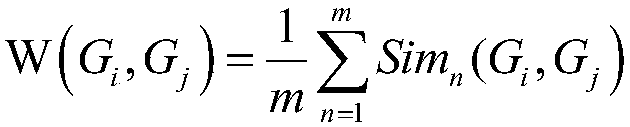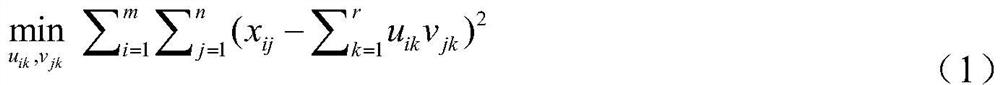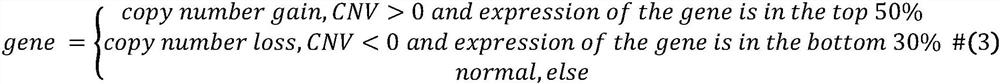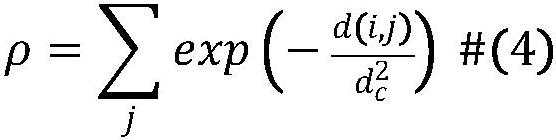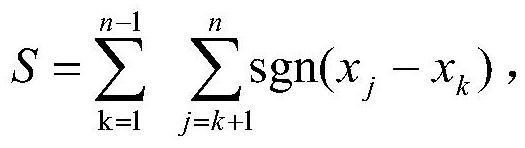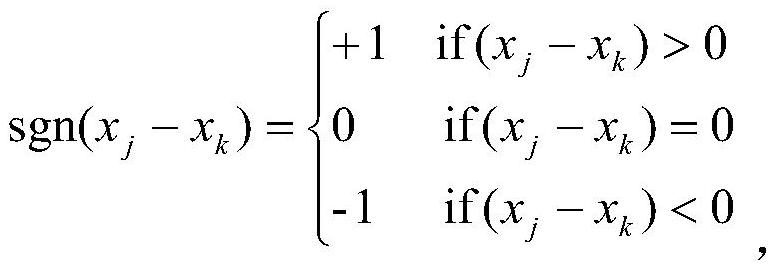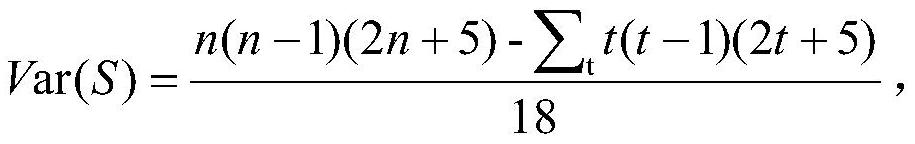Patents
Literature
30 results about "Gene interaction network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
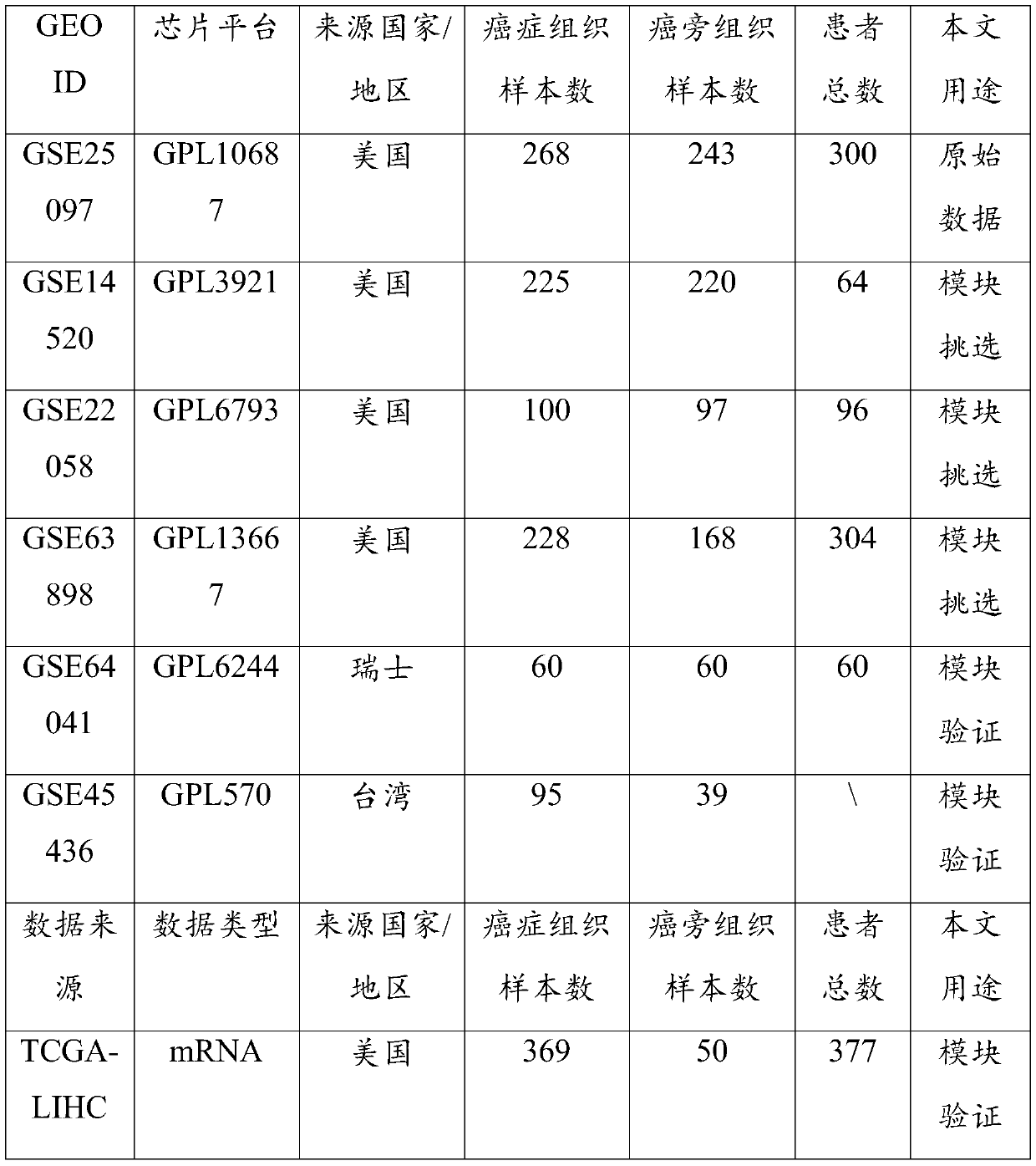
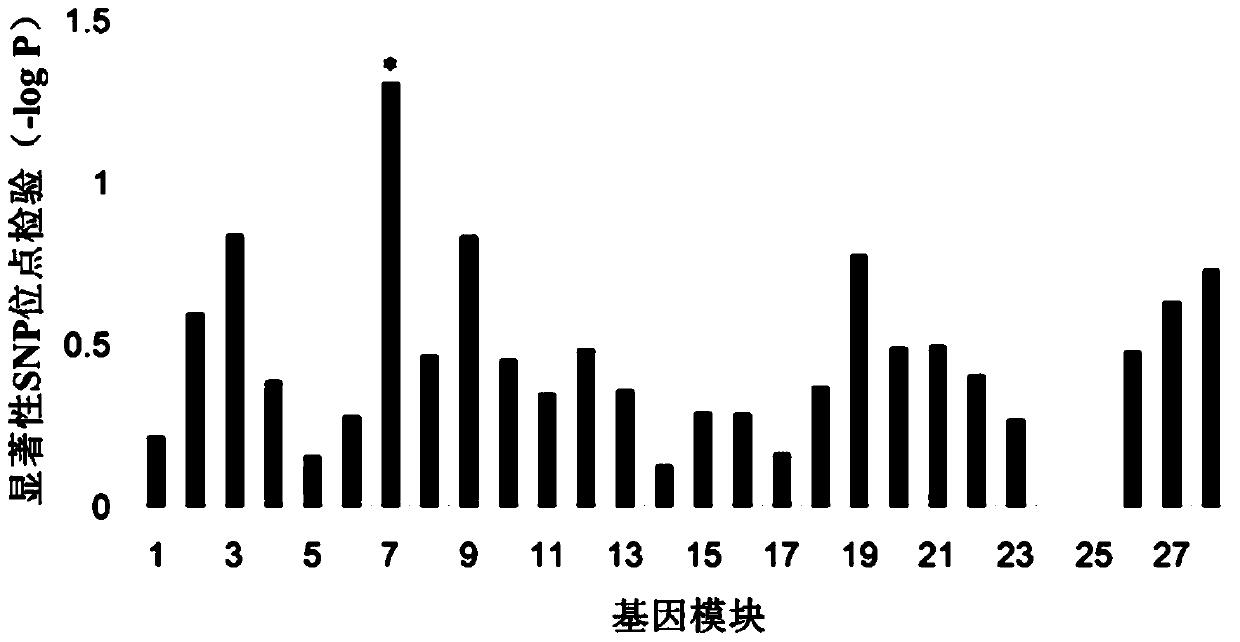
Construction method for specific cancer differential expression gene regulation and control network
InactiveCN105740651AHigh precisionImprove calculation accuracyHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsDifferentially expressed genesBioinformatics
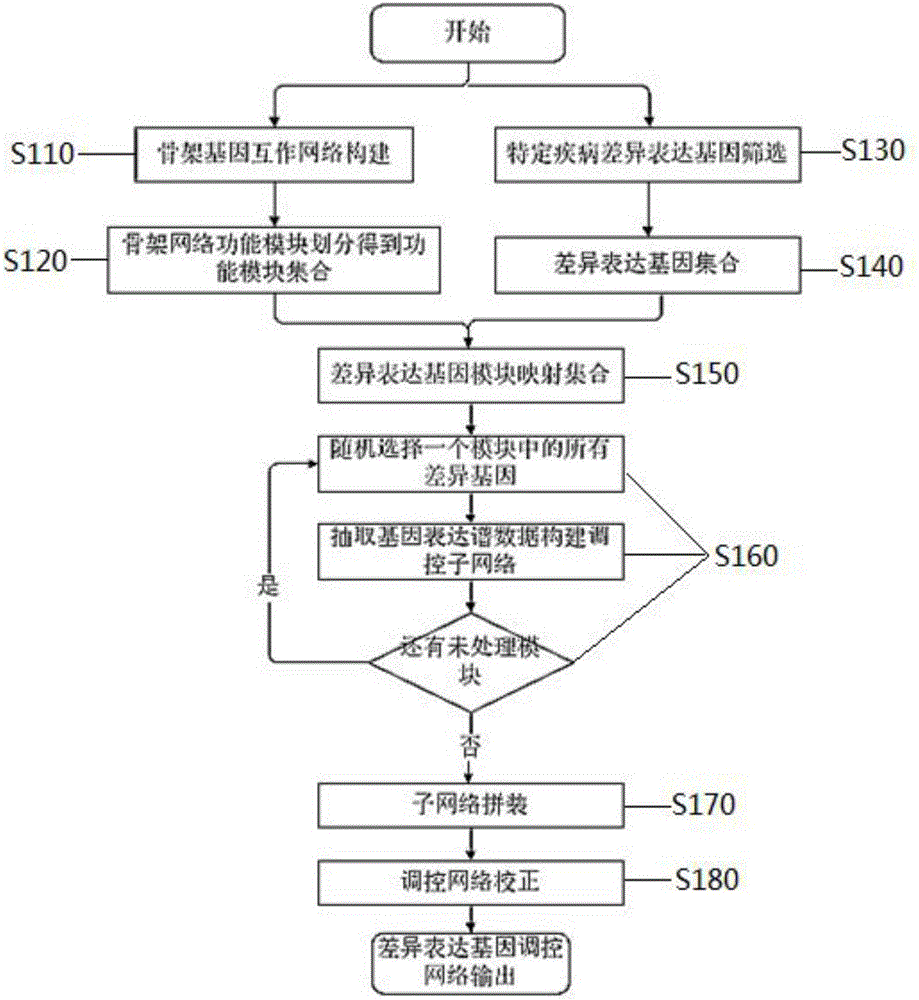
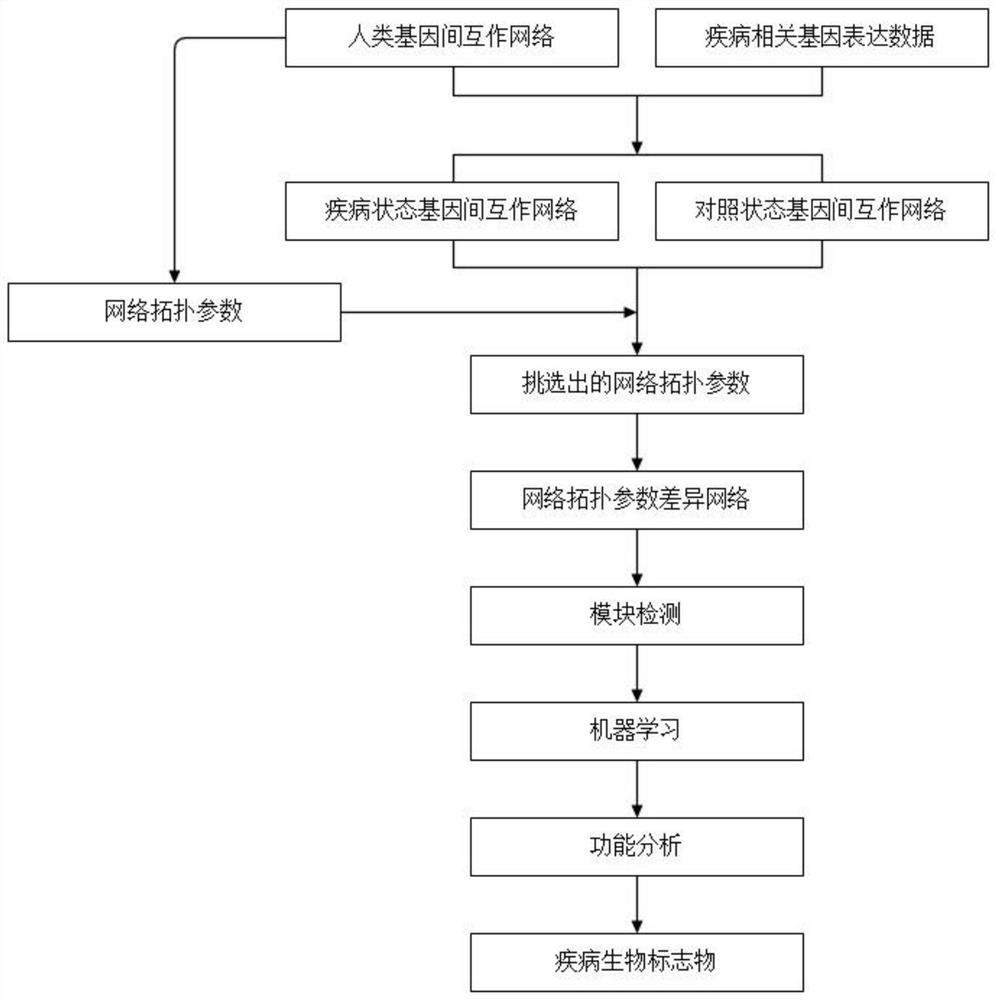
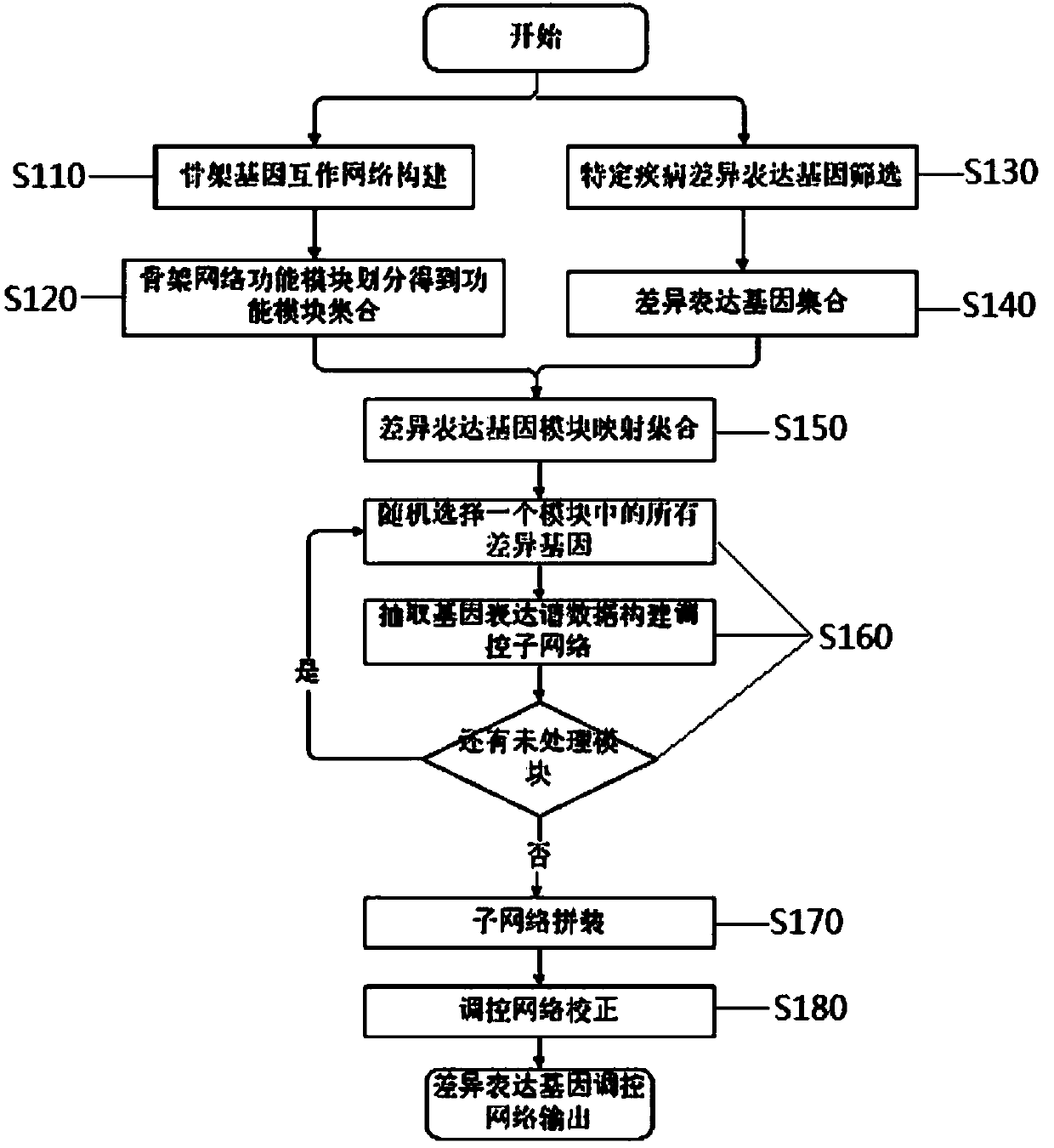
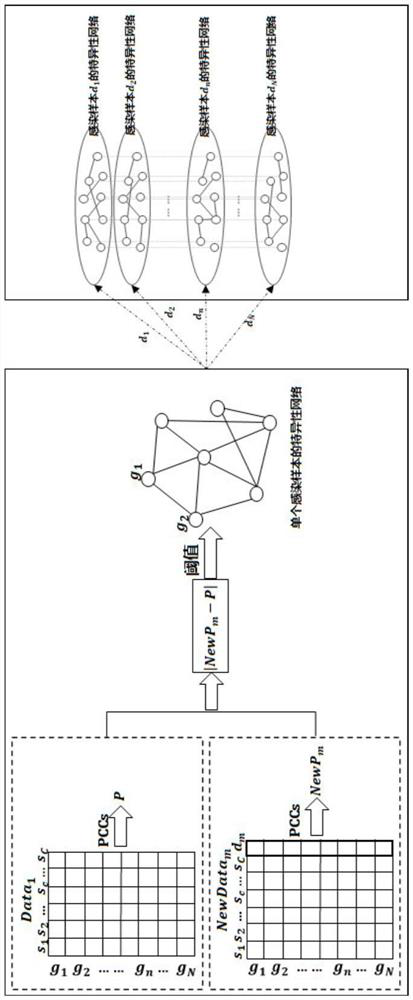
The invention discloses a construction method for a specific cancer differential expression gene regulation and control network.The method includes the following steps of firstly, constructing a framework gene interaction network according to function similarity weight numbers between genes; secondly, conducting module division on the framework gene interaction network through a segmenting method; thirdly, screening out differential expression genes through complete genome methylation data; fourthly, classifying the screened-out differential expression genes according to functions; fifthly, using all the differential expression genes mapped to each same function module as a function classification; sixthly, constructing the regulation and control network of all the genes in each function classification function; seventhly, conducting sub-network splicing under guidance of a framework network.The calculation complexity is greatly reduced, and high precision is achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Cancer biomolecule marker screening method and system based on network topology parameters
ActiveCN110444248ACharacter and pattern recognitionProteomicsBiomarker identificationScreening method
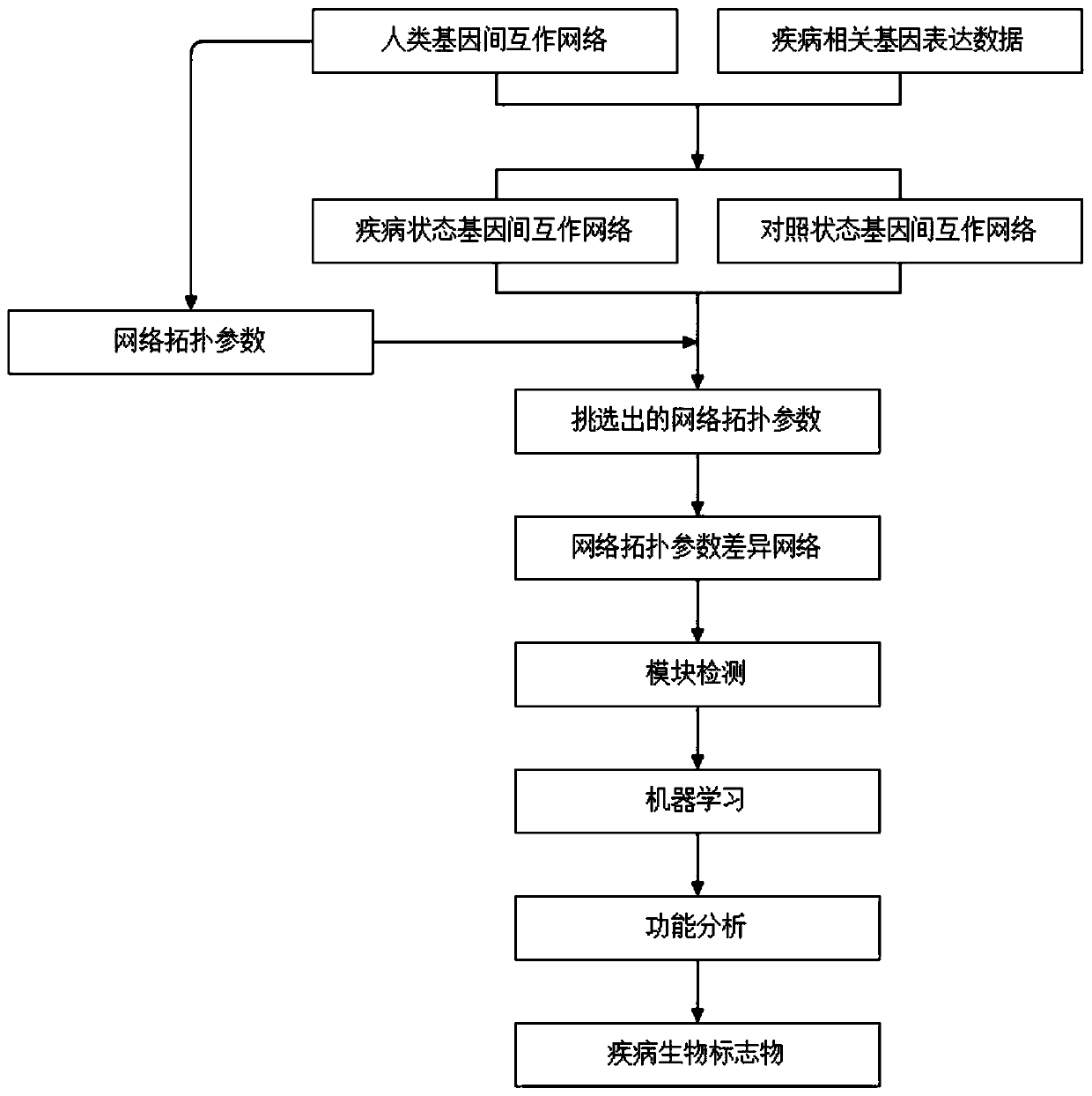
The invention discloses a cancer biomolecule marker screening method and system based on network topology parameters. The method comprises the steps that a human gene interaction network and gene chipexpression data are acquired and integrated to obtain a gene interaction network based on gene expression data; a disease state and control state gene interaction network is constructed; network topology parameter difference genes of the disease state and control state gene interaction network are calculated, and a network topology parameter difference change network is obtained based on the network parameter difference genes; network module mining is performed on the network topology parameter difference network; feature selection is performed on an obtained difference network module to obtain genes capable of distinguishing normality and diseases in all modules; the classification effect of the genes selected from the modules on the diseases is detected, and the difference network module is screened according to the classification effect to serve as a biomolecule marker candidate. The invention provides a novel complex disease biomarker identification method based on omics data, andexperiments prove that the method has certain accuracy and effectiveness.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for supporting analysis of gene interaction network, and computer product
Detailed information of each analysis subject partial network is displayed on a left pane of a screen. The detailed information includes the number of nodes, the number of edges, and accumulative coverage of the analysis subject partial network for each disease. Based on the detailed information, a user can designate the analysis subject partial network of a disease the user wishes to analyze. When the user has designated the disease, a network diagram indicating a partial network related to the designated disease is displayed on a right pane.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for supporting analysis of gene interaction network, and computer product
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
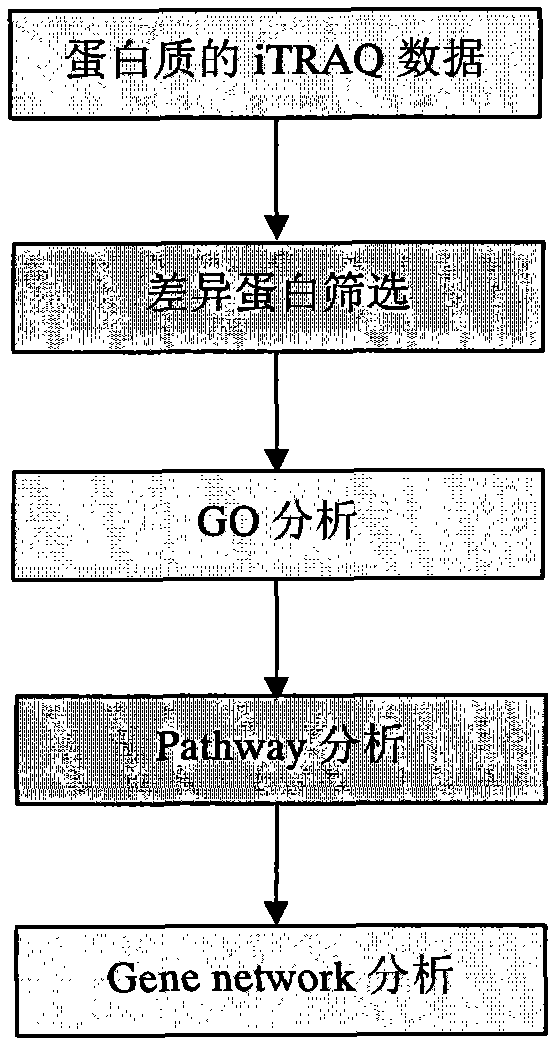
Processing method of cow urine iTRAQ test data
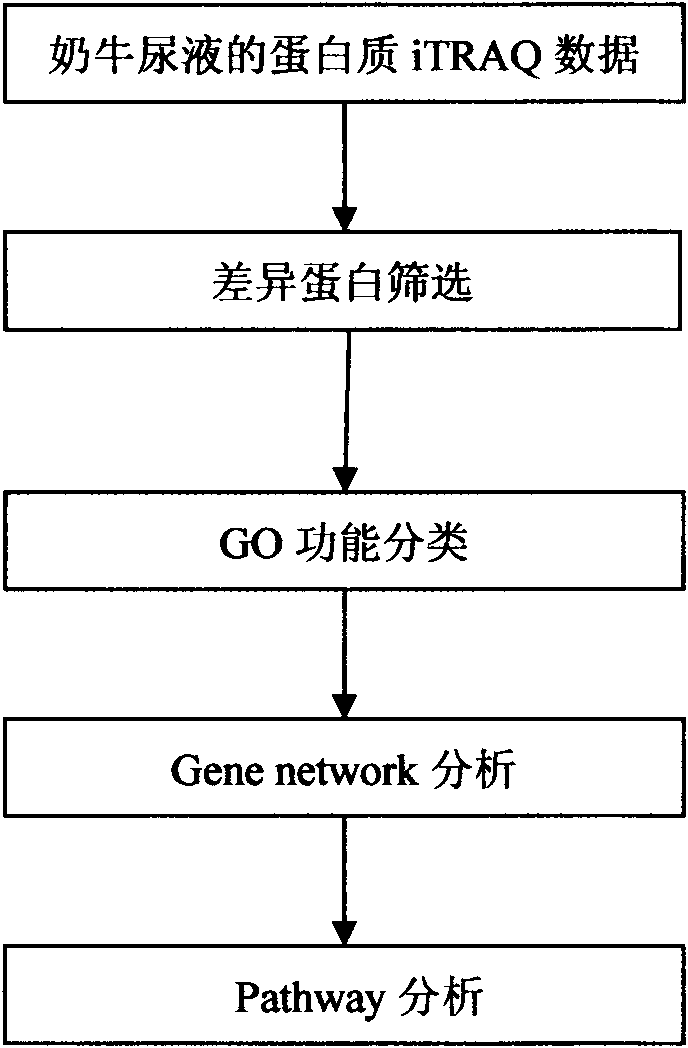
Aiming at the characteristics of iTRAQ protein quantitative analysis, a method for analyzing cow urine iTRAQ data is designed. The main process includes: step one, screening differential proteins and obtaining the differentiated result by grouping and screening the original iTRAQ data; step two, performing GO analysis, including obtaining more comprehensive gene function information displayed as a directed acyclic graph through mapping query to the GO database; step three, performing Pathway analysis, which is similar with the GO analysis, including construction of interaction paths between genes through the comparison and query of the KEGG database; and step four, performing gene network analysis, including obtaining a gene interaction network diagram through the integration of three different types of interactions.
Owner:SHANGHAI CLUSTER BIOTECH
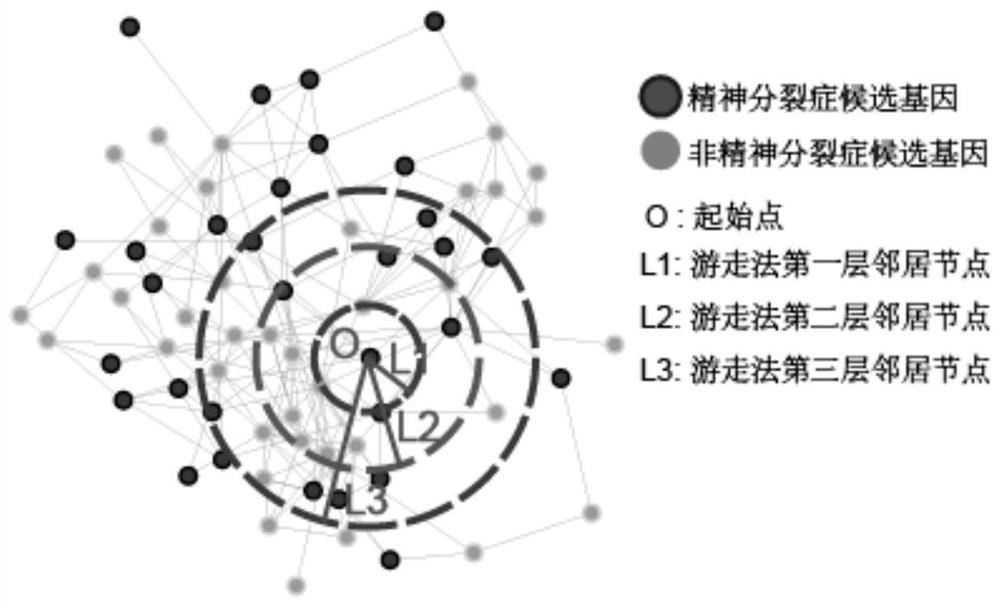
Schizophrenia gene-gene interaction network and construction method thereof
ActiveCN110827916AQuality improvementMental therapiesProteomicsCandidate Gene Association StudyProtein Interaction Networks
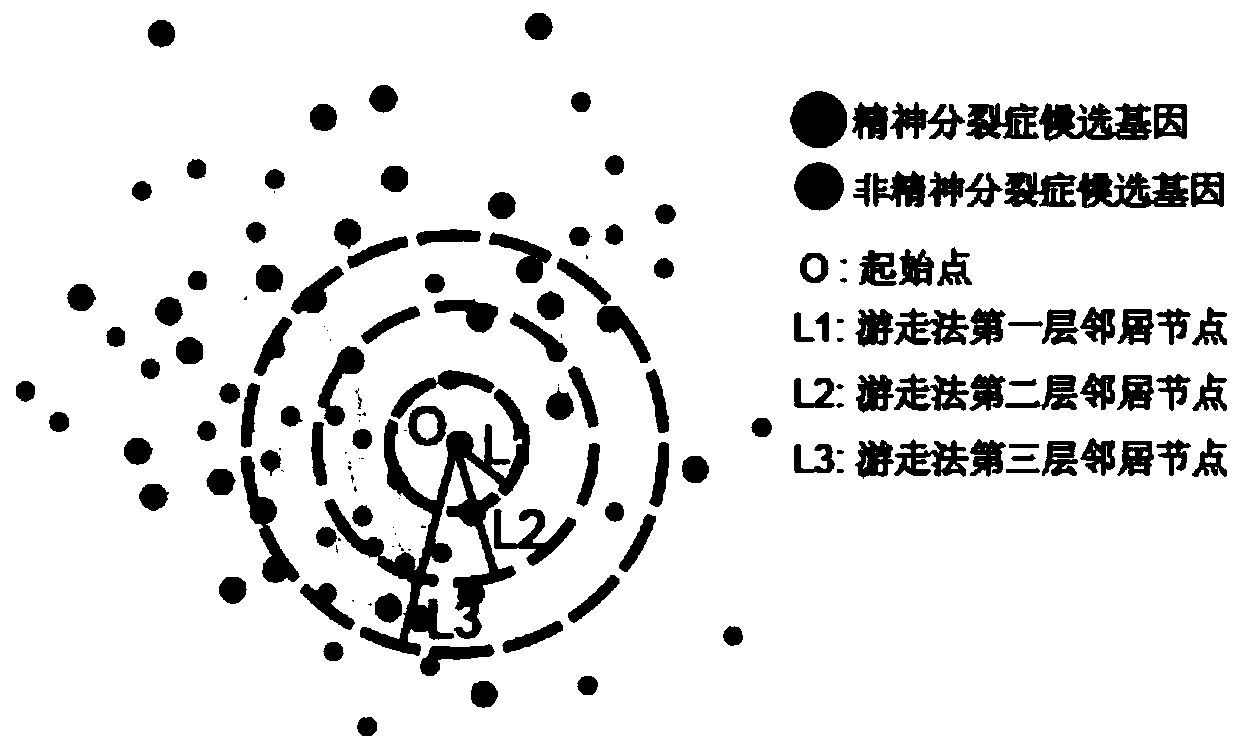
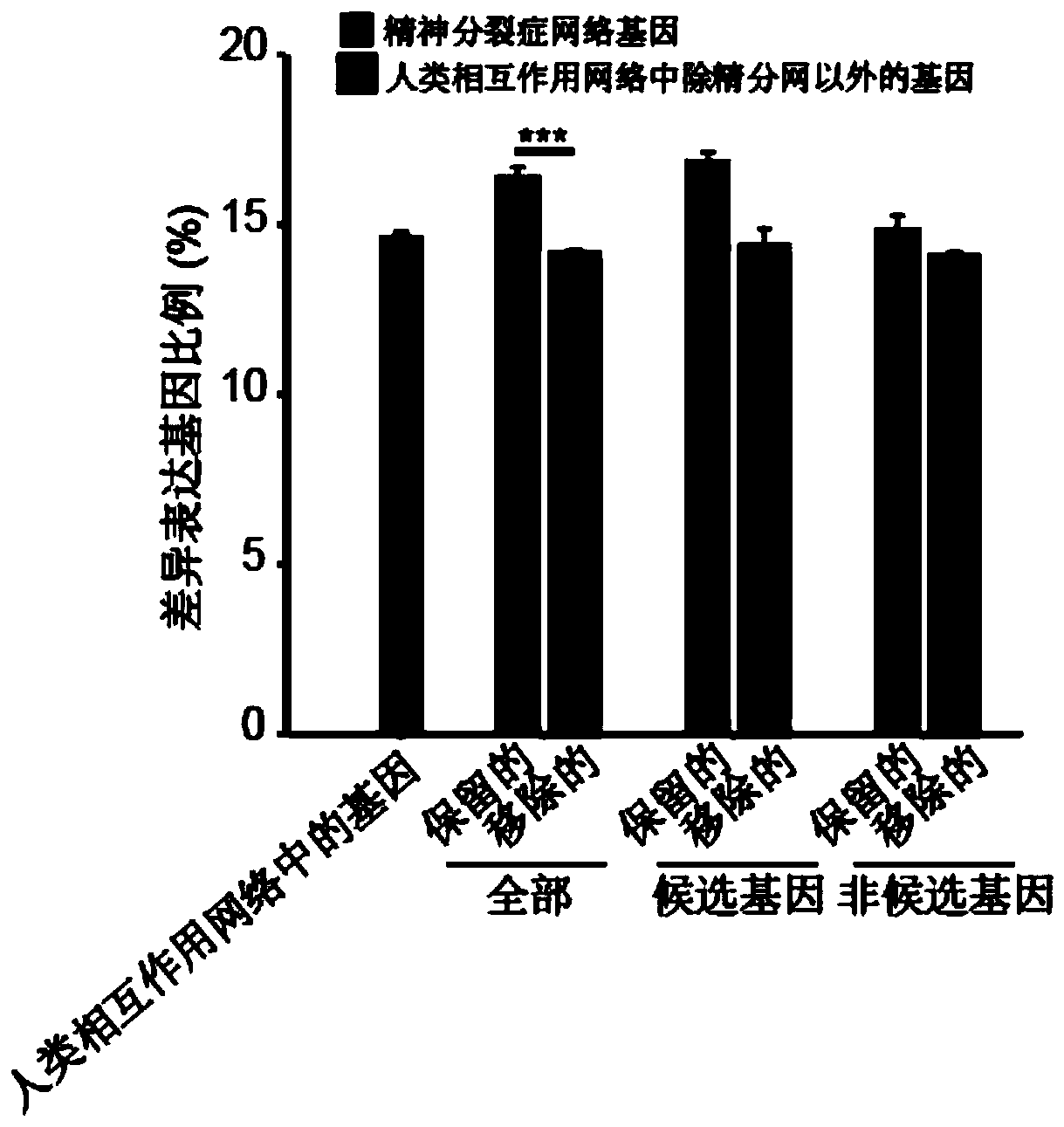
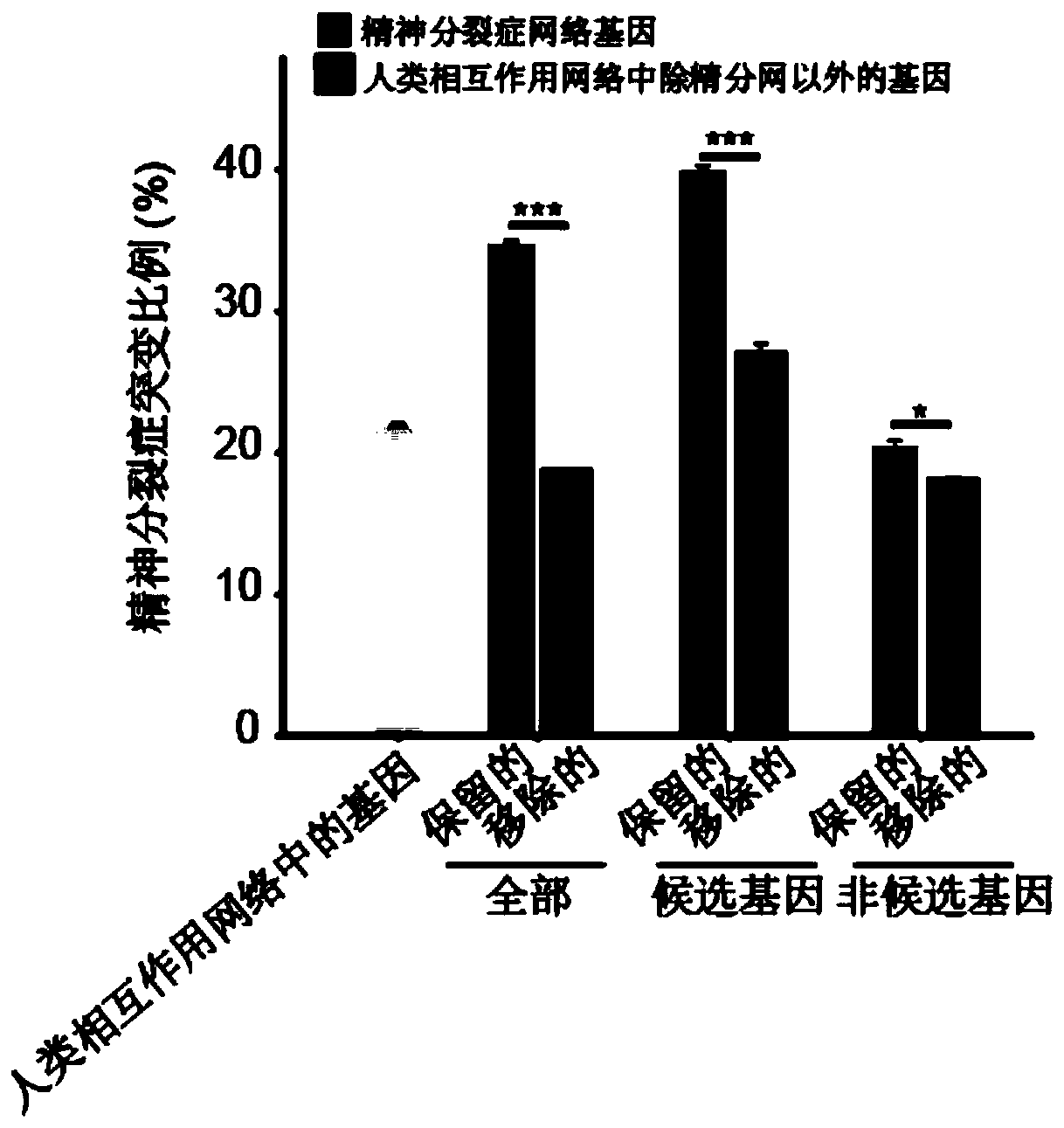
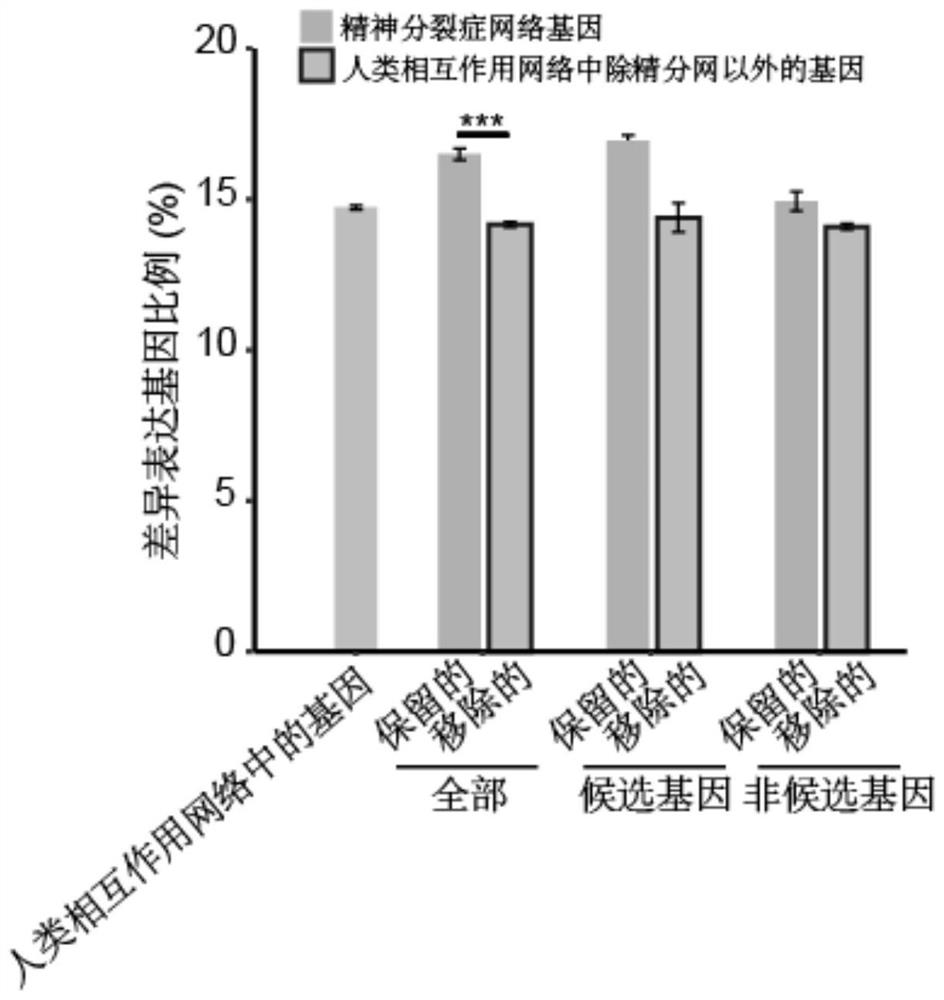
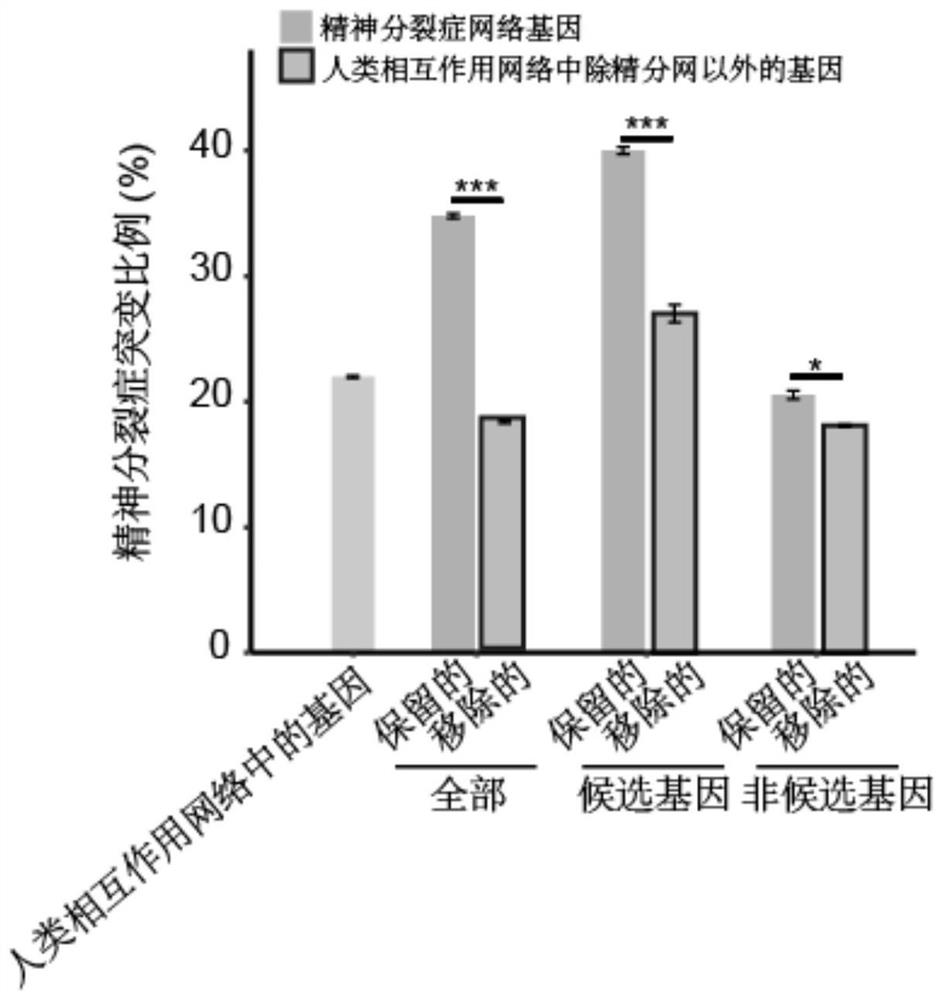
The invention discloses a construction method of a schizophrenia gene-gene interaction network. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1), collecting known schizophrenia candidate genes; (2) mapping the collected known schizophrenia candidate genes into a human protein-protein interaction network, and converting the human protein-protein interaction network into an interaction network named by genes; (3) carrying out R-score assignment on all the genes in the network, carrying out G-score assignment on all the genes in the network, and endowing each edge with a weight; (4) constructing an inter-node shortest path matrix and extracting a preliminary network by using a walk extension method; and (5), extracting a final network and outputting a result. According to the schizophrenia gene-gene interaction network constructed by the invention, part of false positive genes are removed, more potential candidate genes related to schizophrenia are included, and an enrichment analysis result shows that the retained genes are more related to schizophrenia, so that the constructed gene interaction network is better in quality.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
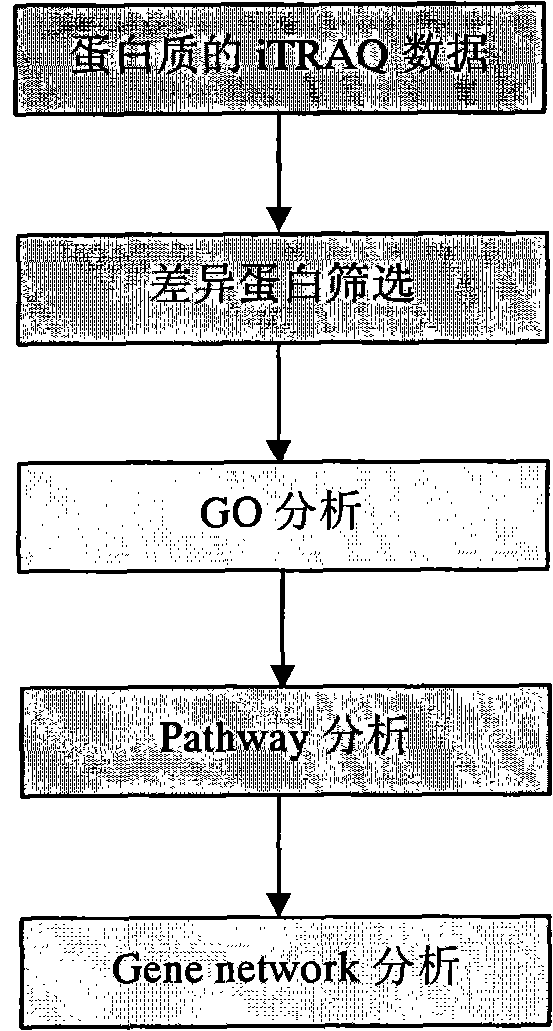
Method for analyzing iTRAQ (isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation) data
InactiveCN102321733AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPathway analysisAnalysis data
The invention designs a method for analyzing iTRAQ (isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation) data aiming at the characteristics of iTRAQ protein quantitative data analysis. The method has a main flow which comprises the following steps of: 1, screening differential protein: screening the initial iTRAQ data in groups to acquire a difference result; 2, performing GO (Gene Ontology) analysis: performing query mapping on a GO database to acquire completer gene function information so as to display a directed acyclic graph; 3, performing Pathway analysis which is similar to GO analysis: performing comparative query with a KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database to construct an interaction pathway between genes; and step 4, performing Gene network analysis: integrating three different interaction relations to obtain a gene interaction network graph.
Owner:SHANGHAI CLUSTER BIOTECH
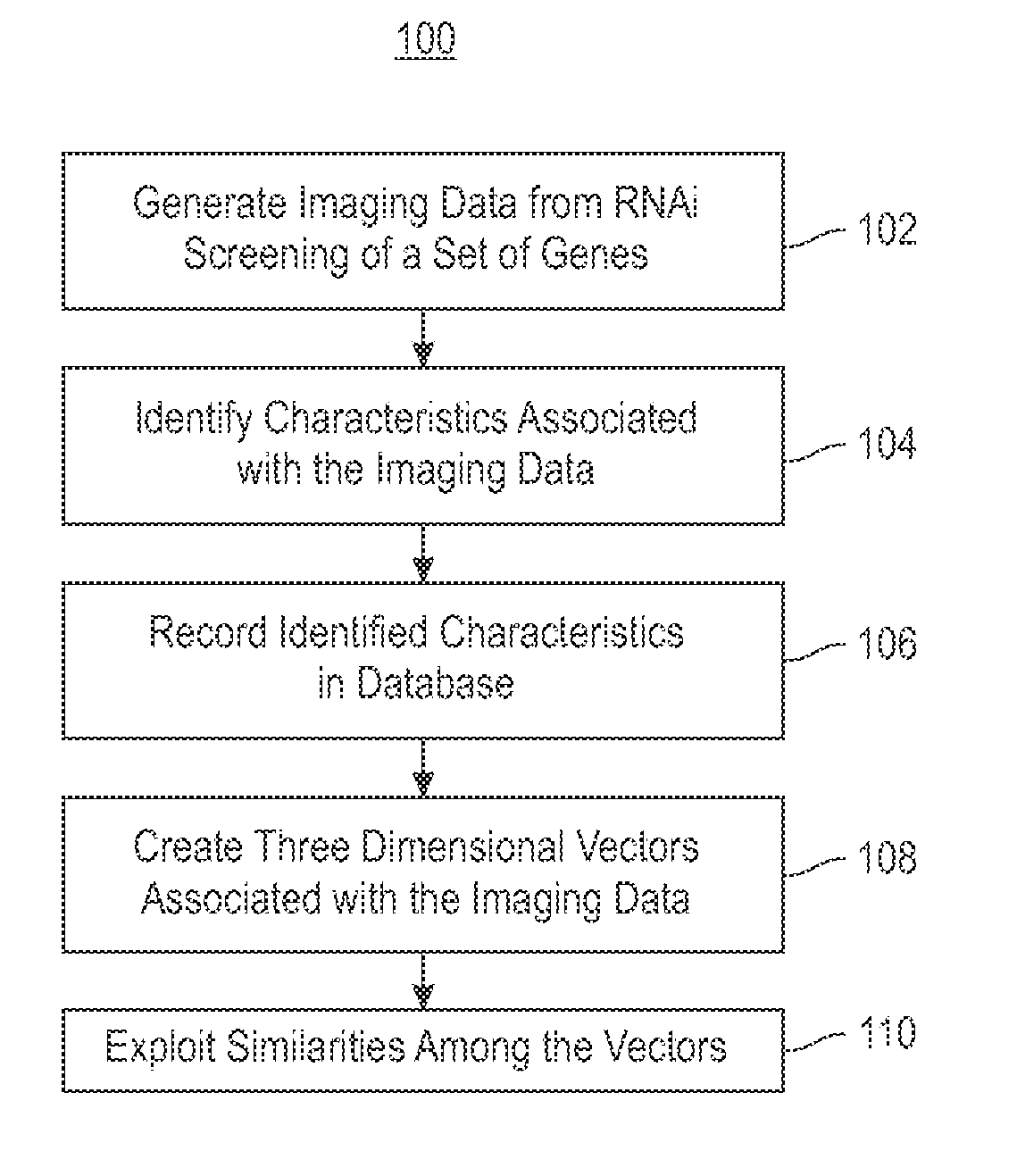
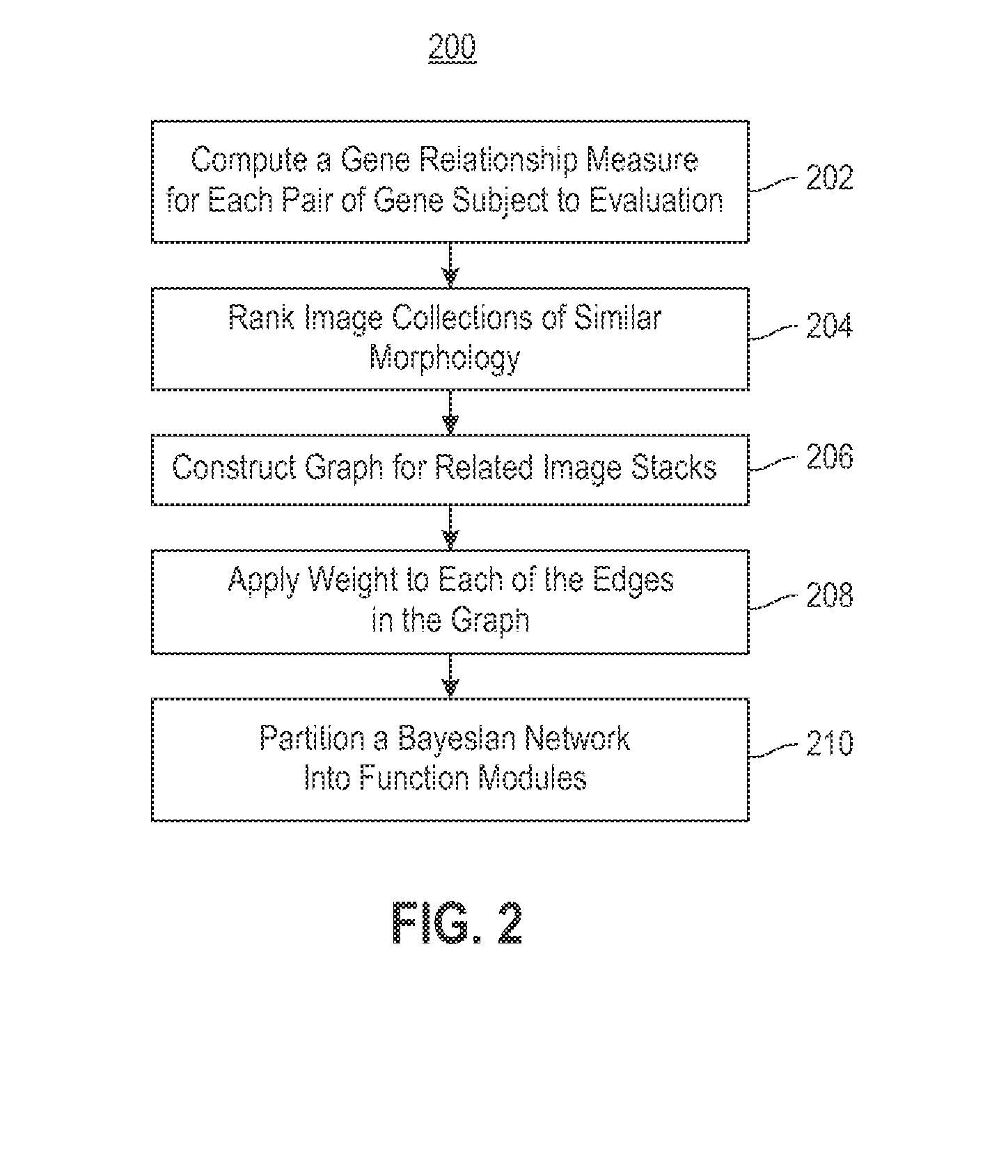
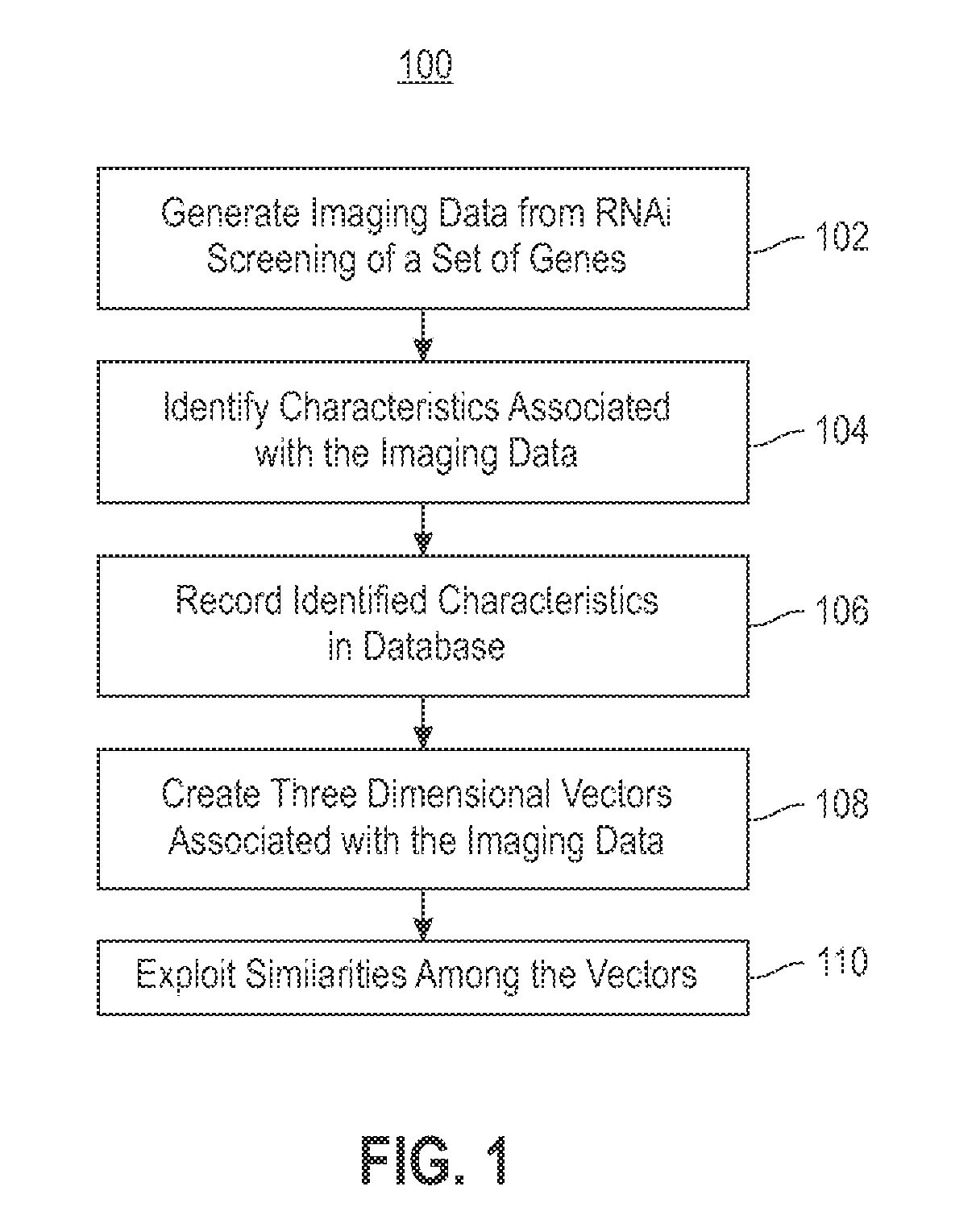
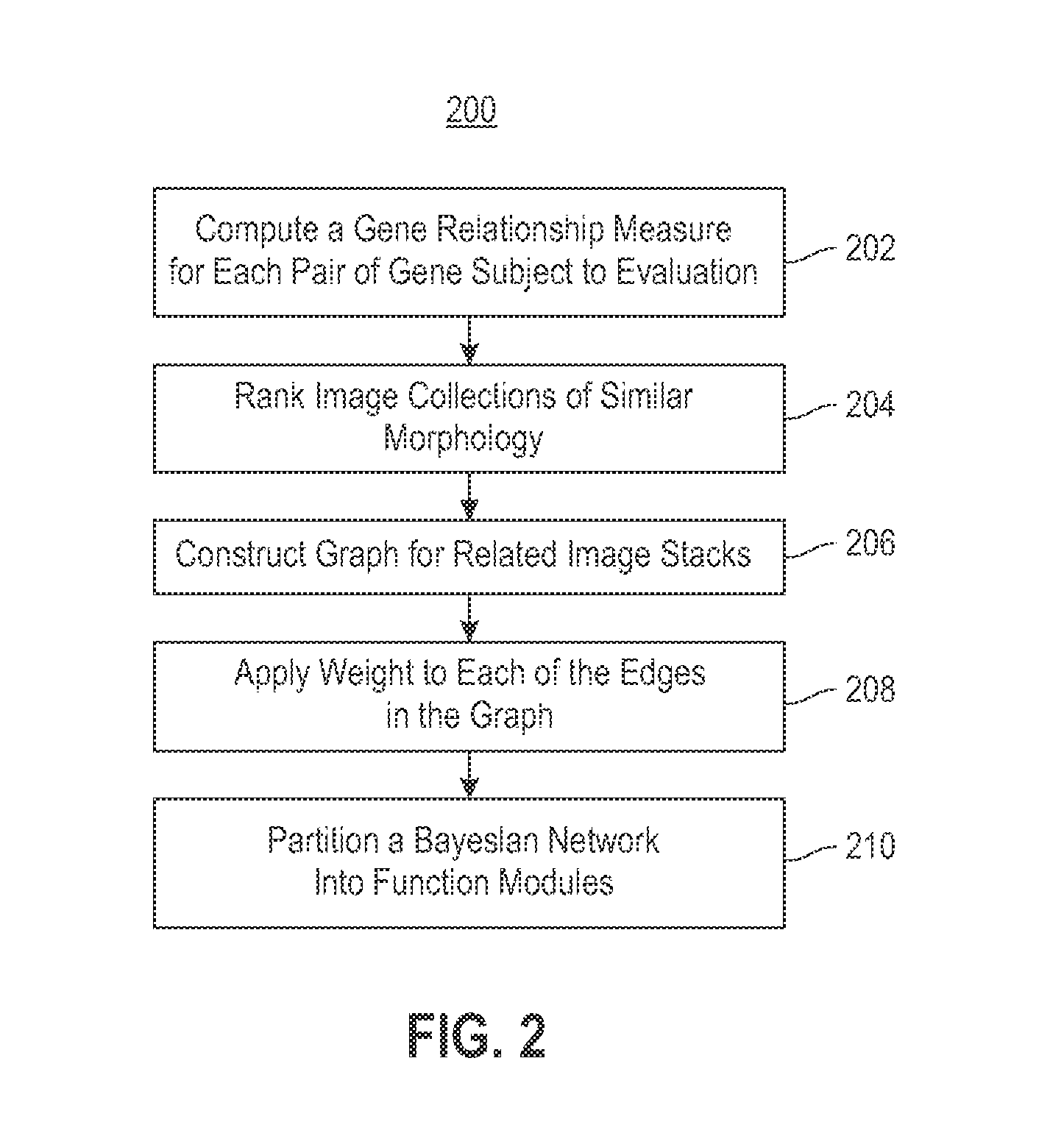
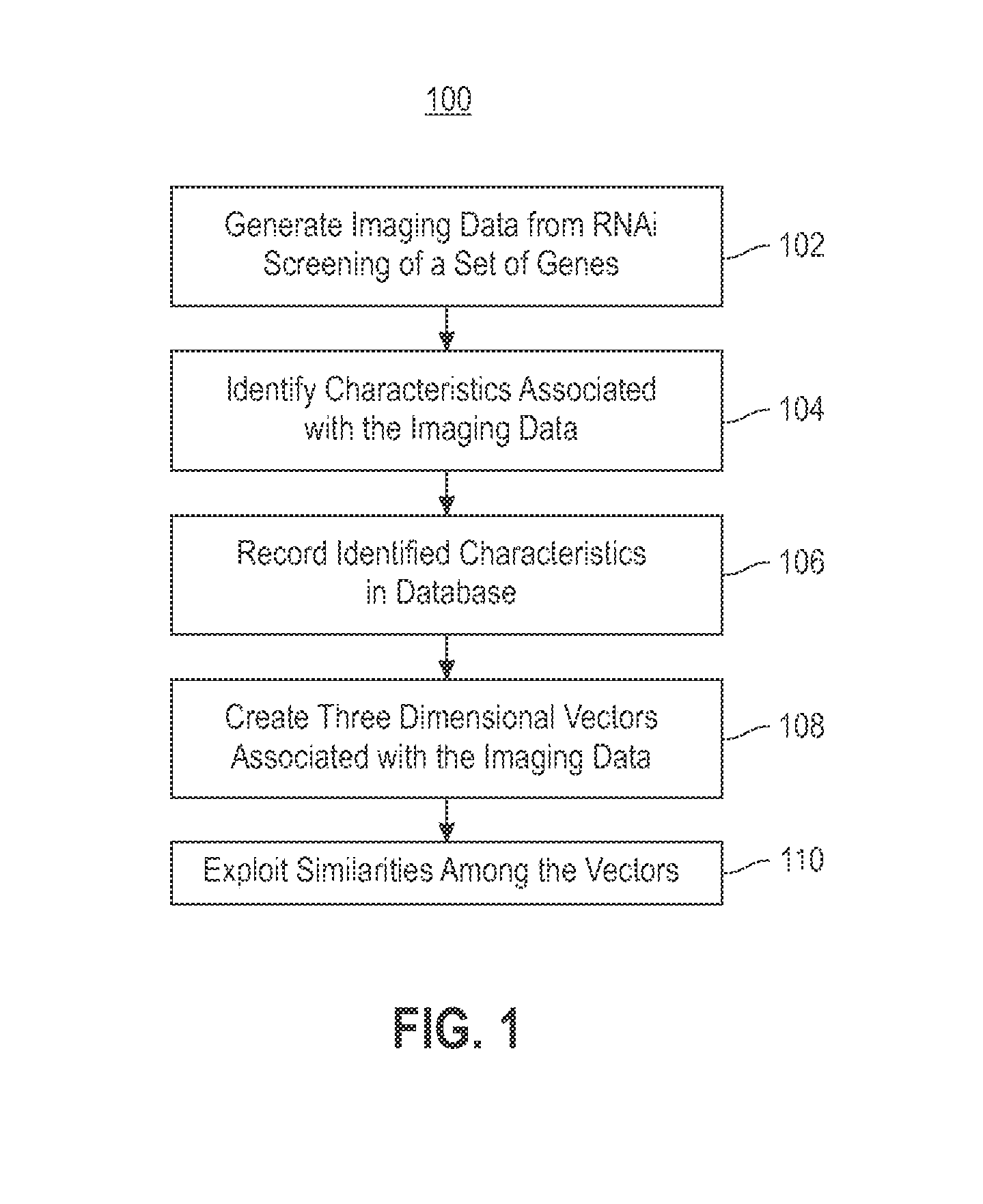
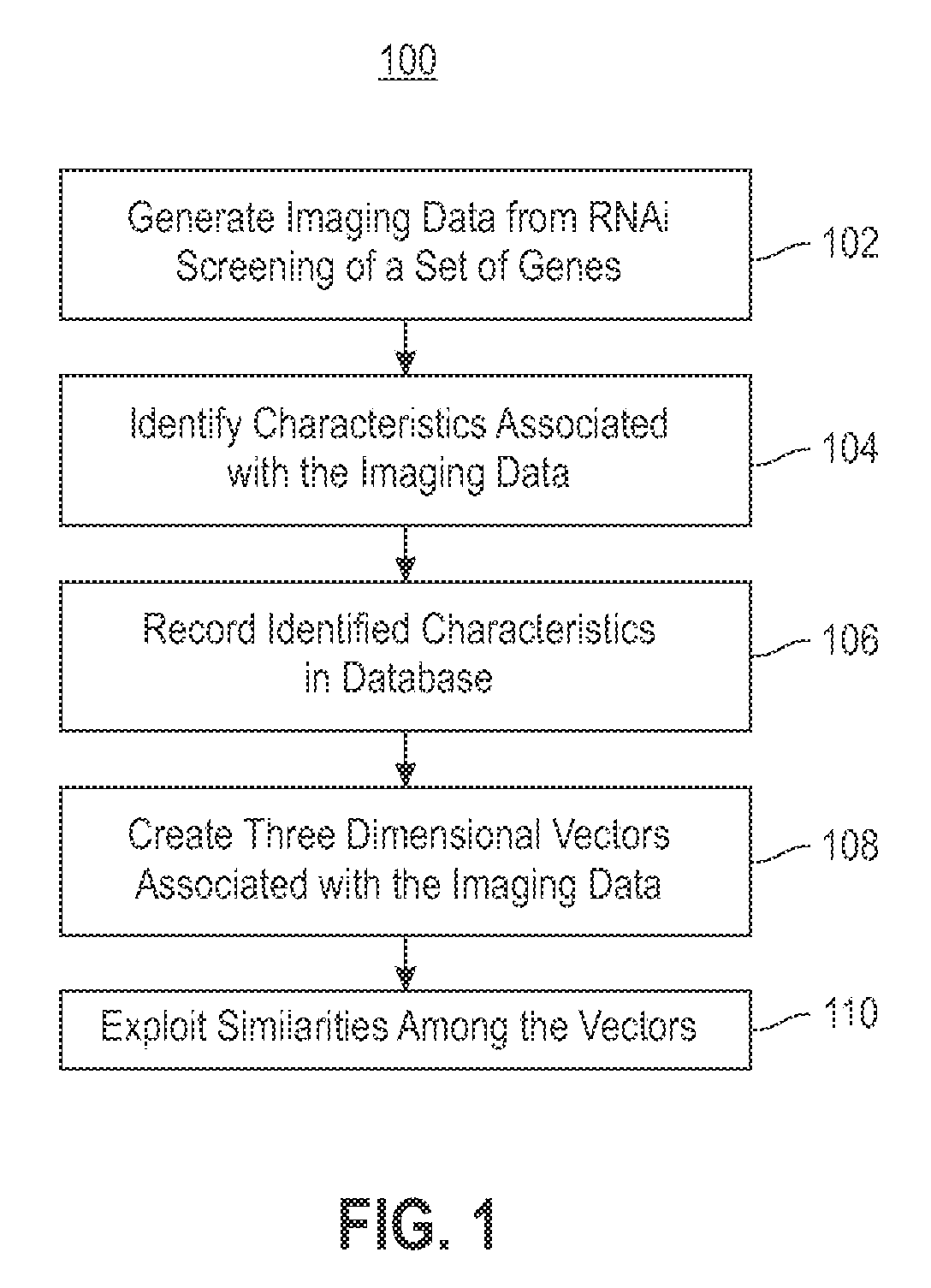
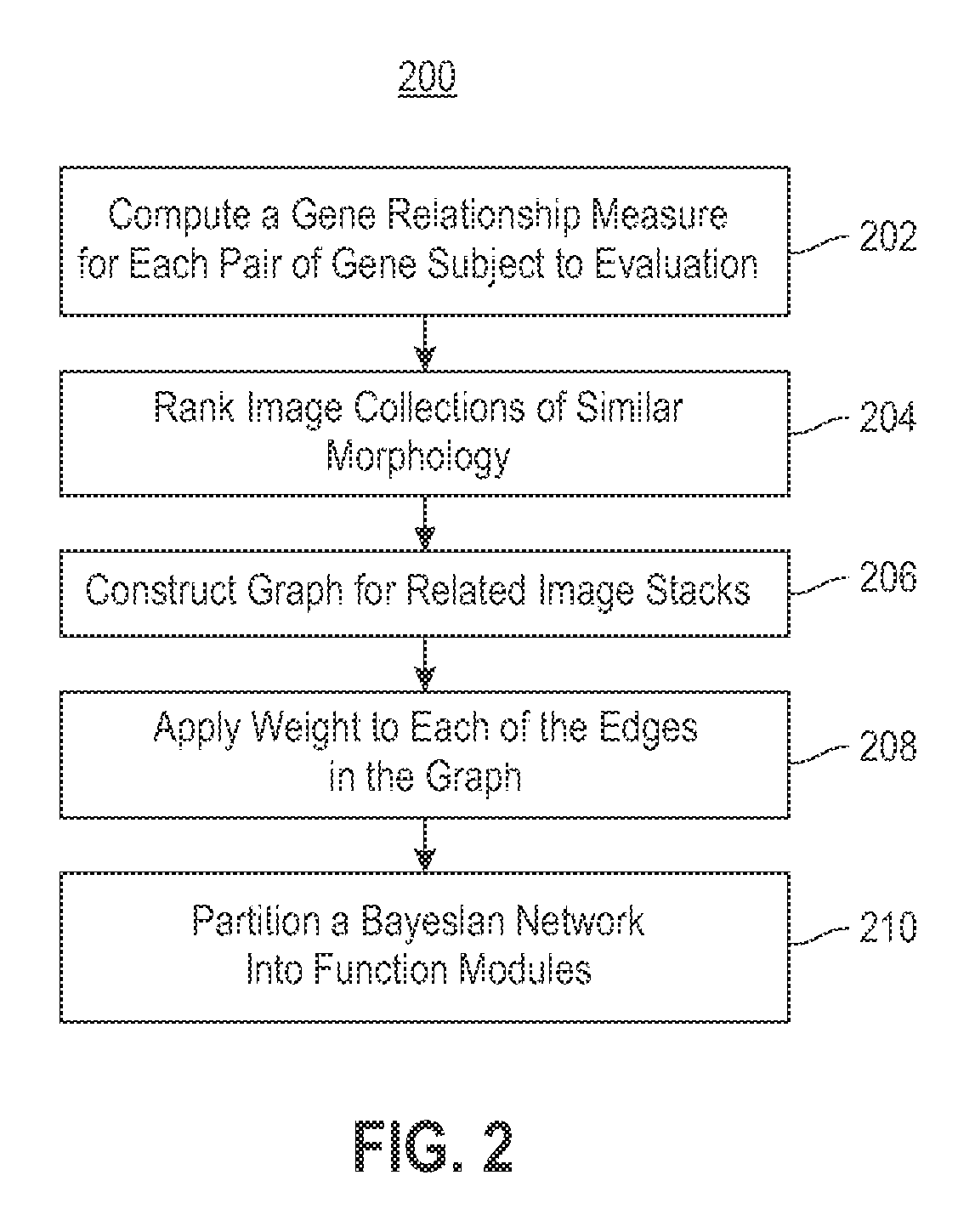
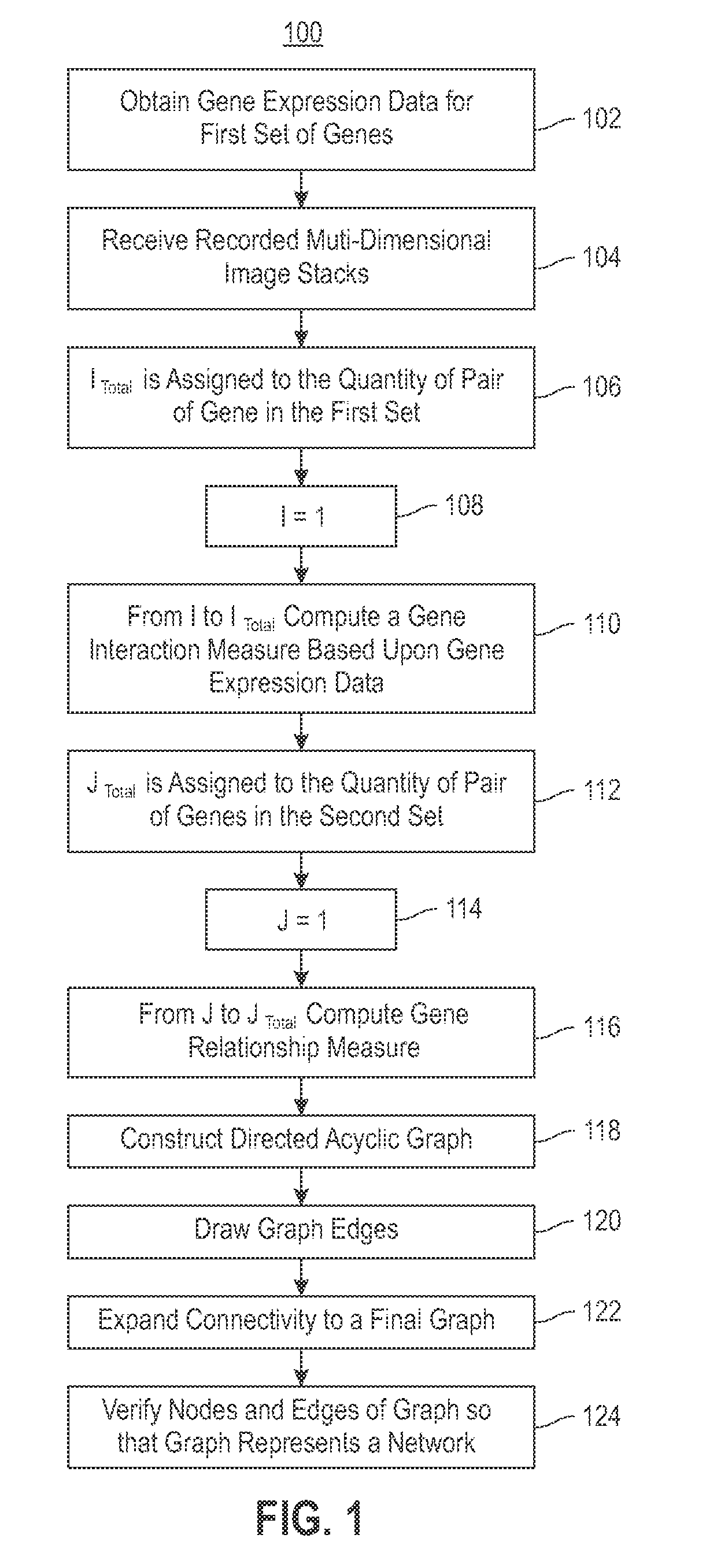
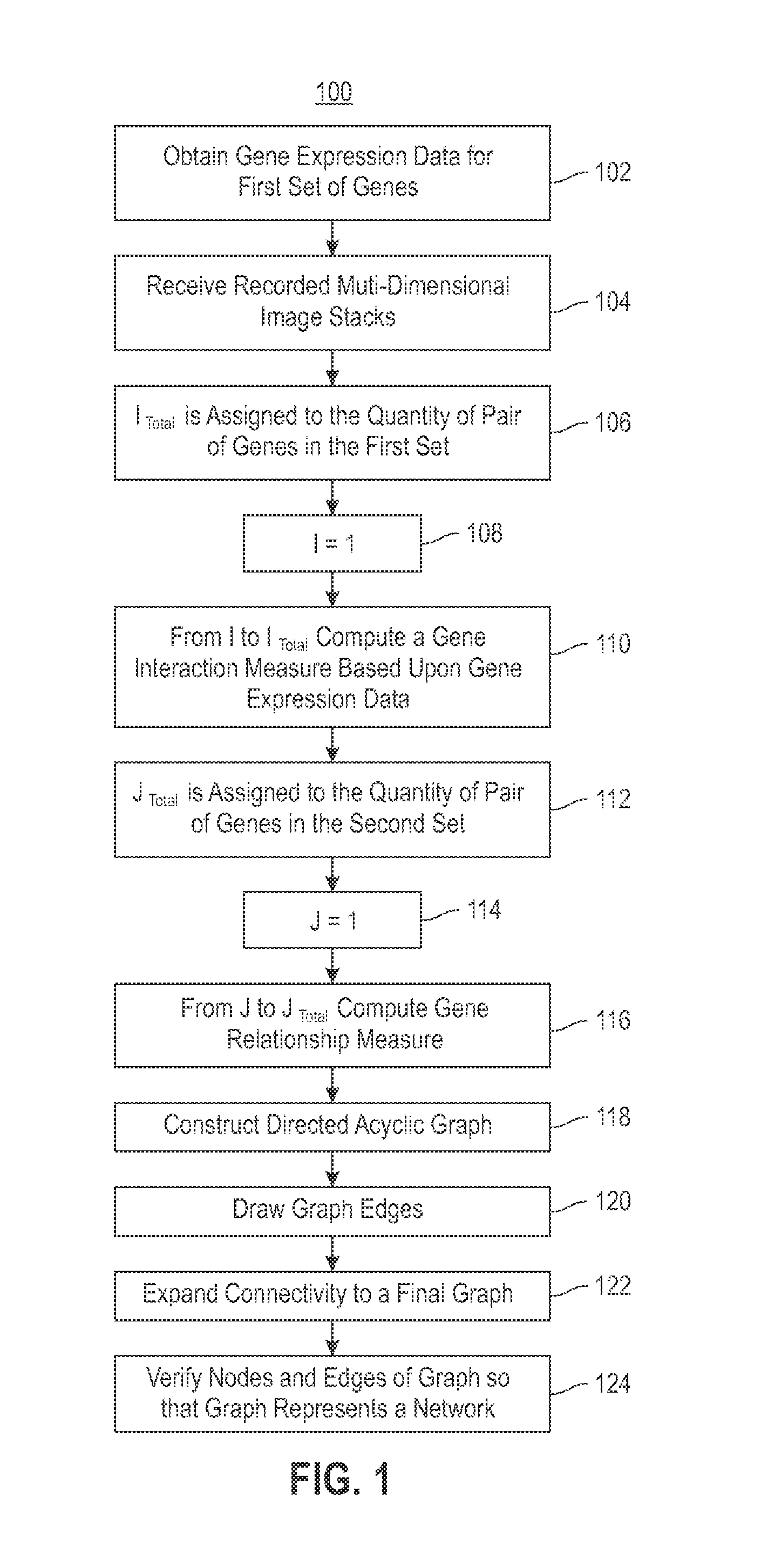
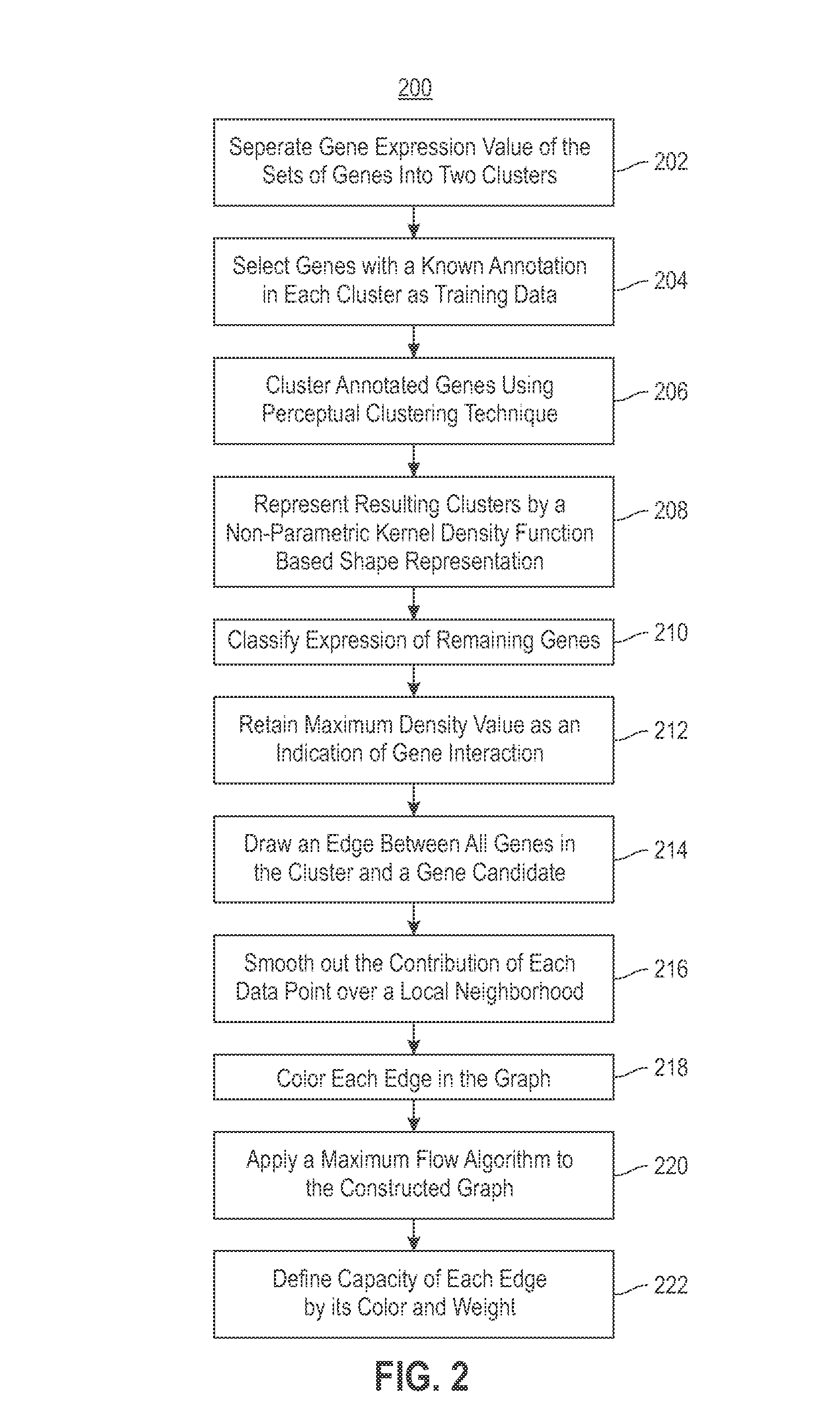
Using RNAi Imaging Data For Gene Interaction Network Construction
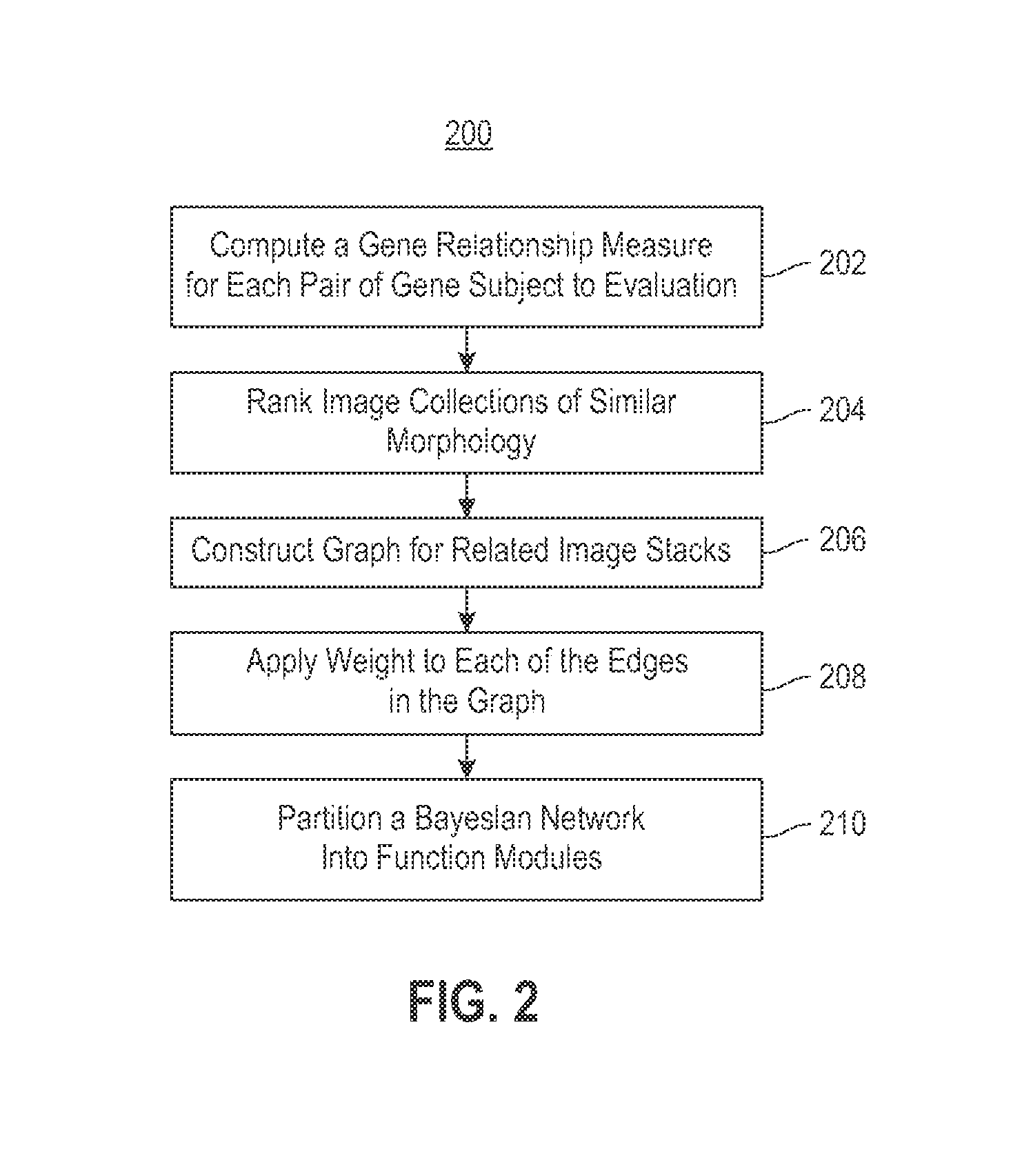
Embodiments of the invention relate to a constructing a gene interaction network. Tools are provided to compute a gene relationship measure based upon cellular images, and to rank image collections having a similar morphology. The ranking is based upon capturing similarity within the ranked collection by modeling a three dimensional shape of a cellular image stack. The graph is constructed for related images stacks. Nodes in the graph represent genes, and edges drawn between the nodes represent corresponding image stacks in a commonly ranked list. Accordingly, the graphical representation mathematically and visually connects respective genes.
Owner:IBM CORP
Using RNAi Imaging Data For Gene Interaction Network Construction
Embodiments of the invention relate to a constructing a gene interaction network. Tools are provided to compute a gene relationship measure based upon cellular images, and to rank image collections having a similar morphology. The ranking is based upon capturing similarity within the ranked collection by modeling a three dimensional shape of a cellular image stack. The graph is constructed for related images stacks. Nodes in the graph represent genes, and edges drawn between the nodes represent corresponding image stacks in a commonly ranked list. Accordingly, the graphical representation mathematically and visually connects respective genes.
Owner:IBM CORP
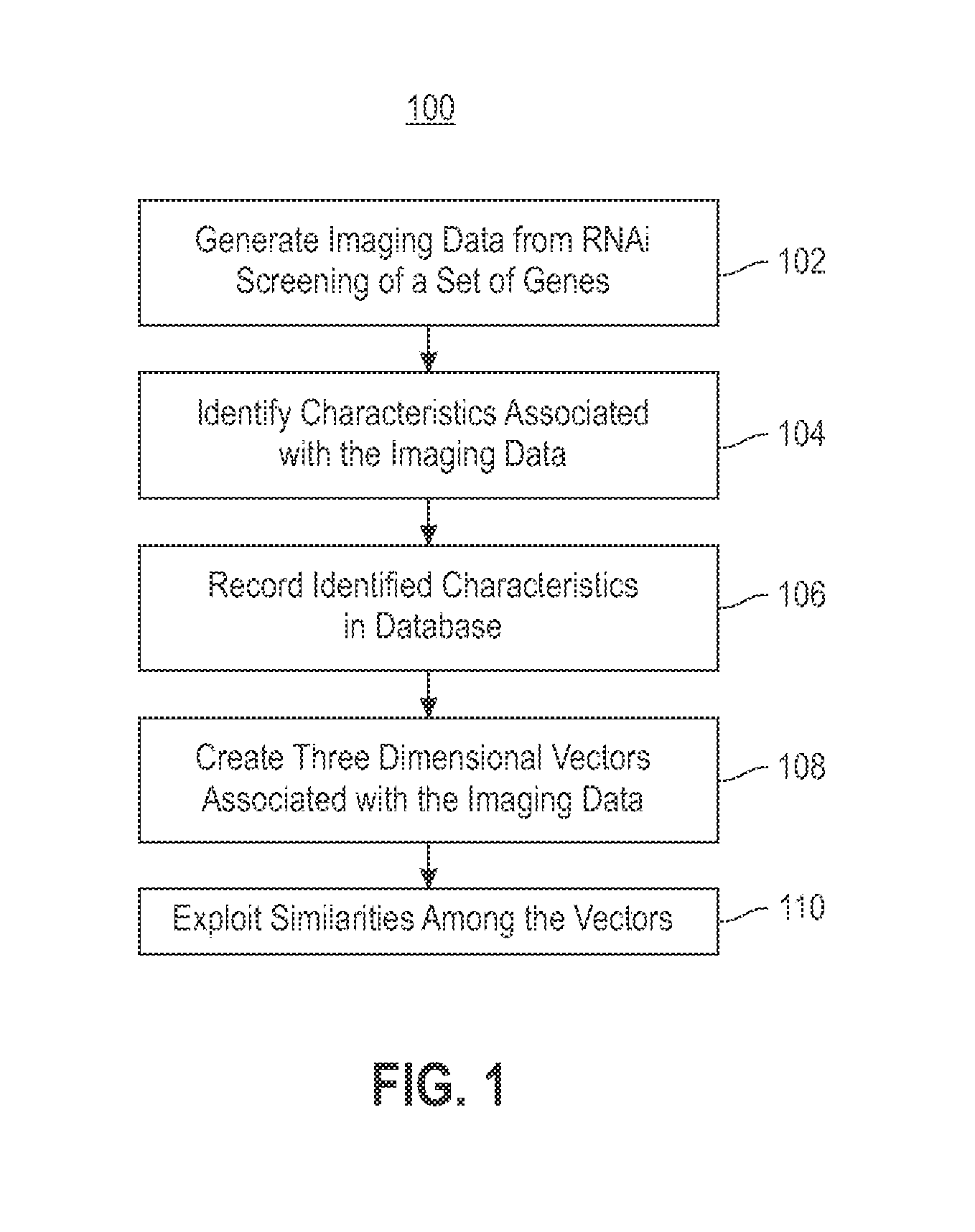
Using RNAi imaging data for gene interaction network construction
Embodiments of the invention relate to a constructing a gene interaction network. Tools are provided to compute a gene relationship measure based upon cellular images, and to rank image collections having a similar morphology. The ranking is based upon capturing similarity within the ranked collection by modeling a three dimensional shape of a cellular image stack. The graph is constructed for related images stacks. Nodes in the graph represent genes, and edges drawn between the nodes represent corresponding image stacks in a commonly ranked list. Accordingly, the graphical representation mathematically and visually connects respective genes.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Using RNAi imaging data for gene interaction network construction
Embodiments of the invention relate to a constructing a gene interaction network. Tools are provided to compute a gene relationship measure based upon cellular images, and to rank image collections having a similar morphology. The ranking is based upon capturing similarity within the ranked collection by modeling a three dimensional shape of a cellular image stack. The graph is constructed for related images stacks. Nodes in the graph represent genes, and edges drawn between the nodes represent corresponding image stacks in a commonly ranked list. Accordingly, the graphical representation mathematically and visually connects respective genes.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for identifying esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on basis of network index difference analysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioinformatics, and relates to a method for identifying esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on the basis of network index difference analysis. The method comprises the following steps of processing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma gene sample data and normal gene sample data to construct an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma gene interactionnetwork and a normal gene interaction network; using a network module identification method to find out key community structures in the two networks, and performing gene function enrichment analysison the key community structures; extracting same nodes from the two networks, and retaining nodes linked to the same nodes to obtain the two simplified networks; using a global index and a local modular index, analyzing the two simplified networks to obtain genes related to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; combining a gene function enrichment analysis result with gene annotations and functionalreferences to finally determine candidate markers for diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. A method for studying the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on the basis of gene network difference analysis is further perfected.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Identification method of markers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma based on difference analysis of network indicators
ActiveCN108108589BHigh precisionFill in the gaps in the analysisProteomicsGenomicsOncogeneCancer research
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioinformatics, and relates to a method for identifying esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on the basis of network index difference analysis. The method comprises the following steps of processing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma gene sample data and normal gene sample data to construct an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma gene interactionnetwork and a normal gene interaction network; using a network module identification method to find out key community structures in the two networks, and performing gene function enrichment analysison the key community structures; extracting same nodes from the two networks, and retaining nodes linked to the same nodes to obtain the two simplified networks; using a global index and a local modular index, analyzing the two simplified networks to obtain genes related to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; combining a gene function enrichment analysis result with gene annotations and functionalreferences to finally determine candidate markers for diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. A method for studying the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on the basis of gene network difference analysis is further perfected.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Method and system for screening cancer biomolecular markers based on network topology parameters
The invention discloses a method and system for screening cancer biomolecular markers based on network topology parameters. The method includes: acquiring human intergenic interaction network and gene chip expression data, and integrating the intergenic interaction based on the gene expression data. Network; construct the interaction network between genes in the disease state and the control state; calculate the network topology parameter difference gene between the disease state and the control state gene interaction network, and obtain the network topology parameter difference change network based on the network parameter difference gene; Mining the network modules of the topological parameter difference network; performing feature selection on the obtained difference network modules to obtain the genes that are distinguishable between normal and disease in each module; detecting the classification effect of the genes selected in each module on diseases, and screening according to the classification effect Differential network modules as biomolecular marker candidates. The present invention provides a new complex disease biomarker recognition method based on omics data, which is proved to have certain accuracy and effectiveness by experiments.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A method for constructing regulatory networks of differentially expressed genes in specific cancers
InactiveCN105740651BHigh precisionImprove calculation accuracyHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsCancer genesGene map
The invention discloses a construction method for a specific cancer differential expression gene regulation and control network.The method includes the following steps of firstly, constructing a framework gene interaction network according to function similarity weight numbers between genes; secondly, conducting module division on the framework gene interaction network through a segmenting method; thirdly, screening out differential expression genes through complete genome methylation data; fourthly, classifying the screened-out differential expression genes according to functions; fifthly, using all the differential expression genes mapped to each same function module as a function classification; sixthly, constructing the regulation and control network of all the genes in each function classification function; seventhly, conducting sub-network splicing under guidance of a framework network.The calculation complexity is greatly reduced, and high precision is achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
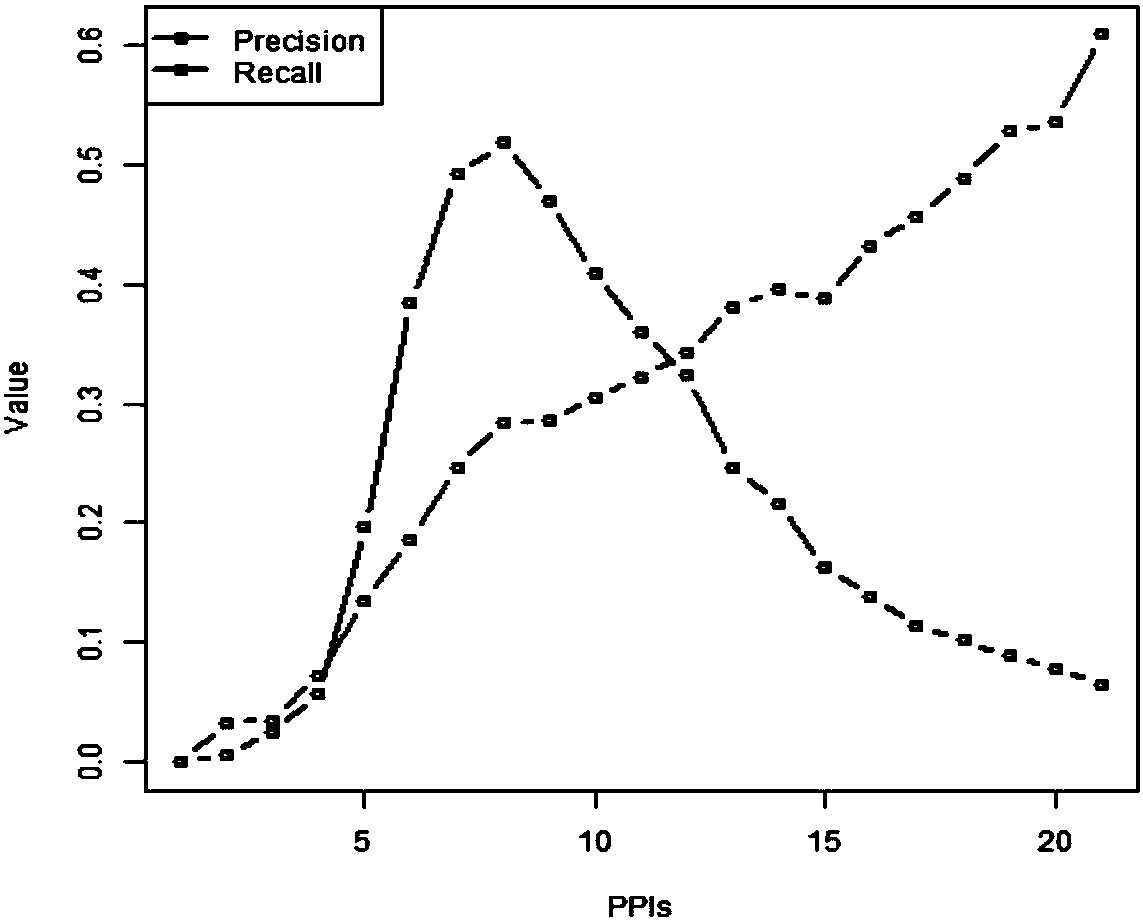
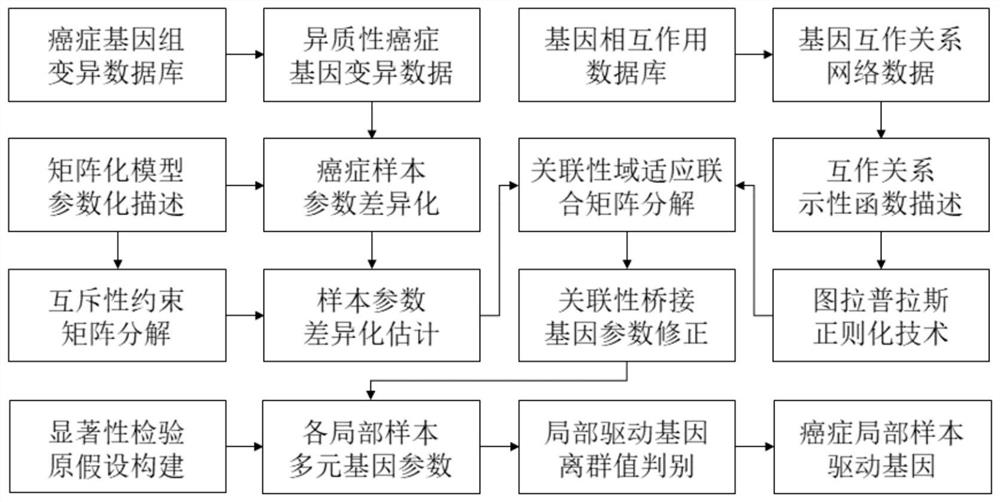
Mutually-exclusively constrained graph Laplacian approach to heterogeneous cancer driver gene identification
ActiveCN111785325BResolve indistinguishableRealize associative bridgingMedical automated diagnosisProteomicsCancer genomeGene recognition
The present invention provides a method for identifying heterogeneous cancer driver genes based on a mutually exclusive constrained graph Laplacian. First, obtain cancer genome variation data and gene interaction network; then, use a matrix model to describe the heterogeneity of cancer, and use mutually exclusive constraint matrix decomposition to estimate the sample parameters of heterogeneity cancer; Then, construct the mutual exclusion constraint matrix decomposition optimization function regularized by the joint association and interaction network, and correct the parameters of the driving genes affected by the interaction in the local samples through iterative solution; finally, use the outlier test method to identify the driving genes . The invention can solve the problem of differential estimation of parameters of cancer samples and effective identification of driver genes in local samples affected by interaction, and realizes the identification of driver genes mutated in local samples from gene variation data of heterogeneous cancer samples.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Screening method of functional peptide
PendingCN114420200AReduce consumptionReduce pollutionBiostatisticsProteomicsGene targetsProtein Interaction Networks
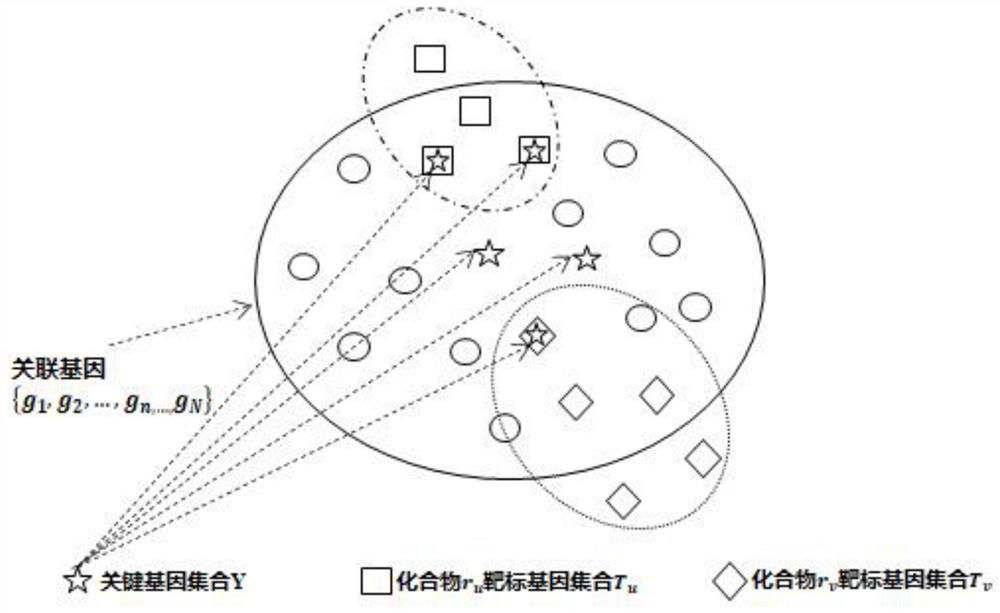
The invention discloses a functional peptide screening method which is low in cost, efficient and environment-friendly and specifically comprises the following steps: calling a regulatory network related to the function type of a functional peptide needing to be screened; finding out a first gene target set related to the function type; performing functional target prediction on each sequenced peptide fragment, and screening to obtain a second gene target set related to the functional type; performing association processing on the second gene target set and the first gene target set to obtain a functional target; constructing a protein interaction network according to the functional targets, carrying out node graph visualization analysis to obtain a gene interaction network graph, and identifying to obtain a core module and a key gene; calculating node edge numbers of proteins and genes by using an R language, and performing normalization processing to obtain a first score of each target in the functional targets; multiplying the first score of each target point of the single peptide fragment by a corresponding similarity coefficient and then summing to obtain a functional score of the single peptide; and selecting the first 20 peptide fragments with hydrophobicity of 0-3 as candidate peptides.
Owner:时代生物科技(深圳)有限公司 +1
A method for constructing schizophrenia gene-gene interaction network
ActiveCN110827916BQuality improvementMental therapiesProteomicsCandidate Gene Association StudyProtein Interaction Networks
The invention discloses a method for constructing a schizophrenia gene-gene interaction network. The construction method comprises the following steps: ① collecting known candidate genes for schizophrenia; ② mapping the collected known candidate genes for schizophrenia In the human protein-protein interaction network, it is converted into an interaction network named after genes; ③ assign R-score to all genes in the network, assign G-score to all genes in the network, and assign weights to each edge ; ④ Construct the shortest path matrix between nodes; Extract the preliminary network with the "walk expansion" method; ⑤ Extract the final network and output the result. The present invention constructs the gene-gene interaction network of schizophrenia, removes some false positive genes, and includes more potential candidate genes related to schizophrenia. The enrichment analysis results show that the retained genes are more closely related to schizophrenia. Correlation indicates that the quality of the gene interaction network constructed by the present invention is better.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
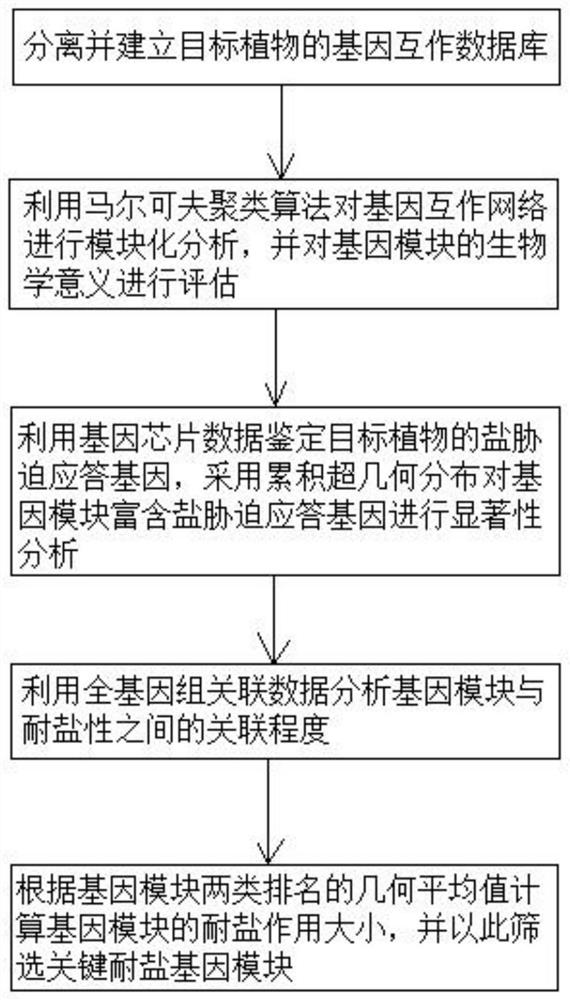
Plant salt-tolerant gene module mining method
PendingCN113990388AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyProteomicsGenomicsCluster algorithmMarkov clustering
The invention discloses a plant salt-tolerant gene module mining method. The method comprises the following steps that: based on a gene interaction network, a Markov clustering algorithm is adopted to carry out modular analysis on the gene interaction network, and gene chip and whole genome associated data are utilized to evaluate the salt tolerances of gene modules; and a key salt-tolerant gene module is screened out according to the salt-tolerant contribution of each gene module. Compared with an existing method, the method focuses on discovery of a brand new salt-tolerant gene group, and greatly improve the efficiency and accuracy of plant salt-tolerant gene mining.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +1
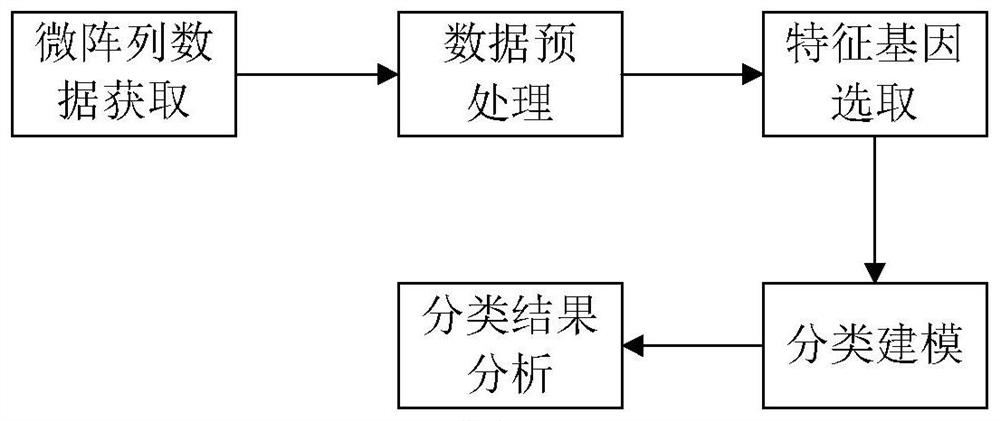
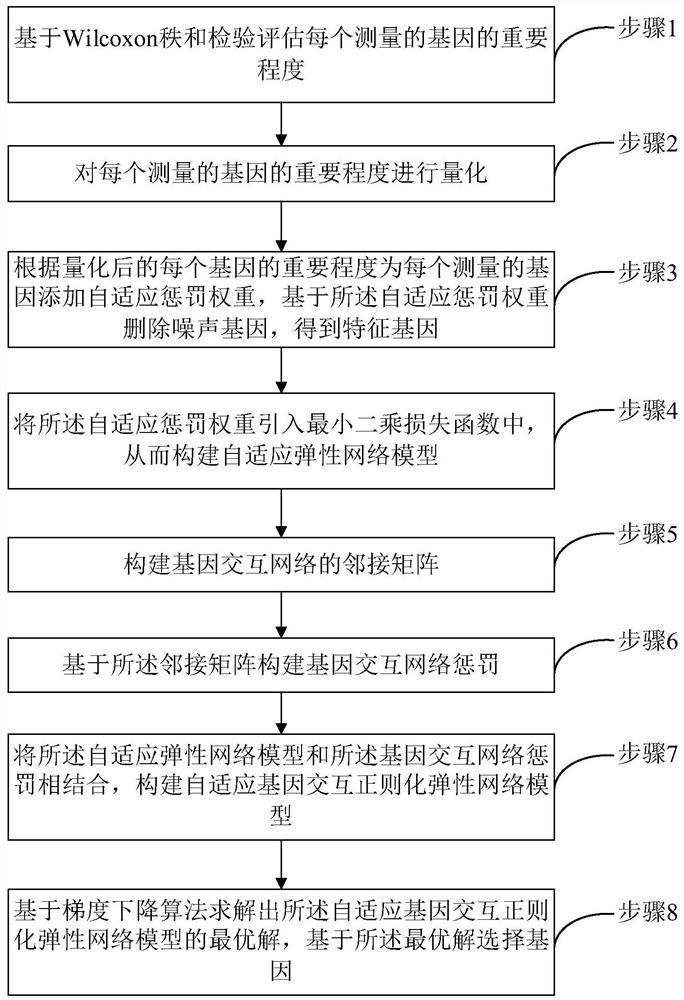
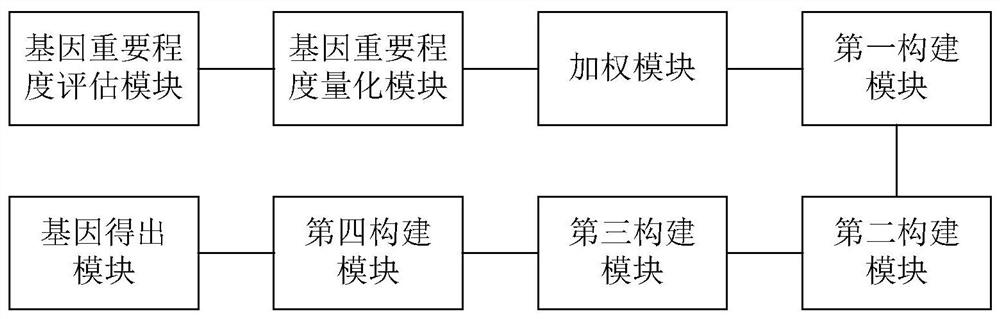
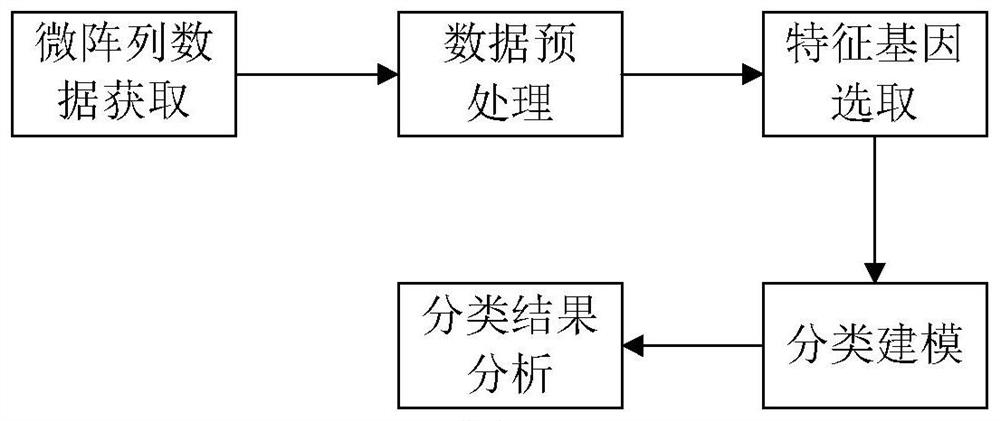
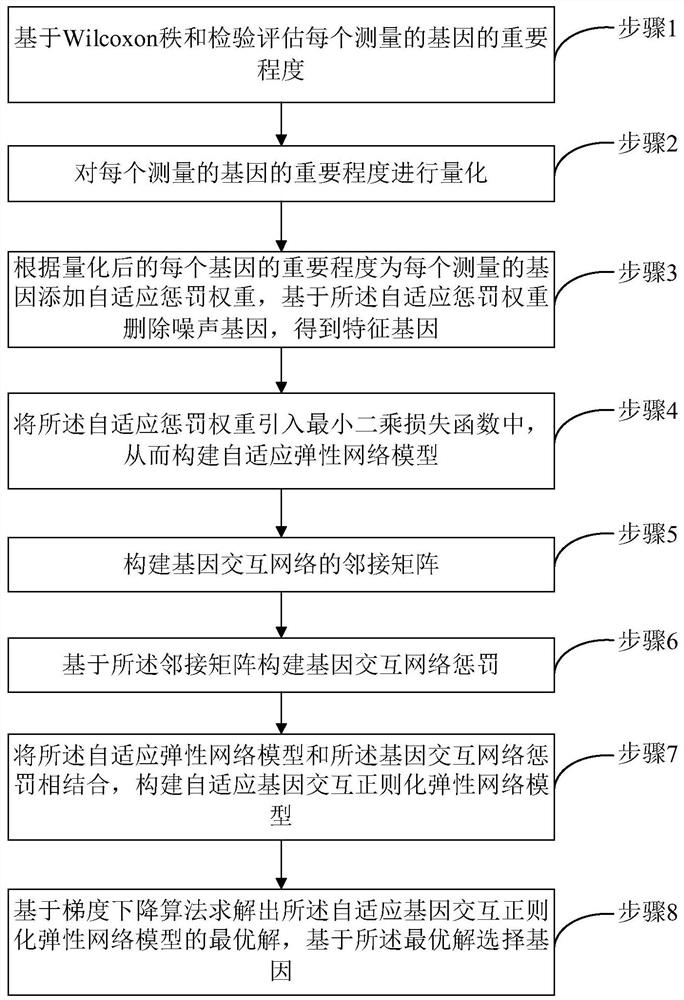
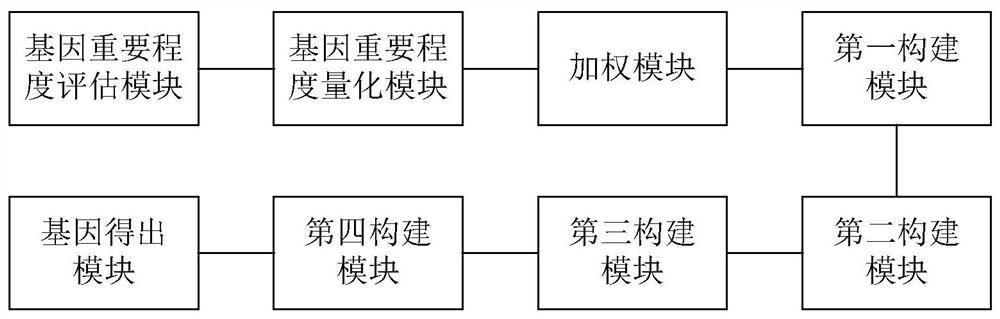
Gene selection method and system based on adaptive gene interaction regularization elastic network model
ActiveCN113838519AEasy to integrateGood for classification purposeBiostatisticsHybridisationAlgorithmGene selection
The invention discloses a gene selection method and system based on a self-adaptive gene interaction regularization elastic network model. The method comprises the following steps: checking and evaluating the importance degree of each measured gene based on a Wilcoxon rank sum; quantifying the importance degree of each measured gene, adding an adaptive penalty weight, and then deleting noise genes to obtain feature genes; introducing the penalty weight into a least square loss function, and constructing a self-adaptive elastic network model; constructing an adjacent matrix of the gene interaction network; constructing a gene interaction network penalty based on the adjacent matrix; combining the self-adaptive elastic network model with gene interaction network penalty to construct a self-adaptive gene interaction regularization elastic network model; solving an optimal solution of the regularization elastic network model based on a gradient descent algorithm, and selecting a gene based on the optimal solution. According to the method, important genes highly related to tumor generation can be adaptively selected, and redundant and unrelated genes and noise genes are removed.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Method for expressing quantitative character and CNV association based on gene interaction network clustering and group sparse learning
The invention relates to the field of data mining in bioinformatics, in particular to a synthetic lethal interaction prediction method based on a heterogeneous graph convolutional neural network. The method mainly comprises the steps of (1) collecting breast cancer FPKMRNA-seq information, breast cancer CNV data and breast cancer high-confidence risk gene information; (2) preprocessing breast cancer copy number variation (CNV) and mRNA data by a rank-based method; (3) establishing a gene-gene interaction network based on protein interaction knowledge and a signal channel, and generating a high-density sub-network by using a network clustering algorithm; and (4) constructing a group sparse learning-based model to describe the incidence relation between the subnet and the mRNA expression of the target gene, measuring the ability of the CNVs to predict the expression change of the target gene by using a root mean square error (RMSE), carrying out cross validation by adopting a k-fold cross validation algorithm, and carrying out correlation analysis on the gene expression and the CNV by using a Sperman correlation research method in combination with pathway enrichment analysis.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for Screening Potentially Important Genes in Population Genome Based on mk-test
Owner:中国科学院昆明植物研究所海盐工程技术中心
An epigenome-based drug discovery method and its application
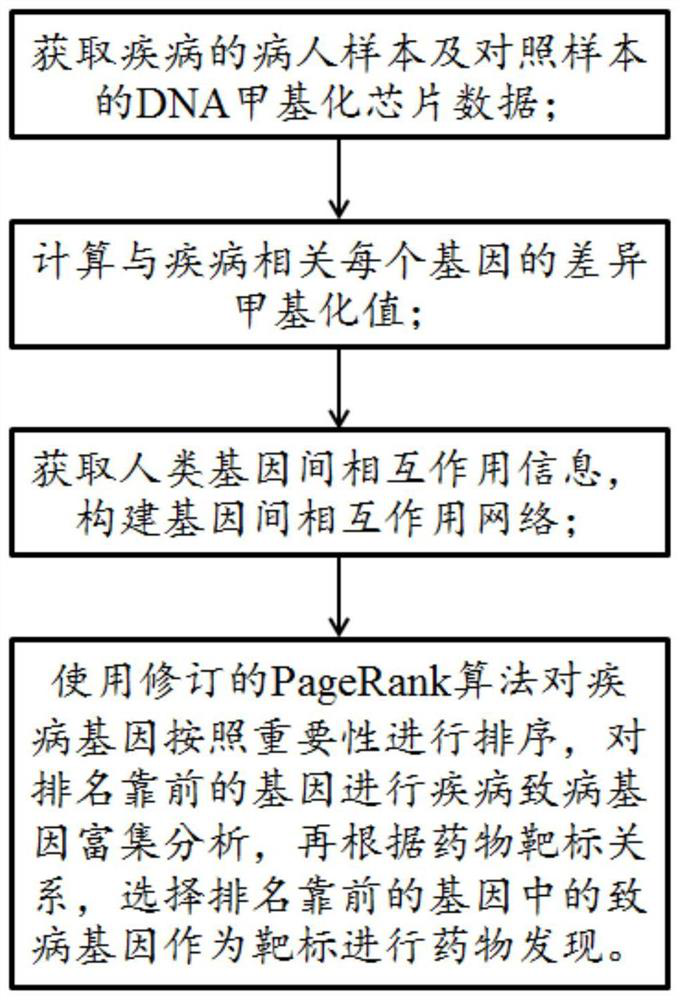
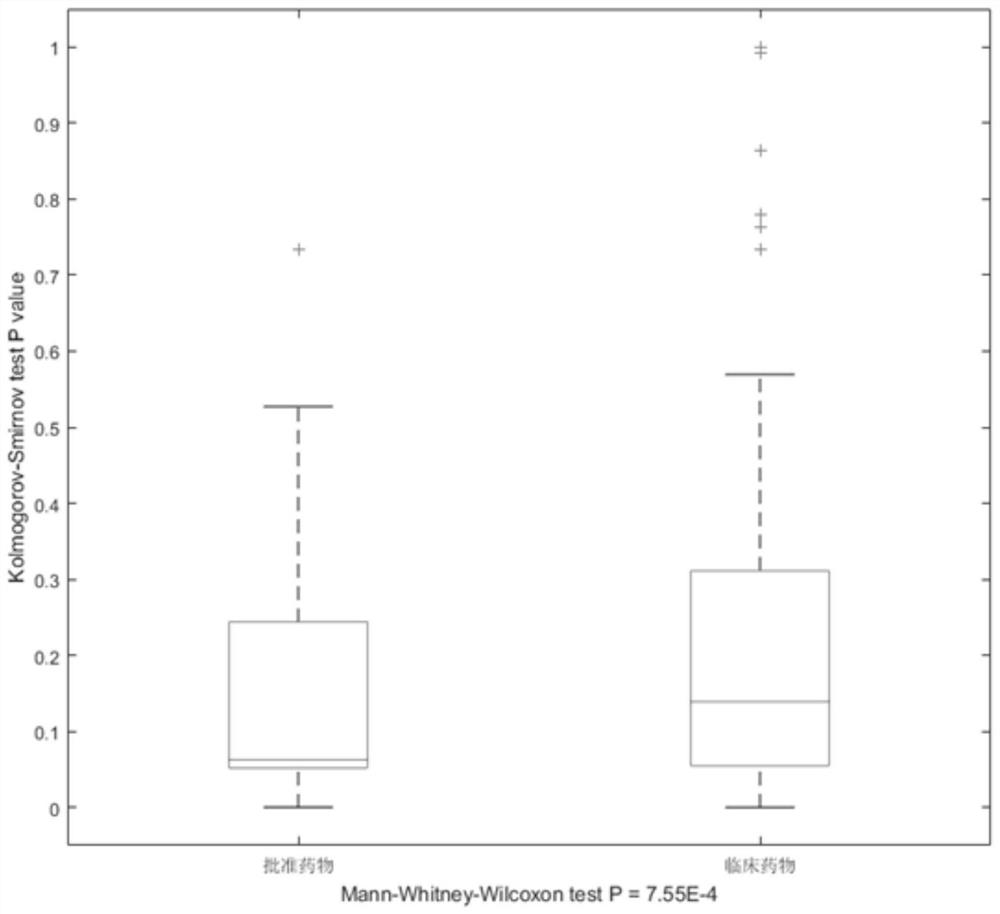
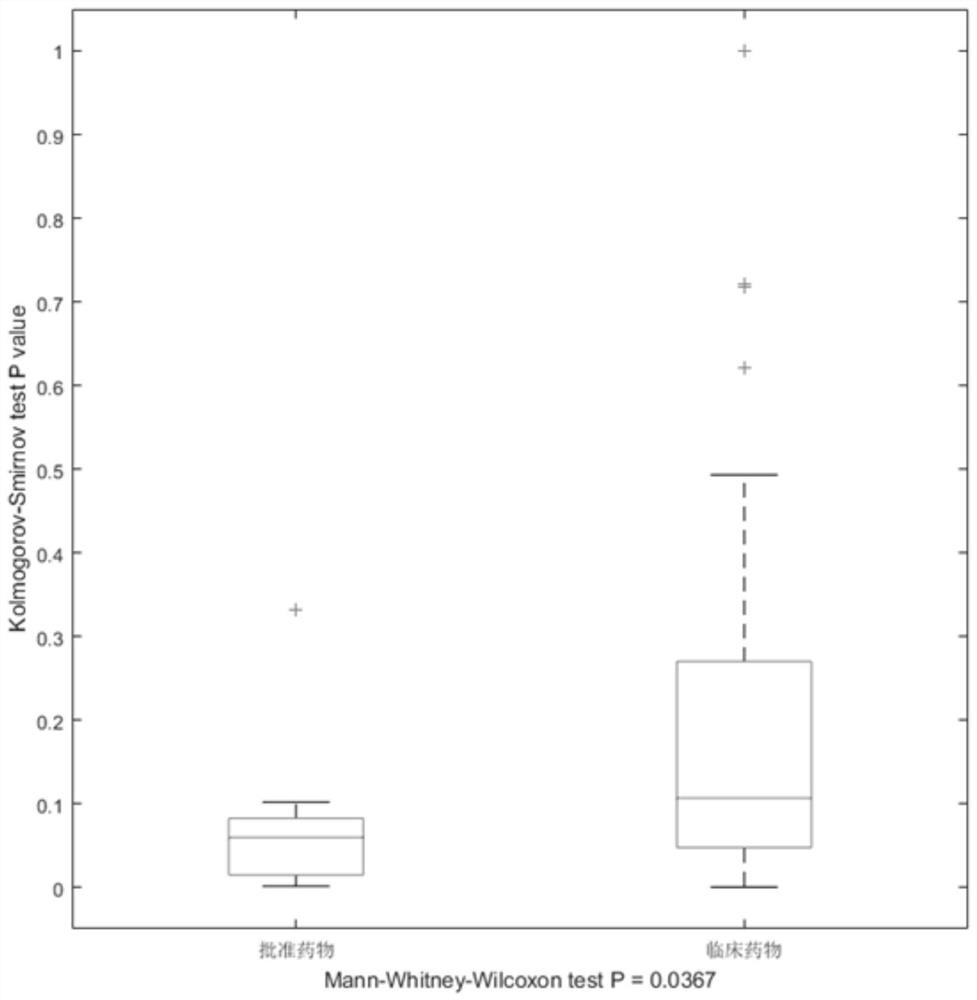
ActiveCN109545276BSolid theoretical foundationEasy to implementMolecular designProteomicsDiseasePagerank algorithm
The invention relates to an epigenome-based drug discovery method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biomedicine. Starting from the basic principle of drug action, the present invention combines the DNA methylation chip data of patient samples and the interaction network between genes, and uses the revised PageRank algorithm to mine the key pathogenic genes in the process of disease pathogenesis, so that according to the corresponding relationship of drug targets , to search for potential drugs to treat diseases. This method has the characteristics of solid theoretical foundation, easy implementation and high efficiency, and has broad application prospects in drug discovery.
Owner:武汉百药联科科技有限公司 +1
Gene selection method and system based on adaptive gene interaction regularization elastic network model
ActiveCN113838519BEasy to integrateGood for classification purposeBiostatisticsHybridisationGene selectionDescent algorithm
The invention discloses a gene selection method and system based on an adaptive gene interaction regularization elastic network model. The method includes: evaluating the importance of each measured gene based on the Wilcoxon rank sum test; Quantify and add adaptive penalty weights, and then delete noise genes to obtain eigengenes; introduce penalty weights into the least squares loss function to construct an adaptive elastic network model; construct the adjacency matrix of gene interaction network; construct genes based on adjacency matrix Interactive network penalty; combine the adaptive elastic network model and gene interaction network penalty to construct an adaptive gene interaction regularized elastic network model; solve the optimal solution of the regularized elastic network model based on the gradient descent algorithm, based on the optimal solution Select genes. The present invention can adaptively select important genes that are highly correlated with the generation of tumors, and remove redundant, irrelevant genes and noise genes.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
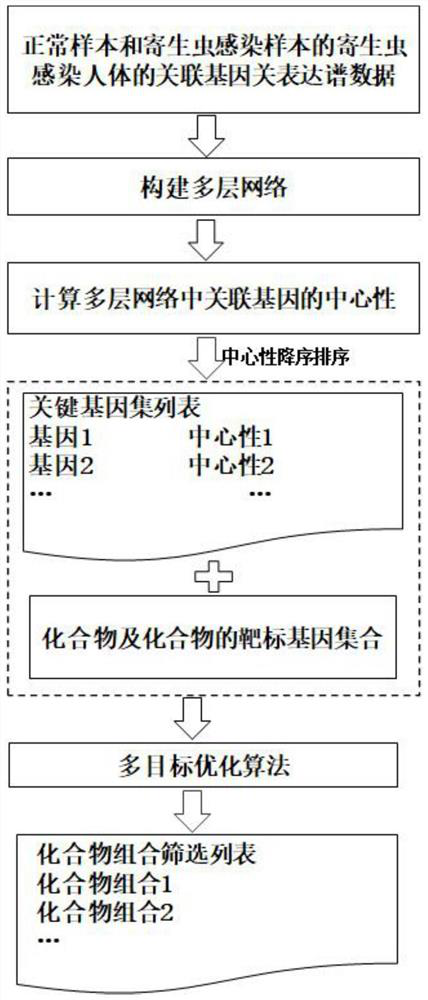
Compound combination screening method based on anti-parasitic infection key genes
PendingCN113990385AImprove screening efficiencyImprove the speed of combination screeningBiostatisticsProteomicsPagerank algorithmComputational gene
The invention discloses a compound combination screening method based on anti-parasitic infection key genes, which comprises the following steps of: 1, preprocessing biological data, constructing a single-layer difference interaction network for each individual infected by parasites, connecting gene nodes corresponding to a plurality of single-layer networks constructing a multi-layer gene interaction network, realizing fusion of multiple networks, calculating scores of genes in each layer of network by using a PageRank algorithm of the multi-layer network, and sorting and screening key genes by using average scores of corresponding same genes in all layers; and 2, designing a multi-objective optimization function model based on the key genes, known FDA approved compounds and a target gene set of each compound, and obtaining a better compound combination by using a multi-objective optimization algorithm. According to the invention, the time efficiency of screening the compound combination for resisting parasitic infection can be improved, and a better compound combination can be screened out.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Method for Rapidly Constructing Cas9 Binary Expression Vector Library of Paired sgRNA
ActiveCN107893086BEfficiently buildEfficient constructionHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionRestriction siteLigation
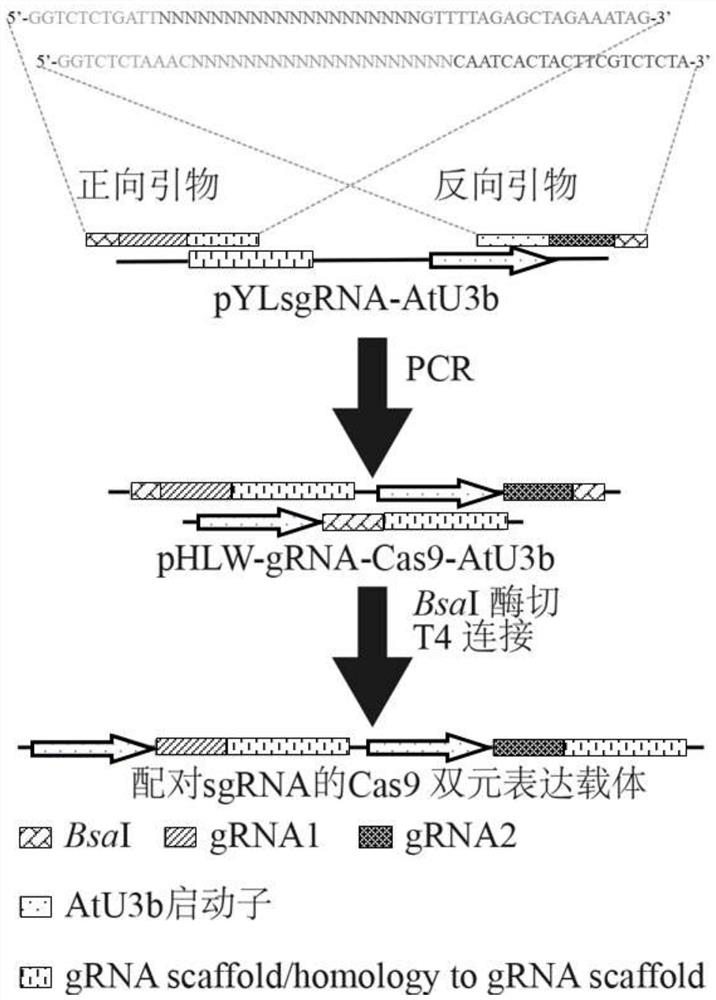
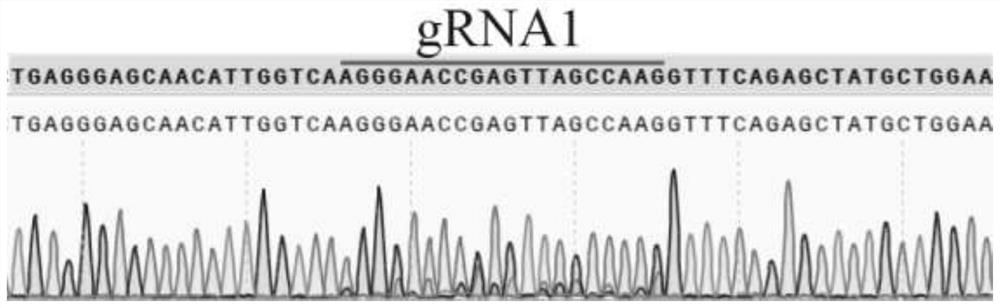
The invention discloses a method for rapidly constructing a Cas9 binary expression vector library paired with sgRNA, and relates to a method for rapidly constructing a binary vector in the field of genetic engineering. In this method, on the basis of constructing the CRISPR-Cas9 binary expression vector, the corresponding forward and reverse primers are designed according to the specific gene design target sequence, and the primer has two BsaI restriction sites; the target sequence and two BsaI sites are obtained by one-step PCR The target fragment, and then construct the above fragment into a binary expression vector with Cas9 gene by simple digestion and ligation to form a paired sgRNA Cas9 vector. The invention can efficiently establish random libraries and non-random libraries, which can be used for large-scale screening of gene functions in plants, and can be used for the construction and research of gene interaction networks between multiple genes; the experimental results prove that this method successfully and efficiently constructs Cas9 binary expression vector library of random paired sgRNAs for 14 targets (from 14 genes).
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for screening population genome latent important gene based on MK-test
The invention provides a method for screening a population genome latent important gene based on MK-test, wherein the method belongs to the field of gene screening technology. The method comprises thesteps of 1), constructing a gene interacting network; 2), acquiring and / or inputting a gene parameter according to the requirement by means of a processing module; 3), outputting an inter-species and / or intra-species variation rate after operation of the gene parameter through a standard formula, and screening the latent important gene of the population genome; and 4), performing functional analysis on the latent important gene, wherein the processing module comprises at least two gene chips, and a computer which is connected with the gene chips. The method can realize large-batch simultaneous analysis to the inter-species or intra-species variation. After operation, the change trend of a non-expression segment proportion and / or expression segment proportion along with a gene change can be effectively analyzed, and an effective approach is supplied for latent important gene screening of the population genome.
Owner:中国科学院昆明植物研究所海盐工程技术中心
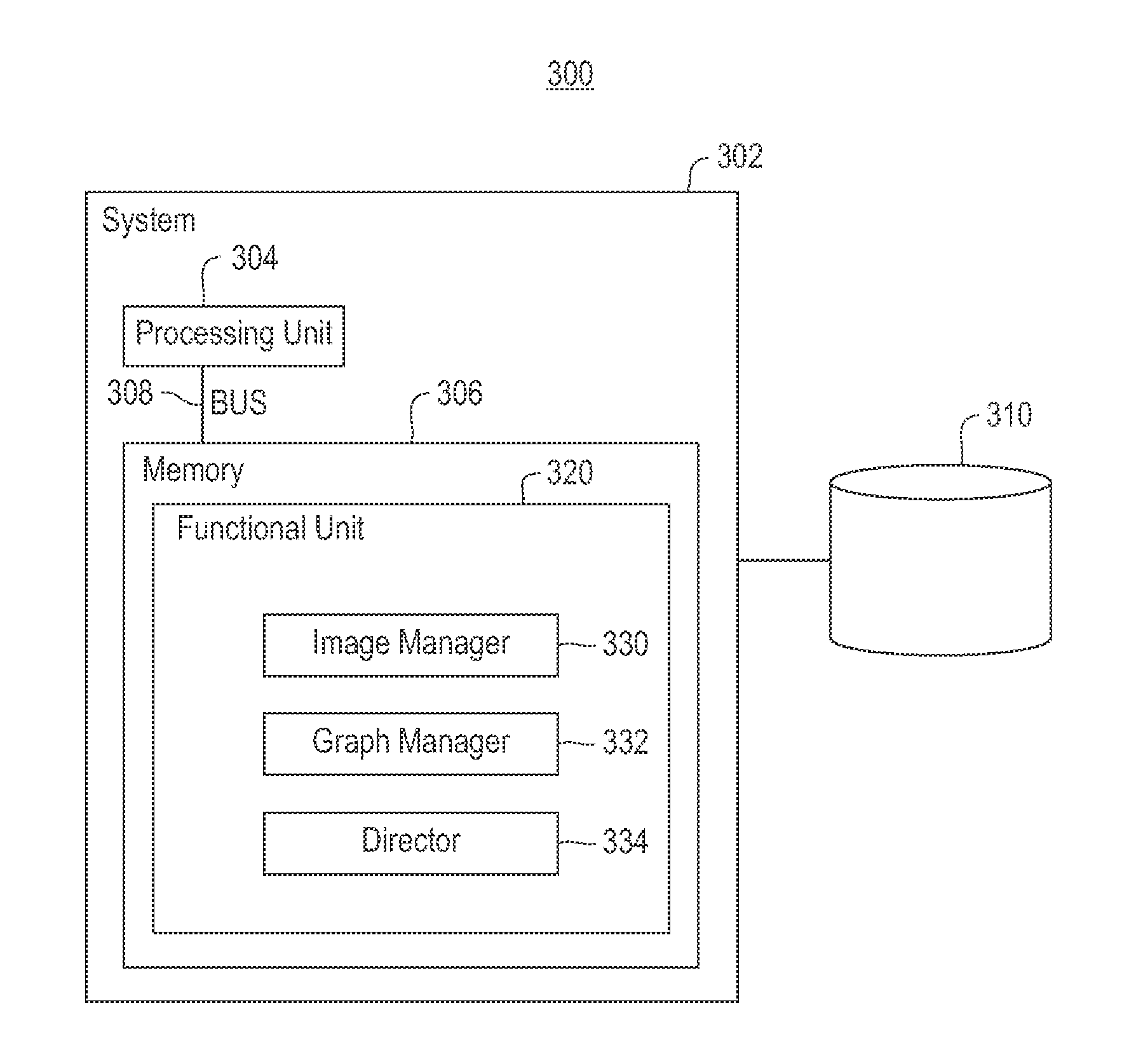
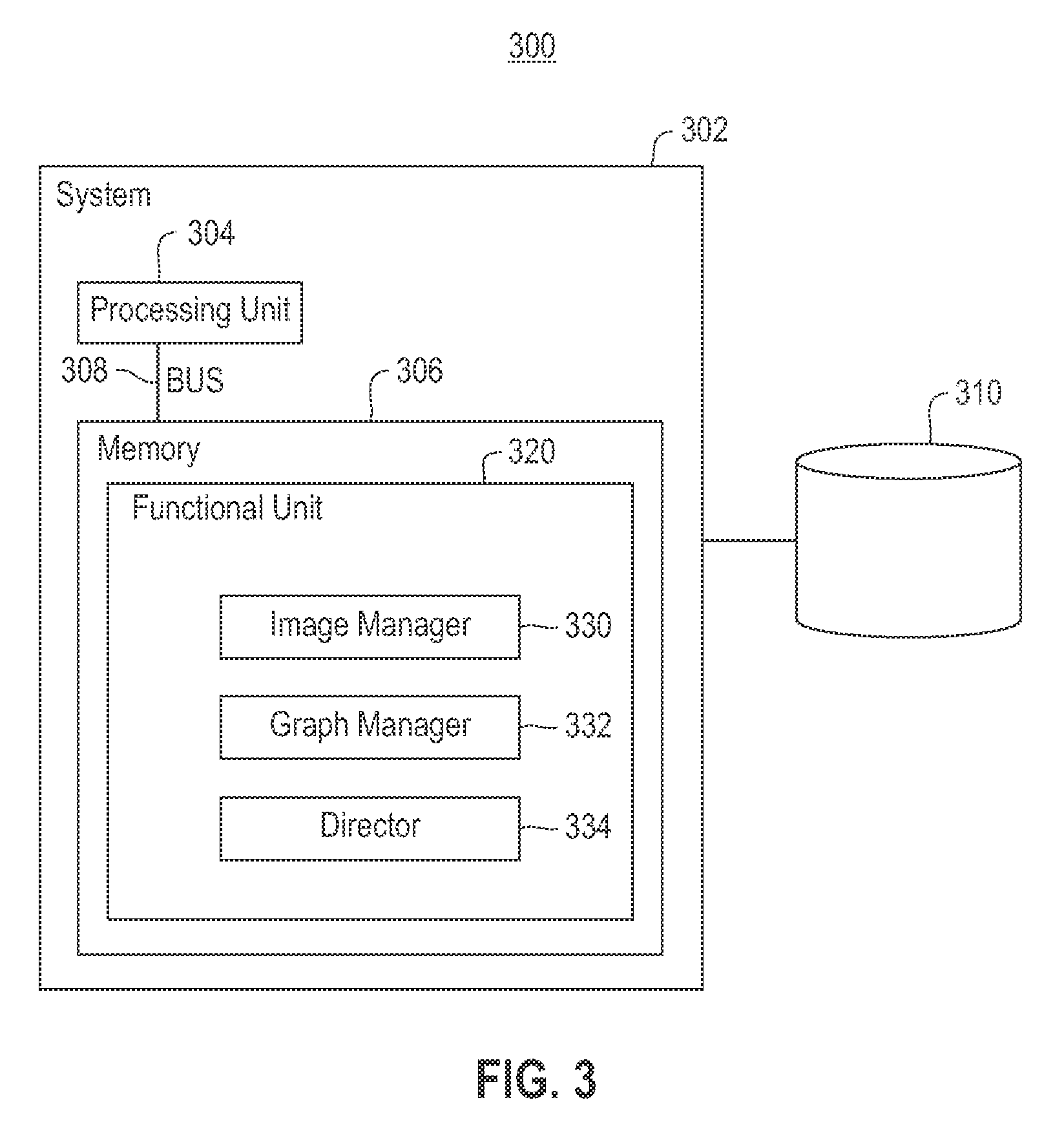
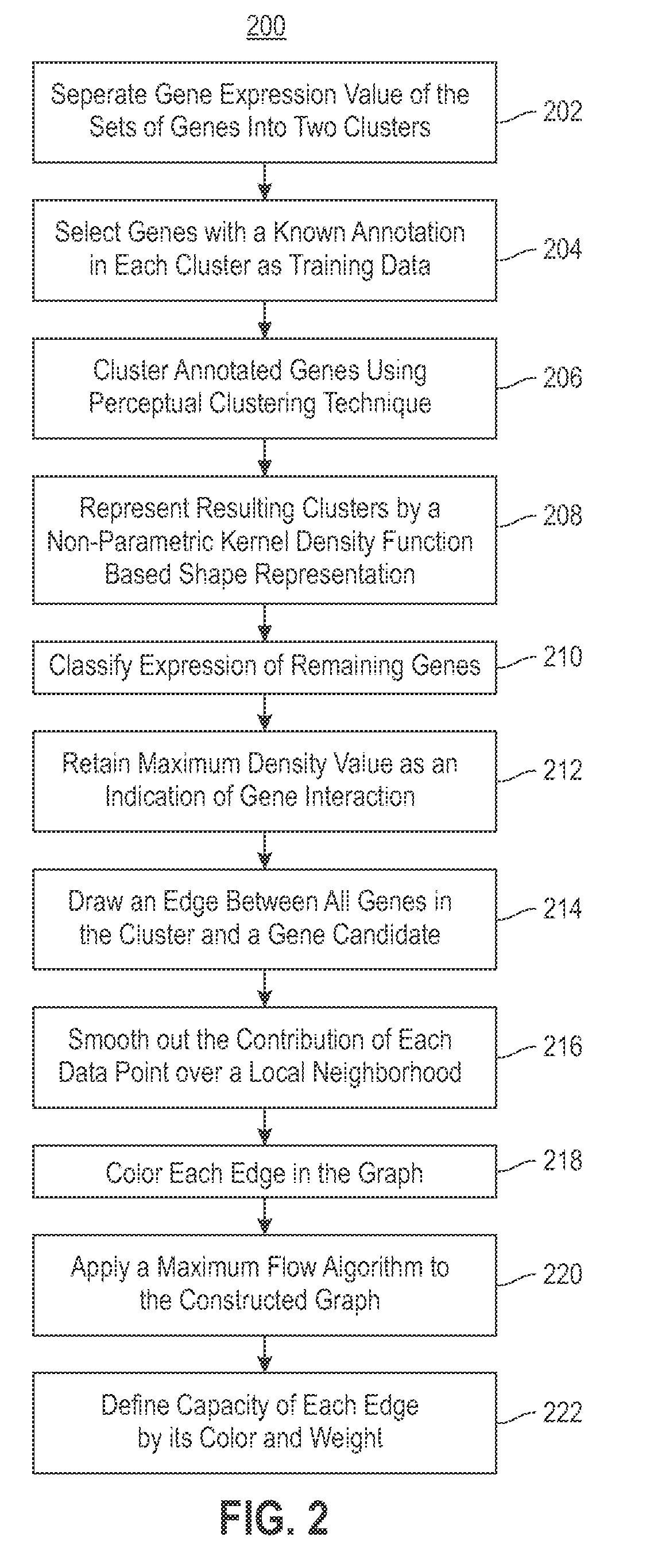
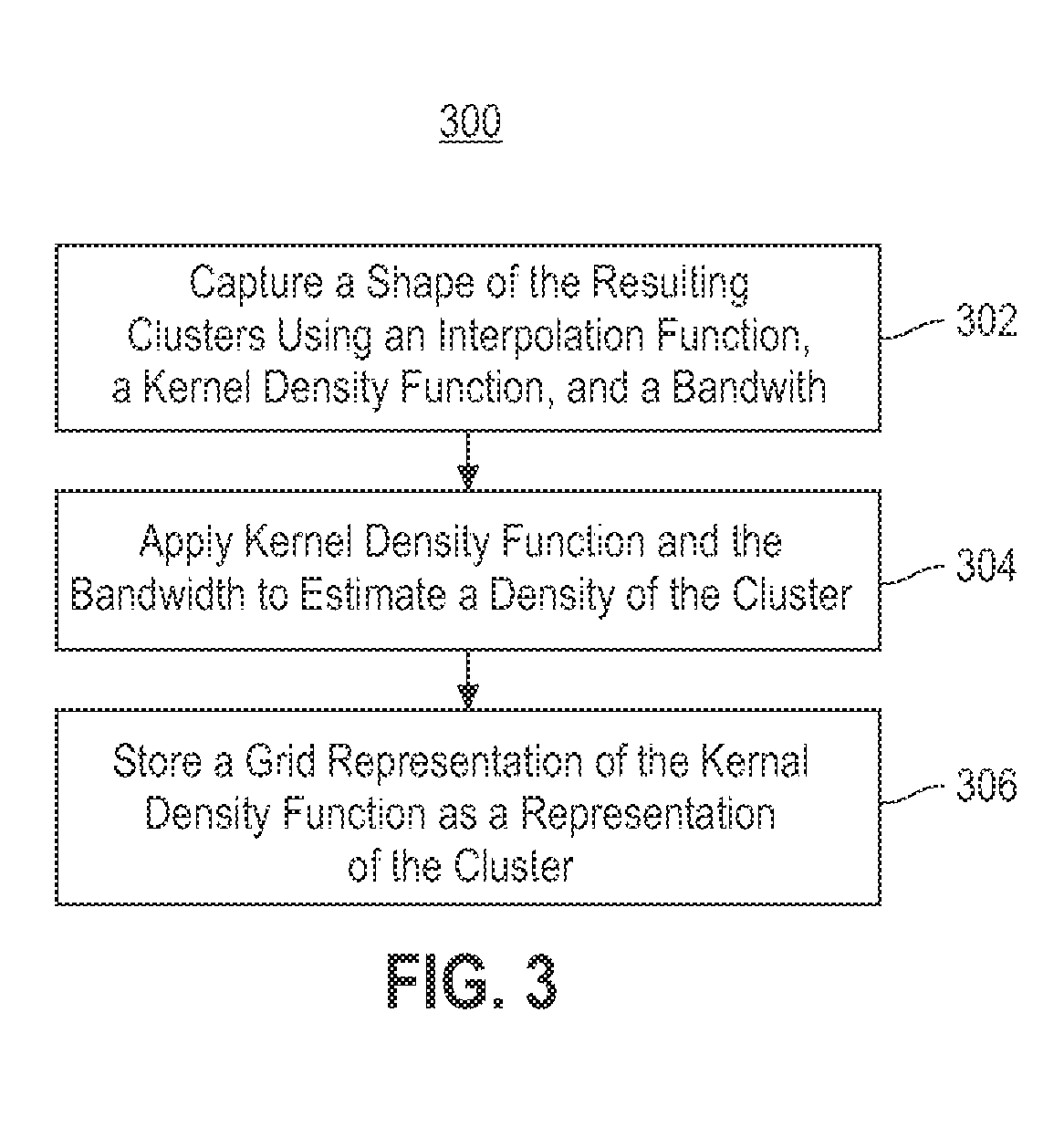
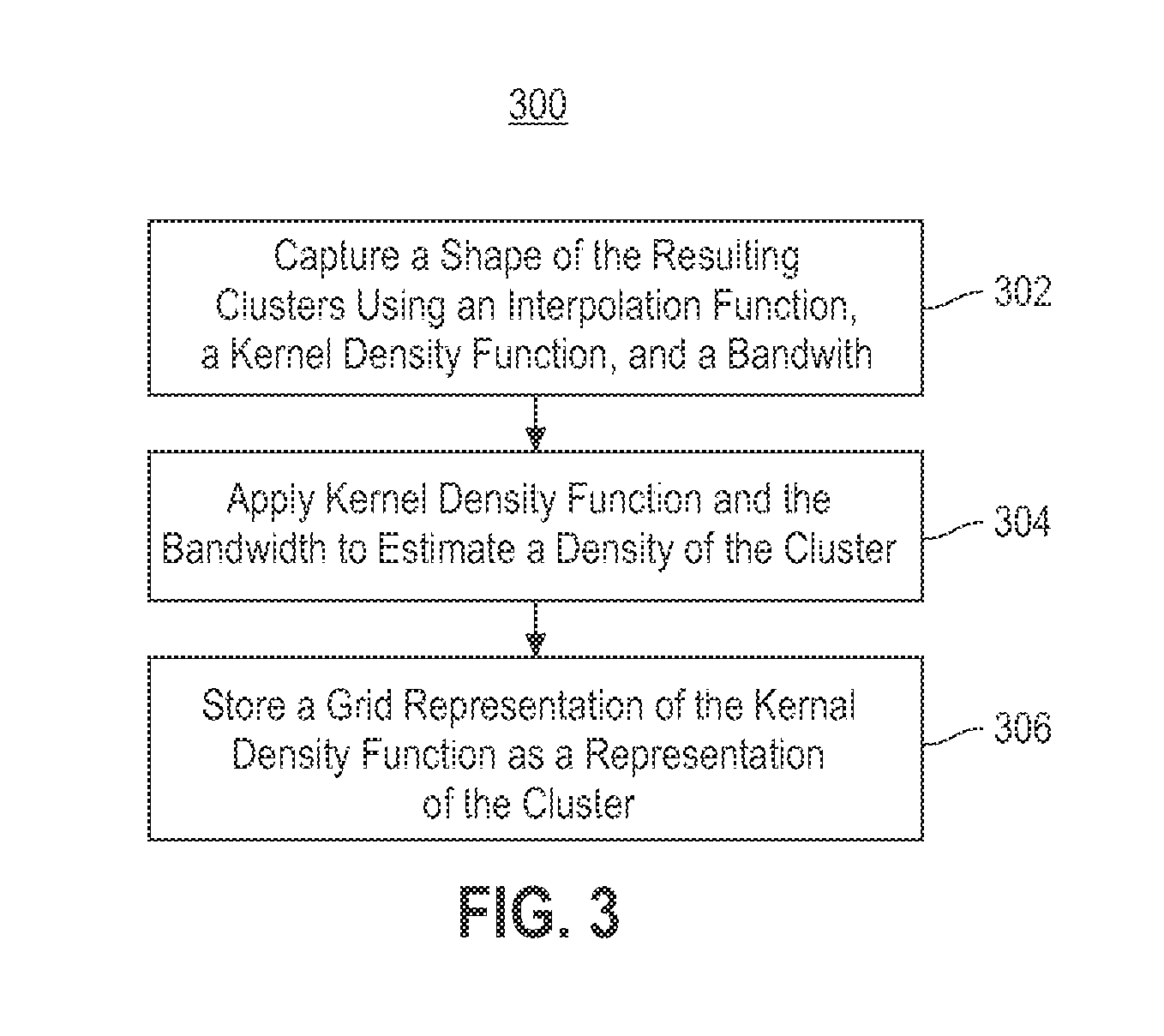
Combining RNAi imaging data with genomic data for gene interaction network construction
Embodiments of the invention relate to a method for constructing a gene interaction network by combining two sources of genomic information, namely RNAi imaging data and gene expression data. Tools are provided to gather data, including gene expression data and gene image data, and to compute measurements and relationships, respectively. A graph is constructed with nodes representing genes and edges drawn between the nodes to form gene clusters. The graph is refined such that the shape captures a structural pattern of the cluster.
Owner:IBM CORP
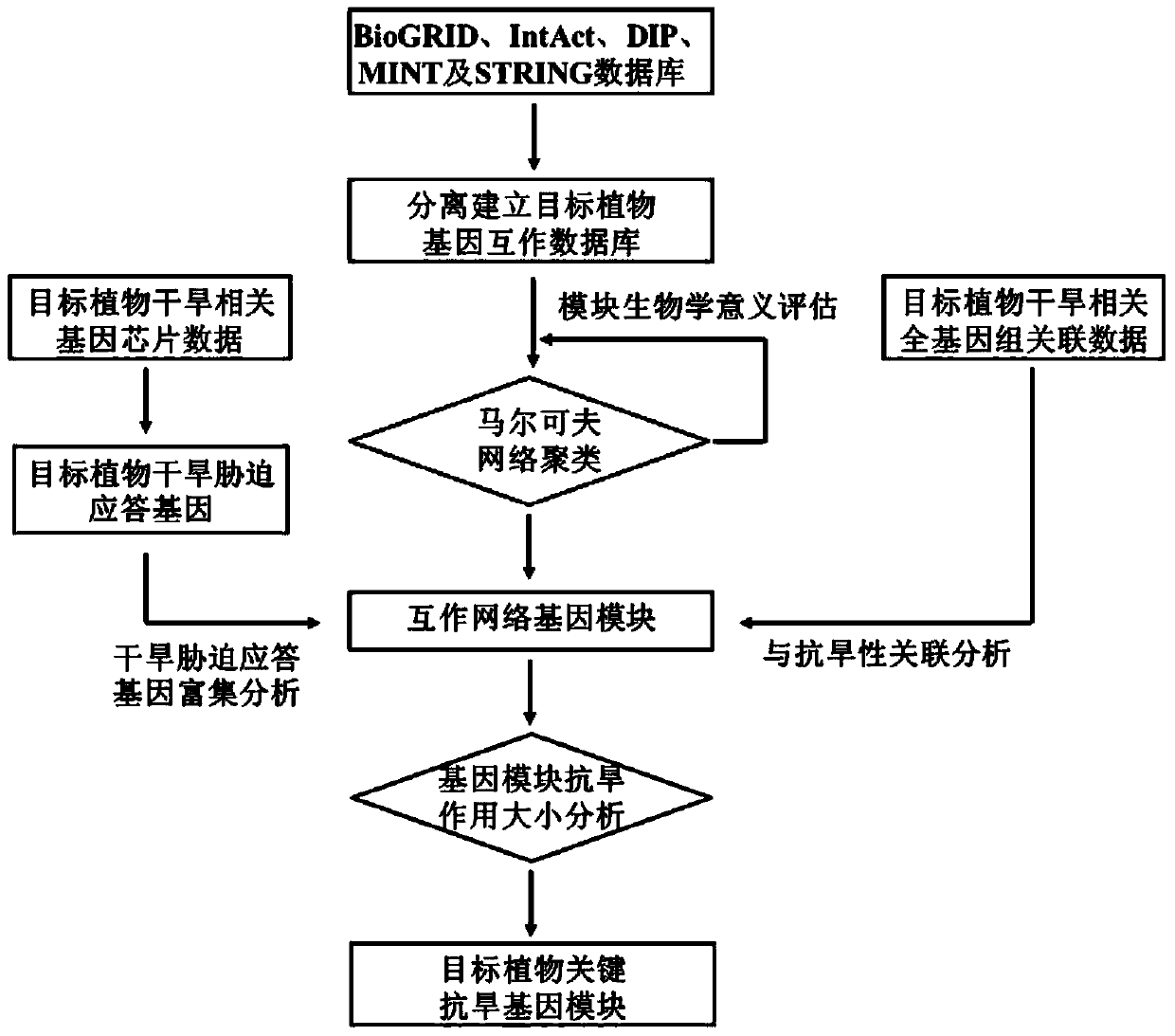
A method of mining drought resistance gene modules in plants
ActiveCN105279396BImprove efficiencyImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsResistant genesMarkov clustering
A method for mining drought-resistant gene modules in plants. The method is based on the gene interaction network, and uses the Markov clustering algorithm to conduct modular analysis on the gene interaction network, and uses gene chip and genome-wide association data to determine the drought-resistance effect of gene modules. to evaluate. According to the drought resistance contribution of each gene module, the key drought resistance gene modules were screened. Compared with existing methods, this method focuses on the discovery of new drought-resistant gene groups, which greatly improves the efficiency and accuracy of plant drought-resistant gene discovery.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Combining RNAi imaging data with genomic data for gene interaction network construction
Embodiments of the invention relate to a method, system, and computer program product to construct a gene interaction network by combining two sources of genomic information, namely RNAi imaging data and gene expression data. Tools are provided to gather data, including gene expression data and gene image data, and to compute measurements and relationships, respectively. A graph is constructed with nodes representing genes and edges drawn between the nodes to form gene clusters. The graph is refined such that the shape captures a structural pattern of the cluster.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com