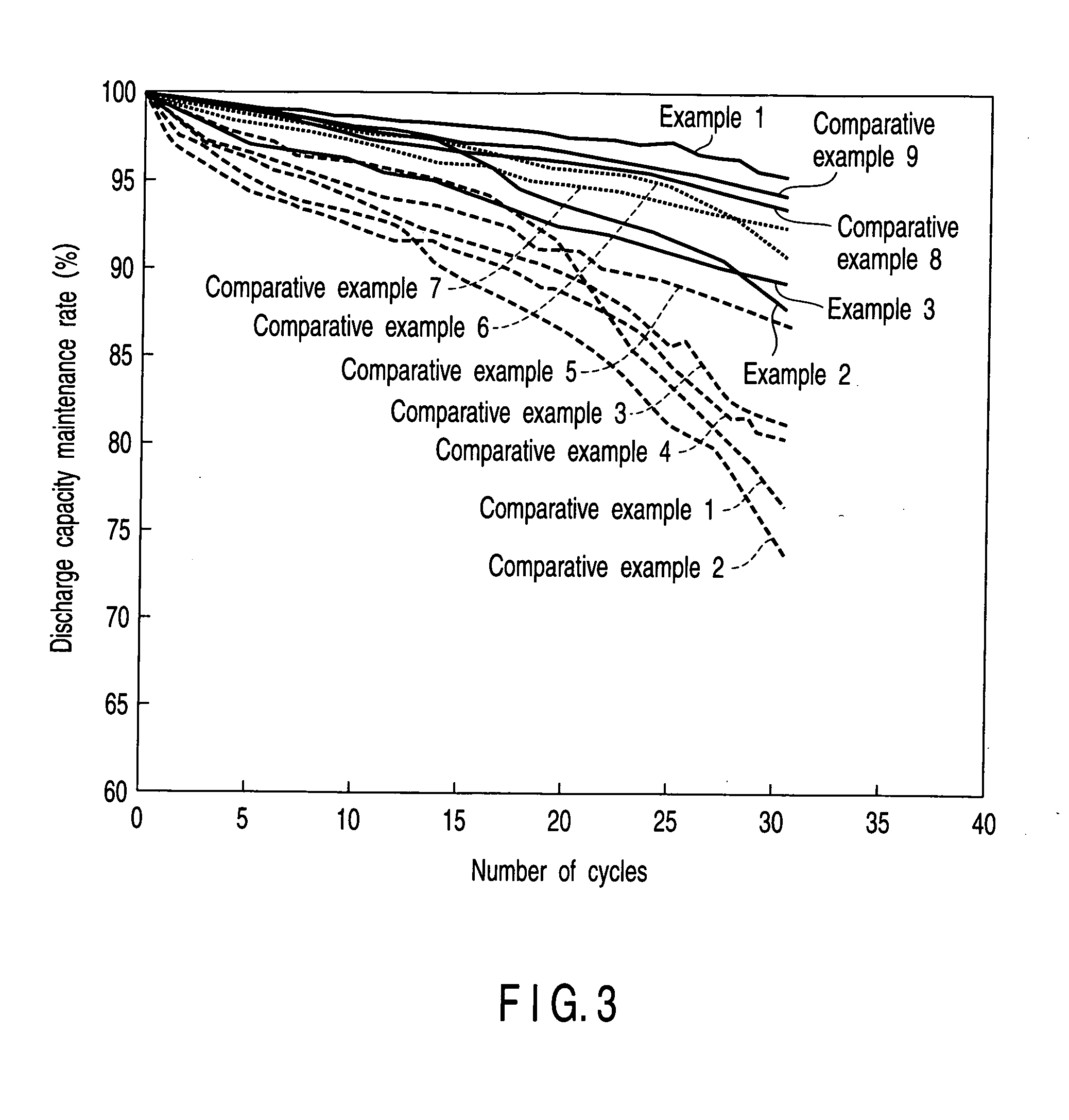
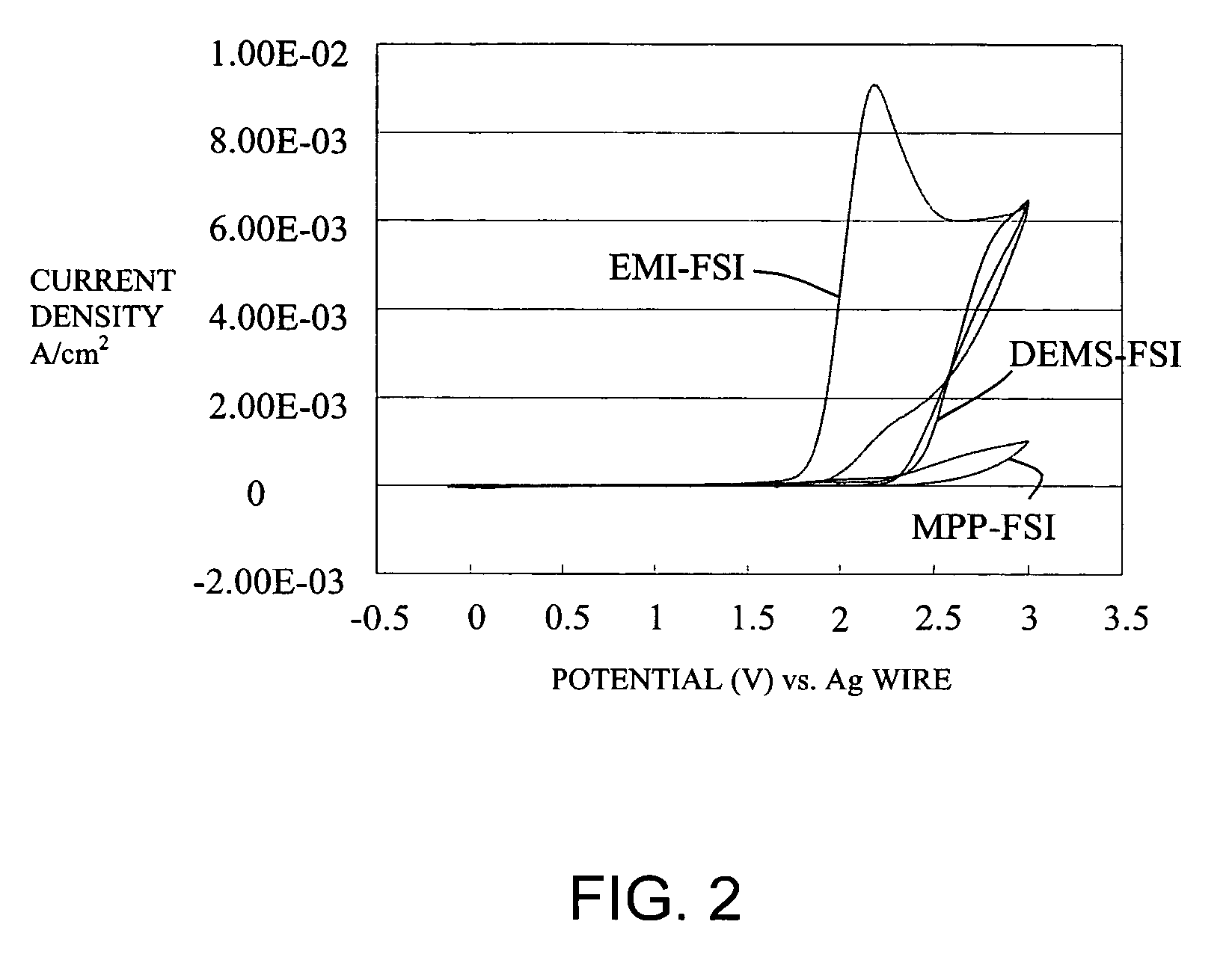
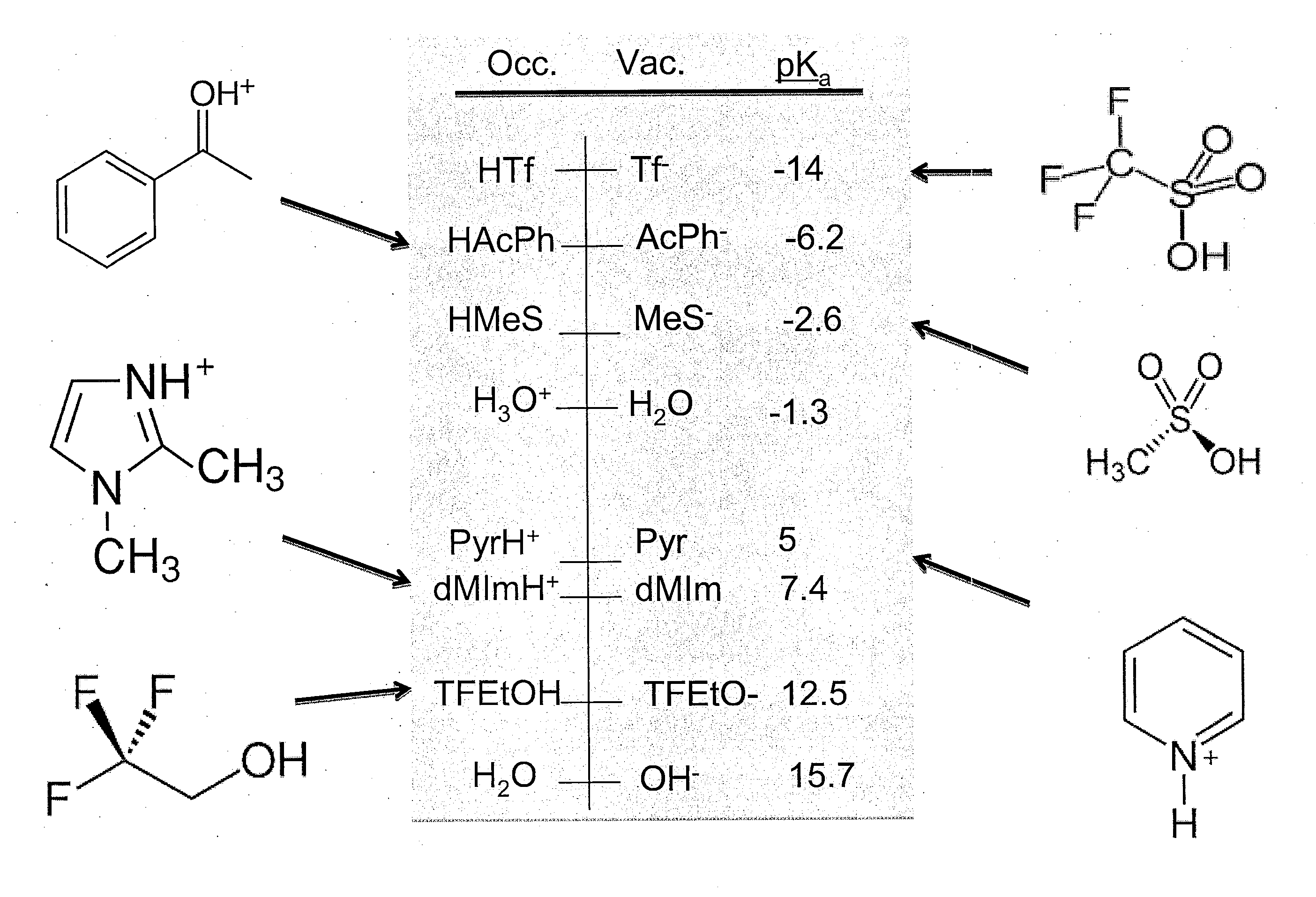
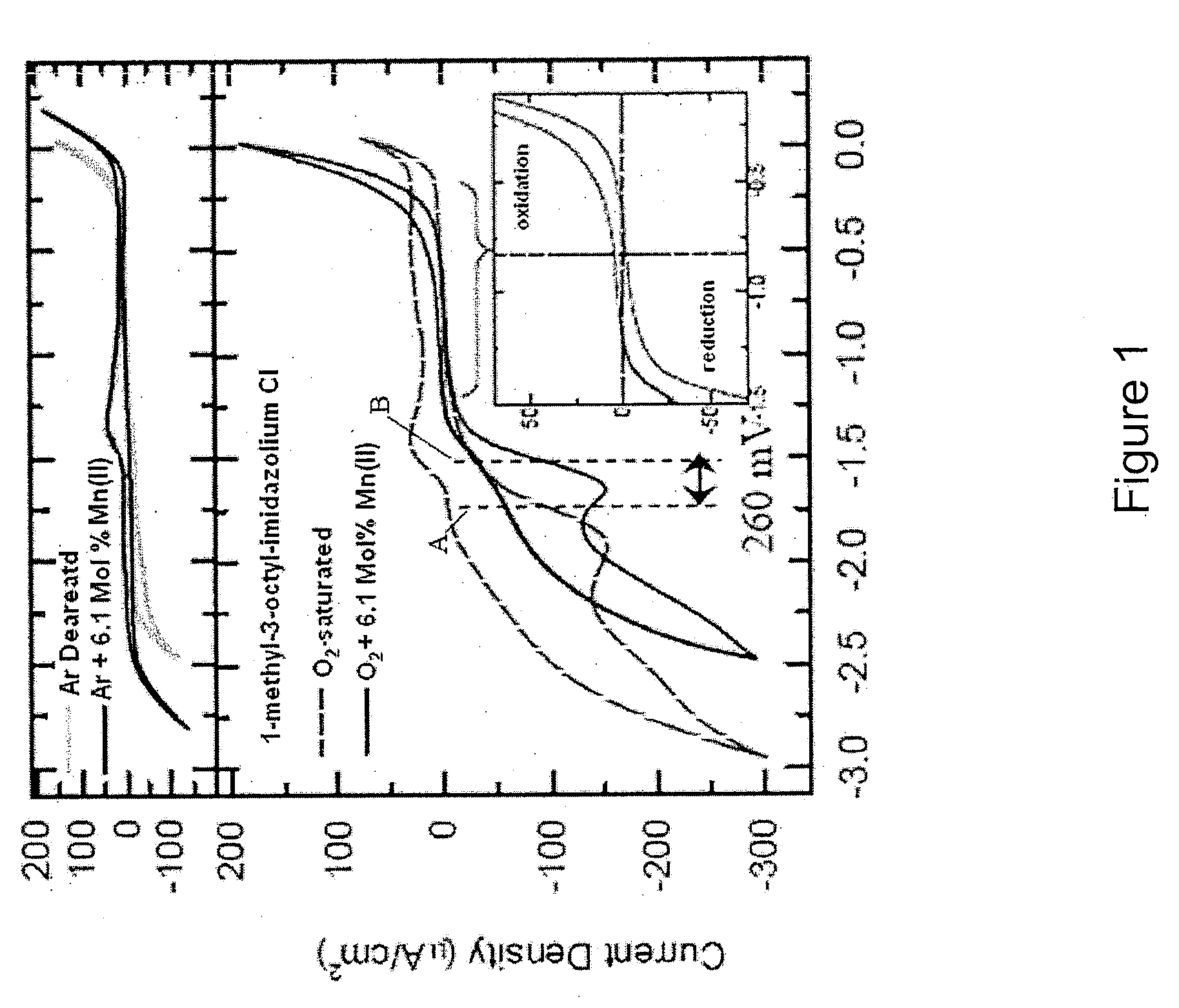
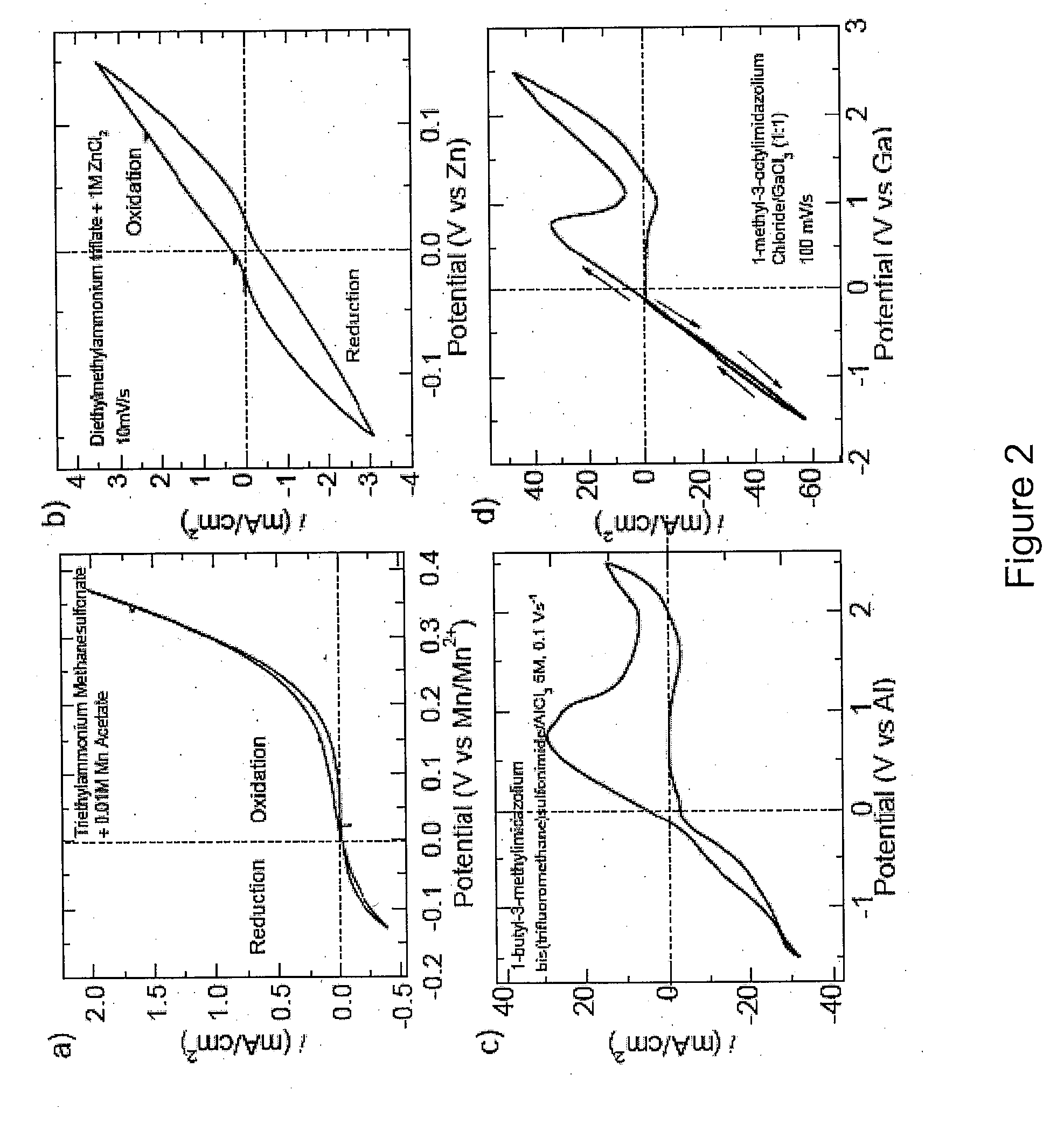
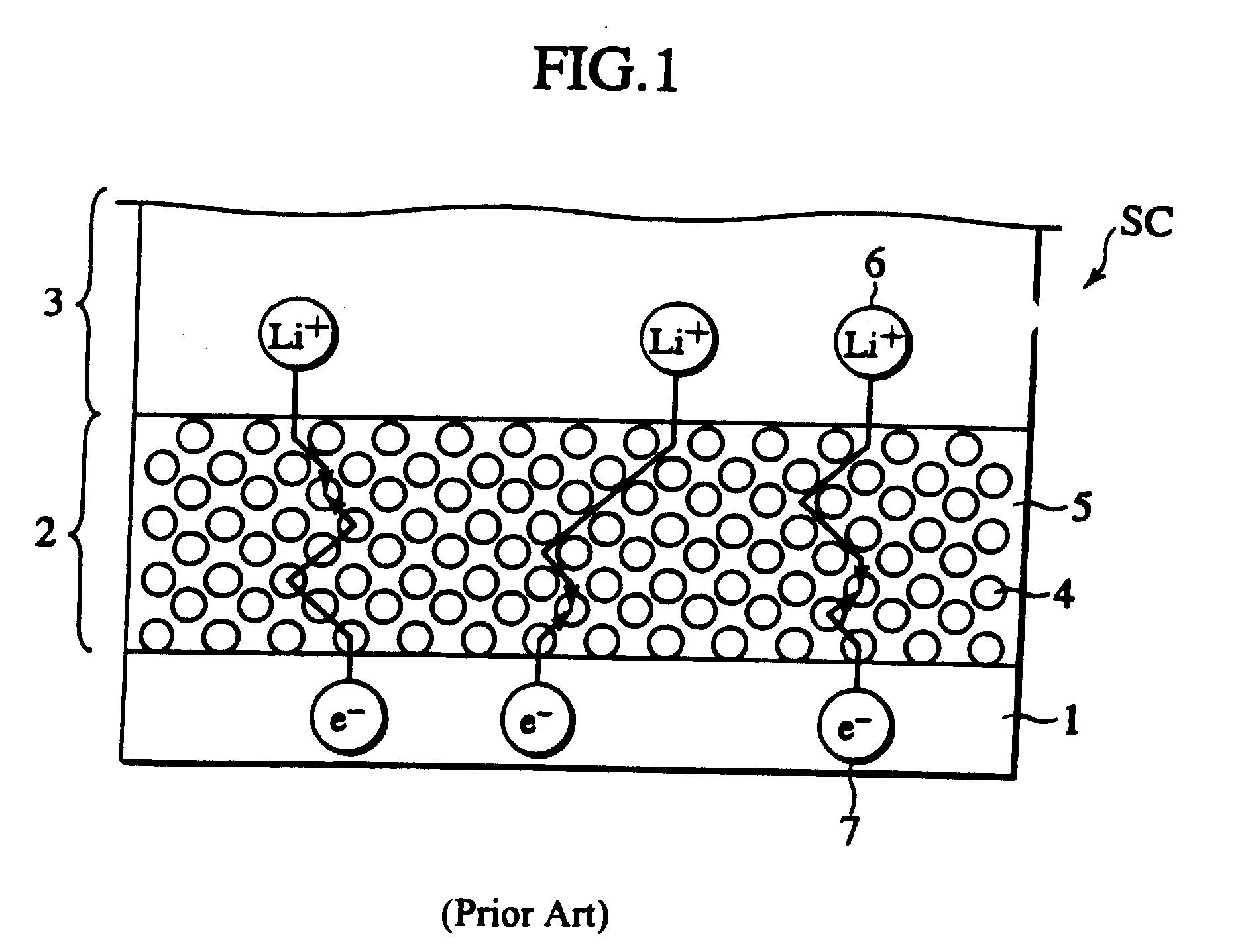
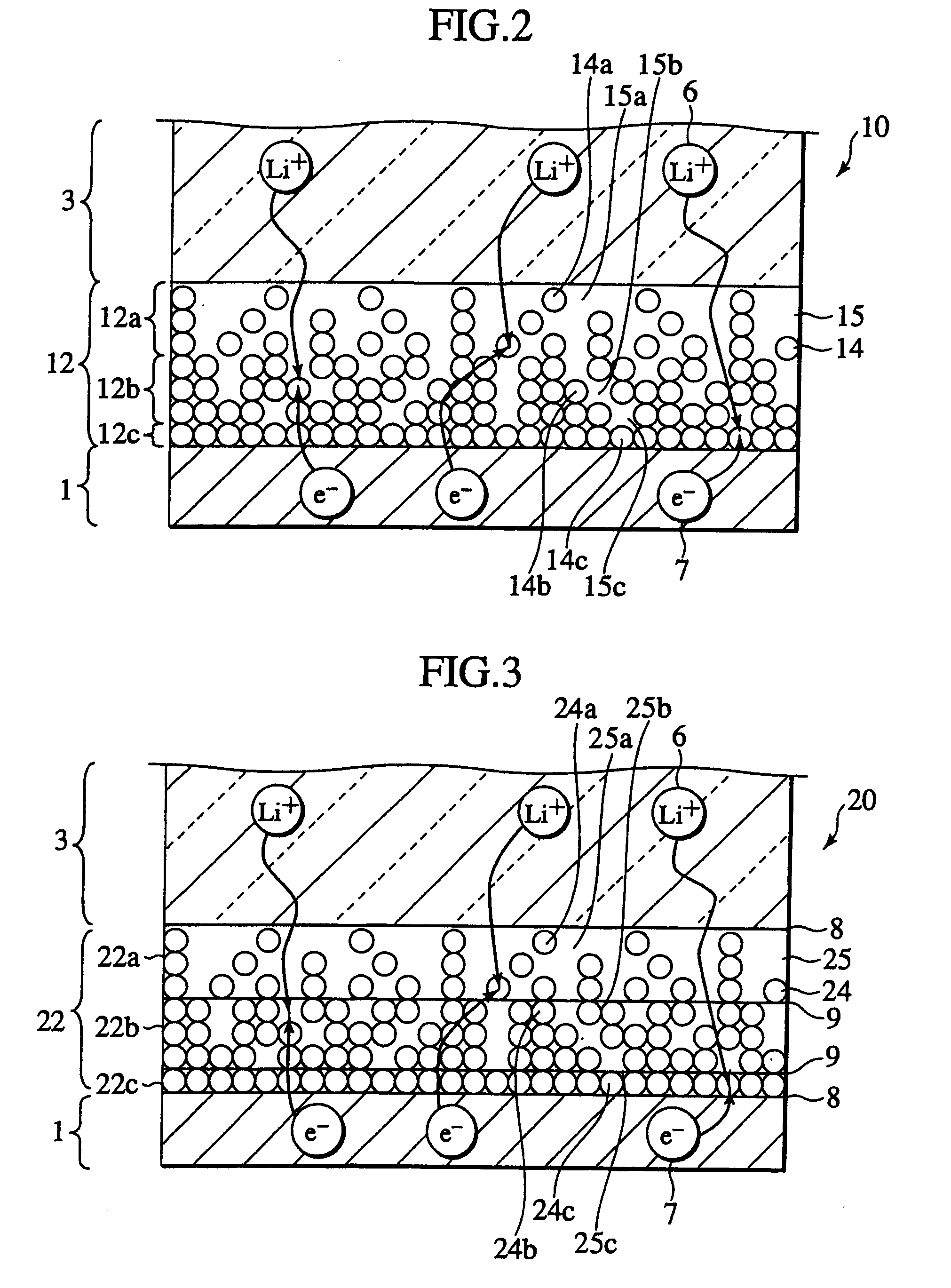
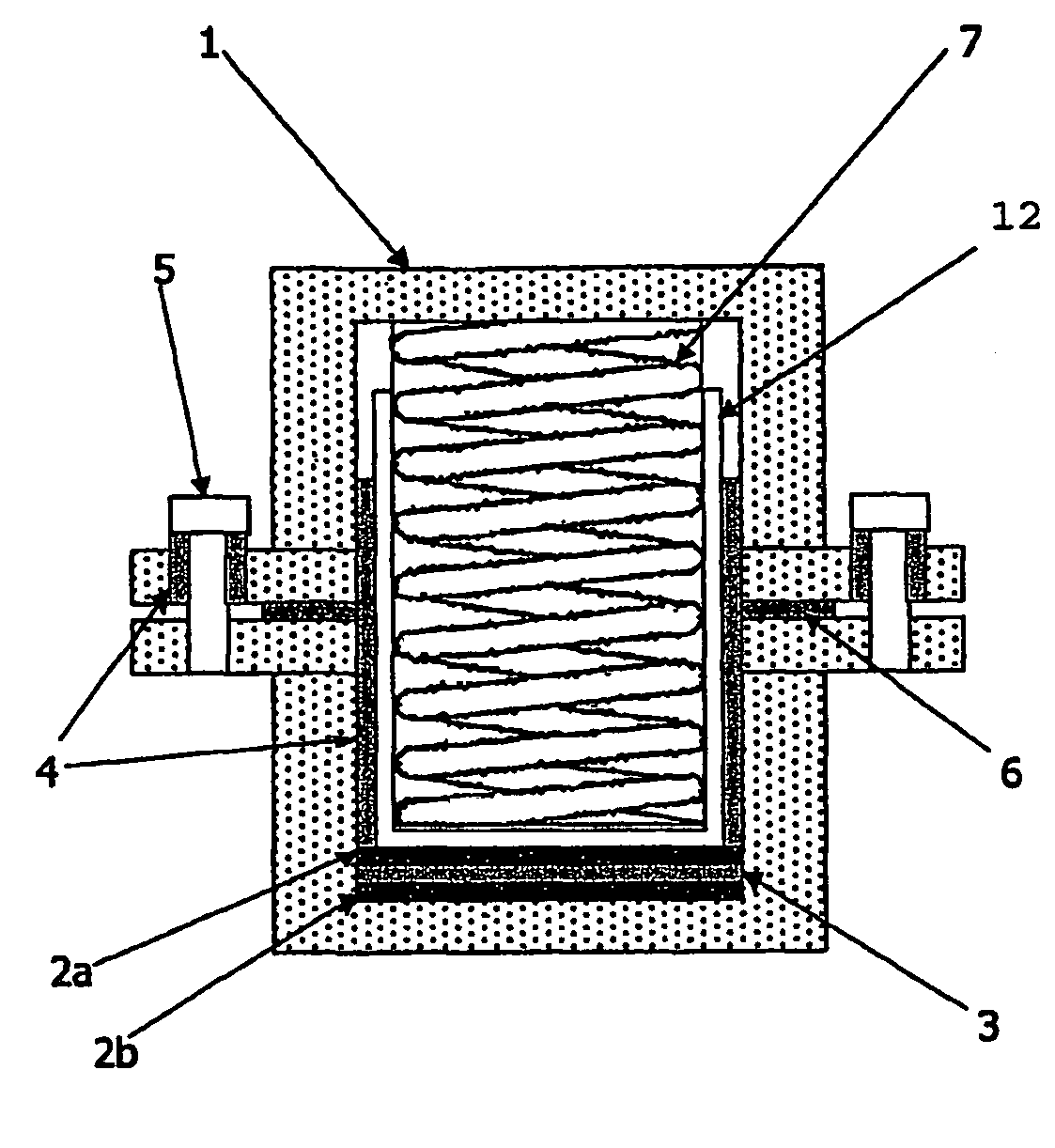
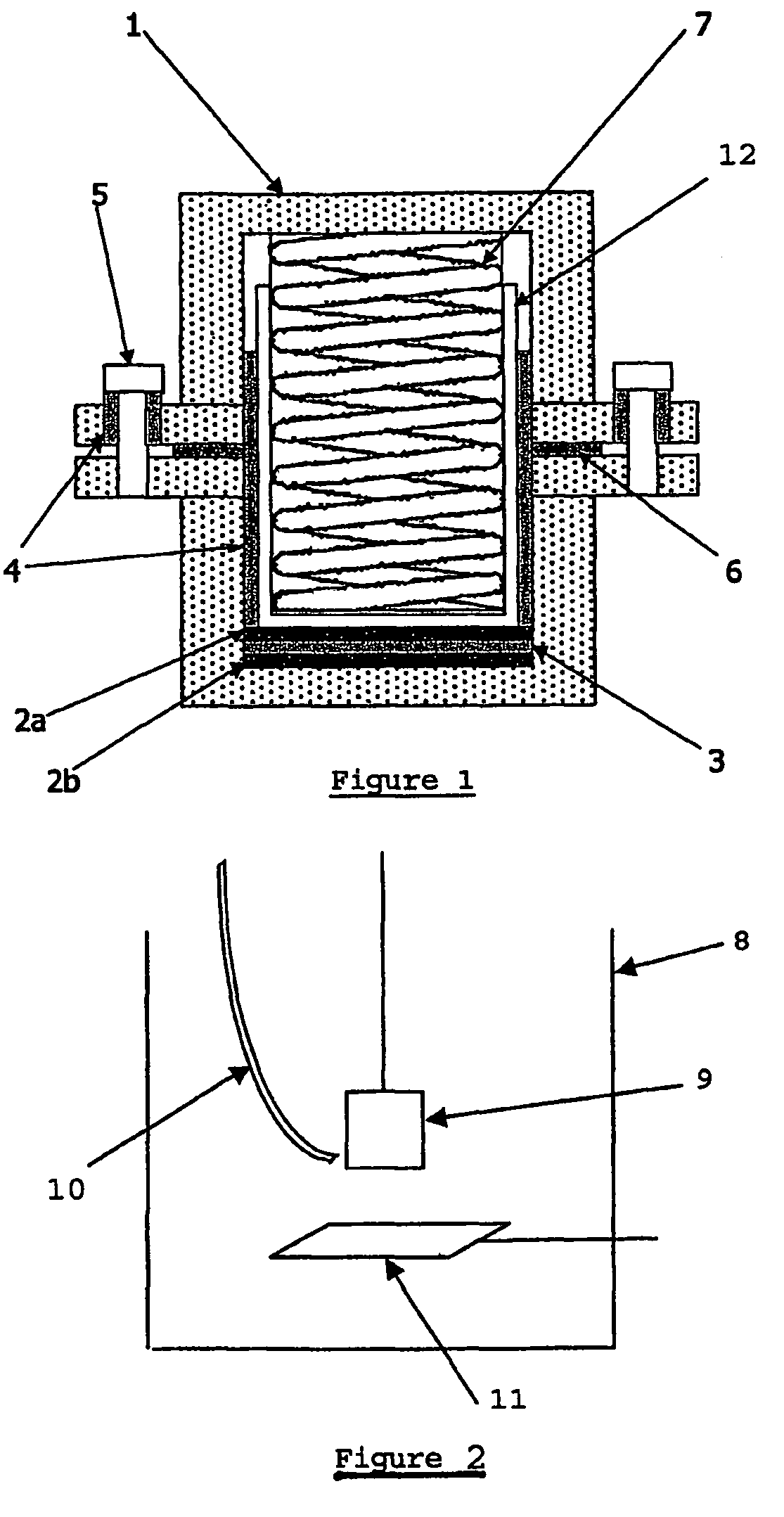
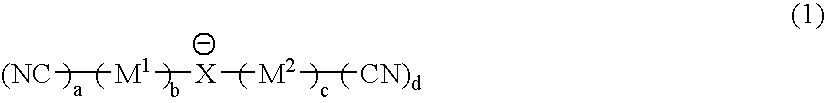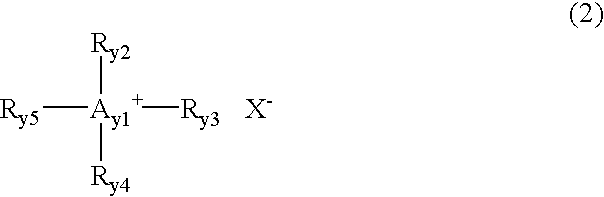Patents
Literature
168results about "Inorganic electrolytes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Material for electrolytic solutions and use thereof
InactiveUS20040002002A1Avoid corrosionImprove ionic conductivityHybrid capacitor electrolytesAlkaline accumulatorsOrganic linkingElectrical conductor
It is an object of the present invention to provide a material for electrolytic solutions suited for use as material in electrolytic solutions serving as ionic conductors in electrochemical devices, such as large-capacity cells or batteries. The present invention is related to a material for electrolytic solutions which comprises, as an essential constituent, an anion represented by the general formula (1): wherein X represents at least one element selected from among B, N, O, Al, Si, P, S, As and Se; M<1 >and M<2 >are the same or different and each represents an organic linking group; a is an integer of not less than 1, and b, c and d each independently is an integer of not less than 0.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Nonaqueous electrolyte
ActiveUS20050221188A1Excellent characteristicsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsElectrode carriers/collectorsLithiumMaterials science
A nonaqueous electrolyte battery includes a positive electrode containing an active material, a negative electrode, and a nonaqueous electrolyte, the negative electrode including a current collector and a negative electrode active material supported by the current collector, the negative electrode active material having a Li insertion potential not lower than 0.2V (vs. Li / Li+) and an average primary particle diameter not larger than 1 μm, and a specific surface area of the negative electrode, excluding a weight of the current collector, as determined by the BET method falls within a range of 3 to 50 m2 / g.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Nonaqueous electrolytes and nonaqueous-electrolyte secondary batteries employing the same
ActiveUS20100099031A1Large capacityImprove cycle performanceCell electrodesOrganic electrolyte cellsHigh current densityChemical structure
A subject is to provide a nonaqueous electrolyte excellent in cycle performances such as capacity retention after cycling, output after cycling, discharge capacity after cycling, and cycle discharge capacity ratio, output characteristics, high-temperature storability, low-temperature discharge characteristics, heavy-current discharge characteristics, high-temperature storability, safety, high capacity, high output, high-current-density cycle performances, compatibility of these performances, etc. Another subject is to provide a nonaqueous-electrolyte secondary battery employing the nonaqueous electrolyte. The subjects have been accomplished with a nonaqueous electrolyte which contains a monofluorophosphate and / or a difluorophosphate and further contains a compound having a specific chemical structure or specific properties.
Owner:MU IONIC SOLUTIONS CORP +1
Non-aqueous electrolyte battery
InactiveUS20060068282A1Improve output performanceImprove cycle performanceNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersMolten saltNon aqueous electrolytes
A non-aqueous electrolyte battery that contains a molten salt electrolyte and has the enhanced output performances and cycle performances can be provided. The electrolyte has a molar ratio of lithium salt to molten salt of from 0.3 to 0.5, and the non-aqueous electrolyte battery has a positive electrode having a discharge capacity of 1.05 or more times that of a negative electrode thereof.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Battery and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060024582A1Decomposition is suppressedFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsDecompositionCarbide
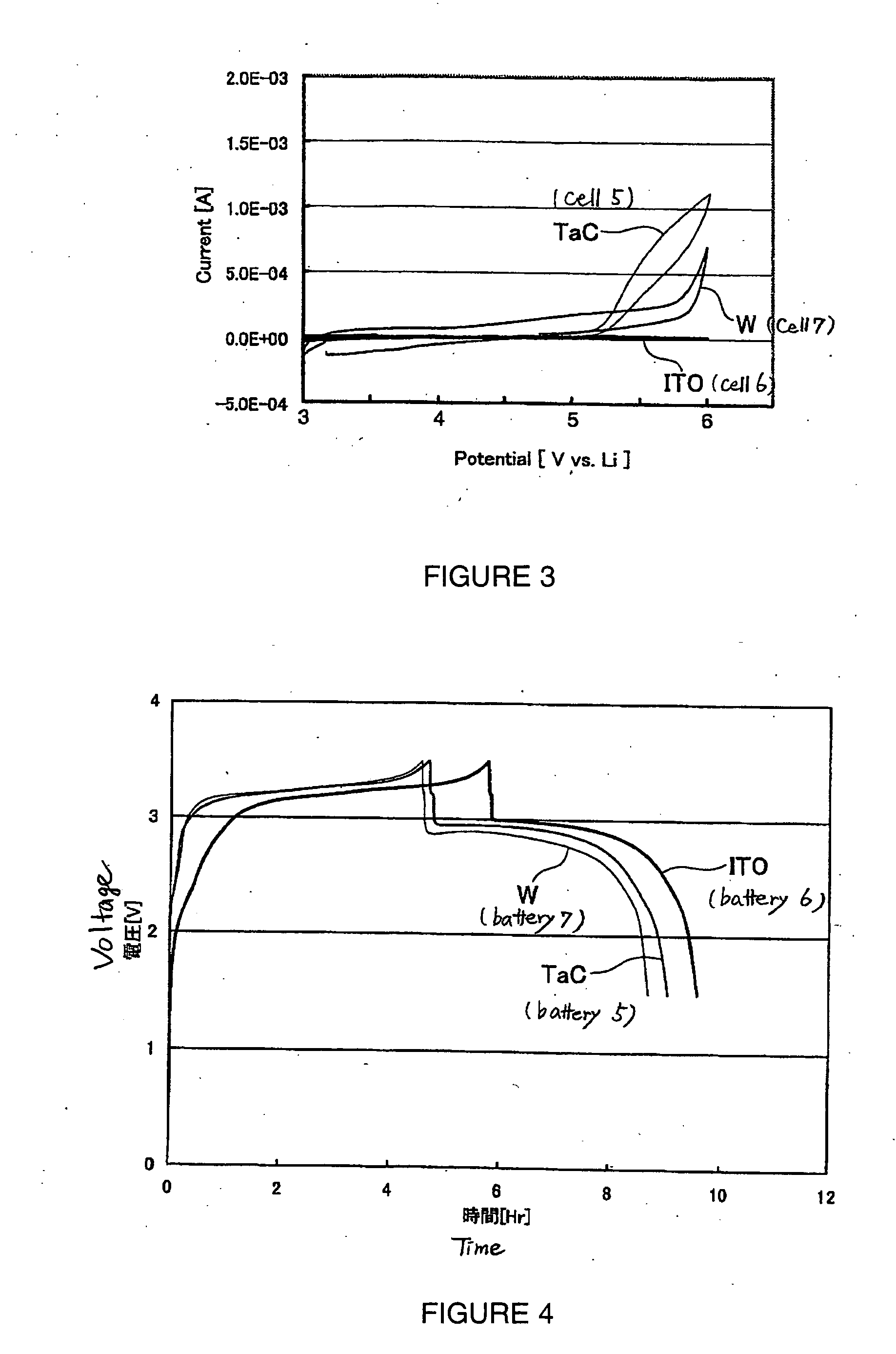
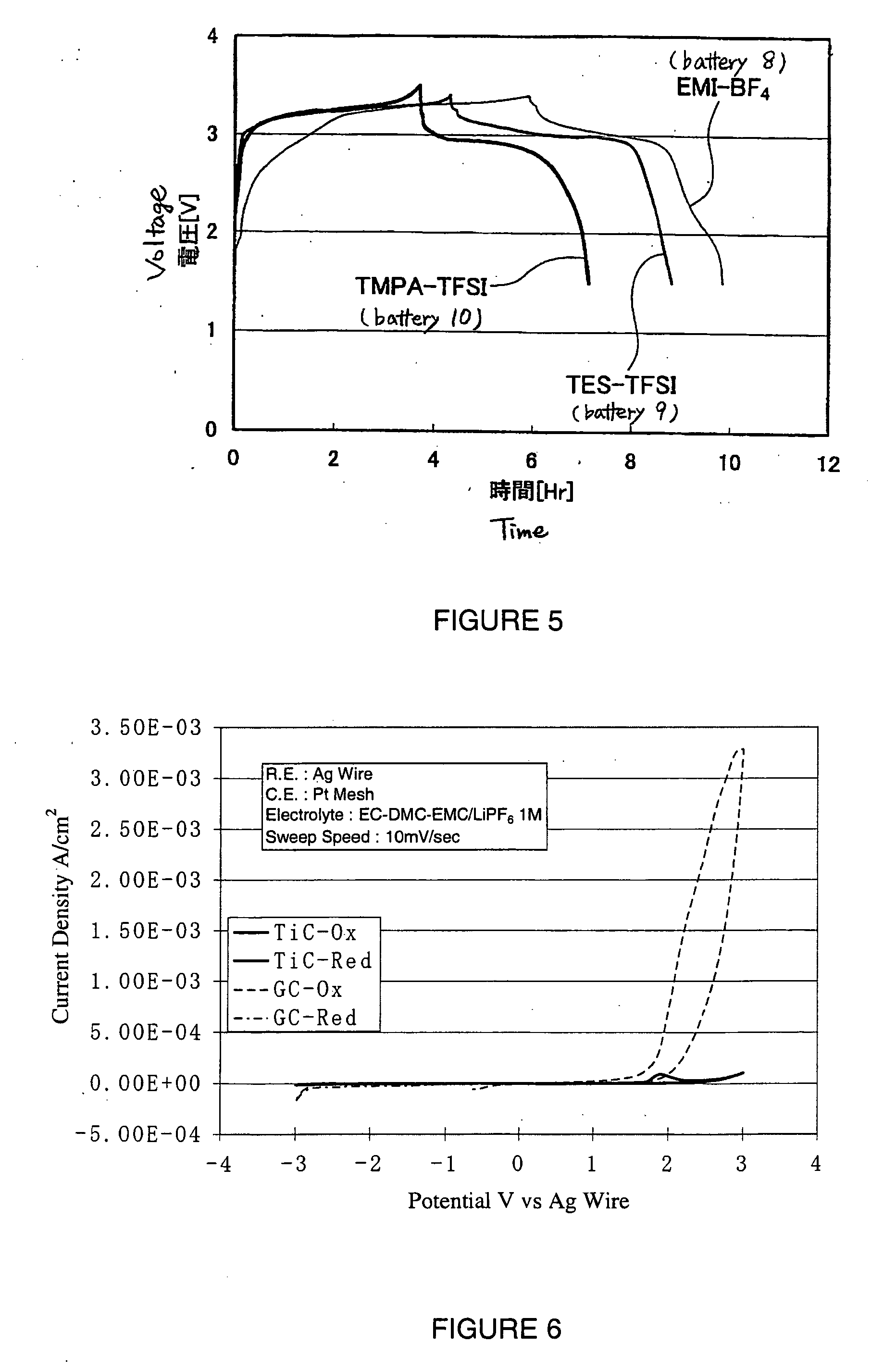
There is provided a battery containing an electrolyte, according to which oxidative decomposition of the electrolyte is suppressed. The battery contains a positive electrode having an active material and an electron conducting material. The electron conducting material has a barrier layer at least on the surface thereof. This barrier layer is substantially constituted from at least one material selected from (a) oxides of elements in group 2 to 14 and the third or subsequent period of the periodic table, (b) carbides of elements in group 2 to 14 and the third or subsequent period of the periodic table, (c) nitrides of elements in group 2 to 14 and the third or subsequent period of the periodic table, and (d) tungsten.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Nonaqueous electrolyte battery
InactiveUS20050164082A1Good rate characteristicsExcellent cycle characteristicsFinal product manufactureCylindrical casing cells/batteryAlkaline earth metalPotential difference
A nonaqueous electrolyte battery includes a positive electrode, a negative electrode containing an active material providing a negative electrode working potential which is nobler than a lithium electrode potential, and whose potential difference from the lithium electrode potential is 0.5V or more, and an electrolyte containing molten salt, ester phosphate and metal salt including at least one of alkaline metal salt and alkaline earth metal salt, the electrolyte satisfying the following formula (1): 0.5≦(M2 / M1)≦1 (1) where M1 is a molar number of the metal salt and M2 is a molar number of the ester phosphate.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Battery with molten salt electrolyte and high voltage positive active material
InactiveUS20060088767A1High voltageActive material electrodesSecondary cellsMolten saltRechargeable cell
A lithium-based rechargeable battery comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and a molten salt electrolyte that is electrically conductive lithium ions. The positive electrode includes a positive active material that has an electrochemical potential of at least approximately 4.0 volts relative to lithium, and more preferably at least approximately 4.5 V relative to lithium. The electrolyte may further include a source of lithium ions, such as a lithium compound. Other rechargeable batteries using other ionic species can be fabricated to an analogous design.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING NORTH AMERICA +1
Metal-air cell with performance enhancing additive
ActiveUS20110281184A1Improves oxygen reduction thermodynamicsImproved kineticsFuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsOxygenElectrochemical cell
Systems and methods drawn to an electrochemical cell comprising a low temperature ionic liquid comprising positive ions and negative ions and a performance enhancing additive added to the low temperature ionic liquid. The additive dissolves in the ionic liquid to form cations, which are coordinated with one or more negative ions forming ion complexes. The electrochemical cell also includes an air electrode configured to absorb and reduce oxygen. The ion complexes improve oxygen reduction thermodynamics and / or kinetics relative to the ionic liquid without the additive.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
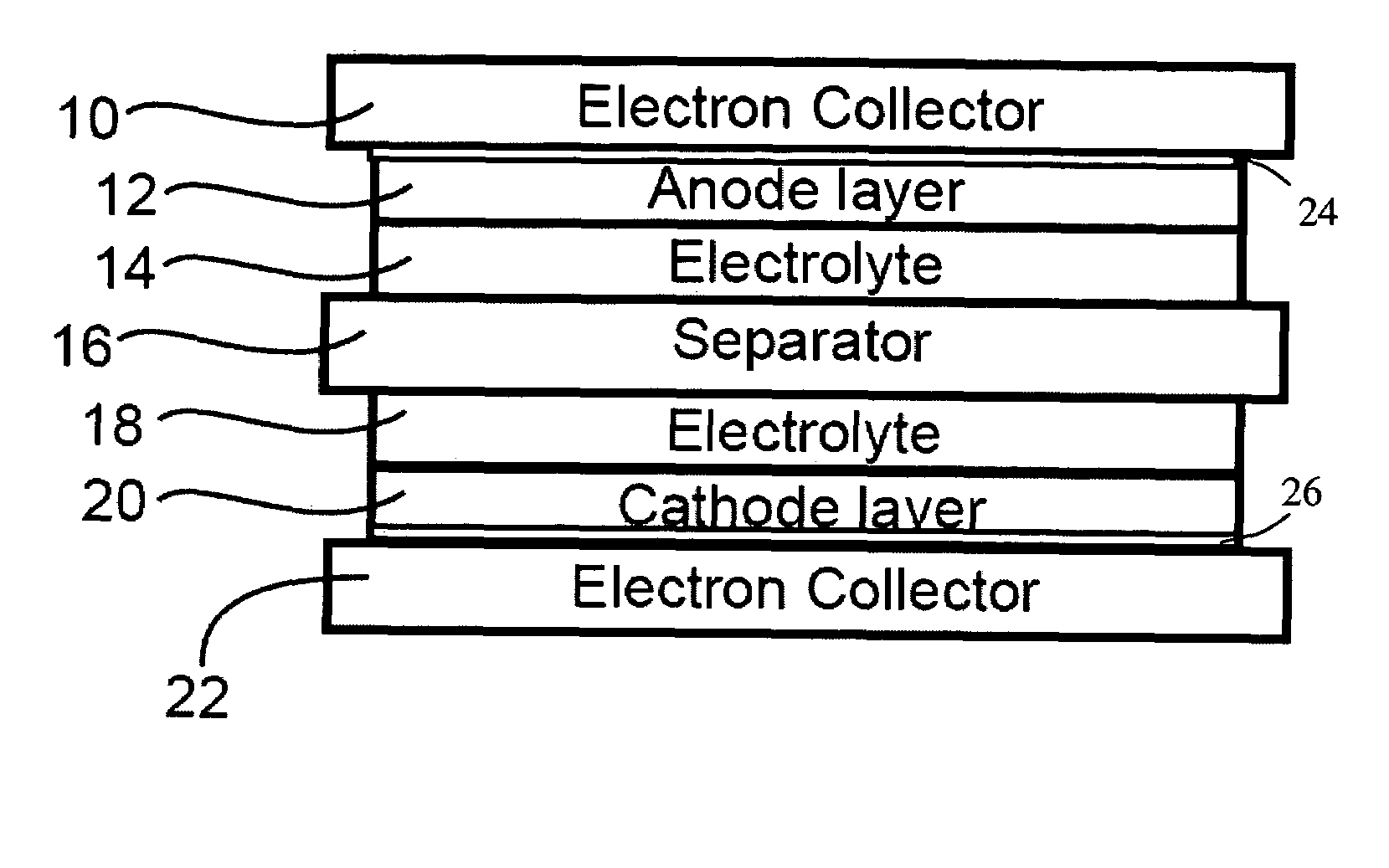
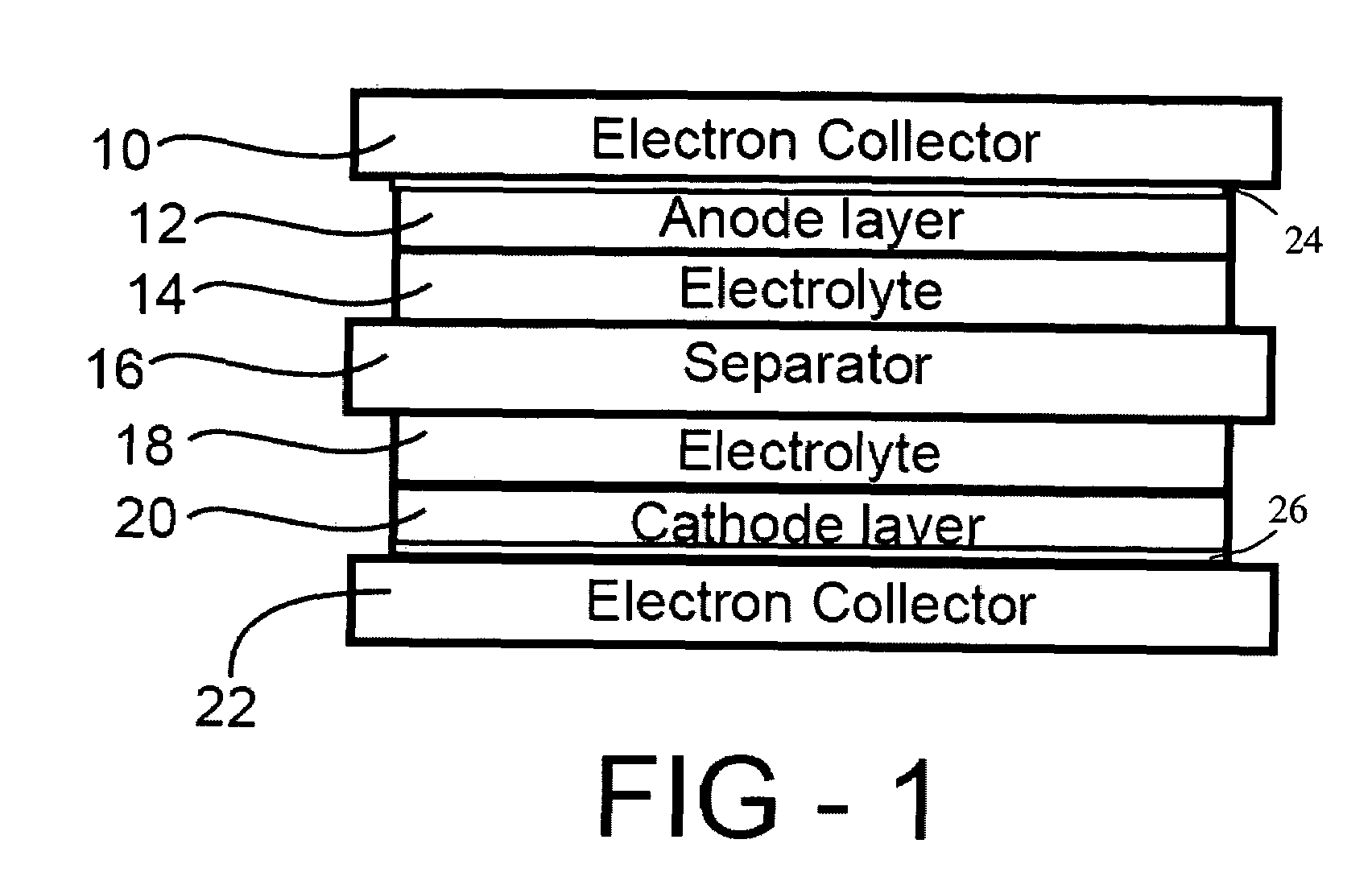
Secondary cell electrode and fabrication method, and secondary cell, complex cell, and vehicle
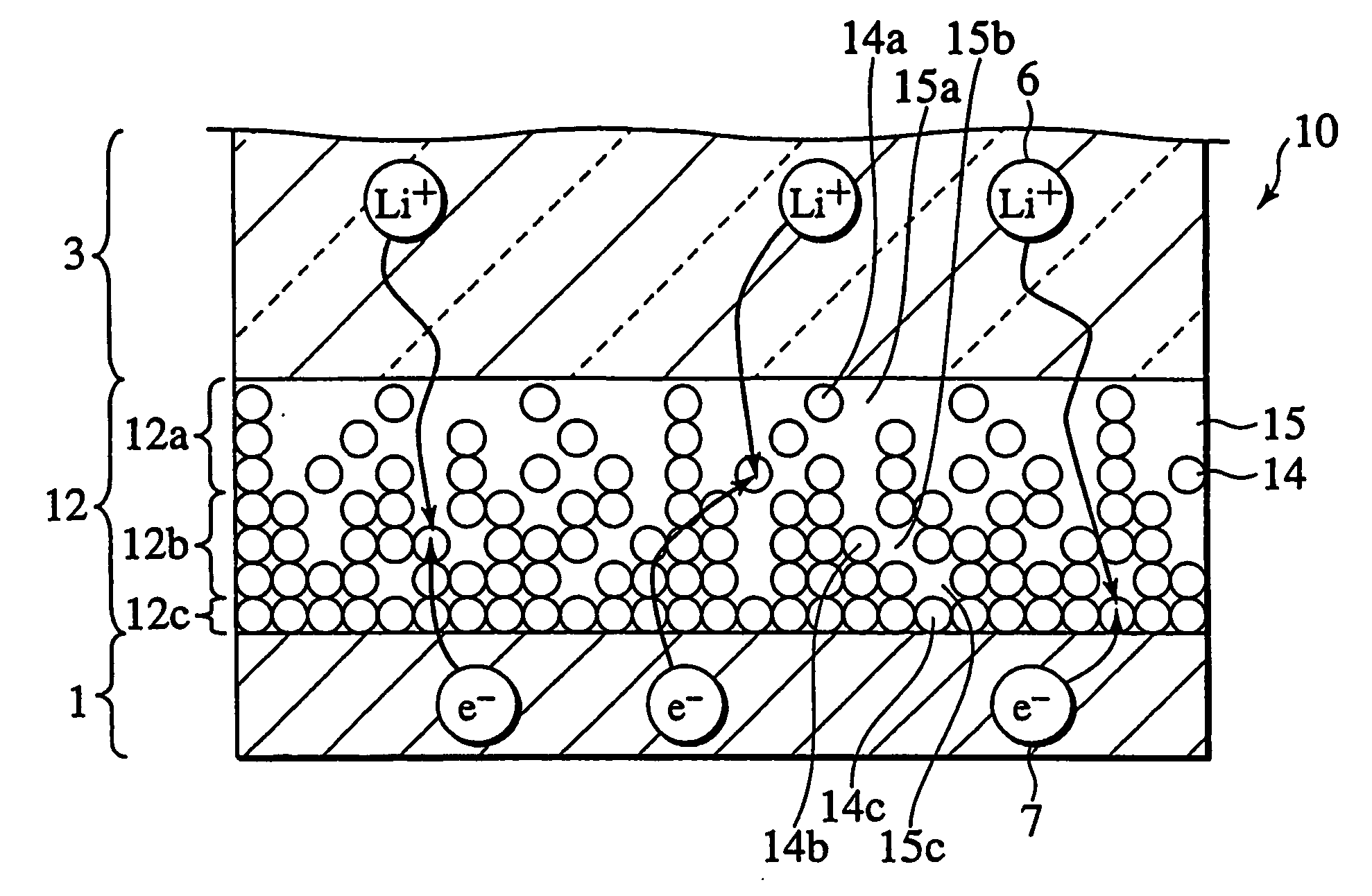
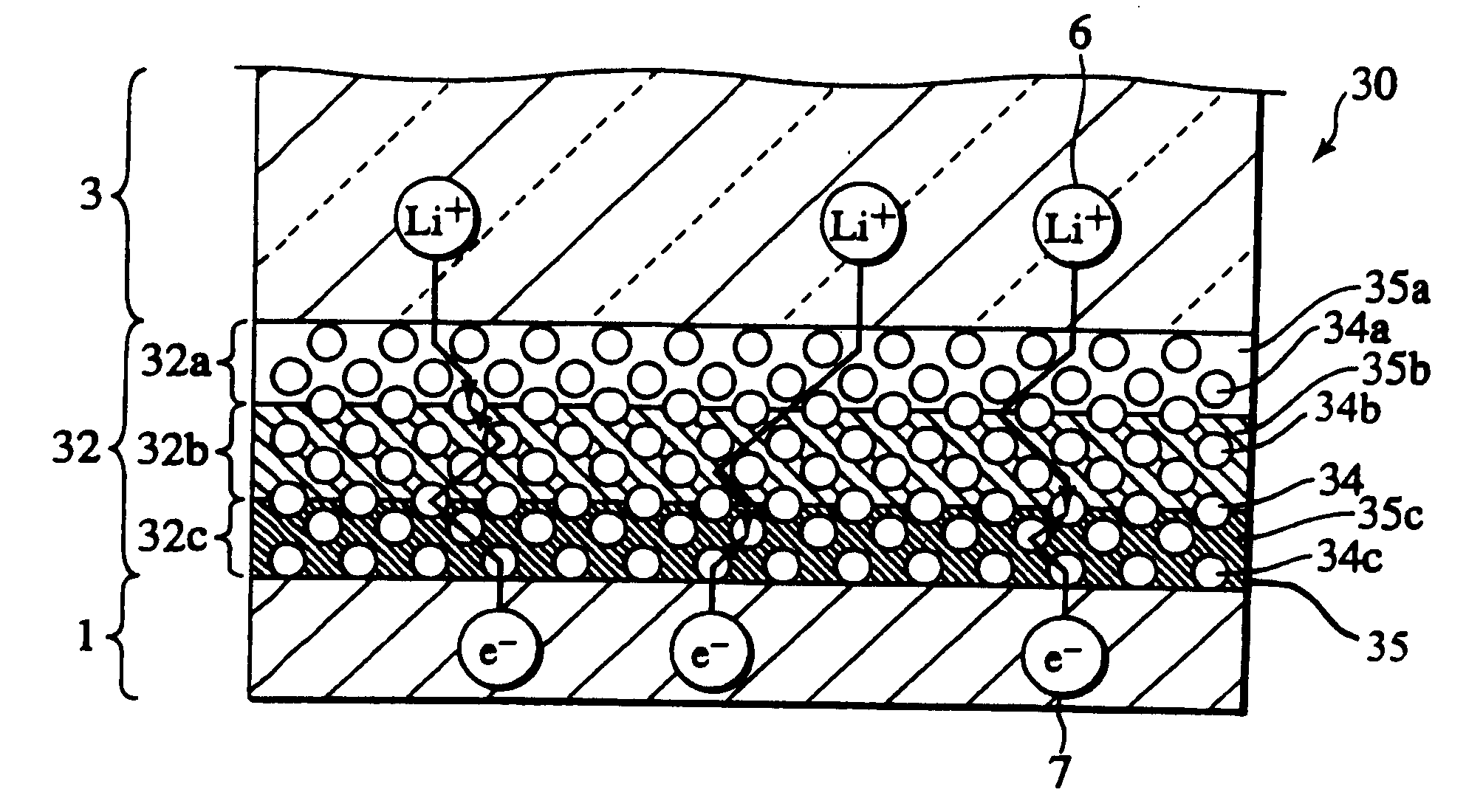
InactiveUS20060251965A1Solid electrolyte cellsActive material electrodesElectrolyteMaterials science
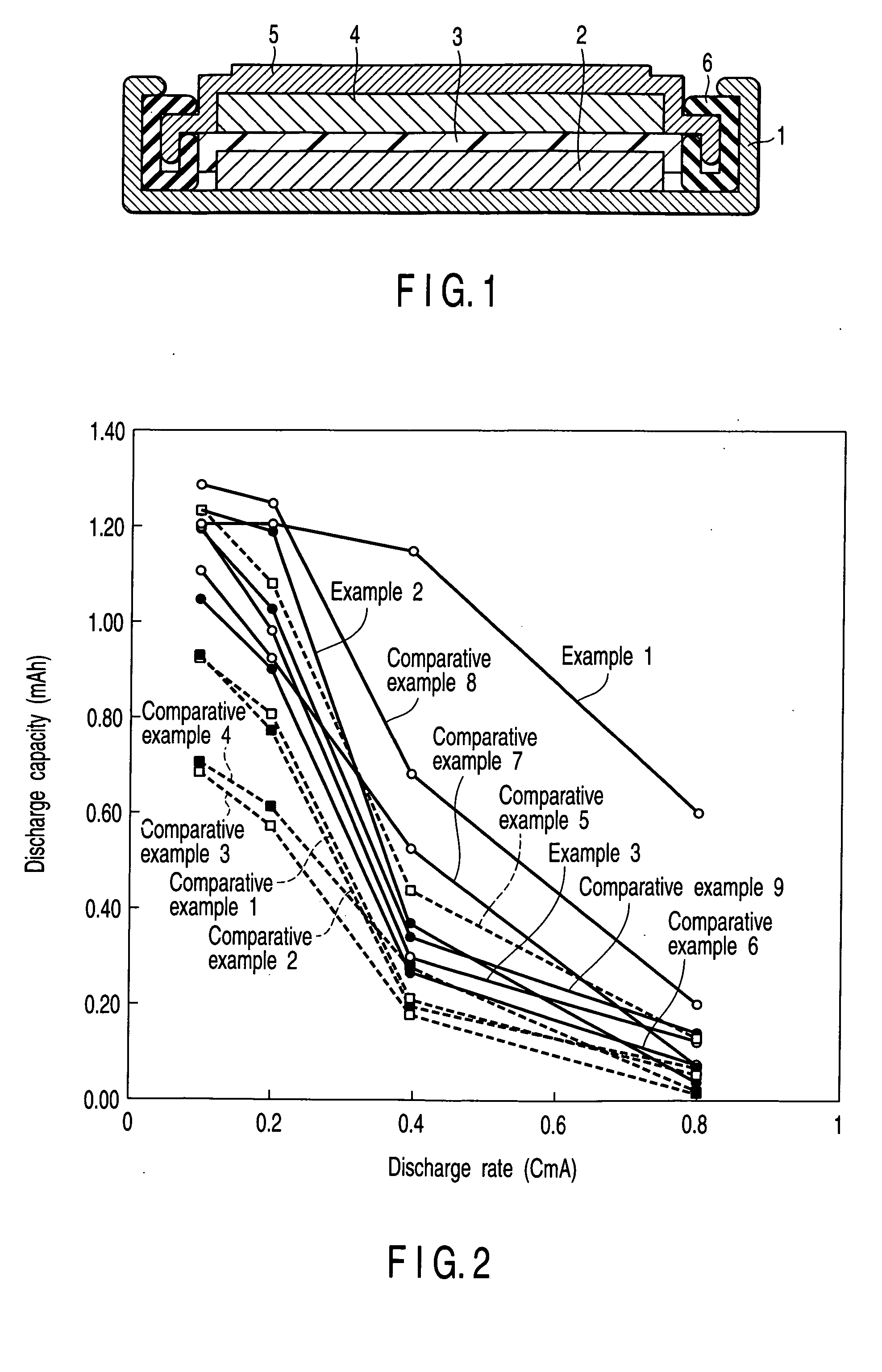
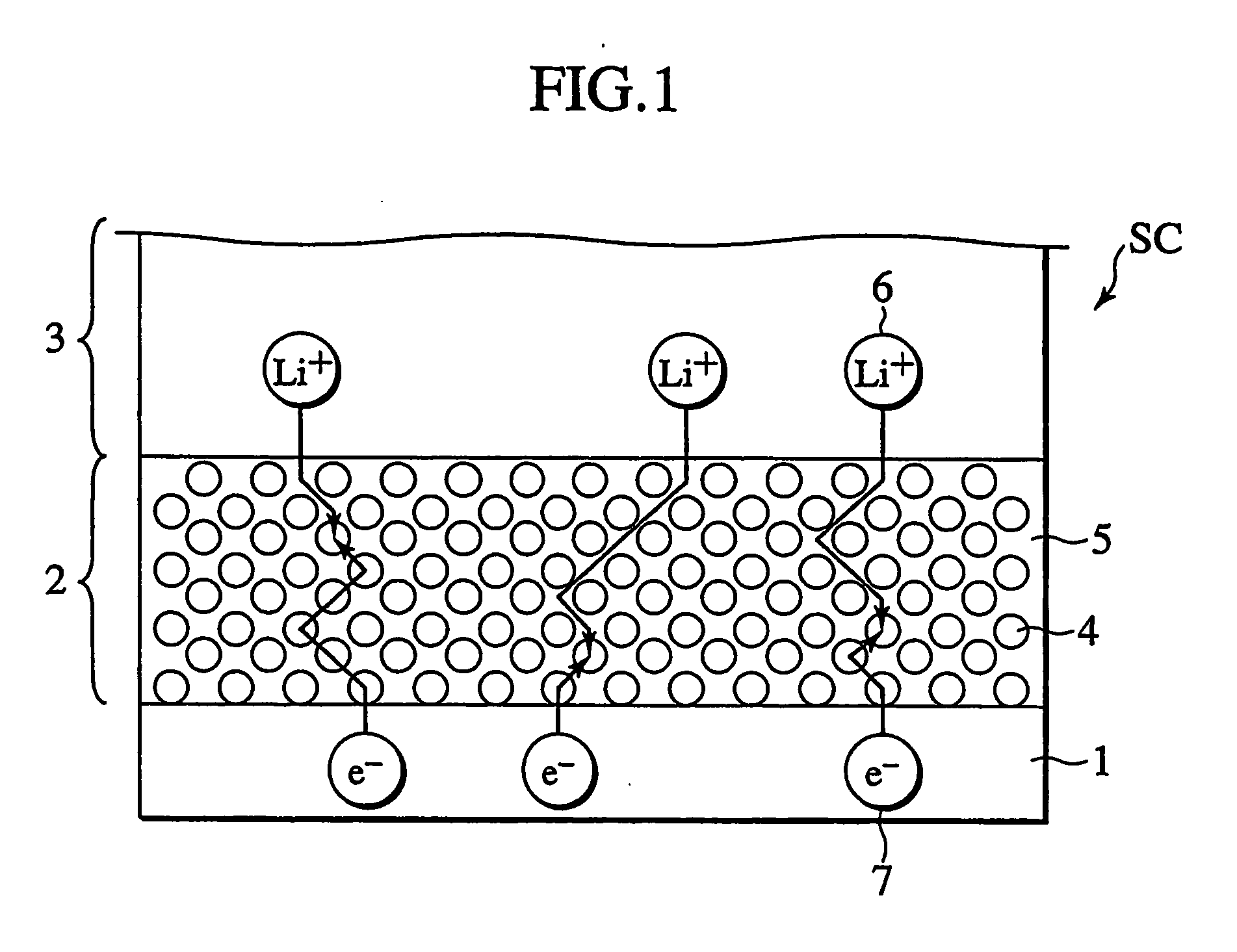
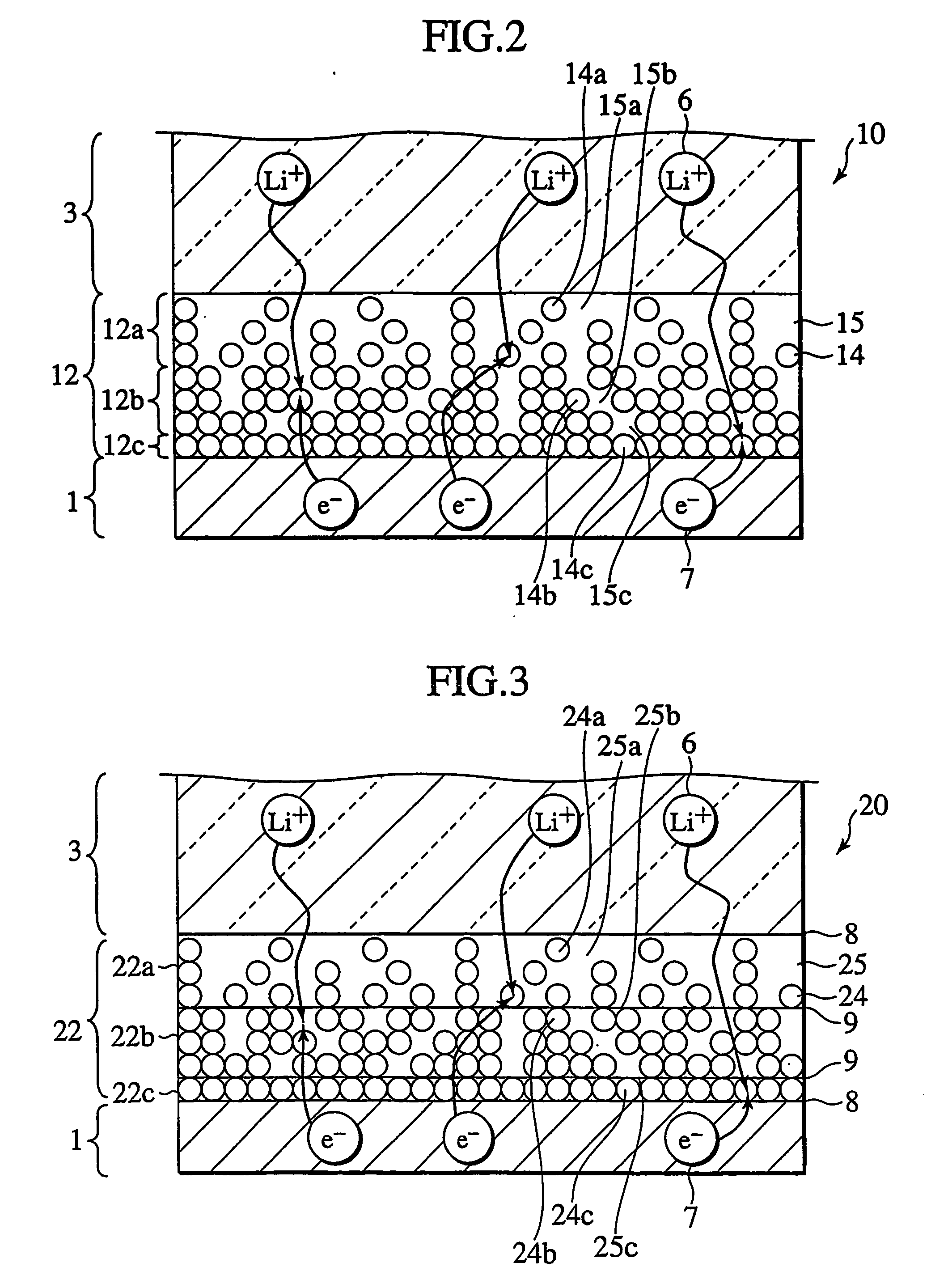
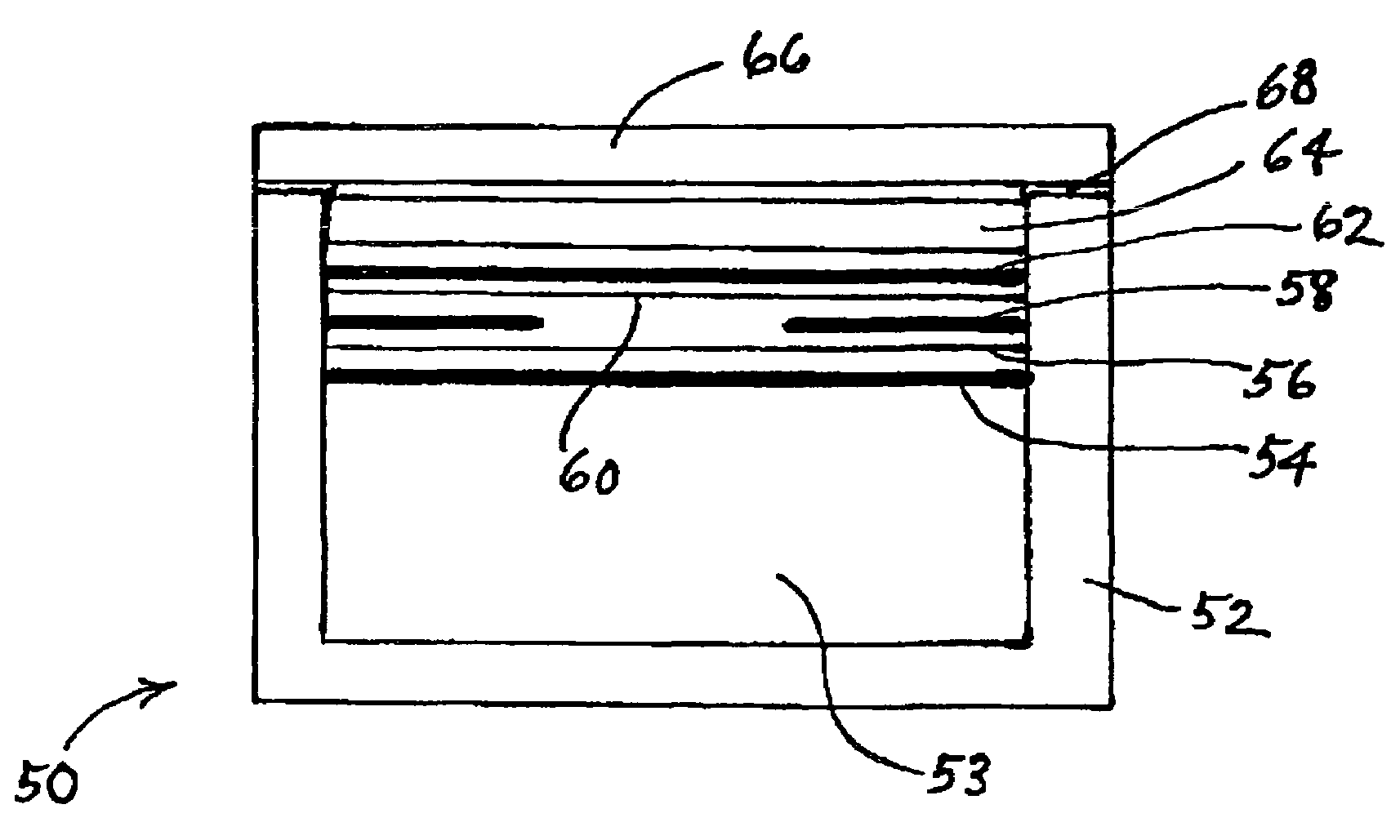
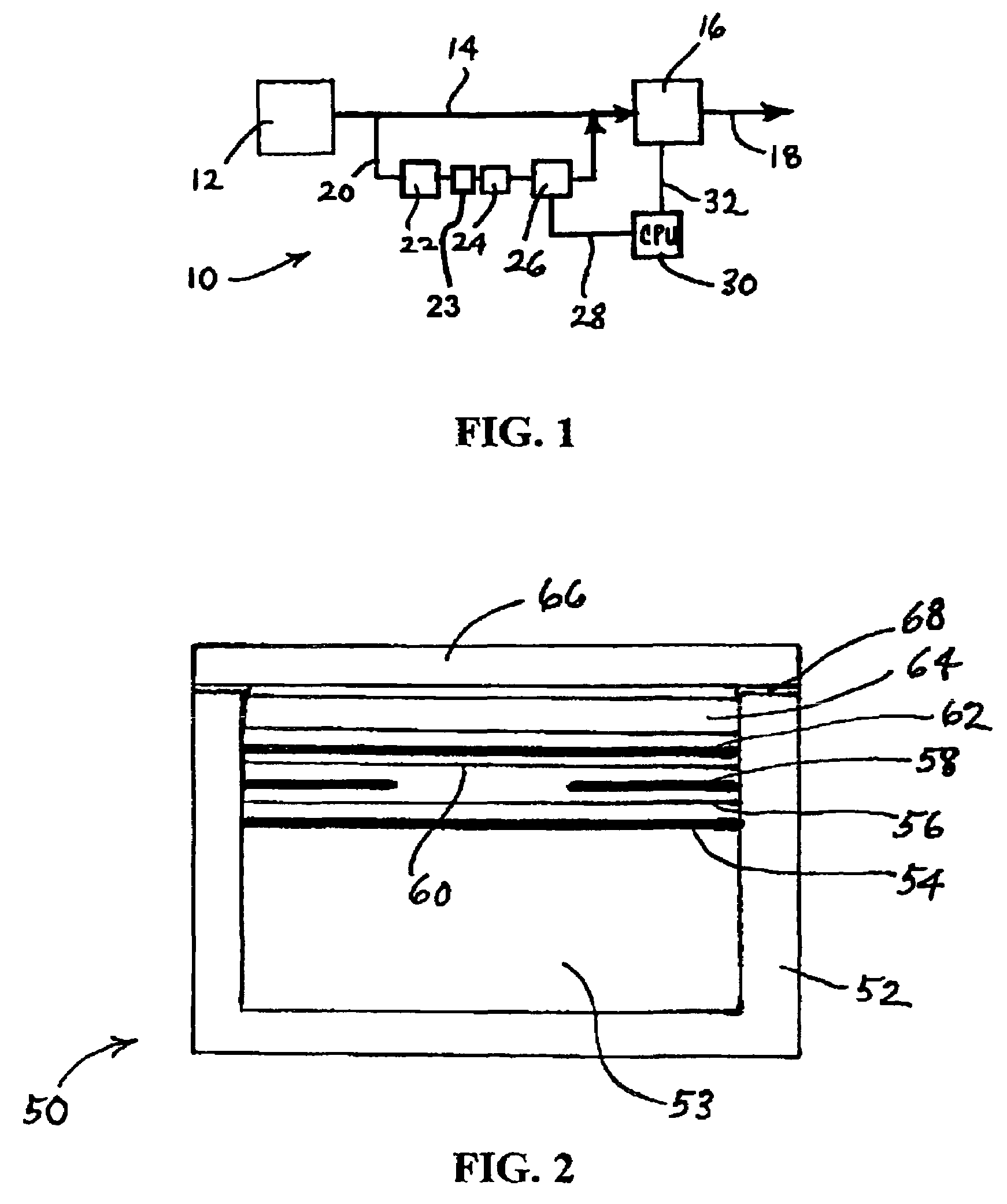
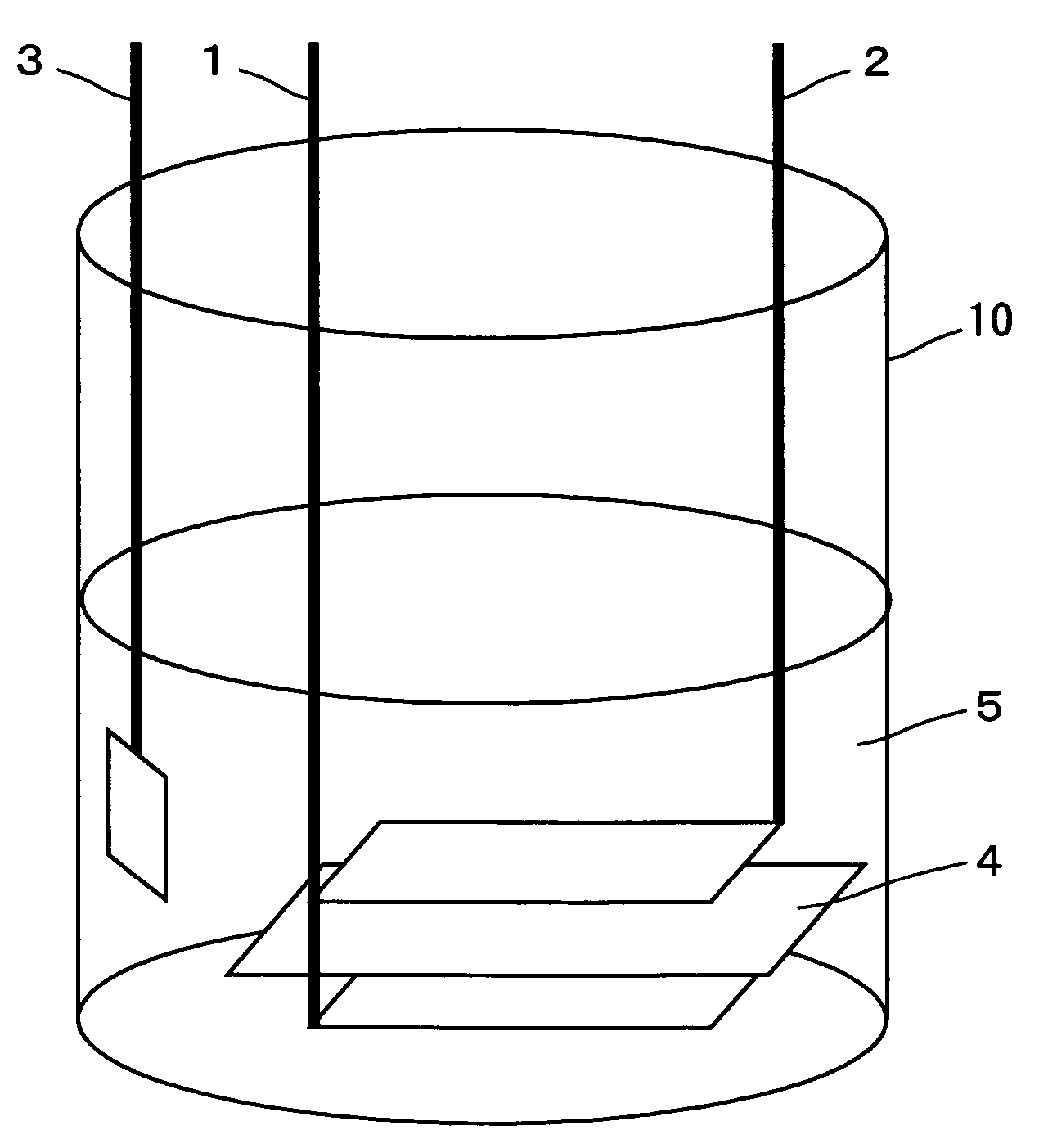
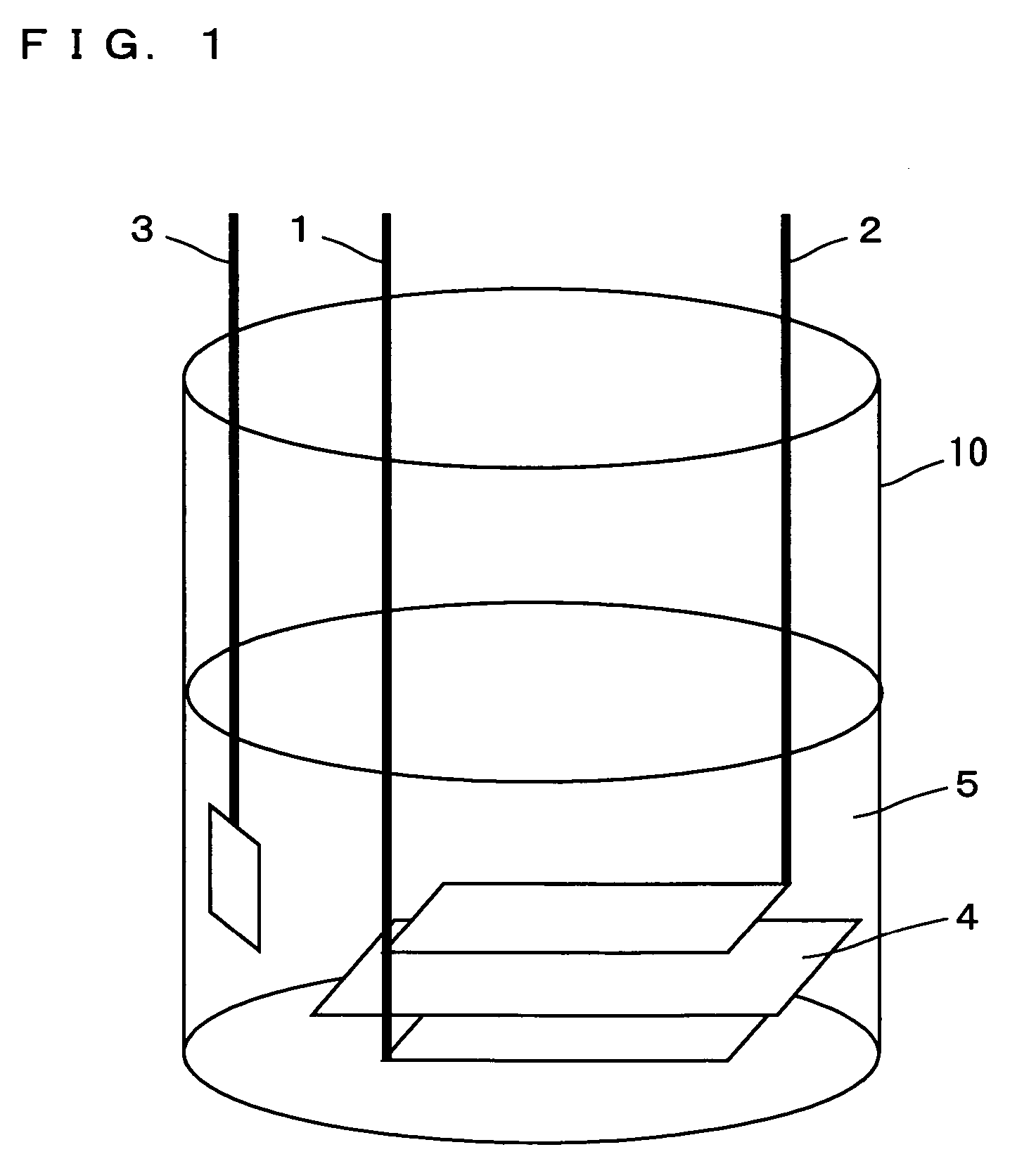
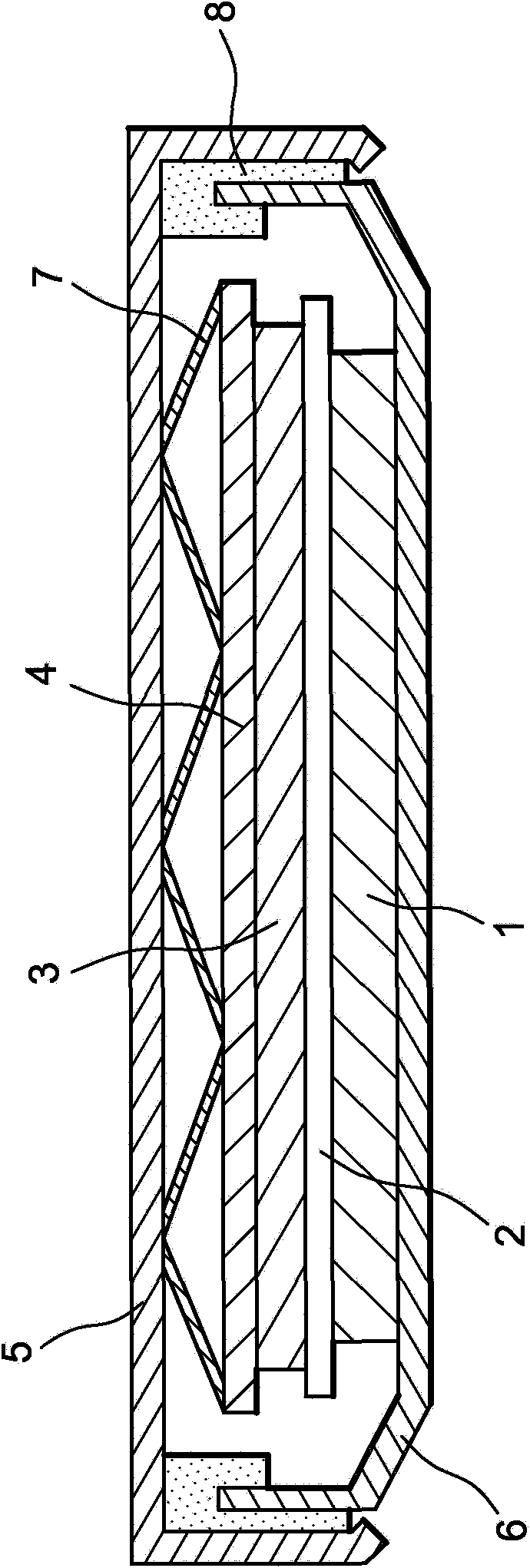
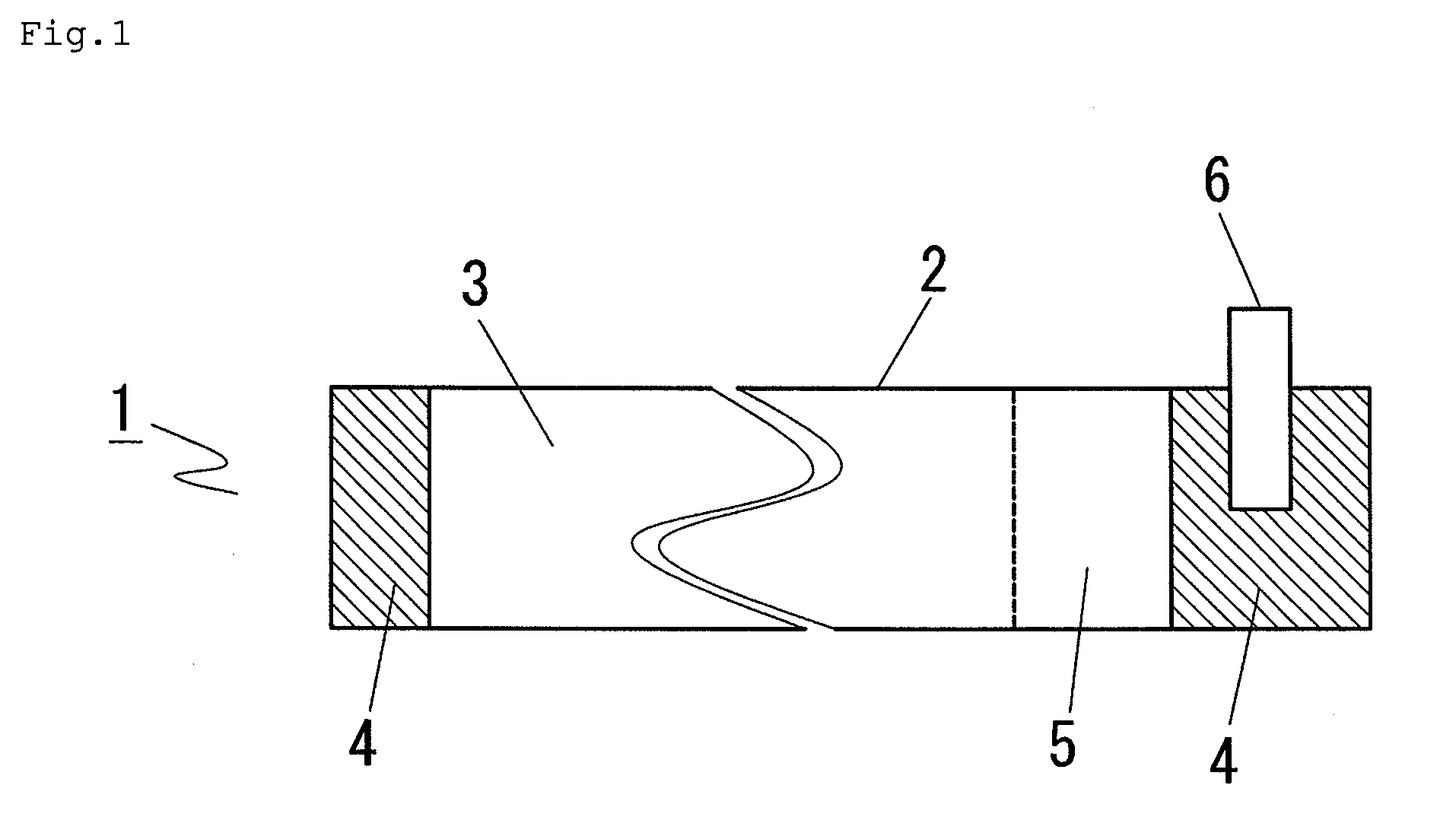
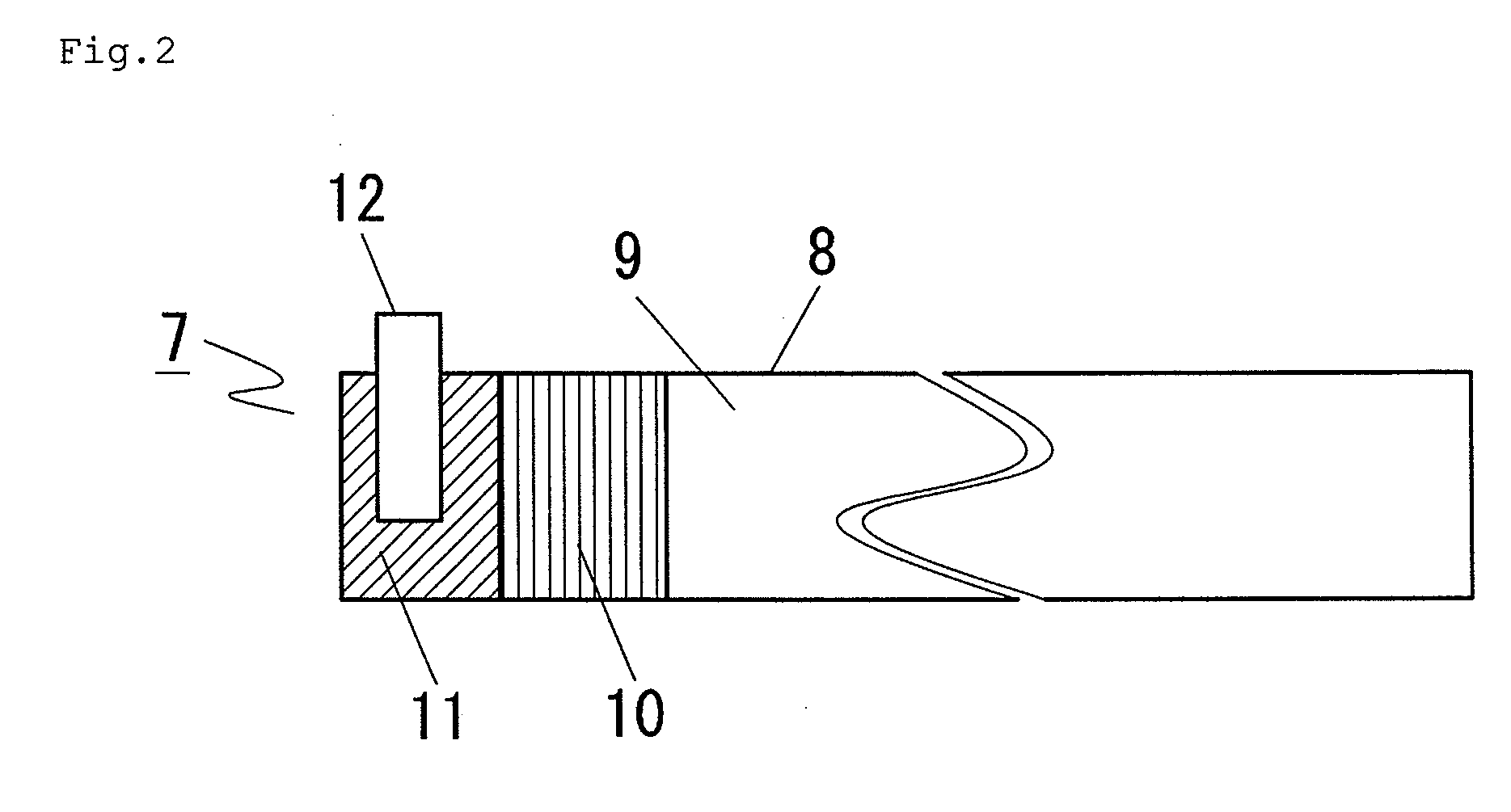
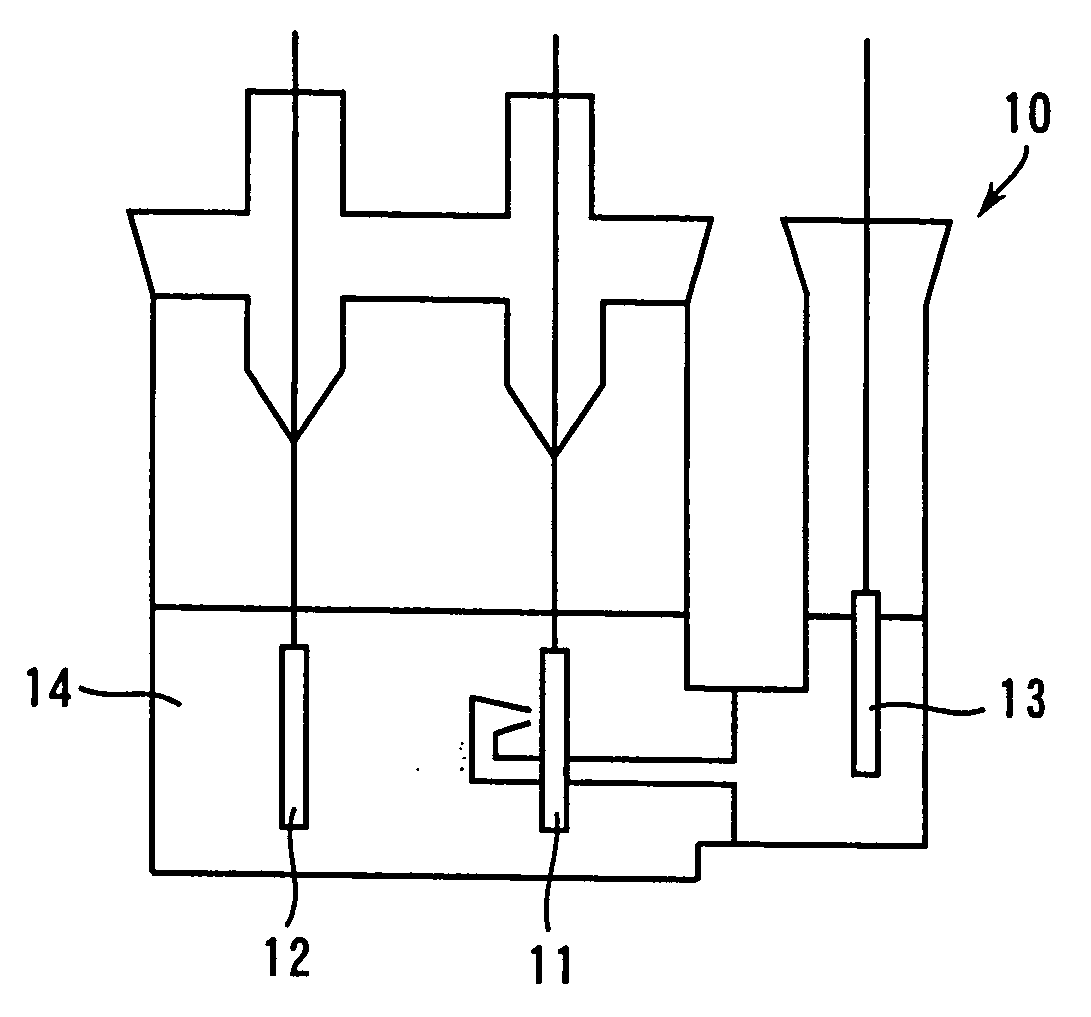
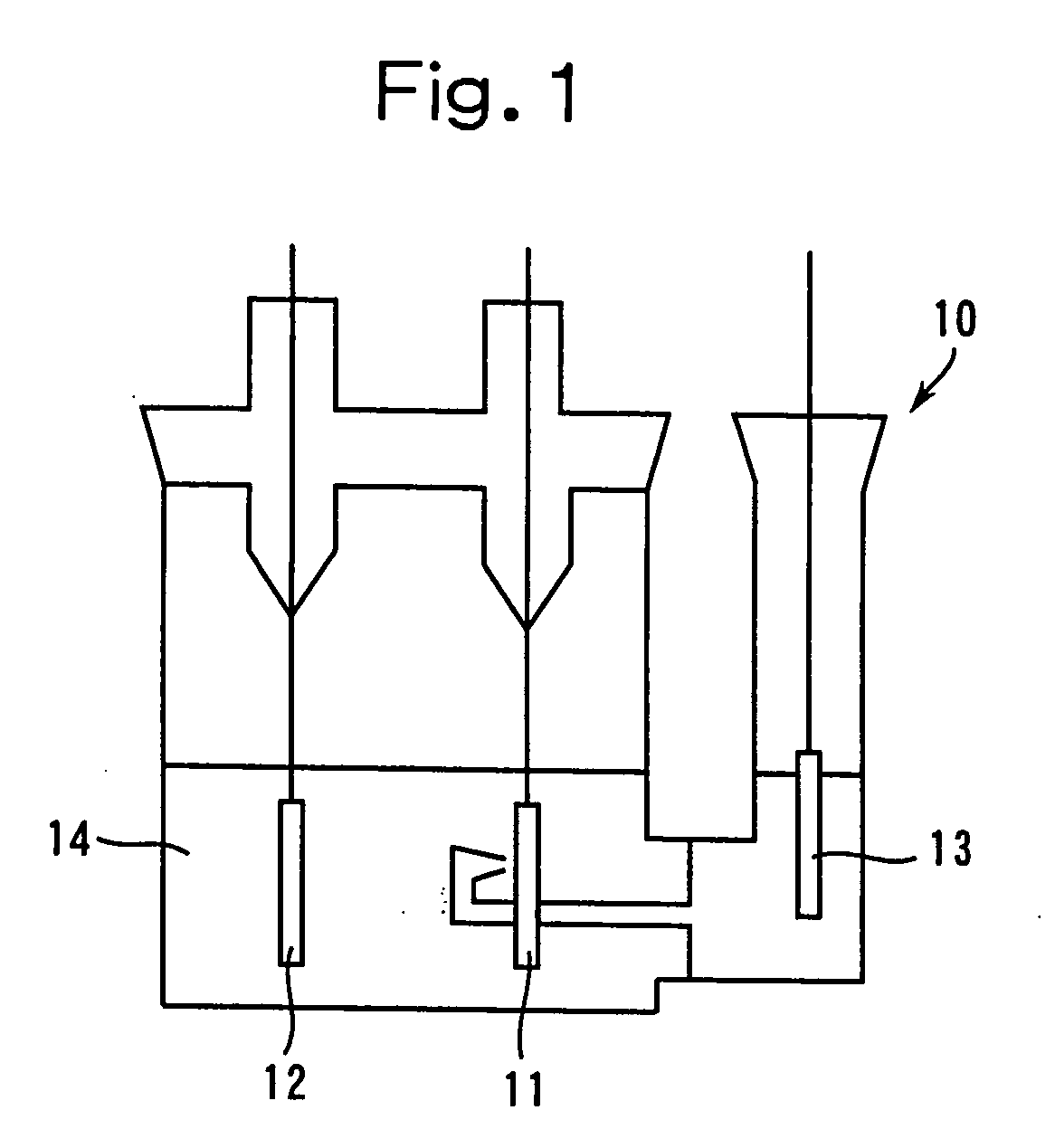
In a nonaqueous electrolyte cell-oriented electrode (10), an electrode active material layer (12) formed on a collector (1) has a density gradient developed with a gradient of a varied concentration of a solid along a thickness from a surface of the electrode active material layer (12) toward the collector (1), and in a gel electrolyte cell-oriented electrode (30), an electrode active material layer (32) formed on a collector (1) has a density gradient developed with (a) gradient(s) of (a) varied concentration(s) of one or both of an electrolyte salt and a film forming material along a thickness from a surface of the electrode active material layer (32) toward the collector (1).
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Battery with molten salt electrolyte and phosphorus-containing cathode
A lithium-ion battery comprises a negative electrode, a positive electrode, and an electrolyte including a molten salt. The positive electrode comprises an electroactive compound including phosphorus, oxygen, lithium, and at least one other metal or semi-metal. The combination of such electrode compositions and a molten salt electrolyte provides a battery with very high thermal stability. Other ions, such as alkal metal ions, may be used in place of lithium ions for applications in other battery technologies.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +2
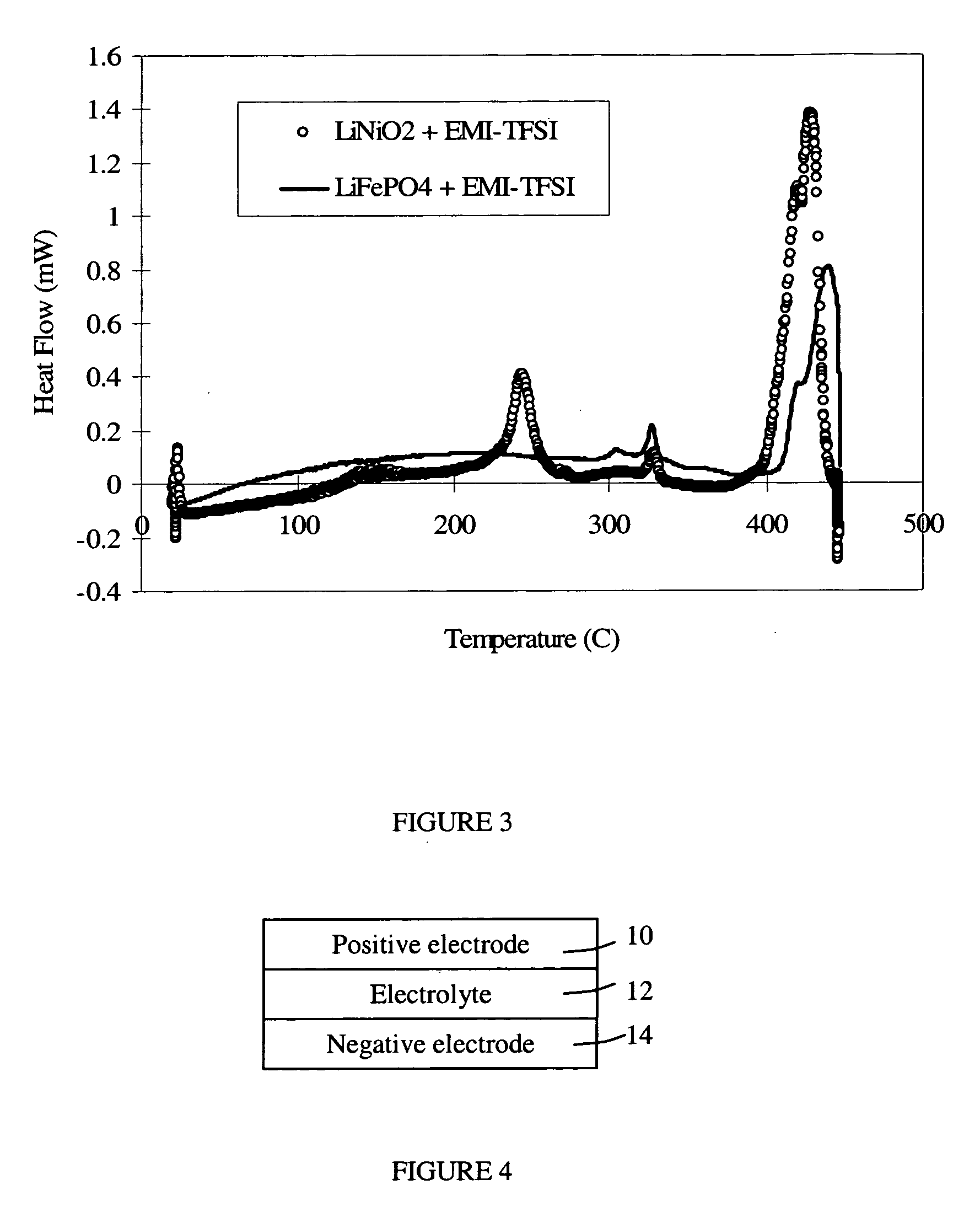
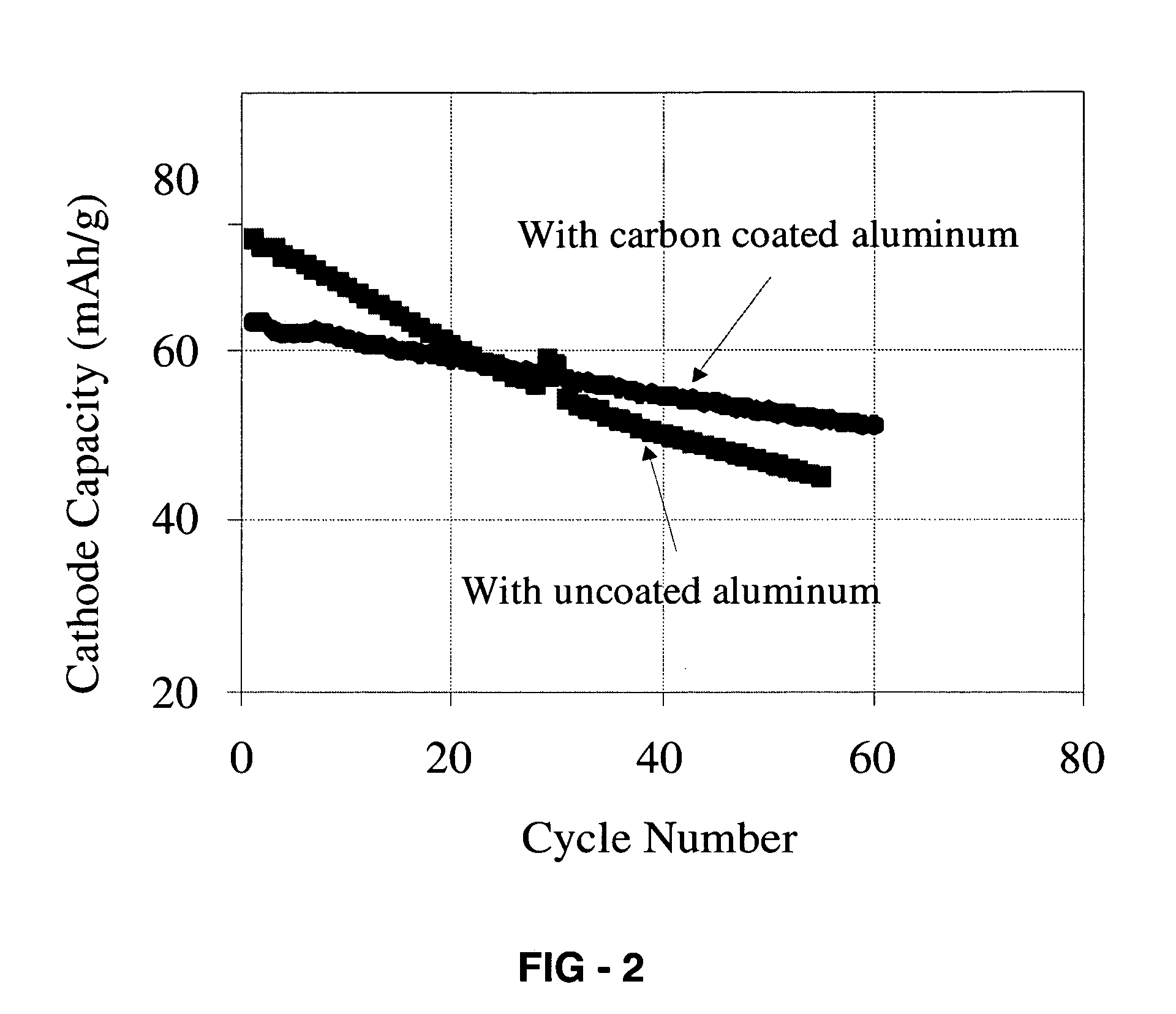
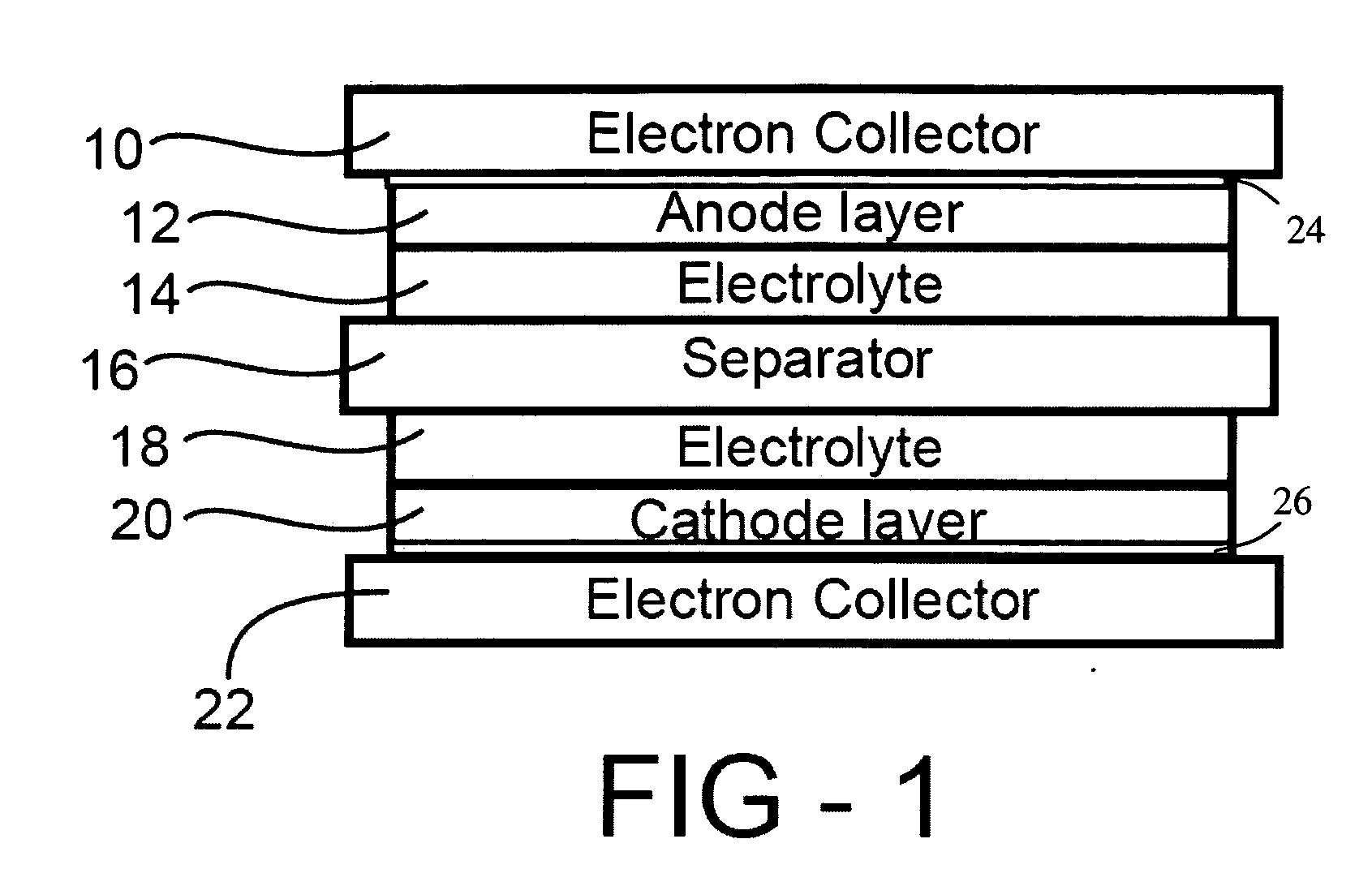
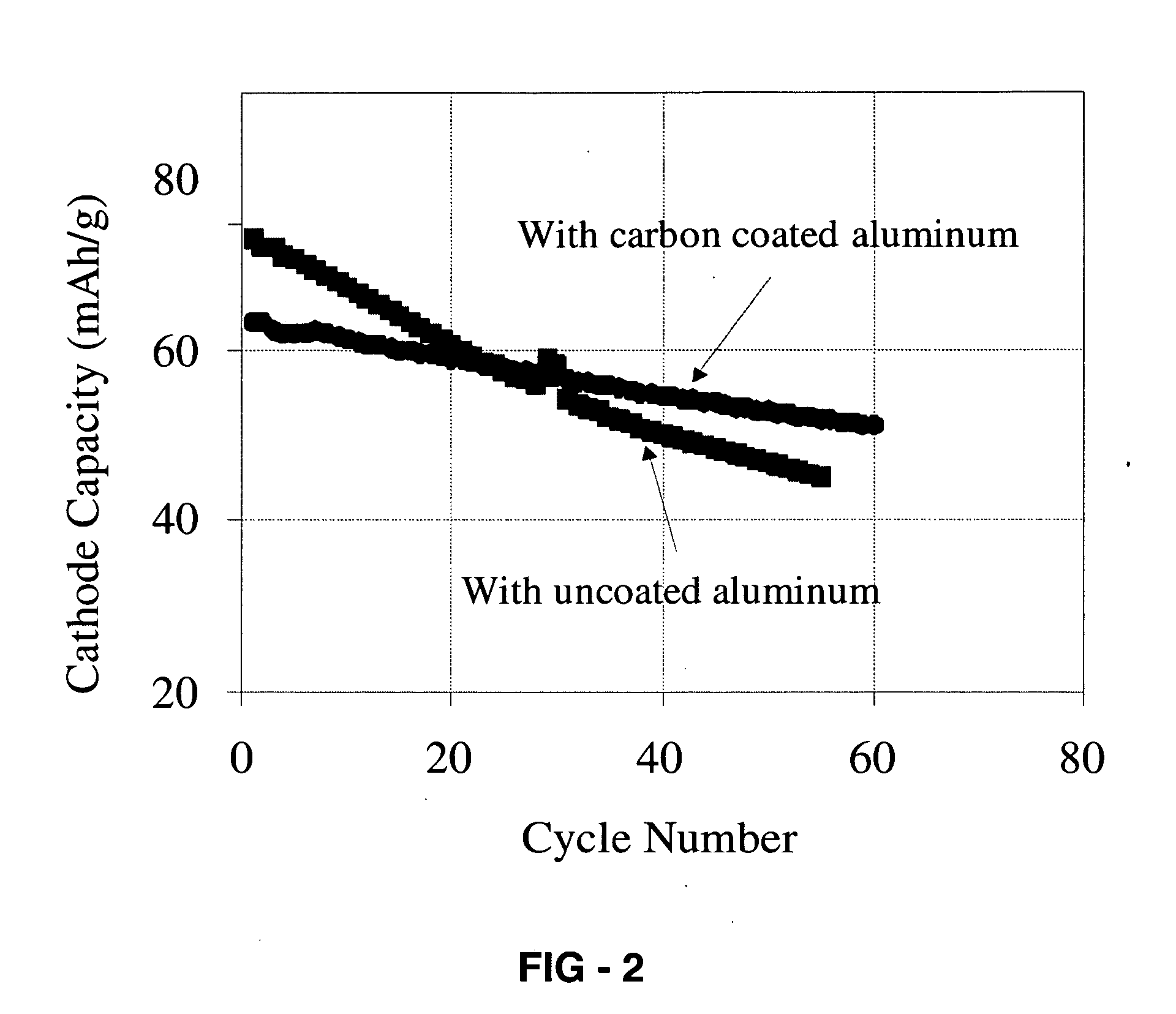
Corrosion protection using carbon coated electron collector for lithium-ion battery with molten salt electrolyte
InactiveUS7348102B2Material nanotechnologyElectrode carriers/collectorsConductive polymerCarbon nanotube
A battery, such as a lithium-ion battery, comprises a first electrode, a second electrode, a molten salt electrolyte, and an electron collector, associated with the first electrode, the electron collector comprising an electrically conducting film. The battery further includes a protection layer separating the electron collector and the first electrode, the protection layer comprising a carbon-containing material. The electron collector may be an electrically conducting material such as aluminum, aluminum alloy, copper, nickel, other metal (such as alloys), conducting polymer, and the like. In one example, the protection layer is a graphite layer. In other examples, the protection layer may be a fullerene film, carbon nanotube film, or other carbon-containing material.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +2
Electrochemical cell for gas sensor
InactiveUS7060169B2Improve electrochemical performanceOrganic chemistryWeather/light/corrosion resistanceElectrolysisFuel cells
An electrochemical cell for applications such as electrochemical fuel cells, or electrochemical cell gas sensors used for detection of target gas species in environments containing or susceptible to presence of same. The electrochemical cell utilizes an ionic liquid as an electrolyte medium, thereby achieving a broader range of operational temperatures and conditions, relative to electrochemical cells utilizing propylene carbonate or other conventional electrolytic media.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Conductive polyamine-based electrolyte
InactiveUS20060210873A1Facilitated releaseImprove efficiencyAlkaline accumulatorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesIonic liquidPolyamine
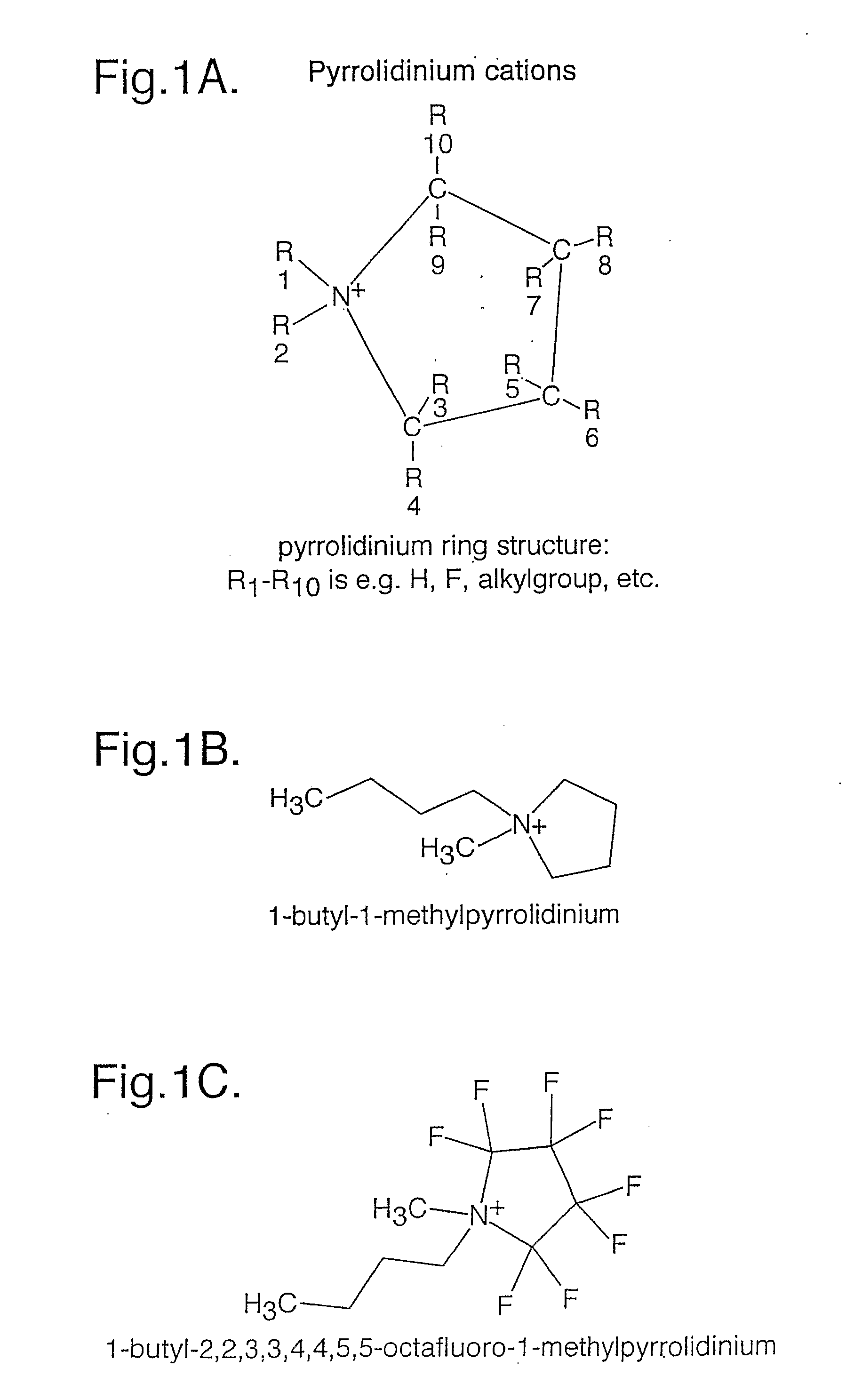
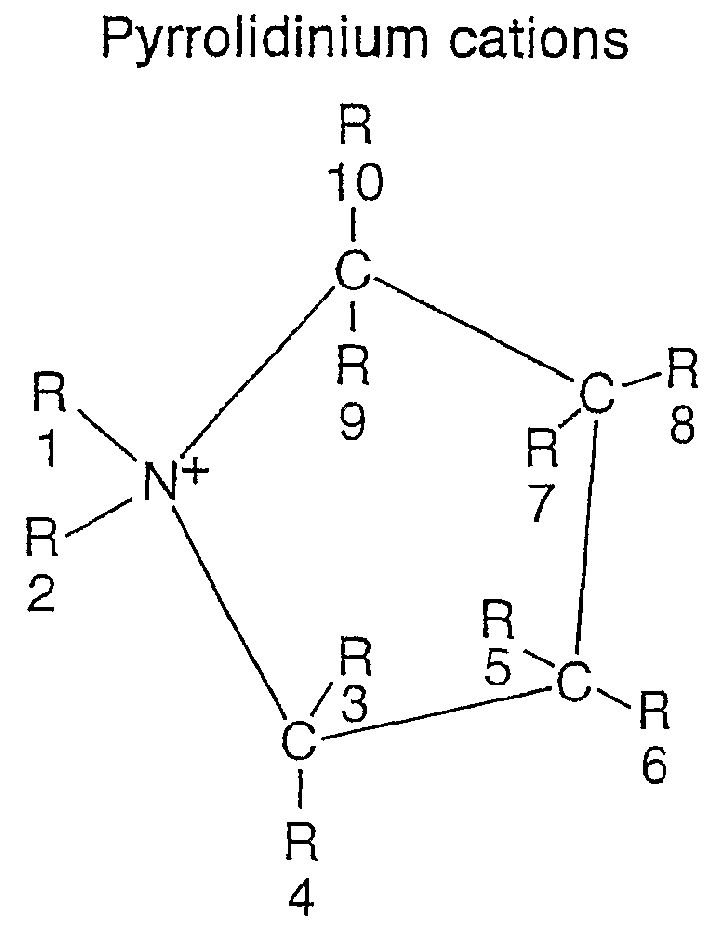
Pyrrolidinium based room temperature ionic liquids, and phosphorous and arsenic analogues, are used as electrolytes in energy storage devices including secondary lithium batteries, supercapacitors and asymmetric battery-supercapacitors. The electrolytes preferably contain lithium ions as the charge-carrying species. The electrolytes are in a liquid state at the operating temperature.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Nonaqueous electrolyte and nonaqueous-electrolyte secondary battery
InactiveUS20060035137A1Good low temperatureLow melting pointOrganic chemistryOrganic electrolyte cellsLithiumMethyl group
A nonaqueous electrolyte which contains an ionic liquid having general formula (1) below and a melting point not higher than 50° C., a compound which reductively decomposes at a more noble potential than the ionic liquid, and a lithium salt. In formula (1), R1 to R4 are each independently an alkyl group of 1 to 5 carbons or an alkoxyalkyl group of the formula R′—O—(CH2)n— (R′ being methyl or ethyl, and the letter n being an integer from 1 to 4), and any two from among R1, R2, R3 and R4 may together form a ring, with the proviso that at least one of R1 to R4 is an alkoxyalkyl group of the above formula. X is a nitrogen atom or a phosphorus atom, and Y is a monovalent anion.
Owner:NISSHINBO IND INC
Electrochemical device
InactiveUS20060210876A1Excellent in charge-discharge cycle characteristicHybrid capacitor electrolytesProtecting/adjusting hybrid/EDL capacitorLamellar crystalsHydrogen atom
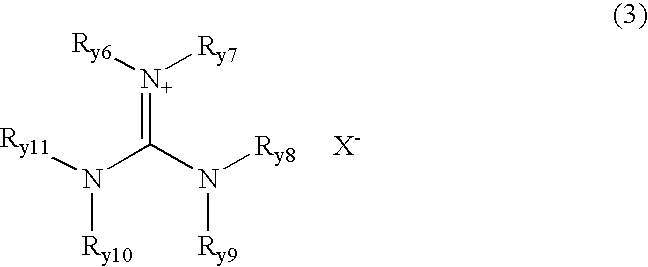
An electrochemical device includes a case, a nonaqueous electrolyte filled in the case and containing a room temperature molten salt in an amount of 1 to 50 vol %, a first electrode housed in the case, and a second electrode housed in the case and containing a substance having a lamellar crystal structure. The room temperature molten salt contains a cation represented by formula (1) or formula (2) given below. R1 includes a carbonic acid ester group. Each of R2 and R3 denotes a substituent having an acyclic structure and having 4 or less carbon atoms, or R2 and R3 are combined to denote a substituent having a cyclic structure and having 4 or 5 carbon atoms. R4 includes a carbonic acid ester group, R5 has an acyclic structure and has 4 or less carbon atoms, and R6 denotes a hydrogen atom or a methyl group.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Electrochemical Element for Use at High Temperatures
ActiveUS20070254213A1Reduces ionic conductivityImprove power densityOrganic electrolyte cellsCapacitor electrolytes/absorbentsCelsius DegreeRechargeable cell
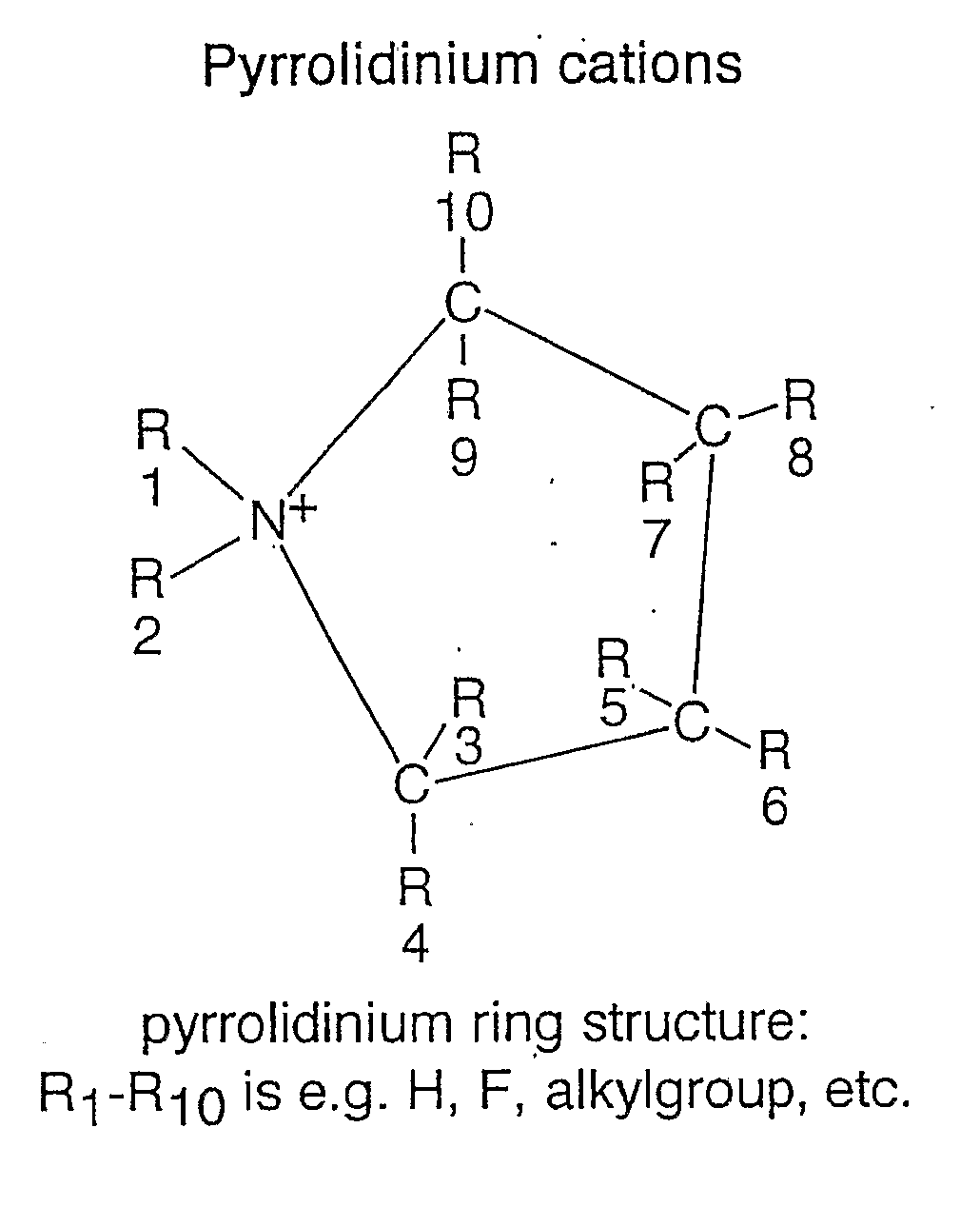
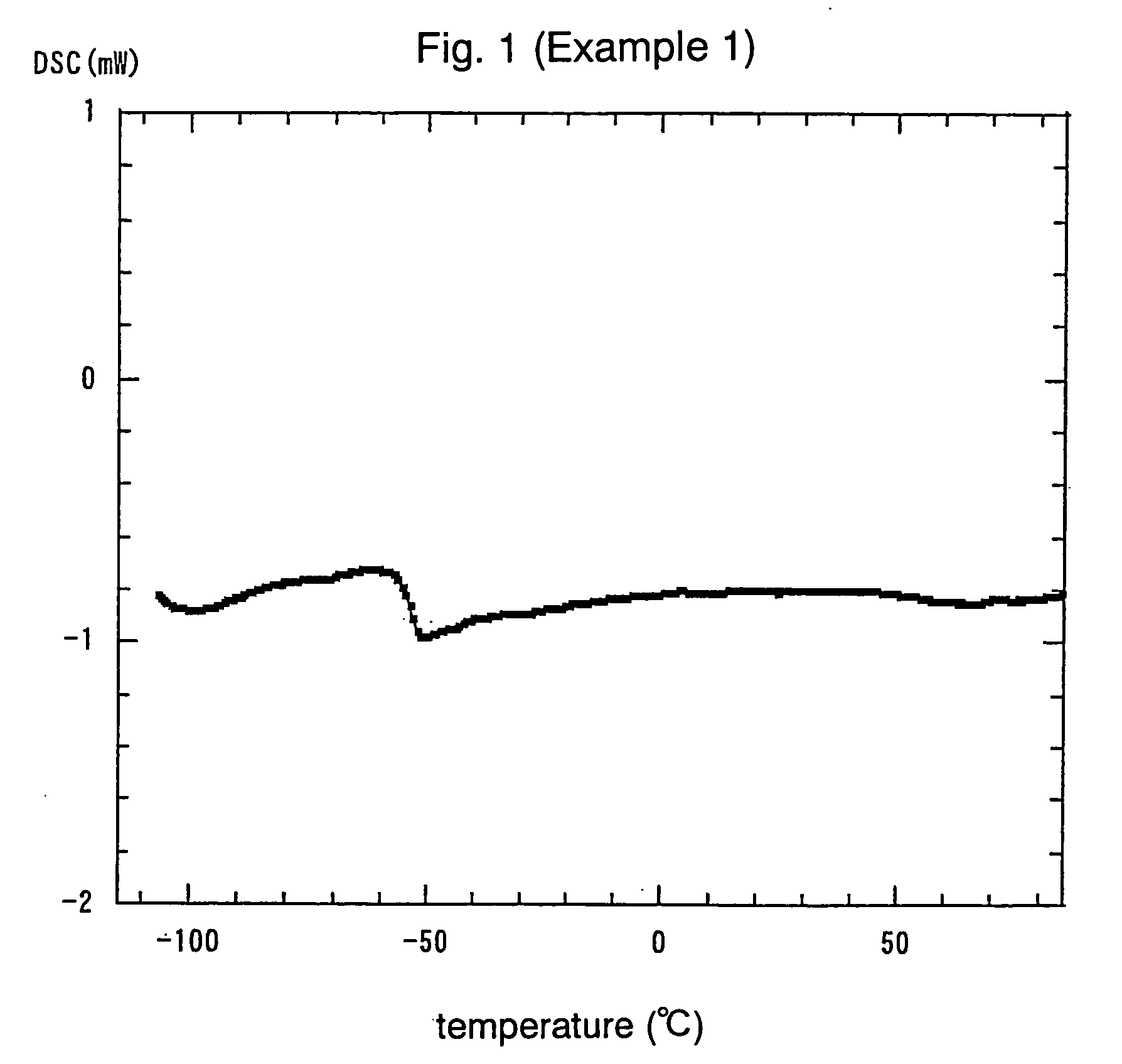
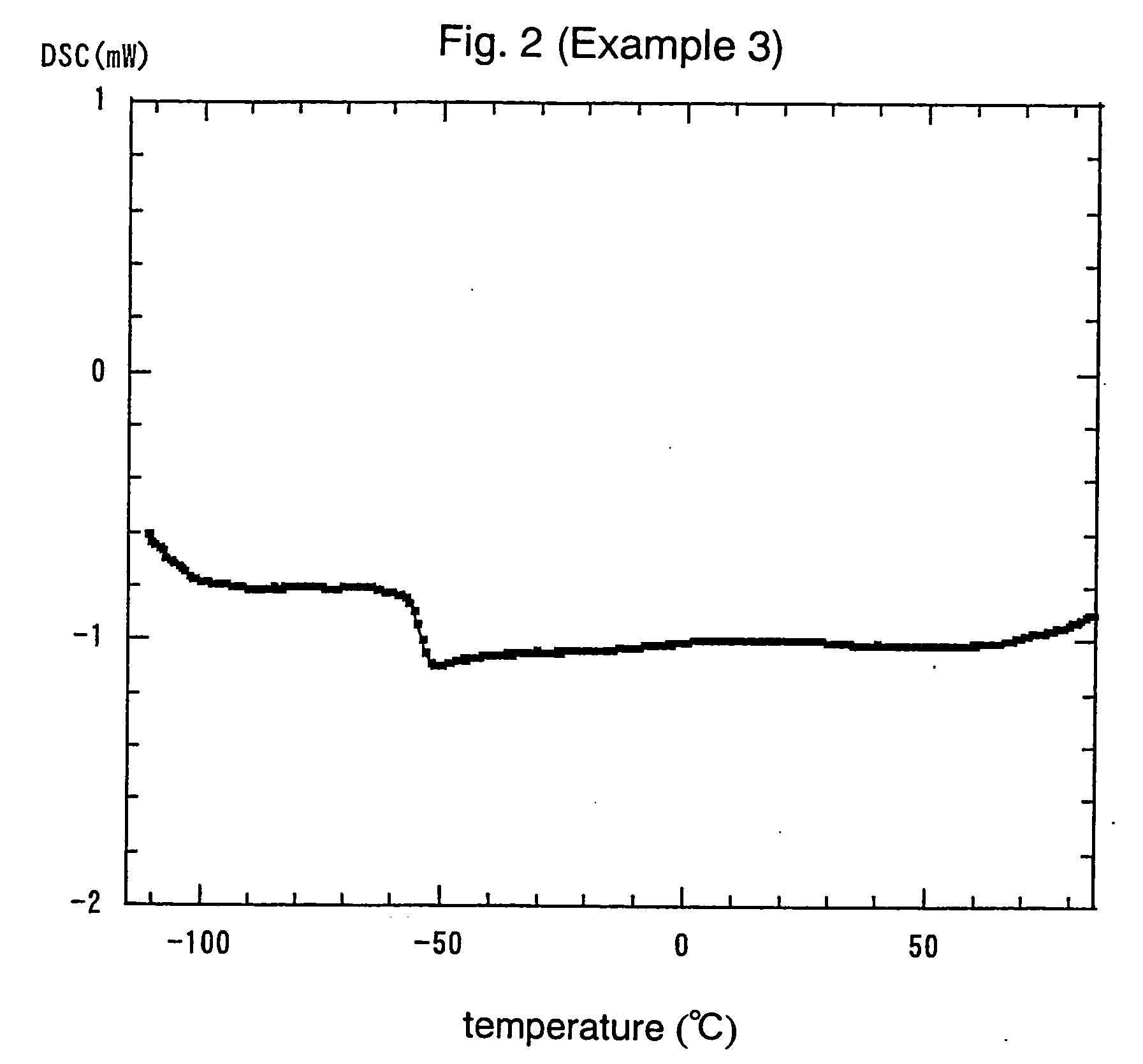
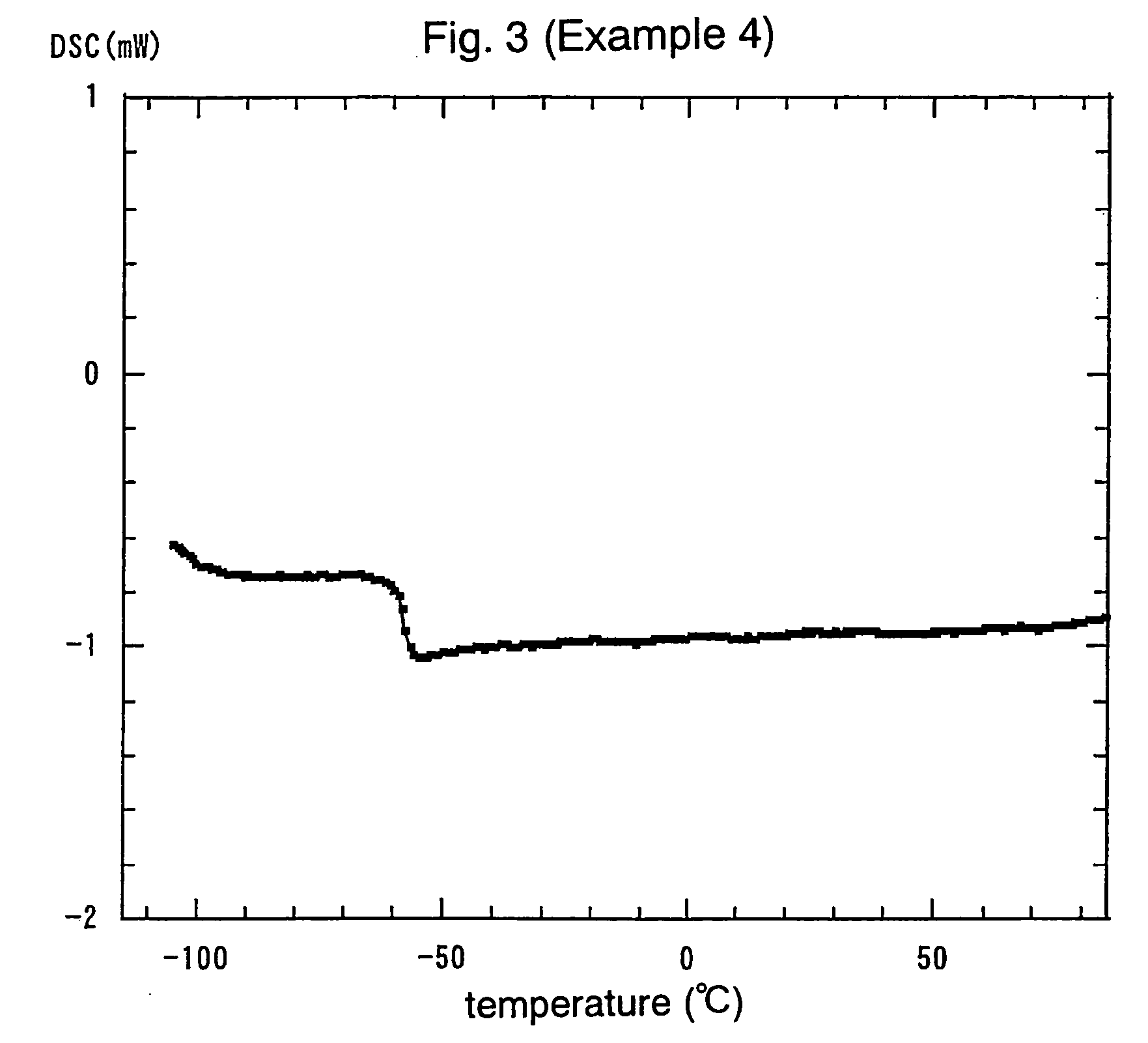
An electrochemical element for use at a high temperature has a cathode comprising an intercalation material as active material, an anode and an electrolyte arranged between the cathode and anode, which electrolyte comprises an ionic liquid with an anion and a cation, which cation comprises a pyrrolidinium ring structure comprising four Carbon atoms and one Nitrogen atom. Experiments revealed that rechargeable batteries comprising N—R1—N—R2-pyrrolidinium, wherein R1 and R2 are alkyl groups and R1 may be methyl and R2 may be butyl or hexyl, are particularly suitable for use at a temperature of up to about 150 degrees Celsius and may be used in oil and / or gas production wells.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Room-temperature molten salt, process for producing the same and applications thereof
InactiveUS20050175867A1Low water solubilityImprove heat resistanceElectrolyte holding meansHybrid capacitor electrolytesMolten saltRoom temperature
The present invention provides a room-temperature molten salt that is obtainable by mixing two or more organic salts and that has a solidifying point lower than the solidifying point (or melting point) of any of the starting organic salts, a process for producing the same, and use of the same. Specifically, the present invention provides a room-temperature molten salt that comprises a mixture of two or more organic salts with different anionic moieties and different organic cationic moieties and that has a melting point lower than any of the individual organic salts, a process for producing the same, and use of the same.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Battery with molten salt electrolyte and protected lithium-based negative electrode material
InactiveUS20060019167A1Inhibition of dissolutionImprove ionic conductivityNon-aqueous electrolyte cellsElectrode carriers/collectorsAlkaline earth metalLithium metal
A battery comprises a negative electrode including a negative electroactive material, a positive electrode, an electrolyte located between the negative electrode and the positive electrode, and a protection layer, the protection layer separating the electrolyte and the negative electroactive material. Example batteries include lithium batteries and lithium-sulfur batteries having a molten salt electrolyte. The negative electroactive material may be a lithium-containing material such as lithium metal, lithium alloy, or other lithium compound. In other battery technologies, the negative electroactive material may comprise another alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, or other material. The protection layer may comprise a solid polymer electrolyte or other ion-transmissive material.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Electrochemical element for use at high temperatures
An electrochemical element for use at a high temperature has an anode, a cathode comprising an intercalation material having an upper reversible potential-limit of at most 4 V versus Li / Li+ as active material, and an electrolyte arranged between the cathode and anode, which electrolyte comprises an ionic liquid with an anion and a cation a pyrrolidinium ring structure having four Carbon atoms and one Nitrogen atom. Experiments revealed that rechargeable batteries comprising such an intercalation material and N—R1—N—R2-pyrrolidinium, wherein R1 and R2 are alkyl groups and R1 may be methyl and R2 may be butyl or hexyl, are particularly suitable for use at a temperature of up to about 150 degrees Celsius and may be used in oil and / or gas production wells.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery
InactiveUS20050136327A1Improve charge/discharge efficiencyImprove cycle performanceOrganic electrolyte cellsLi-accumulatorsLithiumCyclic ether
A positive electrode has a positive-electrode active material obtained from a mixture of elemental sulfur, a conductive agent and a binder. A negative electrode is composed of a carbon material such as graphite, lithium alloy, or the like that can store lithium and release it. A nonaqueous electrolyte contains a first solvent composed of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of cyclic ethers and chain ethers, and a second solvent composed of a room temperature molten salt having a melting point not higher than 60° C. in a volume ratio in the range of 0.1:99.9 to 40:60, and also contains saturated lithium polysulfide.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Lithium-ion rechargeable accumulators including an ionic liquid electrolyte
The present invention relates to a lithium-ion rechargeable accumulator including a negative electrode in which the active material is graphite carbon, a positive electrode in which the active material is LiFePO4, and an ionic liquid electrolyte containing at least one ionic liquid of the formula C+A- in which C+ is a cation and A- is an anion, and at least one conducting salt, wherein the ionic liquid electrolyte further includes an organic additive consisting of vinyl ethylene carbonate (VEC).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Corrosion protection using carbon coated electron collector for lithium-ion battery with molten salt electrolyte
InactiveUS20060063072A1Material nanotechnologyElectrode carriers/collectorsConductive polymerCarbon nanotube
A battery, such as a lithium-ion battery, comprises a first electrode, a second electrode, a molten salt electrolyte, and an electron collector, associated with the first electrode, the electron collector comprising an electrically conducting film. The battery further includes a protection layer separating the electron collector and the first electrode, the protection layer comprising a carbon-containing material. The electron collector may be an electrically conducting material such as aluminum, aluminum alloy, copper, nickel, other metal (such as alloys), conducting polymer, and the like. In one example, the protection layer is a graphite layer. In other examples, the protection layer may be a fullerene film, carbon nanotube film, or other carbon-containing material.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +2
Ionic Liquid
InactiveUS20080008930A1Low viscosityImprove conductivityDouble layer capacitorsConductive materialChemical reactionSolvent
The present invention relates to ionic liquids having low melting points, low viscosities and high electrical conductivities; and more specifically, to ionic liquids including at least one organic onium ion and at least one anion represented by the formula: [Z-BF3]−wherein Z is an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, or a fluoroalkenyl group. The ionic liquids according to the invention are capable of easily dissolving electrolytes such as lithium salts, and are also nonflammable and have low viscosities; therefore, the ionic liquids are suitable for use as electrolyte solvents for lithium batteries such as lithium secondary batteries, electric double-layer capacitors, and the like. The ionic liquids according to the invention are suitable for use in electrochemical devices such as lithium secondary batteries, fuel cells, solar batteries, electrical double-layer capacitors and the like; as solvents for chemical reactions; and as lubricants.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Material for electrolytic solutions and use thereof
InactiveUS7713658B2Avoid corrosionImprove ionic conductivityAlkaline accumulatorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesElectrolytic agentElectrical conductor
It is an object of the present invention to provide a material for electrolytic solutions suited for use as material in electrolytic solutions serving as ionic conductors in electrochemical devices, such as large-capacity cells or batteries.The present invention is related to a material for electrolytic solutions which comprises, as an essential constituent, an anion represented by the general formula (1):wherein X represents at least one element selected from among B, N, O, Al, Si, P, S, As and Se; M1 and M2 are the same or different and each represents an organic linking group; a is an integer of not less than 1, and b, c and d each independently is an integer of not less than 0.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Lithium ion battery
InactiveUS20100092869A1Good rate characteristicsReduce resistanceCell electrodesOrganic electrolyte cellsDecompositionPhysical chemistry
To provide high energy density, good cycle properties and rate characteristics and long-term safety of a lithium ion battery containing at least an ionic liquid and a lithium salt. The above problems are solved by suppressing reduction and decomposition of the ionic liquid on an anode by using a graphite coated with an amorphous carbon or onto which an amorphous carbon is deposited as an anode active material.
Owner:NEC ENERGY DEVICES LTD
Electrolyte composition and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell
InactiveUS20030013021A1Maintain good propertiesPreventing leakage and depletionSolid electrolytesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsMolten saltElectrolyte composition
An electrolyte composition excellent in charge-transporting property that can be prepared with ease, and a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell that comprises the electrolyte composition to exhibit excellent cell characteristics while preventing leakage or depletion of the electrolyte composition. The electrolyte composition comprises: a particular molten salt; a polymer prepared by a reaction between an electrophile having at least two unsaturated bonds polarized by an electron-withdrawing group and a nucleophile having a plurality of nucleophilic groups; and a metal salt containing a Group IA metal ion or a Group IIA metal ion.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Non aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
InactiveUS20030096163A1Improve flame retardant performanceAvoid decompositionLead-acid accumulatorsElectrolytic capacitorsMolten saltRoom temperature
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Secondary cell electrode and fabrication method, and secondary cell, complex cell, and vehicle
InactiveUS20090173632A1Solid electrolyte cellsActive material electrodesMaterials scienceCurrent collector
In a nonaqueous electrolyte cell-oriented electrode (10), an electrode active material layer (12) formed on a collector (1) has a density gradient developed with a gradient of a varied concentration of a solid along a thickness from a surface of the electrode active material layer (12) toward the collector (1), and in a gel electrolyte cell-oriented electrode (30), an electrode active material layer (32) formed on a collector (1) has a density gradient developed with (a) gradient(s) of (a) varied concentration(s) of one or both of an electrolyte salt and a film forming material along a thickness from a surface of the electrode active material layer (32) toward the collector (1).
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Energy storage devices
InactiveUS7479353B2Facilitated releaseImprove efficiencyHybrid capacitor electrolytesAlkaline accumulatorsIonic liquidElectrolyte
Pyrrolidinium-based room temperature ionic liquids, and phosphorus and arsenic analogues, are used as electrolytes in energy storage devices including secondary lithium batteries, supercapacitors and asymmetric battery-supercapacitors. The electrolytes preferably contain lithium ions as the charge-carrying species. The electrolytes are in a liquid state at the operating temperature.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Positive electrode, non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20040191629A1Increase energy densityElectrode manufacturing processesOrganic electrolyte cellsCyclic etherAqueous electrolyte
A non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery comprises a positive electrode including elemental sulfur, a negative electrode including silicon that stores lithium, and a non-aqueous electrolyte including a room temperature molten salt having a melting point of not higher than 60° C. The non-aqueous electrolyte may further include at least one type of solvent selected from cyclic ether, chain ether, and fluorinated carbonate. The non-aqueous electrolyte may include a reduction product of elemental sulfur. The positive electrode has a positive electrode active material made of a mixture of elemental sulfur, a conductive agent, and a binder. The electrode having a positive electrode active material is processed under reduced-pressure while immersed in the non-aqueous electrolyte. A pressure during the reduced-pressure process is preferably not higher than 28000 Pa (-55 cmHg with respect to atmospheric pressure).
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com