Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Compact and durable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
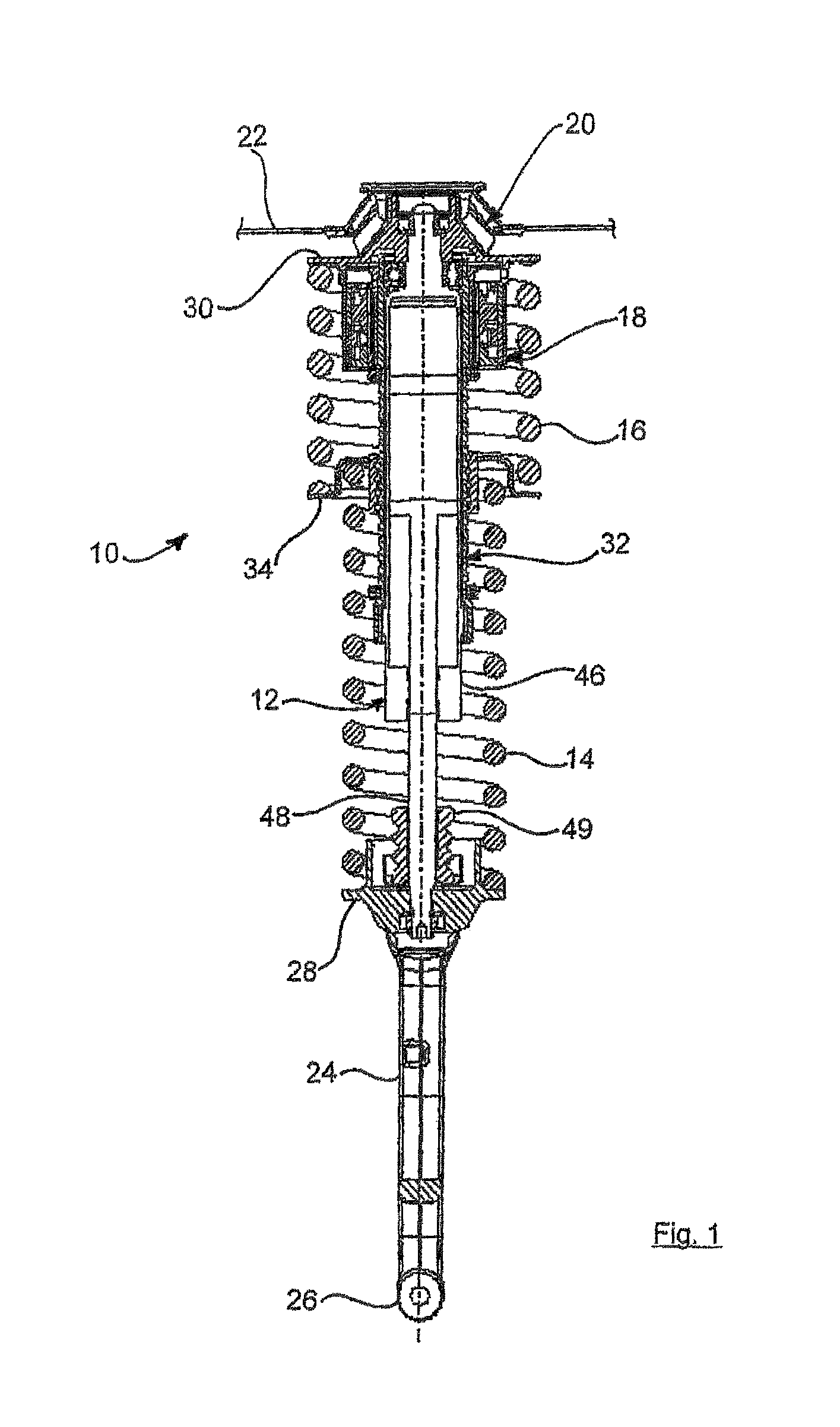
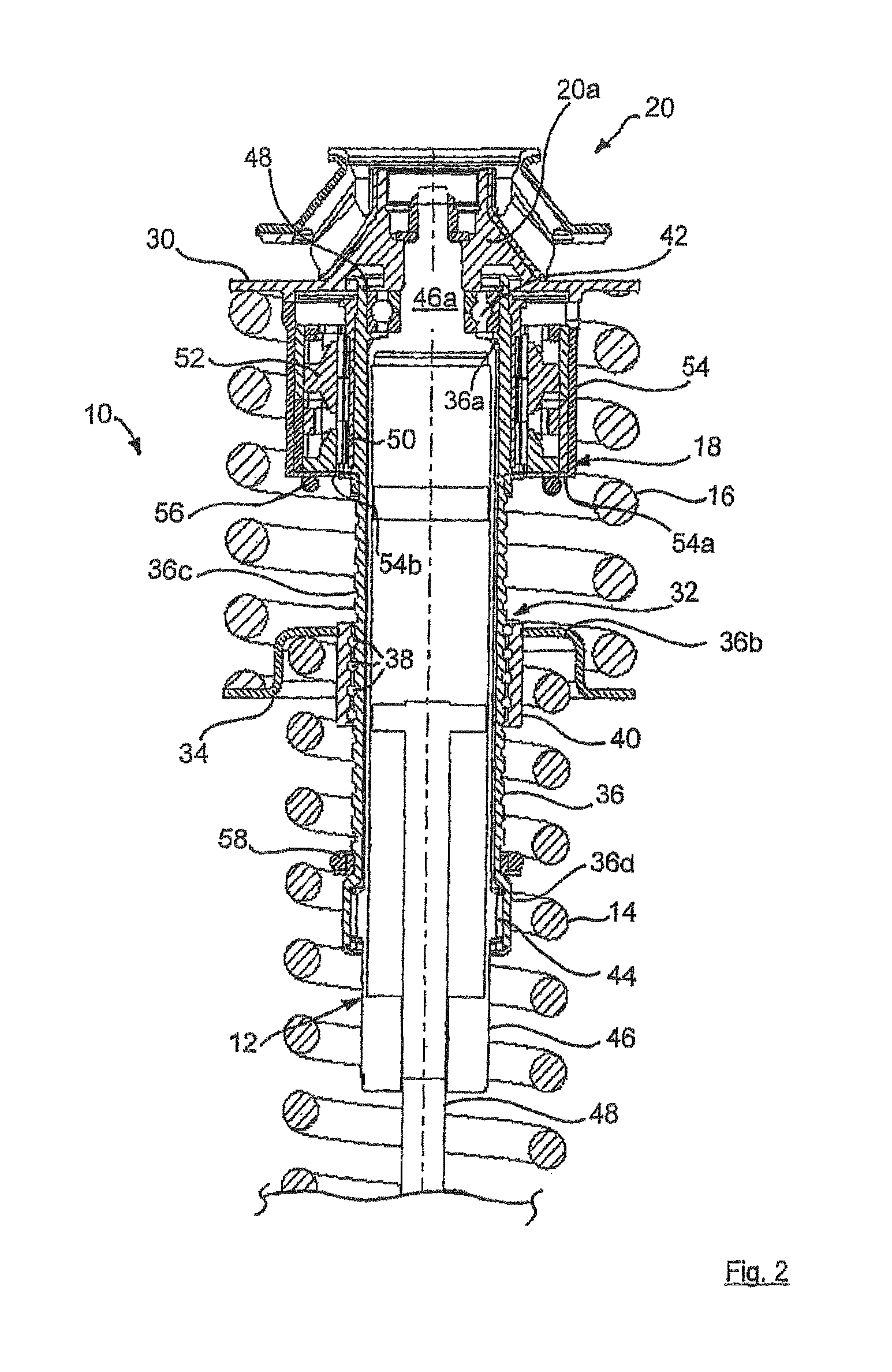
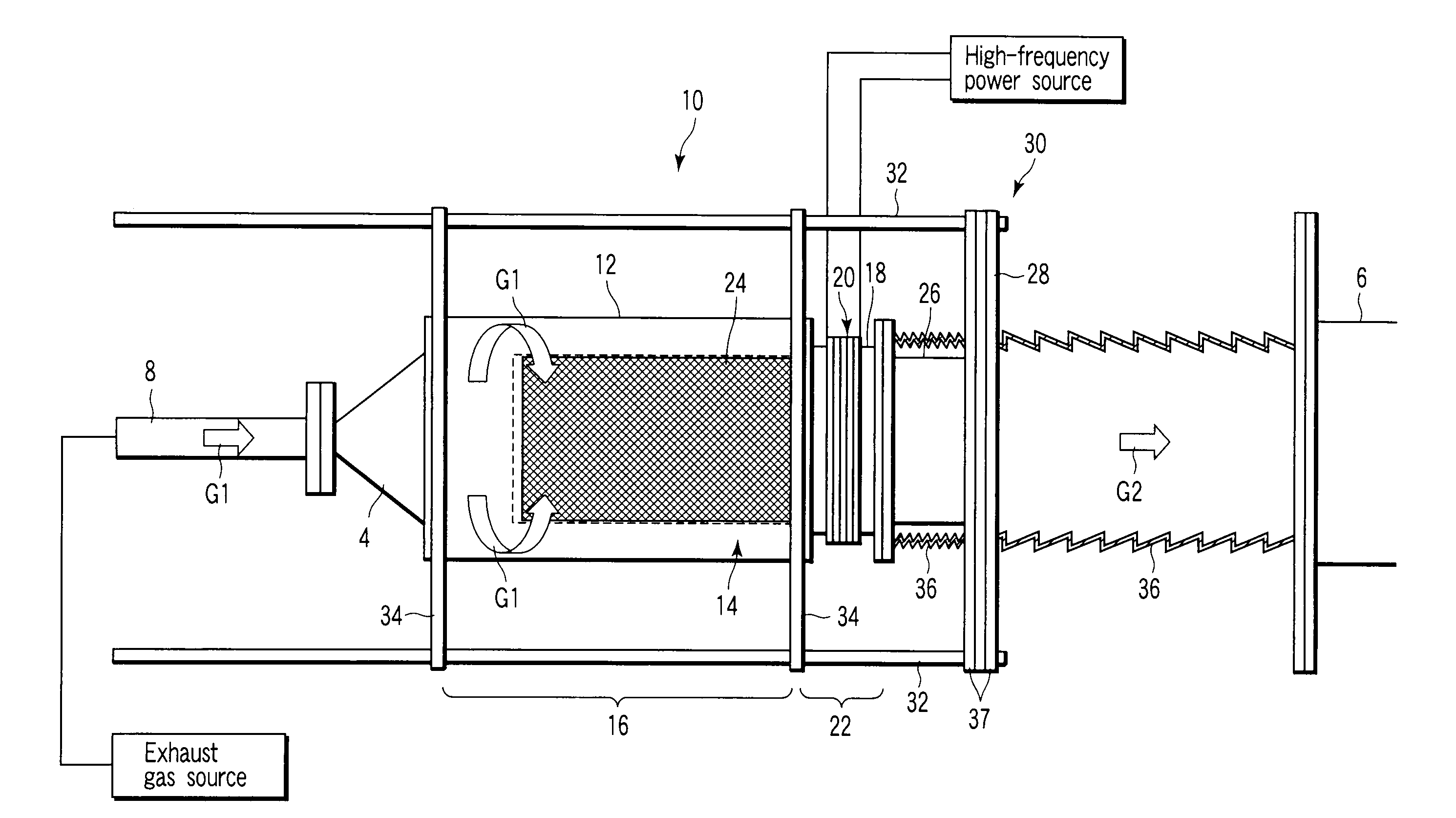
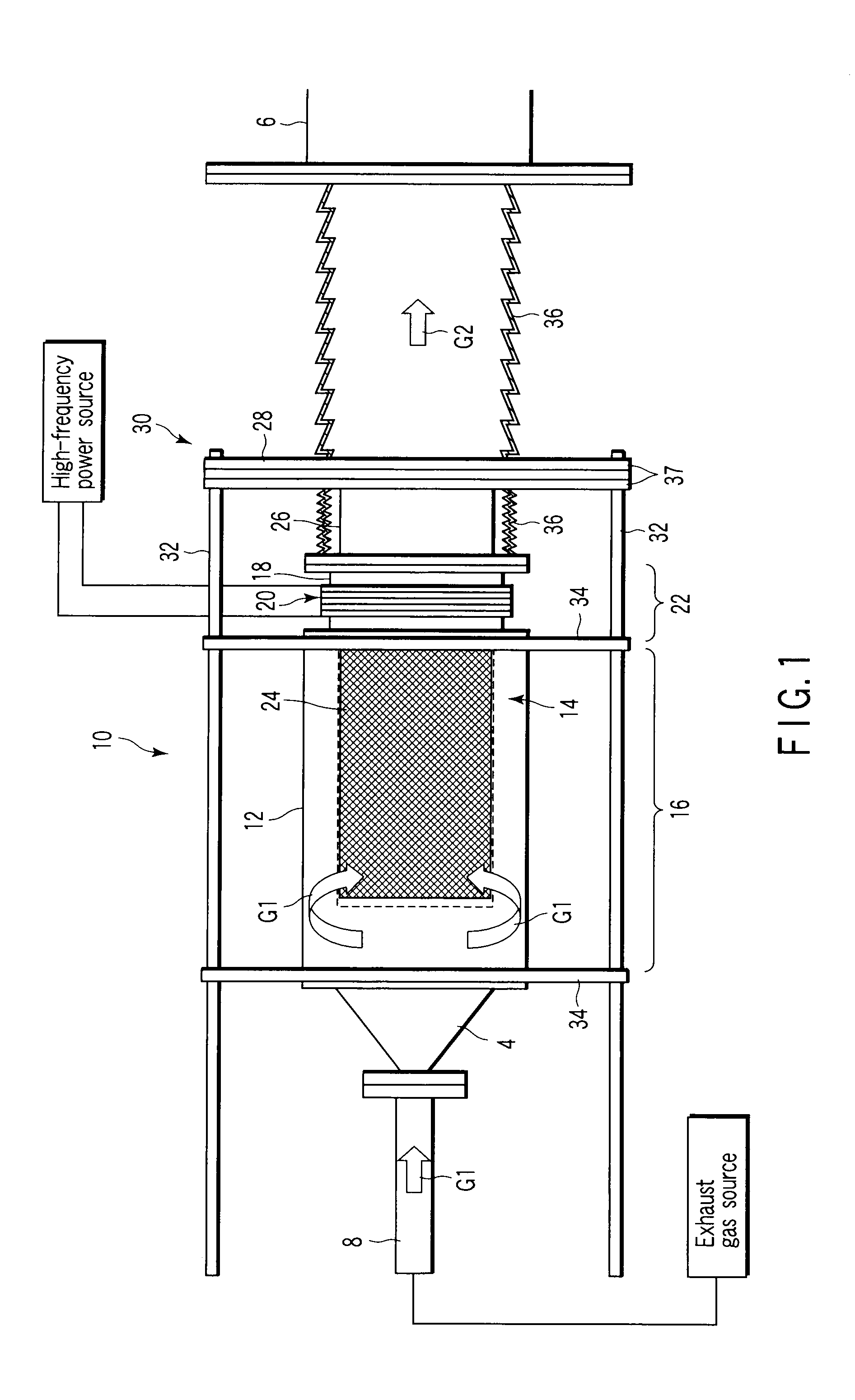
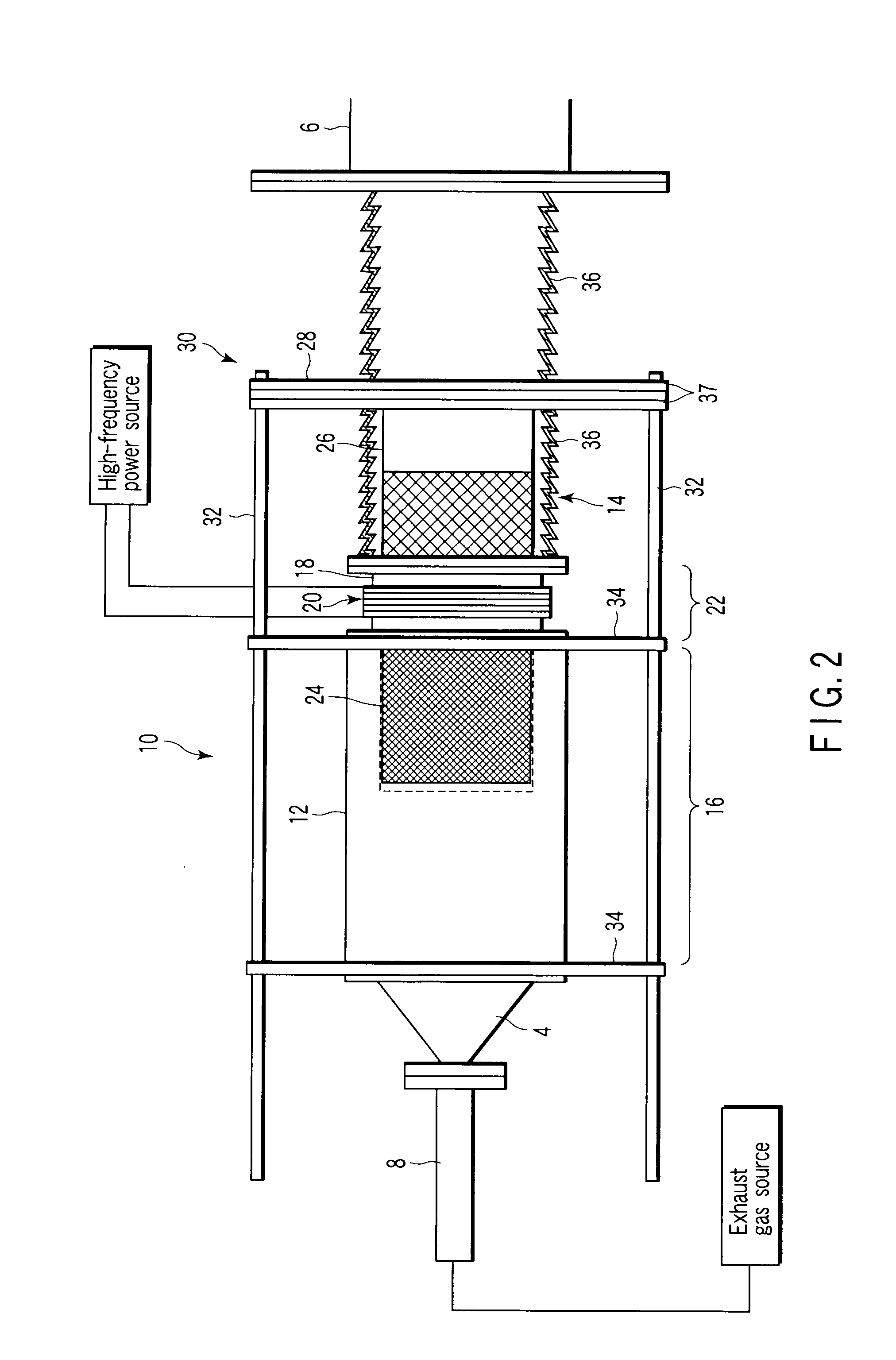
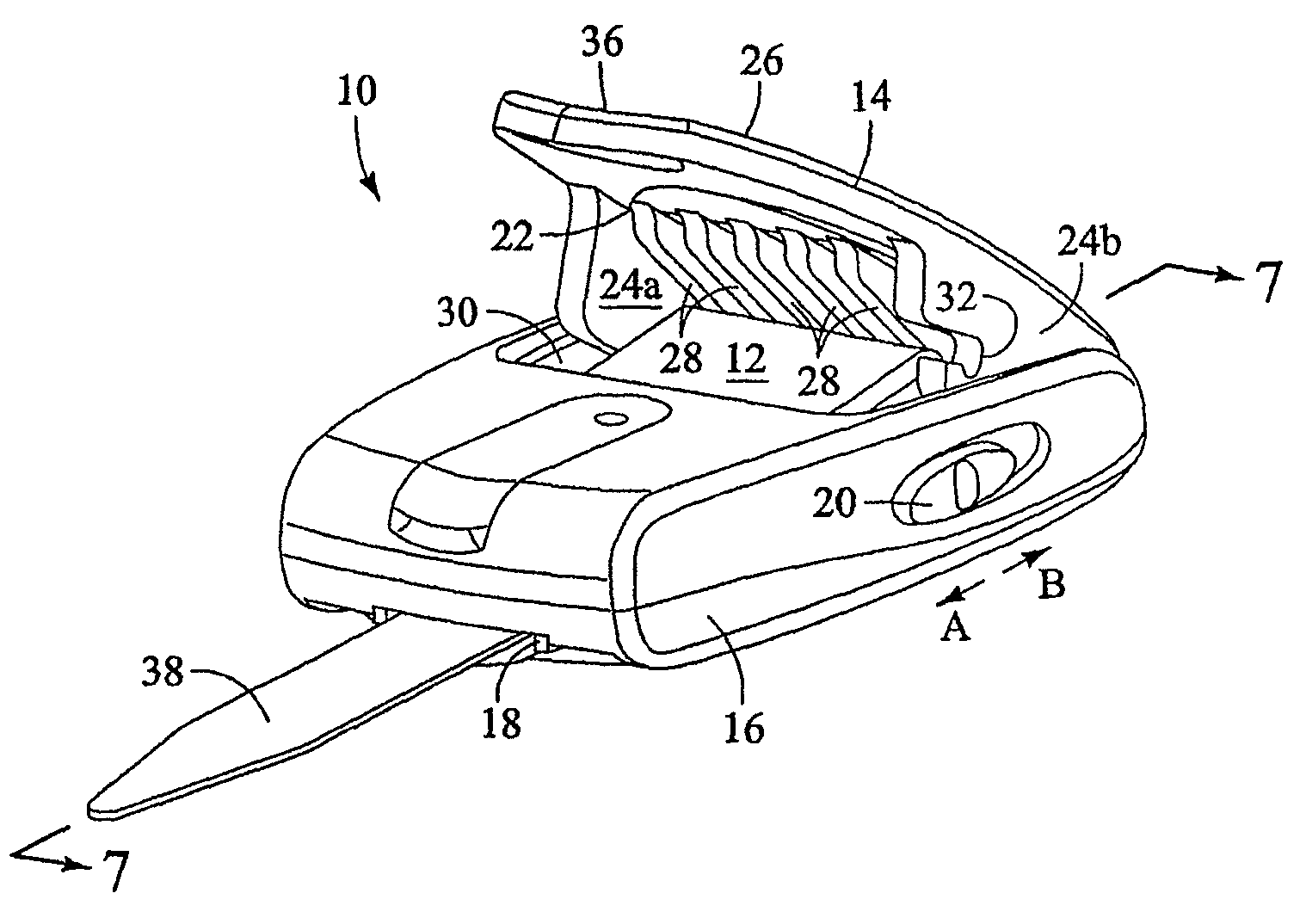
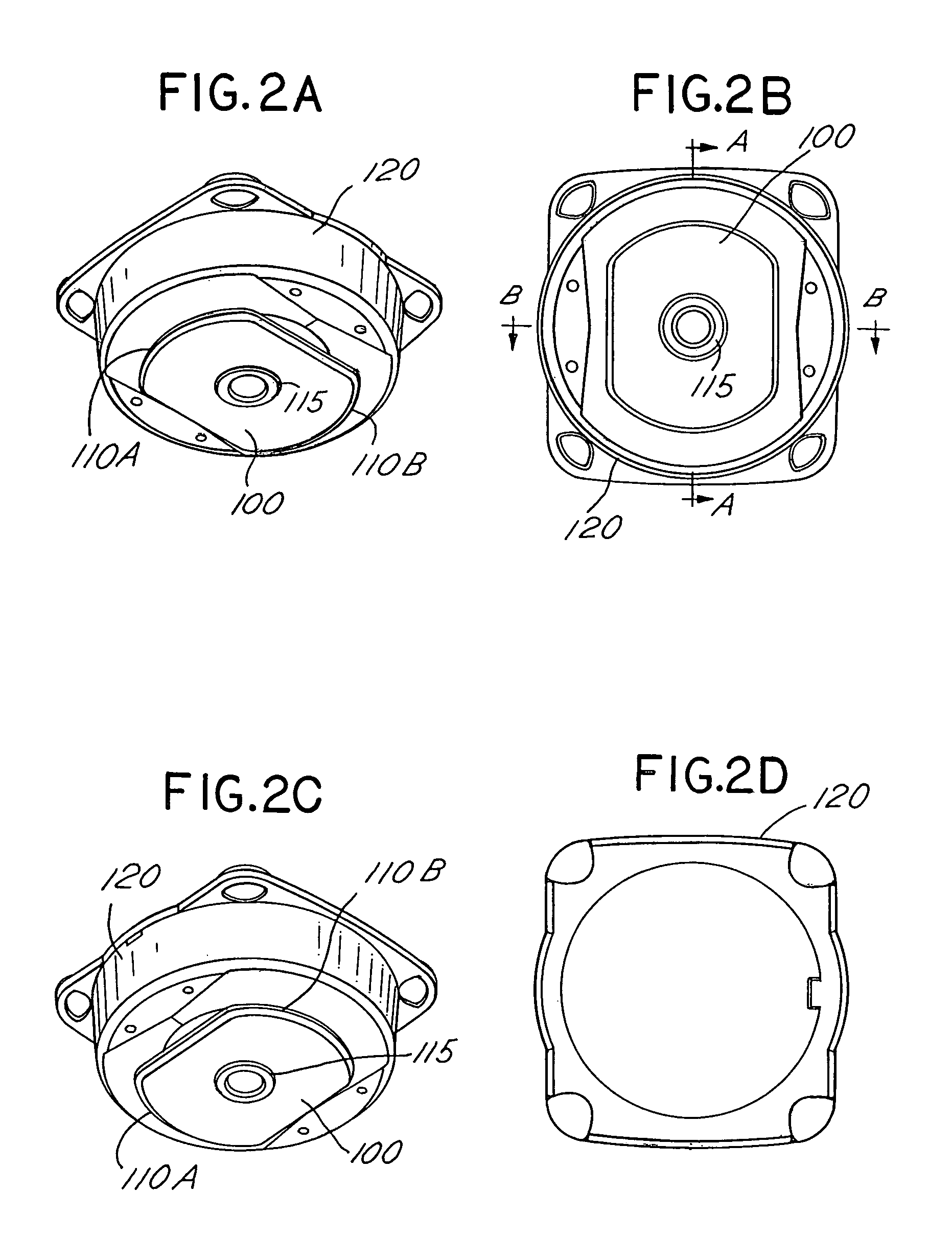
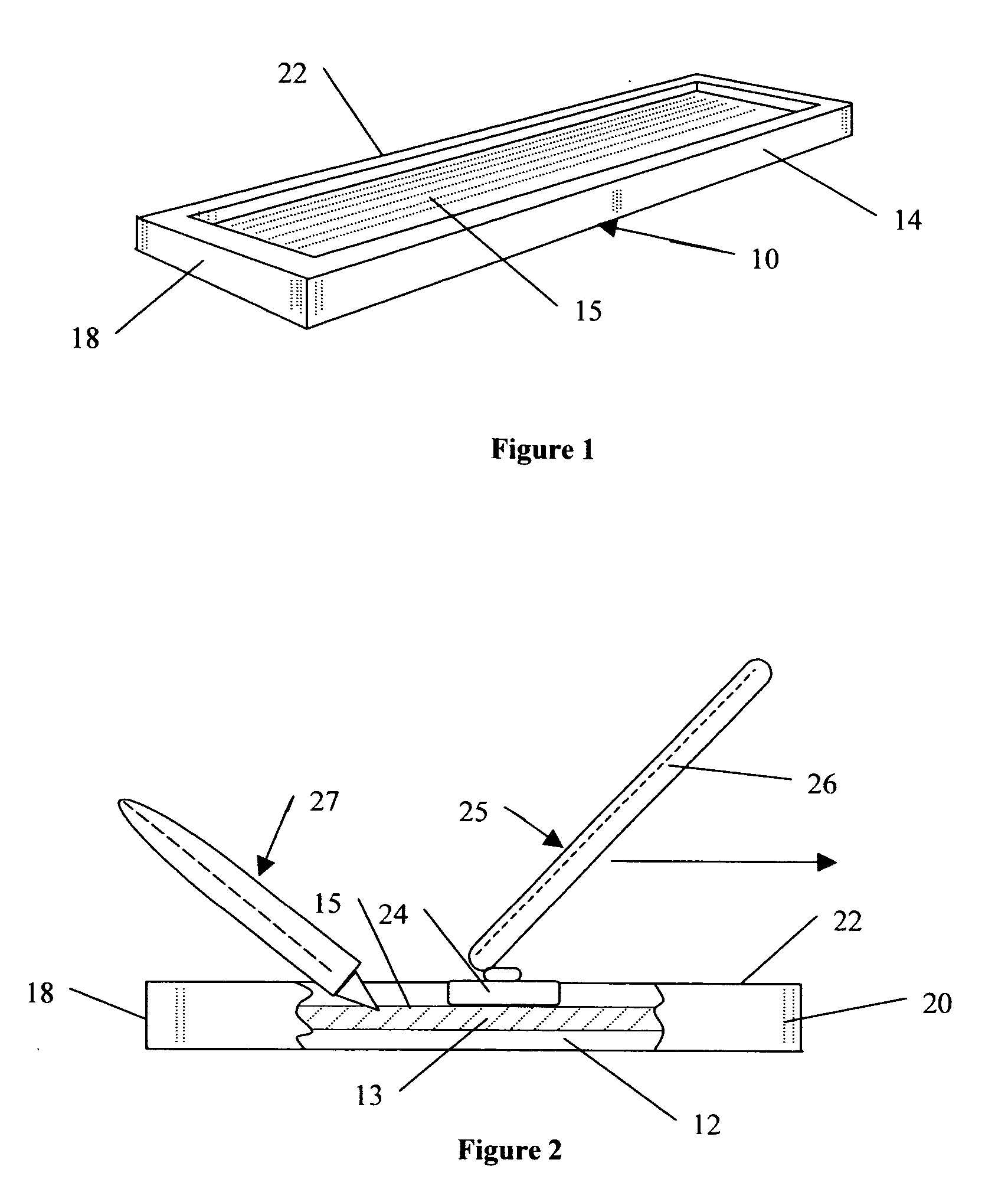
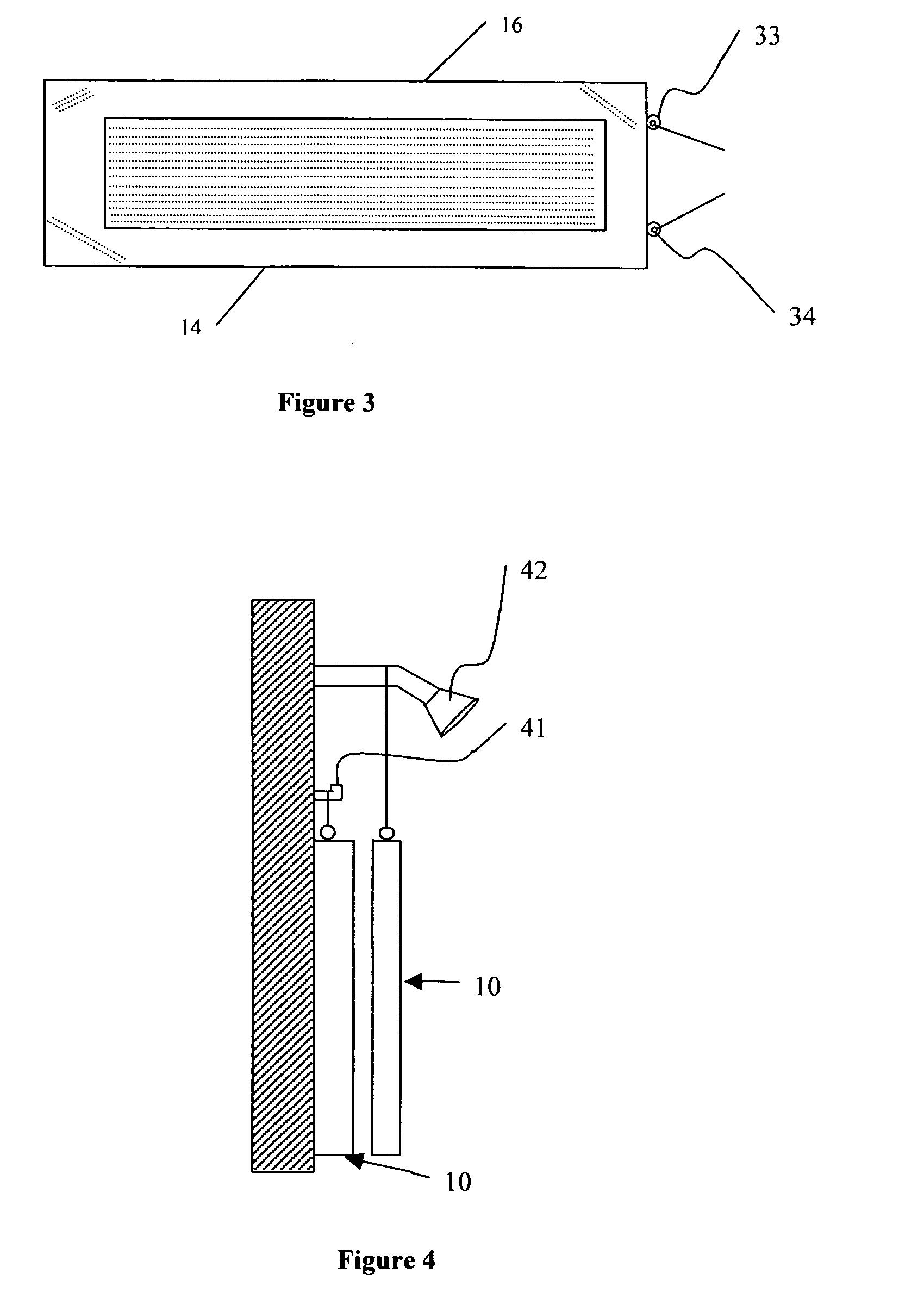
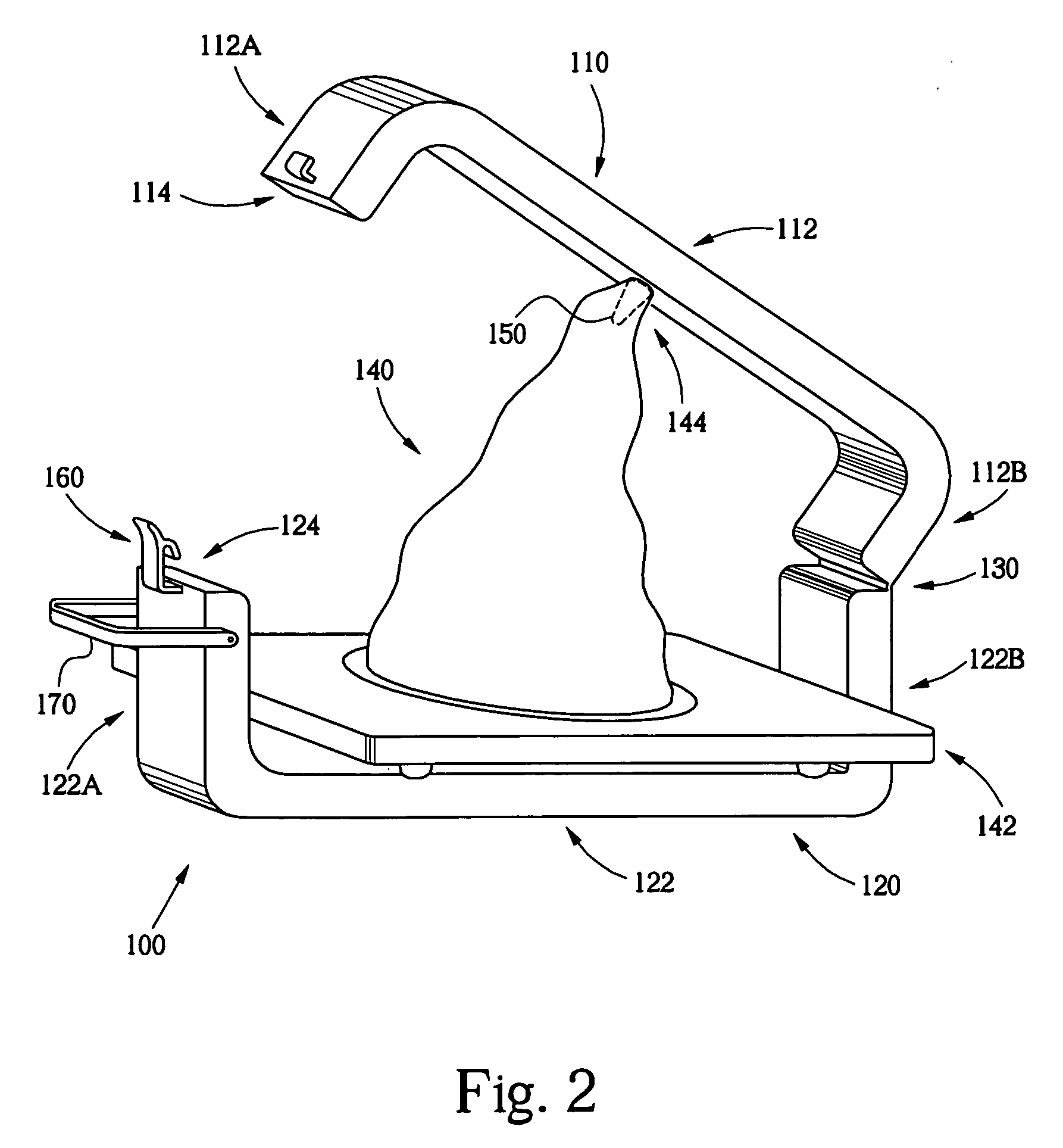
Particle preconcentrator
InactiveUSRE38797E1Compact and durableWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationDesorptionParticle physics
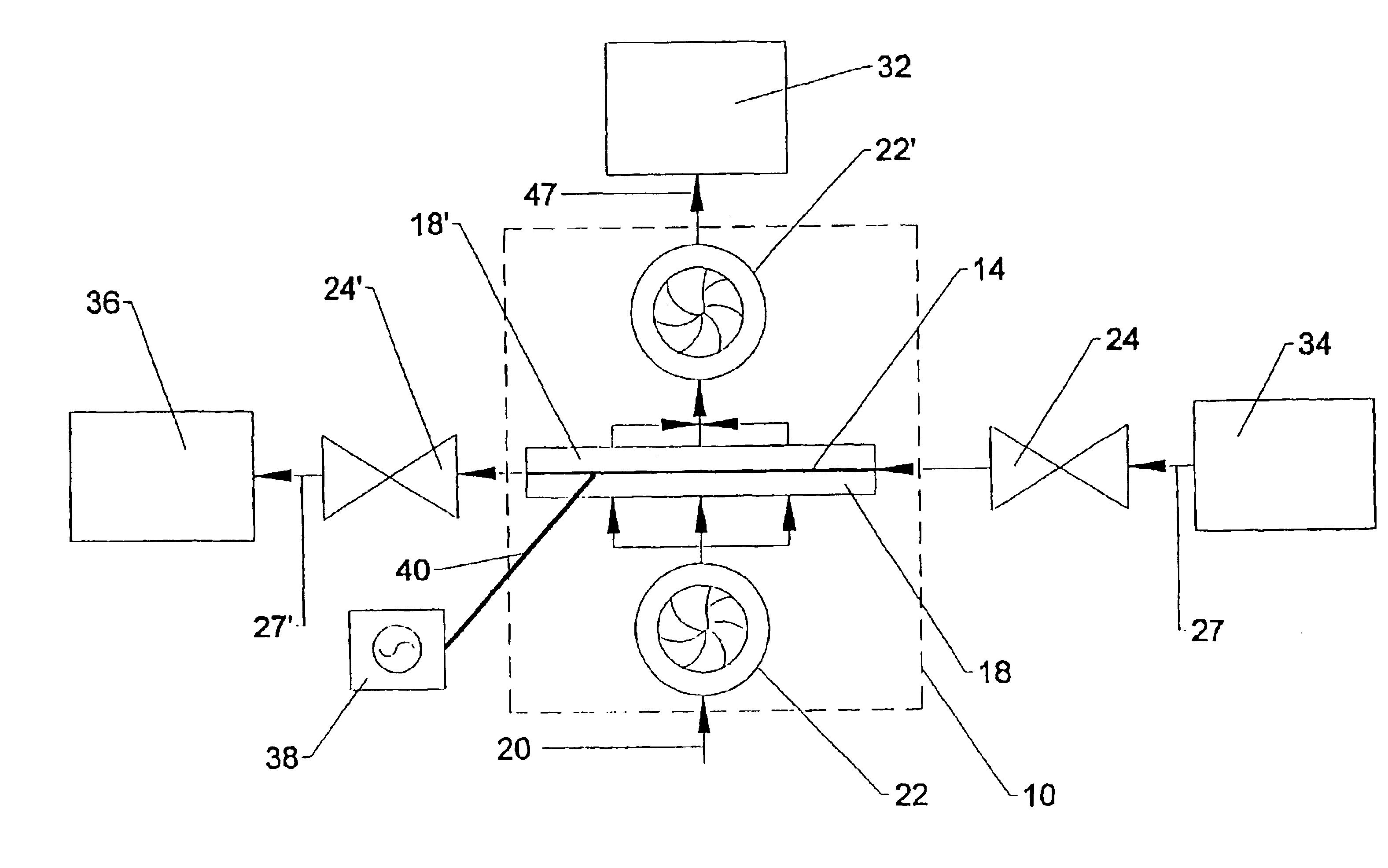
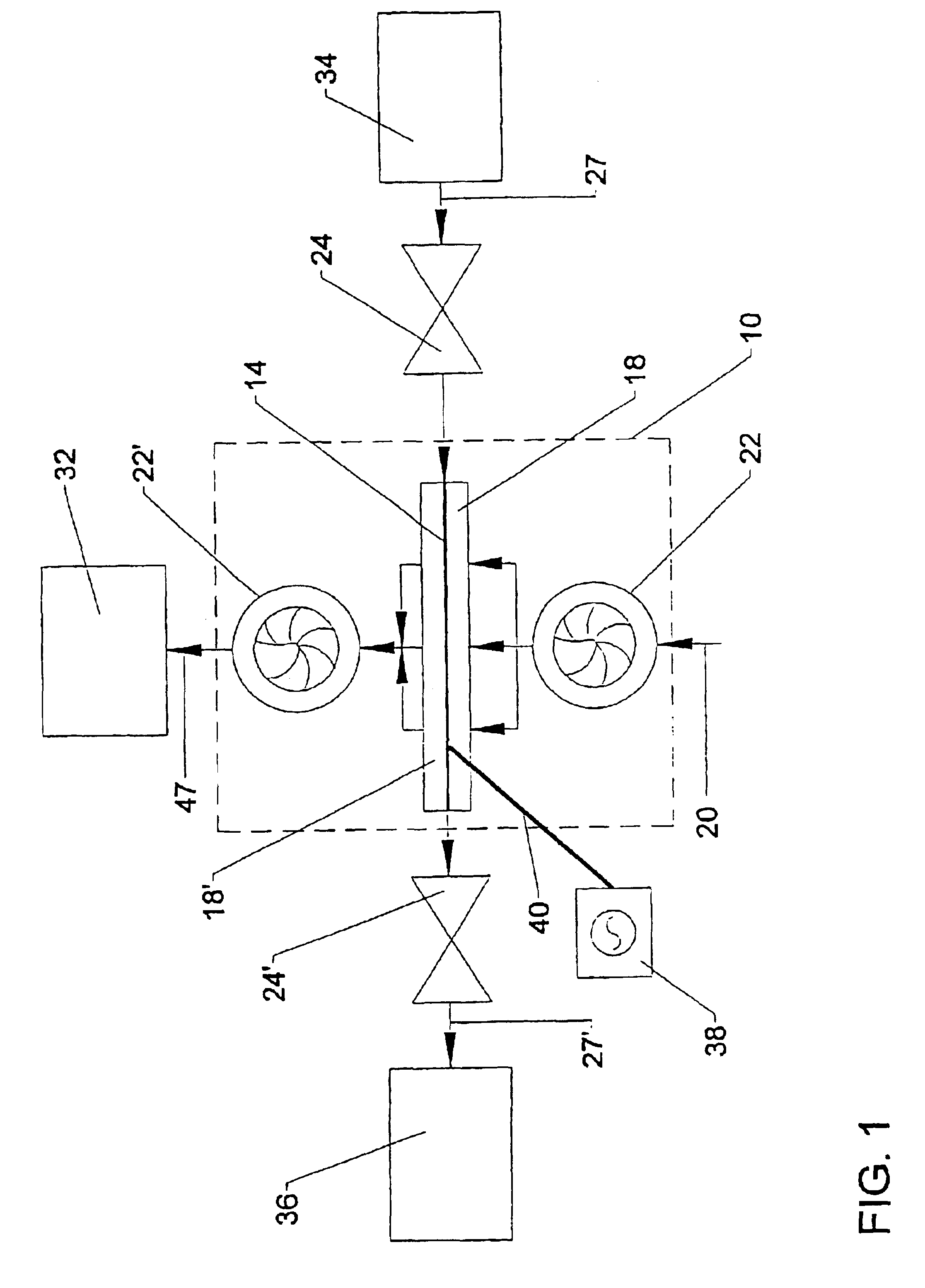
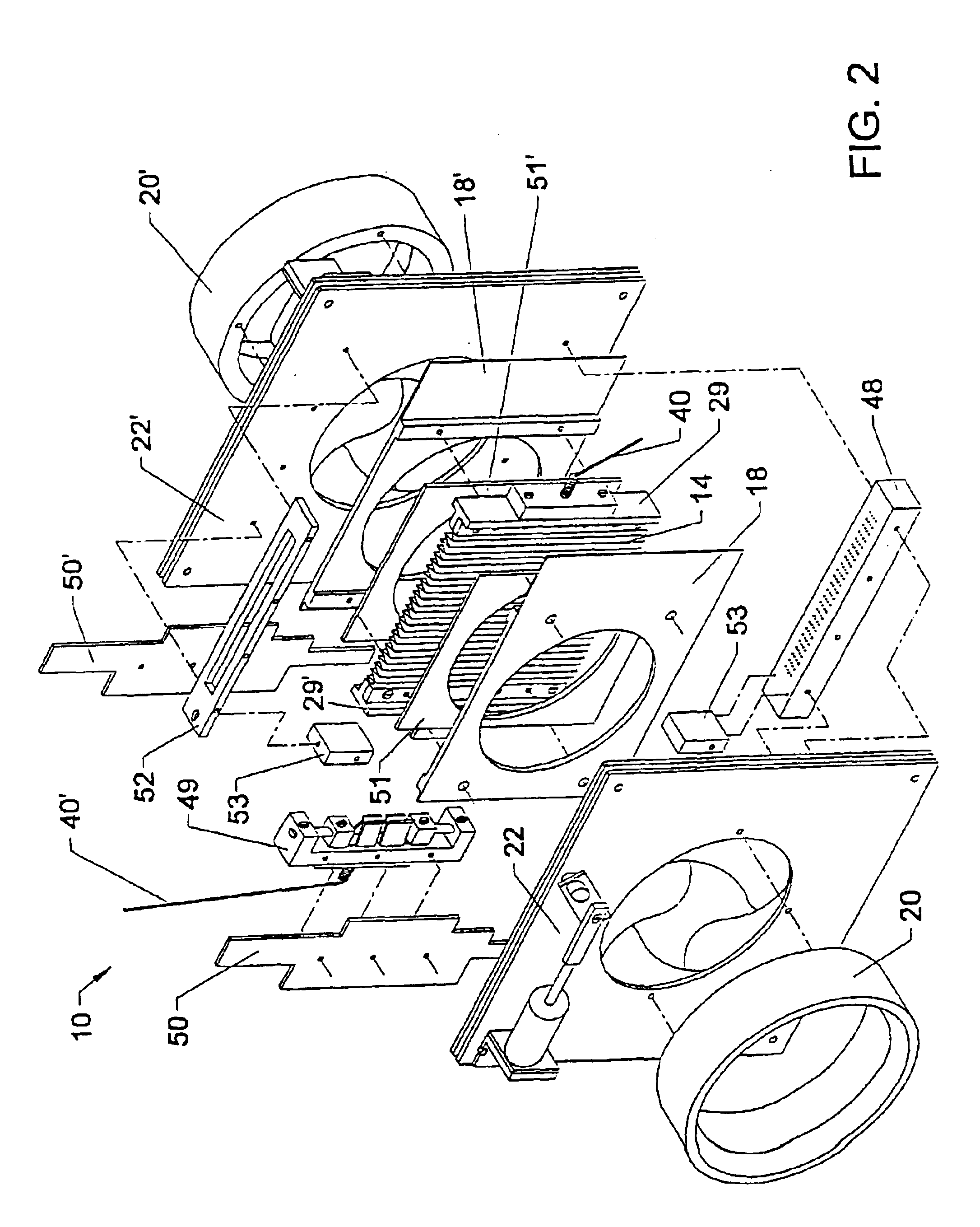
An apparatus and method for preconcentrating particles and vapors. The preconcentrator apparatus permits detection of highly diluted amounts of particles in a main gas stream, such as a stream of ambient air. A main gas stream having airborne particles entrained therein is passed through a pervious screen. The particles accumulate upon the screen, as the screen acts as a sort of selective particle filter. The flow of the main gas stream is then interrupted by diaphragm shutter valves, whereupon a cross-flow of carrier gas stream is blown parallel past the faces of the screen to dislodge the accumulated particles and carry them to a particle or vapor detector, such as an ion mobility spectrometer. The screen may be heated, such as by passing an electrical current there through, to promote desorption of particles therefrom during the flow of the carrier gas. Various types of screens are disclosed. The apparatus and method of the invention may find particular utility in the fields of narcotics, explosives detection and chemical agents.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Slip sheet
InactiveUS7013814B2Substantial shock absorbingCompact and durableRigid containersEngineeringSlide plate
A slip sheet pallet comprising a first sheet engageable with a stacked array which is to be supported; a second sheet attached to the first sheet; at least one flap connected to and extending outwardly from at least one of the first and second sheets and gripable by a lift truck gripping assembly; at least one of the first and second sheets comprising a compound sheet with a plurality of distinct connected layers.
Owner:SIGNODE IND GRP
Spring Strut Arrangement for Wheel Suspension of Motor Vehicles
InactiveUS20100308518A1Low costCompact and durableNon-rotating vibration suppressionResilient suspensionsShock absorberSuspension spring
The invention relates a spring strut arrangement for wheel suspensions of motor vehicles, which is formed from a telescoping shock absorber, a suspension spring element which is preferably made as a helical compression spring, and a preloaded spring element which is preferably made as a helical compression spring, the spring elements being supported by way of spring caps on the body of the motor vehicle and on a wheel suspension element and a third spring cap located in between being movably guided along the longitudinal axis of the shock absorber relative to the body by way of an electrically driven positioning drive which is located within the spring elements, the positioning drive having a positioning spindle which is pivoted around the shock absorber and an adjusting nut which is connected to the movable spring cap. According to the invention, the shock absorber with the shock absorber tube is located at the top on the body of the motor vehicle and the positioning spindle is pivoted on the shock absorber tube.
Owner:AUDI AG
Straddle-type vehicle and power unit
ActiveUS7905803B2Improve responseStable structureChain/belt transmissionToothed gearingsGroove widthPower unit
In a V-belt continuously variable transmission (CVT) of an ATV, a movable sheave half of a primary sheave is disposed on the outer side in the vehicle width direction with respect to a fixed sheave half, and a sheave drive mechanism for controlling the respective groove widths of the primary sheave and a secondary sheave through a driving force by an electric motor is located on the outer side in the vehicle width direction with respect to the movable sheave half of the primary sheave. A footboard of the ATV is located on the outer side of the V-belt CVT in the vehicle width direction and below a primary sheave shaft and a secondary sheave shaft. A portion of the electric motor is located above and in front of the primary sheave shaft as viewed in the sheave shaft direction. A straddle-type vehicle having the compact, yet durable V-belt continuously variable transmission achieves a speed change operation highly responsive to the vehicle running condition.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Gear shifting force detection positioning and clamping device for multi-type shifter assembly
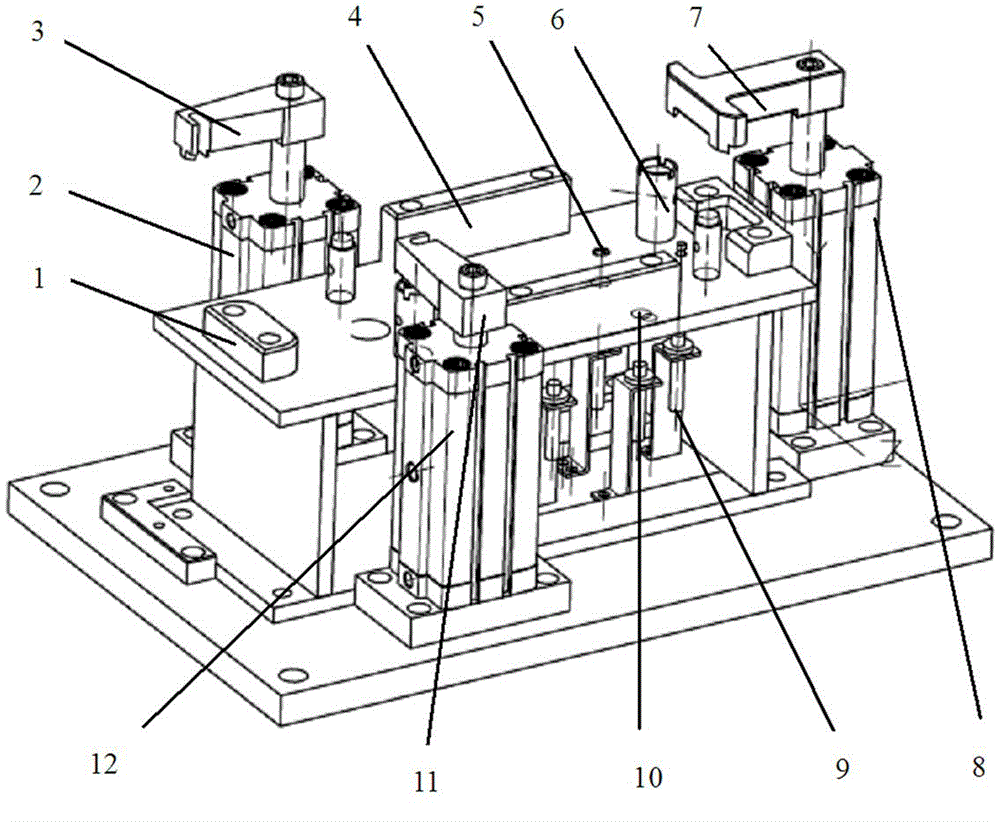
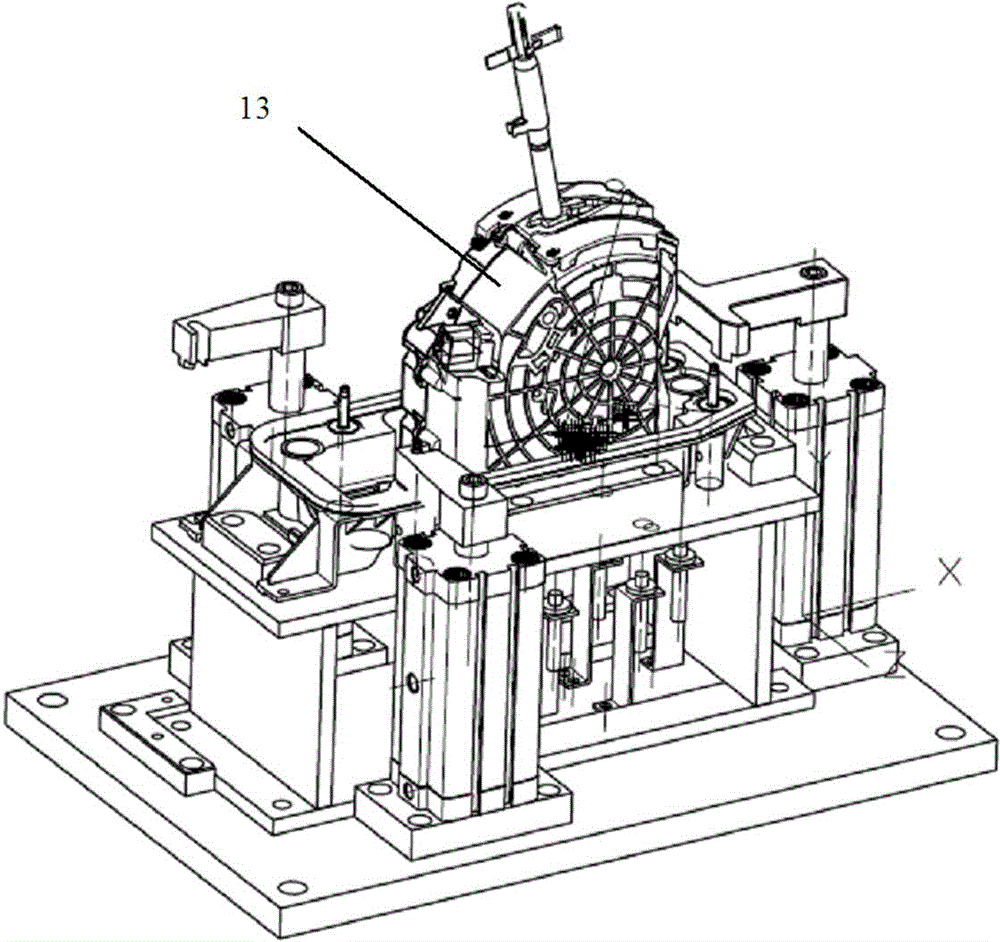
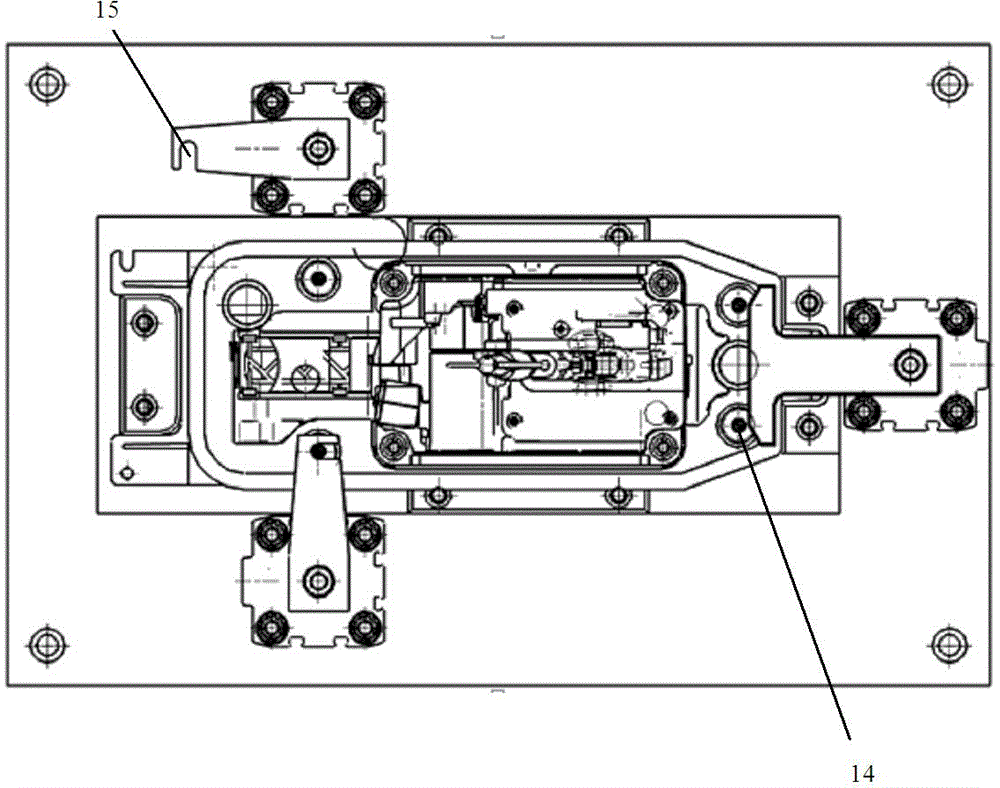
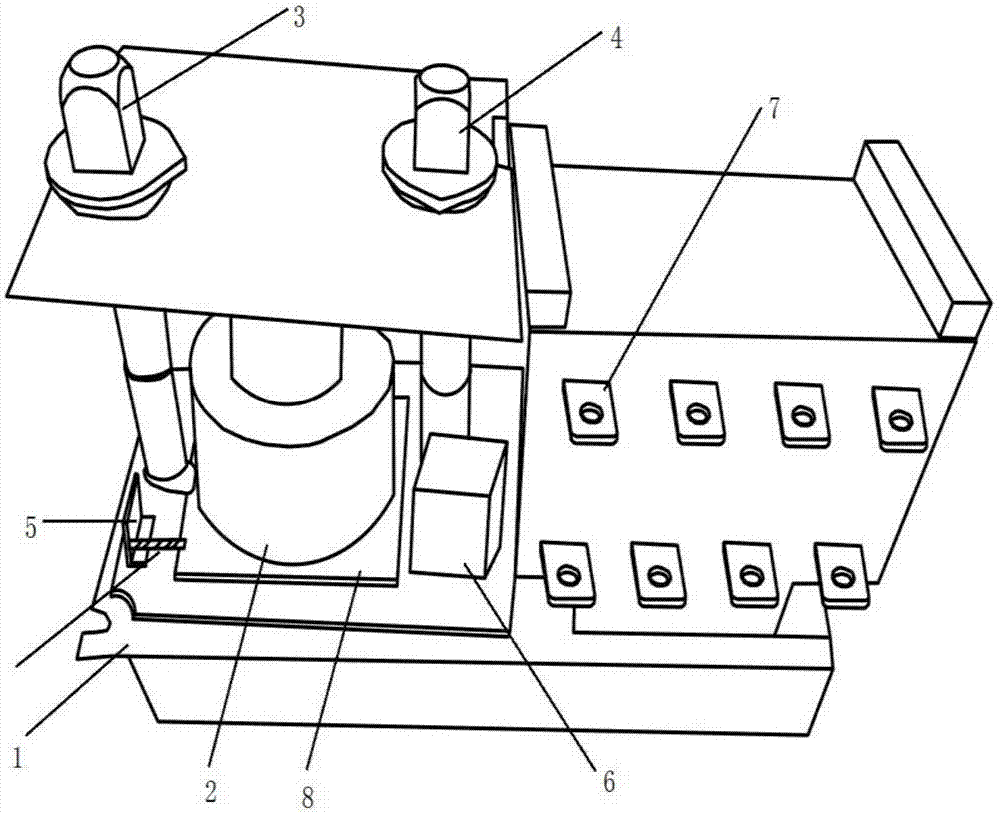
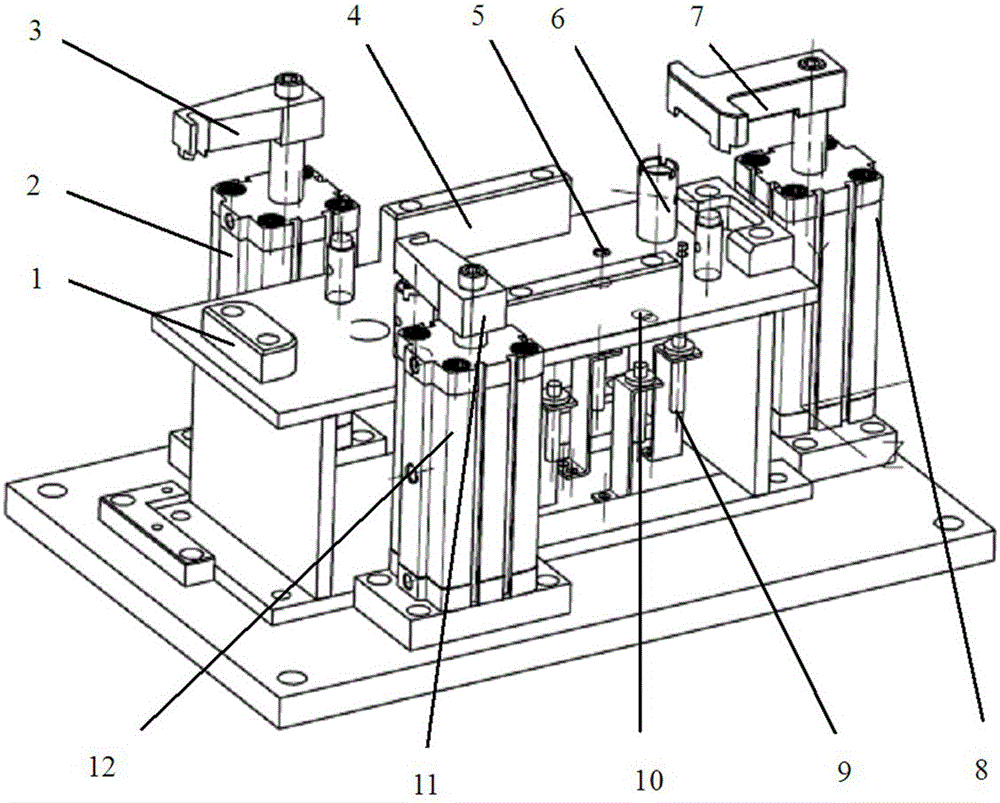
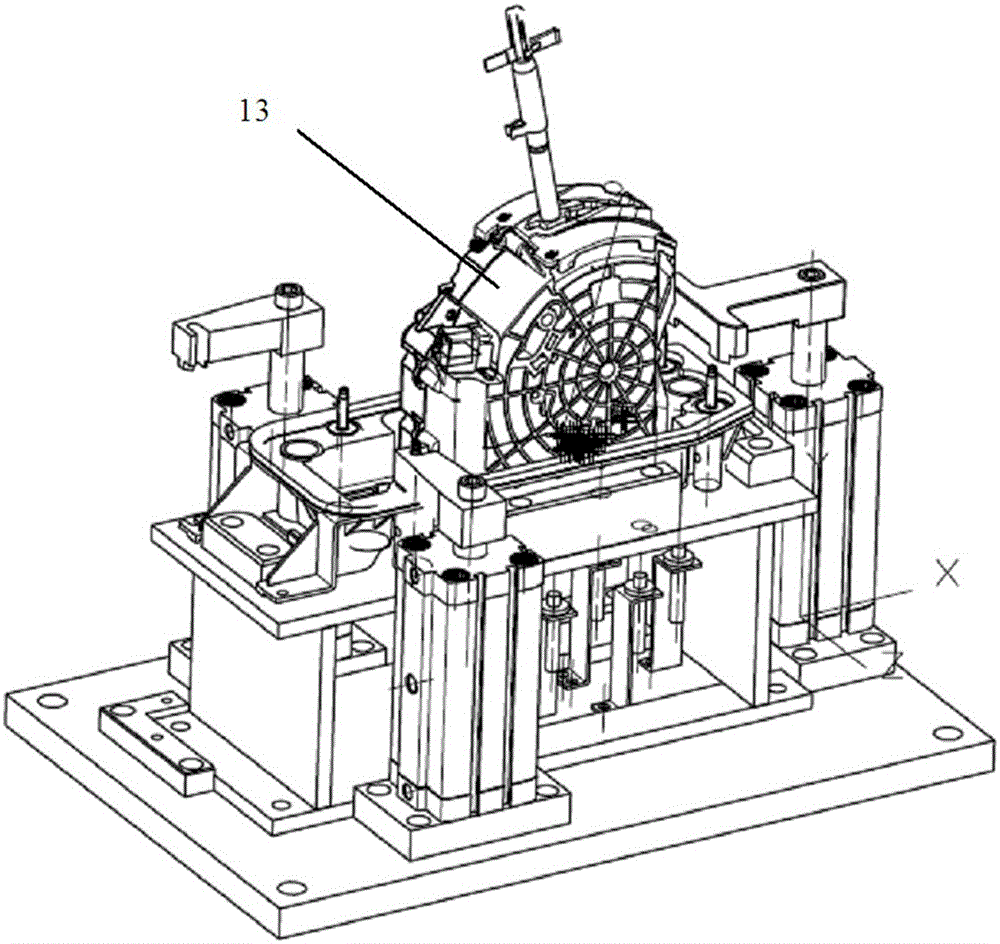
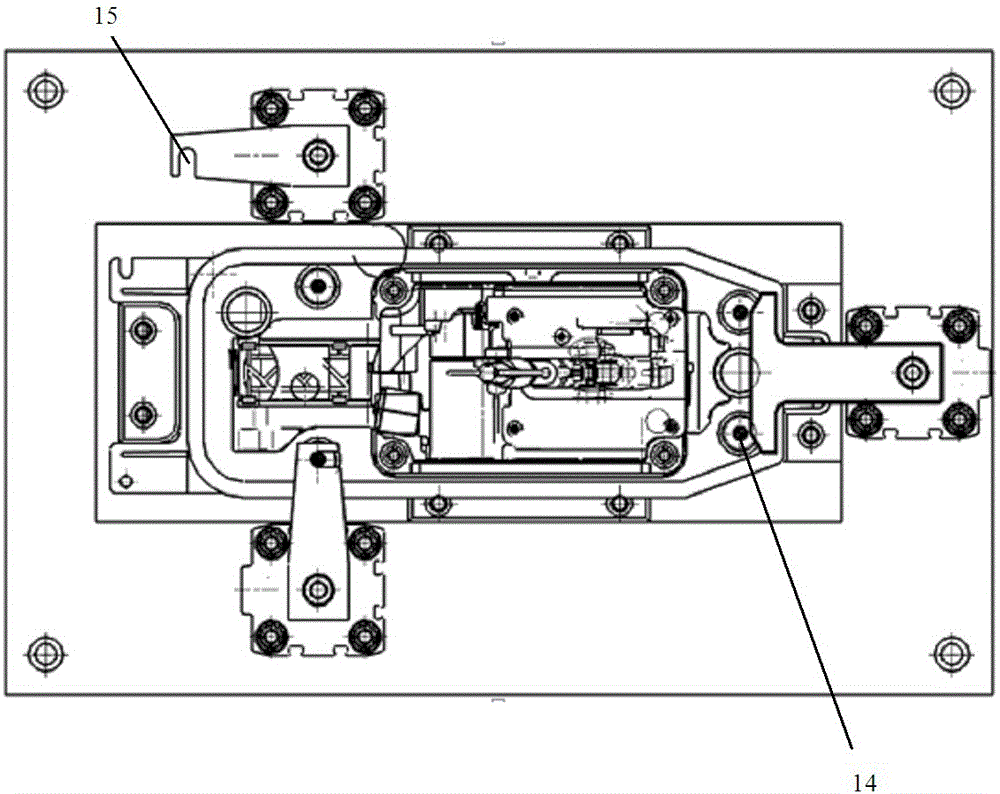
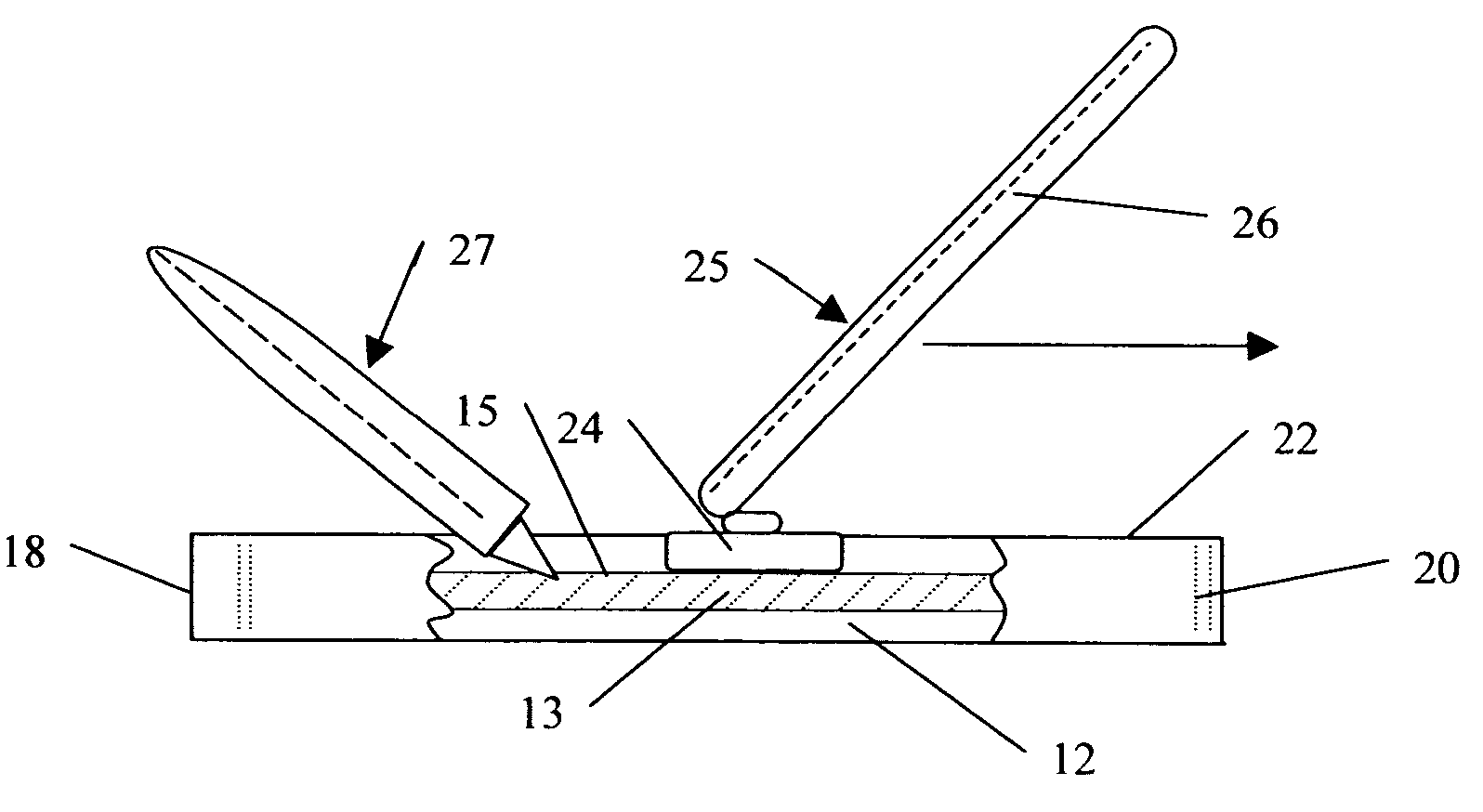
ActiveCN104942731ACompact and durableQuality assuranceWork holdersControl engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a gear shifting force detection positioning and clamping device for a multi-type shifter assembly. A positioning assembly is based on the positioning principle of being provided with two pins on each face, and a coarse positioning mode and a fine positioning mode are combined for positioning. The positioning assembly comprises two positioning plates, two positioning blocks, two type distinguishing detection bars and two positioning in-place detection probes, wherein the two positioning plates and the two positioning blocks are used for conducting coarse positioning. When a shifter is fixed on the positioning assembly, the approximate position of the shifter is fixed preliminarily through the positioning plates and the positioning blocks first, then the two detection bars and sensors fixed below the detection bars can act to judge the type of the shifter, meanwhile, the two positioning in-place detection probes with springs are pressed downwards by the shifter, distance change happens between the positioning in-place detection probes and sensors fixed below the positioning in-place detection probes, and in this way, whether the shifter is fixed in place or not can be judged. The positioning assembly is a detachable module type positioning assembly, and different positioning assemblies can be correspondingly used according to the requirements for different types of shifters.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Spring strut arrangement for wheel suspension of motor vehicles
InactiveUS8573573B2Low costCompact and durableResilient suspensionsVehicle springsShock absorberSuspension spring
The invention relates a spring strut arrangement for wheel suspensions of motor vehicles, which is formed from a telescoping shock absorber, a suspension spring element which is preferably made as a helical compression spring, and a preloaded spring element which is preferably made as a helical compression spring, the spring elements being supported by way of spring caps on the body of the motor vehicle and on a wheel suspension element and a third spring cap located in between being movably guided along the longitudinal axis of the shock absorber relative to the body by way of an electrically driven positioning drive which is located within the spring elements, the positioning drive having a positioning spindle which is pivoted around the shock absorber and an adjusting nut which is connected to the movable spring cap. According to the invention, the shock absorber with the shock absorber tube is located at the top on the body of the motor vehicle and the positioning spindle is pivoted on the shock absorber tube.
Owner:AUDI AG
Unmanned flying device
ActiveUS10093417B2Easy constructionEasy to transportUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftCouplingEngineering
An unmanned flying device including a body, a first blade and at least a second blade, and a coupling assembly for coupling the first blade and the at least second blade to the body. Both the first blade and the at least second blade are rotateable about the body and are deployable away from the body via rotation of the first and the at least second blades about the body. The coupling assembly urges the collapsing of the first blade and the at least second blade towards the body.
Owner:ASCENT AEROSYST INC
Powered trailer steering and hitching assist
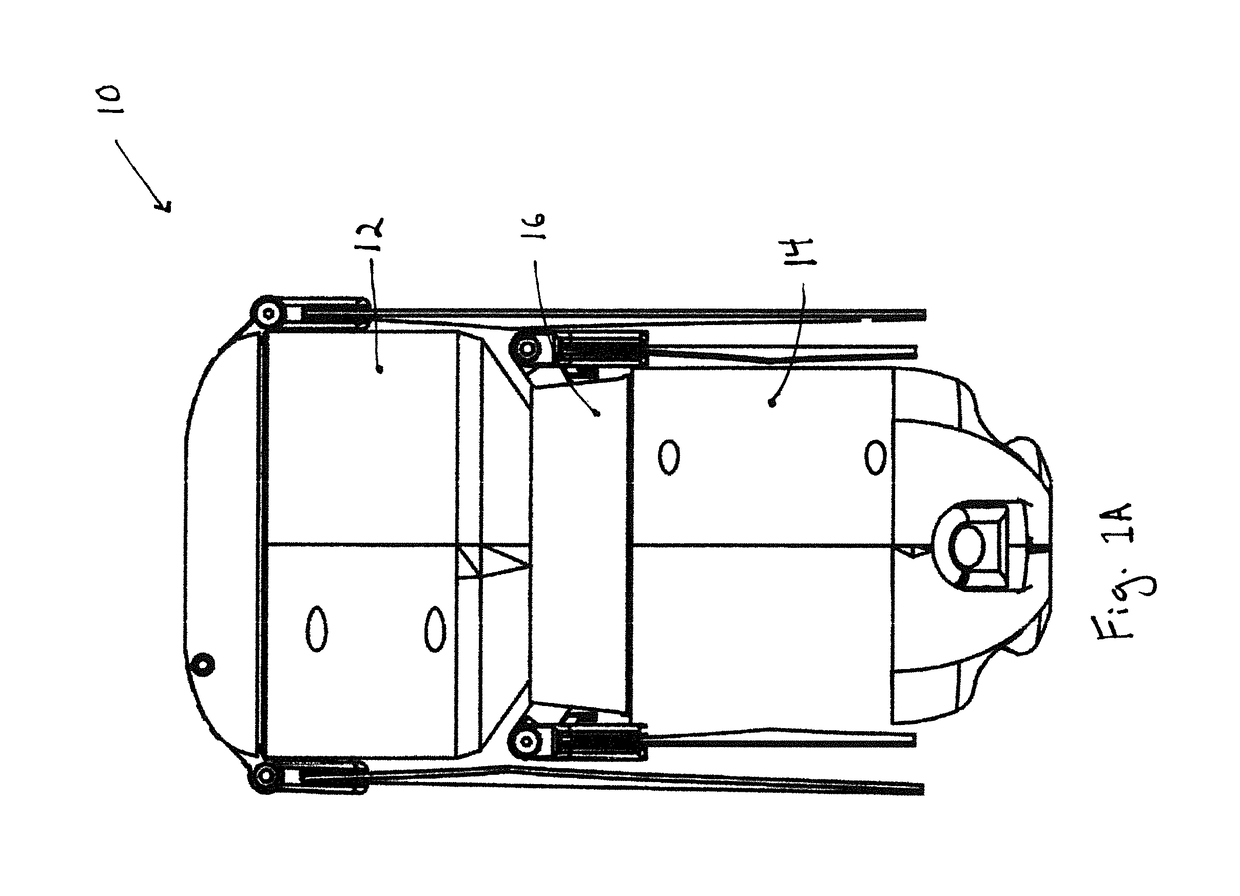
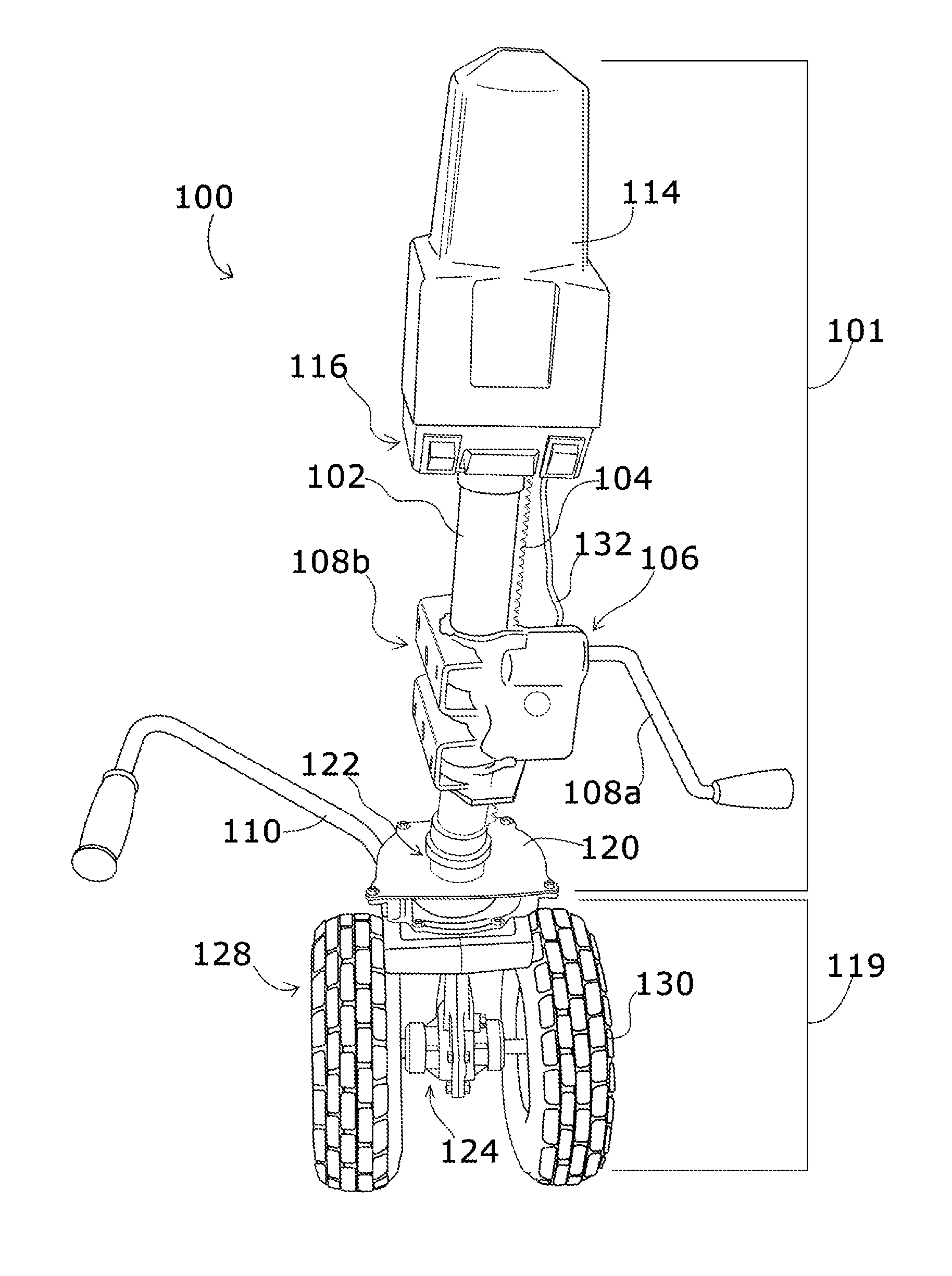
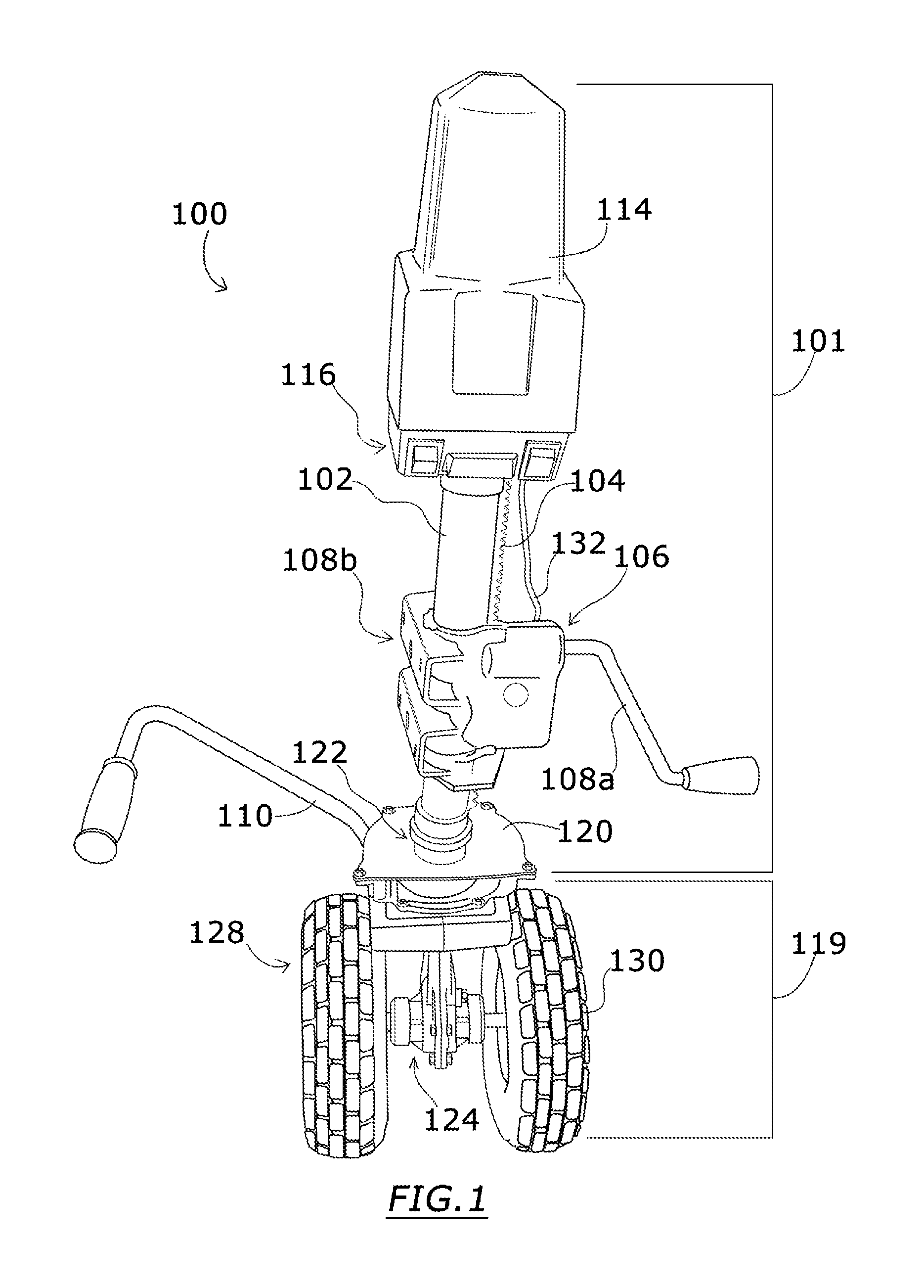
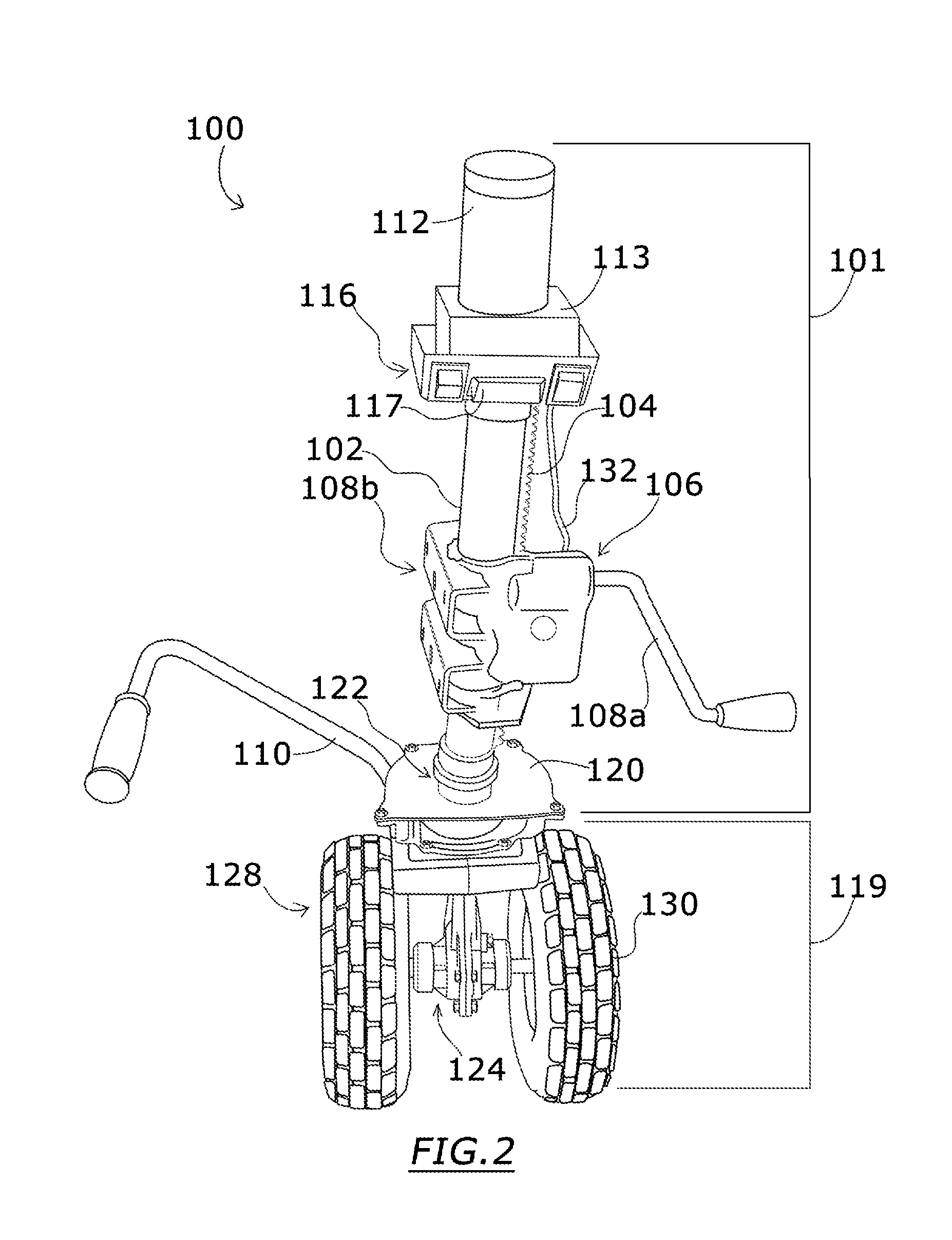
InactiveUS20140202778A1Addressing Traction InsufficiencyCompact and durableVehicle cleaning apparatusTractor-trailer combinationsDrive shaftJackscrew
A stowable powered jack for steering a boat trailer includes an electric motor turning a drive shaft running longitudinally through a support tube which is mounted to a trailer frame. The drive shaft powers a transmission which sits between a pair of wheels driven by a transverse axle. Controls for the motor provide at least forward and reverse motion for wheels. The transmission is sealed within a housing that is swivels in relation to the fixed support tube. An extendable handle facilitates steering.
Owner:BARRETT RICHARD TERRELL +1
Power Tool and Transmission Thereof
InactiveUS20150128429A1Compact and durableAdd supportMetal sawing devicesGearboxesGear driveMedial axis
The disclosure relates to a transmission for a power tool, comprising an input gear driven by a driver, an intermediate shaft carrying first and second intermediate gears, the first intermediate gear being meshed with the input gear, an output shaft carrying an output gear, the output gear being meshed with the second intermediate gear for driving a tool bit, and proximal and distal bearings supporting proximal and distal ends of the intermediate shaft respectively. The first intermediate gear is formed with a receptacle portion which is recessed from a proximal end surface of the first intermediate gear in an axial direction towards a distal side, the proximal bearing being received in the receptacle portion at least in part in the axial direction. The disclosure also relates to a power tool comprising the above transmission. The disclosure provides a compact and robust structure.
Owner:BOSCH POWER TOOLS CHINA +1
Package decoration with pop-up display
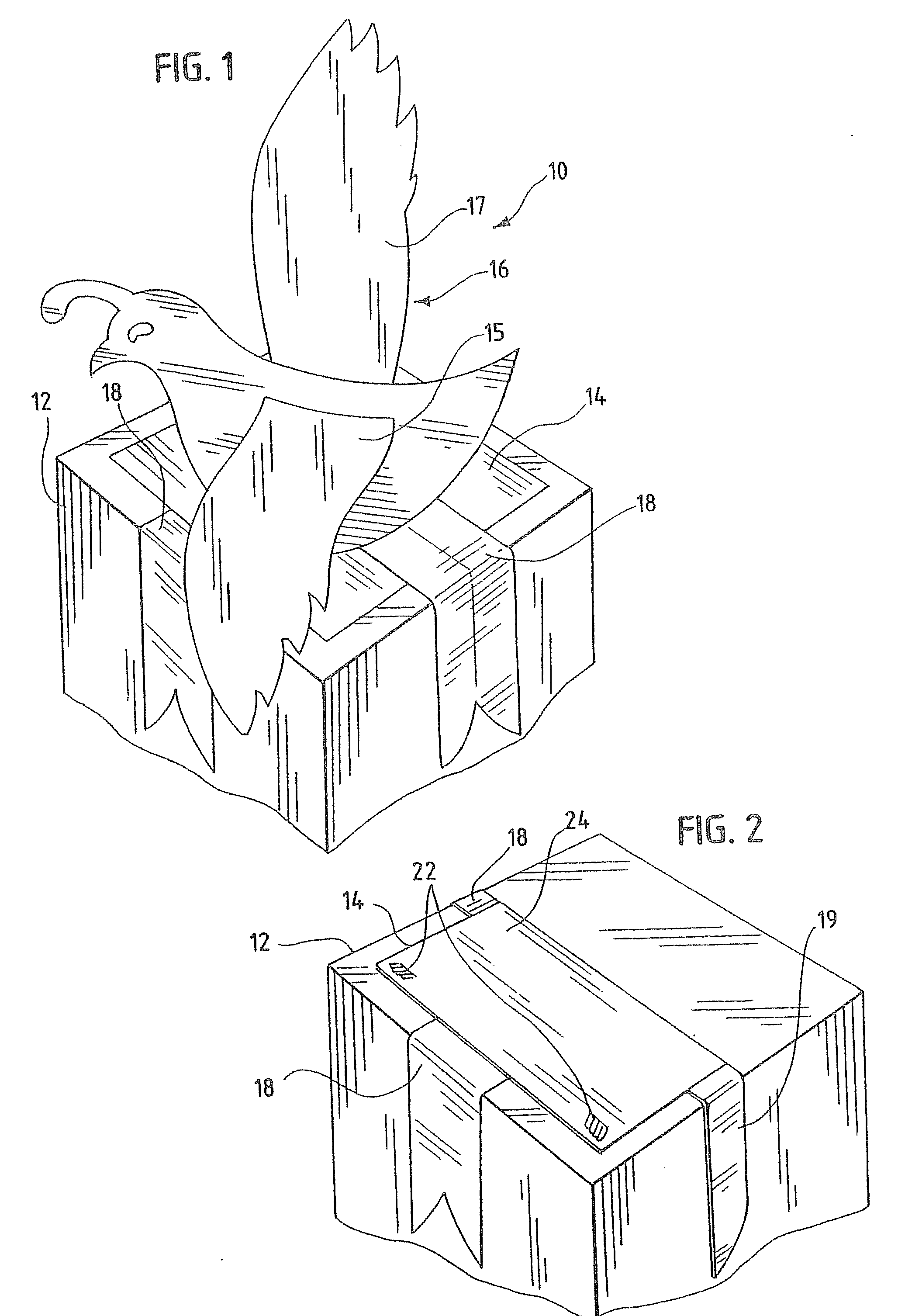
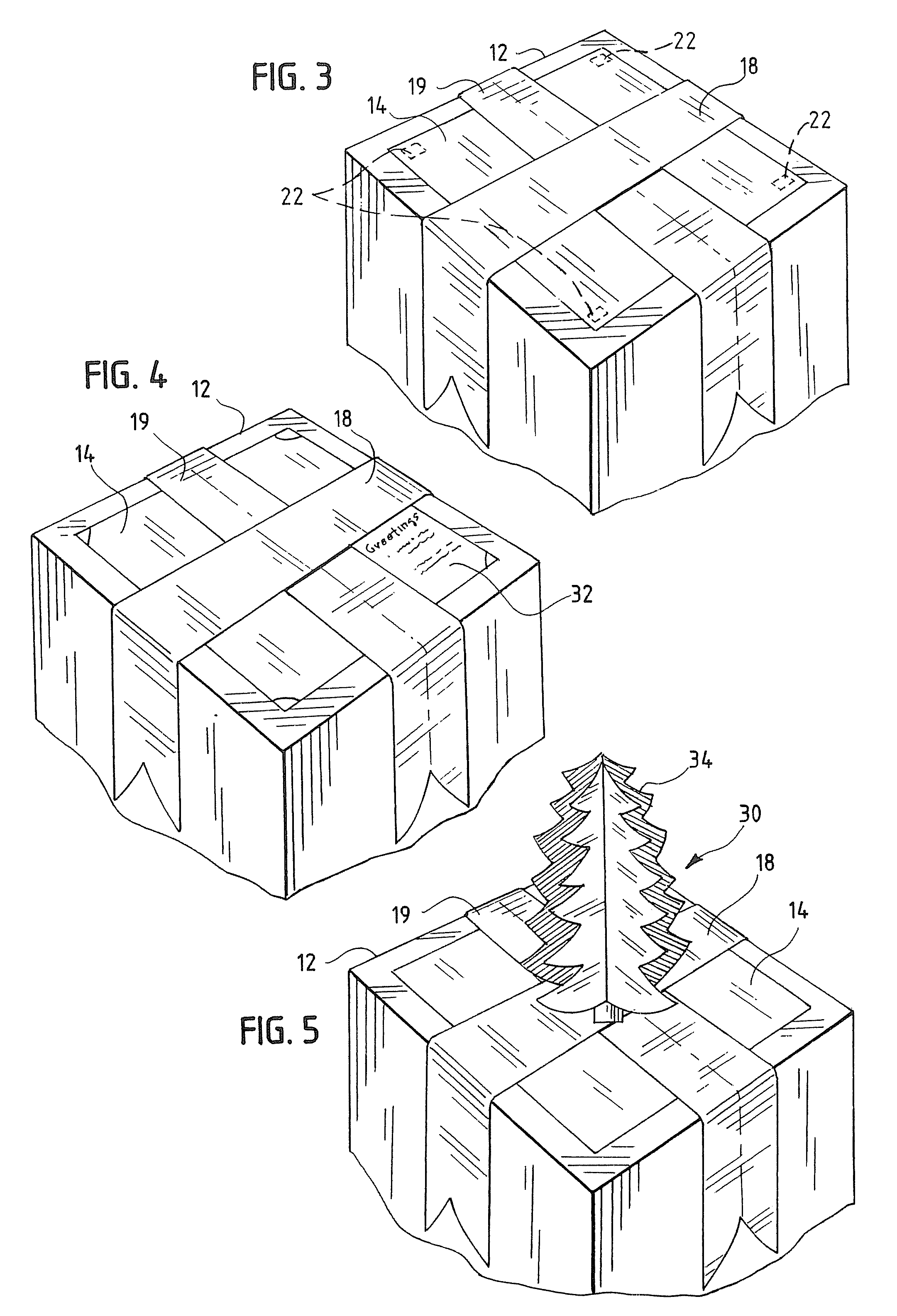
InactiveUS20070007167A1Quick and easy to openCompact and durableOther accessoriesContainer/bottle contructionEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A package decoration having a foldable panel and pop-up decoration affixed to the panel. The panel and the pop-up decoration are foldable into a flat format, the pop-up decoration folding between folded portions of the panel. The pop-up decoration configured and printed, and the panel printed to provide an occasion specific decoration. The panel may include a printed greeting and other package wrappings, such as ribbons may also be included with the panel and pop-up decoration.
Owner:PETTER MARTA
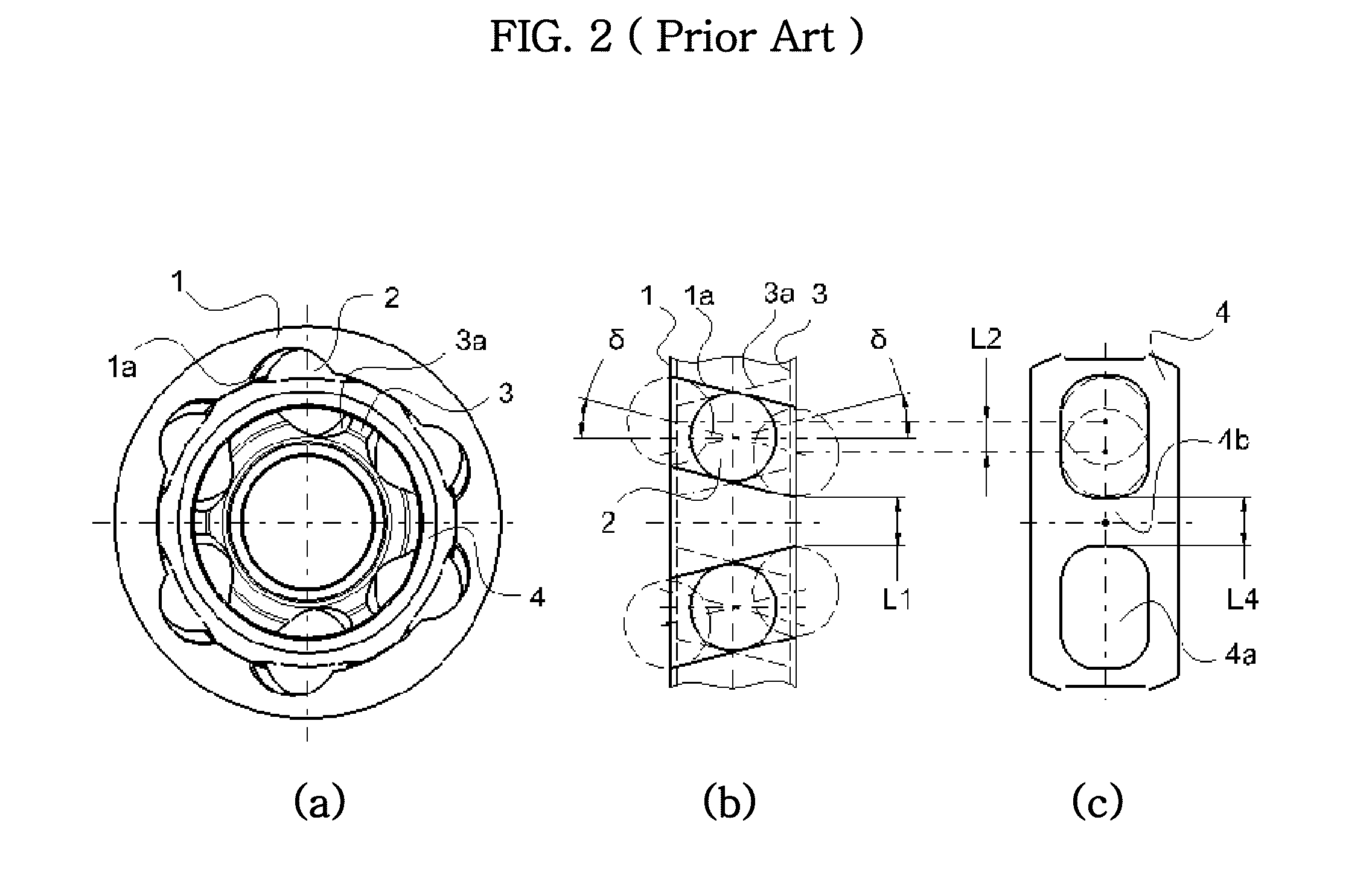
Cross Groove Type Constant Velocity Joint with Composite Groove Patterns
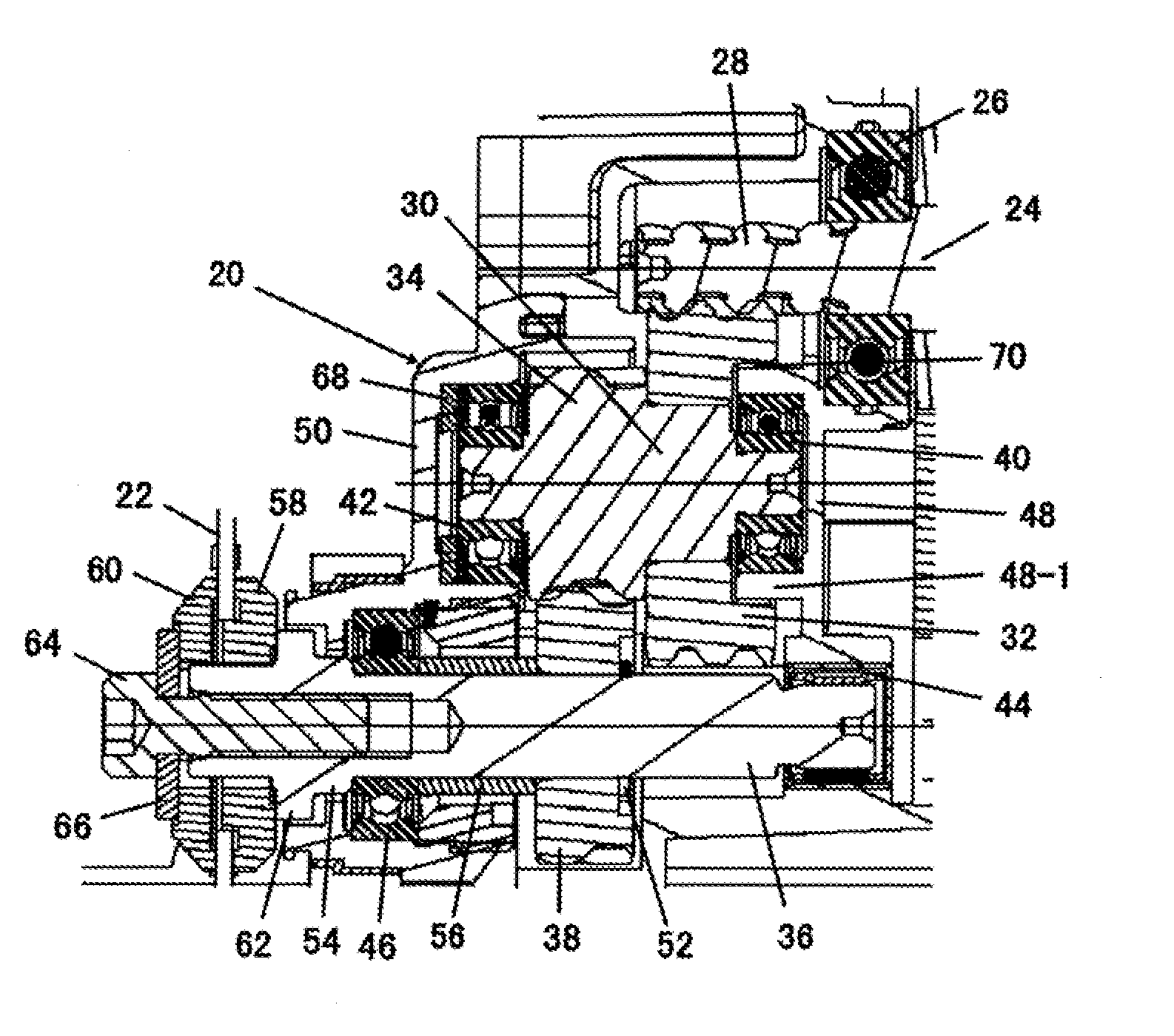
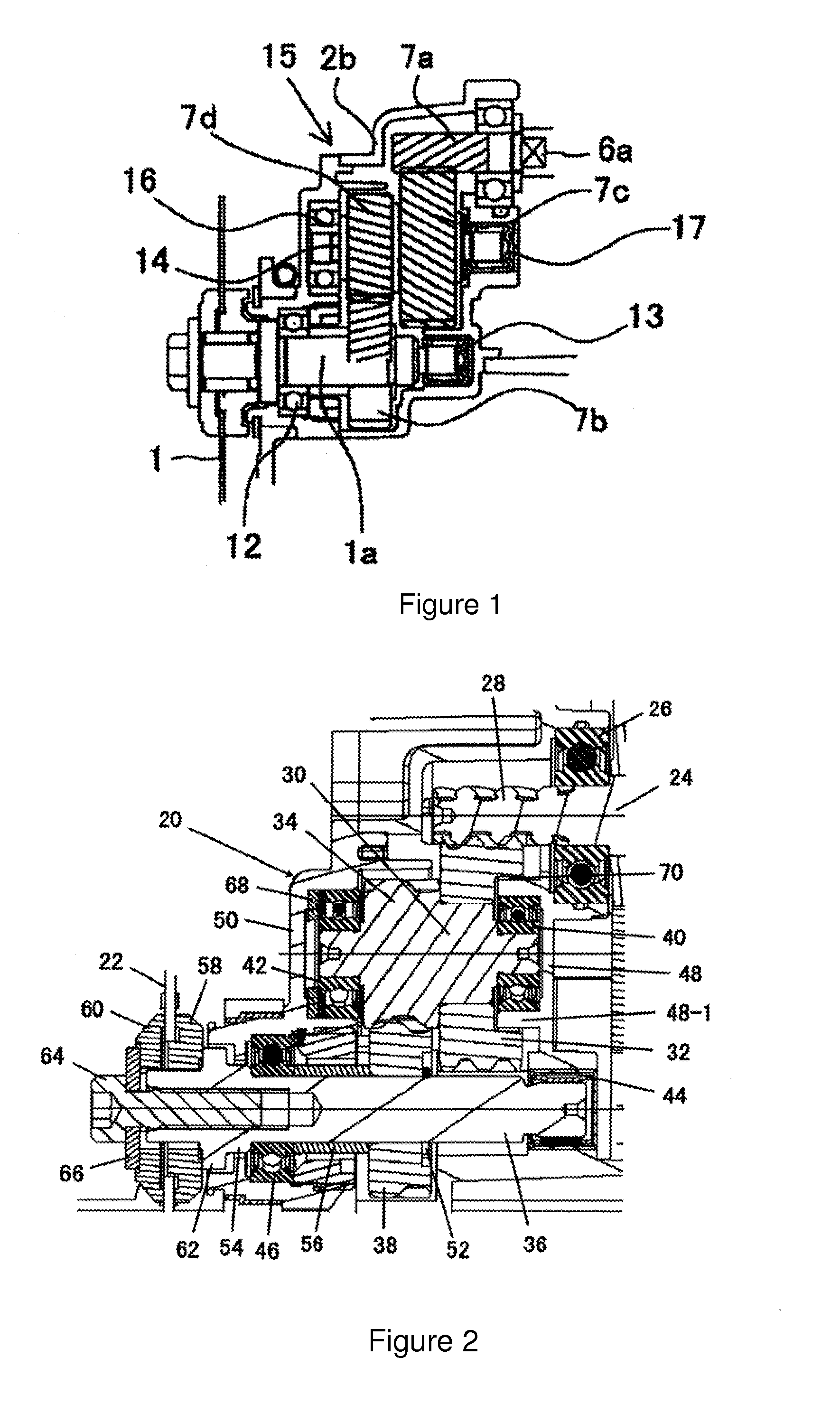
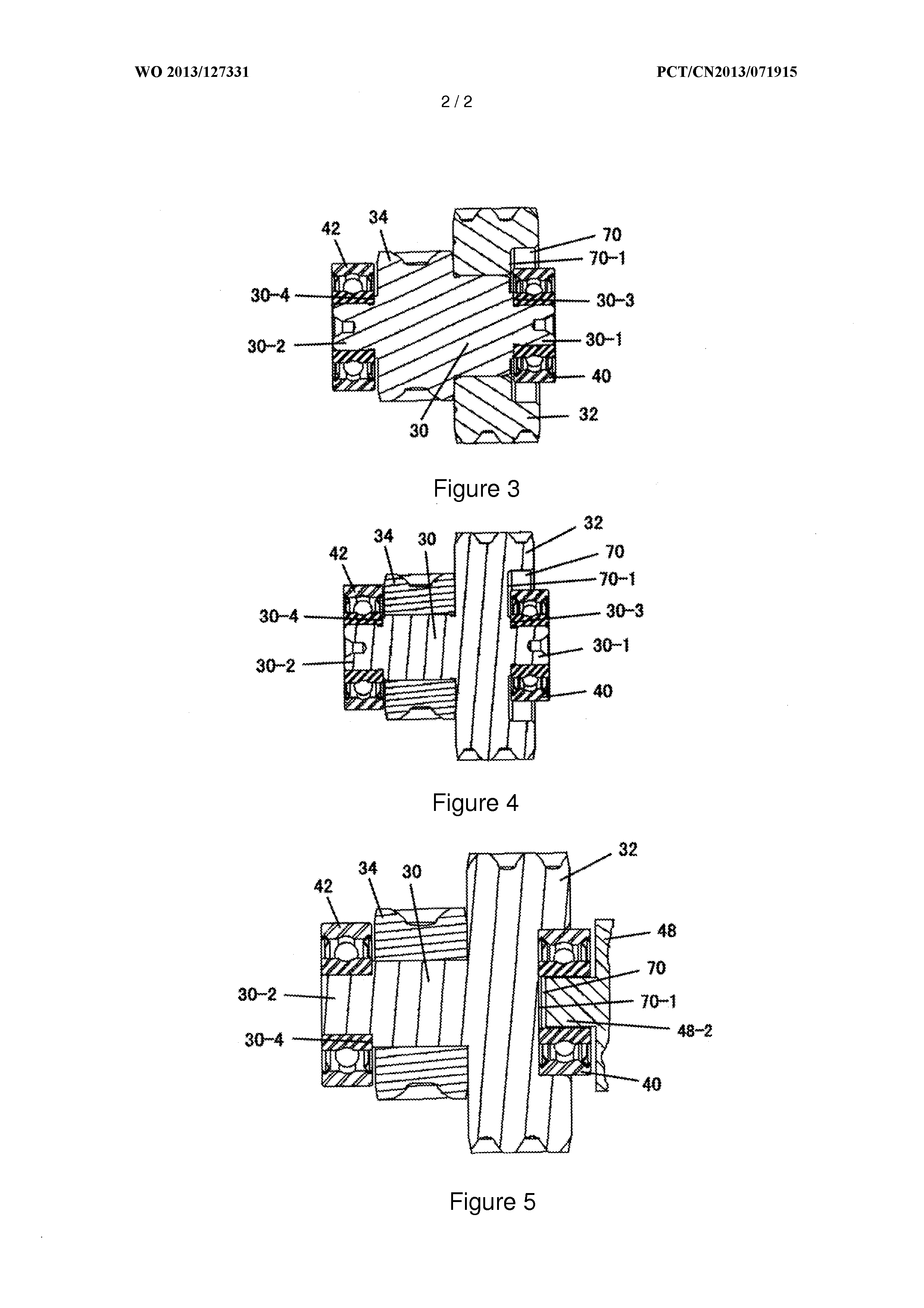
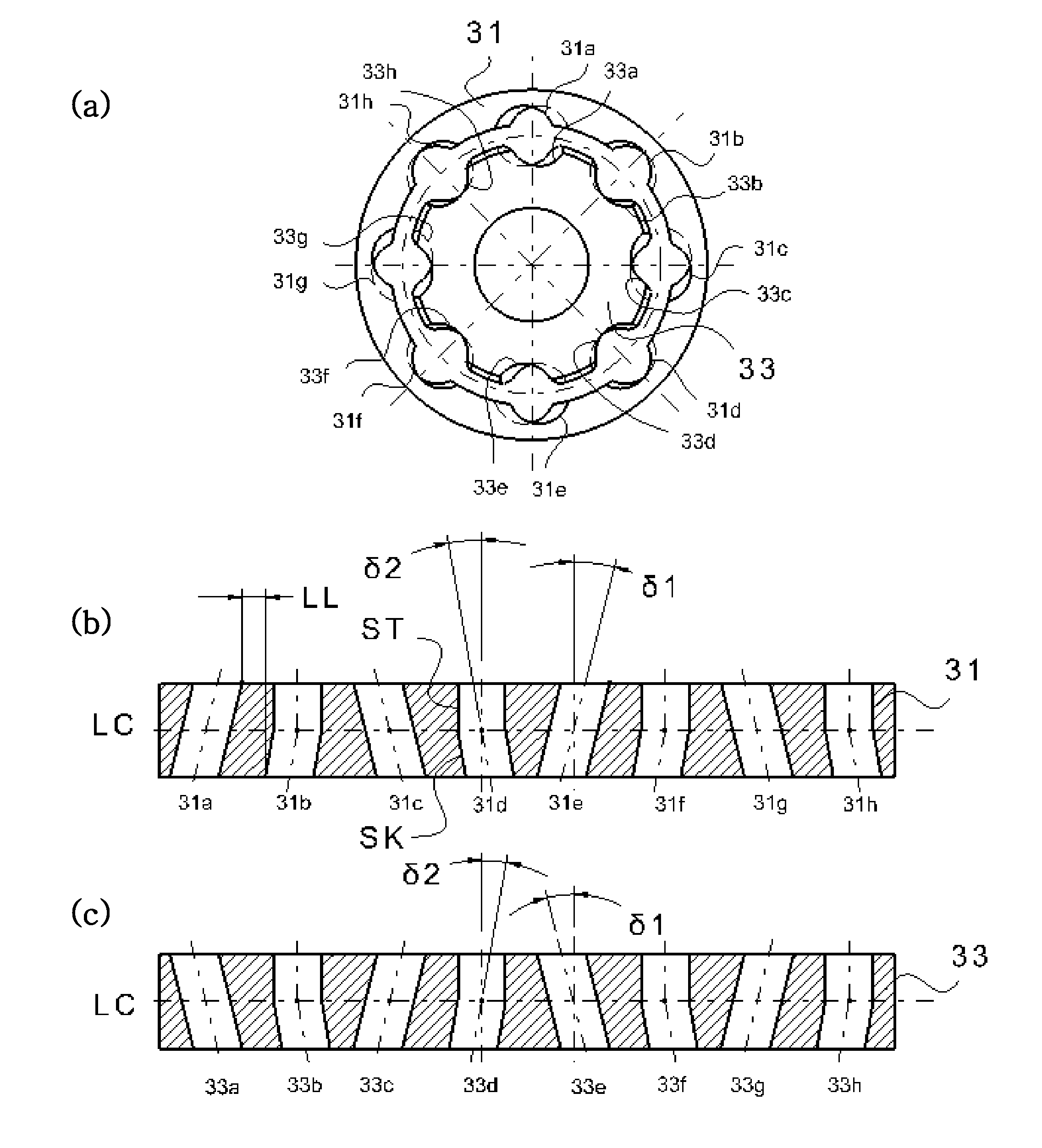
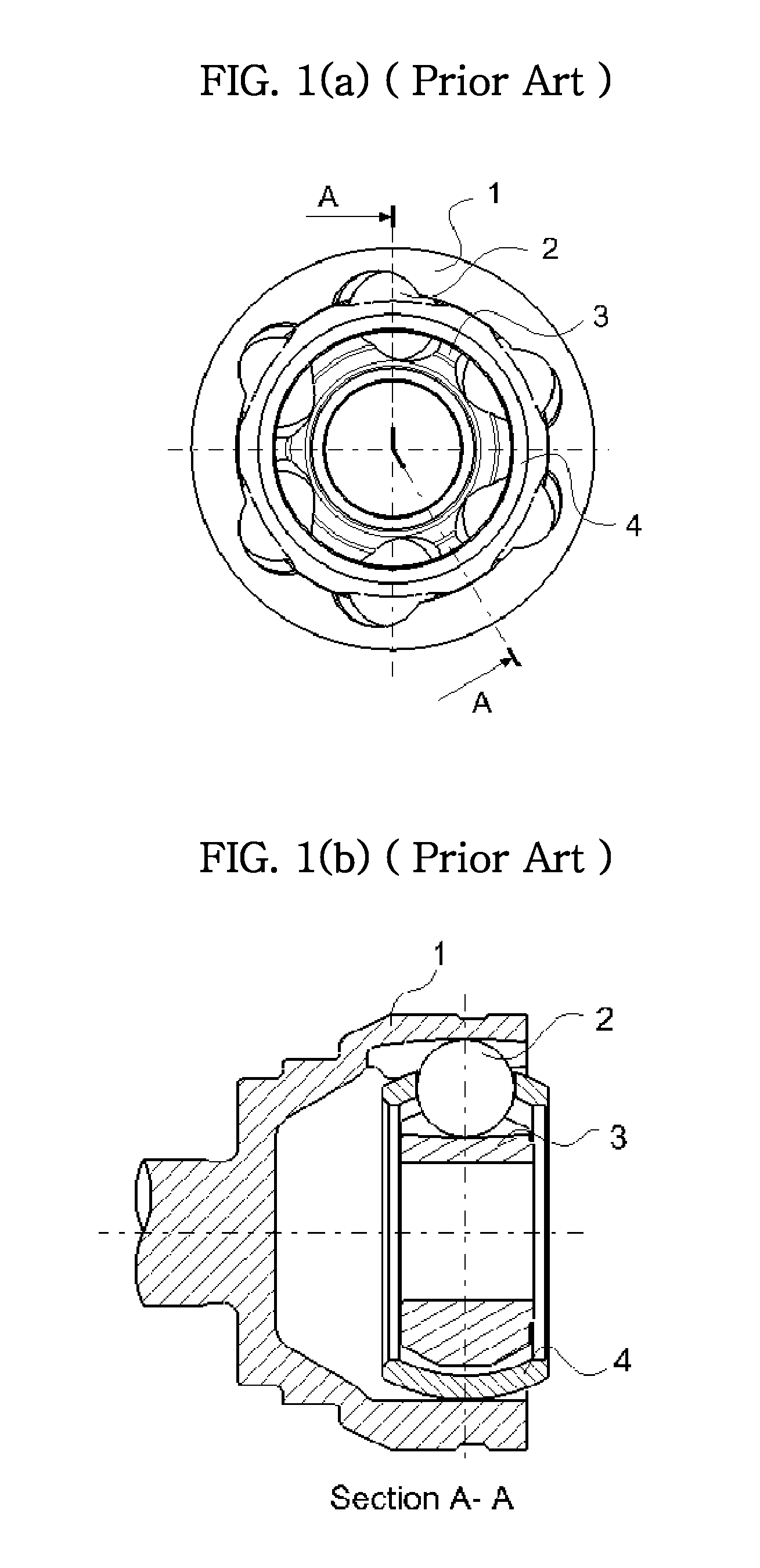
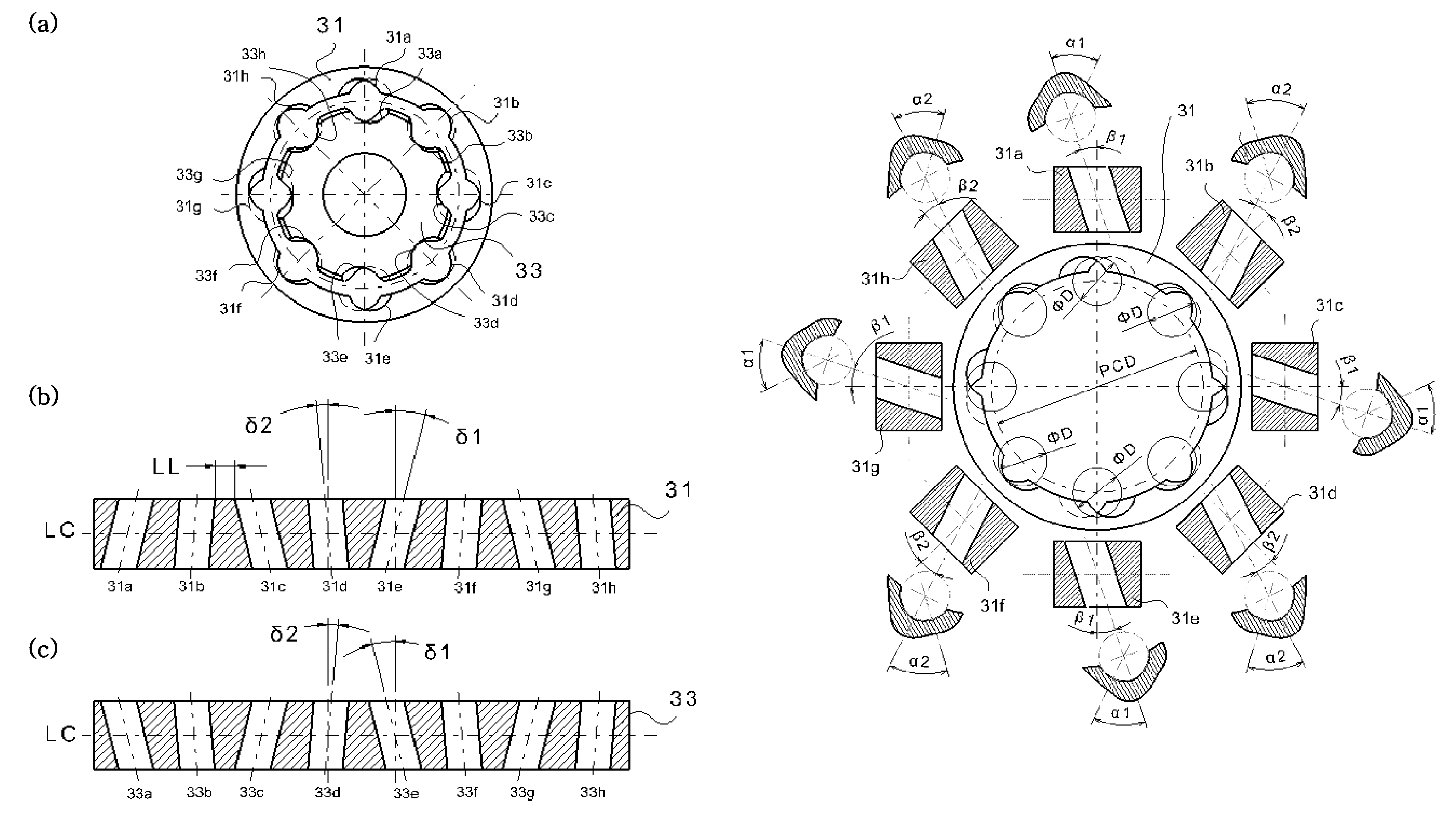
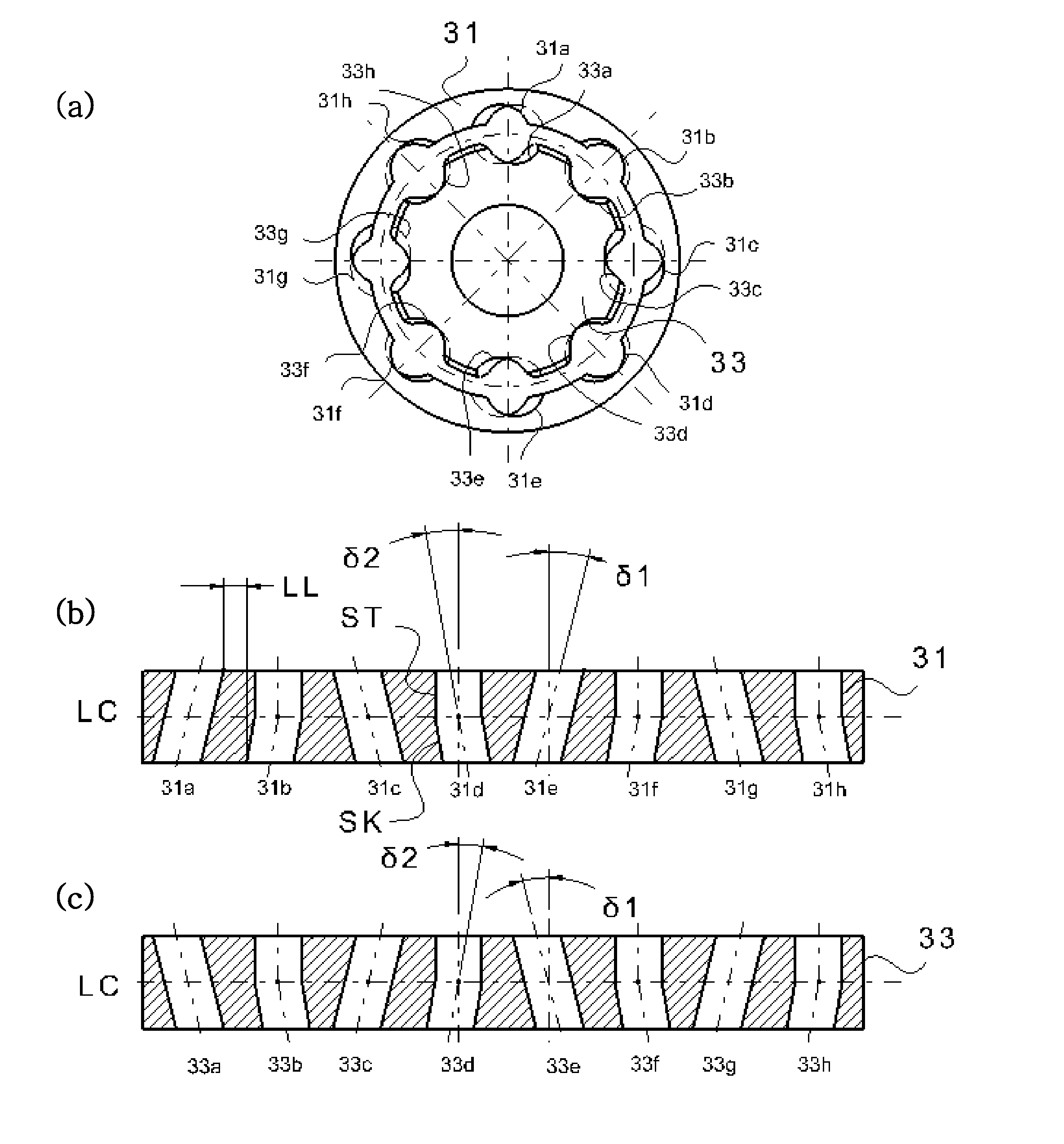
ActiveUS20110070955A1Compact and durable structureEnhanced strengthYielding couplingConstant-velocity jointControl theory
A constant velocity joint for a drive system comprises: an outer joint member having a plurality of inwardly facing outer ball grooves, the outer ball grooves consisting of a first group of grooves and a second group of grooves with composite or non-linear groove pattern; an inner joint member disposed inside the outer joint member and having a plurality of outwardly facing inner ball grooves consisting of a first group of grooves and a second group of grooves with composite or non-linear groove pattern, each inner ball groove of the inner joint member being coupled with a corresponding outer ball groove of the outer joint member generally in crossed pair; and a cage having circumferentially displaced cage windows to accommodate a plurality of balls therein. The groove patterns of the ball grooves can be a combination of skewed grooves and non-linear grooves, a combination of non-linear grooves such as a curved groove or a compositely shaped groove, or a combination of linear grooves and non-linear grooves.
Owner:HYUNDAI WIA
Muffler device
InactiveUS6915877B2Decreasing capacityAvoid accumulationSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesUltrasound attenuationBarrier function
A muffler device, in one preferred embodiment, having four barriers therein. Each barrier functions to form an within which the exhaust stream can be partitioned and redirected. Eventually, the exhaust streams are once again recombined and expelled from the muffler. The partitioning and reassembly of the exhaust streams provides sound attenuation while increasing the horsepower of the engine and without resulting in any build up of unignited fuel.
Owner:KHAYALIAN GARABED
Exhaust gas purifier and filter regenerator
InactiveUS20090084077A1Compact and durableEfficiently gathering particulateCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentExhaust gasEngineering
An exhaust gas cleaning apparatus and a filter regeneration apparatus that are capable of cleaning a large volume of exhaust gas without any increase in size of a nonmagnetic member around which a working coil for induction heating is wound. The exhaust gas cleaning apparatus includes a particulate collecting section and a filter regenerating section placed next to each other in the flow direction of an exhaust gas, and a movable frame. The movable frame holds an extension of a filter unit extending from a casing of the particulate collecting section beyond the support frame of the filter regenerating section, and can move the filter unit in the axial direction of the casing. When the filter unit moved by the movable frame passes through the filter regenerating section, a corresponding part of a holding frame disposed in the filter unit is continuously induction-heated to burn collected particulates, such that the filter unit can be regenerated.
Owner:TOKYO UNIV OF MANNE SCI & TECH
Collar stay punch, storage device and method
InactiveUS7578034B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce shear forceSnap fastenersTravelling carriersClosed loopEngineering
A collar stay perforating device for perforating a portion of a collar stay and a collar stay storage device for storing the perforated collar stay are provided. The collar stay perforating device comprises a base member having a punch hole and a guide to receive an end of a collar stay. A first lever member pivotally attached to the base member has a punch member that cooperates with the punch hole. A second lever member pivotally attached to the base member bears on the first lever member to bring the punch member into cooperation with the punch hole thereby perforating the collar stay. The perforated collar stay may then be stored on a collar stay storage device comprising an openable ring member having releaseably engageable arms for forming a closed loop. The ring is openable permitting one of the arms to be inserted through the perforated collar stay thereby providing ordered and compact storage of collar stays.
Owner:BG & SONS
Method and apparatus for connecting various implantable medical treatment system component devices
InactiveUS7010355B2Efficiently and securely connectedEasy to operateElectrotherapyEngineeringMedical treatment
Disclosed is a universal connector for connecting component devices of an implantable medical treatment system. The universal connector includes a male and a female interface adapted to connectively mate two devices of the implantable medical treatment system. A locking flange and recess are provided, as well as a locking shoulder and ridge combination, to securely connect the mated male and female interfaces. When mated and securely joined, the universal connector of the present invention allows a device of the implantable medical treatment system to interface with any other device of the implantable medical treatment system for simplified handling and bi-directional communications.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
High Voltage Circuit Breaker, System, Vacuum Interrupter Module and Associated Drive Module
ActiveUS20170256374A1Simple structureReduce air resistanceRailway vehiclesHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesElectricityComputer module
A high voltage circuit breaker comprises a vacuum interrupter module, a drive module, and an actuator. The vacuum interrupter module has a vacuum interrupter housing and a pair of electrical contacts disposed in the vacuum interrupter housing. At least one of the pair of electrical contacts is movable relative to the other of the pair of electrical contacts to engage and disengage the electrical contacts from one another for switching a high voltage on and off. The drive module has a drive module housing and a drive member coupled with the at least one movable electrical contact. A central part of the drive member is disposed in the drive module housing and insulated from an ambient air. The actuator is coupled to the drive member and moves the pair of electrical contacts relative to one another.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS (UK) LTD
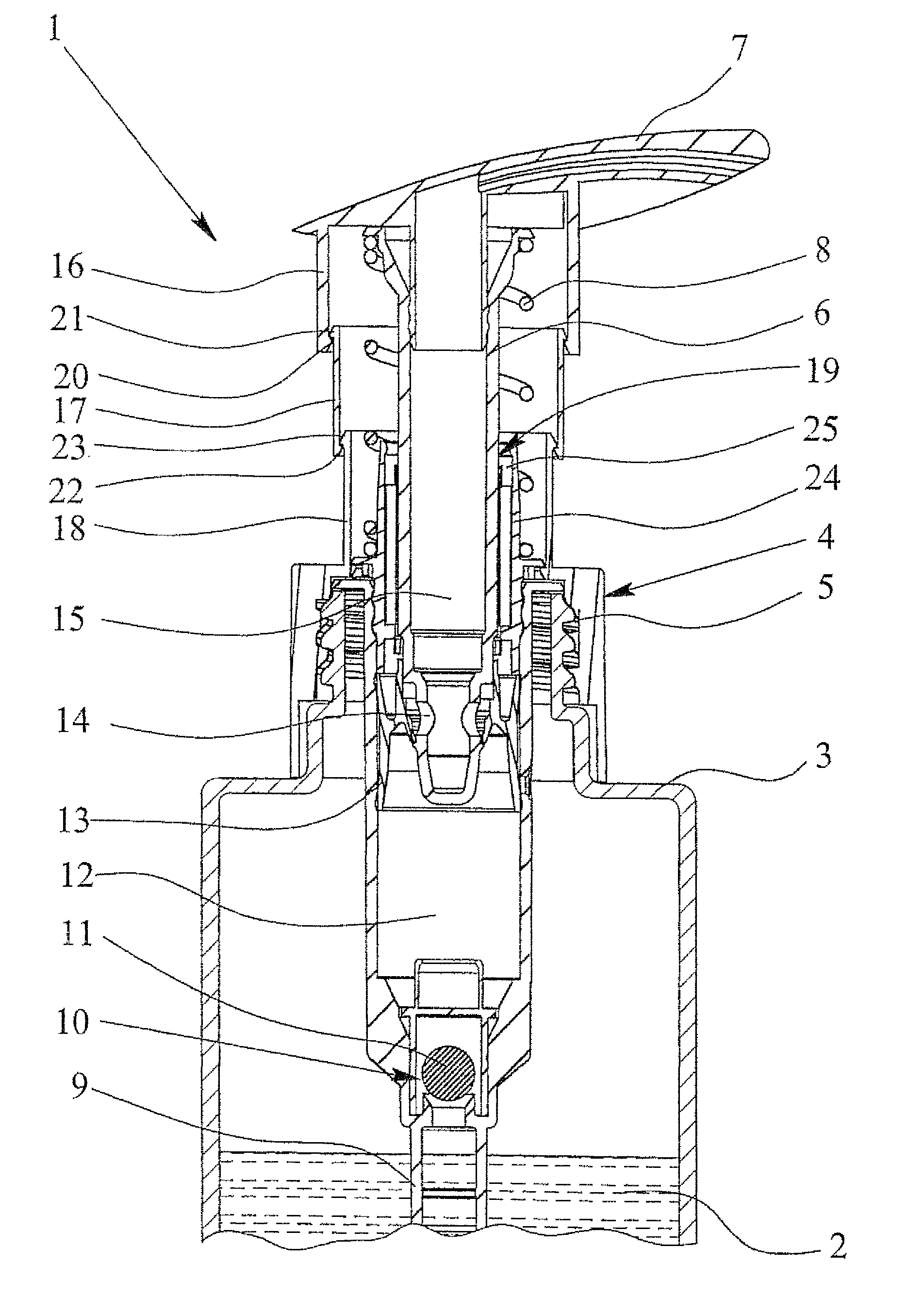
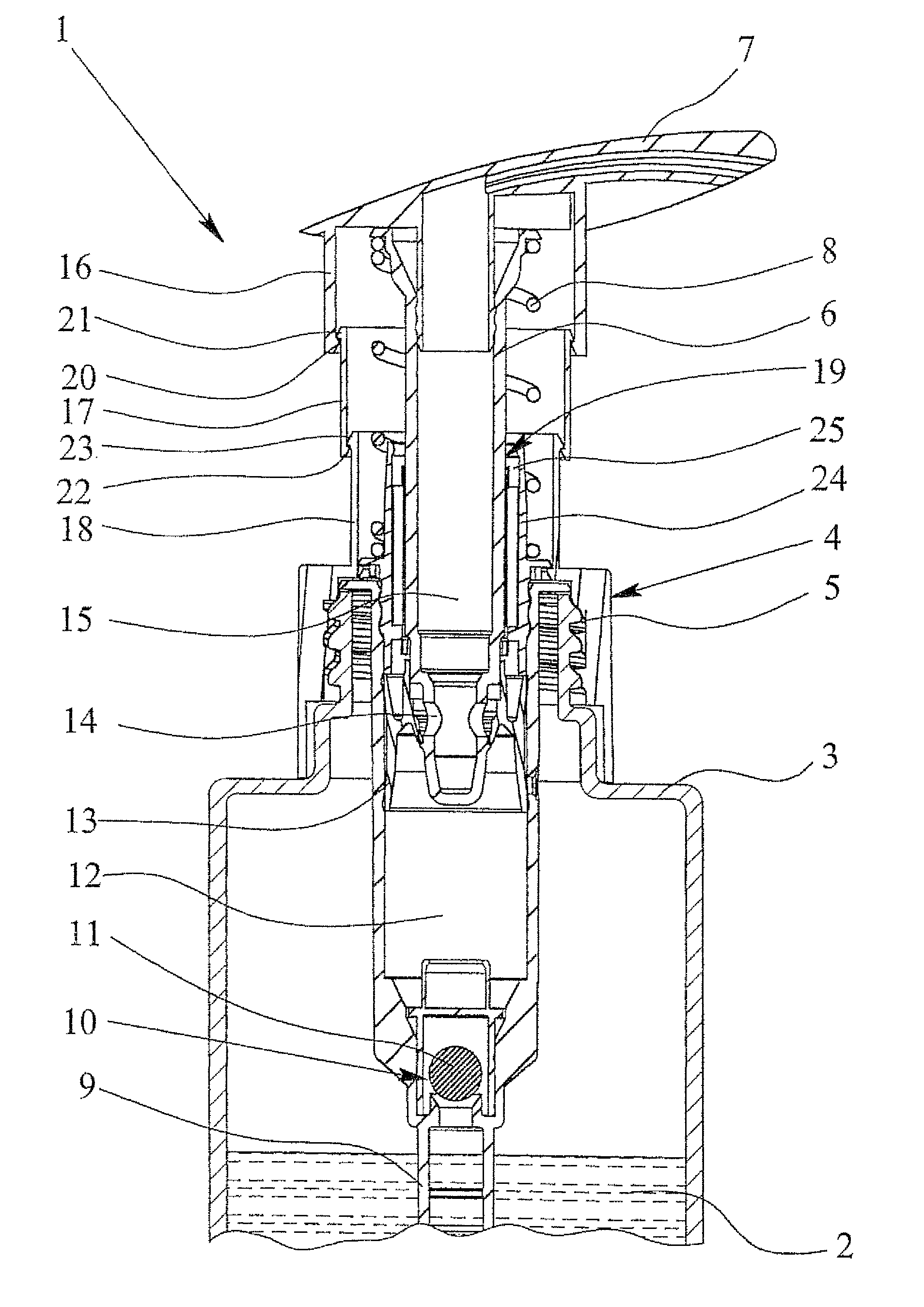
Dispenser pump
ActiveUS7819291B2Compact and durableCompact structureLarge containersSingle-unit apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:APTAR DORTMUND GMBH
Dual-power automatic change-over switch
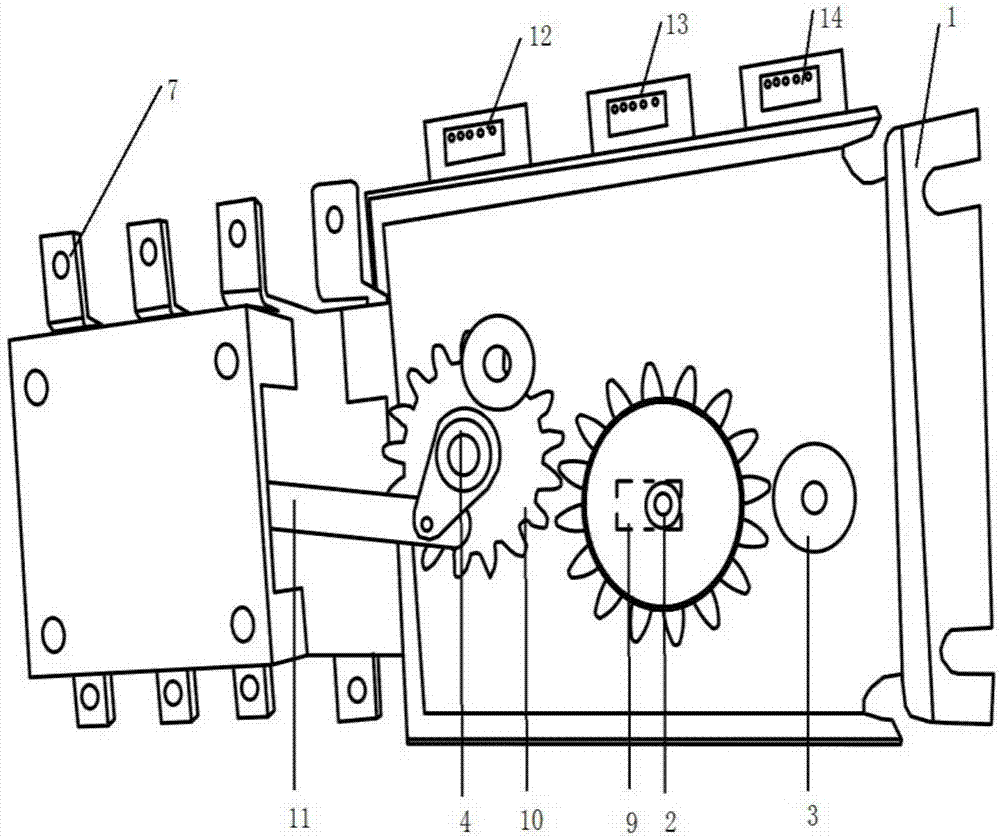
InactiveCN107359060ALow voltage usageLess dangerous to humansContact driving mechanismsSwitch power arrangementsElectricityEngineering
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of change-over switches, in particular relates to a novel dual-power automatic change-over switch comprising a housing (1), a gear motor (2), a relay (6), a dual-power converter (7), a gear set (10) and a control connecting link (11). Besides, the dual-power automatic change-over switch further includes an adjusting shaft (3), a manual rotating shaft (4) and a 12-V direct-current power supply; and the gear motor (2) is connected with the 12-V direct-current power supply electrically. Therefore, the manual and automatic adjustment is realized. The 12-V direct-current power supply provides power for the gear motor directly, so that a defect that a 110-V or 220-V voltage needs to be collected from a wiring terminal of a dual-power converter in the prior art is overcome, the voltage is reduced, and the injury on the human body is reduced.
Owner:XIAN A PU DUN ELECTRICITY TECH
Multi-type shifter assembly shift force detection positioning clamping device
ActiveCN104942731BCompact and durableQuality assuranceWork holdersControl engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a multi-type shifter assembly shift force detection, positioning and clamping device. The positioning assembly is based on the positioning principle of two pins on one side, and adopts a combination of coarse and fine positioning for positioning, including two positioning plates for rough positioning. And two positioning blocks, and there are two models to distinguish the detection rod and two positioning detection probes. When the shifter is fixed on the positioning assembly, the approximate position of the shifter is initially fixed by the positioning plate and the positioning block. , and then the model can be judged by the action of the two detection rods and the fixed sensor below. Change, in order to judge whether the shifter is fixed in place, the positioning assembly is a detachable modular positioning assembly, according to the needs of different types of shifters, different positioning assemblies can be used correspondingly.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Multi-bladed razor cartridge sharpener
InactiveUS20060099894A1Compact and durablePortable grinding machinesGrinding/polishing hand toolsBlades razorSoap solution
Apparatus for sharpening and or honing a multi-bladed razor cartridge including a sharpening member, a housing to secure the sharpening member. A soap solution dispenser provides a lubricant to the sharpening member to lubricate the razor and a housing to limit the travel of the razor on the sharpening member. The sharpening and or honing member is made of a mirrored plate glass secured in a channel within the housing.
Owner:MORITA ANDY K
Cross Groove Type Constant Velocity Joint
ActiveUS20110092299A1Compact and durableHigh strengthYielding couplingShaft for rotary movementSkew angleEngineering
A constant velocity joint for a drive system comprises: an outer joint member having a plurality of inwardly facing outer ball grooves, the outer ball grooves consisting of a first group of grooves, each groove of which having a skewed groove shape with a first skew angle other than zero and alternately arranged in opposite directions relative to an axis of rotation of outer joint member, and a second group of grooves, each groove of which having a skewed groove shape with a second skew angle other than zero and alternately arranged in opposite directions relative to an axis of rotation of outer joint member, the second skew angle less than the first skew angle; and an inner joint member disposed inside the outer joint member and having a plurality of outwardly facing inner ball grooves consisting of a first group of grooves, each groove of which having a skewed groove shape with a first skew angle other than zero and alternately arranged in opposite directions relative to an axis of rotation of inner joint member, and a second group of grooves, each groove of which having a skewed groove shape with a second skew angle other than zero and alternately arranged in opposite directions relative to an axis of rotation of inner joint member, the second skew angle less than the first skew angle, each inner ball groove of the inner joint member being coupled with a corresponding outer ball groove of the outer joint member generally in crossed pair. In addition to the differentiated skew angles, the contact angles of the balls in the first and second group of grooves and other configurations may also be differentiated.
Owner:HYUNDAI WIA
Upper side, in particular paper side, and papermaking-machine fabric
ActiveUS7770606B2Simple and compact and durable structureImprove uniformityMachine wet endPress sectionYarnEngineering
Owner:ANDRITZ TECH & ASSET MANAGEMENT
Workpiece flushing device for scribing machine and scribing machine
ActiveCN114769203ACompact structureCompact and durableCleaning using liquidsWater flowMechanical engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductor cutting, and provides a workpiece washing device for a scribing machine and the scribing machine, and the workpiece washing device comprises at least one water curtain pipe assembly; the water curtain pipe assembly comprises a water curtain pipe, a first water inlet connector and a second water inlet connector, the water curtain pipe comprises a pipe sleeve and a water passing pipe assembly embedded in the pipe sleeve. The water inlet connectors are arranged at the two ends of the water curtain pipe correspondingly, the water flow stroke can be shortened, and therefore the pressure difference in the length direction of the water curtain pipe is reduced; meanwhile, flow channels with different lengths are arranged to be communicated with different water spraying holes in a sealed mode, so that independent closed flow channels with balanced pressure are provided for the water spraying holes in different areas, it is guaranteed that the water outlet pressure of the water spraying holes is balanced, the washing effect is improved, meanwhile, workpieces can be effectively protected against damage, and the service life of the workpieces is prolonged. And the flushing device is more compact in overall structure and small in occupied space, and reasonable layout of parts on the scribing machine is facilitated.
Owner:沈阳和研科技股份有限公司
Ceramic Chute Liner
InactiveUS20160039608A1Compact and durableExtended service lifeChutesRubber membraneComposite material
A ceramic chute liner (10) comprising of a plurality of mechanically interlocked ceramic blocks (1). The corresponding mechanically interlocked ceramic blocks (1) have rubber films between them along respective adjoining surfaces such that, the ceramic blocks (1) are bonded with each other with substantial strength and the impact force is substantially reduced.
Owner:TEGA IND LTD
Cross groove type constant velocity joint
ActiveUS8444495B2Compact and durableHigh strengthYielding couplingShaft for rotary movementEngineeringControl theory
Owner:HYUNDAI WIA
Utility lamp system
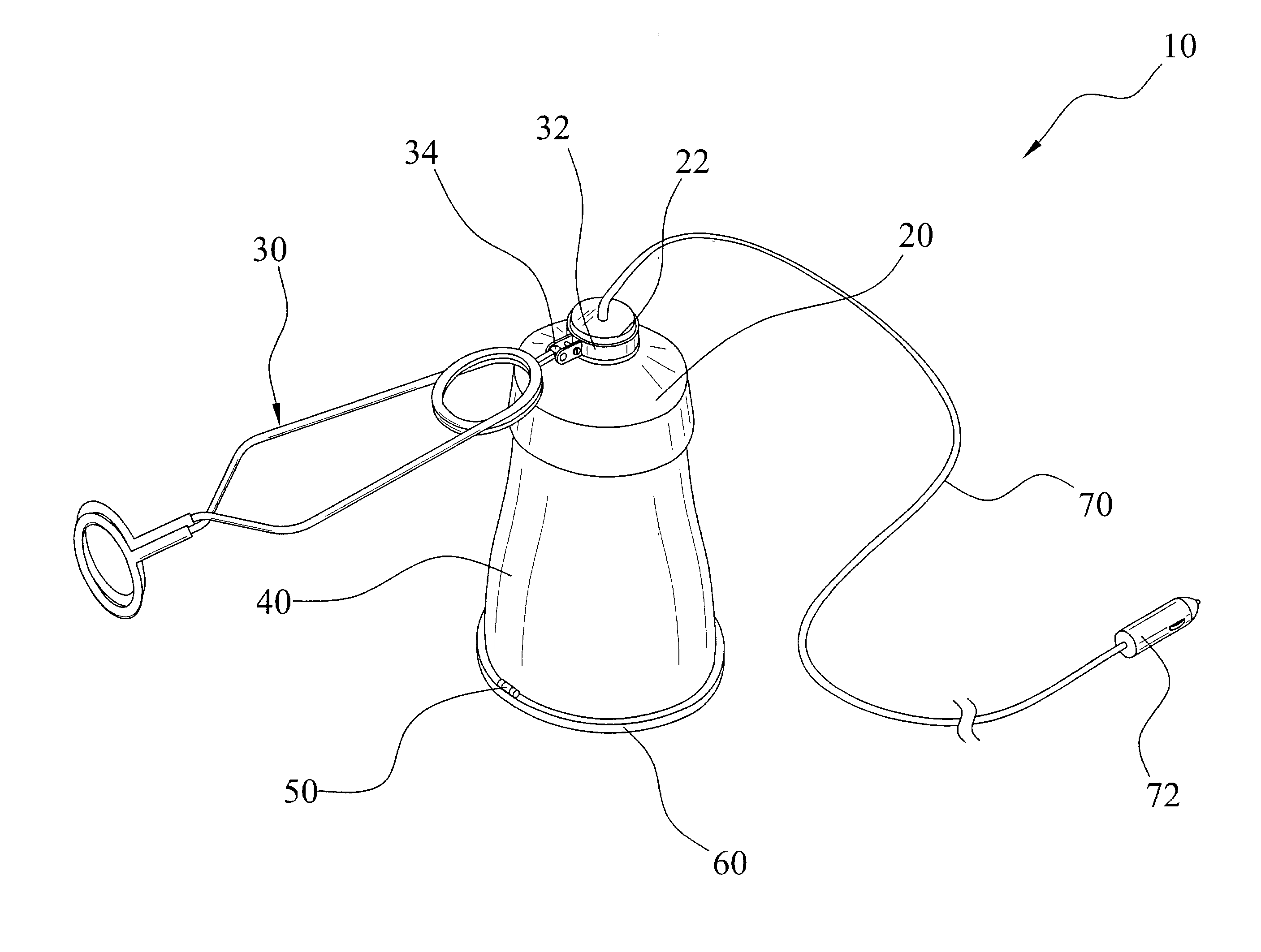
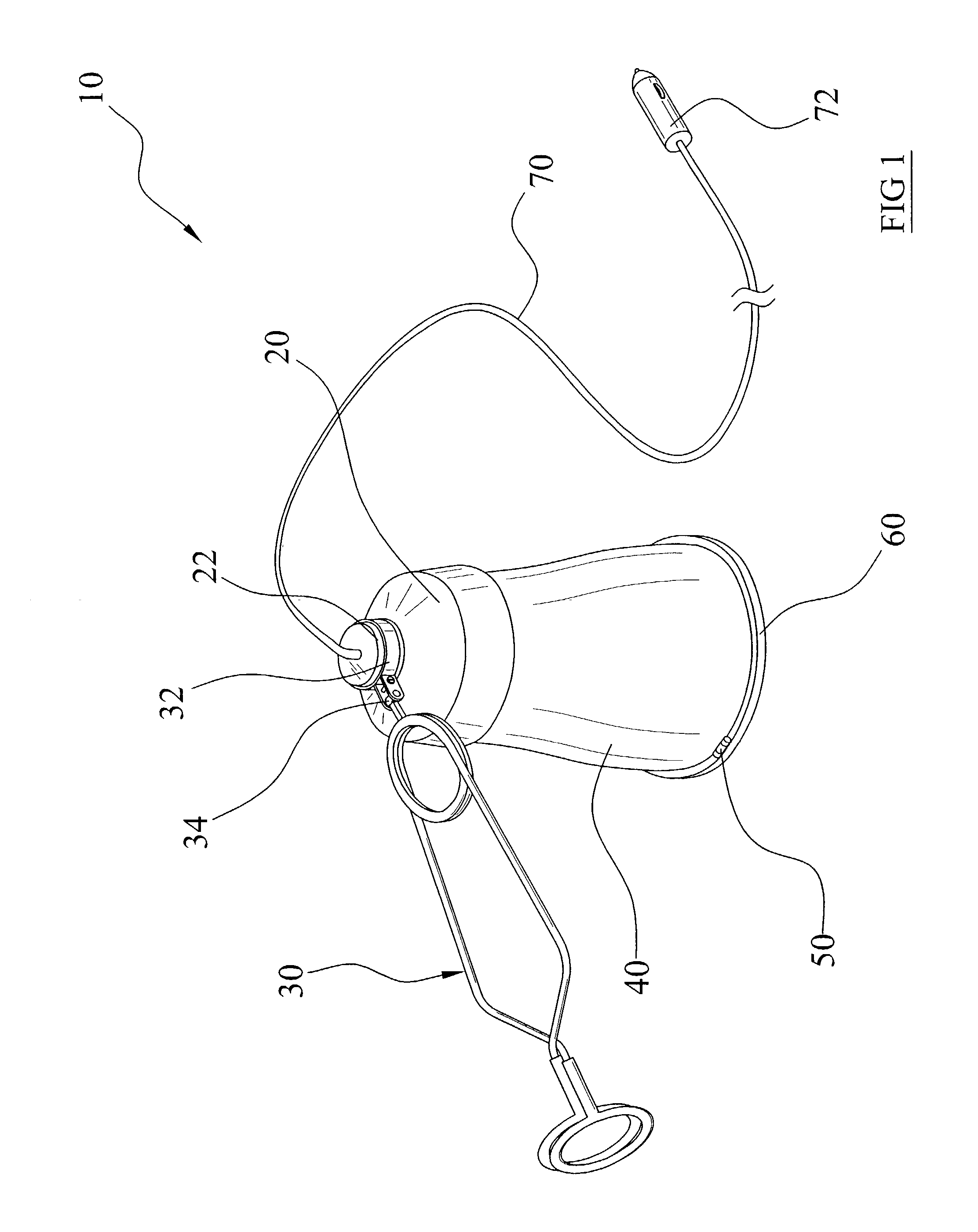
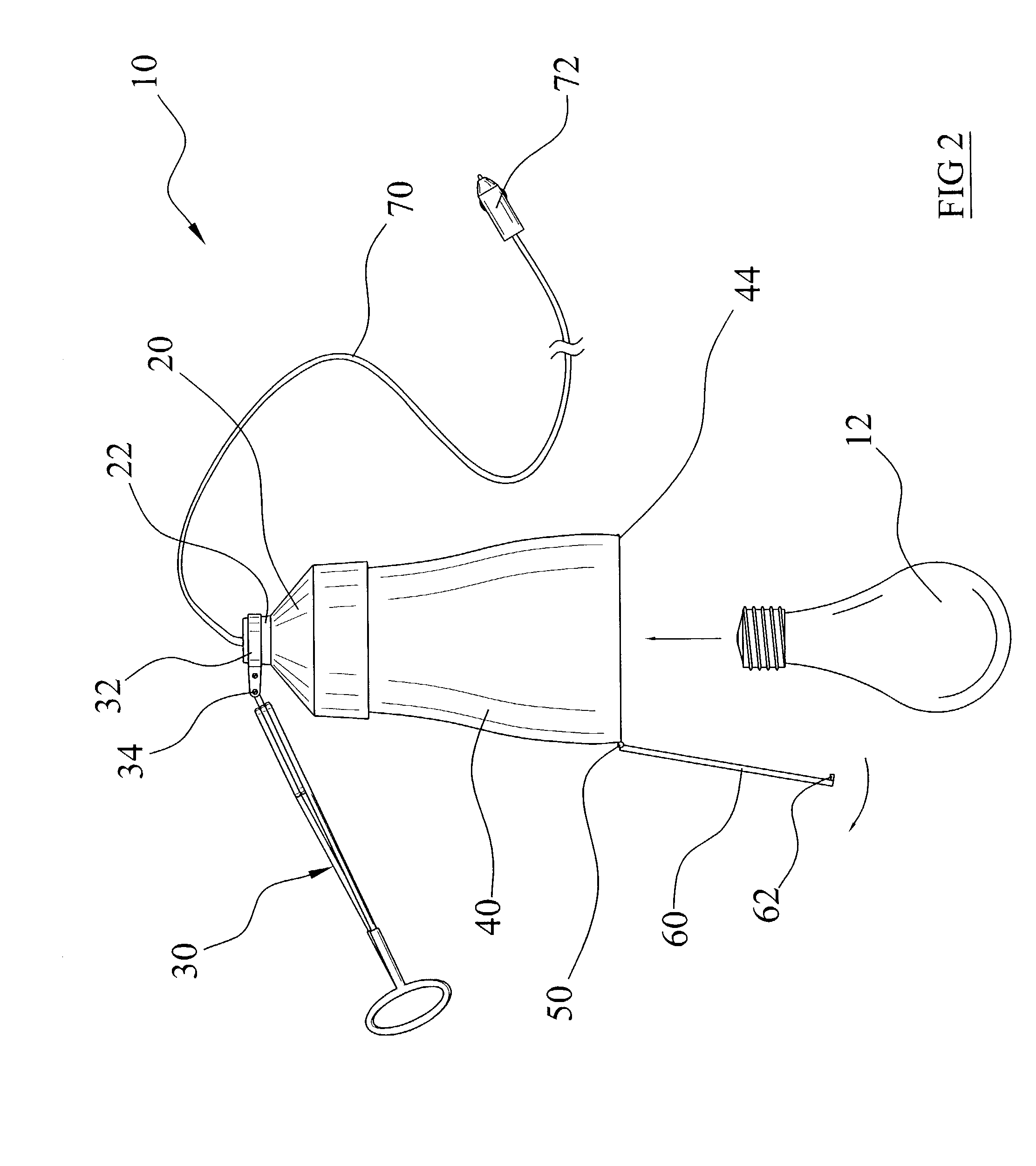
InactiveUS7111960B2Compact and durableElectric lighting for hand-held useLighting support devicesElectricityEngineering
A utility lamp system for use in outdoor and indoor locations in a convenient manner. The device includes a main housing with an electrical receptacle within, a clamp structure movably attached to the main housing, a bulb housing extending from the main housing, and a cover pivotally attached to a lower end of the bulb housing.
Owner:JETLAND DAVID W
Cross groove type constant velocity joint with composite groove patterns
ActiveUS20120238370A1Compact and durableHigh strengthYielding couplingControl theoryConstant-velocity joint
Owner:HYUNDAI WIA
A hidden fixing device for a suitcase
InactiveCN103355905BCompact and durableAvoid damage from collisionsLuggageOther accessoriesBiomedical engineeringSurface cover
The invention discloses a luggage fitting, and particularly relates to a hidden-type fixation device for a luggage. The fixation device comprises a surface cover embedded in the luggage body of the luggage, a pressing buckle buckling with the surface cover, and a contraction mechanism disposed below the surface cover. The pressing buckle comprises a compression block. The compression block is provided with a clamping block. The surface cover is provided with a compression face matched with the compression block. The compression face is provided with a clamping slot matched with the clamping block, and an opening. The contraction mechanism comprises a rotating shaft and a coil. One end of the coil passes through the opening and is fixed to the compression block, and the other end of the coil is fixed to the rotating shaft. The surface cover of the device is embedded in the luggage body of the luggage, and therefore compared with a technical scheme that pothooks are disposed on a luggage body in a protruding manner, and other technical schemes, damage of the fixation device caused by collision to other objects is prevented in the technical scheme provided by the invention. In conclusion, the fixation device has advantages of an ingenious fixation manner, good effects and high reliability. Related components are tightly connected through a coiling manner, and therefore the structure of the fixation device is more compact and durable.
Owner:广州第九城服饰有限公司
Safety cone holder device
ActiveUS20050051452A1Effective and secure mannerCompact and durableConstructionsExternal framesSpring forceStowage
The present invention provides a holder device for securing one or more non-rigid safety cones, each of which having a flexible conical part that can be reduced to a small volume substantially linearly. The holder device has an open frame construction and is lightweight, compact, and durable. The holder device has two bracket-like main components that are movably joined or connected at one common end and that can be secured or locked together at the other ends. By selecting material and strengthening design configuration of the two components to counteract the spring force of the coil or coils held therebetween, by strategically placing a positioning element to secure the cone or cones centrally, and by supporting their base from at least three sides, the holder device of the present invention offers sufficient support and efficient stowage of non-rigid safety cones in a convenient, secure, and cost effective manner.
Owner:TTB PROD +1
Power-consumption-free heat dissipation device of electronic device
InactiveCN110267488APlay a protective effectSpeed up the flowModifications using liquid coolingEngineeringPhase change
The invention discloses a power-consumption-free heat dissipation device of an electronic device. The power-consumption-free heat dissipation device comprises a body, wherein the body comprises a shell and a filling body. The shell wraps the filling body, the shell is made of a solid heat conduction material, and the filling body is made of a phase change material. A first air hole and a second air hole which are communicated are formed in the body, the first air hole transversely extends and forms an opening in the side face of the body, and the second air hole extends upwards and forms an opening in the upper end of the body. The power-consumption-free heat dissipation device is mounted on the electronic device. The phase-change process of the phase-change material and the first air hole and the second air hole are utilized to form a chimney effect, so that the heat dissipation of the electronic device can be conveniently and efficiently realized. The defect that a traditional radiator is subjected to high-power operation in a short time of an electronic device and generates a large amount of heat which cannot be discharged in time is overcome, so that a role in protecting the electronic device is played. Meanwhile, an external power supply does not need to be externally connected, and no noise is generated in the working process, and the heat dissipation device is compact in structure and is stable and durable. The heat dissipation device is used in the field of heat dissipation devices.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com