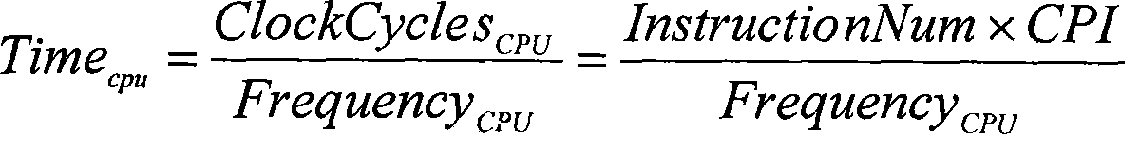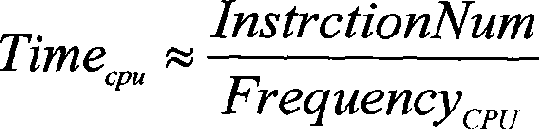Patents
Literature
39 results about "Custom integrated circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
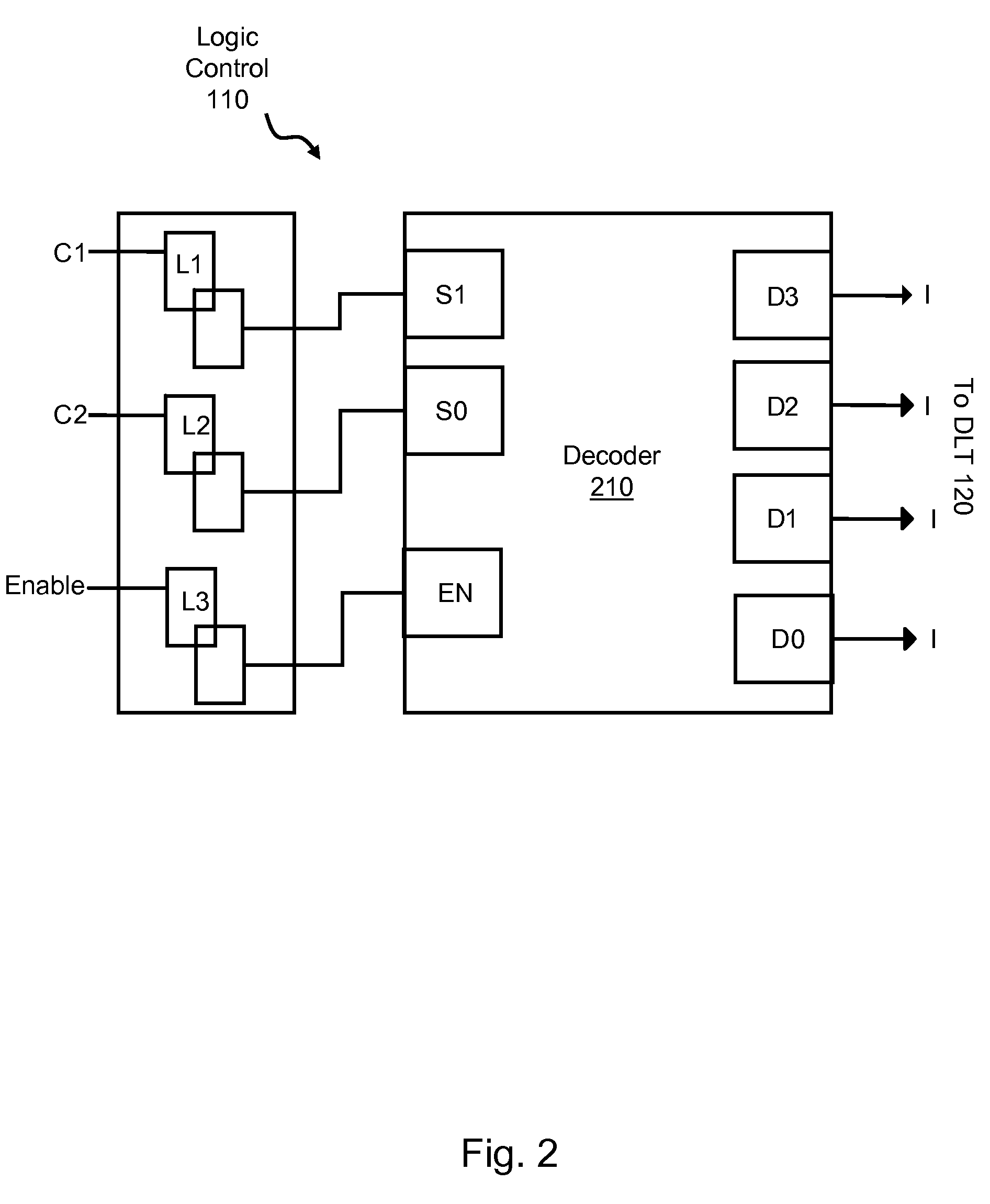
Method and device of using compressed data in far-end fuse box to initialize integrated circuit
InactiveCN1357893ARead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingShift registerCustom integrated circuits
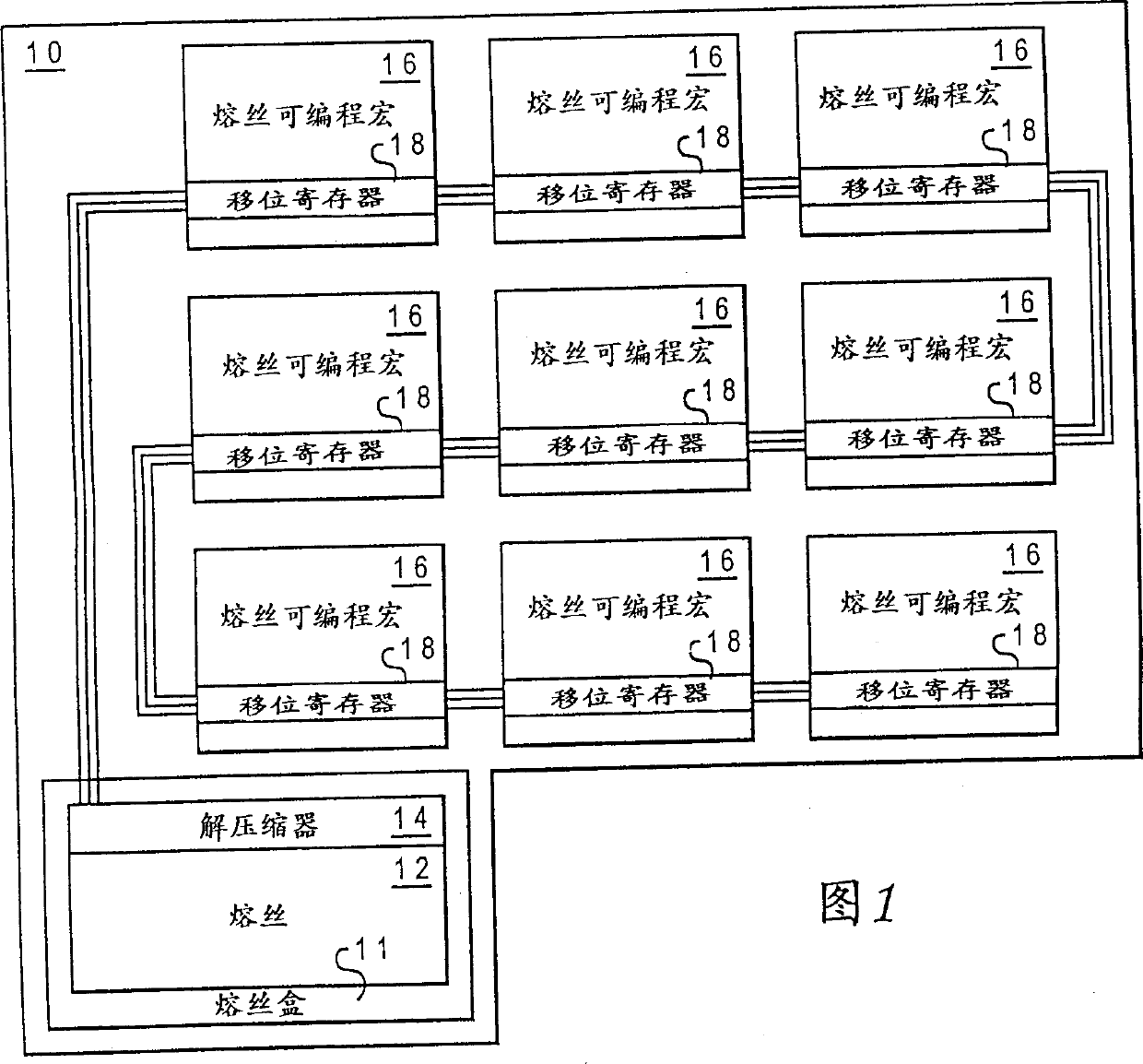
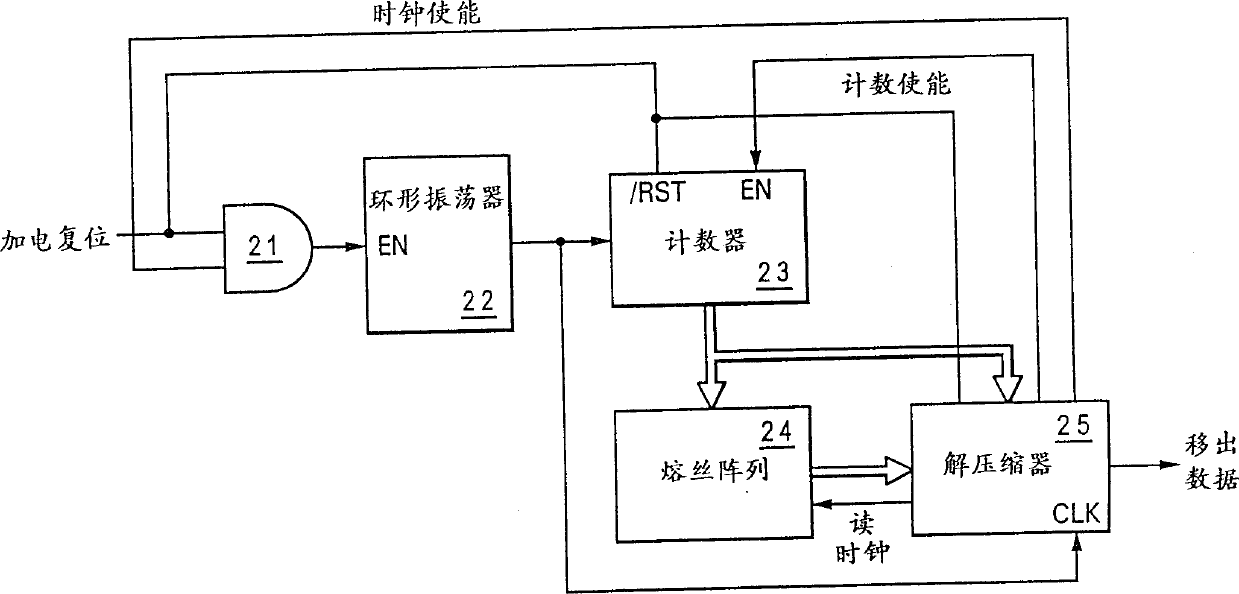
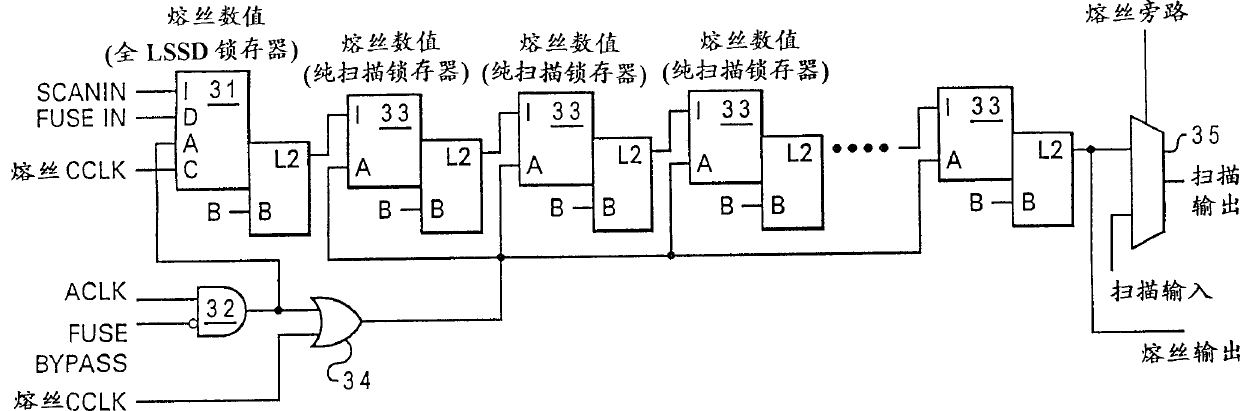
A method and apparatus for initializing an integrated circuit using compressed data from a remote fusebox allows a reduction in the number of fuses required to repair or customize an integrated circuit and allows fuses to be grouped outside of the macros repaired by the fuses. The remote location of fuses allows flexibility in the placement of macros having redundant repair capability, as well as a preferable grouping of fuses for both programming convenience and circuit layout facilitation. The fuses are arranged in rows and columns and represent control words and run-length compressed data to provide a greater quantity of repair points per fuse. The data can be loaded serially into shift registers and shifted to the macro locations to control the selection of redundant circuits to repair integrated circuits having defects or to customize logic.
Owner:格芯公司
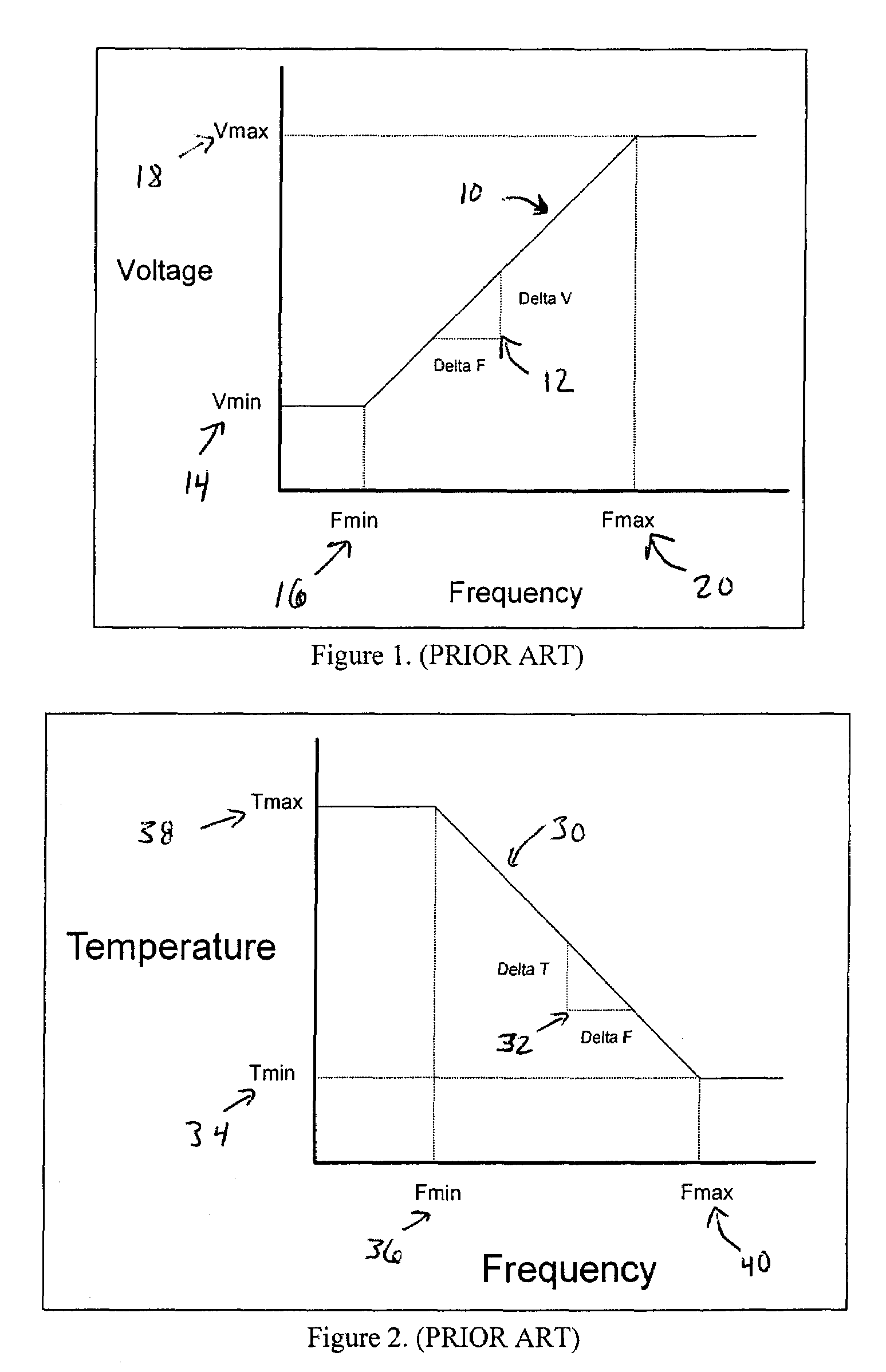
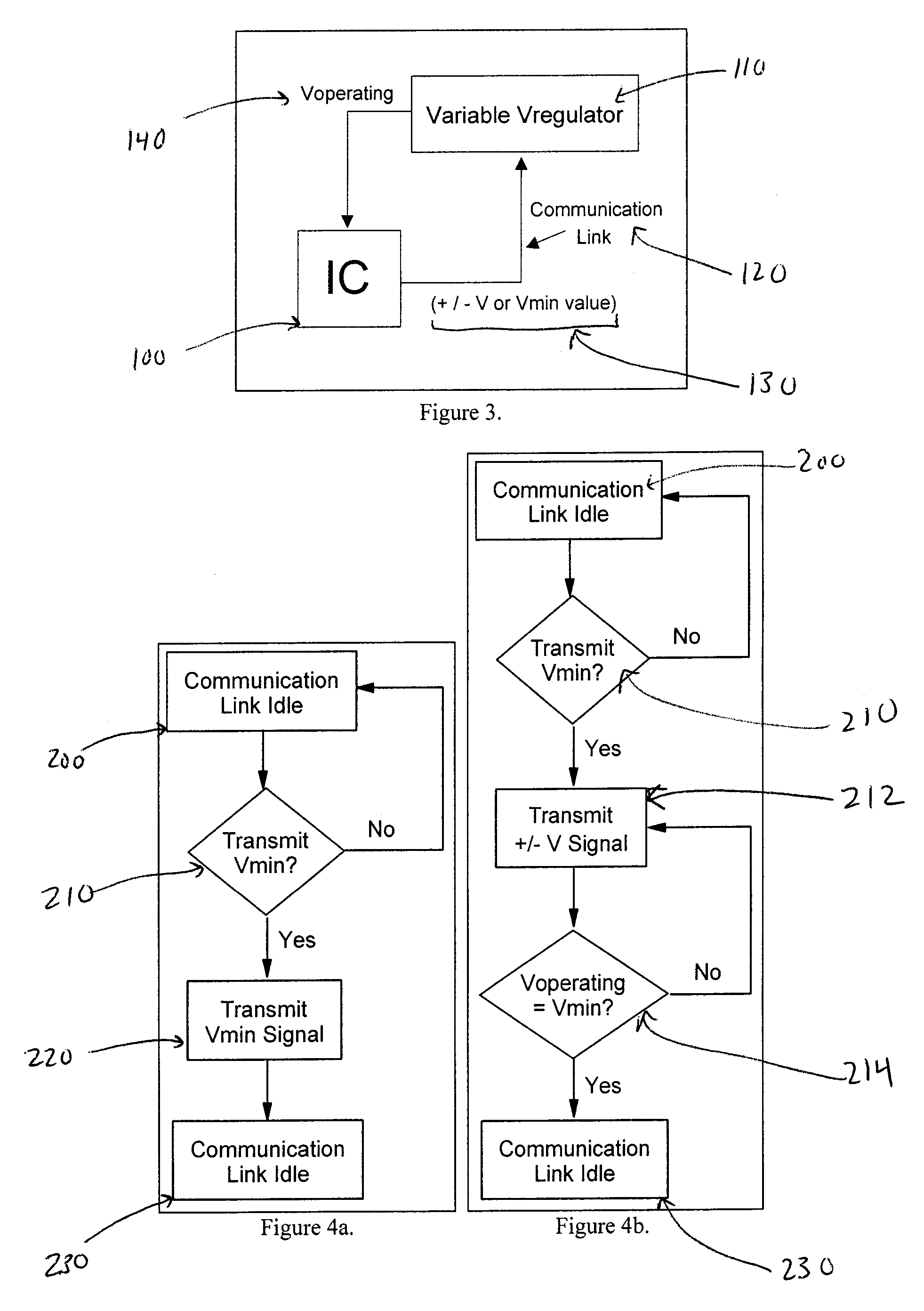
System and method of controlling power consumption in an electronic system by applying a uniquely determined minimum operating voltage to an integrated circuit rather than a predetermined nominal voltage selected for a family of integrated circuits
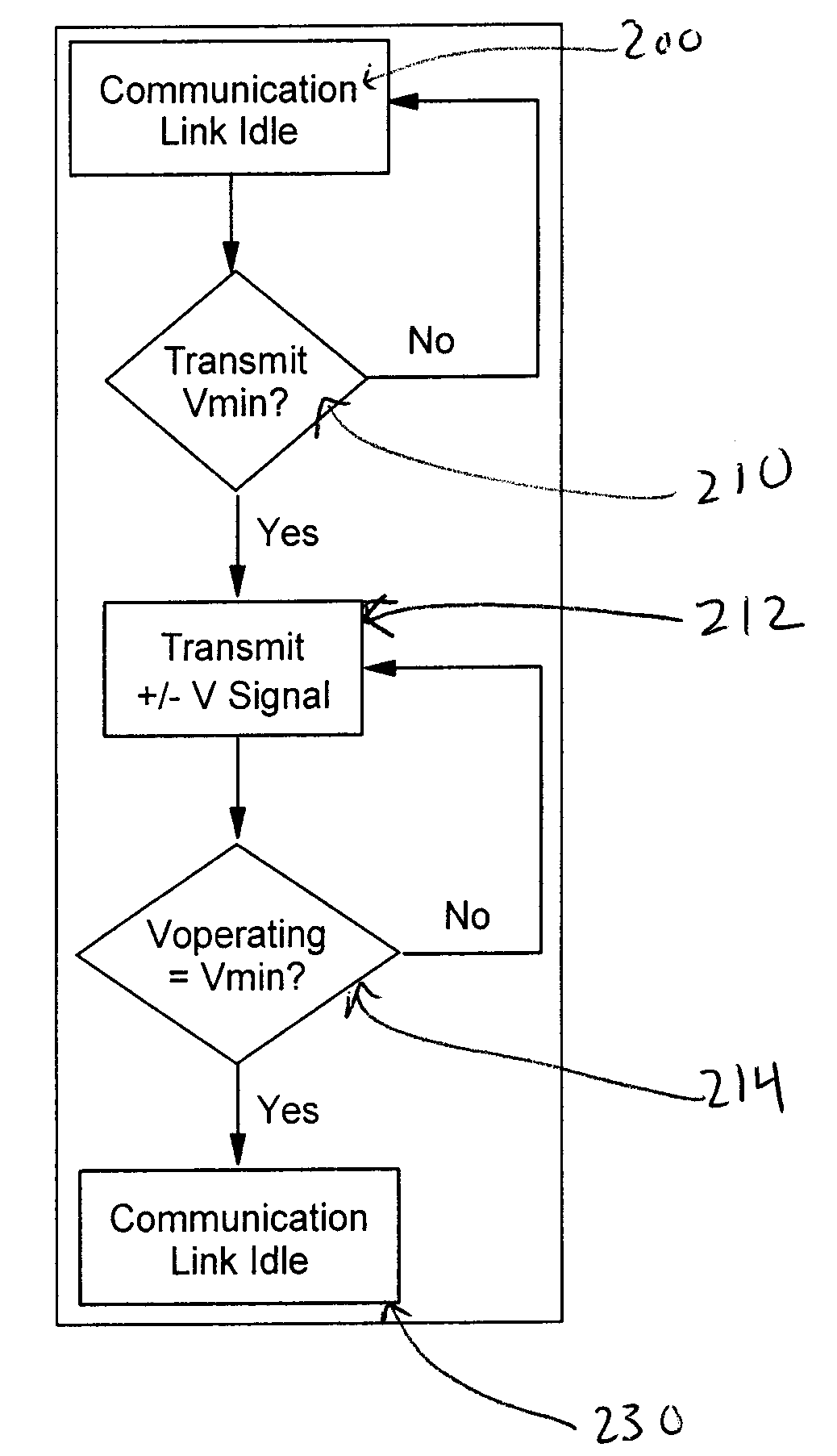
A method and apparatus for adaptively adjusting the operating voltage of an integrated circuit in response to tester-to-system variations, worst-case testing techniques, process variations, temperature variations, or reliability wearout mechanisms. The minimum operating voltage of an integrated circuit is determined either during external testing of the integrated circuit or during built-in-self-testing. The minimum operating voltage is transmitted to a variable voltage regulator where it is used to set the output of the regulator. The output of the regulator supplies the integrated circuit with its operating voltage. This technique enables tailoring of the operating voltage of integrated circuits on a part-by-part basis which results in power consumption optimization by adapting operating voltage in response to tester-to-system variations, worst-case testing techniques, process variations, temperature variations or reliability wearout mechanisms. Alternatively, the invention enables adaptive adjustment of the operating frequency of an integrated circuit. The invention enables system designers to adaptively optimize either system performance or power consumption on a part-by-part basis in response to tester-to system variations, worst-case testing techniques, process variations, temperature variations or reliability wearout mechanisms.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
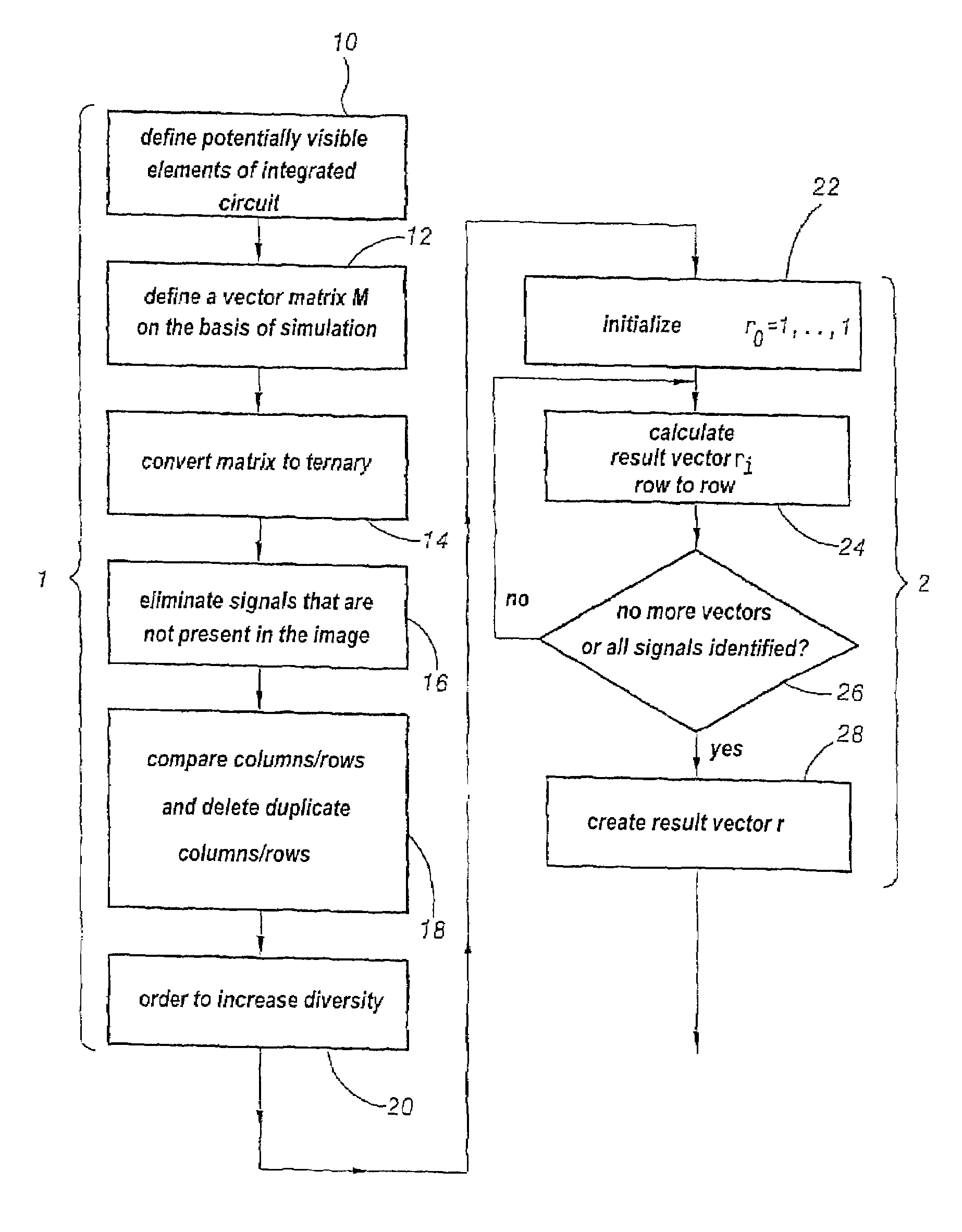
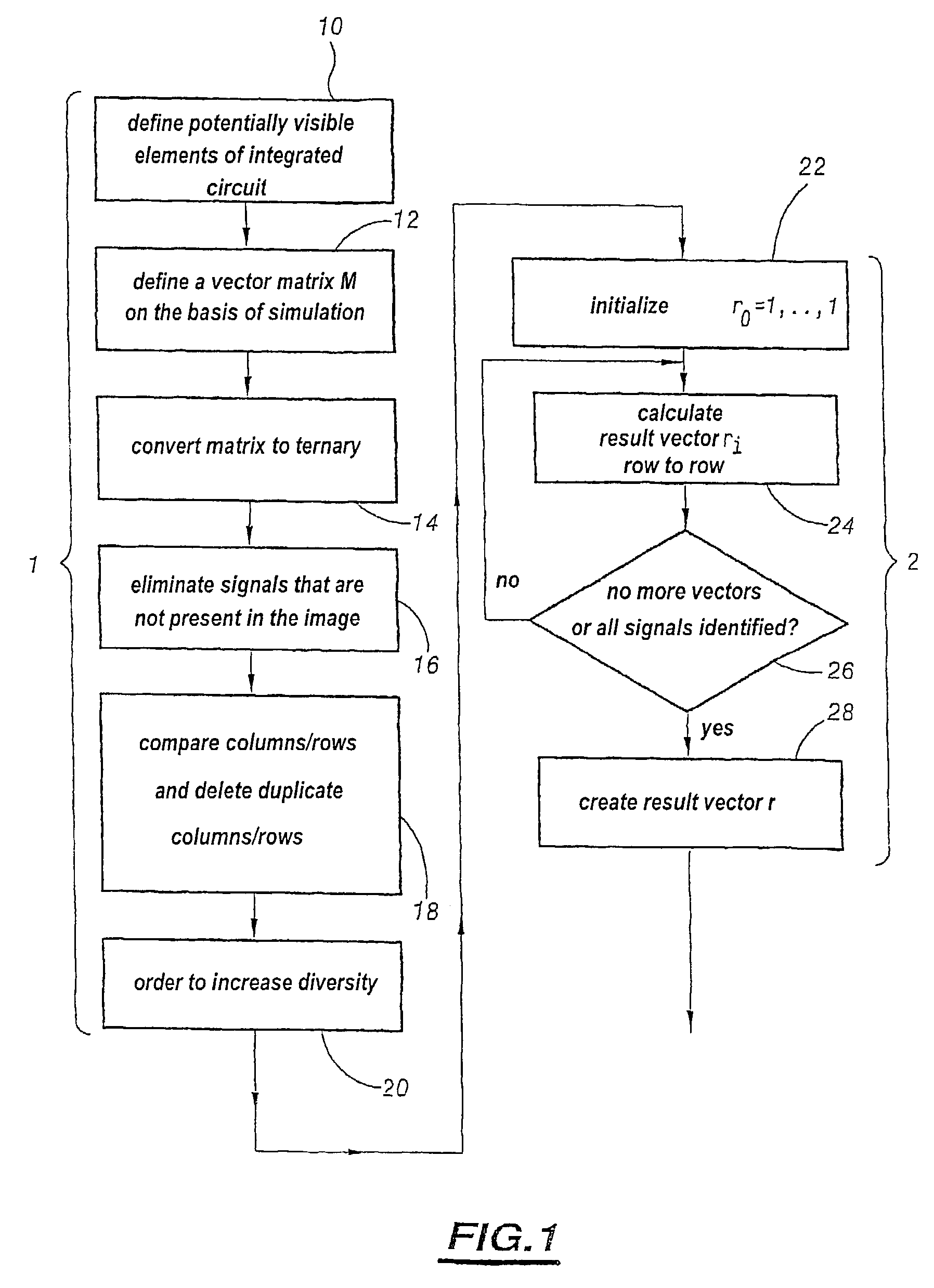
Method for customizing an integrated circuit element
InactiveUS7190822B2Increase diversityDigital circuit testingCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsCircuit models
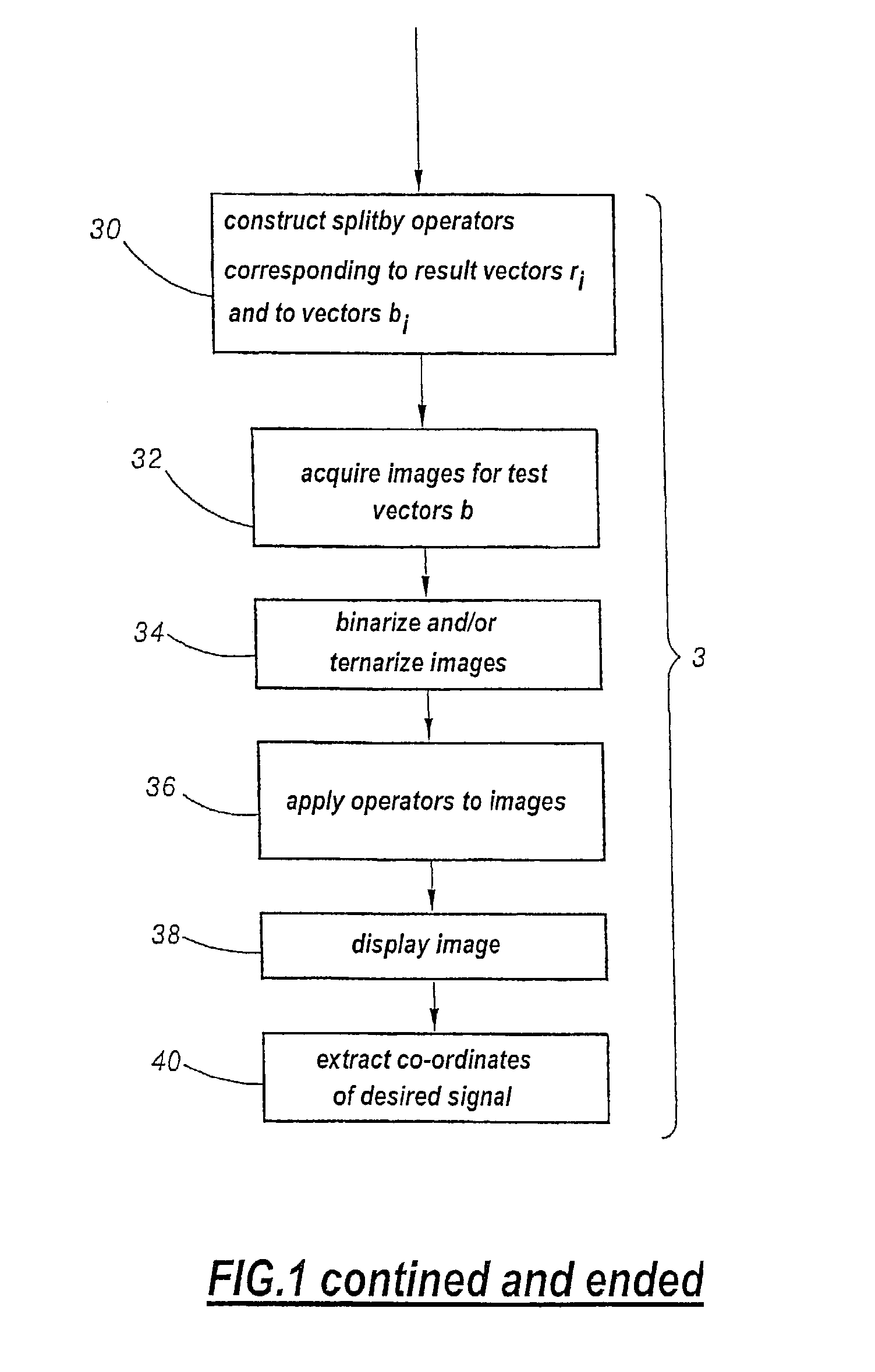
A customizing method includes steps which consist in: a) determining on the basis of a circuit model, a set of vectors each corresponding to a theoretical operating time of the circuit when a predetermined sequence of tests is applied, the coefficients of each vector representing the state of a common set of elements of the circuit among which the element to be customized (12); b) defining on the basis of a comparison of vectors, a composite of logic operators applied on the vectors and enabling to extract the coefficient corresponding to the element to be customized (30); c) producing images of the operating circuit at times corresponding to the vectors whereon is applied the composite of logic operators (32); and d) graphically combining the images produced in accordance with a composite of graphic operators corresponding to the composite of logic operators (36).
Owner:CENT NAT DETUD SPATIALES C N E S
Method for implementing reconfigurable accelerator custom-built for program
InactiveCN101441564AHigh frequencyImprove performanceSpecific program execution arrangementsGeneral purposeGranularity
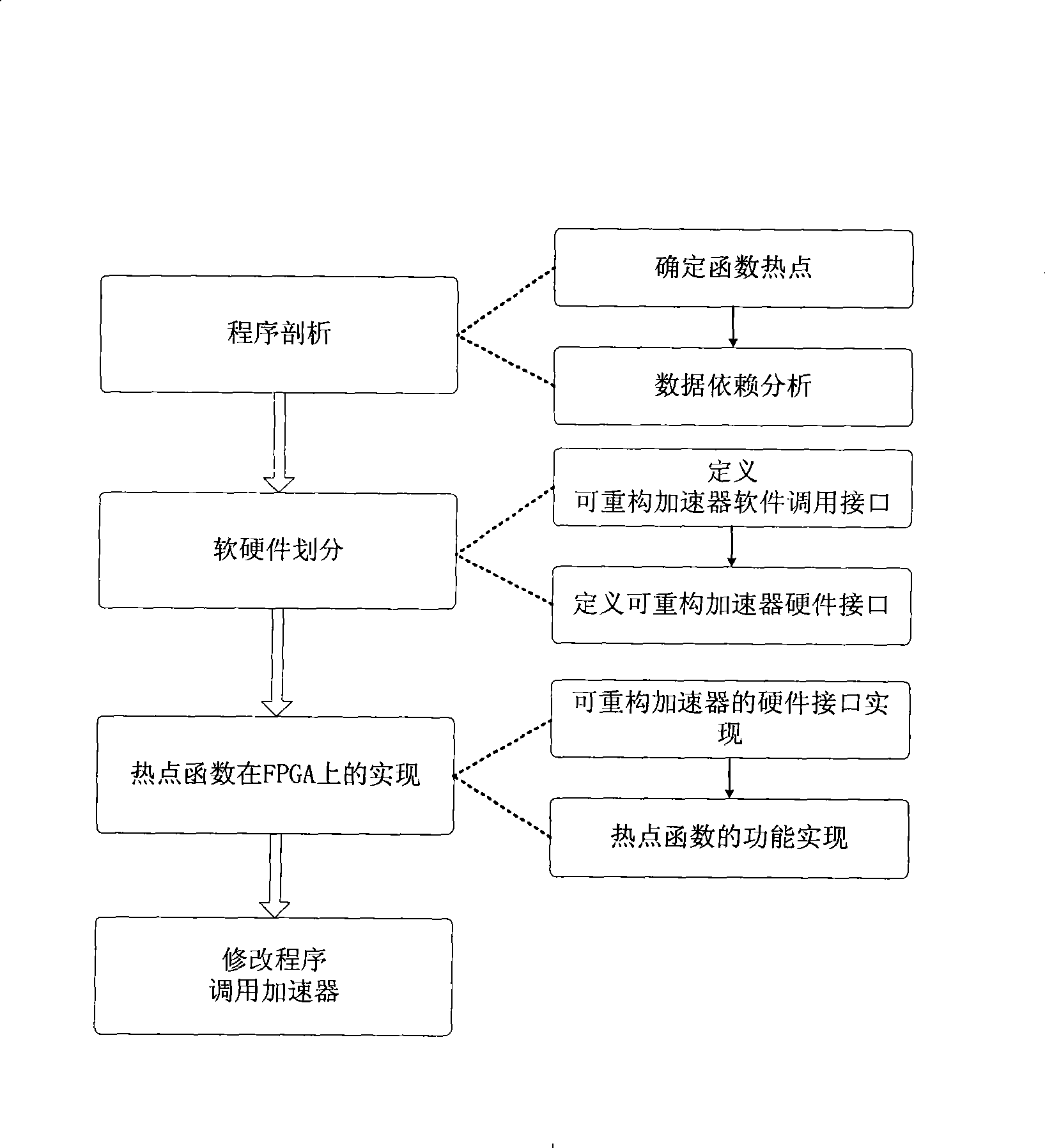
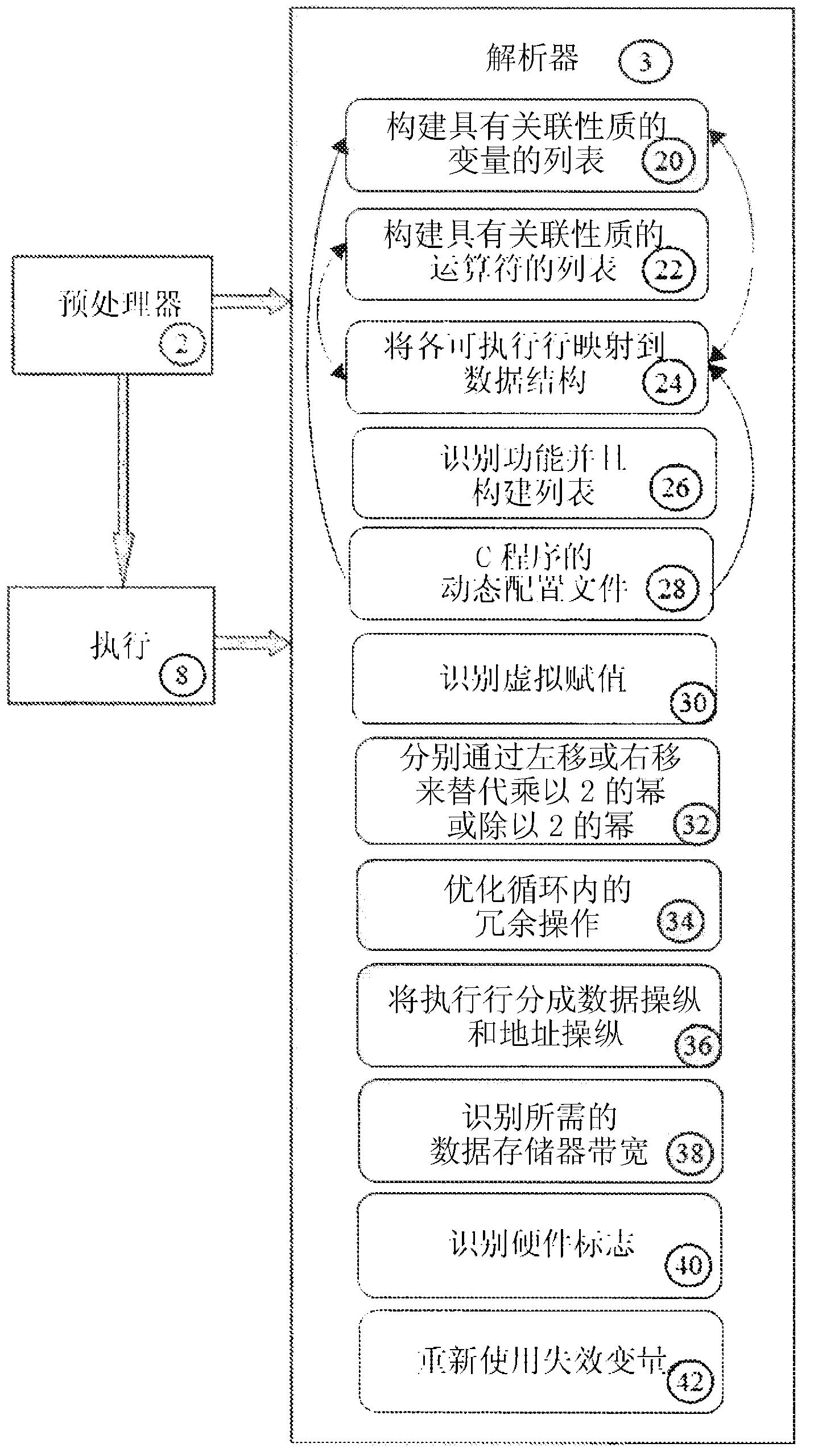
The invention discloses a method for realizing a reconfigurable accelerator customized for a program. The reconfigurable accelerator customized for the program accelerates the program on an FPGA by arranging the FPGA for the prior general-purpose computer system. The method has a main function of analyzing the program, uses functions to calculate information for the runtime of a granularity sampling program, acquires computing-intensive hot spot functions in the program, realizes the hot spot functions as the reconfigurable accelerator on the FPGA, and modifies call of the hot spot functions in the program into call of the corresponding reconfigurable accelerator to accelerate execution of the hot spot functions. The method uses the reconfigurable accelerator to realize the hot spot functions of the program, improves the total speed-up ratio of the program, uses the FPGA to realize the reconfigurable accelerator, achieves the performance of an approximately applied custom integrated circuit, and simultaneously maintains the flexibility of a general-purpose processor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Semiconductor integrated circuit having standard and custom circuit regions
InactiveUS6037666ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a mother chip having a standard integrated circuit and electrodes pads, and an option chip having a custom integrated circuit, the option chip being provided over a part of the mother chip via connectors.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
System for acquiring device parameters
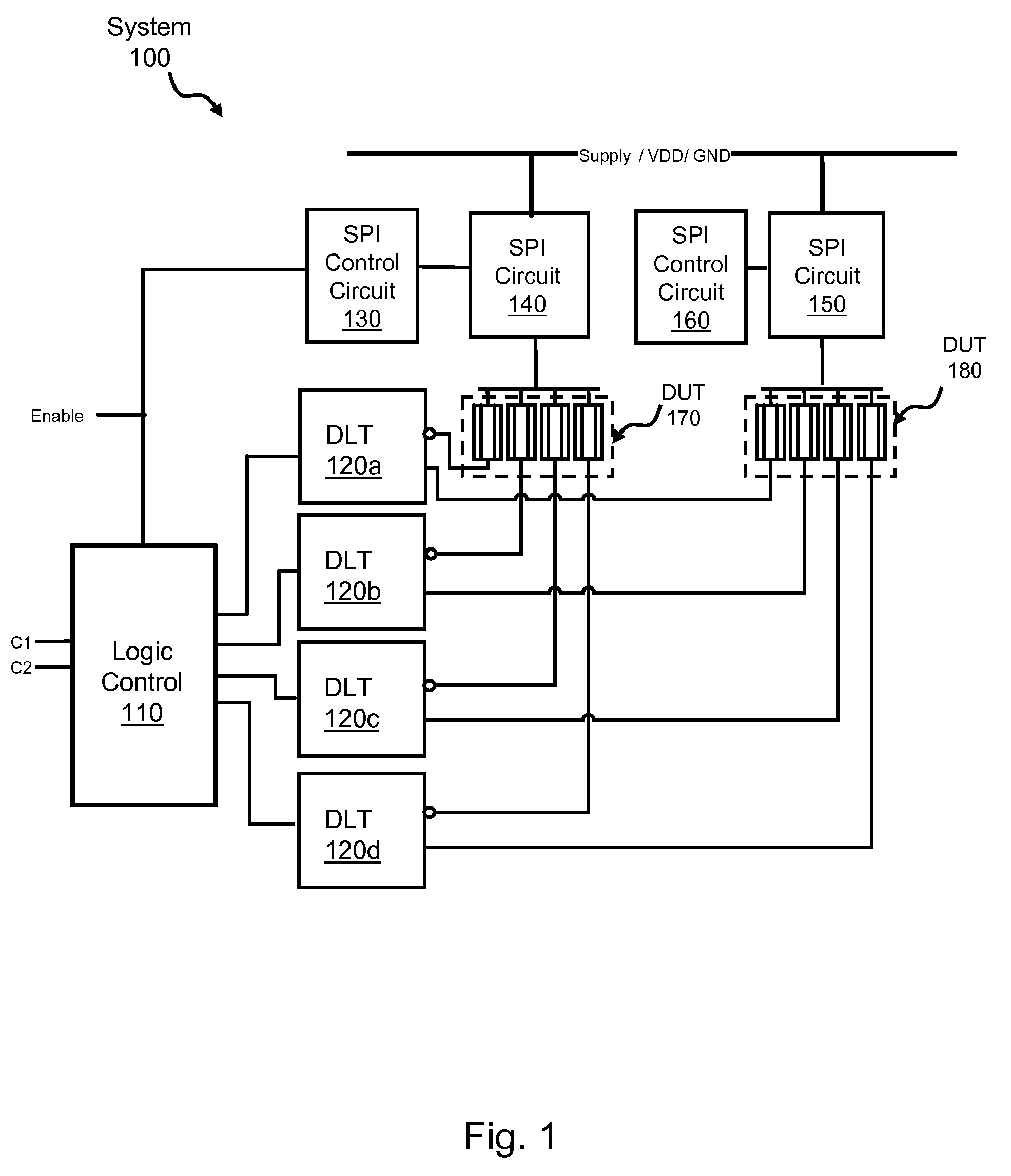
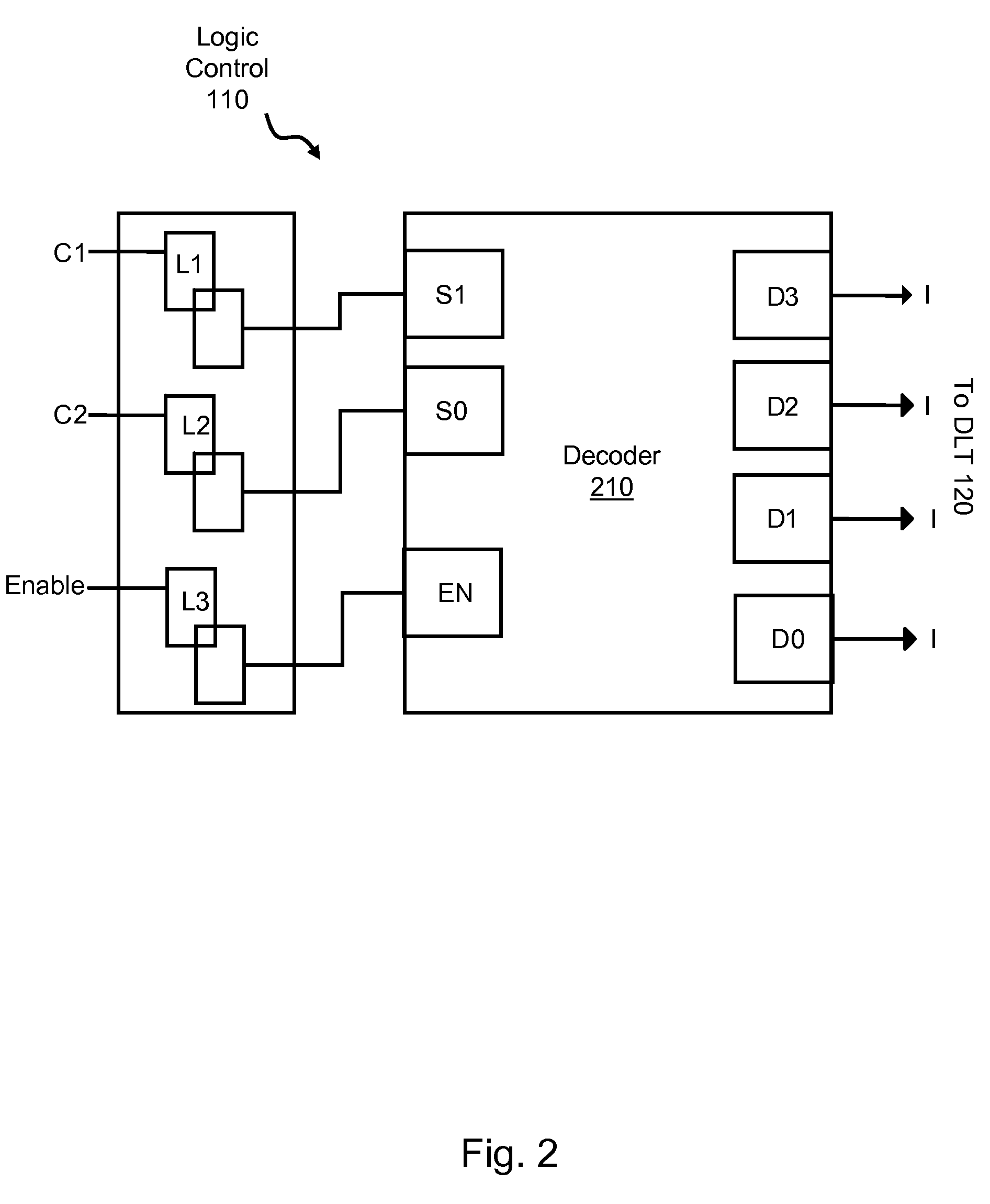
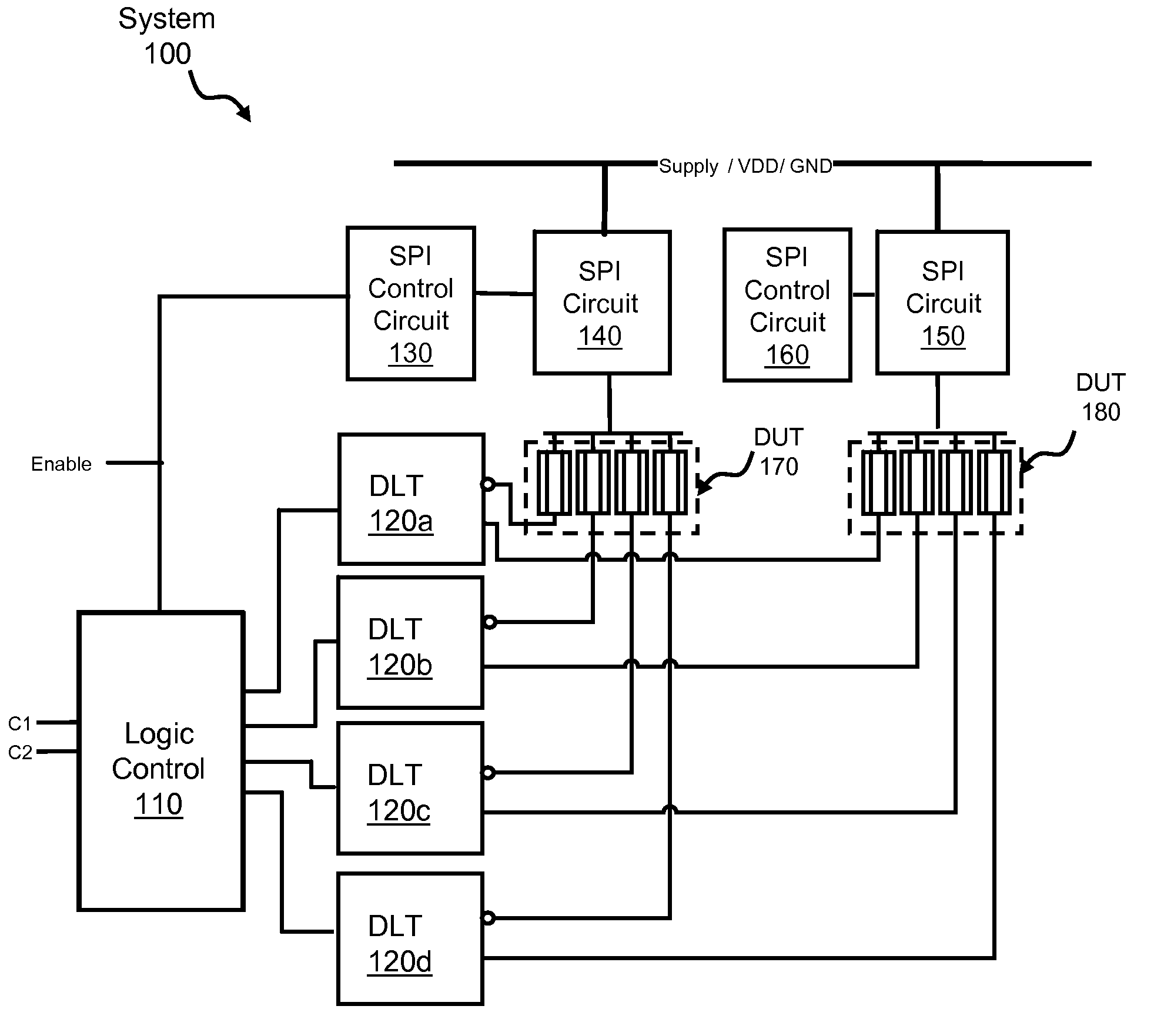
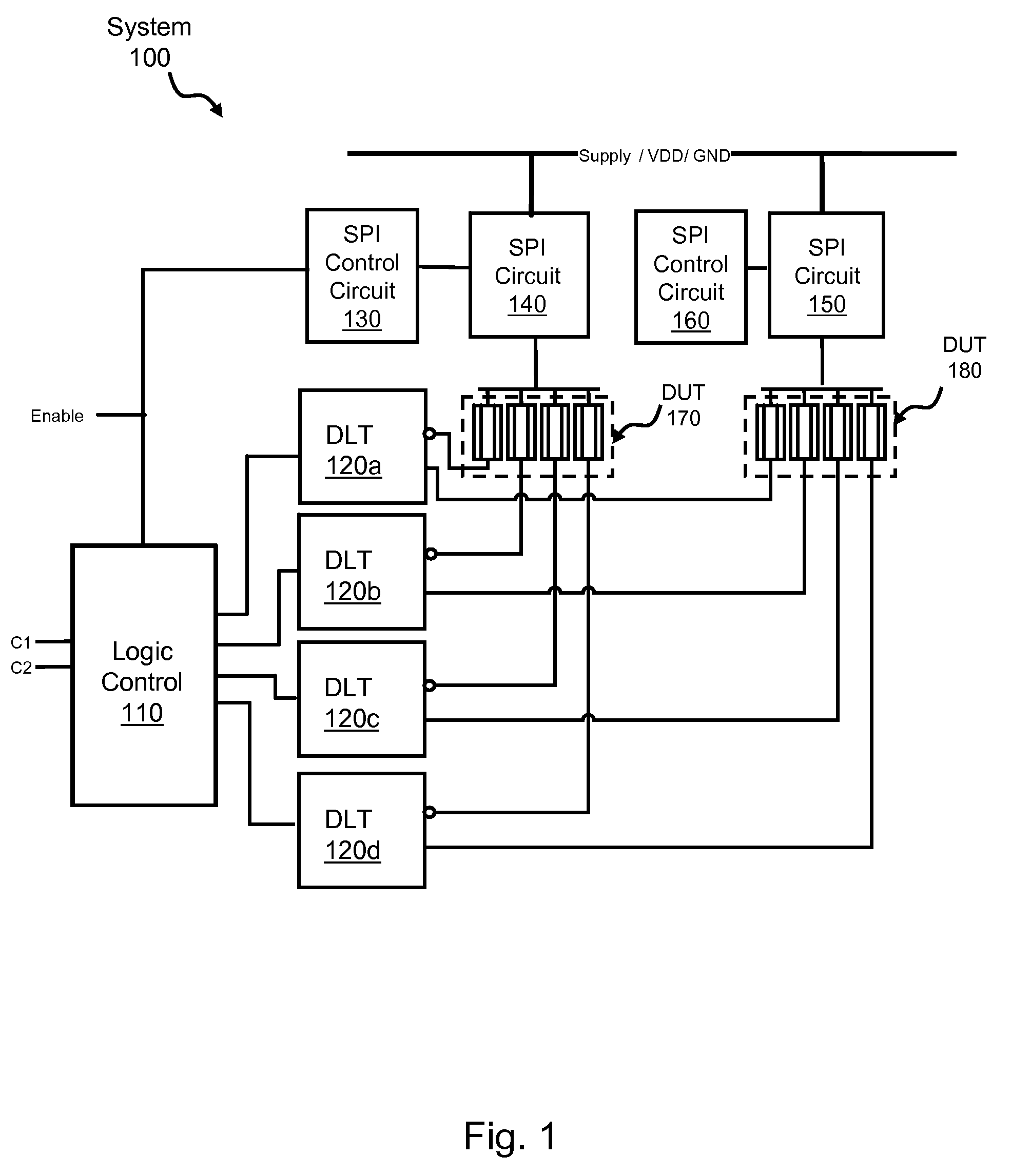
A system for performing device-specific testing and acquiring parametric data on custom integrated circuits, for example ASICs, such that each chip is tested individually without excessive test time requirements, additional silicon, or special test equipment. The testing system includes a device test structure integrated into unused backfill space in an ASIC design which tests a set of dummy devices that are identical to some of those of the ASIC. The device test structure includes control logic for designating the type of test and which device types to activate (e.g. pFETs or nFETs), a protection circuit for protecting the SPM when the test is inactive, an isolation circuit for isolating the devices under test (DUT) from any leakage current during test, and a decode circuit for providing test input (e.g. voltages) to the DUT. By controlling which devices to test and the voltage conditions of those devices, the system calculates the relative product yield and health of the line on a die by die basis.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
A system for acquiring device parameters
ActiveUS20080018356A1High yieldAffecting costResistance/reactance/impedenceTesting circuitsTest inputState of health
A system for performing device-specific testing and acquiring parametric data on custom integrated circuits, for example ASICs, such that each chip is tested individually without excessive test time requirements, additional silicon, or special test equipment. The testing system includes a device test structure integrated into unused backfill space in an ASIC design which tests a set of dummy devices that are identical to some of those of the ASIC. The device test structure includes control logic for designating the type of test and which device types to activate (e.g. pFETs or nFETs), a protection circuit for protecting the SPM when the test is inactive, an isolation circuit for isolating the devices under test (DUT) from any leakage current during test, and a decode circuit for providing test input (e.g. voltages) to the DUT. By controlling which devices to test and the voltage conditions of those devices, the system calculates the relative product yield and health of the line on a die by die basis.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
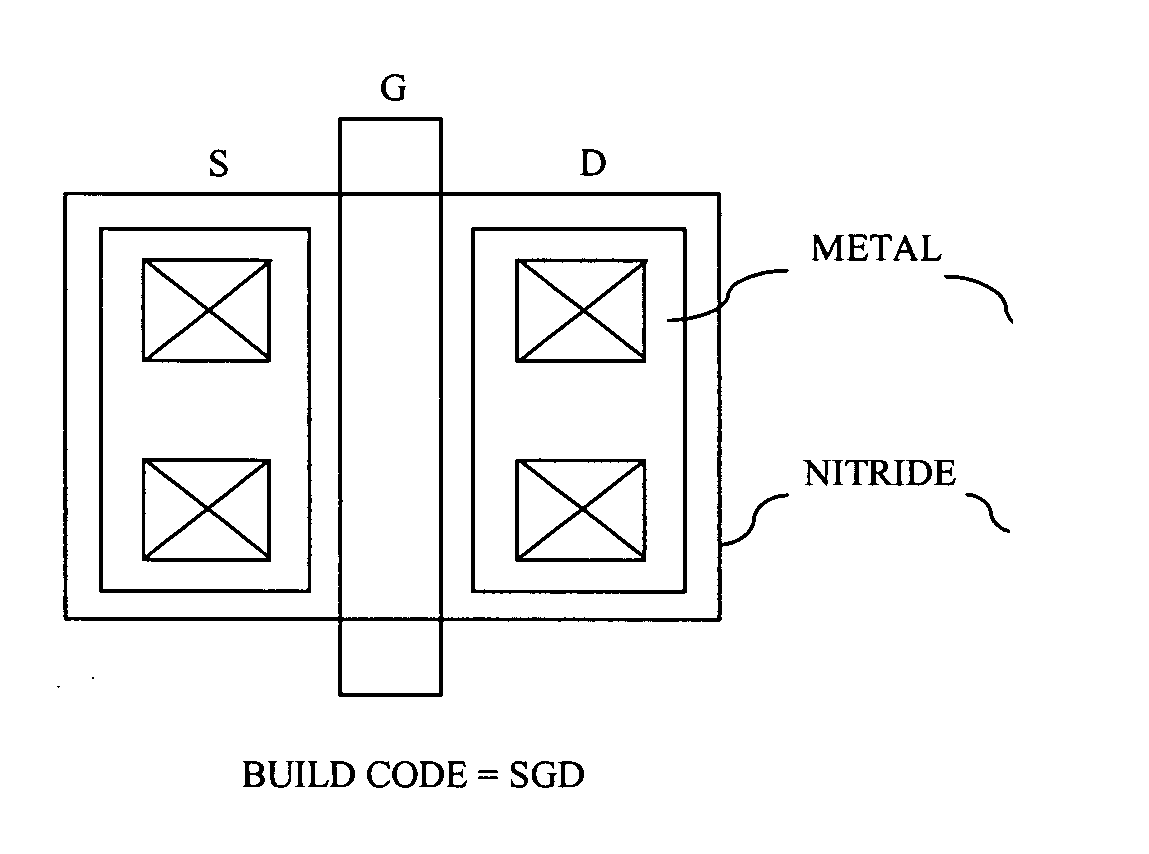
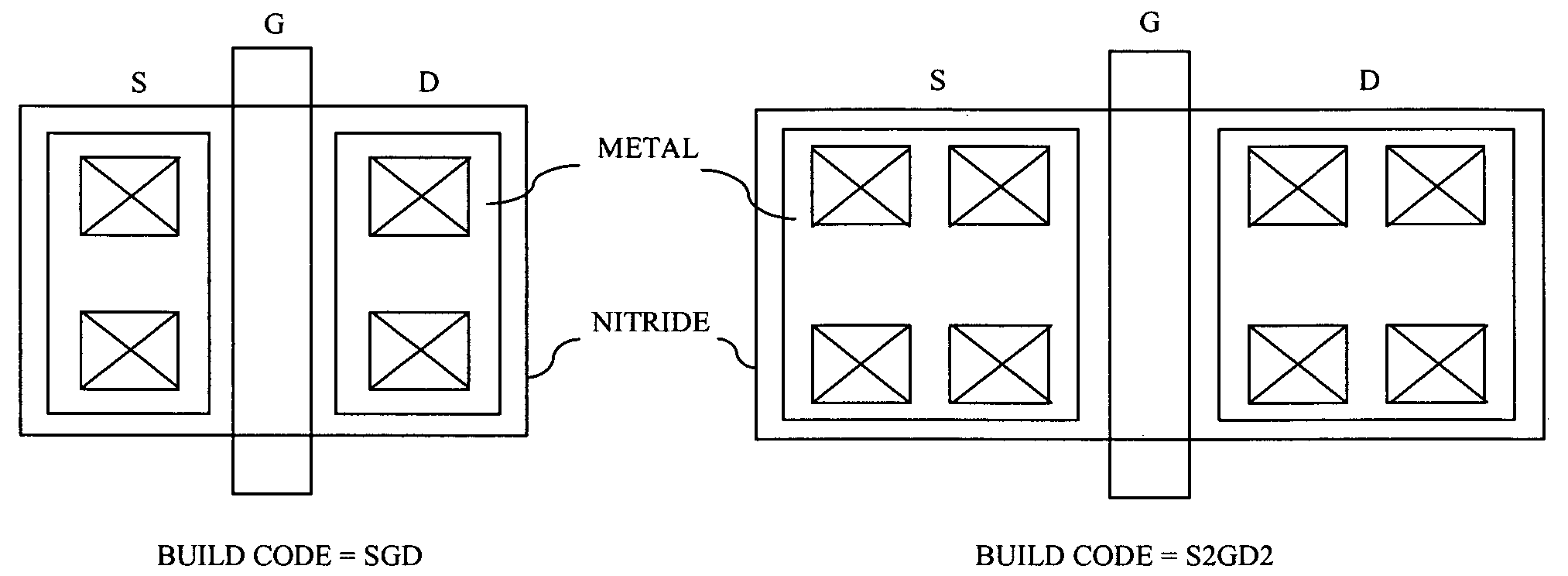
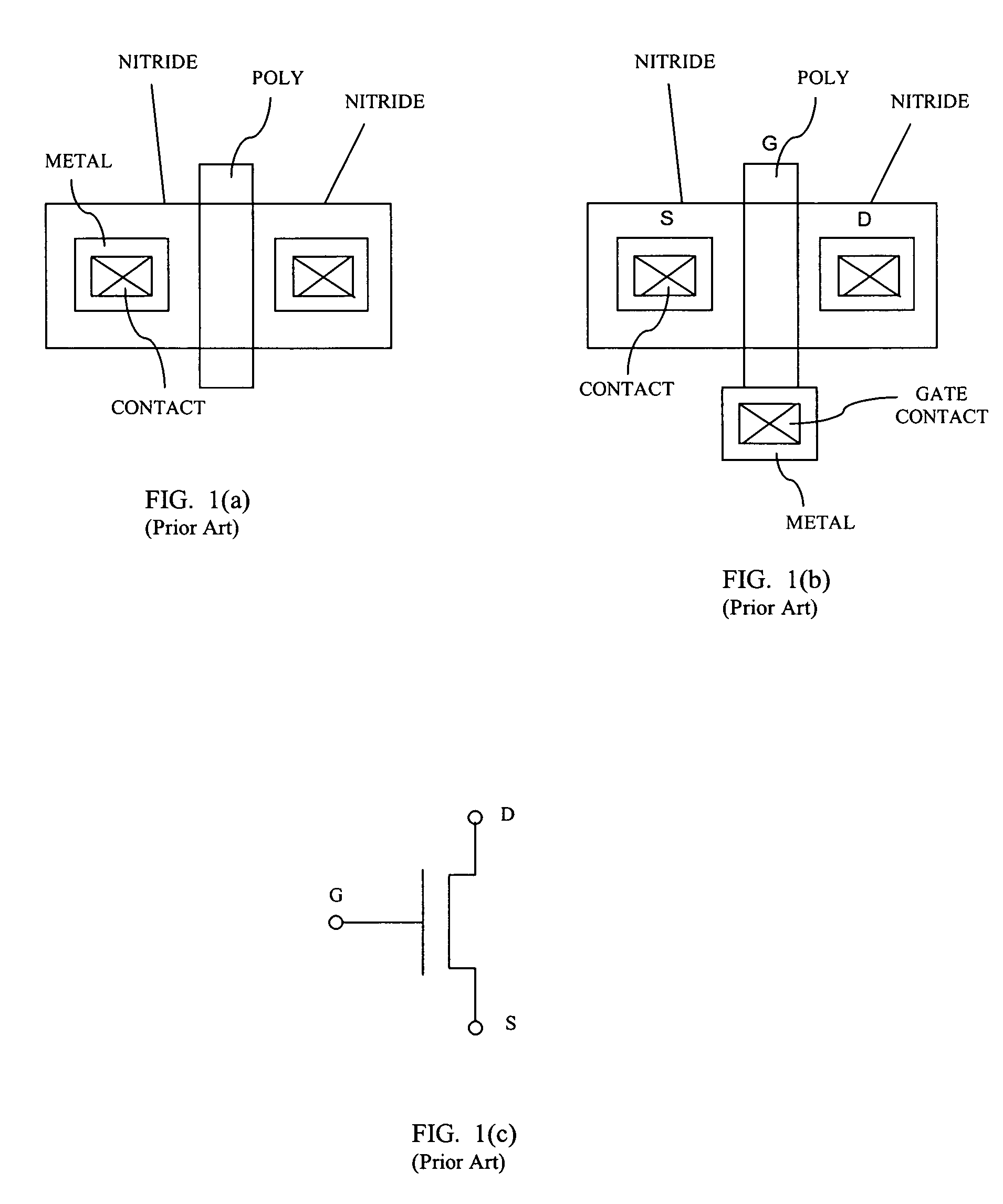
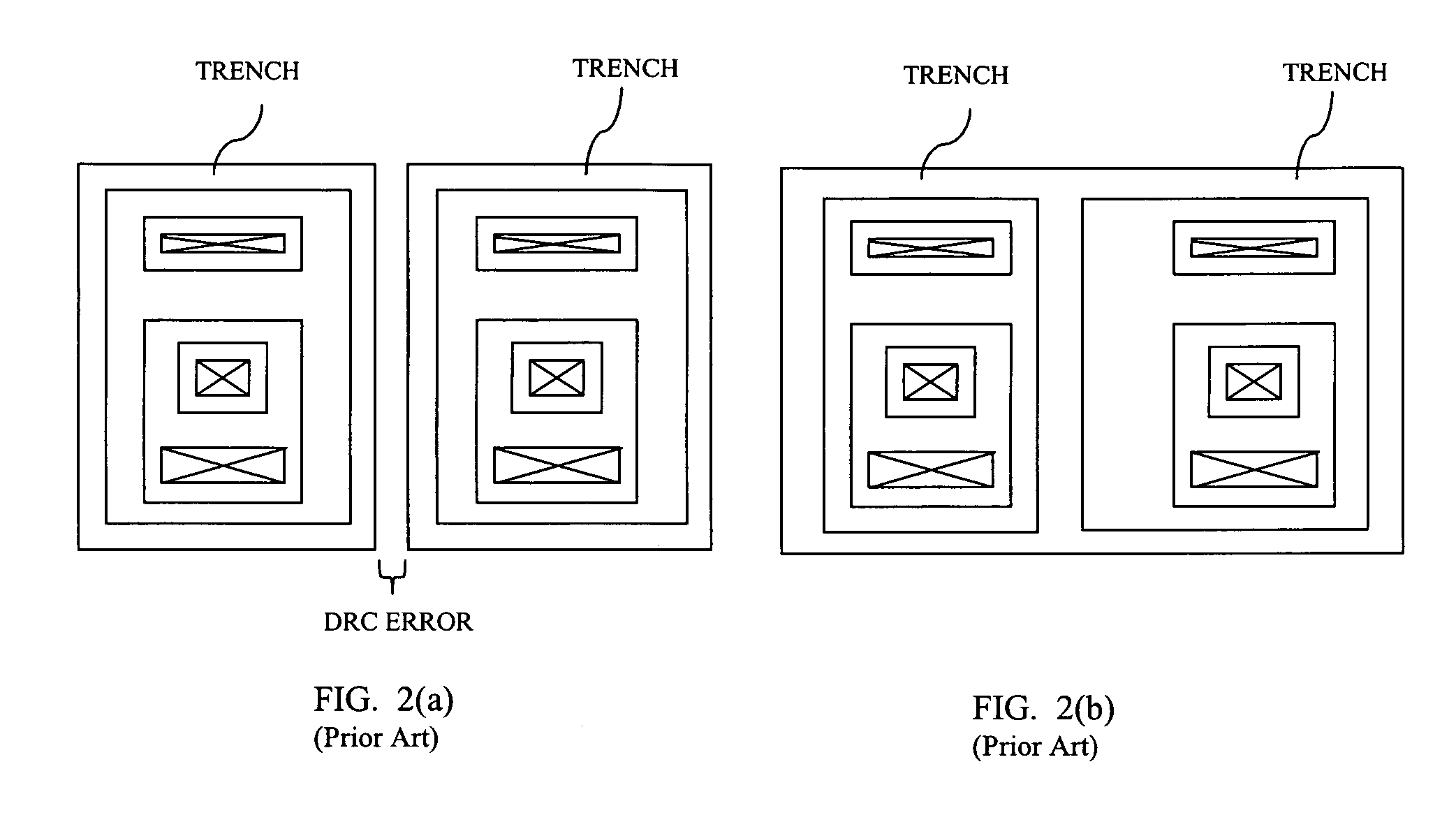
Usage of a buildcode to specify layout characteristics
InactiveUS20070118825A1Reduce in quantityCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsStandardizationCustom integrated circuits
A method for laying out custom integrated circuits includes the steps of preliminarily laying out a custom integrated circuit using a plurality of libraried standardized programmed cells (p-cells). Buildcode representations are then assigned for each of a plurality of circuit components and features thereof to realize customization of at least a portion of the plurality of p-cells. A final layout of the custom integrated circuit is then generated using the buildcode representations.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Usage of a buildcode to specify layout characteristics
A method for laying out custom integrated circuits includes the steps of preliminarily laying out a custom integrated circuit using a plurality of libraried standardized programmed cells (p-cells). Buildcode representations are then assigned for each of a plurality of circuit components and features thereof to realize customization of at least a portion of the plurality of p-cells. A final layout of the custom integrated circuit is then generated using the buildcode representations.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
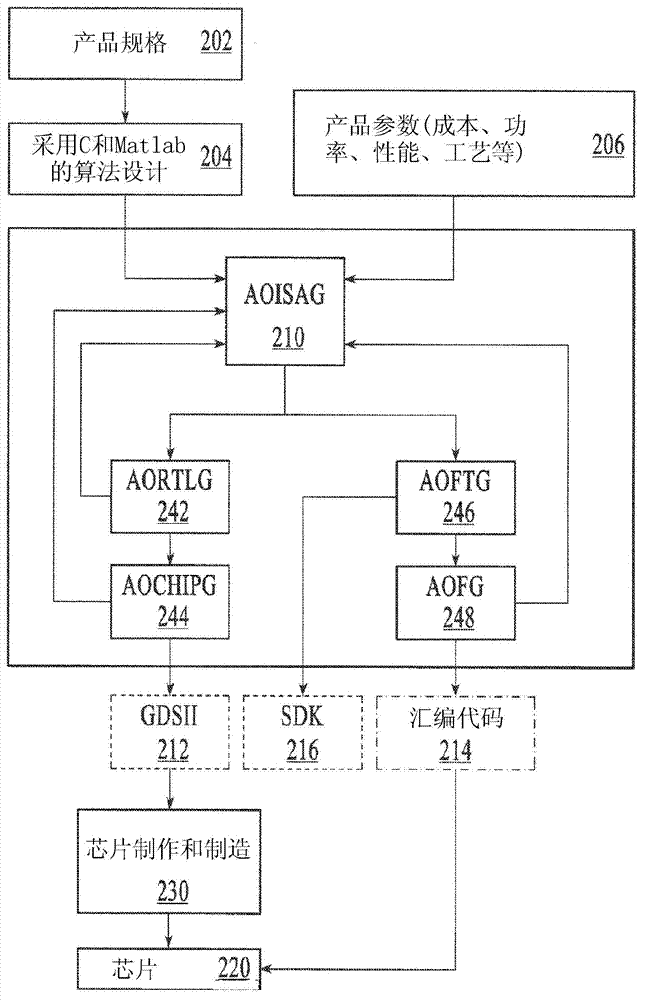
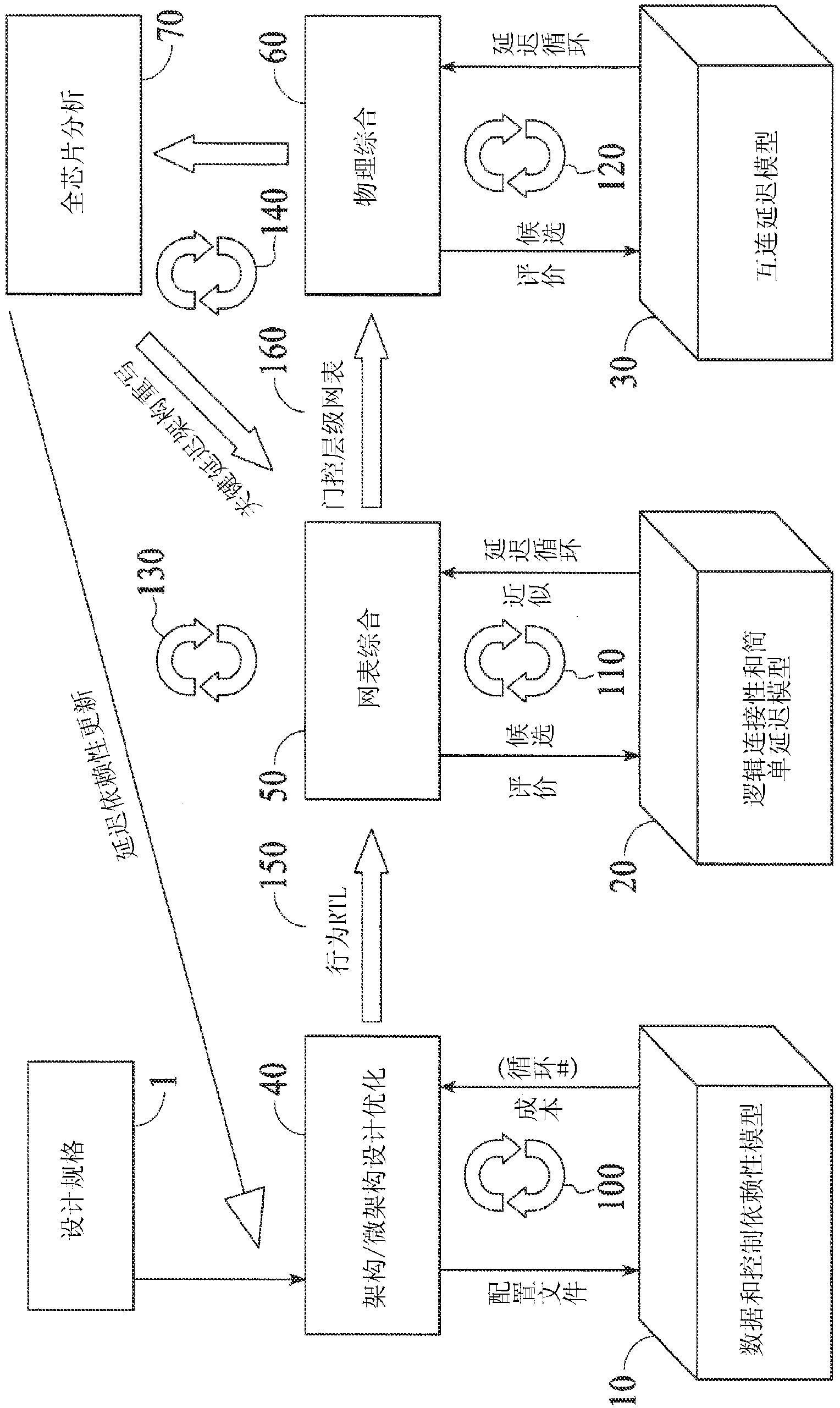
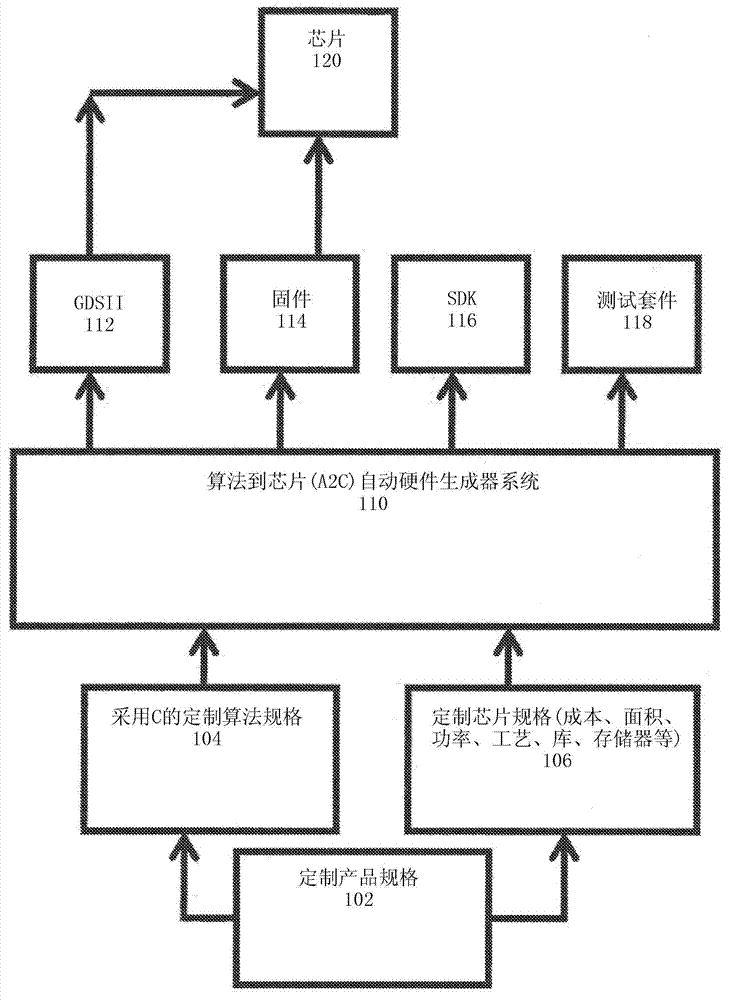
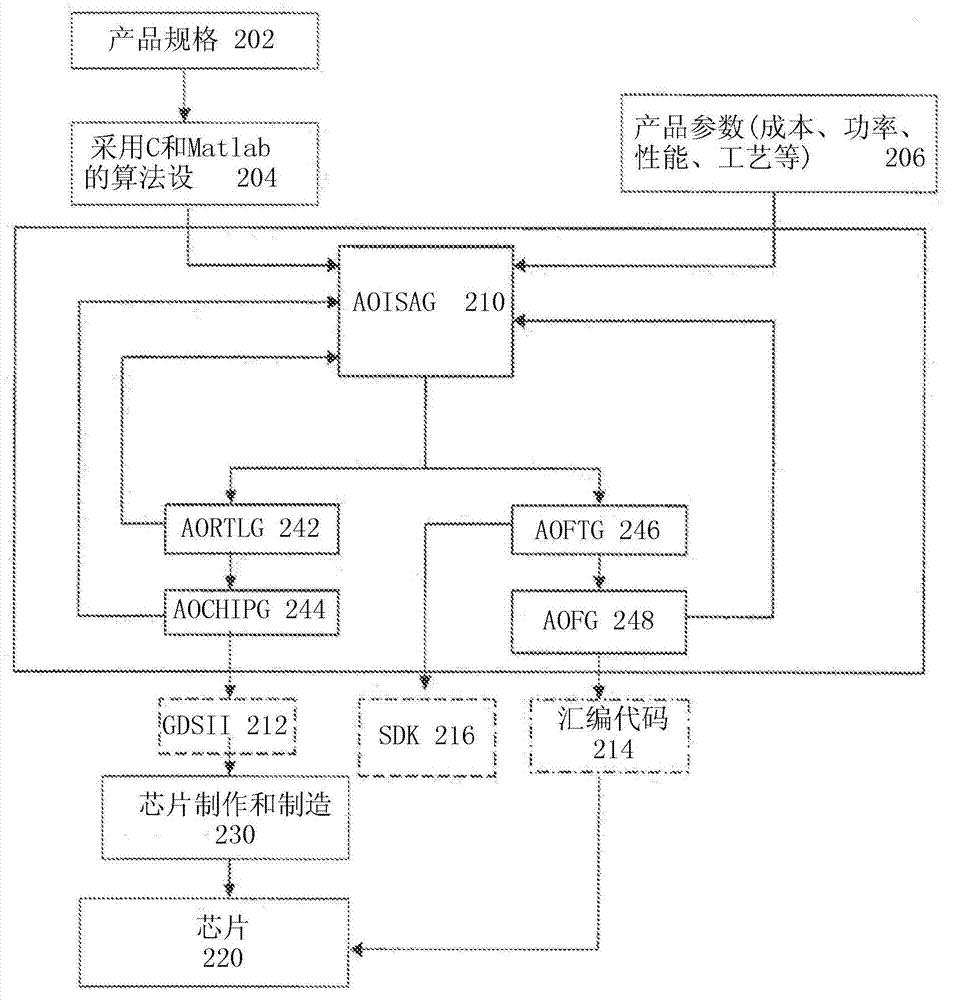
Automatic optimal integrated circuit generator from algorithms and specification
InactiveCN103098059AReduce designEliminate risk by designCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureProcessor register
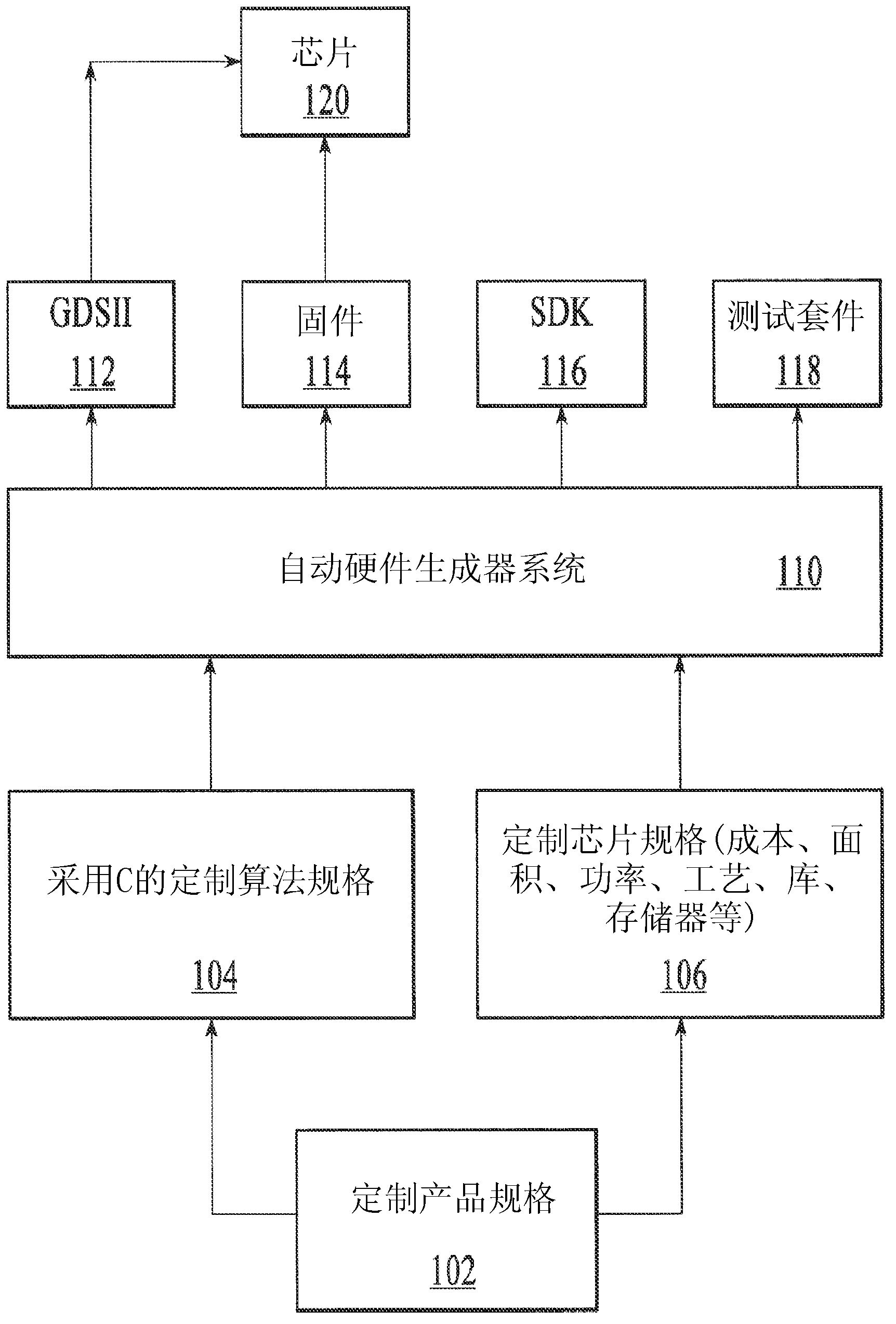
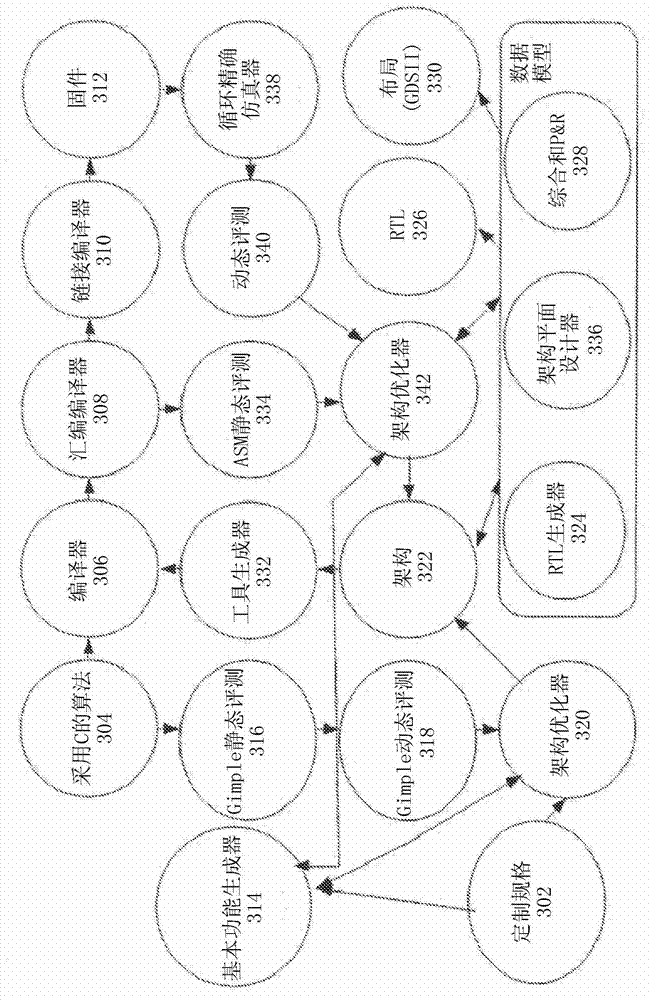
Automated design of a custom integrated circuit based on algorithmic process as input and using highly automated tools that requires virtually no human involvement is disclosed. The method includes receiving a specification of the custom integrated circuit including computer readable code and constraints on the custom integrated circuit; generating a computer-architecture for the computer readable code that best fits the constraints; automatically determining an instruction execution sequence based on the code profile and reassigning or delaying the instruction sequence to spread operation over processing blocks to reduce hot spots; continuously evaluating and optimizing one or more factors including physical implementation, and local and global area, timing, or power at an architecture level above RTL or gate-level synthesis; and automatically synthesizing the designed architecture and generating a computer readable description of the custom integrated circuit for semiconductor fabrication.
Owner:ALGOTOCHIP
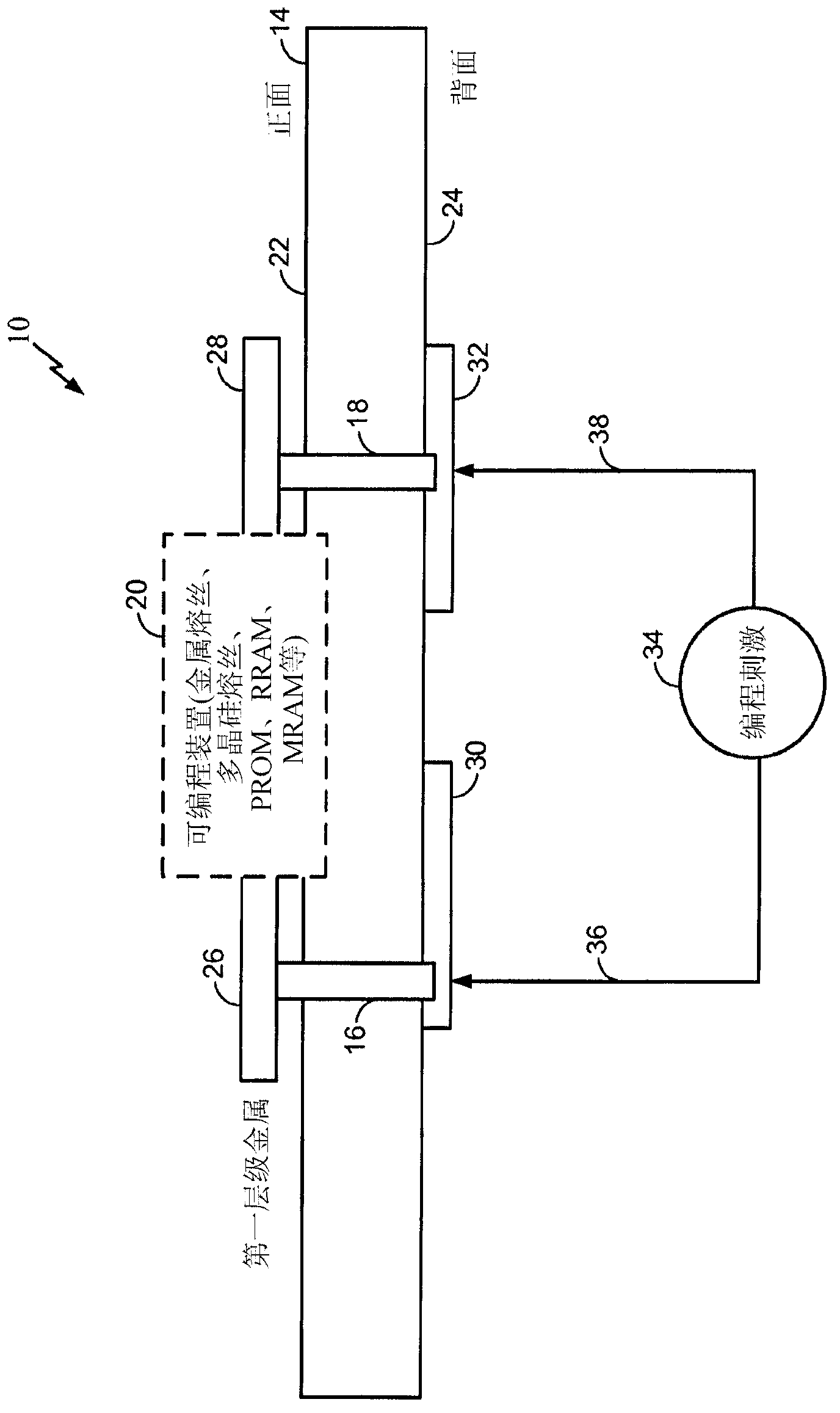
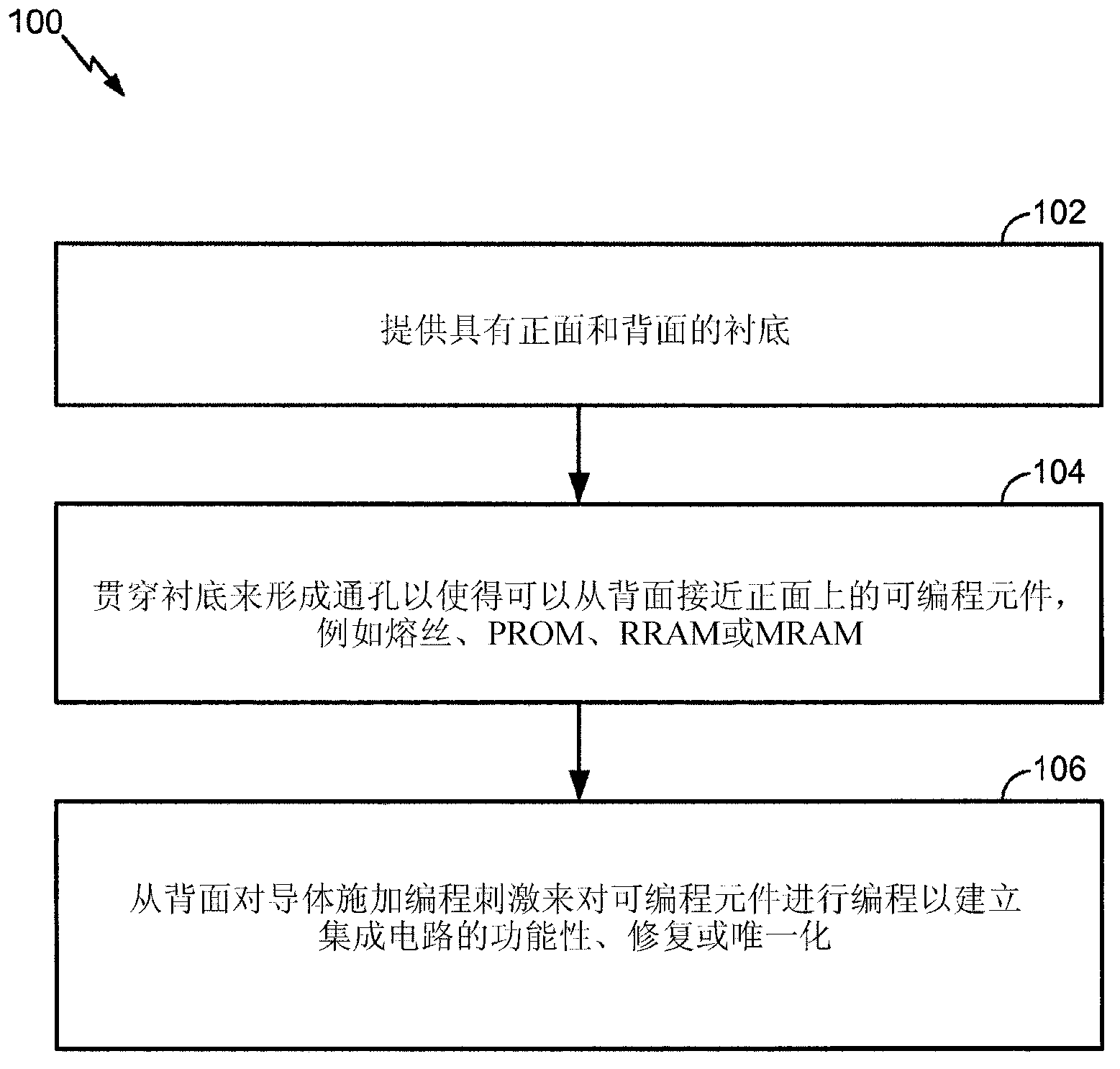
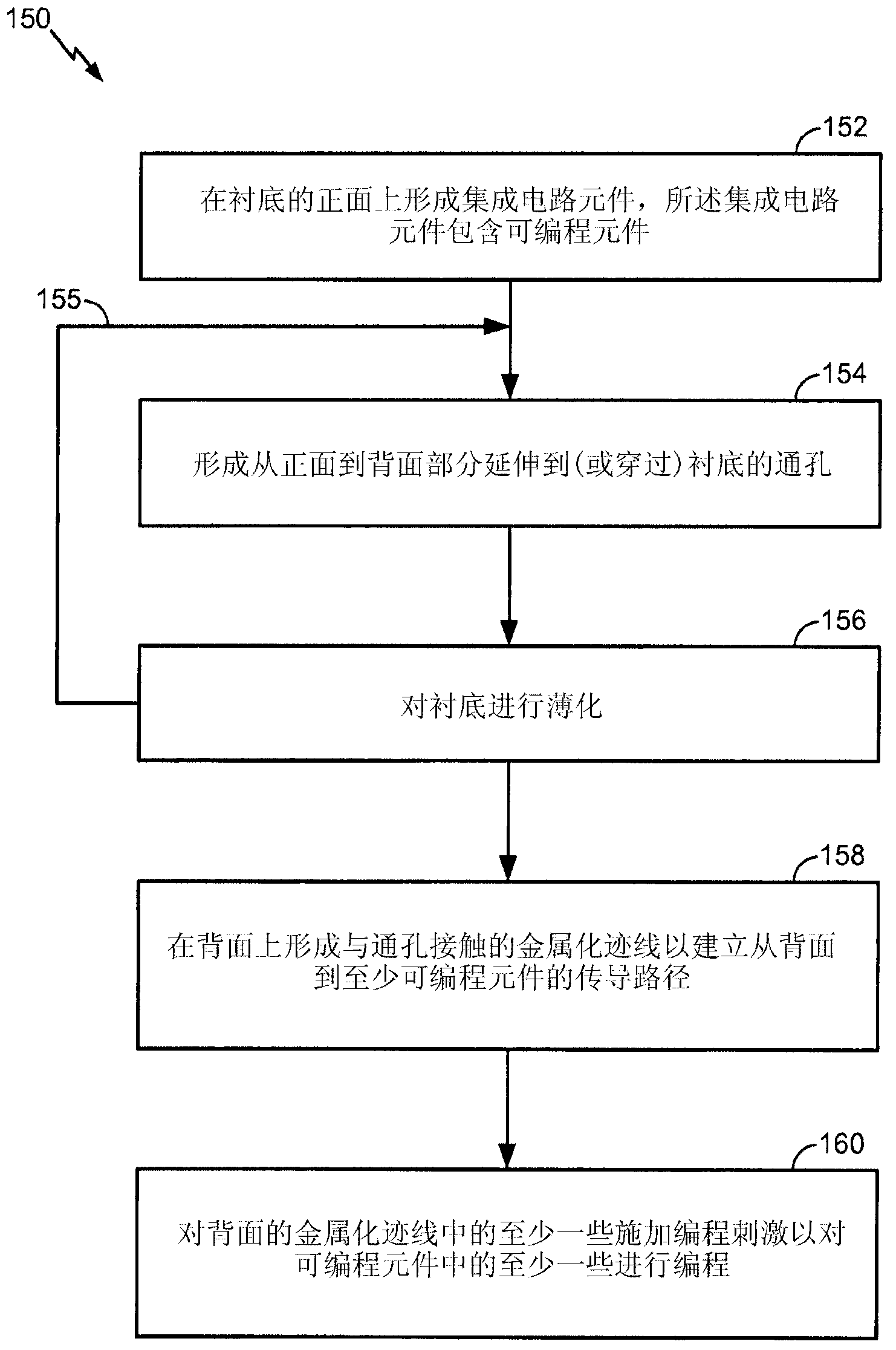
Integrated circuit chip customization using backside access
ActiveCN103189973ABuild functionalitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit design
An integrated circuit, a method for making an integrated circuit product, and methods for customizing an integrated circuit are disclosed. Integrated circuit elements including programmable elements, such as fuses, PROMs, RRAMs, MRAMs, or the like, are formed on the frontside of a substrate. Vias are formed through the substrate from its frontside to its backside to establish conduction paths to at least some of the programmable elements from the backside. A programming stimulus is applied to at least some of the vias from the backside to program at least some of the frontside programmable elements.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
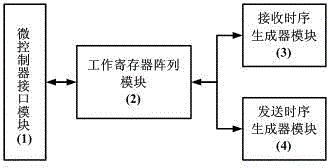
High-speed LVDS serial synchronization communication controller
ActiveCN104144137AMake electrical connectionsReliable exchangeBaseband system detailsElectric digital data processingMicrocontrollerElectronic information
The invention discloses a high-speed LVDS serial synchronization communication controller. The high-speed LVDS serial synchronization communication controller comprises a microcontroller interface module (1), a work register array module (2), a receiving time sequence generator module (3) and a sending time sequence generator module (4). The high-speed LVDS serial synchronization communication controller can be matched with a serializer MAX9217, a deserializer MAX9218 and other customized integrated circuits of a Canada MAXIM company to form a full duplex and high speed LVDS synchronization serial communication interface. A control order, parameters and data given by an X80 series microcontroller can be received, the information exchanging process is controlled, and the working state of the high-speed LVDS serial synchronization communication controller is fed back to an X86 series microcontroller. When one frame of data are received or sent, an interrupt request signal of the X86 series microcontroller can be automatically produced. A user system can be assisted to achieve an information exchange protocol defined by a user, reliable high-speed, serial and synchronous full duplex data exchange between two electronic information systems connected through an LVDS signal line is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL & ELECTRONICS TECH
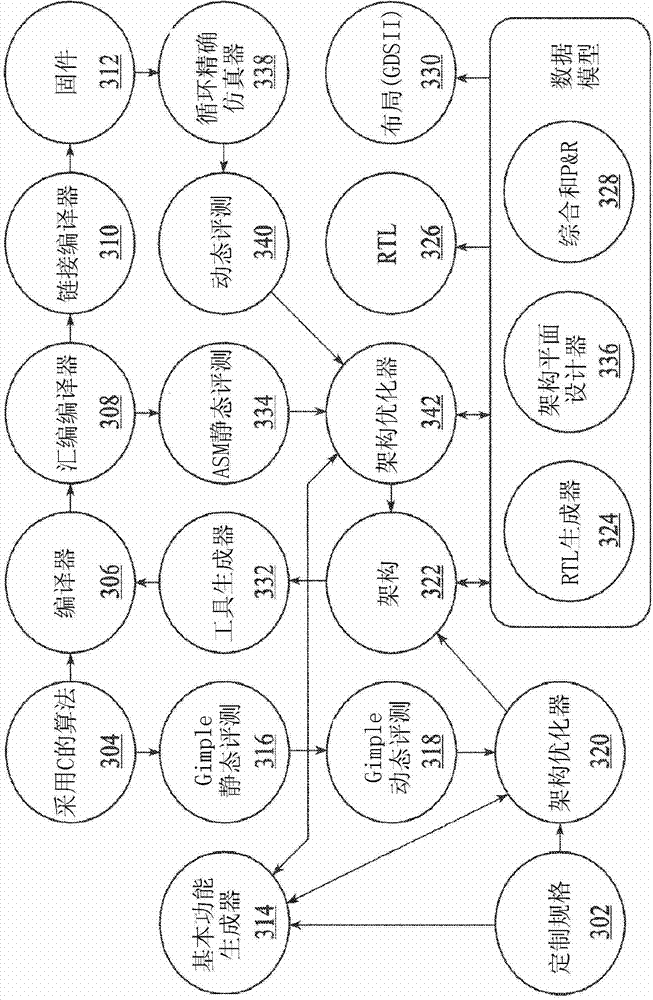
Intelligent architecture creator
InactiveCN103270512AAccurate modelingReduce designGeneral purpose stored program computerCAD circuit designComputer architectureSemiconductor
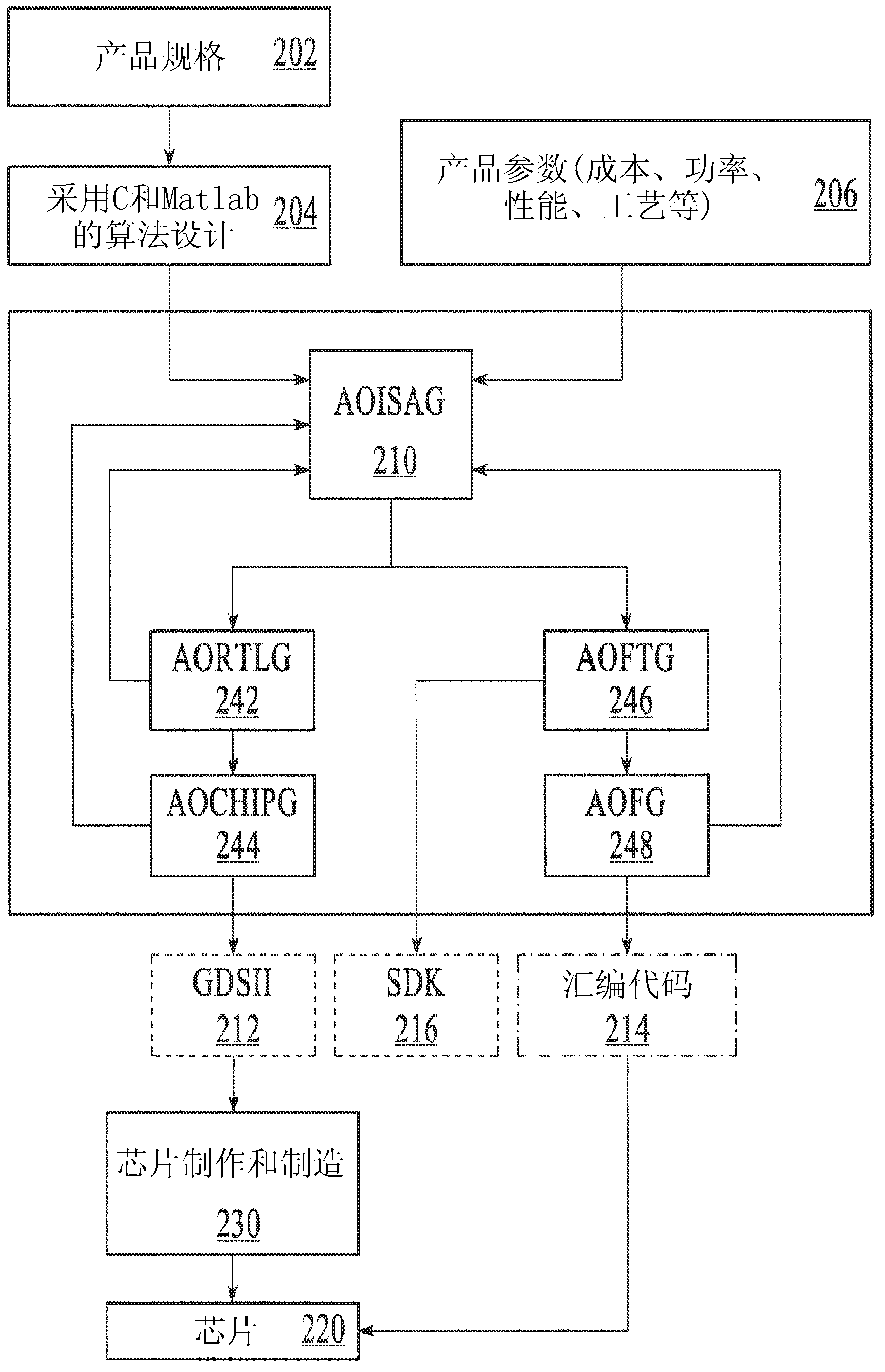
Systems and methods are disclosed to automatically generate a processor architecture for a custom integrated circuit (IC) described by a computer readable code. The IC has one or more timing and hardware constraints. The system extracts parameters defining the processor architecture from a static profile and a dynamic profile of the computer readable code; iteratively optimizes the processor architecture by changing one or more parameters until, all timing and hardware constraints expressed as a cost function are met; and synthesizes the generated processor architecture into a computer readable description of the custom integrated circuit for semiconductor fabrication.
Owner:ALGOTOCHIP
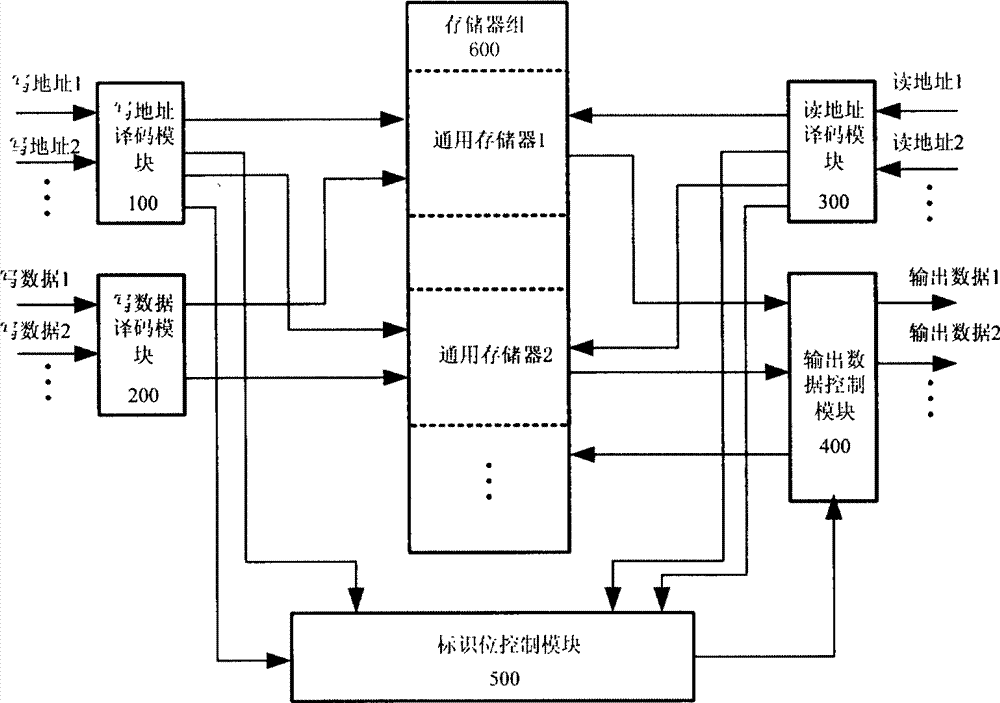
Method of structuring multiport asynchronous storage module
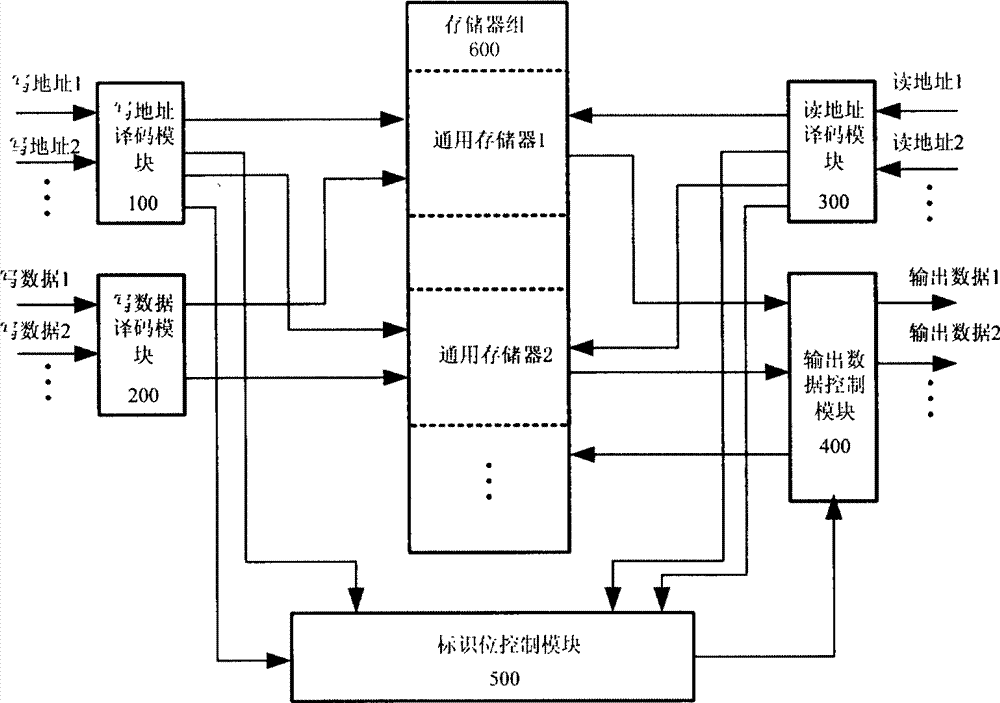
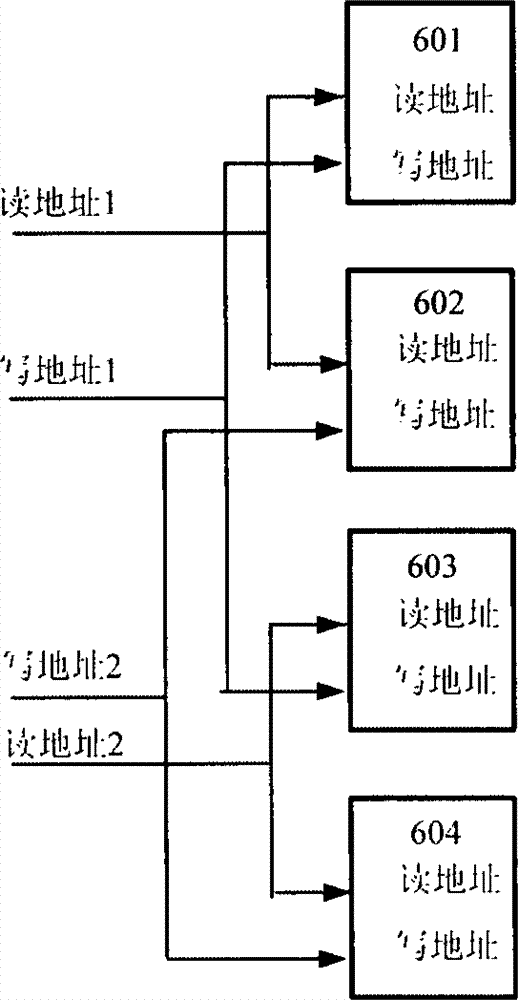
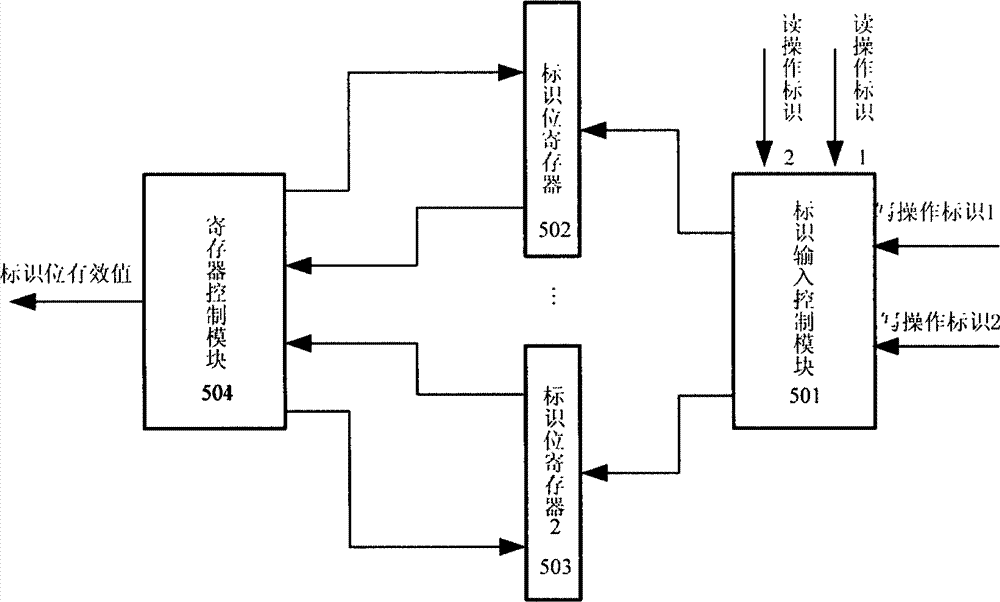
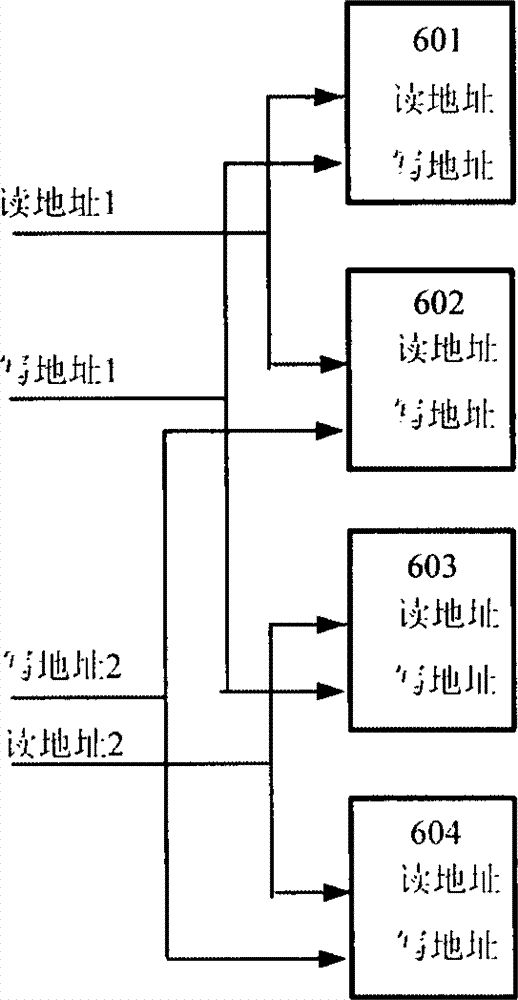
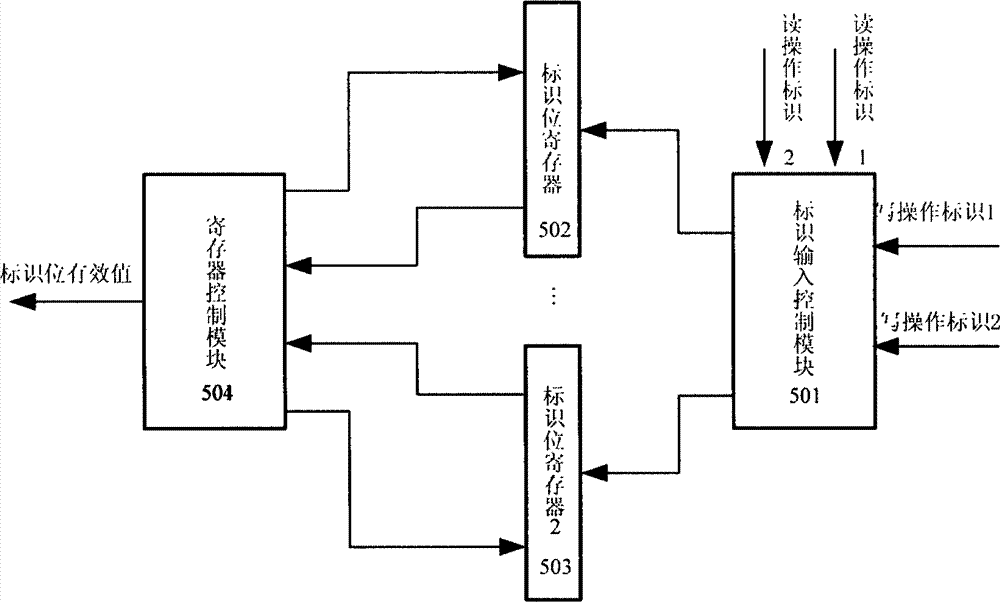
ActiveCN102930898AIncrease the number of portsIncrease storage capacityRead-only memoriesFull customComputer module
The invention discloses a method of structuring a multiport asynchronous storage module and relates to buffer storage and interchange of multichannel parallel data in the process of data interchange and processing. The method of structuring the multiport asynchronous storage module aims at solving the problem that in the process of design of a current semi-custom integrated circuit, a used storer of a technological library just has two types of single ports or double ports and can not meet certain situations of high data throughput rates. An addressing manner of address decoding control partitioning reading and writing is adopted by a plurality of double-port type storers in the technological library to structure the multiport asynchronous storage module, so that the aim that a simple port storage module is structured to the multiport storage module is achieved, and the requirement for the high data throughput rates is reached. The method of structuring the multiport asynchronous storage module has the advantages of flexibly expanding capacity and available access ports of the storer according to design requirements, reducing design difficulty, and shortening development time. Relative to a full-custom multiport storer, the method of structuring the multiport asynchronous storage module has the advantages of being good in flexible performance, high in reliability, small in design risk and the like.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
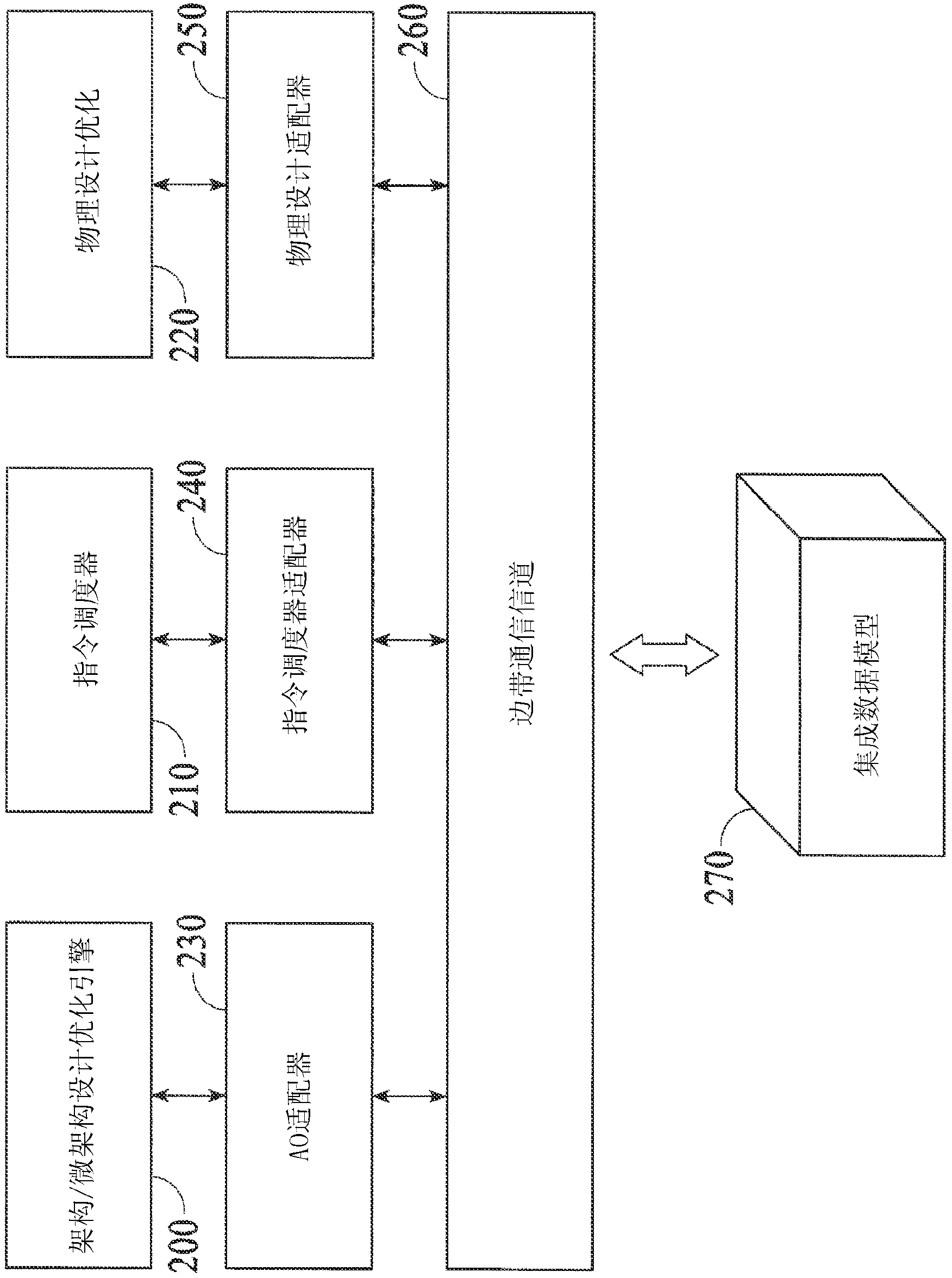
Architectural level power-ware optimization and risk mitigation
InactiveCN103282886AAvoid suboptimal surprisesImprove predictabilityCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationParallel computingInstruction sequence
Systems and methods are disclosed to automatically synthesize a custom integrated circuit by receiving a specification of the custom integrated circuit including computer readable code and generating a profile of the computer readable code to determine instruction usage; automatically generating a processor architecture uniquely customized to the computer readable code, the processor architecture having one or more processing blocks to implement one or more instructions; determining an instruction execution sequence based on the code profile and reassigning the instruction sequence to spread operation to different blocks on the IC to reduce hot spots; and synthesizing the generated processor chip specification into a computer readable description of the custom integrated circuit for semiconductor fabrication.
Owner:ALGOTOCHIP
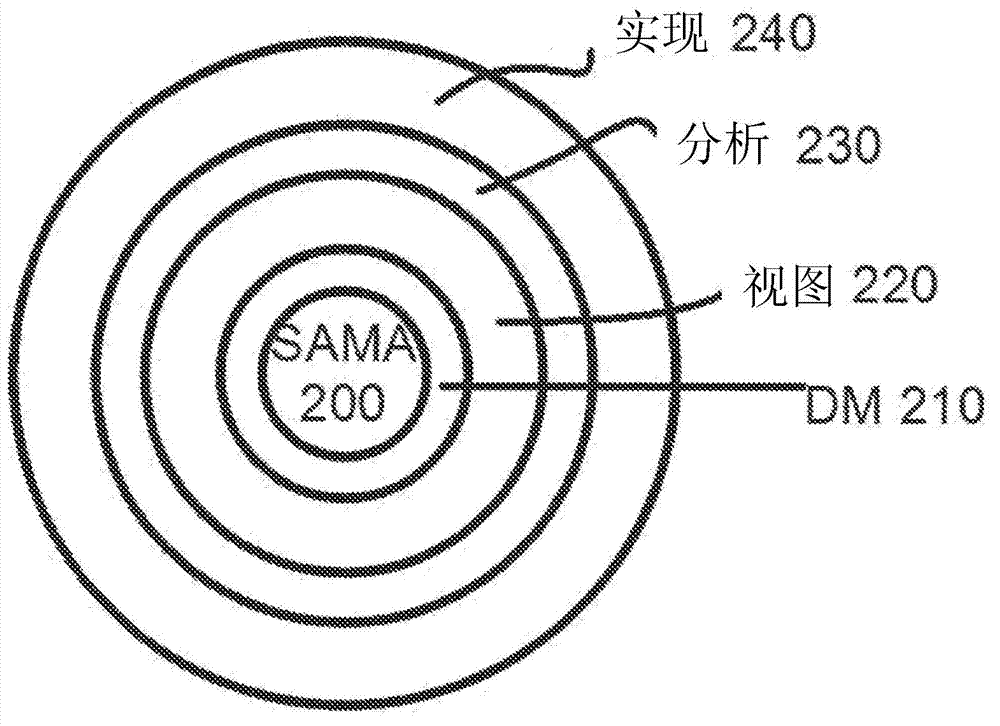
System, architecture and micro-architecture (sama) representation of an integrated circuit
InactiveCN103098026AEasy to useEasy to optimizeComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureSemiconductor
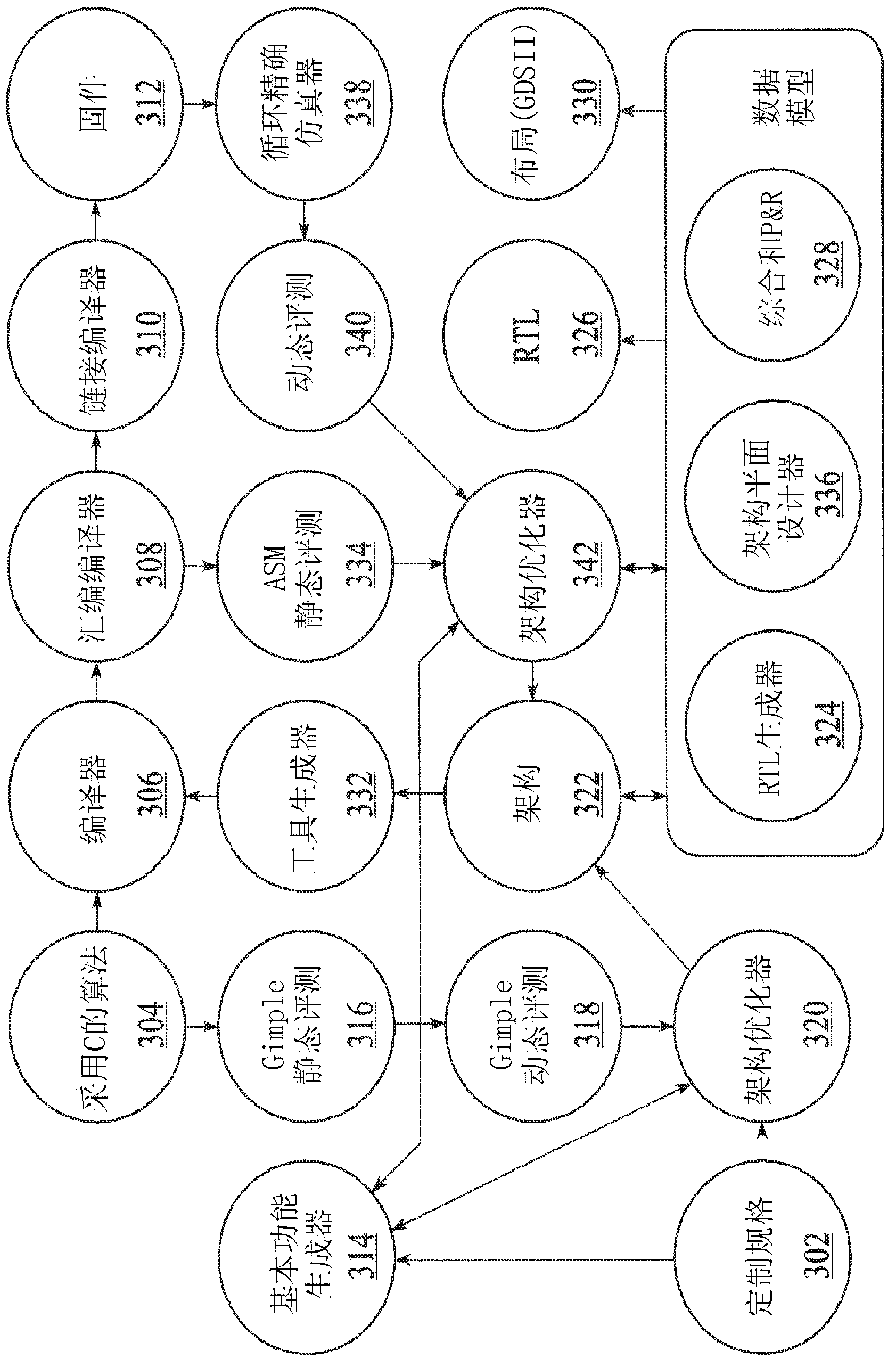
Systems and methods are disclosed to automatically generate a custom integrated circuit (IC) design by receiving a specification of the custom IC including computer readable code to be executed by the custom IC; generating an abstraction of the IC as a system, processor architecture and micro-architecture (SAMA) representation; providing the SAMA representation to a data model having at least an architecture optimization view, a physical design view, and a software tool view; optimizing the processor architecture by iteratively updating the SAMA representation and the data model to automatically generate a processor architecture uniquely customized to the computer readable code which satisfies one or more constraints; and synthesizing the generated architecture into a computer readable description of the custom integrated circuit for semiconductor fabrication. The foregoing can be done with no or minimal human involvement.
Owner:ALGOTOCHIP
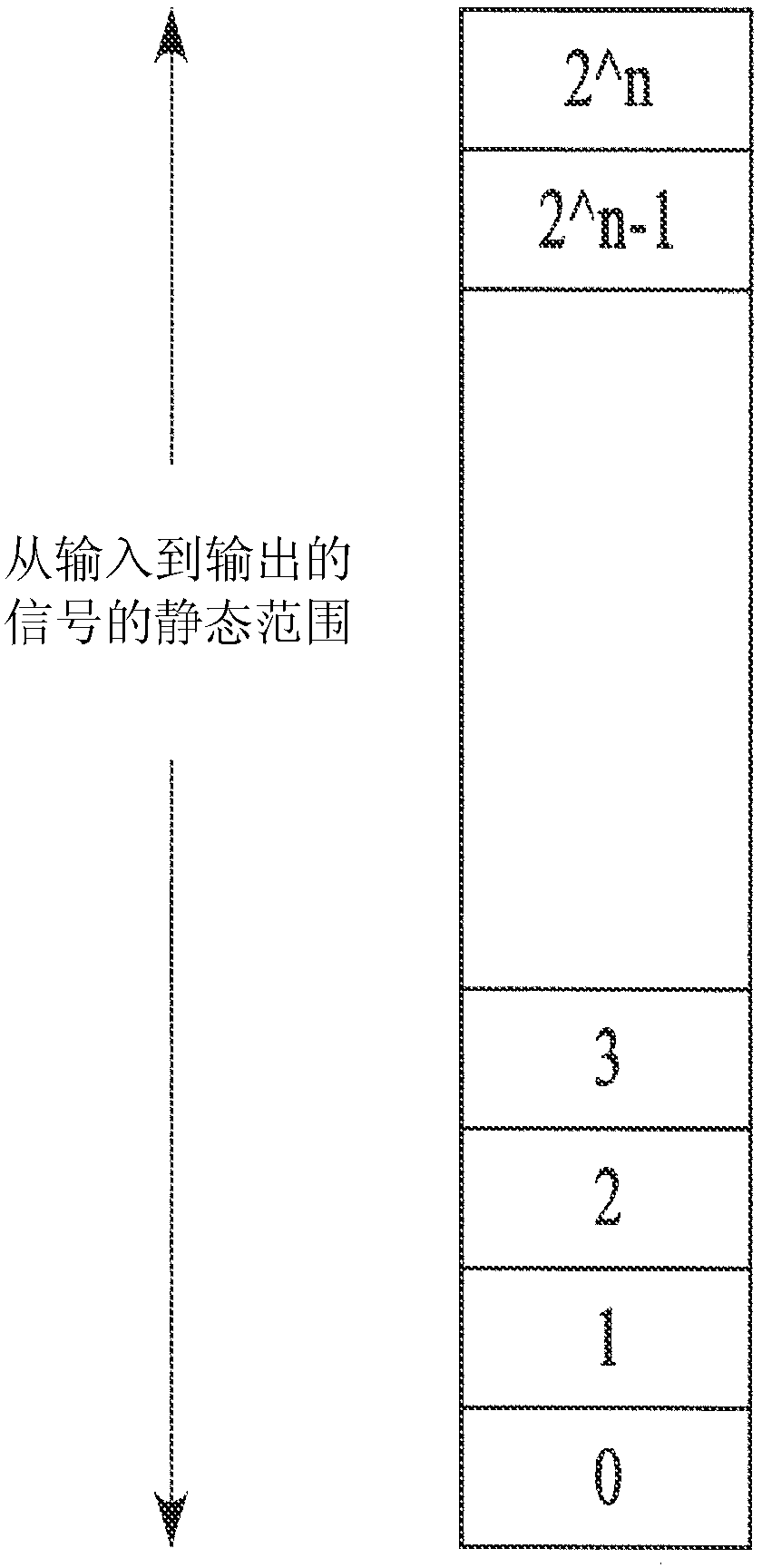
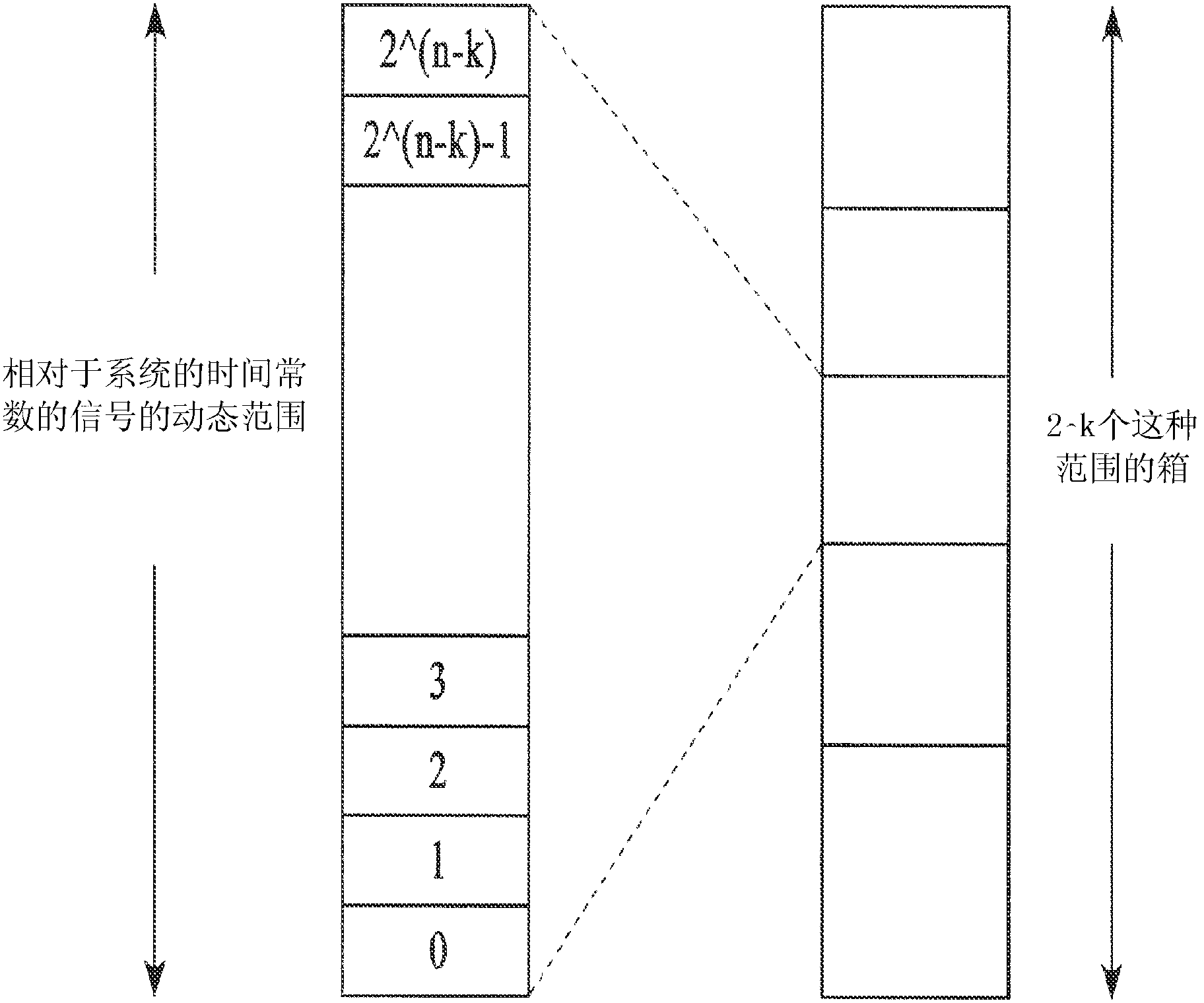
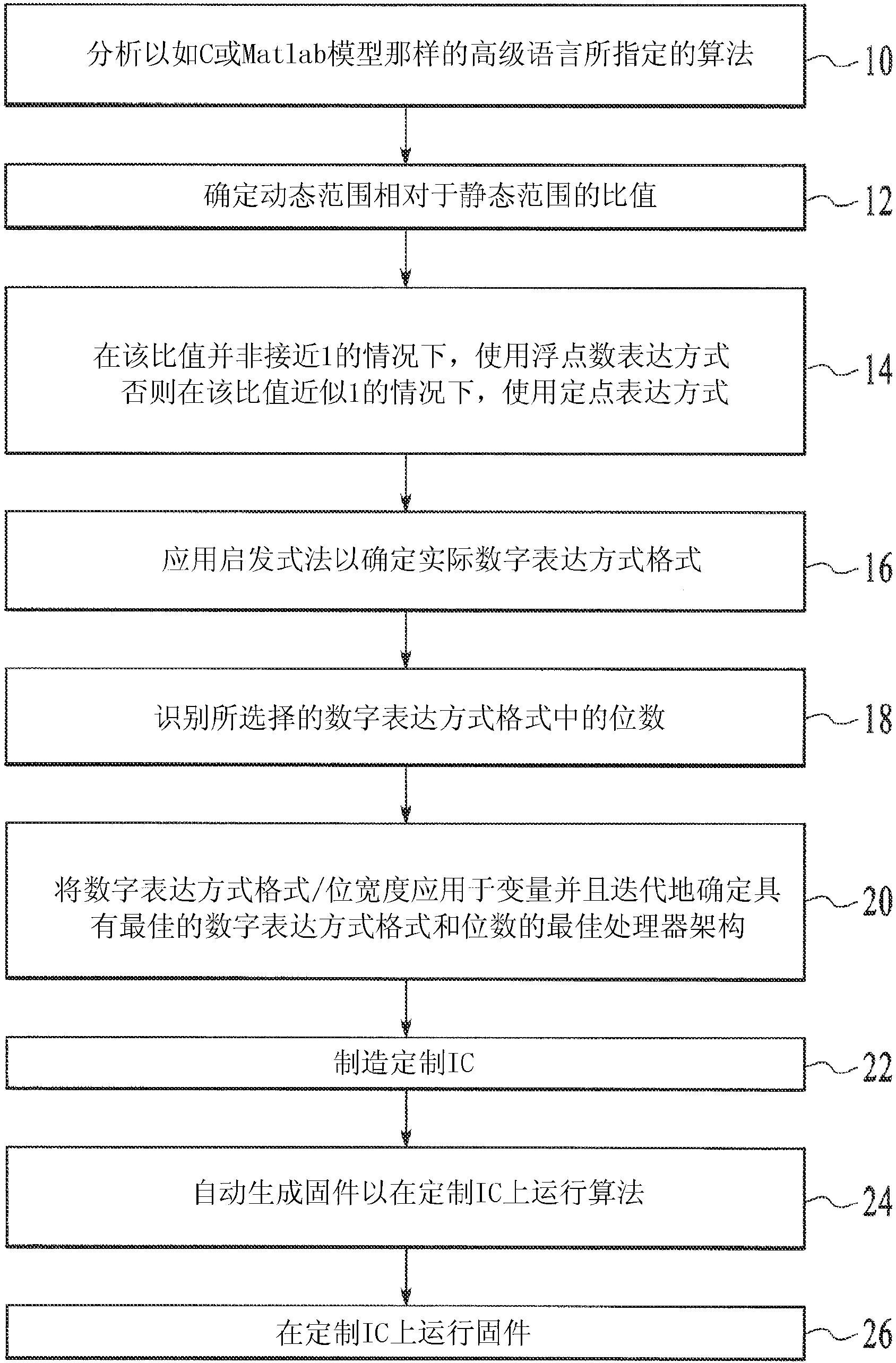
Architecture guided optimal system precision definition algorithm for custom integrated circuit
InactiveCN103314379AIncrease the areaIncrease powerDigital data processing detailsCAD circuit designComputer architectureFloating point
Systems and methods are disclosed to automatically determine an optimal number format representation for a model or code to be implemented in a custom integrated circuit (IC) by determining a ratio of dynamic range to static range in the model or code, and selecting a floating point or a fixed point number representation based on the ratio; determining the optimal number representation format based on a cost function that includes hardware area and power cost associated with a predetermined bit precision arithmetic; automatically generating a processor architecture customized to the optimal number representation format; and synthesizing the generated processor architecture into a computer readable description of the custom integrated circuit for semiconductor fabrication.
Owner:ALGOTOCHIP
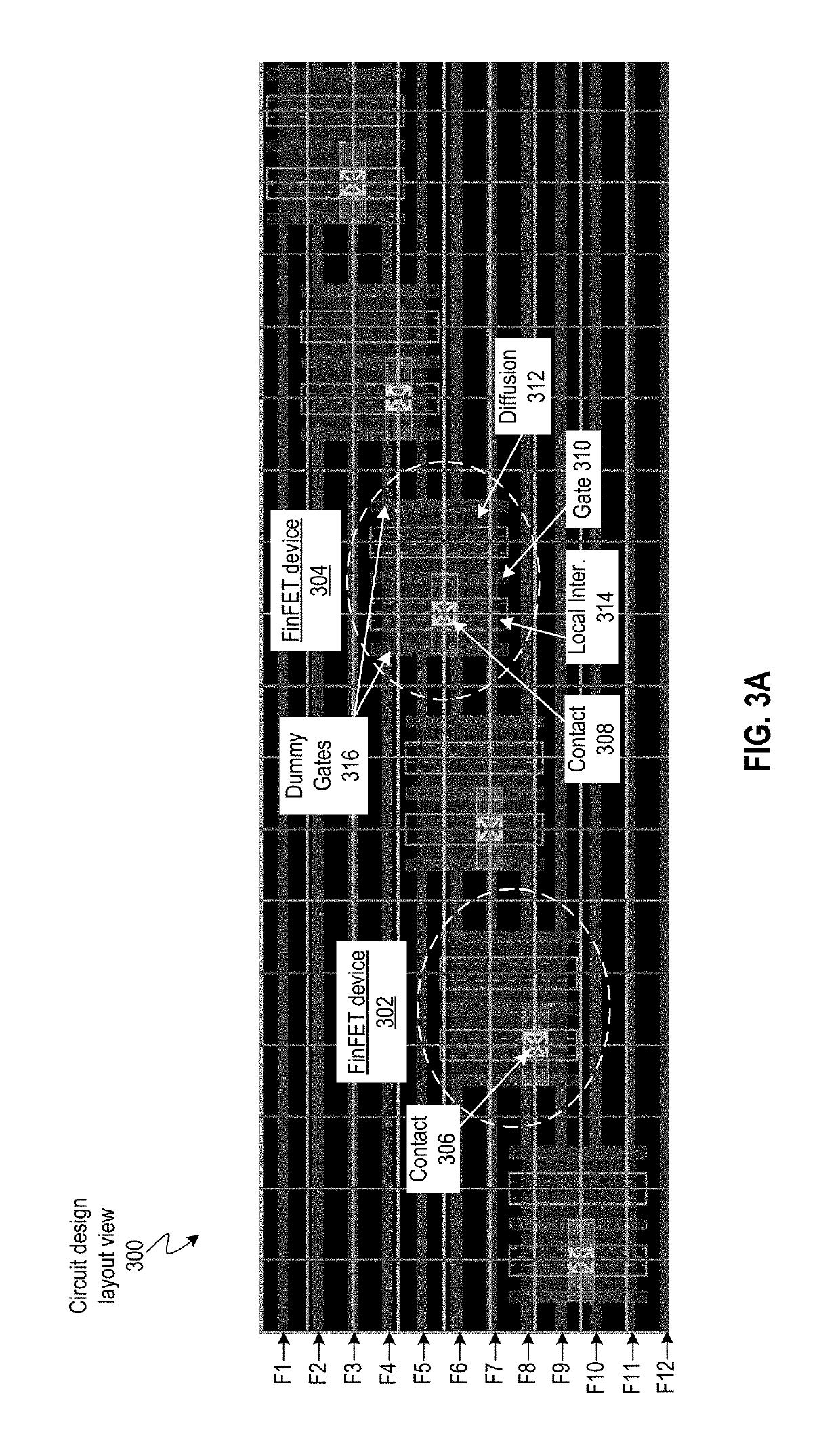
Using color pattern assigned to shapes for custom layout of integrated circuit (IC) designs
Systems and techniques for facilitating layout of an integrated circuit (IC) design are described. A distinct color pattern can be assigned to a set of shapes in a layout of the IC design that correspond to a net. Next, the layout of the IC design can be displayed in a graphical user interface (GUI) of the IC design tool. Some embodiments can move a diffusion region of a multigate device with respect to the location of the device contacts so that the diffusion region is aligned with respect to a set of fin tracks, wherein each fin of each multigate device is located on a fin track.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
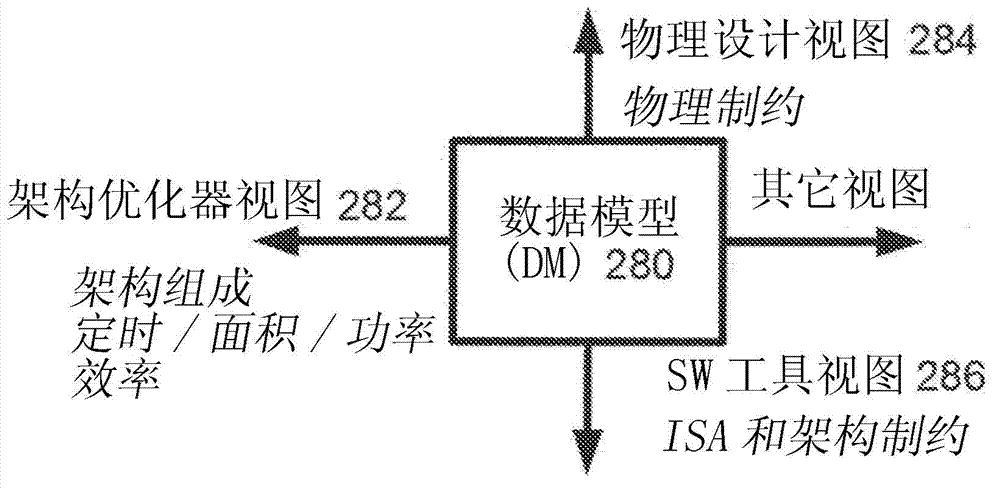
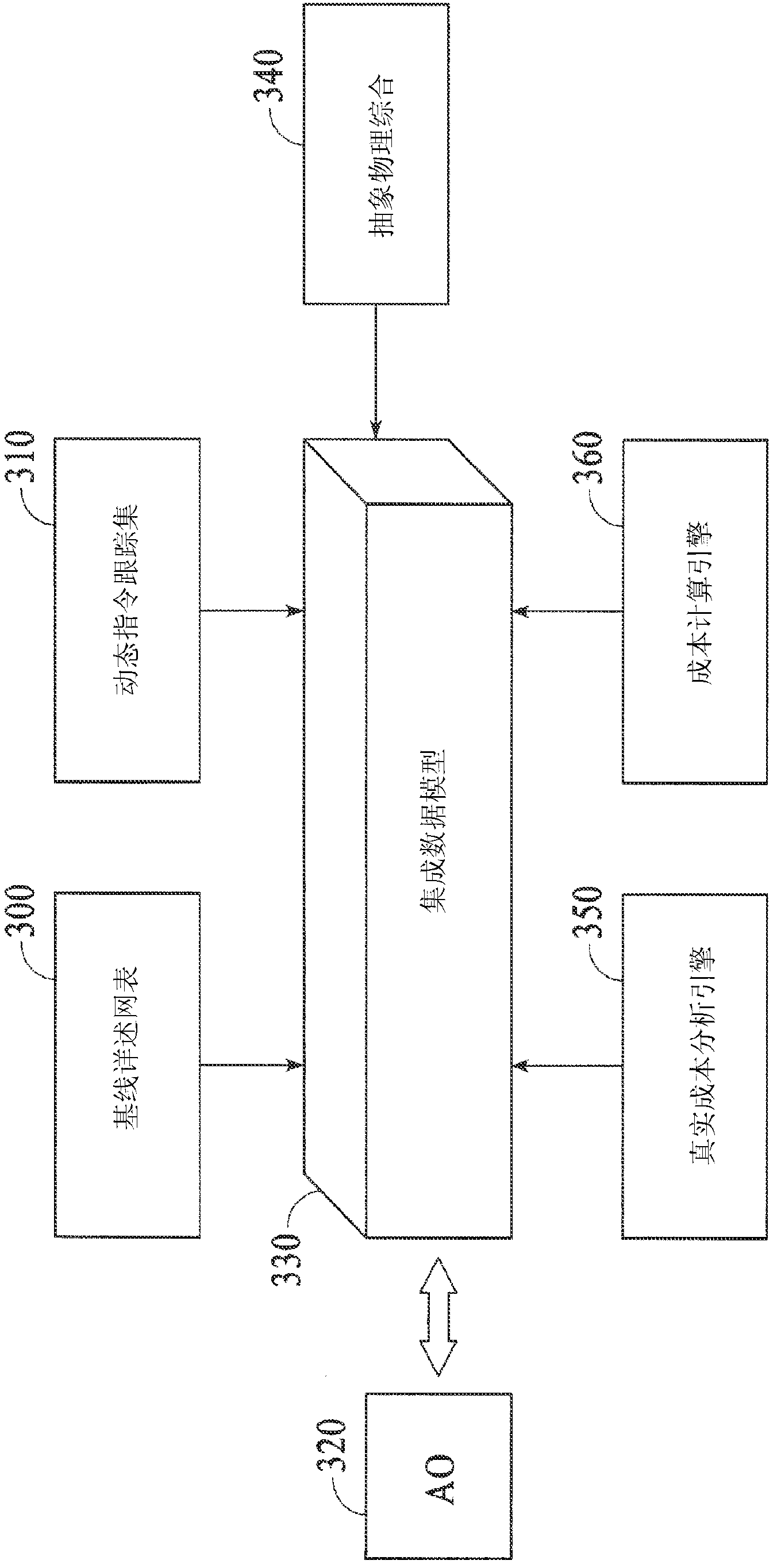
Integrated data model based framework for driving design convergence from architecture optimization to physical design closure
InactiveCN103262081AReduce designQuality improvementConstraint-based CADCAD circuit designTheoretical computer scienceCustom integrated circuits
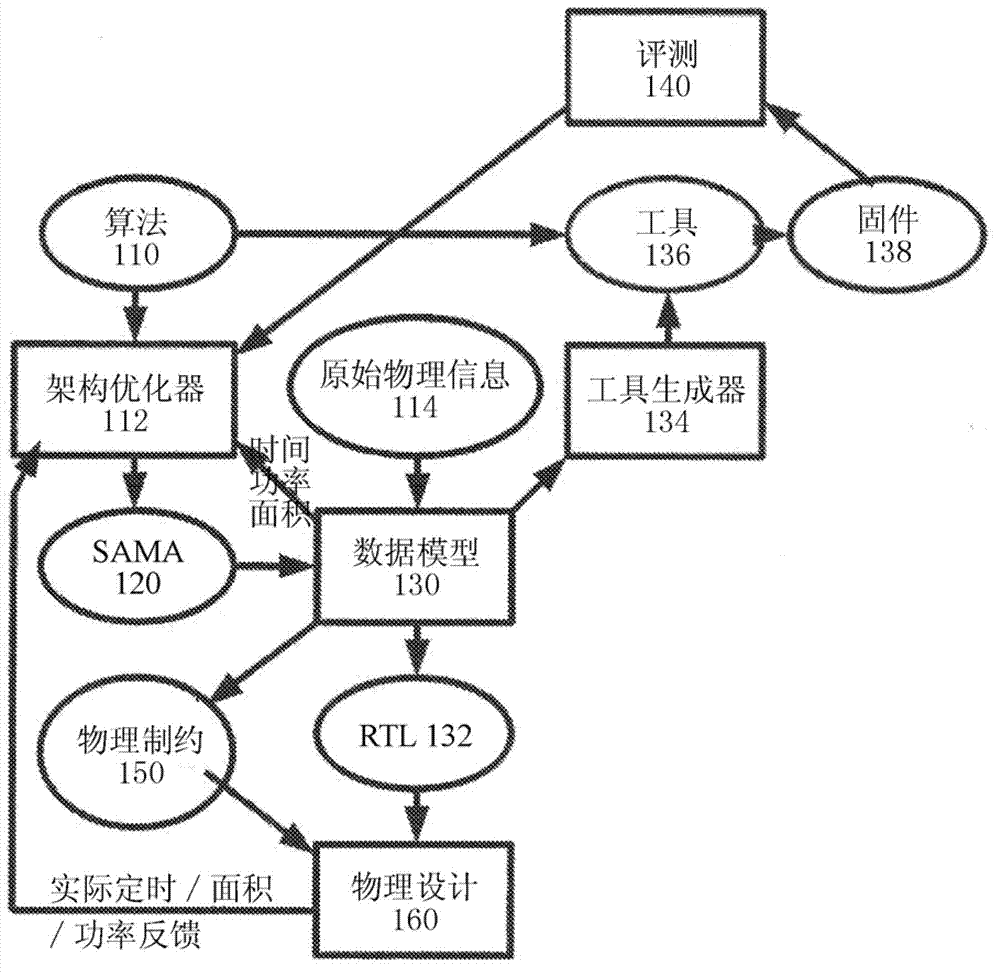
Systems and methods are disclosed to automatically synthesize a custom integrated circuit by receiving a specification of the custom integrated circuit including computer readable code and one or more constraints on the custom integrated circuit, encoding architecture level knowledge in a data model to generate and pass new constraints for physical synthesis of a chip specification uniquely customized to the computer readable code, receiving a look-ahead cost function during architecture optimization consistent with cost observed later in the flow after detailed physical synthesis is performed, wherein the look-ahead cost function is generated from a prior iteration and supplied to a subsequent iteration through the data model, and automatically translating information available at one optimization point into a constraint for another optimization point invoked at a different place in the design flow using the data model.
Owner:ALGOTOCHIP
Reduced memory nucleotide sequence comparison
Comparisons between two nucleotide sequences can be performed by customized integrated circuity that can implement a Smith Waterman analysis in a reduced memory footprint, storing and referencing onlyindividual portions, or subsections, of a two-dimensional matrix that is representative of the comparison between the two nucleotide sequences. As the backtracking proceeds, backtracking metadata corresponding to a cell from a subsection that is not currently retained in memory can be required. Such a subsection can be regenerated from previously generated scores associated with checkpoint cellsof the two-dimensional matrix that comprise two edges of the subsection being regenerated. Moreover, to further reduce memory consumption, the backtracking metadata stored for each cell can comprise four binary digits: two indicative of a directional assignment, one indicative of whether the corresponding cell is part of a deletion stretching across multiple contiguous cells, and one analogously indicative of insertions stretching across multiple contiguous cells.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
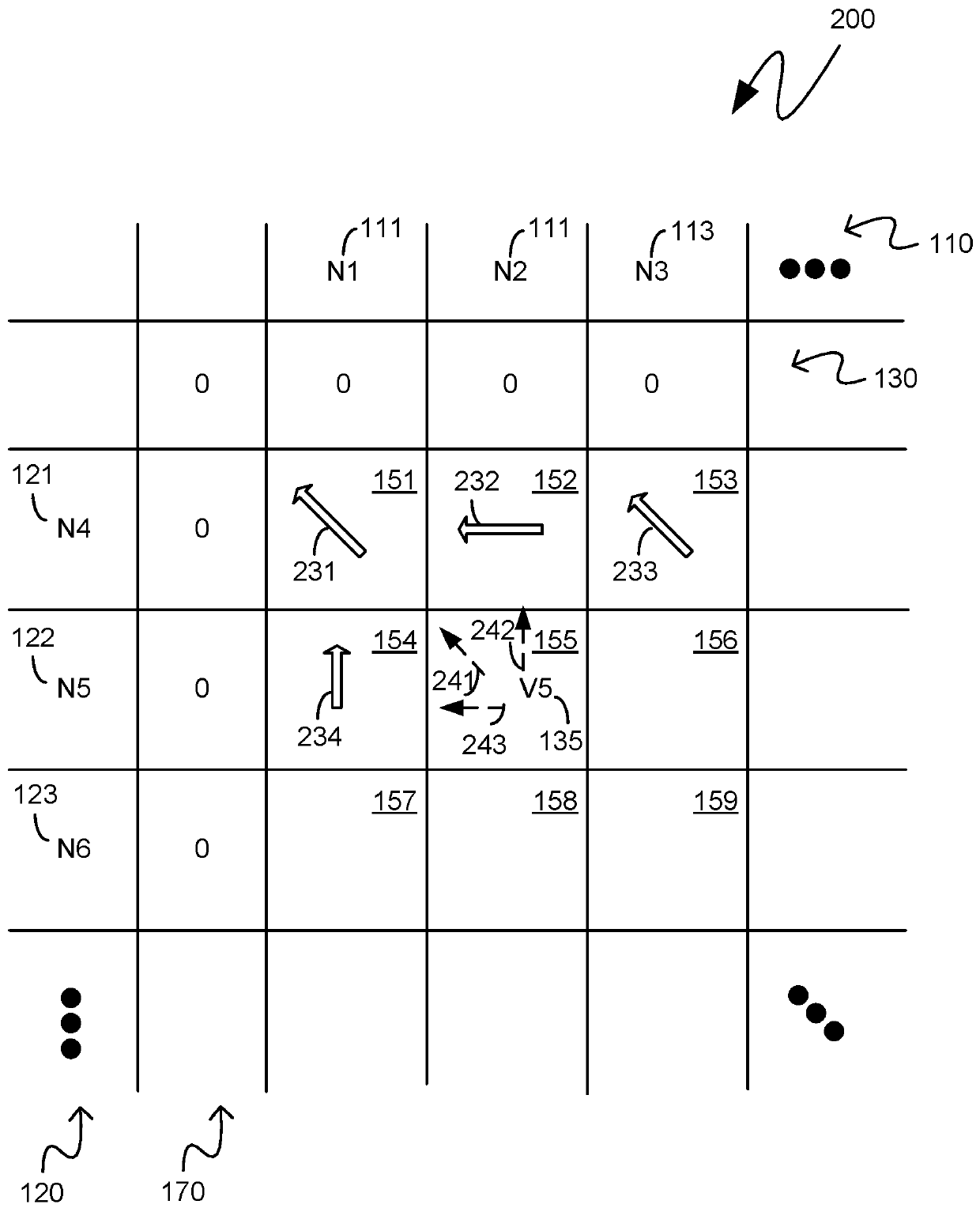
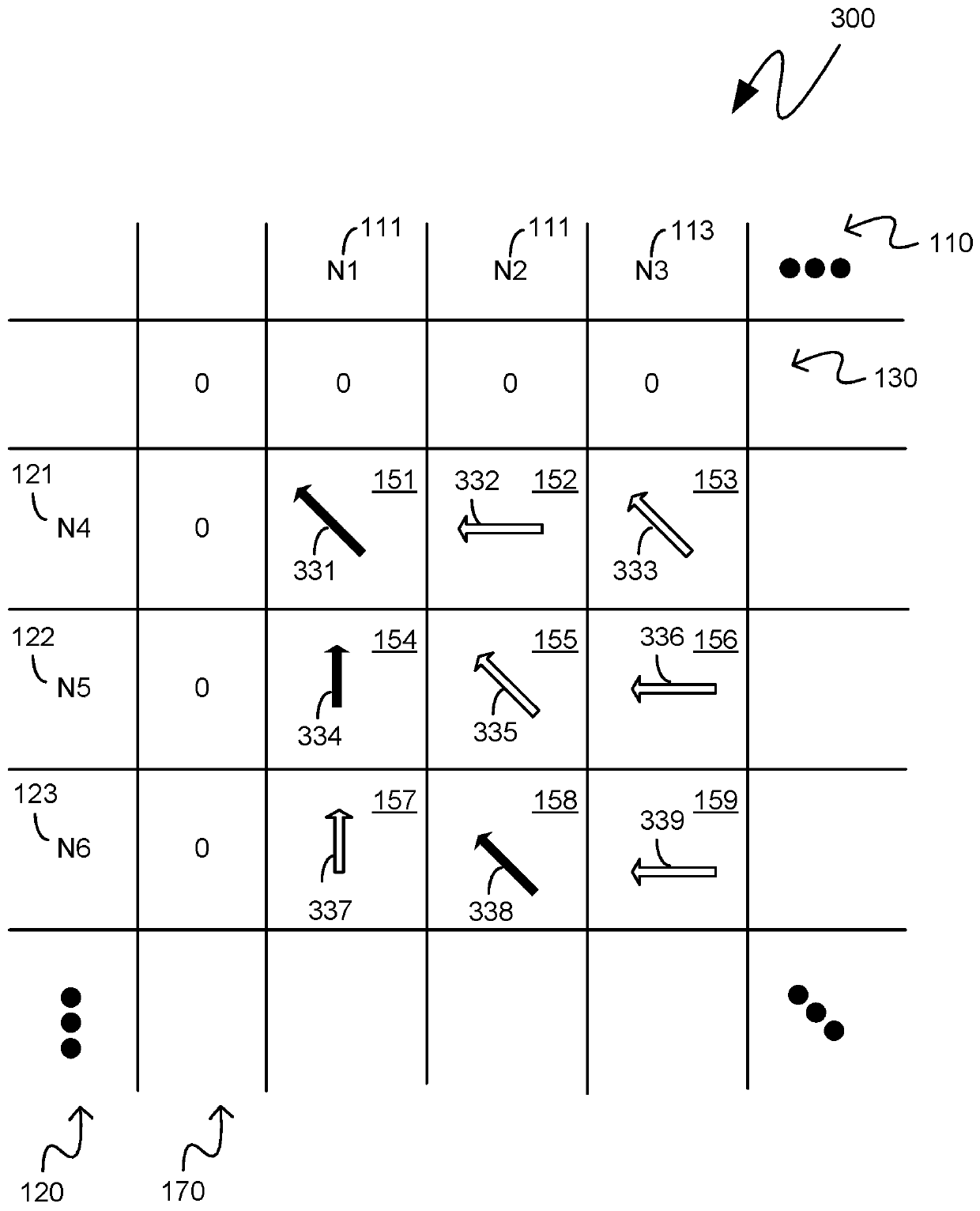
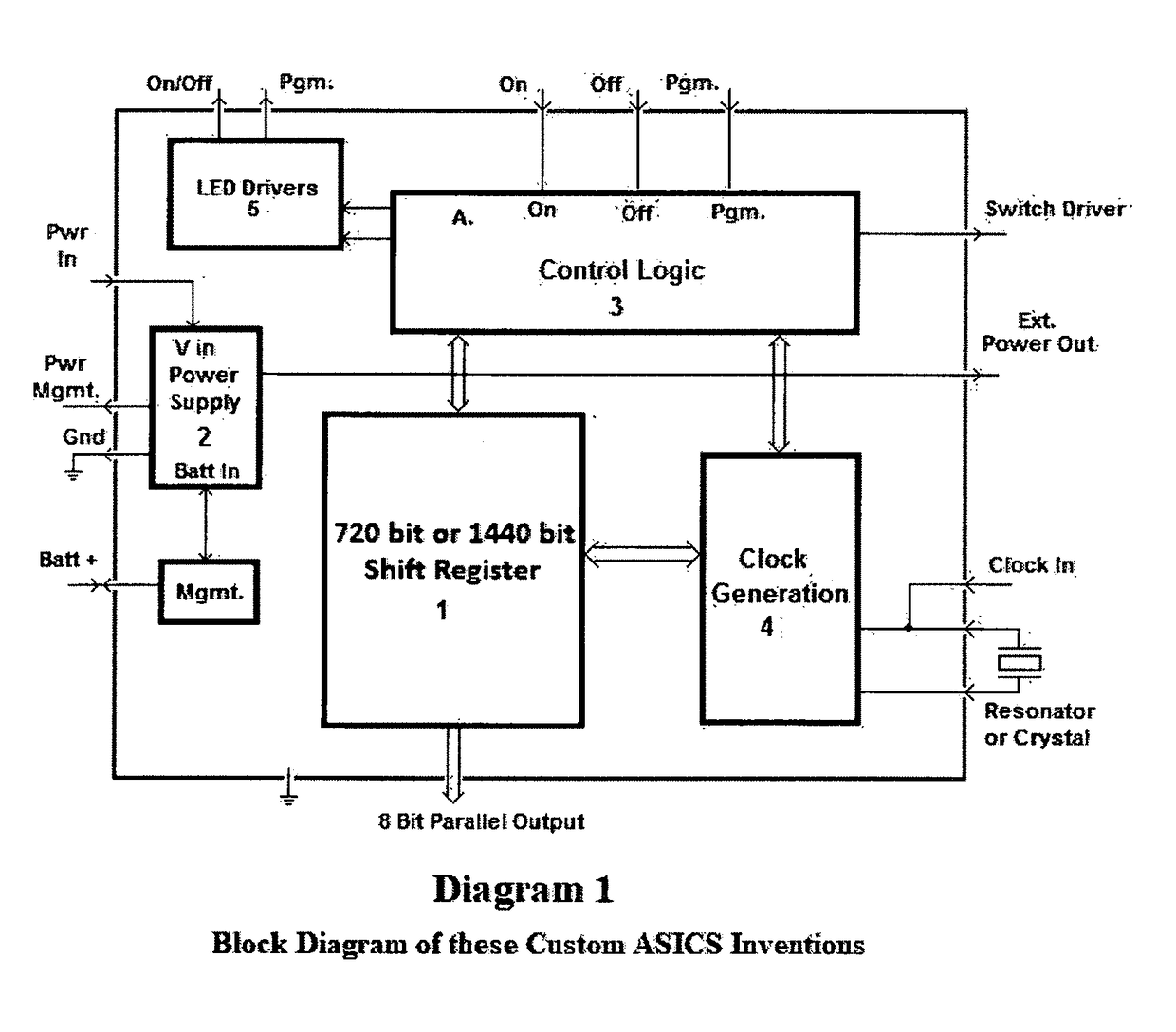
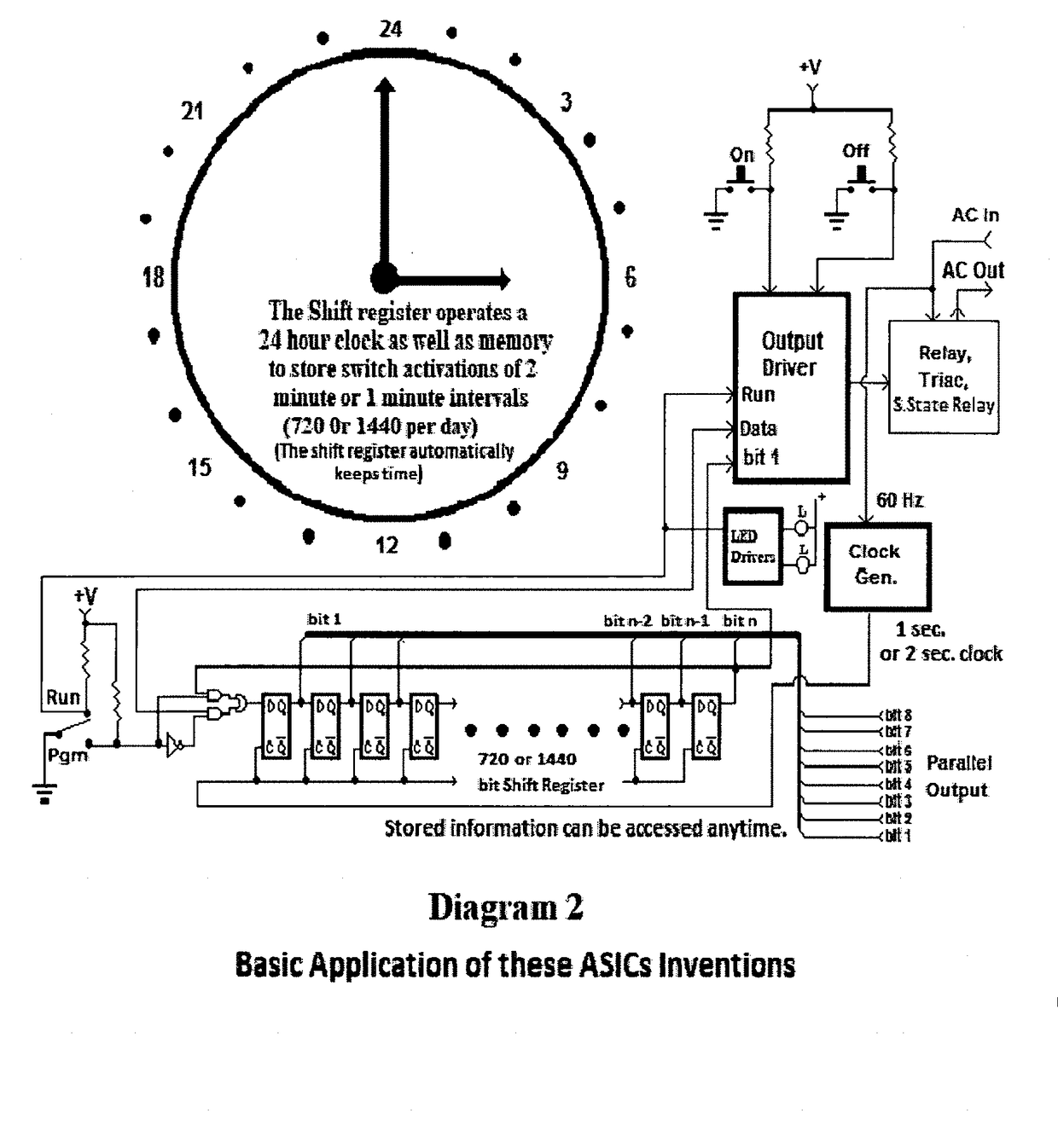
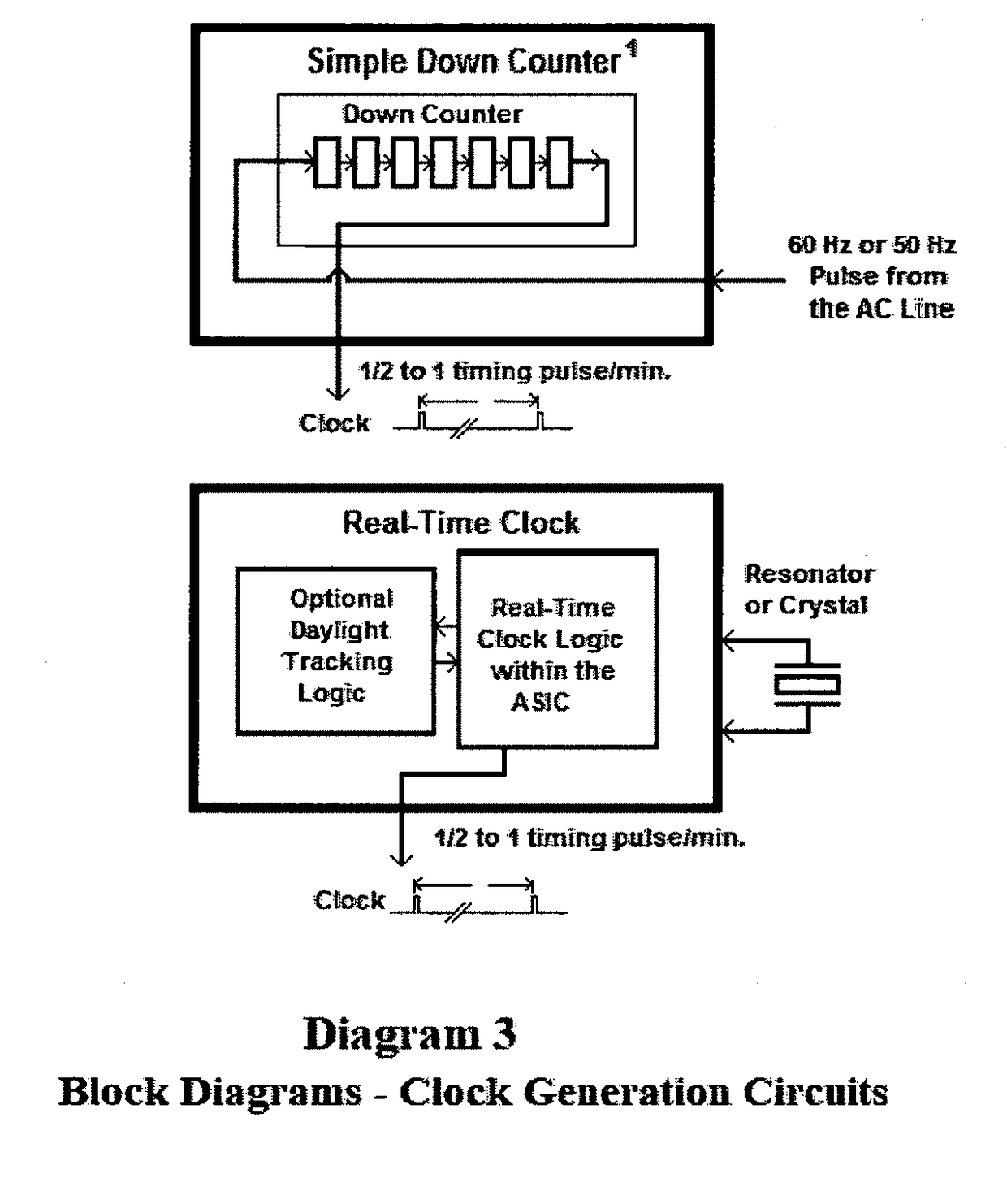
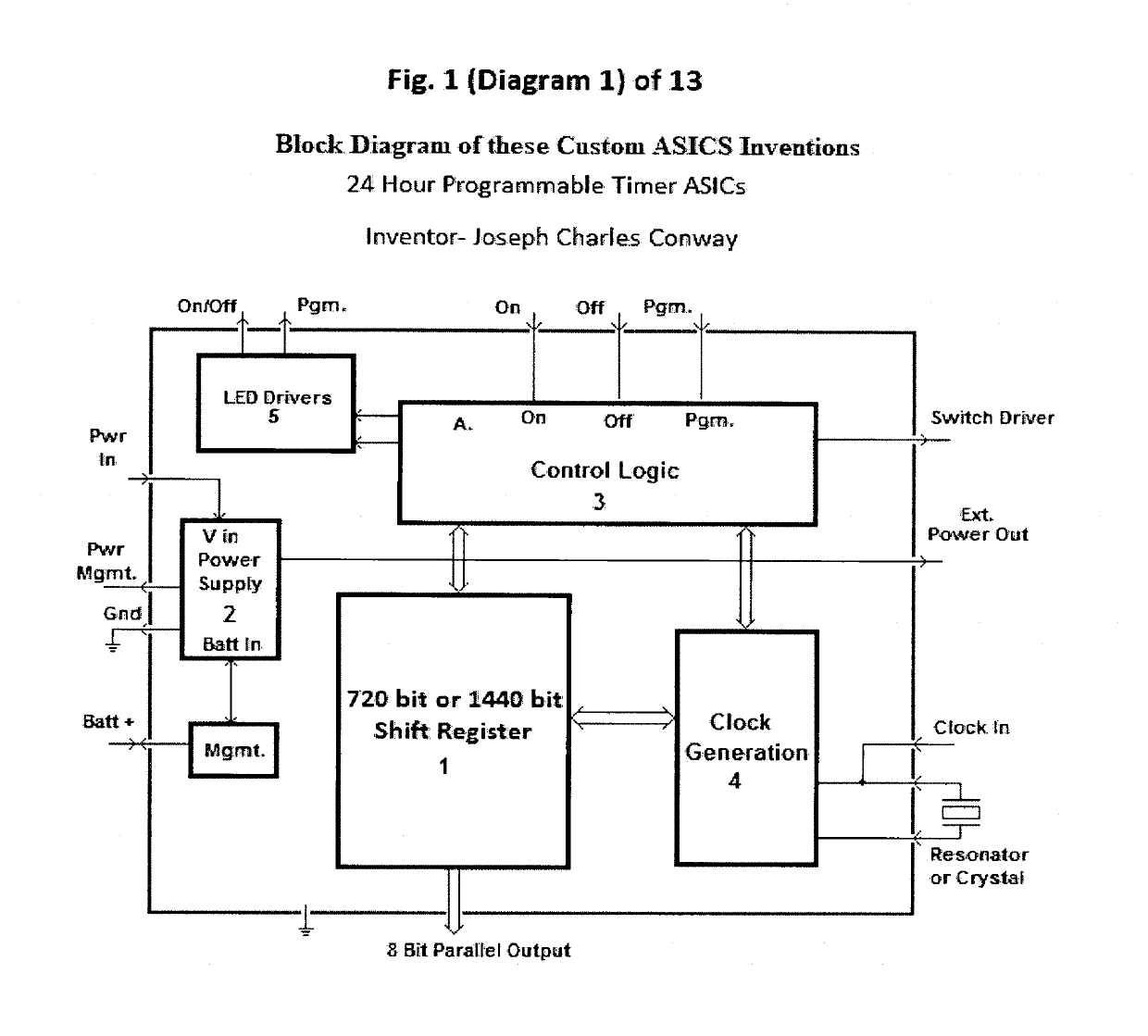
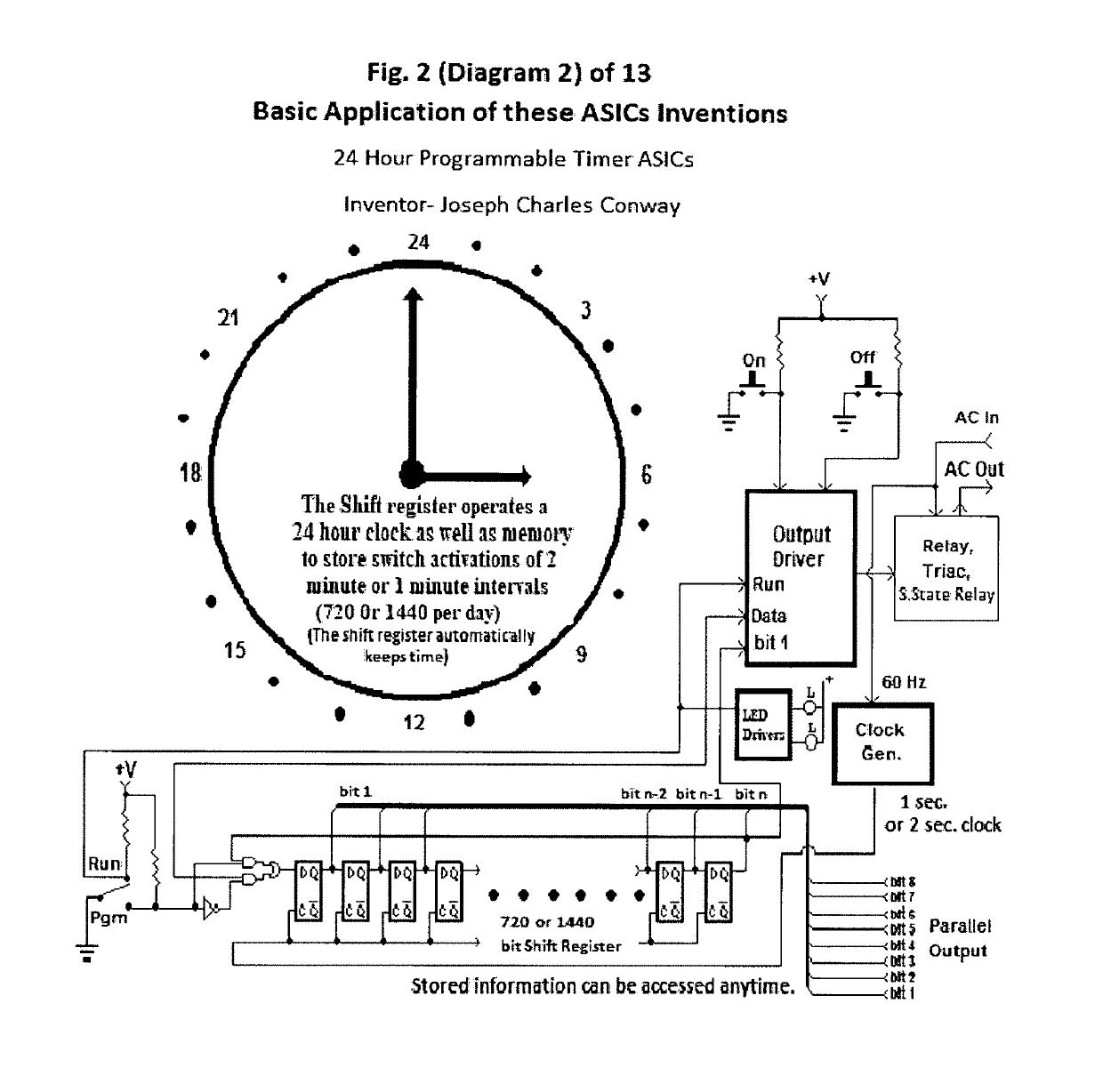
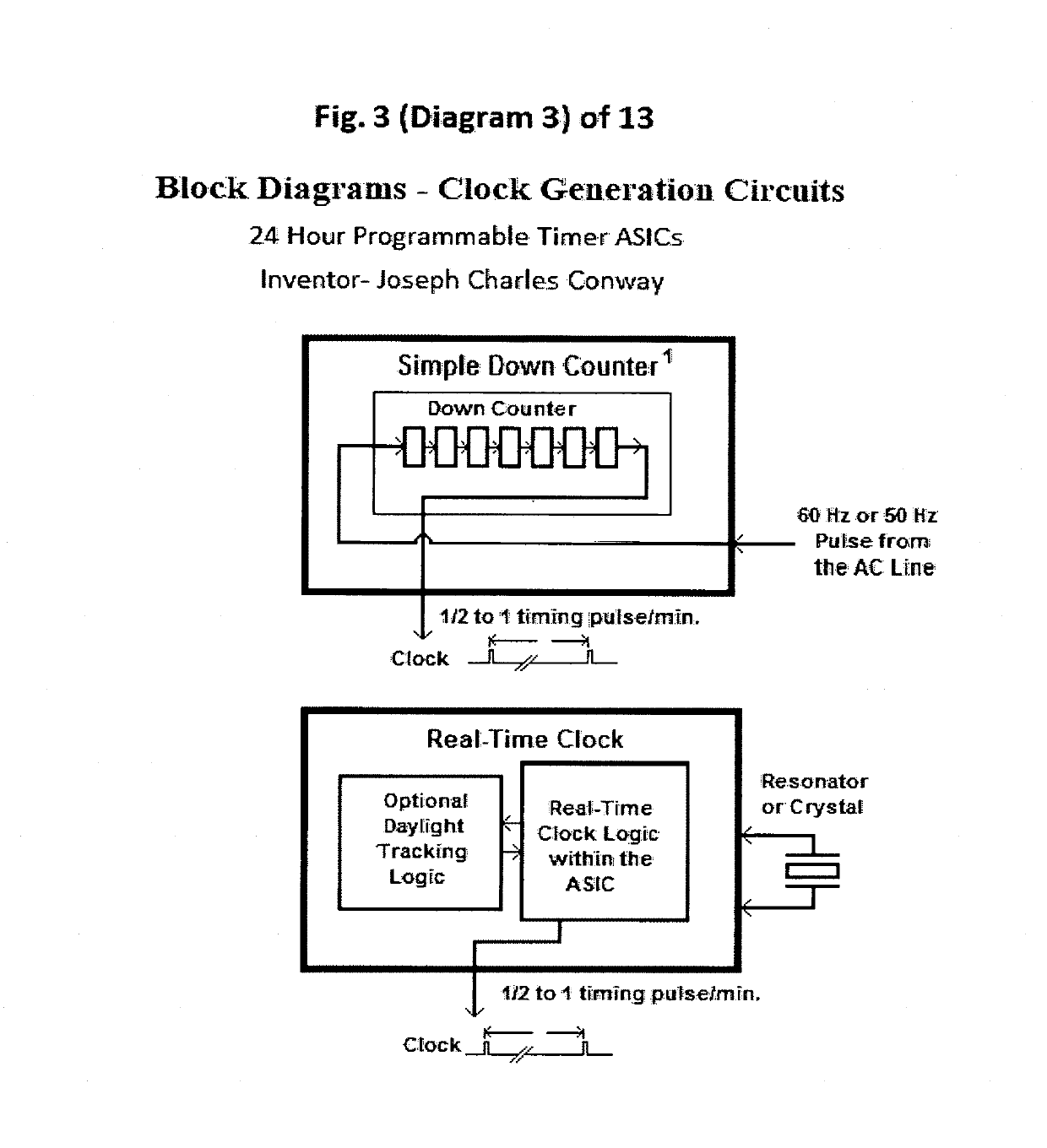
24 Hour Programmable Timer Custom Integrated Circuits
ActiveUS20190082522A1Eliminate needTime indicationDigital data processing detailsShift registerReal-time clock
This patent outlines the design of a family of Applications Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) for specific use in stand-alone end products and other devices needing 24 hour timer functions. These ASICs have a built-in real-time clock as well as a memory storage function remembering On and Off switch activity with the ability to repeat it. The ASICs have LED drivers indicating the function being performed. The power-on indicator also doubles as night light feature.These ASICs can store two minute or one minute intervals of power switch changes per day depending upon the amount of shift register memory placed in the ASICs. The memory function doubles as a static shift register for storage as well as providing a large portion of the real time 24 hour clock. These ASICs fully integrate most of the electronics required for stand-alone memory timers. Only a few additional components are required to fully create products using these ASICs.
Owner:CONWAY JOSEPH CHARLES
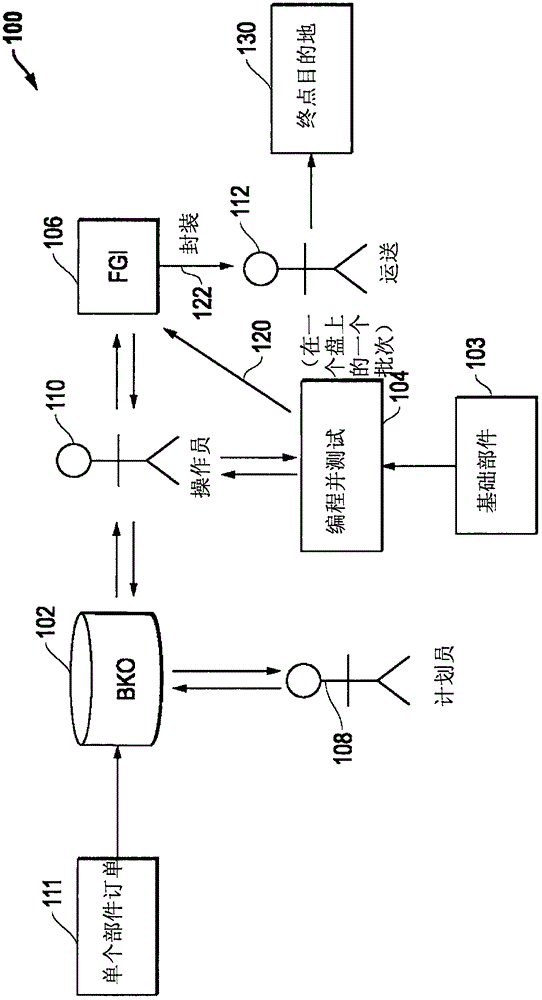
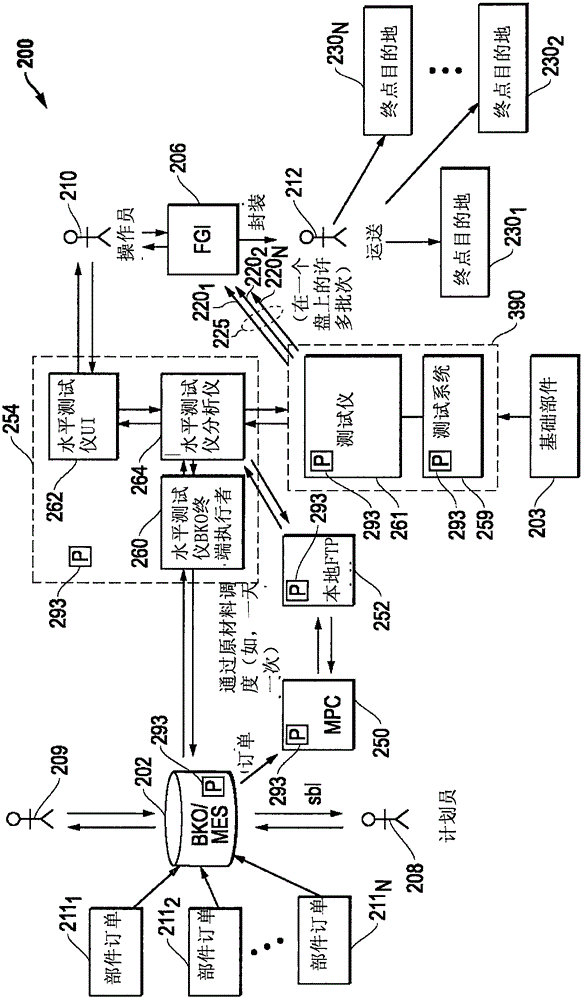
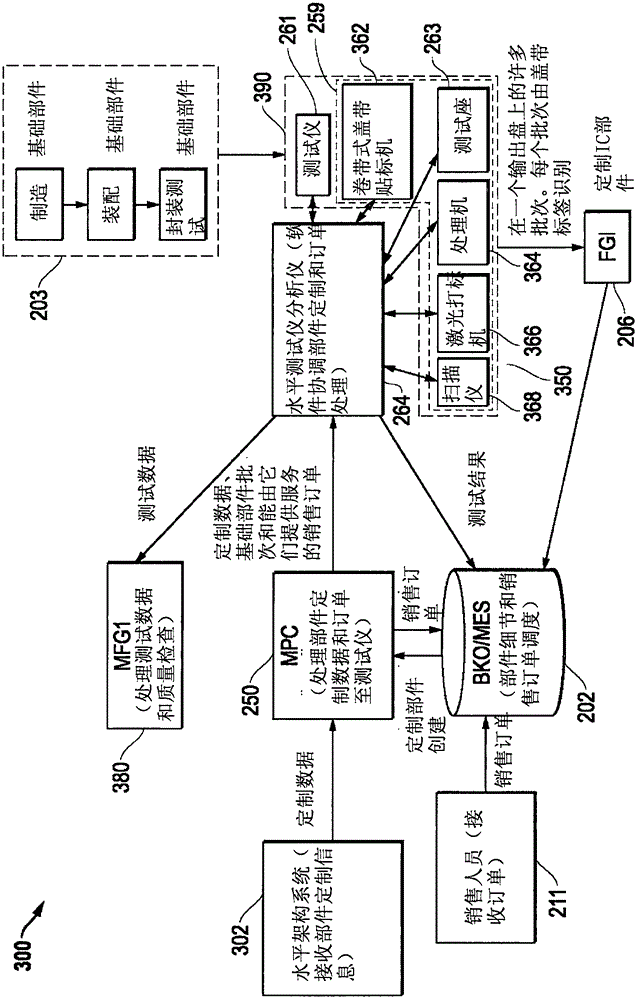
Horizontal Infrastructure Handling For Integrated Circuit Devices
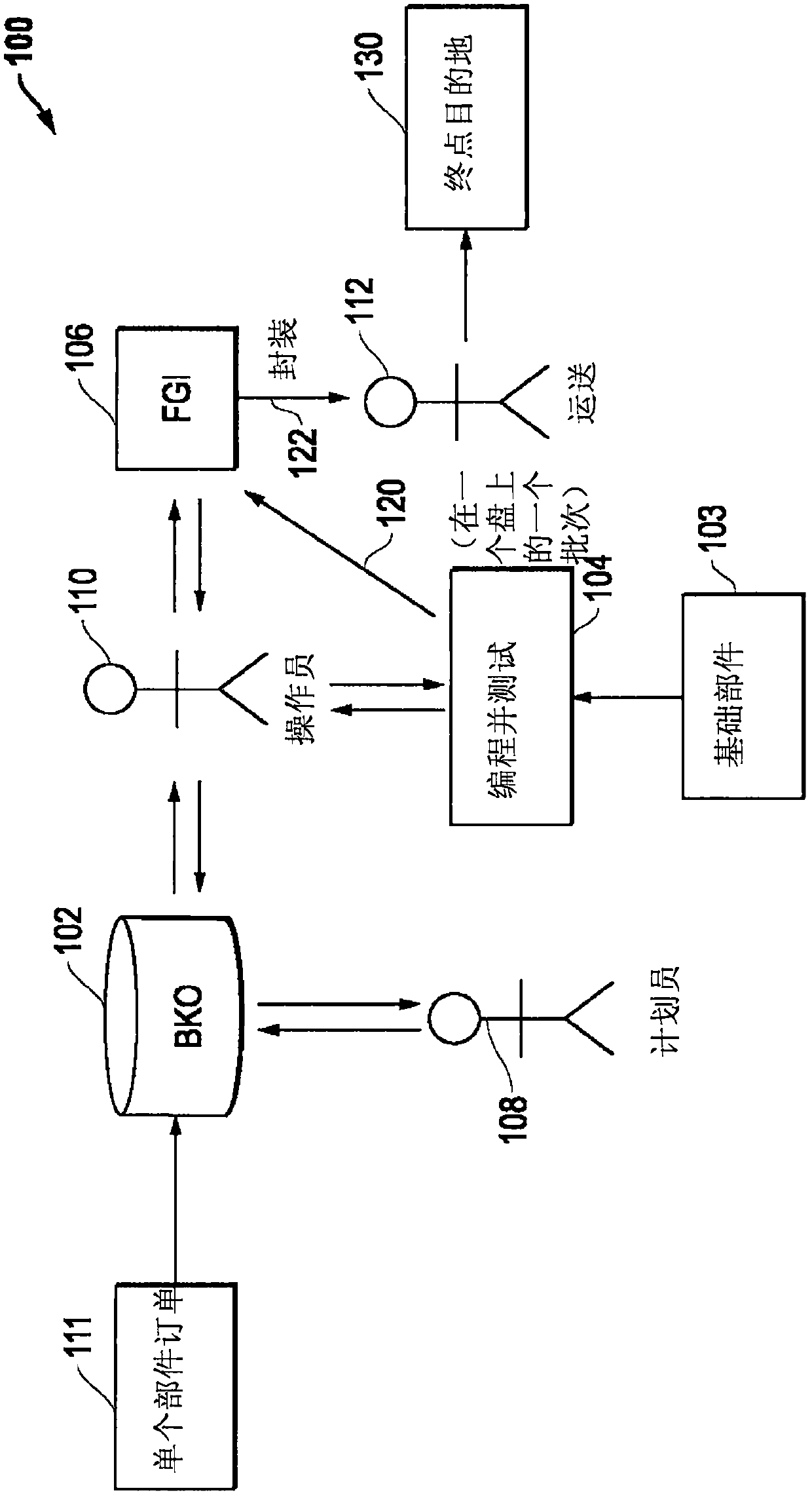
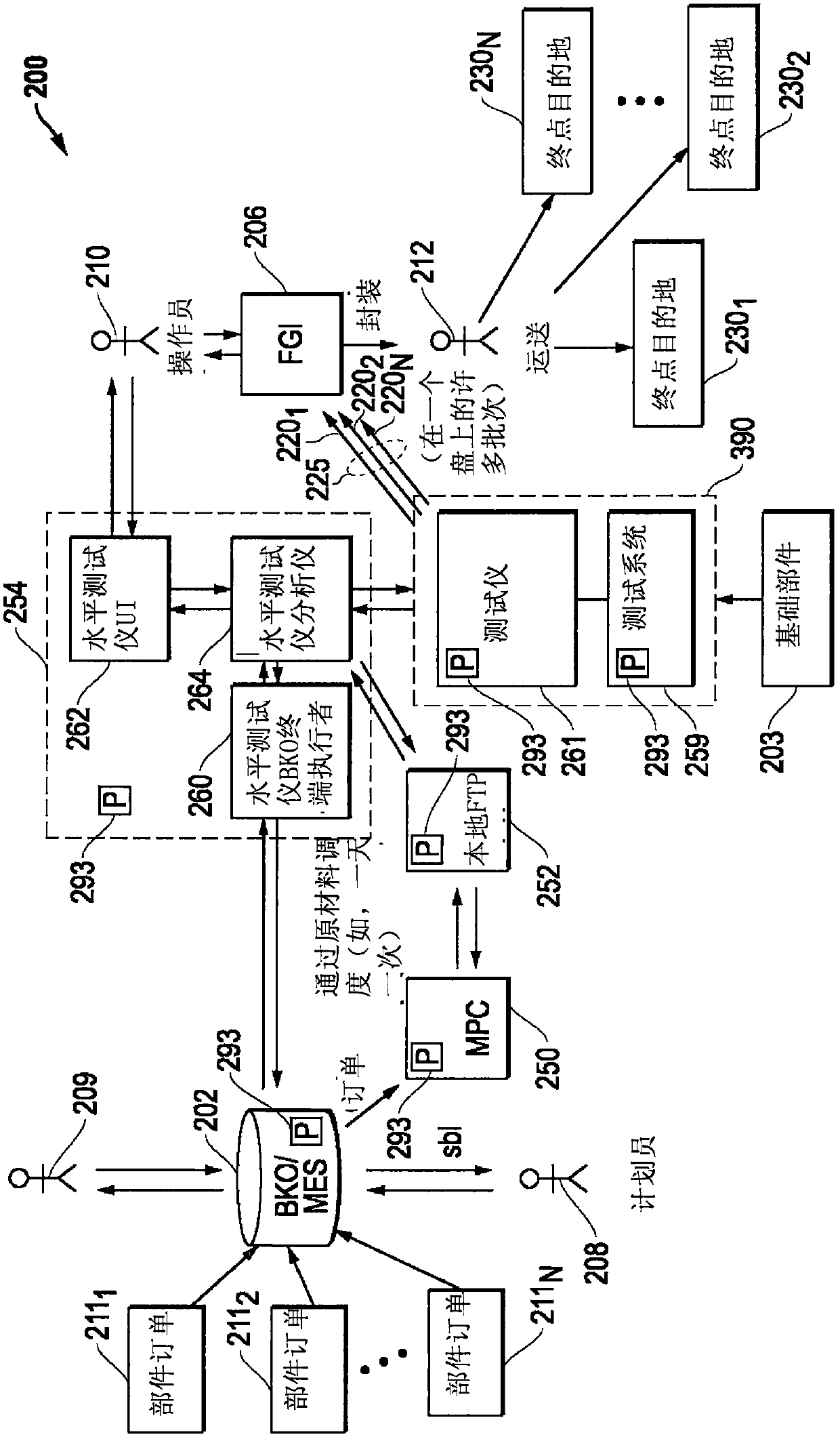
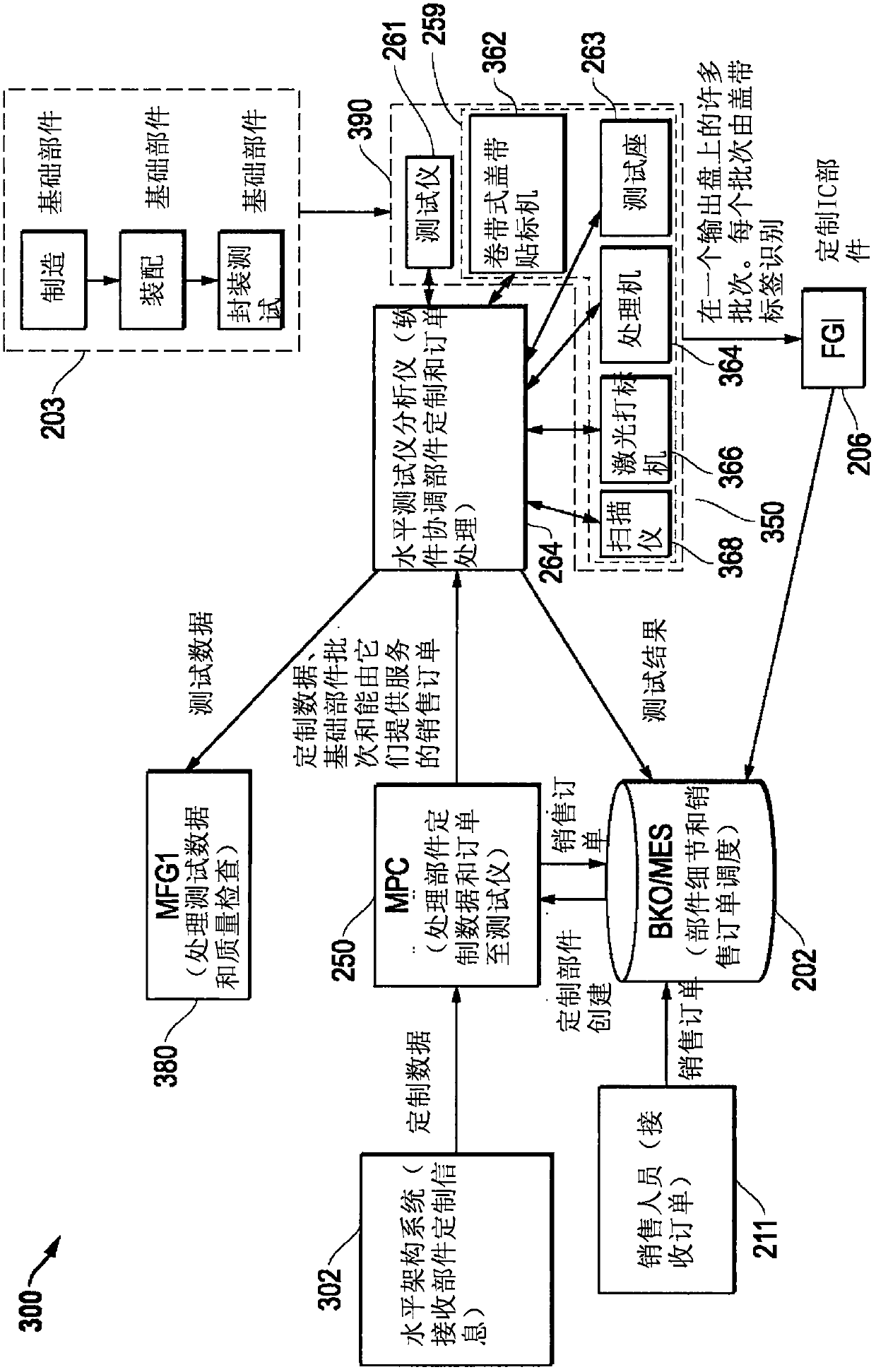
ActiveCN106485563AReliable transportationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingEngineeringIc devices
The invention provides a horizontal infrastructure handling for integrated circuit devices. Systems and methods are provided that may be implemented to produce customized integrated circuit (IC) device parts together from a common base IC device part that is customized with settings or code to build different unique IC device parts for different purposes that are processed and output together from the manufacturing process. Different individual devices of the common base part may be customized (e.g., programmed) with different settings and / or code to build respective uniquely configured parts for different purposes, e.g., such as according to different respective part orders.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
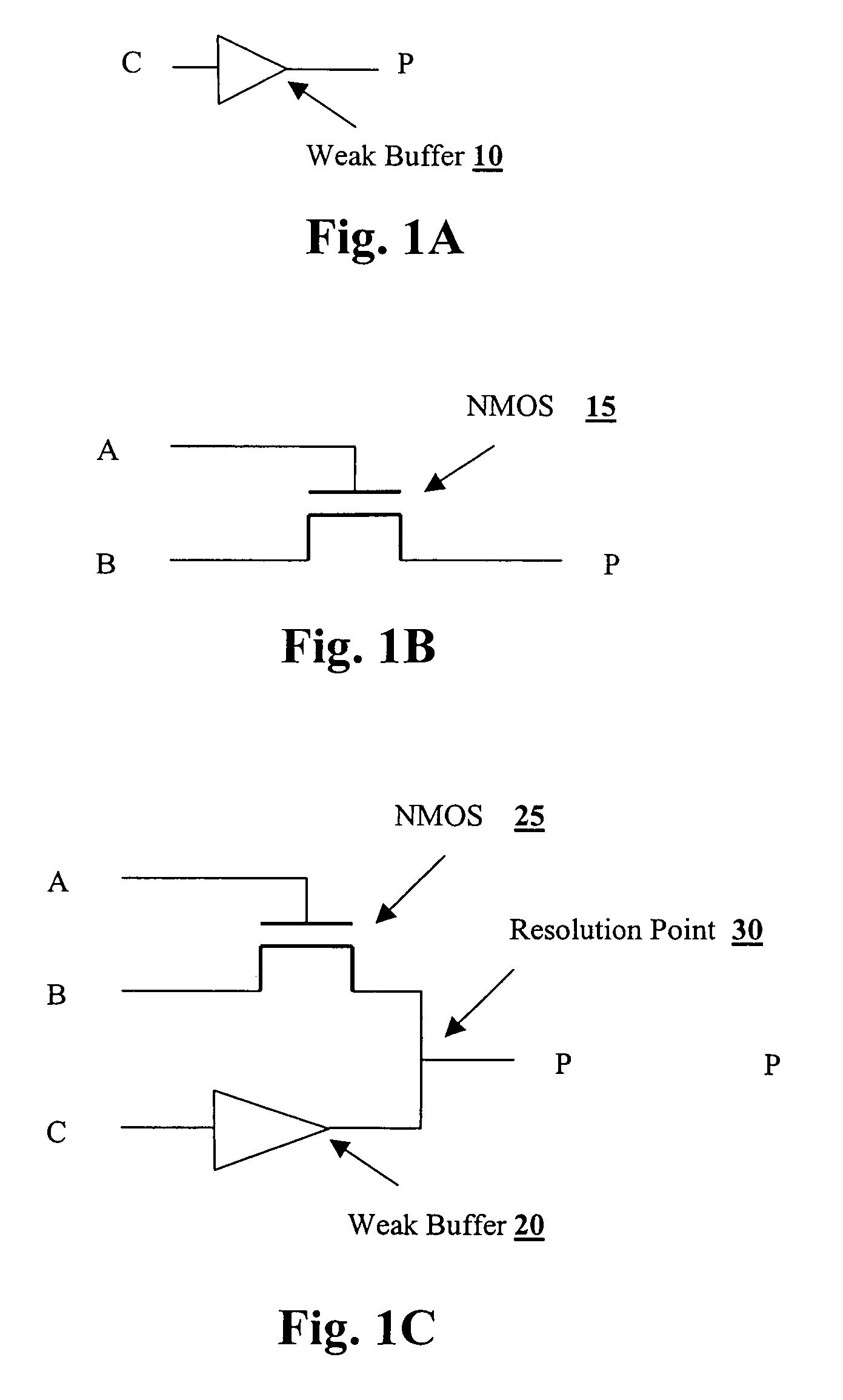
Method and system for creating a boolean model of multi-path and multi-strength signals for verification
InactiveUS7735035B1Obviates abilityAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designTheoretical computer scienceComputer science
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Slim bezel and display having the same
A bezel of a display includes source lines with a same length, gate in panel (GIP) lines, and at least two customized integrated circuit (IC) chips arranged along a straight line in a lateral direction. Each of the customized IC chips is coupled to at least one of the source lines or the GIP lines. Circuit layouts on the customized IC chips are, together, equivalent to a circuit layout on a standard IC chip. A sum of widths of the customized IC chips in the lateral direction is greater than a width of the standard IC chip.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
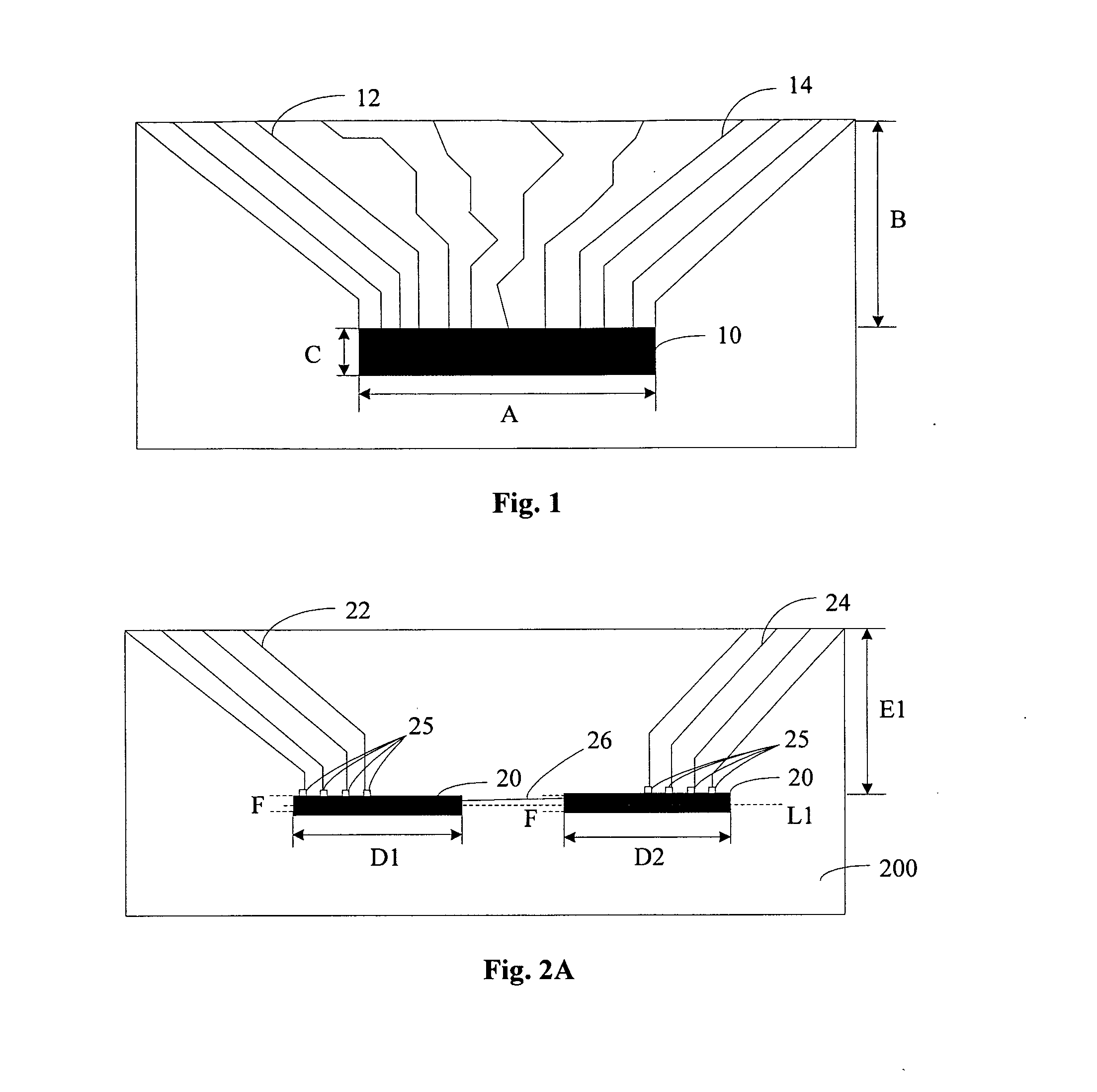
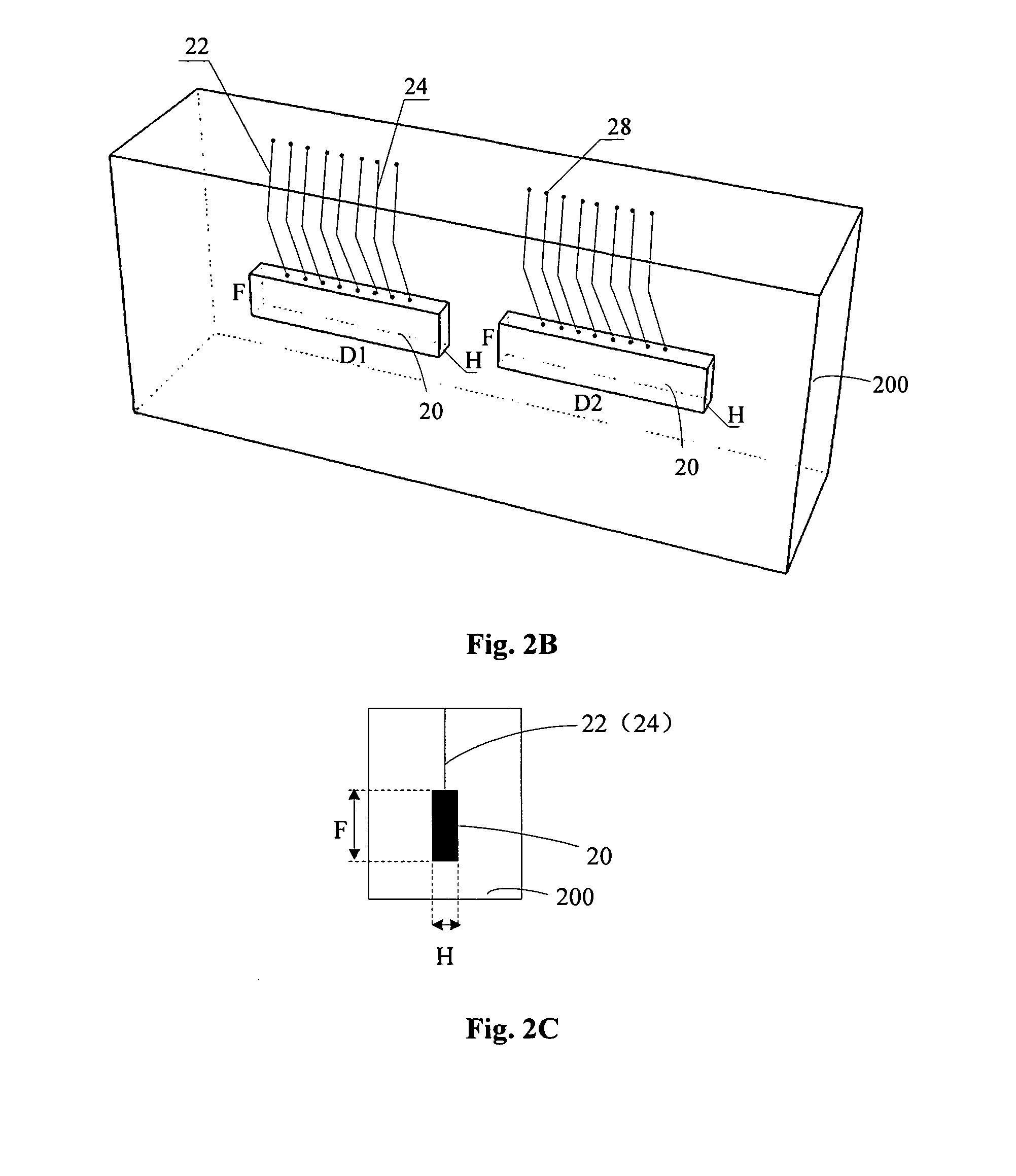
Integrated Circuits Partially Activated Based on Intrinsic Features
ActiveCN106164918BInternal/peripheral component protectionCoding/ciphering apparatusComputer hardwareComputer architecture
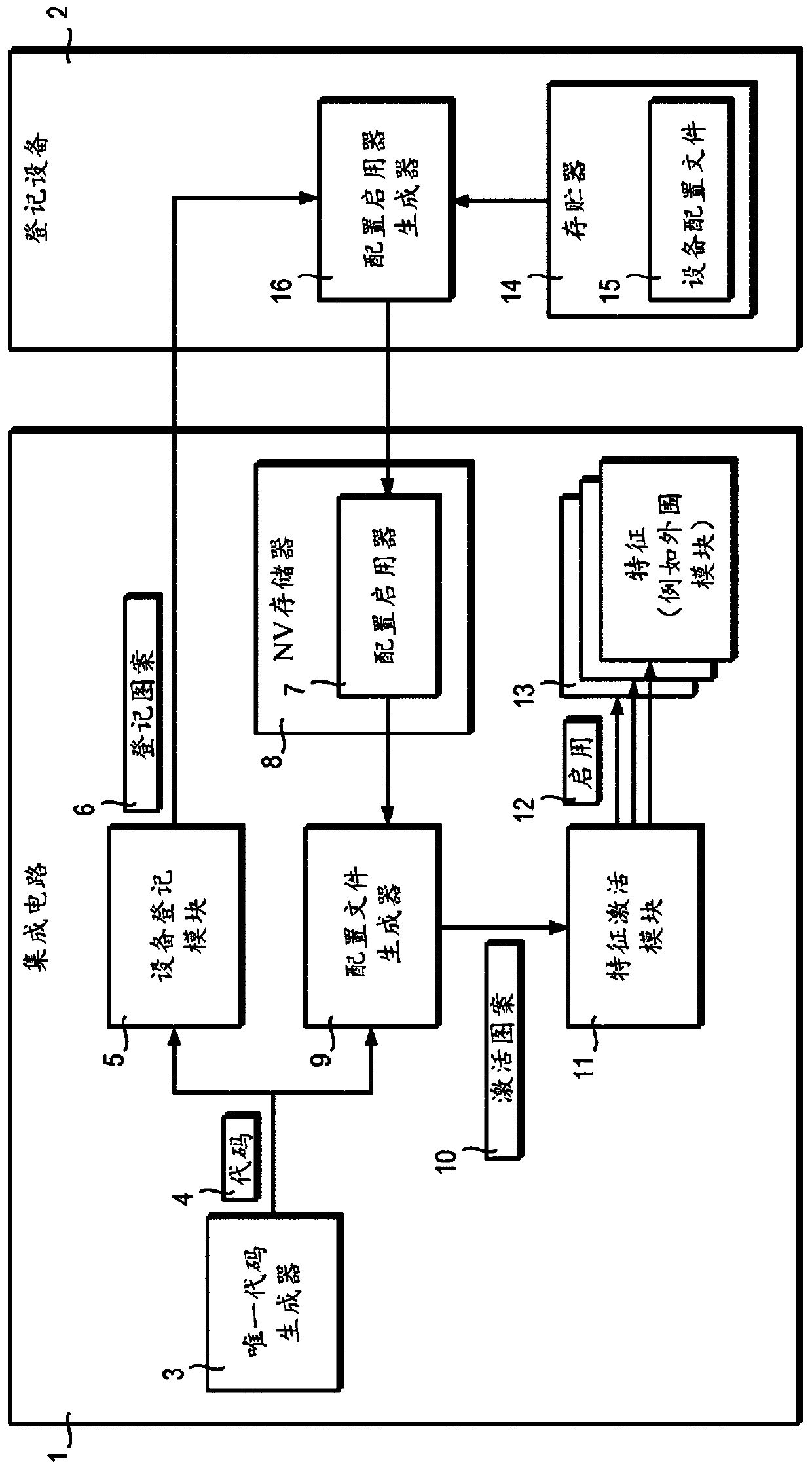
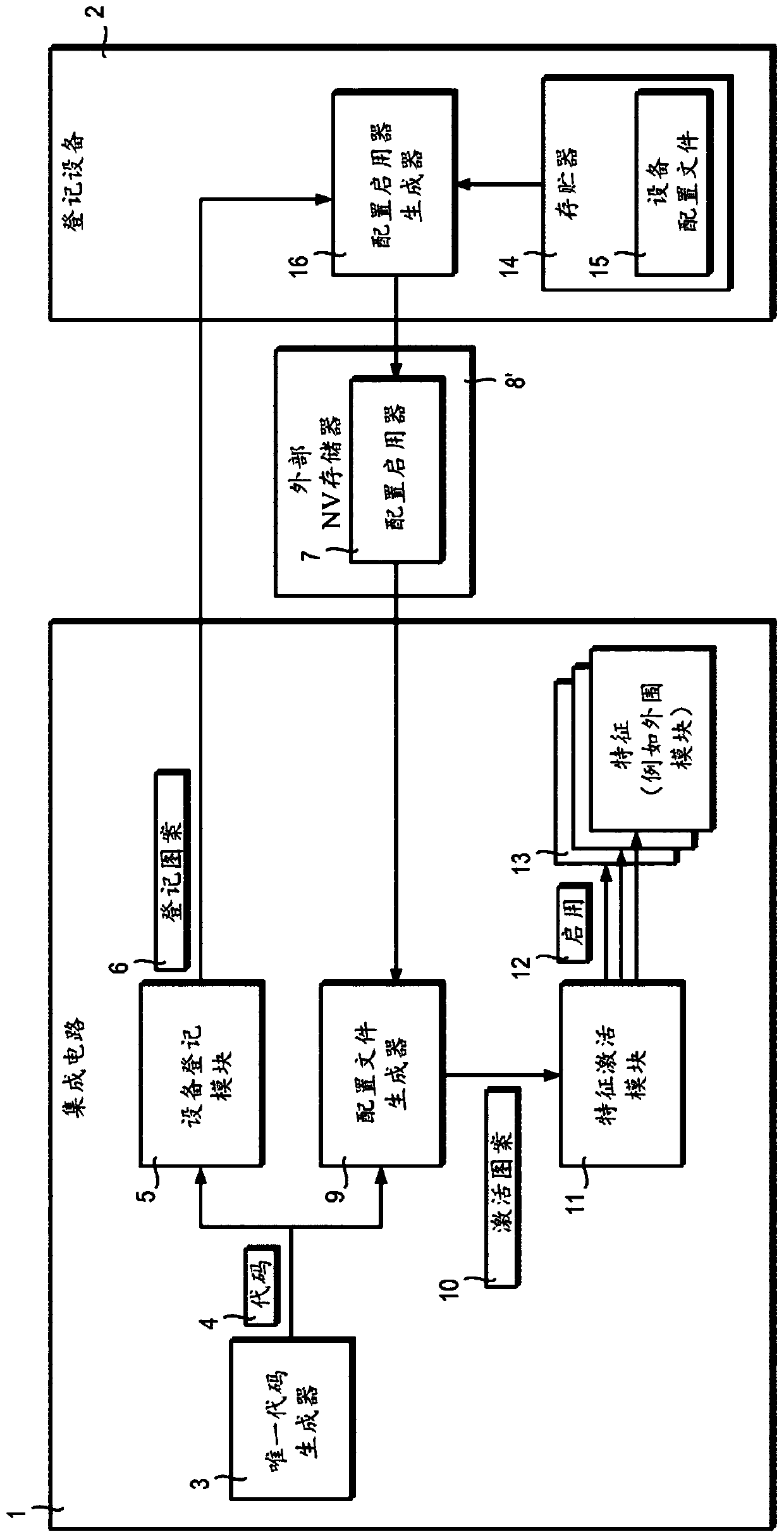
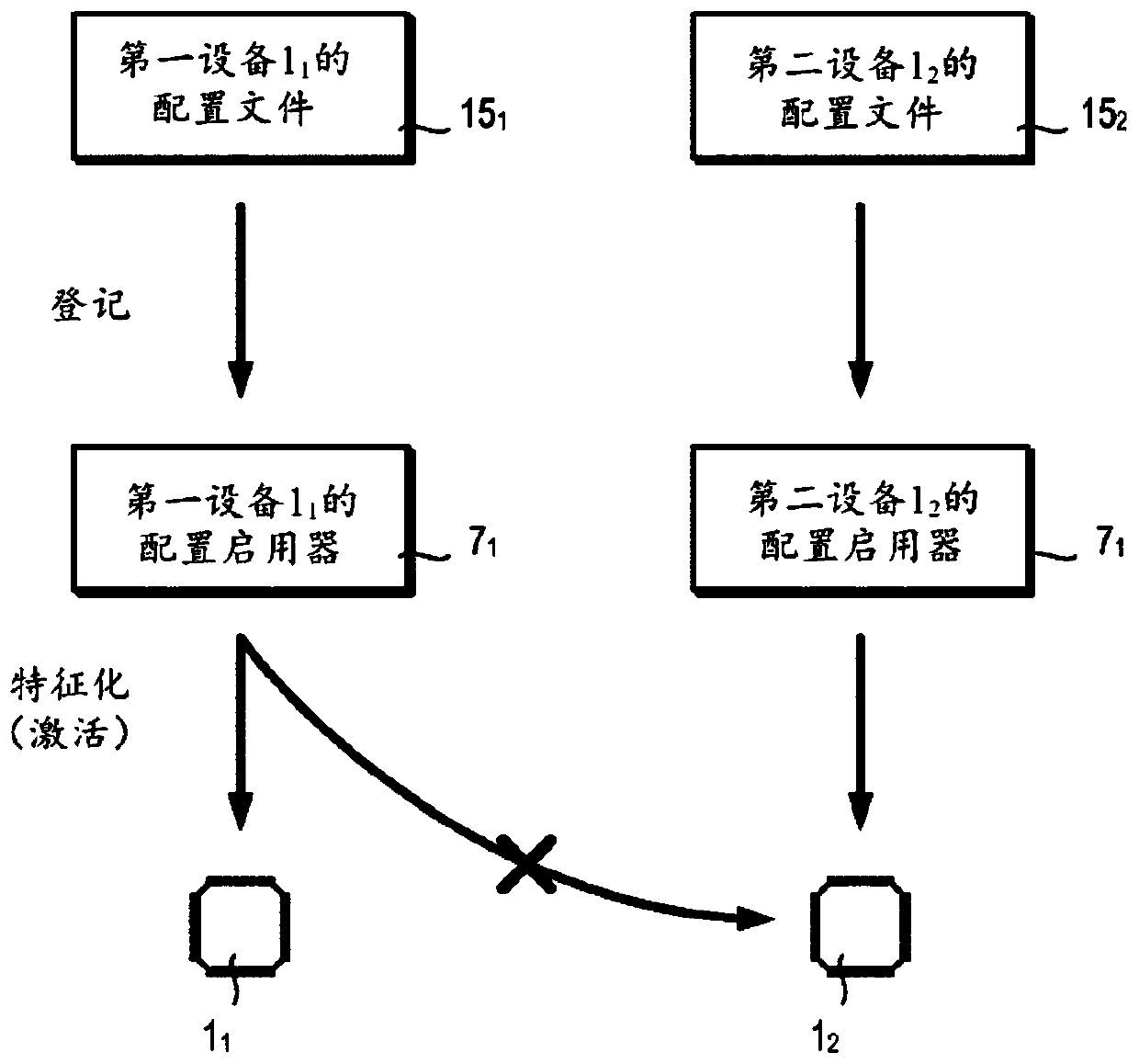
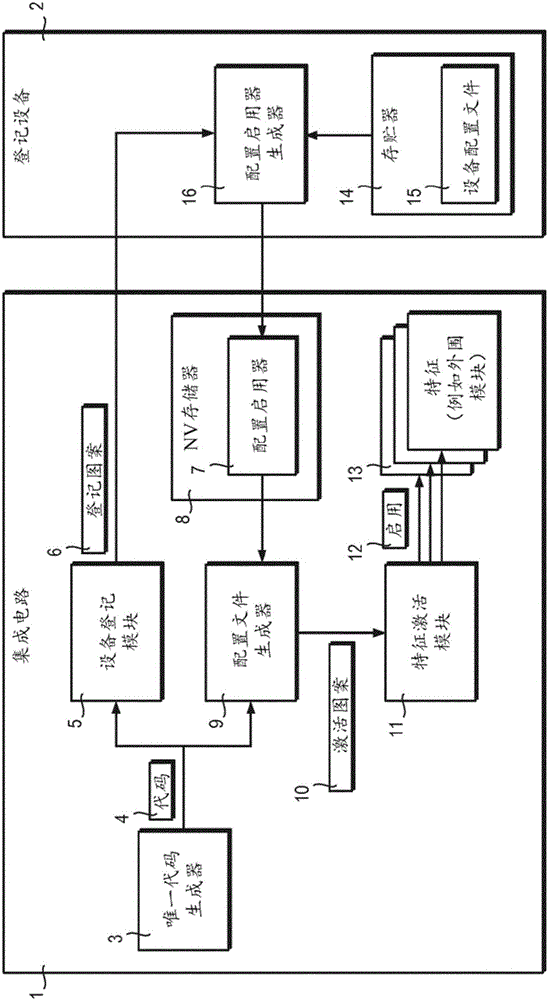
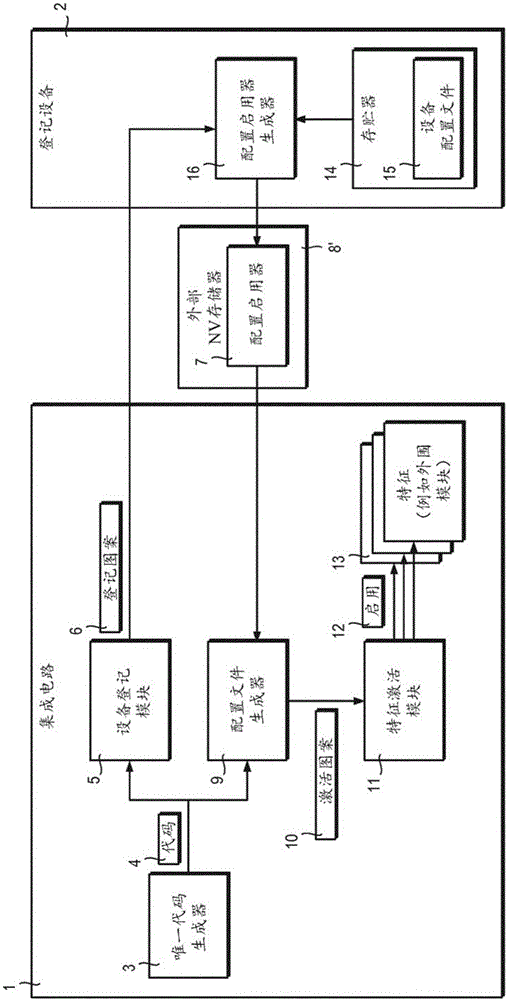
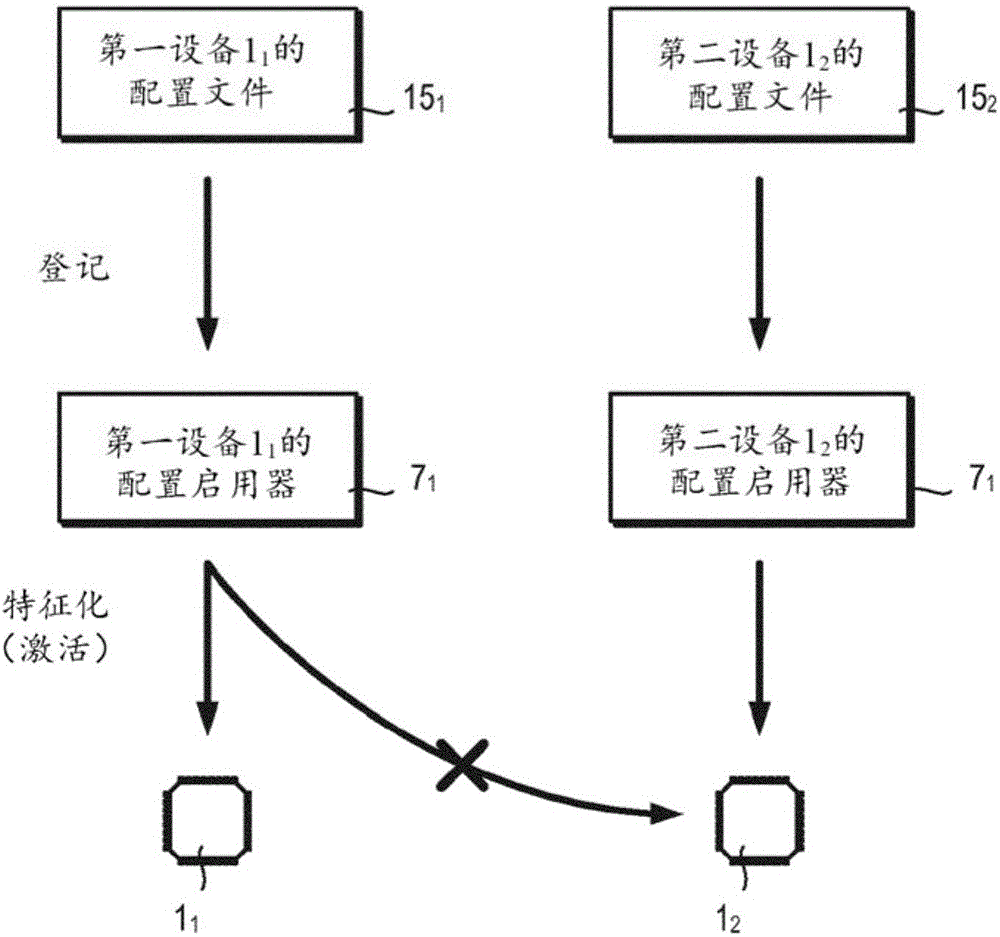
A fixed logic integrated circuit is disclosed. The integrated circuit includes a unique code generator (3) configured to generate a code (4) having a value inherently unique to the integrated circuit, a registration pattern generator configured to generate a registration pattern (6) based on the unique code (4) (5). The integrated circuit is configured to transmit a registration pattern (6) to an external registration device (2) and to receive enabling data (7) from the external registration device. Optionally, the integrated circuit may comprise a memory (8) for storing remotely generated enabling data (7). The integrated circuit includes: a configuration file generator (9) configured to generate configuration data (10) using remotely generated enablement data (7) and a unique code (4); and a feature activation module (11) configured to To activate and / or deactivate features (13) of the integrated circuit and / or to customize the integrated circuit according to the configuration data (10).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS EURO
Integrated circuit with parts activated based on intrinsic features
ActiveCN106164918AInternal/peripheral component protectionCoding/ciphering apparatusComputer moduleEngineering
A fixed logic integrated circuit is disclosed. The integrated circuit comprises a unique code generator (3) configured to generate a code (4) having a value which is intrinsically unique to the integrated circuit, an enrolment pattern generator (5) configured to generate an enrolment pattern (6) based on the unique code (4). The integrated circuit is configured to transmit the enrolment pattern (6) to an external enrolment device (2) and to receive enabling data (7) from the external enrolment device. Optionally, the integrated circuit may include memory (8) for storing remotely- generated enabling data (7). The integrated circuit comprises a configuration file generator (9) configured to generate configuration data (10) using the remotely- generated enabling data (7) and the unique code (4), and a feature activation module (11) configured to activate and / or disable features (13) of the integrated circuit and / or customise the integrated circuit in dependence upon the configuration data (10).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS EURO
Horizontal Architecture Processing for Integrated Circuit Devices
ActiveCN106485563BReliable transportationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingComputer hardwareCommon base
Systems and methods are provided that may be implemented to produce customized integrated circuit (IC) device parts together from a common base IC device part that is customized with settings or code to build different unique IC device parts for different purposes that are processed and output together from the manufacturing process. Different individual devices of the common base part may be customized (e.g., programmed) with different settings and / or code to build respective uniquely configured parts for different purposes, e.g., such as according to different respective part orders.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Method of structuring multiport asynchronous storage module
ActiveCN102930898BIncrease the number of portsIncrease storage capacityRead-only memoriesFull customComputer module
The invention discloses a method of structuring a multiport asynchronous storage module and relates to buffer storage and interchange of multichannel parallel data in the process of data interchange and processing. The method of structuring the multiport asynchronous storage module aims at solving the problem that in the process of design of a current semi-custom integrated circuit, a used storer of a technological library just has two types of single ports or double ports and can not meet certain situations of high data throughput rates. An addressing manner of address decoding control partitioning reading and writing is adopted by a plurality of double-port type storers in the technological library to structure the multiport asynchronous storage module, so that the aim that a simple port storage module is structured to the multiport storage module is achieved, and the requirement for the high data throughput rates is reached. The method of structuring the multiport asynchronous storage module has the advantages of flexibly expanding capacity and available access ports of the storer according to design requirements, reducing design difficulty, and shortening development time. Relative to a full-custom multiport storer, the method of structuring the multiport asynchronous storage module has the advantages of being good in flexible performance, high in reliability, small in design risk and the like.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Automatic optimal integrated circuit generator from algorithms and specification
InactiveCN103098058AReduce designEliminate risk by designCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureCustom integrated circuits
Systems and methods are disclosed to automatically design a custom integrated circuit includes receiving a specification of the custom integrated circuit including computer readable code and one or more constraints on the custom integrated circuit; automatically devising a processor architecture and generating a processor chip specification uniquely customized to the computer readable code which satisfies the constraints; and synthesizing the chip specification into a layout of the custom integrated circuit.
Owner:ALGOTOCHIP
24 hour programmable timer custom integrated circuits
ActiveUS10470281B2Eliminate needEasy to useTime indicationDigital data processing detailsReal-time clockImage resolution
Eight Applications Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) for use in stand-alone end products and other devices requiring a 24 hour memory. They have a real-time clock as well as memory that stores On and Off Switch closures with the ability to repeat them. They also have power management to allow them to operate by receiving their power through the load they are switching. They also have LED drivers to indicate the function being performed. They can store a resolution of two minute or one minute intervals of On and Off Switch closures per 24 hour period depending upon the amount memory integrated into the ASIC. Only a few external components are required to create end products and / or utilize these ASICs in another product.
Owner:CONWAY JOSEPH CHARLES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com