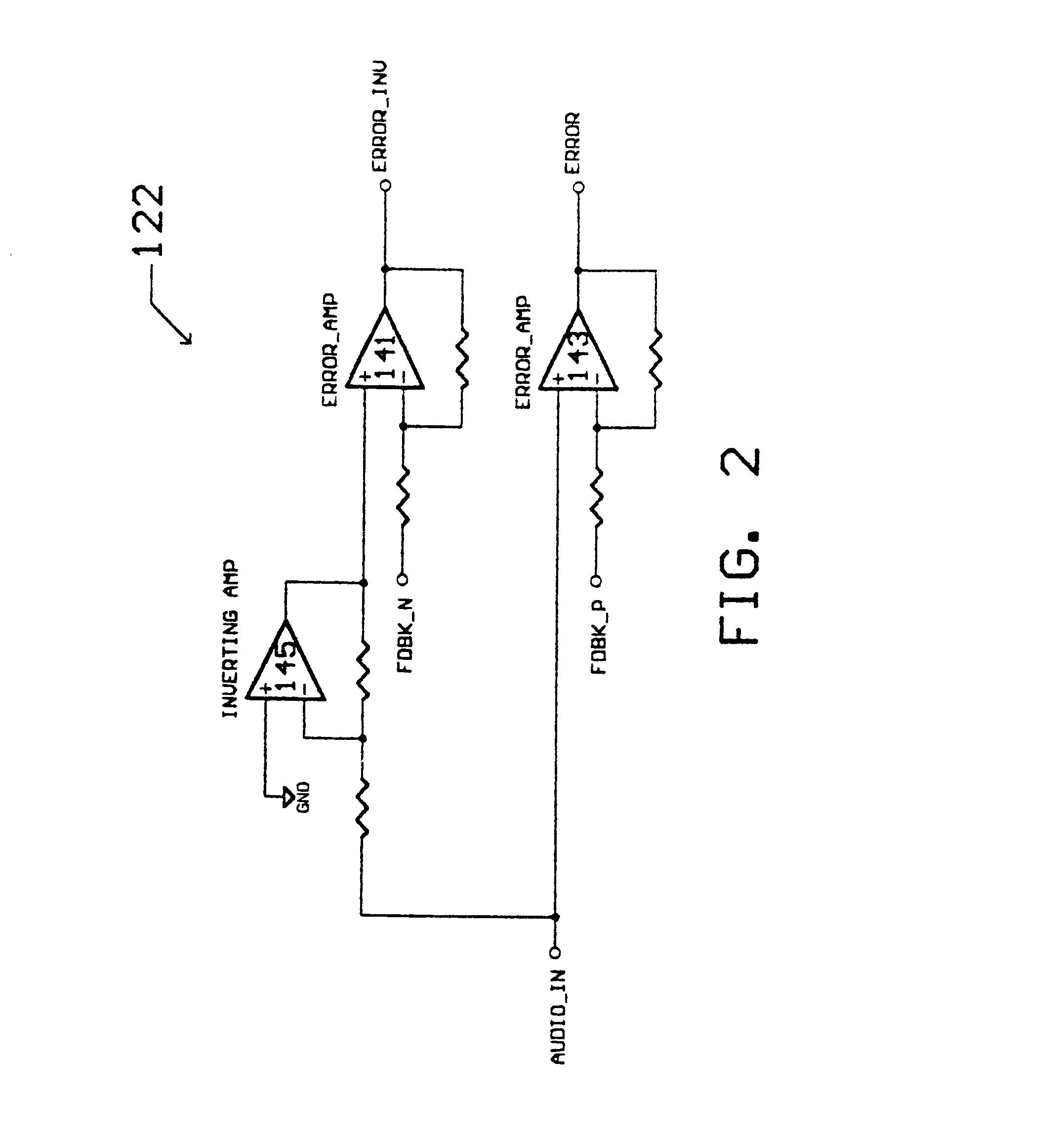
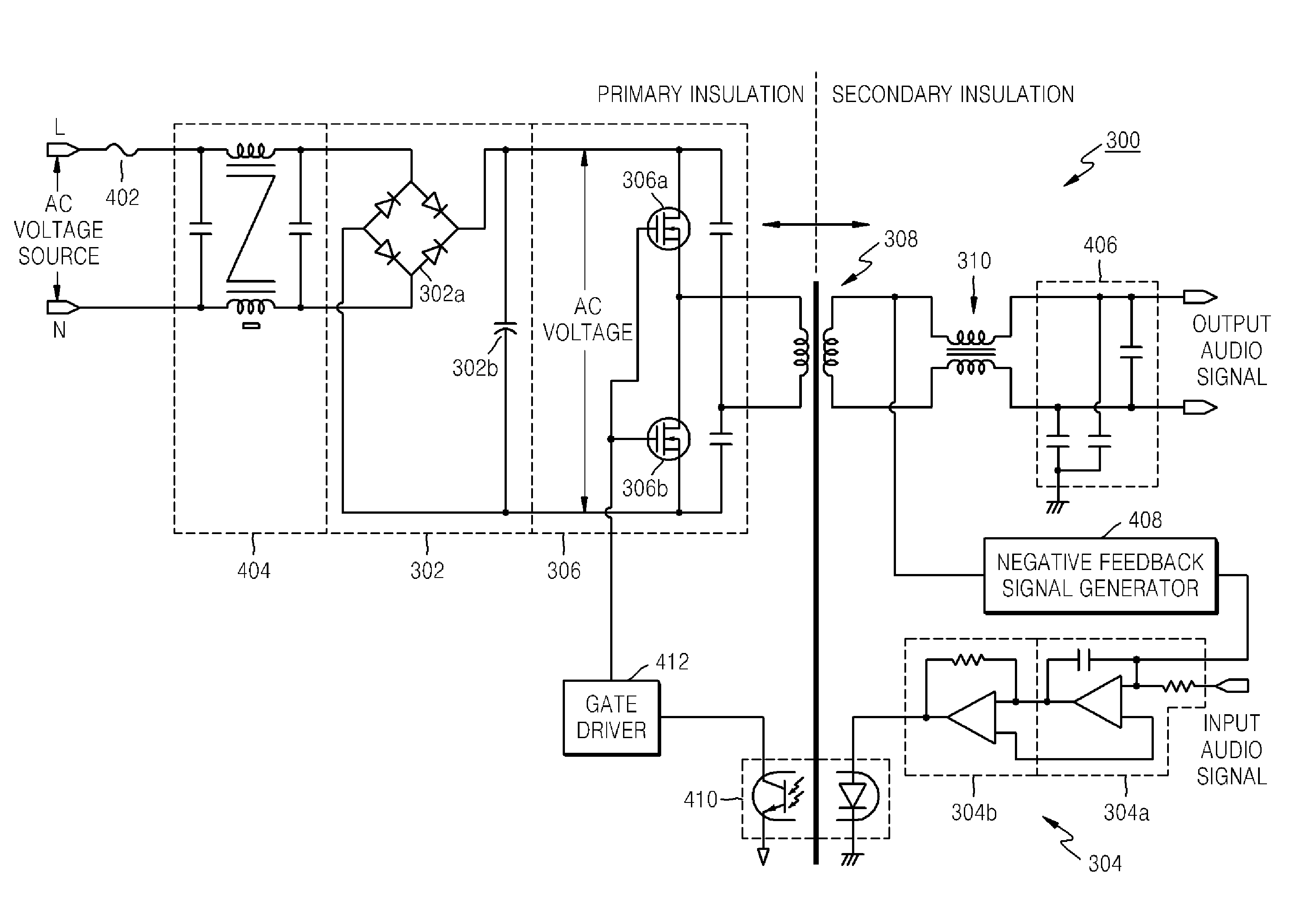
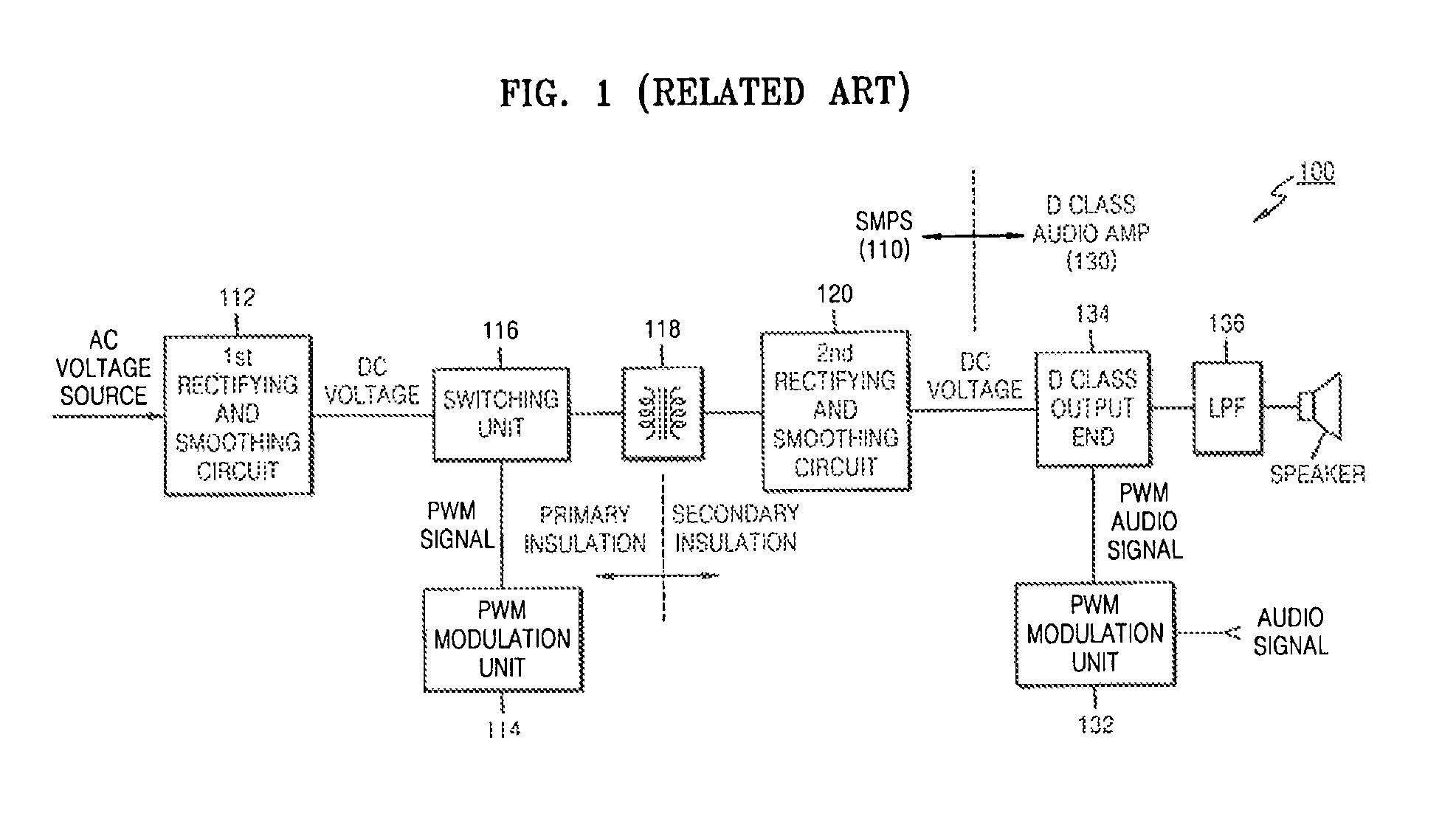
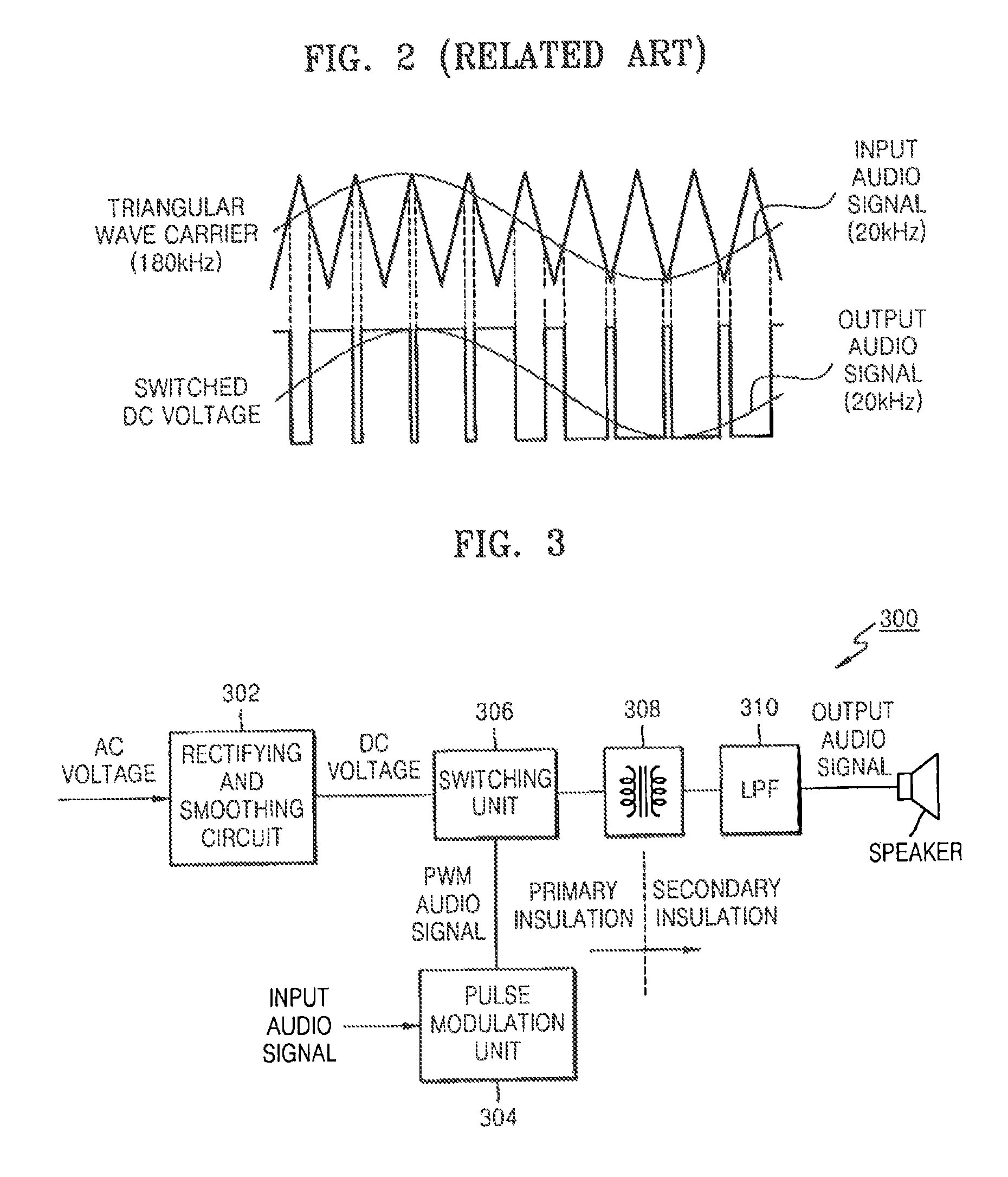
Digital audio amplifier and digital audio amplifying method therefor
InactiveUS7952426B2Improve power efficiencyReduce manufacturing costNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierTransformer
A digital audio signal amplifier and a digital audio signal amplifying method provide safety and power efficiency by integrating a switching mode power supply and a digital audio amplifier into an apparatus. The digital audio amplifier includes a pulse modulation unit generate a pulse modulated audio signal by pulse-modulating an input audio signal, a switching unit to switch a DC voltage based on the pulse modulated audio signal, an insulation transformer to transform the output of the switching unit and to output the result of the transforming, and a low-pass filter to obtain an audio signal corresponding to the input audio signal by low-pass filtering the output of the insulation transformer, and to output the output audio signal. By integrating a switching mode power supply and a digital audio amplifier into an apparatus, the digital audio amplifier satisfies the insulation requirement and at the same time increases power efficiency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Parallel opto-electric structure for high sensitivity and wide bandwidth optical transceiver
InactiveUS20020003649A1Amplifiers controlled by lightElectromagnetic receiversAudio power amplifierTransceiver
An optical receiver circuit including a plurality of PIN diodes, each associated with a dedicated element transimpedance amplifier, the outputs of the element transimpedance amplifiers being connected to a summing amplifier which sums the voltages output from the element transimpedance amplifiers. The optical receiver circuit provides the same output voltage value as a single large PIN diode having an active area comparable to the sum of the active areas of the smaller PIN diodes, and thus has the same high sensitivity as the single large PIN diode but a much wider bandwidth.
Owner:IBM CORP
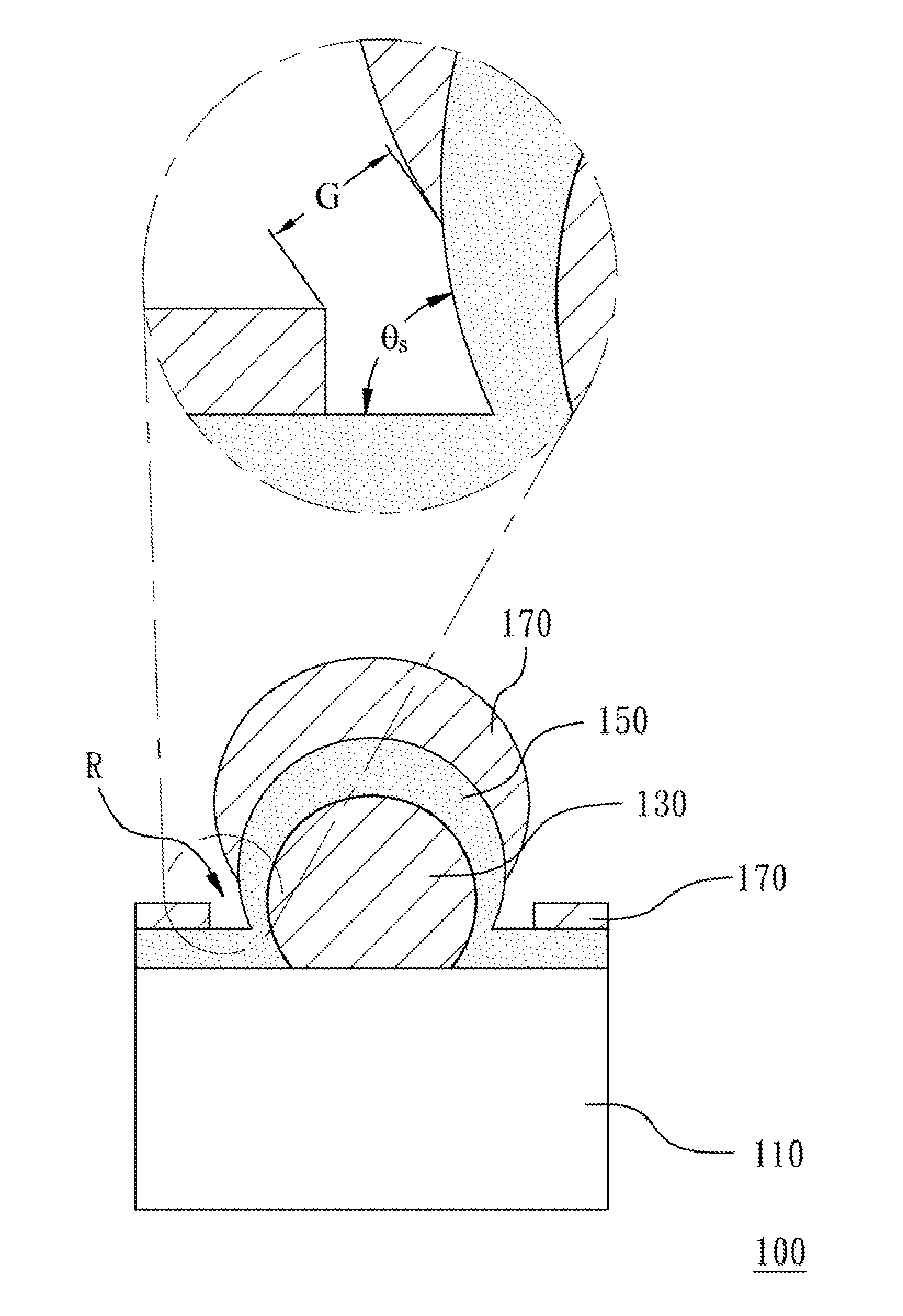
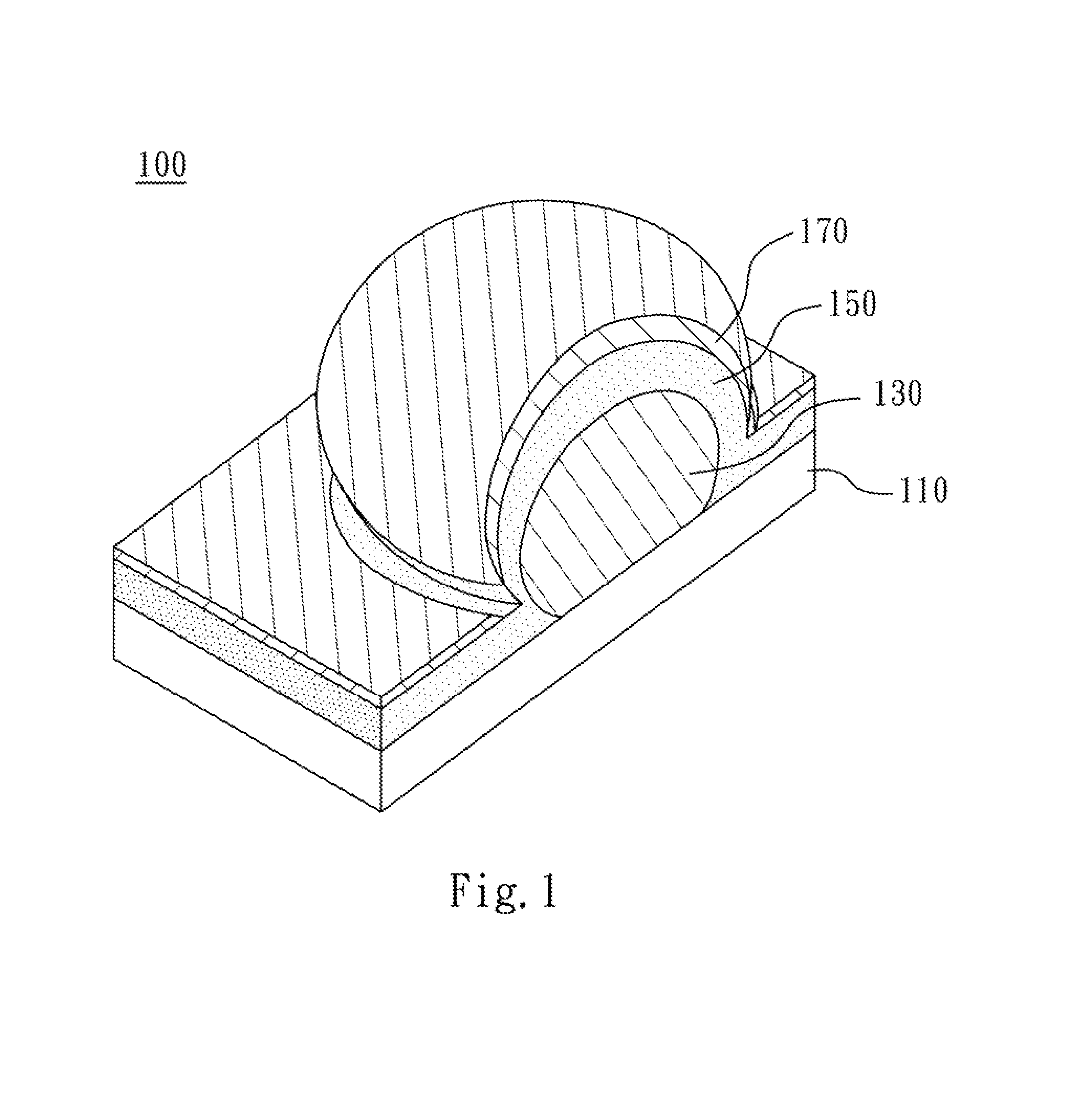
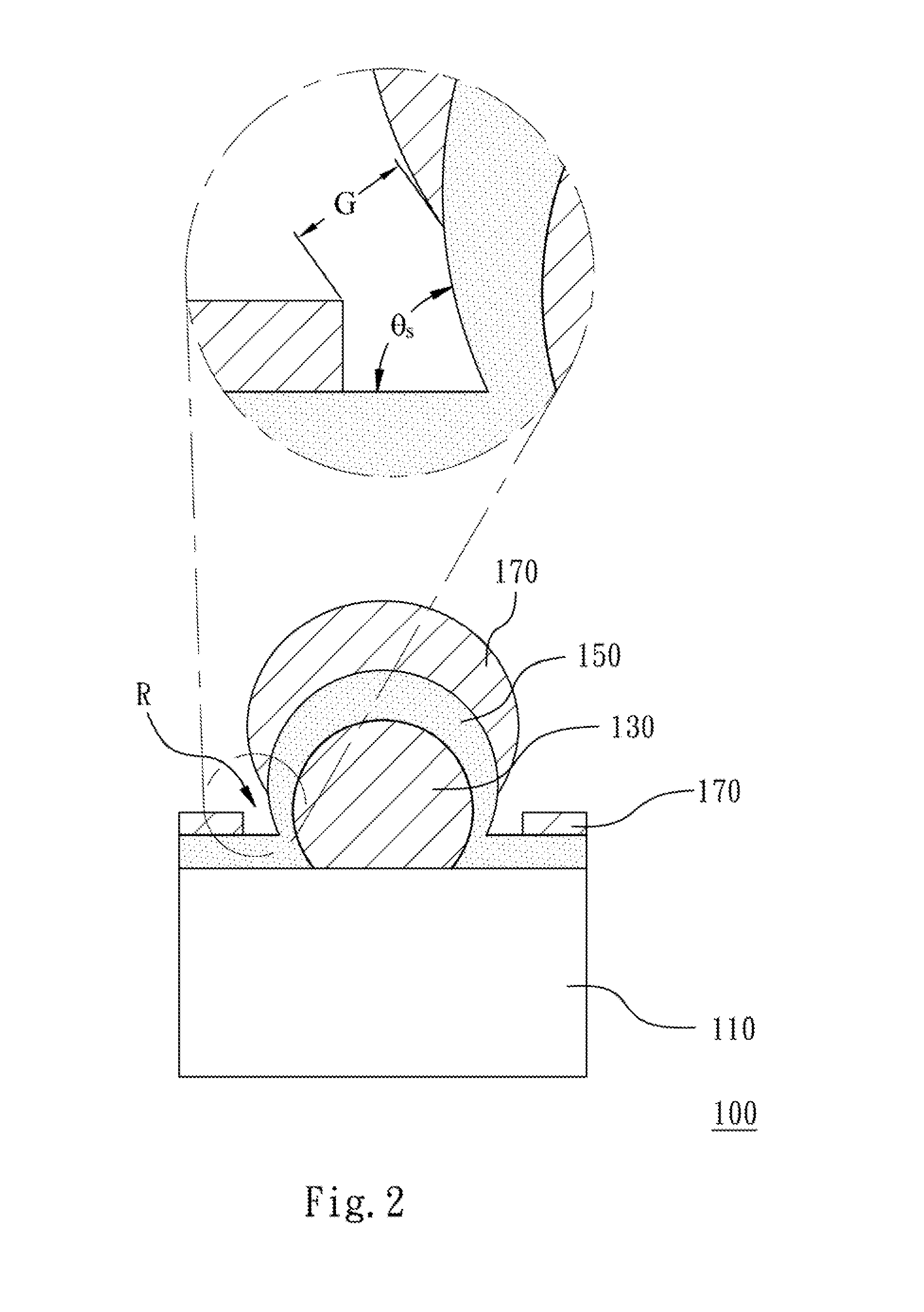
SERS-active structure, fabrication method thereof, and SERS system comprising the same
A SERS-active structure includes a substrate, at least one metal nanoparticle, a dielectric layer and a metal nanolayer. The metal nanoparticles are disposed on the substrate. The substrate and the metal nanoparticles are covered by the dielectric layer, so that the dielectric layer forms a recessed portion with a dihedral angle formed by a surface of the dielectric layer at which the at least one metal nanoparticle contacts the substrate. The dielectric layer is covered by the metal nanolayer and the metal nanolayer has a gap located at and exposing the recessed portion.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
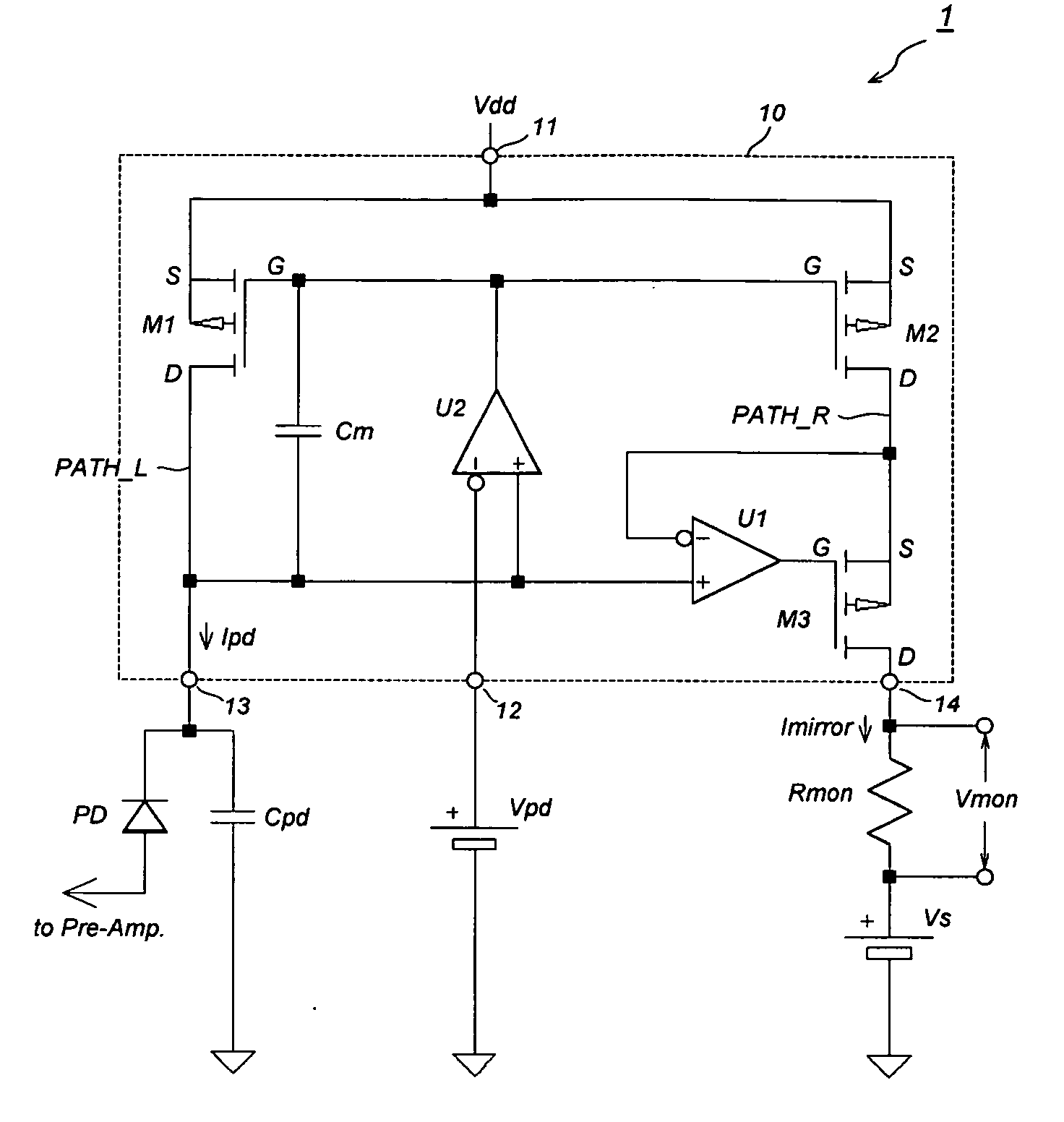
Current mirror circuit and optical receiver circuit using the same
ActiveUS20090202259A1Increase output impedanceGuaranteed uptimeAmplifiers controlled by lightElectromagnetic receiversMOSFETEngineering
A current mirror circuit and an optical receiver circuit implementing with the current mirror circuit are disclosed. The current mirror circuit provides two MOSFETs and two differential amplifiers. The MOSFETs are operated under the same bias condition even the power supply voltage decreases due to the virtual short-circuit characteristic between two inputs of the differential amplifier. One of the differential amplifiers provides a variable gain and output impedance characteristic to stabilize the feedback loop formed by this differential amplifier and one of the MOSFETs.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
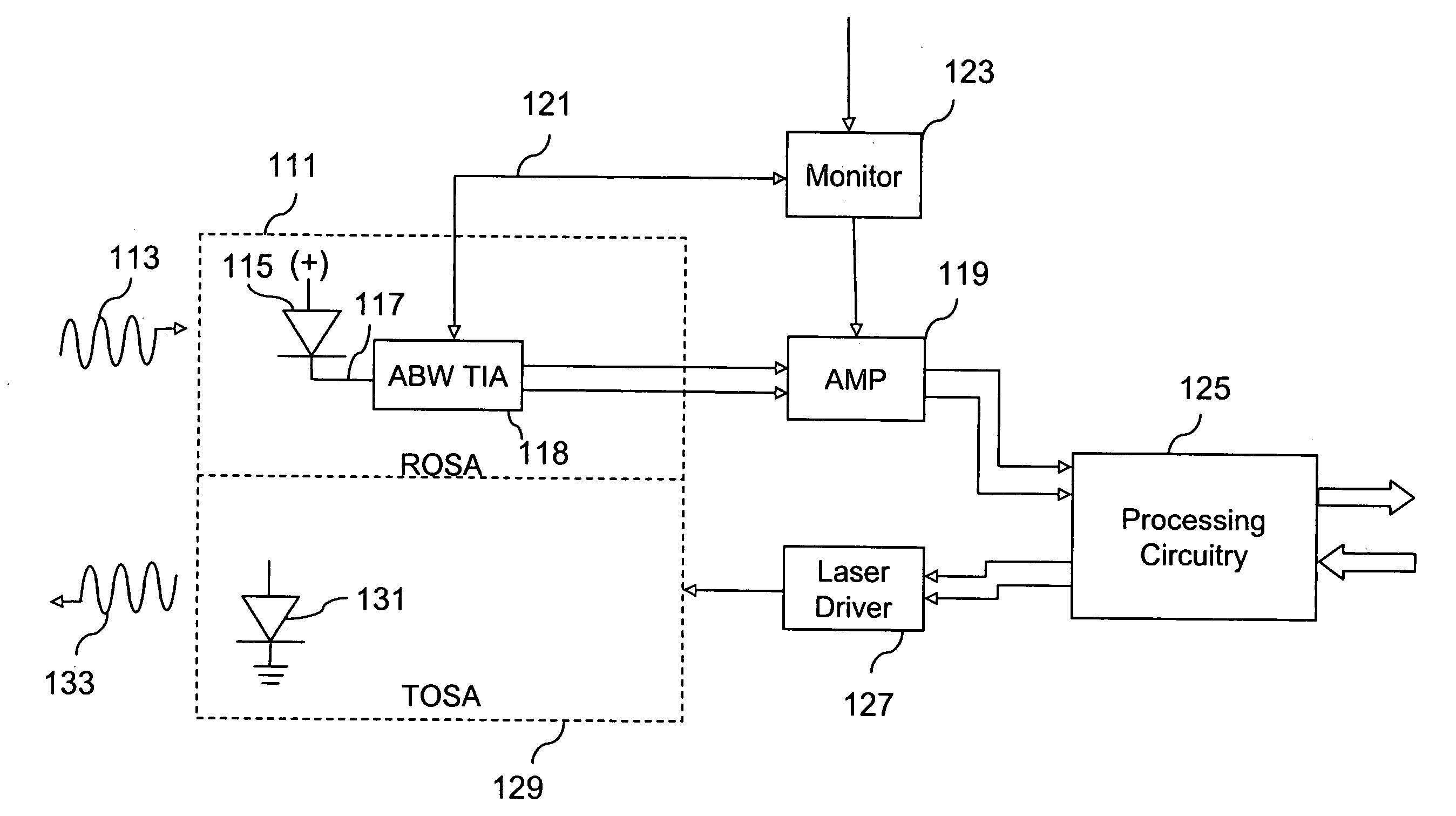
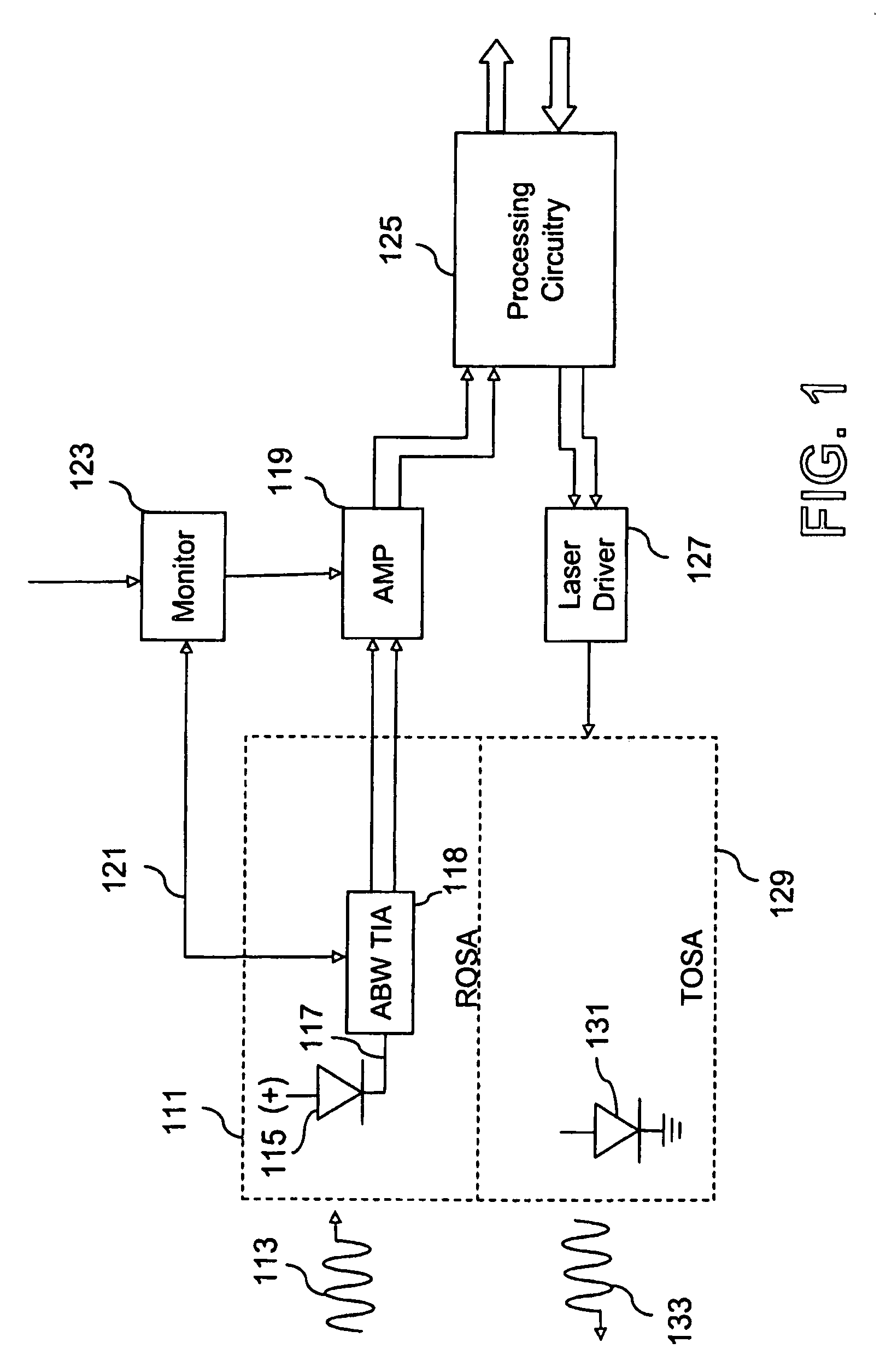
PIN/TIA SYSTEM FOR USE IN FTTx APPLICATIONS
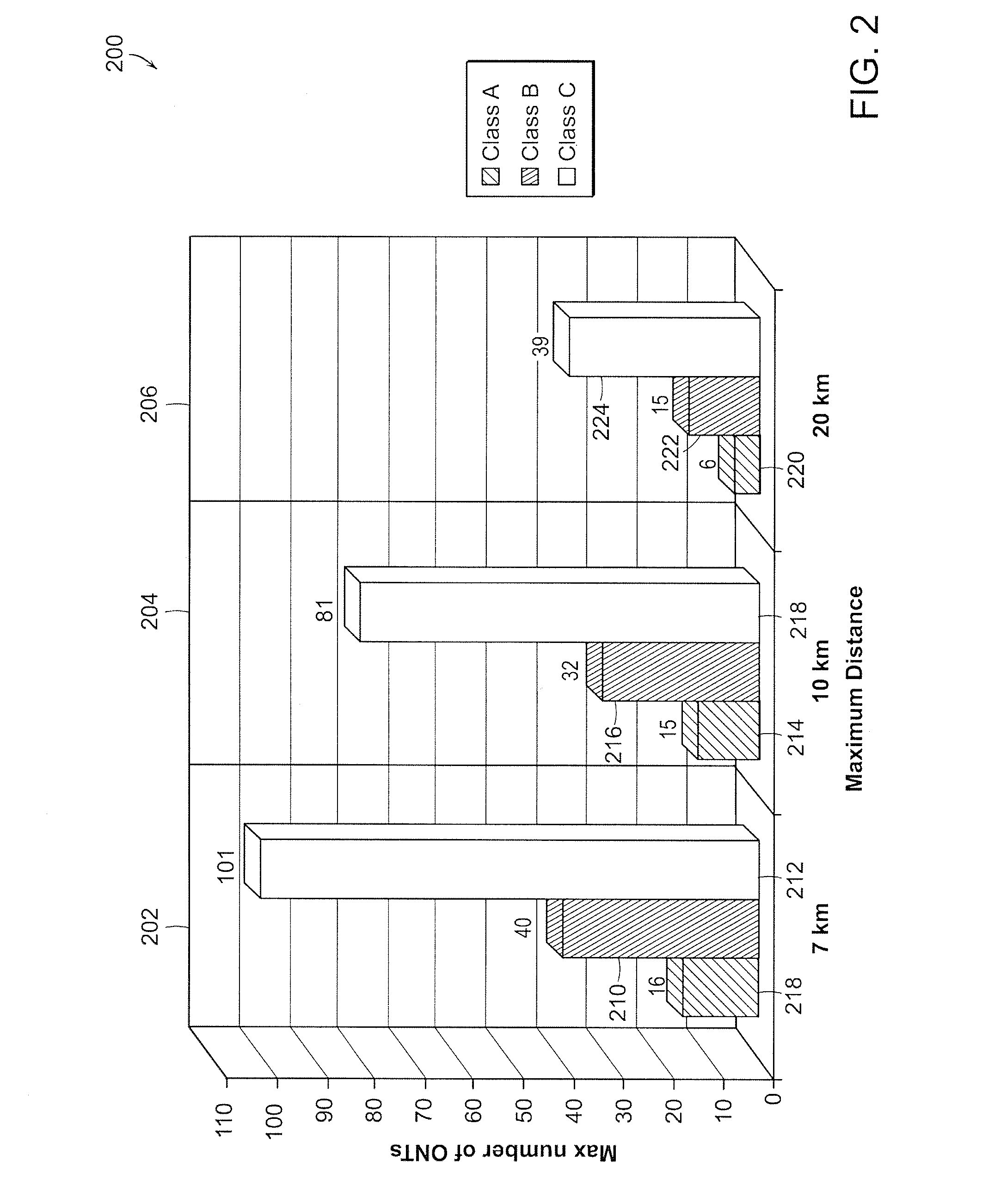
ActiveUS20080247766A1Improved performance characteristicsImprove transmission qualityTime-division optical multiplex systemsAmplifiers controlled by lightOptical ModuleEngineering
A system is disclosed for an improved ROSA that has increased sensitivity for permitting greater numbers of ONTs to be connected to an optical network per defined transmission line distances. ROSA configuration includes a digital optical module with improved performance characteristics. This digital optical module has replaced a conventional photodiode with a PIN detector that is coupled with the TIA. The resulting the digital optical module containing this PIN / TIA configuration when incorporated in a ROSA provides a single ROSA solution that will meet or exceed the ITU / IEEE FTTx standards for short and long distances under substantially all operating conditions.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INT
LED driver circuit capable of adjusting output current
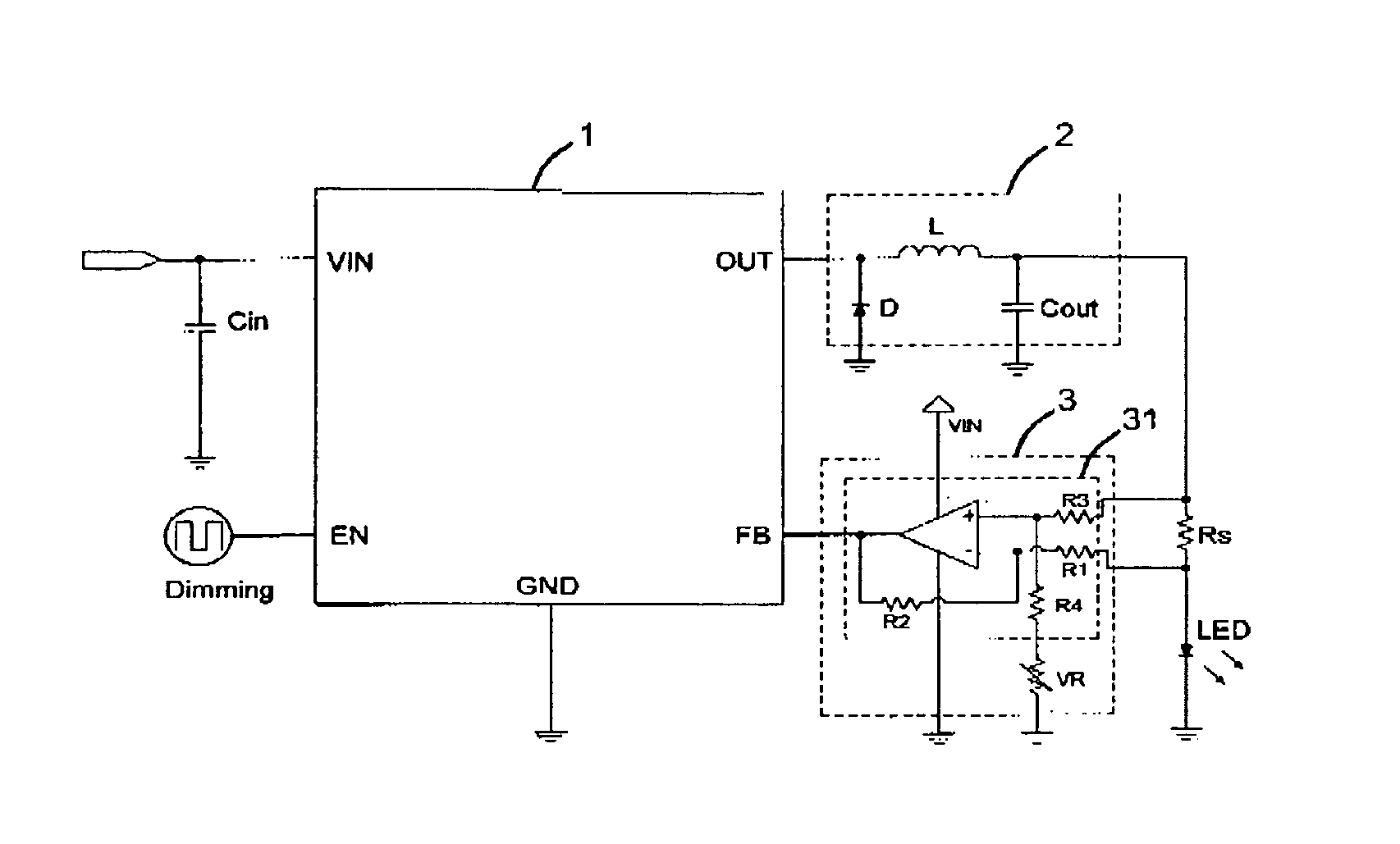
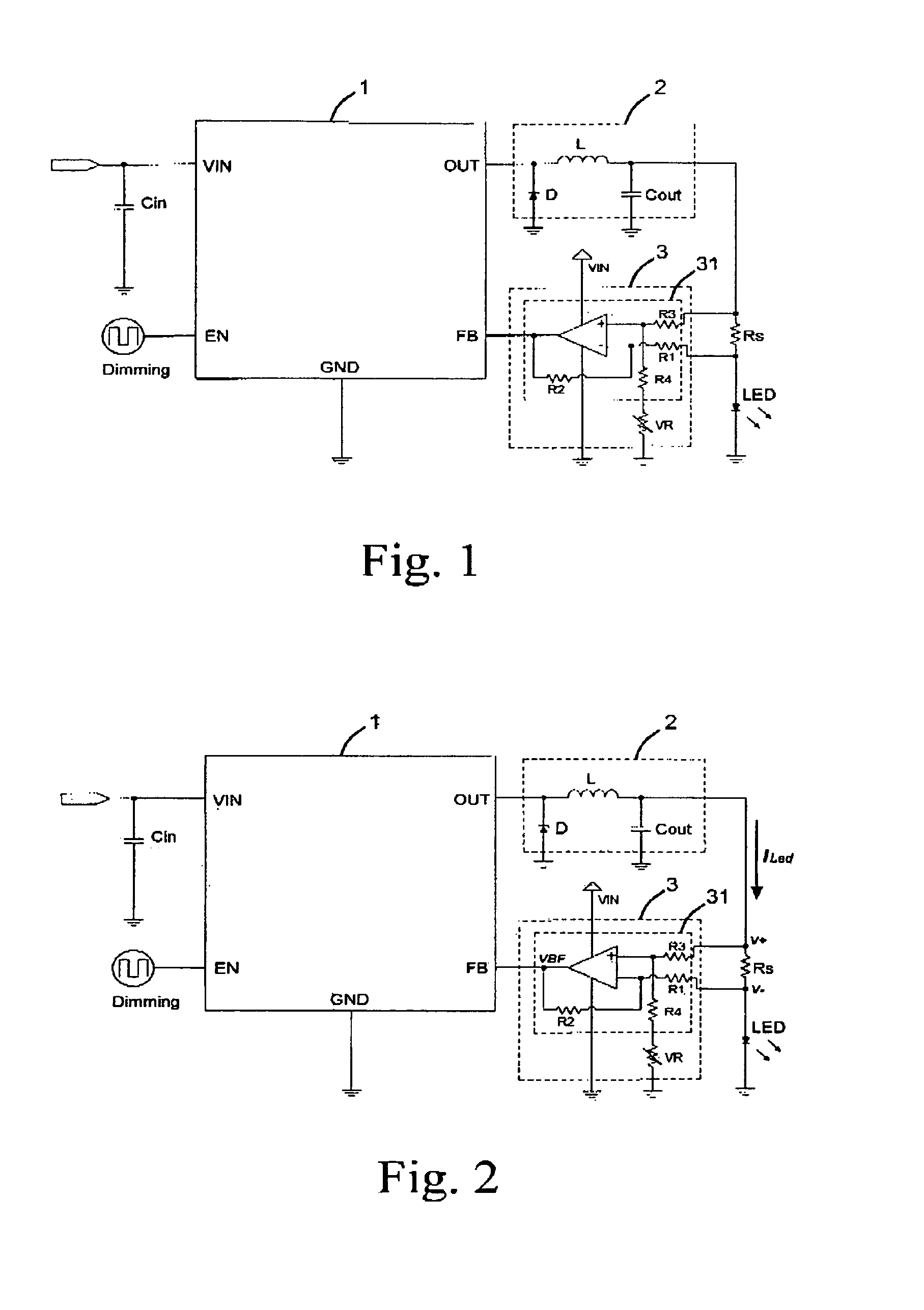
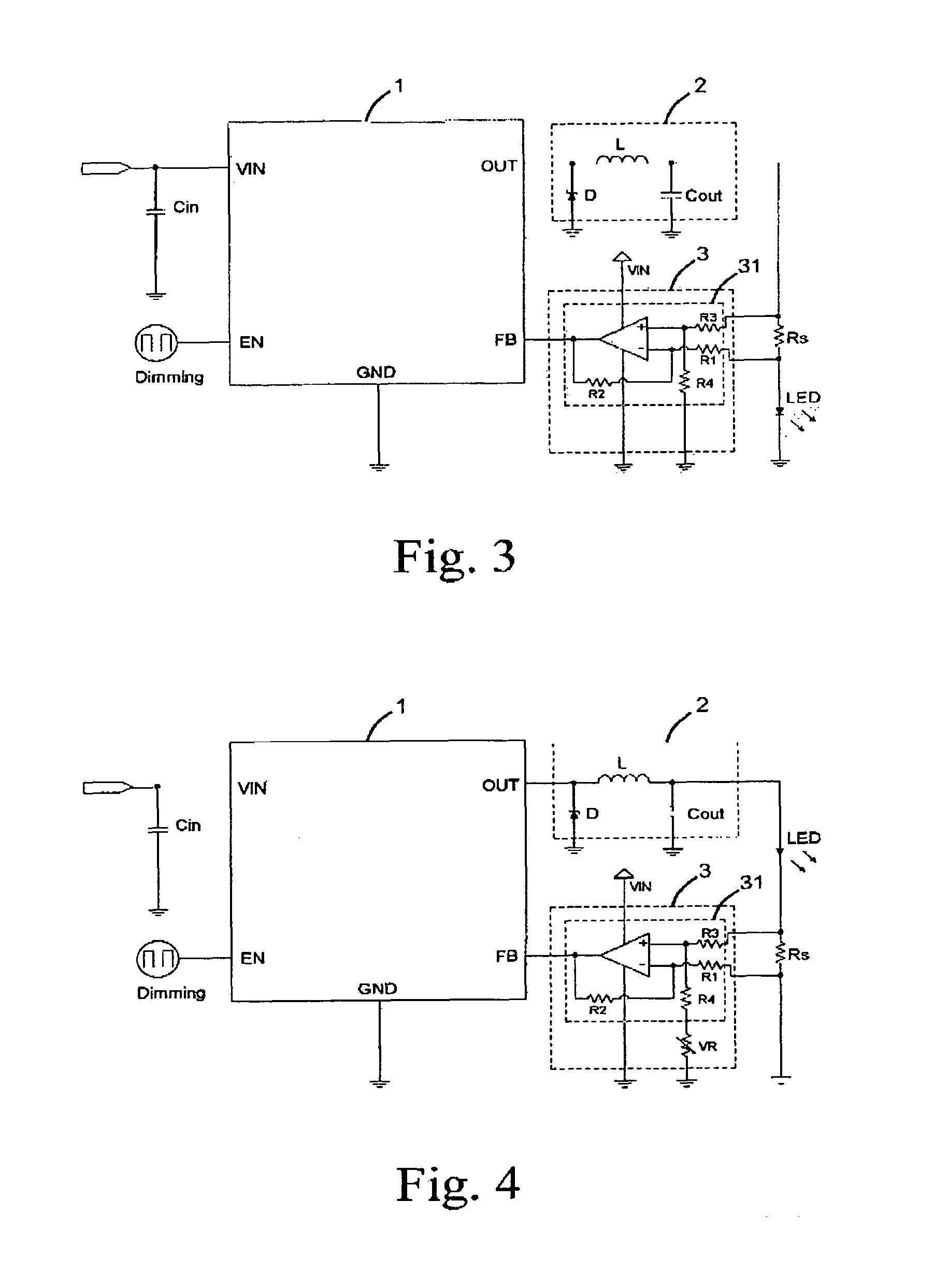
InactiveUS7714520B2Low costControl performanceElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementPower controllerVoltage regulation
An LED driver circuit includes a power controller, a voltage regulator, a detecting resistor, a light emitting device, and a voltage detecting circuit. The voltage detecting circuit has a first input end connected to a higher potential end of the detecting resistor, and a second input end thereof is connected to a lower potential end of the detecting resistor. The output end of the voltage detecting circuit is connected to a feedback end of the power controller so as to output a detected voltage signal to the power controller for adjusting the output voltage and supplying a stable and proper value of current to the light emitting device. The voltage detecting circuit is a differential amplifier capable of detecting the voltage difference between the detecting resistor and amplifying it as a feedback to the power controller. Therefore, the output current from the power controller is precisely controlled.
Owner:LIU DA YI
Optical power monitor for PON telecommunication
InactiveUS7676152B2Gain controlDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCommunications systemOptical power
In an optical telecommunication system in which an intensity of an arriving optical signal is different for each packet, detected is an optical intensity for each packet with little error. For this purpose, contrived is to detect an average optical intensity across header parts for each packet by focusing on the fact that the header part comprising the preamble and delimiter of a packet is in a bit pattern which includes approximately the same numbers of “0” and “1”.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
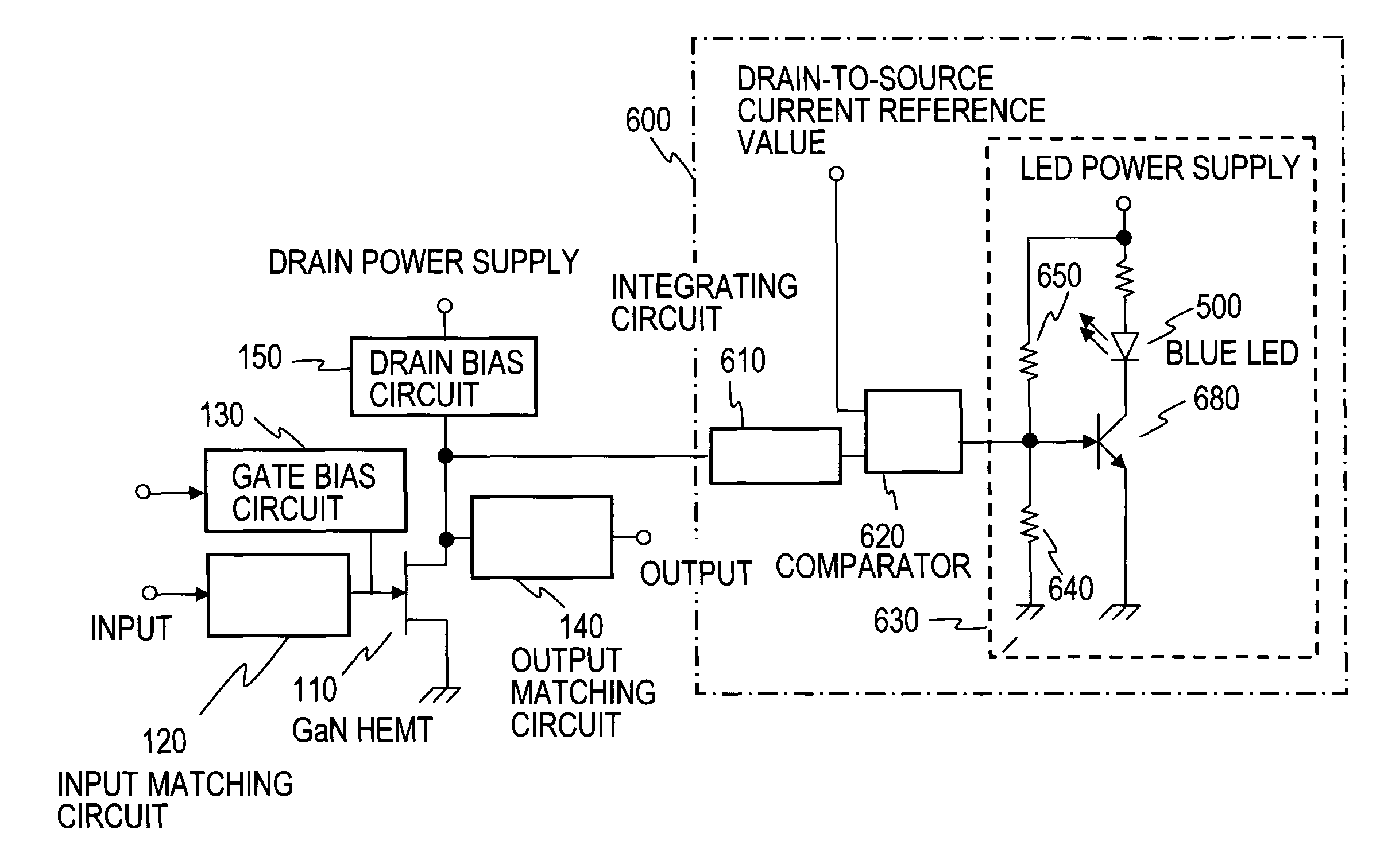
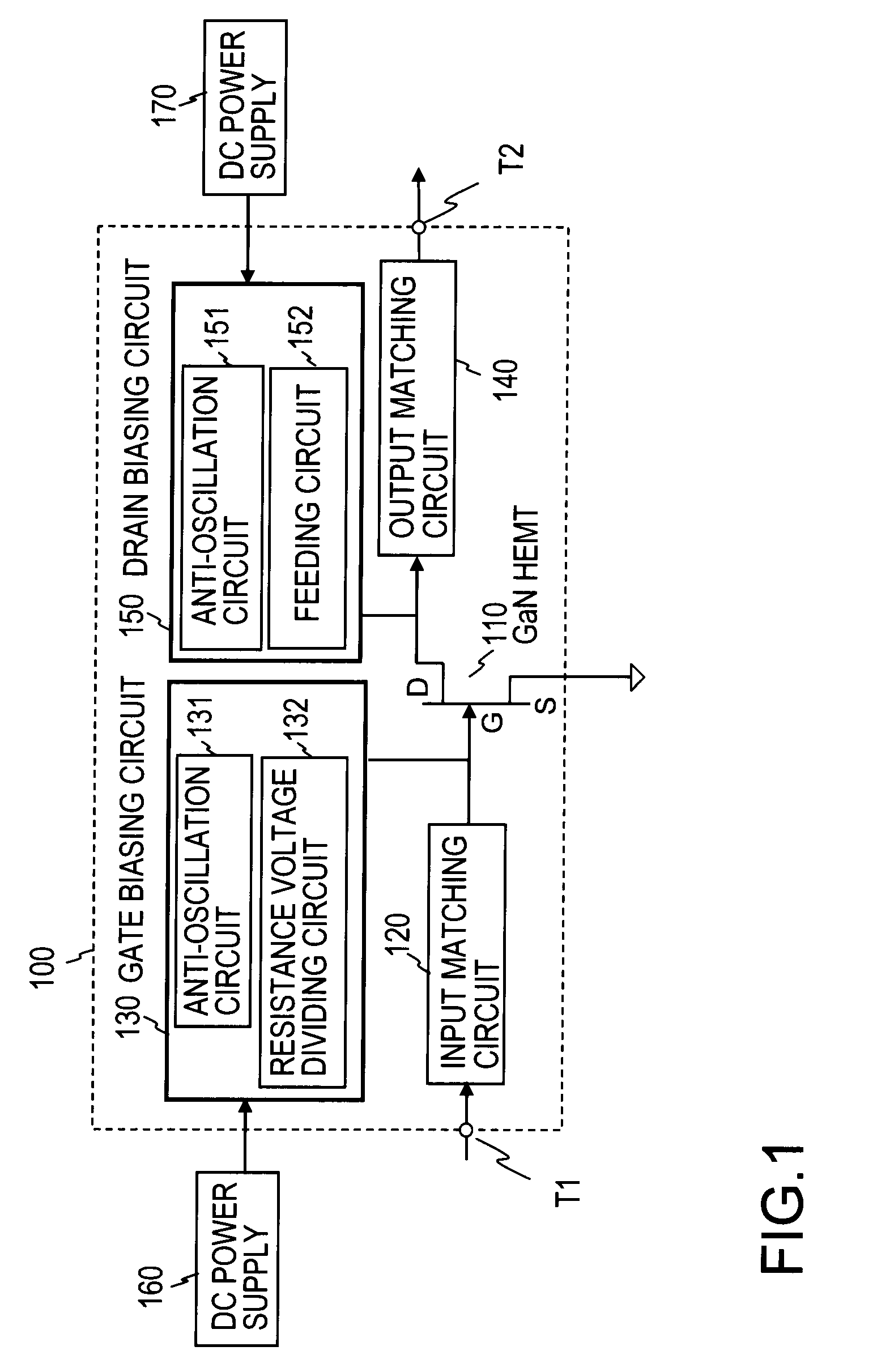
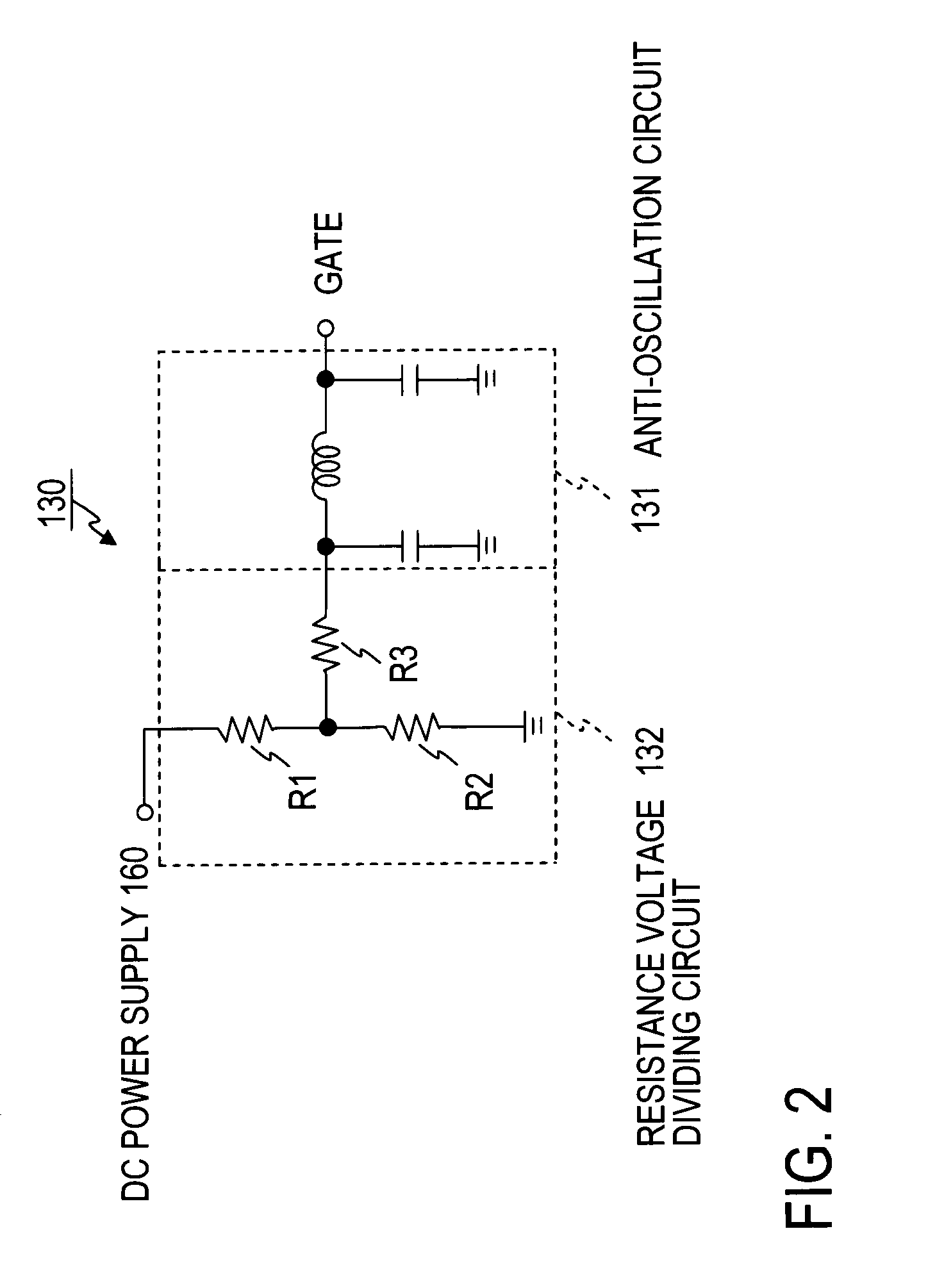
Cryogenic receiving amplifier and amplifying method
InactiveUS7795965B2Reduce additionalAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierImpedance matching
The present invention discloses a cryogenic receiving amplifier using a gallium nitride high electron mobility transistor (GaN HEMT) as an amplifying device in a cryogenic temperature environment. The cryogenic receiving amplifier includes an input matching circuit which makes an impedance matching between a gate of the amplifying device and an outside of an input terminal, a gate biasing circuit which applies a DC voltage to the gate of the amplifying device, an output matching circuit which makes an impedance matching between a drain of the amplifying device and an outside of an output terminal, and a drain biasing circuit which applies a DC voltage to the drain of the amplifying device. The cooled temperature is preferably set to 150 K or below, and the GaN HEMT may be illuminated with light of a blue LED.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Wavelength-division-multiplexing optical transmission system and control method thereof
InactiveUS7606488B2Fast transferLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingTransport system
In a wavelength-division-multiplexing optical transmission system in which optical-node apparatuses that perform relay transmission of wavelength-division-multiplexed light are located at specified nodes in a main optical transmission path, an optical amplifier switches level control to constant-gain control when there is a notification of a change in the number of multiplexed wavelengths, and then after a specified amount of time restarts level control so that the level becomes a target level that corresponds to the actual number of wavelengths. When doing this, an optical-transmission-system-control unit controls the optical-transmission system so that the equationT<Y / (N·v)is satisfied, wherein T denotes a period from the time when a change in the number of multiplexed wavelengths occurs until said constant-gain control starts v denotes output-level-recovery speed of the optical amplifier, Y denotes fluctuation allowance of a receiving unit after wavelength-division-multiplexing transmission, and N is a maximum number of spans.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High sensitivity optical receiver employing a high gain amplifier and an equalizing circuit
An optical receiver includes a light receiving element for converting an optical signal to an electrical signal having a first bandwidth and an amplifier for amplifying the electrical signal. The amplifier has a first gain response that yields a second bandwidth that is less than the first bandwidth. The optical receiver also includes an equalizing circuit operationally coupled to the amplifier. The equalizing circuit has a second gain response that compensates for the first gain response of the amplifier so that a substantially constant net gain is imparted by the amplifier and the equalizing circuit to the electrical signal over the first bandwidth.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
High speed preamplifier circuit, detection electronics, and radiation detection systems therefrom
ActiveUS20090224835A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifiers controlled by lightAudio power amplifierTransimpedance amplifier
A preamplifier circuit for processing a signal provided by a radiation detector includes a transimpedance amplifier coupled to receive a current signal from a detector and generate a voltage signal at its output. A second amplification stage has an input coupled to an output of the transimpedance amplifier for providing an amplified voltage signal. Detector electronics include a preamplifier circuit having a first and second transimpedance amplifier coupled to receive a current signal from a first and second location on a detector, respectively, and generate a first and second voltage signal at respective outputs. A second amplification stage has an input coupled to an output of the transimpedance amplifiers for amplifying the first and said second voltage signals to provide first and second amplified voltage signals. A differential output stage is coupled to the second amplification stage for receiving the first and second amplified voltage signals and providing a pair of outputs from each of the first and second amplified voltage signals. Read out circuitry has an input coupled to receive both of the pair of outputs, the read out circuitry having structure for processing each of the pair of outputs, and providing a single digital output having a time-stamp therefrom.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Microstructures, method for producing microstructures, and optical field amplifying device
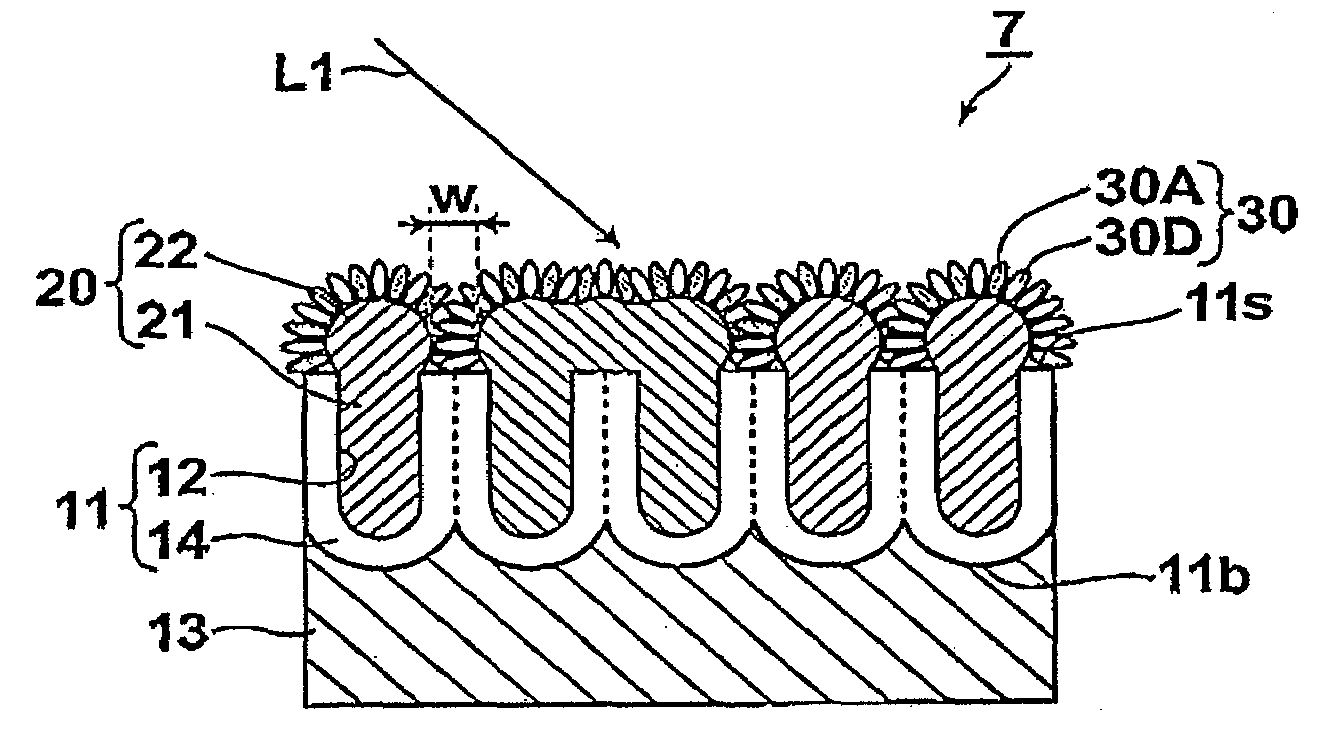
InactiveUS20080304060A1Increase in sizeImprove visual effectsOptical radiation measurementLiquid surface applicatorsDielectricElectrical conductor
A microstructure is formed on a conductor. The microstructure is equipped with a dielectric base material, in which a great number of fine holes having substantially the same shape in plan view are formed. The fine holes are open at the surface of the dielectric base material, and are substantially uniformly provided therein. A plurality of micro metal members are fixed to the dielectric base material. The micro metal members include filling portions that fill one or more of the fine holes, and protruding portions that protrude from the surface of the dielectric base material and are of diameters greater than the fine holes, capable of inducing local plasmon. The plurality of micro metal members include those that have different numbers of filling portions.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical offset signal cancellation for optical receiver
InactiveUS20050232637A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansLow-pass filterOffset cancellation
A laser driver for high speed interconnections may convert a digital signal to a current train of a bias mode to represent logical zero and of a modulation mode to represent logical one. An optical signal thus produced may include an optical offset. An optical receiver may include a photo-detector to receive the optical signal and generate a current signal, which includes a corresponding current offset. A first amplifier stage converts the current signal to a voltage signal and a second amplifier stage generates a digital output from the voltage signal. One or more low-pass filters may be used to filter the digital output and generate a filtered offset signal for a differential amplifier to generate an offset cancellation signal. The offset cancellation signal may be provided to offset cancellation circuitry to remove the current offset from the current signal generated by the photo-detector.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Popular searches
Dc amplifiers with modulator-demodulator Electroluminescent amplifiers Star/tree networks Transmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systems Star-type electromagnetic networks Electronic switching Optical elements Photoelectric discharge tubes Photometry electrical circuits Differential amplifiers
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com