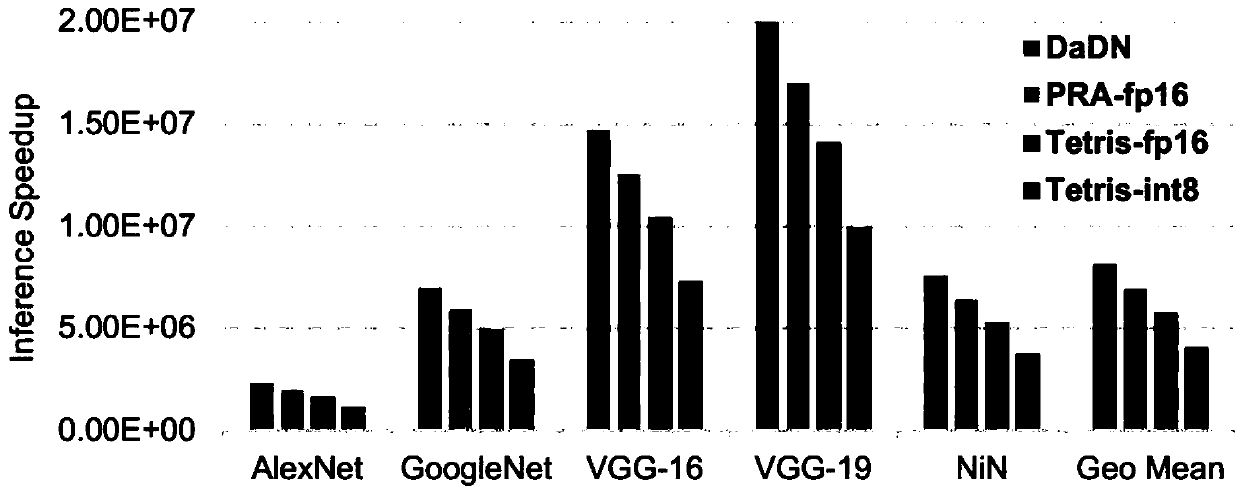
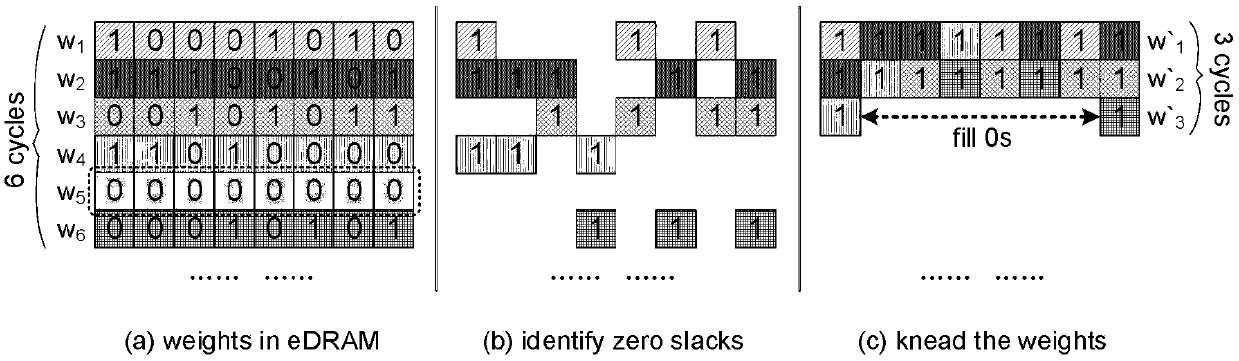
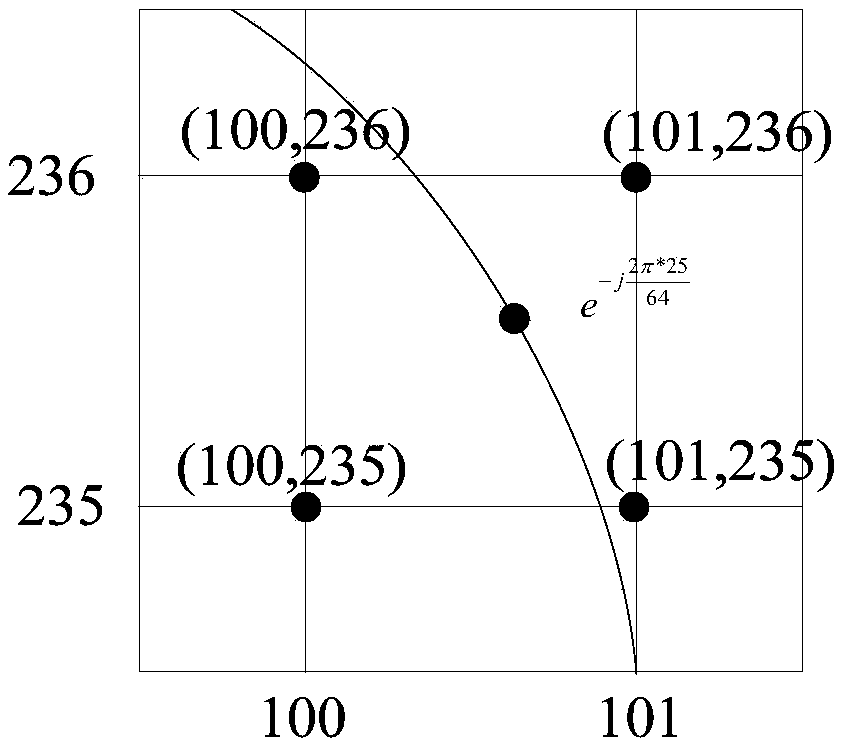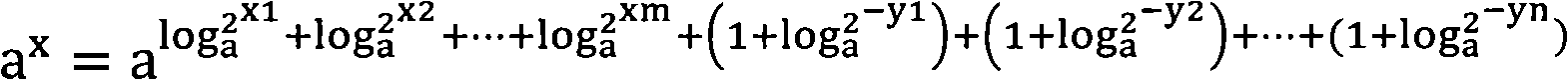Patents
Literature
36 results about "Shift-and-add" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
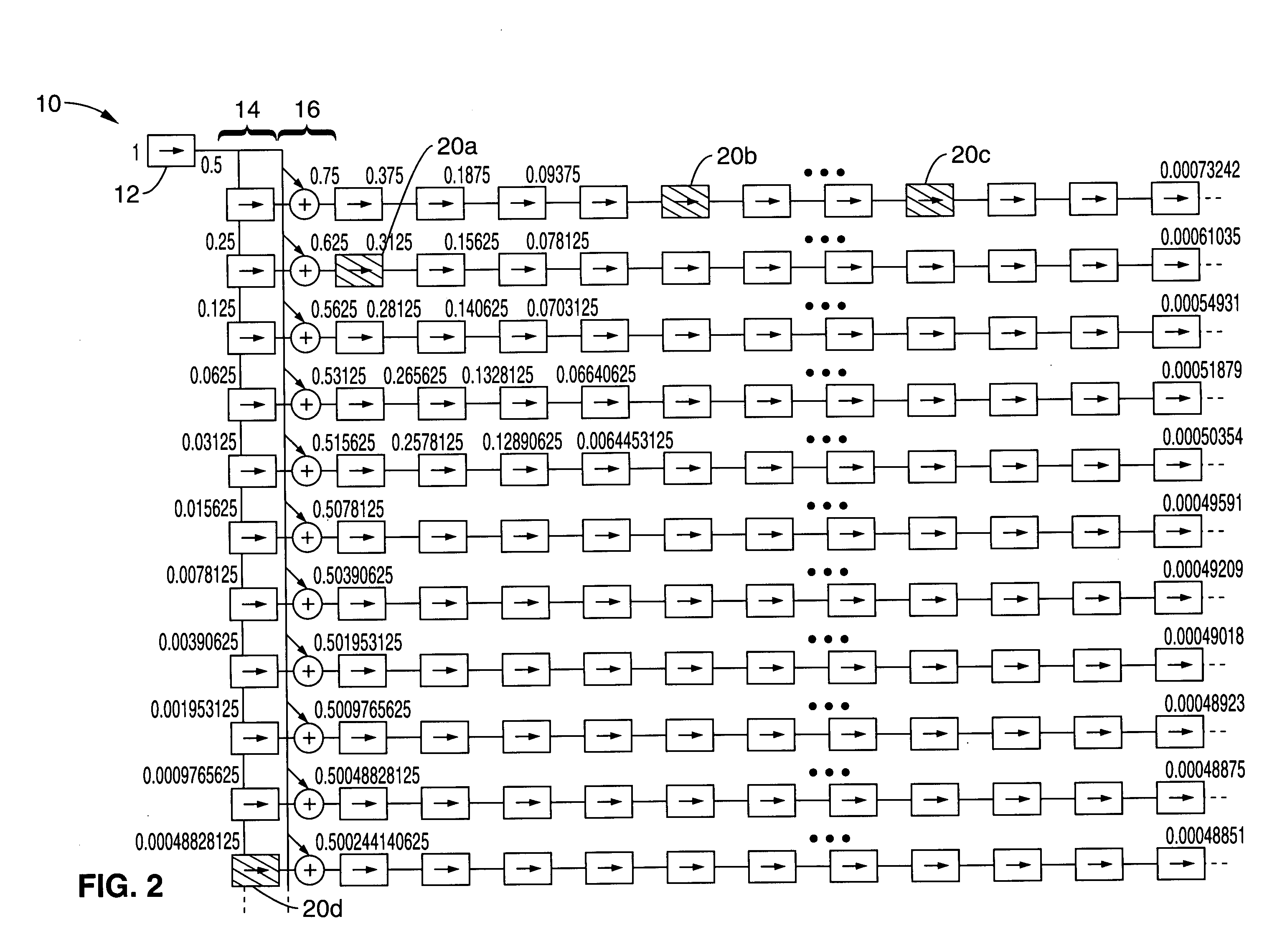
The shift-and-add method (more recently "image-stacking" method) is a form of speckle imaging commonly used for obtaining high quality images from a number of short exposures with varying image shifts. It has been used in astronomy for several decades, and is the basis for the image stabilisation feature on some cameras. The method involves calculation of the differential shifts of the images. This is easily accomplished in astronomical images since they can be aligned with the stars. Once the images are aligned they are averaged together. It is a basic principle of statistics that variation in a sample can be reduced by averaging together the individual values. In fact, when using an average, the signal-to-noise ratio should be increased by a factor of the square root of the number of images. A number of software packages exist for performing this, including IRAF, RegiStax, Autostakkert, Keiths Image Stacker, Hugin, and Iris.
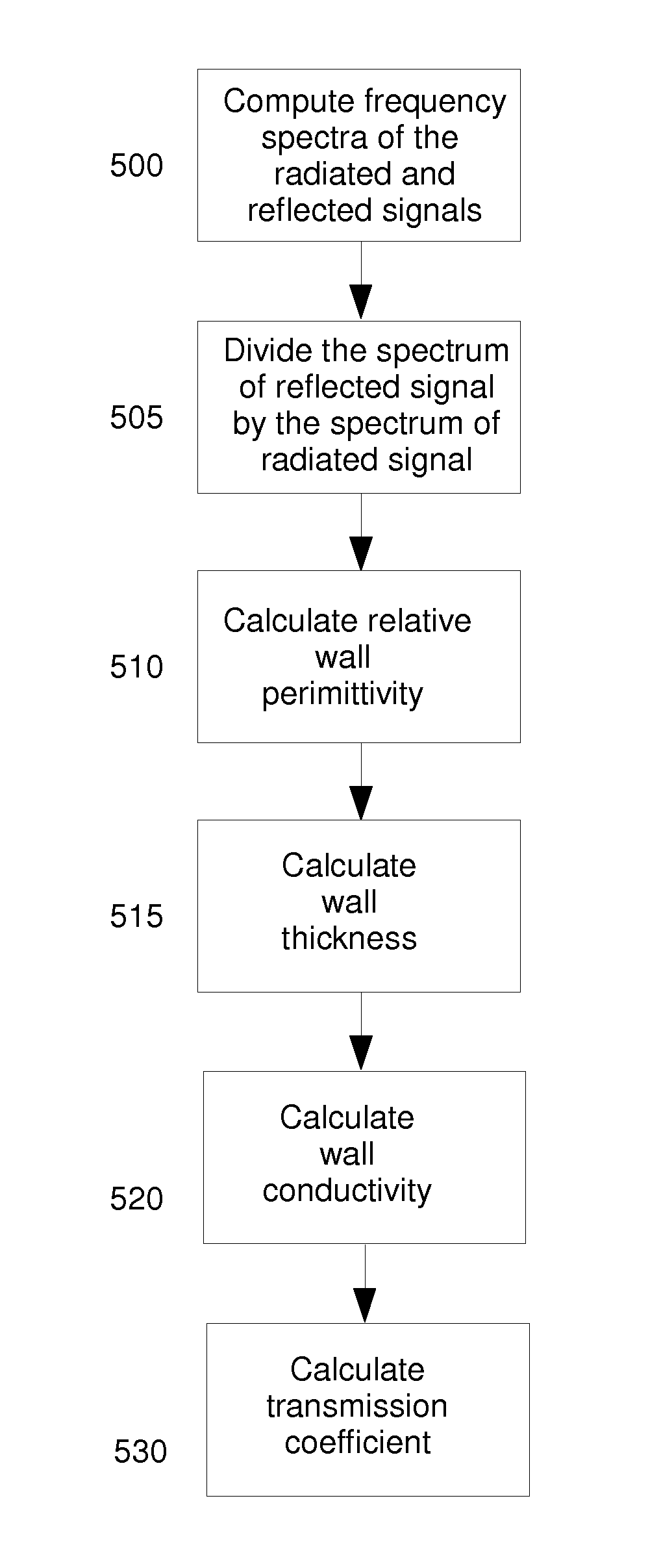
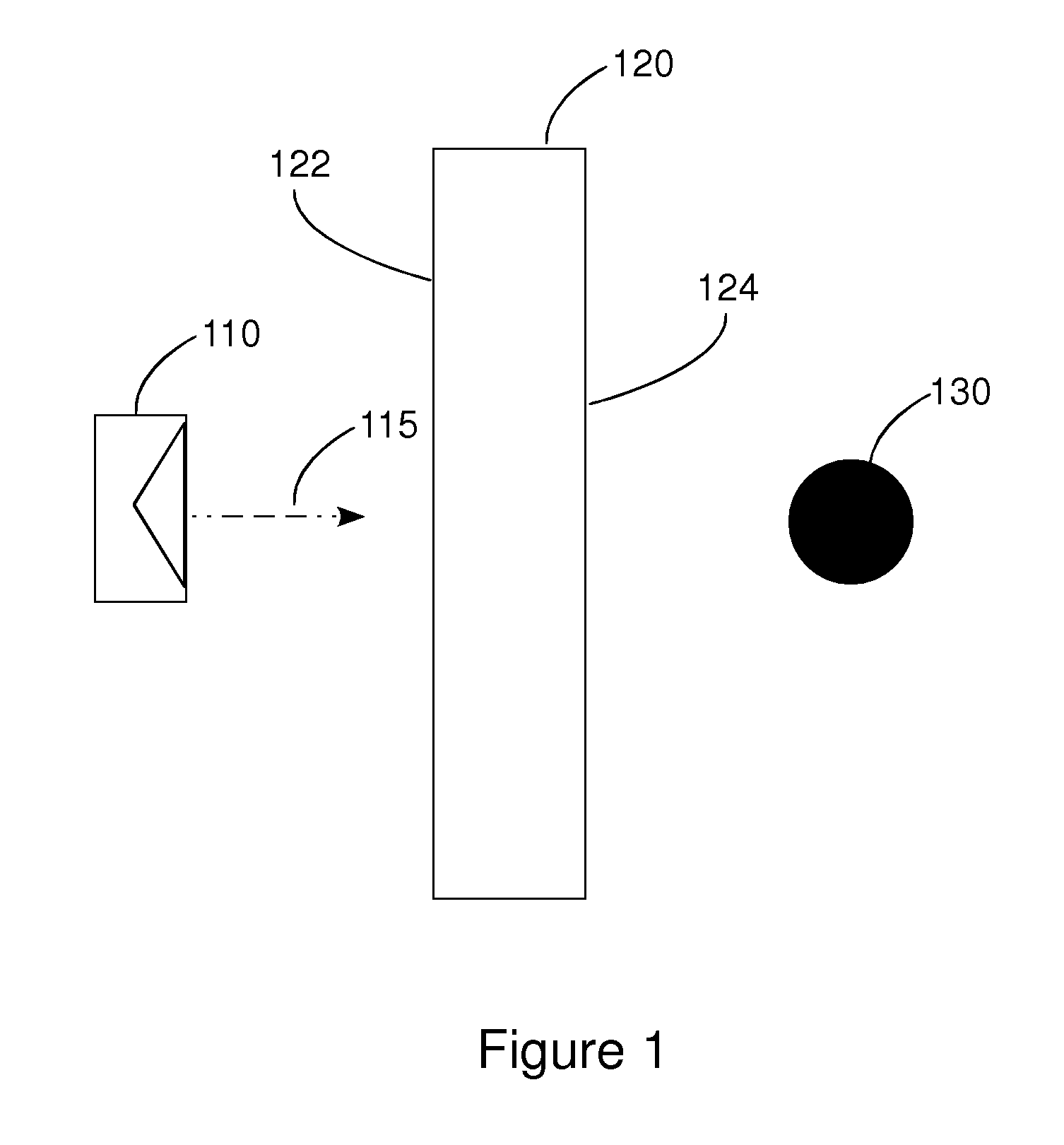
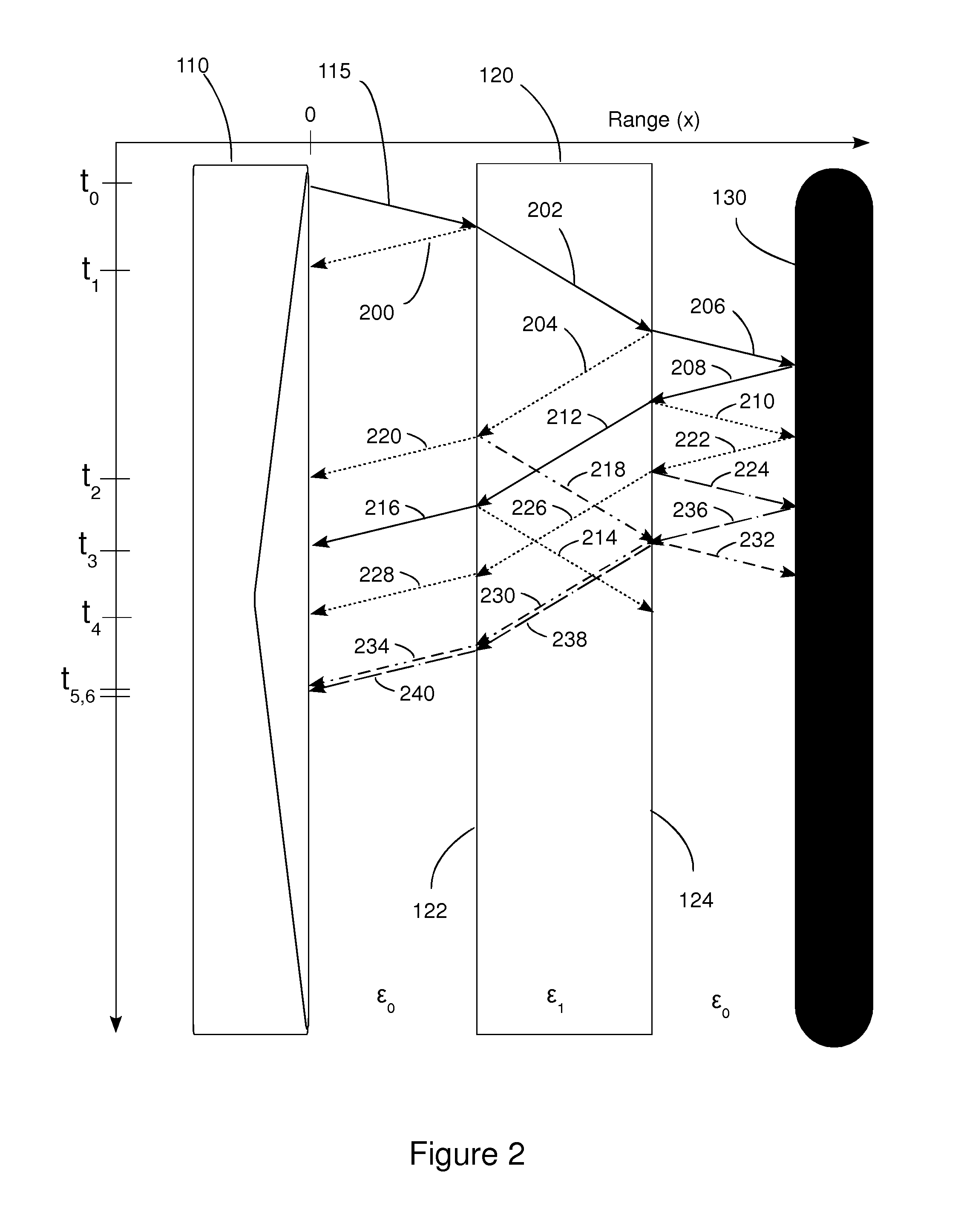
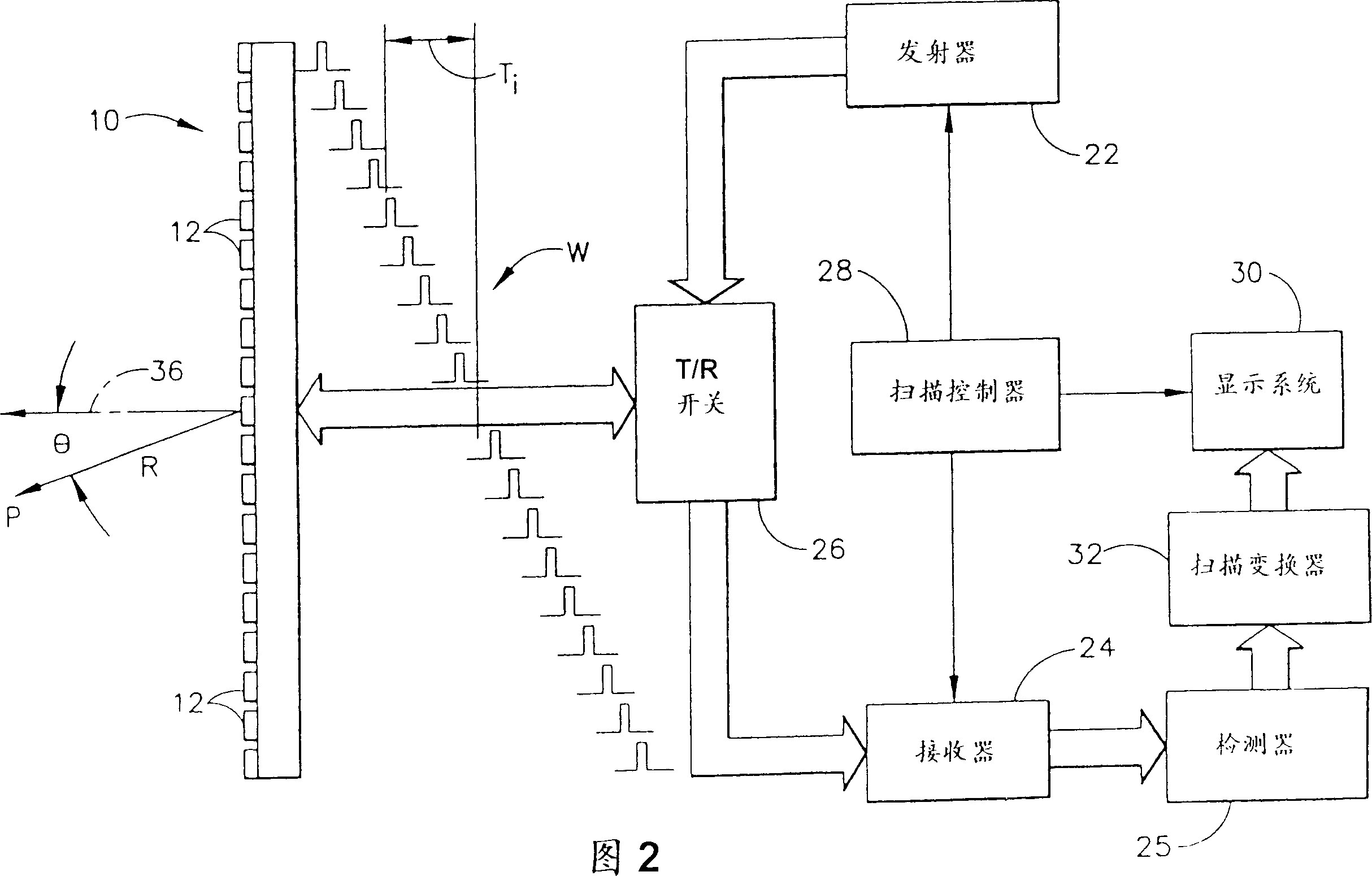
Method and apparatus for through the wall radar imaging
InactiveUS20120235849A1Reduce componentsCompensation DistortionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandTime domain
The present invention comprises a method for through the wall radar imaging. An impulse synthetic aperture radar system transmits short, ultra-wideband carrierless microwave pulses at an obstacle behind which a target of interest is located. The return signals are received, stored and analyzed. Portions of the return signals that represent reflections from the obstacle are identified and analyzed in the time domain to estimate the transmission coefficient of the wall, either by estimating wall parameters or by using a novel shift and add procedure. The estimated transmission coefficient is used to filter the received signals to reduce the components of the received signal that are generated by the obstacle, and to compensate for distortion caused by the obstacle in the portions of the transmitted signal that are reflected by the target and returned, through the obstacle, to the radar system.
Owner:TATOIAN JAMES Z +1
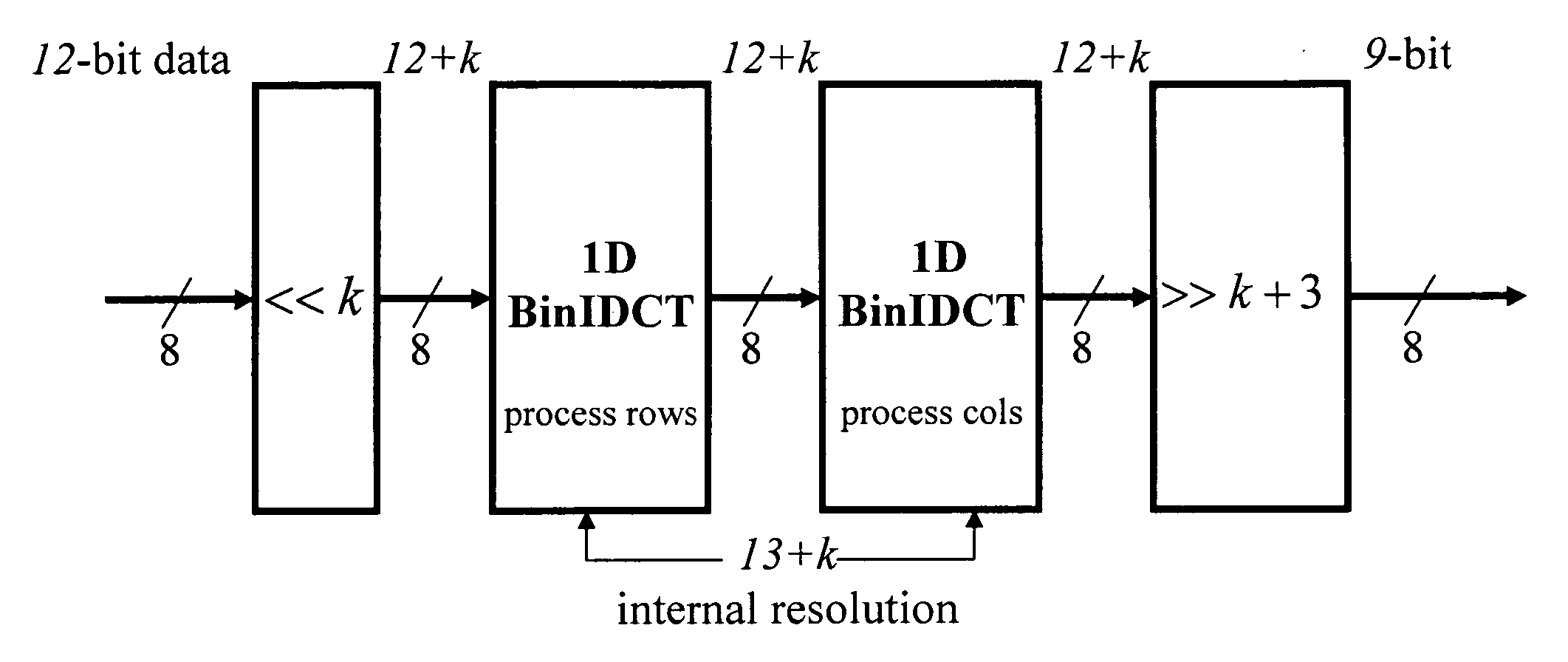
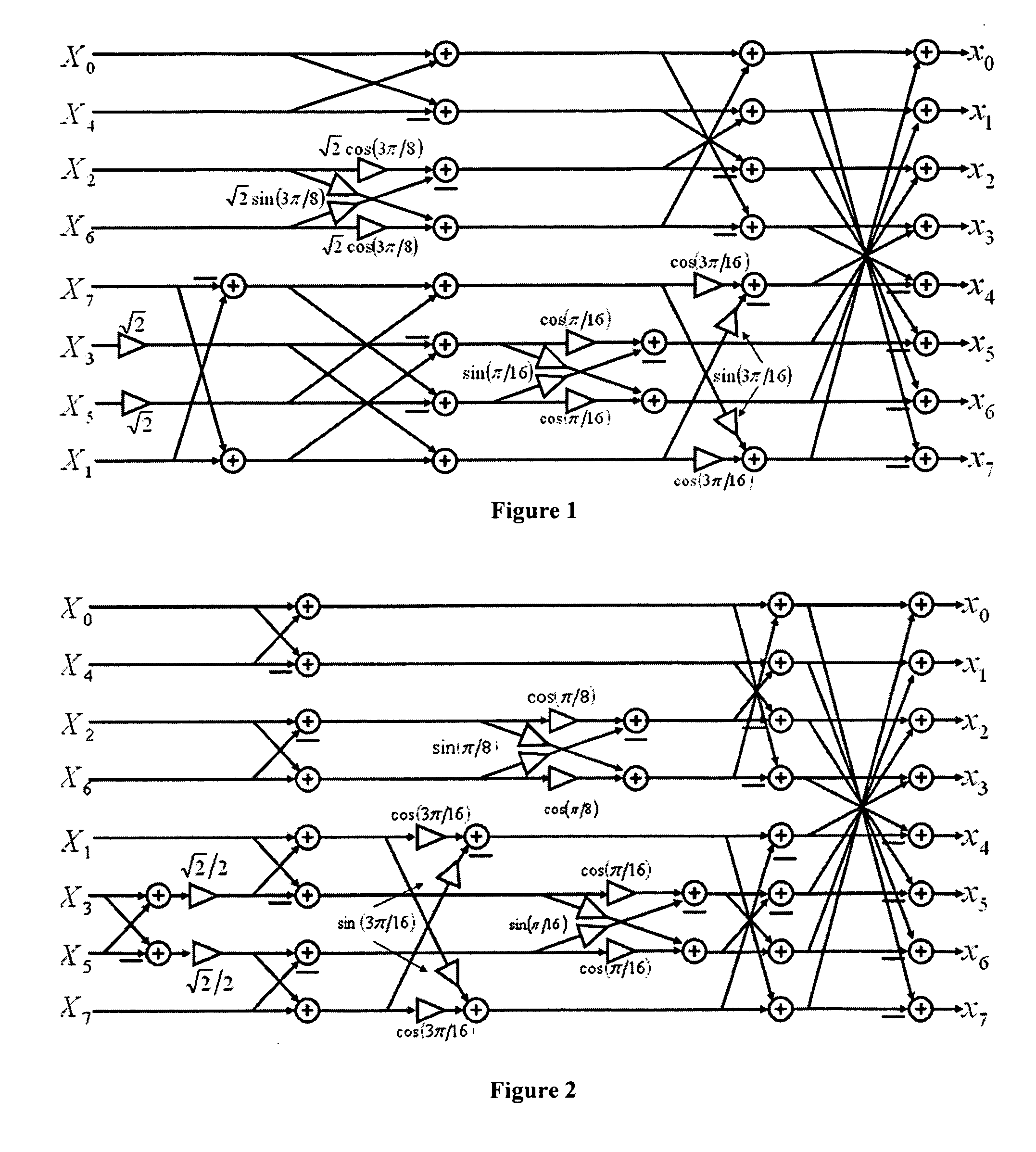
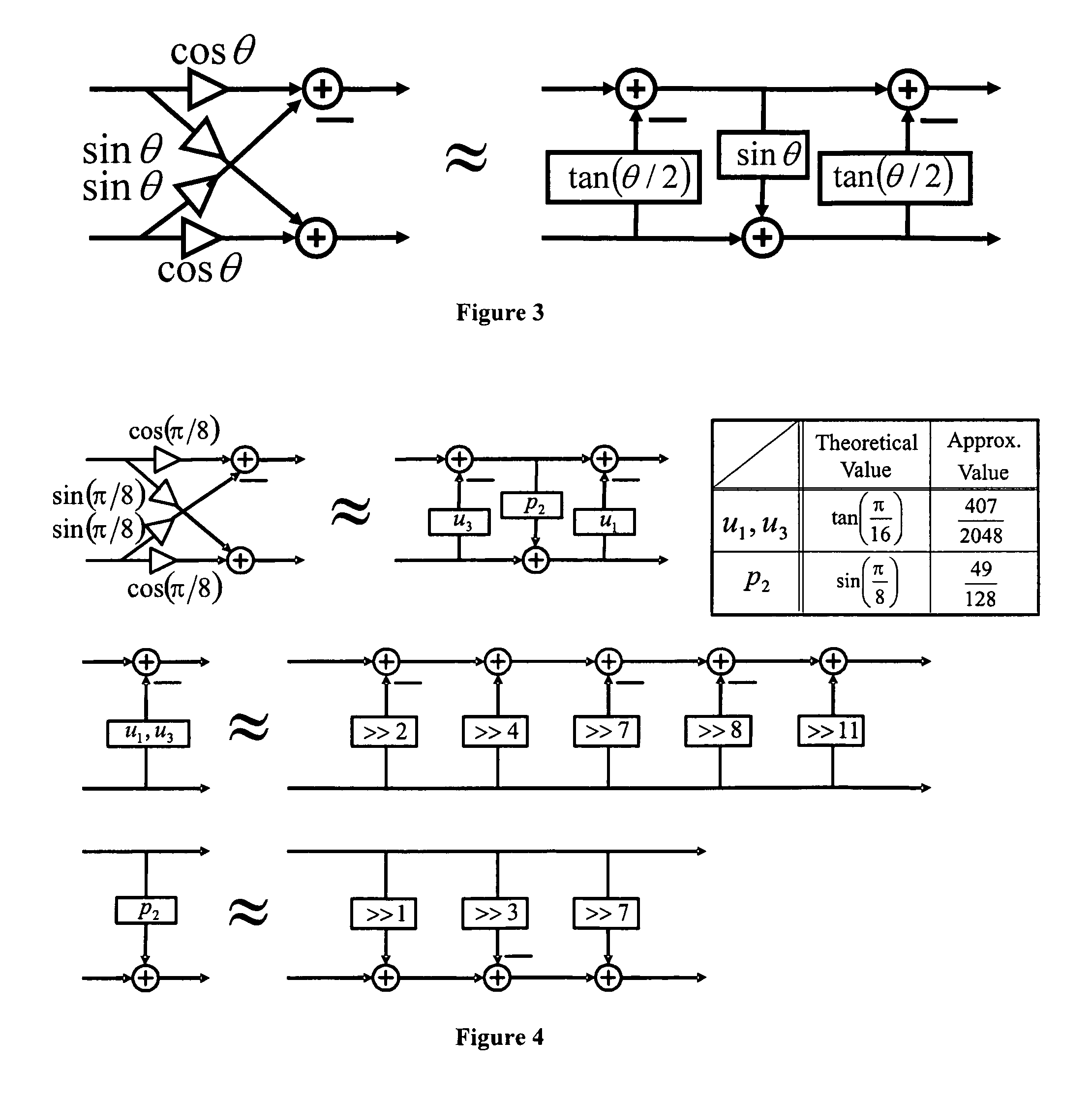
Fast multiplierless integer invertible transforms
ActiveUS20070196025A1Satisfactory compatibilityFast and efficient multiplierless hardware implementationCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationExtensibilityShift-and-add
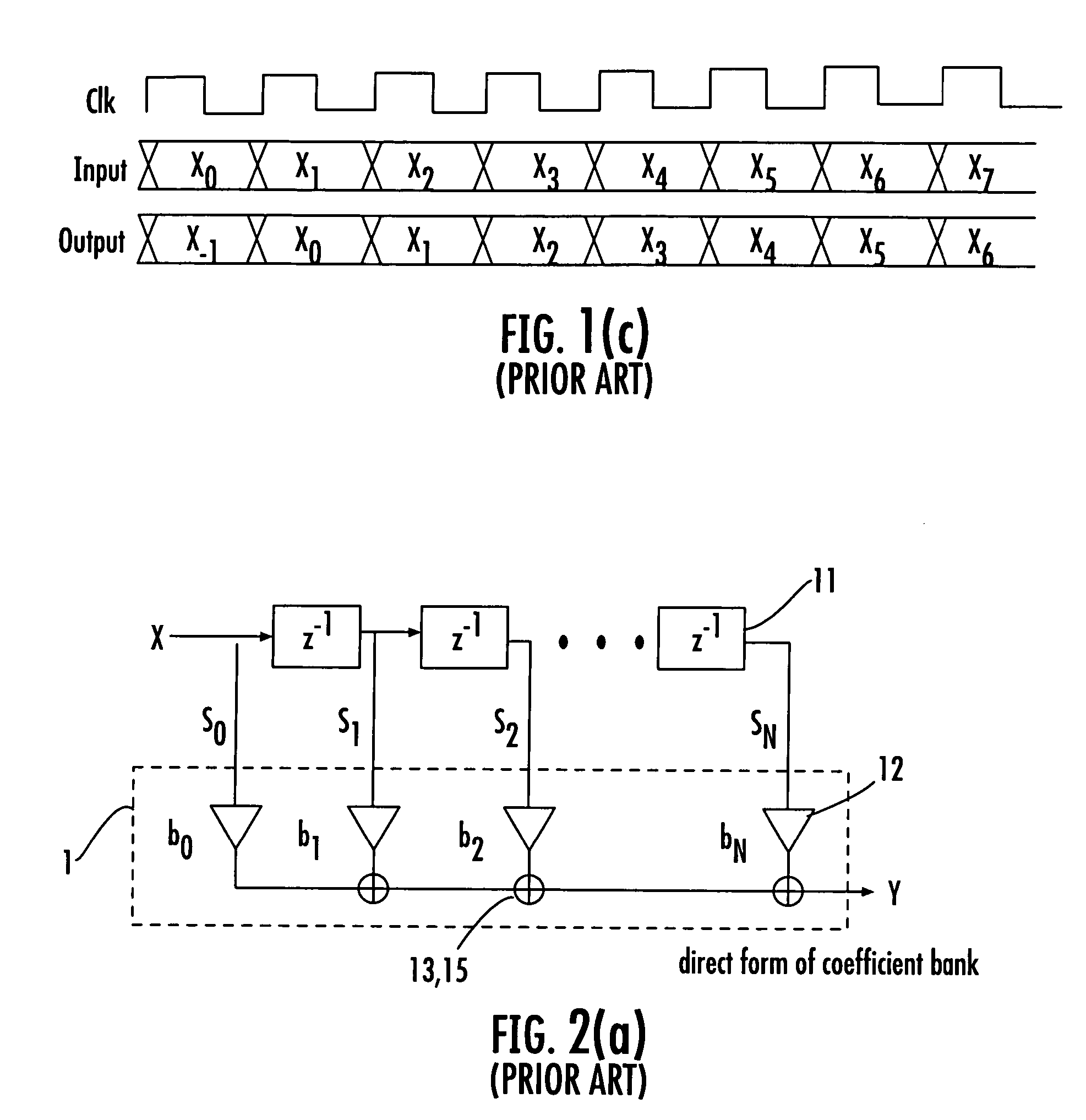
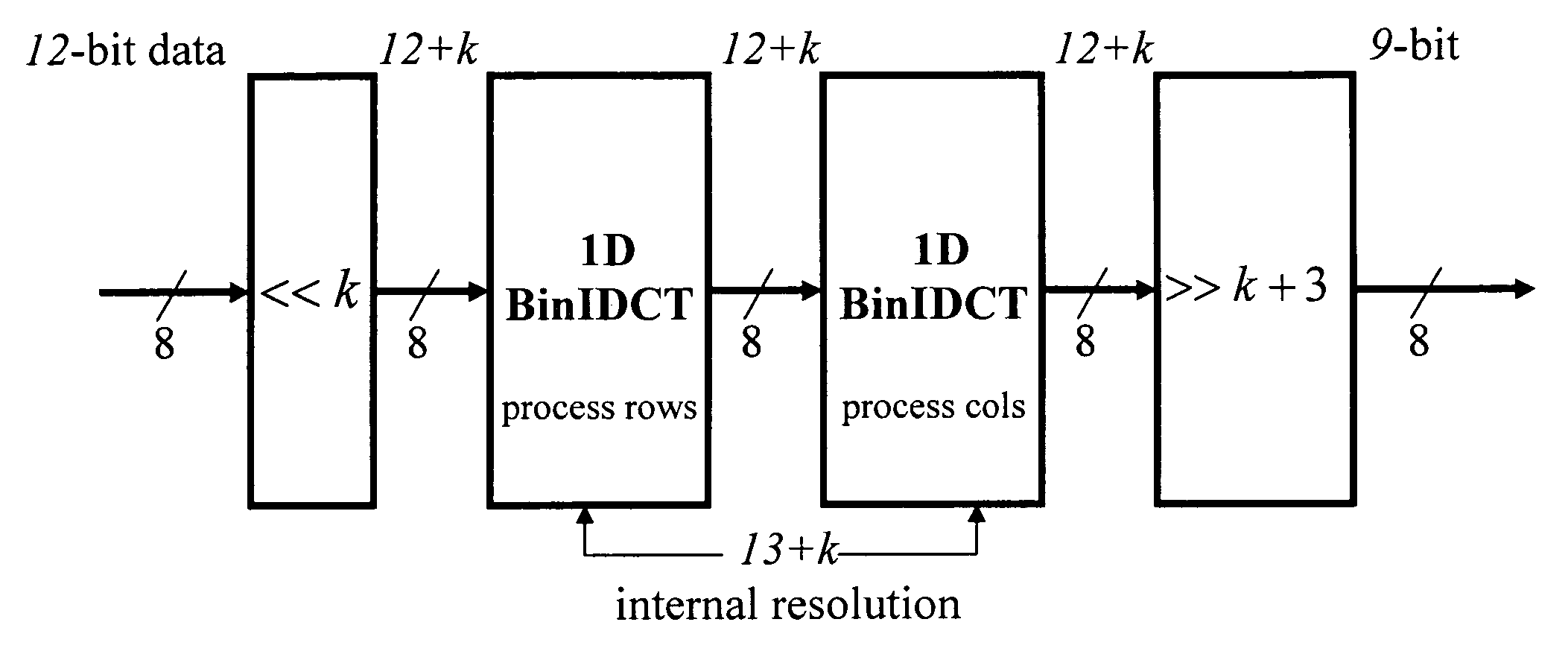
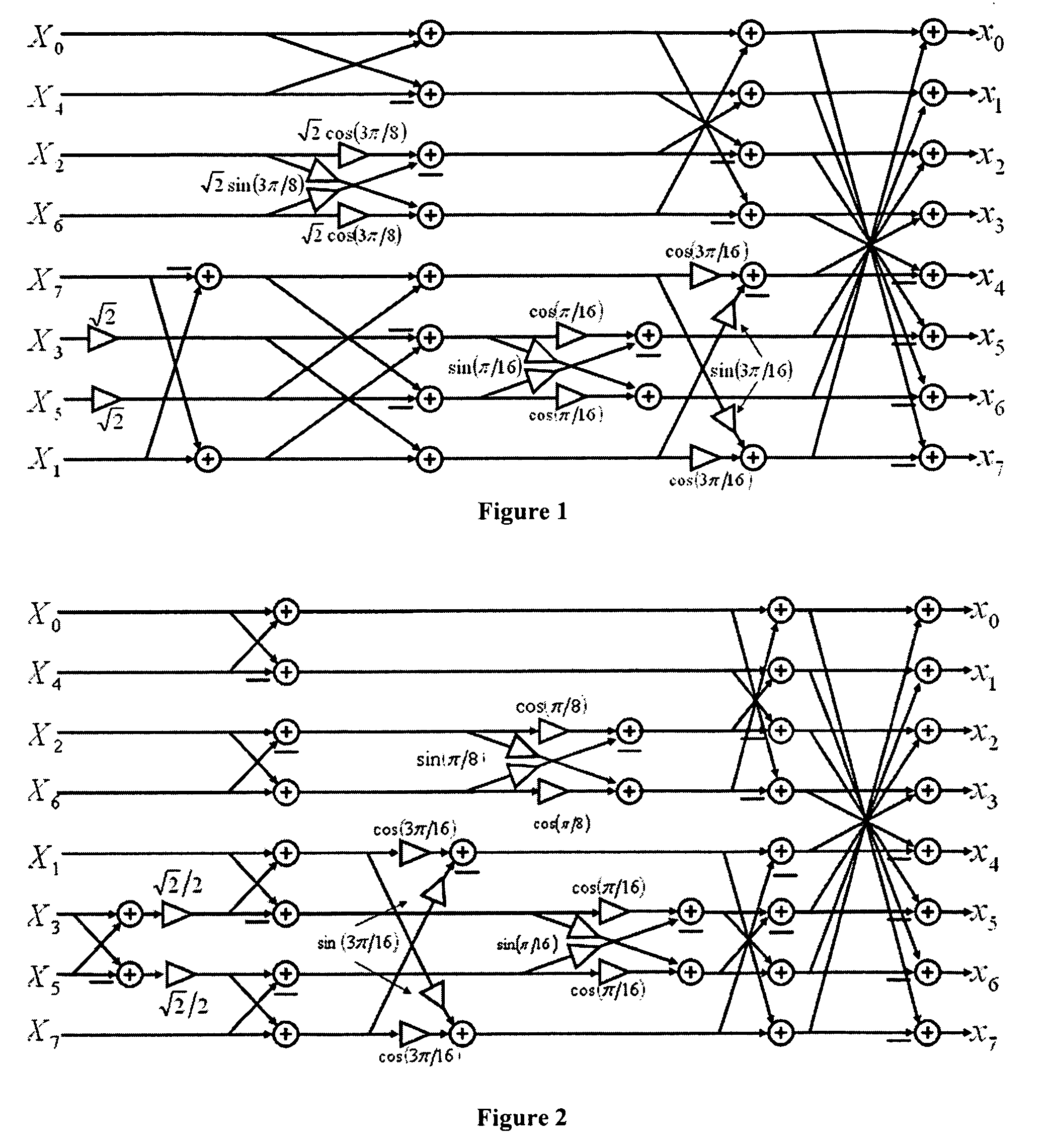
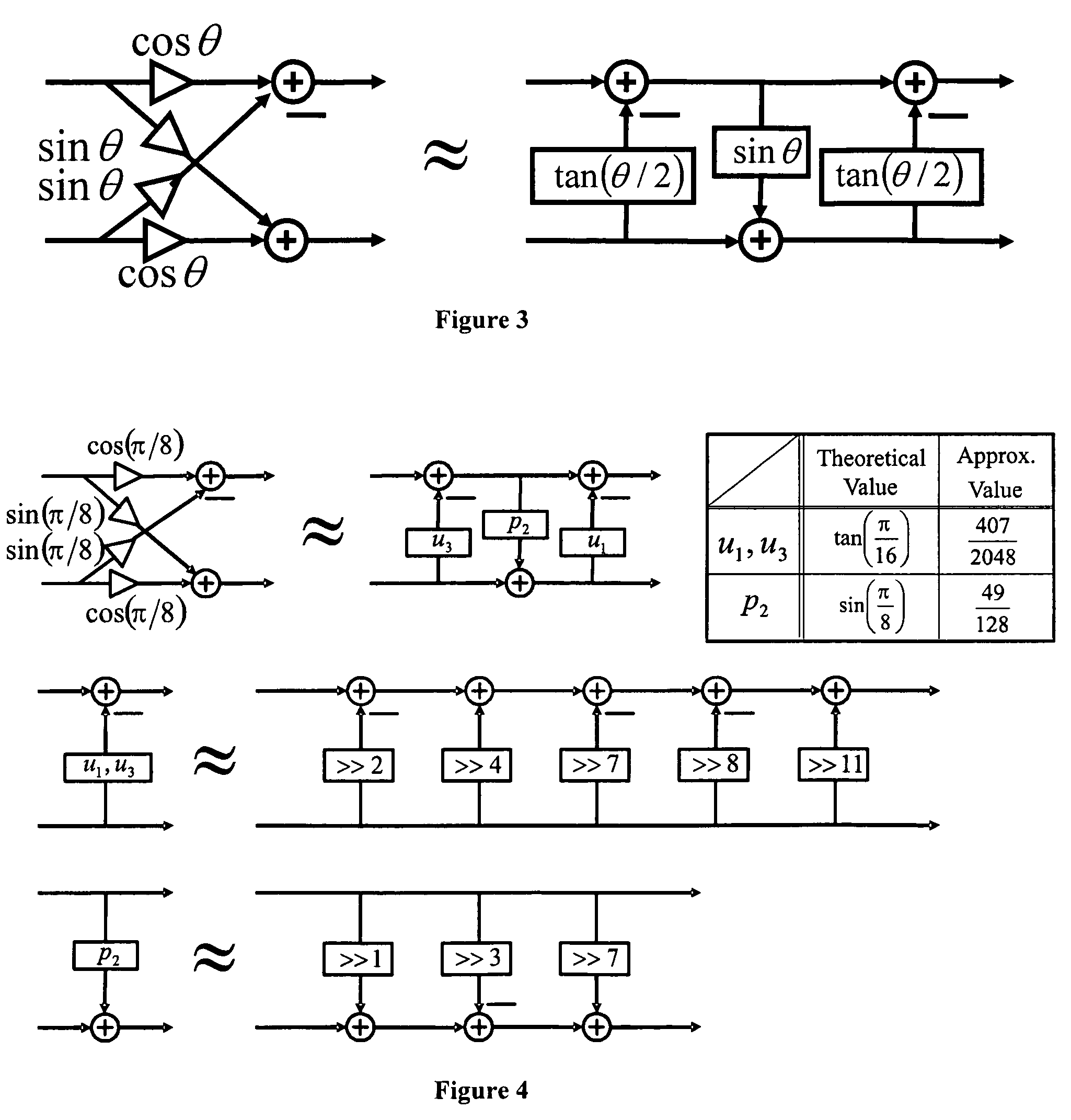
This invention relates to the design and implementation of a large family of fast, efficient, hardware-friendly fixed-point multiplierless inverse discrete cosine transforms (IDCT) and the corresponding forward transform counterparts. All of the proposed structures comprises of butterflies and dyadic-rational lifting steps that can be implemented using only shift-and-add operations. The approach also allows the computational scalability with different accuracy-versus-complexity trade-offs. Furthermore, the lifting construction allows a simple construction of the corresponding multiplierless forward DCT, providing bit-exact reconstruction if properly pairing with our proposed IDCT. With appropriately-chosen parameters, all of the disclosed structures can easily pass IEEE-1180 test. The high-accuracy algorithm of the present invention is over 100 times more accurate than IEEE-1180 specifications, leading to practically drifting-free reconstruction in popular MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 codecs even at the lowest quantization setting.
Owner:FASTVDO
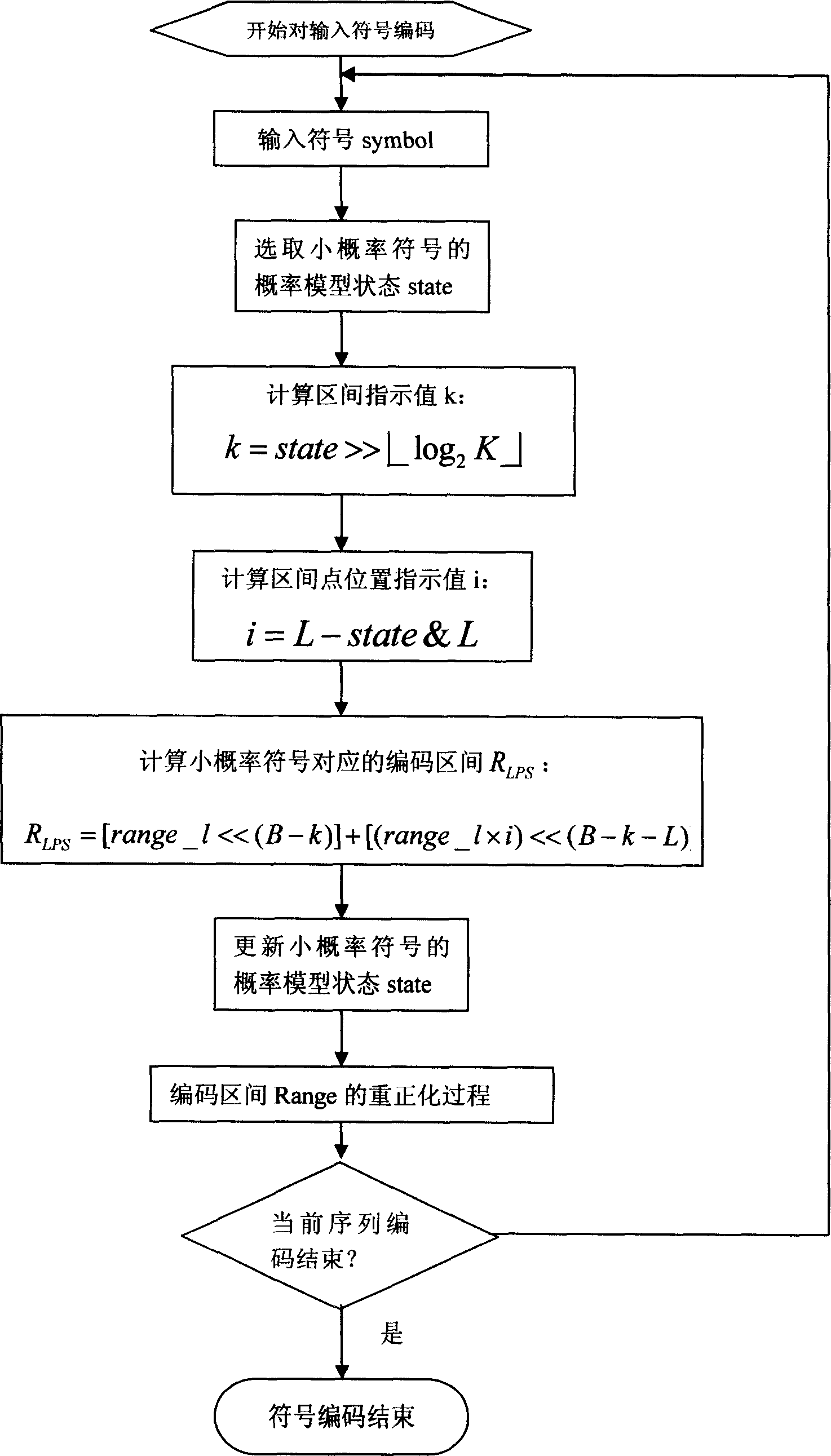
A two-value arithmetic coding method of digital signal
InactiveCN1703089AReduce complexityCoding efficiency is quiteCode conversionTelevision systemsDirect computationComputer architecture
This invention relates to signal process arithmetic coding field and relates to image or video coding method, which is characterized by the following: designing new small possibility quantity scheme and the coding range and uses the displacement and adding technique to reduce the possibility of the complexity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
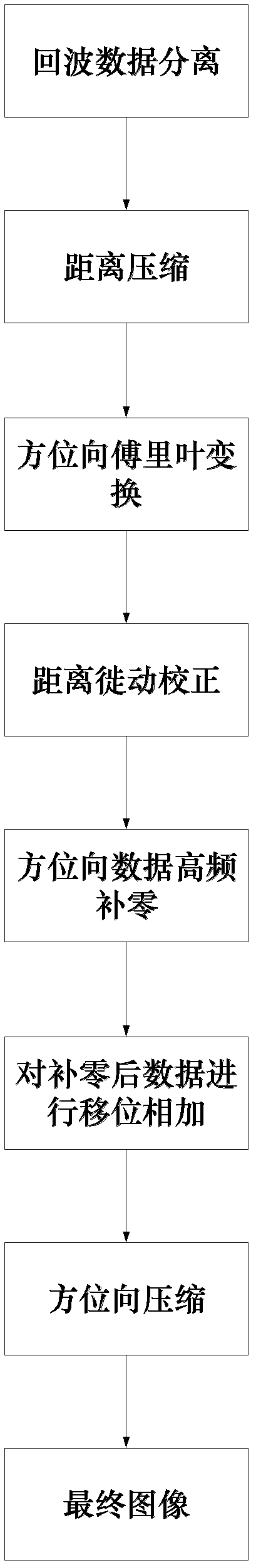
Ultralow sidelobe synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on complete complementary sequence
InactiveCN102608602ARadar signal waveform is easyEasy generationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging qualityImage quality
The invention discloses an ultralow sidelobe synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on a complete complementary sequence. The ultralow sidelobe synthetic aperture radar imaging method includes steps of 1, dividing echo data based on signal waveforms of the complete complementary sequence into echo data which are obtained by means of utilizing two complementary sequences as radar transmitting signals independently; 2, compressing range pulses based on matched filtering; 3, performing azimuth Fourier transformation; 4, correcting range migratory motion; 5, performing azimuth data high-frequency zero fill; 6, shifting and adding the data after zero rill; and 7, performing azimuth compressing to obtain a final image. The ultralow sidelobe synthetic aperture radar imaging method has theadvantages that radar signal waveforms are easy to be generated, pulse compressing is easy to be realized, azimuth ultralow sidelobe is realized, and azimuth resolution and image quality are high.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
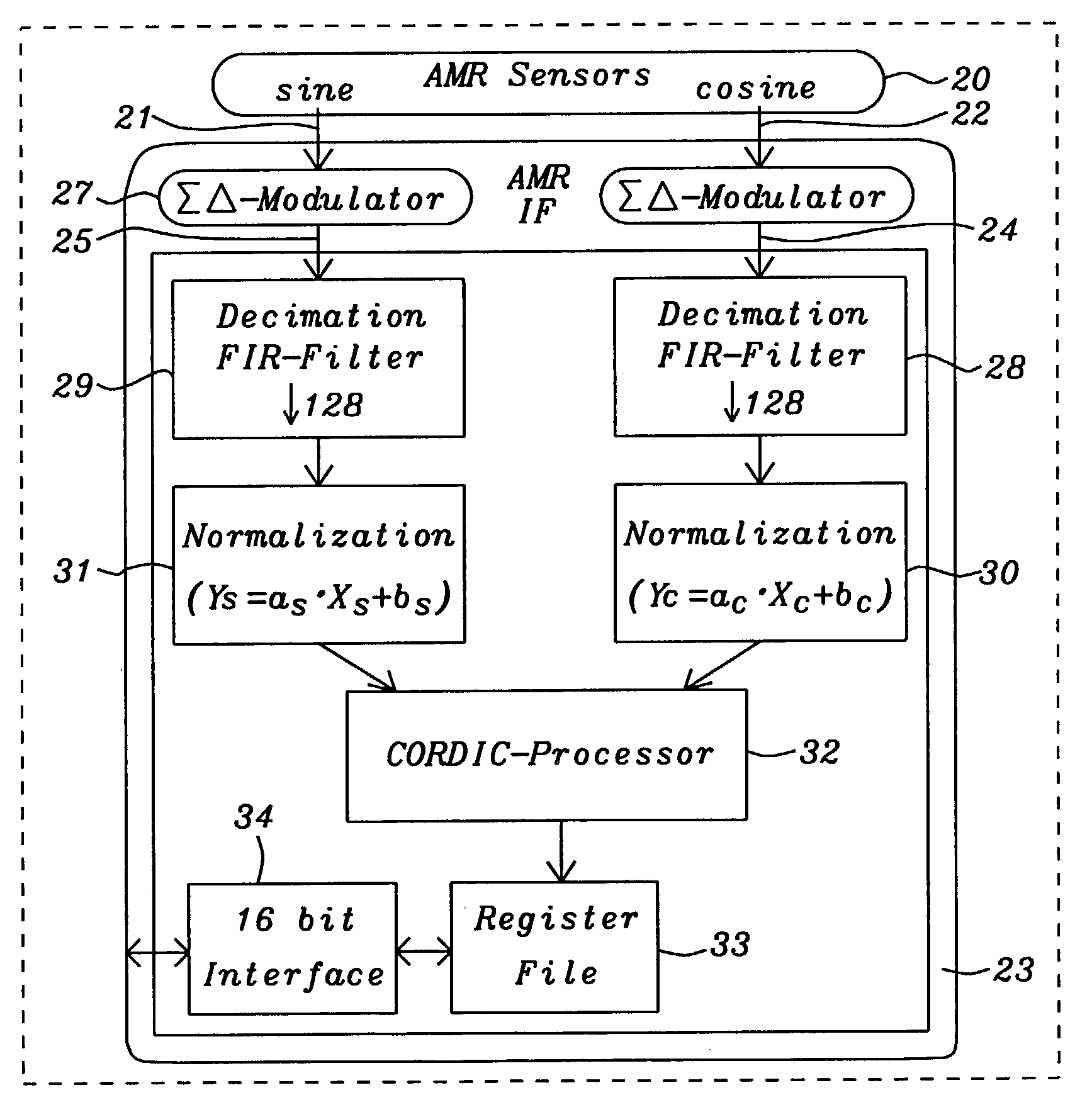
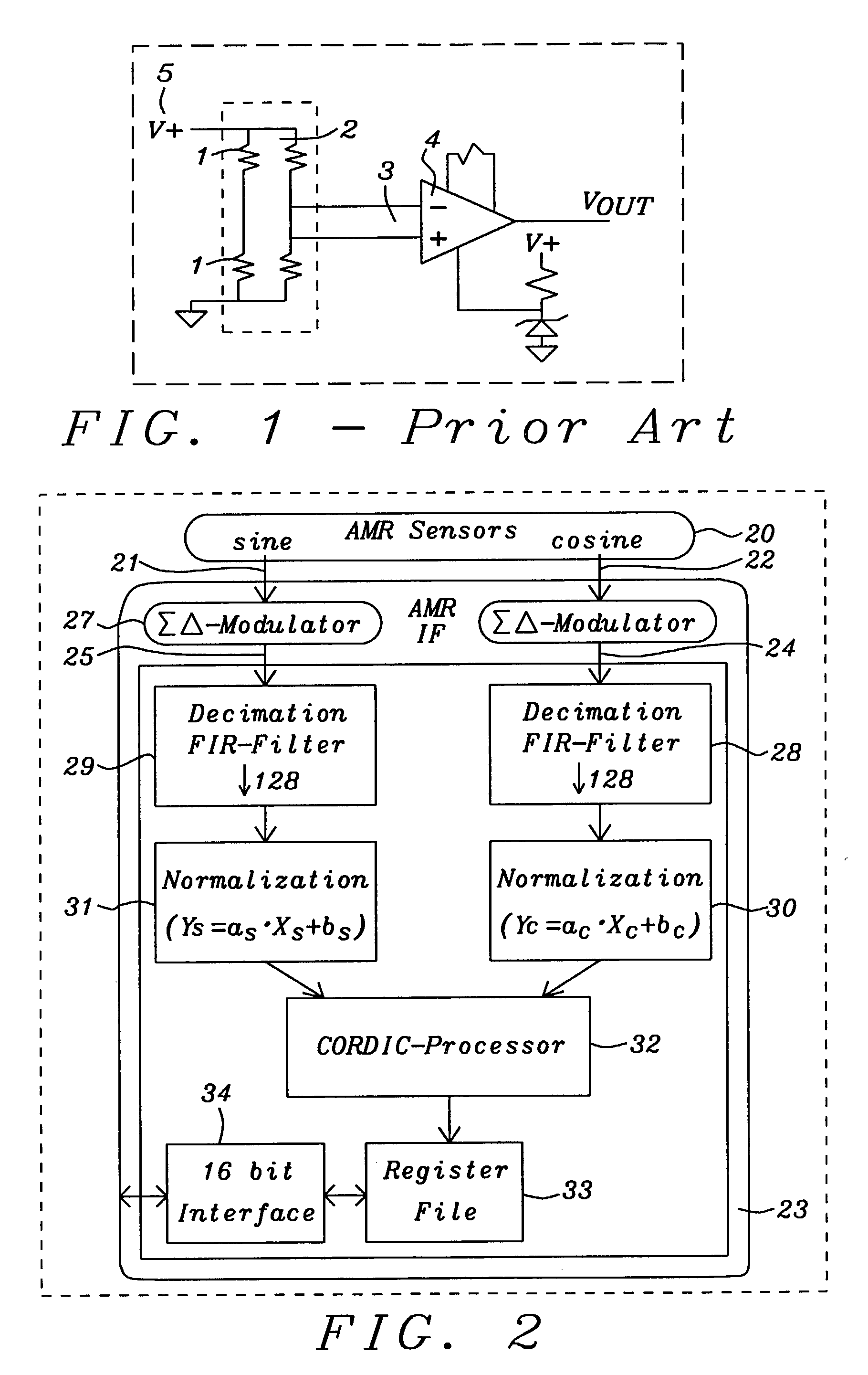
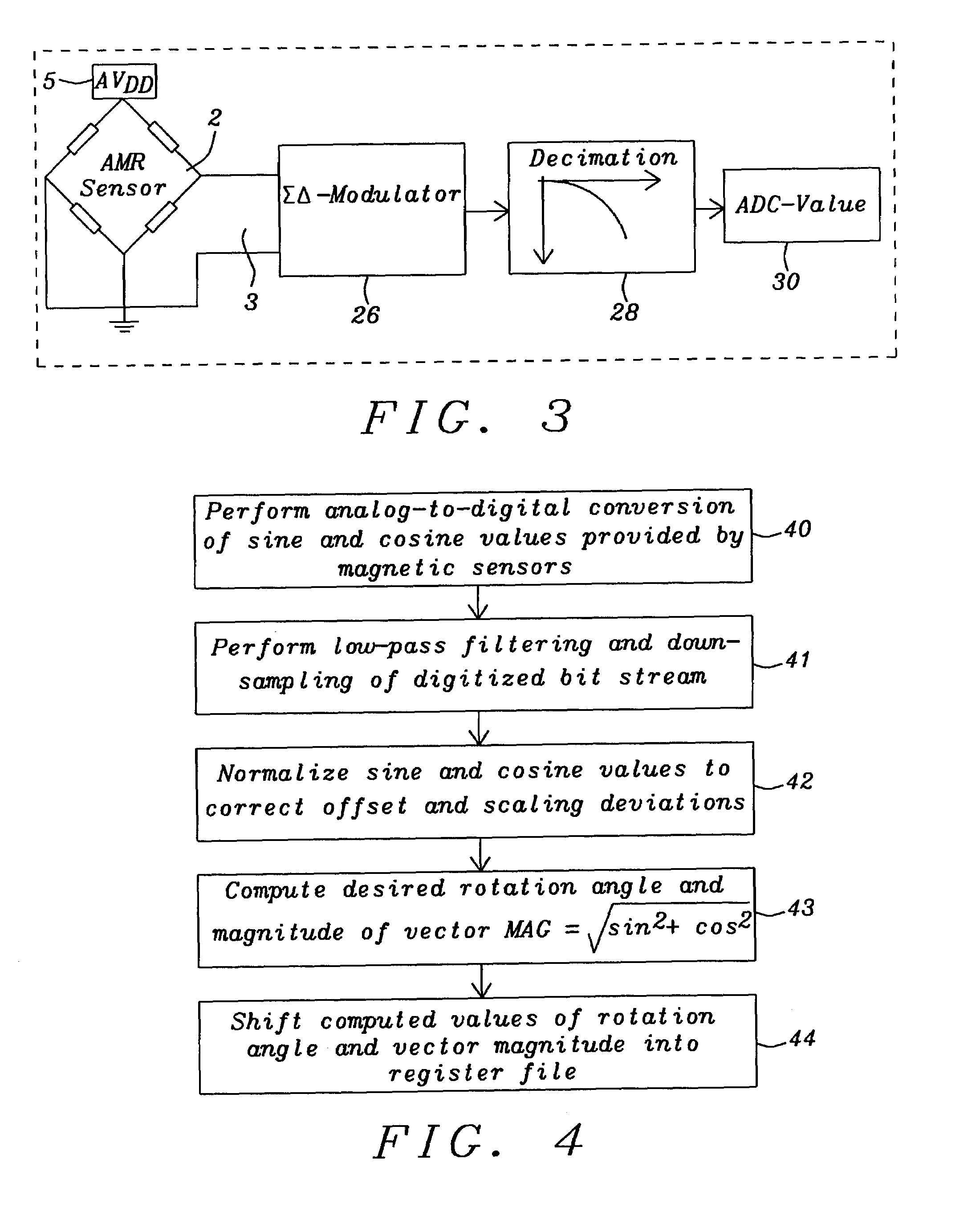
Magnetic sensor digital processing interface for electrical motor application
InactiveUS7064538B2Pulse generation by non-linear magnetic/dielectric devicesSolid-state devicesShift-and-addAnalog signal
A system and methods for an interface for magnetic sensors to determine a rotational angle has been achieved. This interface can be used for magnetic sensors providing analog signals of the sine and cosine values of the angle to be determined. Analog signals are being processed in two measurement paths for the sine and cosine signal each until the desired angle is computed by a CORDIC processor. The first stage of the measurement path is the conversion of the sine and cosine signals from analog to digital by 2nd order delta-sigma modulators with an over-sampling ratio. A low-pass decimation filter with sinc3 characteristic performs the digital value computation. The next stage normalizes the digitized sine and cosine values to correct offset and scaling deviations. The CORDIC processor computes the angle by decomposing the desired rotation angle into iterations of pre-defined elementary rotation angles performing the rotation operation by simple shift-and-add operations and the magnitude of the vector using the output from the normalization stages.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
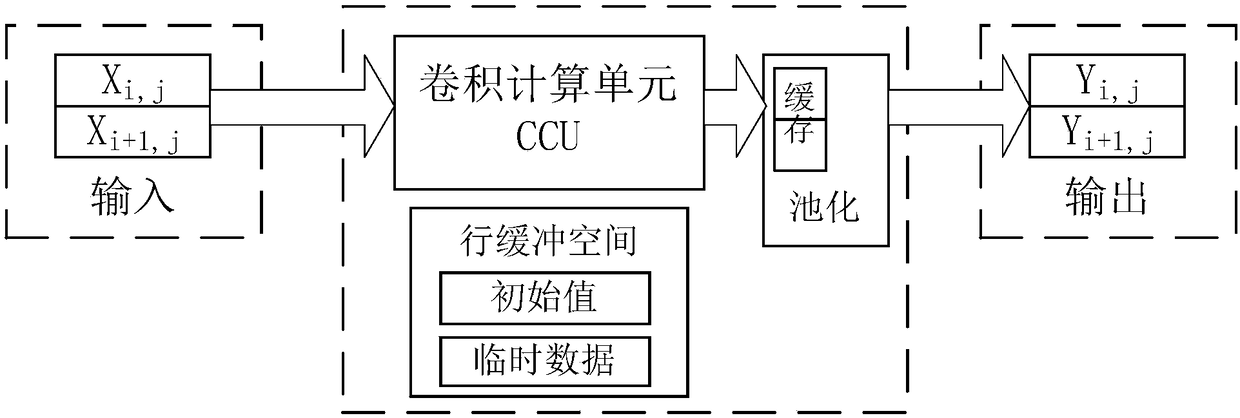
Convolution calculating apparatus and method for neural network
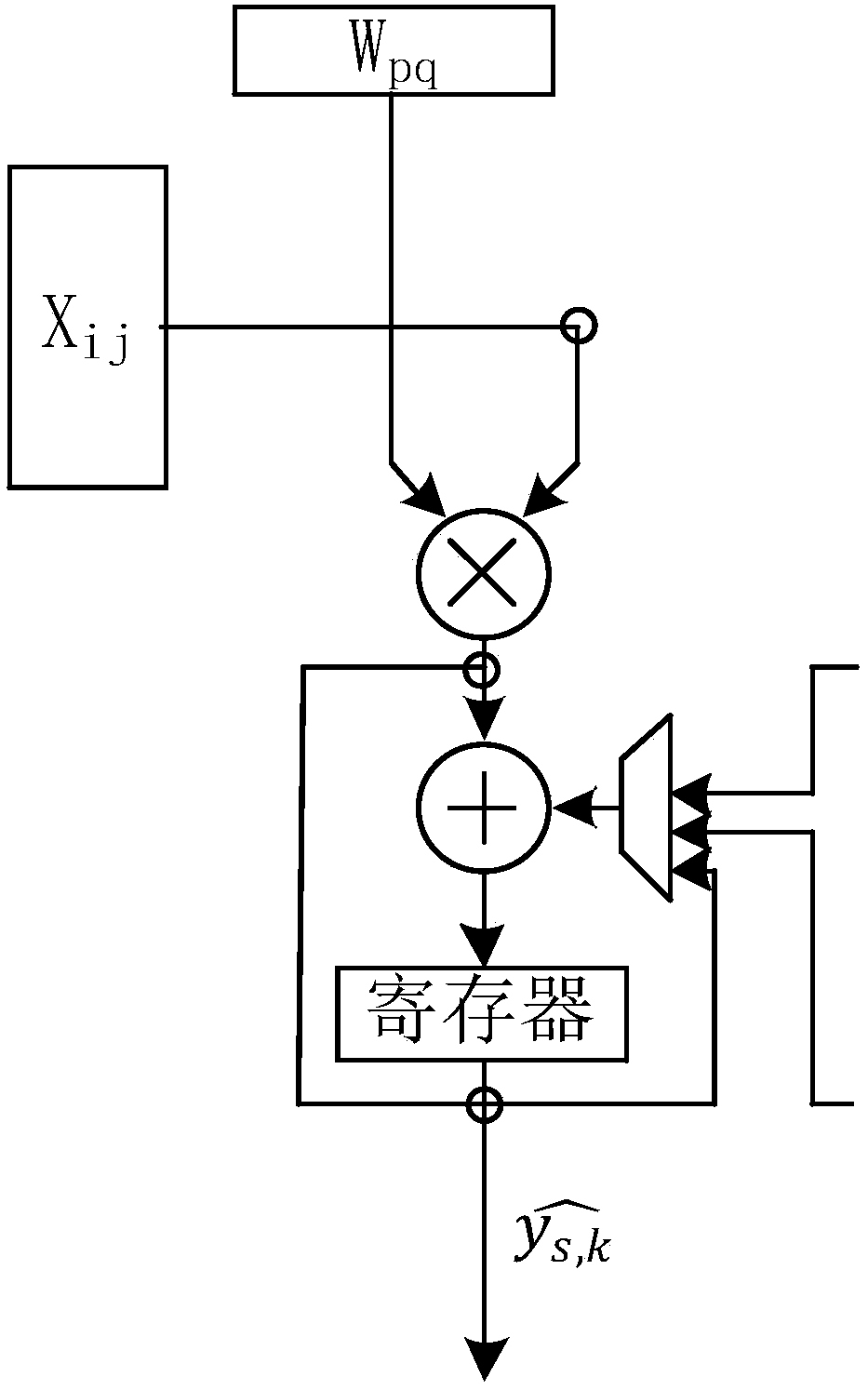
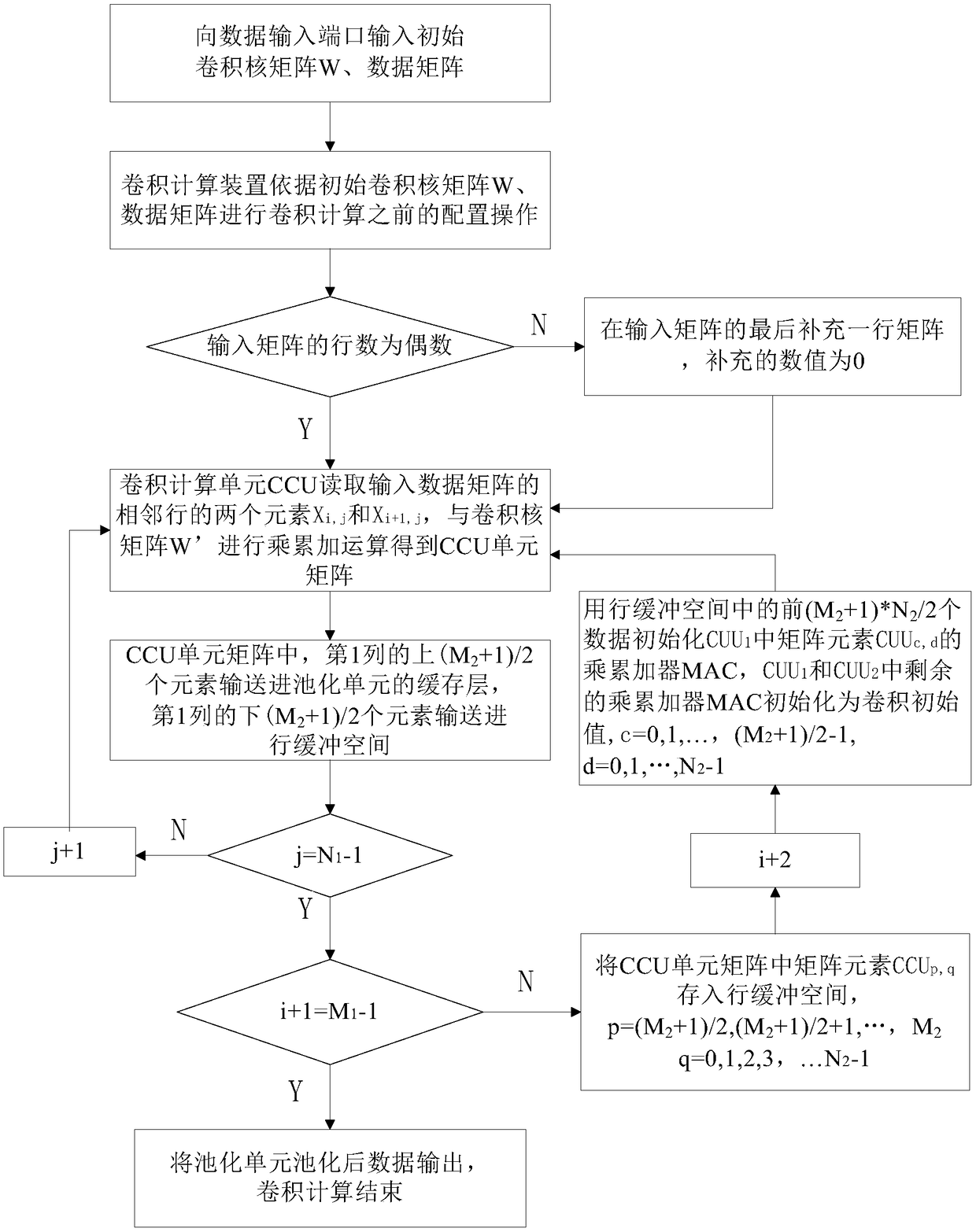
ActiveCN108537330AReduce read and write operationsImprove computing efficiencyNeural architecturesPhysical realisationDigital signal processingAlgorithm
The invention belongs to the digital signal processing field, and specifically relates to a convolution calculating apparatus and method for a neural network. The convolution calculating apparatus andmethod for a neural network aims at solving the problem that consumption of resources is great and the utilization rate of the read in data is low during the process of convolution calculation. The convolution calculating method for a neural network includes the steps: input data matrixes are processed in rows, and every two rows of data are input serially row by row into multiply accumulator arrays for carrying out multiply and accumulate operations; the multiply accumulator arrays perform deployment according to a convolution kernel dimension (M2, N2), and can process 2*M2*N2 times of multiplication in parallel; and by means of the convolution operation law, the two groups of multiply accumulator arrays can be shifted and added, and the data operation is accelerated. The convolution calculating apparatus and method for a neural network can excavate parallelism during the calculating process and improve the calculating efficiency of the system, and at the same time can reuse the input data and directly put the calculation results into a pooling unit, thus being able to reduce data reading and writing. Besides, the convolution calculating apparatus and method for a neural networkonly need one row cushion space, thus having a small demand for resources, can realize calculation of different dimension convolution, and have the advantages of calculating flexibility, universality,high effectiveness and low power consumption property.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for reconstructing GPU (Graphic Processing Unit) accelerating X-ray image based on CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture)
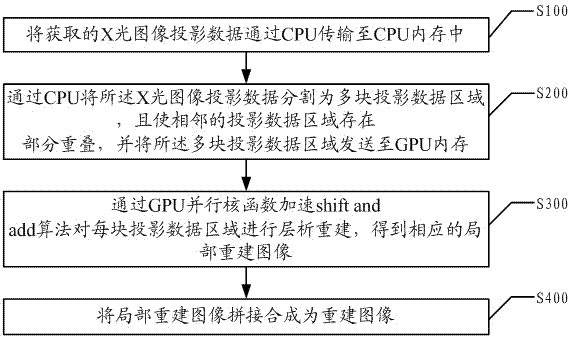
ActiveCN103700123AFast operationLow costImage enhancement2D-image generationShift-and-addTomographic reconstruction
The invention discloses a method and a device for reconstructing a GPU (Graphic Processing Unit) accelerating X-ray image based on a CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture). The method comprises the following steps: transmitting acquired X-ray image projection data into a CPU (Central Processing Unit) memory by virtue of a CPU; partitioning the X-ray image projection data into multiple projection data regions by virtue of GPU, partially overlapping the adjacent projection data regions, and sending the multiple projection regions to the CPU memory; performing tomographic reconstruction on each projection data region by virtue of a GPU parallel kernel function accelerating shift and add algorithm, so as to obtain corresponding partial reconstruction images; splicing and synthesizing the partial reconstruction images into the reconstruction image. According to the method and the device, the parallel shift and add algorithm is realized by virtue of GPU hardware acceleration under the CUDA, so that the computing speed is greatly improved, meanwhile the cost is saved, and great convenience is brought to a user.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMAI MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
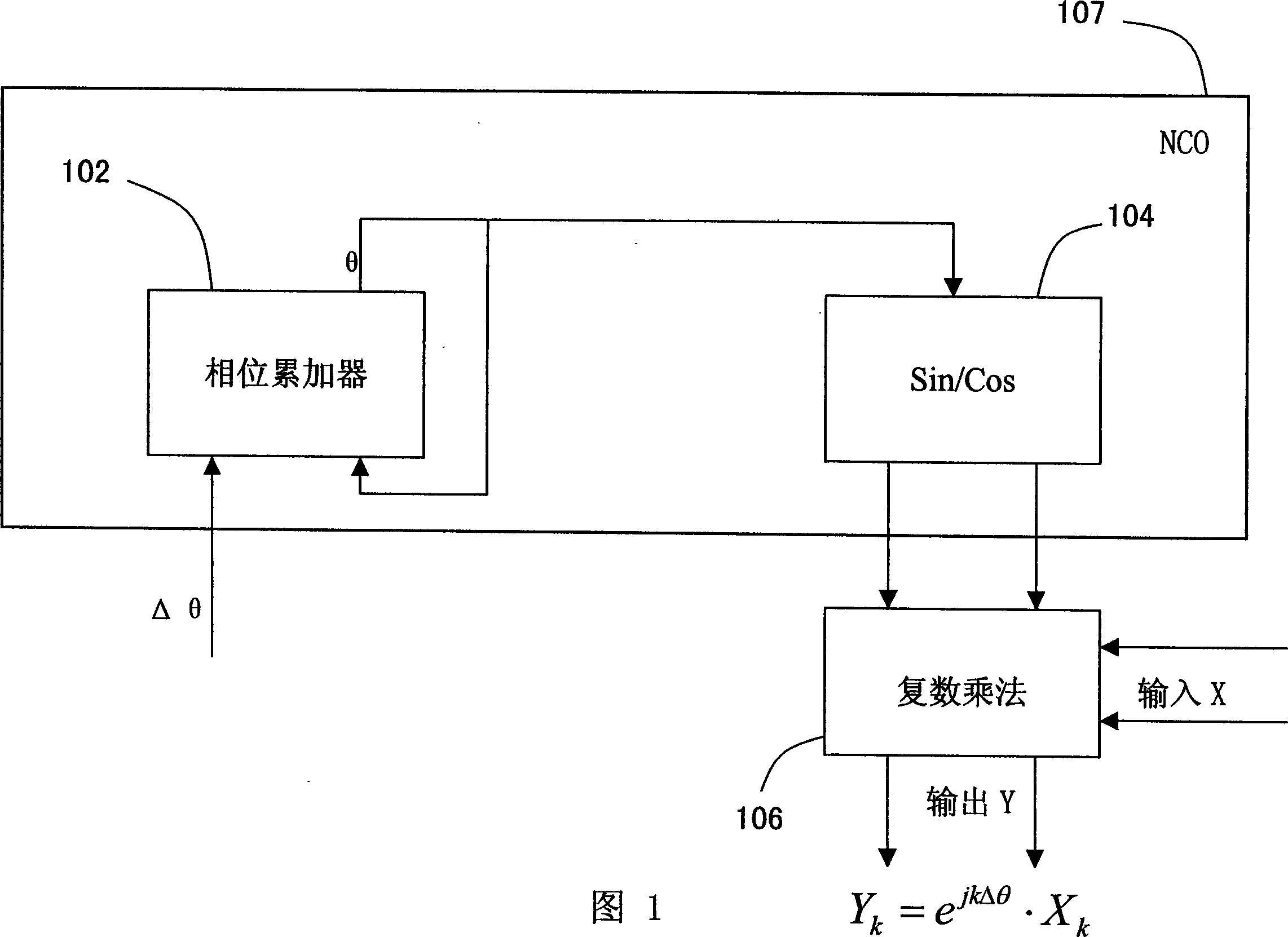
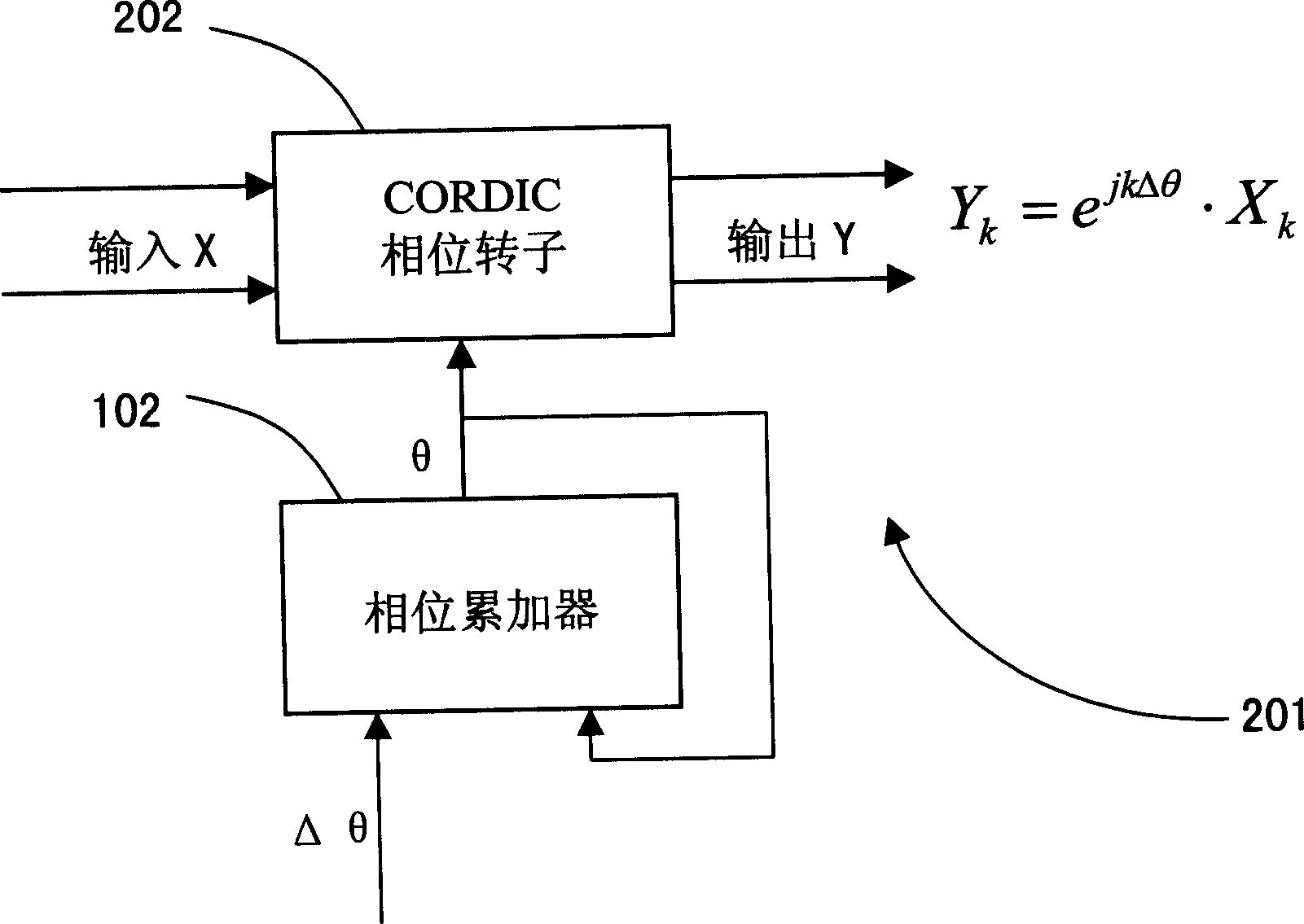
Frequency translator using a cordic phase rotator
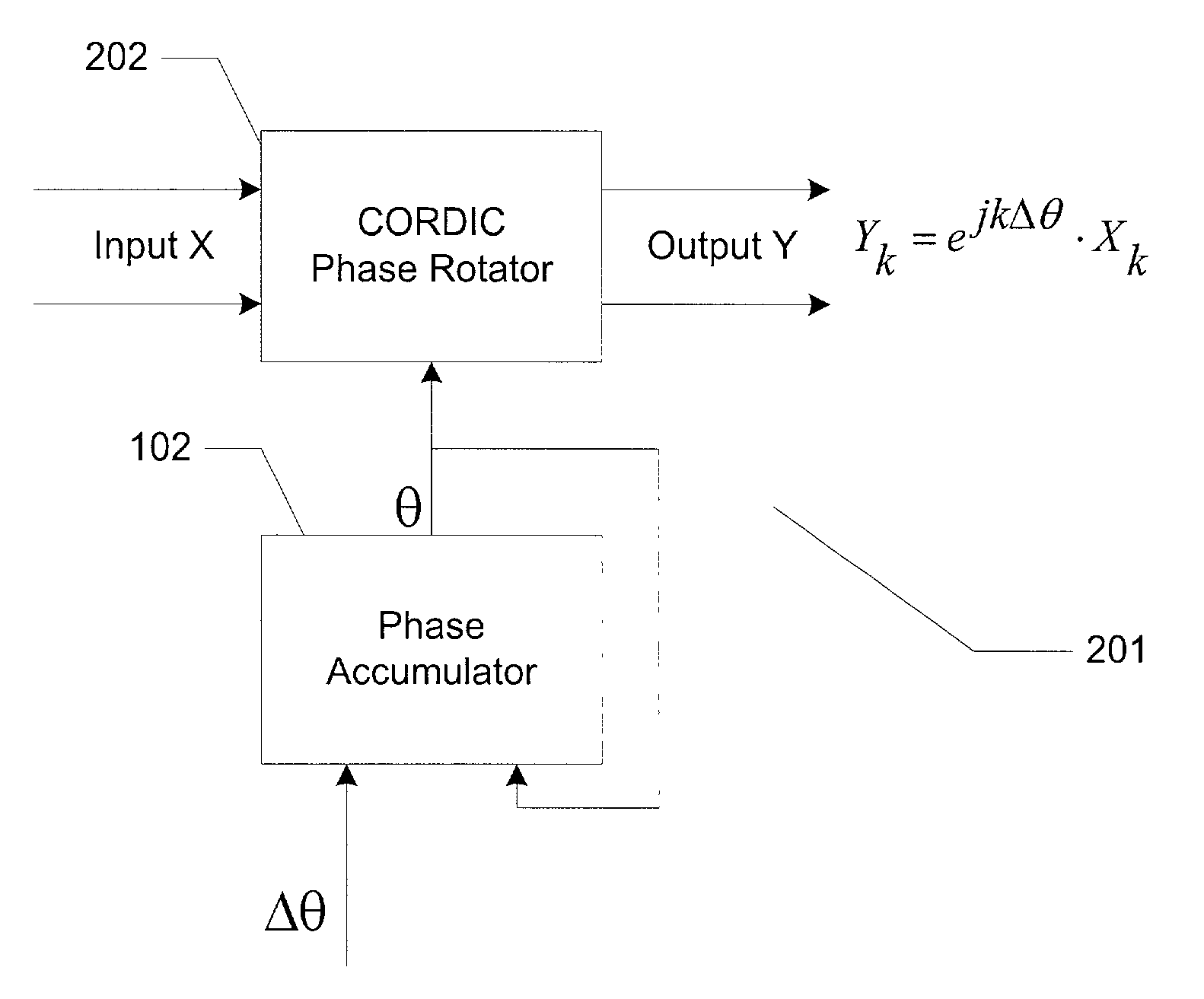
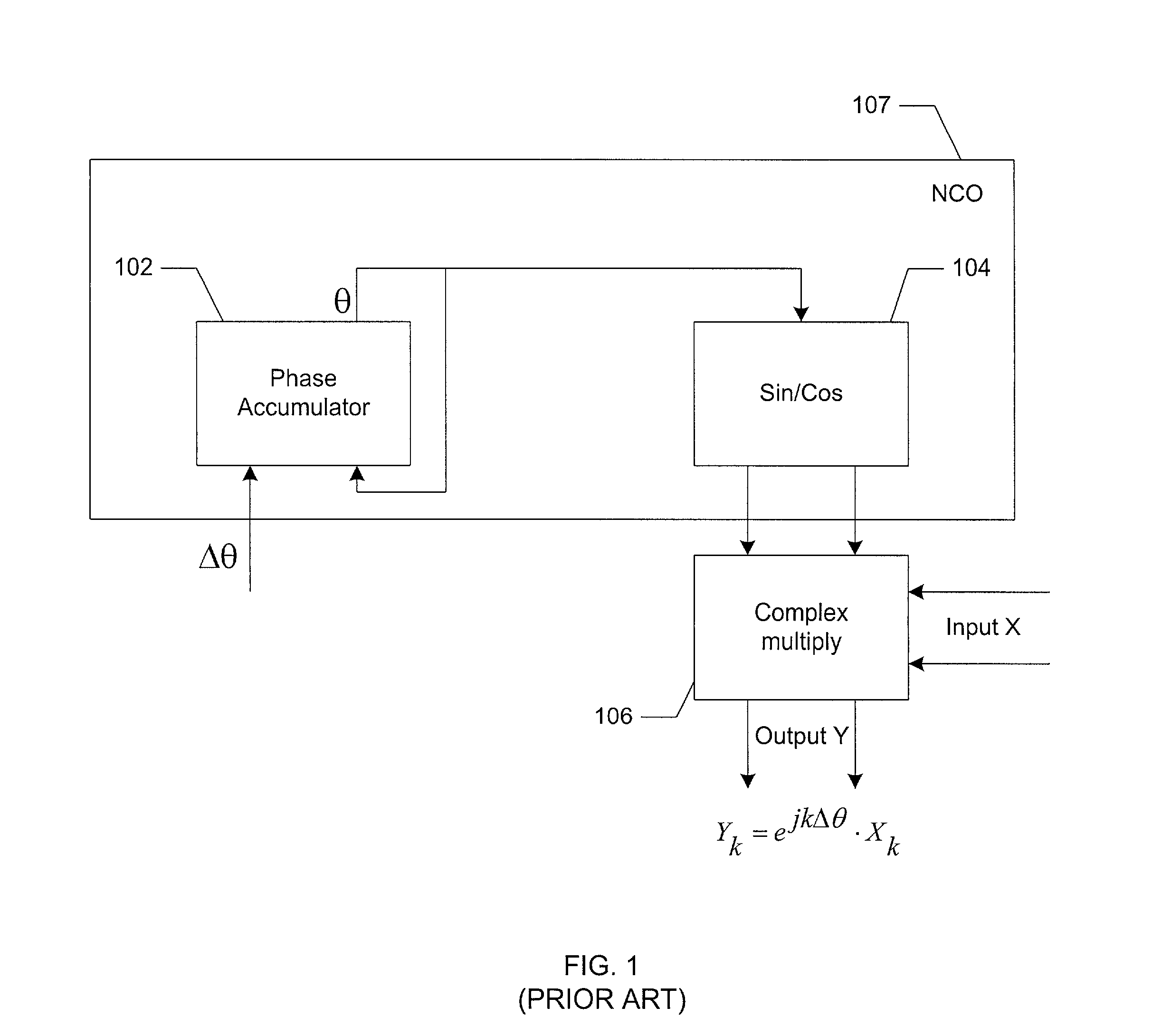
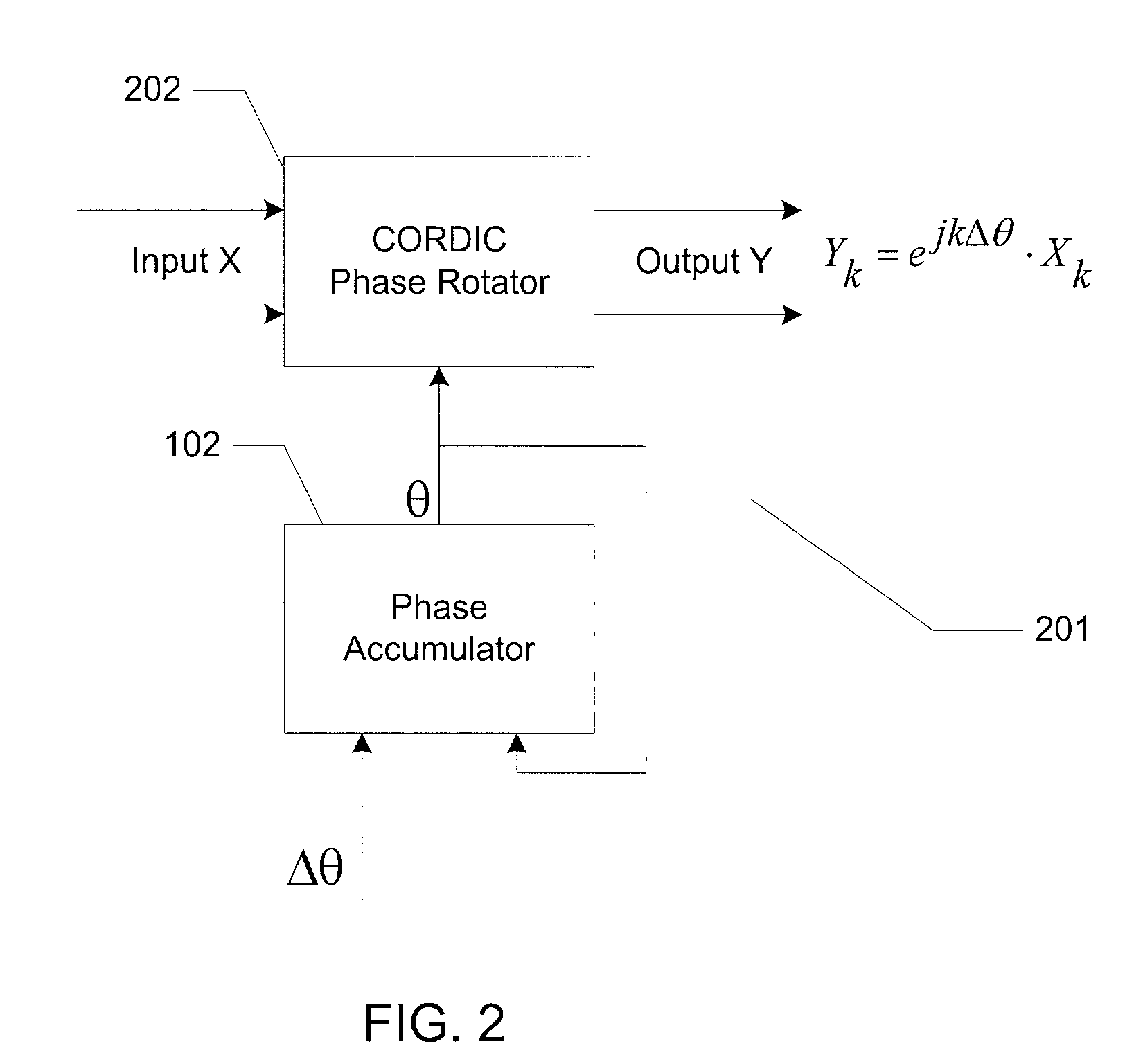
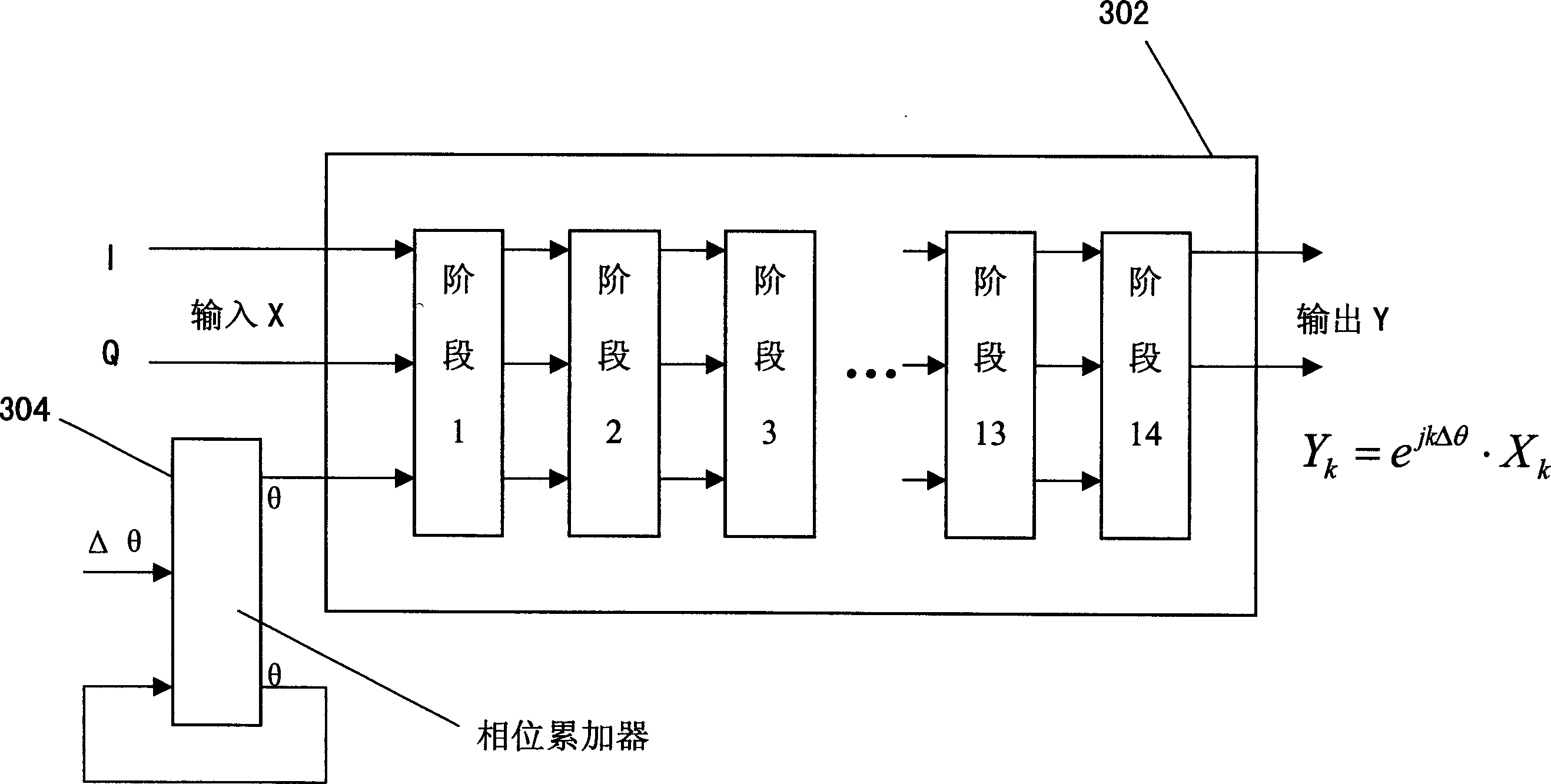
ActiveUS7020190B2Easy to implementNoise minimizationModulation transferenceComputation using non-contact making devicesRoundingShift-and-add
A frequency translator uses a CORDIC phase rotator coupled to a phase accumulator to translate an input signal in frequency. The CORDIC phase rotator performs required phase angle rotations of input vectors using only shift and add operations. Thus, the frequency translator can be readily implemented in hardware. Higher precision arithmetic is used in the CORDIC phase rotator operations than the input vectors contain. To avoid truncation error at the output of the CORDIC phase rotator, stochastic rounding is employed. A dither signal is added to avoid errors due to nonlinear operation of D / A converters, where D / A conversion of the frequency translated signal is required.
Owner:SKYBITZ INC
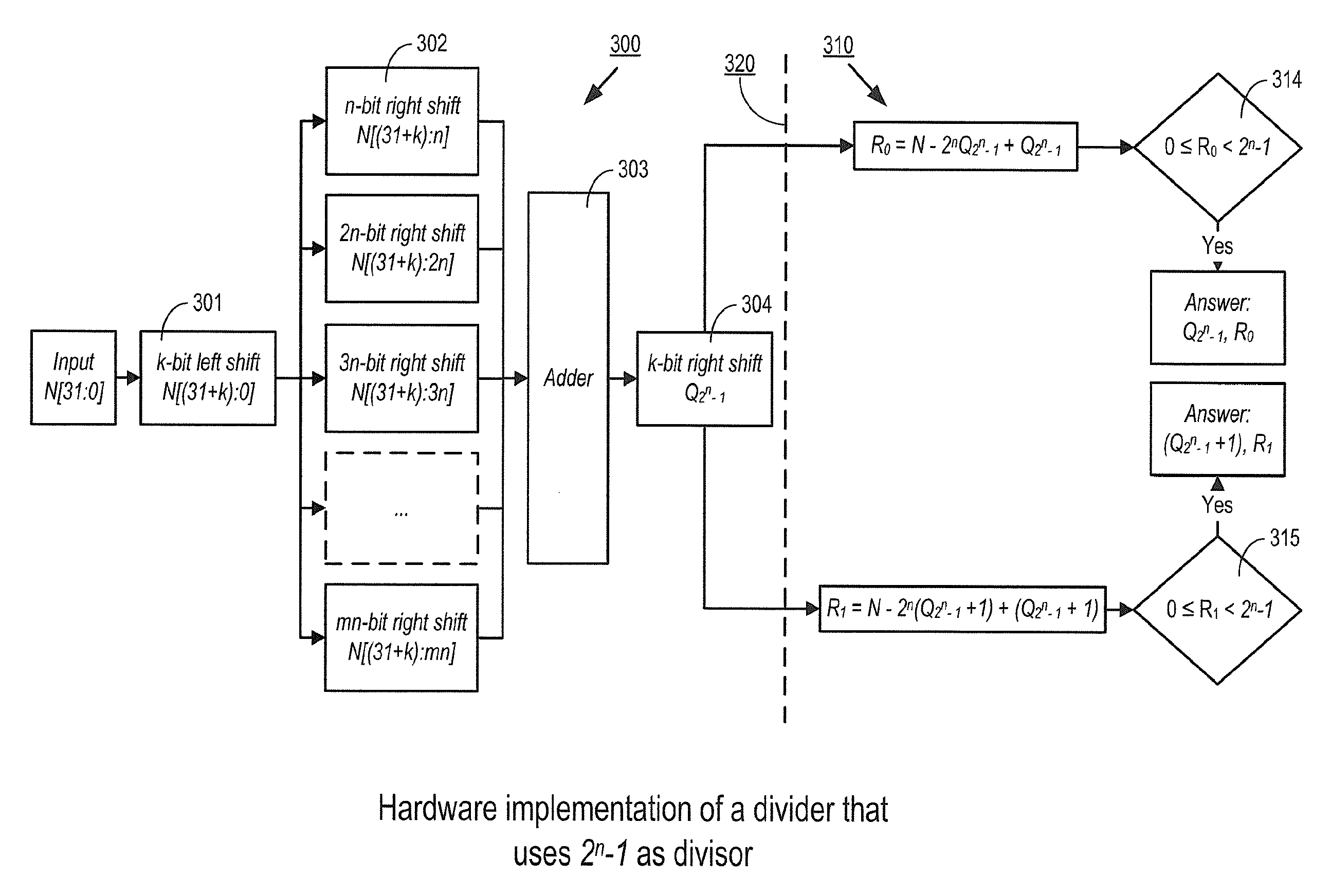
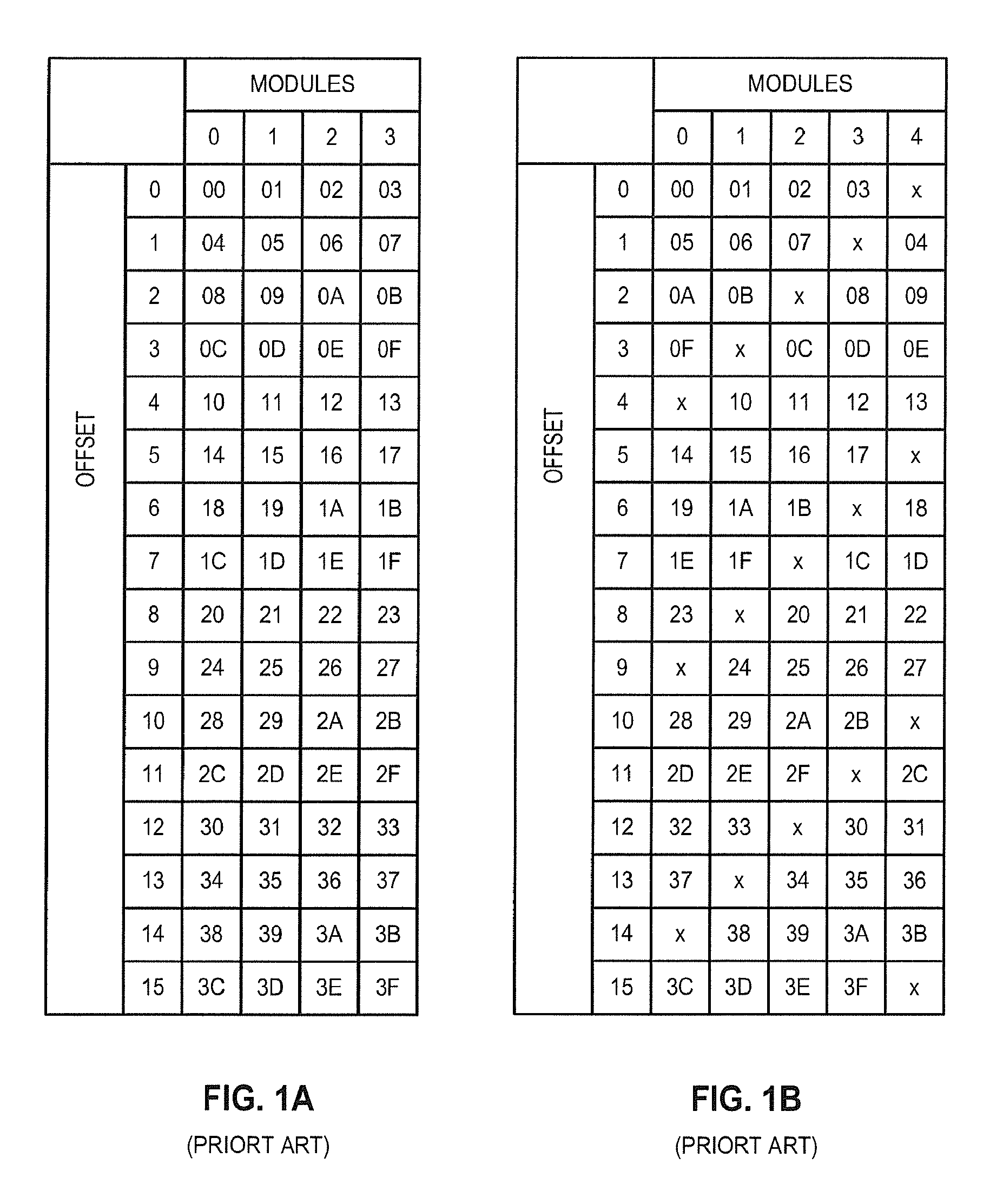
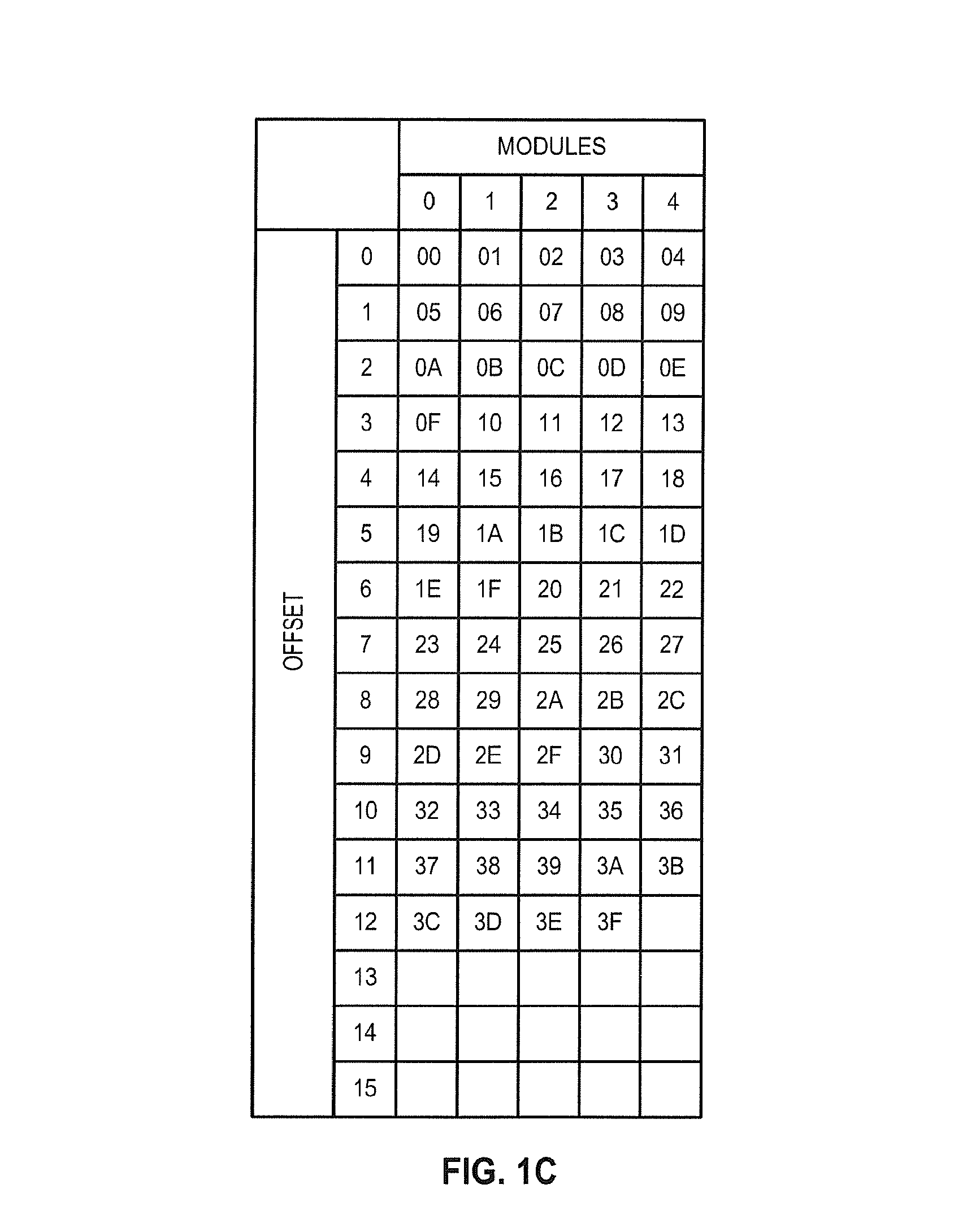
FAST MECHANISM FOR ACCESSING 2n±1 INTERLEAVED MEMORY SYSTEM
InactiveUS20140025908A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationShift-and-addInterleaved memory
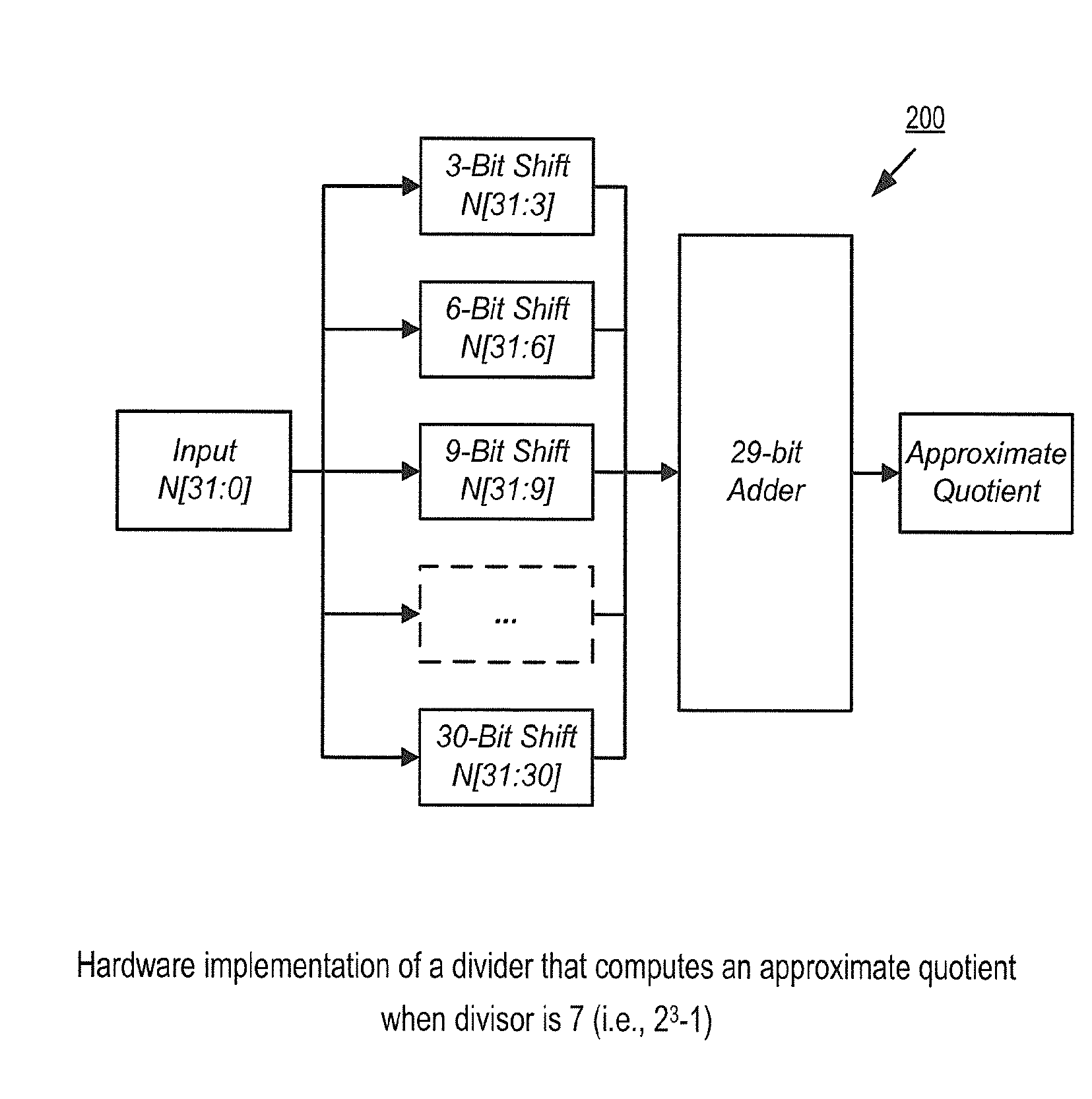
A mechanism implemented by a controller enables efficient access to an interleaved memory system that includes M modules, M being (2n+1) or (2n−1), n being a positive integer number. Upon receiving an address N, the controller performs shift and add / subtract operations to obtain a quotient of N divided by M based on a binomial series expansion of N over M. The controller computes a remainder of N divided by M based on the quotient. The controller then accesses one of the modules in the memory based on the remainder.
Owner:INTEL CORP
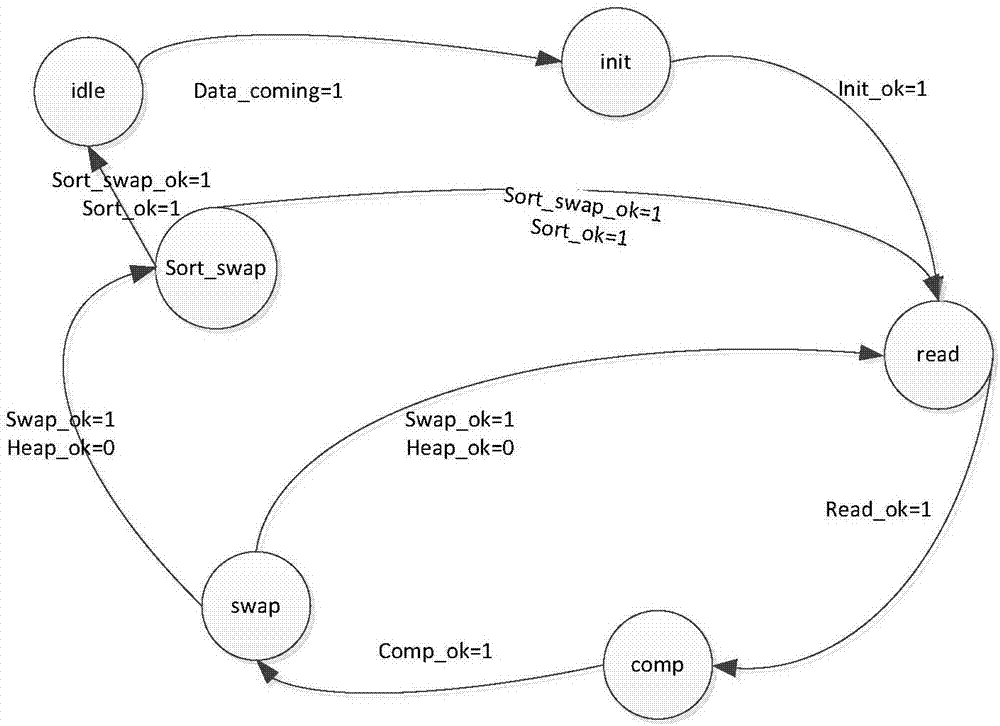
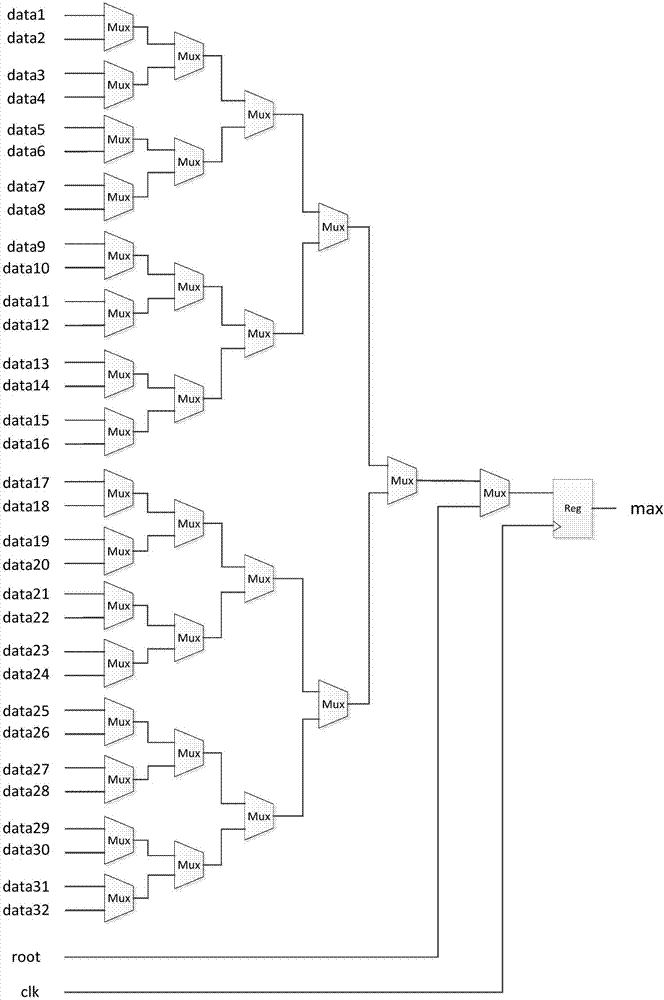
Sorting method suitable for FPGA implementation
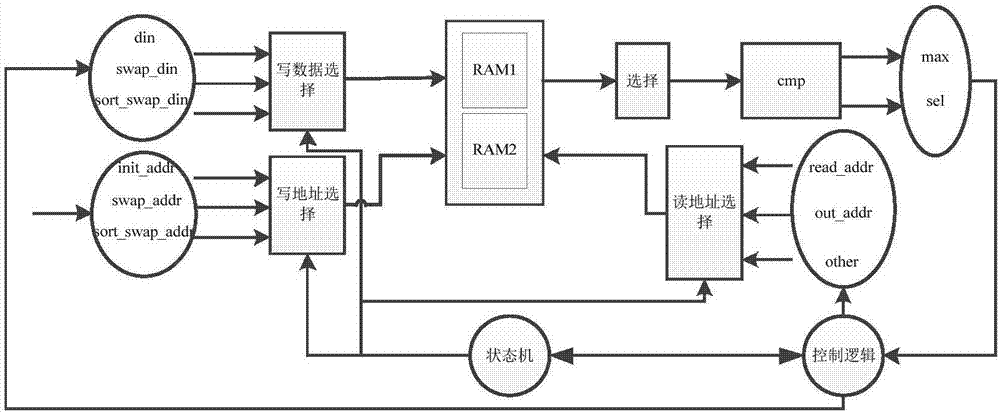
The invention belongs to the field of heapsort, and especially relates to a sorting method suitable for FPGA implementation. According to the sorting method suitable for FPGA implementation, through designing a new data structure, a binary tree structure of an existing heapsort algorithm is modified to be a 2k-ary tree, k>=2, the degree of parallelism of data comparison is increased, the number of layers of the tree is reduced, and therefore the number of times accessing the data is decreased. By utilization of the function of outputting multiple data in one clock of an RAM of an FPGA, 2k child nodes to be compared can be read out in one clock, and the data reading time is reduced. The 2k-ary tree structure is used, addresses of the child nodes are simply obtained by shifting and adding non-leaf node addresses, thereby facilitating data access in the implementation and reduction of complexity of the implementation. Sorting time delay can be largely reduced by the method, and real-time performance of a sorting module is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Device for implementing a sum of products expression
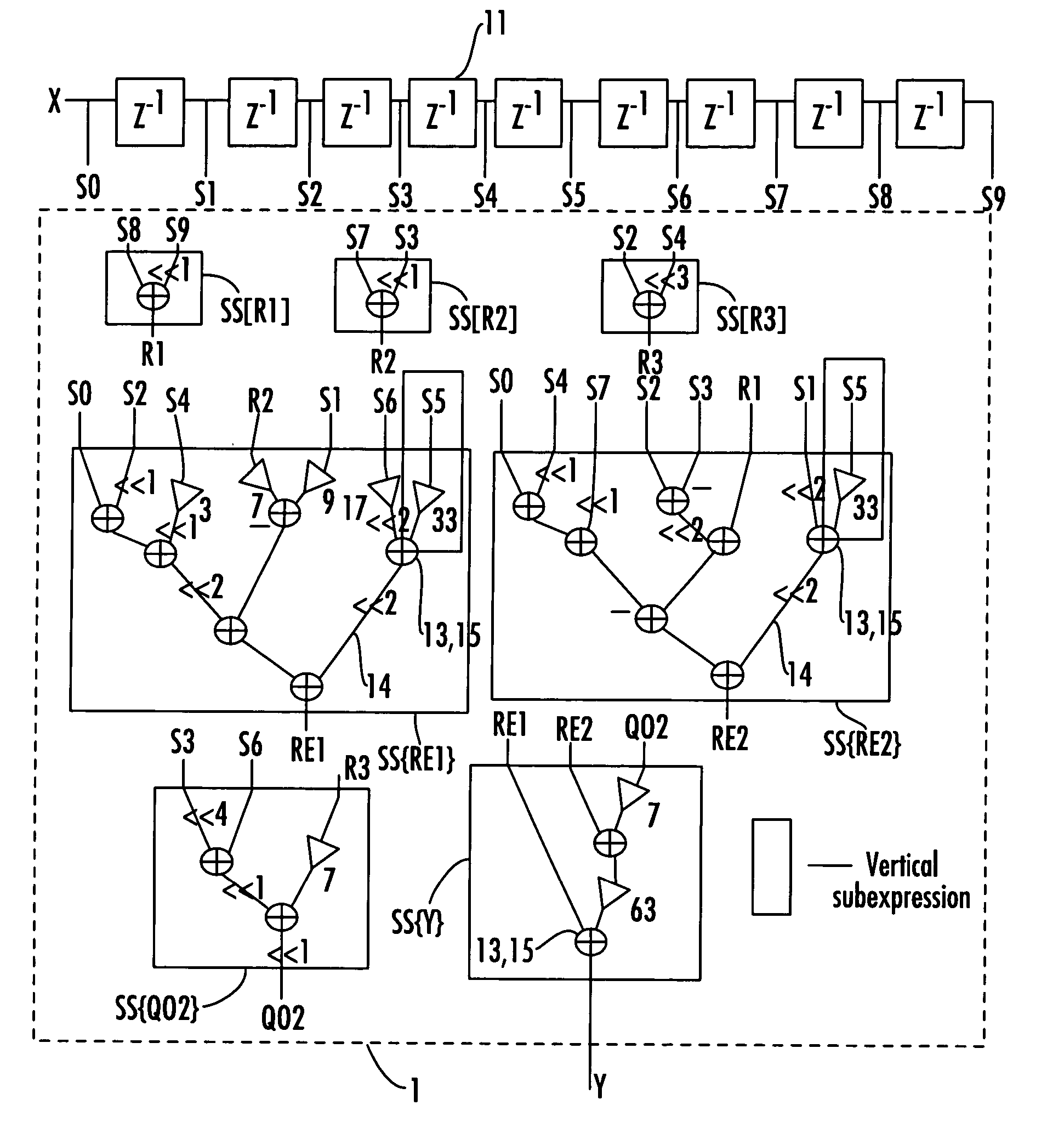
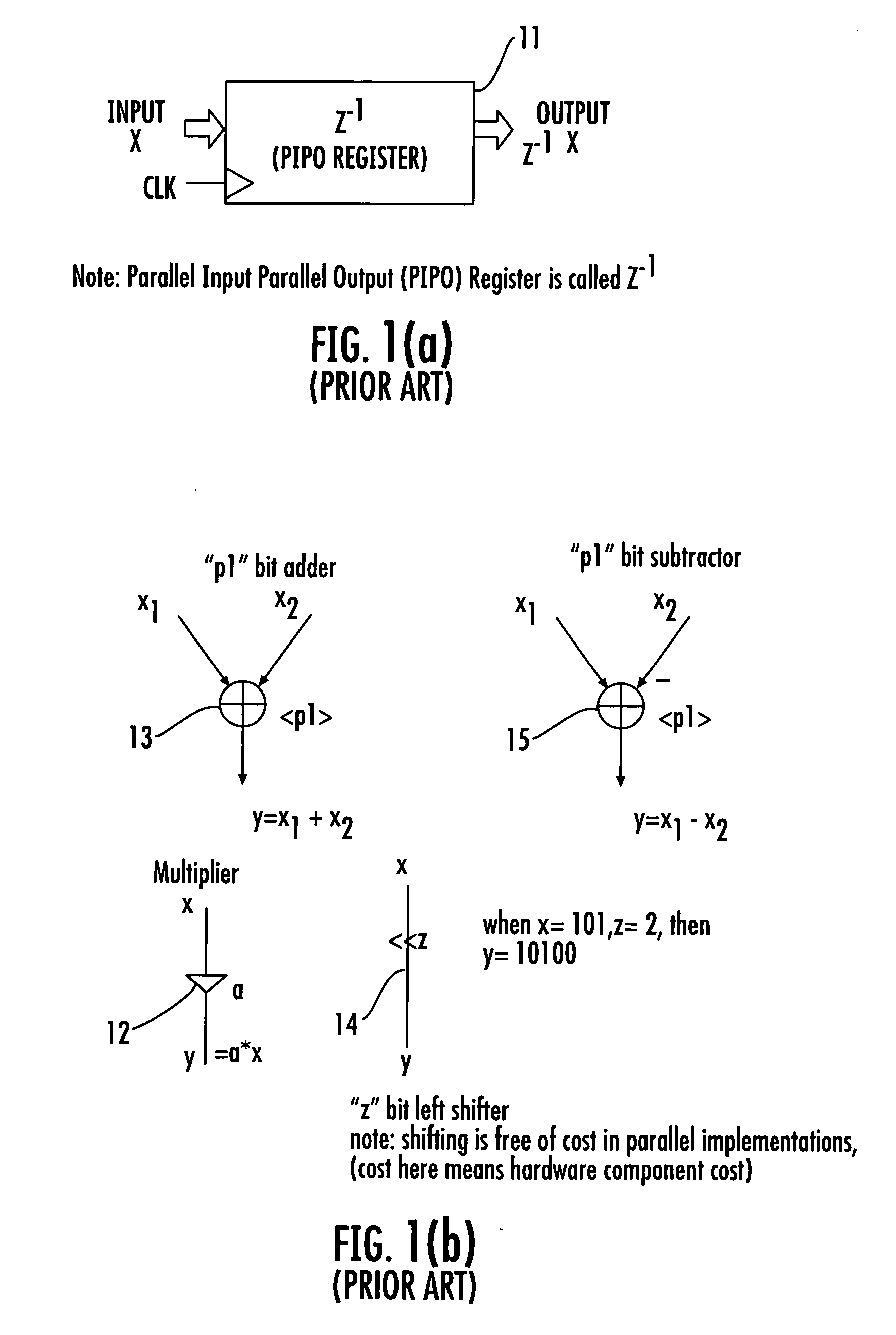
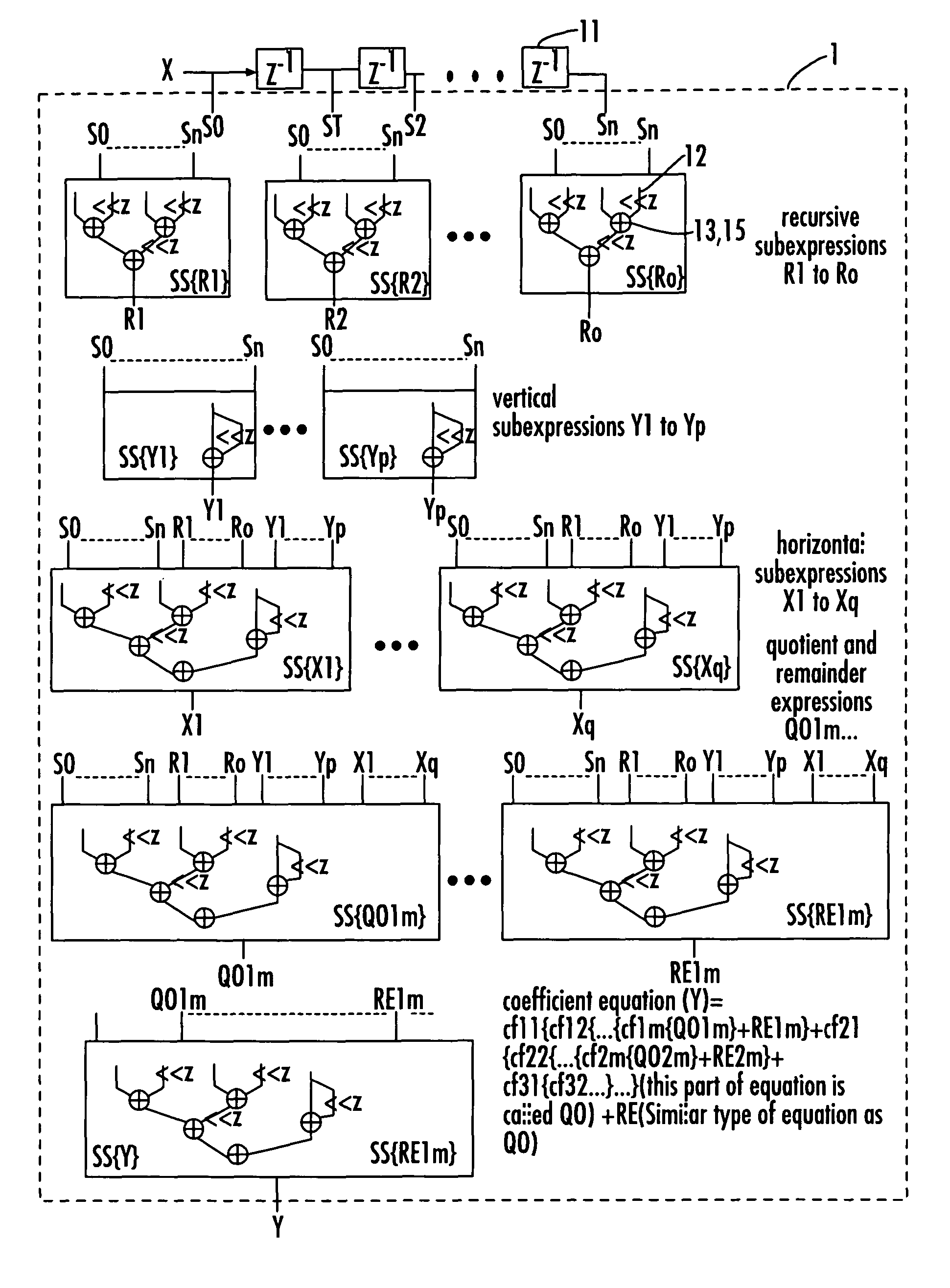
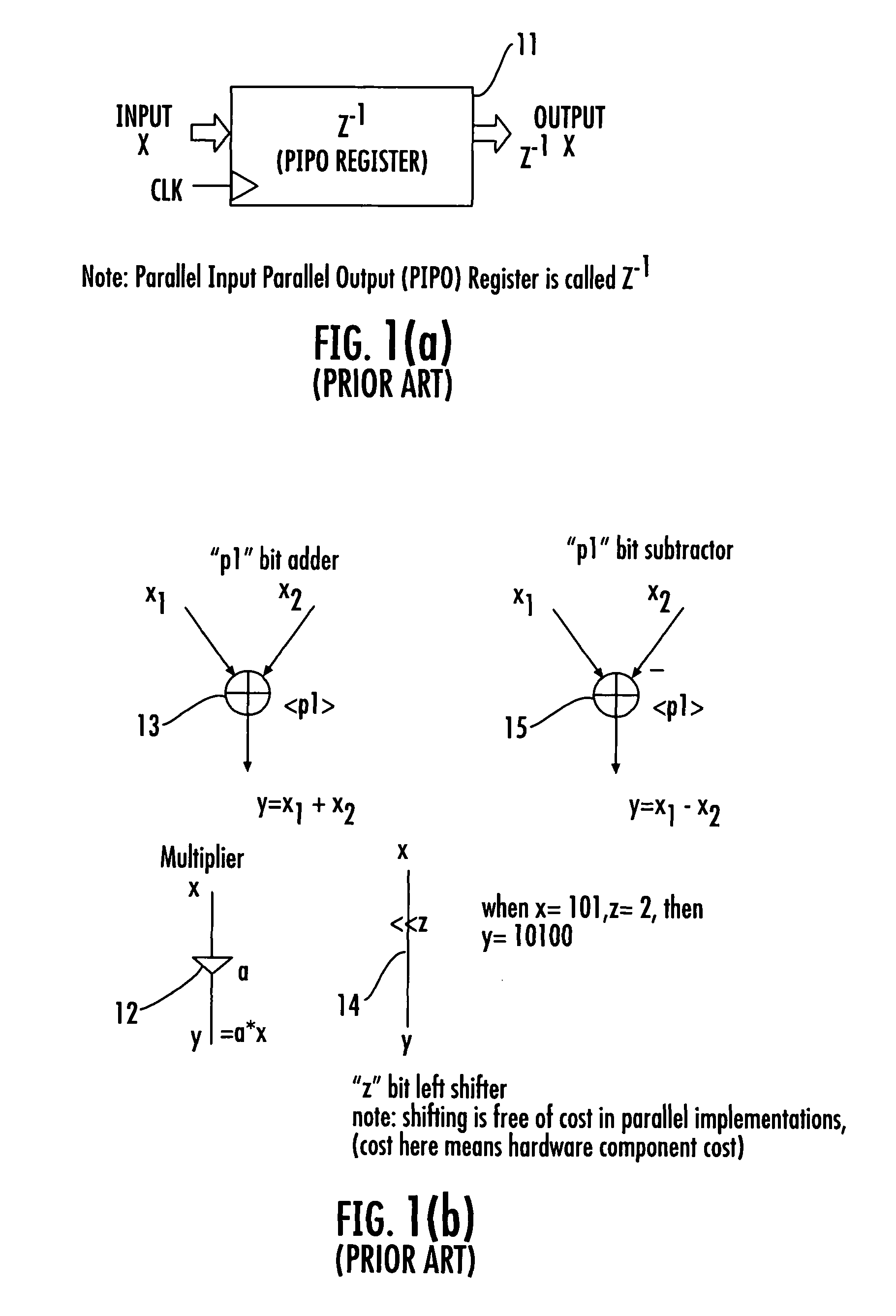
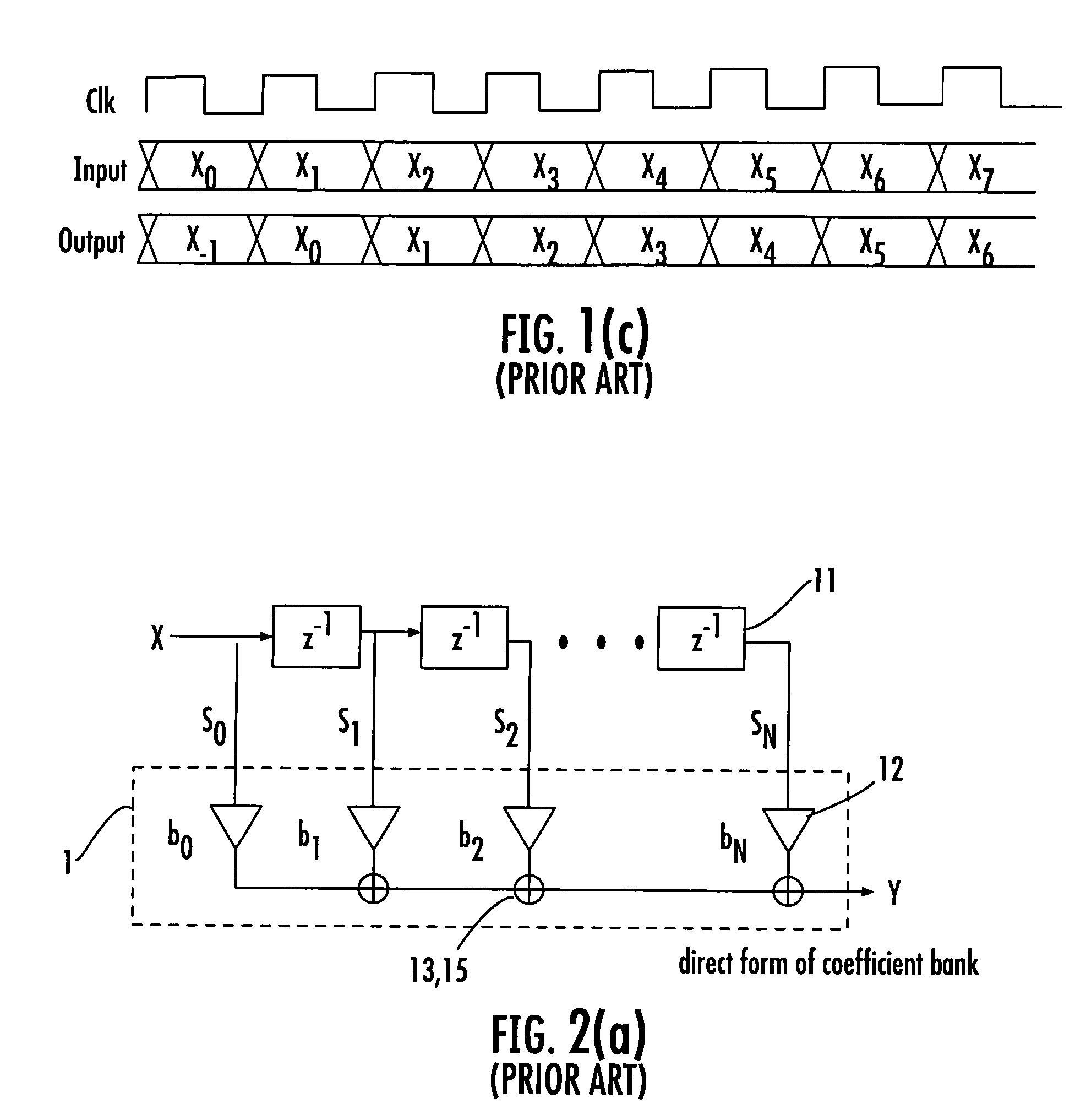
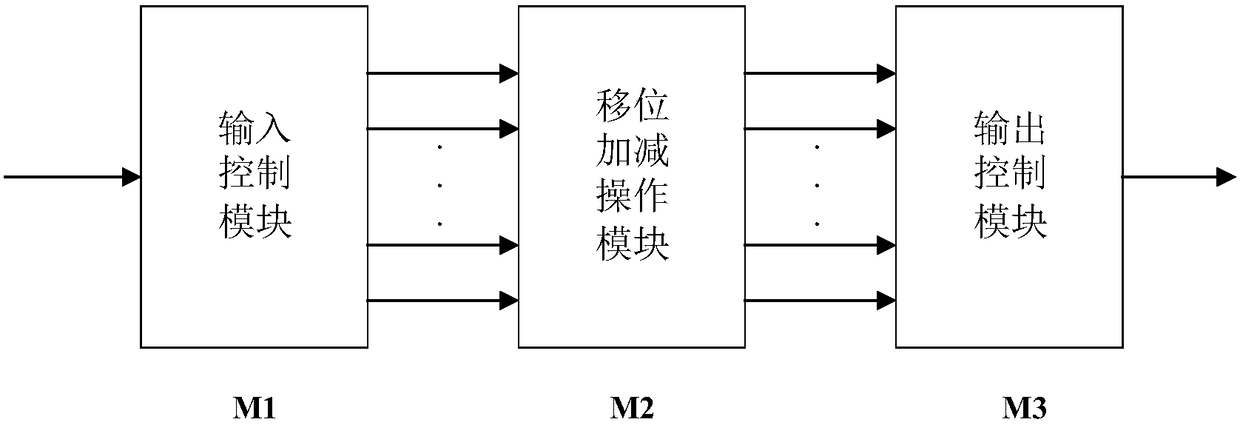
InactiveUS20060153321A1Digital technique networkDigital data processing detailsDecompositionShift-and-add
A device for implementing a sum-of-products expression includes a first set of 2-input Shift-and-Add (2SAD) blocks receiving a coefficient set / complex sum-of-products expression for generating a first set of partially optimized expression terms by applying recursive optimization therein, a second set of 1-input Shift-and-Add (1SAD) blocks receiving response from the 2SAD blocks for generating a second set of partially optimized expression terms by applying vertical optimization therein, a third set of 2SAD blocks receiving recursively and vertically optimized response from the first set of 2SAD block and the second set of 1SAD blocks for generating a third set of partially optimized expression terms by applying horizontal optimization therein, a fourth set of 2SAD blocks receiving response from the blocks for generating a fourth set of partially optimized expression terms by applying decomposition and factorization, and a fifth set of 2SAD blocks receiving response from the fourth set of 2SAD blocks, for generating the final output.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS PVT LTD
Fast multiplierless integer invertible transforms
ActiveUS8548265B2Satisfactory compatibilityFast and efficient hardware implementationCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationShift-and-addTrade offs
This invention relates to the design and implementation of a large family of fast, efficient, hardware-friendly fixed-point multiplierless inverse discrete cosine transforms (IDCT) and the corresponding forward transform counterparts. All of the proposed structures comprises of butterflies and dyadic-rational lifting steps that can be implemented using only shift-and-add operations. The approach also allows the computational scalability with different accuracy-versus-complexity trade-offs. Furthermore, the lifting construction allows a simple construction of the corresponding multiplierless forward DCT, providing bit-exact reconstruction if properly pairing with our proposed IDCT. With appropriately-chosen parameters, all of the disclosed structures can easily pass IEEE-1180 test. The high-accuracy algorithm of the present invention is over 100 times more accurate than IEEE-1180 specifications, leading to practically drifting-free reconstruction in popular MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 codecs even at the lowest quantization setting.
Owner:FASTVDO
A low-complexity multiplier-free fixed-point FFT optimization method based on dynamic truncation
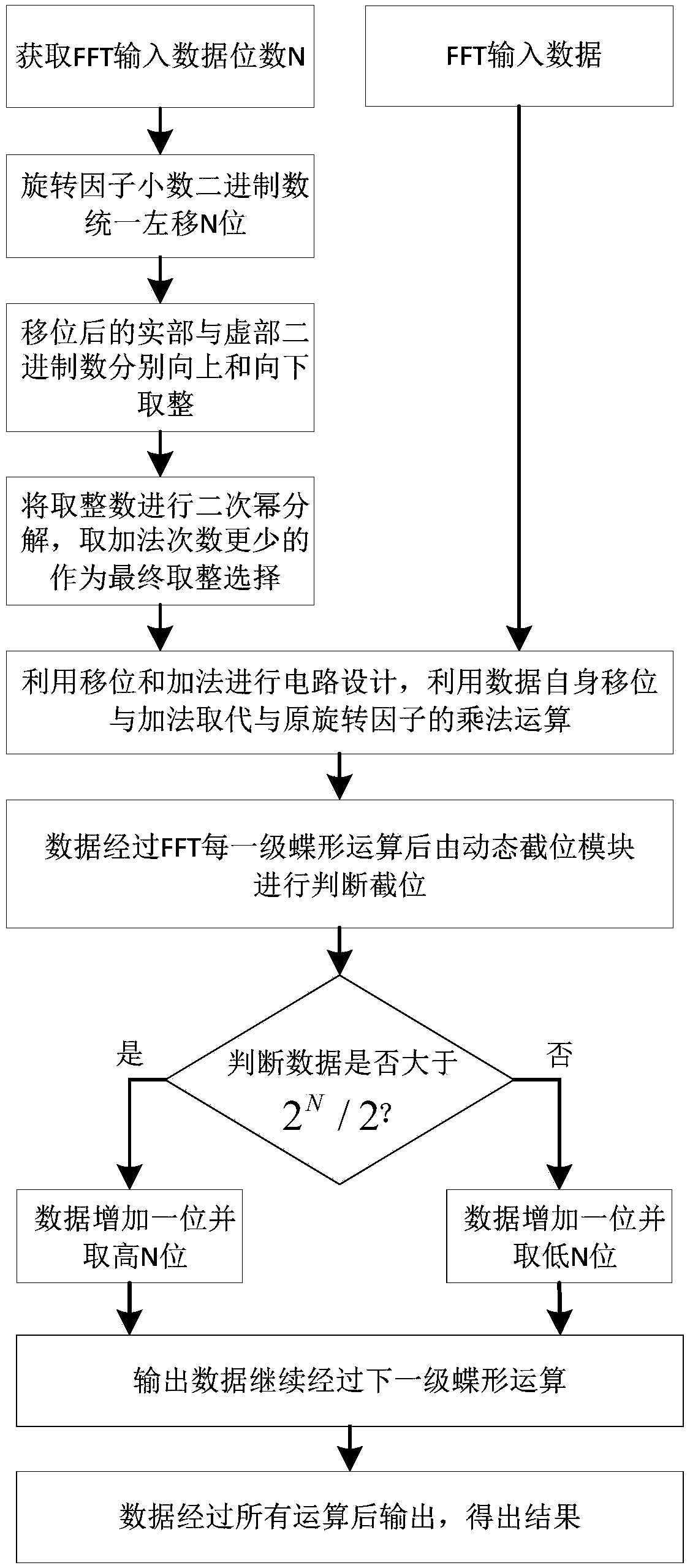
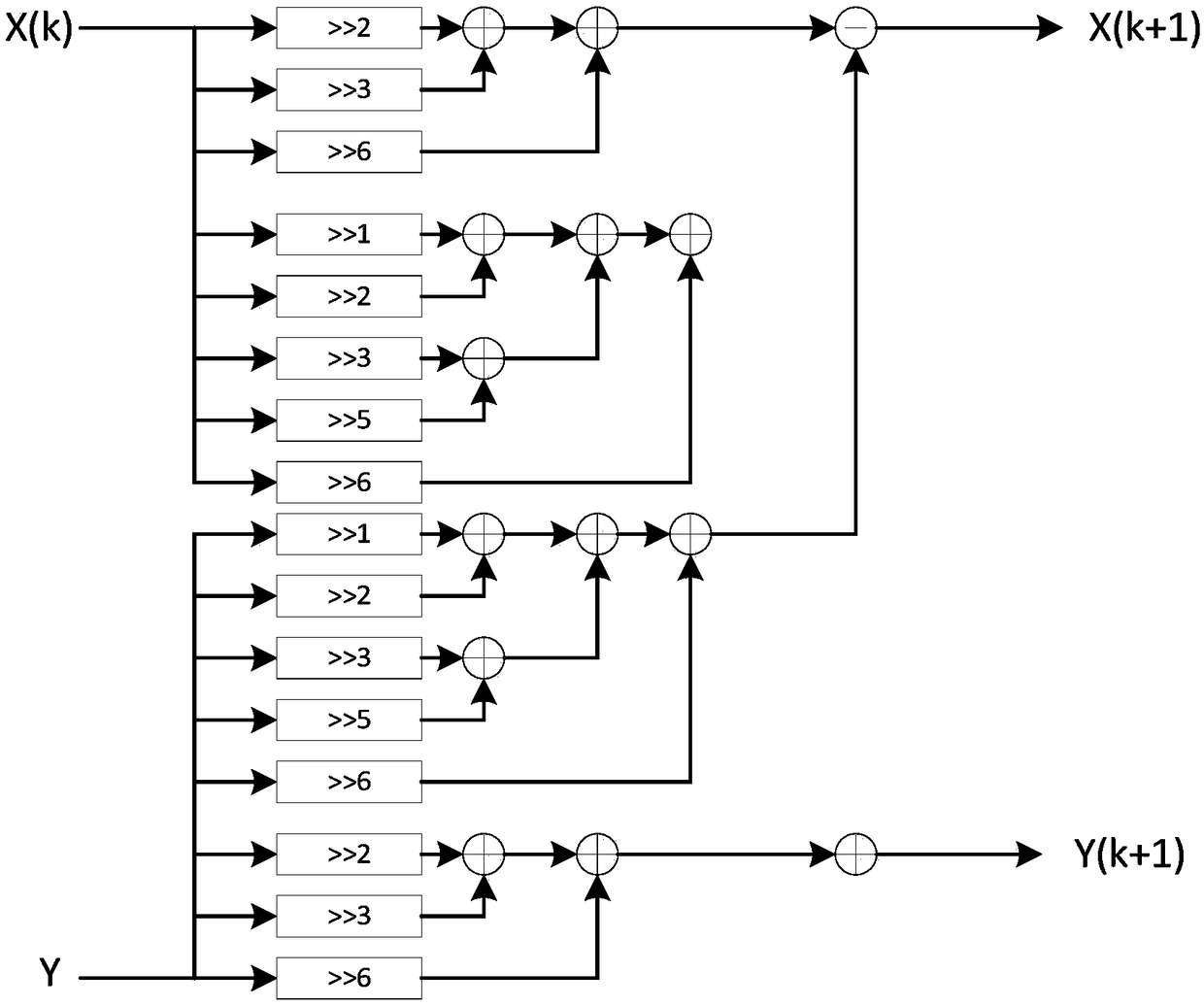
ActiveCN109359267AReduce in quantityImprove performanceComplex mathematical operationsRotation factorDigital signal processing
The invention belongs to the application field of software radio and digital signal processing thereof, in particular to a low-complexity multiplier-free fixed-point FFT optimization method based on dynamic truncation. The method includes obtaining FFT input data bits N and input data; shifting the decimal fraction of each rotation factor by N bits to the left, and dividing the data into a real part and an imaginary part, wherein N is the number of bits of the input data; rounding up the real part and the imaginary part up and down respectively, so that they are approximated to integers; All integers are factorized to the second power, and the integer with the least number of additions is selected; The circuit is designed by using shift and addition, and the multiplication of the originalrotation factor is replaced by the shift and addition of the data itself. The present invention further reduces the number of adders while replacing conventional complex multipliers with shift and add-subtract. At the same time, the dynamic bit-truncation module is added to restrain the growth of data bits, reduce the consumption of hardware resources, improve the computing speed and improve the performance of the circuit.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A convolution neural network accelerator
ActiveCN109543140AReduce storageFast operationComputation using non-contact making devicesCode conversionAlgorithmShift-and-add
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Frequency translator using a cordic phase rotator
A frequency translator uses a CORDIC phase rotator coupled to a phase accumulator to translate an input signal in frequency. The CORDIC phase rotator performs required phase angle rotations of input vectors using only shift and add operations. Thus, the frequency translator can be readily implemented in hardware. Higher precision arithmetic is used in the CORDIC phase rotator operations than the input vectors contain. To avoid truncation error at the output of the CORDIC phase rotator, stochastic rounding is employed. A dither signal is added to avoid errors due to nonlinear operation of D / A converters, where D / A conversion of the frequency translated signal is required.
Owner:思凯比特兹公司
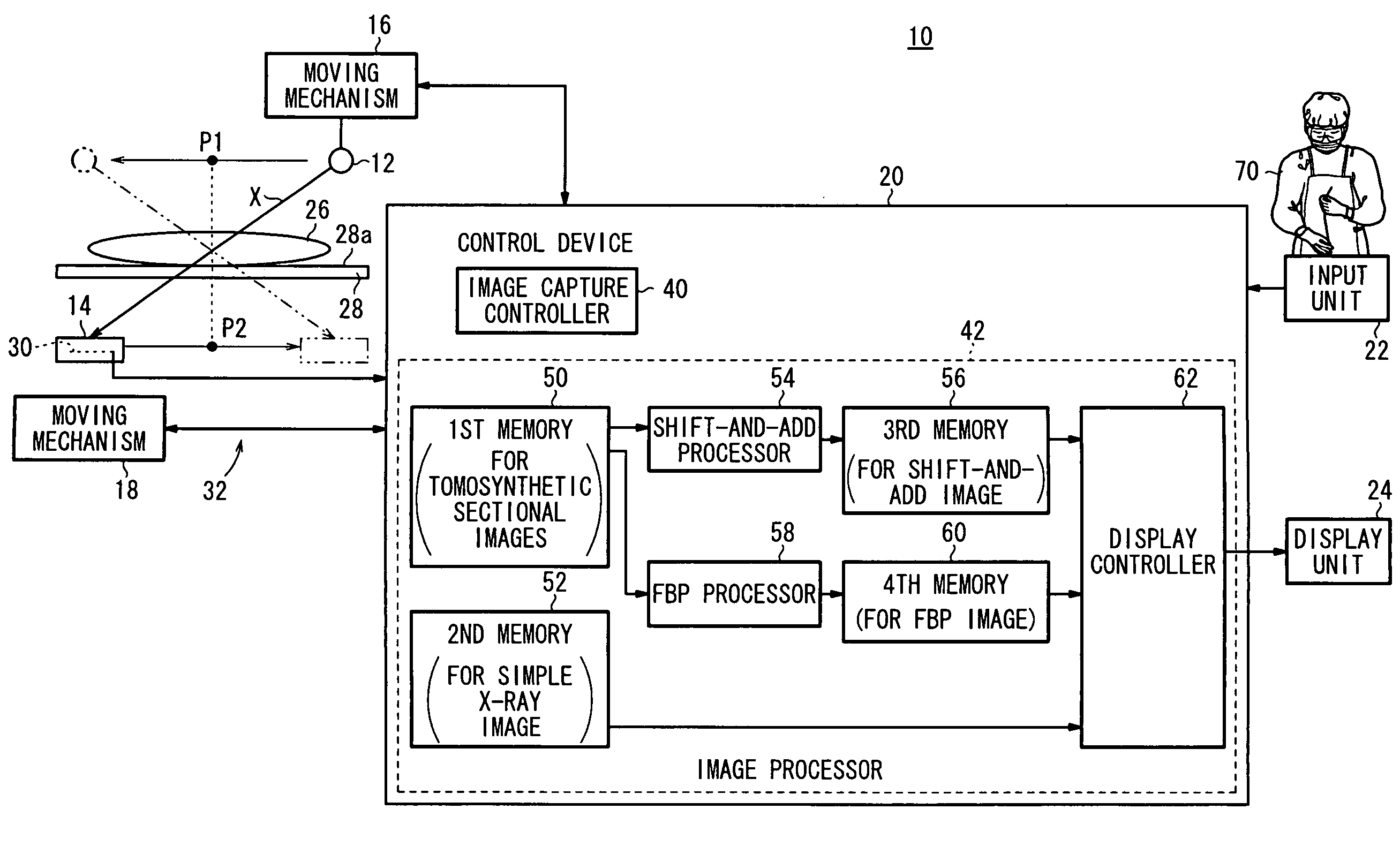
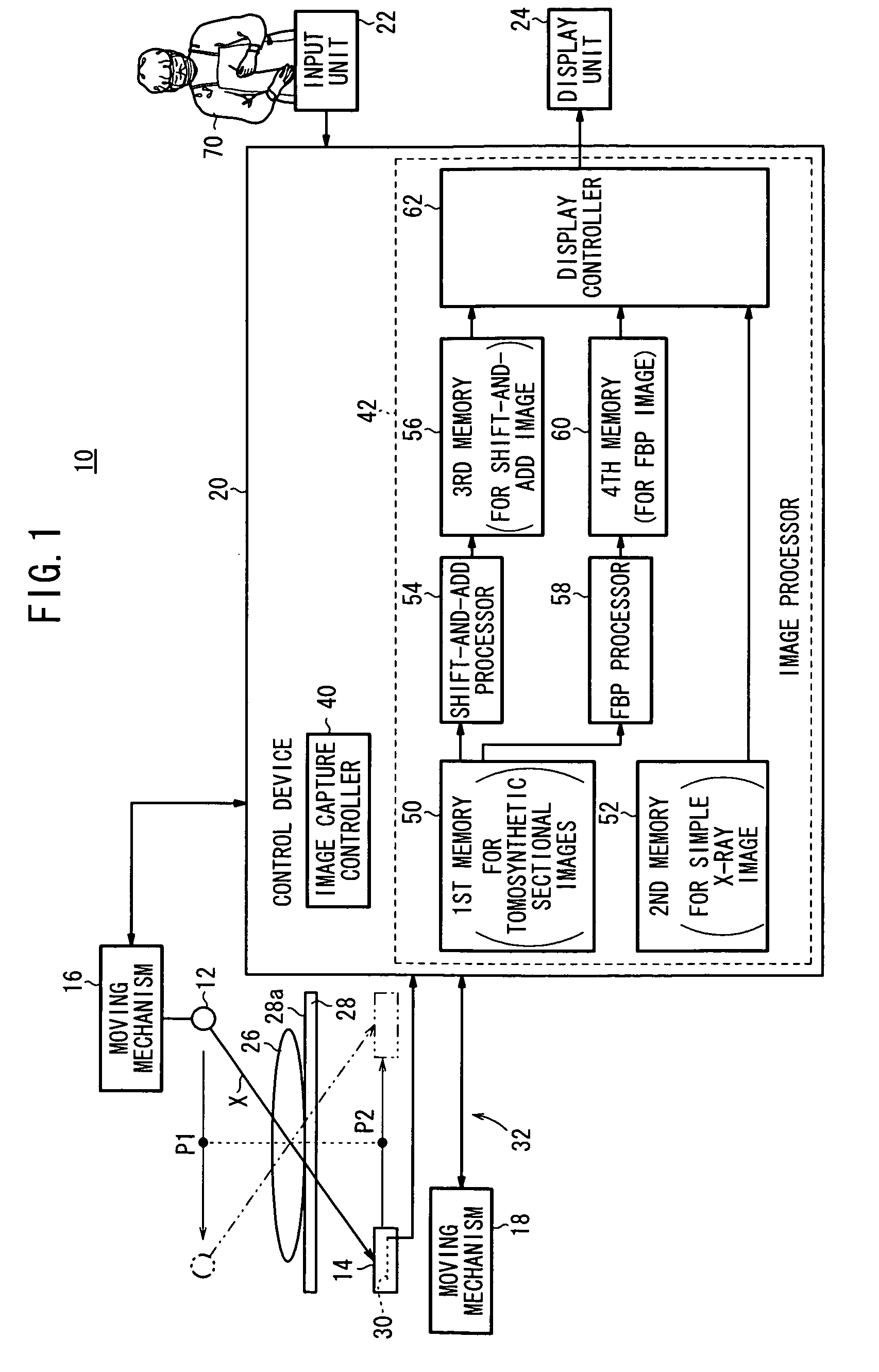
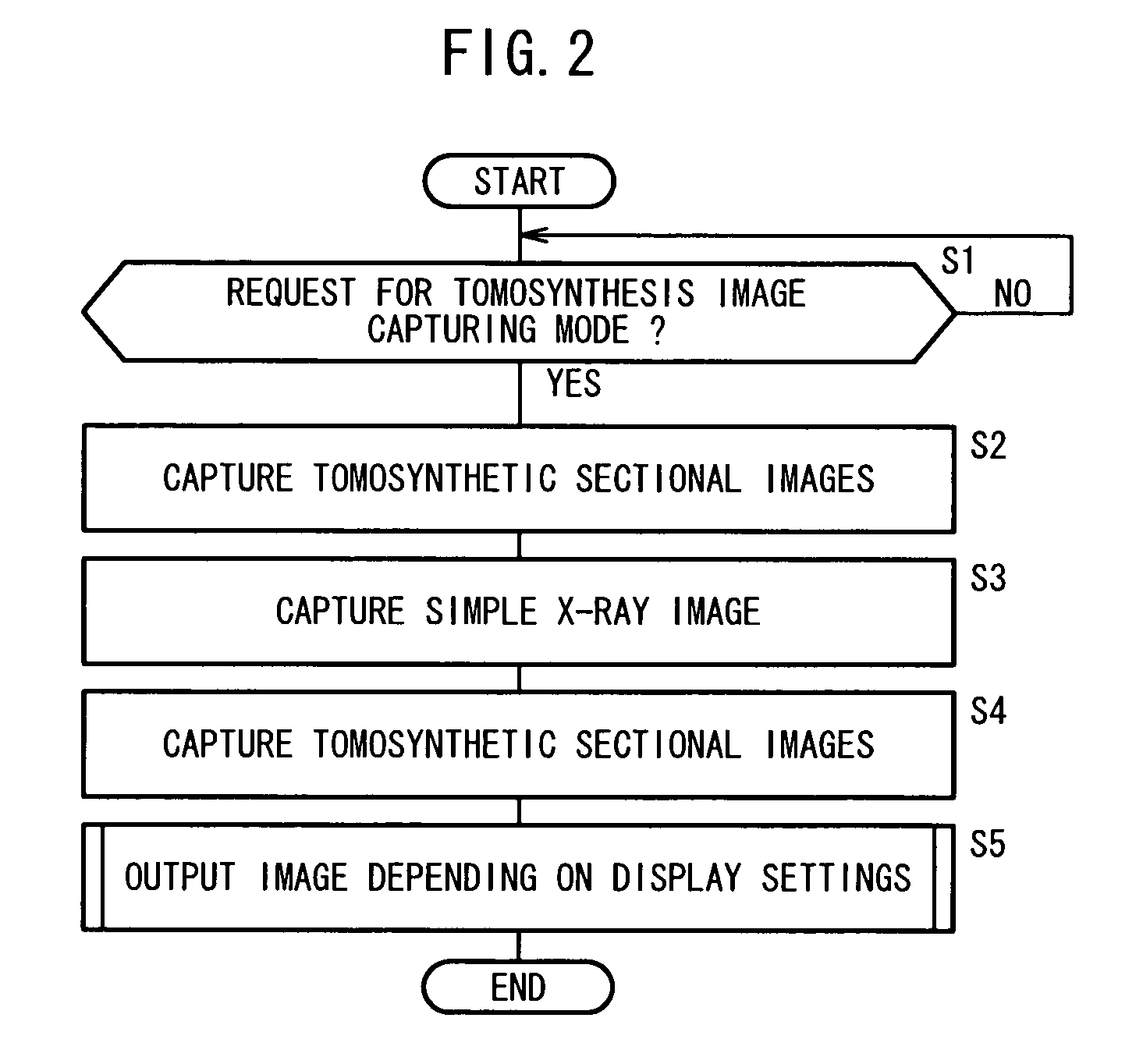
Radiation image diagnosing system
InactiveUS20100080438A1Effective diagnosisDiagnose the subject efficientlyReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomosynthesisShift-and-add
A radiation image diagnosing system includes a tomosynthesis image capturing assembly for acquiring the data of a plurality of tomosynthetic sectional images. The acquired data of the tomosynthetic sectional images are processed to reconstruct a shift-and-add image by a shift-and-add processor. The acquired data of the tomosynthetic sectional images are also processed to reconstruct an FBP image by an FBP processor. The shift-and-add image and the FBP image are displayed parallel to each other on a display unit.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
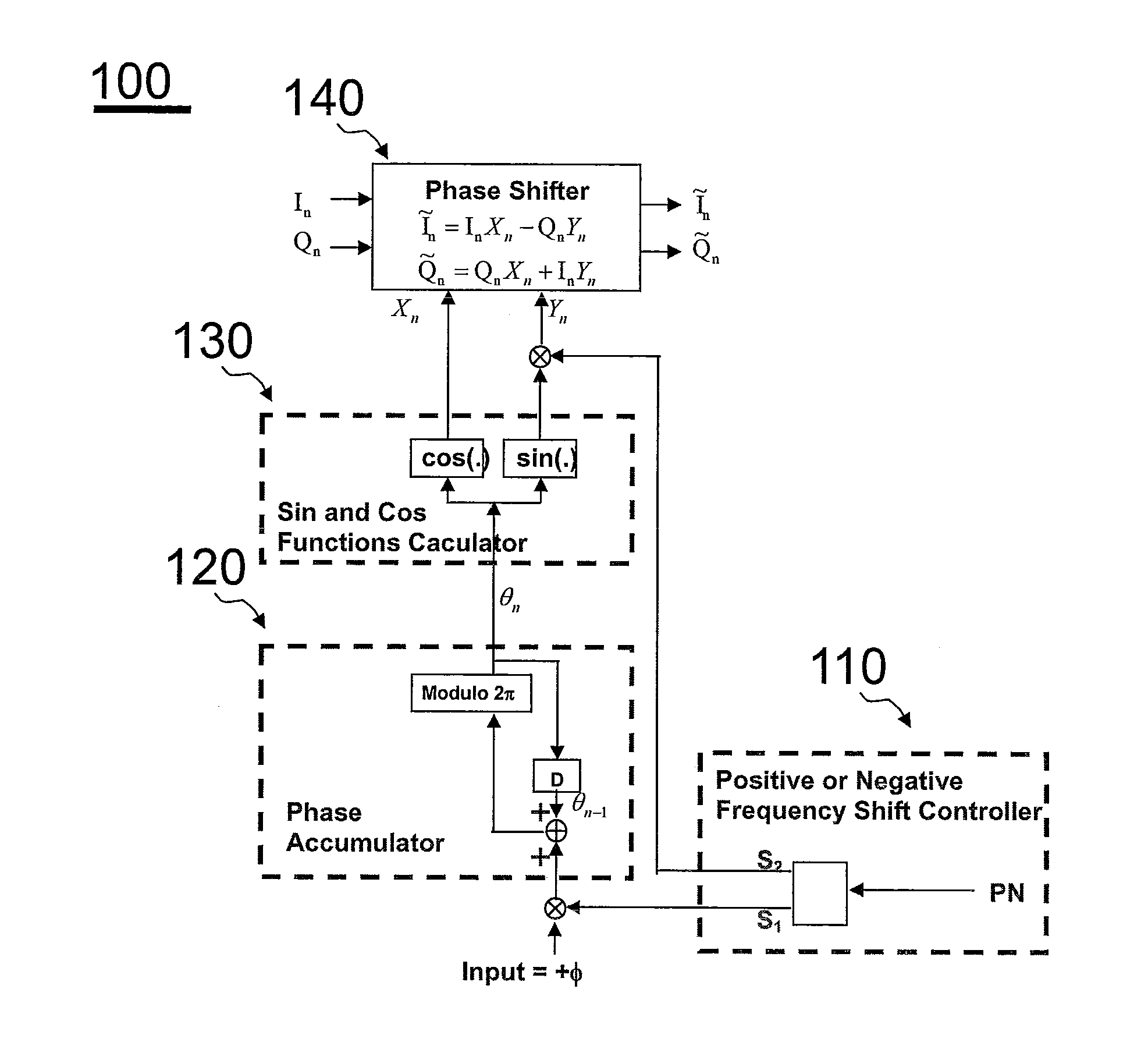
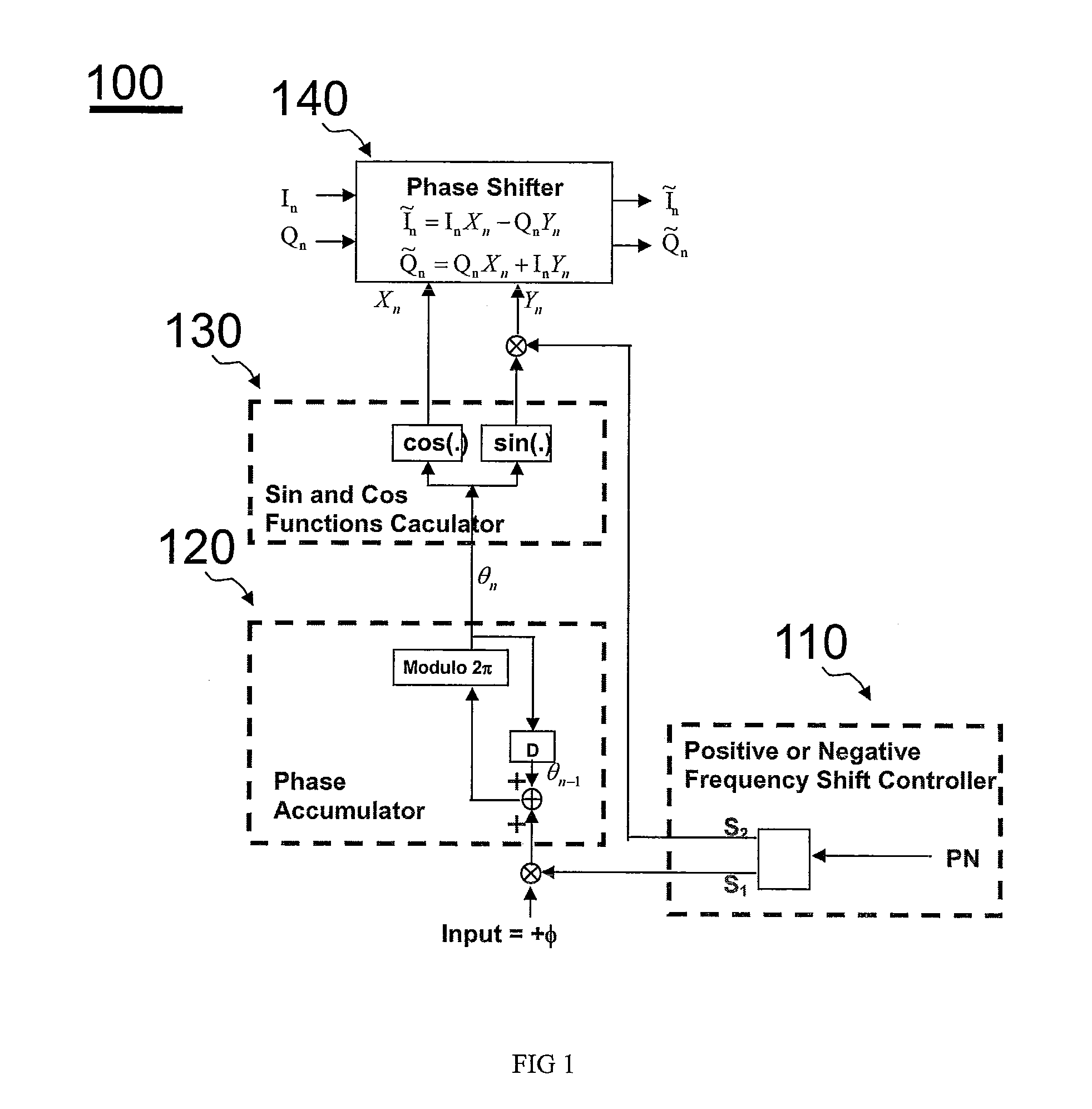
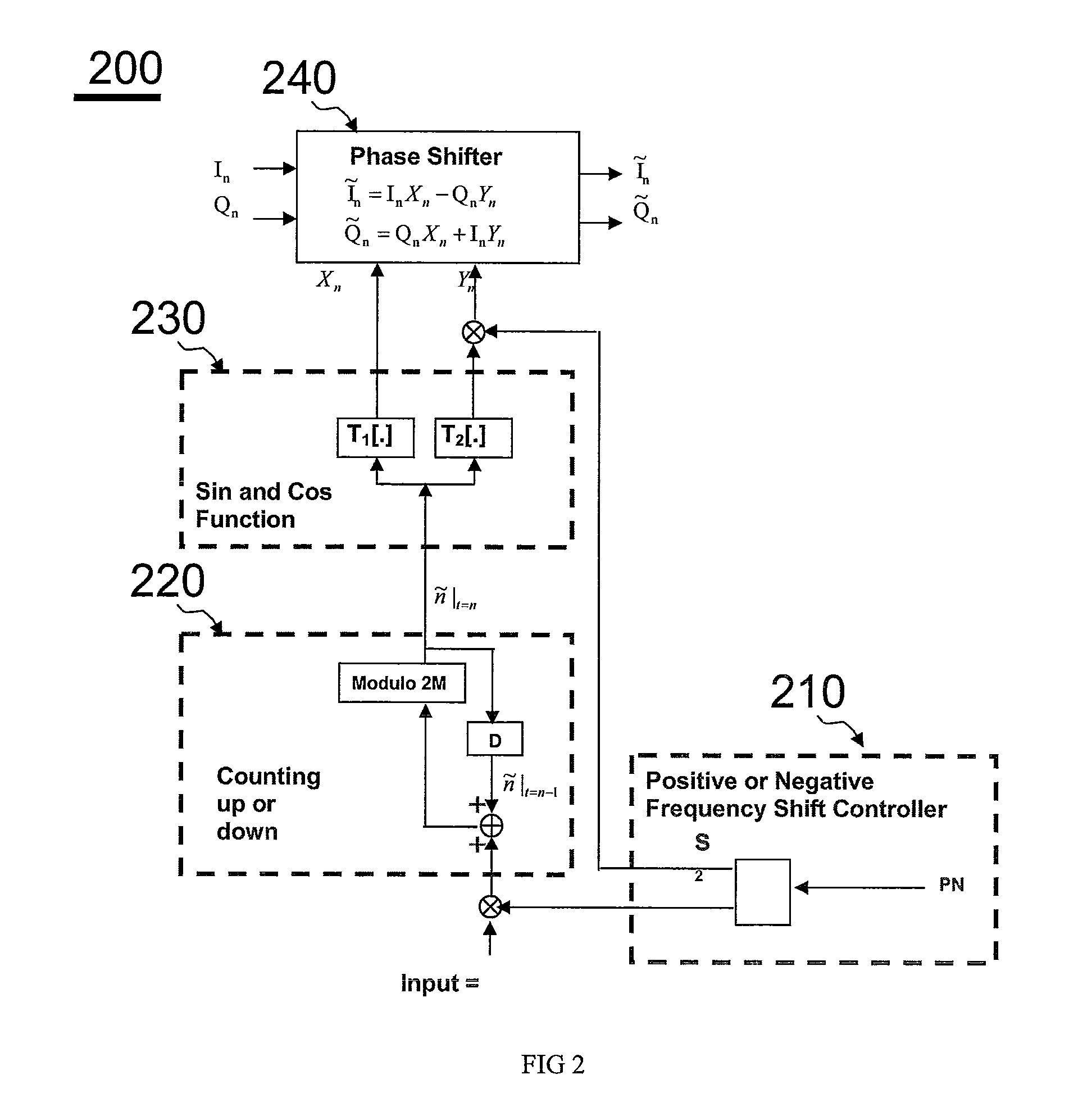
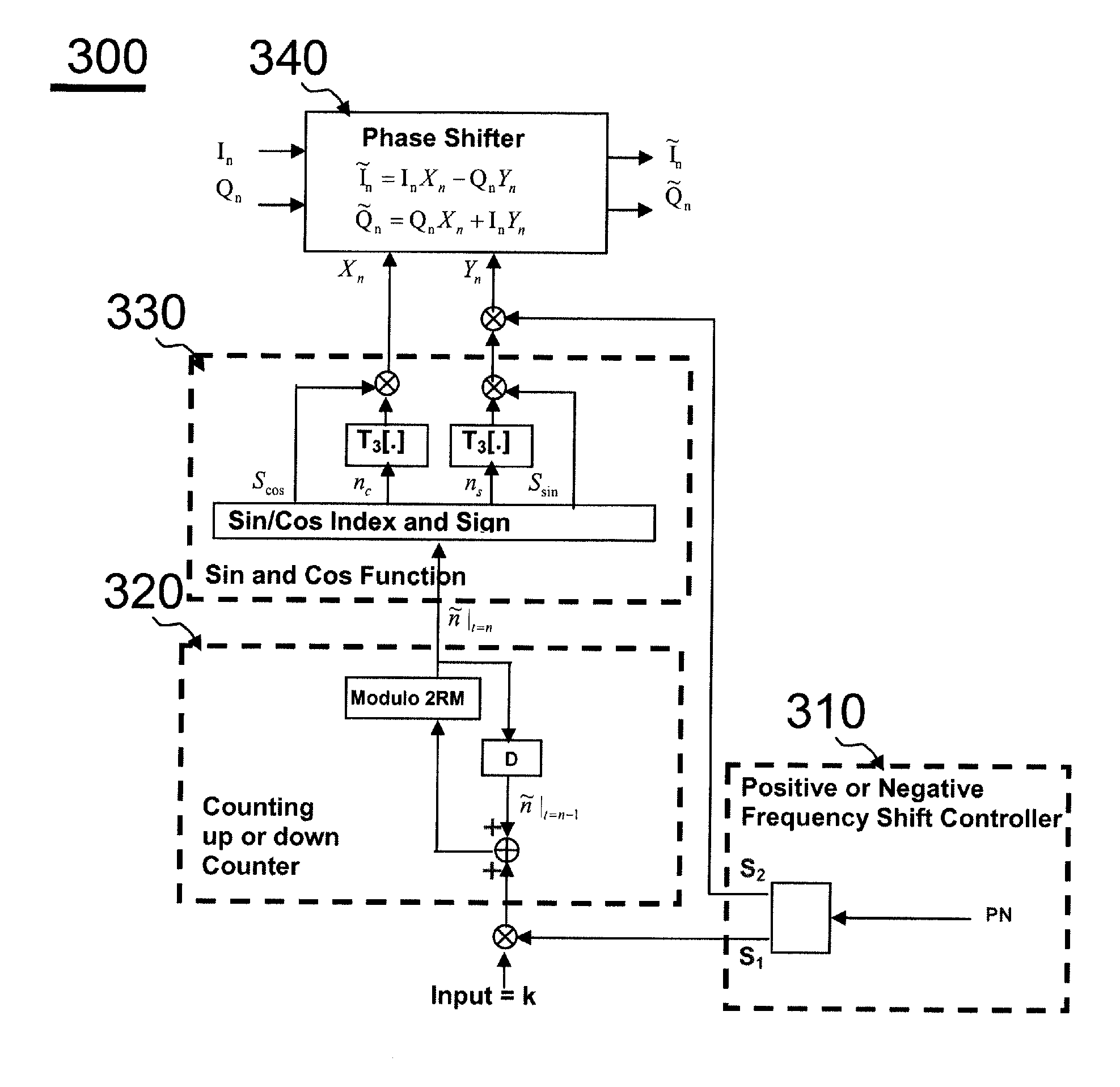
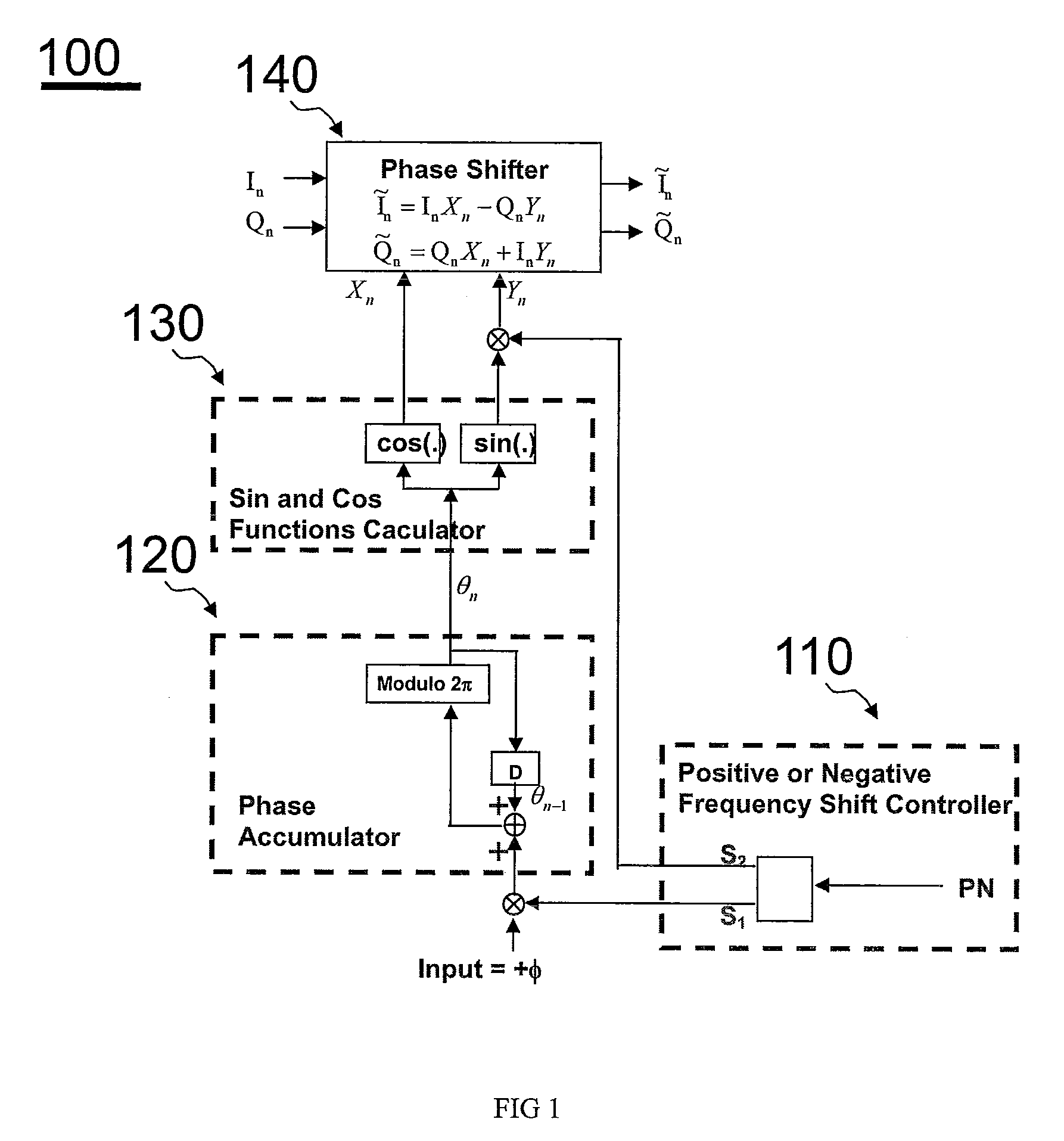
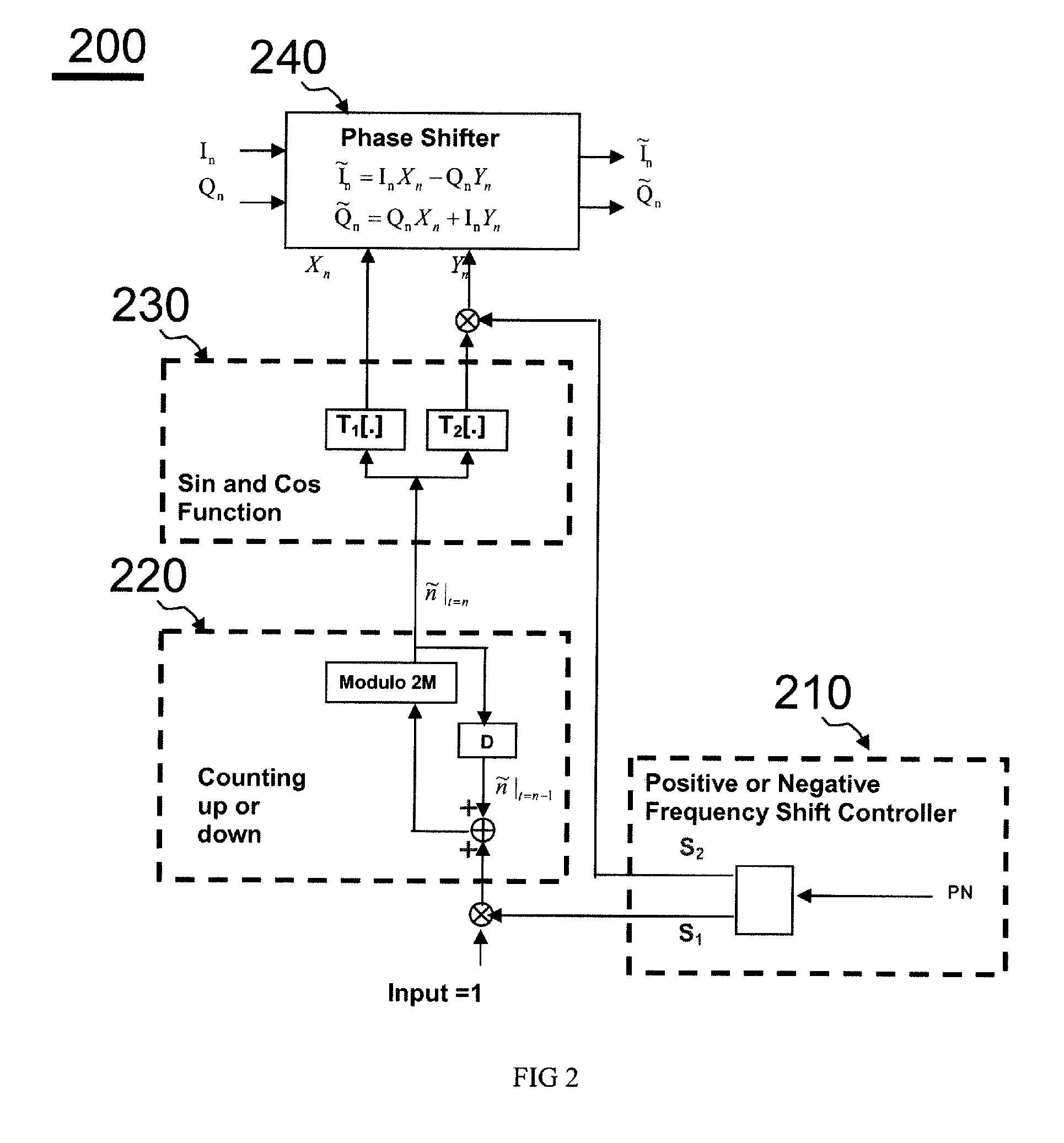
Arbitrary frequency shifter in communication systems
ActiveUS20110076952A1Easy to implementModulated-carrier systemsDigital data processing detailsSampling instantReal arithmetic
This invention describes a programmable, digital implementation to shift an arbitrary frequency, or various frequencies in various communication systems of the original signal in the frequency domain. The correspondent phase accumulation to perform the desired frequency shift per sampling instant is perfectly tracked by counting up or down a simple integer. Several arbitrary frequency shifters with different mathematical models are provided. The correspondent implementations with Look-Up-Tables (LUT) are derived for high-speed implementations without further calculations of the values of the sine and cosine functions every sampling instant. Furthermore, a simple shift-and-add phase rotation is described to replace the four required real multiplications. If the original complex signal contains only one-bit each from real part and imaginary part, a surprisingly simple implementation is derived and disclosed for the overall arbitrary frequency shift operation. Further simplifications are also disclosed to make this invention feasible for high sampling frequencies and small frequency drifts.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
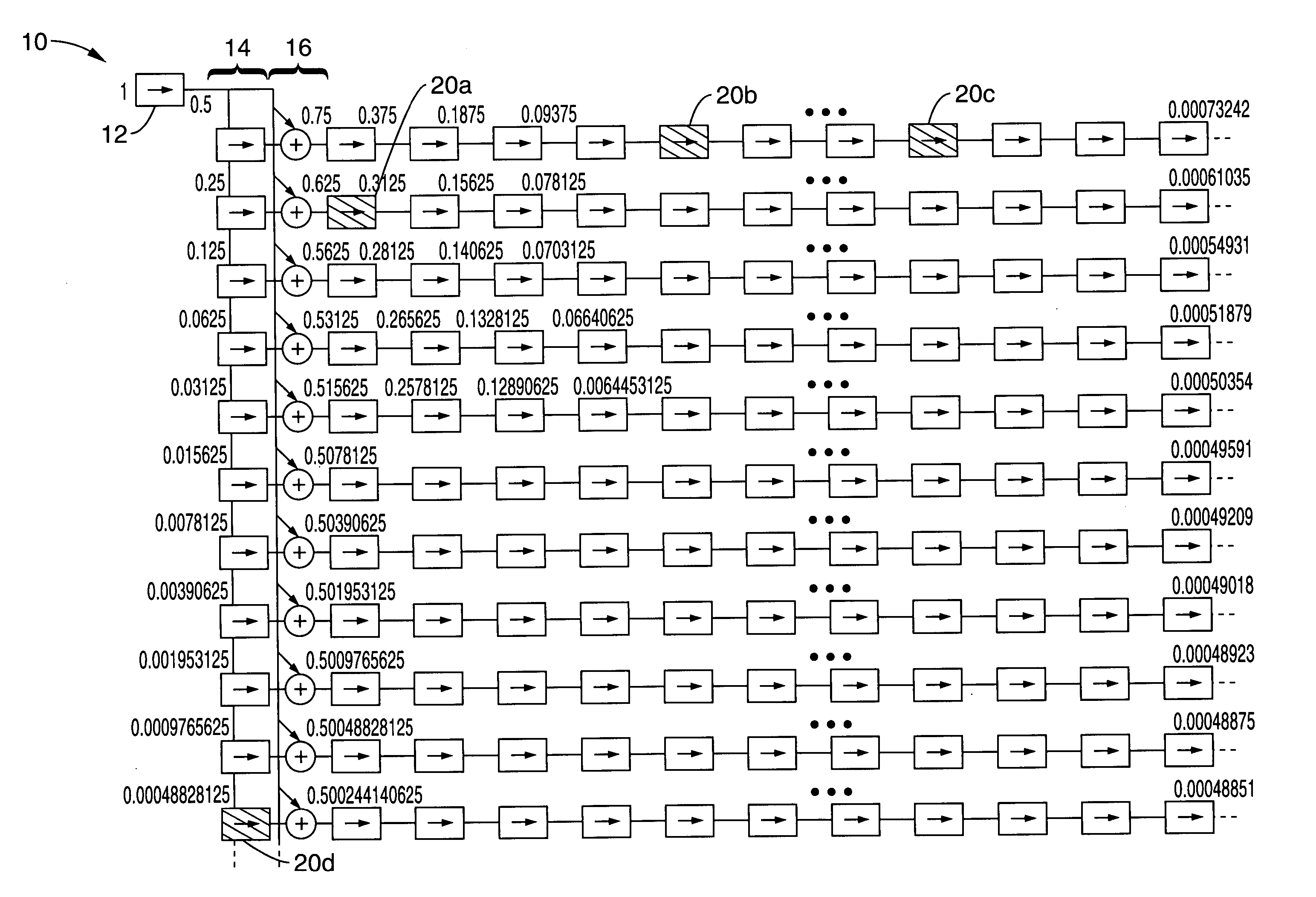
Power of two multiplication engine
InactiveUS20060095496A1Efficient implementationMinimal hardwareComputation using non-contact making devicesShift-and-addEngineering
A multiplication engine is described in which a decision threshold engine utilizes a Y-adder powers of two shift table to iteratively generate shift-add combinations. The shift-add combinations are output in a sequence with decreasing levels of contribution wherein the accuracy of the associated multiplication increases up to any desired level of accuracy to meet the requirements of the application. The multiplication engine can be used for generating the combinations either statically or dynamically. One embodiment describes a Y-adder hardware slider table engine in which the shift table is implemented with shifters and adders that can be set for active state or pass through state, and selectively summed to generate a product result directly from the table without the need to combine shift and add hardware.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Method and system for determining a number of data packets required to transport a data block
InactiveUS7839936B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNetwork packetShift-and-add
A method and system for determining a number of non-power of two sized data packets required to transport a data block. A data block size is shifted rightward by a number of bits equal to a base-two exponent of a divisor, with the bits remaining stored as a first value, and the bits removed stored as a second value. At least one binary shift is performed to calculate a third and fourth value. The fourth value is shifted and added to the second value to calculate a fifth value. At least one comparison is performed on the fifth value to process a sixth and seventh value. A number of non-power of two sized data packets is determined by summing the first, third, and sixth values, then adding one if the seventh value is not zero.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Device for implementing a sum of products expression
InactiveUS7917569B2Digital technique networkDigital data processing detailsShift-and-addDecomposition
A device for implementing a sum-of-products expression includes a first set of 2-input Shift-and-Add (2SAD) blocks receiving a coefficient set / complex sum-of-products expression for generating a first set of partially optimized expression terms by applying recursive optimization therein, a second set of 1-input Shift-and-Add (1SAD) blocks receiving response from the 2SAD blocks for generating a second set of partially optimized expression terms by applying vertical optimization therein, a third set of 2SAD blocks receiving recursively and vertically optimized response from the first set of 2SAD block and the second set of 1SAD blocks for generating a third set of partially optimized expression terms by applying horizontal optimization therein, a fourth set of 2SAD blocks receiving response from the blocks for generating a fourth set of partially optimized expression terms by applying decomposition and factorization, and a fifth set of 2SAD blocks receiving response from the fourth set of 2SAD blocks, for generating the final output.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS PVT LTD
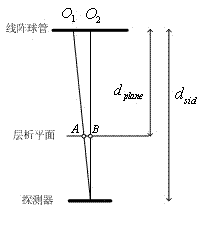
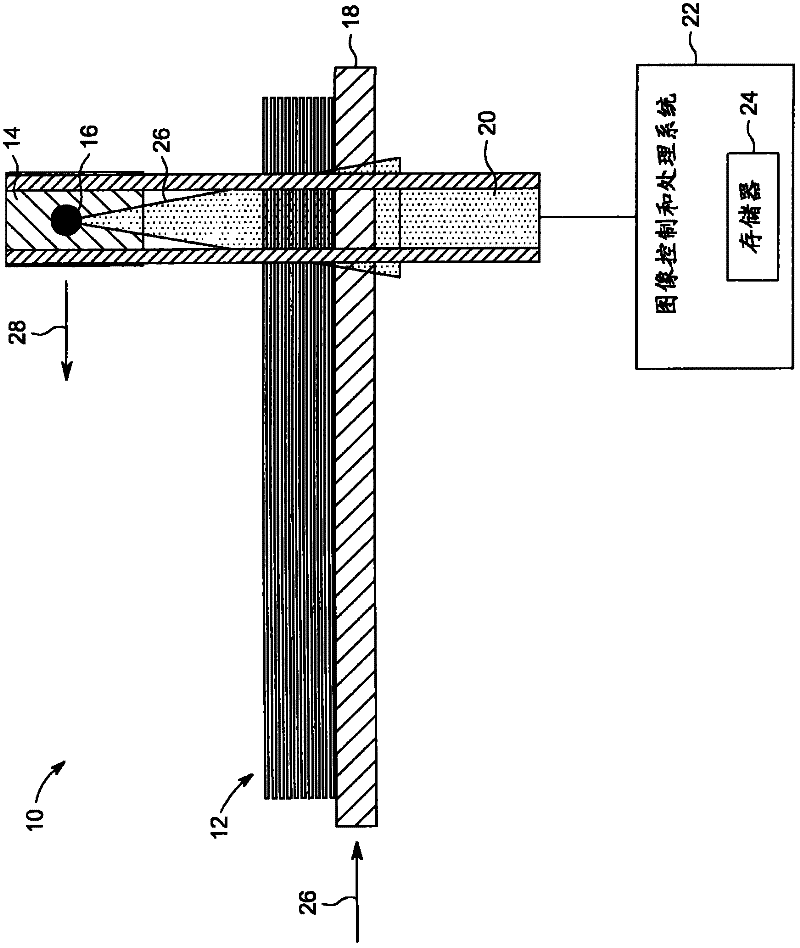
Method and apparatus for laminography inspection
InactiveCN102539456AEliminate travel timeEliminates the need to move timeUsing wave/particle radiation meansX-ray tube multi-cathode assemblyShift-and-addProjection image
Imaging systems including a multiple focal spot x-ray source adapted to irradiate an object with a series of angularly displaced x-ray beams, one at a time, without substantial rotation or translation of the multiple focal spot x-ray source are provided. Such systems also includes a detector adapted to receive at least a fraction of the angularly displaced x-ray beams after being attenuated by the object to produce at least two x-ray projection images of the object. The imaging systems also include a processor adapted to shift and add the at least two x-ray projection images to bring at least two planes of the object into focus, one at a time.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multiplex signal error correction method and device
InactiveUS7583770B2Reduce errorsMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPhase correctionShift-and-add
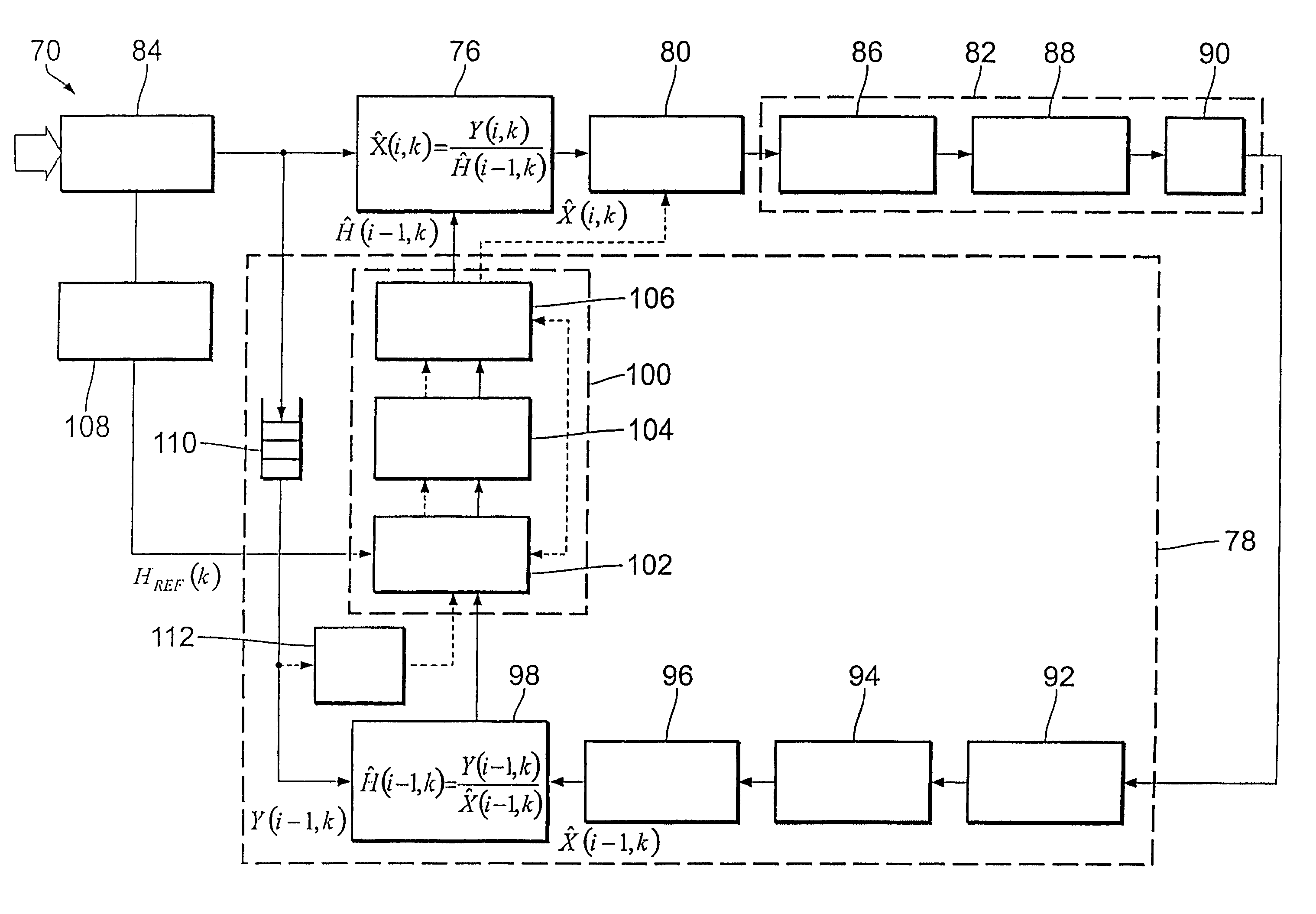
A method of reducing a phase error caused by a plurality of error sources in a signal in the form of a sequence of a plurality of digital partial signals associated with a number of subcarriers (k) of a carrier, the method including, for each partial signal: equalization of the partial signal (Y(i,k)), estimation of the phase error of the equalized partial signal (X(i,k)), and correction of the estimated phase error of the equalized partial signal. One embodiment provides the equalization with elimination of an accumulation of a phase error over the sequence of the partial signals. In addition the estimation includes detecting a plurality of predetermined pilot signals and determining a phase correction factor on the basis of the detected pilot signals, with at least one multiplication operation carried out solely by means of shift and adding operations. A corresponding apparatus is also described.
Owner:IHP GMBH INNOVATIONS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE MICROELECTRONICS LEIBNIZ INST FUR INNOVATIVE
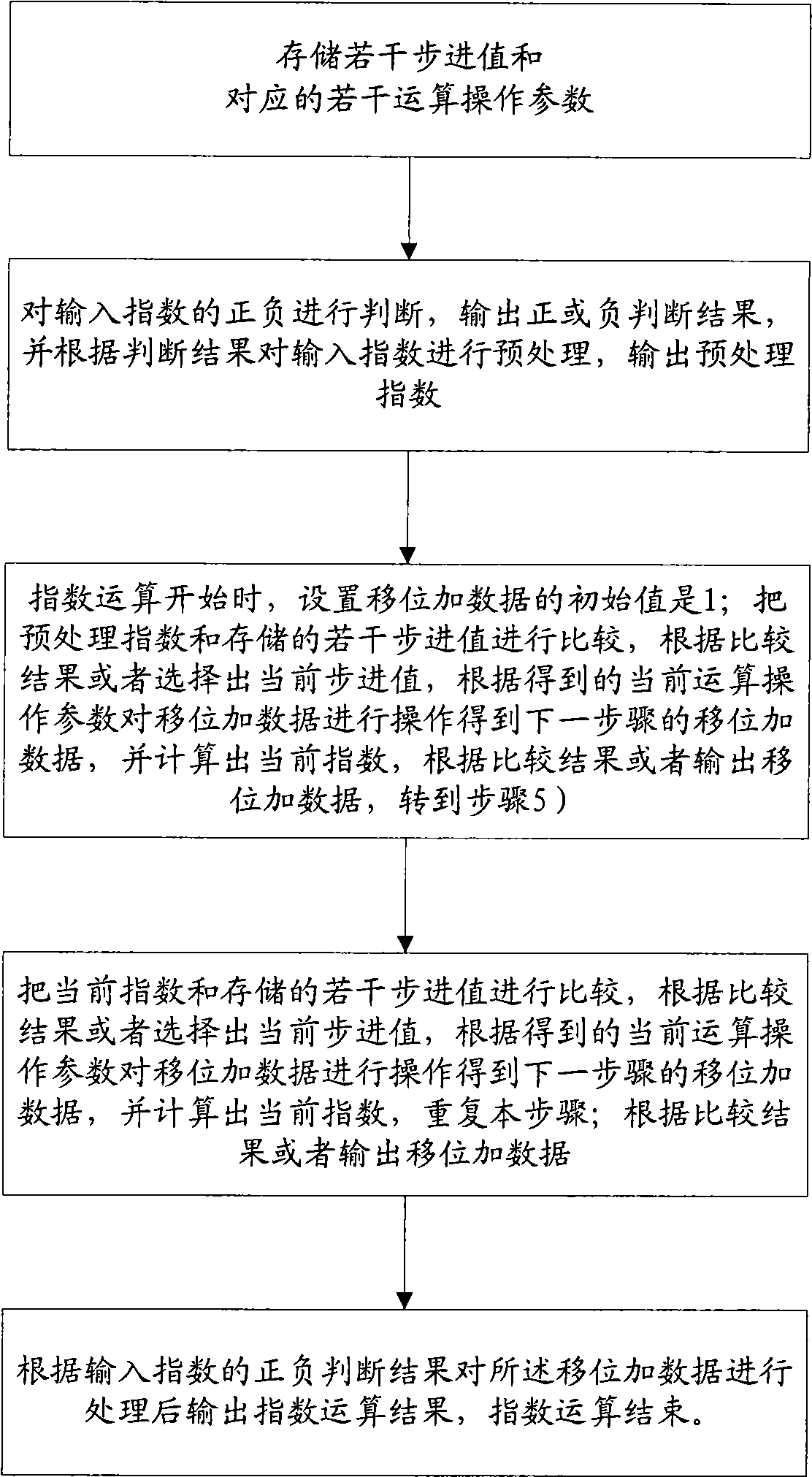
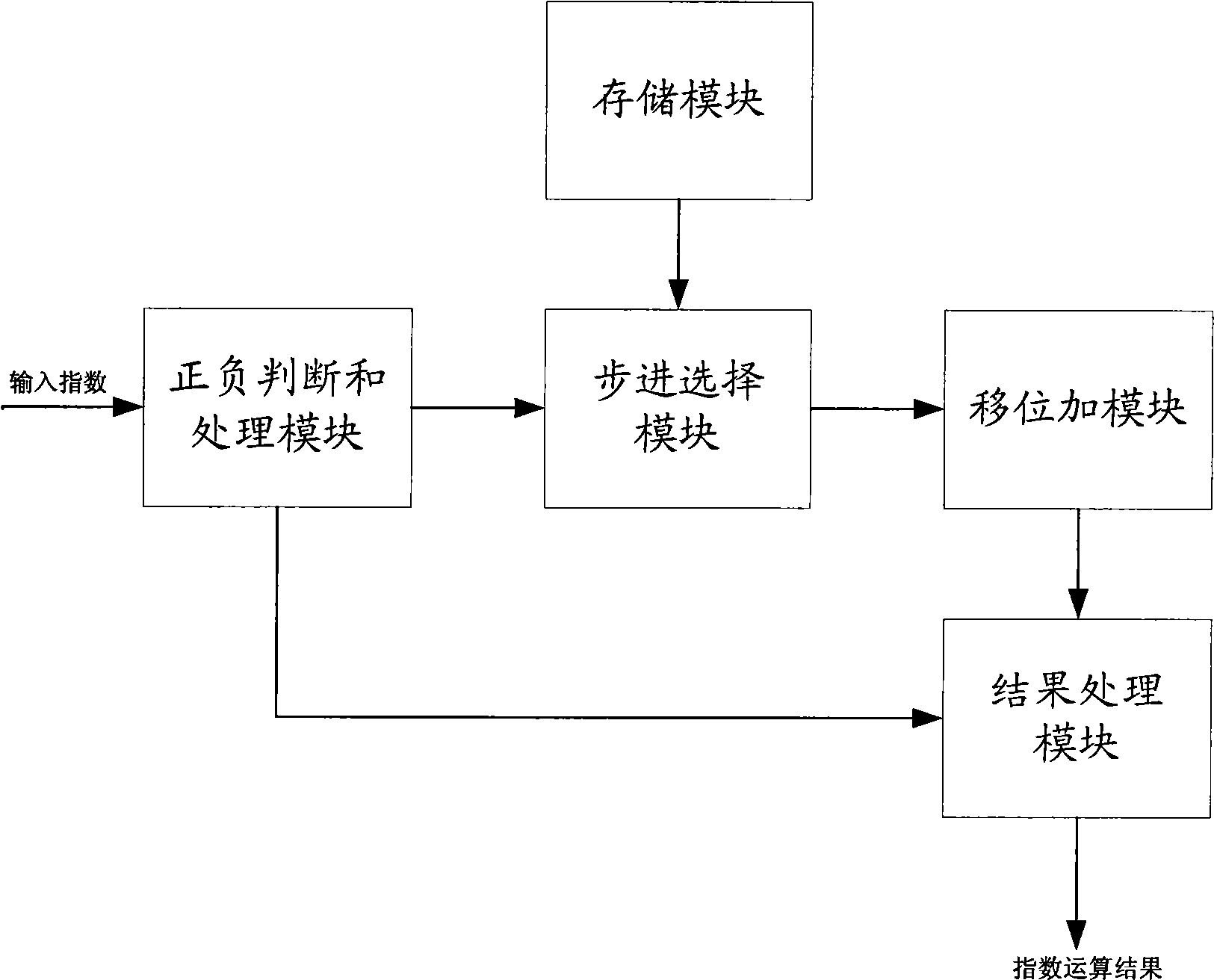
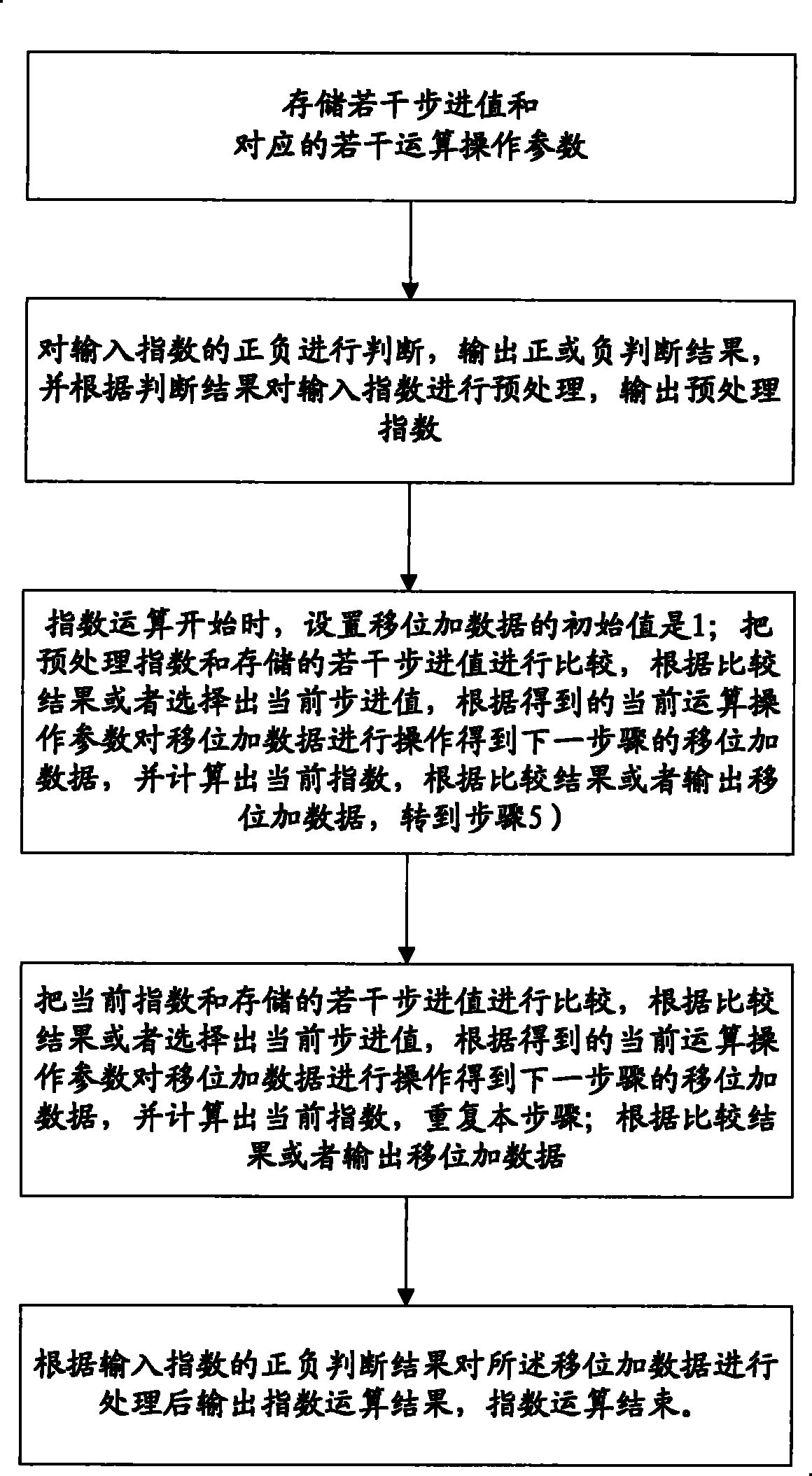
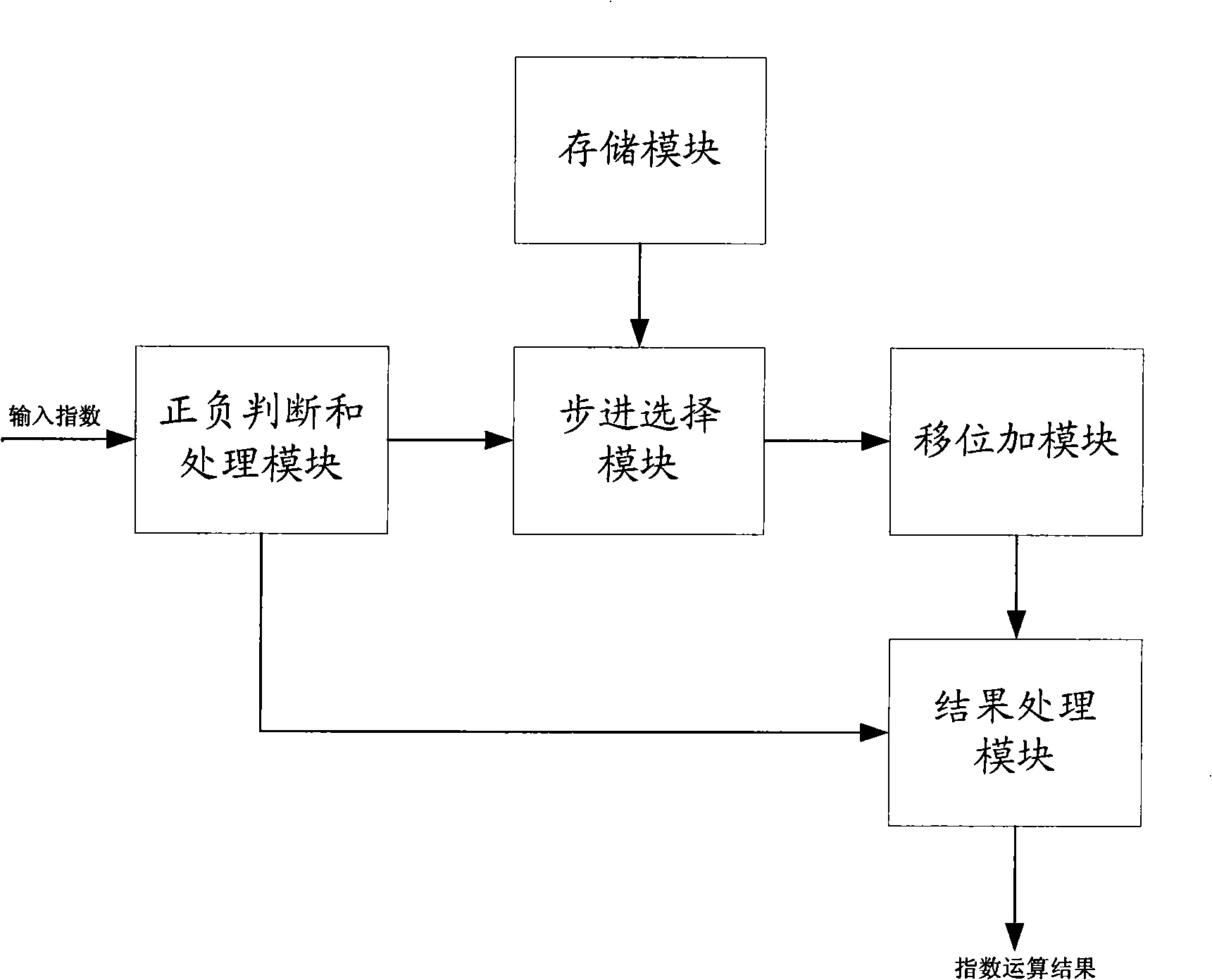
Index operation method and device
ActiveCN101510148AExcellent precisionExcellent resourcesDigital data processing detailsShift-and-addComputer science
The invention provides an exponent arithmetic method and device; the method comprises the steps of storing a plurality of step values and corresponding calculation operating parameters; preprocessing input indexes according to the plus-minus of the input indexes; setting the initial value of add and shift data to be 1 when the exponent arithmetic is started; firstly comparing the processed indexes with the plurality of stored step values to select the step values of the indexes and corresponding exponent arithmetic parameters; carrying out substraction to the processed indexes and the selected step values and taking the result as the current indexes; comparing the current indexes with the plurality of stored step values to select the step values of the indexes and corresponding exponent arithmetic parameters again; in this way, comparing the current indexes with the stored step values without repetition until the current indexes are smaller than all the stored step values; carrying out shift operation or shift and add operation to the add and shift data according to the obtained exponent arithmetic parameters in each step; and finally processing the add and shift data according to the plus-minus of the input indexes and outputting the exponent arithmetic result.
Owner:VIMICRO ELECTRONICS CORP
Fast mechanism for accessing 2n±1 interleaved memory system
InactiveUS9268691B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationShift-and-addComputer module
A mechanism implemented by a controller enables efficient access to an interleaved memory system that includes M modules, M being (2n+1) or (2n−1), n being a positive integer number. Upon receiving an address N, the controller performs shift and add / subtract operations to obtain a quotient of N divided by M based on a binomial series expansion of N over M. The controller computes a remainder of N divided by M based on the quotient. The controller then accesses one of the modules in the memory based on the remainder.
Owner:INTEL CORP
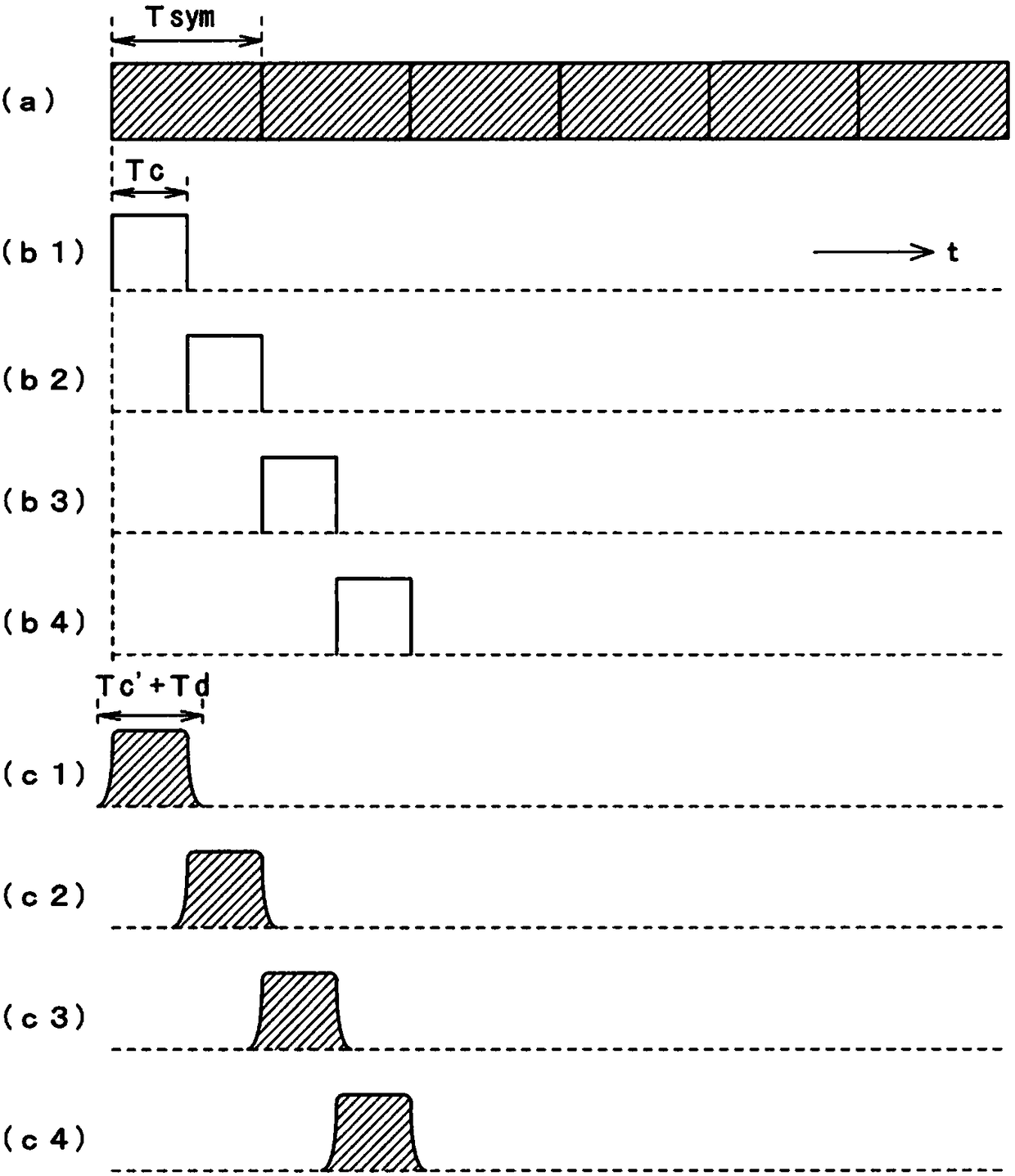
Device and method for testing MIMO scheme system
ActiveCN108206718ASmall scaleGreat reduction effectSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
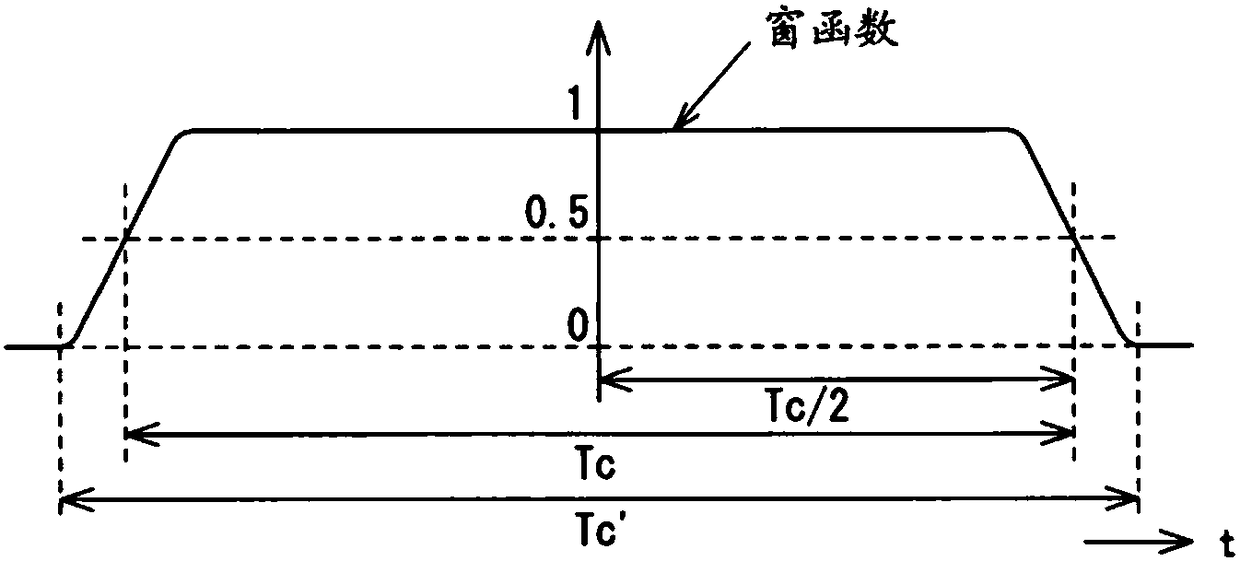
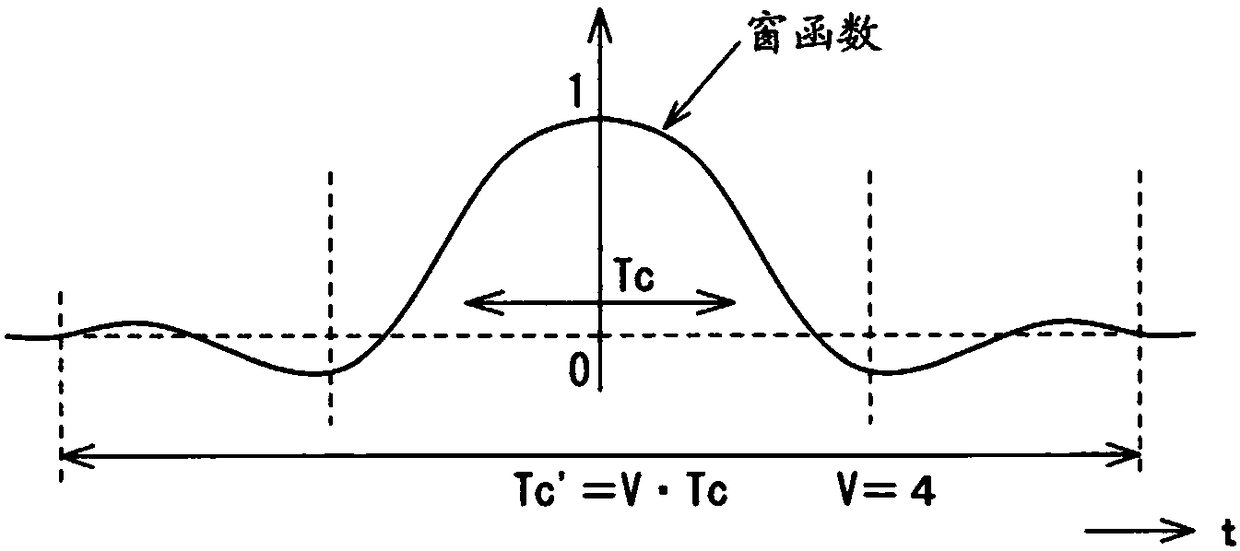
The invention provides a testing device for a system, and the device is small in circuit scale and uses little electricity. The system combines multi-carrier, a MIMO scheme, and beam forming processing. For modulation signals of each carrier of an R layer quantity output by a layer frequency domain signal generation unit (31), a window function arithmetic operation unit (32) performs convolution arithmetic operation of frequency characteristics of a window function. On another aspect, for a beam forming equivalence arithmetic operation unit (52) performs an arithmetic operation process equivalent to the beam forming process with the input of propagation channel characteristics of each path which are output by a fading setting unit (51), and a Fourier transform unit (53) performs Fourier transform with the input of the arithmetic operation results. An arithmetic operation unit (54) performs multiplication on two operation results Ht and Fsym, obtains spectrum information of signals to be received in receiving antennas, and converts the obtained spectrum information into signals in the time domain through inverse Fourier transform processes performed by a time domain signal generation unit. A shift addition unit (34) shifts and adds the converted signals, to generate received signals of the receiving antennas.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
A fully automatic multi-mode 3D color measurement method based on multi-view
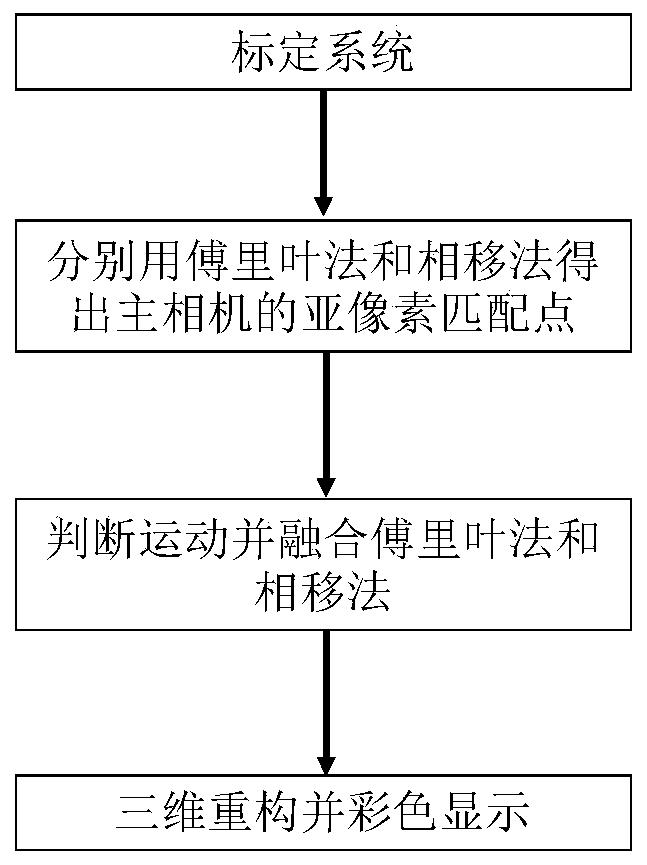
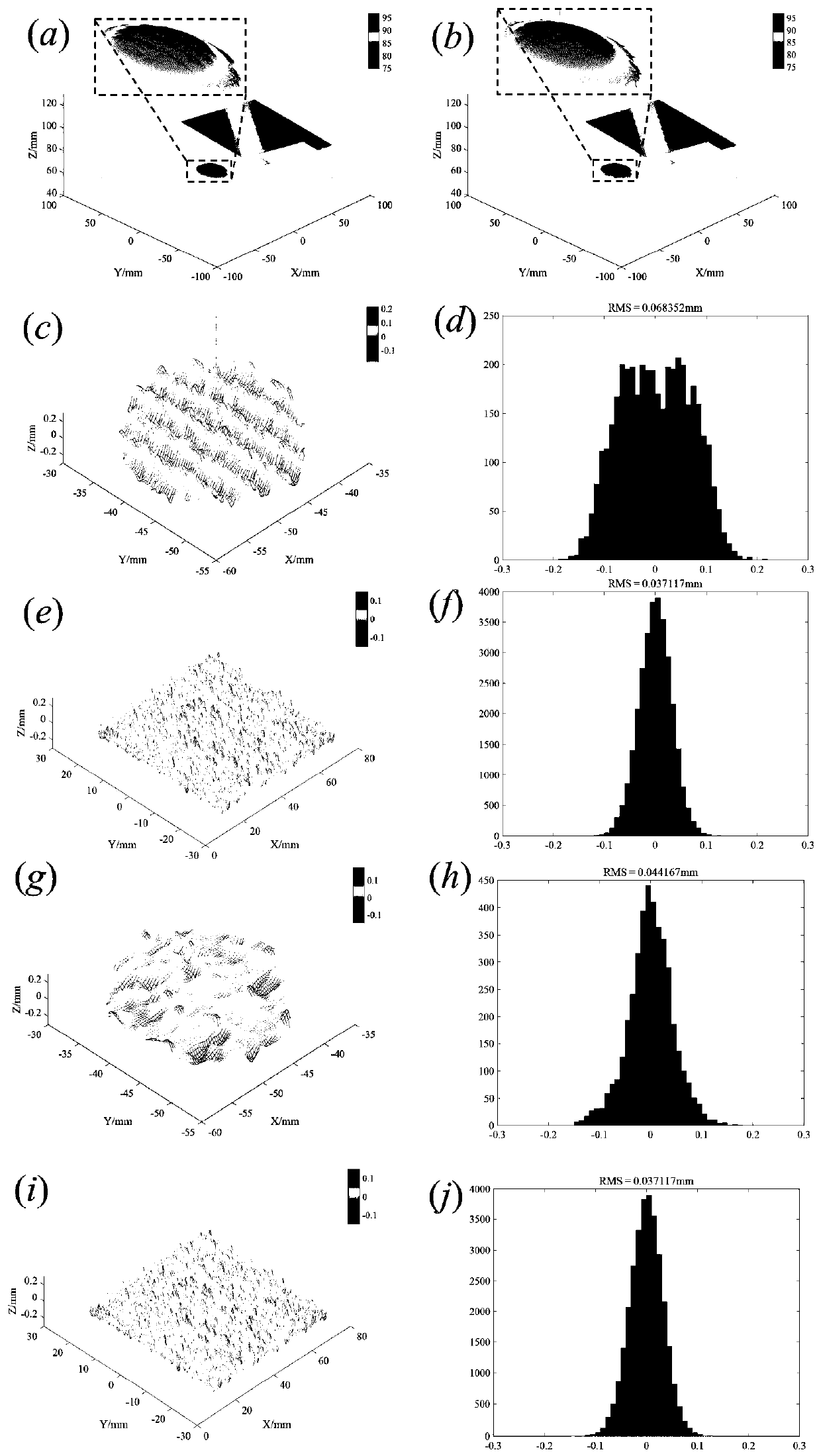
ActiveCN109579741BHigh speedHigh precisionUsing optical meansPattern recognitionFourier profilometry
The invention discloses a multi-view-based full-automatic multi-modal three-dimensional color measurement method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly performing phase-shift profilometryby adopting a three-step phase-shift method, and performing Fourier profilometry by utilizing the second fringe in the three-step phase-shift and adding an all-white graph, and unwrapping phase basedon a stereo phase unwrapping method; and then judging a movement region of a measured object pixel by pixel through the change of two adjacent moment phases; acquiring the high-precision profile by utilizing the phase-shift profilometry when measuring a static object; and effectively extracting the motion object profile by utilizing the Fourier profilometry when measuring a dynamic object. The advantages of the Fourier profilometry and the phase-shift profilometry can be sufficiently utilized under a complex scene (the scene contains the moving object and the static object or the object is inmoving and static states at the same time), thereby obtaining a reconstruction result with better precision.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Arbitrary frequency shifter in communication systems
ActiveUS8437427B2Easy to implementModulated-carrier systemsDigital data processing detailsSampling instantCommunications system
This invention describes a programmable, digital implementation to shift an arbitrary frequency, or various frequencies in various communication systems of the original signal in the frequency domain. The correspondent phase accumulation to perform the desired frequency shift per sampling instant is perfectly tracked by counting up or down a simple integer. Several arbitrary frequency shifters with different mathematical models are provided. The correspondent implementations with Look-Up-Tables (LUT) are derived for high-speed implementations without further calculations of the values of the sine and cosine functions every sampling instant. Furthermore, a simple shift-and-add phase rotation is described to replace the four required real multiplications. If the original complex signal contains only one-bit each from real part and imaginary part, a surprisingly simple implementation is derived and disclosed for the overall arbitrary frequency shift operation. Further simplifications are also disclosed to make this invention feasible for high sampling frequencies and small frequency drifts.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
A kind of exponent calculation method and device
The invention provides an exponent arithmetic method and device; the method comprises the steps of storing a plurality of step values and corresponding calculation operating parameters; preprocessing input indexes according to the plus-minus of the input indexes; setting the initial value of add and shift data to be 1 when the exponent arithmetic is started; firstly comparing the processed indexes with the plurality of stored step values to select the step values of the indexes and corresponding exponent arithmetic parameters; carrying out substraction to the processed indexes and the selected step values and taking the result as the current indexes; comparing the current indexes with the plurality of stored step values to select the step values of the indexes and corresponding exponent arithmetic parameters again; in this way, comparing the current indexes with the stored step values without repetition until the current indexes are smaller than all the stored step values; carrying out shift operation or shift and add operation to the add and shift data according to the obtained exponent arithmetic parameters in each step; and finally processing the add and shift data according to the plus-minus of the input indexes and outputting the exponent arithmetic result.
Owner:VIMICRO ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for providing dynamically variable time delay for ultrasound beamformer
InactiveCN1184474CUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersWallace treeShift-and-add
A phased array sector scanning ultrasonic system includes a separate receive channel for each respective element in an ultrasonic transducer array. Each receive channel imparts a delay to the echo signal produced by each respective element. The delayed echo signals are summed to form a steered, dynamically focused and dynamically windowed receive beam even when the transmit beam does not emanate from the center of the array. The receiver has a beamformer including a multiplicity of beamformer channels. The beamformer dynamically increases delays to each channel without introducing unwanted discontinuities, by combining and synchronizing a FIFO and an interpolator. The interpolator uses "Wallace tree" adders to accumulate bit-shifted versions of the inputs. The number of additions is less than the number of bits which would be needed to represent equivalent coefficients. This reduces the hardware relative to a conventional implementation which incorporates multipliers with shifts and adds equaling the number of bits in the coefficients.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Inverse Fourier transformation algorithm applied to NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet of Things)
InactiveCN108111458AIncrease profitReduce usageMulti-frequency code systemsRotation factorShift-and-add
The invention provides an inverse Fourier transformation algorithm applied to NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet of Things). The algorithm is characterized in that the characteristics of an implementation method for realizing mapping of 12 sub-carriers of the NB-IoT to 128-point IDFT (Inverse Discrete Fourier Transformation) are analyzed, and available information in each output is decomposed to optimize a processing process. The regularity of rotation factors is utilized, and shifting and adding methods are used, so that the utilization rate of hardware resources is increased; the use of a multiplier is reduced; the hardware area can be saved greatly; and the power consumption of an inverse Fourier transformation device is lowered. More importantly, compared with a conventional N-point IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transformation) module, the inverse Fourier transformation algorithm can realize lower inverse Fourier transformation processing delay when being applied to the NB-IoT.
Owner:SYSU HUADU IND SCI & TECH INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com