Patents
Literature
77 results about "Interrupt latency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
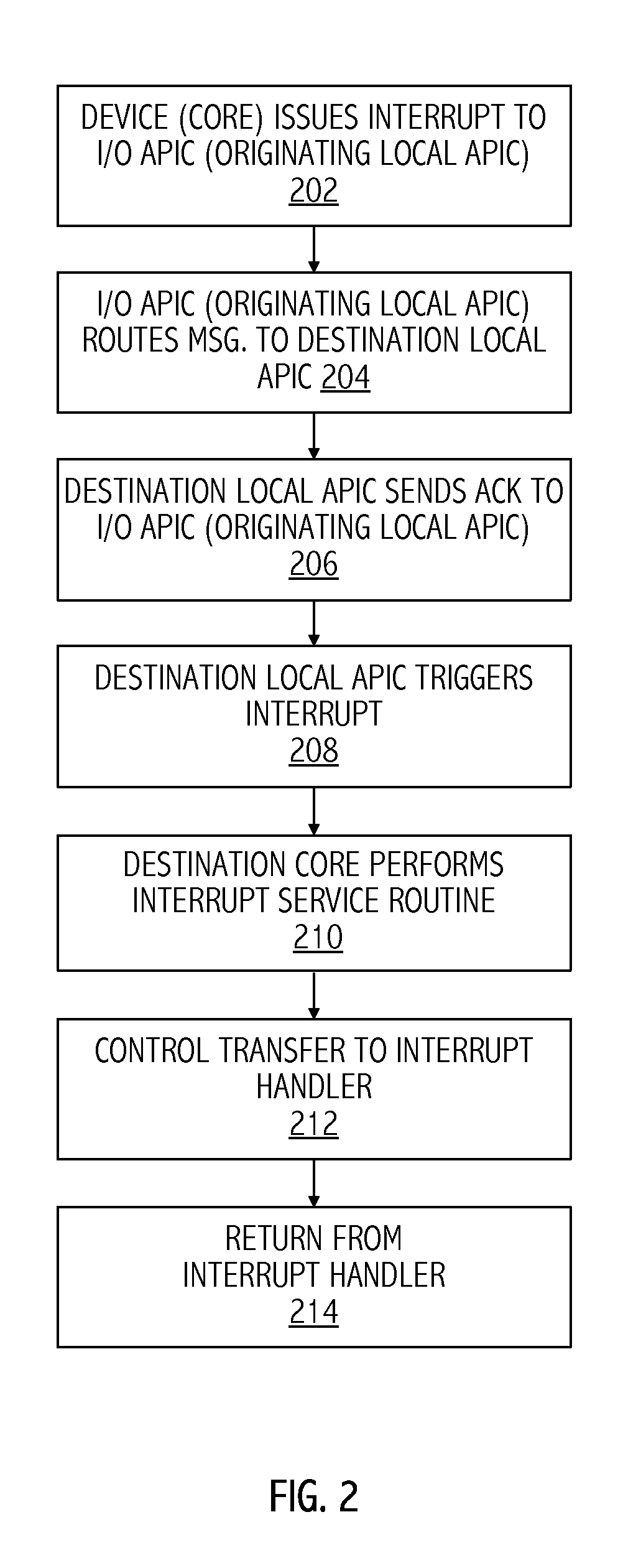
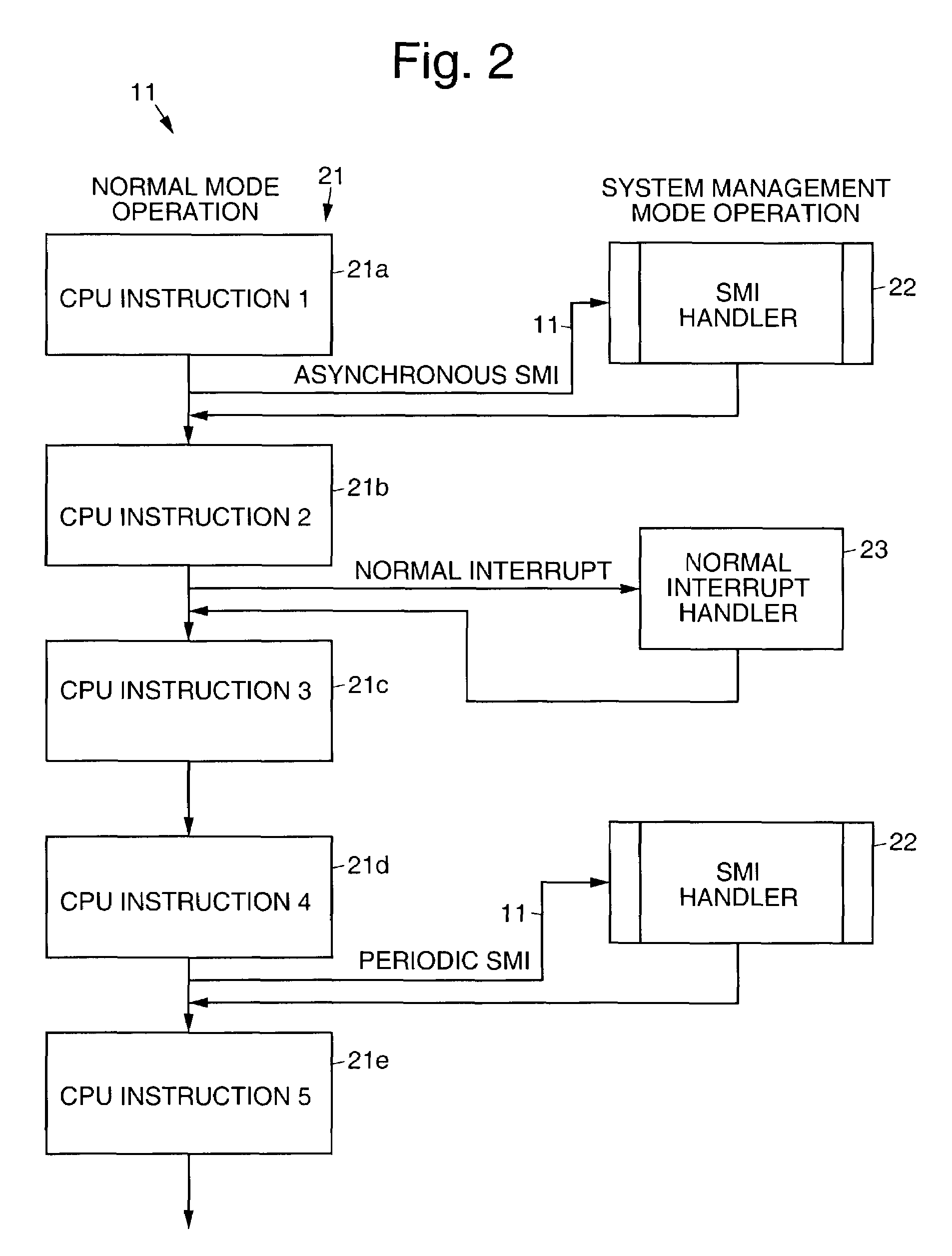
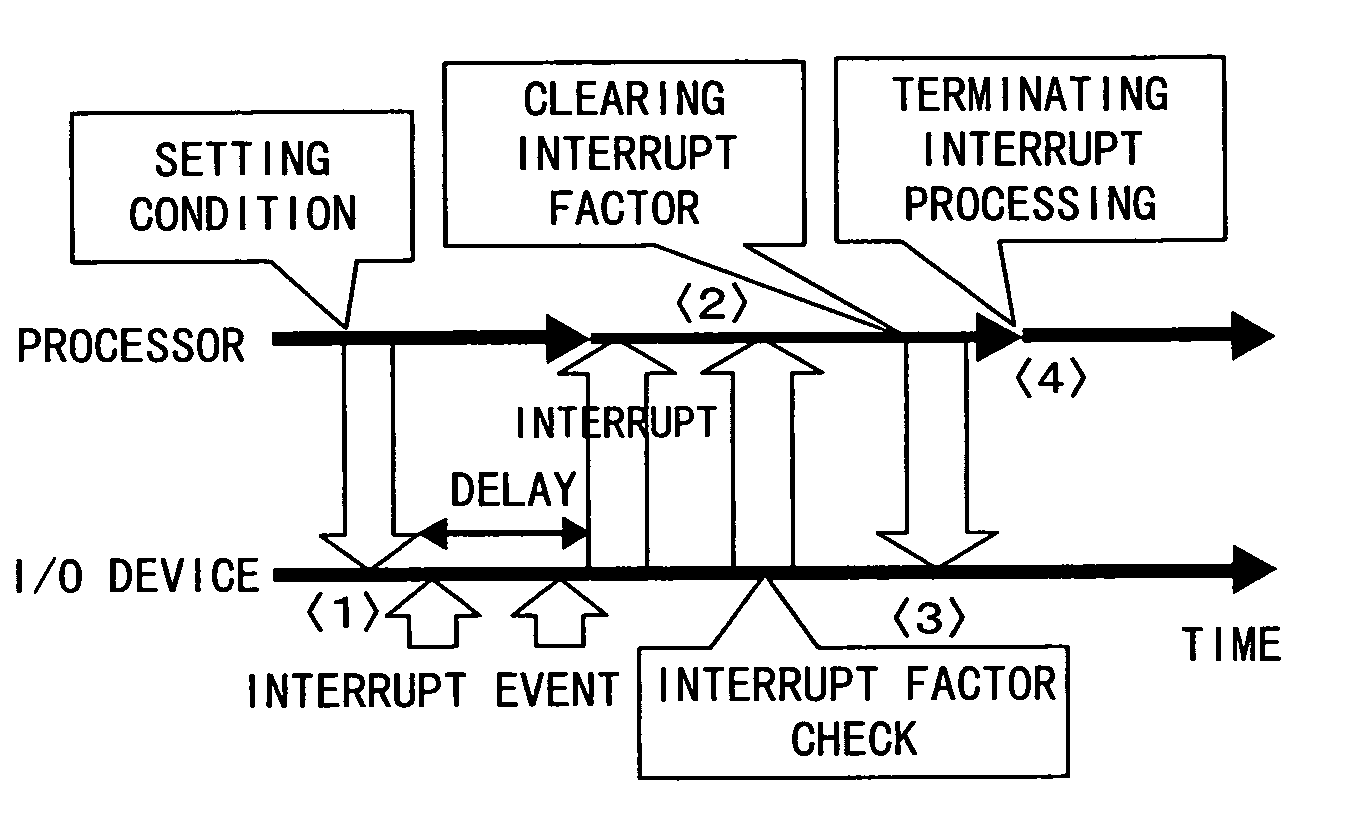
In computing, interrupt latency is the time that elapses from when an interrupt is generated to when the source of the interrupt is serviced. For many operating systems, devices are serviced as soon as the device's interrupt handler is executed. Interrupt latency may be affected by microprocessor design, interrupt controllers, interrupt masking, and the operating system's (OS) interrupt handling methods.
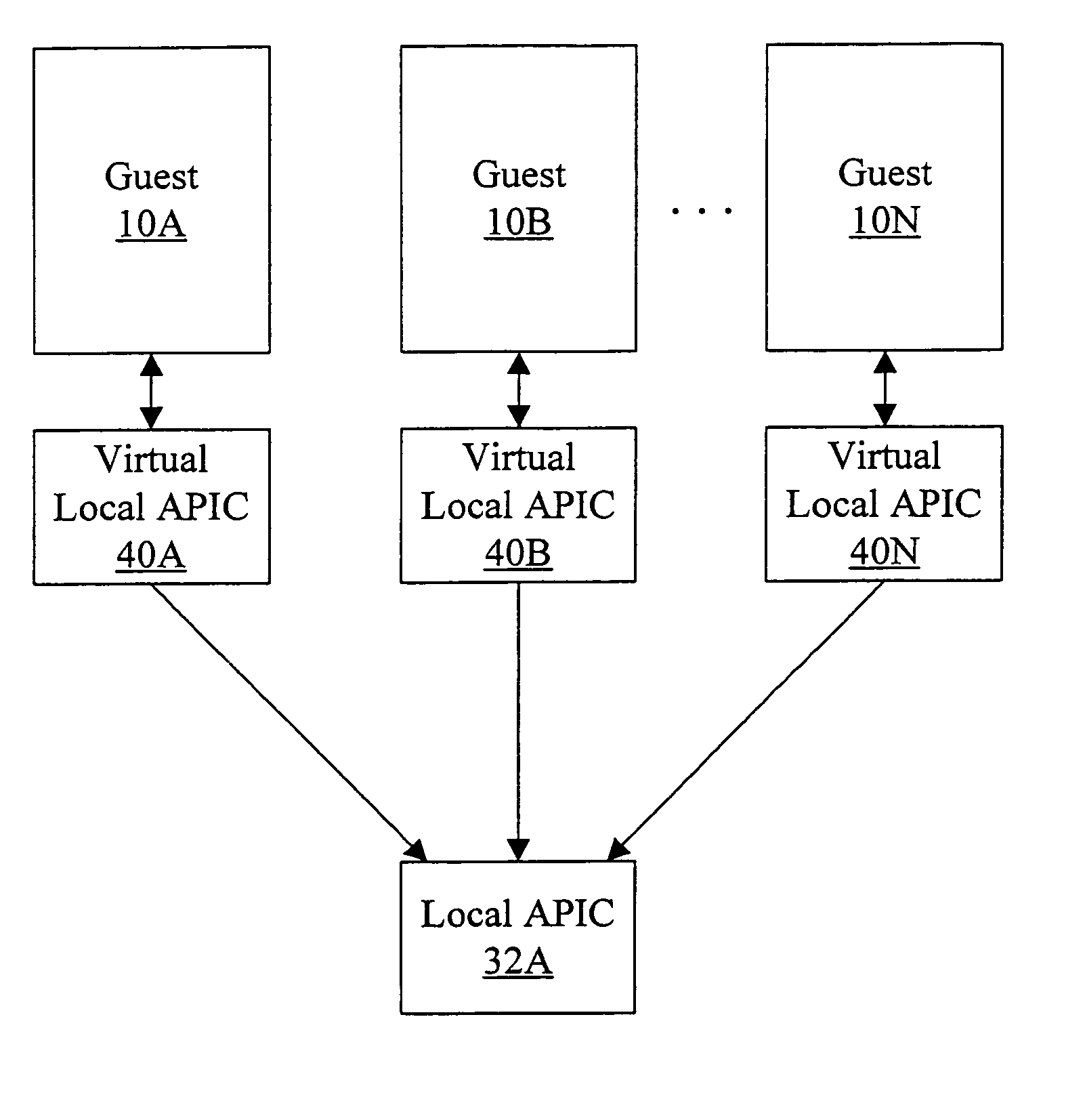
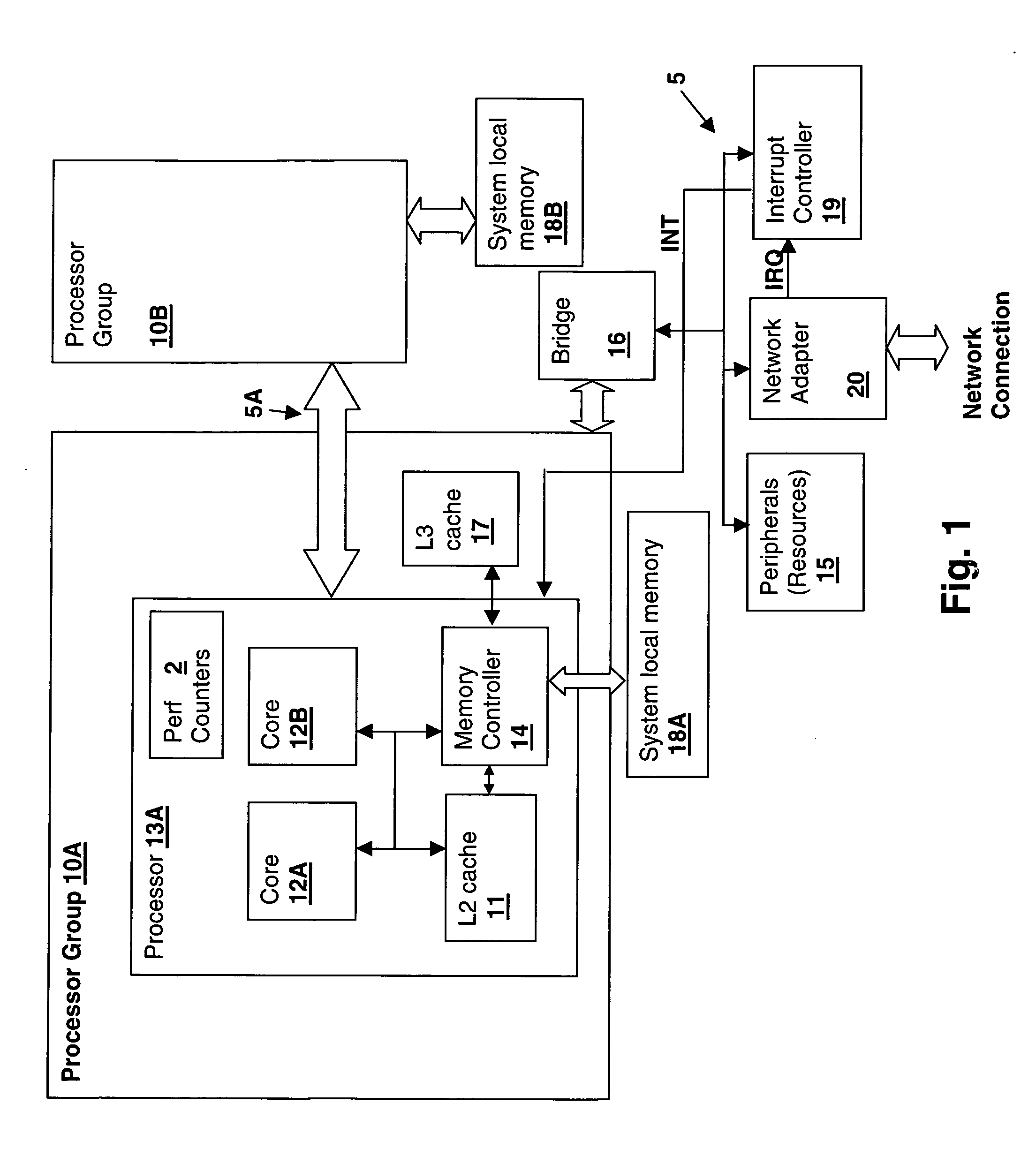
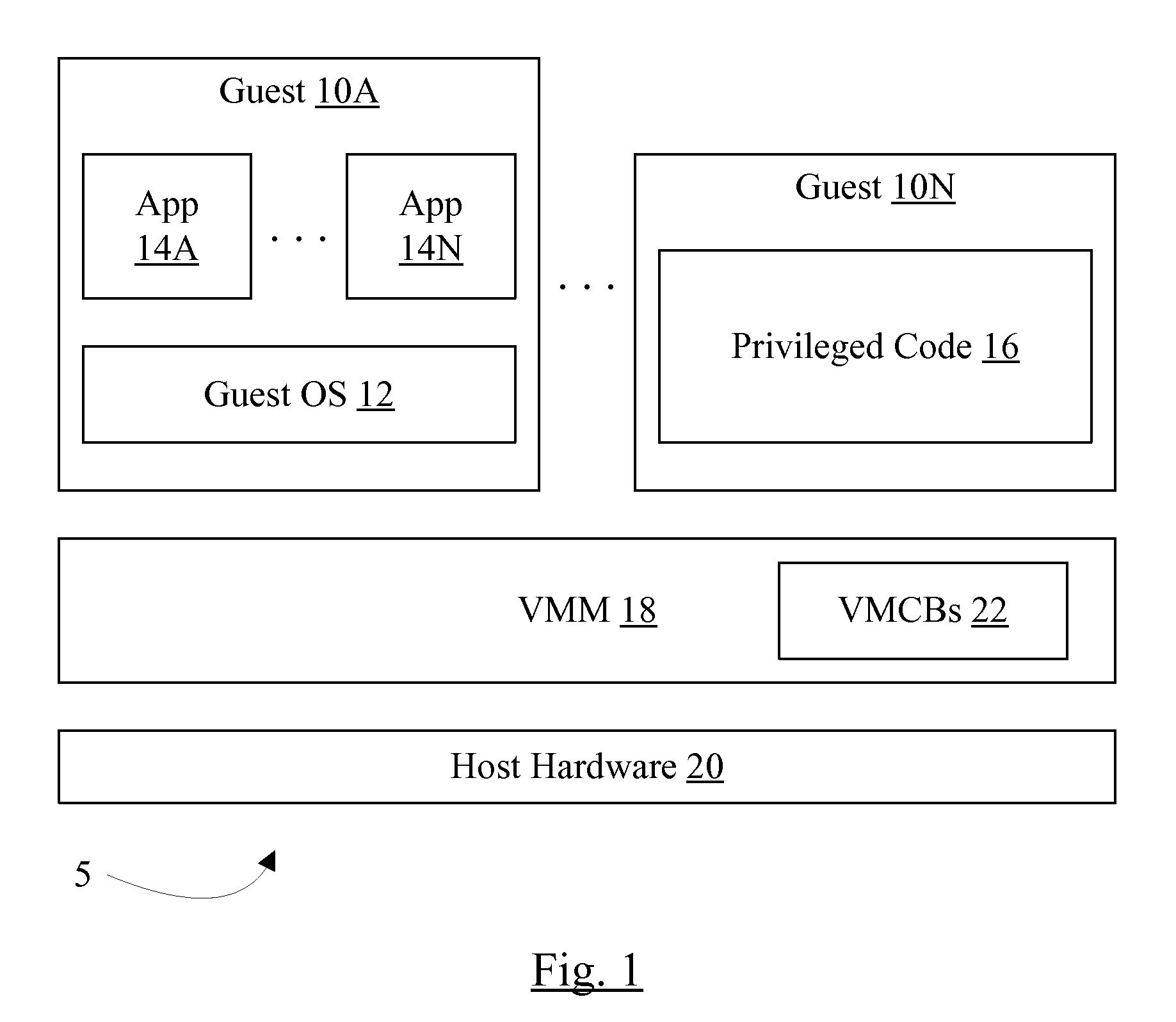
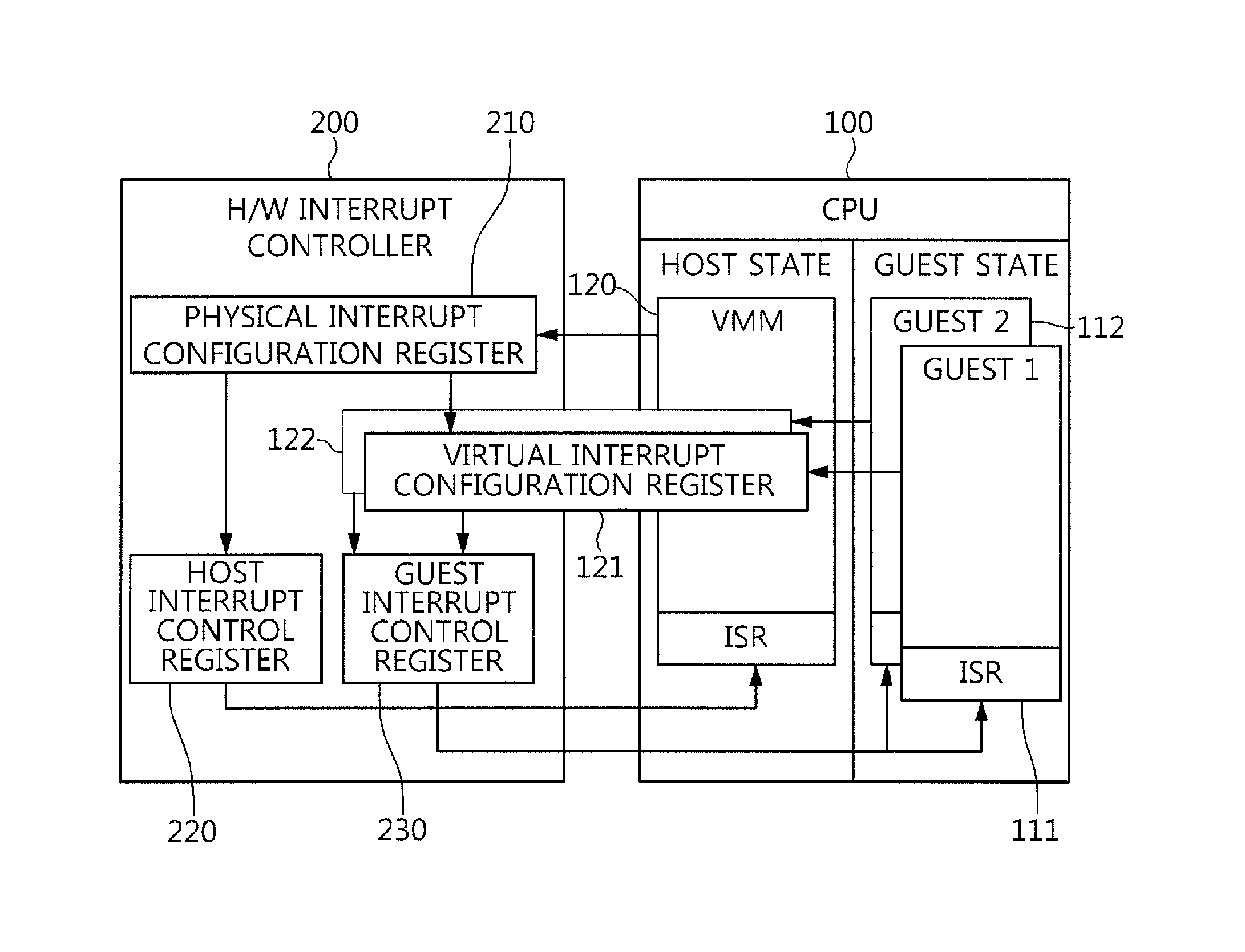
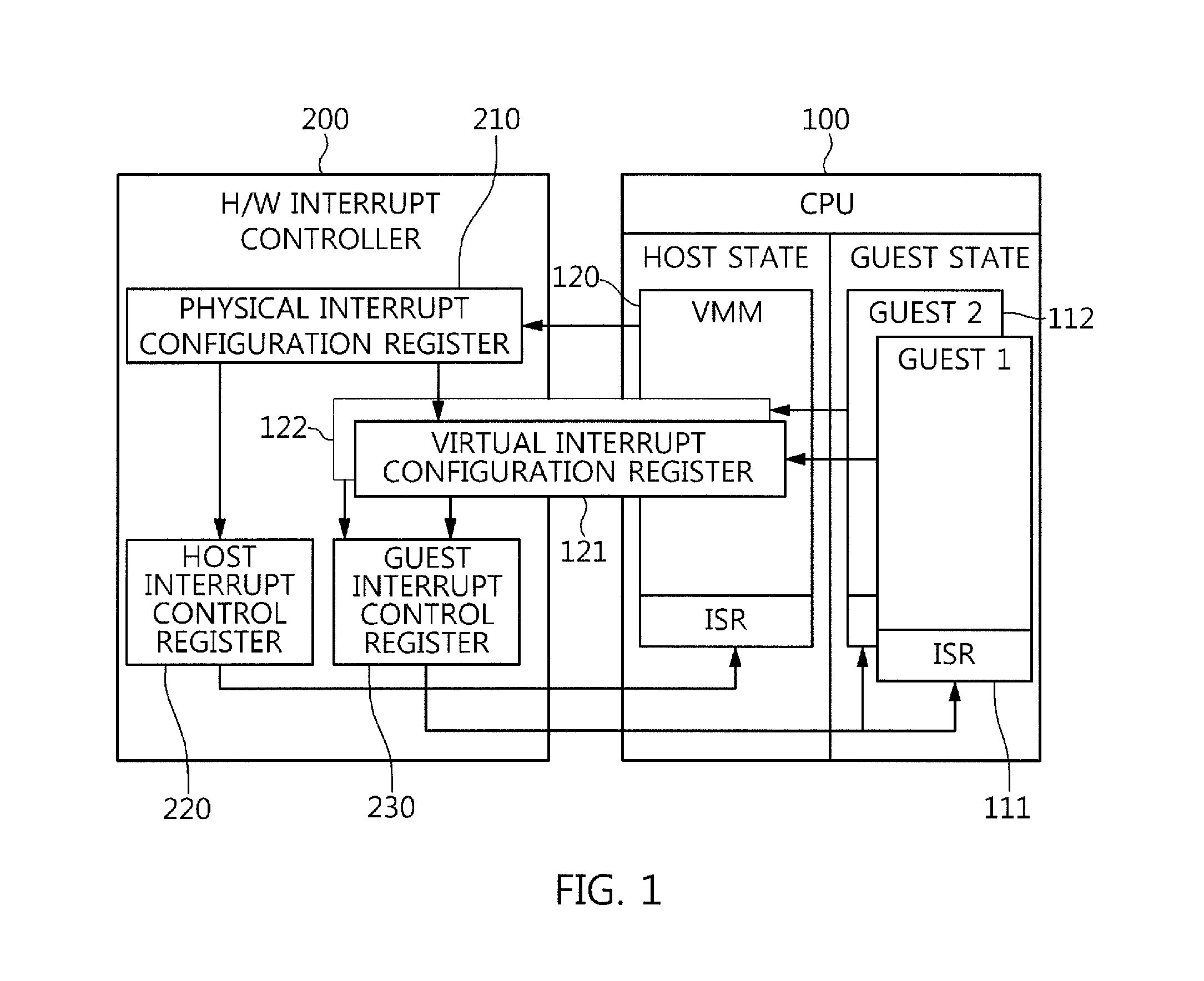
Processor that maintains virtual interrupt state and injects virtual interrupts into virtual machine guests
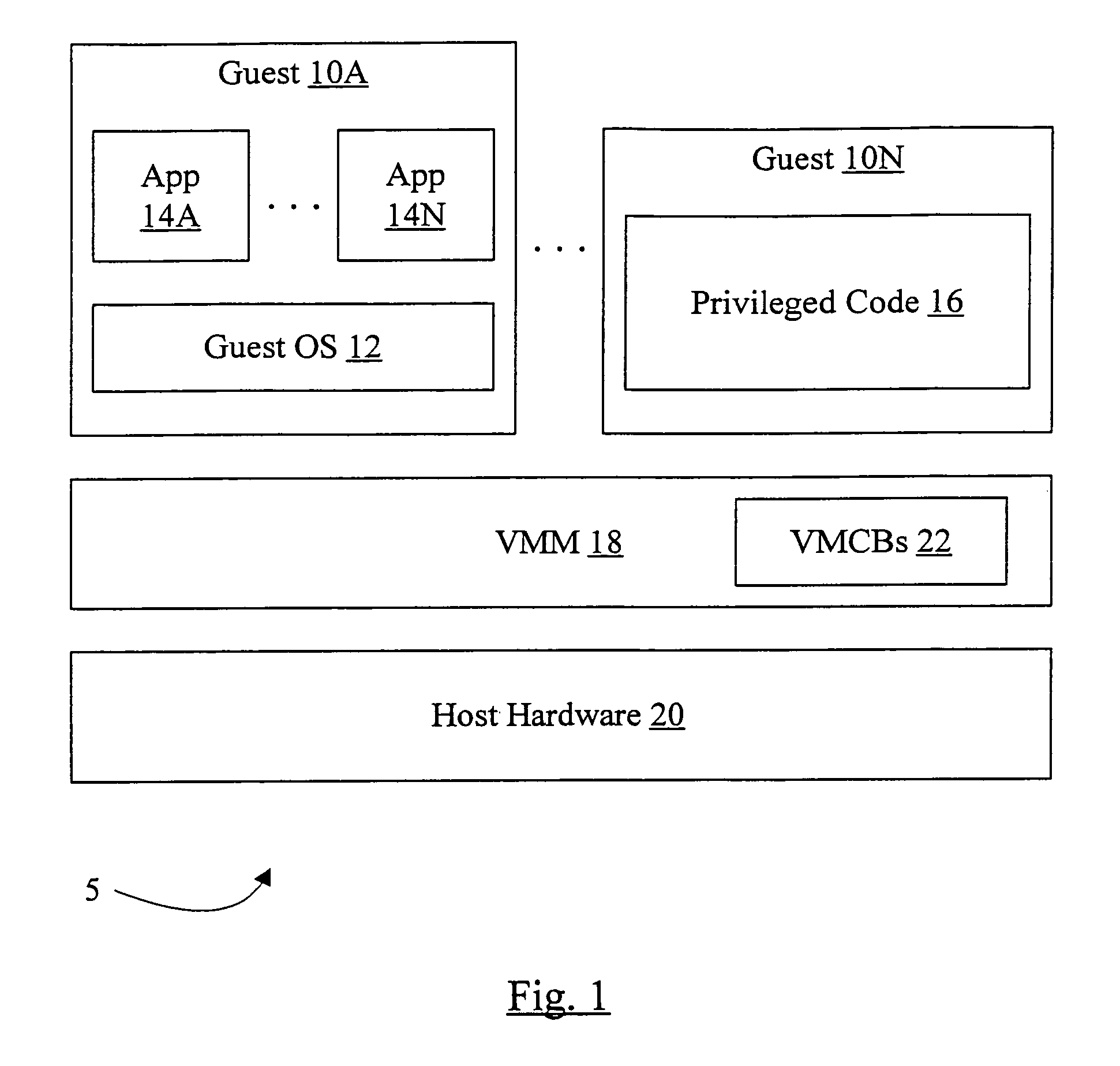
In one embodiment, a processor comprises one or more registers and a control unit. The registers are configured to store interrupt state describing a virtual interrupt. The control unit is configured to initiate the virtual interrupt responsive to the interrupt state. In another embodiment, a method comprises storing an interrupt state describing a virtual interrupt in a storage area allocated to a guest. A processor initiates the virtual interrupt subsequent to initiating execution of the guest, responsive to the interrupt state. In still another embodiment, a computer accessible medium stores a plurality of instructions comprising instructions which, when executed on a processor in response to a physical interrupt: determine a guest into which a virtual interrupt corresponding to the physical interrupt is to be injected; and store an interrupt state describing the virtual interrupt in a storage area allocated to the guest.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
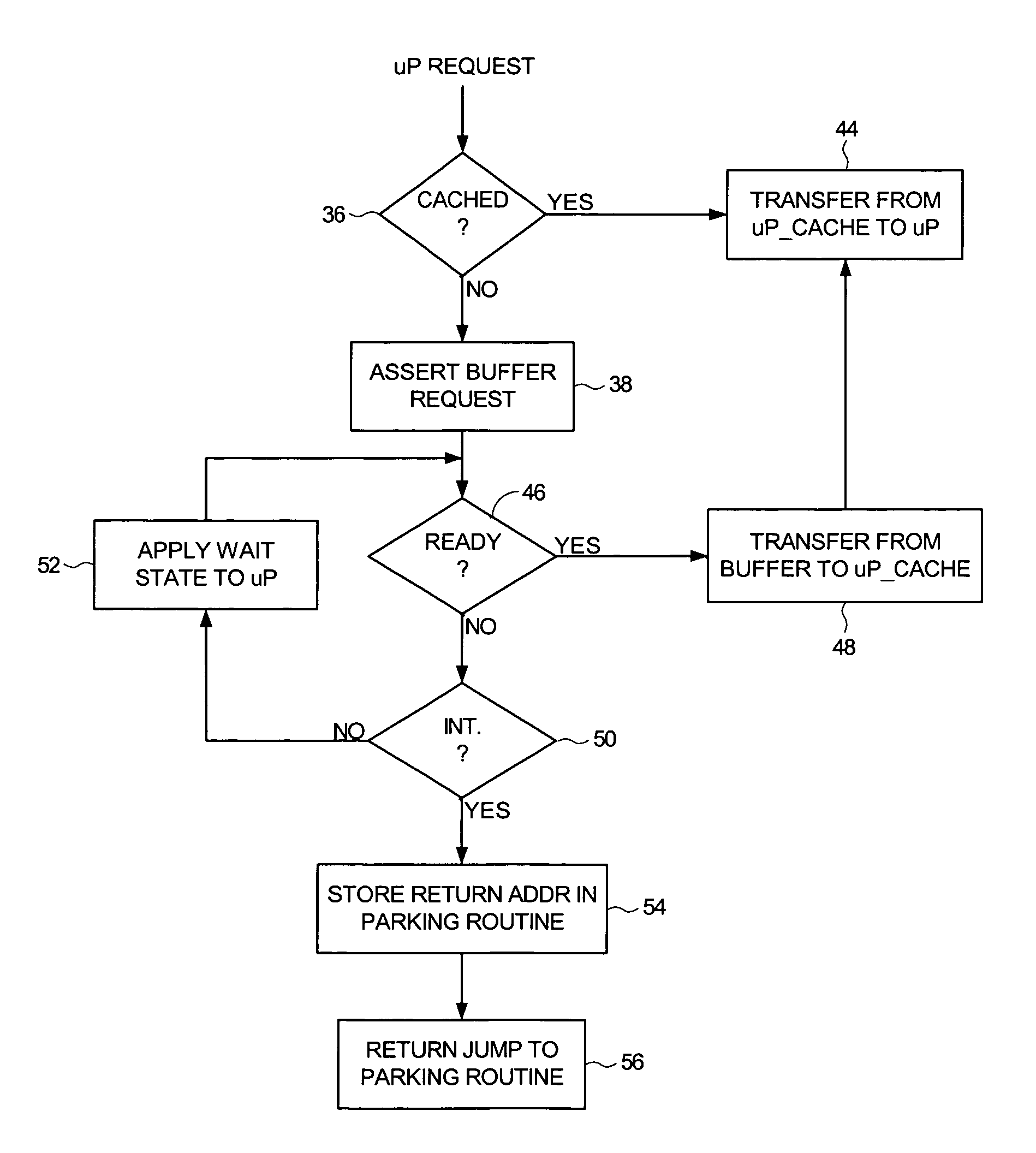
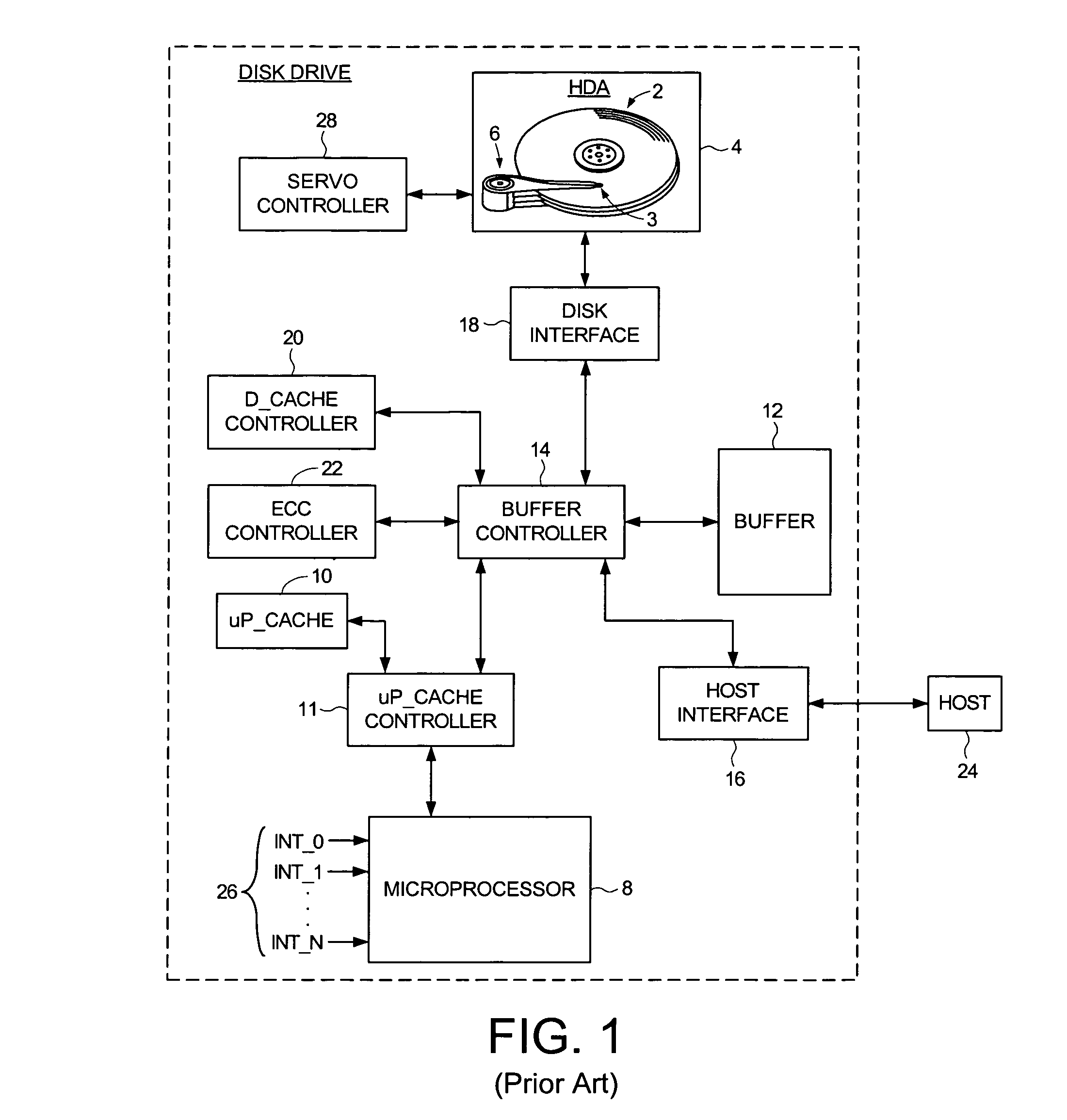
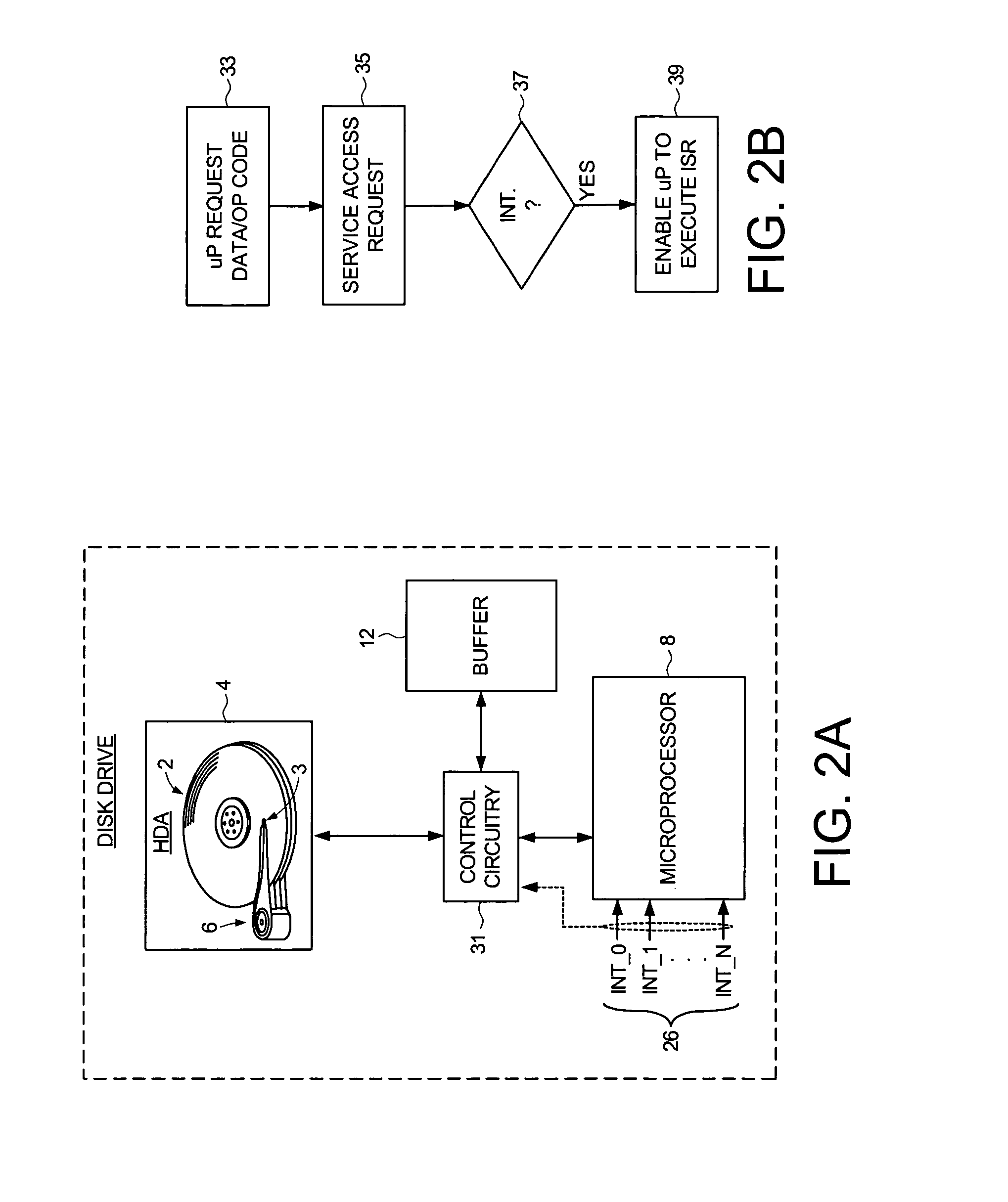
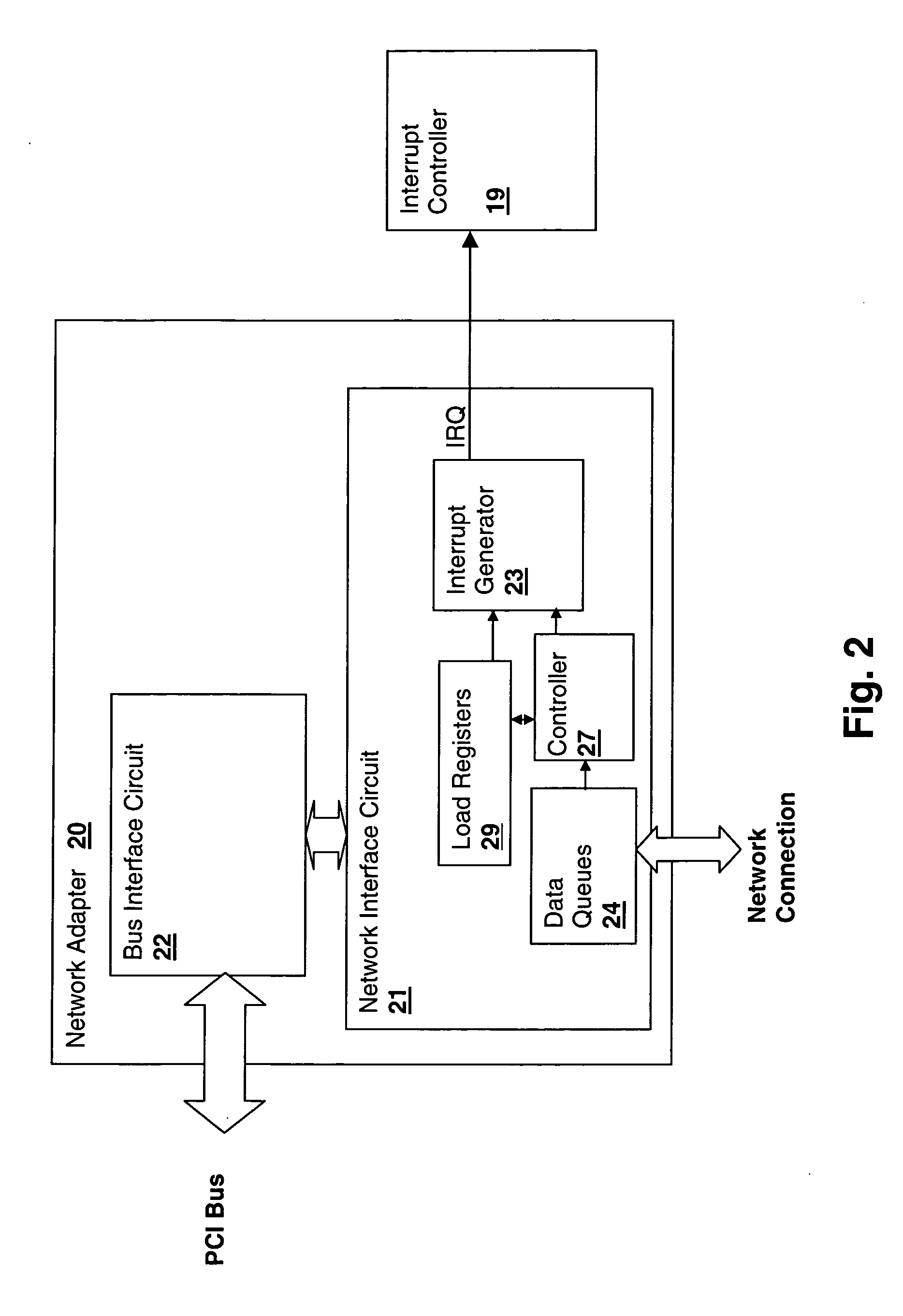
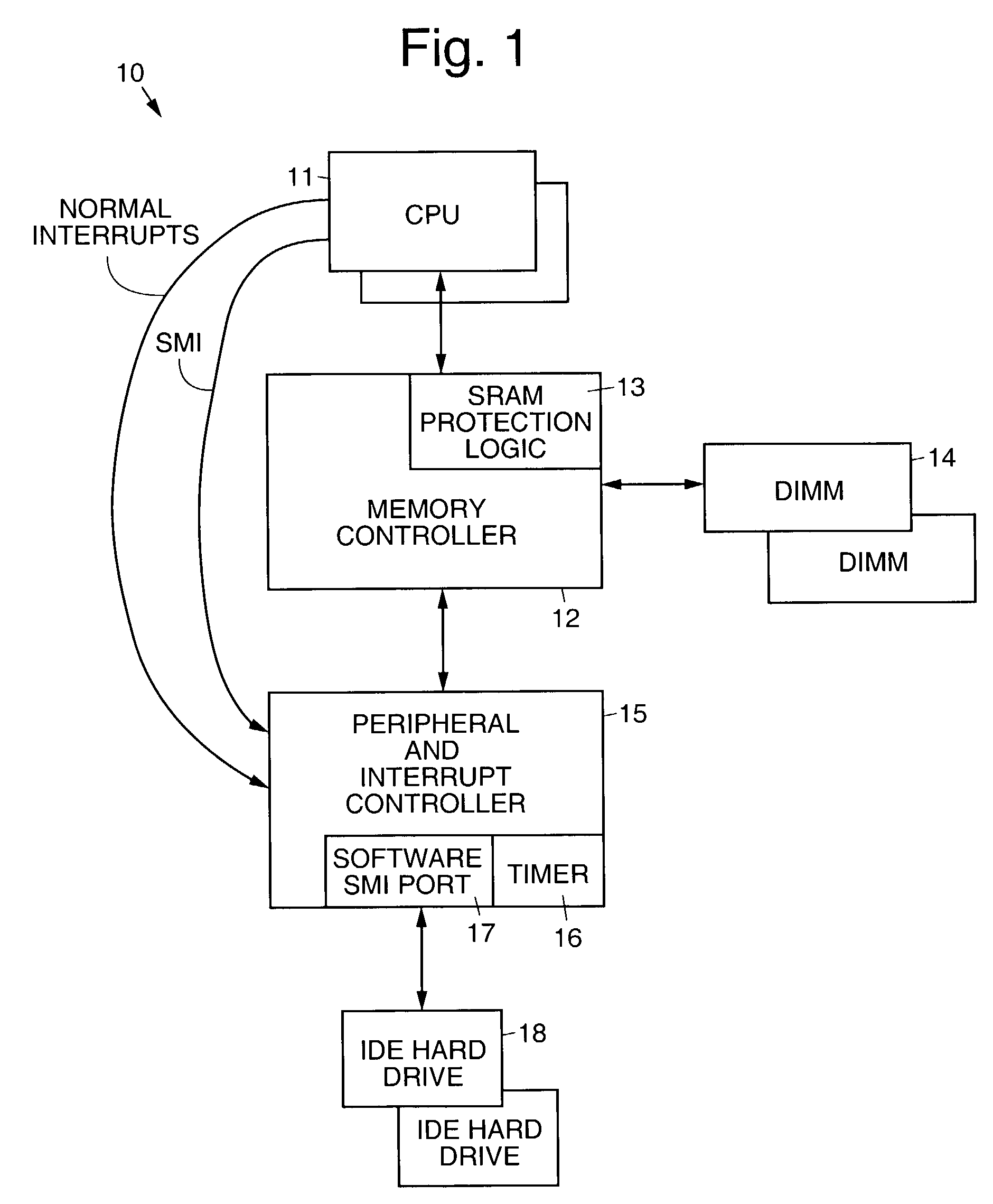
Disk drive implementing shared buffer memory with reduced interrupt latency
InactiveUS8019914B1Reduce Interrupt LatencyInput/output processes for data processingData conversionControl circuitComputer science
A disk drive is disclosed having a disk, a head actuated over the disk, a buffer memory for storing control routine op codes and control routine data, and a microprocessor for receiving the control routine op codes and control routine data. Control circuitry within the disk drive services an access request generated by the microprocessor by accessing the buffer memory, and monitors at least one interrupt. If the interrupt occurs while servicing the access request, the control circuitry enables the microprocessor to execute an interrupt service routine corresponding to the interrupt. Enabling the microprocessor to execute the interrupt service routine rather than wait for the access request reduces the latency in servicing the interrupt.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
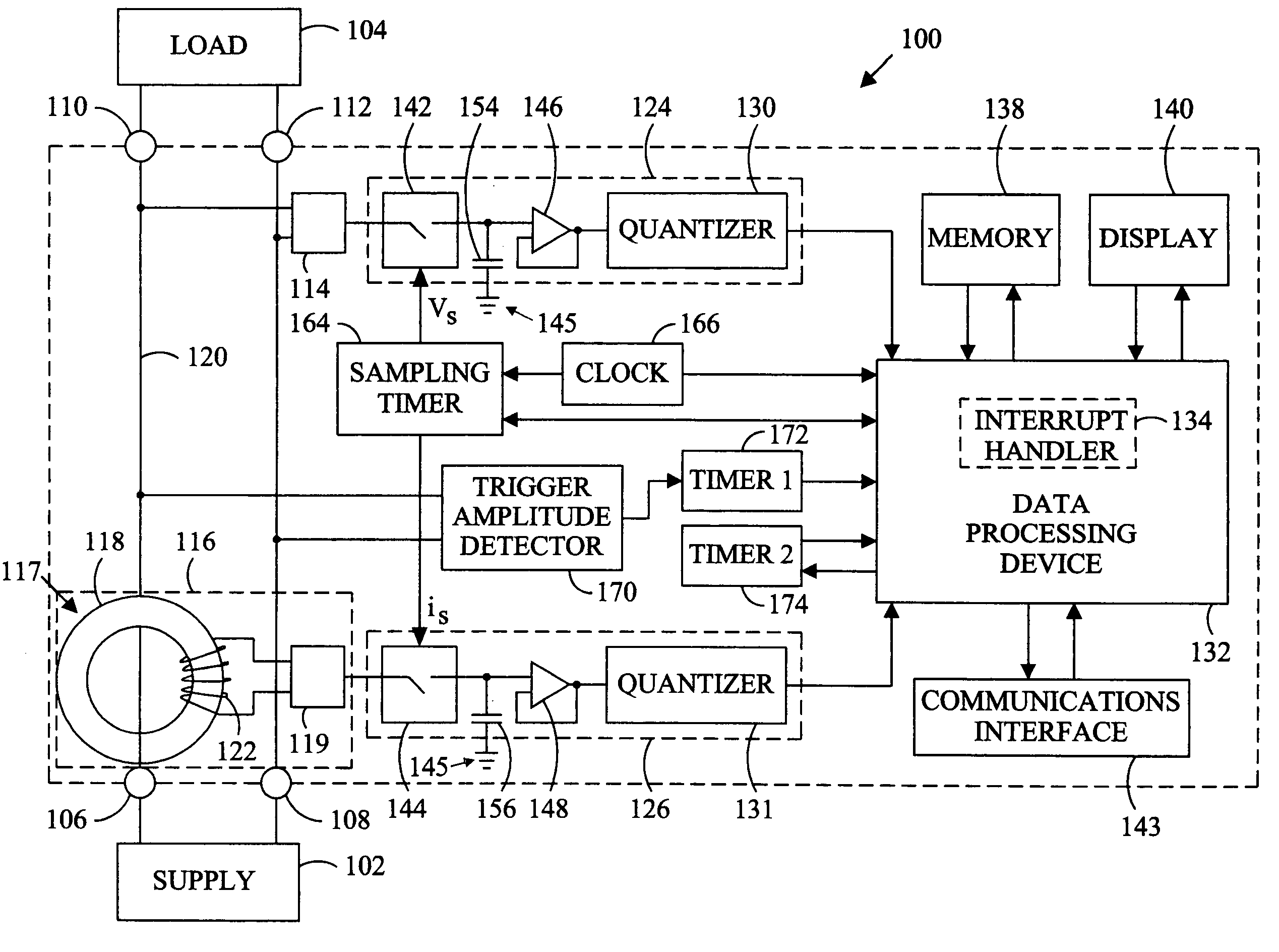
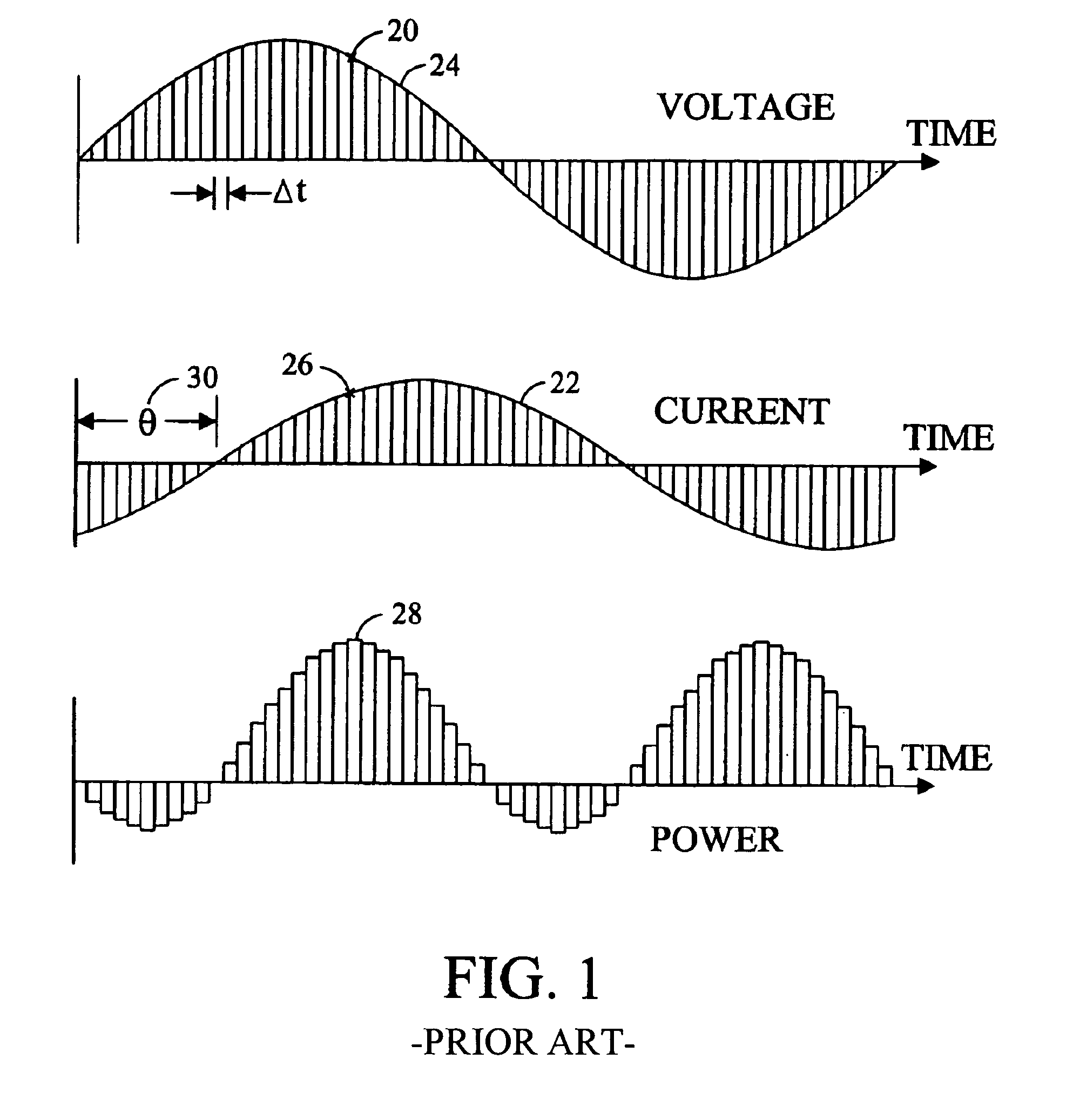
Power meter
The computational resources of a digital power meter can be reduced by utilizing an interrupt requested in anticipation of interrupt latency to perform real-time tasks, an approximation of a root mean square load current at an earlier time to compensate for a phase shift between the load current and the current transducer output, and an amplitude that is neither zero nor maximum to distinguish the cycles of a harmonically distorted waveform.
Owner:VERIS INDS
Staggered polling of buffer descriptors in a buffer descriptor ring direct memory access system
InactiveUS6182165B1Radio transmissionInput/output processes for data processingMicrocontrollerDirect memory access
A microcontroller implements a buffer descriptor ring direct memory access (DMA) unit that polls buffer descriptors when in idle mode. This polling is to determine whether the software has set up a buffer or group of buffers transmission and transfer ownership of those buffers to the DMA unit. To reduce interrupt latency and bandwidth occupation, the polling of these buffer descriptor ownership flags is staggered for the DMA channels. For example, if eight DMA channels are implemented, the polling of their buffer descriptors can be distributed throughout a 1.28 millisecond polling interval.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
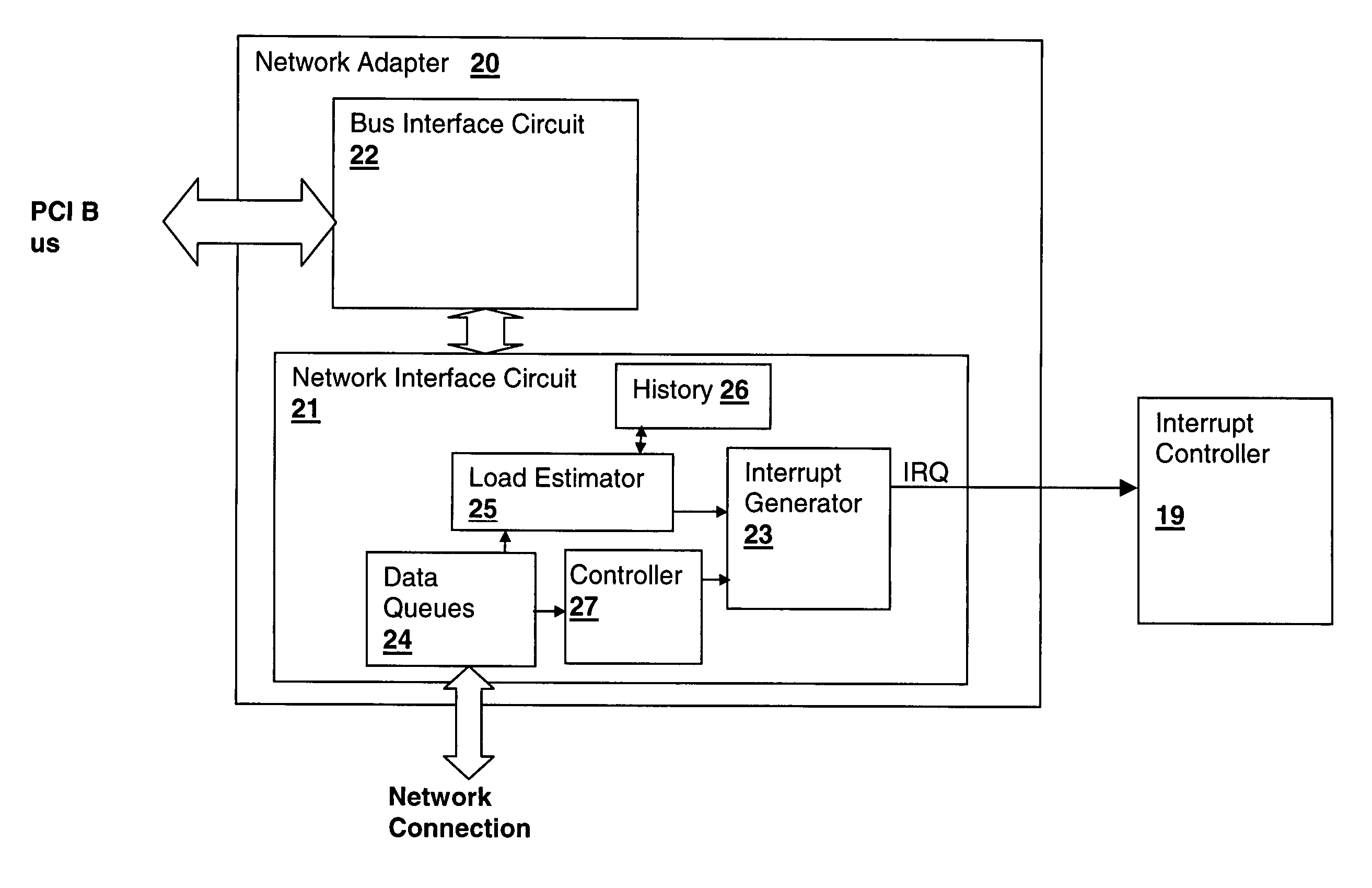
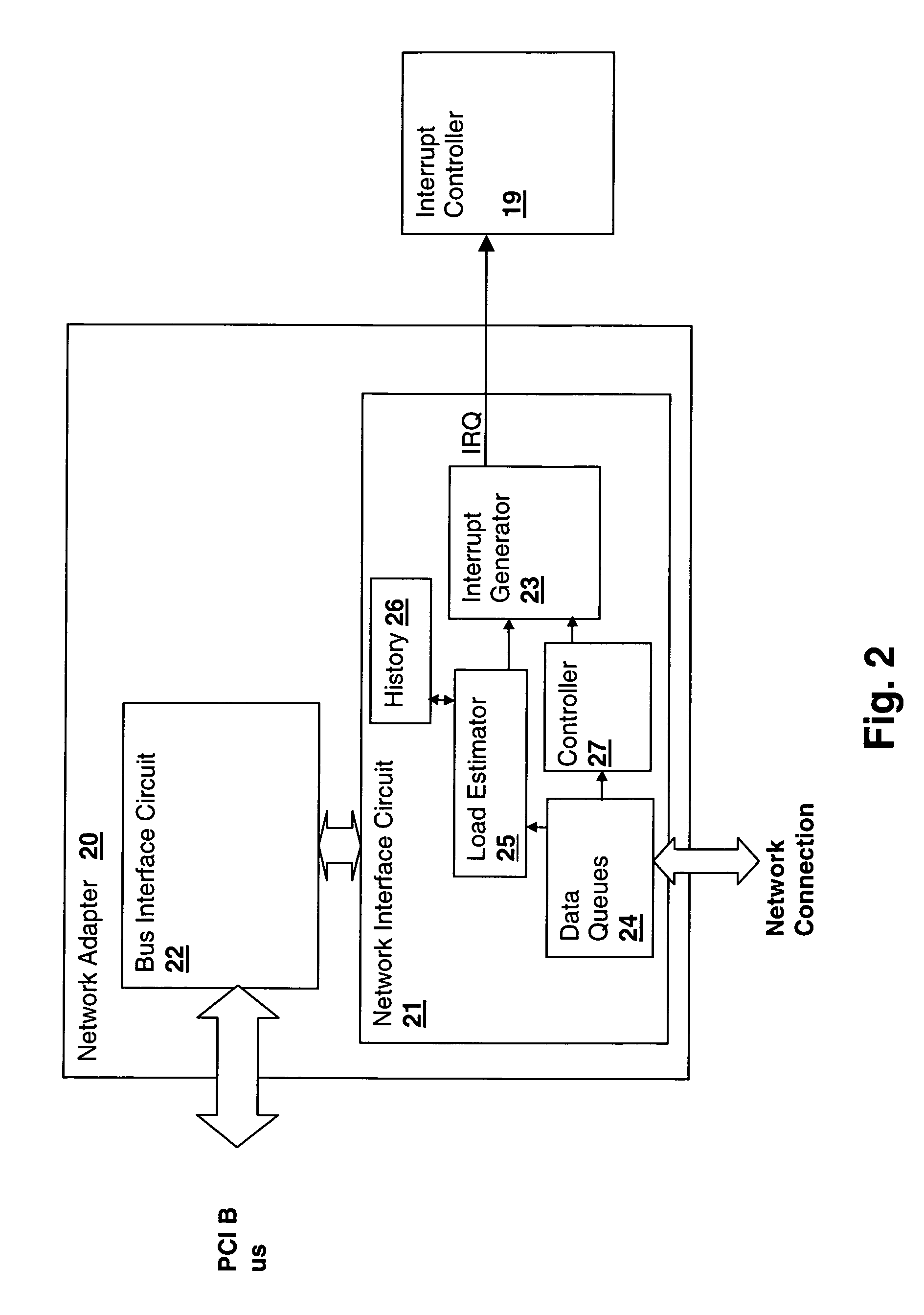
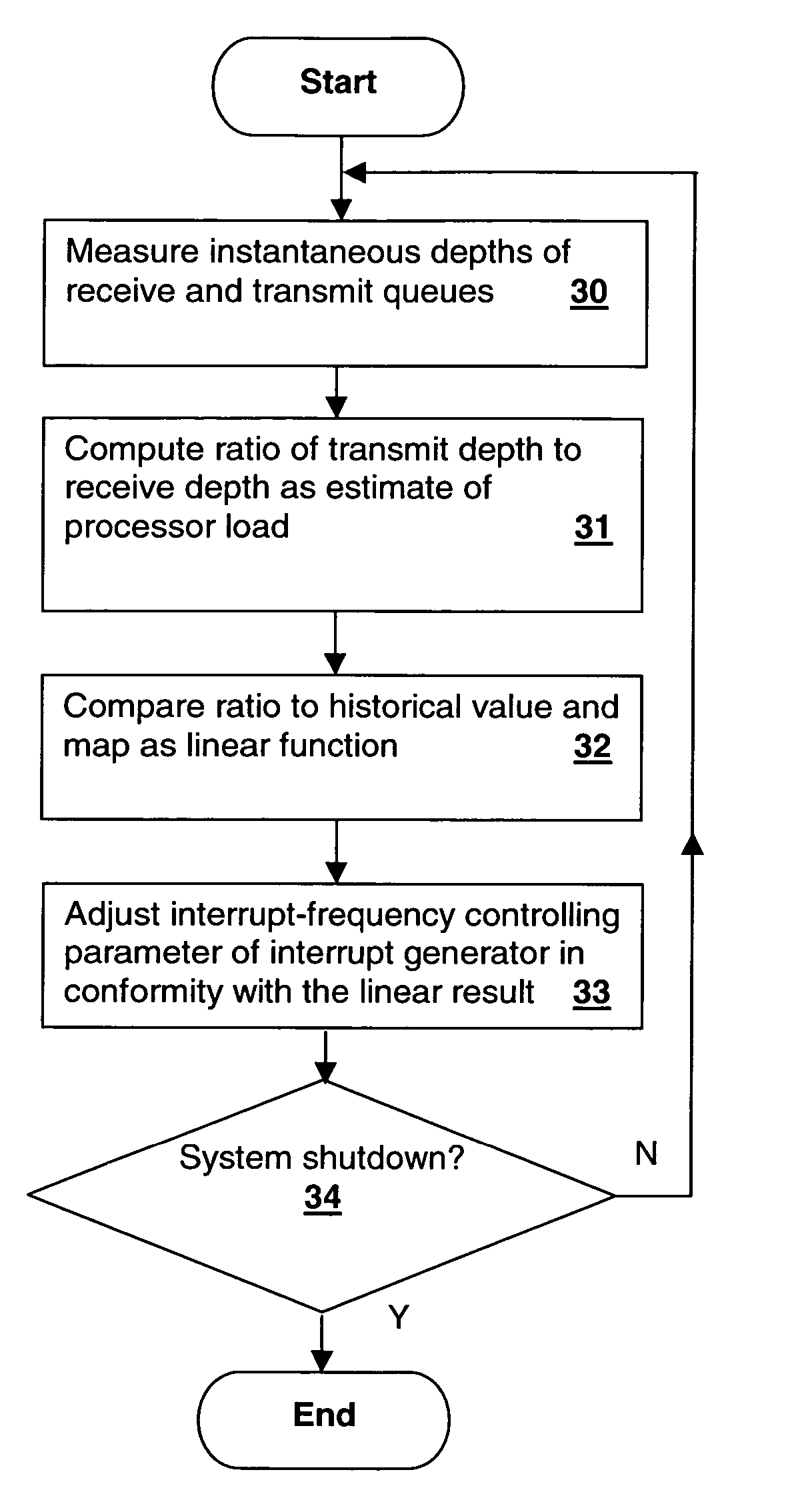
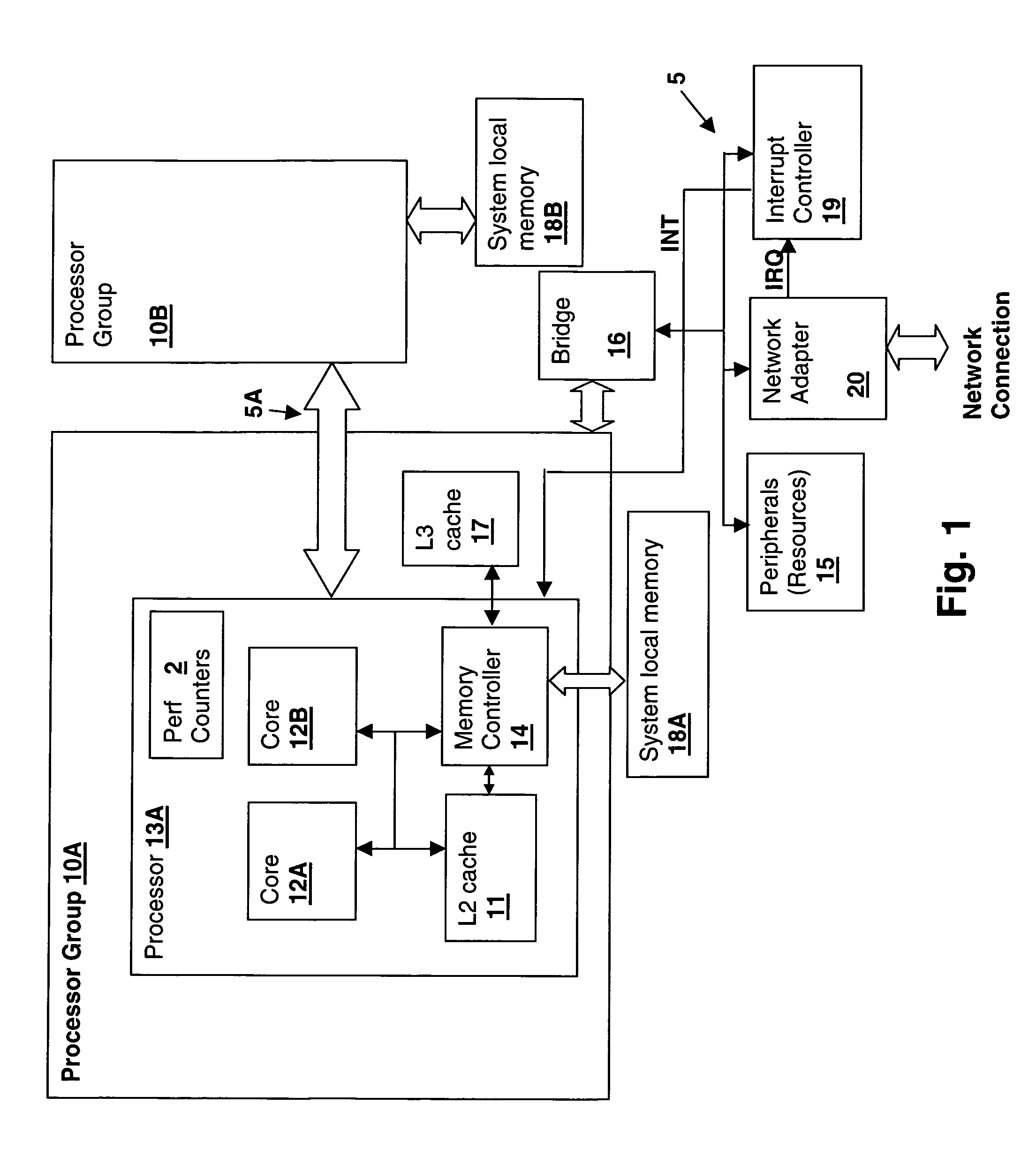
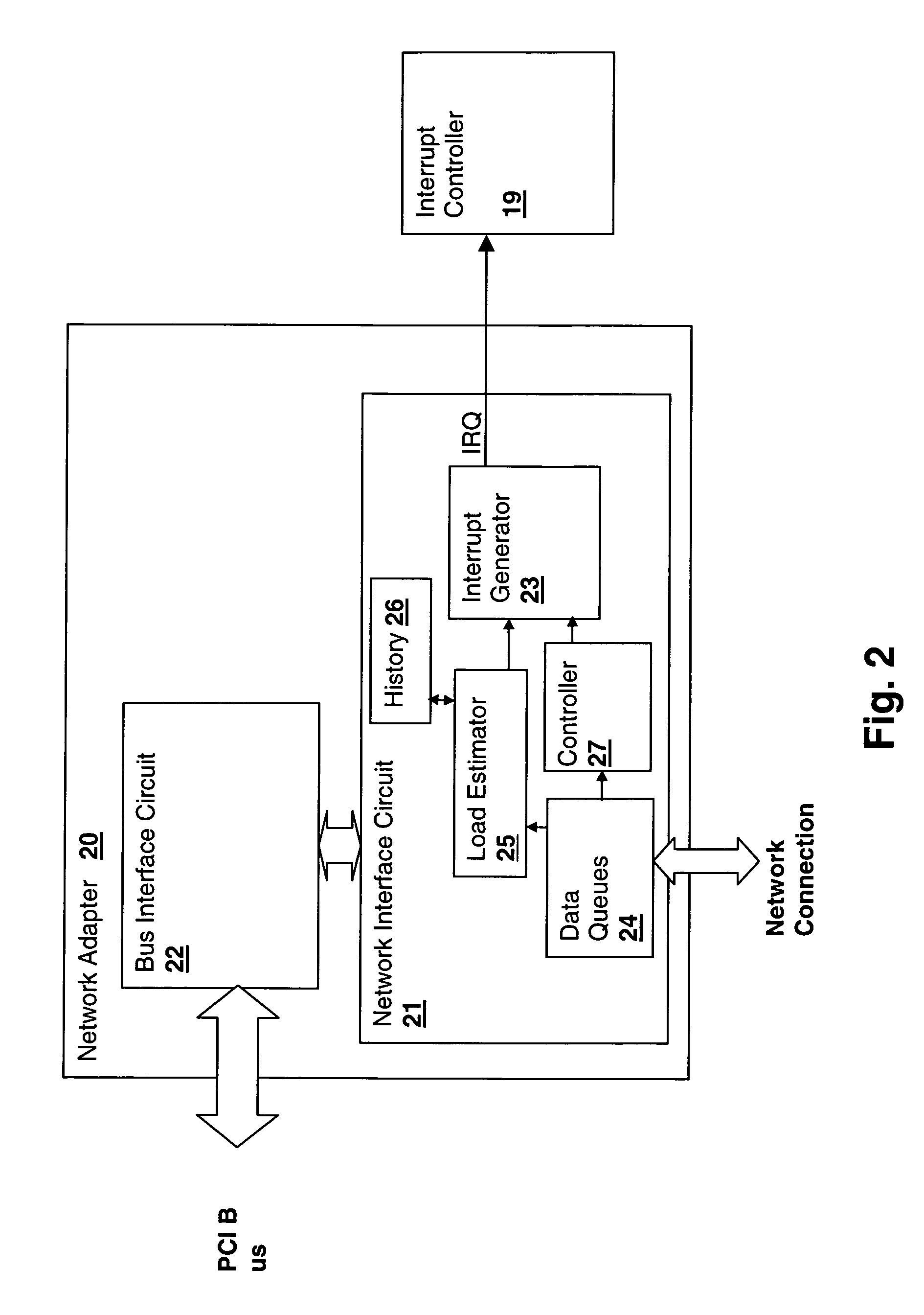
Method and apparatus for controlling peripheral adapter interrupt frequency by estimating processor load in the peripheral adapter
InactiveUS20060064520A1Reduce interrupt overheadLower latencyStore-and-forward switching systemsInput/output processes for data processingControl breakDelayed time
A method and system for controlling interrupt frequency by estimating processor load in the peripheral adapter provides adaptive interrupt latency to improve performance in a processing system. A mathematical function of the depth of one or more queues of the adapter is compared to its historical value in order to provide an estimate of processor load. The estimated processor load is then used to set a parameter that controls the frequency of an interrupt generator, which may be controlled by setting an interrupt queue depth threshold, packet frequency threshold or interrupt hold-off time value. The mathematical function may be the ratio of the transmit queue depth to the receive queue depth and the historical value may be predetermined, user-settable, obtained during a calibration interval or obtained by taking a long-term average of the mathematical function of the queue depths.
Owner:IBM CORP
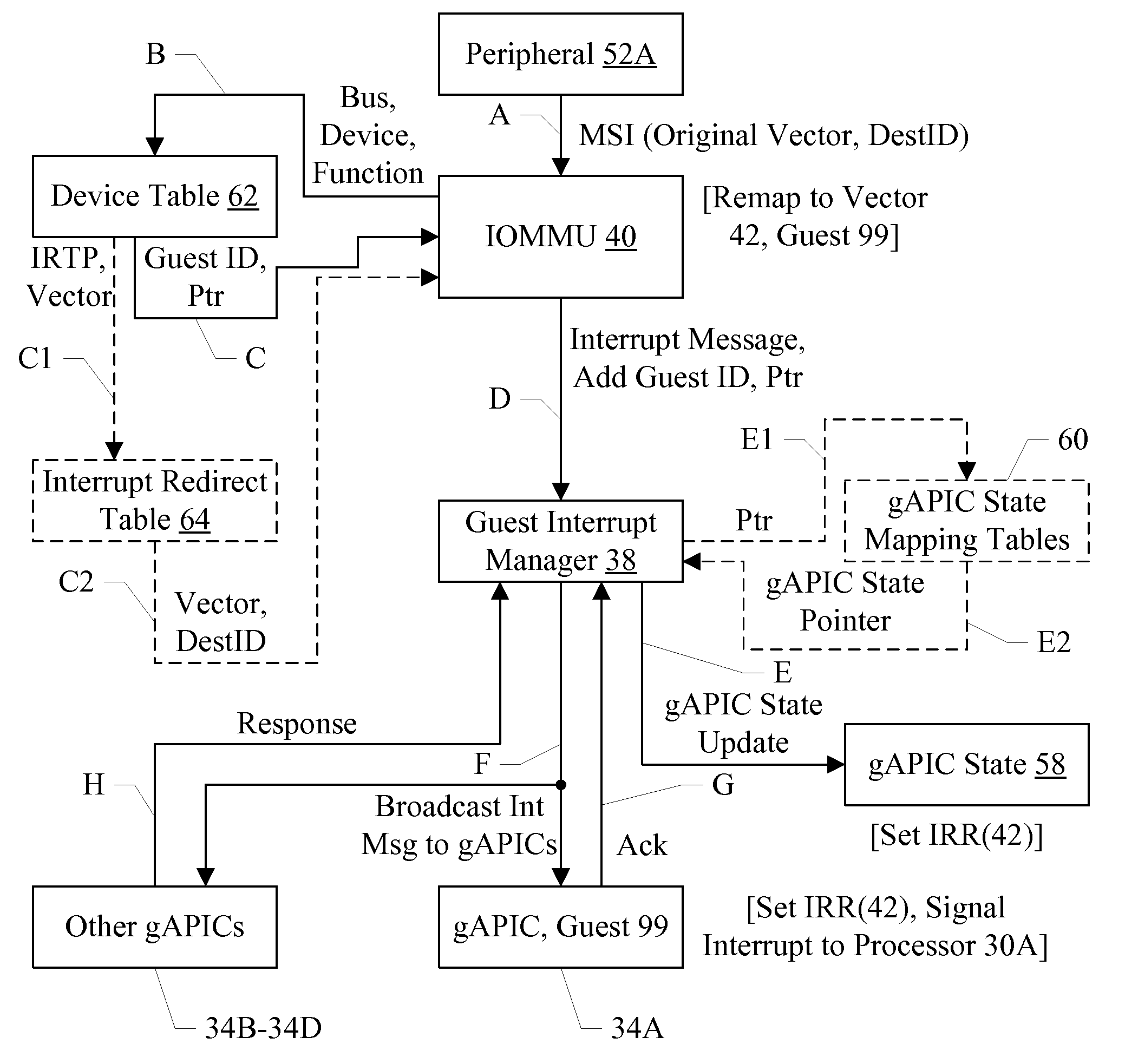
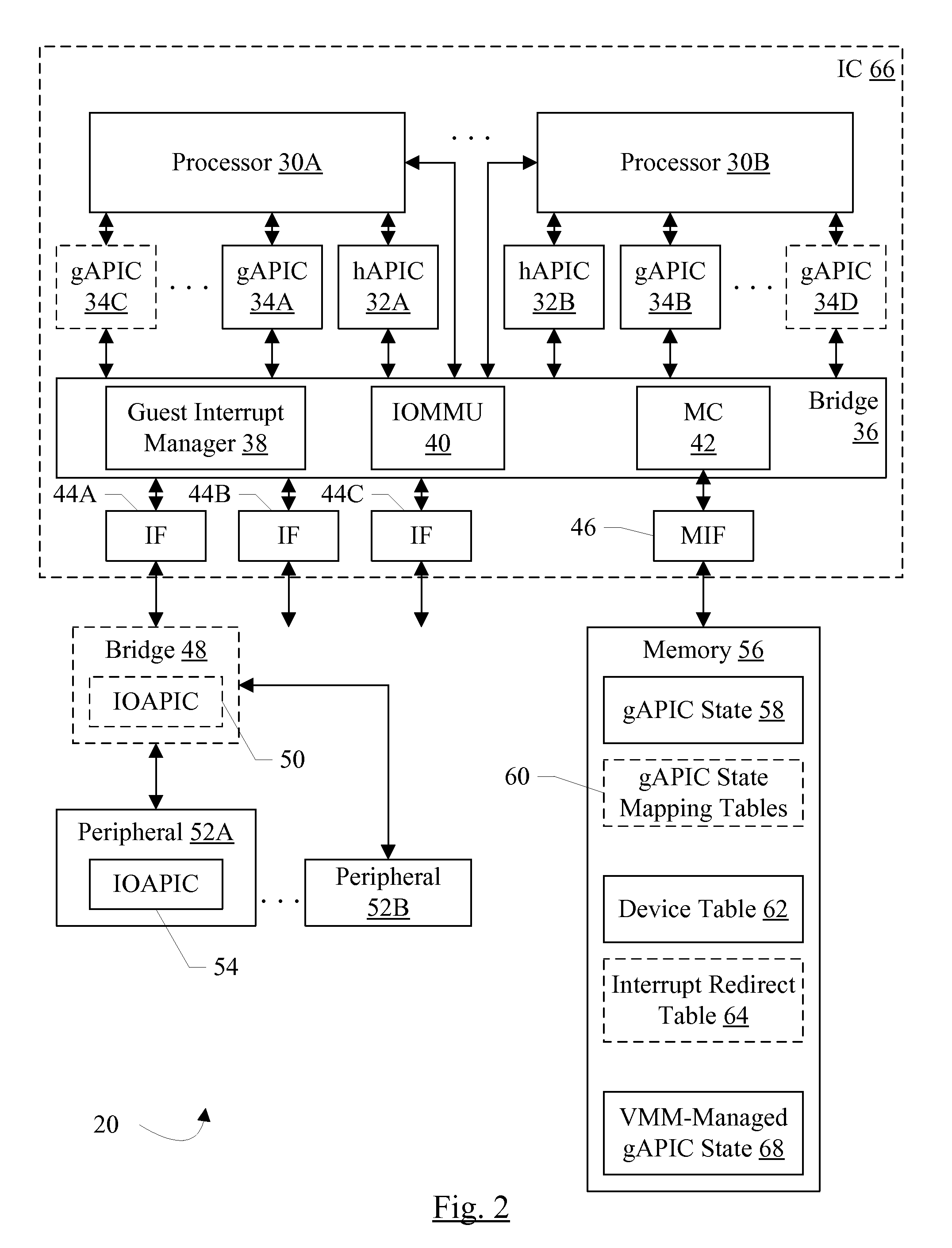
Memory structure to store interrupt state for inactive guests
ActiveUS20100191889A1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsMemory systemsVirtual machine
In an embodiment, a system comprises a memory system configured to store a data structure. The data structure stores at least an interrupt request state for each destination in each of a plurality of guests executable on the system. The interrupt request state identifies which interrupts have been requested at the corresponding interrupt controller in the corresponding guest of the plurality of guests. A guest interrupt manager is coupled to receive an interrupt message targeted at a first destination in a first guest of the plurality of guests, and the guest interrupt manager is configured to update the interrupt request state in the data structure that corresponds to the first destination and the first guest.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and system for controlling peripheral adapter interrupt frequency by transferring processor load information to the peripheral adapter
InactiveUS20060064529A1Reduce interrupt overheadLower latencyElectric digital data processingControl breakOperational system
A method and system for controlling interrupt frequency by transferring processor load information to a peripheral adapter provides adaptive interrupt latency to improve performance in a processing system. A device driver obtains current processor load information from an operating system or directly from processor usage counters. The estimated processor load is then used to set a parameter in the adapter that controls the frequency of an interrupt generator, which may be controlled by setting an interrupt queue depth threshold, packet frequency threshold or interrupt hold-off time value. The result is that the relative frequency of interrupts is managed in conformity with the current processor load, provide reduced processing latency when the system is relatively idle, which avoids loading the processor with additional interrupt processing overhead when the processor is busy.
Owner:IBM CORP
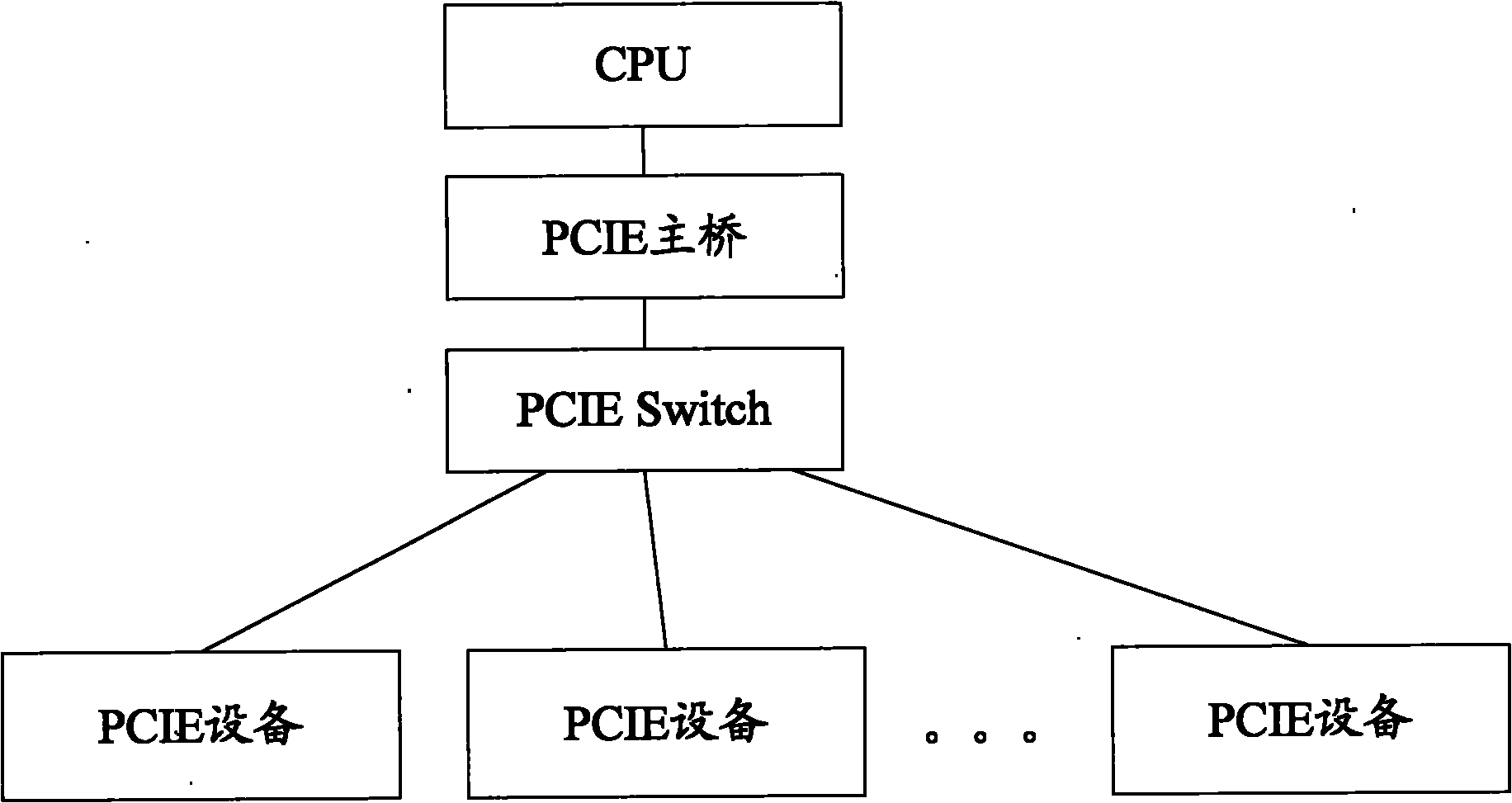
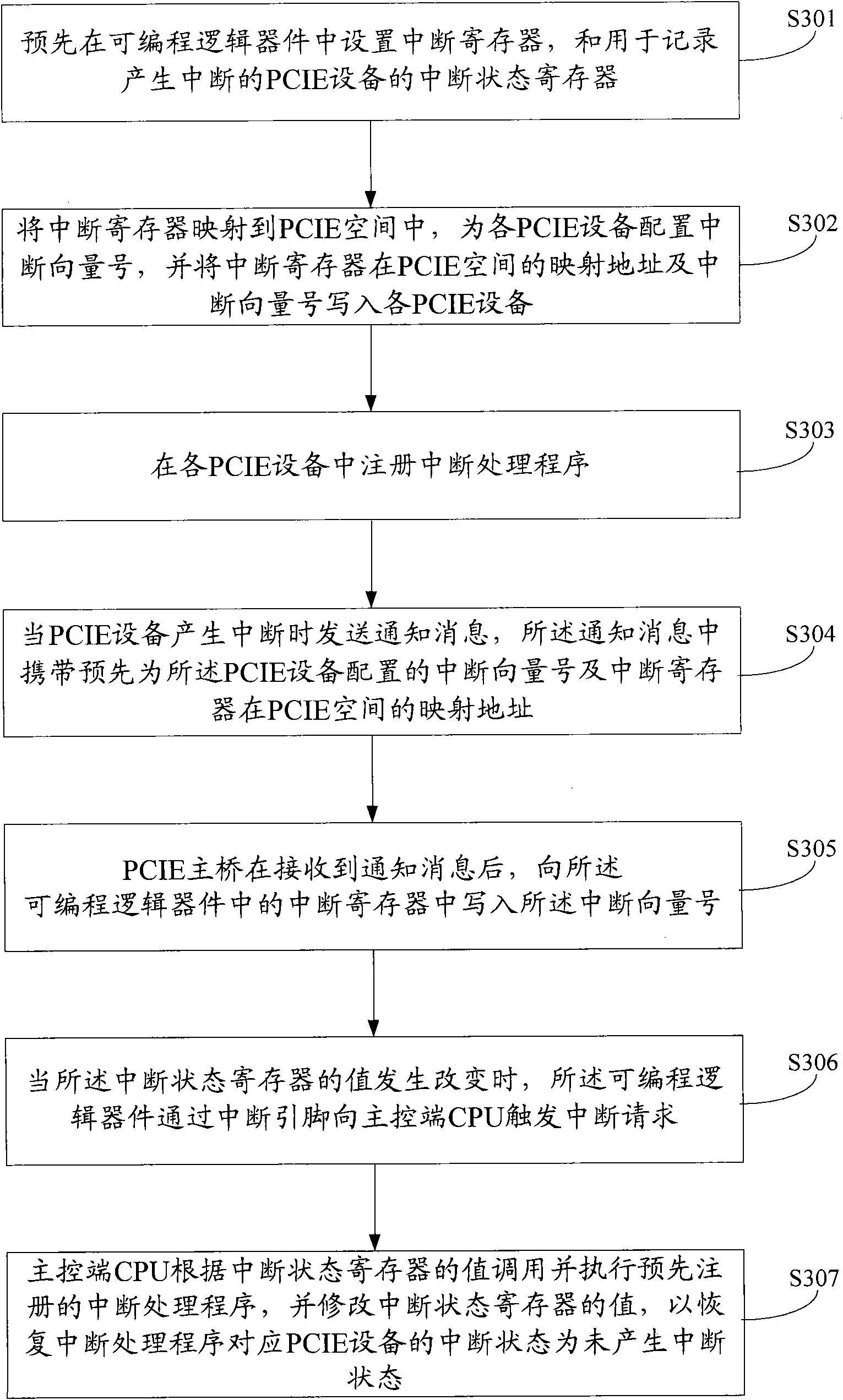
Interrupt processing method of multi-PCIE (Peripheral Component Interface Express) equipment system
ActiveCN101872330AReduce Interrupt LatencyImprove interrupt handling efficiencyElectric digital data processingAutomatic controlMedium scale integration
The invention discloses an interrupt processing method of a multi-PCIE (Peripheral Component Interface Express) equipment system, relating to the field of automatic control. In the invention, an interrupt register and an interrupt state register are arranged in advance, and the value of the interrupt state register changes along with the variation of a value of the interrupt register based on a preset rule; a notification message is sent when PCIE equipment generates interrupt, and an interrupt vector number and an interrupt register address which are configurated to the PCIE equipment in advance are carried in the message; after receiving the notification message, a main control end writes the interrupt vector number into the interrupt register corresponding to a mapping address; and an interrupt processing program which is registered in advance is called and executed based on the value of the interrupt state register, and the value of the interrupt state register is revised to restore an interrupt state of the PCIE equipment corresponding to the interrupt processing program into a non-interrupt state. The invention can process interrupt simultaneously generated by a plurality of PCIE equipments, and PCIE equipment which does not support an MSI (Medium-scale Integration) interrupt mode can apply the invention, therefore, the interrupt processing efficiency of the system is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
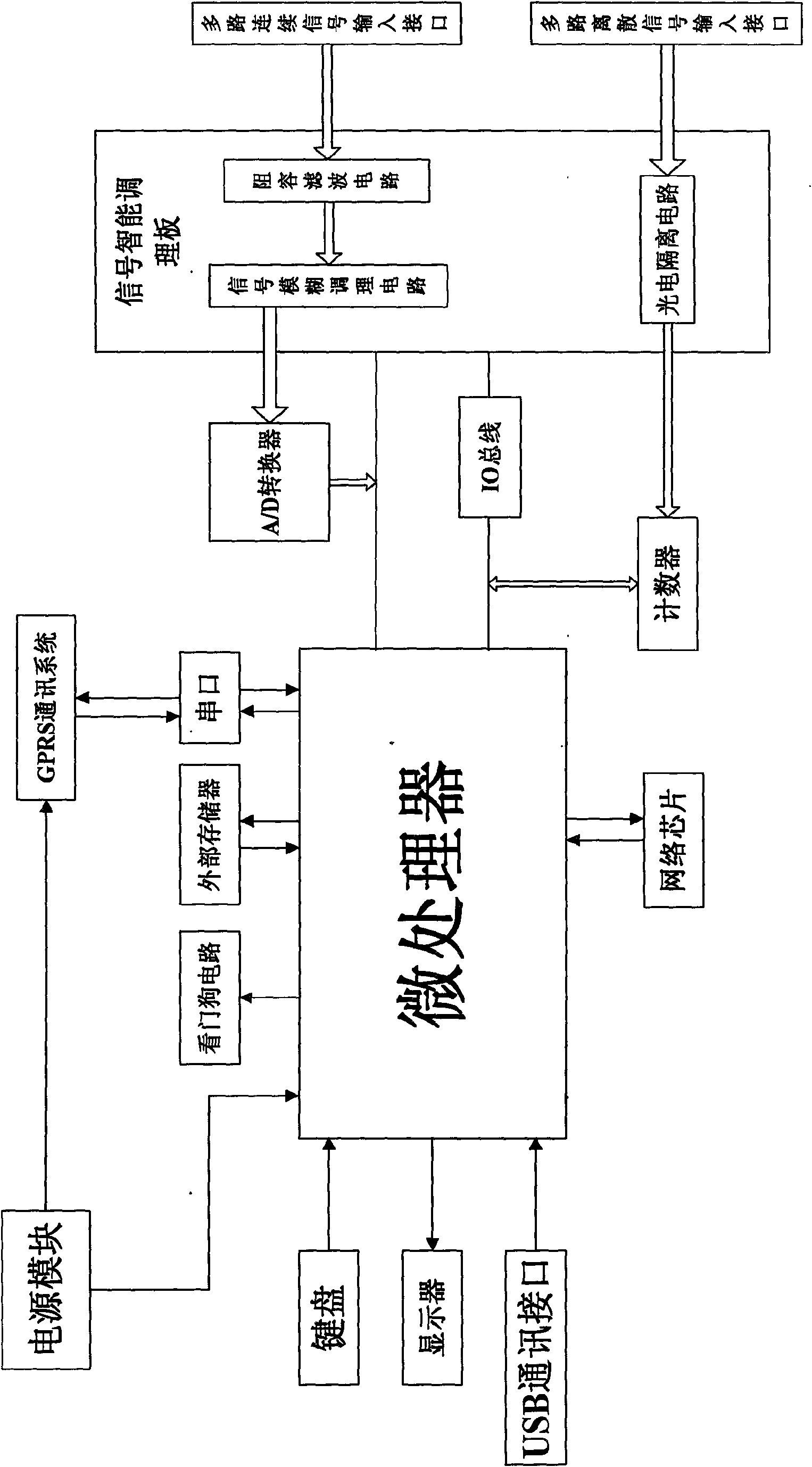
Universal data acquisition unit and data acquisition method thereof
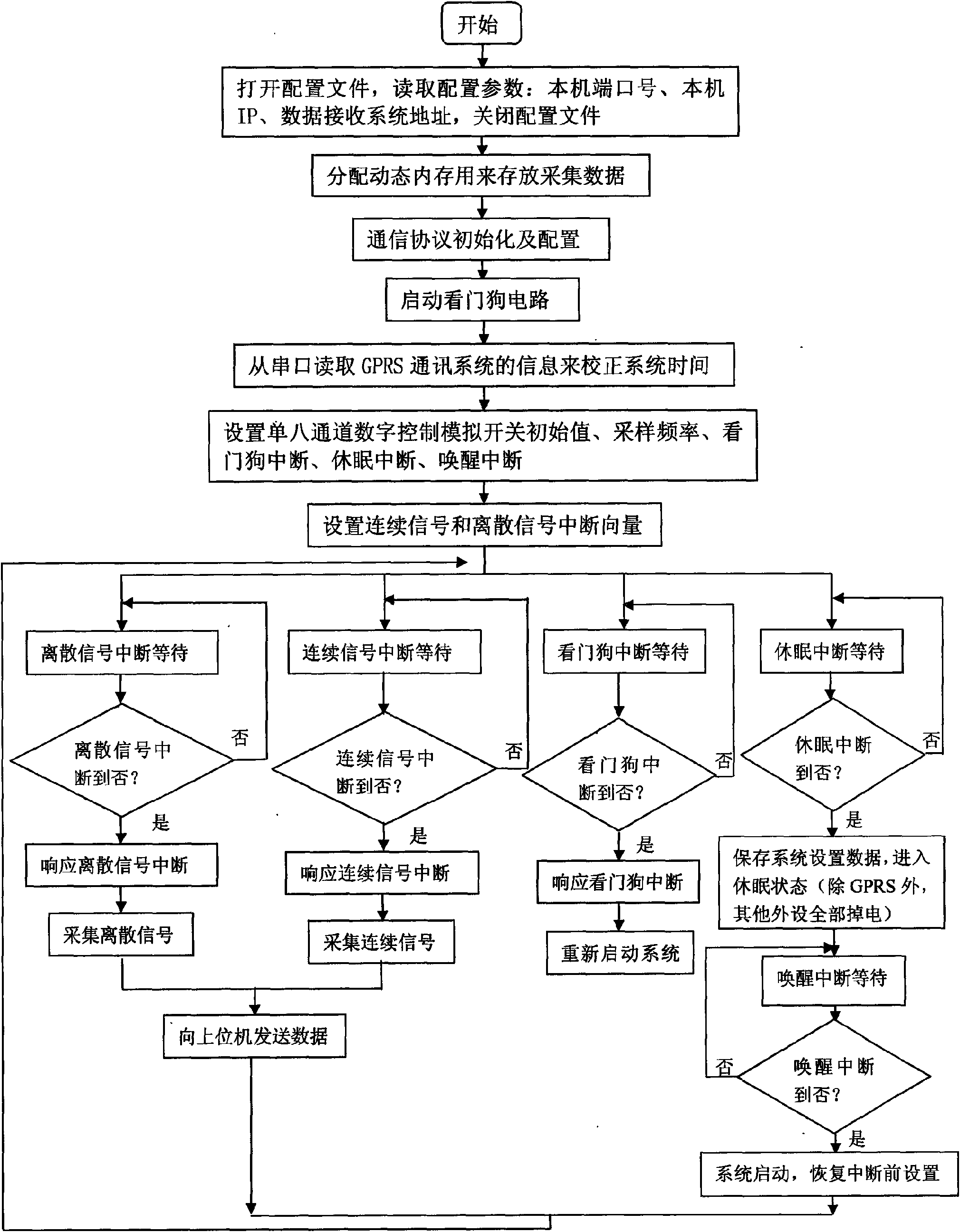
InactiveCN101661276AImprove performanceReduce power consumptionProgramme controlComputer controlData acquisitionContinuous signal
The invention relates to a universal data acquisition unit and a data acquisition method thereof, belonging to the technical field of data acquisition; the universal data acquisition unit comprises amicroprocessor; a multi-path discrete signal input interface is connected with the input end of a counter by a photoelectric isolating circuit, and a multi-path continuous signal input interface is connected with the input end of an A / D converter, and a microprocessor is connected with the input ends of the A / D converter and the counter. The data acquisition method comprises that: system initialization is carried out; continuous and discrete signal interrupt vector is set; interrupt latency is carried out, if the discrete signal is interrupted, the discrete signal is acquired; if the continuous signal is interrupted, the continuous signal is acquired; if a watchdog is interrupted, a system is restarted; if hibernation is interrupted, system setting data is stored, and then a hibernation state is carried out; and then, interrupt latency awaken operation is carried out, if awakening is interrupted, the system is started, and the setting is restored before interruption; if the continuoussignal and the discrete signal are acquired, interrupt latency is continuously carried out after data is transmitted to an upper computer; if not, interrupt latency is carried out directly.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
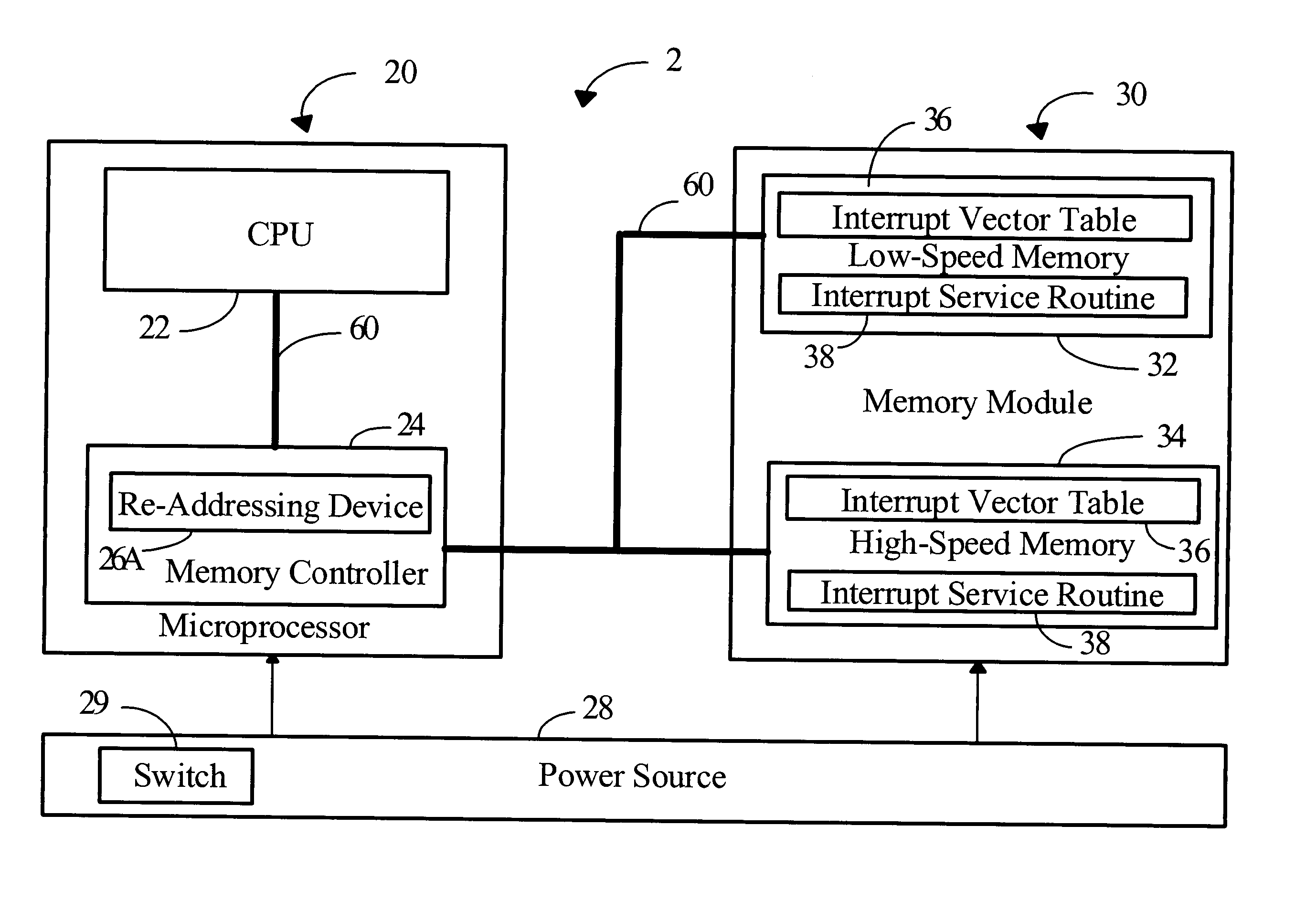
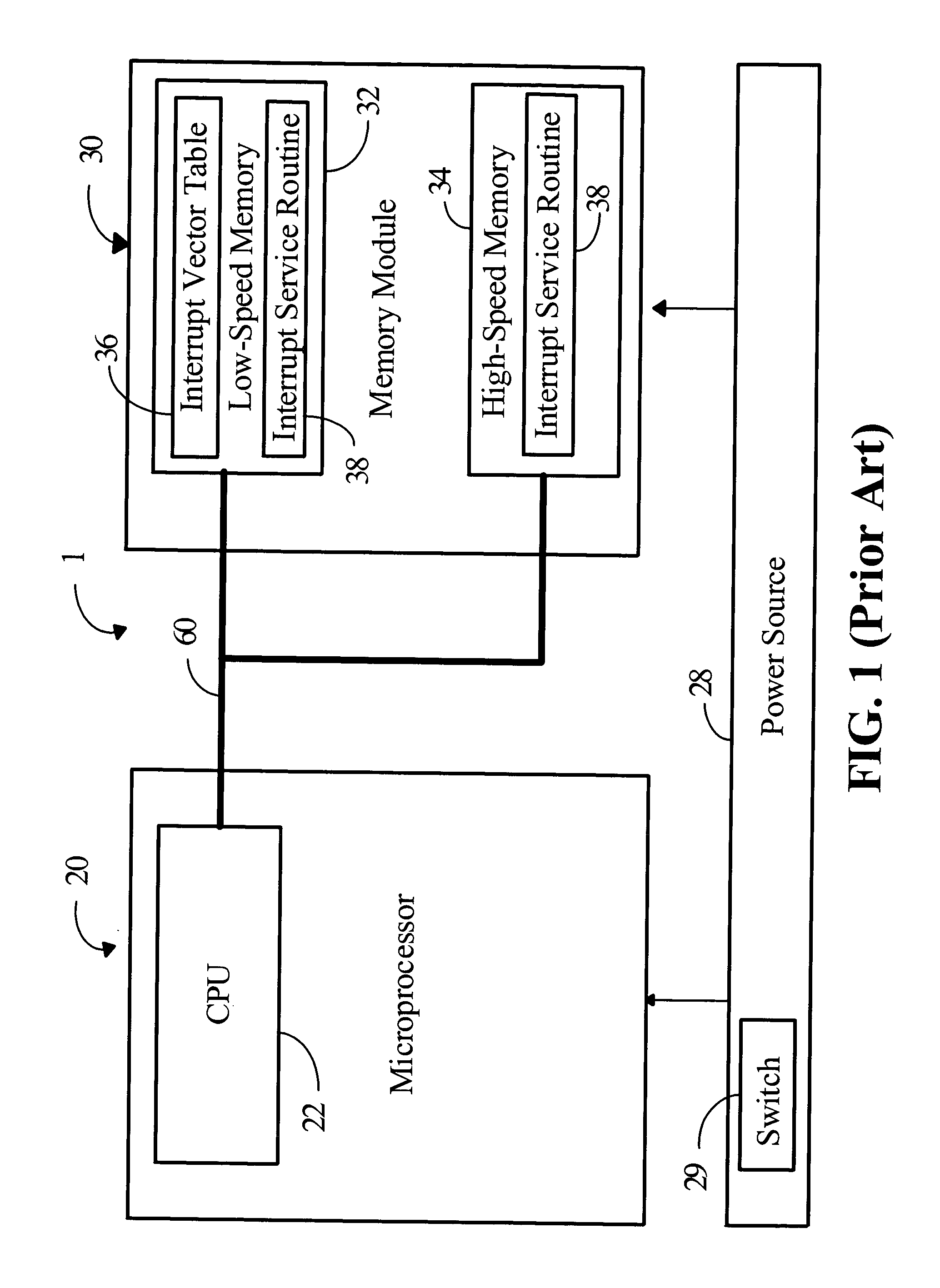
Interrupt-processing system for shortening interrupt latency in microprocessor
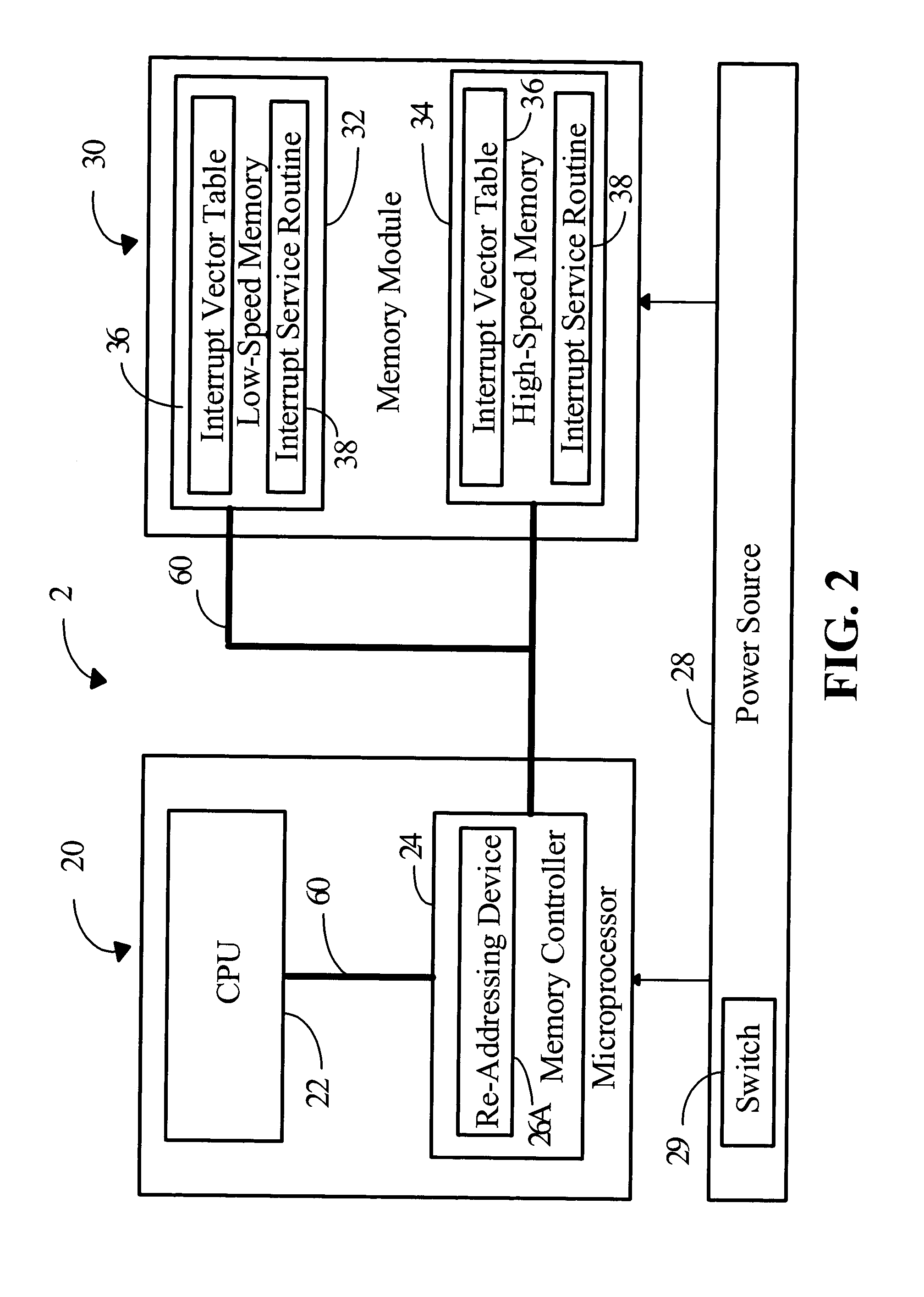
ActiveUS20050060461A1Reduce Interrupt LatencyIncrease interrupt service efficiencyMemory systemsMicro-instruction address formationHigh speed memoryLow speed
The invention relates to a data processing system which comprises a memory module and a microprocessor. The memory modules comprise at least one low-speed memory and one high-speed memory; both store an interrupt vector table individually for recording the entry instruction of interrupt service routines. The microprocessor comprises a central processing unit (CPU) and a memory controller with a re-addressing device. Once an interruption occurs, the CPU generates and sends an interrupt vector address to the memory controller. If the vector is located in the range of interrupt vector table, the re-addressing device sends an enable signal to the high-speed memory to enable the CPU to fetch the entry instruction of interrupt service routines from the high-speed memory, not from the pre-determined low-speed memory. Hence, the interrupt latency is reduced.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method, apparatus, and computer program product for dynamically tuning amount of physical processor capacity allocation in shared processor systems
InactiveUS7296133B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsData processing systemPhysics processing unit
A method, apparatus, and computer program product in a shared processor data processing system are disclosed for dynamically tuning an amount of physical processor capacity that is allocated to each one of multiple logical partitions. A physical processor is shared among the logical partitions. A service window is allocated to each logical partition during each dispatch time slice. Processes that are defined by a first one of the logical partitions are executed during a first service window that was allocated to the first logical partition. A determination is made dynamically during runtime as to whether a length of the first service window should be increased to optimize interrupt processing and reduce interrupt latency.If it is determined that the length should be increased, the length of the first service window is dynamically increased during runtime.
Owner:IBM CORP
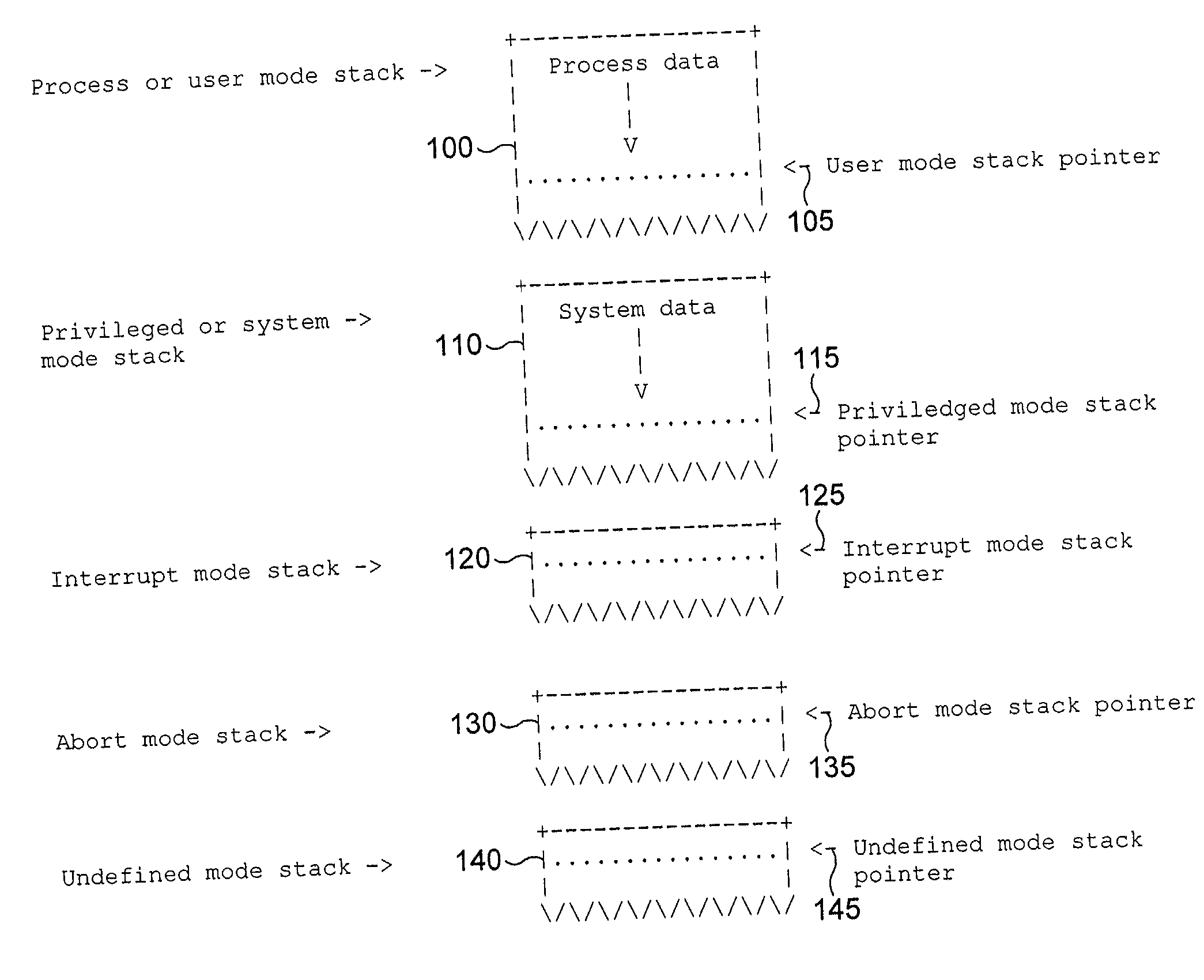
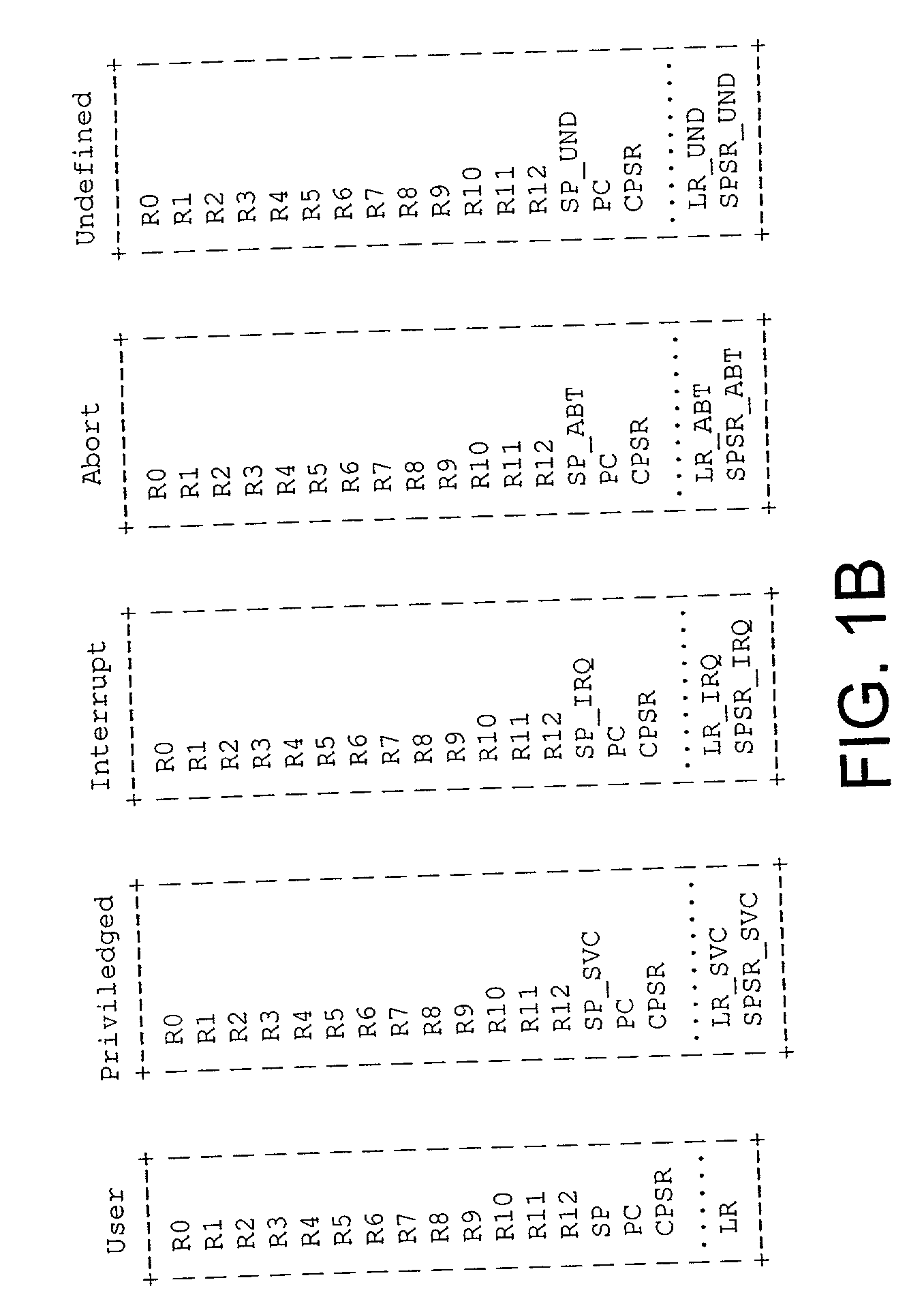
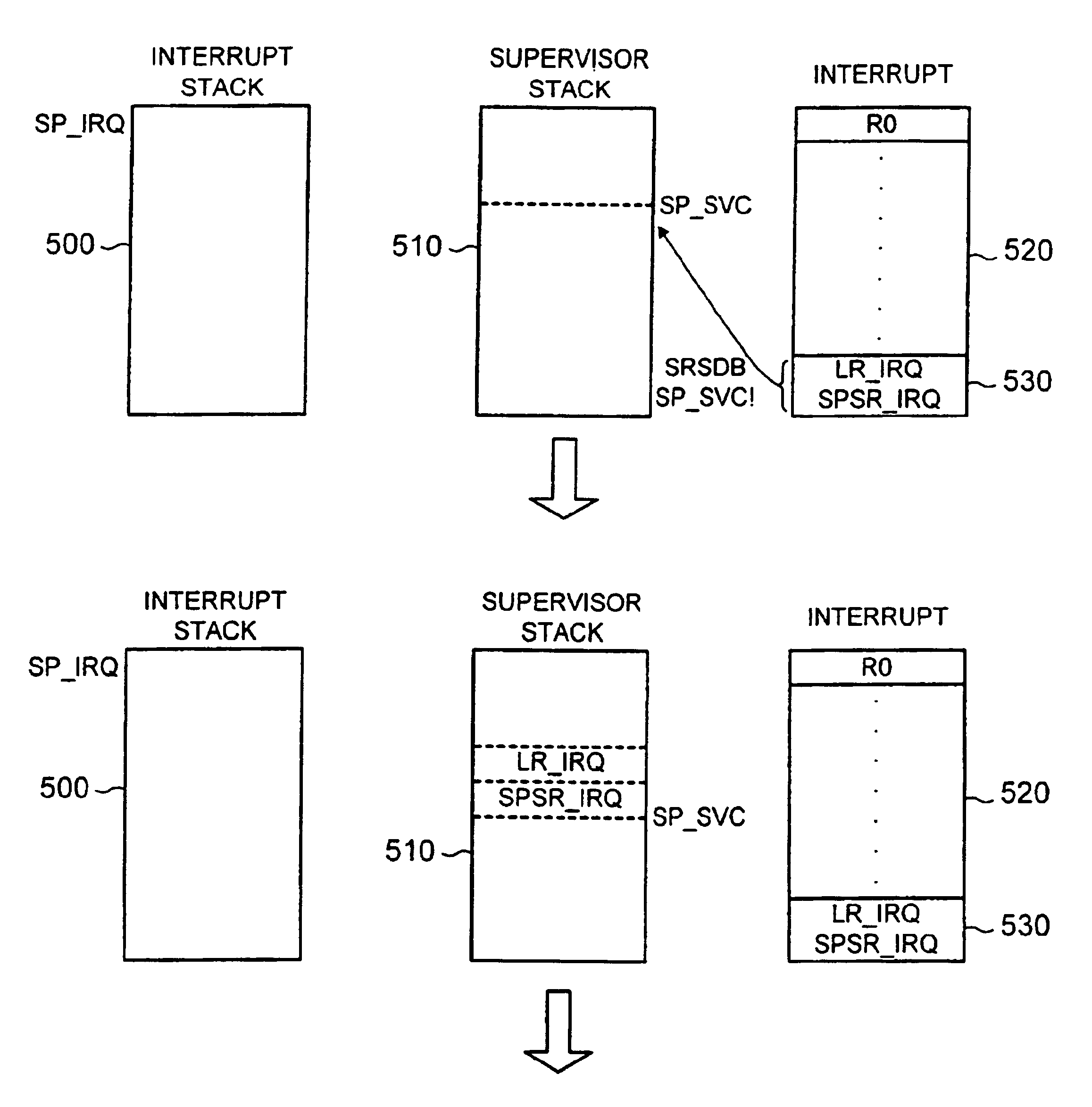
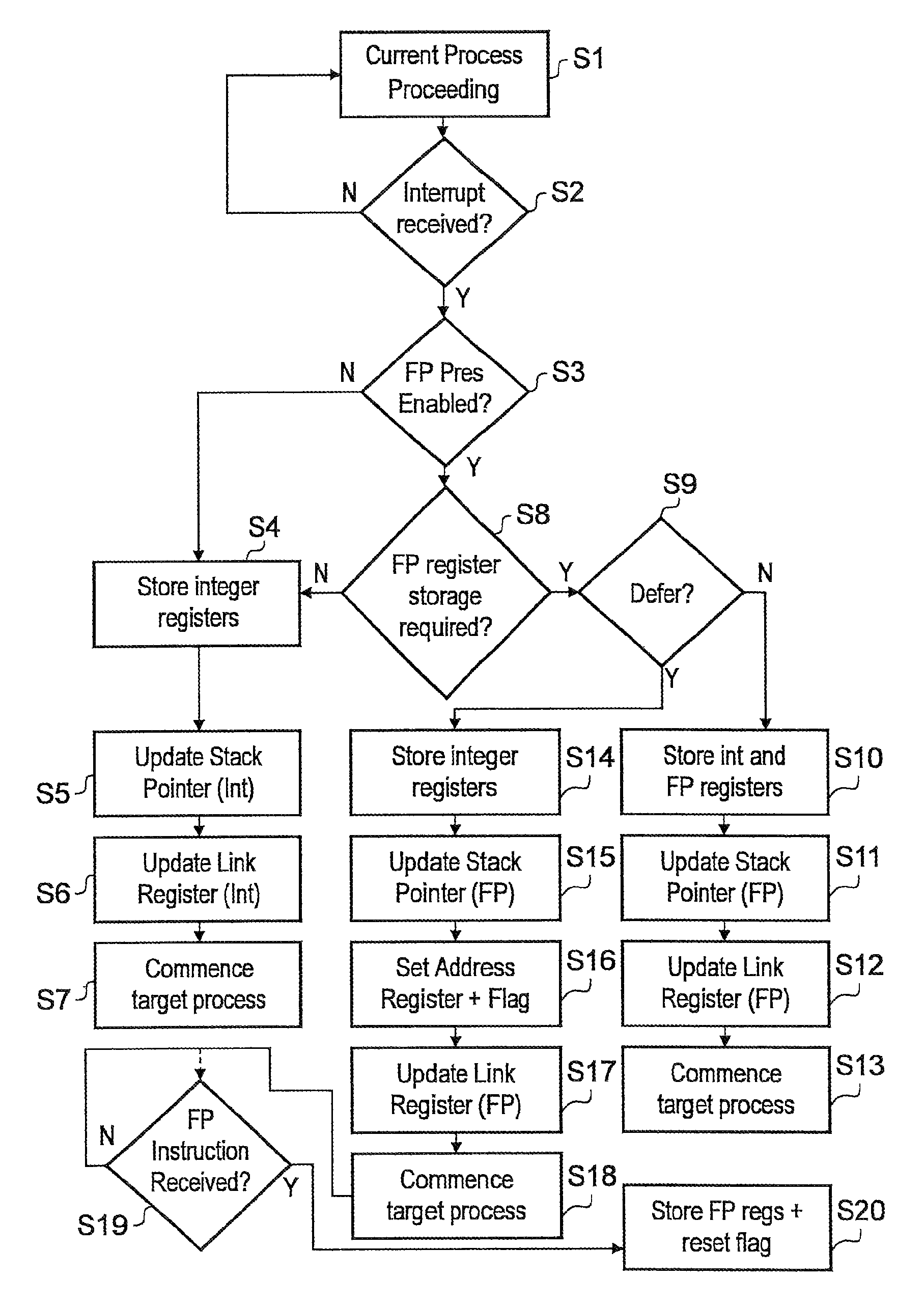
Data processing apparatus and method for saving return state
InactiveUS20020099933A1Program initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsParallel computingOperation mode
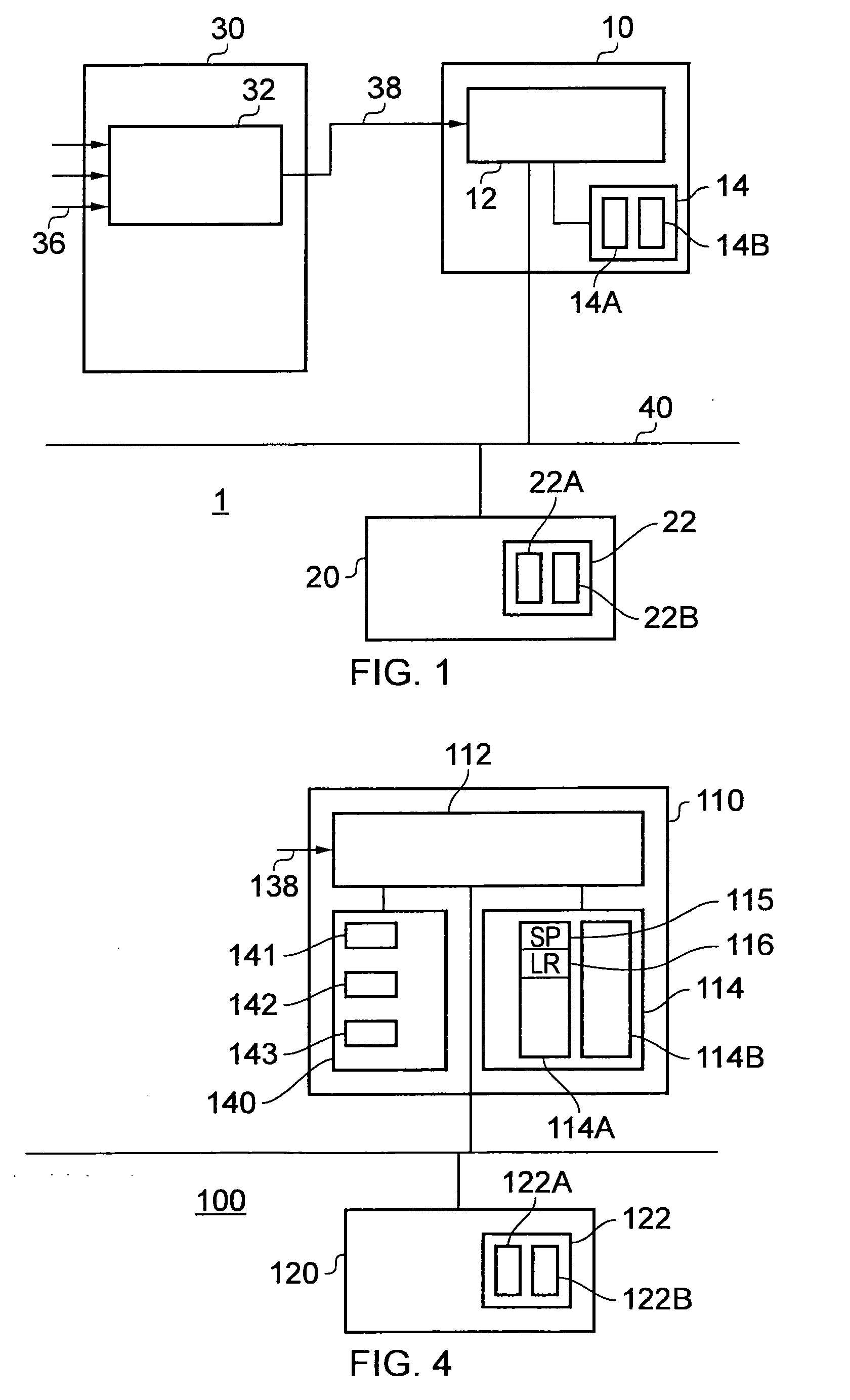
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for saving return state. The data processing apparatus comprises a processing unit for executing data processing instructions, the processing unit having a plurality of modes of operation, with each mode of operation having a corresponding stack for storing data associated with that mode. The processing unit is responsive to a return state data processing instruction to write return state data of the processing unit from its current mode of operation to a stack corresponding to a different mode of operation to the current mode of operation. This approach significantly reduces code size and improves interrupt latency over known prior art techniques.
Owner:ARM LTD
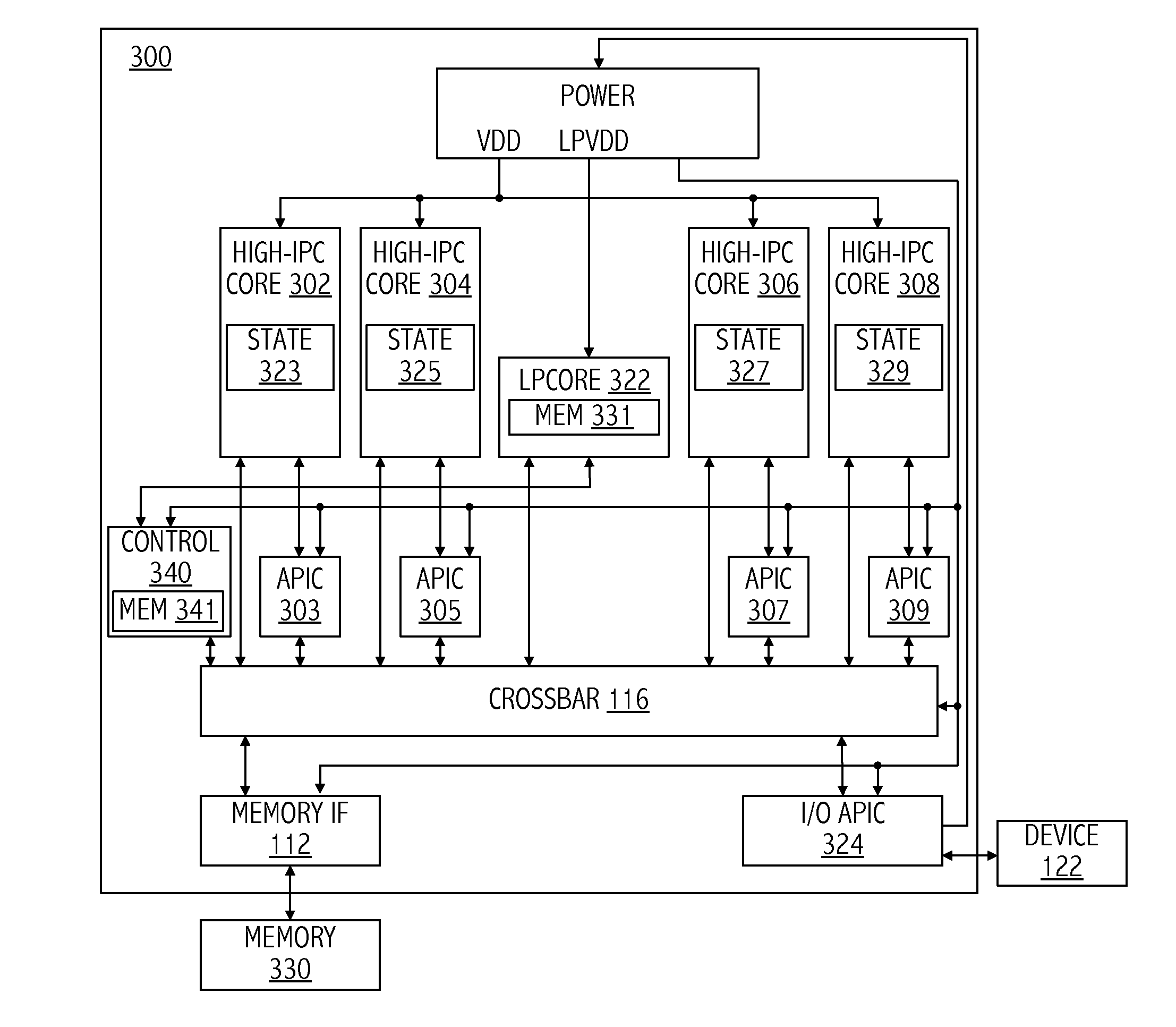
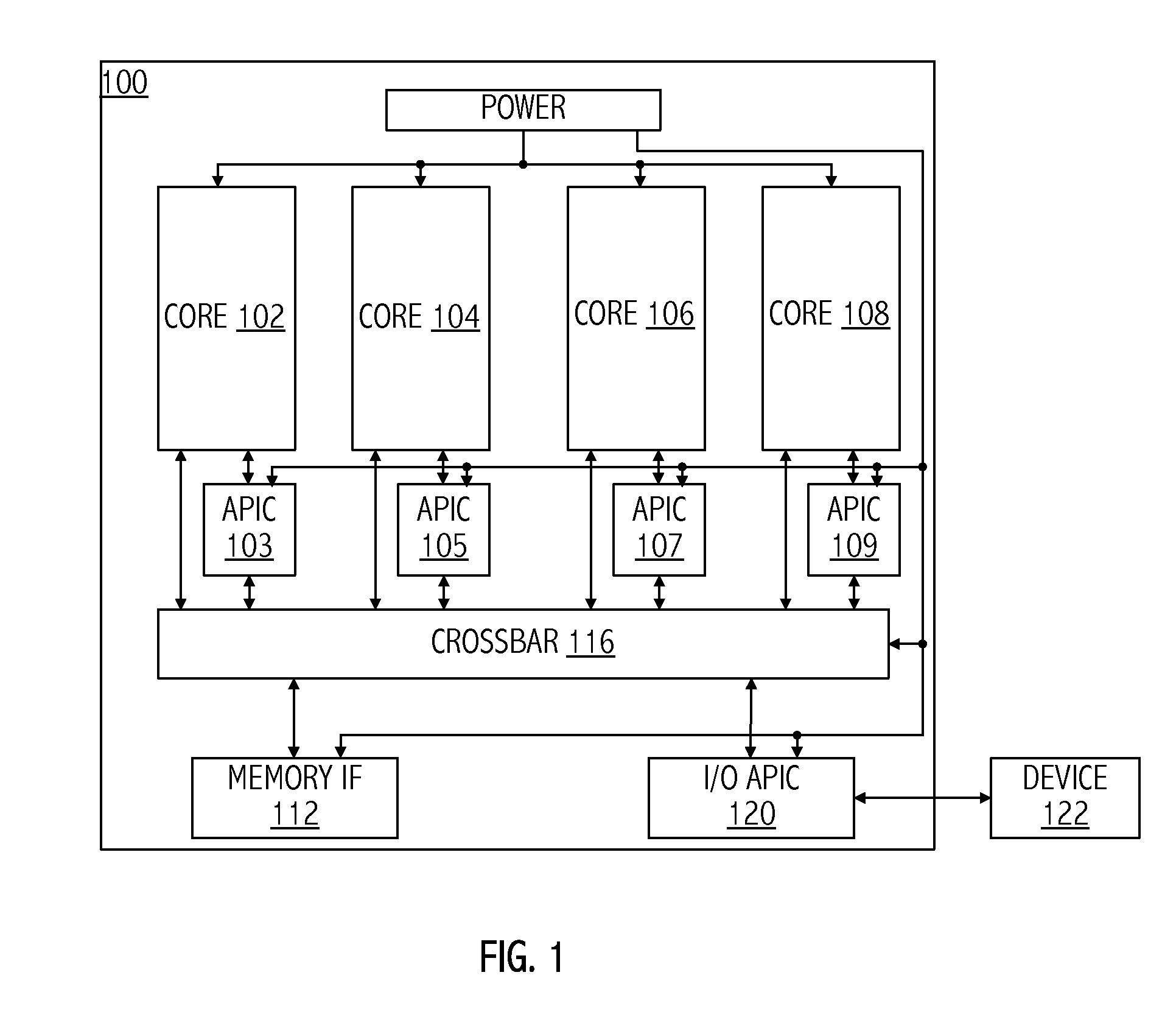
Mechanism for reducing interrupt latency and power consumption using heterogeneous cores
ActiveUS20140068289A1Less powerIncrease the number ofVolume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsHeterogeneous networkComputer science
A technique for operating a processor includes detecting an interrupt having a first core of the processor as a destination core. The technique includes handling the interrupt by a second core of the processor in response to the first core being in a low-power state. The first core may be capable of executing a greater number of instructions-per-cycle than the second core and the second core may consume less power than the first core. The first core may be coupled to a first voltage plane and the second core may be coupled to a second voltage plane having lower power than the first voltage plane.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
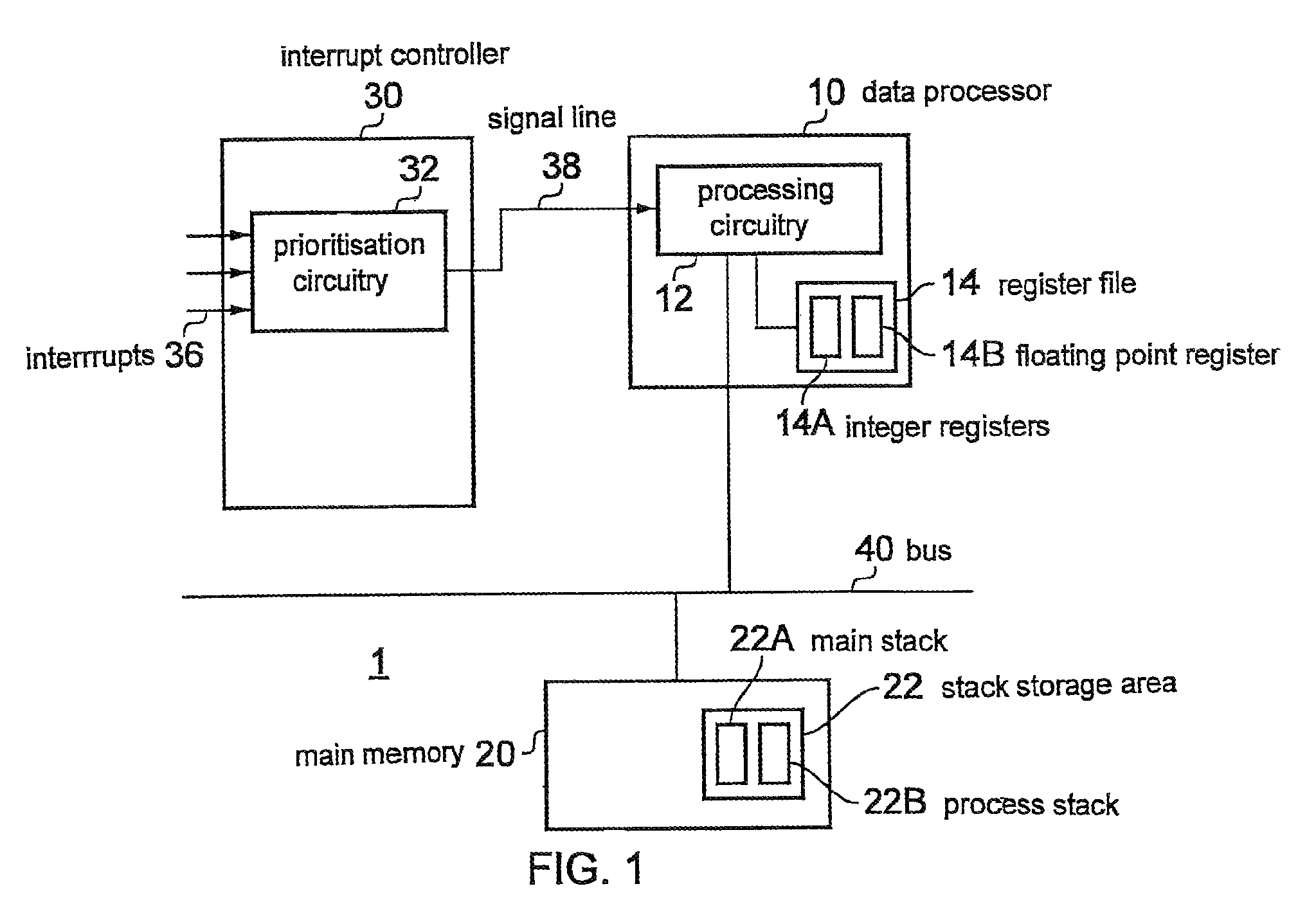
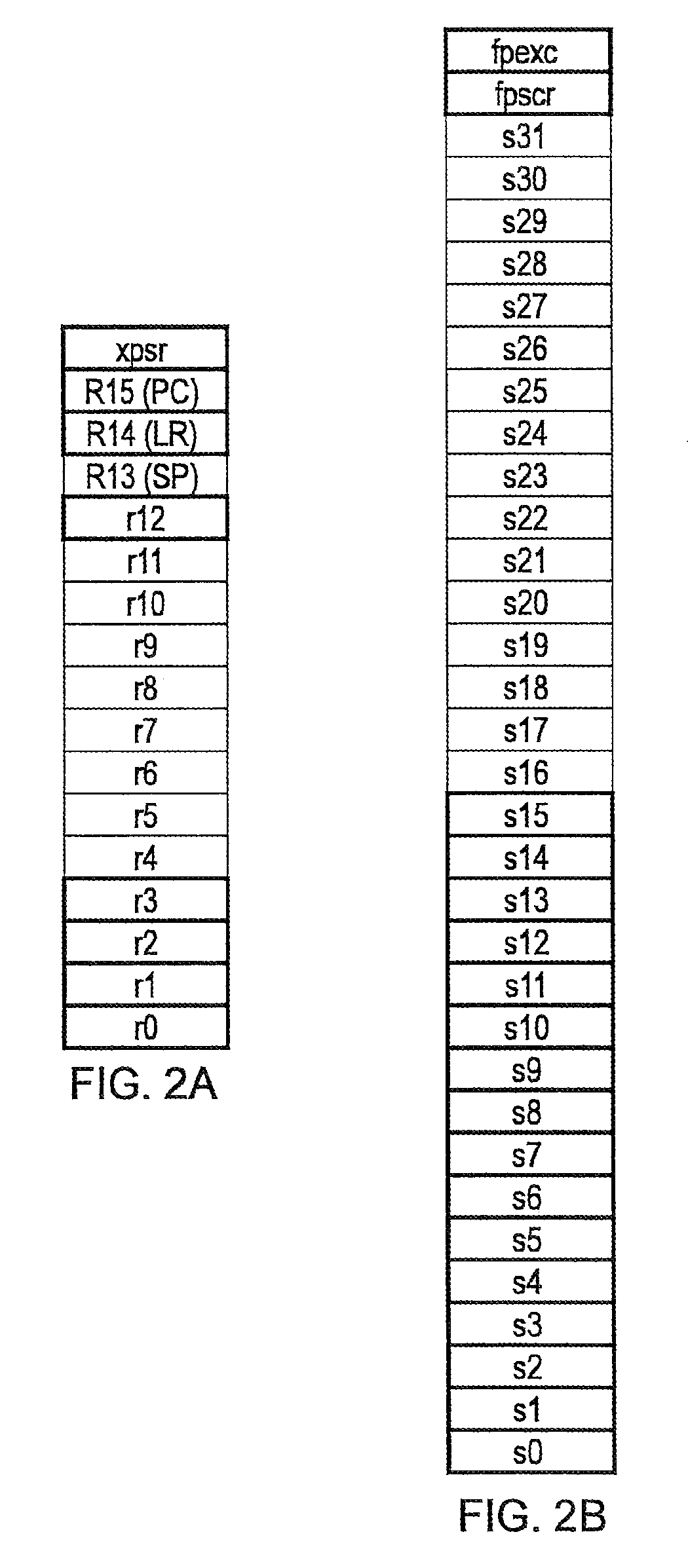
Data processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20100325397A1Improve timelinessReduce processRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsProcessor registerParallel computing
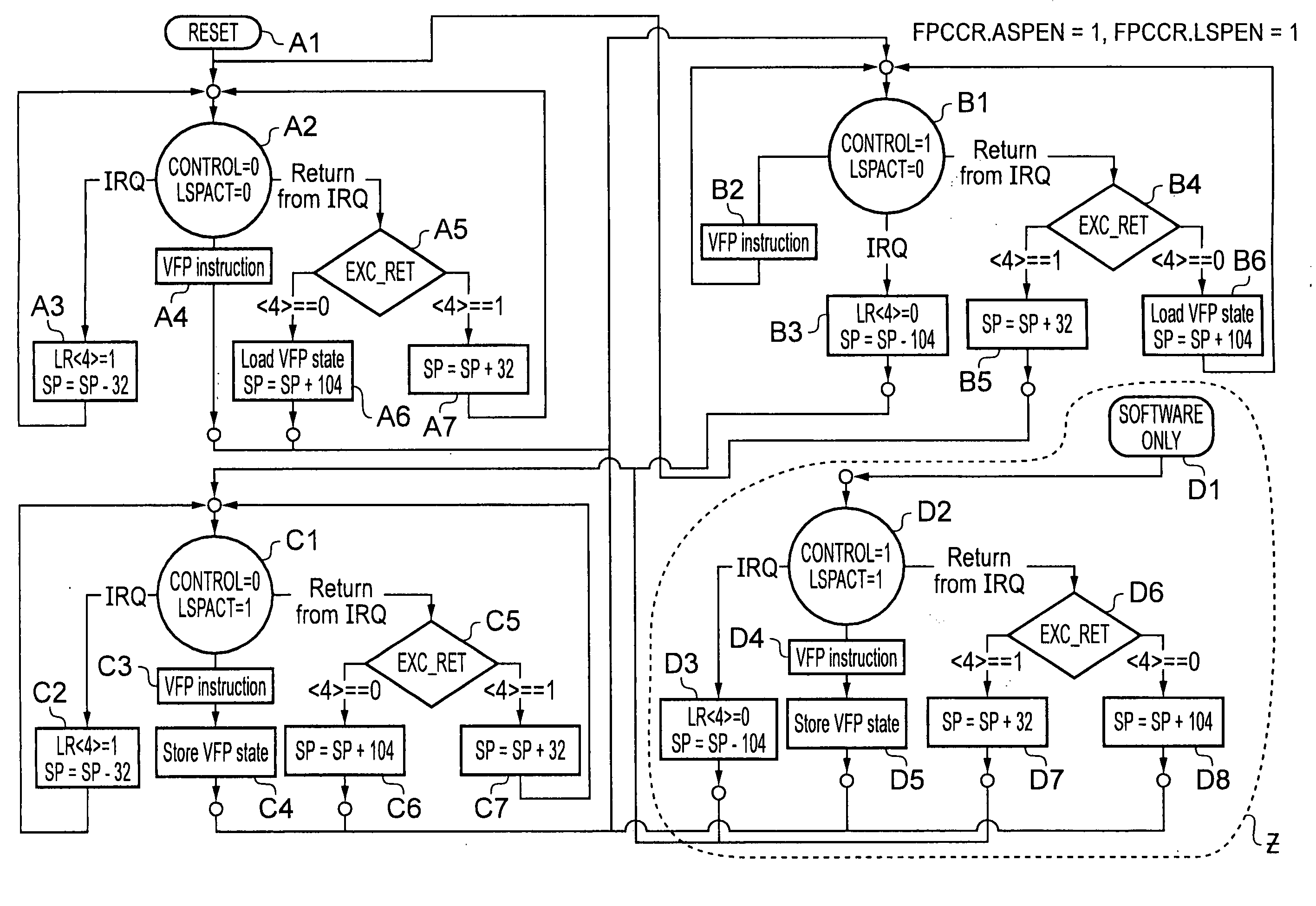
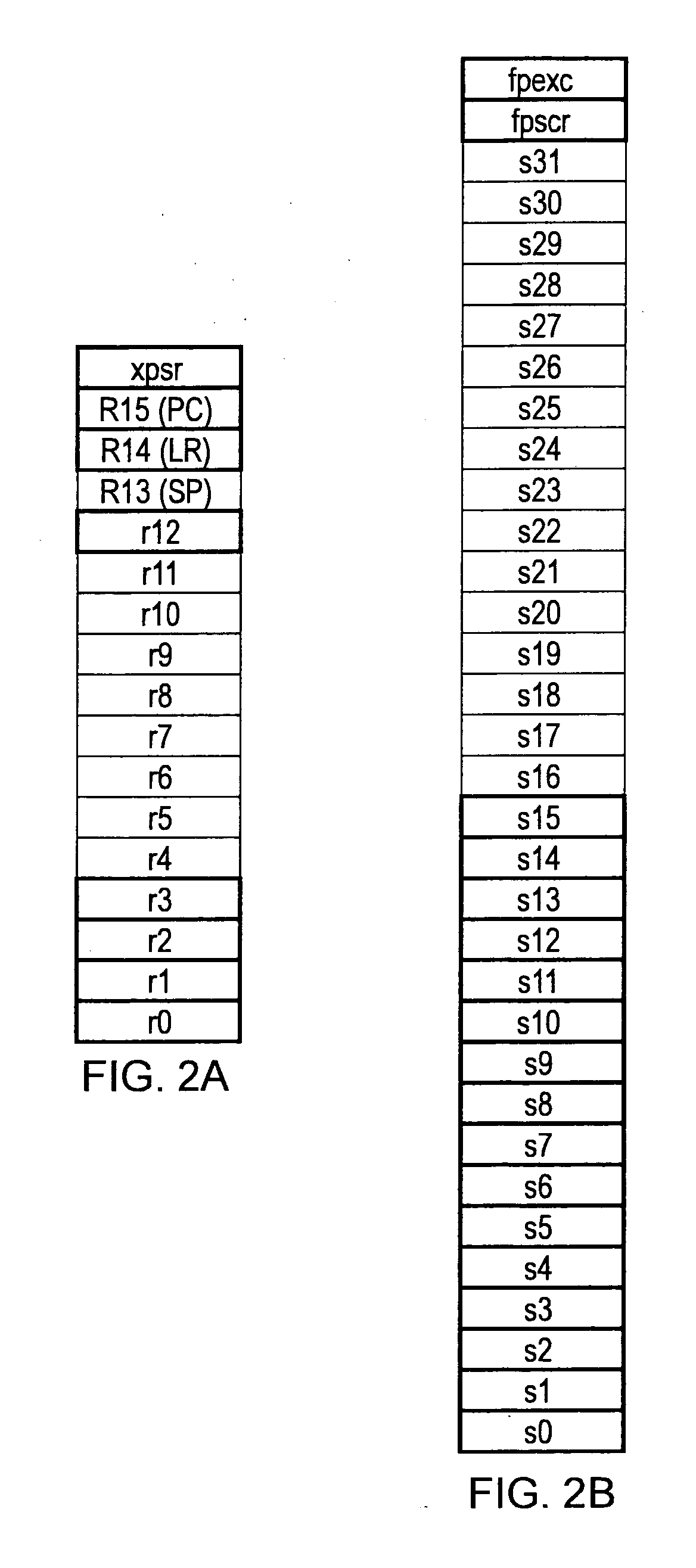
A data processing apparatus is described which comprises processing circuitry responsive to data processing instructions to execute integer data processing operations and floating point data processing operations, a first set of integer registers useable by the processing circuitry in executing the integer data processing operations, and a second set of floating point registers useable by the processing circuitry in executing the floating point data processing operations. The processing circuitry is responsive to an interrupt request to perform one of an integer state preservation function in which at least a subset of only the integer registers are copied to a stack memory, and a floating point state preservation function in which at least a subset of both the integer registers and the floating point registers are copied to the stack memory, the one of said integer state preservation function and the floating point state preservation function being selected by the processing circuitry in dependence on state information. In this way, it is possible to reduce the memory size requirement through reduced stack sizes, and to reduce the number of memory accesses required compared with the basic solution of always preserving floating point registers. As a result, power usage and interrupt latency can be reduced.
Owner:ARM LTD
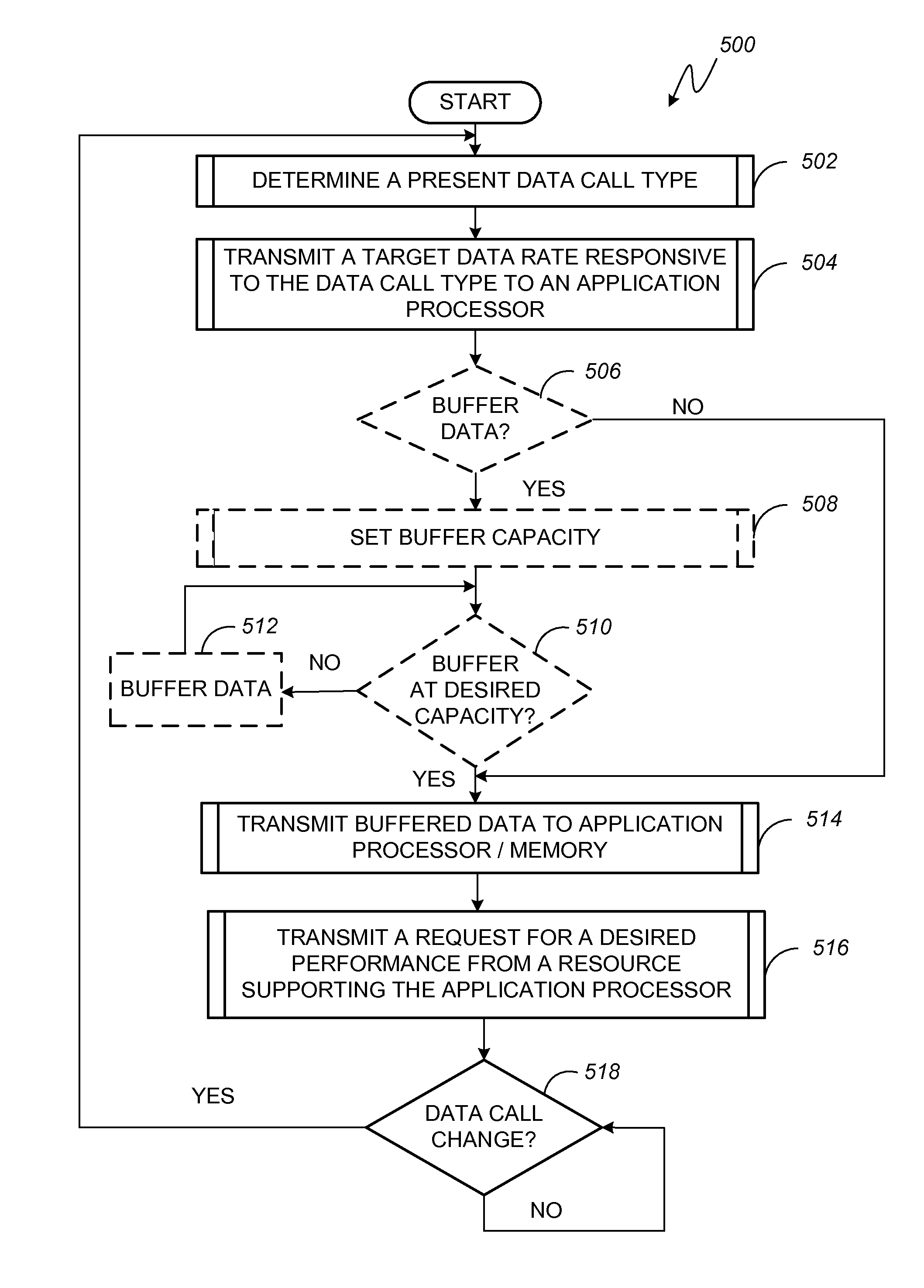
Dynamic adjustment of an interrupt latency threshold and a resource supporting a processor in a portable computing device
ActiveUS20140122689A1Conserve data consumptionNot adversely affecting user experienceDigital computer detailsDigital data protectionModem deviceComputer science
A portable computing device includes a modem and an application processor communicatively coupled by a data bus. The modem communicates a target data throughput in accordance with an identified data call. In response, the application processor determines whether an adjustment of an interrupt latency threshold is warranted to support the target data throughput identified by the modem. Otherwise, the application processor executes no such adjustment. In addition, the modem requests a desired performance of an application processor resource. In response, the application processor adjusts a control input of the application processor controlled resource. A change in a present data transfer session triggers the modem to communicate a revised target data throughput and / or a revised request for a desired performance of an application processor resource.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
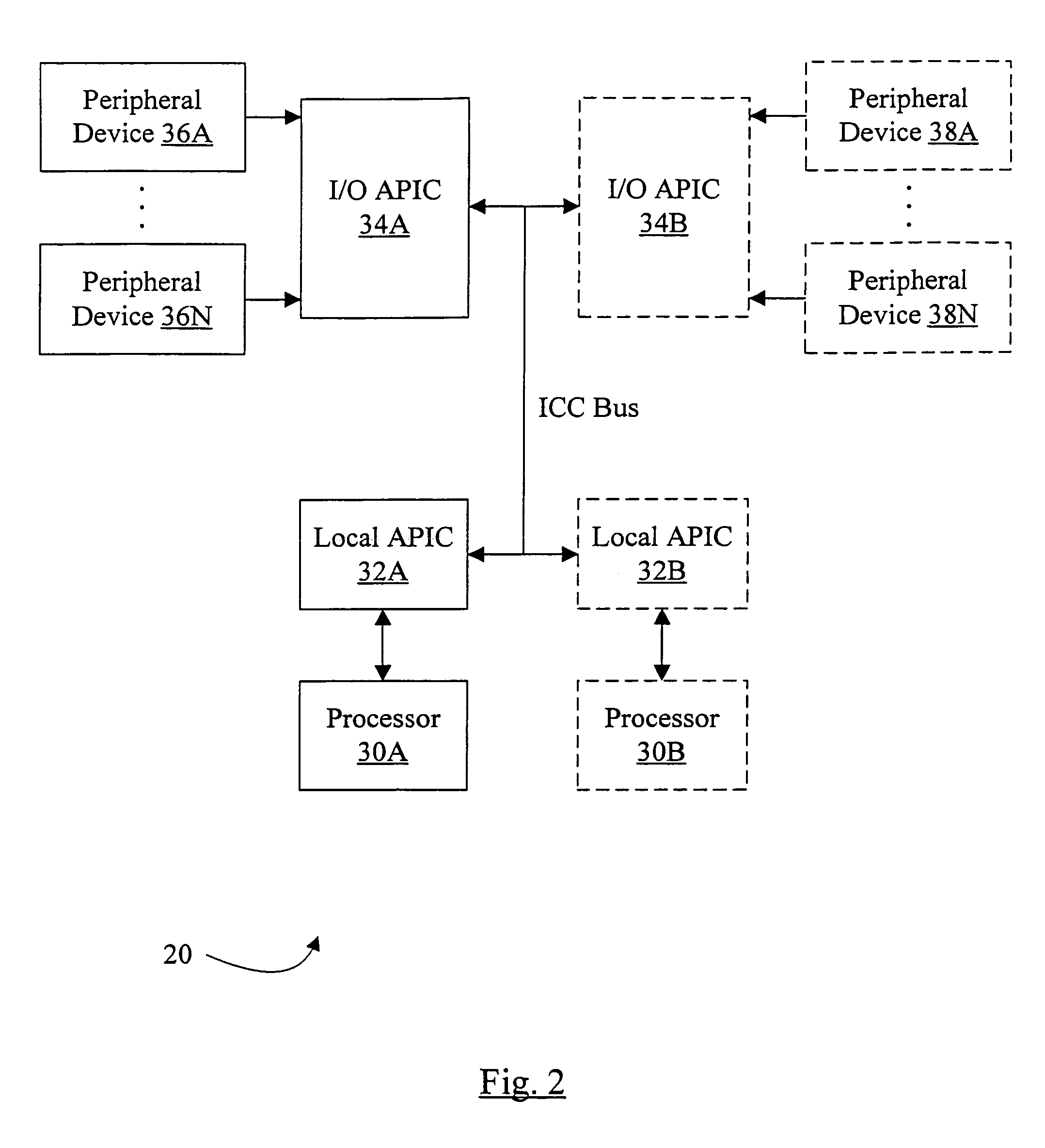
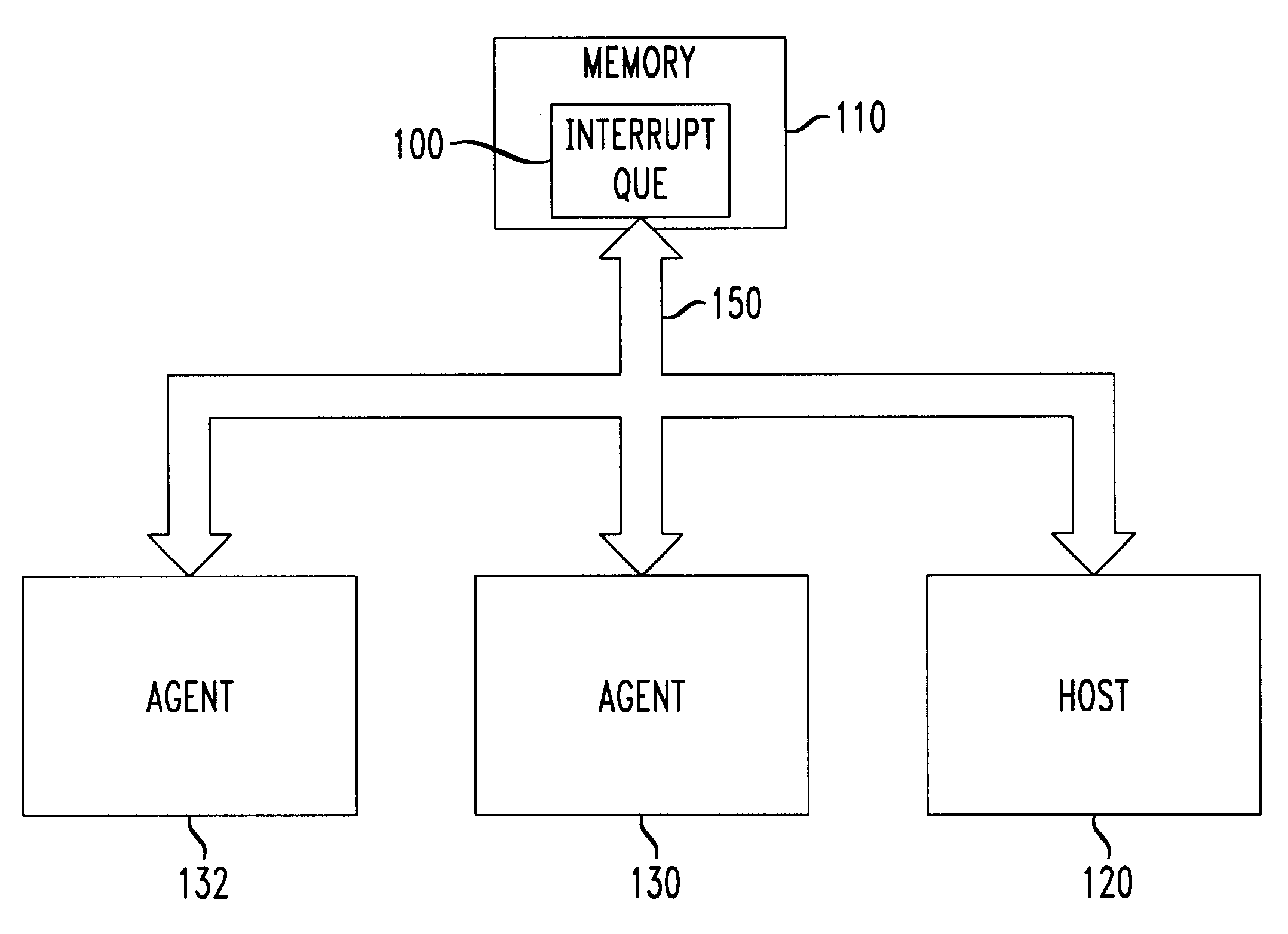
System for memory based interrupt queue in a memory of a multiprocessor system
InactiveUS6240483B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationHardware monitoringMulti processorStatus register
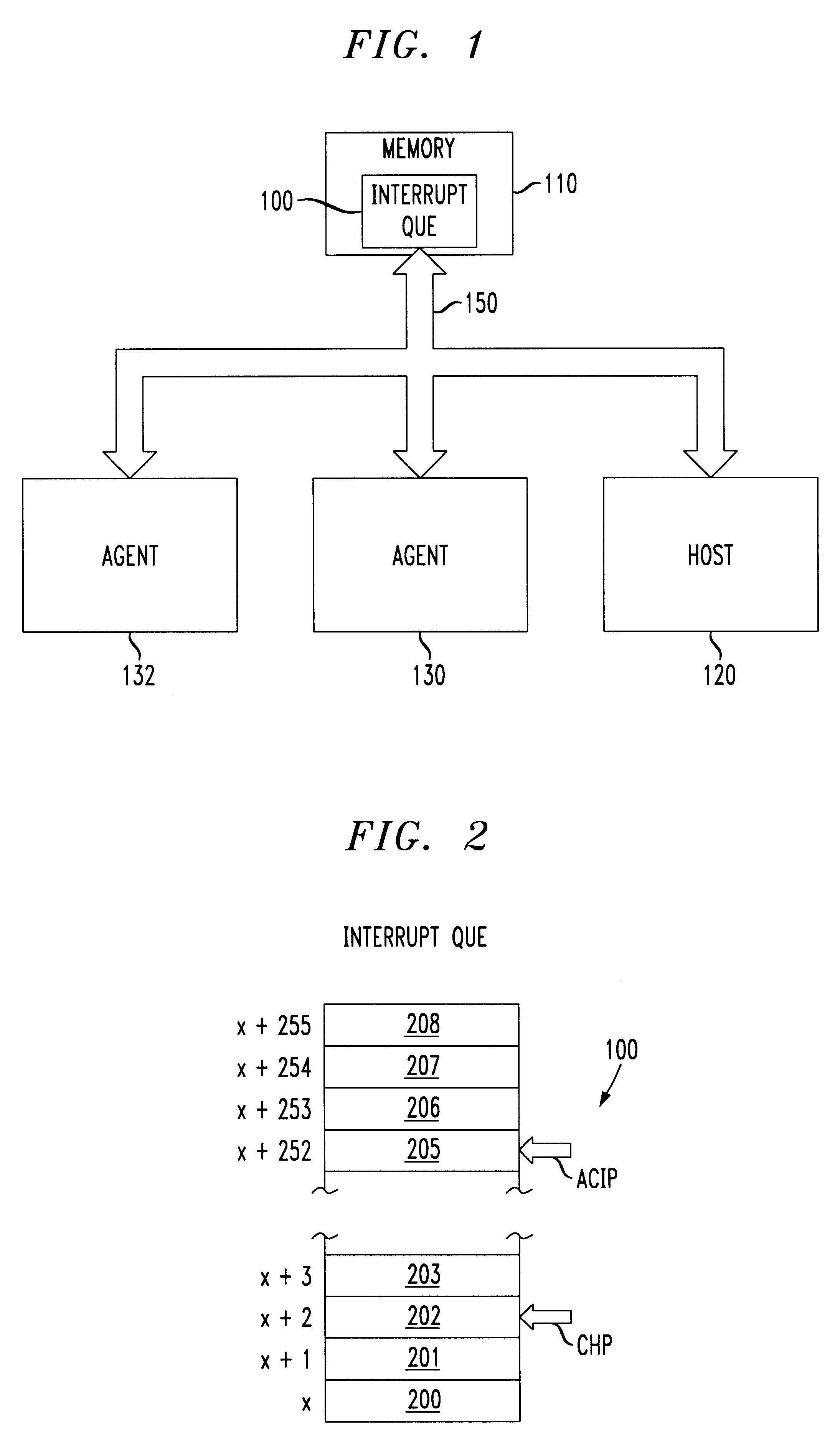
An interrupt mechanism which reduces or eliminates the need for an interrupt status register while at the same time provides suitable information to a host or other processor with respect to the cause and parameters surrounding an interrupt signal. An interrupt queue is maintained in shared memory accessible by both a host and an interrupting agent. The interrupt queue has a capacity or two or more separate interrupt requests, either from a same interrupting agent or from two different interrupting agents. As interrupting agents write to the interrupt queue, an agent current interrupt pointer (ACIP) is incremented to a next position in the interrupt queue. As the host services interrupts, the current host pointer is incremented to clear the serviced interrupt request entry.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
System and method for adjusting power usage to reduce interrupt latency
ActiveUS20130111092A1Interrupt handlingEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingSufficient timeTime critical
A system and method are described for warming a processor from a low power state in anticipation of a time critical interrupt. For example, one embodiment of a method comprises: detecting that a time-critical interrupt will require processor resources at some point in the future; estimating a time at which the time-critical interrupt will be triggered; scheduling a timer interrupt to fire at a specified time prior to the estimated time that the time-critical interrupt will be triggered, the timer interrupt being scheduled with sufficient time to ensure that the processor is warmed to a level at which it is capable of handling the time-critical interrupt at the time that the time-critical interrupt is triggered; and responsively triggering the timer interrupt at the specified time prior to the time critical interrupt.
Owner:APPLE INC
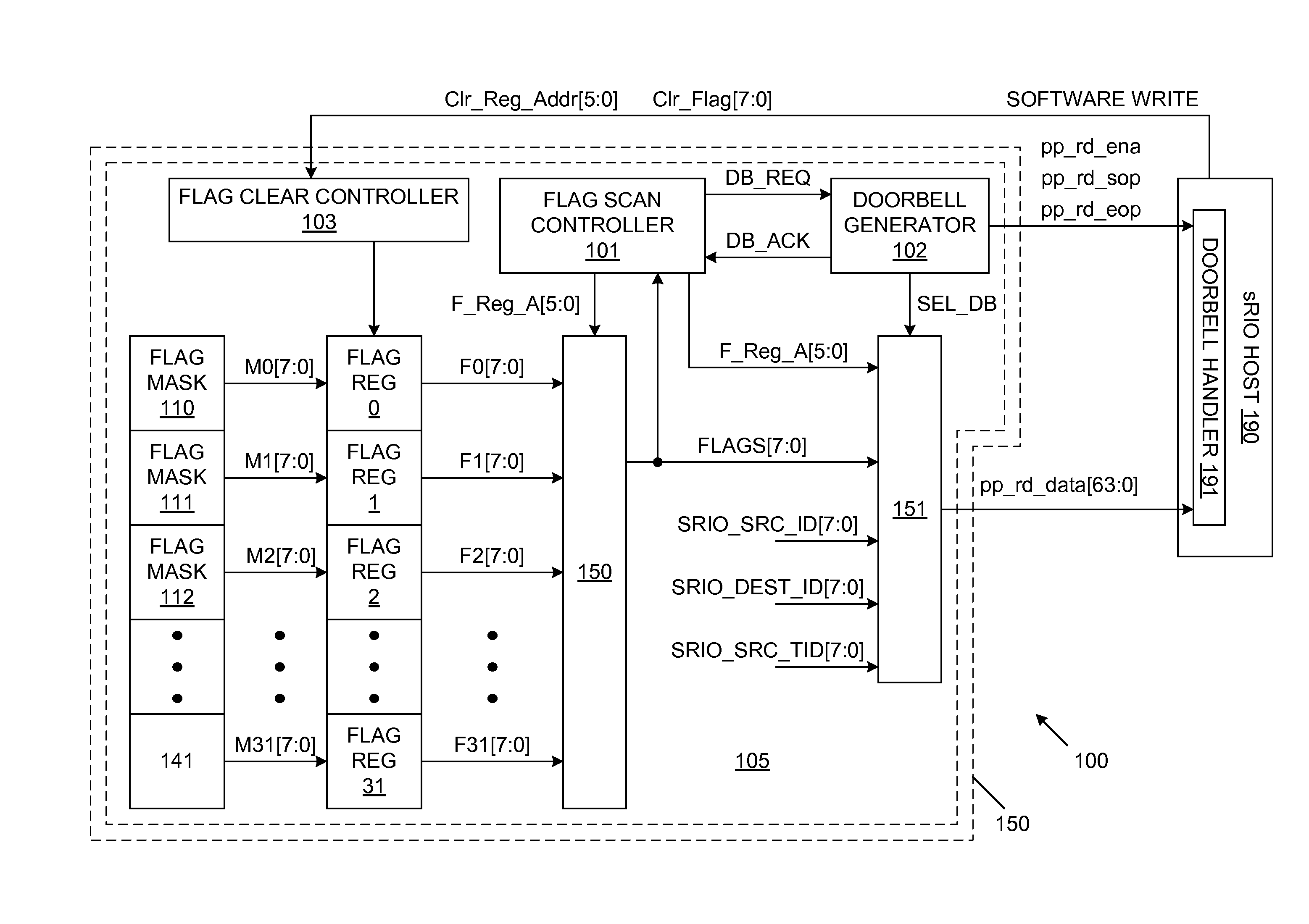
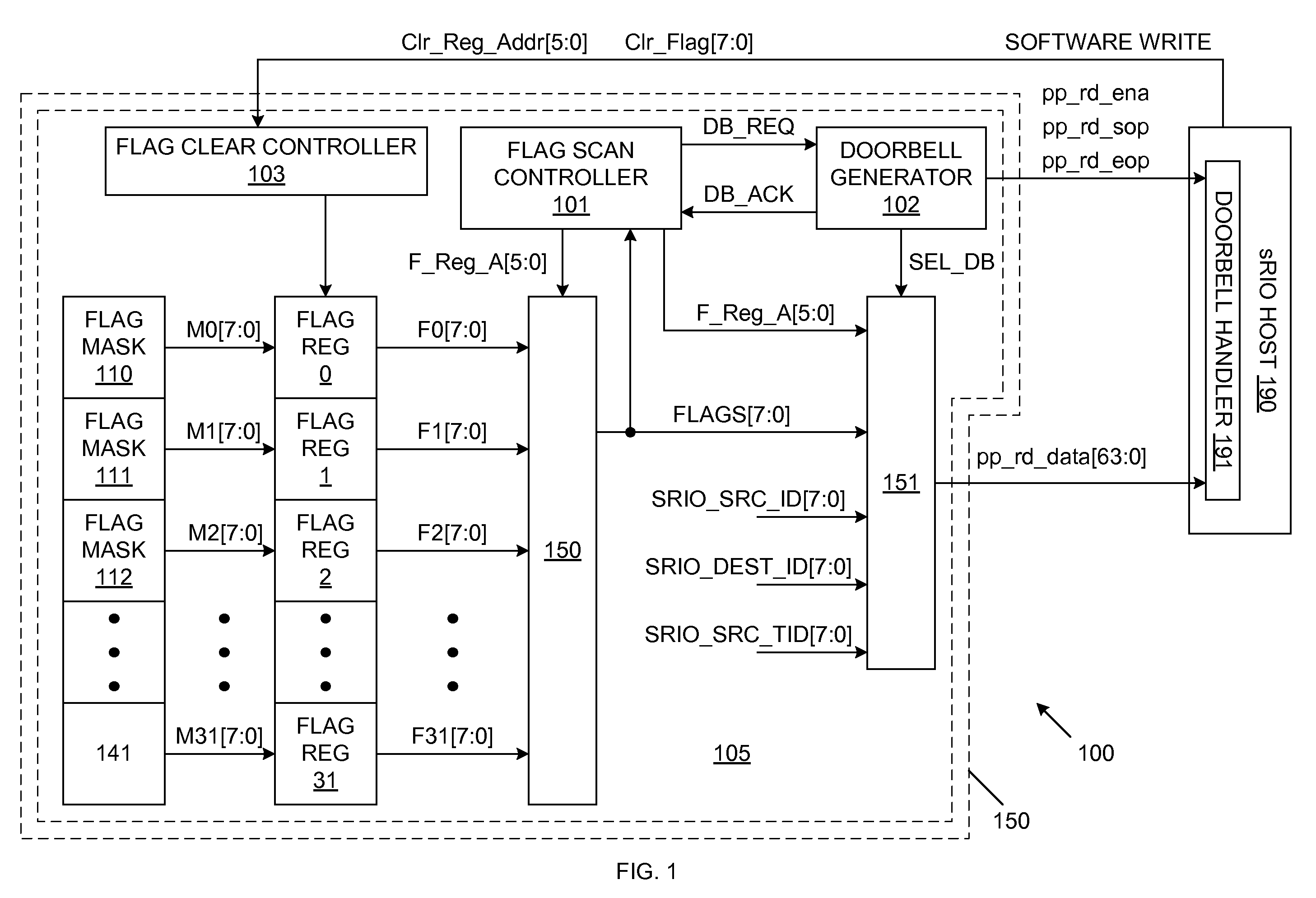
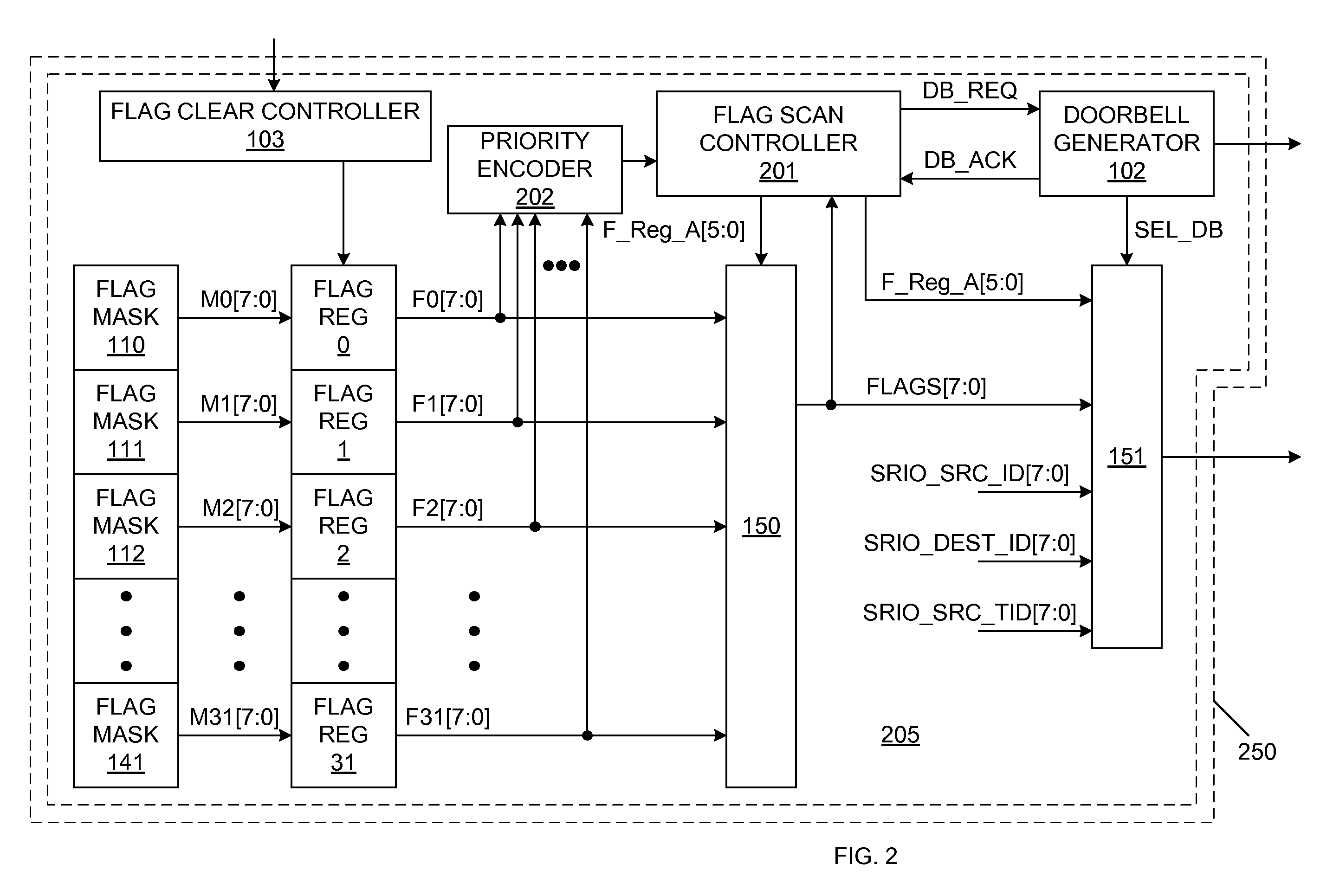
Rapid input/output doorbell coalescing to minimize CPU utilization and reduce system interrupt latency
ActiveUS7617346B2Eliminates race conditionConditional code generationMemory systemsDoorbellProcessor register
Status / error reporting is implemented using a doorbell system. A plurality of flag registers are included on a system device, such as a serial buffer. Each flag register has a corresponding address, and stores a plurality of flags. A flag scan controller accesses the flag registers in a predetermined priority order, using the flag register addresses. Upon detecting that one or more of the flags of a flag register are activated, the flag scan controller causes a doorbell command to be generated. The doorbell command includes the flag register address and the corresponding flags. A system processor receives the doorbell command and services the activated flags. Once the activated flags are serviced, the system processor performs one or more software write operations to clear the flags within the system device. The system processor can simultaneously service multiple flags. The system processor can also simultaneously clear multiple flags.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Data processing apparatus and method for saving return state
InactiveUS6904517B2Suppresses increase in code sizeImprove performanceProgram initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsParallel computingOperation mode
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for saving return state. The data processing apparatus comprises a processing unit for executing data processing instructions, the processing unit having a plurality of modes of operation, with each mode of operation having a corresponding stack for storing data associated with that mode. The processing unit is responsive to a return state data processing instruction to write return state data of the processing unit from its current mode of operation to a stack corresponding to a different mode of operation to the current mode of operation. This approach significantly reduces code size and improves interrupt latency over known prior art techniques.
Owner:ARM LTD
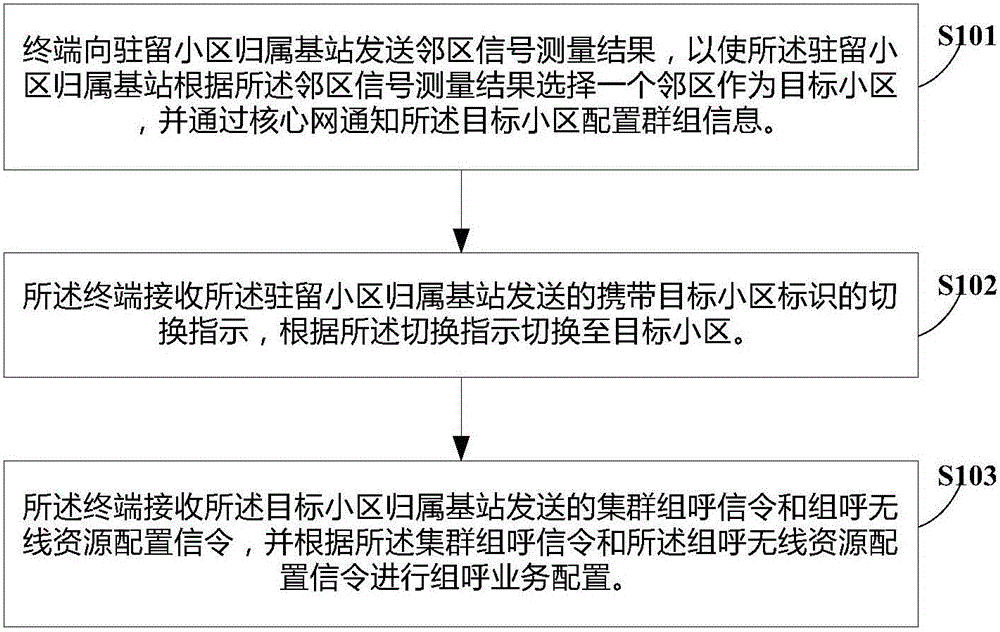
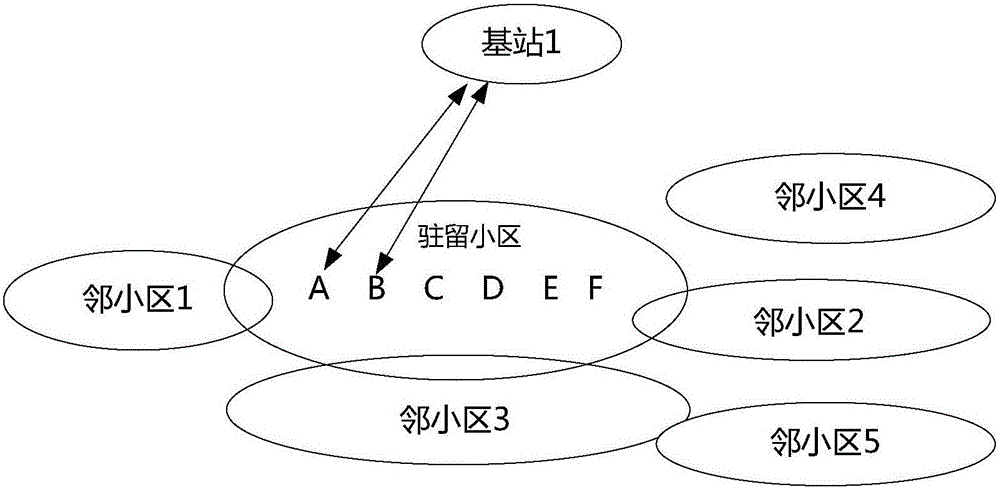
Movement control method for terminal in RRC idel state, terminal and base station
ActiveCN106489274AReduce Interrupt LatencyAssess restrictionConnection managementComputer terminalCluster group
Disclosed are a movement control method for a terminal in an RRC idle state, a terminal and a base station. The method is applied to a terminal side and comprises: a terminal sends a neighbor cell signal measurement result to a base station to which a camp-on cell belongs, so that the base station to which the camp-on cell belongs selects a neighbor cell as a target cell according to the neighbor cell signal measurement result, and informs the target cell of configuration of group information by means of a core network; the terminal receives a switching indication carrying a target cell identifier from the base station to which the camp-on cell belongs, and switches to the target cell according to the switching indication; and the terminal receives cluster group call signaling and group call radio resource configuration signaling that are sent by a base station to which the target cell belongs, and configures a group call service according to the cluster group call signaling and the group call radio resource configuration signaling. The technical solution of the present invention can reduce the interrupt latency of a group call service during movement of a terminal.
Owner:HYTERA COMM CORP
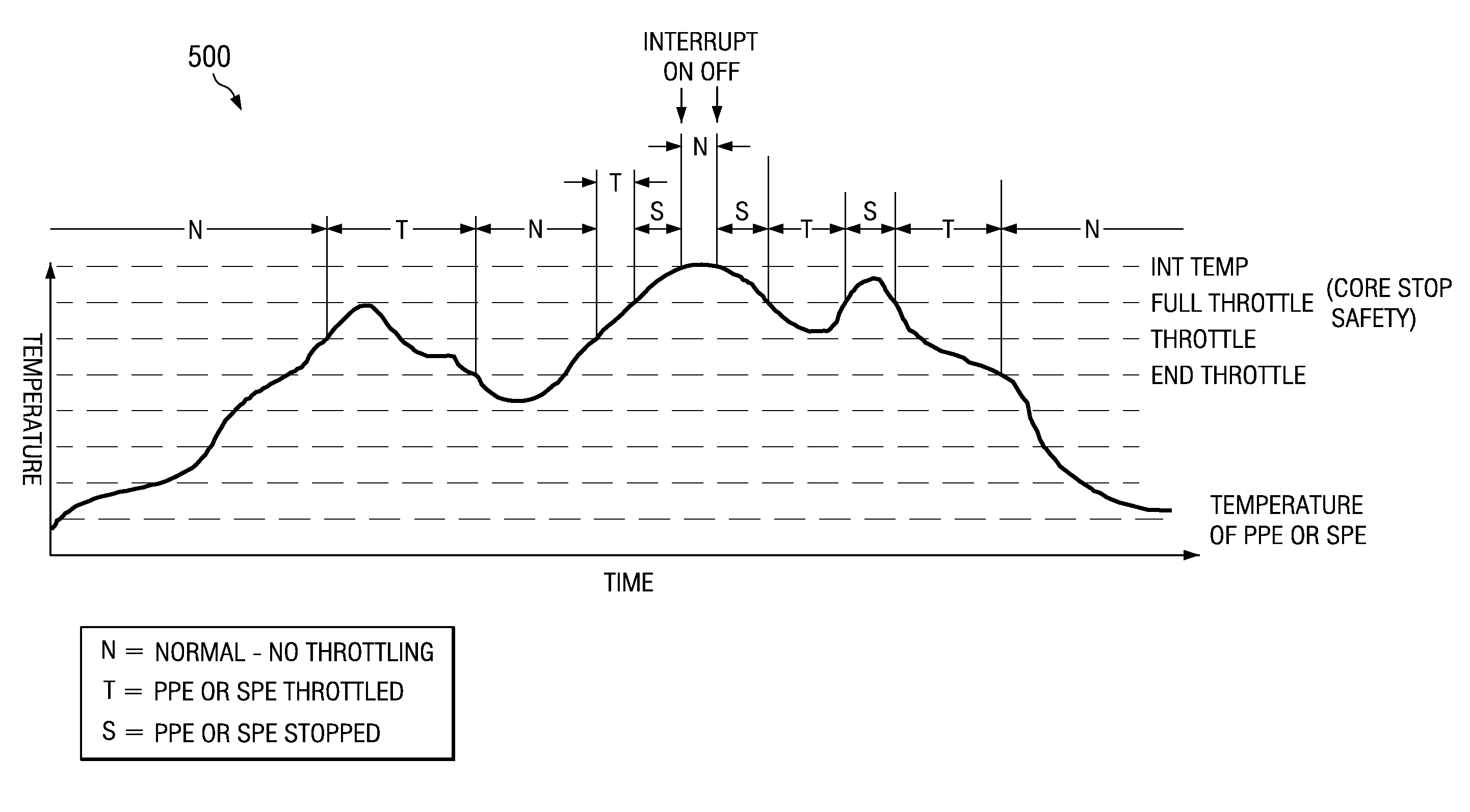
Thermal throttle control with minimal impact to interrupt latency
InactiveUS20070124611A1Minimal impactReduce Interrupt LatencyThermometer detailsTemperatue controlThrottle controlData processing system
A computer implemented method, data processing system, and processor are provided for thermal throttle control with minimal impact to interrupt latency. A setting of an interrupt status bit is monitored. A determination is made as to whether an interrupt associated with the interrupt status bit is an unmasked interrupt in response to the interrupt status bit being set. An existing throttling mode is disabled and the interrupt handled in response to the interrupt being unmasked, where the interrupt latency of the integrated circuit is reduced.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for controlling peripheral adapter interrupt frequency by estimating processor load in the peripheral adapter
InactiveUS7634589B2Lower latencyReduce overheadStore-and-forward switching systemsInput/output processes for data processingControl breakEmbedded system
A method provides adaptive interrupt latency to improve performance in a processing system. A ration of transmit queue depth to receive queue depth of the adapter is compared to its historical value in order to provide an estimate of processor load. The estimated processor load is then used to set a parameter that controls the frequency of an interrupt generator, which may be controlled by setting an interrupt queue depth threshold, packet frequency threshold or interrupt hold-off time value. The historical value may be predetermined, user-settable, obtained during a calibration interval or obtained by taking a long-term average of the ratio.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
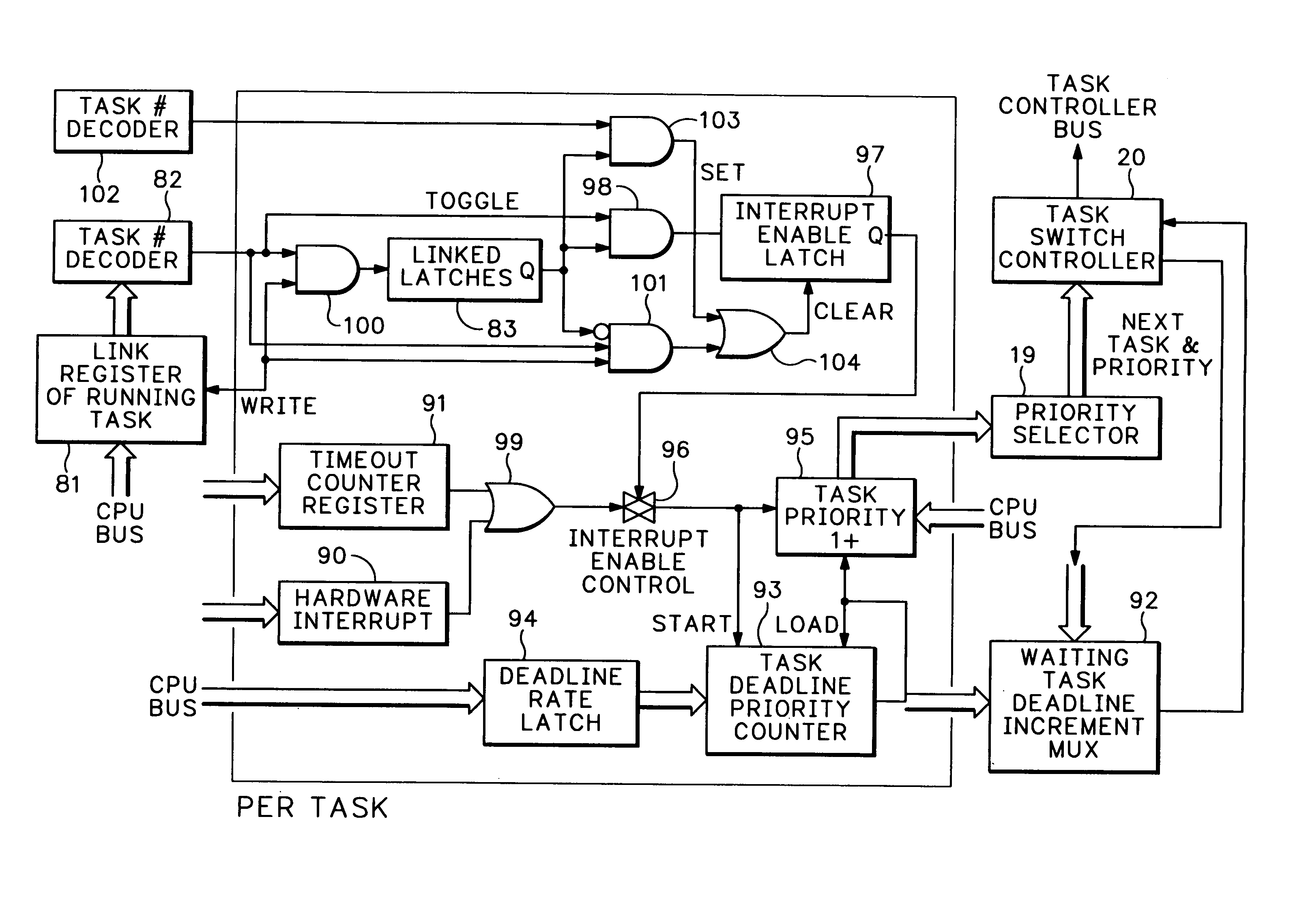
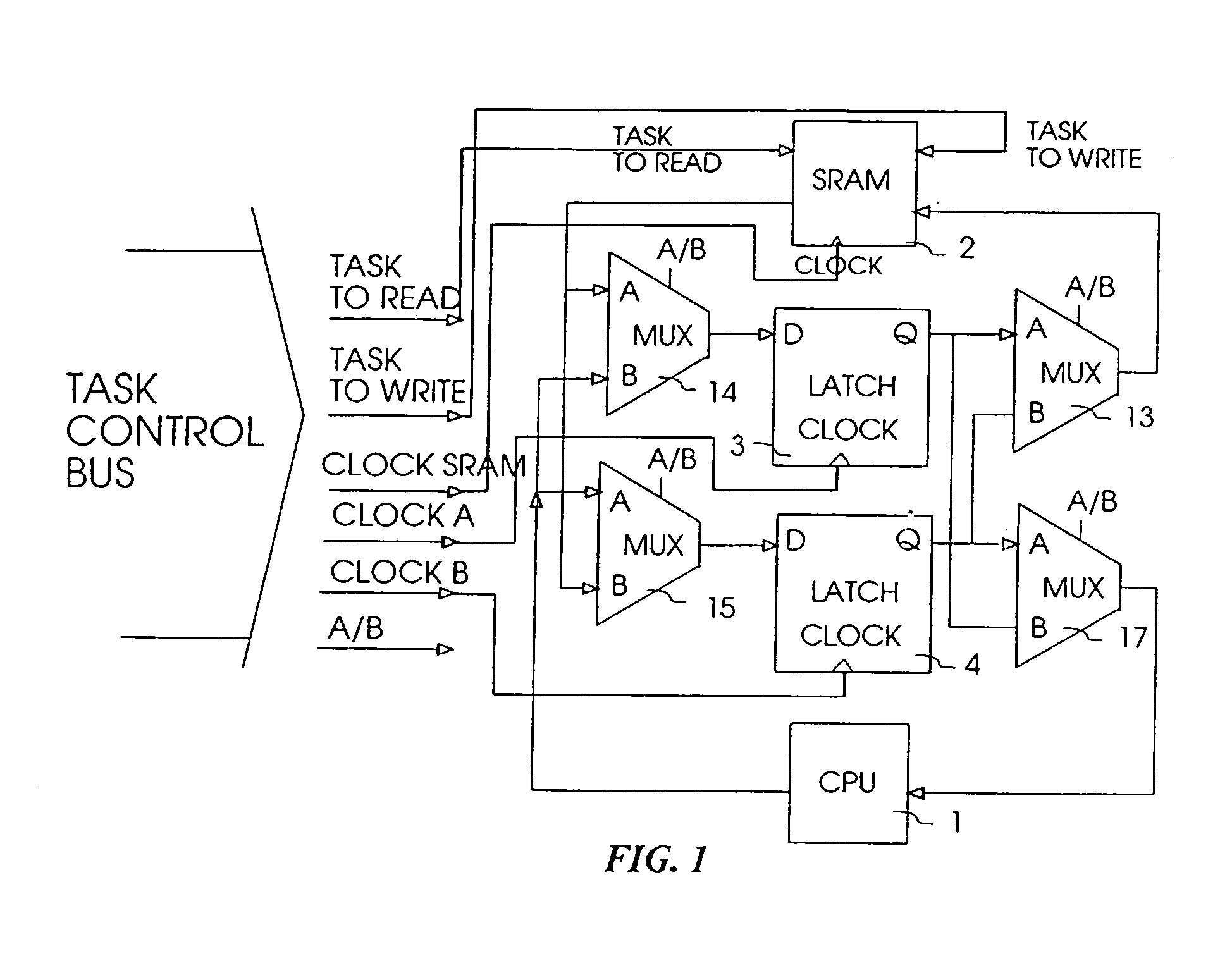
Zero overhead computer interrupts with task switching
InactiveUS6981133B1Avoid lostProgram initiation/switchingProgram control using stored programsTime limitArchitecture of Integrated Information Systems
The invention constitutes a unique hardware zero overhead interrupt and task change mechanism for the reduction or elimination of interrupt latency and task change processing overhead delays in computer architectures. Without loss of time, the system performs complete task state saving and restoration between one cycle and the next without software intervention. For each Central Processing Unit (1) register, the invention uses one or more auxiliary latches (3, 4) wherein one latch (3, 4) is used as the “running” latch and one of the auxiliary latches is attached to task storage memory. The invention swaps connections between alternate “running” registers and auxiliary registers while transferring other tasks to and from task storage memory (2). The invention provides a task linking system to allow the linking of tasks for the mandatory sequential execution of the linked tasks. Further, the invention includes a priority “impatience” counter system to increase the relative priorities of various tasks as they approach their task deadlines.
Owner:XYRON INC
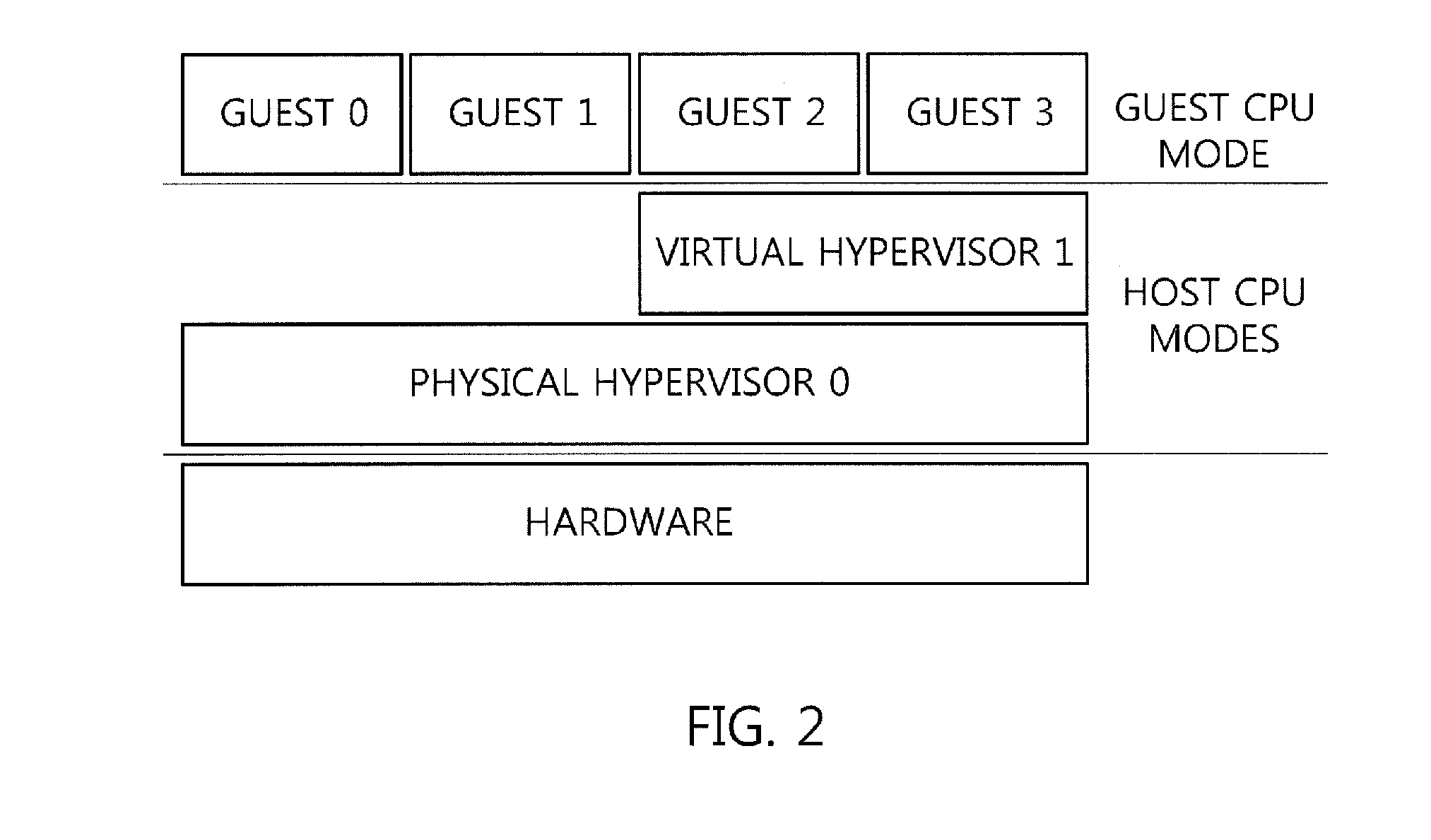
Hybrid virtualization method for interrupt controller in nested virtualization environment
InactiveUS20160085568A1Reduce Interrupt LatencyProgram initiation/switchingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationNested virtualizationVirtual machine
Disclosed is a hybrid virtualization method for an interrupt controller in nested virtualized environment, which can reduce guest interrupt latency. A hybrid virtualization method includes operating a Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) which enables a program executed on a host and a program executed on a guest to be simultaneously used, providing, by the VMM, a virtual interrupt configuration register to the guest, and selectively utilizing full virtualization and partial virtualization. Full virtualization is used when guests which are running simultaneously request the same interrupt. In this case, the interrupt is trapped by the VMM before being injected to the different guests. Partial virtualization allows a guest to directly handle incoming interrupt and avoids expensive traps to the hypervisor to reduce the latency. This virtualization technique can be used by any kind of VMM which is physical hypervisor or virtual hypervisor for processing interrupts of their respective guests.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
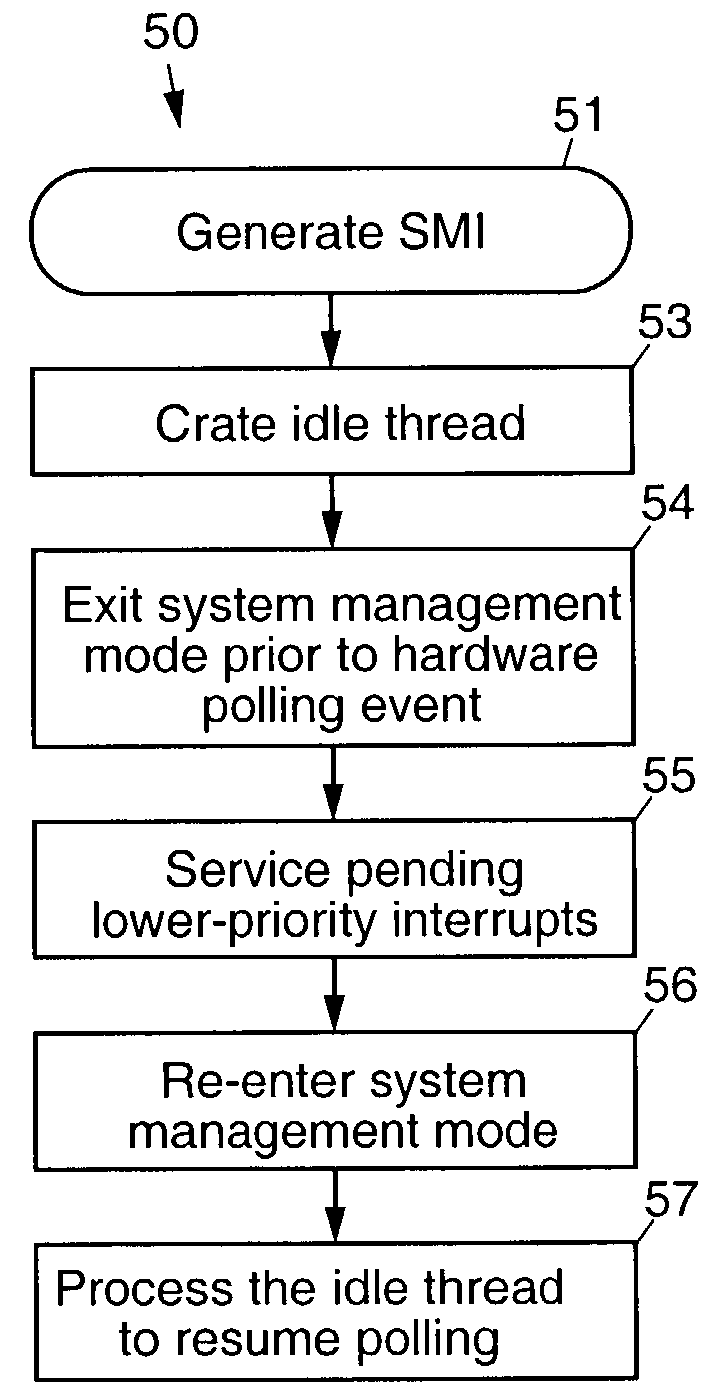
Reducing interrupt latency while polling
InactiveUS7043729B2Reduce system management interrupt (SMI) latencyReduce managementProgram initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsPolling systemSystem Management Mode
Systems, methods, and software for reducing system management interrupt (SMI) latency while operating in system management mode. The present invention implements a technique for exiting system management mode while waiting for polled hardware events, handling any pending lower-priority interrupts and then resuming polling. The present invention does this by multi-threading SMI source handlers, using an idle thread, and using protocols for software-generated system management interrupts that insure that lower priority interrupts are serviced.
Owner:PHOENIX TECH EMEA LTD
Data processing apparatus and method having integer state preservation function and floating point state preservation function
ActiveUS9201651B2Reduce size requirementsIncrease spaceRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareProcessor register
A data processing apparatus is described which comprises processing circuitry responsive to data processing instructions to execute integer data processing operations and floating point data processing operations, a first set of integer registers useable by the processing circuitry in executing the integer data processing operations, and a second set of floating point registers useable by the processing circuitry in executing the floating point data processing operations. The processing circuitry is responsive to an interrupt request to perform one of an integer state preservation function in which at least a subset of only the integer registers are copied to a stack memory, and a floating point state preservation function in which at least a subset of both the integer registers and the floating point registers are copied to the stack memory, the one of said integer state preservation function and the floating point state preservation function being selected by the processing circuitry in dependence on state information. In this way, it is possible to reduce the memory size requirement through reduced stack sizes, and to reduce the number of memory accesses required compared with the basic solution of always preserving floating point registers. As a result, power usage and interrupt latency can be reduced.
Owner:ARM LTD
Computer for dynamically determining interrupt delay
InactiveUS7415561B2Program initiation/switchingInput/output processes for data processingDelayed timeEmbedded system
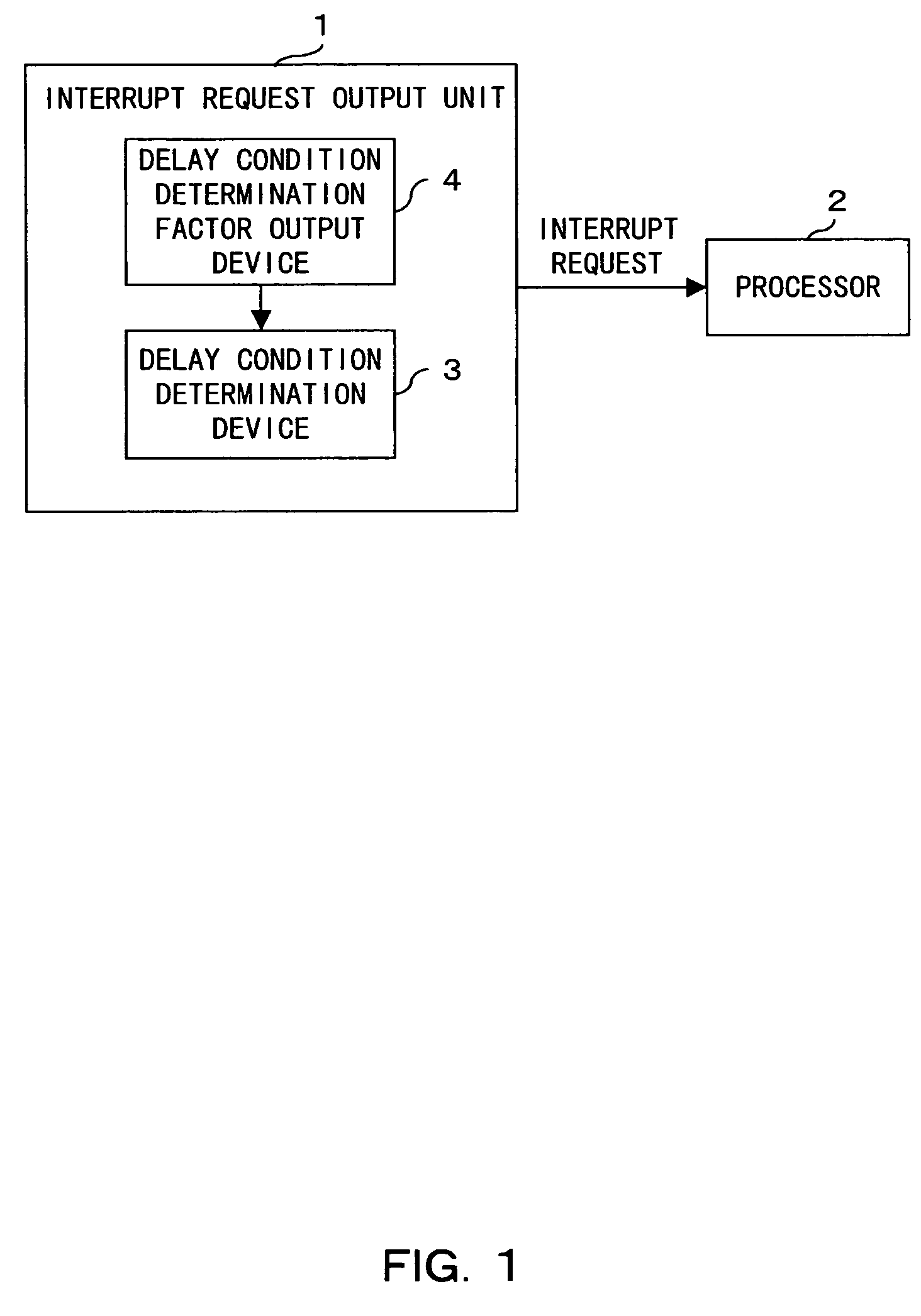
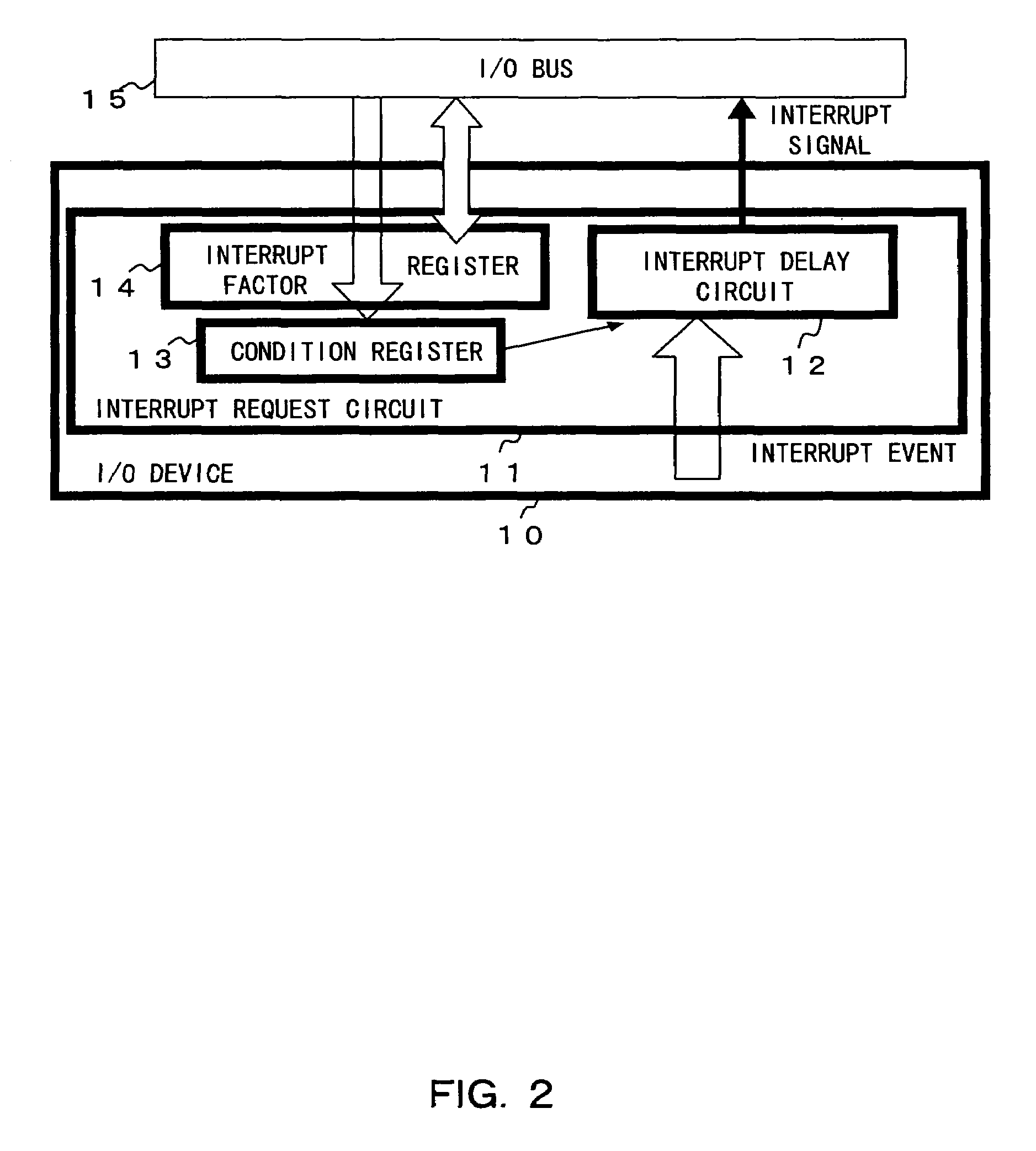
In a computer having a unit for outputting an interrupt request to a processor, a delay condition from occurrence of an interrupt event to issue of an interrupt request to the processor can be dynamically determined depending on the processor load status, etc. The interrupt request output unit includes a unit for obtaining a determination factor of a delay condition from the occurrence of an interrupt event to the issue of an interrupt request to the processor, and a unit for determining a delay condition corresponding to the obtained determination factor. For example, a time up to a read of an interrupt factor by the processor is obtained as a determination factor, and is multiplied by a coefficient, thereby determining a delay time as a delay condition.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Mmpp analysis of network traffic using a transition window
InactiveUS20080101228A1Accuracy of the selectionFlexibilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBoundary valuesInternet traffic
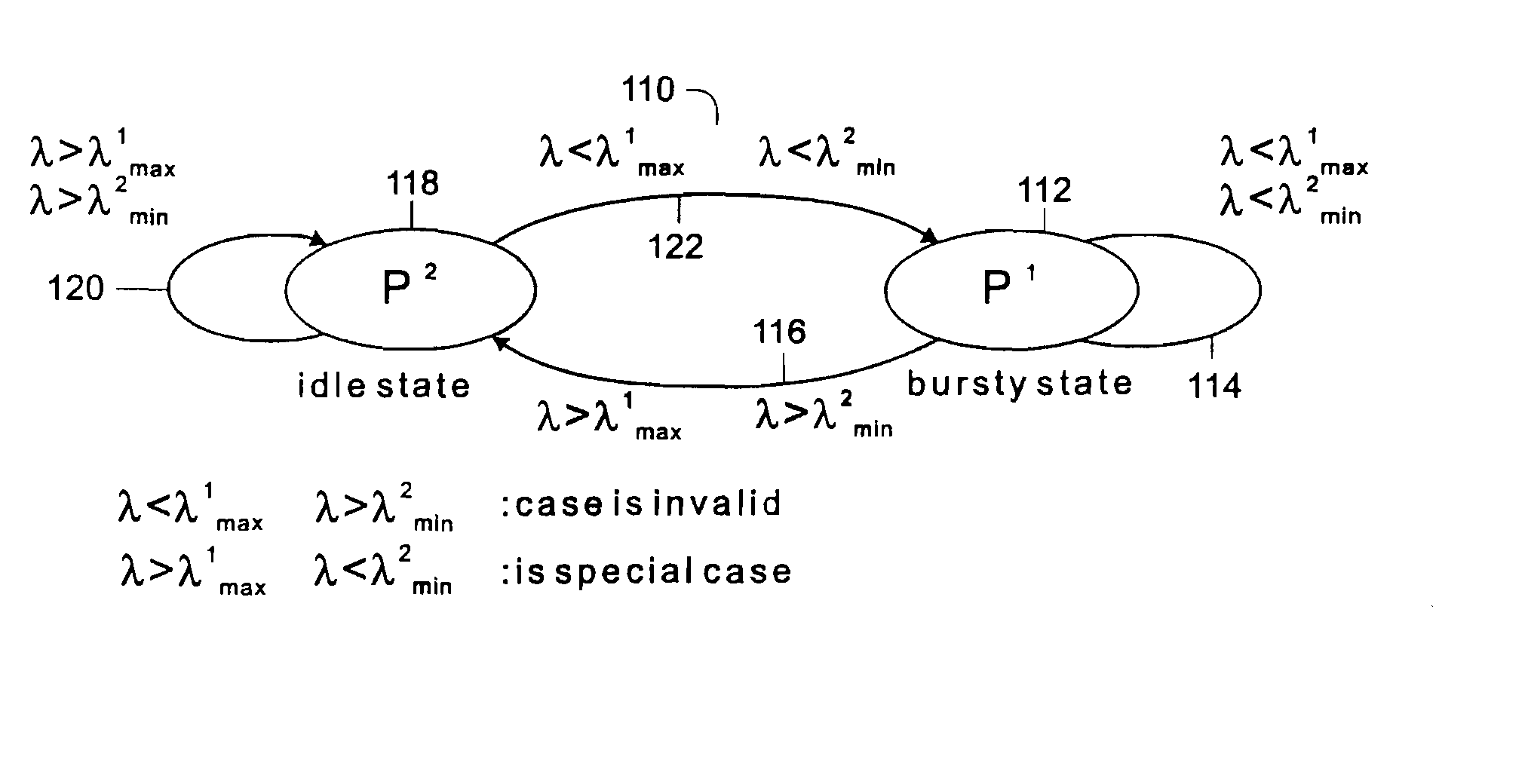
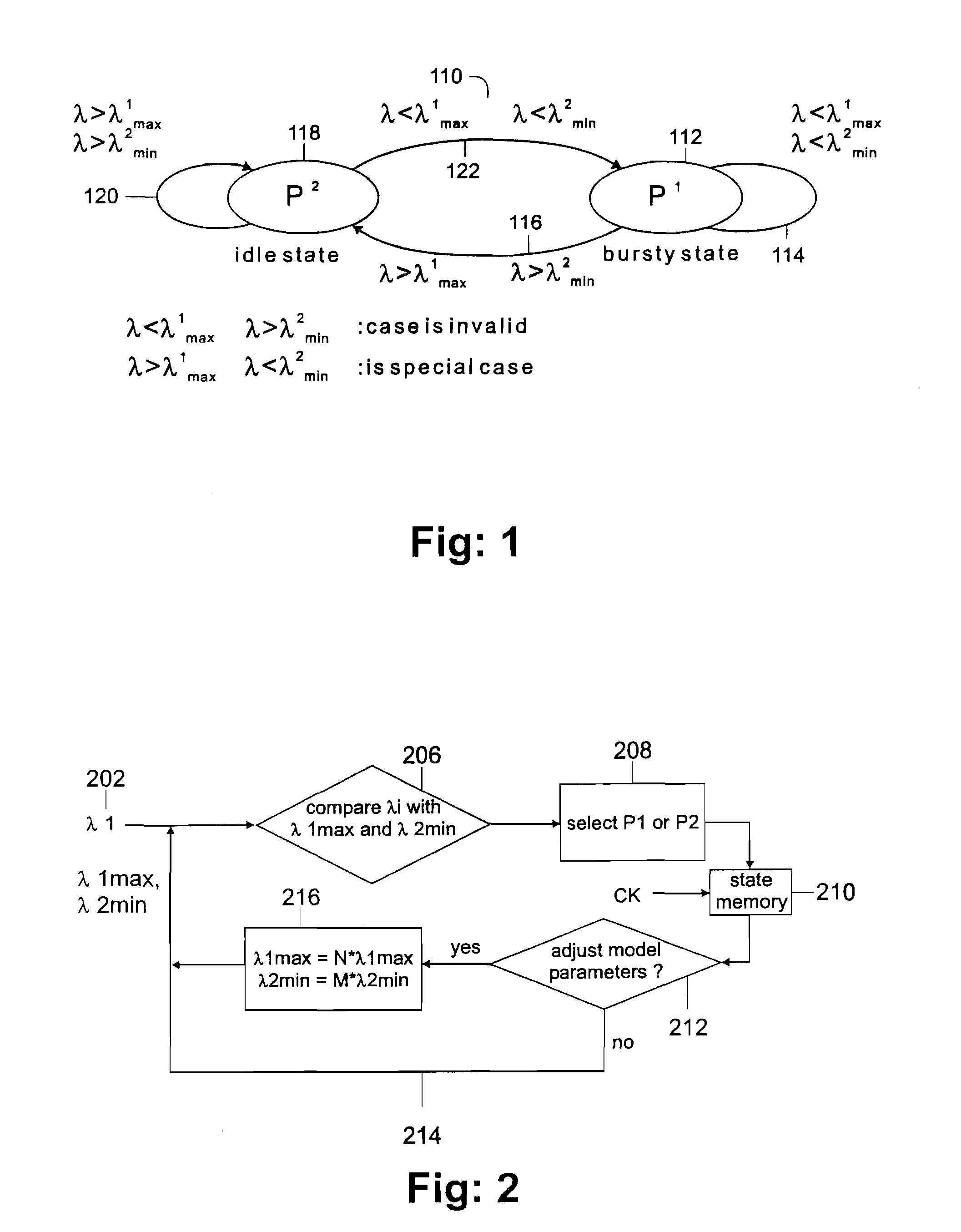
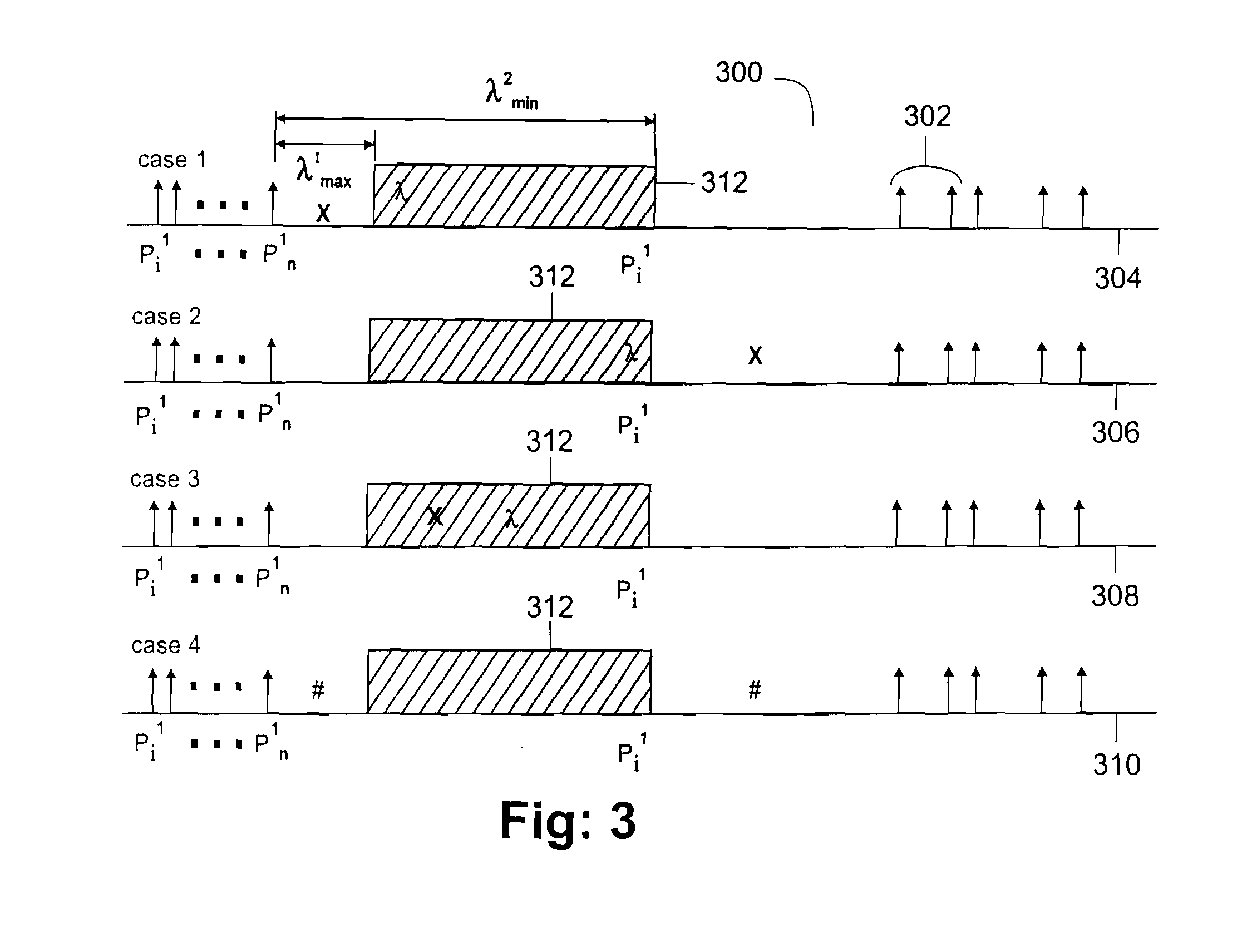
Data communication in network traffic is modeled in real time and is analyzed using a 2-state Markov modified Poissen process (MMPP). The traffic inter-arrival times for bursty and idle states define a transition window [λ1max, λ2min] represented by the boundary values λ1max for the inter-arrival time for bursty traffic, and λ2min for the inter-arrival time for idle traffic. Changes in the values of λ1max and λ2min are tracked over time, and the size of the transition window is enlarged or decreased based upon relative changes in these values. If the inter-rival times for the bursty state and the idle state become approximately equal, the model defaults to a single state model. The modeling is applicable to the synchronization of polling and blocking in a low-latency network system. This permits the adoptive selection of poll or block to maximize CPU utilization and interrupt latency.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Method for Mitigating Adverse Processor Loading in a Personal Computer Implementation of a Wireless Local Area Network Adapter
ActiveUS20080019277A1Low costMinimizing processing loadEnergy efficient ICTError preventionInternet trafficPeak value
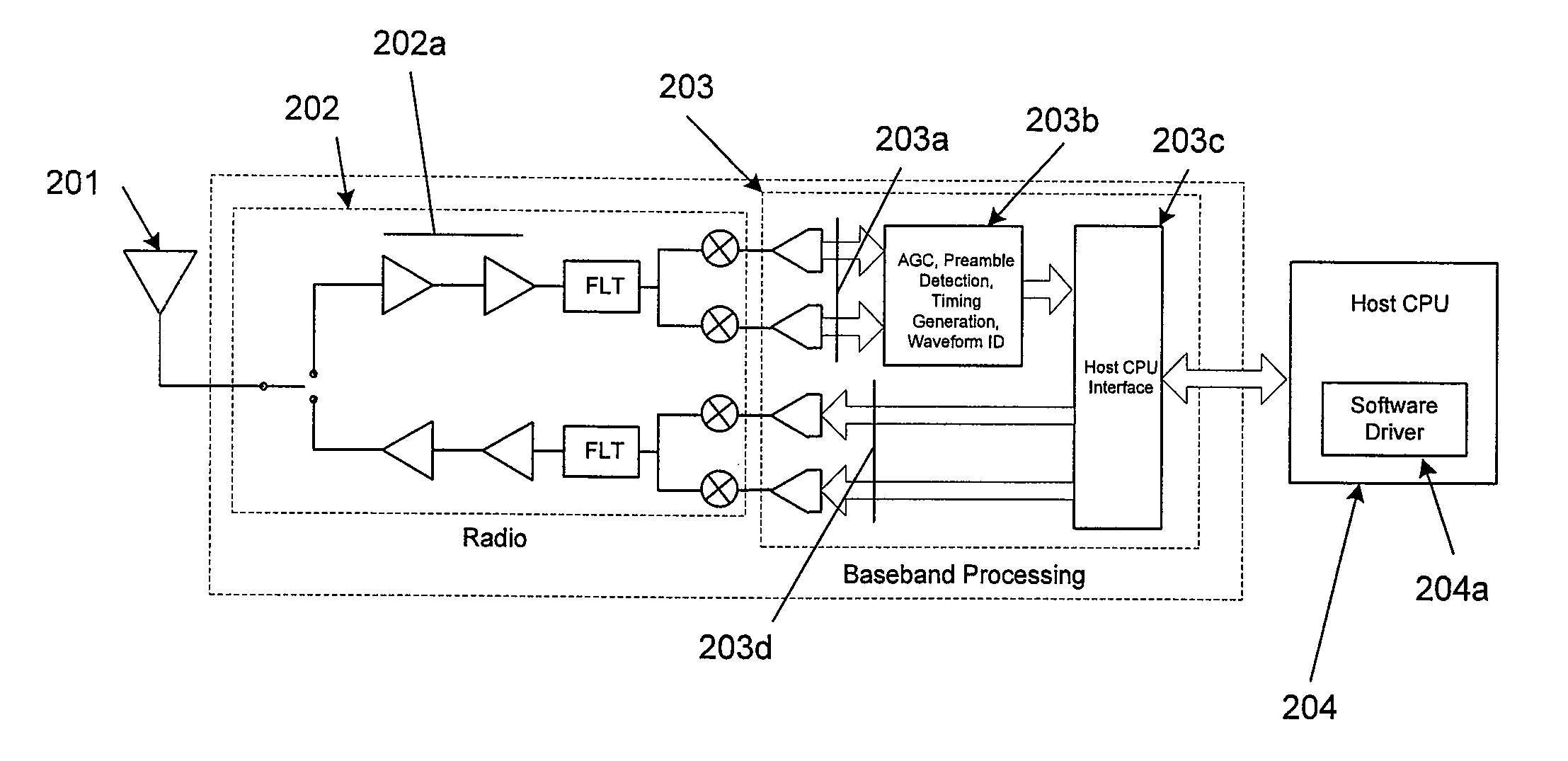
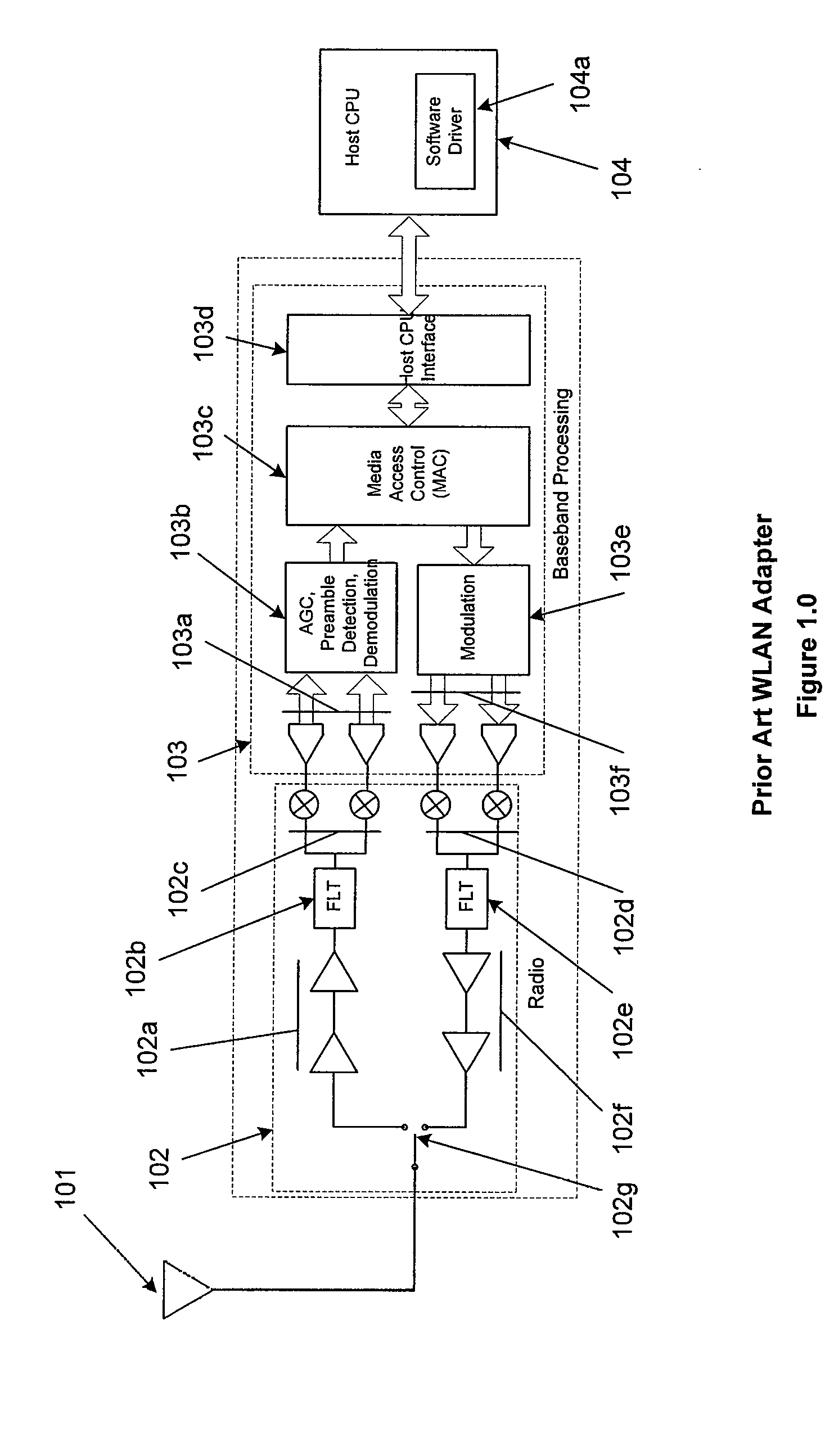
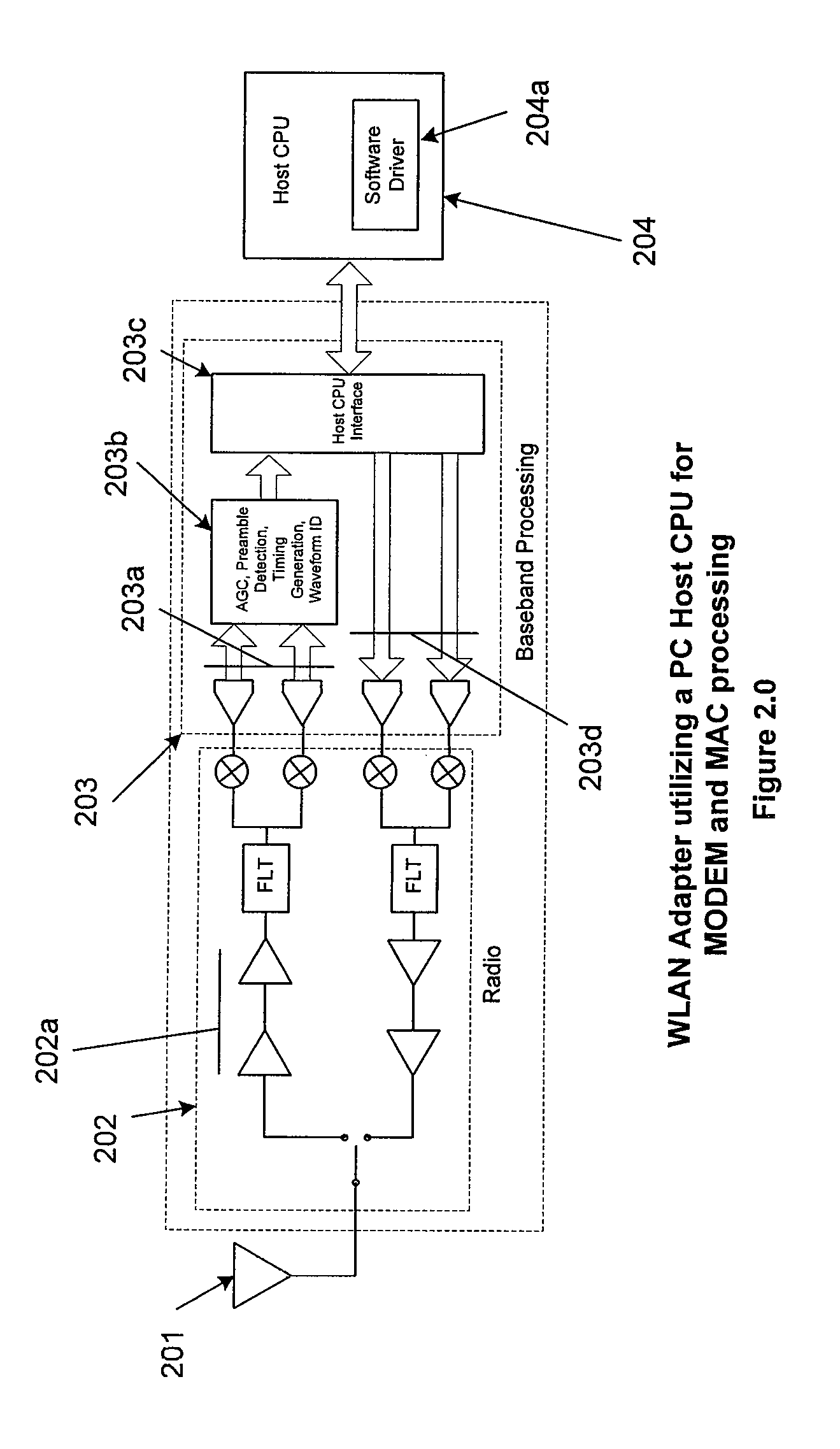
A personal computer's (PC) microprocessor is used to provide both the physical layer (PHY) and media access control (MAC) processing functions required to implement a wireless local area network (WLAN) adapter. This technique uses the polling mechanism associated with the power save (PS) functionality of WLAN protocol to relieve networking stress on the host processing system. It does this while maintaining networking integrity and packet delivery. The WLAN protocol polling mechanism is used to briefly inhibit the transfer of packets from the WLAN access point (AP) during peak periods of network traffic and / or host processor loading. Because the modulation, demodulation, and MAC functions, typically implemented in dedicated hardware on existing adapters are implemented in software running on the host PC microprocessor, other host system processes and applications can interfere with these time critical functions. Conversely, latency introduced by WLAN specific processing tasks during peak periods of network traffic may cause unacceptable delays to the other processes and applications requiring microprocessor attention. In addition to its primary stated purpose of allowing WLAN mobile stations to save power, this technique will use power save polling as a method for controlling delivery of network packets when the host is heavily loaded or when peak interrupt latencies make reliable packet delivery difficult or impossible.
Owner:GLOBESPANVIRATA +1
Interrupt signal processing system
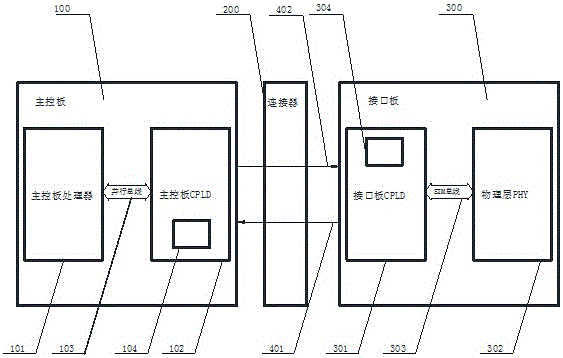
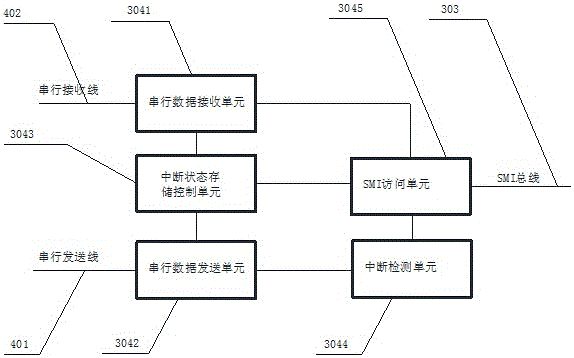
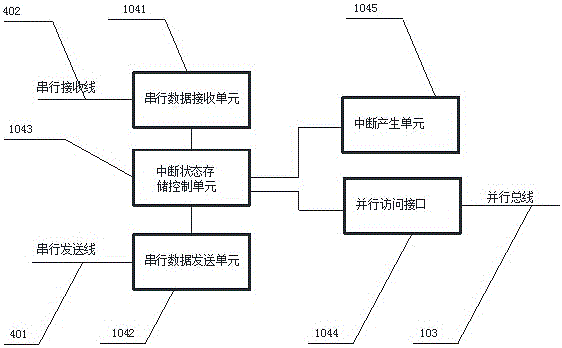
ActiveCN106294253AReduce loadReduce the number of instructionsElectric digital data processingControl registerComputer module
The invention relates to the field of communication and in particular to an interrupt signal processing system. According to the system disclosed by the invention, an interrupt processing module function is increased on CPLD between a master control board and an interface board, and the operation of interrupt state and control register between the master control board and the interface board is realized by utilizing two serial signal lines. All interrupt states of the interface board are reported to the CPLD of the master control board in a serial bus manner, the master control board processor only needs to execute once and perform bus access when interrupt happens, and the interrupt state is acquired from the CPLD of the master control board. Therefore, instruction per cycle allowing the processor to access peripherals is greatly reduced, load of the processor is reduced, and the interrupt response time is accelerated. The interrupt needs to be transferred between the interface board and the master control board by two signal lines only, and signal pins are greatly saved.
Owner:ANHUI WANTONG POSTS & TELECOMM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com