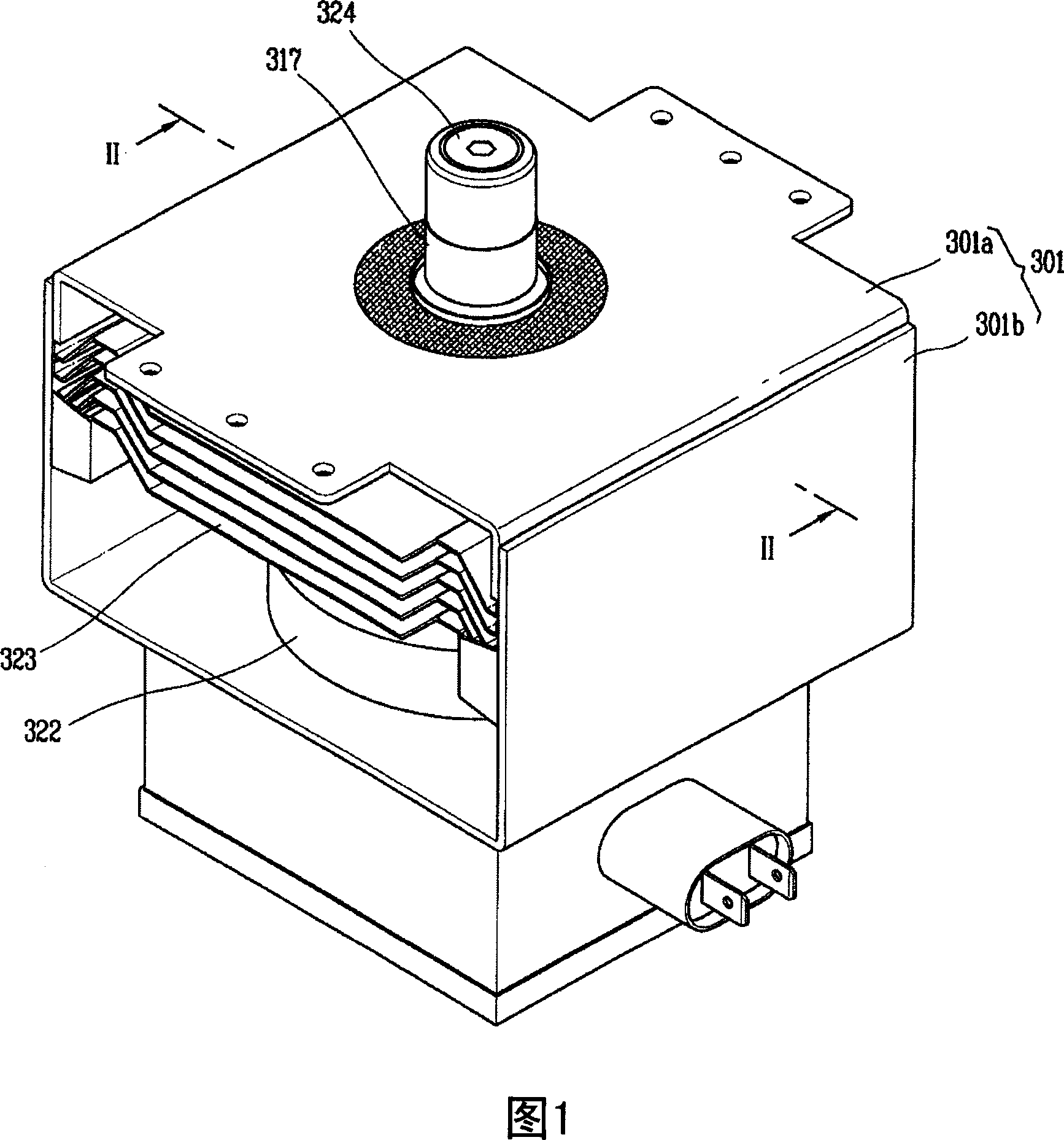
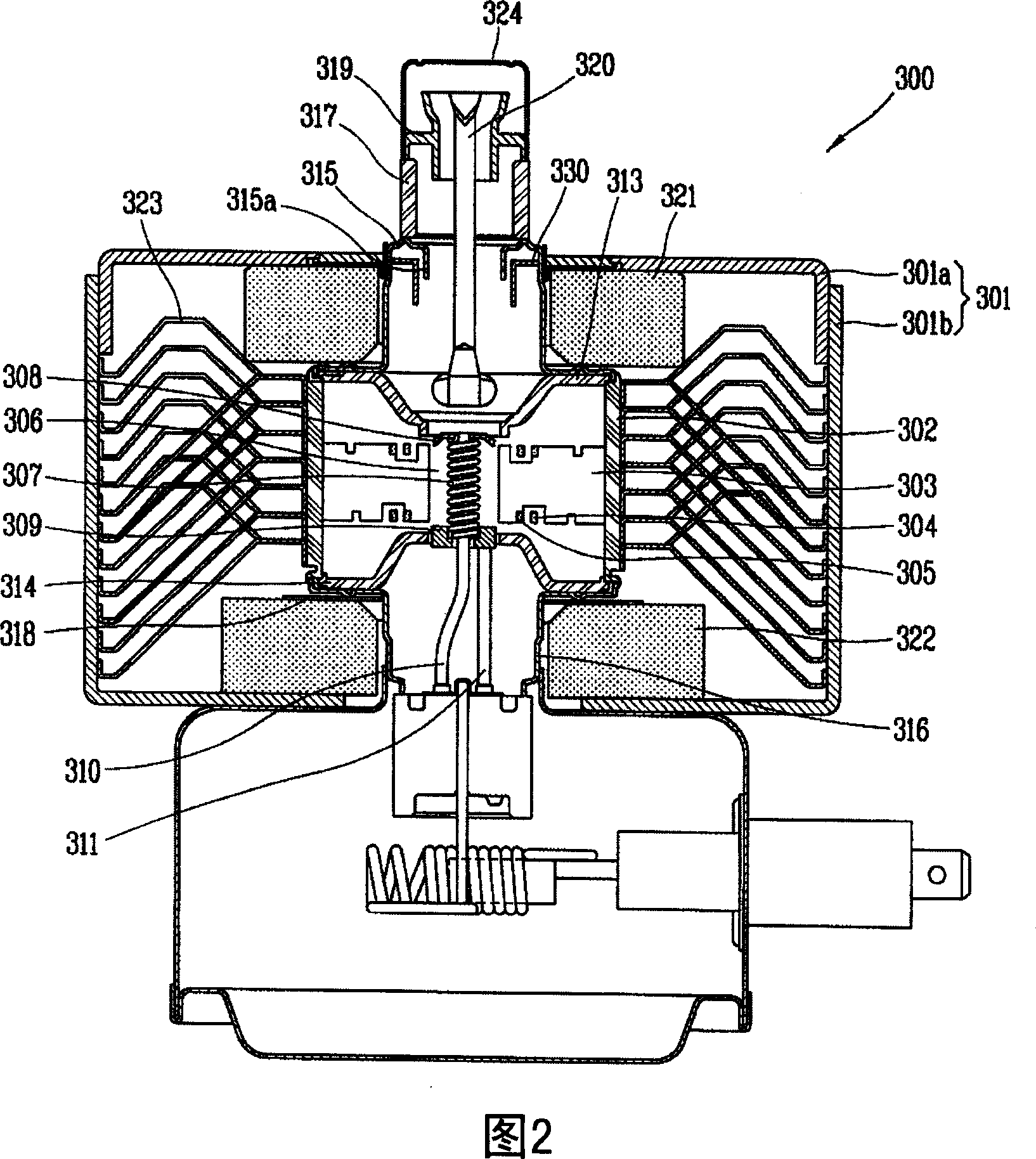
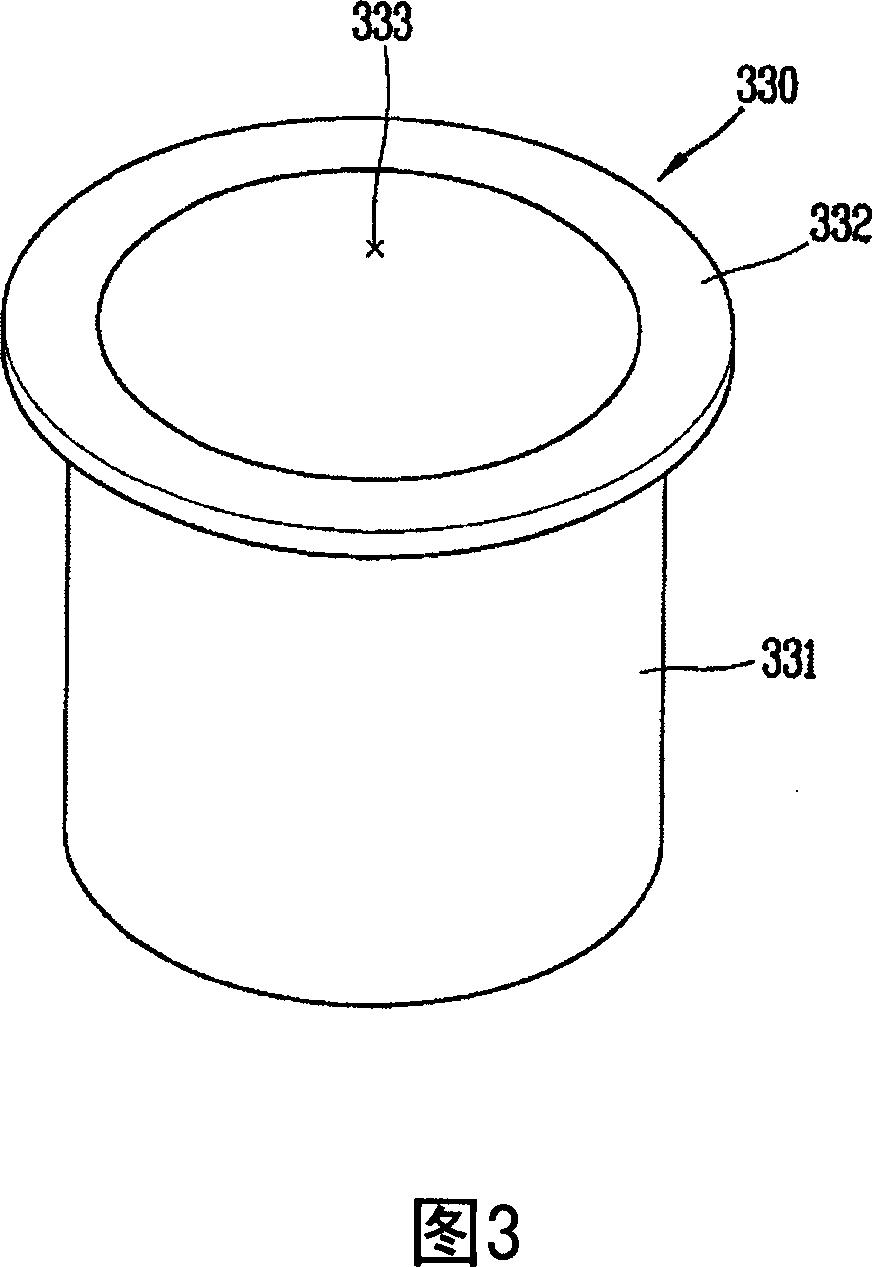
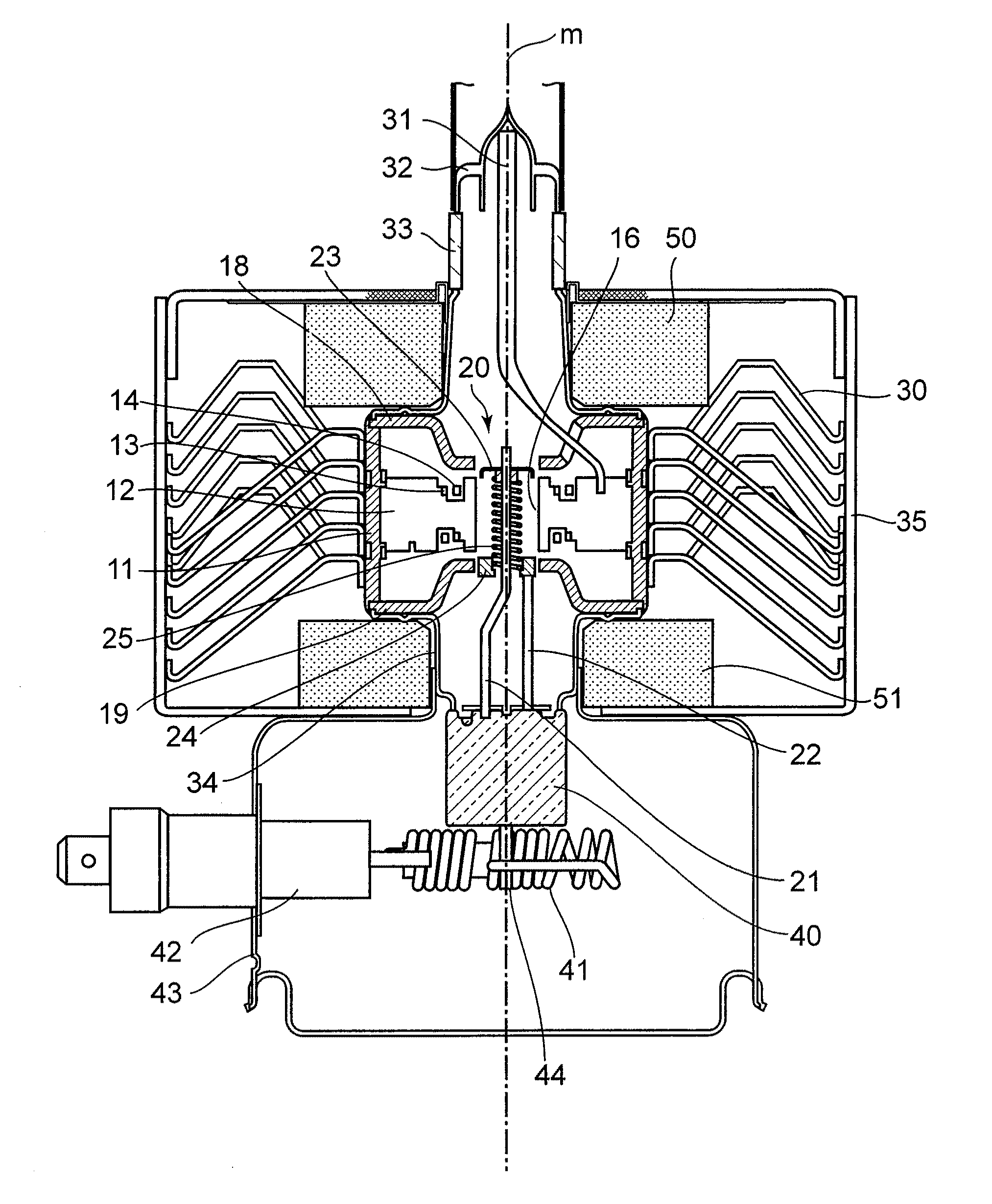
Patents
Literature
154results about "Multi-cavity magnetrons" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
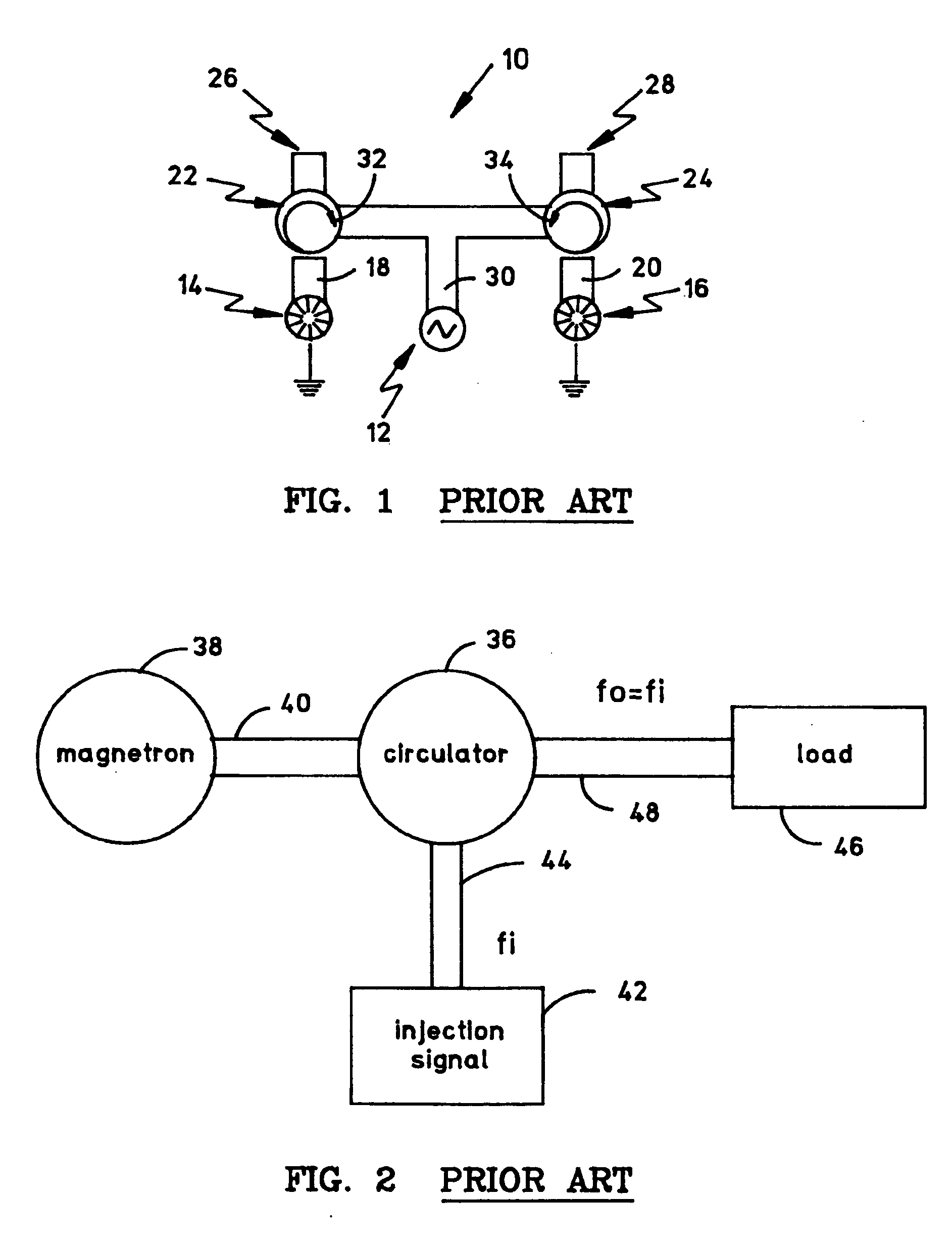
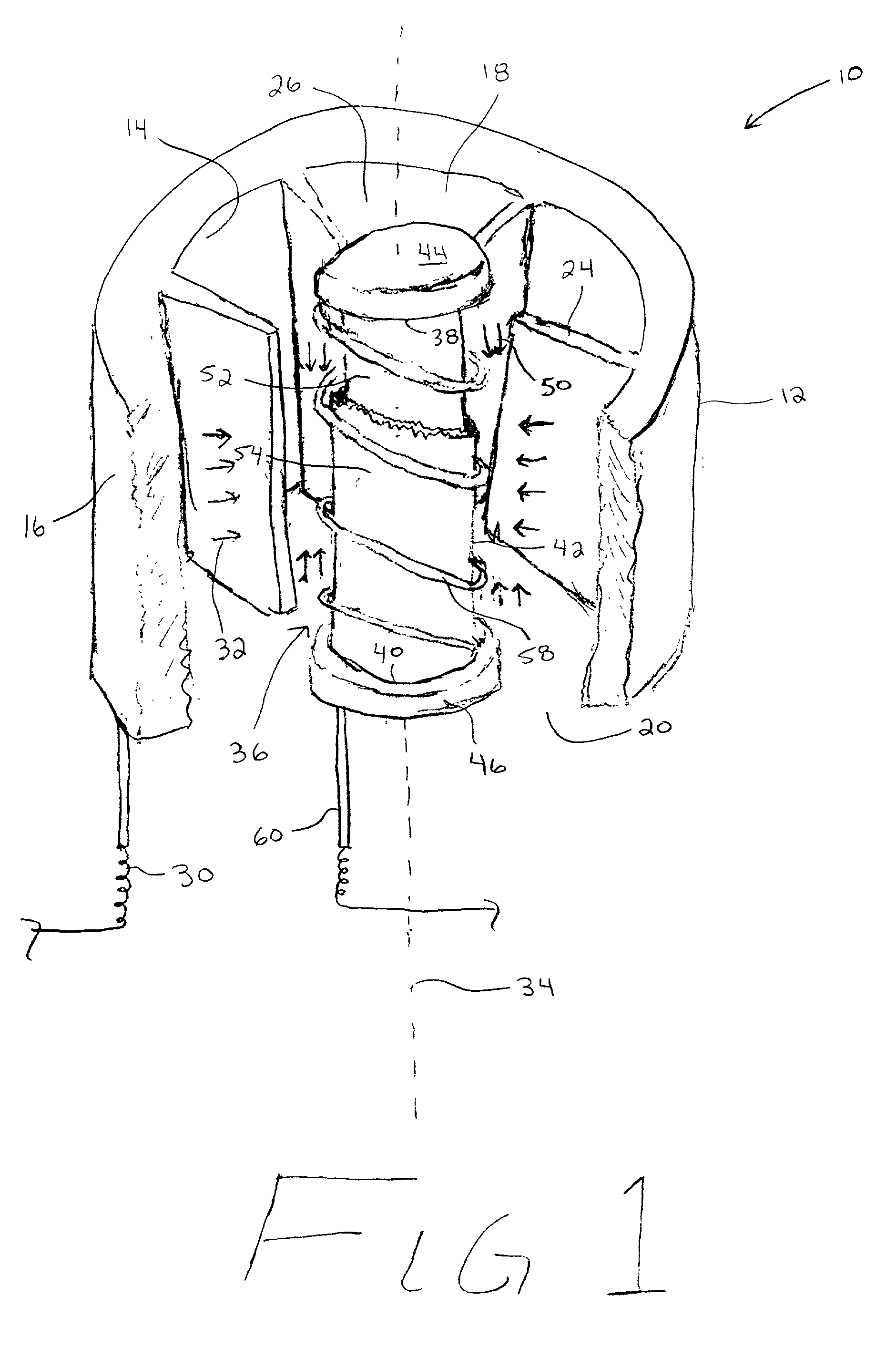
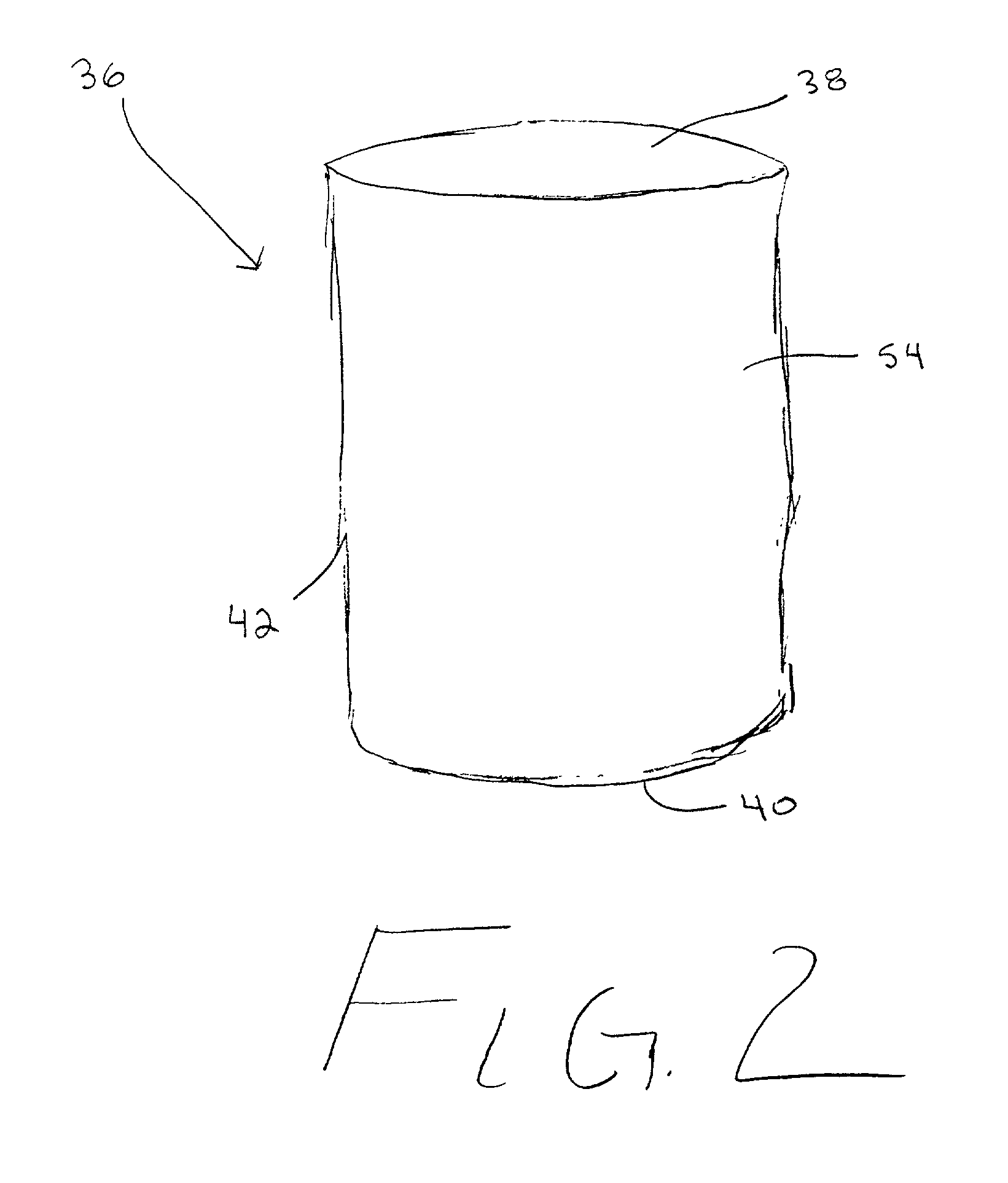
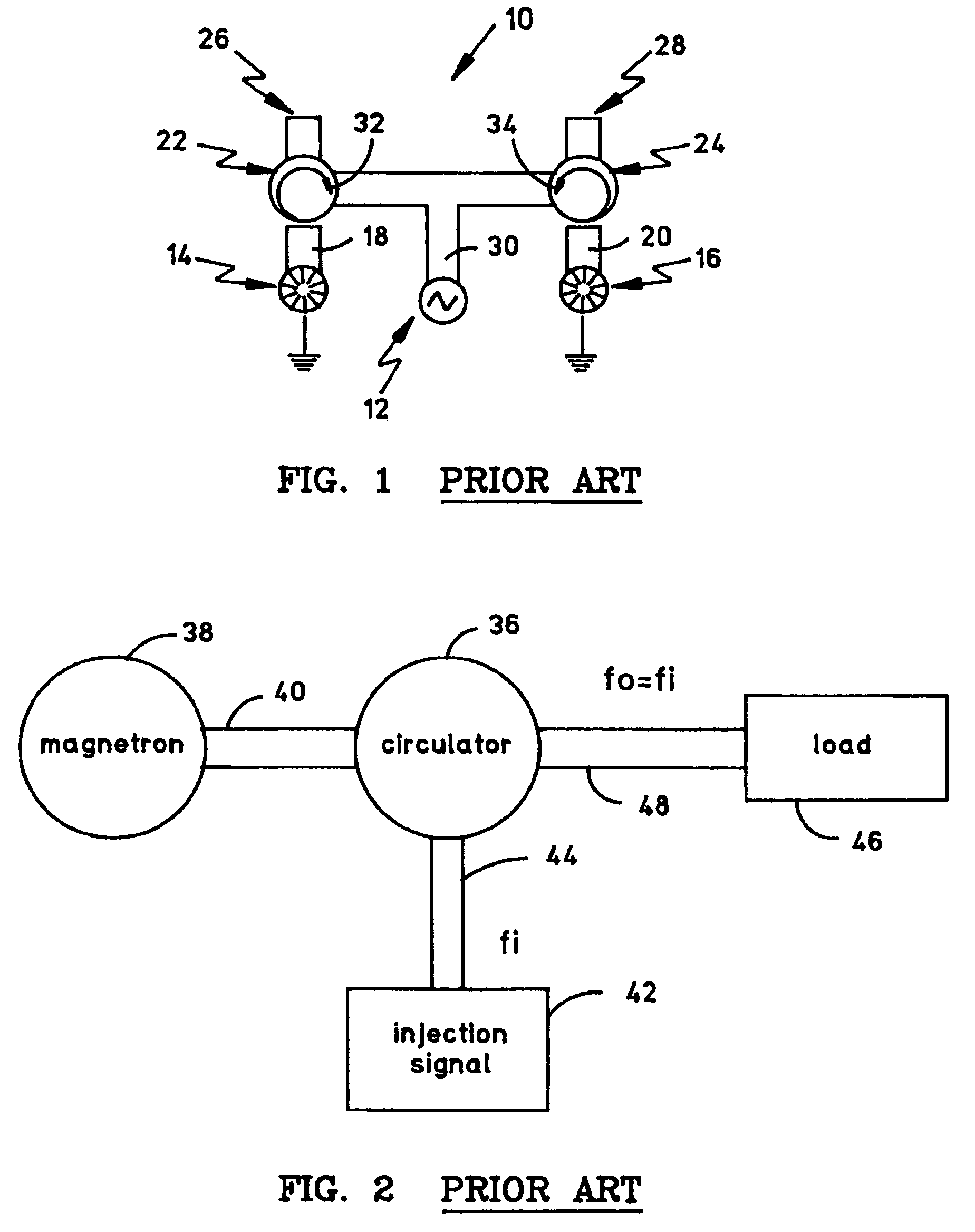
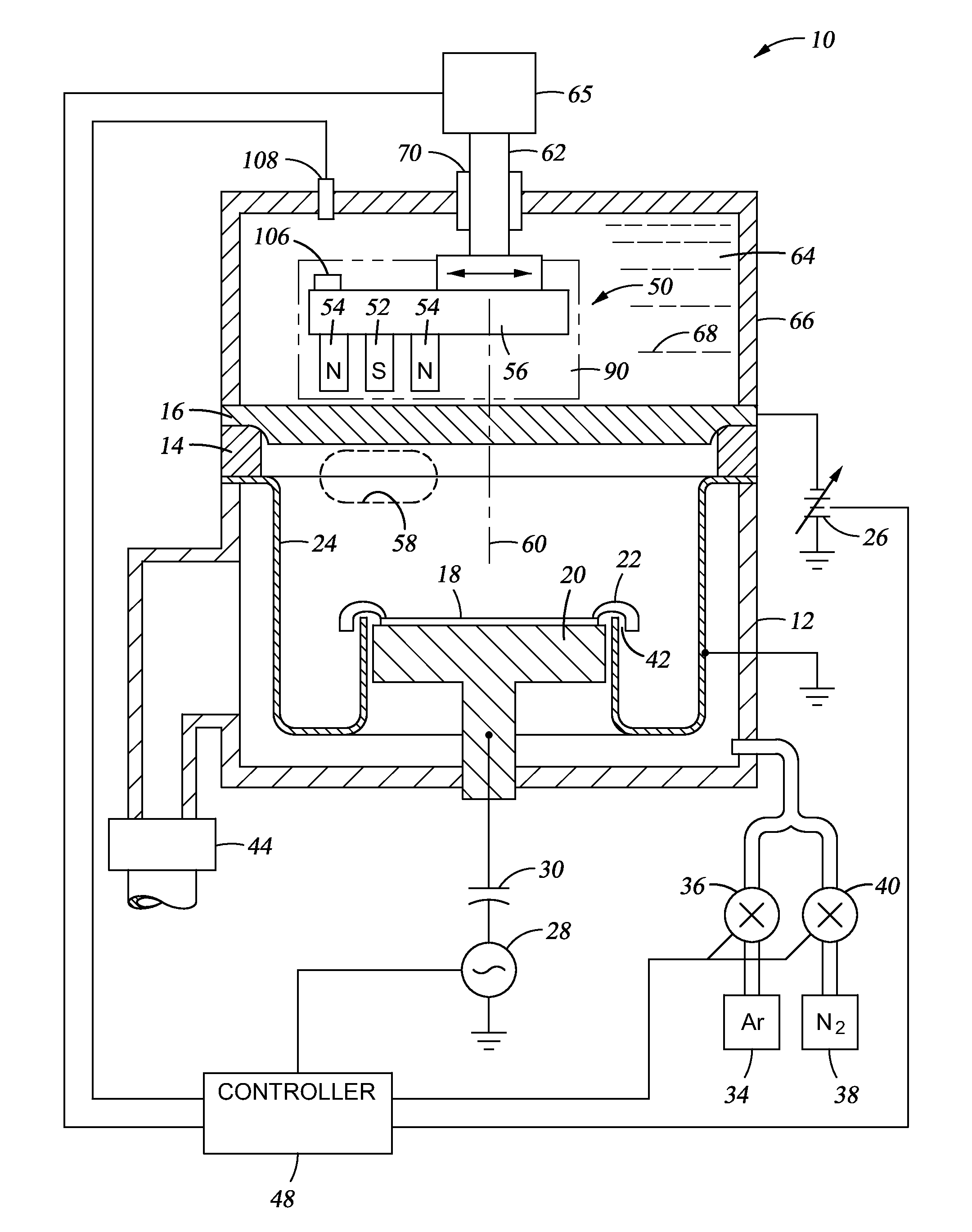
High-power microwave system employing a phase-locked array of inexpensive commercial magnetrons
InactiveUS20060208672A1Facilitates coherent combinationEfficient and inexpensiveTravelling-wave tubesRF amplifierMicrowave applicationsAs Directed
A high-power microwave generator employing a plurality of inexpensive commercial magnetron tubes cross-coupled by means of a secondary coupling path between each magnetron output pair, whereby a portion of the output energy from a first magnetron tube is injected into a second magnetron tube and a portion of the output energy from the second magnetron tube is similarly injected into the first magnetron tube. The resulting cross-injection of microwave energies brings the respective magnetron tube pair into a phase-lock sufficiently stable to permit coherent combination of their outputs for many high-power microwave applications, such as directed energy weapon systems. The magnetron phase-locking system requires no external components other than the secondary coupling paths of this invention.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Magnetron device with mode converter and related methods
ActiveUS20090058301A1Simple radiation patternIncrease the number ofAntenna supports/mountingsStructural circuit elementsRadiation modeMode transformation
The present invention provides a relativistic magnetron with axial extraction, or magnetron with diffraction output (MDO), with a mode converter placed directly within the diffraction output of radiation to effectively convert the operating π-mode into a radiated mode of simpler radiation patterns.
Owner:STC UNM
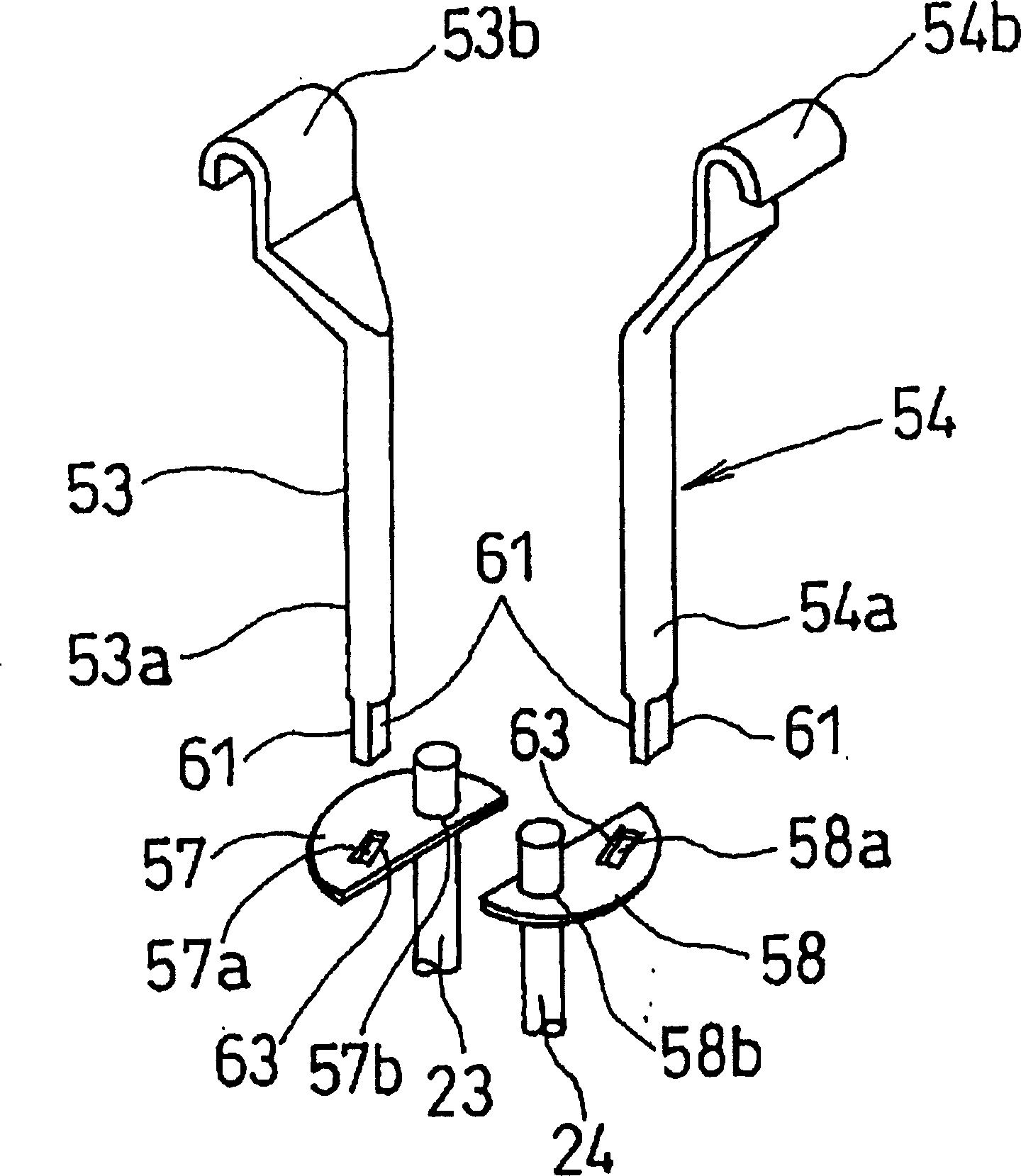
Magnetron
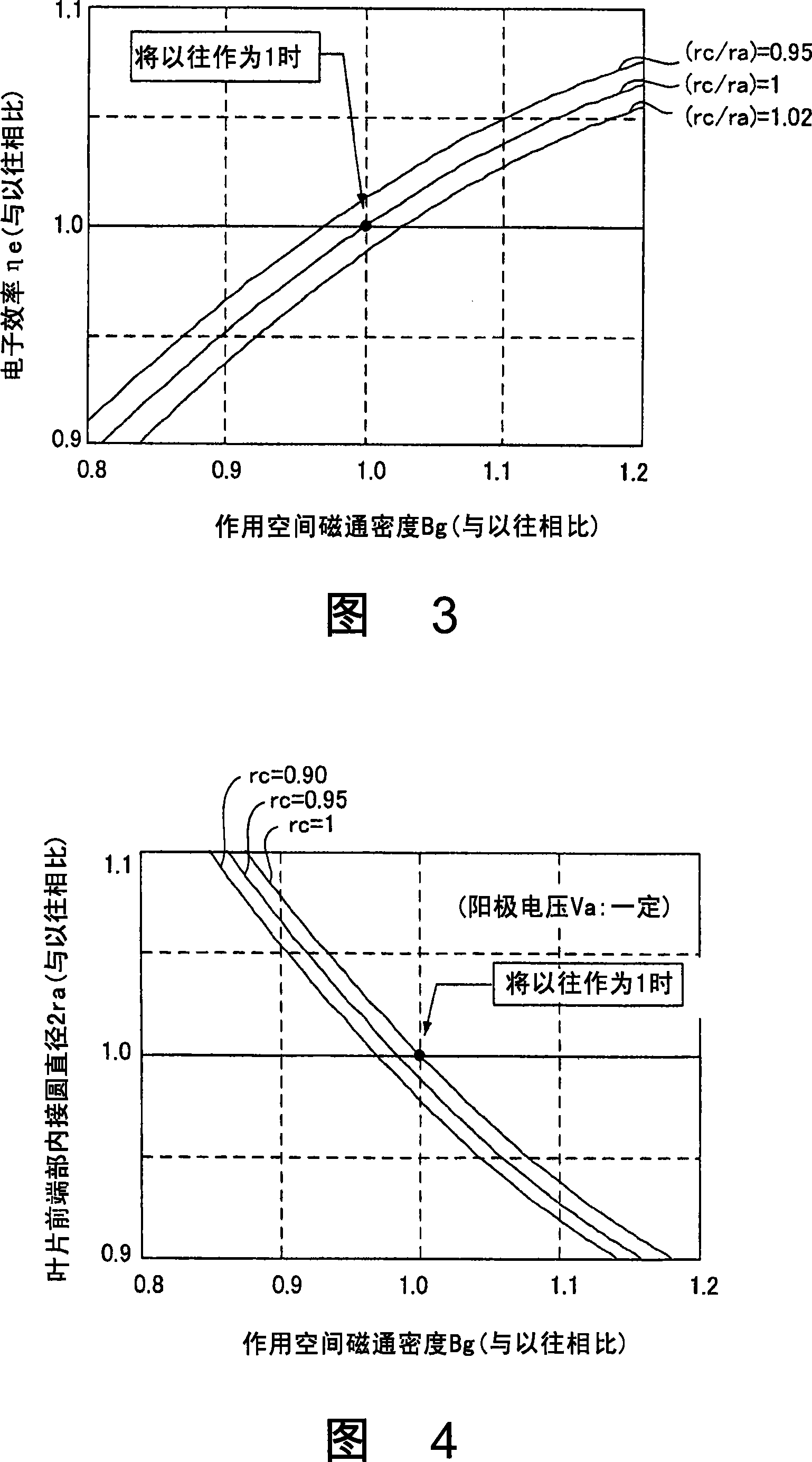
InactiveUS7023137B2Improve electronic efficiencyImprove oscillation efficiencyCellsTransit-tube leading-in arrangementsMicrowaveMagnetic poles
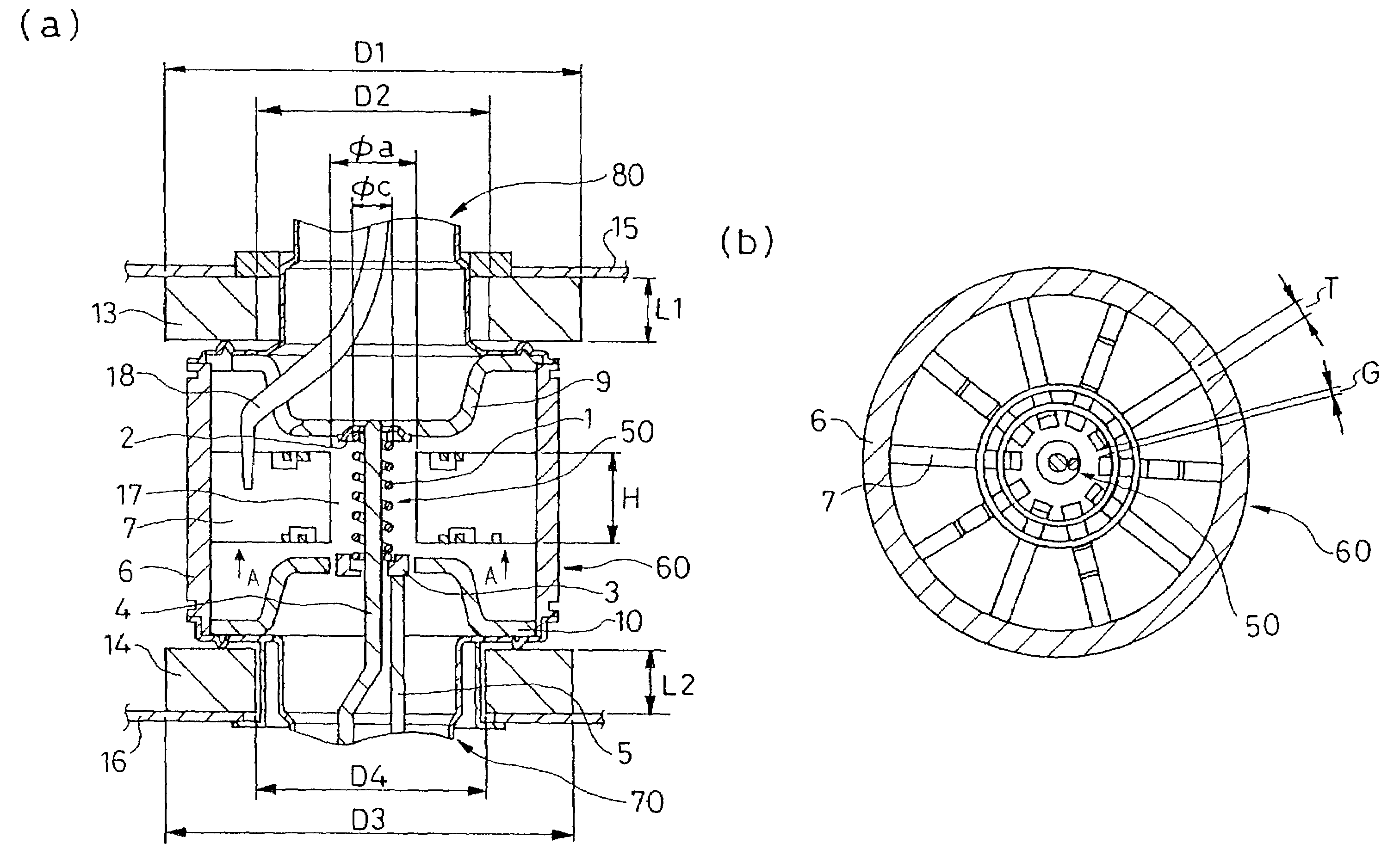
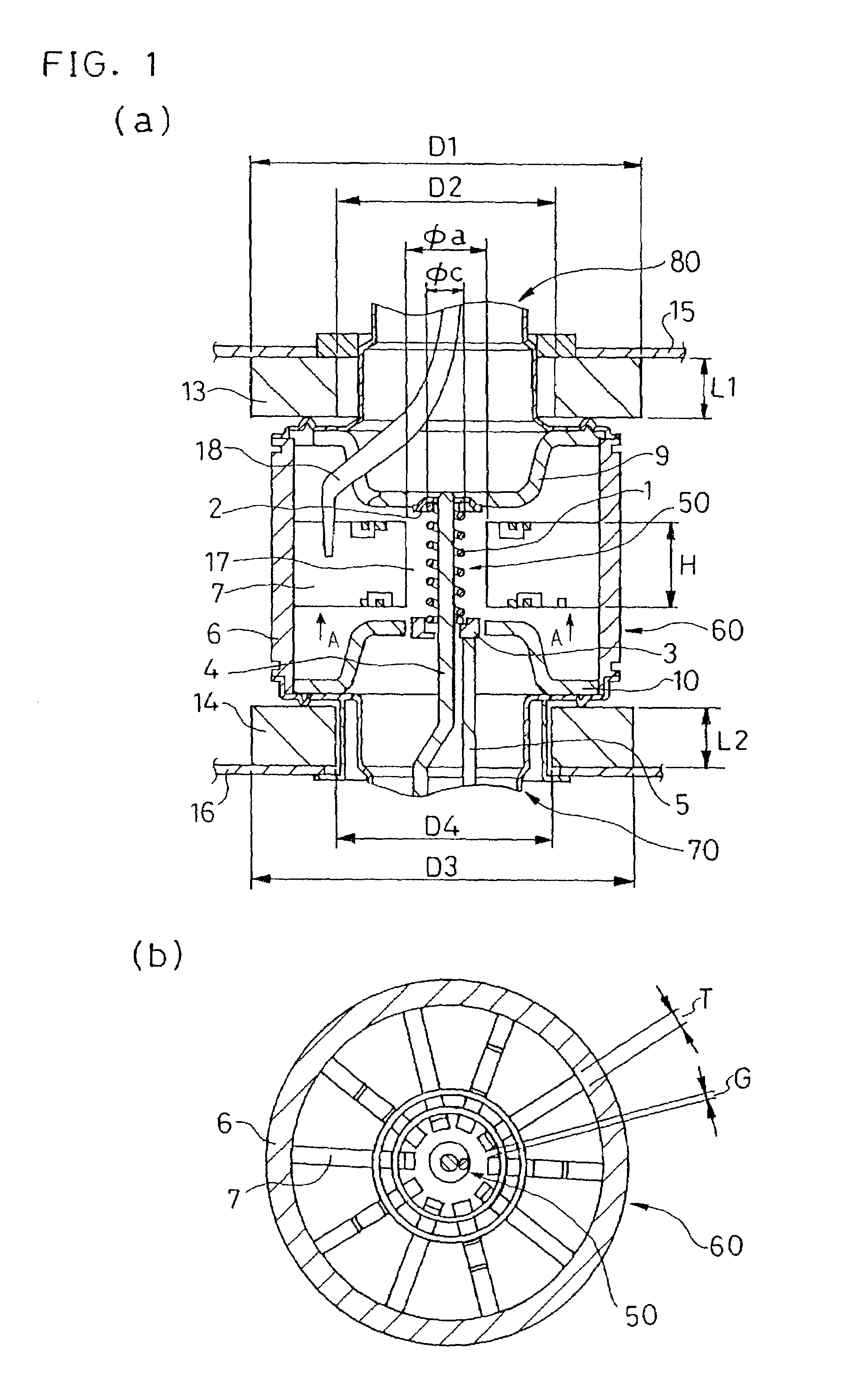
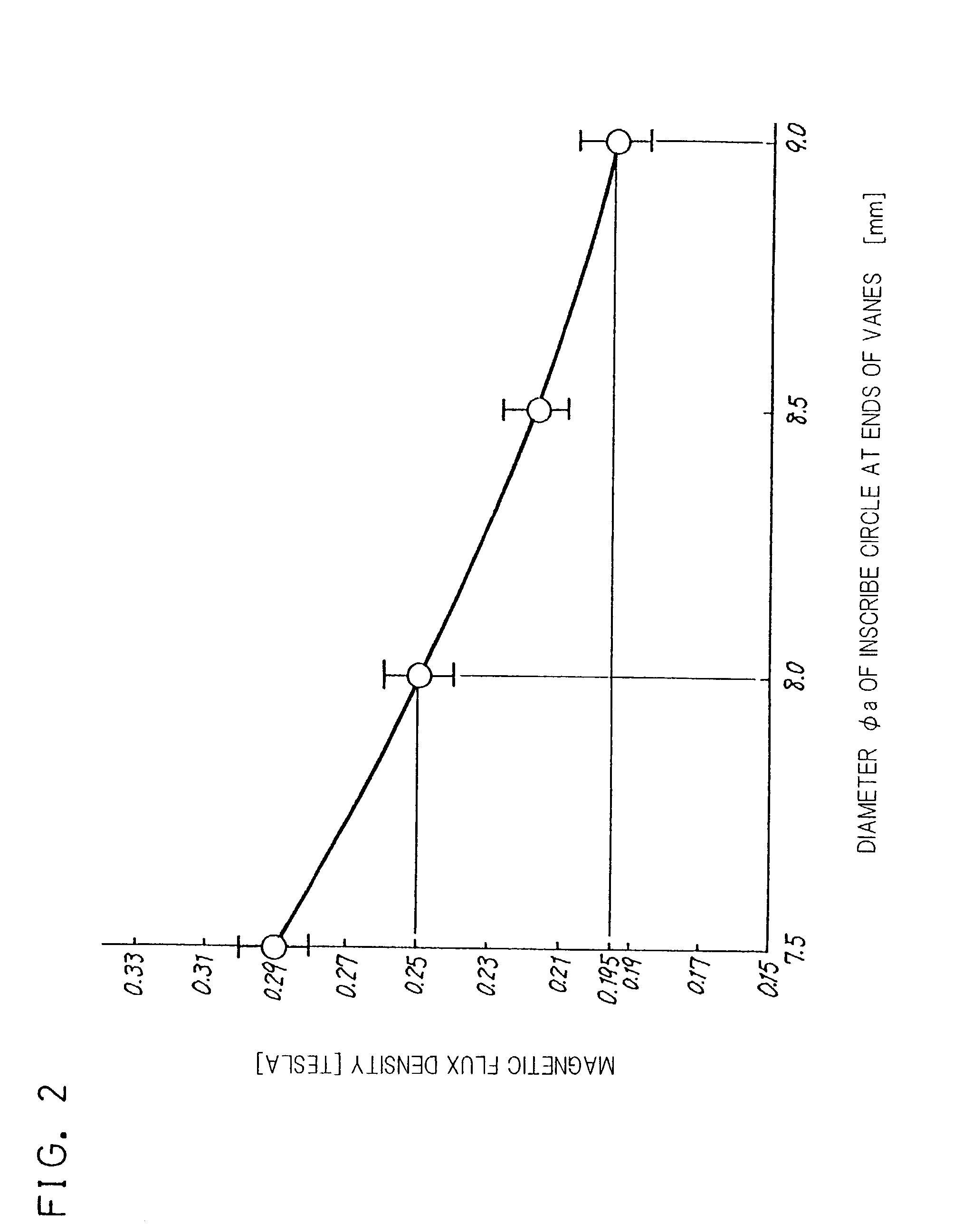
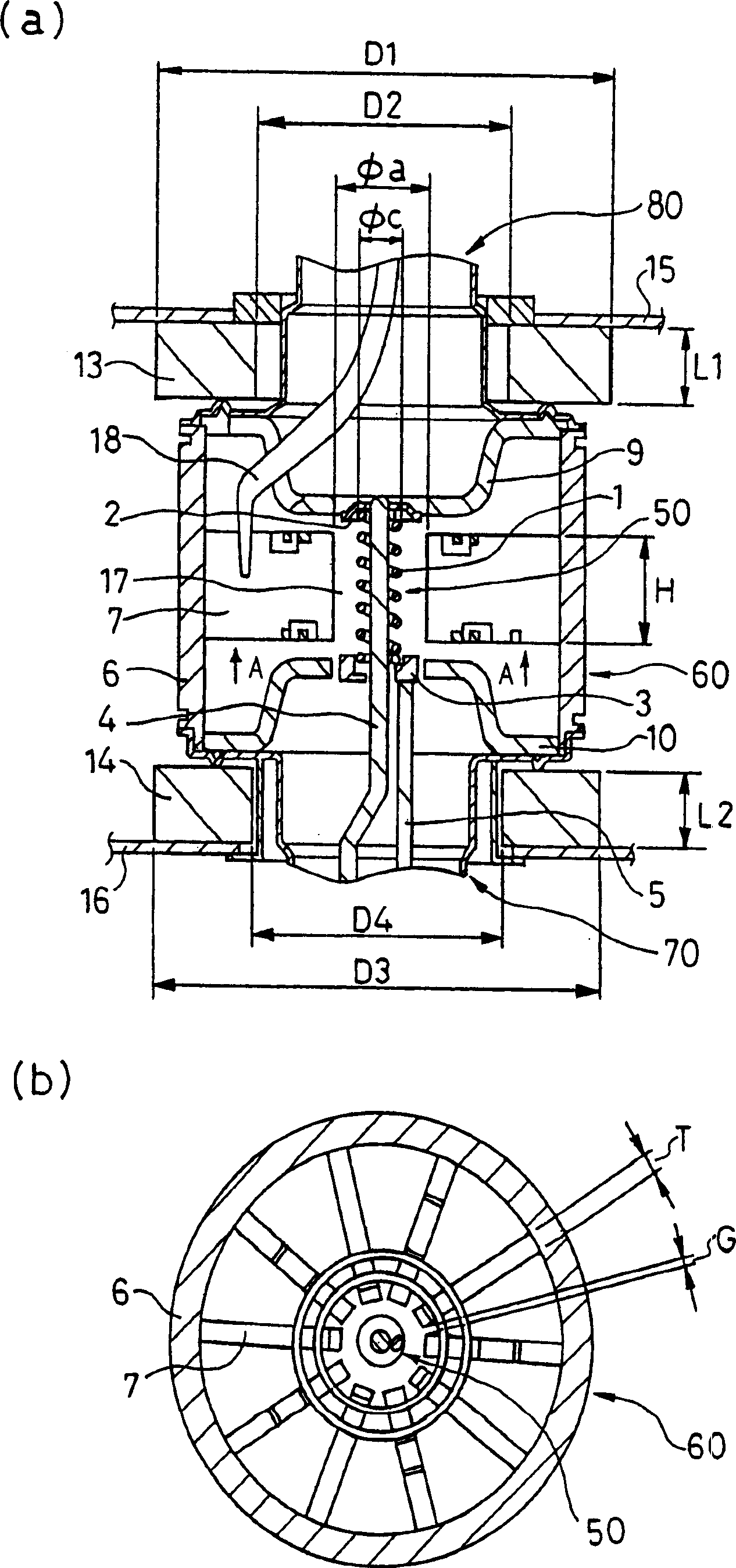
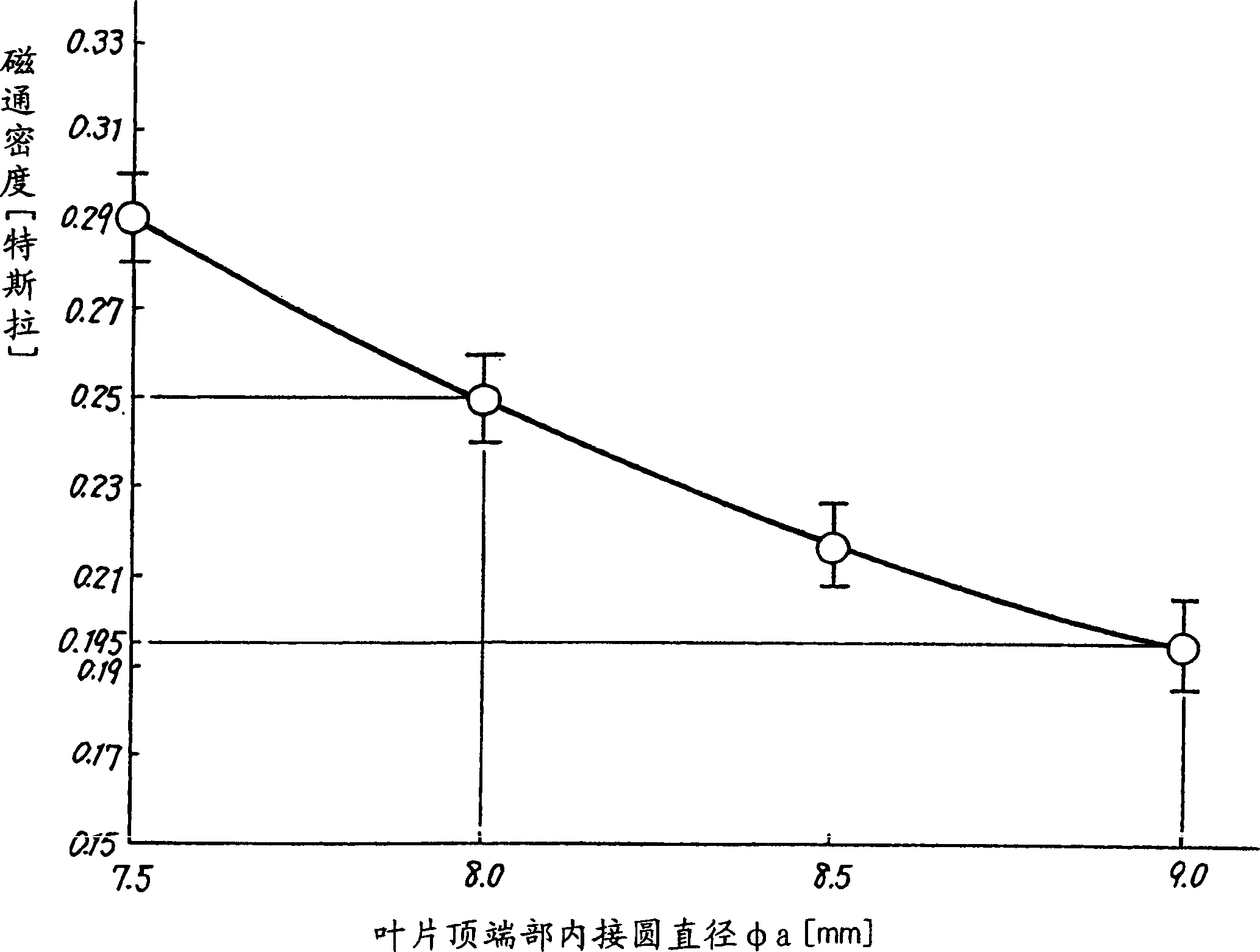
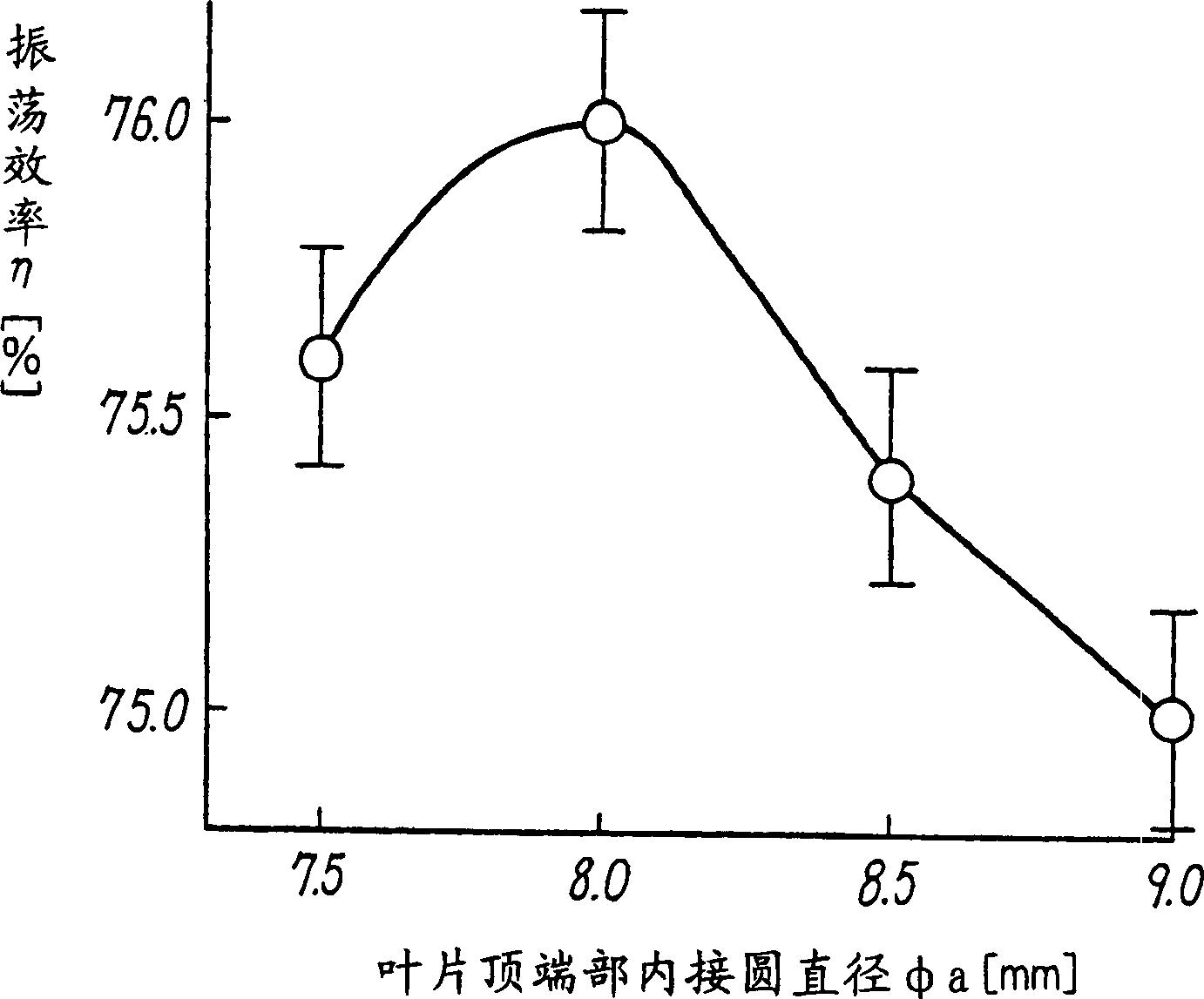
A magnetron comprising an anode portion having an anode cylinder and vanes, a cathode portion having a coil-shaped filament, magnetic poles disposed at the upper and lower ends of the filament, ring-shaped permanent magnets made of a Sr ferrite magnet containing La—Co, an input portion and an output portion. The diameter φa of the inscribed circle at the ends of the vanes constituting the anode portion is in the range of 7.5 to 8.5 mm, and the outside diameter φc of the coil-shaped filament 1 constituting the cathode portion is in the range of 3.4 to 3.6 mm.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Mode seeding cathode for a relativistic magnetron
A high-power relativistic magnetron wherein the cathode geometry is shaped to form a DC electric field that has a non-negligible azimuthal component causing preferential selection of the pi mode at startup (suppression of mode competition), a significant increase in radiated power output and time integrated efficiency when compared to standard relativistic magnetron cathode designs.
Owner:AIR FORCE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SERETARY OF THE
Magnetron
InactiveCN1404093AImprove electronic efficiencyImprove oscillation efficiencyTransit-tube leading-in arrangementsVacuum evaporation coatingMagnetic polesOptoelectronics
A magnetron comprising an anode portion having an anode cylinder and vanes, a cathode portion having a coil-shaped filament, magnetic poles disposed at the upper and lower ends of the filament, ring-shaped permanent magnets made of a Sr ferrite magnet containing La-Co, an input portion and an output portion. The diameter phia of the inscribed circle at the ends of the vanes constituting the anode portion is in the range of 7.5 to 8.5 mm, and the outside diameter phic of the coil-shaped filament 1 constituting the cathode portion is in the range of 3.4 to 3.6 mm.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetron with diamond coated cathode
InactiveUS20020125827A1Reduce operating costsMinimizes electronic noiseTransit-tube electron/ion gunsTransit-tube cathodesSecondary electronsPole piece
A radio frequency magnetron device for generating radio frequency power includes a cathode at least partially formed from a diamond material. An anode is disposed concentrically around the cathode. An electron field is provided radially between the anode and the cathode. First and second oppositely charged pole pieces are operatively connected to the cathode for producing a magnetic field in a direction perpendicular to the electric field. A filament is provided within the electron tube which when heated produces primary electrons. Alternatively, a voltage is applied to the anode which causes primary electrons to emit from the diamond coated cathode. A portion of the primary electrons travel in a circular path and induce radio frequency power. Another portion of the primary electrons spiral back and collide with the cathode causing the emission of secondary electrons. The secondary electron emission sustains operation of the magnetron device once the device has been started.
Owner:TERAPHYSICS CORP
High efficiency, low voltage, low L-band, mega-watt class magnetron
InactiveUS8878433B1Reduce input voltageCompact designTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureResonant cavity
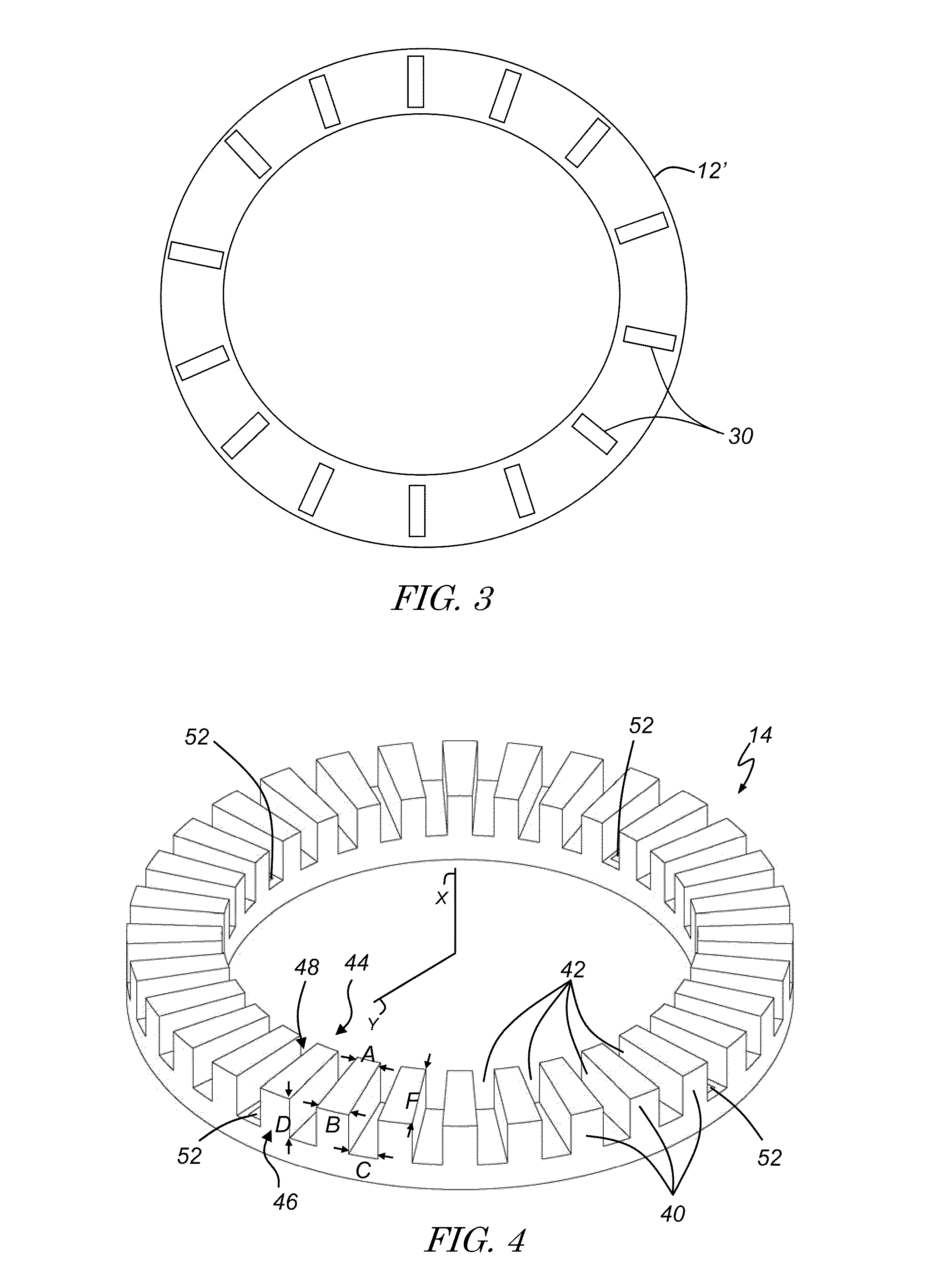
A conventional (non-relativistic) magnetron provides megawatt-levels of power. The magnetron includes a fourteen vane slow wave structure that surrounds a fourteen turn helical cathode. An upstream coaxial waveguide is surrounded by a dish-shaped flange that accommodates a reflector chamber in communication with an upstream void and a downstream interaction chamber. The vanes of the slow wave structure are shaped to define fourteen resonant chambers therebetween with each of the resonant cavities having a wedge portion in communication with a neck portion.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
High-power microwave system employing a phase-locked array of inexpensive commercial magnetrons
InactiveUS7164234B2Facilitates coherent combinationEfficient and inexpensiveTravelling-wave tubesRF amplifierMicrowave applicationsAs Directed
A high-power microwave generator employing a plurality of inexpensive commercial magnetron tubes cross-coupled by means of a secondary coupling path between each magnetron output pair, whereby a portion of the output energy from a first magnetron tube is injected into a second magnetron tube and a portion of the output energy from the second magnetron tube is similarly injected into the first magnetron tube. The resulting cross-injection of microwave energies brings the respective magnetron tube pair into a phase-lock sufficiently stable to permit coherent combination of their outputs for many high-power microwave applications, such as directed energy weapon systems. The magnetron phase-locking system requires no external components other than the secondary coupling paths of this invention.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Magnetron
InactiveUS20070151847A1Improve efficiencyReduce heating powerCellsVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringHeating power
A magnetron comprises an anode, a cathode disposed at a center of the anode, a plurality of vanes radially protruding from an inner surface of the anode towards the cathode, and an upper end shield and a lower end shield respectively coupled to an upper end and a lower end of the cathode so that a length of an effective heating portion of the cathode may be less than a height of the vane. A heating power for the cathode is reduced thus to decrease an input power for the same output, thereby enhancing an efficiency of the magnetron
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Magnetron anode design for short wavelength operation
ActiveUS7265360B2Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsElectrical conductorPole piece
An electromagnetic radiation source is disclosed. The electromagnetic radiation source includes an anode having a first conductor, a second conductor positioned relative to the first conductor, a plurality of pole pieces coupled to at least one of the first conductor and the second, and at least one mechanical phase reversal positioned along the first conductor or second conductor. Adjacent pole pieces are separated by a gap. The electromagnetic radiation source also includes a cathode separated from the anode by an anode-cathode space, electrical contacts for applying a dc voltage between the anode and the cathode and establishing an electric field across the anode-cathode space, and at least one magnet arranged to provide a dc magnetic field within the anode-cathode space generally normal to the electric field. Electrons emitted from the cathode are influenced by the electric and magnetic fields to follow a path through the anode-cathode space and pass in close proximity to the plurality of pole pieces, and the gaps between adjacent pole pieces provide fringing fields which interact with the electrons to produce single mode operation at a desired operating frequency.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
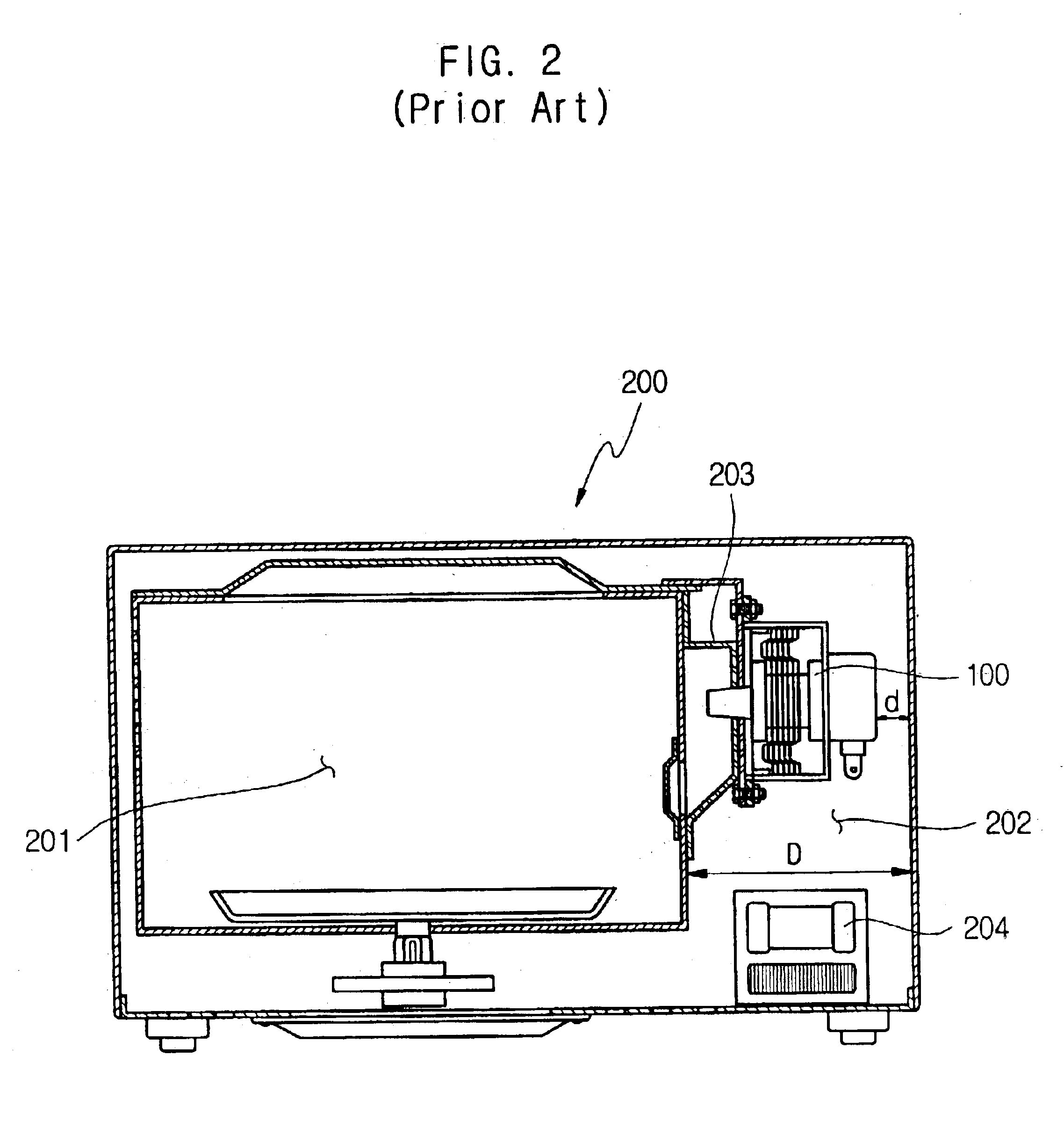
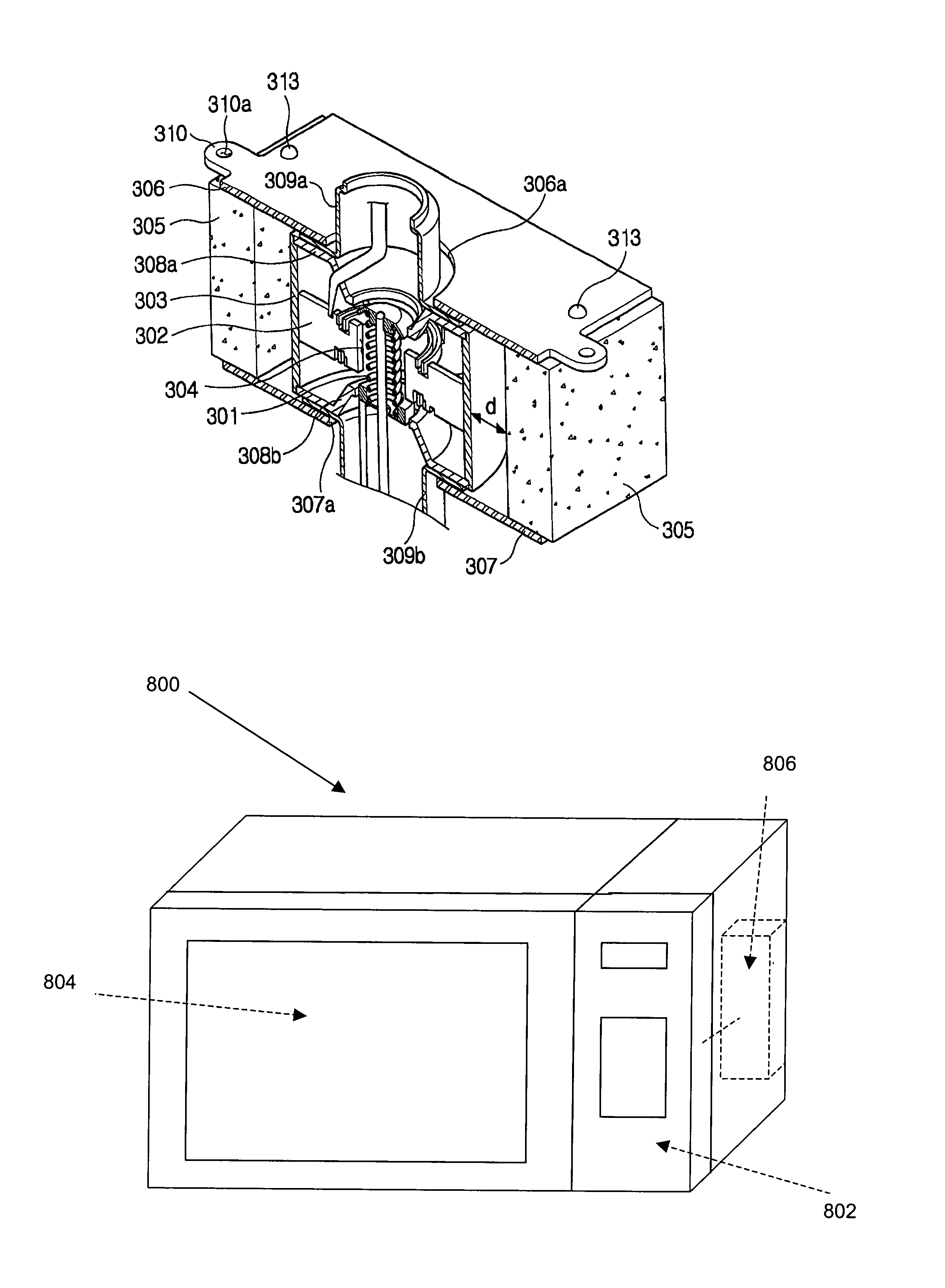
Magnetron for microwave ovens
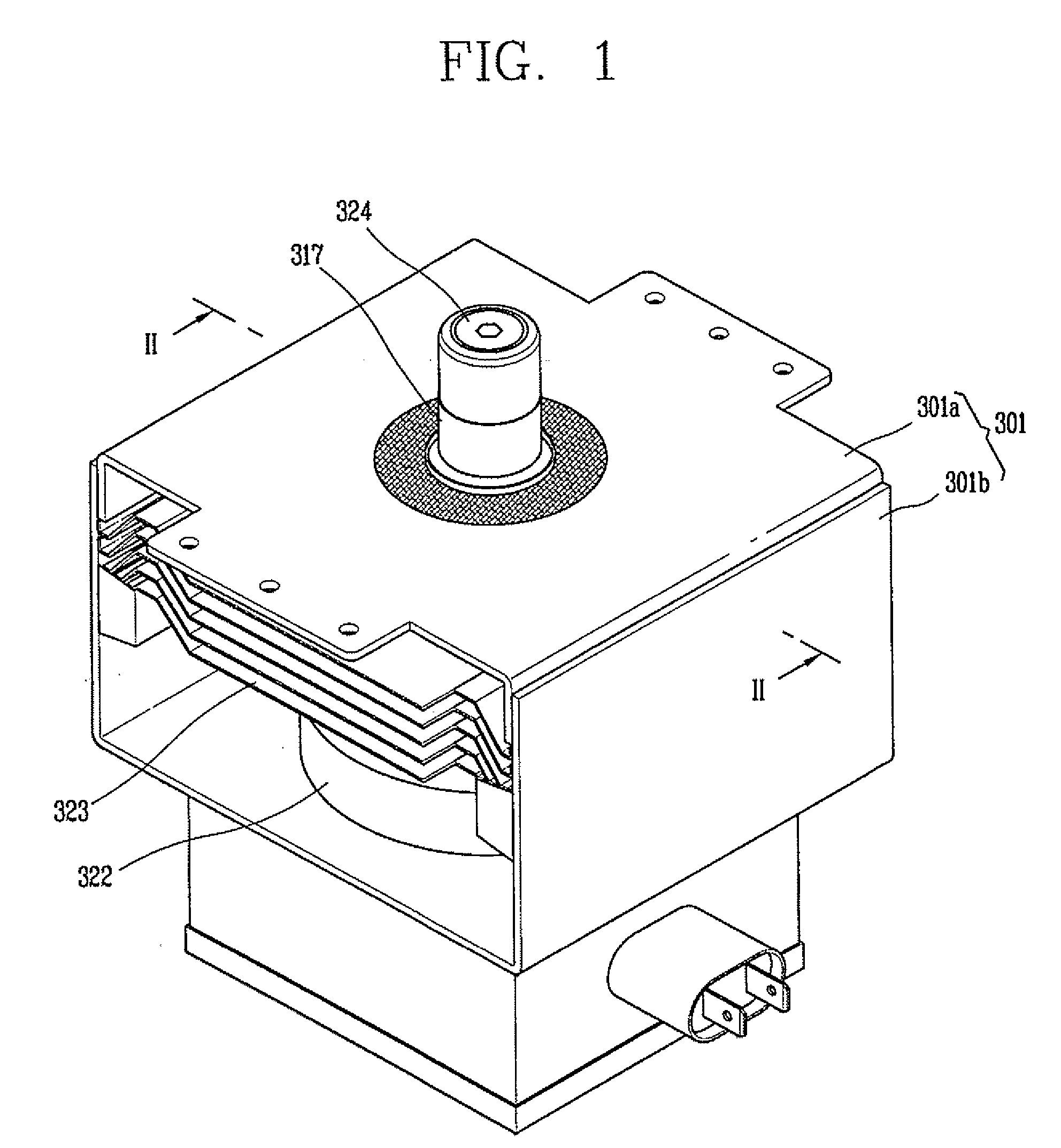
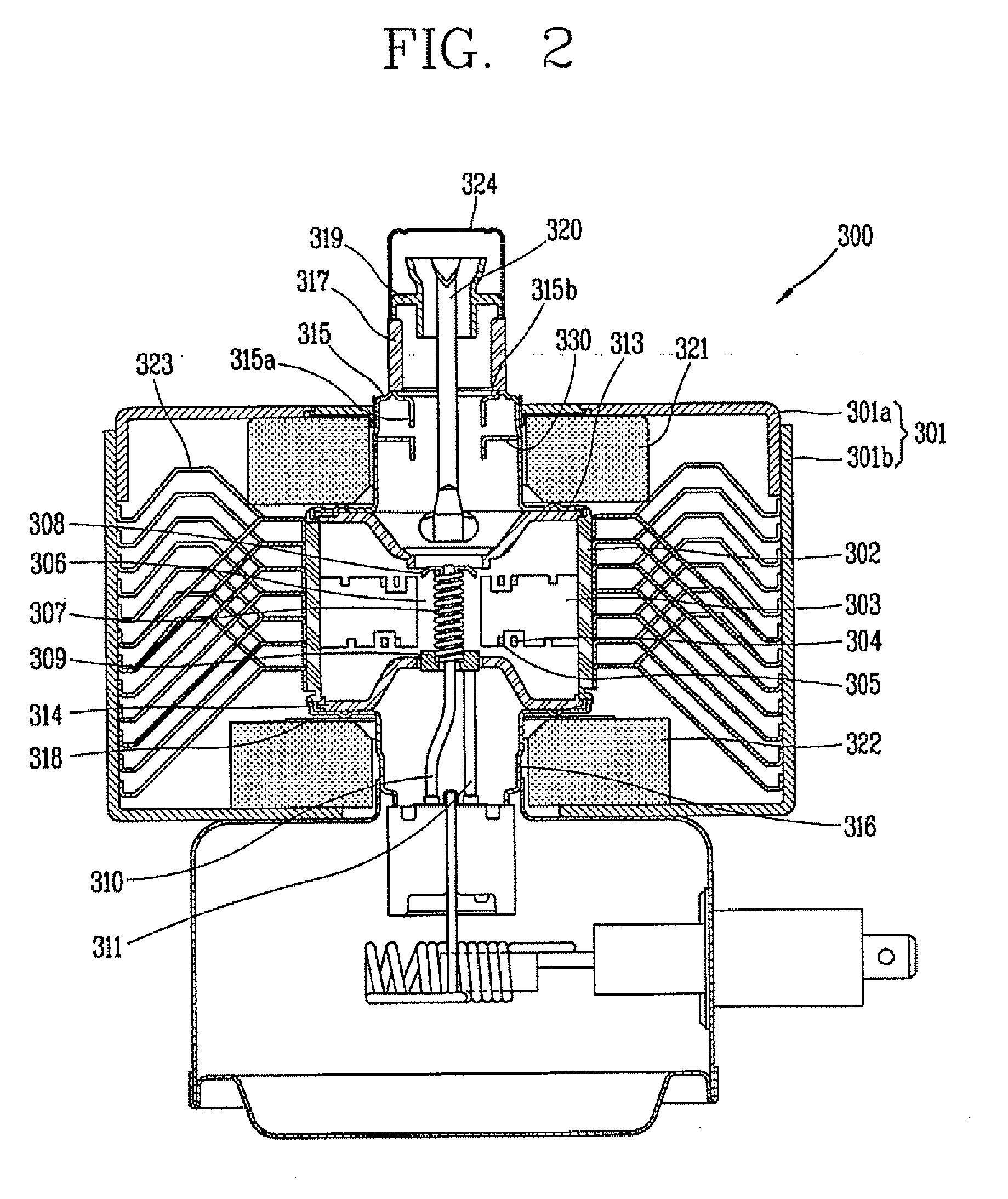
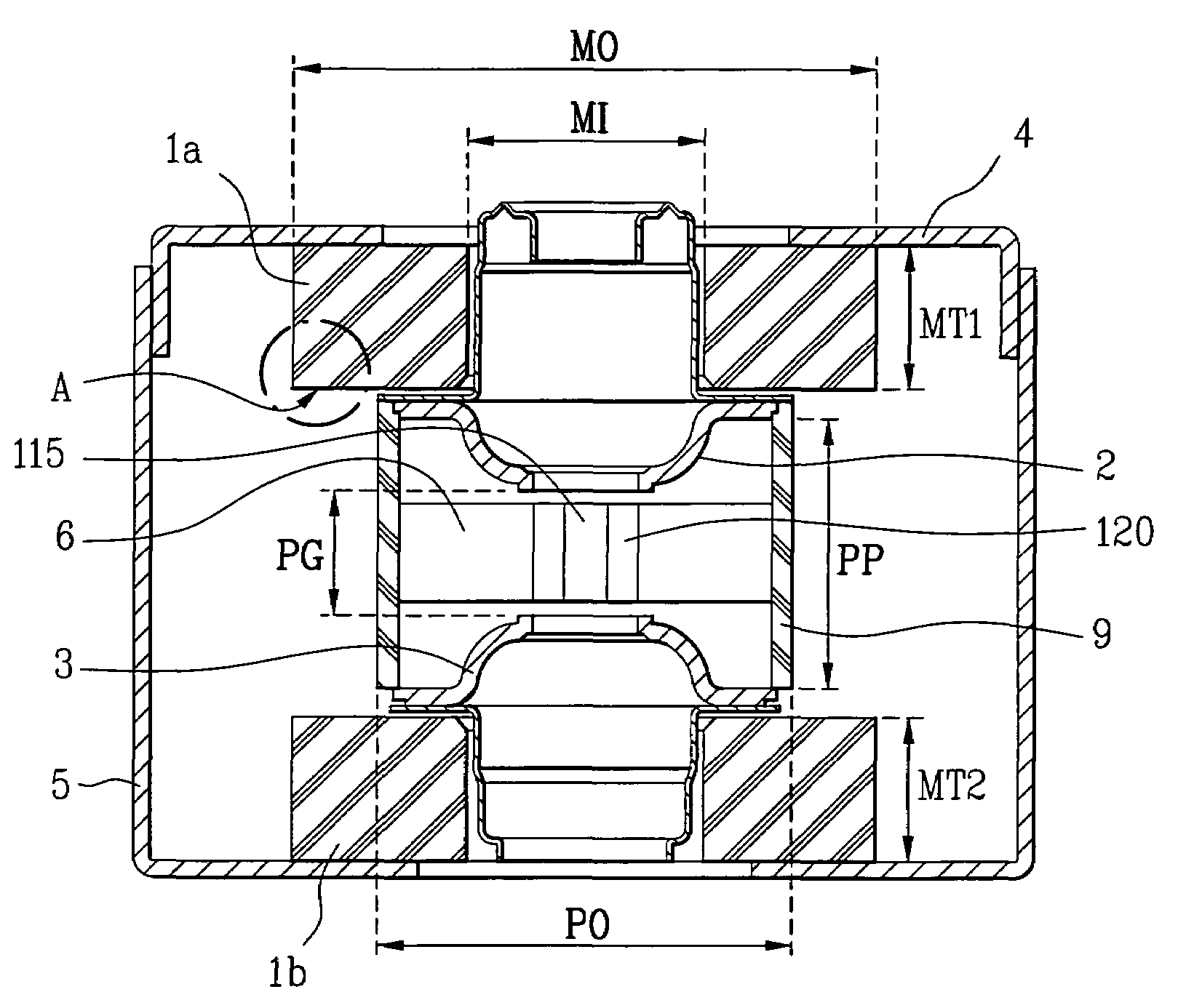
InactiveUS6847023B2Reduce the overall heightReduce insulation distanceTransit-tube leading-in arrangementsMicrowave heatingMicrowave ovenMiniaturization
A magnetron for microwave ovens including a second insulator interposed between a connection part and a bottom of a yoke to form a relatively lengthened insulation distance, or a molded insulating plate attached to a bottom of the filter box to reduce a distance between the connection part and a bottom of the filter box. In the magnetron, an entire height of the magnetron is reduced, so that a miniaturization of the magnetron can be implemented and a design of a product including the magnetron, such as a microwave oven, can be freely carried out, thus allowing an appearance of the product to be variously designed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetron for microwave oven
A magnetron for a microwave oven includes a yoke, an anode cylindrical body installed inside the yoke, a plurality of veins mounted inside the anode cylindrical body, a filament installed in a center of the veins, and an upper magnet and a lower magnet respectively mounted on an upper side and a lower side of the anode cylindrical body. The magnetron also includes an upper pole piece and a lower pole piece respectively installed between the anode cylindrical body and the upper and lower magnets. A length (L) from an external tip of a central part of the upper pole piece to an internal tip thereof, on which a hollow part is formed, is adjusted to suppress harmonics in the magnetron. Thus, generation of the harmonics may be effectively attenuated, and an output of a microwave may be enhanced by preventing power consumption of the magnetron which may be large due to interrupting harmonics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
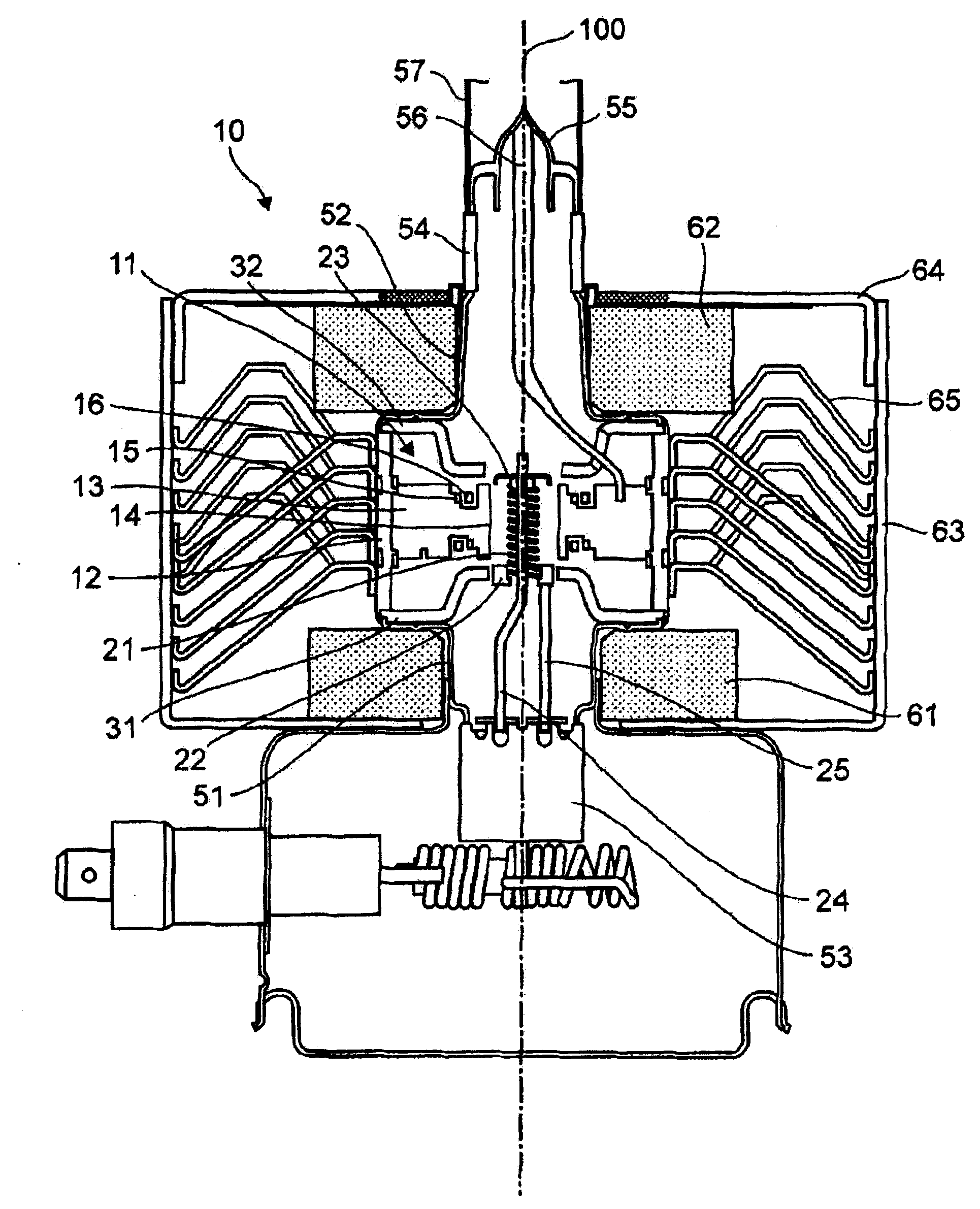
Encapsulated magnetron
ActiveUS20150048735A1Transit-tube vessels/containersAngle modulation by transit-time tubeMagnetic polesEngineering
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Magnetron
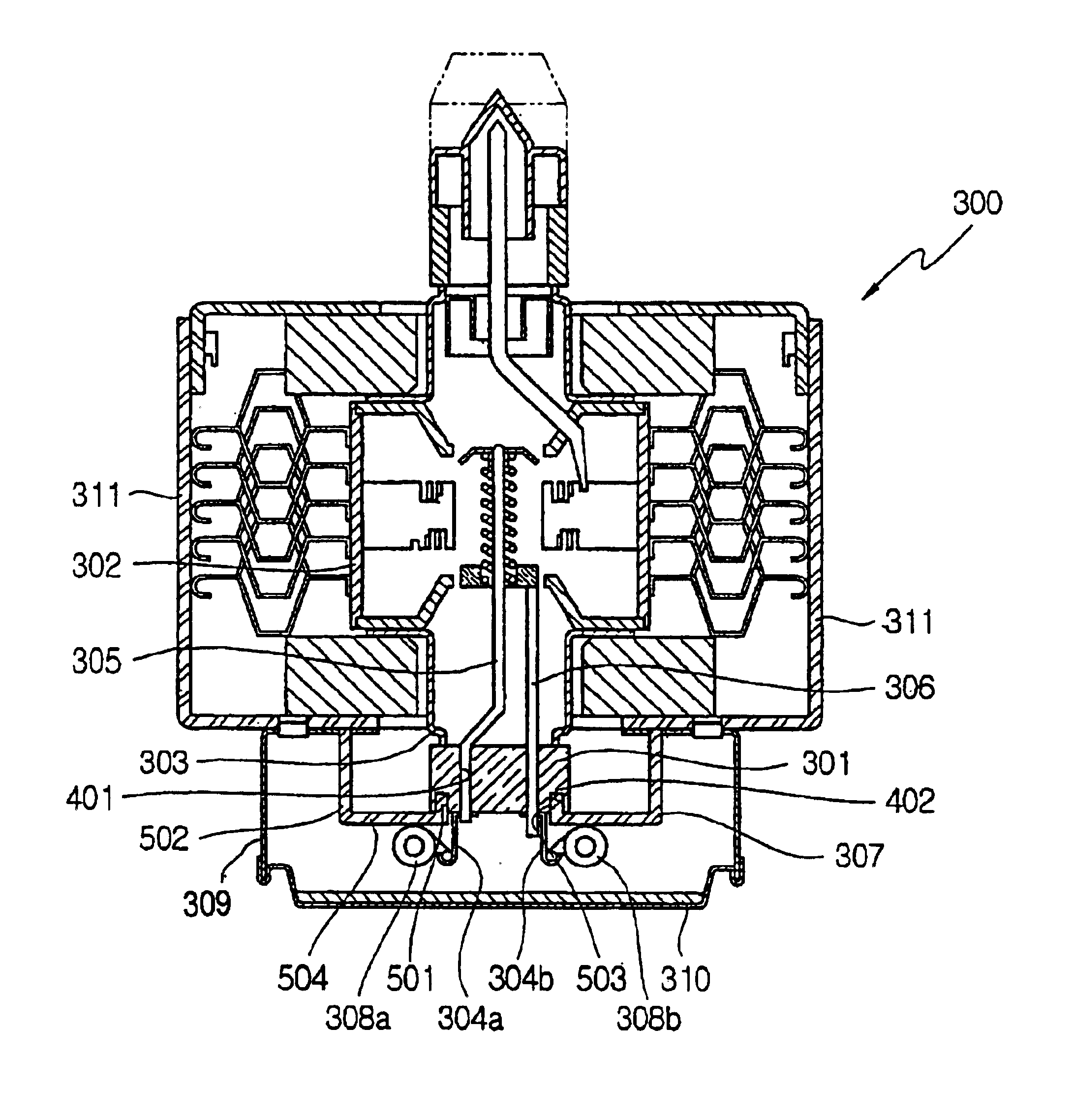
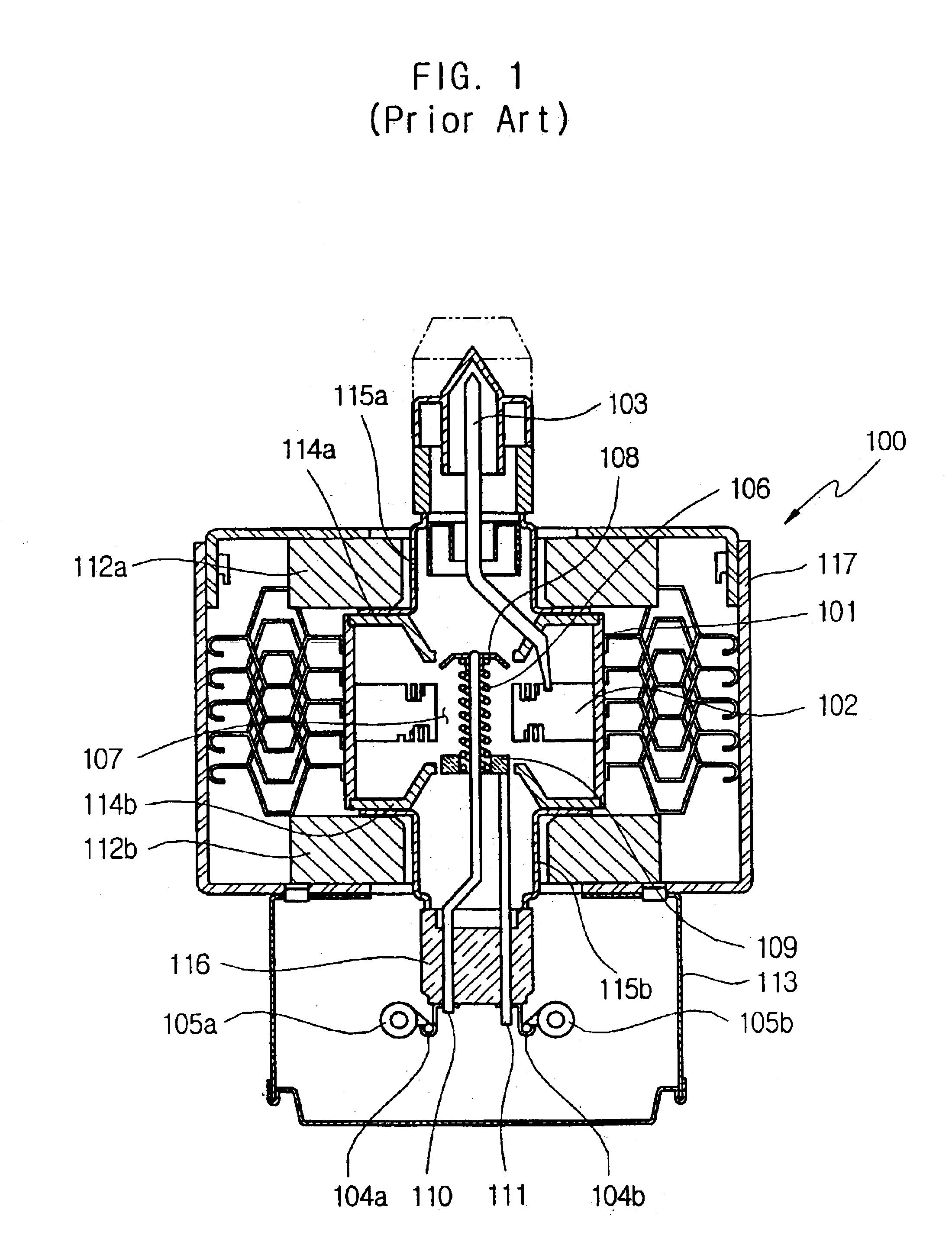
InactiveUS20070139125A1Transit-tube leading-in arrangementsPulse automatic controlRadio frequency energyEngineering
A magnetron is provided including a yoke having an internal space, a first magnet provided at one end of the internal space, a second magnet provided at a second end of the internal space, the second magnet being axially spaced from the first magnet. Further, an anode cylinder that generates radio frequency energy may be provided axially between the first and second magnets, a first pole piece and a second pole piece may be provided proximate first and second openings of the anode cylinder, respectively. Additionally, the magnetron may also include a seal that intercepts external leakage, the seal may have an inward protrusion extending axially towards the anode cylinder; and a choke filter that intercepts external leakage provided proximate the seal.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
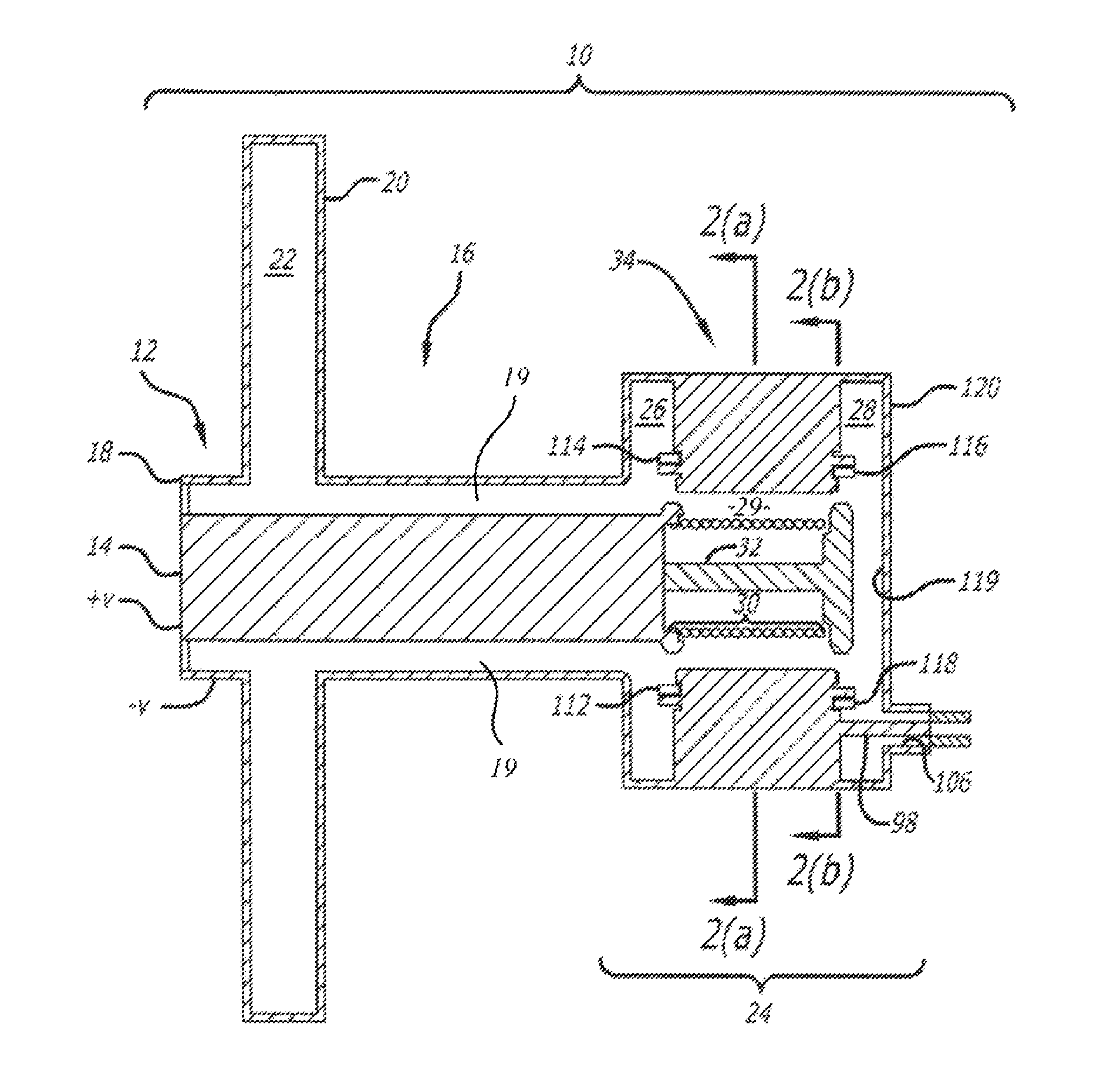
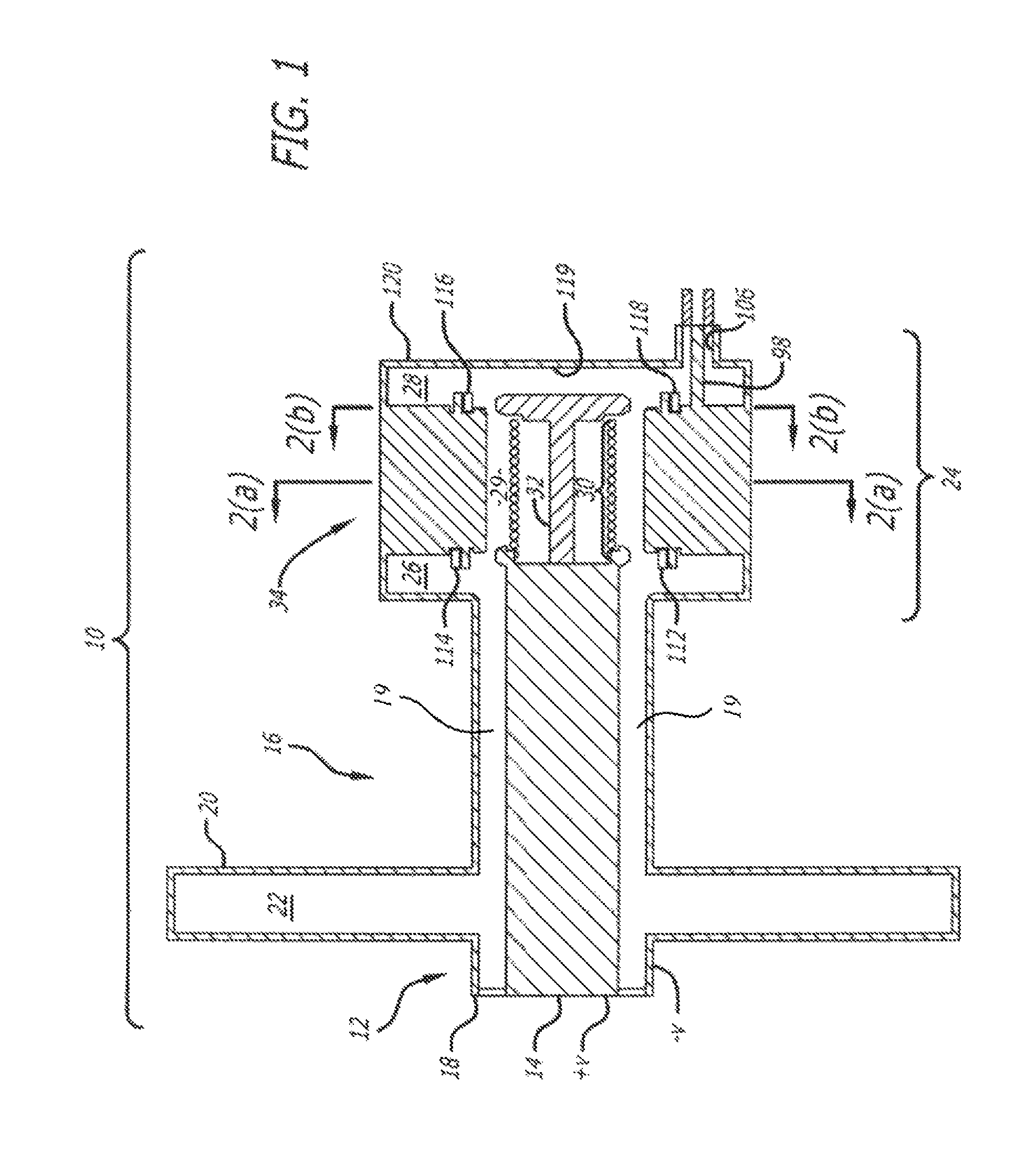
Phase and frequency locked magnetron
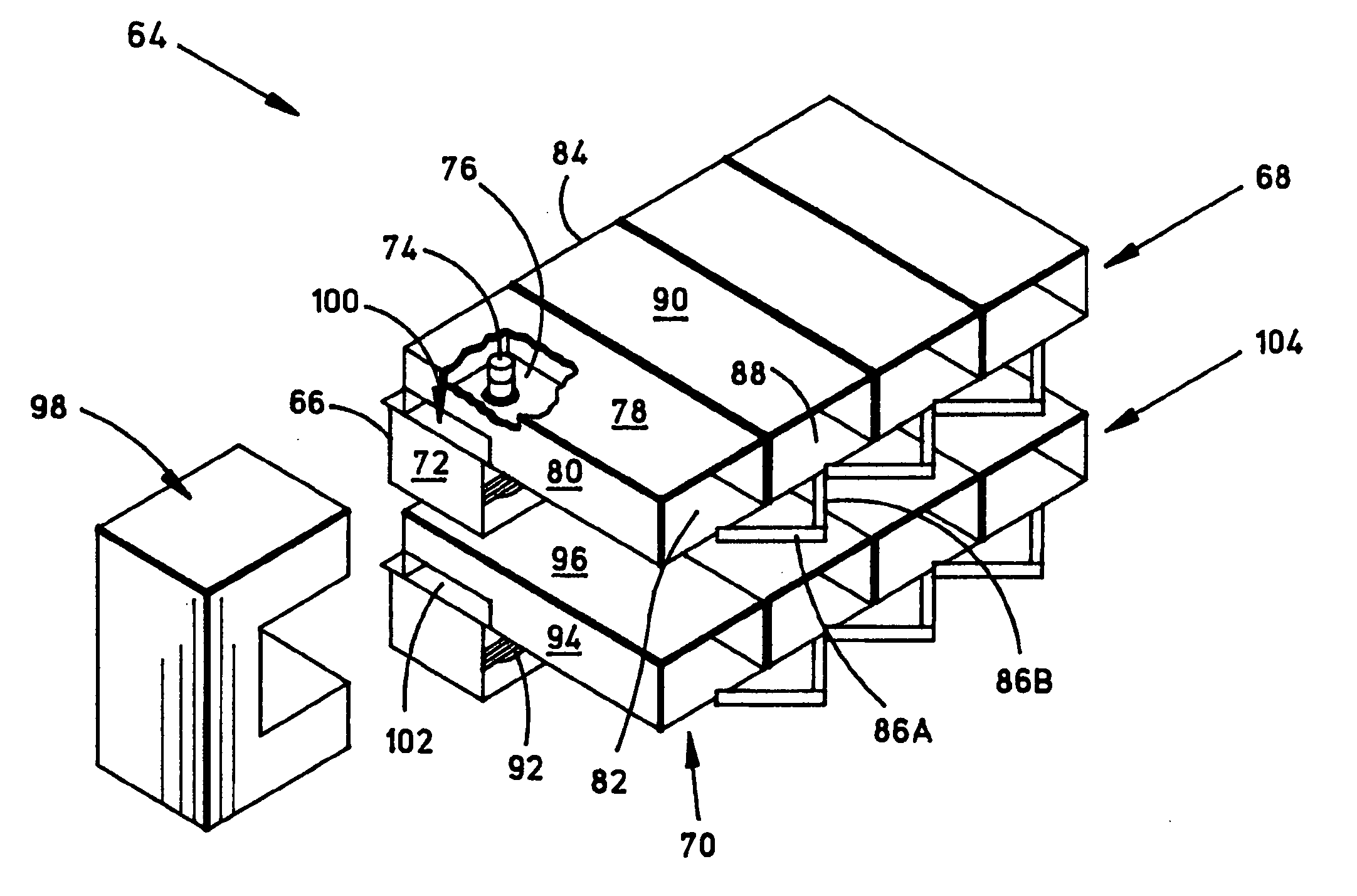
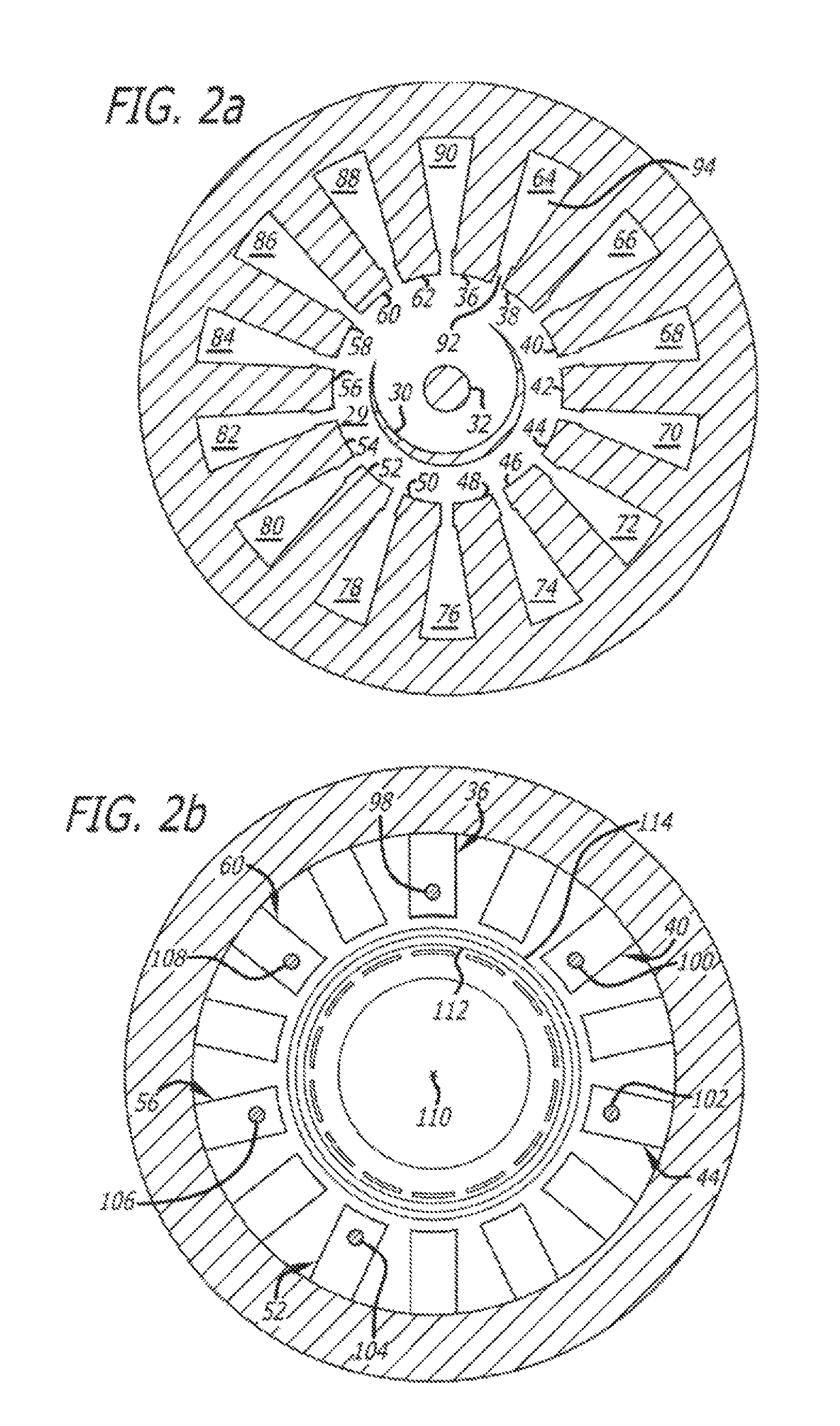
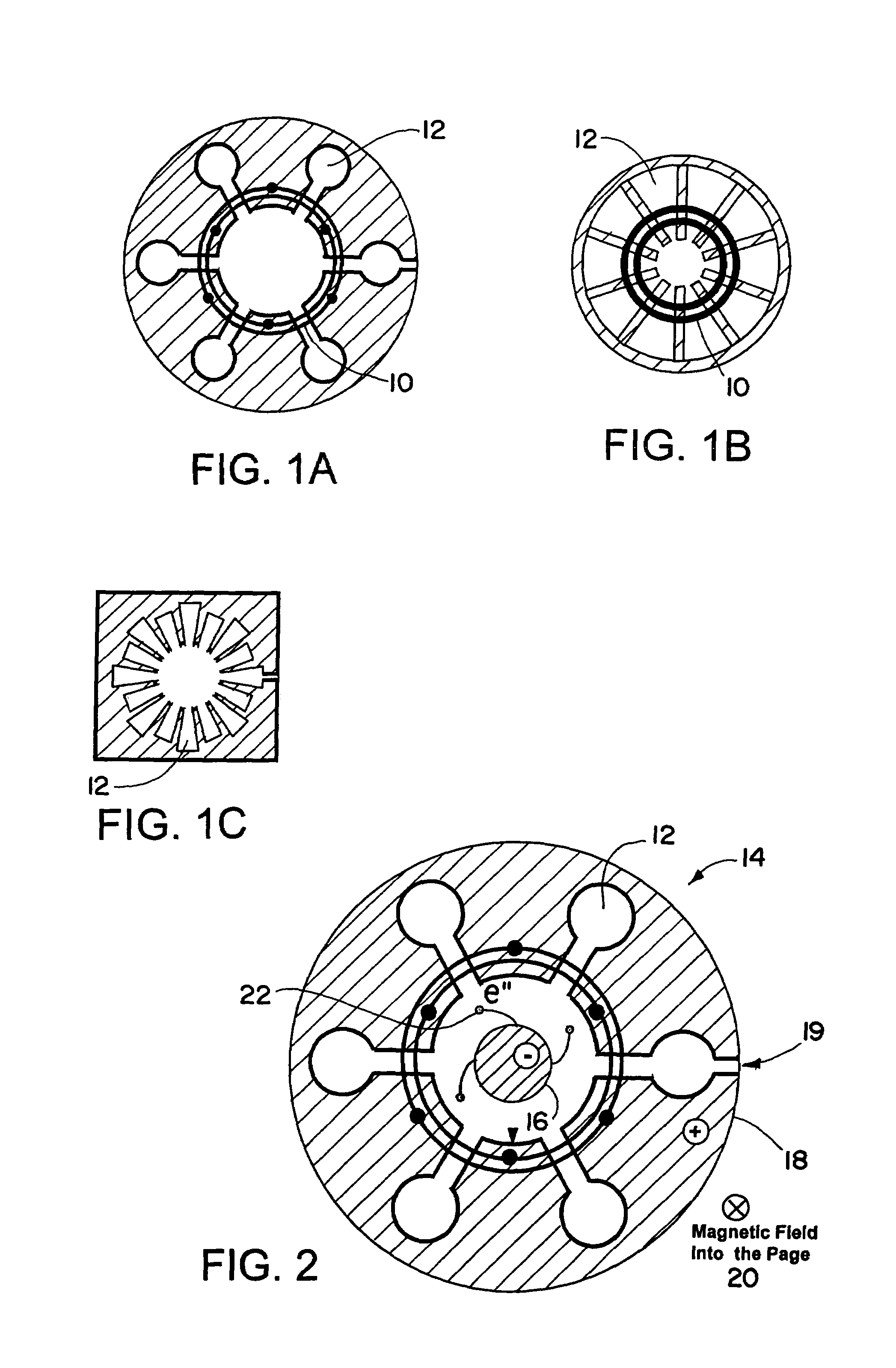
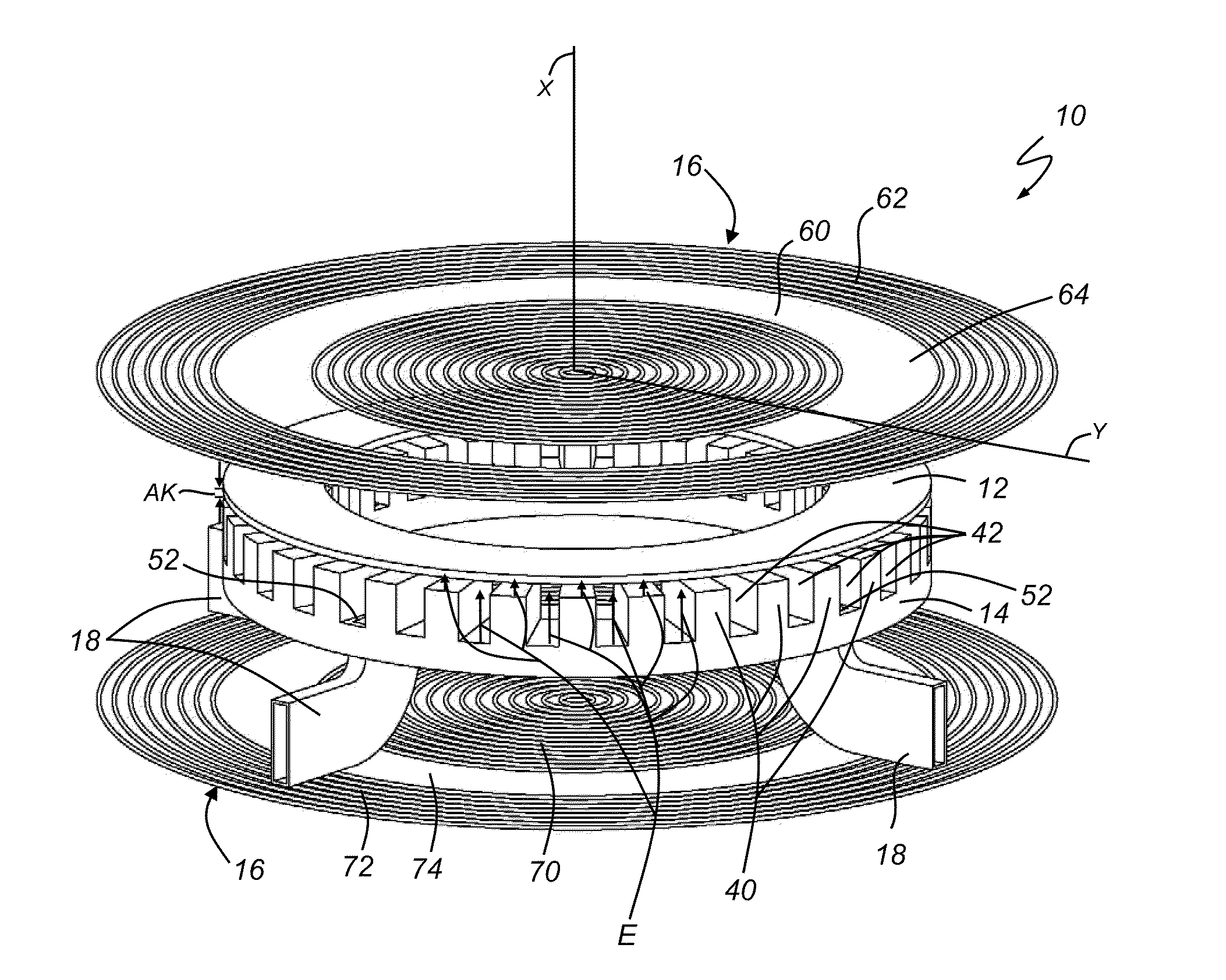
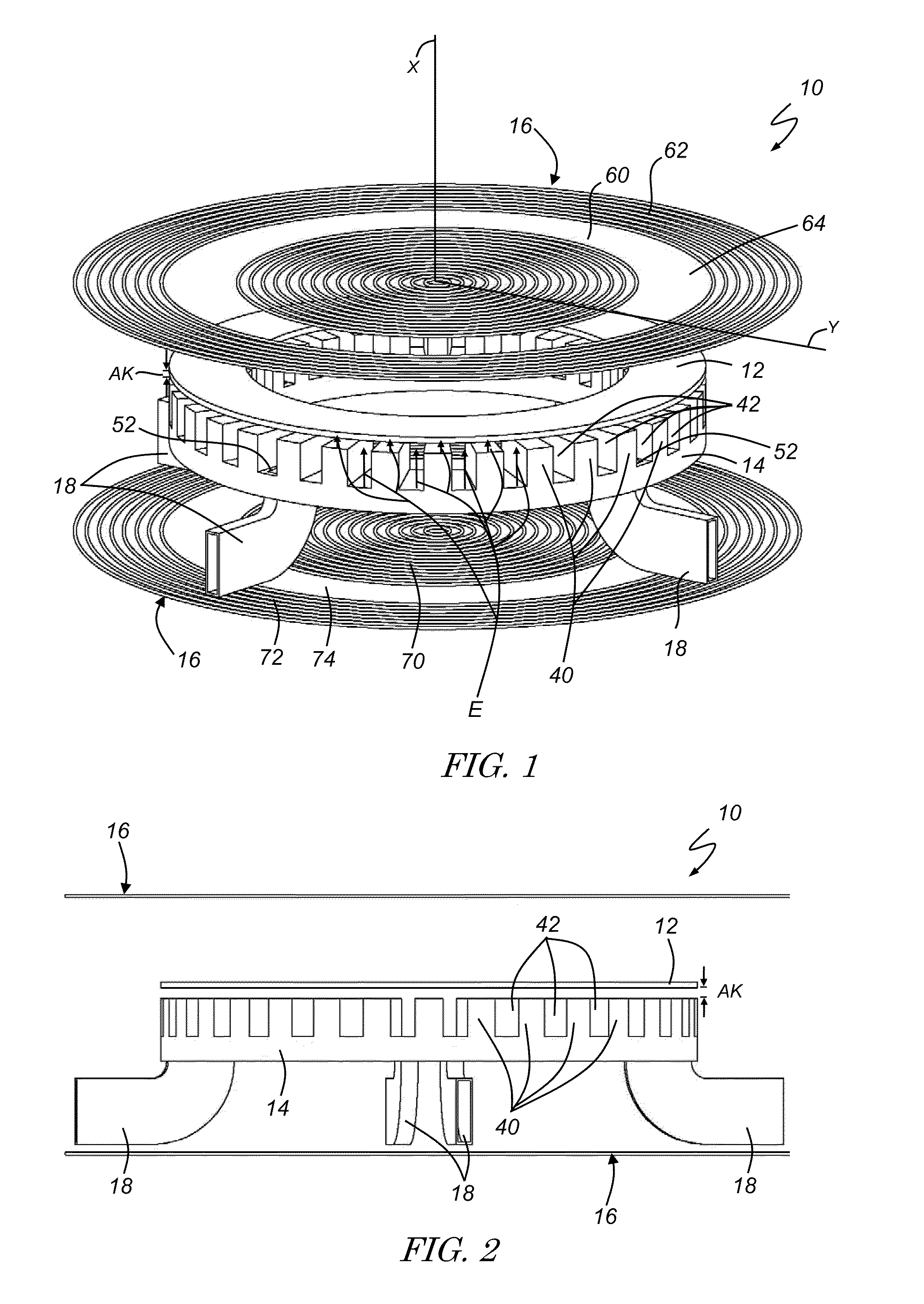
InactiveUS20110254443A1Multi-cavity magnetronsTransit-tube coupling devicesParticle acceleratorAccelerated particle
A magnetron of improved performance capable of stabilizing the frequency and phase of magnetron output for use in particle accelerators and other applications. Thin variable-permeability blocks are attached inside the resonant anode structures of a standard magnetron design. A variable bias electromagnet, with field orthogonal in direction to the RF magnetic field, is used to vary the permeability of each block and therefore the resonant frequency of each anode structure. An electronic feedback control circuit adjusts the bias magnetic fields to lock in the frequency and phase of the magnetron output to an external low-level reference signal. Such devices may be used to provide synchronized high-power RF to many locations (e.g. the RF cavities of a particle accelerator), while requiring the distribution only of electrical power and an appropriate low-level RF reference signal.
Owner:MUONS
Magnetron
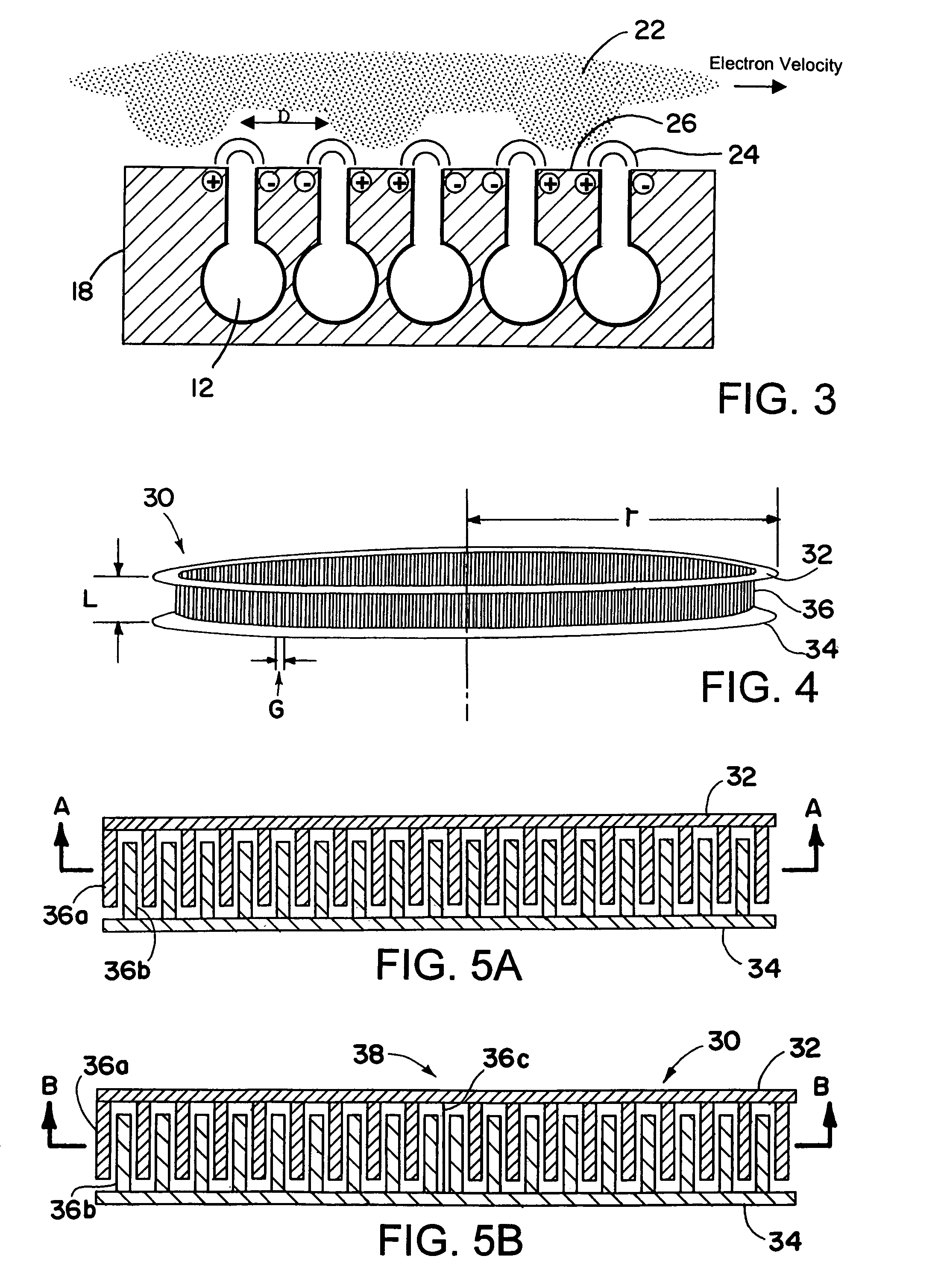
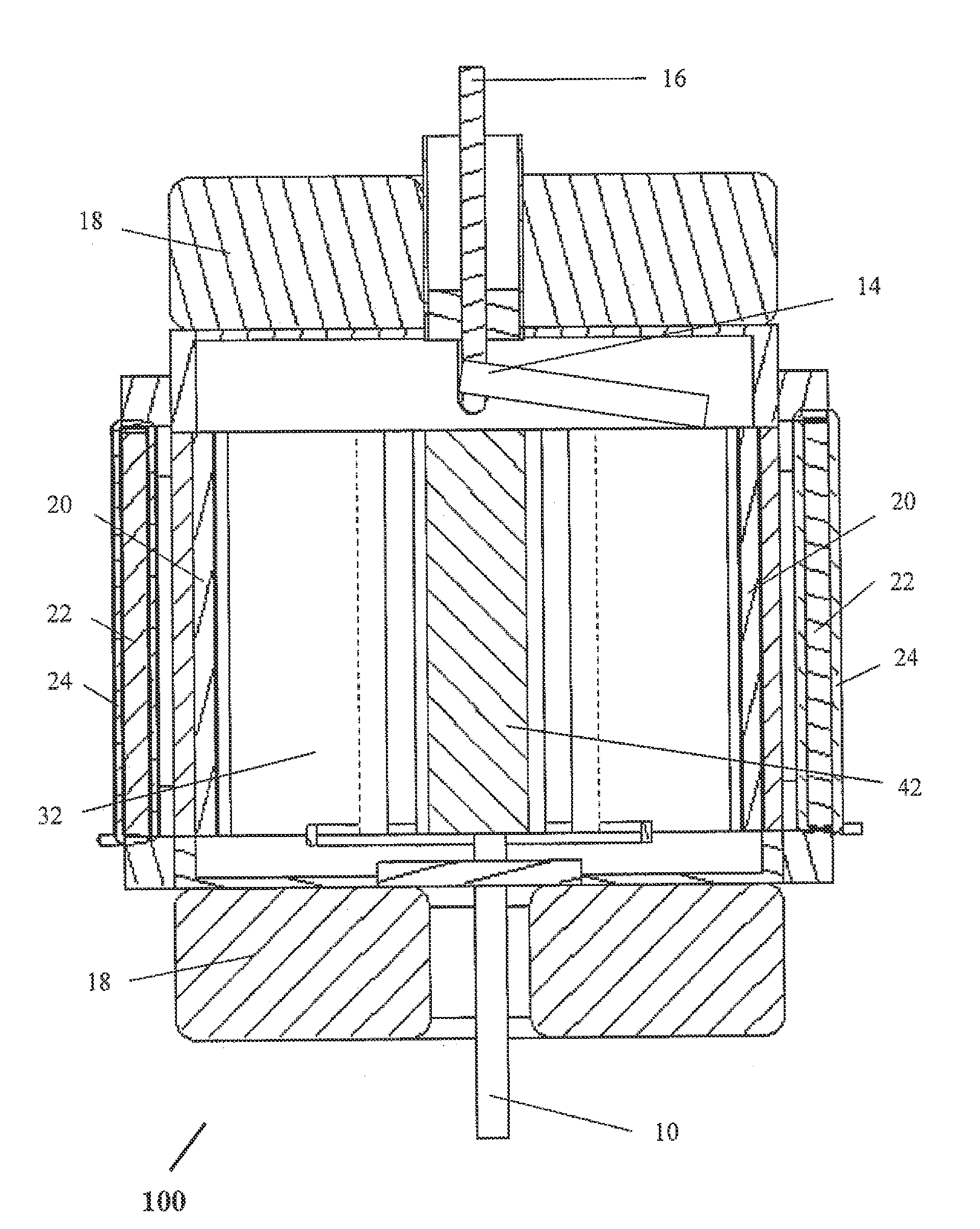
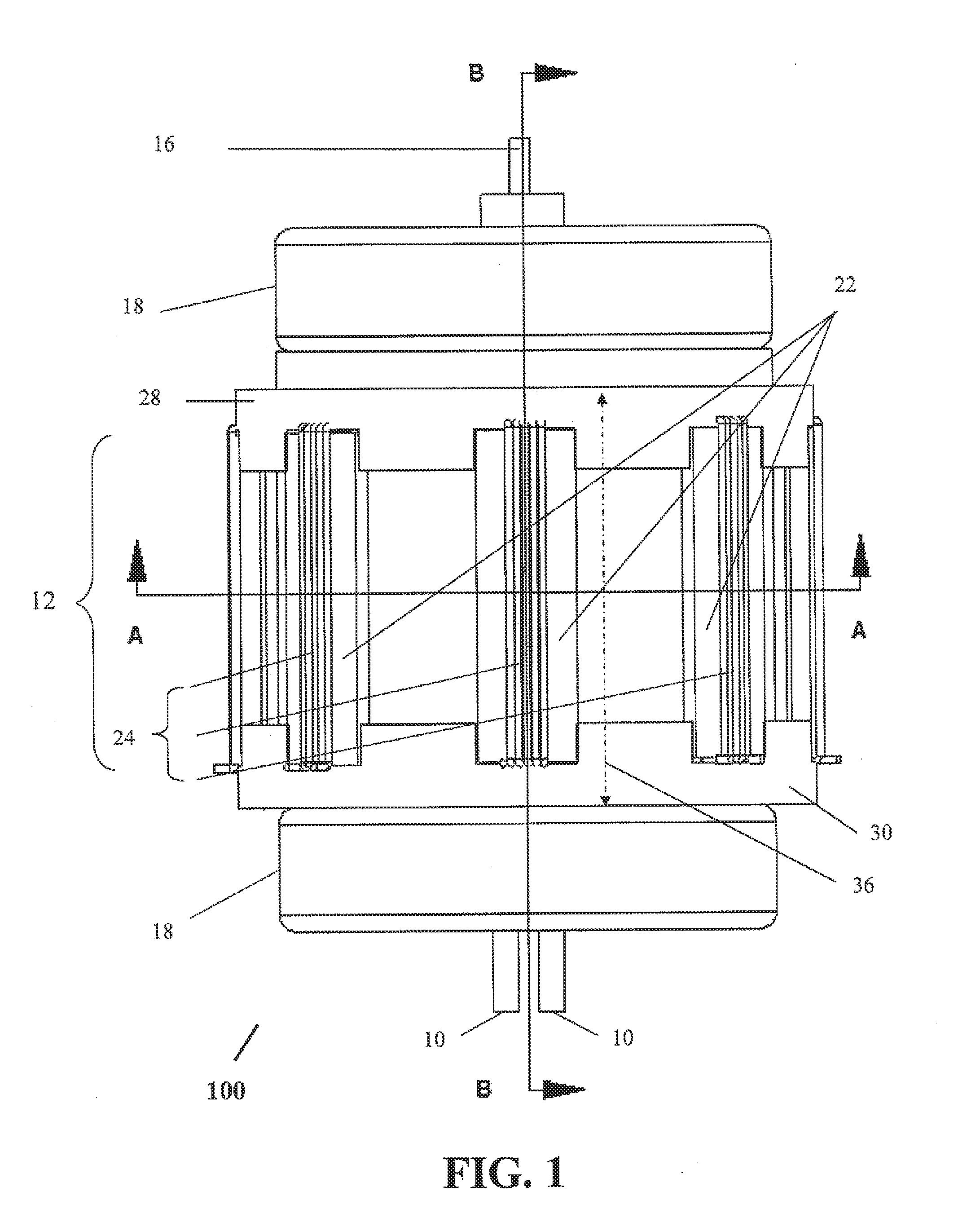
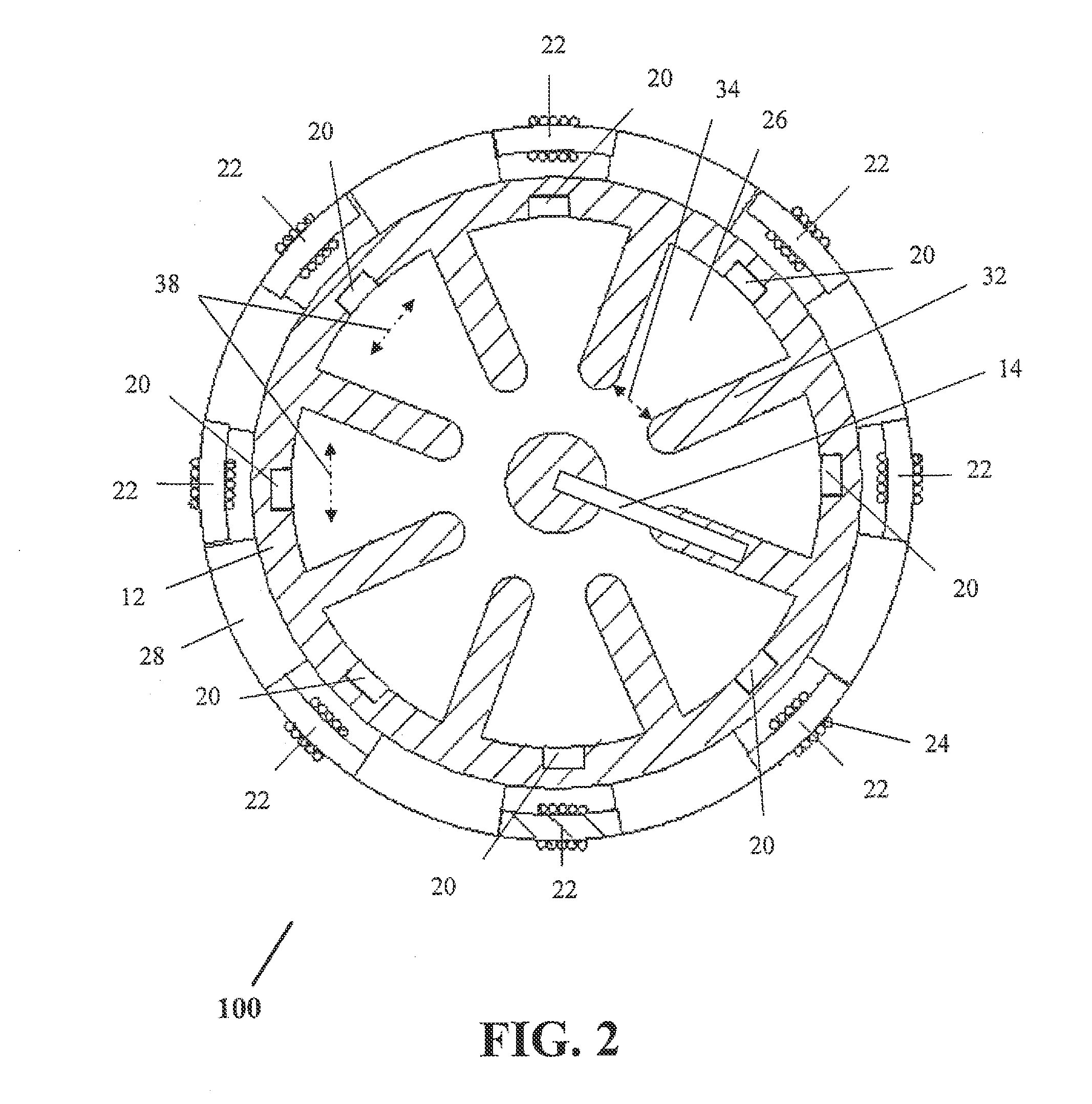
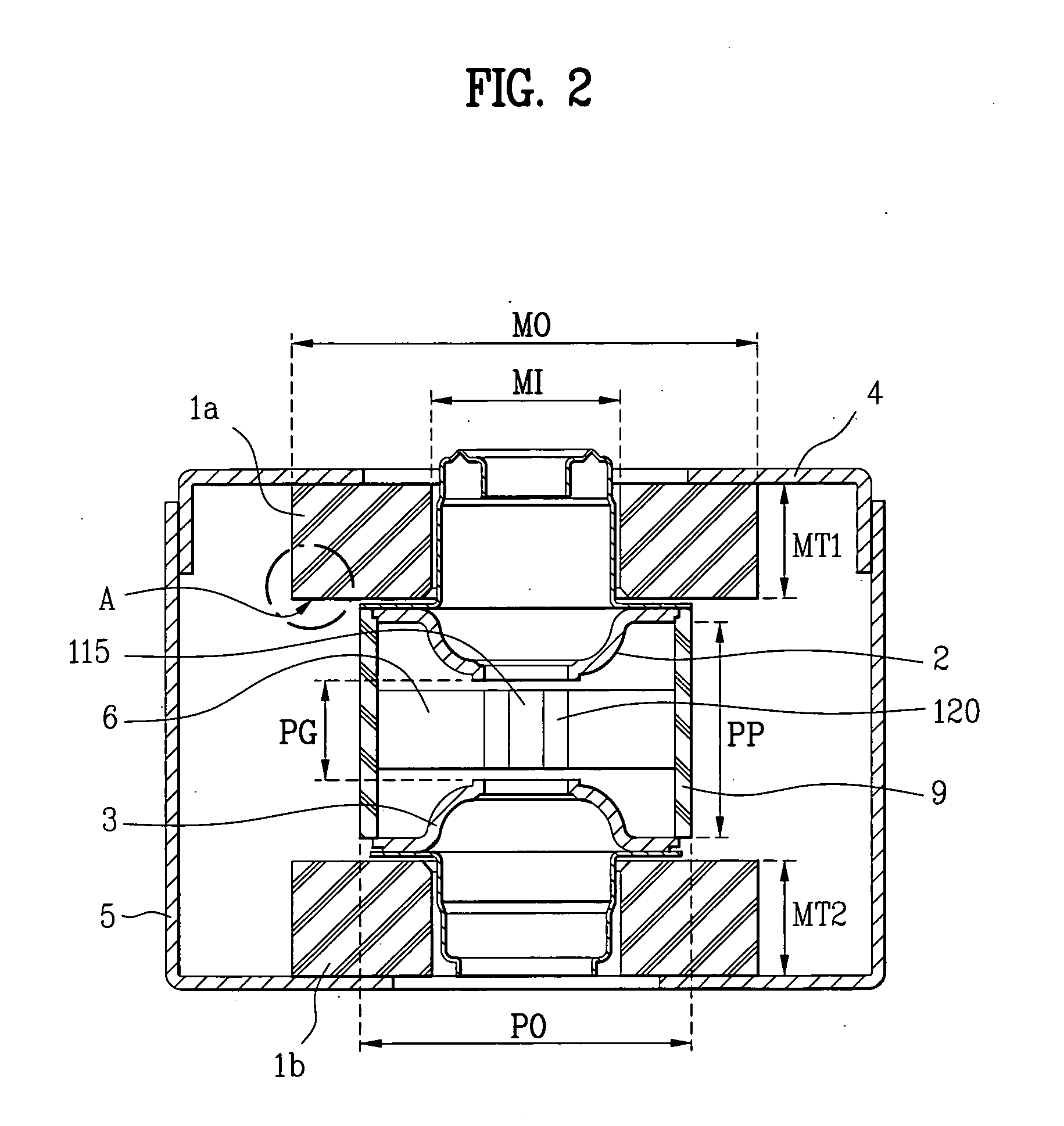
ActiveUS20060220566A1Reduce reflectionReduce mismatchMulti-cavity magnetronsTransit-tube coupling devicesCapacitanceResonant cavity
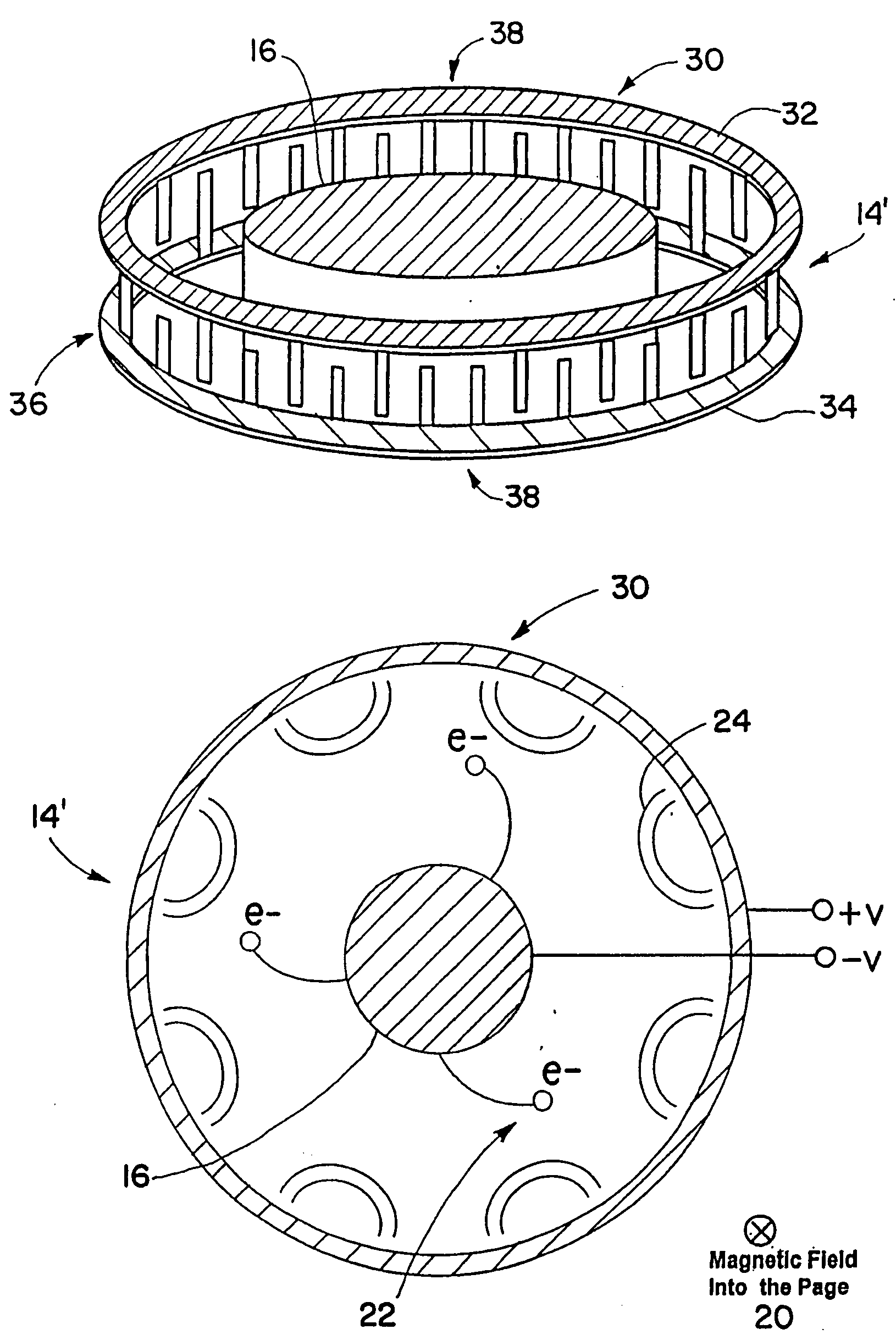
In a magnetron having a body 1 defining an anode 2 divided into resonant cavities 4 by vanes 3 and having a coaxial cathode 5, r.f. energy produced when a magnetic field is applied parallel to the axis of the anode is launched along a waveguide 8 by an antenna 6 in an evacuated region of the magnetron closed by a dielectric window 19. The latter has sector shaped conducting areas on its surface symmetrically arranged with respect to the antenna, the inductance of which balance the capacitance of the dielectric window, thereby reducing reflections at the window.
Owner:E2V TECH (UK) LTD
Magnetron
InactiveUS20060219548A1Small sizeReduce output capacityCellsTransit-tube vessels/containersMagnetic polesPhysics
Disclosed herein is a magnetron. The magnetron comprises an anode cylinder, upper and lower magnets provided to upper and lower portions of the anode cylinder, and upper and lower magnetic poles connected to the magnets, respectively. Each of the magnets has an inner diameter of 19˜21 mm, a thickness of 11.5˜12.5 mm, and an outer diameter of 50˜54 mm.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
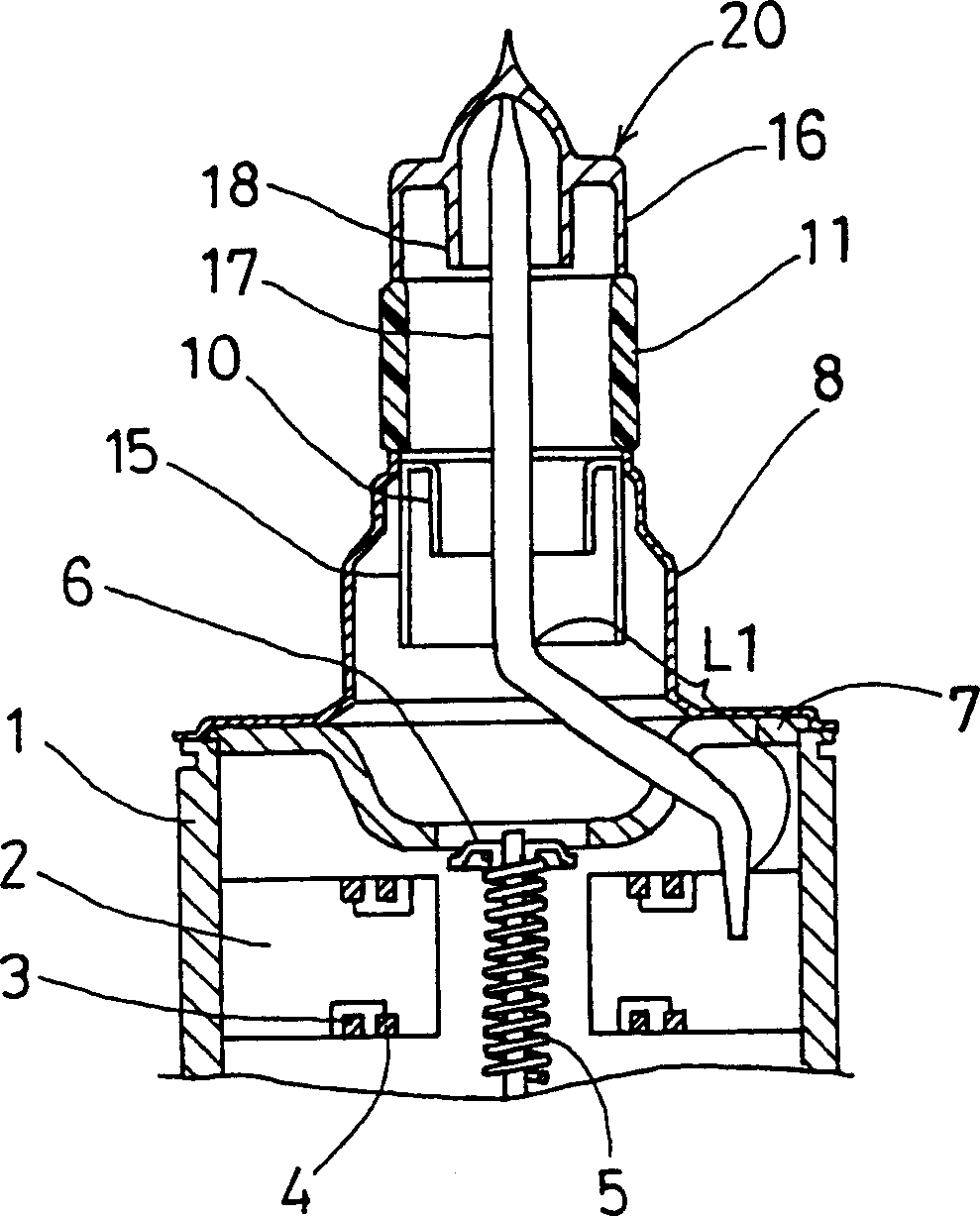
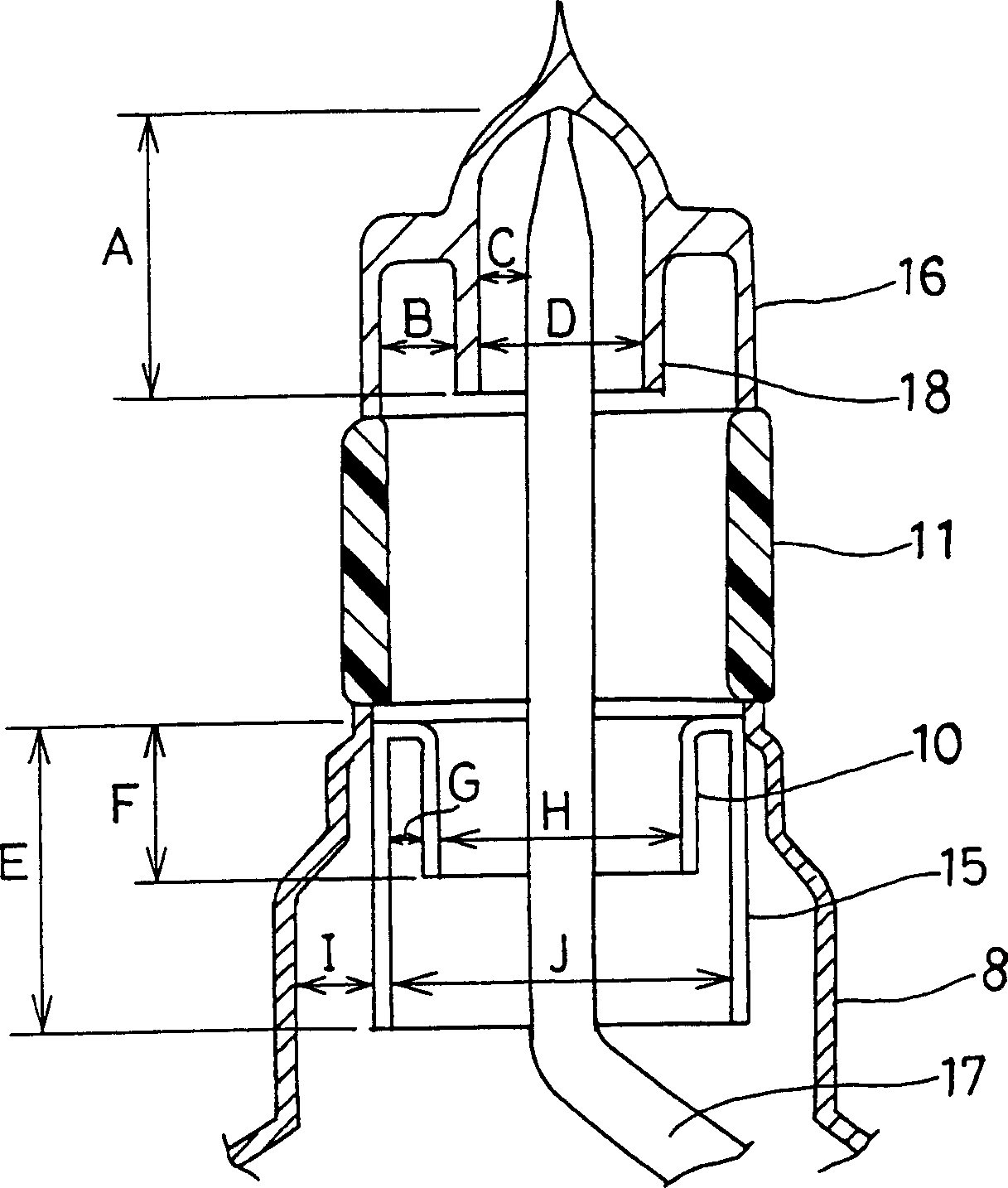
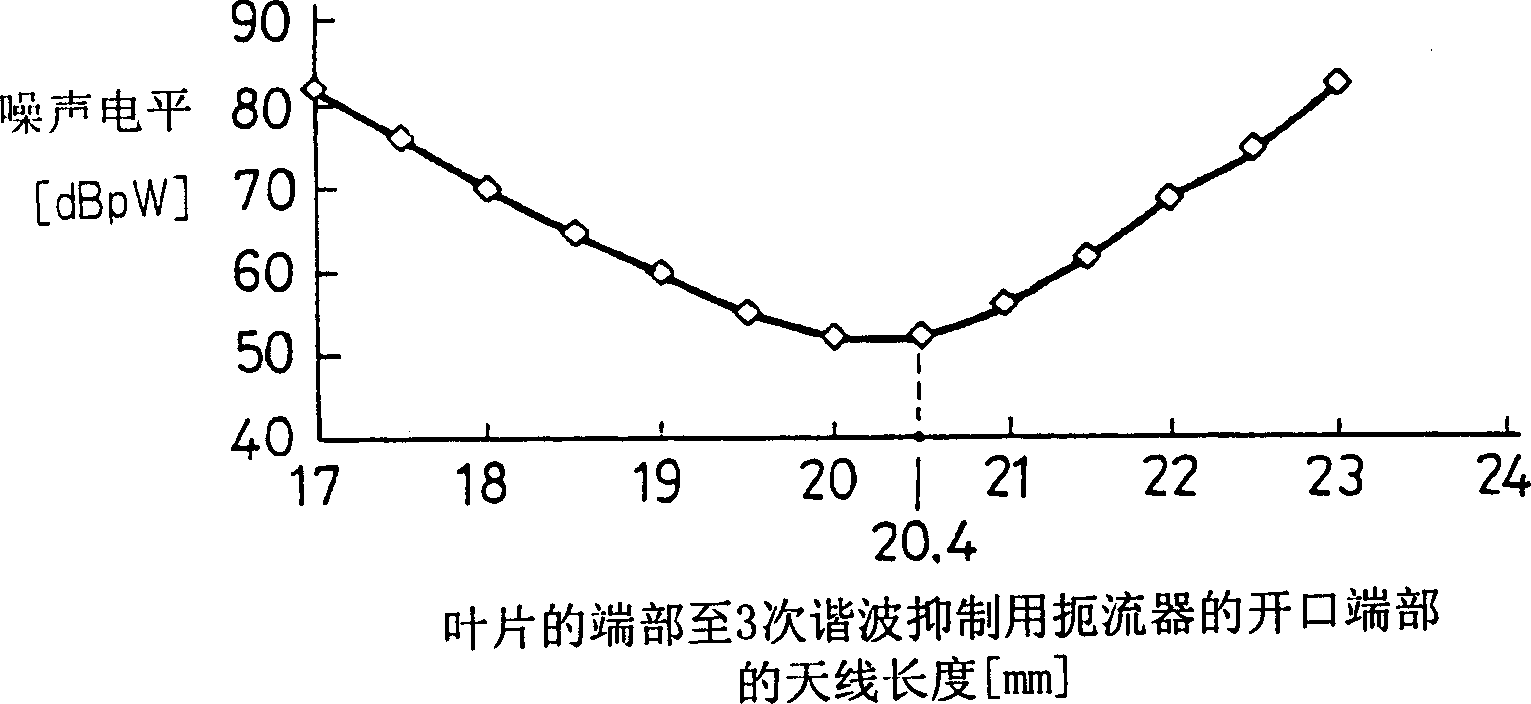
Magnetron
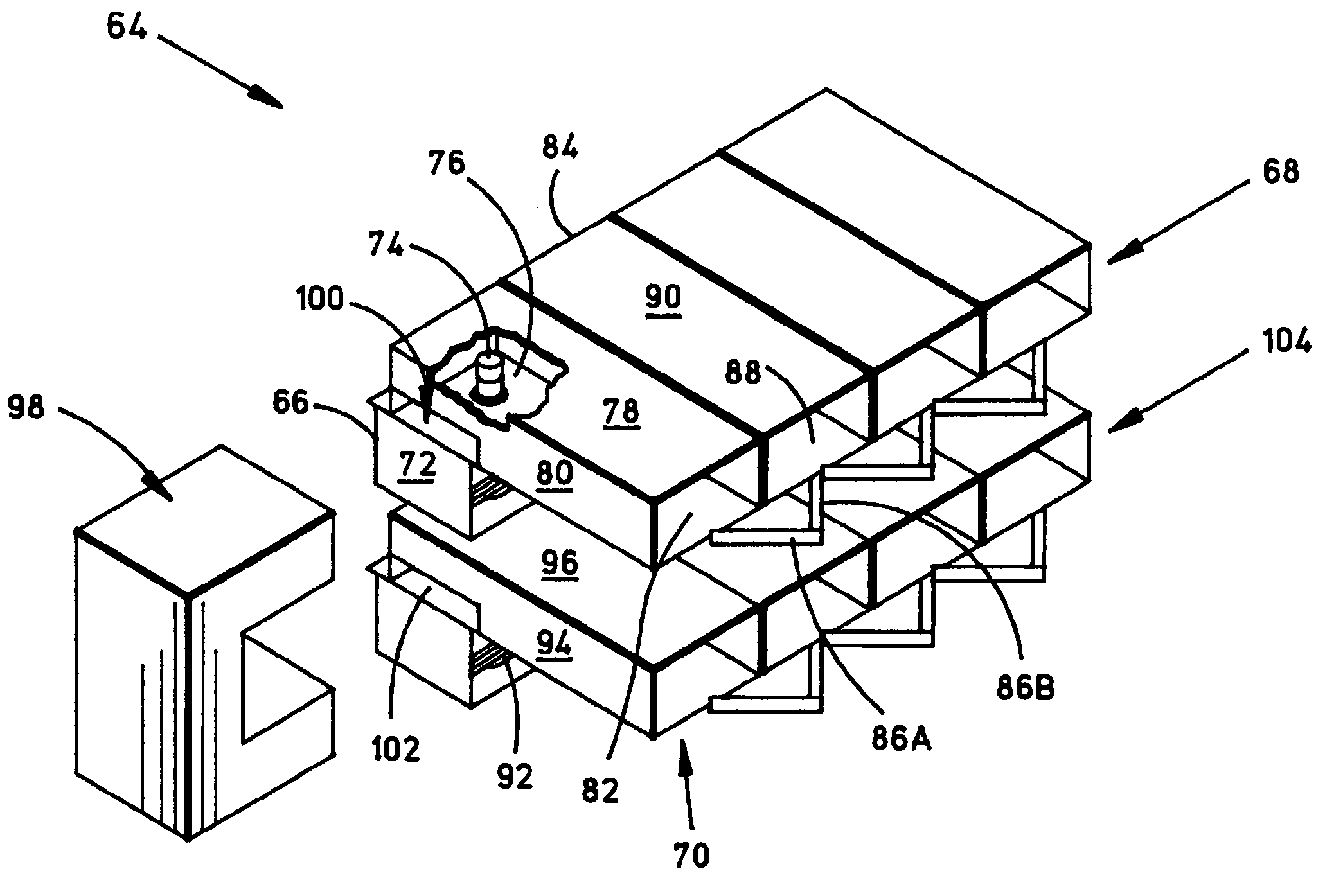
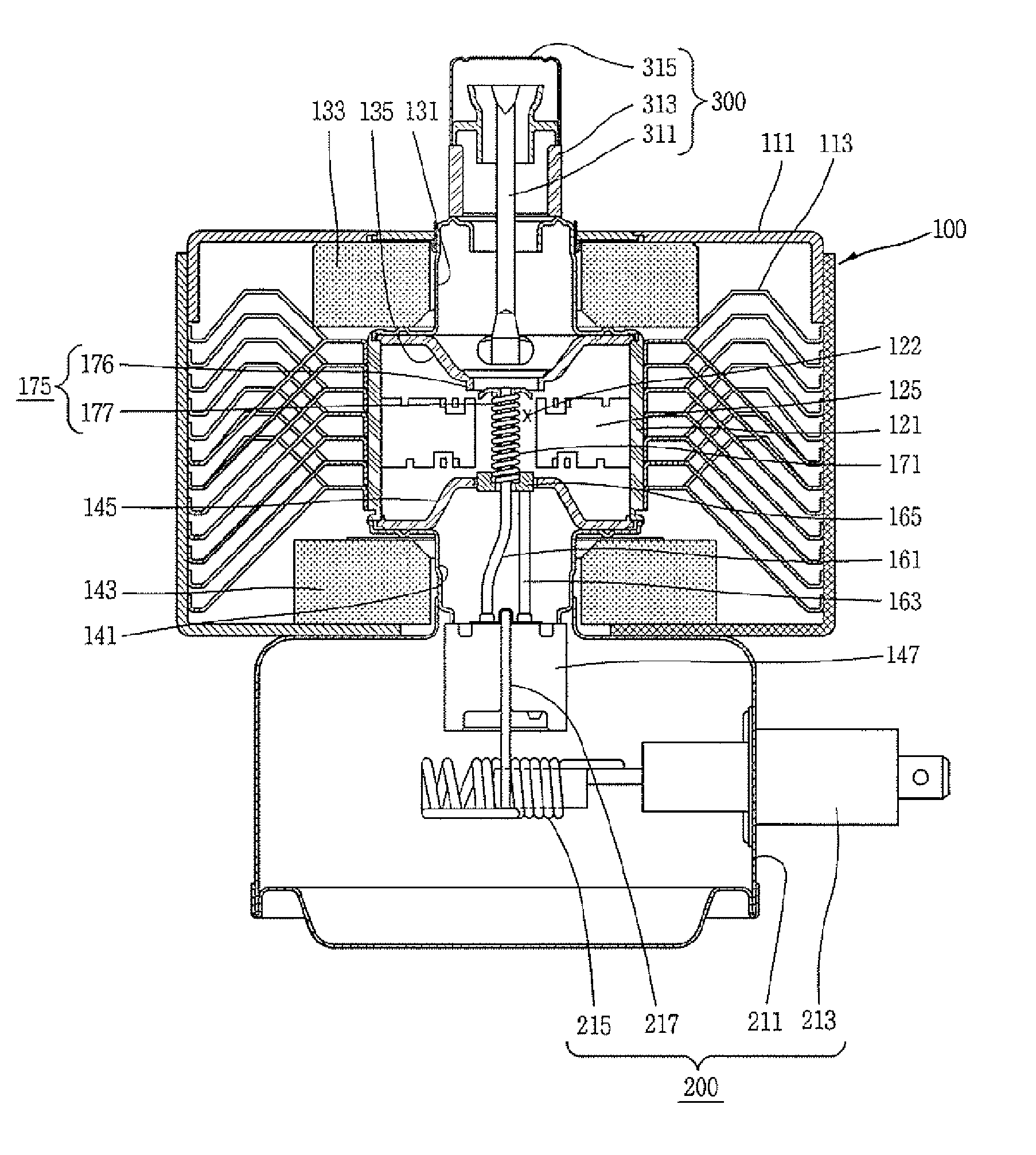
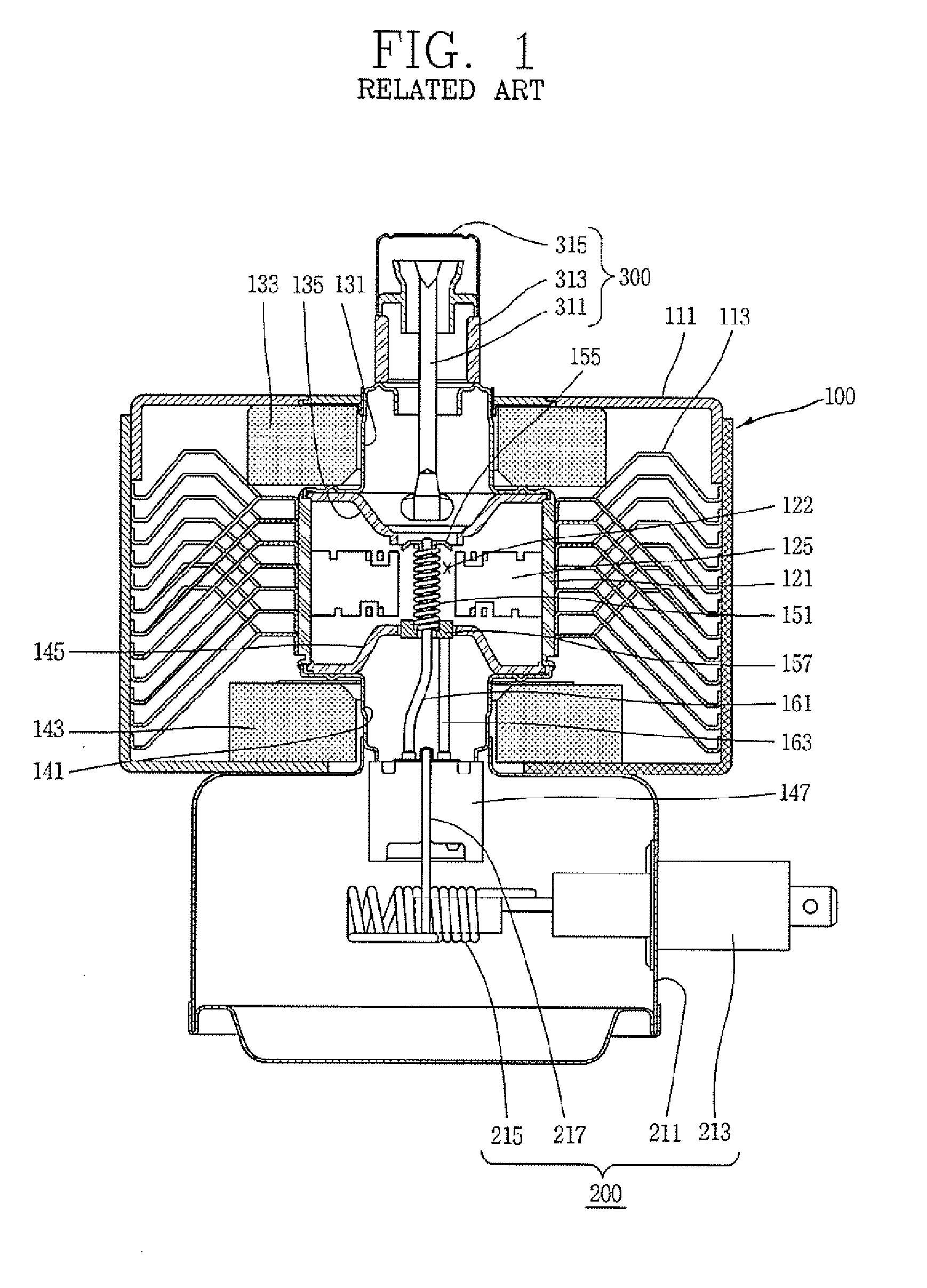
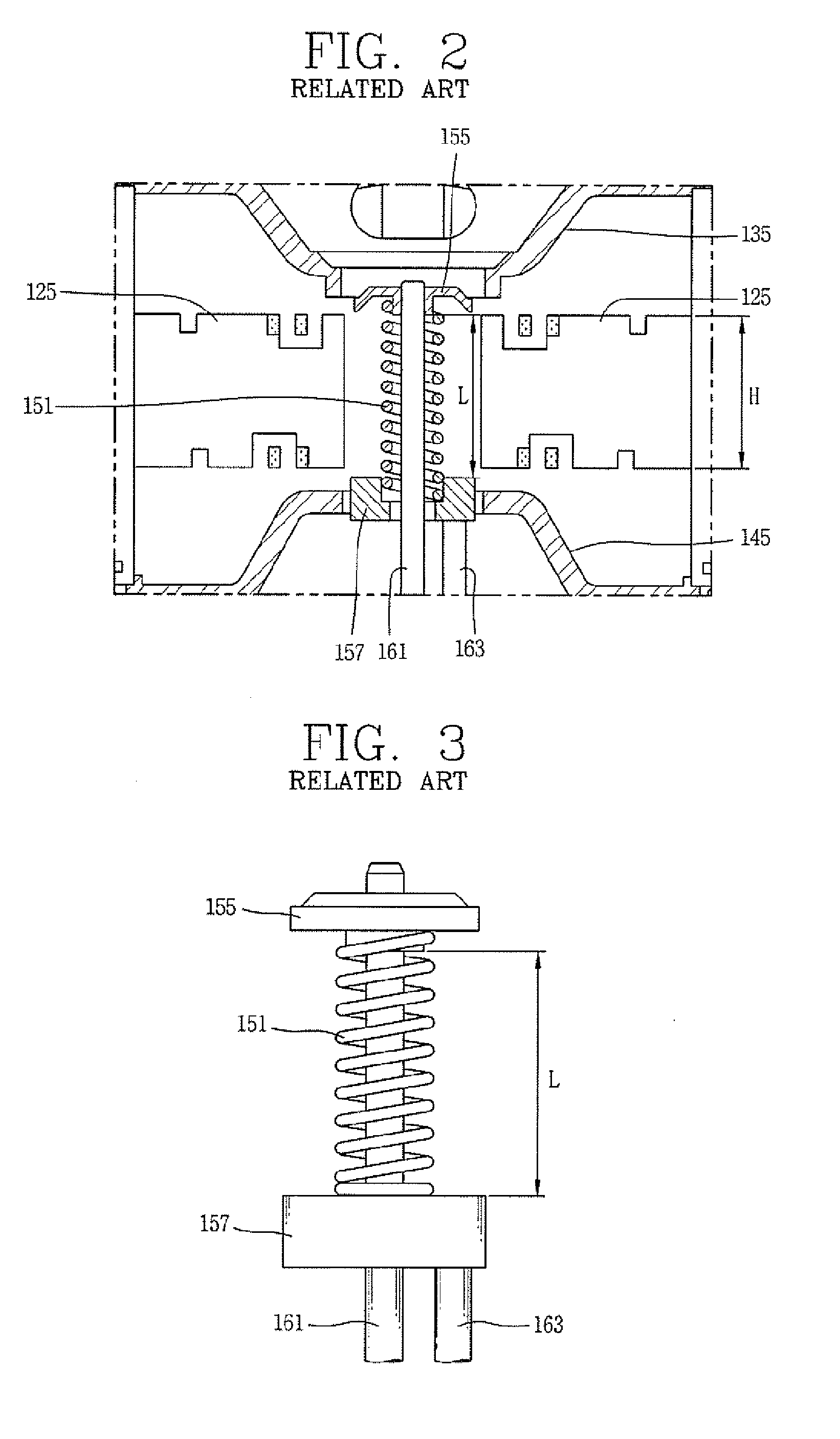
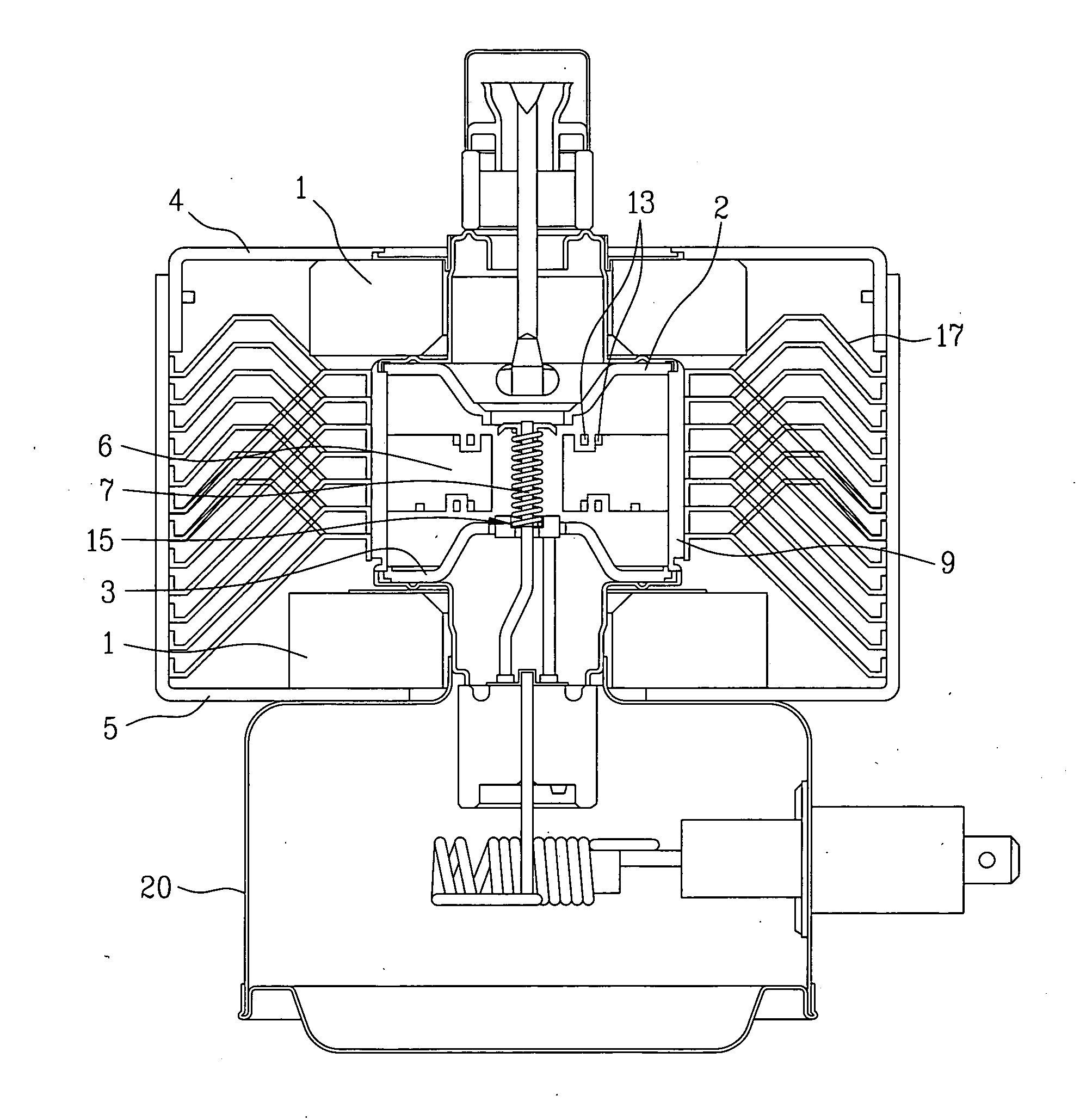
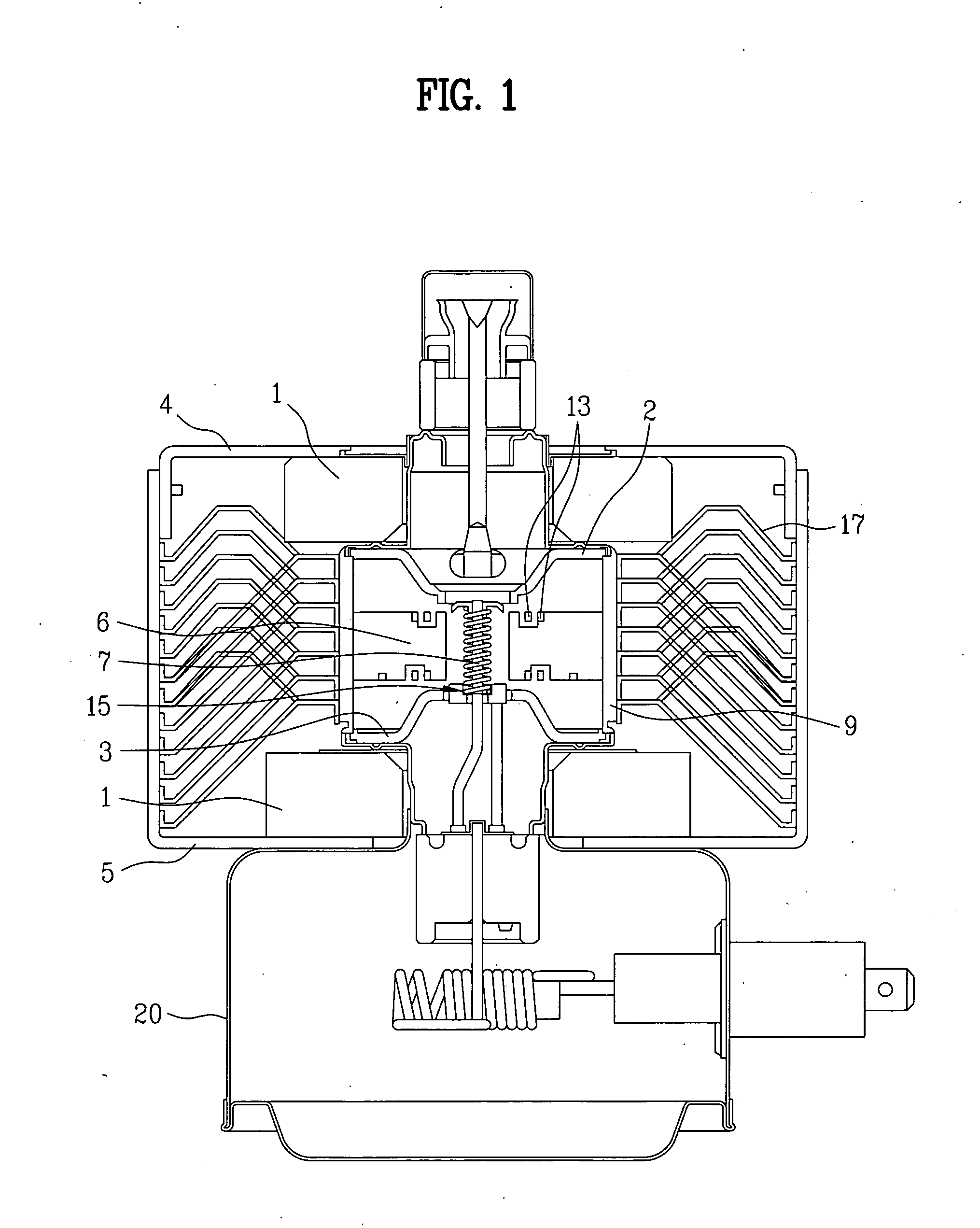
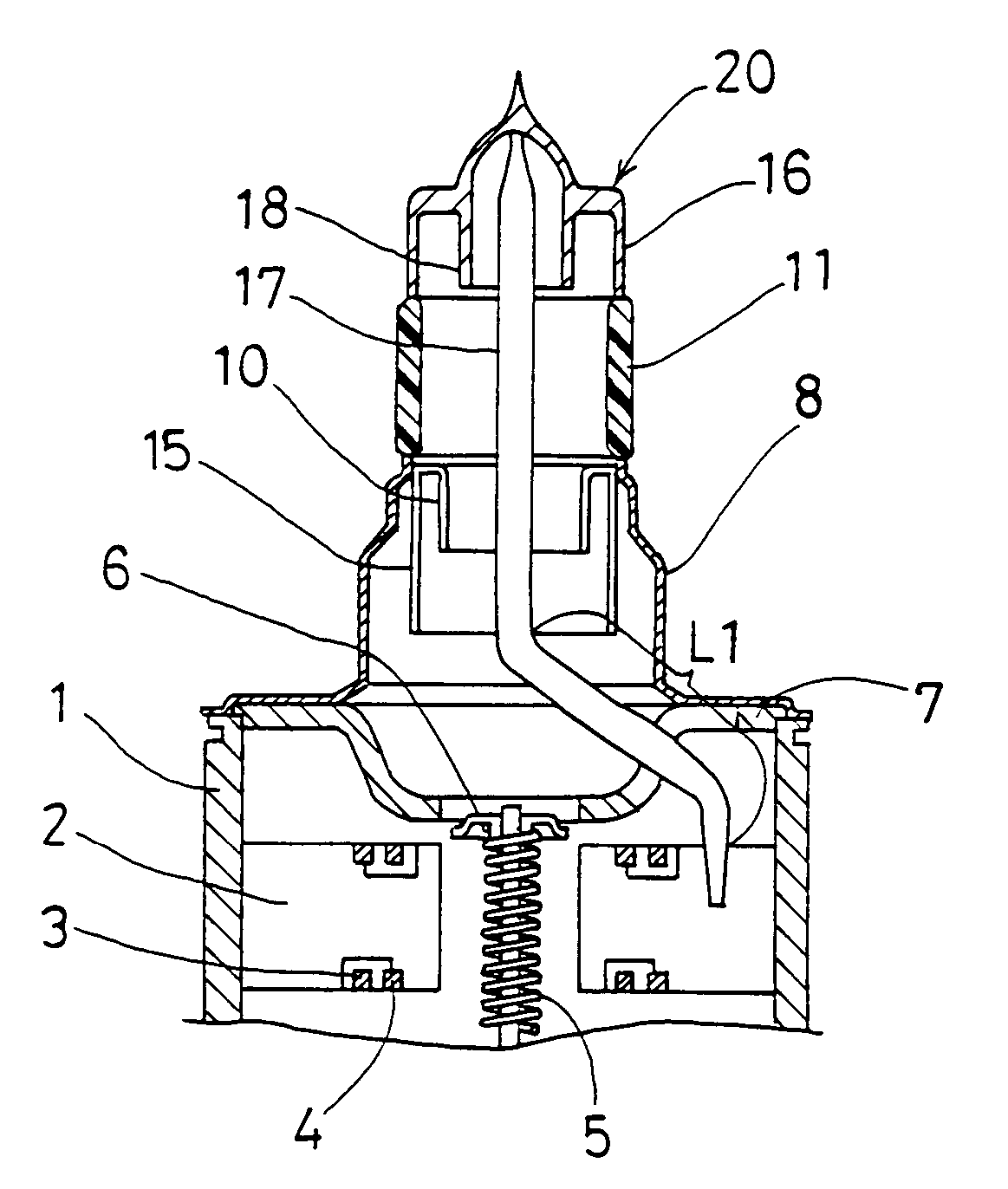
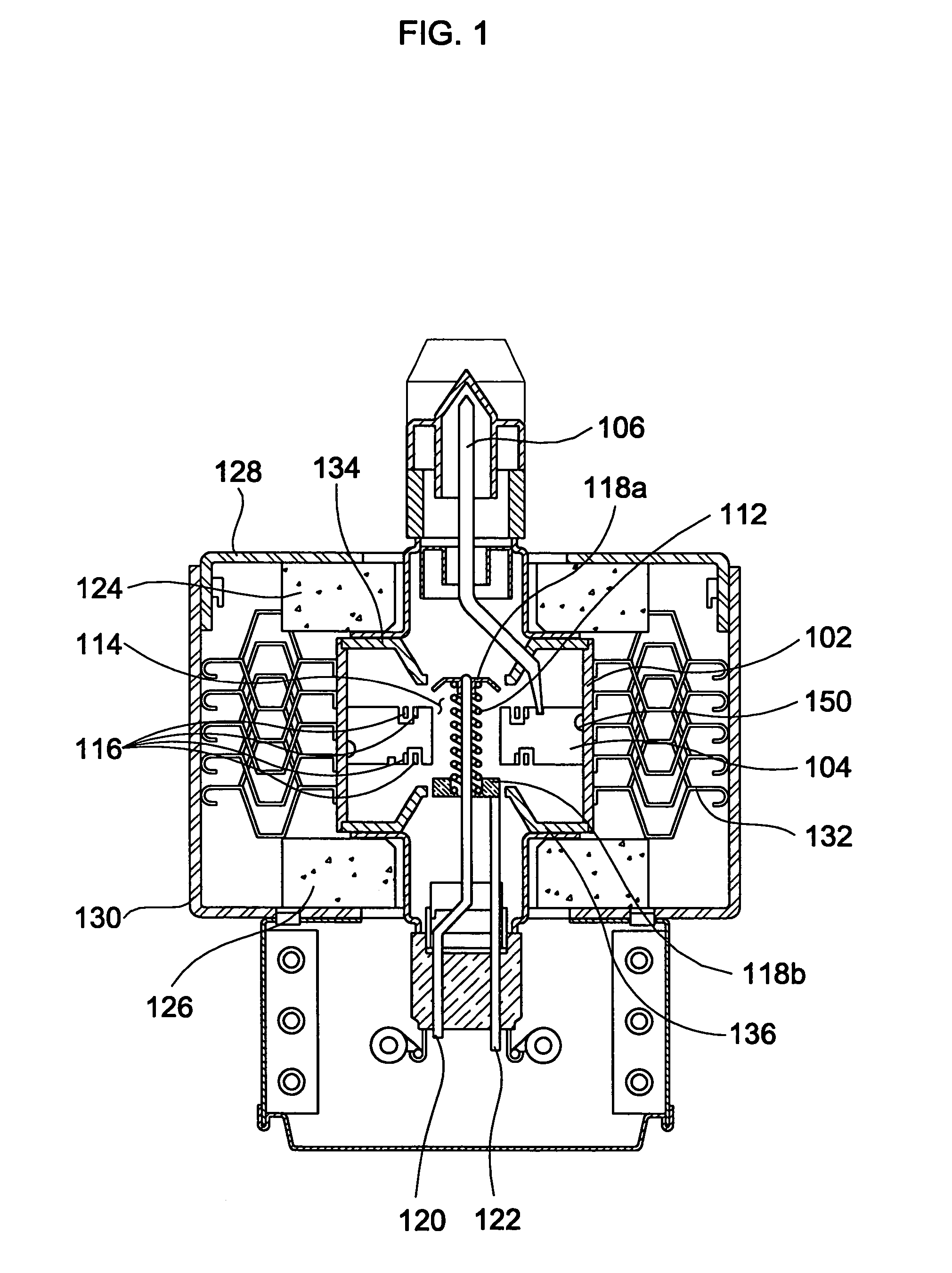
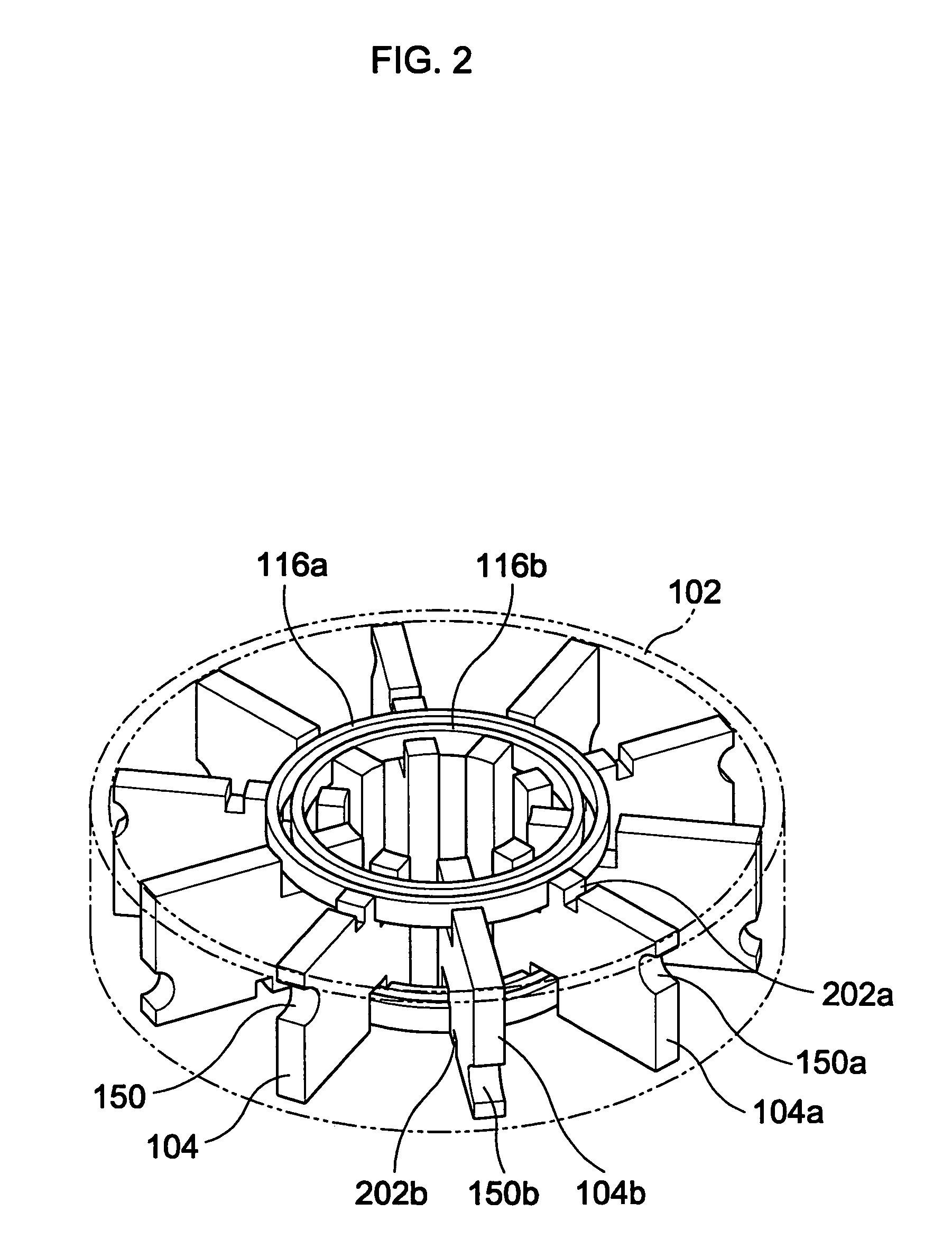
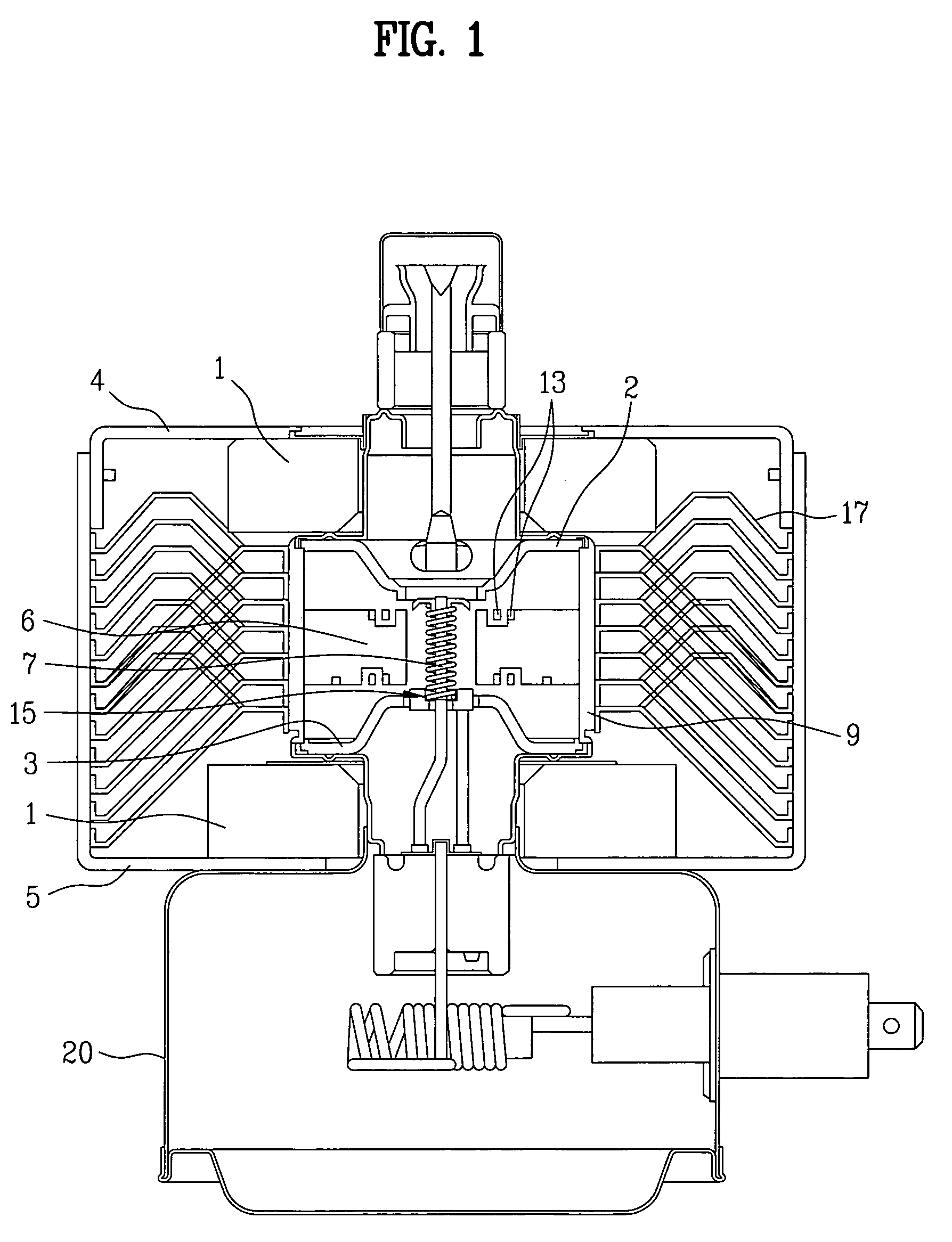
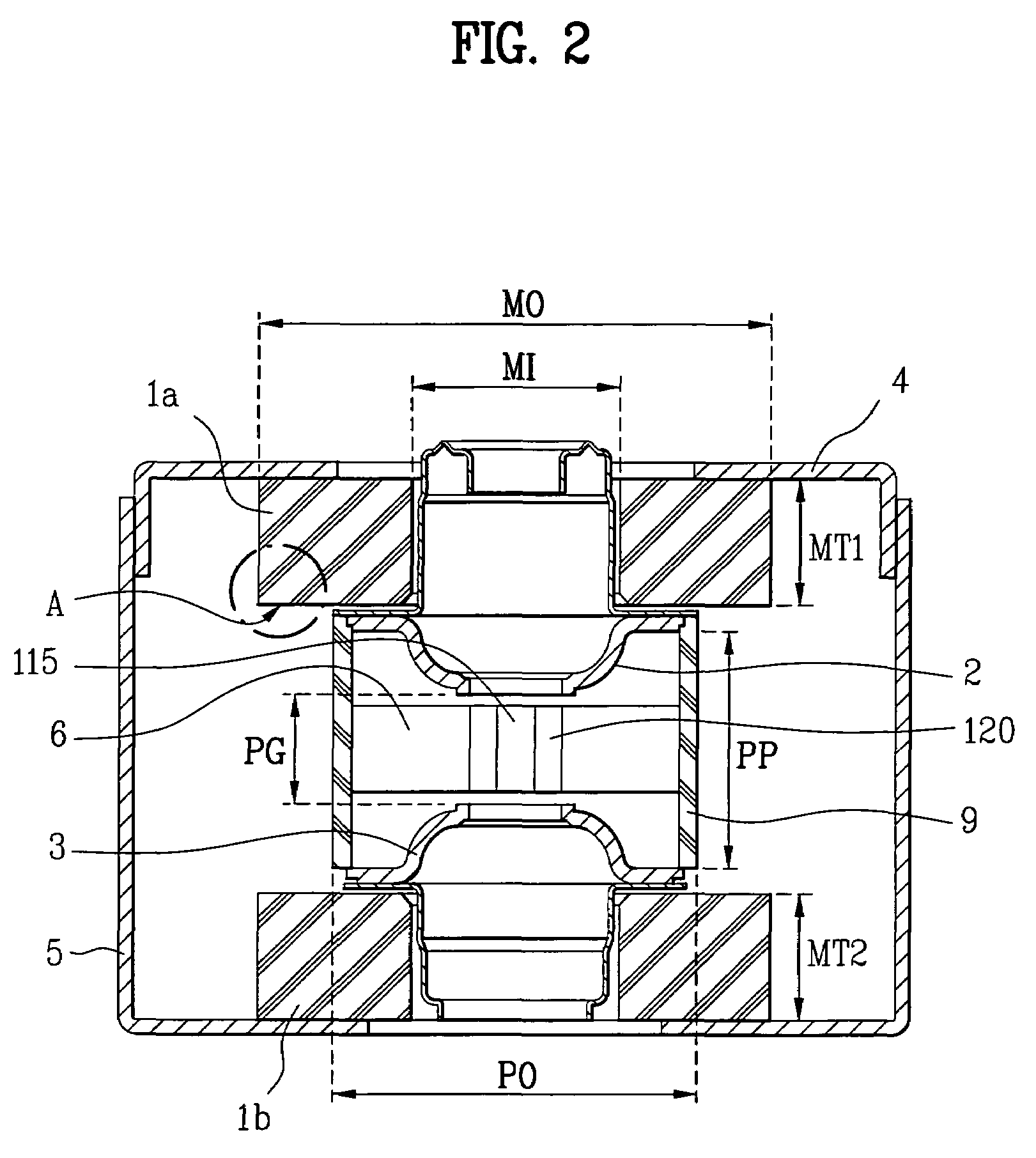
ActiveUS7148627B2Reduce noise levelSecurely lowering noise levelTransit-tube leading-in arrangementsMulti-cavity magnetronsMicrowaveMagnetic poles
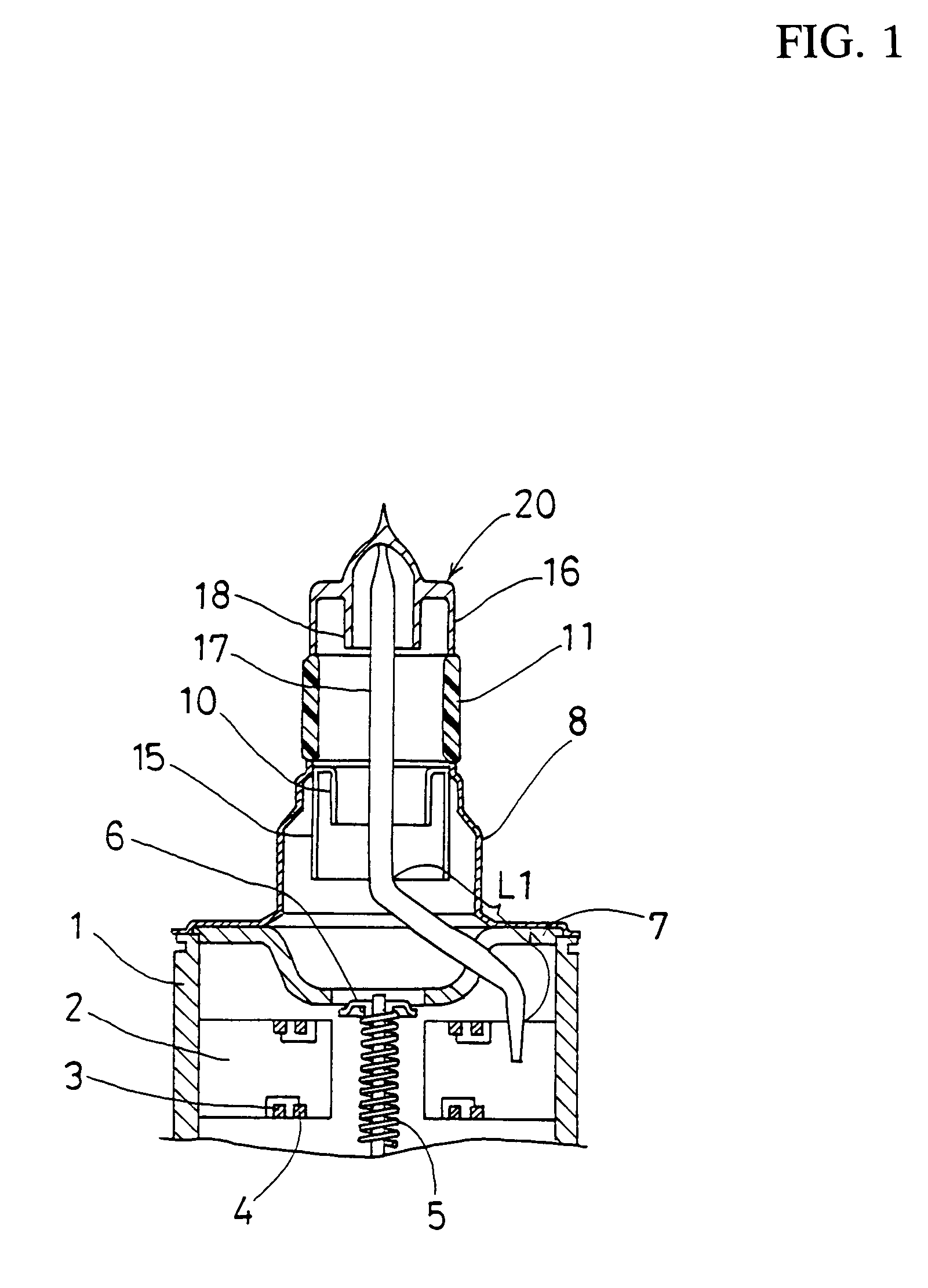
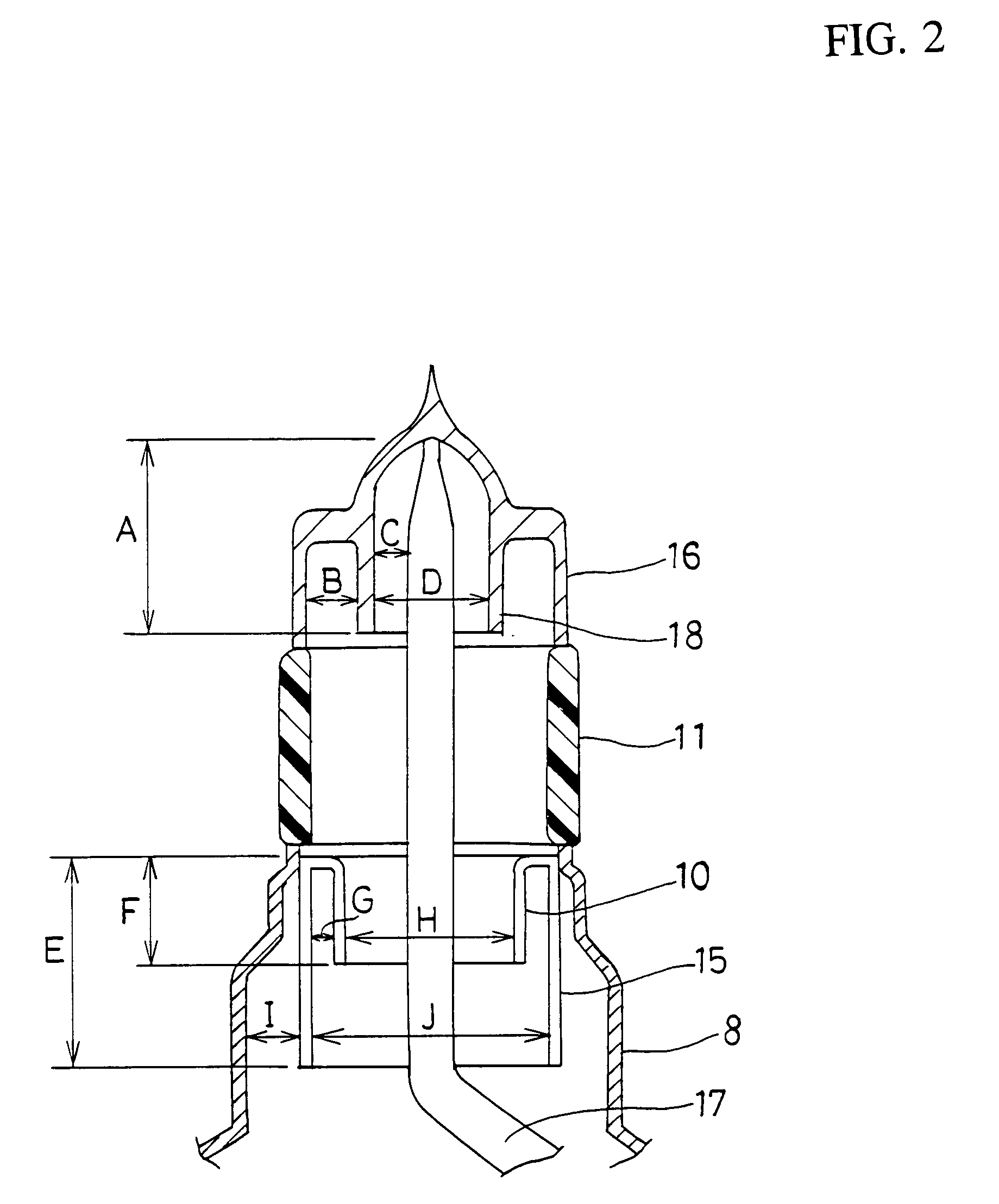
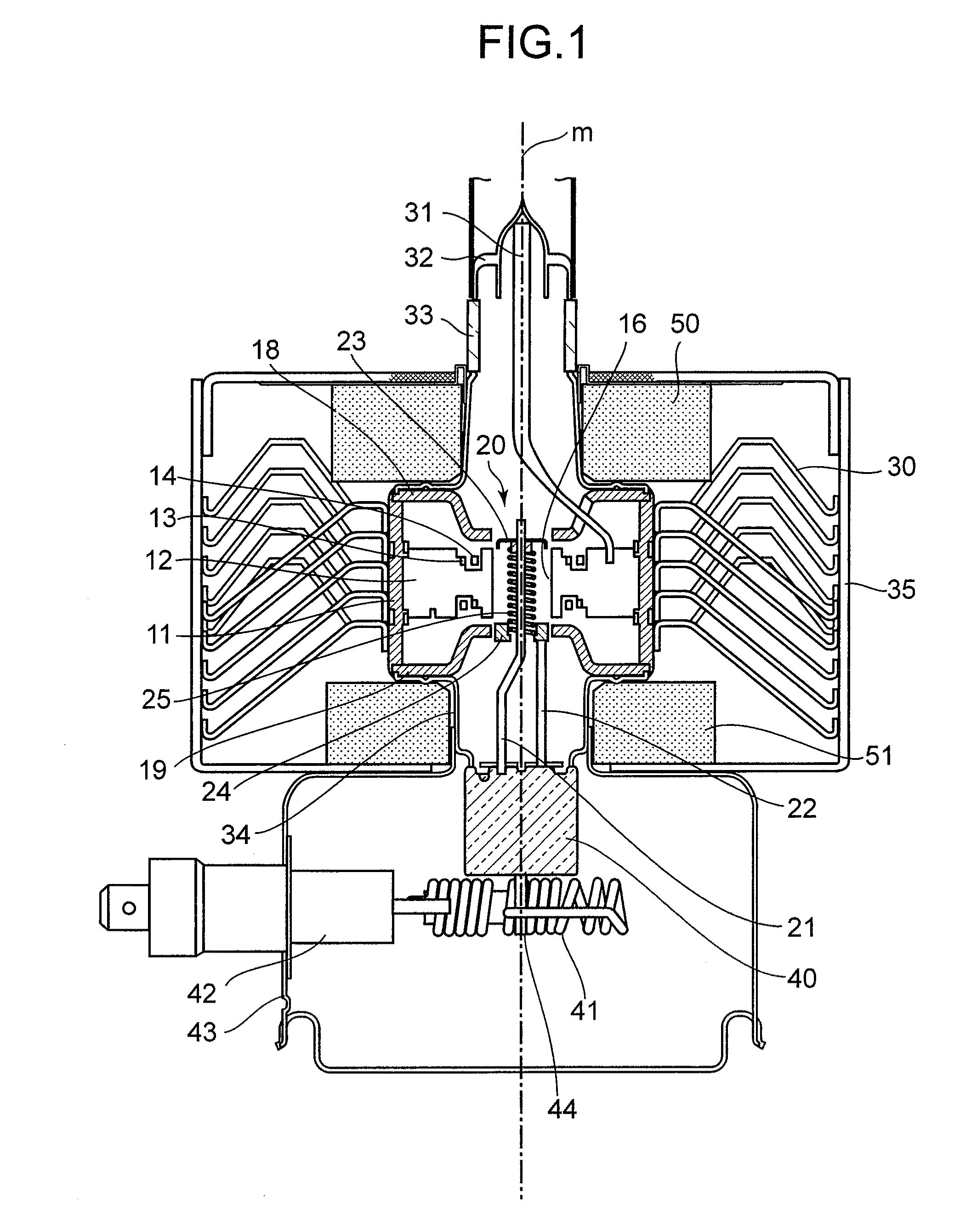
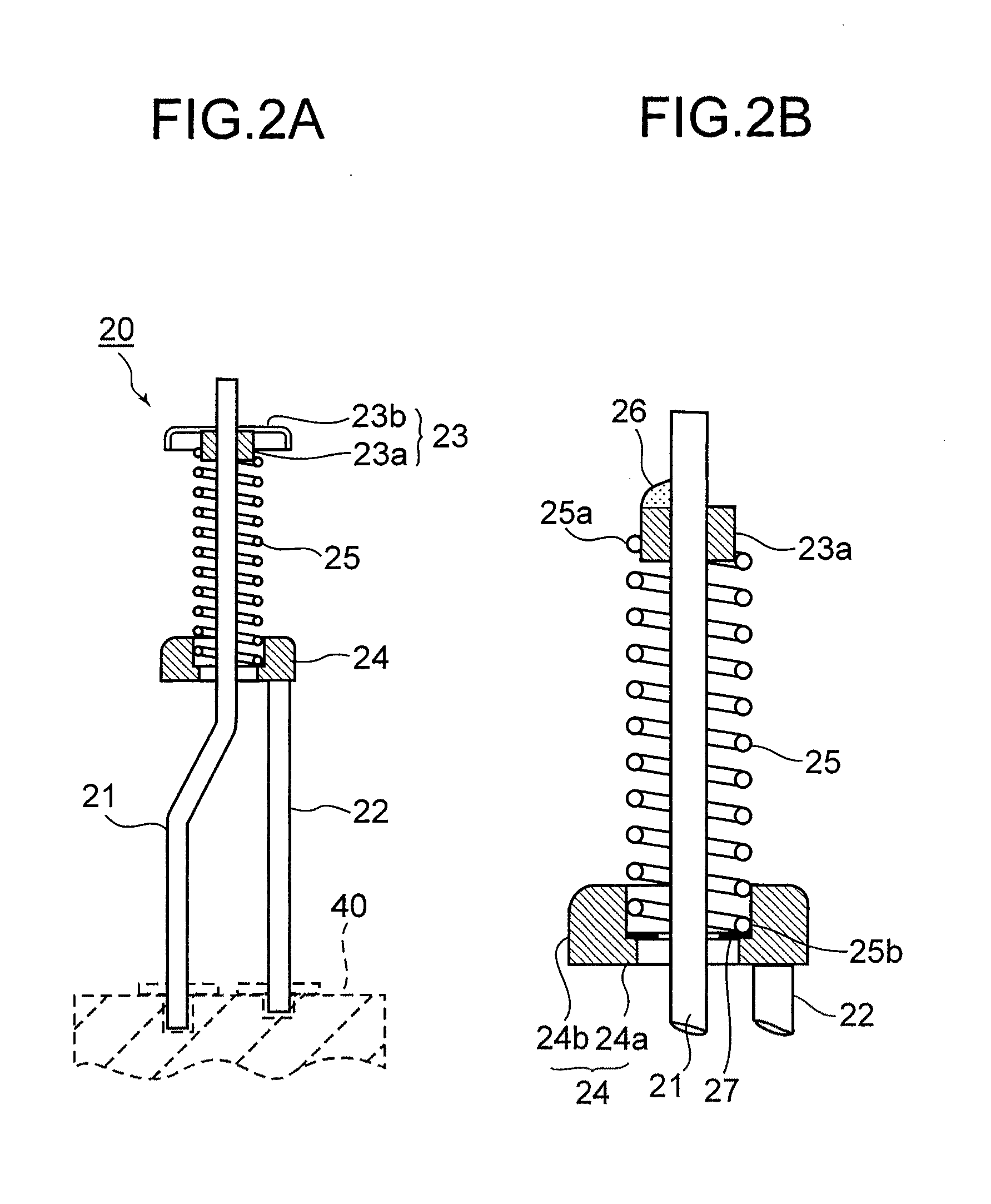
A magnetron is configured so that an antenna lead 17 connected to a desired position of an anode segment 2 passes through a magnetic pole piece 7 and a metal cylinder 8 so as not to make contact therewith and is connected to the output portion of the magnetron, and so that the electrical length L1 of this antenna lead 17 between the opening end of a third harmonic restraint choke 15 and the connection portion of the anode segment 2 is 1 / 2 of the wavelength (λ) of the third harmonic, thereby restraining the third harmonic and the side bands of the third harmonic.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetron cathode assembly
InactiveCN1599012AHigh positioning accuracyImprove connection strengthTransit-tube leading-in arrangementsTransit-tube cathodesMetalCathode
A magnetron cathode assembly which realizes stopping of turn of an external terminal inserted into a stem insulator without increasing a manufacturing cost. A leading end of a base end axial portion of an external terminal has a non-circular section by providing a flat surface in at least one position on its peripheral surface, and a straight stop edge that fits to the flat surface thereby to carry out stopping of turn of the external terminal is provided for a terminal fitting hole of a sealing metal plate into which the leading end of this external terminal is fitted.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetron
InactiveCN1472767AReduced parts countReduce noise levelTransit-tube leading-in arrangementsMulti-cavity magnetronsMagnetic polesThird harmonic
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetron
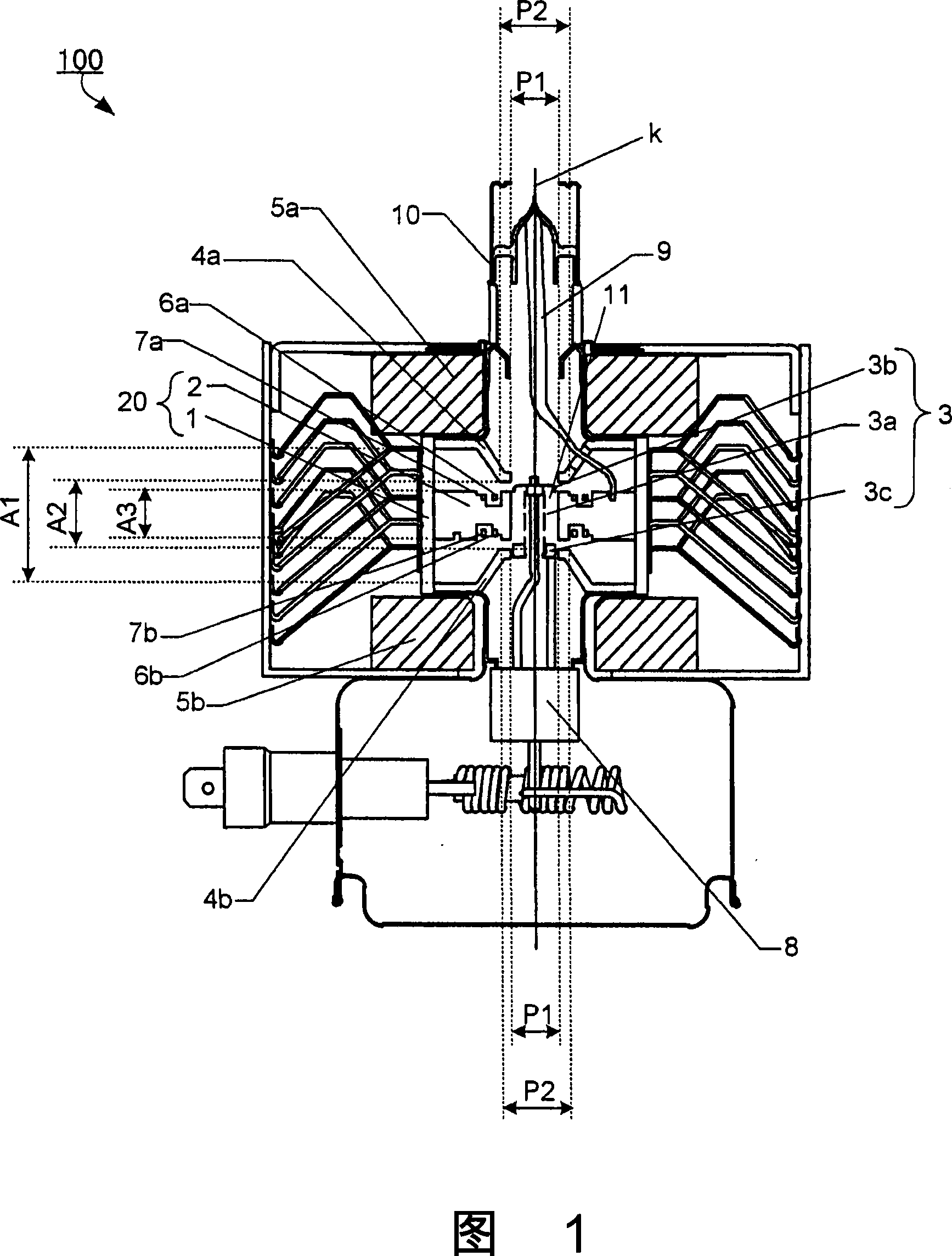
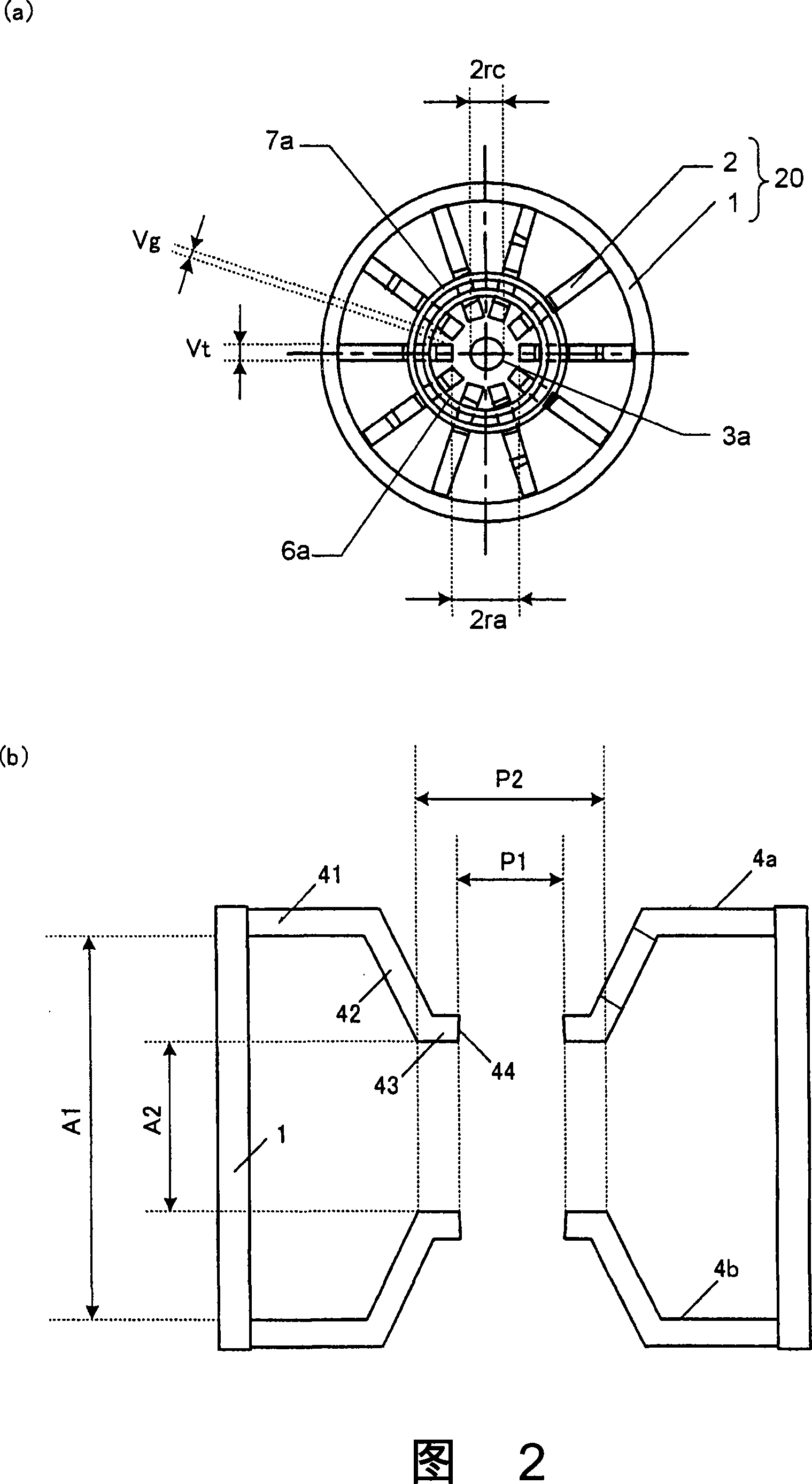
InactiveUS20070296515A1Enhanced oscillationTransit-tube vessels/containersAngle modulation by transit-time tubeElectrical and Electronics engineeringFunnel shape
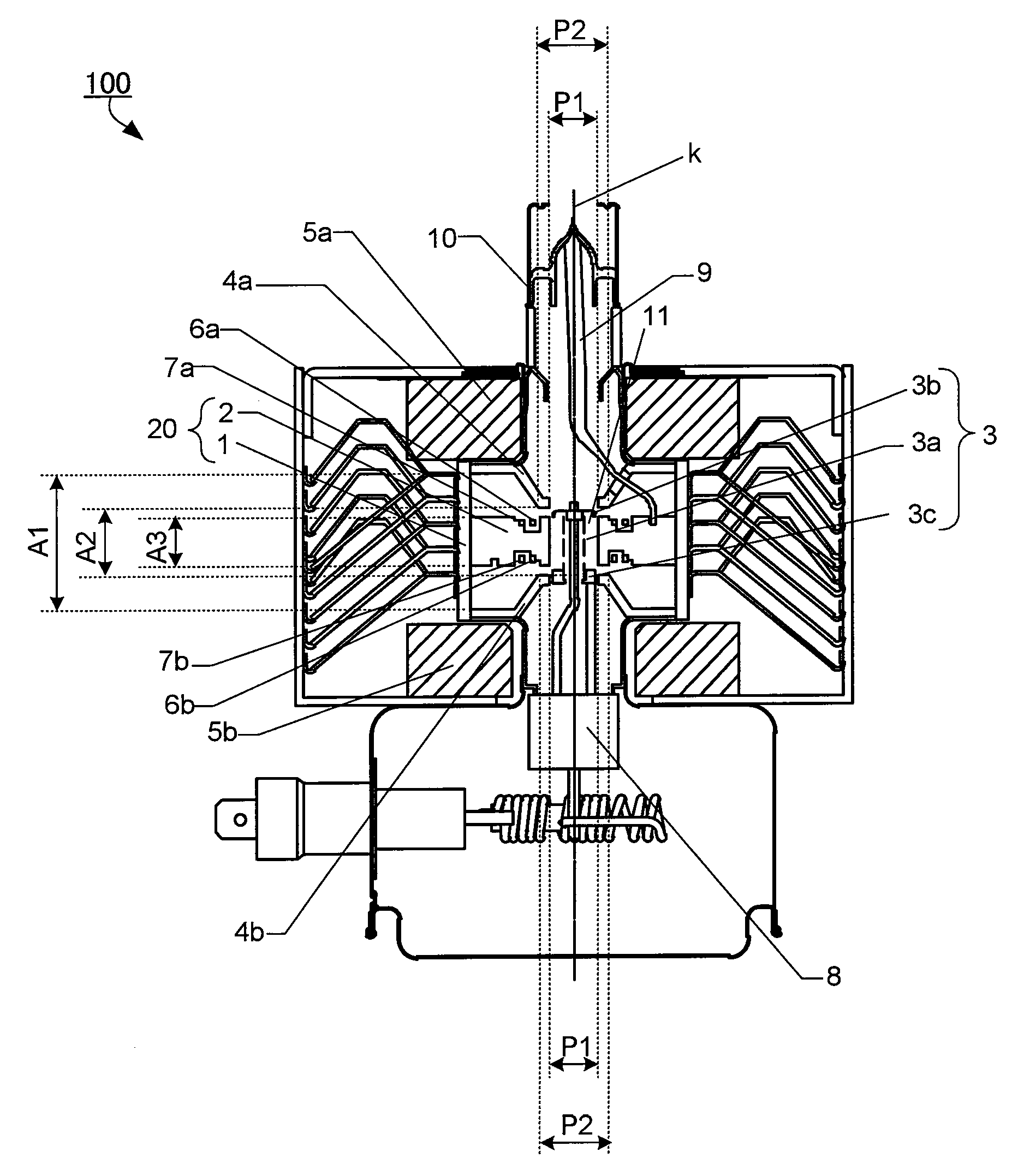
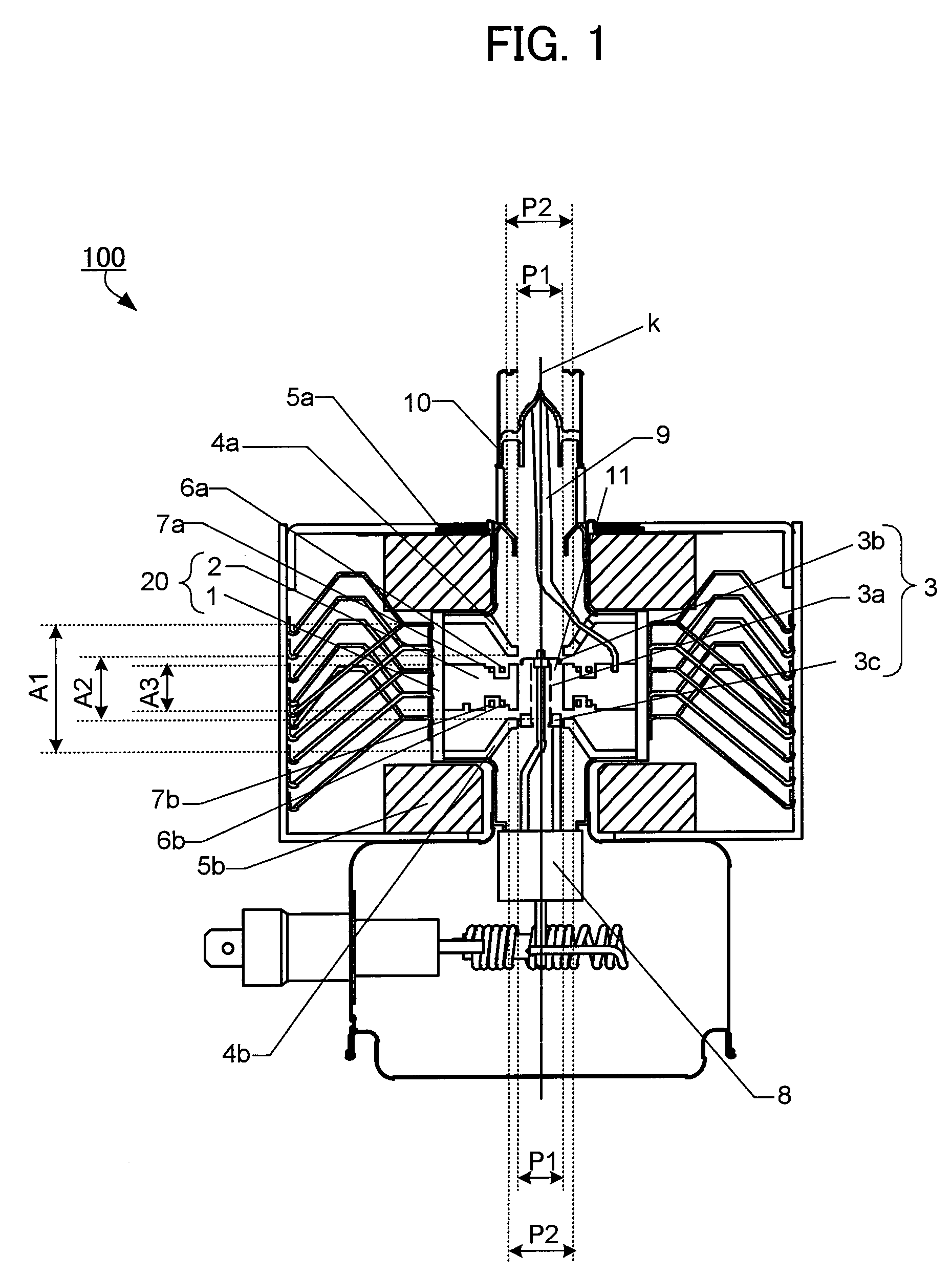
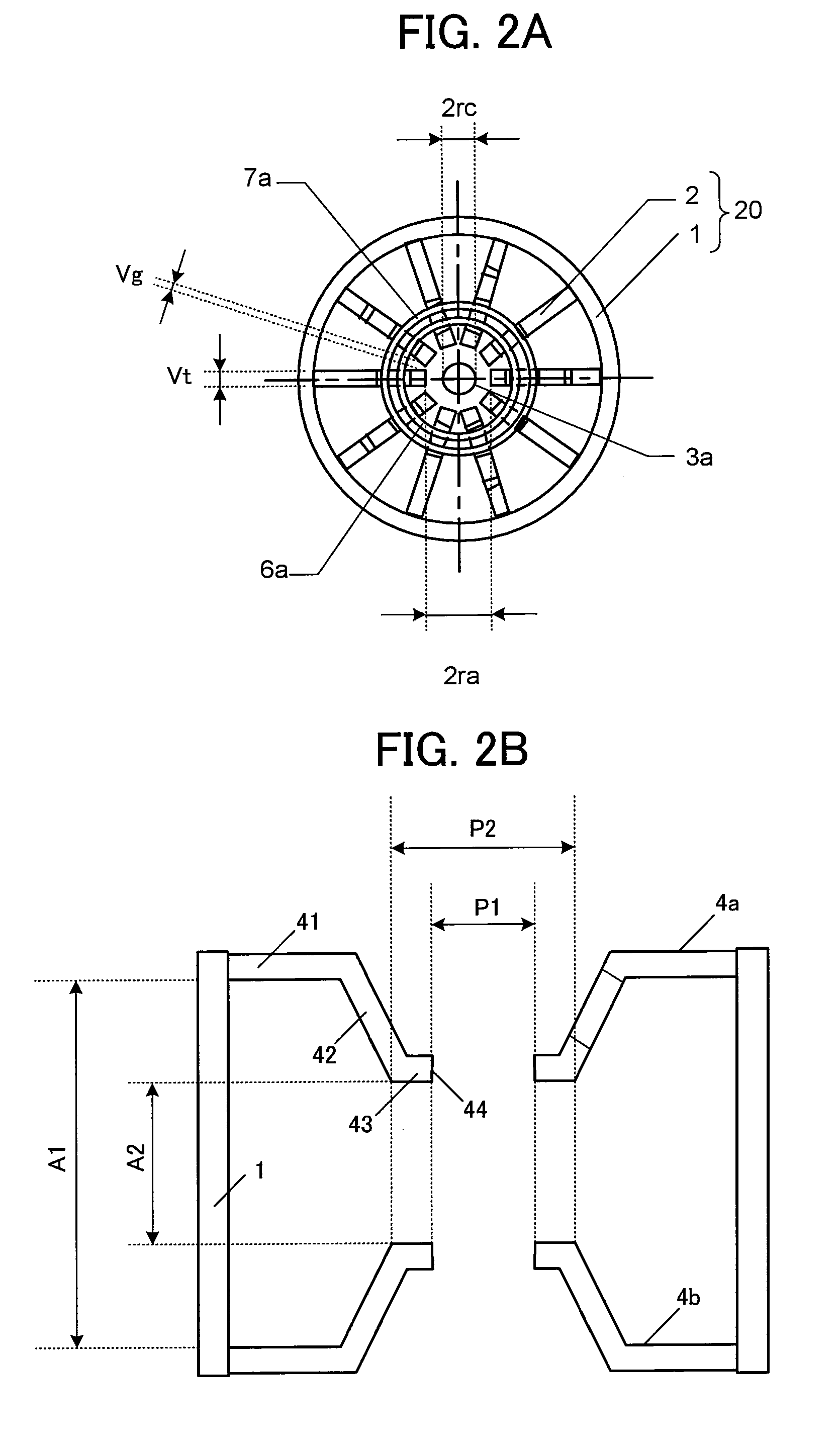
At an oscillation frequency of 2450 MHz band, number of the vanes constituting the anode part of the magnetron being, the diameter 2ra of the circle inscribing tip portions of the vanes on the cathode side being 8.0 to 8.8 mm, the diameter 2rc of the outer periphery of the filament constituting the cathode part being 3.5 to 3.9 mm, the height A3 of the vane in the direction of the tube axis is 7.0 to 8.0 mm, the mutual distance A1 between the bases of the pair of funnel-shaped pole pieces fixed to both sides of the anode part being 21.5 to 23.5 mm, the mutual distance A2 between the bottom portions of the pair of pole pieces being 10.2 to 11.2 mm, the inner diameter P1 of the through-hole of the pole piece being 8.3 to 8.5 mm, and the outer diameter P2 of the bottom portion being 11.0 to 16.0 mm are set up.
Owner:TOSHIBA HOKUTO ELECTRONICS CORP
Vane structure of magnetron
ActiveUS7135820B2Reduce generationEvenly distributedCellsVacuum evaporation coatingHarmonicEngineering
A magnetron includes semi-circularly shaped electric field adjusting grooves provided on surfaces of outer ends of vanes brought into contact with an inner surface of a positive polar body to make distribution of an electric field uniform on the surfaces of the outer ends of the vanes. Accordingly, the electric field becomes uniform by the electric field adjusting grooves provided on the surfaces of the outer ends of the vanes, so that generation of undesirable harmonics is suppressed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetron, and microwave oven and high-frequency heating apparatus each equipped with the same
InactiveUS7026762B2Low costImprove oscillation efficiencyTransit-tube leading-in arrangementsDomestic stoves or rangesMicrowave ovenResonance
A magnetron includes a ring-shaped anode, a cathode, an activating space, at least one permanent magnet and a magnetic flux carrying unit. The ring-shaped anode forms a plurality of resonance circuits. The cathode is disposed at the axial center of the anode to emit thermions. The activating space is formed between the anode and the cathode. The at least one permanent magnet is provided beside the anode. The magnetic flux carrying unit carries magnetic flux generated by the at least one permanent magnet to the activating space. A microwave oven and / or high frequency heating apparatus may utilize the magnetron.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetron
ActiveCN101093770AImprove oscillation output efficiencyMiniaturizationTransit-tube vessels/containersTransit-tube circuit elementsEngineeringFunnel shape
At an oscillation frequency of 2450 MHz band, number of the vanes constituting the anode part of the magnetron being, the diameter 2 ra of the circle inscribing tip portions of the vanes on the cathode side being 8.0 to 8.8 mm, the diameter 2 rc of the outer periphery of the filament constituting the cathode part being 3.5 to 3.9 mm, the height A 3 of the vane in the direction of the tube axis is 7.0 to 8.0 mm, the mutual distance A 1 between the bases of the pair of funnel-shaped pole pieces fixed to both sides of the anode part being 21.5 to 23.5 mm, the mutual distance A 2 between the bottom portions of the pair of pole pieces being 10.2 to 11.2 mm, the inner diameter P 1 of the through-hole of the pole piece being 8.3 to 8.5 mm, and the outer diameter P 2 of the bottom portion being 11.0 to 16.0 mm are set up.
Owner:TOSHIBA HOKUTO ELECTRONICS CORP
Magnetron
InactiveUS7375470B2Small sizeReduce output capacityCellsTransit-tube vessels/containersMagnetic polesPhysics
Disclosed herein is a magnetron. The magnetron comprises an anode cylinder, upper and lower magnets provided to upper and lower portions of the anode cylinder, and upper and lower magnetic poles connected to the magnets, respectively. Each of the magnets has an inner diameter of 19˜21 mm, a thickness of 11.5˜12.5 mm, and an outer diameter of 50˜54 mm.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
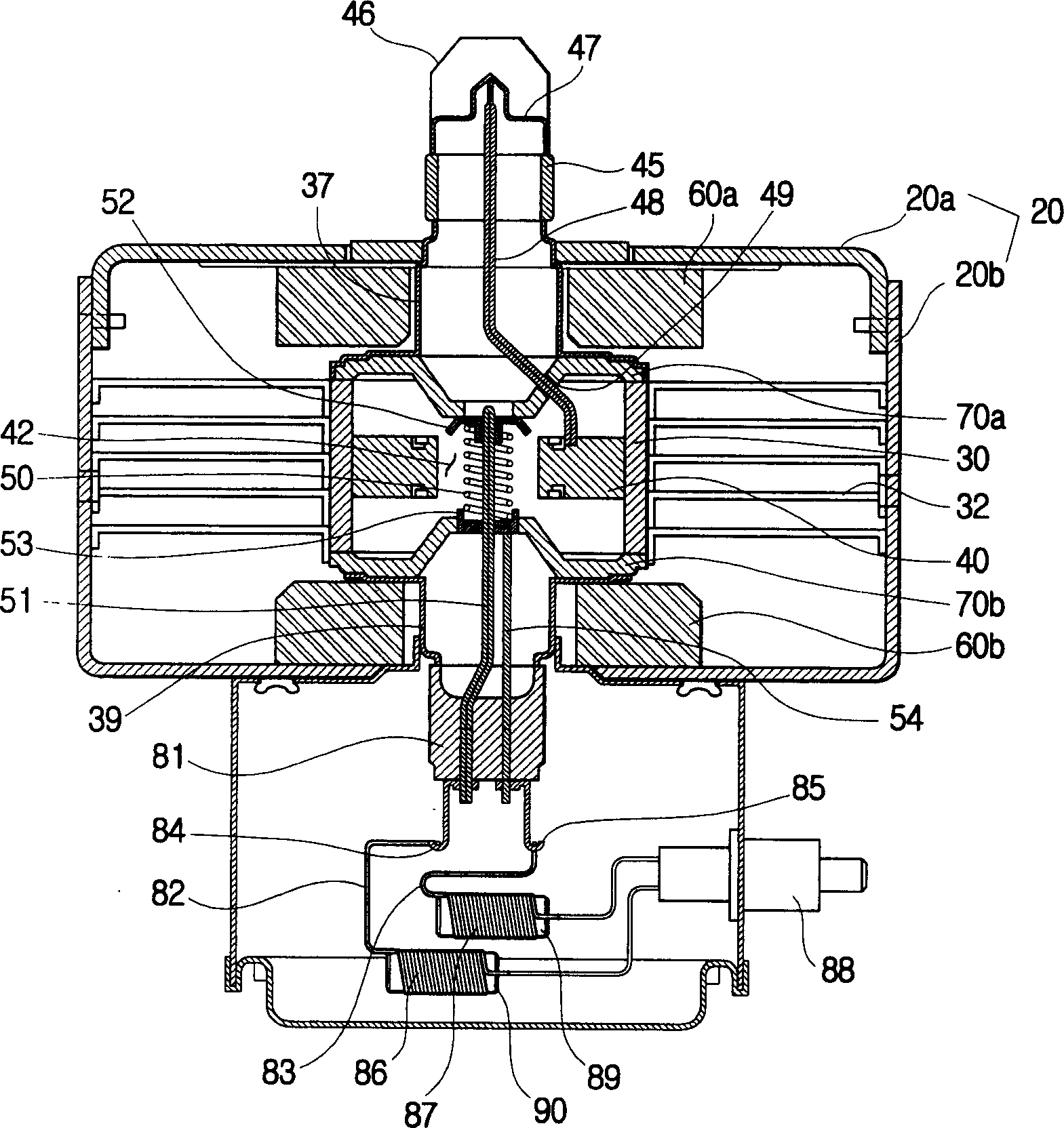
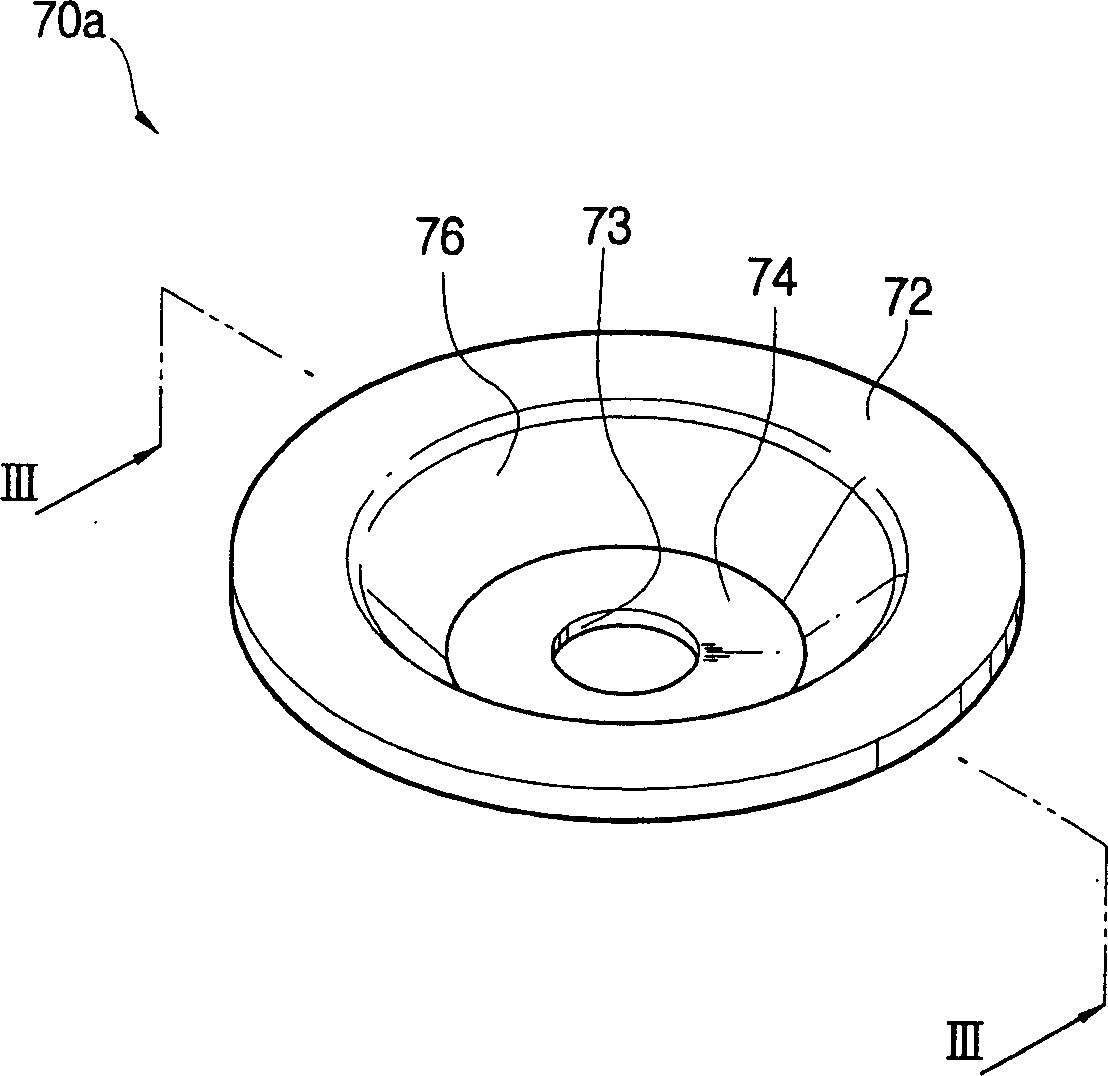
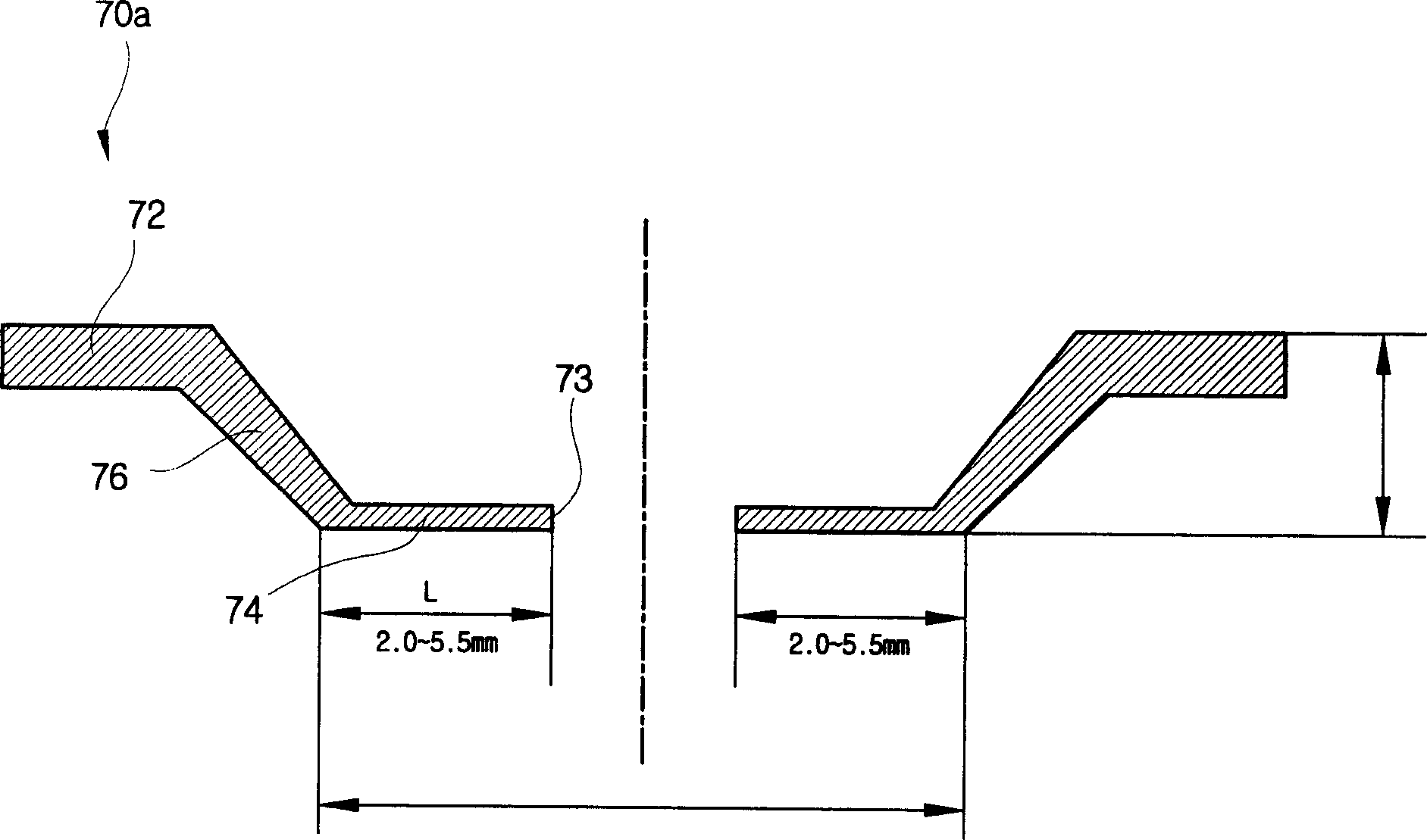
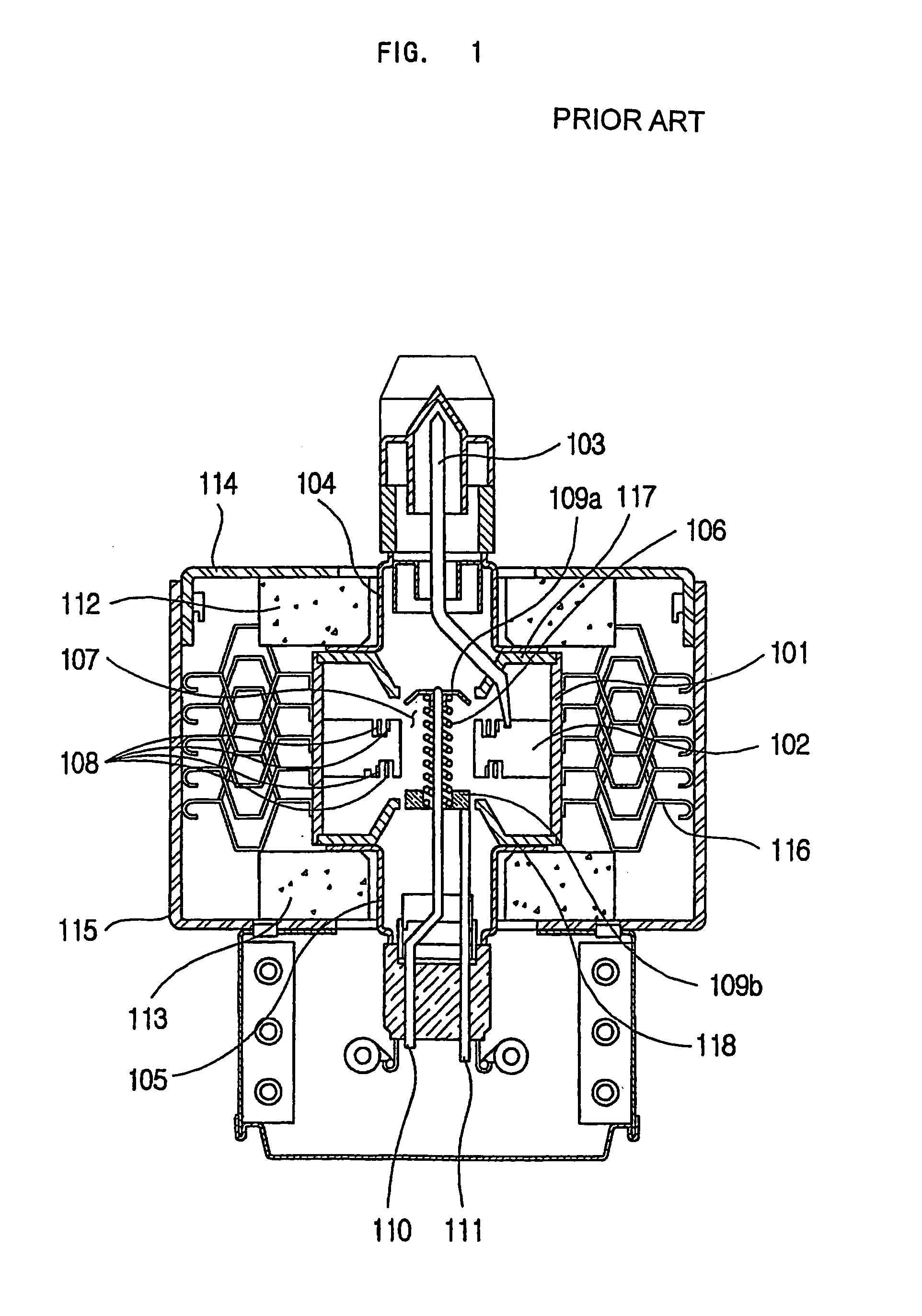
Magnetron for microwave oven
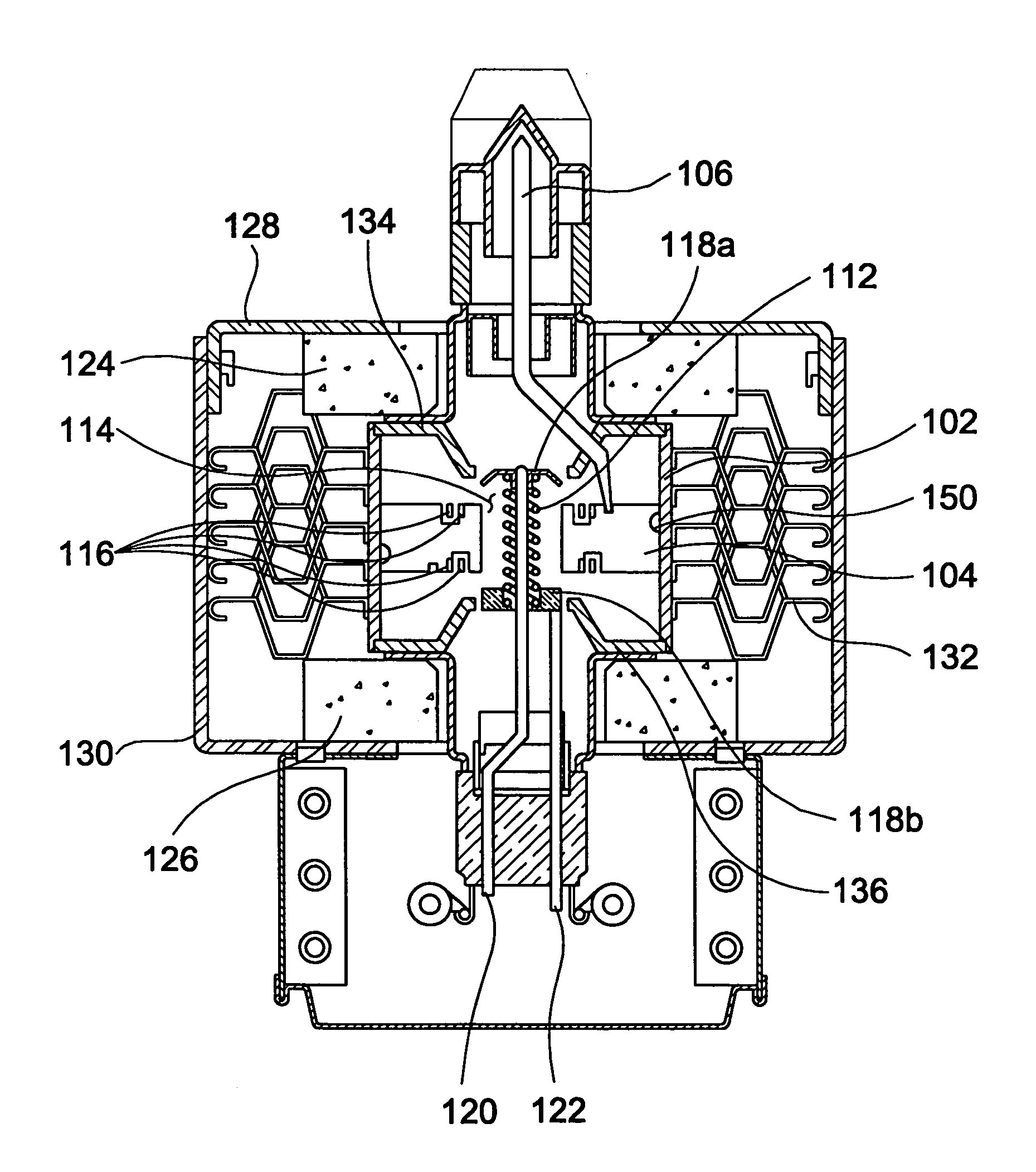
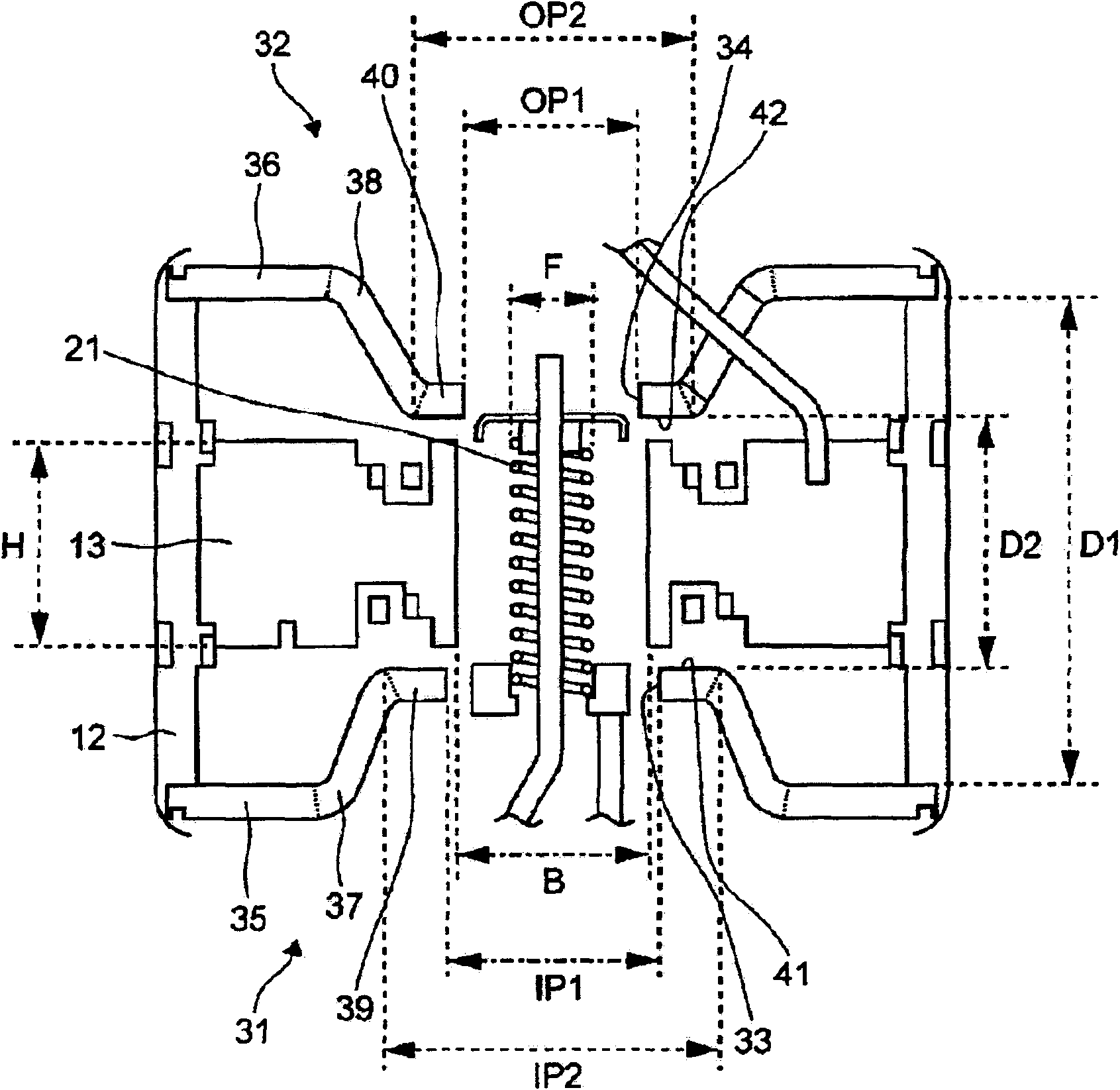
Unnecessary noises generated from a magnetron for a microwave oven are suppressed. In a magnetron 10 for a microwave oven, the diameter IP1 of the through-hole 33 of the input side pole piece 31 is 8.6 to 9.1 mm and the outer diameter IP2 of the internal surface 41 of the input side pole piece 31 is 15 to 16 mm, while the diameter OP1 of the through-hole 34 of the output side pole piece 32 is 7.9 to 8.1 mm and the outer diameter OP2 of the internal surface 42 of the output side pole piece 32 is 11 to 13 mm. Additionally, the interval distance D1 between the outer annular portion 35 of the input side pole piece 31 and the outer annular portion 36 of the output side pole piece 32 is 11.5 to 13.5 mm and the interval distance D2 between the inner annular portion 39 of the input side pole piece 31 and the inner annular portion 40 of the output side pole piece 32 is 10.2 to 11.2 mm.
Owner:TOSHIBA HOKUTO ELECTRONICS CORP
Crossed field device
ActiveUS8841867B2Travelling-wave tubesStructural circuit elementsAudio power amplifierCrossed-field amplifier
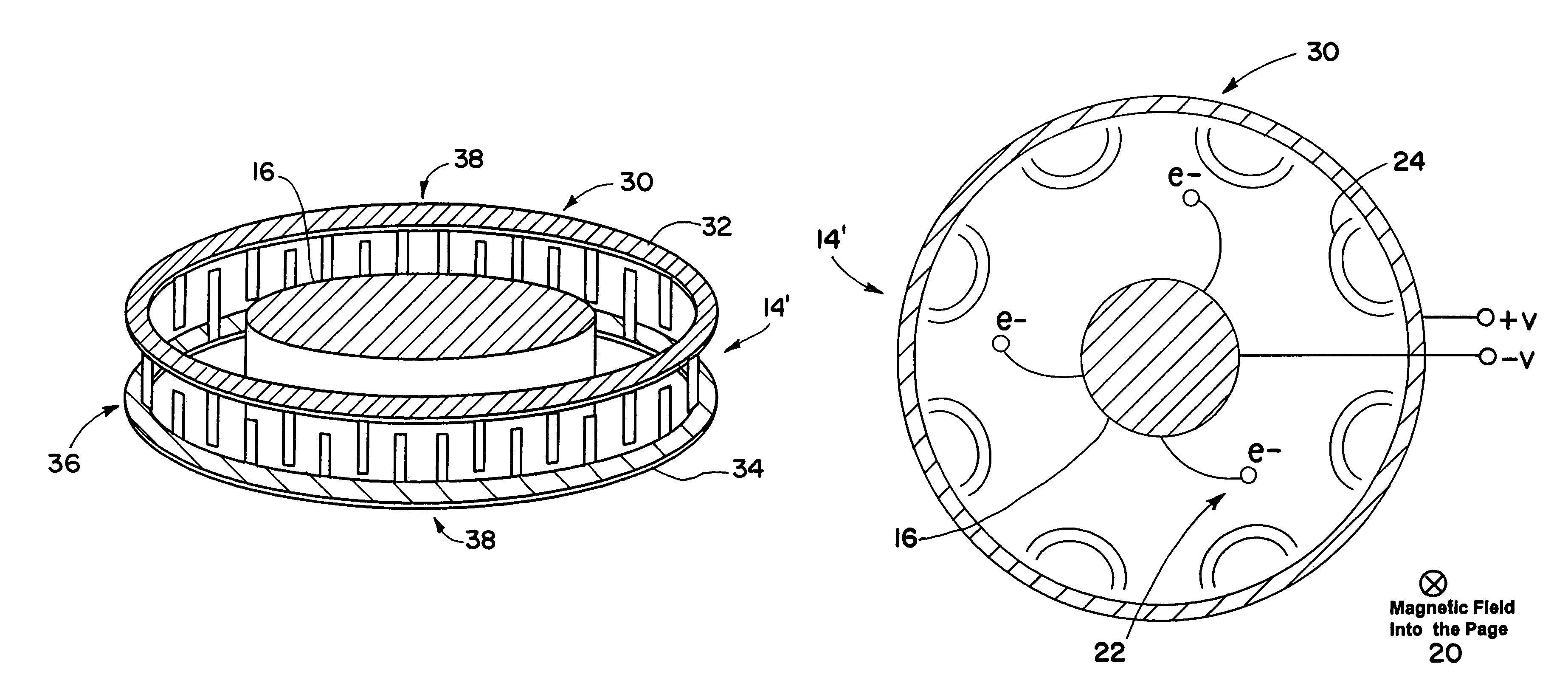
A crossed field device, such as a magnetron or crossed field amplifier, that includes a cathode, an anode, one or more magnetic elements, and one or more extraction elements. In one embodiment, the crossed field device includes an annular cathode and anode that are axially spaced from one another such that the device produces an axial electric (E) field and a radial magnetic (B) field. In another embodiment, the crossed field device includes an oval-shaped cathode and anode that are radially spaced from one another such that the device produces a radial electric (E) field and an axial magnetic (B) field. The crossed field device may produce electromagnetic (EM) emissions having a frequency ranging from megahertz (MHz) to terahertz (THz), and may be used in one of a number of different applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Optical magnetron for high efficiency production of optical radiation and related methods of use
InactiveUS20080296508A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsOptical radiationElectric power transmission
An electromagnetic radiation source is disclosed that produces a single mode operation at a desired operating frequency. The electromagnetic radiation source is included in a wide variety of applications including a wireless power transmission system, a system for providing wireless / high-bandwidth communications in accordance with the present invention, a lighting system, an irradiation system, a weapons system, etc.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Magnetron
A magnetron is provided including a yoke having an inner space; a first magnet provided at one end of the inner space, a second magnet provided at a second end of the inner space, the second magnet being axially spaced from the first magnet. Further, there is an anode cylinder that generates a high frequency provided between the first magnet and the second magnet; a first pole piece and a second pole piece provided proximate first and second openings of the anode cylinder, respectively. Additionally, a seal that prevents outward leakage and has an inward protrusion extending axially toward the anode cylinder; and a choke filter, provided beneath a free end of the inwardly bent end of the seal to prevent outward leakage, may be provided.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Brazing material, electron tubes, magnetron and method for brazing
InactiveUS20100052501A1Low costHigh melting pointElectrode assembly support/mounting/spacing/insulationIncadescent body mountings/supportMetallurgyElectron
Owner:TOSHIBA HOKUTO ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com