Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Surface potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
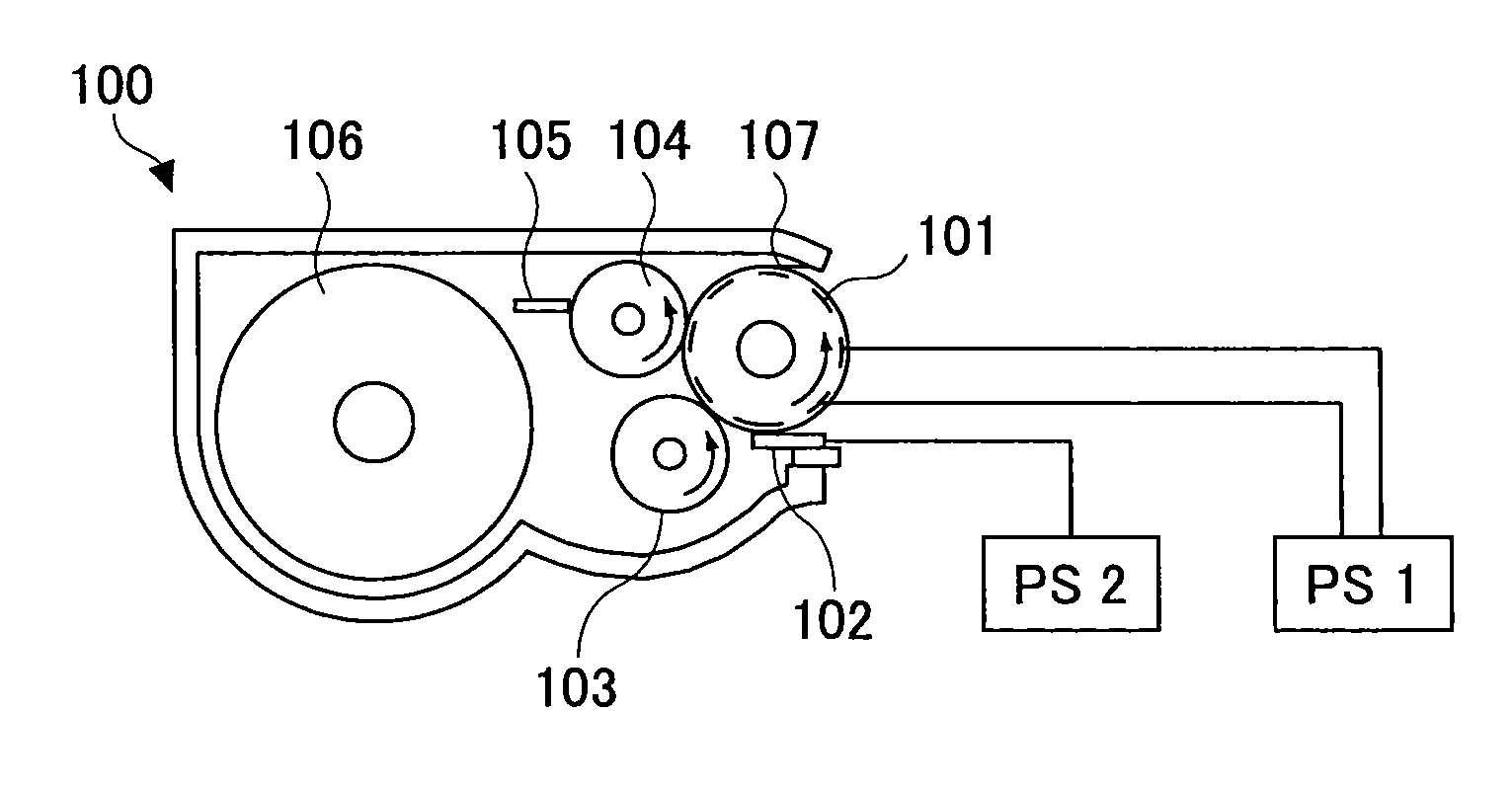
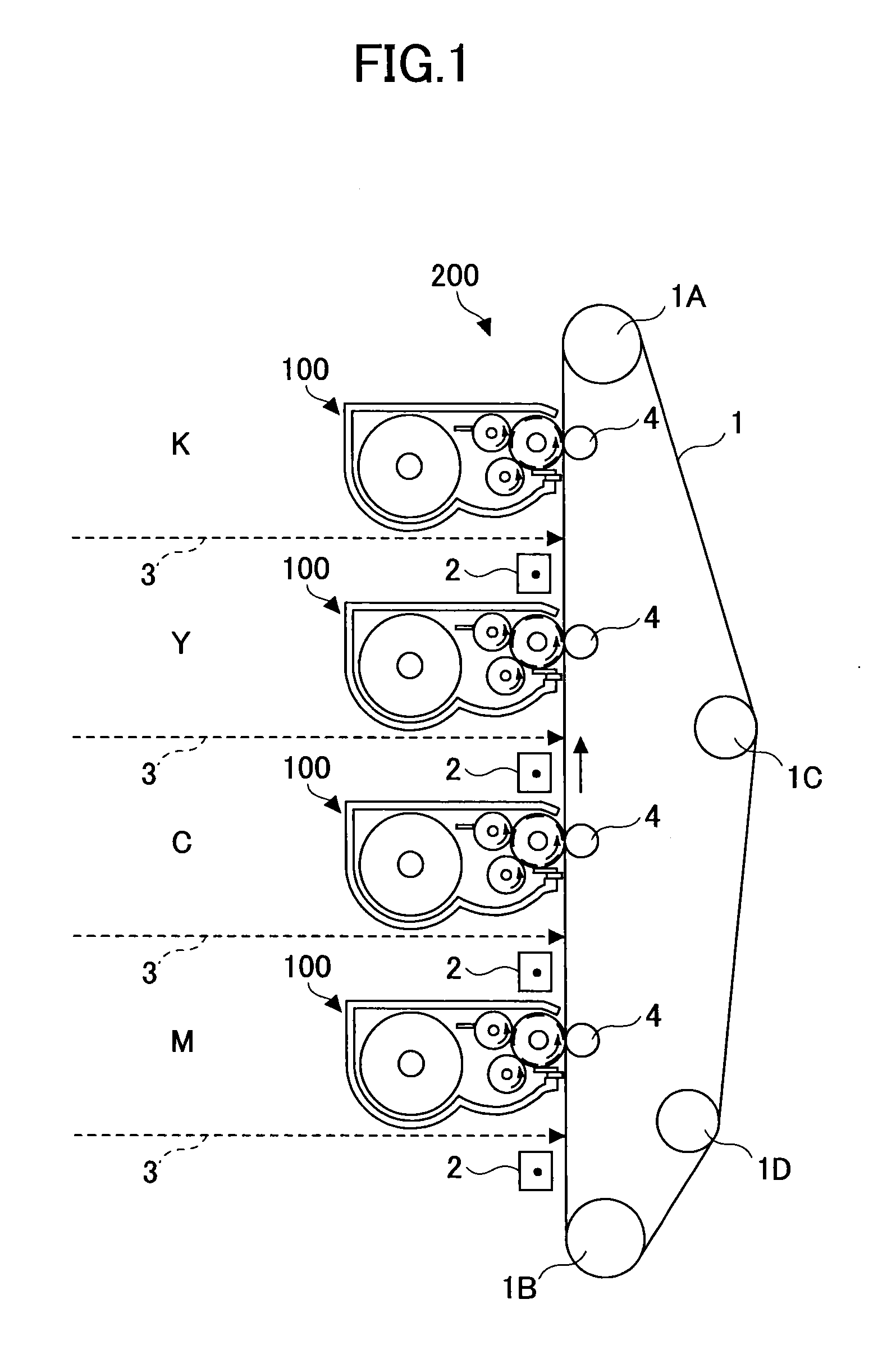
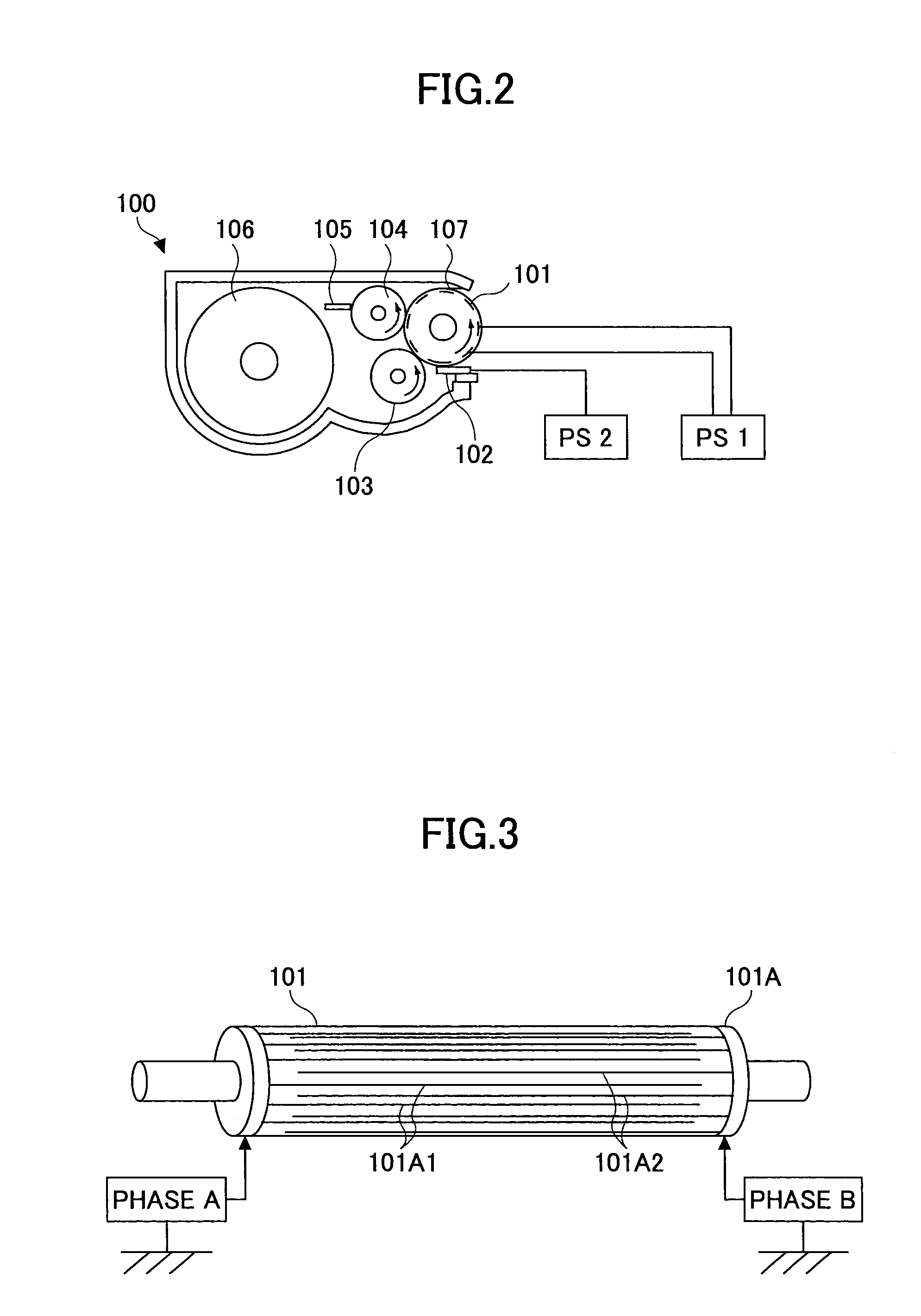
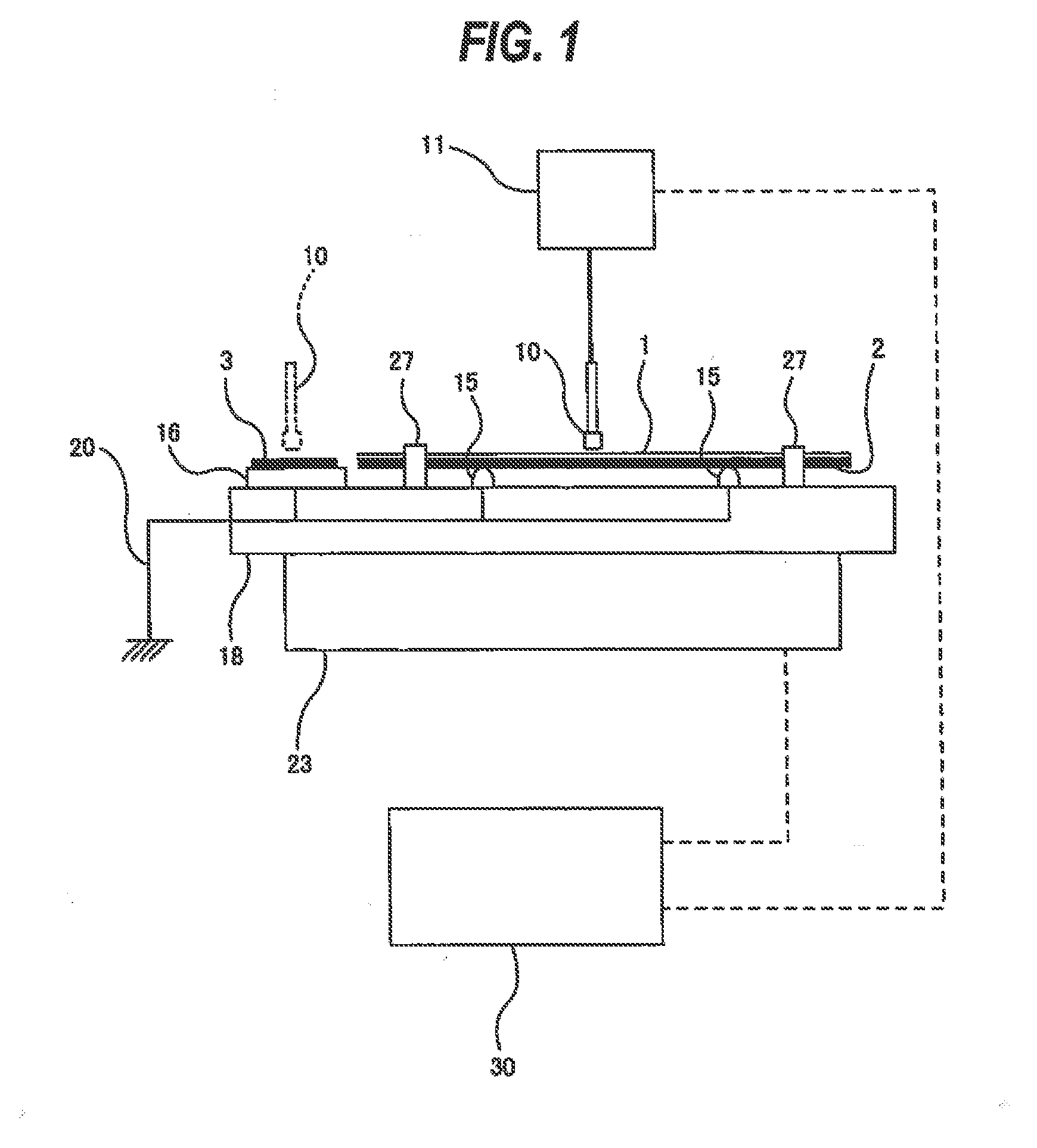
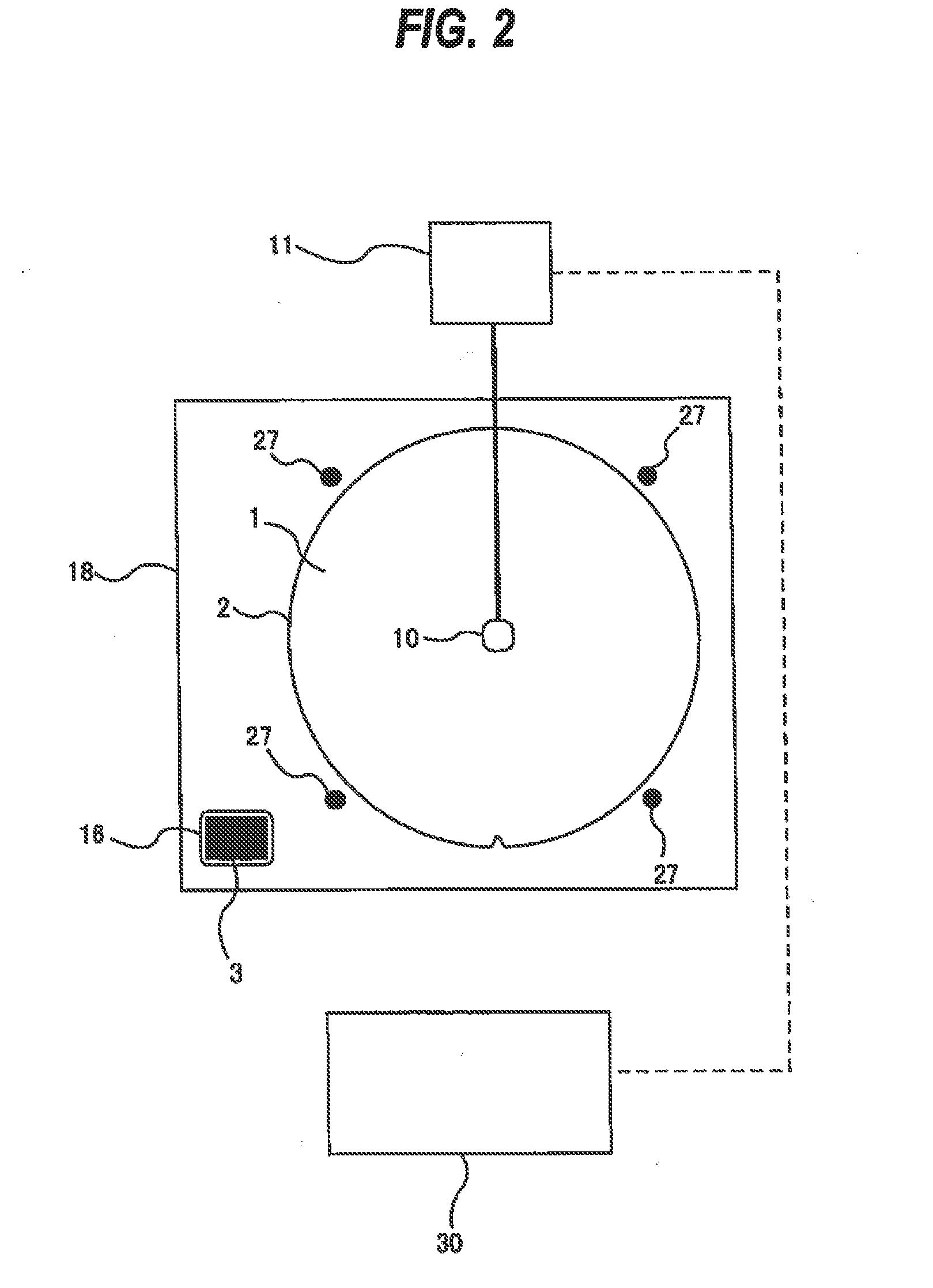
Developing apparatus, image forming apparatus, and process cartridge
InactiveUS20090035025A1Surface potentialEnhance the imageElectrographic process apparatusPotential differenceLatent image
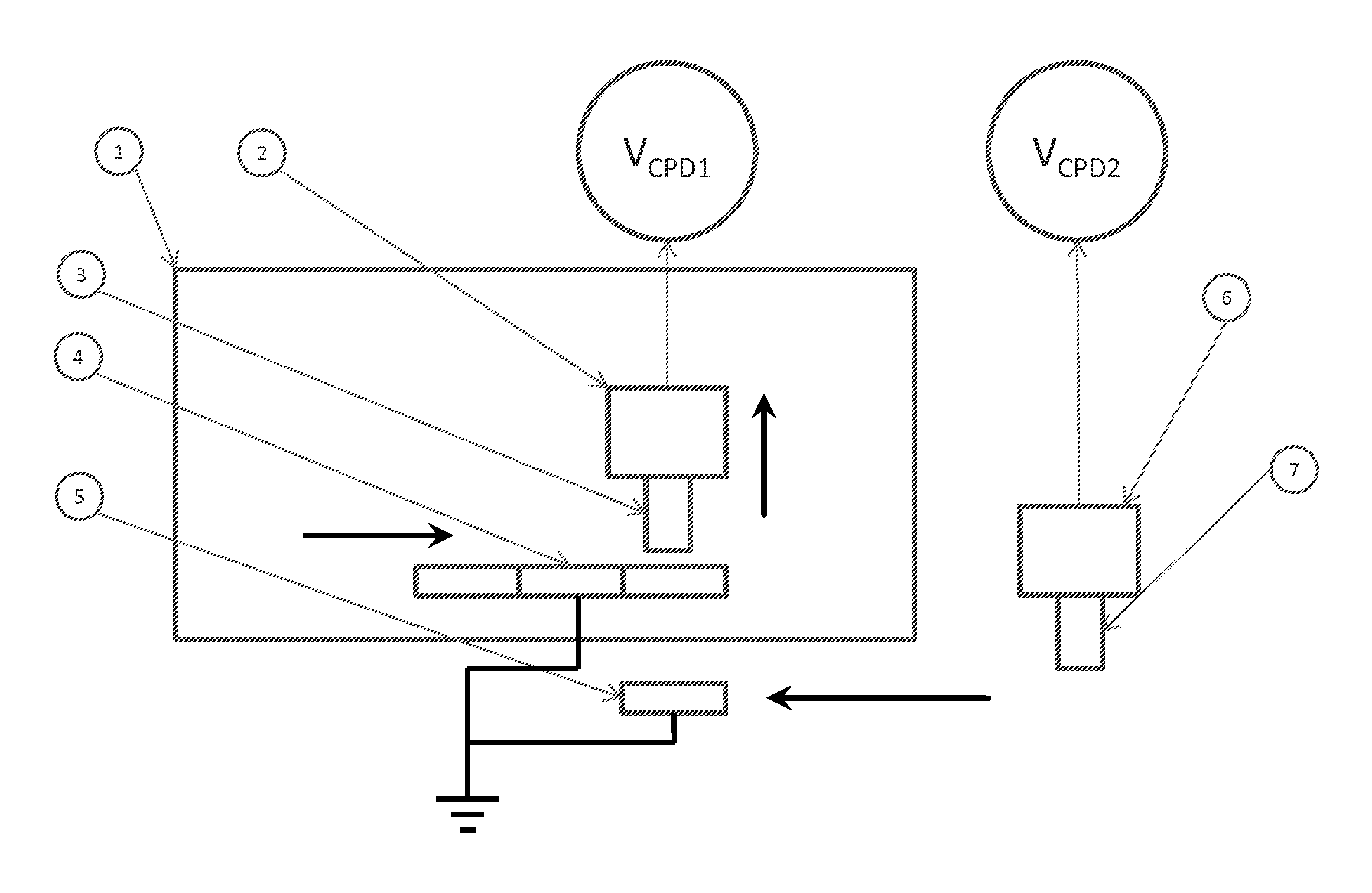
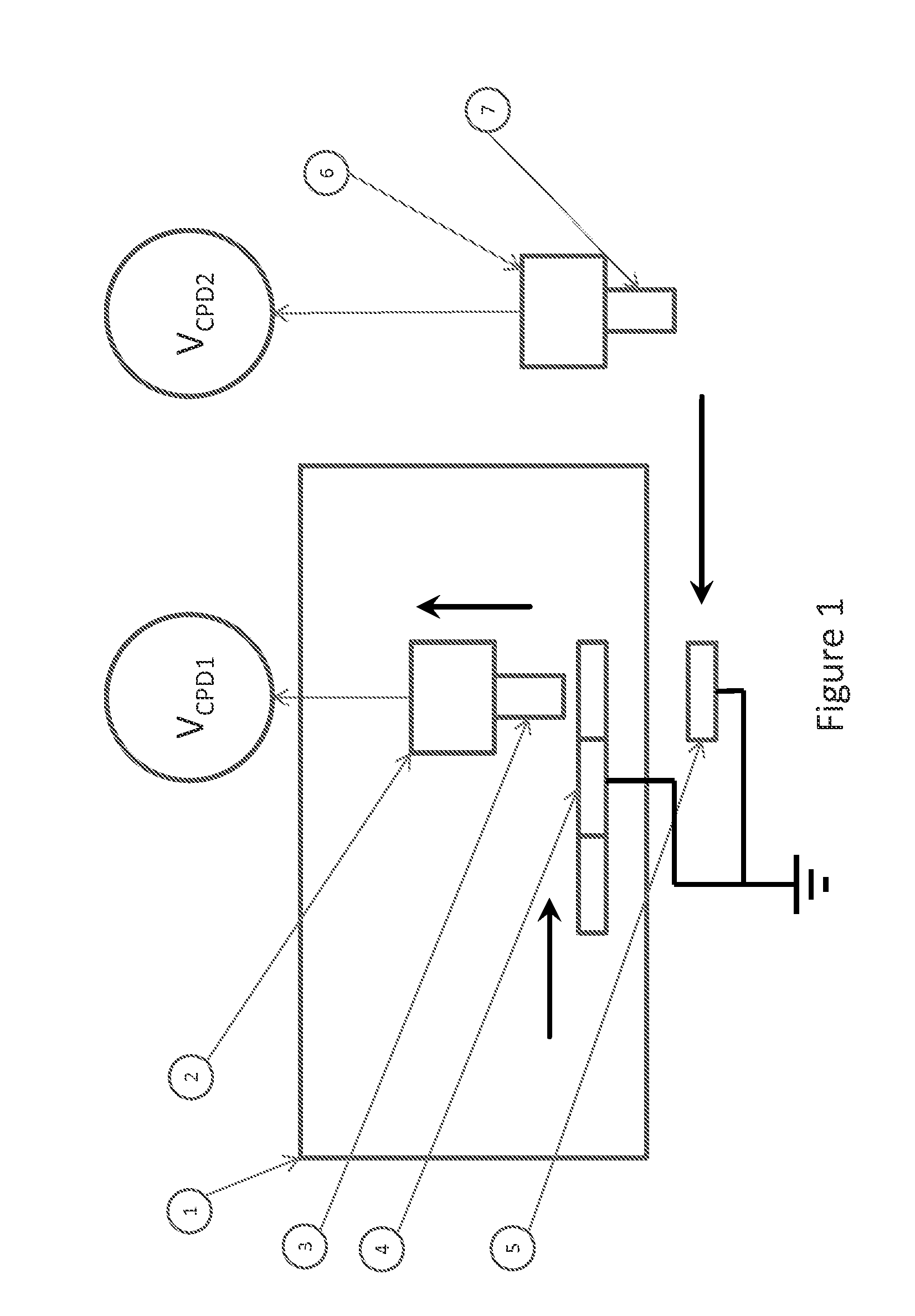
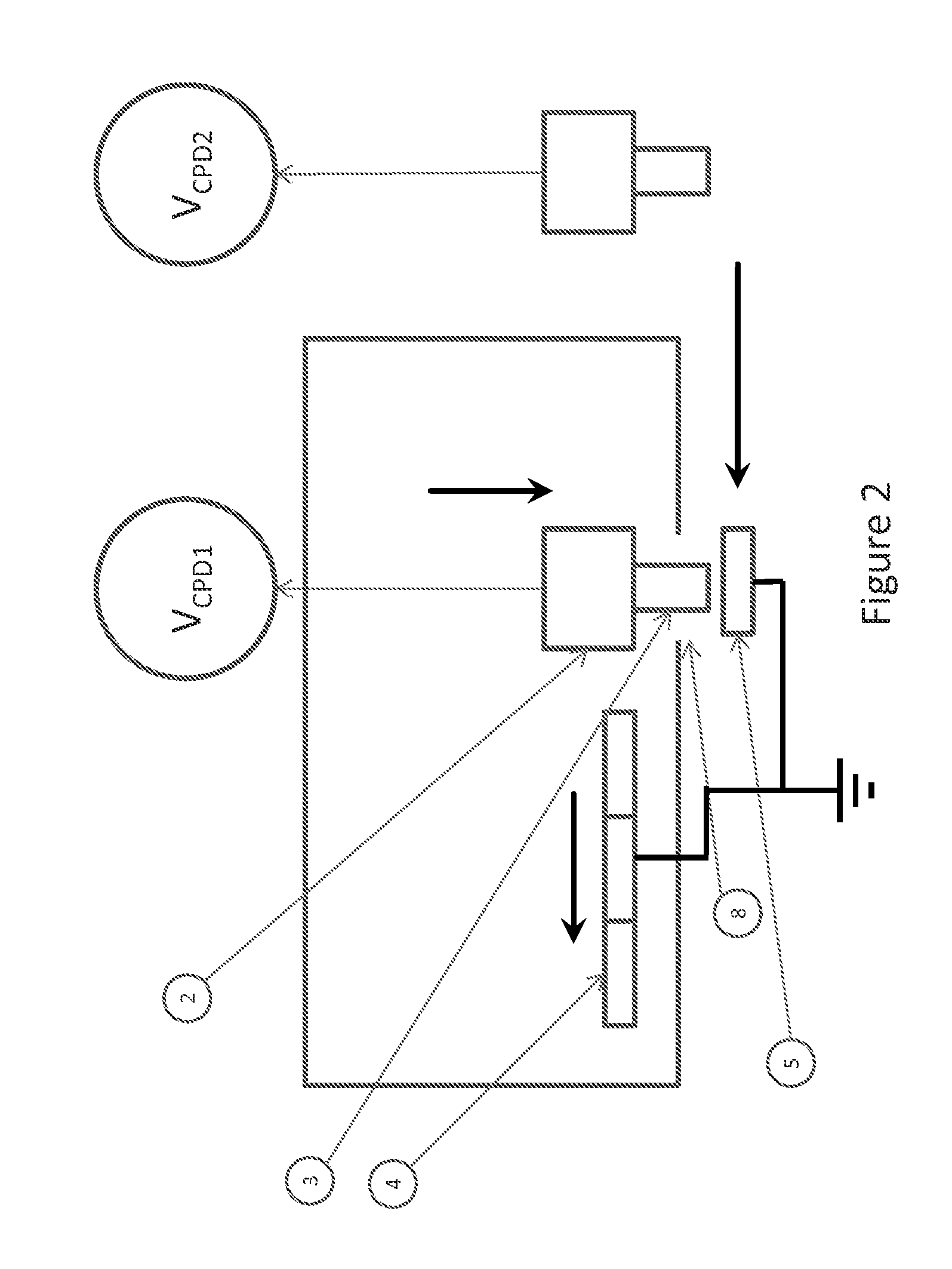
A disclosed developing apparatus employs a flare roller that is a toner carrier in which electrodes of two different phases are provided at fine intervals. Density irregularities or scumming in a developed image due to a potential difference between the flare roller and a latent image carrier are prevented by maintaining a constant potential on the flare roller surface. A voltage is applied to the electrodes on the flare roller such that an electric field that varies with time is generated between the electrodes, whereby a toner cloud is produced by the movement or hopping of toner over the flare roller. Thereby the toner attaches to a latent image on the latent image carrier, thus developing the latent image. In one embodiment, a bias with an average potential equal to an average potential of the bias applied to the electrodes is applied to a toner layer thickness regulating member.
Owner:RICOH KK
Image forming apparatus
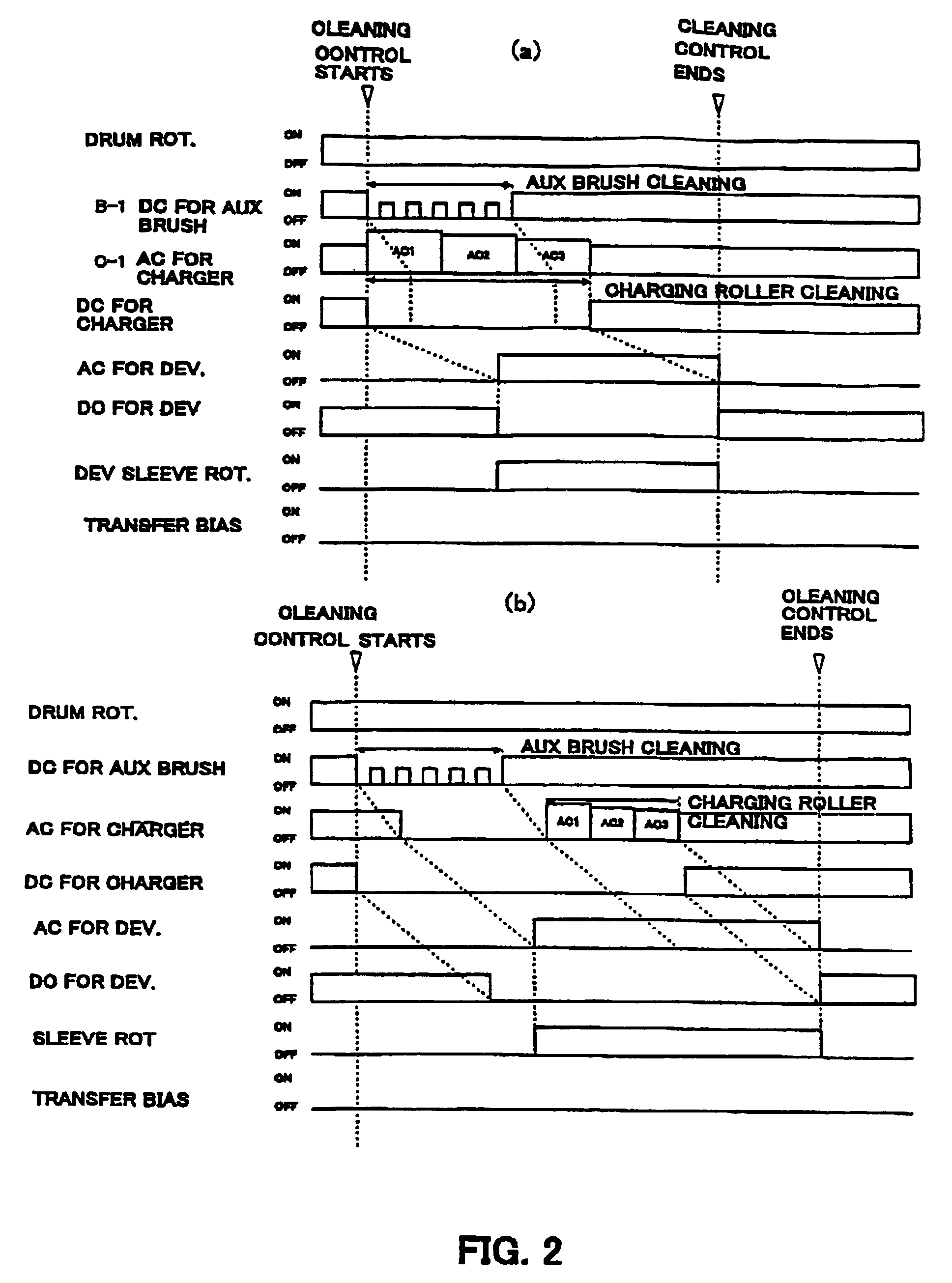
InactiveUS20050078981A1Enhance the imageEasy to cleanElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeImage formationEngineering
An image forming apparatus includes an image bearing member; charging means for electrically charging the image bearing member while contacting to the image bearing member; transferring means for transferring a developed image on the image bearing member onto a transfer material; developer charging means for electrically charging a developer remaining on the image bearing member after the image is transferred, the developer charging means being disposed downstream of the transferring means and upstream of the charging means with respect to a moving direction of the image bearing member; and electric field forming means for forming a cleaning electric field in a direction of transferring the developer from the developer charging means onto a predetermined region of the image bearing member and for forming a cleaning electric field for transferring the developer from the charging means onto the image bearing member after the predetermined region of the image bearing member passes through a contact portion between the charging means and the image bearing member.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for preparing powder exhibiting low susceptibility to electrification
InactiveUS20070009444A1Excellent in kneading propertyCharging tendencyBiocideCosmetic preparationsPolyethylene glycolCompound (substance)
A method of producing lowly-charged powder comprising drying a liquid composition containing a highly-charged compound and polyethyleneglycol.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Image forming apparatus
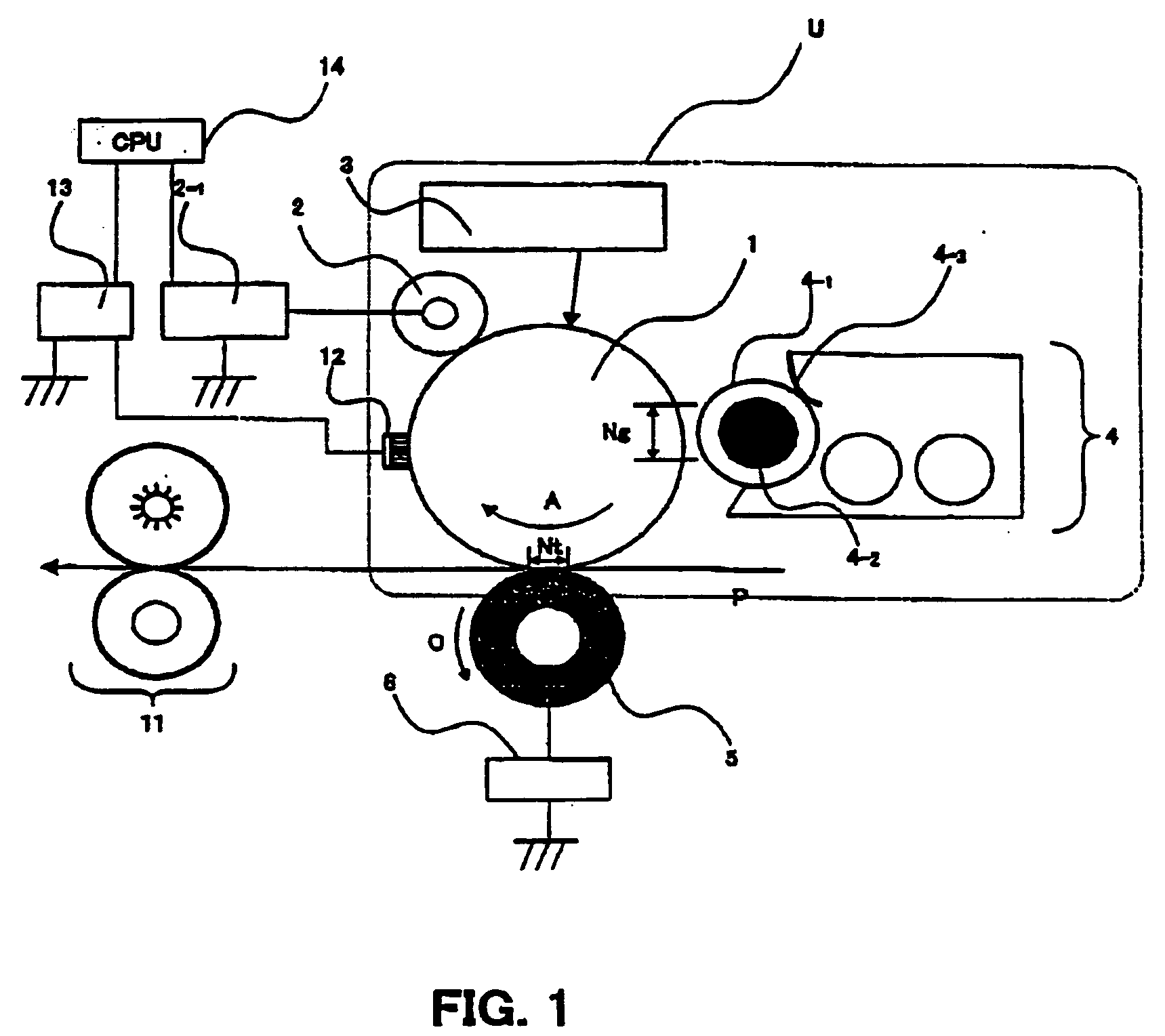
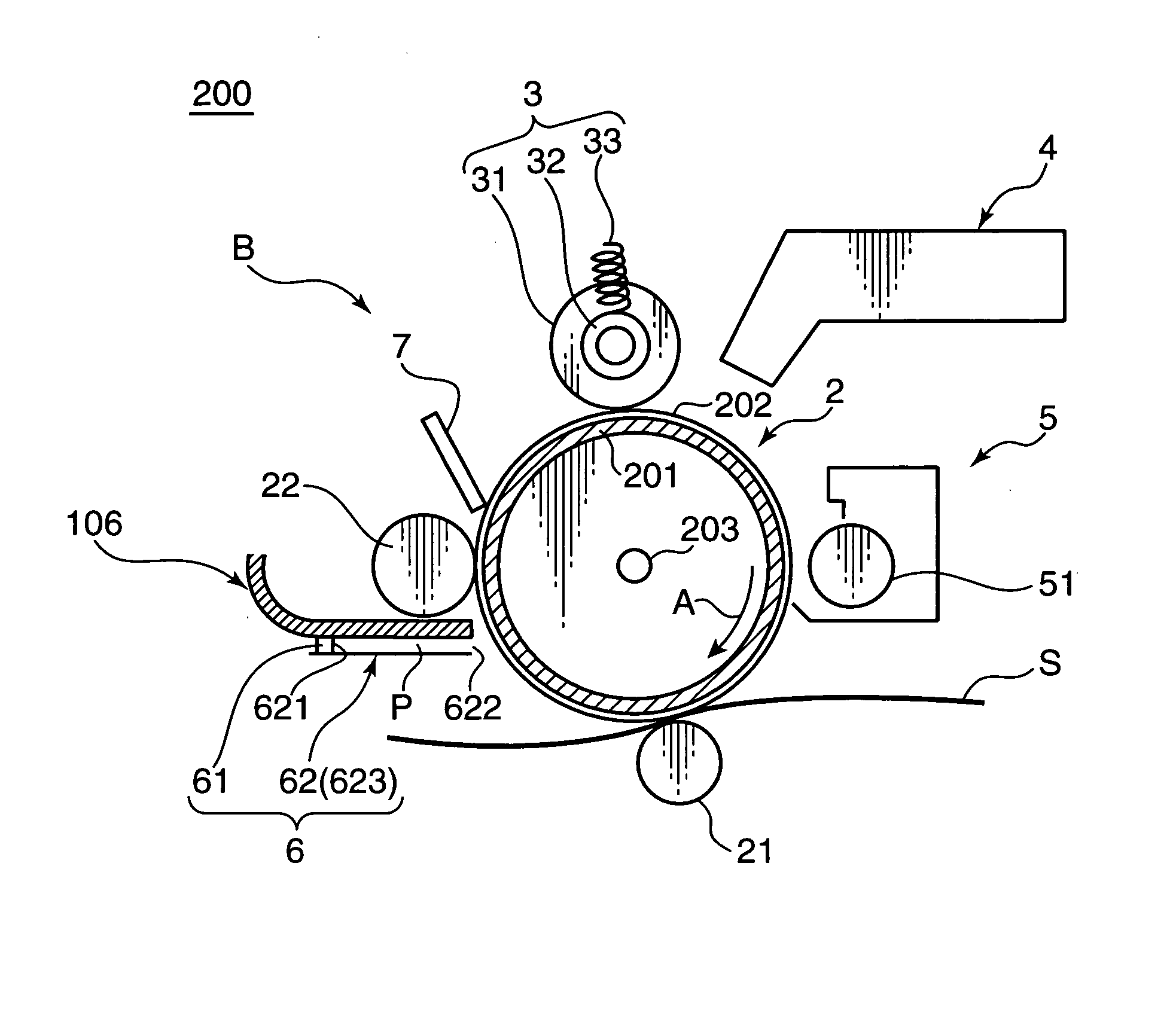
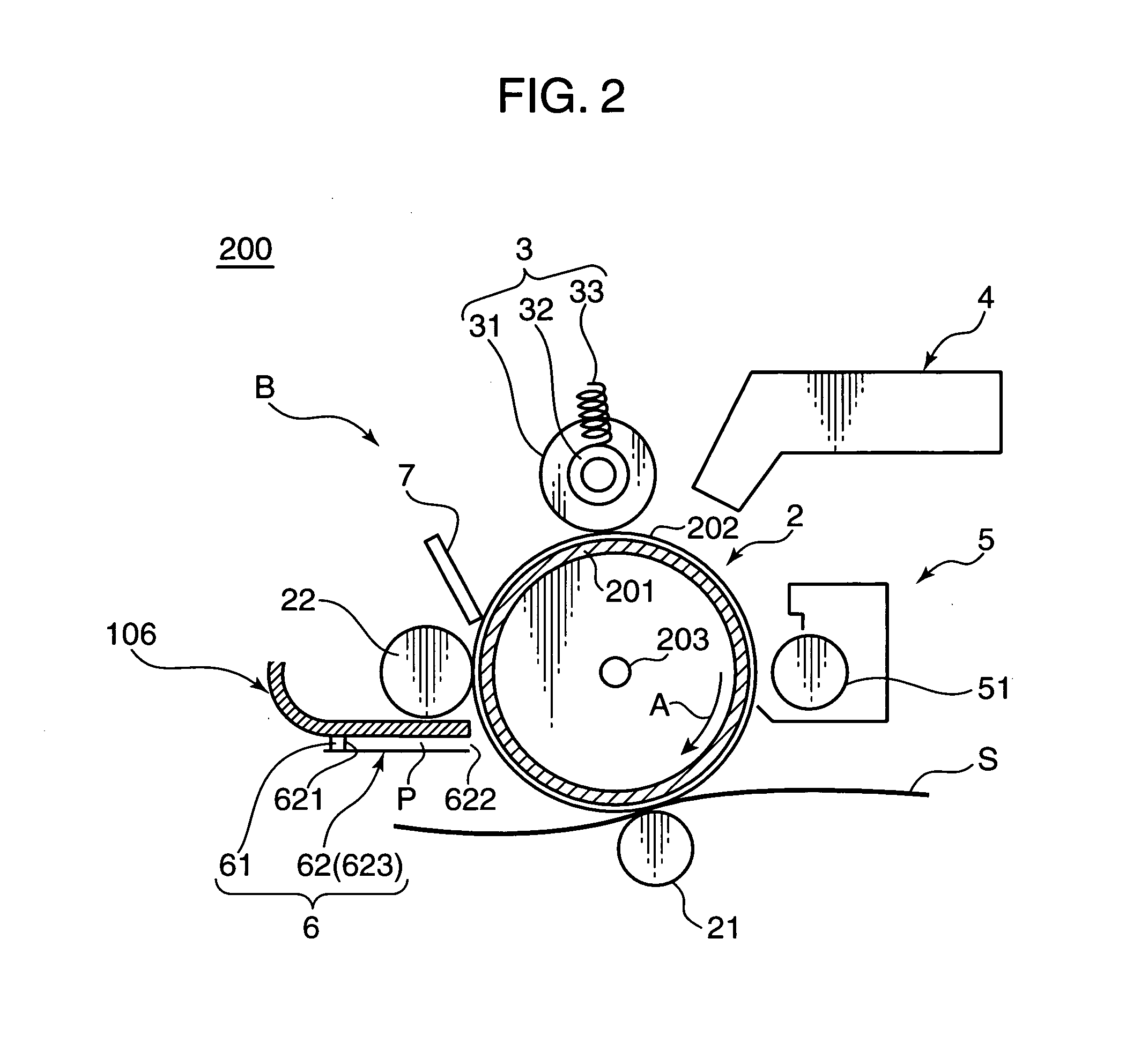
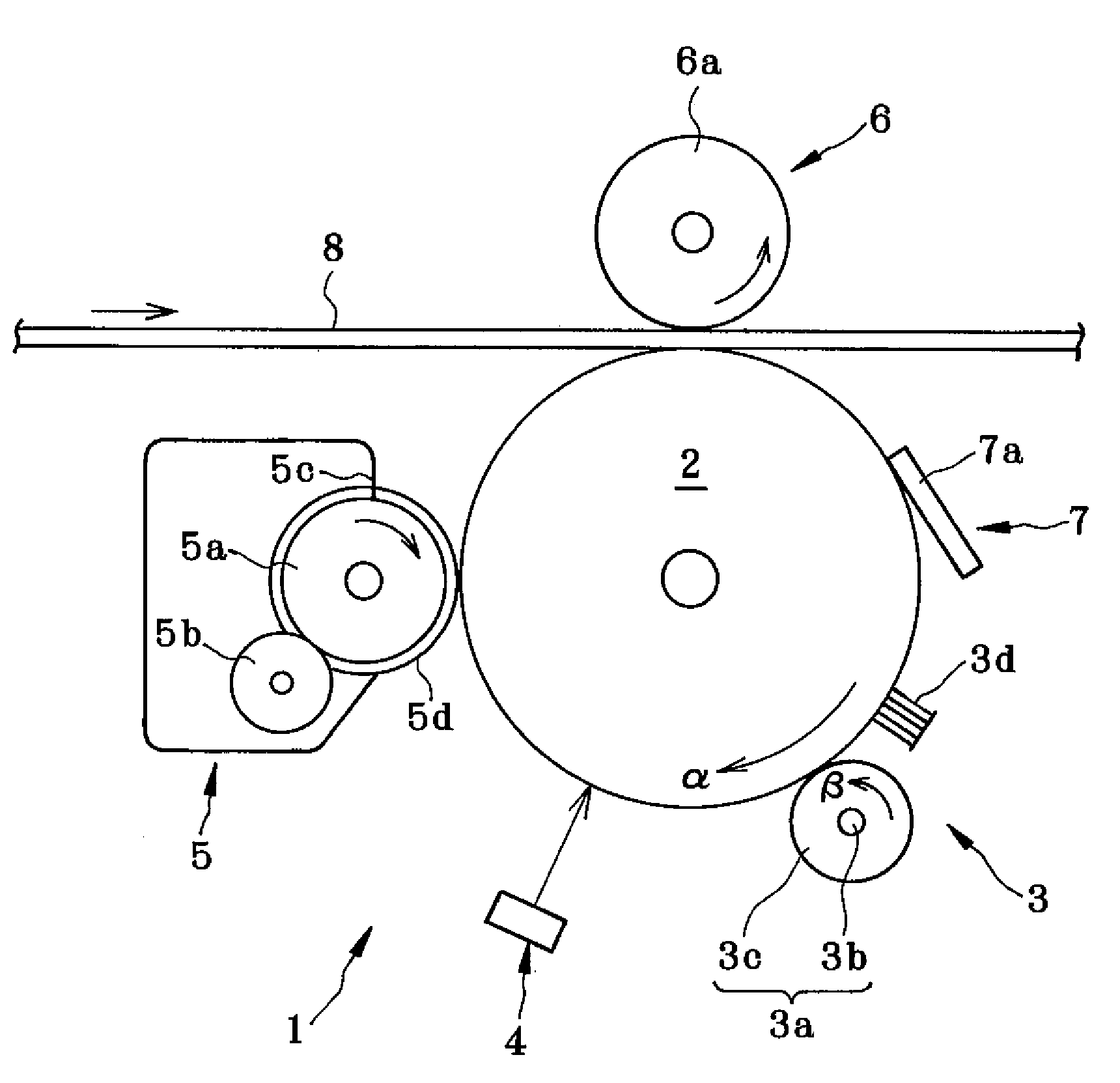
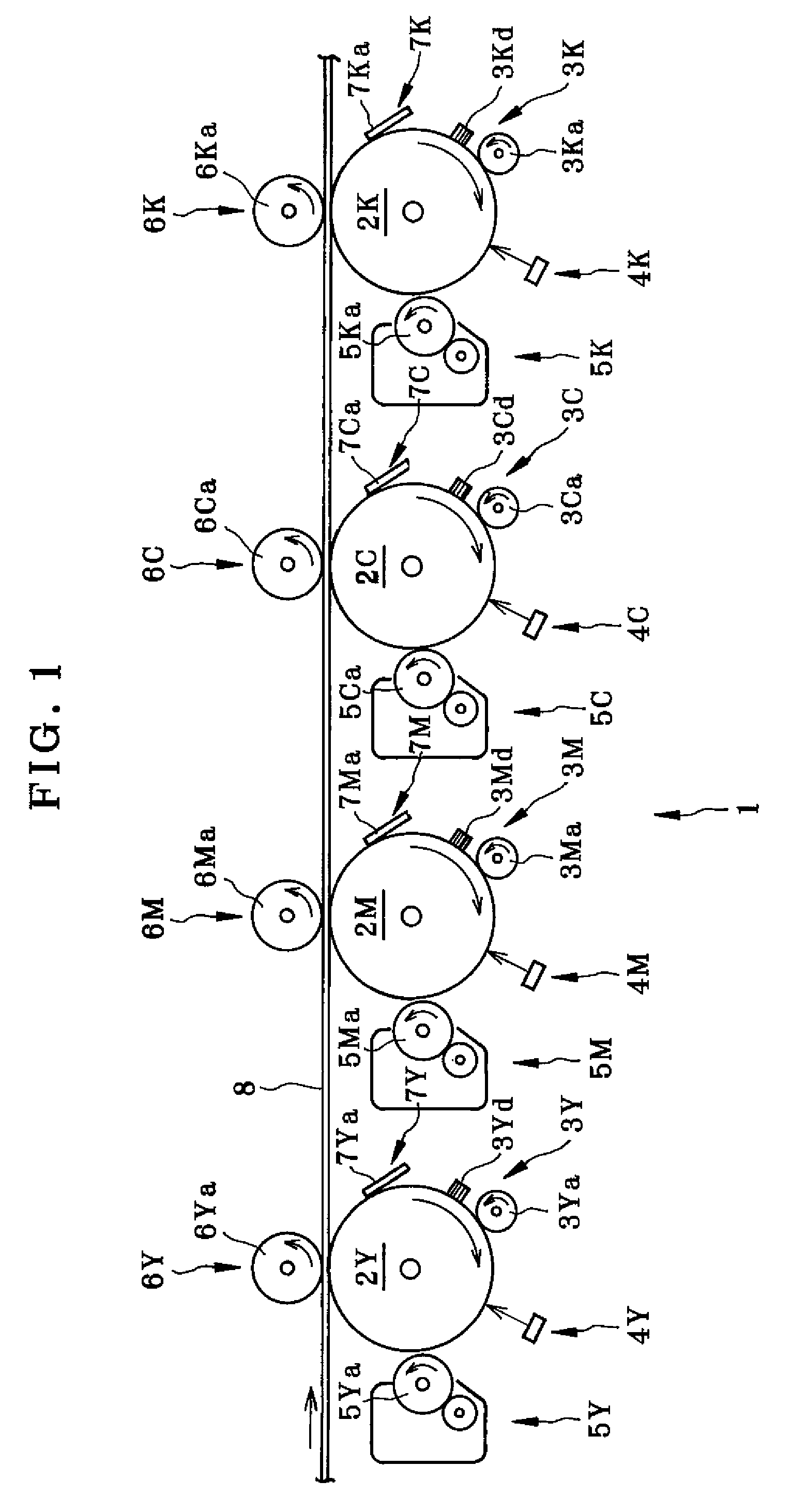
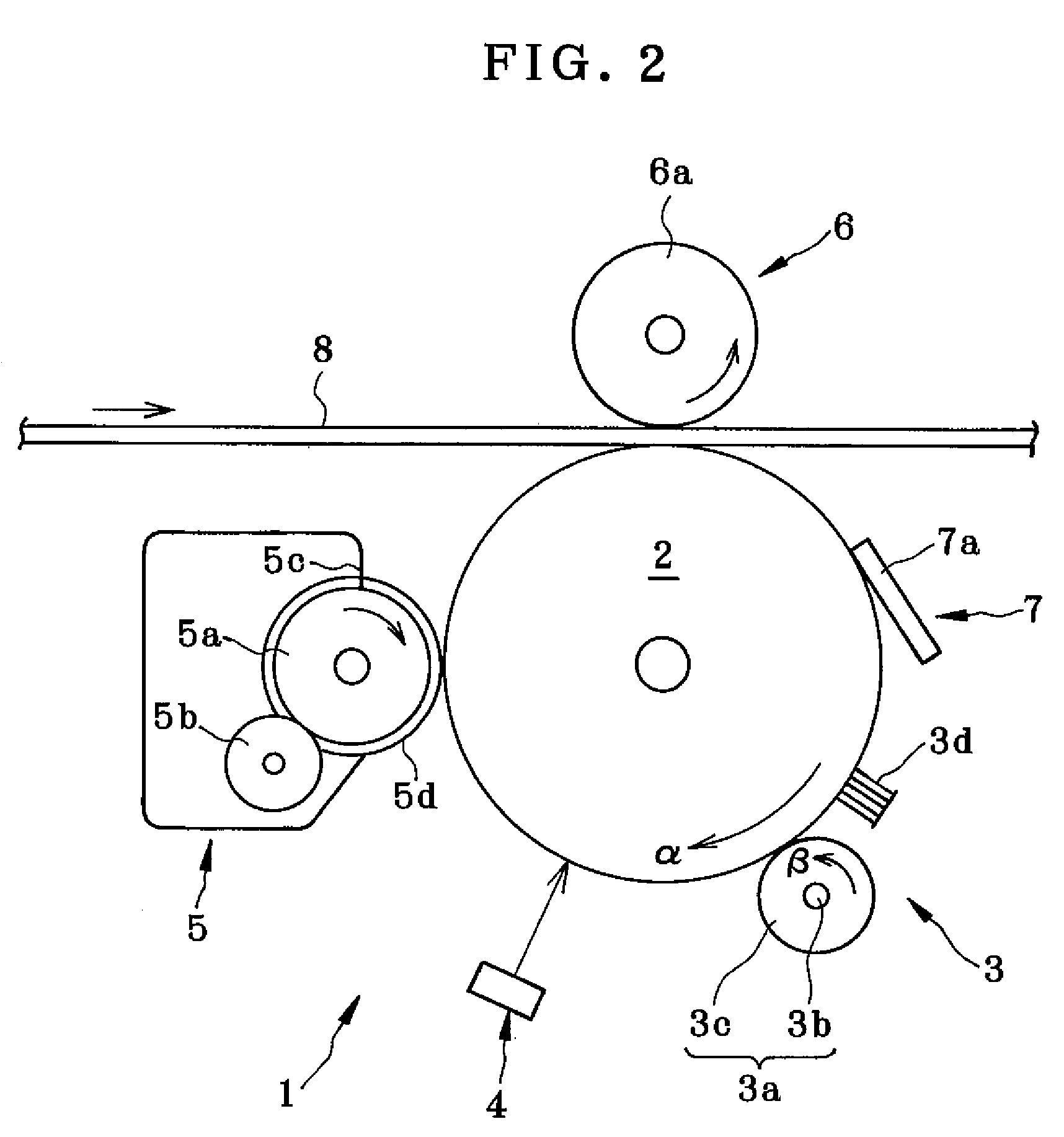
ActiveUS20060188288A1Avoid it happening againSurface potentialElectrography/magnetographyImage formationEngineering
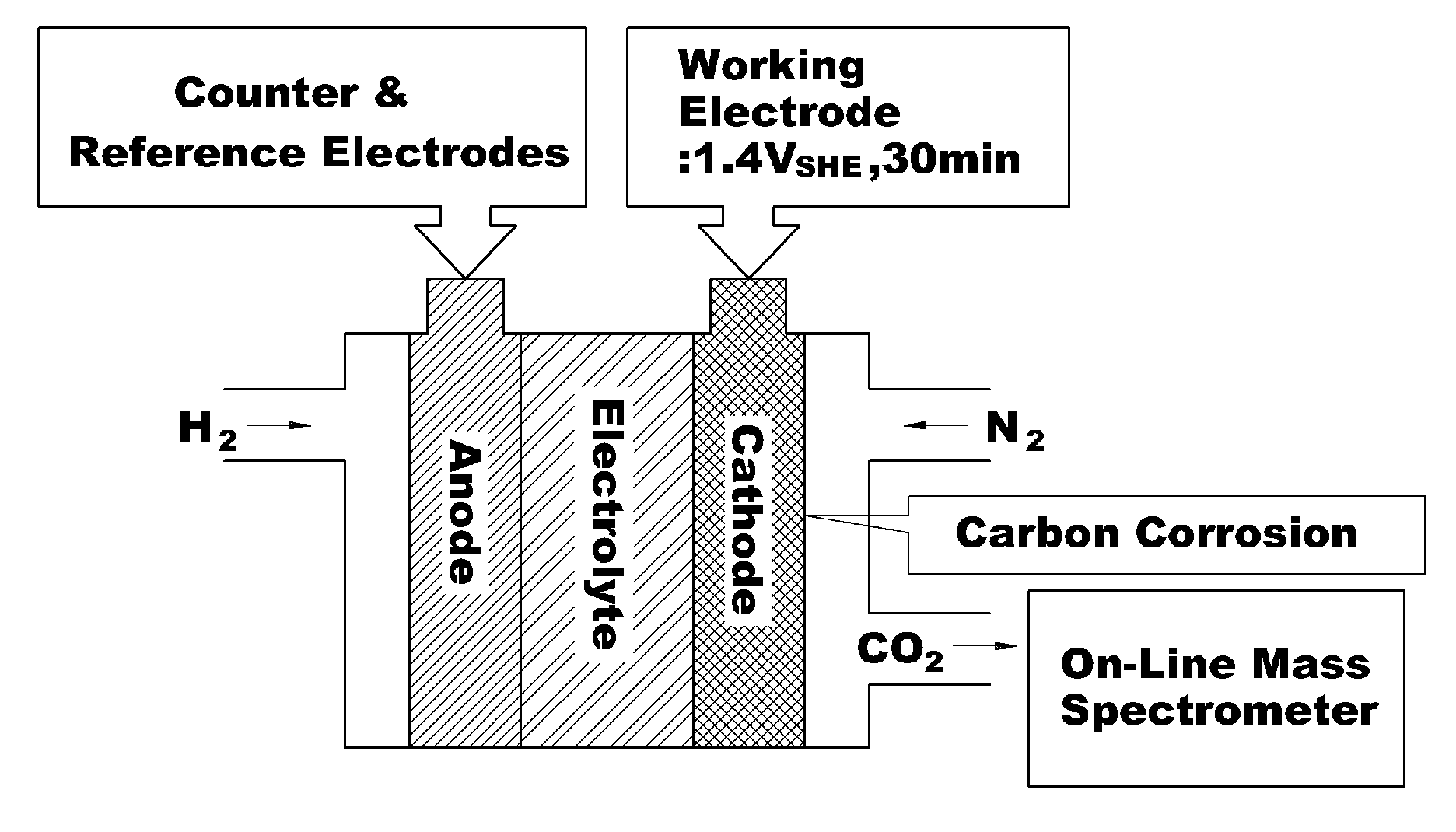
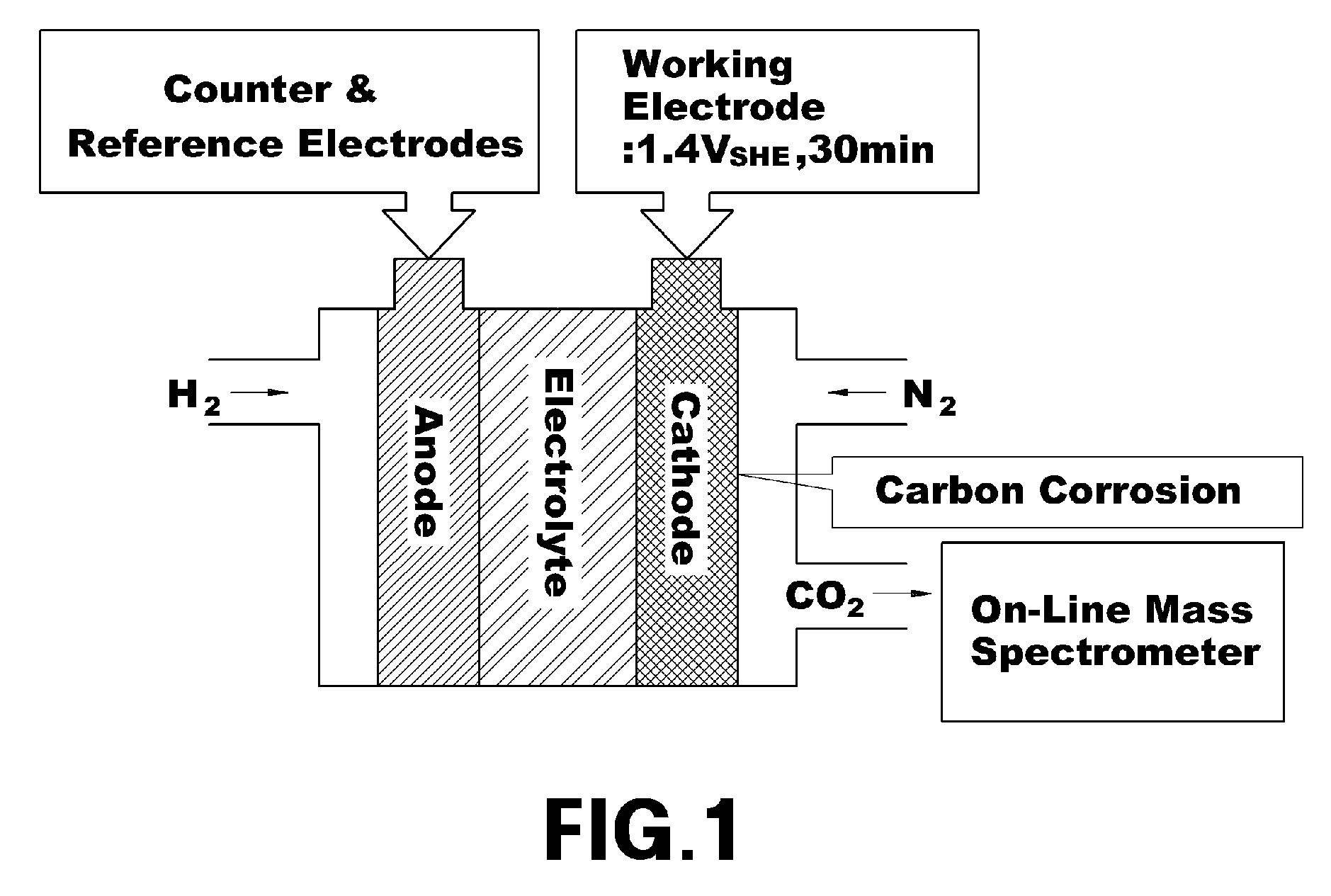
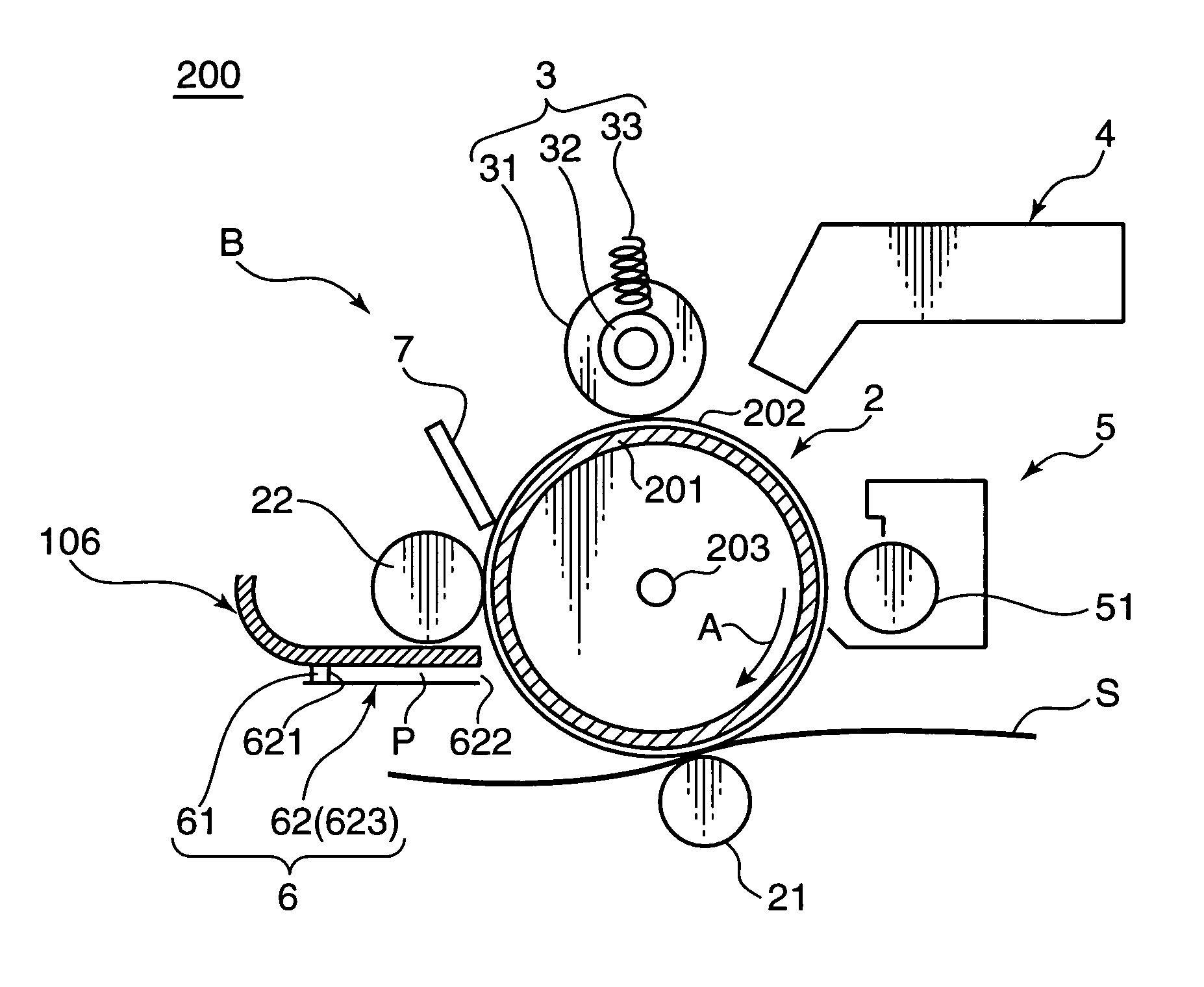
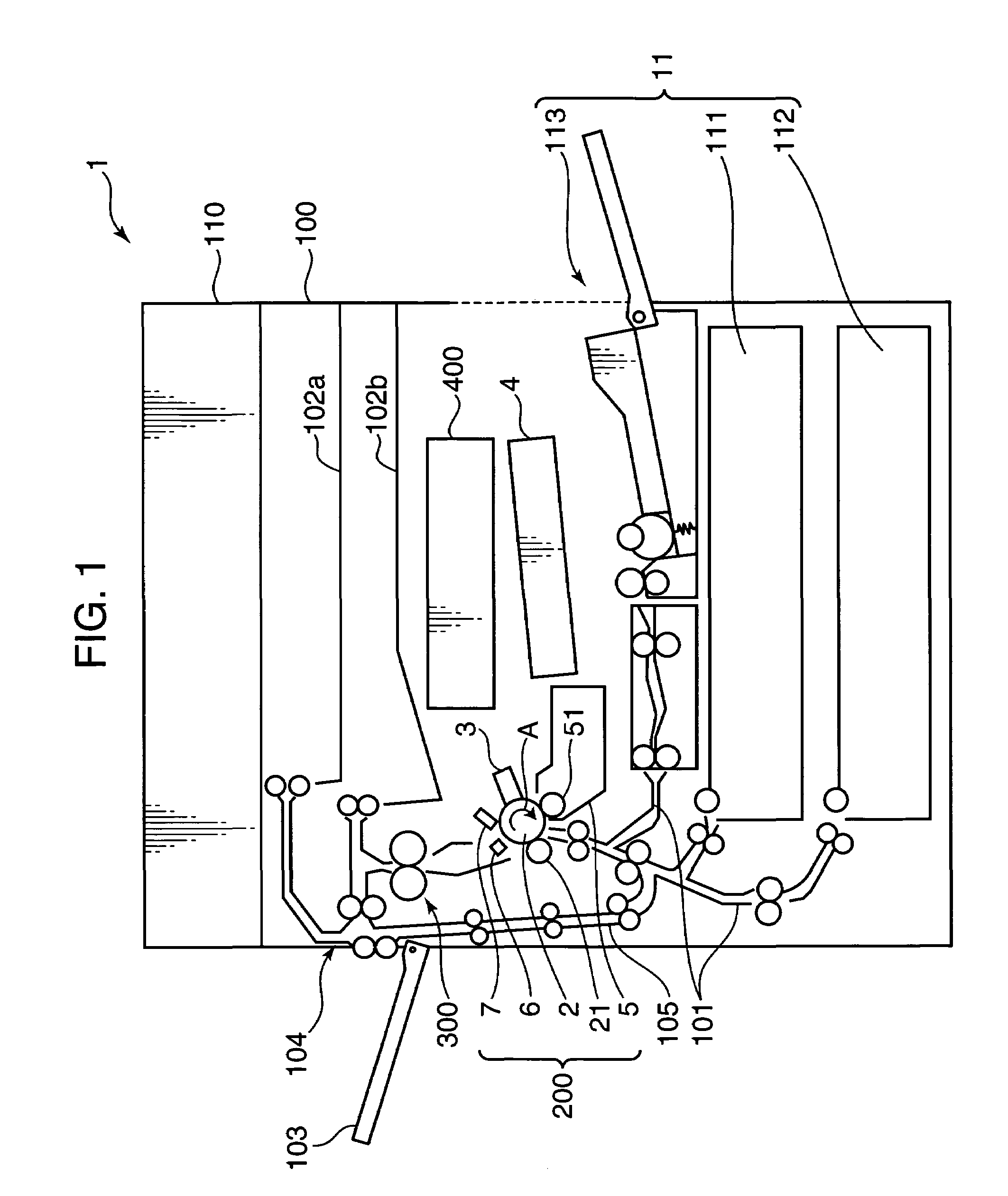
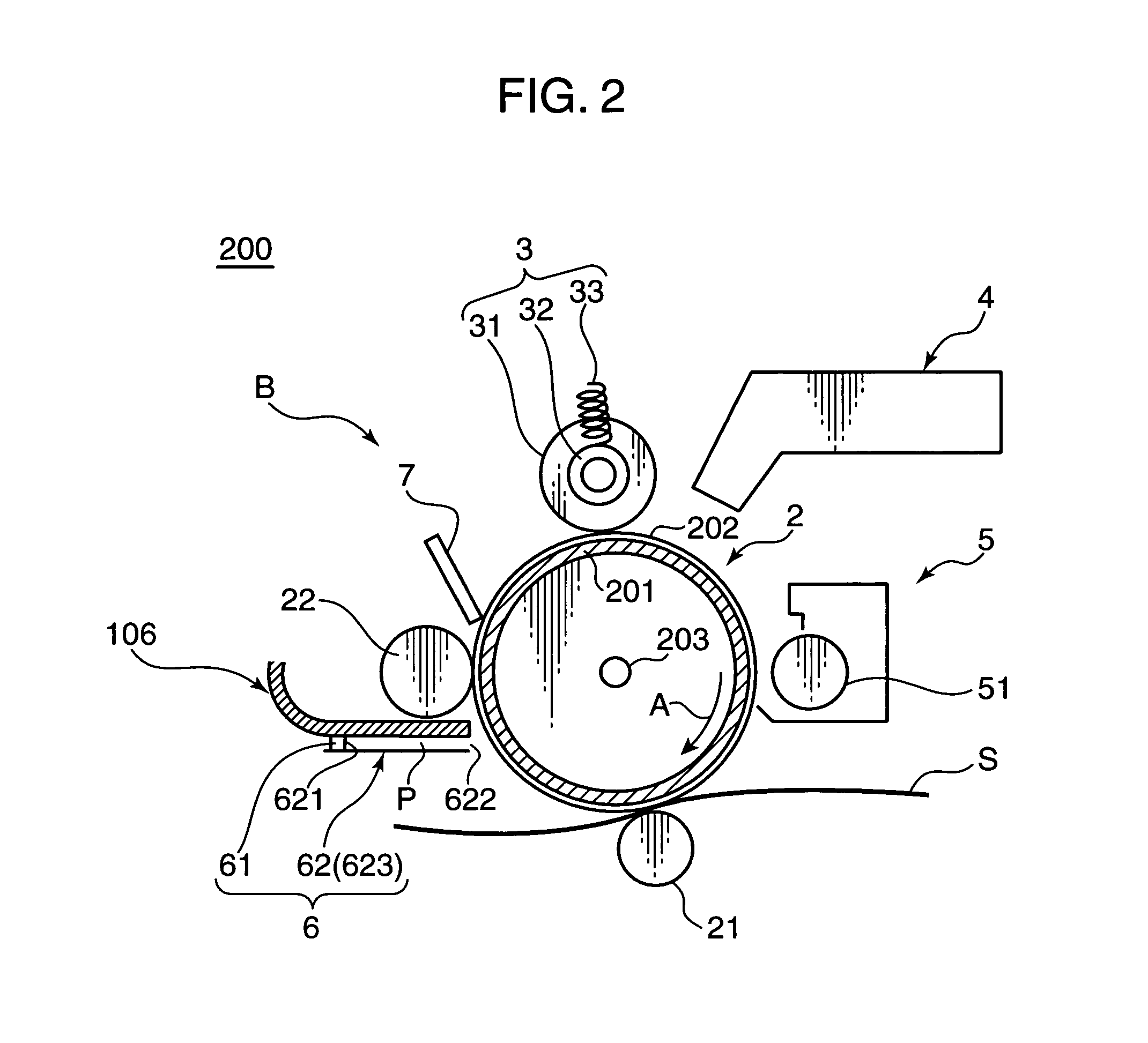
Charge removing light is guided by an optical path defining member (623) from a charge removing unit (6) toward a photosensitive drum (2). A distance between an end surface (623e) of the optical path defining member (623) and a surface on an axially central part of the photosensitive drum (2) is less than a distance between the end surface (623e) and the surface on the axially opposite ends of the photosensitive drum (2). Thus an irradiation width and an amount of the charge removing light projected onto the surface of the photosensitive drum (2) are increased on the opposite ends. With this arrangement, the amount of generated light carriers can be reduced on the axially central part, as compared with the axially opposite ends, and a surface potential distribution non-uniformity due to a difference in nip distance between the photosensitive drum (2) and a charging roller (31) can be eliminated.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
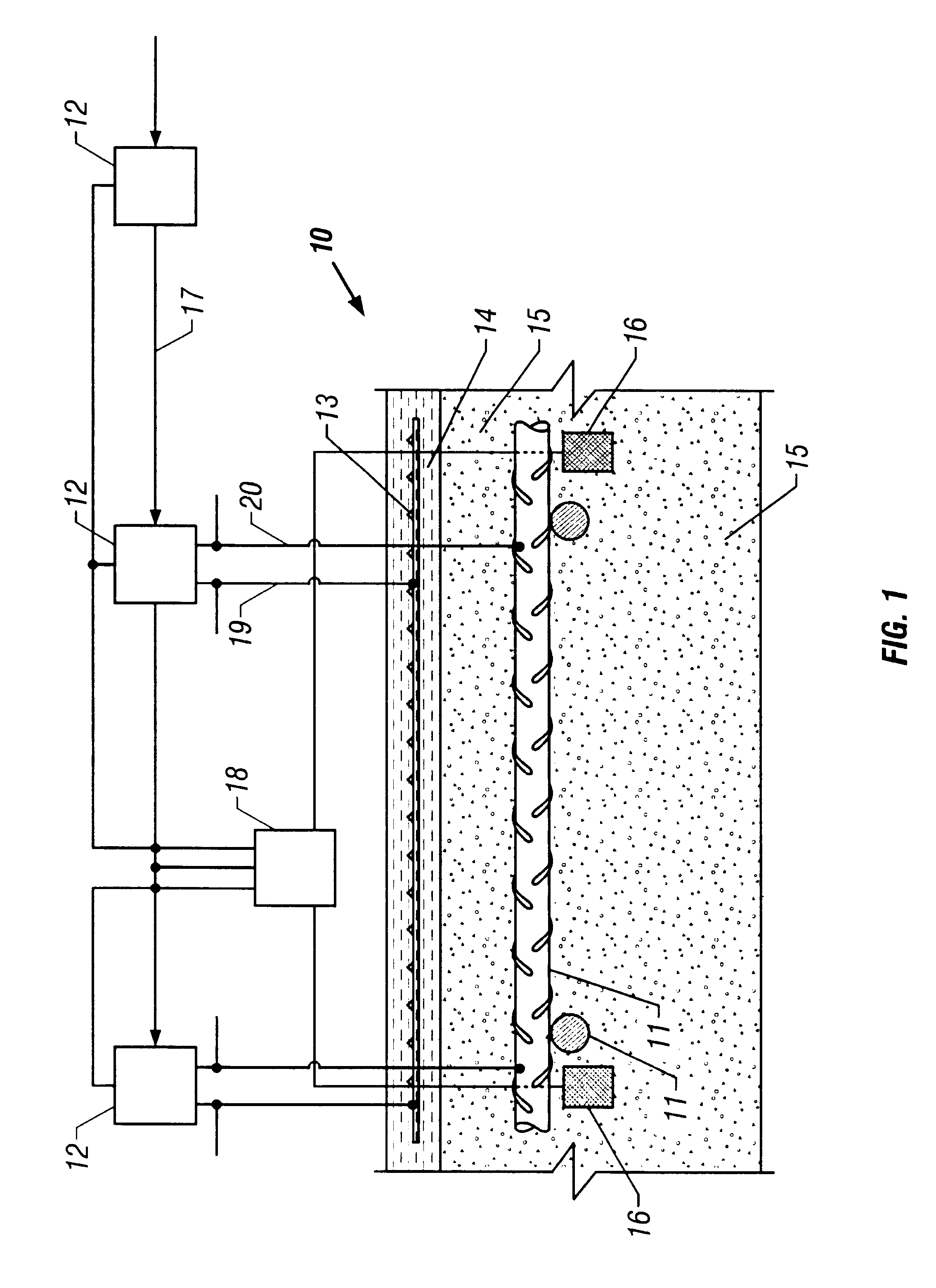
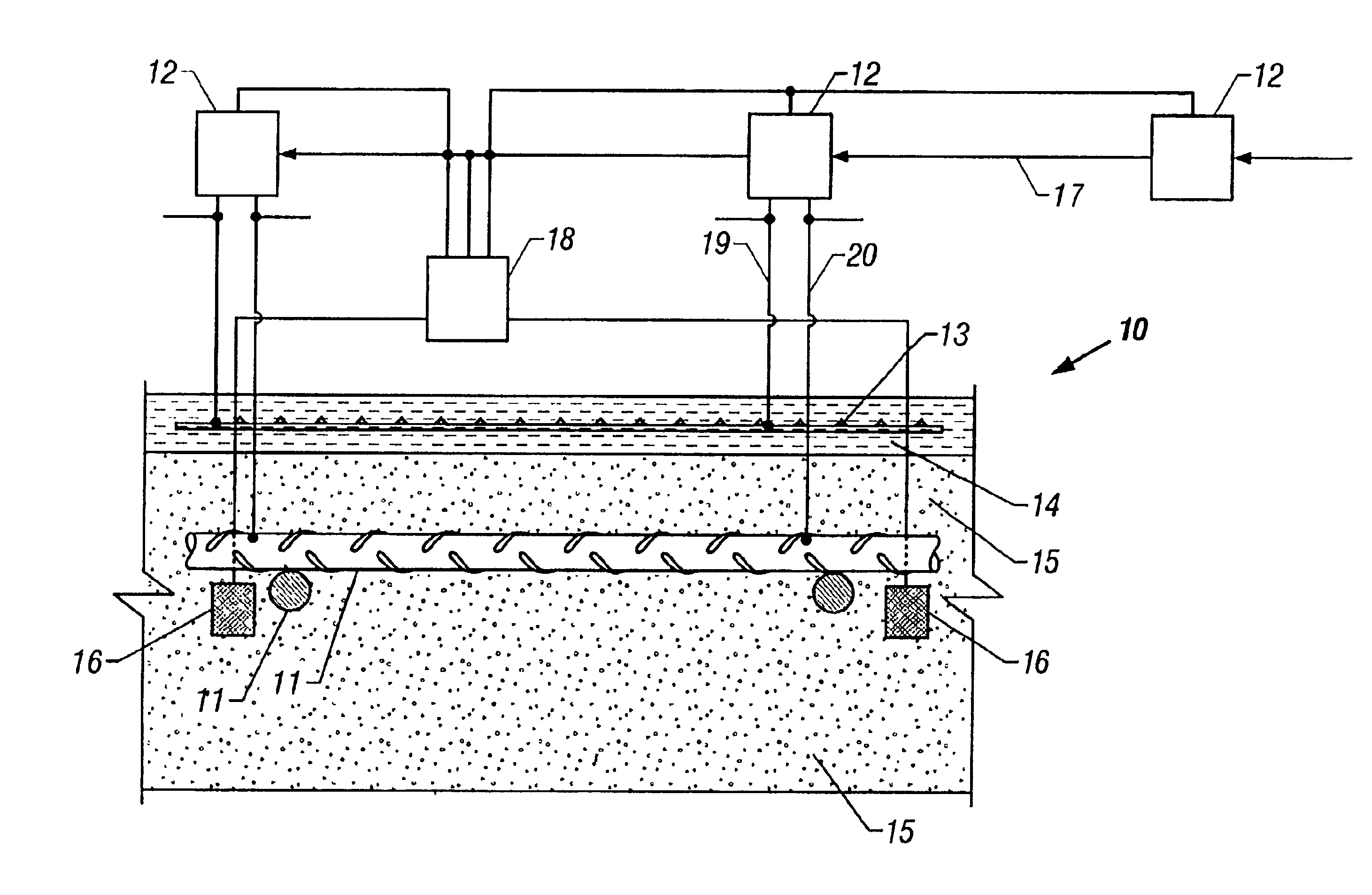
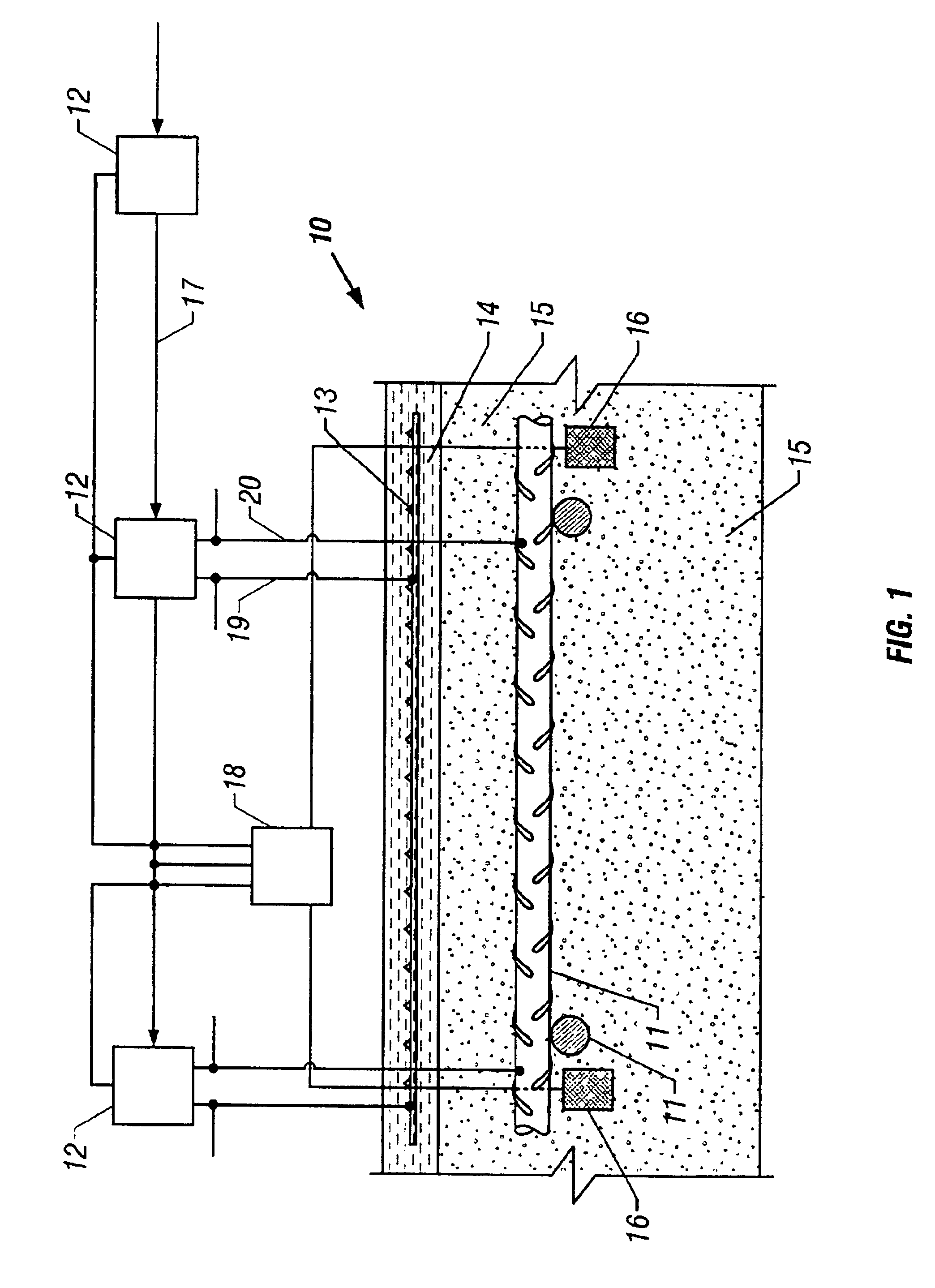
Method of treating corrosion in reinforced concrete structures by providing a uniform surface potential
InactiveUS6398945B1Inhibiting and preventing corrosionEliminate differencesRebar corrosionPower flow
The invention provides a method of inhibiting or preventing corrosion of reinforced steel in concrete by eliminating the differences in surface potentials that result in the total passivation of corrosion activity and create an environment in the steel that does not allow corrosion. The method, optionally includes measuring the active non-uniform surface potential in the steel and passing a DC voltage through the concrete and steel to stop corrosion providing a substantially uniform surface potential on the reinforced steel. The current is controlled and adjusted to send pre-determined amounts of electrical energy to individual areas targeted for treatment. A corrosion potential survey may be conducted to determine the energy requirements necessary for the corrosion condition or a reference electrode may be strategically placed on the concrete structure. The amount of energy passed is sufficient to polarize the reinforcing steel sufficiently to stop corrosion and establish substantially uniform surface potentials on all the reinforcing steel. The invention also includes changing conditions on the surface of steel from a condition of non-uniform surface potential to a condition of substantially uniform surface potential.
Owner:INFRASTRUCTURE REPAIR TECH
Method of treating corrosion in reinforced concrete structures by providing a uniform surface potential
The present invention provides a method of inhibiting or preventing corrosion of reinforced steel in concrete by eliminating the differences in surface potentials that result in the total pasivation of corrosion activity and create an environment in the steel that does not allow corrosion. The method, optimally includes measuring the active non-uniform surface potential in the steel and passing a DC voltage through the concrete and steel to stop corrosion providing a substantially uniform potential on the reinforced steel. The current is controlled and adjusted to send pre-determined amounts of electrical energy to individual areas targeted for treatment. A corrosion potential survey may be conducted to determine the energy requirements necessary for the corrosion condition or a reference electrode may be strategically placed on the concrete structure. The amount of energy passed is sufficient to polarize the reinforcing steel sufficiently to stop corrosion and establish substantially uniform surface potentials on all the reinforcing steel. The invention also includes changing conditions on the surface of steel from a condition of non-uniform surface potential to a condition of substantially uniform surface potential.
Owner:INFRASTRUCTURE REPAIR TECH
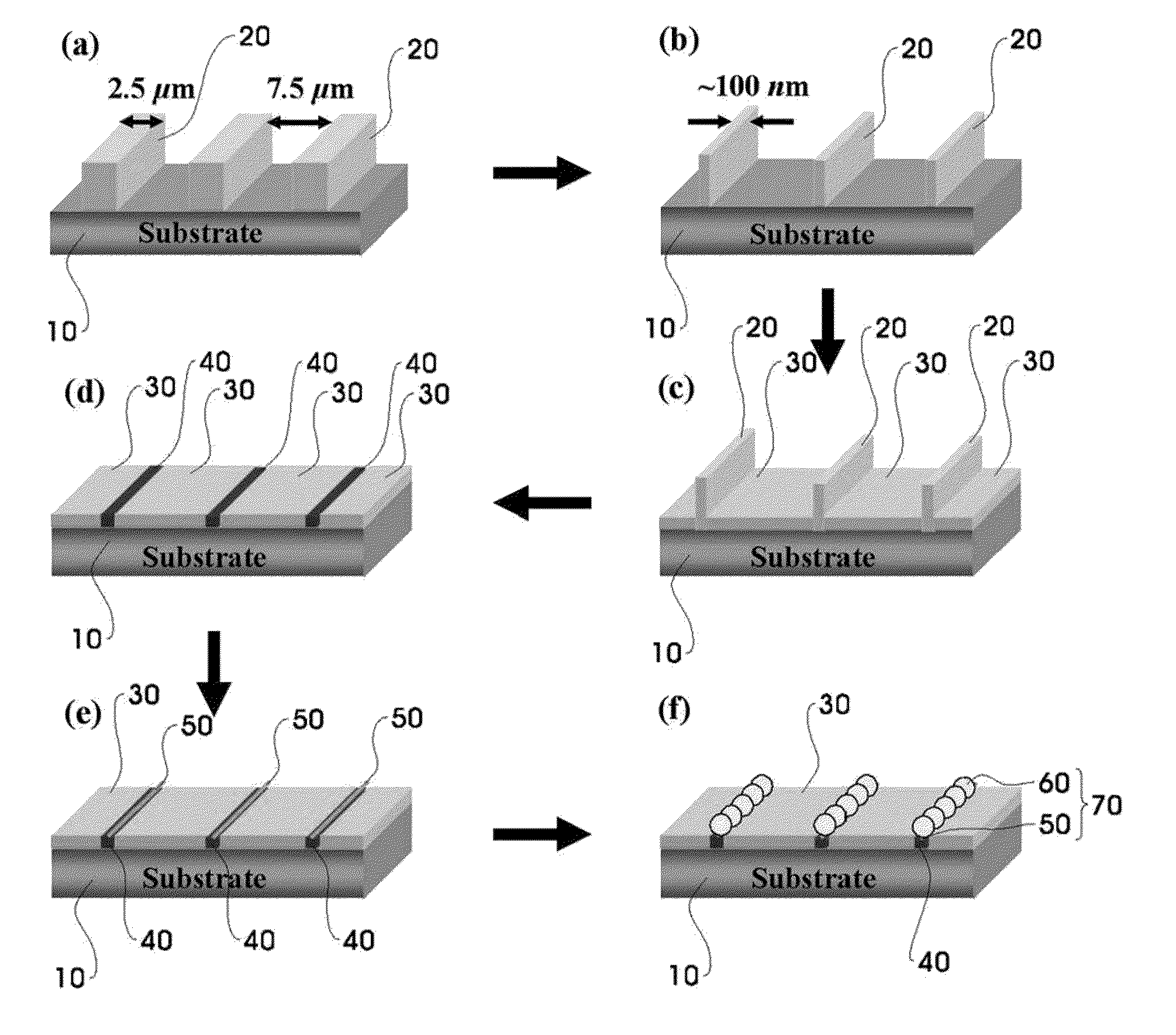
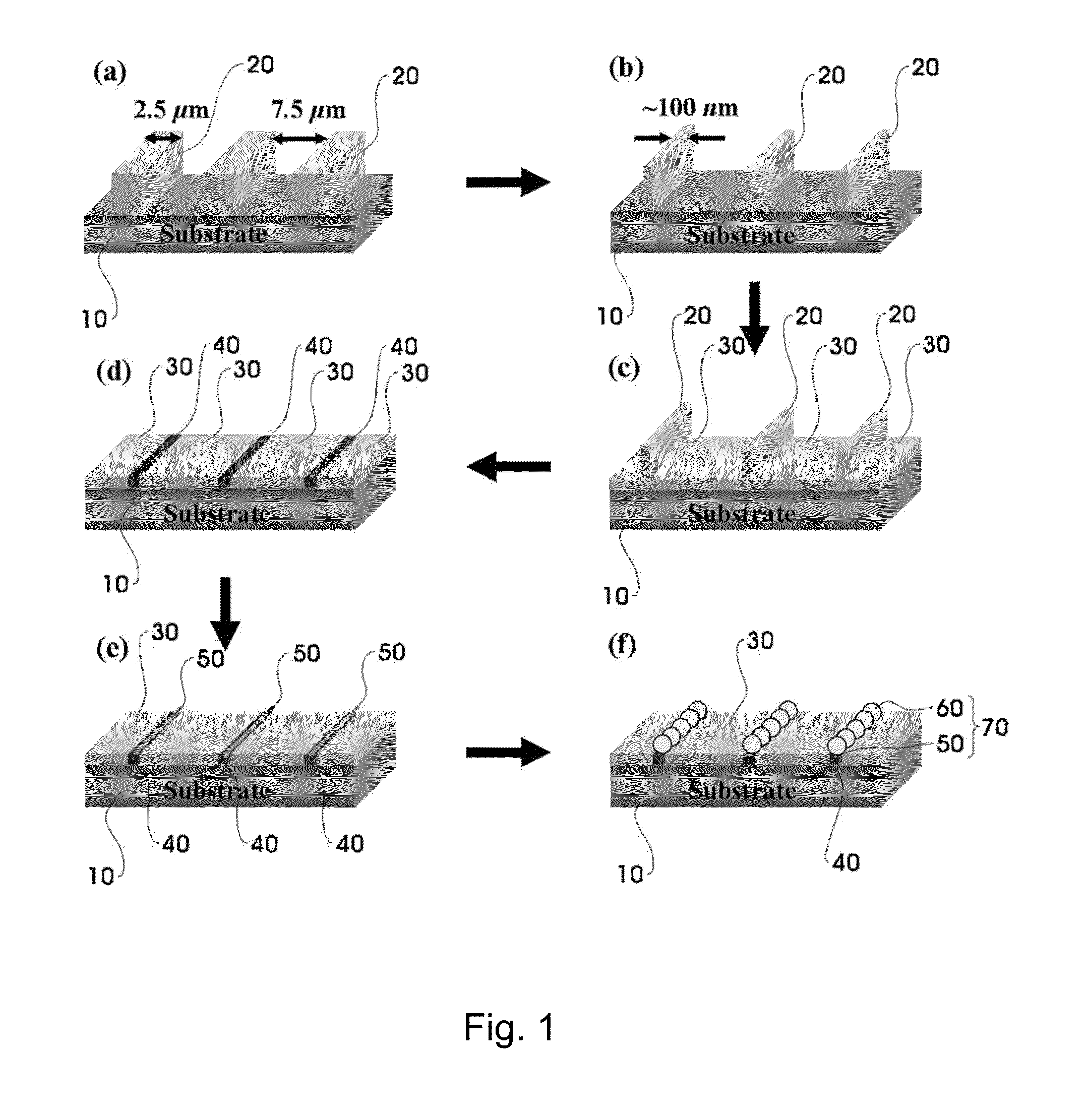
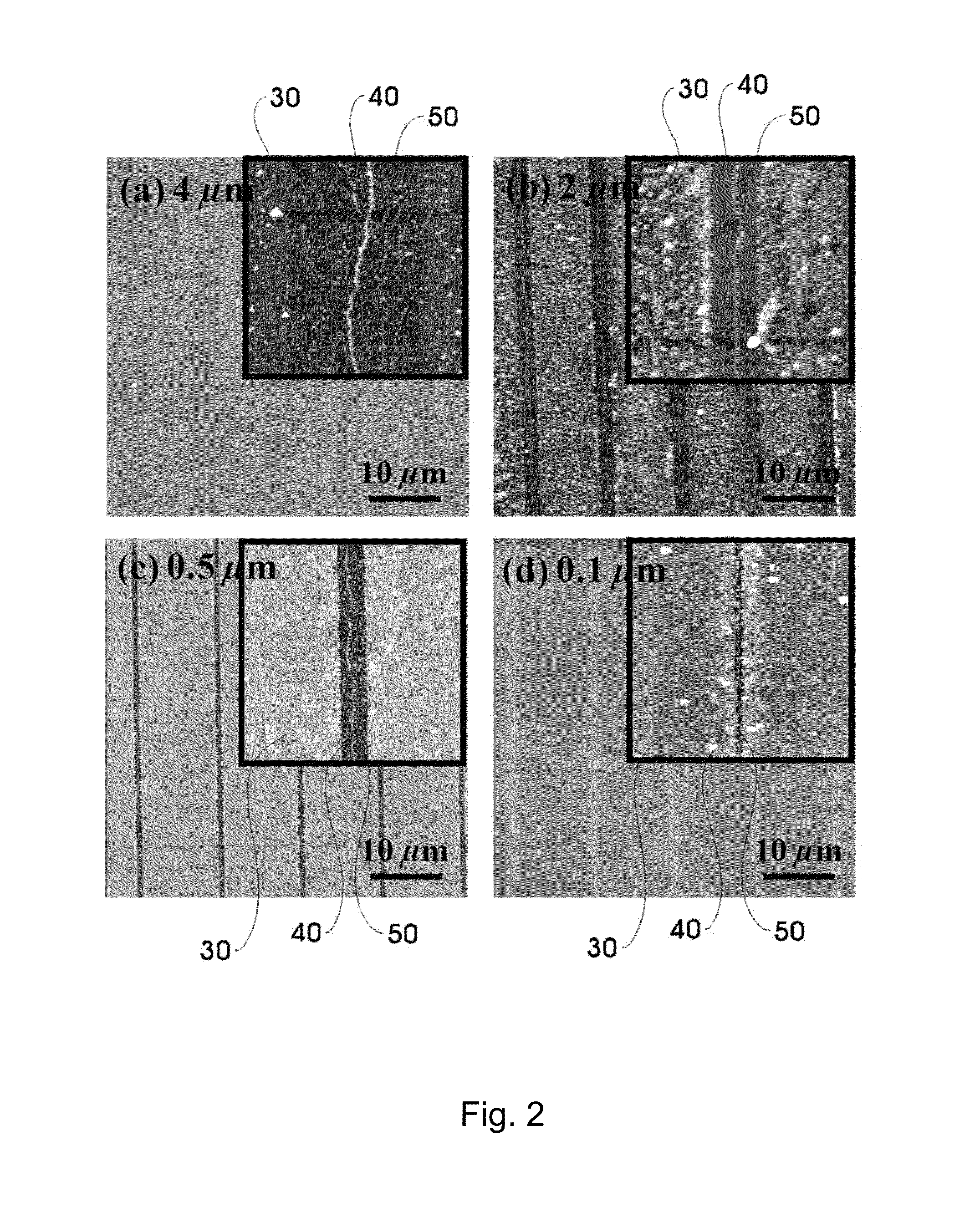
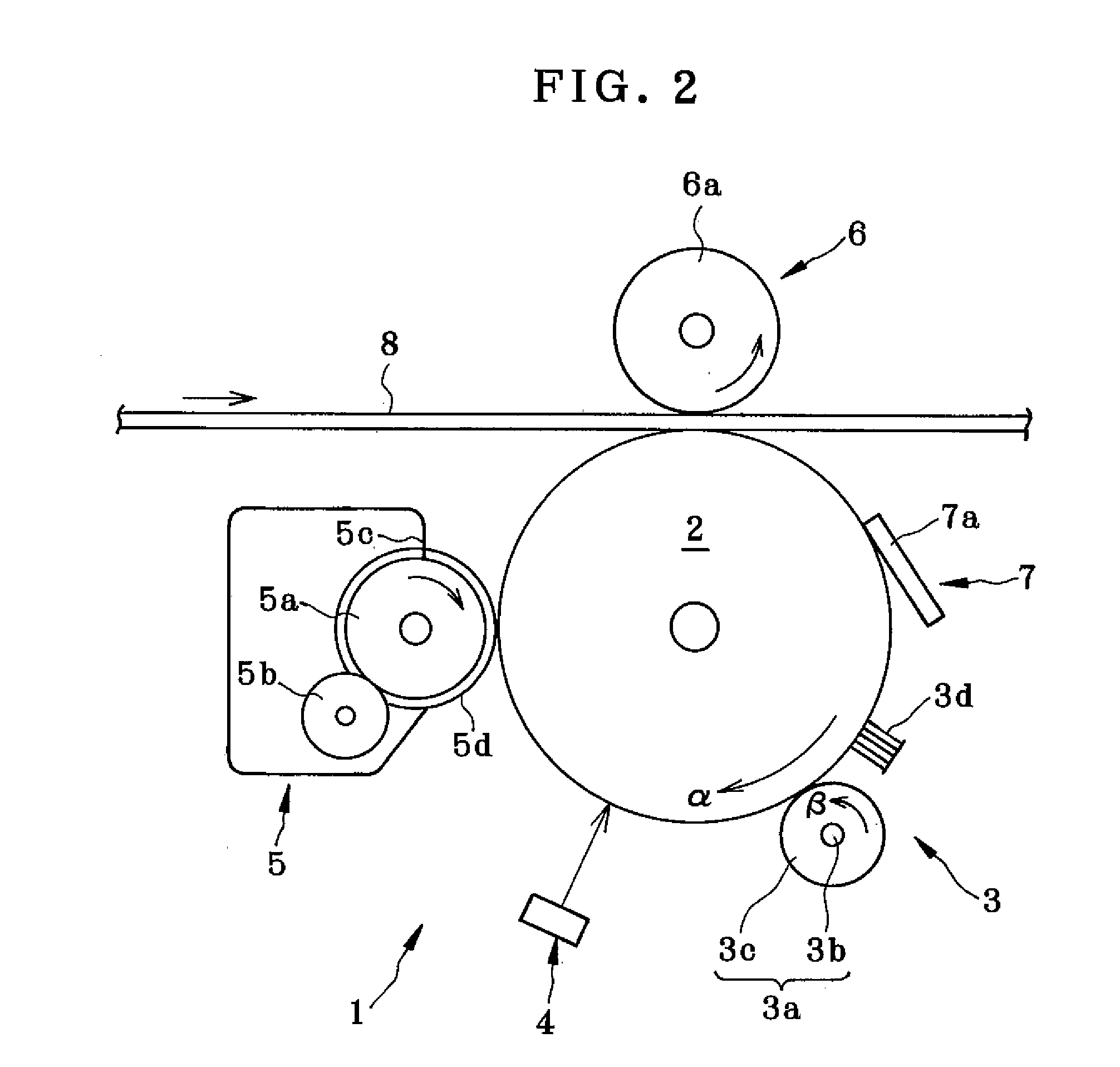
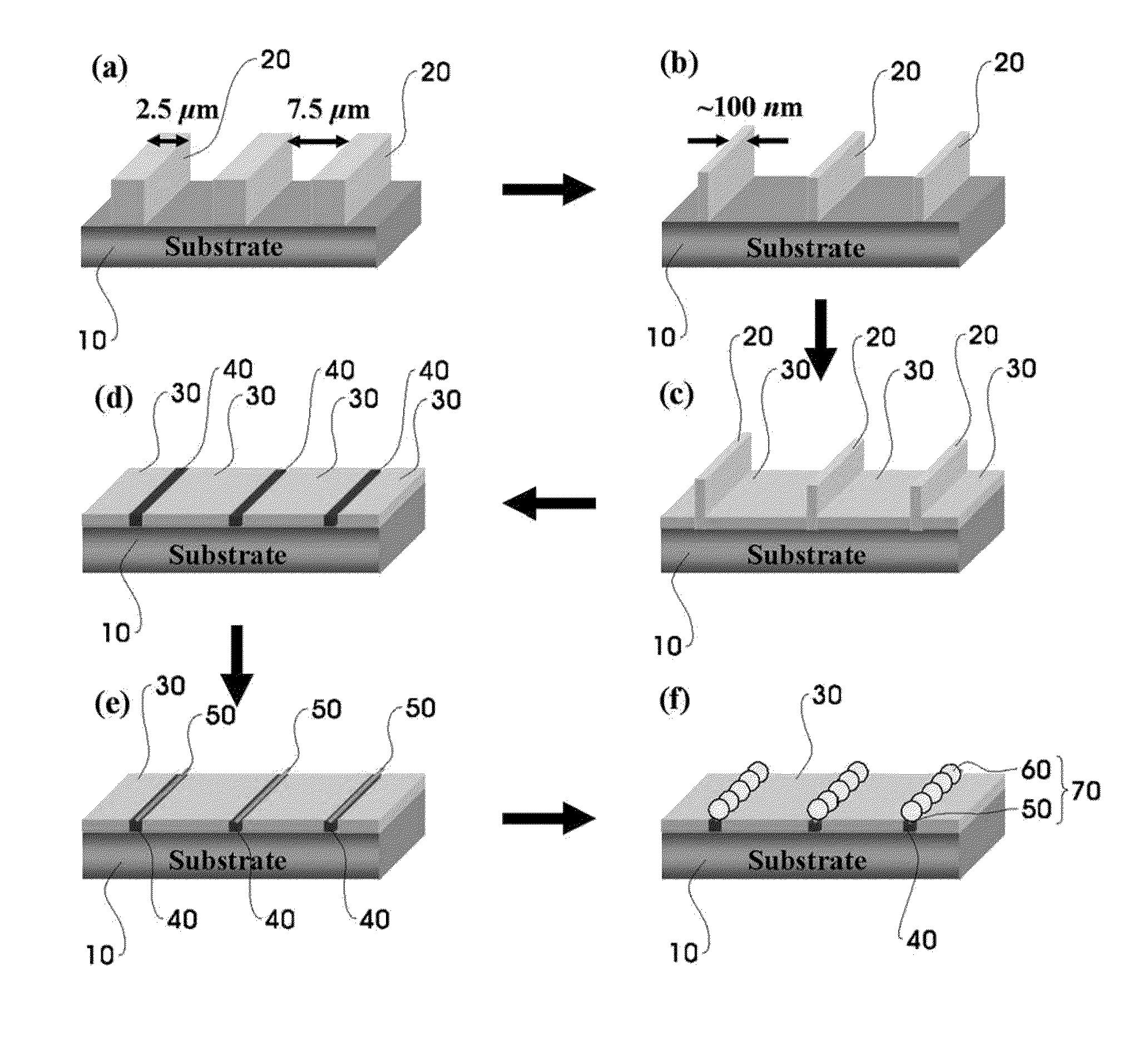
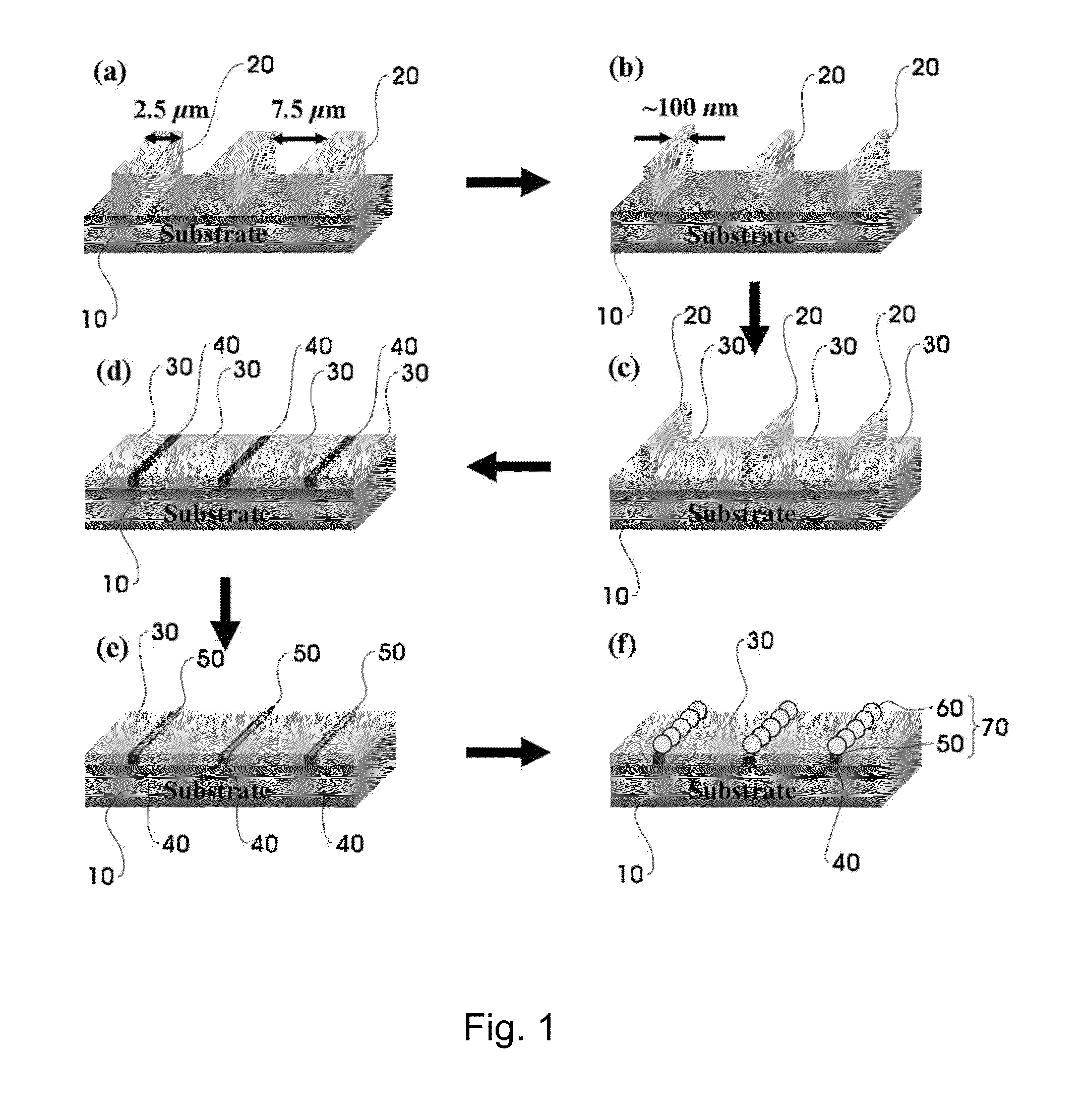
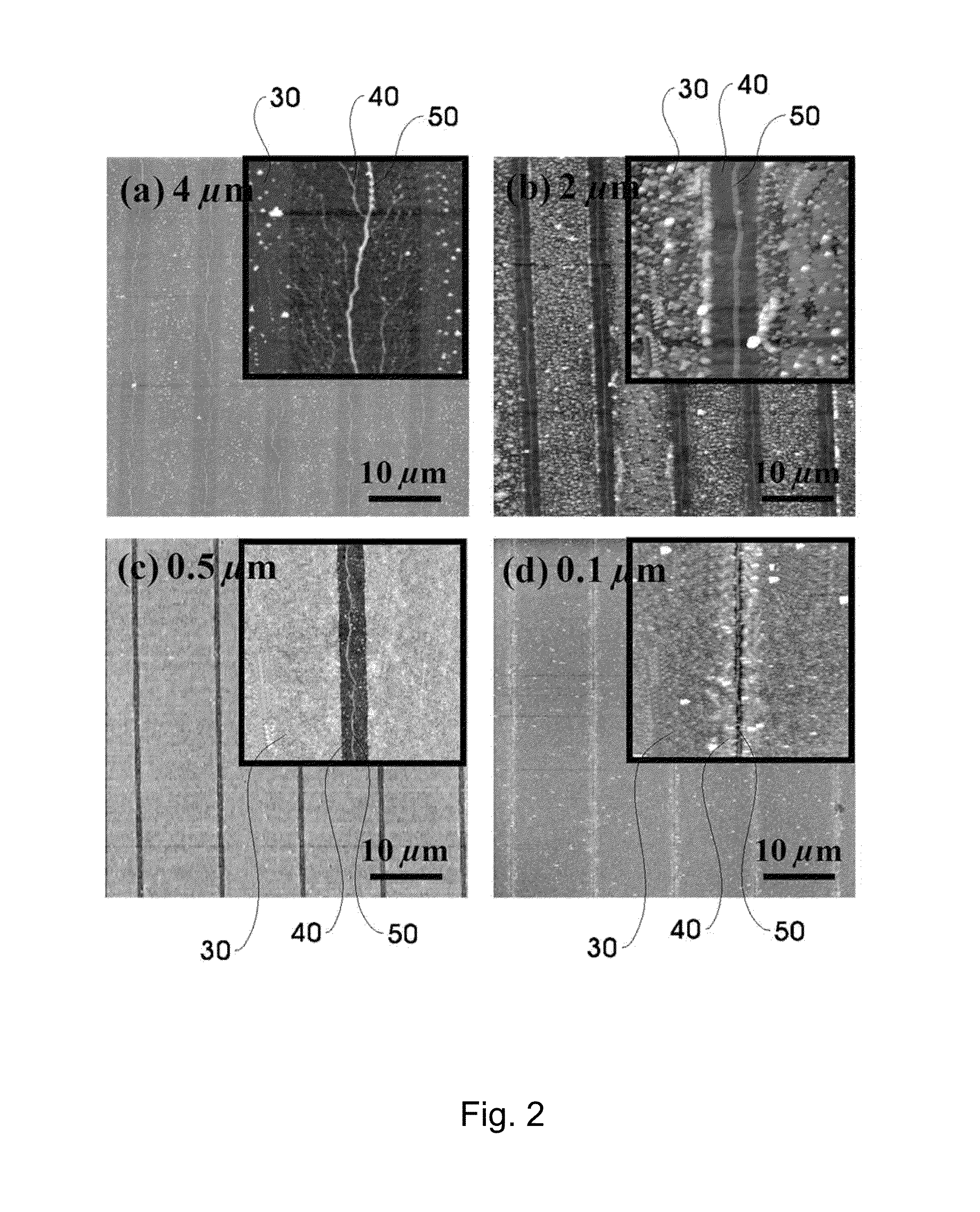
Method to assemble nano-structure on a substrate and nano-molecule device comprising nano-structure formed thereby
ActiveUS20100216076A1Reduce widthSurface potentialMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure assemblyResistNanolithography
A method of selectively positioning nanostructures on a substrate is provided which includes: a first step of forming a photoresist pattern on the substrate and then control the line width of the photoresist pattern in a nano unit to form a nanometer photoresist layer; a second step of forming a protective layer for preventing adsorption of a nano-material in a patter-unformed area on the substrate on which the nanometer photoresist layer has been formed; a third step of removing the photoresist layer formed on the substrate; a fourth step of forming a positively-charged or negatively charged adsorbent layer in the area from which the photoresist layer has been removed; and a fifth step of applying a nano-material-containing solution charged in the opposite polarity of the adsorbent layer to the substrate on which the adsorbent layer has been formed.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
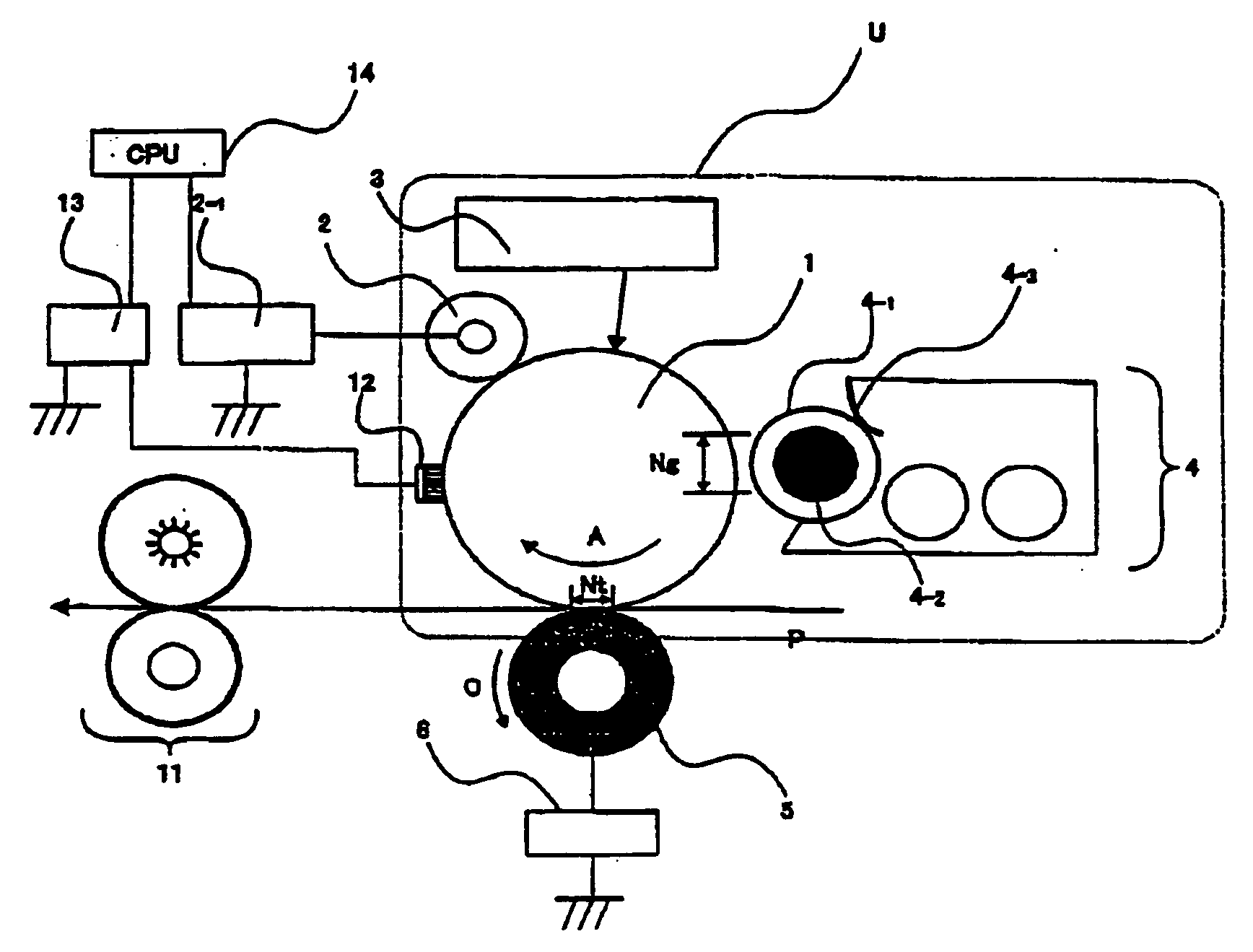
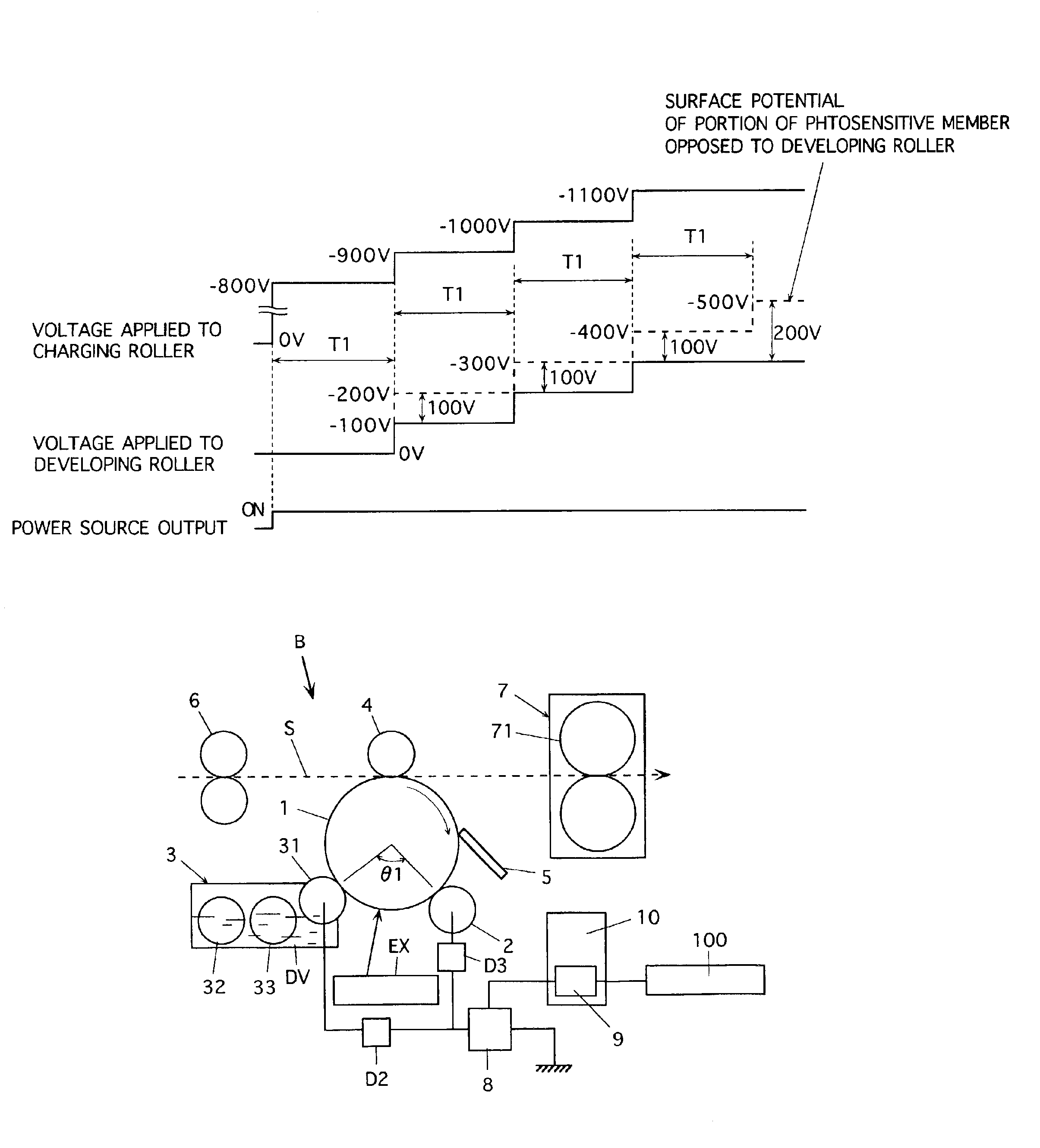
Image forming method and image forming apparatus for suppressing movement of developer onto the electrostatic latent image carrier when the voltages applied to the charging and developing devices are raised or lowered
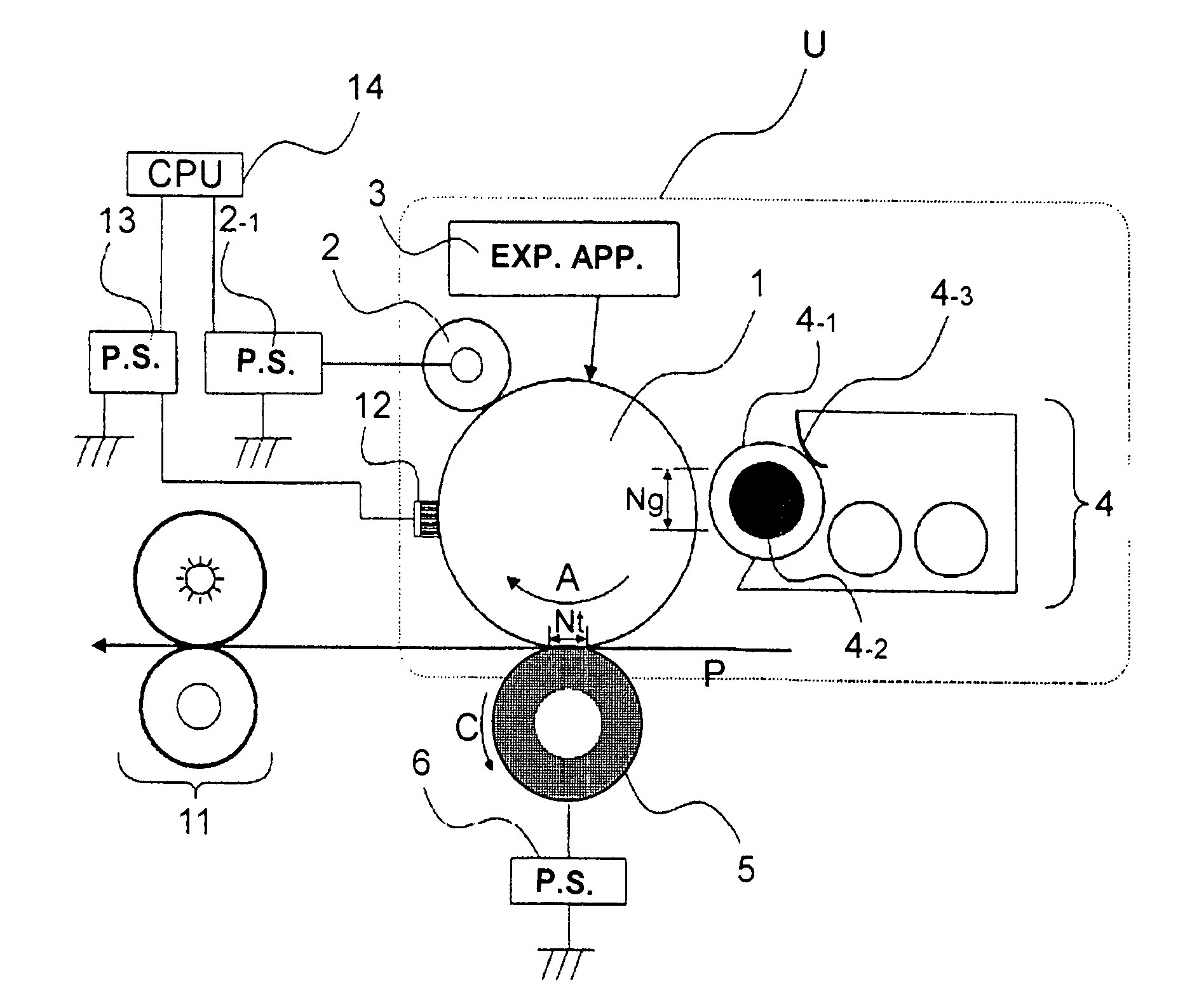
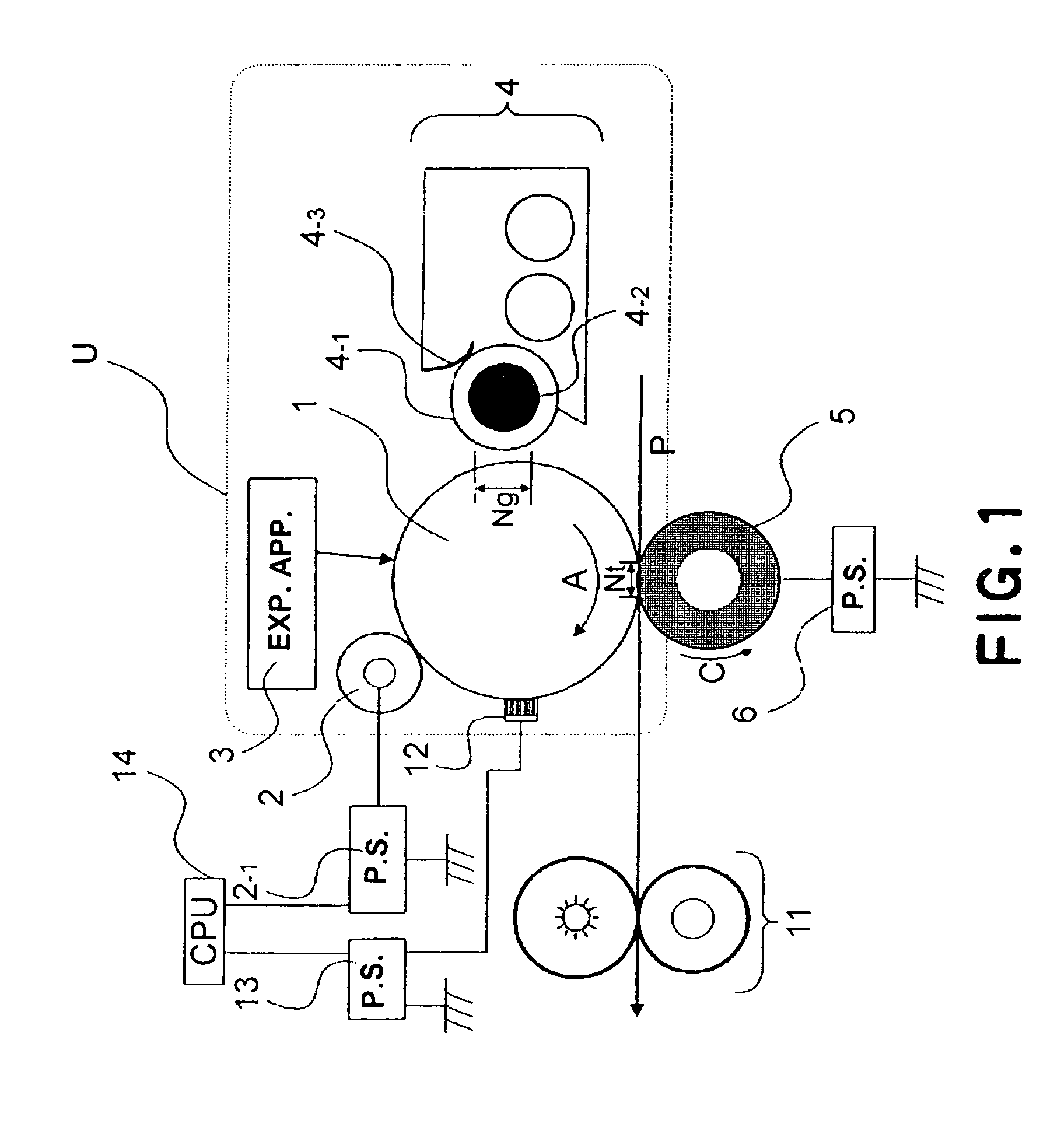
InactiveUS6845222B2Reduce in quantityConsumption can be suppressedElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeLatent imagePotential difference
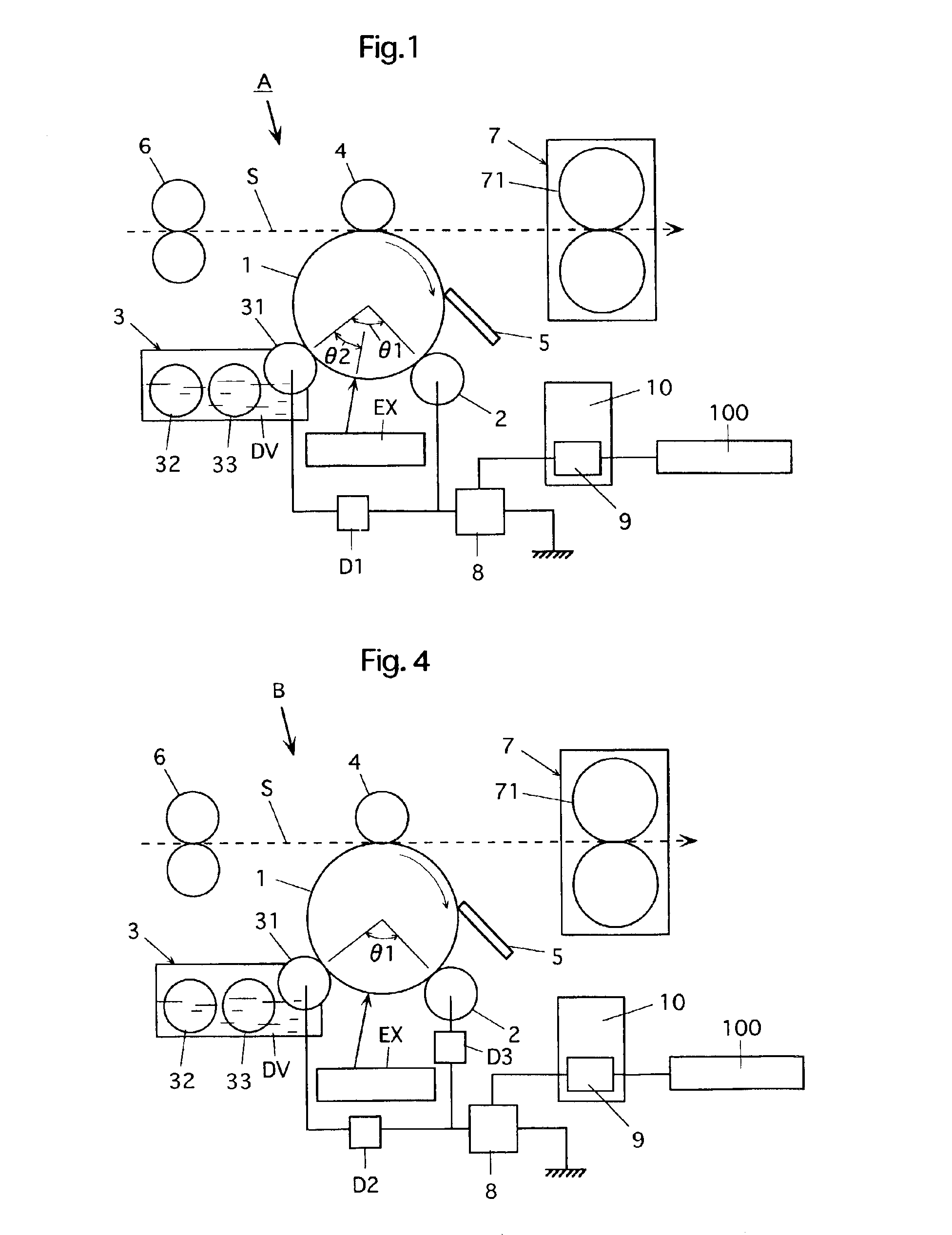
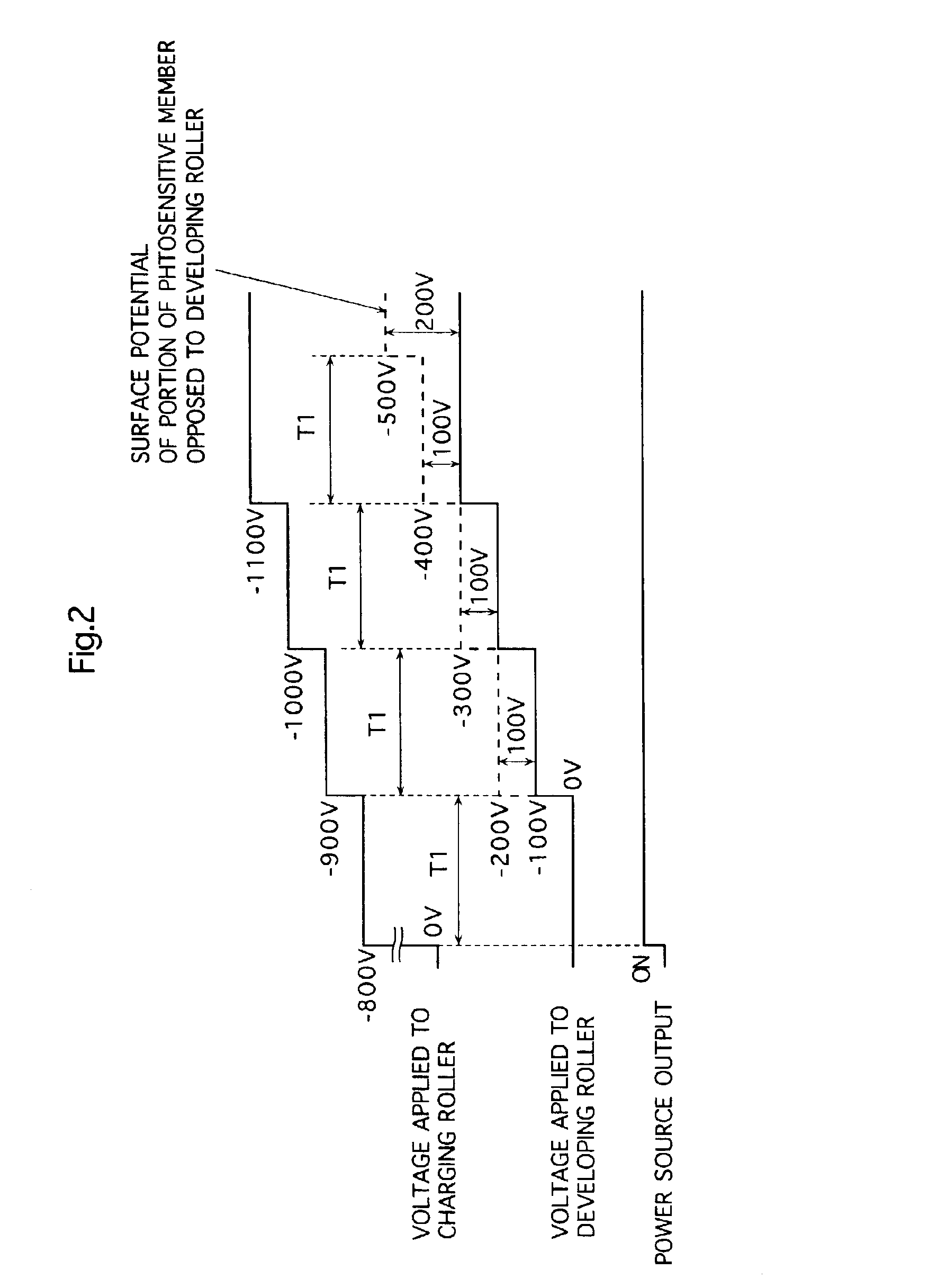
An electrophotographic image forming apparatus having a photosensitive member 1, a charging roller 2 and a developing roller 31, and including an output variable power source 8 common to the charging and the developing rollers 2 and 31 for applying voltages to the charging and developing rollers 2 and 31, respectively, a power source output control portion 9, and a voltage changing device (Zener diode D1) interposed between the developing roller 31 and the power source 8, wherein, when the voltages applied to the charging and developing rollers 2 and 31 are raised to and lowered from voltages required for image formation, respectively, the control portion 9 controls an output of the power source 8 to perform the raising and lowering of the applied voltages for a predetermined time while keeping a potential difference for suppressing movement of developer onto the photosensitive member 1 between the voltages applied to the charging and developing rollers 2 and 31.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
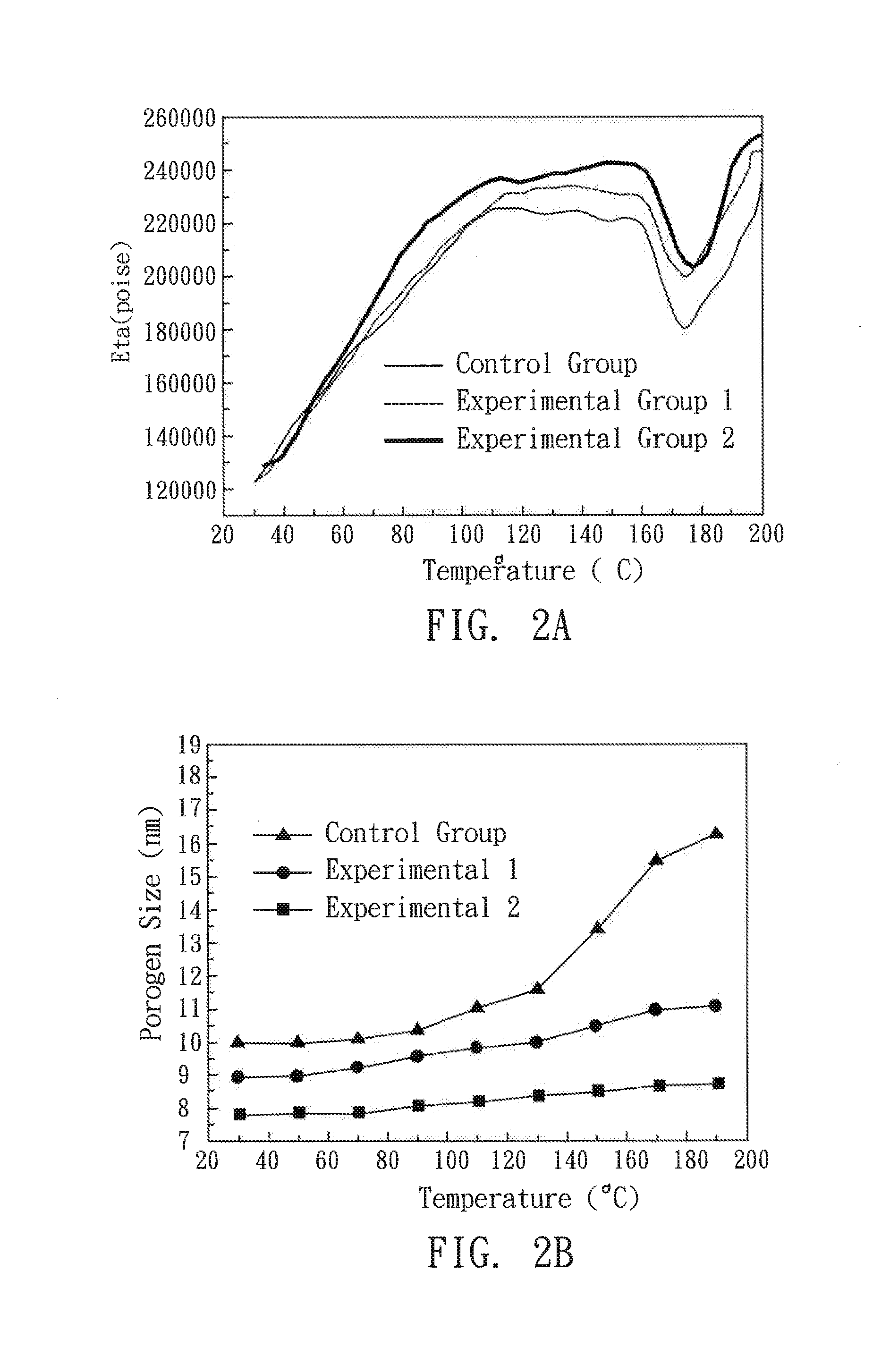
Method for Making Porous Materials
InactiveUS20140030432A1Low dielectric constantLess dielectric lossSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolventSurface modification
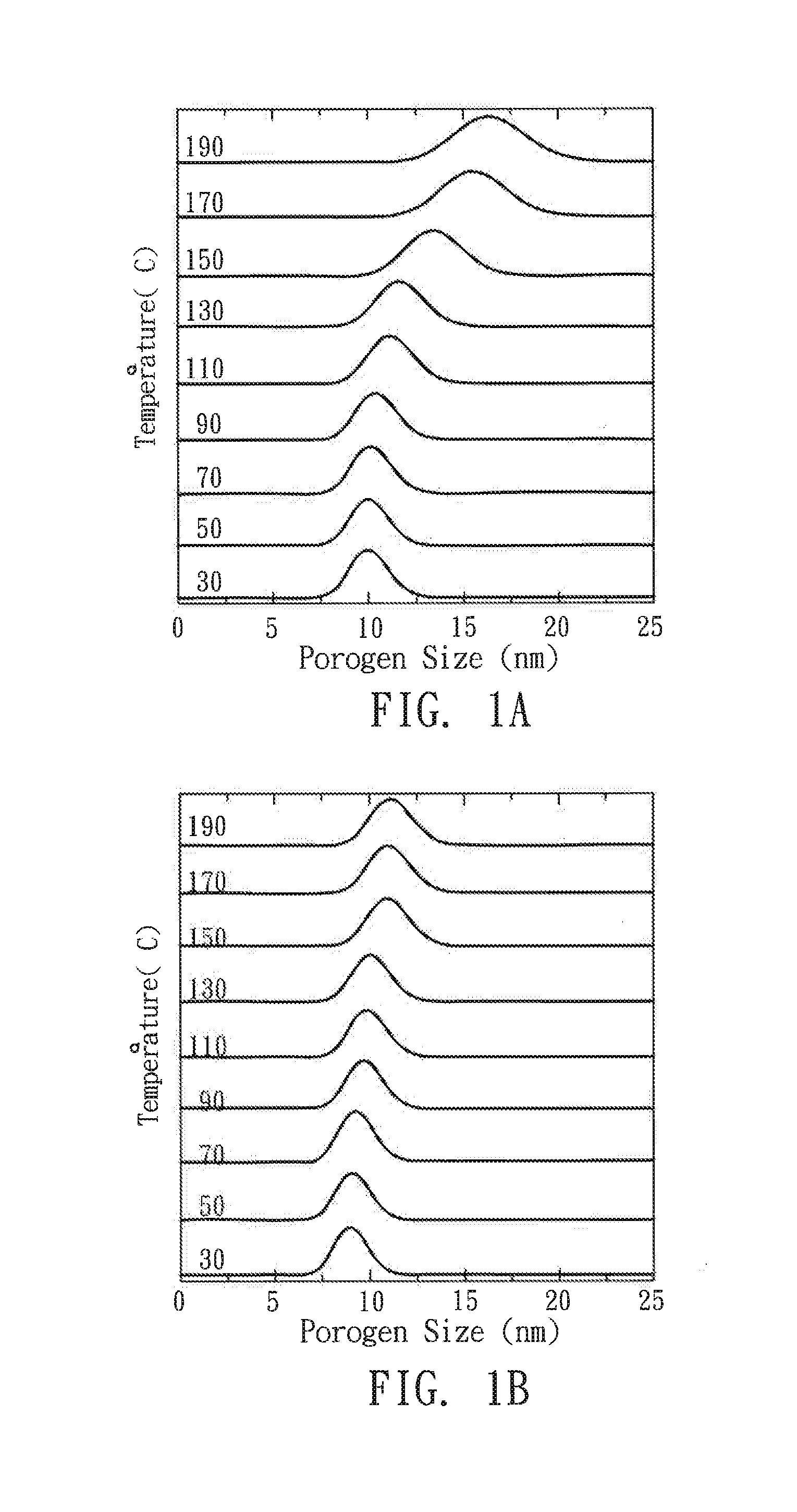
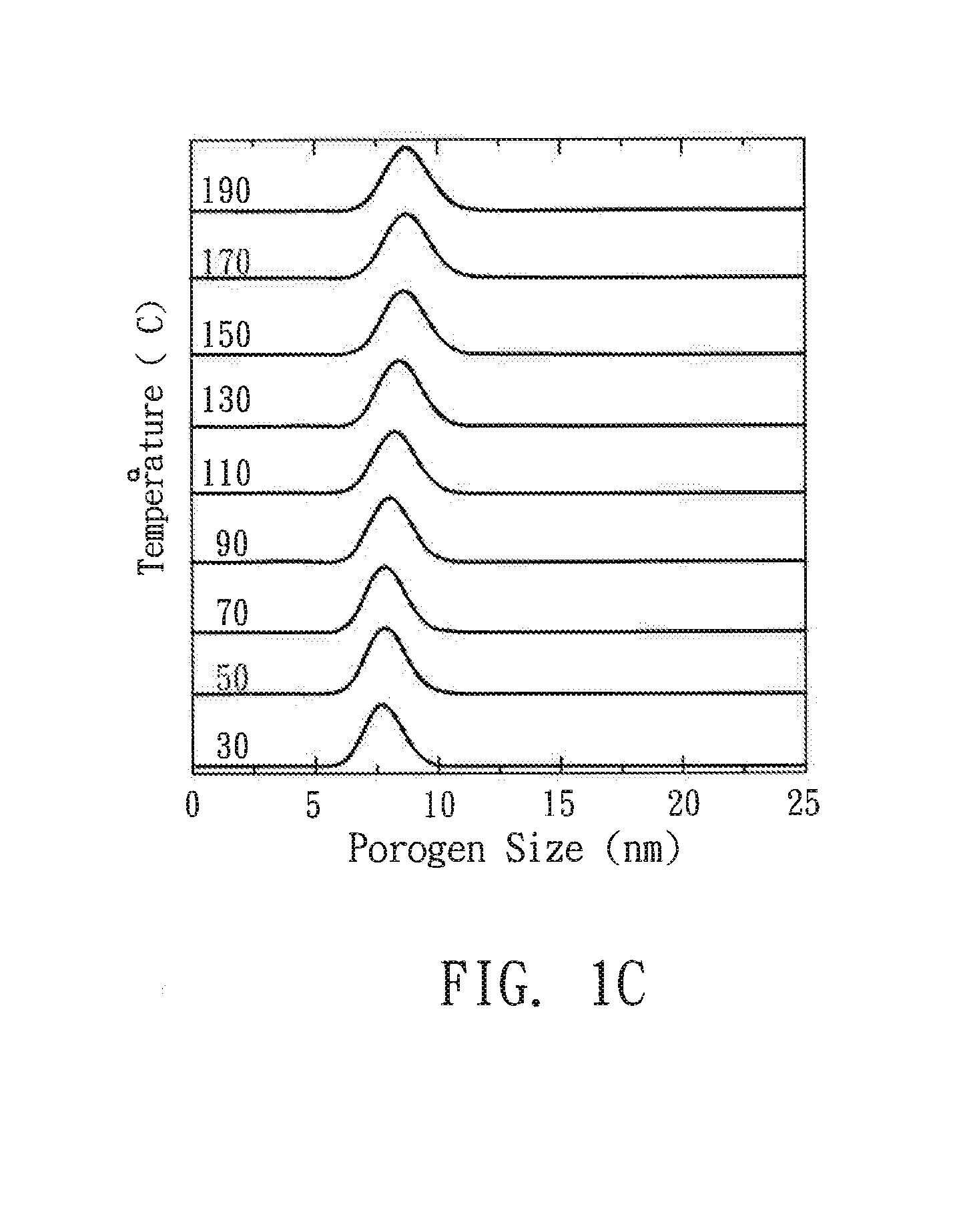
A method for manufacturing a porous material is disclosed, which comprises the following steps: providing a substrate; coating the substrate with a precursor solution to form a precursor film, wherein the precursor solution includes a precursor compound, a porogen, and a solvent, and the porogen is modified by a surface modification to have an absolute surface electric potential of >25 mV; and treating the precursor film with a thermal curing profile to remove the porogen and form a porous material.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
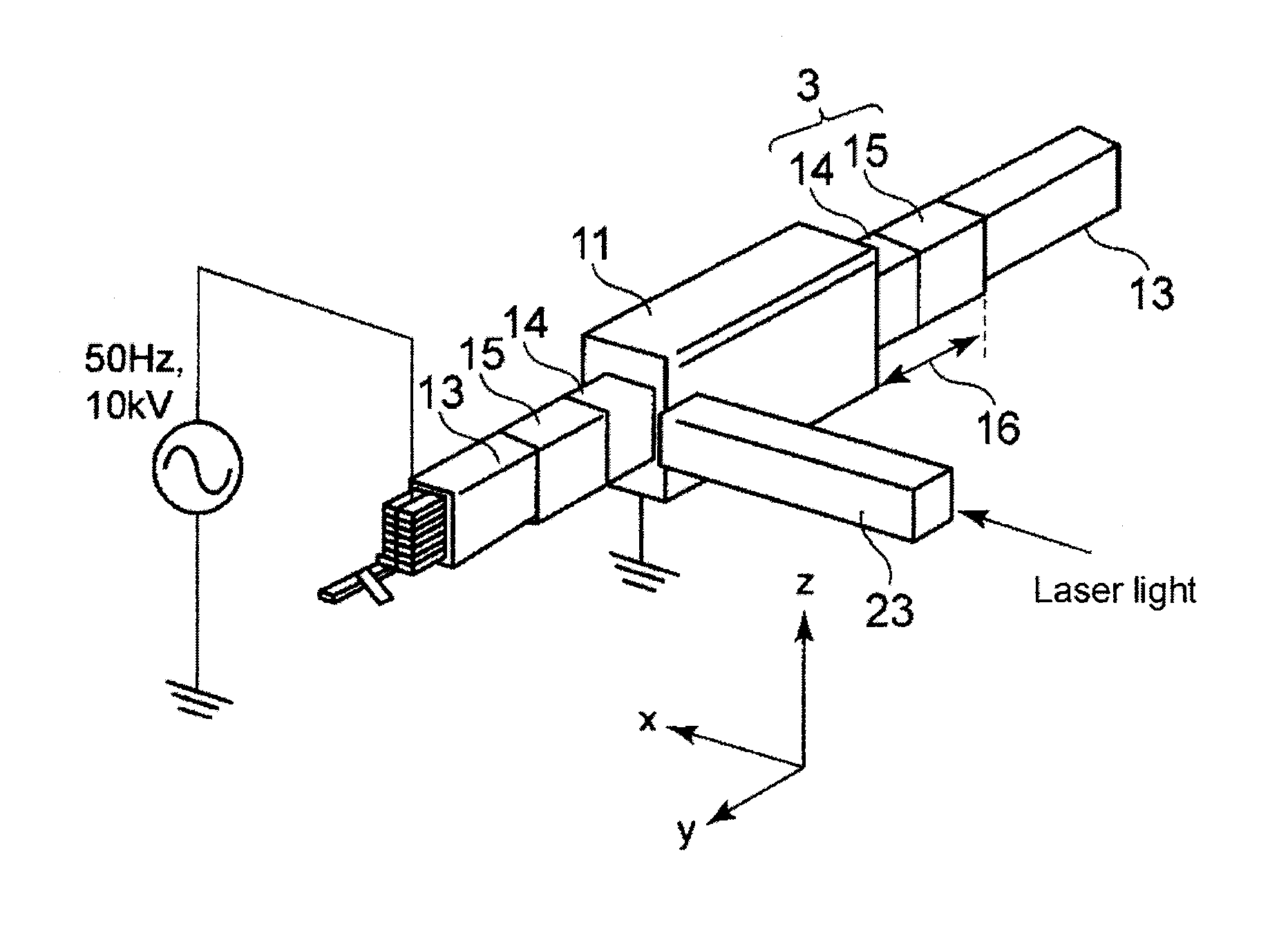
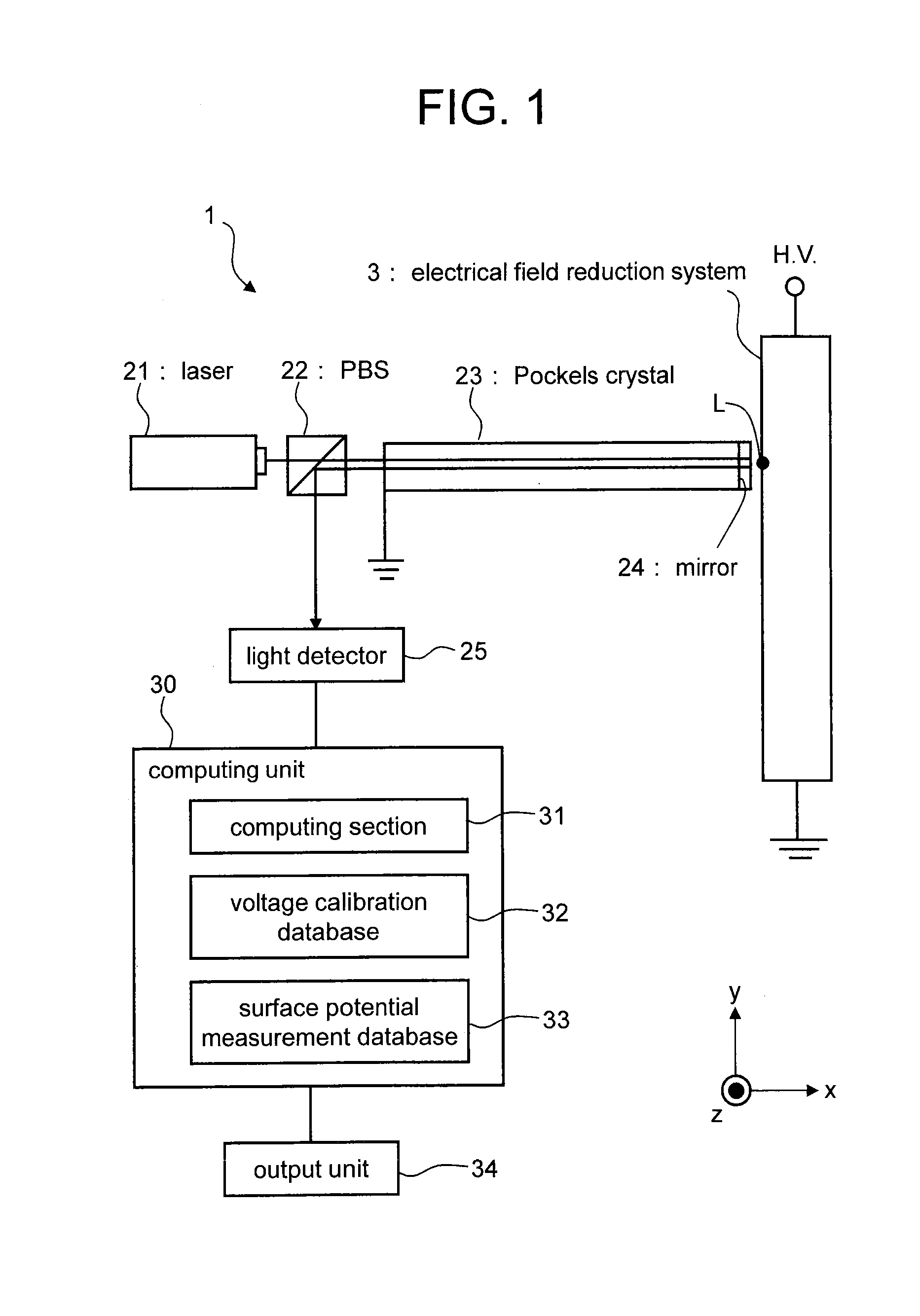
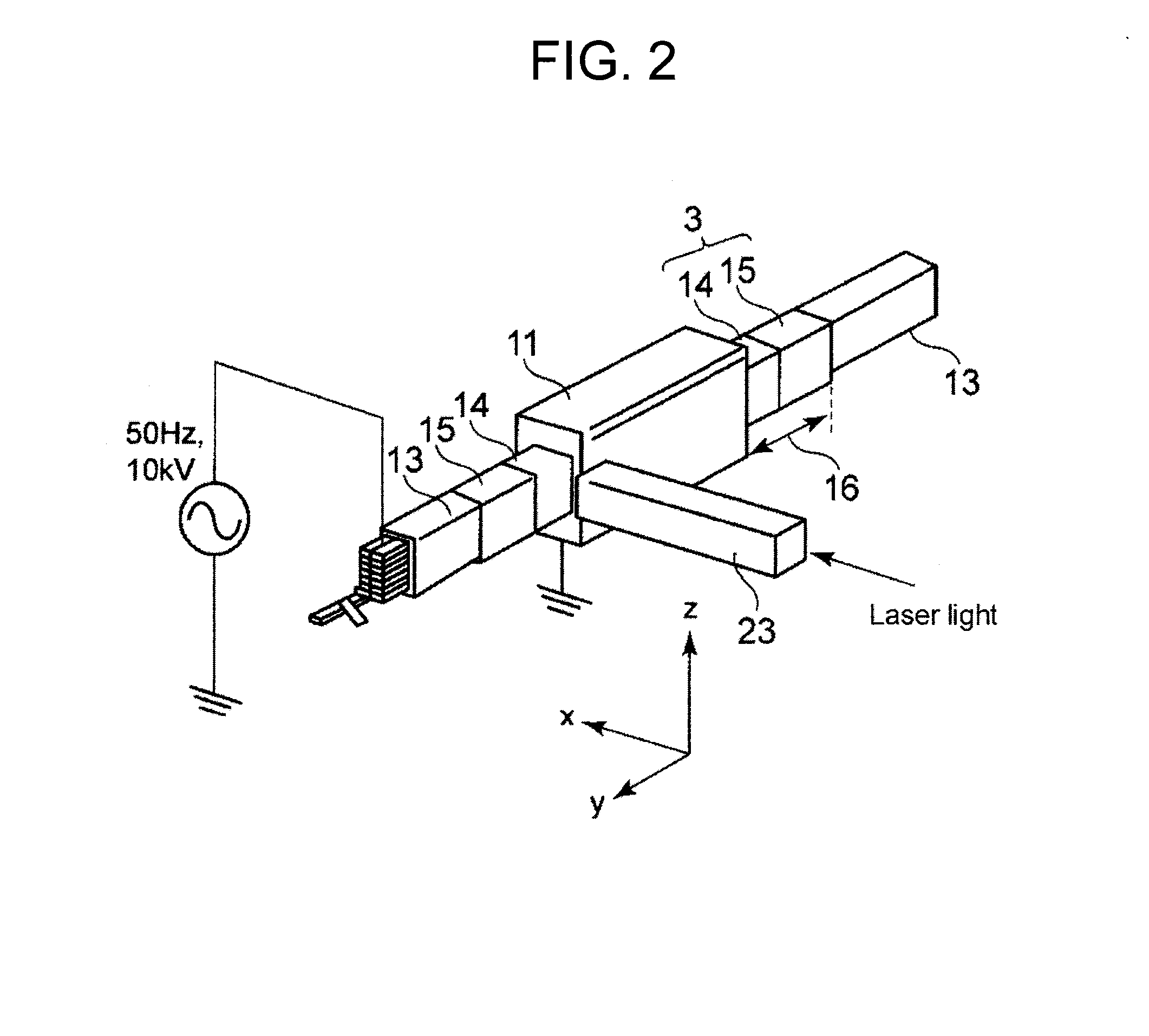
Surface potential distribution measuring device and surface potential distribution measuring method
ActiveUS20140300368A1Surface potentialDynamo-electric machine testingElectrostatic field measurementsOptoelectronicsPulse voltage
In a surface potential distribution measuring device for an electric field reduction system of a rotating electrical machine, a Pockels crystal is used between a laser and the surface (test location) of the electric field reduction system. Thus, the light Light intensity of a laser beam reflected on a mirror provided between the Pockels crystal and the test location corresponds to an output voltage that is the voltage difference between the first end surface and the second end surface of the Pockels crystal. Even when an inverter voltage is generated, by using a light detector having a frequency band capable of following the high frequency components of the inverter pulse voltage, the light intensity is detected by the light detector. Therefore, from the light intensity (output voltage), the surface potential distribution measuring device can measure the surface potential of the electric field reduction system in which an inverter pulse voltage is generated.
Owner:TOSHIBA MITSUBISHI-ELECTRIC IND SYST CORP +1
Method for manufacturing catalyst for fuel cell
InactiveUS20100227756A1Improve corrosion resistanceReducing the platinum precursorMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesFuel cellsEngineering
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Image forming apparatus
ActiveUS7421229B2Avoid it happening againSurface potentialElectrography/magnetographyImage formationEngineering
Charge removing light is guided by an optical path defining member (623) from a charge removing unit (6) toward a photosensitive drum (2). A distance between an end surface (623e) of the optical path defining member (623) and a surface on an axially central part of the photosensitive drum (2) is less than a distance between the end surface (623e) and the surface on the axially opposite ends of the photosensitive drum (2). Thus an irradiation width and an amount of the charge removing light projected onto the surface of the photosensitive drum (2) are increased on the opposite ends. With this arrangement, the amount of generated light carriers can be reduced on the axially central part, as compared with the axially opposite ends, and a surface potential distribution non-uniformity due to a difference in nip distance between the photosensitive drum (2) and a charging roller (31) can be eliminated.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
Image forming apparatus with two cleaning electric fields for transferring developer from a developer charging device onto an image bearing member
InactiveUS6987939B2Enhance the imageEasy to cleanElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeDevice formImage formation
Owner:CANON KK
Charger, image forming apparatus, and charge control method
InactiveUS7835655B2Avoid bandsEffectively realizing high quality image formationElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeCharge controlImage formation
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electrophotographic photosensitive member, method for manufacturing the same, and electrophotographic apparatus
InactiveUS20140242506A1High surface potentialIncrease surface potentialElectrographic process apparatusCoatingsEngineeringSurface layer
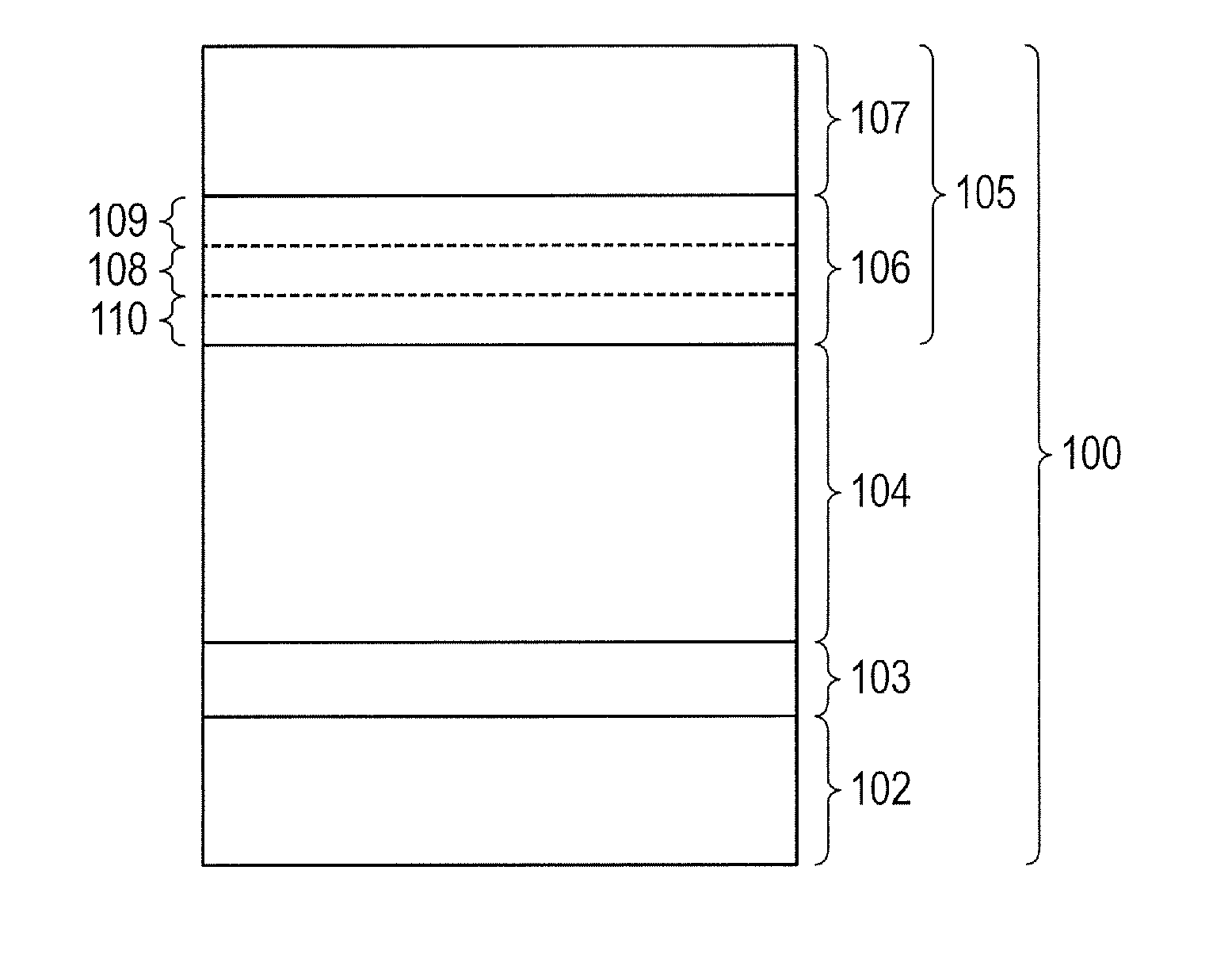
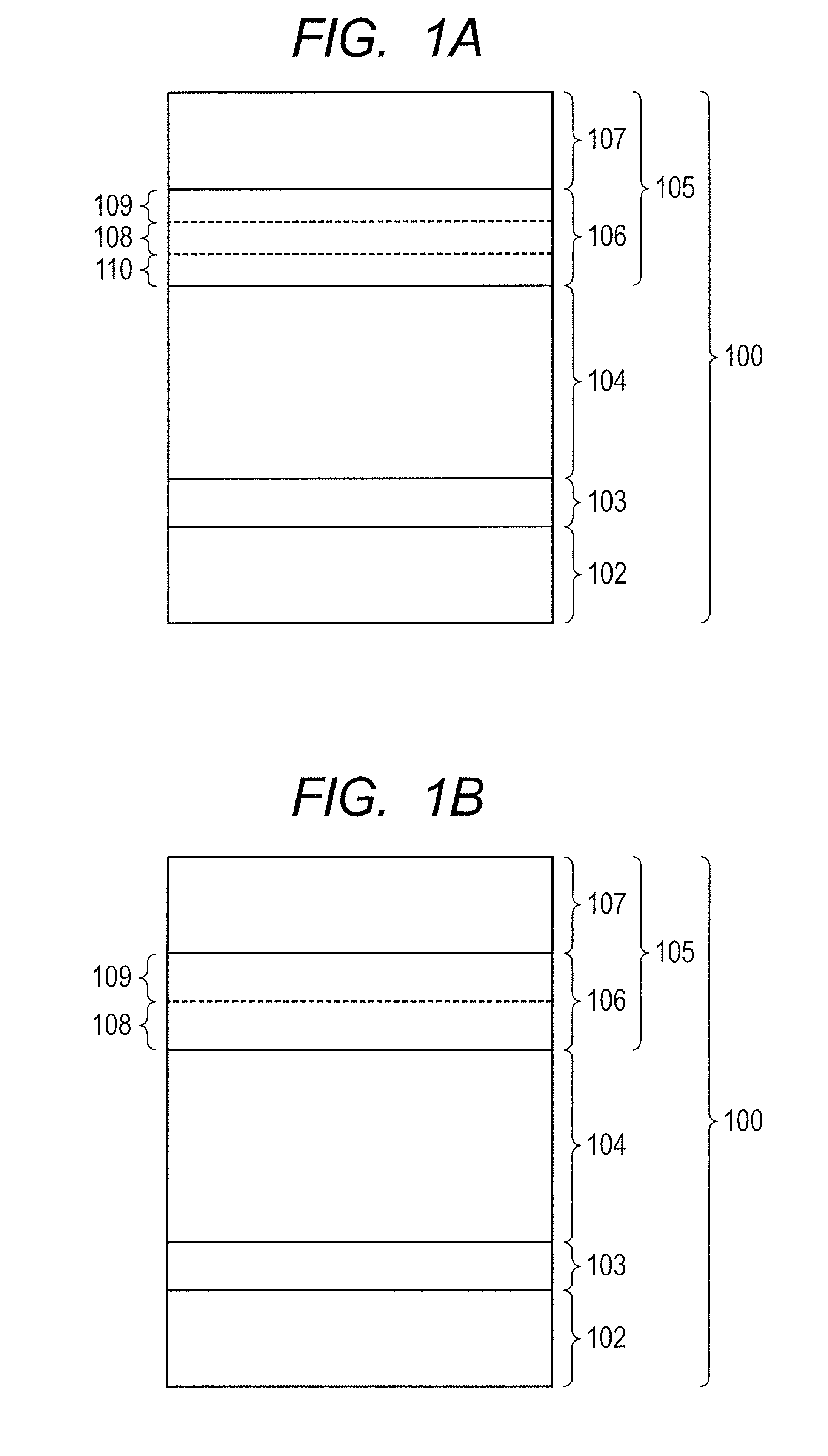
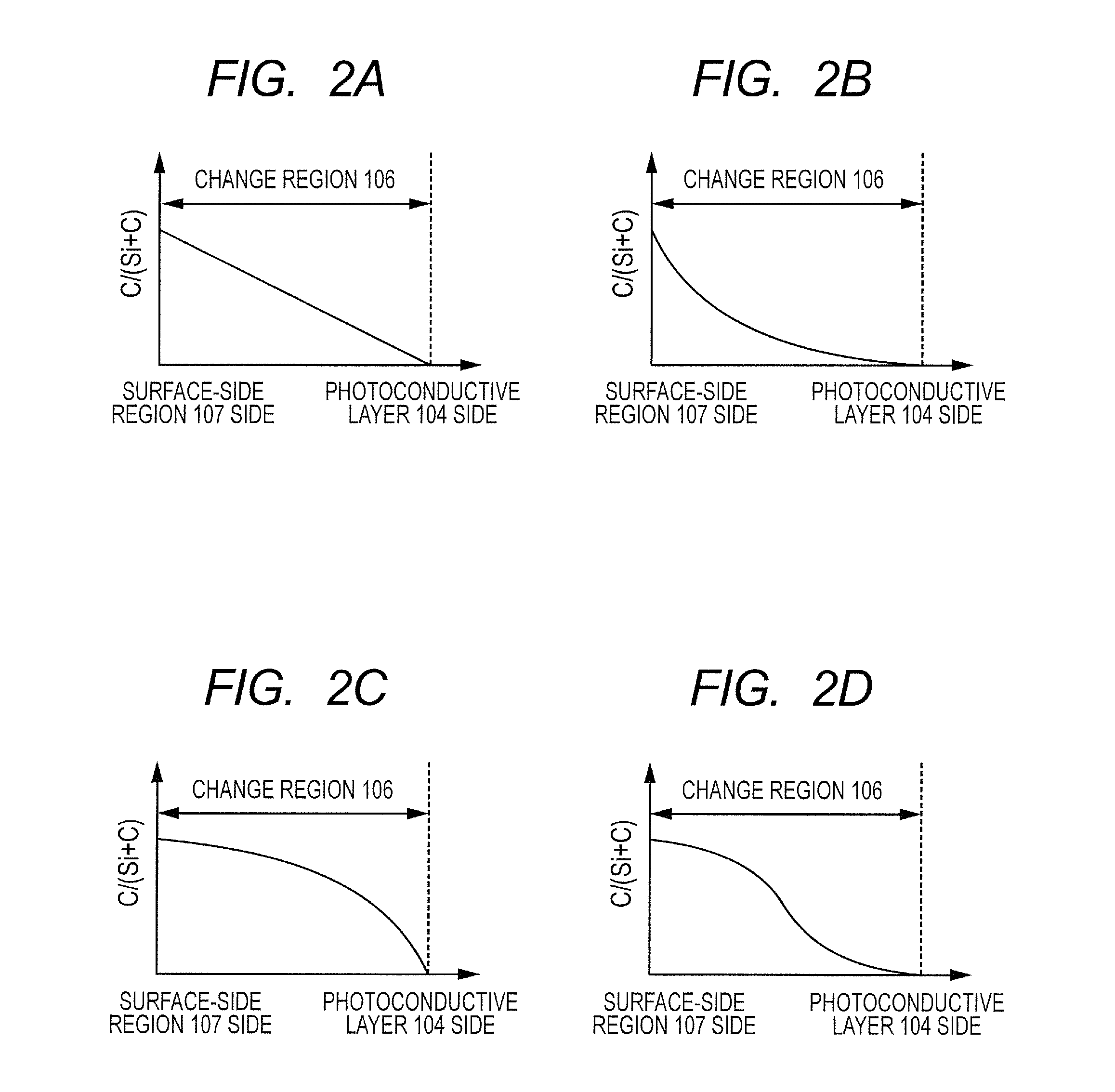
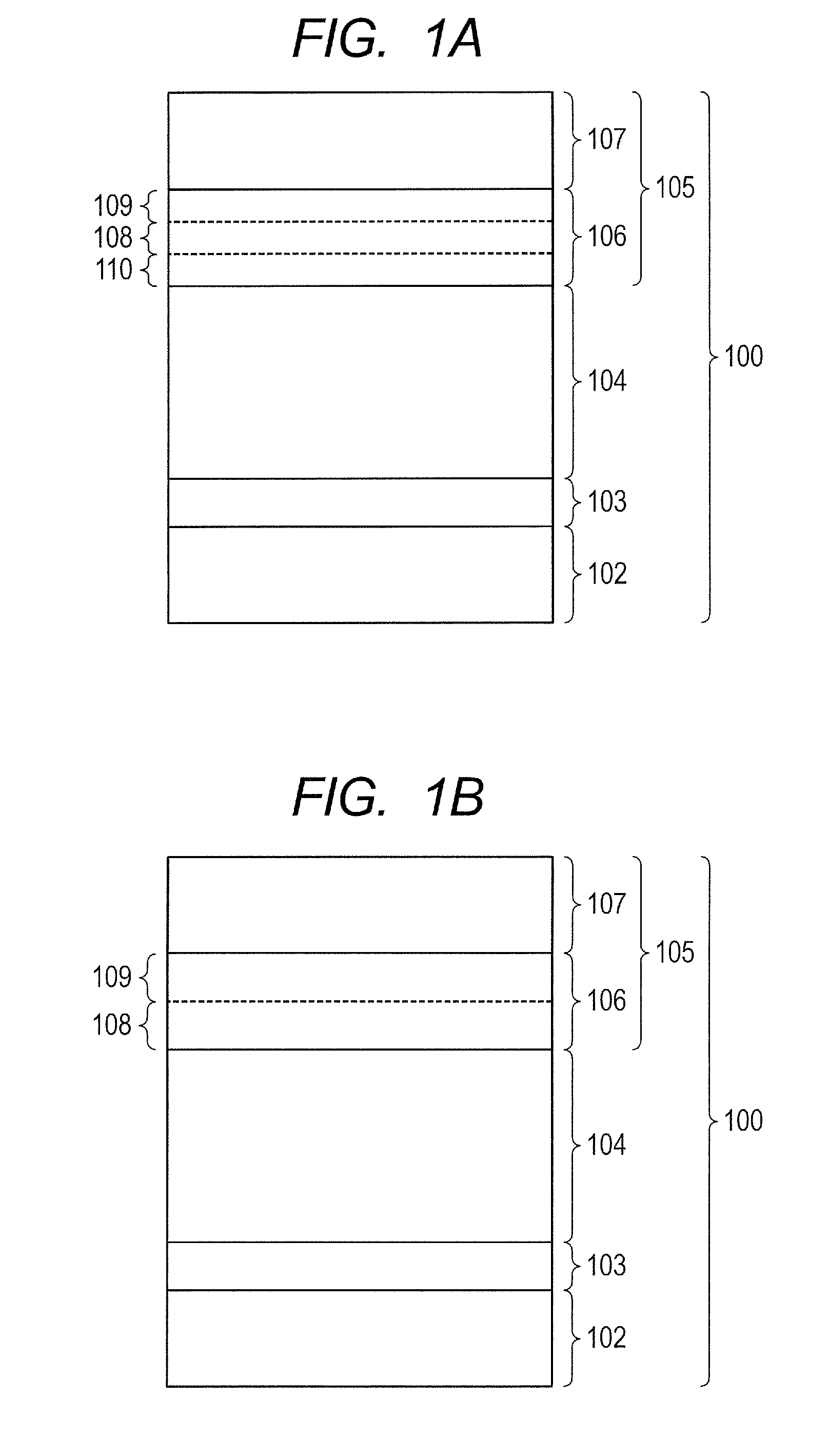
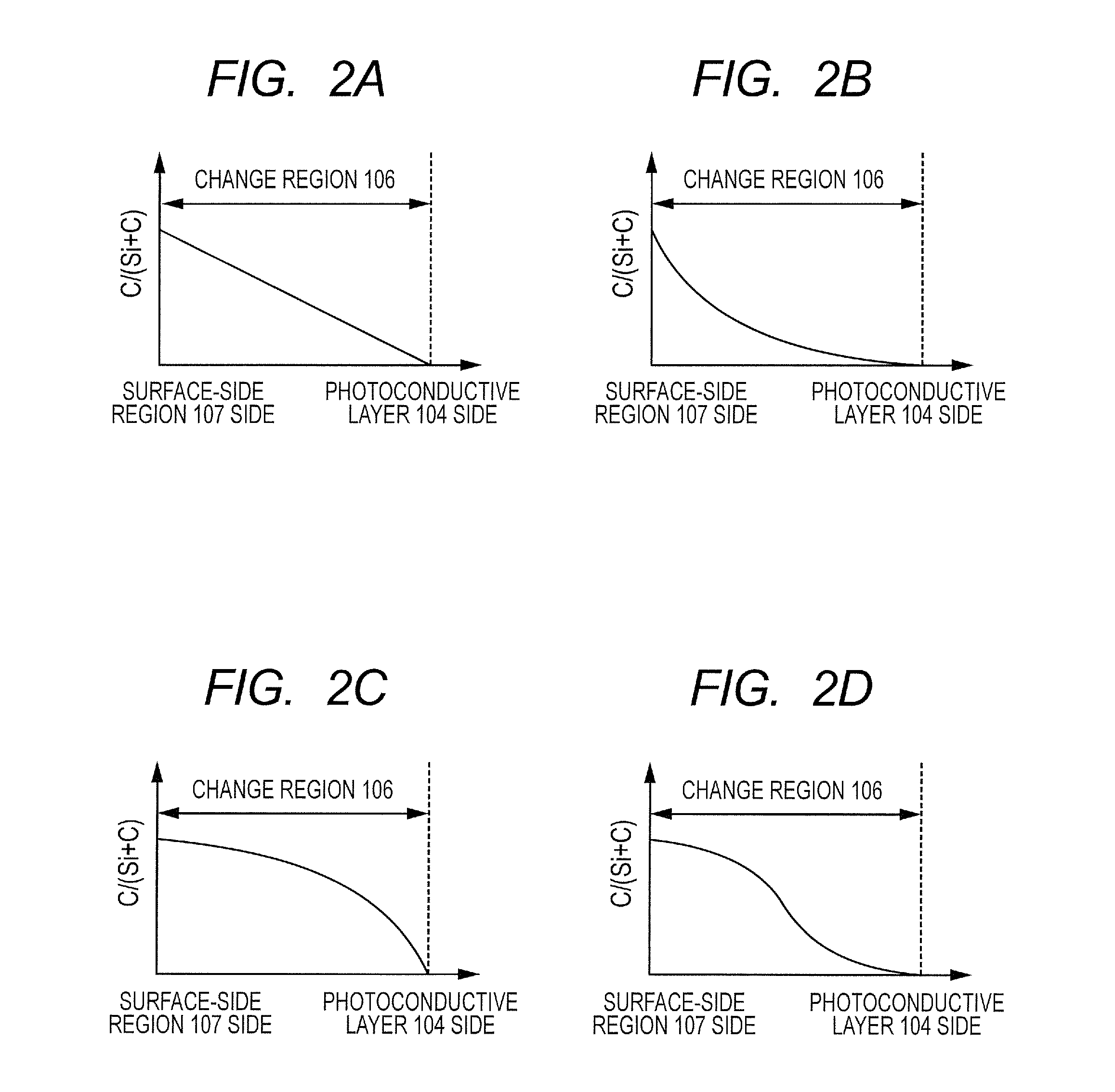
A surface layer of the electrophotographic photosensitive member has a change region in which a ratio of the number of carbon atoms with respect to the sum of the number of silicon atoms and the number of carbon atoms gradually increases toward a surface side of the electrophotographic photosensitive member from a photoconductive layer side, wherein the change region has an upper charge injection prohibiting portion containing a Group 13 atom, and a surface-side portion which is positioned closer to the surface side of the electrophotographic photosensitive member than the upper charge injection prohibiting portion and does not contain the Group 13 atom, and the distribution of the Group 13 atom in a boundary portion between the surface-side portion and the upper charge injection prohibiting portion is precipitous.
Owner:CANON KK
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
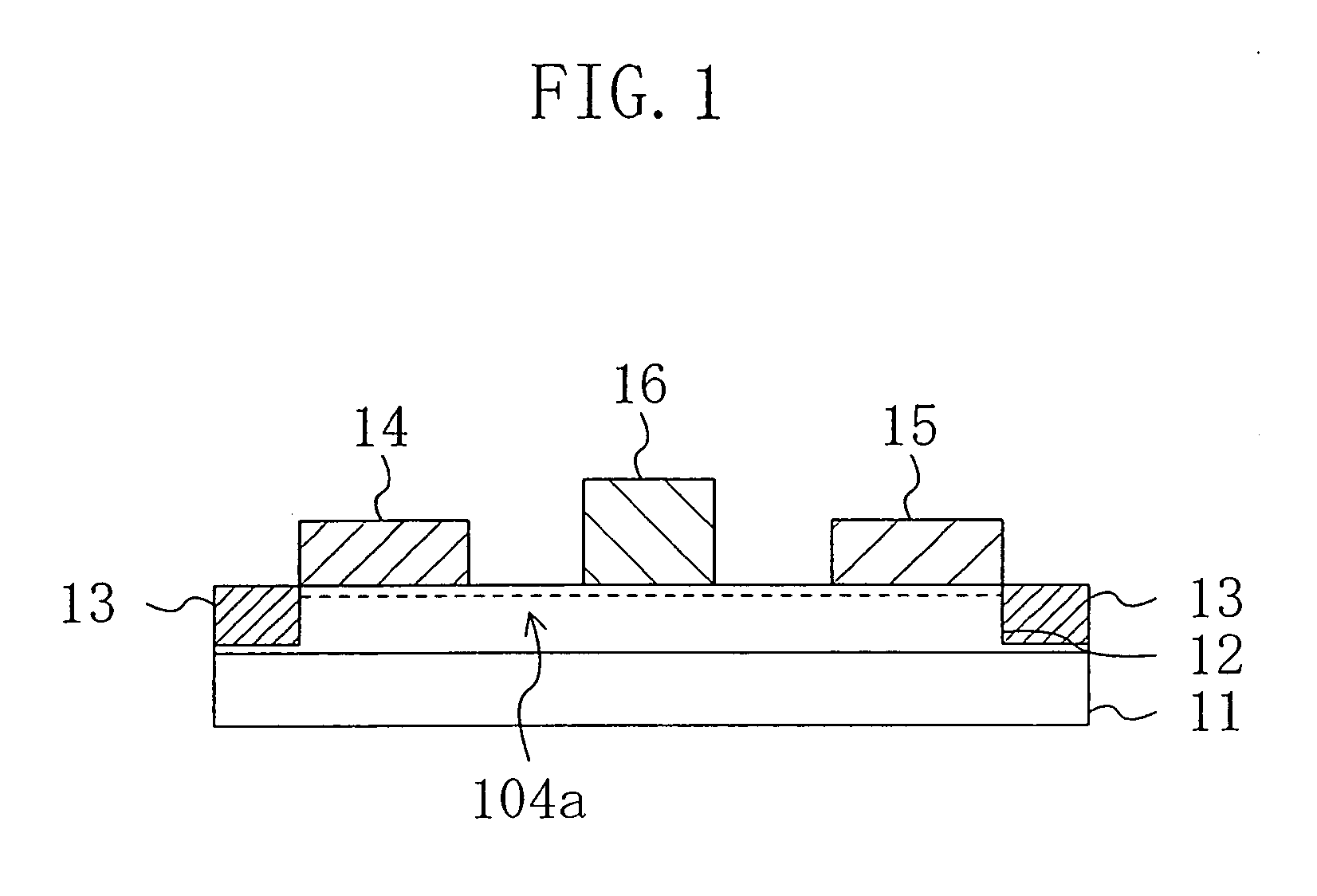
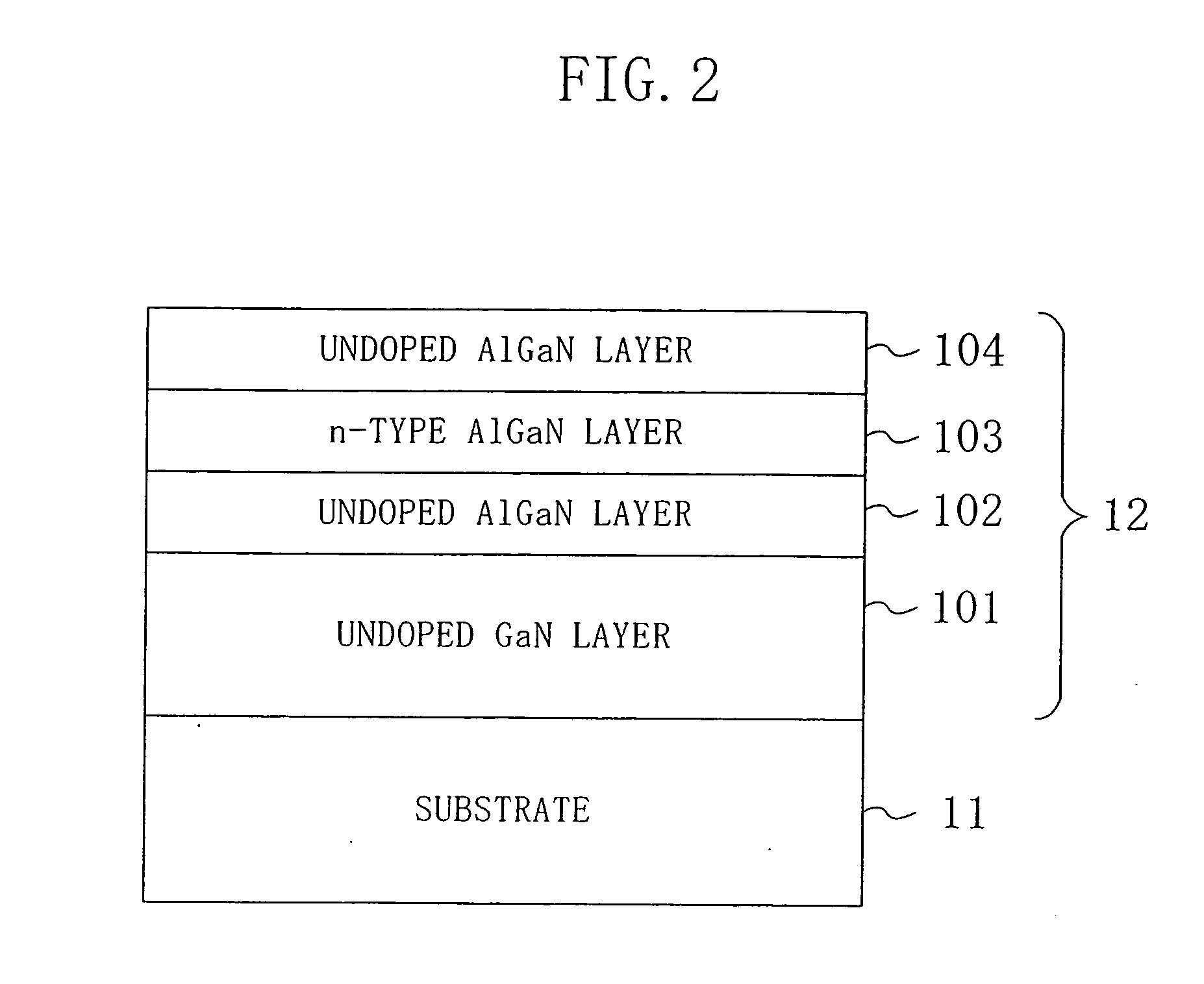
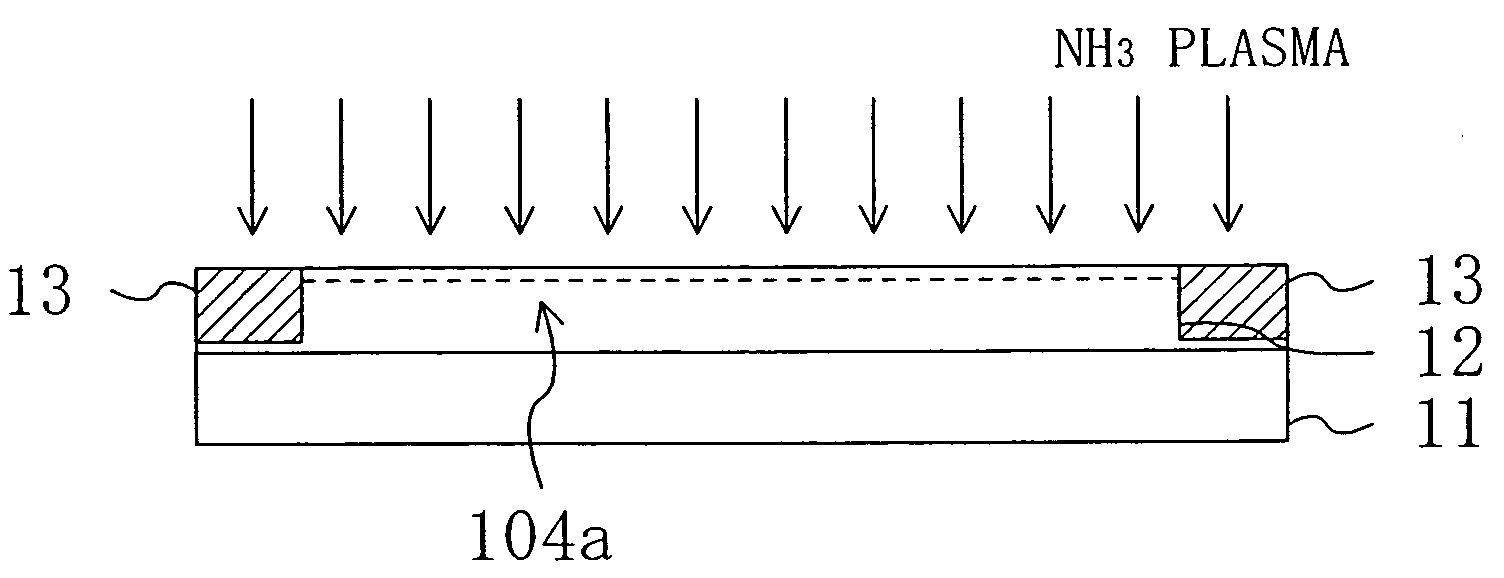
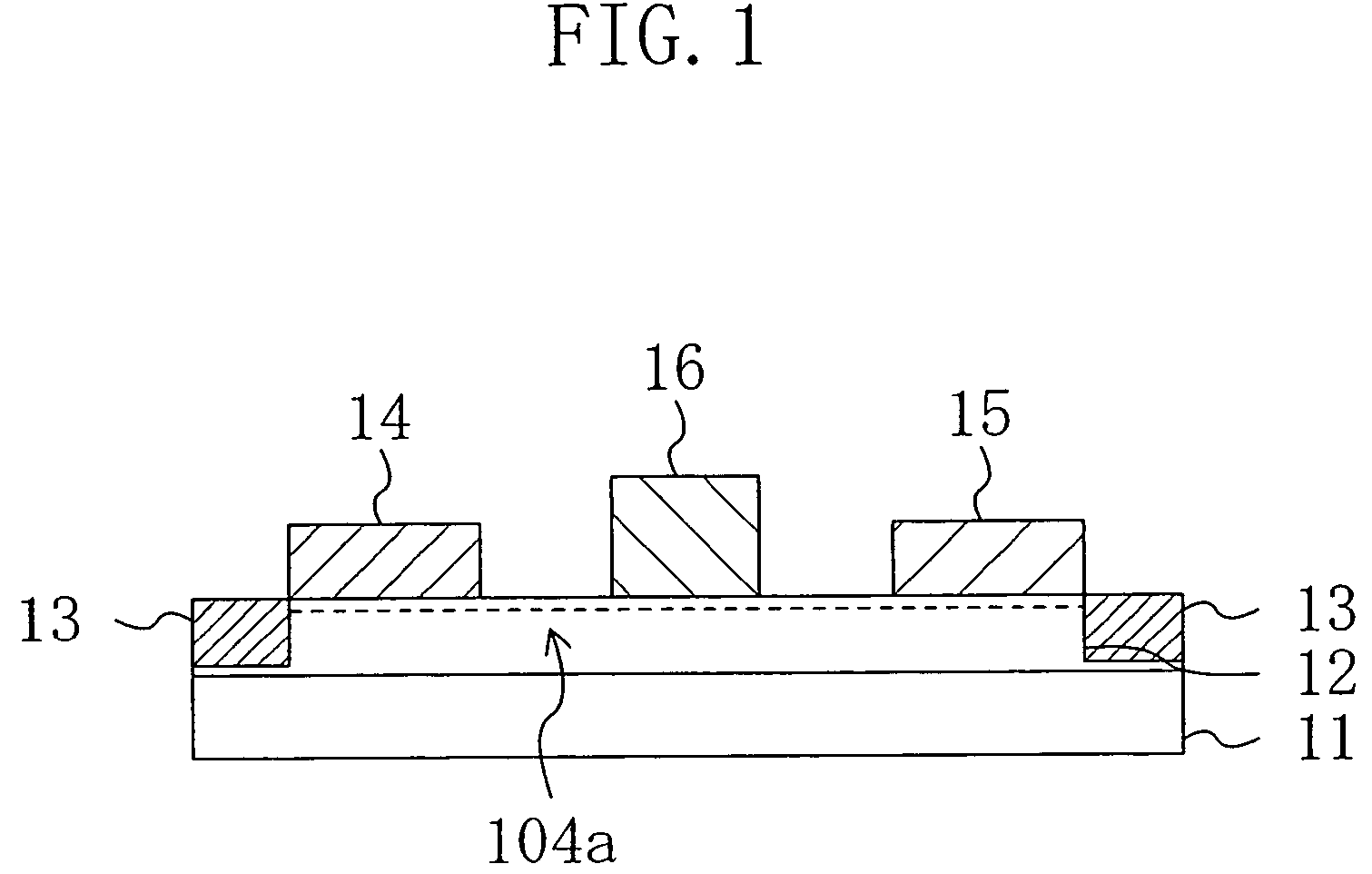
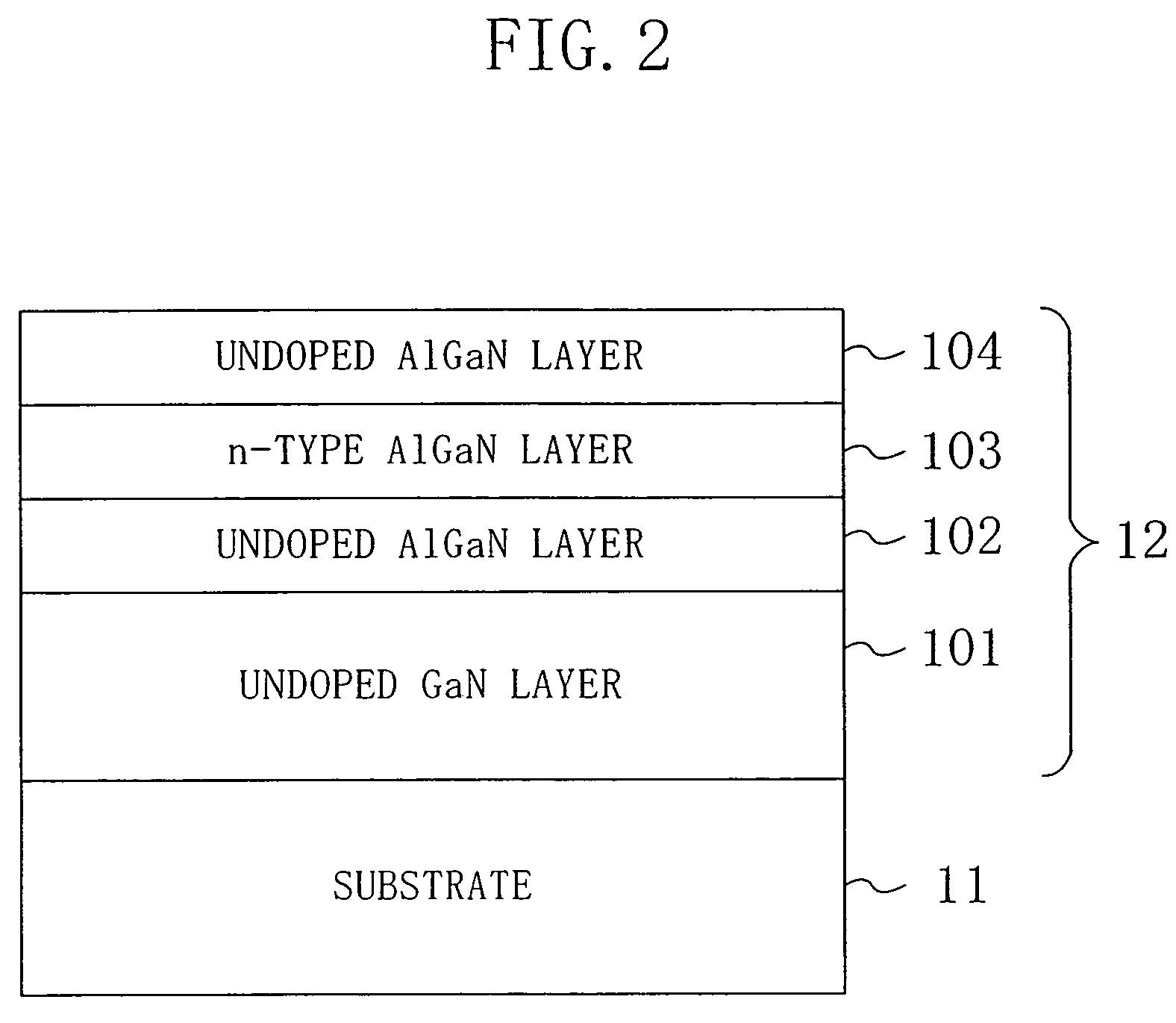
InactiveUS20070020896A1Decrease in surface potentialReduce resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialElectron
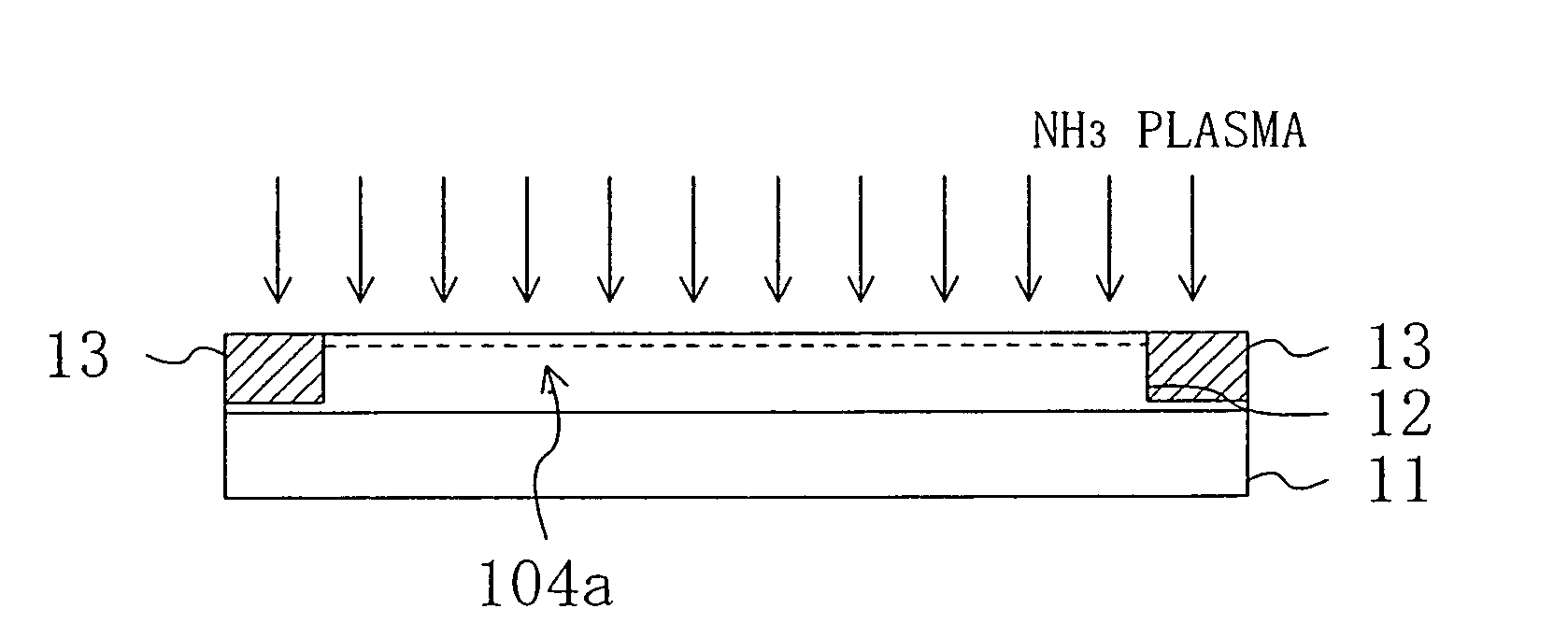
A semiconductor device has an active region composed of a group III-V nitride semiconductor and ohmic electrodes and a gate electrode each formed on the active region. The active region has an entire surface thereof exposed to a plasma such that a surface potential for electrons therein is lower than in the case where the entire surface is not exposed to the plasma.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for fabricating a semiconductor device including exposing a group III-V semiconductor to an ammonia plasma
InactiveUS7122451B2Decrease in surface potentialImprove drain current valueSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesAmmoniaElectron
A semiconductor device has an active region composed of a group III–V nitride semiconductor and ohmic electrodes and a gate electrode each formed on the active region. The active region has an entire surface thereof exposed to a plasma such that a surface potential for electrons therein is lower than in the case where the entire surface is not exposed to the plasma.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Combined-source Mos Transistor with Comb-shaped Gate, and Method for Manufacturing the Same
ActiveUS20120181585A1Increase the on-currentReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricSchottky barrier
The present invention discloses a combined-source MOS transistor with a Schottky Barrier and a comb-shaped gate structure, and a method for manufacturing the same. The combined-source MOS transistor includes: a control gate electrode layer, a gate dielectric layer, a semiconductor substrate, a highly-doped source region and a highly-doped drain region, wherein a Schottky source region is connected to a side of the highly-doped source region which is far from a channel, one end of the control gate extends to the highly-doped source region, the extended gate region is an extension gate in a form of a comb-shaped and the original control gate region is a main gate; an active region covered by the extension gate is also a channel region, and is a substrate material; the highly-doped source region which is formed by highly doping is located on both sides of each comb finger of the extension gate; and a Schottky junction is formed at a location where the Schottky source region and the channel under the extension gate are located. As compared with an existing MOSFET, in the invention, a higher turn-on current, a lower leakage current and a steeper subthreshold slope may be obtained under the same process condition and the same active region size.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
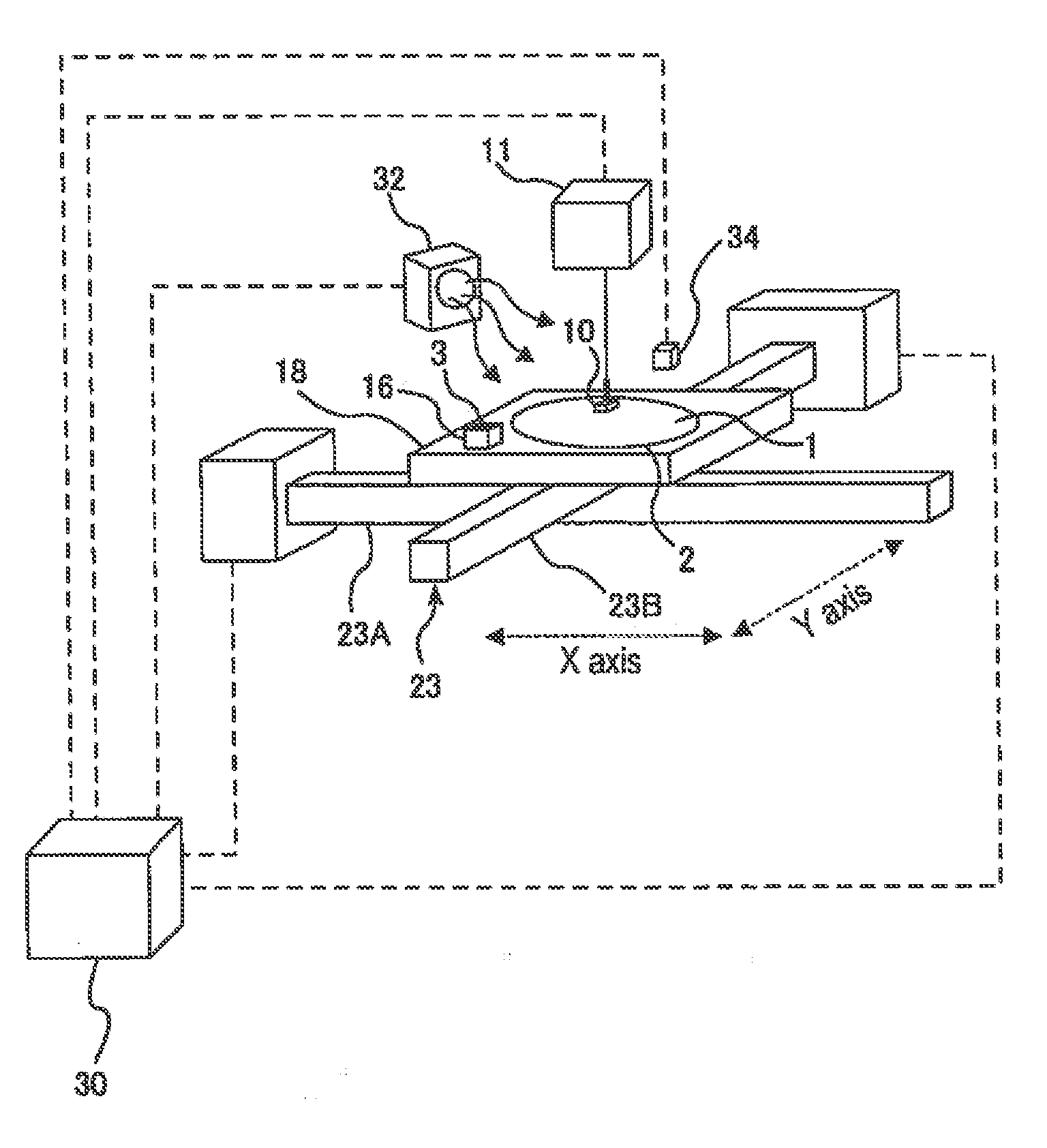
Surface potential measuring apparatus and surface potential measuring method
ActiveUS20140253136A1Accurate measurementLow priceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesPotential measurementMeasurement device
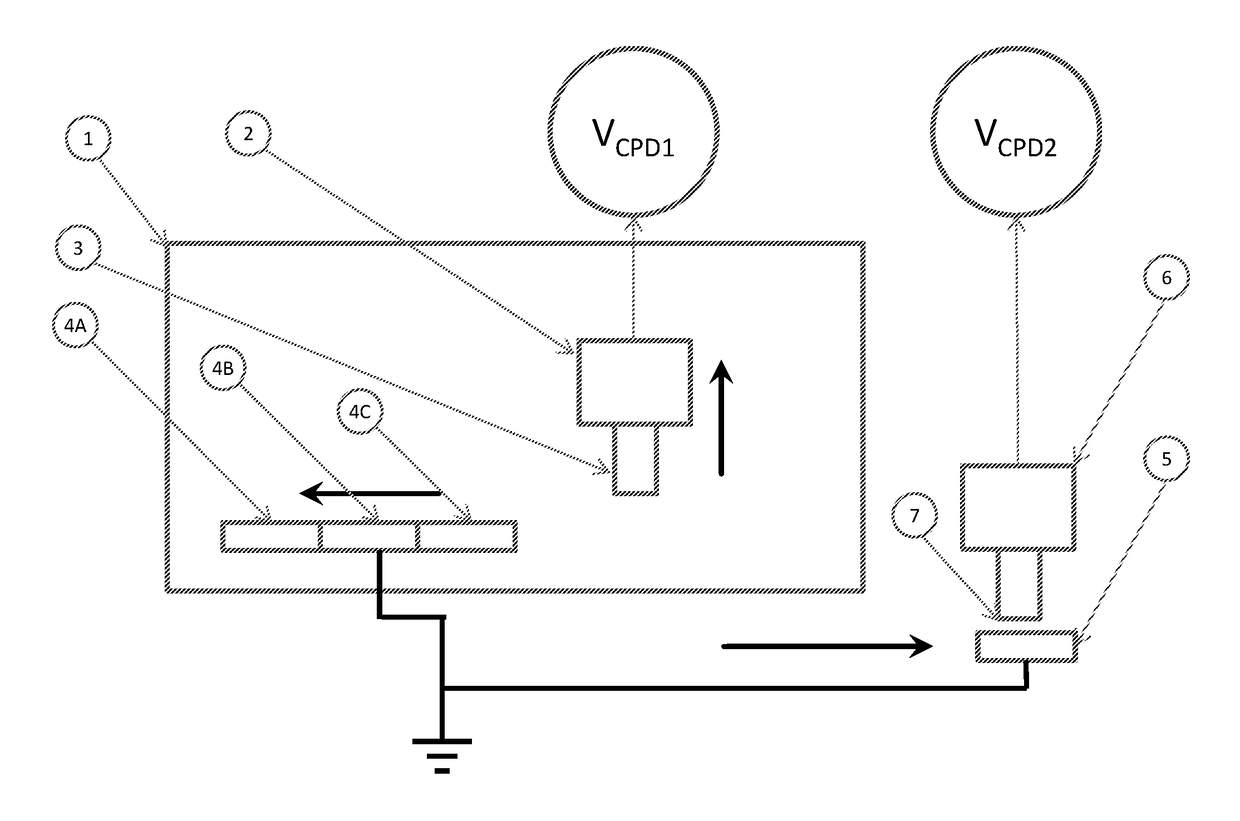
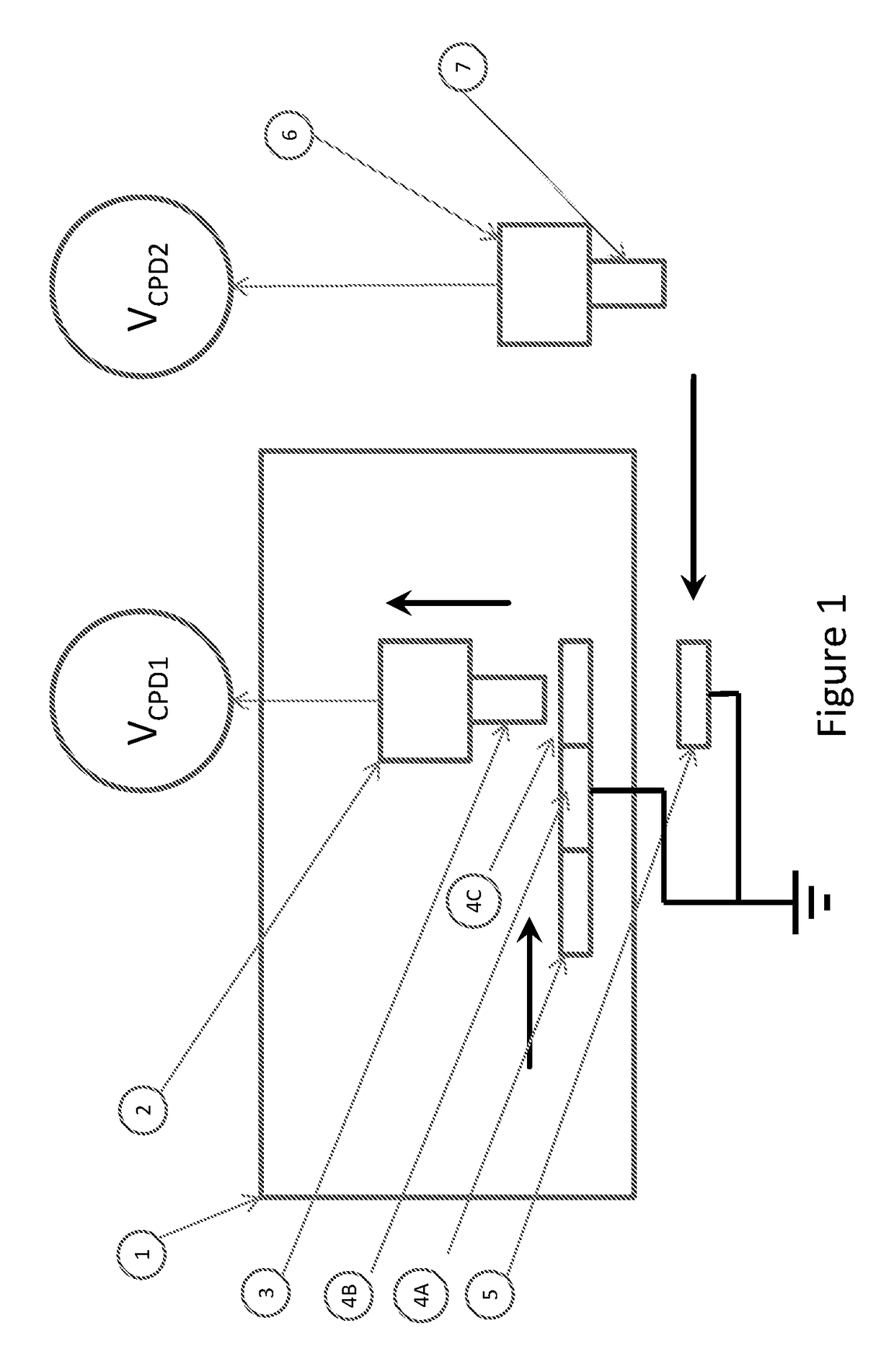
An apparatus for measuring a surface potential of an object on an underlying structure is disclosed. A relatively-moving mechanism moves a probe and a second support member relative to each other until the probe faces a reference structure on the second support member, an electric potential measuring device measures the surface potential of the reference structure through the probe, the controller calibrates the electric potential measuring device such that a measured value of the surface potential of the reference structure becomes 0, the relatively-moving mechanism moves the probe and a first support member relative to each other until the probe faces the object on the first support member after the calibration, and the electric potential measuring device measures the surface potential of the object through the probe.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Combined-source MOS transistor with comb-shaped gate, and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8507959B2Reduce power consumptionIncrease the areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricSchottky barrier
The present invention discloses a combined-source MOS transistor with a Schottky Barrier and a comb-shaped gate structure, and a method for manufacturing the same. The combined-source MOS transistor includes: a control gate electrode layer, a gate dielectric layer, a semiconductor substrate, a highly-doped source region and a highly-doped drain region, wherein a Schottky source region is connected to a side of the highly-doped source region which is far from a channel, one end of the control gate extends to the highly-doped source region, the extended gate region is an extension gate in a form of a comb-shaped and the original control gate region is a main gate; an active region covered by the extension gate is also a channel region, and is a substrate material; the highly-doped source region which is formed by highly doping is located on both sides of each comb finger of the extension gate; and a Schottky junction is formed at a location where the Schottky source region and the channel under the extension gate are located. As compared with an existing MOSFET, in the invention, a higher turn-on current, a lower leakage current and a steeper subthreshold slope may be obtained under the same process condition and the same active region size.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS8280266B2Prevent foggingImprove image qualityElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
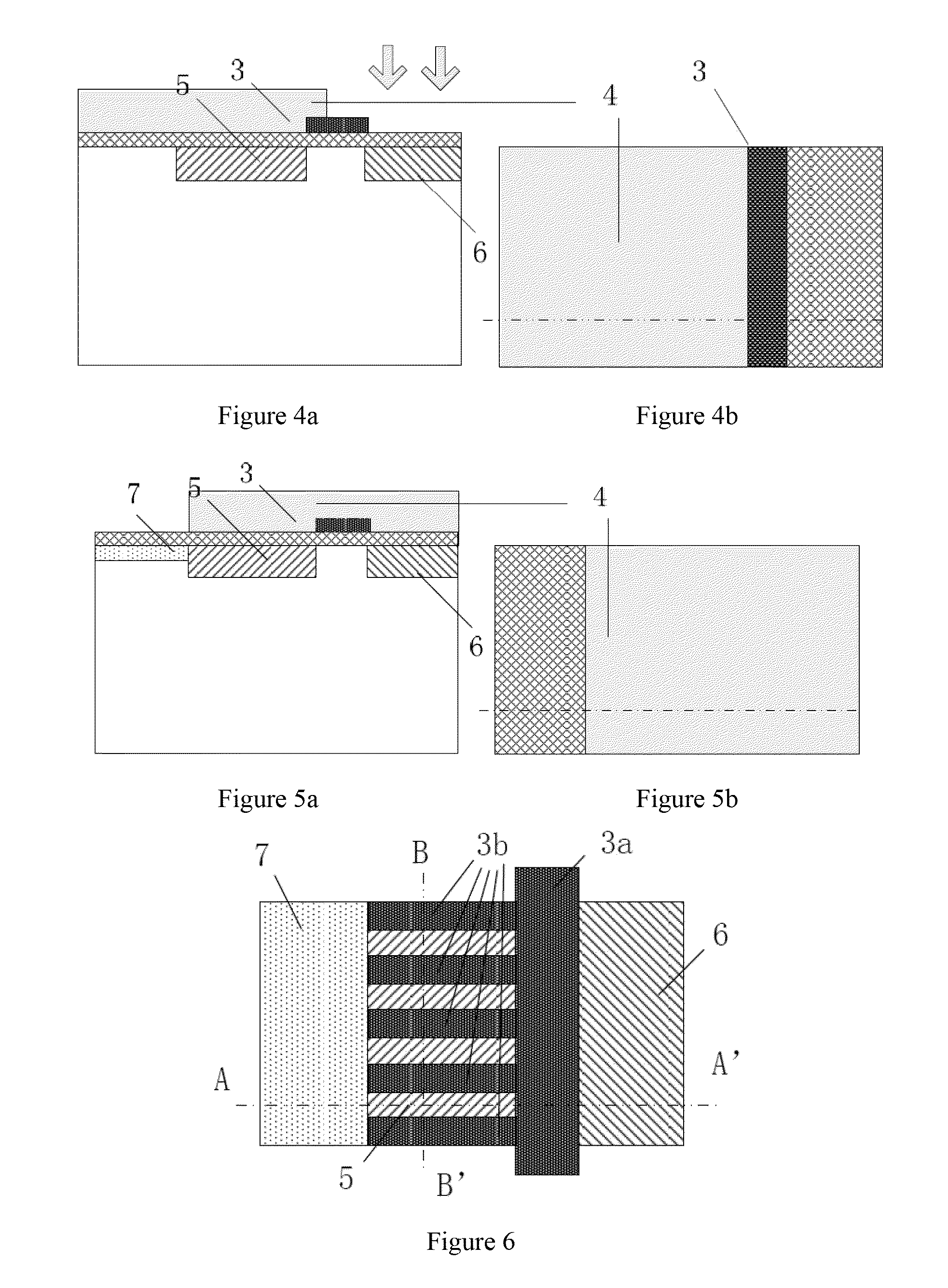
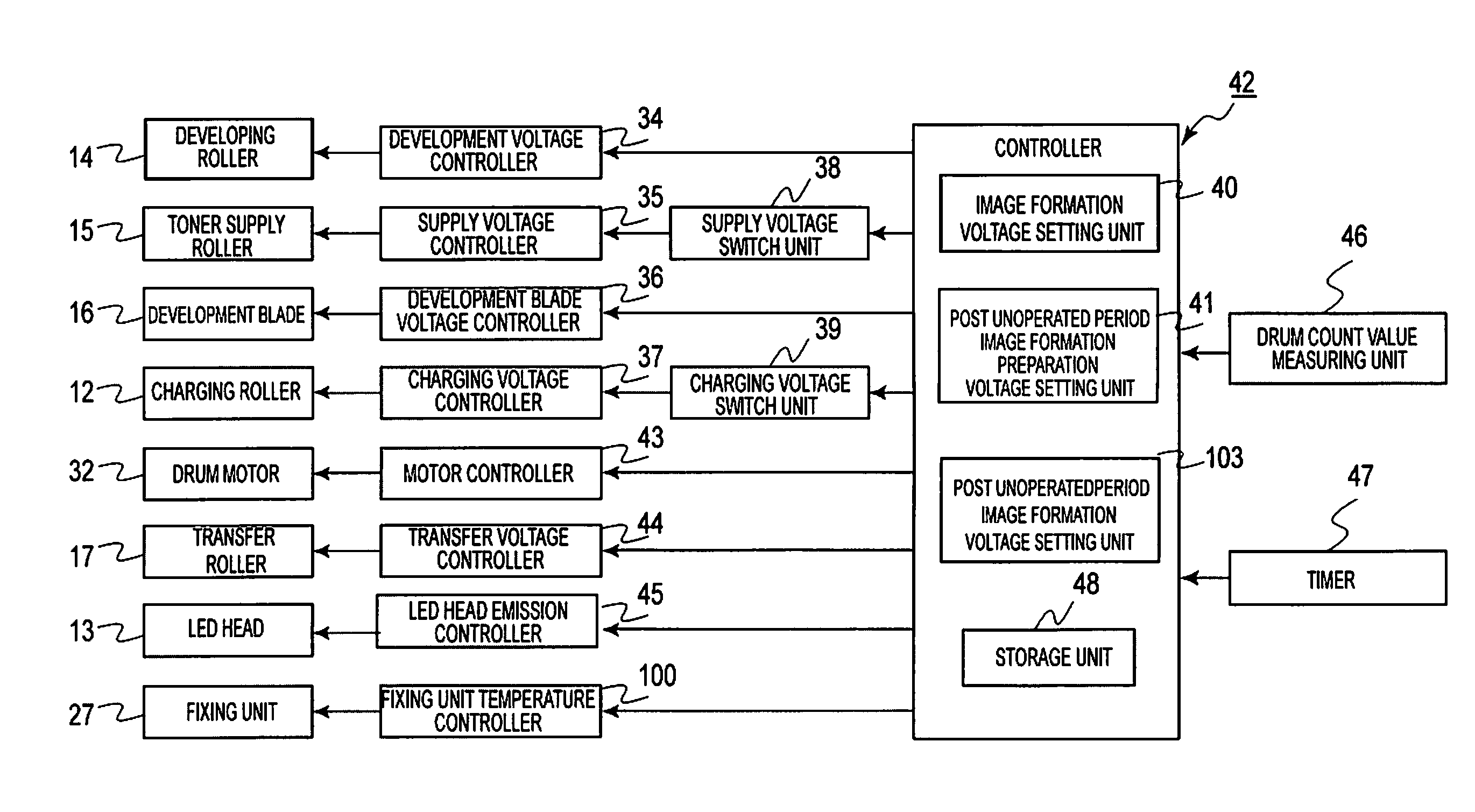
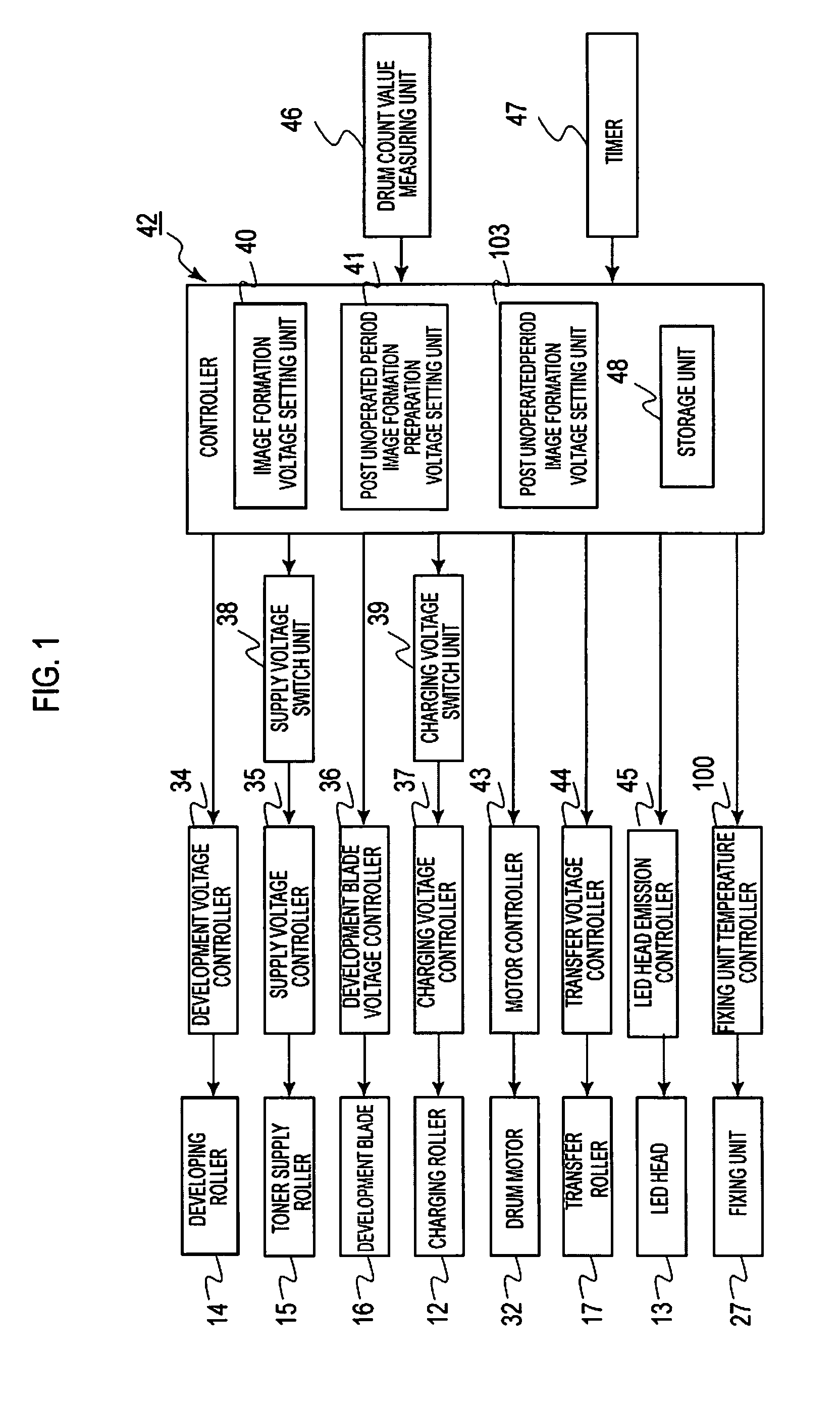
An image forming apparatus includes an image forming unit having image forming elements and a fixing unit. The image forming elements includes an image carrier, a charging unit, a developer carrier, and a developer supplier. The image forming apparatus further includes a post unoperated period image formation preparation processor operable to, when the unoperated period, which is a time period from an end of an image forming operation to a start of a subsequent image forming operation is equal to or greater than a threshold, perform an idling operation to rotate the image carrier while applying a post unoperated period image formation preparation voltage, which is different from a normal image formation voltage, to a given one or more of the image forming elements.
Owner:OKI DATA CORP
Work function calibration of a non-contact voltage sensor
InactiveUS20150338494A1Accurately determineEasy to measureContactless testingReference sampleWork function
A method and a system for calibrating the work function or surface potential of a non-contact voltage sensor probe tip are provided. The method includes preparing one or more reference sample surfaces and a reference non-contact voltage sensor probe tip to have stable surface potentials, measuring the voltage between the reference samples and the reference sensor probe tip, measuring the voltage between a point on a non-reference sample surface and the reference sensor probe tip, measuring the voltage between the same point on the non-reference sample surface and a non-reference non-contact voltage sensor probe tip, and determining a surface potential correction factor for the non-reference, non-contact voltage sensor.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
Image forming apparatus and image forming process
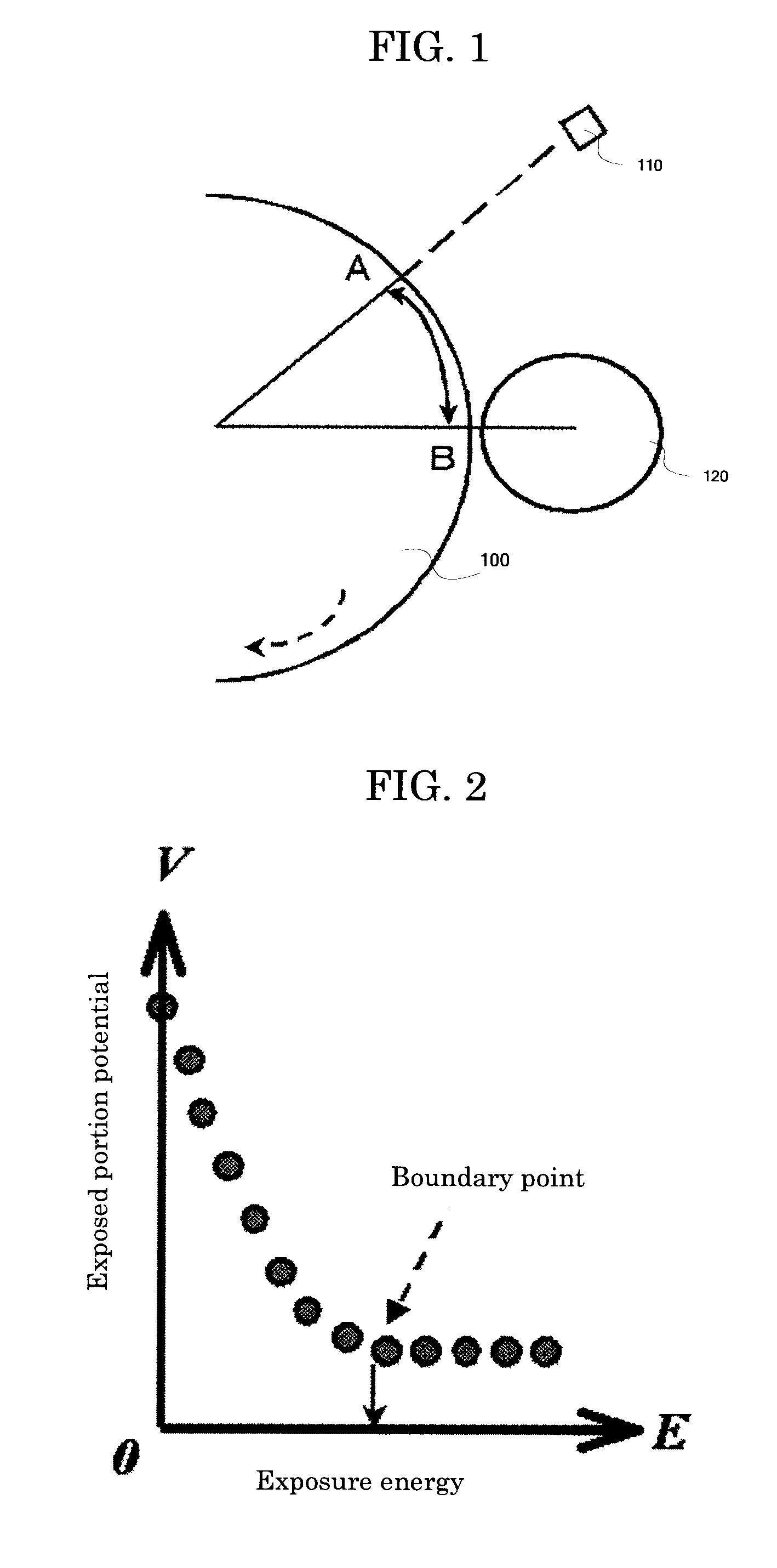
InactiveUS7714882B2High durabilitySuperior effectElectrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternTransit timeEngineering
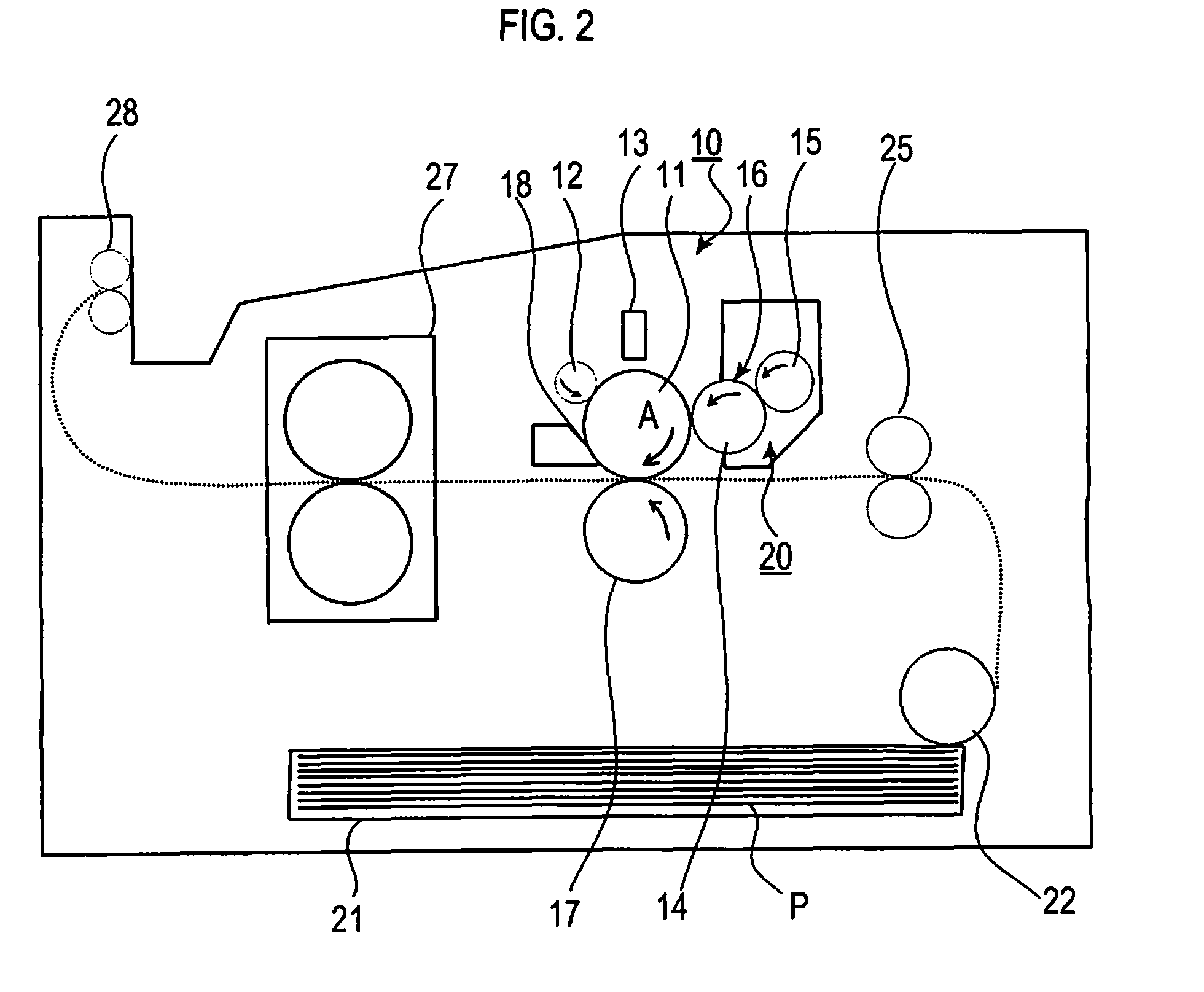
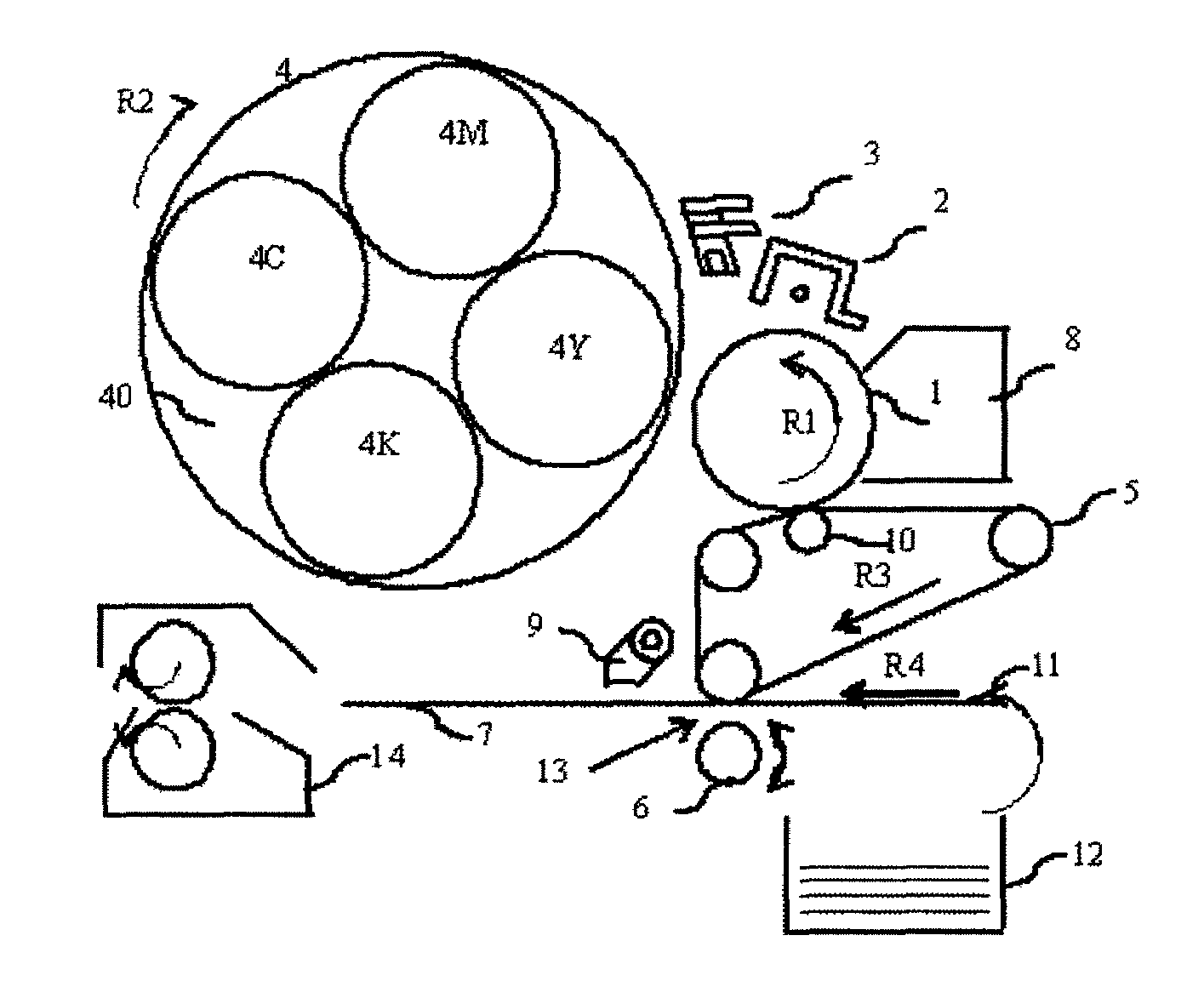
The present invention provides an image forming apparatus including a photoconductor, a charging unit configured to charge the photoconductor, a writing unit configured to form a latent electrostatic image, a toner image forming unit configured to form a toner image by developing the latent electrostatic image, the toner image forming unit having a plurality of developing devices housing a plurality of color developers for each color, a transfer unit configured to transfer the toner image formed on the photoconductor onto a transfer material, and a fixing unit configured to fix the transferred toner image on the transfer material, wherein the time spent by an arbitrary point on the photoconductor in moving from a position in which to face the writing unit to a position in which to face the developing unit is shorter than 50 ms and longer than the transit time of the photoconductor.
Owner:RICOH KK
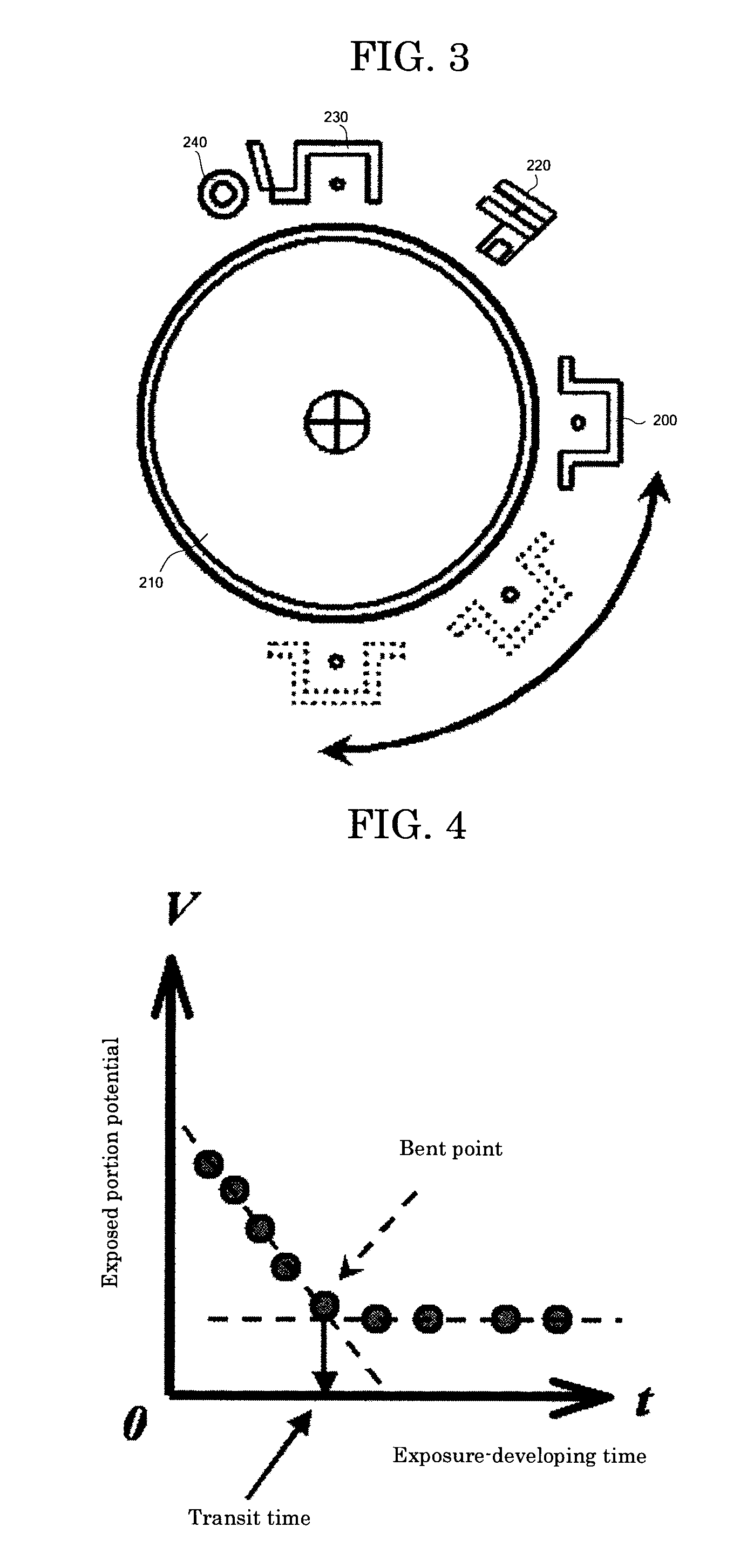
Charger, Image Forming Apparatus, and Charge Control Method
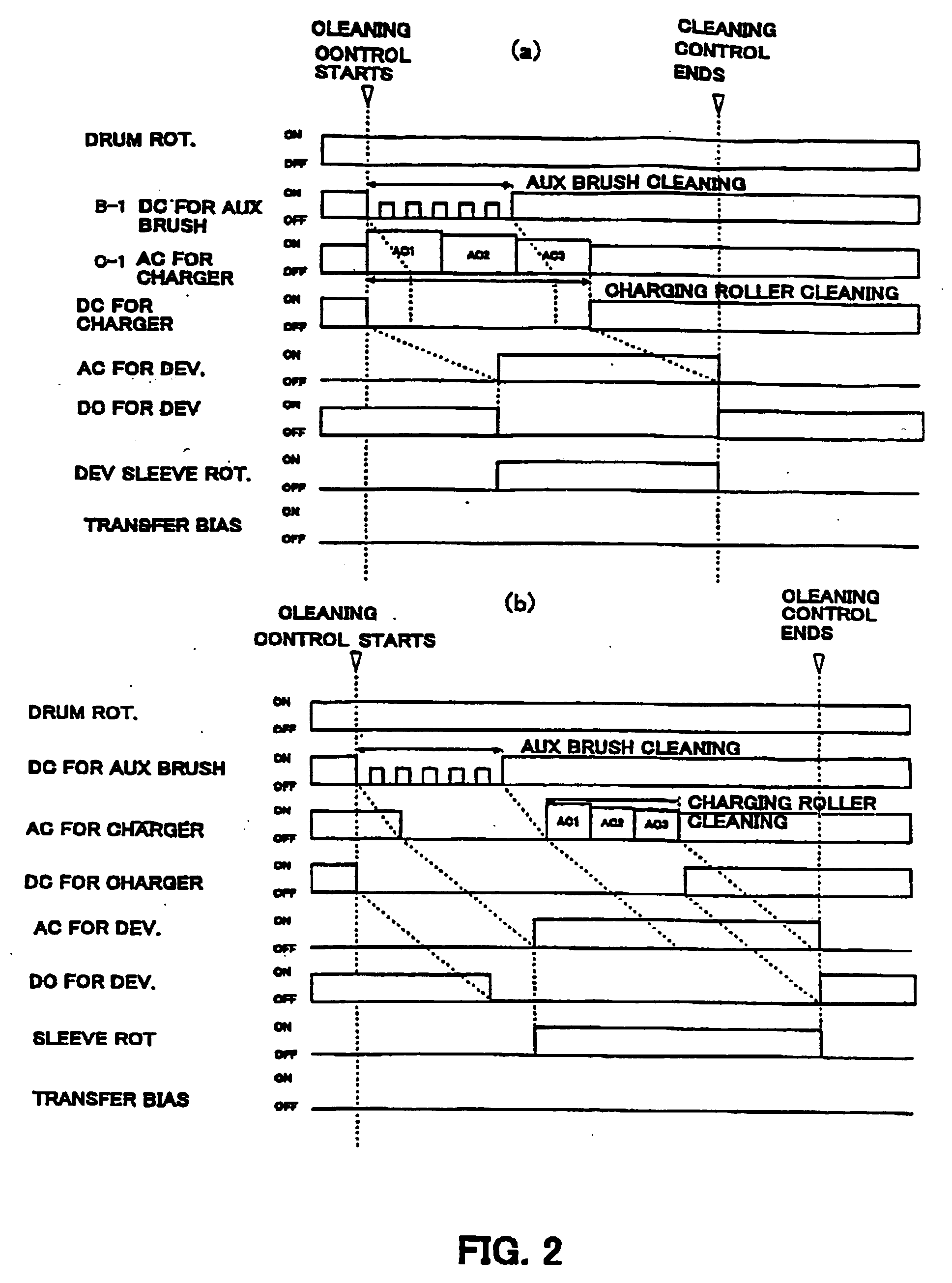
InactiveUS20080131154A1Avoid bandsPreventing resist shiftElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeImage formationCharge control
A charger includes: a primary charging member which is rotatably provided and is brought into contact with an image carrier to charge the surface of the image carrier; a secondary charging member which is brought into contact with the image carrier at a portion on the downstream side relative to the first charging member in the rotational direction of the image carrier to charge the surface of the image carrier; and a controller which controls voltages applied to the first and second charging members, wherein at the time of image formation, the controller applies, to the first charging member, a voltage whose absolute value is higher than the absolute value of the discharge start voltage of the first charging member and applies, to the second charging member, a voltage whose absolute value is lower than the absolute value of the discharge start voltage of the second charging member and whose absolute value is lower than the voltage applied to the first charging member, and at the time when an image is not formed, the controller applies, to the first charging member, a voltage whose absolute value is lower than the absolute value of the discharge start voltage of the first charging member and applies, to the second charging member, a voltage whose absolute value is higher than the absolute value of the discharge start voltage of the second charging member and whose absolute value is higher than the voltage applied to the first charging member.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method to assemble nano-structure on a substrate and nano-molecule device comprising nano-structure formed thereby
ActiveUS8329386B2Reduce widthSurface potentialMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure assemblyResistEngineering
A method of selectively positioning nanostructures on a substrate is provided which includes: a first step of forming a photoresist pattern on the substrate and then control the line width of the photoresist pattern in a nano unit to form a nanometer photoresist layer; a second step of forming a protective layer for preventing adsorption of a nano-material in a patter-unformed area on the substrate on which the nanometer photoresist layer has been formed; a third step of removing the photoresist layer formed on the substrate; a fourth step of forming a positively-charged or negatively charged adsorbent layer in the area from which the photoresist layer has been removed; and a fifth step of applying a nano-material-containing solution charged in the opposite polarity of the adsorbent layer to the substrate on which the adsorbent layer has been formed.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Surface potential sensor and copying machine
ActiveUS20150028881A1MiniaturizeHigh measurement sensitivityCurrent/voltage measurementSemiconductor operation lifetime testingElectricityReduced size
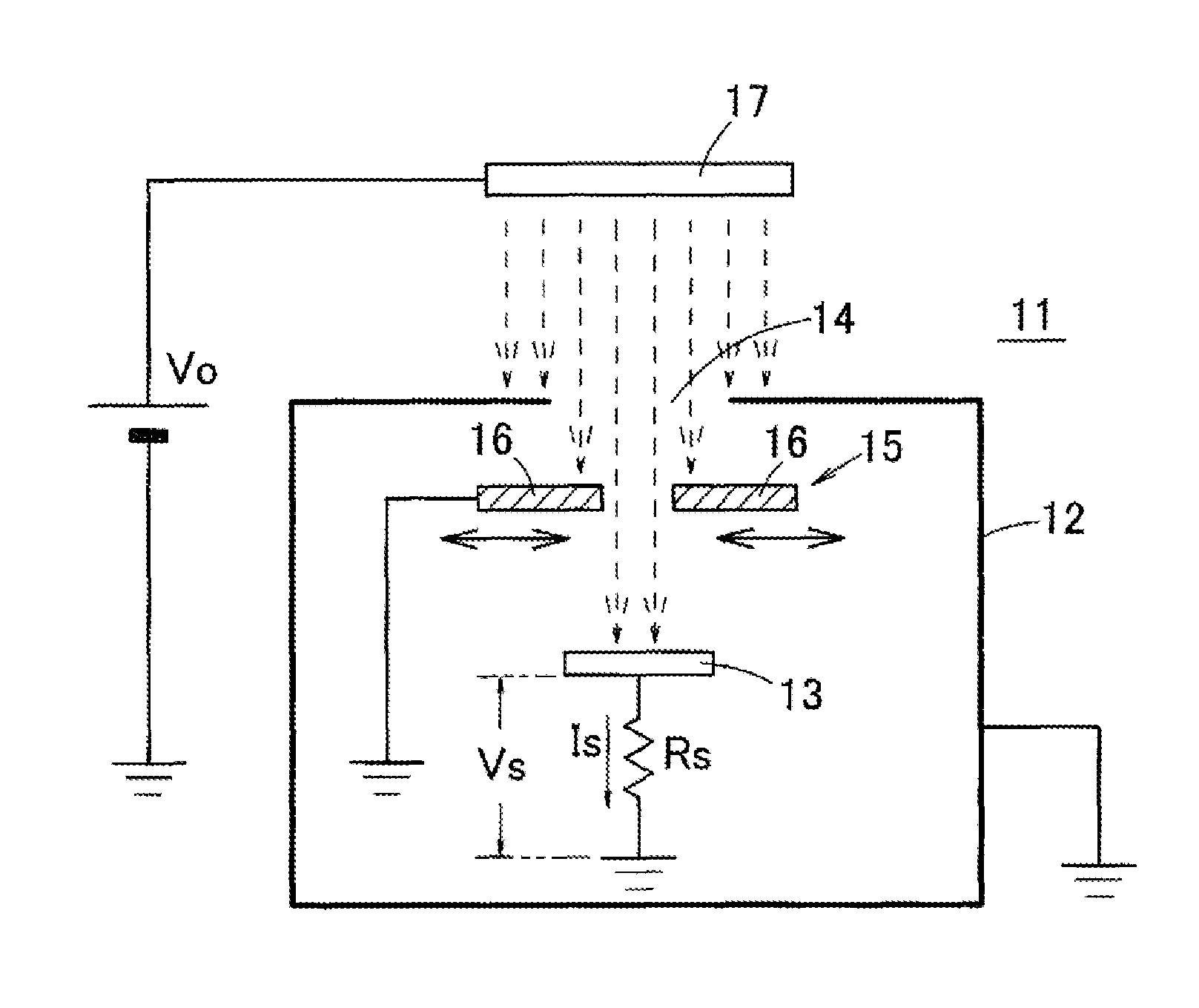
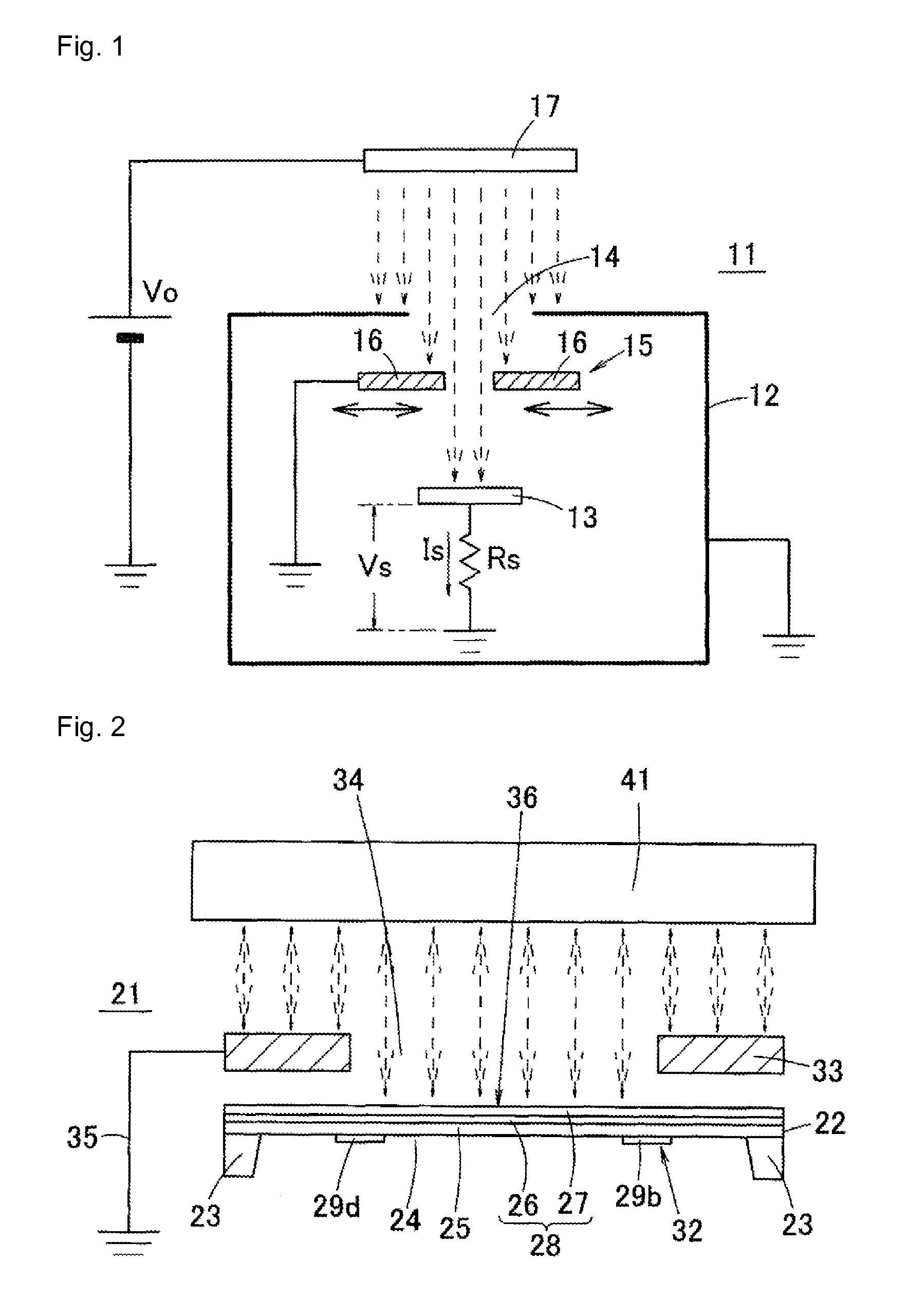
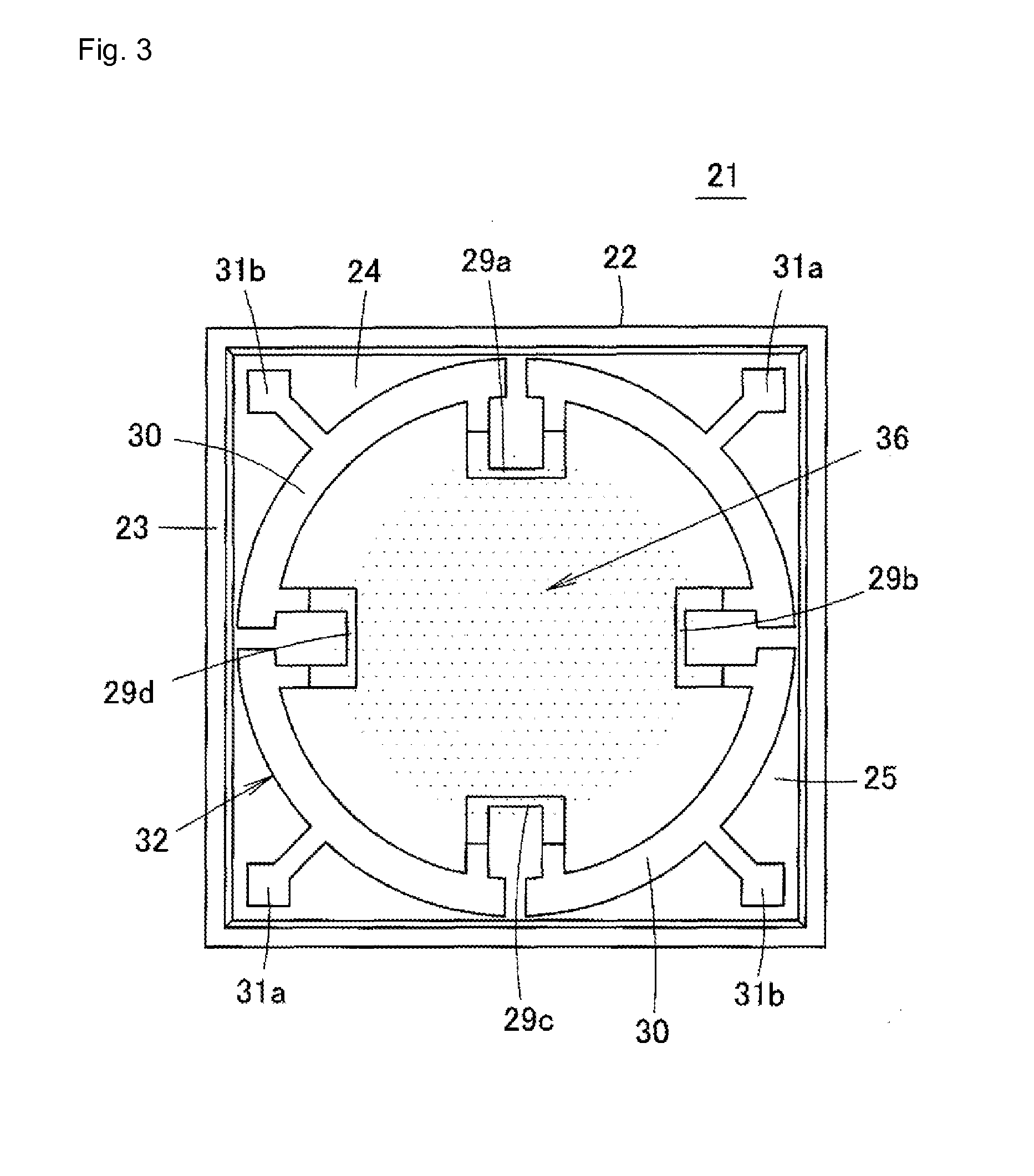
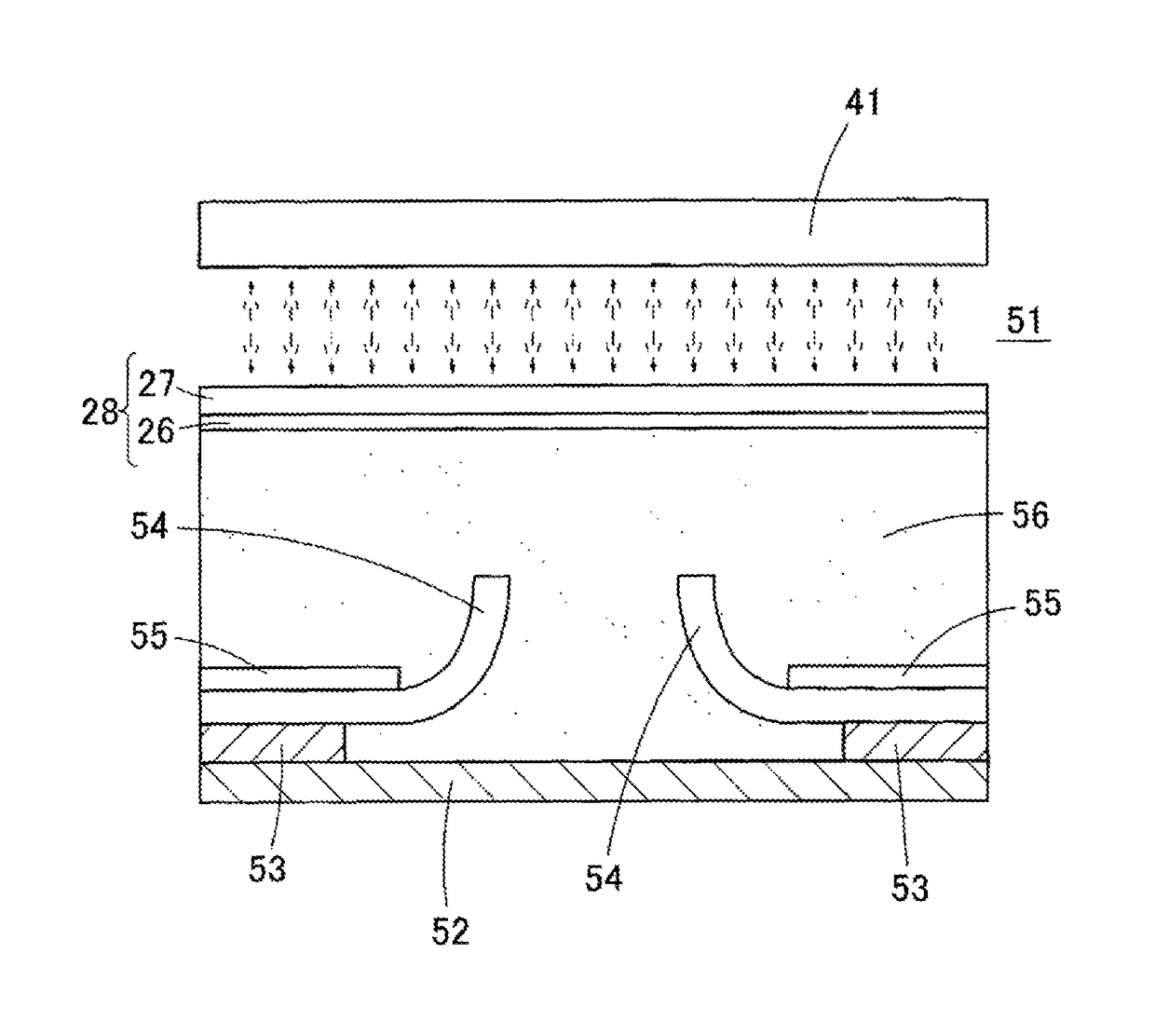
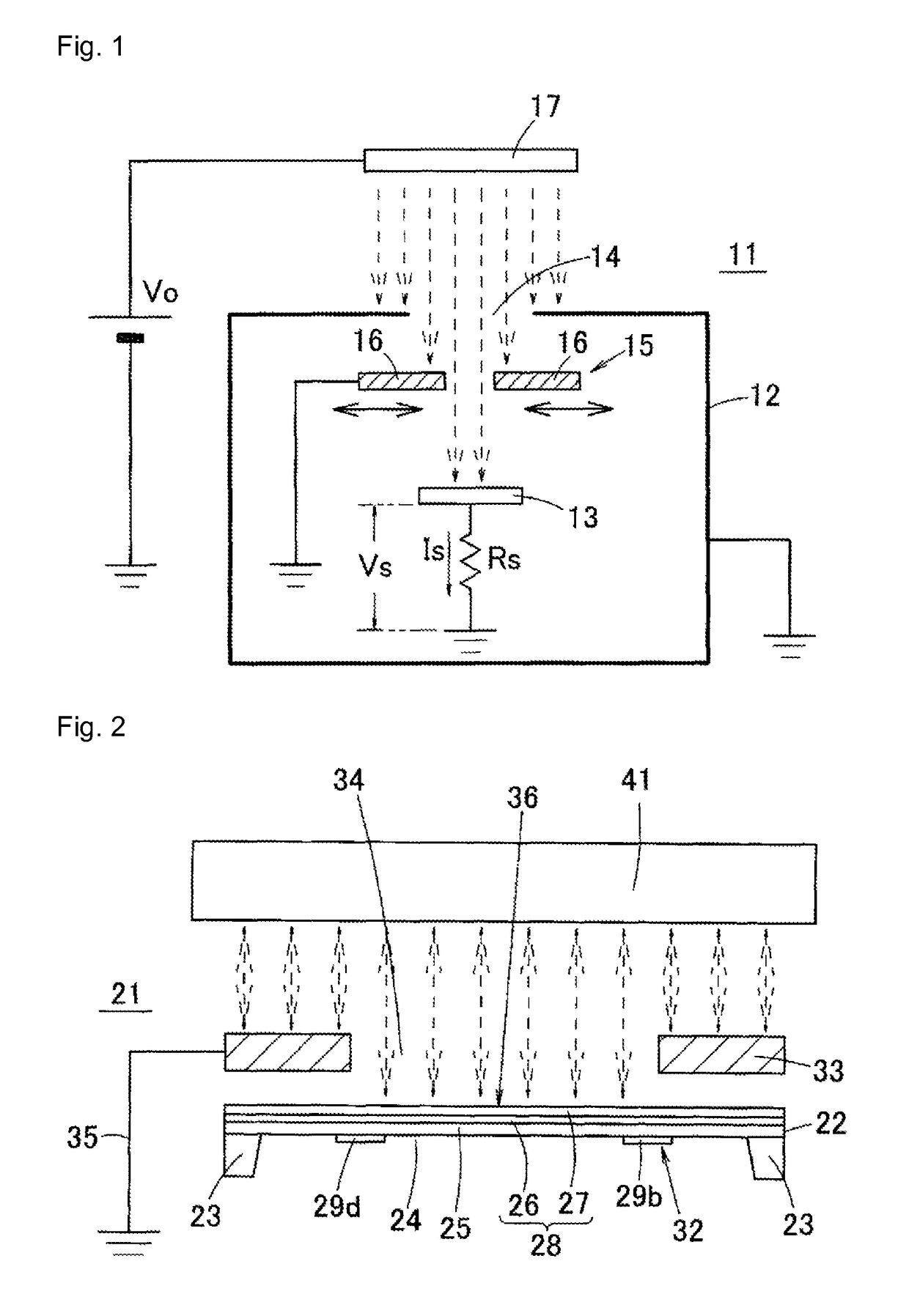
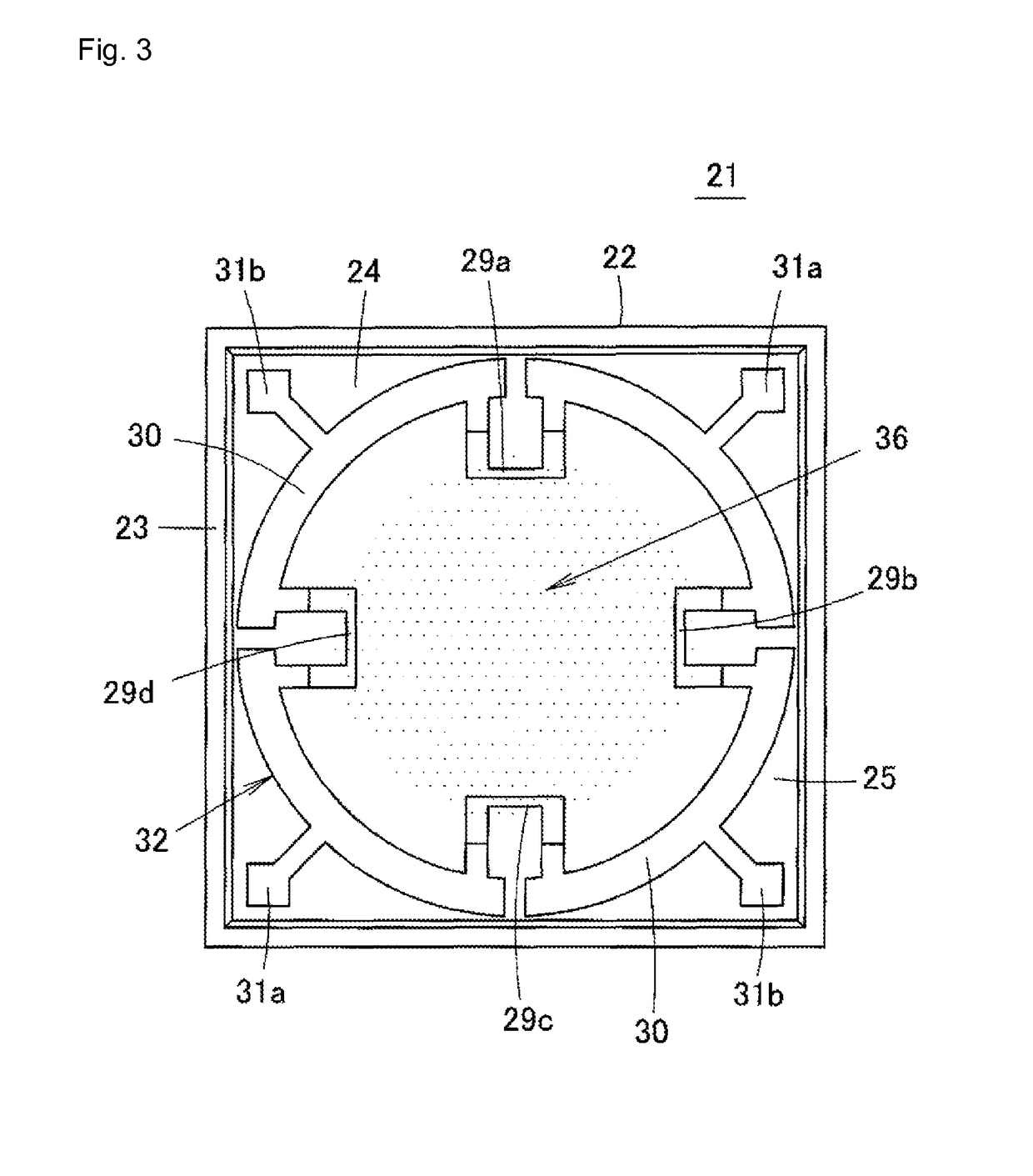
This surface potential sensor is provided with an electret electrode (28), which is configured of a metal film (26) and an electret film (27), said electret electrode being provided on an upper surface of a diaphragm (25) of a semiconductor substrate. Four piezoresistors (29a, 29b, 29c, 29d) are formed on the diaphragm (25), and a distortion quantity detecting unit (32) is configured by forming a bridge circuit using the piezoresistors. Since an electrostatic force that operates between an object and the electret electrode (28) changes corresponding to potential of the object, and the electret electrode (28) warps corresponding to the change, the potential of the object can be detected by measuring a distortion quantity of the electret electrode (28) by means of the distortion quantity detecting unit (32). Consequently, not only the potential of the object but also a polarity thereof can be detected with reduced size and high sensitivity.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Electrophotographic photosensitive member, method for manufacturing the same, and electrophotographic apparatus
InactiveUS9091948B2Increase surface potentialSurface potentialElectrography/magnetographyCoatingsSurface layerEngineering
A surface layer of the electrophotographic photosensitive member has a change region in which a ratio of the number of carbon atoms with respect to the sum of the number of silicon atoms and the number of carbon atoms gradually increases toward a surface side of the electrophotographic photosensitive member from a photoconductive layer side, wherein the change region has an upper charge injection prohibiting portion containing a Group 13 atom, and a surface-side portion which is positioned closer to the surface side of the electrophotographic photosensitive member than the upper charge injection prohibiting portion and does not contain the Group 13 atom, and the distribution of the Group 13 atom in a boundary portion between the surface-side portion and the upper charge injection prohibiting portion is precipitous.
Owner:CANON KK
Work function calibration of a non-contact voltage sensor
InactiveUS9625557B2Accurate repeatable measurementAccurately determinedContactless testingReference sampleWork function
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20210080851A1Surface potentialElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeInformation controlImage formation
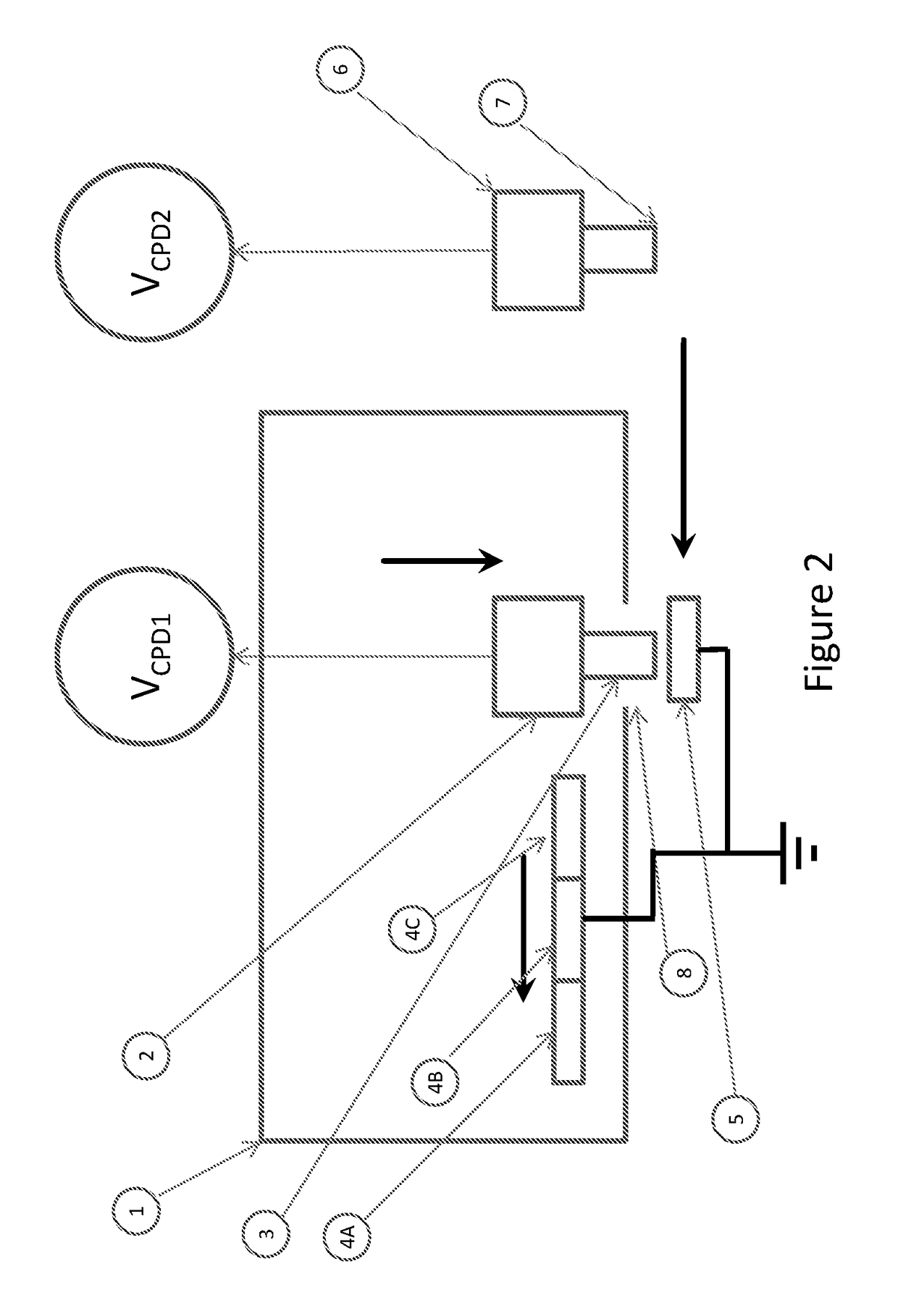
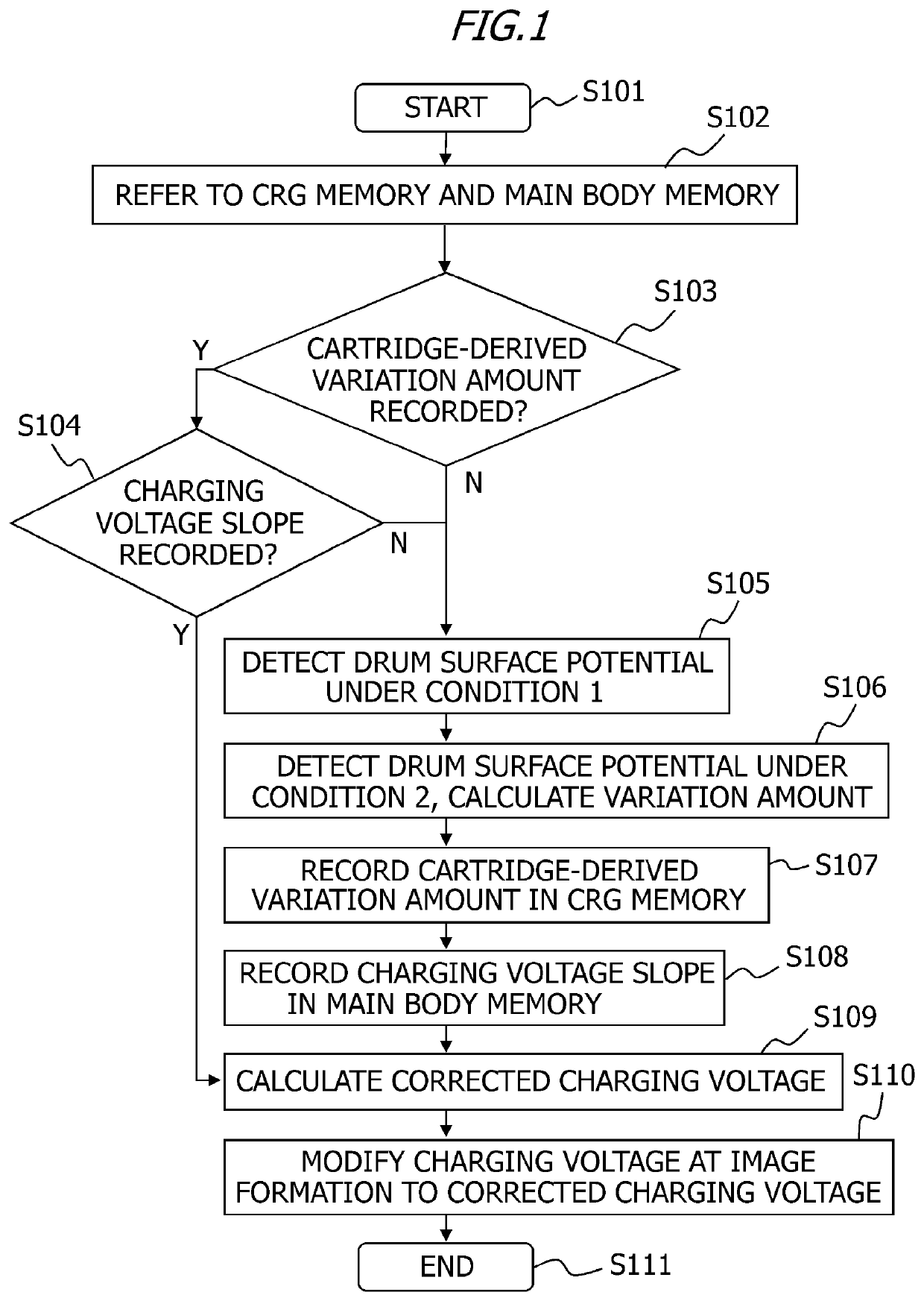
An image forming apparatus, including: a potential detection portion that detects information relating to a surface potential formed on a surface of an image bearing member; and a control portion that calculates a first charging voltage, at which the surface potential has a first value, on the basis of the information, and that controls the potential detection portion, wherein the potential detection portion acquires a plurality of the information items under a plurality of conditions where charging voltage differs, and wherein the control portion calculates the first charging voltage from a deviation of the charging voltage, which is a deviation deriving from an apparatus main body and calculated on the basis of the plurality of the information items and the first value, and controls a power supply portion so that the first charging voltage is applied to a charging member during an image forming operation.
Owner:CANON KK
Surface potential sensor and copying machine
ActiveUS10073127B2Simple structureResistant to breakdownCurrent/voltage measurementSemiconductor operation lifetime testingElectricityElectrical polarity
This surface potential sensor is provided with an electret electrode (28), which is configured of a metal film (26) and an electret film (27), said electret electrode being provided on an upper surface of a diaphragm (25) of a semiconductor substrate. Four piezoresistors (29a, 29b, 29c, 29d) are formed on the diaphragm (25), and a distortion quantity detecting unit (32) is configured by forming a bridge circuit using the piezoresistors. Since an electrostatic force that operates between an object and the electret electrode (28) changes corresponding to potential of the object, and the electret electrode (28) warps corresponding to the change, the potential of the object can be detected by measuring a distortion quantity of the electret electrode (28) by means of the distortion quantity detecting unit (32). Consequently, not only the potential of the object but also a polarity thereof can be detected with reduced size and high sensitivity.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com