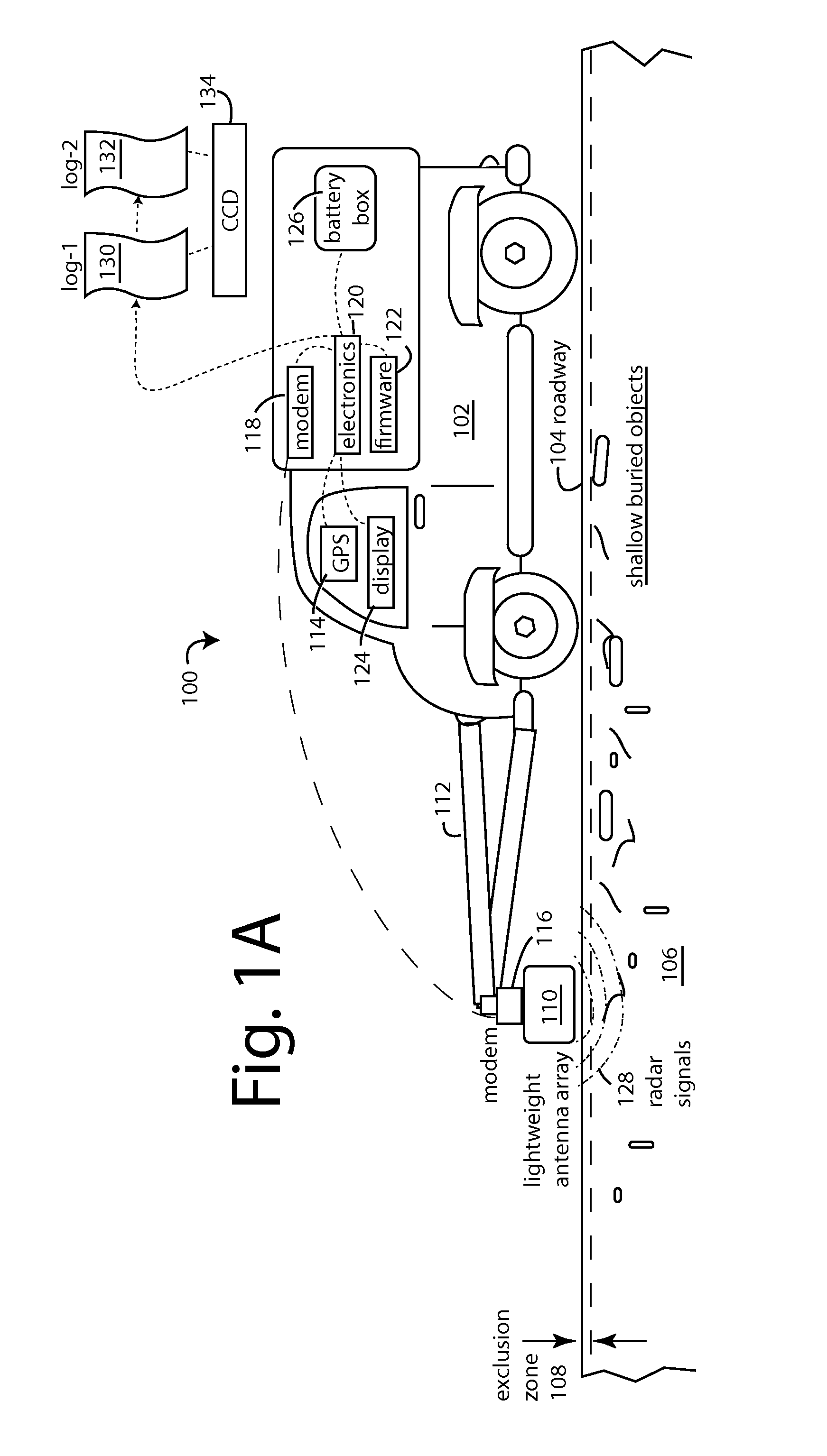
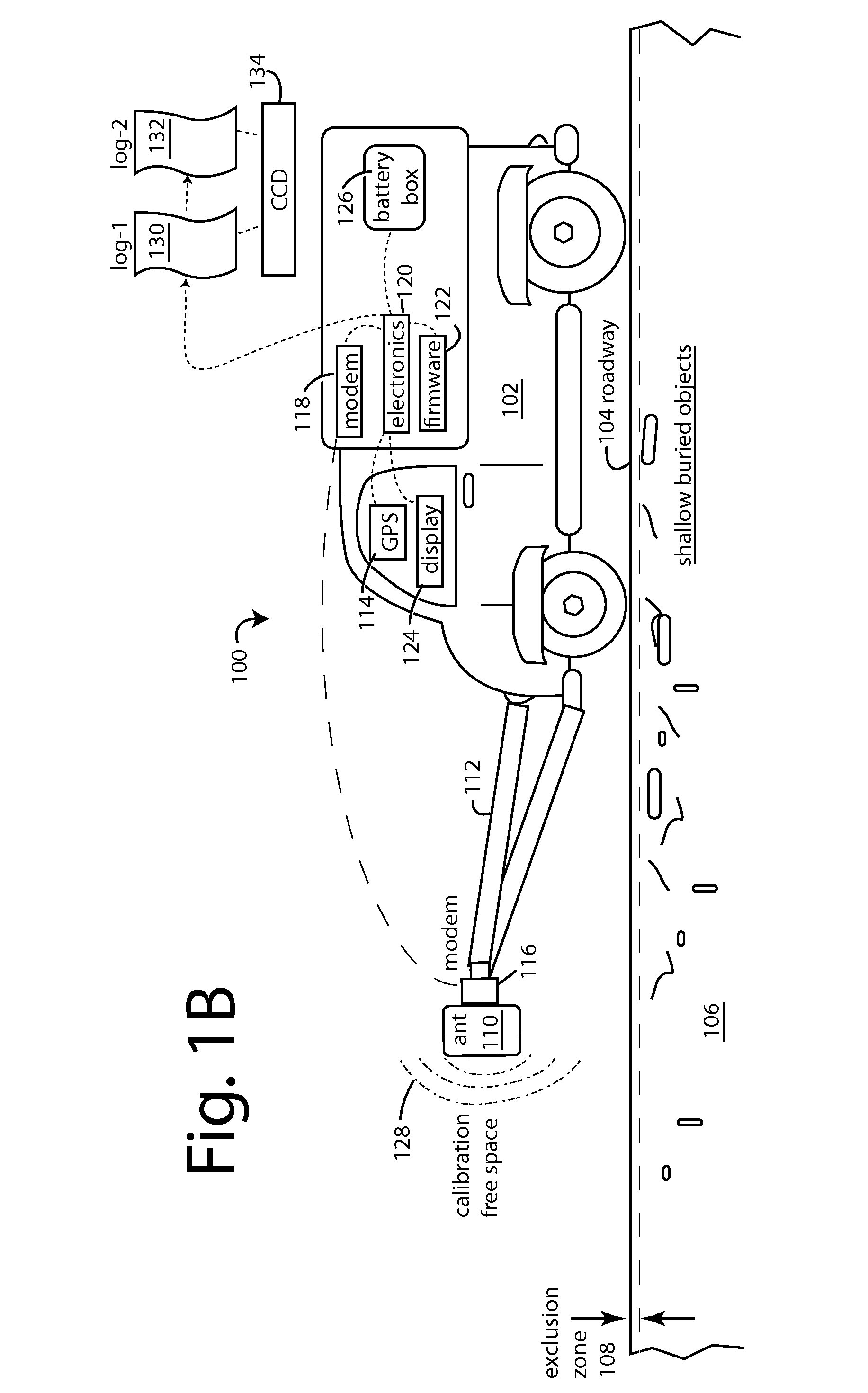
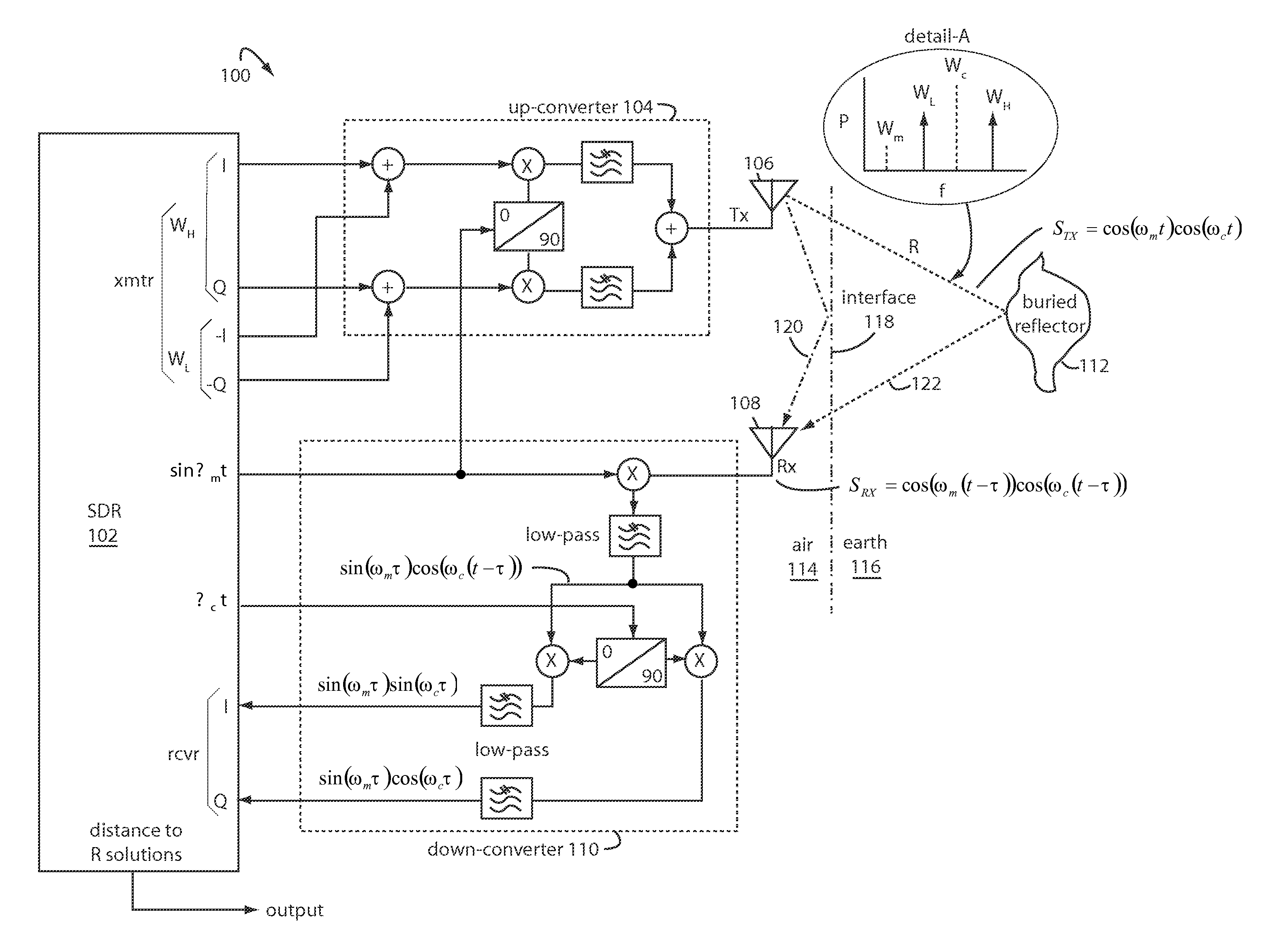
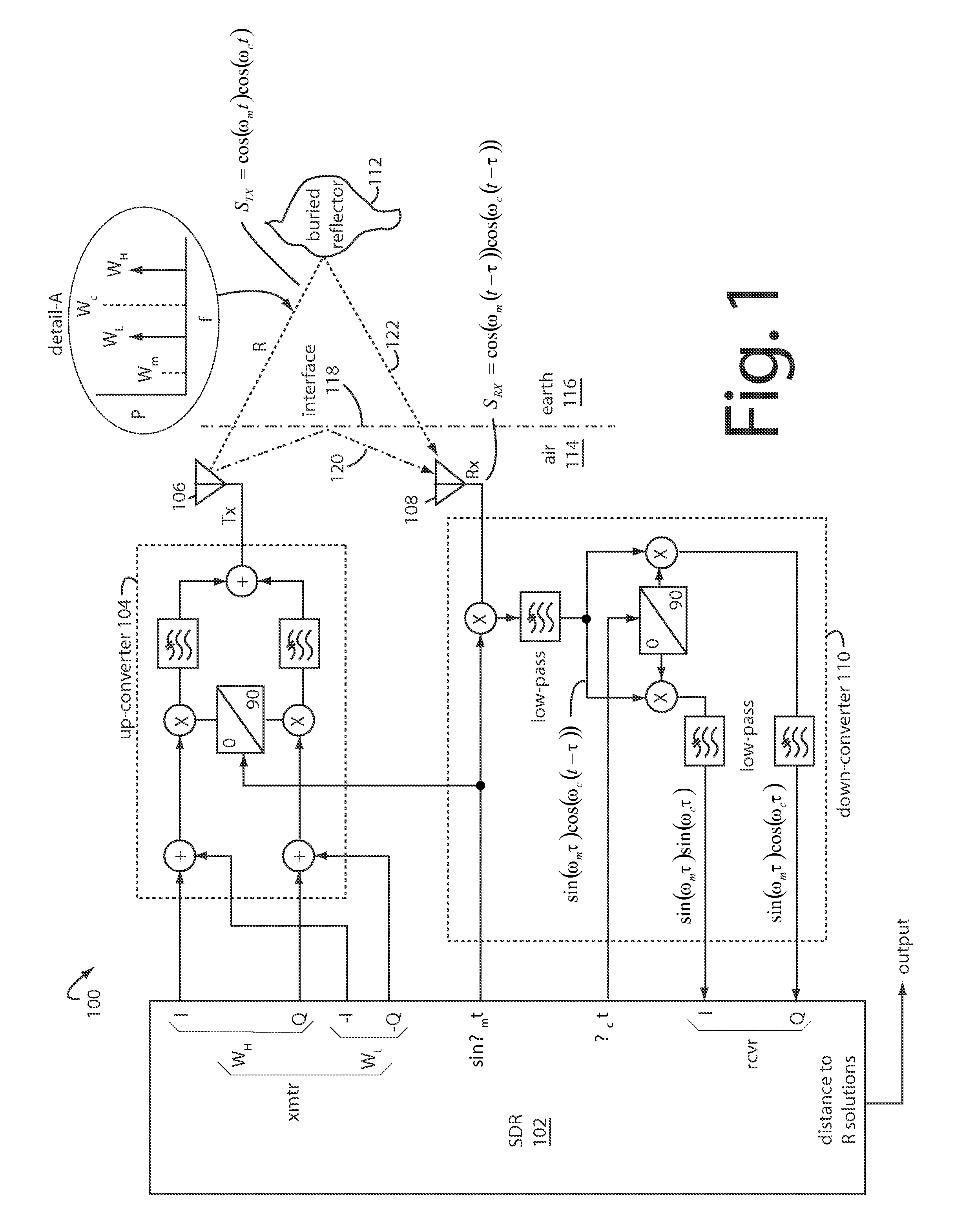
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Ground penetration radar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
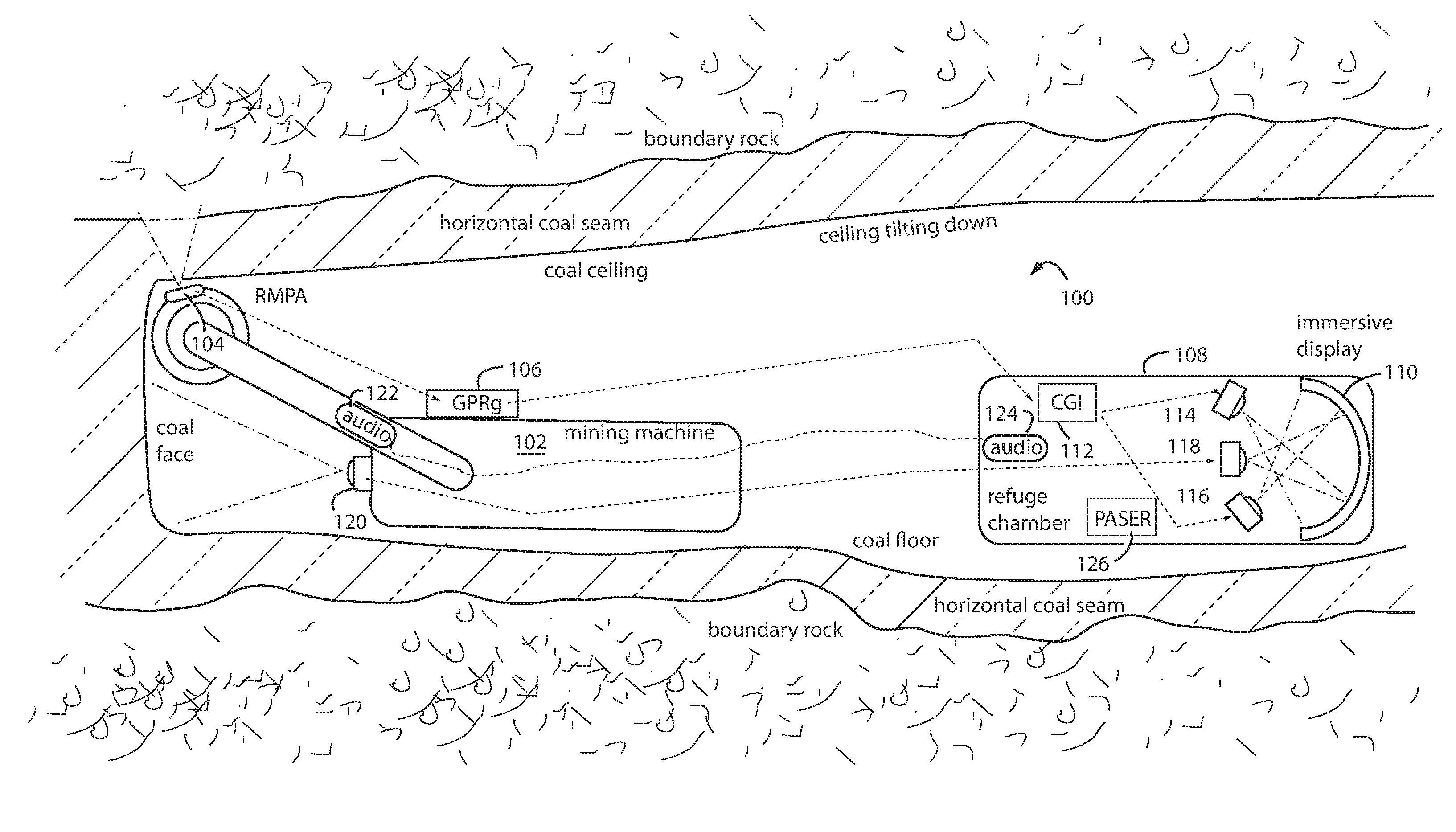
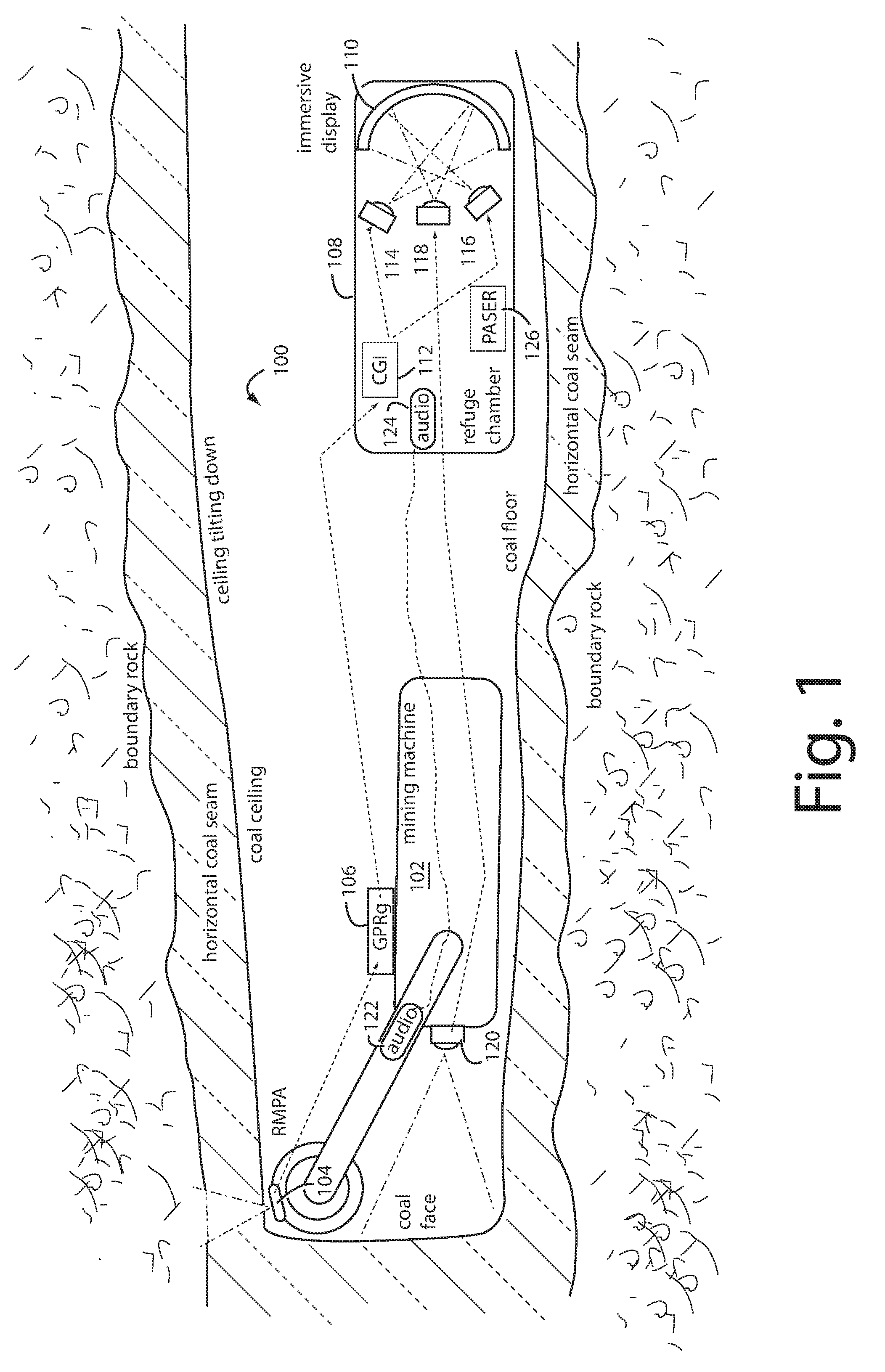
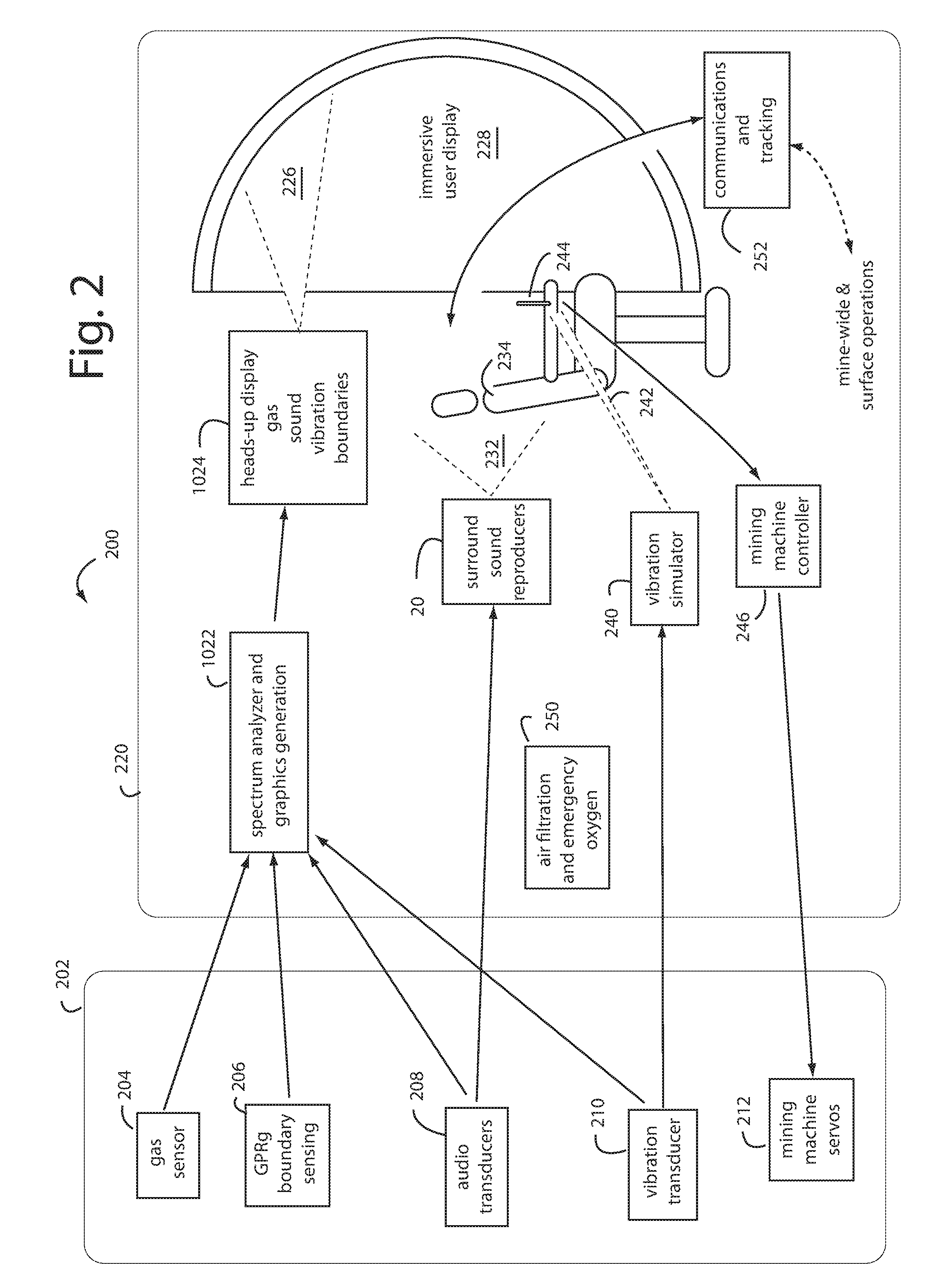
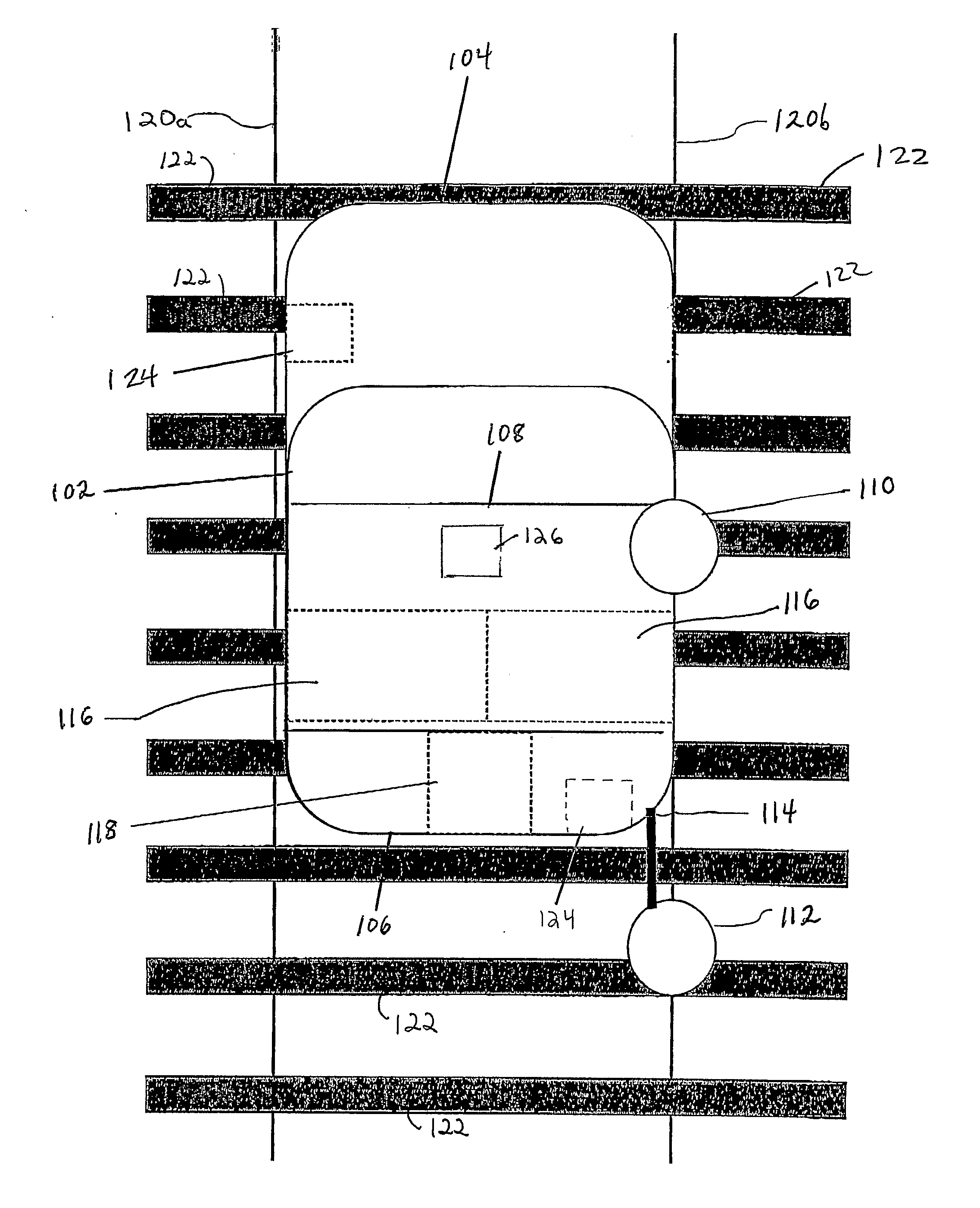
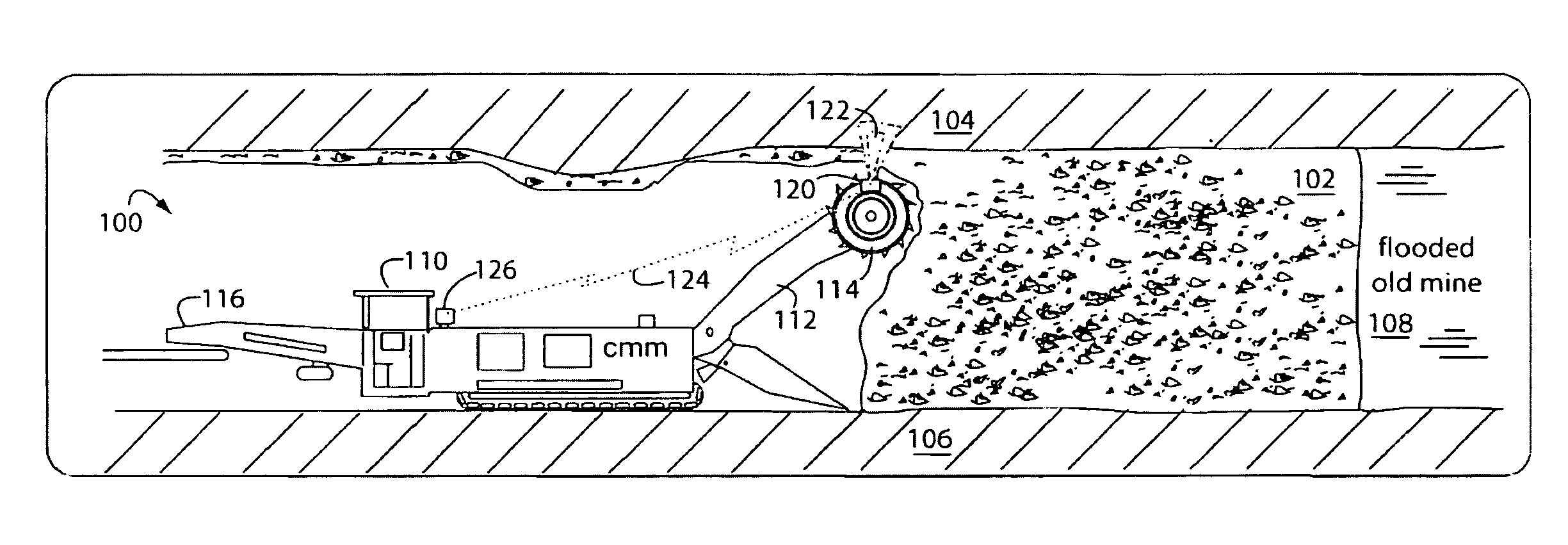
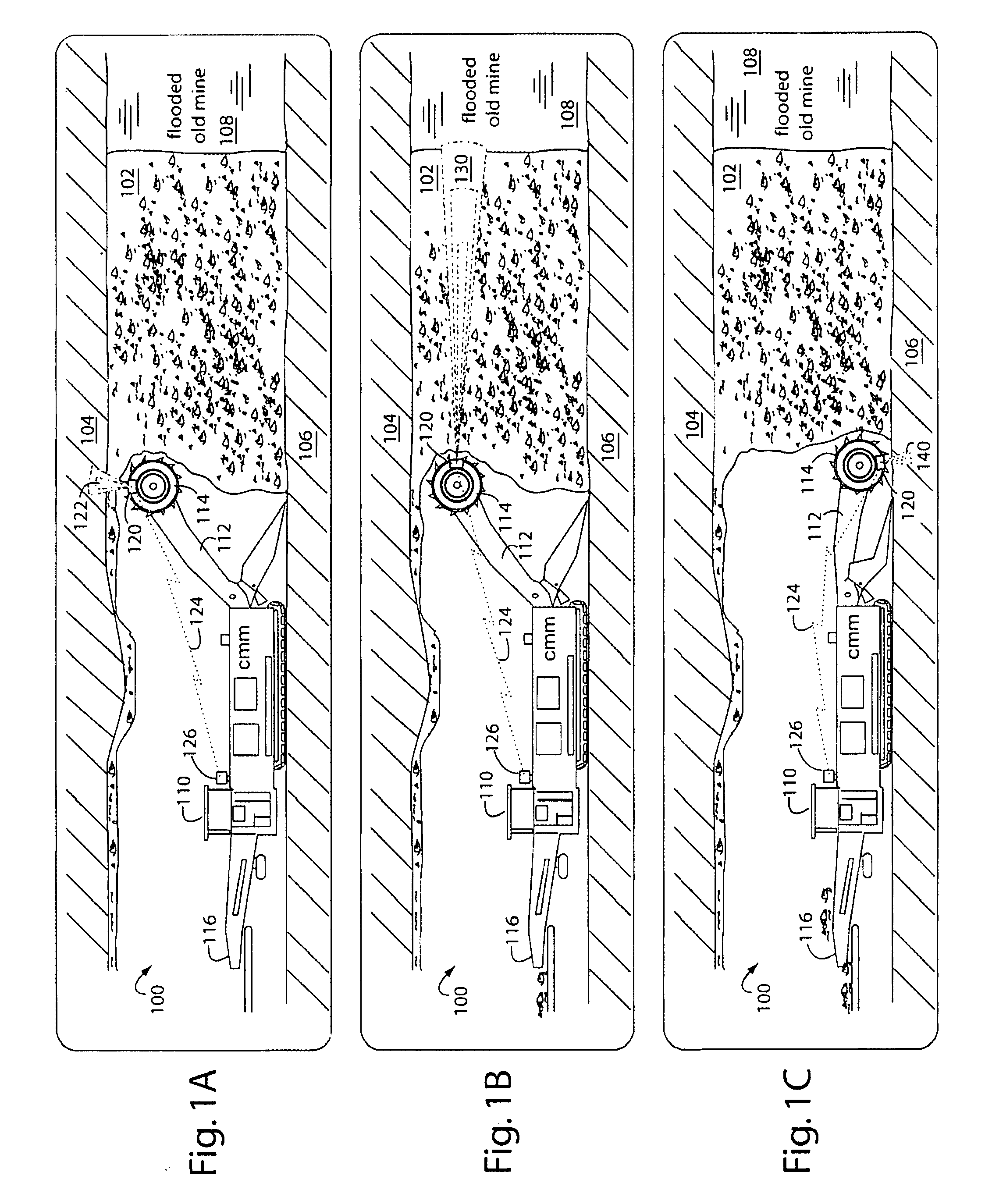
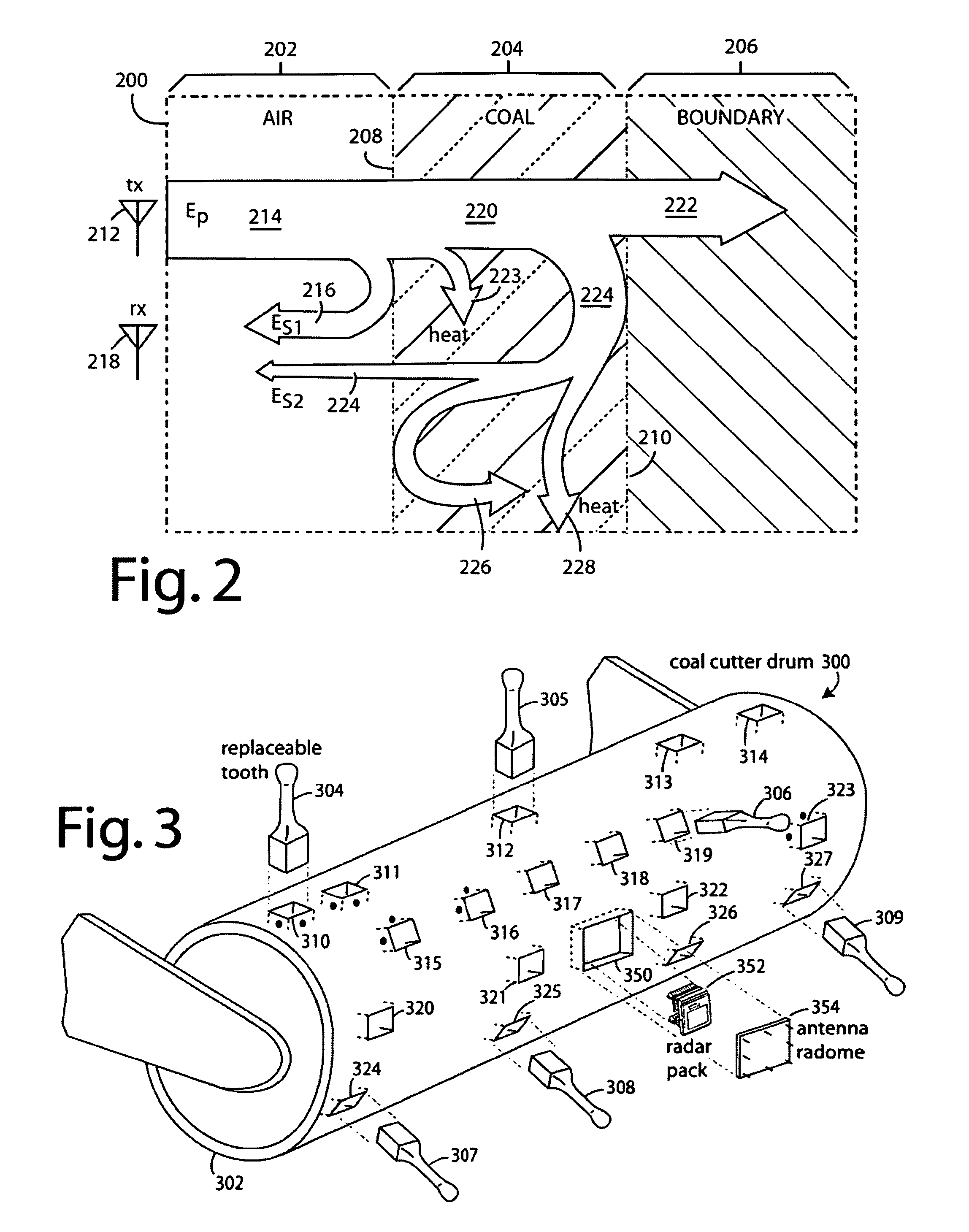
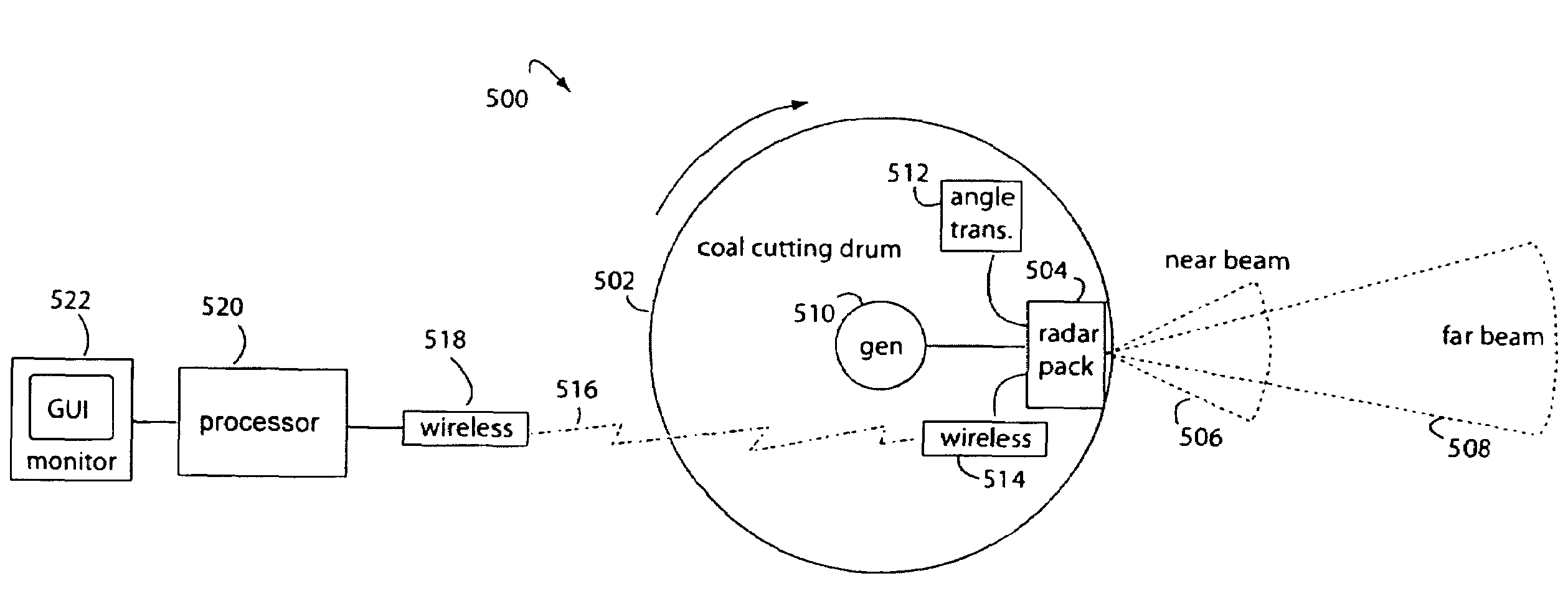
Method of protecting the health and well-being of coal mine machine operators
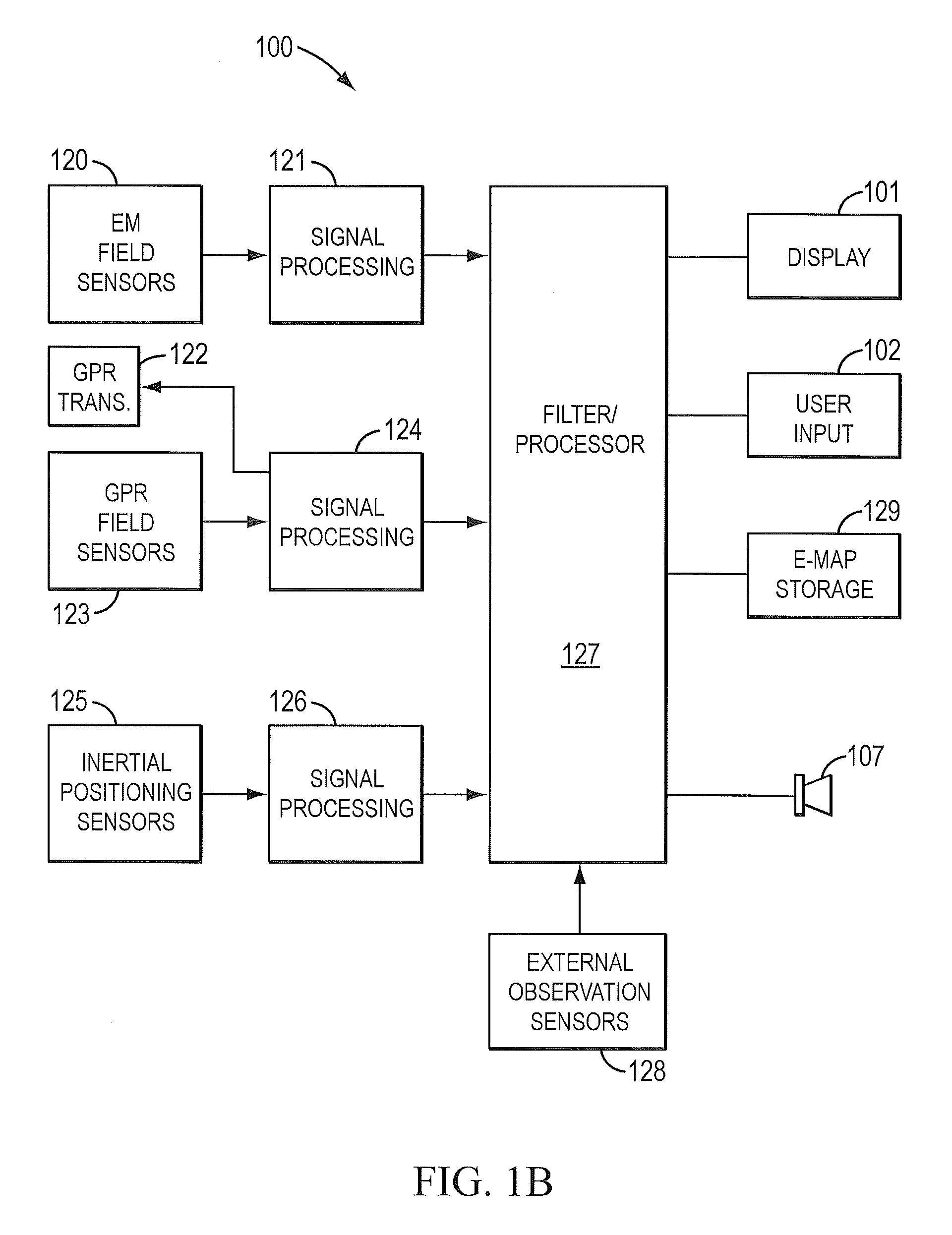
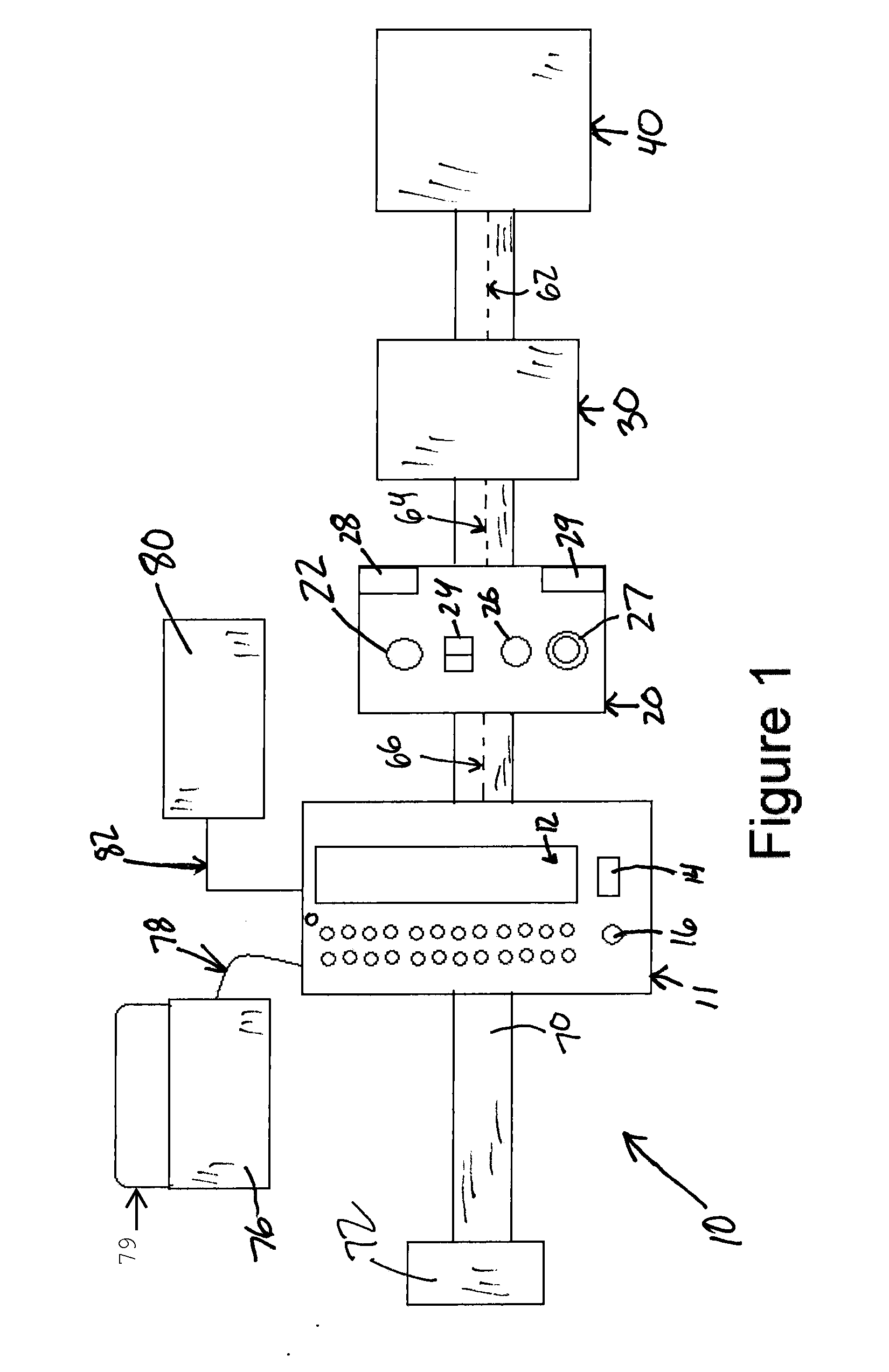
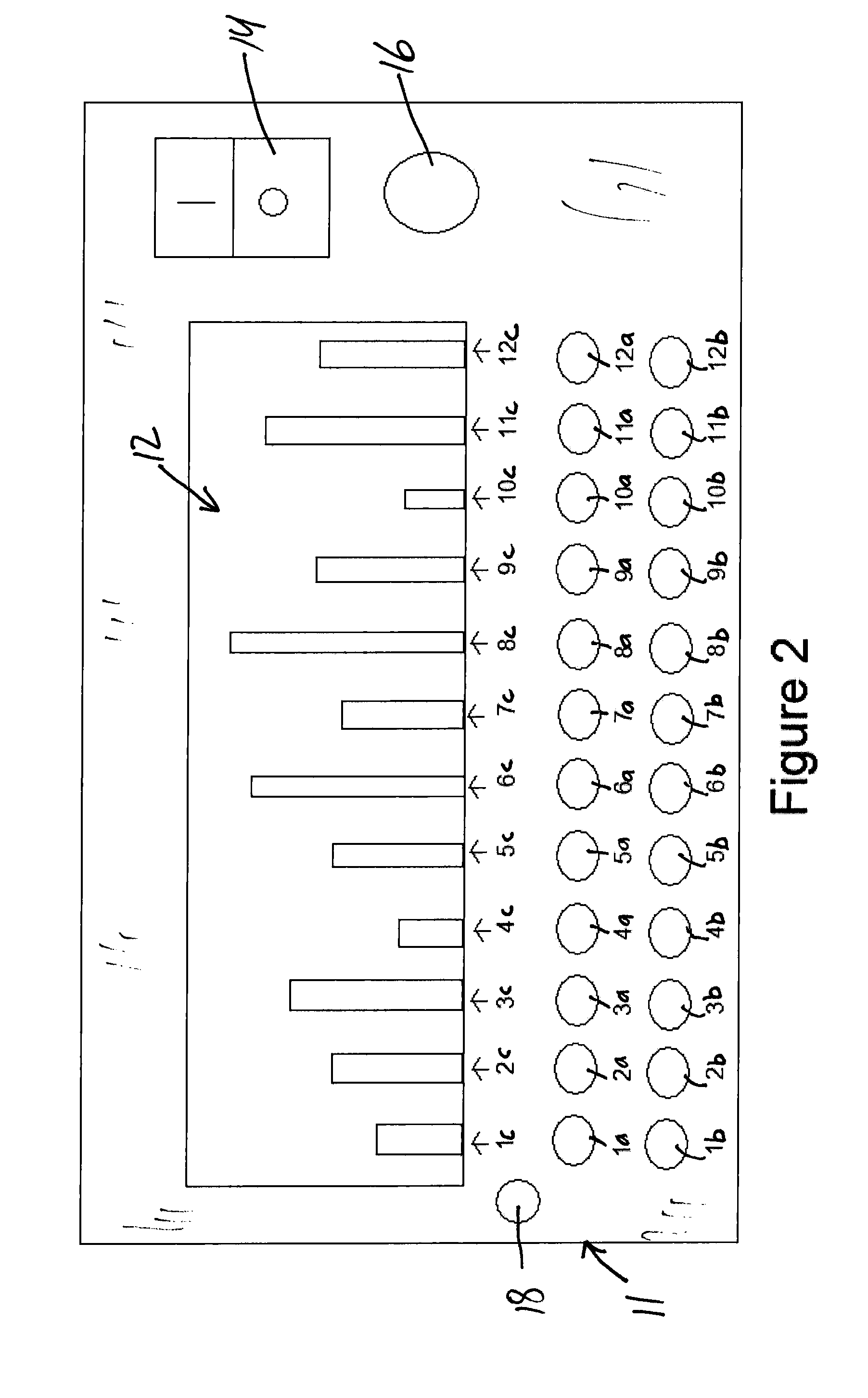
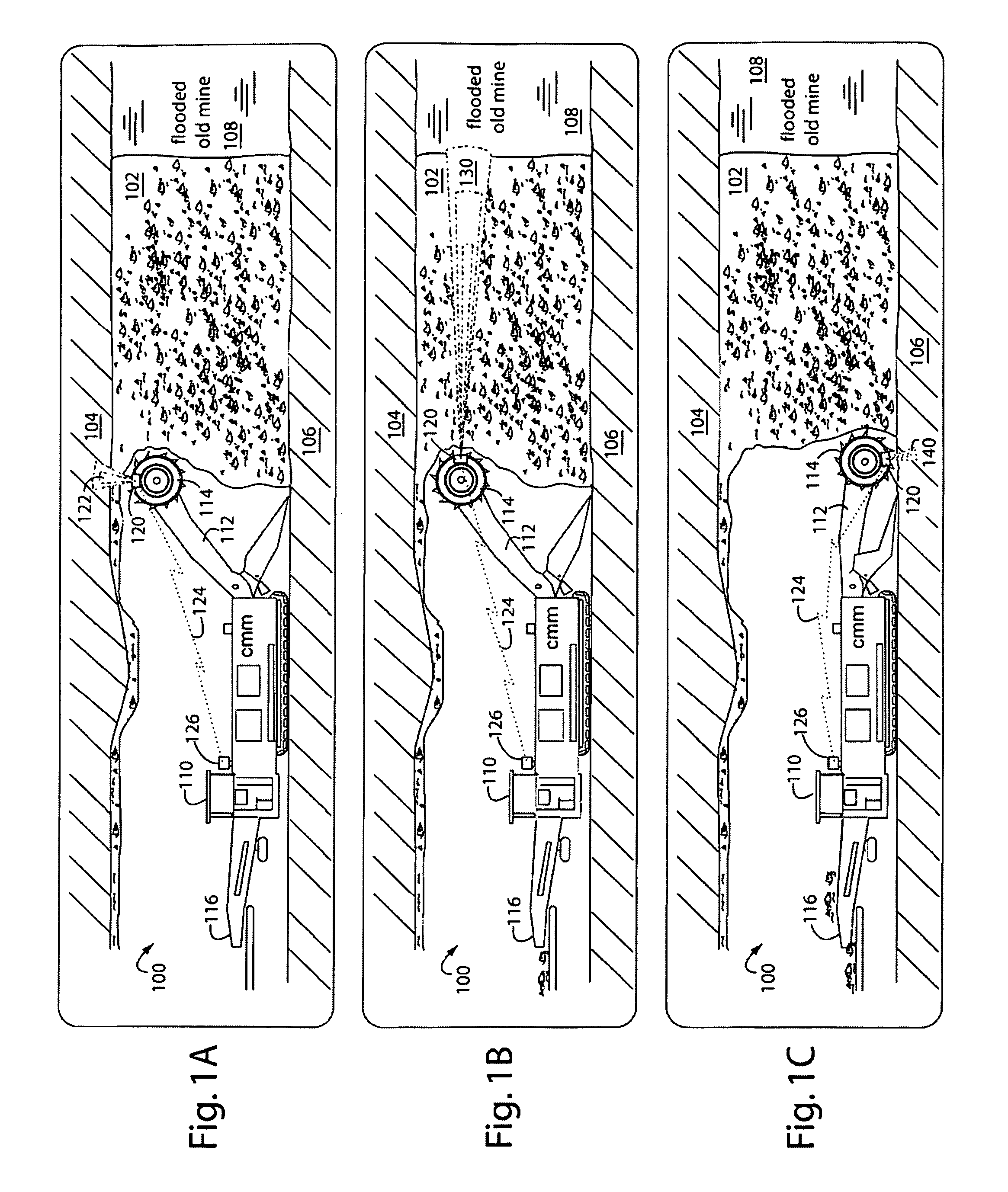
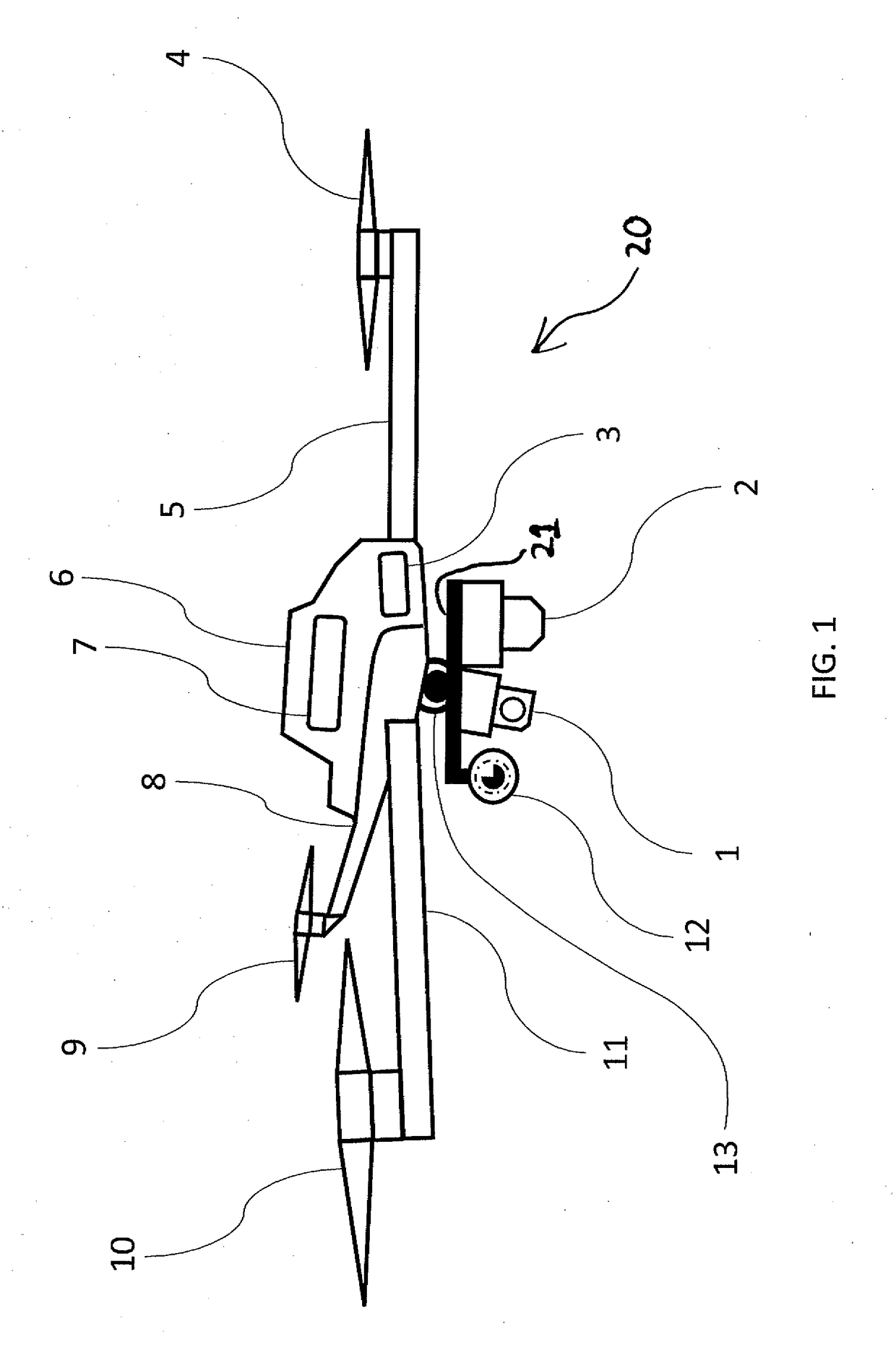
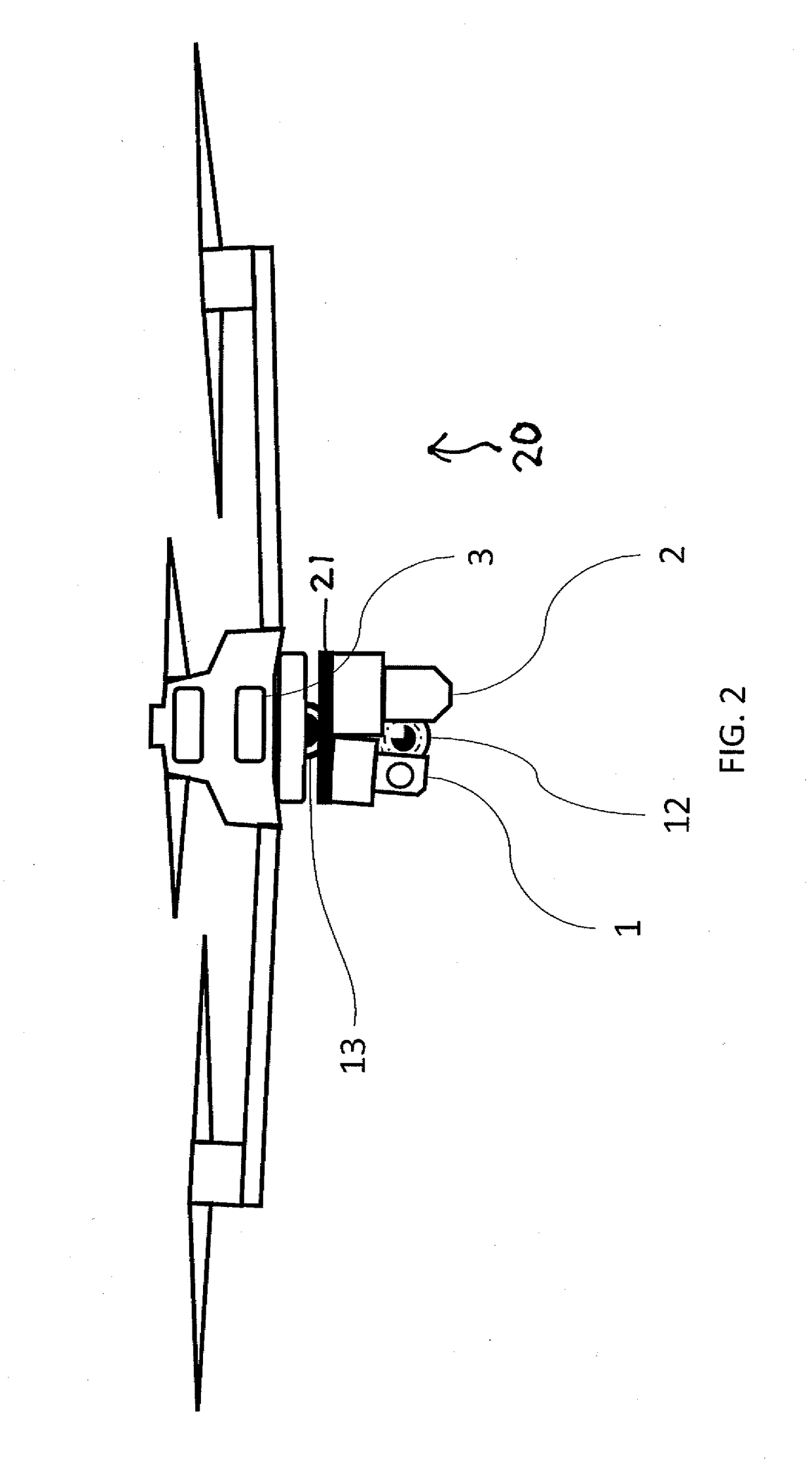
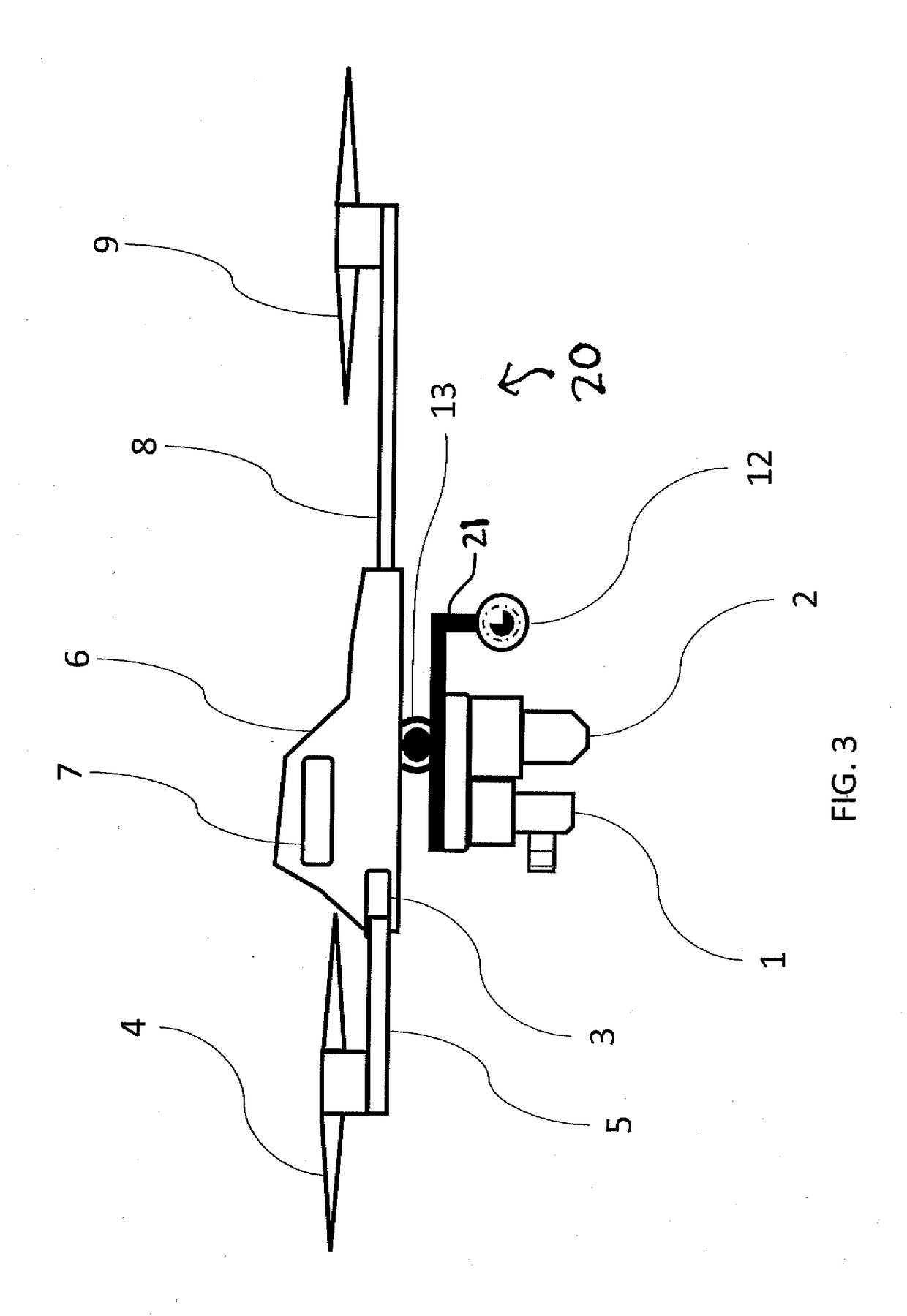
A method of operating coal mine machinery that protects and maintains machine operators' health and well-being removes the machine operators to a clean, low-noise environment inside a refuge chamber. Inside, are controls, cameras, audio, and informational displays needed to run continuous mining machines nearby and communicate mine-wide with other personnel. Cameras fitted to the mining machines provide straight-ahead views, ground penetrating radars fitted to the cutting drums measure the coal depths in the ceilings above, the floors below, and the coal face ahead. Guidance data is presented on informational displays, and the data from the ceilings and floors is used to drive computer graphics special effects to graphically represent the coal ceilings and coal floors overlaying boundary rock. Audio pickups on the mining machine allow the operator to hear and feel how the machine is functioning, just as operators have always employed their other senses.
Owner:STOLARCZYK LARRY G
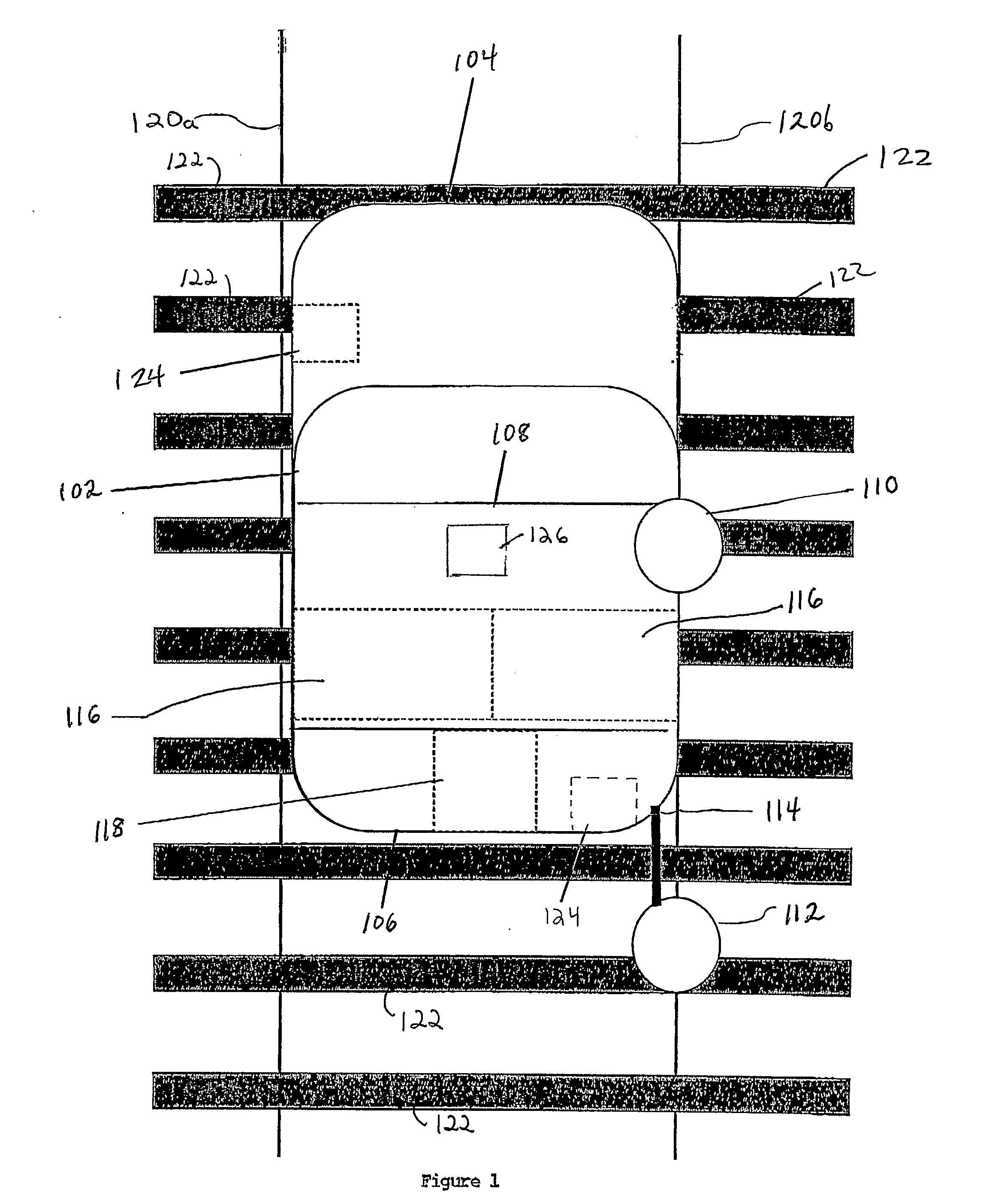
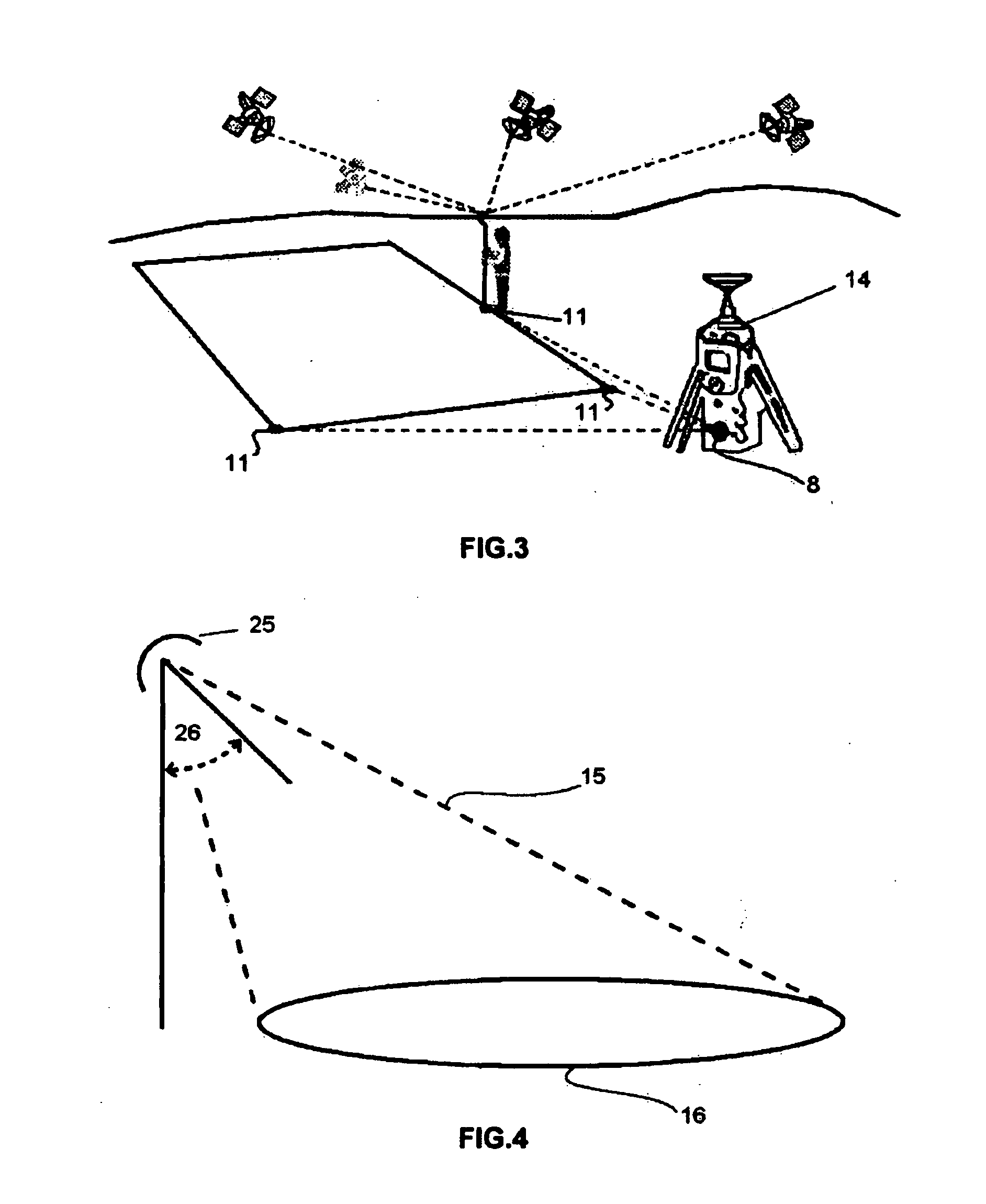
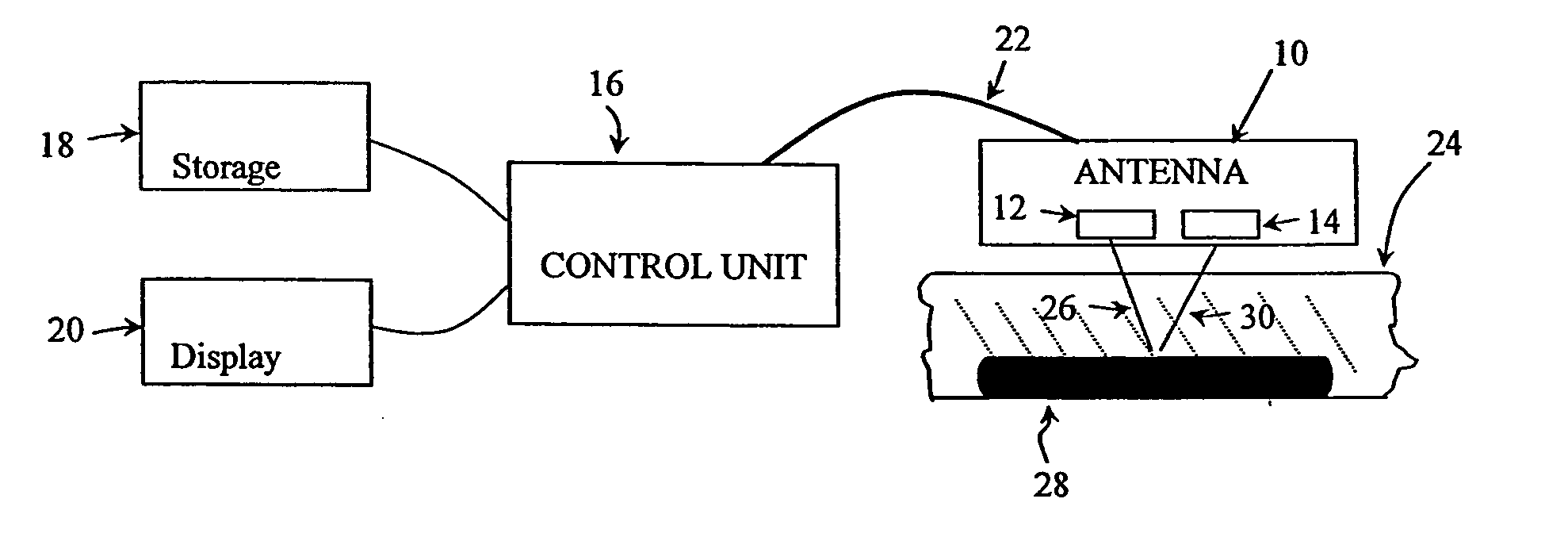
Railroad surveying and monitoring system
InactiveUS20100026551A1Easy to adaptOptimizationPosition fixationTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTerrainLandform
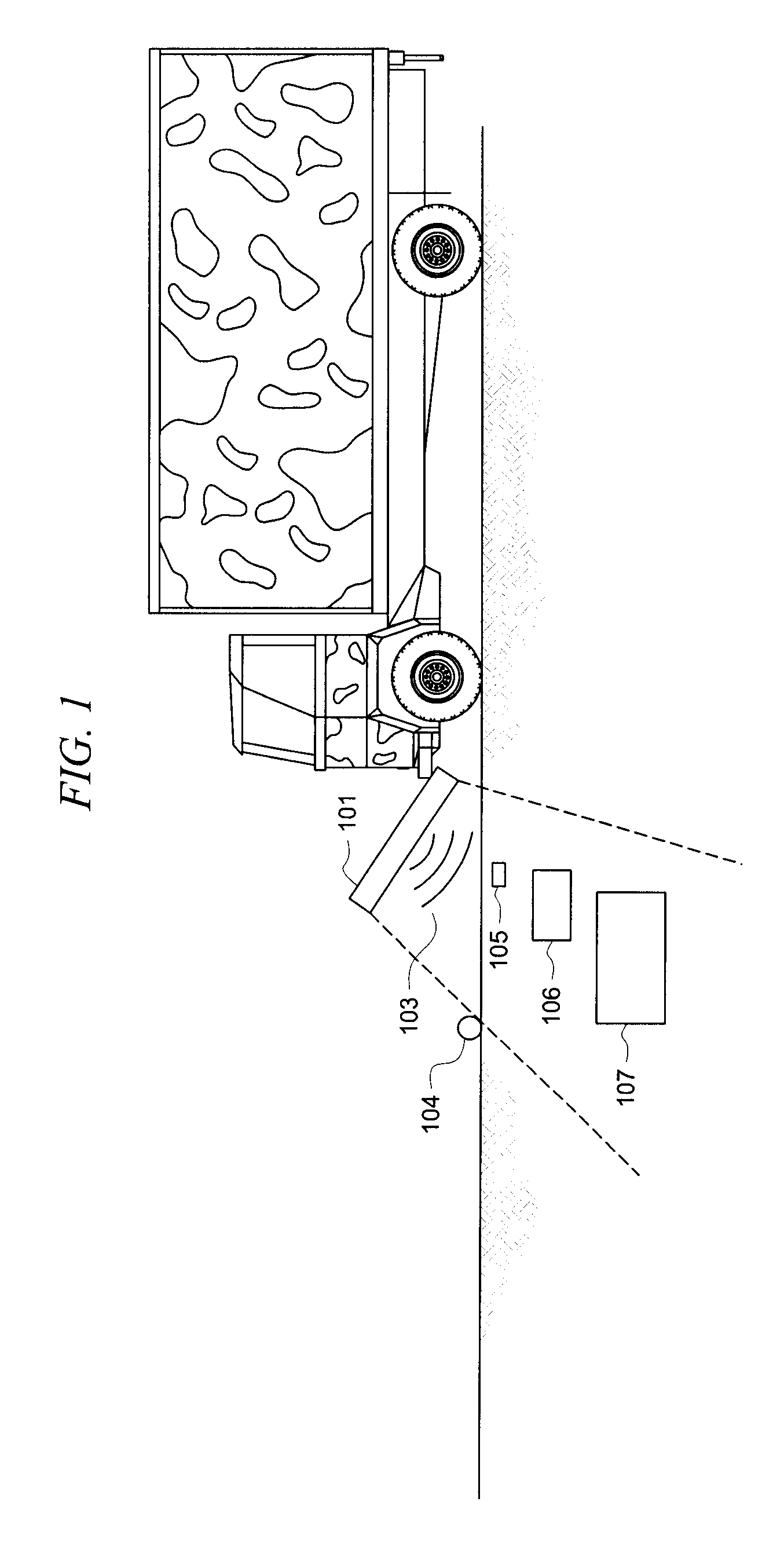
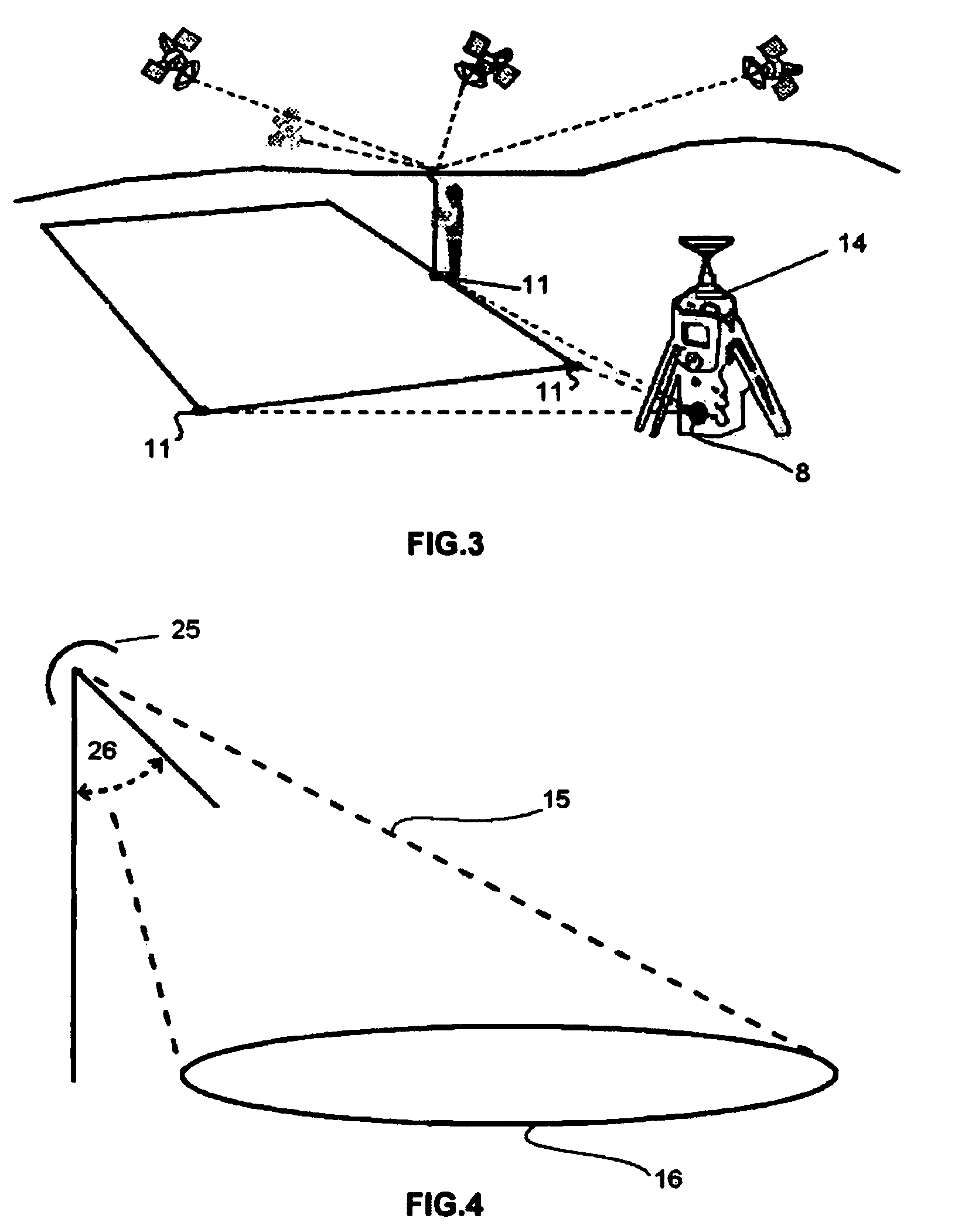
A Railroad Surveying and Monitoring System configured on a mobile platform for surveying, monitoring, and analyzing rail position and superstructure and terrain substructure of railroad tracks (20a,b) or other structures. The system employs two or more High Accuracy Differential Global Positioning System devices (110,112), ground penetrating radar devices (116), terrain conductivity instruments (118), optical cameras (124), and data receivers and processors (126), which in turn process, display, and store the data in a usable database. Precise coordinate data generated from a High Accuracy Global Positioning System provides both location data for subsurface sensors and surface sensors and rail position coordinates to monitor track displacements during track inspection in real time.
Owner:MARSHALL UNIV RES
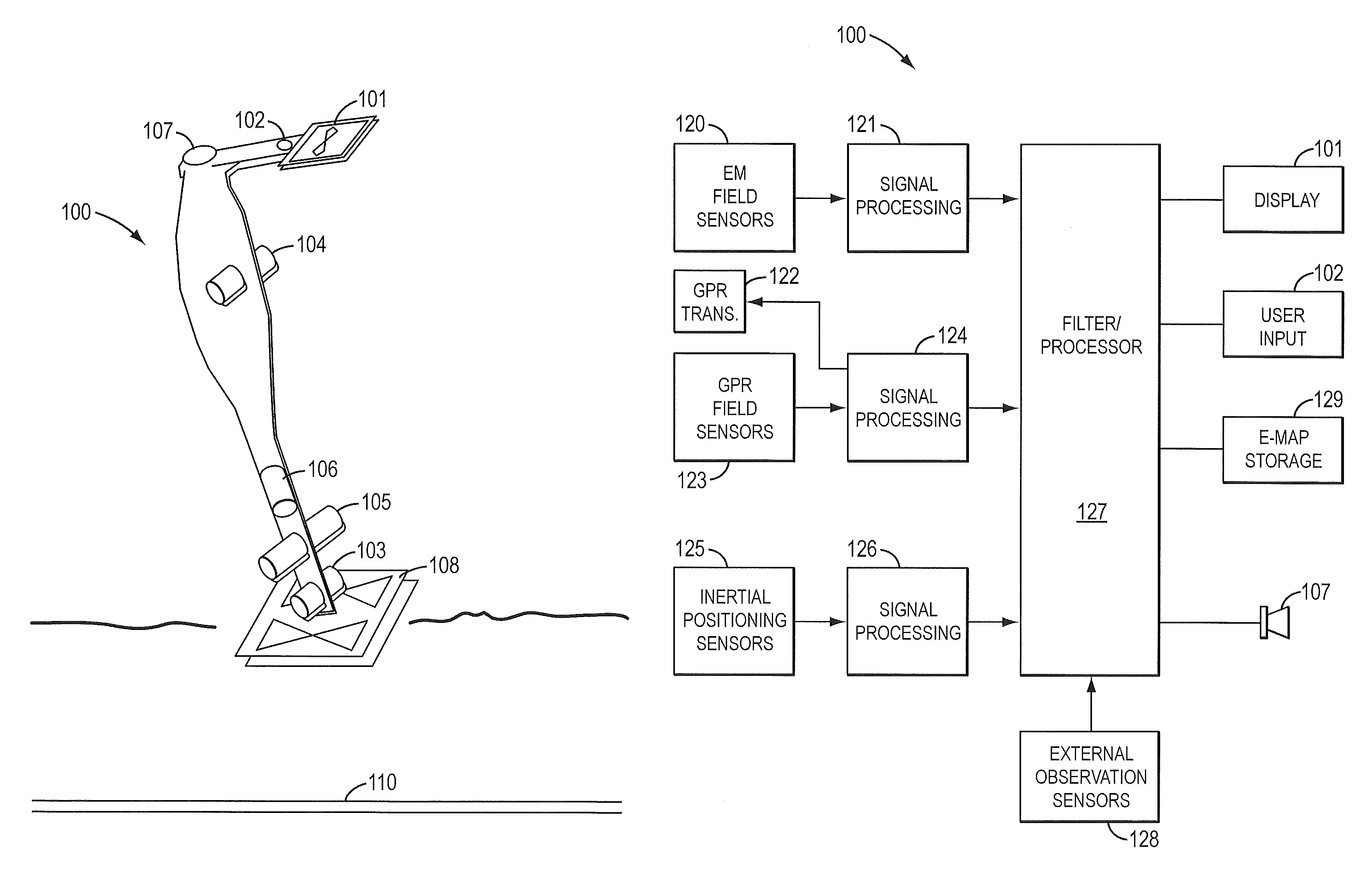
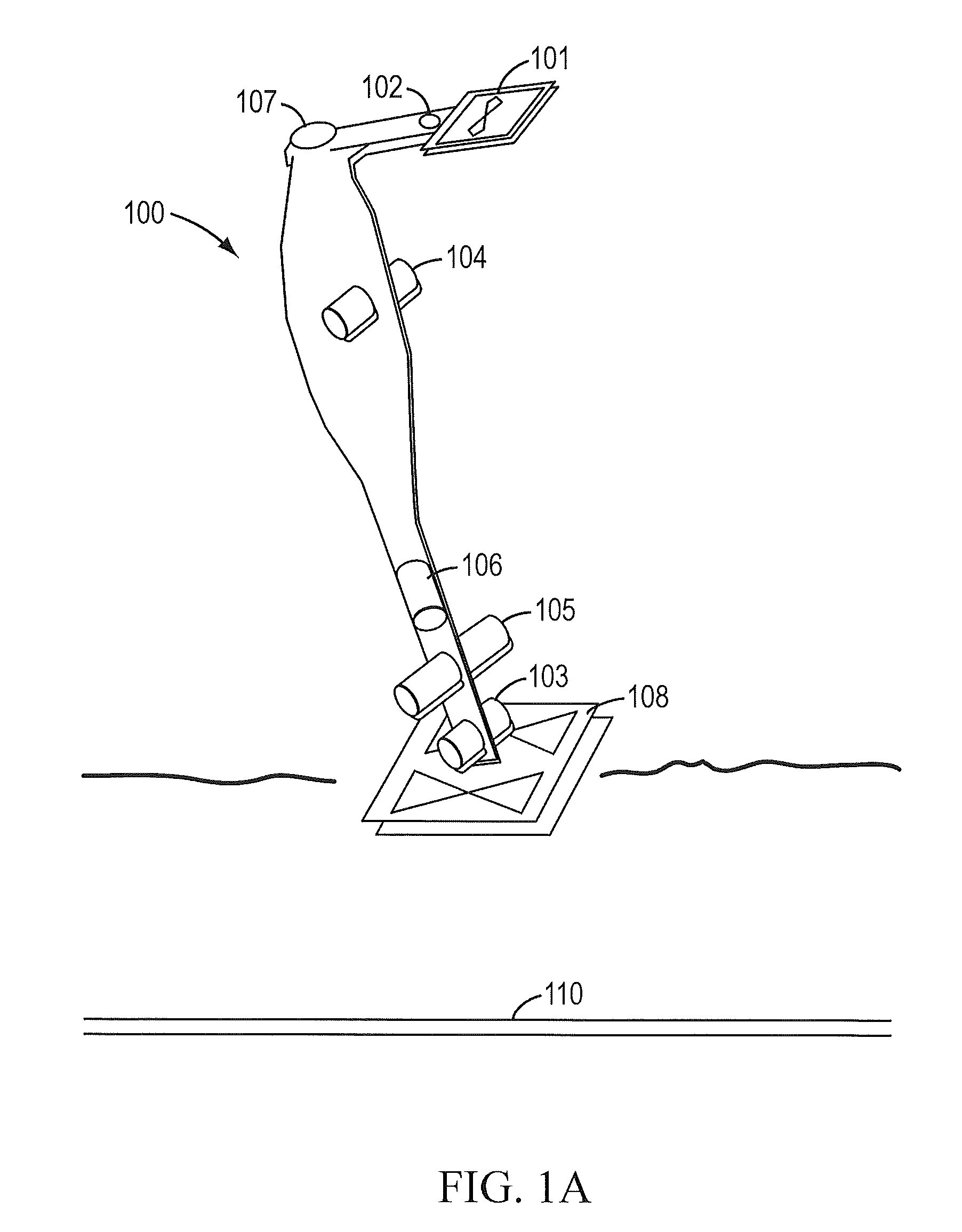
Sensor fusion for model-based detection in pipe and cable locator systems
ActiveUS7834801B2Improve positionSatellite radio beaconingElectric/magnetic detectionGyroscopeAccelerometer
Line locator systems that fuse traditional sensors used in a combined pipe and cable locator (electromagnetic coils, magnetometers, and ground penetrating radar antennas) with low cost inertial sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) in a model-based approach are presented. Such systems can utilize inexpensive MEMS sensors for inertial navigation. A pseudo-inertial frame is defined that uses the centerline of the tracked utility, or an aboveground fixed object as the navigational reference. An inertial sensor correction mechanism that limits the tracking errors over time when the model is implemented in state-space form using, for example, the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is disclosed.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for detecting leaks in buried pipes by using a selected combination of geophysical instruments
InactiveUS6667709B1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidEngineeringWave speed
A method and apparatus for detecting and locating leaks in buried pipes is disclosed in which ground penetrating radar, induction, acoustic, and vacuum excavation systems are selected based on soil conditions and then employed in selected combinations. The conductivity and wave speed of the soil are used in the selection process and in the process of detecting and locating a leak based on the measurements obtained from the selected combination of detection systems.
Owner:UNDERGROUND IMAGING TECH +1
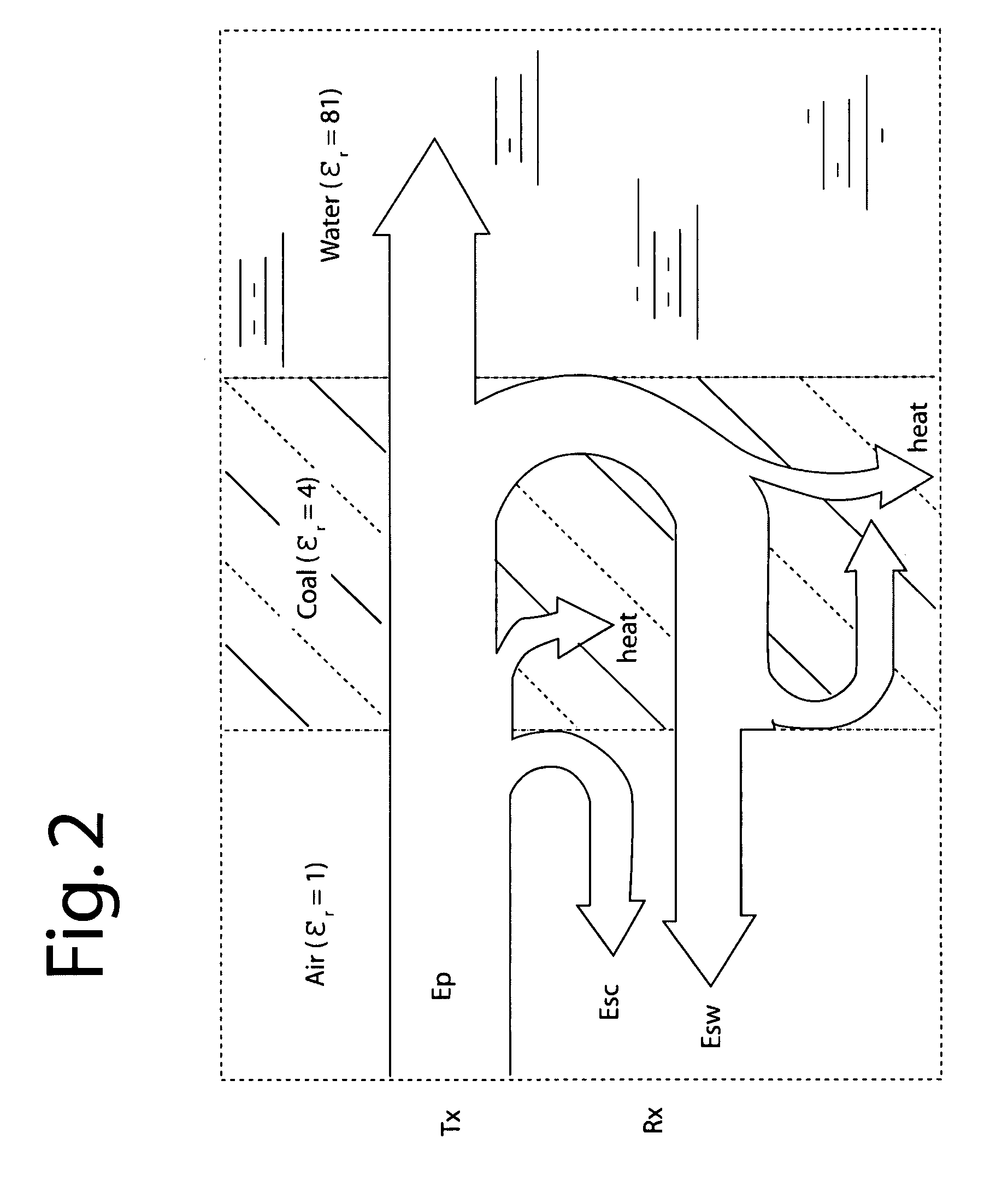
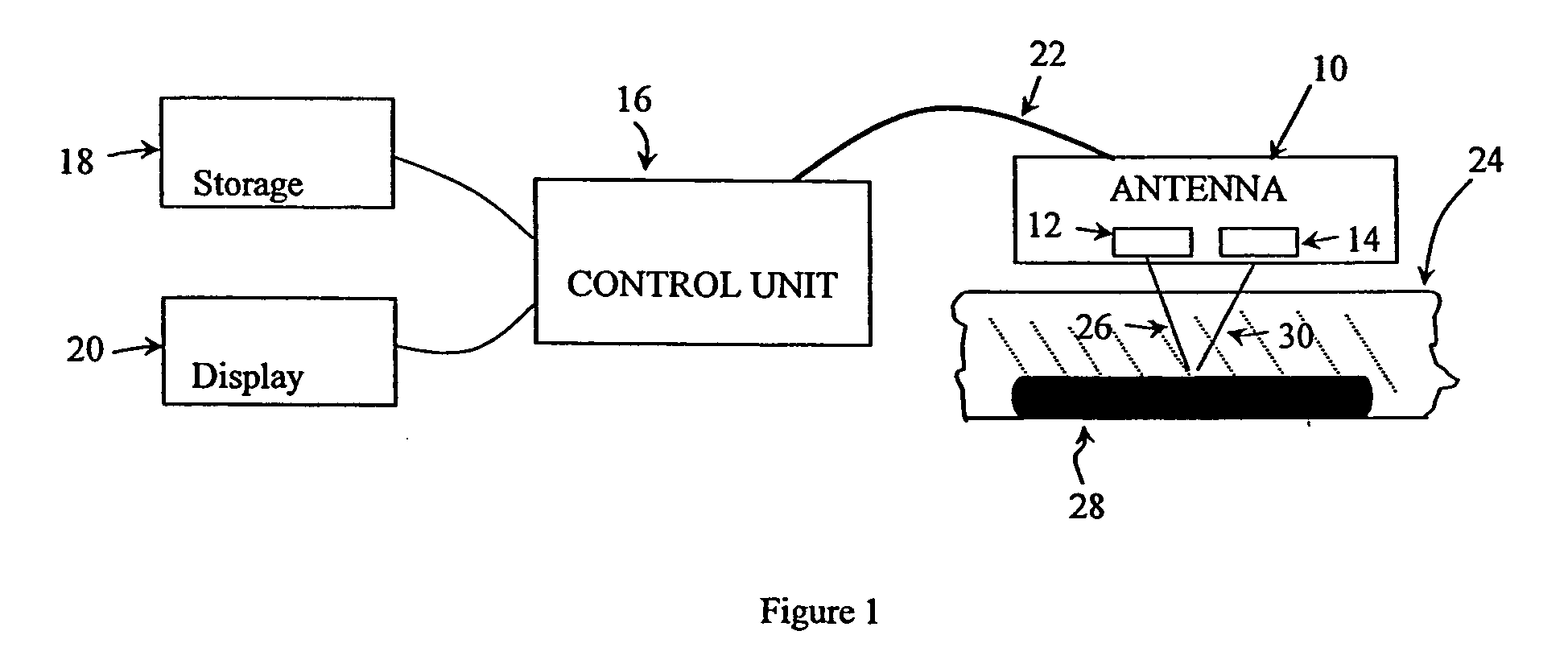
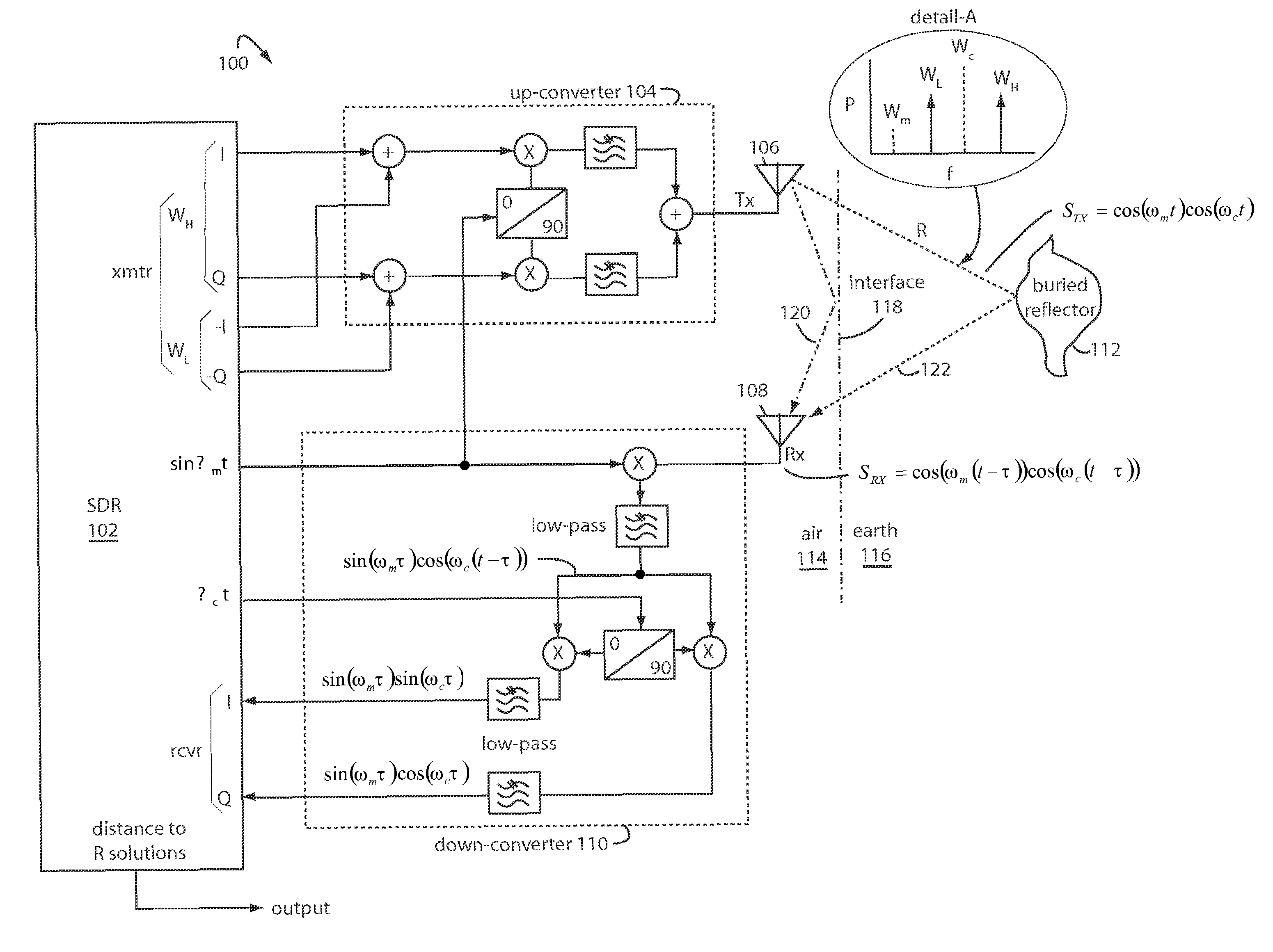
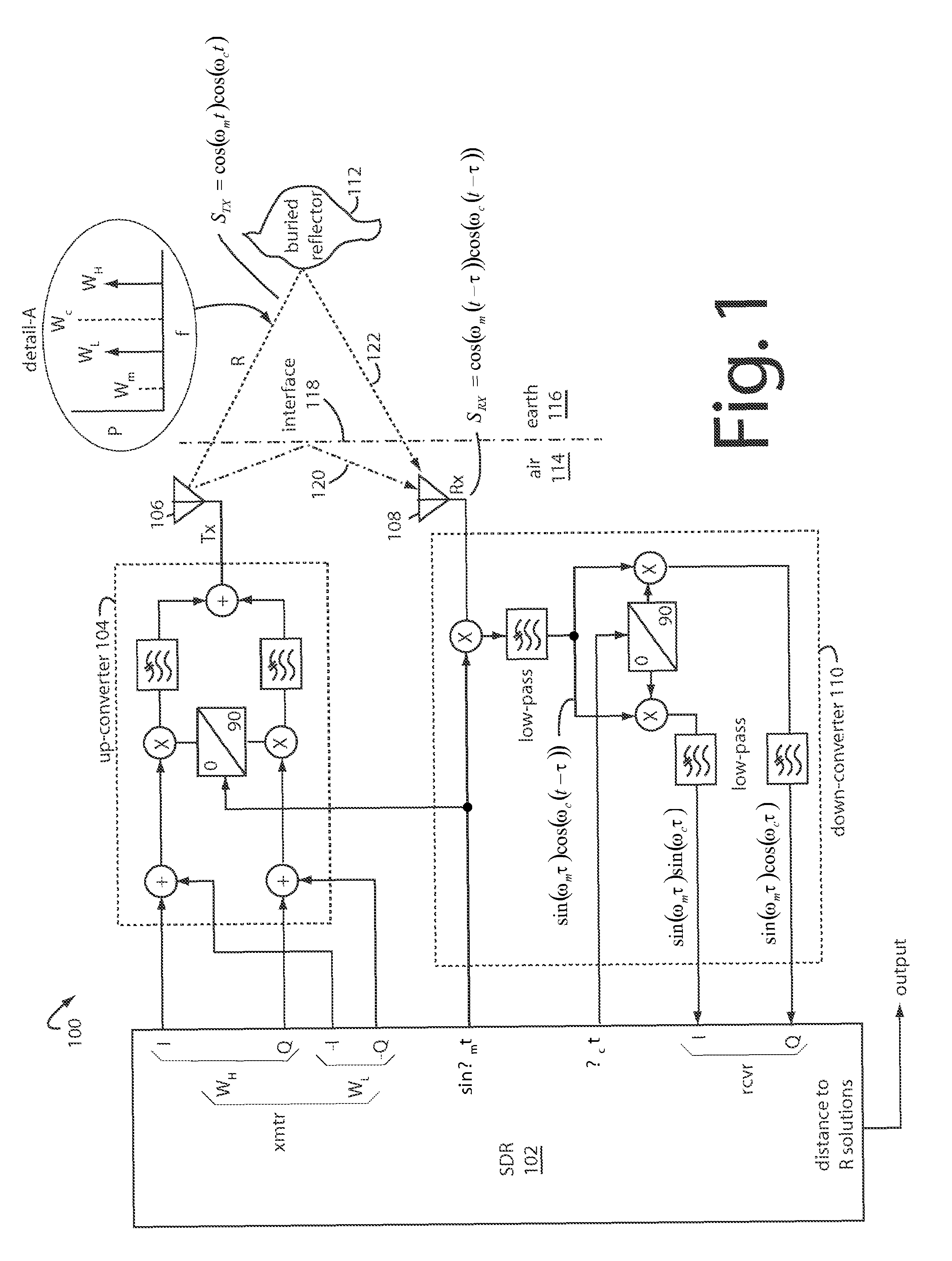
Double-sideband suppressed-carrier radar to null near-field reflections from a first interface between media layers
InactiveUS20080218400A1Increase reflectionSlitting machinesDetection using electromagnetic wavesMicrostrip patch antennaAntenna design
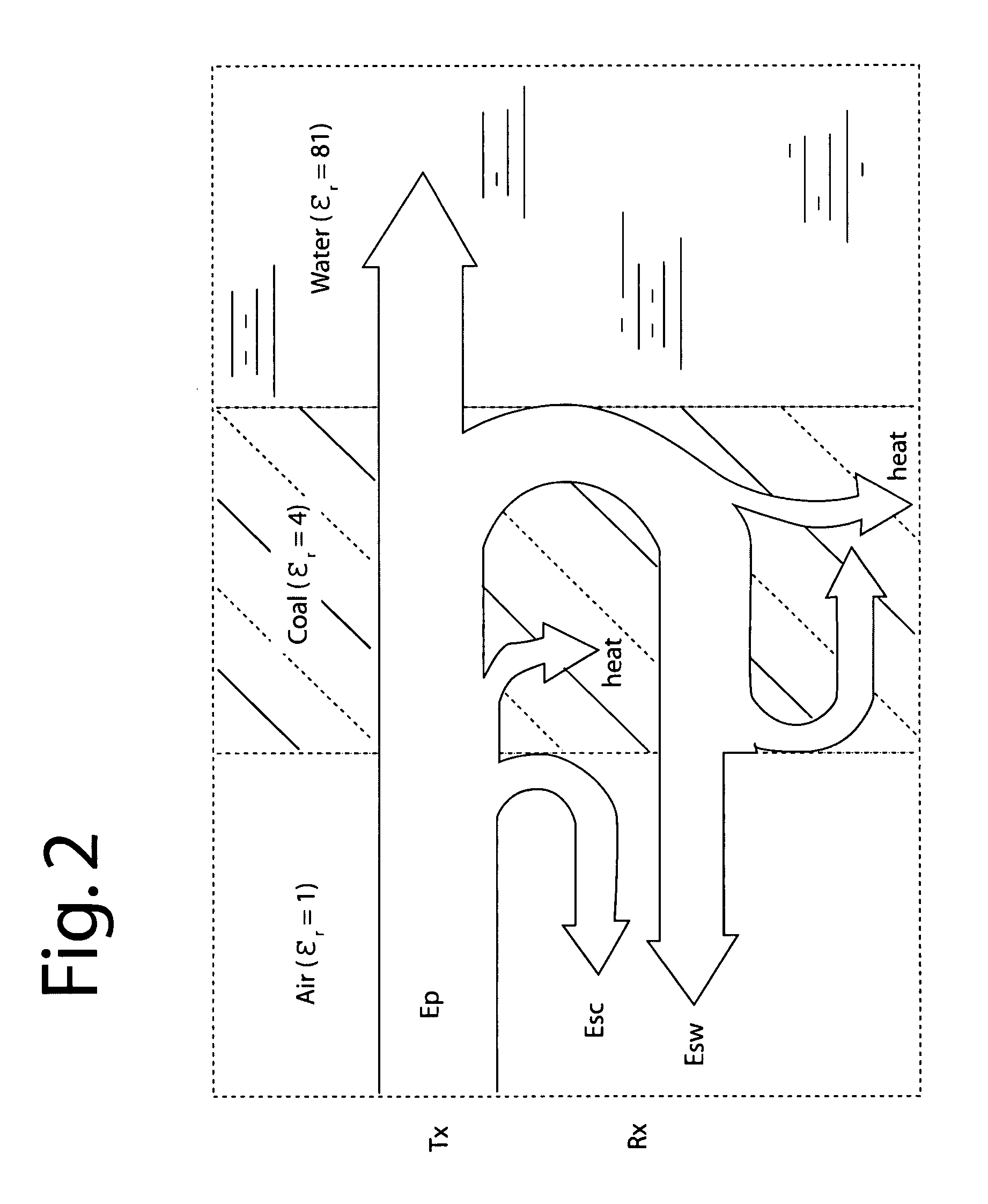
A ground-penetrating radar comprises a software-definable transmitter for launching pairs of widely separated and coherent continuous waves. Each pair is separated by a constant or variable different amount double-sideband suppressed carrier modulation such as 10 MHz, 20 MHz, and 30 MHz Processing suppresses the larger first interface reflection and emphasizes the smaller second, third, etc. reflections. Processing determines the electrical parameter of the natural medium adjacent to the antenna.The modulation process may be the variable or constant frequency difference between pairs of frequencies. If a variable frequency is used in modulation, pairs of tunable resonant microstrip patch antennas (resonant microstrip patch antenna) can be used in the antenna design. If a constant frequency difference is used in the software-defined transceiver, a wide-bandwidth antenna design is used featuring a swept or stepped-frequency continuous-wave (SFCW) radar design.The received modulation signal has a phase range that starts at 0-degrees at the transmitter antenna, which is near the first interface surface. After coherent demodulation, the first reflection is suppressed. The pair of antennas may increase suppression. Then the modulation signal phase is changed by 90-degrees and the first interface signal is measured to determine the in situ electrical parameters of the natural medium.Deep reflections at 90-degrees and 270-degrees create maximum reflection and will be illuminated with modulation signal peaks. Quadrature detection, mixing, and down-conversion result in 0-degree and 180-degree reflections effectively dropping out in demodulation.
Owner:STOLAR
Light-Weight Analyzer For Odor Recognition
The invention provides a light weight analyzer, e.g., detector, capable of locating clandestine graves. The detector utilizes the very specific and unique chemicals identified in the database of human decompositional odor. This detector, based on specific chemical compounds found relevant to human decomposition, is the next step forward in clandestine grave detection and will take the guess-work out of current methods using canines and ground-penetrating radar, which have historically been unreliable. The detector is self contained, portable and built for field use. Both visual and auditory cues are provided to the operator.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
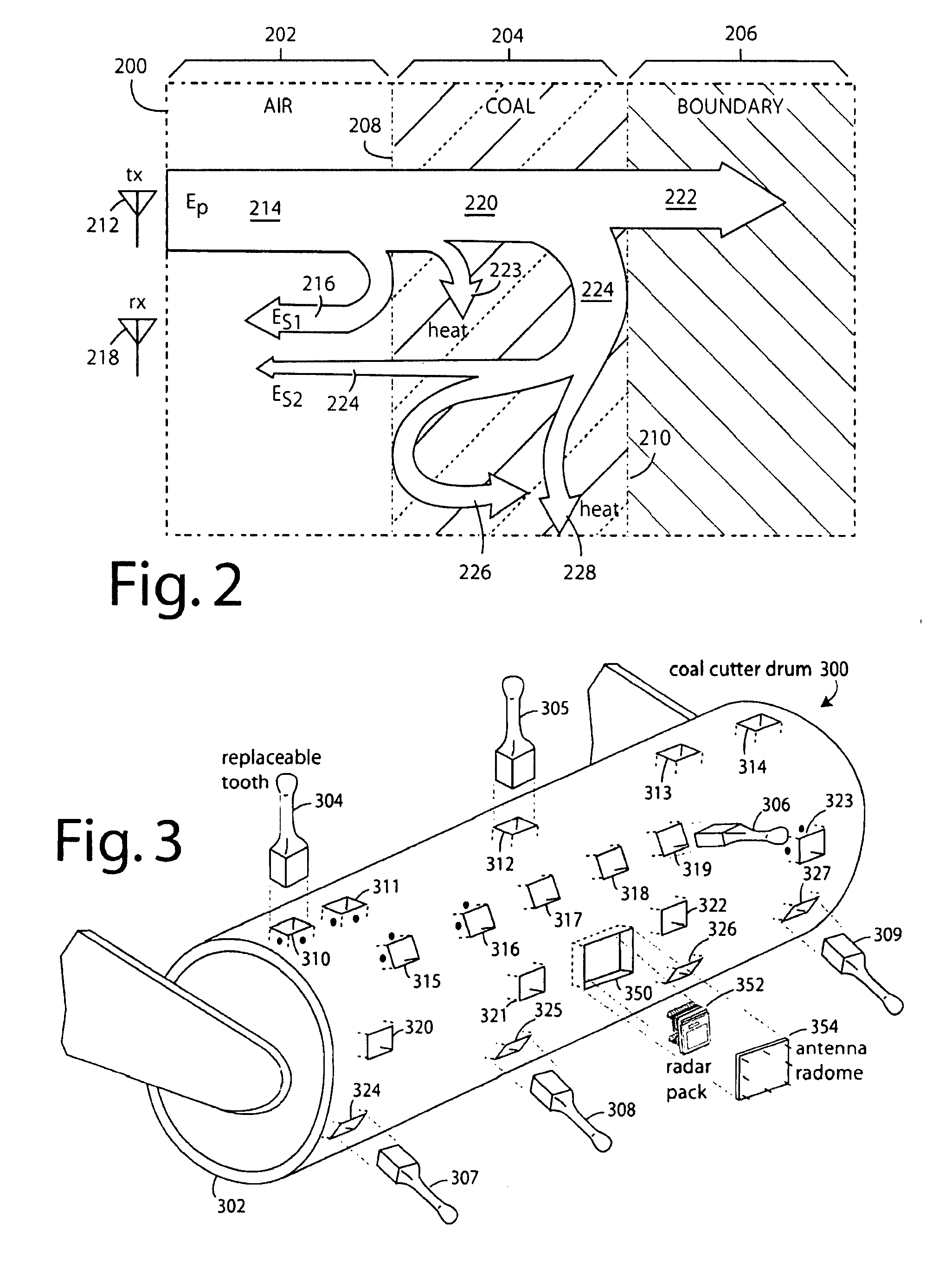
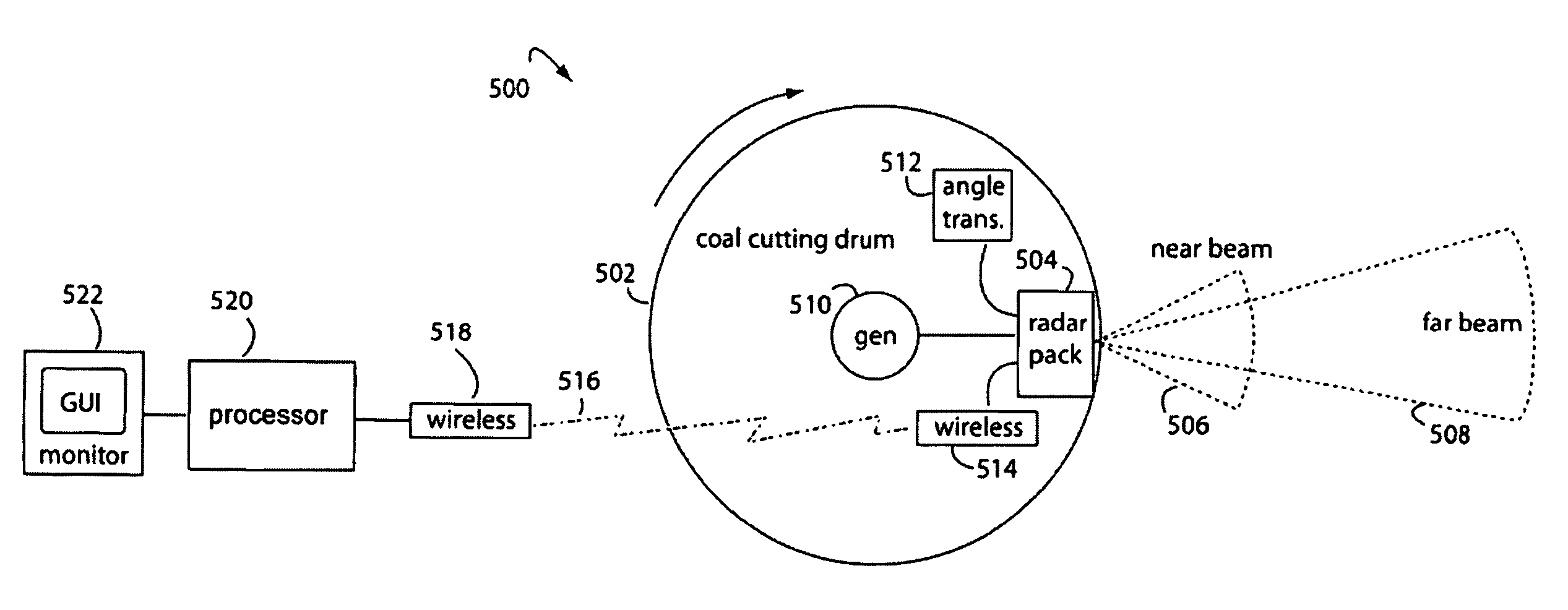
Radar mining guidance control system
InactiveUS7659847B2Increase reflectionSlitting machinesDetection using electromagnetic wavesGuidance controlCarrier signal
A coal-mining machine uses a ground-penetrating radar based on a software-definable transmitter for launching pairs of widely separated and coherent continuous waves. Each pair is separated by a constant or variable different amount double-sideband suppressed carrier modulation such as 10 MHz, 20 MHz, and 30 MHz. Processing suppresses the larger first interface reflection and emphasizes the smaller second, third, etc. reflections. Processing determines the electrical parameter of the natural medium adjacent to the antenna. Deep reflections at 90-degrees and 270-degrees create maximum reflection and will be illuminated with modulation signal peaks. Quadrature detection, mixing, and down-conversion result in 0-degree and 180-degree reflections effectively dropping out in demodulation.
Owner:STOLAR
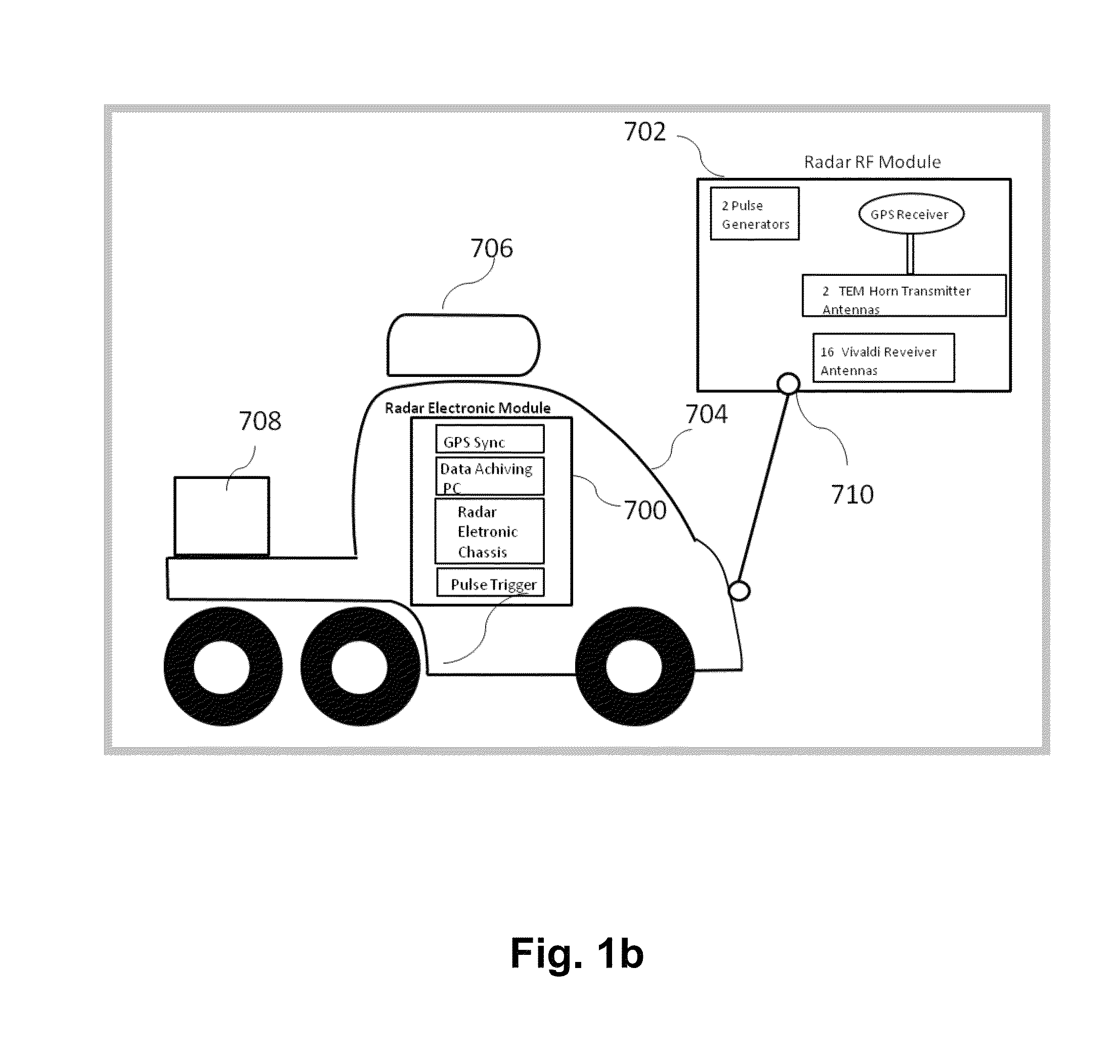
Moving Multi-Polarization Multi-Transmitter/Receiver Ground Penetrating Radar System and Signal Processing for Buried Target Detection
InactiveUS20160061948A1Enhance signatureQuality improvementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsDiversity scheme
A moving ground penetrating radar is comprised of multiple transmitters and receivers with multiple, e.g., Horizontal and Vertical, polarizations to detect buried targets with standoff capability. Novel signal and imaging techniques are used to form high quality radar imagery with low artifacts that are due to various sources of self-induced resonances, e.g., transmitter-receiver coupling, calibration errors, and motion errors in the multi transmitter / receiver channels of the radar system. The irradiated target area image is formed via exploiting both the spatial diversity of the physical multi-transmitter and multi-receiver array and synthetic aperture / array that is generated by the motion of the platform that carries the radar system. The images that are formed from the multiple polarizations are combined to remove surface targets / clutter and, thus, enhance signatures of buried targets.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Double-sideband suppressed-carrier radar to null near-field reflections from a first interface between media layers
InactiveUS7656342B2Increase reflectionSlitting machinesDetection using electromagnetic wavesMicrostrip patch antennaAntenna design
Owner:STOLAR
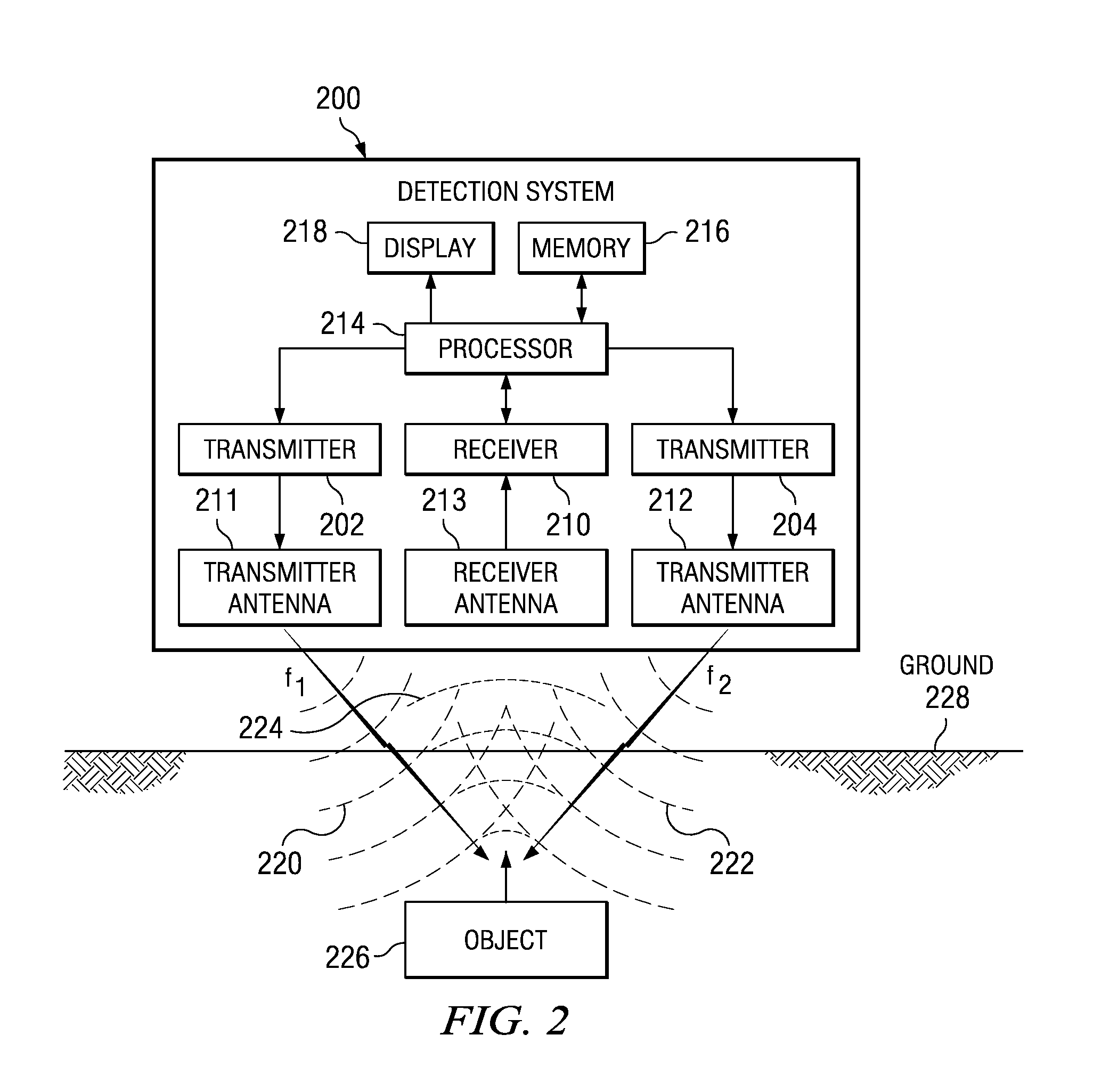
Method and apparatus for using collimated and linearly polarized millimeter wave beams at brewster's angle of incidence in ground penetrating radar to detect objects located in the ground
InactiveUS20090040093A1Defence devicesDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio frequency signalLight beam
A detection system comprises a transmitter unit, a receiver, and a processor. The transmitter unit is capable of transmitting a first collimated beam having a first frequency and a second collimated beam having a second frequency into a ground, wherein the first collimated beam and the second collimated beam overlap in the ground. The receiver is capable of monitoring for a response radio frequency signal having a frequency equal to a difference between the first frequency and the second frequency. The response radio frequency signal is generated by an object having non-linear conductive characteristics in response to receiving the first collimated beam and the second collimated beam. The processor is capable of controlling an operation of the transmitter unit and the receiver. The processor is connected to the transmitter unit and the receiver. The object is detected when the response radio frequency signal is detected by the receiver.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
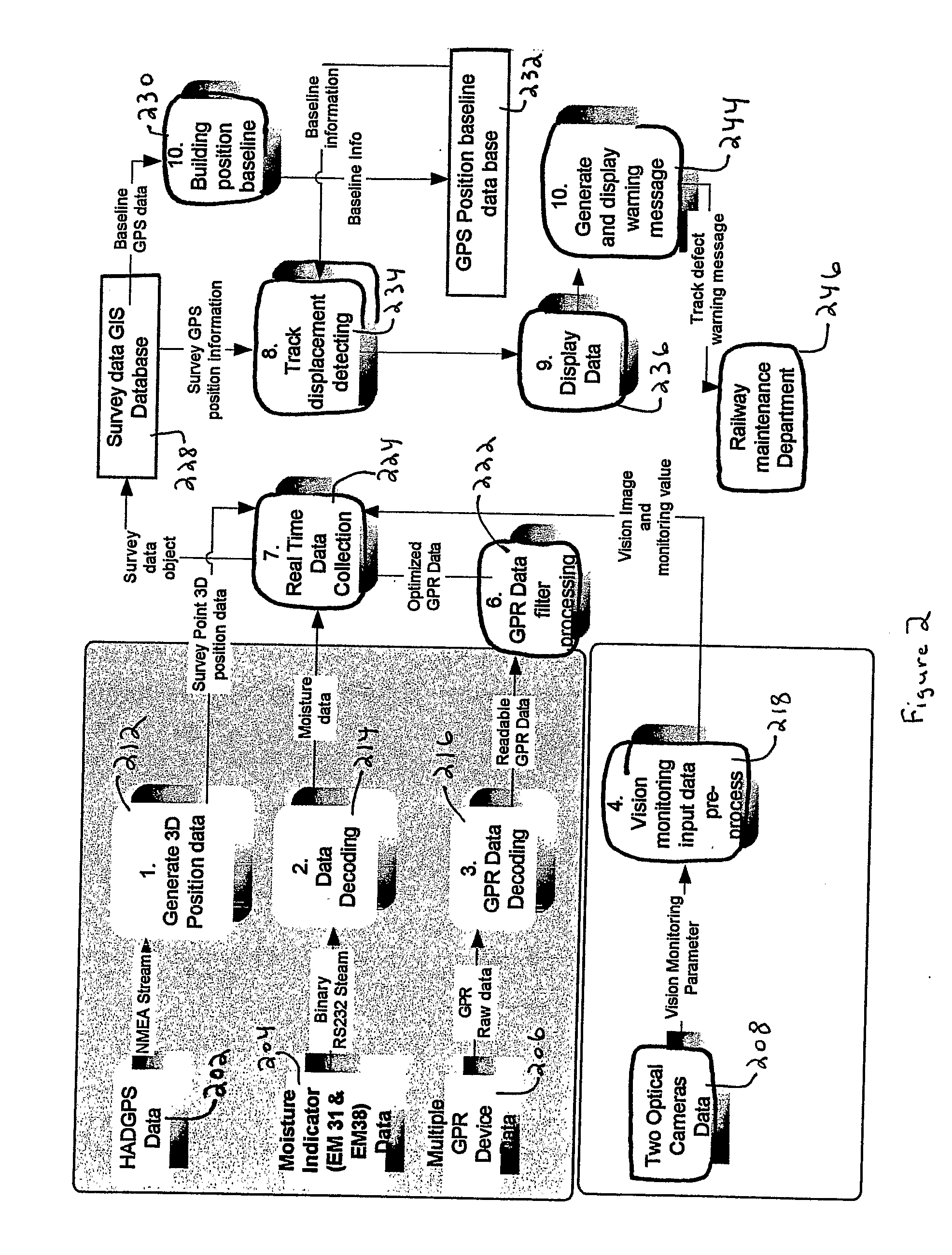
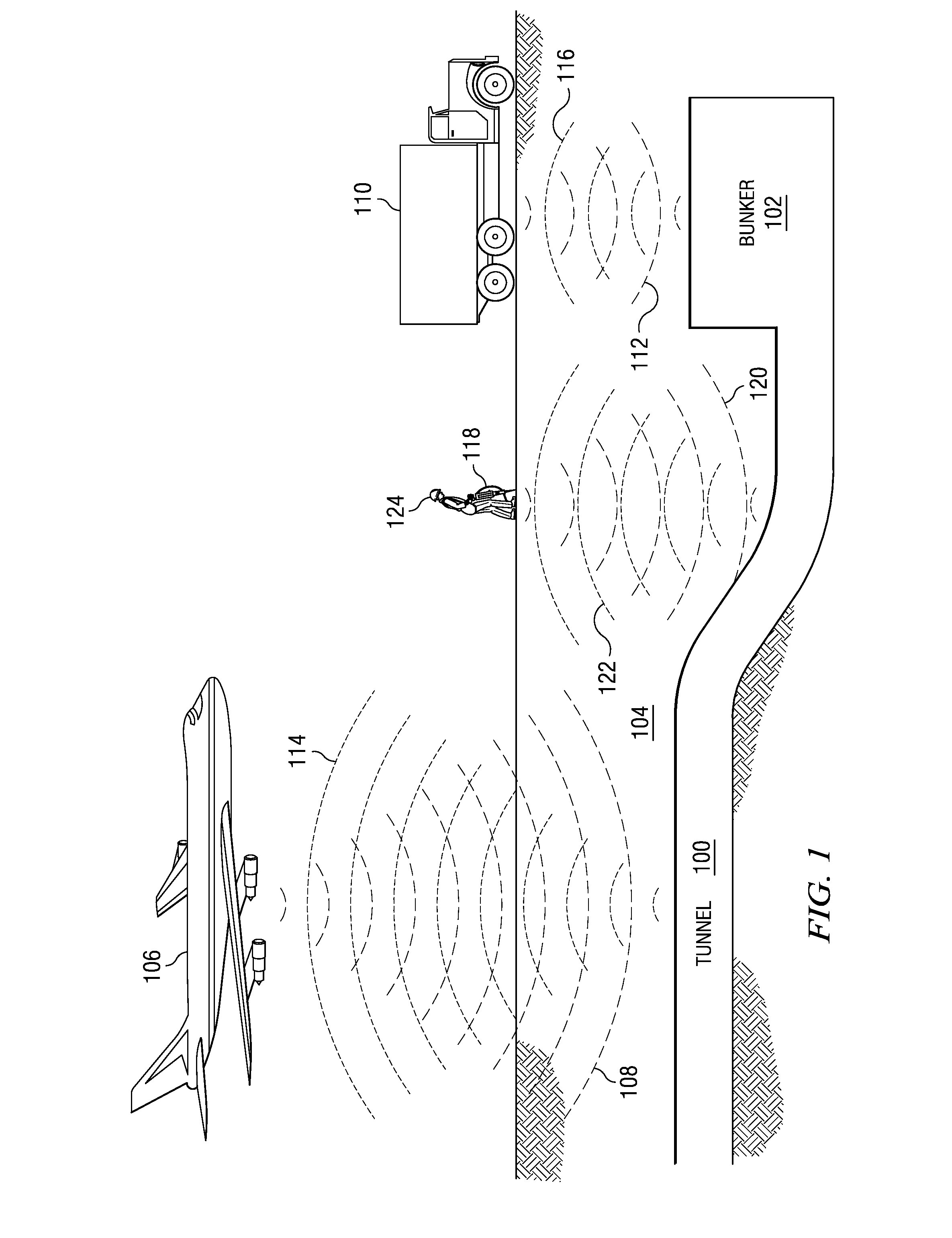
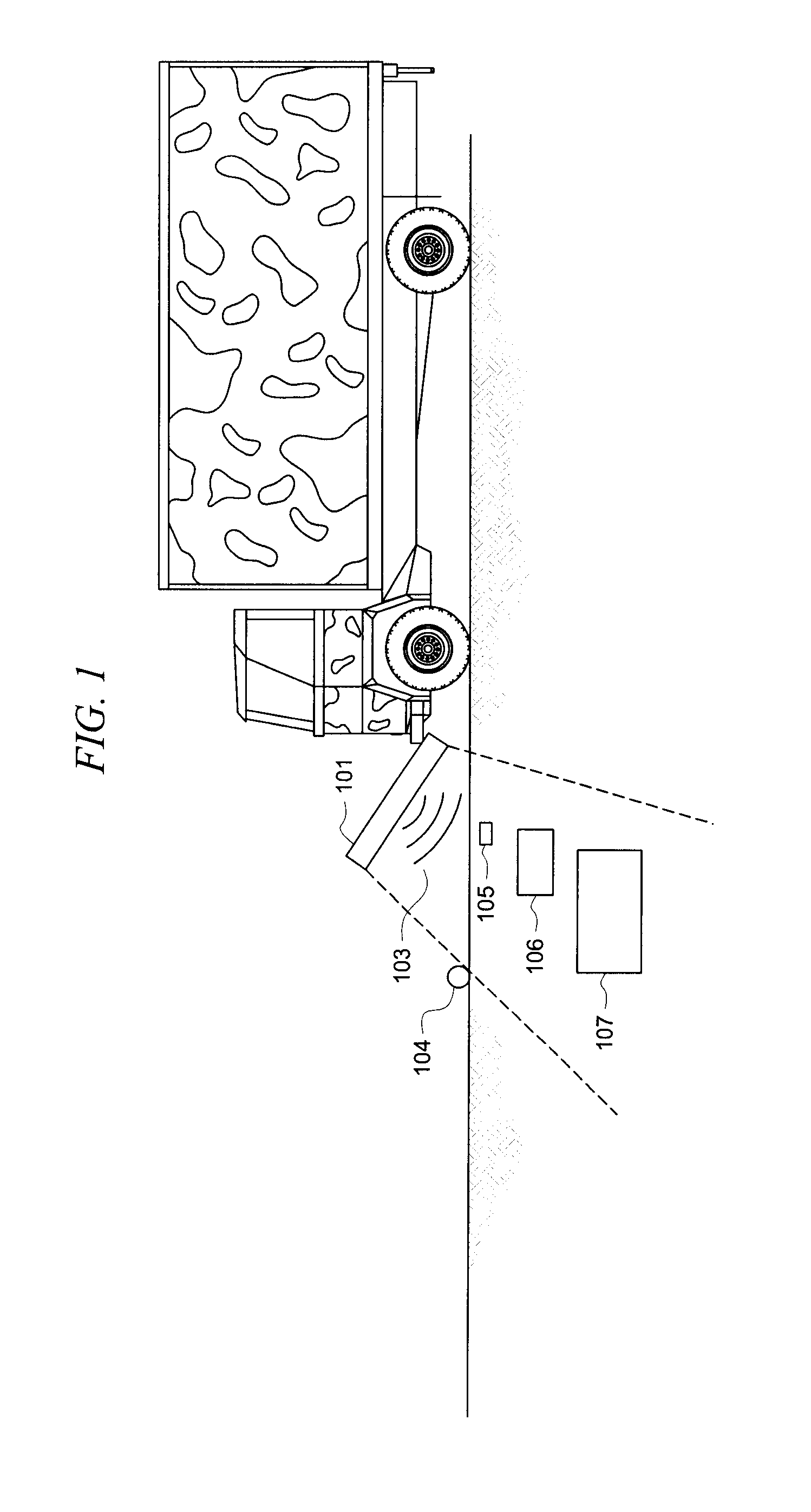
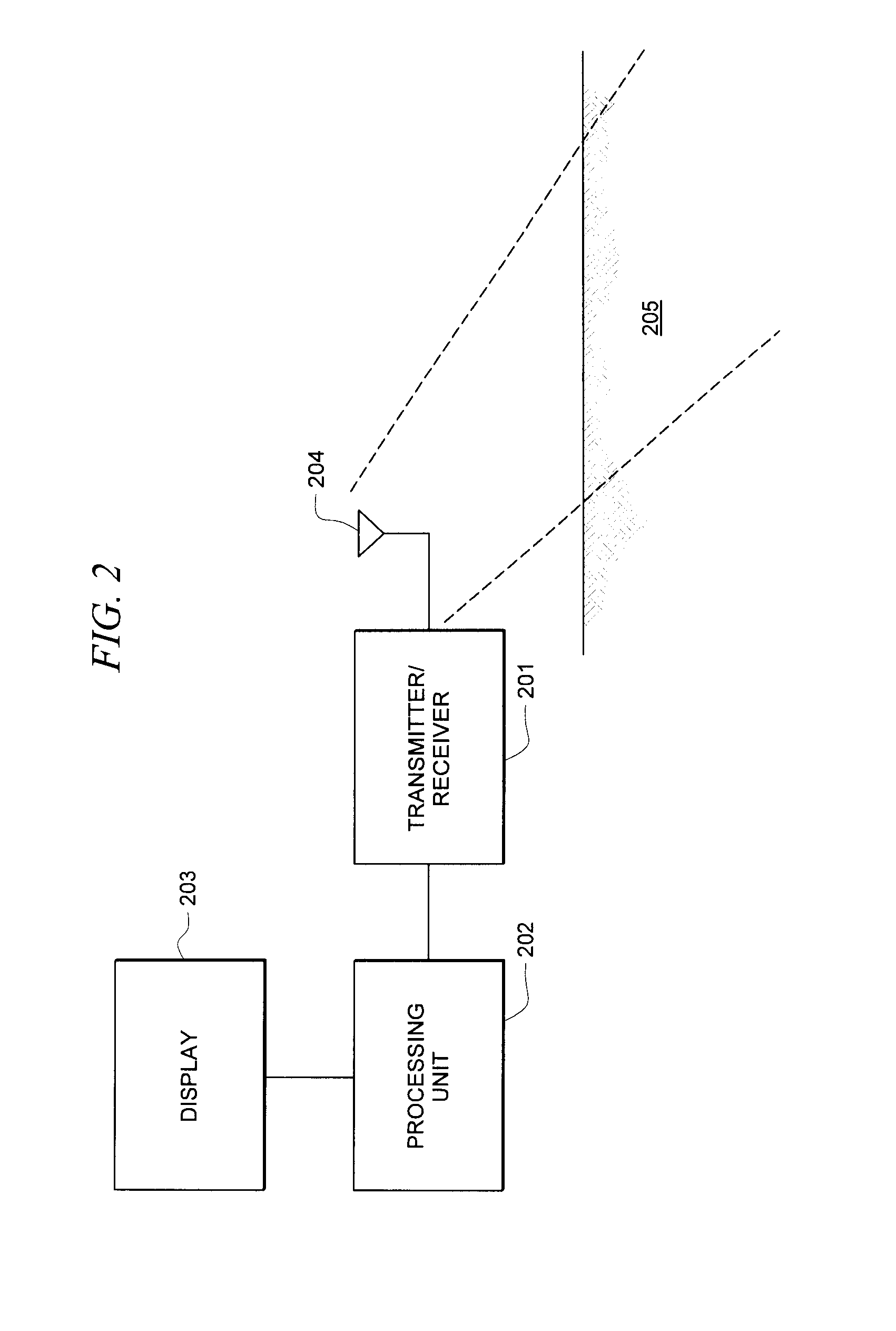
System and method for detecting, locating and identifying objects located above the ground and below the ground in a pre-referenced area of interest
InactiveUS20110037639A1Surveying instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingContinuous scanningAbove ground
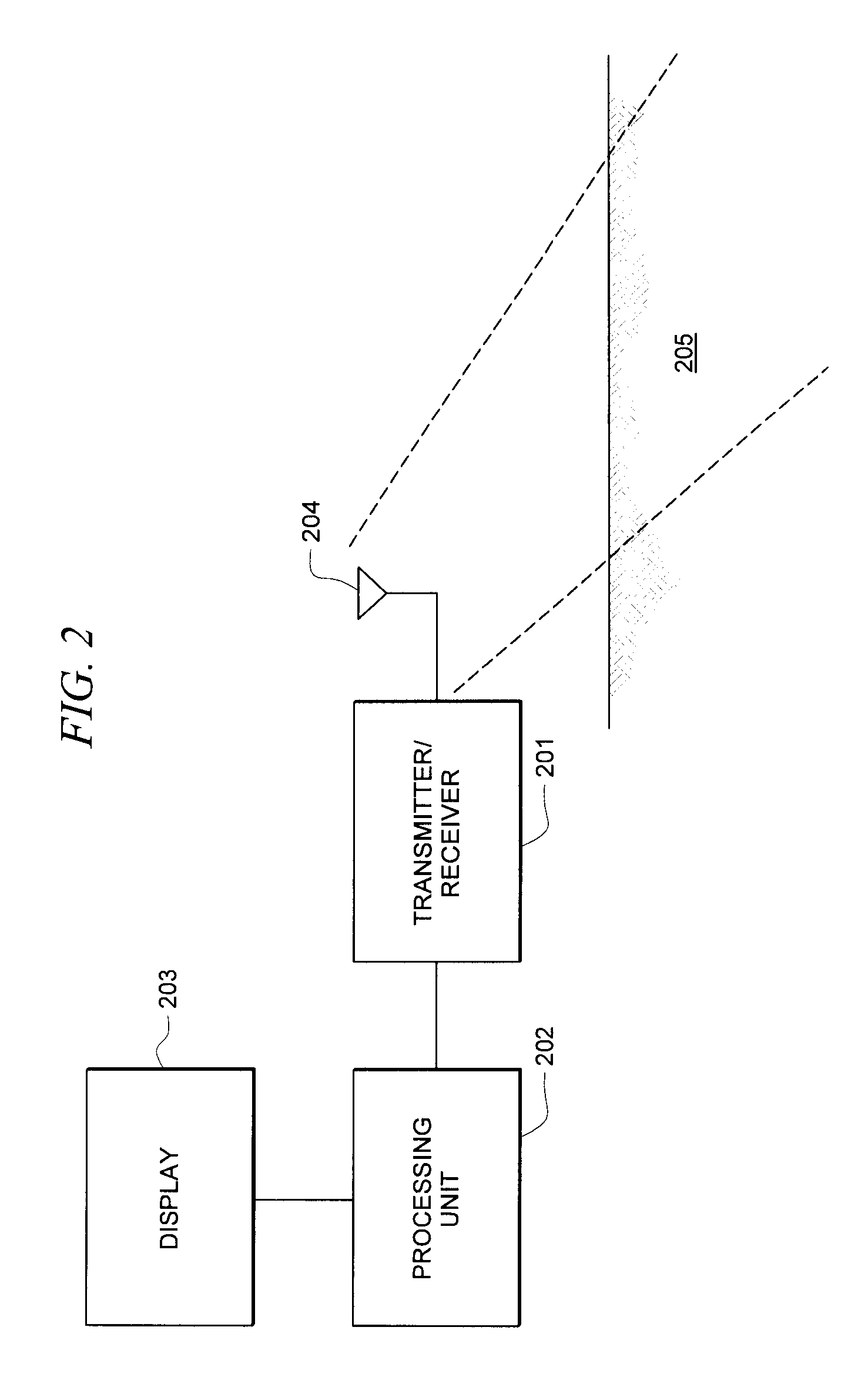
The invention relates to a system and method for detecting, locating and identifying objects located above ground or below ground in an area of interest, comprising an airborne vehicle which circumscribes the area of interest and which includes a built-in radar having an antenna with a respective transmitter and receiver, signal-processing means, data-storage means and graphical interface means. According to the invention, the area of interest has been pre-referenced and the radar is a heterodyne ground penetration radar (GPR). The signal transmitted by the antenna generates a beam that illuminates a strip of earth, consisting of a sinusoidal electromagnetic signal having a frequency that is varied in precise pre-determined progressive steps. This signal is mixed with the received (reflected) signal, thereby producing two sets of values corresponding to the phases of each frequency step or stage Said sets of values, which are obtained throughout successive sweeps (as the antenna moves), are stored in the storage means and subsequently processed in the processing means in order to obtain a final map or image of the location of the objects above ground or below ground.
Owner:PONTIFISIA UNIVERSIDAD KATOLIKA DE CHILE
Dual mode ground penetrating radar (GPR)
InactiveUS20120133543A1High sensitivityHigh impedanceAntenna feed intermediatesIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsDual modeAntenna feed
A dual mode ground penetrating radar includes an enclosure which houses radar electronics. The dual mode ground penetrating radar includes an enclosure housing radar electronics. The dual mode ground penetrating radar further includes a first antenna feed having ferrite loading and extending outside of the enclosure. The dual mode ground penetrating radar further includes a second antenna feed spaced apart from the first antenna feed, the second antenna feed having ferrite loading and extending outside of the enclosure. An RF signal is provided in at least one of the first and second antenna feeds by the radar electronics.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ CITY FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Remote scanning and detection apparatus and method
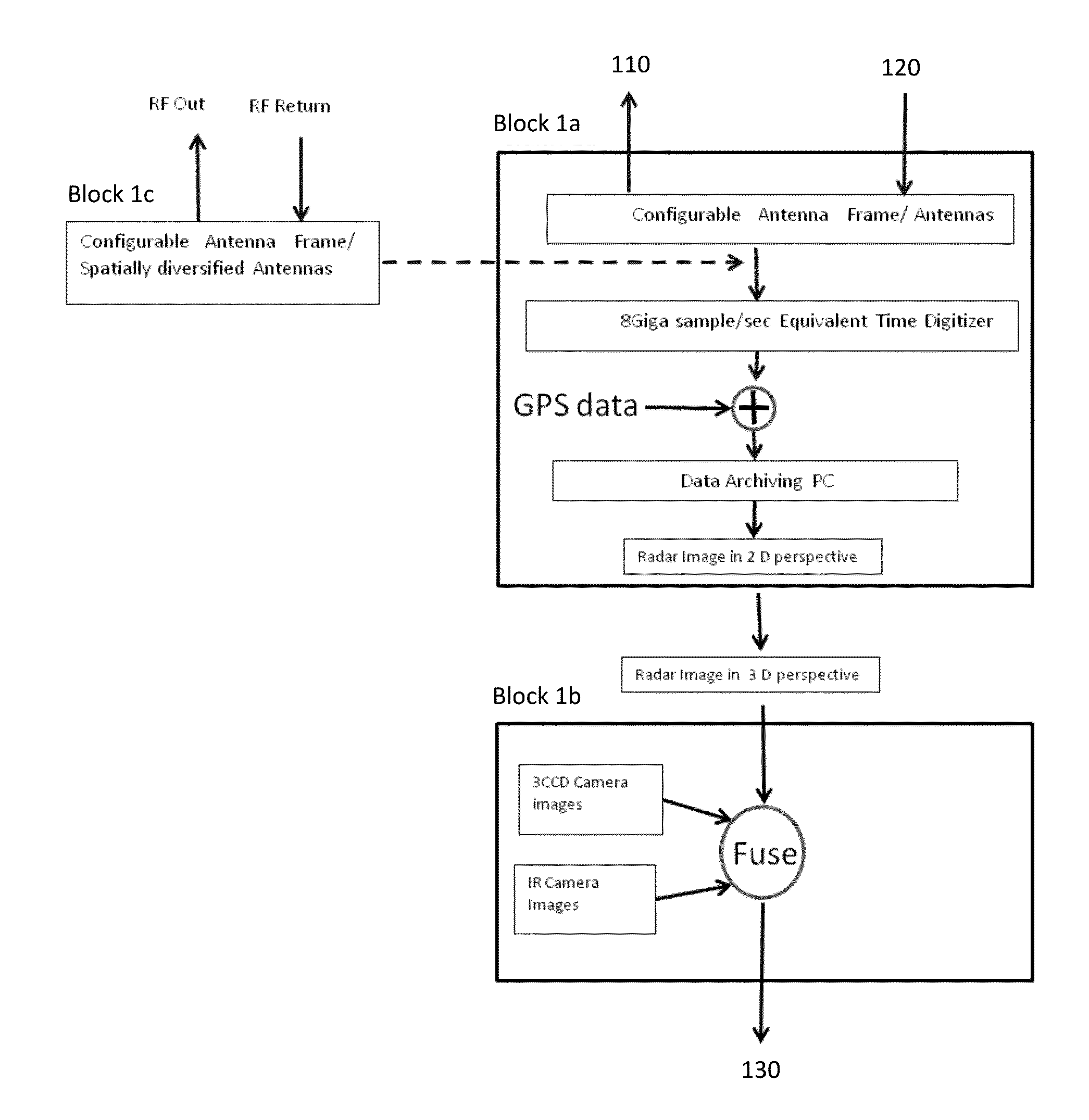
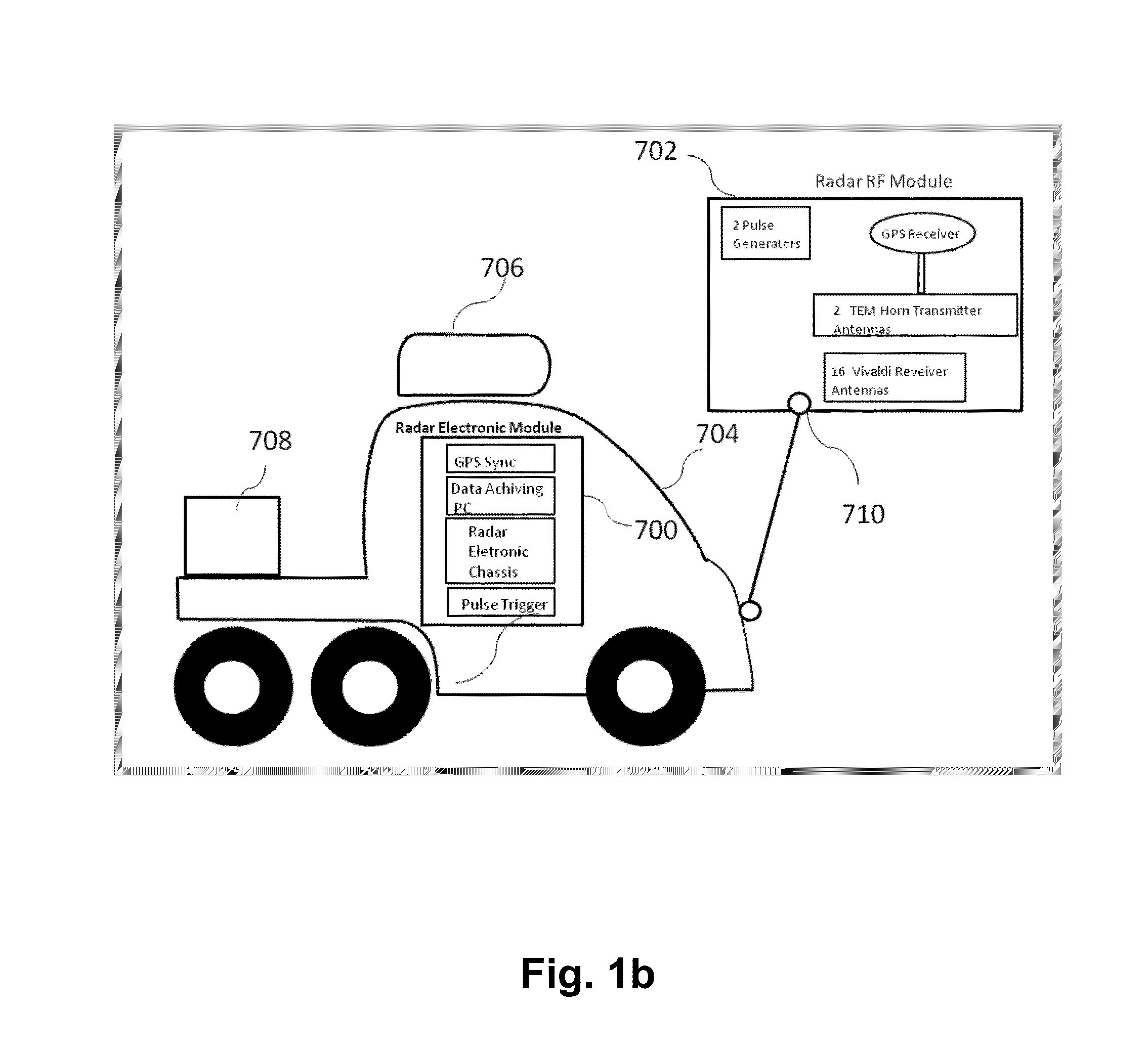
ActiveUS20160350907A1Accurate rapid collection recordationEasy to handleTelevision system detailsImage enhancementInfraredEngineering
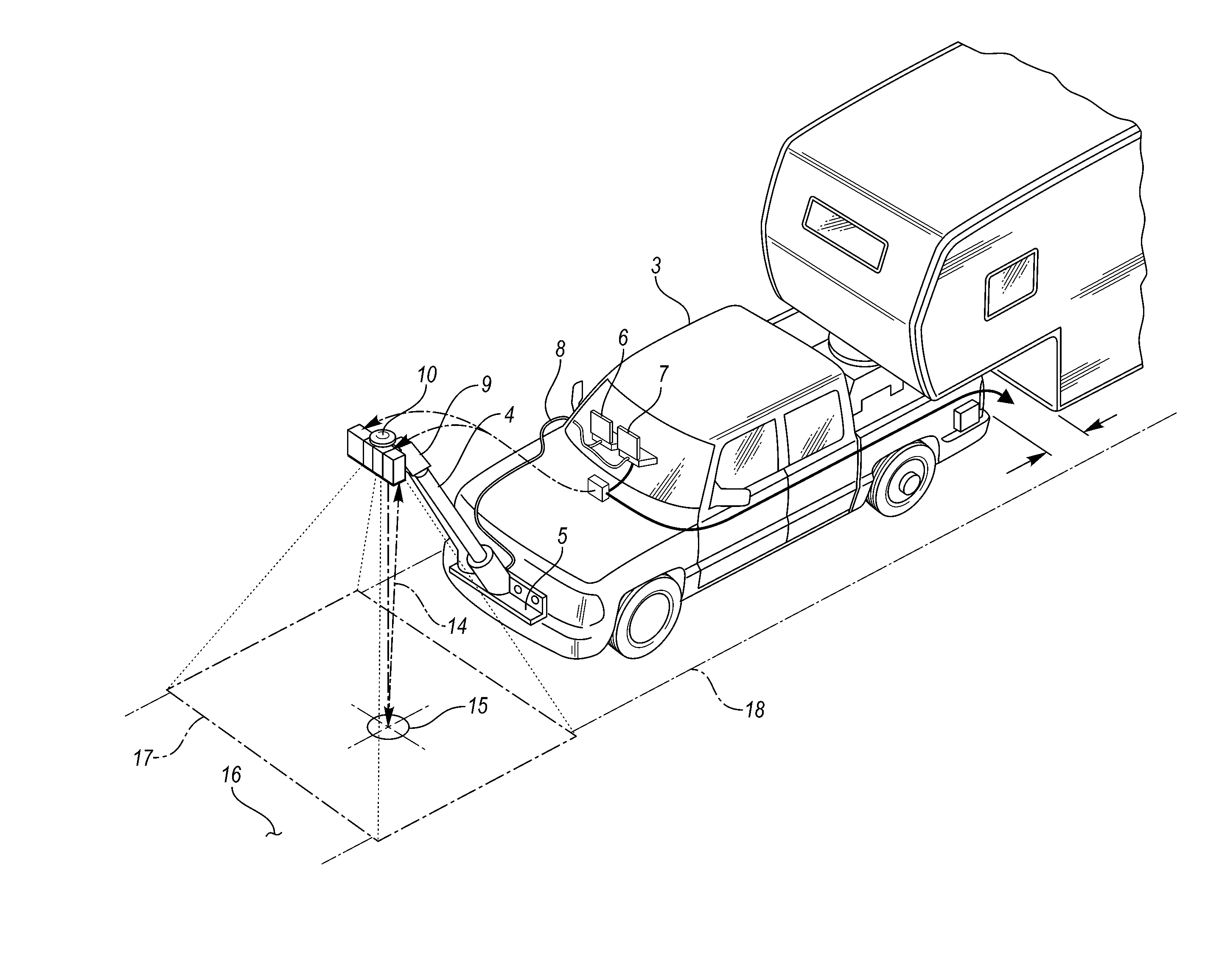
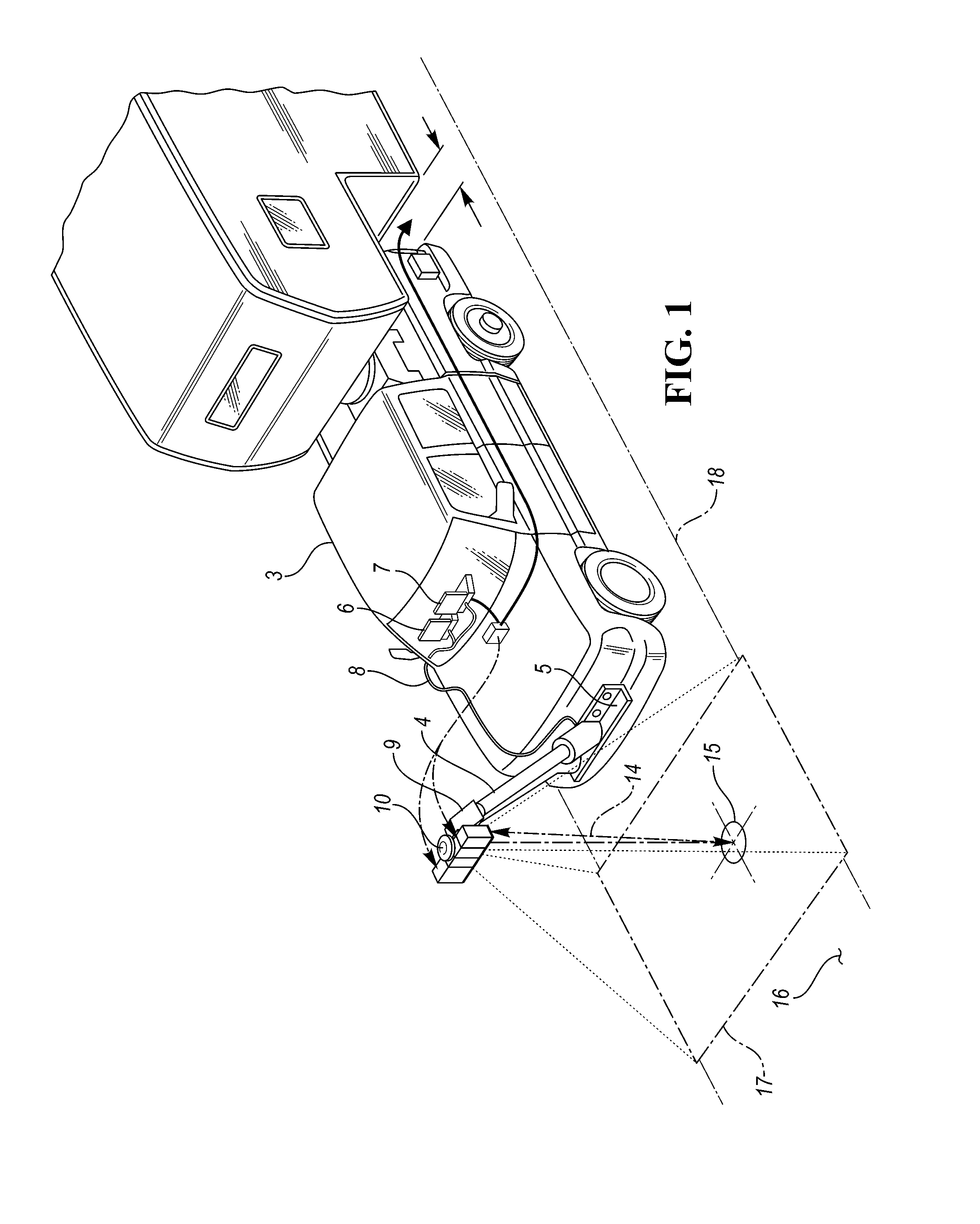
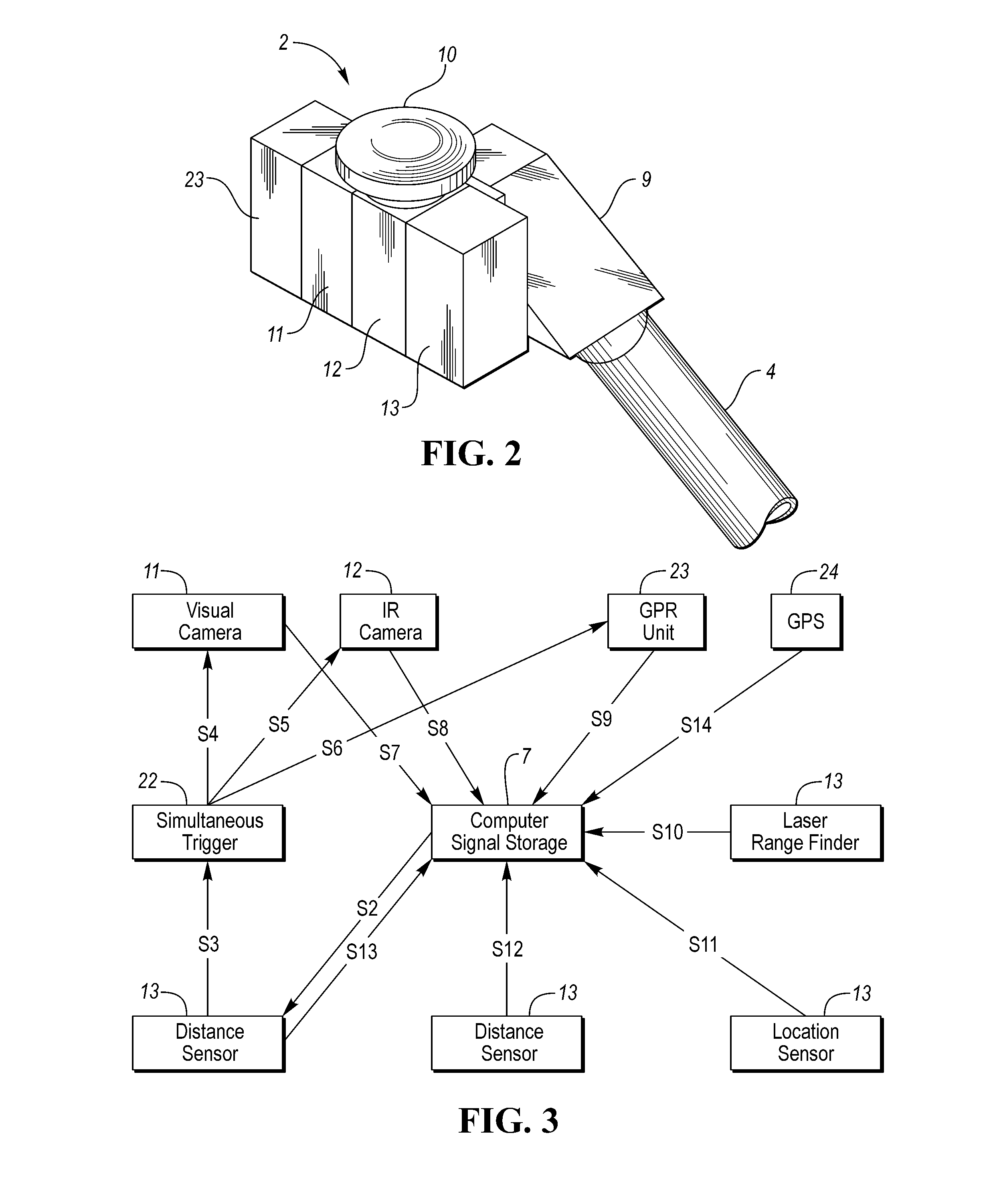
A surface scanning apparatus attached to a movable highway vehicle, mobile equipment or a drone (collectively, “platform”) that passes over a substrate, at least some of the features of which are to be sensed and characterized. The apparatus includes a variously adaptable, complete, and ready to operate packaged kit including configured sensor suites with components selected from the group consisting of a visual scanning sensor; an infra-red scanning sensor; a ground-penetrating radar unit; a laser range finder for sensing elevation of the apparatus above the substrate; a distance sensor for measuring displacement of the apparatus from a point of origin; a position sensing unit for determining a position of the apparatus; a simultaneous trigger mechanism; a structural boom assembly attached to the platform; and a processor for digitally processing measurements and signals collected by one or more of the group of components.
Owner:GSE TECH
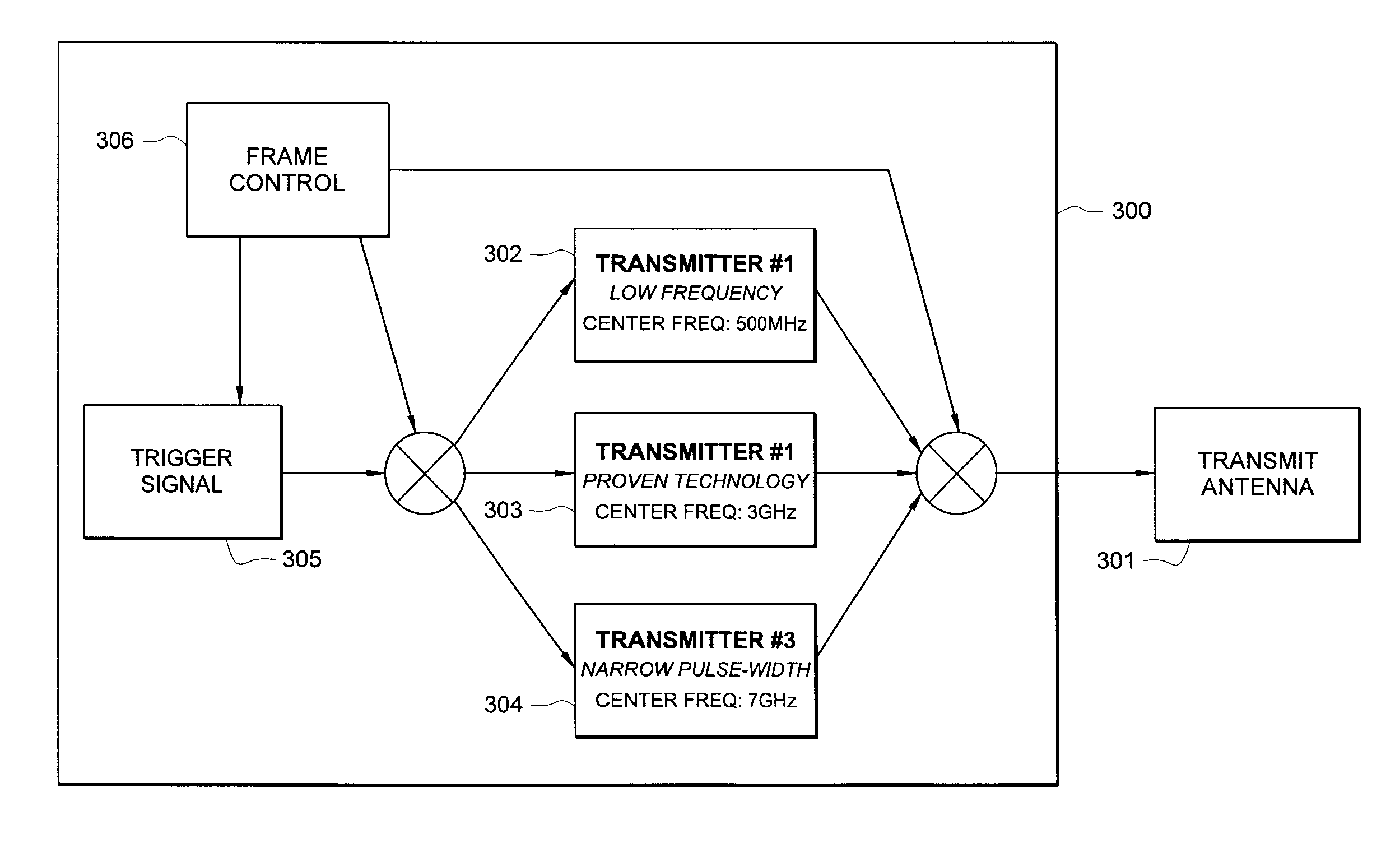
Adjustable pulse width ground penetrating radar
A ground penetrating radar system is described that is able to create both low frequency, wide pulses, and high frequency, narrow pulses, to enable both deep and shallow operation of the ground penetrating radar on demand, including simultaneous operation.
Owner:NIITEK
Land mine detector
A forwarding looking ground penetrating mine detection apparatus includes a radiation source for irradiating a sample of ground suspected of containing at least one mine with a plurality of frequency swept ground penetrating radar signals. A detector receives target signals backscattered from the ground responsive to the radar signal. The detector includes a time-frequency analyzer which transforms the target signals into a time-frequency image representation (TFR). In a preferred embodiment, the detector can include a wavelet packet transformer (WPT) for extracting time-frequency localized information from the TFR in the form of feature set constructed from a wavelet table. The apparatus can also include a data dimensionality reducer for selecting features to form a feature subset from the feature set, preferably based on reference to a training data set. A multilayer neural network classifier can be based on the feature subset, and be adaptable to the surrounding environment through learning.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Precise infrastructure mapping using full-waveform inversion of ground penetrating radar signals
ActiveUS10234552B1Accurate estimateAccurate dataDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFilling materialsFull waveform
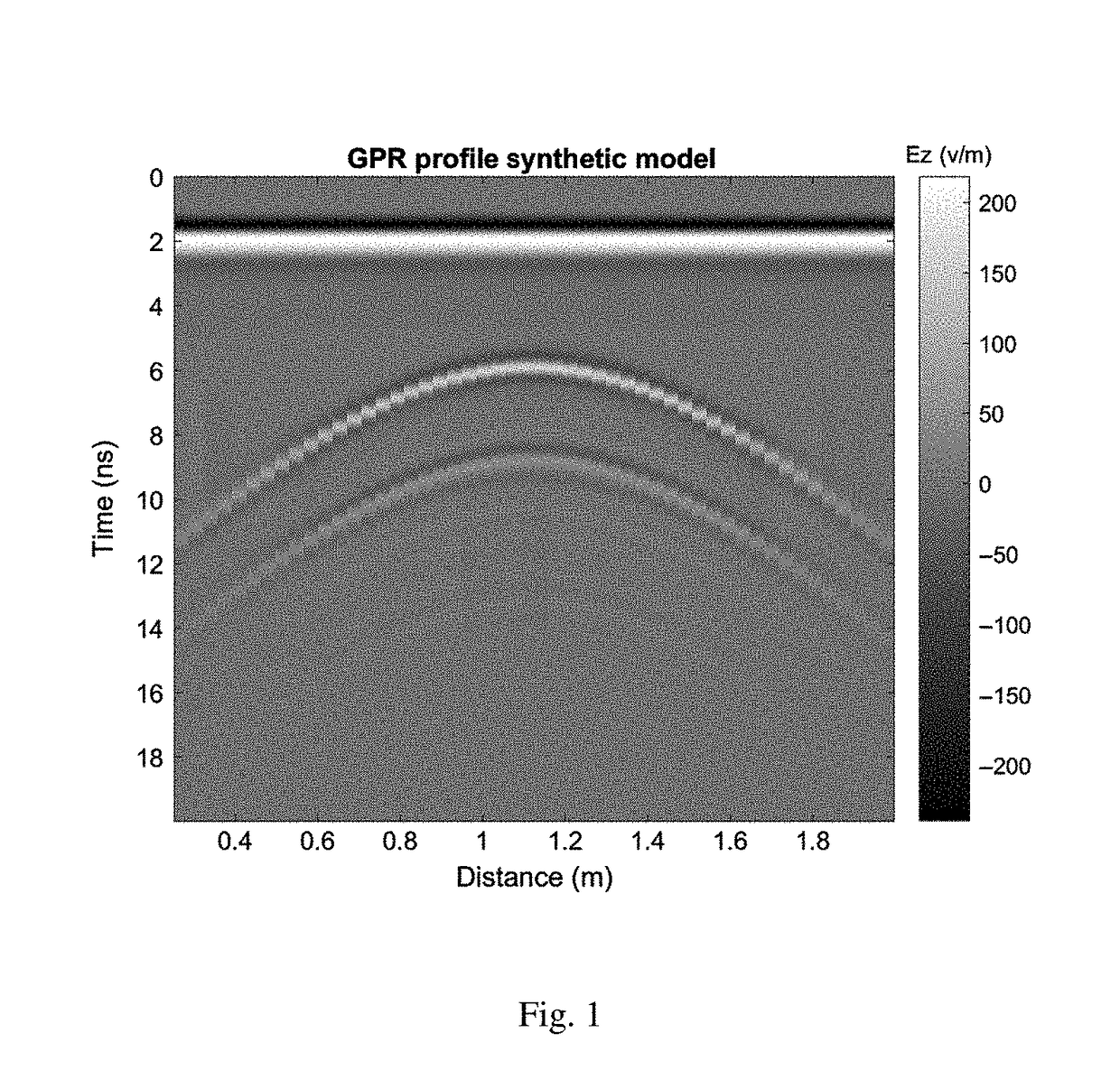
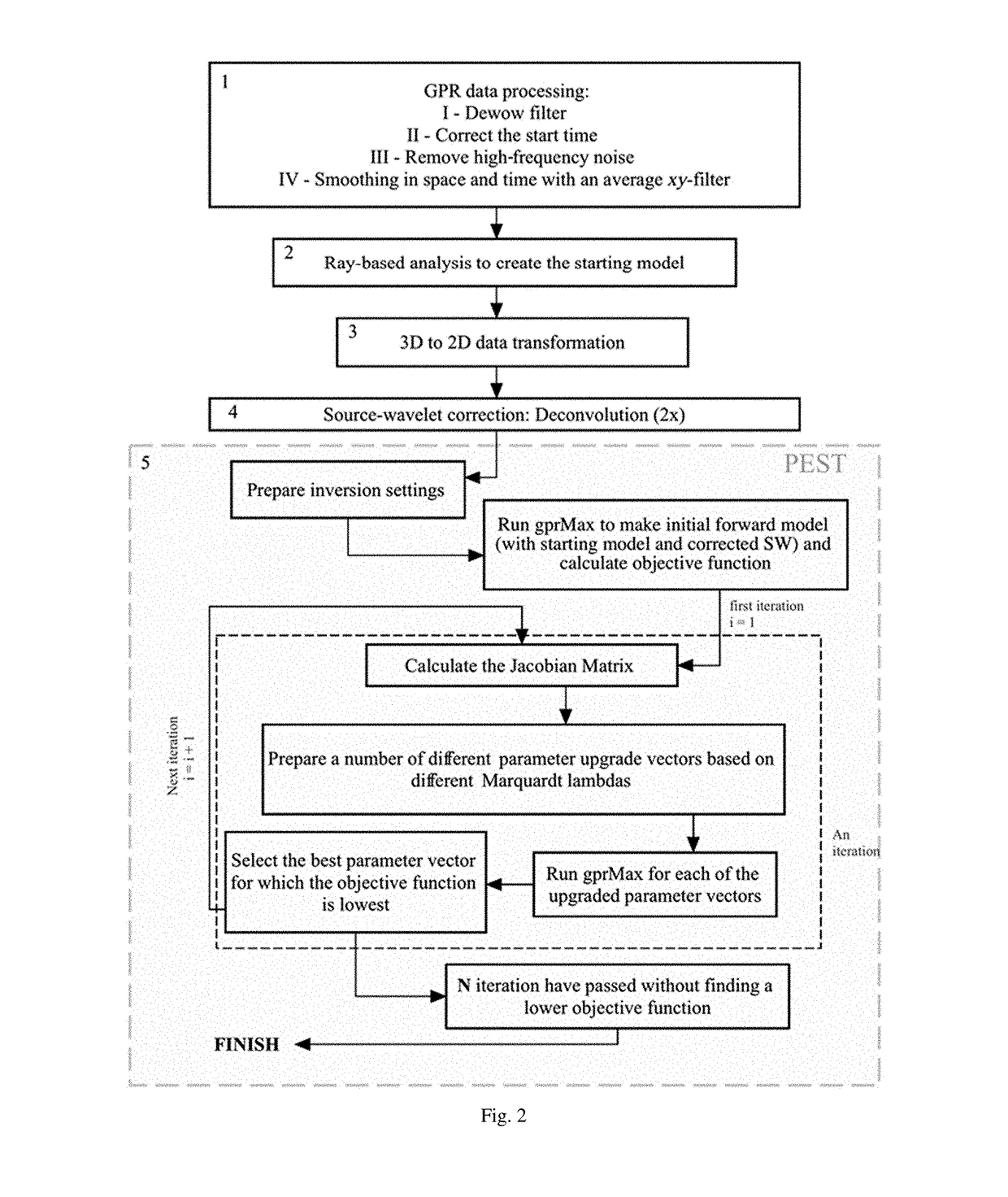
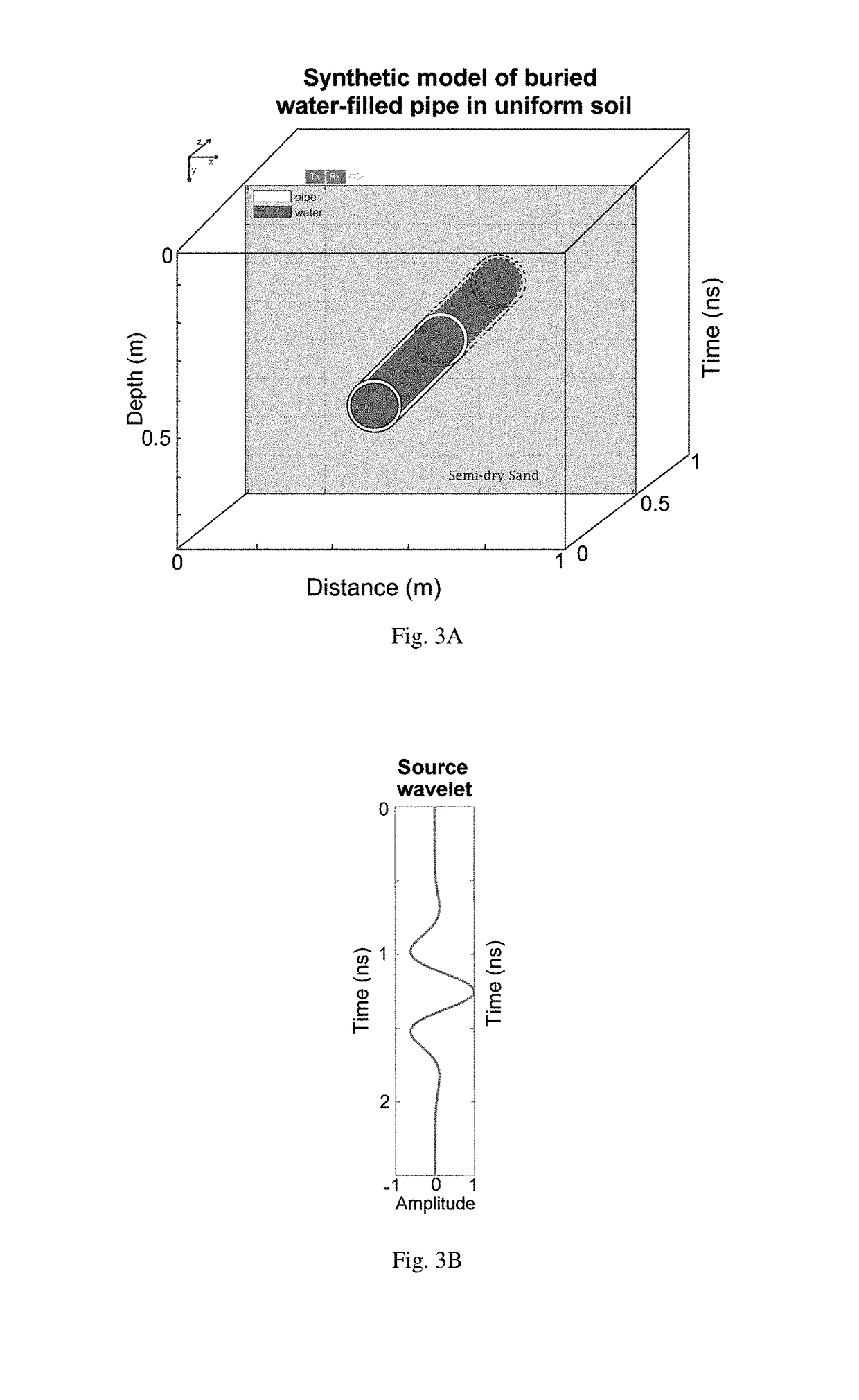
A new method for FWI of common-offset GPR data, particularly targeting the dimensions and infilling material of buried pipes. The method is useful in situation where clear isolated diffraction hyperbolas indicate the presence of a pipe, but pipe dimensions and filling may be unknown. The invention is a method of taking GPR data and applying advanced numerical methods to get the depth and size of an underground pipe in a very accurate manner. An embodiment of the method consists of five main steps: GPR data processing, ray-based analysis to set a good initial model, 3D to 2D transformation of data, effective SW estimation, and FWI.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
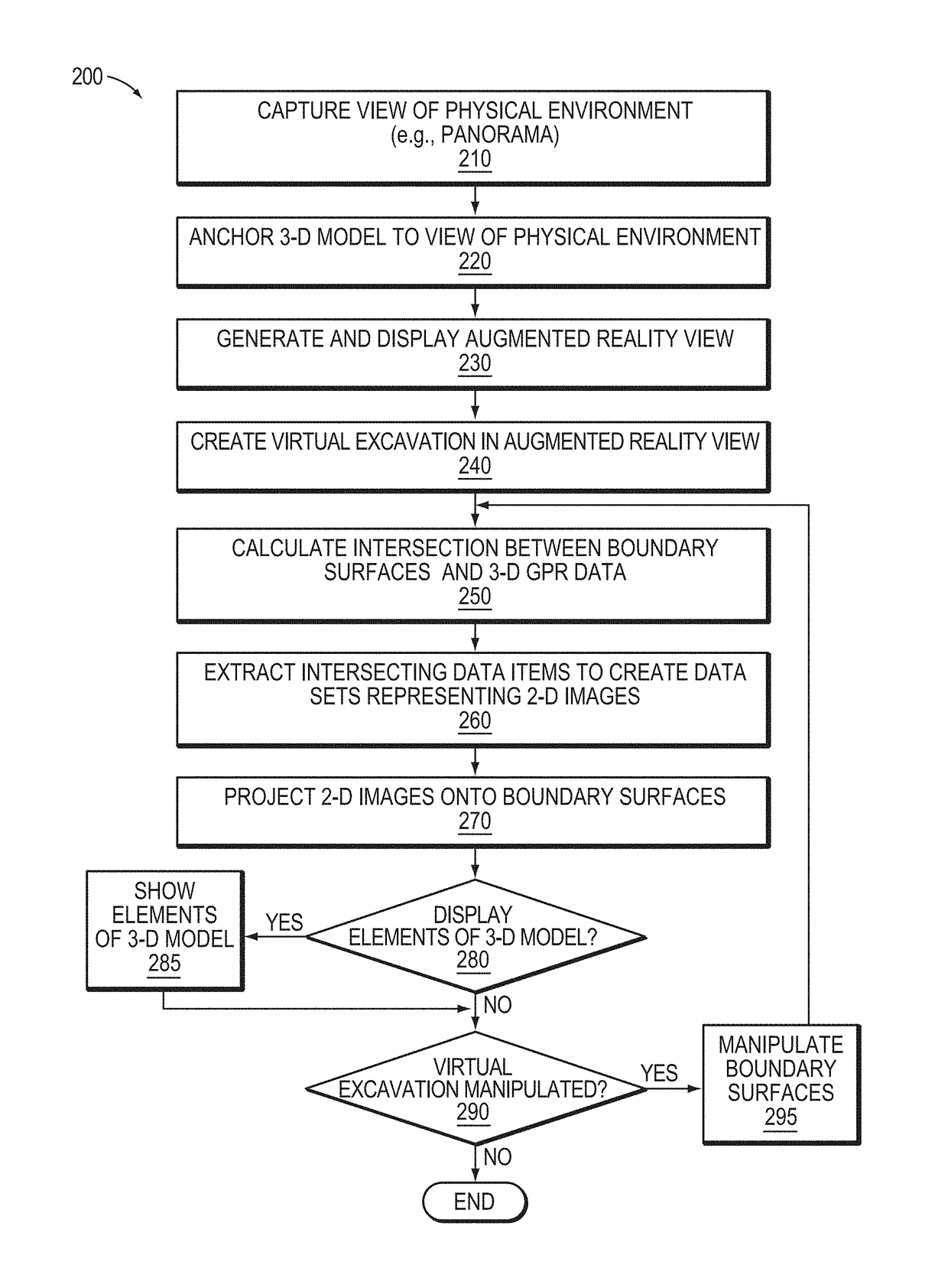
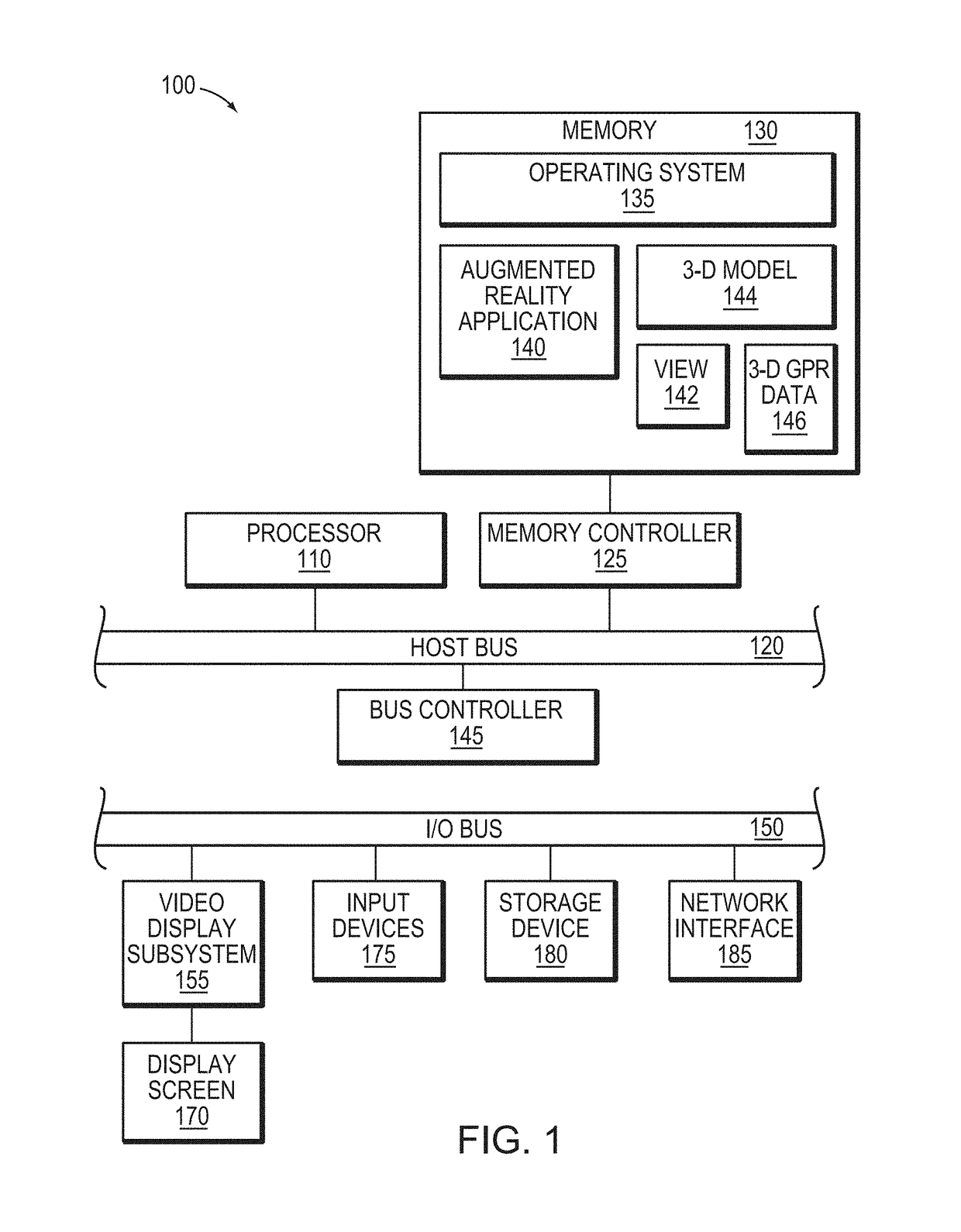
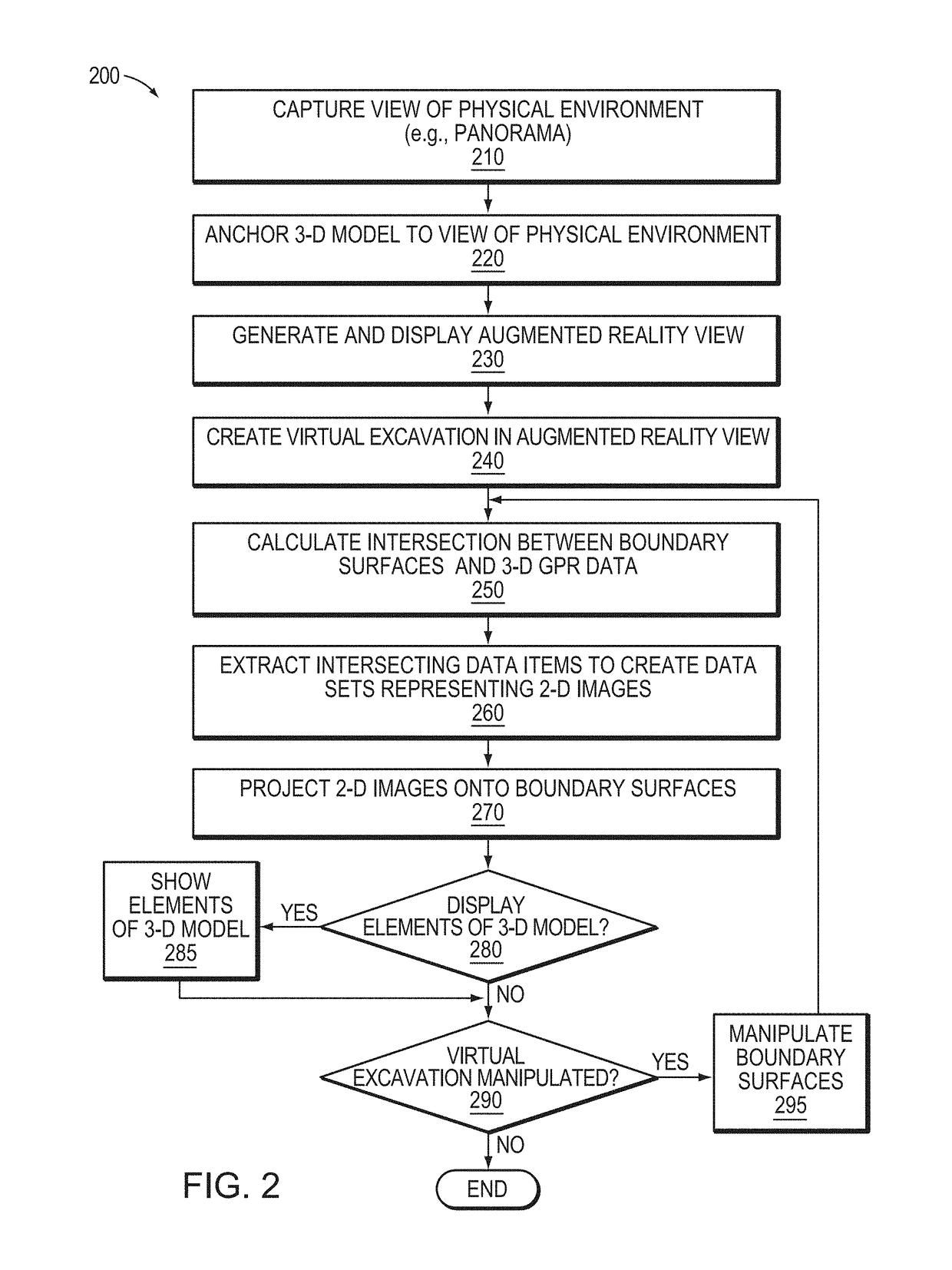
Visualization of 3-D GPR data in augmented reality
In one embodiment, an augmented reality application generates an augmented reality view that displays three-dimensional (3-D) ground penetrating radar (GPR) data on boundary surfaces of a virtual excavation. The augmented reality application calculates an intersection of the one or more boundary surfaces of the virtual excavation and the 3-D GPR data, and extracts data items of the 3-D GPR data that intersect the one or more boundary surfaces of the virtual excavation. The augmented reality application then projects two-dimensional (2-D) images based on the extracted data items onto the one or more boundary surfaces of the virtual excavation to show subsurface features in the augmented reality view that can be manipulated (e.g., moved, rotated, scaled, have its depth changed, etc) by a user.
Owner:BENTLEY SYST INC
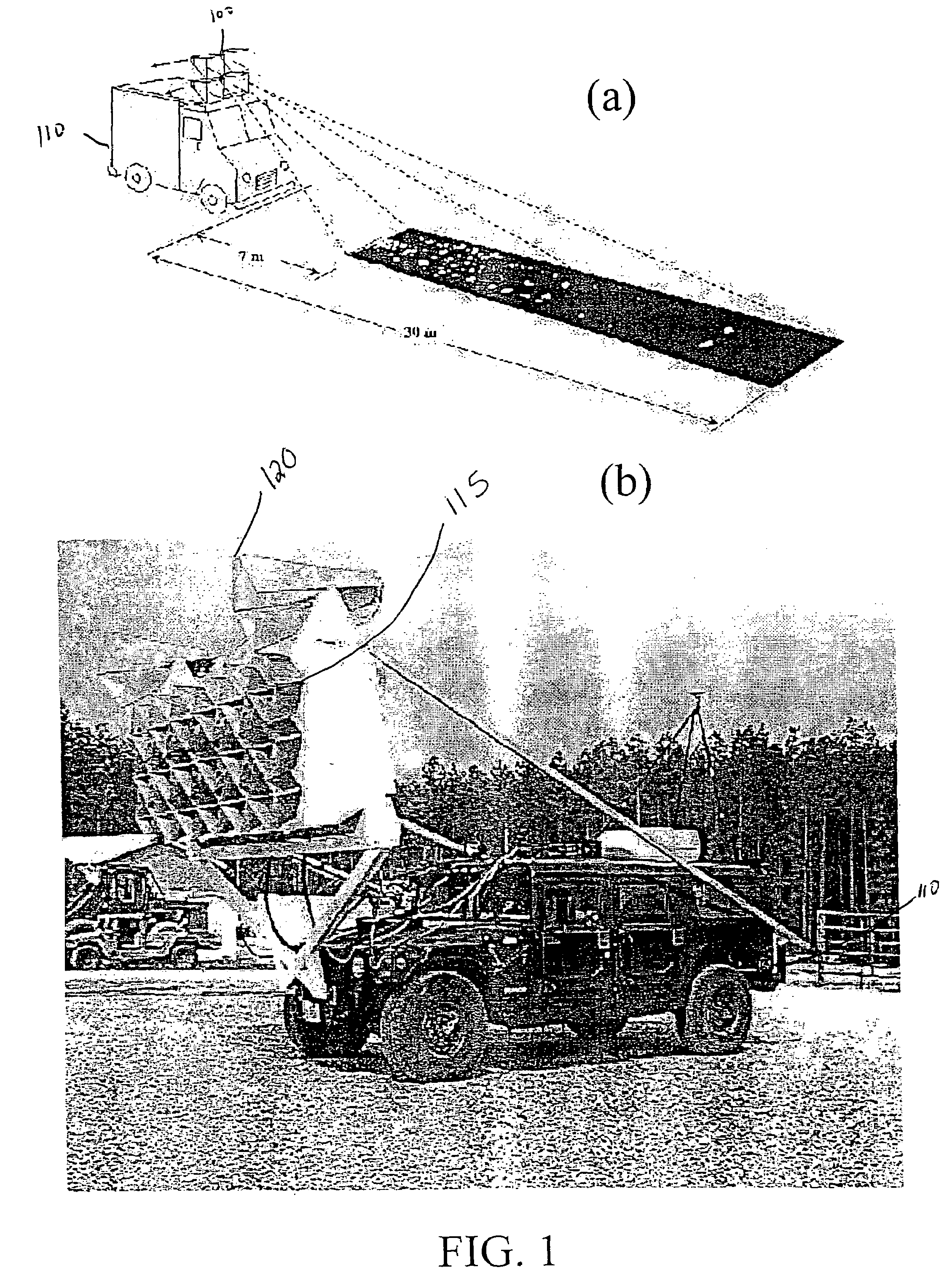
Large area ground monitoring
InactiveUS20140125508A1Improving false positive performanceImprove performanceAntenna arraysAntenna detailsAluminum honeycombGround vehicles
A municipal infrastructure maintenance system uses a ground vehicle to move an antenna array in back-and-forth sweeps over large areas or distances. The antenna array comprises dozens of compartmentalized radio dipole antennas arranged laterally, shoulder-to-shoulder across the width of each sweep. An antenna switch matrix is connected between the antenna array and a ground-penetrating-radar (GPR) set and provides electronic aperture switching and selection, and the ability to laterally register one sweep to the next. The antenna array is extended out in front of the ground vehicle on a pivotable boom, and the cantilevered weight is a primary concern. The antenna array is constructed with aluminum-on-aluminum honeycomb panels slotted and folded around dozens of resistive-card compartment separators. Printed circuit boards with matching baluns are also slotted to receive tabs on the resistive cards, and their dipole elements are resistive loaded to quench crosstalk and near field effects.
Owner:STOLAR
Earth-penetrating radar with inherent near-field rejection
InactiveUS20090167589A1Effective imagingGain to be increasedDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionContinuous waveTransmitter antenna
Owner:STOLAR
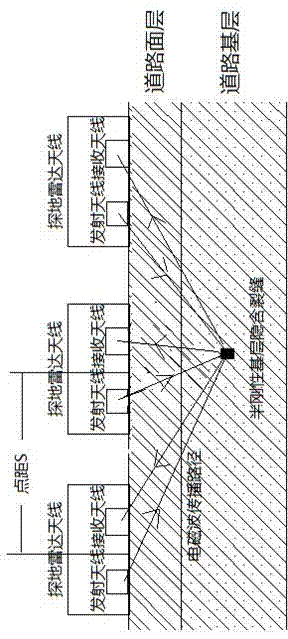
Nondestructive test method for depth and horizontal position of hidden crack of road base
InactiveCN103675920AHigh positioning accuracyPrecise positioningDetection using electromagnetic wavesContinuous measurementRadar
The invention discloses a nondestructive test method for the depth and horizontal position of a hidden crack of the road base. The method comprises that corresponding data images are obtained by continuous measurement via a ground penetration radar and manual spot measurement, the position of the crack is approximately determined, on the basis, the data images are analyzed in an ellipse method to improve the positioning precision, and the length and depth of the crack in the semi-rigid base are accurately positioned. Via continuous measurement based on the ground penetration radar and the manual spot measurement, the error of the obtained horizontal position of the crack of the semi-rigid base reaches 4.4%, and the error of the upper depth of the crack reaches 32%. After data analysis via the ellipse method, the error of the horizontal position of the crack of the semi-rigid base reaches 2.2%, and the error of the upper depth of the crack reaches 22%, wherein the precision of the horizontal position is improved by 2.2%, and the precision of the upper depth of the crack is improved by 10%. Thus, accurate data basis can be provided for crack maintenance, and the nondestructive test method of the invention has significant theoretical and practical values.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Adjustable pulse width ground penetrating radar
A ground penetrating radar system is described that is able to create both low frequency, wide pulses, and high frequency, narrow pulses, to enable both deep and shallow operation of the ground penetrating radar on demand, including simultaneous operation.
Owner:NIITEK
Moving multi-polarization multi-transmitter/receiver ground penetrating radar system and signal processing for buried target detection
InactiveUS9395437B2Enhance signatureQuality improvementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsDiversity scheme
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Method and Apparatus for Detecting Subsurface Targets Using Data Inversion and a Temporal Transmission Line Model
ActiveUS20140240162A1Better target detectionFew false alarmGeological detection using milimetre wavesDetection using electromagnetic wavesVariation of parametersGround penetration radar
A method and apparatus for detects one or more subsurface targets by receiving a reflectivity data from two or more subsurface reflectors using a ground penetrating radar. The two or more subsurface reflectors may include the one or more subsurface targets and a medium surrounding the one or more subsurface targets. An impedance data for the two or more subsurface reflectors is calculated by inverting the reflectivity data using a temporal transmission line model with a “layer-peeling” method. One or more constitutive parameters of the two or more subsurface reflectors are calculated based on the impedance data. The one or more subsurface targets are detected based on a change in the one or more constitutive parameters.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Apparatus and method for determining defects in dielectric materials and detecting subsurface objects
ActiveUS20190064362A1Efficient integrationElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGround penetration radarVehicle control
An apparatus travels within a 3-dimensional space collecting data that may be used to expose defects in structures and objects beneath the ground surface. In a preferred embodiment, the apparatus includes an unmanned aerial vehicle controlled by a user. The apparatus carries LIDAR and ground penetrating radar and correlates data received from both to facilitate displaying a map with data superimposed on it representing locations of defects in structures and buried objects.
Owner:SCOTT MICHAEL LEON
System and methods for obtaining ground conductivity information using GPR data
InactiveUS20050078028A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceDetection using electromagnetic wavesGround conductivityAtmospheric sciences
A method for inferring information about the conductivity of a medium from ground penetrating radar (GPR) data using a calculated effective penetration limit of the GPR system, including various methods for calculating the effective penetration limit.
Owner:CIST DAVID B
Earth-penetrating radar with inherent near-field rejection
InactiveUS7548181B1Efficient earth-penetrating imagingHigh gainDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionContinuous wavePeak value
A ground-penetrating radar comprises a transmitter for launching pairs of widely separated and coherent continuous waves. Each pair is separated by a different amount, such as 10 MHz, 20 MHz, and 30 MHz. These are equivalent to modulation that have a phase range that starts at 0-degrees at the transmitter antenna which is near the ground surface. Deep reflectors at 90-degrees and 270-degrees will be illuminated with modulation signal peaks. Quadrature detection, mixing, and down-conversion result in 0-degree and 180-degree reflections effectively dropping out in demodulation.
Owner:STOLAR
Systems and methods for detecting soil characteristics
InactiveCN105246319AWatering devicesMaterial analysis using microwave meansSoil characteristicsSoil science
Owner:ELWHA LLC
SAR autofocus for ground penetration radar
ActiveUS20140015710A1Improve errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarAutofocus
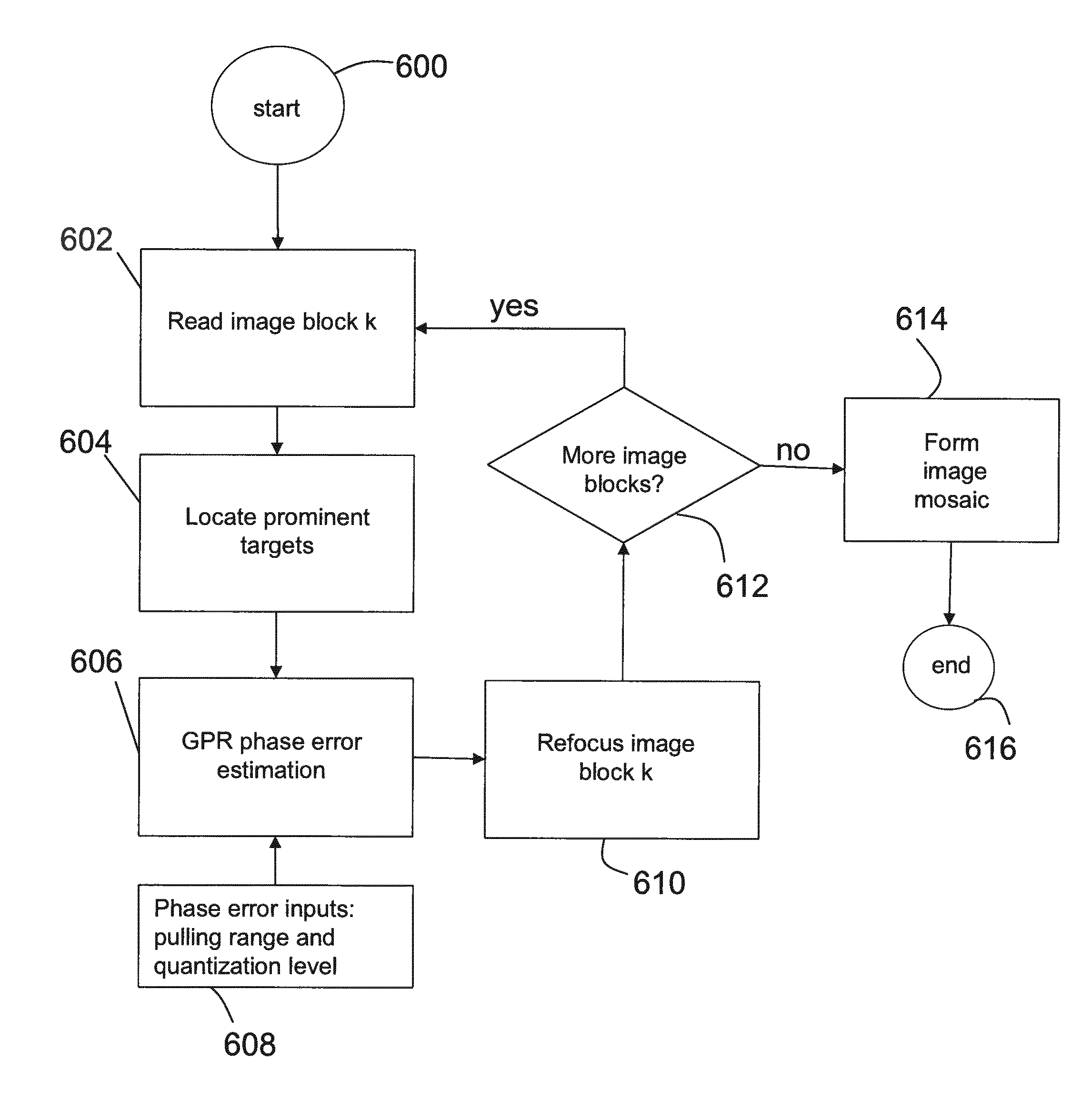
A method of synthetic aperture radar autofocus for ground penetration radar (100). The method includes transmitting a signal via an antenna (102); receiving a reflected signal comprising a plurality of image blocks via the antenna (102); reading each image block from the reflected signal (602) via a processor (108); locating prominent targets in each image block (604) via the processor (108); estimating ground penetration phase error (606) via the processor (108) in each image block via phase error inputs (608) including pulling range and quantization level by generating a 1D phase error (706) and converting the 1D phase error into a 2D phase error of an image spectra (708); refocusing each image block according to estimated ground penetration phase error for that image block (610) via the processor (108); and forming an image mosaic comprising each refocused image block (614) via the processor (108).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and system for characterization of subsurface cavities using joint inversion of gravity and ground penetrating radar data
InactiveUS20160313443A1Gravitational wave measurementDetection using electromagnetic wavesGround penetration radarGravitation
A system and associated methodology determines the porosity and water saturation of a cavity using a joint inversion of gravity and ground penetrating radar data. The system exhibits high accuracy. In one embodiment, the cavity is spherical.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
System and method for detecting, locating and identifying objects located above the ground and below the ground in a pre-referenced area of interest
The invention relates to a system and method for detecting, locating and identifying objects located above ground or below ground in an area of interest, comprising an airborne vehicle which circumscribes the area of interest and which includes a built-in radar having an antenna with a respective transmitter and receiver, signal-processing means, data-storage means and graphical interface means. According to the invention, the area of interest has been pre-referenced and the radar is a heterodyne ground penetration radar (GPR). The signal transmitted by the antenna generates a beam that illuminates a strip of earth, consisting of a sinusoidal electromagnetic signal having a frequency that is varied in precise pre-determined progressive steps. This signal is mixed with the received (reflected) signal, thereby producing two sets of values corresponding to the phases of each frequency step or stage. Said sets of values, which are obtained throughout successive sweeps (as the antenna moves), are stored in the storage means and subsequently processed in the processing means in order to obtain a final map or image of the location of the objects above ground or below ground.
Owner:PONTIFISIA UNIVERSIDAD KATOLIKA DE CHILE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com