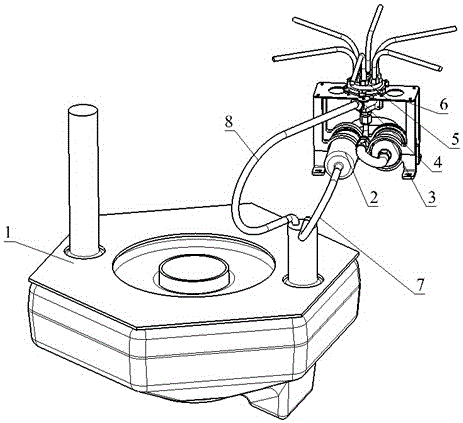
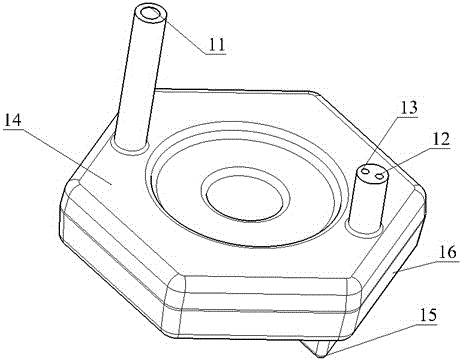
Patents
Literature
301results about How to "Improve flight stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rotary-wing vehicle system and methods patent
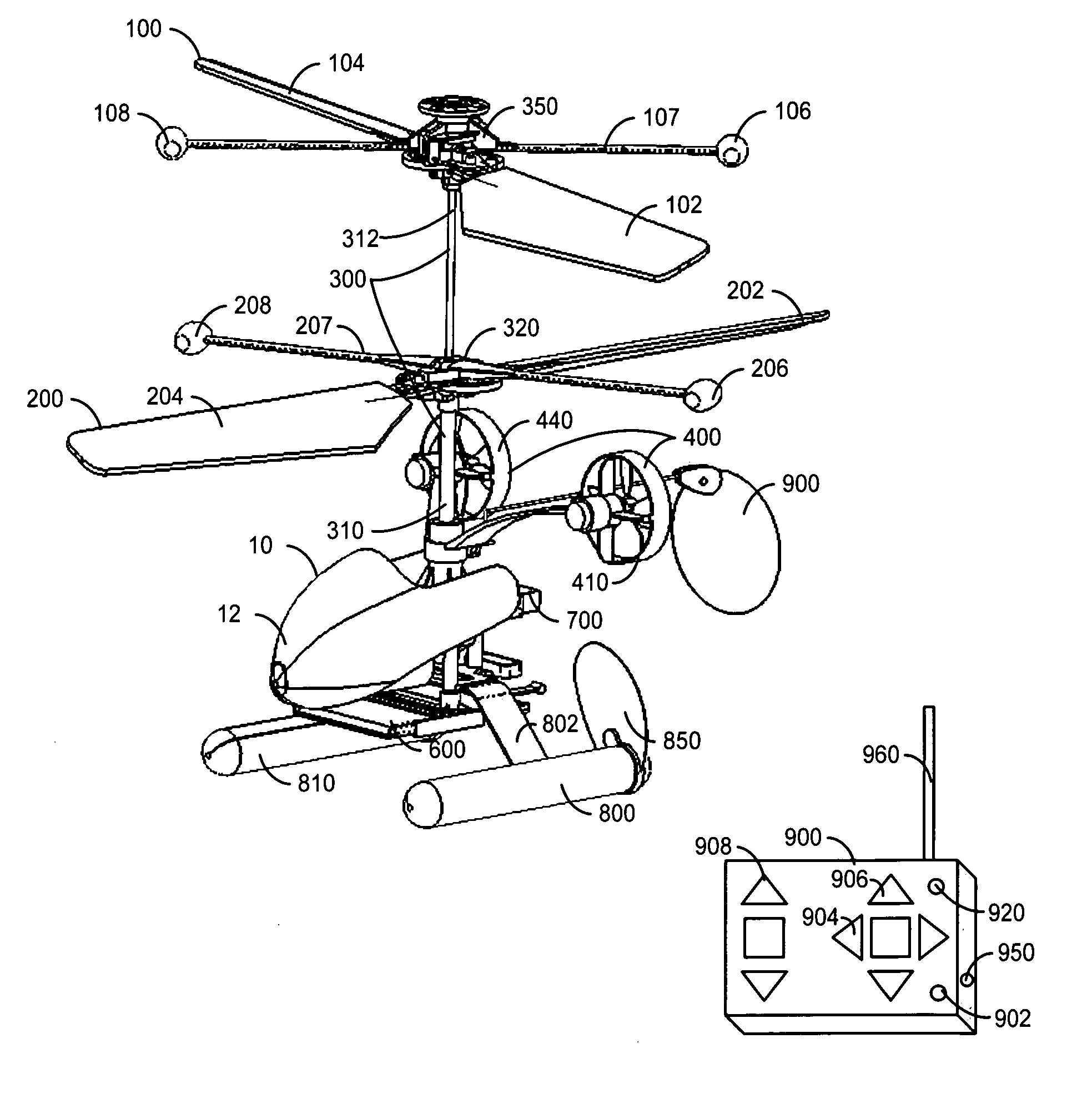
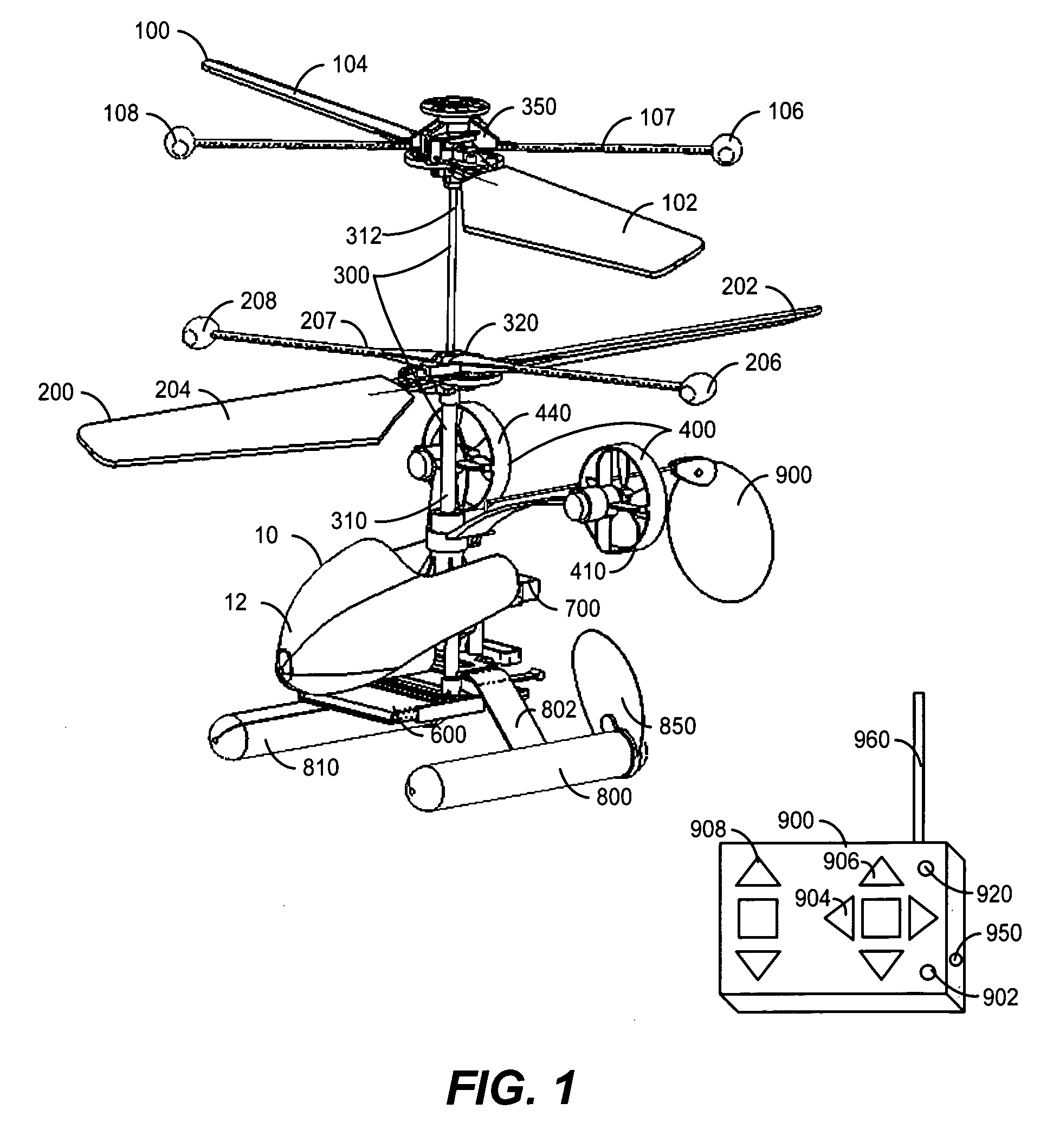
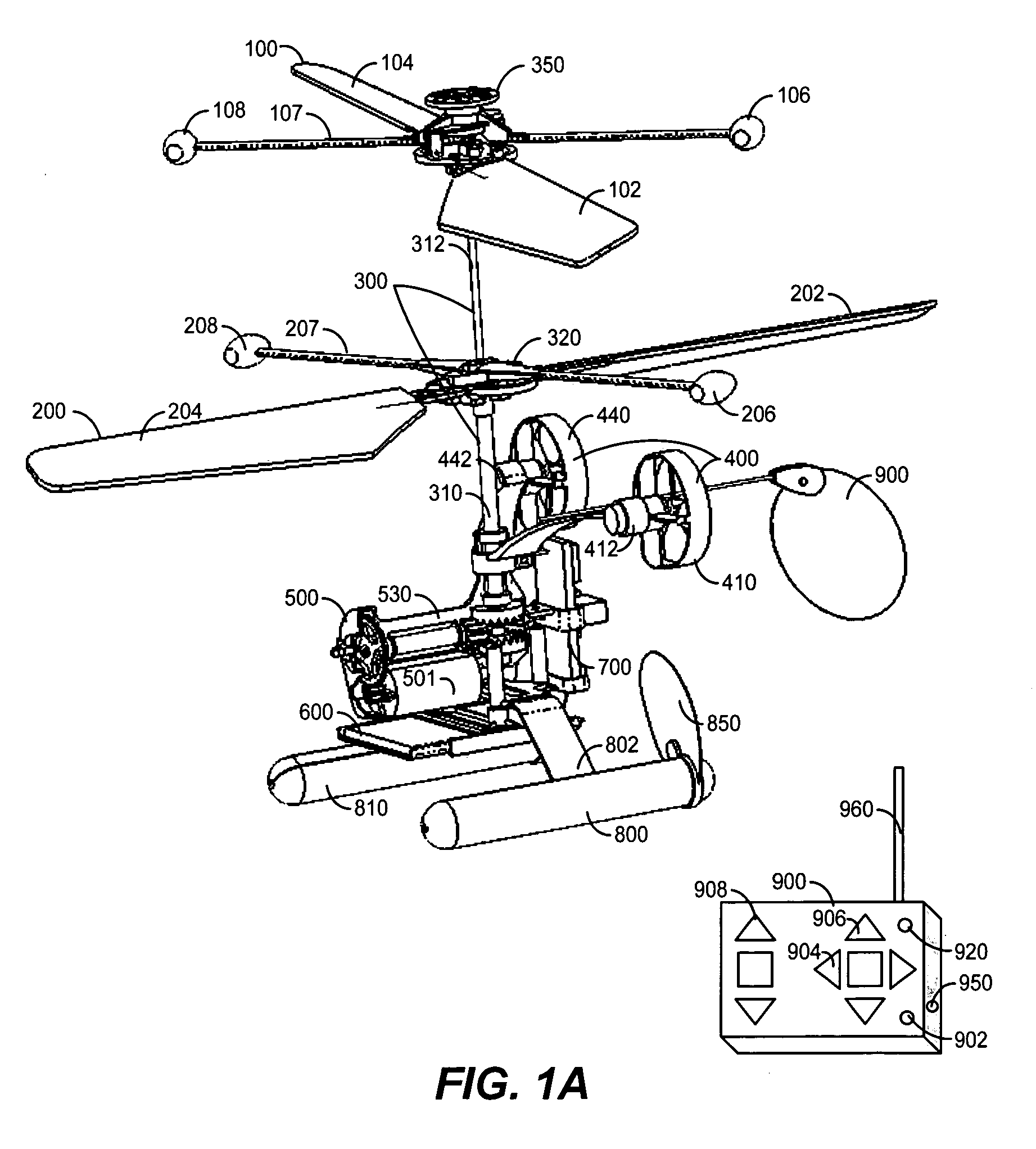
InactiveUS20060231677A1Improved yaw stabilityImprove flight stabilityToy aircraftsRotocraftAviationFlight vehicle
A rotary-wing apparatus that is aeronautically stable, easy to fly with a multidimensional control, small size, and safe to fly and low cost to produce. The rotary-wing apparatus includes a coaxial counter rotating rotor drive providing lifting power with an inherent aeronautical stability; Auxiliary propellers that face the direction of flight and are located on opposite sides of said coaxial Rotary-wing apparatus and enable flying forwards, backwards and perform yawing; A rotary-wing coaxial helicopter toy that is remotely controlled and safe to fly in doors and out doors, while performing exciting maneuvers even by untrained kids
Owner:ZIMET NACHMAN +1
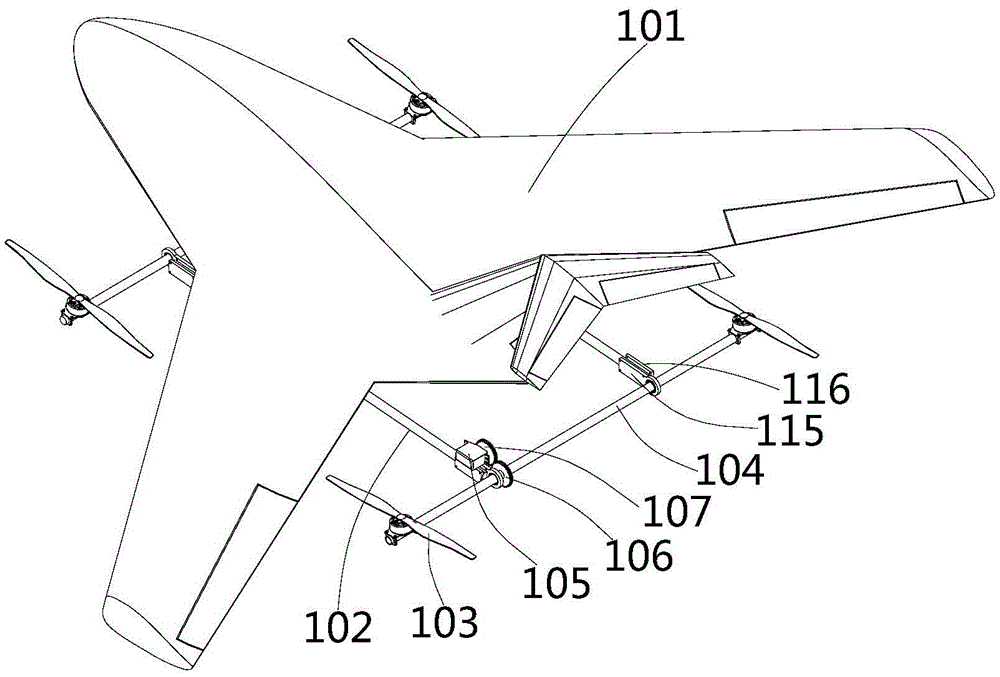
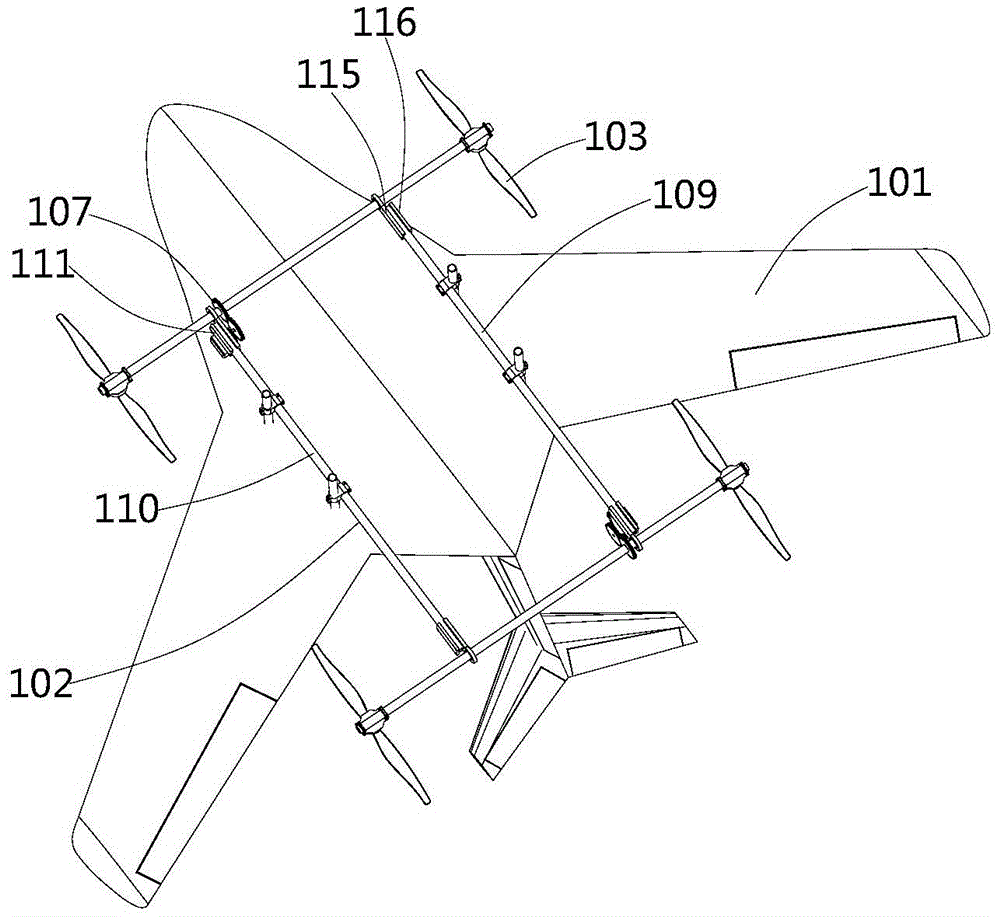
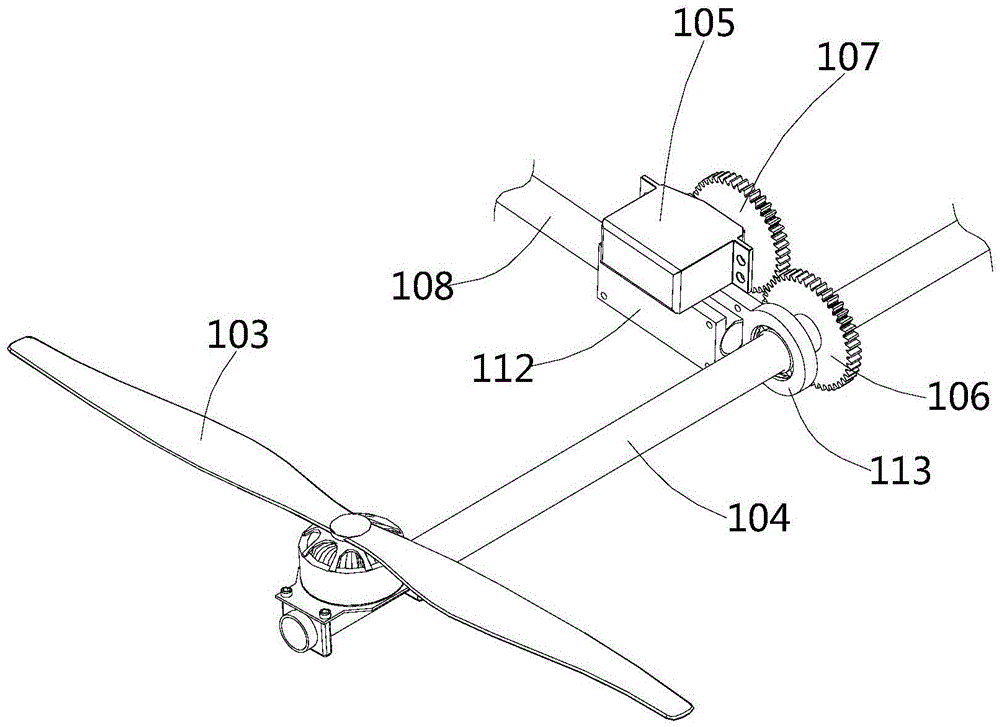
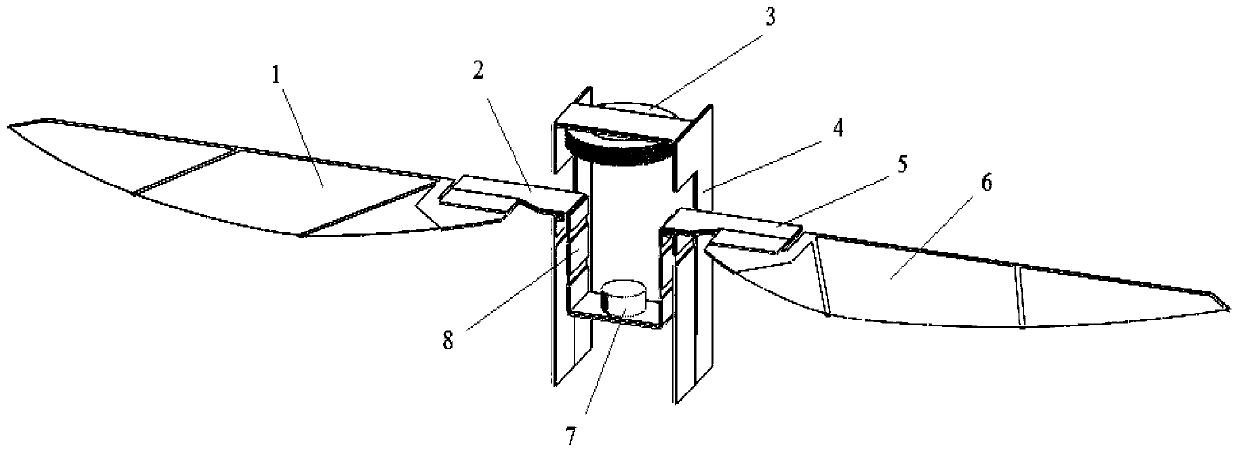
Fixed-wing multi-shaft aircraft
ActiveCN105539833AImprove flight efficiencyImprove operational efficiencyRotocraftFixed wingRotary wing
The invention provides a fixed-wing multi-shaft aircraft, and belongs to the field of aircrafts. The fixed-wing multi-shaft aircraft comprises a fixed wing and a multi-shaft rotor wing rack which are connected with each other, and the multi-shaft rotor wing rack is provided with multiple rotor wing mechanisms; the rotor wing mechanisms comprise propellers and rotating shafts, the propellers are rotatably connected with drive devices, the drive devices are fixedly connected with the rotating shafts, and the rotating shafts are connected with rotating control mechanisms. The fixed-wing multi-shaft aircraft has the advantages of both a fixed-wing aircraft and a multi-shaft aircraft, can achieve a multi-shaft mode, a fixed-wing mode and a fixed-wing and multi-shaft mixed mode and also has the advantages of achieving vertical taking-off and landing and hovering and being high in flying speed and long in flying time.
Owner:CHENGDU XUESHANG TECH CO LTD
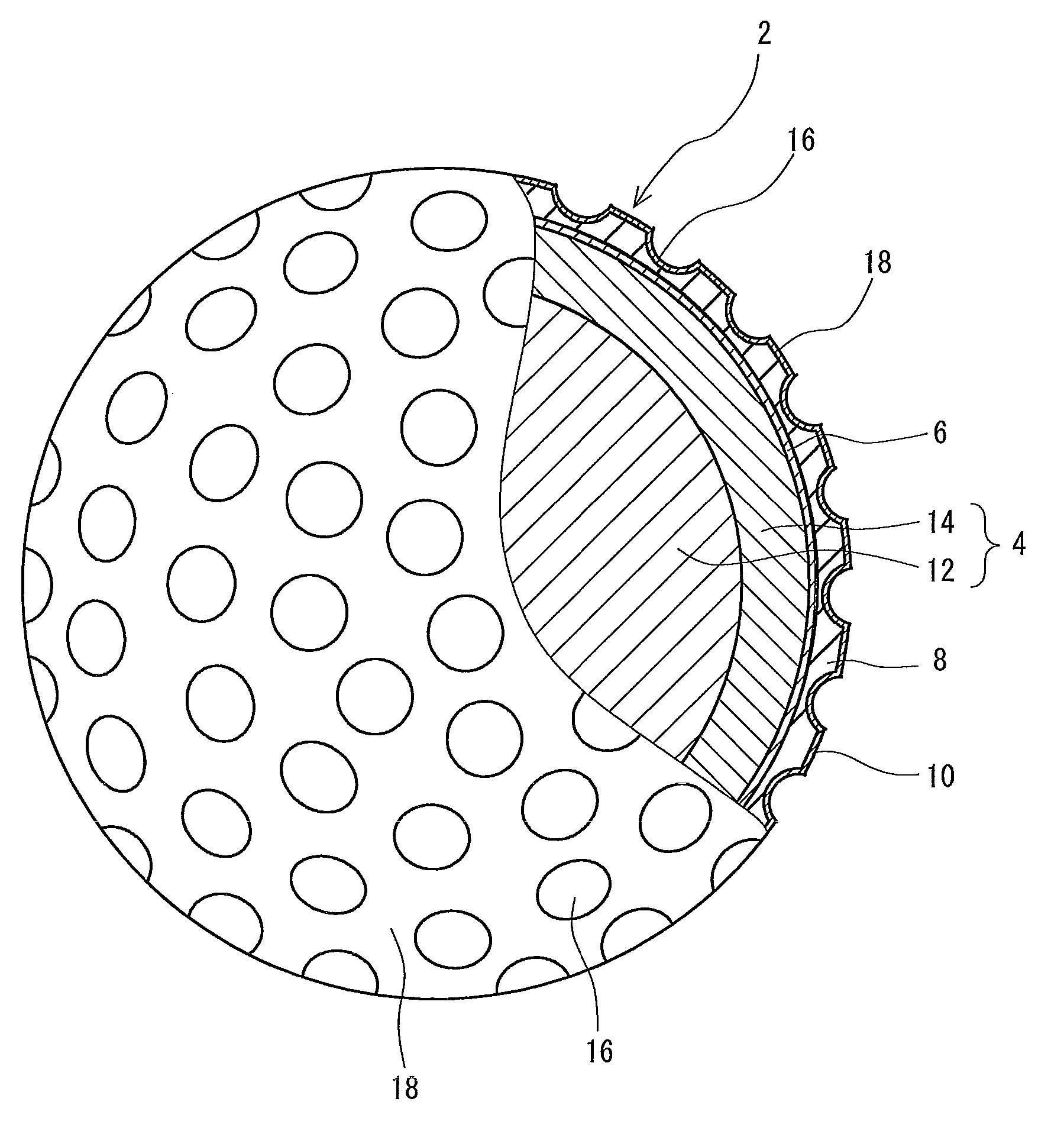
Golf ball
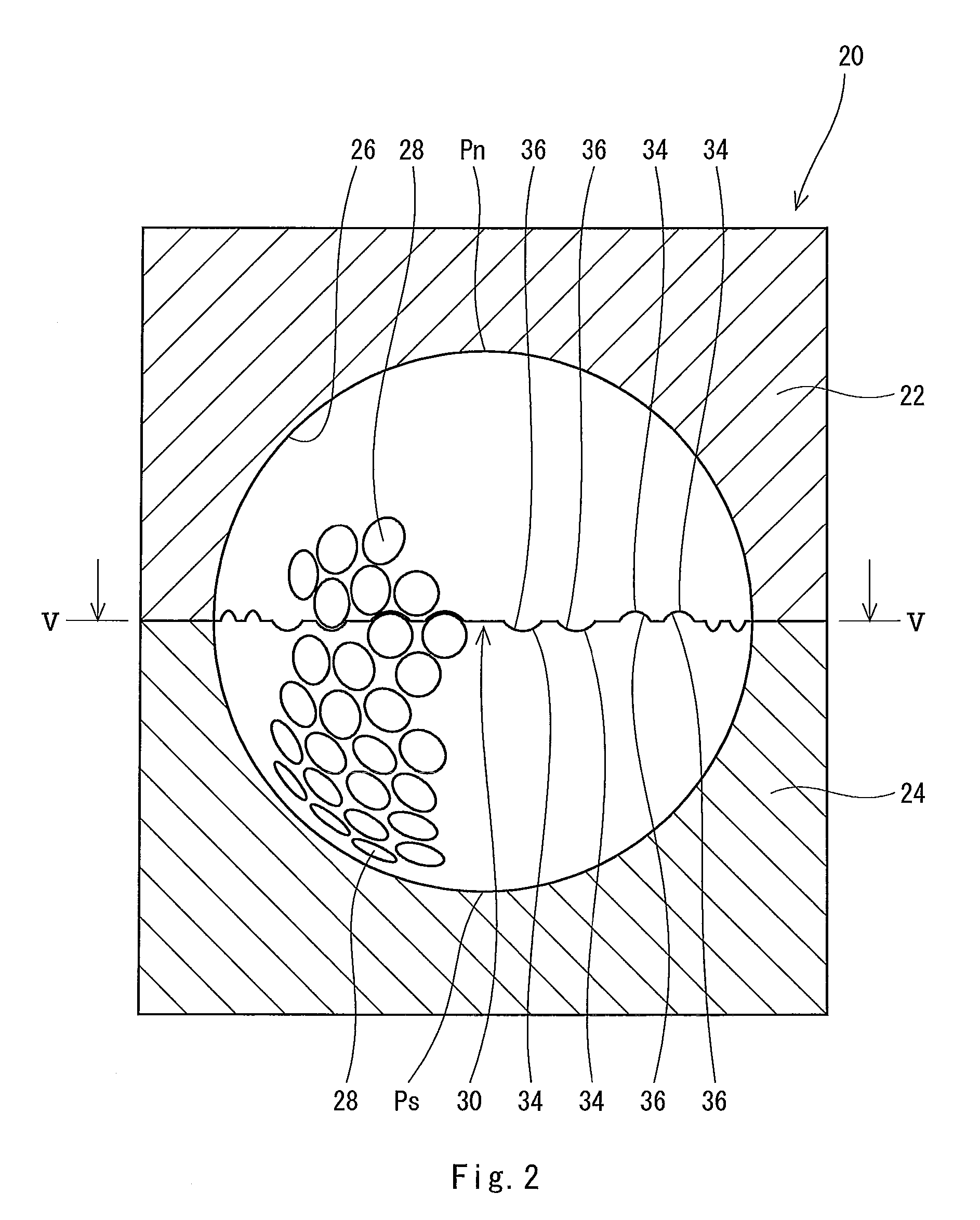
ActiveUS20090247328A1Suppresses spinLong distanceGolf ballsSolid ballsCarbamateThermoplastic polyurethane
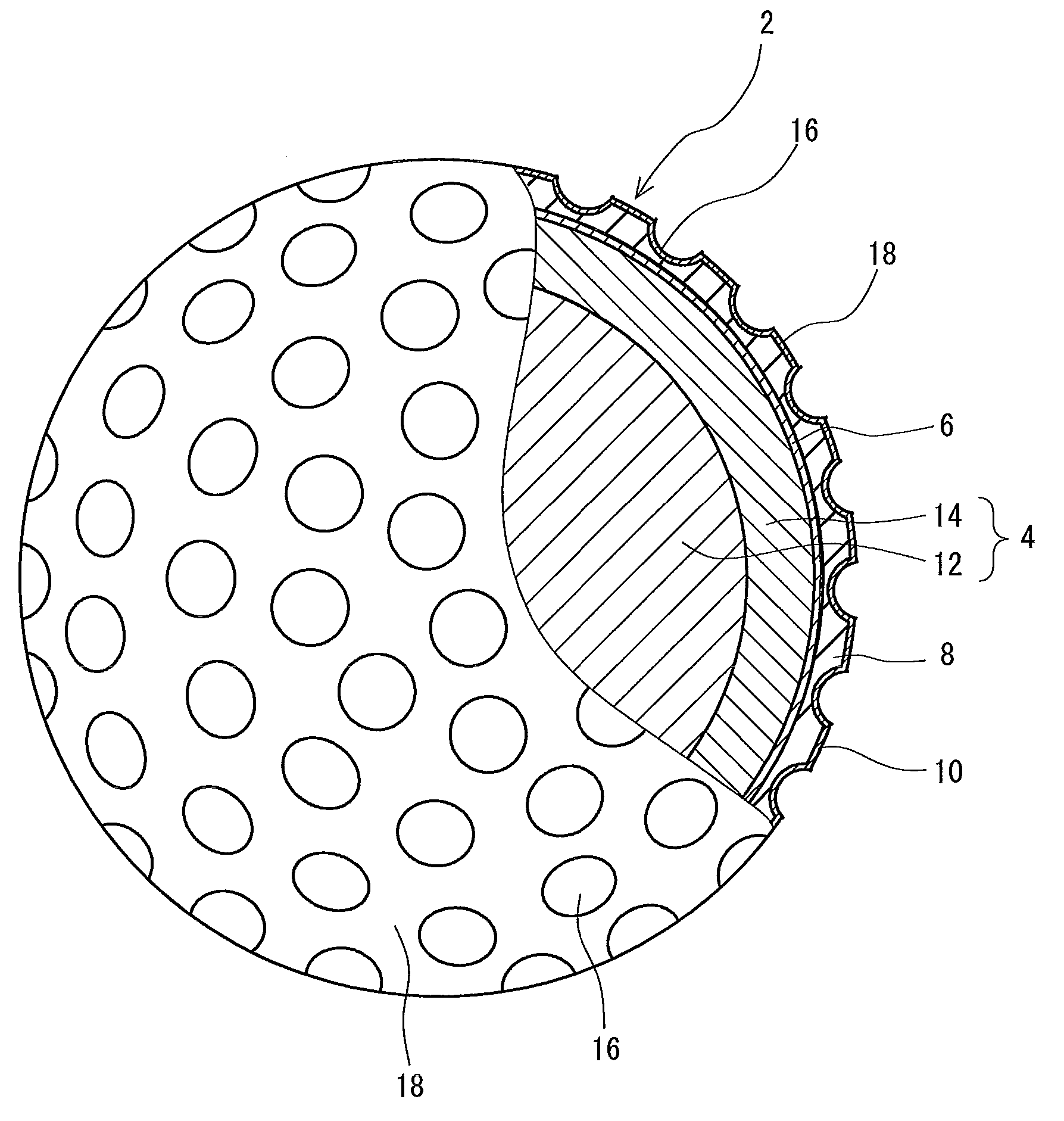
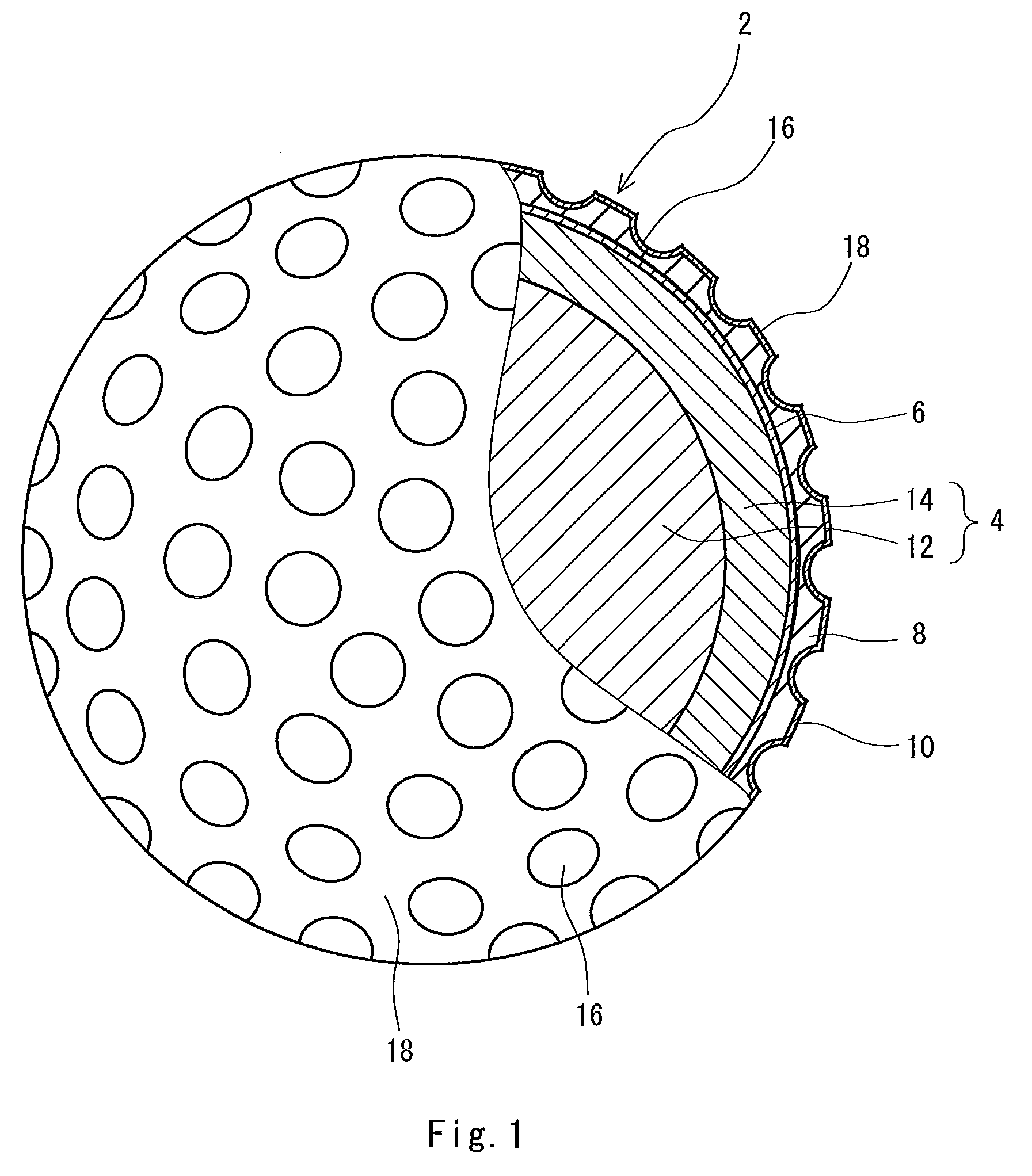
A golf ball 2 includes a center 12, a mid layer 14, a reinforcing layer 6, a cover 8 and a paint layer 10. The golf ball 2 has a large number of dimples 16 on the surface thereof. The cover 8 is formed of a resin composition including thermoplastic polyurethane (A) and a polyisocyanate mixture (B). The polyisocyanate mixture (B) includes a urethane prepolymer (B1) having two or more isocyanate groups or an isocyanate compound (B2) having three or more isocyanate groups. The polyisocyanate composition (B) further includes a thermoplastic resin (B3) which substantially does not react with an isocyanate goup. The golf ball 2 is obtained by a mold having protrusions which projects from the equator of the mold. Each protrusion includes a part of a pimple.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Flying wing type double-duct vertical taking-off and landing aircraft
InactiveCN107089316AImprove flight efficiencyImprove stealth performanceFuselagesVertical landing/take-off aircraftsFlight vehicleWingtip device
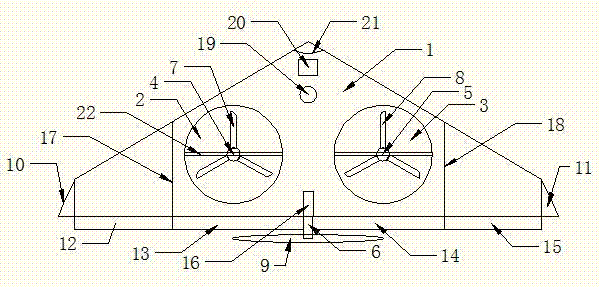
A flying-wing double-ducted vertical take-off and landing aircraft. It mainly consists of five parts. The first part is the fuselage 1, the second part is the No. 1 ducted engine 4, the No. 2 ducted engine 5 and the rear engine 6, the third part is the vertical tail 16, the No. 1 horizontal tail 12, the No. 2 horizontal tail 13, No. 3 horizontal stabilizer 14, No. 4 horizontal stabilizer 15, No. 1 winglet 10, No. 2 winglet 11. The fourth part is the support rod 19 , and the fifth part is the externally mounted pan / tilt head and the camera or photoelectric sensor 20 . The fuselage 1 is a flying wing type, the fuselage 1 can be folded, and the fold line 17 and the fold line 2 18 are the folding points of the fuselage. There are No. 1 duct 2 and No. 2 duct 3 distributed on the fuselage 1. No. 1 ducted engine 4 and No. 2 ducted engine 5 are located in the center of No. 1 duct 2 and No. 2 duct 3, respectively, and are connected by connecting The rod 22 is fixed. The No. 1 ducted engine 4 and the No. 2 ducted engine 5 are respectively equipped with a No. 1 propeller 7 and a No. 2 propeller 8 . The rear engine 6 is located in the center of the tail of the fuselage 1 , and a rear propeller 9 is installed on the rear engine 6 . The No. 1 horizontal stabilizer 12 , the No. 2 horizontal stabilizer 13 , the No. 3 horizontal stabilizer 14 , and the No. 4 horizontal stabilizer 15 of the aircraft are respectively located at the rear of the fuselage 1 . The No. 1 winglet 10 and the No. 2 winglet 11 of the aircraft are located on the left and right sides of the fuselage 1 respectively, and are bent downward. The vertical tail 16 of the aircraft is located in the middle of the tail of the fuselage 1 , on the upper part of the fuselage 1 . The support rod 19 is located in the middle of the front part of the fuselage 1 , and is located in the lower part of the fuselage 1 . The camera or photoelectric sensor is located in the middle of the front of the body 1 and is installed under the body 1 . The sweep angle 21 is the sweep angle of the flying wing fuselage 1 .
Owner:张飞
Multi-rotor aircraft driven by duct lift fans with diversion helms
The invention discloses a multi-rotor aircraft driven by duct lift fans with diversion helms. The multi-rotor aircraft comprises the multiple duct lift fans with diversion helms, and an aircraft fuselage, wherein the aircraft fuselage comprises a frame, a landing gear, a power module, a flight control module , a load cabin and other function modules; the duct lift fans with the diversion helms are mounted on the aircraft fuselage and mainly consist of propellers, propeller driving units, the diversion helms, diversion helm driving units, ducts and the like, and the ducts are arranged at the peripheries of the propellers and used for improving the efficiency of the propellers, protecting the propellers and reducing the noise of the propellers; the propellers are driven by the propeller driving units; and the diversion helms driven by the diversion helm driving units are arranged on the air inlet sides or the air outlet sides of the duct lift fans.
Owner:刘朝阳
Shuttlecock and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103127683AIncrease profitReduce dosageBall sportsRacket sportsEngineeringAgricultural engineering
Owner:ANHUI SANCAI SPORTS GOODS
Tilted four-rotor aircraft
The invention relates to a tilted four-rotor aircraft. The tilted four-rotor aircraft comprises a fuselage, wherein the fuselage is provided with a front wing and a rear wing, two ends of the front wing and two ends of the rear wing are respectively provided with a set of rotor system, and the front wing and the rear wing are respectively and internally provided with a worm-wheel shaft which passes through the fuselage and is used for driving a rotor wing system to do tilted rotating motion; each set of rotor wing system comprises a direct-current brushless motor and a propeller, and the direct-current brushless motor is arranged at the end of the worm-wheel shaft and provided with the propeller. Compared with a conventional tilted double-rotor aircraft, the safety and reliability of the tilted four-rotor aircraft provided by the invention are higher; four rotors have strong lift force, so that the payload, flight radius and flight stability are all greatly improved. The tilted four-rotor aircraft provided by the invention can realize three flight modes, namely a helicopter mode, a transition mode and a horizontal propulsion mode, and has the characteristics of simple structure, high strength, reliable function realization and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Culvert-type vertical take-off and landing lifting body unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN107600405AReduce forward flight resistanceReduce resistanceVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftUncrewed vehicleFuselage
The invention discloses a culvert-type vertical take-off and landing lifting body unmanned aerial vehicle and relates to the technical field of vertical take-off and landing unmanned aerial vehicles.The culvert-type vertical take-off and landing lifting body unmanned aerial vehicle comprises a fuselage (1), lifting force rotor wings (2), a take-off and landing culvert (3), tilting-rotating thrustculverts (7) and tilting-rotating thrust rotor wings (8). The take-off and landing culvert (3) is composed of a through hole penetrating through the upper surface and the lower surface of the fuselage (1), and the lifting force rotor wings (2) are arranged in the take-off and landing culvert (3). The tilting-rotating thrust culverts (7) are hinged to the rear end of the fuselage (1) through tilting-rotating control mechanisms (9), the tilting-rotating control mechanisms (9) are configured to be capable of enabling the included angle between the axis of each tilting-rotating thrust culvert (7)and the axis of the fuselage (1) to be variable, and the tilting-rotating thrust rotor wings (8) are arranged in the tilting-rotating thrust culverts (7). Under the conditions that the vertical take-off and landing capacity of the unmanned aerial vehicle is maintained and the overall weight of the unmanned aerial vehicle is not excessively increased, the flight speed of the unmanned aerial vehicle is increased, the flight stability of the unmanned aerial vehicle is improved, the rotor wing exposed problem is avoided through the culverts, and the flight safety and the take-off and landing hovering efficiency are improved.
Owner:CHINA HELICOPTER RES & DEV INST
Four-rotor aircraft provided with telescopic and foldable undercarriages
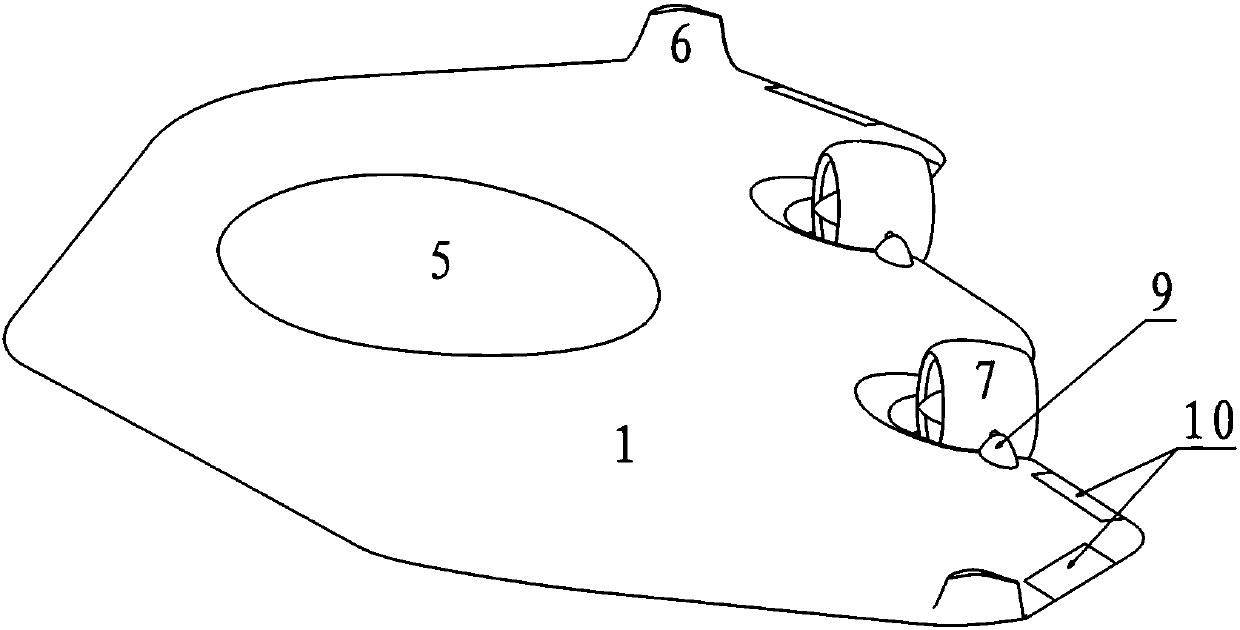
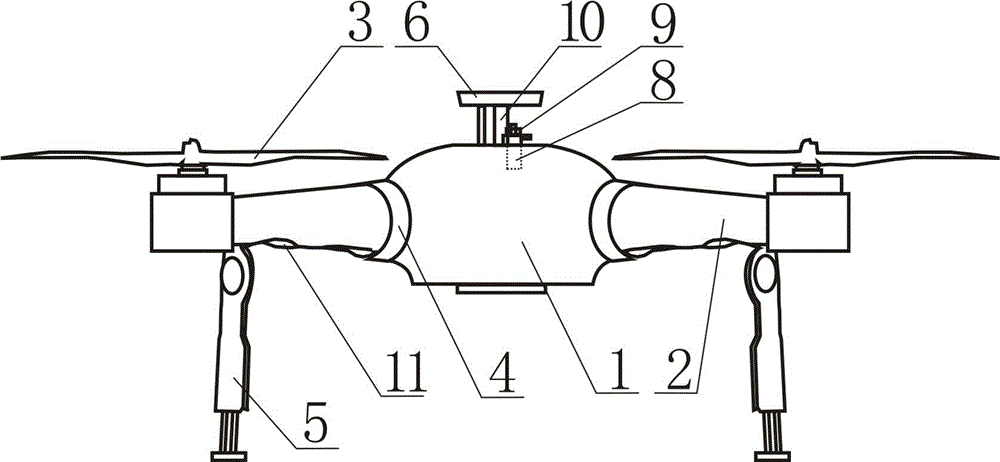
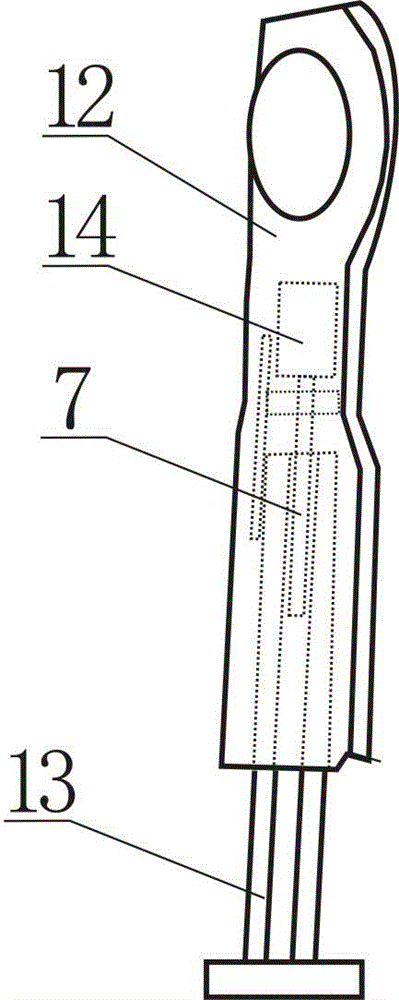
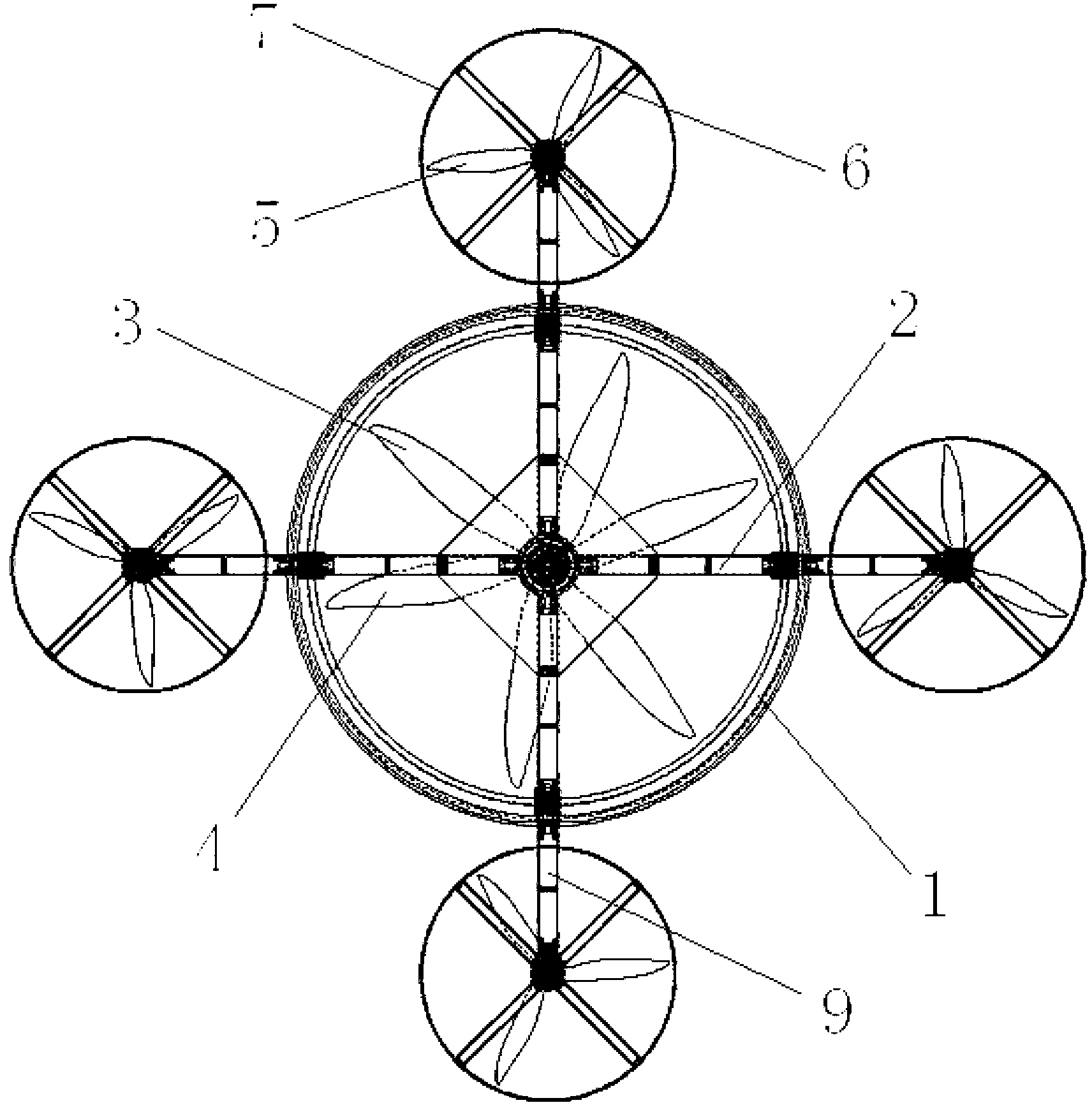
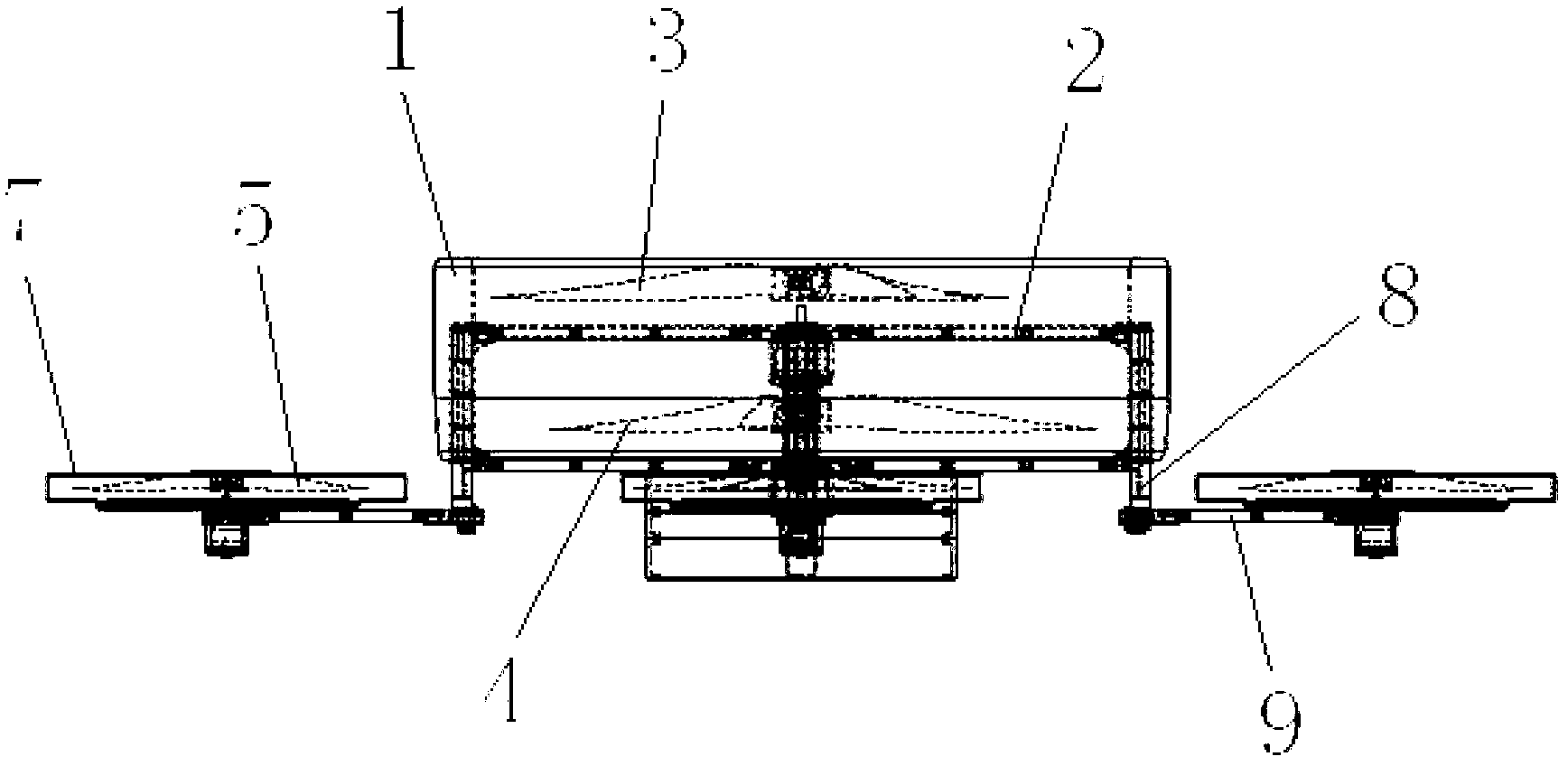
InactiveCN104787319AReduce signal interferenceImprove flight stabilityRotocraftUndercarriagesFlight vehicleDrive motor
Owner:张杰
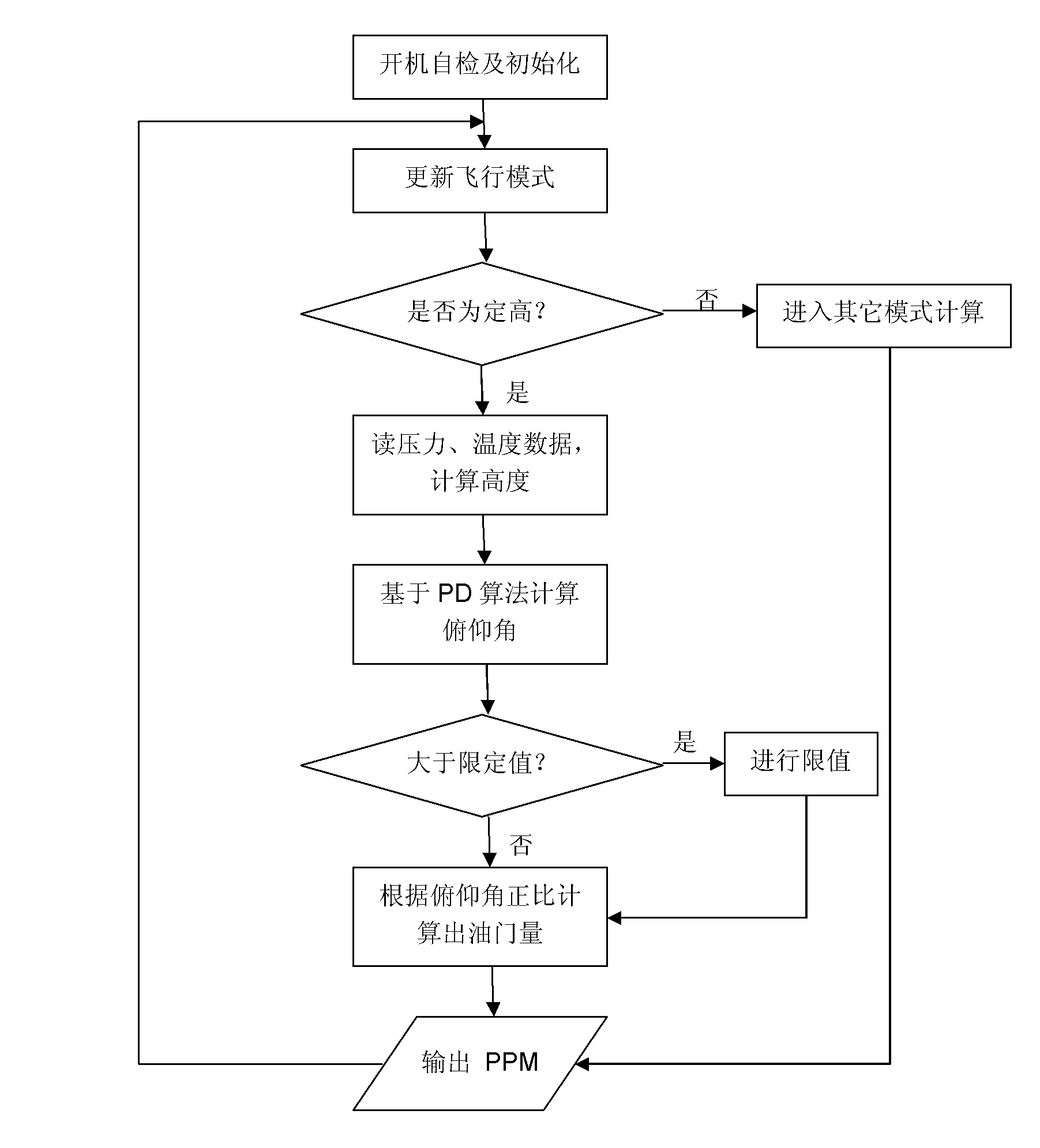
System and method for controlling fixed-height flight of fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN102442424ASatisfied with low-altitude and fixed-altitude flightEasy to operateActuated automaticallyMicrocomputer systemEngineering
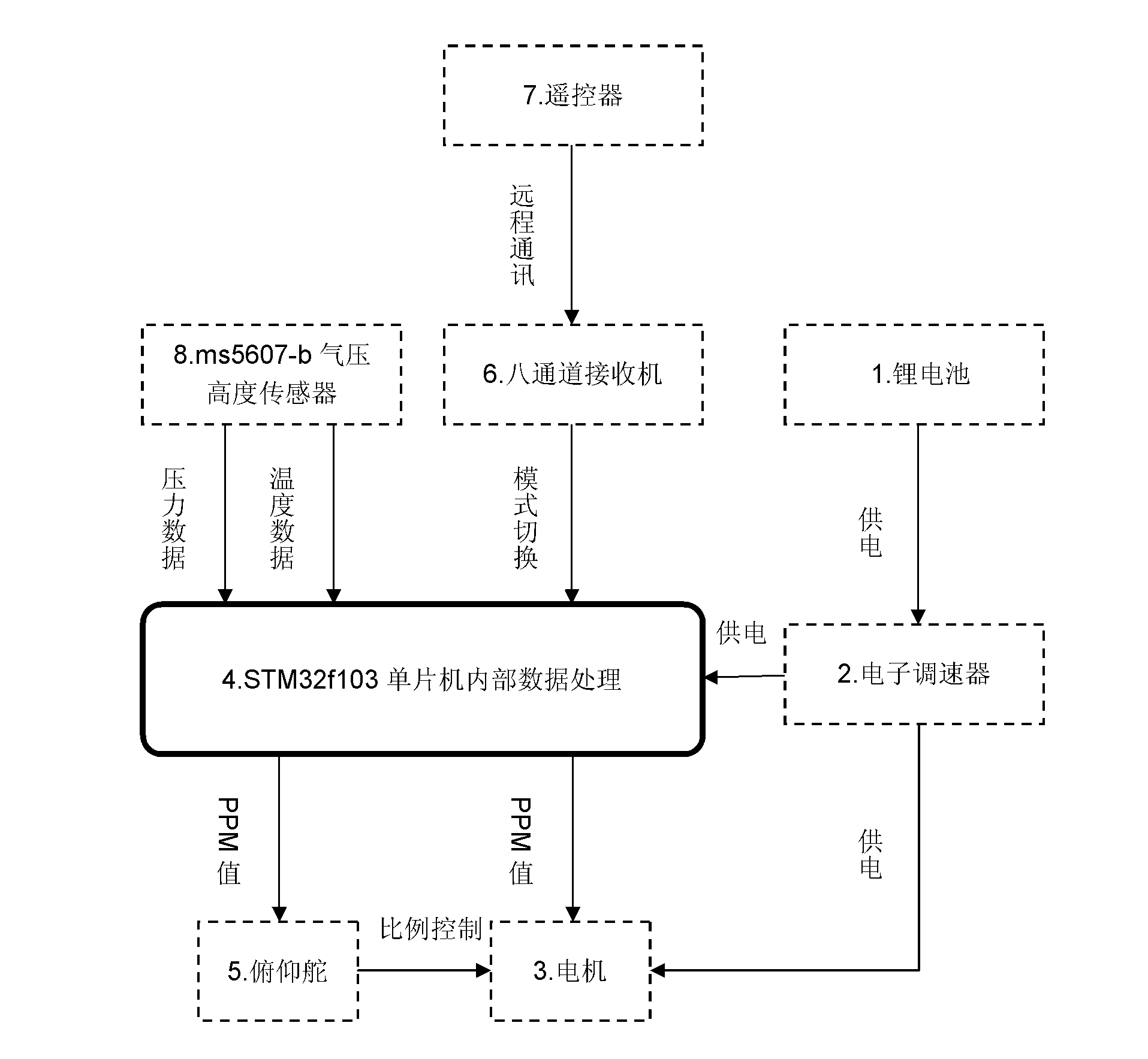
The invention discloses a system and a method for controlling fixed-height flight of a fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle, relating to the field of unmanned aerial vehicle control. By using the system and the method, a barometric height sensor is used as a height measuring element, an external lithium battery is used for supplying power to the whole system, and the sensor is protected by using a wind filtering device to reduce the influence, caused by wind pressure at a high altitude, on the sensor so that errors are reduced. After related information is measured by the barometric height sensor, an I2C bus (internal integrated circuit bus) transmits data to a single-chip microcomputer system, a series of data calculations are performed in a single-chip microcomputer to obtain corresponding height information; and finally, an elevating rudder and a gasoline throttle on the plane are linked together for PD (proportional plus derivative) control so as to control angle changes of a steering engine and the size of the gasoline throttle, and a height over-ascending and over-descending protection program is added in the programs to further improve the safety and realize autonomous height fixing of the unmanned aerial vehicle. The system has the advantages of low cost, small error, stable structure, small interference from external environment, easy implementation and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Electromagnetic drive insect-like flapping-wing micro air vehicle
ActiveCN103274049AReduce frictionImprove transmission efficiencyOrnithoptersFlapping wingSpiral coil
The invention provides an electromagnetic drive insect-like flapping-wing micro air vehicle. Two wings are respectively connected with two ends of a carapace through flexible hinges; the wings, the carapace and a baffle block form a 'baffle' structure; the carapace is rigidly connected to a chest; a cylindrical permanent magnet is attached to the center position at the lower part of the chest; a spiral coil is attached to the center position at the upper part of a machine body opposite to the permanent magnet; the spiral coil and the permanent magnet are respectively located at the upper side and the lower side of each wing when being assembled; and the spiral coil overlaps with the axis of the permanent magnet. By adopting the traditional four-connecting rod drive mechanism, the transmission efficiency of the air vehicle is greatly improved; better flight stability can be obtained by adjusting the center of gravity to overlap with a lift center; by adopting simple structures of the flexible hinges and the baffle block, a certain degree of passive reverse can be obtained in a flapping process due to interaction of inertia force and aerodynamic force; the assembly precision is improved by folding and assembling; and miniaturization of the air vehicle is easily achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
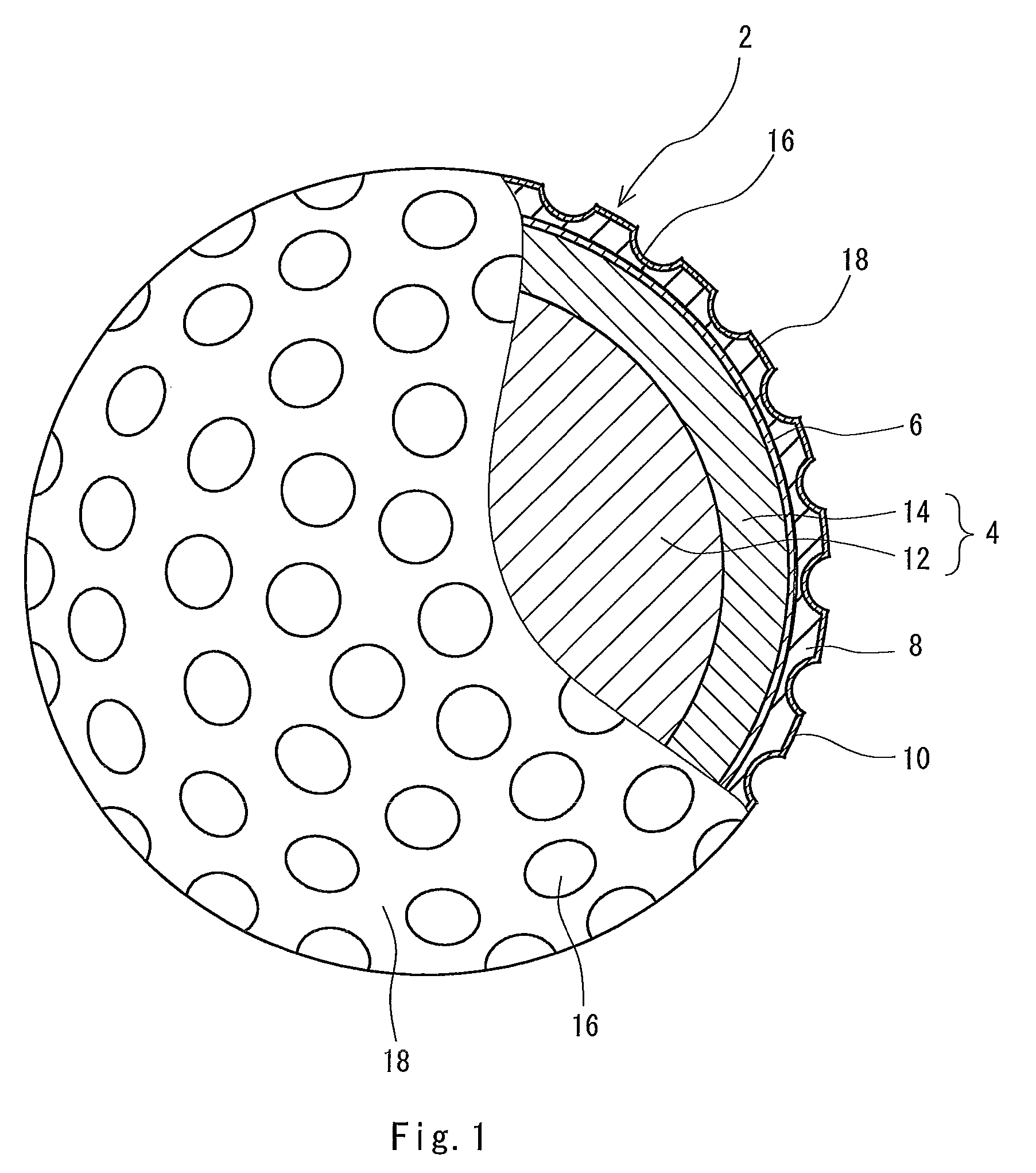
Golf ball
A golf ball 2 includes a center 12, a mid layer 14, a reinforcing layer 6, a cover 8 and a paint layer 10. The golf ball 2 has a large number of dimples 16 on the surface thereof. The cover 8 is formed of a resin composition including thermoplastic polyurethane (A) and a polyisocyanate mixture (B). The polyisocyanate mixture (B) includes a urethane prepolymer (B1) having two or more isocyanate groups or an isocyanate compound (B2) having three or more isocyanate groups. The polyisocyanate mixture (B) further includes a thermoplastic resin (B3) which substantially does not react with an isocyanate group. The golf ball 2 is obtained by a mold having protrusions which project from the equator of the mold. Each protrusion includes a part of a pimple.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Multielement seeding combustion explosion type rainfall-increasing and anti-hail rocket
InactiveCN101726219ANo pollution in the processLarge coverage areaWeather influencing devicesSelf-propelled projectilesCombustionEngineering
The invention relates to a multielement seeding combustion explosion type rainfall-increasing and anti-hail rocket. In the rocket, one end of a safety system (2) is connected with a flame bullet seeding catalyst system (1), the other end is connected with the front end of a solid motor (3); the back end of the motor (3) sticks to an empennage; four catalyst seeding holes are evenly distributed in the middle part of a nozzle (5), a plurality of flame bullets (12) are sleeved together to be arranged in a shell (15), safety fuses (16) are arranged in the centre bores of the flame bullets (12), a propelling medicine (13) is filled to one end of each flame bullet (12); a cladding medicine block(9) is filled in the threaded connection section capsule of the shell (15), an ignition medicine package (8) is arranged in the counter bore of the cladding medicine block(9), and the ignition wire of the ignition medicine package passes through the centre bore of the nozzle (5). The invention adopts the flame bullet burning mode that catalyst is burnt and seeded continuously and a plurality of flame bullets are thrown along the parent trajectory, for seeding the catalyst, thus requiring that the flame bullets are thrown reliably and the burning is stable. The flame bullets of the invention adopt casting moulding for structure design, the technology is easy and stable, and the flame bullets are easy for the batch production.
Owner:SHAANXI ZHONGTIAN ROCKET TECH CO LTD
Upward-anticyclone UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) pesticide sprayer
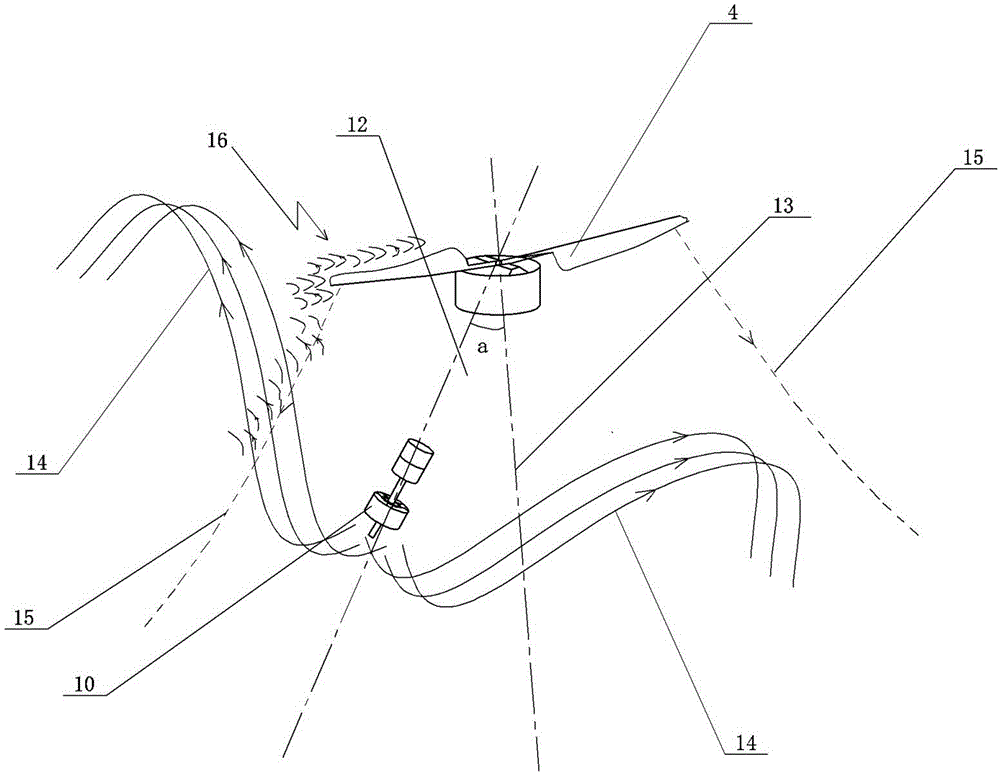
The invention discloses an upward-anticyclone UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) pesticide sprayer comprising a support, a control unit, a propeller and a pesticide box. N supporting rods are symmetrically and evenly fixed around the support. A supporting base is fixed above the upper ends of the supporting rods. A propeller motor is mounted on the supporting base. The propeller is provided above a motor. The outer ends of at least two of the supporting rods are provided with spray rods which are adjustable, below the propeller. A nozzle is mounted on the lower portion of each spray rod and linearly mounted on the spray rod. The included angle a made by the axes of every spray rod and the propeller is 30 to 45 degrees. The upward-anticyclone UAV pesticide sprayer has the advantages that after sprayed out of the nozzles, pesticide particles are not directly sprayed to the ground but brought outside by air to the top of the propeller, pesticide is sprayed up and rotated down and is sprayed in parabolic curves, mists are evenly distributed by the air generated by the propeller and can be sprayed wider, spraying uniformity is guaranteed, and pesticide effect is greatly improved.
Owner:广西乐维科技有限公司
Wing deformation type bionic unmanned aerial aircraft and deformation control method
ActiveCN107054645AImprove wind resistance and maneuverabilityImprove flight stabilityOrnithoptersTerrainFlight vehicle
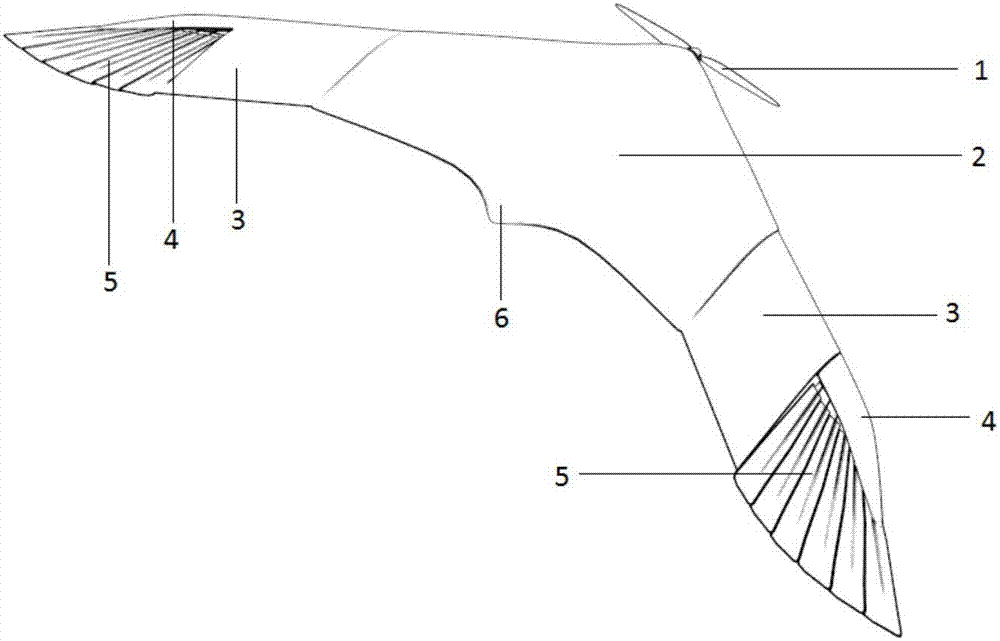
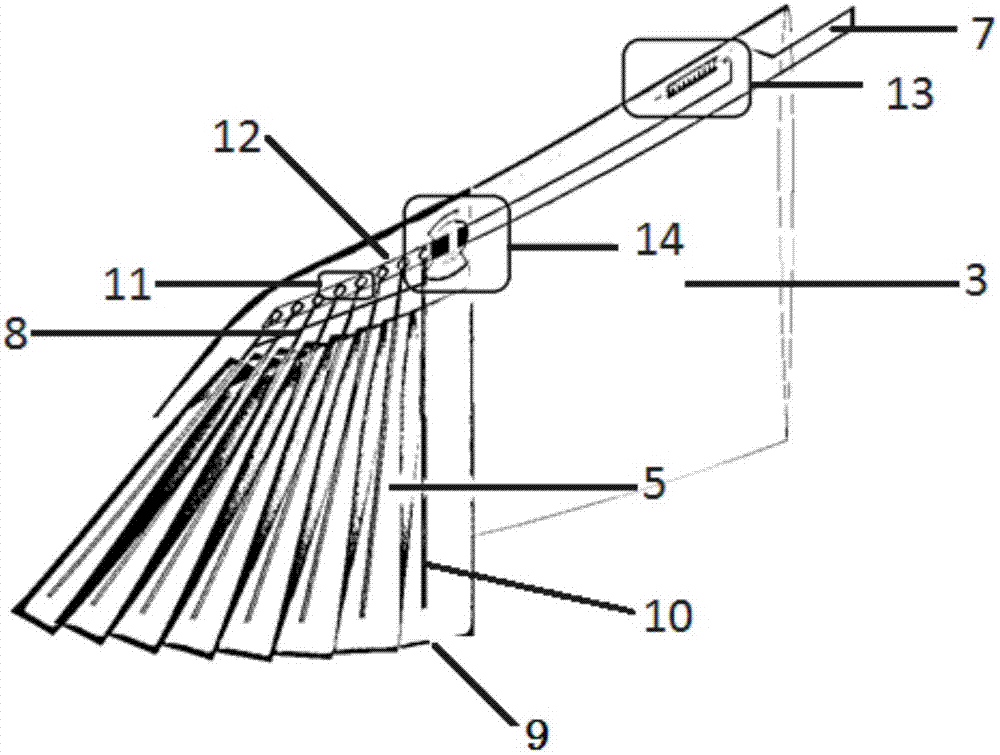
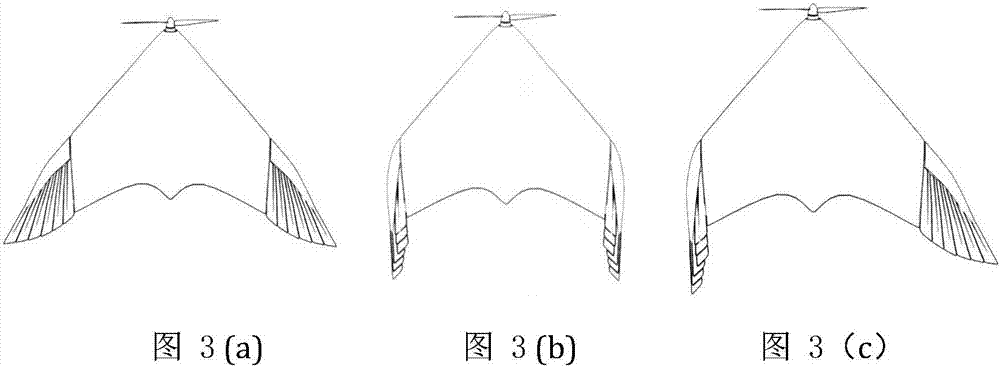
The invention relates to a wing deformation type bionic unmanned aerial aircraft and a deformation control method. The wing deformation type bionic unmanned aerial aircraft consists of six functional parts, such as a propeller, a wing body integration wing section, telescopic wing sections, folded wing control sections, bionic wings and a stable tail wing section. The wing deformation type bionic unmanned aerial aircraft has the advantages that by adopting the two types of basic deformation bionic combinations of extending and retraction of the telescopic wing sections and folding of the bionic wings, the pneumatic configuration of a bird in flying is simulated, so that the wing deformation type bionic unmanned aerial aircraft can flexibly and stably fly under the complicated terrains of cities, forests, mountains and the like and the limited space, random, turbulence flow, low-altitude and ultralow-altitude environments; the defect of difficulty in quickly, flexibly, stably and flexibly flying across the complicated near-ground turbulent flow environment in the traditional fixed-wing or multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is overcome.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
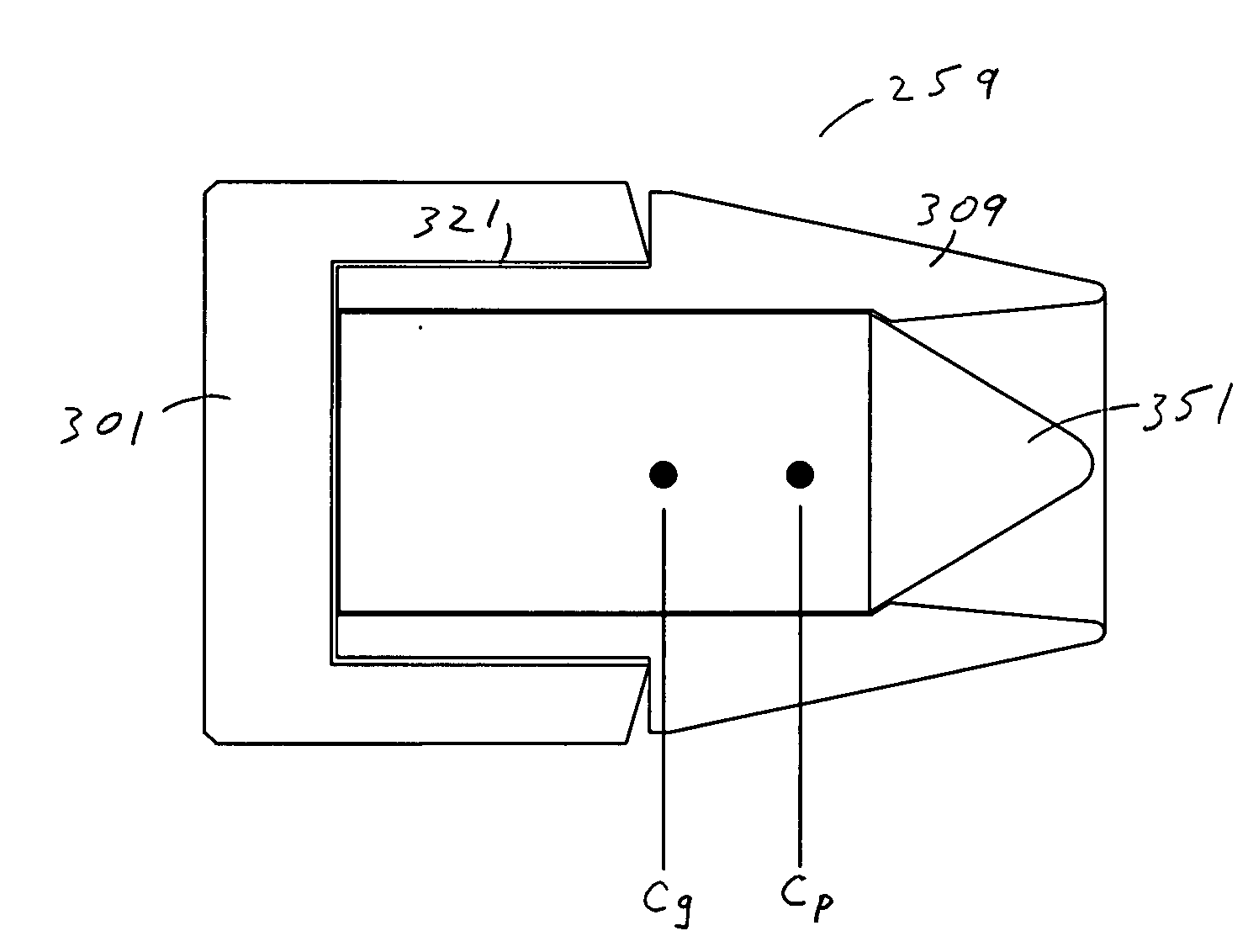
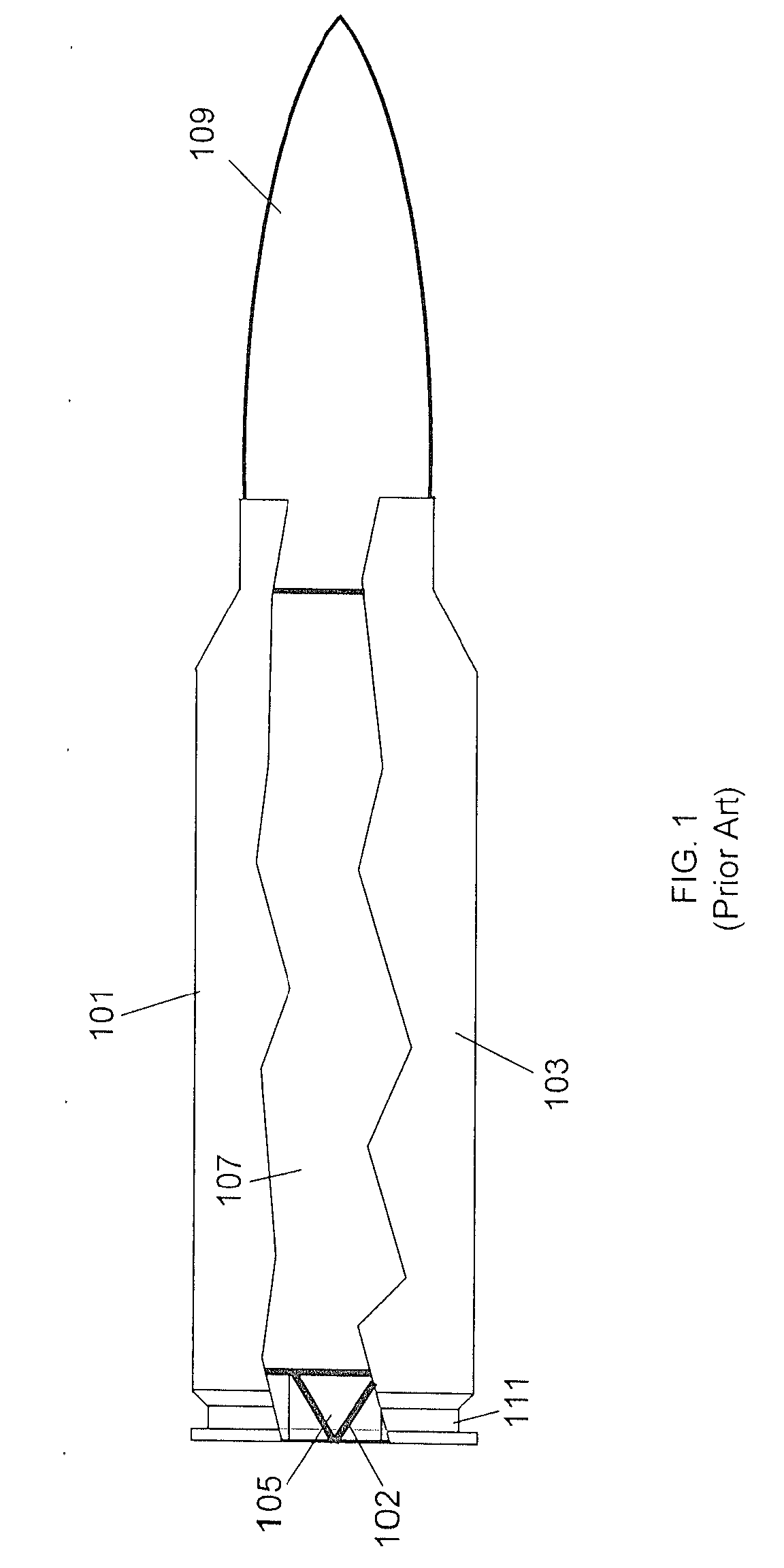
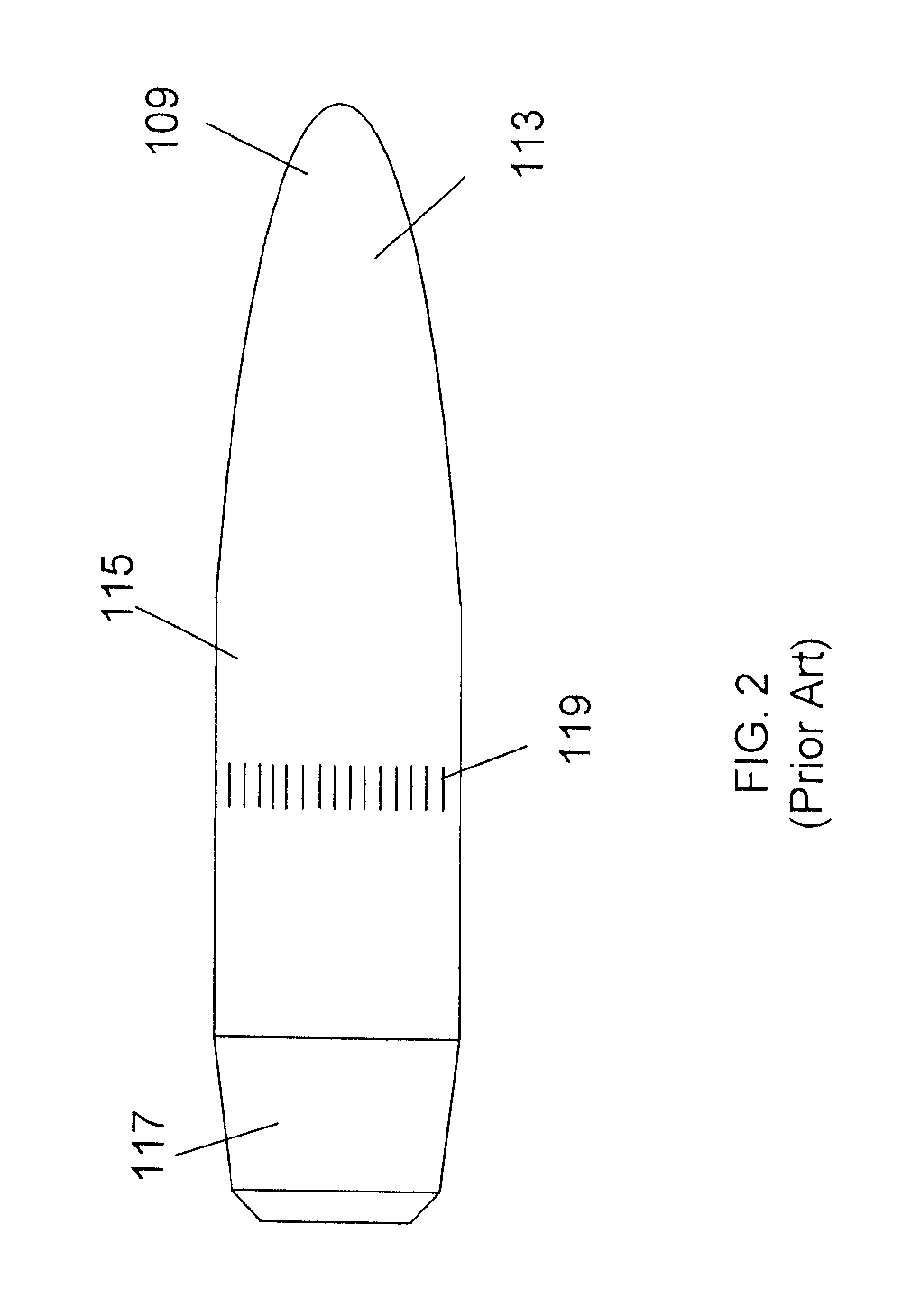
Special purpose small arms ammunition
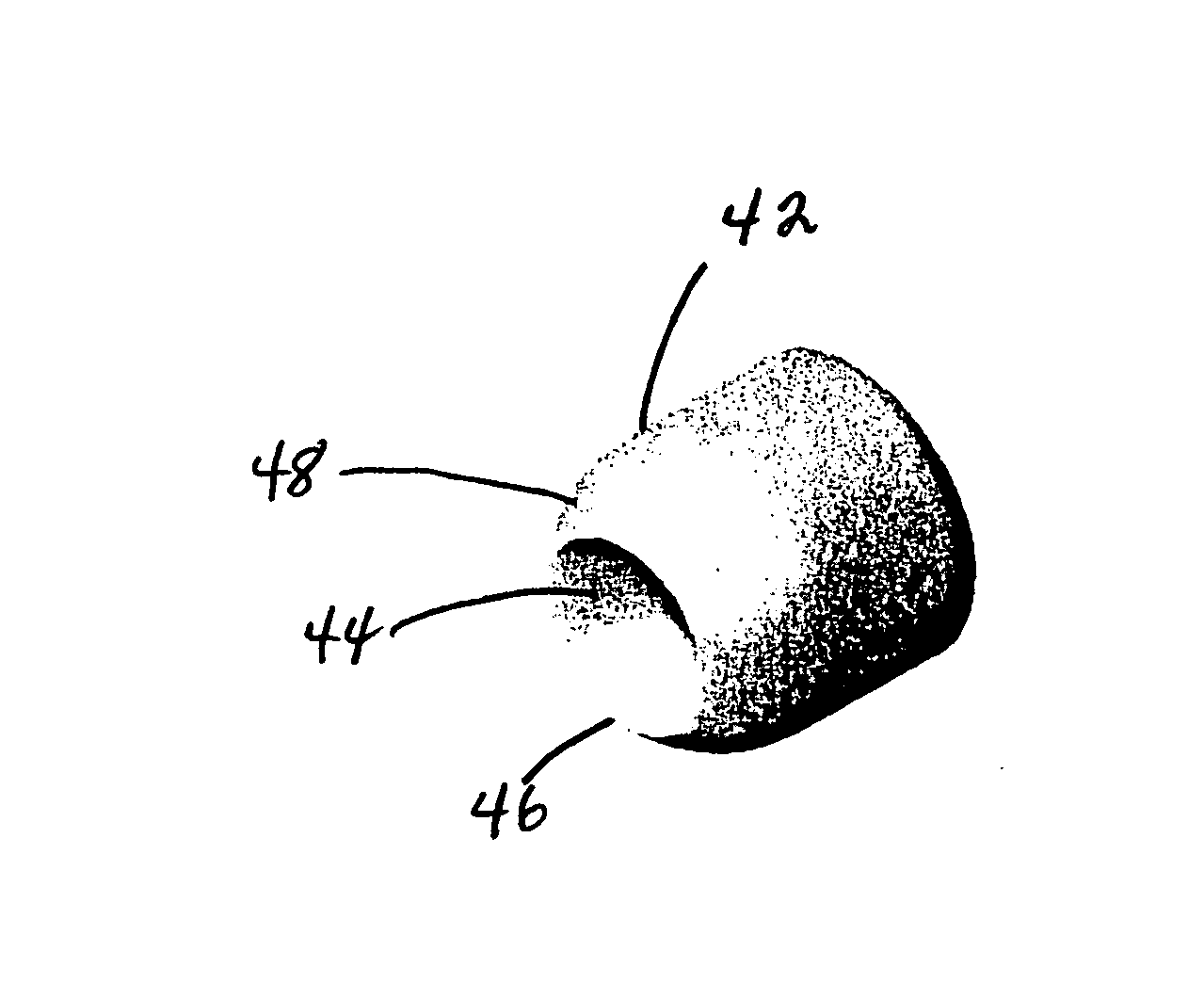
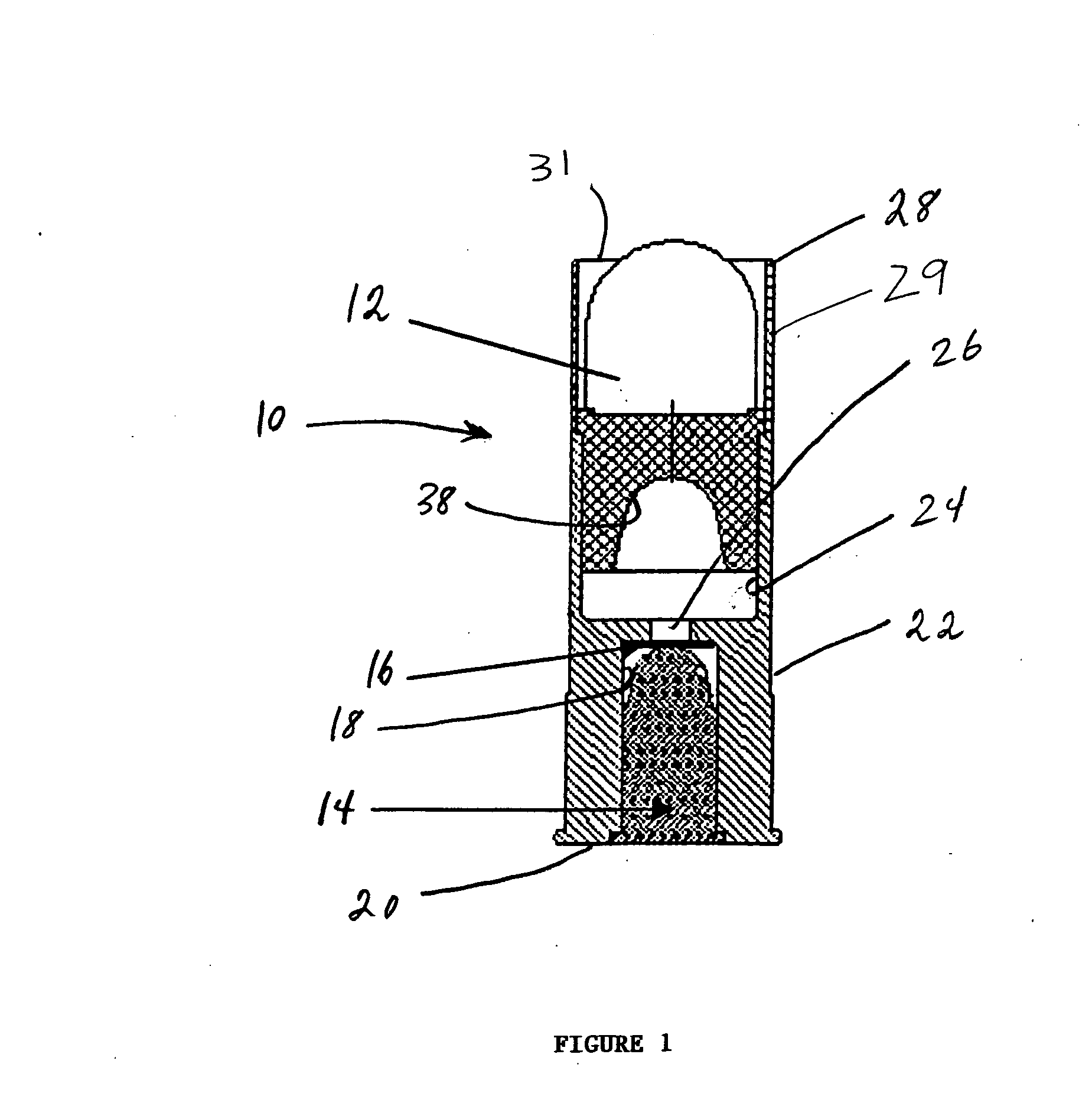
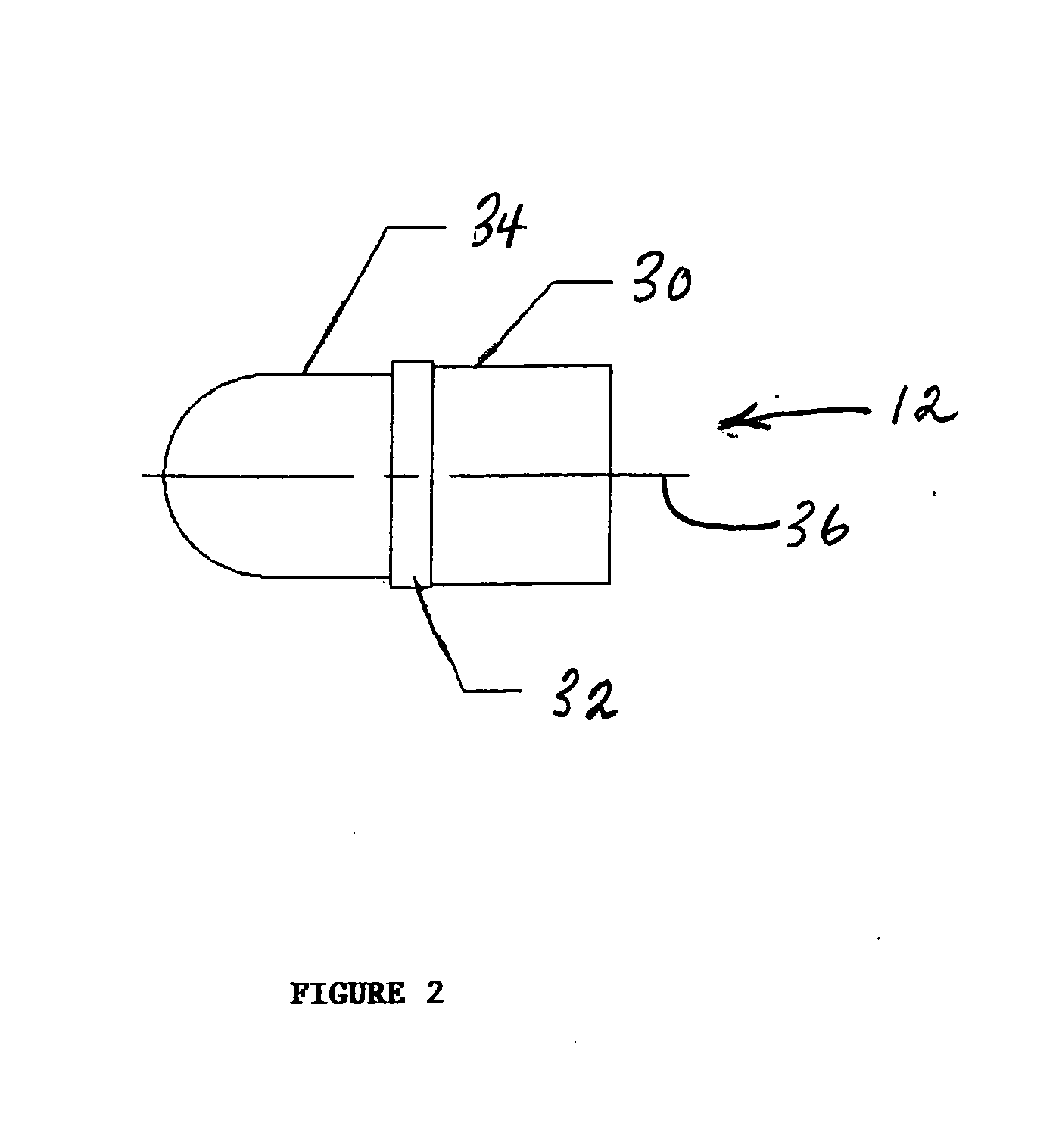
ActiveUS20080092768A1Improve flight stabilityFast spinAmmunition projectilesProjectilesHigh densityEngineering
A multi-piece projectile for a small arms cartridge includes a metal cup that has a bore, a plastic sheath having a through hole and a high-density core. The cup is a cylindrical metal structure having a bore. The sheath is a cylindrical end and a conical end and a through hole. The core is a cylindrical structure having conical end and a blunt end. The projectile is assembled by placing the core in the through hole of the sheath and then pressing the sheath into the bore of the cup. The assembled projectile is attached to the cartridge by crimping the cup to the orifice in the end of the cartridge casing after it is filled with the propellant. When the projectile is fired all of the components remain coupled together but break apart upon impact with a target. Because the core has a higher mass than the other components the components separate very easily, the majority of the kinetic energy remains in the core. Once separated from the other components, the core is able to penetrate through various protective materials.
Owner:XTEK
Heavy-load low-structure-complexity double-coaxial-twin-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN104859854AIncrease payloadIncrease output powerPropellersRotocraftDrive shaftThrough transmission
The invention discloses a heavy-load low-structure-complexity double-coaxial-twin-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle, wherein rotor transmission mechanisms are arranged at the left side and the right side of a vehicle body of an unmanned aerial vehicle body; through transmission mechanisms arranged on the unmanned aerial vehicle body, power is transmitted to the rotor transmission mechanisms arranged at the two sides of the unmanned aerial vehicle body through driving shafts; the rotor transmission mechanisms transmit the power to an upper rotor and a lower rotor through an upper rotor transmission rod and a lower rotor transmission rod via the transmission among four mutually engaged bevel gears; and the identical-rotating-speed and opposite-direction rotation of the upper rotor and the lower rotor is realized. A total variable-pitch mechanism is arranged between the upper rotor transmission rod and the upper rotor, and the regulation of the pitch angle and the roll angle of the unmanned aerial vehicle is realized; a variable-total-pitch mechanism is arranged between the lower rotor transmission rod and the lower rotor, the regulation of the total pitch of the unmanned aerial vehicle is realized; and the yaw angle and the total lift of the unmanned aerial vehicle are controlled. The heavy-load low-structure-complexity double-coaxial-twin-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle has the advantages that the characteristics of heavy effective load and high output power are realized; and a redundancy design method is adopted, and the flight stability of the unmanned aerial vehicle is improved through the design of multiple rotors and multiple sets of variable-pitch mechanisms.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
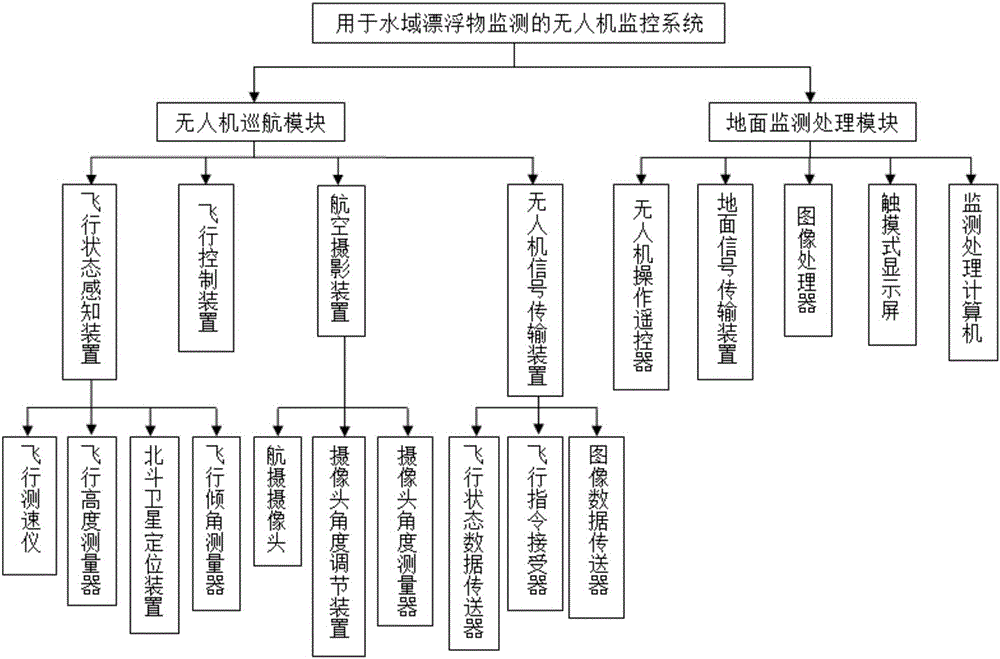
Unmanned aerial vehicle monitoring system for monitoring floating objects in water
InactiveCN106534811AReduce energy consumptionHigh degree of intelligenceClosed circuit television systemsObservation pointWater flow
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle monitoring system for monitoring floating objects in water. The system comprises a UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) cruise module and a ground monitoring processing module. By using the UAV cruise module to carry out monitoring, most water areas can be reached, the implementation difficulty of monitoring is small, a UAV does not carry monitoring personnel, the UAV cruise module reaches an observation point in the air, the disadvantages of power safety reliability and the interference of water area velocity and water flow direction by using an observation ship are overcome, the possibility of accidents is little, the reliability and safety of monitoring are improved, the floating objects in a large water area can be monitored in a short time, the monitoring efficiency is improved, a lot of manpower and resources are saved, the energy consumption of monitoring personnel is reduced, a monitoring area and a water area floating object area can be accurately calculated, the density of the water area floating objects is accurately calculated, and the analysis decision and further measures are facilitated according to provided detailed monitoring data.
Owner:王昱淇
Composite rotor craft
InactiveCN103318406AImprove all-terrain passing abilityImprove efficiencyRotocraftFlight control modesCantilever
The invention relates to a composite rotor craft. The composite rotor craft comprises a craft main body, an energy device, a plug-in connector and a control device, wherein the craft main body comprises a main propeller and a plurality of auxiliary propellers; the main propeller comprises a main rotor I, a main rotor II and a main duct; the main rotor I and the main rotor II are fixed in the main duct through a main duct supporting frame; the part, in the main duct, of the outer edge of the main duct supporting frame is provided with a plurality of vertical connecting rods; cantilevers are outward and horizontally arranged at the bottoms of all the vertical connecting rods; the auxiliary propellers are arranged at the outer ends of all the cantilevers. The composite rotor craft has the benefits that the integration of various rotor flight modes is adopted, the flight efficiency is greatly improved, the flexibility of the craft is greatly improved, and the flight stability and reliability are also greatly improved; an advanced flight control mode is adopted, a plurality of rotors can be simultaneously controlled and adjusted, the control difficulty of the craft is greatly reduced, and the flight efficiency of the craft is improved.
Owner:长源动力(北京)科技有限公司
Special purpose small arms ammunition
A multi-piece projectile for a small arms cartridge includes a metal cup that has a bore, a plastic sheath having a through hole and a high-density core. The cup is a cylindrical metal structure having a bore. The sheath is a cylindrical end and a conical end and a through hole. The core is a cylindrical structure having conical end and a blunt end. The projectile is assembled by placing the core in the through hole of the sheath and then pressing the sheath into the bore of the cup. The assembled projectile is attached to the cartridge by crimping the cup to the orifice in the end of the cartridge casing after it is filled with the propellant. When the projectile is fired all of the components remain coupled together but break apart upon impact with a target. Because the core has a higher mass than the other components the components separate very easily, the majority of the kinetic energy remains in the core. Once separated from the other components, the core is able to penetrate through various protective materials.
Owner:XTEK
Bendable wing for micro air vehicle
InactiveUS7331546B2Improve flight stabilityRigid enoughAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesMicro air vehicleWingspan
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Non-lethal ammunition
ActiveUS20080017064A1Maximize flight stabilitySufficient weightAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionEngineeringHigh pressure
Owner:DEFENSE TECH
Multi-rotor plant protection unmanned aerial vehicle
PendingCN107344618AImprove space occupancyOverall small sizeFuselagesInsect catchers and killersUncrewed vehicleElectric machinery
The invention discloses a multi-rotor plant protection unmanned aerial vehicle which comprises a vehicle body and a power module, a spraying module and a control module arranged on the vehicle body, wherein the vehicle body comprises an engine body, engine arms and a foot stool; the power module comprises a power source, a driving module and a motor module; the power source is equipped with a power supply output end; a power end of the driving module is connected with the power supply output end; and the output end of the driving module is connected with the motor module. The invention aims to provide the multi-rotor plant protection unmanned aerial vehicle; a drug kit and a battery can be directly arranged on the engine body and the flying property of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be promoted; a liquid level detection device is arranged on the engine body and can be used for monitoring the liquor storage in the drug kit at any time; and the drug kit and the engine body are in inserted connection with each other, the drug kit can be quickly and conveniently replaced, the time can be saved and the working efficiency can be increased.
Owner:超农力浙江智能科技有限公司
Controllable control surface-based rocket and attitude self-correction control method thereof
InactiveCN108681329AEliminate spinSolve the problem of unstable flight attitudeCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsFlight heightGyroscope
The invention relates to a controllable control surface-based rocket and attitude self-correction control method thereof, belongs to the technical field of spaceflight, and aims to solve the problem of instable attitude when a rocket takes off and the problem of spinning of the rocket in the process of operating in air. The rocket includes controllable control surfaces and an electronic control board used for controlling the controllable control surfaces; each controllable control surface is connected with a rocket body through a corresponding steering engine; and the electronic control boardincludes a gyroscope used for measuring the triaxial angular velocity and attitude angle of the rocket, a barometer used for measuring rocket flight height and a processor. The gyroscope and the barometer are utilized to obtain current actual measurement attitude data, Kalman filtering is utilized to filter triaxial angular velocity input to a PID controller; the eventually obtained flight height,triaxial angular velocity and attitude angle are input to the PID controller; the PID controller compares the read actual measurement attitude data with ideal attitude data, and provides a reasonablePID controlled quantity through operation of the processor; and the PID controlled quantity drives a rocker arm of the steering engine to act, thereby achieving the purpose of controlling the attitude of the rocket eventually.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Aerial propelling device suitable for amphibious unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN103204237AGood for flight controlMaintain propulsion performancePropellersDepending on number of propellersMotor driveBevel gear
The invention discloses an aerial propelling device suitable for an amphibious unmanned aerial vehicle. A first blade and a second blade of the propelling device are mounted at two ends of a second flange. A third blade and a fourth blade are mounted at two ends of a first flange. A first bevel gear, a third bevel gear and a fourth bevel gear are connected to a cross shaft through bearings. The second bevel gear is mounted on the first flange. The fourth bevel gear is mounted on the second flange. A blade motor drives a middle shaft to transmit motion to the first flange, the rotation of the first flange drives the first bevel gear to move so as to allow the other three bevel gears to move, and then four blades are moved. The front blade layer and the rear blade layer of the propelling device rotates coaxially, the rotation directions of the front blade layer and the rear blade layer are opposite, and accordingly influence, caused by deflection torque of one-way rotation, on flying attitude of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be balanced, and aerial flight control of the unmanned aerial vehicle is facilitated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Special purpose small arms ammunition
ActiveUS20110107937A1Fast spinImprove stabilityAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionHigh densityEngineering
A multi-piece projectile for a small arms cartridge includes a metal cup that has a bore, a plastic sheath having a through hole and a high-density core. The cup is a cylindrical metal structure having a bore. The sheath is a cylindrical end and a conical end and a through hole. The core is a cylindrical structure having conical end and a blunt end. The projectile is assembled by placing the core in the through hole of the sheath and then pressing the sheath into the bore of the cup. The assembled projectile is attached to the cartridge by crimping the cup to the orifice in the end of the cartridge casing after it is filled with the propellant. When the projectile is fired all of the components remain coupled together but break apart upon impact with a target. Because the core has a higher mass than the other components the components separate very easily, the majority of the kinetic energy remains in the core. Once separated from the other components, the core is able to penetrate through various protective materials.
Owner:XTEK
Transverse arrangement type composite thrust high-speed helicopter
InactiveCN108045572ASmall aerodynamic interferenceReduce distractionsRotocraftRigid rotorVariable pitch propeller
The invention relates to a transverse arrangement type composite thrust high-speed helicopter. The helicopter comprises a helicopter body, wings symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the helicopter body, a tail wing arranged at the tail of the helicopter body, engines arranged at the ends of the two sides of the wings, transversely arranged rotor wings arranged above the engines and variablepitch propellers arranged at the positions, close to the direction of the tail wing, of the rears of the engines, wherein the tail wing comprises horizontal tails used for achieving effects of stabilizing pitching and vertical fins used for providing yaw direction motion, the axes of the variable pitch propellers are parallel to the axis of the helicopter body. The transverse arrangement type composite thrust high-speed helicopter sufficiently utilizes advancing blades of the rigid rotor wings at a high speed, and thus pneumatic interference among the rotor wings is reduced; the flying stability can be improved through V-shaped arrangement; the rotor wing / wing interference is effectively reduced by the rigid blade characteristic in the forward flying process, and the transverse distancebetween the two rotor wings sharply reduces the rigidness and the weight of the wings; and propellant blades are arranged below the rotor wings, a transmission system is simplified, and the helicopterbody space is saved.
Owner:CHINA HELICOPTER RES & DEV INST
Fluid ejecting apparatus
InactiveUS20090295853A1High strengthIncrease the speed at which a bubble disappearsOther printing apparatusHelmholtz resonatorBiomedical engineering
A fluid ejecting apparatus that ejects fluid includes: a pressure chamber that is filled with the fluid; a pressure generating element that deforms a wall face of the pressure chamber to change a volume of the pressure chamber; a nozzle that is in fluid communication with the pressure chamber and that is used for ejecting the fluid; and a control unit that generates a drive pulse for controlling the pressure generating element. The control unit is able to generate a maintenance drive pulse for ejecting a bubble together with the fluid from the pressure chamber. The maintenance drive pulse includes a first pulse portion that drives the pressure generating element to cause the pressure chamber to expand into an expanded state and a second pulse portion that causes the pressure chamber to contract from the expanded state. The width of the second pulse portion is equal to or smaller than half the Helmholtz resonance period of the fluid with which the pressure chamber is filled.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Aircraft
InactiveCN103112587AImprove lifting efficiencyImprove lifting stabilityPropellersAircraftsFlight vehiclePropeller
The invention discloses an aircraft which comprises a controller, wherein the controller is uniformly provided with and connected with a lifting propeller 1, a lifting propeller 2, a lifting propeller 3, a lifting propeller 4, a horizontal propeller 1, a horizontal propeller 2, a horizontal propeller 3 and a horizontal propeller 4. The lifting of the aircraft mainly depends on the cooperation of the four lifting propellers, and the intelligent lifting can be realized comprehensively by individual control on each lifting propeller caused by the lifting controller, so that the lifting efficiency of the aircraft is high, and the lifting stability is good. The horizontal motion of the aircraft is achieved mainly through the cooperation of the four horizontal propellers, the operation and control technique requirements on operators are not too high, and compared with the traditional aircraft, the horizontal motion flexibility of the aircraft is improved greatly. Through the individual and cooperative control on the four lifting propellers and the four horizontal propellers of the aircraft, the flying flexibility and flying stability of the aircraft are improved.
Owner:曾小敏
Fuel-powered multi-rotor unmanned plane fuel supply scheme
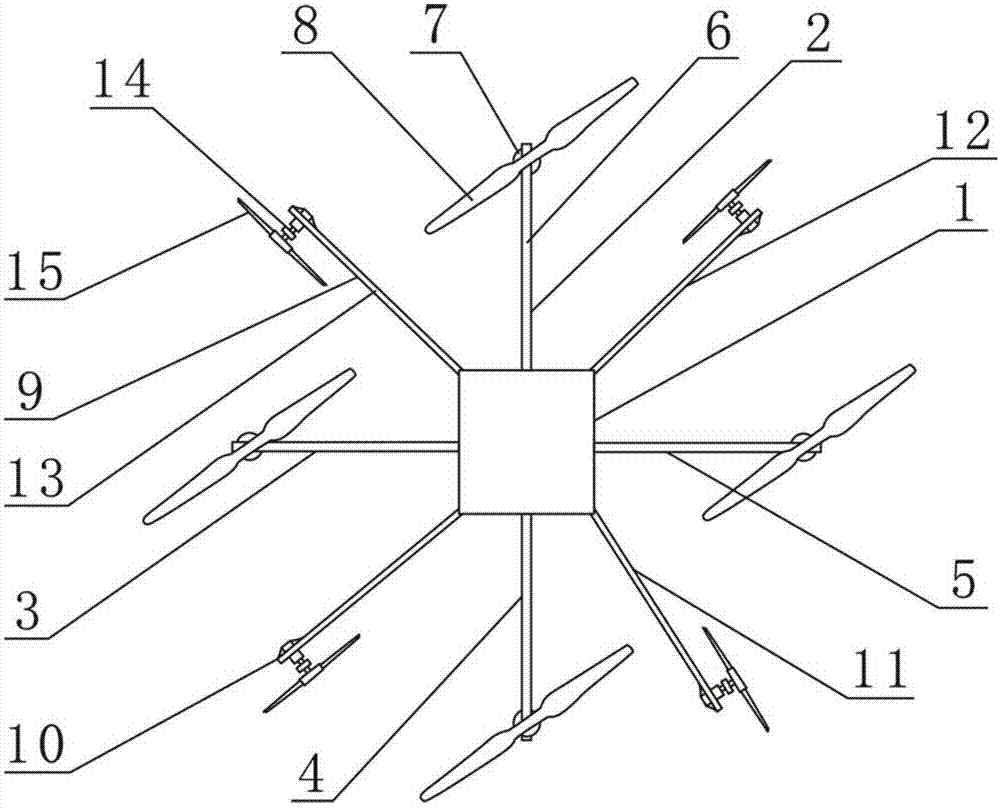
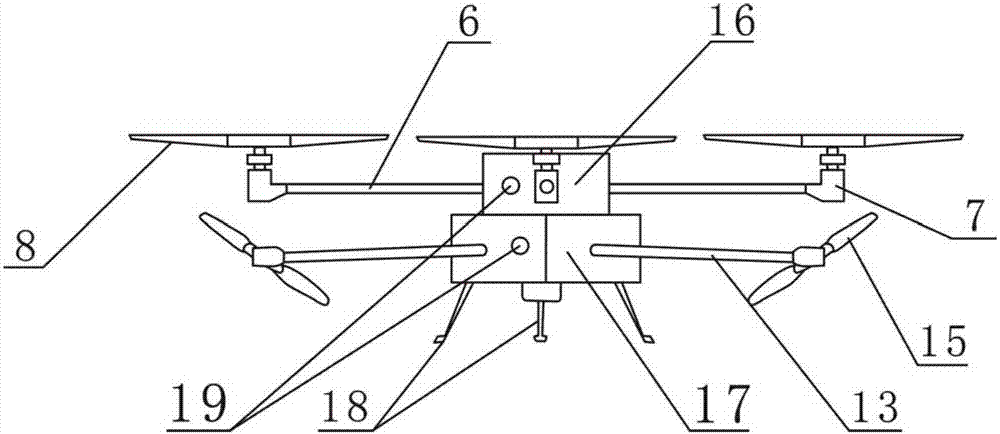
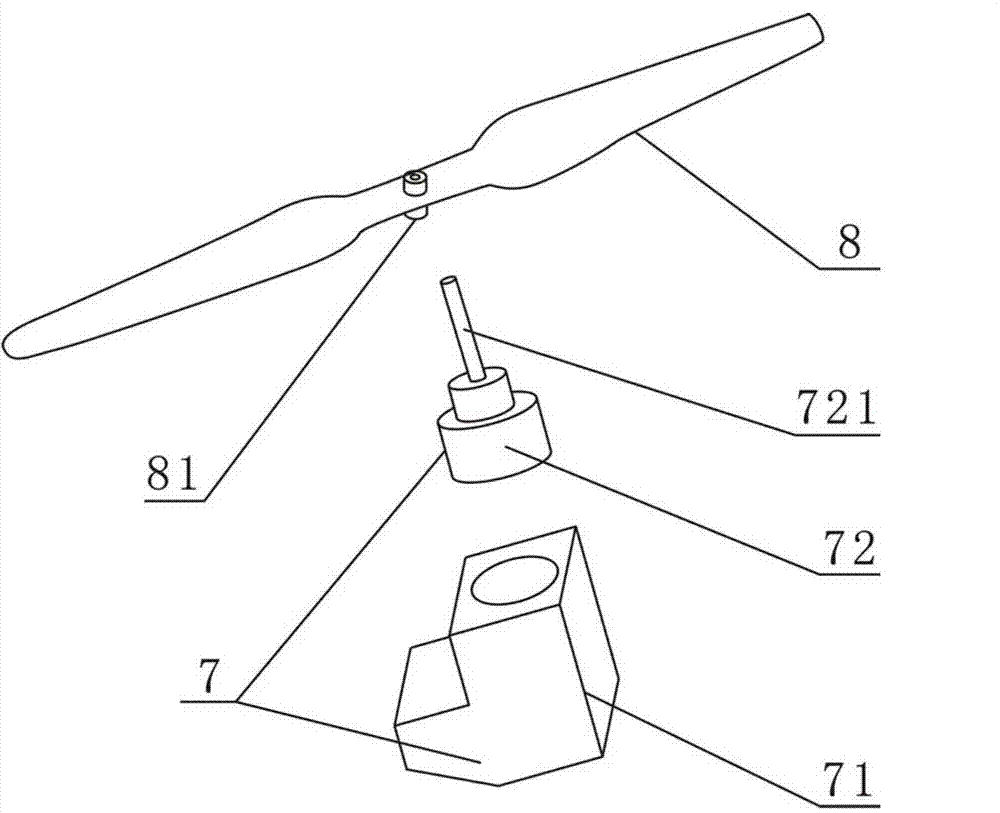
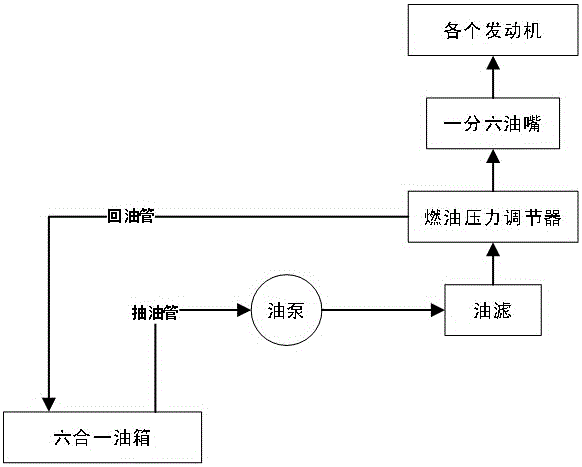
ActiveCN106081132AReduce weightLow costPower plant fuel tanksFuel injection apparatusFuel tankFuel supply
The invention relates to a fuel-powered multi-rotor unmanned plane fuel supply scheme. An all-in-one fuel tank, a fuel pump, a fuel strainer, a fuel pressure regulator, a one-to-more nipple and a fixed support constitute a whole fuel supply system. The central idea of the scheme is all-in-one one-to-more combined design. The fuel tank adopts the all-in-one design: a plurality of partitions with smaller height than the fuel tank are arranged inside the fuel tank, and the upper and lower ends of each partition do not contact the upper and lower surfaces of the fuel tank, so that the whole fuel tank is divided into a plurality of independent small fuel tanks which communicate with each other. The nipple adopts the one-to-more design: one fuel inlet is divided into a plurality of fuel outlets. The fuel pressure regulator and the one-to-more nipple form an integral body, and do not need special arrangement. The scheme solves the following problems: fuel shortage of a certain engine can easily occurs when the fuel-powered multi-rotor unmanned plane is inclined, each engine of the fuel-powered multi-rotor unmanned plane needs one fuel supply system, bubbles can easily appear in the fuel supply system, and the fuel pressure regulator needs to be independently arranged.
Owner:辽宁大壮无人机科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com