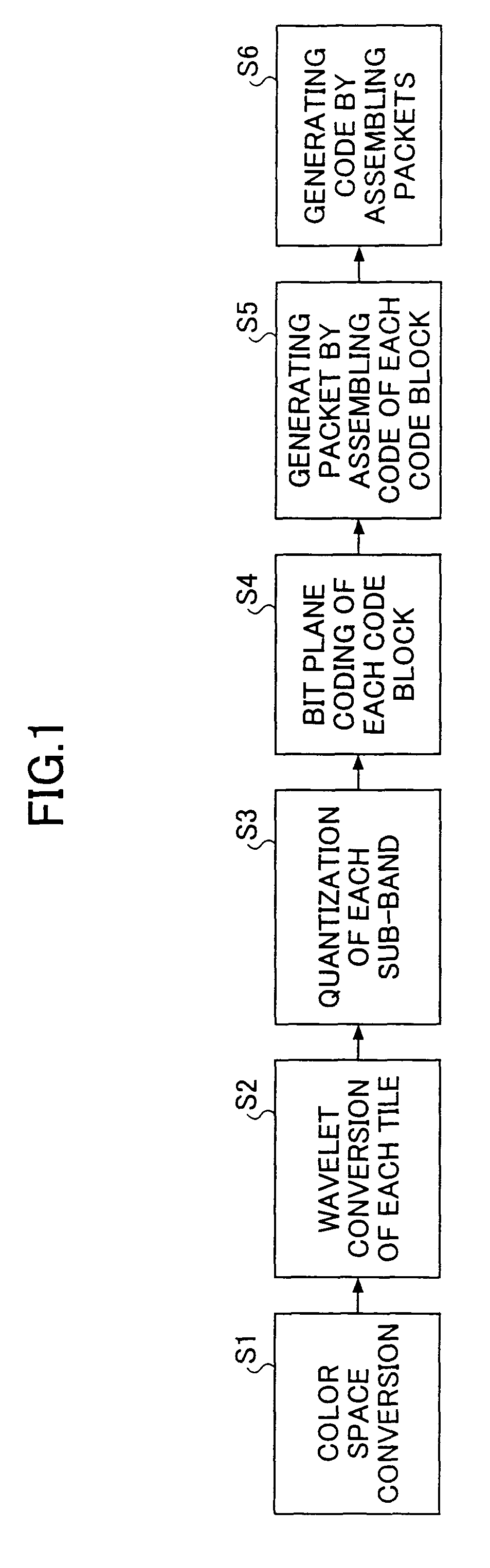
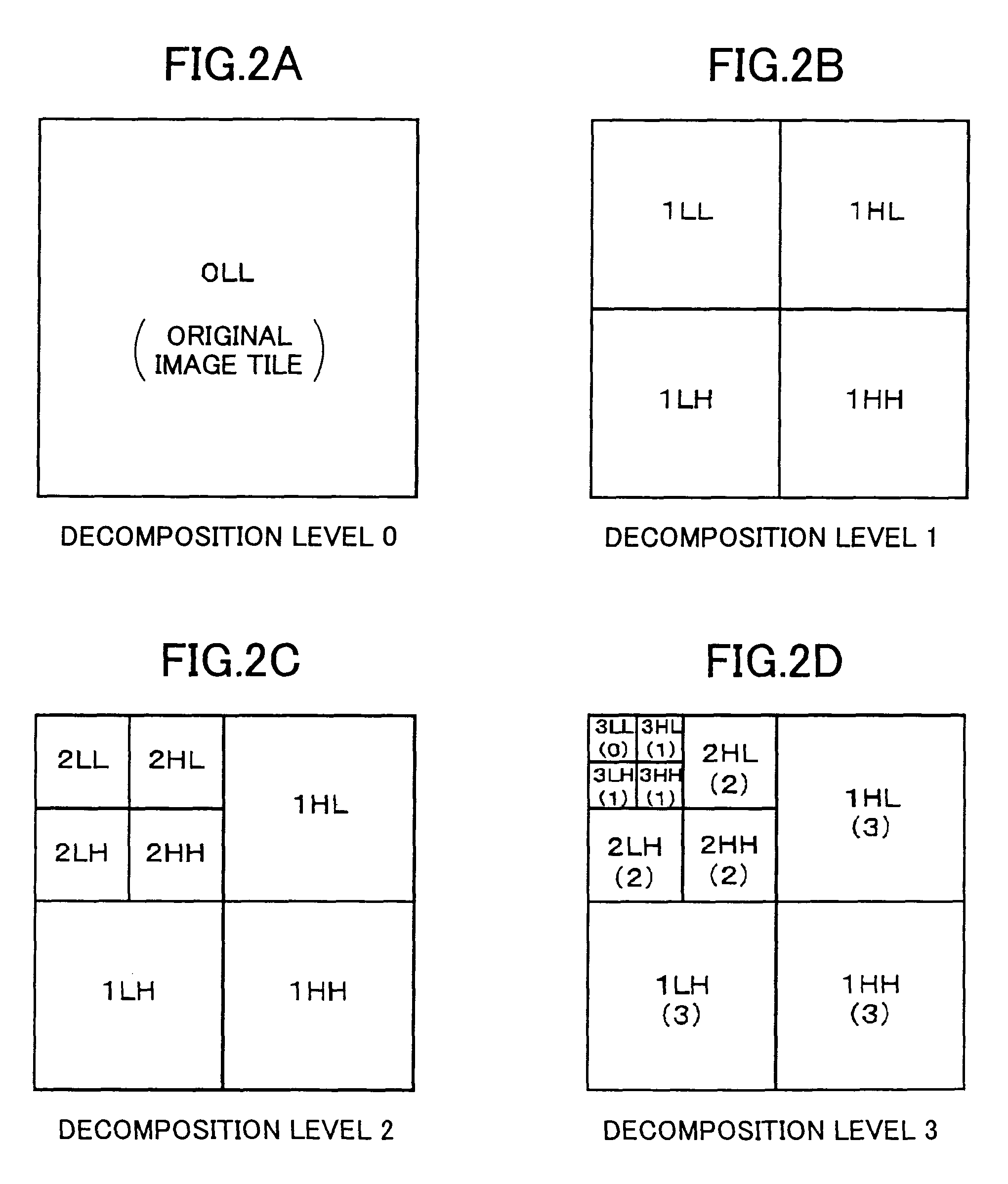
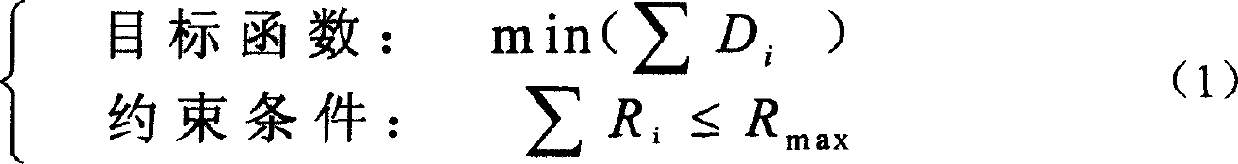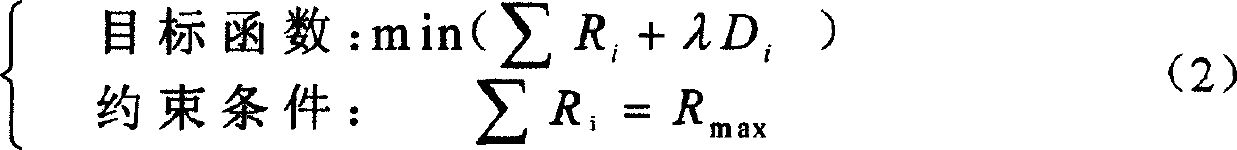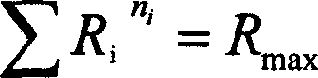Patents
Literature
99 results about "JPEG 2000" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
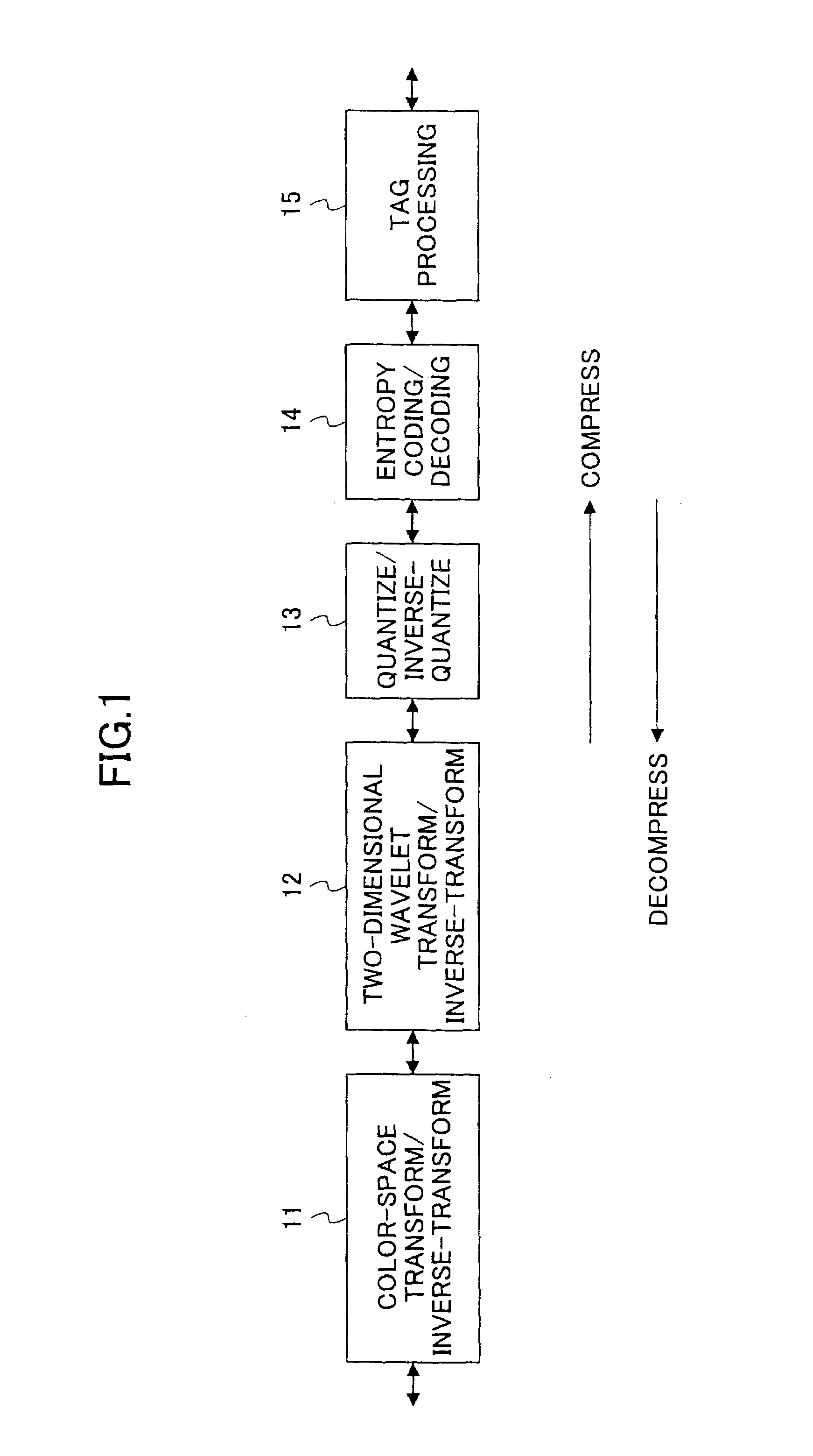
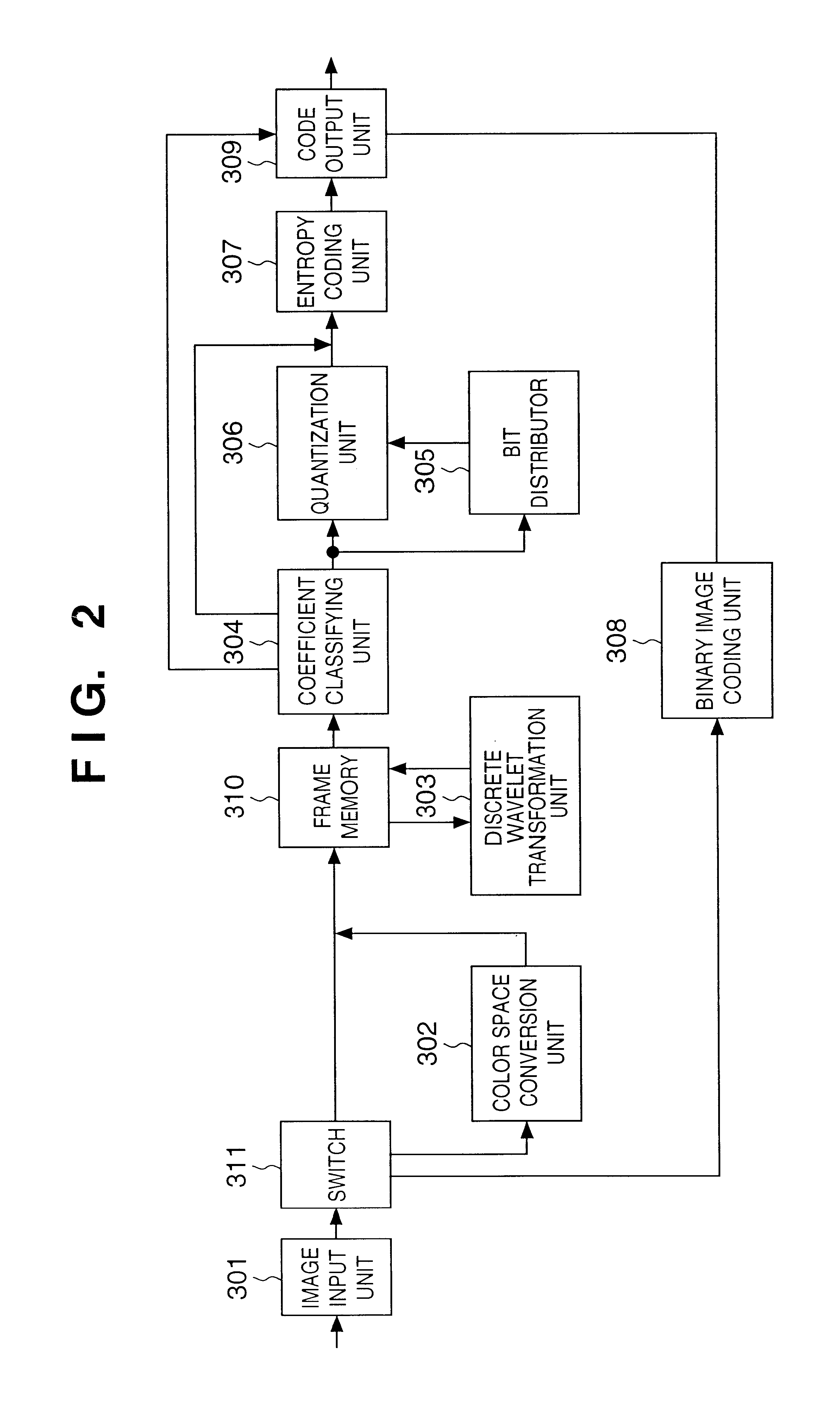
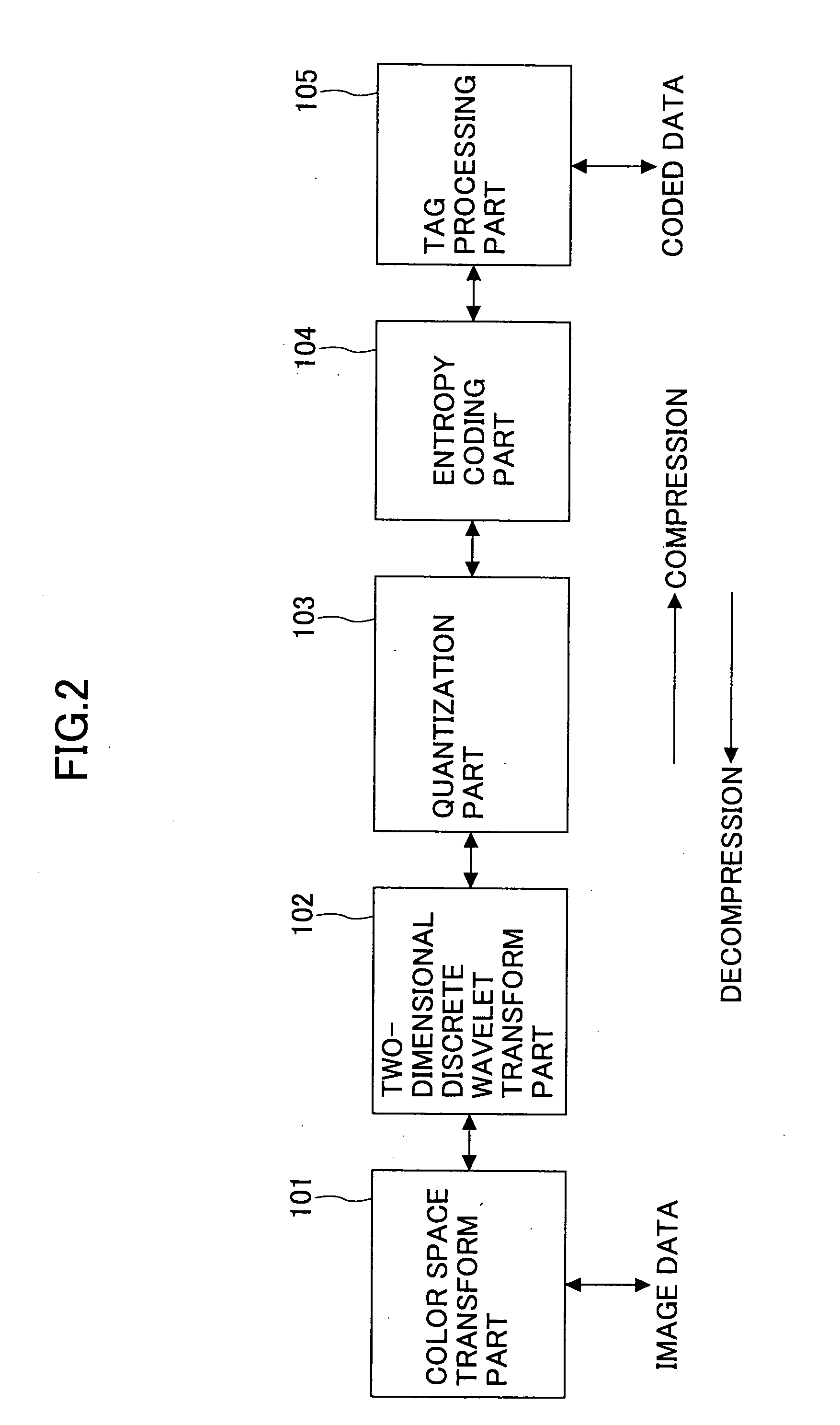
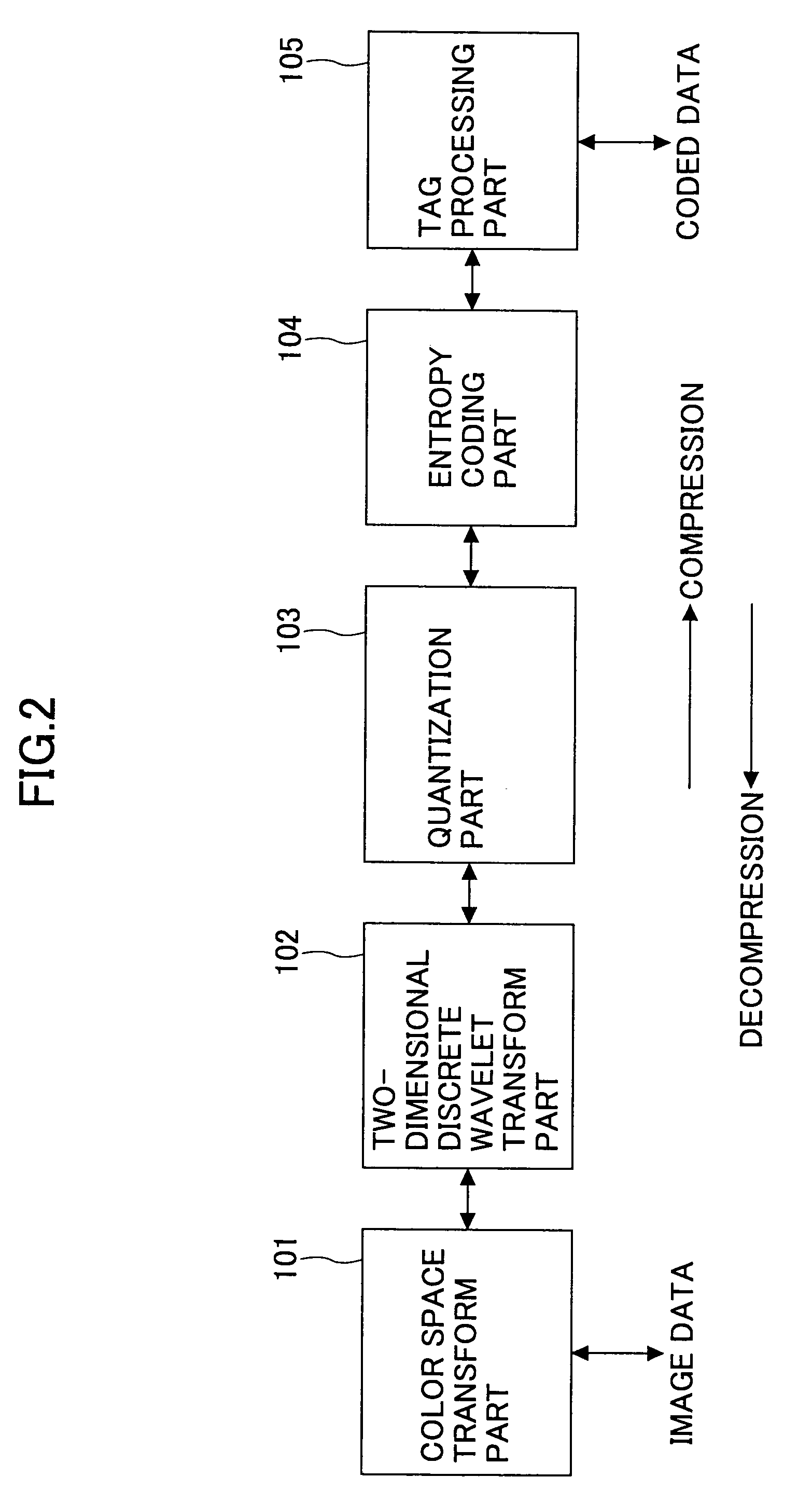
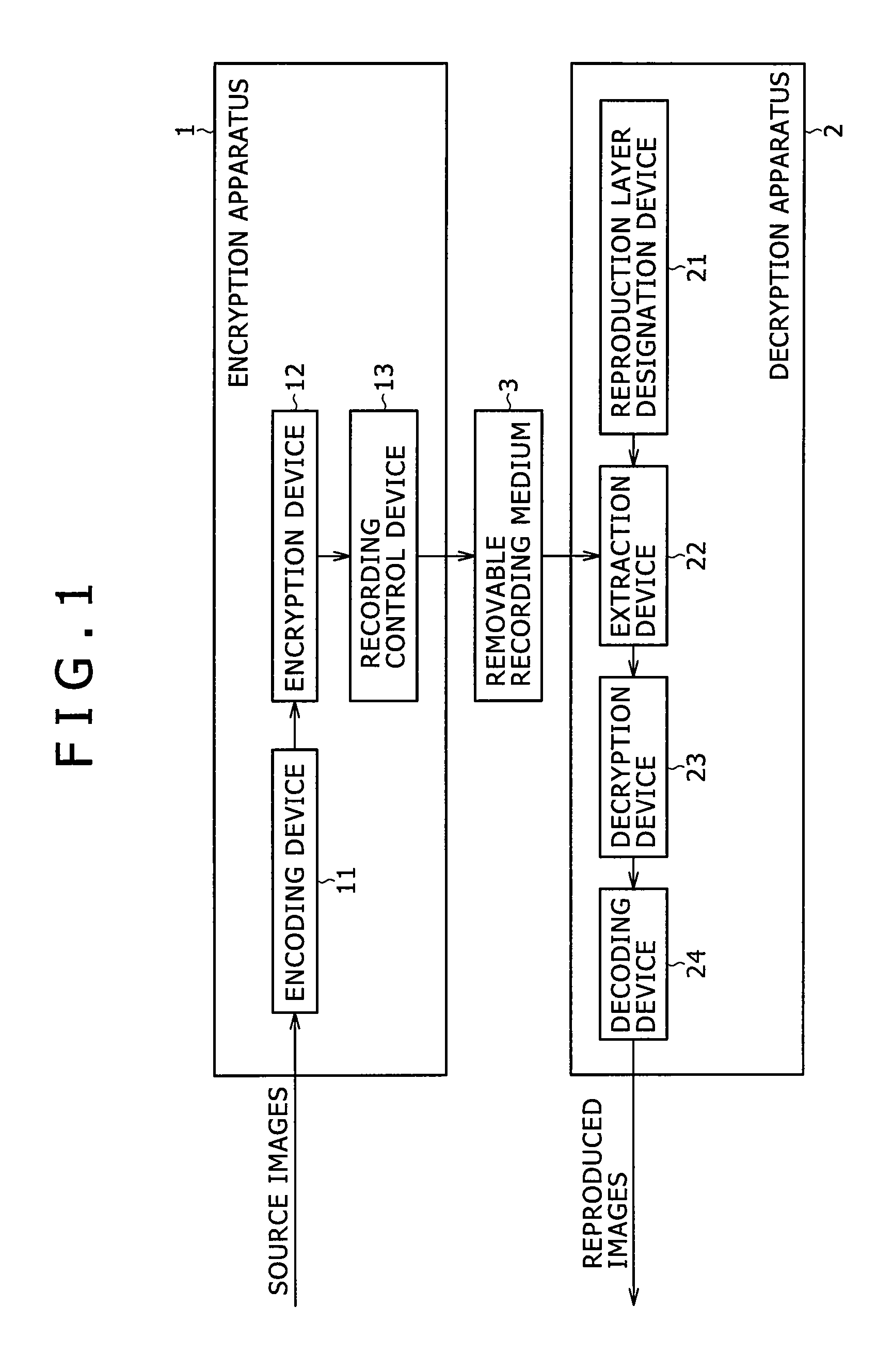
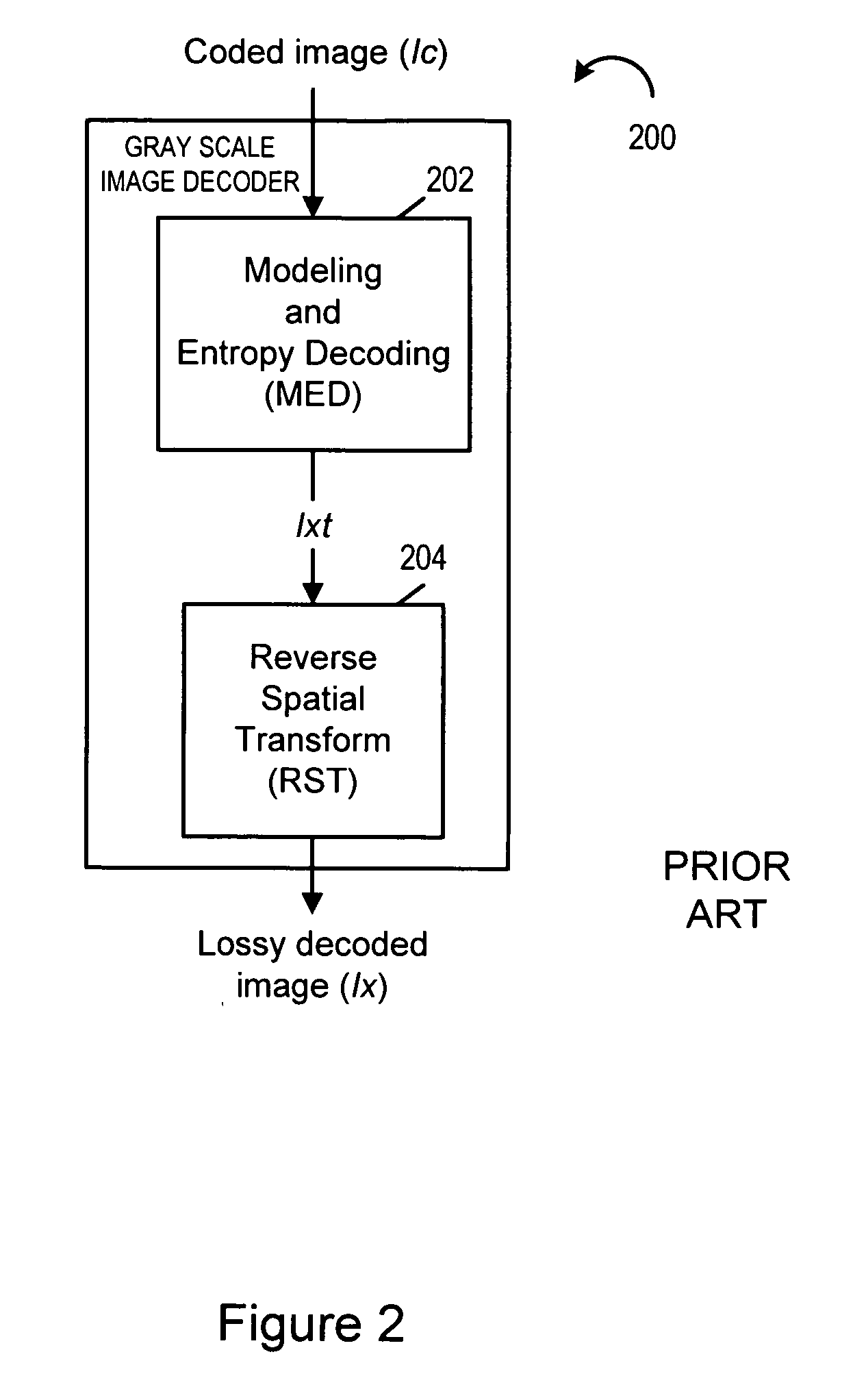
JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president), with the intention of superseding their original discrete cosine transform (DCT) based JPEG standard (created in 1992) with a newly designed, wavelet-based method. The standardized filename extension is .jp2 for ISO/IEC 15444-1 conforming files and .jpx for the extended part-2 specifications, published as ISO/IEC 15444-2. The registered MIME types are defined in RFC 3745. For ISO/IEC 15444-1 it is image/jp2.
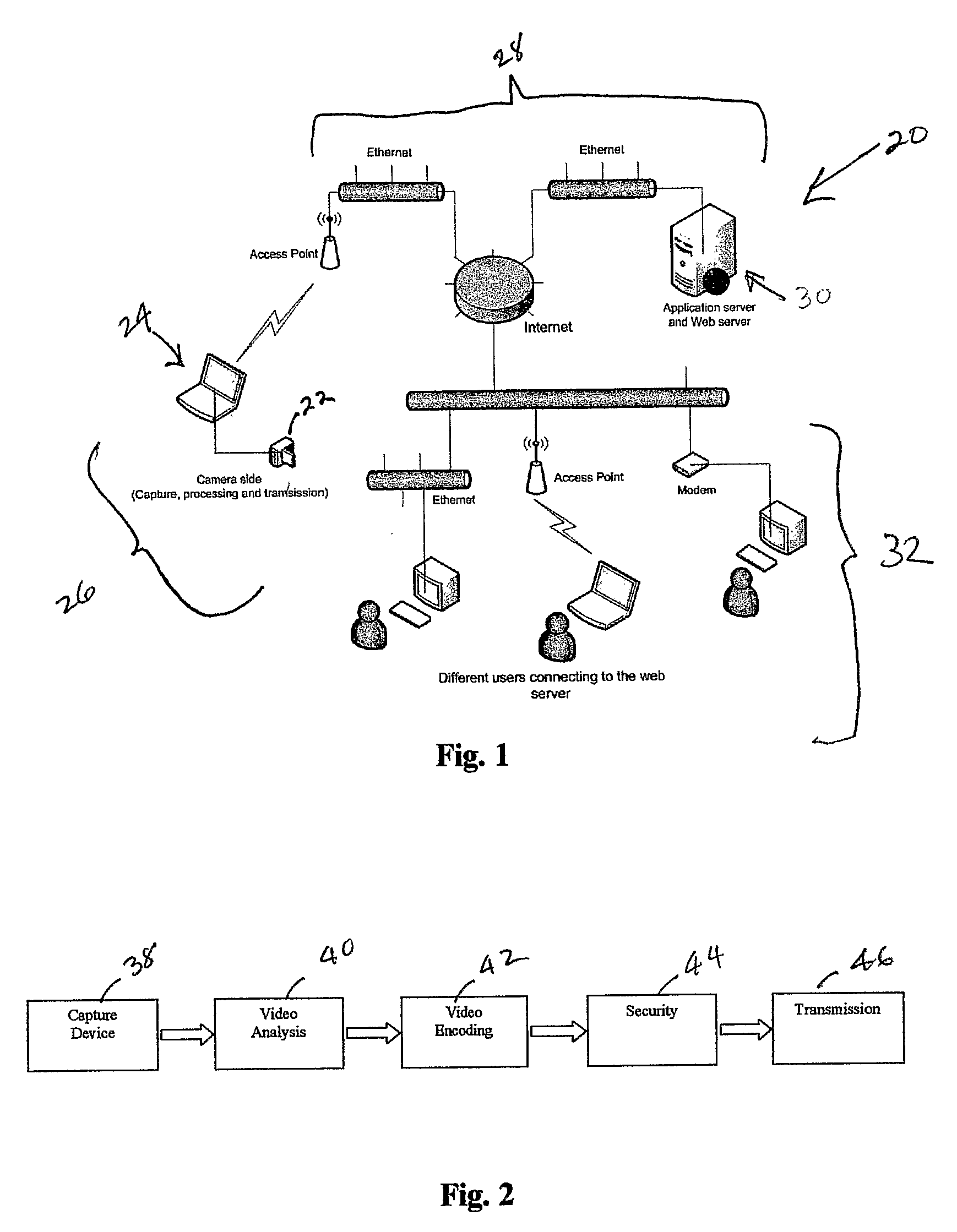
Smart Video Surveillance System Ensuring Privacy
InactiveUS20070296817A1Closed circuit television systemsBurglar alarmComputer hardwareVideo monitoring
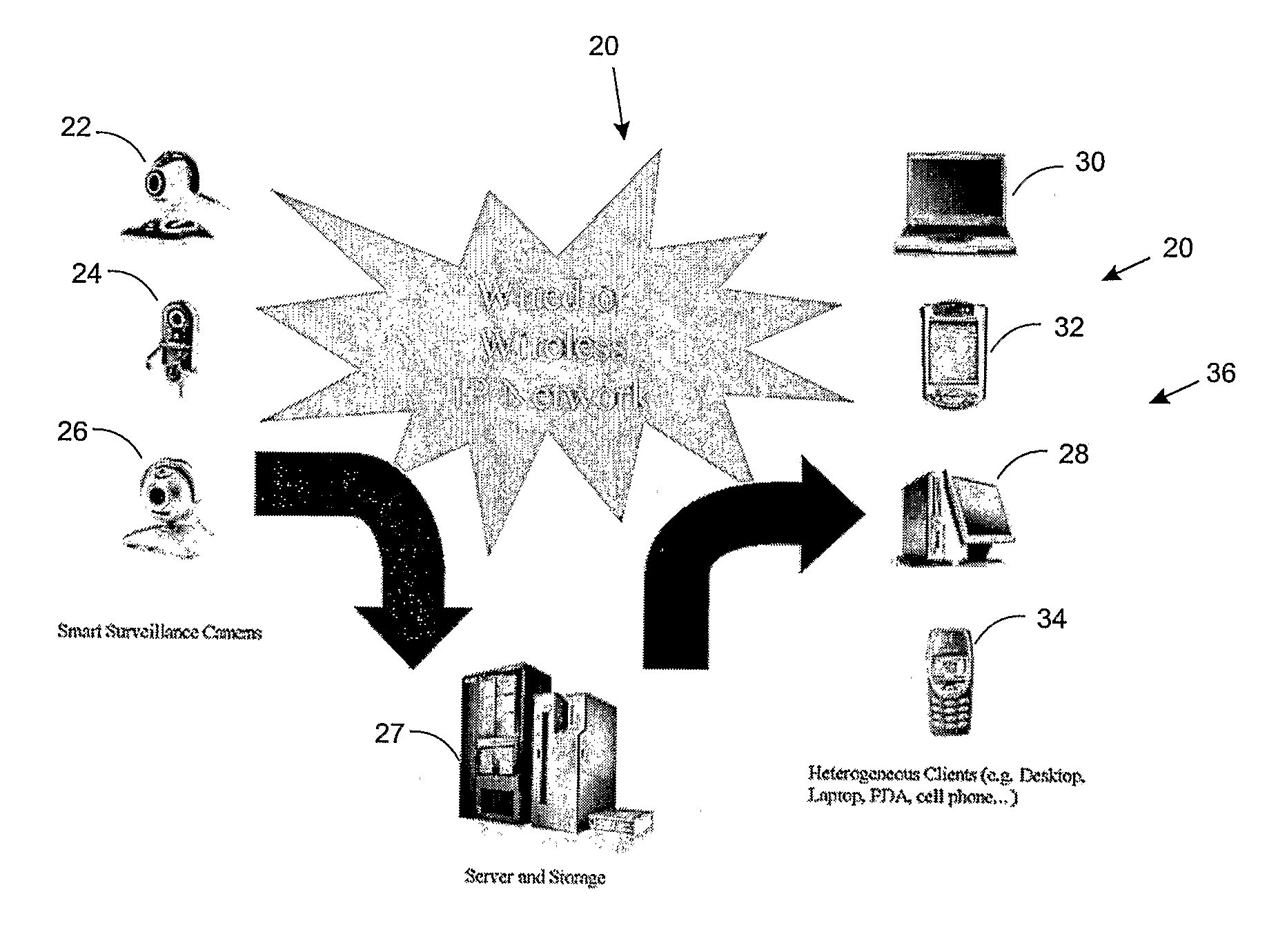
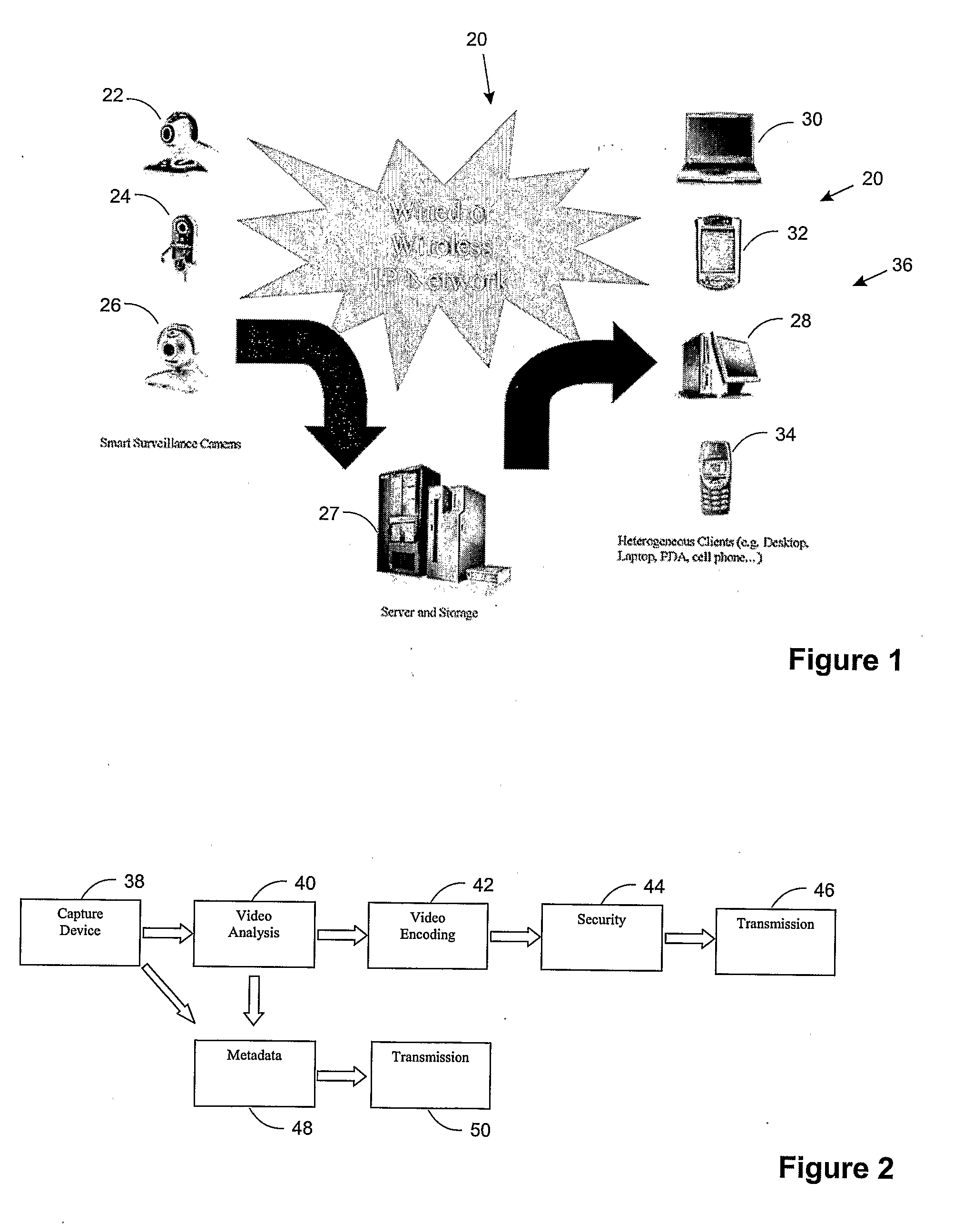
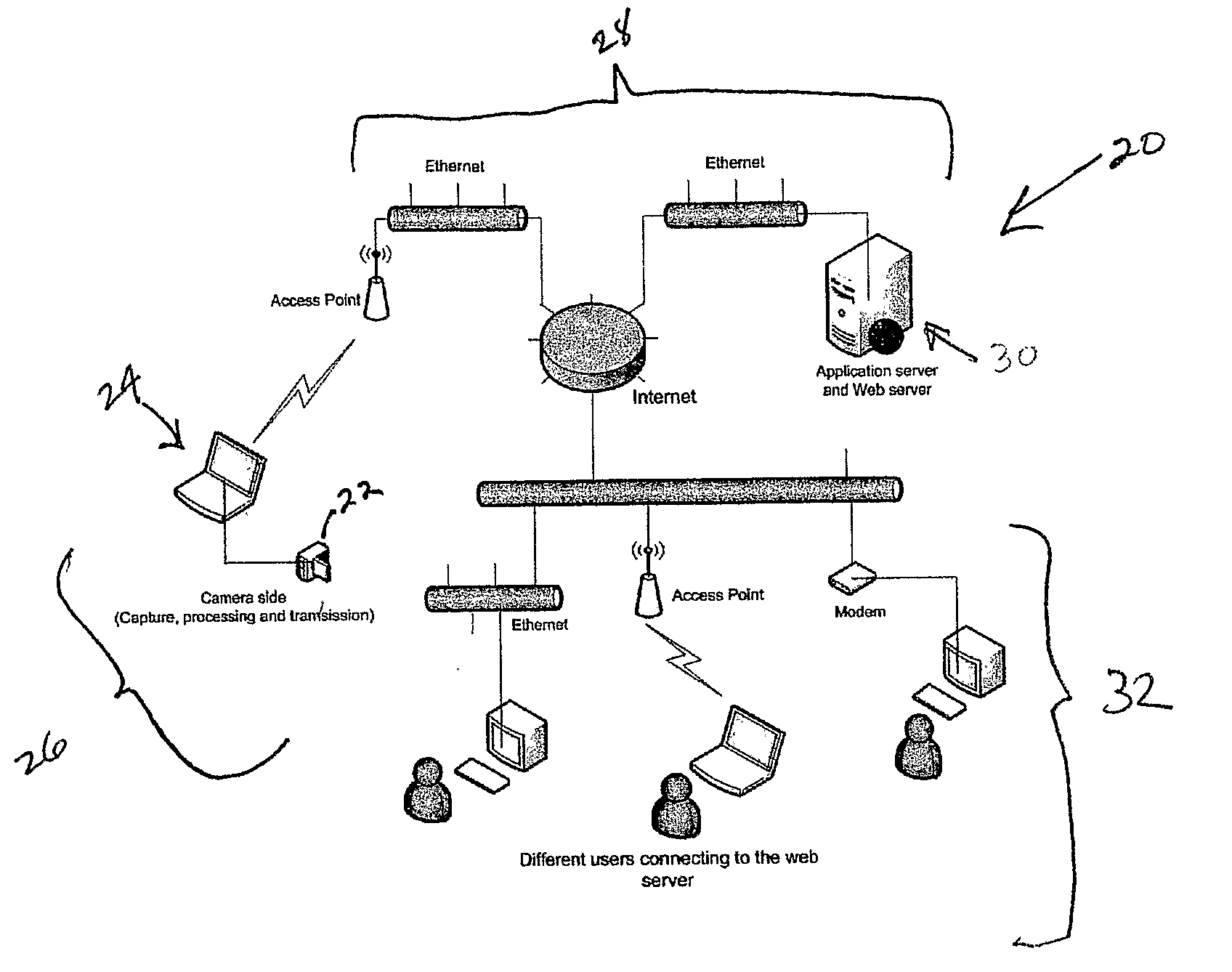
This invention describes a video surveillance system which is composed of three key components 1—smart camera(s), 2—server(s), 3—client(s), connected through IP-networks in wired or wireless configurations. The system has been designed so as to protect the privacy of people and goods under surveillance. Smart cameras are based on JPEG 2000 compression where an analysis module allows for efficient use of security tools for the purpose of scrambling, and event detection. The analysis is also used in order to provide a better quality in regions of the interest in the scene. Compressed video streams leaving the camera(s) are scrambled and signed for the purpose of privacy and data integrity verification using JPSEC compliant methods. The same bit stream is also protected based on JPWL compliant methods for robustness to transmission errors. The operations of the smart camera are optimized in order to provide the best compromise in terms of perceived visual quality of the decoded video, versus the amount of power consumption. The smart camera(s) can be wireless in both power and communication connections. The server(s) receive(s), store(s), manage(s) and dispatch(es) the video sequences on wired and wireless channels to a variety of clients and users with different device capabilities, channel characteristics and preferences. Use of seamless scalable coding of video sequences prevents any need for transcoding operations at any point in the system.
Owner:EMITALL SURVEILLANCE
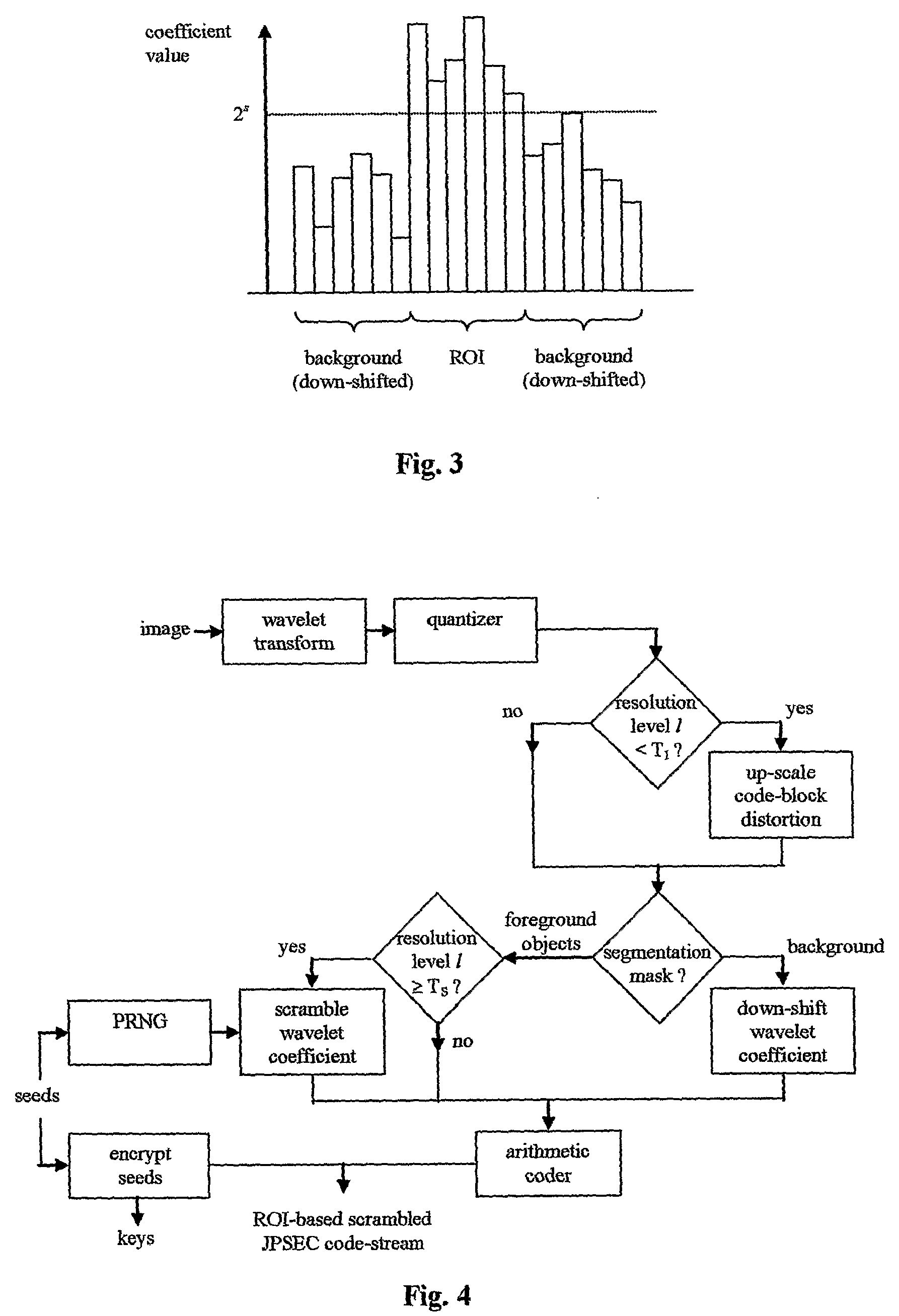
Efficient Scrambling Of Regions Of Interest In An Image Or Video To Preserve Privacy
InactiveUS20080117295A1Drawbacks of known code block scrambling techniques are avoidedLimited degreeCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsFace detectionCoding block
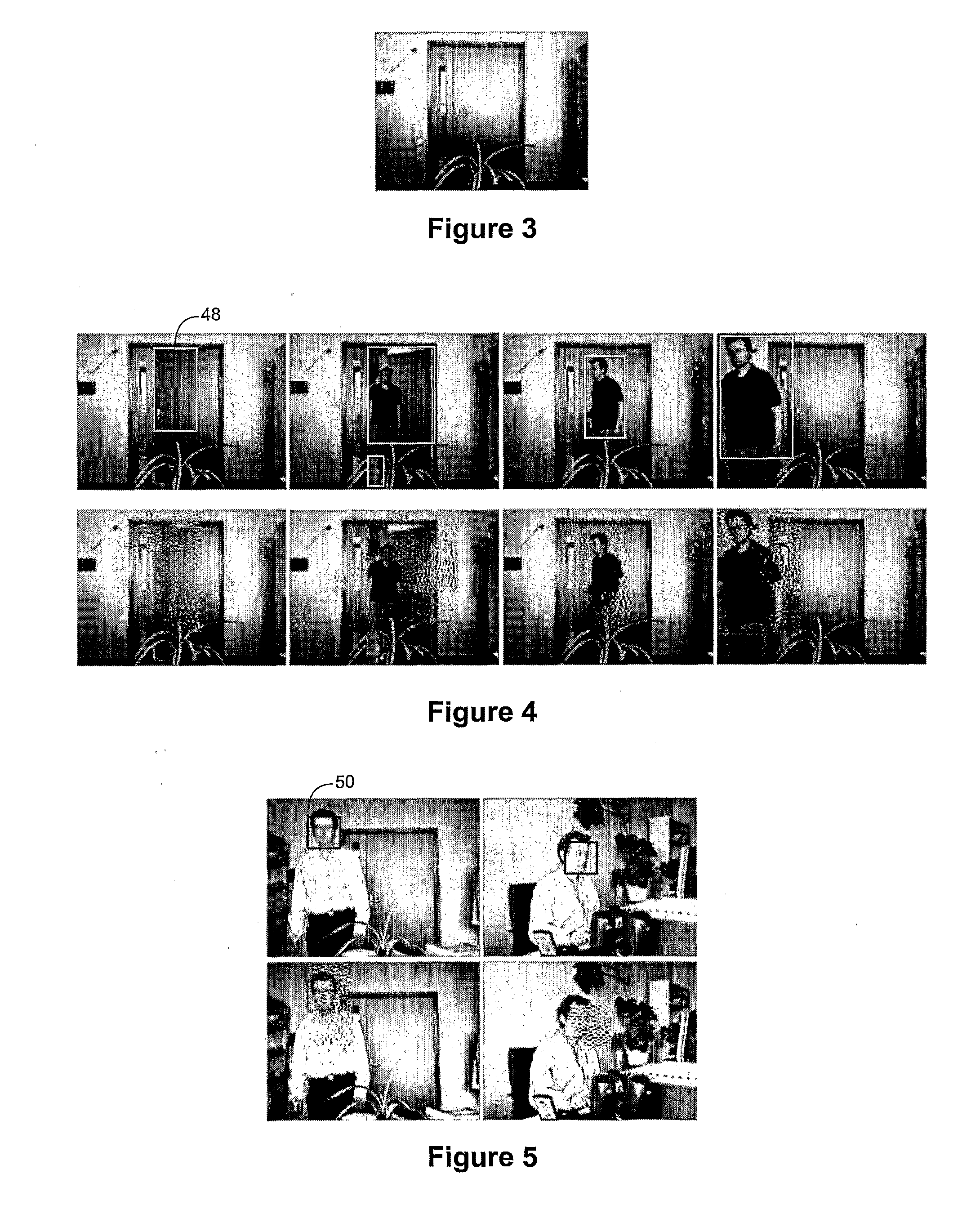
A video surveillance system is disclosed which addresses the issue of privacy rights and scrambles regions of interest in a scene in a video scene to protect the privacy of human faces and objects captured by the system. The video surveillance system is configured to identify persons and or objects captured in a region of interest of a video scene by various techniques, such as detecting changes in a scene or by face detection. In accordance with an important aspect of the invention regions of interest are automatically scrambled, for example, by way of a private encryption key, while the balance of the video scene is left in tact and is thus recognizable. Such region of interest scrambling provides distinct advantages over known code block scrambling techniques. The entire video scenes are then compressed, by one or more compression standards, such as JPEG 2000. In accordance with one aspect of the invention, the degree of scrambling can be controlled.
Owner:EMITALL SURVEILLANCE
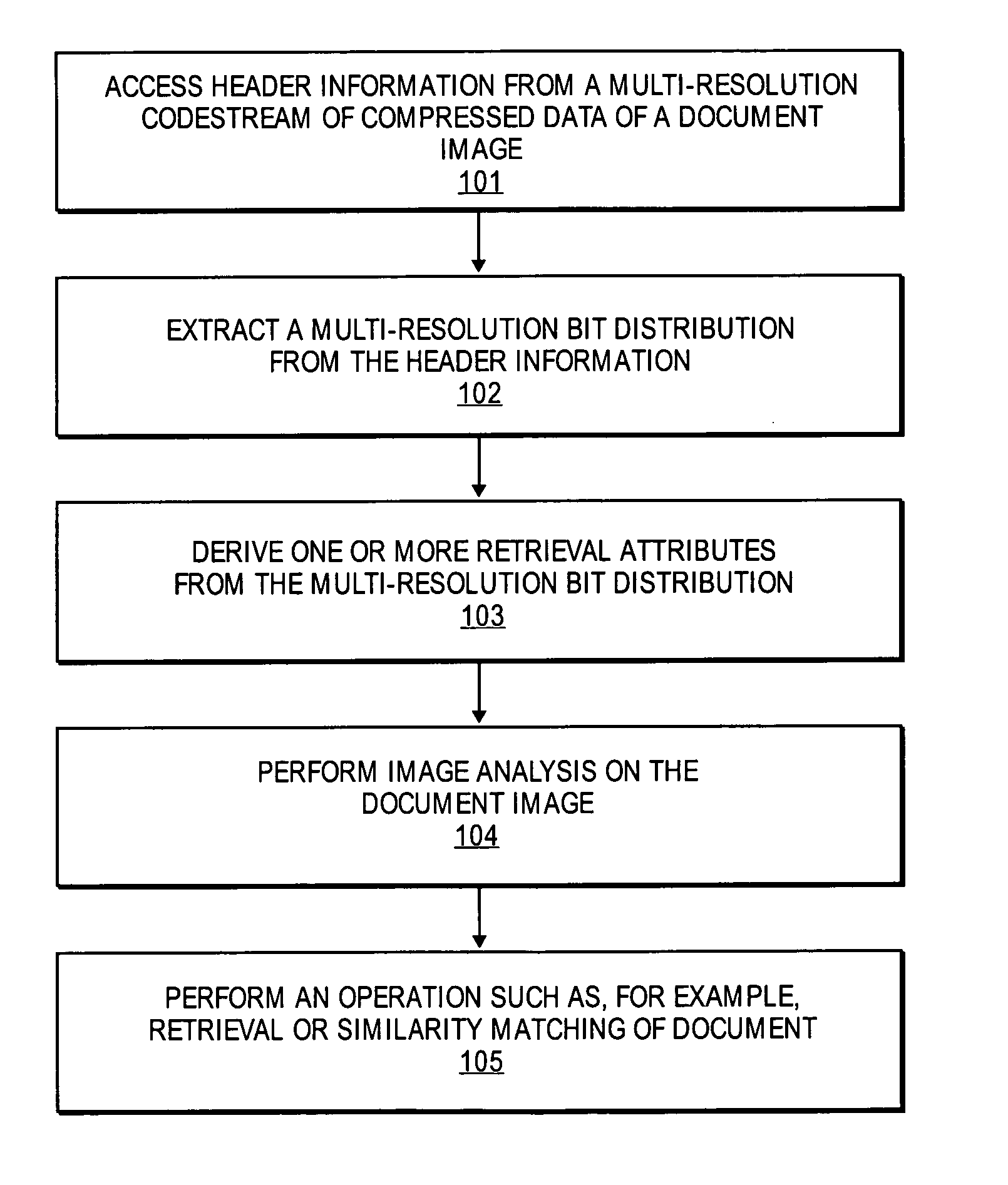
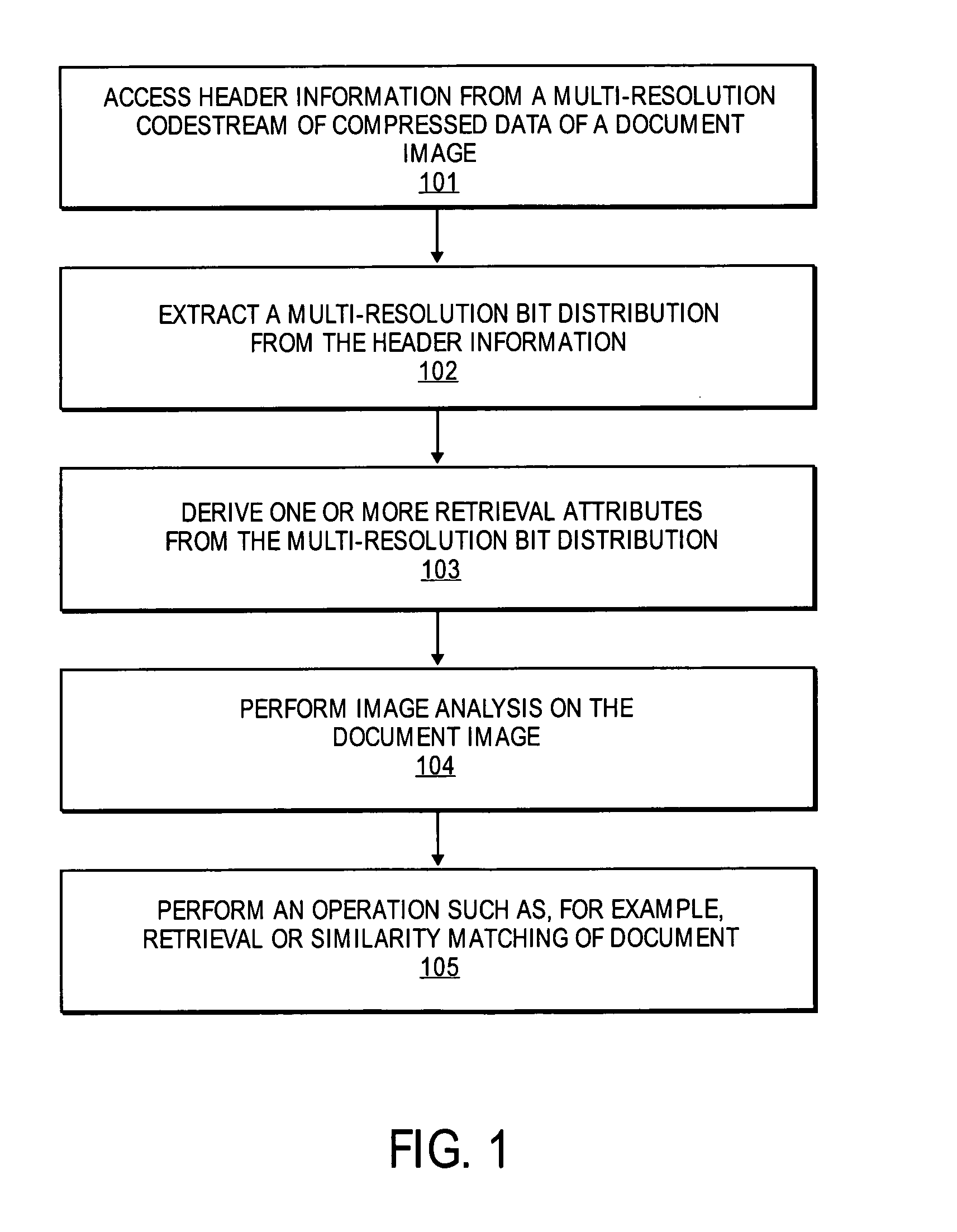
Features for retrieval and similarity matching of documents from the JPEG 2000-compressed domain
InactiveUS20050100219A1Digital data information retrievalImage analysisImaging processingImaging analysis
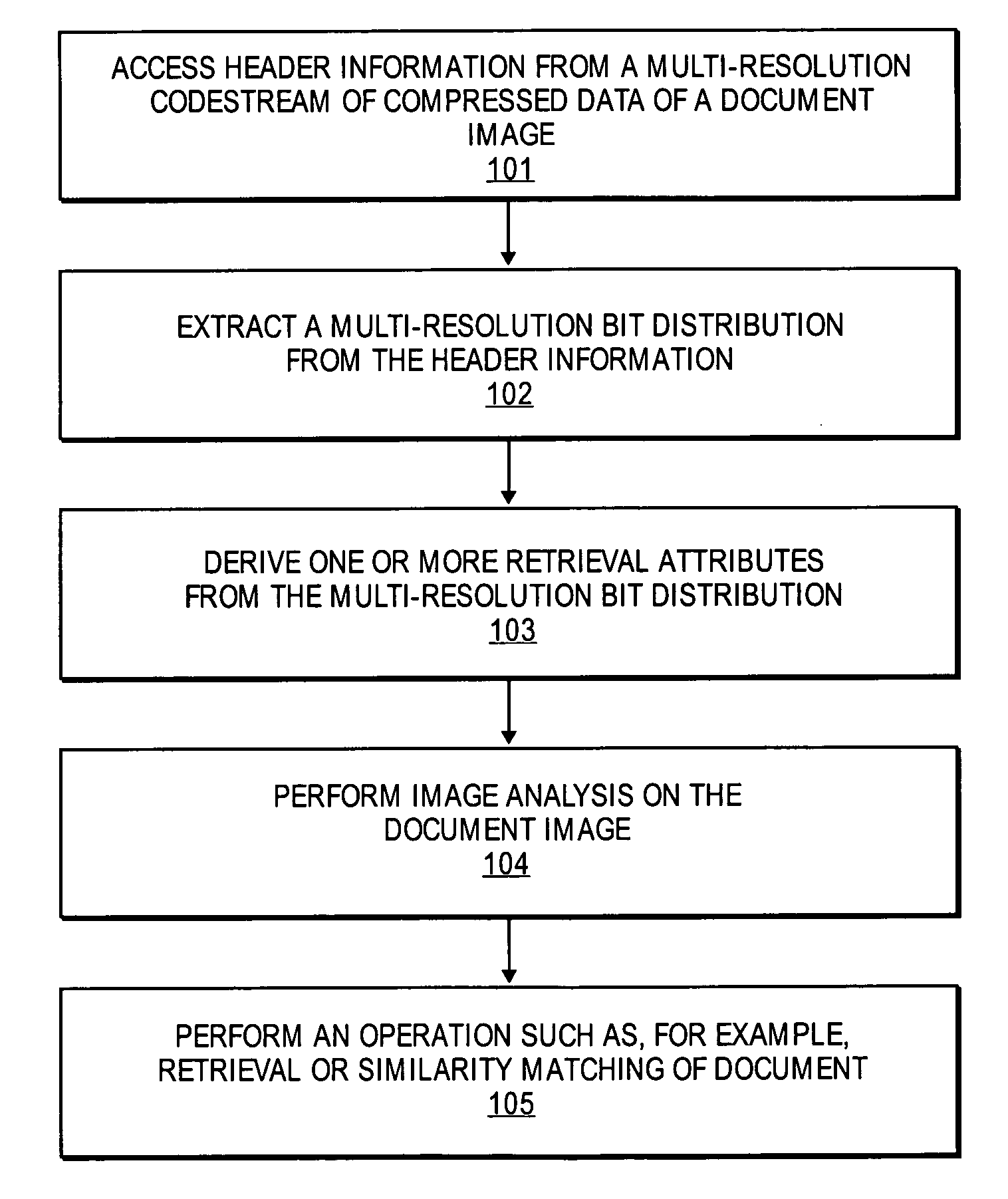
A method and apparatus for image processing is described. In one embodiment, the method comprises accessing header data from a multi-resolution codestream of compressed data of a first document image, deriving one or more retrieval attributes from the header information, and performing image analysis between the first document image and a second document image based on the one or more retrieval attributes.
Owner:RICOH KK
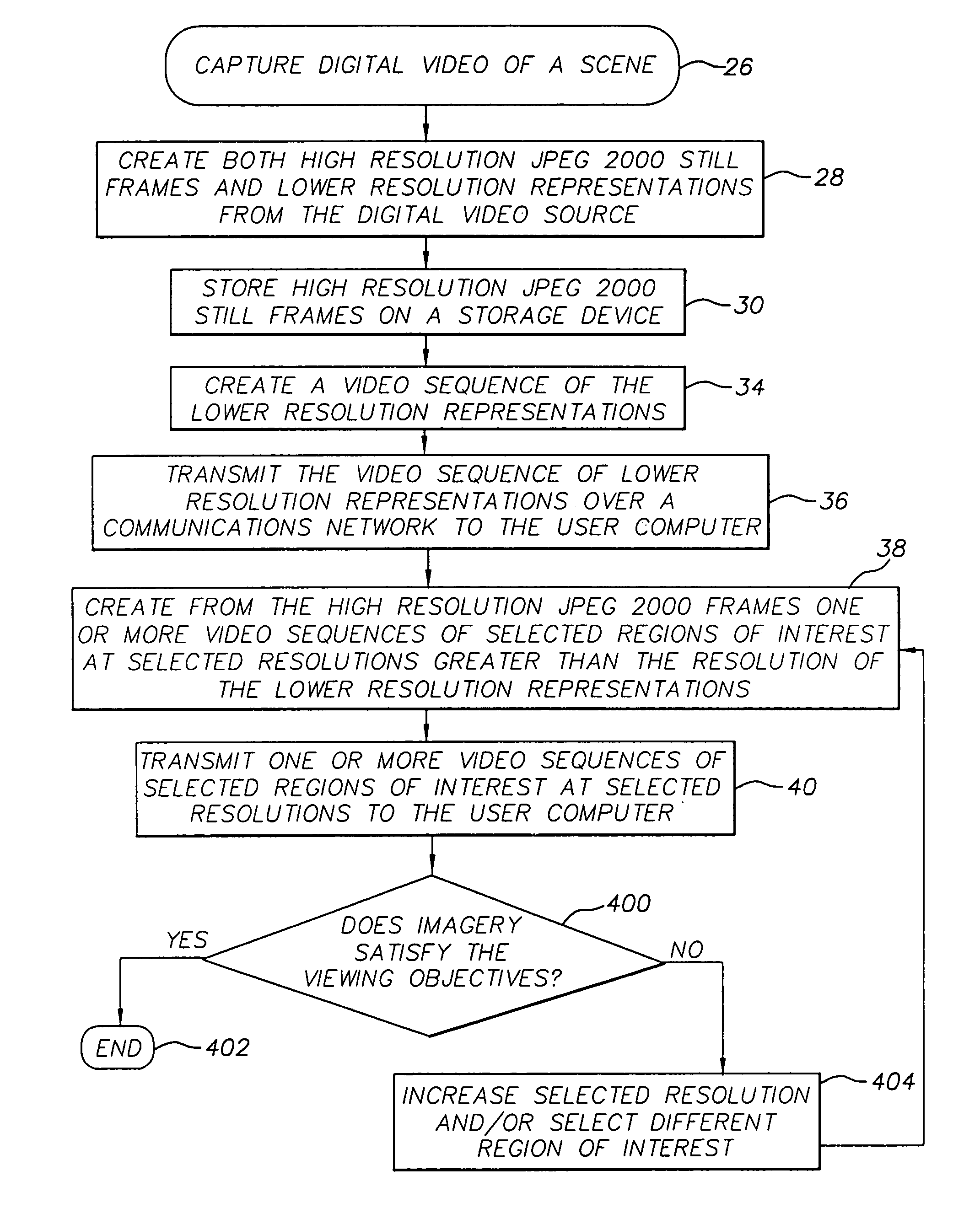
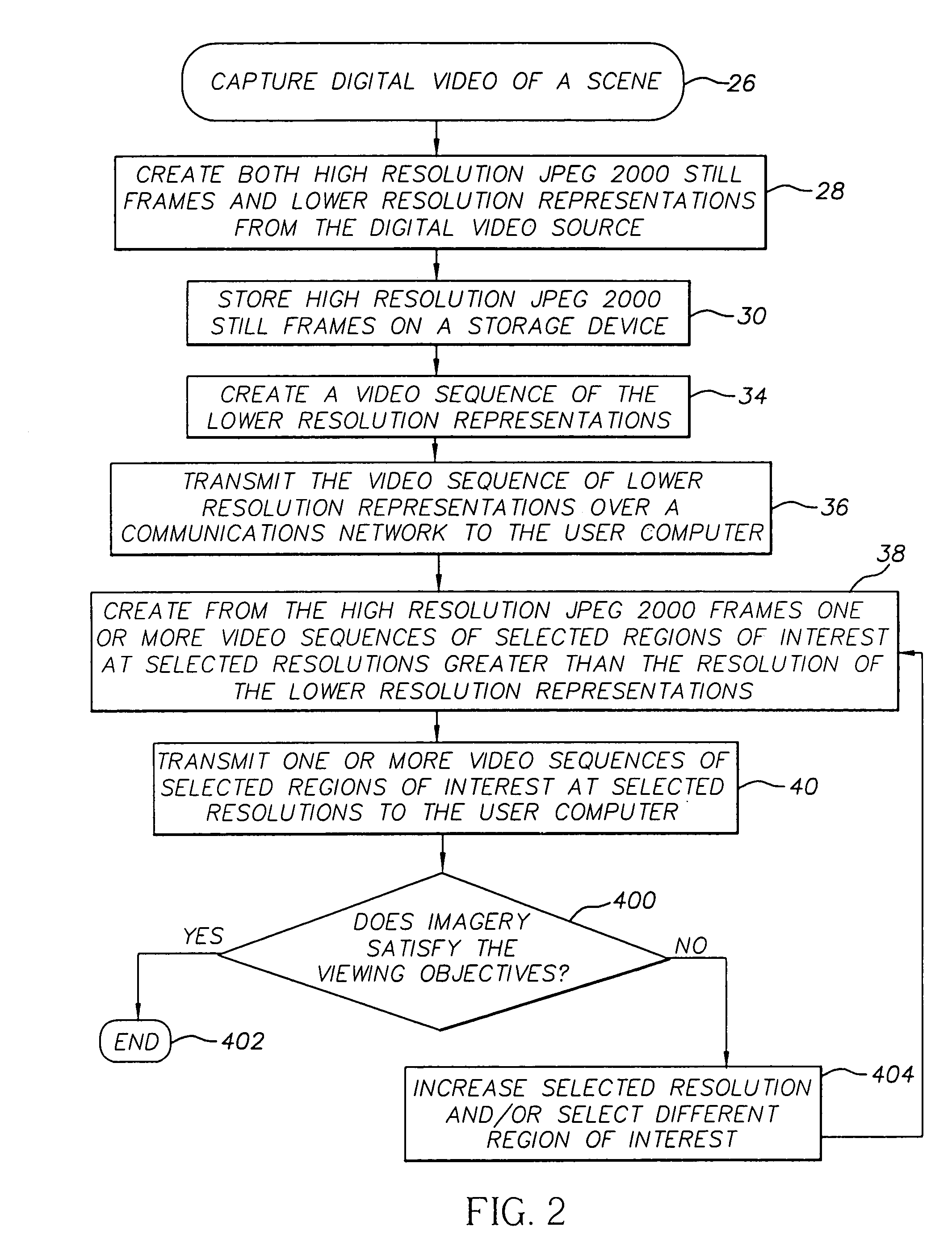
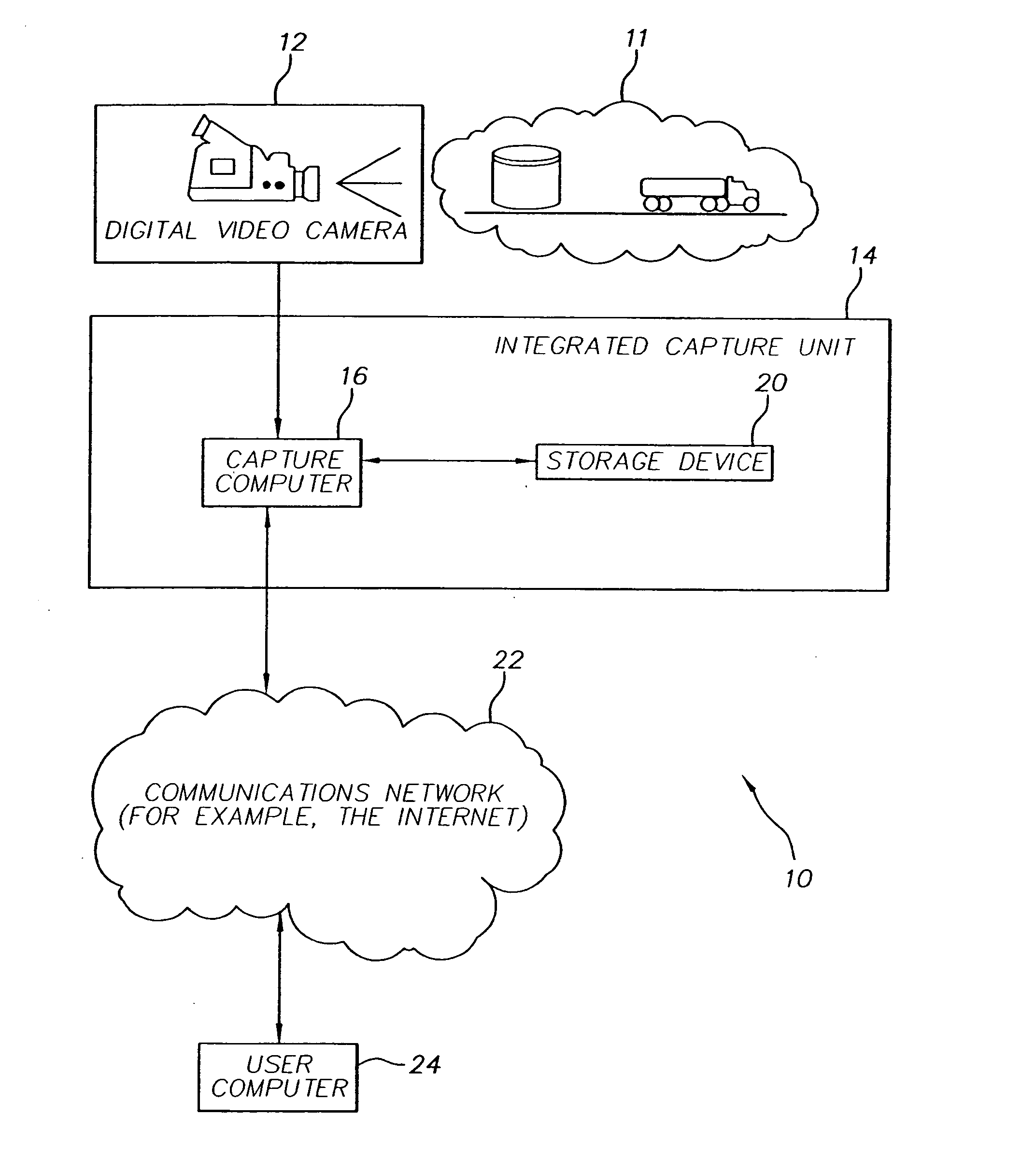
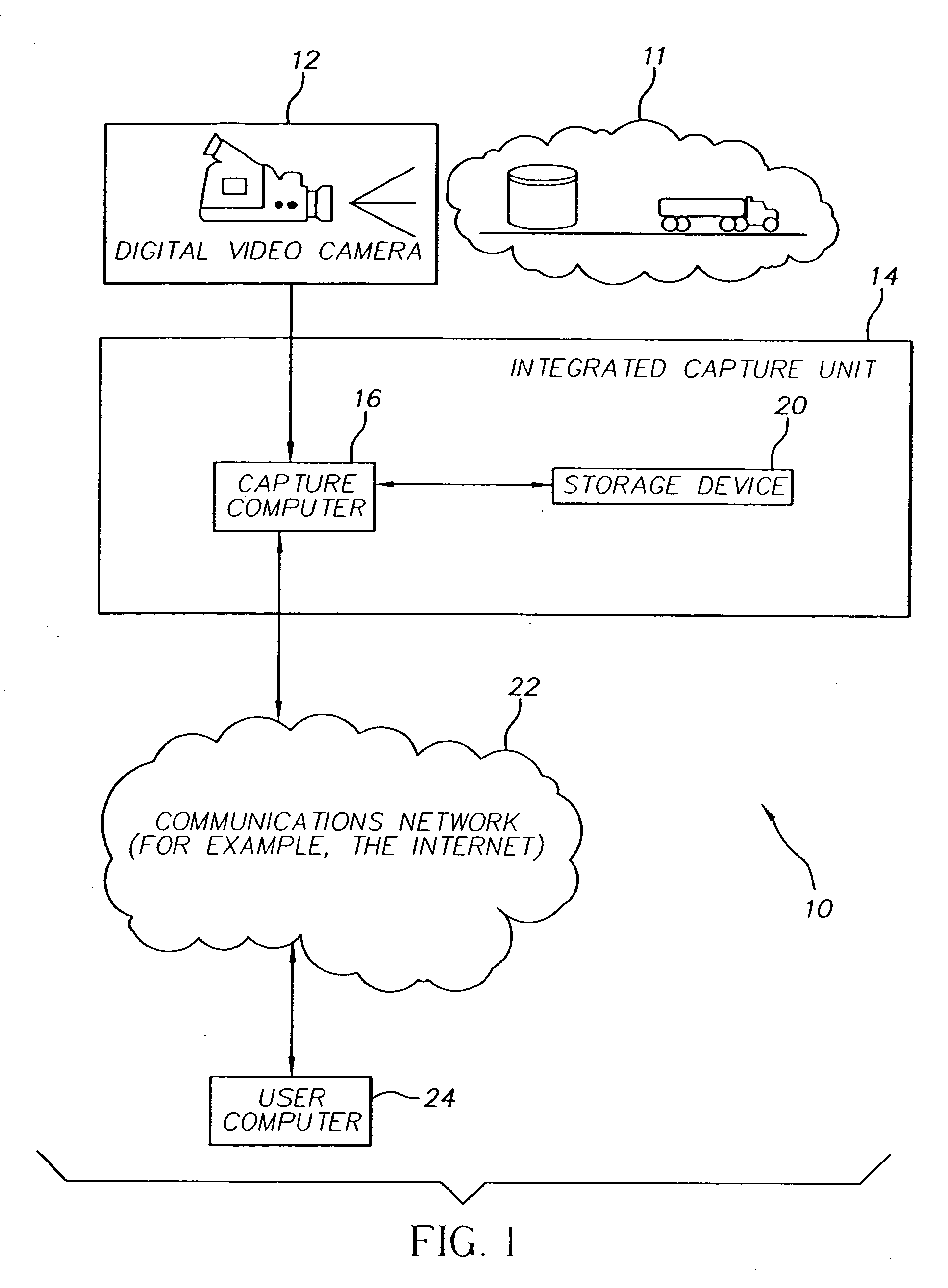
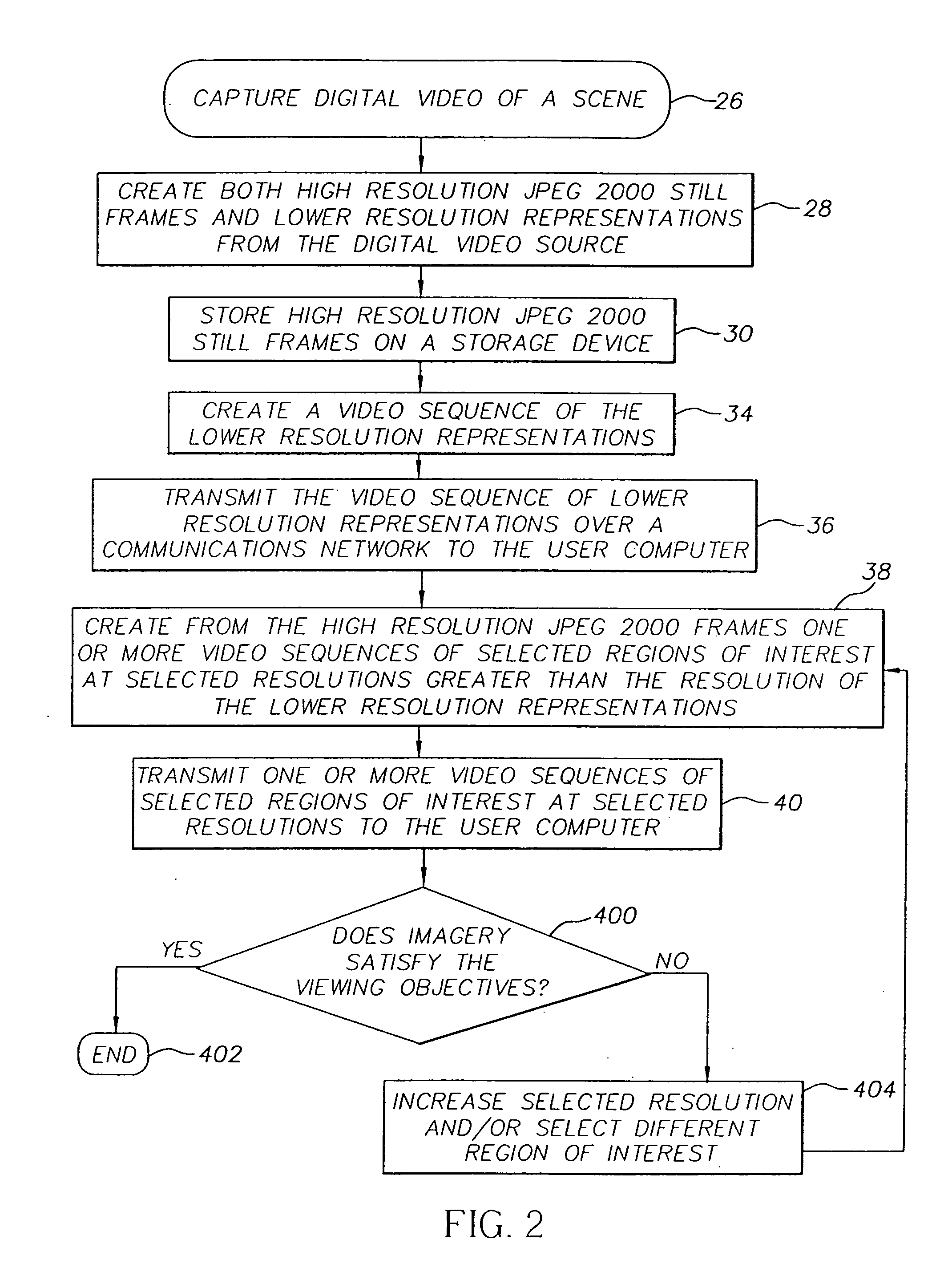
Method of transmitting selected regions of interest of digital video data at selected resolutions
InactiveUS7116833B2High resolutionPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoImage resolution
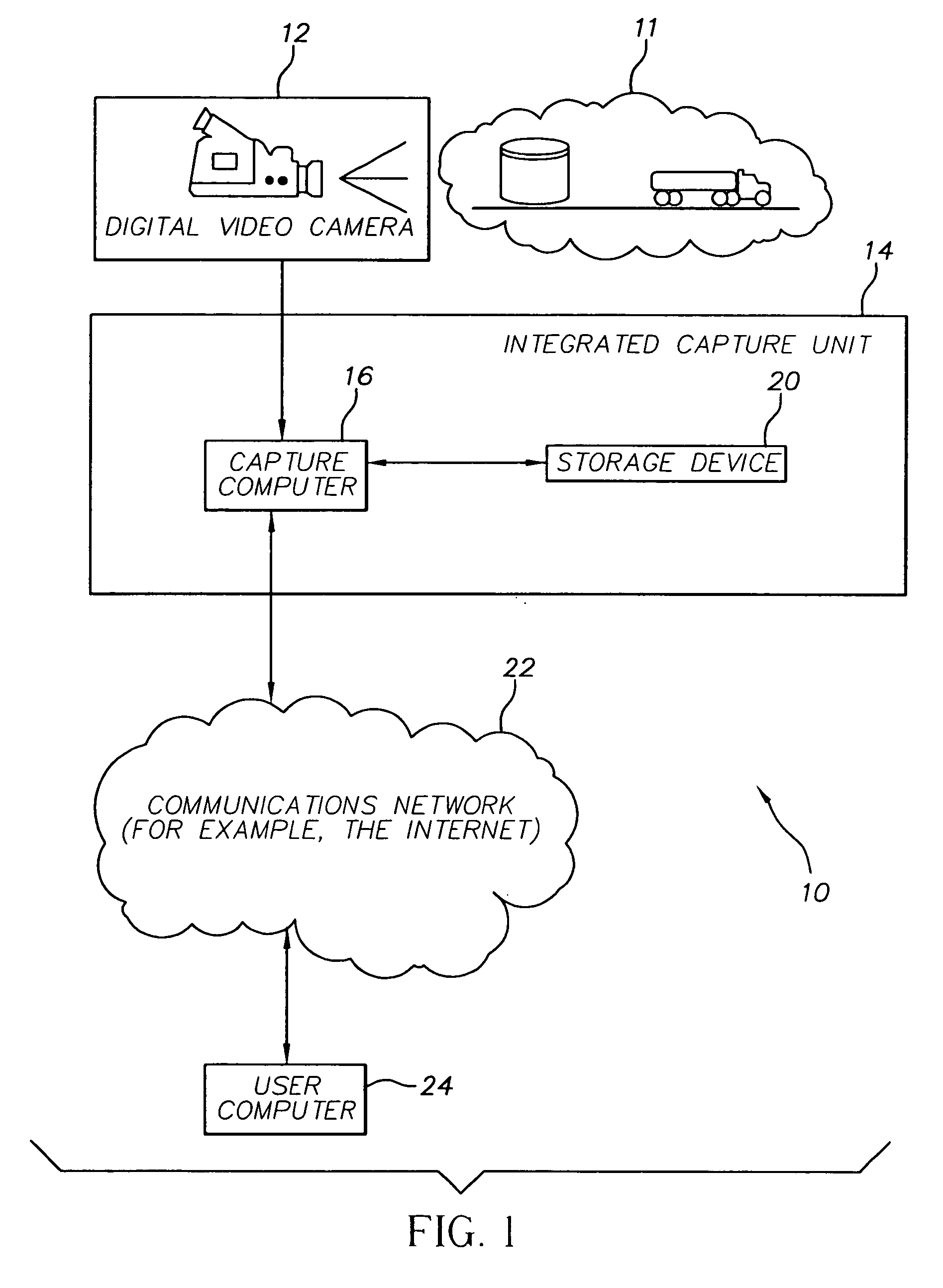
A method of transmitting selected regions of interest of digital video data at selected resolutions, including: capturing digital video; compressing the digital video into a sequence of individual high resolution JPEG 2000 frames and simultaneously extracting from the compressed high resolution JPEG 2000 frames a lower resolution; storing the individual high resolution JPEG 2000 frames in a storage device; creating a video sequence of the lower resolution representation; transmitting the video sequence of the lower resolution representation to a user; creating one or more video sequences of selected regions of interest at selected resolutions greater than the resolution of the video sequence of the lower resolution representation; transmitting one or more video sequences of selected regions of interest at selected resolutions; and repeating the prior two steps at incrementally increased resolutions until a desired resolution of the selected region of interest is reached according to a viewing objective.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
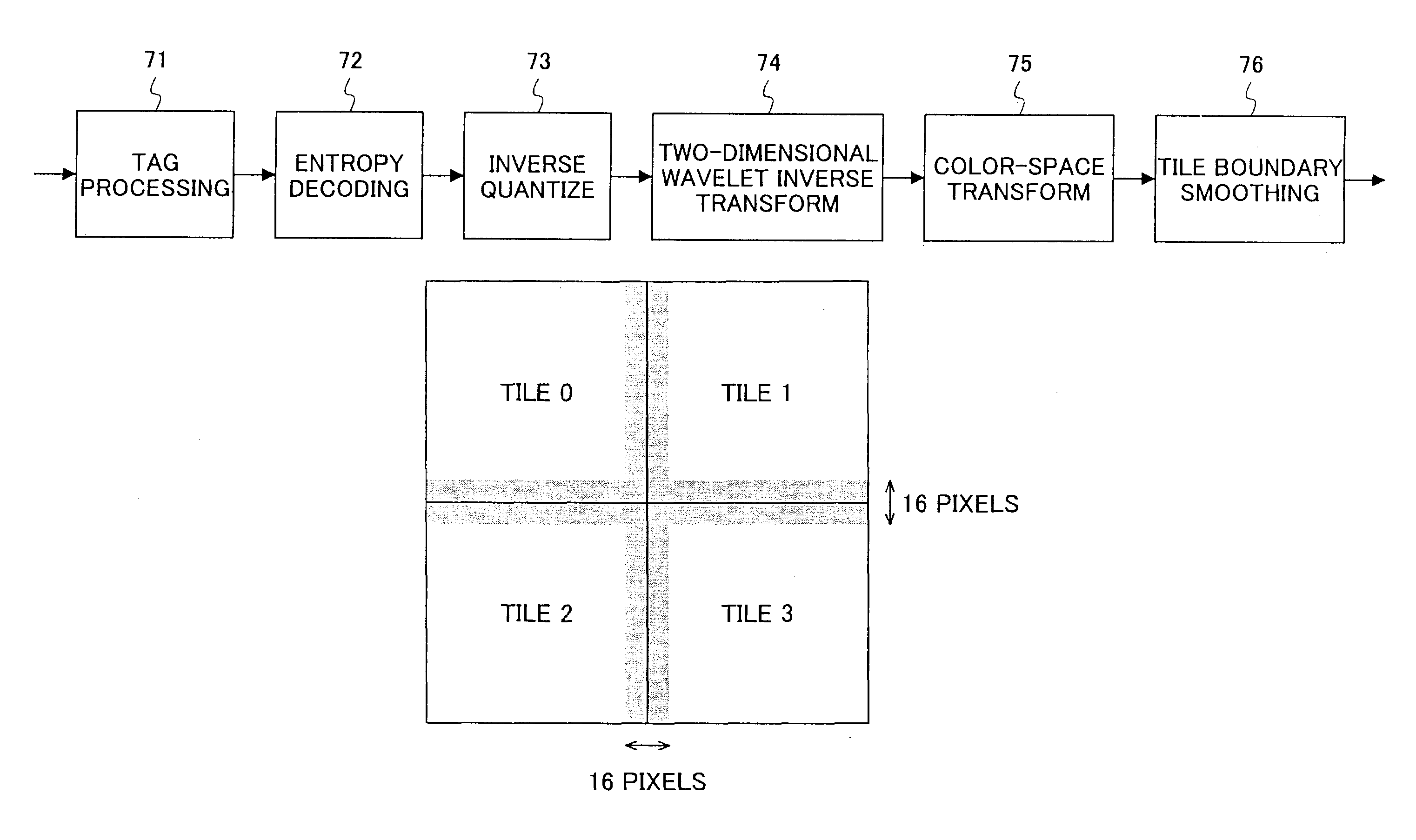
Smoothing tile boundaries of images encoded and decoded by JPEG 2000
An image processing apparatus and method for decompressing compressed image data is described. In one embodiment, the image processing apparatus decompresses compressed image data that is obtained by dividing an original image into blocks and compressing each block. The apparatus may comprise a decompression unit to decompress the compressed image data to provide an image which is a collection of the respective blocks, and a smoothing unit to perform a smoothing operation on the decompressed image to control the smoothing effect applied to the image based on distance from a block boundary and based on an edge amount.
Owner:RICOH KK
Image sensing apparatus, method and recording medium storing program for method of setting plural photographic modes and variable specific region of image sensing, and providing mode specific compression of image data in the specific region
InactiveUS6917384B1Uniform Image QualityIncrease flexibilityTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer graphics (images)Single image
When a region of interest of an image is compressed with high quality by an image sensing apparatus, such as a digital camera or the like, the region of interest (ROI) can be compressed by a compression coefficient different from that of other regions of the image according to the so-called JPEG 2000 method. However, setting the ROI is a complicated operation for a user. In the present invention, when a continuous photographing mode is not set, a single image sensing operation is assumed and the ROI is automatically set in a first region, which is the largest of three regions. Whereas in the continuous photographing mode, if a low-speed mode is set, the ROI is set in a second region smaller than the first region, and if a high-speed mode is set, the ROI is set in a third region, which is the smallest. In other words, the ROI is automatically set in the largest region in the single photographing mode, and when the continuous photographing mode is set, the ROI is automatically set larger in the low-speed mode than in the high-speed mode.
Owner:CANON KK
Massive image data compression method
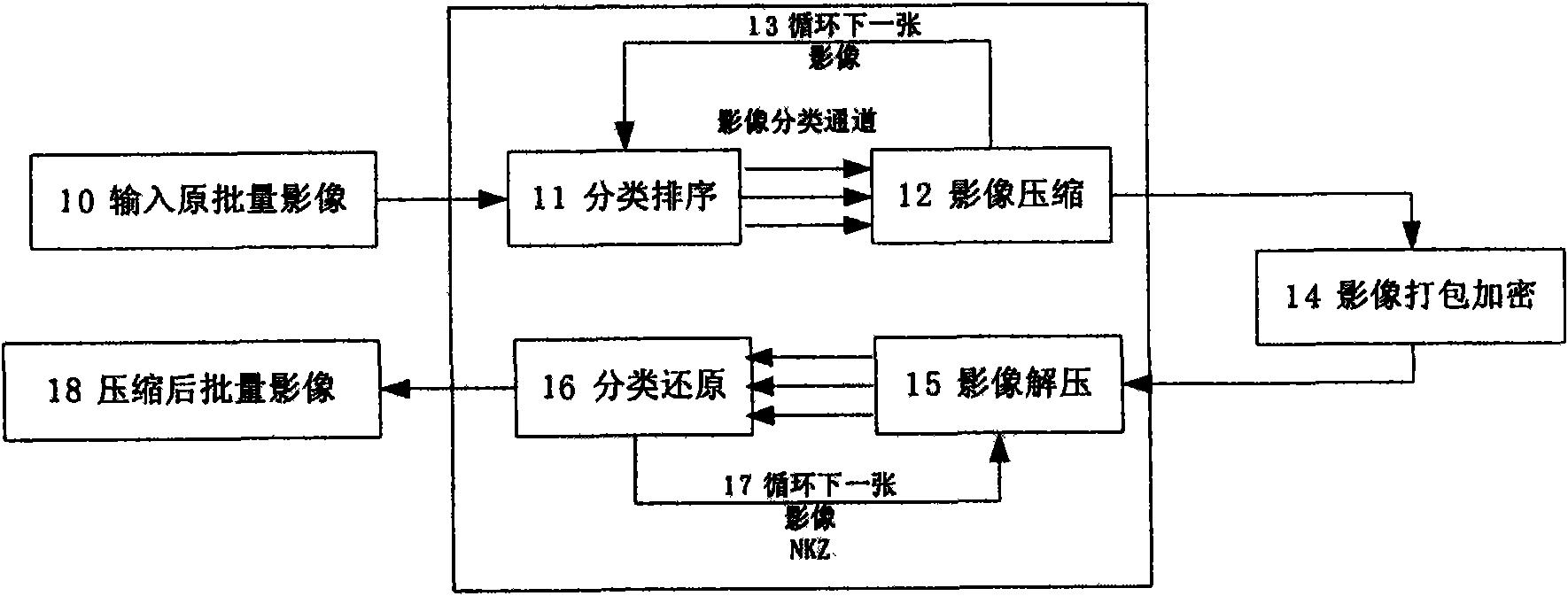
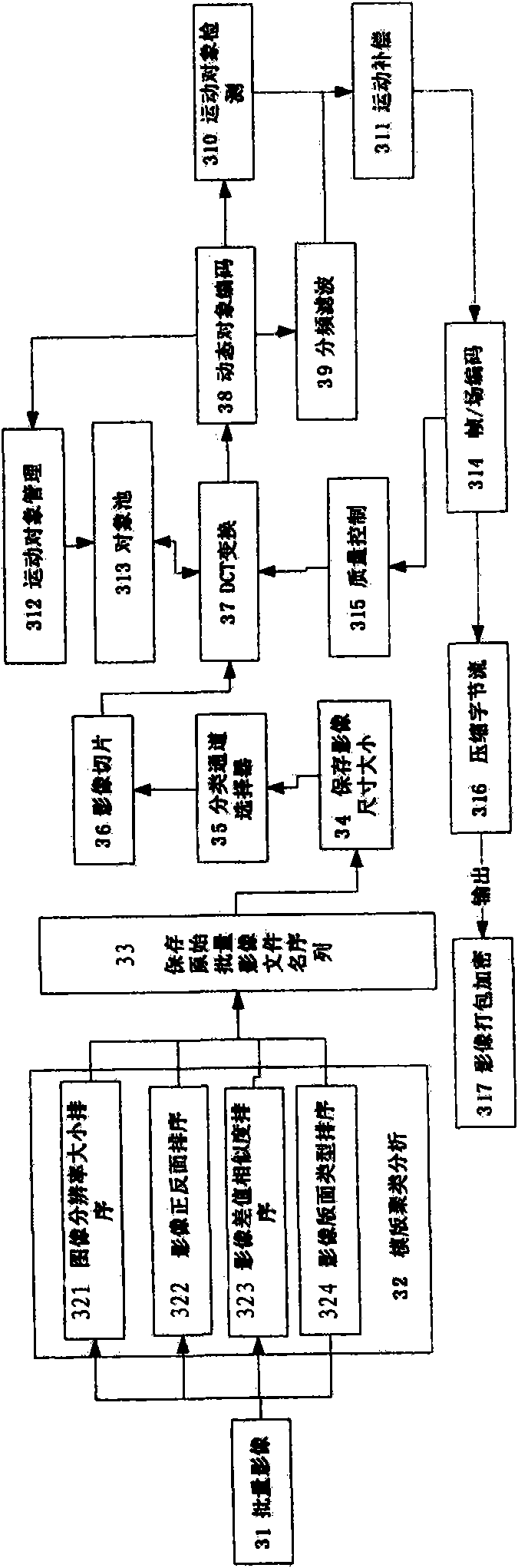
ActiveCN101594537AIncrease the compression ratioHigh speedTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImage decompressionCompression method
The invention relates to a compression method and belongs to a method of data compression technology in the field of information technology. The method comprises the following steps: inputting large-batch bill images; sorting and sequencing the bill images; utilizing a dynamic image compression algorithm to compress the images; packing and encrypting the images; adopting a dynamic image decompression algorithm to decompress the images and reducing and taking each image picture out; and outputting the batch images after the sorting and reduction. Compared with JPEG 2000, the compression algorithm provided by the invention has the advantages that: the compression speed is improved by 4 times; the size of resulting file of the compression is one-tenth of that of the original image; and after the decompression, the discrimination rate of OCR is kept unchanged basically. Based on the property, the compression method can transmit a real-time image in the network by using only small bandwidth.
Owner:京北方信息技术股份有限公司
Method of transmitting selected regions of interest of digital video data at selected resolutions
InactiveUS20060239574A1High resolutionPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoImage resolution
A method of transmitting selected regions of interest of digital video data at selected resolutions, including: capturing digital video; compressing the digital video into a sequence of individual high resolution JPEG 2000 frames and simultaneously extracting from the compressed high resolution JPEG 2000 frames a lower resolution; storing the individual high resolution JPEG 2000 frames in a storage device; creating a video sequence of the lower resolution representation; transmitting the video sequence of the lower resolution representation to a user; creating one or more video sequences of selected regions of interest at selected resolutions greater than the resolution of the video sequence of the lower resolution representation; transmitting one or more video sequences of selected regions of interest at selected resolutions; and repeating the prior two steps at incrementally increased resolutions until a desired resolution of the selected region of interest is reached according to a viewing objective.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
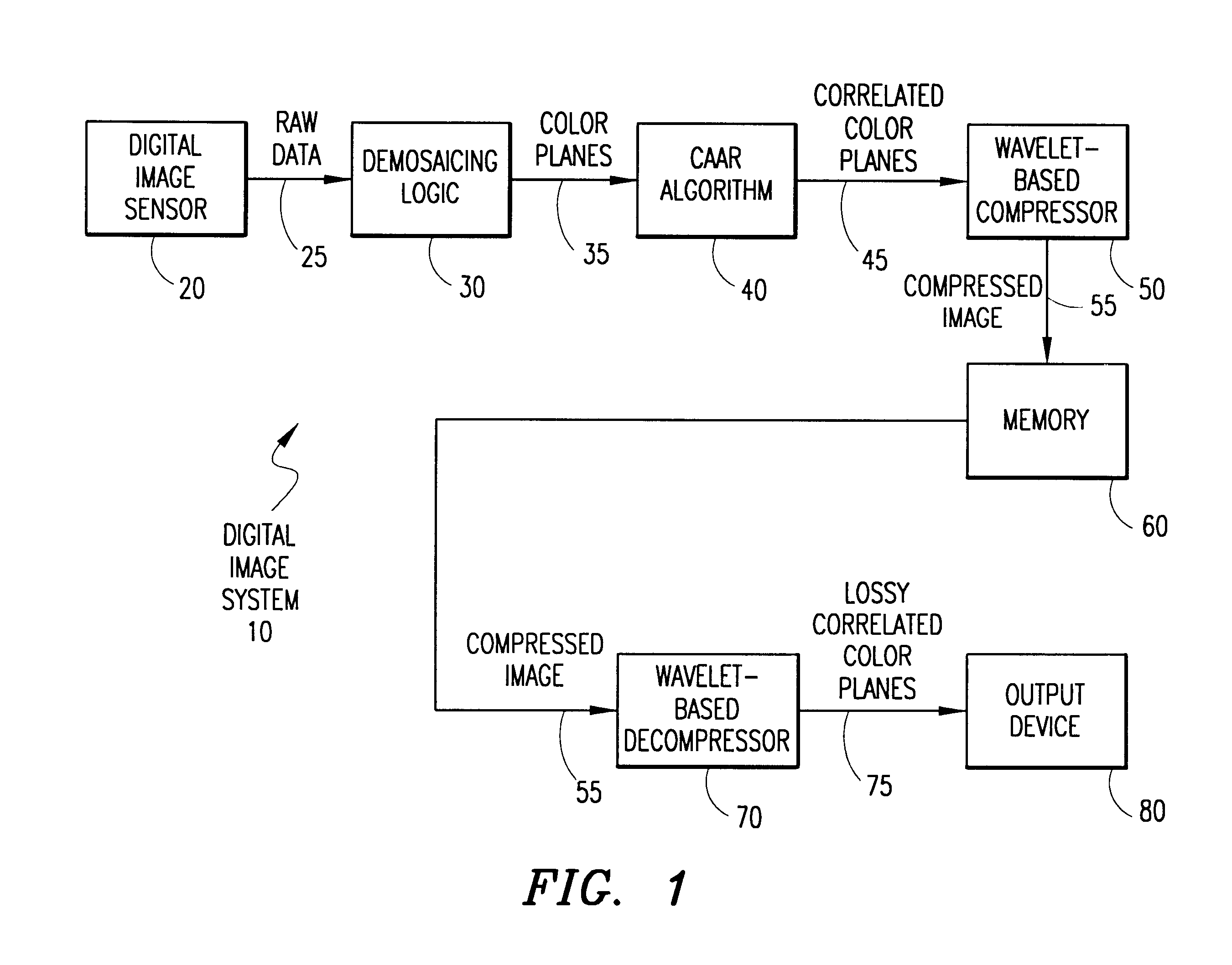
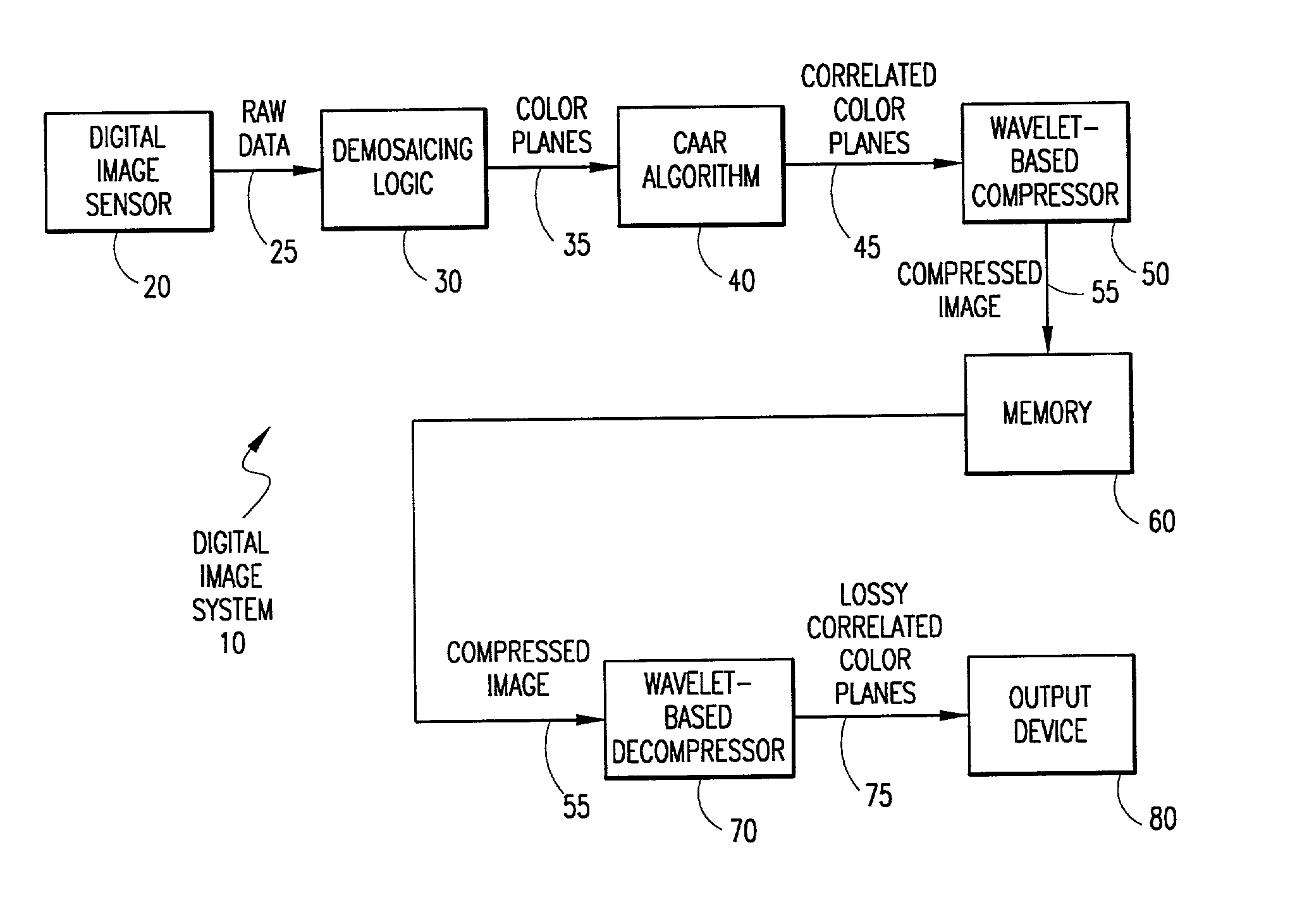
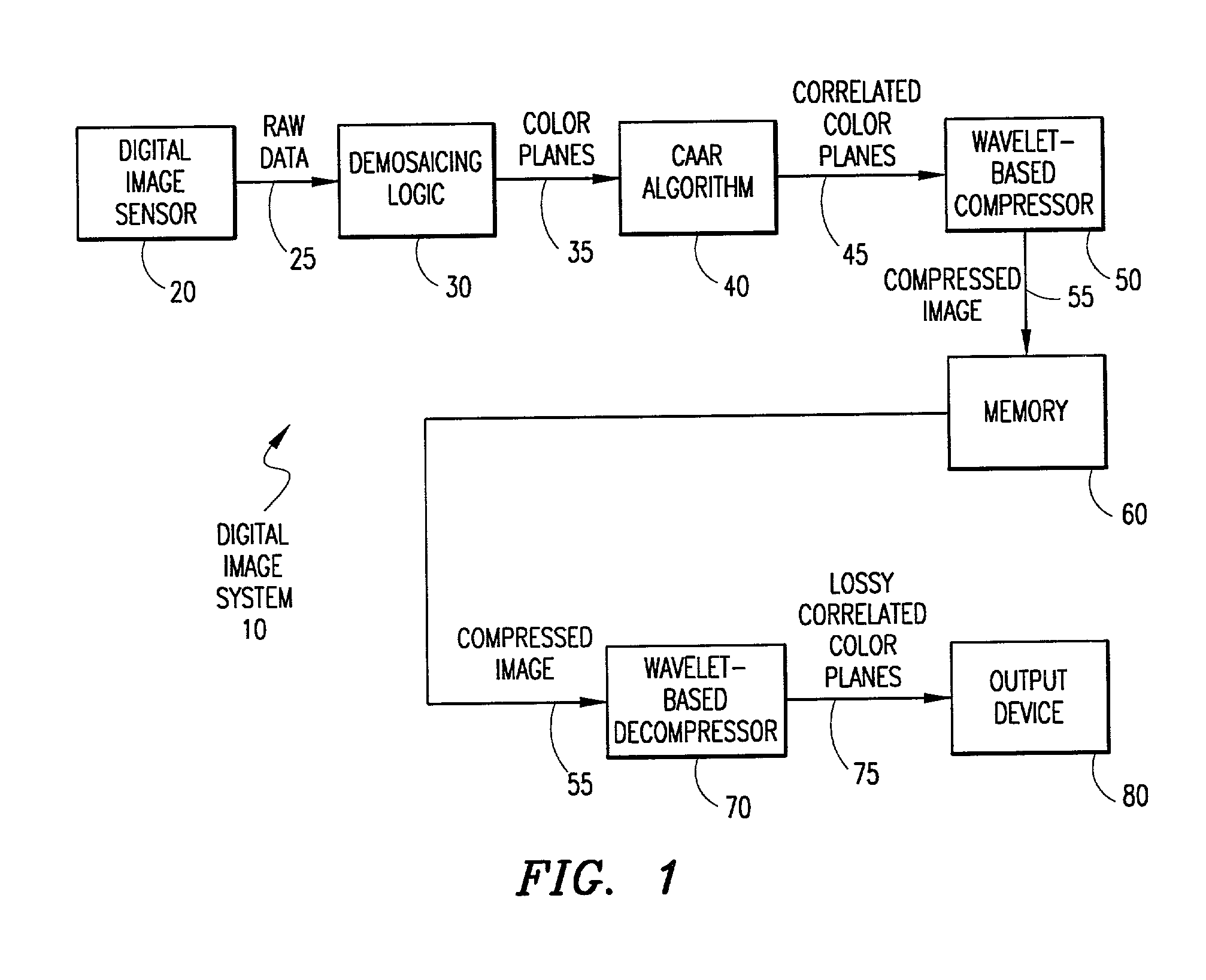
System and method for processing demosaiced images to reduce color aliasing artifacts
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
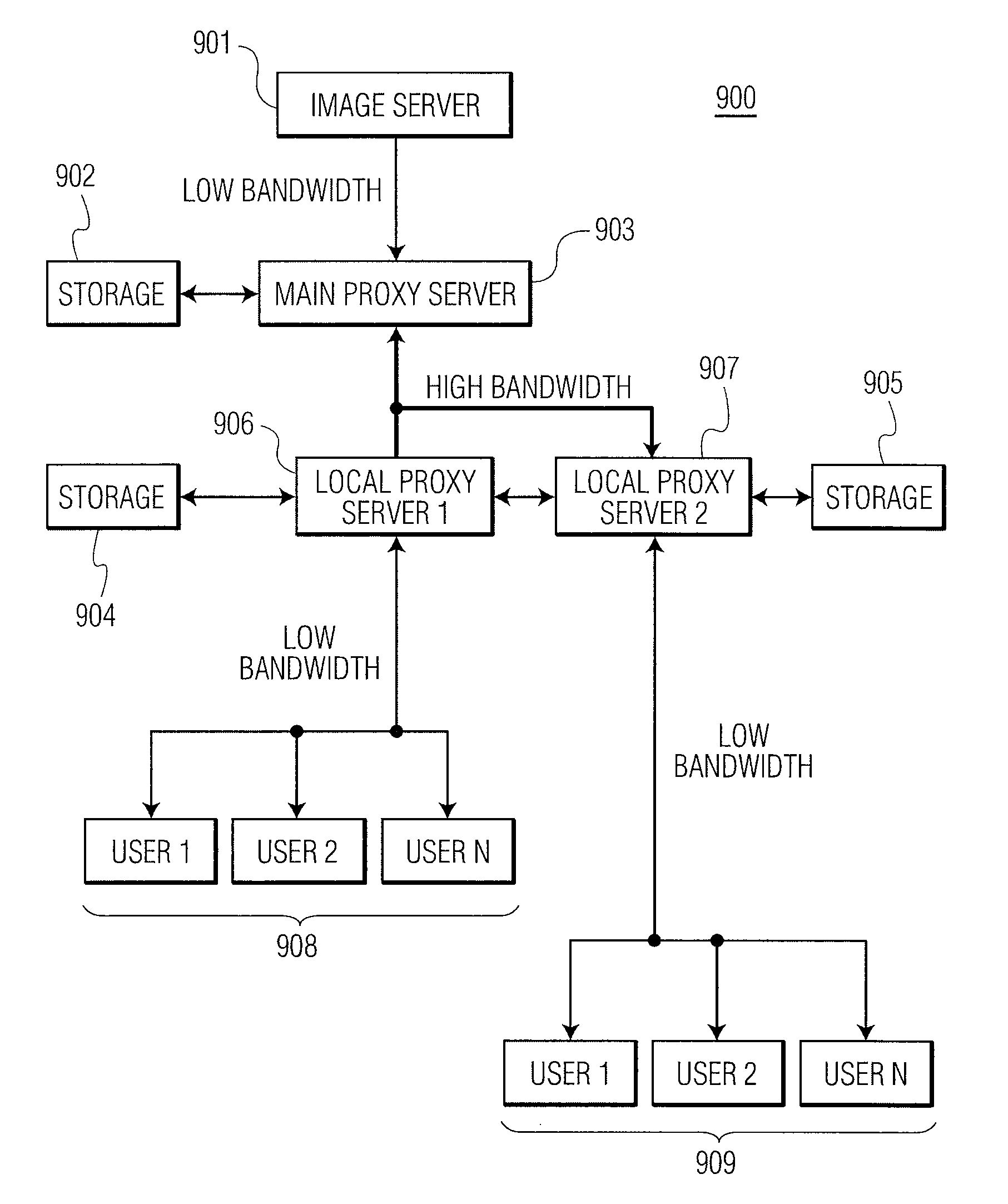
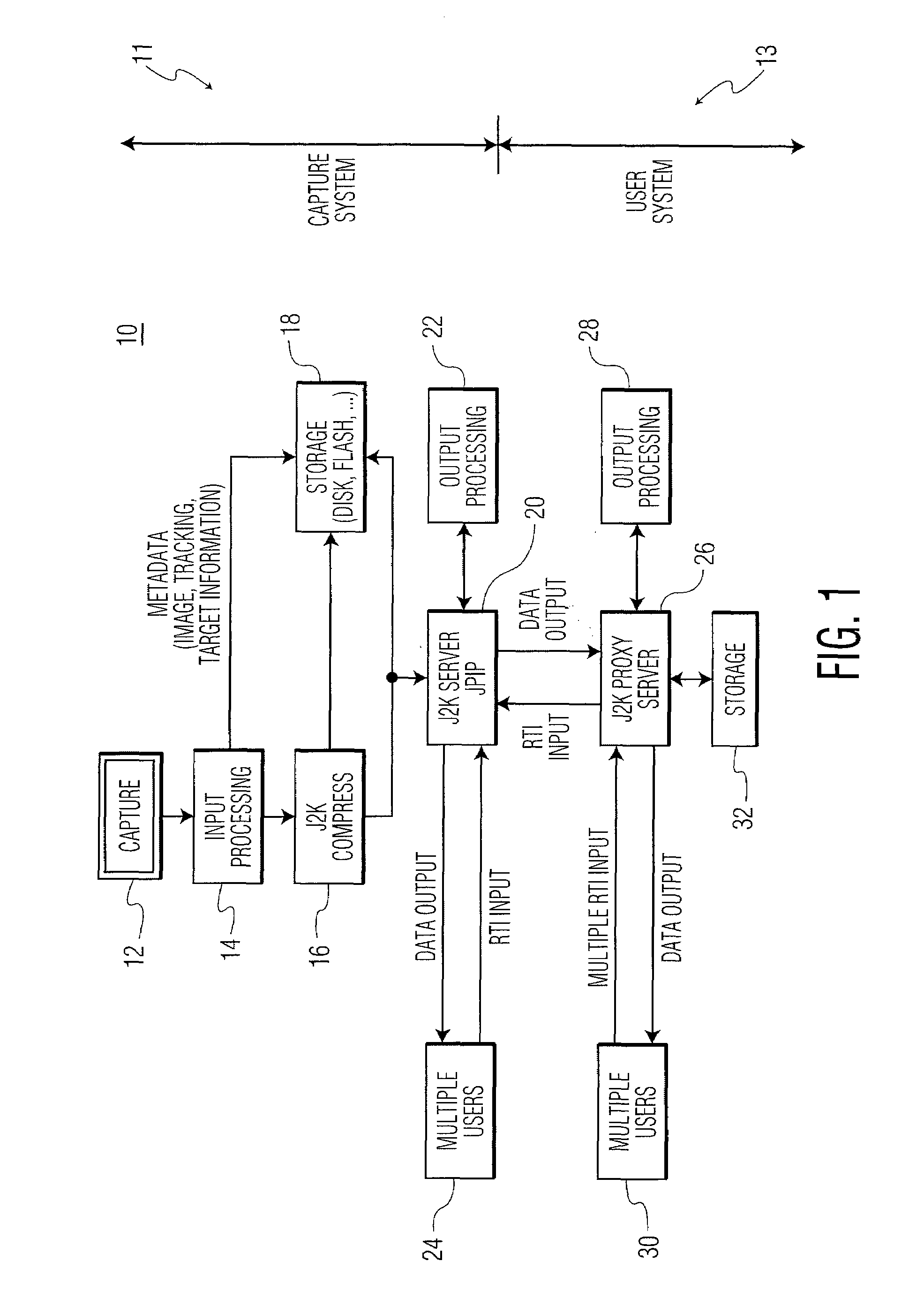
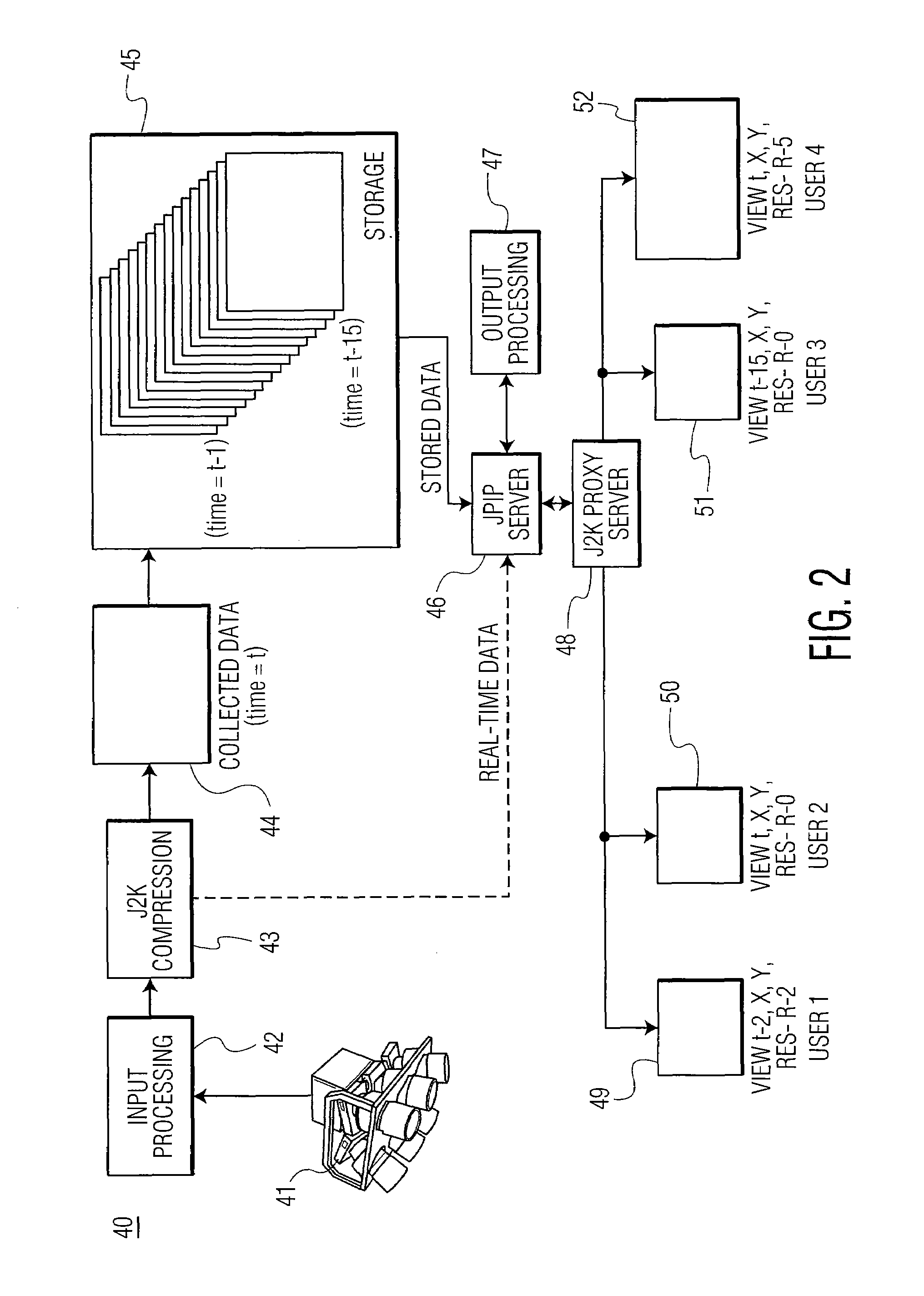
Imaging architecture for region and time of interest collection and dissemination
A server fulfills region and time of interest (RTI) requests for images from multiple users. The server includes a receiver for receiving a RTI request from a user, a processor for assembling a compressed image based on the RTI request, and a transmitter for transmitting the compressed image to the user. The processor is configured to extract a first portion of the compressed image from a local storage device. If the first portion is insufficient to fulfill the RTI request, the processor is configured to request a second portion of the compressed image from another server, and combine the first and second portions of the compressed image to fulfill the RTI request from the user. The compressed image includes an image compressed by a JPEG 2000 compressor.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
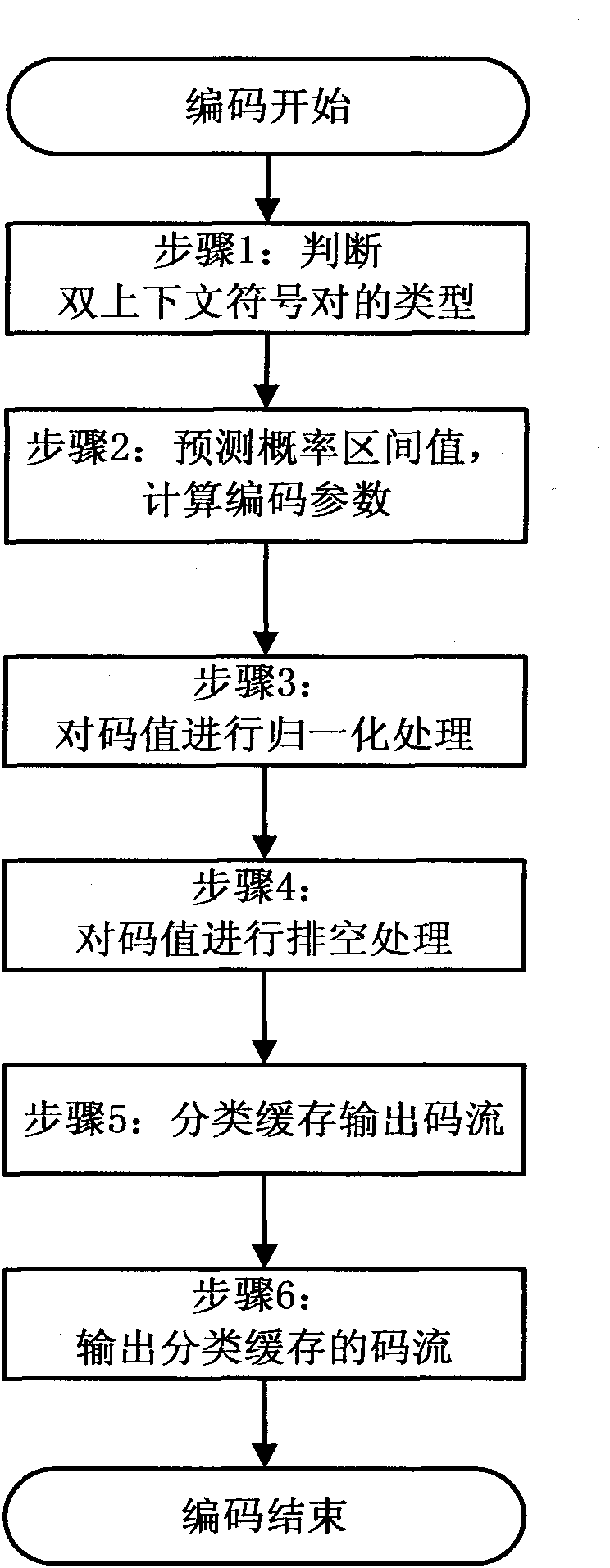
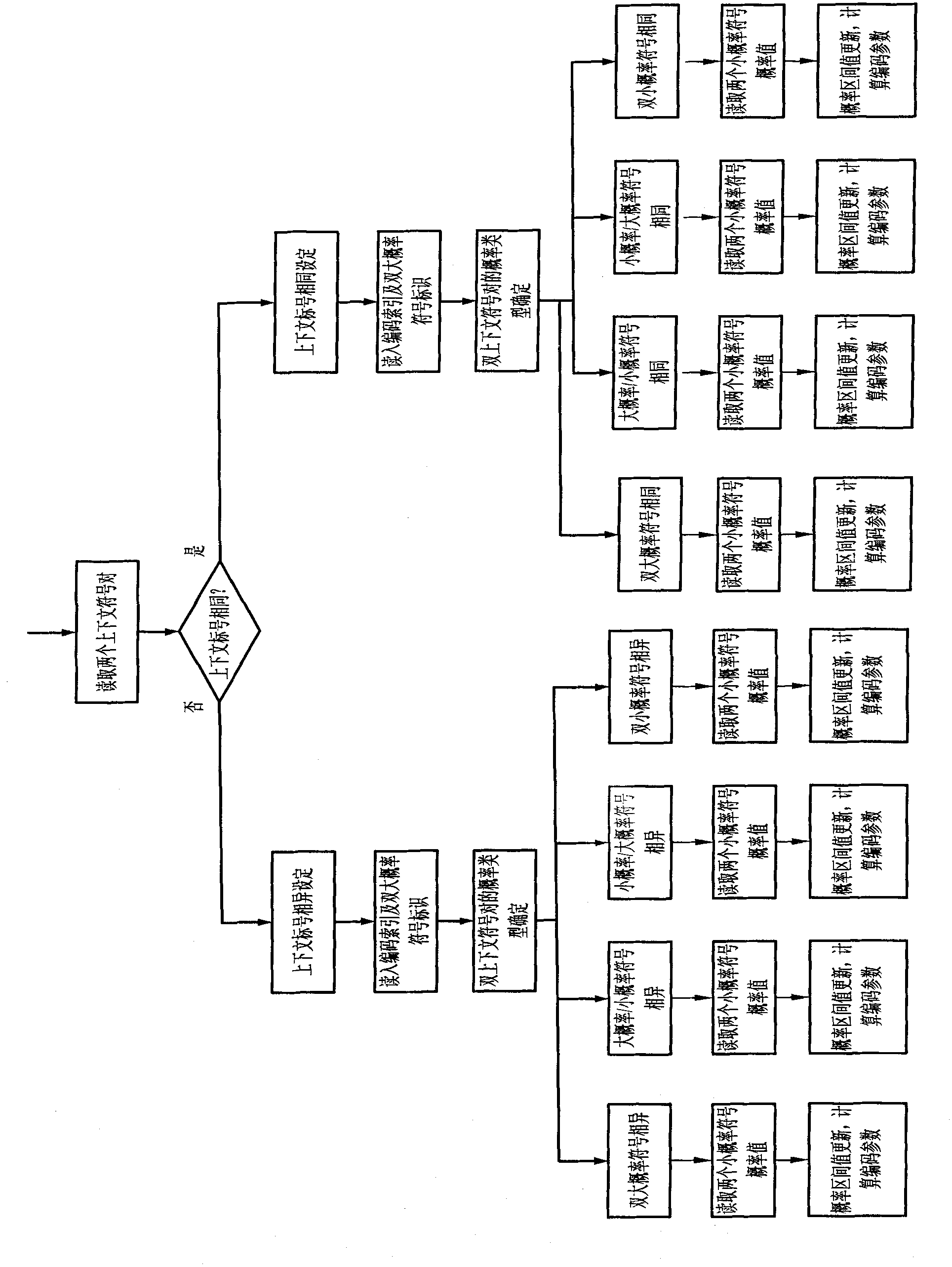
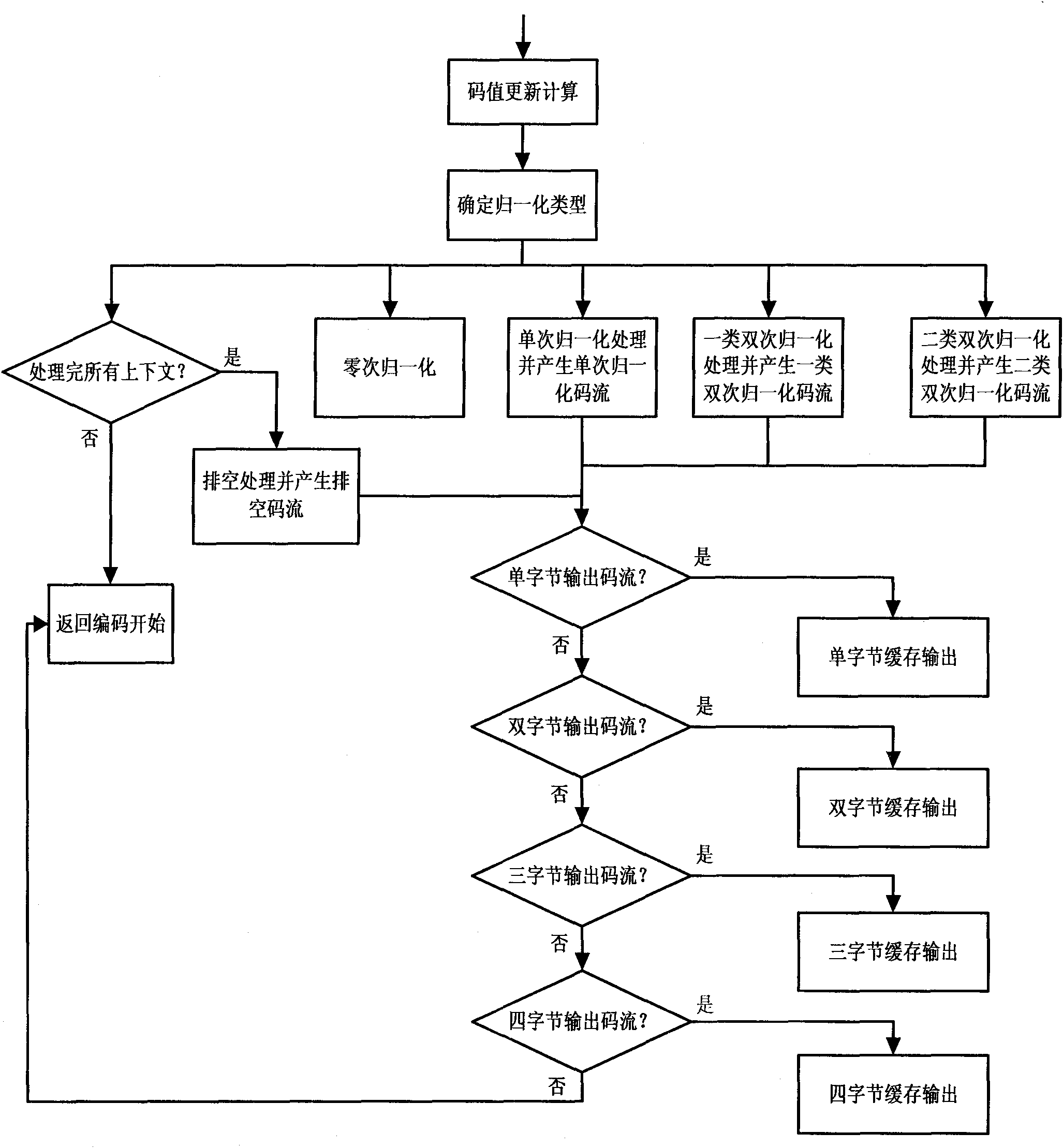
High-speed real-time processing arithmetic coding method based on JPEG 2000 standard
InactiveCN101841707AAvoid coding pausesImprove encoding speedTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationArithmetic codingInterval valued
The invention discloses a high-speed real-time processing arithmetic coding method based on a JPEG 2000 standard, which mainly solves the problem of the traditional coding method that the complexity is high and the coding speed is low. The coding process comprises the following steps of: judging the types of double context symbol pairs, respectively predicting the probability interval values according to the types and calculating the coding parameter; updating the code values, judging the current normalization type and normalizing the code values; if no new context symbol is input, emptying the code values; caching the code streams upon normalization and emptying process according to the byte and class; and finally, outputting the classified cached code streams in turn according to the priority order. The invention has the advantages of high coding speed and low complexity, and is applicable to the image compression coding of various high-speed digital apparatuses, in particular to the high-speed real-time satellite remote sensing image coding.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Image processing apparatus, image reading apparatus, image forming apparatus and recording medium for image processing program
InactiveUS20050031215A1Eliminate the problemReduce total usageGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
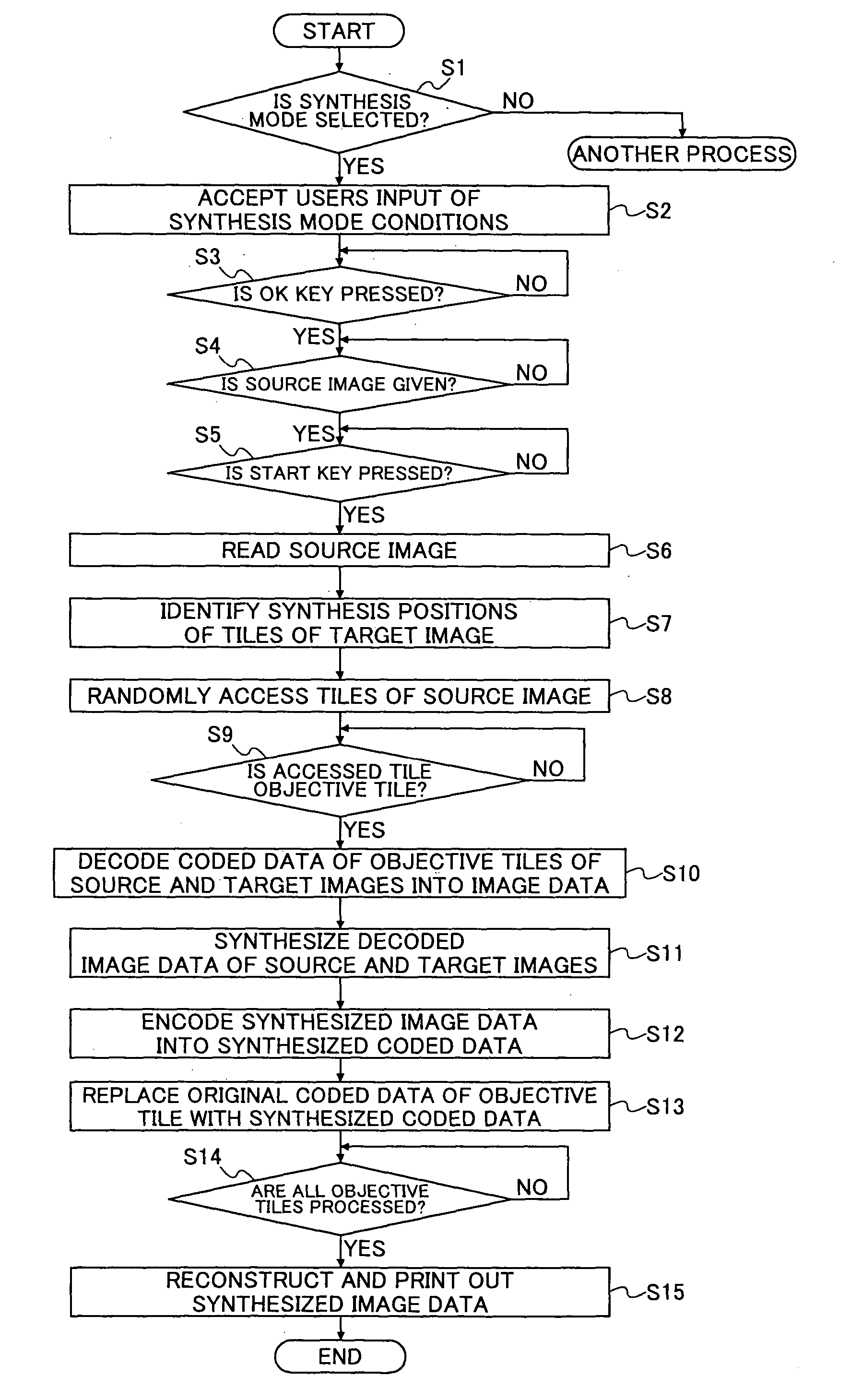
An image processing apparatus, an image reading apparatus, an image forming apparatus and a computer-readable recording-medium for storing an image processing program are disclosed. The image processing apparatus can synthesize coded data encoded in accordance with JPEG 2000 standard from source and target images at a higher speed with less use of a memory. The image processing apparatus includes a search part and an objective block synthesis part. The search part searches coded data of the source image per predetermined independently processable block for an objective block corresponding to a designated synthesis area. The objective block synthesis part synthesizes detected coded data of the objective block of the source image and coded data of the objective block of the target image.
Owner:RICOH KK
Enhancement of compressed image data
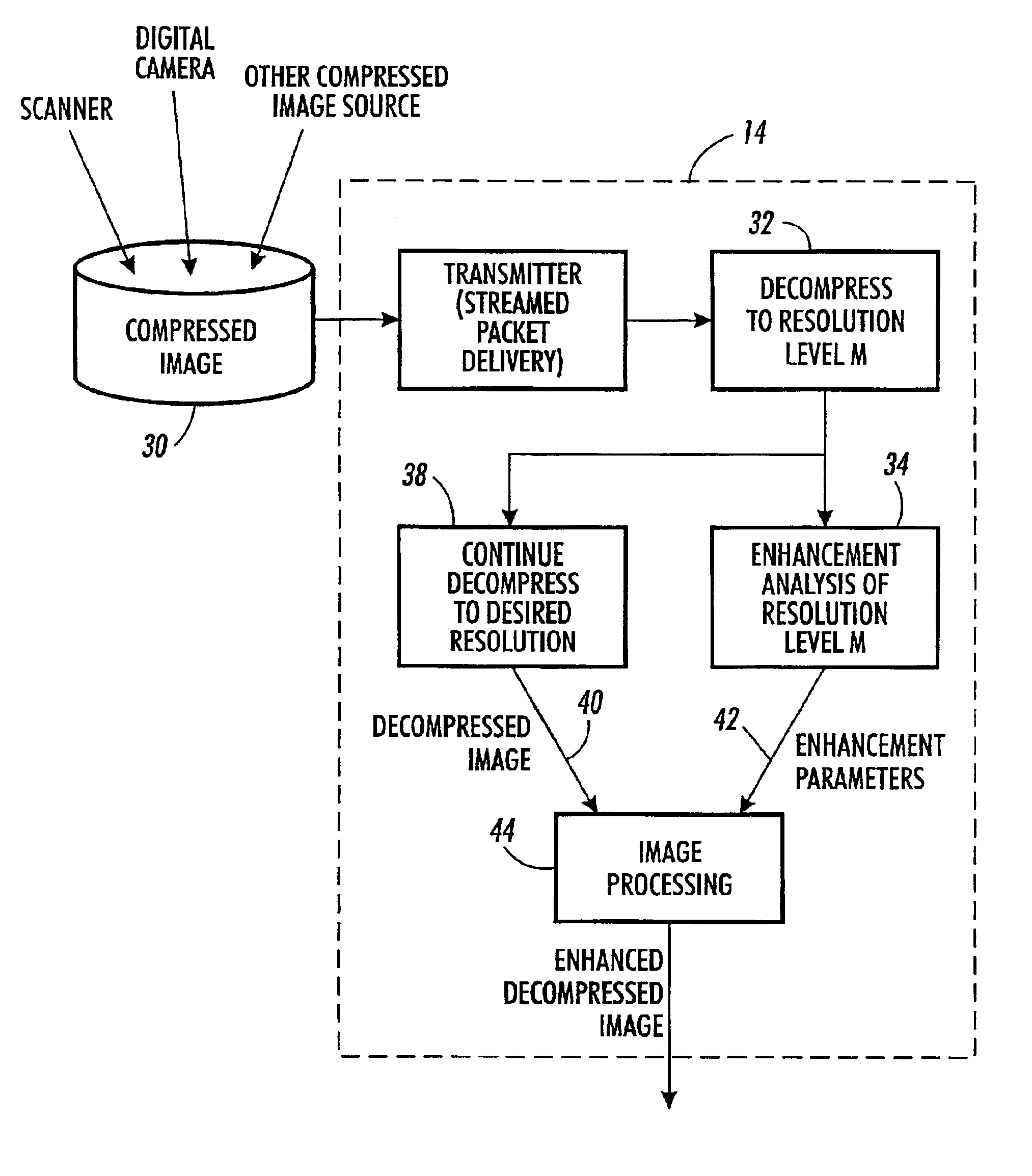
ActiveUS7031534B2Increase investmentEnhanced image dataImage enhancementCode conversionTone reproductionImage resolution
A xerographic apparatus, a printer, a printer server, and the like processes wavelet domain image data and includes means for receiving the wavelet domain image data representative of an input digital image. The wavelet domain image data may be formatted as a JPEG 2000 compressed file or other wavelet domain file including N levels of wavelet decompositions. An M-level extractor extracts an Mth level wavelet decomposition from the wavelet domain image data where M is <N. The extracted Mth level wavelet decomposition is a low resolution representation of the input digital image. An image enhancement system receives the extracted Mth level wavelet decomposition and derives an enhancement process such as a tone reproduction curve, a sharpness filter, and the like from the extracted Mth level wavelet decomposition. The enhancement process is used to enhance a higher resolution representation of the digital input image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Image processing apparatus, image reading apparatus, image forming apparatus and recording medium for image processing program
InactiveUS7336852B2Eliminate the problemReduce total usageGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing apparatus, an image reading apparatus, an image forming apparatus and a computer-readable recording-medium for storing an image processing program are disclosed. The image processing apparatus can synthesize coded data encoded in accordance with JPEG 2000 standard from source and target images at a higher speed with less use of a memory. The image processing apparatus includes a search part and an objective block synthesis part. The search part searches coded data of the source image per predetermined independently processable block for an objective block corresponding to a designated synthesis area. The objective block synthesis part synthesizes detected coded data of the objective block of the source image and coded data of the objective block of the target image.
Owner:RICOH KK
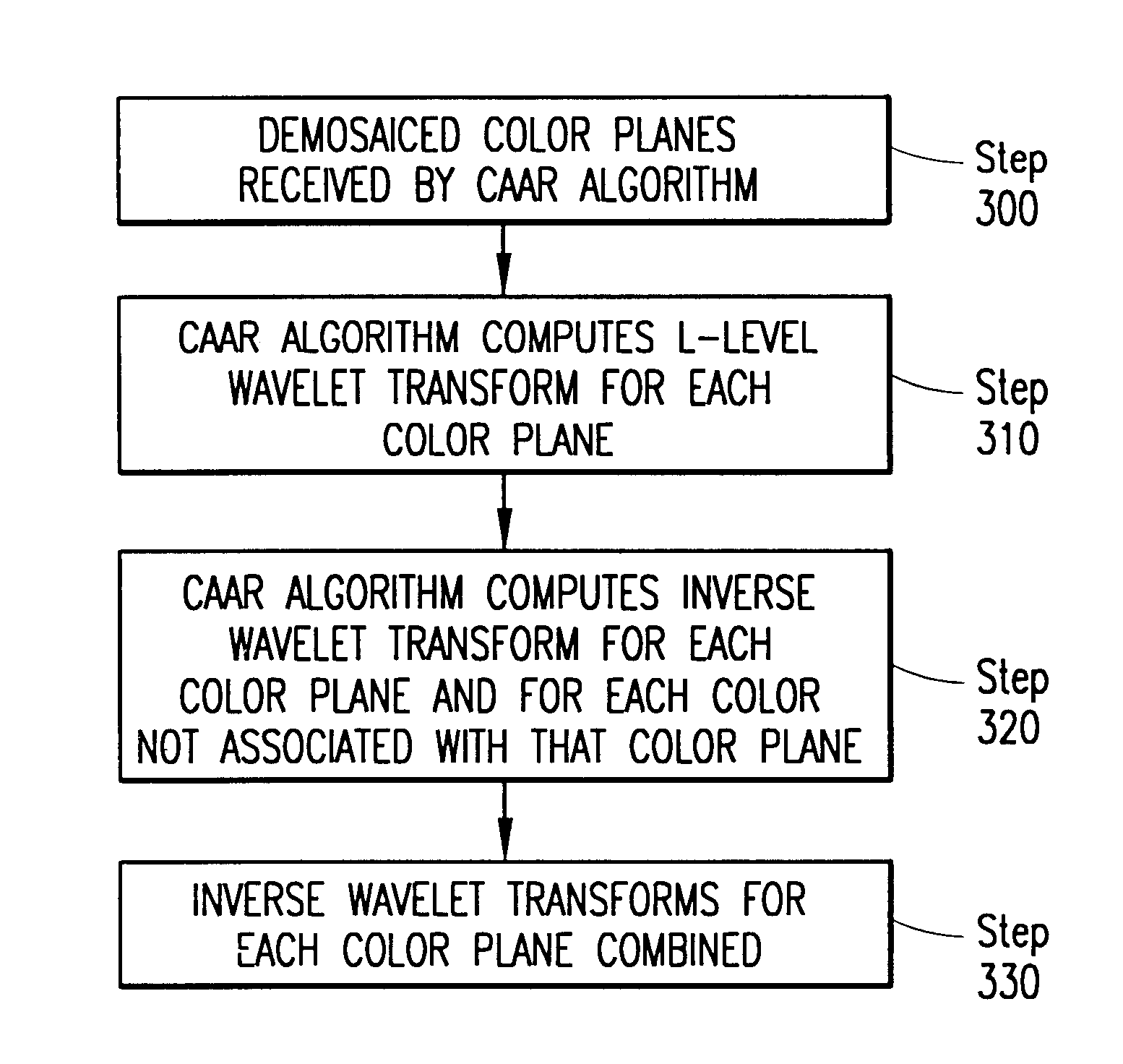
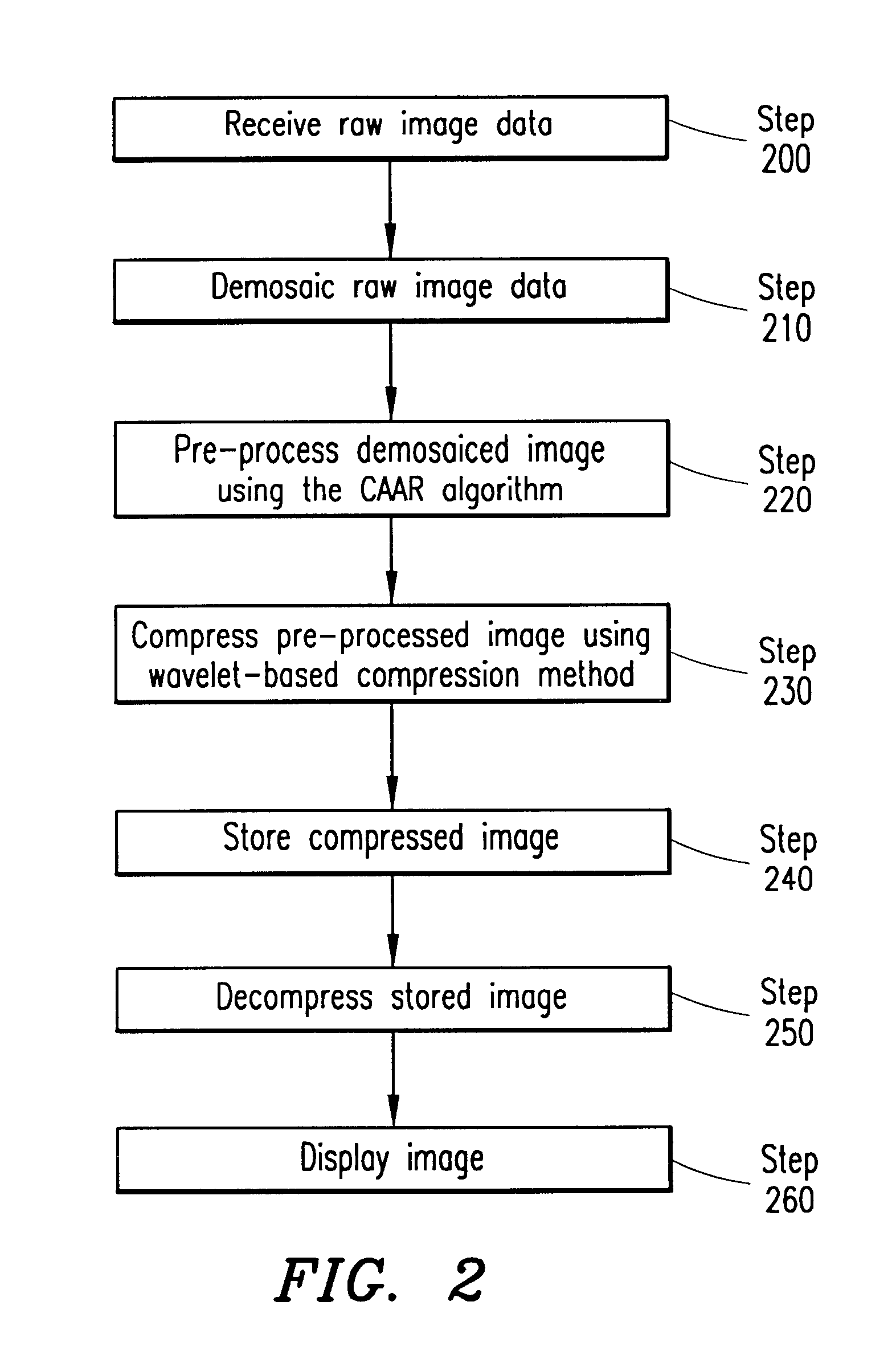
System and method for processing demosaiced images to reduce color aliasing artifacts
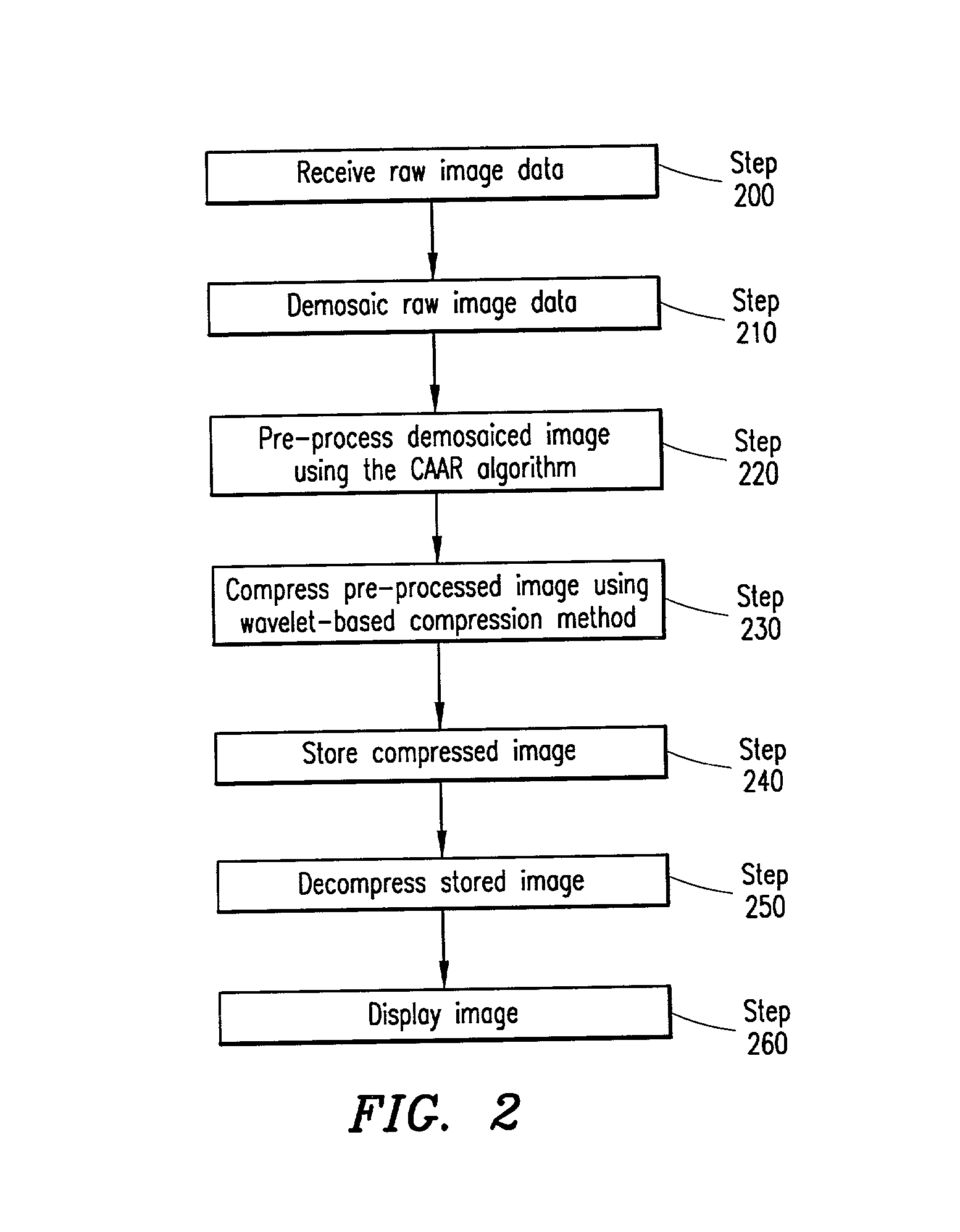
A system and method is provided for processing a demosaiced image using a color aliasing artifact reduction (CAAR) algorithm in order to reduce color aliasing artifacts. The CAAR algorithm computes the L level wavelet transform for the demosaiced color planes R, G and B. Thereafter, the CAAR algorithm estimates the correct color value at each pixel location for the colors not associated with that pixel location. For example, to determine the green value at red pixel locations, the CAAR algorithm performs an inverse wavelet transform using the green approximation signal and the red detail signals. This process is repeated for each of the colors (e.g., green values at blue pixel locations, red values at green pixel locations, etc.). In addition, the CAAR algorithm performs an inverse wavelet transform on each of the color planes themselves, so that the pixel values of the color associated with each pixel location are not altered. Thereafter, the inverse wavelet transform of each color plane is combined with the inverse wavelet transform of each of the estimated color values for that color plane to produce correlated R, G and B color planes. It is these correlated R, G and B color planes that may later be compressed using a wavelet-based image compression method, such as the JPEG 2000 standard.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
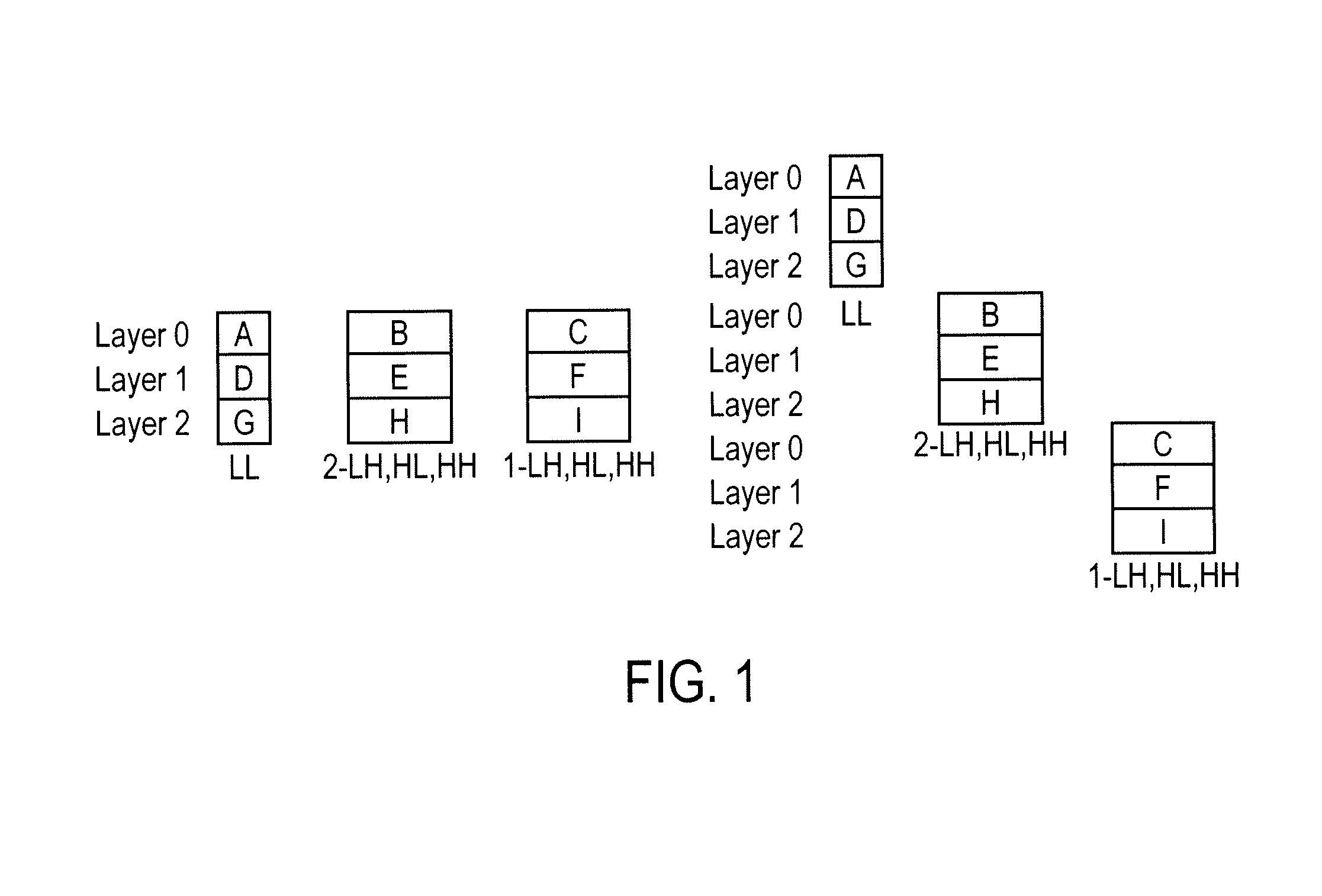
Information Processing System And Information Processing Method For Use Therewith, Information Processing Apparatus And Information Processing Method For Use Therewith, And Program
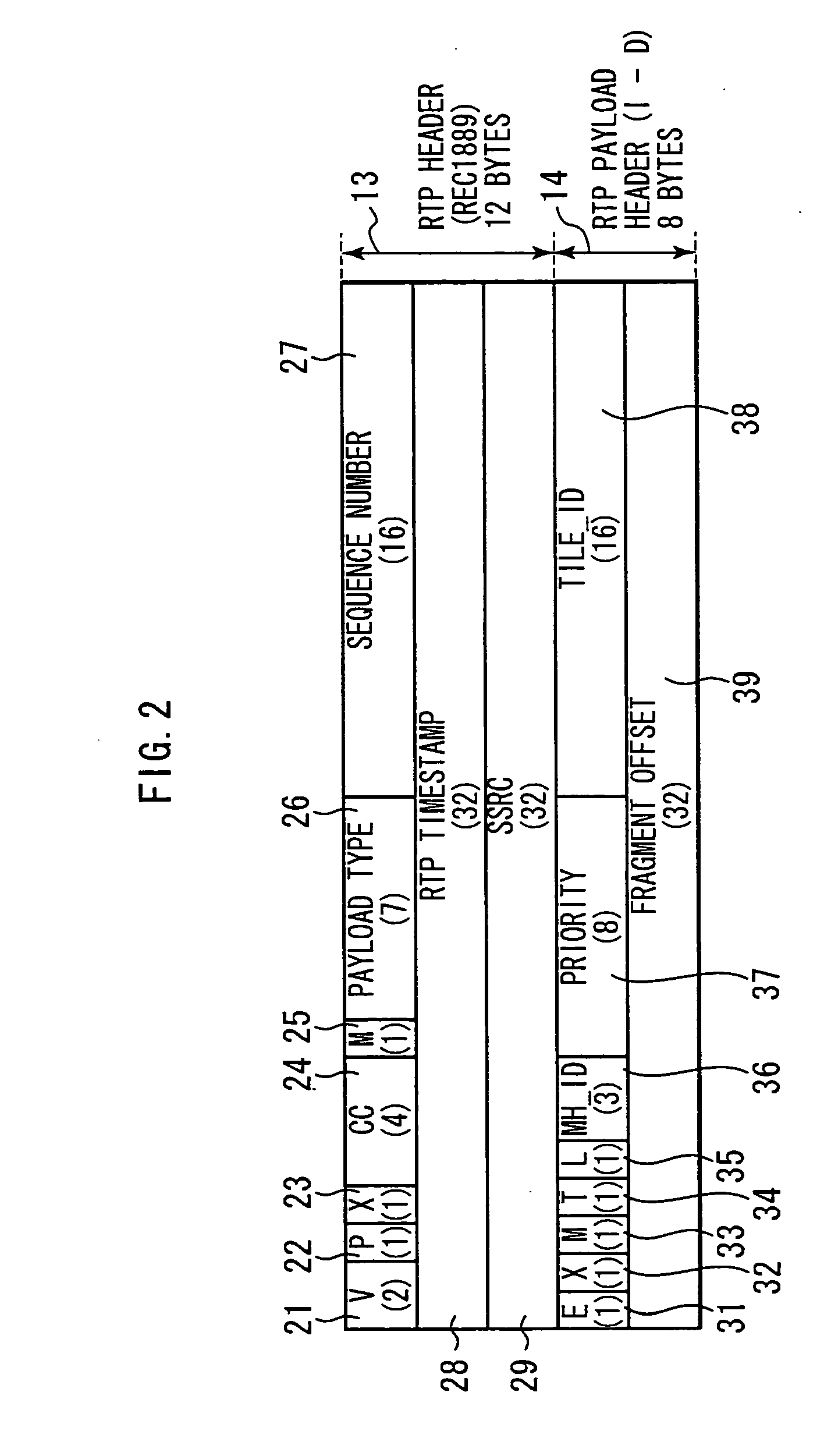
InactiveUS20070223697A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiple keys/algorithms usageInformation processingImage resolution
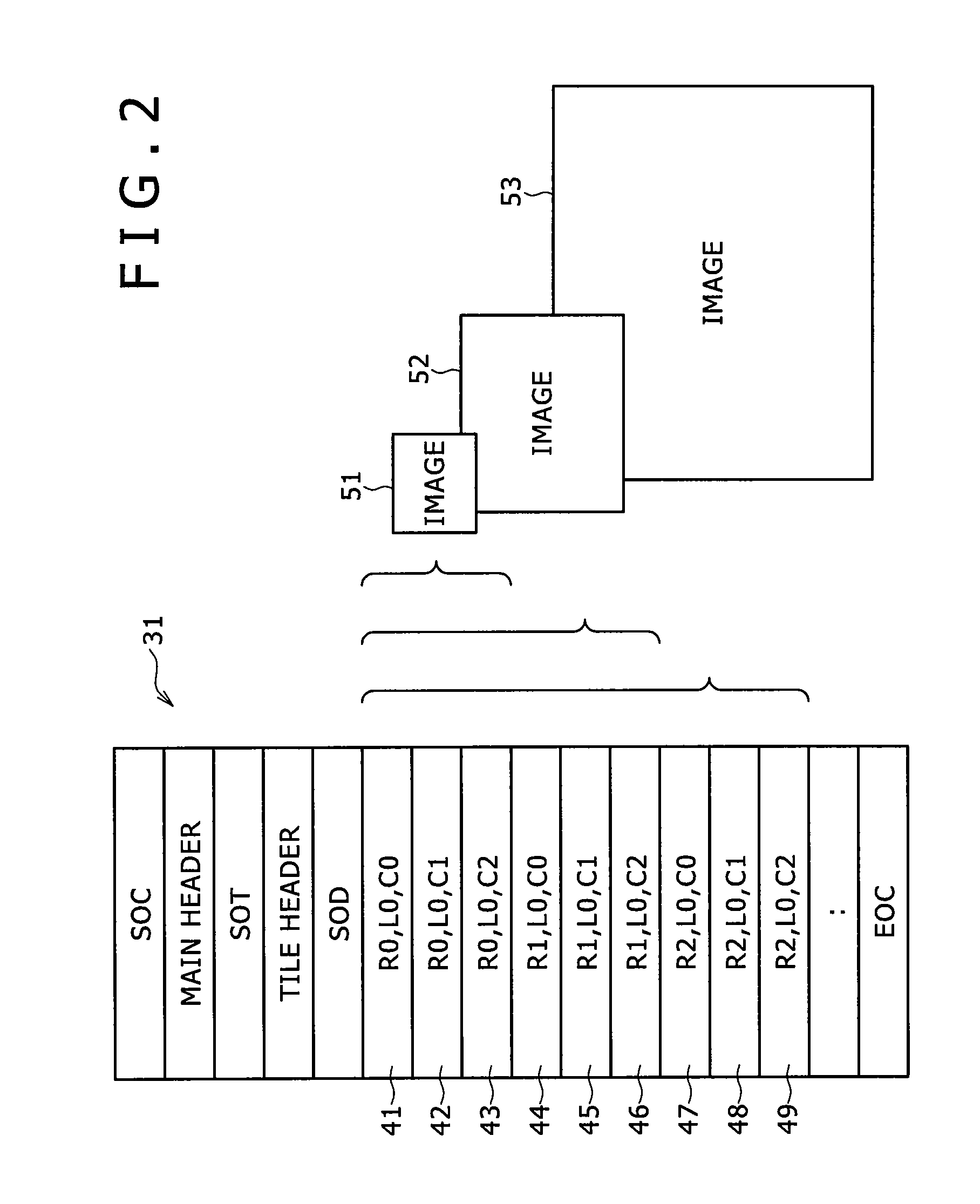
The present invention relates to an information processing system and a method for use therewith, an information processing apparatus and a method for use therewith, and a program which are capable of decrypting desired portions of encrypted data. Of packets 211 through 216 constituting a bit stream of layered-encoded image data 201 according to JPEG 2000, the packets 211 through 213 are each encrypted independently of the packets 214 through 216 which are also encrypted each. This produces encrypted split data 262 with the resolution at level zero (corresponding to R0) and encrypted split data 263 with the resolution at level one (corresponding to R1). The header (ranging from SOC to SOD) of layered-encoded image data 201 is appropriated for a header 261, followed by encrypted split data 262 and 263 and an EOC 264, in that order, the whole data array constituting data 251 that is output as the definitive encrypted data. This invention is particularly applicable to image delivery apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image-processing apparatus, an image-processing method, a program, and a memory medium
InactiveUS7626733B2Television system detailsDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareImaging processing
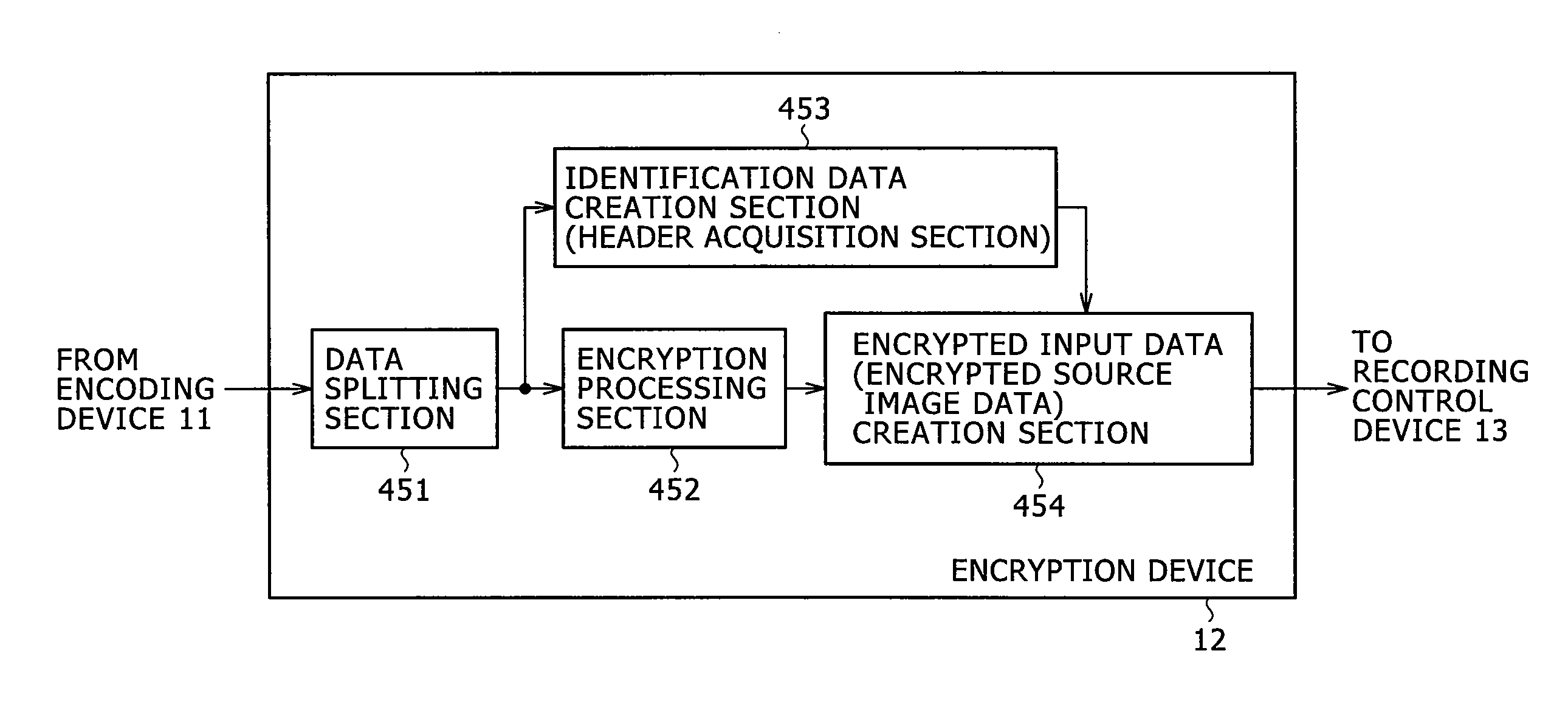
Efficient utilization of a memory medium is enhanced in an image-processing apparatus, in which encoded data of JPEG 2000 or Motion-JPEG 2000 are stored in the memory medium as a file. File size of the encoded data is adjusted close to, but not to exceed an integer multiple of a memory domain management unit (sector size) of the memory medium. Thereby, a memory domain assigned to the image file in its entirety, or almost in its entirety, is used effectively, improving the efficient utilization of the memory medium.
Owner:RICOH KK
JPEG 2000 speed control method through real time cut-off
Disclosed method predicts effective bit plane in a internal code block within sub band, and puts forward a scheme for controlling preallocation rate of code block and code stream. Wavelet weight omega and quantization coefficient delta are as weights in allocating code rates between code blocks, and rate of block is allocated according to total number of channel contained in code block. Based on the algorithm said above, VLSI structure in real time coding and real time blocking is put forward, and JPEG 2000 does this requirement, according to the experiment proof. The invention raises coding speed and compression ratio in duplication so as to solve bottleneck in image video compression.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
System and method for compressing satellite images with low bit rate
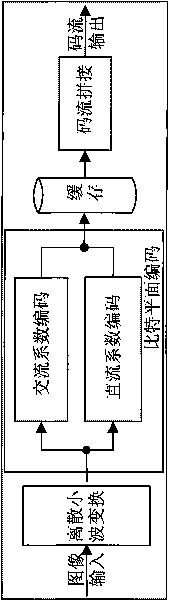
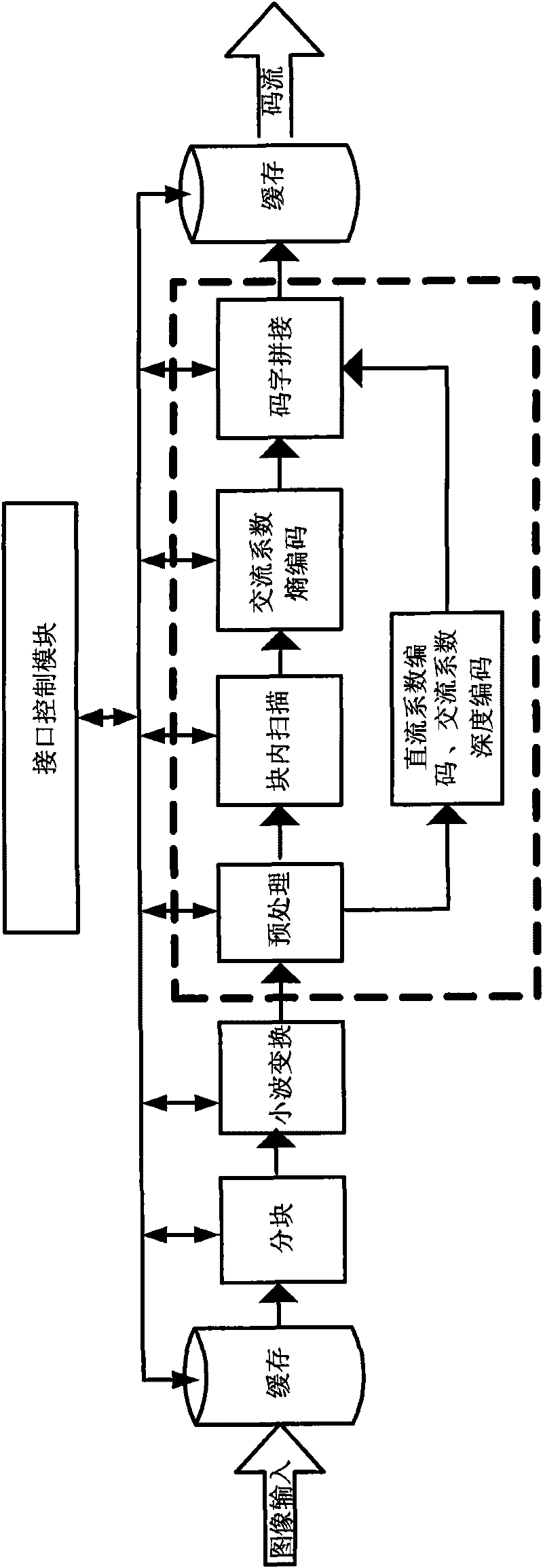
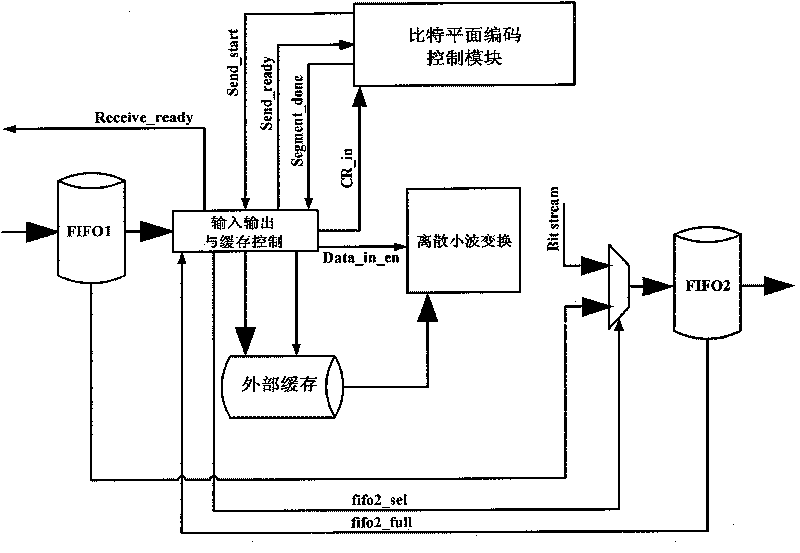
InactiveCN101742300APrevent error propagationReduce power consumptionTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCode moduleSatellite image
The invention discloses a system and a method for compressing satellite images with low bit rate. The system comprises a control module, a wavelet transformation module, a CCSDS scanning coding module and a code stream splicing module. In the system and the method, image data are divided into a plurality of 32X32 (or 64X64 and 128X128) small images; then, the small images are transmitted into the wavelet transformation module, the scanning coding module and the code stream splicing module for obtaining compressing code streams. The wavelet transformation module, the scanning coding module and the code stream splicing module are used for line production among image blocks; and the scanning coding module is used for the line production along bit planes. The compressing effect of the system and the method for compressing the images is between JPEG 2000 and EZW; when the compression is carried out at a low bit rate, the compressing effect is equivalent to JPEG2000; a decoding re-synchronization mechanism is adopted for preventing error codes of space data from diffusing in transmission, with low power consumption; and extensively used parallel operation and a line structure increase the processing speed of a chip and meet the macro compressing requirement of the satellite images.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Methods and systems for scalable streaming of images with client-side control
InactiveUS7260614B2Image degradationLower latencyCathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb serviceClient-side
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for managing and transmitting image data. Some embodiments are particularly suited to streaming JPEG 2000 images from a web server.
Owner:SHARP KK
Information processing device and method, recording medium, and program
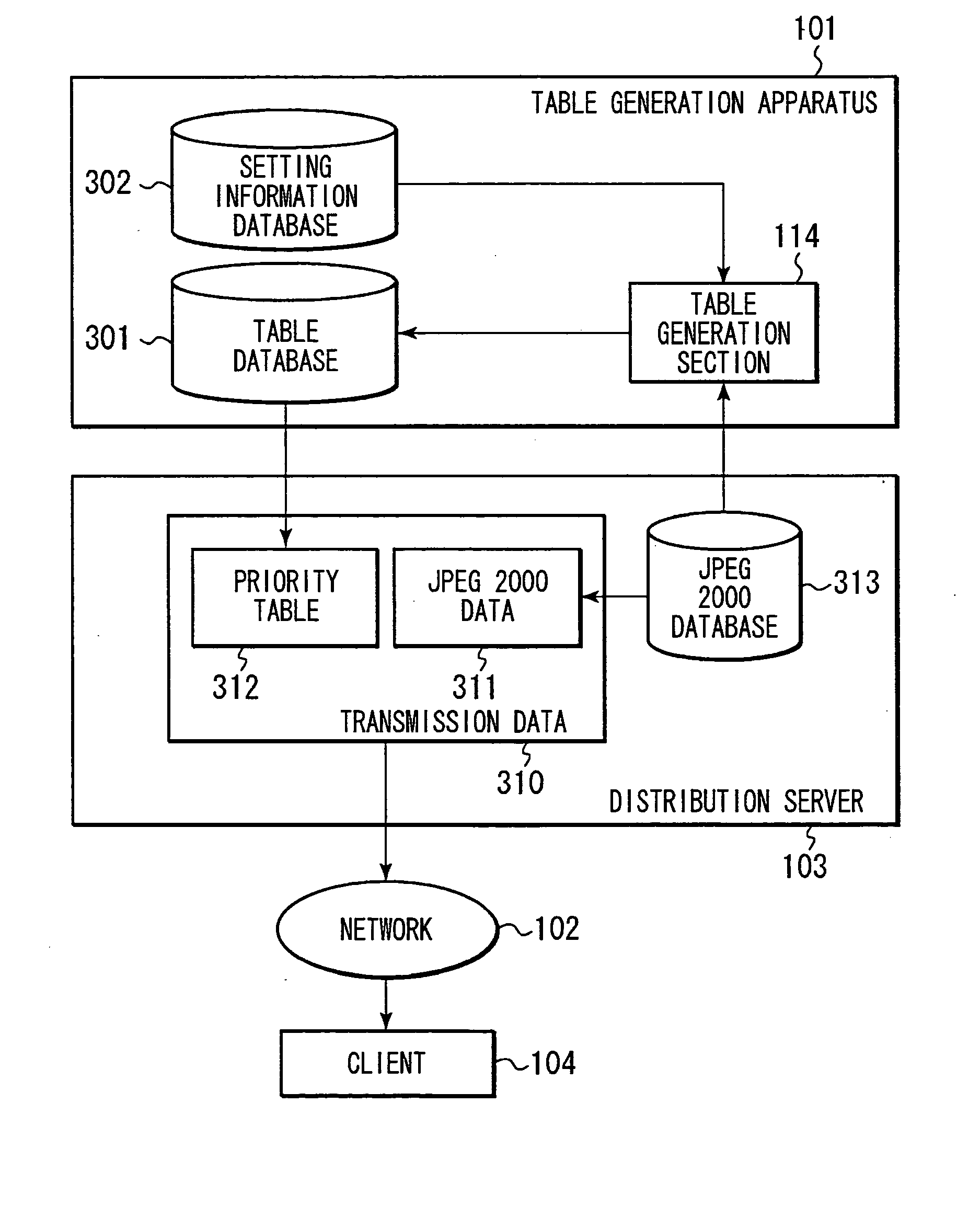
InactiveUS20050226252A1Simple wayData switching by path configurationTwo-way working systemsInformation processingValue set
The present invention relates to an information processing apparatus and method, recording medium, and program capable of generating a priority table in a straightforward manner. JPEG 2000 data 151 inputted to a table generation section 114 is held by a JPEG 2000 data reading section 161, and is provided to a JP2 packet information extraction section 162 at a prescribed timing. After the necessary JP2 packet information has been extracted in packet form, this is provided to a priority table editing section 164. Then, at the priority table editing section 164, a priority table with priority values set for all of the JP2 packets is made based on setting information 152 designating priority values for some of the JP2 packets corresponding to the JPEG 2000 data 151 provided by the setting information reading section 163 and is outputted by the priority table output section 165. The present invention can be applied to personal computers.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image processing apparatus, image display system, program, and storage medium
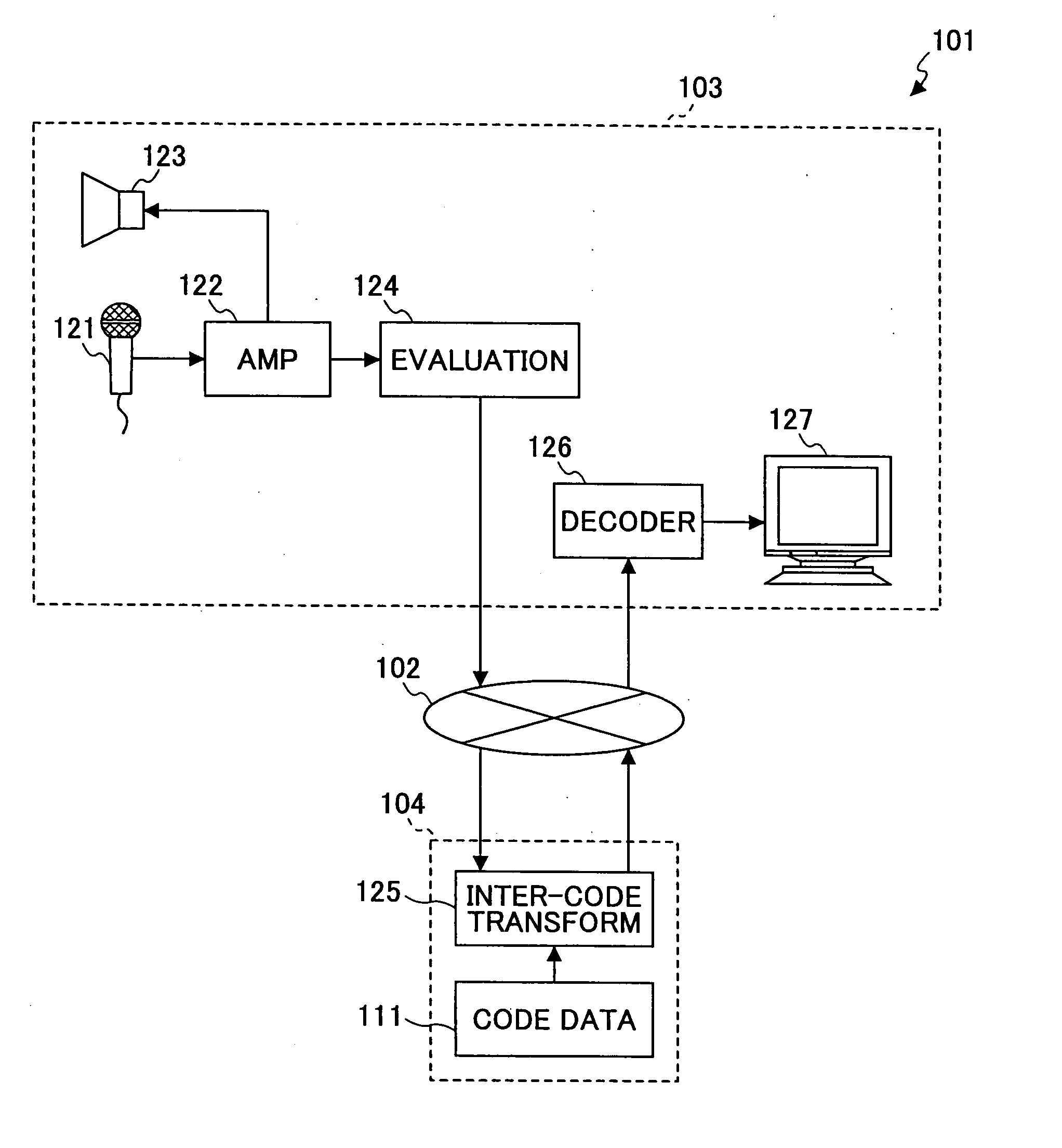
InactiveUS20050031212A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisComputer hardwareImaging processing
A technique is disclosed for evaluating an audio characteristic such as singing ability, and processing an image to be displayed according to the evaluation result in a manner that can attract the interest of a user. JPEG 2000 code data of a moving image for a karaoke system, for example, are transmitted from a server to a client along with accompanying audio data, and the code data are then decoded at a decoder to form an image to be displayed. An audio signal such as the voice of the user that is input to a microphone is evaluated at an evaluation unit, and the evaluation result is transmitted to the server. Based on this evaluation result, an inter-code transform unit conducts image processing by selectively discarding codes from code data of an image that are to be transmitted to the client.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features for retrieval and similarity matching of documents from the JPEG 2000-compressed domain
InactiveUS7912291B2Digital data information retrievalImage analysisImaging processingImaging analysis
A method and apparatus for image processing is described. In one embodiment, the method comprises accessing header data from a multi-resolution codestream of compressed data of a first document image, deriving one or more retrieval attributes from the header information, and performing image analysis between the first document image and a second document image based on the one or more retrieval attributes.
Owner:RICOH KK
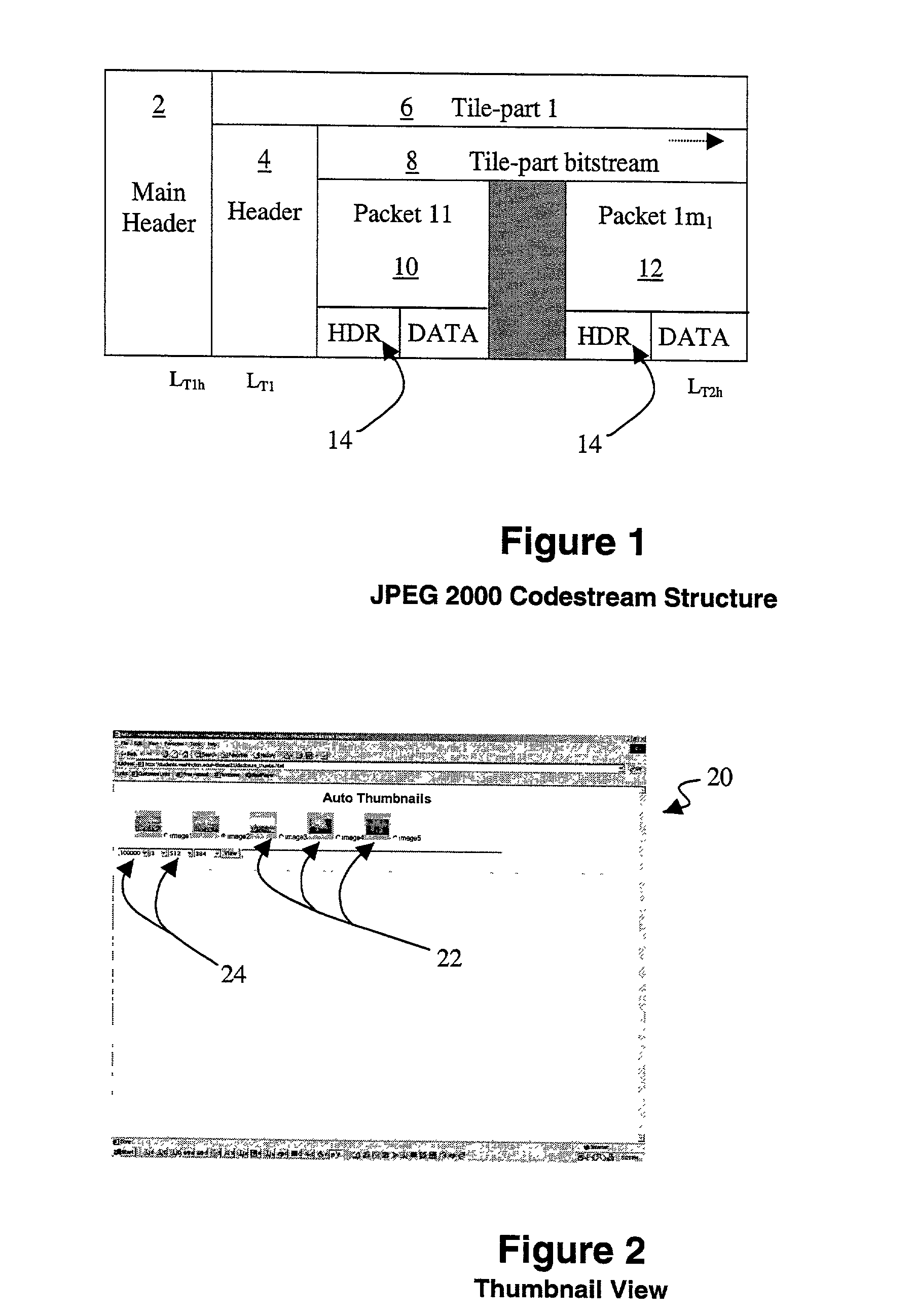
JPP-stream to JPEG 2000 codestream conversion
InactiveUS7460724B2Adjustable lengthImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionNetwork packet
A method and apparatus for converting a JPP-Stream to JPEG 2000 codestream is described. In one embodiment, the method comprises writing a main header data-bin to an output JPEG 2000 codestream with a marker segment specifying use of a progression order with a layer progression last. The method also includes, for each tile, writing a legal tile header; and for each component, position and resolution in said each tile, determining a number of completely received layers, writing one or more bytes of precinct data-bin corresponding to completed layers to the output JPEG 2000 codestream, and writing an empty packet header for each packet of each layer that is not complete. Also for each tile, the method includes updating the SOT marker segment to adjust a length to the number of bytes of packet data. The method further includes writing an EOC marker at the end of the output JPEG 2000 codestream.
Owner:RICOH KK
Data transform for improved compression of multicomponent images
ActiveUS20050276486A1Simplifies implementation issueReduce redundancyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningColor imageComputer architecture
Owner:ACCUSOFT CORP
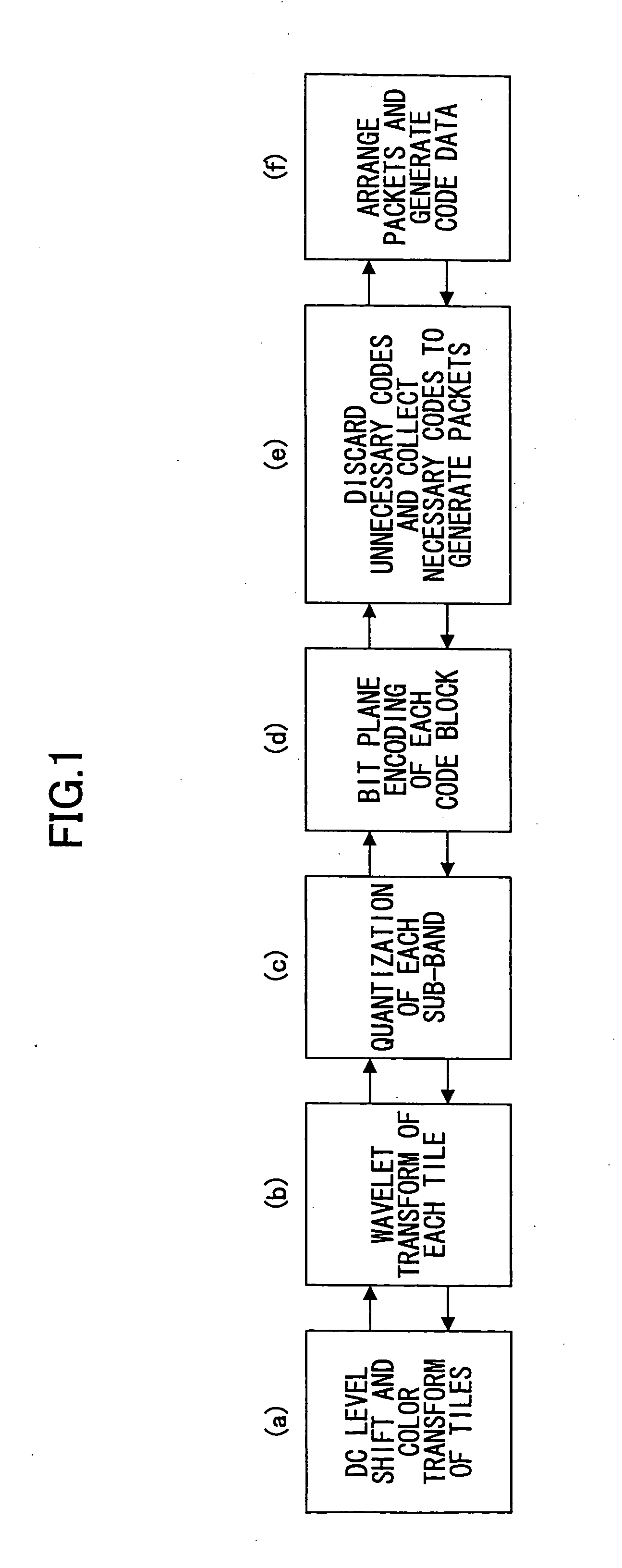
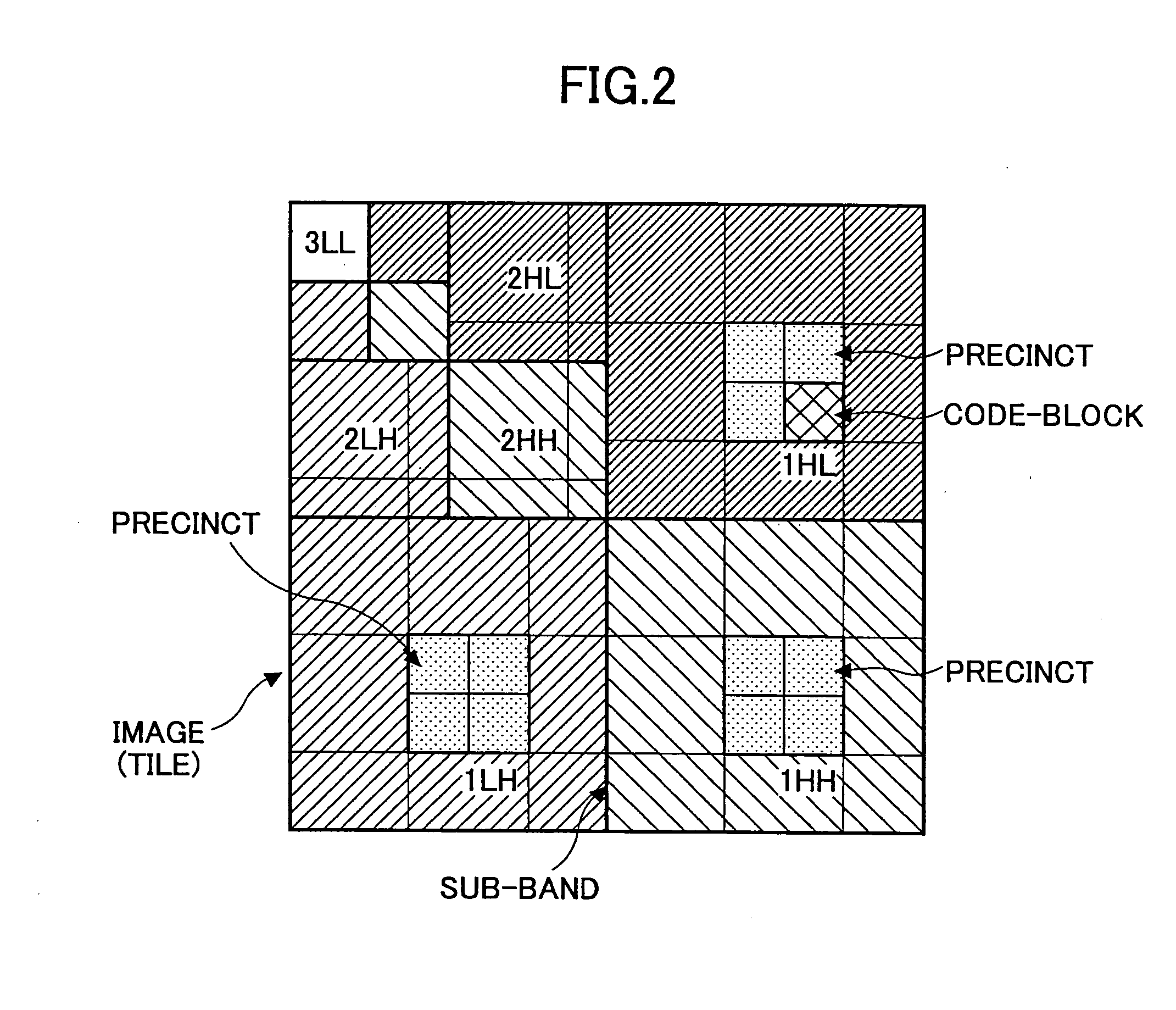
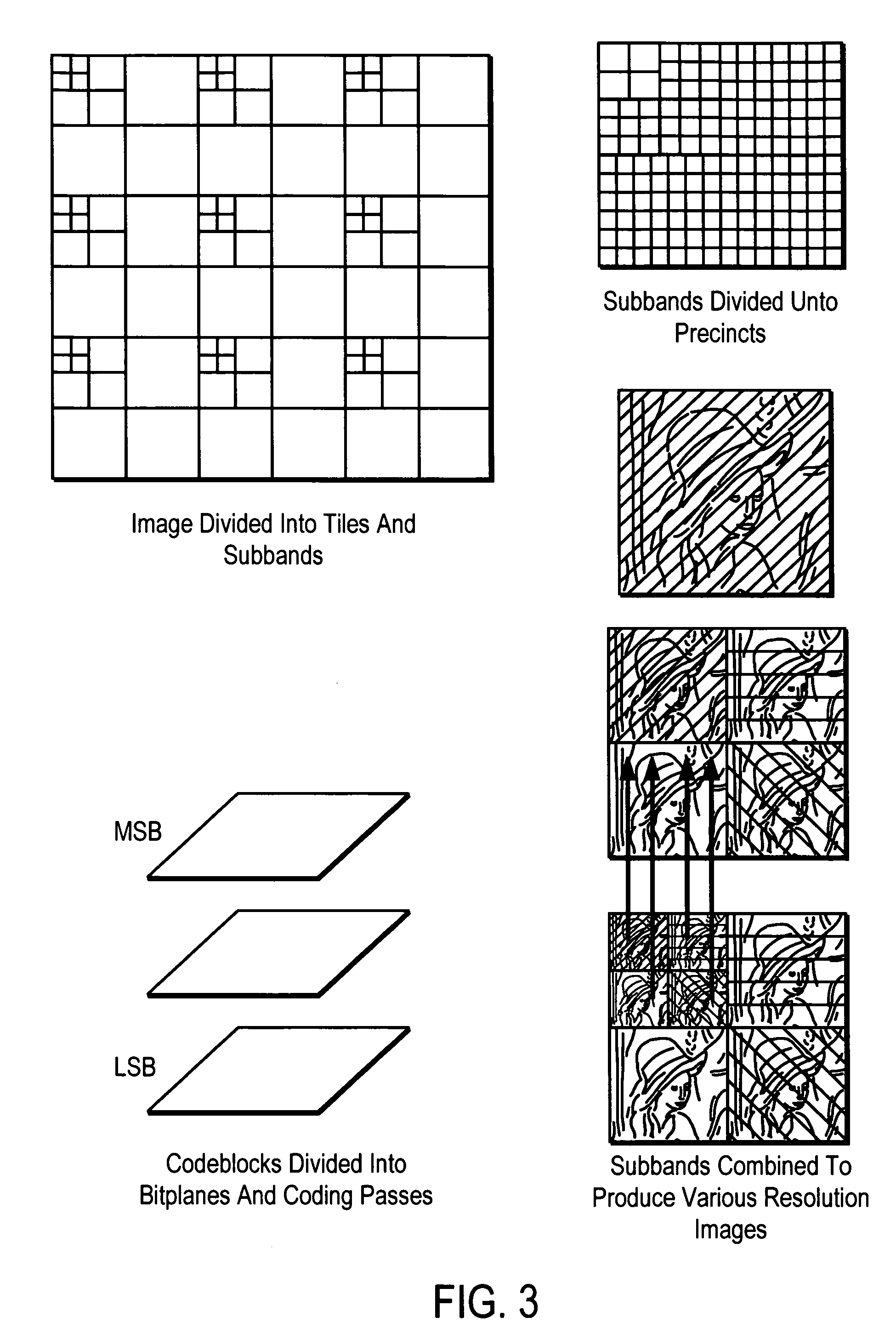
Pre-compression rate-distortion optimization method for JPEG 2000
ActiveUS20060008162A1Minimize processing timeMinimize system resourceCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationCoding blockRate distortion
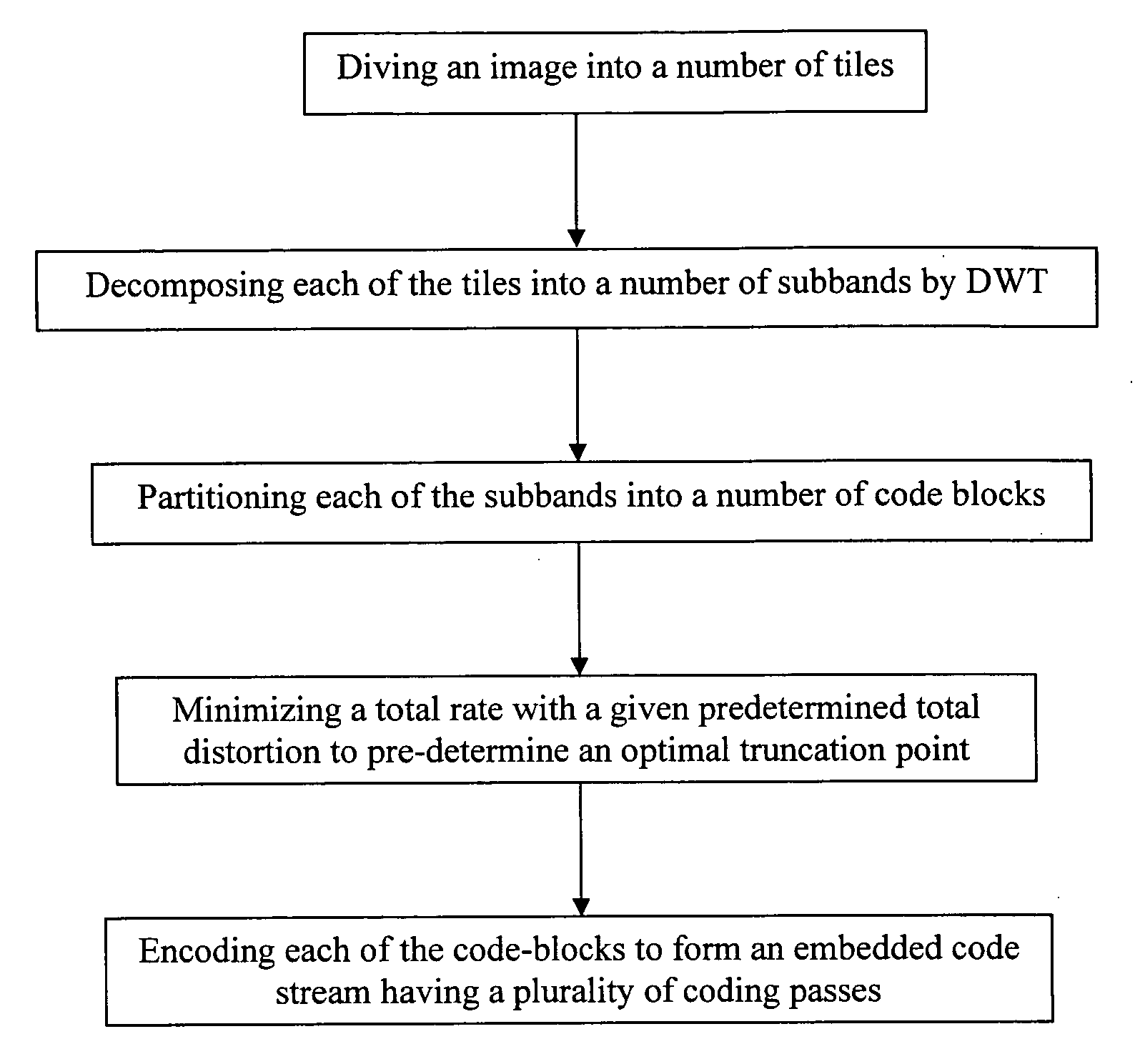
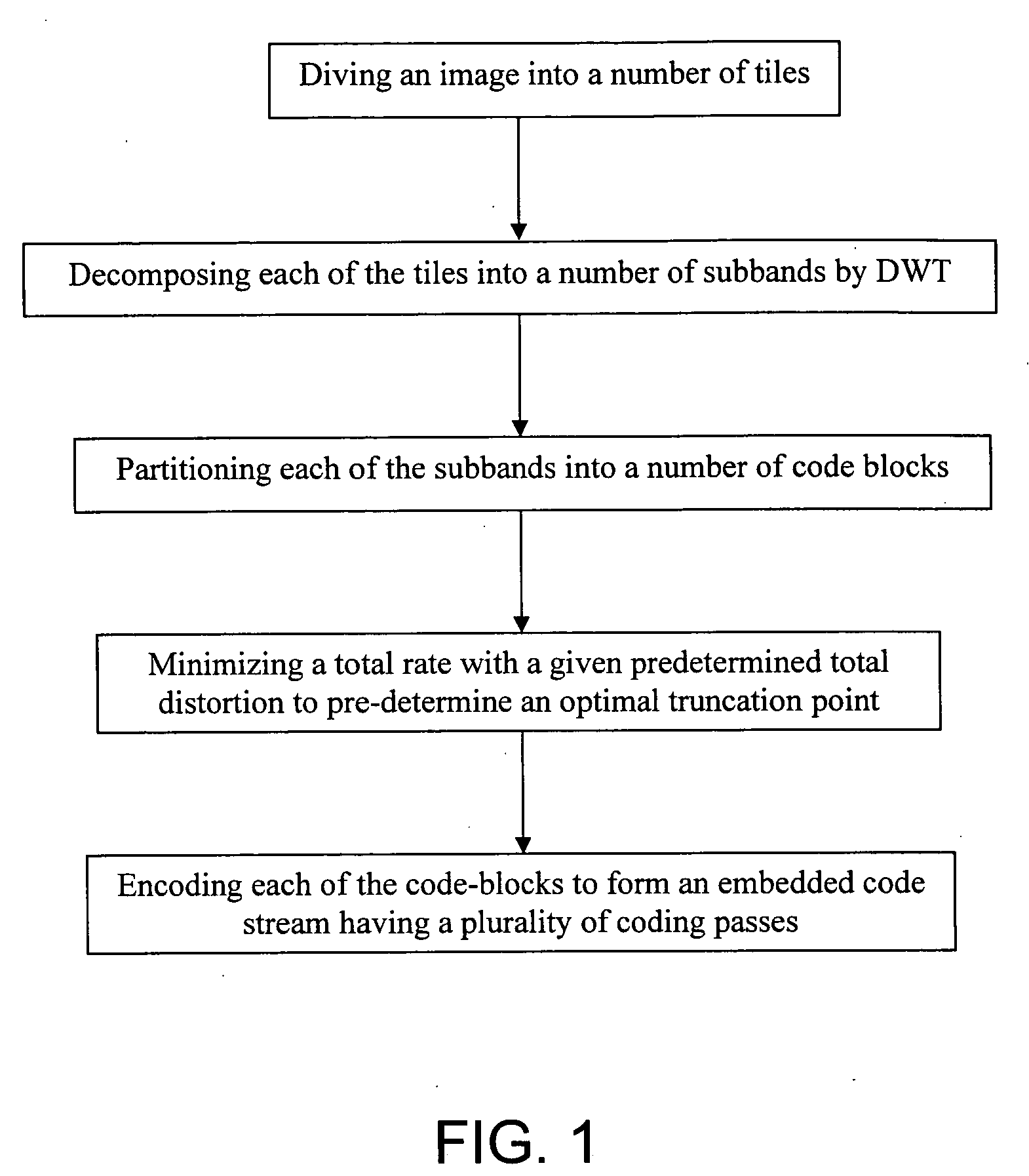
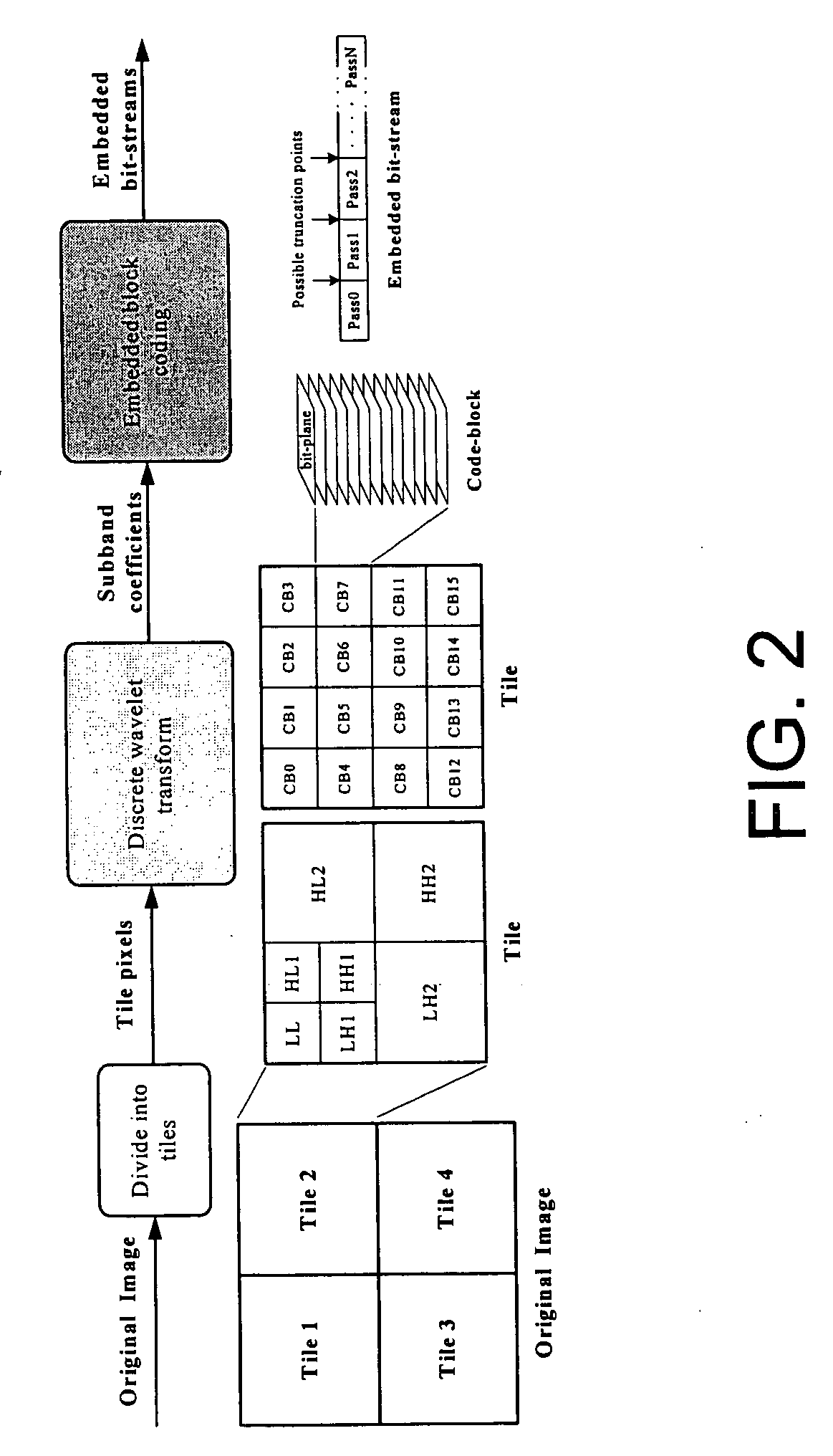
A method of optimizing a compression of a still image in JPEG 2000 format, which includes the steps of: (a) dividing an image into a predetermined numbers of tiles each having a predetermined numbers of tile pixels; (b) decomposing each of the tiles into a predetermined number of subbands by Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) partitioning each of the subbands into a predetermined number of code-blocks which are arranged into a plurality of bit-planes respectively; (d) minimizing a total rate with a given predetermined total distortion of image so as to pre-determine an optimal truncation point for each of the code-blocks; (e) truncating a predetermined part of the DWT coefficients for each of the code-blocks so as to reduce computational resource; and (f) encoding each of the code-blocks by embedded block-coding to form an embedded code-stream having a plurality of code passes.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
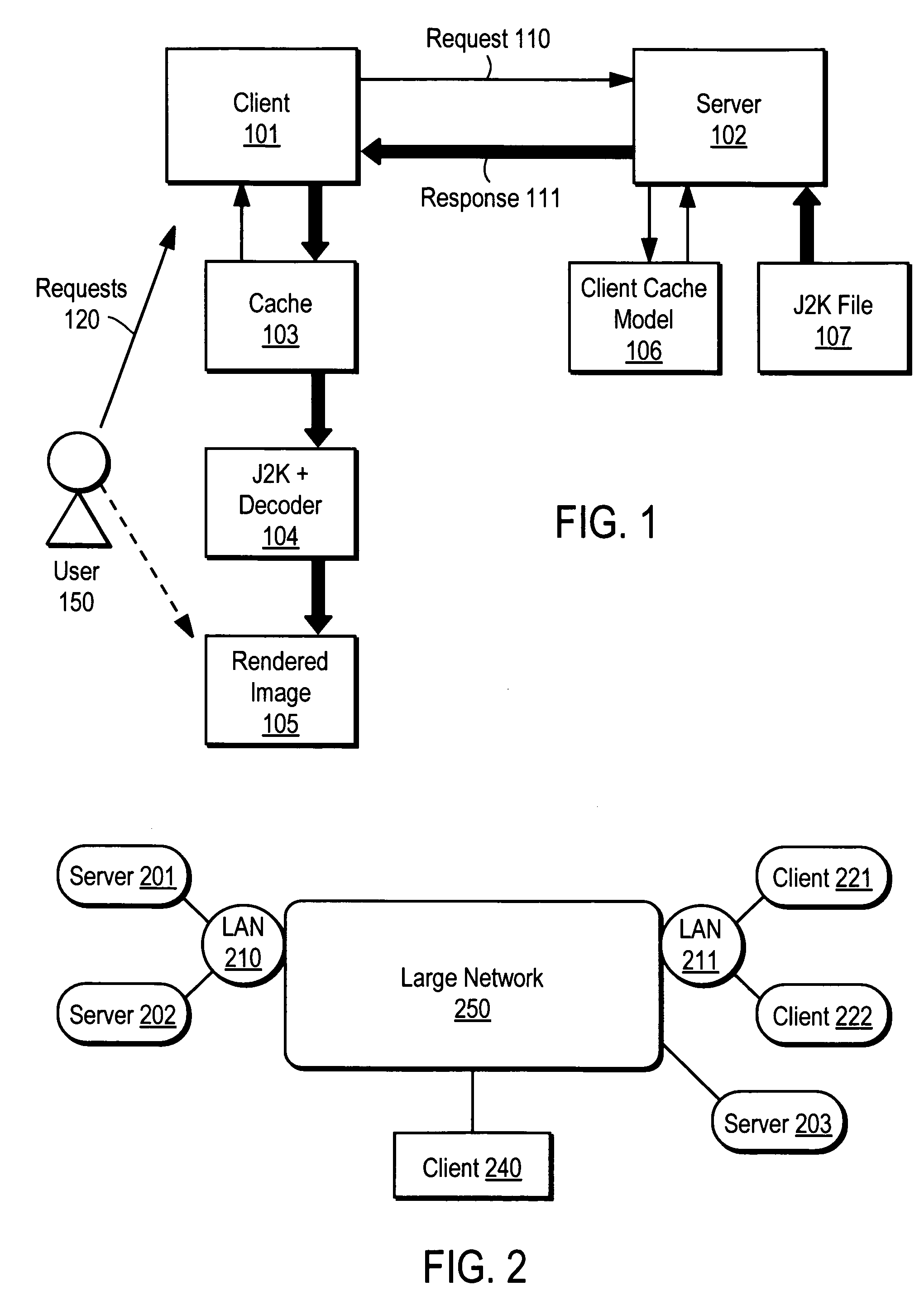
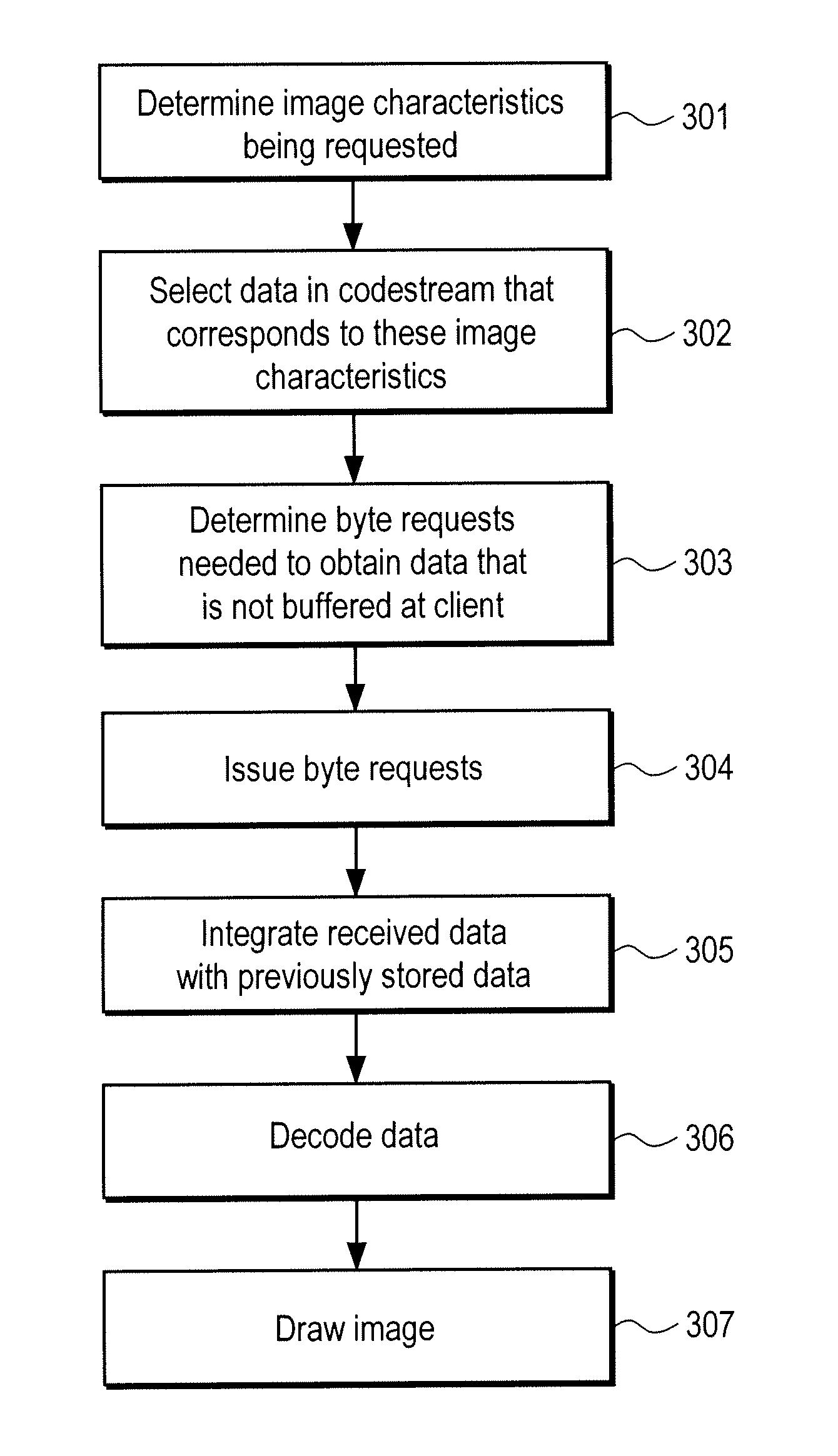
JPEG 2000 for efficent imaging in a client/server environment
InactiveUS7581027B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTelevision systemsClient-sideApplication software
In one embodiment, the system comprises a server and a client. The server stores a compressed codestream corresponding to image data. The client is coupled to the server via a network environment. The client includes a memory having an application and a data structure stored therein. The data structure identifies positions of packets of the compressed codestream on the server and identifies data of the compressed codestream already buffered at the client. The client requests bytes of the compressed codestream from the server that are not already stored in the memory and generates decoded image data requested by a user from the bytes of the compressed codestream requested from the server and any portion of the compressed codestream previously stored in the memory necessary to create the image data.
Owner:RICOH KK
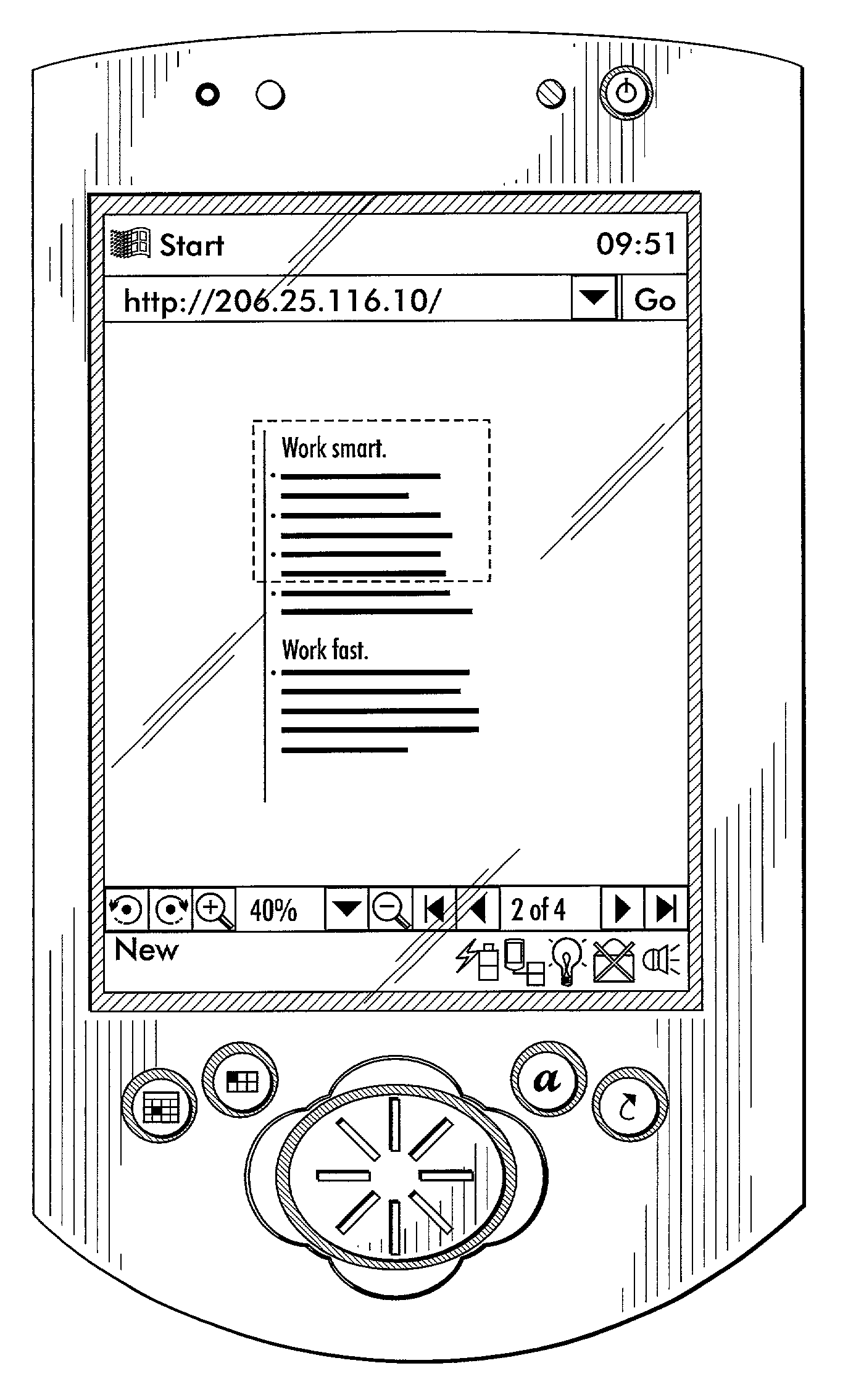
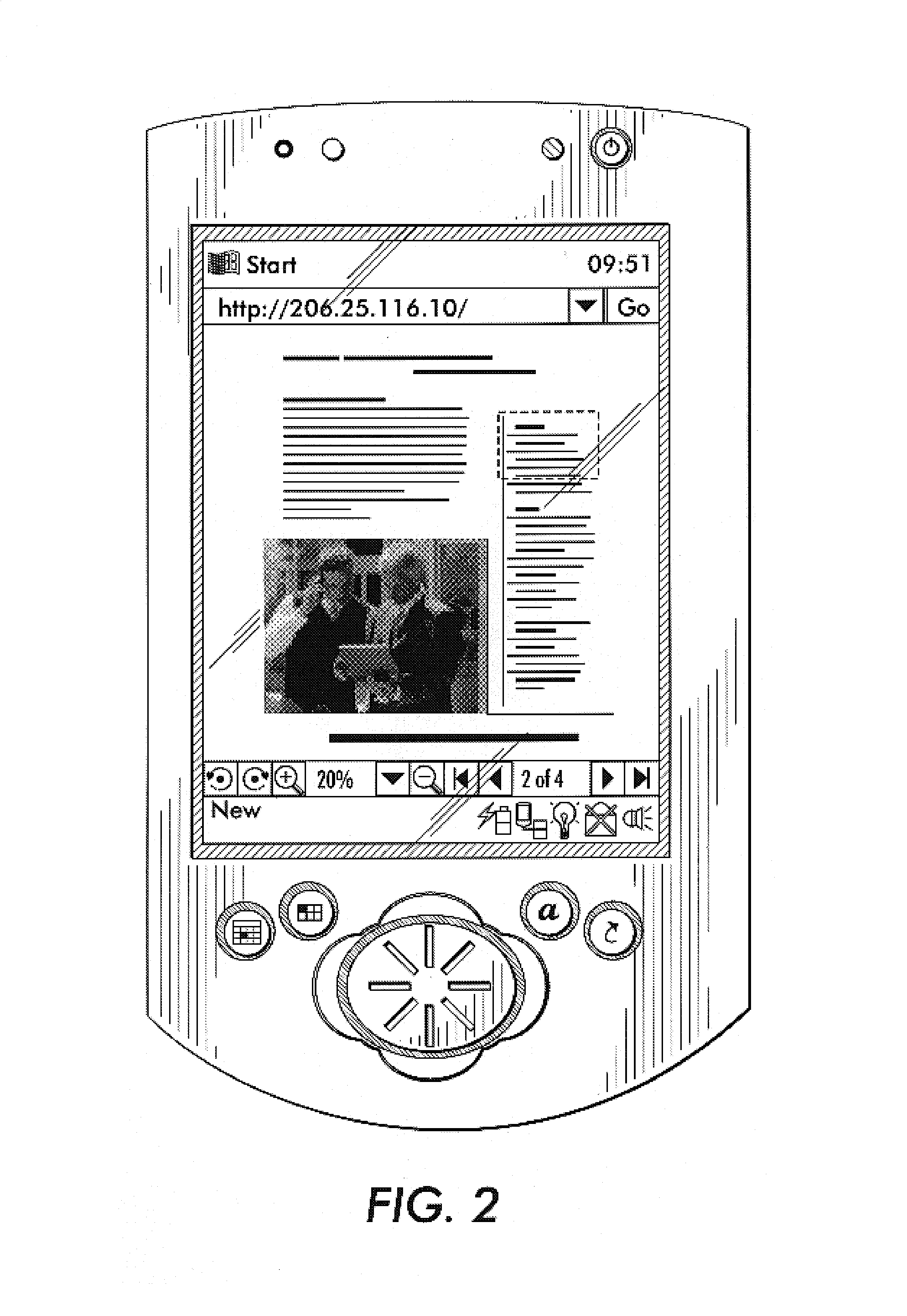
Method for document viewing
ActiveUS7284069B2Improved end-to-end system responsivenessLow latency)Data processing applicationsStatic indicating devicesMegabyteDocument preparation
What is disclosed is a method by which a client-side handheld device requests a server to convert server-side documents into a compression format prior to transmission of said documents to the client. The server retrieves and converts the requested documents to a raster image that is then compressed according to attributes based on information received from the client device in the initial document request. Instead of having to manipulate multiple formats which the original documents are in and supported by the server, the client-side device is preferably optimized in hardware and / or software to support and otherwise take advantage of the requested compression format. The compressed document is then delivered to the client device, in whole or in part, selectively or progressively over time per individual requests prior to displaying the received data to the end-user. Depending on the requested delivery mode, server-side documents are preferably compressed using wavelet compression methods, such as the JPEG 2000 standard, known in the arts. Through such a compression format, documents of sizes (in total bytes) exceeding one or more Megabytes can be compressed down to as small as 30 kilobytes or less.
Owner:MAJANDRO LLC
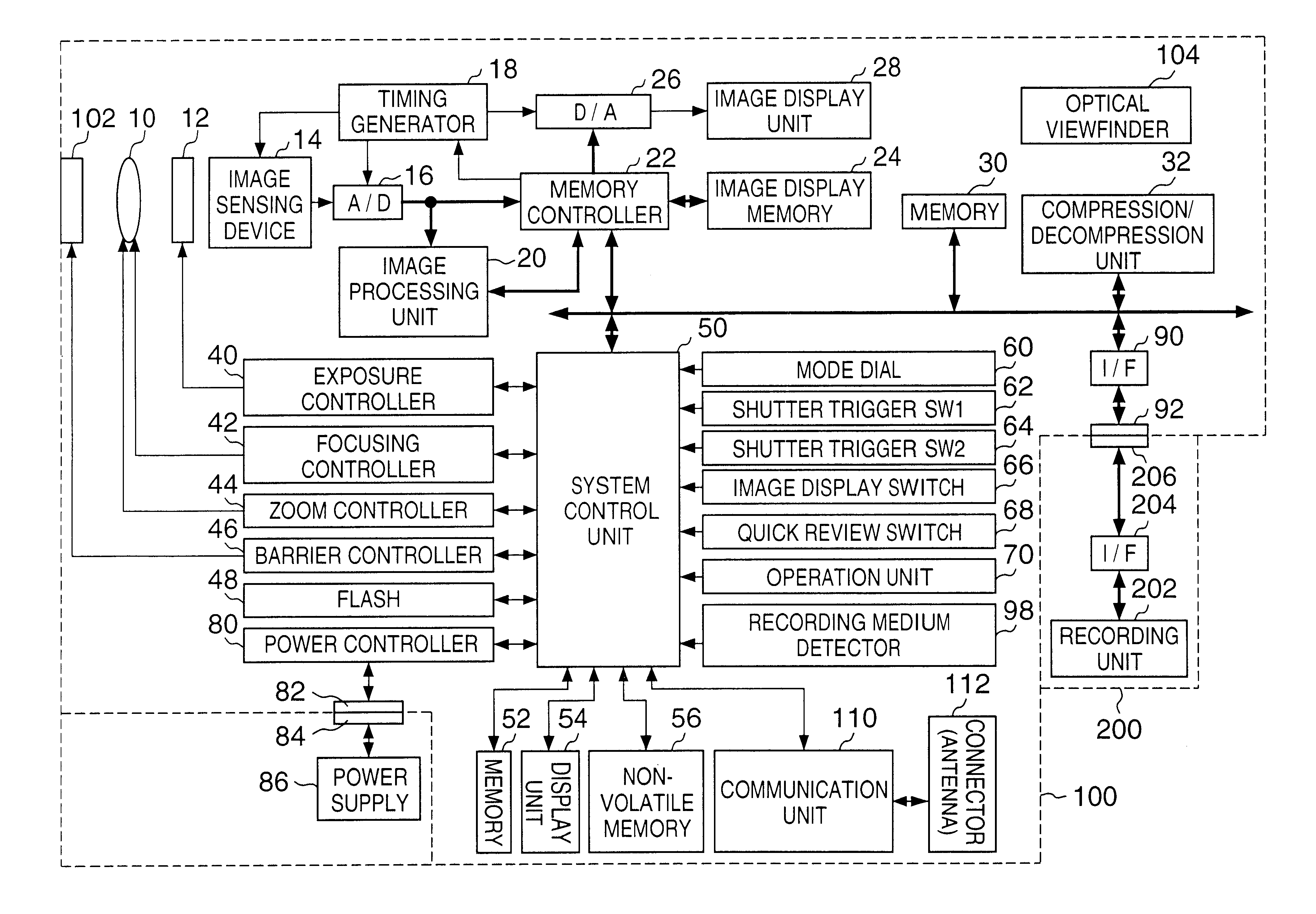
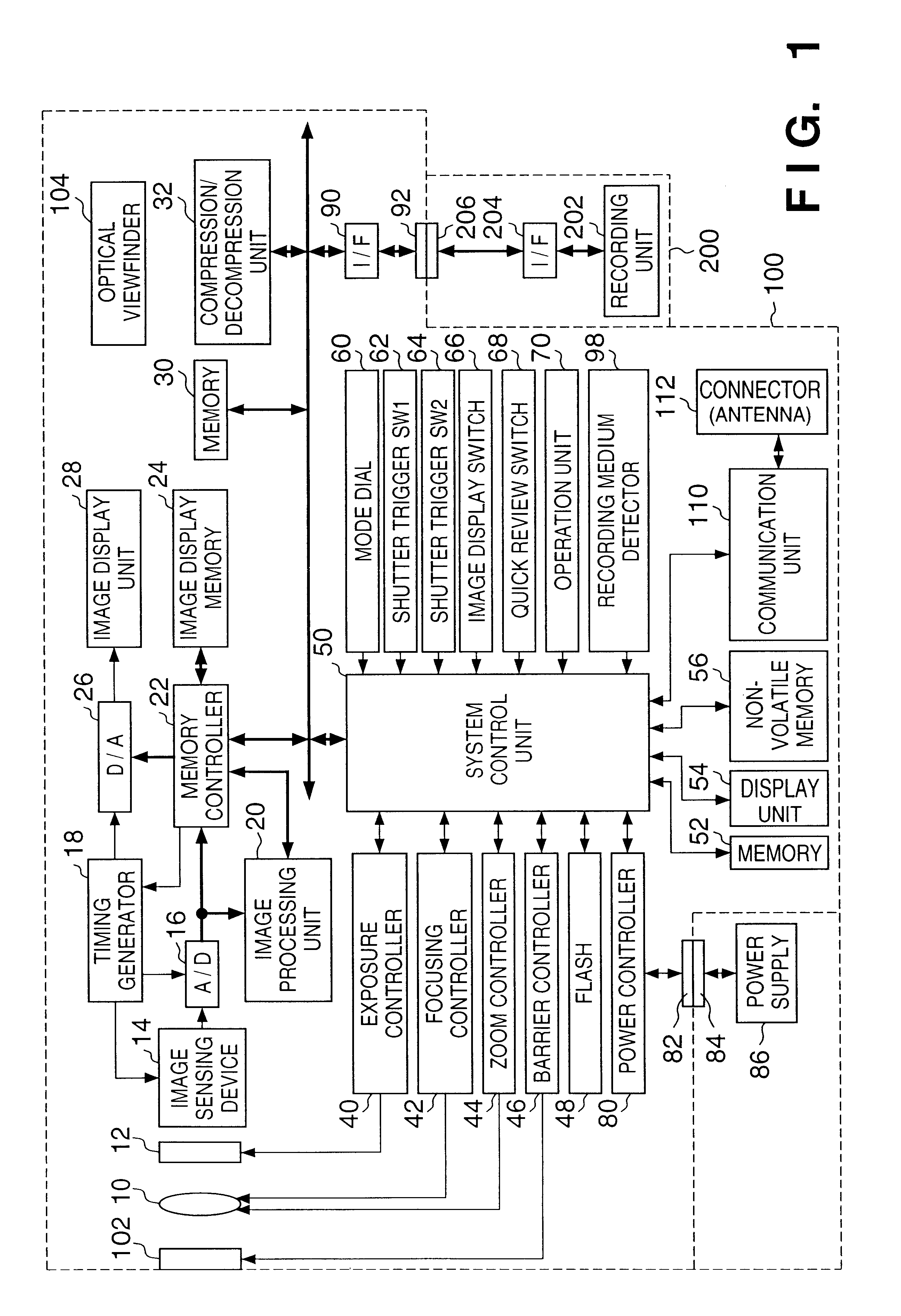
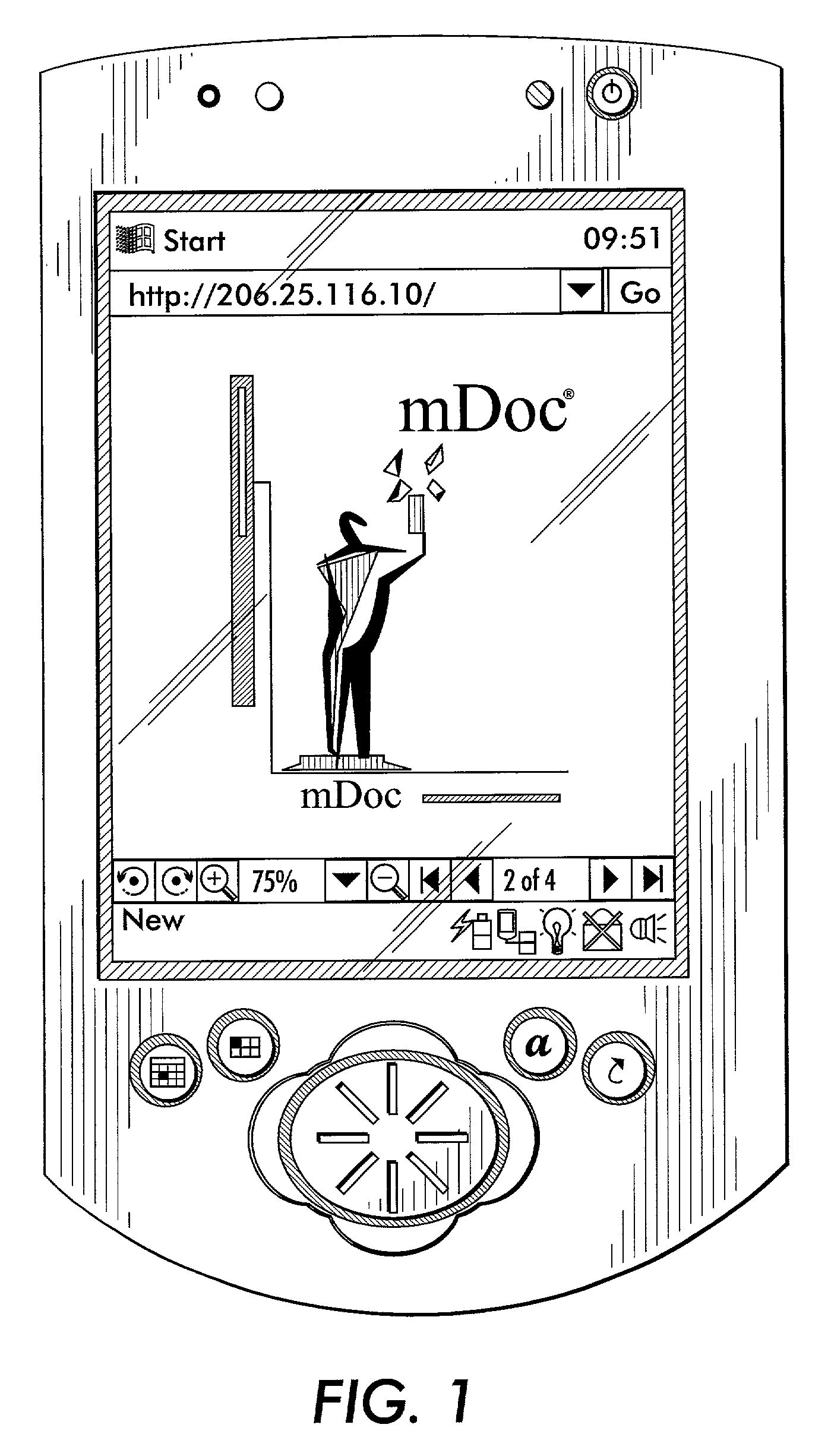
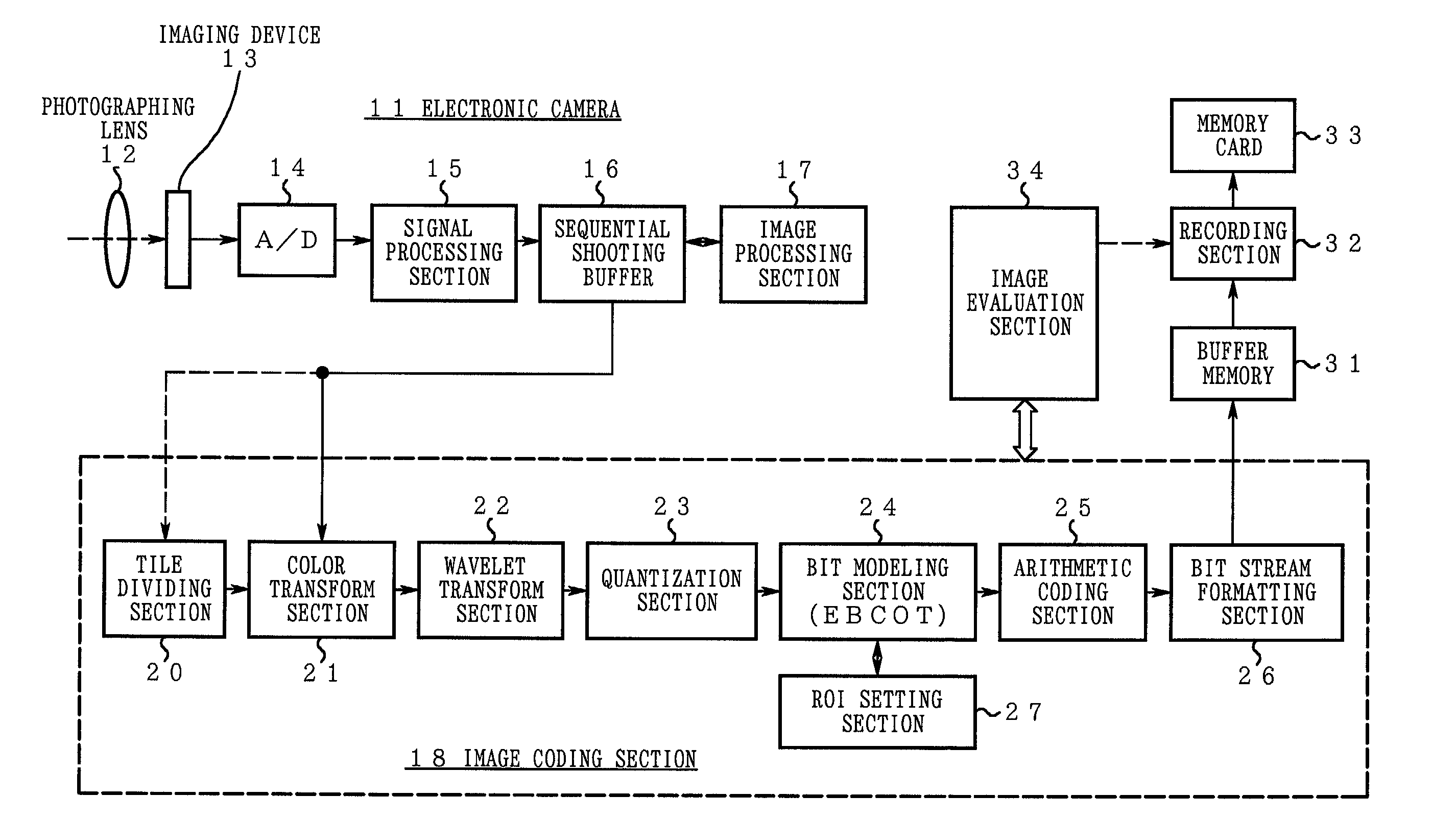
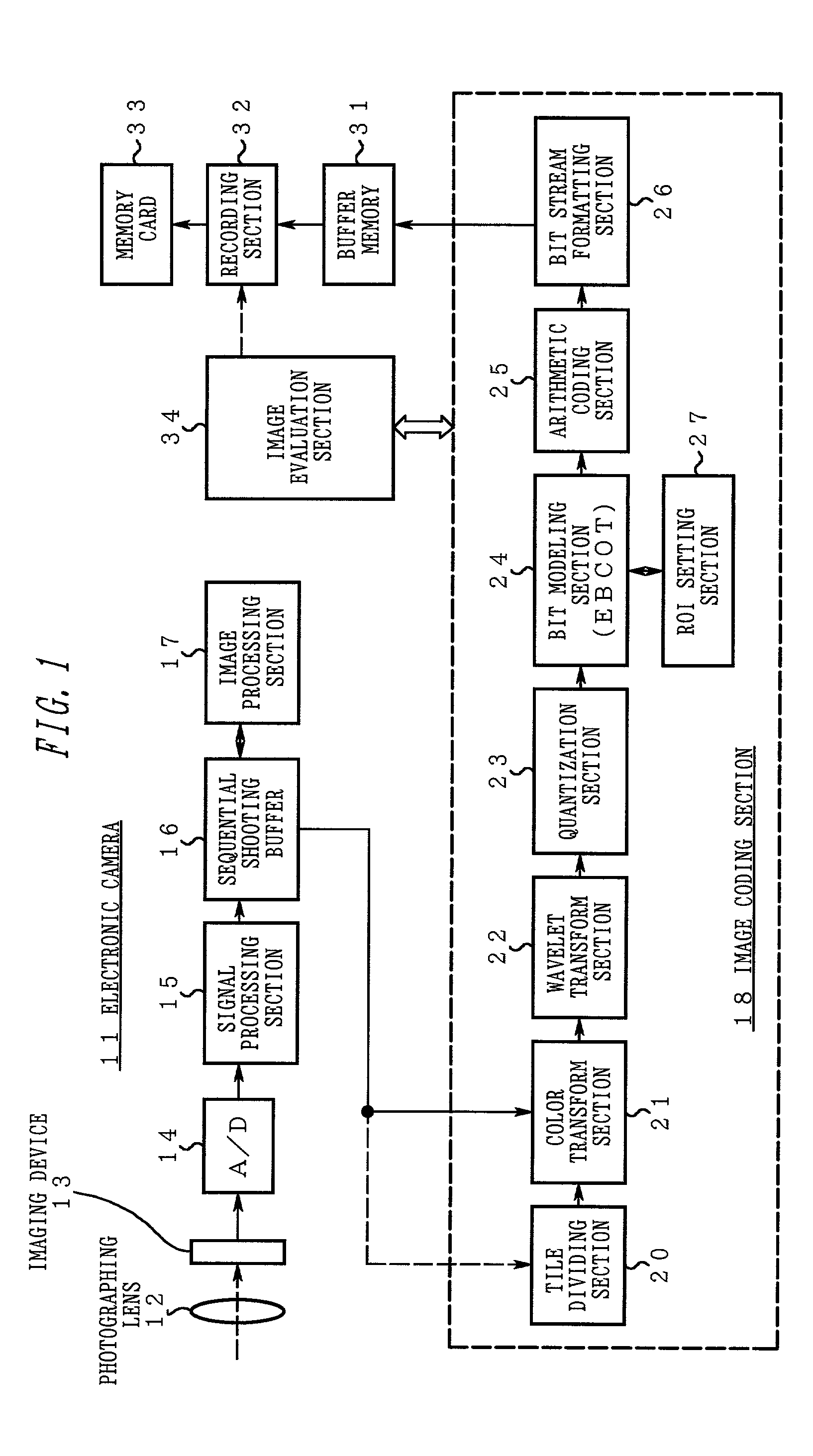
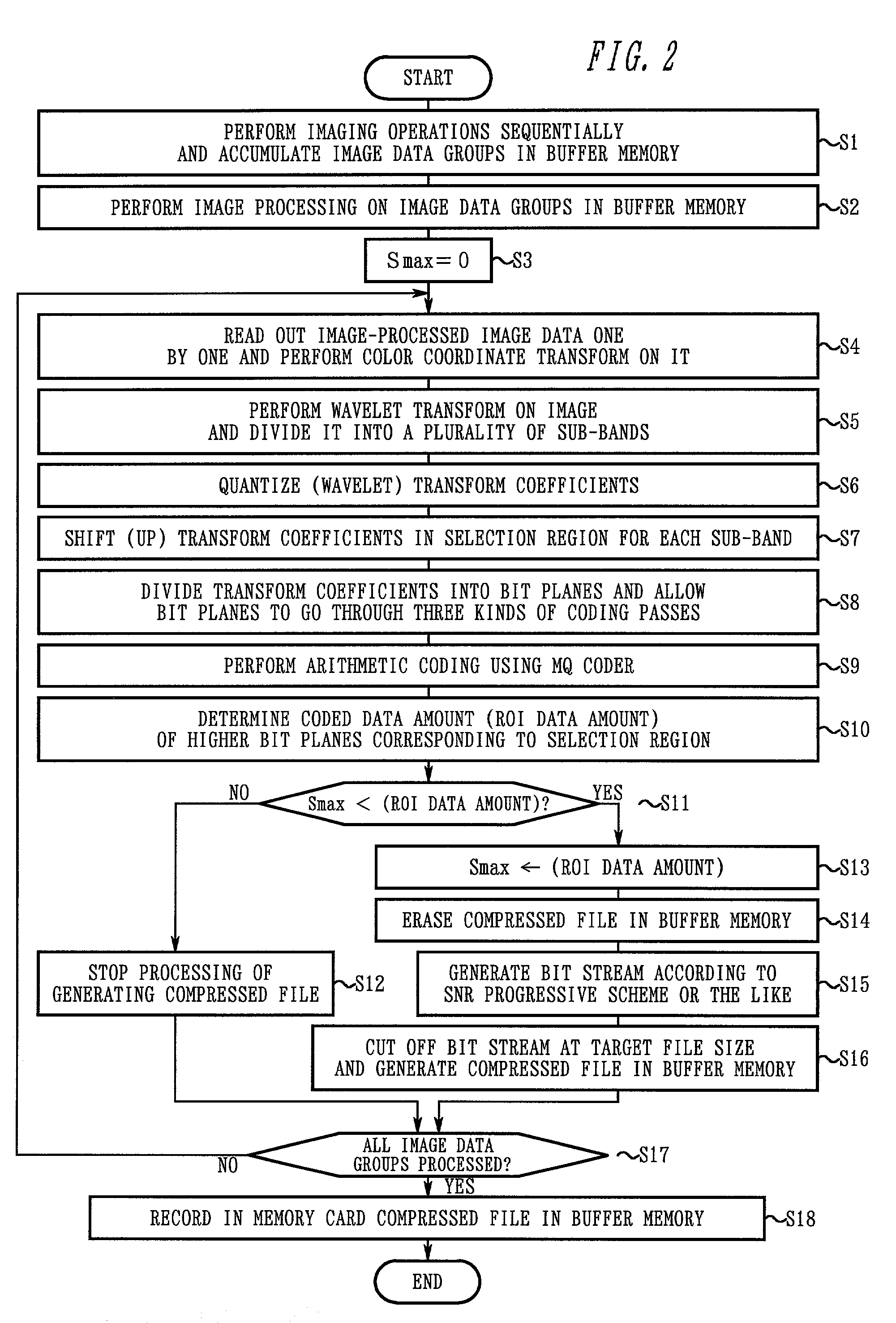
Electronic camera and image processing program
ActiveUS7039250B2Prevents unnecessary compression processingImprove processing speedTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingQuality assessment
The invention provides a technique for compression processing according to JPEG 2000 or the like in an electronic camera that evaluates the quality of each of image data groups taken sequentially by an imaging section and records high-rank image data selectively, and in a related image processing program. The quality of an image is evaluated based on: an amount of data in a selection region of ROI coding; an amount of data to a predetermined position of a bit stream; a cutoff position of a bit stream; a signal level of a high-frequency-range sub-band component; or an amount of data of a predetermined tile. This quality evaluation makes it possible to achieve an image selection function that matches the compression processing of JPEG 2000 or the like very well.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Image processor
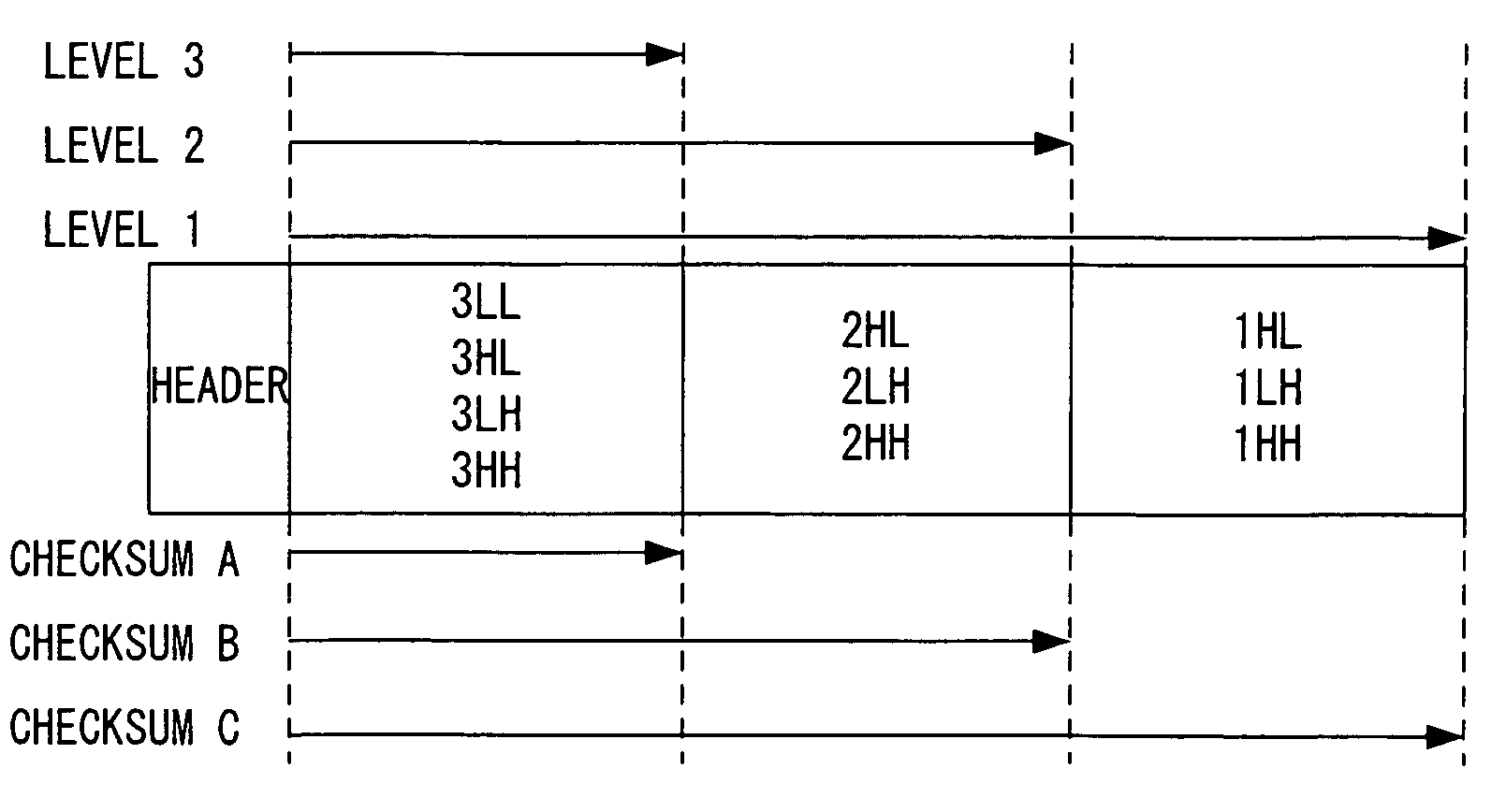
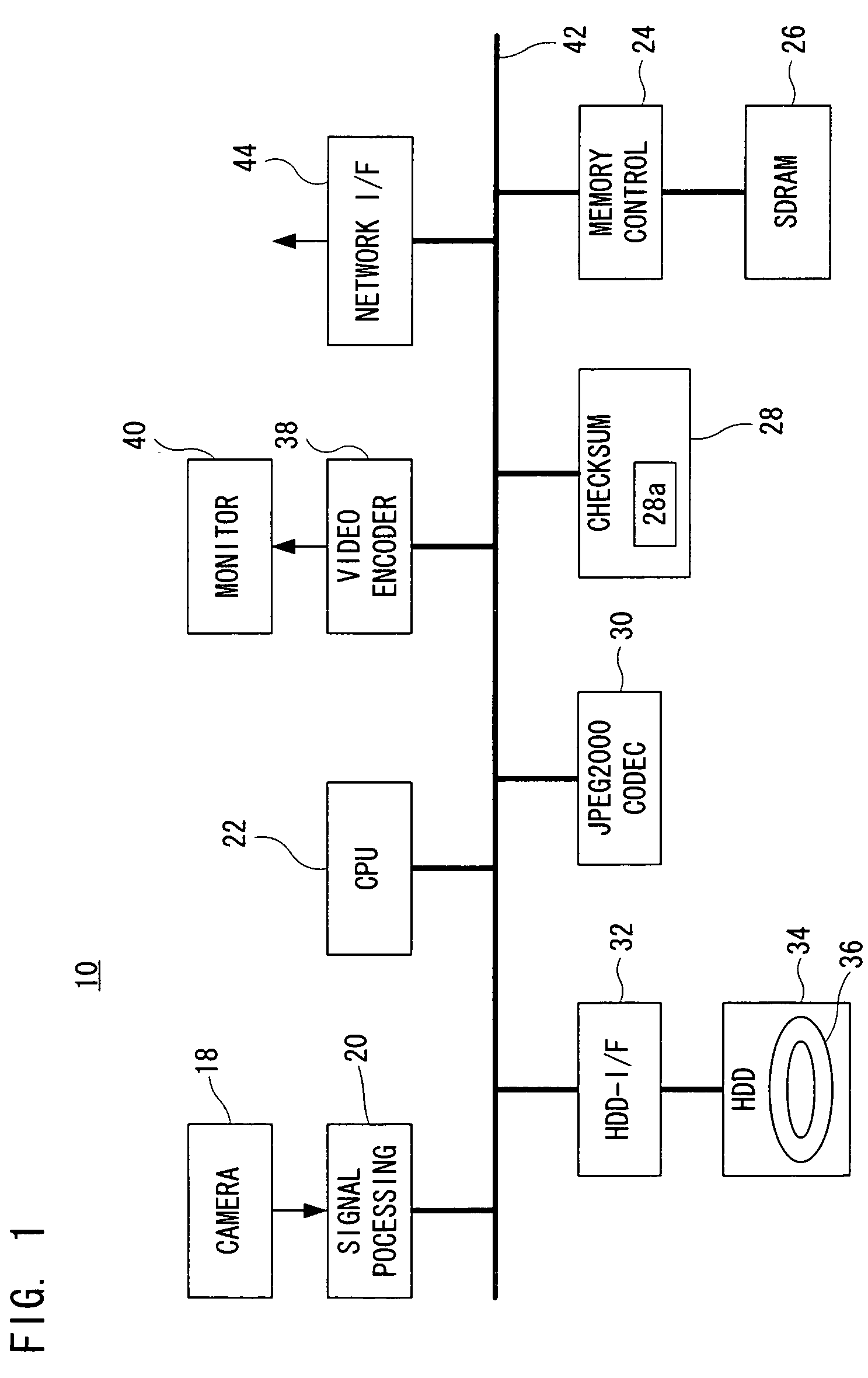
InactiveUS7620257B2Easy to detectCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareChecksum
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com