Patents
Literature
44 results about "Mycobacterial cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cell envelope of mycobacteria, i.e., the compounds that surround the cytoplasm and protect the micro-organisms from their environment, is important for the bacterial physiology because inhibition of the production of some of its constituents, e.g., mycolic acids and arabinogalactan, kills the cells.
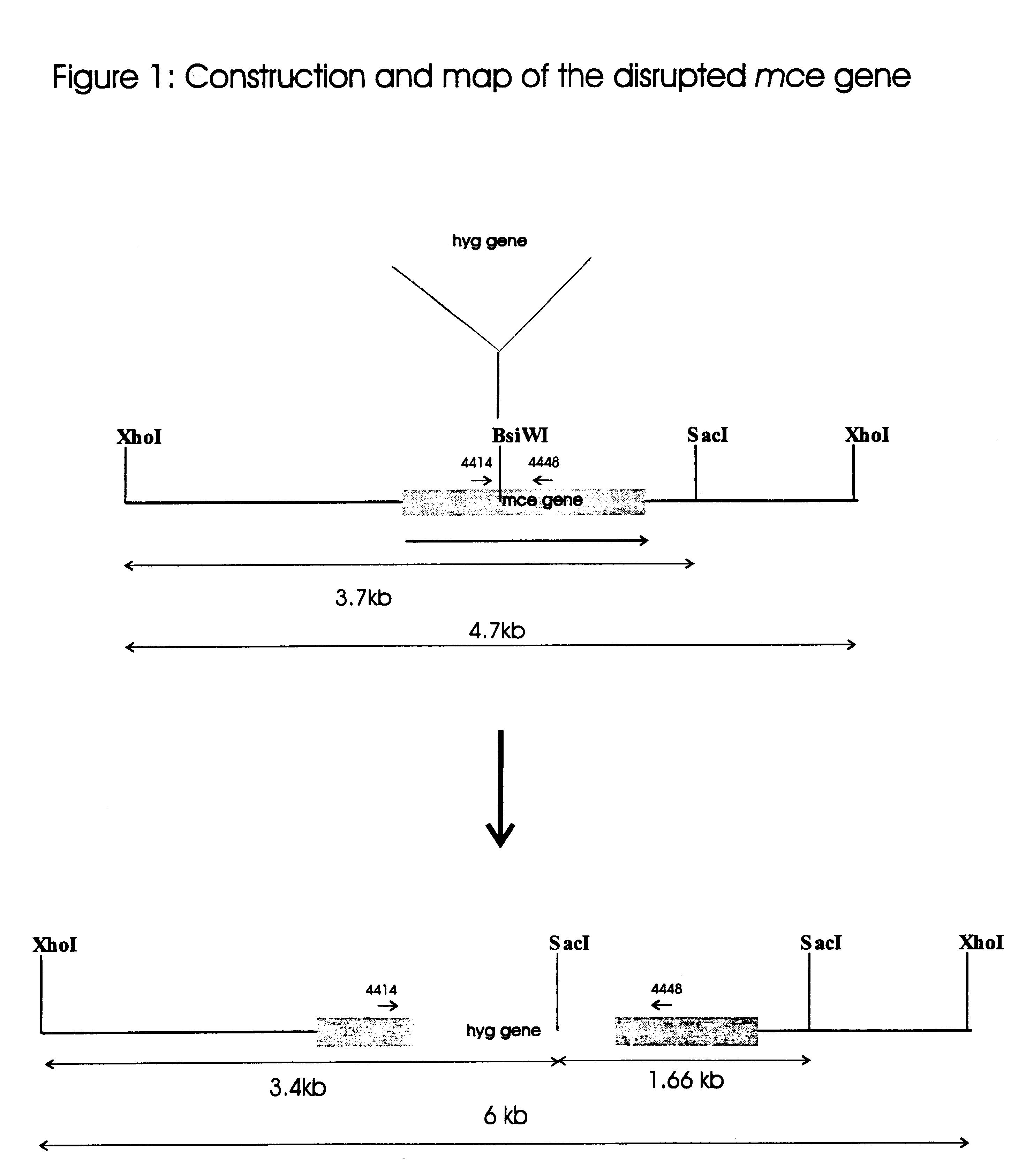
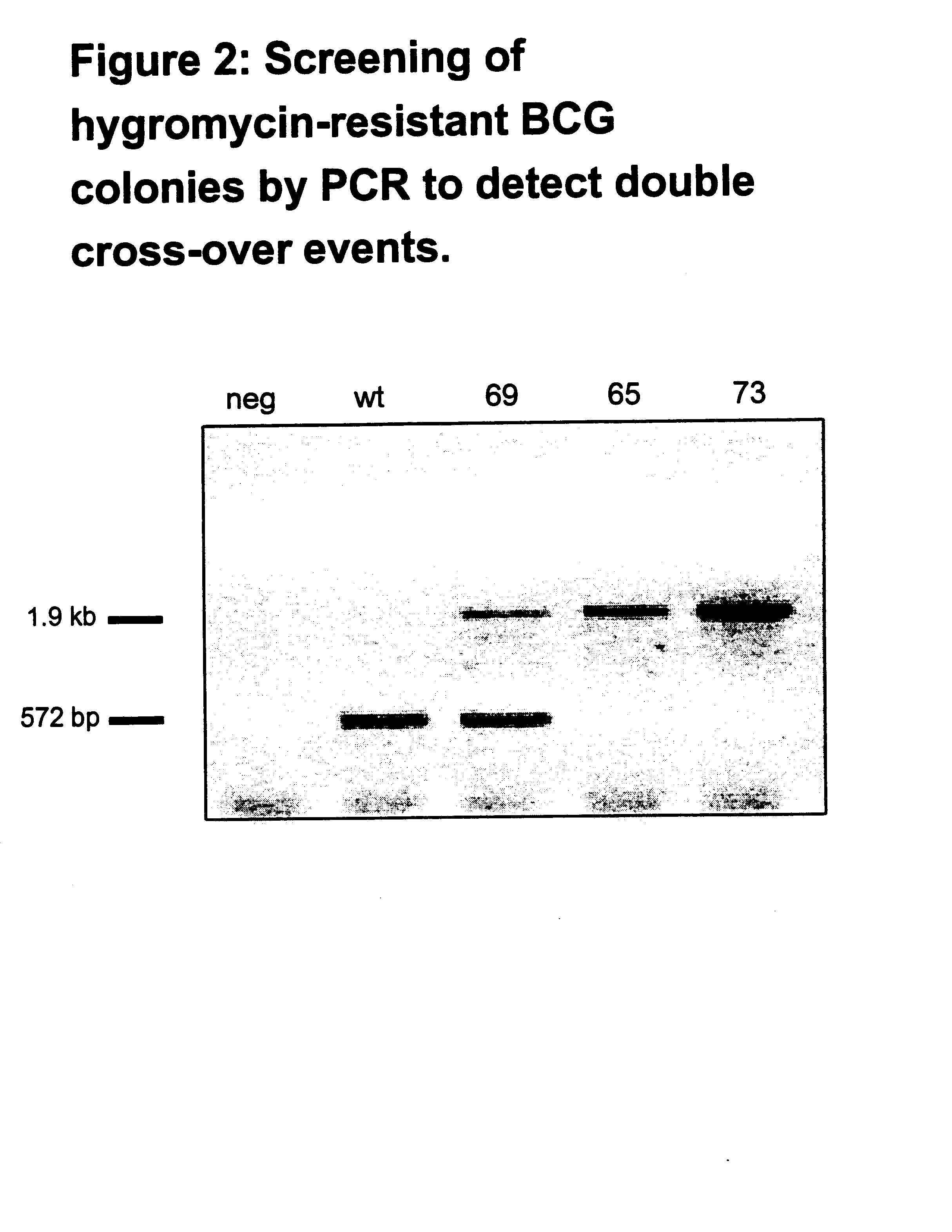
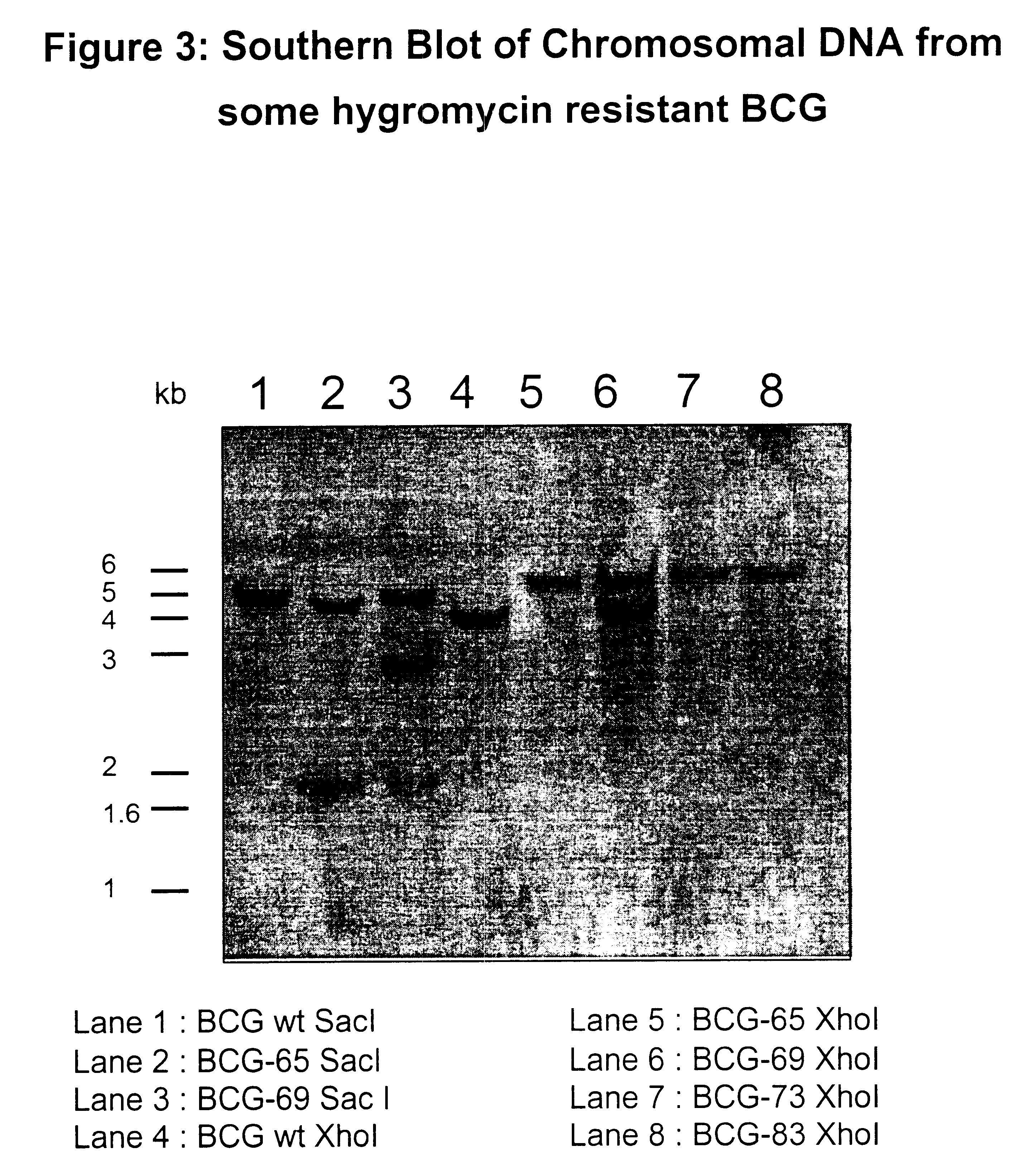
Attenuated strains of mycobacteria
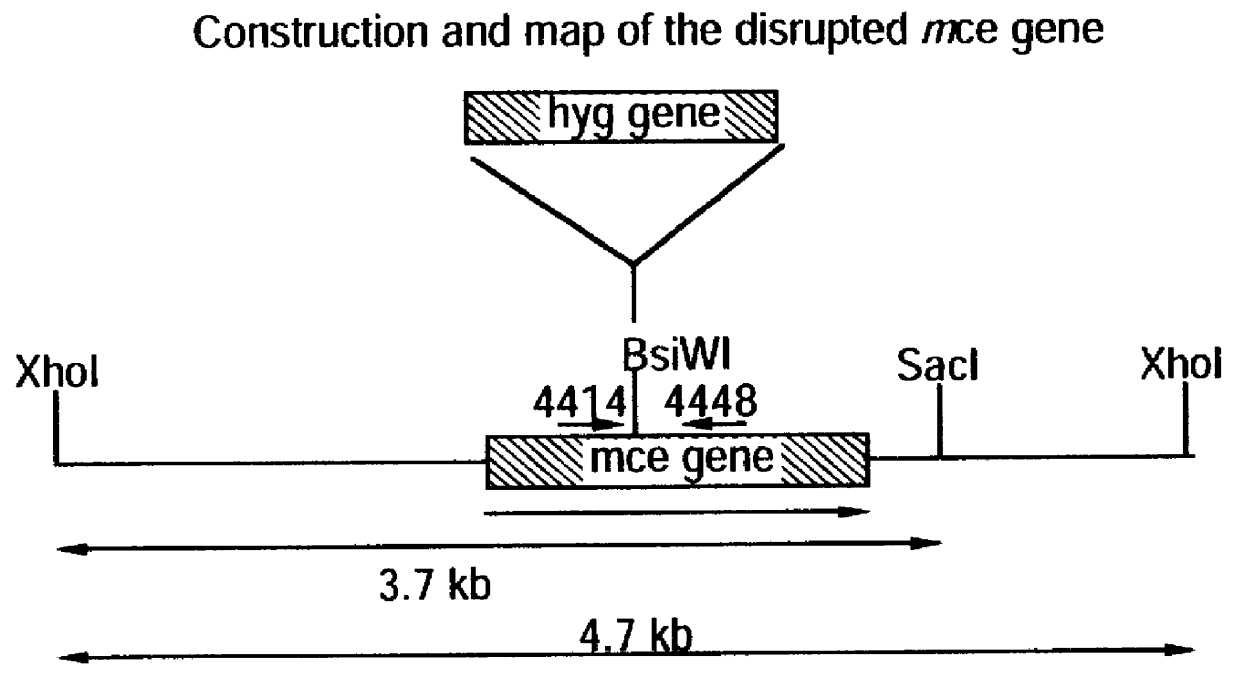
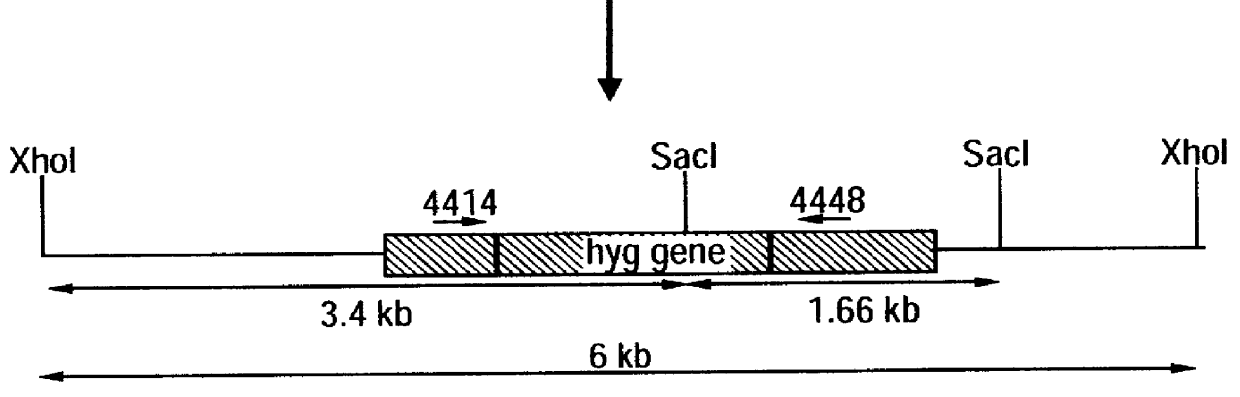
Attenuated strains of Mycobacterium, particularly species of the tuberculosis complex, have the mycobacterial cell entry (mce) gene functionally disabled. The gene may be disabled by an insertion into the gene which disrupts the mycobacterial cell entry function thereof of a selectable marker which is used for screen for homologous recombinants in which a double cross-over event has been effected. The attenuated strains may be used in the immunization of hosts against Mycobacterium disease.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Composition and method for regulating cell proliferation and cell death
InactiveCN1290171ABacteria material medical ingredientsCarbohydrate active ingredientsMycobacterial cellCell wall
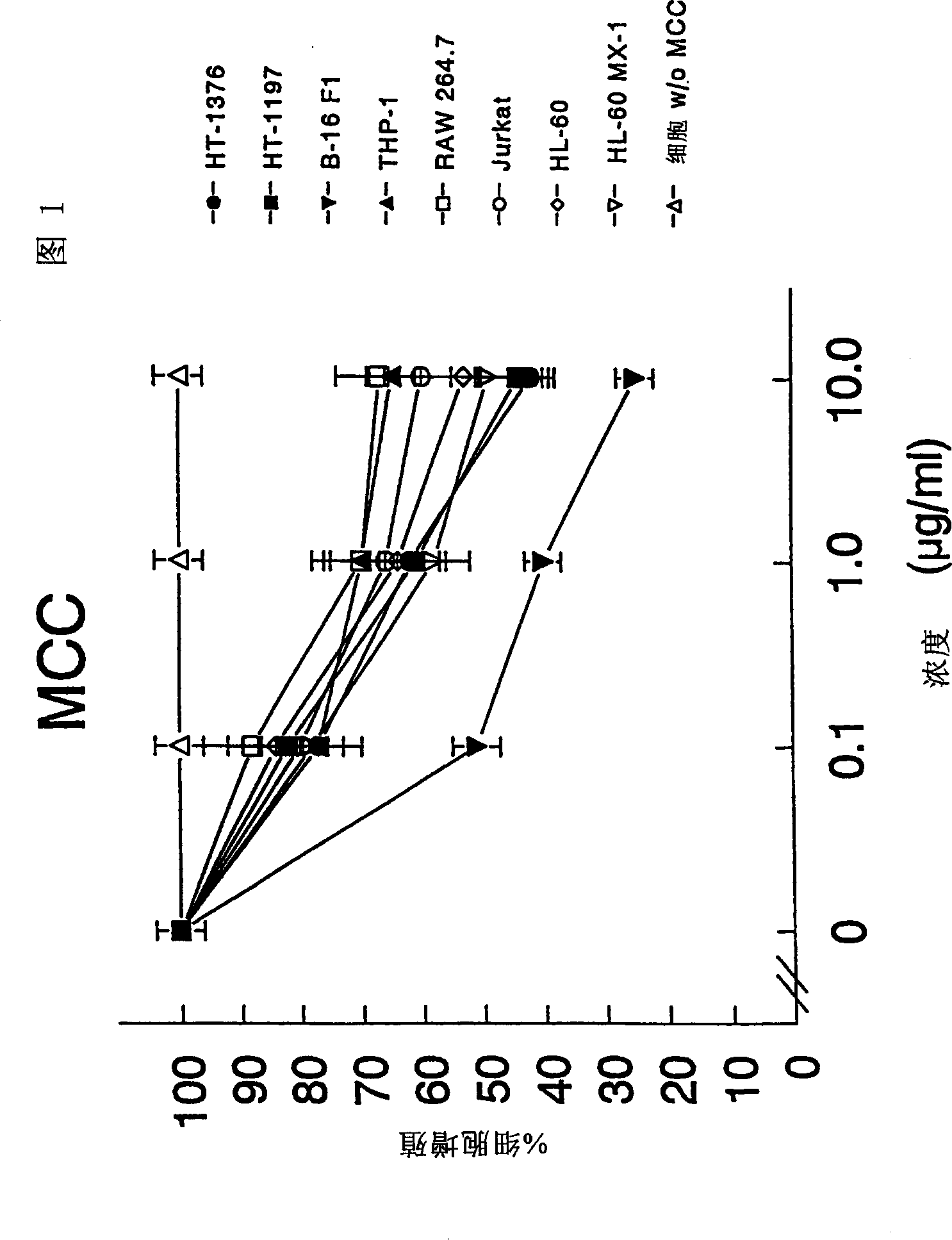
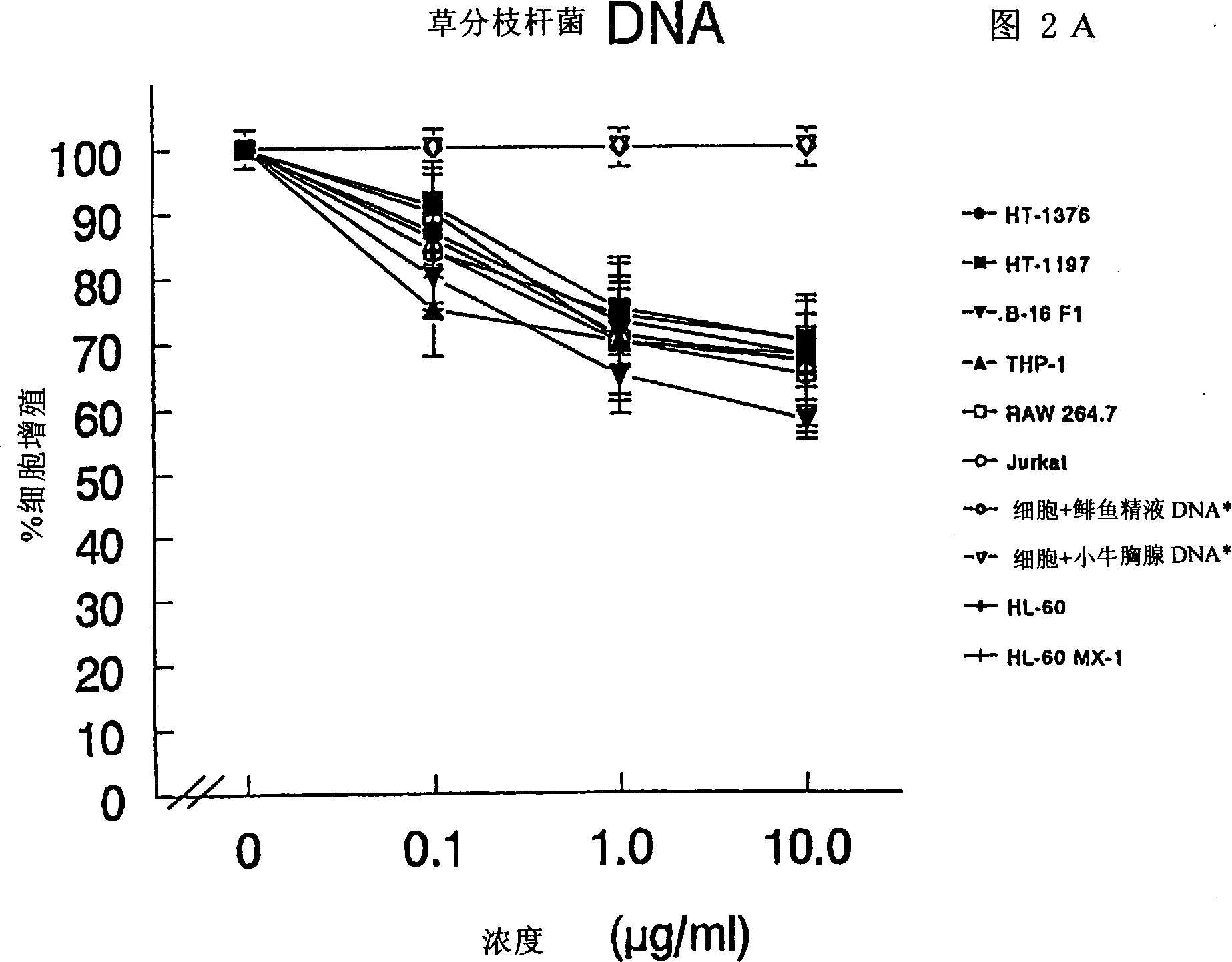
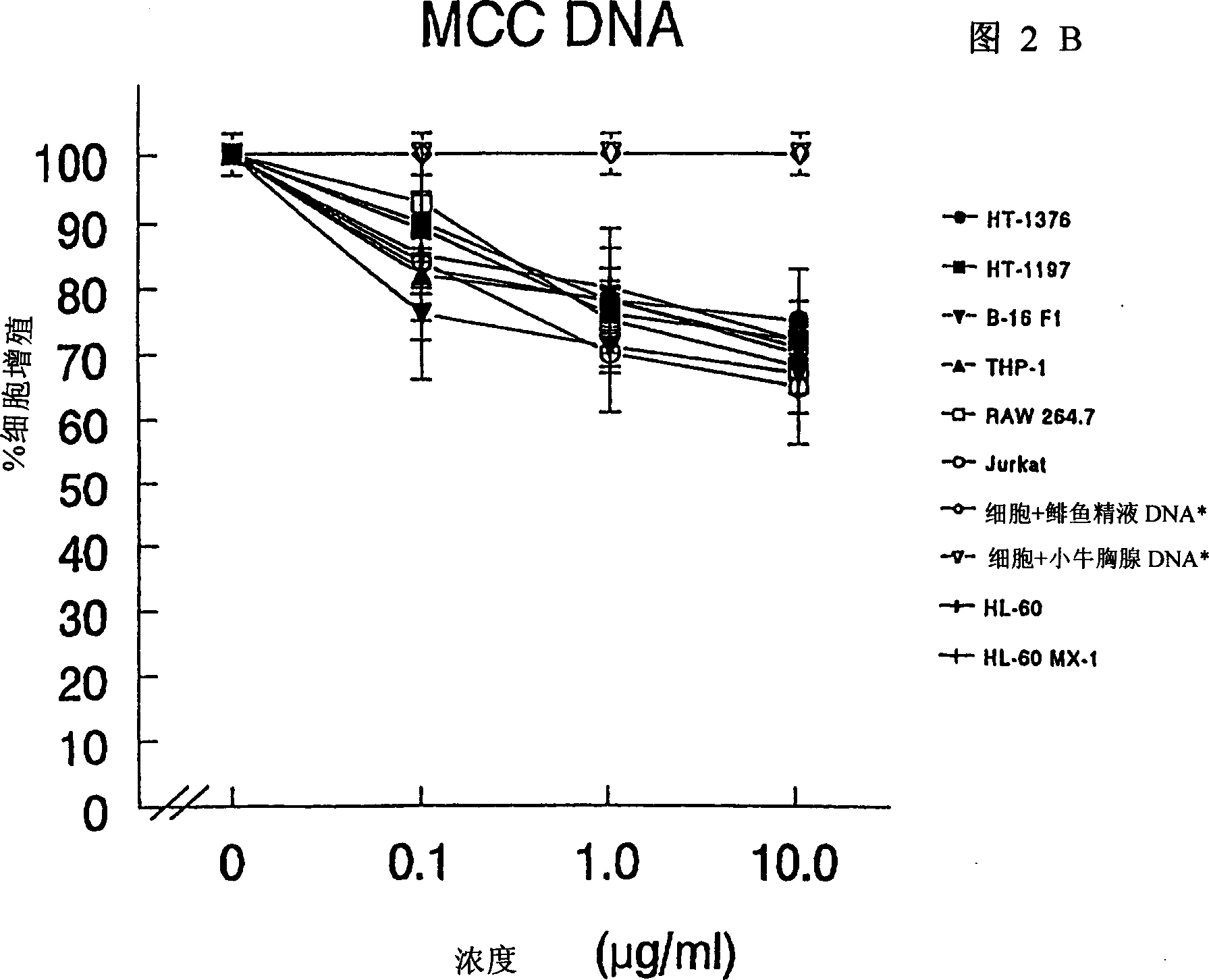
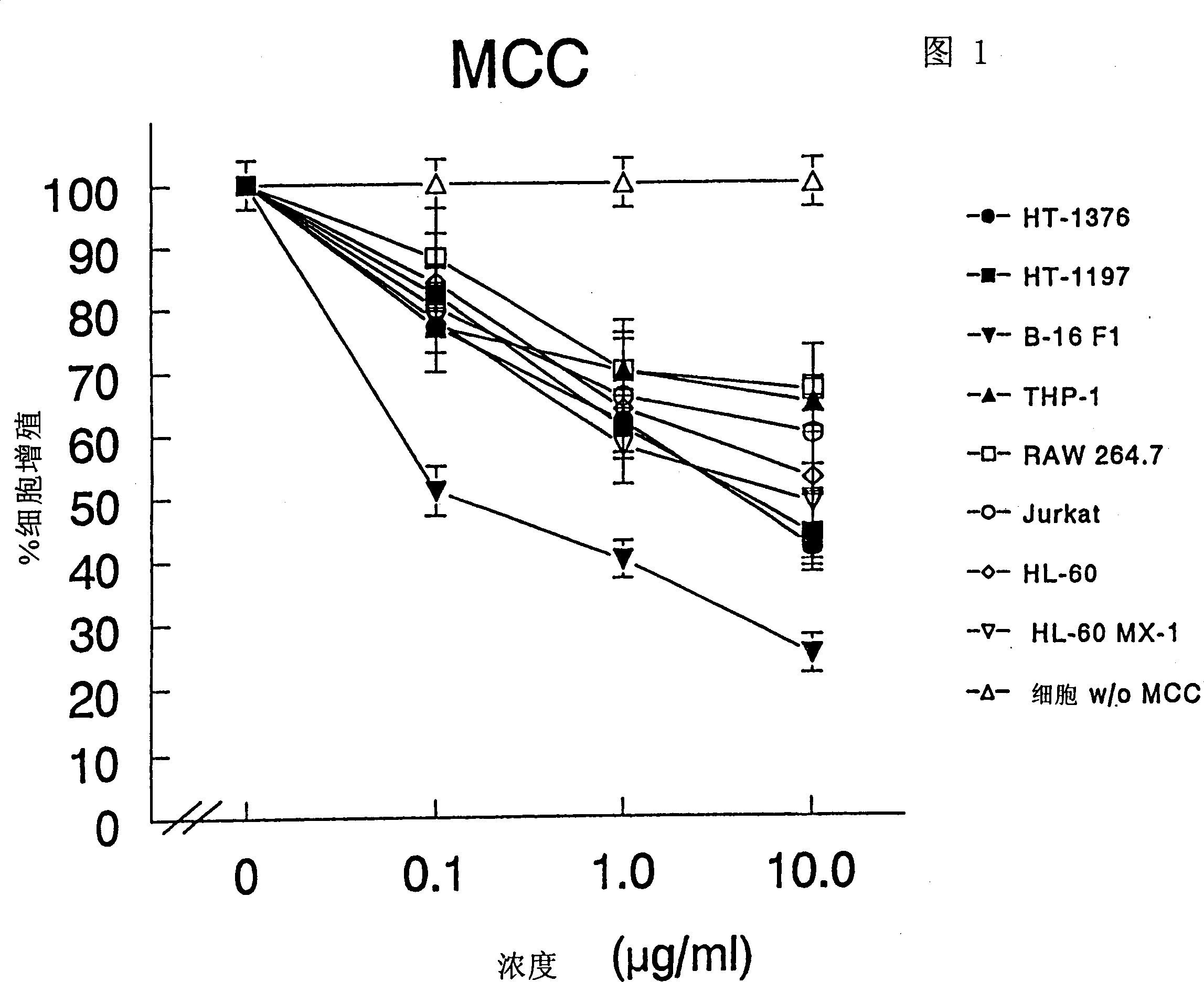
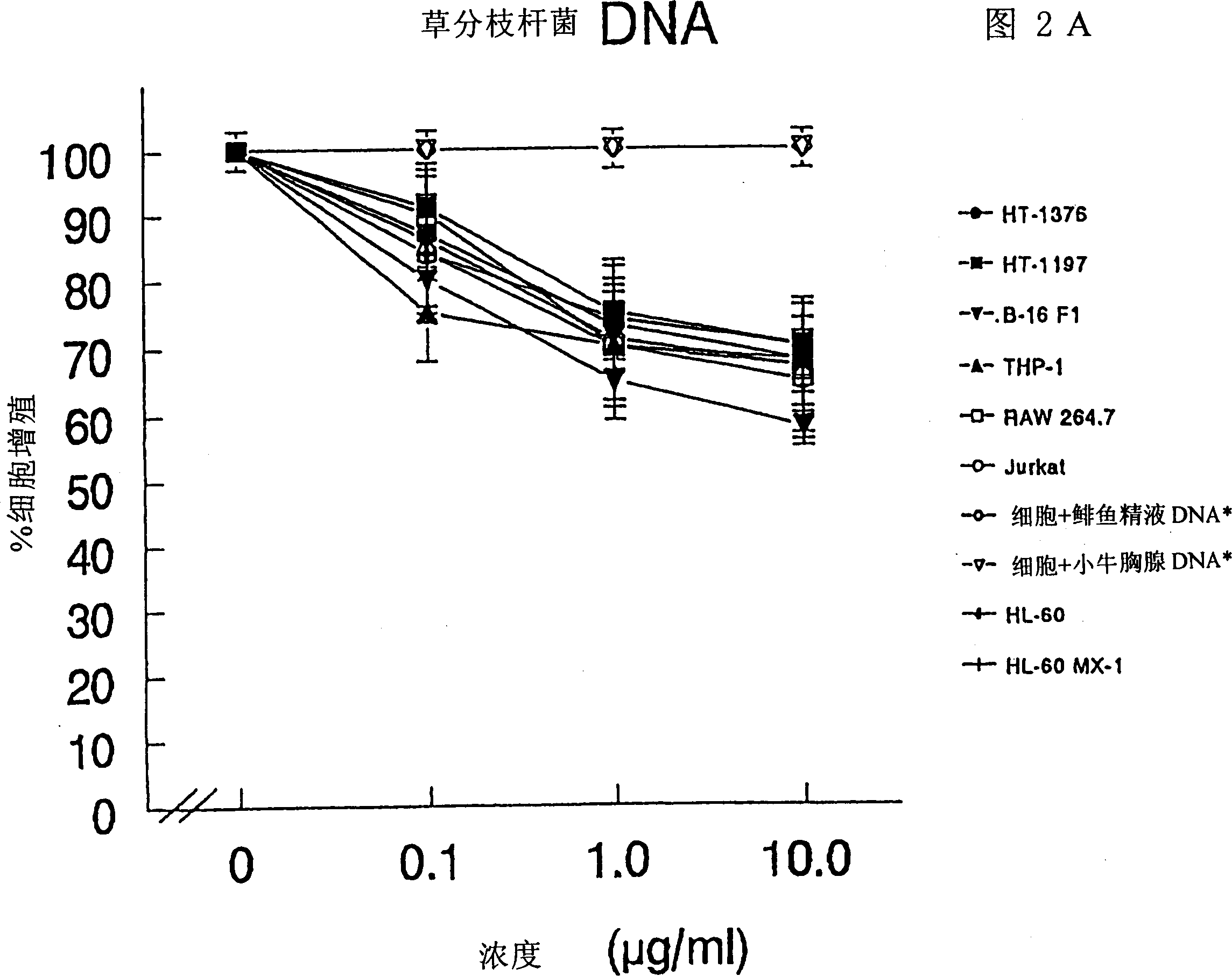
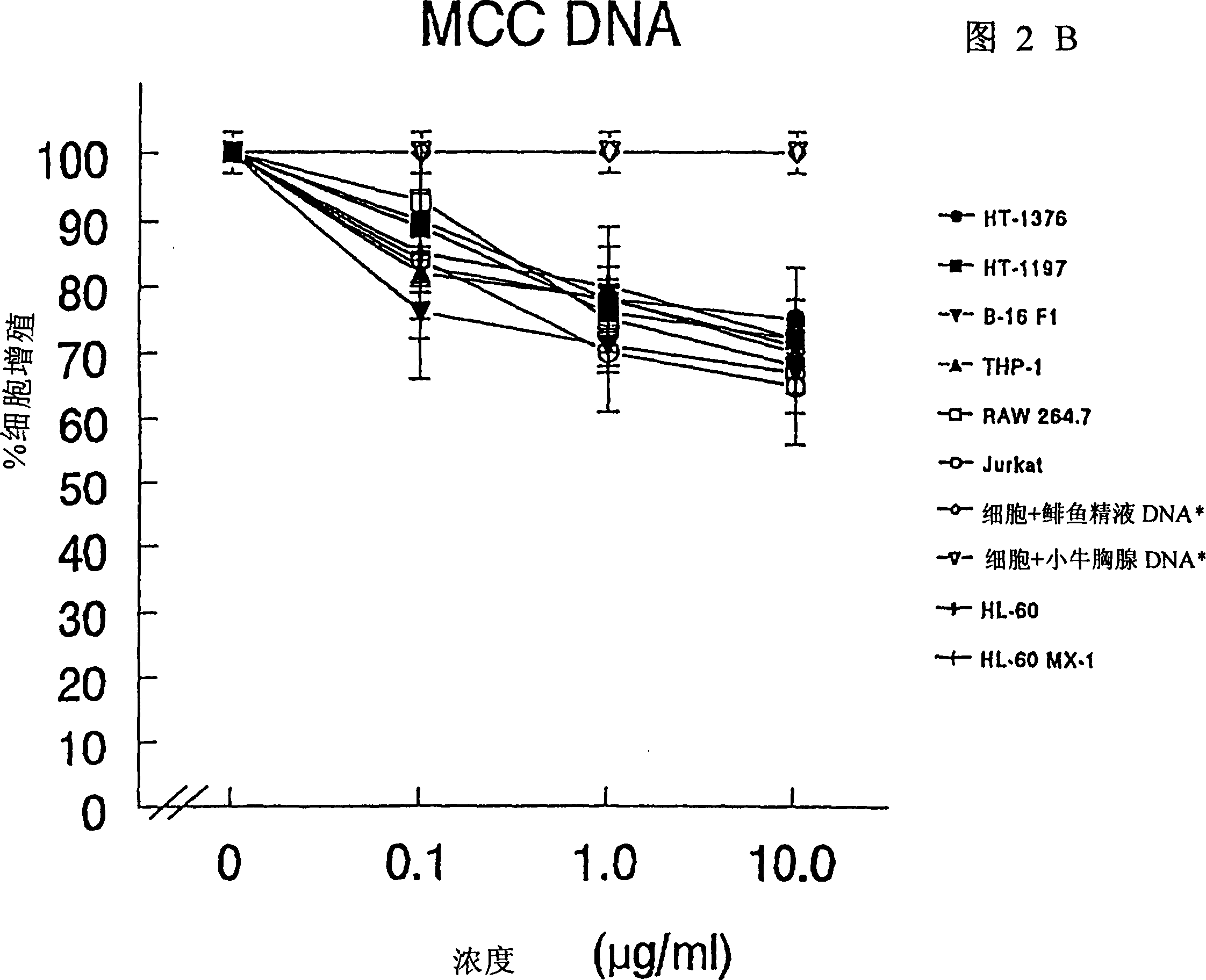
The present invention relates to a composition and method for treating cancer in the urinary bladder. More particularly, the present invention relates to a composition comprising a Mycobacterium phlei (M. phlei) deoxyribonucleic acid (M-DNA)-M. phlei cell wall complex (MCC), wherein the M-DNA is preserved and complexed on the M. phlei cell wall, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The MCC composition inhibits proliferation of and induces apoptosis in the cancer cells in the urinary bladder of the animal.
Owner:贝尔尼奇泌尿知识产权公司
Benzofuran and benzofuran coumarin derivatives and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109942523AStrong anti-tuberculosis activityImprove bioavailabilityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsResistant tuberculosisMycolic acid
The invention discloses benzofuran and coumestans derivatives as shown in formulae (I|), (II) and (III) and a preparation method and an application thereof in treating multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. The benzofuran and coumestans derivatives are anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis compounds which are novel in structure and obvious in antibacterial effect. The compounds taking polyketone synthase coded by a mycobacterium tuberculosis pks13 gene fragment as an acting target spot inhibits growth and reproduction of microorganisms, in particular synthesis of mycolic acid in mycobacterium tuberculosis cell walls. The derivatives have a potential application prospect in the medical field.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +2
Methods and compounds for the treatment of immunologically-mediated skin disorders
InactiveUS20030007976A1Reduce productionImprove bindingAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
Methods for the treatment of skin disorders, including psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, alopecia areata, skin cancers, and related disorders, such as psoriatic arthritis are provided, such methods comprising administering a composition having antigenic and / or adjuvant properties. Compositions which may be usefully employed in the inventive methods include inactivated M. vaccae cells, delipidated and deglycolipidated M. vaccae cells, M. vaccae culture filtrate and compounds present in or derived therefrom, together with combinations of such compositions.
Owner:GENESIS RES & DEV
Construction method and application of mycobacteria genetic engineering bacteria
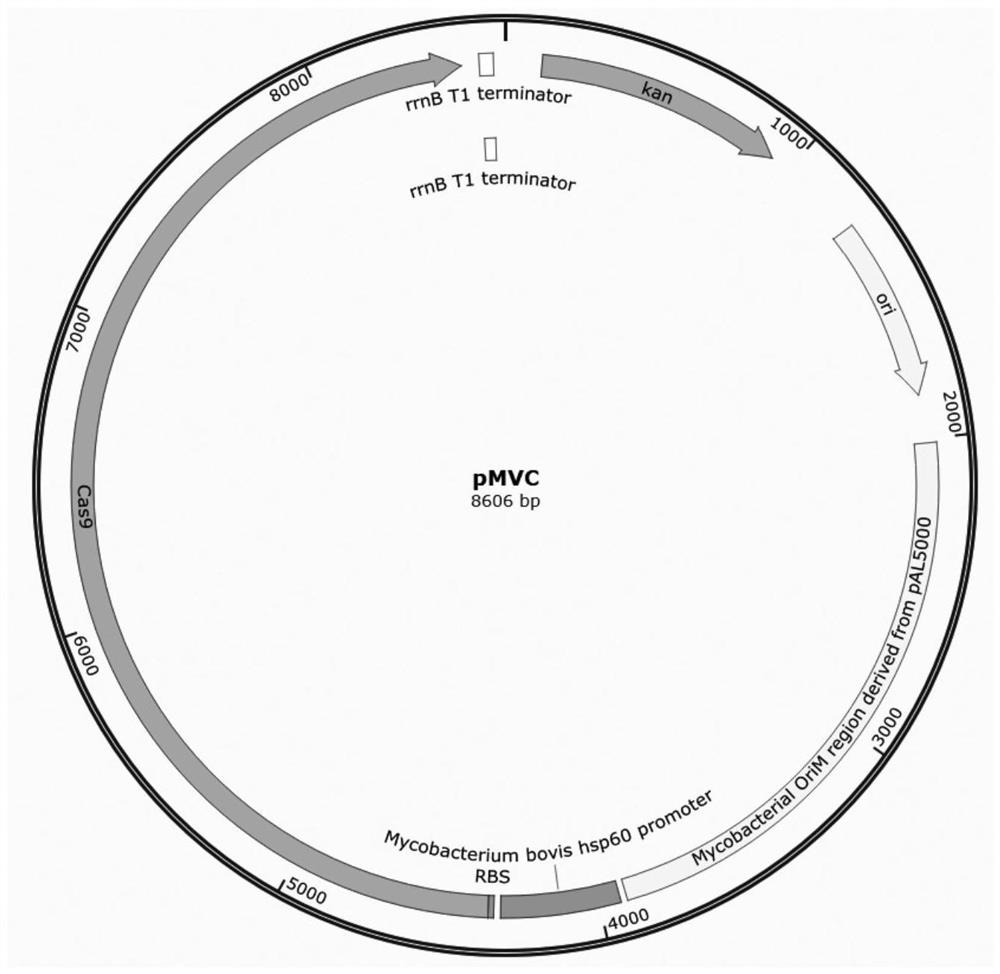
The invention discloses a construction method and application of mycobacteria genetic engineering bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. A recombinant plasmid is transformed into a mycobacteria LY-1 cell, sgRNA can distinguish a specific region on a genome and lead Cas9 protein to be combined to a target site; and under the action of the protein, a double-strand breaknotch is formed in the target site, and most of cells are dead. Under the action of recombinase, a homologous repairing sequence led along with the recombinant plasmid is integrated to the notch through double exchange, and the cells successfully repaired homologously by genes can survive, and form genotypes which are artificially designed for gene inactivation, exogenous gene insertion and the like. The knockout efficiency for the same gene by the constructed CRISPR-Cas9 system is 60%, and compared with a conventional mycobacteria gene editing manner, the constructed CRISPR-Cas9 system is more convenient and higher in efficacy.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel antimycobacterial compounds
Novel compounds belonging to the class of oxazolidinones possessing potent antimycobacterial properties especially useful in the treatment of acid fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex, M. fortuitum and M. kansai. The compound and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof act as antibacterial agents. Also disclosed is a method for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial conditions such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex, M. fortuitum and M. kansai, comprising administering an antimycobacterially effective amount of the said compound and / or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. There is also disclosed a process for the manufacture of the said compound or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
Methods for the treatment of immunologically-mediated skin disorders
InactiveUS6328978B1Easy to useEnhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
Methods for the treatment of skin disorders, including psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, alopecia areata and skin cancers are provided, such methods comprising administering a composition having antigenic and / or adjuvant properties. Compositions which may be usefully employed in the inventive methods include inactivated M. vaccae cells, delipidated and deglycolipidated M. vaccae cells, M. vaccae culture filtrate and compounds present in or derived therefrom, together with combinations of such compositions.
Owner:GENESIS RES & DEV
Method for the treatment of inflammation
InactiveUS6890911B1Reduce inflammationCheap preparationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineCell wall
Owner:BIONICHE UROLOGY IP
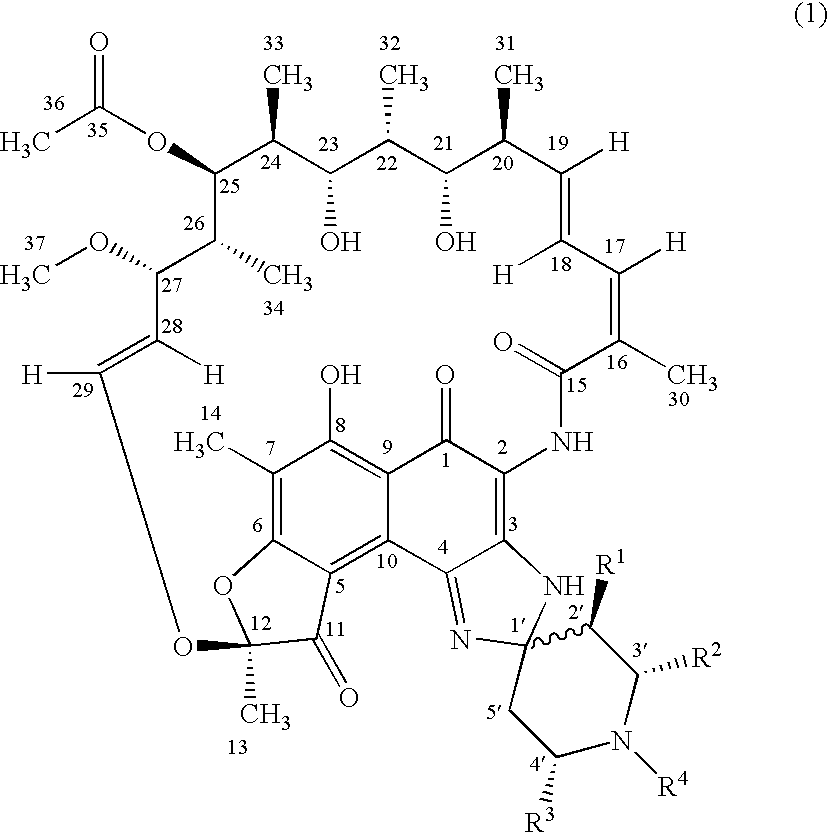
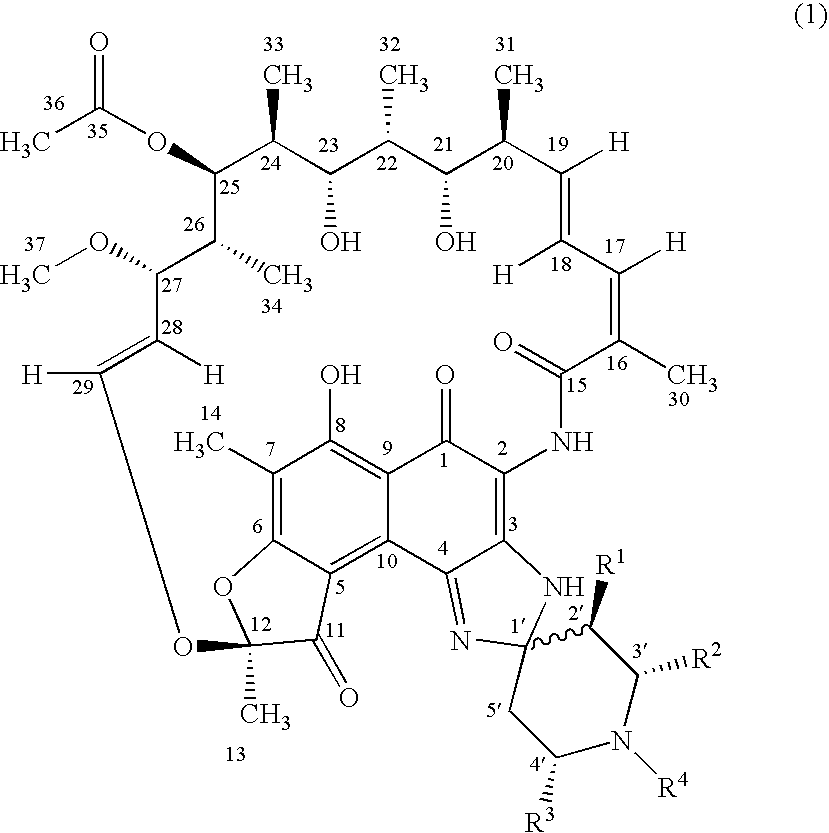
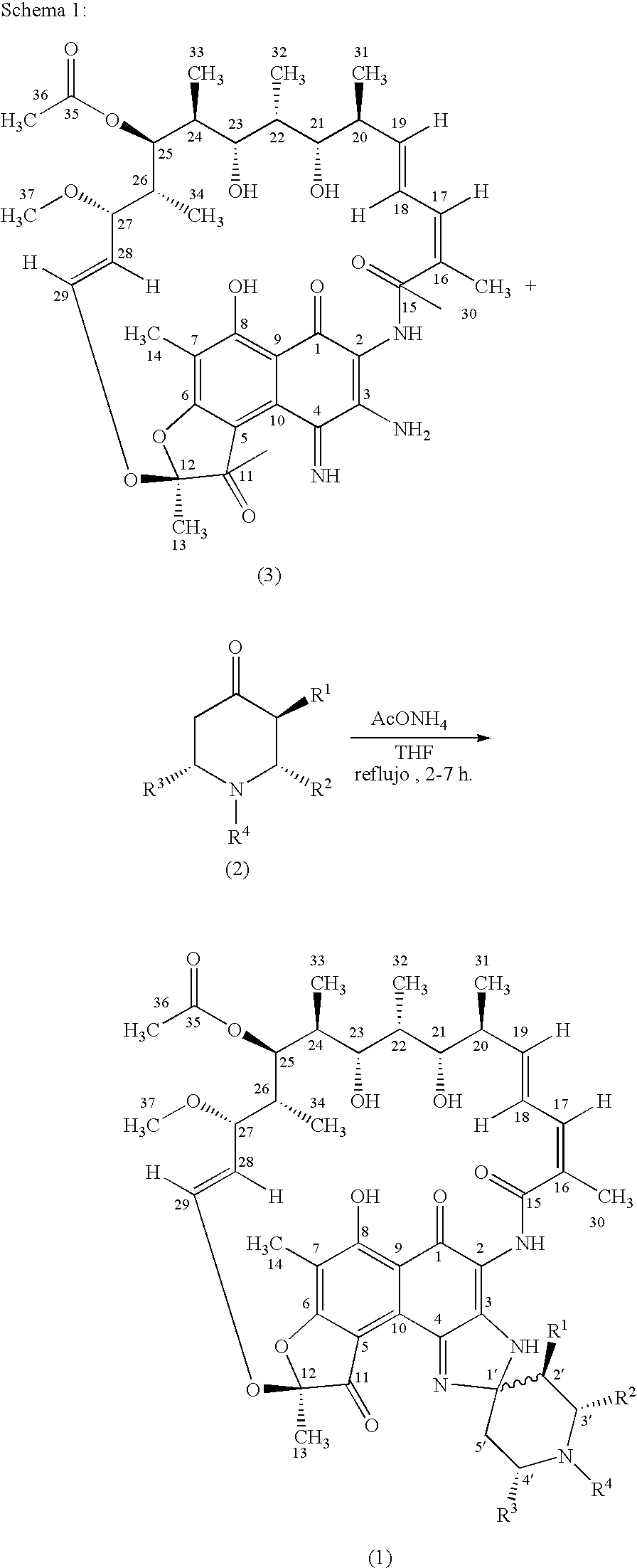
Spiropiperidylrifamycins for the Treatment of Mycobacterial Infections
The compounds of formula (1), their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and their solvates, wherein R1 is a radical selected between hydrogen and alkyl; R2 is selected from hydroxyalkyl, phenyl, phenyl mono-substituted and phenyl di-substituted in positions 3 and 4; R3 is selected from phenyl, phenyl mono-substituted and phenyl di-substituted in positions 3 and 4; the substituents of the phenyl of R2 and R3 selected from halogen, (C1-C4)-alkyl and (C1-C4)-alkoxyl and R4 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl allyl and homoallyl, they are useful for the treatment of mycobacterial infections, in particular for the treatment of infections produced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex or Mycobacterium kansasii.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OVIEDO
Carbohydrate chip for quickly diagnosing tuberculosis, preparation method thereof and tuberculosis diagnostic kit adopting carbohydrate chip
InactiveCN102707053AIncreased antigen specificityStrong specificityMaterial analysisAntigenLipomannan
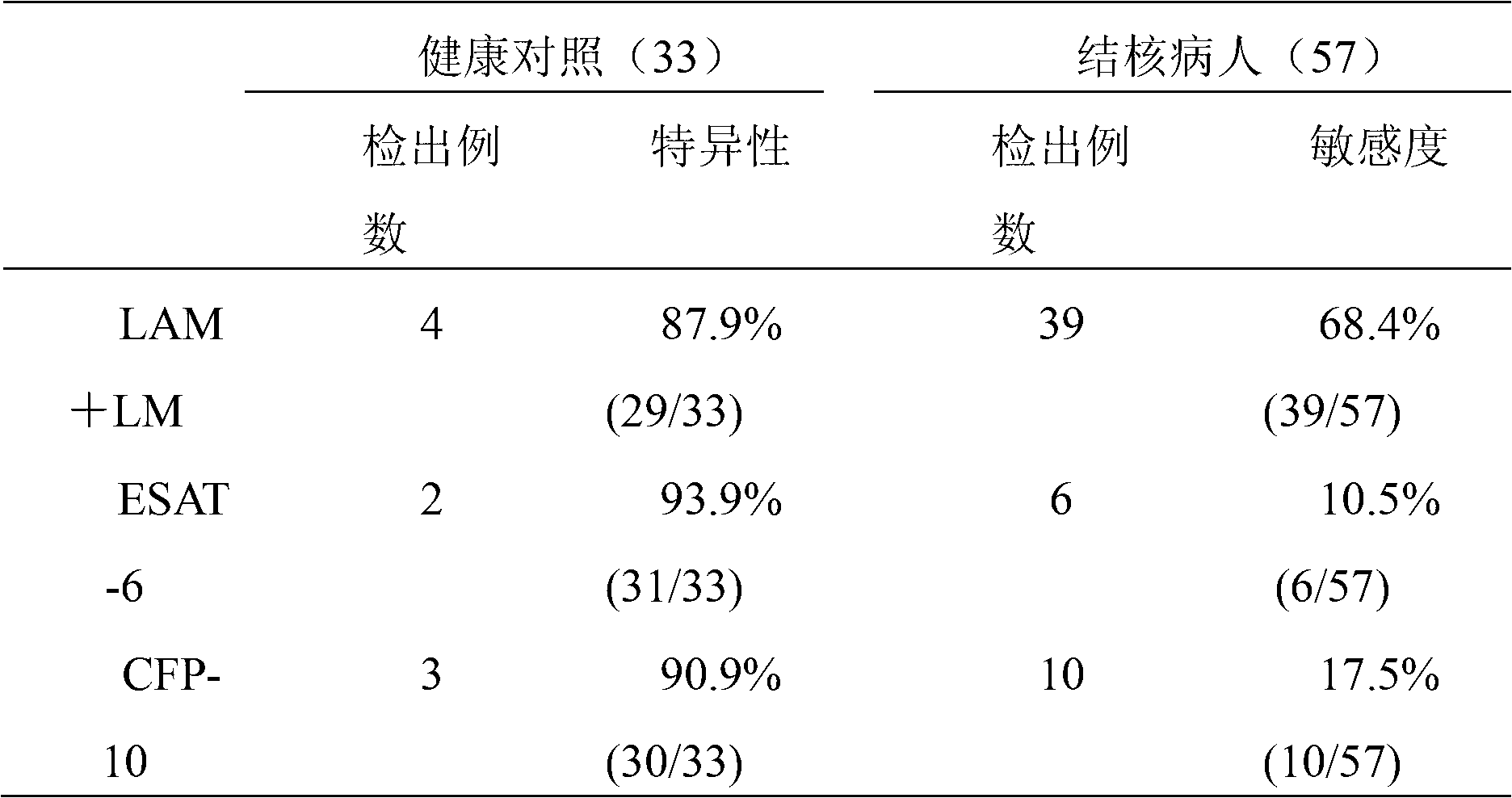
The invention relates to a carbohydrate chip for quickly diagnosing tuberculosis, which comprises a solid-phase carrier. The carbohydrate chip is characterized by further comprising a mycobacterium tuberculosis lipopolysaccharides antigen probe which is fixed on the solid-phase carrier through oximation reaction. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the carbohydrate chip and a tuberculosis diagnostic kit adopting the carbohydrate chip. The preparation method comprises the following steps: separating, extracting and purifying lipopolysaccharides in a mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall; fixing LAM (lipoarabinomannan) and LM (lipomannan) probes in the solid-phase carrier, such as a nitrocellulose membrane or porous plate, and the like, by utilizing a method of oximation reaction, thereby obtaining the carbohydrate chip; and judging if the mycobacterium tuberculosis is infected, by bonding the carbohydrate chip with a corresponding antibody in blood serum and performing enzyme linked color-developing reaction. A cell wall lipopolysaccharides antigen with species specificity adopted by the carbohydrate chip only can be combined with a specific tuberculosis antibody, so that the detecting specificity and sensitivity of the tuberculosis are greatly increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
glmm gene knock-out bacterial strain as well as preparation method and application in sieving mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase inhibitors
InactiveCN101928691AIntegrity breachImprove efficacyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention discloses a glmM gene knock-out bacterial strain ML2009 (mycobacterium smegmatis), CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) 3418, which is constructed by using phosphoglucomutase participating in the biosynthesis of key components in a mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall. The bacterial strain ML2009 can be used as a cell model for sieving phosphoglucomutase inhibitors with high flux, be used for sieving effective phosphoglucomutase inhibitors from a combined compound library, traditional Chinese medicine and natural products to prepare tuberculosis-resisting medicaments with high medicine effects; and in addition, in the cells of a human body, the synthesis approach of UDP (Uridine Diphosphate)-acetyl glucosamine is different from that of mycobacterium tuberculosis, no phosphoglucomutase exists in the UDP-acetyl glucosamine, therefore, the reaction catalyzed by the mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase does not exist in the cells of the human body so that the tuberculosis-resisting medicaments developed by using the phosphoglucomutase as a target enzyme are harmless to the human body, and the defect that the traditional antibacterial medicament also kill normal cells is overcome.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Attenuated strains of mycobacteria
Attenuated strains of Mycobacterium, particularly species of the tuberculosis complex, have the mycobacterial cell entry (mce) gene functionally disabled. The gene may be disabled by an insertion into the gene which disrupts the mycobacterial cell entry function thereof of a selectable marker which is used for screen for homologous recombinants in which a double cross-over event has been effected. The attenuated strains may be used in the immunization of hosts against Mycobacterium disease.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
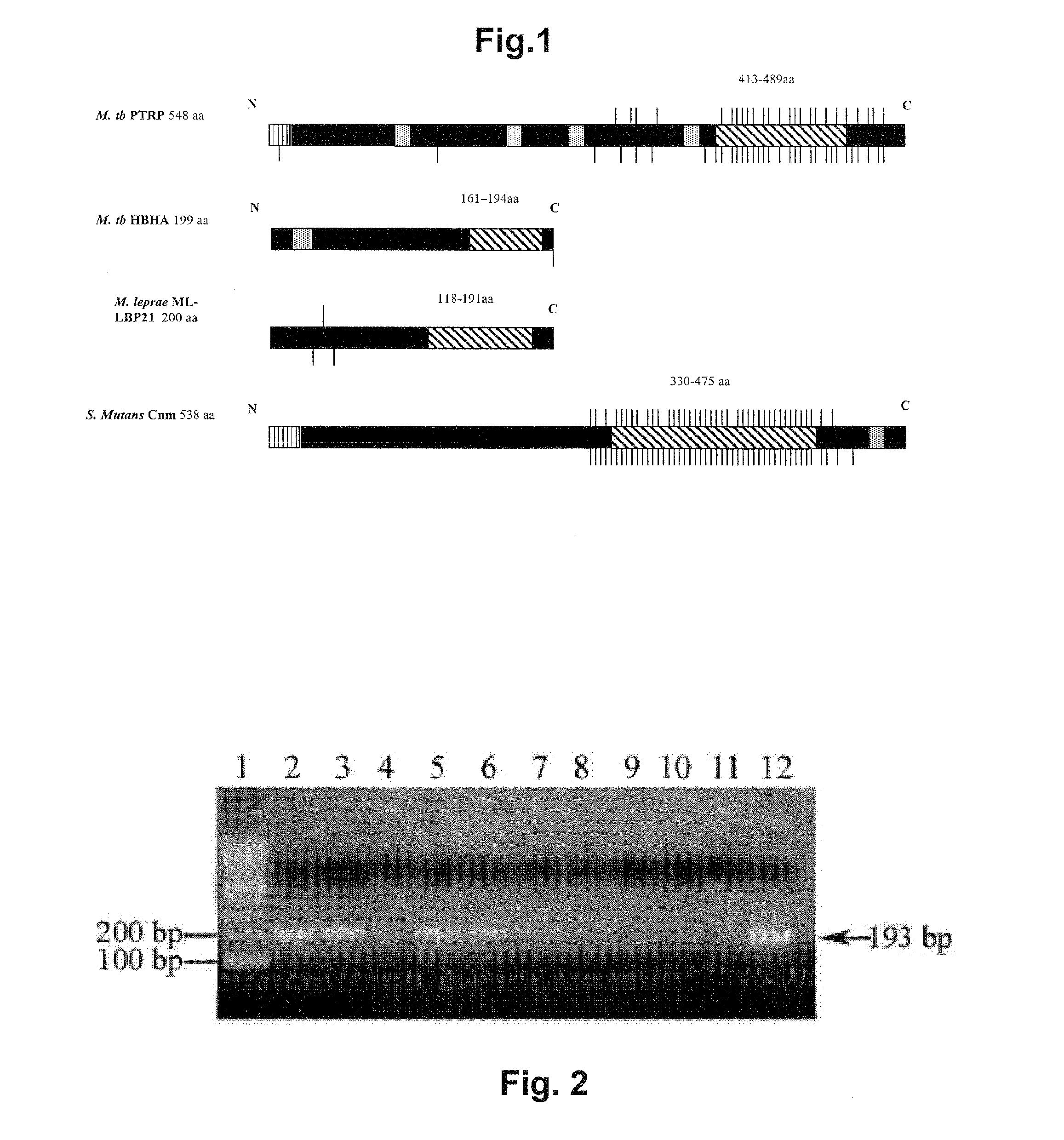
Immunodominant mycobacterium tuberculosis peptides from cell wall proteins for early diagnosis and immunization
A number of peptide epitopes and fragments from three Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) cell wall proteins have been identified as early antigens that induce antibodies early during Mtb infection in humans. The proteins are Proline-Threonine Repetitive Protein (PTRP), PE-PGRS51, and LipC. These peptides, alone or in mixtures, or as parts of fusion polypeptides or peptide multimers, are useful as antigens for serological detection of early in infection by detecting the presence of early antibodies against these proteins, thereby permitting earlier diagnosis of Mtb infection than was heretofore possible by conventional means. The above peptides and other peptide-based compositions are also used as immunogens for inclusion in TB vaccines. Also provided are methods for early diagnosis of Mtb infection and for immunizing a subject to prevent or treat Mtb infections and tuberculosis.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
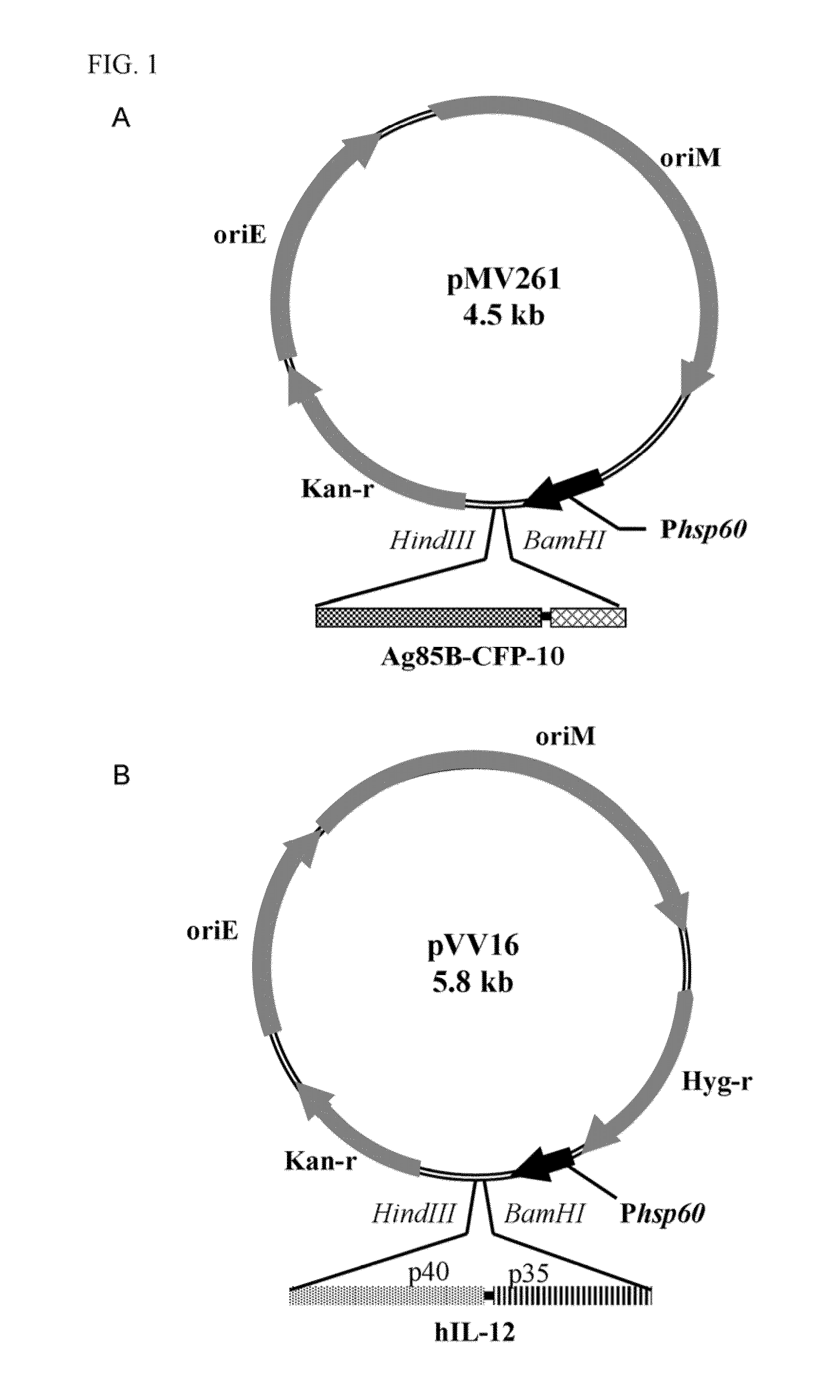
Recombinant bcg strains with enhanced ability to inhibit intracellular mycobacterial growth
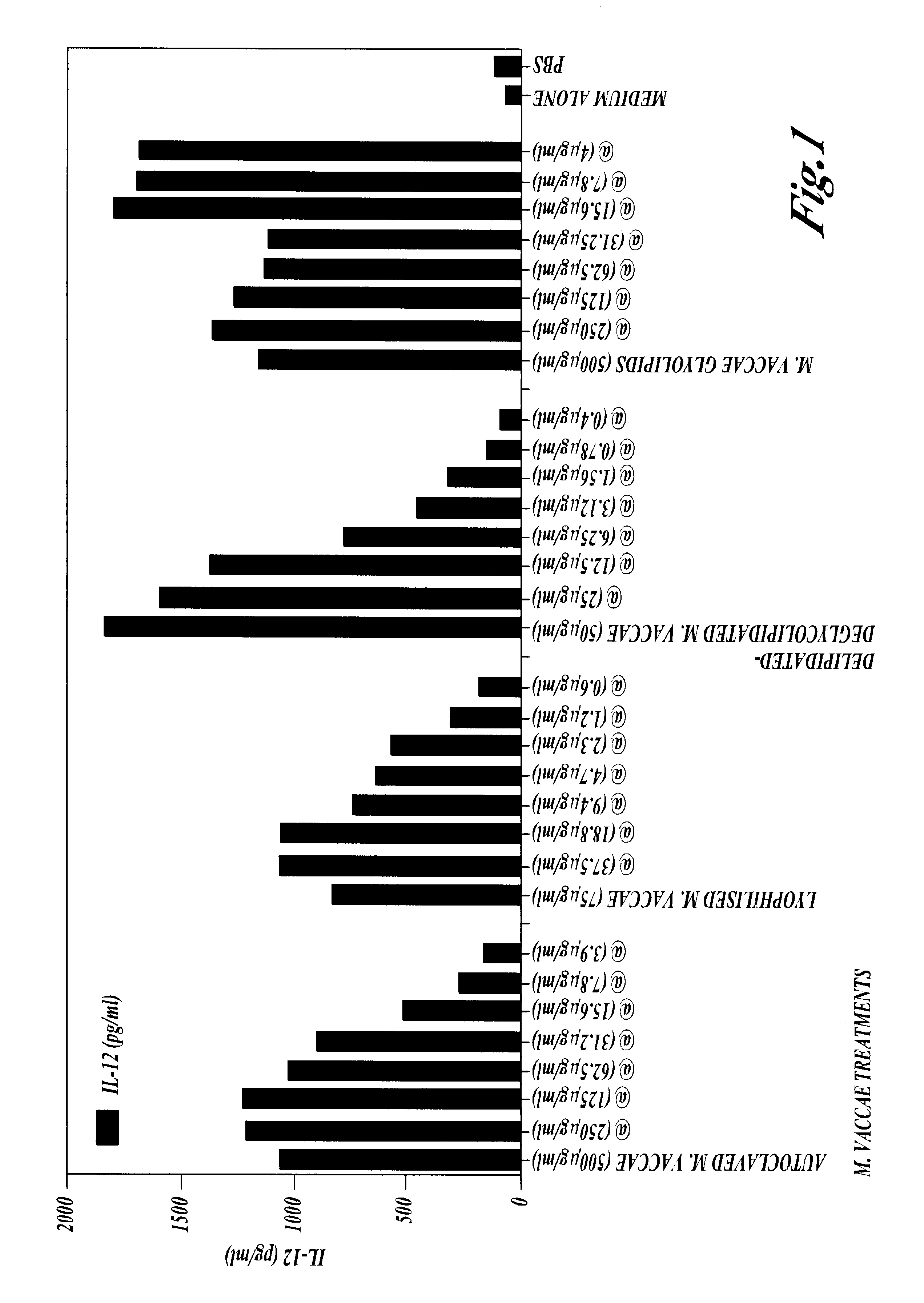
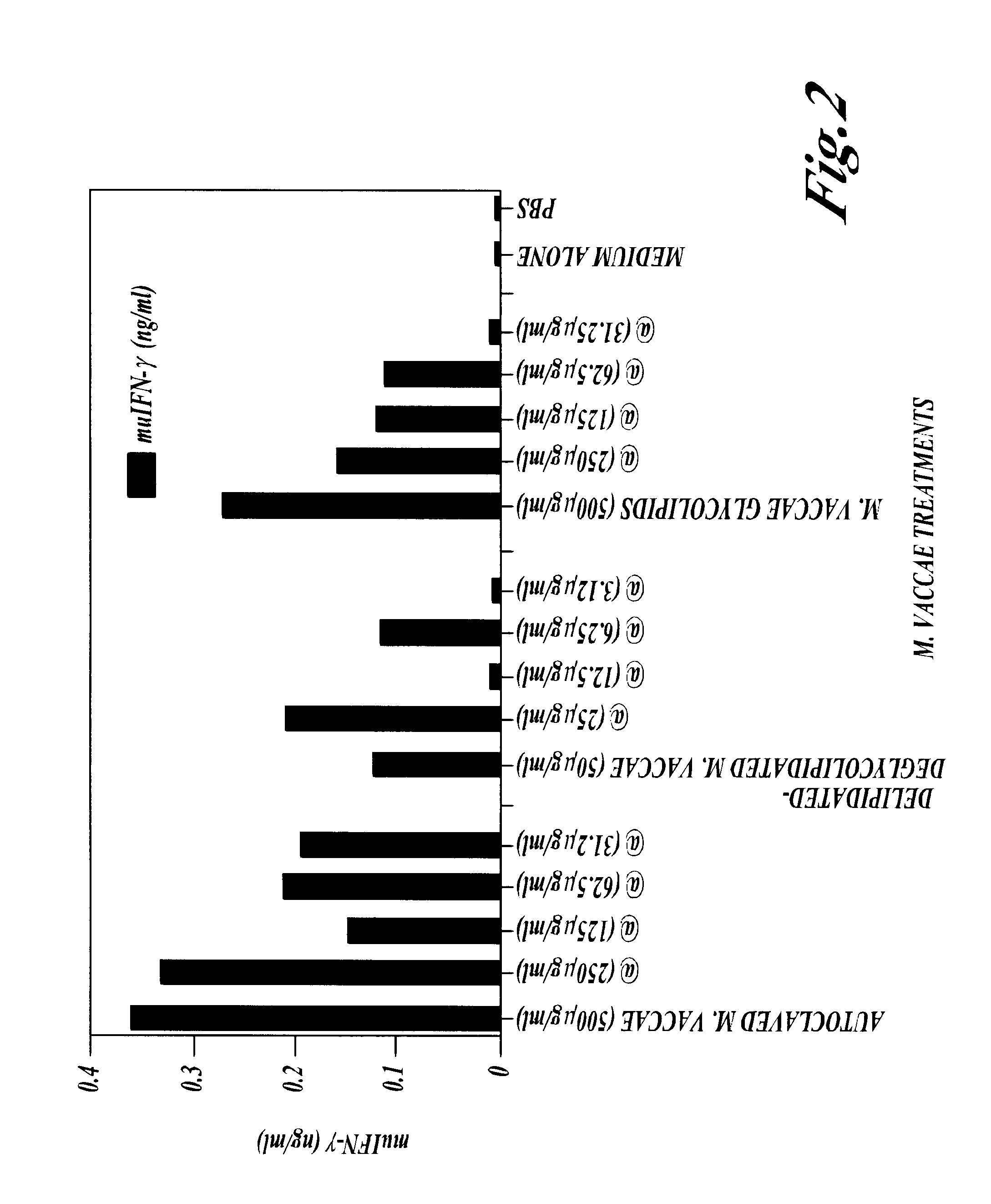
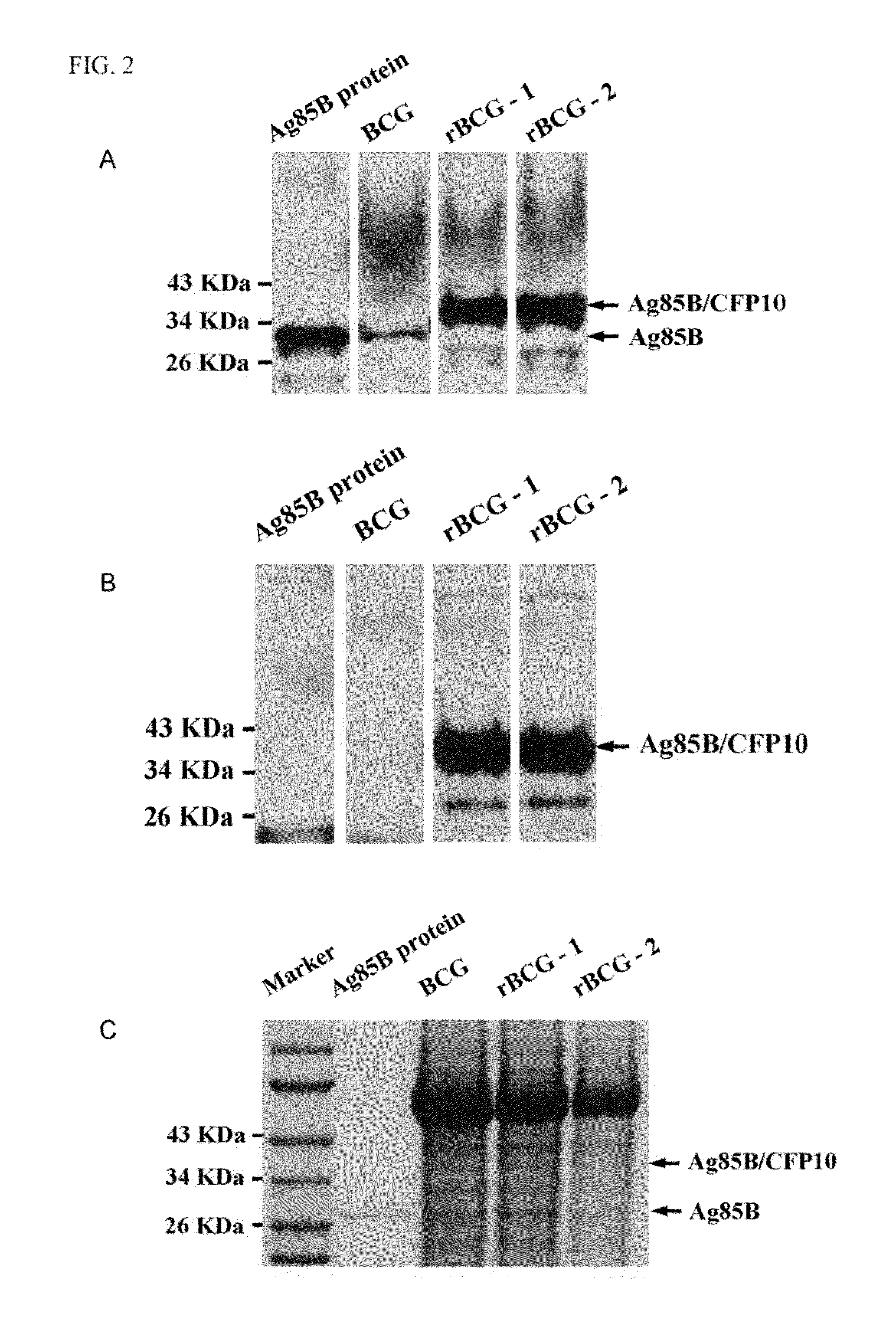
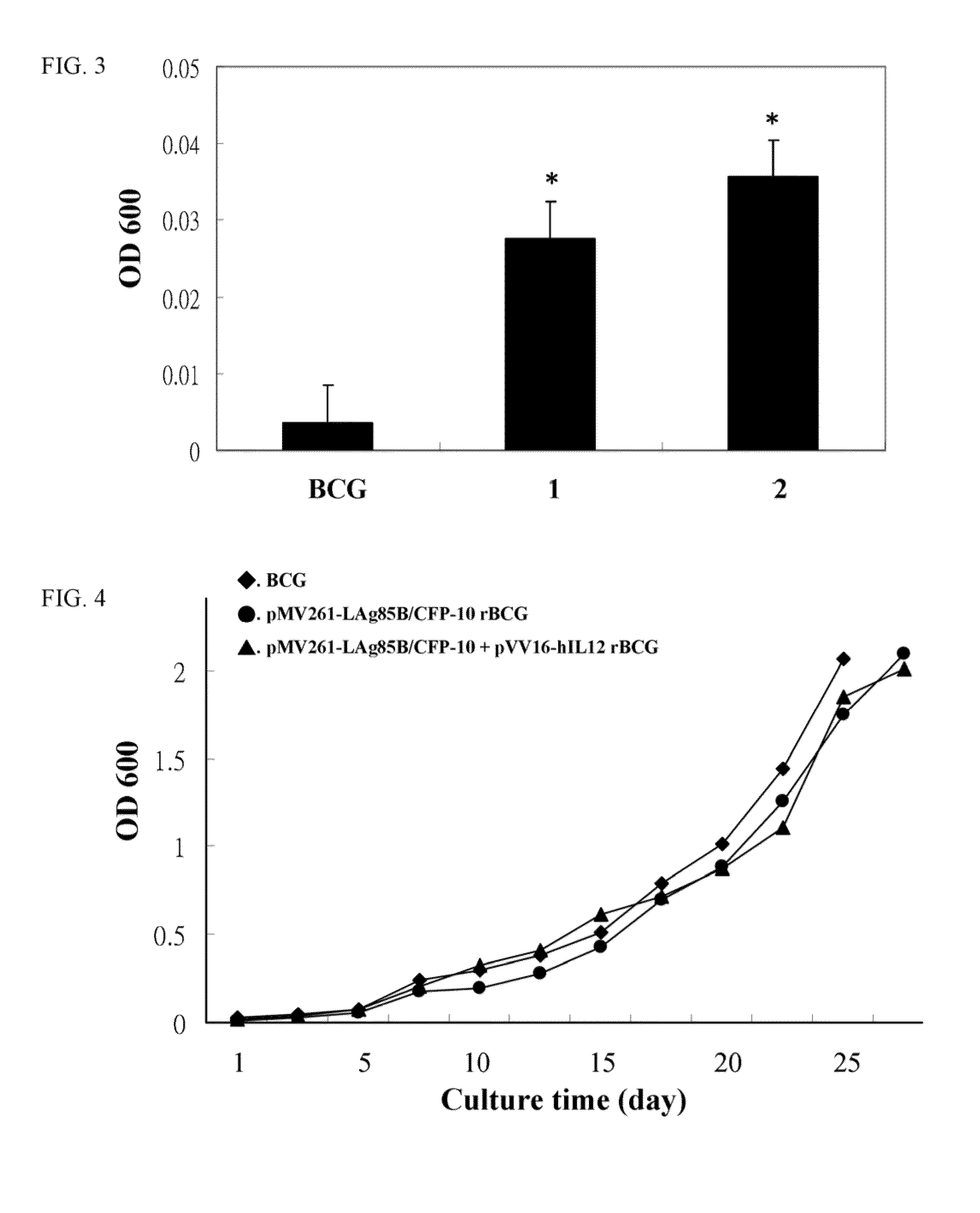
A recombinant bacterial cell strain is disclosed. It comprises: a) a first vector comprising a fusion transgene encoding Ag85B-CFP10 fusion protein, the fusion transgene being operably linked to a promoter effective for expression of the Ag85B-CFP10 fusion protein; and b) a second vector comprising a transgene encoding interleukin-12 (IL-12), the transgene being operably linked to a promoter effective for expression of the IL-12 protein. A method of inhibiting intracellular growth of Mycobacterium in a subject is also disclosed.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Mycobacterium brumae cell wall extracts that can be used in therapy of superficial bladder cancer
Invention is using M. brumae is a mycobacterium strain which stimulates immune system cells strongly, is non-pathogen for humans and has all of the defining attributes of the strain with catalog number 51384, American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) for therapy of superficial bladder cancers.
Owner:ACAN NACIYE LEYLA +9
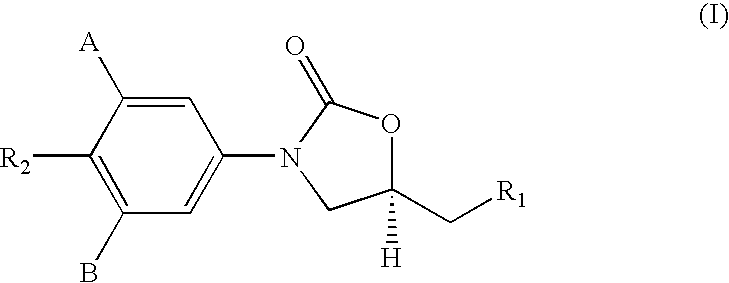
Oxazolidinone compounds and methods of use thereof as antibacterial agents
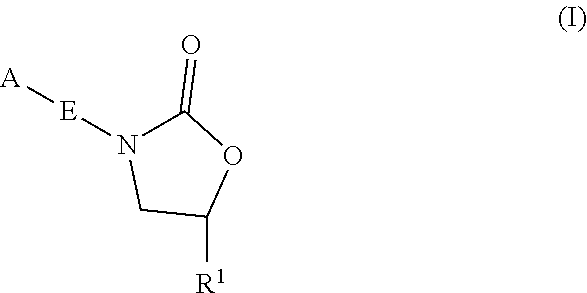
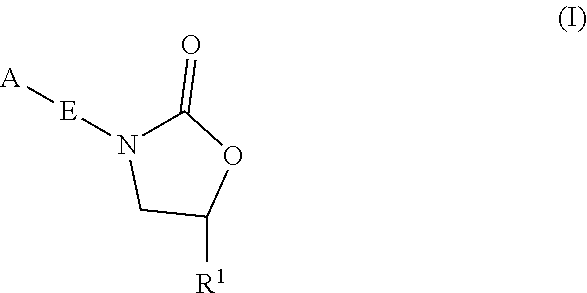
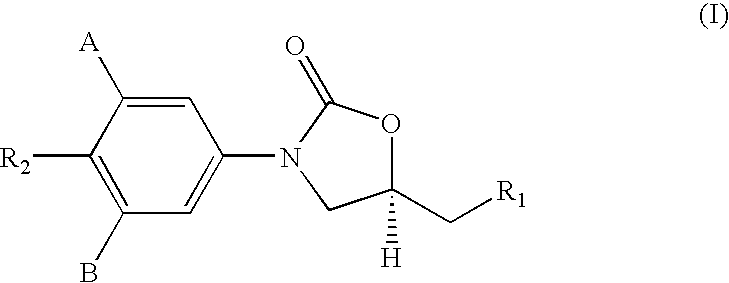
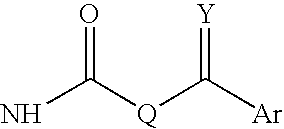
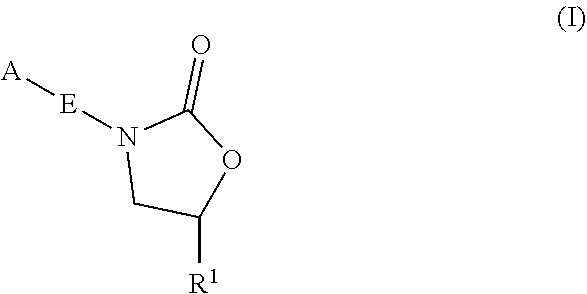
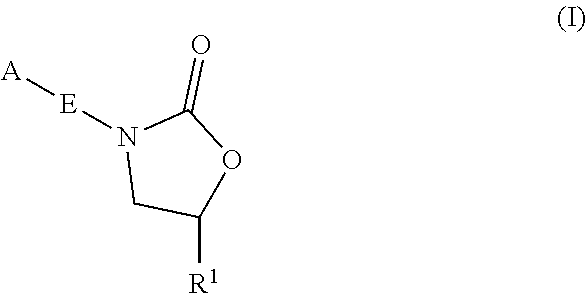
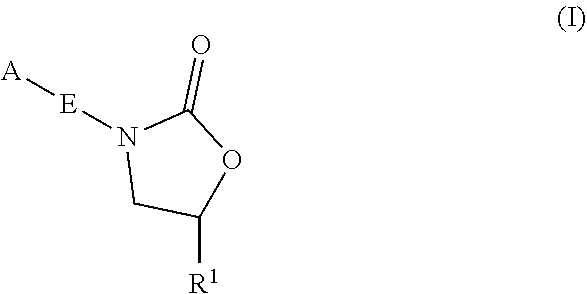
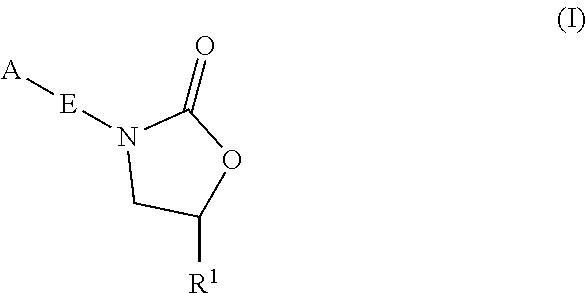
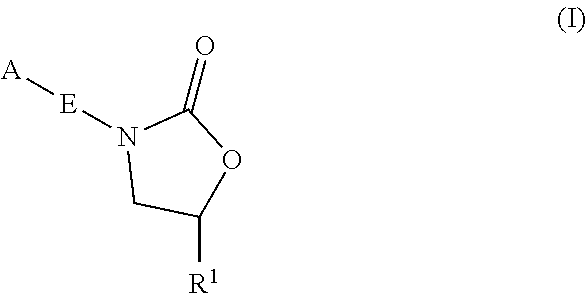
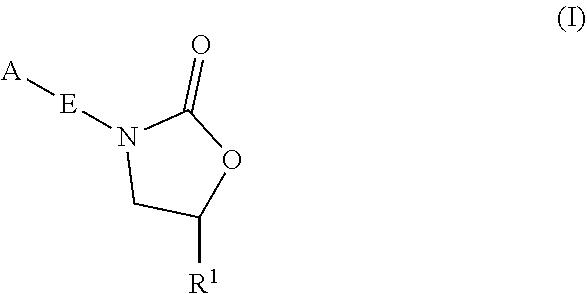
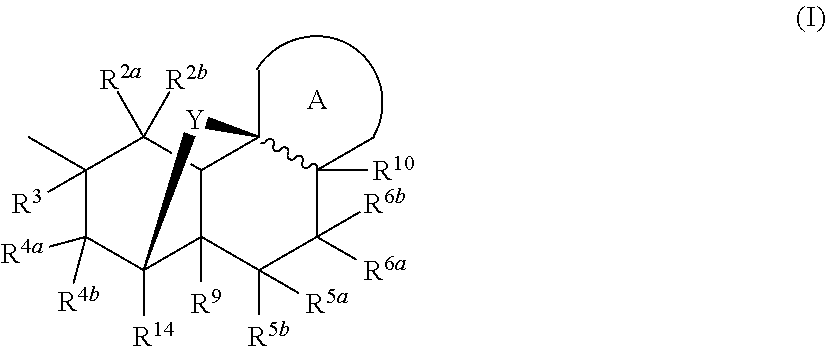
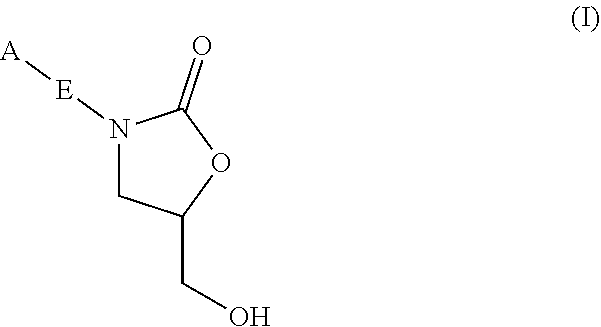
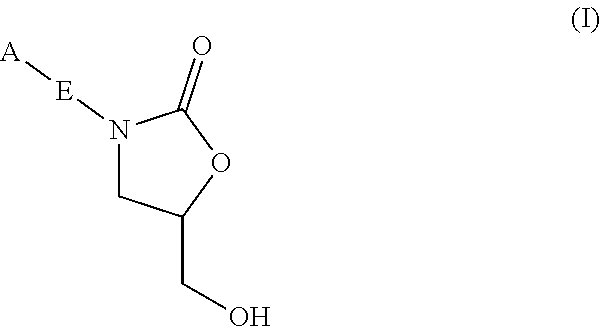
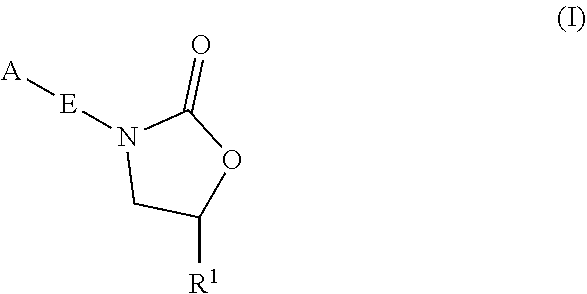
InactiveUS20180290987A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMycobacterium InfectionsMycobacterial cell
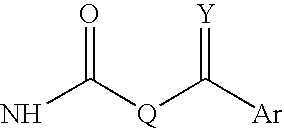
The present invention relates to oxazolidinone compounds of Formula (I): and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein A, E, and R1 are as defined herein. The present invention also relates to compositions which comprise at least one oxazolidinone compound of the invention. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an oxazolidinone of the invention and / or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a composition comprising such compound and / or salt.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Primer and Probe for Use in Detection of Mycobacterium Kansasii and Method for Detection of Mycobacterium Kansasii Using the Same
InactiveUS20090298057A1Quick checkImprove accuracyElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementBacteroidesDiagnosis methods
The present invention discloses an oligonucleotide which comprises a part or the entire sequence of the nucleotide sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 3 or 4, or a part or the entire sequence of a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence, wherein the oligonucleotide is capable of hybridizing with the nucleotide sequence of Mycobacterium kansasii; a primer and a probe for use in the detection of Mycobacterium kansasii comprising the oligonucleotide; and a method for detecting Mycobacterium kansasii using the primer and / or probe.The method for detecting Mycobacterium kansasii enables the detection of M. kansasii more rapidly and with higher accuracy compared with a conventional bacterium identification method performed by culture examination on a bacterium. Further, the method can exclude any false positive result for the diagnosis and can also detect and diagnose M. kansasii with higher accuracy compared with a diagnosis method performed by PCR using a conventional primer and / or probe. Still further, the method can quantify a M. kansasii cell.
Owner:WAKO PURE CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES
Kit for detecting sensitive mycobacterium tuberculosis and detection method of kit
The invention relates to the technical field of detection, in particular to a kit for detecting sensitive mycobacterium tuberculosis and a detection method of the kit. The kit is used for testing mycobacterium tuberculosis, and the preparation steps of a reagent include putting a sputum sample into a sodium hydroxide solution, and shaking and removing mucin components on the surface of the sputumsample; preforming high-speed centrifugation on the sputum sample to extract required mycobacterium tuberculosis cells; crushing the extracted Mycobacterium tuberculosis cells, centrifuging, washing with distilled water, and dissolving the obtained precipitate with a membrane dissolving solution to obtain an outer membrane protein; separating membrane outer proteins to obtain three outer membraneproteins, and purifying and recombining the three outer membrane proteins to obtain three recombined proteins; diluting the purified three recombined protein solution and using an enzyme label plate;closing the enzyme label plate and washing; and putting the enzyme label plate into a vacuum aseptic dryer for drying and then putting into a reagent bottle. The method can detect an antibody in the sample and a source of the antibody.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
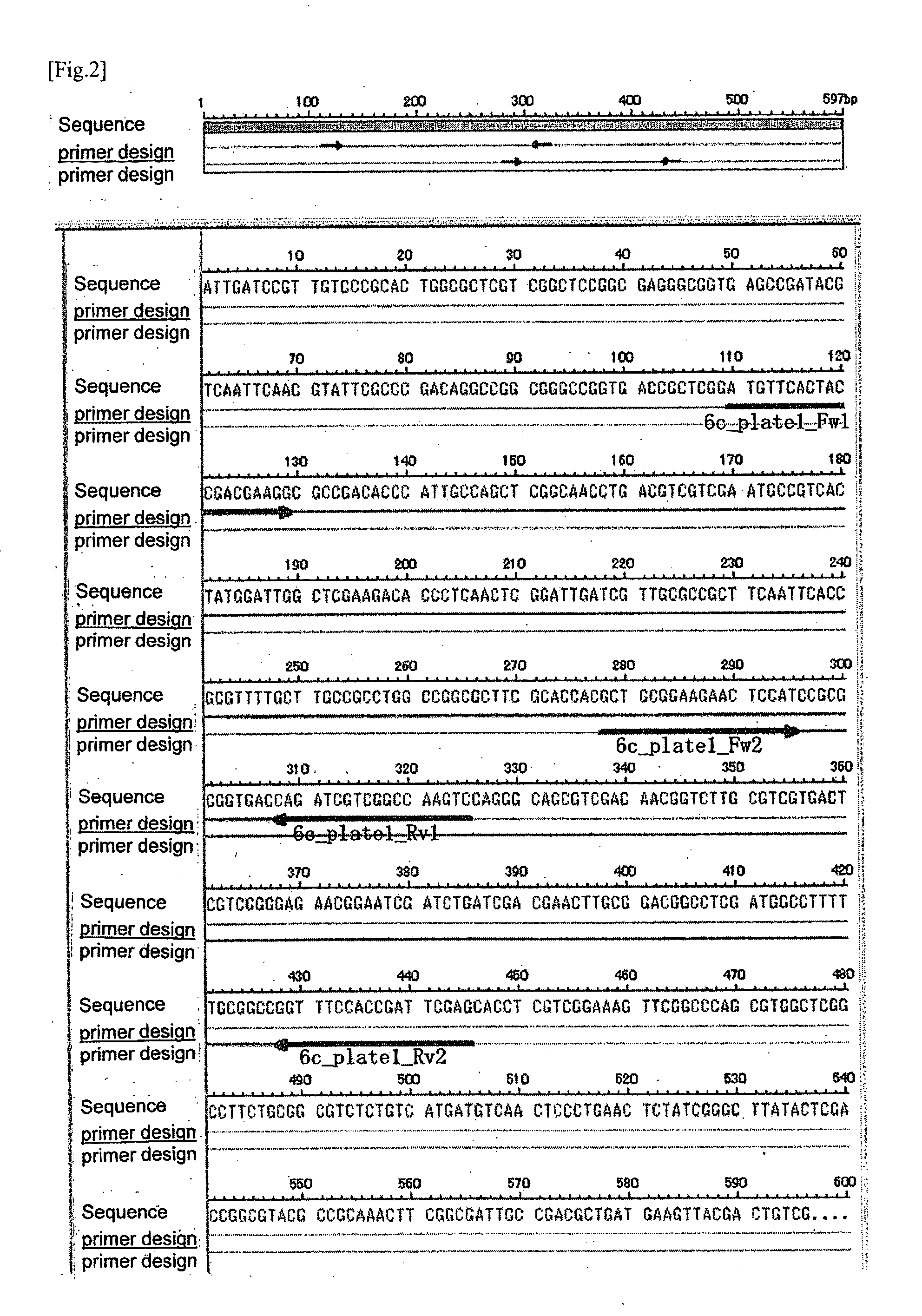
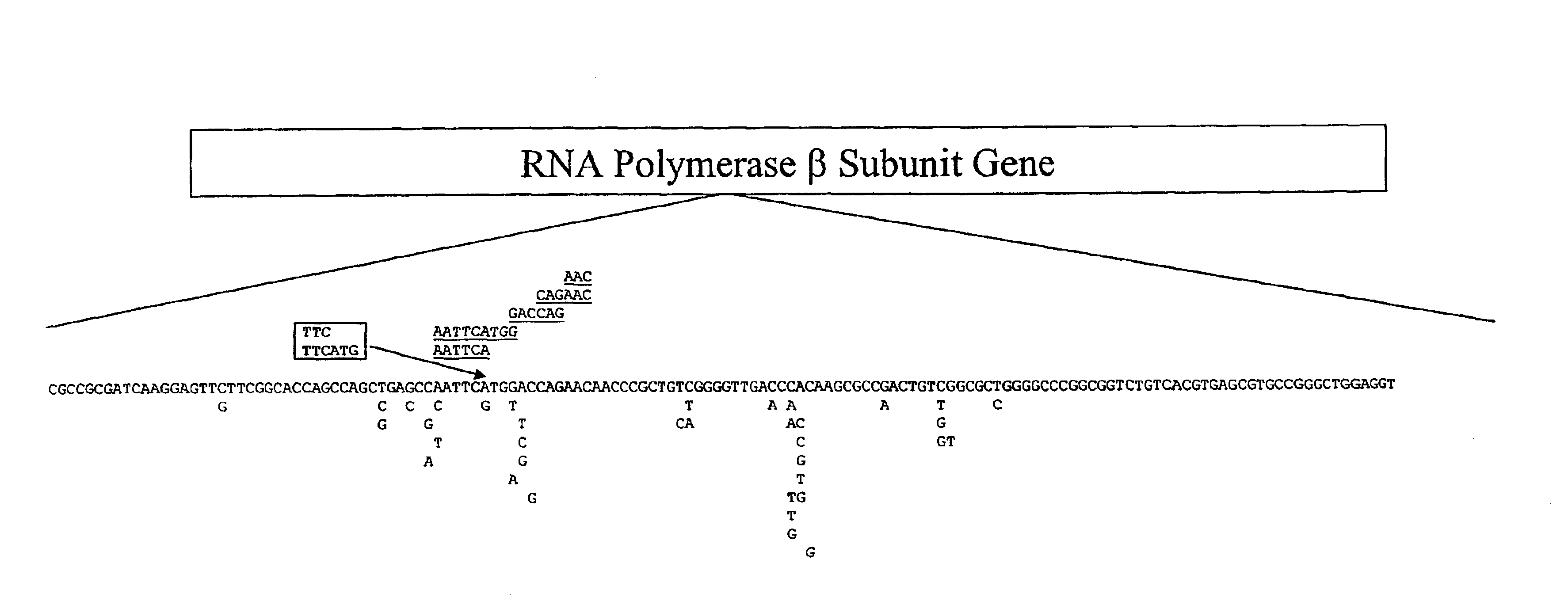
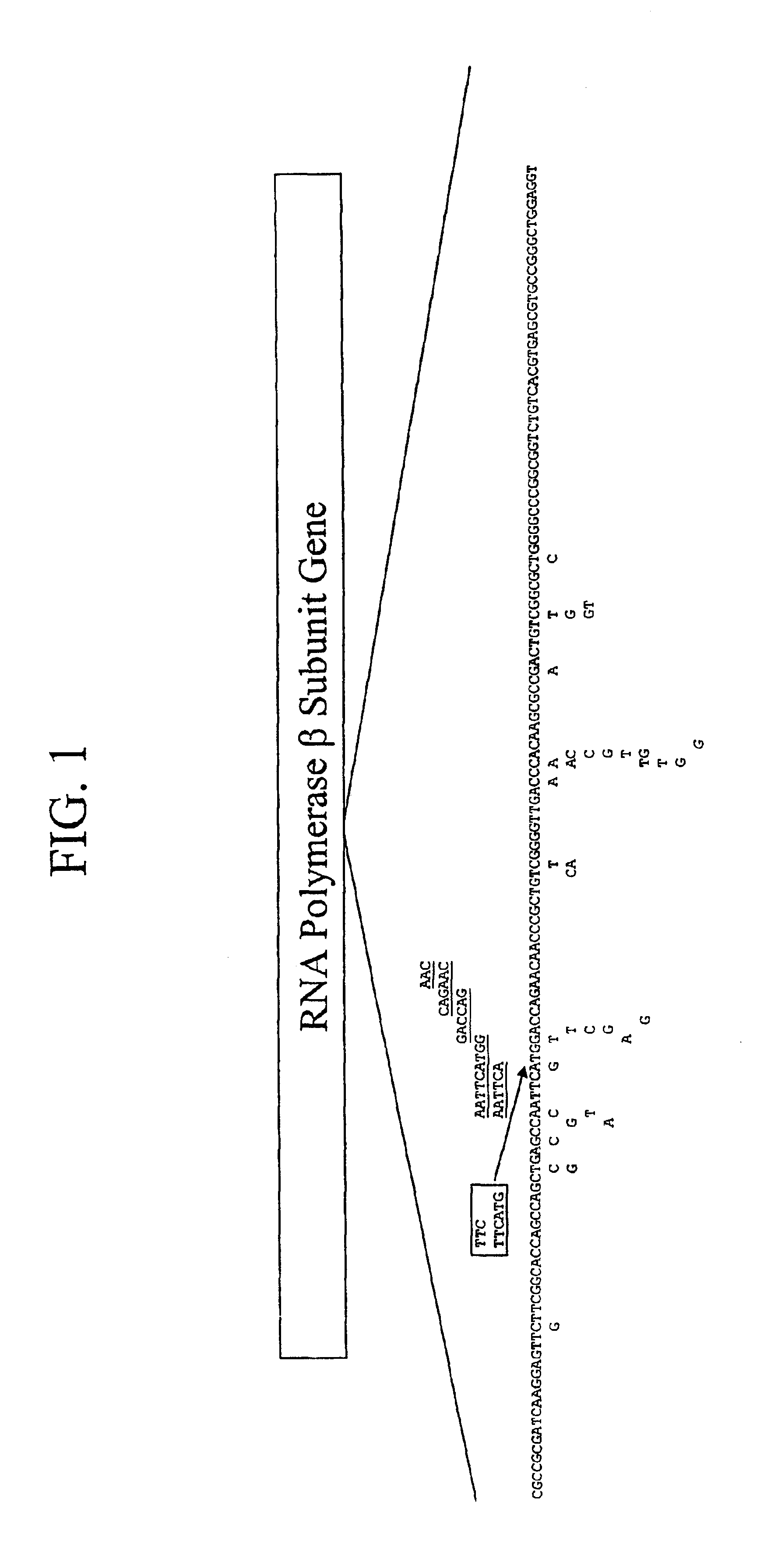
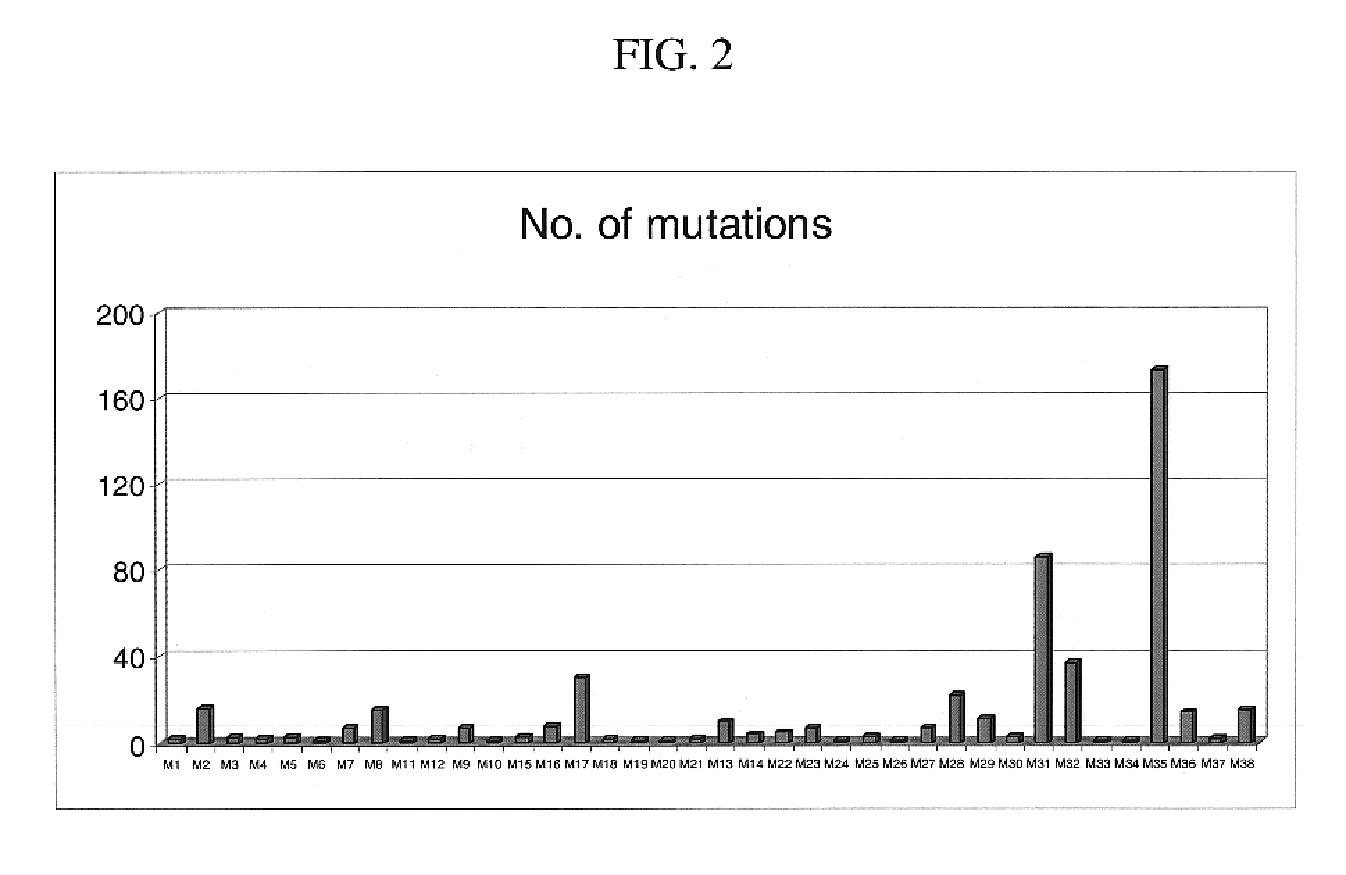
Mutation detection on RNA polmerase beta subunit gene having rifampin resistance
InactiveUS6902894B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceNucleotide
The present invention provides a diagnostic test method for detecting a tendency to rifampin resistance caused by mutations in a rpoB gene of M. tuberculosis, comprising the steps of (i) extracting genomic DNA from a biological sample containing M. tuberculosis cells; (ii) amplifying from the extracted genomic DNA the rpoB gene coding sequence or at least one distinct fragment thereof containing nucleotides encoding at least one test amino acid of the group consisting of amino acid numbers 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 522, 526, 529, 531, 533 to produce fluorescently labeled amplification product; (iii) contacting said fluorescently labeled amplification product with a first control array of oligonucleotide probes having DNA sequences specific to the wildtype M. tuberculosis rpoB gene coding sequence, including the nucleotides encoding the at least one test amino acid, and with a second test array of oligonucleotide probes having DNA sequences specific to the M. tuberculosis rpoB gene coding sequence, including nucleotides encoding mutations in the at least one test amino acid, wherein at least 3 mutations of the rpoB gene are probed for by the second test array of oligonucleotide probes; detecting any fluorescent hybridization signal of said purified fluorescently labeled amplification product which hybridized with the first and second arrays of oligonucleotide probes; (iv) correlating said detected hybridization with a tendency to rifampin resistance; and (v) correlating the detected hybridization to a tendency to rifampcin resistance and MDR.
Owner:GENETEL PHARMA
Fluorescent probe for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis as well as preparation method and detection method thereof
PendingCN114836193ARealize detectionEasy and fast detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesTuberculosis mycobacterium
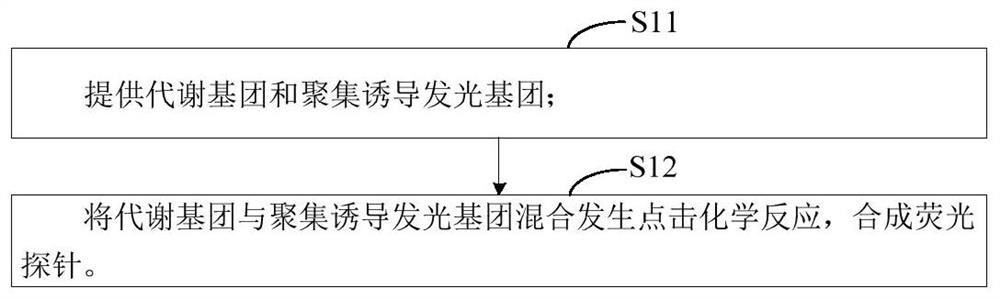
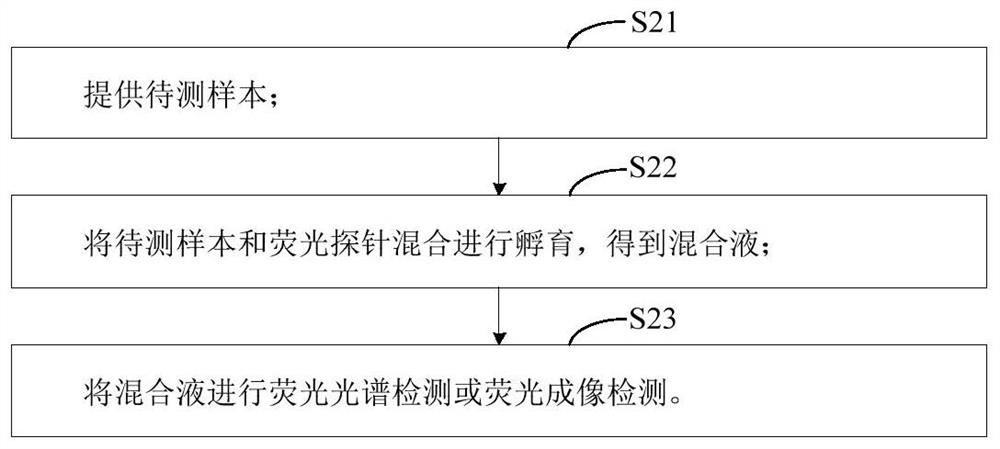
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, and provides a fluorescent probe for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis, the fluorescent probe comprises a metabolic group and an aggregation-induced emission group, the metabolic group is connected with the aggregation-induced emission group through a chemical bond, and the metabolic group is used for synthesizing mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall peptidoglycan. According to the fluorescent probe provided by the invention, mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall peptidoglycan is synthesized through the contained metabolic group, a large amount of mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall peptidoglycan is gathered to the mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall in a metabolic labeling manner, and the aggregation-induced emission group generates a fluorescence signal due to aggregation, so that the detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis is realized. In addition, the fluorescent probe can rapidly and conveniently detect mycobacterium tuberculosis, and is high in specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:THE THIRD PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN +1
Antimycobacterial compounds
Novel compounds belonging to the class of oxazolidinones possessing potent antimycobacterial properties especially useful in the treatment of acid fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex, M. fortuitum and M. kansai. The compound and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts act as antibacterial agents. Also mentioned is a method for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial conditions such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex, M. fortuitum and M. kansai., including administering an antimycobacterially effective amount of the compound and / or pharmaceutically acceptable salts. There is also mentioned a process for the manufacture of the compound or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
Oxazolidinone compounds and methods of use thereof as antibacterial agents
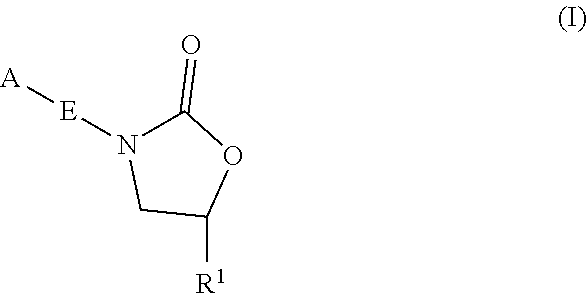
ActiveUS20190248753A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMycobacterium InfectionsMycobacterial cell
The present invention relates to oxazolidinone compounds of Formula (I):and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein A, E, and R1 are as defined herein. The present invention also relates to compositions which comprise at least one oxazolidinone compound of the invention. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an oxazolidinone of the invention and / or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a composition comprising such compound and / or salt.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Oxazolidinone compounds and methods of use thereof as antibacterial agents
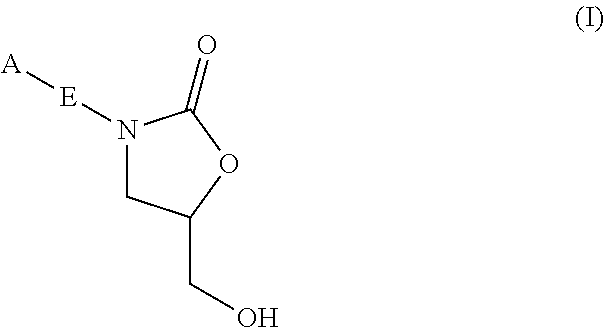
ActiveUS10752621B2Antibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryTuberculosis mycobacteriumMycobacterium Infections
The present invention relates to oxazolidinone Compounds of Formula (I): (I) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein A, E, and R1 are as defined herein. The present invention also relates to compositions which comprise at least one oxazolidinone compound of the invention. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an oxazolidinone of the invention and / or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a composition comprising such compound and / or salt.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Nargenicin compounds and uses thereof as antibacterial agents
ActiveUS20180186808A1Antibacterial agentsGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsTuberculosis mycobacteriumNargenicin
The present invention relates to novel nargenicin related compounds which can inhibit DnaE and have antibacterial, particularly antimycobacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The present invention also relates to method for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis by administering an antimycobacterially effective amount of nargenicin or a nargenicin-related compound and / or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Oxazolidinone compounds and methods of use thereof as antibacterial agents
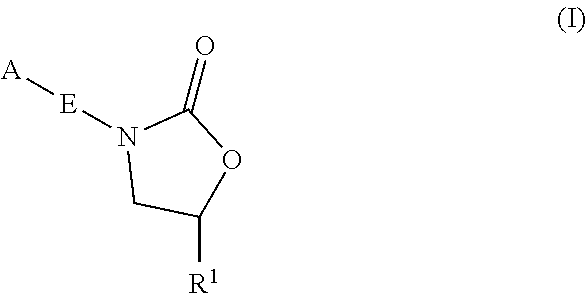
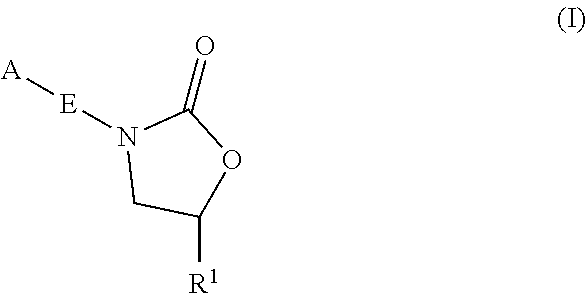
PendingUS20220081403A1Pronounced antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsOxazolidonePharmaceutical medicine
The present invention discloses oxazolidinone compounds of Formula (I): (I) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein A and E, are as defined herein. The present invention also relates to compositions which comprise at least one oxazolidinone compound of the invention. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an oxazolidinone of the invention and / or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a composition comprising such compound and / or salt.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Oxazolidinone compounds and methods of use thereof as antibacterial agents
ActiveUS20200010463A1Pronounced antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryTuberculosis mycobacteriumMycobacterium Infections
The present invention relates to oxazolidinone Compounds of Formula (I): (I) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein A, E, and R1 are as defined herein. The present invention also relates to compositions which comprise at least one oxazolidinone compound of the invention. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an oxazolidinone of the invention and / or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a composition comprising such compound and / or salt.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Primer and probe for use in detection of Mycobacterium kansasii and method for detection of Mycobacterium kansasii using the same
InactiveUS8242249B2Diagnosed more rapidlyImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleotide
The present invention discloses an oligonucleotide which comprises a part or the entire sequence of the nucleotide sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 3 or 4, or a part or the entire sequence of a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence, wherein the oligonucleotide is capable of hybridizing with the nucleotide sequence of Mycobacterium kansasii; a primer and a probe for use in the detection of Mycobacterium kansasii comprising the oligonucleotide; and a method for detecting Mycobacterium kansasii using the primer and / or probe.The method for detecting Mycobacterium kansasii enables the detection of M. kansasii more rapidly and with higher accuracy compared with a conventional bacterium identification method performed by culture examination on a bacterium. Further, the method can exclude any false positive result for the diagnosis and can also detect and diagnose M. kansasii with higher accuracy compared with a diagnosis method performed by PCR using a conventional primer and / or probe. Still further, the method can quantify a M. kansasii cell.
Owner:WAKO PURE CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES
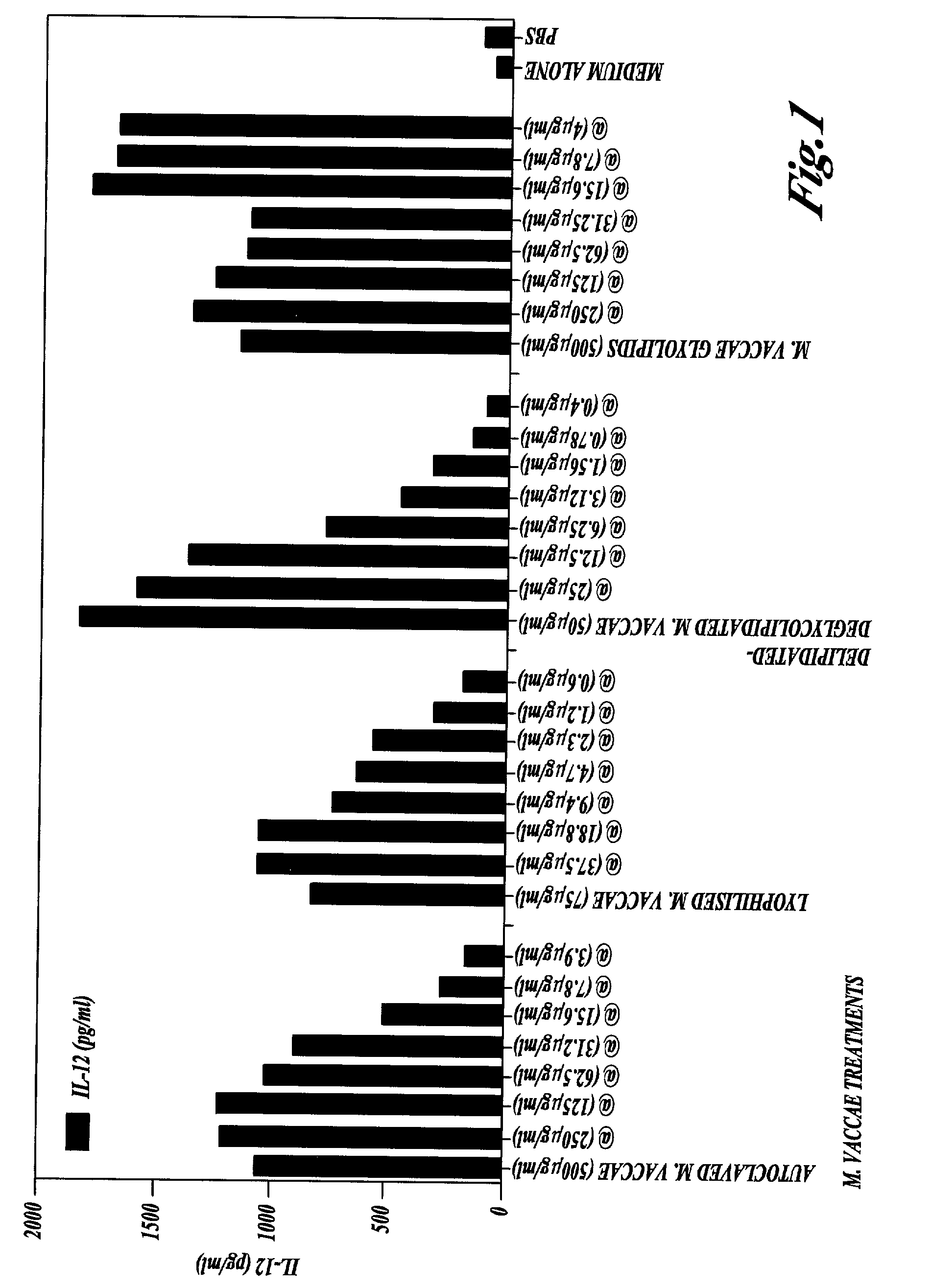
Compsns. derived from i(mycobacterium vaccae) and methods for their use
The present invention provides compositions which are present in or may be derived from Mycobacterium vaccae, together with methods for their use in the treatment, prevention and detection of disorders including infectious diseases, immune disorders and cancer. Methods for enhancing the immune response to an antigen including administration of M. vaccae culture filtrate, delipidated M. vaccae cells, delipidated and deglycolipidated M. vaccae cells depleted of mycolic acids, and delipidated and deglycolipidated M.vaccae cells depleted of mycolic acids and arabinogalactan are also provided.
Owner:GENESIS RES & DEV
Construction method and application of a kind of mycobacterium genetically engineered bacteria
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a mycobacterium genetically engineered bacterium, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. In the present invention, after the recombinant plasmid is transformed into mycobacterium LY-1 cells, the sgRNA will recognize a specific region on the genome and guide the Cas9 protein to bind to the target site. Under the action of the protein, a double strand is formed at the target site Most of the cells die because of the broken gap: the homologous repair sequence introduced with the recombinant plasmid is integrated into the gap through double exchange under the action of recombinase, and the cells with successful gene homologous repair survive and form gene loss. Artificially designed genotypes such as living and exogenous gene insertions. The CRISPR-Cas9 system constructed by the present invention has a knockout efficiency of 60% for the same gene, which is more convenient and efficient than the existing mycobacterial gene editing methods.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Composition and method for treating bladder cancer
InactiveCN1153576CBacteria material medical ingredientsCarbohydrate active ingredientsBladder cancerApoptosis
The present invention relates to a composition and method for treating cancer in the urinary bladder. More particularly, the present invention relates to a composition comprising a Mycobacterium phlei (M. phlei) deoxyribonucleic acid (M-DNA)-M. phlei cell wall complex (MCC), wherein the M-DNA is preserved and complexed on the M. phlei cell wall, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The MCC composition inhibits proliferation of and induces apoptosis in the cancer cells in the urinary bladder of the animal.
Owner:贝尔尼奇泌尿知识产权公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com