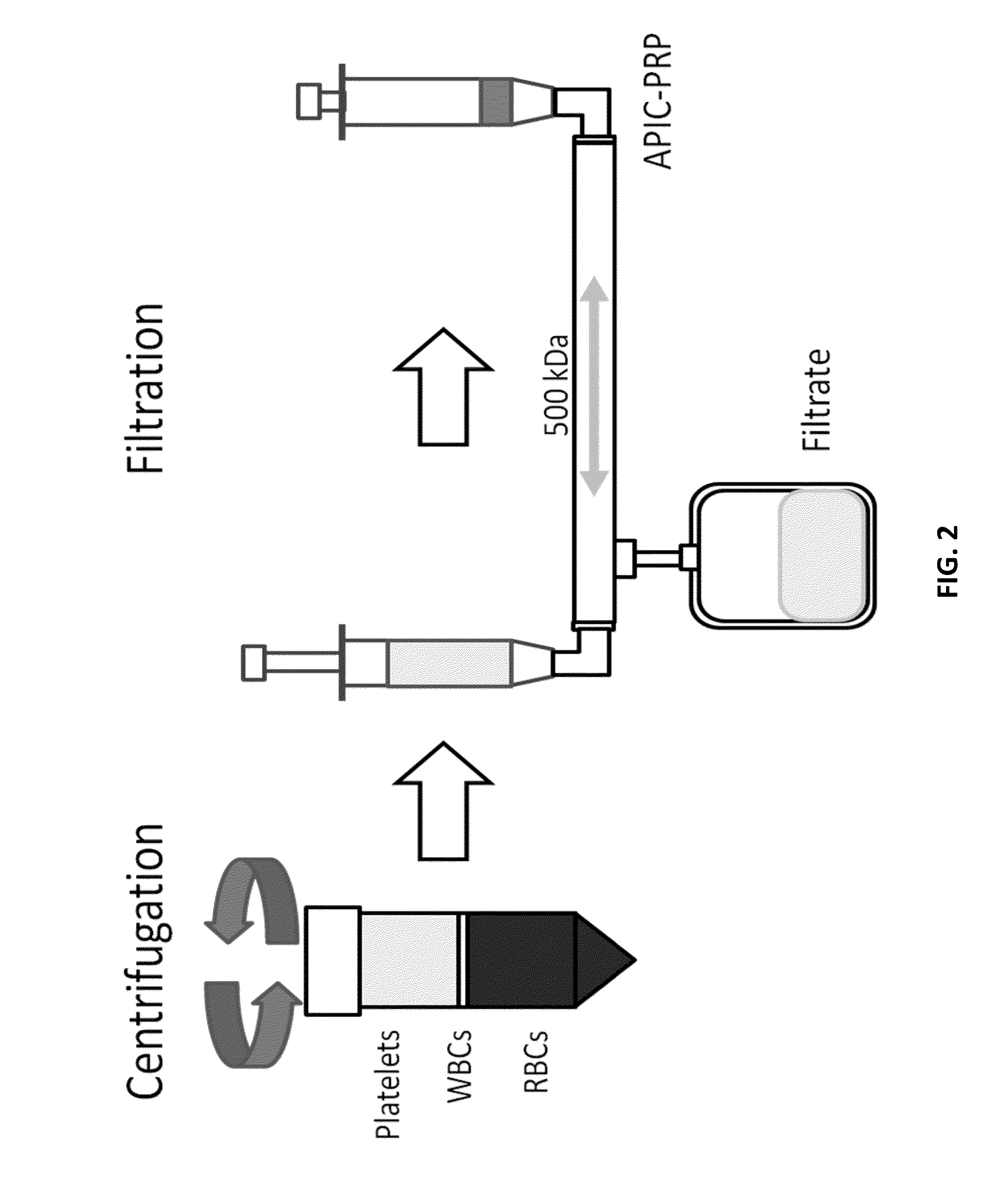
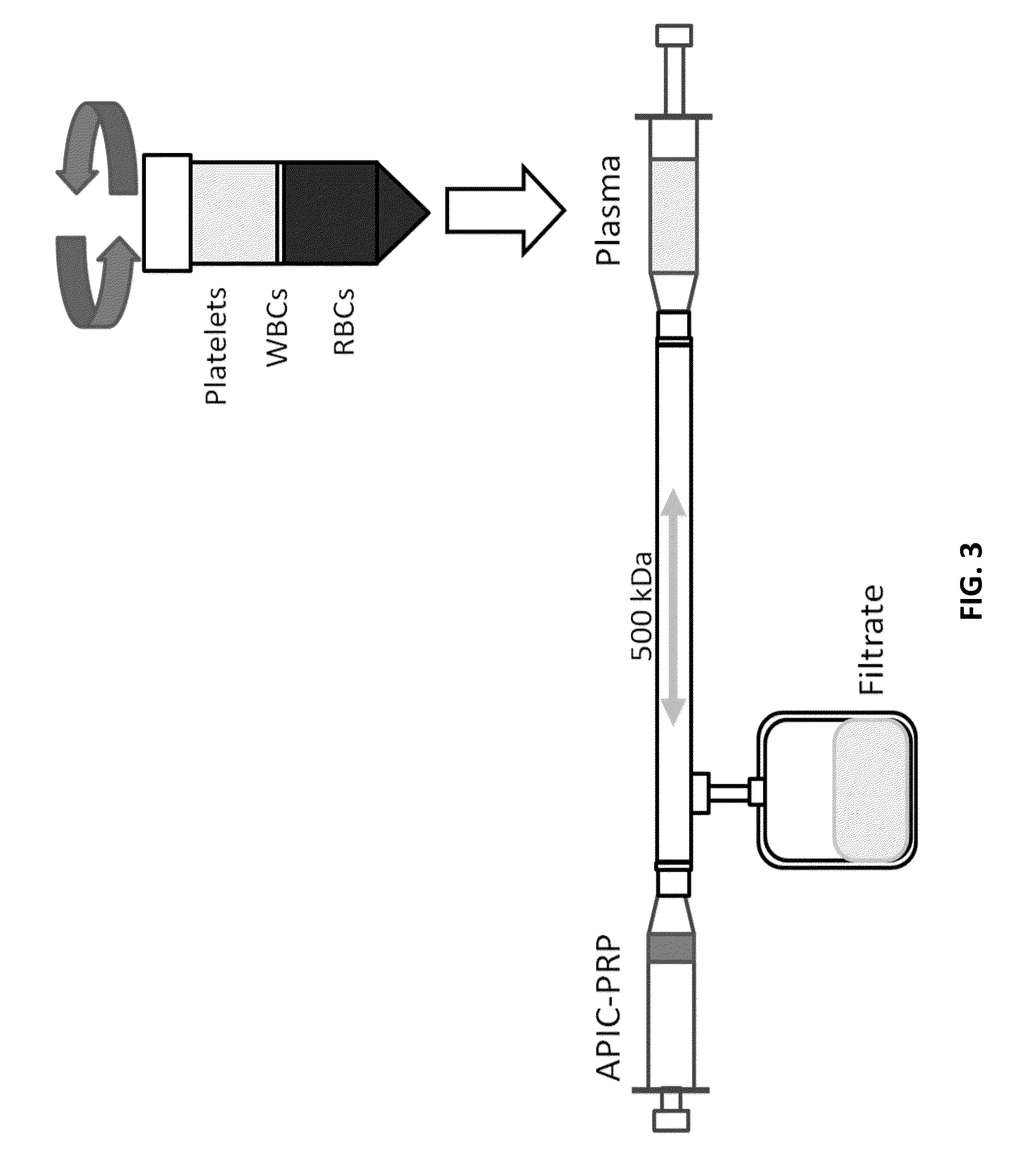
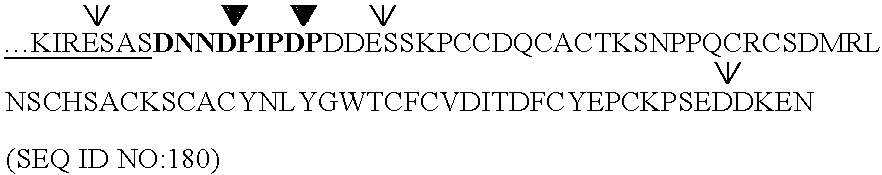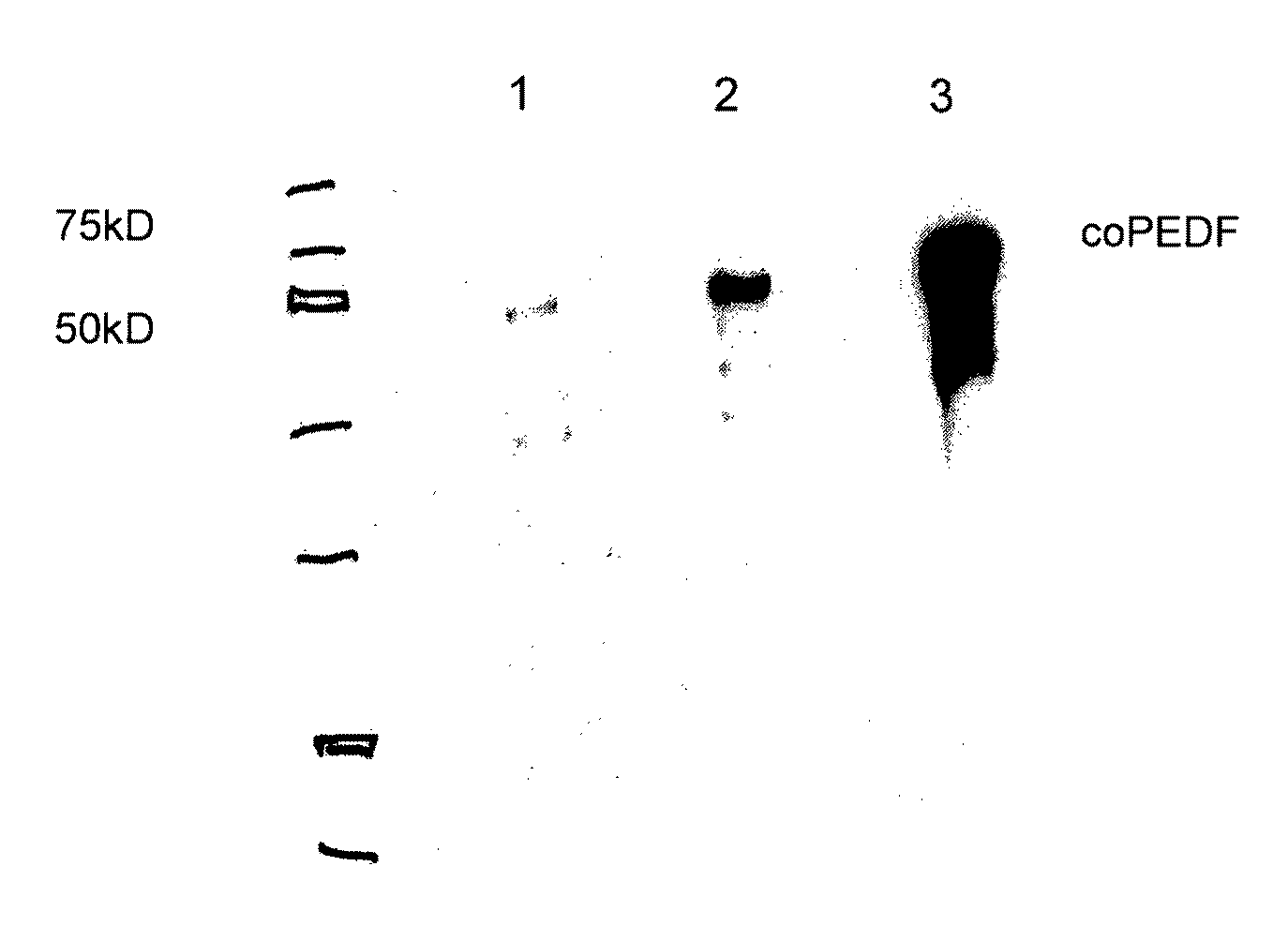Patents
Literature
239results about "Endopeptidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacterial expression of protease inhibitors and variants thereof
ActiveUS20050202535A1Reduce disulfide bondBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityProtease
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
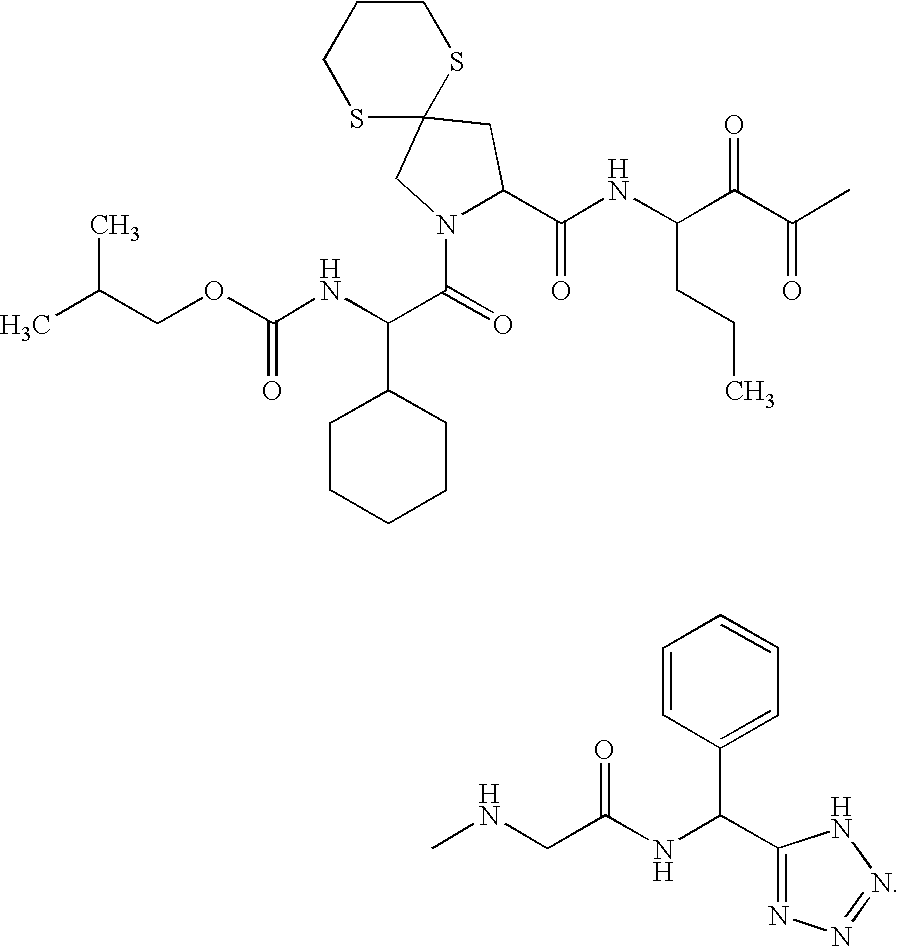
Macrocyclic Proline Derived HCV Serine Protease Inhibitors
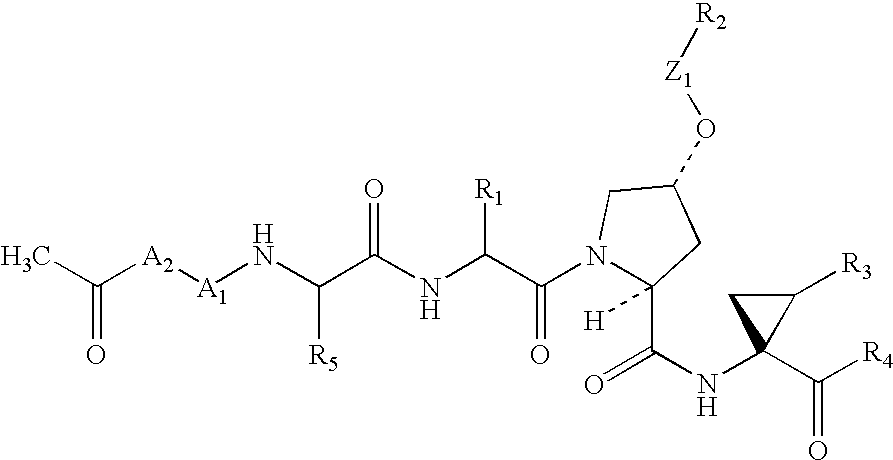
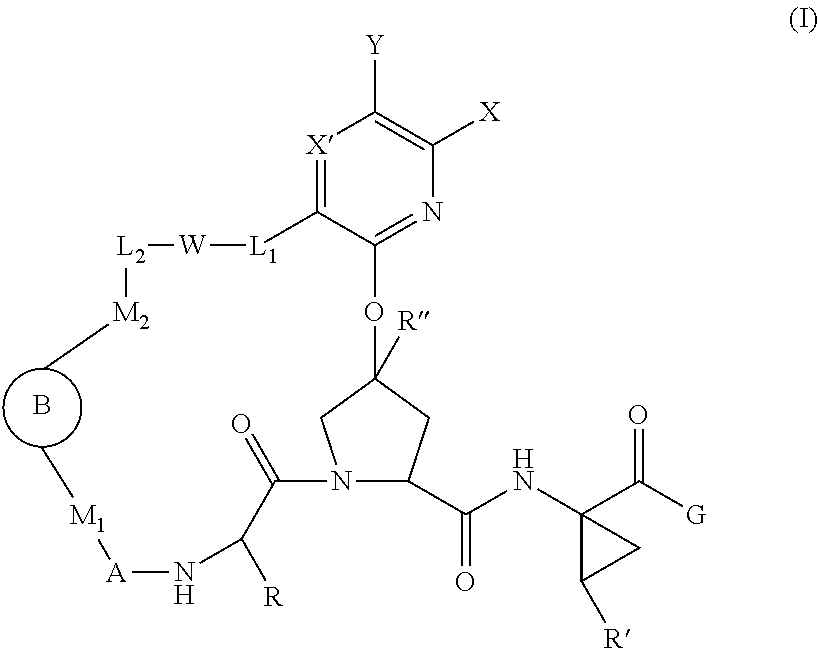
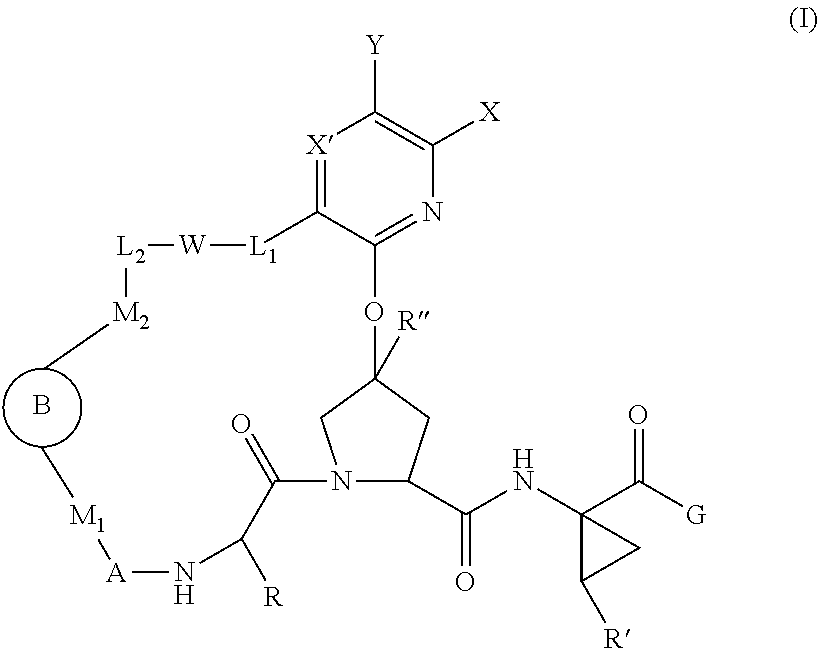
The present invention discloses compounds of Formula I or pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, or prodrugs thereof:which inhibit serine protease activity, particularly the activity of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3-NS4A protease. Consequently, the compounds of the present invention interfere with the life cycle of the hepatitis C virus and are also useful as antiviral agents. The present invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the aforementioned compounds for administration to a subject suffering from HCV infection. The invention also relates to methods of treating an HCV infection in a subject by administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compounds of the present invention.
Owner:ENANTA PHARM INC
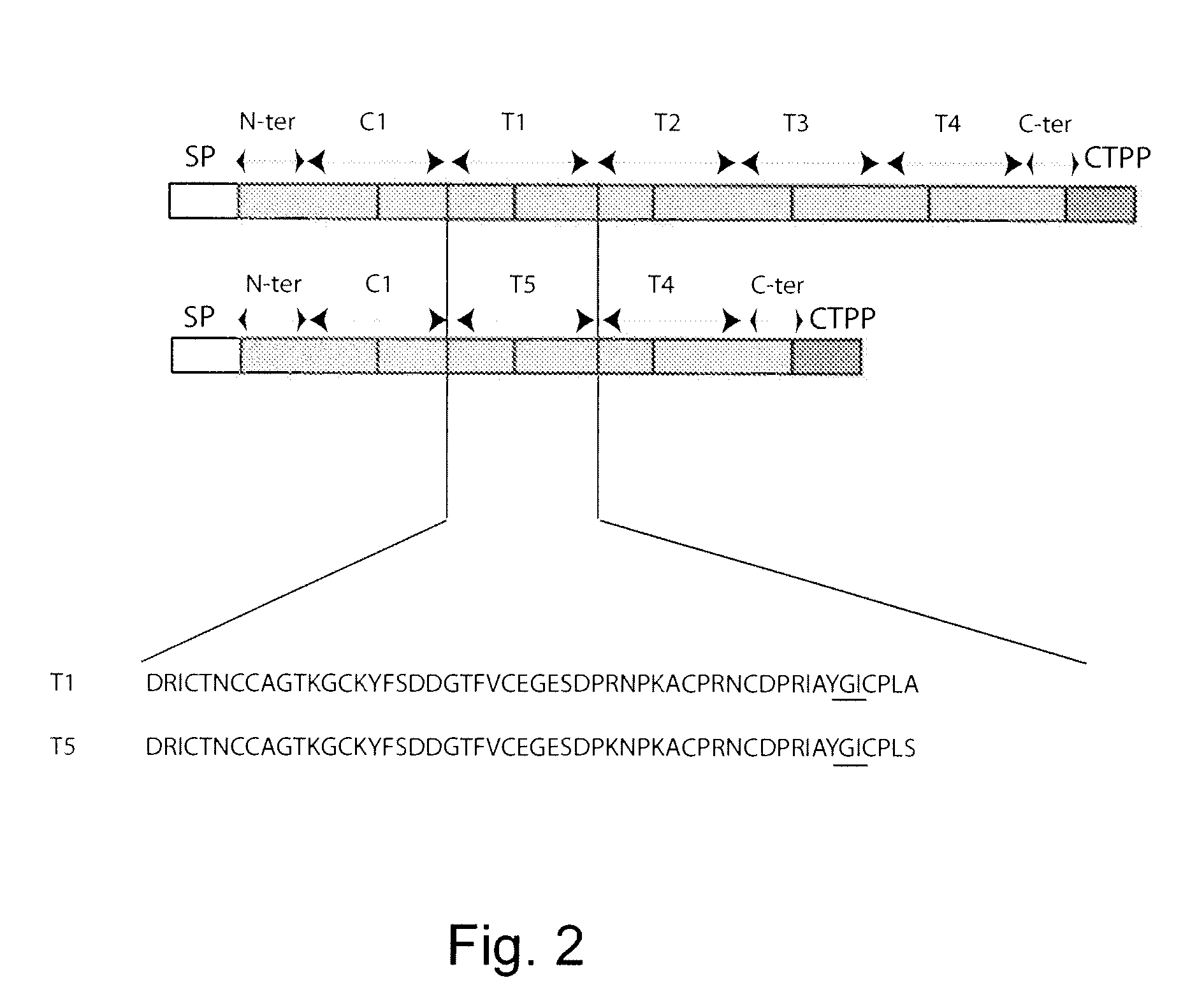
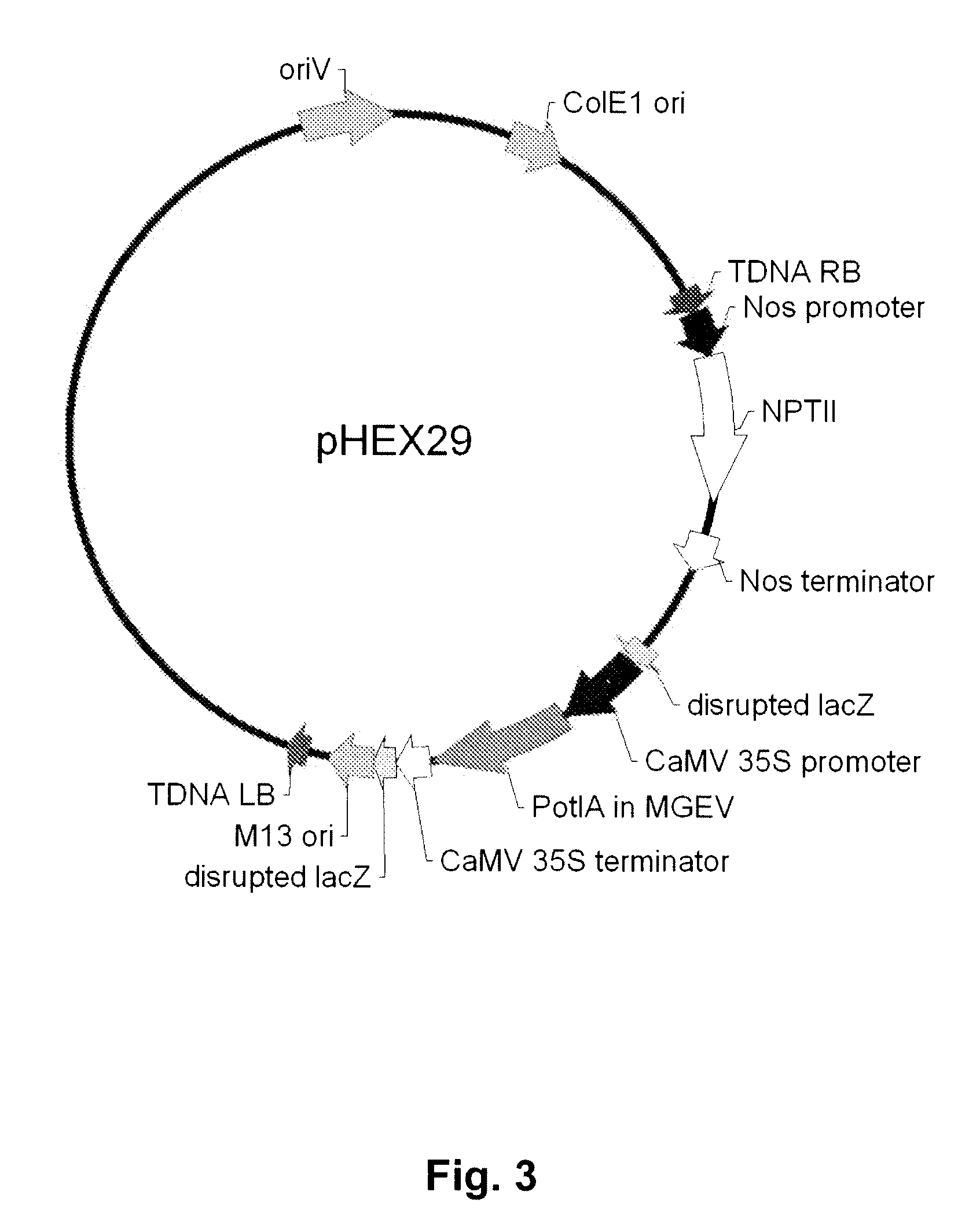
Multi-gene expression vehicle
InactiveUS20070277263A1Lack featureClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesMultigene expressionNucleotide
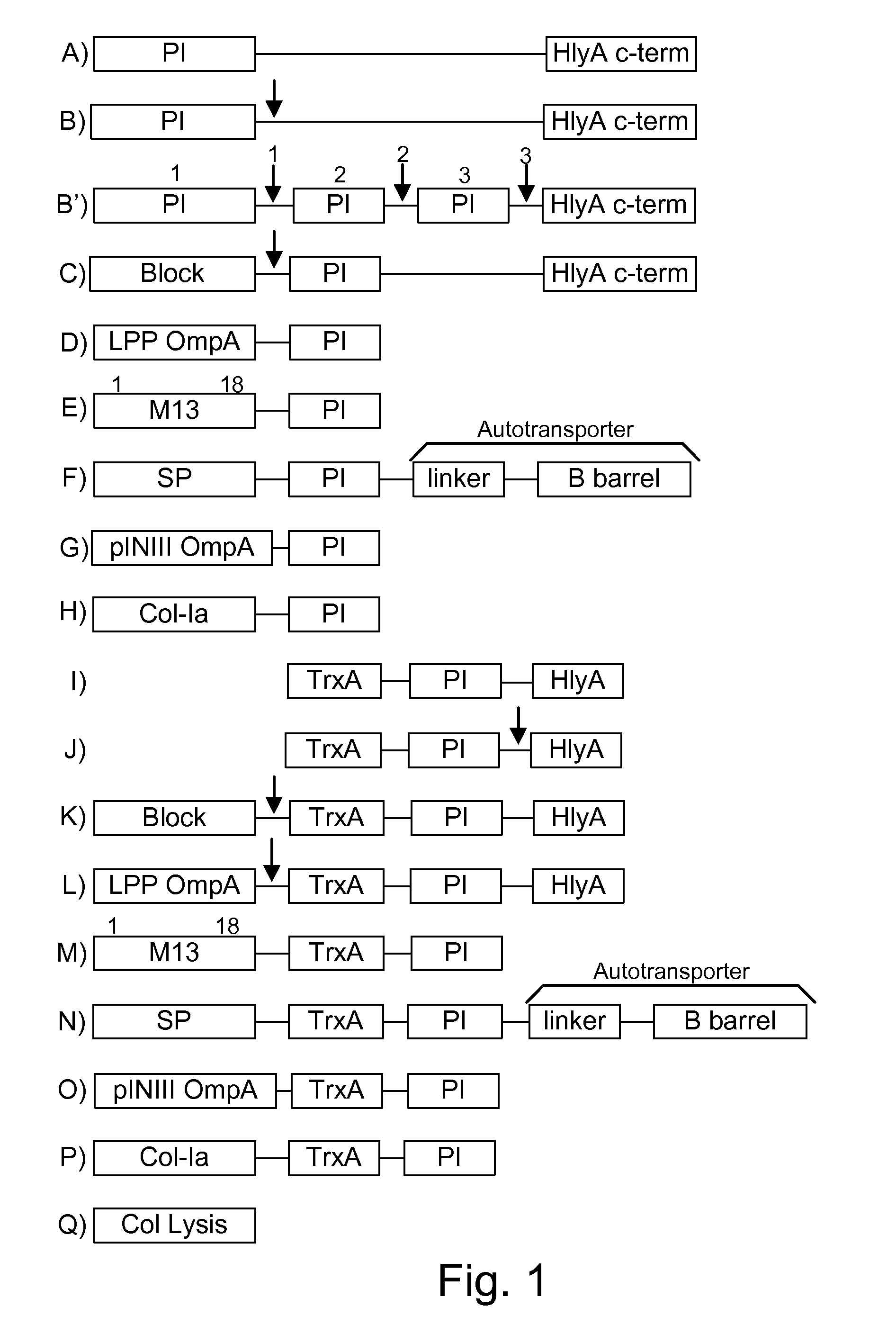
A multigene expression vehicle (MGEV) consisting essentially of a polynucleotide comprising 2 to 8 domain segments, D, each domain encoding a functional protein, each domain being joined to the next in a linear sequence by a Linker (L) segment encoding a Linker peptide, the D and L segments all being in the same reading frame, and at least one of the domains is not a type two protease inhibitor.
Owner:HEXIMA LTD
Compositions and Methods for Use of Pigment Epithelial Derived Factor (PEDF) Peptide Fragments
InactiveUS20090069241A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderPIGMENT EPITHELIUM-DERIVED FACTORPeptide fragment
The invention provides PEDF peptides which retain the biological activity of full-length PEDF. Fusion proteins comprising a PEDF peptide are also provided. The invention further provides a codon-optimized PEDF coding sequence and method of expressing it in bacteria. Compositions, methods of use and kits are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Bacterial expression of bowman-birk protease inhibitors and variants thereof
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Protease inhibitor: protease sensitivity expression system composition and methods improving the therapeutic activity and specificity of proteins delivered by bacteria
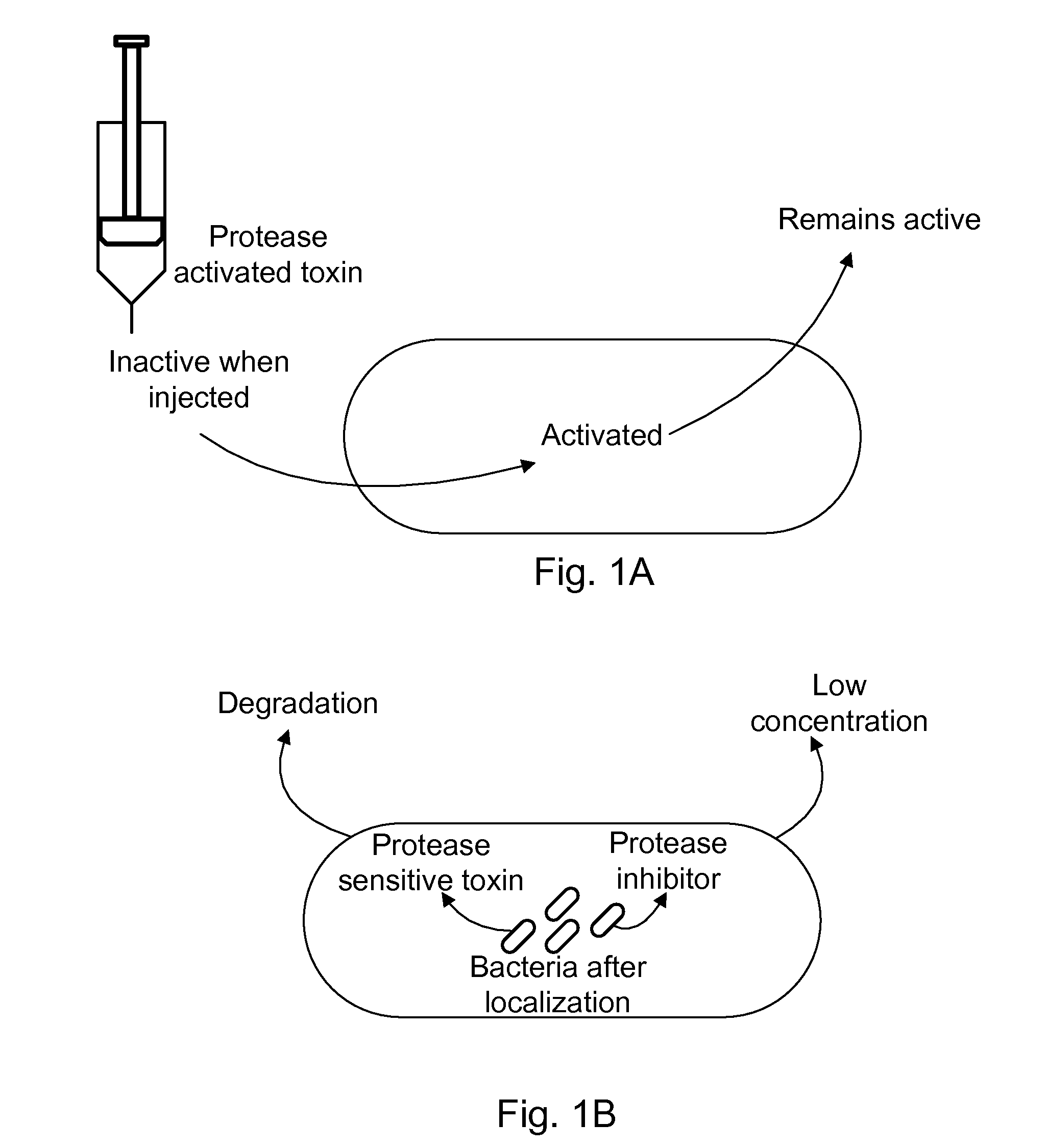
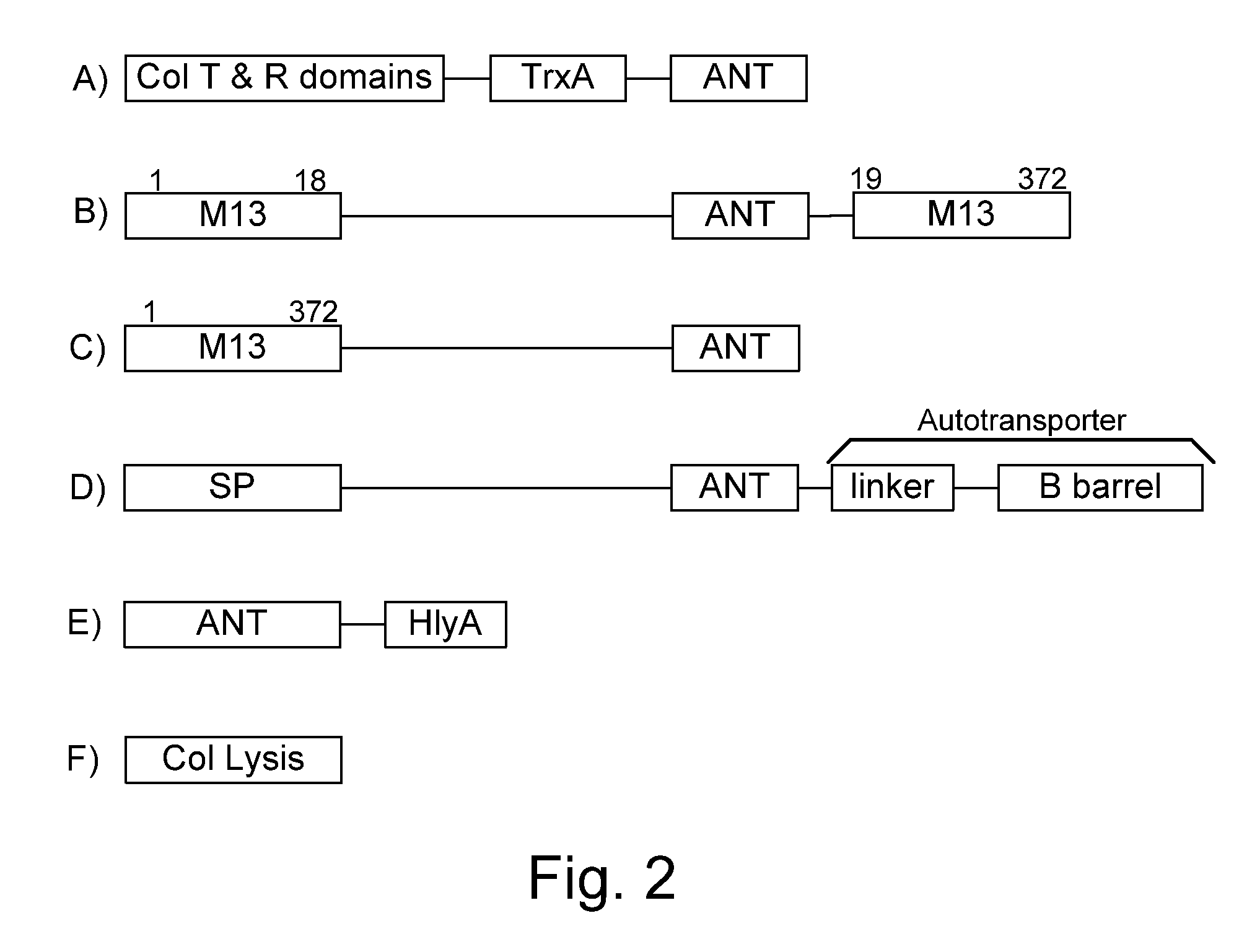
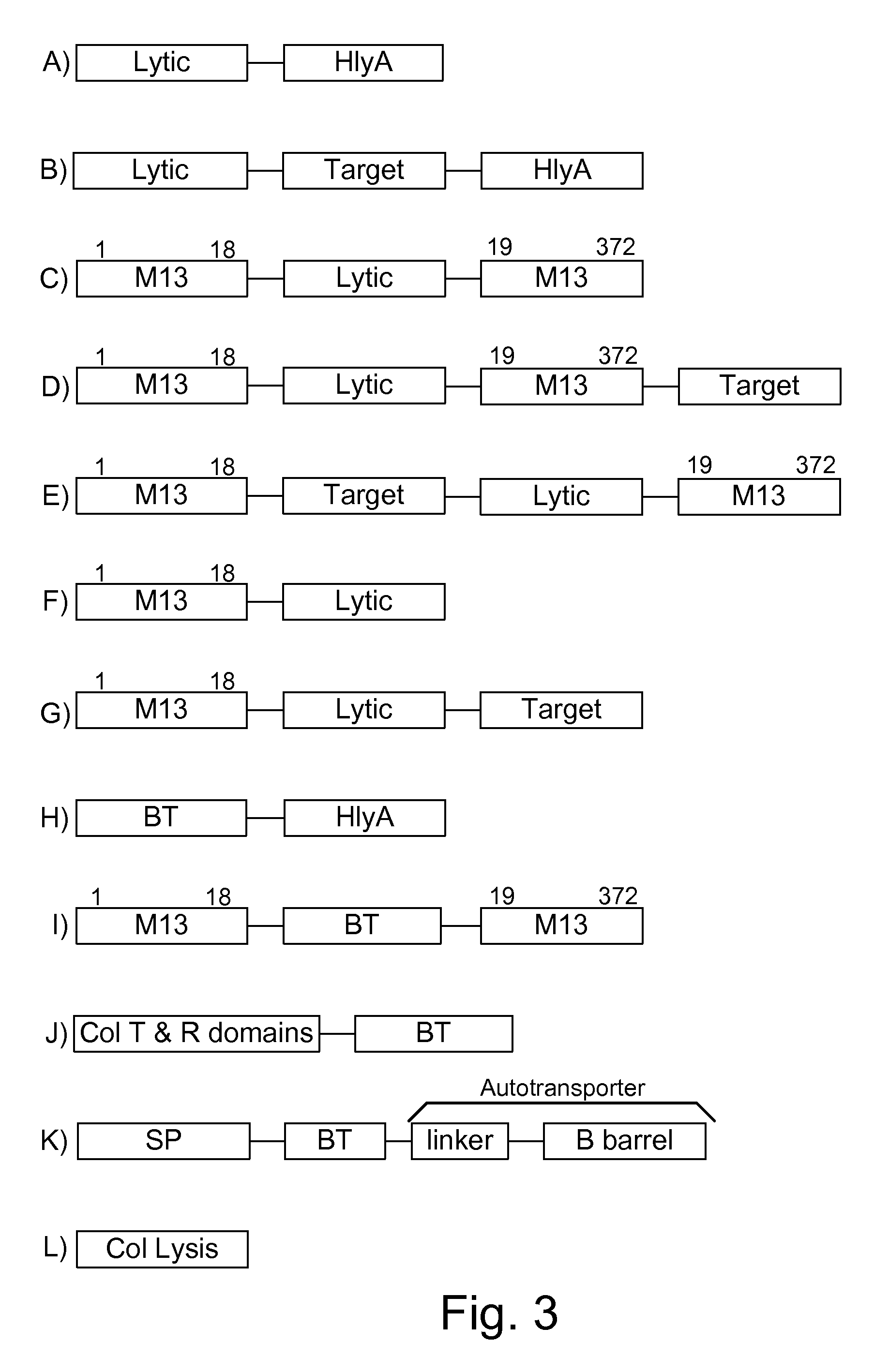
Bacteria which co-express protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents, which are surface displayed, secreted and / or released and result in their localized production and maintenance within a target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue, thereby increasing therapeutic activity and reducing the systemic toxicity. The bacteria may be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic or a probiotic. Protease sensitivity may be further accomplished by engineering protease degradation sites within the therapeutic agents, further enhancing the inactivation outside of the target tissue while retaining activity within the target tissue through co-expression of a protease inhibitor. Novel chimeric proteins secreted by bacteria, including chimeric toxins targeted to neoplastic cells, tumor matrix cells and cells of the immune system, and combination therapies of these protease inhibitor:chimeric toxin-expressing bacteria together with small-molecule and biologic agents are also described. Non-conjugative bacteria limiting exchange of genetic material, and antibody resistant bacteria are also provided.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
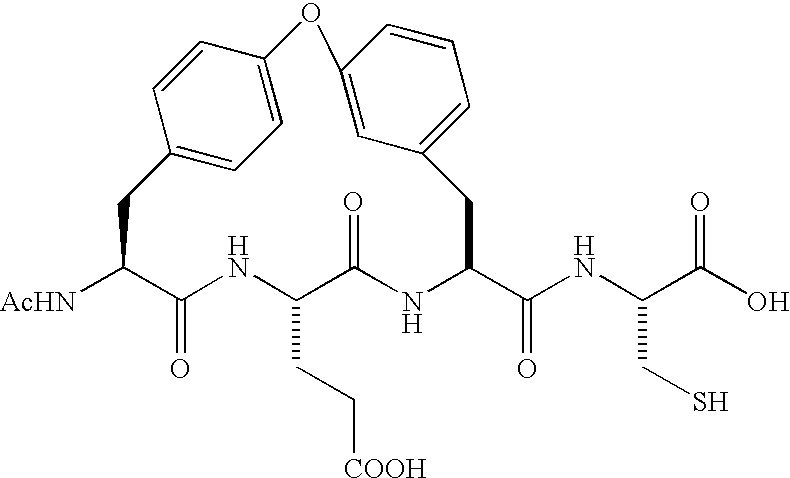
Diagnosis of ovarian carcinomas
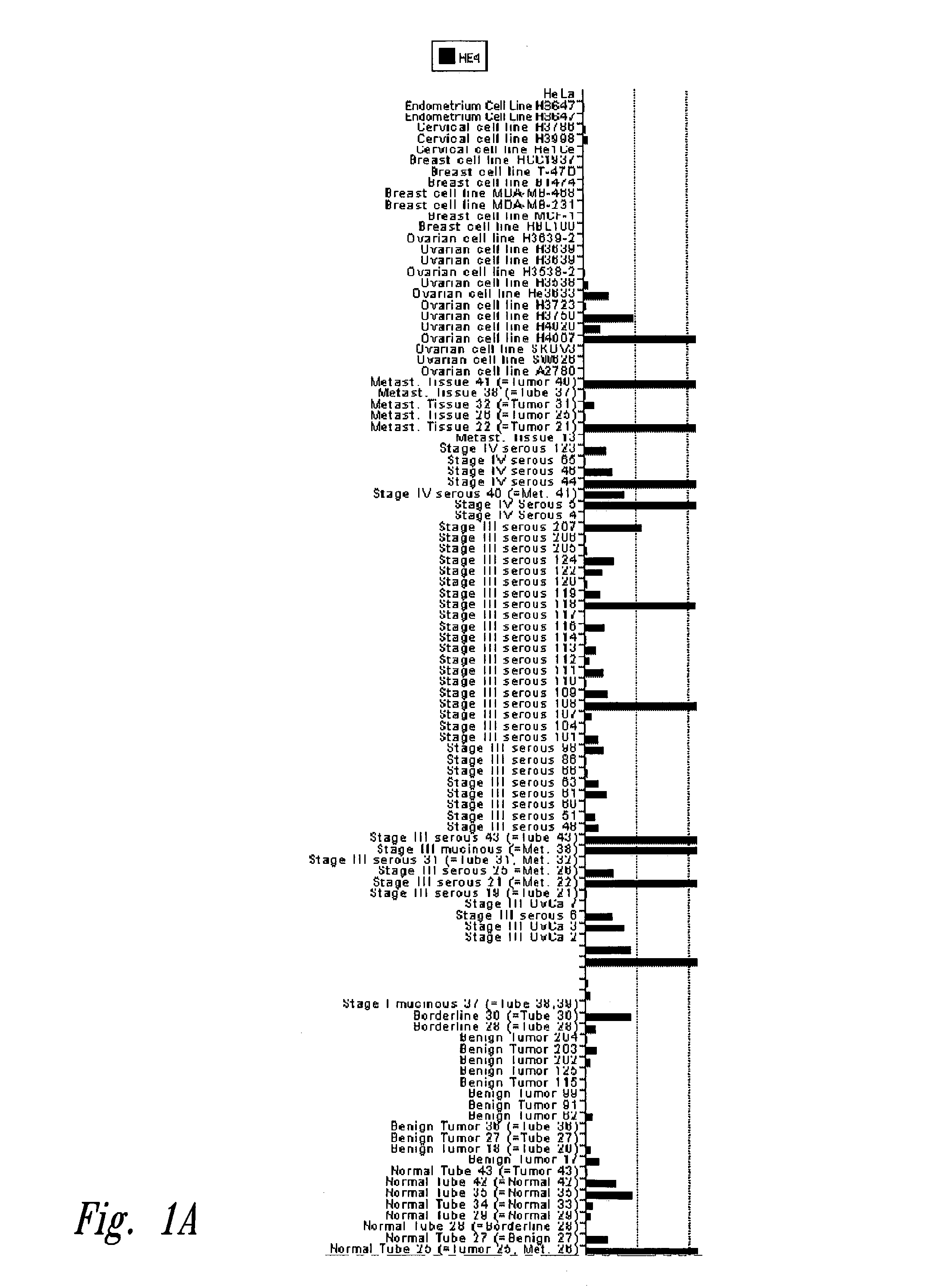
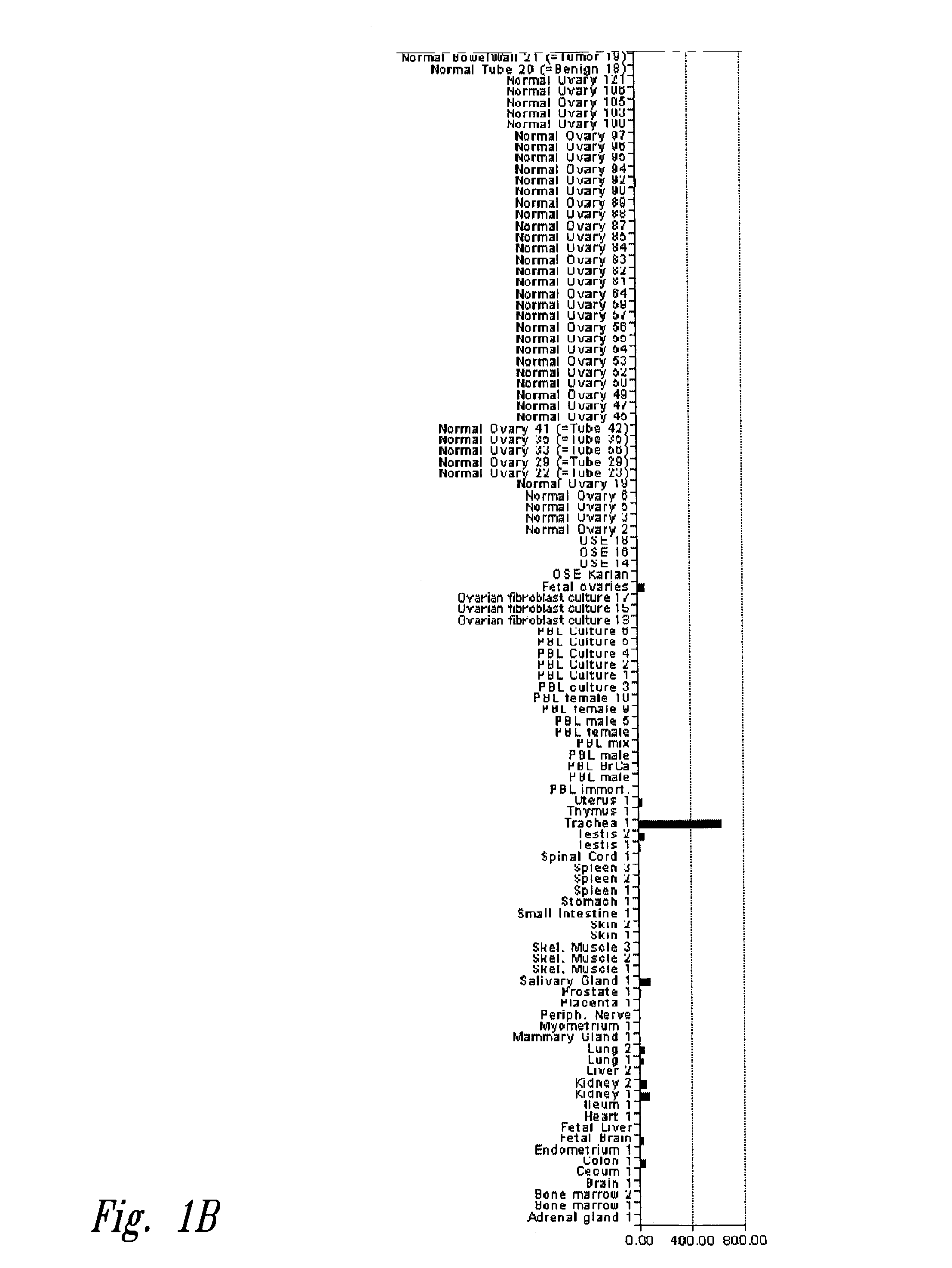
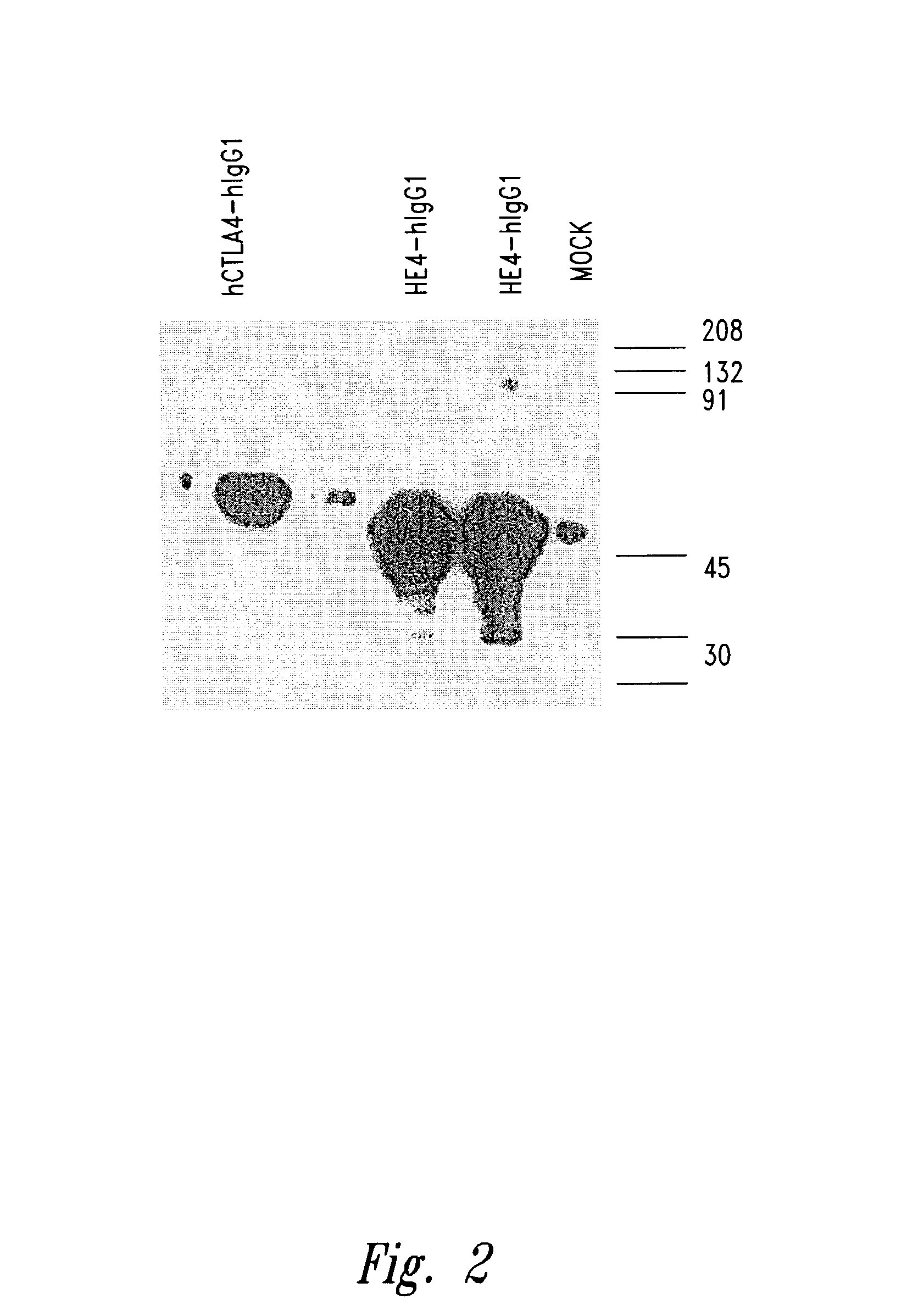
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for the detection of a malignant condition, and relates to the discovery of soluble and cell surface forms of HE4a polypeptides, including HE4a that is overexpressed in ovarian carcinomas. In particular the invention provides a nucleic acid sequence encoding HE4a, and also provides a method of screening for the presence of a malignant condition in a subject by detecting reactivity of an antibody specific for a HE4a polypeptide with a molecule naturally occurring in soluble and / or cell surface form in a sample from such a subject, and by hybridization screening using an HE4a nucleotide sequence, as well as other related advantages.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Protease inhibitor: protease sensitivity expression system composition and methods improving the therapeutic activity and specificity of proteins delivered by bacteria
ActiveUS9068187B1Direct cytotoxicDirect inhibitoryBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesSurface display
Bacteria which co-express protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents, which are surface displayed, secreted and / or released and result in their localized production and maintenance within a target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue, thereby increasing therapeutic activity and reducing the systemic toxicity. The bacteria may be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic or a probiotic. Protease sensitivity may be further accomplished by engineering protease degradation sites within the therapeutic agents, further enhancing the inactivation outside of the target tissue while retaining activity within the target tissue through co-expression of a protease inhibitor. Novel chimeric proteins secreted by bacteria, including chimeric toxins targeted to neoplastic cells, tumor matrix cells and cells of the immune system, and combination therapies of these protease inhibitor:chimeric toxin-expressing bacteria together with small-molecule and biologic agents are also described. Non-conjugative bacteria limiting exchange of genetic material, and antibody resistant bacteria are also provided.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
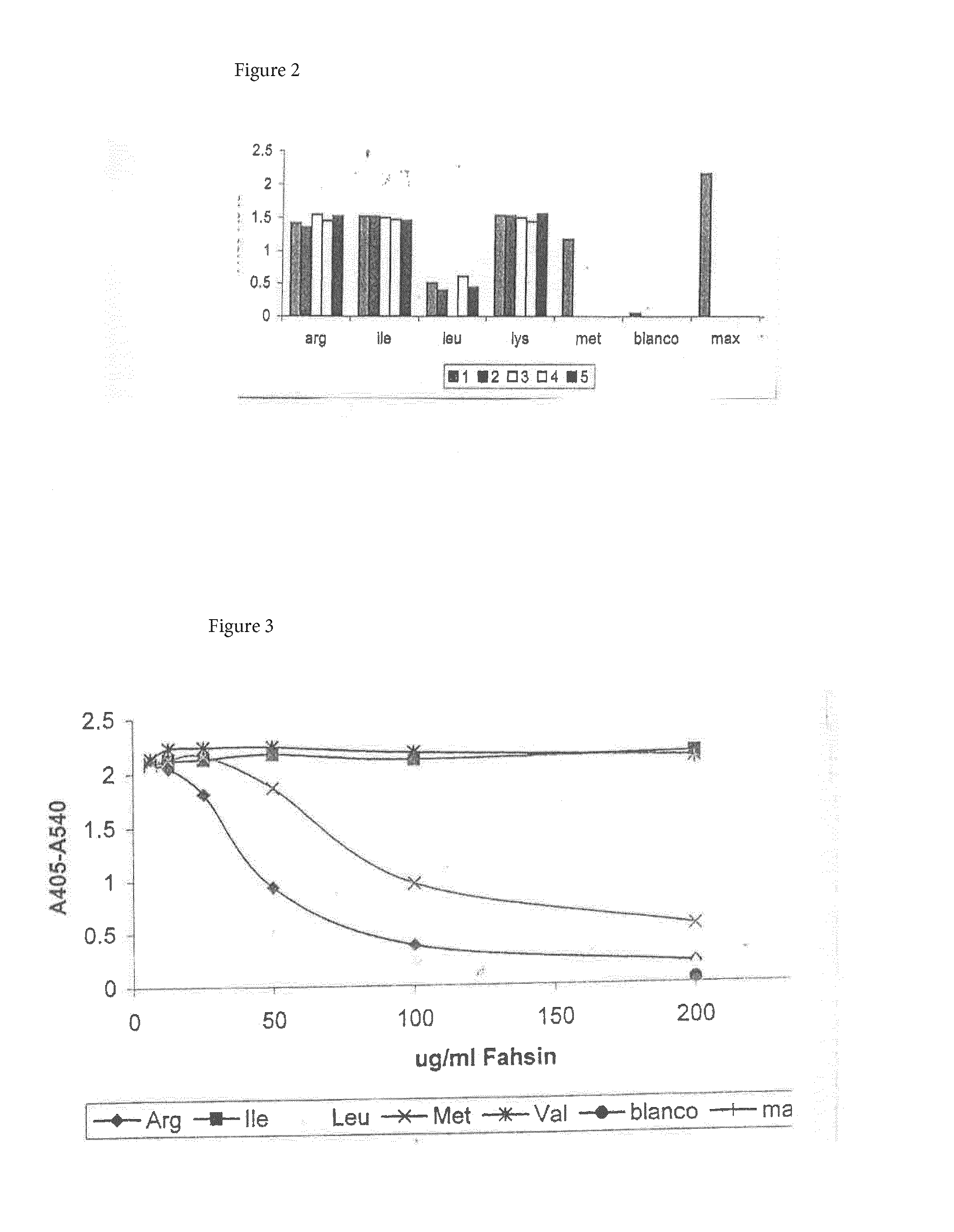
Novel means to decrease the negative effects of smoking
InactiveUS20160177285A1Preferable effectNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCOPDInhalation
The present invention relates to the use of an elastase inhibitor, preferably fahsin for the treatment or prevention of emphysema, COPD or lung cancer. The elastase inhibitor is preferably administered through inhalation, preferably thorough inhalation of tobacco smoke. The invention also comprises smoking articles comprising such an elastase inhibitor.
Owner:VOERMAN GERARD
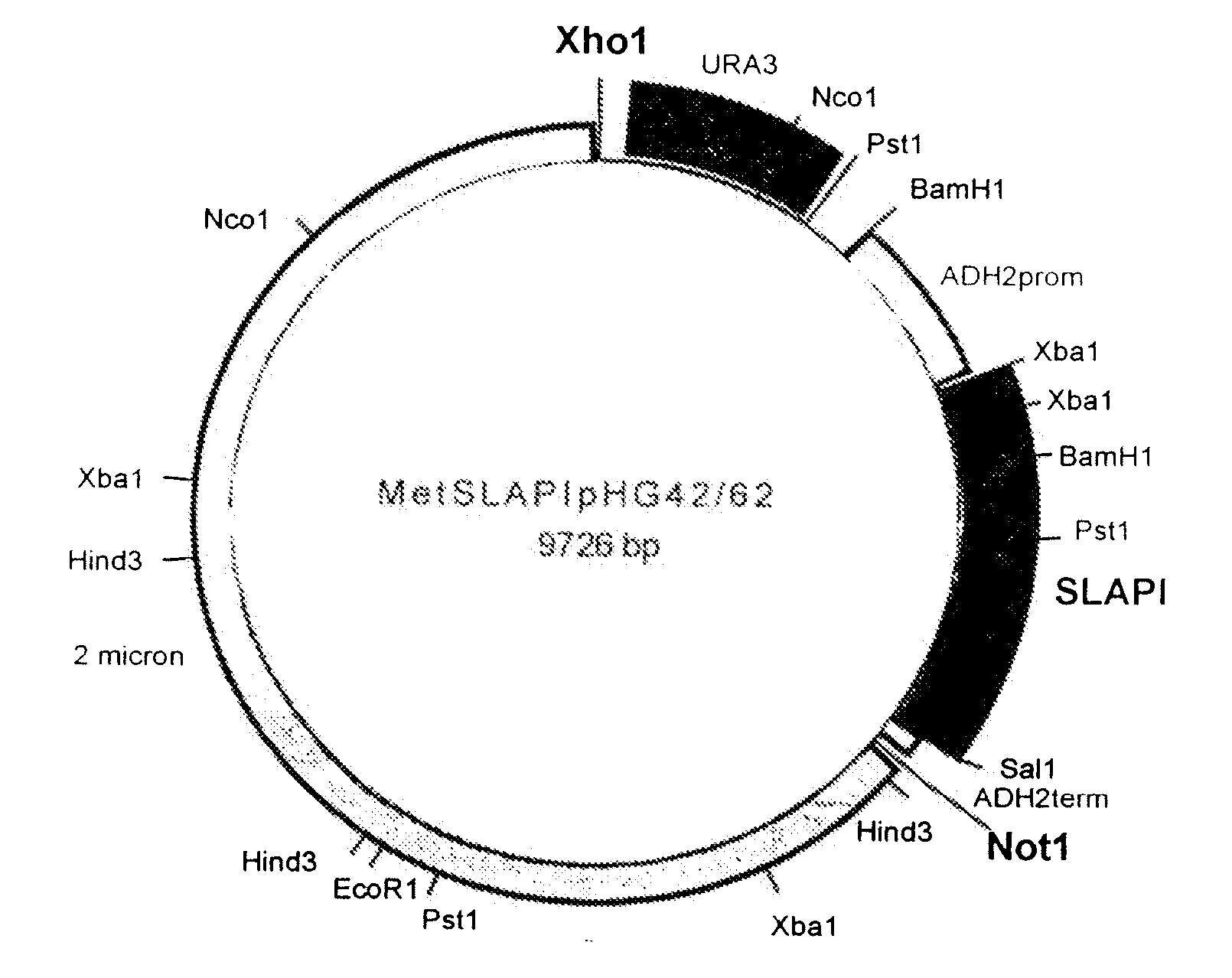
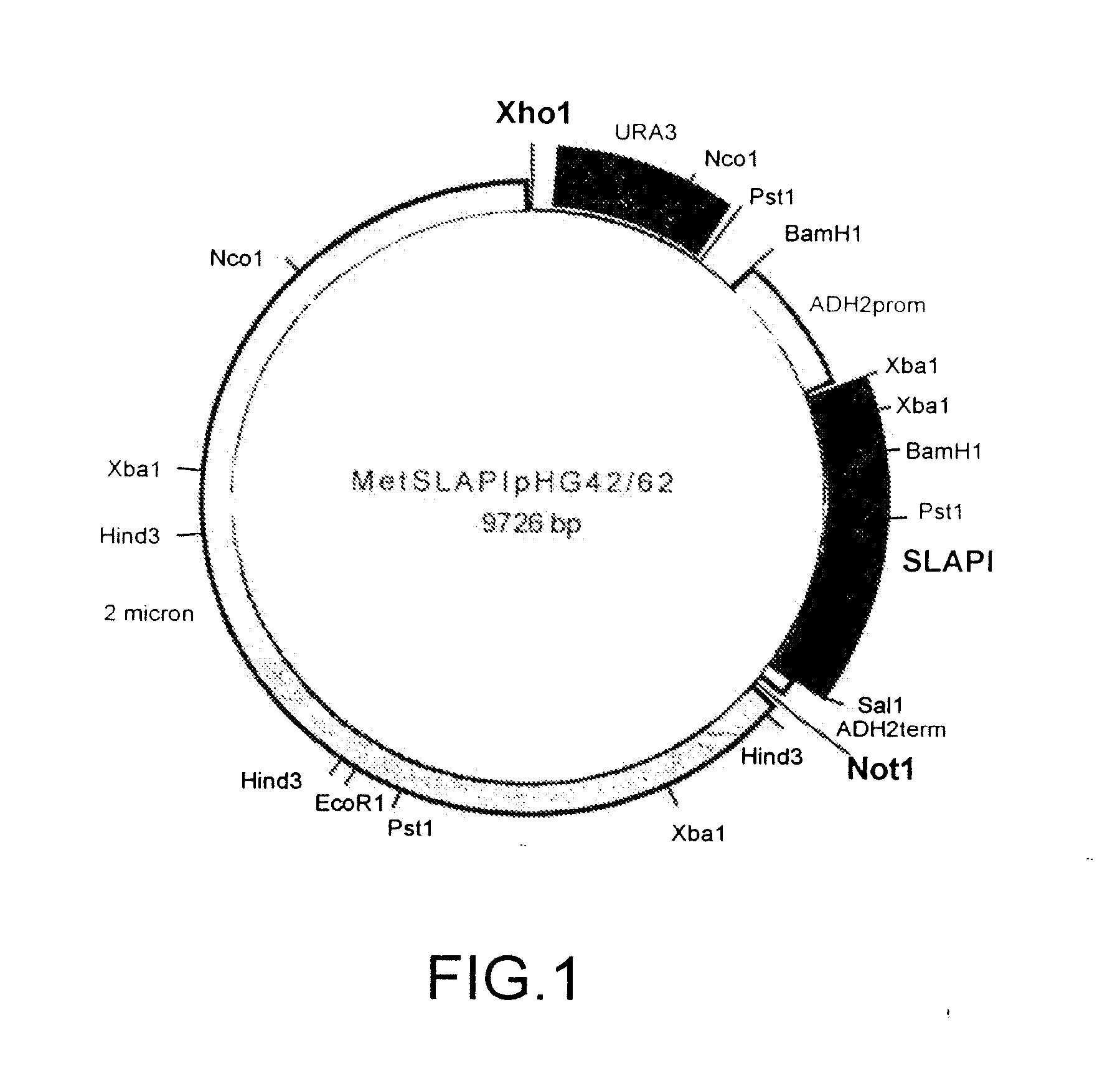
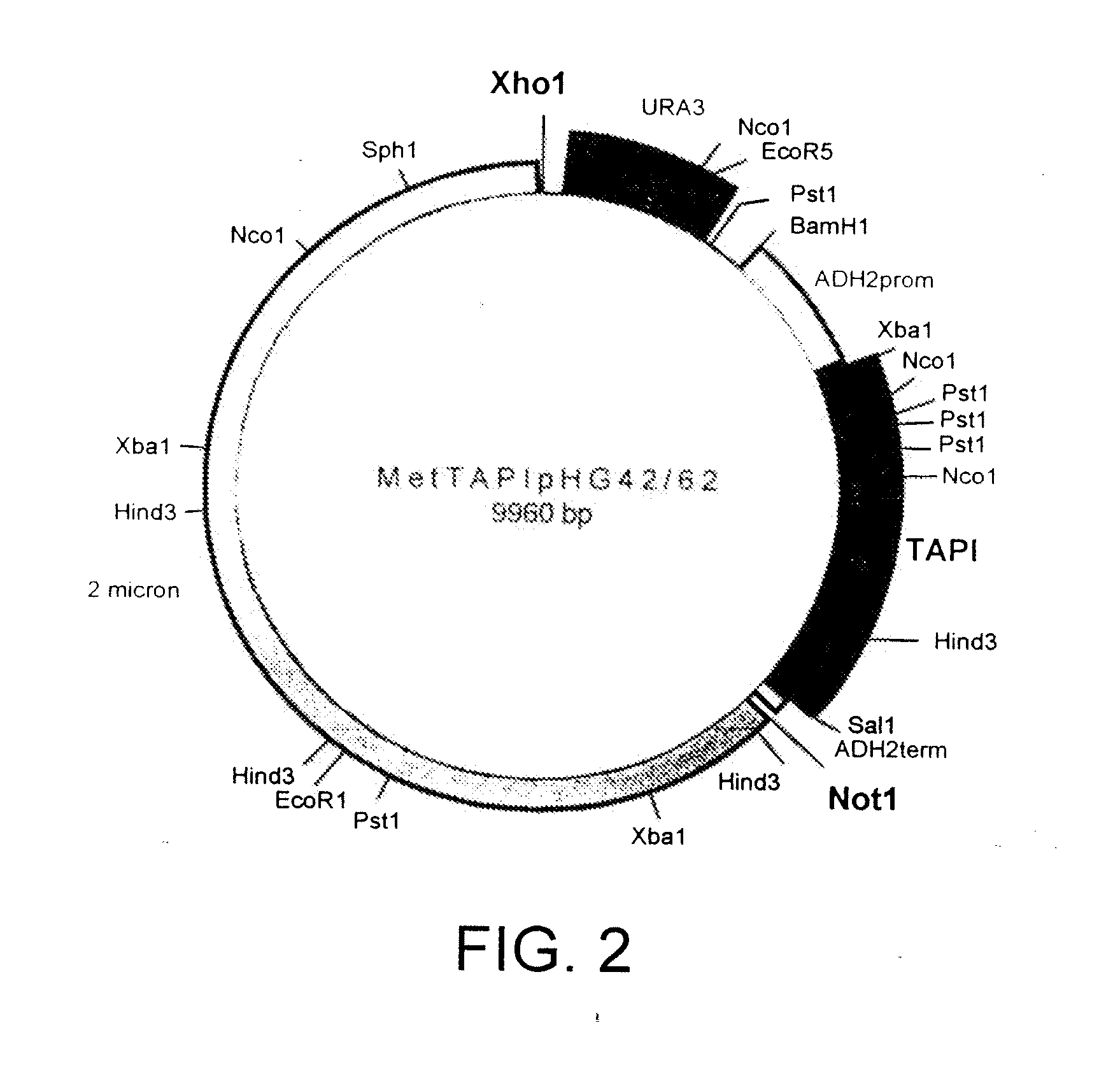
Methods of protein production in yeast
Vectors, host cells, and methods are provided for the production of proteins in yeast. The vectors generally contain a selection gene, a yeast 2 micron sequence, and a polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide, where the polynucleotide is operably linked to promoter, and where the polynucleotide contains one or more yeast-preferred codons. Host cells are cultured under conditions where, after an initial batch phase, oxygen concentration is kept high and glucose feed is regulated so that the yeast cells stay in respiratory metabolism.
Owner:ARRIVA PHARMA
Therapeutic formulations using heat shock/stress protein-peptide complexes
InactiveUS20020192230A1Elicit immune responseBacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsCancer cellStress Proteins
The present invention relates to methods for making compositions comprising heat shock proteins or alpha (2) macroglobulin ("alpha2M"), which compositions are immunogenic against a type of cancer or an agent of an infectious disease, and the compositions produced by the methods described herein. The invention further relates to methods for eliciting an immune response and the prevention and treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases and infectious diseases. Specifically, the present invention provides a method of eliciting an immune response comprise administering to an individual a composition made by mixing an amount of a purified first complex comprising a first heat shock protein or alpha2M complexed to a peptide which displays antigenicity of an antigen of said type of cancer or antigenicity of an antigen of an agent of said infectious disease; and an equal or greater amount of a second heat shock protein or alpha2M that is not complexed in vitro to a peptide which displays antigenicity of an antigen of said type of cancer or antigenicity of an antigen of an agent of said infectious disease, respectively; and is not in the form of a complex, said complex having been isolated as a complex from cancerous tissue of said type of cancer or cells infected with said agent of infectious disease, respectively. Optionally, the methods further comprise administering antigen presenting cells sensitized with hsp-peptide or alpha2M-peptide complexes comprising peptides antigenic to cancer cells or to an agent of an infectious disease.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT HEALTH CENT
Methods and compositions for inhibiting angiogenesis
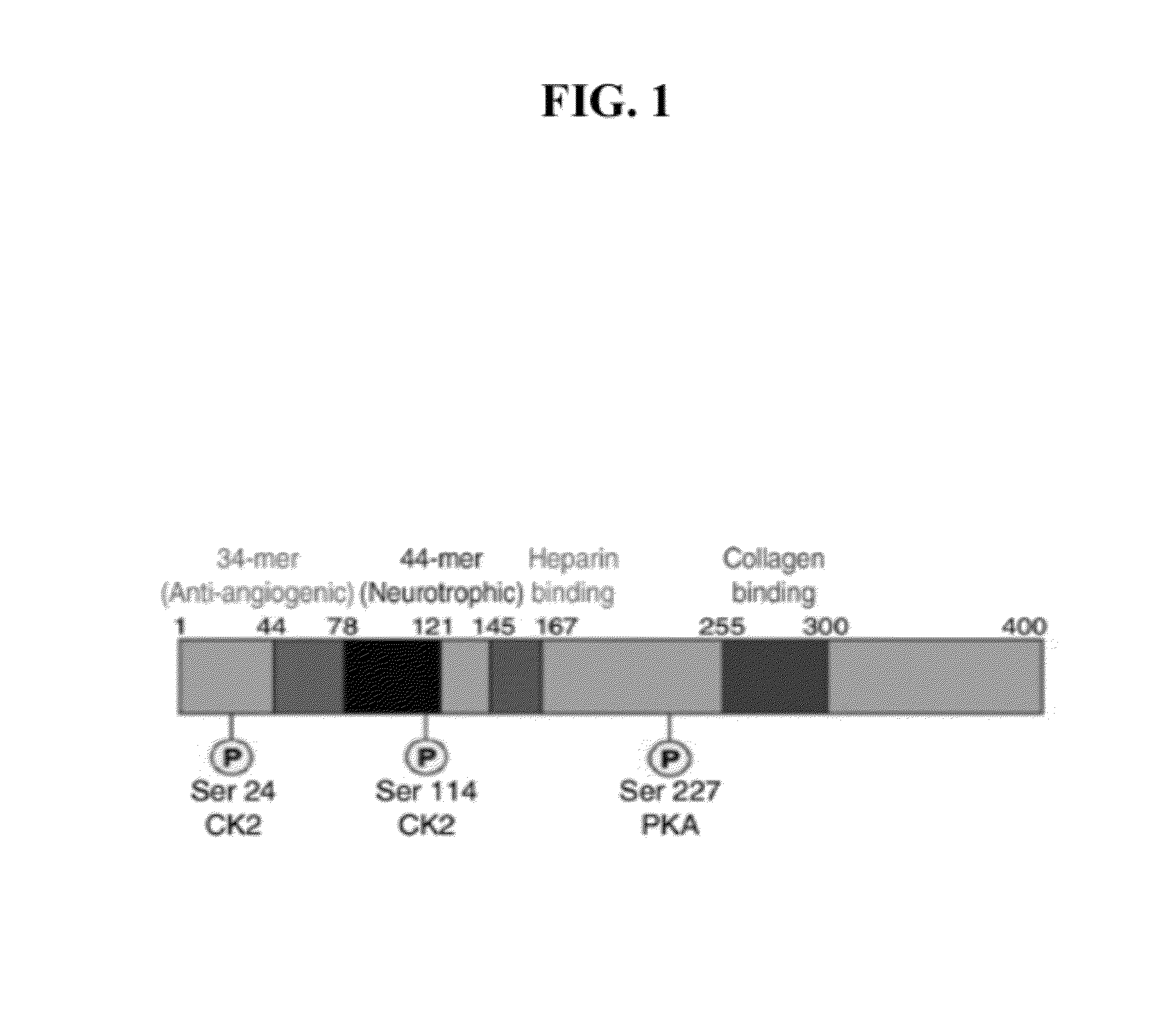
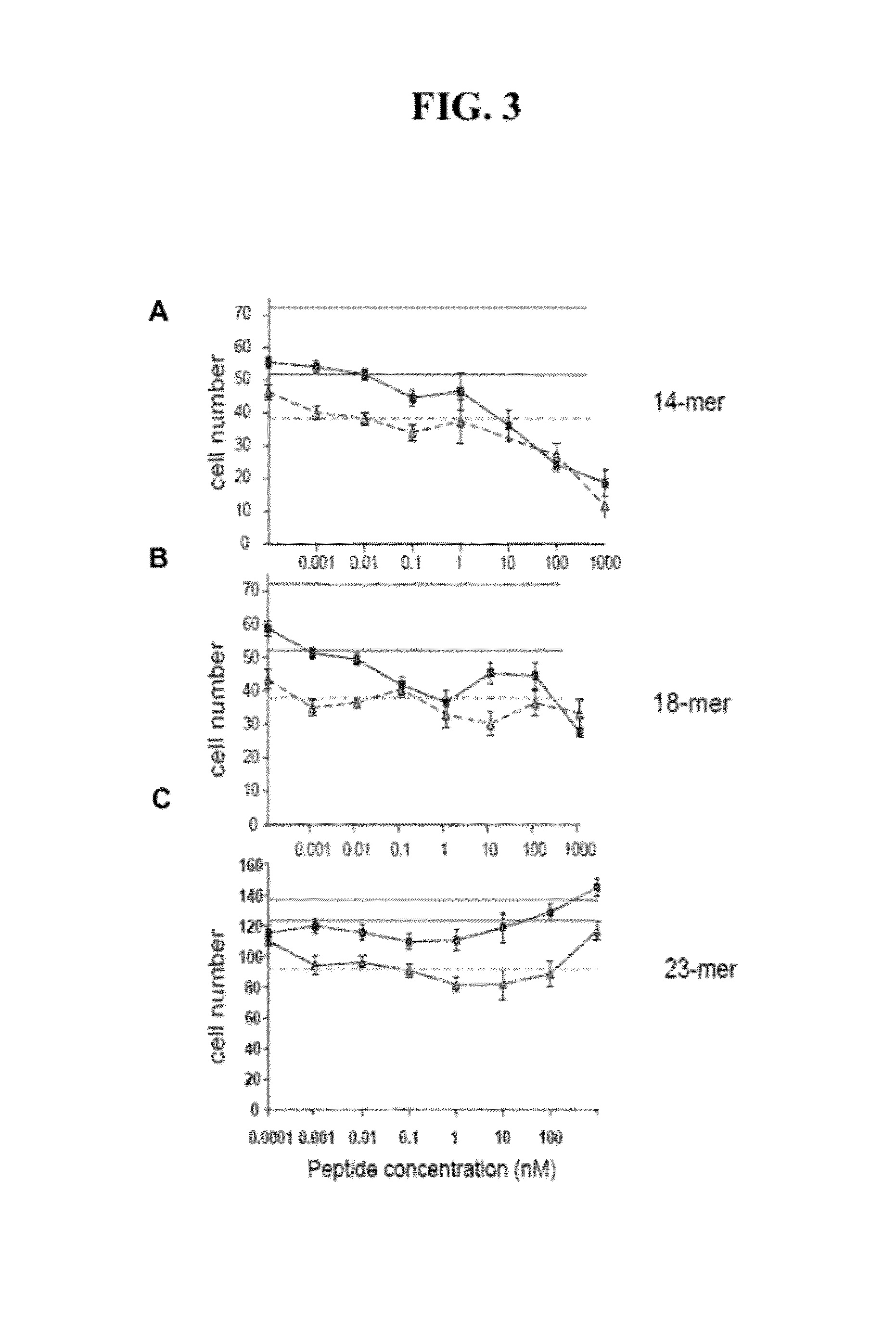
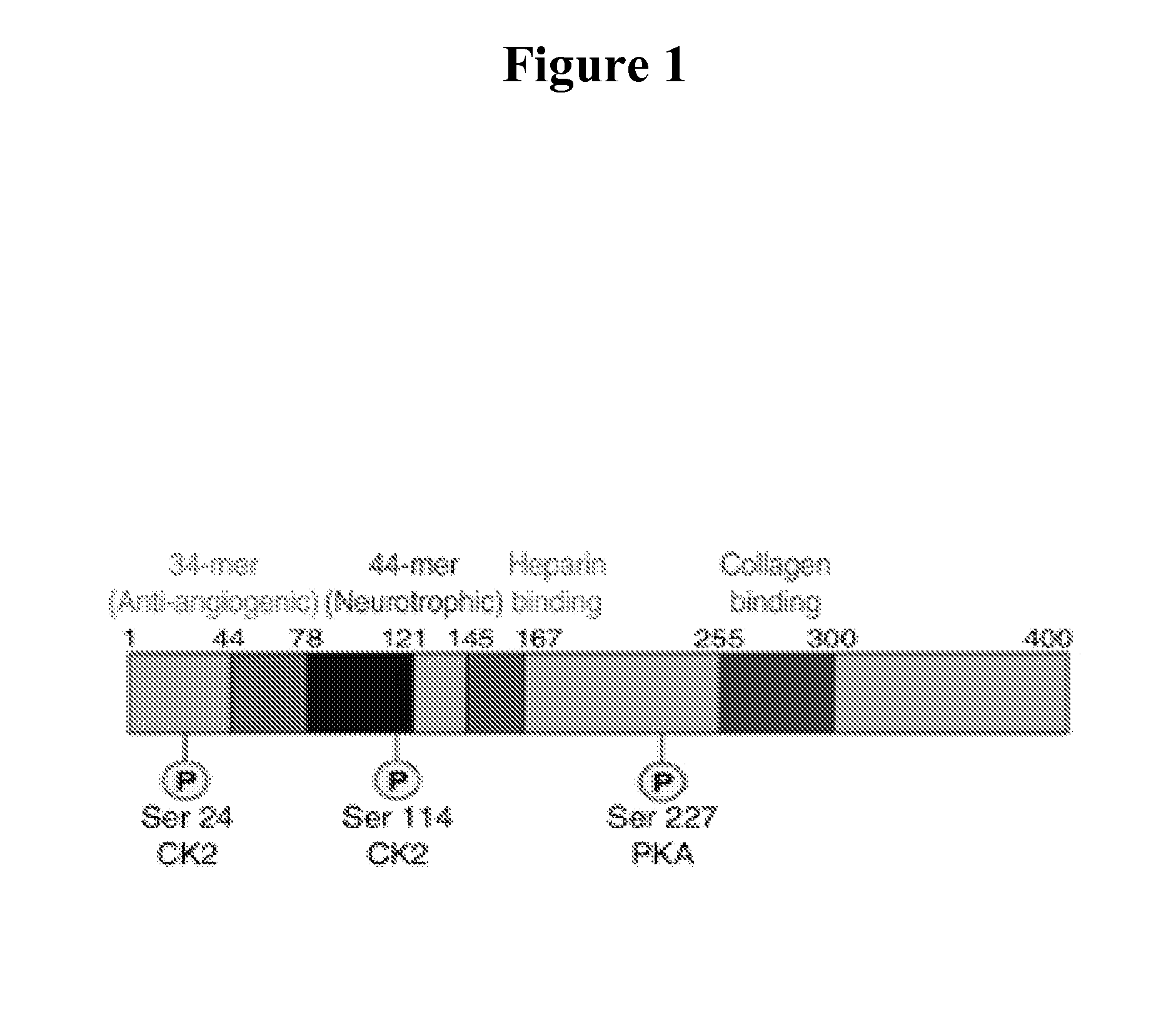
ActiveUS20120316115A1Peptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseasePIGMENT EPITHELIUM-DERIVED FACTOR
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for modulating angiogenesis. In particular, the present invention relates to Pigment Epithelial-derived Factor (PEDF) fragments for use in modulating angiogenesis and treating angiogenesis mediated disease.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Expression in filamentous fungi of protease inhibitors and variants thereof
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Methods and compositions for inhibiting angiogenesis
ActiveUS20100331263A1Inhibit angiogenesisReducing angiogenesisPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseasePIGMENT EPITHELIUM-DERIVED FACTOR
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for modulating angiogenesis. In particular, the present invention relates to Pigment Epithelial-derived Factor (PEDF) fragments for use in modulating angiogenesis and treating angiogenesis mediated disease.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
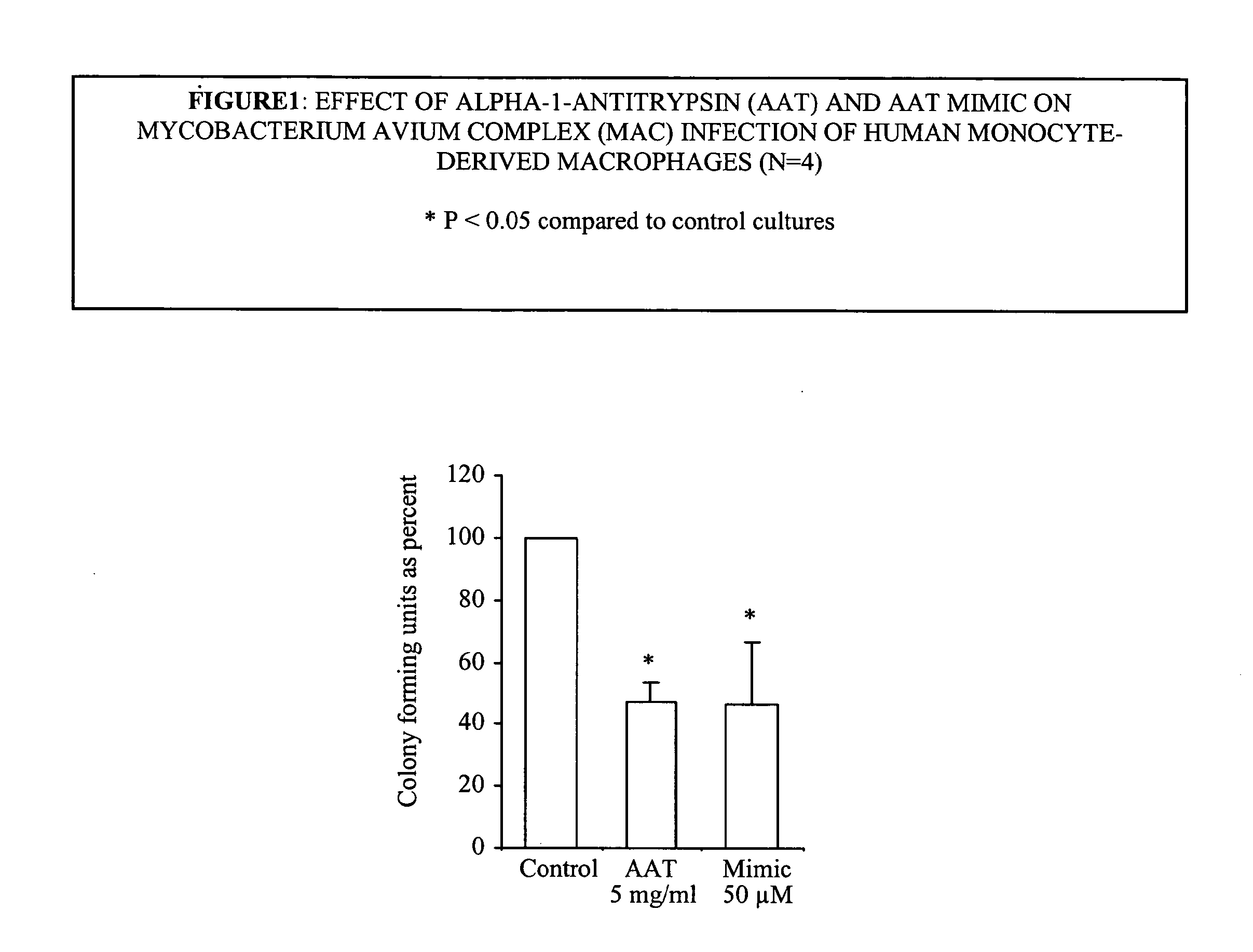
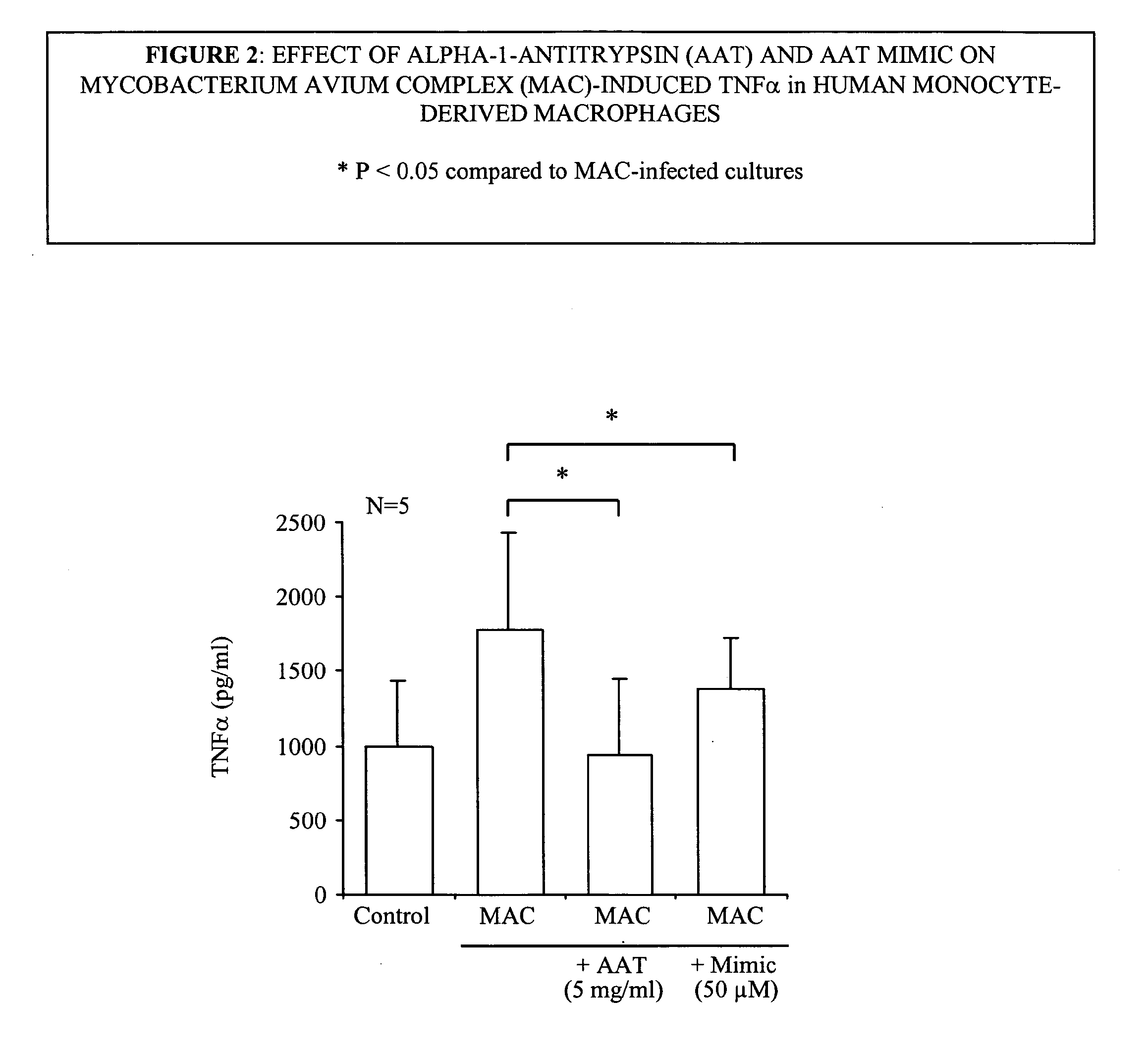
Compositions and methods for treating or ameliorating mycobacterial infections
InactiveUS20100137192A1Inhibit functioningAvoid symptomsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAcid-fastMycobacterium Infections
A novel method of treating and preventing bacterial diseases is provided. In particular, the present invention relates to compositions and methods for inhibition of Gram negative, Gram poitive and acid fast bacilli in general and tuberculosis (TB), mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), and anthrax in particular. Thus, the invention relates to modulation of cellular activities, including macrophage activity, and the like. More particularly, the present invention relates to the inhibitory compounds comprising naturally occurring and man-made inhibitors of serine protease.
Owner:SHAPIRO LELAND
Anti-angiogenic compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20060034932A1Effective occlusionInhibit angiogenesisBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsUrethraMedicine
Owner:ANGIOTECH PHARMA INC
Alteration of amino acid compositions in seeds
InactiveUS7053282B1High nutritional valueReduce the amount of solutionOther foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesPlant cellPlanting seed
The present invention provides a plant seed the endosperm of which is characterized as having an elevated level of a preselected amino acid. The present invention also provides expression cassettes, vectors, plants, plant cells and a method for enhancing the nutritional value of seeds.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Expression in filamentous fungi of protease inhibitors and variants thereof
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Method for controlling the yield and purity of proteinase inhibitor II during extraction
InactiveUS7371418B2Increase surface areaSmall sizeBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsUltrafiltrationFiltration
The present invention provides a method for adjusting the yield and purity of a proteinase inhibitor extract from plant tissue, preferably potato tubers. The extraction and isolation of the proteinase inhibitor from potatoes begins with the addition of an organic acid, preferably formic acid, and a salt, preferably sodium chloride, to raw potatoes. The mixture is subjected to process steps to extract soluble proteins. The extract is subjected to heat treatment at an adjusted temperature and adjusted duration whereby purity of the proteinase inhibitor is enhanced by heating at a relatively high temperature for a relatively short duration and whereby yield of the proteinase inhibitor is enhanced by heating at a relatively low temperature for a relatively long duration. If the removal of soluble protein impurities that are not denatured during the heat treatment step is desired, ultrafiltration is used. By adjusting the cycles of filtration, purity of the proteinase inhibitor can be adjustably selected.
Owner:KEMIN FOODS L C
Modified variant bowman birk protease inhibitors
The present invention relates to modified variant Bowman Birk Protease Inhibitor proteins (BBPIs) that comprise peptides that bind target proteins, and that are further modified to have greater protease inhibitory activity and / or be produced at greater yields than the unmodified BBPIs. The invention encompasses polynucleotide constructs and expression vectors containing polynucleotide sequences that encode the modified variant BBPIs, the transformed host cells that express and produce the modified variant BBPIs, the modified variant BBPI proteins, the compositions comprising the modified variant BBPIs, and the methods for making and using the modified variant BBPIs in personal care.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Multifunctional protease inhibitors and their use in treatment of disease
InactiveUS20080085854A1HydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase
Fusion proteins of protease inhibitors are provided, in particular fusion proteins of alpha 1-antitrypsin (AAT) and a second protease inhibitor, such as secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) or tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases (TIMP). Polynucleotides encoding the fusion proteins, vectors comprising such polynucleotides, and host cells containing such vectors are also provided. Methods of making the fusion proteins of the invention are also provide, as well as methods of using the fusion proteins, for example to inhibit protease activity in a biological sample or in the treatment of an individual suffering from, or at risk for, a disease or disorder involving unwanted protease activity.
Owner:ARRIVA PHARMA
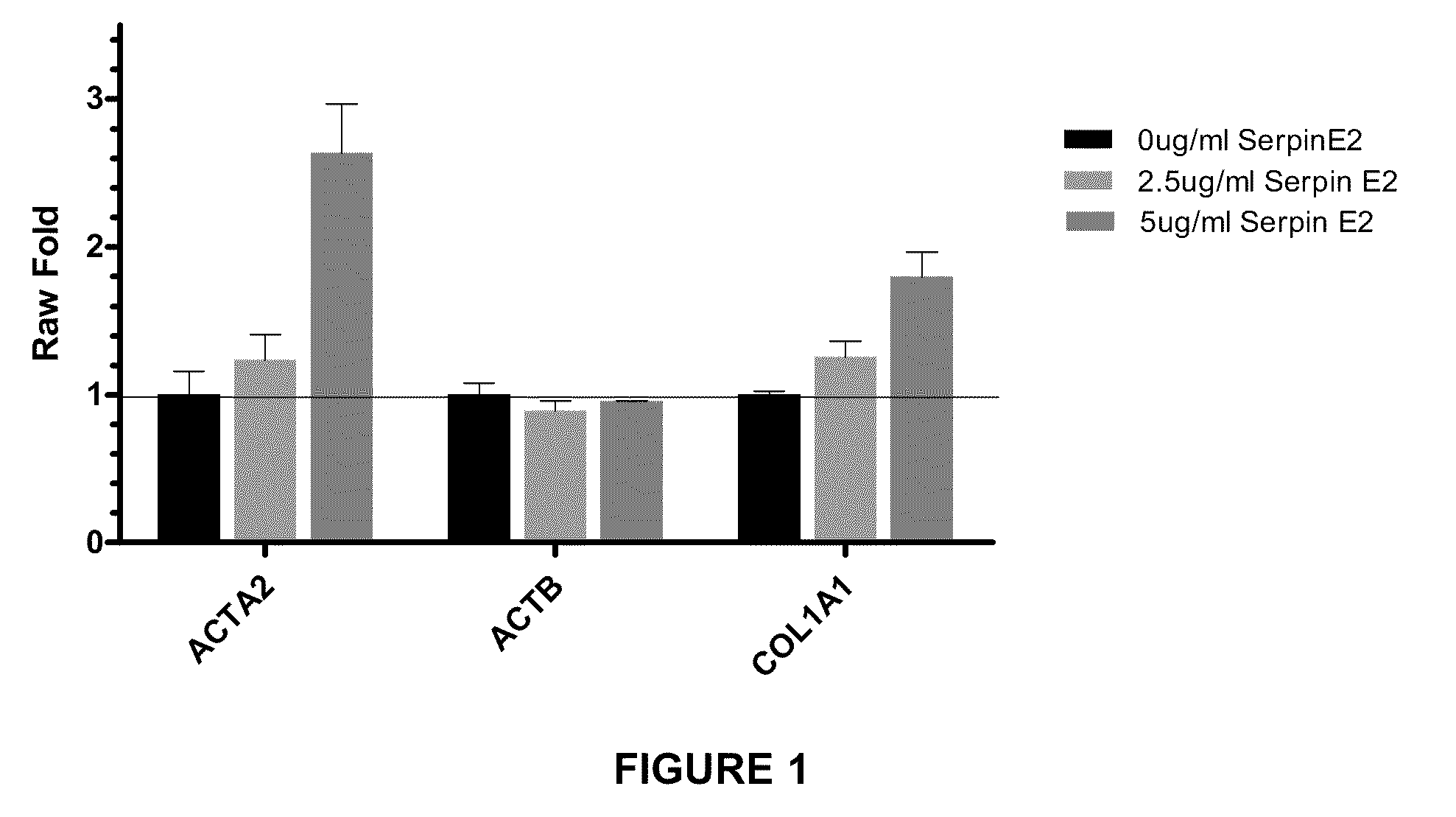
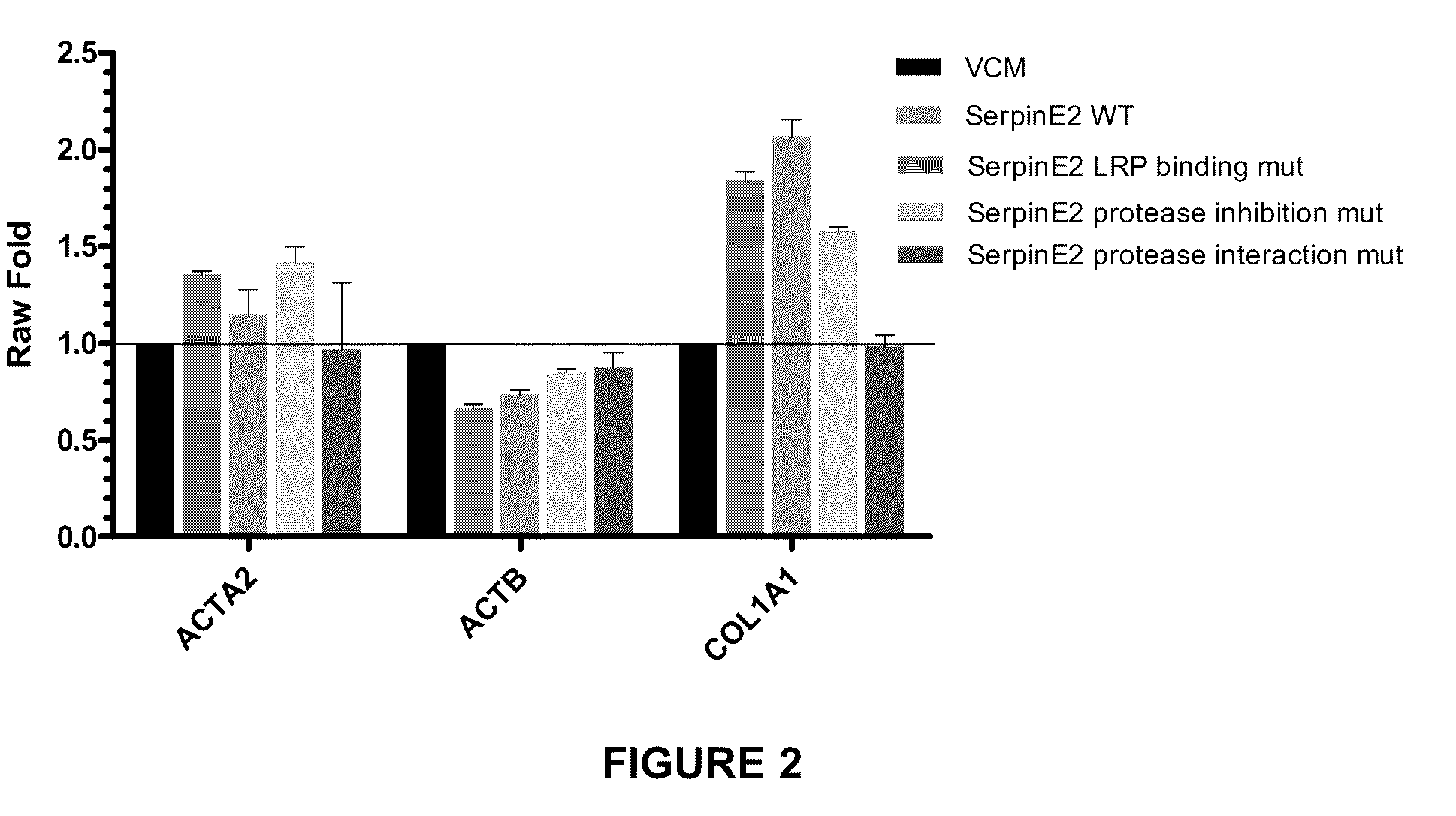
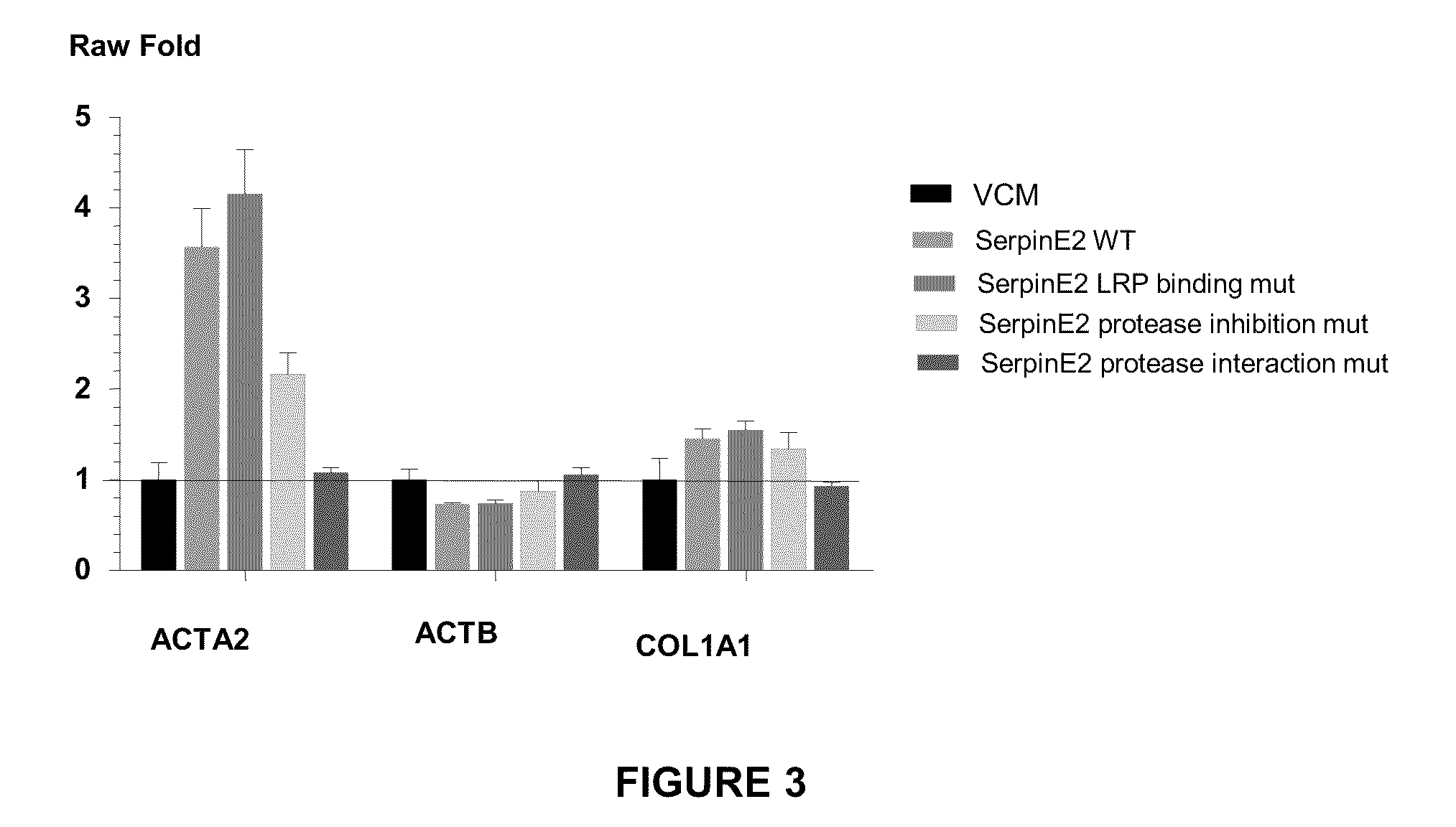
Compositions and methods for regulating collagen and smooth muscle actin expression by serpine2
InactiveUS20100183620A1Reduce expressionReduce formationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesActin
The invention encompasses methods and compositions for increasing or decreasing collagen 1A1 expression and / or α-smooth muscle actin expression in lung fibroblasts using SERPINE2 and antagonists of SERPINE2. The invention also encompasses methods and compositions for increasing or decreasing the formation of myofibroblasts. The invention further provides methods and compositions for treatment of lung diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC +1
Immunization and/or treatment of parasites and infectious agents by live bacteria
ActiveUS9486513B1Reducing or eliminating the targeted parasite, infectious diseaseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHuntingtons choreaAntiparasitic
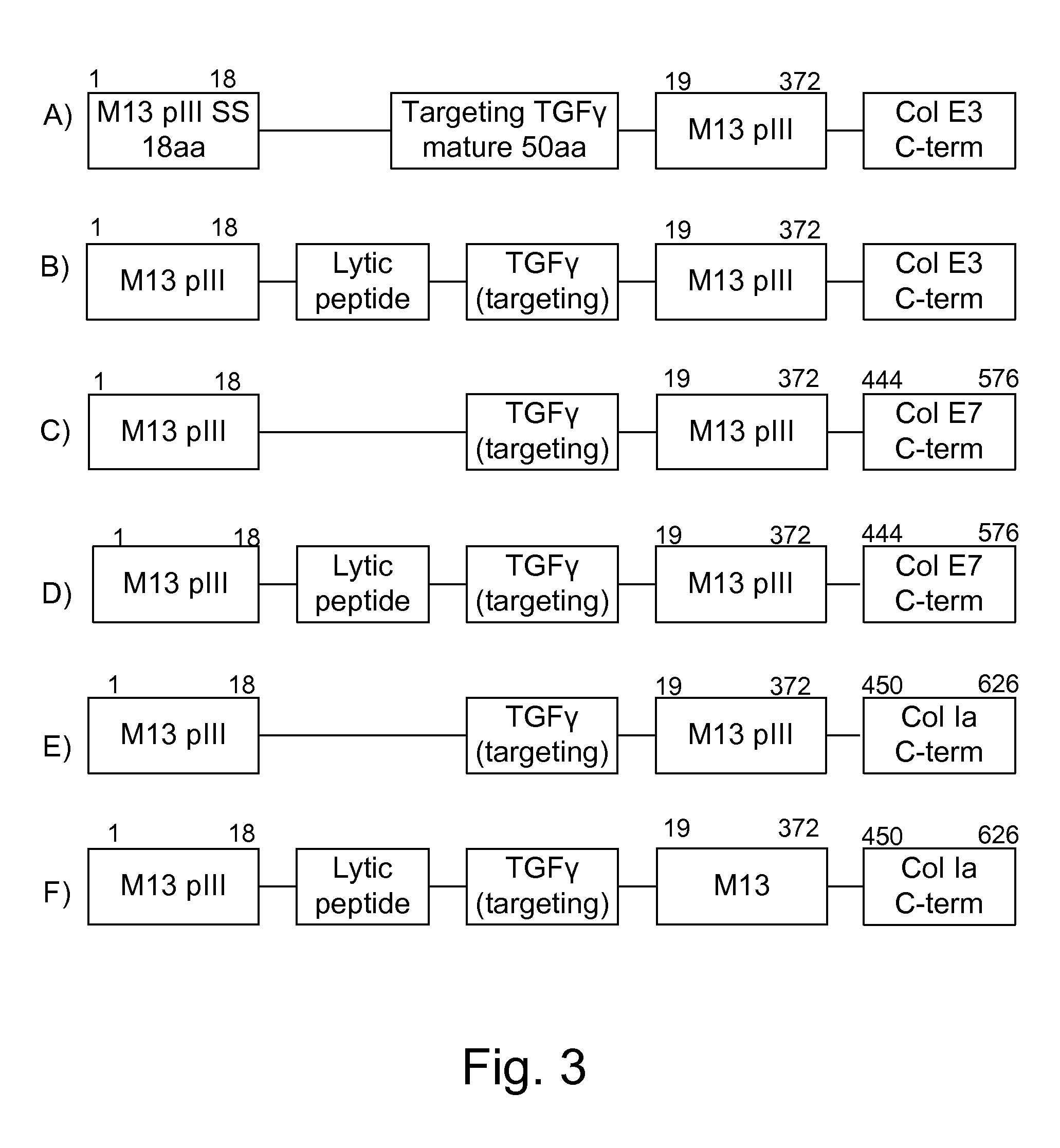
Chimeric proteins are expressed, secreted or released by a bacterium to immunize against or treat a parasite, infectious disease or malignancy. The delivery vector may also be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic, or a probiotic bacterium. The chimeric proteins include chimeras of, e.g., phage coat and / or colicin proteins, bacterial toxins and / or enzymes, autotransporter peptides, lytic peptides, multimerization domains, and / or membrane transducing (ferry) peptides. The active portion of the immunogenic chimeric proteins can include antigens against a wide range of parasites and infectious agents, cancers, Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases, and have enhanced activity when secreted or released by the bacteria, and / or have direct anti-parasite or infectious agent activity. The activity of the secreted proteins is further increased by co-expression of a protease inhibitor that prevents degradation of the effector peptides. Addition of an antibody binding or antibody-degrading protein further prevents the premature elimination of the vector and enhances the immune response.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
Novel calpastatin (CAST) alleles
ActiveUS20070172848A1Improve eating qualityGood quality meatSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCalpastatinGene polymorphism
Disclosed herein are novel alleles characterized by polymorphisms in the CAST gene. The alleles may be used to genetically type animals. In a preferred embodiment, the alleles may be used as markers for animal meat quality and / or growth. Methods for identifying such markers, and methods of screening animals to determine those more likely to produce desired meat quality and / or growth and preferably selecting those animals for future breeding purposes are also disclosed.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
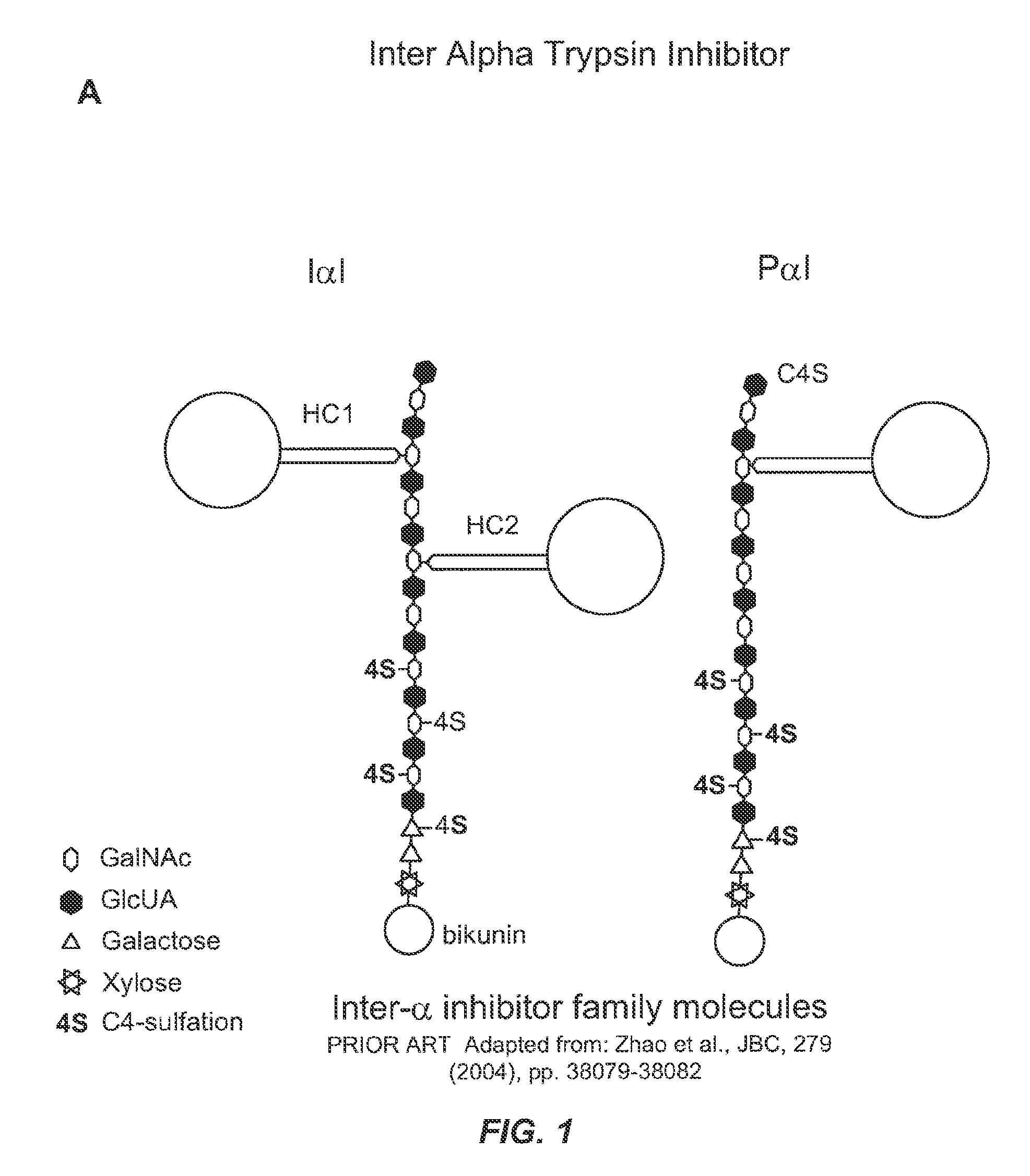
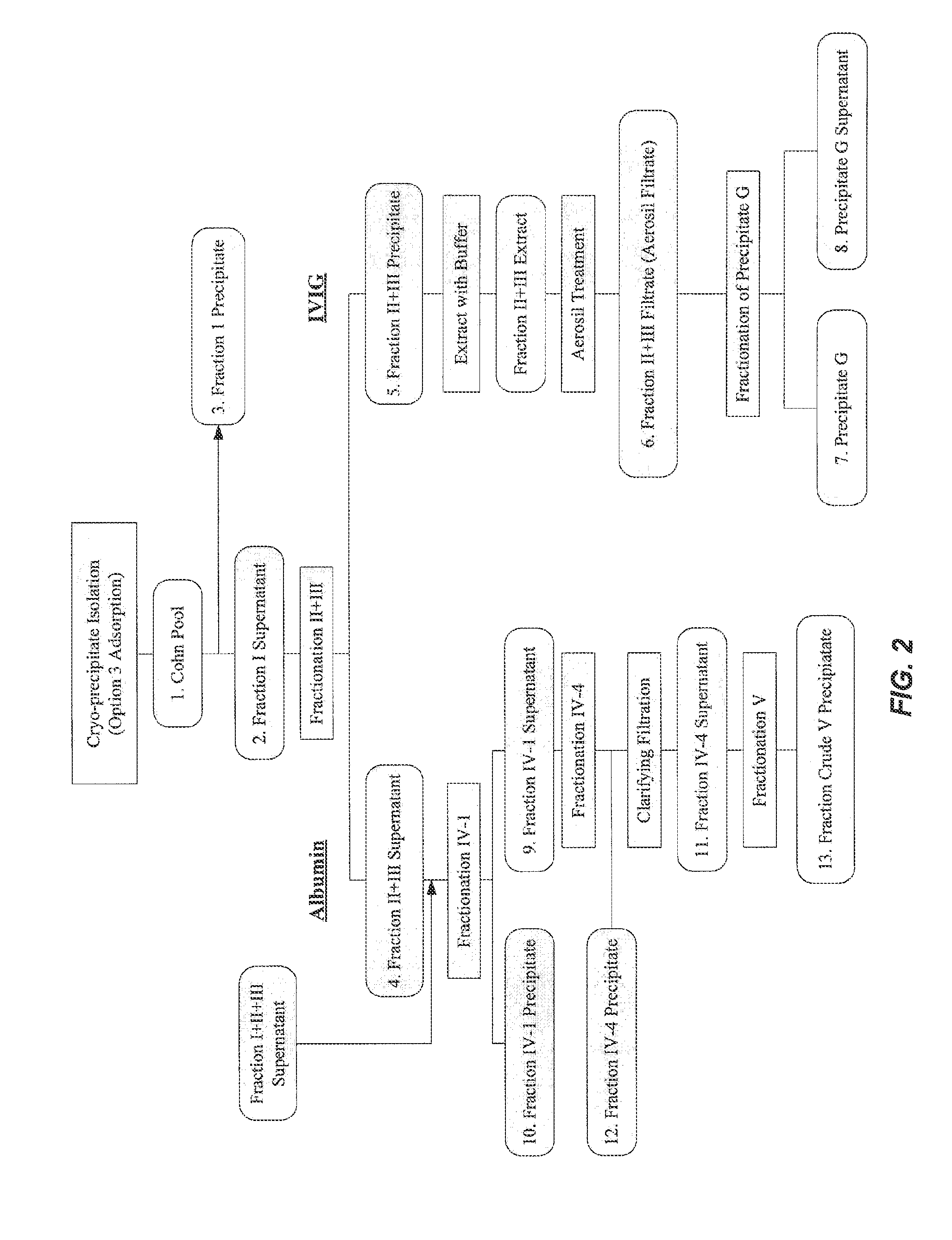
MANUFACTURE OF INTER-ALPHA-INHIBITOR (IaIp) FROM PLASMA
The present invention provides compositions and pharmaceutical formulations of IaIp derived from plasma. Also provided are methods for the manufacture of the IaIp compositions and formulations, as well as method for the treatment of diseases associated with IaIp dysfunction.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Anti-angiogenic compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20060035830A1Effective occlusionInhibit angiogenesisHeavy metal active ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsUrethraMedicine
Owner:ANGIOTECH PHARMA INC
Systems, compositions, and methods for transplantation and treating conditions
Systems and methods for purification and concentration of autologous alpha-2 macroglobulin (A2M) from whole blood and or recombinant A2M are provided. Also provided are methods of treating wounds with A2M. Methods for utilizing A2M in combination with other treatments (e.g., platelets and other growth factors) are provided in addition to combinations with exogenous drugs or carriers. Also provided is a method of producing recombinant A2M wild type or variants thereof where the bait region was modified to enhance the inhibition characteristics of A2M and / or to prolong the half-life of the protein for treating wounds.
Owner:CYTONICS CORP
Method for recovery of Kunitz and Bowman-Birk trypsin inhibitors from soybean whey
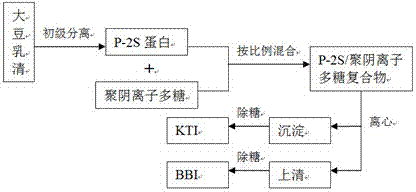
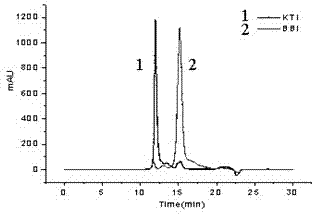
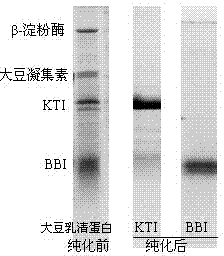
ActiveCN104513307ANo pollution in the processHigh recovery ratePeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesProtein solutionUltrafiltration
Belonging to the field of agricultural product processing and by-product comprehensive utilization, the invention relates to a method for recovery of Kunitz and Bowman-Birk trypsin inhibitors from soybean whey. The method of the invention comprises the steps of: (1) pretreatment of soybean whey; (2) primary separation of whey soy protein; (3) complex coacervation of soybean whey protein and polyanionic polysaccharide; and (4) recovery of Kunitz and Bowman-Birk trypsin inhibitors. By subjecting the raw material to pretreatment, primary separation and complex coacervation, a final protein polysaccharide compound can be obtained, and after ultrafiltration for sugar removal, ultrafiltration for desalination, and twice centrifugation on the final protein polysaccharide compound, a protein solution containing purified Kunitz and Bowman-Birk trypsin inhibitors can be obtained, and through vacuum freeze drying of the protein solution, Kunitz and Bowman-Birk trypsin inhibitor high purity samples can be obtained. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of comprehensive utilization of soybean whey, low equipment requirement, simple operation, and no environmental pollution. And the trypsin inhibitors have high recovery rate, high purity, and high protein activity.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com