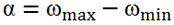Patents
Literature
101 results about "Flow shop scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flow shop scheduling problems, are a class of scheduling problems with a workshop in which the flow control shall enable an appropriate sequencing for each job and for processing on a set of machines or with other resources 1,2,...,m in compliance with given processing orders. Especially the maintaining of a continuous flow of processing tasks is desired with a minimum of idle time and a minimum of waiting time. Flow shop scheduling is a special case of job shop scheduling where there is strict order of all operations to be performed on all jobs. Flow shop scheduling may apply as well to production facilities as to computing designs.
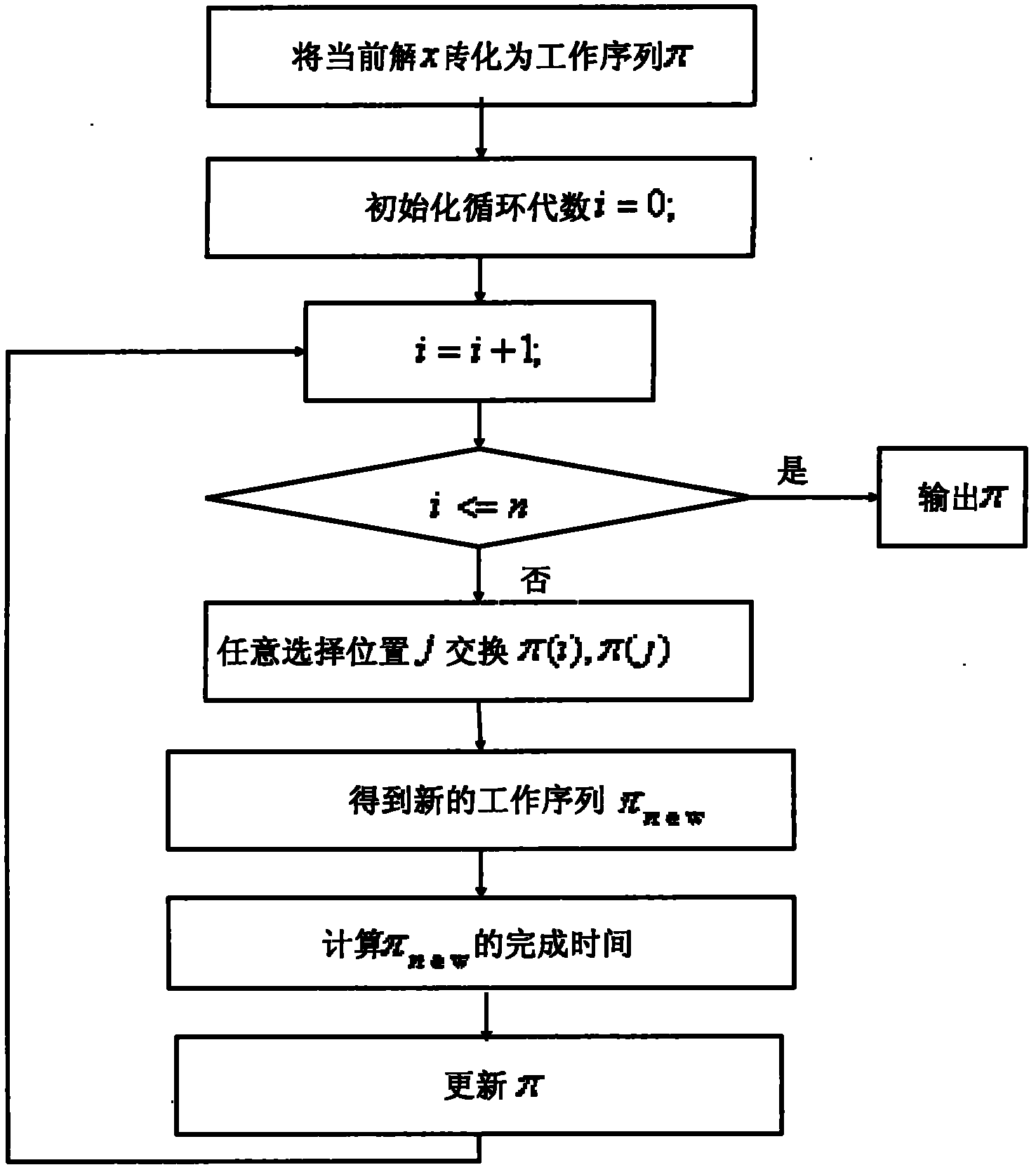
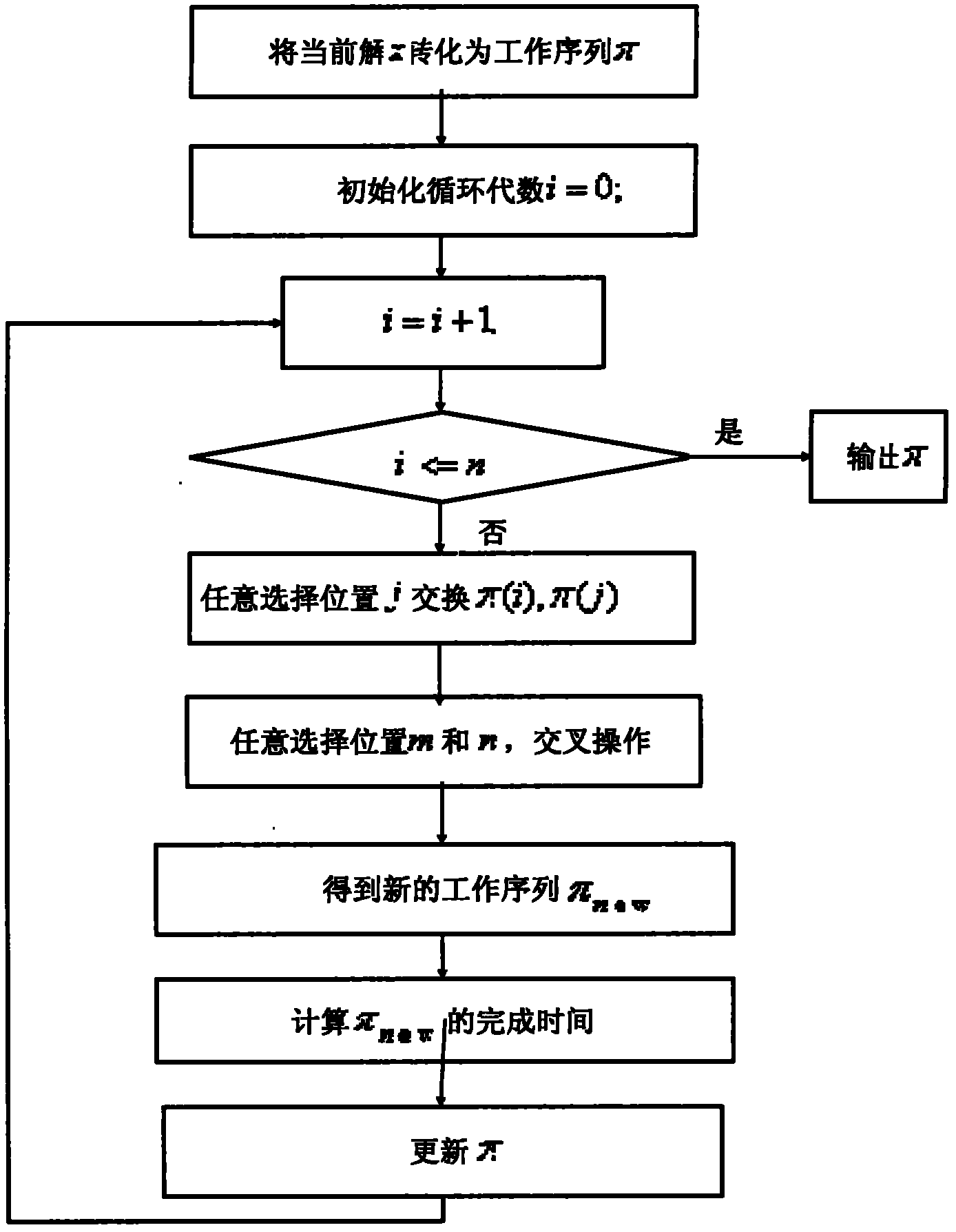
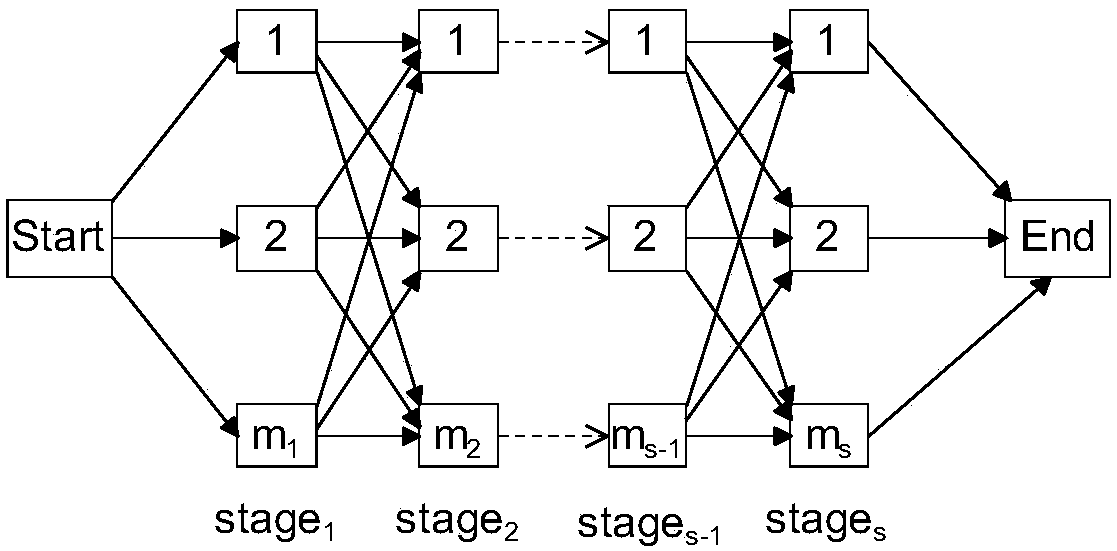
Hybrid flow shop scheduling method
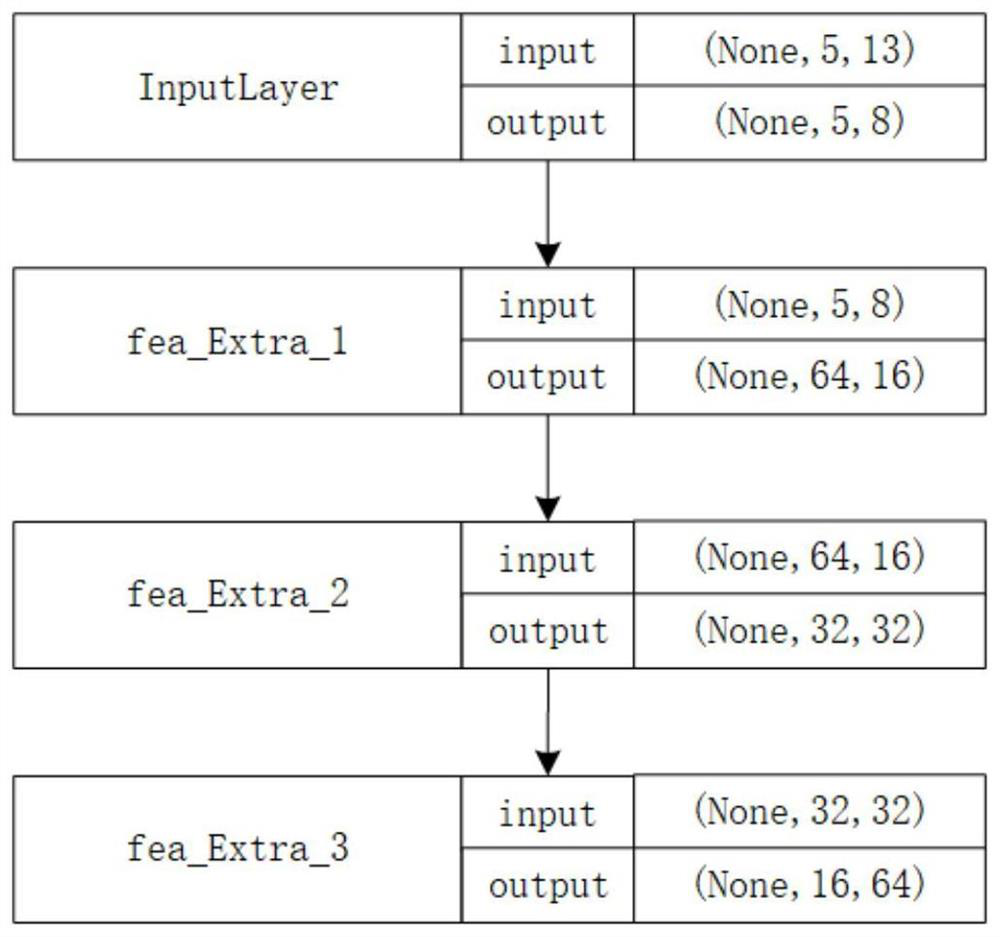
InactiveCN102929263ASolving Scheduling Optimization ProblemsSolve the real problemProgramme total factory controlBatch processingBatch phase
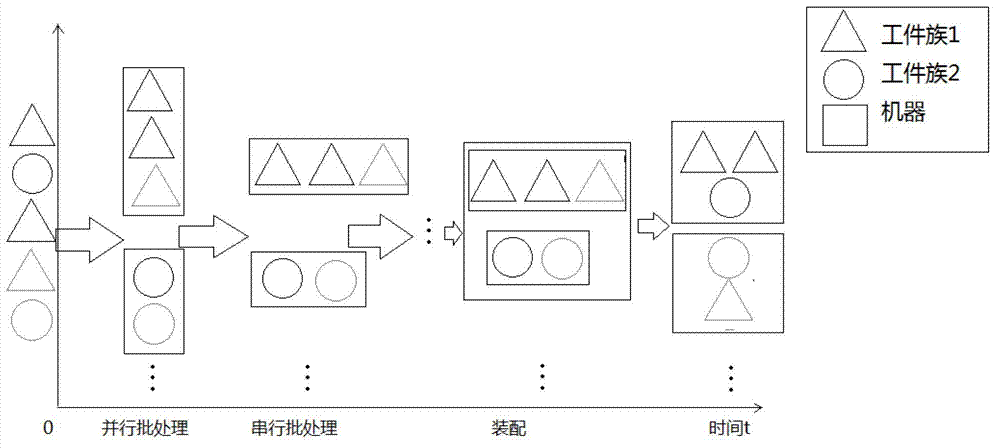
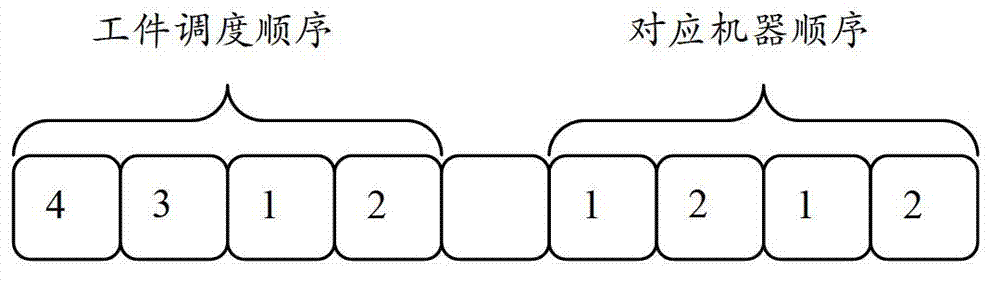
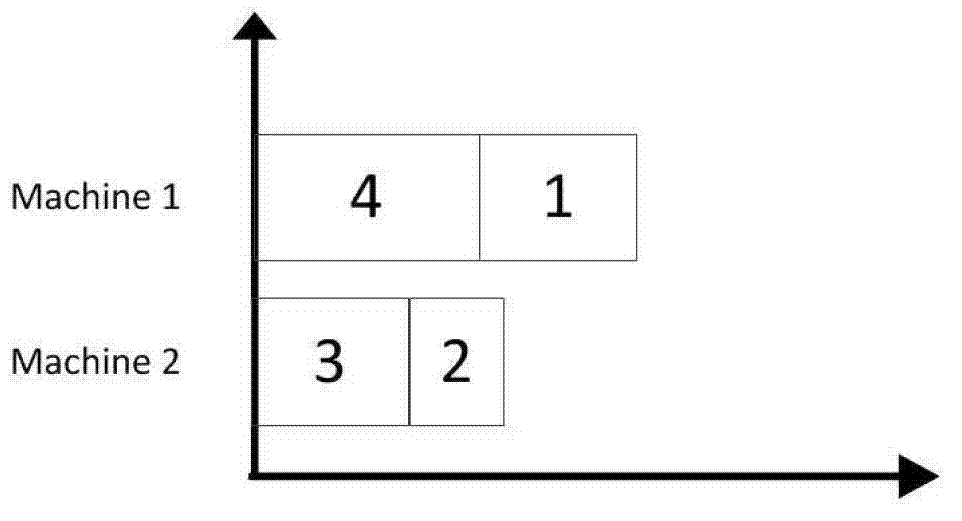
The invention relates to a hybrid flow shop scheduling method, which comprises the following steps of: dividing parts into multiple part sets based on different part families of the required parts; establishing a new batch for each part and performing batching based on the volume of a thermal treating funnel; after the batching, making a serial number for each batch and a machine, and encoding at each stage, wherein each stage comprises two sections of chromosomes, the first section of chromosome is a batch number, and the second chromosome is a machine serial number corresponding to the batch number; generating chromosomes at random when a user meets the conditions restricted by the machines; selecting N chromosomes, carrying out a pairwise cross operation on N selected chromosomes, carrying out a mutation operation on each chromosome, and then repairing the chromosomes; and repeating the steps of selection, cross operation, mutation and repairing till the maximum number of iterations is reached. With the method, the problem of a hybrid flow shop where the assembling affects the batching in the parallel batch processing phase can be solved, and the algorithm operation efficiency can be ensured.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for scheduling flow shop based on multi-swarm hybrid particle swarm algorithm
InactiveCN102222268AStrong local search abilityOvercome the defect of poor local search abilityGenetic modelsLocal optimumProbit model
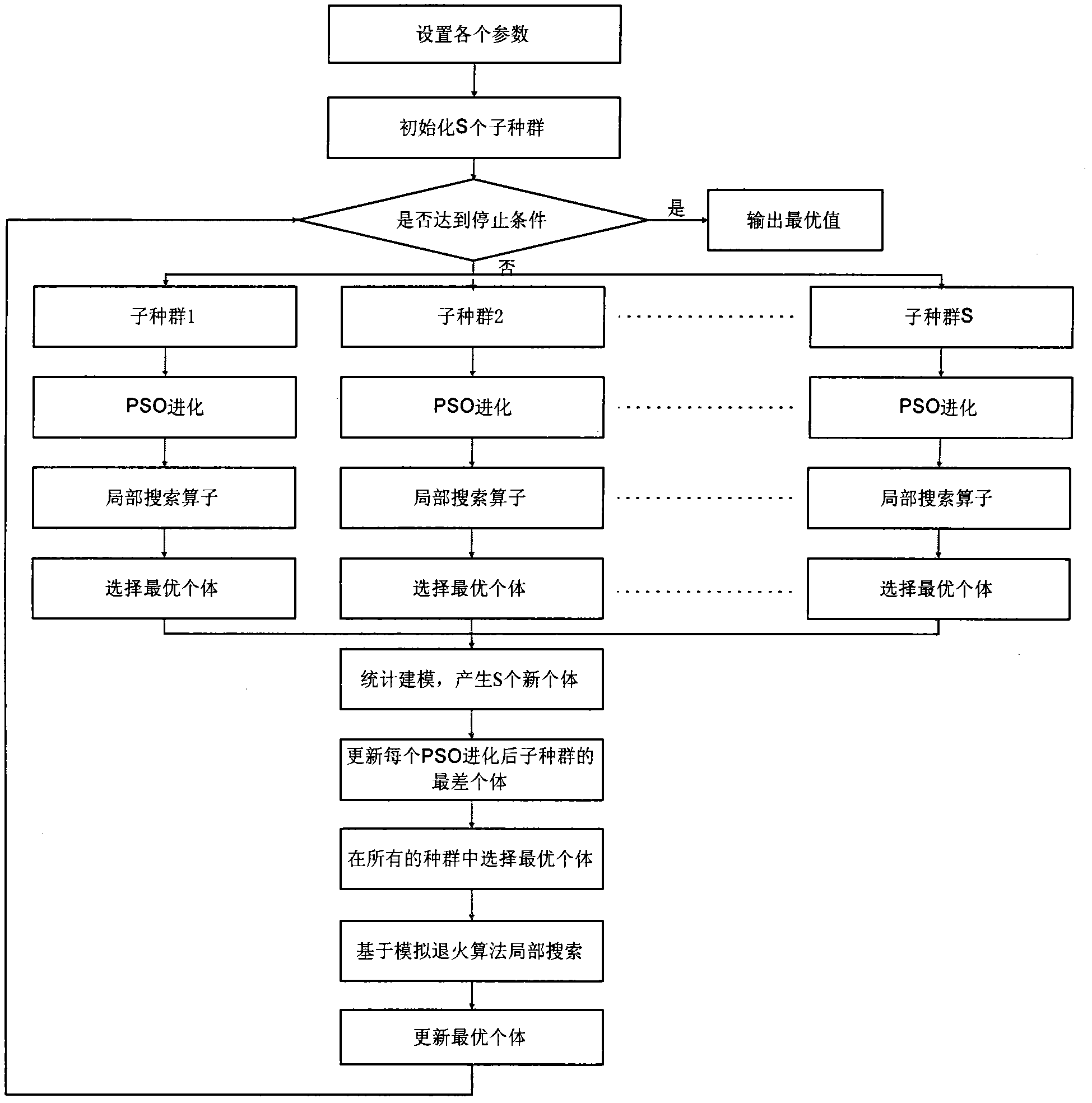
The invention belongs to the computer field, and discloses a method for scheduling a flow shop based on a multi-swarm hybrid particle swarm algorithm, which solves the problems that the flow shop scheduling method based on the hybrid particle swarm algorithm is easy to result in premature convergence and local optimum. The method comprises the following steps of: setting parameters and generating S sub-swarms; judging whether the terminal condition is satisfied, if so, outputting a current optimum scheduling scheme, otherwise, updating positions of particles in each sub-swarm with the particle swarm algorithm, carrying out a local search on odd and even sub-swarms respectively by using searching operators 1 and 2 to obtain an optimum scheduling sequence of each sub-swarm; sharing information of the obtained optimum scheduling sequence by using a statistics-based probability model; and optimizing an optimum working sequence with a simulated annealing algorithm. In the invention, multiple swarms are added, the local search is carried out by using different searching operators, a good flow shop scheduling scheme is obtained, the production time is shortened, and the method can be used for the selection of the job shop scheduling scheme.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
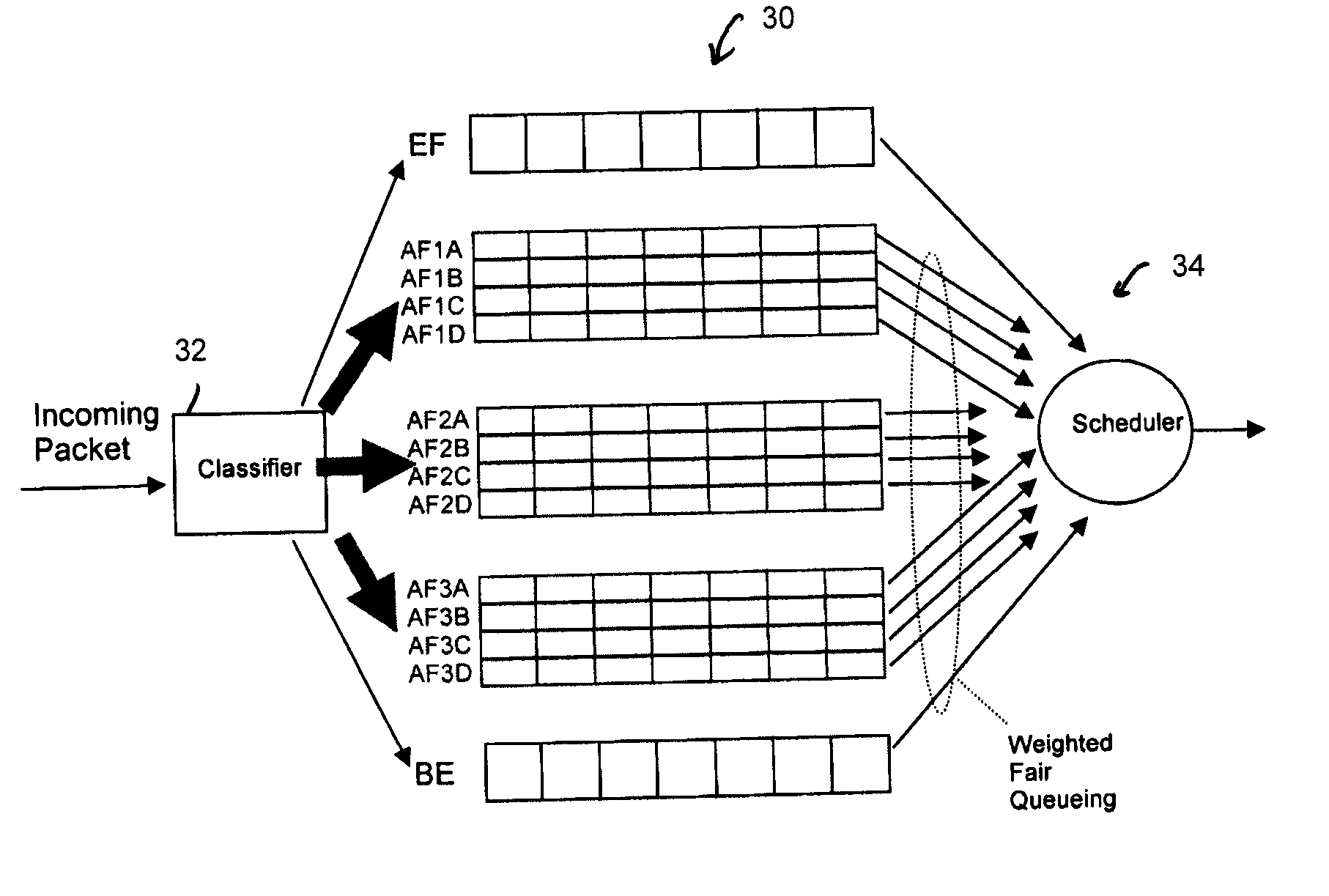
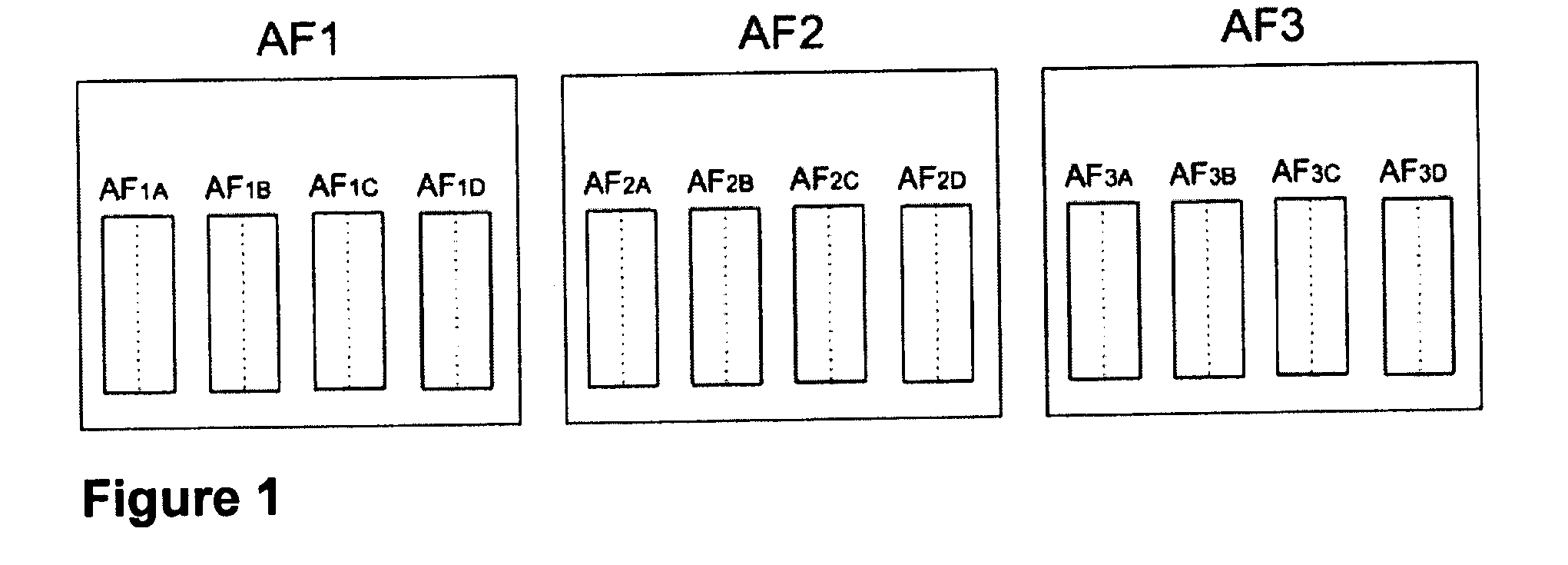
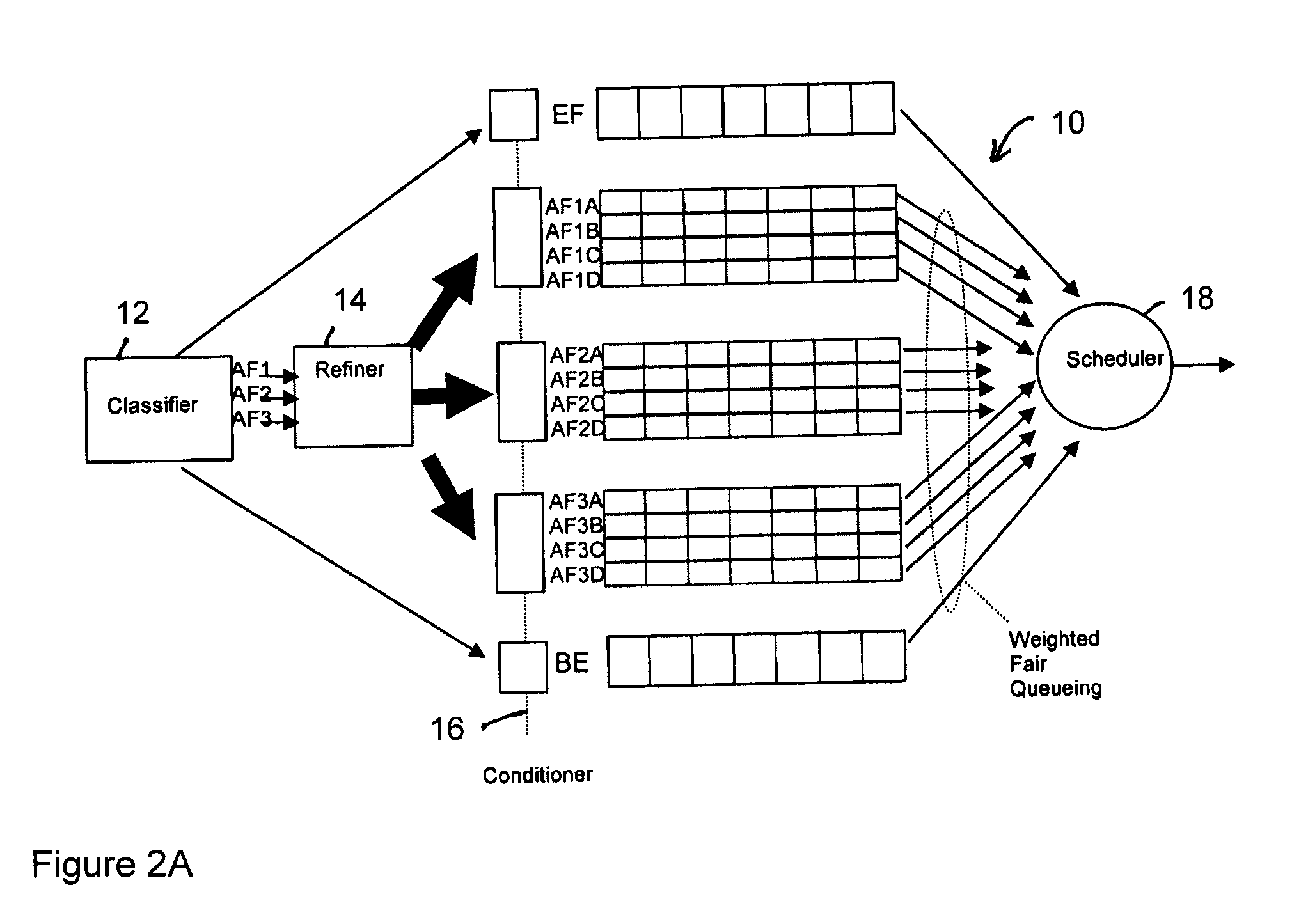
Refined Assured Forwarding Framework for Differentiated Services Architecture
InactiveUS20080080382A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesTraffic capacity
The DiffServ architecture is an increasingly preferred approach for providing varying levels of Quality of Service in an IP network. This discovery presents a new framework for improving the performance of the DiffServ architecture where heterogeneous traffic flows share the same aggregate class. The new framework requires minimal modification to existing DiffServ routers by adding a second layer of classification of flows based on their average packet sizes and using Weighted Fair Queueing for flow scheduling. The efficiency of the new framework is demonstrated by simulation results for delay, packet delivery, throughput, and packet loss, under different traffic scenarios.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
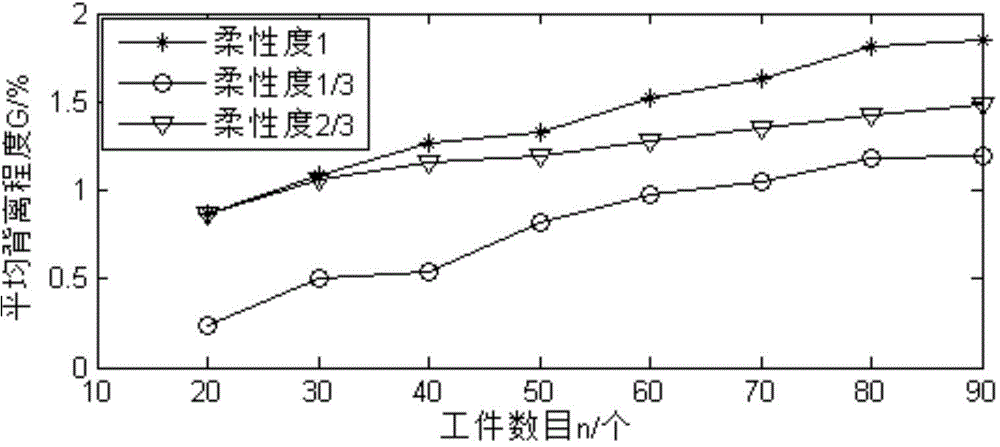
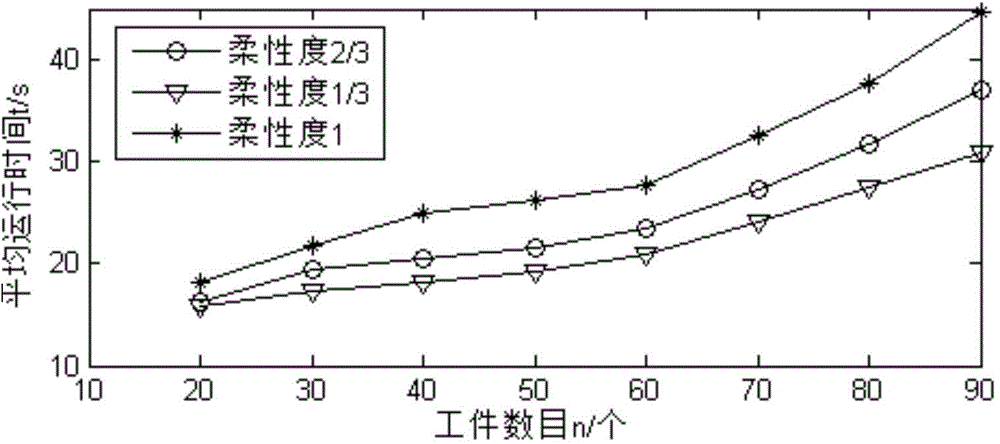
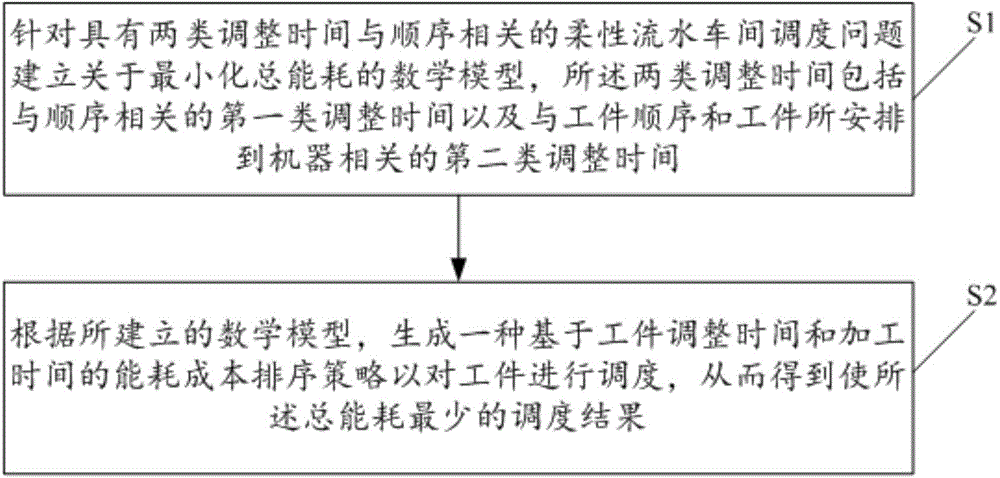
Flexible flow shop energy consumption optimization scheduling method
ActiveCN104808636ALow total energy costHigh energy consumptionTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlMathematical modelComputer science
The invention discloses a flexible flow shop energy consumption optimization scheduling method which has two kinds of adjustment time and is sequence dependent. The method includes the steps: (1) establishing a mathematical model in regard to minimization of total energy consumption for a flexible flow shop scheduling problem which has two kinds of adjustment time and is sequence dependent, wherein the two kinds of adjusting time include a first kind of adjusting time related to sequence and a second kind of adjusting time related to workpiece sequence and machines that workpieces are arranged to; (2) according to the established mathematical model, generating an energy consumption cost ordering strategy based on the workpiece adjusting time and processing time to schedule the workpieces so as to obtain scheduling results enabling the total energy consumption to be least.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
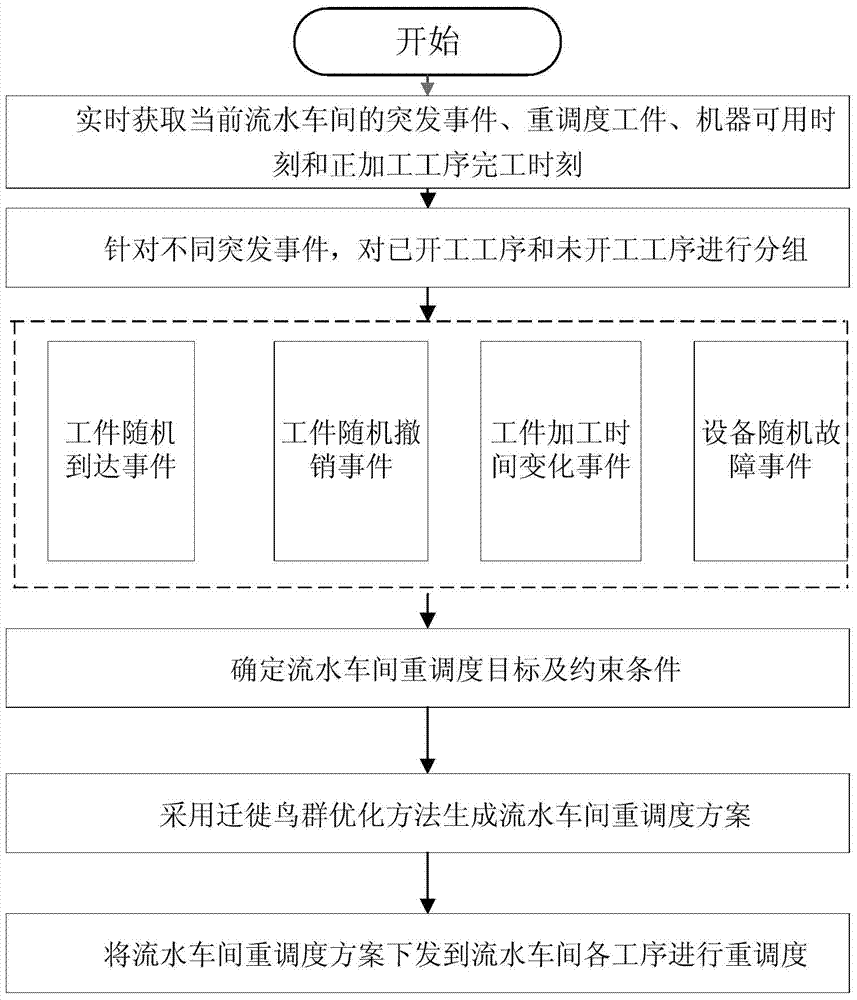
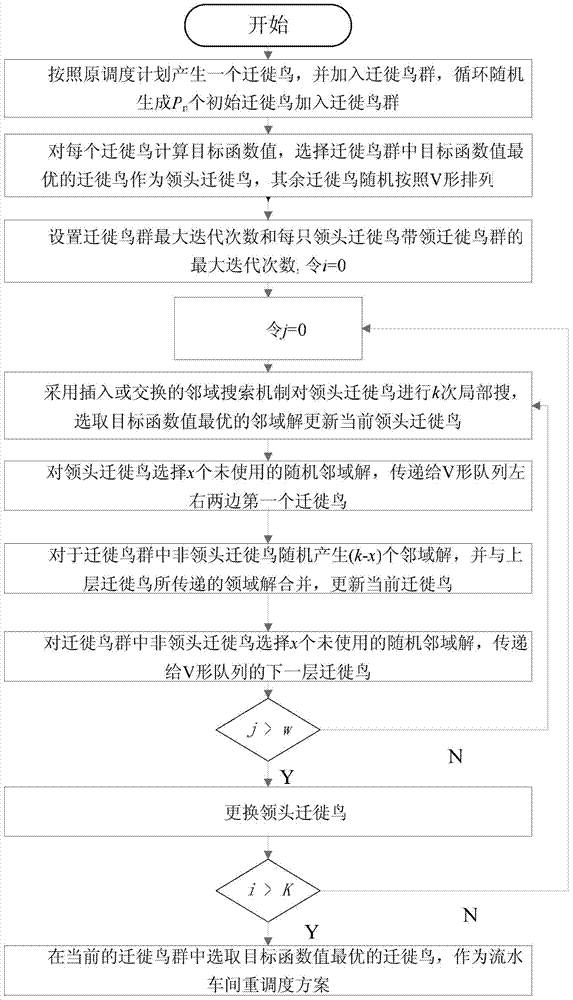
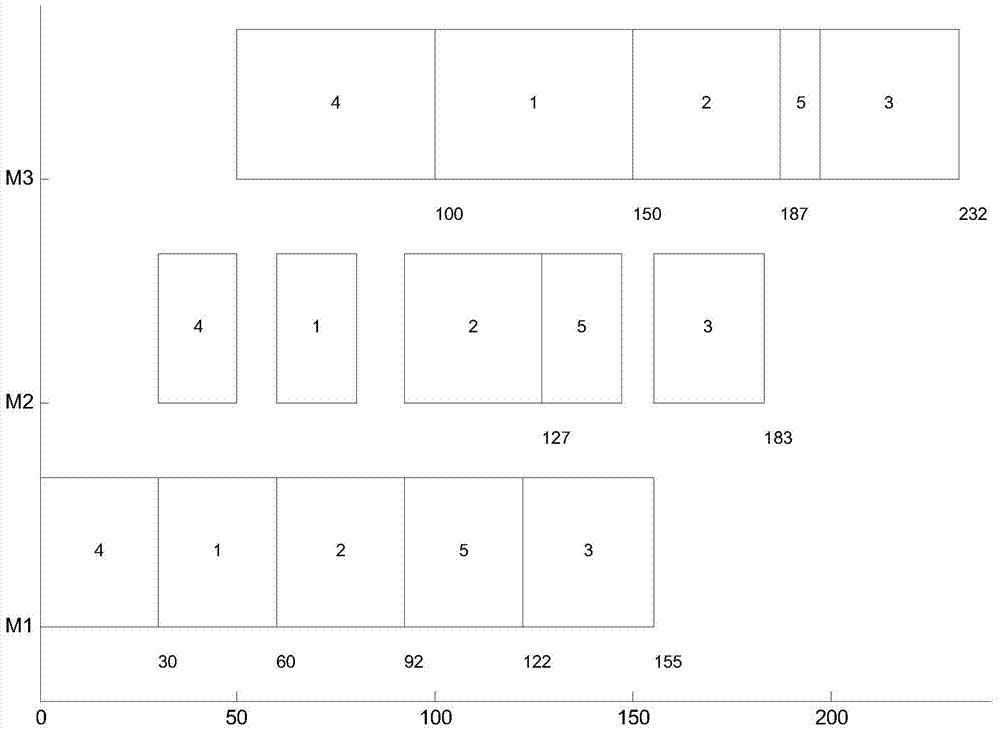
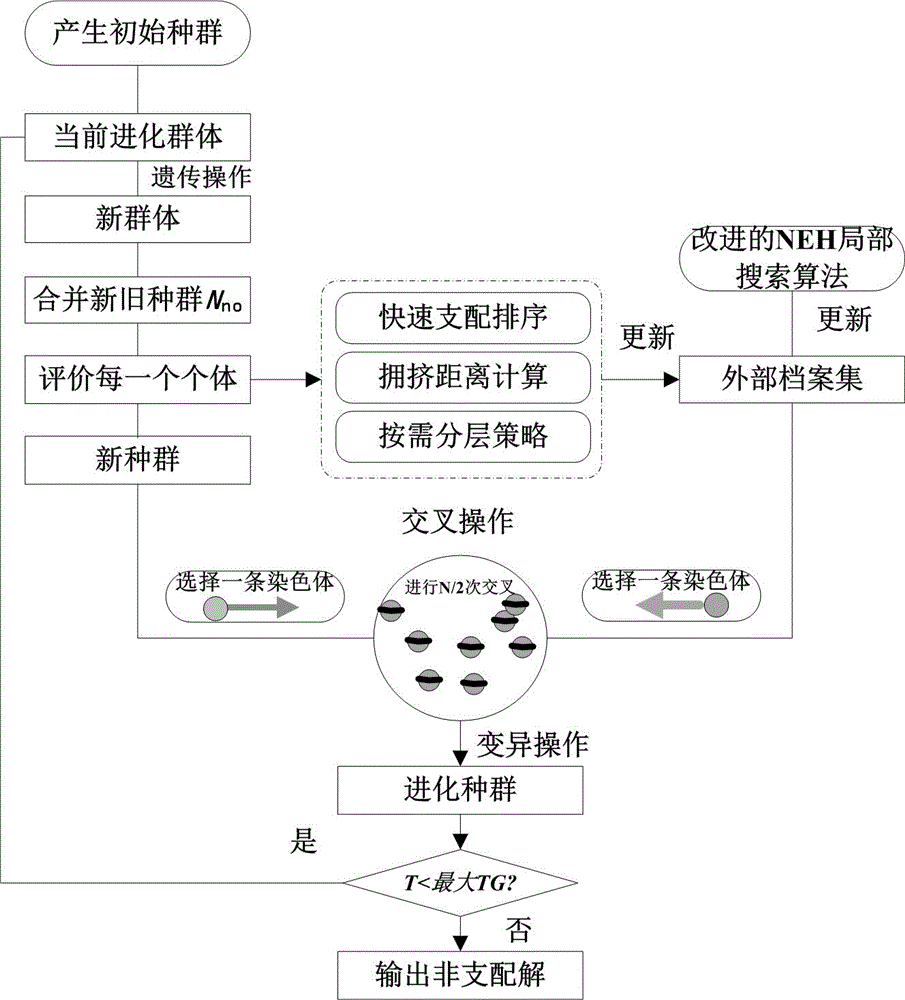
Flow shop rescheduling method
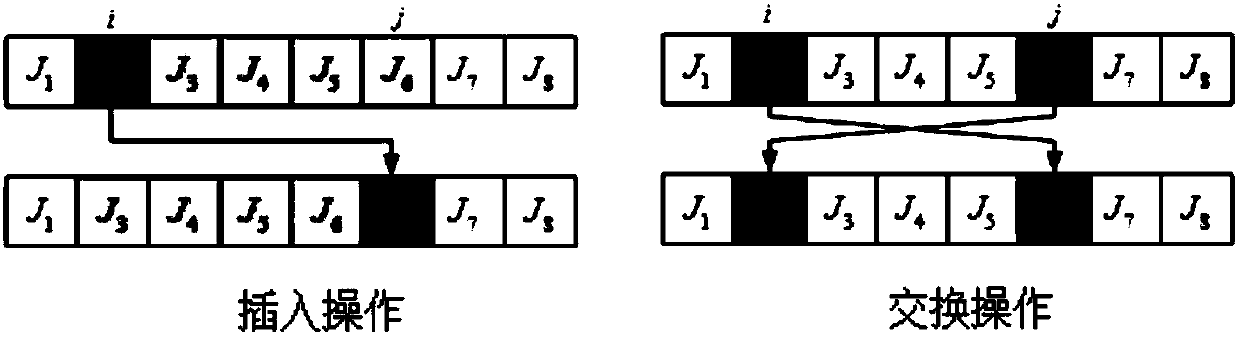
ActiveCN103676902AEnsure diversityGuarantee stabilityProgramme total factory controlCompletion timeNeighborhood search
The invention provides a flow shop rescheduling method which belongs to the technical field of shop scheduling. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring unexpected events, rescheduling workpieces, time available for machinery and manufacturing process completion time of a current flow shop in real time; for different unexpected events, grouping processes which are started and processes which are not started; determining rescheduling objectives and constraints of the flow shop; generating a rescheduling scheme of the flow shop using the particle swarm optimization; sending the rescheduling scheme of the flow shop to each process of the flow shop for rescheduling. The rescheduling method uses a particle swarm optimization to solve the problem of flow shop rescheduling, takes account of a variety of unexpected events, to guarantee rapid response among the unexpected events, uses inserted or exchanged neighborhood search mechanisms to effectively guarantee that the rescheduling scheme is used for processing in time between two unexpected events, constantly transmits search information to the subsequent migratory birds, and constantly swaps the lead bird, thereby ensuring the diversity and stability of scheduling schemes.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Optimizing and dispatching method of energy consumption of flexible flow shop with associated adjustment time and sequence
InactiveCN104391488AHigh energy consumptionLow costEnergy industryProgramme total factory controlMathematical modelHeuristic
The invention discloses an optimizing and dispatching method of energy consumption of a flexible flow shop with associated adjustment and sequence. The method comprises the following steps: S1, searching on the dispatching problem of the flexible flow shop having adjustment time associated with sequence, wherein the adjustment time is defined into one associated with workpiece sequence and the other one associated with workpiece sequence and machines; S2, establishing the following mathematic models; S3, using the minimum overall energy consumption as a target and providing three heuristics algorithms with respect to a problem existing in the problems resolved with an NEH algorithm; S4, verifying the above three algorithms, providing two lower bounds of the problem and designing one simulation experiment based on a split block experiment; S5, analyzing factors, algorithms, lower bounds and CPU operational time according to the simulation results. According to the optimizing and dispatching method of energy consumption of the flexible flow shop with associated adjustment and sequence, the energy consumption is optimized and the cost is saved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Improved particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm of solving zero-waiting flow shop scheduling problem
ActiveCN108053119AImproved Particle Swarm Optimization AlgorithmImprove global search performanceArtificial lifeResourcesCompletion timeNew population
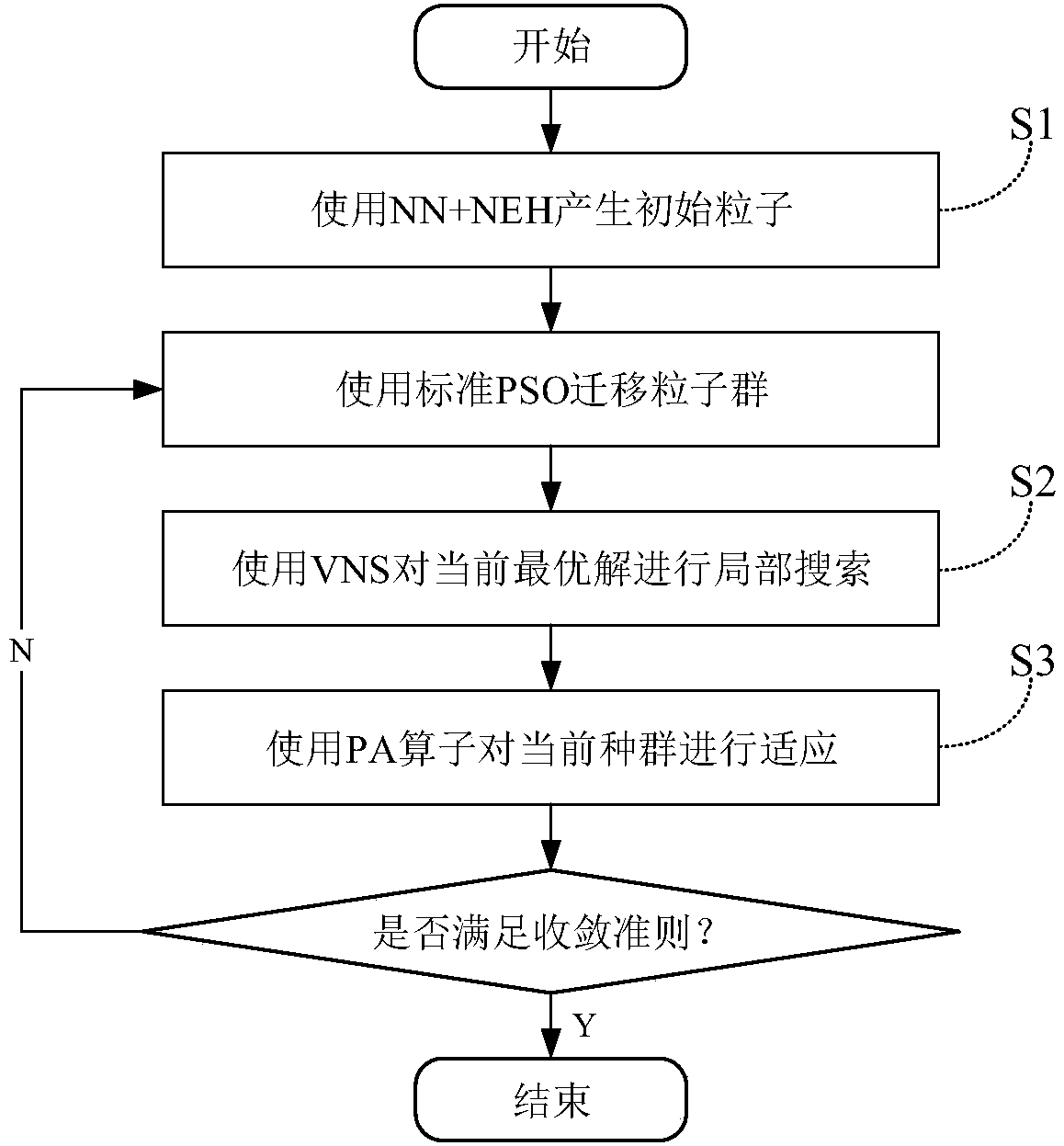
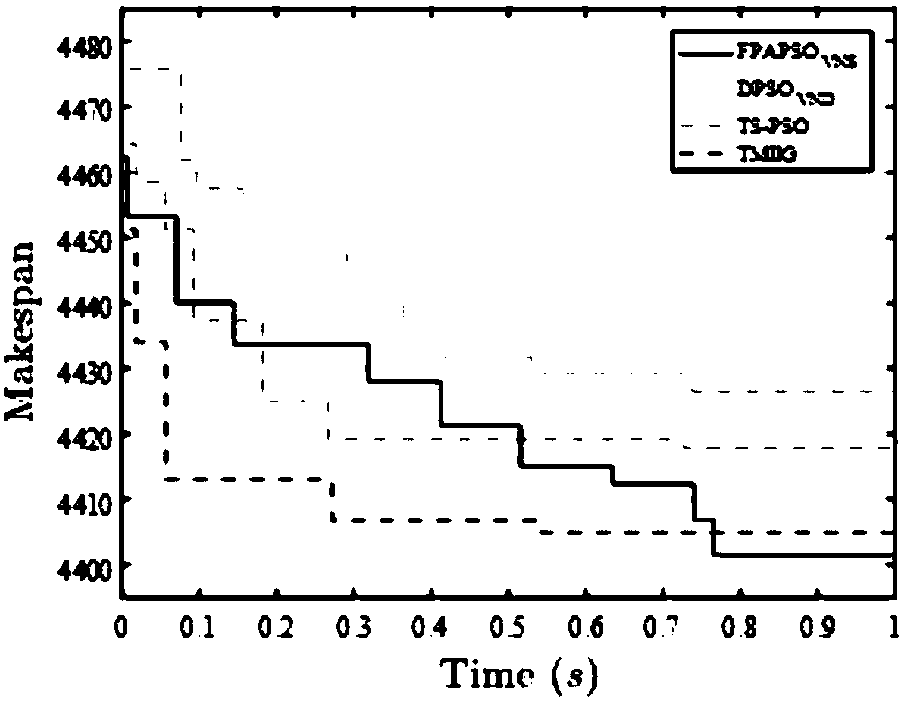
The invention discloses an improved particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm of solving the zero-waiting flow shop scheduling problem. Firstly, parameter initialization and population initialization are carried out, wherein initial workpiece sequences are generated, then a factorial encoding method is used to map all permutations to integers to form an initial population, and finally, a feasible initial velocity set is randomly generated; particles are moved; the population is updated through an original PSO population updating strategy, a new population is mapped to corresponding workpiecesequences, and work completion time of each new workpiece sequence is evaluated; an improved variable neighborhood search (VNS) algorithm is used for a local search, and results obtained by the search are used for replacement; a population adaption (PA) operator is used to increase diversity of the population; and checking of a termination condition is carried out, if the termination condition ismet, a process is stopped, and values of variables and corresponding sequences are returned to be used as a final solution, and otherwise, particle velocity is continuously updated. The method has the advantages of improving a particle swarm optimization algorithm, improving global search capability, and avoiding too early convergence.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
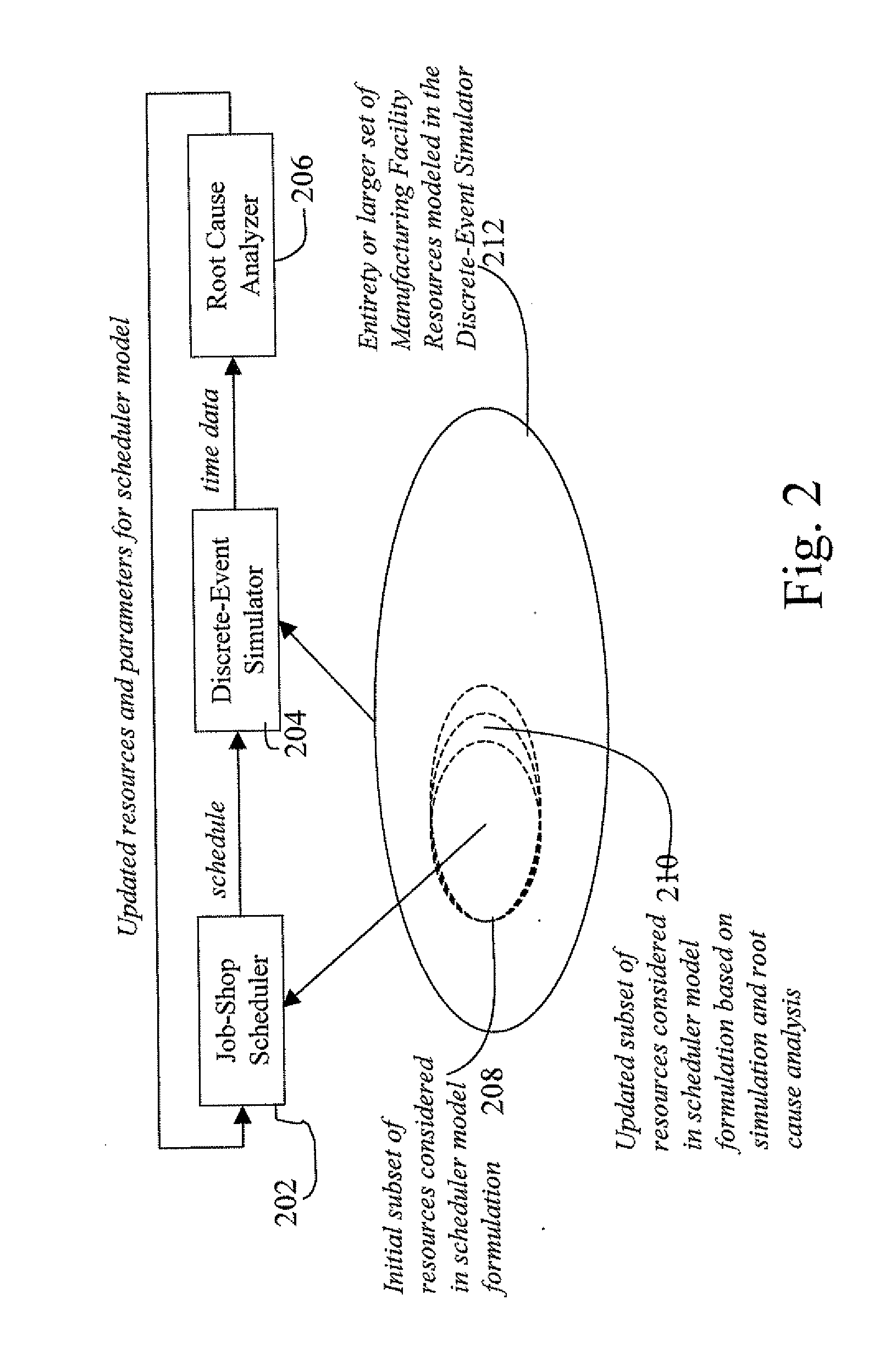
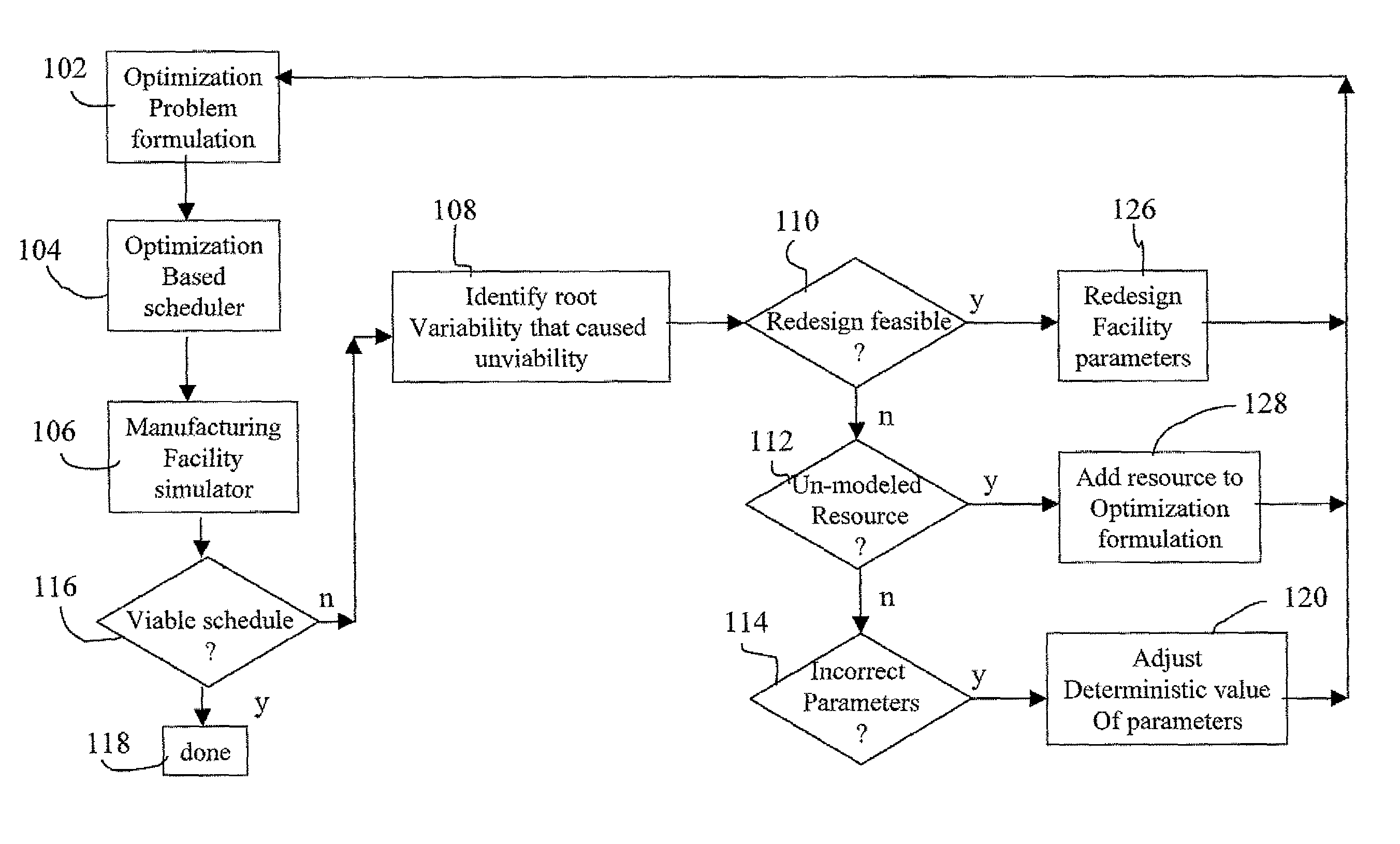
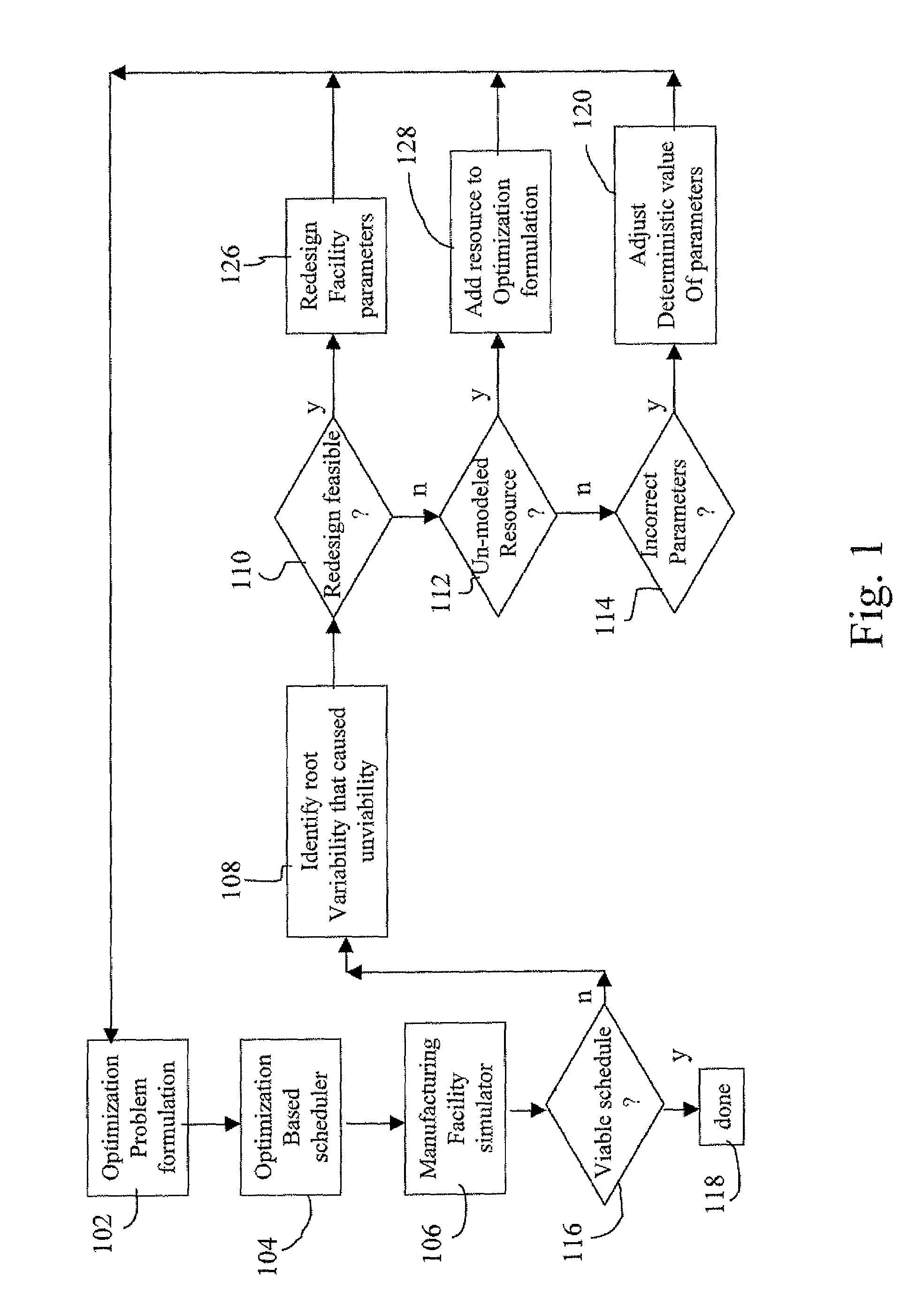
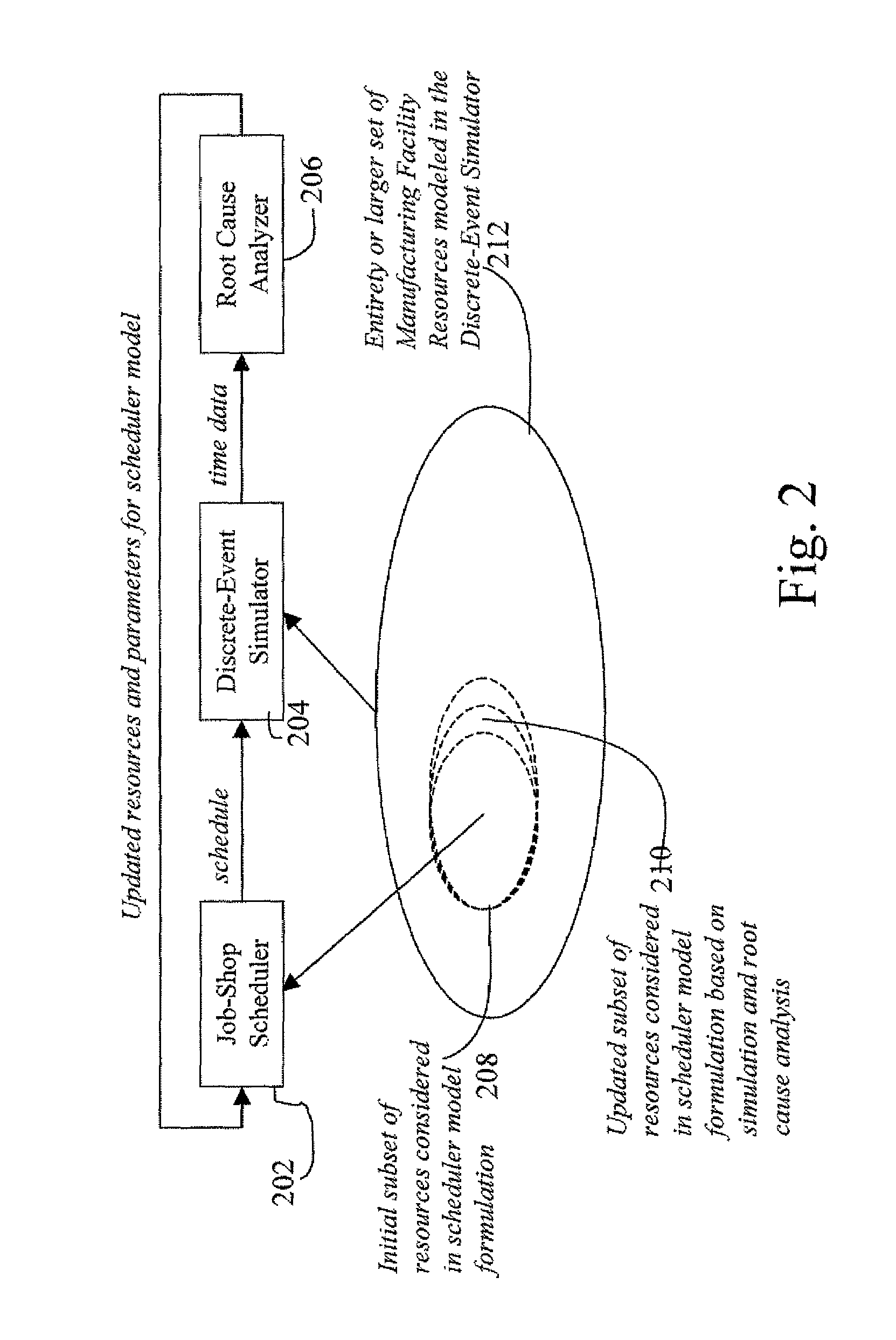
Integration of job shop scheduling with discrete event simulation for manufacturing facilities
ActiveUS20080300705A1Enhancing job shop scheduling formulationRobust scheduleProgramme controlResourcesProgram planningDiscrete event simulation
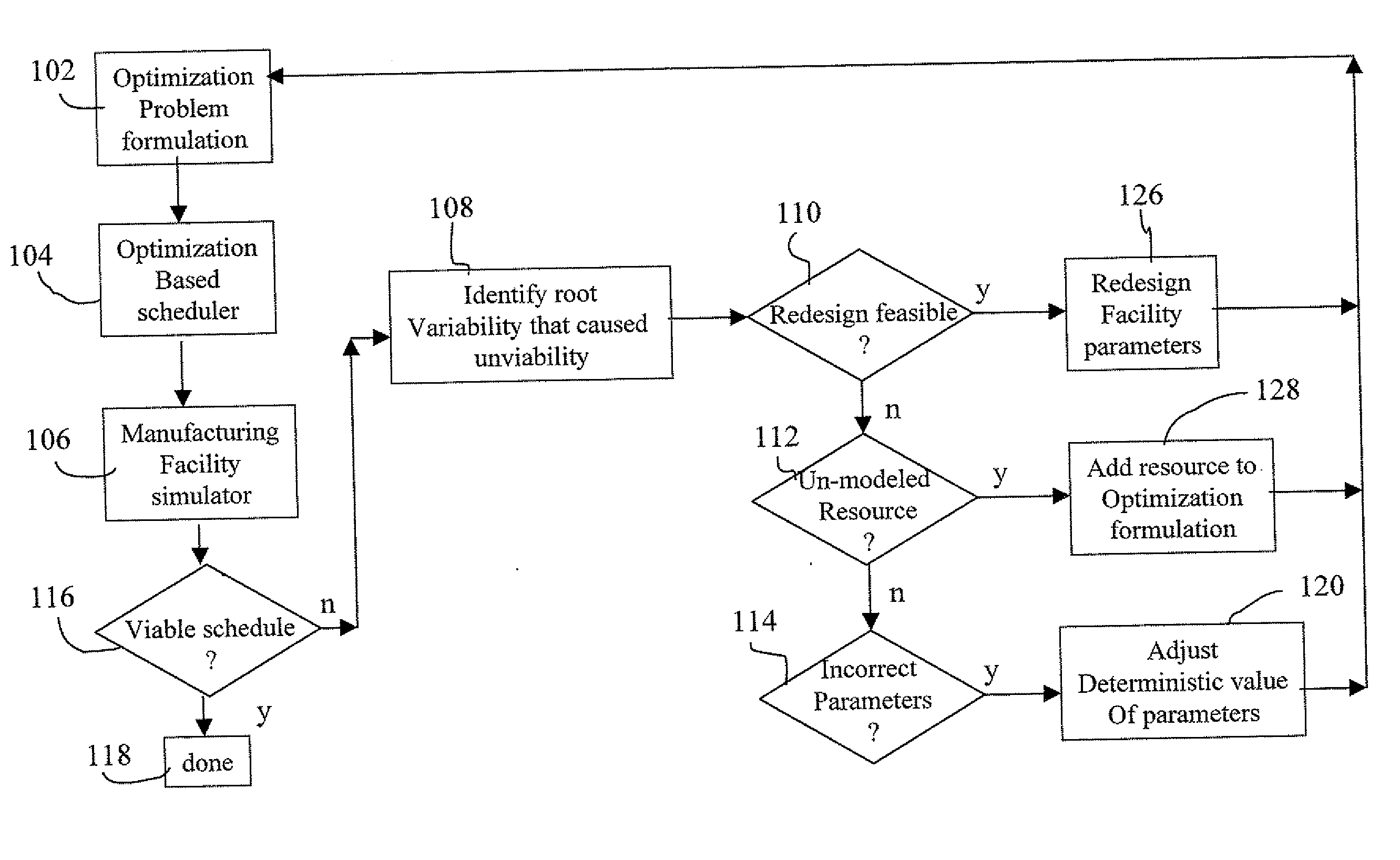
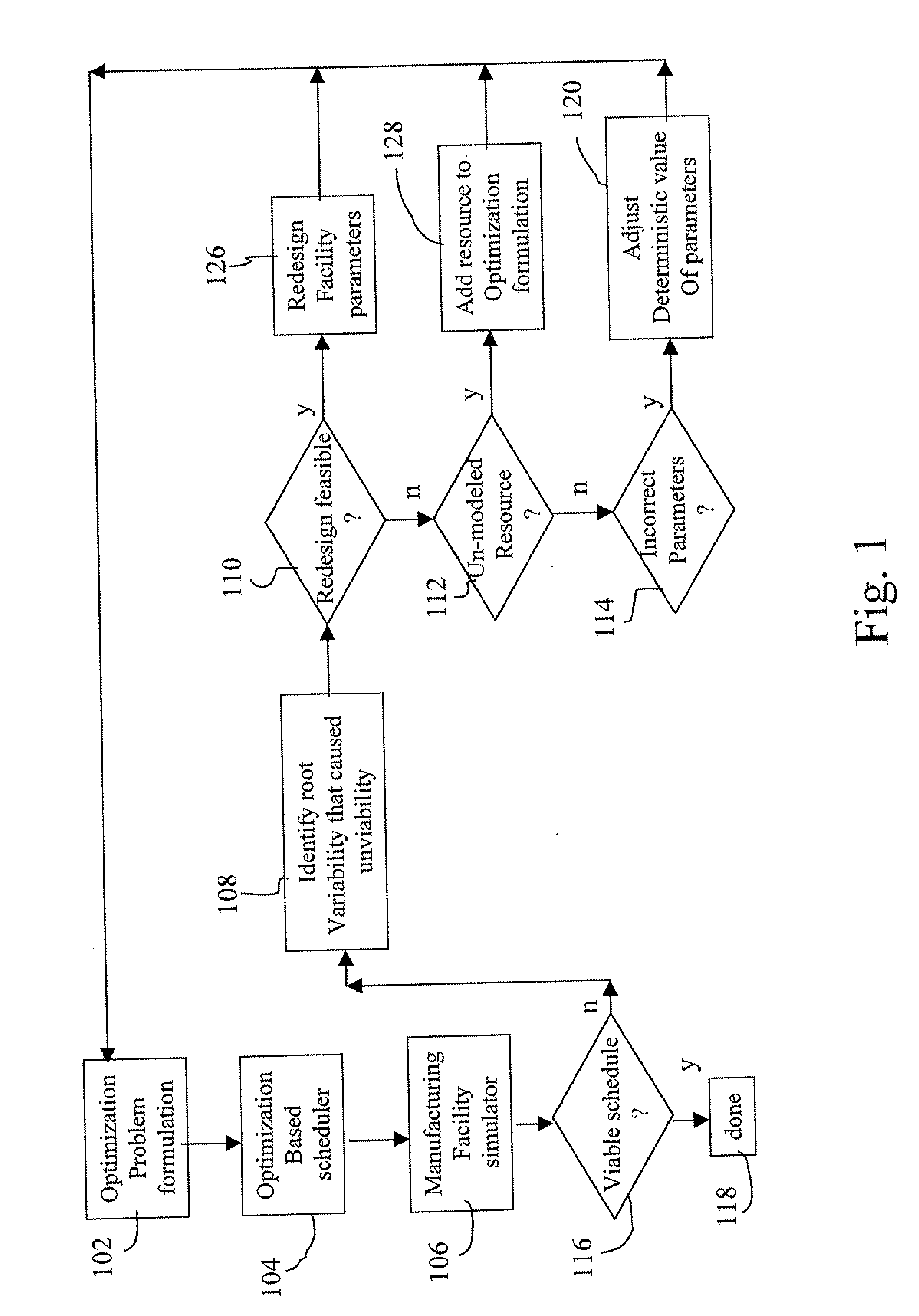
A method and system for integrating job shop scheduling with discrete event simulation for manufacturing facilities are provided. In one aspect a simulator simulates discrete events of a facility using a job schedule generated by a scheduler. The simulator simulates the facility based on one or more local rules, one or more resources, and one or more parameters associated with said locals rules and said resources. The simulator further models said one or more parameters as random variables and using said random variables in its simulation of the facility. The scheduler receives feedback based on output from the simulating step. The feedback includes at least an instruction to the scheduler to include at least one of said one or more resource and to change said one or more parameters based on said modeling of said one or more parameters as random variables. The scheduler uses the feedback for generating an updated schedule.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Integration of job shop scheduling with discreet event simulation for manufacturing facilities
Owner:TWITTER INC
Flexible job shop batch optimization scheduling method having intermediate storage constraint
ActiveCN106971235AFast solutionImprove search abilityForecastingResourcesOptimal schedulingComputer science
The invention discloses a flexible job shop batch optimization scheduling method having intermediate storage constraint, and belongs to the technical field of shop scheduling. The method includes: establishing a flexible job shop optimization scheduling problem model and initializing parameters; considering a constrained condition of a limited storage amount of an intermediate storage warehouse; obtaining machining paths of any different types of workpiece batches; batching the different types of workpieces, and determining a batch dividing scheme thereof; selecting production equipment of each process for the workpiece batches in a random sequence according to the preference probabilities thereof; selecting proper workpiece sub-batches from a waiting batch queue thereof for machining by the equipment according to the preference probabilities thereof; obtaining the scheduling scheme until the number of accomplished batches is equal to the total batch number; and performing iterative operation, and outputting an optimal scheduling method. According to the method, the utilization rate of the equipment can be greatly increased, the whole production cycle is shortened, the production efficiency is improved, and flexile job shop batch optimization scheduling is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Improved particle swarm optimization method based on streamline production scheduling of fuzzy due date
InactiveCN101859100AImprove optimization solution effectImprove the ability to jump out of local optimal solutionsAdaptive controlNeighborhood searchTabu search
The invention relates to an improved particle swarm optimization method based on flow production scheduling of a fuzzy due date. The optimal solution of the existing algorithm can not be found easily. The method comprises the following steps: using the penalty function for neighborhood block design of key lines based on the needs of the flow shop scheduling of the fuzzy due date, establishing a taboo table, and adopting the neighborhood search strategy, thereby enhancing the effect of optimal solution of the improved particle swarm algorithm. Since the stagnation can easily occur to the particle swarm optimization, the concepts of exchange operators and exchange sequences are introduced to reconstruct the particle location formula and the speed optimization formula of the particle swarm optimization, and the introduction of the taboo search algorithm helps the particle swarm optimization to search the best solution in the local area. Simulation experiments on the flow production scheduling of the fuzzy due date demonstrate that the improved particle swarm optimization method facilitates the overall solution.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Particle swarm optimization manufacturing system double-target production scheduling method based on bionic strategy
InactiveCN110598941AFast convergenceAvoid premature convergenceForecastingArtificial lifeInformatizationDecision taking
The invention discloses a particle swarm optimization manufacturing system double-target production scheduling method based on a bionic strategy, and the method comprises the steps: firstly building amixed flow shop scheduling mathematic model, and determining a scheduling process constraint condition and a target function needing to be solved; proposing particle encoding and decoding based on matrix expression; proposing a speed updating rule based on a hormone regulation mechanism; and proposing a particle swarm optimization algorithm based on a bionic strategy, solving the workshop scheduling model and obtaining a scheduling scheme. The invention provides a particle swarm optimization manufacturing system double-target production scheduling method based on a bionic strategy. Accordingto the system, resource arrangement, capacity balance, quality management, cost and delivery time of enterprises can be controlled, problems on a production line are analyzed and explored, correct technology and management decisions are made for informatization, standardization and automatic construction of the enterprises, and therefore the operation efficiency of the manufacturing enterprises isimproved, and benefits are obtained to the maximum extent.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Distributed assembly type permutation flow shop scheduling optimization method and system
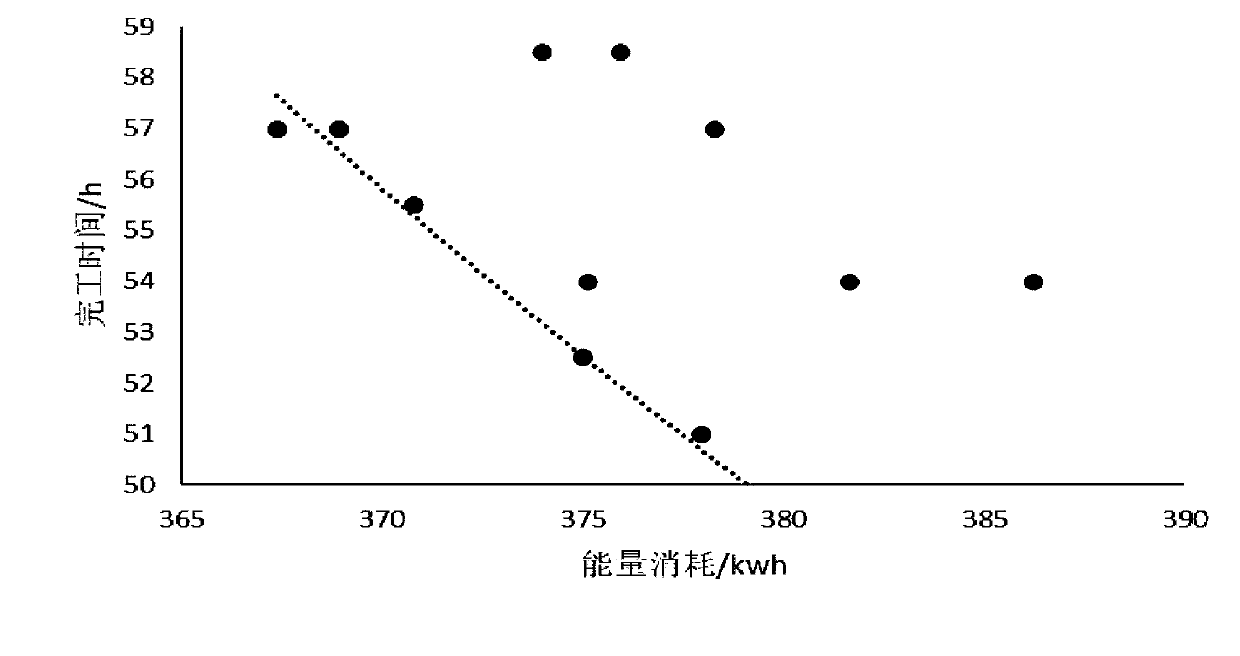
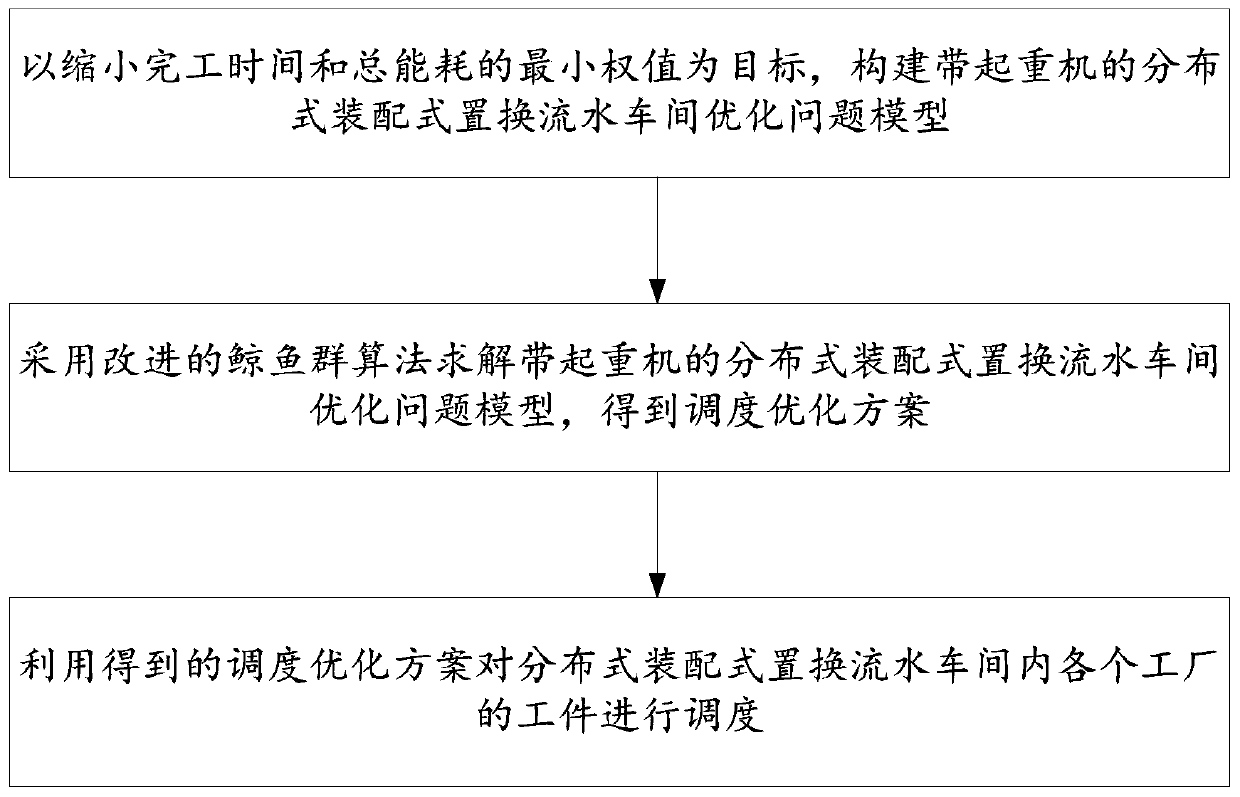
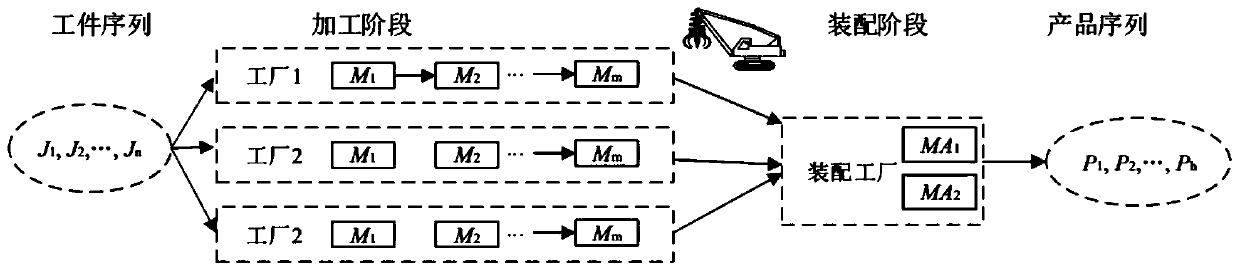
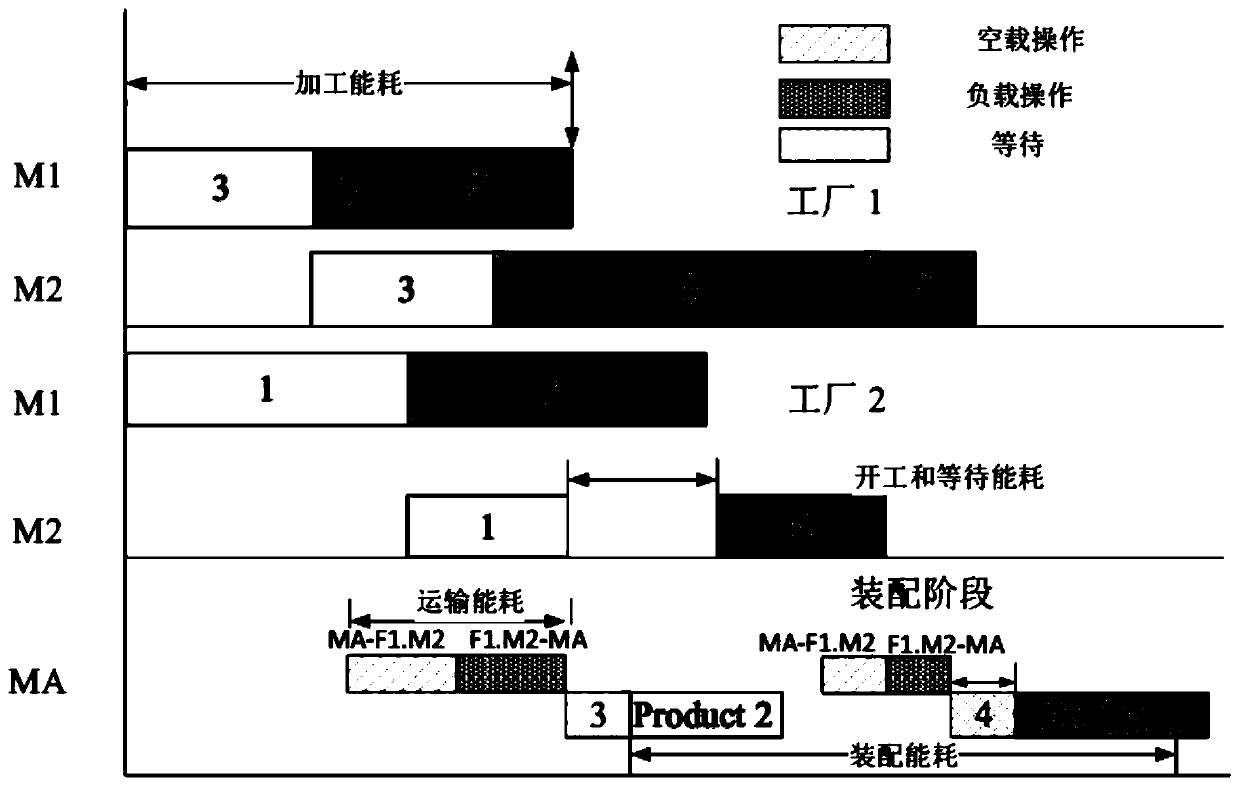
ActiveCN110632907AShorten completion timeReduce energy consumptionProgramme total factory controlCompletion timeMinimum weight
The invention discloses a distributed assembly type permutation flow shop scheduling optimization method and system. The efficiency of a distributed permutation flow shop is increased; and the completion time and the energy consumption are reduced. The method comprises the steps of: with the purpose of reducing the minimum weight value of the completion time and the total energy consumption, constructing a distributed assembly type permutation flow shop optimization problem model with a crane; solving the distributed assembly type permutation flow shop optimization problem model with the craneby adopting an improved whale swarm algorithm, so that a scheduling optimization scheme is obtained; and scheduling work-pieces of various factories in the distributed assembly type permutation flowshop by utilizing the obtained scheduling optimization scheme.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Improved solving algorithm for flexible flow shop scheduling problem
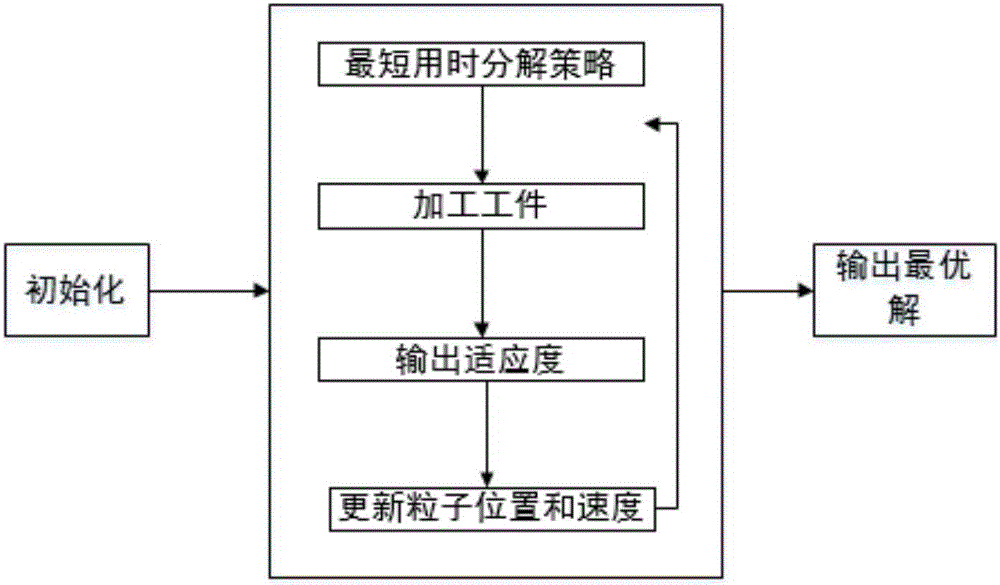
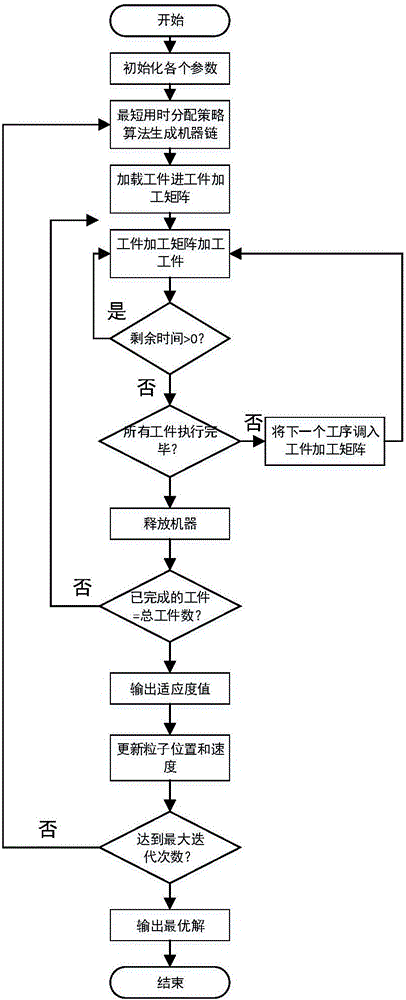
The invention provides an improved solving algorithm for a flexible flow shop scheduling problem. Particle velocity and position correlation operators are redefined. A coding matrix and a decoding matrix are introduced to represent the relationship among workpiece, machine and scheduling. In order to improve the initial group quality of the improved discrete particle swarm algorithm for the flexible flow shop scheduling problem, a shortest time decomposition policy algorithm based on an NEH algorithm is proposed for the first time by analyzing the relationship between initial machine selection and total completion time of scheduling. The improved discrete particle swarm algorithm is used for global optimization. The algorithm has the advantages that the quality of the initial solution of a particle population is improved; and the time for particles to find the optimal solution is shortened; and an inertial weighting method with exponential decrease is used to effectively avoid the premature convergence of the particles and enhance the early global search ability of the particles.
Owner:SICHUAN YONGLIAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
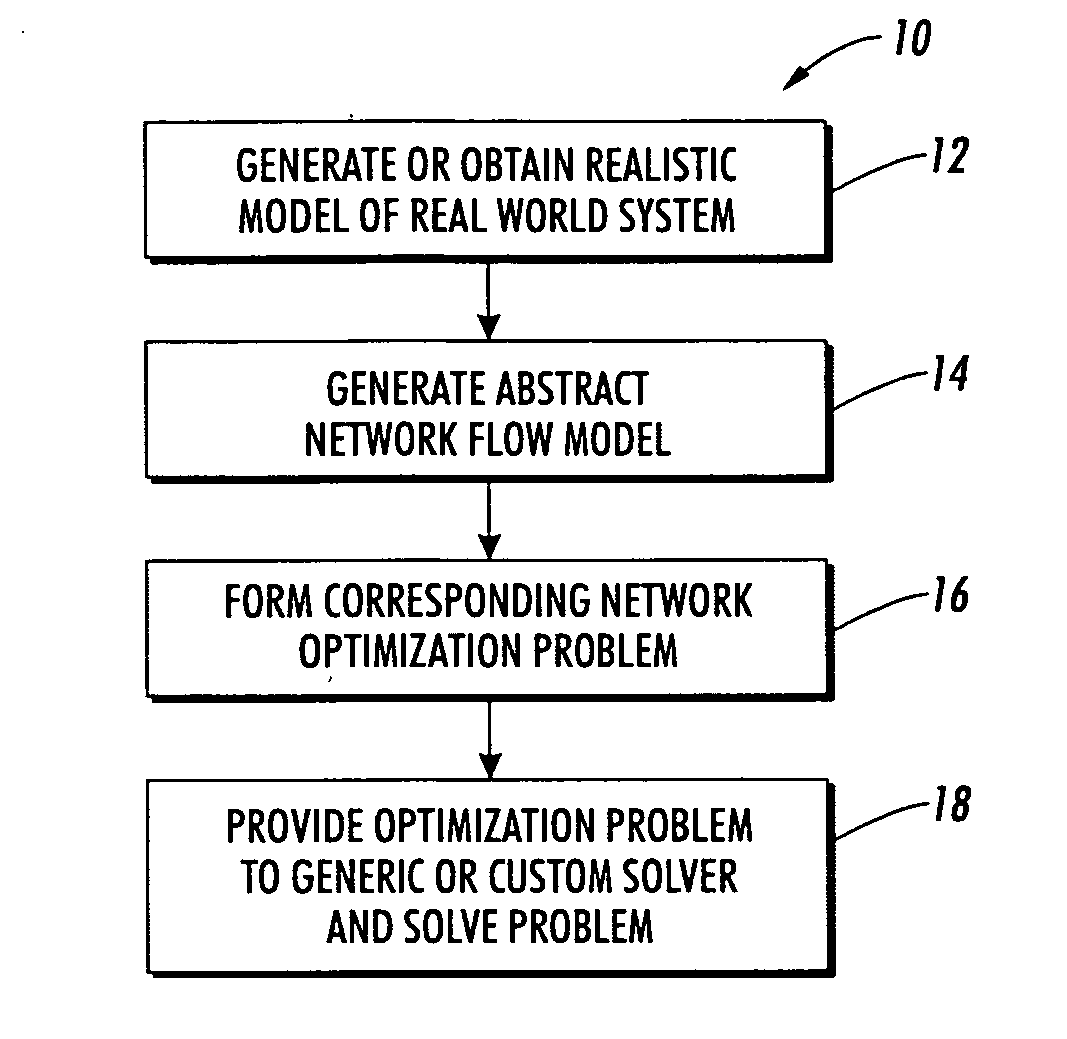
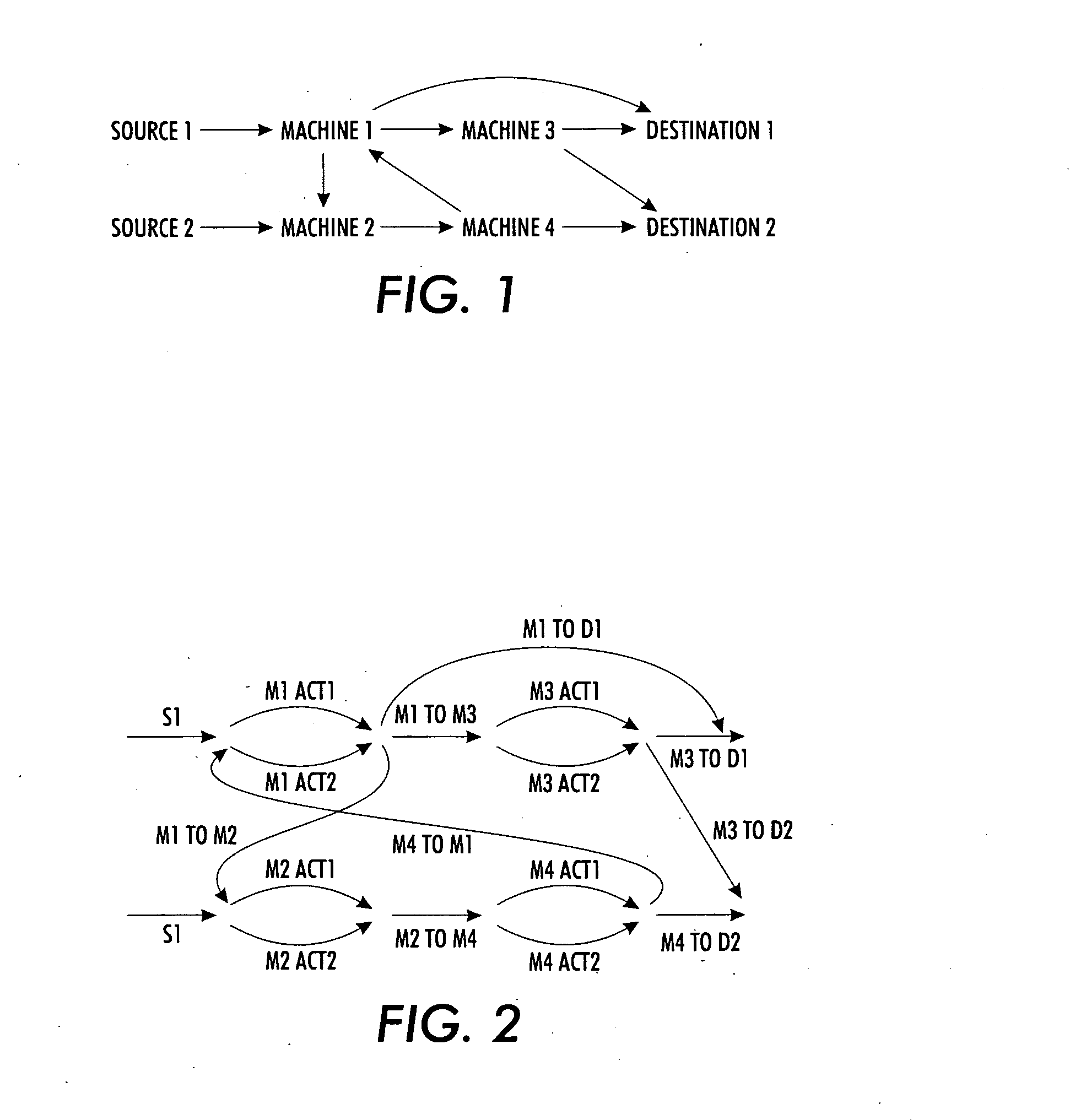
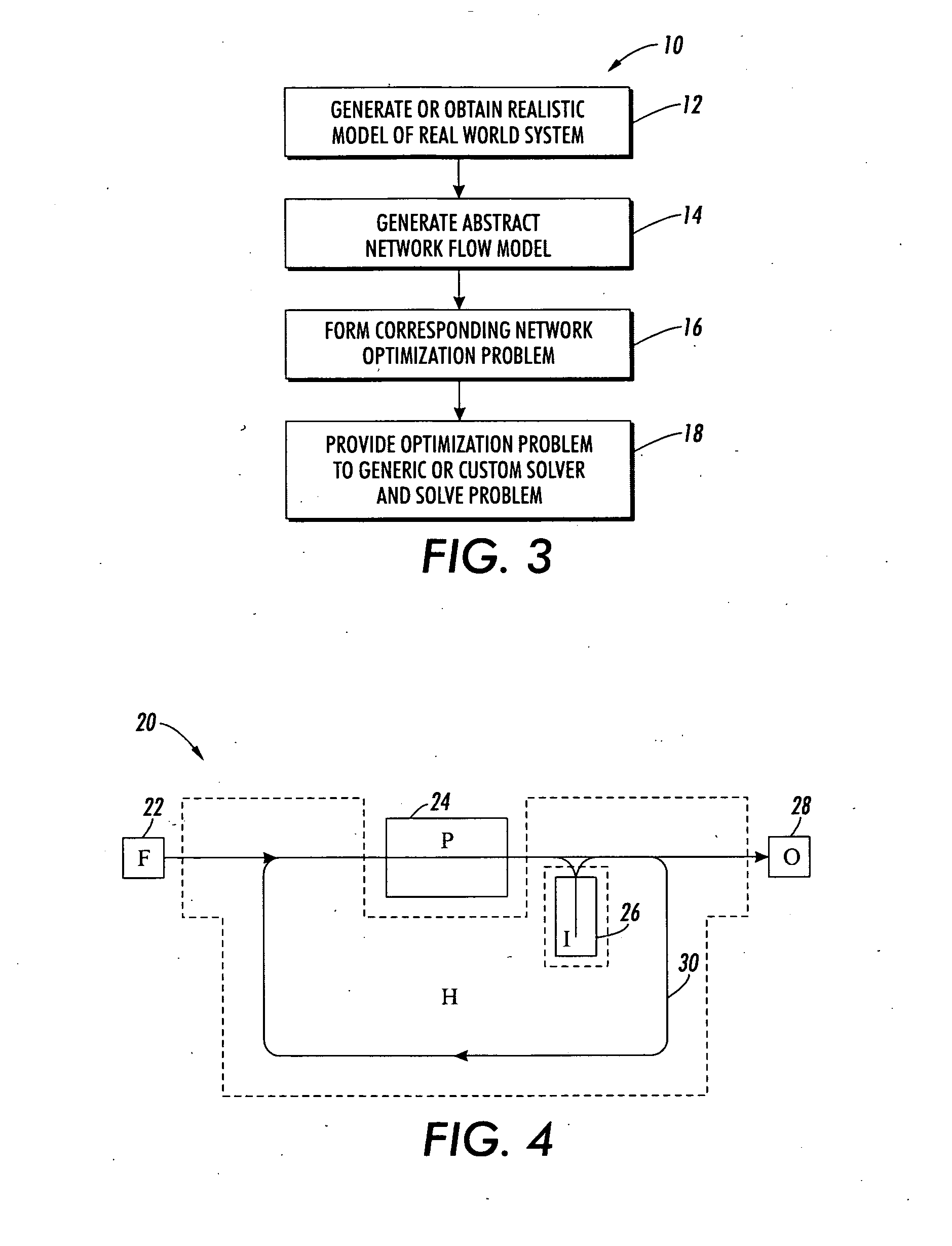
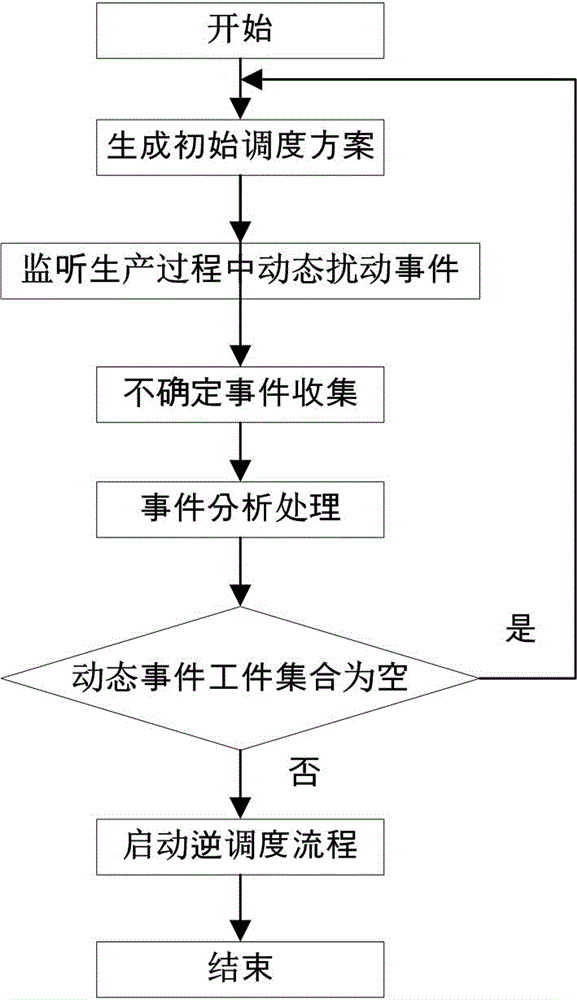
System and method for manufacturing system design and shop scheduling using network flow modeling
A method and tool is provided to obtain an optimistic estimate or exact optimal value of an operational parameter for a realistic system model under investigation. The realistic system model includes components and paths arranged to process continuous or discrete commodities. The system could be a model of a manufacturing system with different machines (some of which may be identical) processing multiple job types, with different sequences of operations with different processing rates on the different machines at different stages. A network flow model of the realistic system model under investigation is generated. Constraints are applied to the abstracted network flow model, and a plurality of steady state network flows, which take into consideration the applied constraints, are performed. The network flows are combined or cascaded into an aggregate network flow, which captures a transformation of the commodities from a first state to a final output state. The network flow problem is solved using a general purpose or custom solver. The optimistic estimate or exact optimal value operational parameter estimate of the realistic system model under investigation is then returned. The method can be used to perform tradeoff studies between machine allocations, job mixes, operating costs, reliability and throughput, or to speed up scheduling and machine control.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Multi-target flow shop inverse scheduling method based on uncertain environment
InactiveCN106125684AIncrease diversityQuality improvementProgramme total factory controlGenetic algorithmComputer science
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
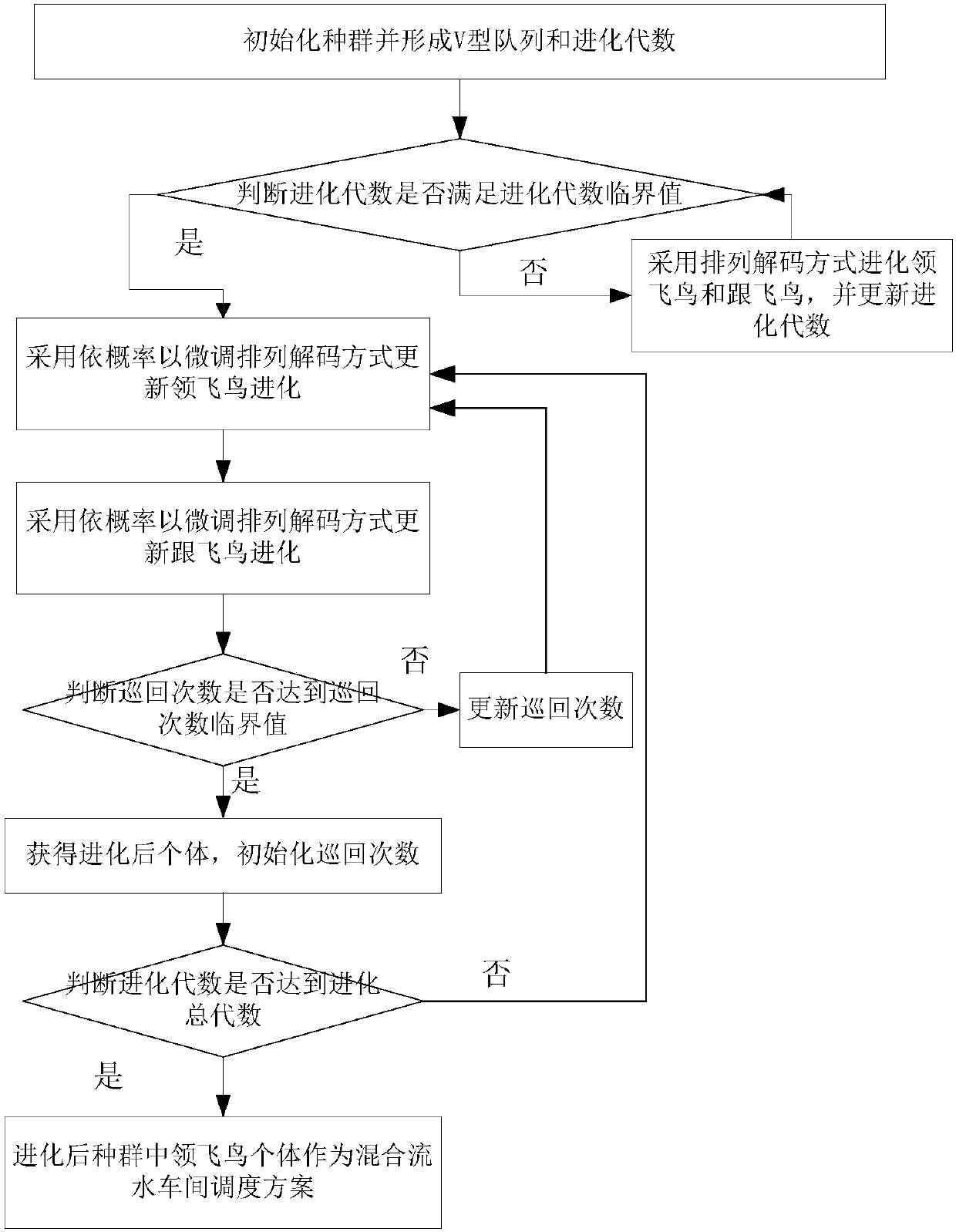
Improved migratory bird optimization method for hybrid flow-shop scheduling problem
InactiveCN108287531AFast convergenceTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlDecoding methodsRate of convergence
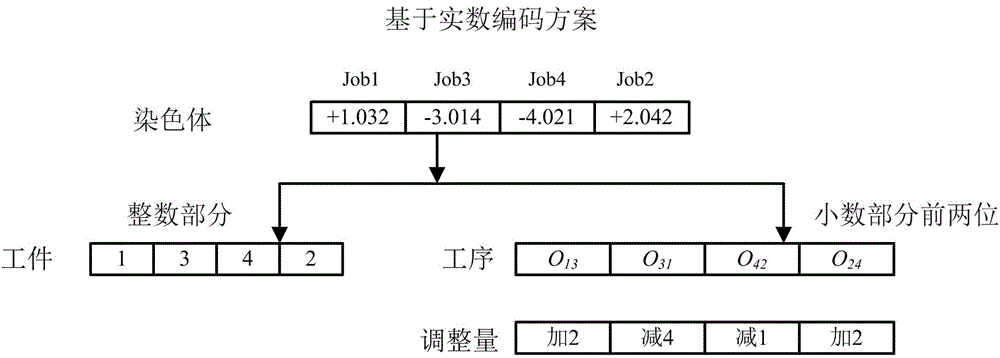
The invention discloses an improved migratory bird optimization method for a hybrid flow-shop scheduling problem, which comprises: before evolutionary algebra, decoding a following bird individual anda leading bird individual by using an arrangement decoding method so as to realize the evolution of the following bird individual and the leading bird individual; after exceeding an evolutionary algebra critical value, decoding the following bird individual and the leading bird individual by a fine-tuning arrangement decoding method according to probability so as to realize the evolution of the following bird individual and the leading bird individual; obtaining a hybrid flow-shop scheduling optimal scheme by determining whether the evolutionary algebra meets a requirement. In the improved migratory bird optimization method provided by the present invention, the fine-tuning arrangement decoding is not in strict accordance with the first-come-first-processing principle in the arrangement decoding method, which increases the possibility of searching out a better solution. The combination of the arrangement decoding step and the fine-tuning arrangement decoding step accelerates the convergence speed of the improved migratory bird optimization algorithm using fine-tuning arrangement decoding.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
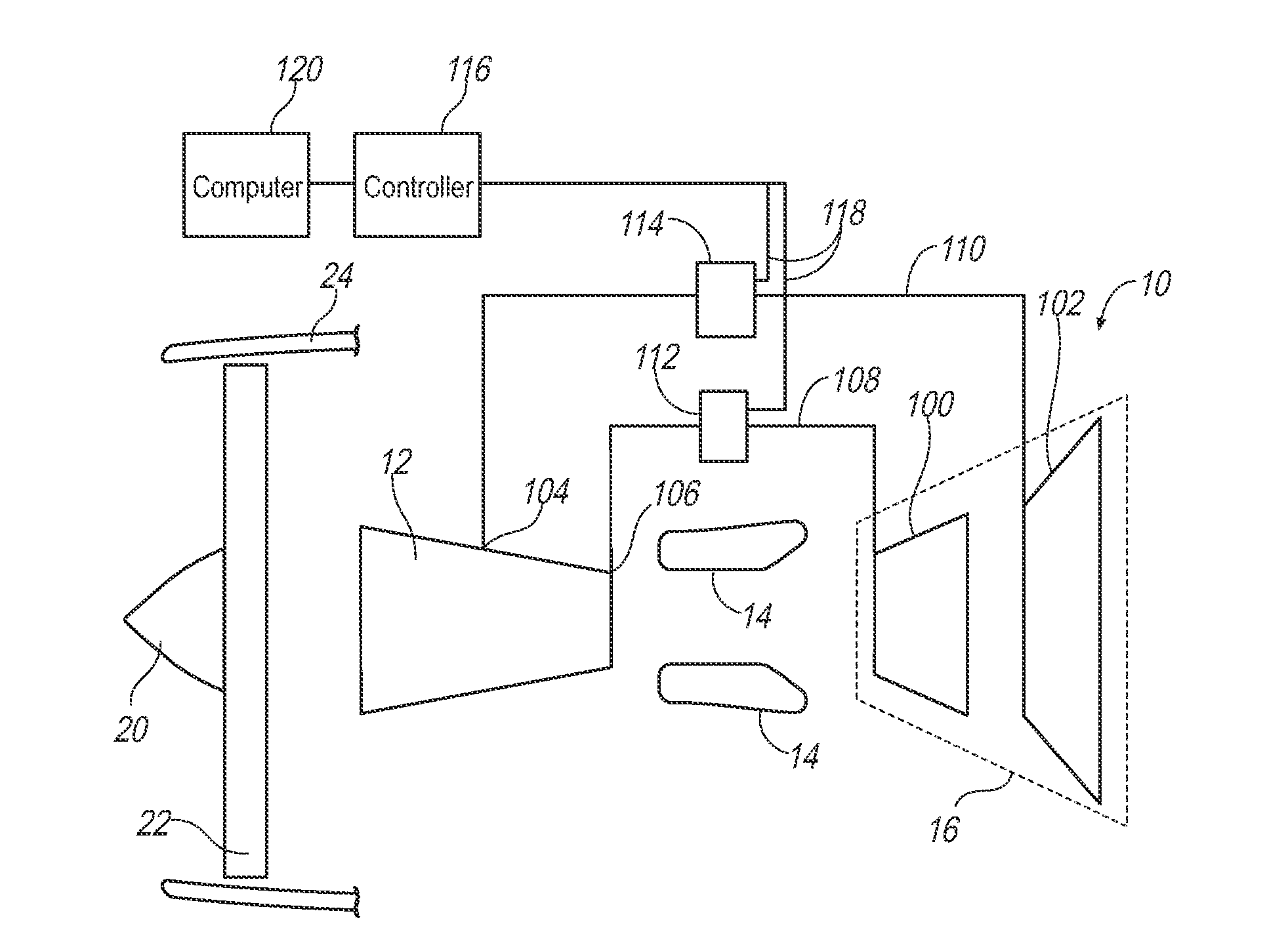
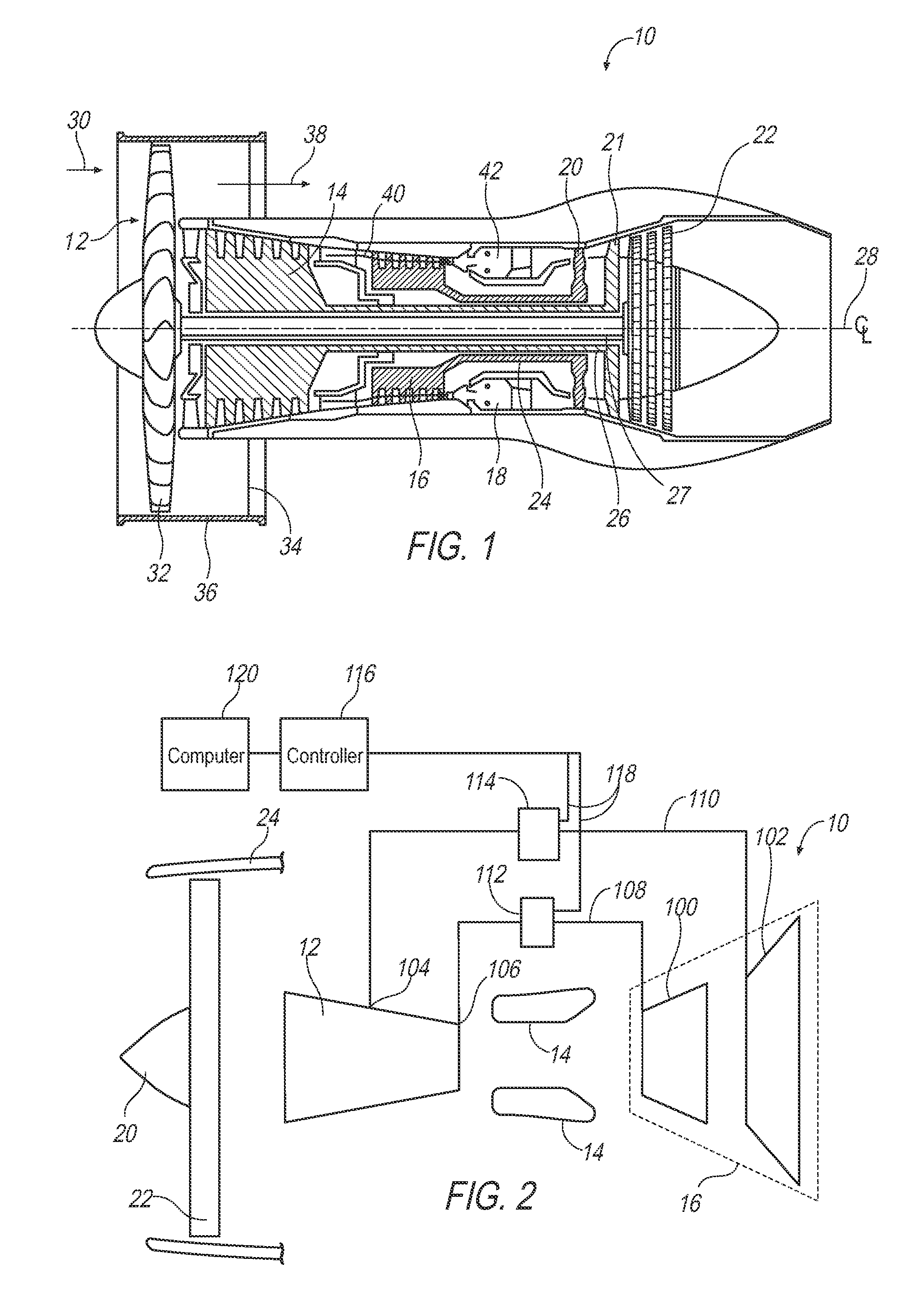
Modulated cooling flow scheduling for both sfc improvement and stall margin increase
A turbine engine includes a compressor, and high and low pressure turbines. The configuration includes a mid-compression station which can be, in the case of a single compressor in the middle of that compressor, or at the exit of the first compressor in the case of two compressors. Also, there is an exit pressure station at the exit of the compression system. A first gas flow line is interposed between the mid-compression station of the compressor and the low pressure turbine, and a second gas flow line is interposed between the exit pressure station of the compression system and the high pressure turbine. A first valve is coupled to the first gas flow line and modulates a low pressure flow rate of coolant in the first gas flow line, and a second valve is coupled to the second gas flow line and modulates a high pressure flow rate of coolant in the second coolant flow line. A controller is configured to operate the first and second valves based on an operating condition of the turbine engine so as to improve the specific fuel consumption while ensuring acceptable stall margin.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE CORP
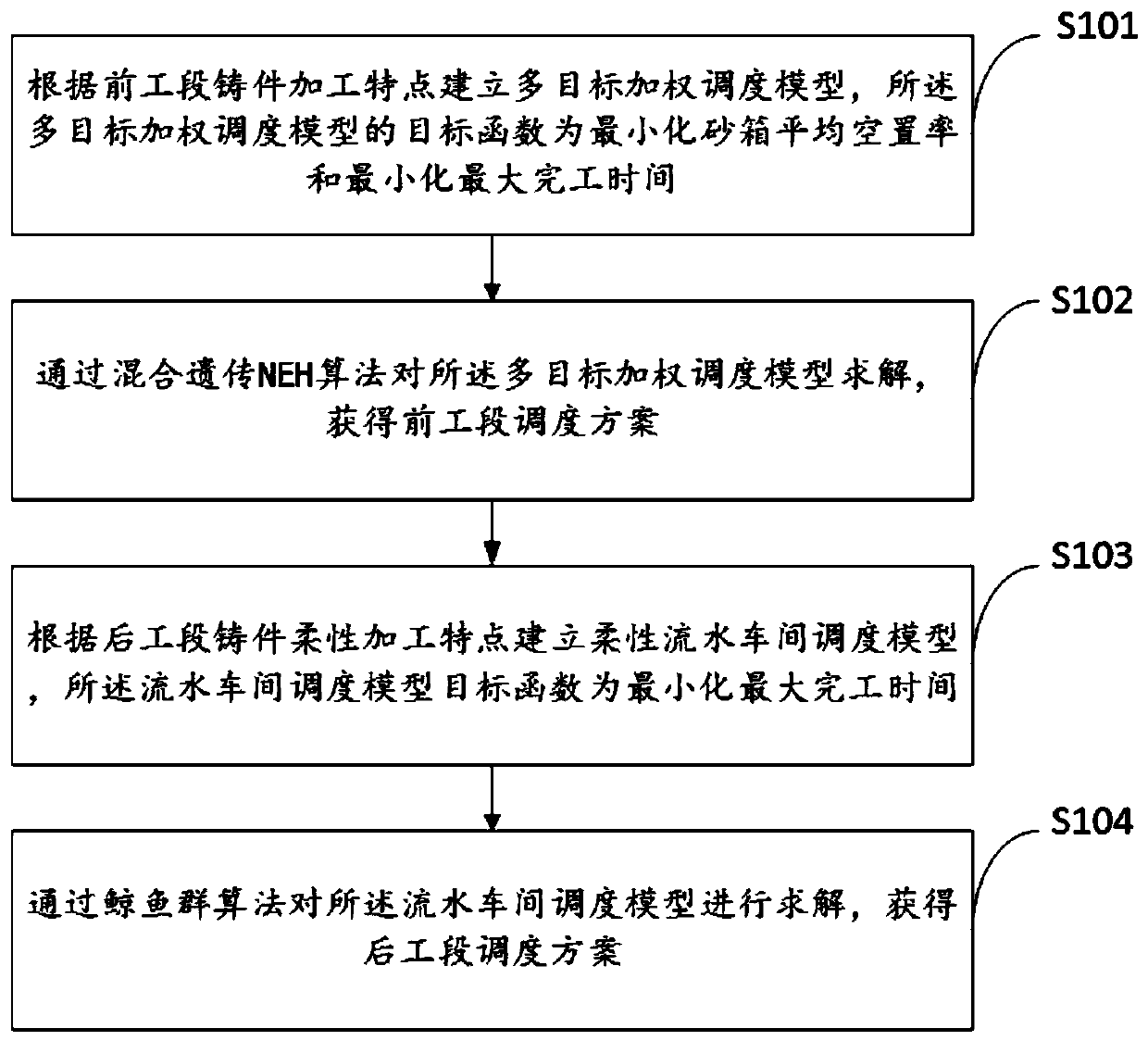
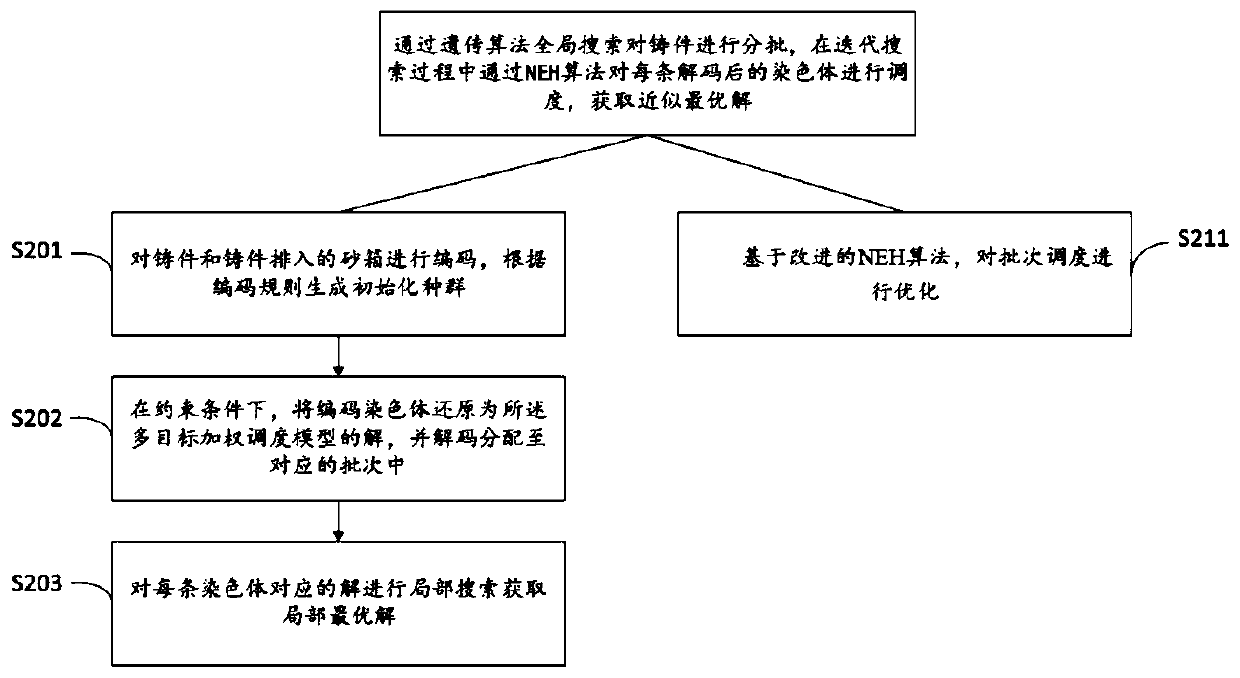
Casting production scheduling method and system
ActiveCN110782085ASolve low production efficiencyFacilitate automated fine-grained controlForecastingArtificial lifeCompletion timeResource utilization
The invention provides a casting production scheduling method and system, and the method comprises the steps: building a multi-objective weighted scheduling model according to the processing characteristics of a casting at a previous section, wherein an objective function of the multi-objective weighted scheduling model is the minimization of the average vacancy rate of a sand box and the minimization of the maximum completion time; solving the multi-objective weighted scheduling model through a hybrid genetic NEH algorithm to obtain a front workshop section scheduling scheme; establishing a flexible flow shop scheduling model according to the flexible machining characteristics of the castings in the later working section, wherein the objective function of the flow shop scheduling model isthe minimum maximum completion time; and solving the flow shop scheduling model through a whale swarm algorithm to obtain a rear workshop section scheduling scheme. According to the scheme, the problem of low casting production efficiency is solved, the production efficiency and the resource utilization rate are effectively improved, and integrated refined management and control are facilitated.
Owner:武汉晨曦芸峰科技有限公司
Handling equipment scheduling method considering AGV collision avoidance
ActiveCN107678433ASolve scheduling problemsImprove performancePosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesGraphicsDynamic models
The invention presents a handling equipment scheduling method considering AGV collision avoidance. A dynamic model of container terminal handling equipment and two types of collision avoidance modelsare built. The discrete event of the equipment is dynamically considered as a hybrid flow shop scheduling problem, and all container tasks in the hybrid flow shop are scheduled through an overall graphic order approach. Finally, under the condition of considering two kinds of collision avoidance cases, a state monitoring controller sends operation time windows to a phase controller according to ahierarchical control structure introduced, the phase controller assigns the operation time windows to specific equipment, and the operation time of AGVs is updated according to the minimum time control problem to realize collision-free scheduling of all the tasks of AGVs. The scheduling method considering both AGV collision avoidance and handling equipment can meet the optimization requirements ofscheduling and management of large automated container terminals.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
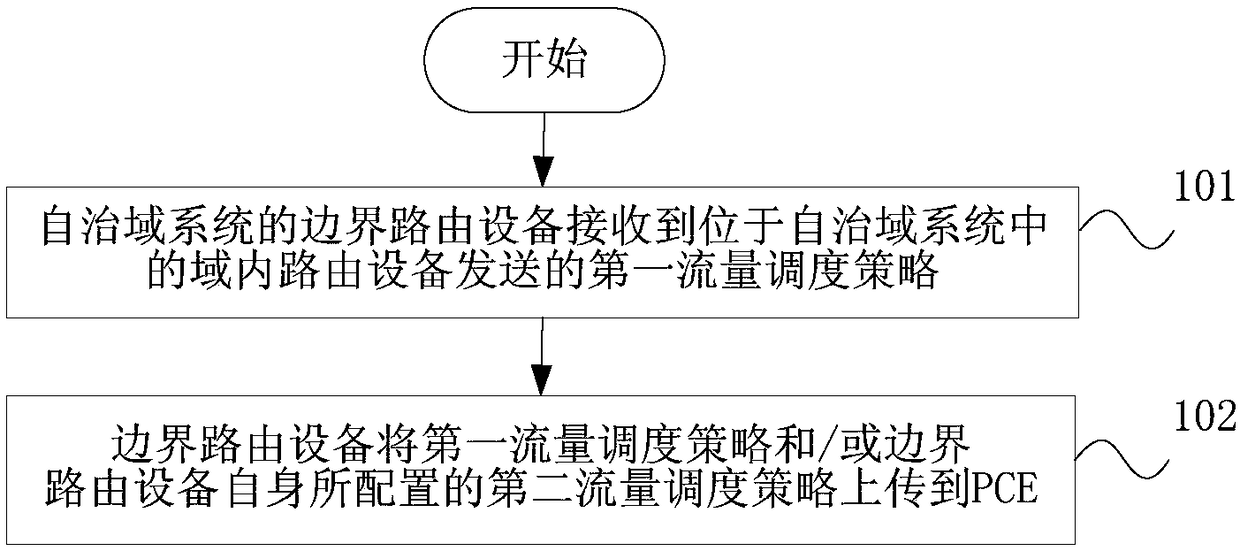
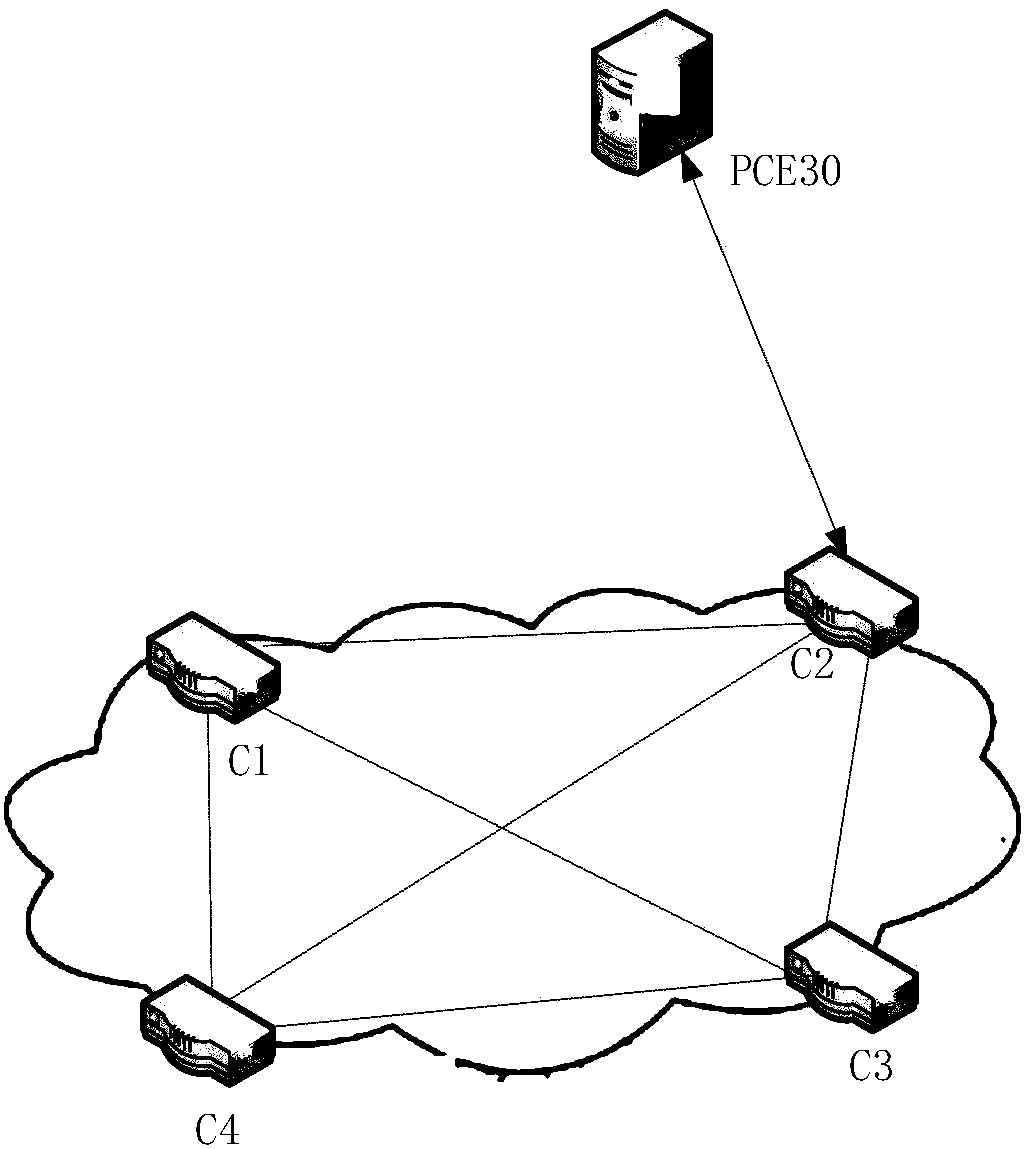
Flow scheduling policy reporting method, autonomous domain system and SDN network system
ActiveCN108206780ARealize centralized schedulingReduce manual interventionData switching networksGlobal optimizationDistributed computing
The invention discloses a flow scheduling strategy reporting method, an autonomous domain system and an SDN network system, and relates to the field of communications. The method comprises the following steps of boundary routing equipment of an autonomous domain system receiving a first flow scheduling strategy sent by the intra-domain routing equipment in the autonomous domain system, wherein a first flow scheduling strategy is configured in the intra-domain routing equipment; and boundary routing equipment uploading a first flow scheduling strategy and / or a second flow scheduling strategy configured by the boundary routing equipment itself to PCE. The method, the autonomous domain system and the SDN network system are provided. manual intervention can be reduced, and the real-time performance and accuracy of global optimization calculation are guaranteed, so that the centralized automatic adjustment of the flow can be realized. Expansion is carried out on the basis of the existing OSPF / IS-IS protocol, and implementation is easy. Centralized scheduling is guaranteed, the consistency of the simulation result and the actual flow forwarding behavior is achieved, and the flow scheduling and optimization capability of an operator in the network can be improved.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Optimized scheduling method applied to distributed production and manufacture process of notebook parts
ActiveCN107831740AOvercome the problem of disrupted distribution informationImprove local search capabilitiesTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlCompletion timeComputer science
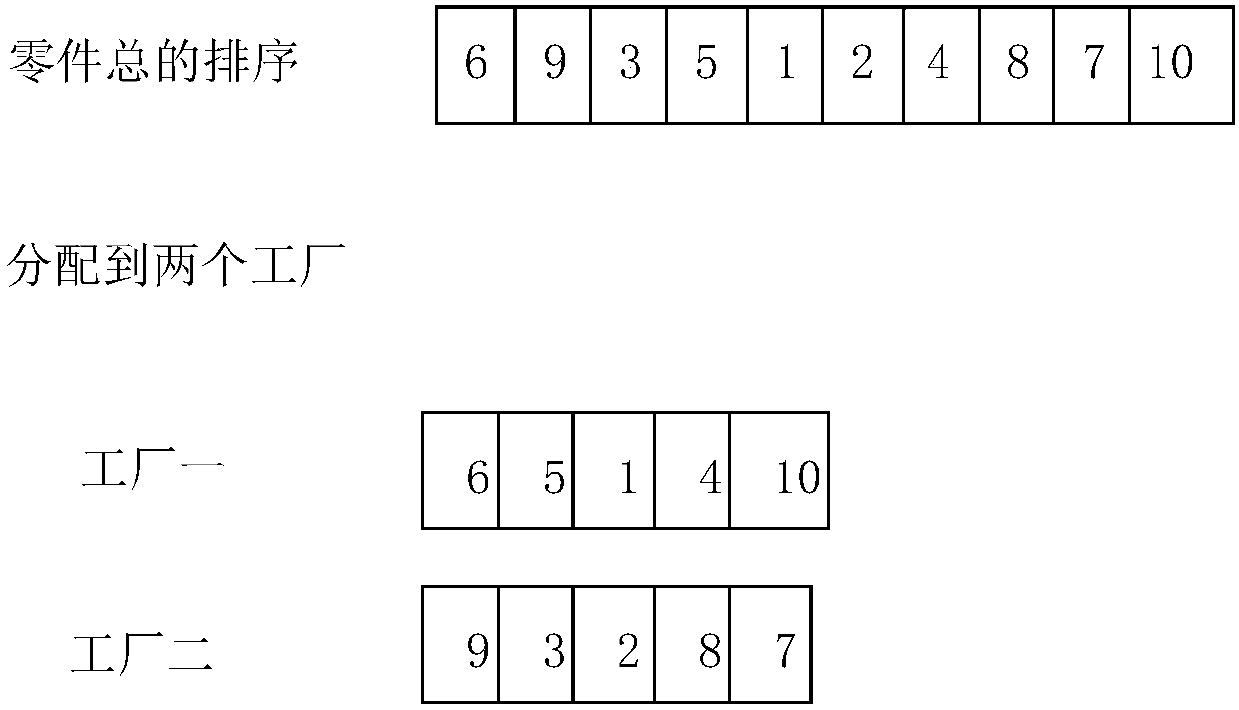
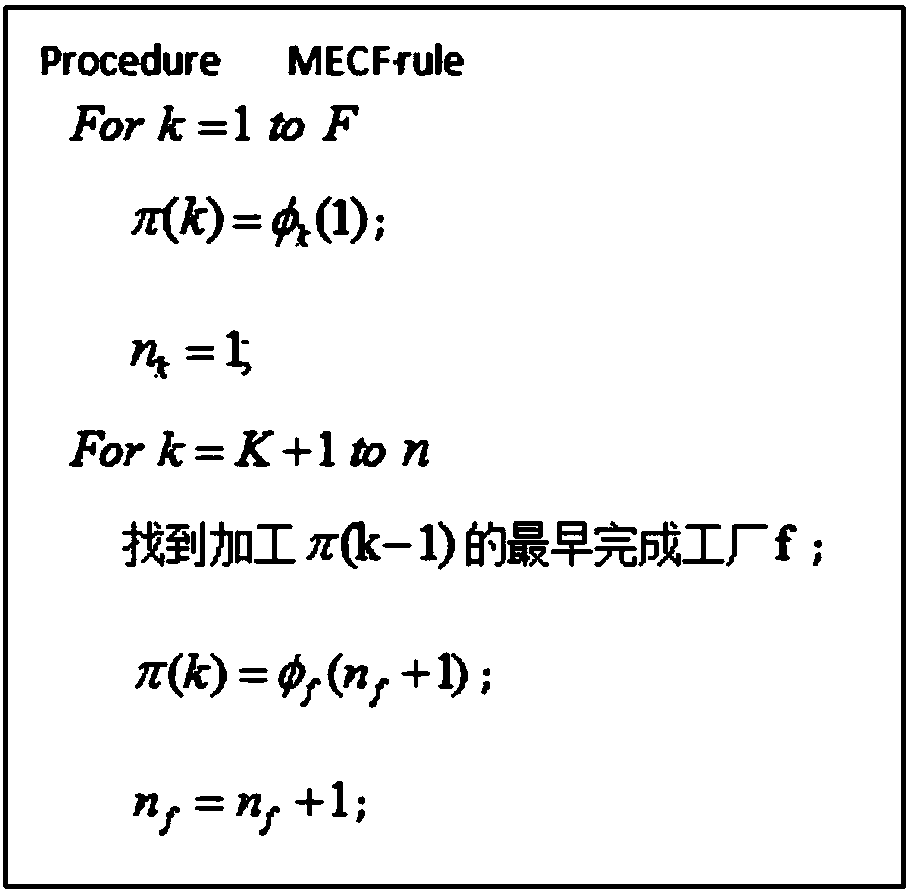
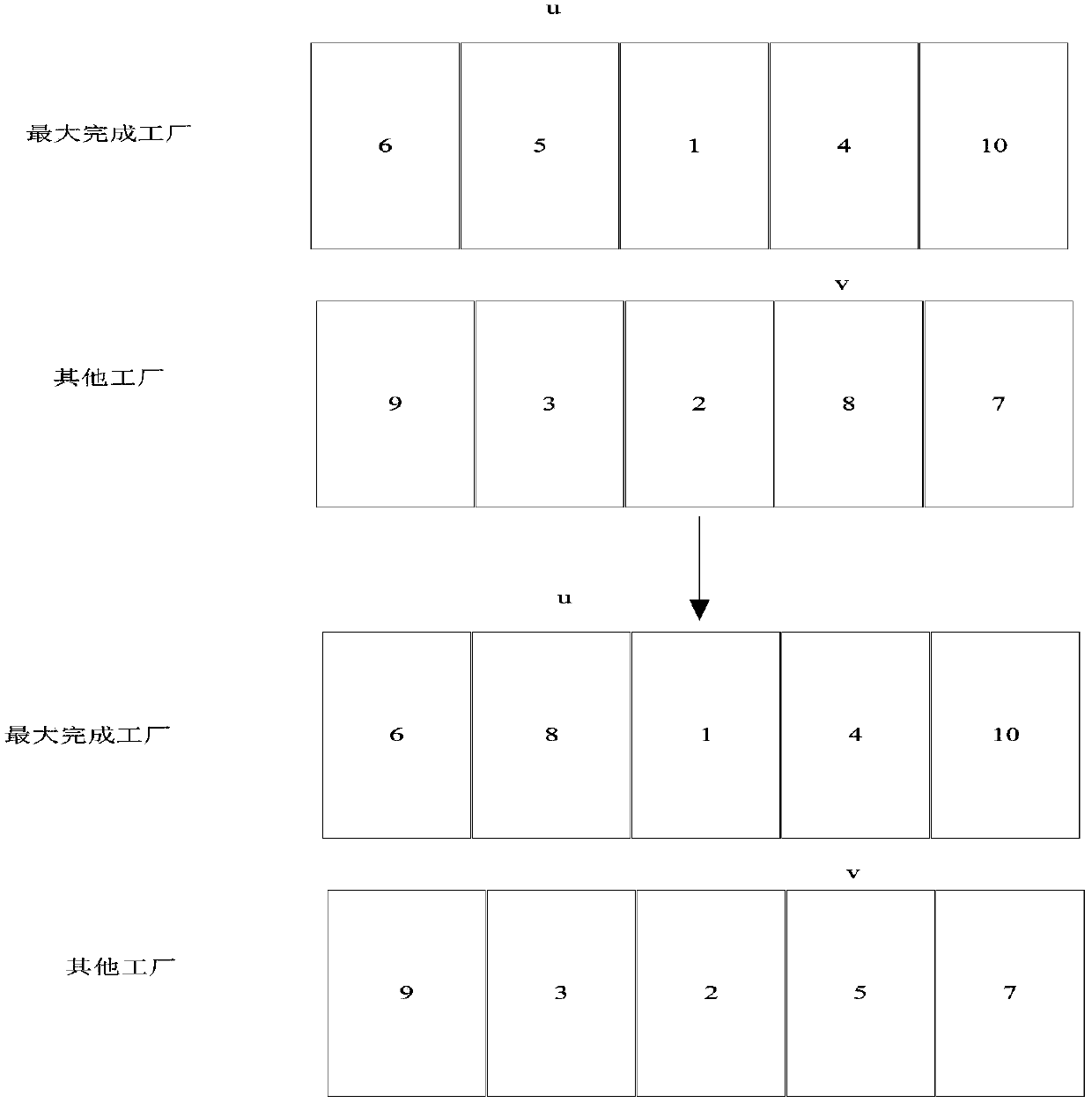
The invention relates to an optimized scheduling method applied to a distributed production and manufacture process of notebook parts. According to the method, a distributed permutation flow shop scheduling model with limited buffers and an optimization object are determined, and the optimization object are optimized via an optimization method with effective estimation of distribution algorithm. The scheduling model is established according to processing time of each part in different machines, and the object is to minimize the total completion time. According to the invention, effective estimation of distribution algorithm is used to solve a distributed production scheduling problem of the notebook parts, and the EDA based intelligent algorithm is used to solve such type of problems for the first time; an earliest completed factor mapping rule MECF is provided for the first time according to a factory distribution rule ECF, and the problem that distribution information of the parts isdisorganized after local searching of optimal individuals; and the local searching capability of the algorithm is further reinforced via local searching based on Swap and Inverse neighborhood.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
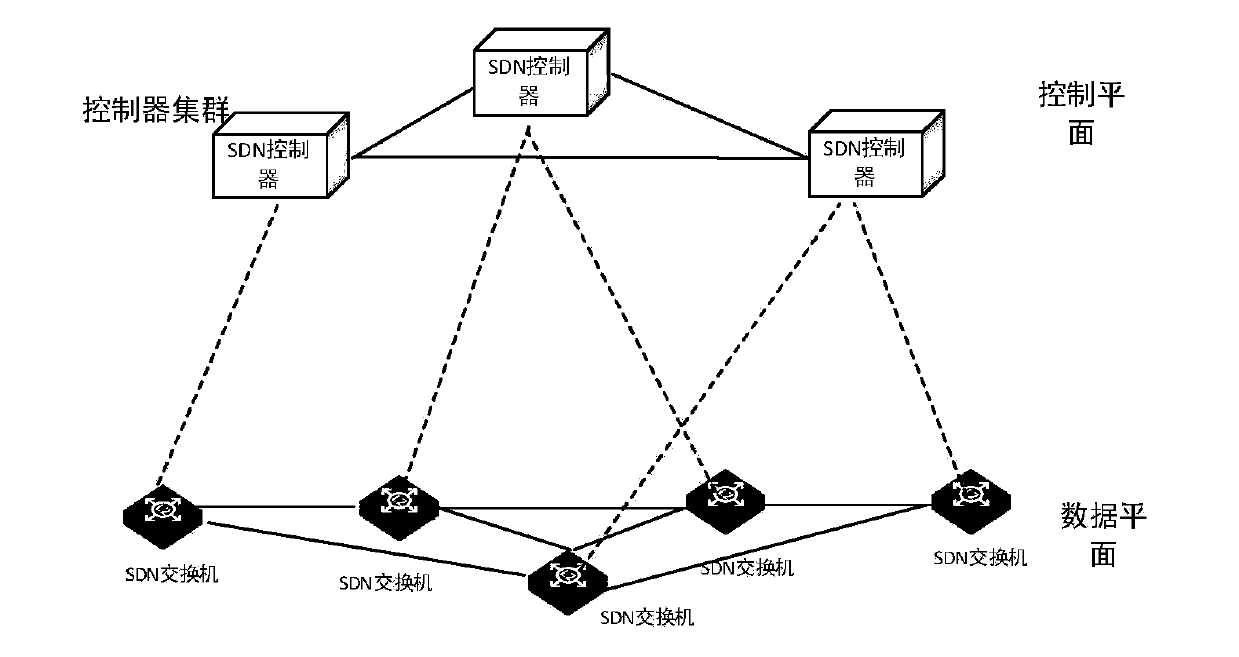
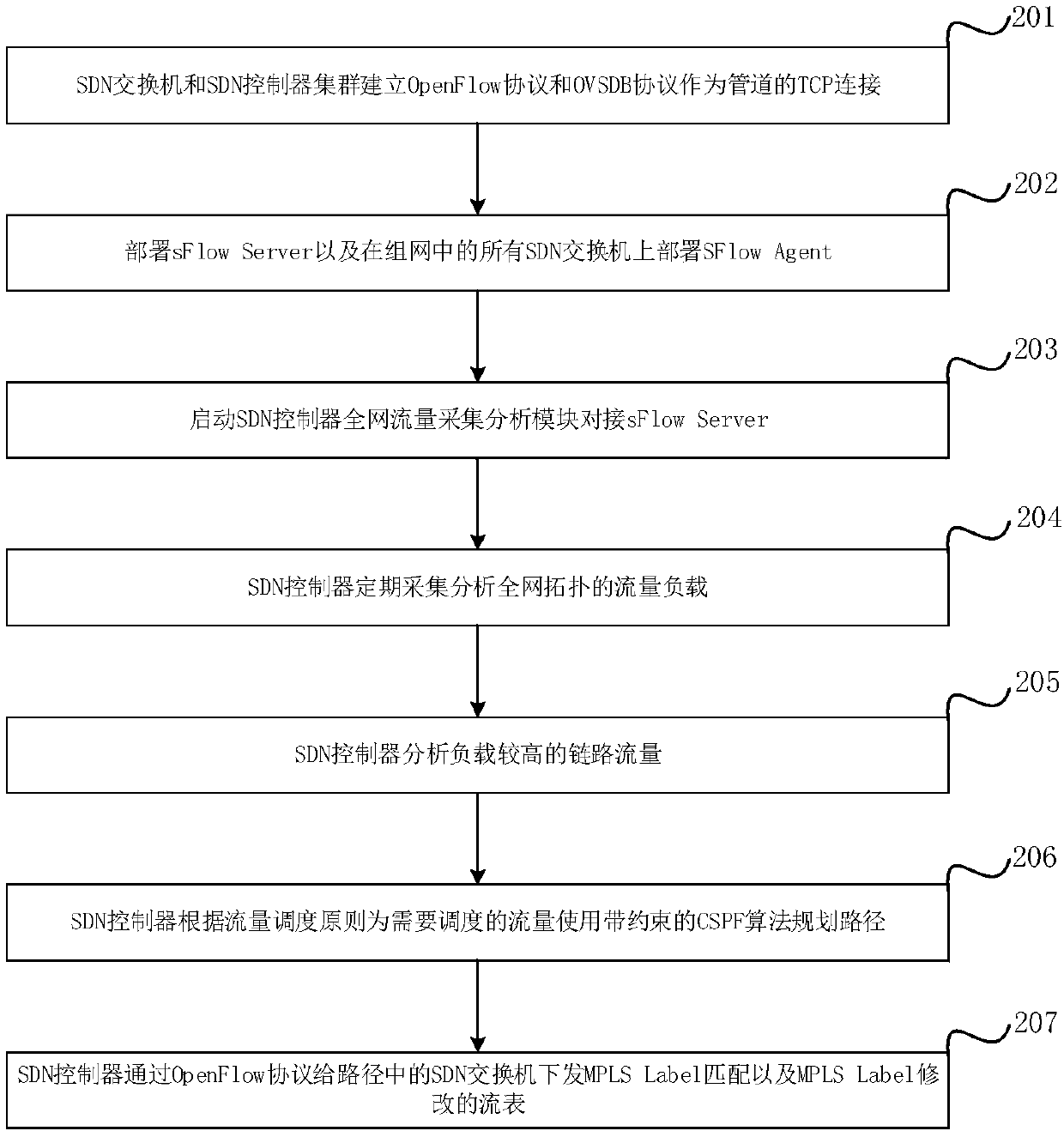
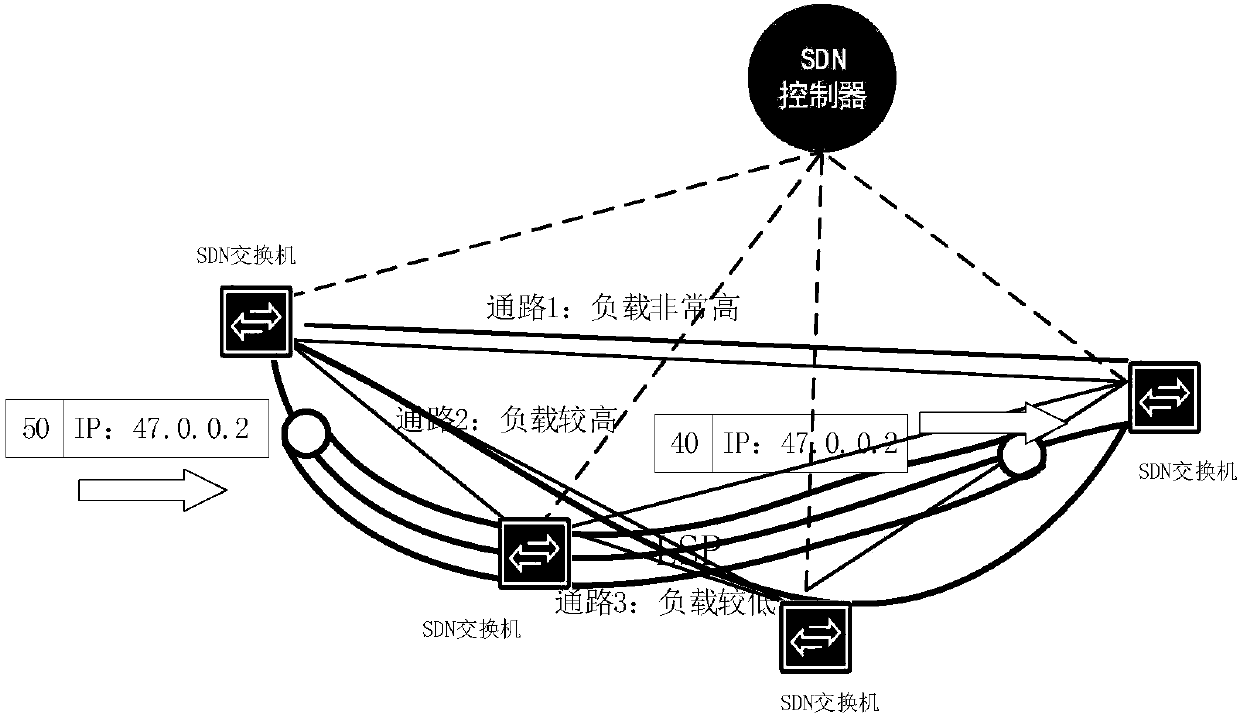
Method and system for flow scheduling based on MPLS in SDN technology
The present invention relates to a method and a system for flow scheduling based on an MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) in SDN (Software Defined Network) technology. The method is based on an SDNnetworking technology, an SDN controller senses total network topology to obtain real-time network topology of the total network, flow load statistics for each link is regularly performed, flow scheduling paths are subjected to optimization calculation based on a multi-constraint CSPF algorithm, and an OpenFlow protocol is employed to issue forwarding flow table of label matching and label exchange based on the MPLS technology to an SDN switch in an LSP path to perform scheduling optimization of the flow.
Owner:JIANGSU FUTURE NETWORKS INNOVATION
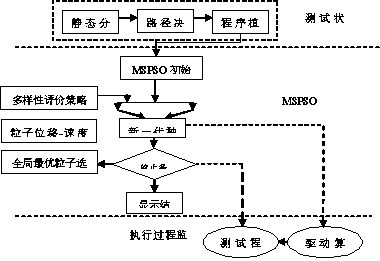
Multi-strategy particle swarm optimization method and system for solving permutation flowshop scheduling problem
InactiveCN107506866AAvoid subjective settingsImprove search abilityForecastingArtificial lifeLocal optimumComputer science
The invention belongs to the optimized control field and discloses a multi-strategy particle swarm optimization method and system for solving a permutation flowshop scheduling problem. The multi-strategy particle swarm optimization method comprises steps of constructing a diversified evaluation strategy, measuring population diversity of particle colonies according to an information entropy mode through subintervals divided by gravitational values, directing alternative execution of local exploration and global searching during an optimizing process, during global optimal particle selection which borrows an ant-city selection strategy in a particle speed-displacement model, calculating a probability of each particle choosing another particle as a global optimal particle, determining a global optimal particle which is following during a particle moving process according to the probability, designing a set variation, and guiding the particle swarm to jump out of a local optimal solution area to perform particle swarm global searching. The set variation operation of the multi-strategy particle swarm optimization method can better help the particle to escape which falls into the local optimal region, prevents a premature convergent phenomenon, can perform continuous optimizing in a global range and can obtain a better result.
Owner:JINGDEZHEN CERAMIC INSTITUTE
Hybrid flow shop scheduling method based on time sequence difference
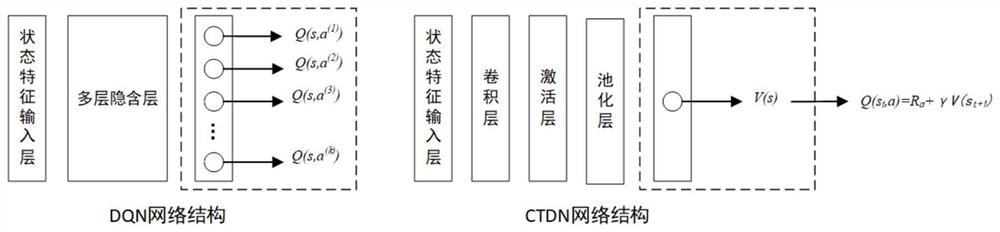
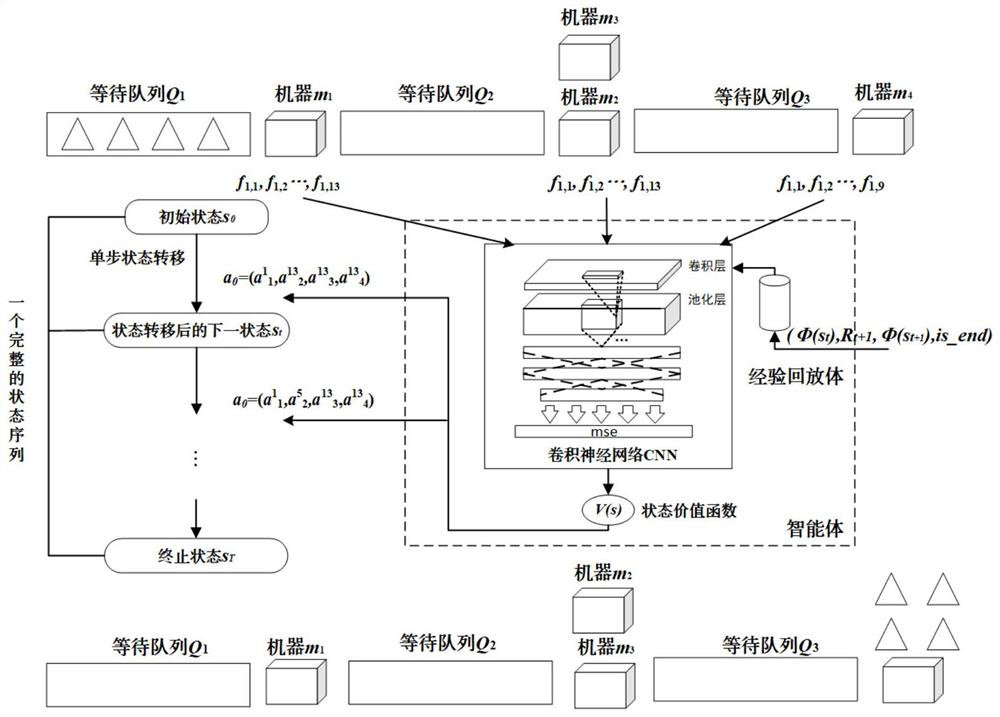
ActiveCN112734172AAvoid overestimationScheduling problem solvingNeural architecturesResourcesReinforcement learning algorithmEngineering
The invention discloses a deep reinforcement learning algorithm based on time sequence difference, which is used for solving a hybrid flow shop scheduling problem of a related parallel machine, combines a convolutional neural network with TD learning in reinforcement learning, and performs behavior selection according to input state features; and therefore, the scheduling decision process of the actual order response type production and manufacturing system is better met. A scheduling problem is converted into a multi-stage decision problem, a convolutional neural network model is used to fit a state value function, manufacturing system processing state characteristic data is input into a model, a time sequence difference method is used to train the model, a heuristic algorithm or an allocation rule is used as a scheduling decision candidate behavior, and a reinforcement learning reward and punishment mechanism is combined, thus selecting an optimal combined behavior strategy for each scheduling decision. Compared with the prior art, the algorithm provided by the invention has the advantages of strong real-time performance, high flexibility and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hybrid flow shop scheduling method for different parallel machines
InactiveCN105741181AImprove scheduling efficiencyImprove the ability to respond to market changesData processing applicationsBiological modelsMetapopulationComputer science
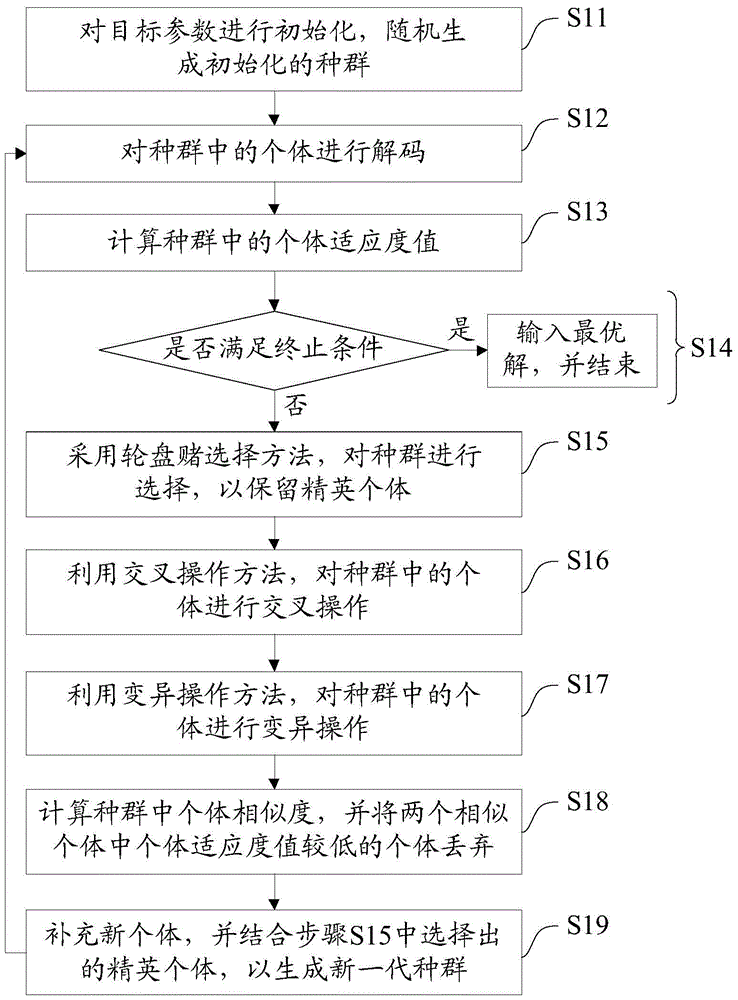
The invention discloses a hybrid flow shop scheduling method for different parallel machines. The method comprises the steps of step S11: initializing target parameters and randomly generating an initialized population; step S12: decoding individuals in the population; step S13: calculating the fitness values of the individuals in the population; step S14: judging whether a stop condition is met or not, and if not, entering the step S15; step S15: performing selection on the population by adopting a roulette wheel selection method to remain elite individuals; step S16: performing crossover operation; step S17: performing mutation operation; step S18: calculating the similarity of the individuals in the population and discarding the individuals with relatively low fitness values; and step S19: supplementing new individuals, generating a new-generation population in combination with the selected elite individuals in the step S15, and returning to the step S12. According to the method, the shop scheduling efficiency is effectively improved and the production cost is reduced, so that the method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:四川索牌科技股份有限公司
Three-stage flexible flow workshop scheduling method based on ST heuristic algorithm
InactiveCN104392124ASolve scheduling problemsData processing applicationsTotal factory controlAlgorithmThree stage
The invention relates to a three-stage flexible flow workshop scheduling method based on an ST heuristic algorithm. The three-stage flexible flow workshop scheduling based on the ST heuristic algorithm comprises the following steps: step one, proposing a type of problem of the three-stage flexible flow workshop scheduling with groups of constraints and arrival of batches of workpieces in consideration, and describing the type of problem by a three-element group of Graham as a formula which is shown in the specification; step two, building an optimization model of the three-stage flexible flow workshop scheduling problem; step three, proposing an ST-idea-based heuristic algorithm; step four, designing a simulation experiment and carrying out simulation scheduling of the ST heuristic algorithm. The invention discloses a set of complete solution algorithm in order to solve the flexible flow workshop scheduling problem with groups of constraints; the three-stage flexible flow workshop scheduling problem with the groups of constraints is solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Intelligent algorithm-based method for optimizing tire building-vulcanizing production energy consumption in real time
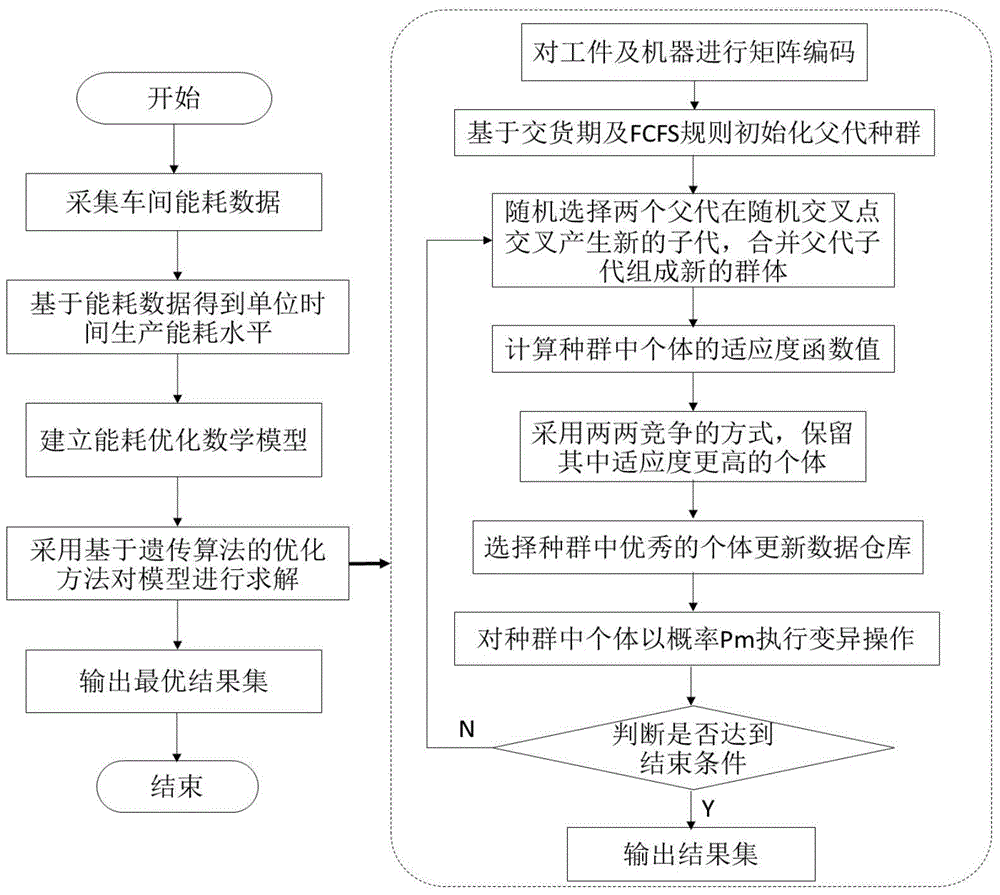
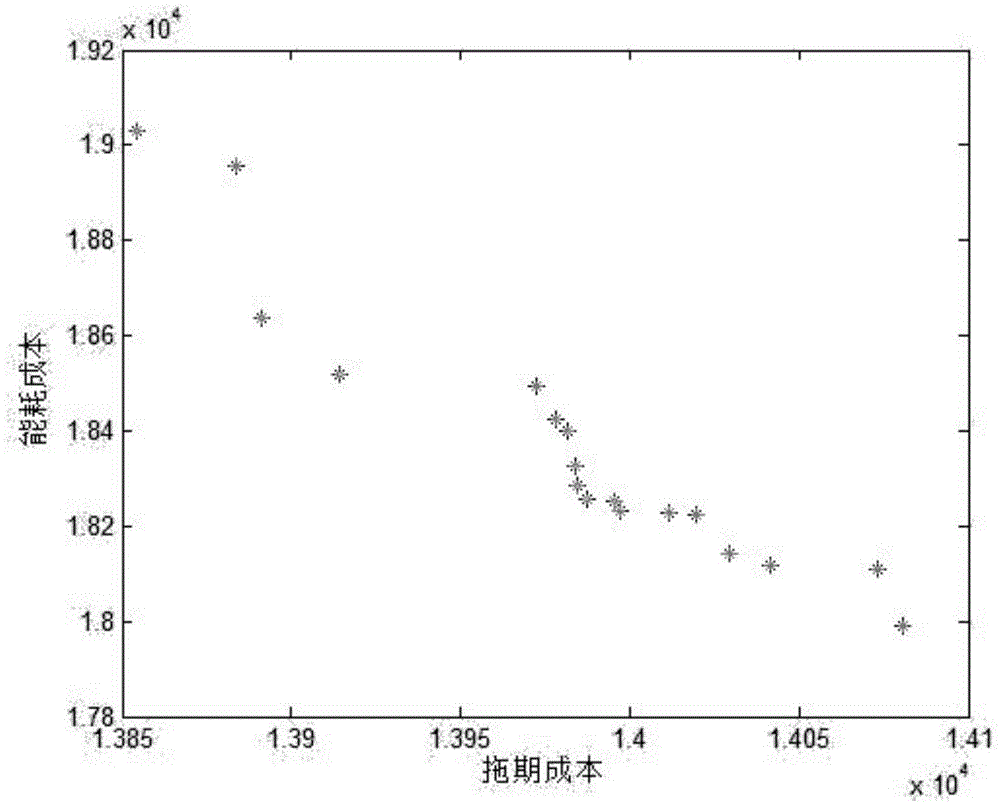
ActiveCN105117801ATimely and accurate scheduling basisHigh production process requirementsForecastingManufacturing computing systemsData acquisitionEnergy consumption
The invention discloses an intelligent algorithm-based method for optimizing tire building-vulcanizing production energy consumption in real time. According to the method, workshop production energy consumption data and real-time production status are obtained through effectively arranging data acquisition equipment in a building-vulcanizing workshop, and a production processing system energy consumption model is established by combining the history energy consumption data, so that the building and vulcanizing processes are abstracted into a flexible flow-shop scheduling problem, the machines and workpieces are coded and an intelligent algorithm is adopted to reasonably schedule the processes, so as to obtain a feasible solution with the optimum fitness.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +2
Improved sparrow search optimization method for blocking flow shop scheduling problem
PendingCN113902174AFast convergenceImprove sufficiencyForecastingArtificial lifeLocal optimumReal arithmetic
The invention discloses an improved sparrow search optimization method for blocking a flow shop scheduling problem, and belongs to the technical field of shop scheduling. The method comprises the steps: employing an integer-real number hybrid coding mode to code a sparrow individual and workpiece production sequence; using a new collaborative initialization strategy to initialize the positions of the sparrows; dividing the sparrow population into a plurality of subgroups for mutual learning; obtaining a good workpiece production sequence solution set, namely a sparrow individual elite solution set, through an improved sparrow individual search strategy; and carrying out local enhancement on the obtained elite solution set, and obtaining an optimal sparrow individual, namely an optimal workpiece machining sequence. The method can solve the problems that the population diversity is reduced and the algorithm is easy to fall into local optimum in the later stage of iteration of the sparrow algorithm; and the processing efficiency of the blockage flow workshop can be effectively improved, and the economic benefits of factories are improved.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Modeling method for hybrid flow shop energy-saving scheduling by considering shutdown and restart strategy
InactiveCN107817771AResolve correctnessAddress effectivenessProgramme total factory controlComputation complexityStart time
The invention discloses a modeling method for hybrid flow shop energy-saving scheduling by considering a shutdown and restart strategy, which comprises the steps of introducing a machining position ending time variable, a machining position starting time variable and a shutdown and restart strategy variable, building a model based on the idle time, further introducing a standby energy consumptionvariable between two adjacent positions on a machine tool, and building a model based on the idle energy consumption; building five mixed integer linear programming models considering the shutdown andrestart strategy; then performing detailed comparative analysis on the mathematical models from the aspects of the modeling process, the model size complexity, the calculation complexity and the like; solving an HFSP (Hybrid Flow Shop Scheduling Problem) example by using a CPLEX solver, and proving the correctness and the effectiveness of the MILP (Mixed Integer Linear Programming) model. Experiments show that MILP models based on different modeling ideas are greatly different in size complexity and calculation complexity, and the solving effect of the MILP model based on the idle energy consumption is better than that of the MILP model based on the idle time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com