Patents
Literature
158results about "Simultaneous television signal transmission by multiple carrier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
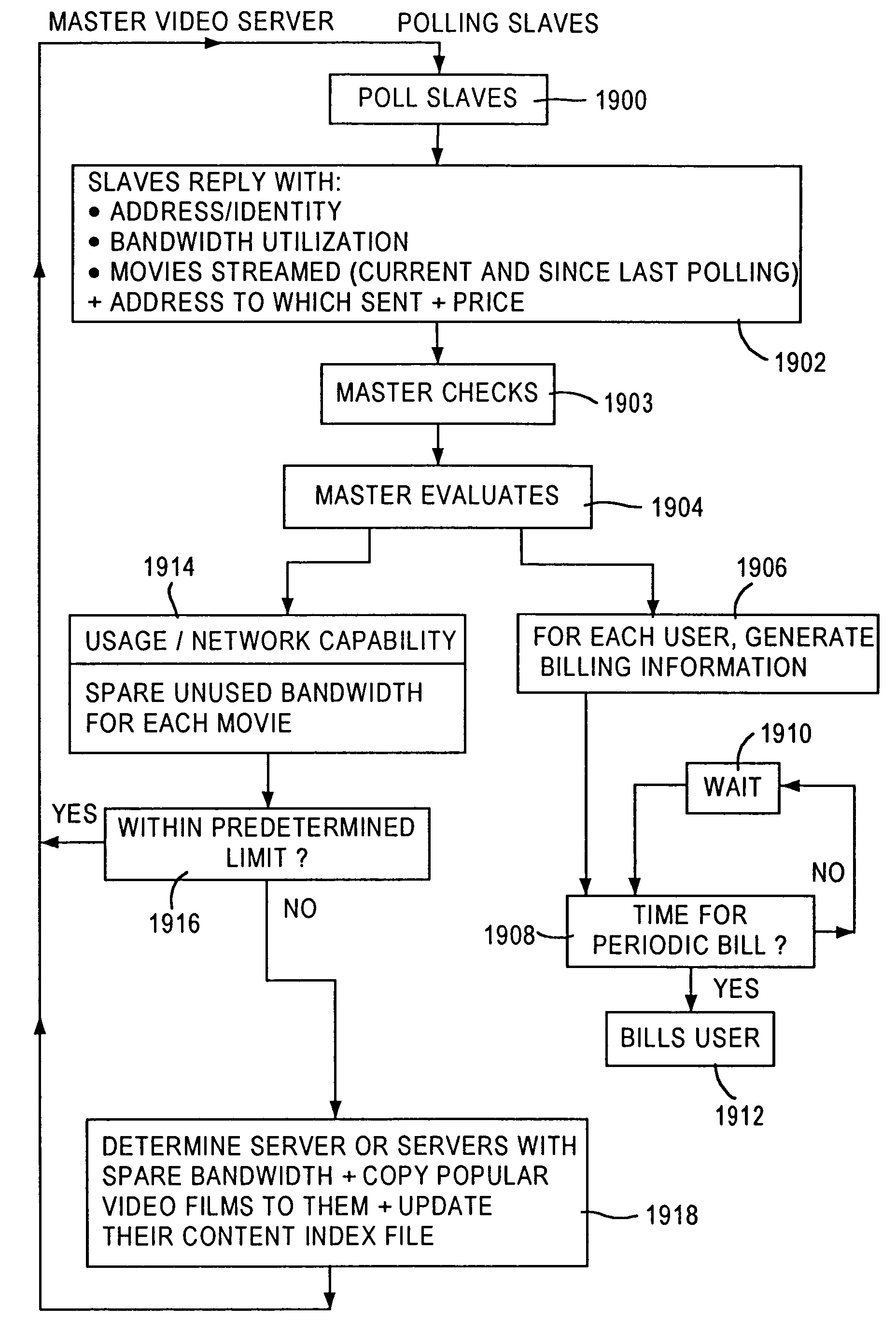
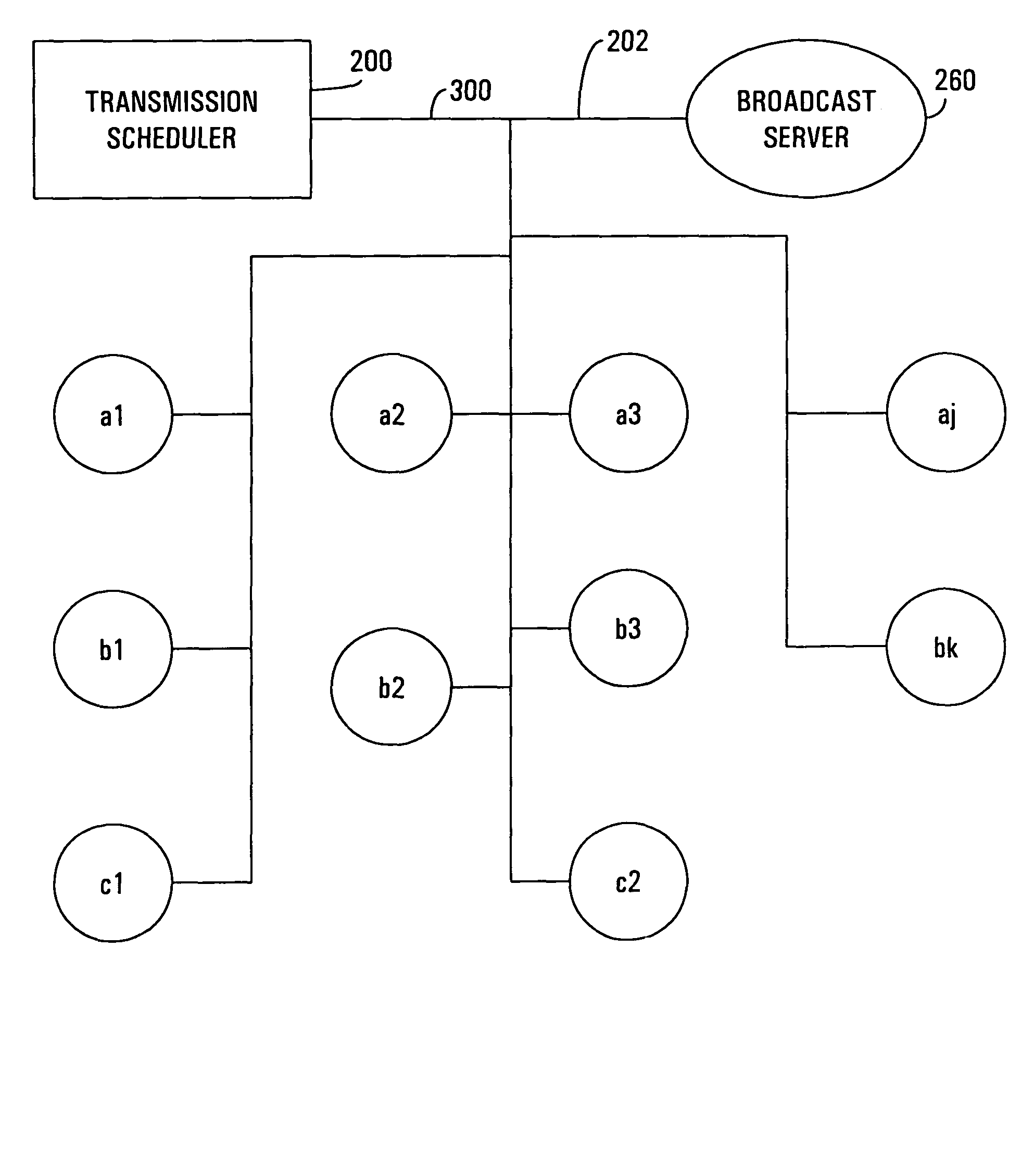
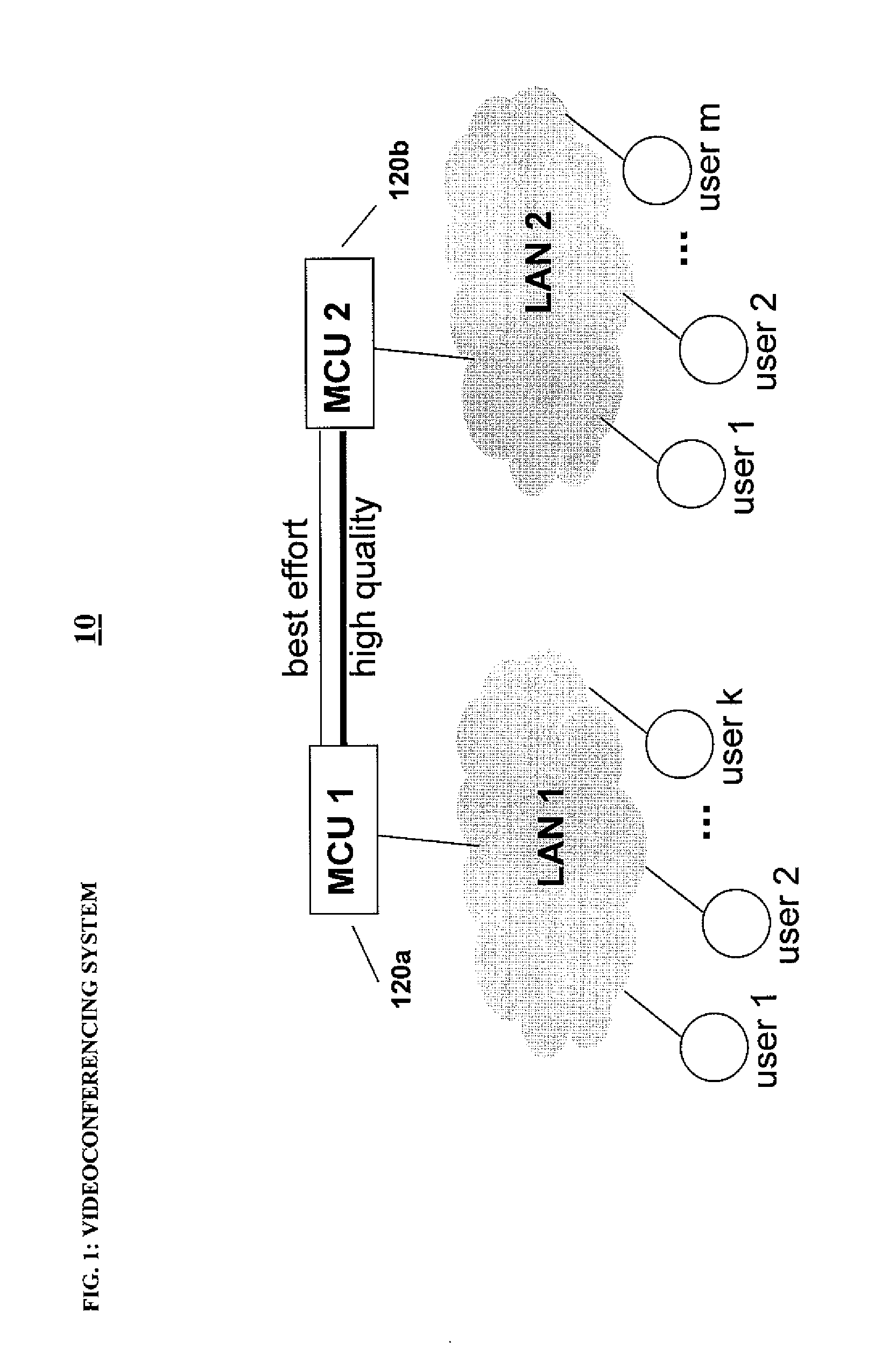
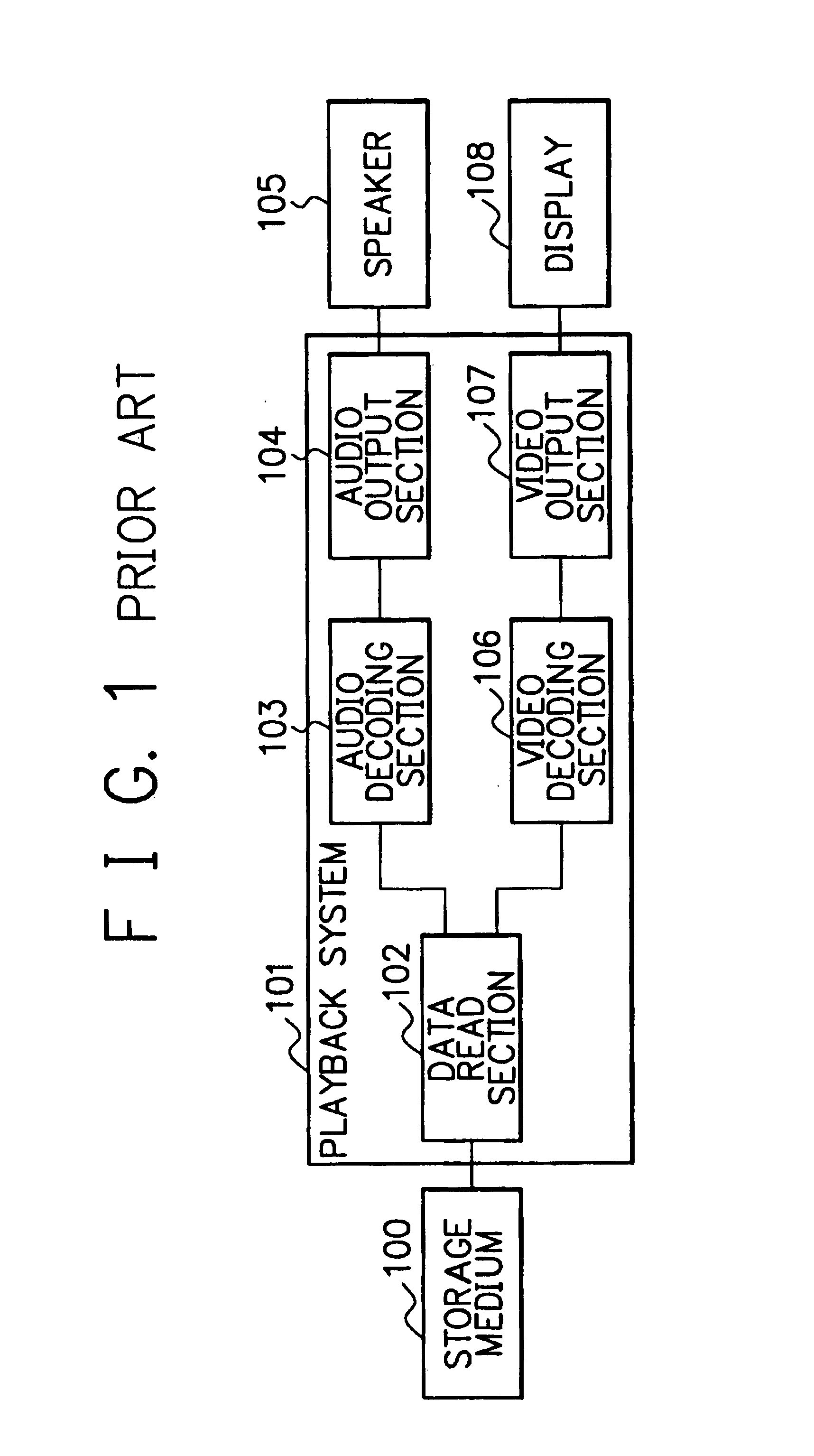
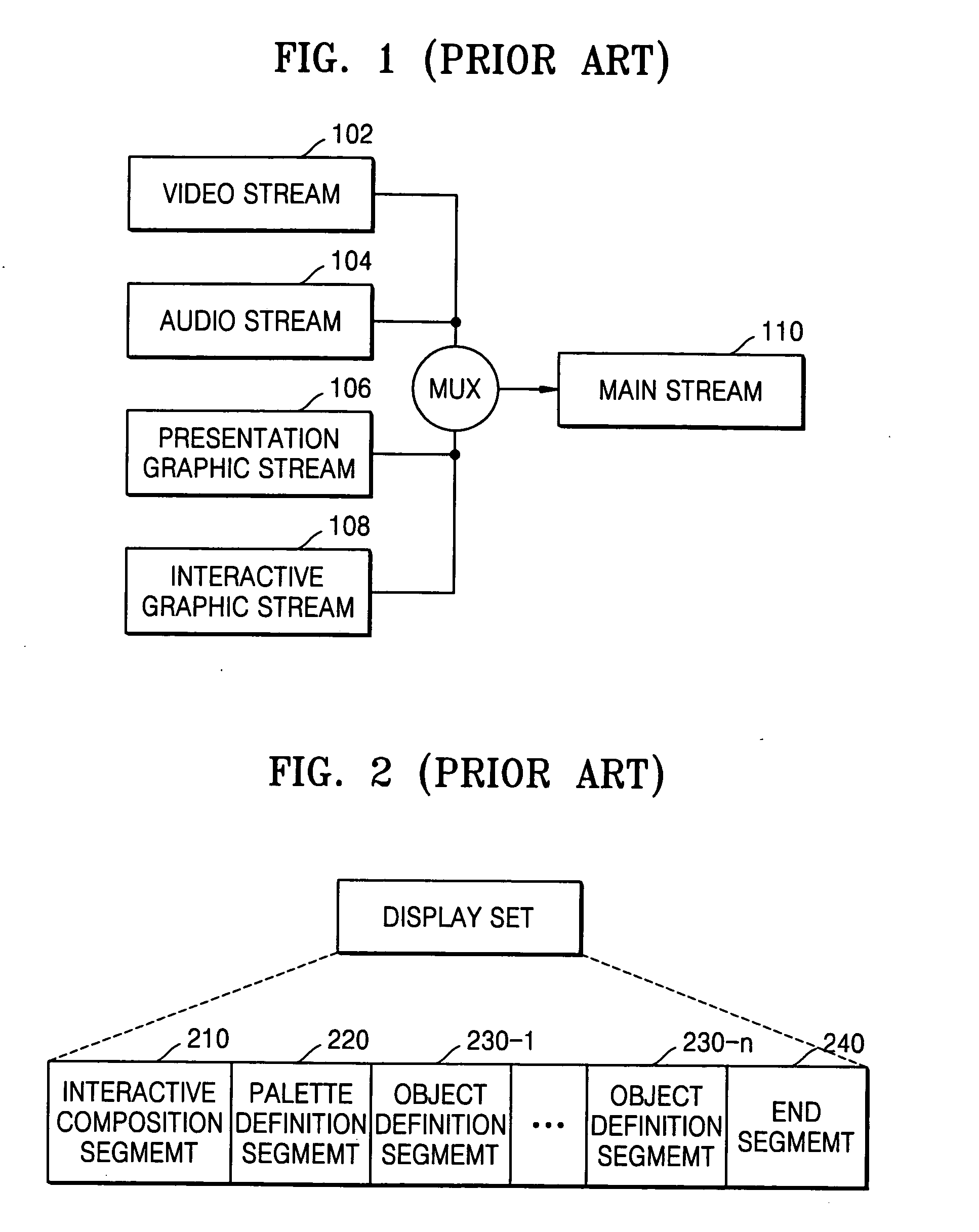
Video system varying overall capacity of network of video servers for serving specific video
ActiveUS7441261B2Improve usabilityImprove network performanceTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVideo server
A method of serving out video over a network of video servers includes evaluating a capacity of the network as a whole to serve out specific video items by establishing, for each video server in the network, an established ability of each server to serve out the specific items that are potentially servable from each video server. The method further includes using the established abilities of each video server to evaluate an overall capability of the network as whole to serve out each of the specific video items. The method also includes varying the overall capability to serve out at least a selected one of the specific video items in accordance with the overall capability of the network.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
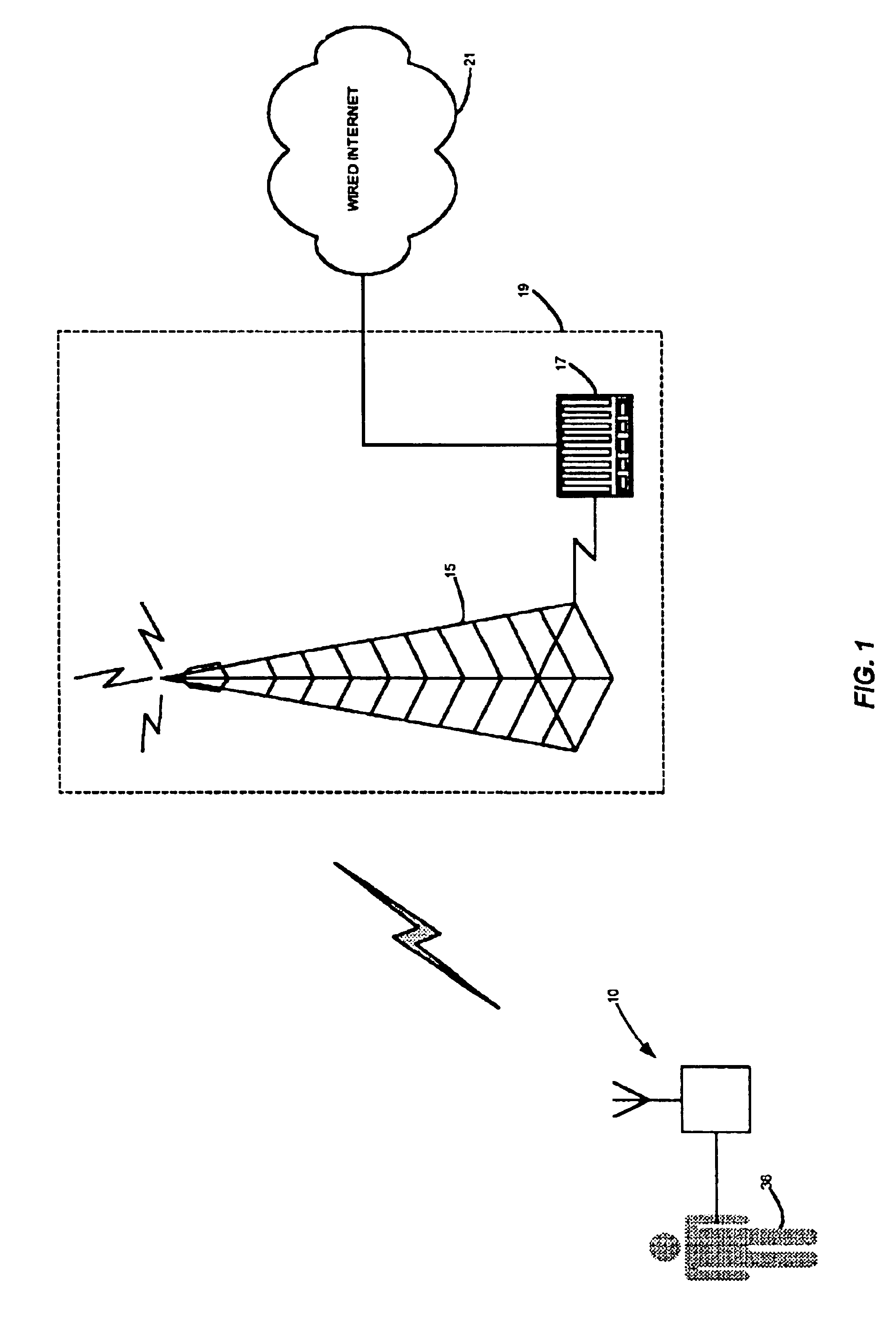
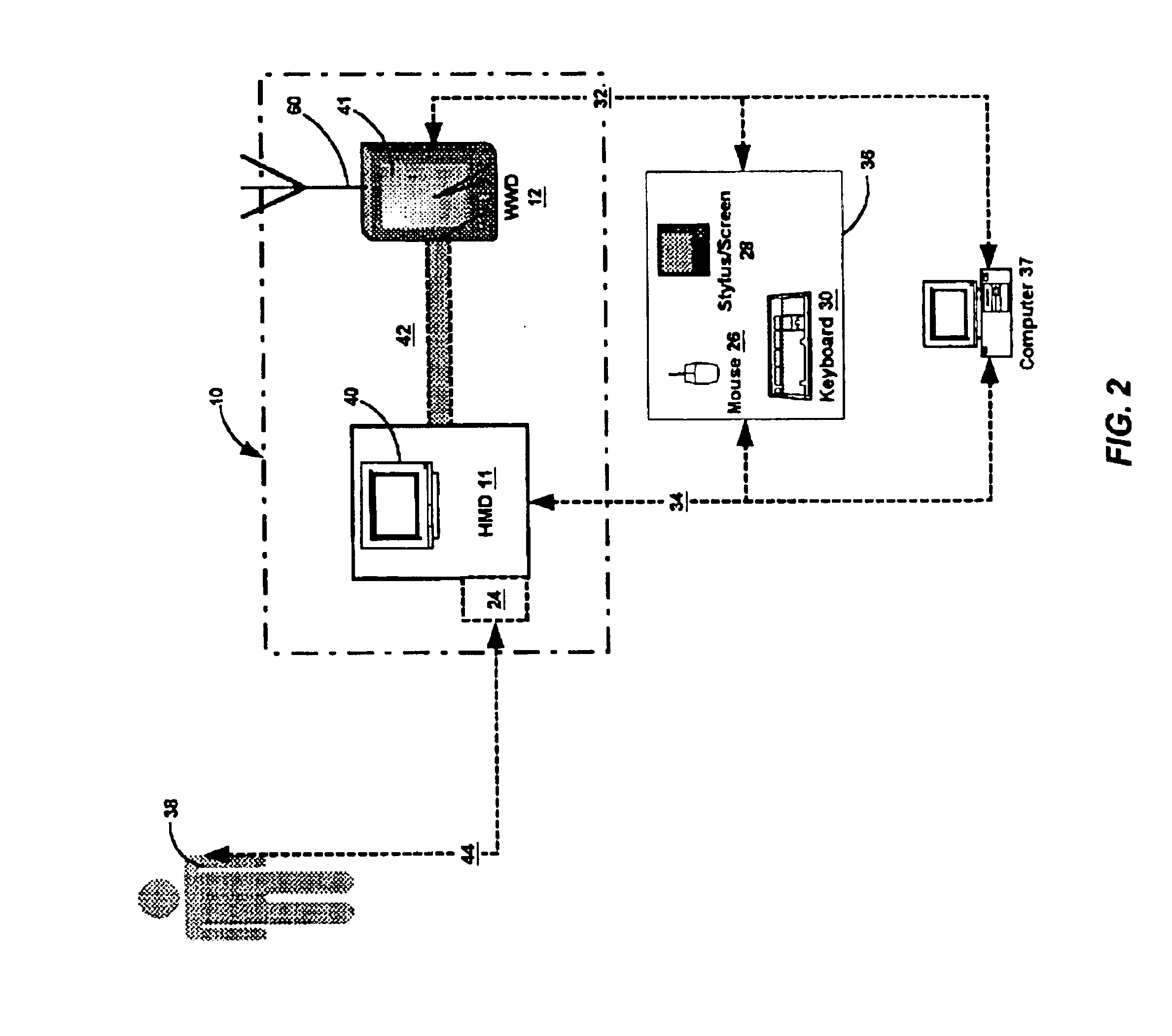
Method and apparatus for health and disease management combining patient data monitoring with wireless internet connectivity
InactiveUS6976958B2Maintain abilityLess memoryTwo-way working systemsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateComputer hardwareDisease
Embodiments of the invention provide a method and apparatus for a wireless health monitoring system for interactively monitoring a disease or health condition of a patient by connecting an internet-enabled wireless web device (“WWD”) to a digital camera or other health monitoring device. The WWD may accommodate a memory device for enhanced storage capabilities that may be particularly pertinent to data-intensive tasks such as the handling and storage of images or other visual data. The health related data is transmitted from the WWD to a server using standard internet protocols and may be integrated with various operating systems for handheld or wireless devices, especially those with enhanced capabilities for handing images and visual data.
Owner:Q TEC SYST +1
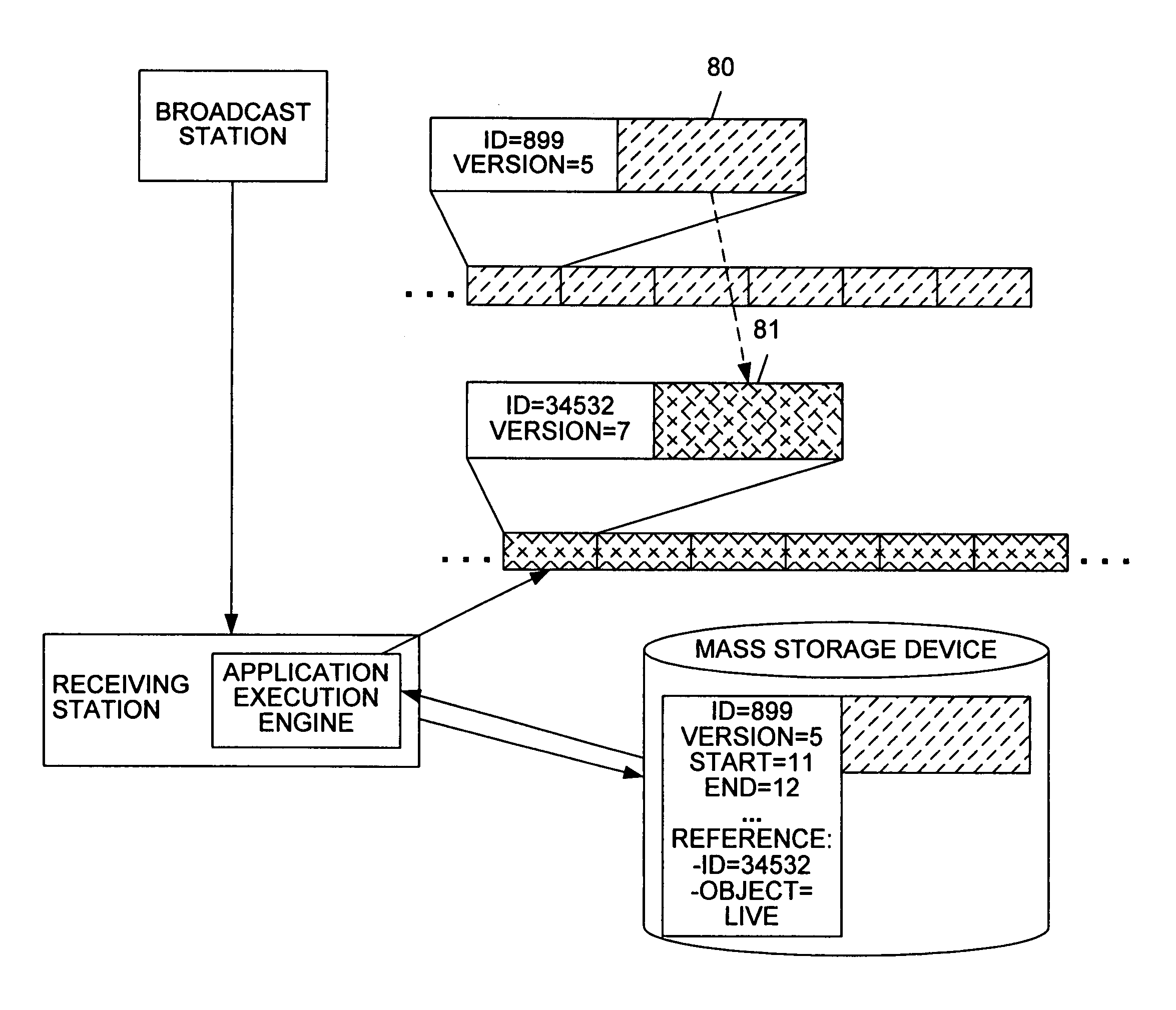
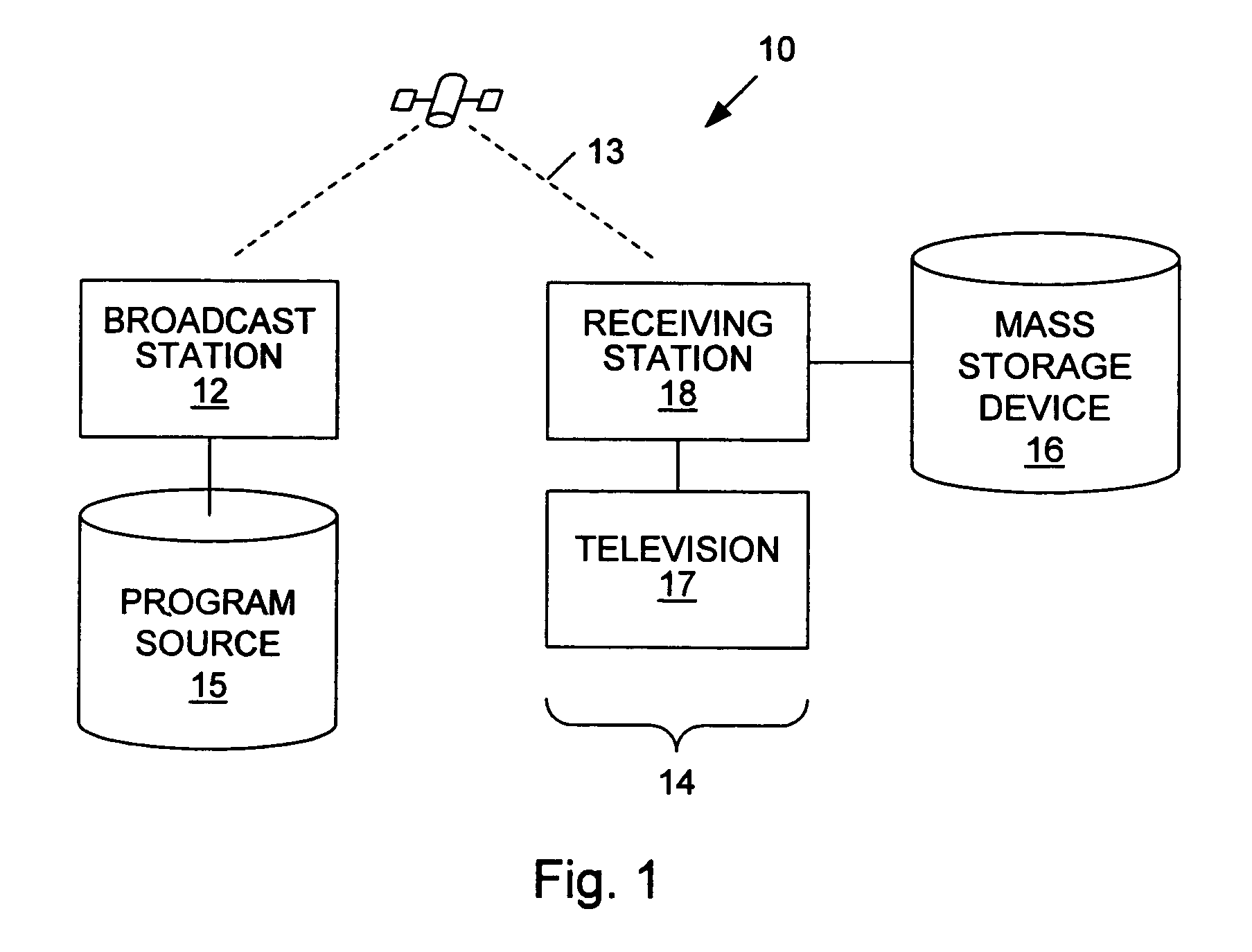
System and method for recording pushed data
InactiveUS7000245B1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsReal-time dataData stream
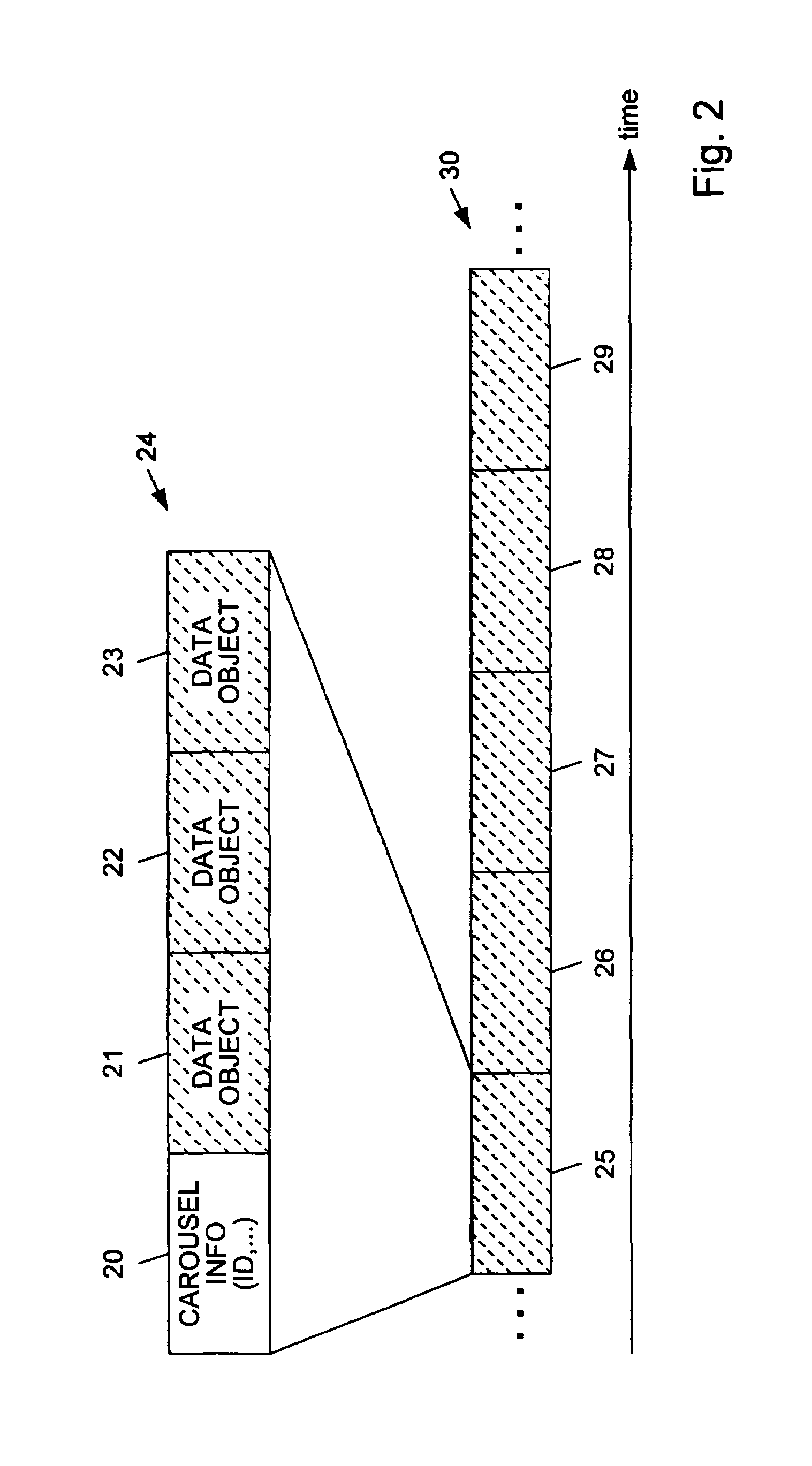
A method for recording pushed interactive data streams of a program. A pushed data stream is broadcast to a receiving station. The data stream includes one or more data objects. The data stream may also reference to live data objects which are intended for immediate consumption and become obsolete thereafter. The data stream may include a file table and object properties corresponding to the data objects. When the data stream is received by the receiving station, the individual data objects are extracted from the data stream. The data objects, accompanying object properties and the file table are then stored on a storage device. Data objects which are external to the data stream or to the program (e.g., data objects from other carousels) are retrieved and are also stored. Live data objects are not stored, but references to these data objects are stored, so that when the program is replayed, current versions of the referenced live data objects can be used. A program not being recorded may contain data objects which are flagged to be cached which are recorded automatically. Consequently, other programs may subsequently access them from the recording when they are played.
Owner:OPEN TV INC
Method and apparatus to synchronize audio and video
InactiveUS20060078305A1Television system detailsColor television signals processingControl delayTime difference
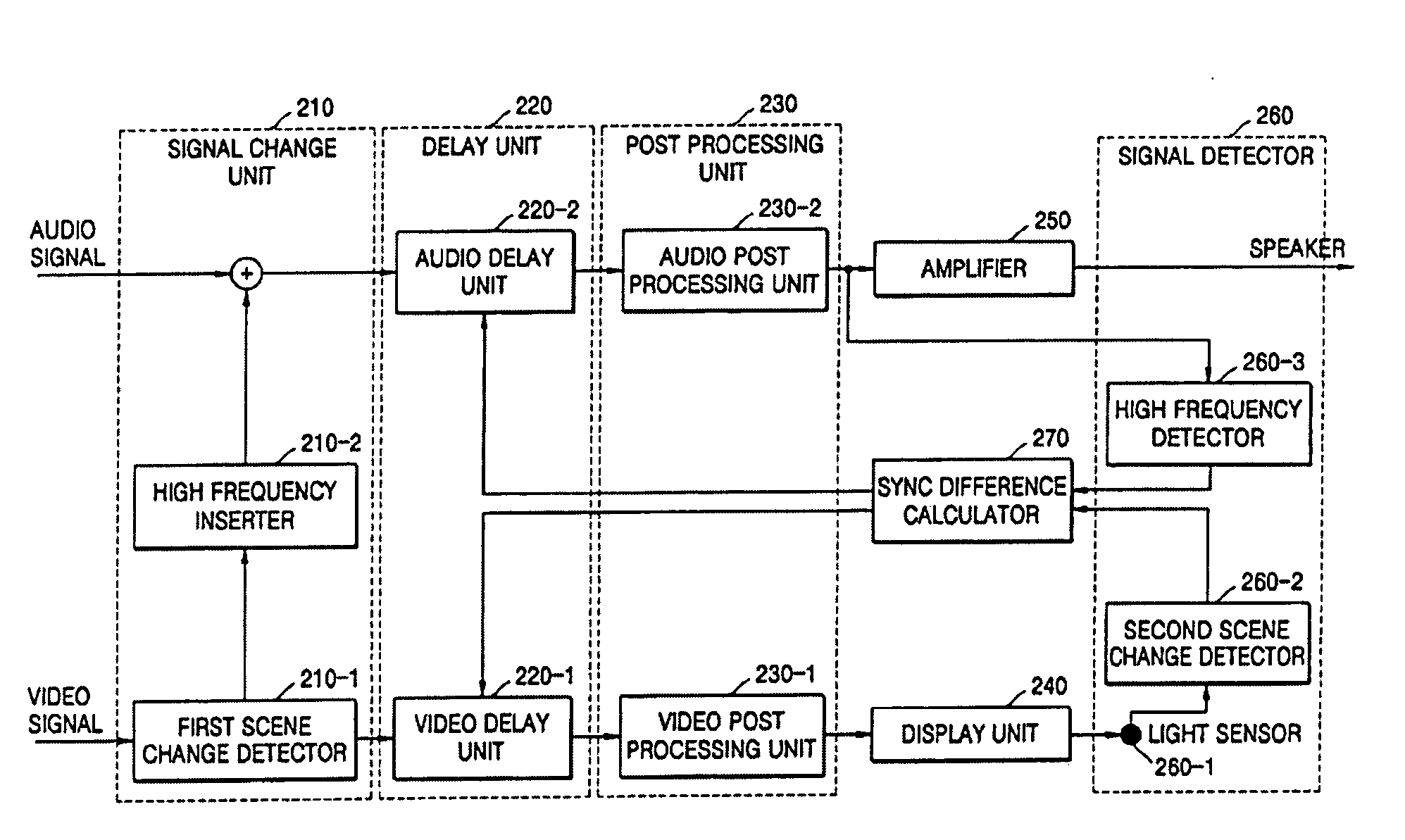
A method and an apparatus to synchronize an audio signal and a video signal. The method includes: displaying video on a screen that corresponds to an audio signal including a high frequency component having a predetermined pattern inserted therein to indicate when a scene change occurs in a video signal, detecting a scene change in the displayed video and detecting the high frequency component having the predetermined pattern in the audio signal, calculating a time difference between a time when the scene change is detected in the displayed video and a time when the high frequency component having the predetermined pattern is detected in the audio signal, and controlling delay times of the audio signal and the video signal according to the calculated time difference. Accordingly, the audio signal and the video signal can be automatically synchronized without performing a separate measuring operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for enhancing recorded radio or television programs with information on the world wide web
ActiveUS20040133919A1Enhanced informationEasy access to informationTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionHyperlinkBroadcasting
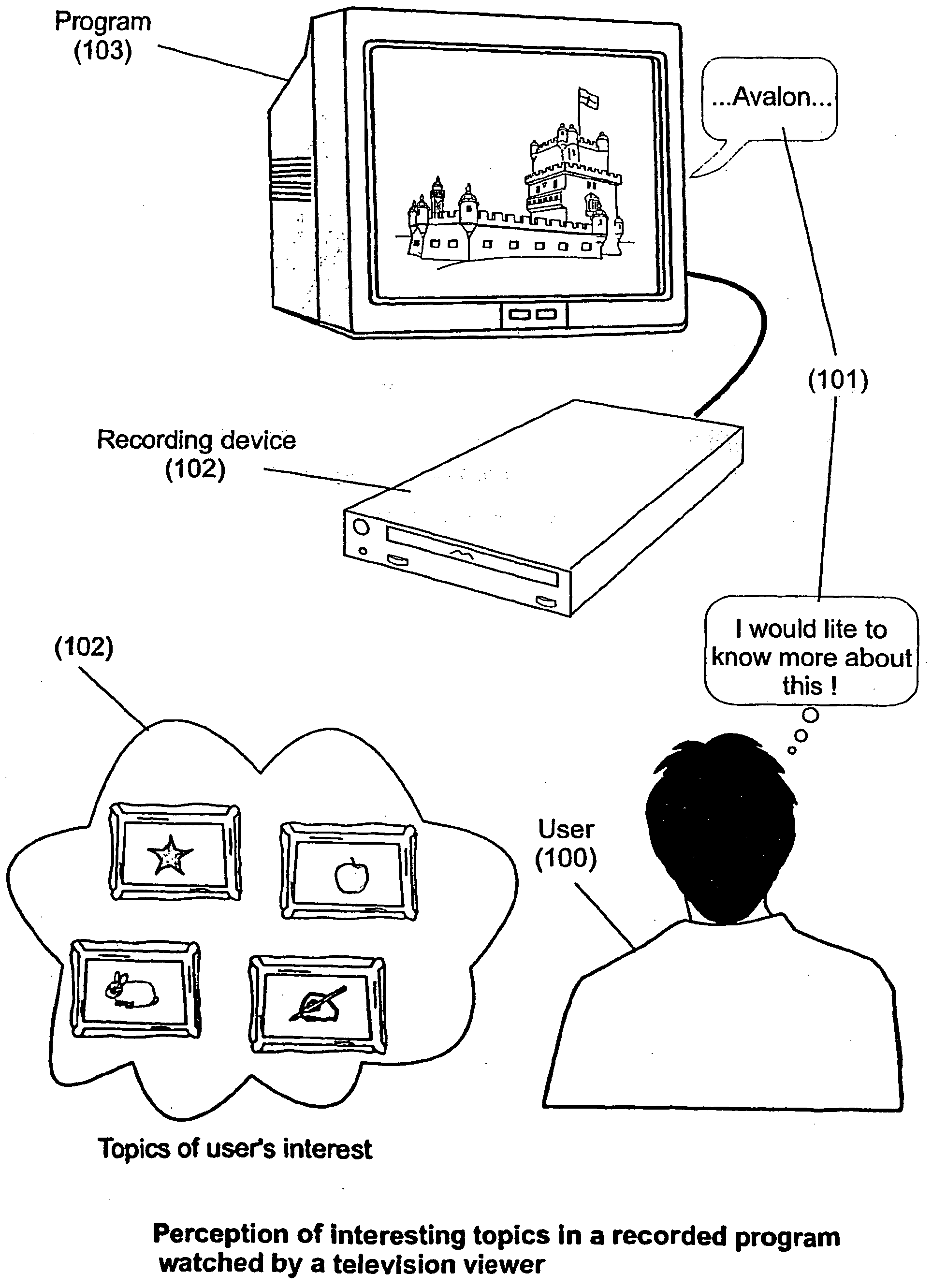
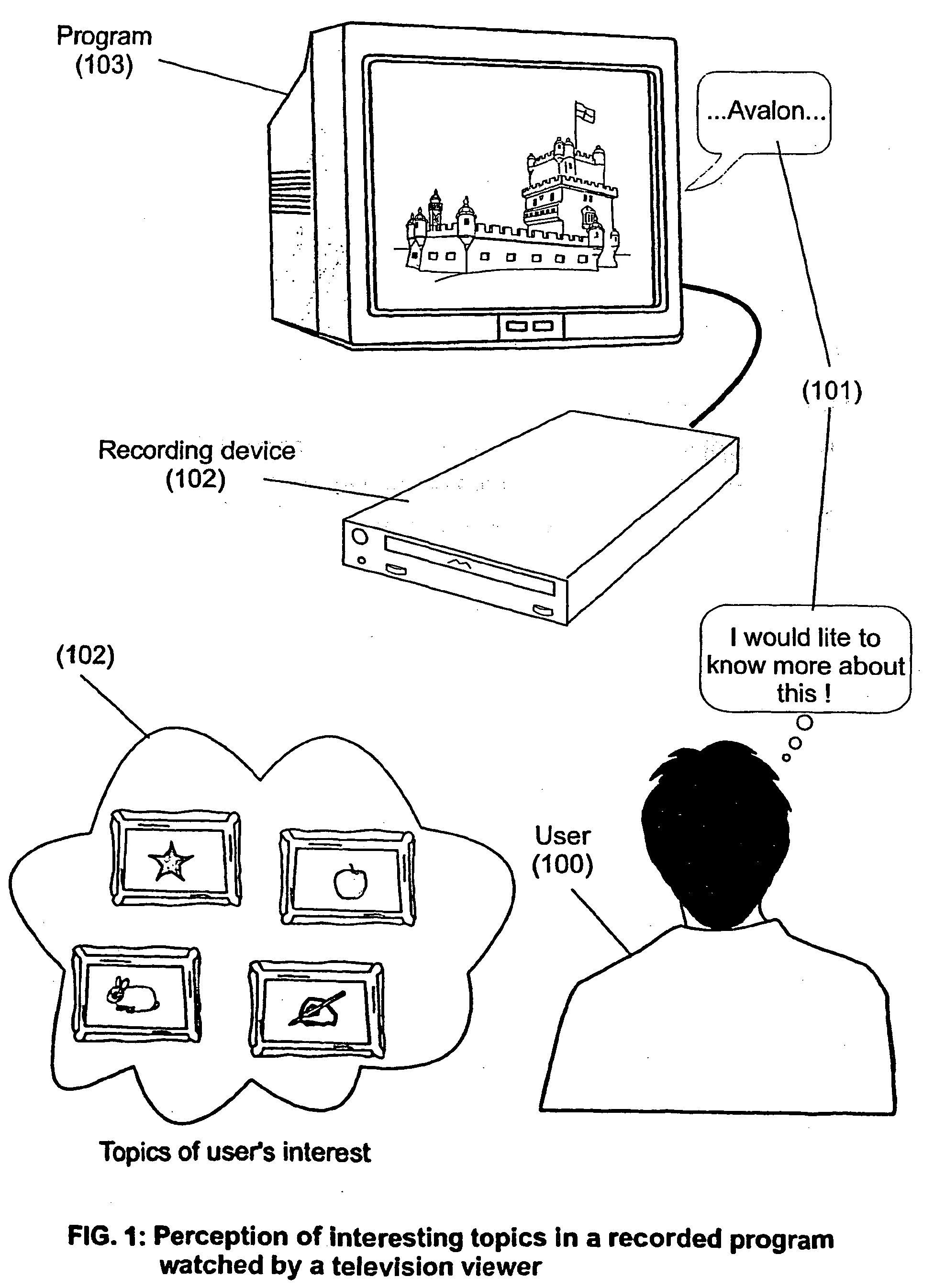
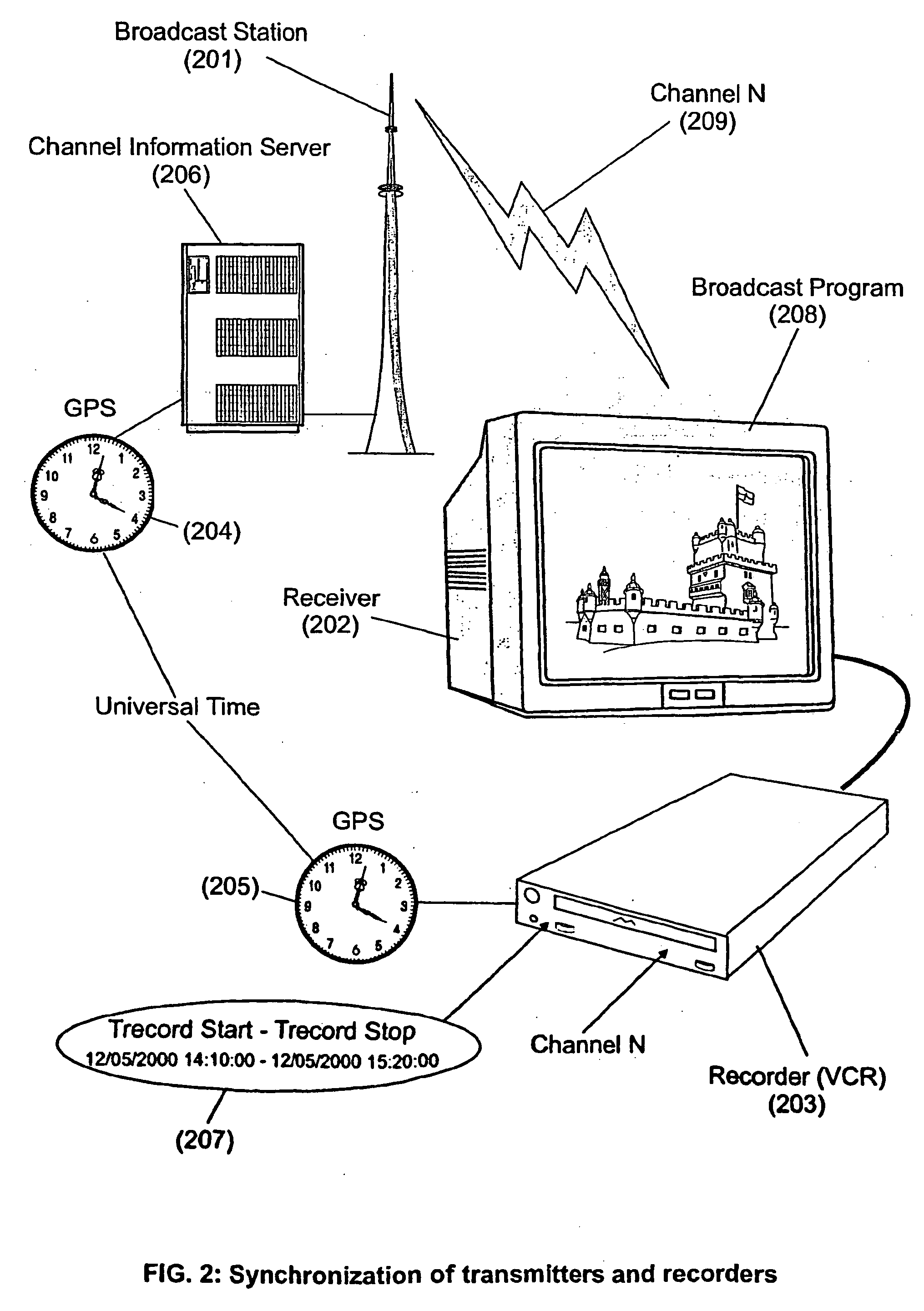
The present invention is directed to a system, method and computer program for enabling a user (100) (an auditor or a viewer) to access complementary information related to one or a plurality of sequences or topics of interest (102) in a recorded program (103) previously broadcast on the radio or television and played back on a device, such as an audio or video tape or disk recorder / player (104). The preferred embodiment of the invention relates to a system and method for enabling a person (100) listening to or watching a recorded program (103), to select one or a plurality of topics (101) (102) drawing his or her attention and for immediately receiving further information related to these topics from the World Wide Web. The system is based on the synchronization of local times (204) (205) of transmitters (201) and recorders (203). The flow of information transmitted, received and recorded is always synchronized, independently of the relative positions of recorders and transmitters. The synchronization is done referring to an absolute or universal time such as the Global Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a satellite system. The GPS or GLONASS receivers are integrated or connected to the broadcasting stations. At the receiver side, GPS or GLONASS receivers may be integrated or connected to the audio or video recorders. The system is also based on a plurality of hyperlinks defined during the production and recording of the broadcast program, for given sequences corresponding to particular intervals of time synchronized with the universal (absolute) time. The hyperlinks are associated wit the information that is broadcast in the program. They can be selected by users during the playback of the recorded program during predefined intervals of time and activated to access additional information and services.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC +1
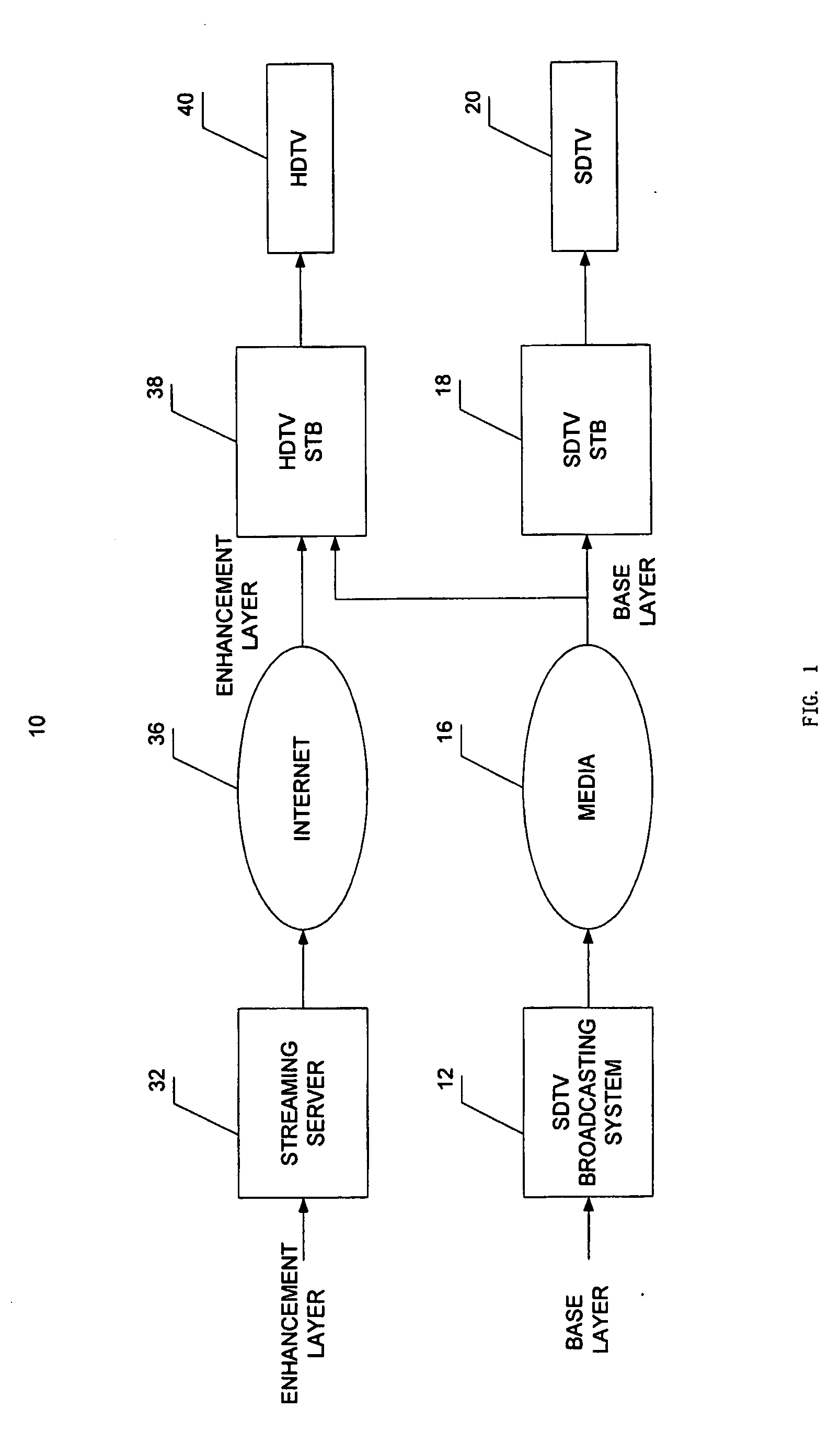
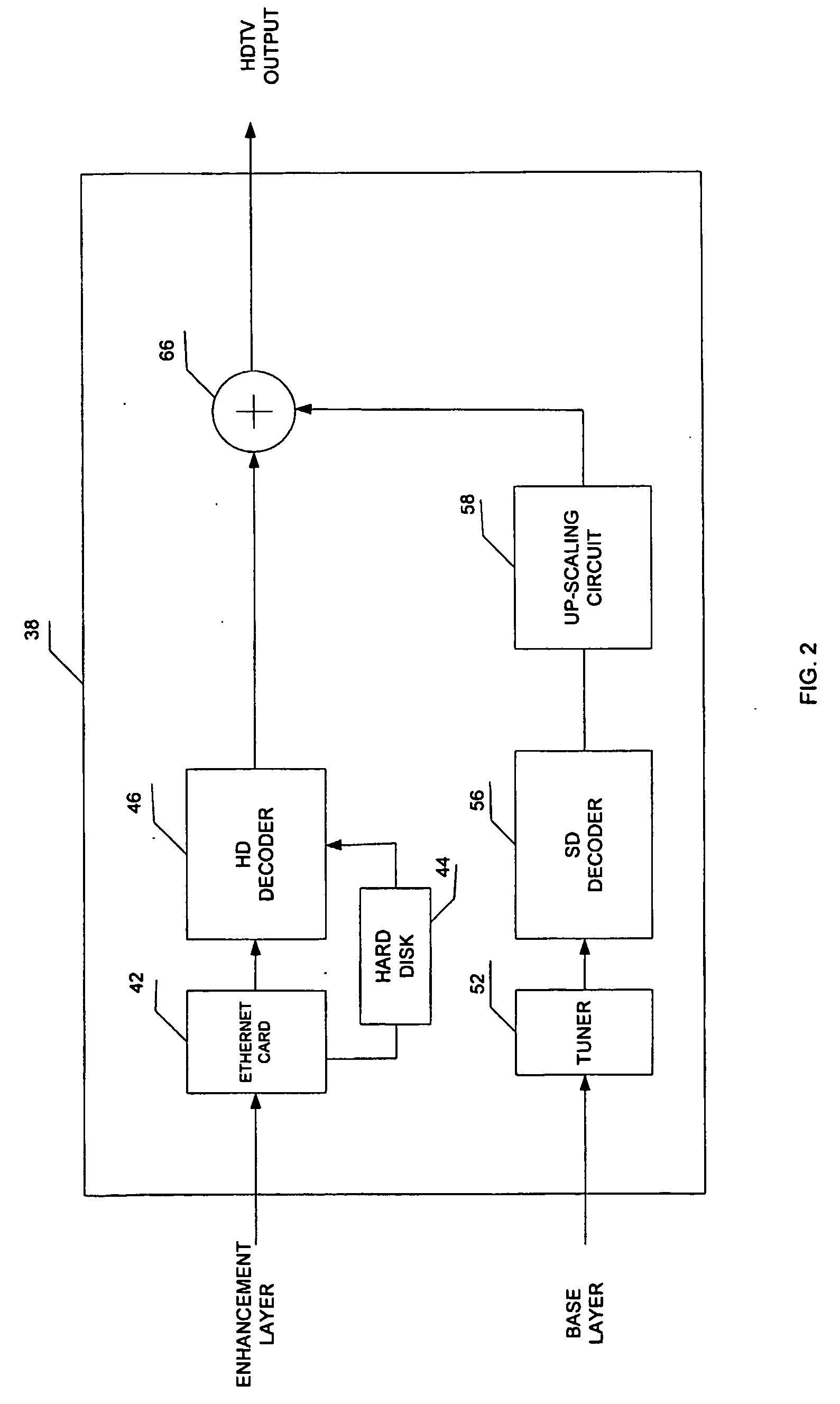
Method and system for delivering dual layer hdtv signals through broadcasting and streaming
InactiveUS20060197828A1Significant bandwidth savingSave bandwidthPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData streamNetworked system
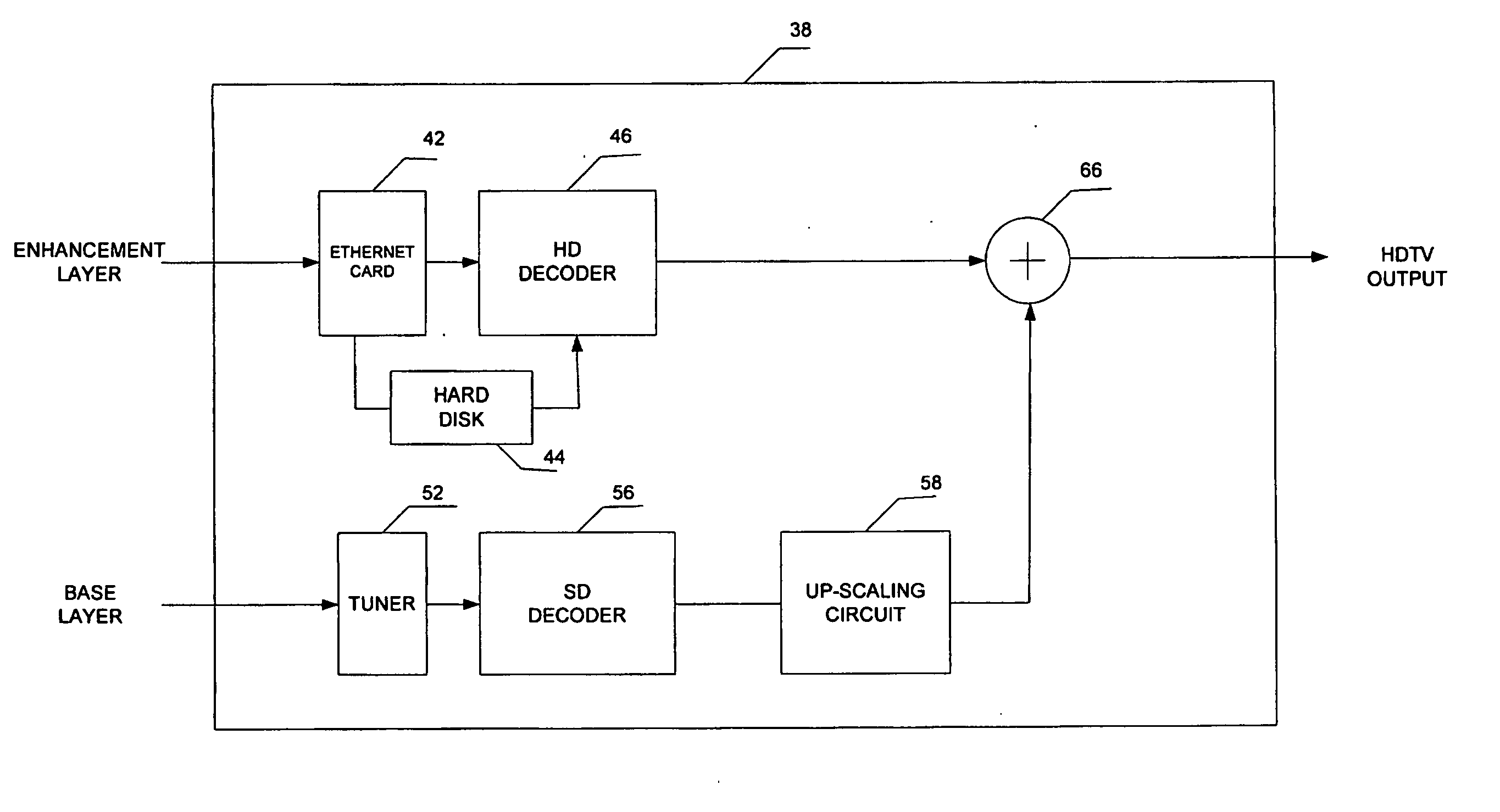
The present invention provides a method and system for delivering SDTV / HDTV services that achieves significant bandwidth savings, while keeping the existing SDTV transmission unchanged. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, a system is provided for delivering HDTV signals. In this system, an HD enhancement layer containing an HD enhancement data stream is obtained\. The HD enhancement layer is delivered to a server to enable a subscriber to access the server, via a set top terminal, to receive the HD enhancement layer over a network system. In another embodiment of the invention, a base layer containing a SD data stream is also delivered to the set top terminal to allow the terminal to integrate the HD enhancement layer and the base layer into a HDTV output.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Movies channel
InactiveUS20050278750A1Easy accessQuicker and less wayTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsHuman–computer interactionMobile device
The present invention provides a movie channel to a user on a mobile device. Movie based content associated with a movie channel is automatically delivered and stored on a mobile electronic device for access by a user. Using the device, users can quickly and efficiently access movie information without having to type in information, or specifically request the movie information to be downloaded to the device. The movie channel includes several different modes for categorically displaying different types of movie information. Some example modes include: a movies mode; a theaters mode; and a current top movies mode. The movies mode is organized to display information relating to particular movies on the electronic device. The theaters mode is arranged to display information relating to particular theaters on the electronic device. The current top movies mode displays information relating to the current “hot” movies.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
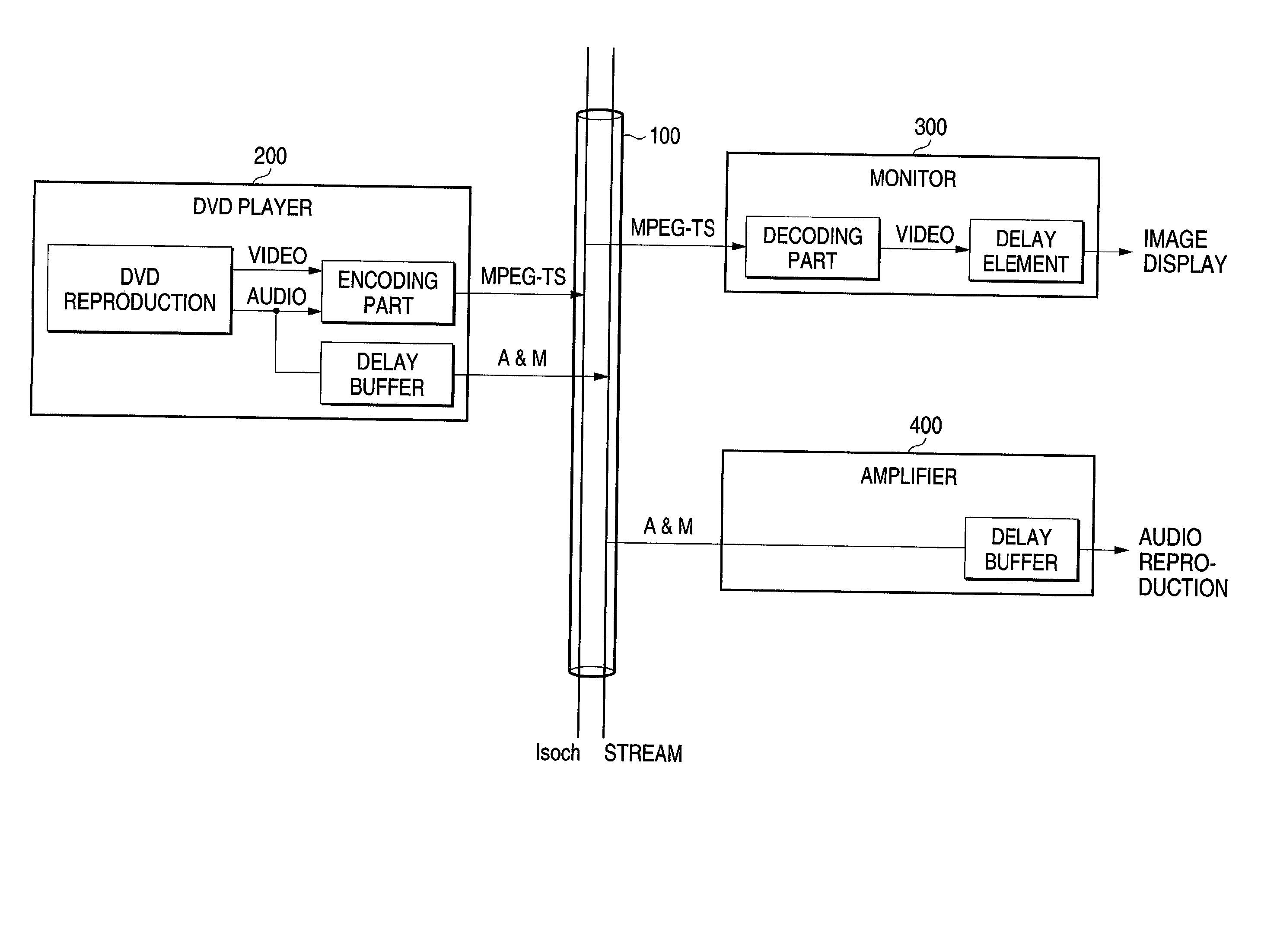
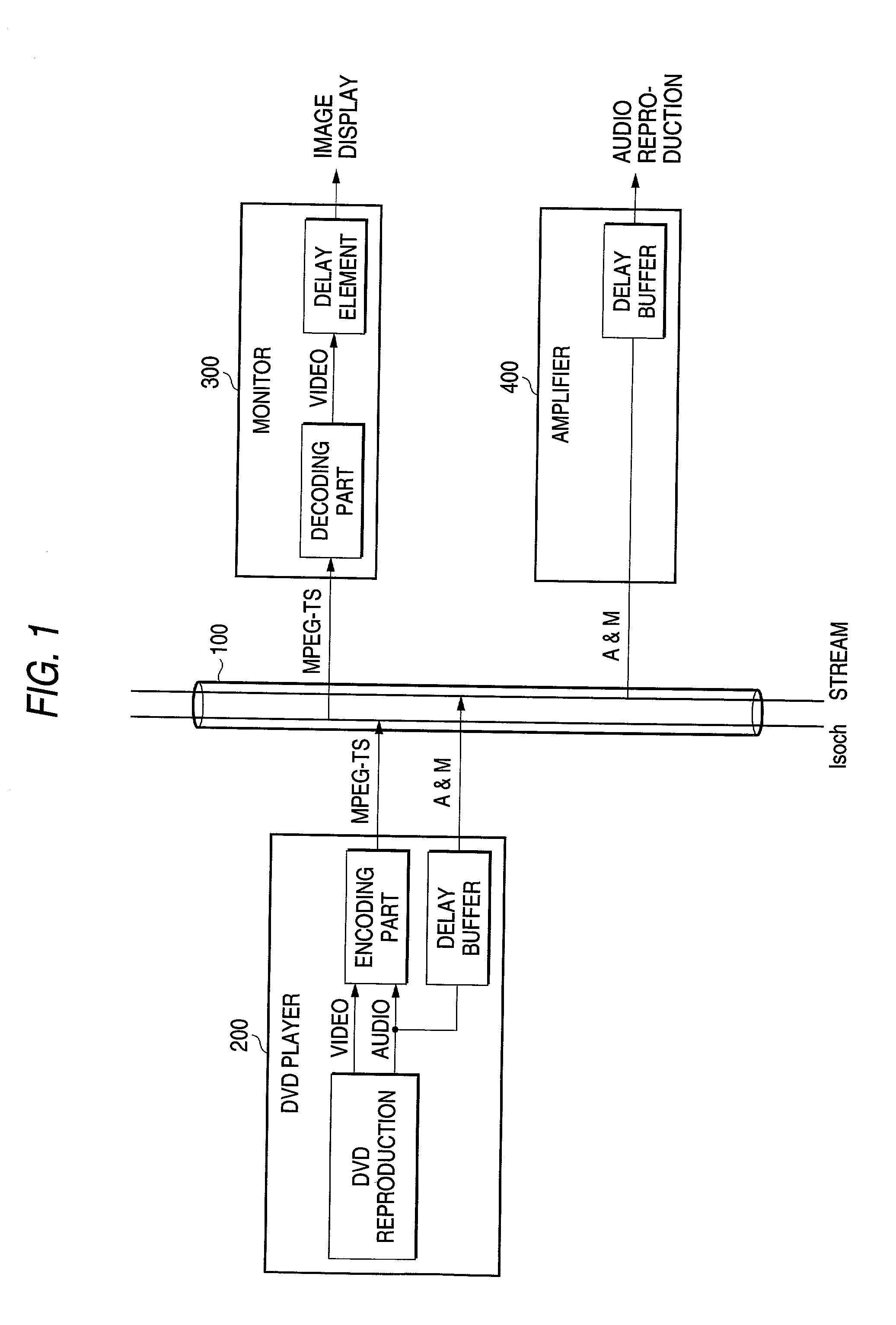
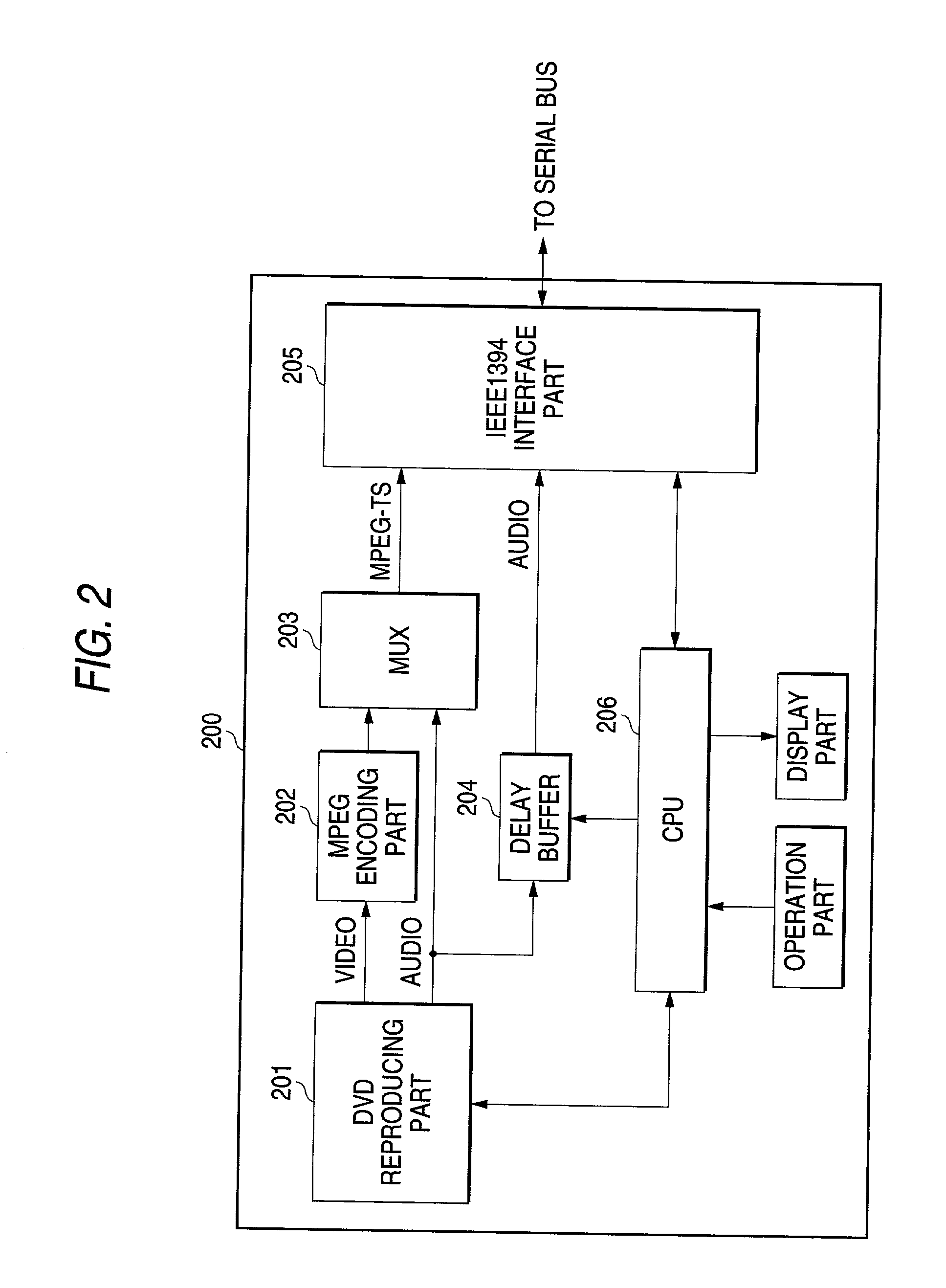
Video display apparatus, audio mixing apparatus, video-audio output apparatus and video-audio synchronizing method
InactiveUS20020174440A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionAudio power amplifierDelay
In a video-audio synchronizing method for synchronizing video and audio reproduced respectively by a monitor 300 and an amplifier 400 connected to a serial bus 100 to which video from a DVD player 200 and audio associated with the video are supplied, the monitor 300 sends out delay time information caused by an intrinsic delay element for video display to the amplifier 400 through the serial bus 100 as a control command, and the amplifier 400 delays the audio by time necessary for synchronization between the video and the audio according to the control command and outputs the audio.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
System and method of performing digital multi-channel audio signal decoding
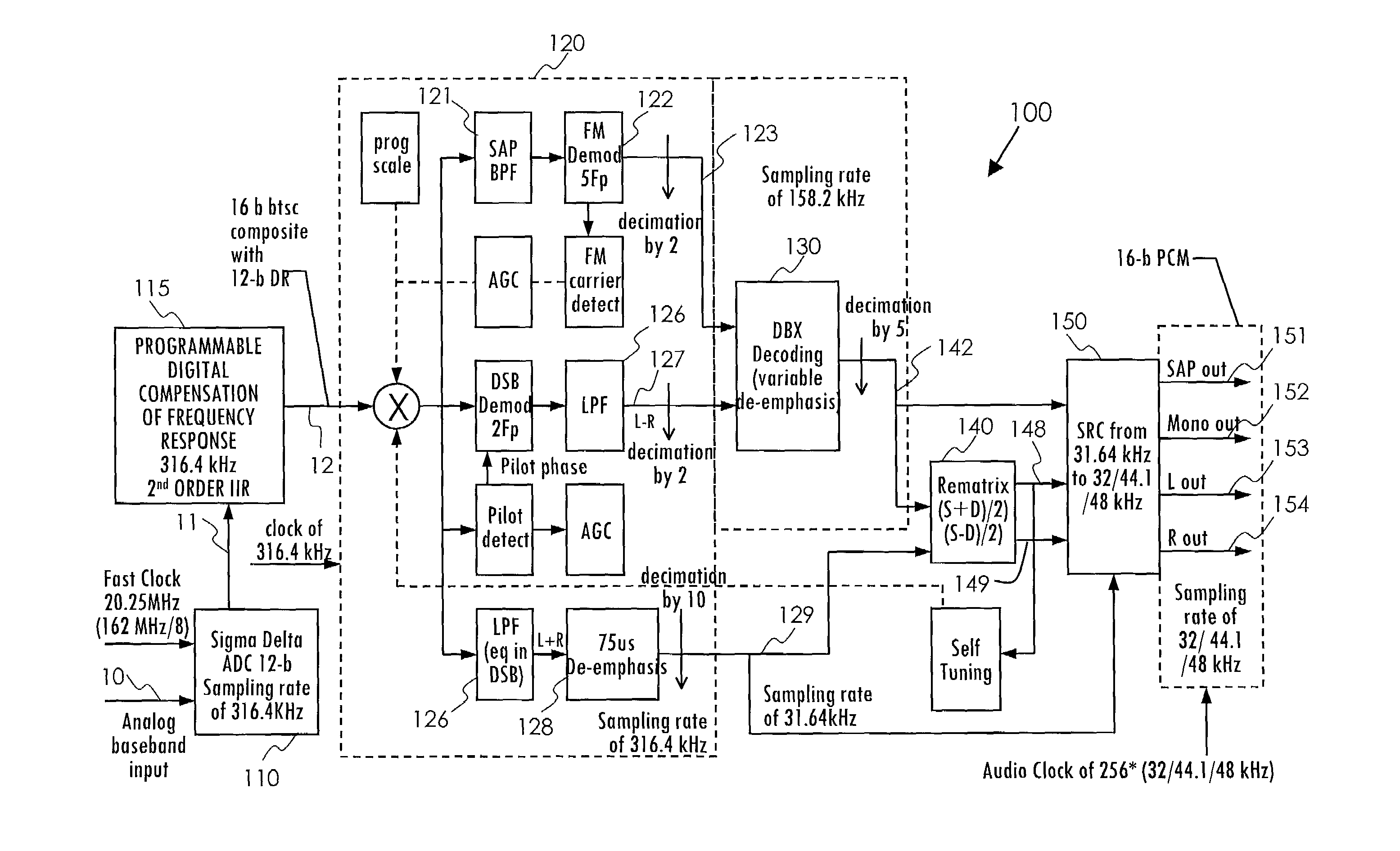
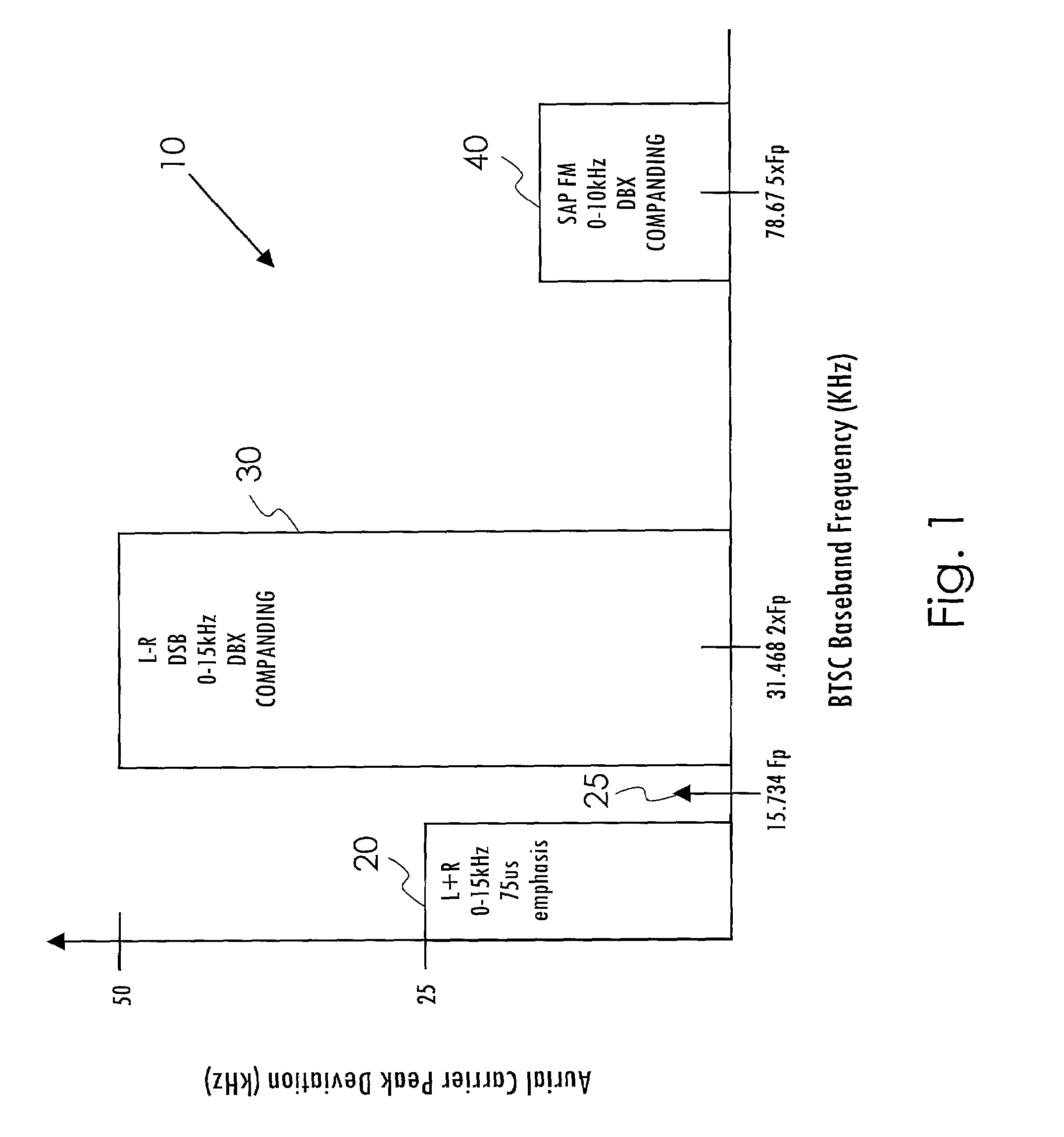
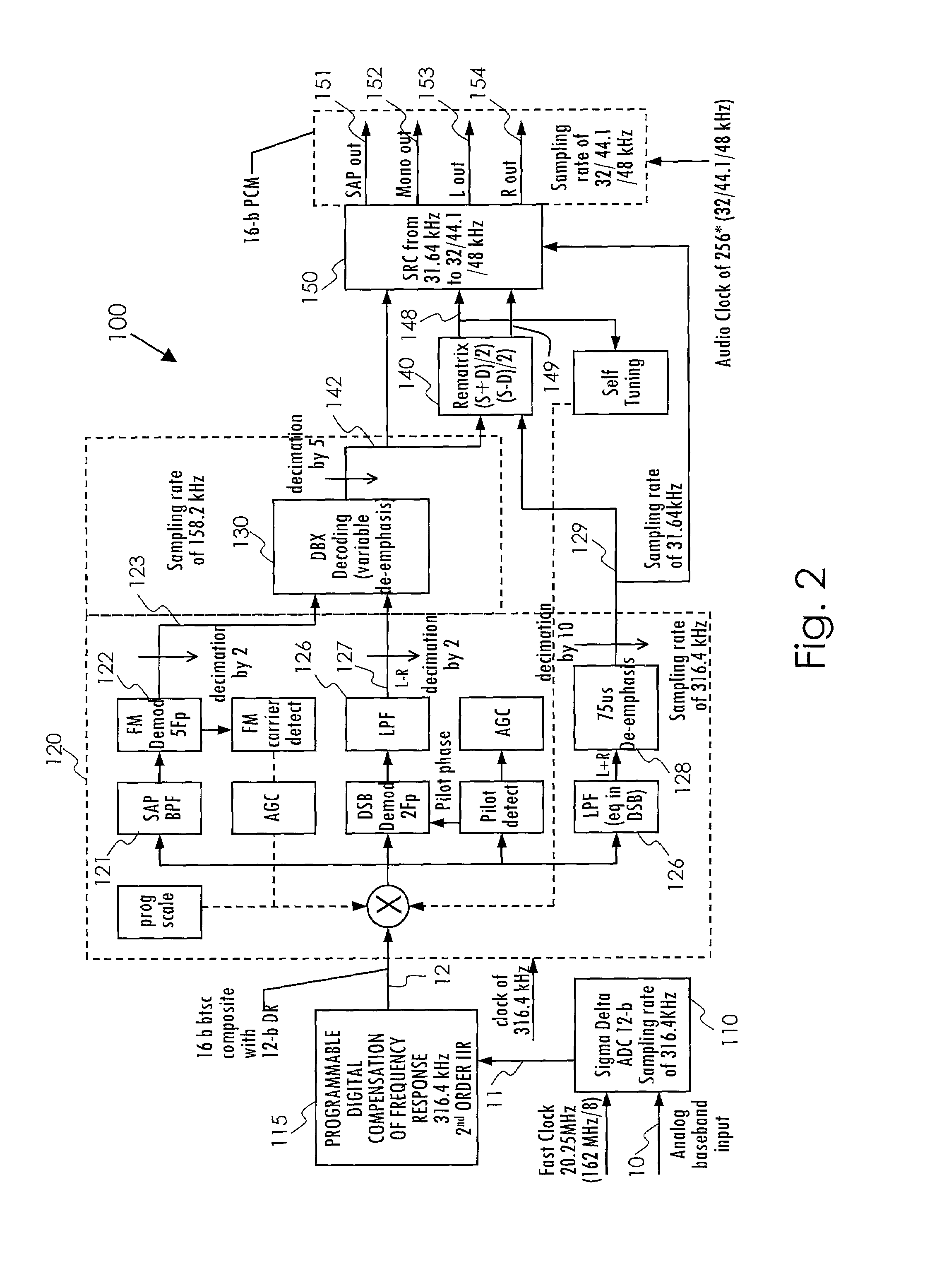
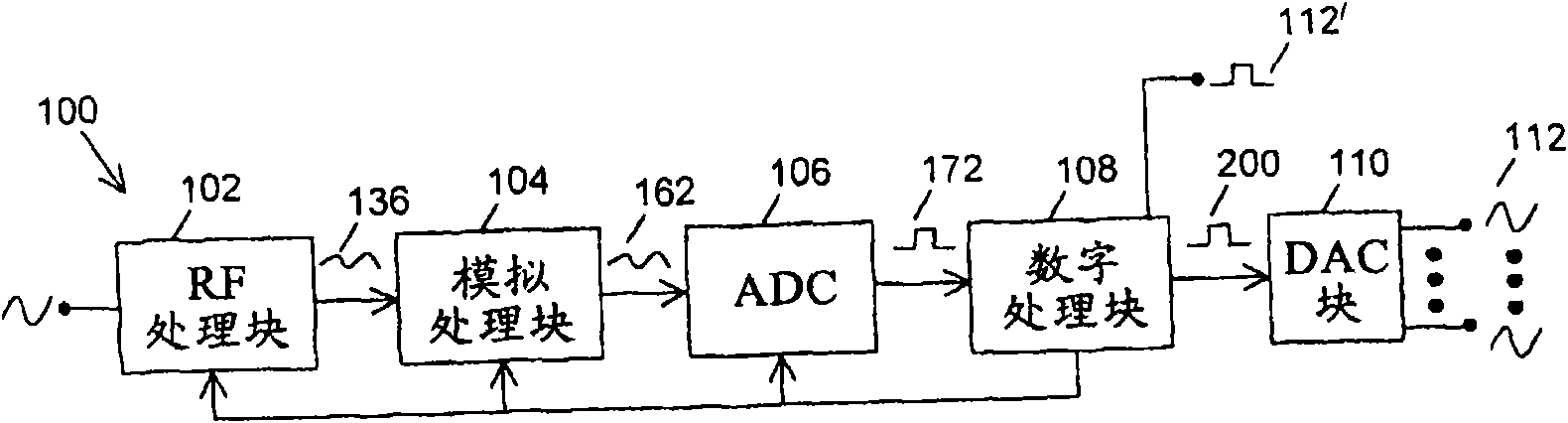
InactiveUS7079657B2Low costLow-cost and efficientTelevision system detailsBroadcast information characterisationFrequency compensationClock rate
A system and method are disclosed for performing digital multi-channel decoding of a BTSC composite audio signal. Analog-to-digital conversion is performed on a composite analog audio signal at a fast clock rate to generate a composite digital audio signal at a first sample rate. Digital frequency compensation is performed on the composite digital audio signal at the first sample rate to generate a compensated composite audio signal. Digital channel demodulation and filtering are performed on the compensated composite audio signal at the first sample rate to generate a first single channel audio signal at a second sample rate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
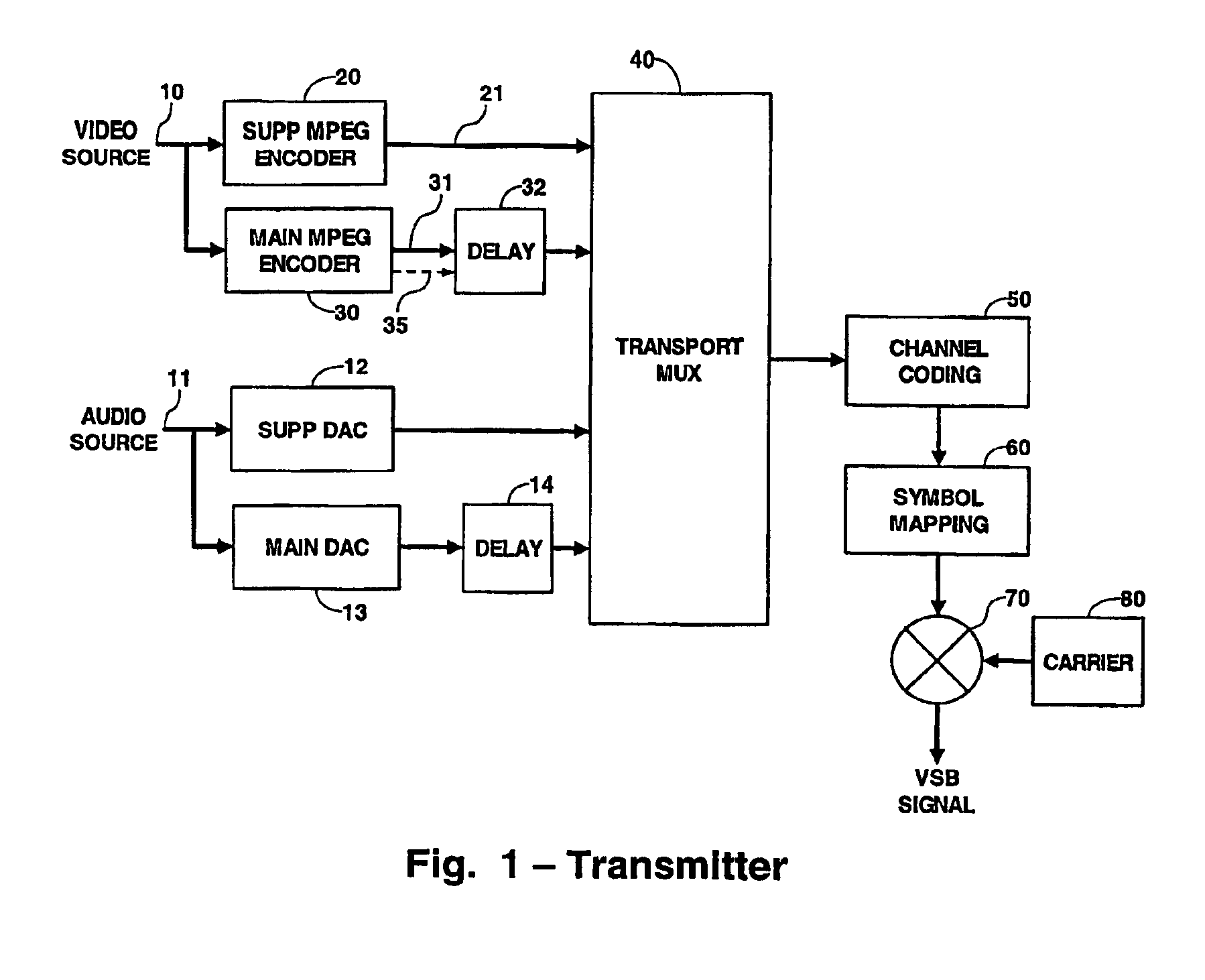
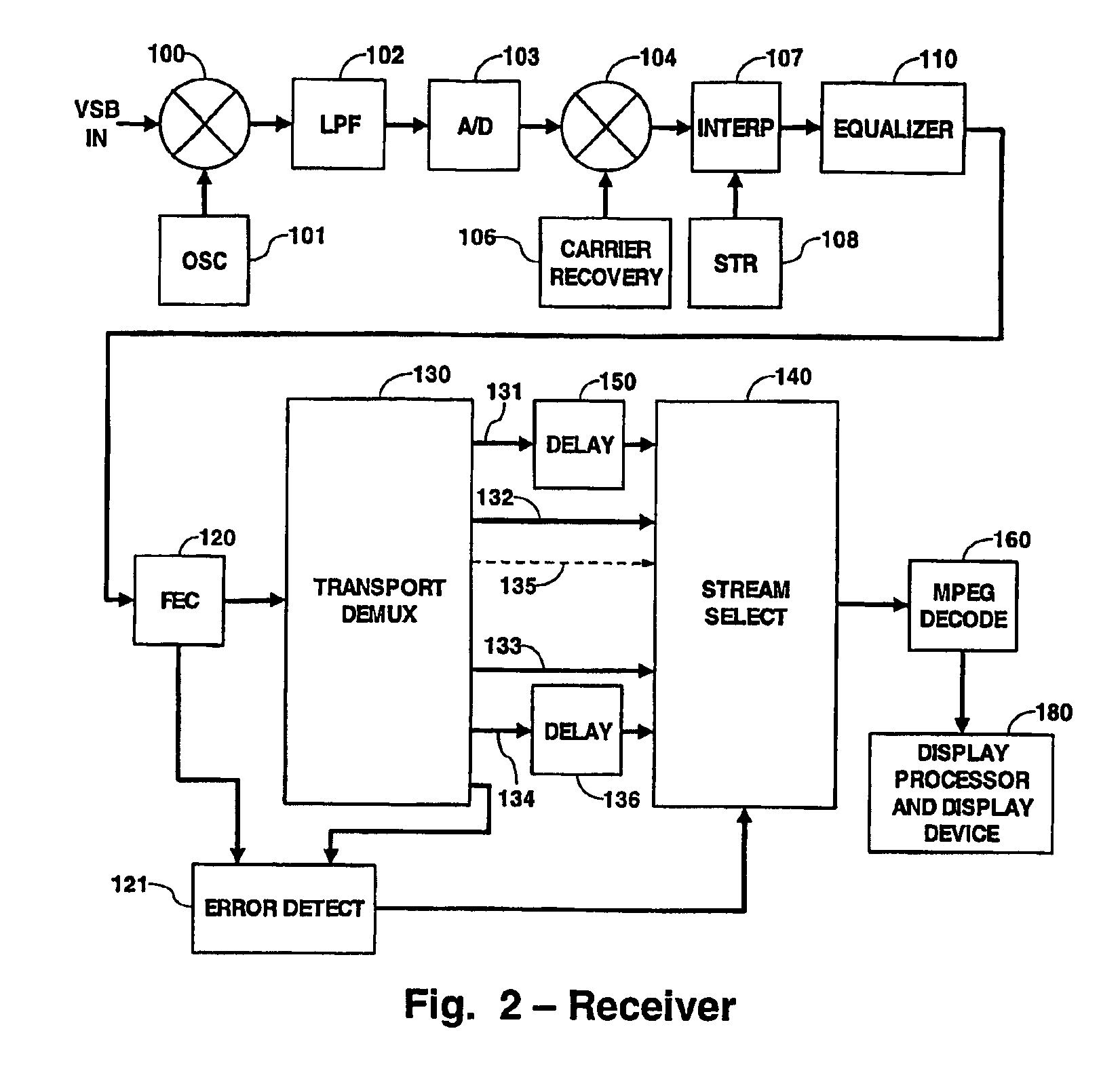
Fade resistant digital transmission and reception system
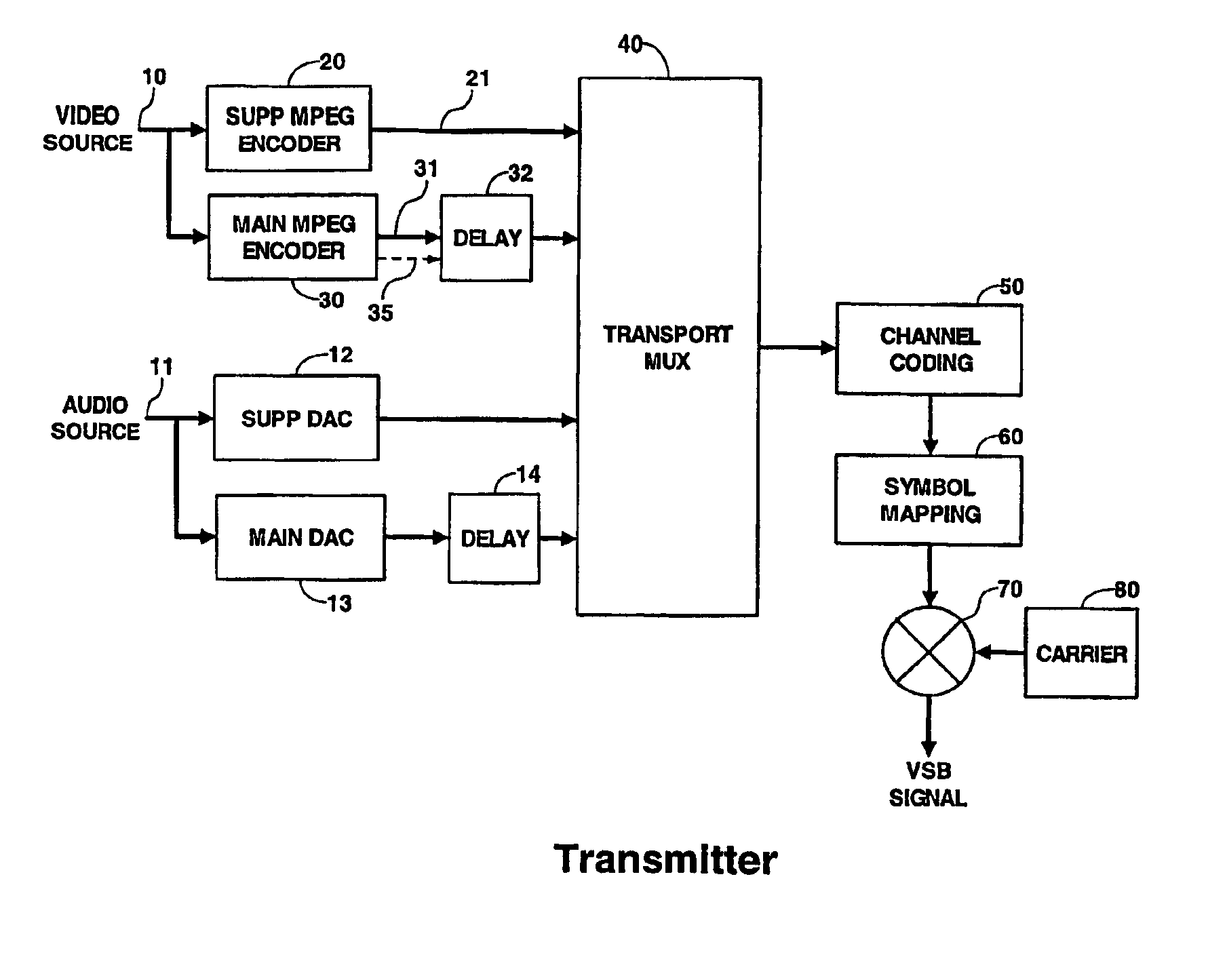
InactiveUS6900828B2Raise priorityTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionCommunications systemDigital broadcasting
In a digital broadcast communications system, a higher priority component and a lower priority component are broadcast from a transmitter to a receiver. Each of these components generates a main and a supplemental signal, and each supplemental signal is advanced in time with respect to the corresponding main signal. The main and supplemental signals for both the higher and lower priority components are combined into a single signal, which is broadcast to a receiver. In the receiver, the time advanced supplemental signals are stored in a buffer to time align them with their corresponding main signals. Both main signals are processed in the normal manner in the receiver, and are also monitored to detect a fading event. When a fading event is detected, the corresponding buffered supplemental signals are substituted for the faded main signals and normal processing continues.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
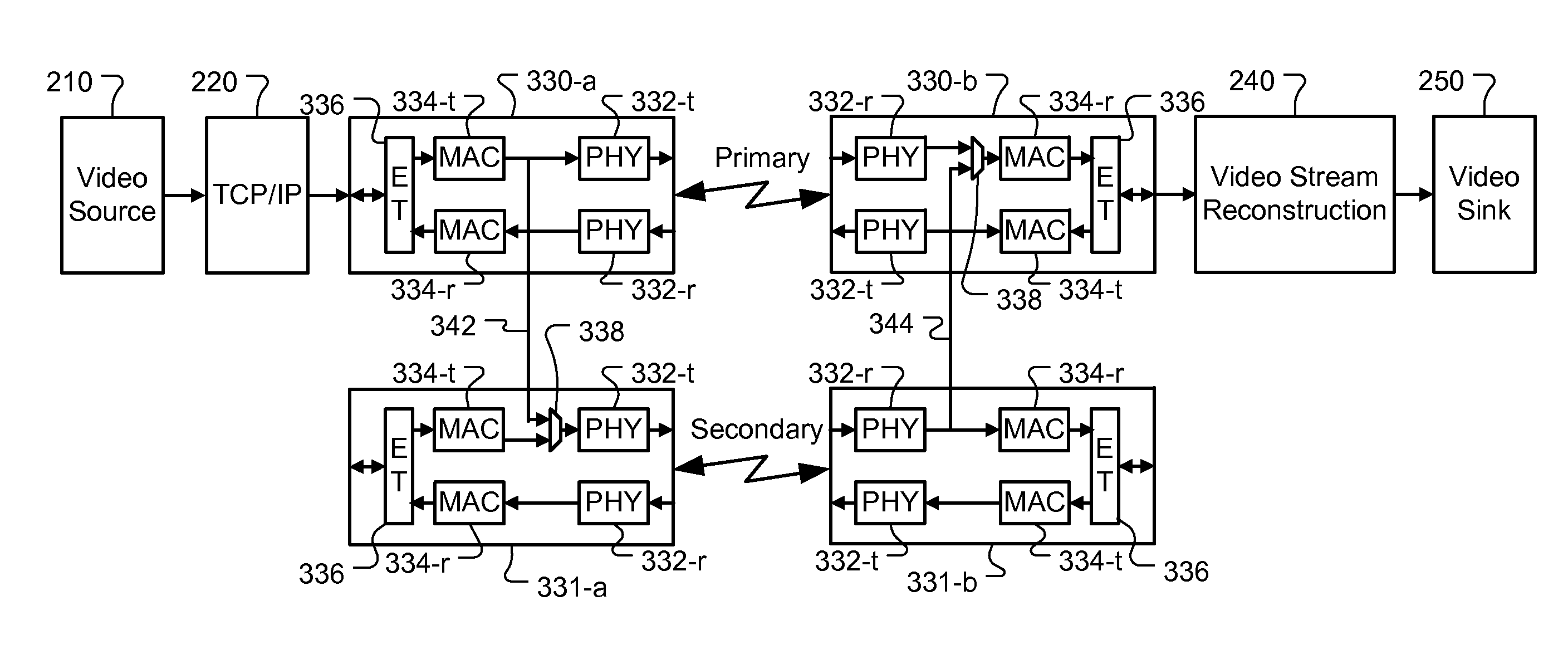
Method and Apparatus for Quick-Switch Fault Tolerant Backup Channel
In a network environment, the Quality of Service becomes an important issue particularly for applications involved with real-time multimedia streaming. Any transmission failure may cause service disruption and the failure has to be quickly recovered to minimize the impact. A unified home networking standard based on existing media in home has been developed to meet the increasing demand for bandwidth, reliability and availability. However, the fault tolerant protocol adopted by the home networking standard is based on an advanced selective ARQ (Automatic Retransmission Request) protocol which may take hundreds of millisecond to establish a backup channel. Alternatively, a hot standby backup channel has to be used to achieve quick switch without data loss at the expense of increased power consumption by the hot standby channel. The present invention discloses a quick-switch modem that can quickly switch from a primary channel to a backup channel upon detection of transmission failure. The quick-switch modem contains an additional interface between the modems for the primary channel and the secondary channel. In order to achieve quick failure detection and data re-route, the quick-switch modem relies on lower layers of the network link to facilitate failure detection and data re-route. Consequently, the switching time is substantially reduced without the need of hot standby. Alternatively, the quick-switch modem can be configured for load sharing to enhance overall available bandwidth.
Owner:RYSHAKOV IGOR
Output-oriented network transmission technique of multi-screen splicing system
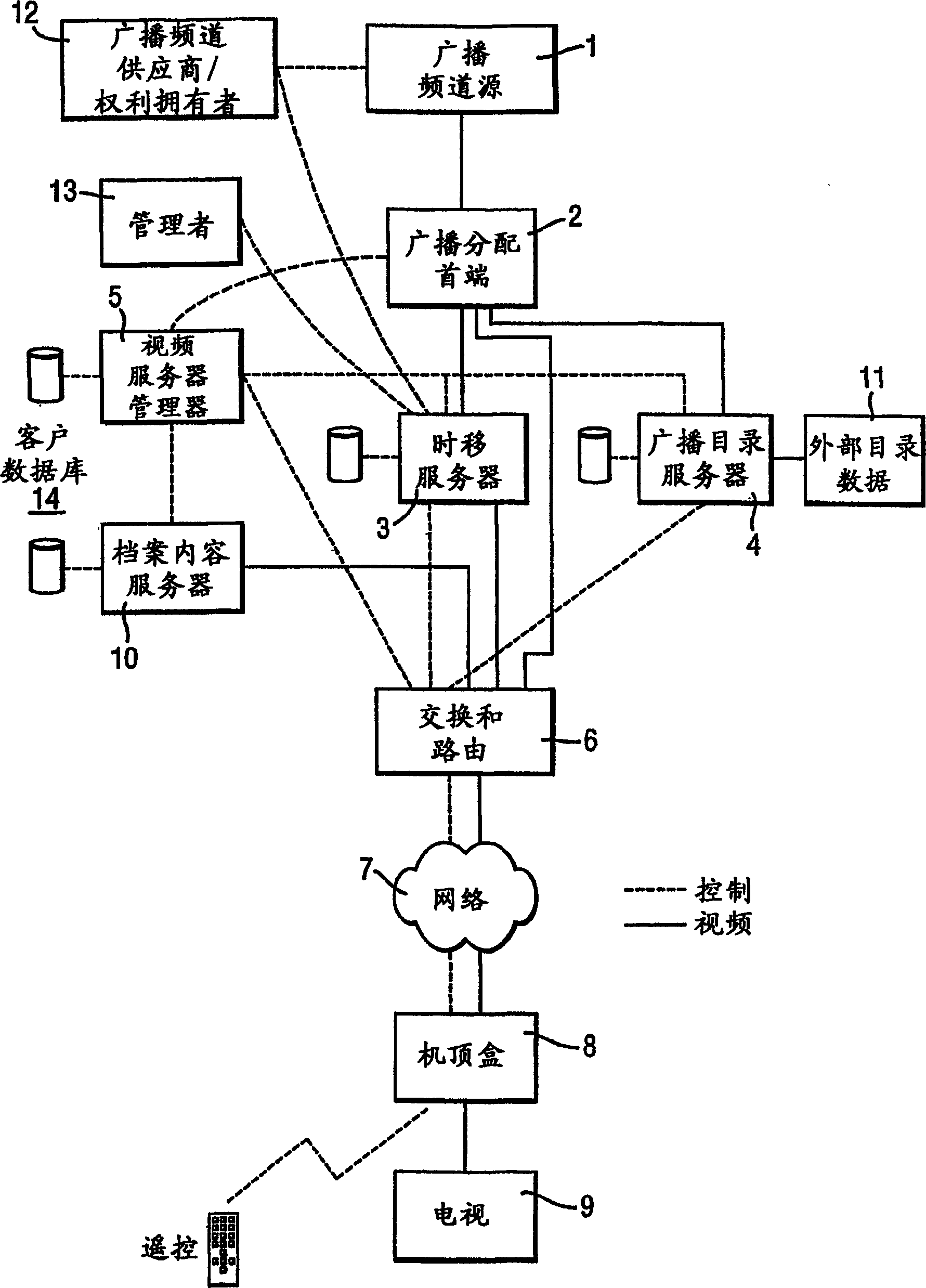
InactiveCN102611869AImprove clarityIncrease refresh ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionSimultaneous television signal transmission by multiple carrierSignal sourceImaging data
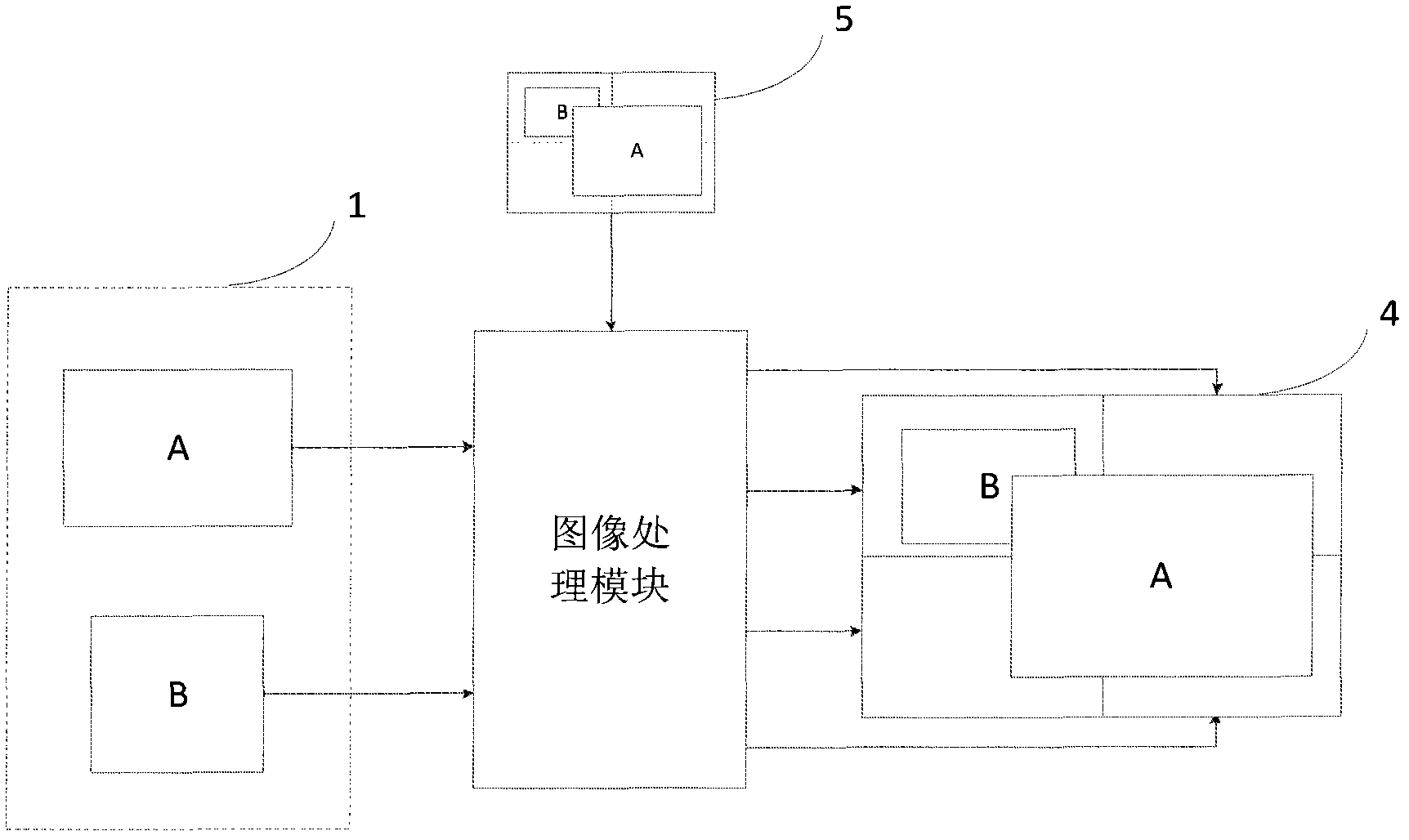
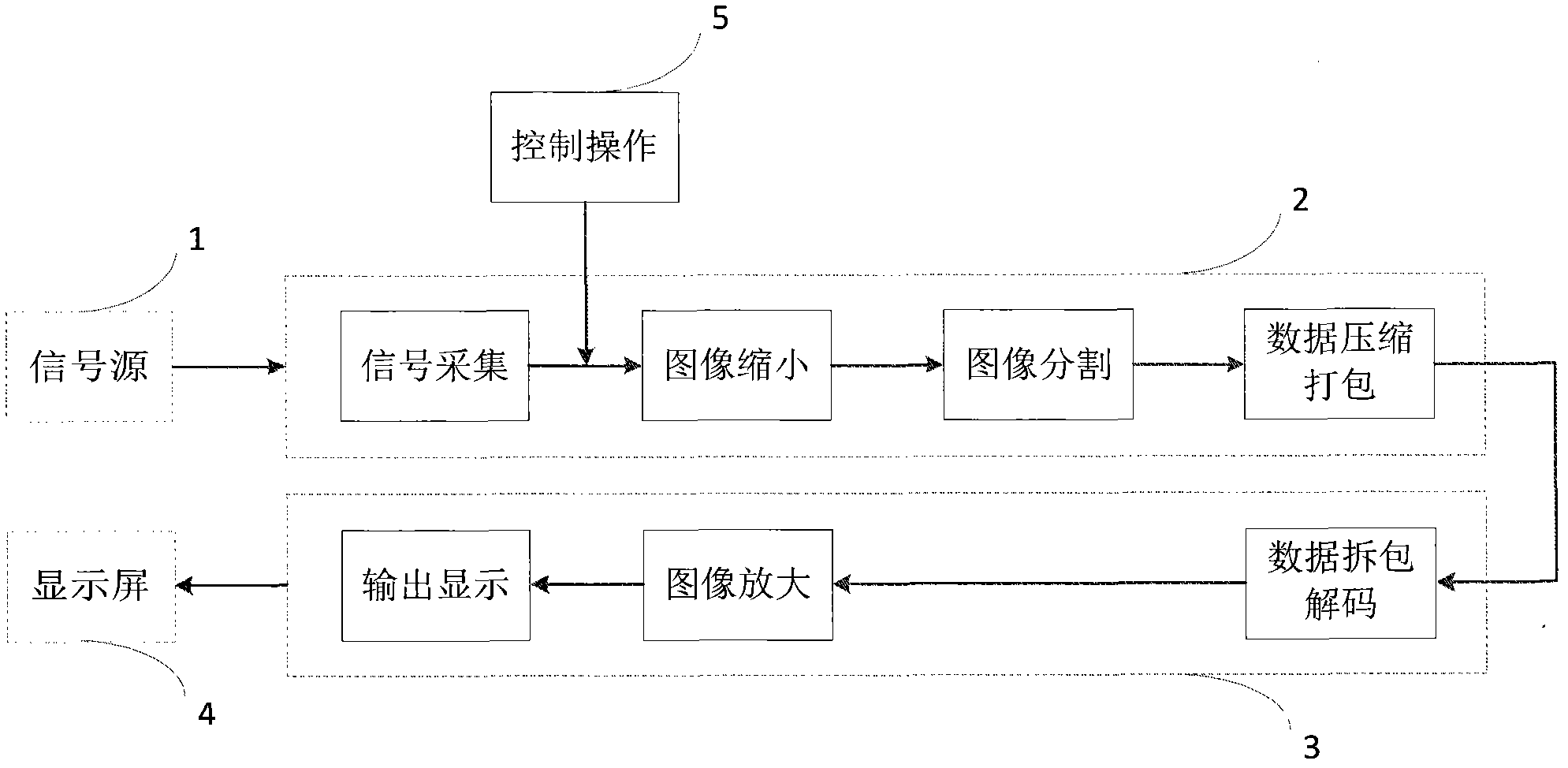
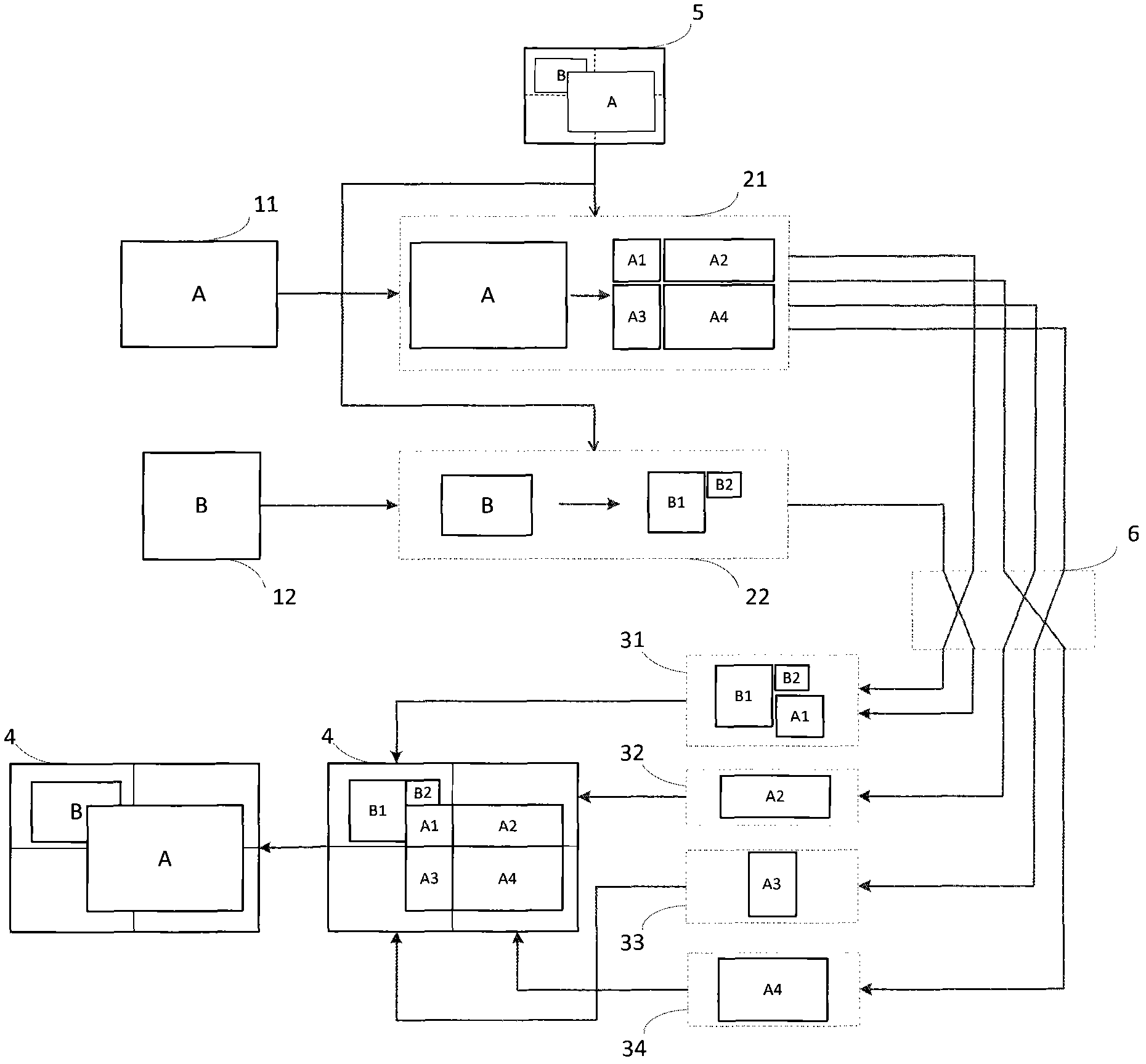
The invention relates to an output-oriented network transmission technique of a multi-screen splicing system. The core of the technique is output-oriented smart segmentation and accurate transmission; in other words, segmentation processing is performed on signals in a smart way according to the requirements of output display, and then each part of data is accurately transmitted to a corresponding display unit. The technique comprises the following main steps that: step 1, an input acquisition end processor (2) acquires a signal from a signal source (1), and performs compression processing on the corresponding signal according to a display policy sent by a control host (5); step 2, the acquisition end processor (2) segments the signal according to the display policy, compresses and packs the segmented image data and then transmits the same to an output display end through a network; step 3, a display end processor (3) unpacks and decodes the data and performs amplification processing on the signal according to the display policy; and step 4, the display end processor outputs and displays the image on a corresponding spliced display screen (4). In the whole process, the data is segmented in advance at the input end and each part of data is accurately transmitted to the corresponding display unit; and the compression of the signal is completed at the input end while amplification is realized by the output end; therefore, the data in the whole network system is transmitted at the lowest flow rate and the waste of bandwidth is avoided.
Owner:江苏清投视讯科技有限公司
Method and system for ensuring continuous data flow between re-transmitters within a chaincast communication system
InactiveUS7831991B1Reduce bandwidth requirementsEfficient content communicationSpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsTechnical communicationThe Internet
Owner:SIM WONG HOO +1
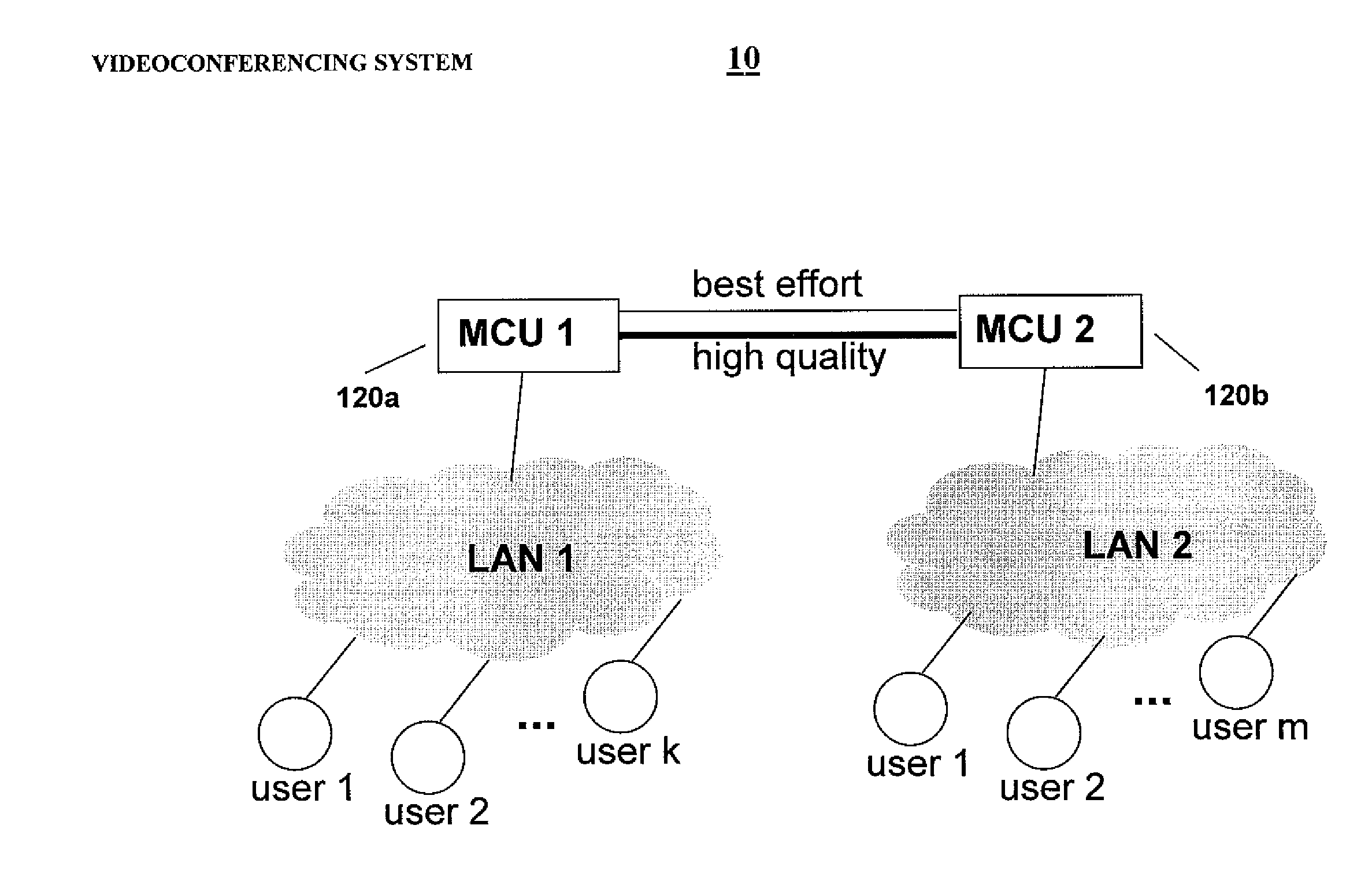
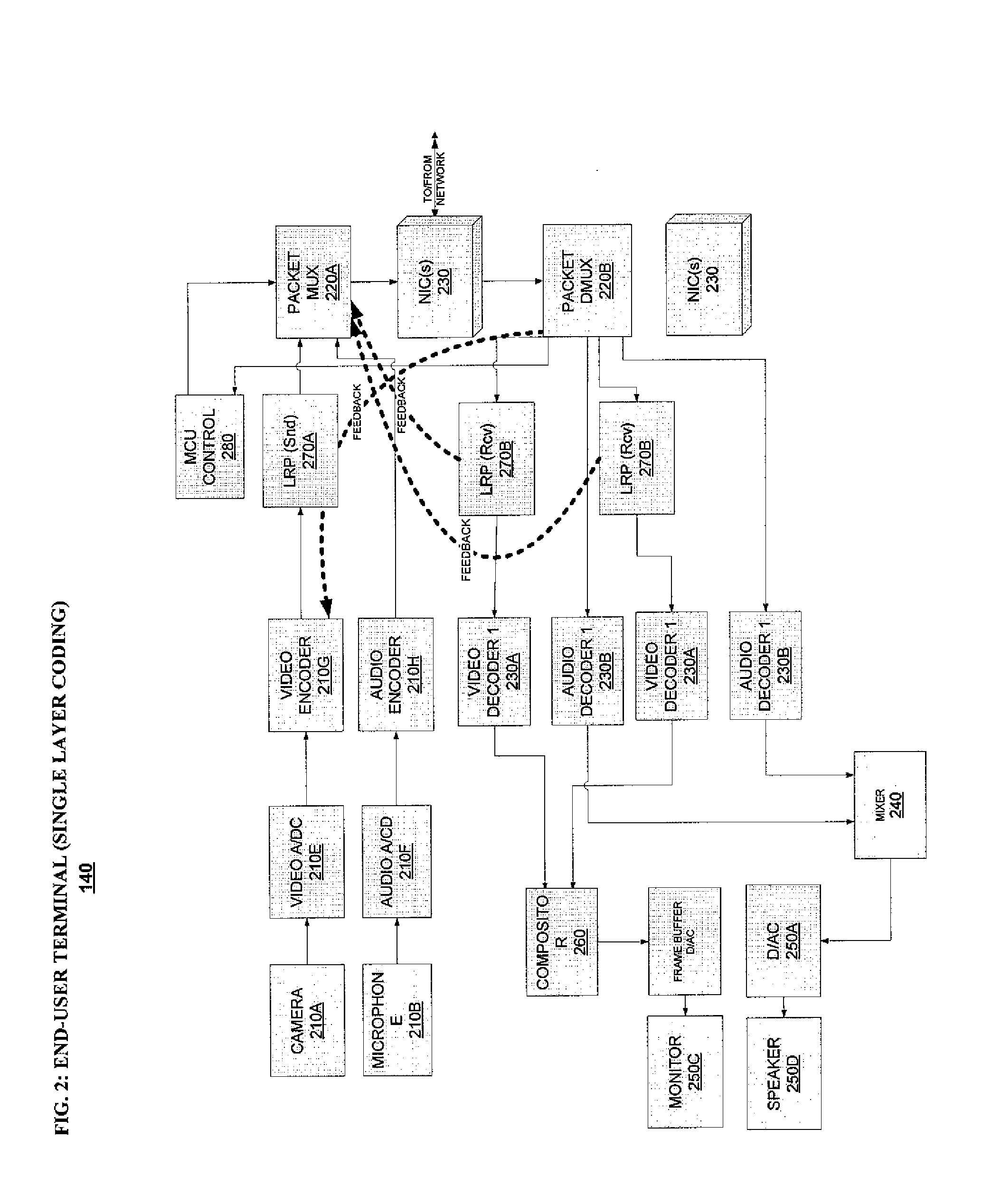
Systems and methods for error resilience and random access in video communication systems
ActiveUS20120069135A1Improve fault toleranceError preventionTelevision conference systemsCommunications systemVideo encoding
Systems and methods for error resilient transmission and for random access in video communication systems are provided. The video communication systems are based on single-layer, scalable video, or simulcast video coding with temporal scalability, which may be used in video communication systems. A set of video frames or pictures in a video signal transmission is designated for reliable or guaranteed delivery to receivers using secure or high reliability links, or by retransmission techniques. The reliably-delivered video frames are used as reference pictures for resynchronization of receivers with the transmitted video signal after error incidence and for random access.
Owner:VIDYO
System and method for identification and insertion of advertising in broadcast programs
InactiveCN1748417APulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision signal transmission by single/parallel channelsData streamBroadcast data
The invention provides a broadcast system and method for identifying and inserting advertisements into a broadcast, wherein the method comprises receiving a broadcast data stream, identifying advertisements in the broadcast data stream, and updating an advertisement catalog containing information for identifying the advertisements and position of the advertisements in programs of the broadcast data stream. During playback, the advertisements or replacing advertisements are inserted into the position or the other position of the program.
Owner:VIDEO NETWORKS IP HLDG
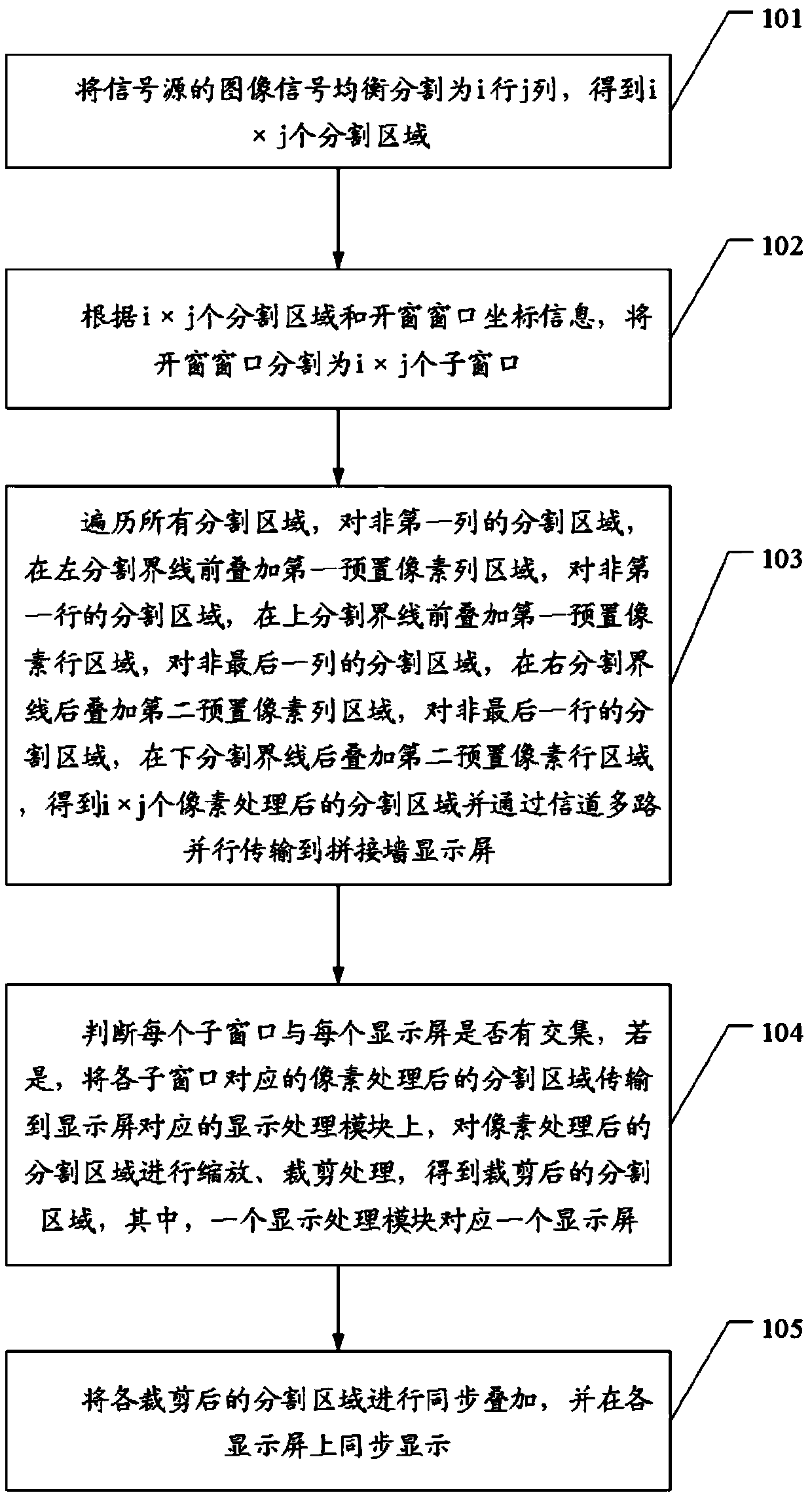
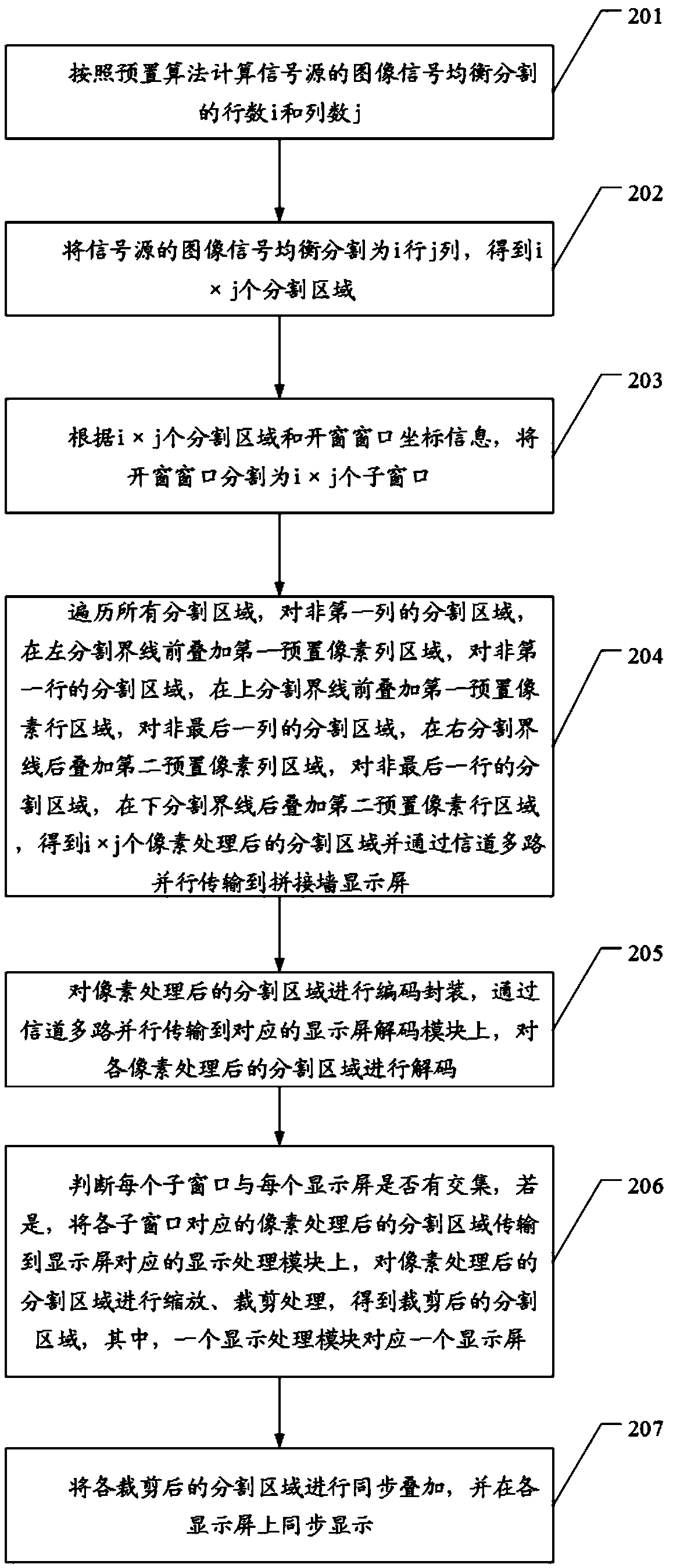
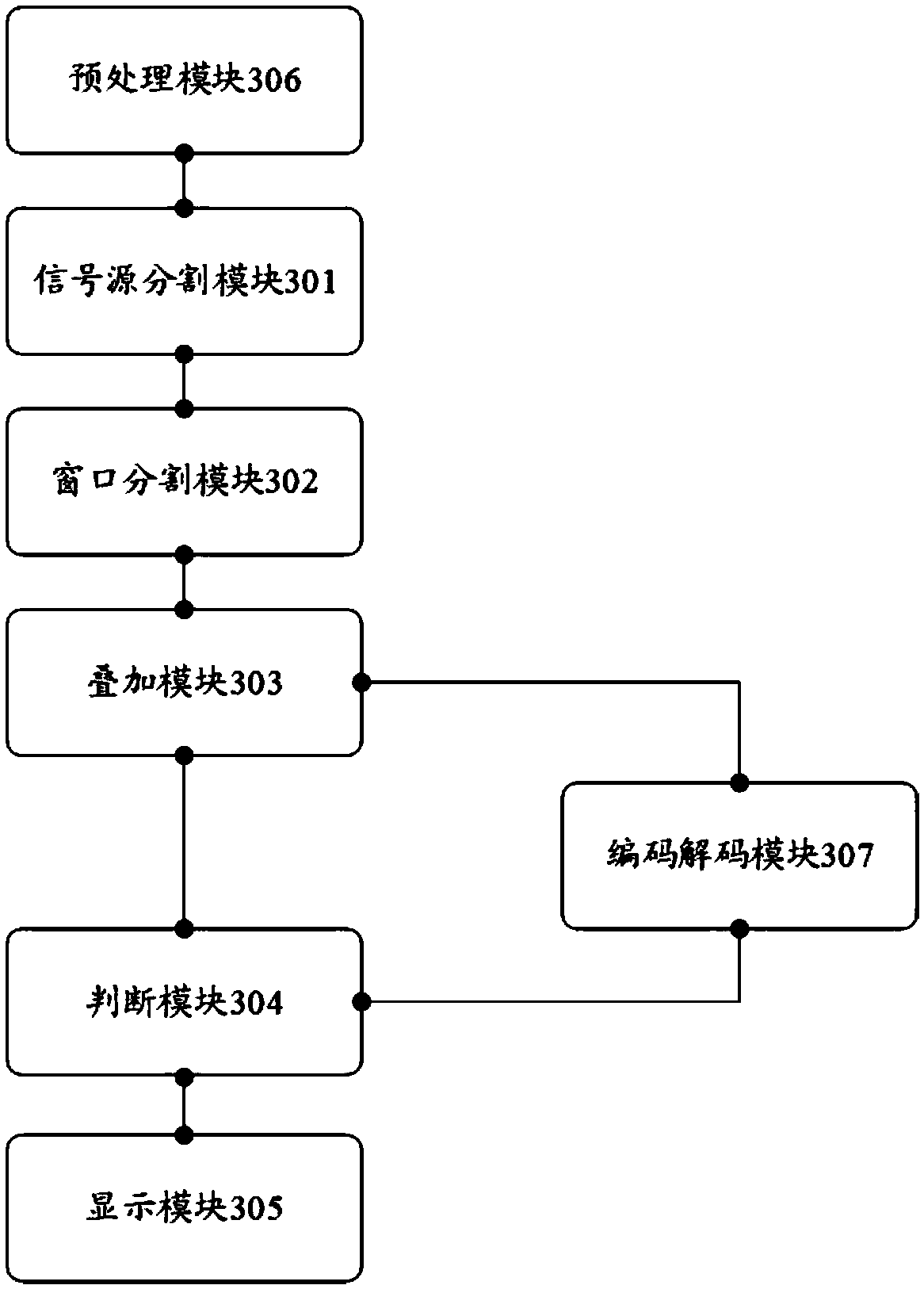
High resolution signal source splicing wall displaying methods, device and equipment
ActiveCN109640026ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)High resolution image
The invention discloses high resolution signal source splicing wall displaying methods. I-line-j-column balanced segmentation is carried out on high resolution image signals which are difficult to transmit through utilization of a signal channel; a windowing window is segmented into ixj subwindows; preset pixel region overlaying processing is carried out on segmented regions; whether each subwindow and each display screen have an intersection or not; if each subwindow and each display screen have the intersection, the pixel processed segmented region corresponding to each subwindow is sent toa corresponding displaying processing module for zooming and clipping processing; and synchronous overlaying and displaying are carried out on the segmented regions obtained through clipping processing, so the high resolution image signals of a signal source are transmitted to a splicing wall for real-time displaying. The technical problem that a technology of transmitting the high resolution image signals to the splicing wall for real-time displaying is deficient at present is solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTRON TECH CO LTD
Image processing device
InactiveUS7176966B2Increase speedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionImaging processing
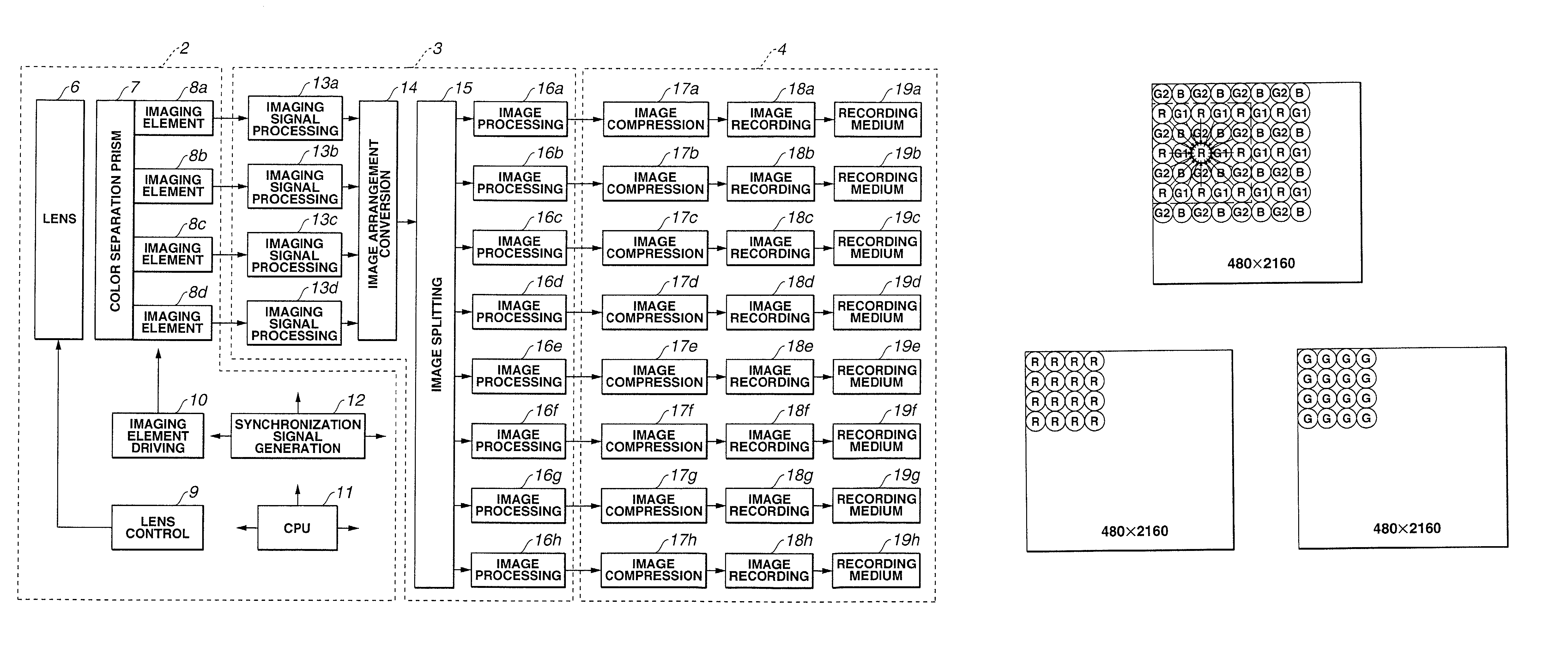
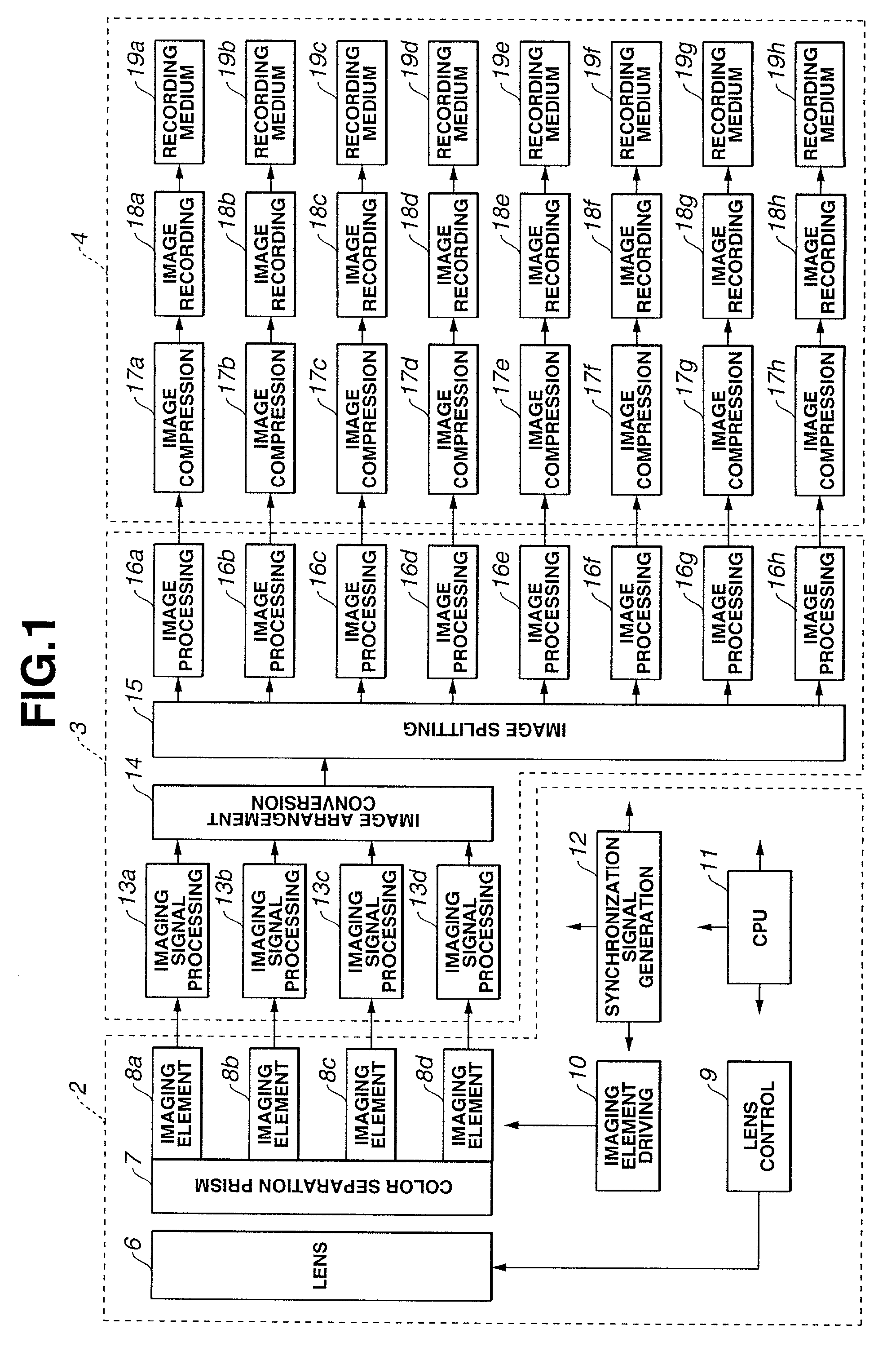
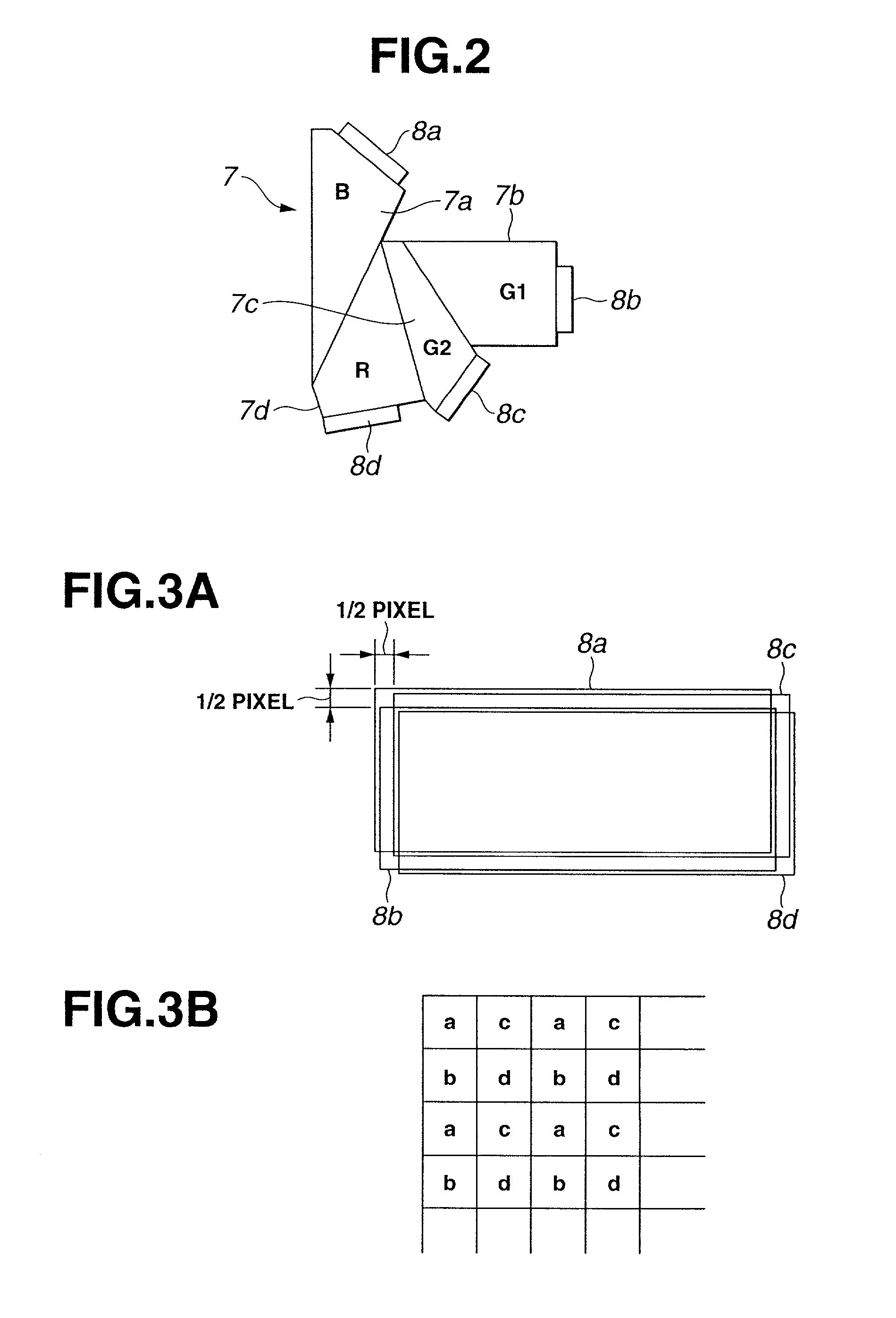
In short, the image processing device for obtaining a single image by using a plurality of image-pickup elements comprises a plurality of image-pickup signal processing circuits that are provided for each of the image-pickup elements, an image arrangement conversion circuit which converts the read-out order of the images corresponding to the respective image-pickup elements that are output from the image-pickup signal processing circuits, an image splitting processing circuit for performing image splitting on the image that is output from the image arrangement conversion circuit, an image processing circuit for performing image processing in parallel on each of the split images, and an image compression circuit for compressing in parallel each of the split images that are output from the image processing circuit.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
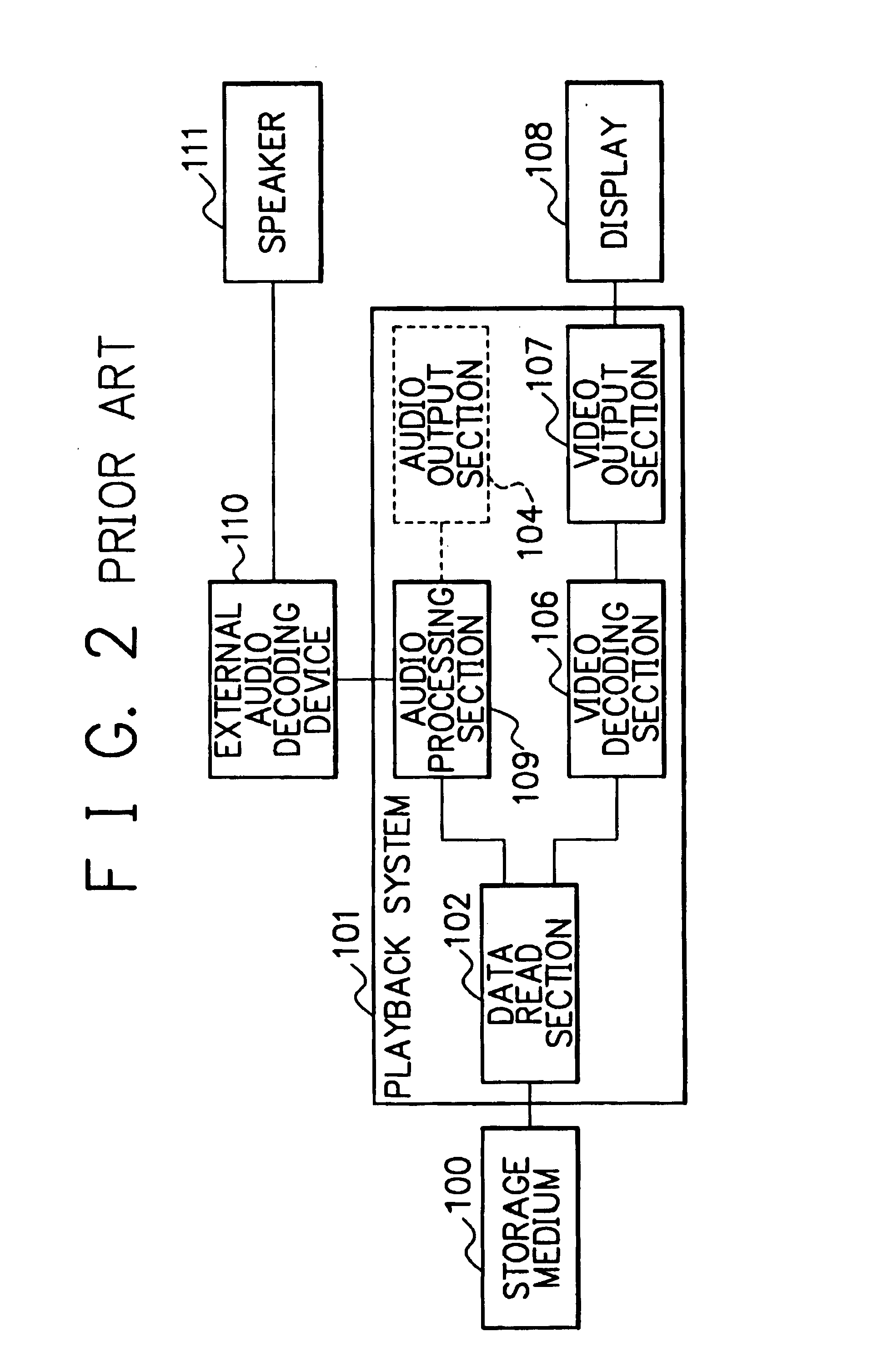
System, method and record medium for audio-video synchronous playback
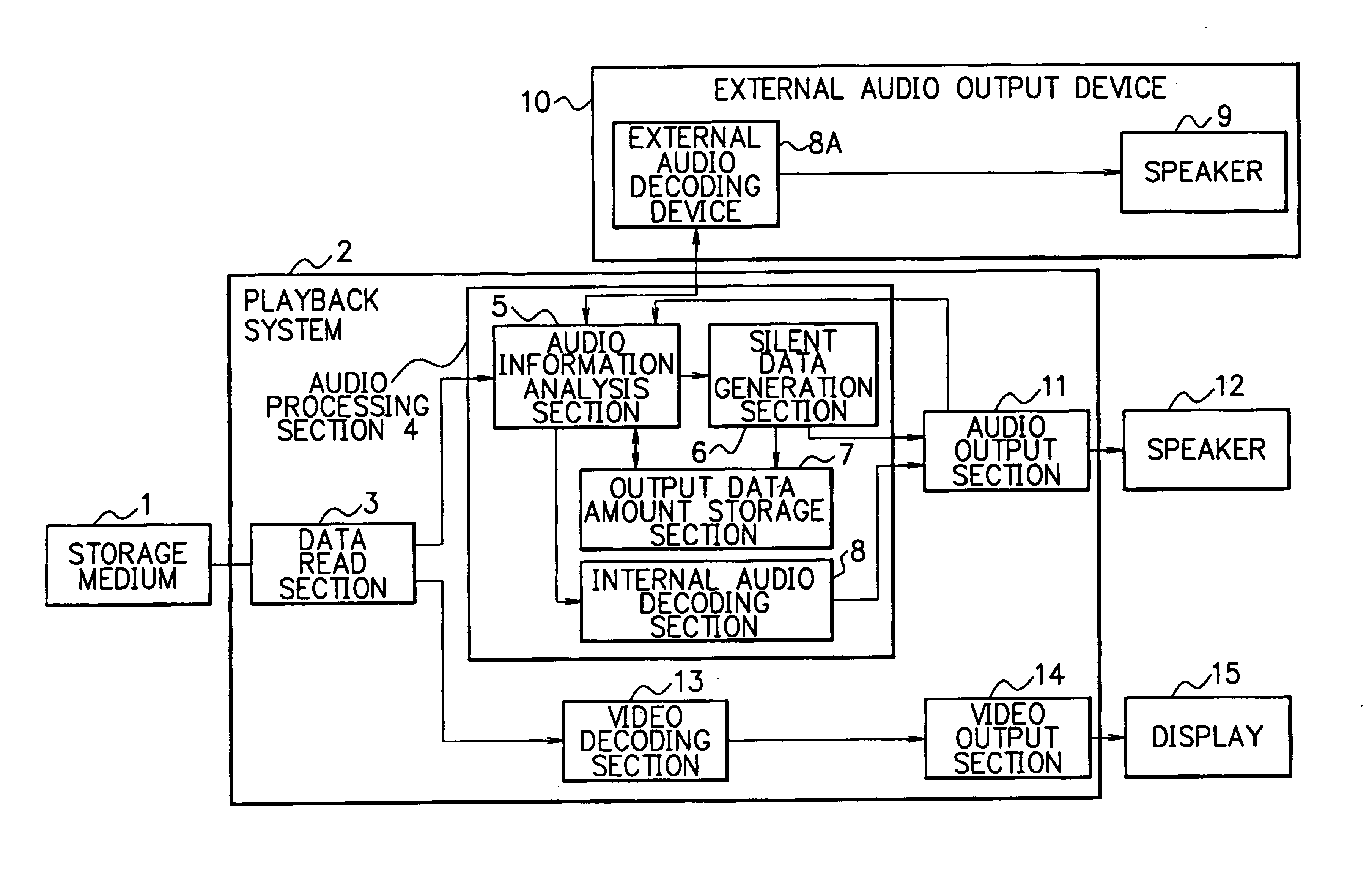
InactiveUS7054544B1Keep in syncTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareInformation analysis
In an audio-video synchronous playback control system which outputs coded audio data to an external audio decoding device so as to be decoded and played back by the external audio decoding device while playing back video data maintaining synchronization with the audio data playback of the external audio decoding device, an audio information analysis section figures out the size of one unit of the coded audio data and the size of audio data which is obtained by decoding the one unit of the coded audio data. A silent data generation section generates silent data of a size corresponding to the size of audio data. The video data playback of the video decoding / output section is controlled based on the amount of the silent data which are played back or processed by the audio output section.
Owner:NEC PERSONAL COMPUTERS LTD
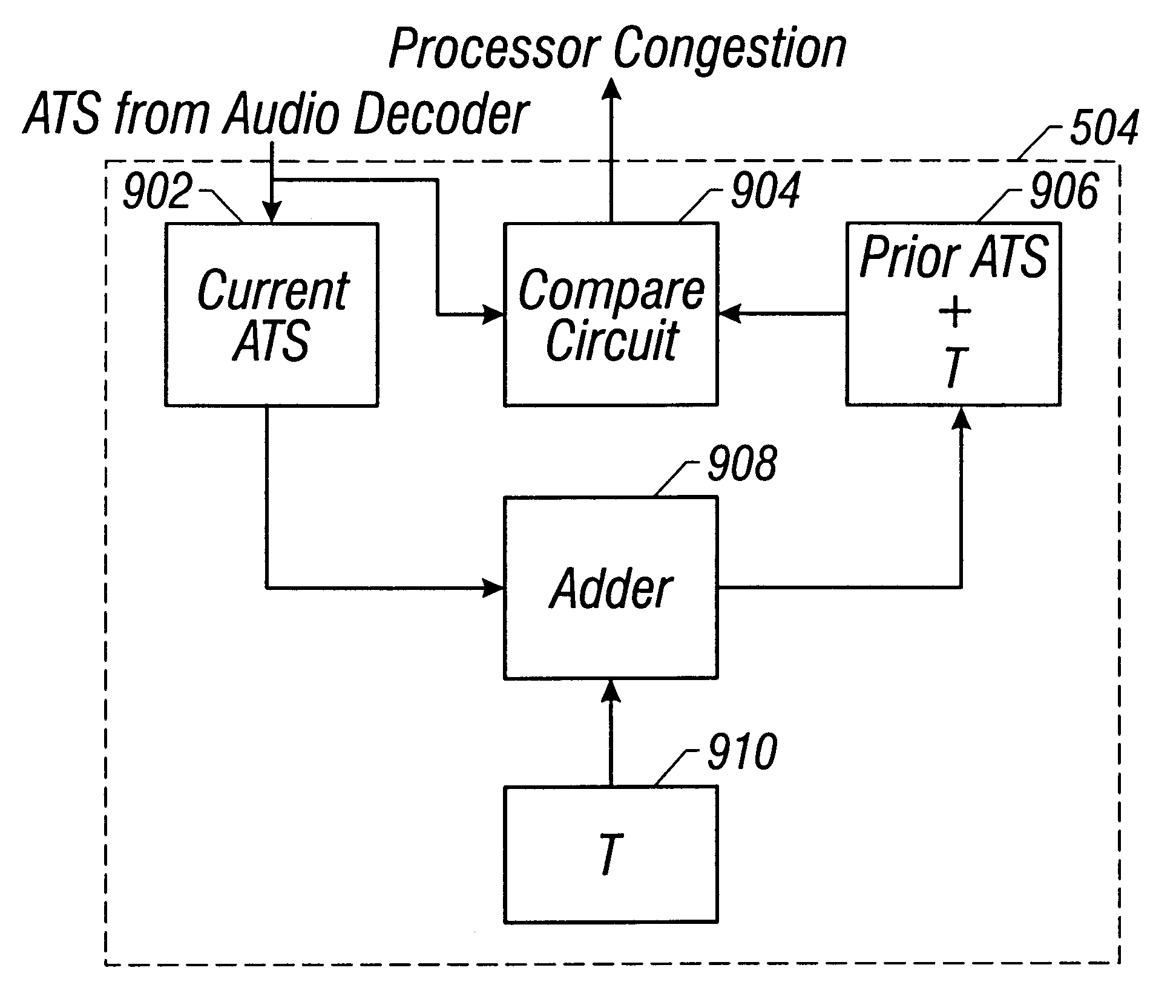
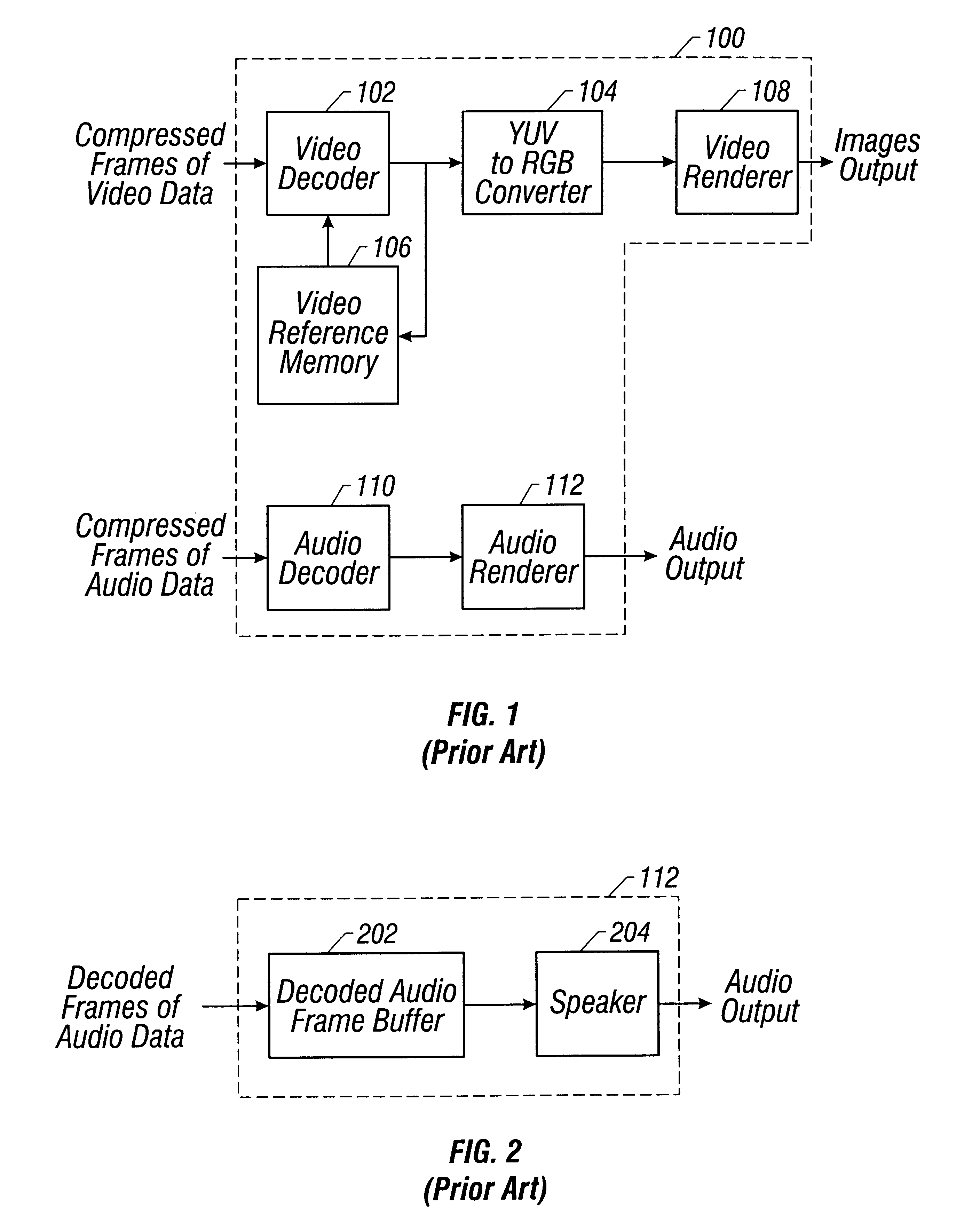
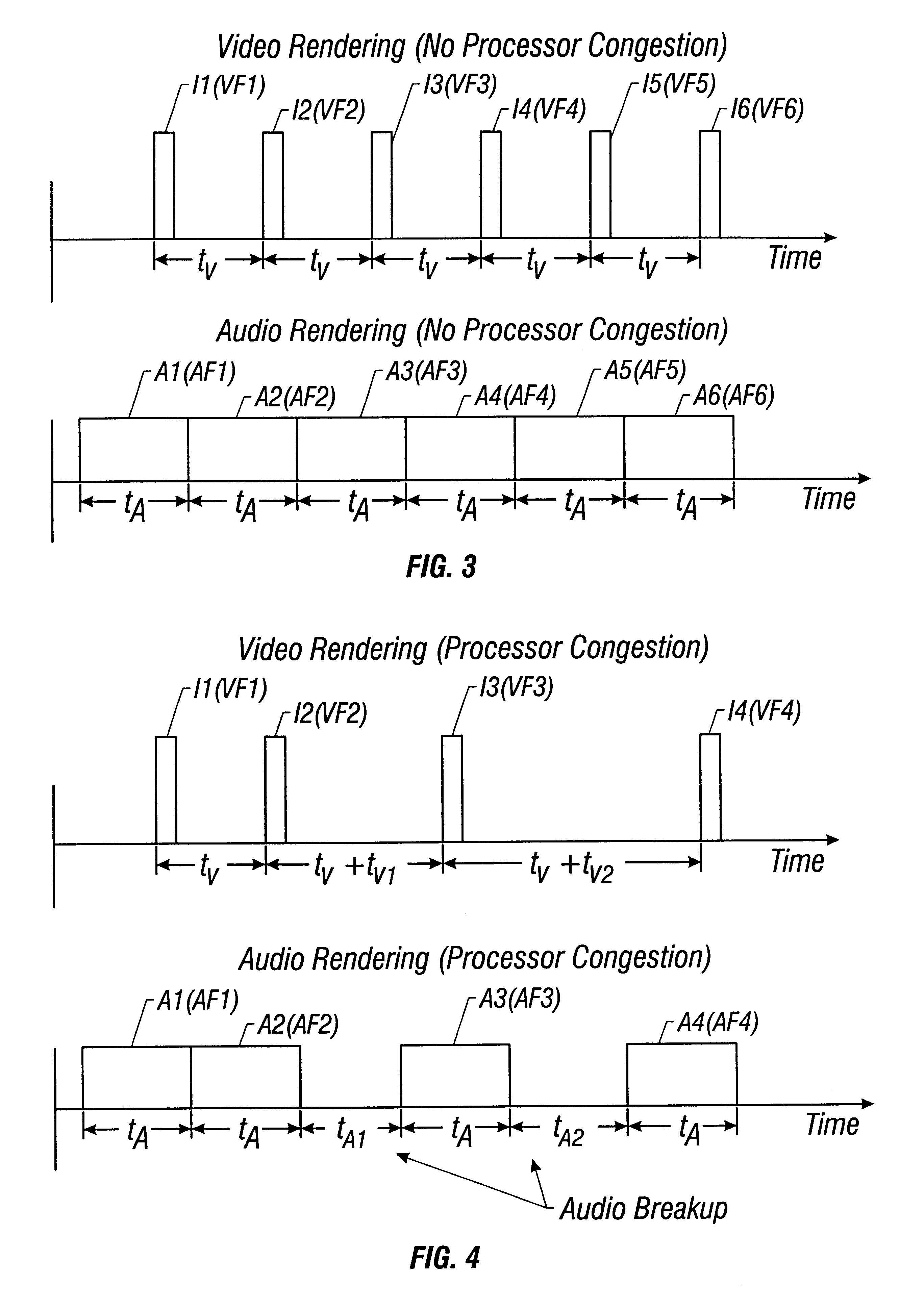
Method and apparatus for detecting processor congestion during audio and video decode
Disclosed is a method and system for detecting processor congestion during decompression of a stream of video and audio data. The system and method includes a processor receiving and decoding a first frame of audio data in accordance with an audio decode software algorithm. The processor generates a first audio time stamp ATS1 indicating the time at which the processor finishes decoding the first frame of audio data. Subsequently, the processor receives and decodes a second frame of audio data in accordance with the same audio decode software algorithm and generates a second audio time stamp ATS2 indicating the time at which the processor finishes decoding the second audio data frame. The first audio time stamp ATS1 is added to a predetermined amount of time T, the result of which is compared with ATS2. T, in one embodiment, is the time it takes a speaker to generate audio corresponding to a decoded frame of audio data. If ATS2 is later in time than (ATS1+T) by a predetermined amount TMIN, a signal is generated indicating that the processor is not decoding received audio frames fast enough due to processor congestion. In response to this signal, the processor workload can be redistributed in favor of increased audio decoding. If ATS2 is not later in time than (ATS1+T) by a predetermined amount TMIN, then no modifications to the processor workload need be made.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
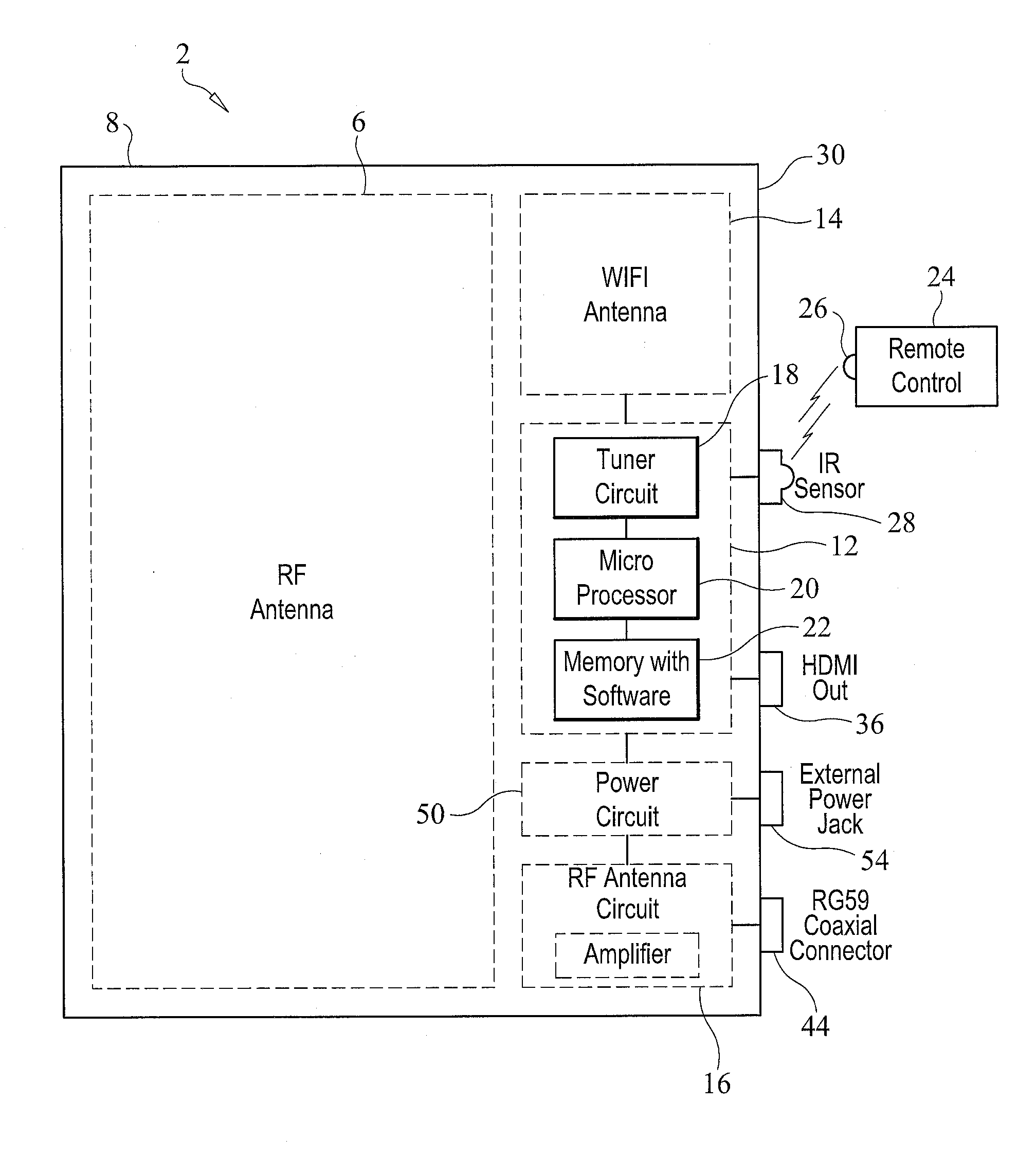
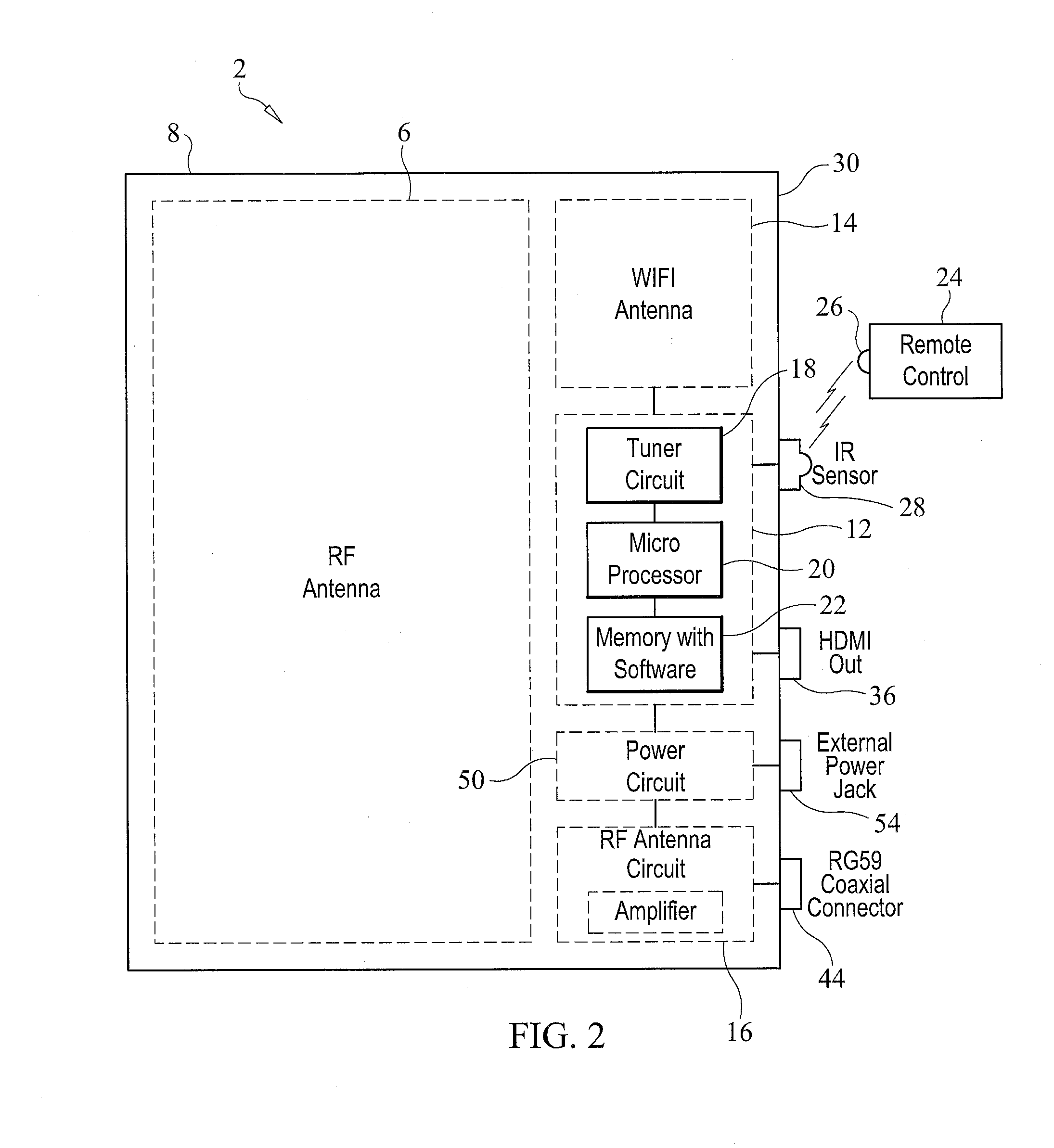
Low profile omni-directional planar antenna with WIFI video streaming capability through broadband network
ActiveUS20140191909A1Improve WiFi signal receptionSolve needsAntenna supports/mountingsSimultaneous television signal transmission by multiple carrierHigh definition tvHigh-definition television
An antenna device includes a housing defining an interior cavity, and an RF antenna situated within the housing. The RF antenna receives high definition television signals broadcast over the air. An MHL connector is mounted on the housing. An external audio or video streaming signal device is coupleable to the MHL connector. An MHL to HDMI converter circuit situated within the interior cavity of the housing receives signals from the external audio or video streaming signal device and processes these signals into an HDMI signal format. The HDMI signals are provided on an HDMI output connector mounted on the housing. RF signals from the RF antenna are provided to an RF coaxial cable connector also mounted on the housing.
Owner:VOXX INT CORP
Communication system
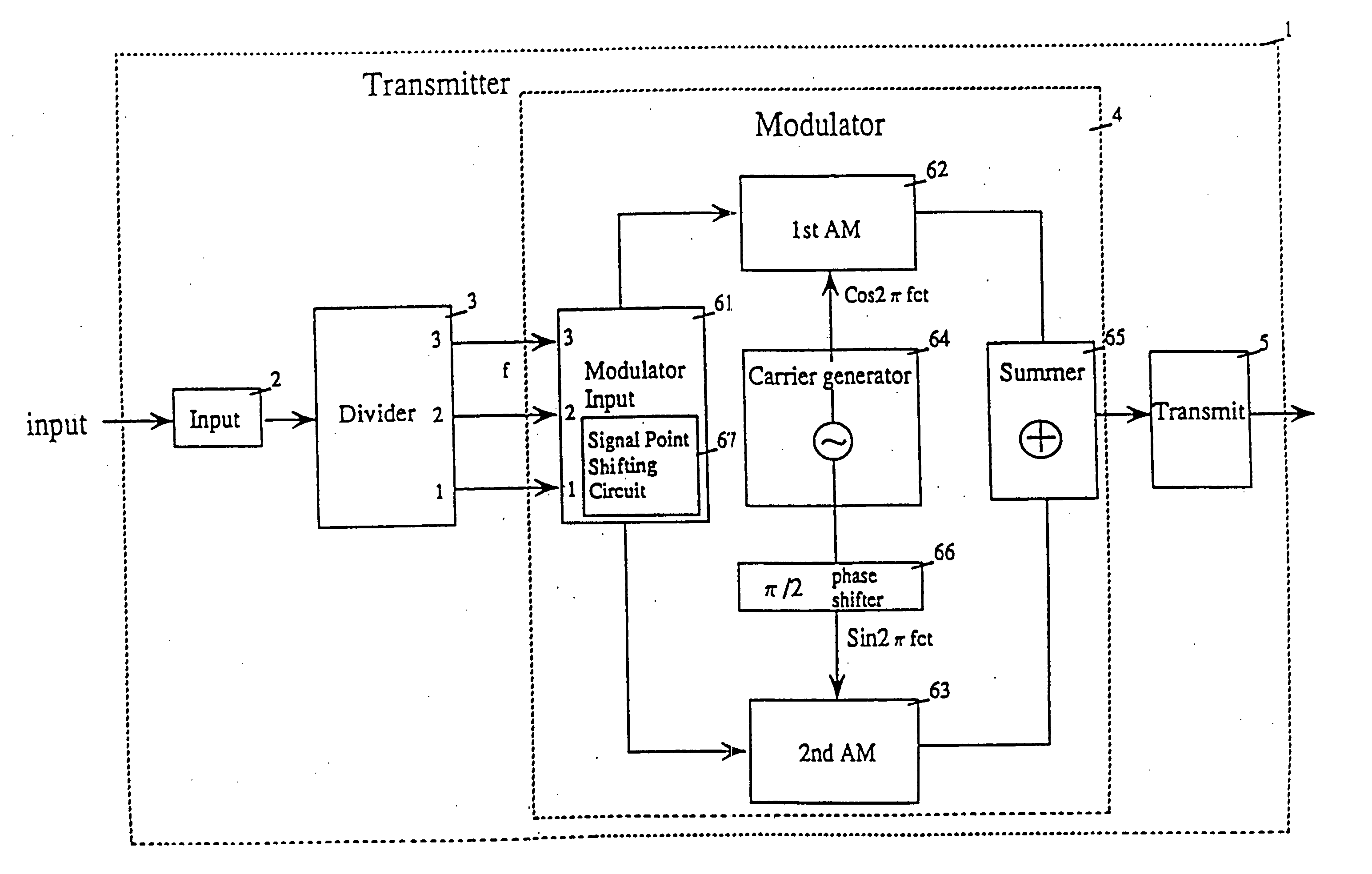
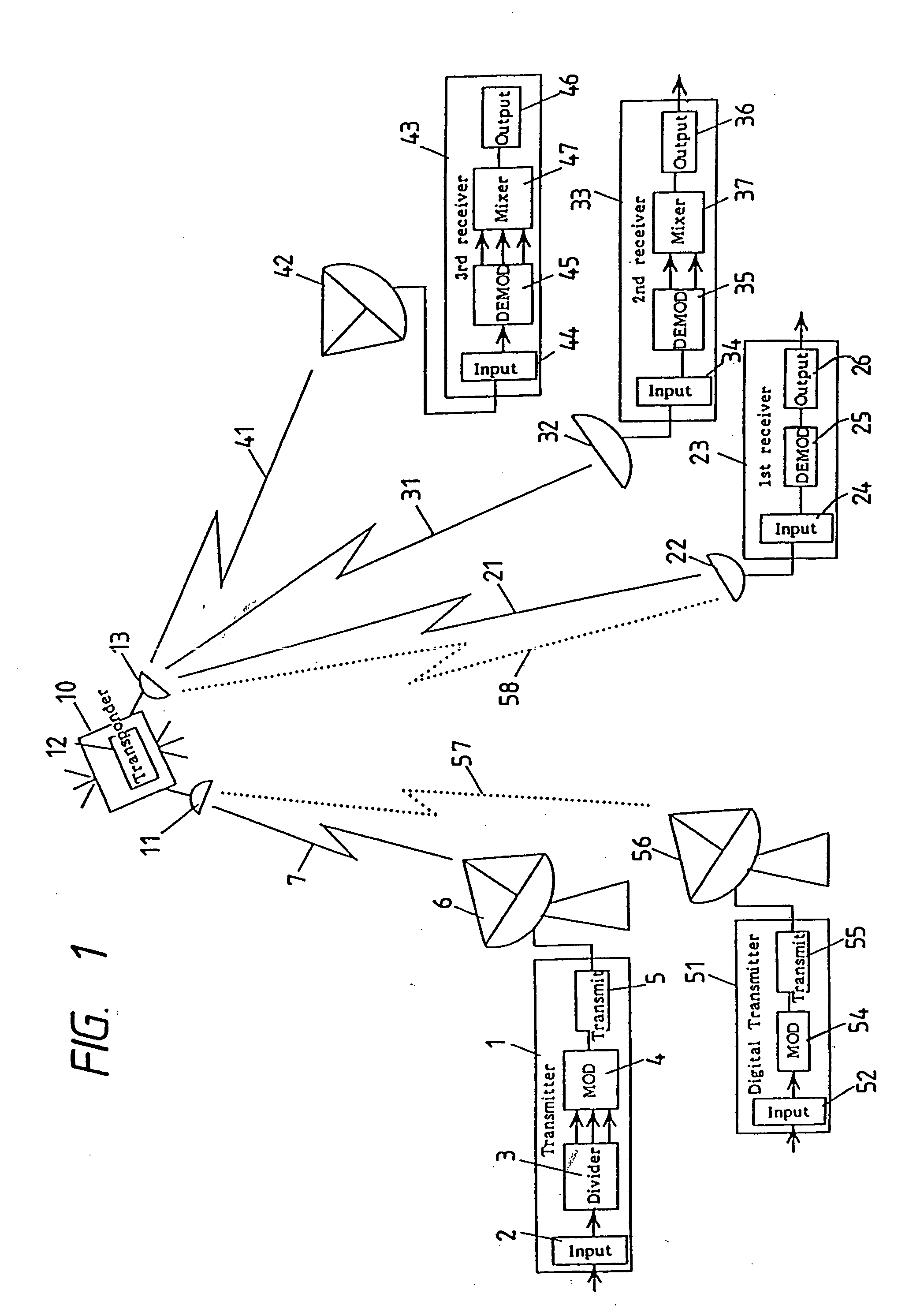
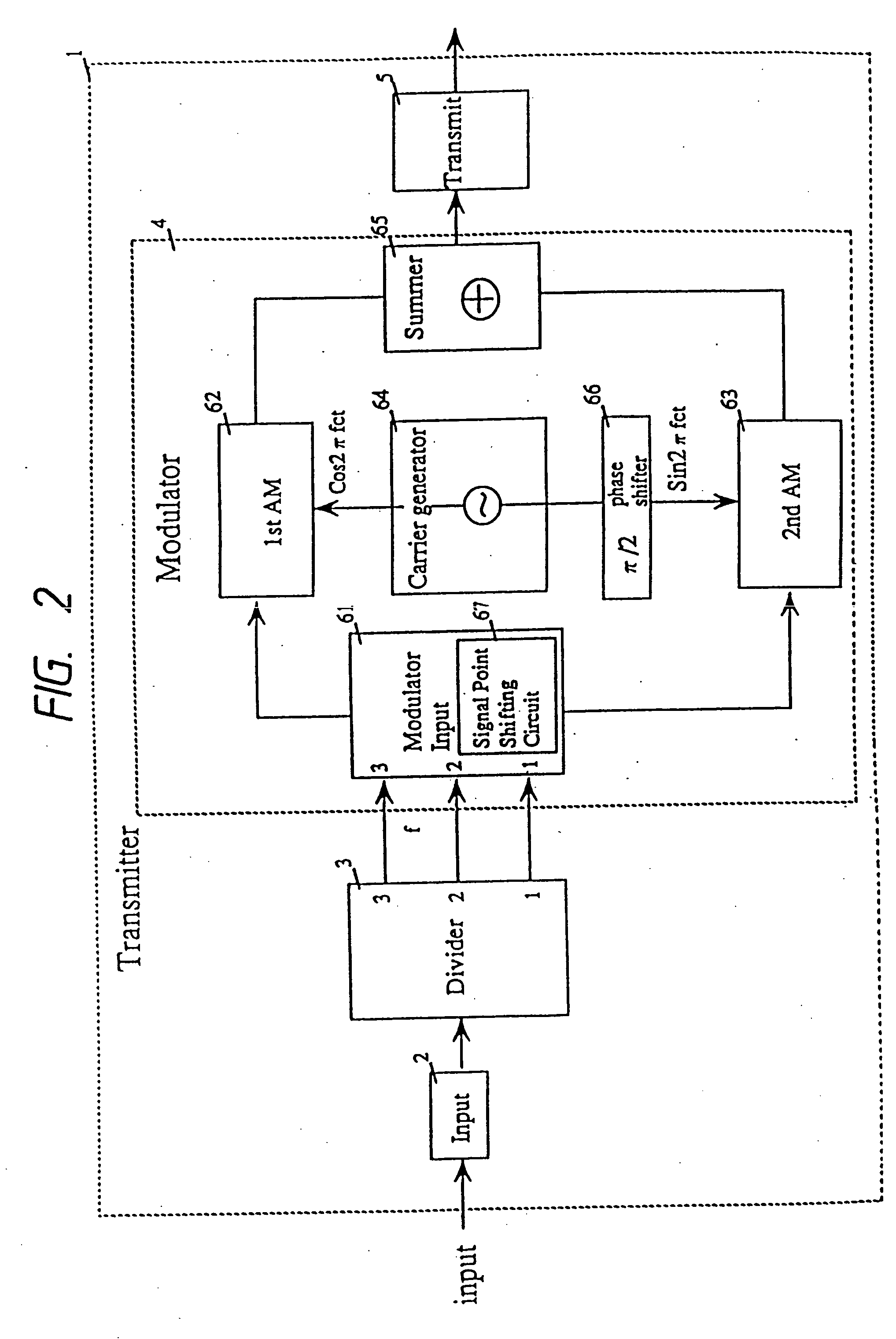
InactiveUS20050018785A1Large service areaReduce areaData representation error detection/correctionPulse modulation television signal transmissionData streamCarrier signal
At the transmitter side, carrier waves are modulated according to an input signal for producing relevant signal points in a signal space diagram. The input signal is divided into, two, first and second, data streams. The signal points are divided into signal point groups to which data of the first data stream are assigned. Also, data of the second data stream are assigned to the signal points of each signal point group. A difference in the transmission error rate between first and second data streams is developed by shifting the signal points to other positions in the space diagram. At the receiver side, the first and / or second data streams can be reconstructed from a received signal. In TV broadcast service, a TV signal is divided by a transmitter into, low and high, frequency band components which are designated as a first and a second data stream respectively. Upon receiving the TV signal, a receiver can reproduce only the low frequency band component or both the low and high frequency band components, depending on its capability.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
A universal television receiver
ActiveCN101682705ATelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision receiversDigital broadcasting
Various embodiments are described herein for a universal television receiver that is capable of processing television channel signals broadcast according to a variety of analog and digital broadcast standards.
Owner:FRESCO MICROCHIP
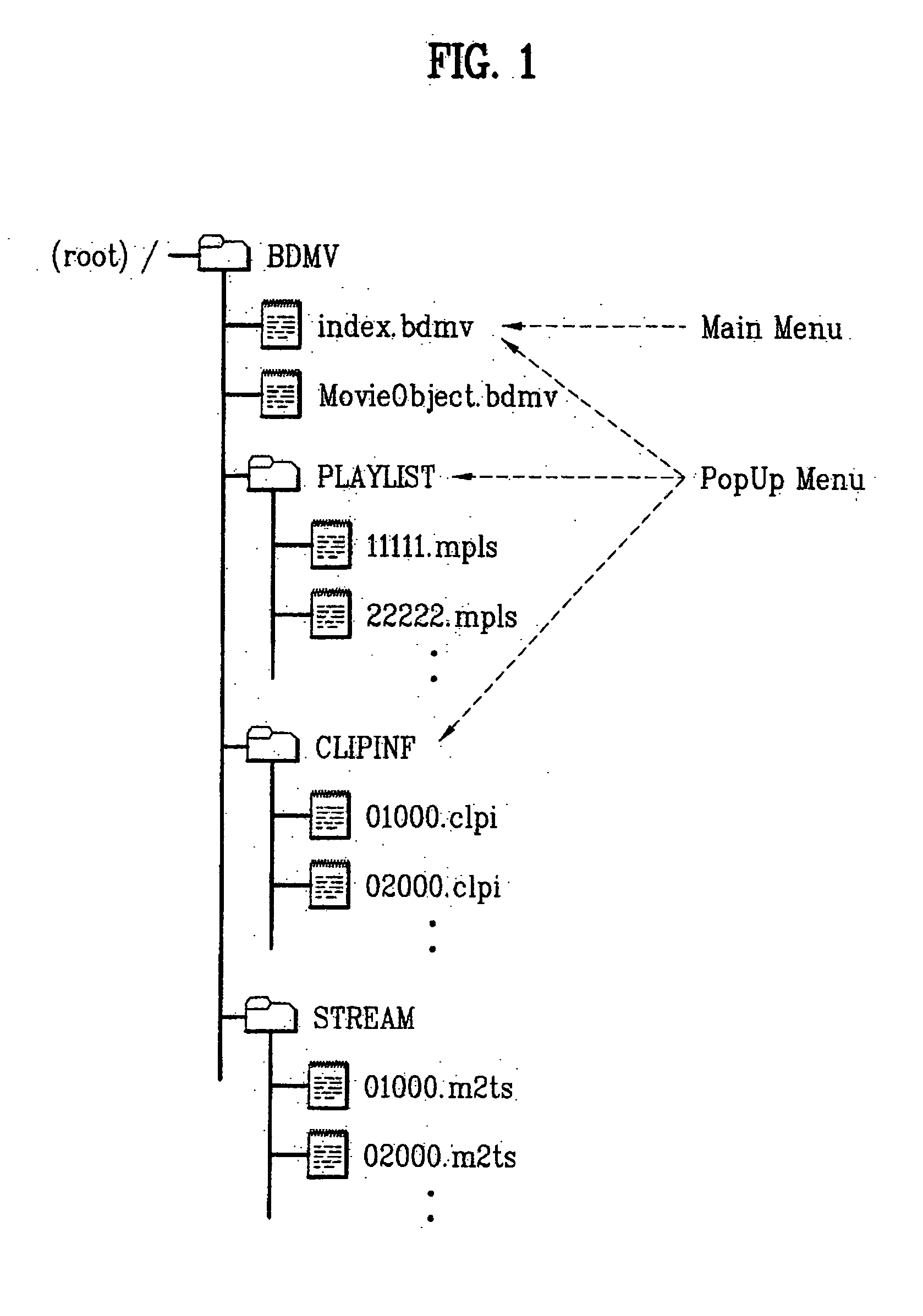
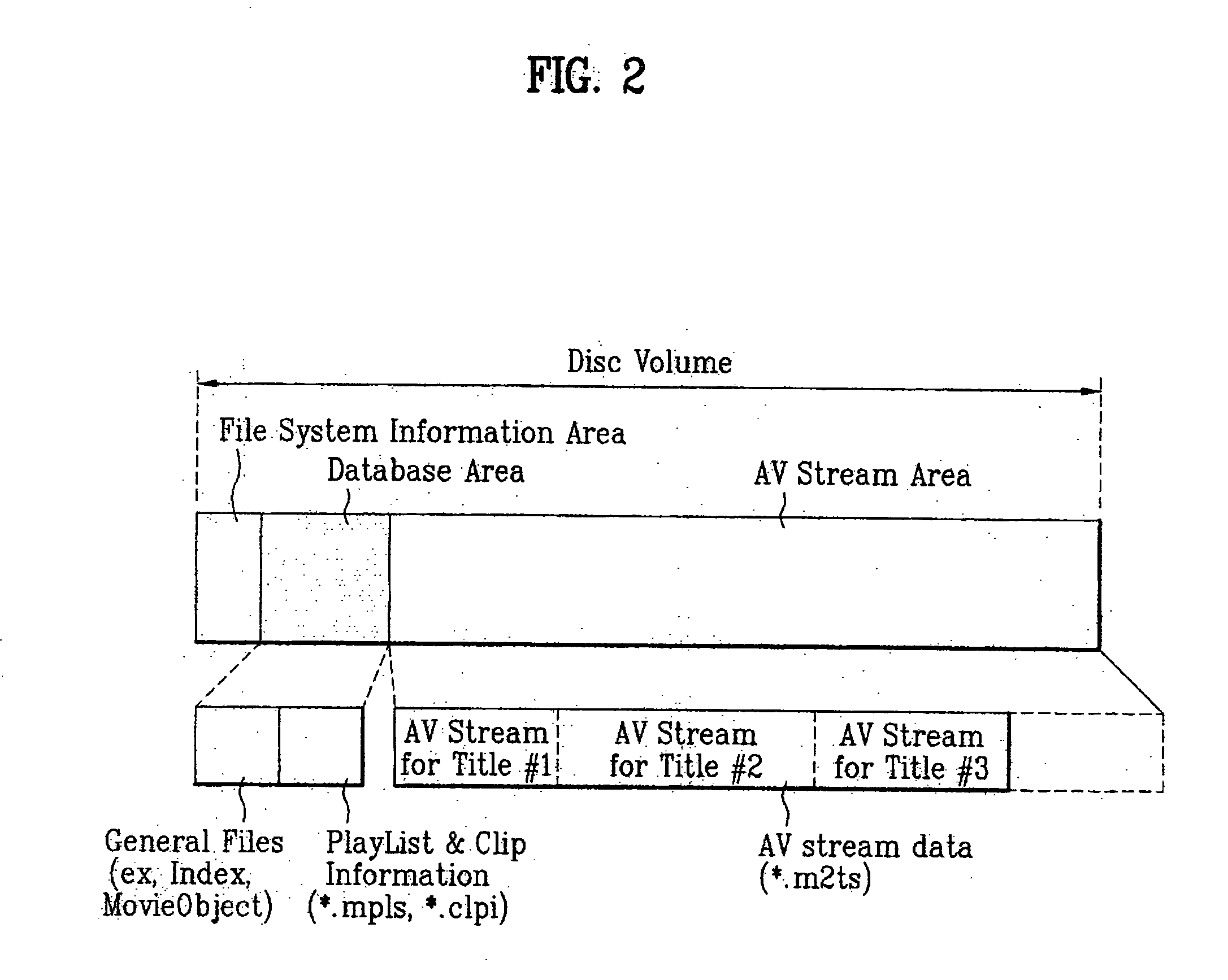
Recording medium having a data structure for managing graphic information and recording and reproducing methods and apparatuses
ActiveUS20050141877A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionGraphicsData structure
In the data structure for managing reproduction of graphic information, first graphic information is stored multiplexed with main data in a first clip file and second graphic information is stored in a second clip file separate from the first clip file.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
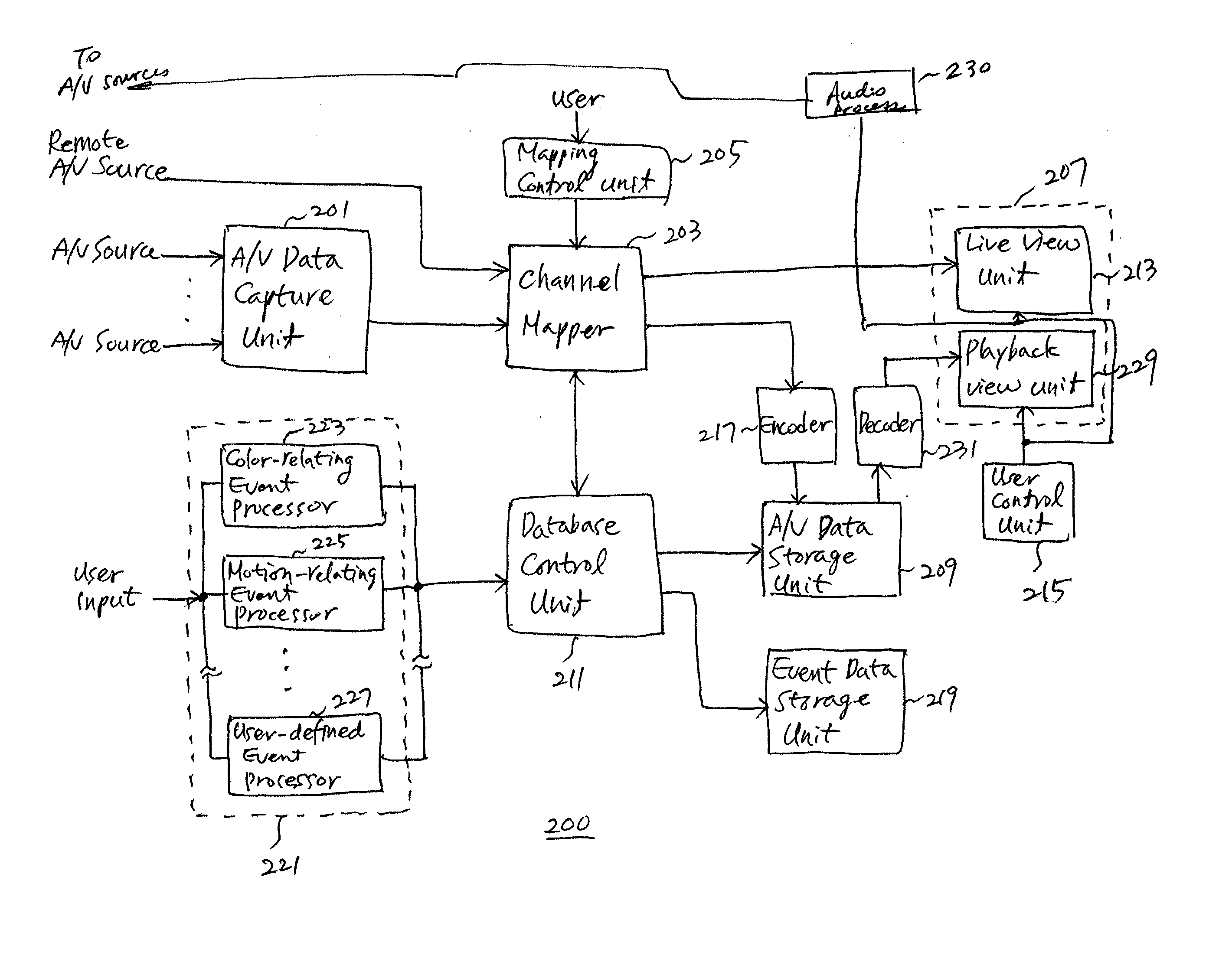
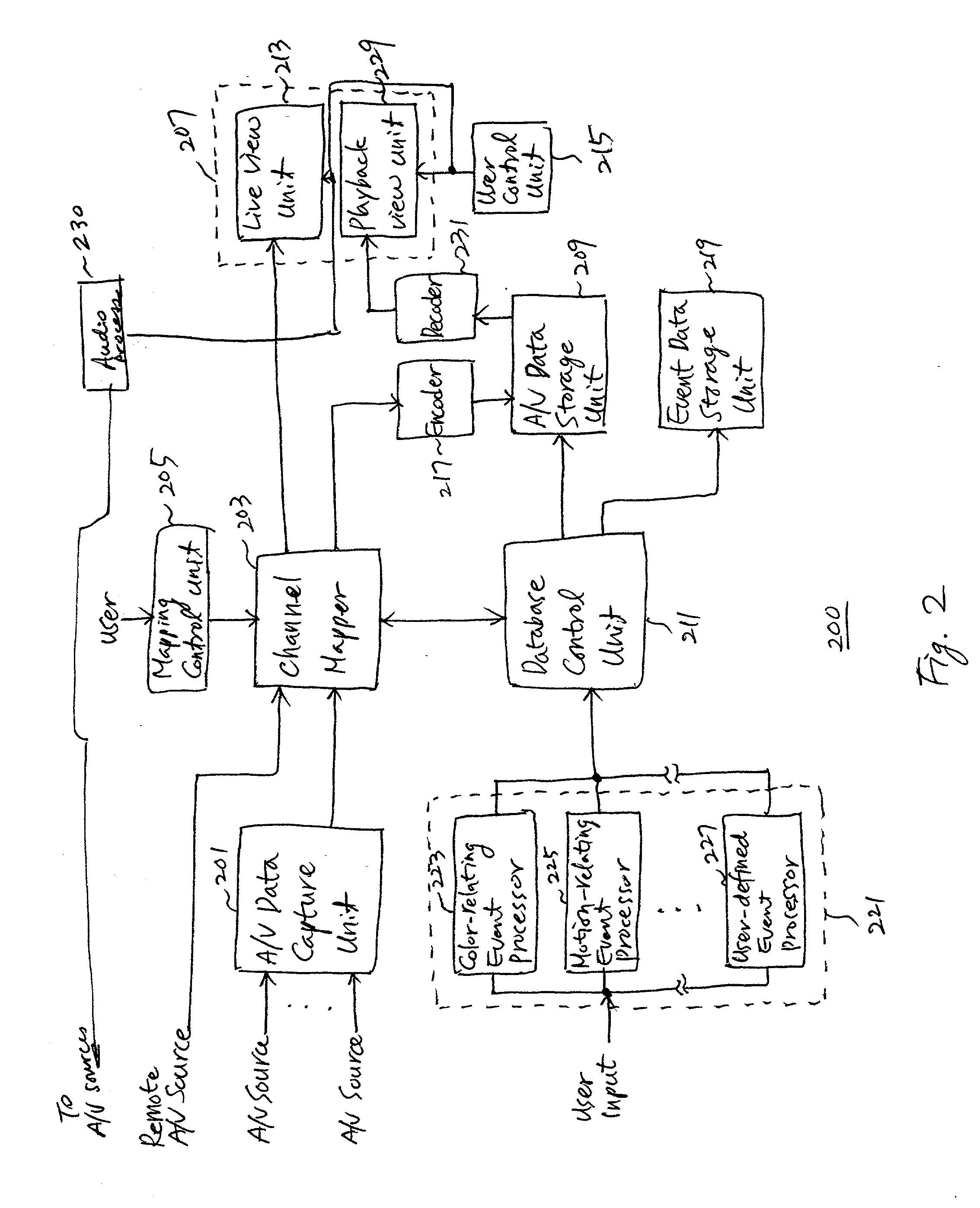
System and method of processing audio/video data in a remote monitoring system
InactiveUS20030215218A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMonitoring systemComputer science
A system and method are provided for processing audio / video (A / V) data provided from multiple A / V sources. The system includes A / V data capture devices for receiving the A / V data, each of which receives A / V data from a predetermined number of A / V sources; drivers for driving output data of the A / V data capture devices for a first set of application programs, each of the drivers receiving output data from corresponding one of the A / V data capture devices and being associated with corresponding one of the first set of application programs; virtual drivers for driving input data for a second set of application programs, each of the virtual drivers being associated with corresponding one of the second set of application programs; and a channel mapping unit for mapping data from the drivers into the virtual drivers.
Owner:INTELLIGENT DIGITAL SYST
Mobile communication terminal
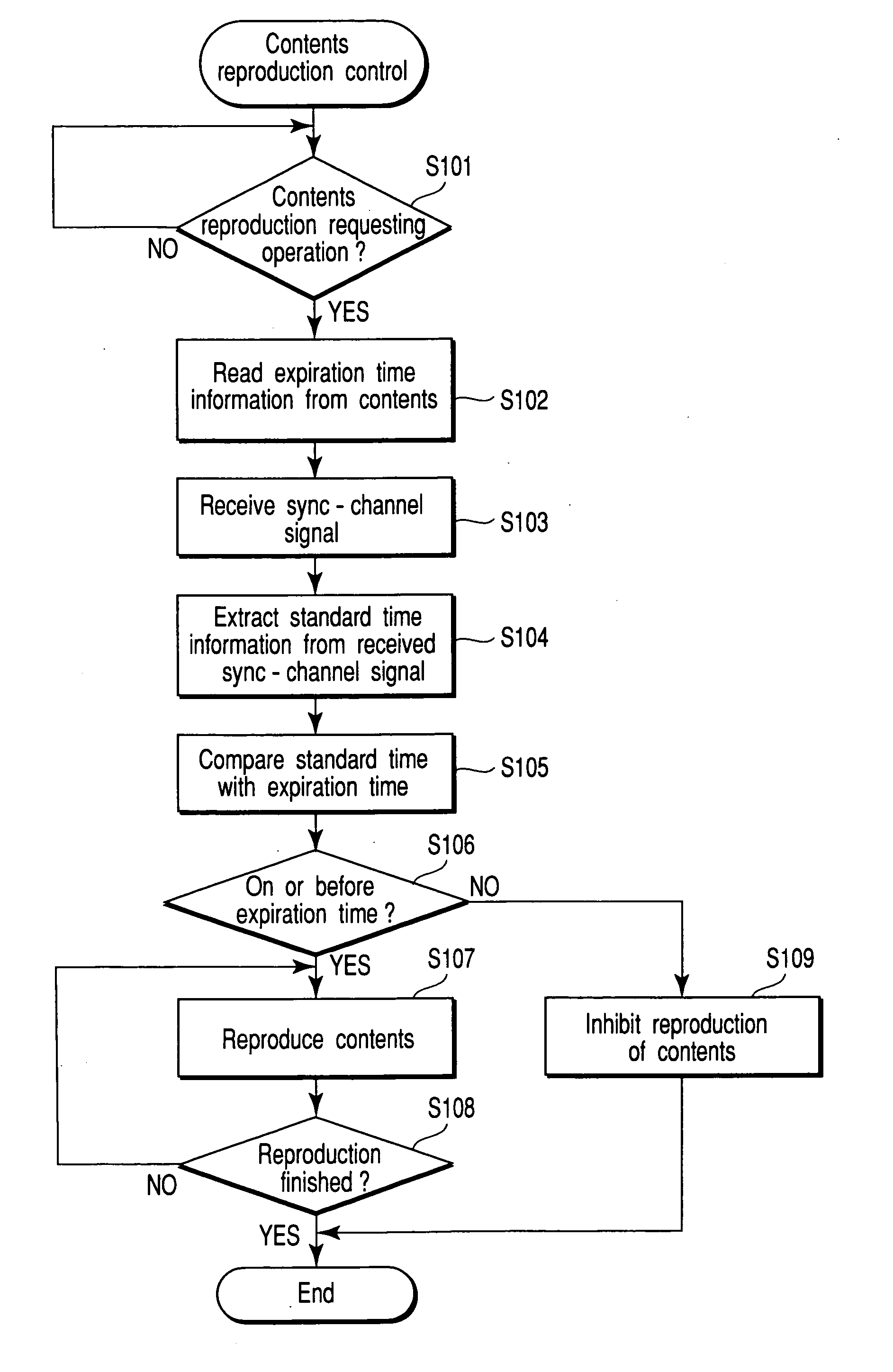
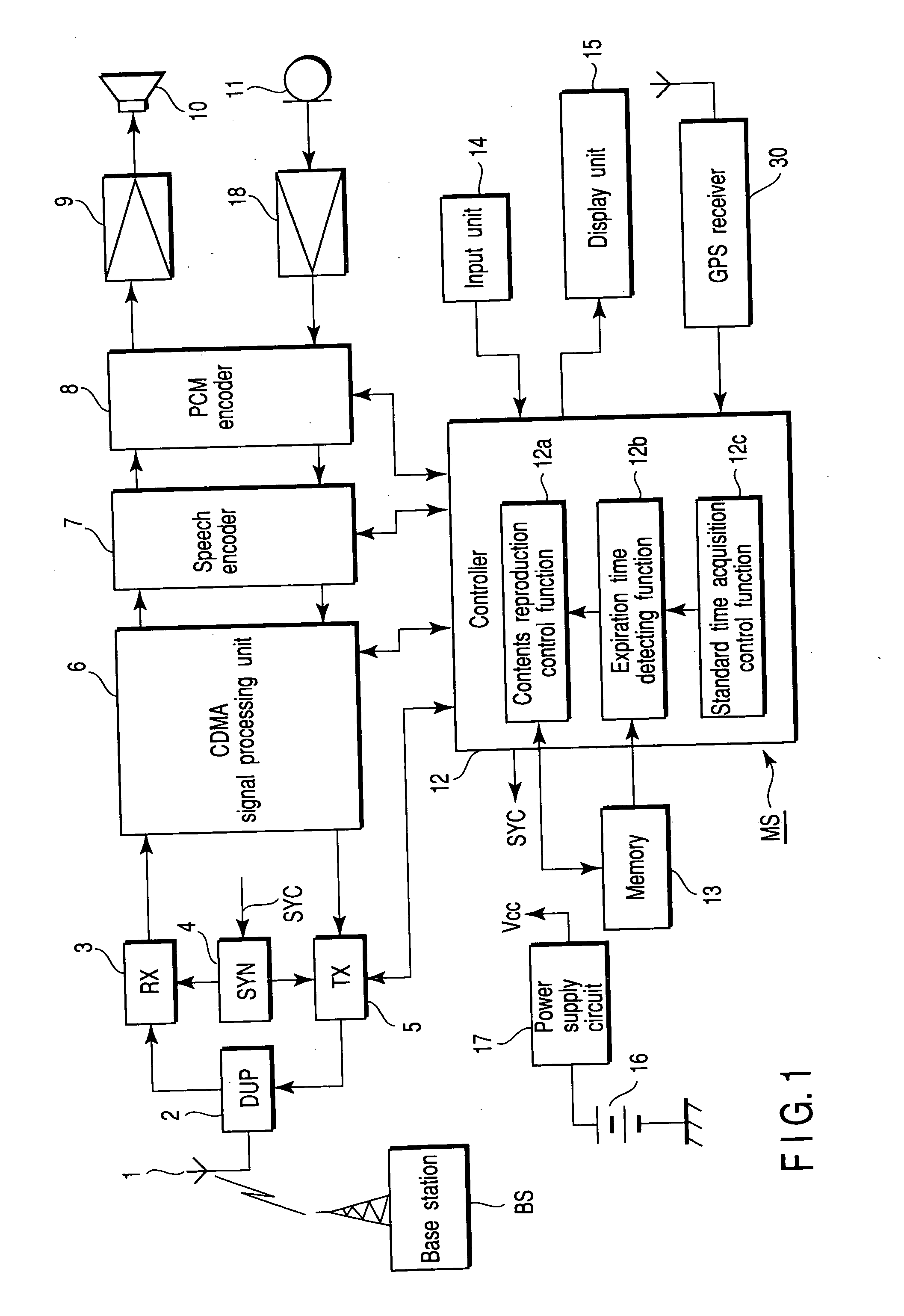
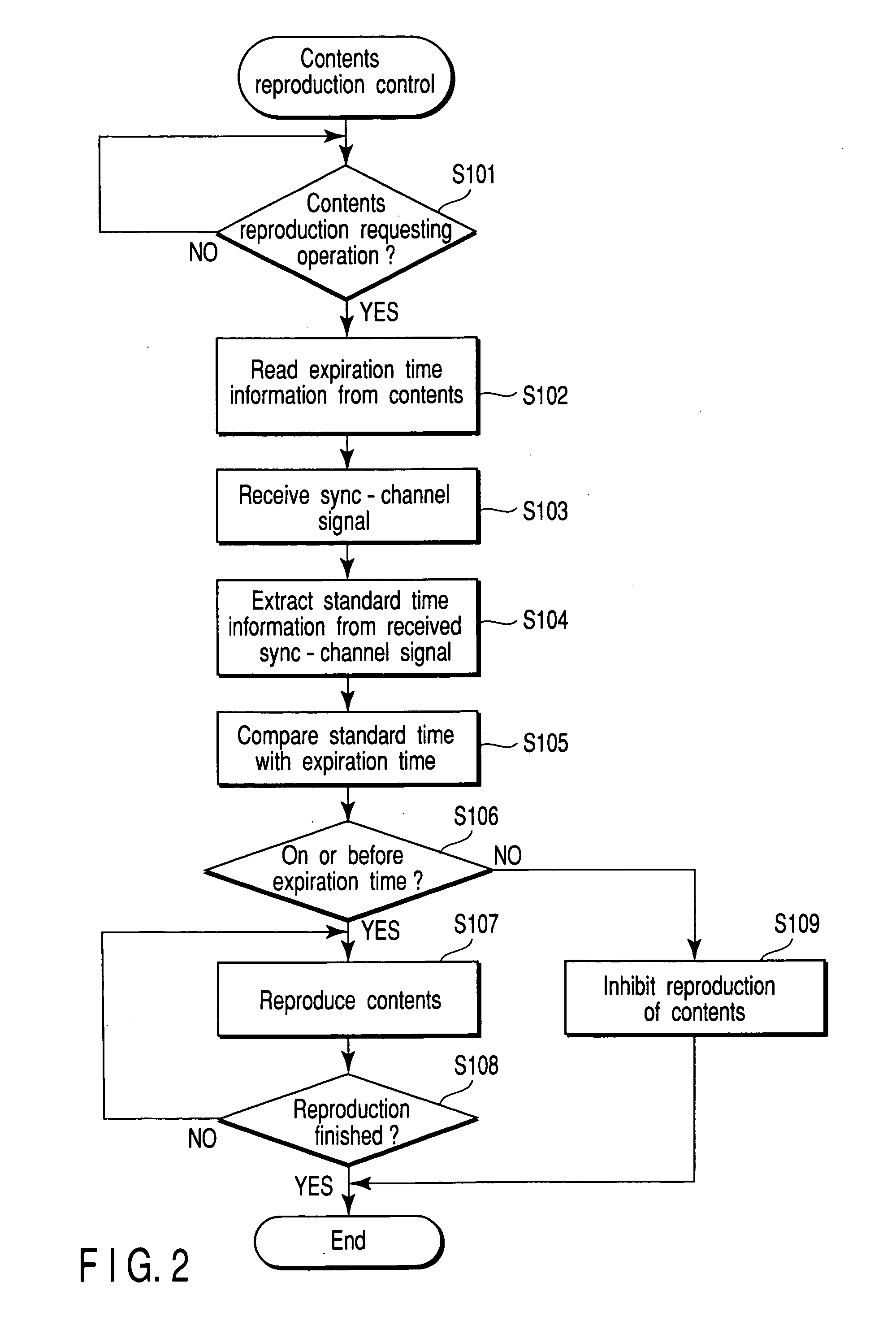
InactiveUS20050020285A1Precise managementEffectively preventSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementExpiration TimeSystem time
A CDMA mobile communication terminal MS receives system time data, as standard time information, the system time data being transmitted from a base station BS via a sync-channel. When reproducing contents, a reproduction expiration time contained in the contents is compared with the received standard time information, thereby detecting whether or not the contents can be reproduced. If it is detected that the contents may be reproduced, reproduction of the contents is permitted, whereas if it is detected that the contents should not be reproduced, reproduction of the contents is inhibited.
Owner:KDDI CORP +1
Multichannel television sound stereo and surround sound encoder suitable for use with video signals encoded in plural formats
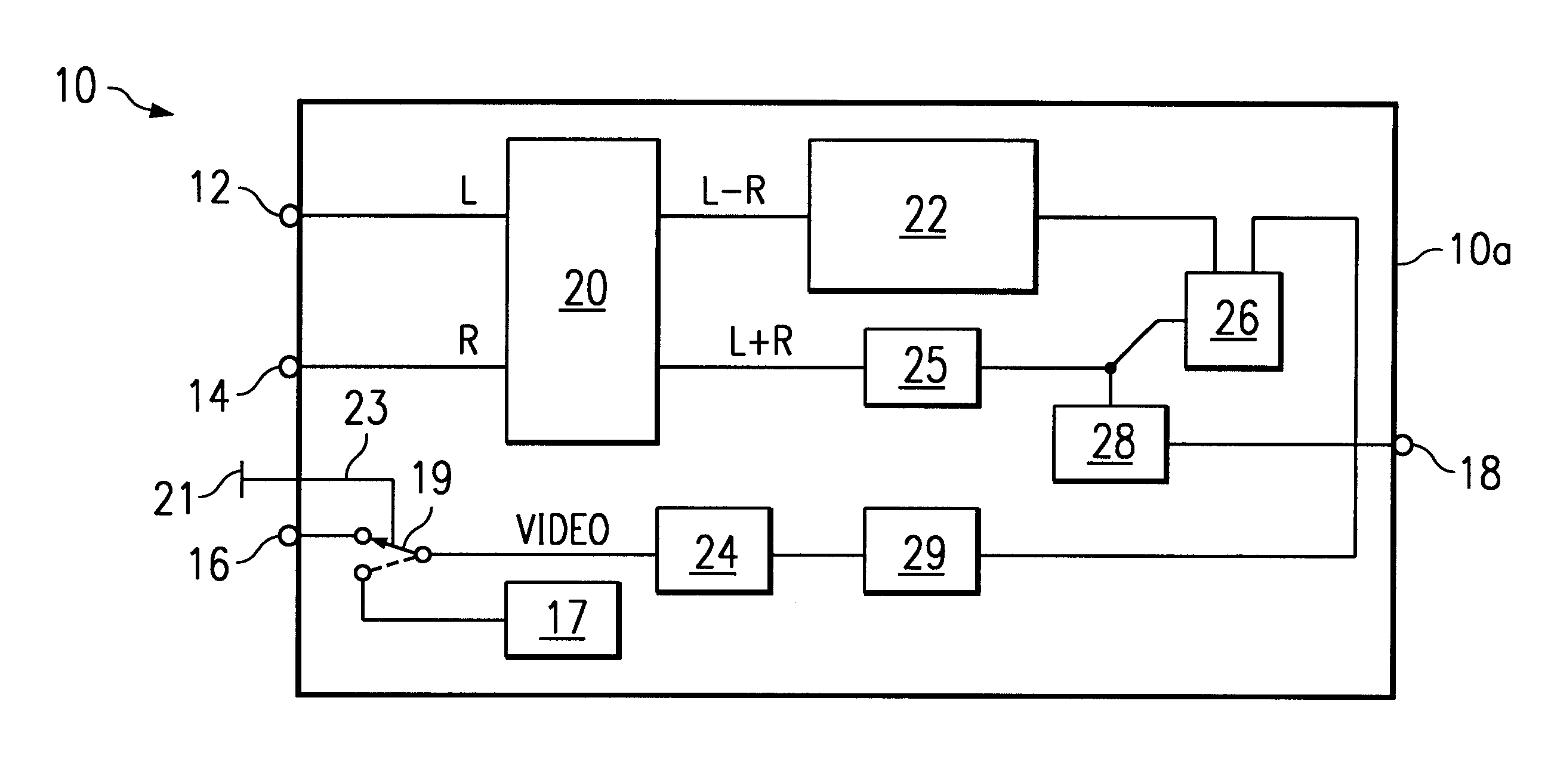
InactiveUS6288747B1Television system detailsBroadcast information characterisationVideo-signal generatorAudio signal
Method and apparatus for generating a composite audio signal clocked to a selected frequency from left and audio input signals. A video / audio signal generator transmits the left and right audio input signals, together with a video signal having a horizontal synchronization signal embedded therein. If copy protection has not been applied to the video signal, the embedded horizontal synchronization signal will have a frequency of 15.734 KHz. If applied to the video signal, copy protection techniques will shift the frequency of the horizontal synchronization signal. To avoid distortion of the composite audio signal, a switch configured to selectively couple the video signal or a secondary video signal generated by an internal video signal generator to an audio signal processor which generates the composite audio output signal from the left and right audio input signals. Embedded within the secondary video signal is a horizontal synchronization signal having a frequency of 15.734 KHz. Thus, if copy protection features cause the frequency of the signal embedded within the primary video signal to shift, the switch may be used to couple the audio signal processor to the internal video signal generator, thereby ensuring that the composite audio signal will always be clocked to the selected frequency.
Owner:CE LABS LLC
Digital audio/video apparatus and method that can perform additional operations
InactiveUS20050008345A1Simple structureEasy to implementTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationImage resolutionVideo equipment
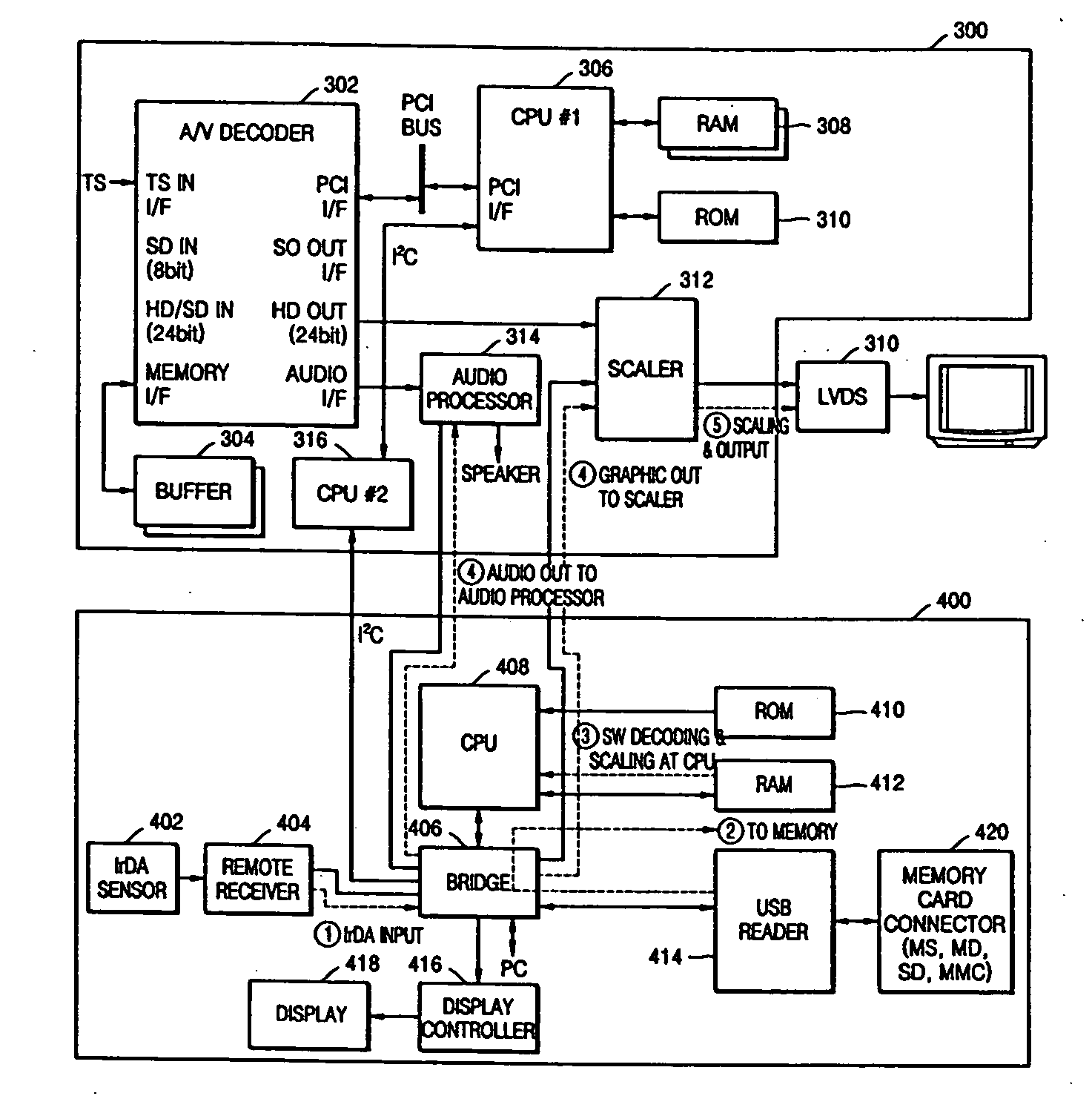
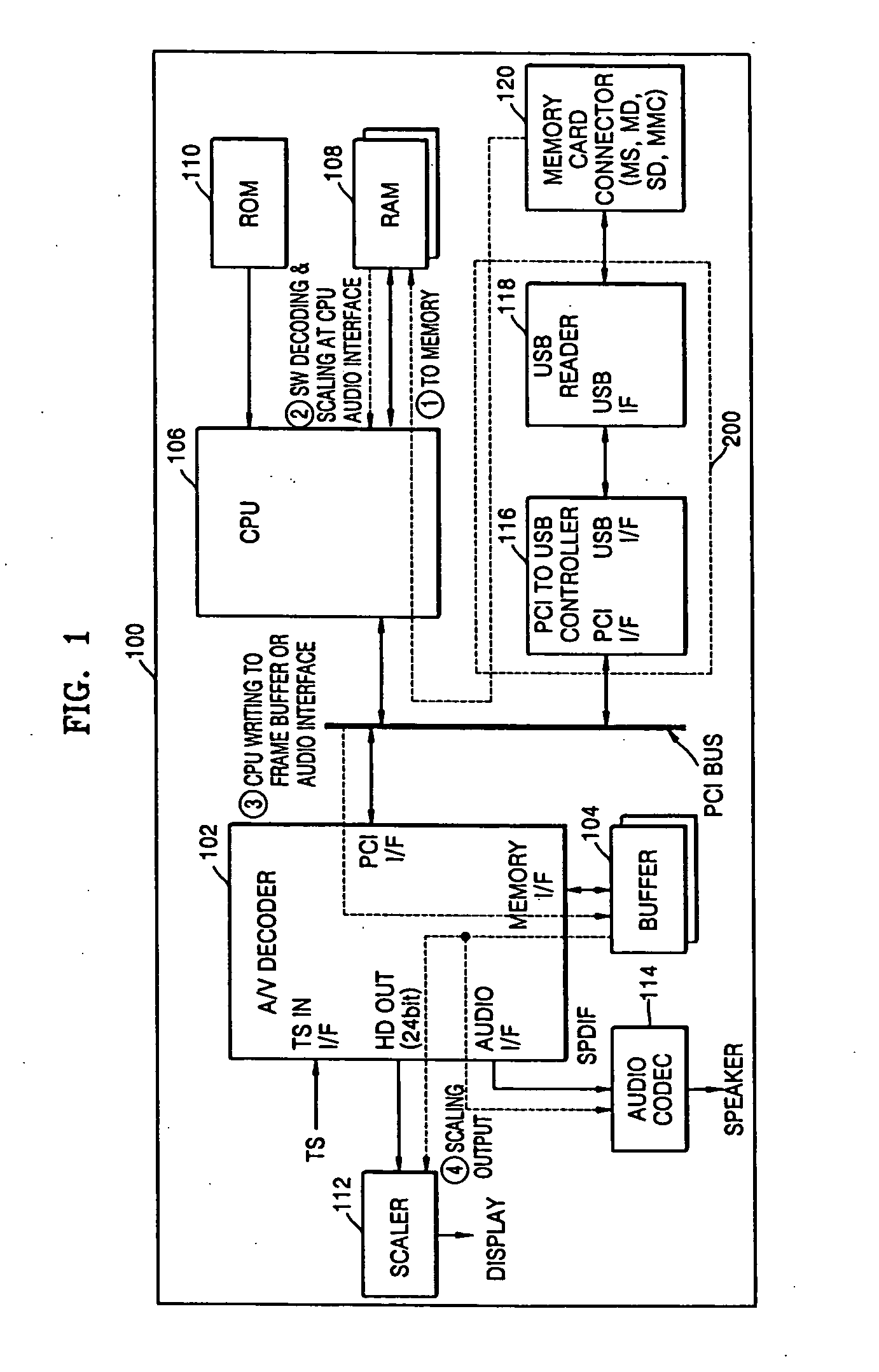
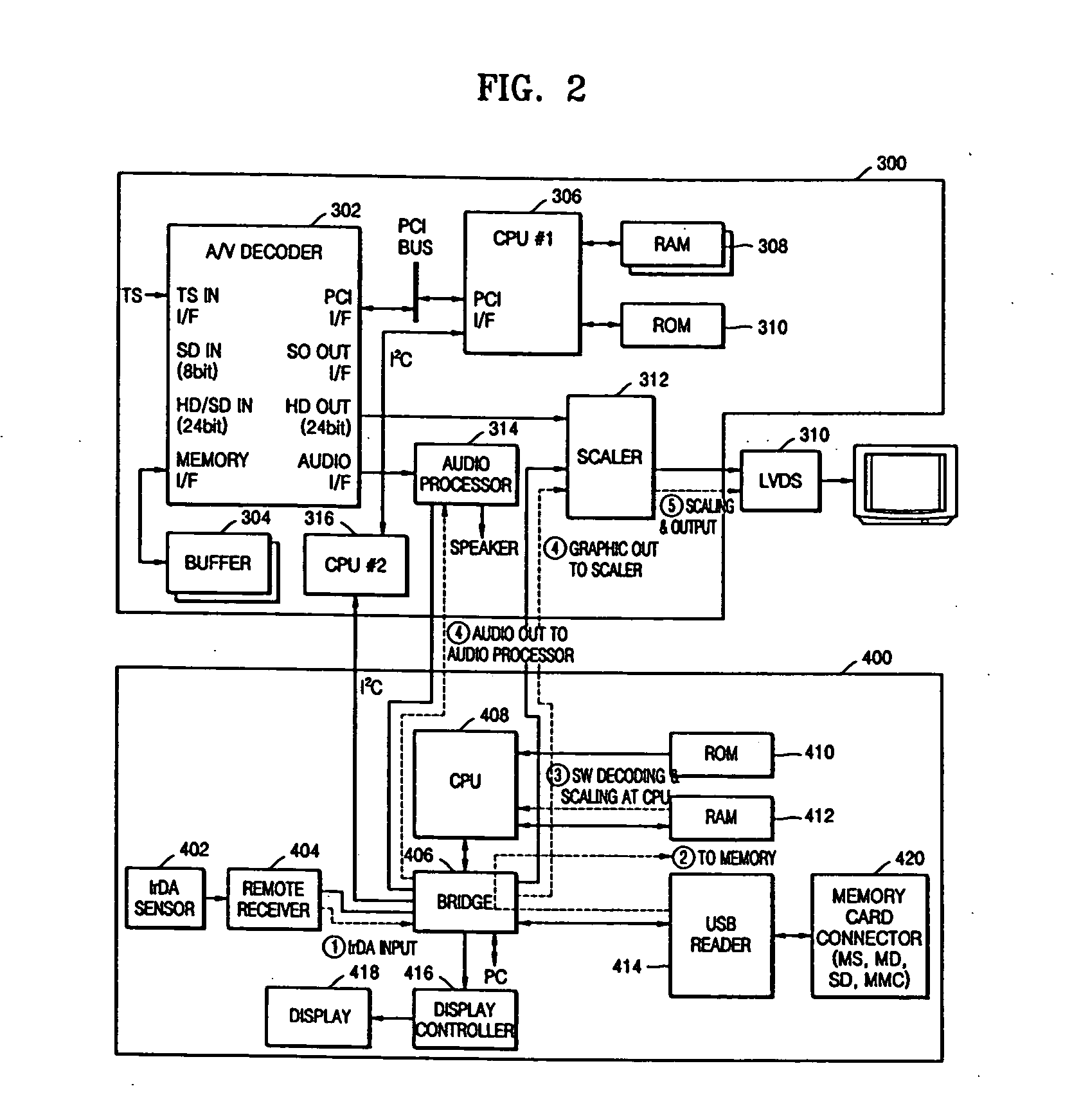
An audio / video (AV) apparatus such as a digital television set and a digital set-top-box device, which can perform additional operations such as an electronic album, MP3 and FIMS, and an additional operation performing apparatus appropriate for the digital AV apparatus. The digital AV apparatus can include an AV decoder to output video and audio data, a scaler to adjust resolutions of video data output from the AV decoder and additional information video data provided from an external video source and to output the adjusted resolution, an audio processor to process audio data output from the AV decoder and additional information audio data provided from an external audio source, and a controller to receive a command provided from an external commander and to control a selection operation of the scaler and the audio processor based on the command.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Video and audio recording with audio being recorded in plural channels independently of video on different recording media
InactiveUS6587640B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionRAIDAudio frequency
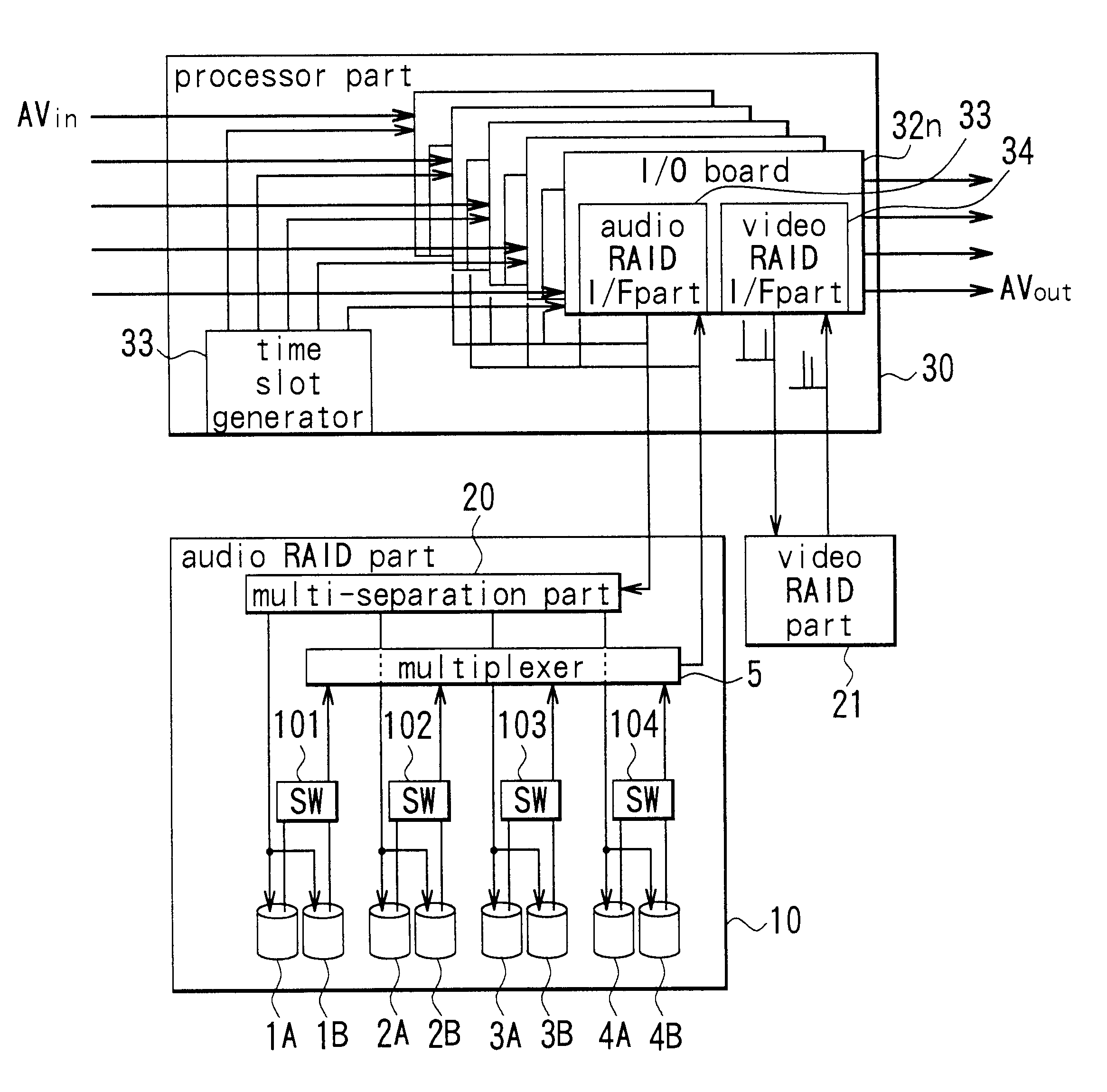
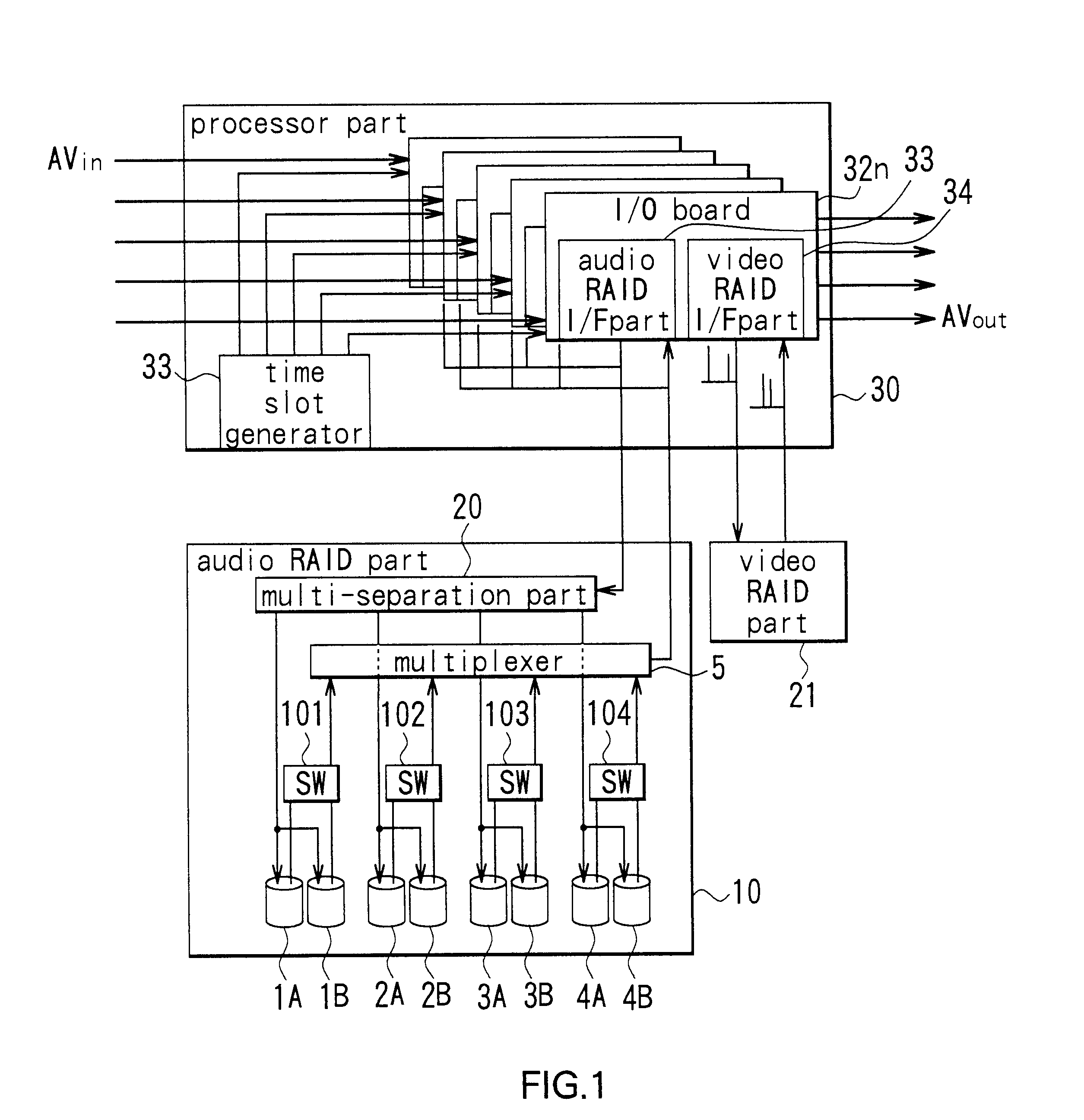
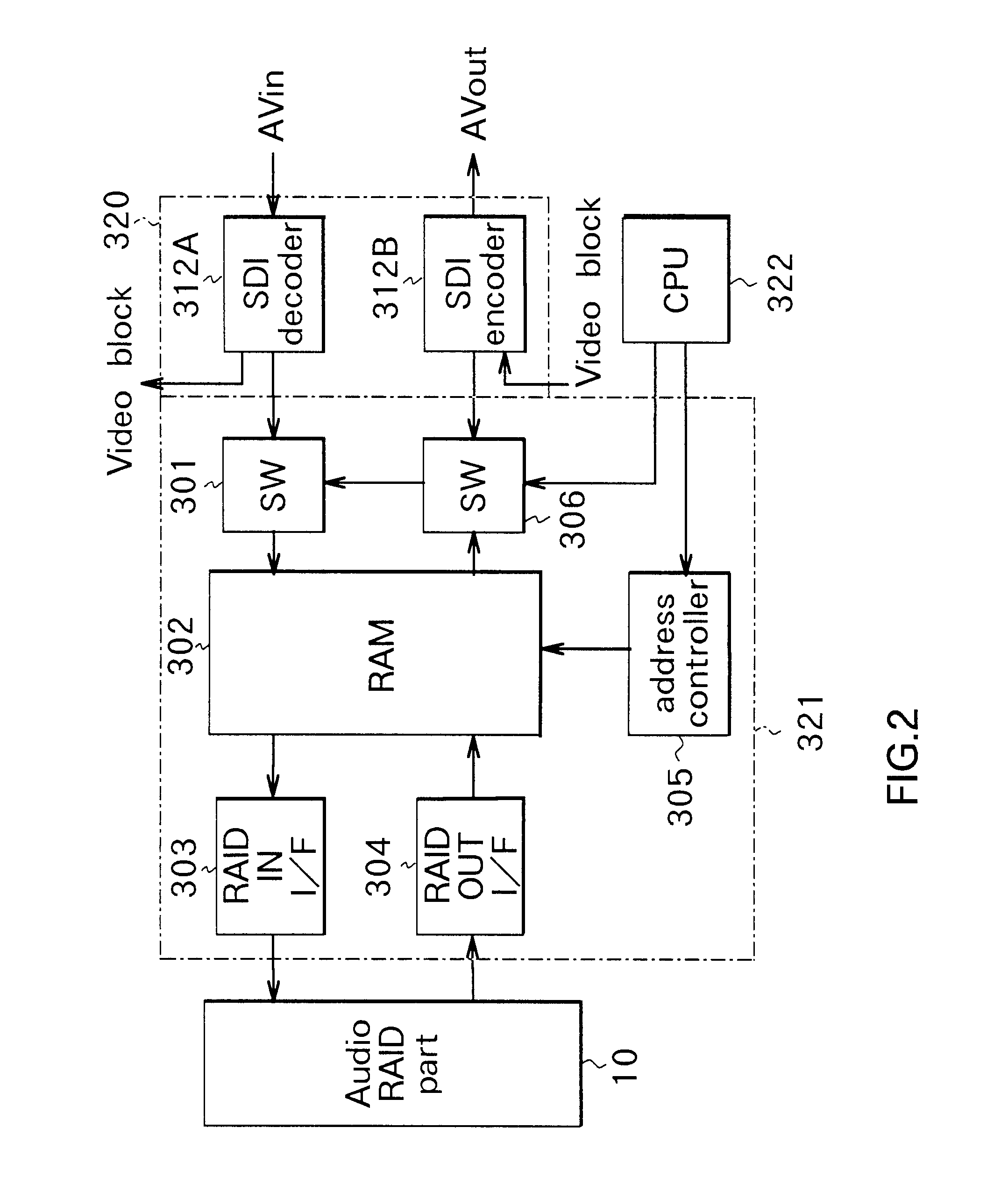
An AV server comprises a processor part (30) for performing various signal processing, such as compression-expansion, of inputted video and audio signals, a video RAID part (21) for storing video signals, and an audio RAID part (10) for storing audio signals. The processor part (30) has a plurality of I / O boards (32n), provided for each channel, for supplying audio signals and video signals to the audio RAID part (10) and the video RAID part (21) respectively, and for receiving audio signals and video signals from the audio RAID part (10) and the video RAID part (21) respectively. The video RAID part (21) is of RAID-3 configuration. The audio RAID part (10) performs writing and reading of audio signals corresponding to each of a plurality of audio signal channels independent of the video RAID part (21).
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for performing multimedia operations
InactiveUS20050071747A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionGraphicsDigital signal processing
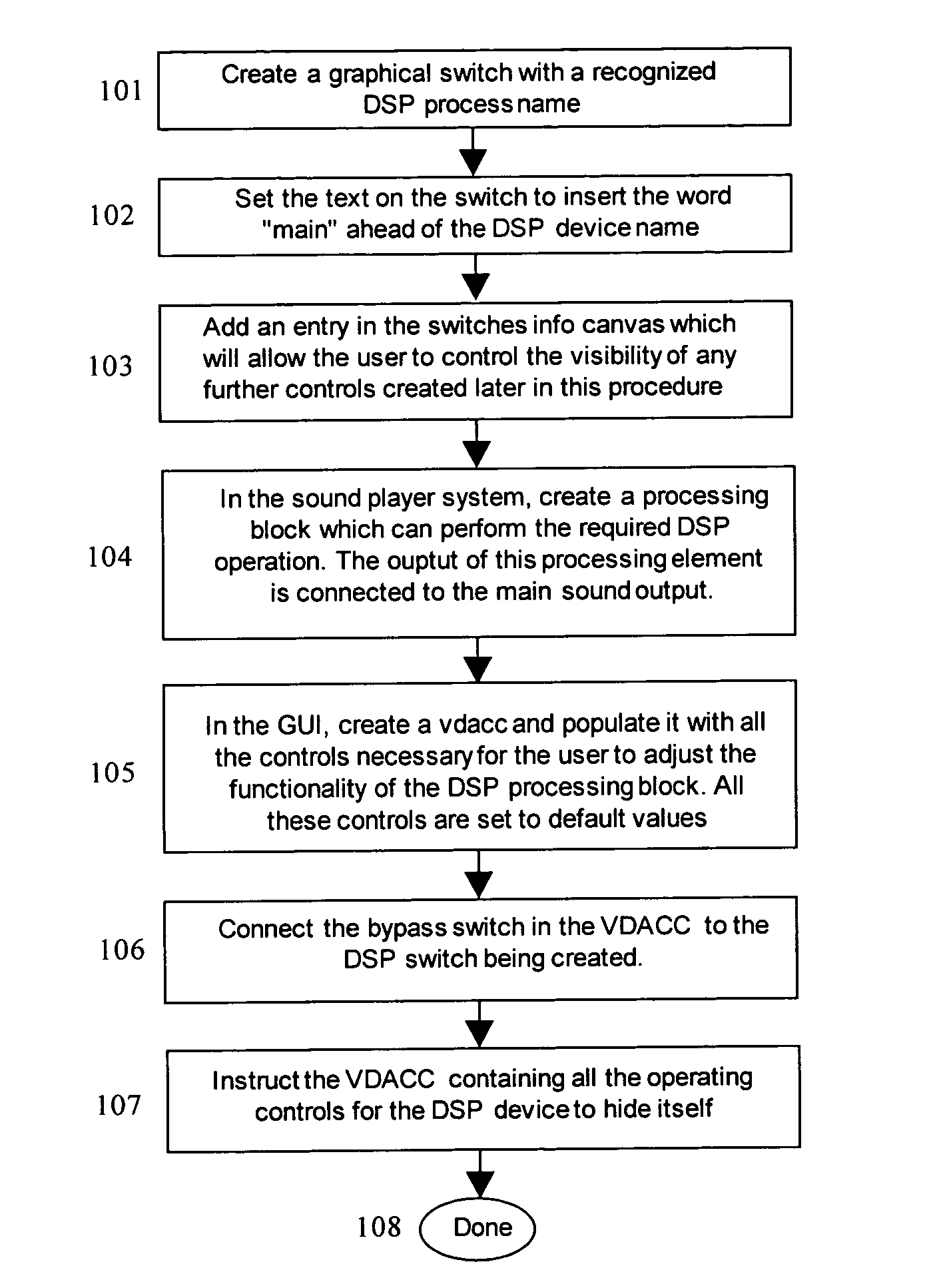
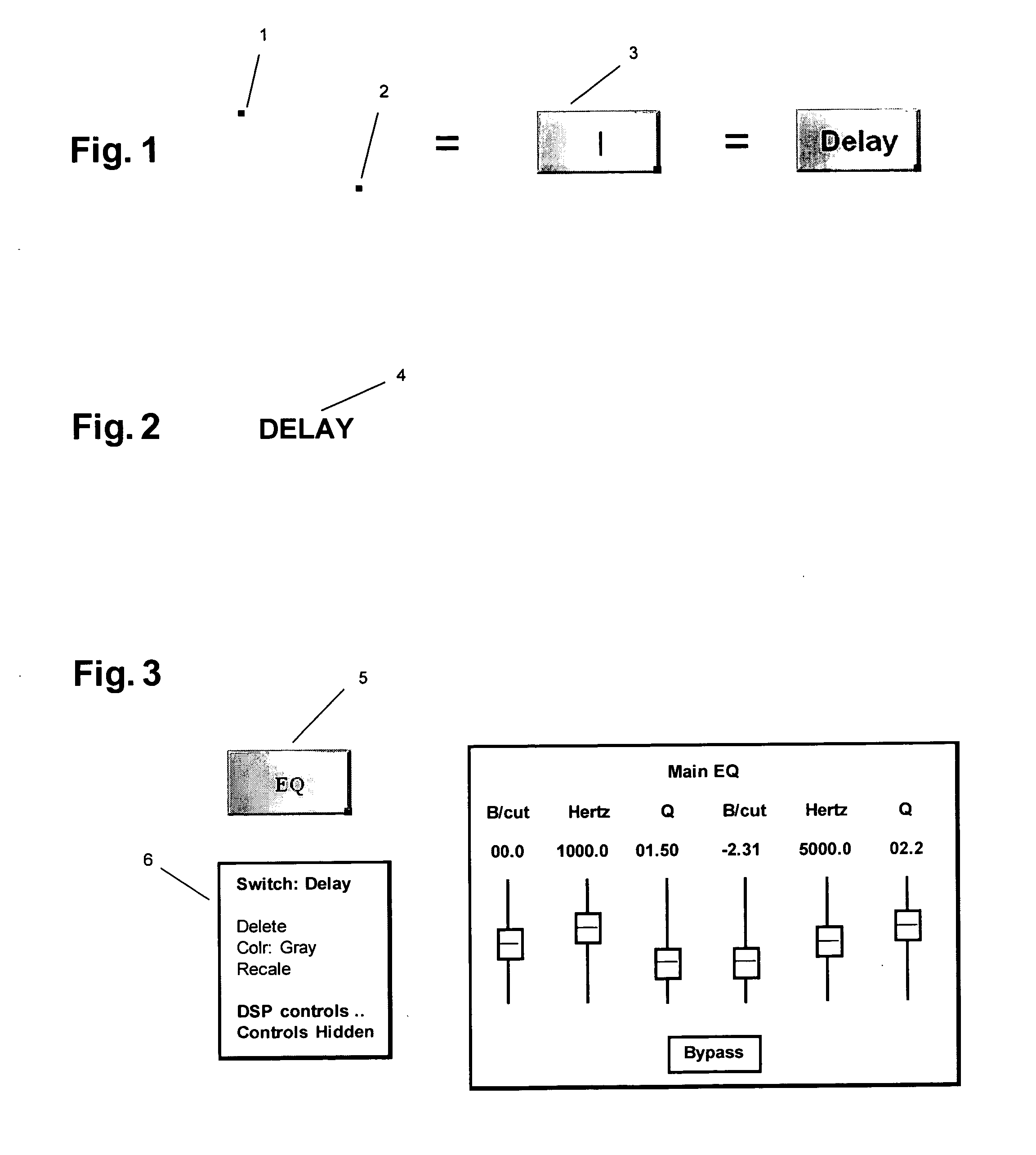
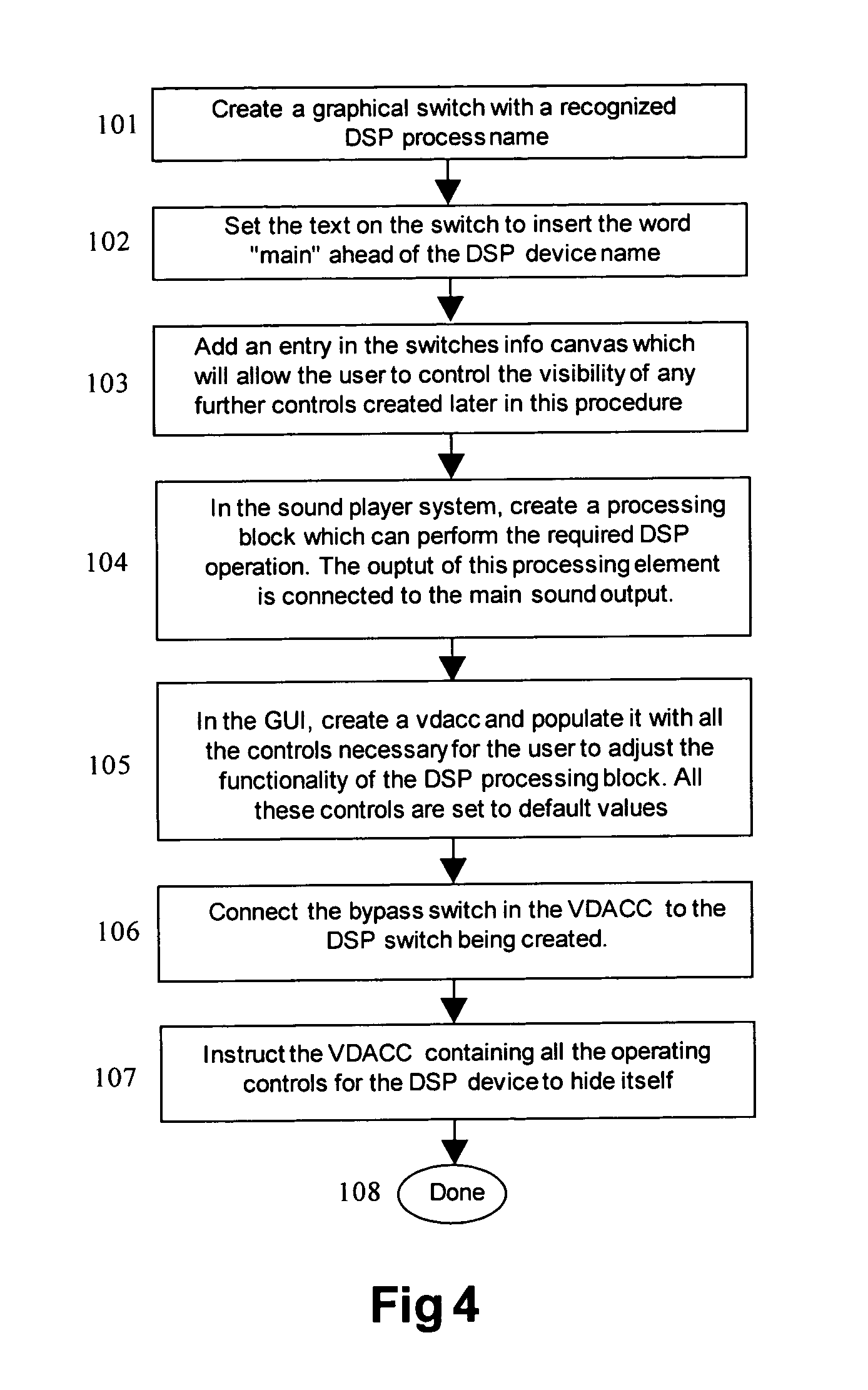
A method for performing multimedia operations involves drawing a graphic directional indicator to establish a signal path between at least one graphical switch, such as a digital signal processing (DSP) or sound switch, and a graphic control device, such as another graphical switch or a fader.
Owner:NBOR CORP
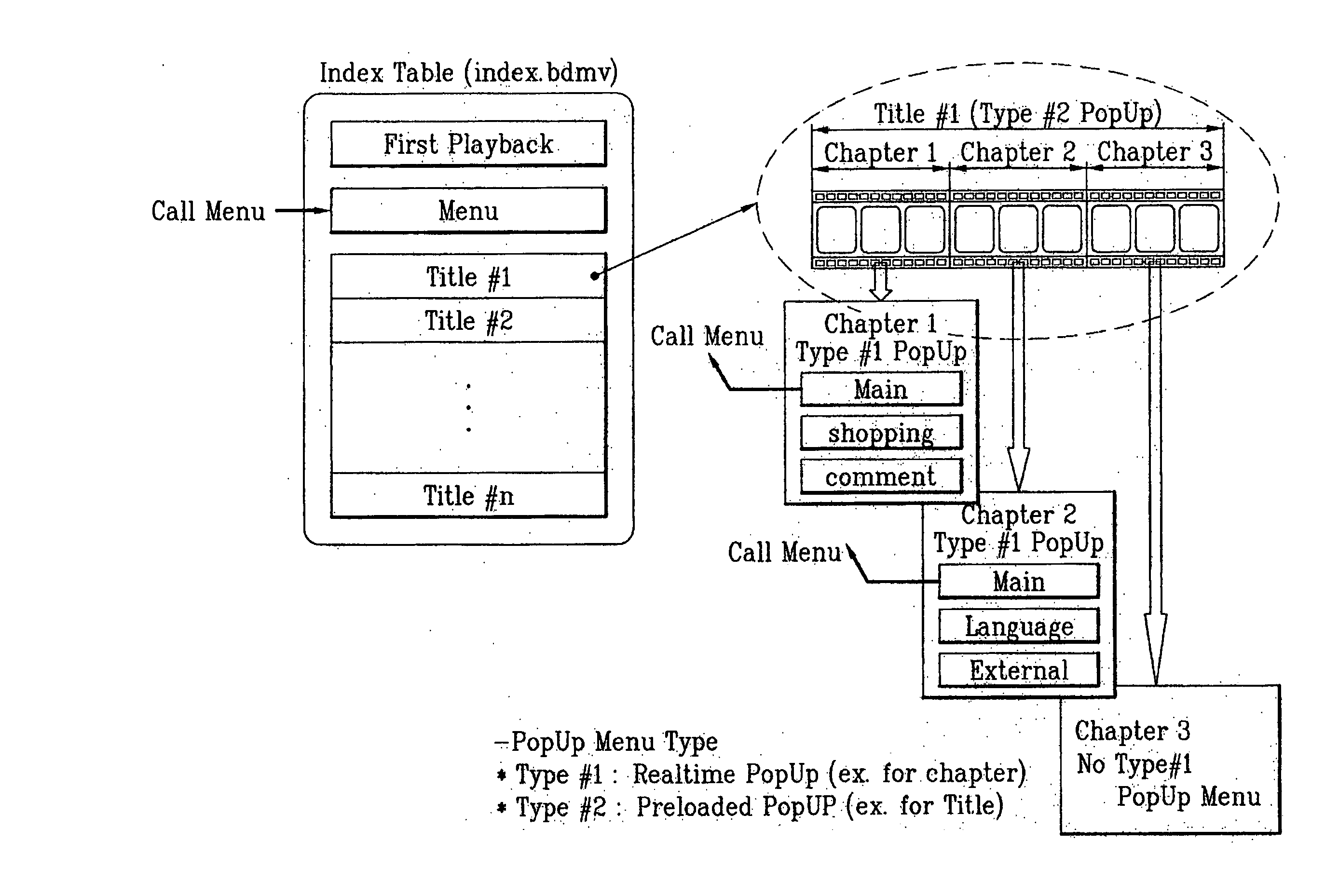
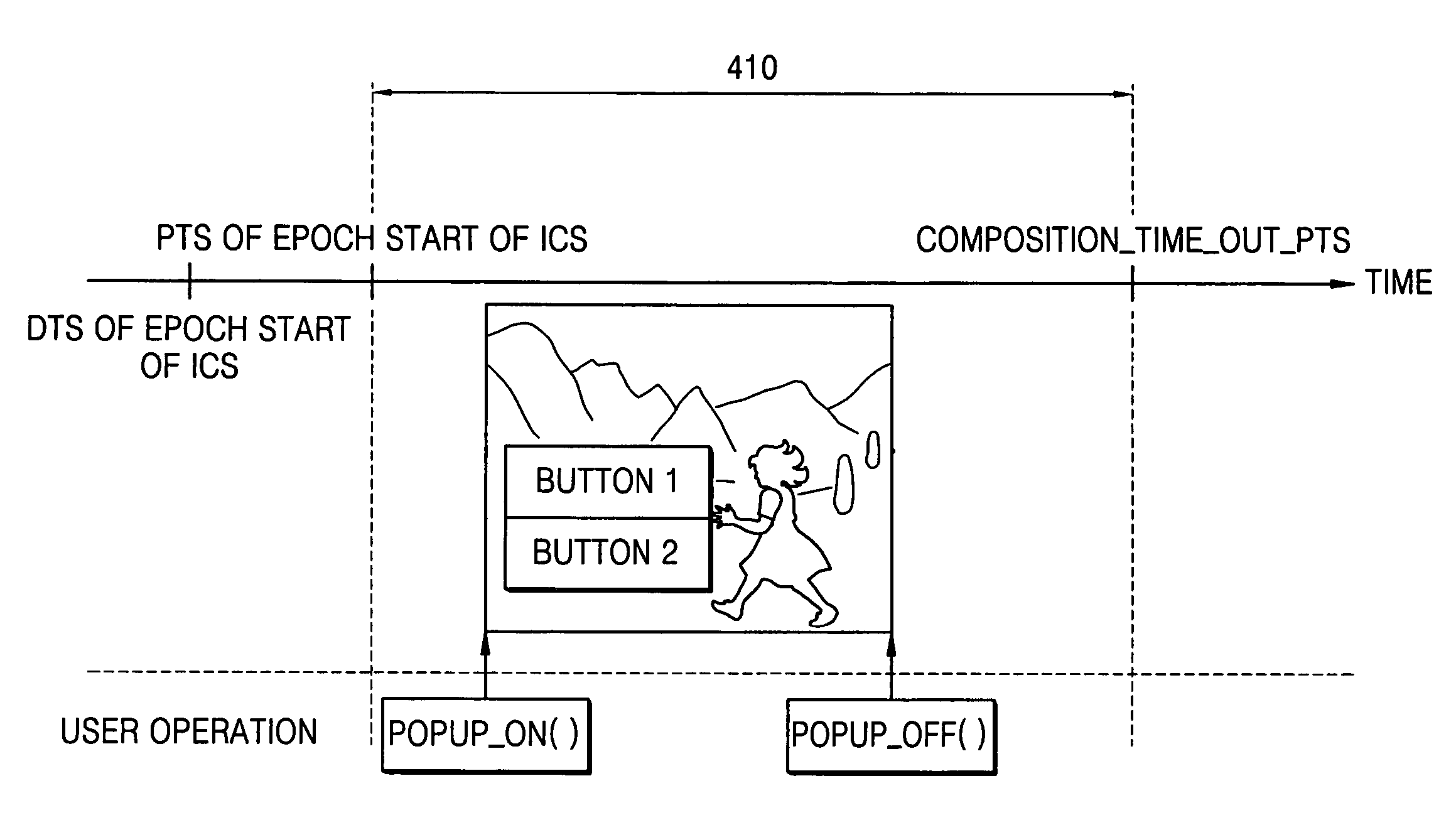
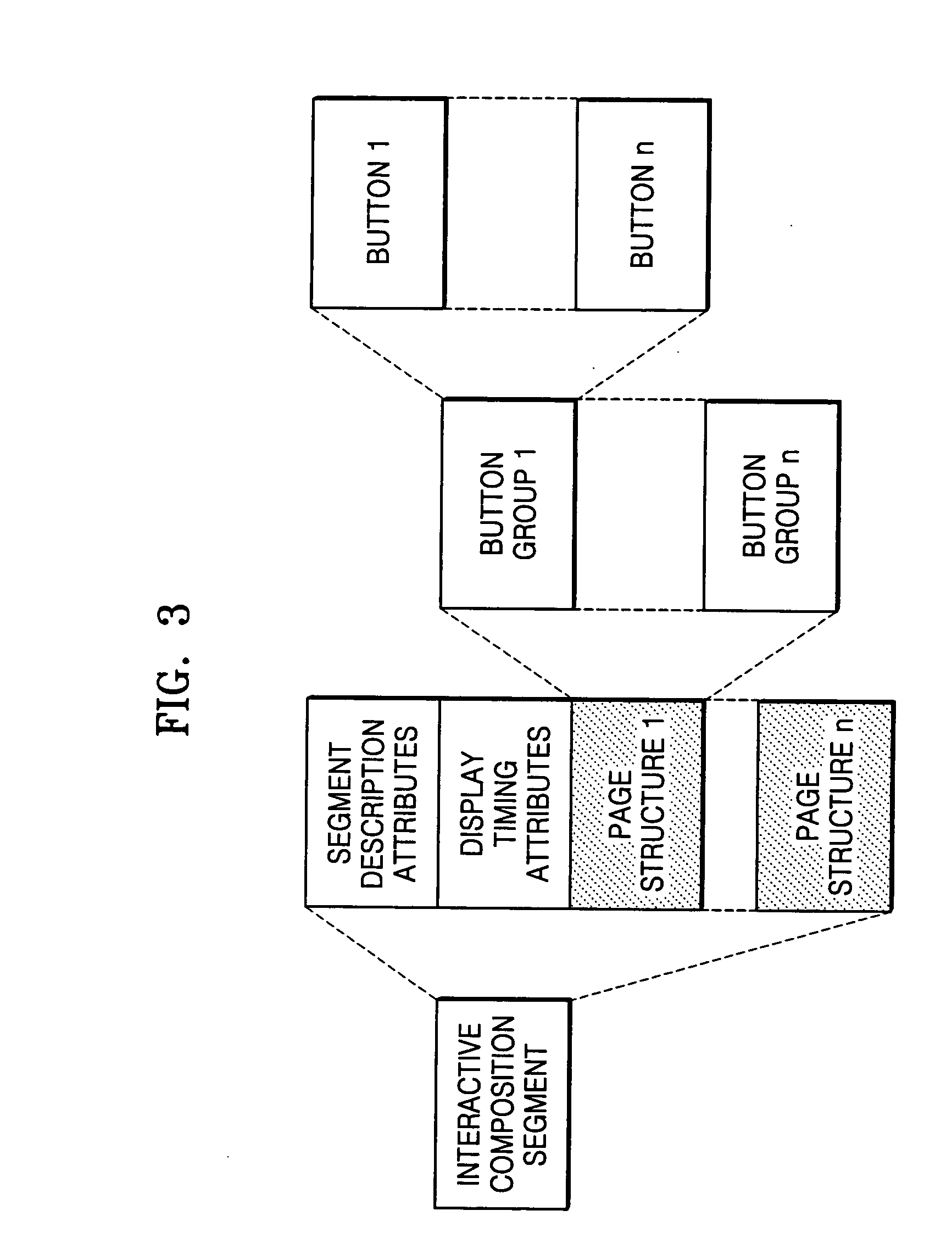
Information storage medium containing interactive graphics stream for change of AV data reproducing state, and reproducing method and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20050177863A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionInteractive graphicsMarine navigation
An information storage medium including AV data; presentation graphics data including subtitle information corresponding to the AV data; and interactive graphics data including menu data; wherein the interactive graphics data further includes a reproducing state change navigation command to change the reproducing state of the AV data and / or the presentation graphics data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com