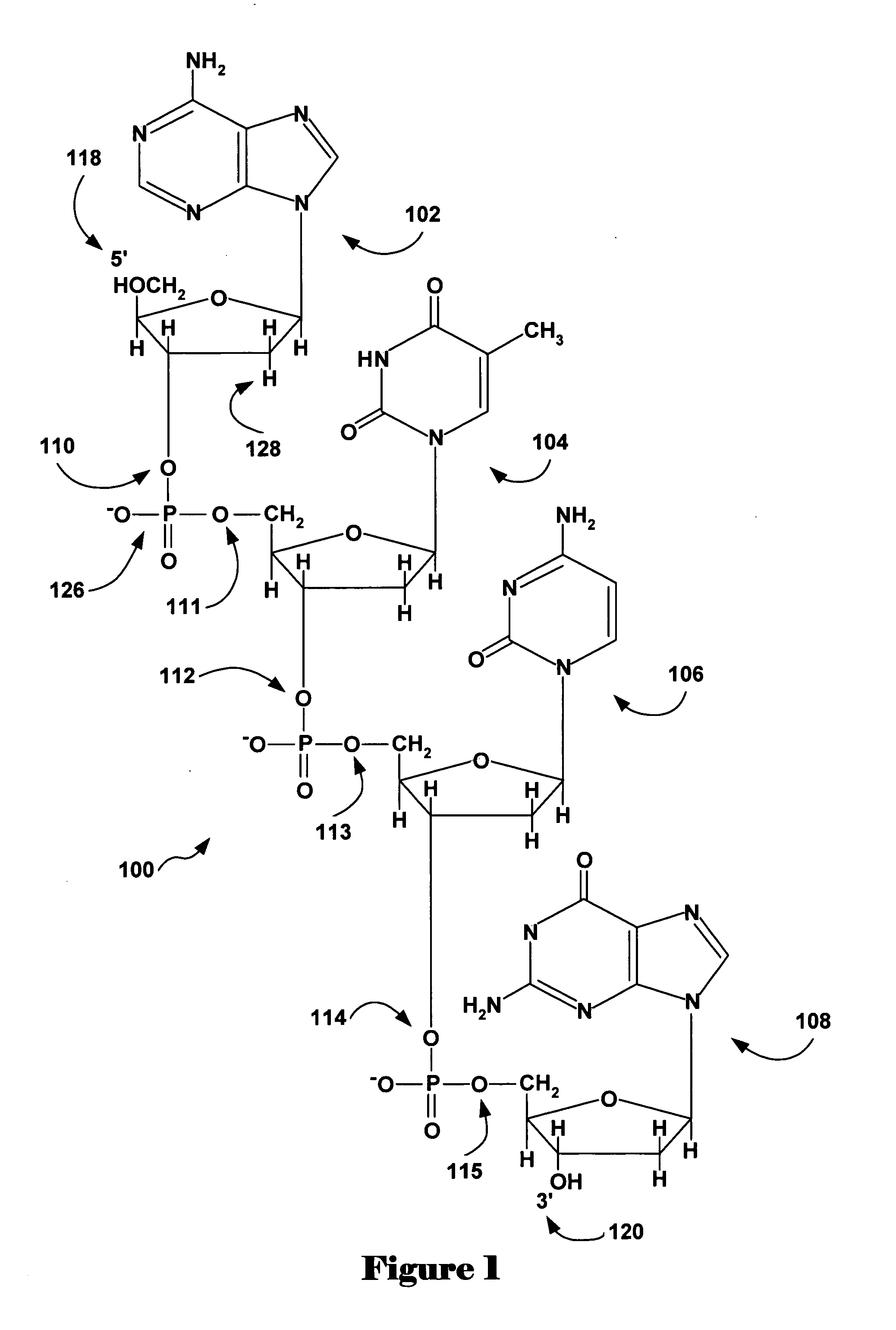
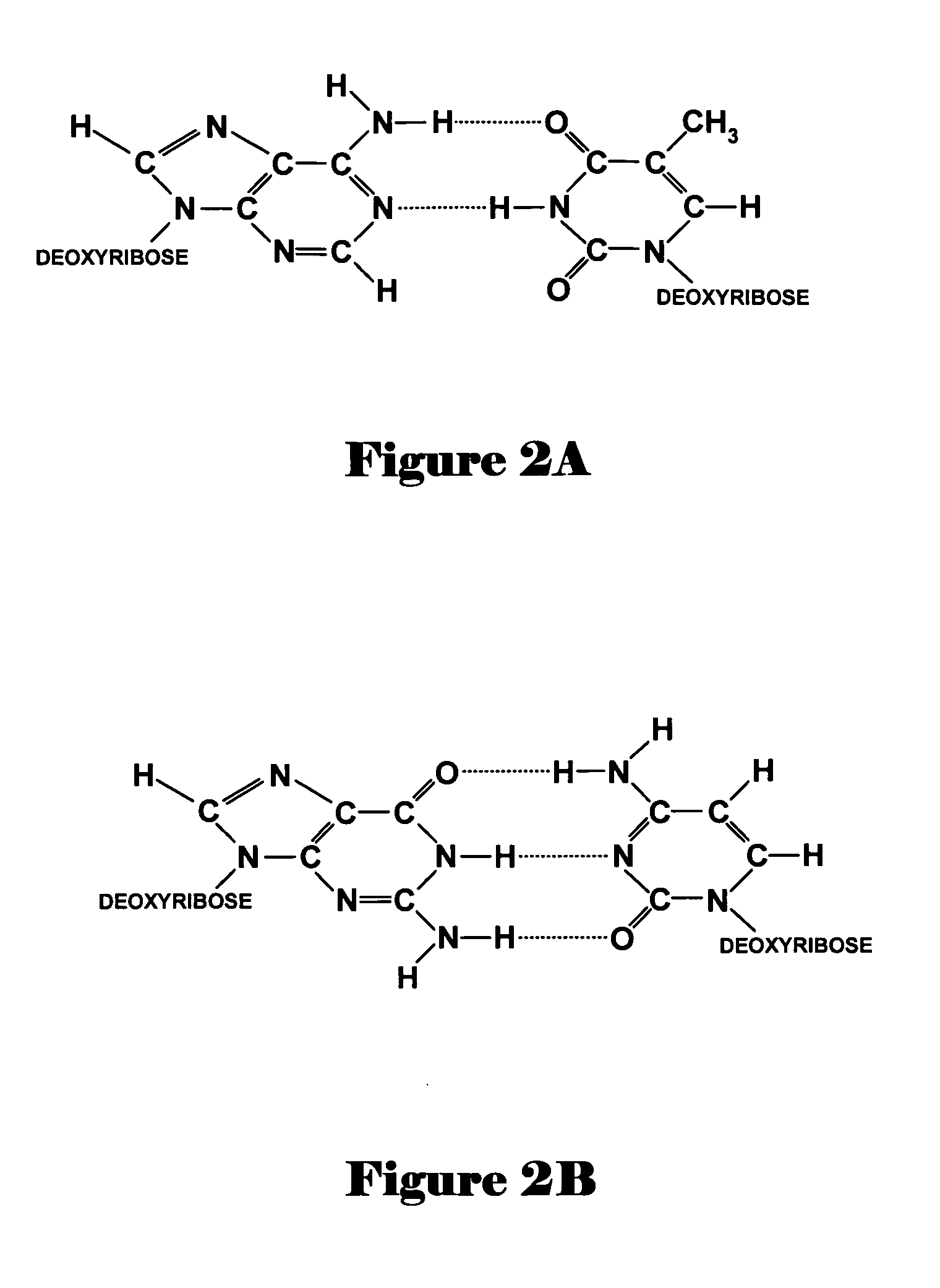
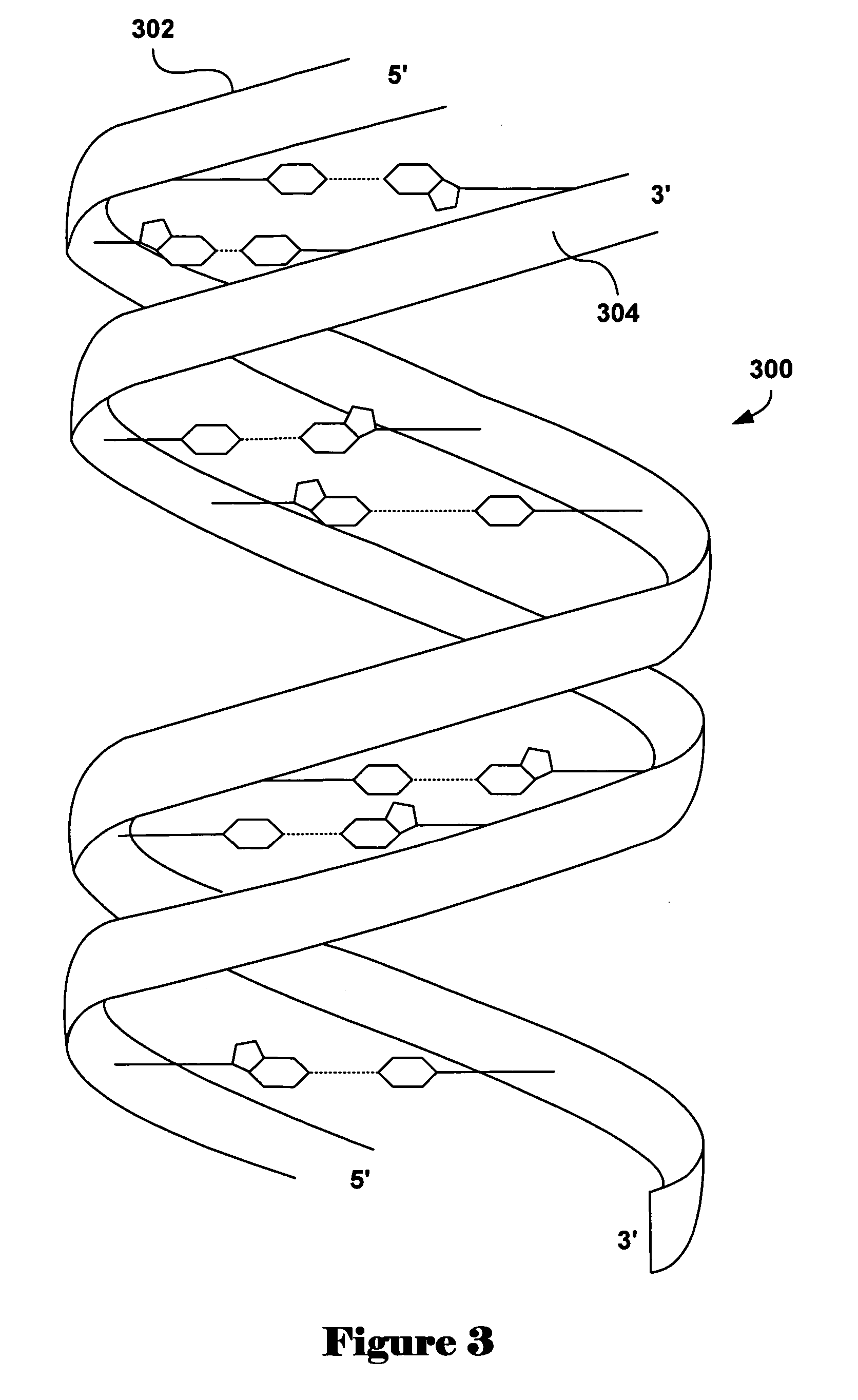
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Microarray image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
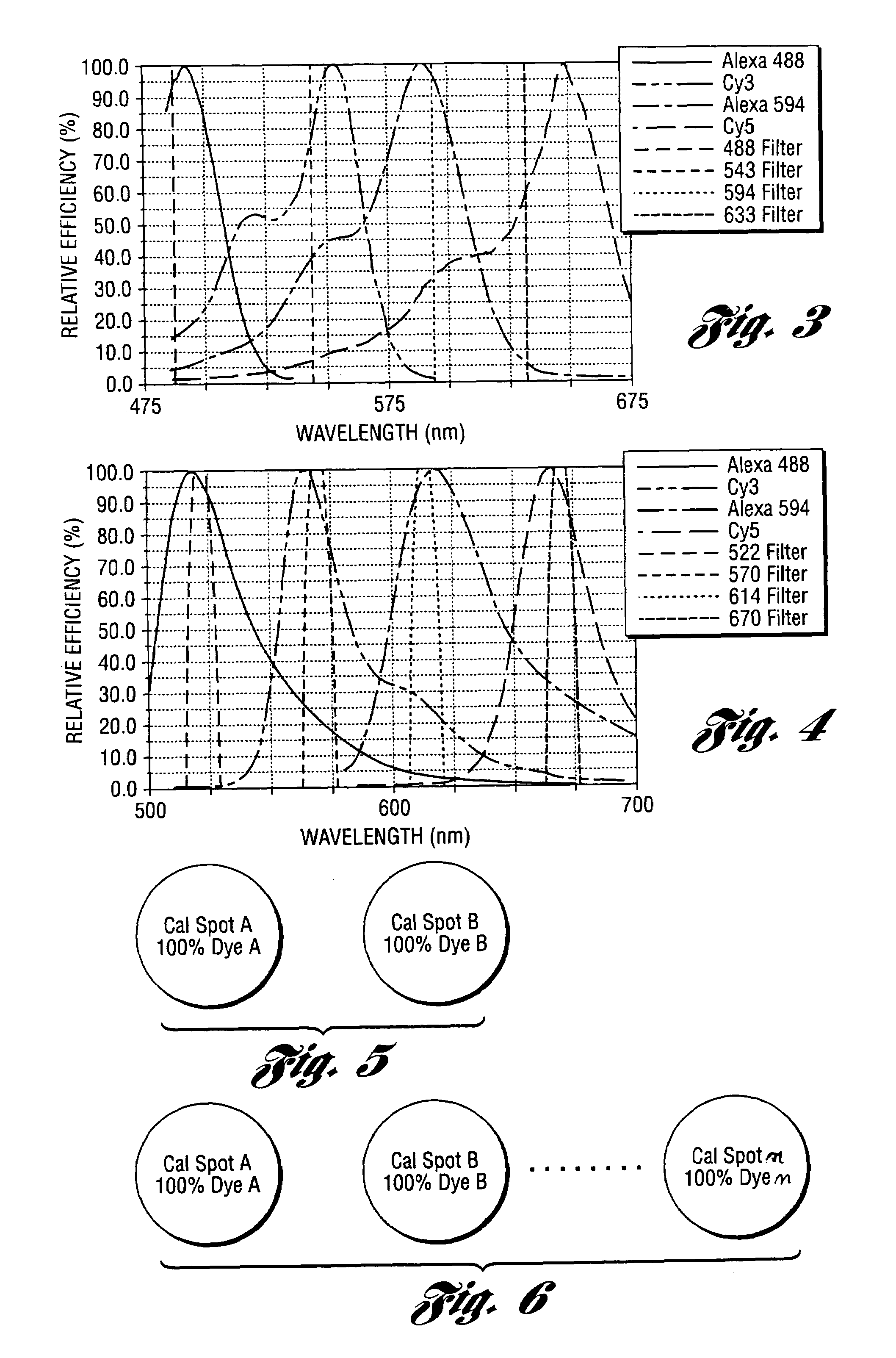
Method and system for automatically creating crosstalk-corrected data of a microarray
InactiveUS7209836B1Microbiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsComputer scienceCrosstalk
A method and system are disclosed for automatically creating crosstalk-corrected data of a microarray utilizing calibration dye spots each of which comprises a single pure dye. A microarray scanner, such as a confocal laser microarray scanner, generates dye images, each of which contains at least one of the calibration dye spots for each of the output channels of the scanner. For each of the calibration dye spots, an output of each of the output channels is measured to obtain output measurements. A set of correction factors is computed from the output measurements to correct the data subsequently gathered from the microarray scanner. In other words, the correction factors are applied to quantitation or measurement data obtained from microarray images which contain spots having dyes of known or unknown excitation or emission spectra to obtain crosstalk-corrected data.
Owner:PACKARD BIOSCI +1
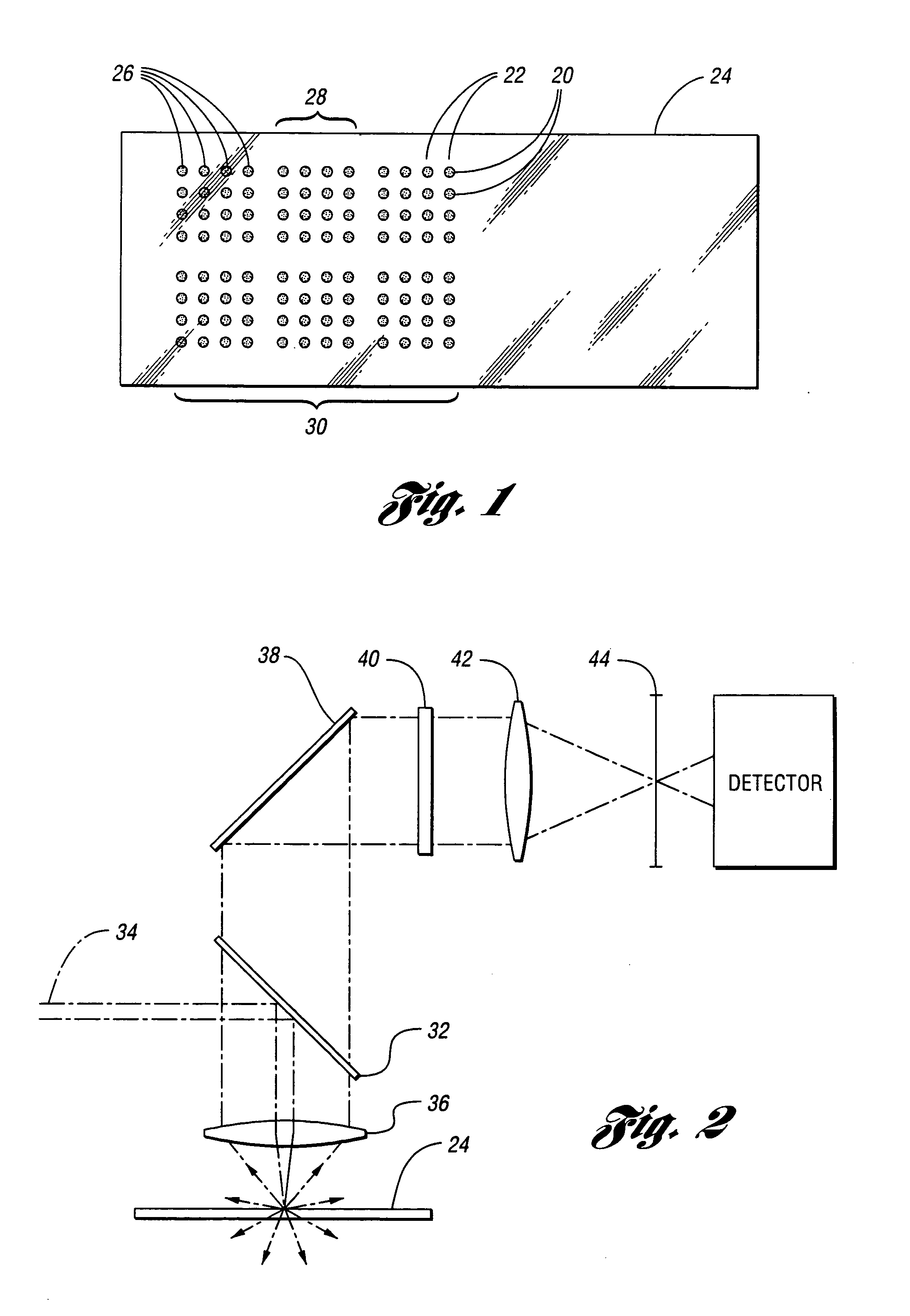
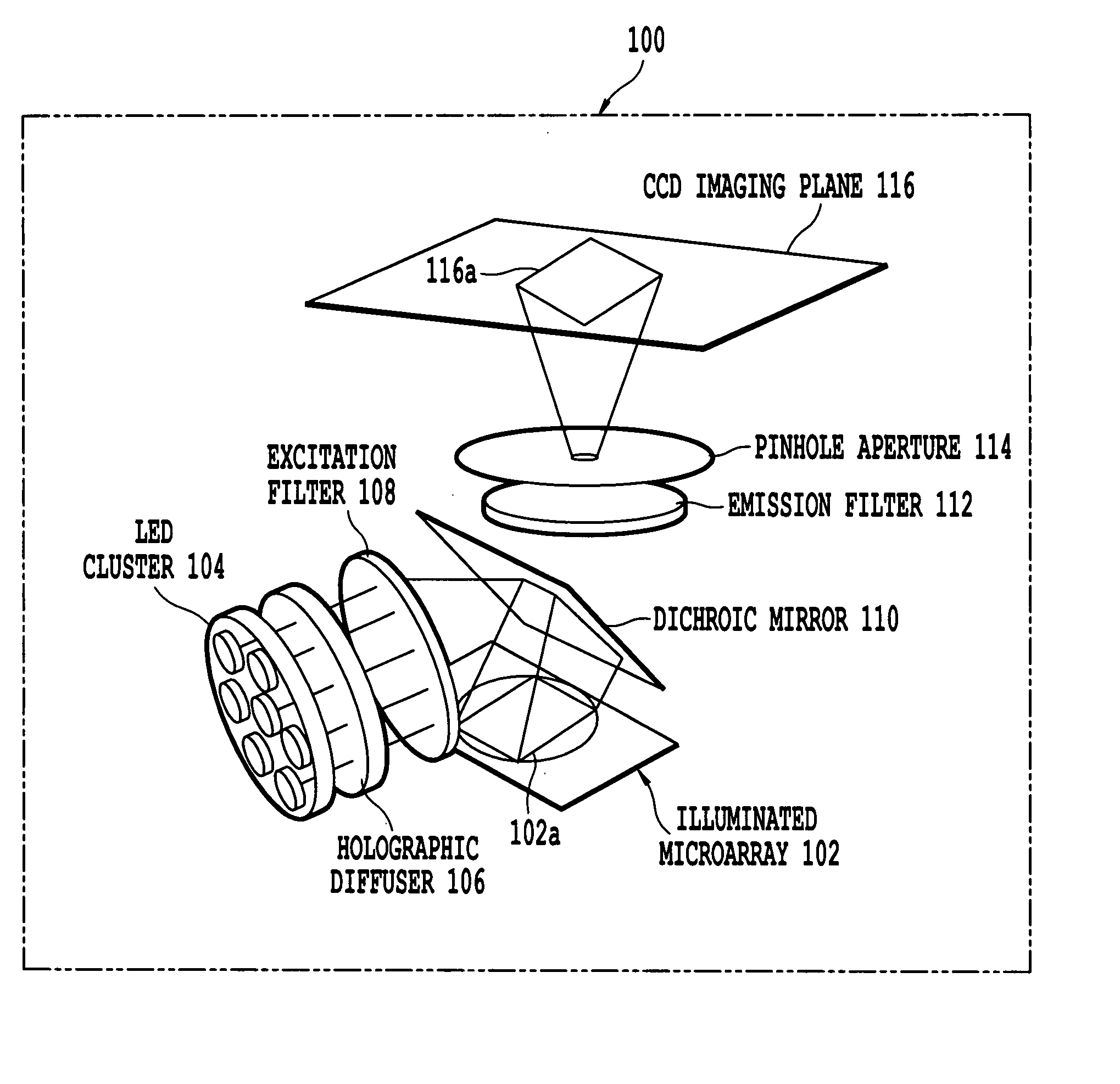
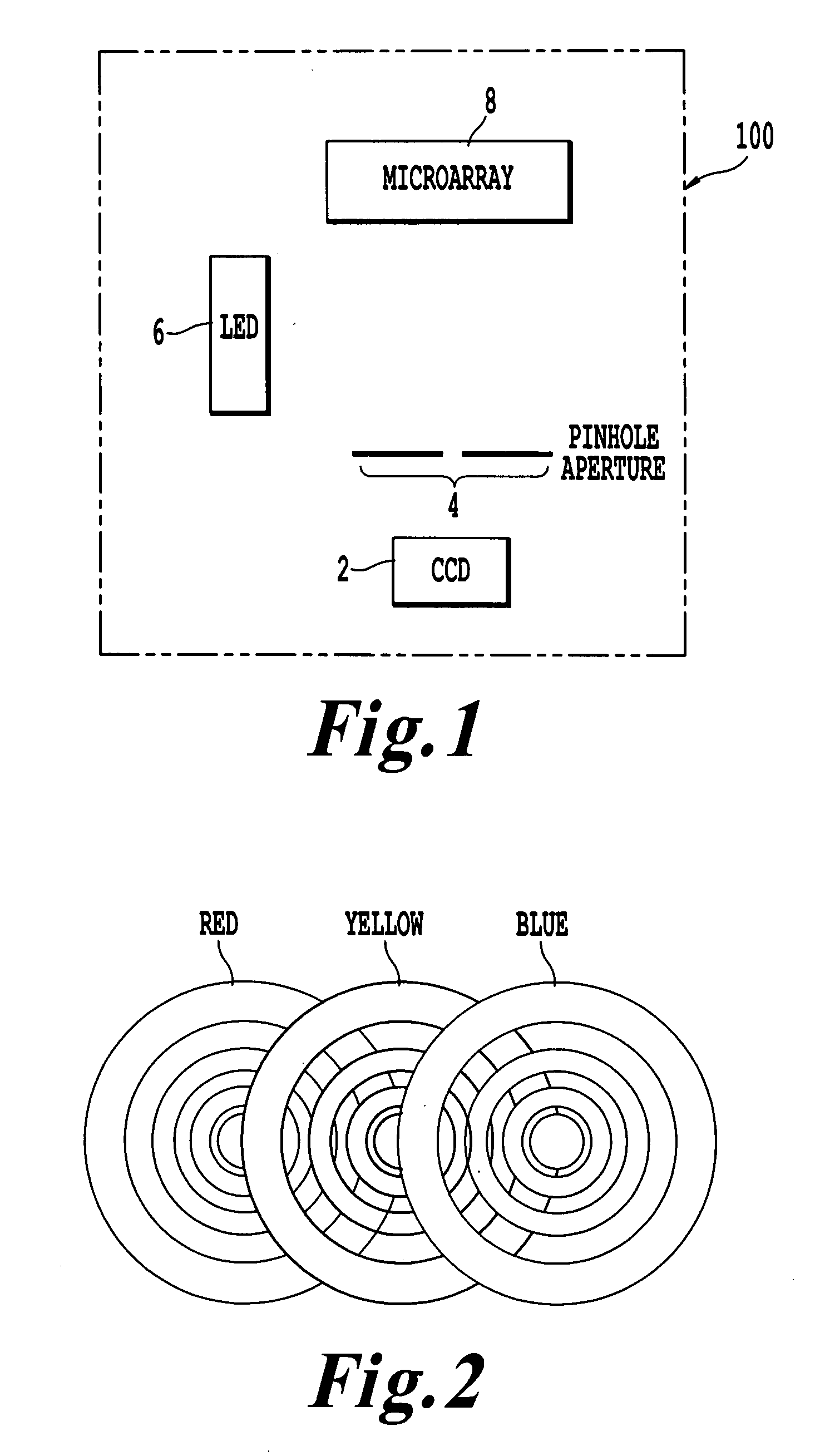
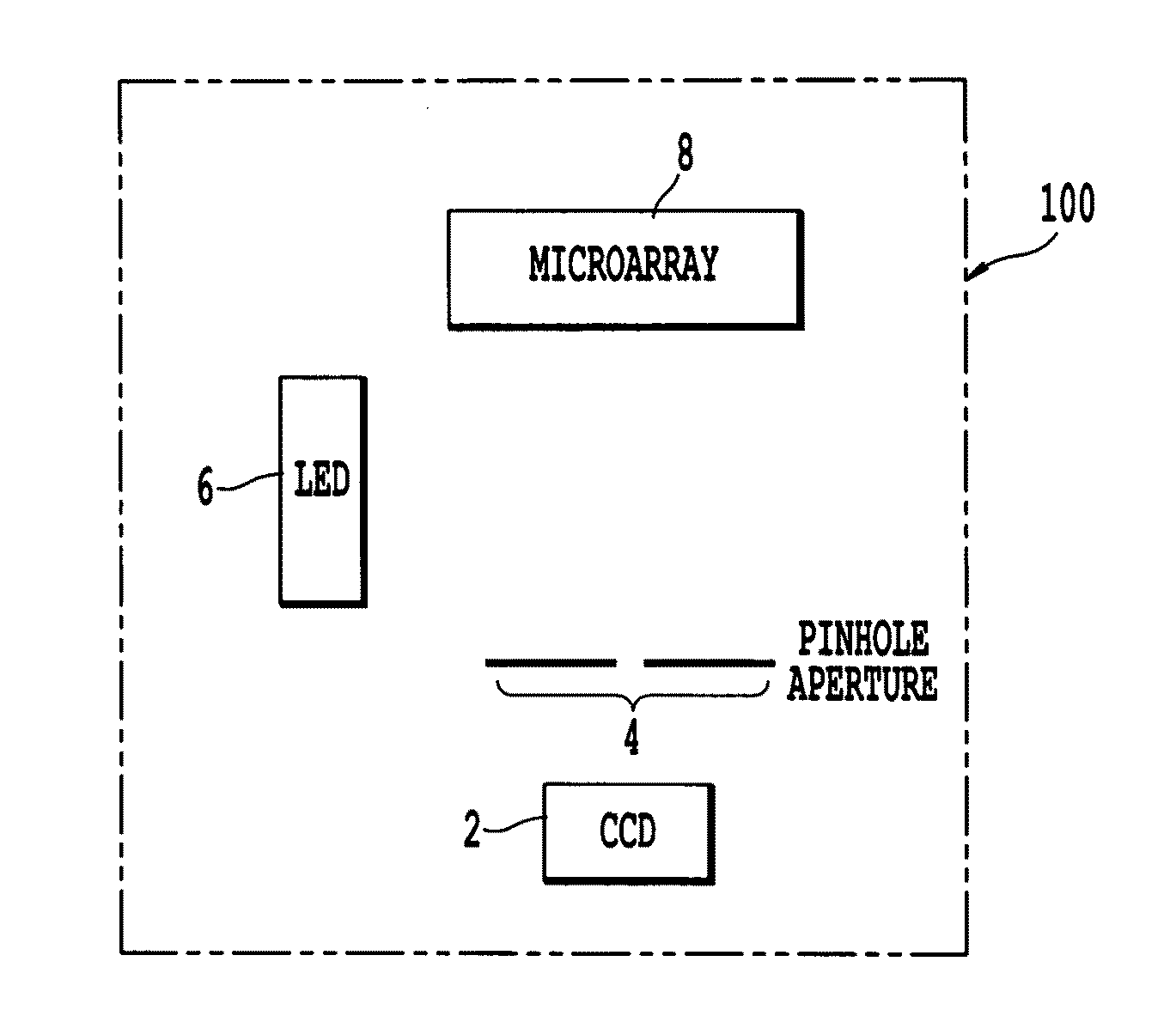
Microarray imaging system and associated methodology
InactiveUS20070263914A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionLight filterCharge couple device
An apparatus and method are provided for creating an image of a microarray. The apparatus includes at least one light source configured to direct light toward the microarray. The apparatus includes an excitation filter configured to filter the light into a first frequency band towards dichromatic mirror. The dichromatic mirror reflects light onto the microarray causing the microarray to emit electromagnetic energy. The apparatus includes emission filter configured to filter the electromagnetic energy within a second frequency band. The apparatus further includes an imaging unit having a charged coupled device (CCD), the CCD having an imaging surface masked by a pinhole blind such that when the pinhole blind receives electromagnetic energy from the emission filter, an image is created of the entire micro array.
Owner:TESSARAE LLC
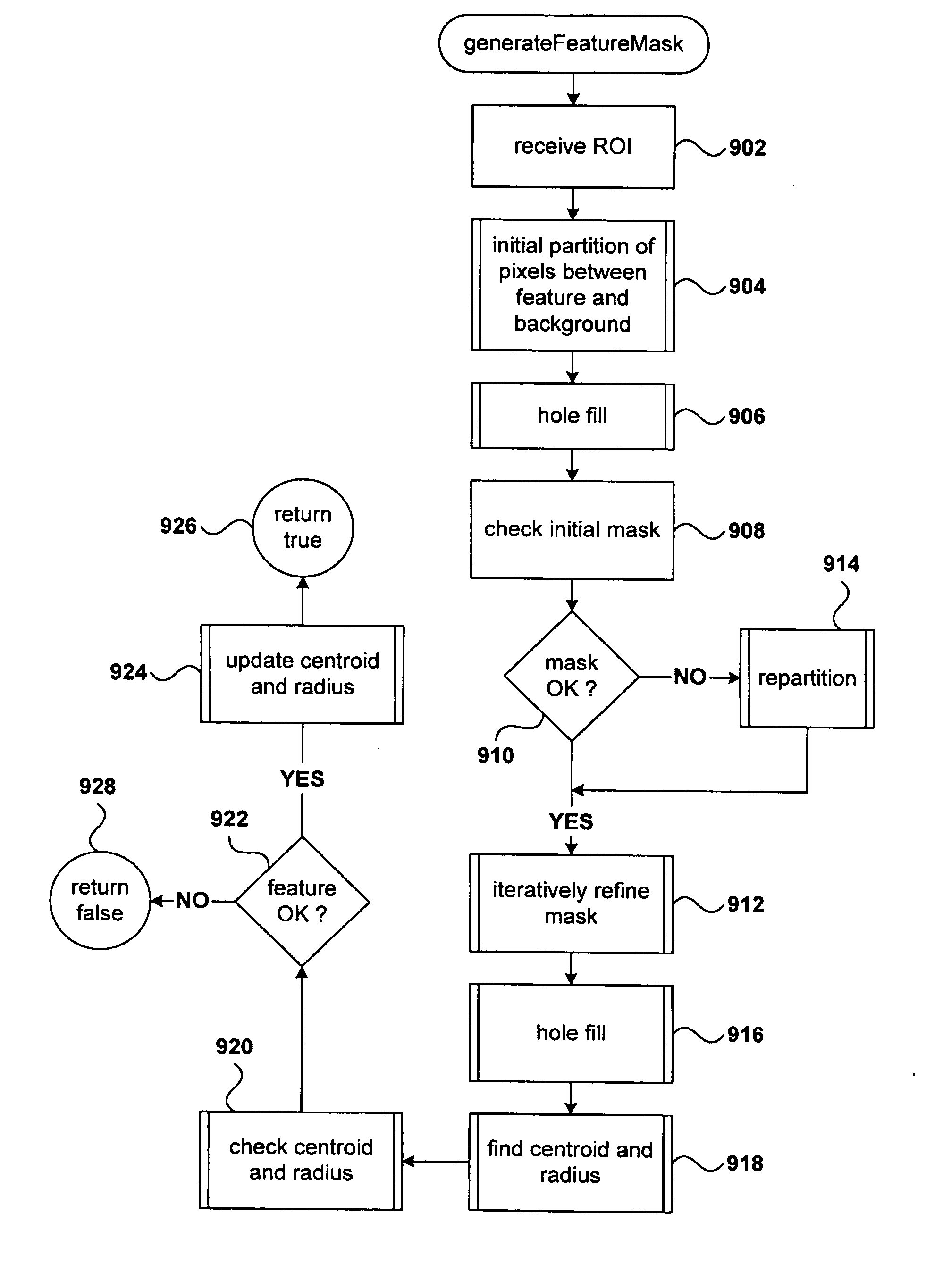
Classification of pixels in a microarray image based on pixel intensities and a preview mode facilitated by pixel-intensity-based pixel classification
One disclosed embodiment is a method based on an iteratively employed Bayesian-probability-based pixel classification, used to refine an initial feature mask that specifies those pixels in a region of interest, including and surrounding a feature in the scanned image of a microarray, that together compose a pixel-based image of the feature within the region of interest. In a described embodiment, a feature mask is prepared using only the pixel-based intensity data for a region of interest, a putative position and size of the feature within the region of interest, and mathematical models of the probability distribution of background-pixel and feature-pixel signal noise and mathematical models of the probabilities of finding feature pixels and background pixels at various distances from the putative feature position. In a described embodiment, preparation of a feature mask allows a feature-extraction system to display feature sizes and locations to a user prior to undertaking the computationally intensive and time-consuming task of feature-signal extraction from the pixel-based intensity data obtained by scanning a microarray.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System for the automatic analysis of images such as DNA microarray images
InactiveUS20020097900A1Efficient and rapid automatic analysis of imageImage enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCMOSDNA microarray
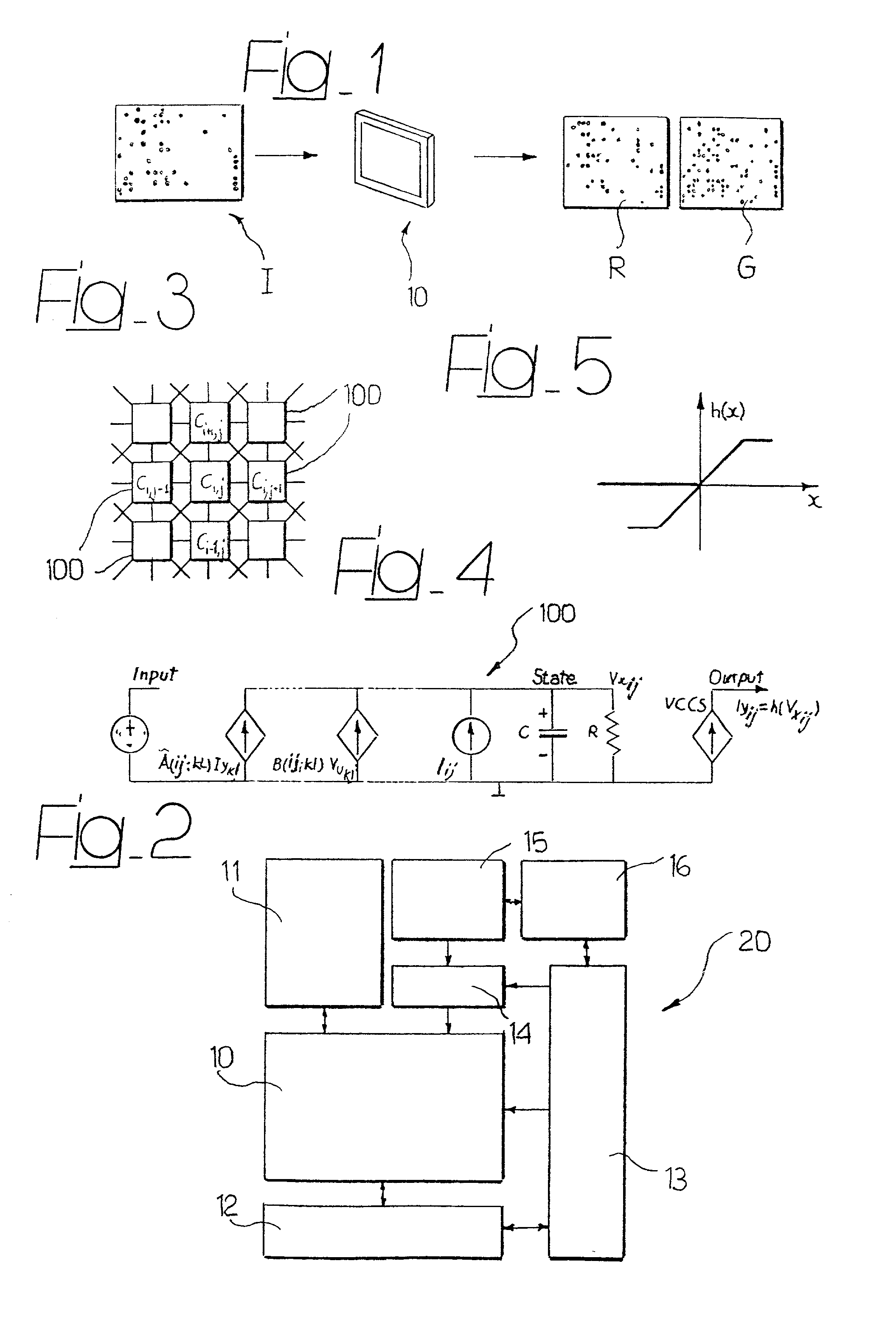
The system can be used for the automatic analysis of images (I), comprising a matrix of spots, such as images of DNA microarrays after hybridisation. The system can be associated-and preferably integrated in a single monolithic component implementing VLSI CMOS technology-to a sensor (10) for acquiring said images (I). The system comprises a circuit (20) for processing the signals corresponding to the images (I), configured according to a cellular neural network (CNN) architecture for the parallel analogue processing of signals.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Microarray imaging system and associated methodology
InactiveUS7961323B2Color/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingTissue microarrayElectromagnetic shielding
Owner:TESSARAE LLC
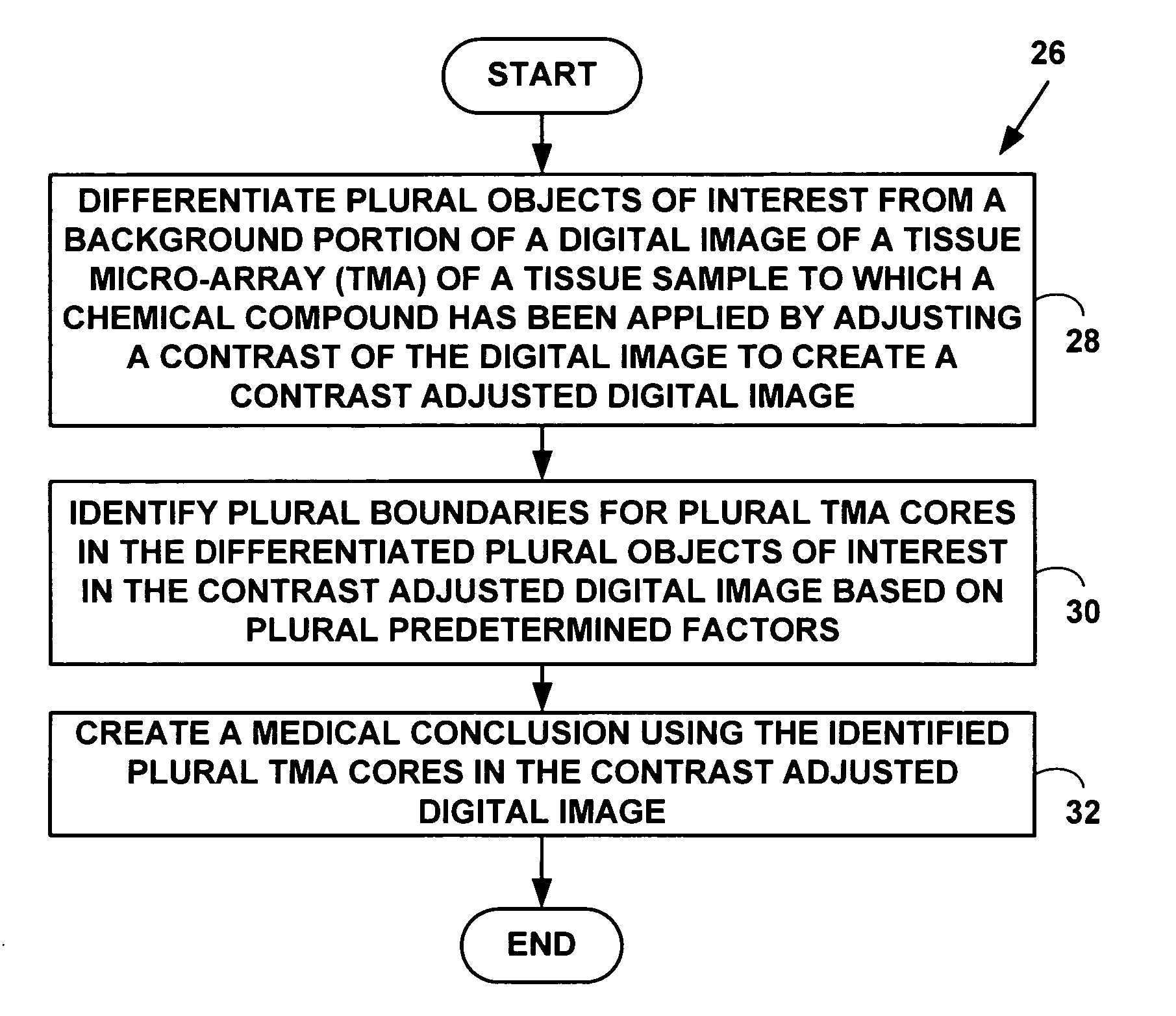
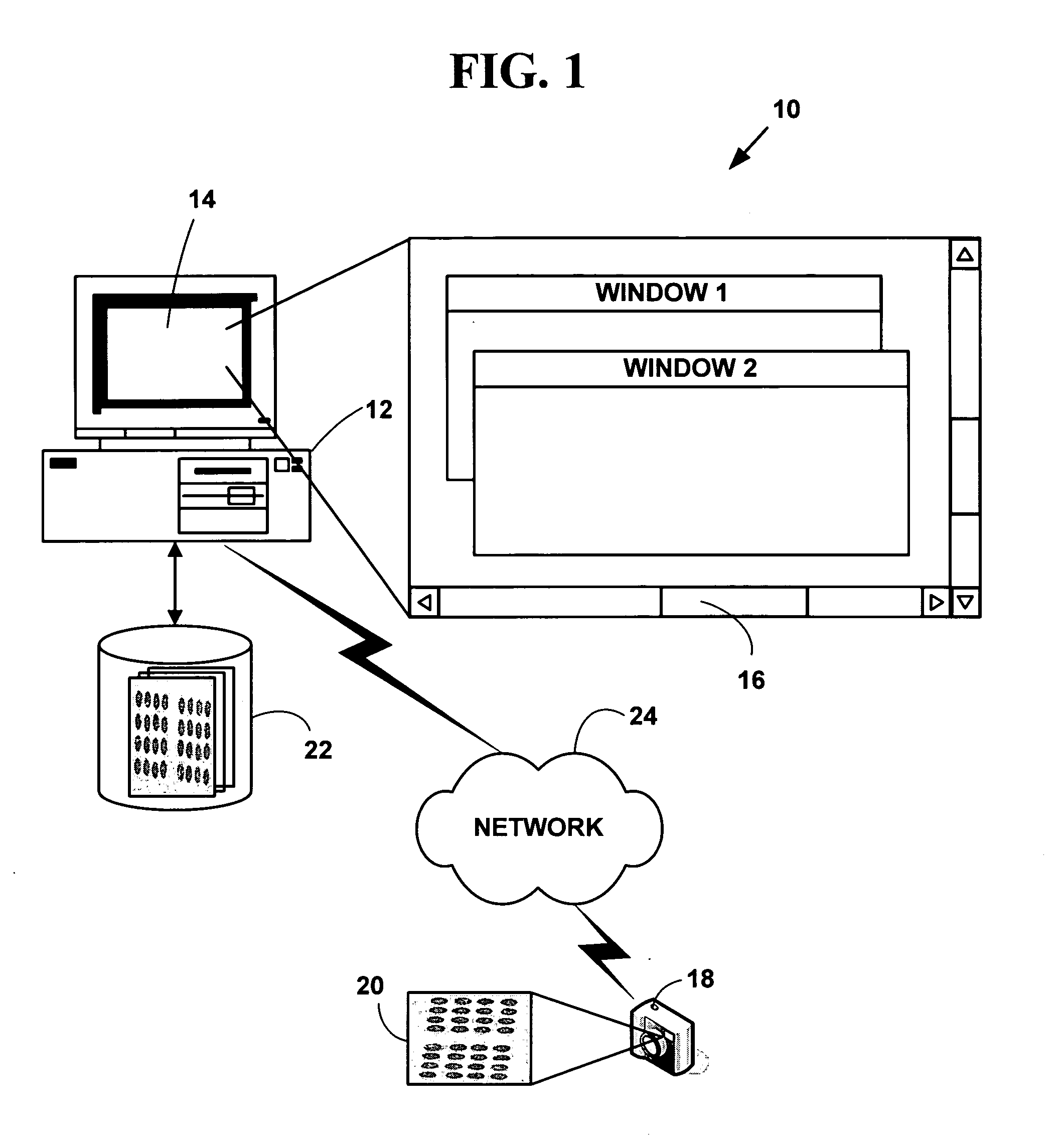
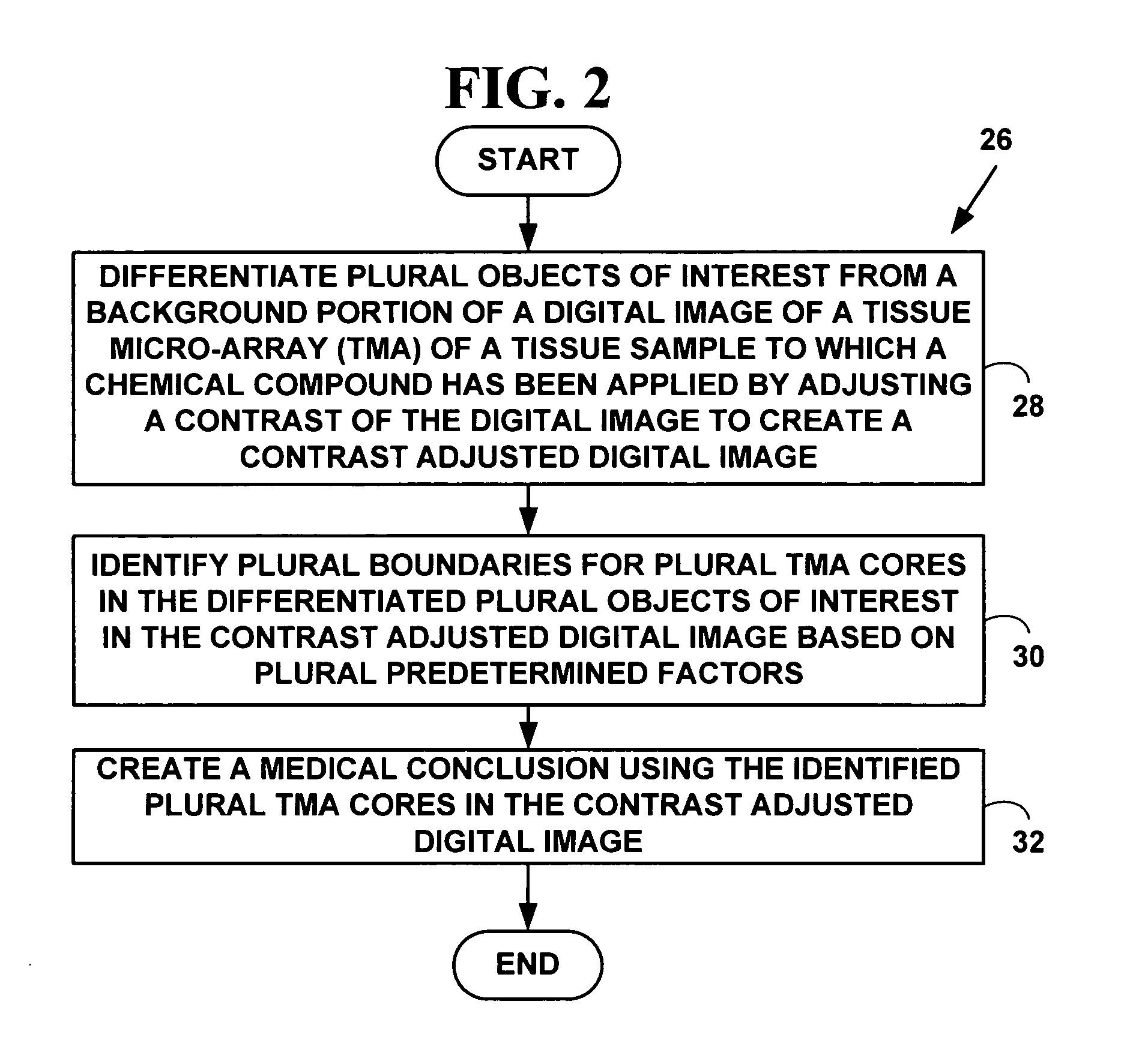
Method and system for automated quantitation of tissue micro-array (TMA) digital image analysis
ActiveUS20060015262A1Facilitates automated analysisAuxiliary diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsHuman cancerTissue microarray
A method and system for automated quantitation of tissue micro-array image (TMA) digital analysis. The method and system automatically analyze a digital image of a TMA with plural TMA cores created using a needle to biopsy or other techniques to create standard histologic sections and placing the resulting needle cores into TMA. The automated analysis allows a medical conclusion such as a medical diagnosis or medical prognosis (e.g., for a human cancer) to be automatically determined. The method and system provides reliable automatic TMA core gridding and automated TMA core boundary detection including detection of overlapping or touching TMA cores on a grid.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
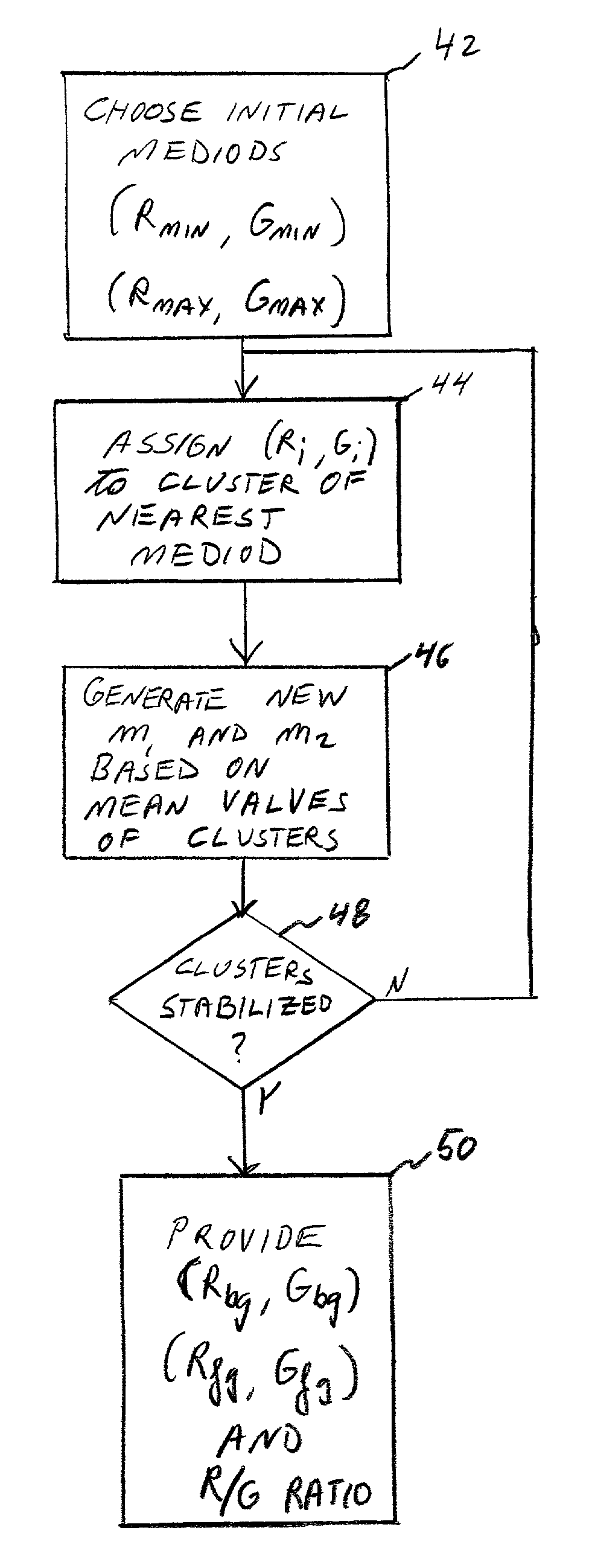
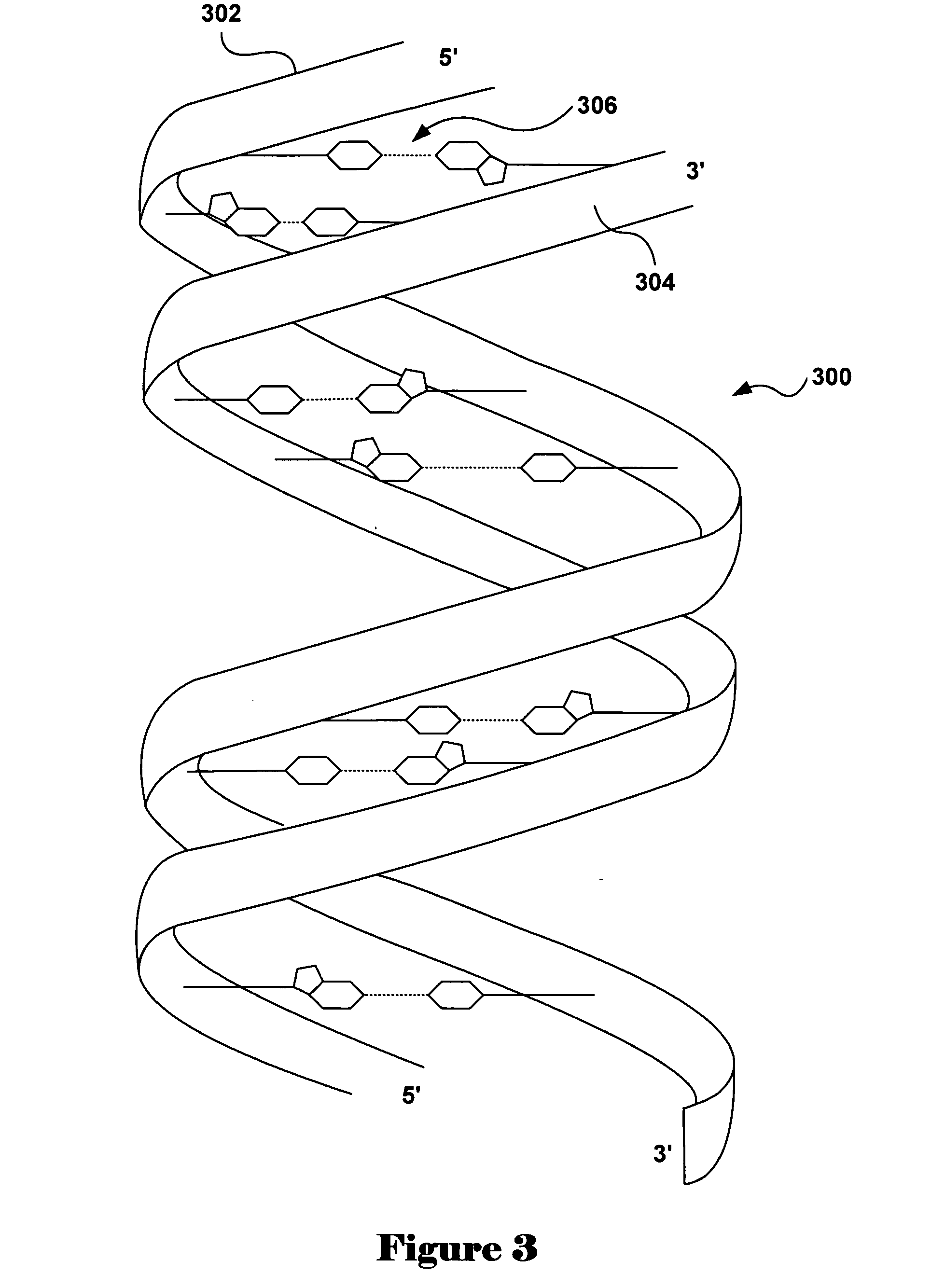
Cluster analysis of genetic microarray images
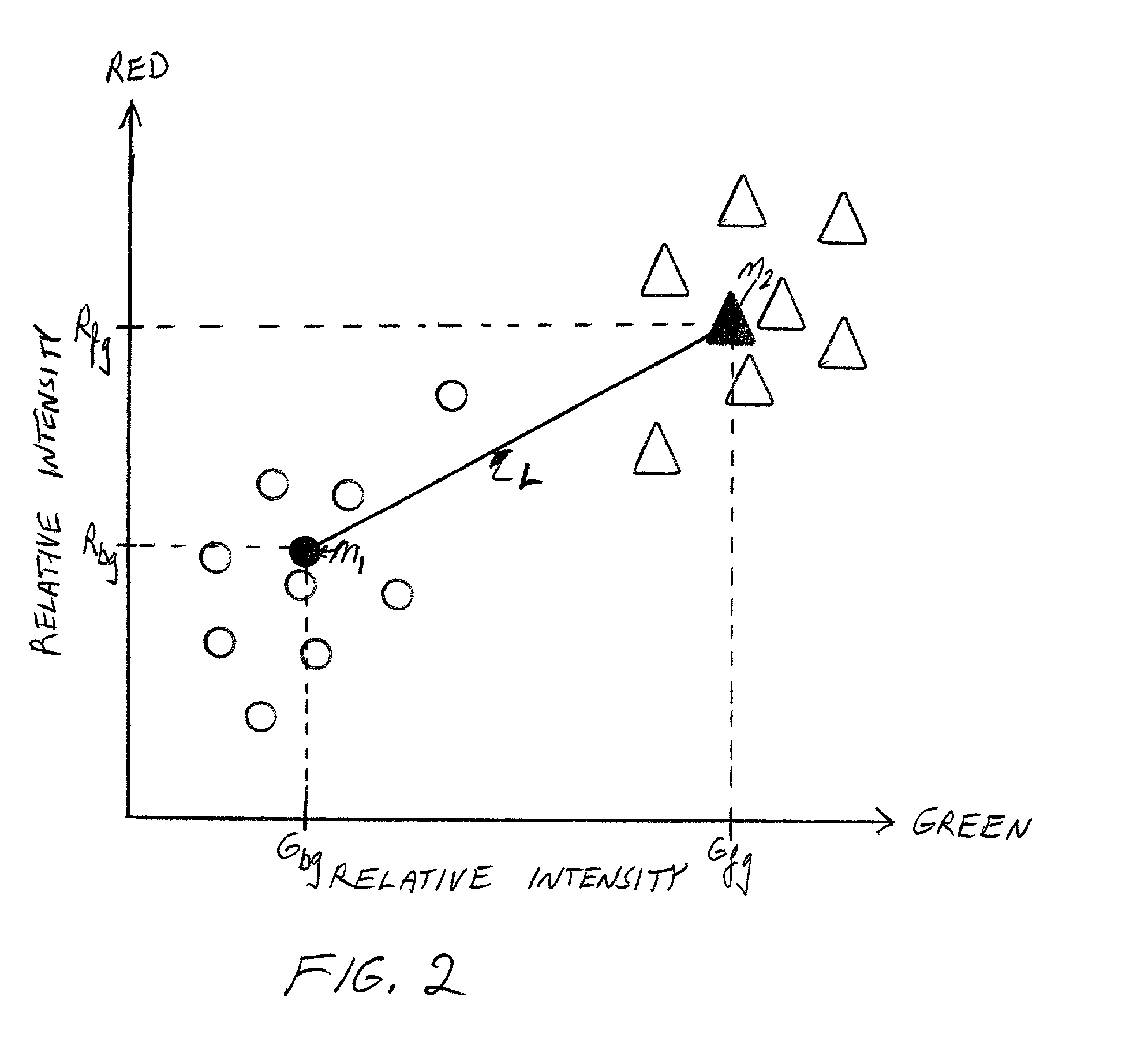
A method for determining relative incidence of a binding substance within two biological samples is provided. The two samples are labeled with luminescent materials having different chromatic properties. An image of the luminescent materials upon a binding site of a microarray is analyzed as two clusters of data points scattered about respective representative pairs of chromatic intensity values. The relative incidence of the binding substance is determined as a ratio of differences between corresponding indices of the representative pairs.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
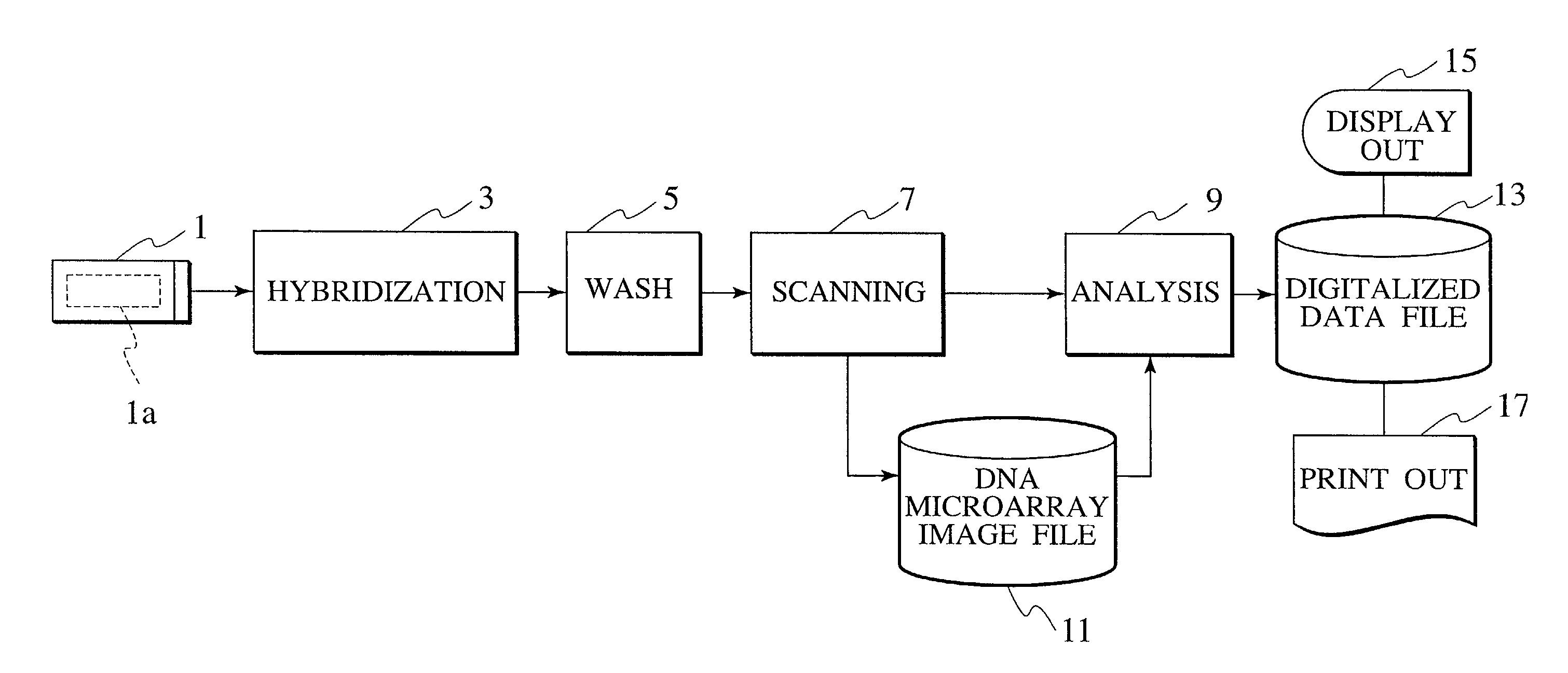
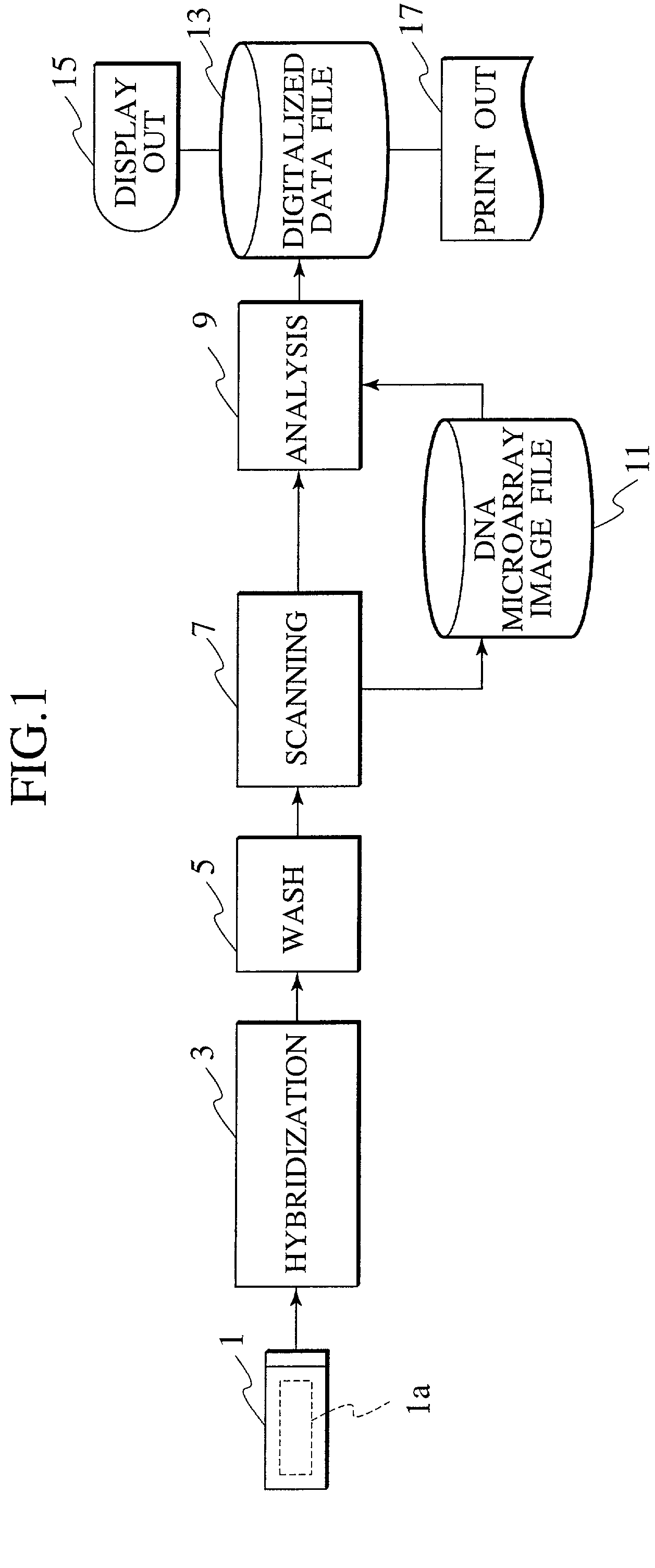
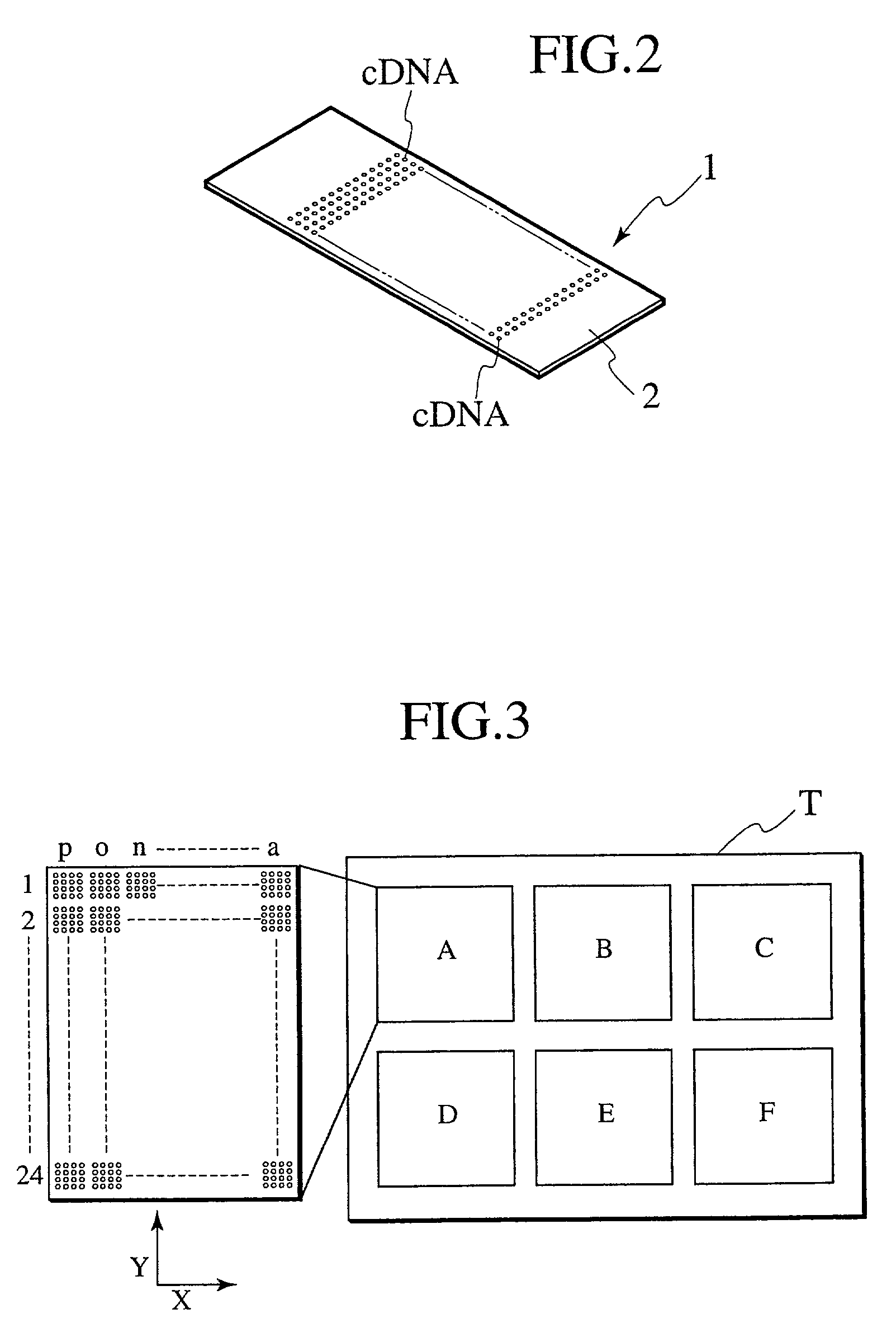
Probe reactive chip, apparatus for analyzing sample and method thereof
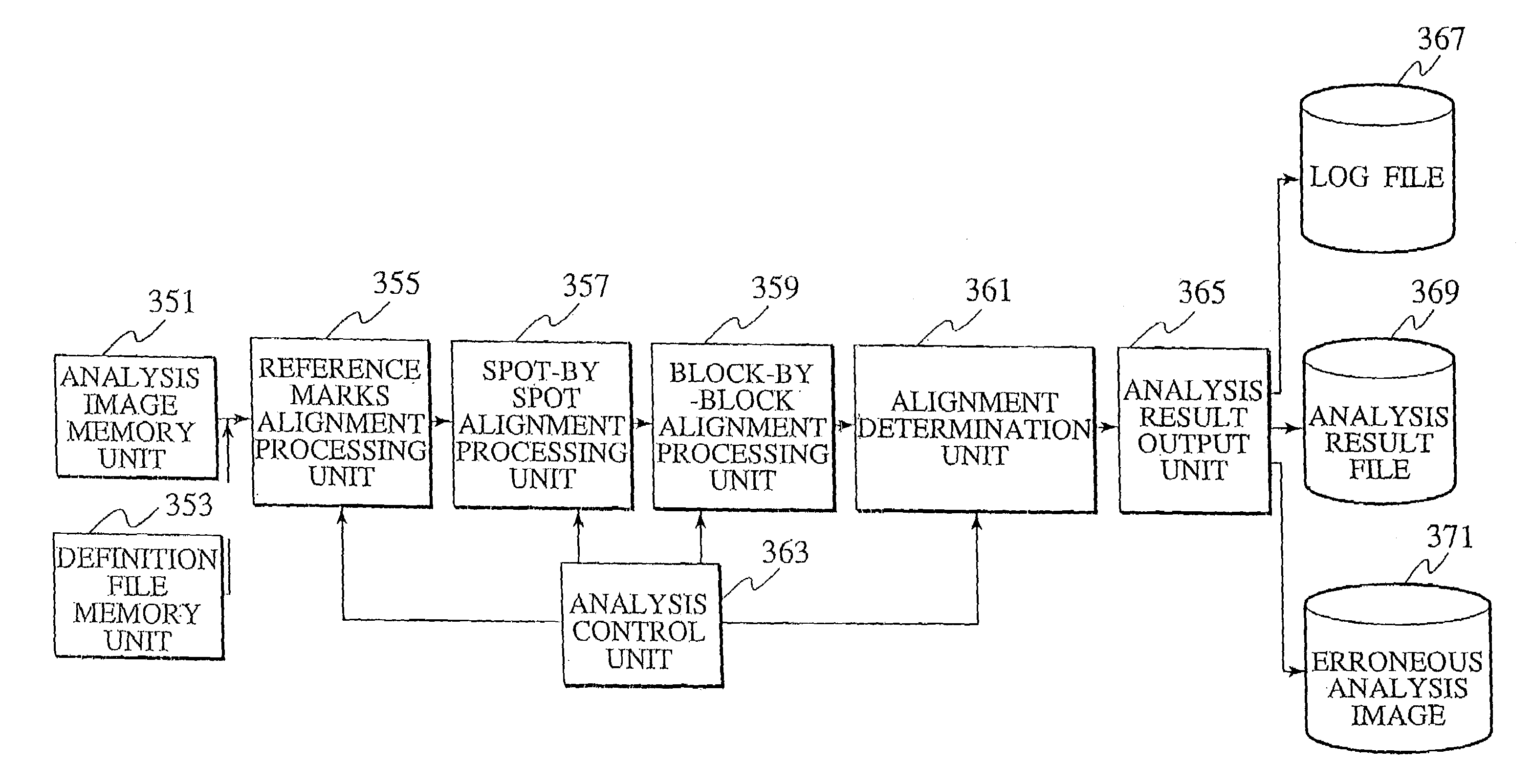
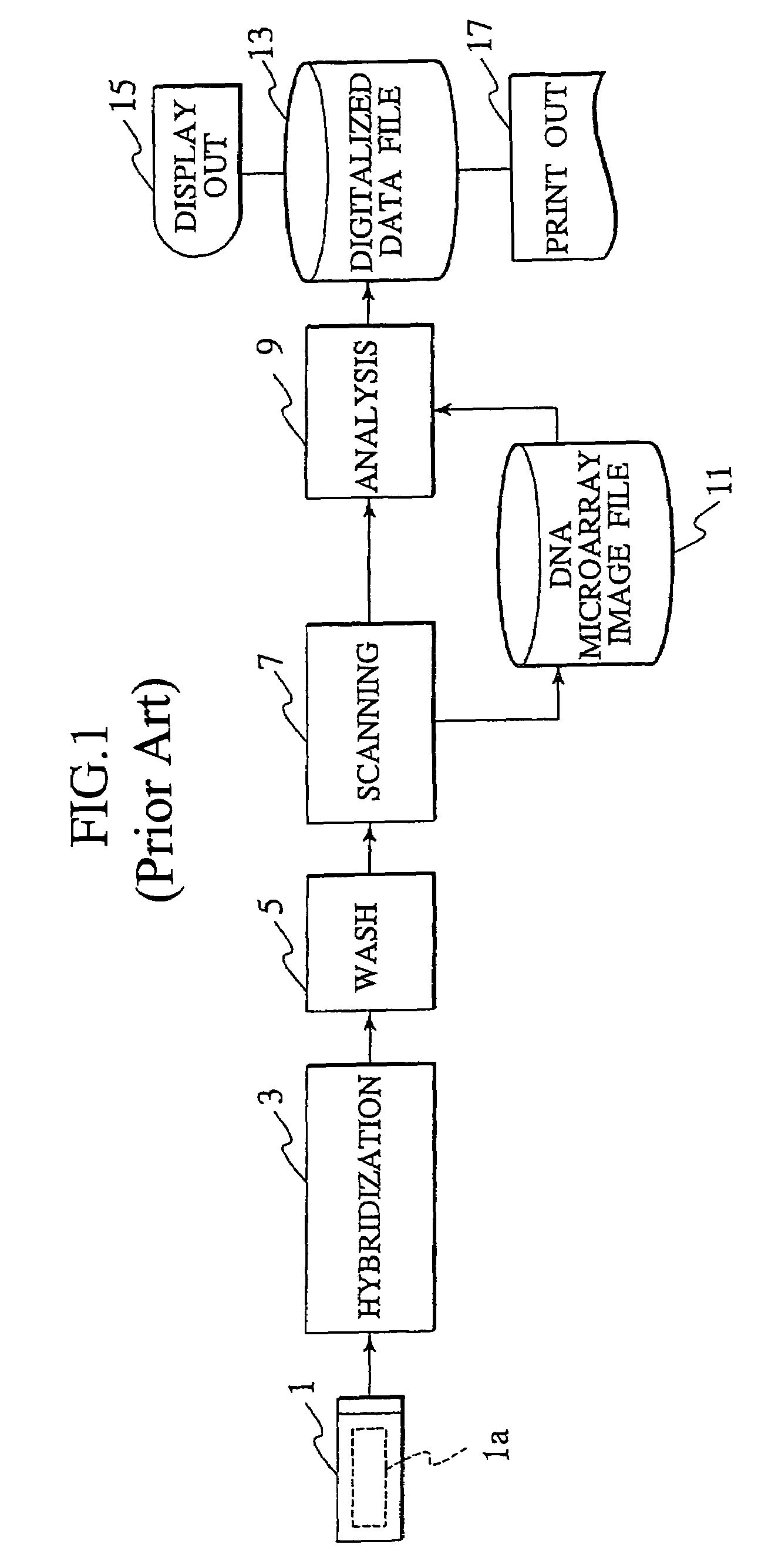
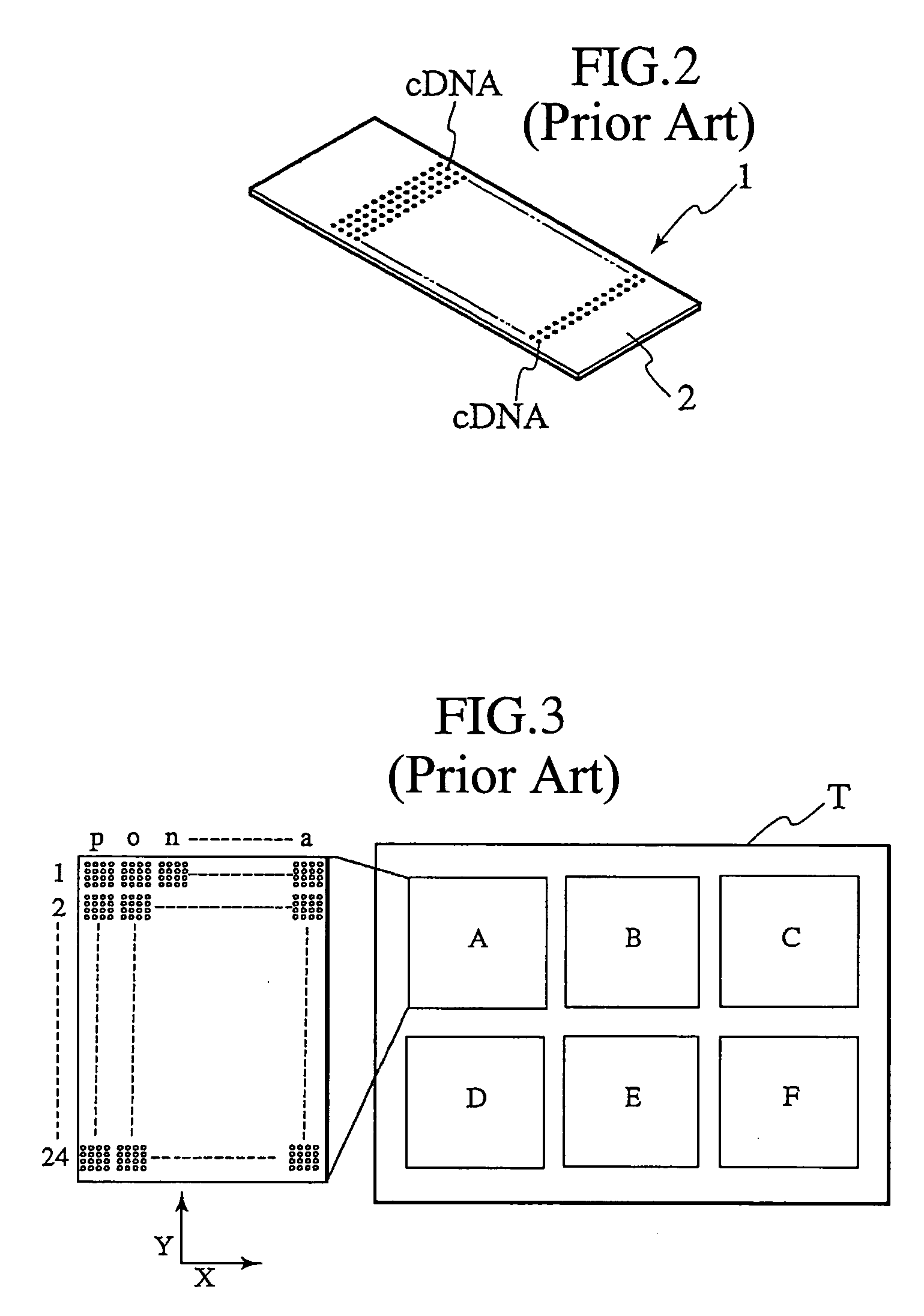
InactiveUS20030152255A1Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsQuantitative determinationReference patterns
Technology is disclosed for highly accurate automated execution of processing for alignment of a detection area to a DNA microarray image file and processing for quantitative determination of success / failure of the alignment during DNA microarray analysis. A probe reactive chip used for the technology comprises a substrate; a spot area wherein spots for fixing a probe capable of specifically reacting to a sample marked so as to be optically detectable are formed in a matrix on a surface of the substrate; and a reference pattern area, which is arranged within the spot area or approximate to the spot area, and comprises a plurality of different alignment marks in order to correct misalignment of the spot during analysis of the sample on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
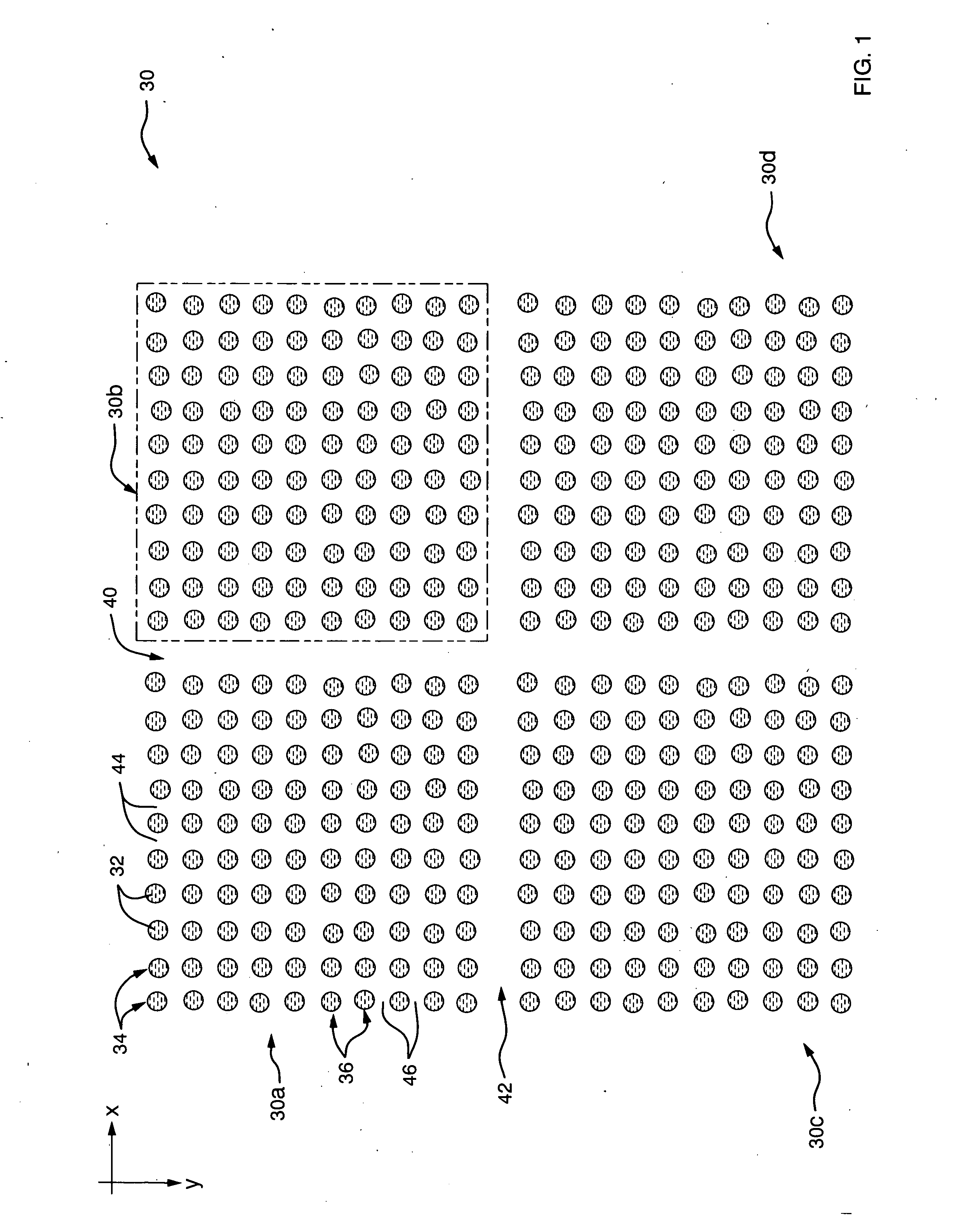
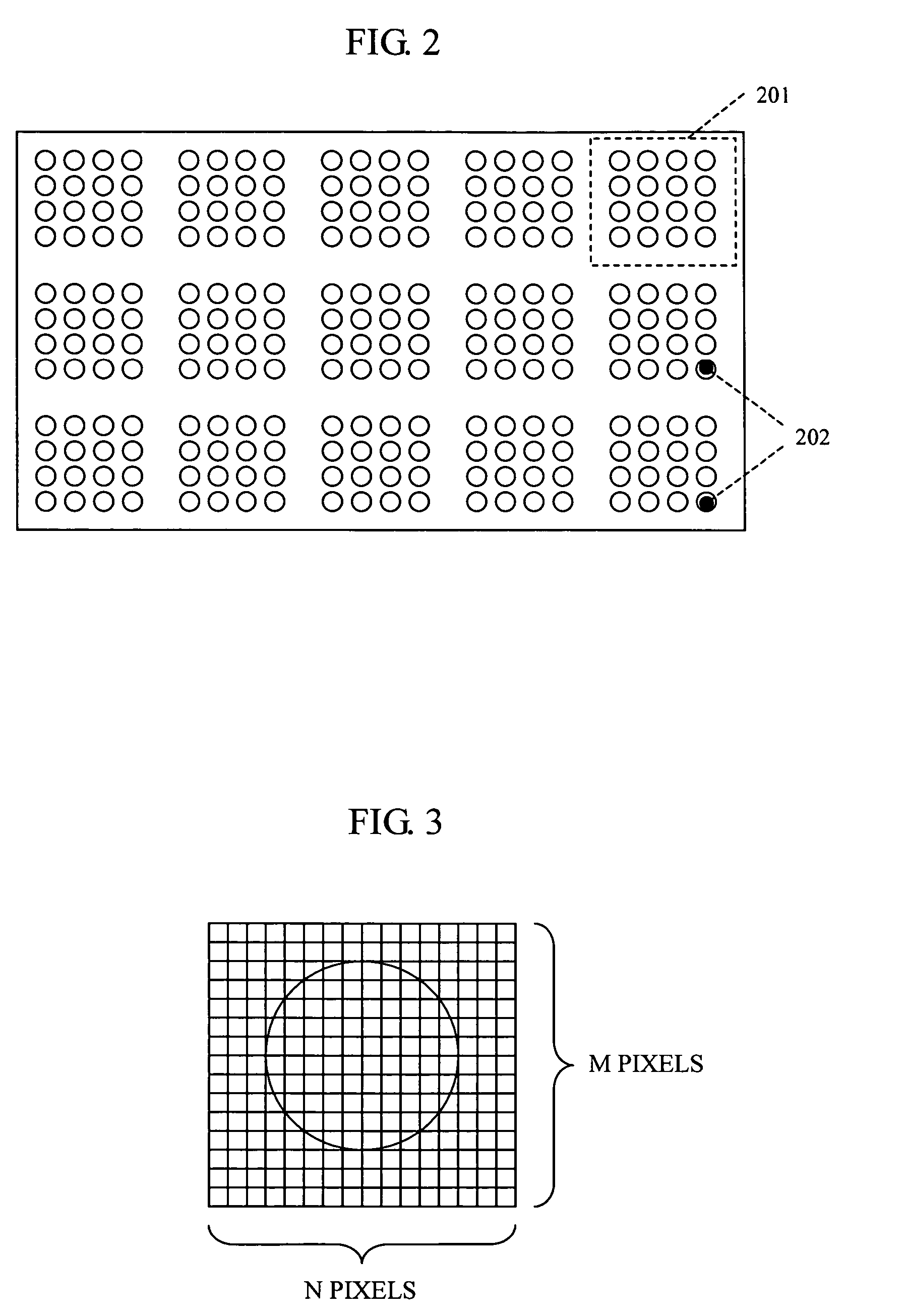
Method and system for determining feature-coordinate grid or subgrids of microarray images
The present invention provides various embodiments that are directed to methods and systems for determining a feature-coordinate grid of a microarray image so that individual features can be located and isolated for statistical analysis. The method receives microarray-image data and determines centroid coordinates for each feature of the microarray image. The methods and systems of the present invention determines uses the centroid coordinates to determine horizontal grid lines and vertical grid lines that are superimposed on the microarray image so that intersections of the grid lines coincide with features of the microarray image. The horizontal grid lines and vertical grid lines provide grid lines of the feature-coordinate grid.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
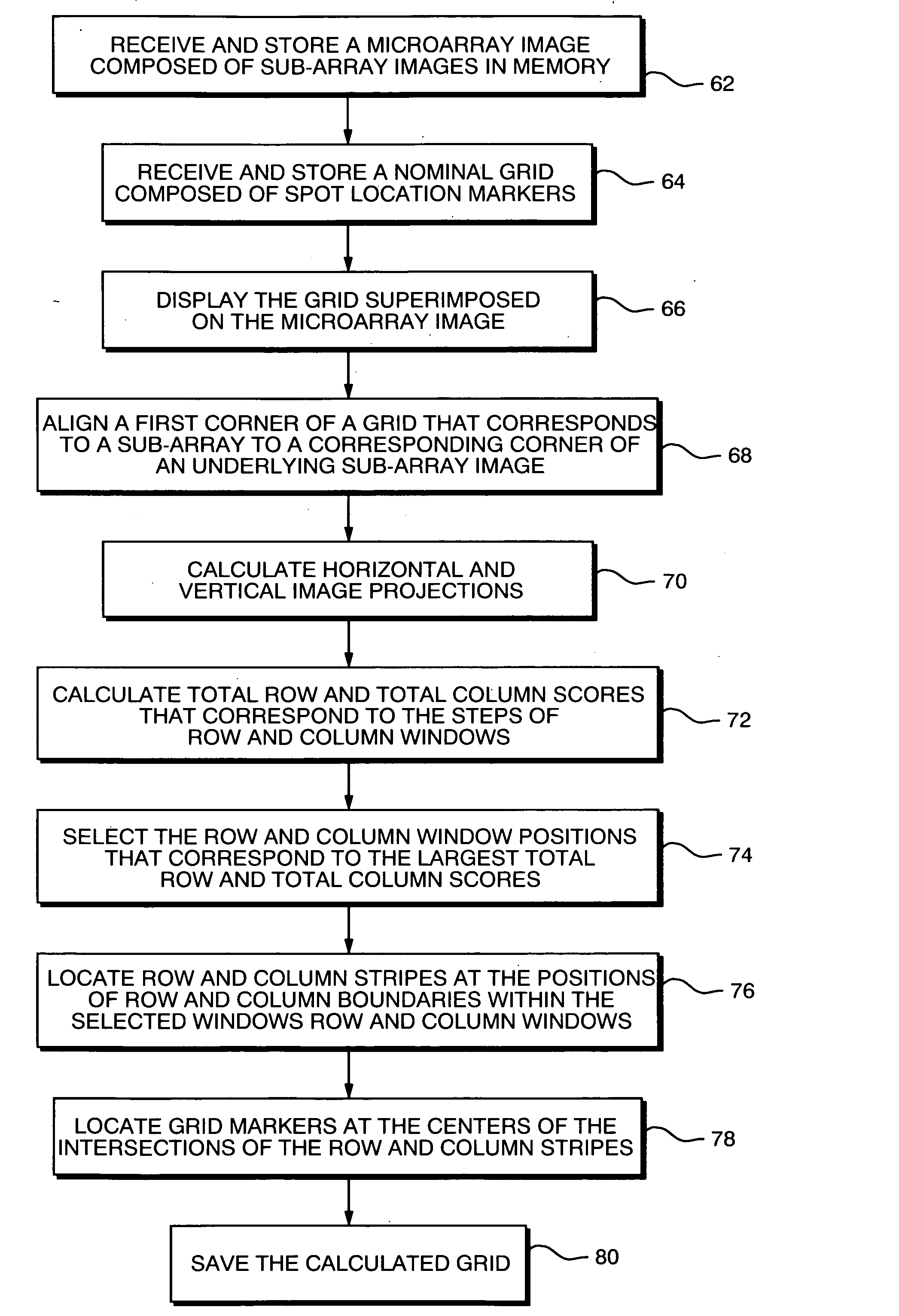
Method and apparatus for automatically segmenting a microarray image
InactiveUS20050244040A1Precise alignmentAccurate segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceMesh grid
A microarray image is segmented into discreet segments for respective spots in the microarray image based on locating microarray image rows and columns by maximizing scores associated with vertical and horizontal image projections. To determine the locations of the rows and columns that extend through artifacts that involve multiple spots and / or multiple columns and rows, the scores may also include contributions from the gaps between adjacent rows and columns. The scores are calculated by stepping windows containing nominally spaced spot-sized row or column boundaries, over the horizontal projection curves. At each step a total row or column score is calculated that represents the areas of the projection curves that fall within the row boundaries. The system then selects the window positions that correspond to the maximum total row score and total column score, and uses the locations of the boundaries as the locations of row and column “stripes” that are sized to the spot diameters. The intersections of the row and column stripes define the segments for the respective spots, and the centers of the intersections are the locations for the spot location, or grid, markers. The system may also determine the best spot size, column and row gap sizes and sub-array gap sizes by changing the boundaries accordingly and determining corresponding maximum scores.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
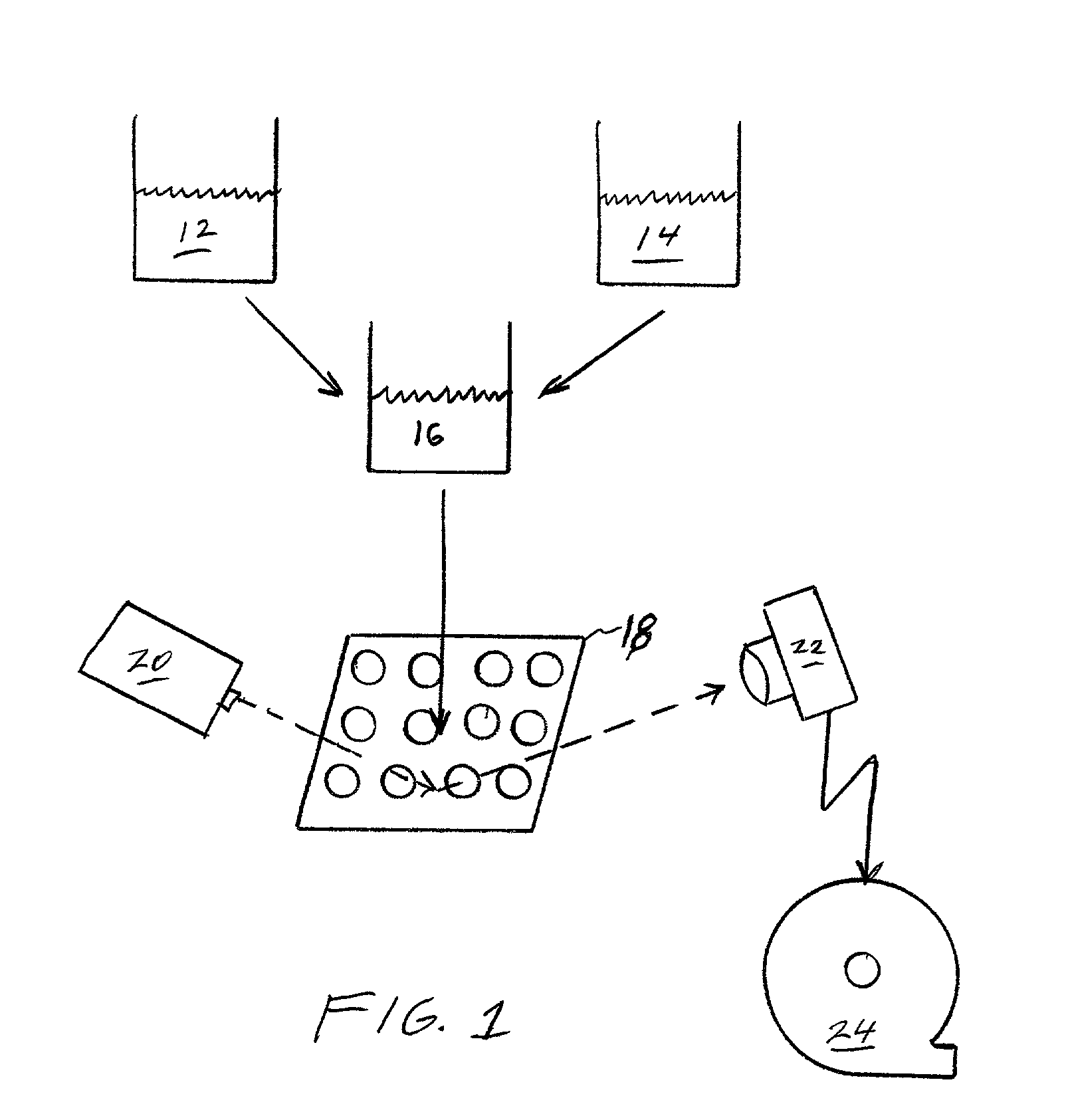
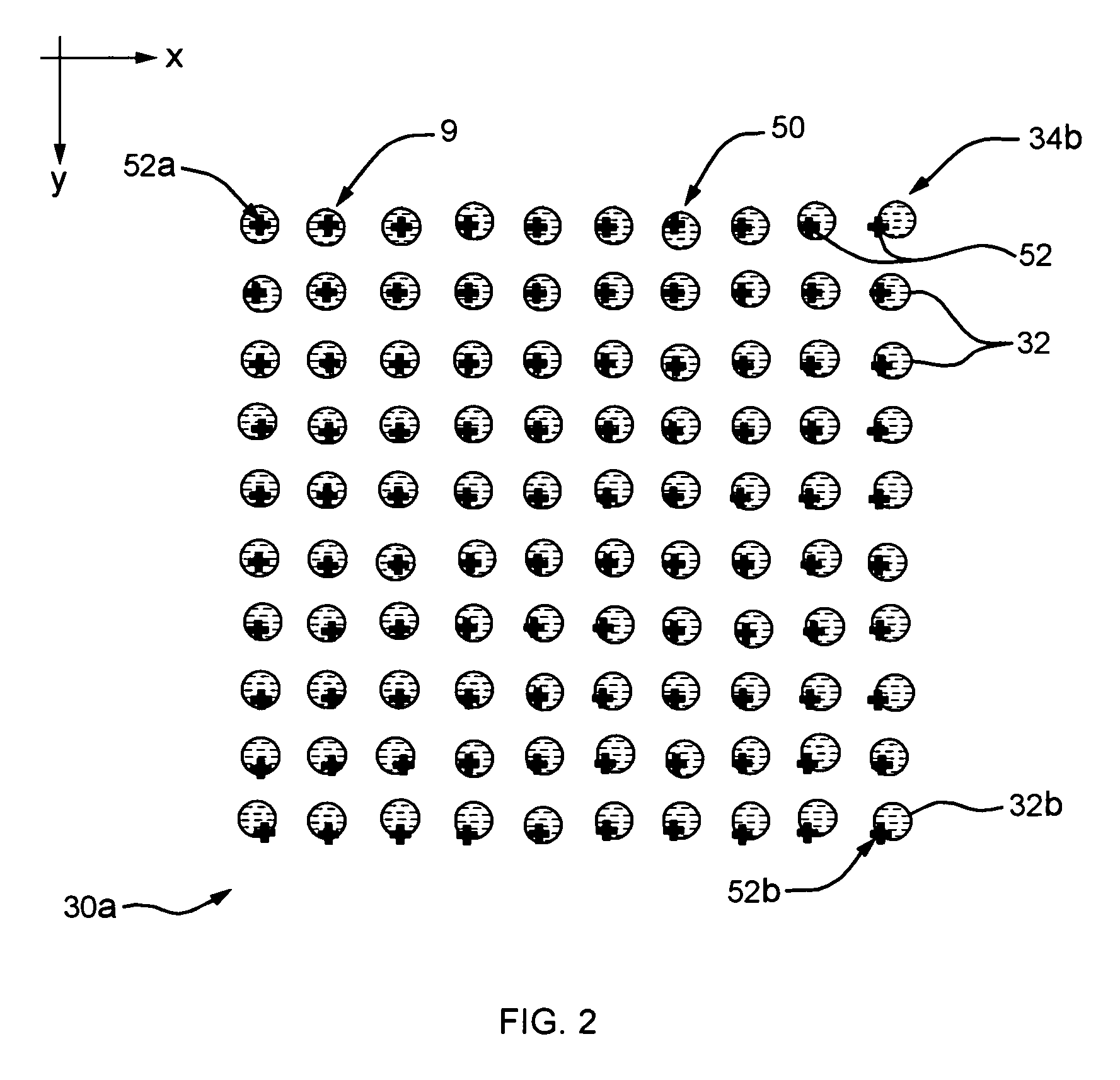
System and apparatus for the remote analysis of chemical compound microarrays
ActiveUS20120201437A1Reduce resource consumptionSimplerImage enhancementImage analysisChemical compoundRemote analysis
A remote microarray analysis system, method and apparatus for use in the remote analysis of a chemical compound microarray supported on a substrate is disclosed. Pixel image data is received from a remote location including image data that depicts (a) a calibration scale associated with the substrate and (b) the microarray. A transformation action of said pixel data corresponding to the calibration scale is determined and the received image data corresponding to at least the microarray is adjusted by applying the transformation action. The adjusted image of the microarray is compared with a database of stored microarray pixel data to extract information from said image.
Owner:DAKADOO AG
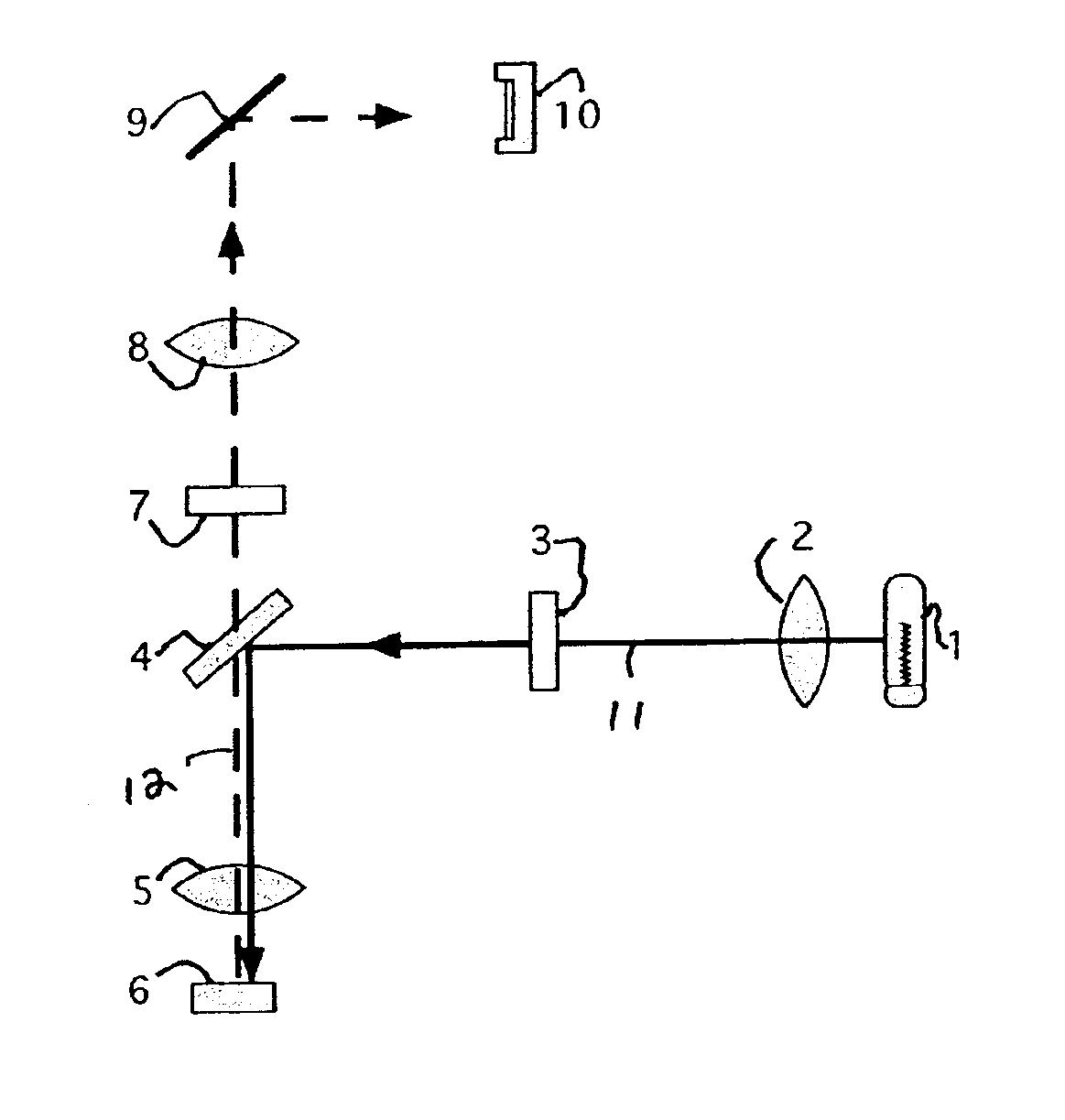
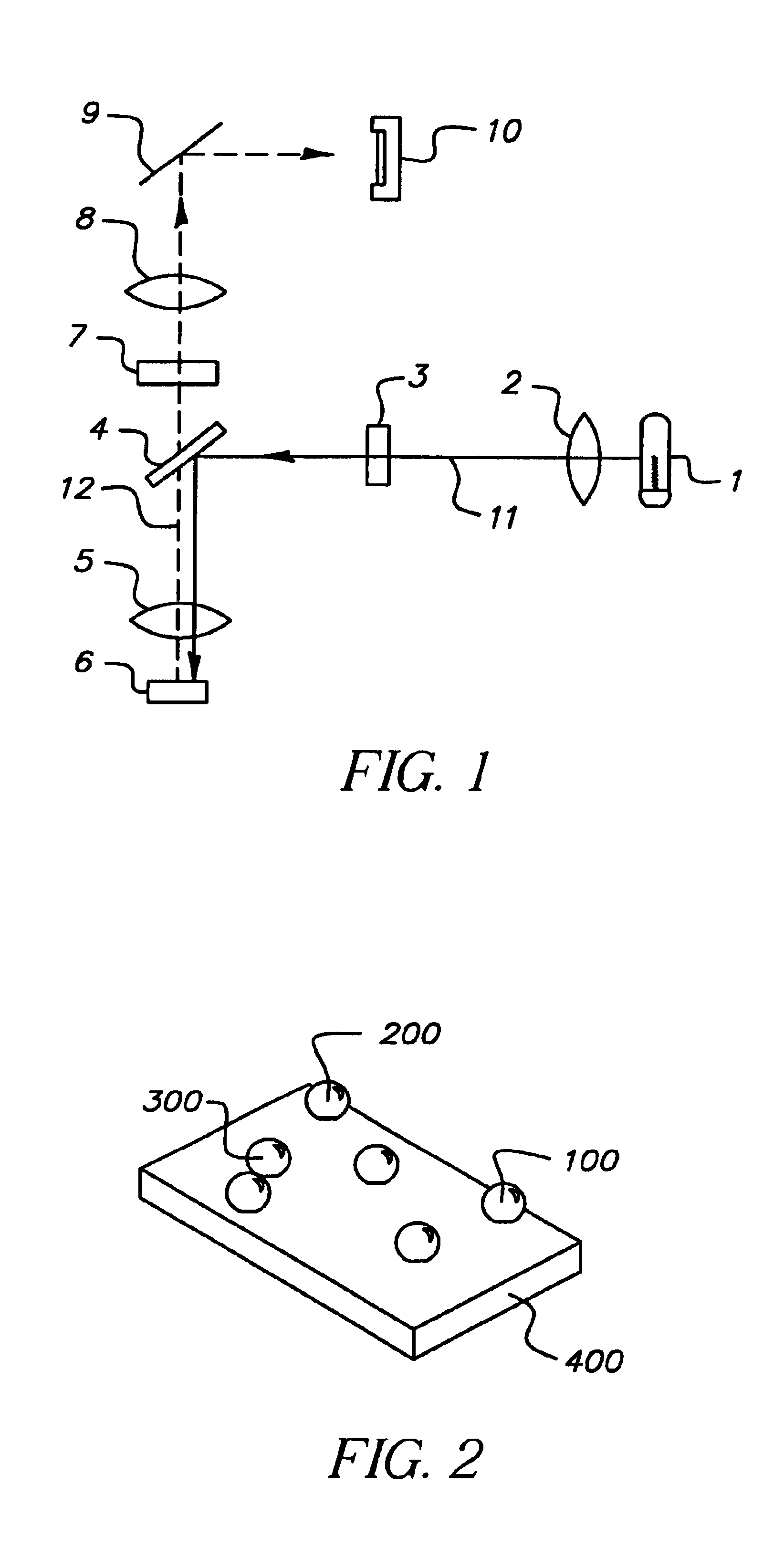
Imaging of microarrays using fiber optic exciter
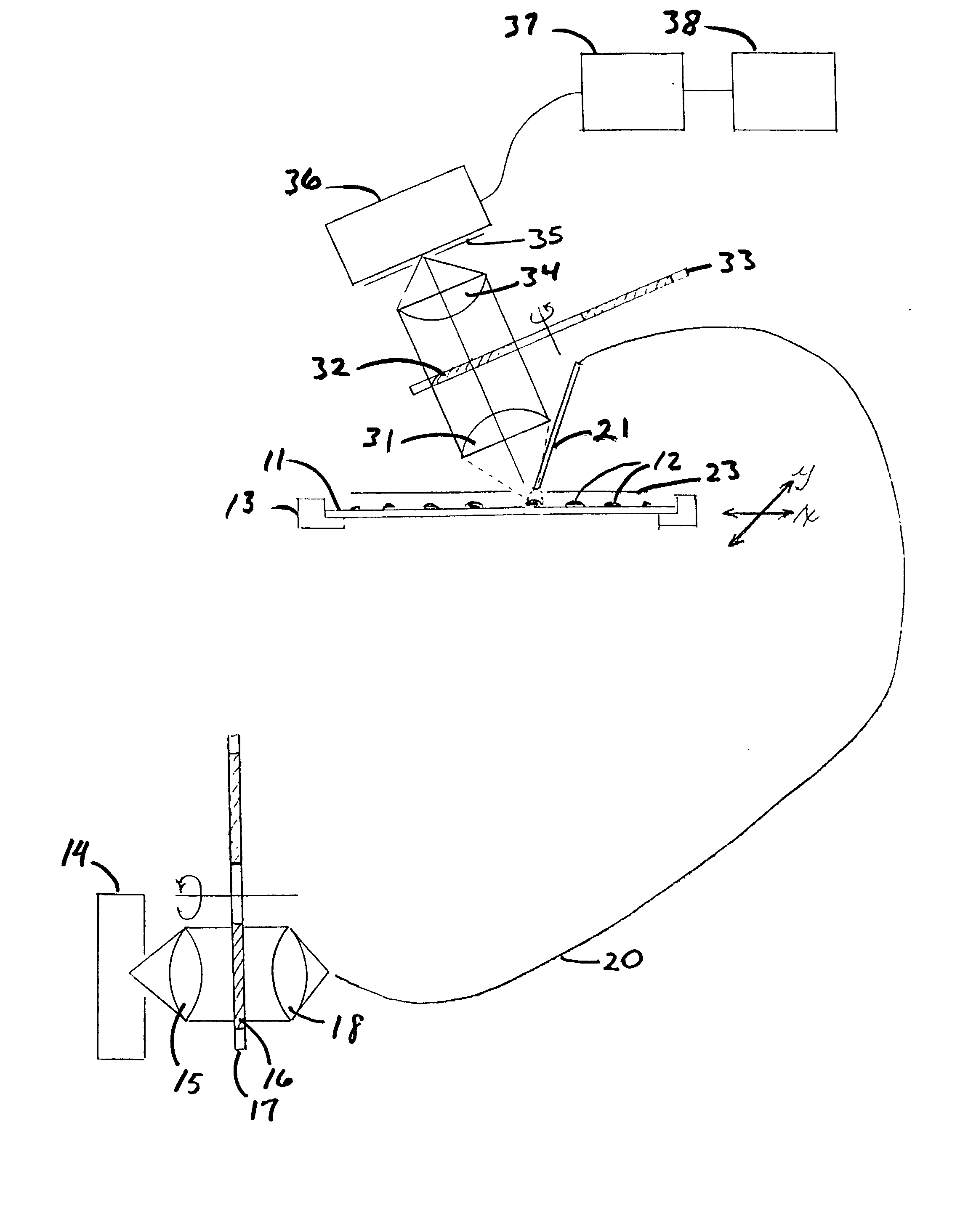
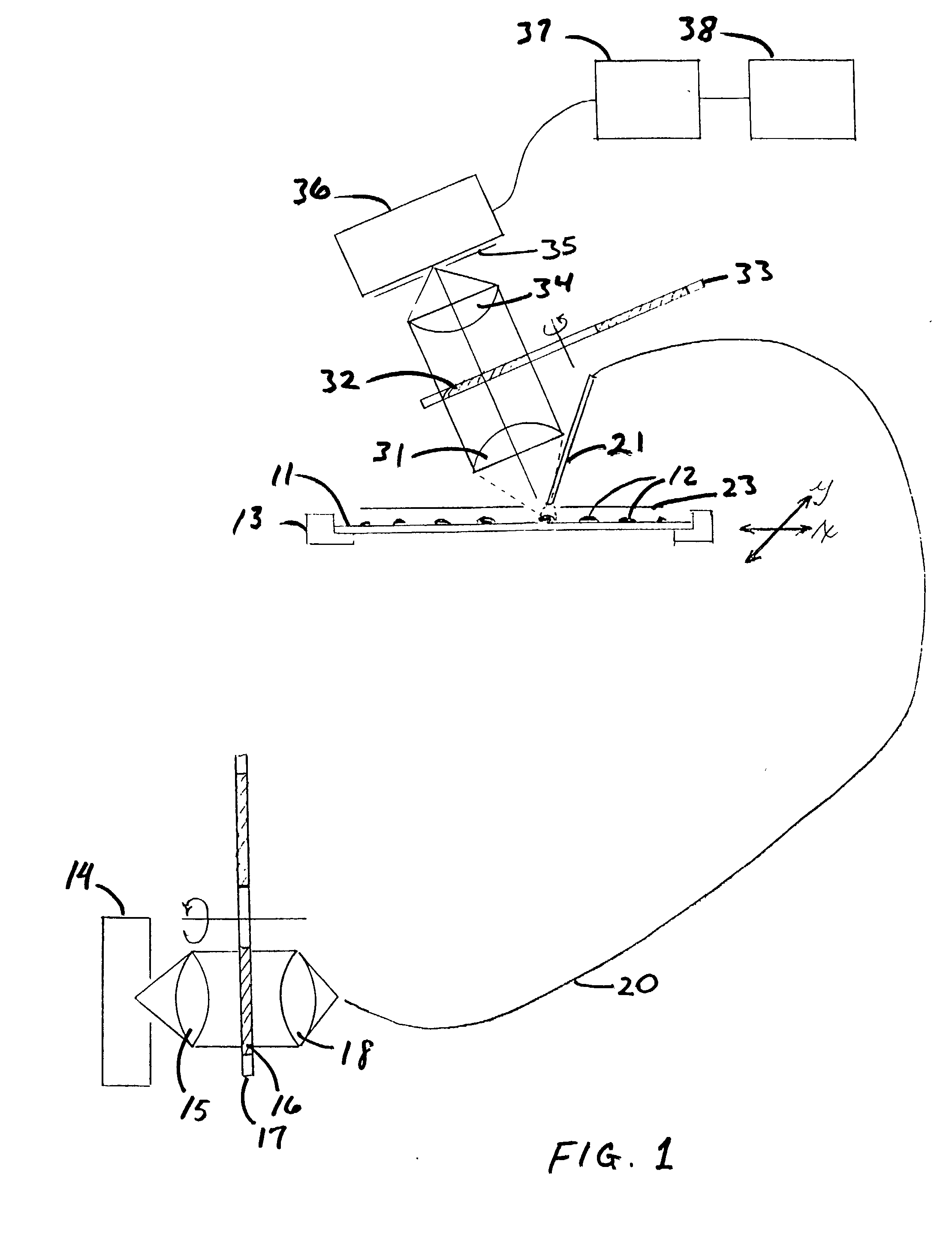
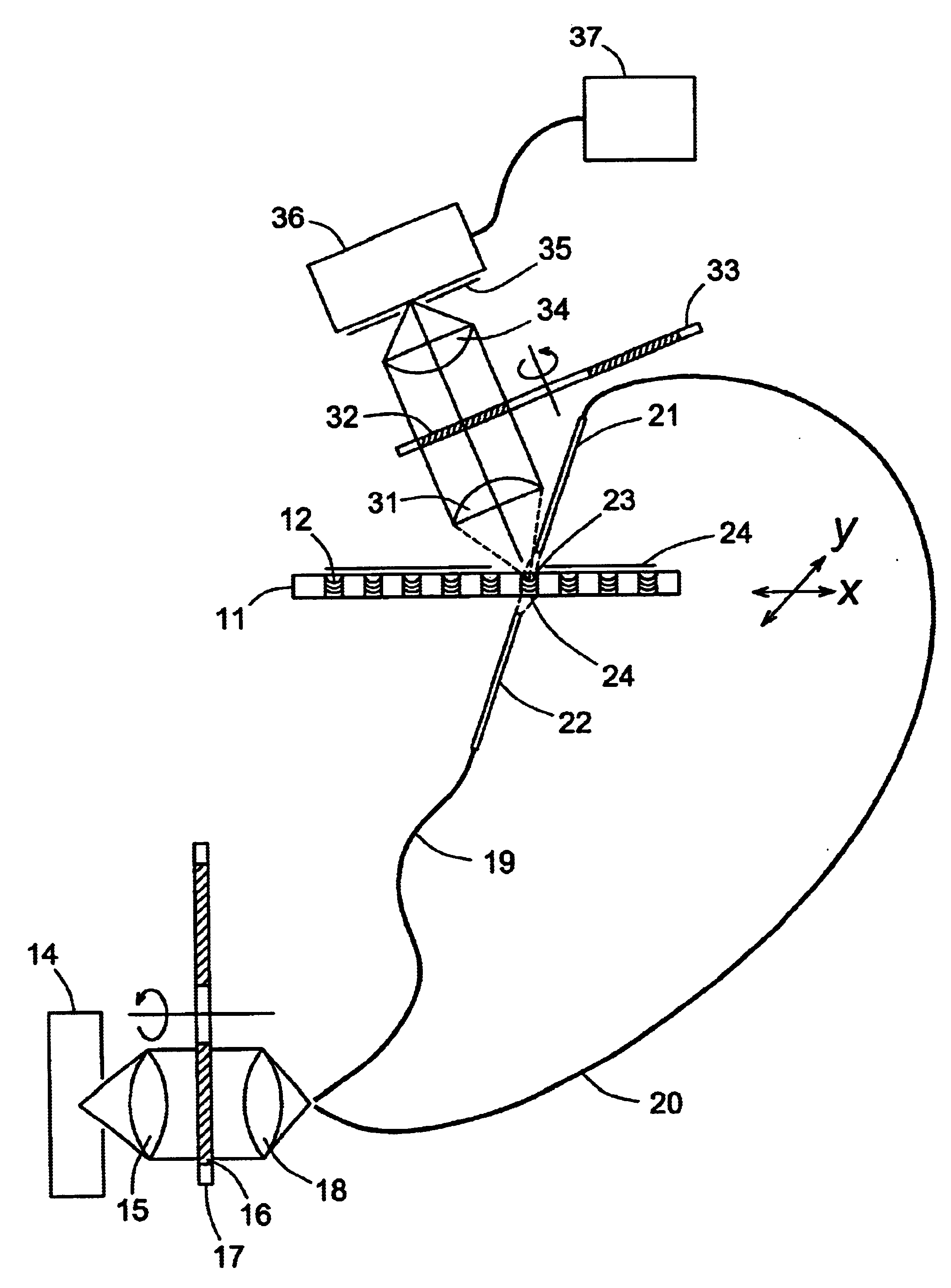
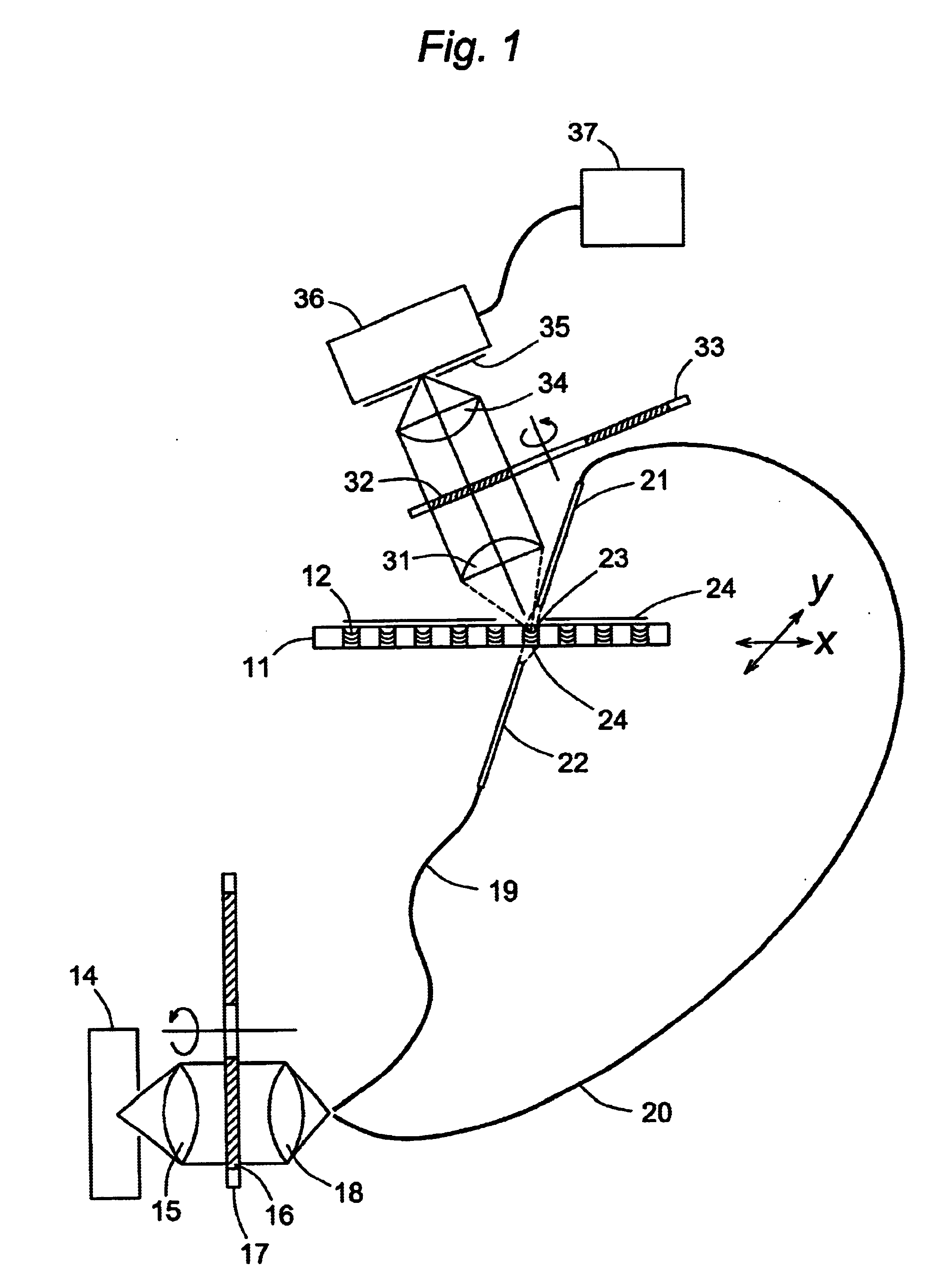
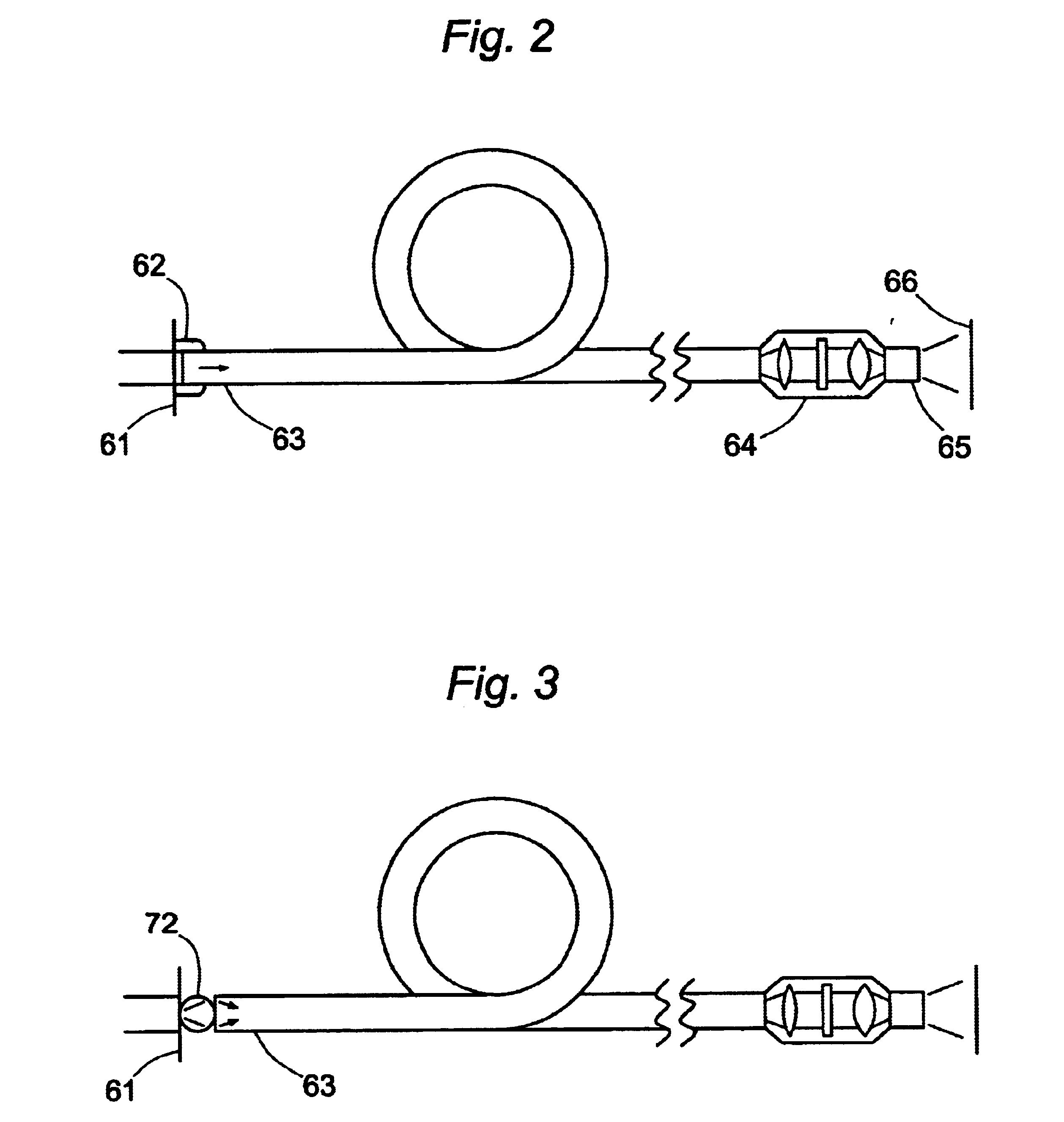
Microarrays are imaged by an illumination and detection system that supplies excitation light through one or more optical fibers, each fiber transmitting excitation light from an excitation light source to a single spot in the microarray. Emission light from each spot is then collected by a collimating lens and converted to a signal that is compiled by conventional software into an image of the entire microarray. The optical fiber(s) and the collimating lens are arranged such that the direction of travel of the excitation light and the direction along which the emission light is collected are not coaxial, and preferably both are at an acute angle to the axis normal to the plane of the microarray.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Probe reactive chip, sample analysis apparatus, and method thereof
InactiveUS7200254B2Improve accuracyMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsQuantitative determinationReference patterns
Technology is disclosed for highly accurate automated execution of processing for alignment of a detection area to a DNA microarray image file and processing for quantitative determination of success / failure of the alignment during DNA microarray analysis. A probe reactive chip used for the technology comprises a substrate; a spot region wherein spots for fixing a probe capable of specifically reacting to a sample marked so as to be optically detectable are formed in a matrix on a surface of the substrate; and a reference pattern area, which is arranged within the spot region or approximate to the spot region, and comprises a plurality of different alignment marks in order to correct misalignment of the spot during analysis of the sample on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Imaging of microarrays using fiber optic exciter
Microarrays are imaged by an illumination and detection system that supplies excitation light through one or more optical fibers, each fiber transmitting excitation light from an excitation light source to a single spot in the microarray. Emission light from each spot is then collected by a collimating lens and converted to a signal that is compiled by conventional software into an image of the entire microarray. The optical fiber(s) and the collimating lens are arranged such that the direction of travel of the excitation light and the direction along which the emission light is collected are not coaxial, and preferably both are at an acute angle to the axis normal to the plane of the microarray.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
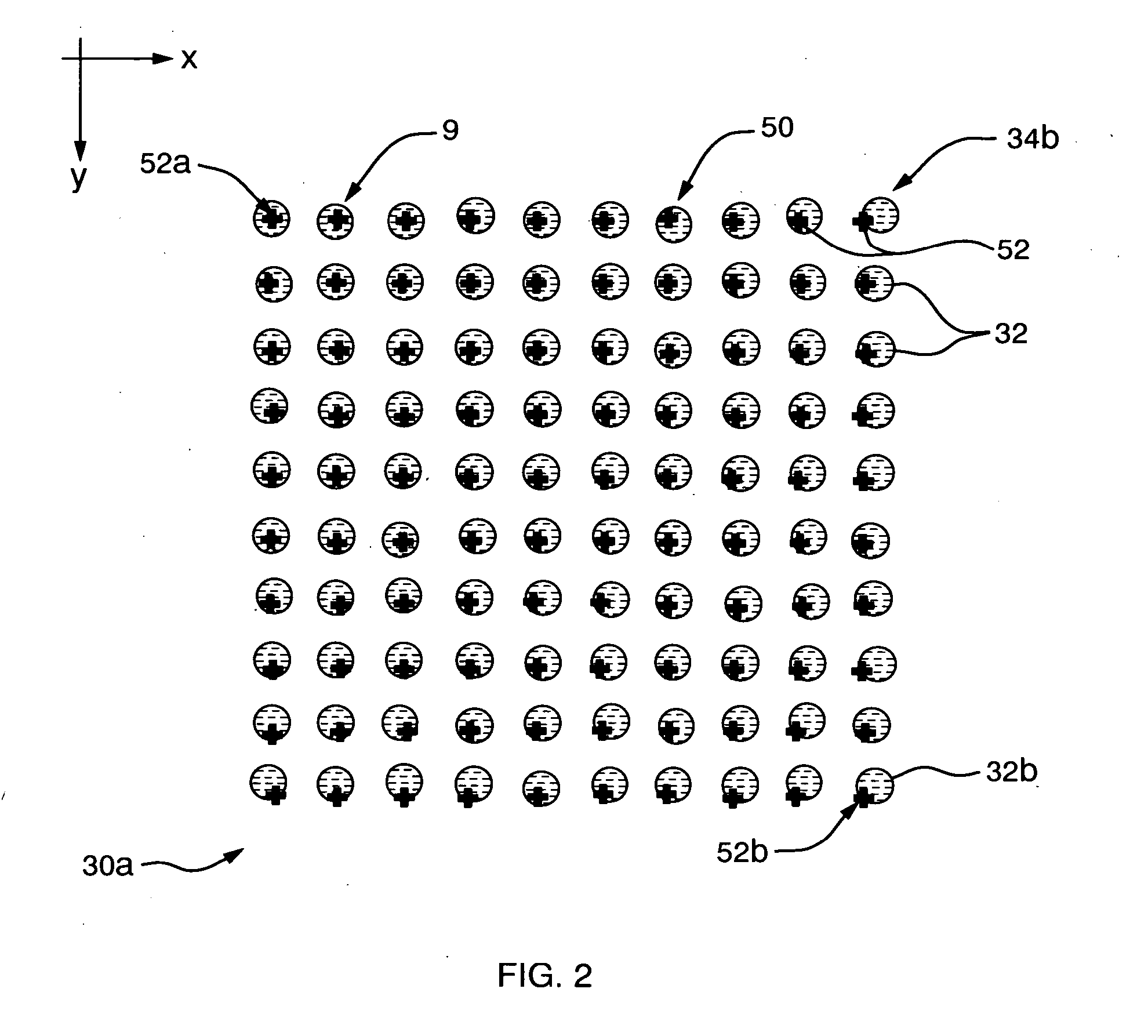
Feature extraction of partial microarray images
InactiveUS20050177315A1Suitable for feature extractionBiological testingHybridisationFeature extractionContour line
A microarray processing system provides to a user an ability to draw one or more contour lines around portions of the microarray considered by the user to be undamaged, non-defective, and otherwise not compromised and therefore suitable for feature extraction. The microarray processing system then constructs one or more rectangular regions of feature extractability based on the user-indicated subregions of feature extractability, and proceeds to extract data from the one or more rectangular regions of feature extractability.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Color detection in random array of microspheres
InactiveUS6947142B2Simple and cost-effective and efficientRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementPattern recognitionColor image
A method of determining one or more color characteristics of a colored microsphere comprising: providing a microarray of microspheres, at least one of which has a color characteristic; capturing the microarray with an electronic color image sensor assembly having a matrix of pixels to produce an electronic microarray image; detecting the location of a microsphere within the captured microarray image; and identifying a color characteristic of the detected microsphere.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
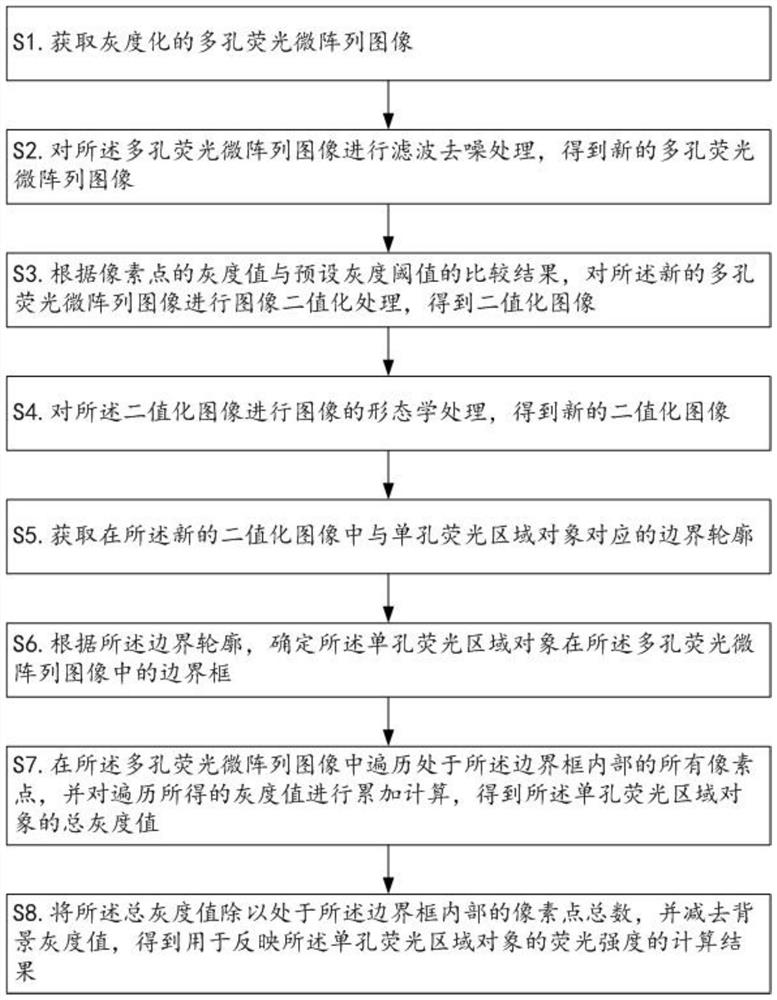
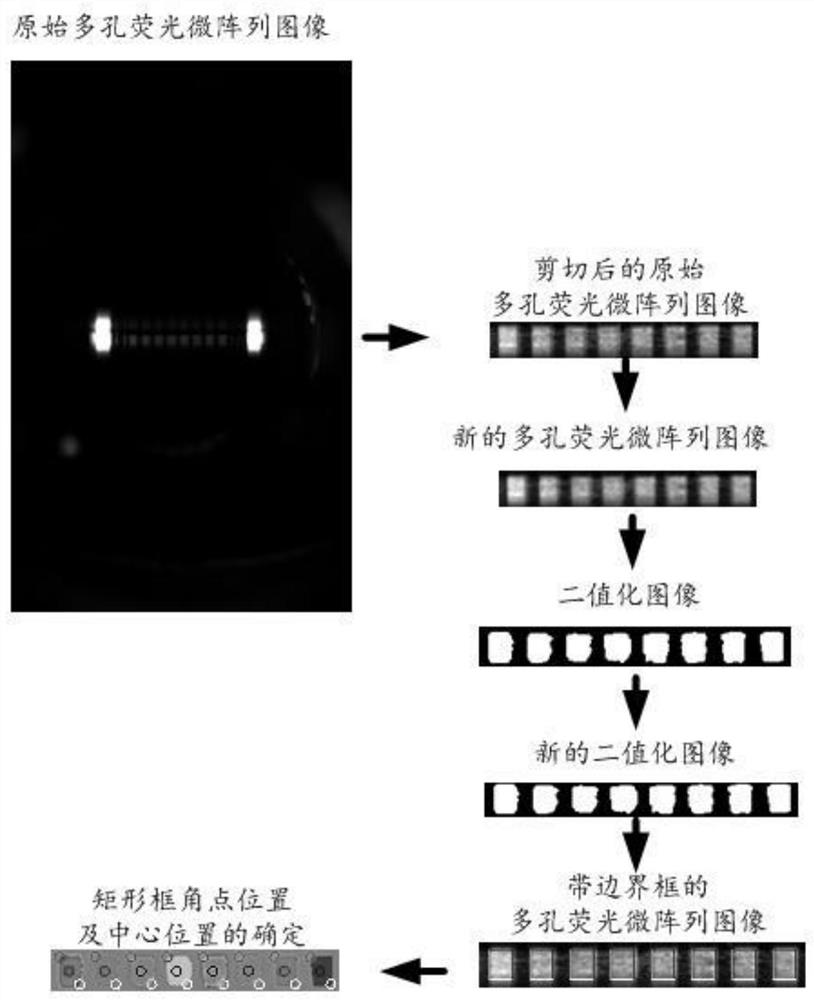
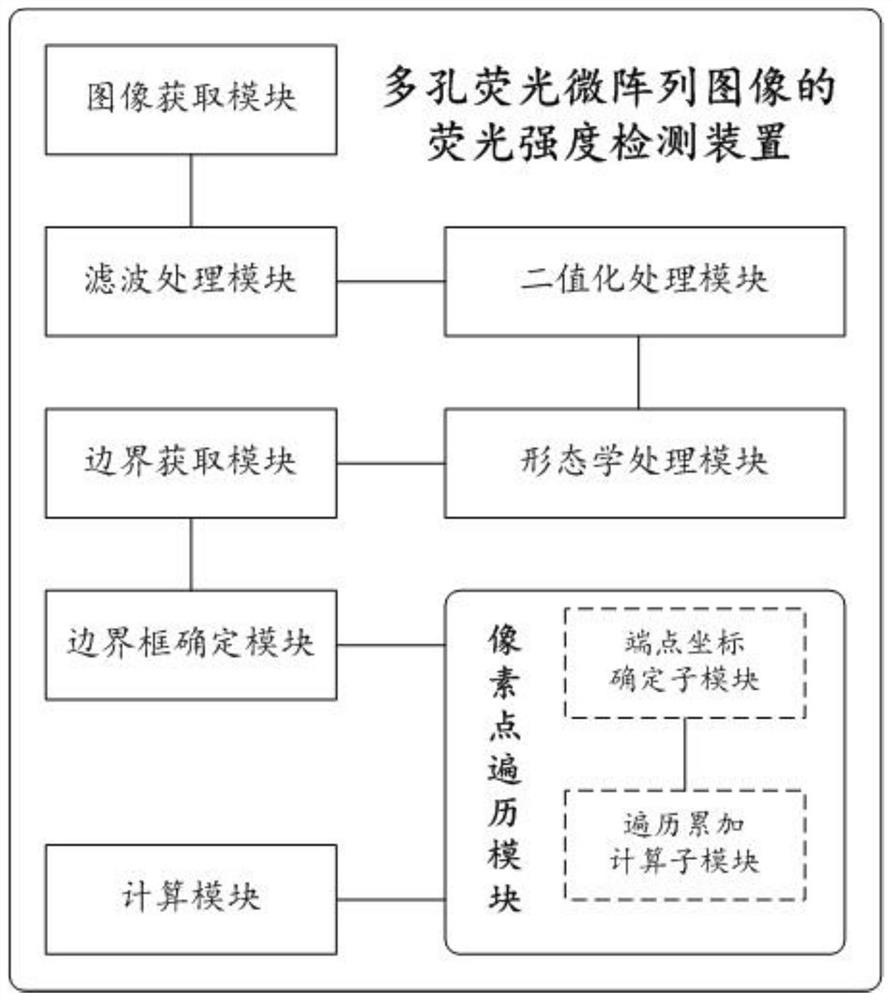
Fluorescence intensity detection method and device for porous fluorescent microarray image, computer equipment and computer readable storage medium
The invention relates to the technical field of digital image processing, and discloses a fluorescence intensity detection method and device for a porous fluorescent microarray image, computer equipment and a computer readable storage medium. After a porous fluorescent microarray image is subjected to filtering and denoising processing, image binarization processing and morphological processing in sequence, a binarized image which is easy to perform contour extraction accurately can be obtained, and for a boundary contour extracted from the binarized image, determination of a bounding box, gray value traversal calculation of pixel points in the box and final background removal calculation of an average gray value are performed in sequence, so that the algorithm operation speed can be improved, the accuracy of the finally obtained fluorescence intensity detection result can be ensured, the fluorescence intensity data of each single-hole fluorescence region object can be quickly and accurately obtained, the purposes of real-time detection and quantitative analysis can be realized, and the method is convenient for practical application and popularization.
Owner:维柯基科技上海有限公司
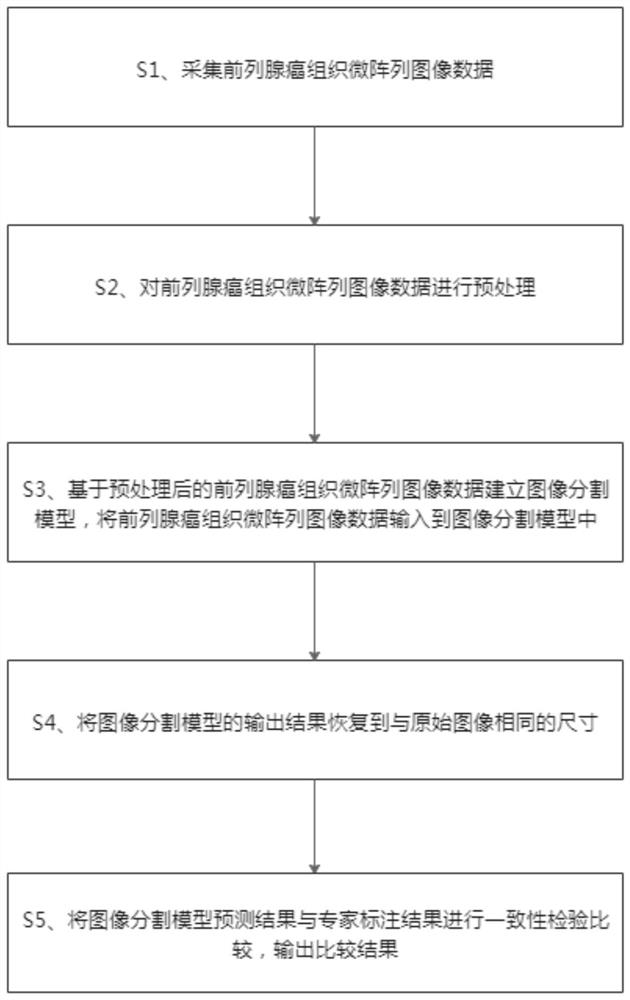
Prostate cancer tissue microarray grading method based on convolutional neural network
The invention provides a prostate cancer tissue microarray grading method based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring prostate cancer tissue microarrayimage data; preprocessing the prostate cancer tissue microarray image data; establishing an image segmentation model based on the preprocessed prostate cancer tissue microarray image data, and inputting the prostate cancer tissue microarray image data into the image segmentation model; restoring an output result of the image segmentation model in the size the same with that of the original image;and performing consistency check and comparison on the prediction result of the image segmentation model and the expert labeling result, and outputting a comparison result. According to the method, the characteristics of the deep layer and the shallow layer can be fused through the multi-scale self-attention network, meanwhile, the characteristics of each scale are supervised, network parameterscan be reduced, the calculation efficiency can be improved, and the effectiveness of the method is verified on a completely marked data set.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
System and method of automated processing of multiple microarray images
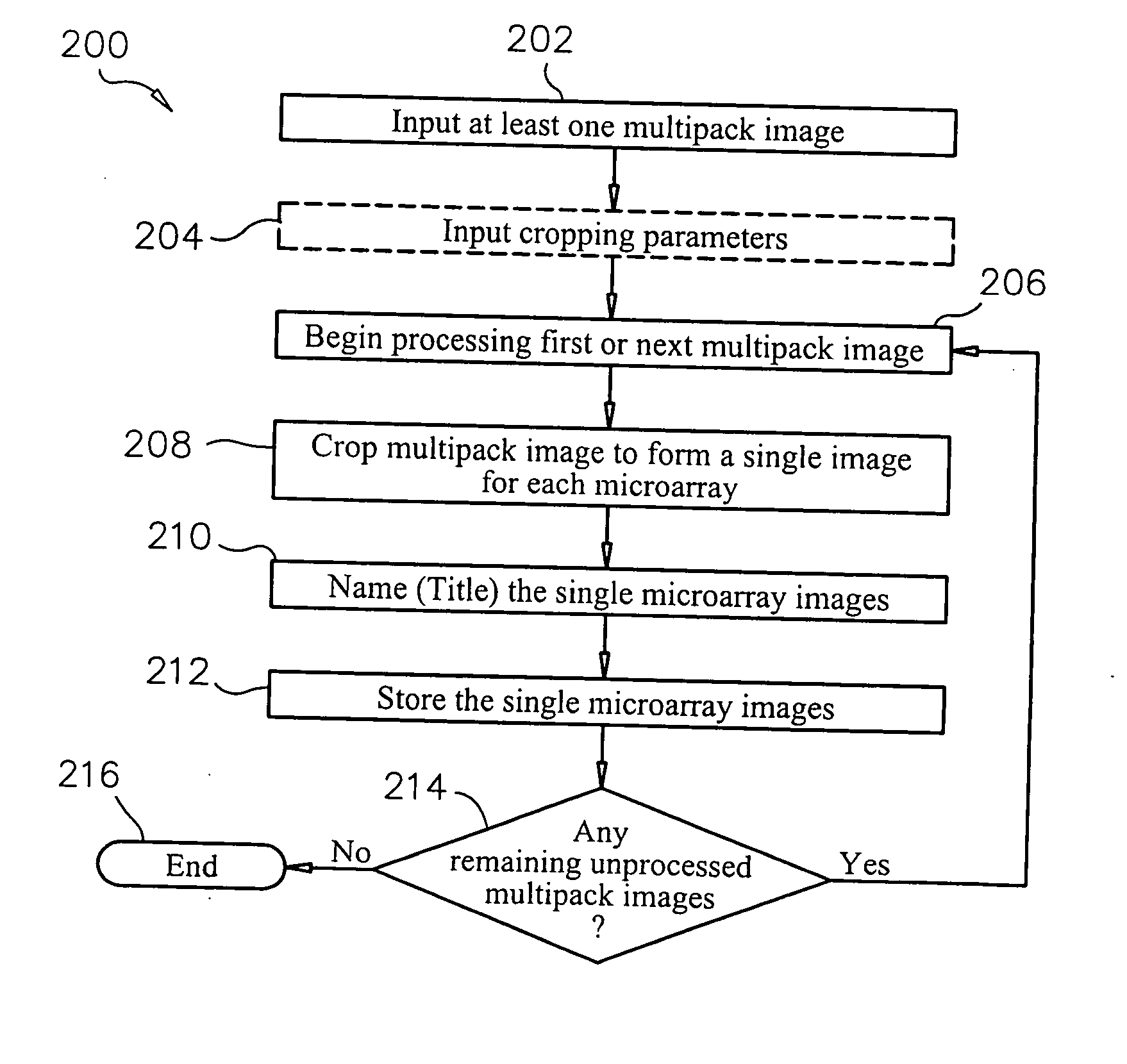
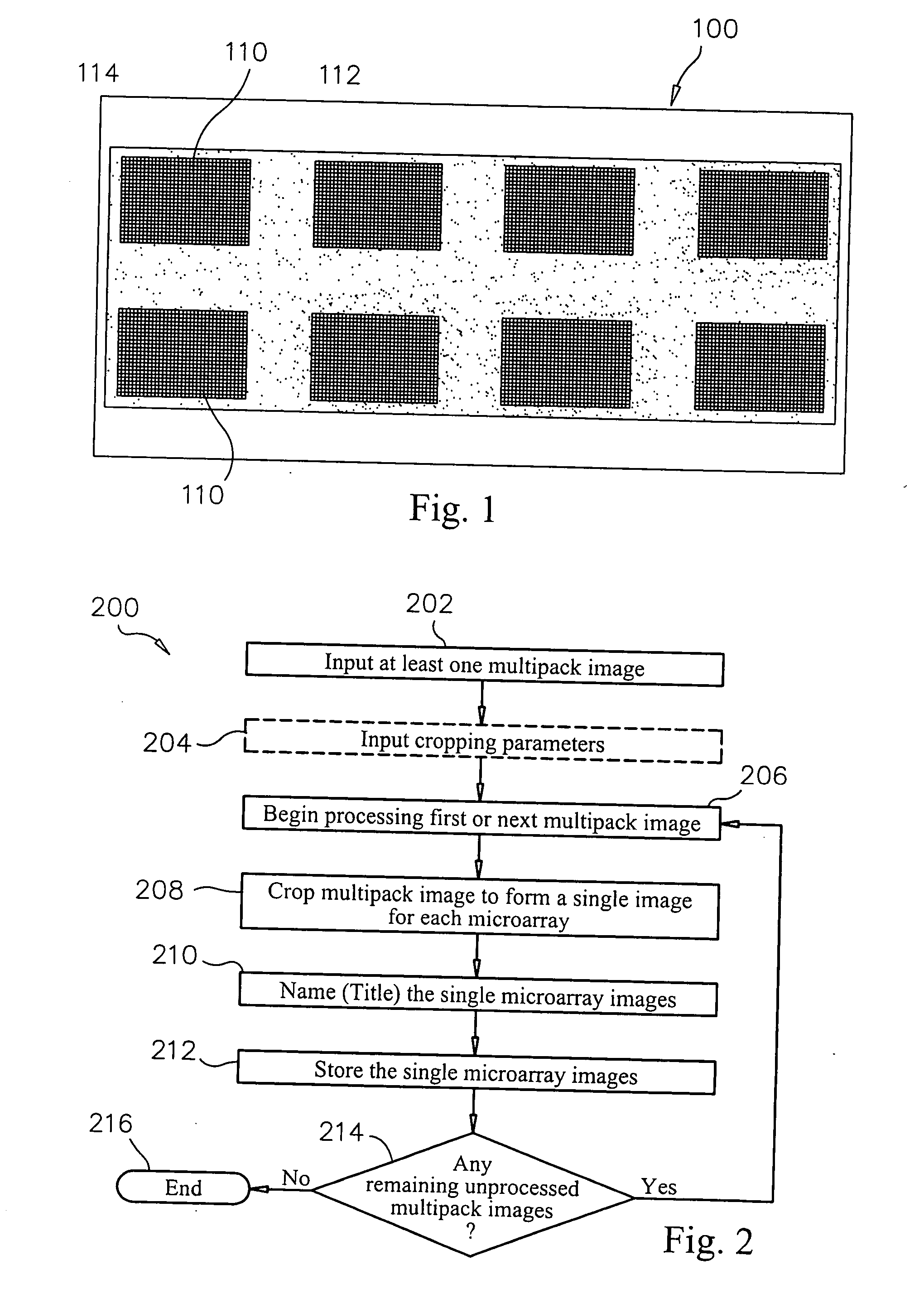
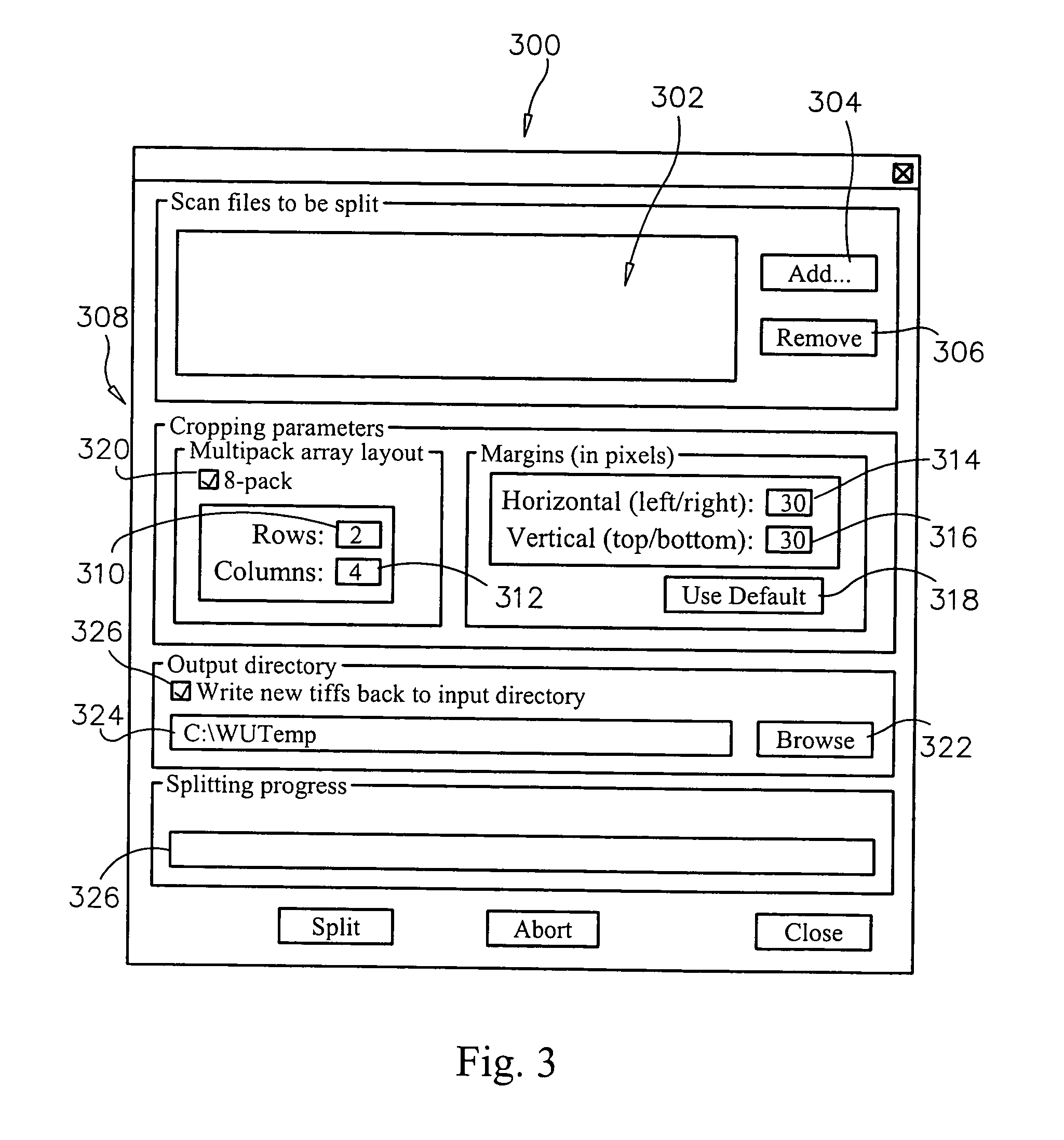
Methods, systems and computer readable media for automatically separating multiple microarray images provided as a single combined image of the multiple microarray images. Methods, systems and computer readable media are provided for providing at least one image containing multiple microarray images thereon, automatically locating the features in the microarray images, automatically determining the boundaries of each microarray image based on the locations of the features, and automatically cropping the image containing multiple microarray images to form a group of single images, each containing only one microarray image cropped from the image containing multiple microarray images. Methods, systems and computer readable media are provided for evaluating separation locations of multiple microarray images in a single combined image of the multiple microarray images, and separating the multiple microarray images along the separation locations, wherein the images are represented in a two-dimensional array.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Tissue microarray analysis
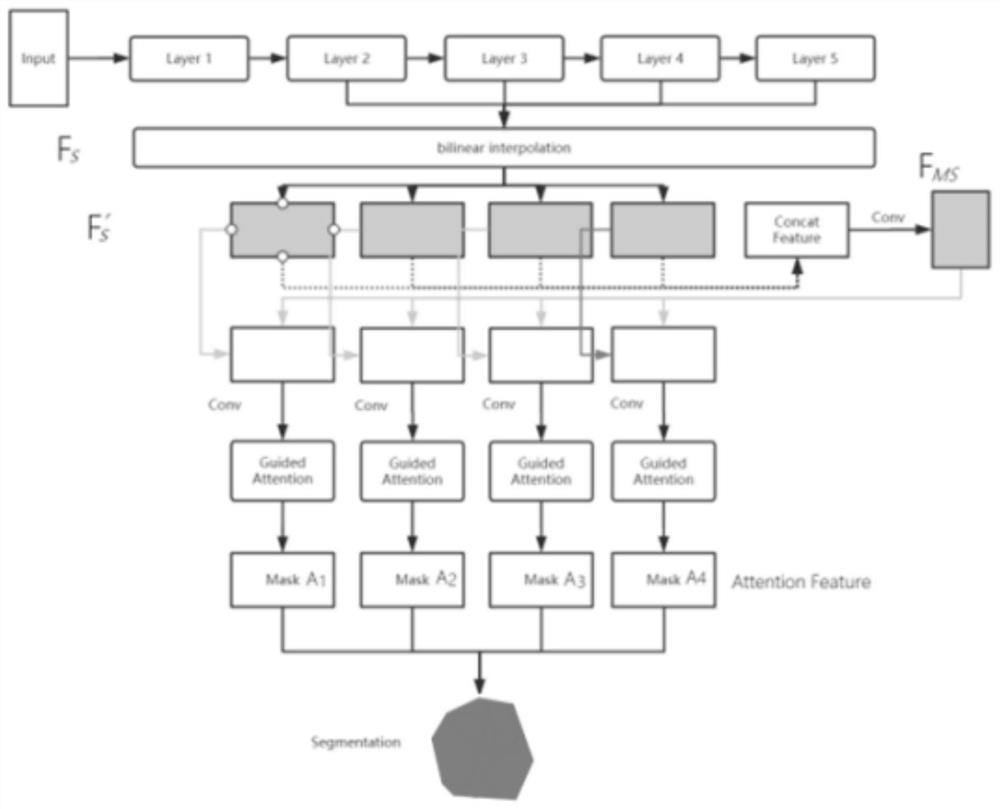
ActiveUS20180247101A1Increase impressionFacilitate viewing overlapping areaImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineTissue sample
The present invention relates to digital pathology. In order to facilitate analyzing a tissue microarray, an apparatus is provided for tissue examination. The apparatus comprises a data input (102), a tissue microarray analyzing unit (104), and an output (106). The data input is configured to receive a reference image of a reference slice obtained from a tissue sample block; and to receive a microarray image of a microarray slice comprising at least one tissue core obtained from at least the tissue sample block. The tissue microarray analyzing unit is configured to register tissue core images of at least one tissue core with the reference image based on a spatial arrangement of the respective tissue core within the tissue sample block. The output is configured to provide a registered result obtained from the tissue microarray analyzing unit for further analyzing purposes.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
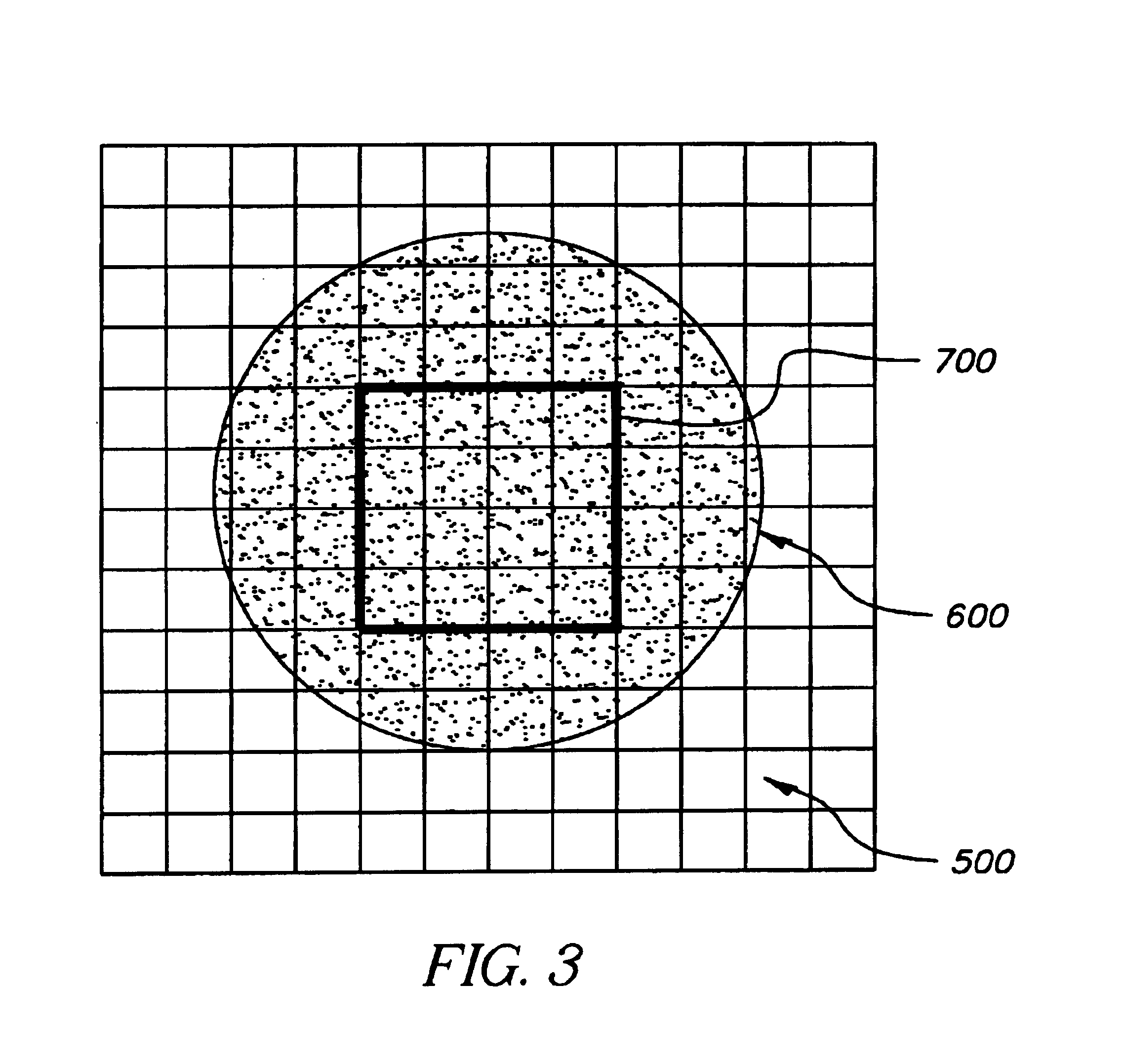
Masking to prevent overexposure and light spillage in microarray scanning
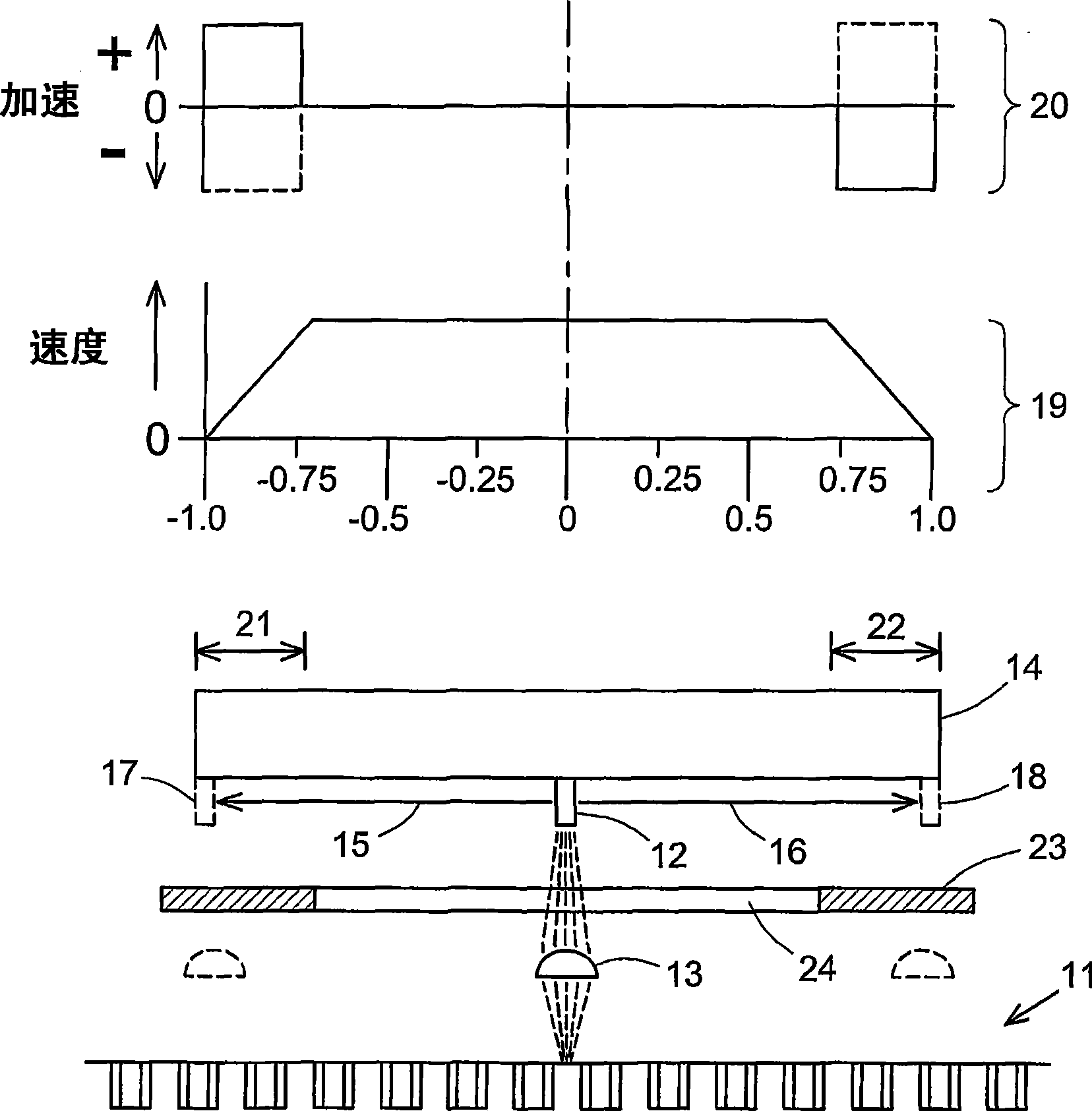
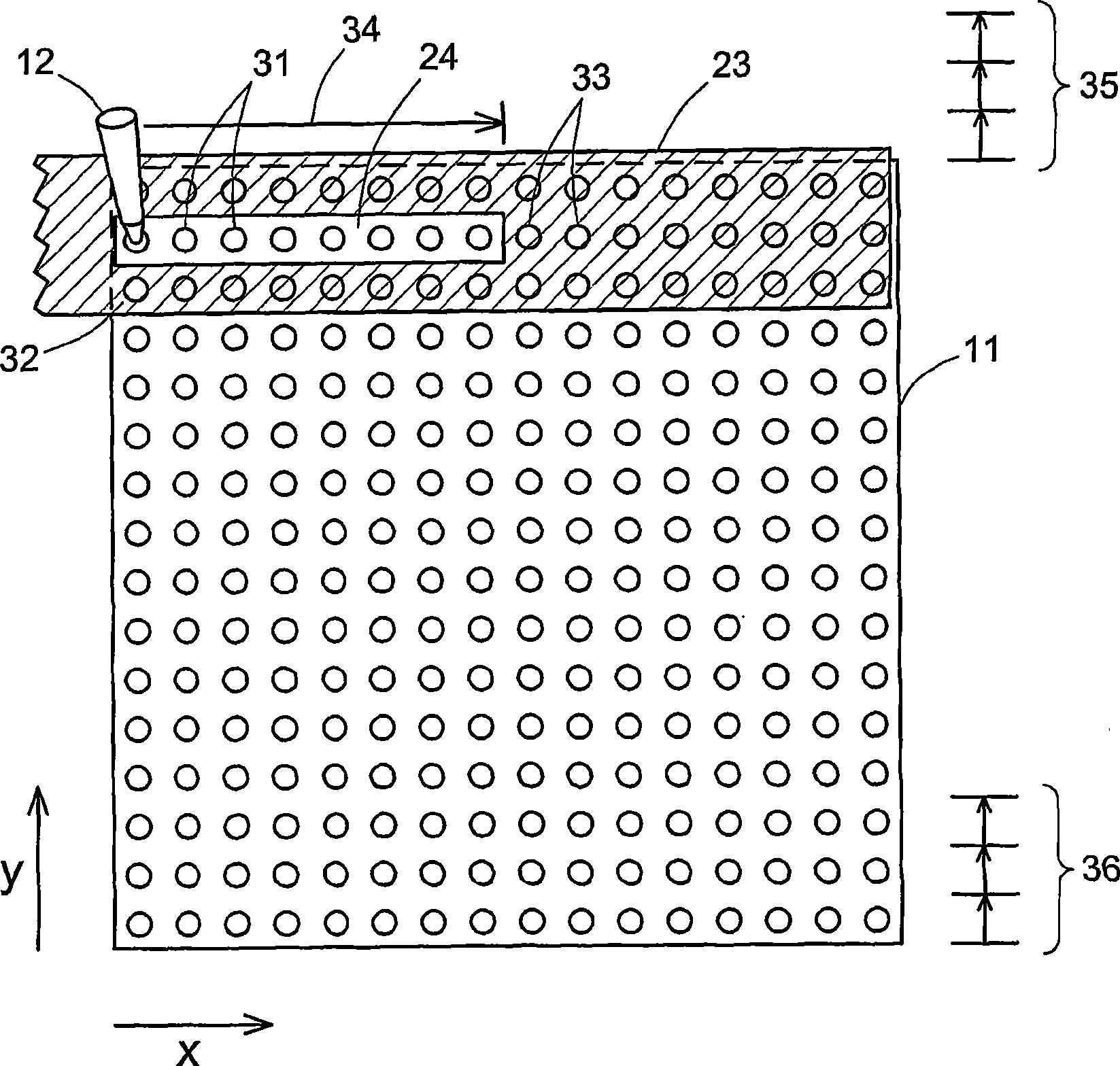
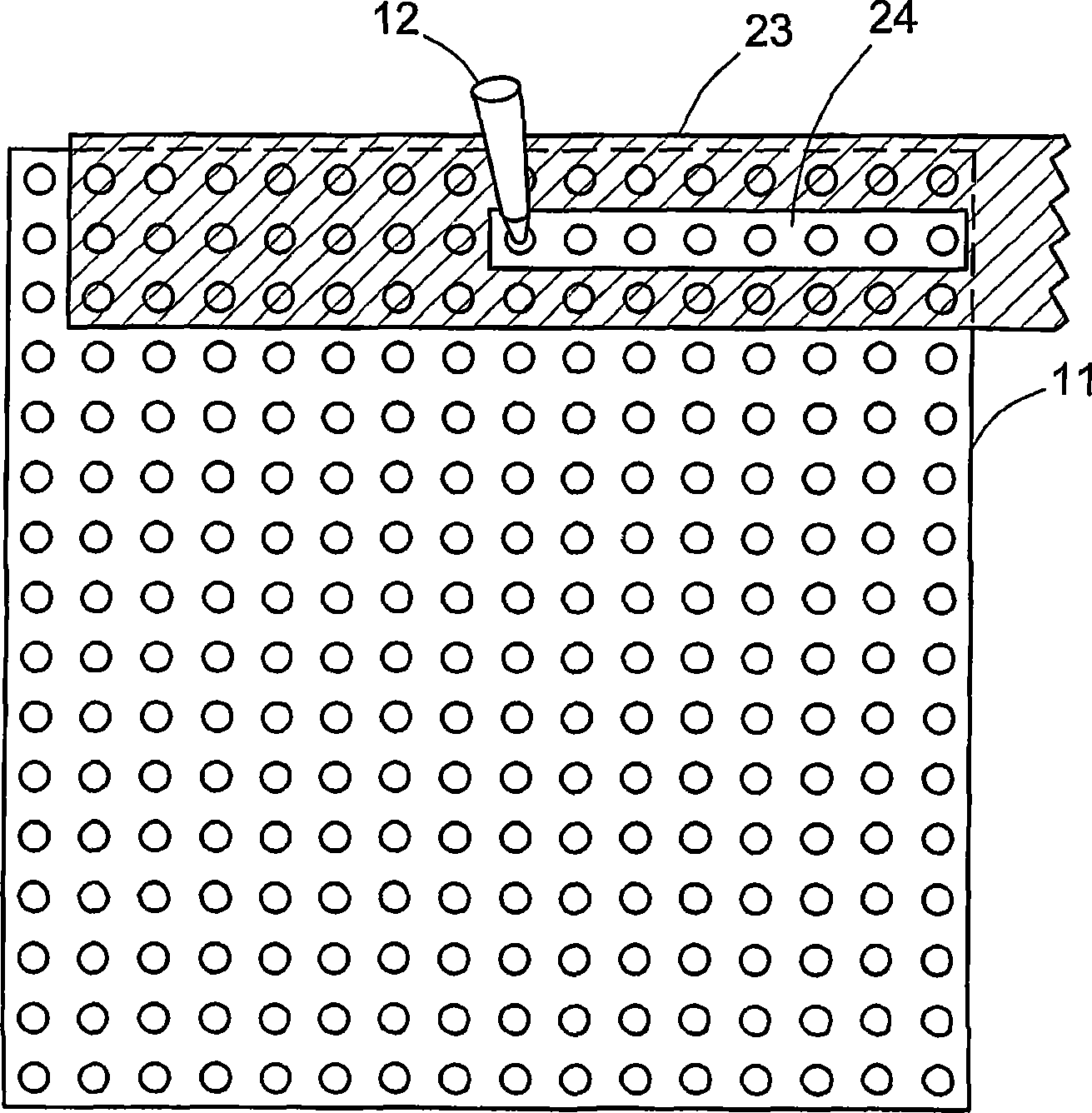
InactiveUS20070132831A1Prevent overflowShorten the lengthInking apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansBackground noiseOptics
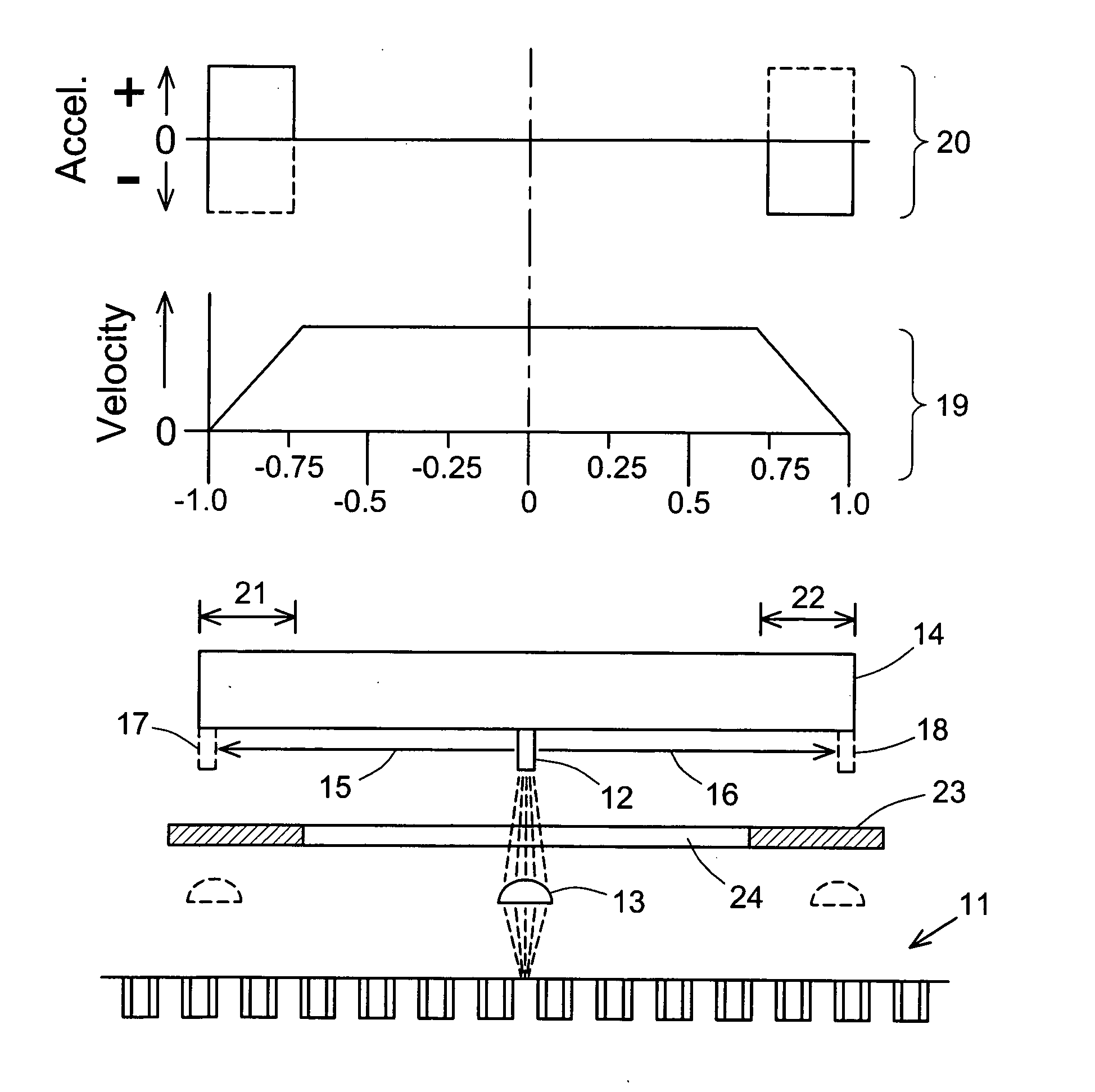
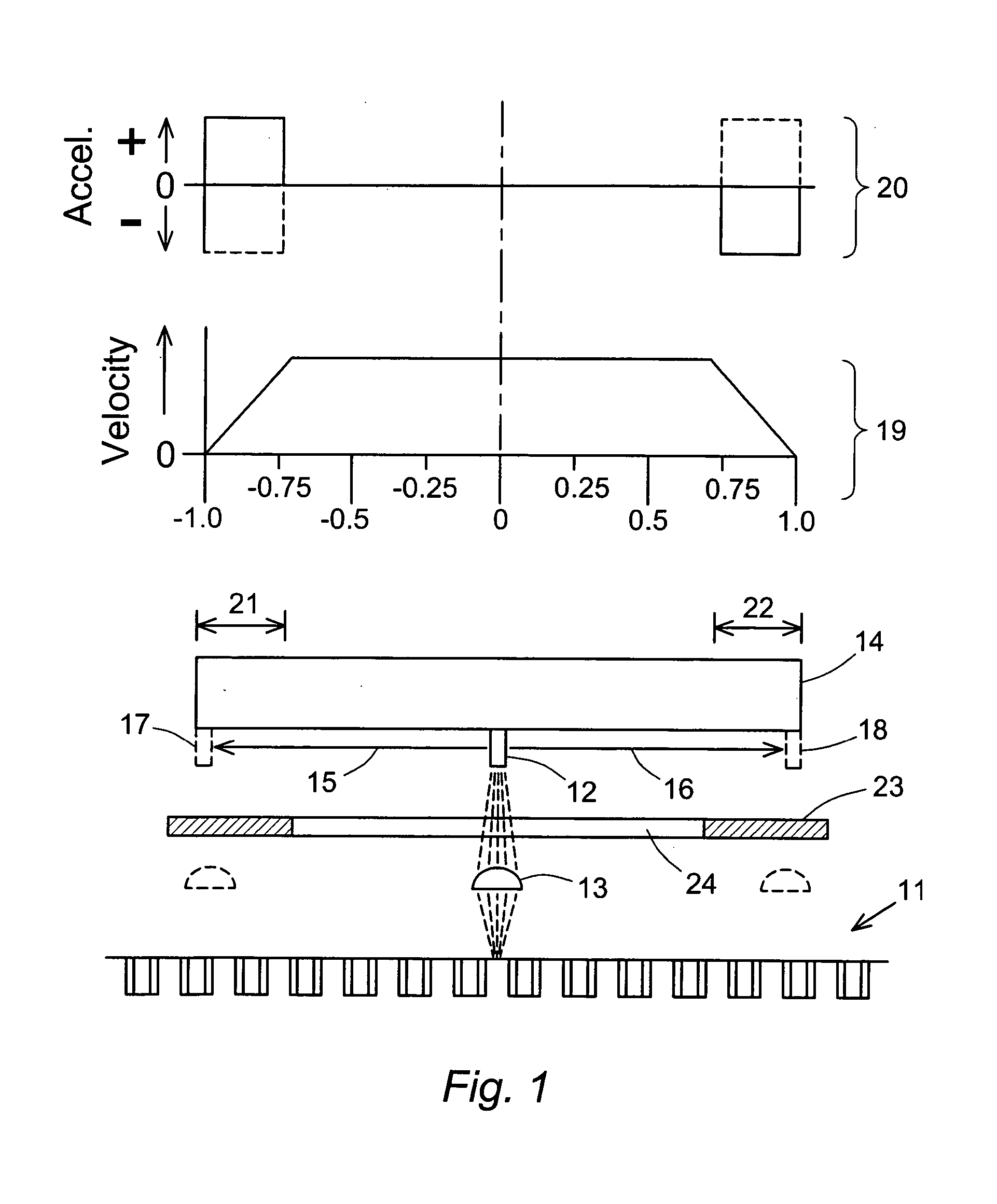
Scanning of a microarray is performed through a mask that exposes a plurality, but not all, of the sites of the microarray, and either the mask is movable relative to the microarray or the microarray is movable relative to the mask, or both. The mask is useful as a means of restricting the illumination of sites on the microarray to those that can be illuminated while the scan head is traveling at a steady, target velocity, blocking the passage of light between the scan head and the microarray at those points in the scan head trajectory where the scan head is either accelerating or decelerating. The mask is also useful for reducing background noise in the microarray image by preventing light spillage to sites adjacent to those being scanned.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
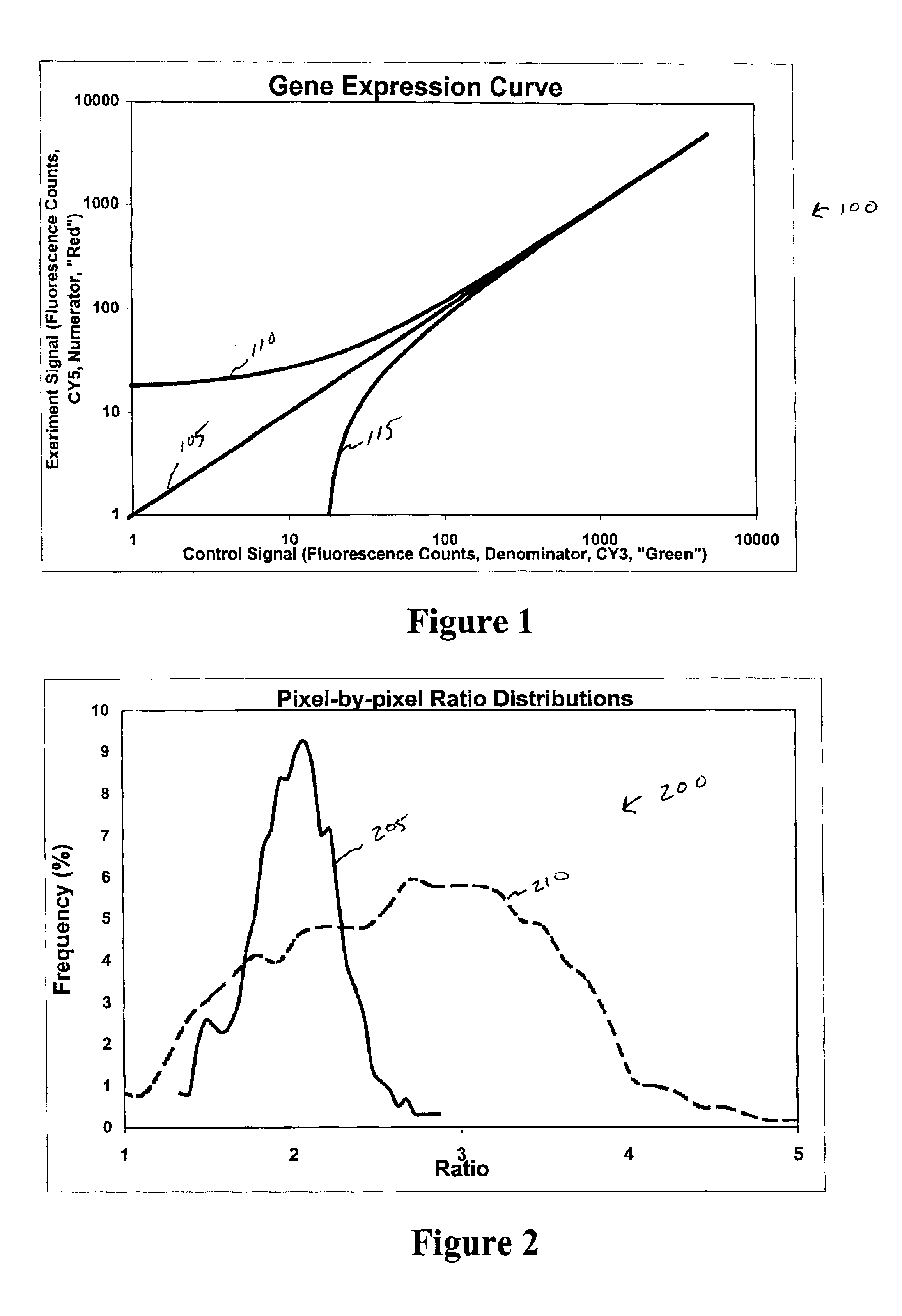
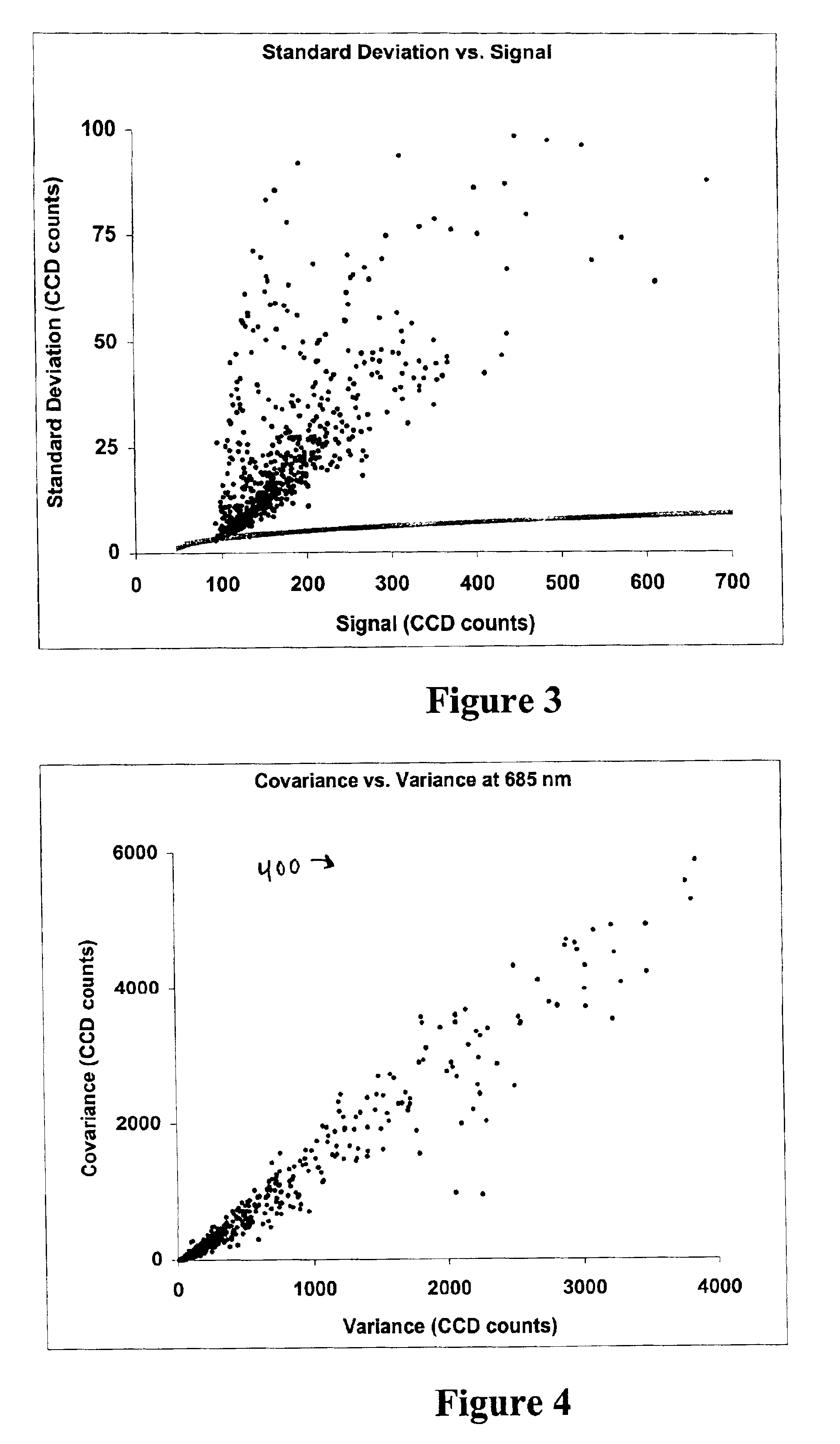
Image metrics in the statistical analysis of DNA microarray data
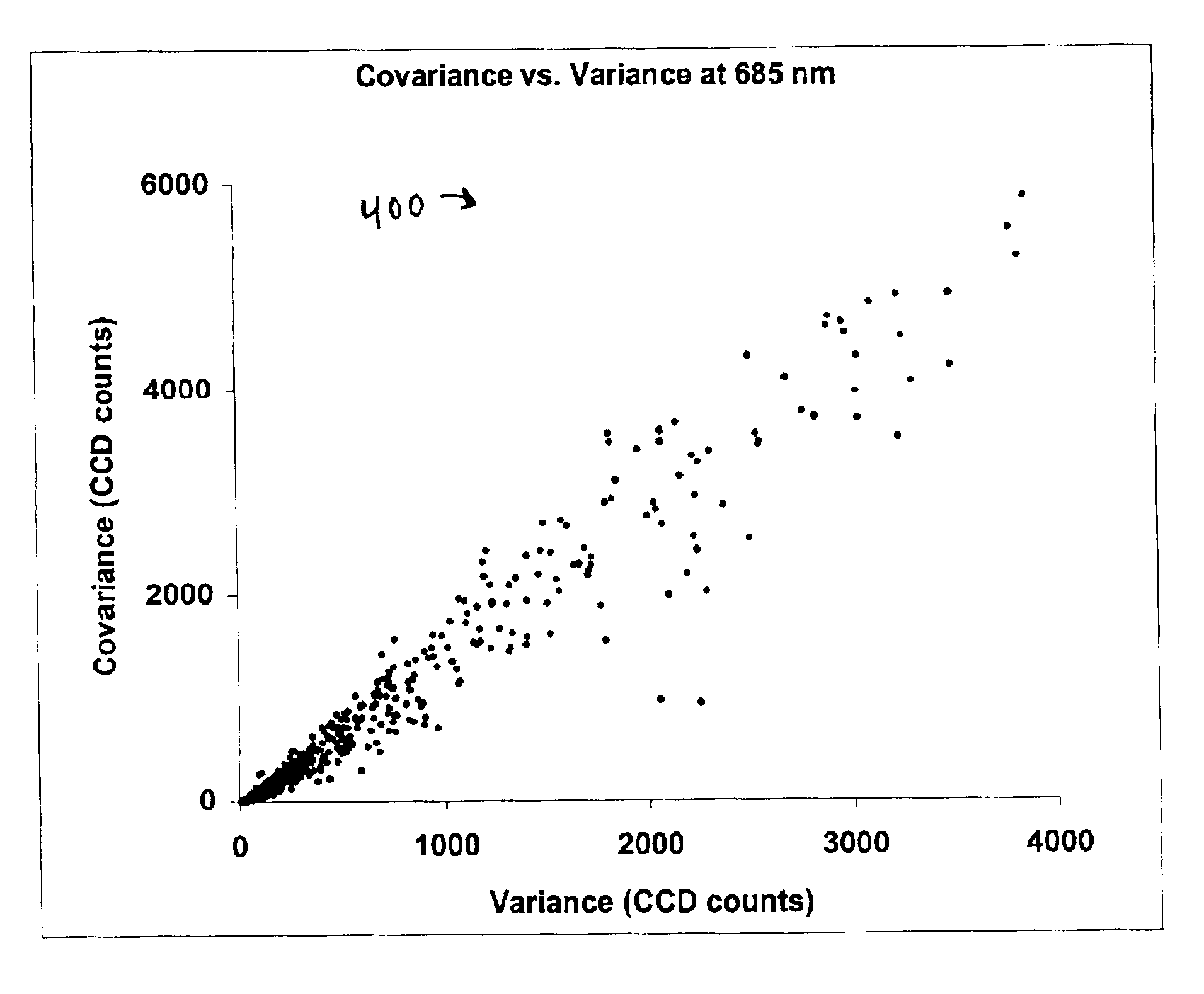
Expression profiling using DNA microarrays is an important new method for analyzing cellular physiology. In “spotted” microarrays, fluorescently labeled cDNA from experimental and control cells is hybridized to arrayed target DNA and the arrays imaged at two or more wavelengths. Statistical analysis is performed on microarray images and show that non-additive background, high intensity fluctuations across spots, and fabrication artifacts interfere with the accurate determination of intensity information. The probability density distributions generated by pixel-by-pixel analysis of images can be used to measure the precision with which spot intensities are determined. Simple weighting schemes based on these probability distributions are effective in improving significantly the quality of microarray data as it accumulates in a multi-experiment database. Error estimates from image-based metrics should be one component in an explicitly probabilistic scheme for the analysis of DNA microarray data.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Method and apparatus for automatically segmenting a microarray image
InactiveUS7599090B2Positioning is simple and fastMaximizing scoreImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersAlgorithmComputer vision
A microarray image is segmented into discreet segments for respective spots in the microarray image based on locating microarray image rows and columns by maximizing scores associated with vertical and horizontal image projections. To determine the locations of the rows and columns that extend through artifacts that involve multiple spots and / or multiple columns and rows, the scores may also include contributions from the gaps between adjacent rows and columns. The scores are calculated by stepping windows containing nominally spaced spot-sized row or column boundaries, over the horizontal projection curves. At each step a total row or column score is calculated that represents the areas of the projection curves that fall within the row boundaries. The system then selects the window positions that correspond to the maximum total row score and total column score, and uses the locations of the boundaries as the locations of row and column “stripes” that are sized to the spot diameters. The intersections of the row and column stripes define the segments for the respective spots, and the centers of the intersections are the locations for the spot location, or grid, markers. The system may also determine the best spot size, column and row gap sizes and sub-array gap sizes by changing the boundaries accordingly and determining corresponding maximum scores.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
System and apparatus for the remote analysis of chemical compound microarrays
ActiveUS8873815B2Simplifies CMA processImprove portabilityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionChemical compound
A remote microarray analysis system, method and apparatus for use in the remote analysis of a chemical compound microarray supported on a substrate is disclosed. Pixel image data is received from a remote location including image data that depicts (a) a calibration scale associated with the substrate and (b) the microarray. A transformation action of said pixel data corresponding to the calibration scale is determined and the received image data corresponding to at least the microarray is adjusted by applying the transformation action. The adjusted image of the microarray is compared with a database of stored microarray pixel data to extract information from said image.
Owner:DAKADOO AG
Method and apparatus for segmenting a microarray image
InactiveUS20050196042A1Amount of timeImage segmentationRadiation/particle handlingCharacter and pattern recognitionImage segmentationComputer vision
In a method for providing rapid and simple manually driven alignment of image segmentation grids to images of imperfect mircroarrays, an image of a microarray composed of multiple sub-arrays or blocks is displayed and a nominal grid composed of corresponding sub-arrays or blocks is superimposed on that image. Comer markers of a grid block are dragged to coincide with the spots at the corresponding corners of the underlying image block. The locations of the intervening grid markers in that block are automatically adjusted by linear interpolation in two dimensions. The corrections generated for this grid block are then applied automatically to all of the other blocks in the grid. Following this, the corner grid blocks are dragged to align a single corner marker within each corner grid block with an image spot at the corresponding corner block of the image, and all of the intervening grid blocks are automatically aligned to these by linear interpolation in two dimensions.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Method to automatically decode microarray images
ActiveCN101553824AError Distortion MinimizationImage enhancementImage analysisFast Fourier transformHigh density
A method of automatically identifying the microarray chip corners and probes, even if there are no probes at the corners, in a high density and high resolution microarray 5 scanned image having an image space, wherein the method minimizes the error distortions in the image arising in the scanning process by applying to the image a multipass corner finding algorithm comprising: (a) applying a Radon transform to an input microarray image to project the image into an angle and distance space where it is possible to find the orientation of the straight lines; (b) applying a fast Fourier transform to the projected image 10 of (a) to find the optimal tilting angle of the projected image; (c) determining the optimal first and last local maxima for the optimal tilting angle; (d) back projecting the determined first and last local maxima to the image space to find the first approximation of the first and last column lines of the image; (e) rotating the image and repeating steps (a) through (d) to find the first approximation of the top and bottom row lines of the image; (f) determining 15 the first approximation of the four corners of the image from the intersection of the column and row lines; (g) applying a heuristic for determining if the first approximation of step (f) is sufficient; and (h) optionally trimming the scanned image around the first approximation of the four corners and repeating steps (a) through (f).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Masking to prevent overexposure and light spillage in microarray scanning
InactiveCN101507256AClear performancePhotometryAnalysis by material excitationBackground noiseOptics
Scanning of a microarray is performed through a mask that exposes a plurality, but not all, of the sites of the microarray, and either the mask is movable relative to the microarray or the microarray is movable relative to the mask, or both. The mask is useful as a means of restricting the illumination of sites on the microarray to those that can be illuminated while the scan head is traveling at a steady, target velocity, blocking the passage of light between the scan head and the microarray at those points in the scan head trajectory where the scan head is either accelerating or decelerating. The mask is also useful for reducing background noise in the microarray image by preventing light spillage to sites adjacent to those being scanned.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
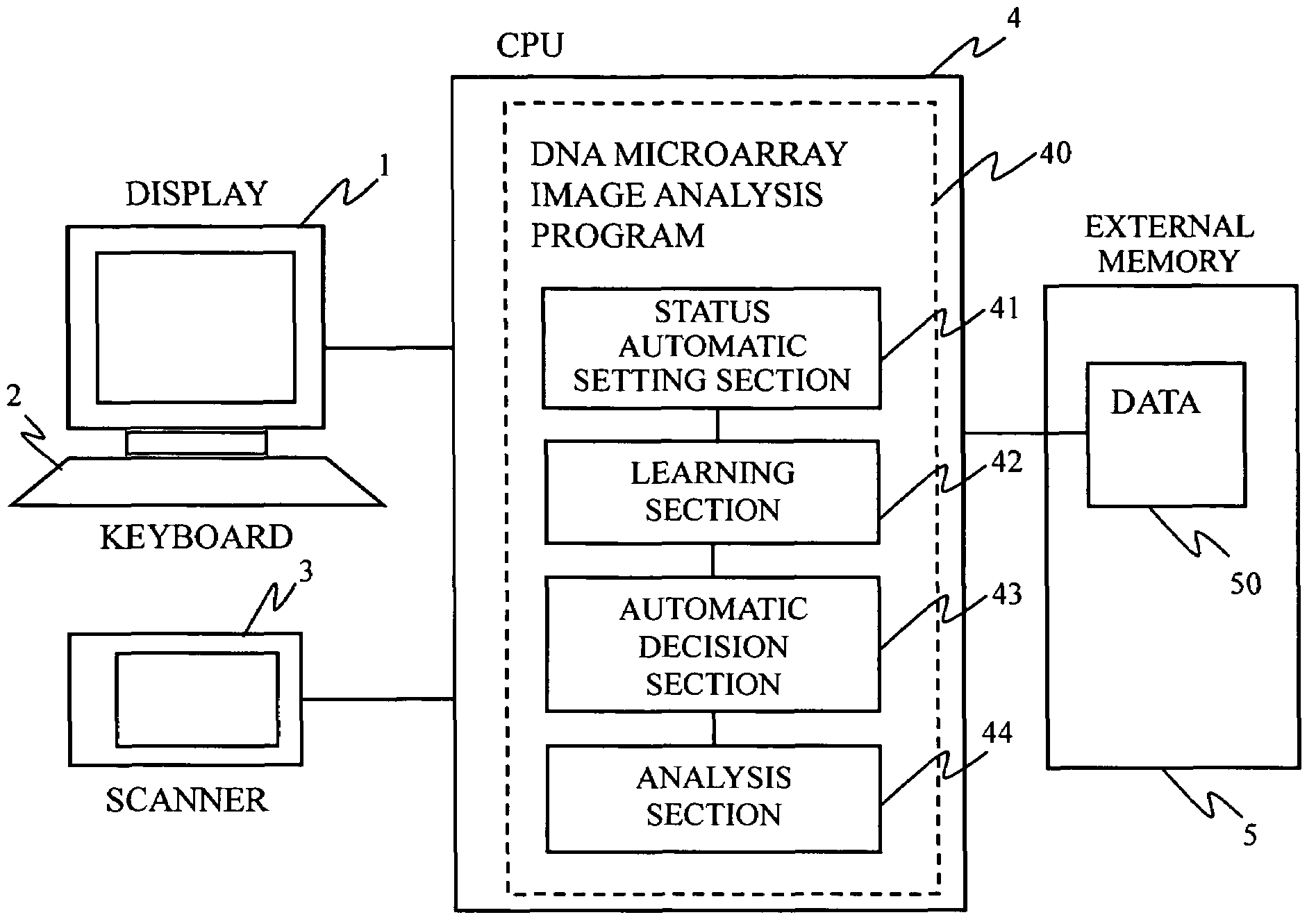
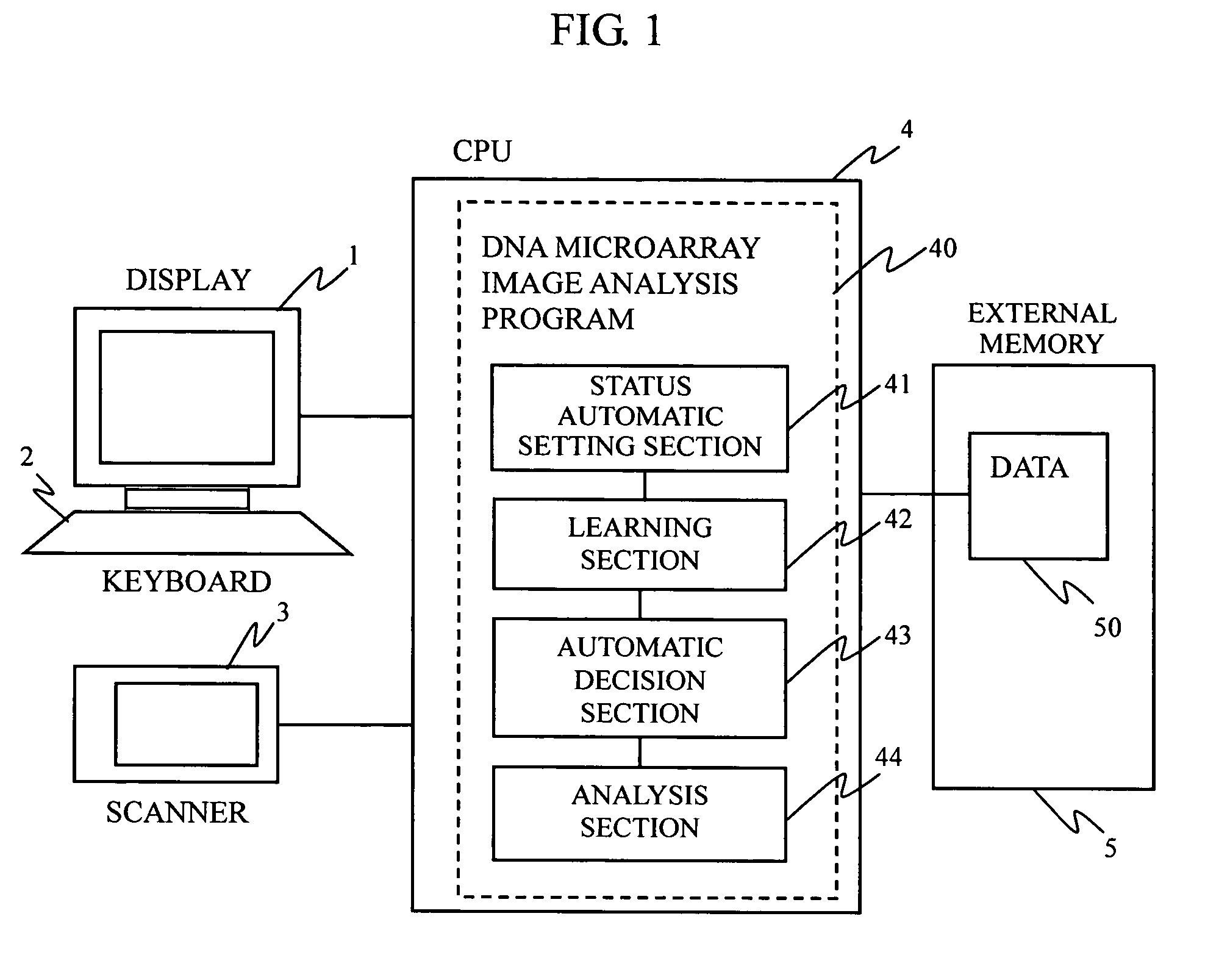
DNA microarray image analysis system
InactiveUS7359537B2Improve abilitiesImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisNeural network learning
In a microarray image analysis system, when one of a plurality of statuses is set for a spot of a microarray by the user, the status of a similar spot is automatically determined. In a microarray image, the user determines a status of a spot, the pixel value matrix of an image in a spot region is learned by a neural network, a vertically and horizontally symmetrical image and an image rotated about the center of the region are formed and are learned by the neural network, and the neural network formed by repeating these steps is used for automatically recognizing the status of an undecided spot.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG
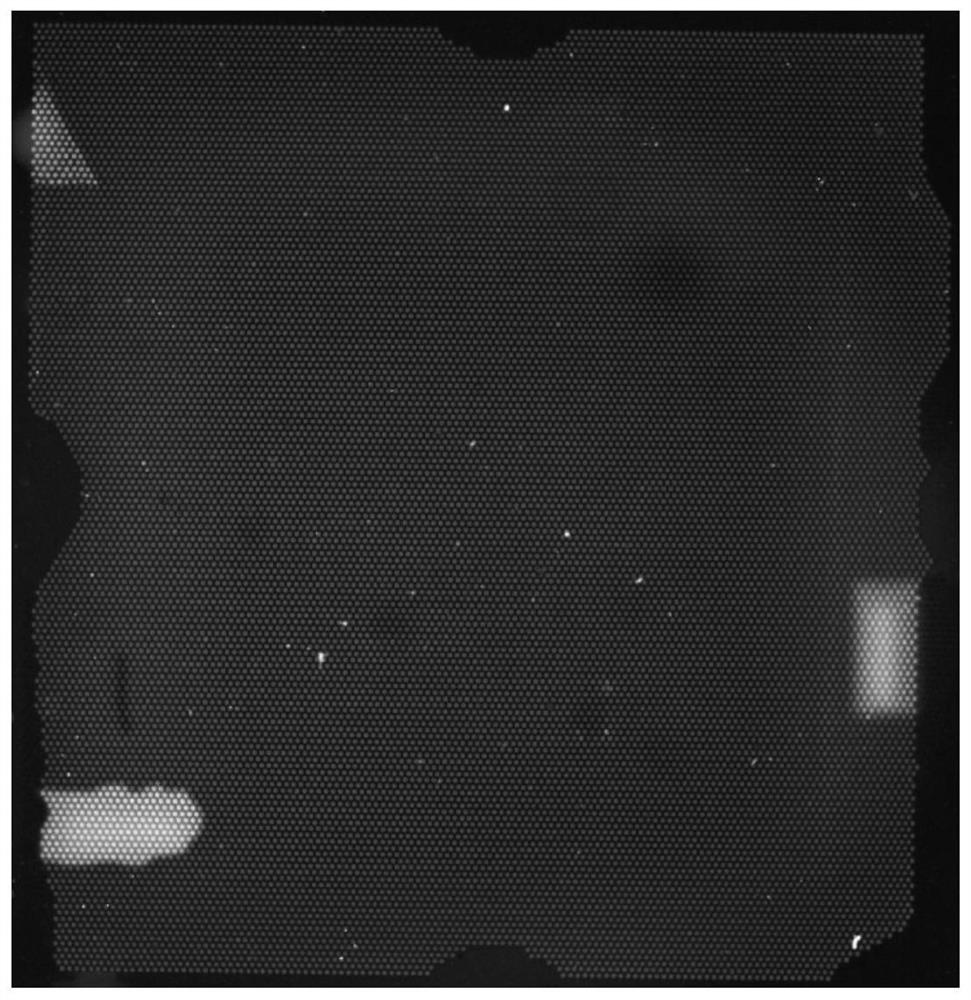
Digital PCR microarray image analysis method
InactiveCN112927182AAchieving Absolute Quantitative AnalysisImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisImage segmentation
The invention provides a digital PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) microarray image analysis method, which comprises the following steps of: inputting a first channel fluorescence image, and preprocessing the first channel fluorescence image; carrying out image segmentation on the preprocessed fluorescence image; identifying effective units of the segmented image, and extracting centroid coordinates of the effective units; positioning and extracting effective units in the second and third channel images according to the coordinates, and counting fluorescence signal intensity of the effective units in the second and third channel images according to the effective units; according to the signal intensity, drawing a scatter diagram and a histogram of the fluorescence intensity of the reaction units in the second channel image and the third channel image, counting the proportion of the positive units, combining Poisson distribution, and calculating the concentration of the target nucleic acid molecules in the original reaction liquid. The mask is established by the first channel image so as to indirectly analyze the second channel image and the third channel image, so that the multi-channel digital PCR microarray image under non-uniform illumination can be effectively analyzed, the accuracy of image analysis is improved, and absolute quantitative analysis of target nucleic acid molecules is realized.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV OF TECH
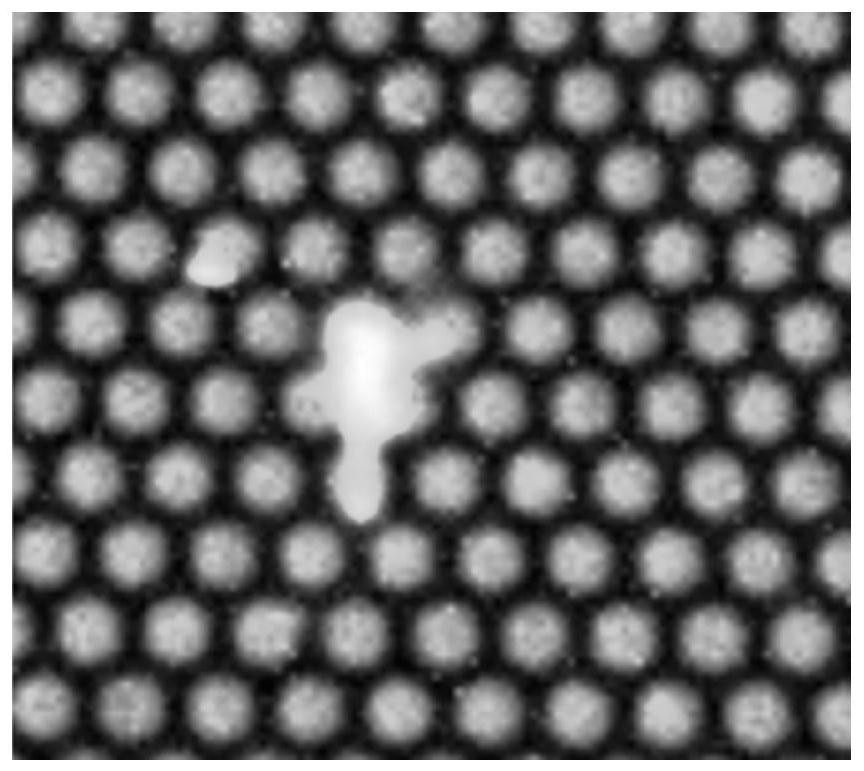
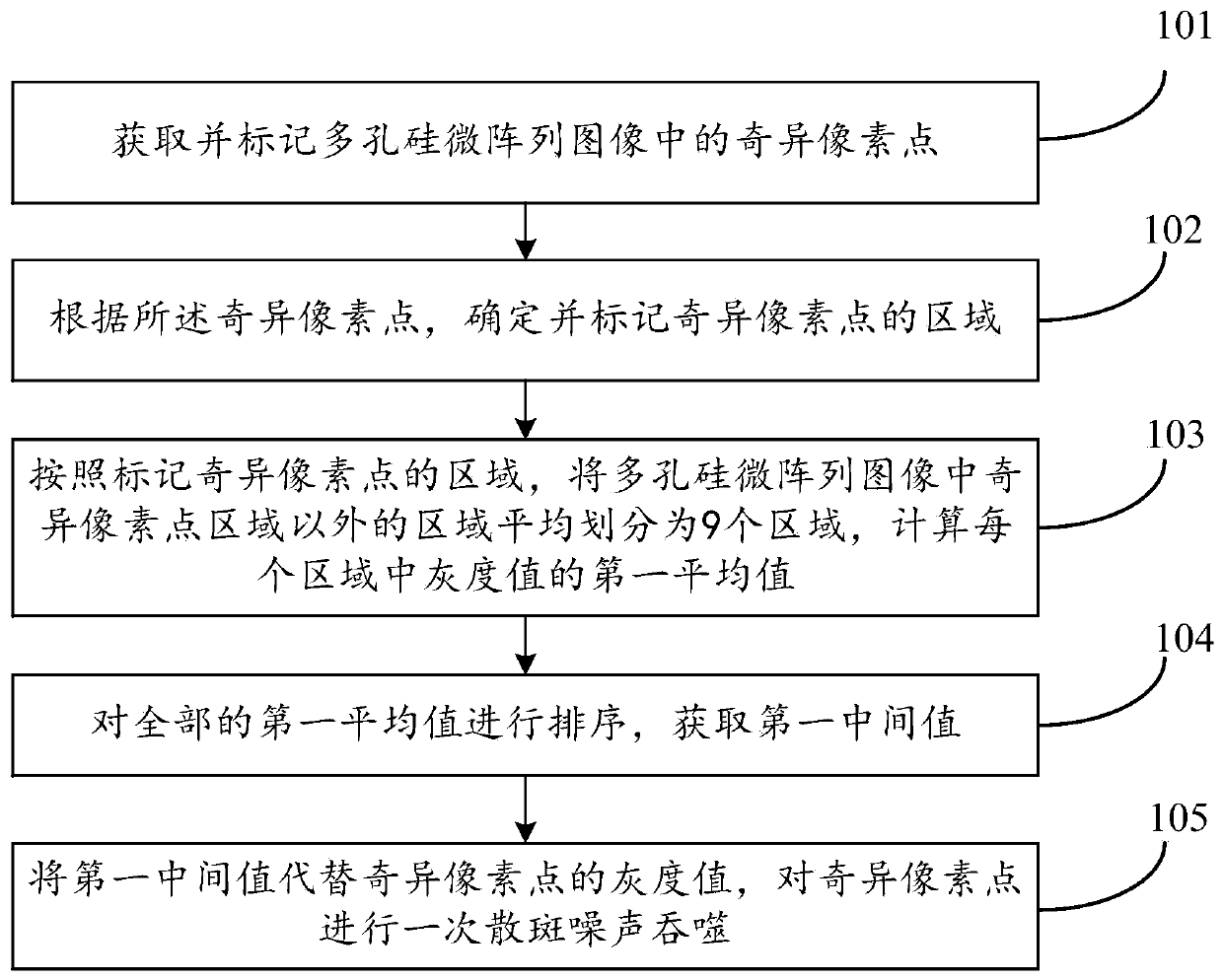
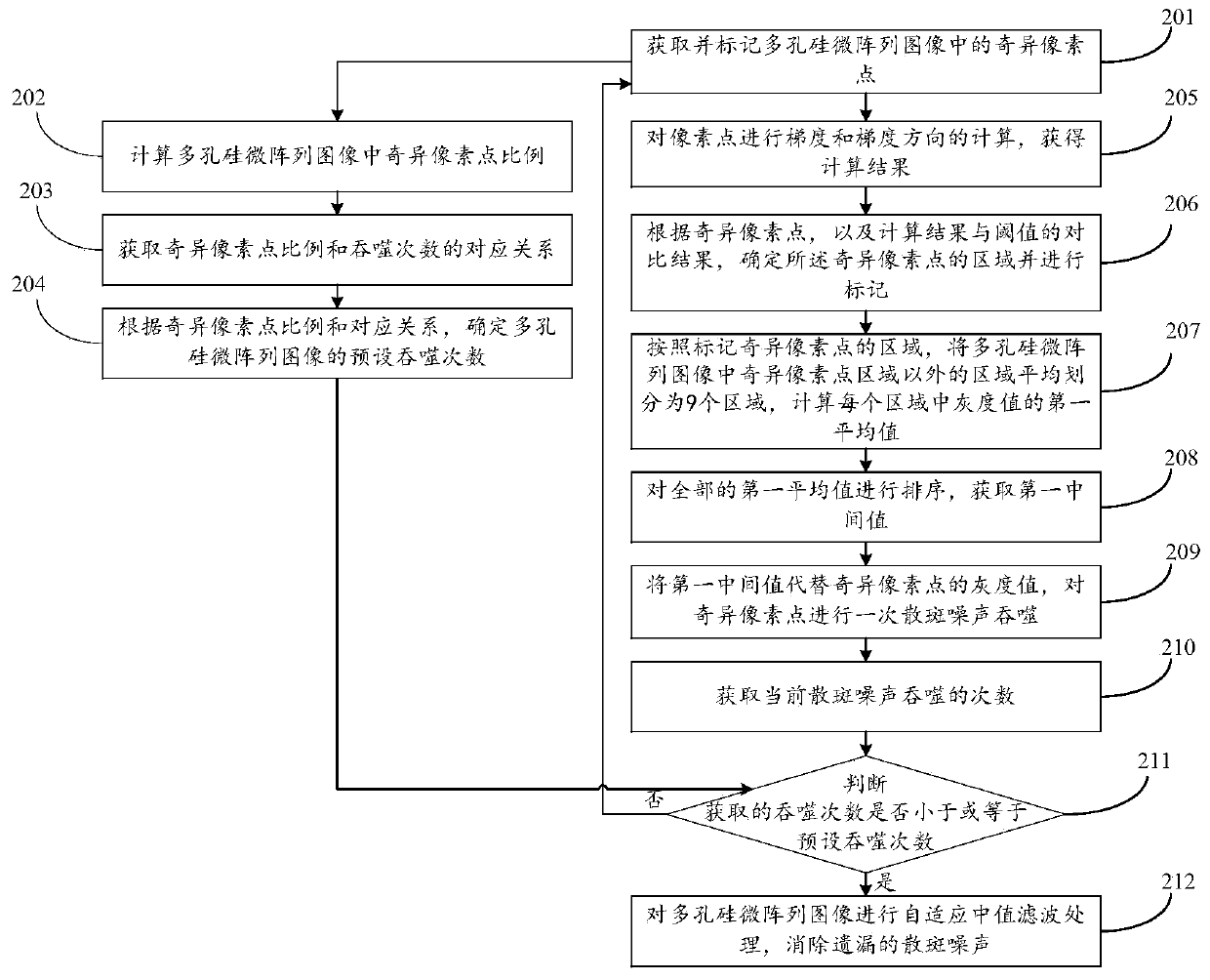
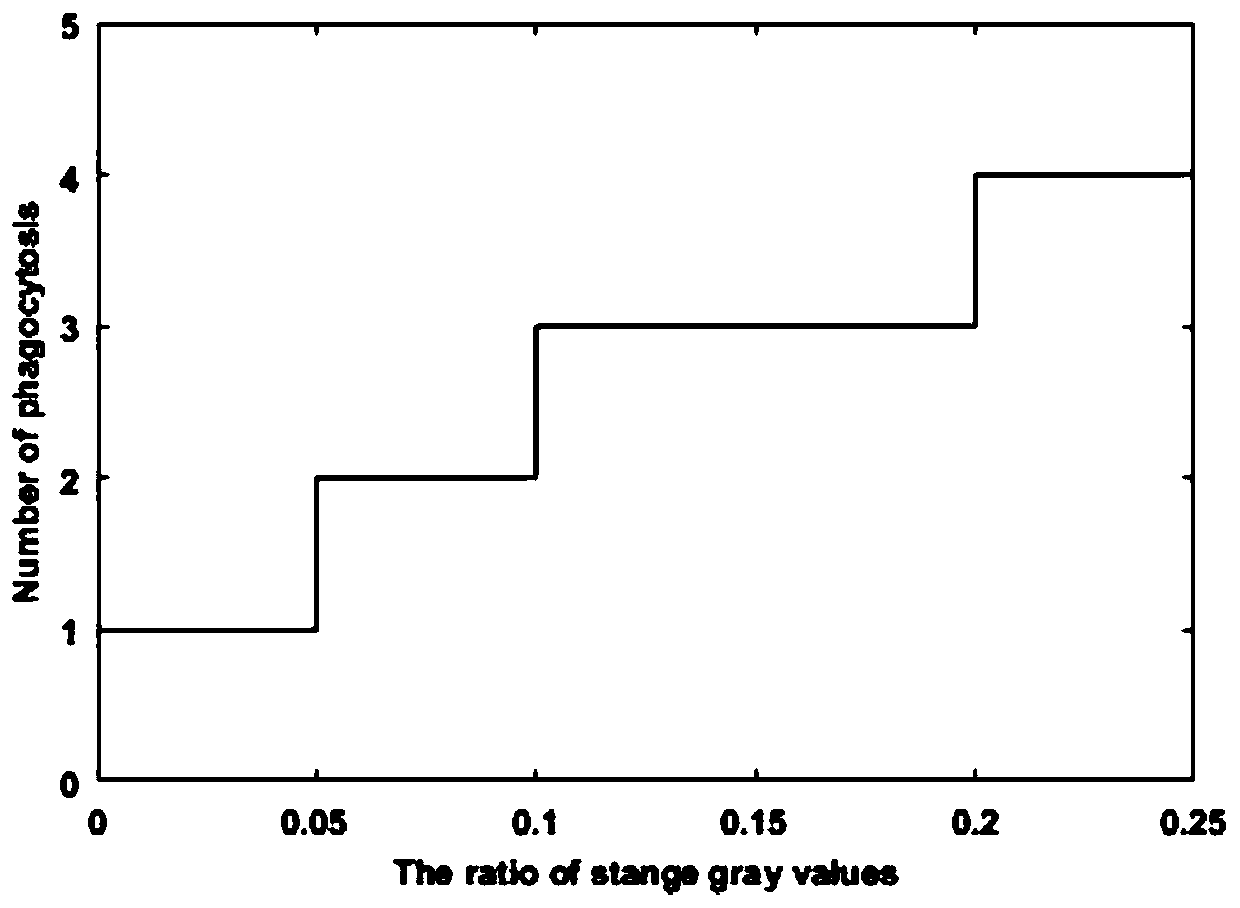
A method and a device for removing speckle noise in a porous silicon microarray image
ActiveCN109712130AGray value restorationEliminate the effects ofImage analysisComputer visionBiochip
The invention discloses a method and a device for removing speckle noise in a porous silicon microarray image, relates to the field of biochips, and can solve the problem of influence of speckle noiseon microarray image detection in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring singular pixel points in a porous silicon microarray image, and marking the singular pixel points;determining and marking an area of the singular pixel point according to the singular pixel point; averagely dividing the region except the singular pixel point region in the porous silicon microarrayimage into nine regions according to the region marked with the singular pixel point, and calculating a first average value of gray values in each region; Sorting all the first average values to obtain a first intermediate value; and replacing the gray value of the singular pixel with the first intermediate value, and carrying out primary speckle noise phagocytosis on the singular pixel. The method can be widely applied to scenes for processing image speckle noise.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com