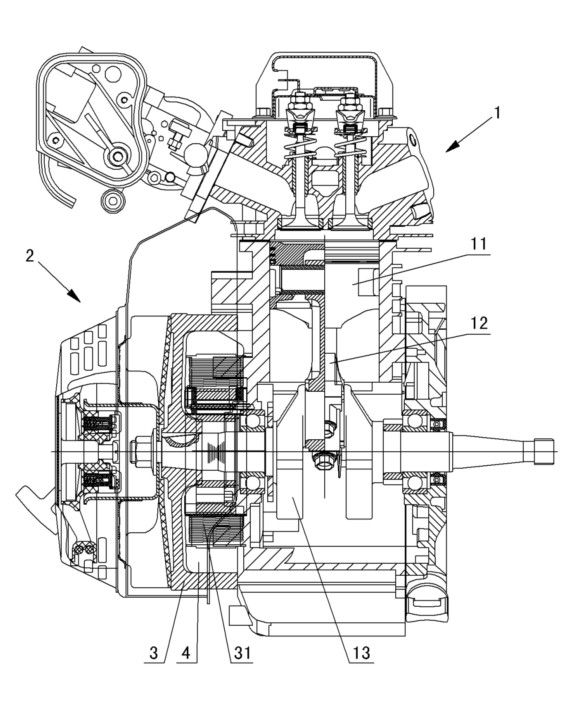
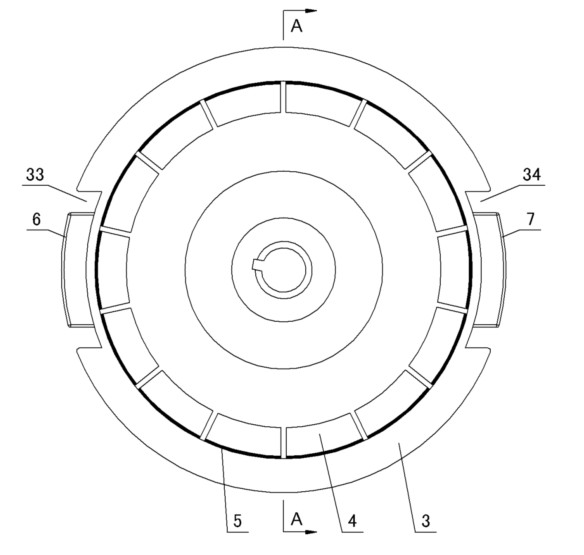
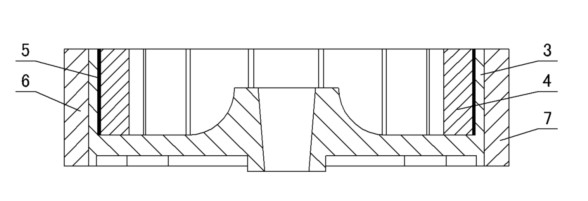
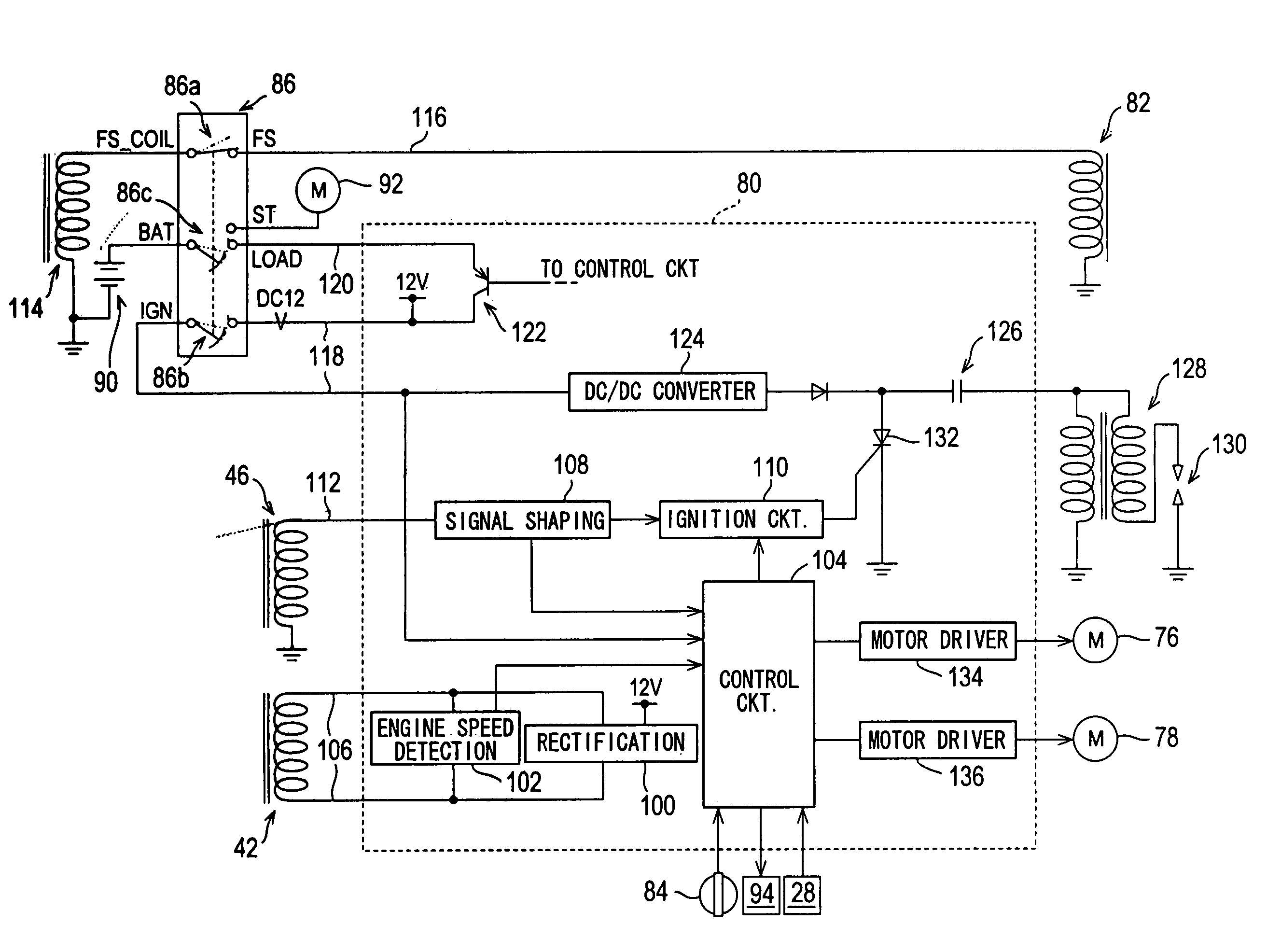
Patents
Literature
47results about "Ignition generator rotor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
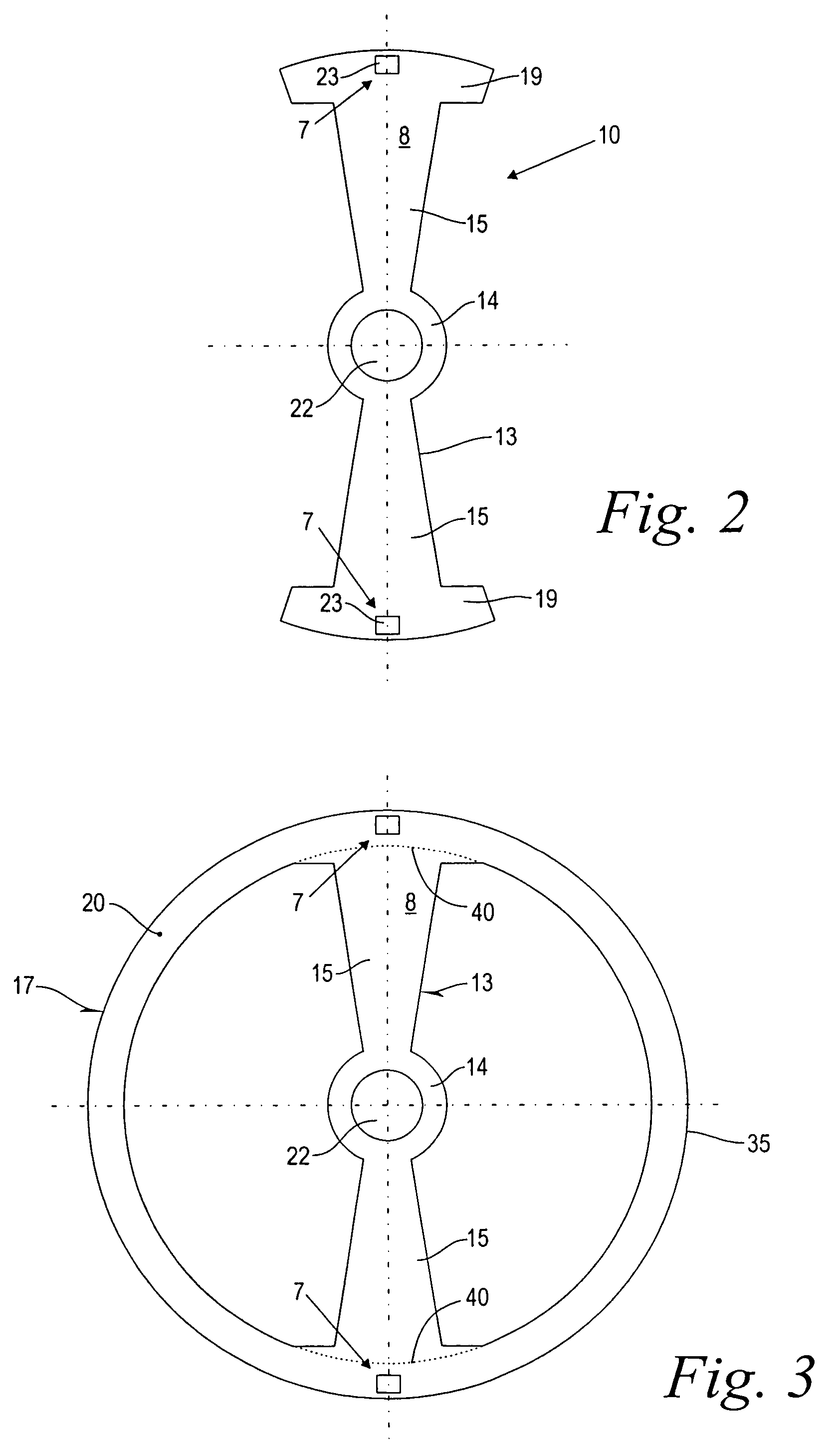
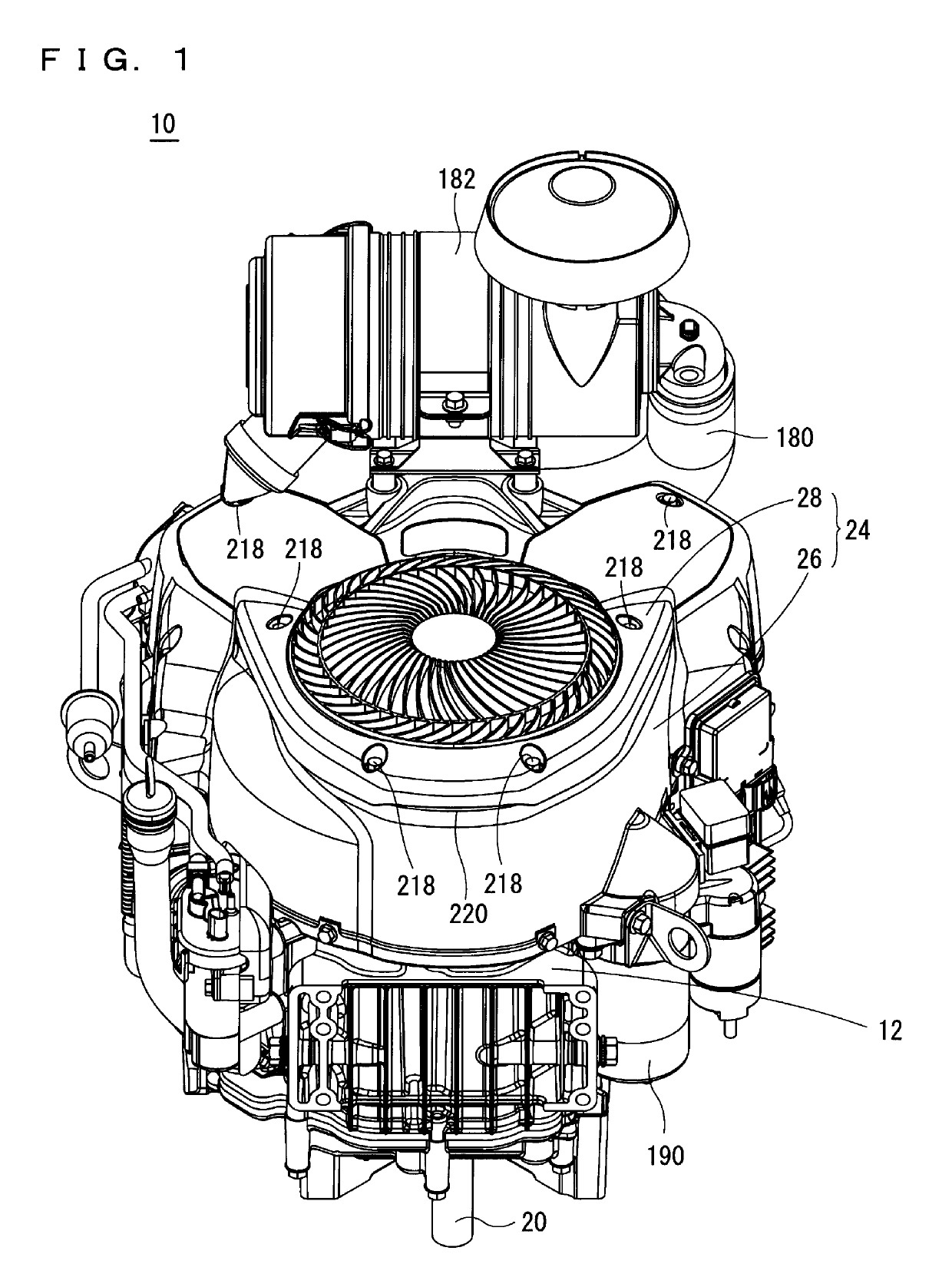
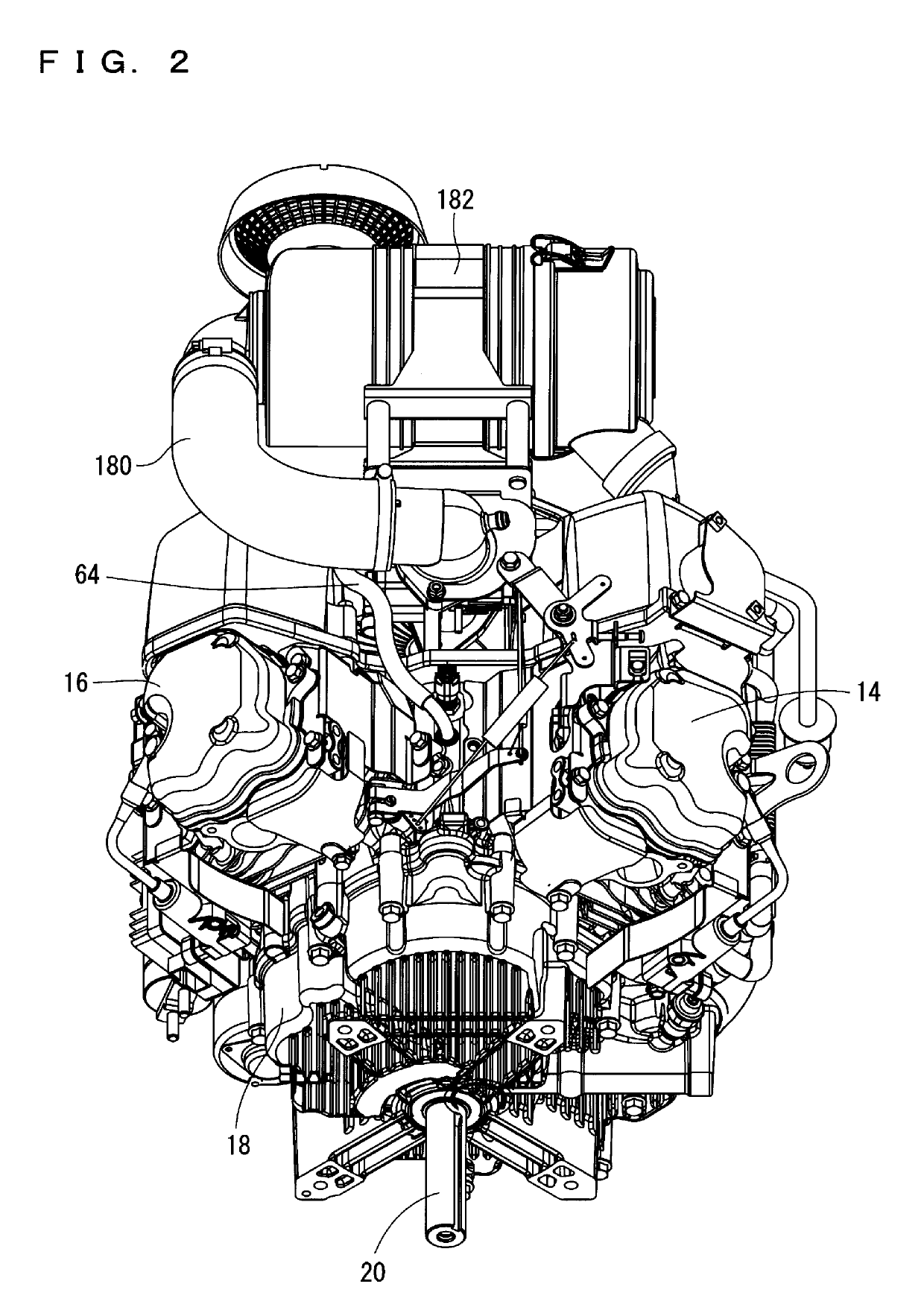
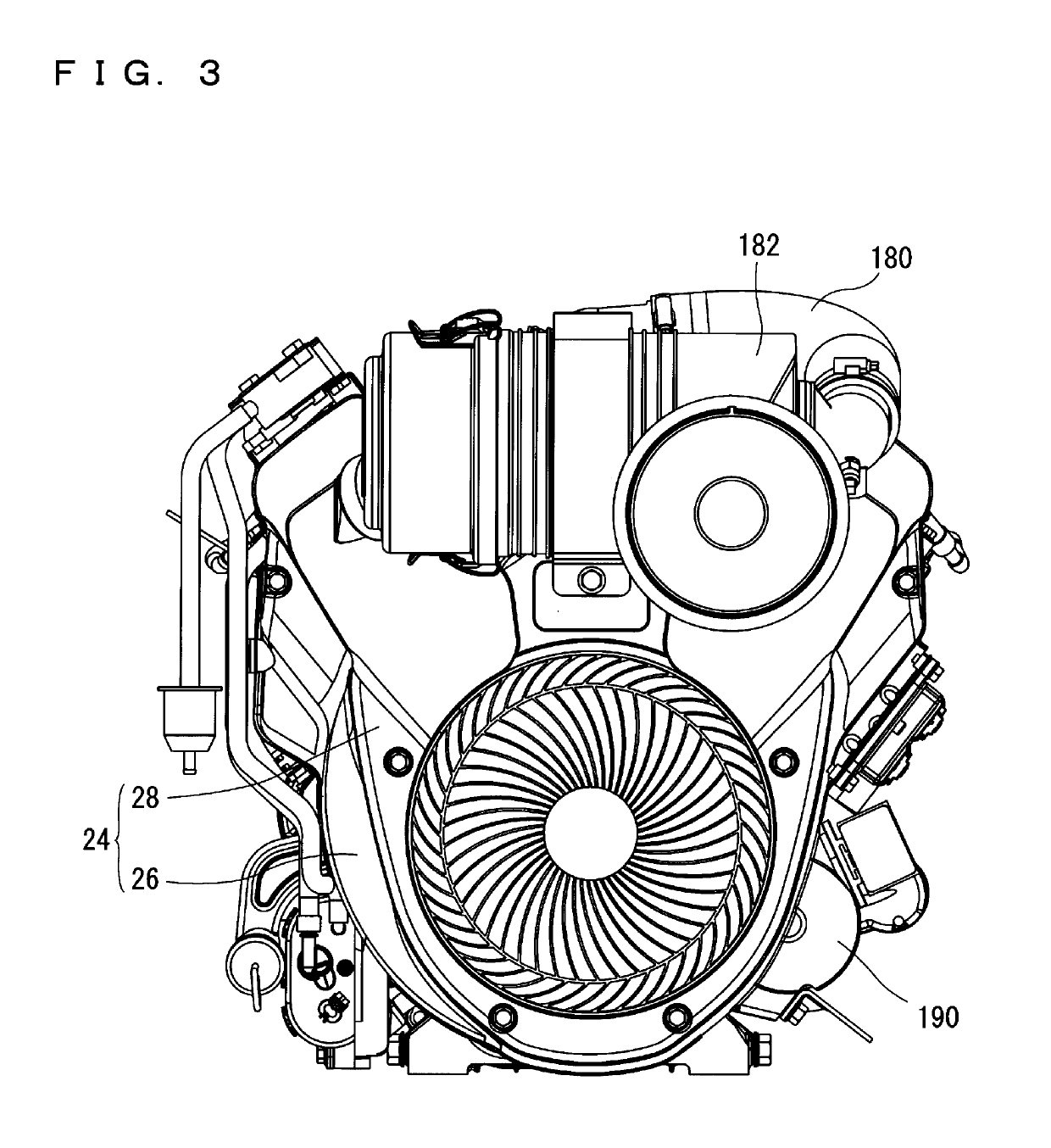
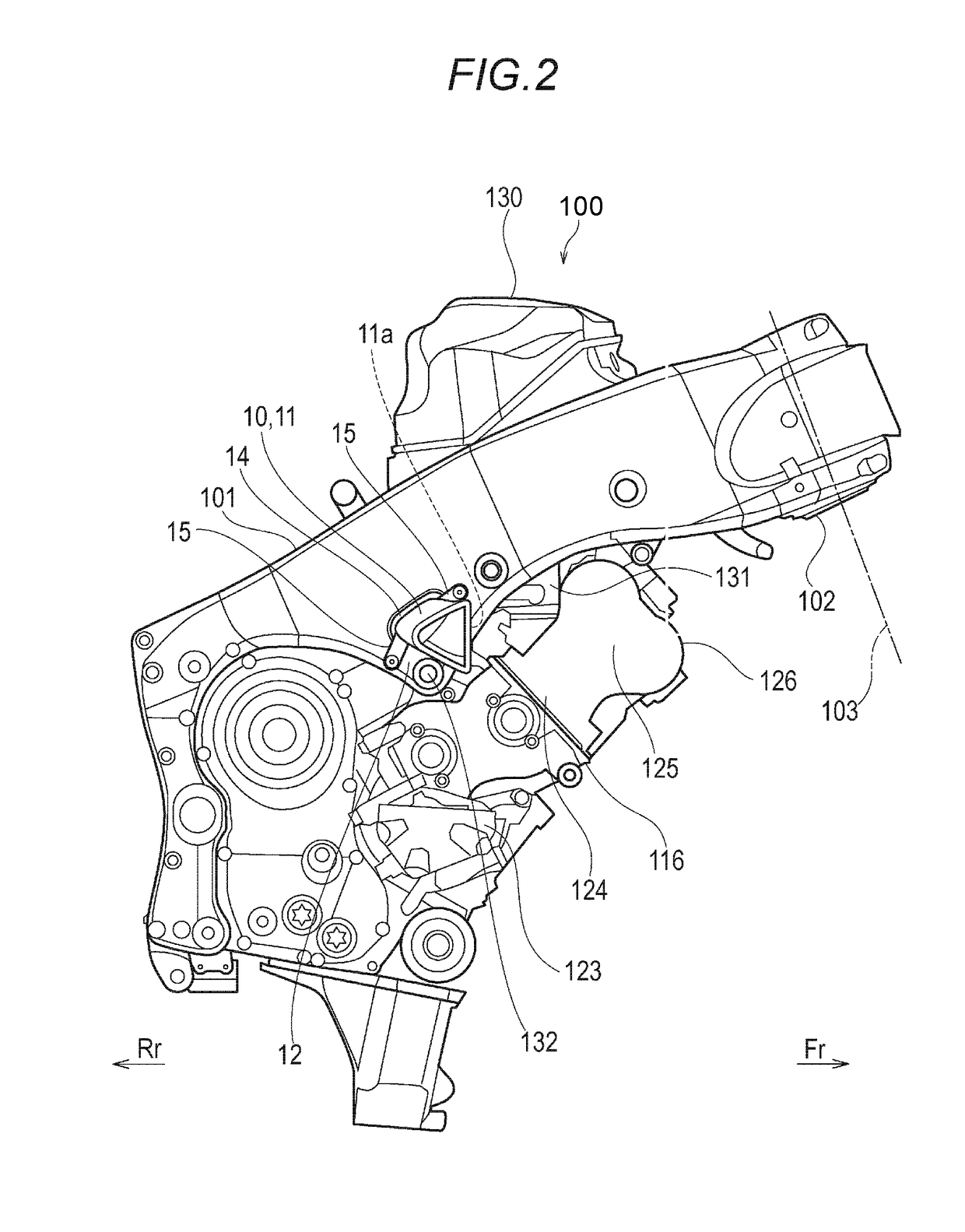
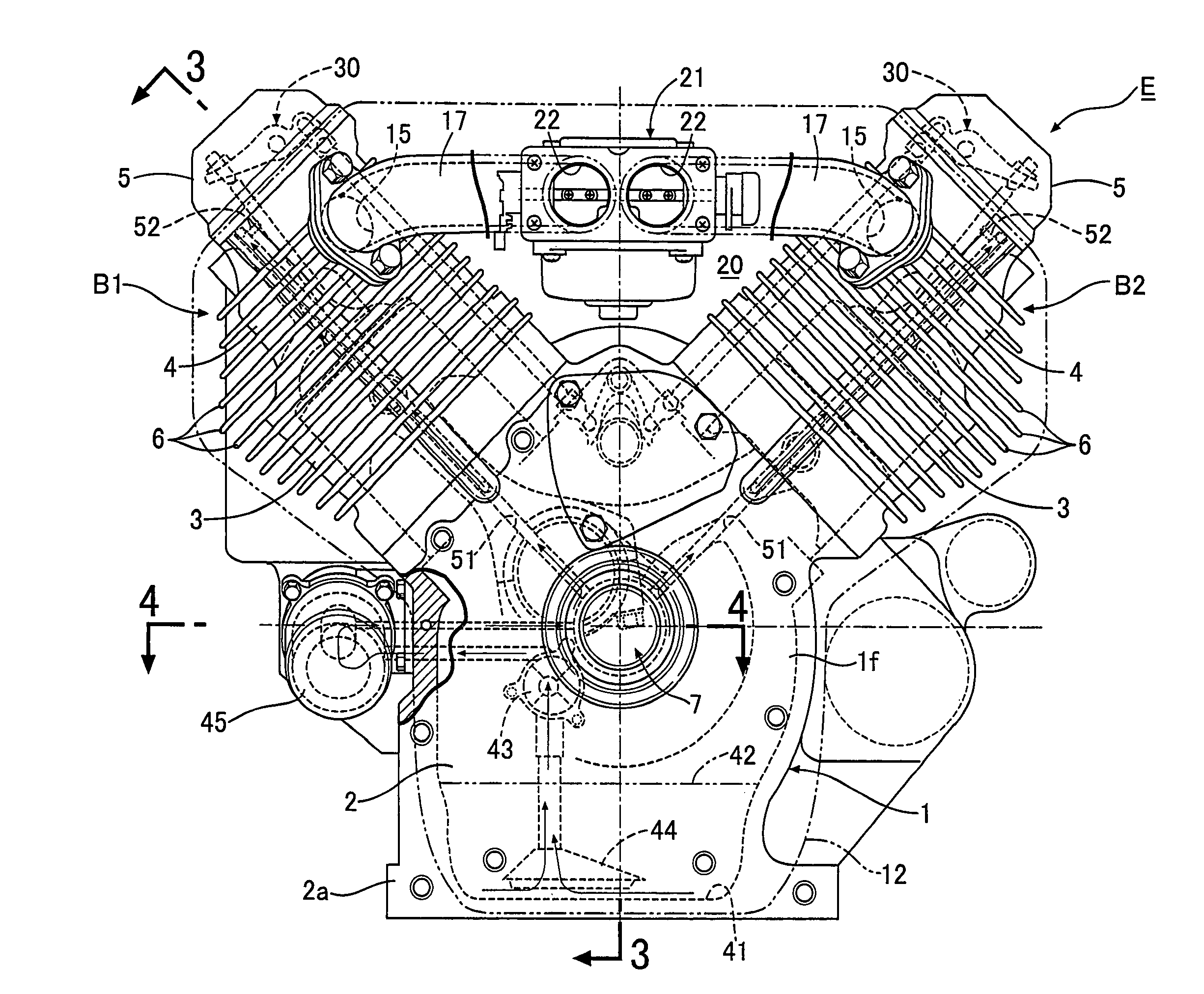
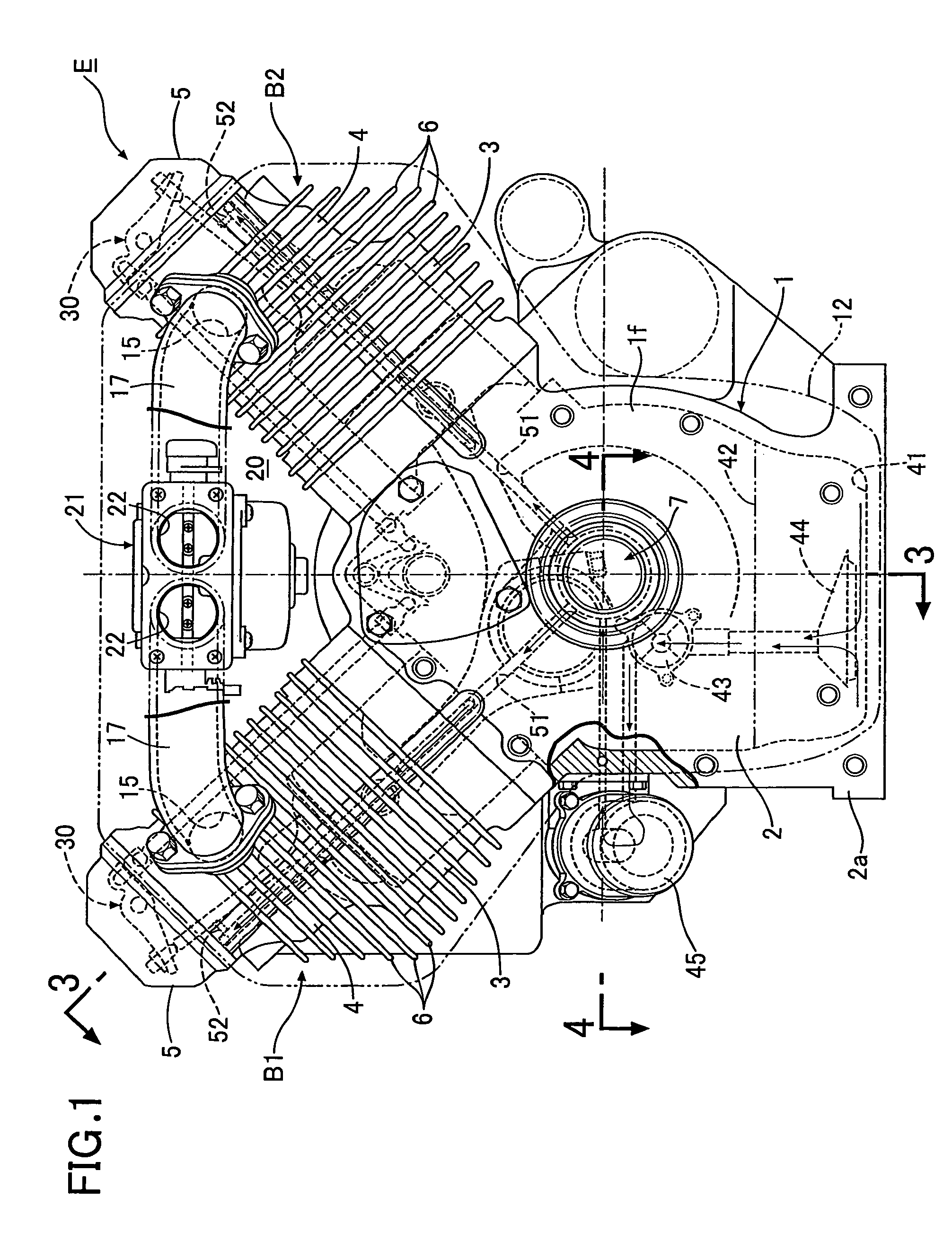
Drive unit with an electric machine
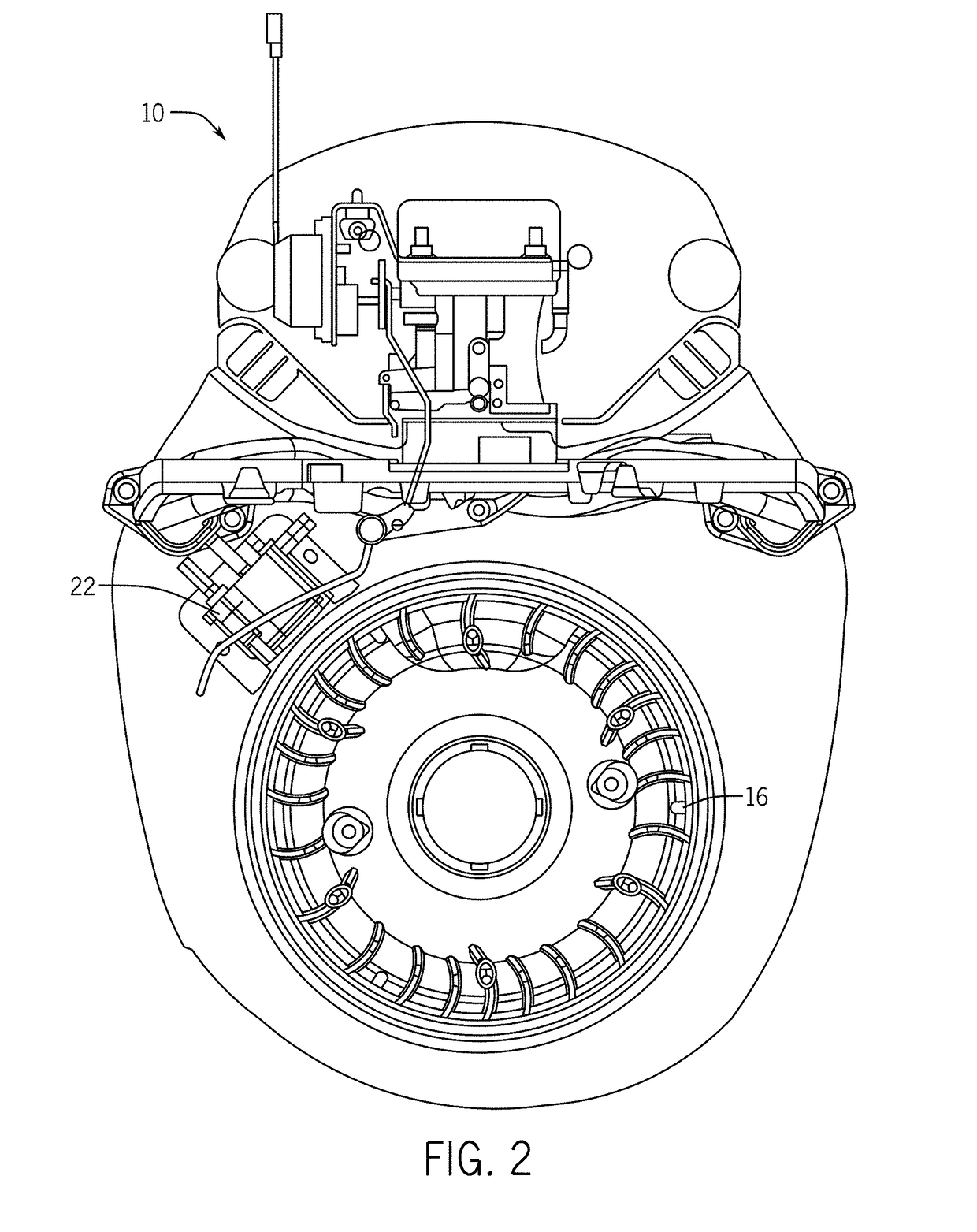
InactiveUS6700280B1Simple designGuaranteed uptimeWindingsIgnition generator rotorElectrical and Electronics engineeringDrive shaft
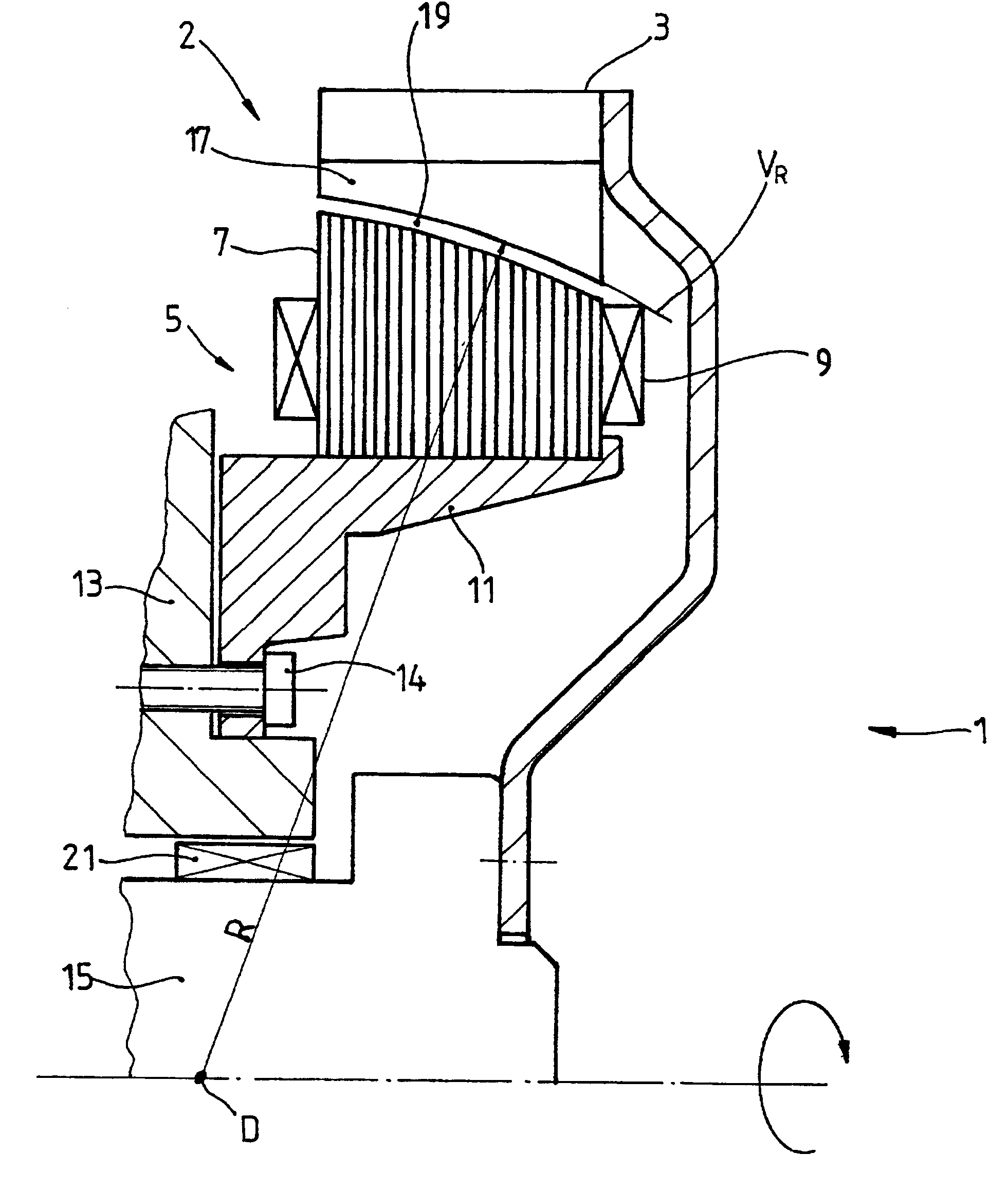
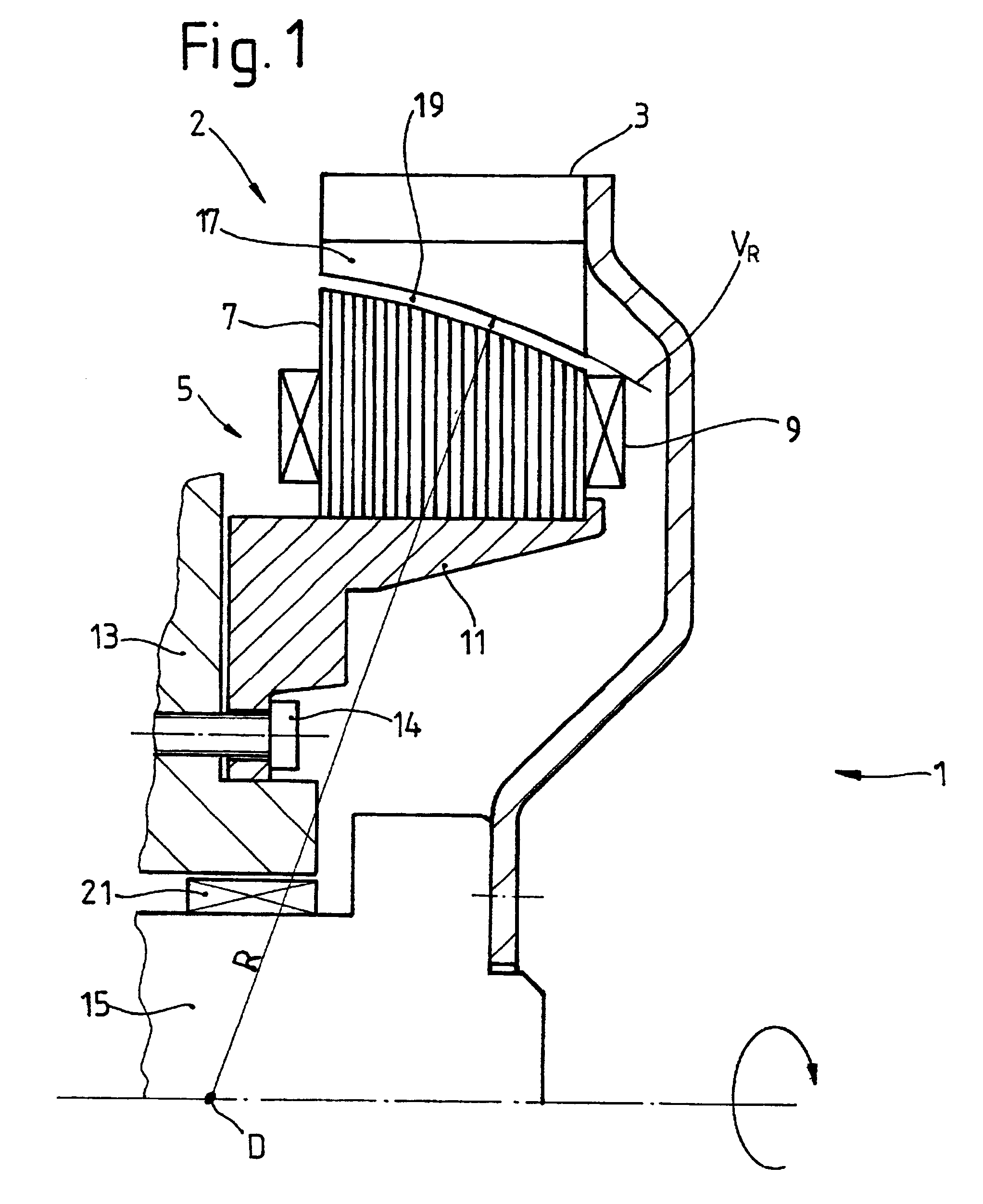
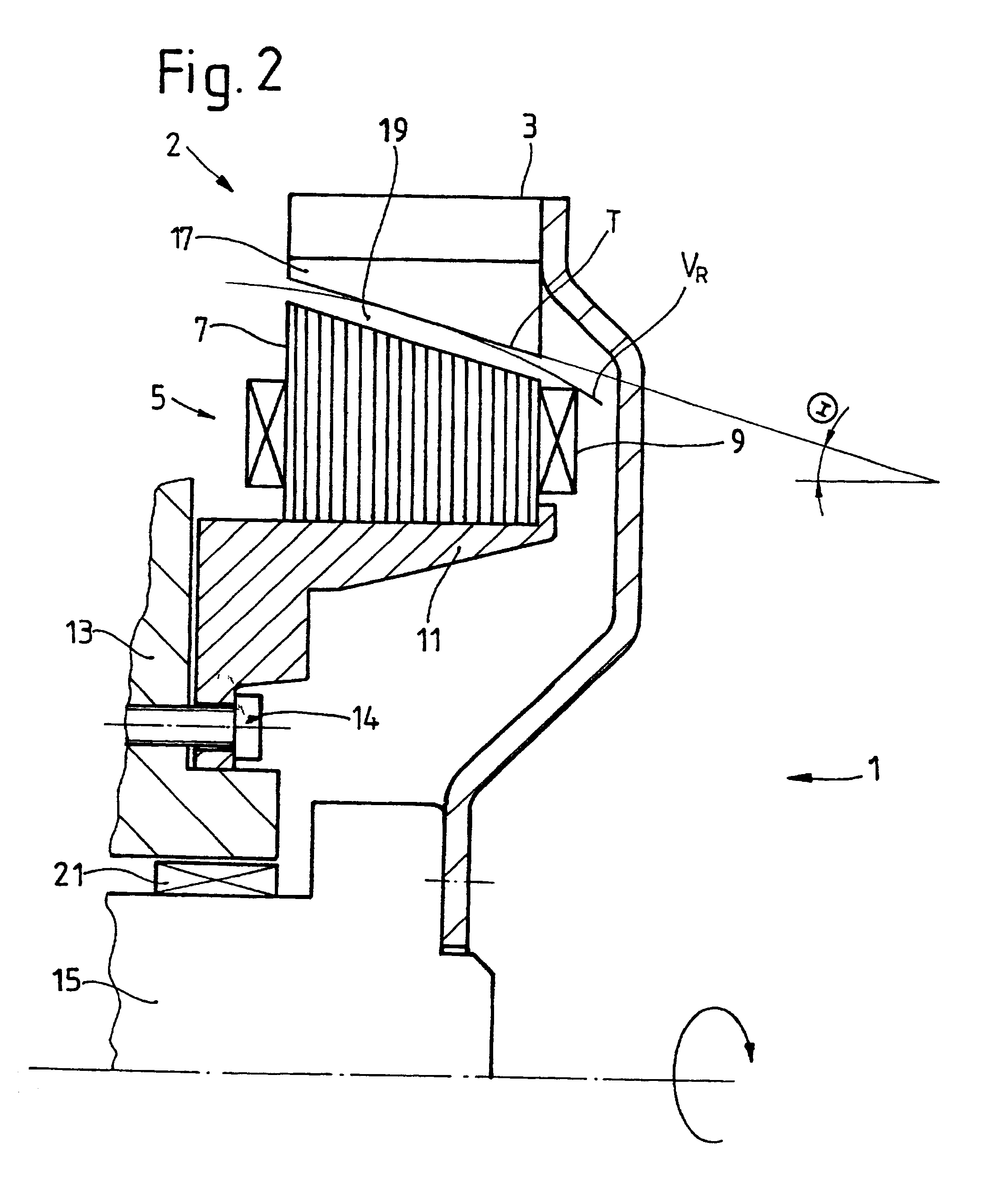
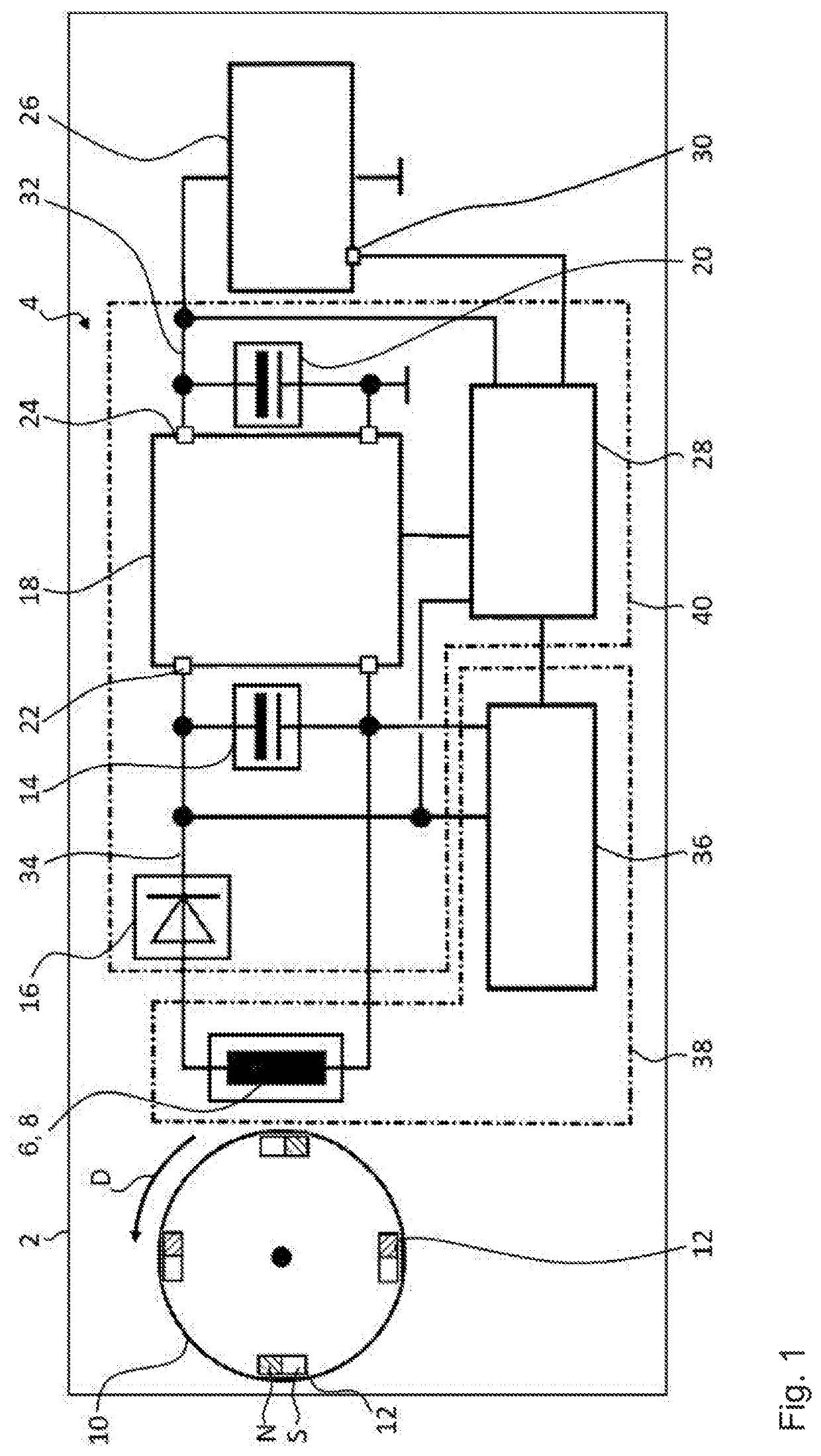
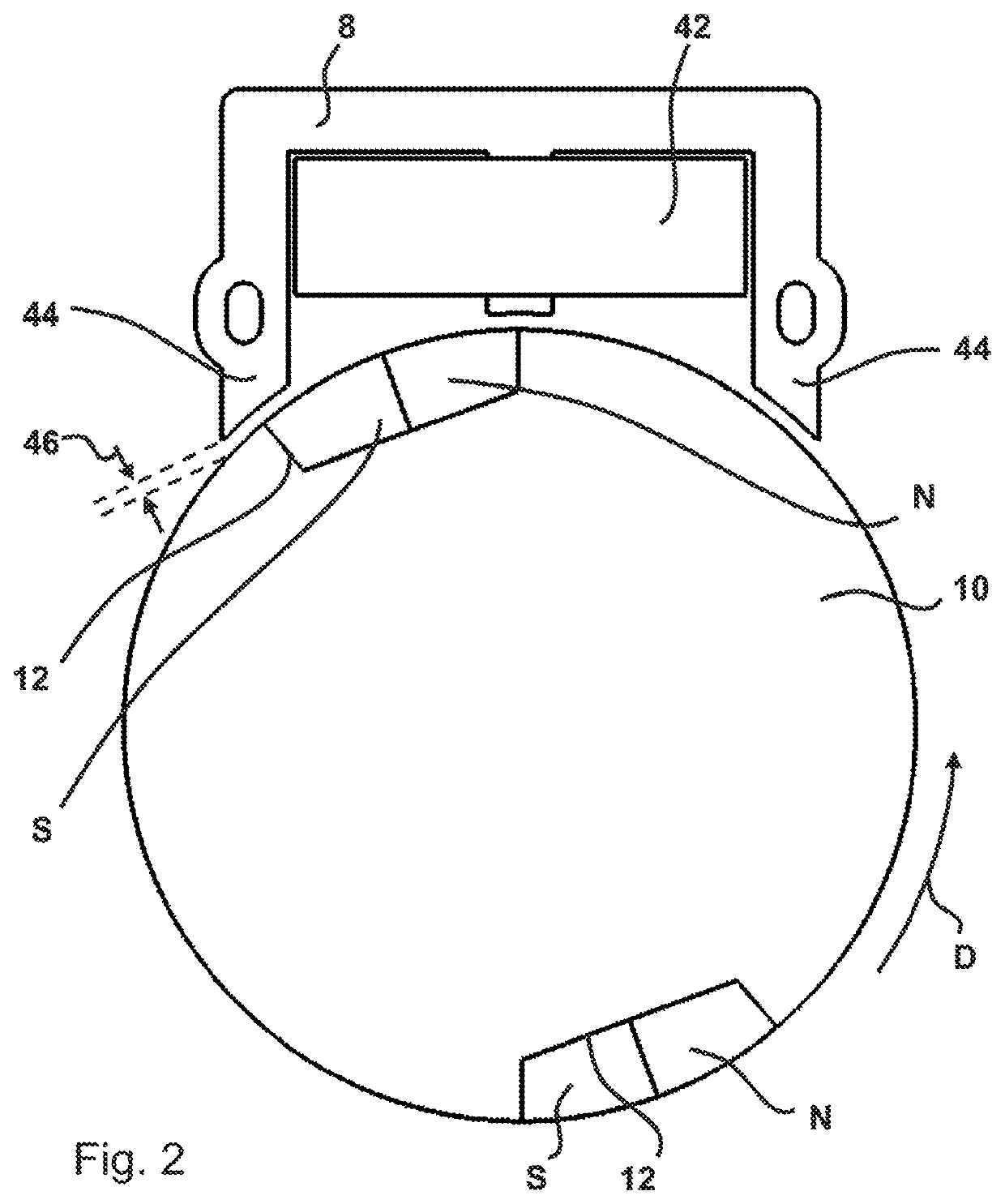
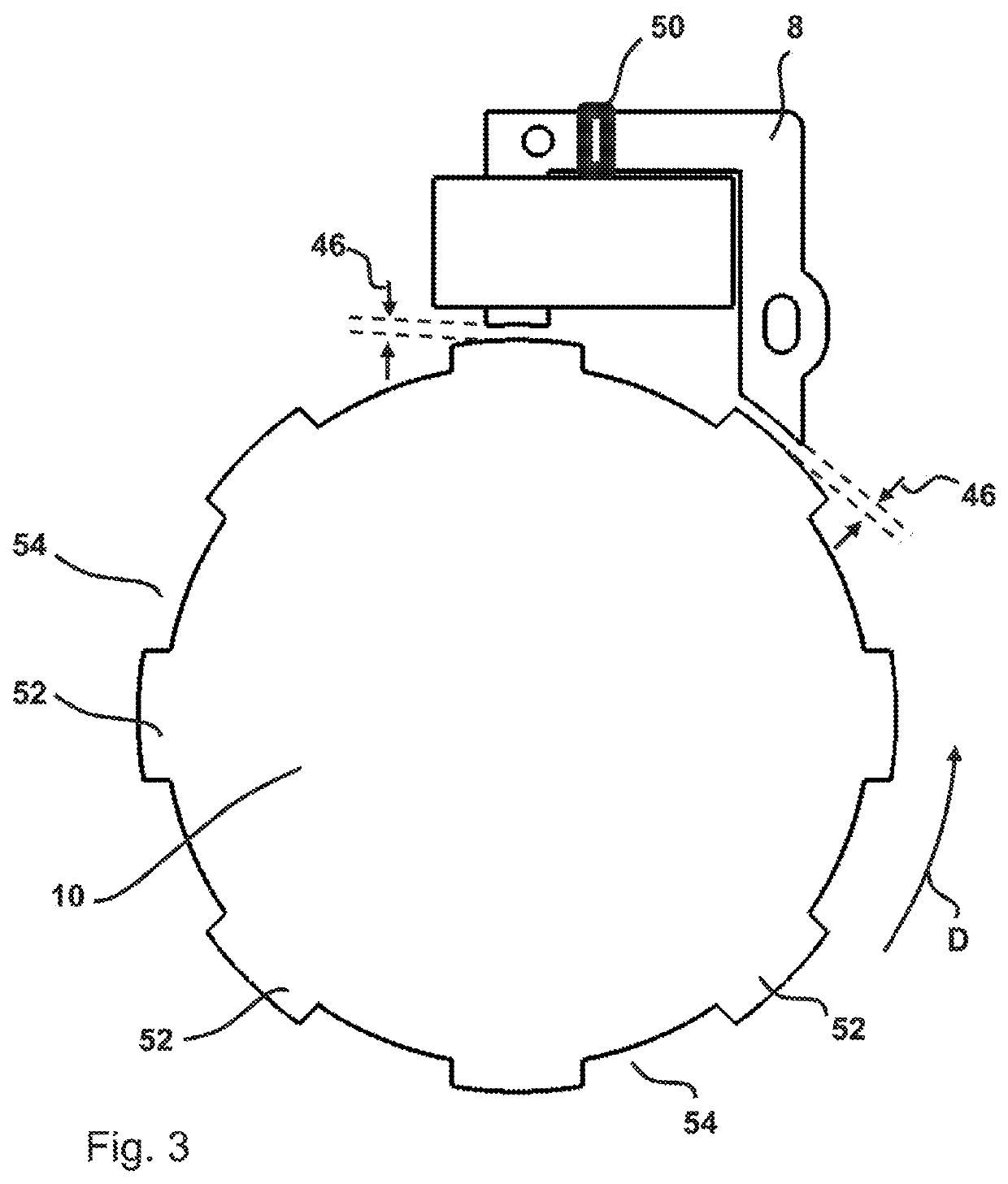
A drive unit with a drive and an electric machine, the drive being equipped with a drive shaft and the electric machine with a stator and a rotor. The rotor is coaxial to the stator and connected to the drive shaft for the transmission of torque, where the stator and the rotor interact with each other across an air gap, and where the drive shaft causes the rotor to execute a wobbling motion. In a cross section parallel to the drive shaft, the geometric course of at least one of the two surfaces forming the boundaries of the air gap, i.e., the surface of the rotor or the surface of the stator, is designed so that it at least approximates the geometric slowing curve (VR) described by the wobbling motion of the rotor.
Owner:MANNESMANN SACHS AG
Engine exhaust control
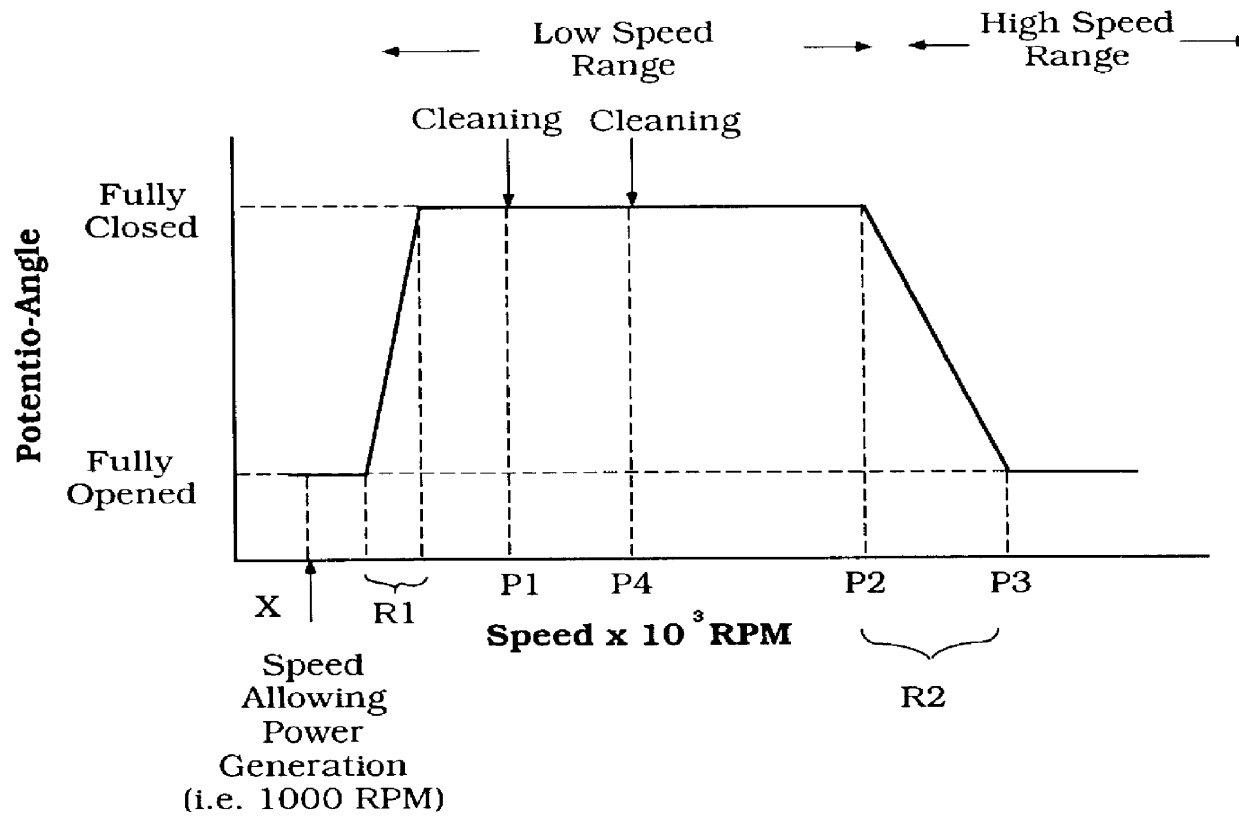
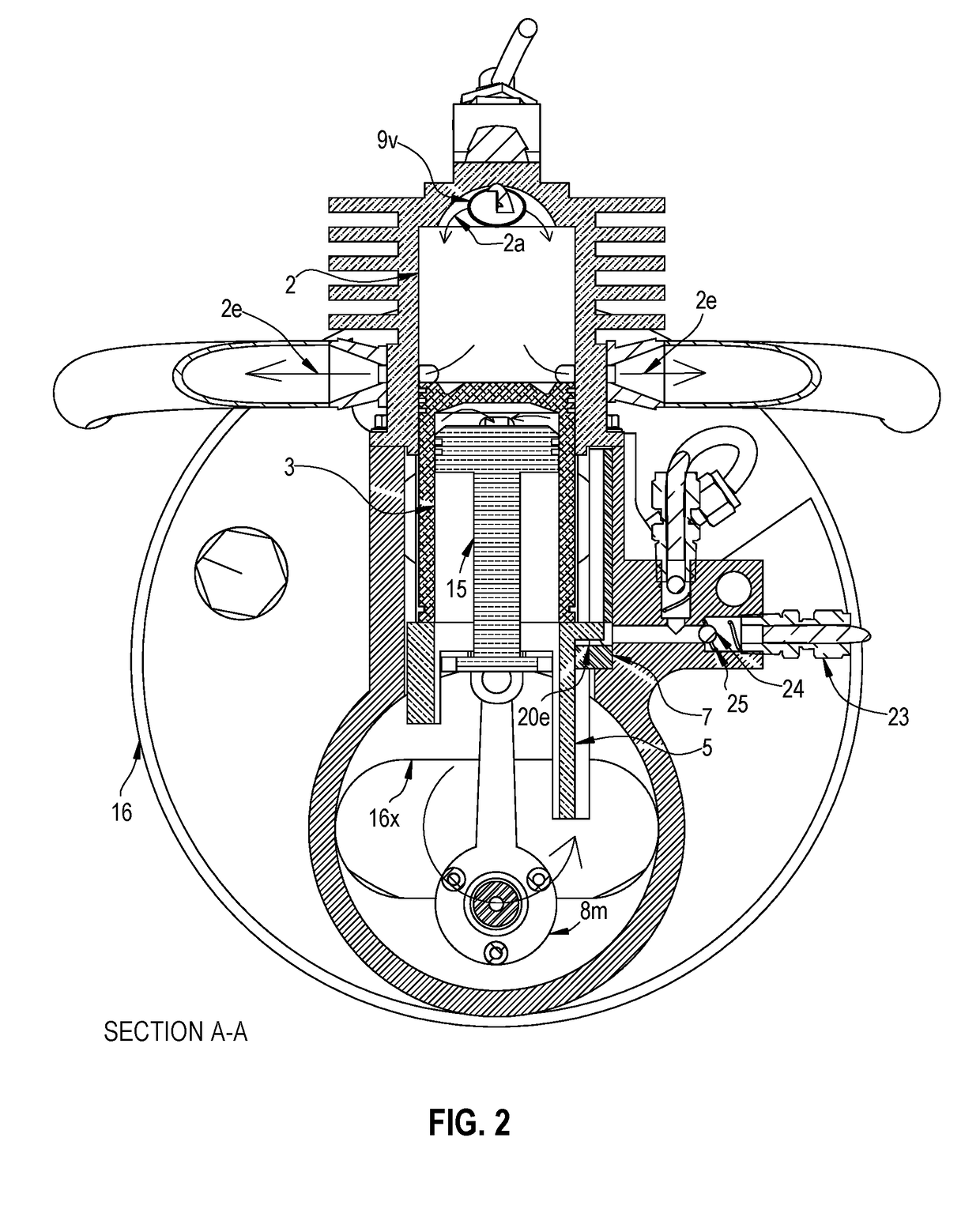
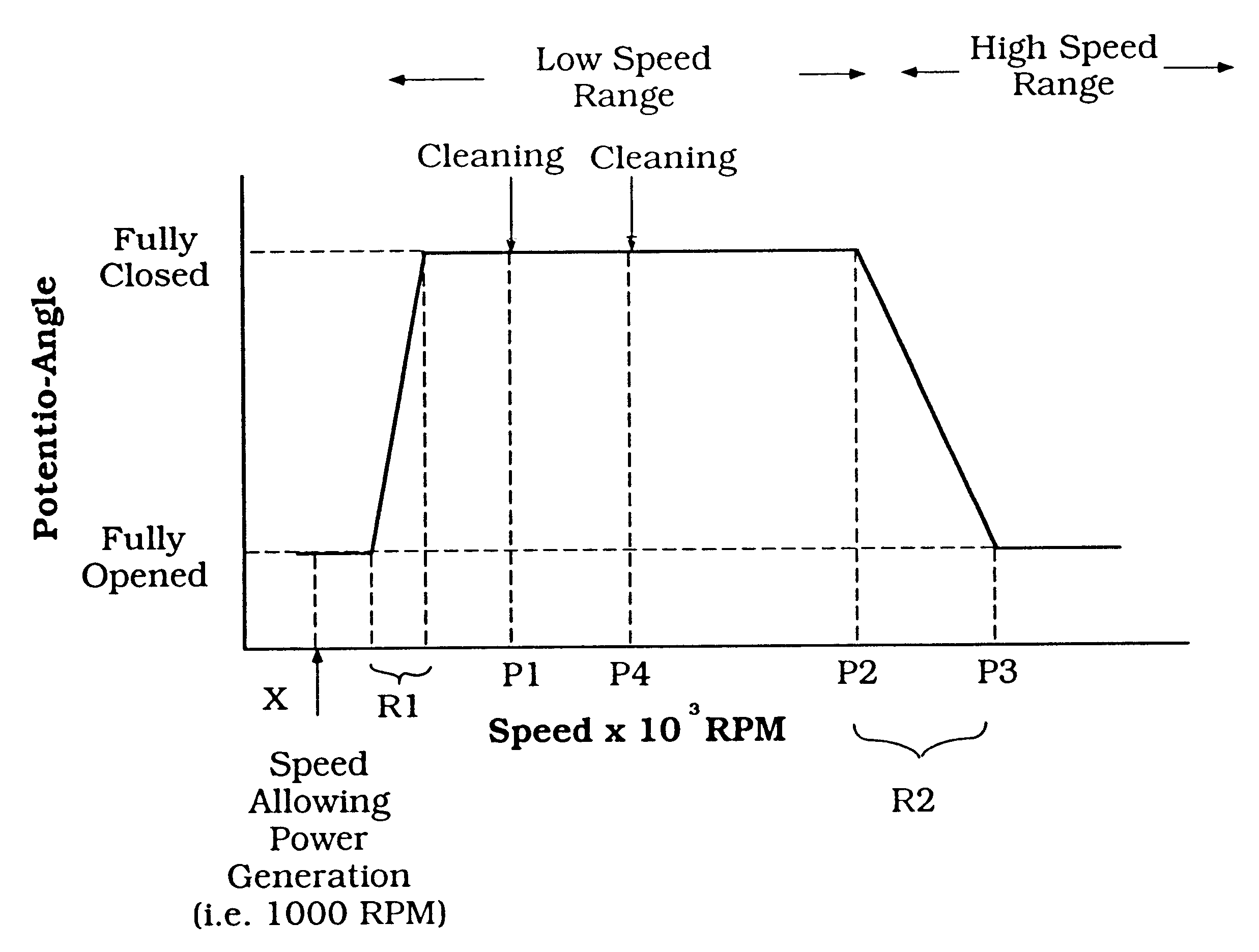
A snowmobile is powered by an internal combustion engine. The engine has an exhaust timing control valve, a control unit and a generator. The control unit determines the positioning of the control valve as a function of engine speed. Additionally, the control unit initiates a control valve cleaning cycle when the engine speed first exceeds a first predetermined speed within a predetermined range of engine speeds. The first predetermined speed is desirably an engine speed at which the generator generates sufficient power to render the control unit operable. The control unit retracts the control valve when the engine speed exceeds the upper limit of the predetermined range. Thereafter, the control unit initiates another control valve cleaning cycle when the engine speed decreases below a second predetermined engine speed.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Magnet wheel of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7281501B2Raise the ratioSimple configurationCoolant flow controlIgnition generator rotorElectric machineryHand held
A magnet wheel (1) for an internal combustion engine, especially a drive motor (2) for a portable handheld work apparatus includes a hub (4) for fixing to a crankshaft (5) of the drive motor (2) and a magnet carrier (6) having at least one magnet holder (7) provided peripherally on the magnet wheel (1). The magnet carrier (6) is a sheet-metal packet (9) of lamella-like layered plates (8). The sheet-metal packet (9) is layered modular-like from at least two differently configured profiled sheet-metal piece types (10, 11, 12). At least one profiled sheet-metal piece type (10) is configured as an arm plate (13) with a hub section (14) as part of the hub (4) as well as an arm section (15) which extends from the hub section (14) radially outwardly up to the region of the magnet carrier (6). At least one additional profiled sheet-metal piece type (11) is configured as a centrifugal mass sheet-metal piece (16) which lies essentially radially outwardly in the peripheral region of the magnet carrier (6).
Owner:ANDREAS STIHL AG & CO KG
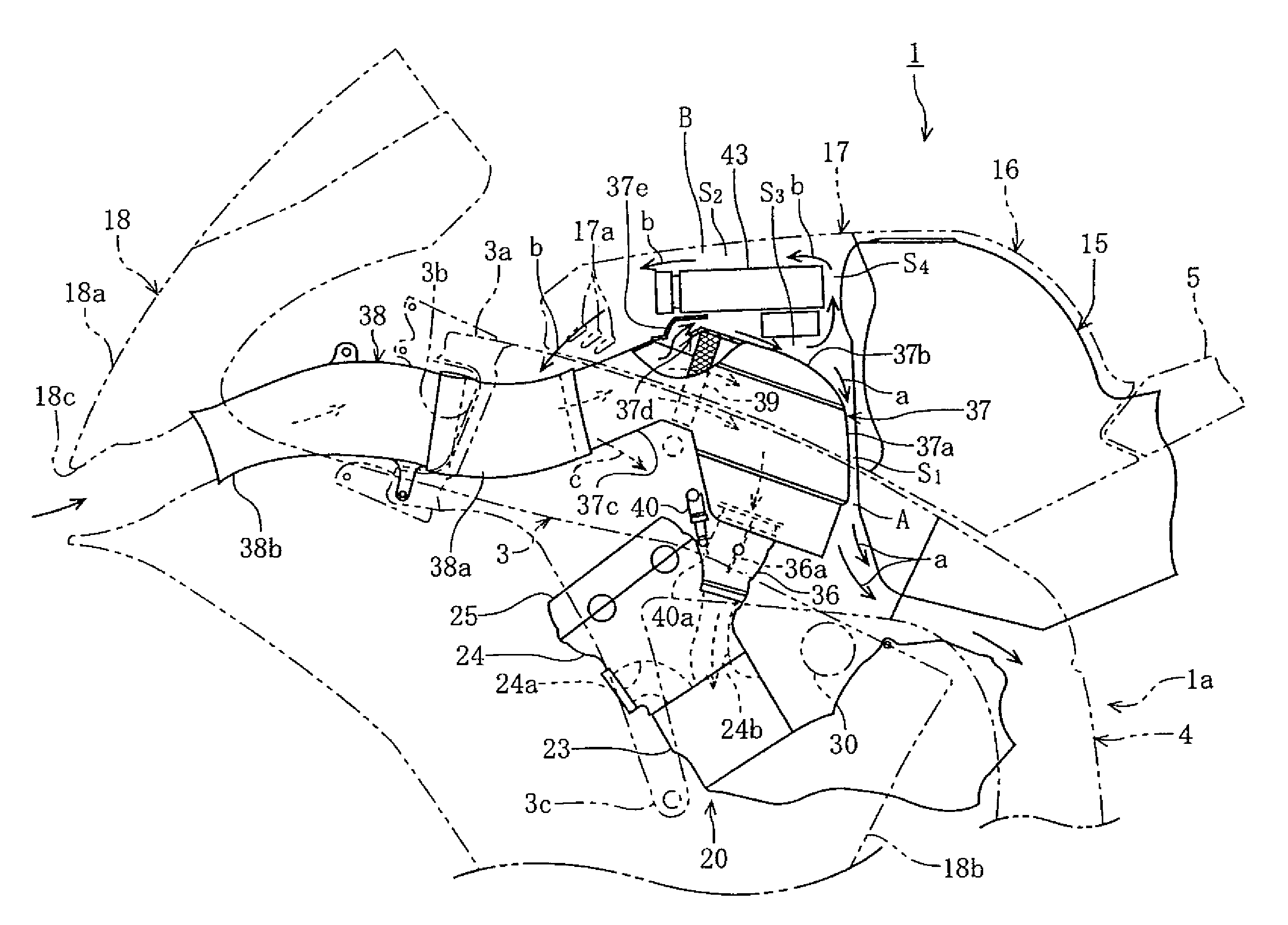
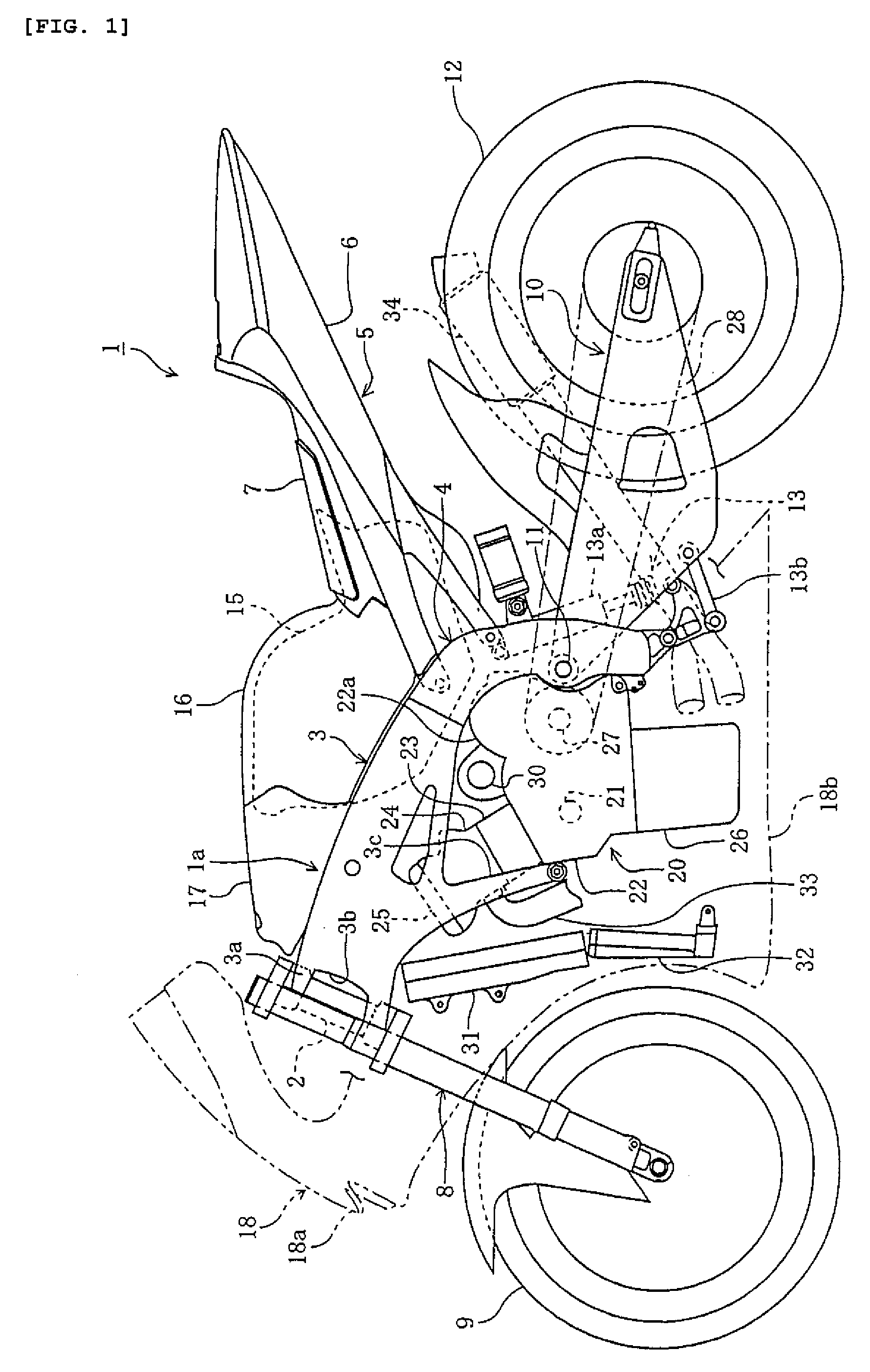
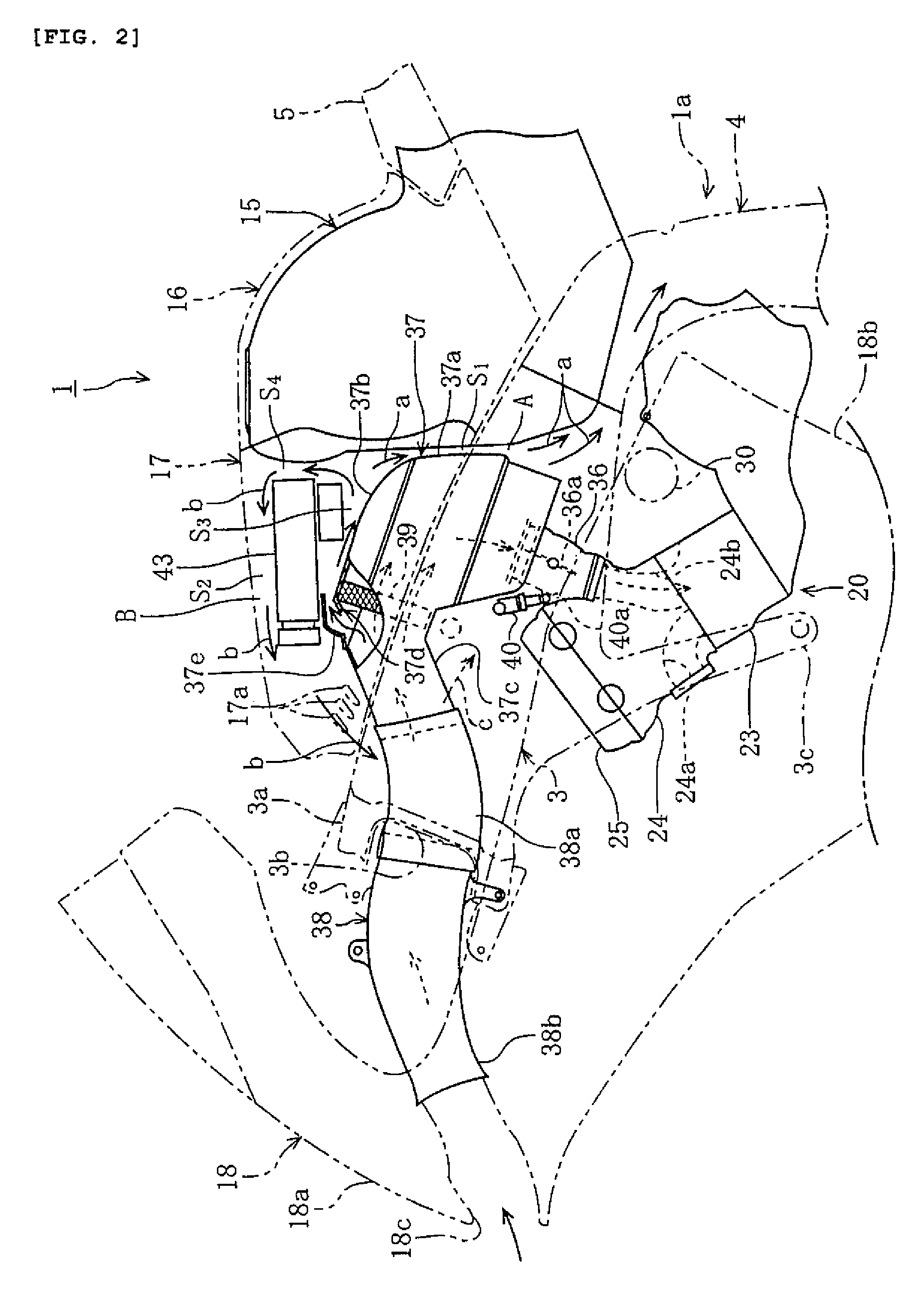
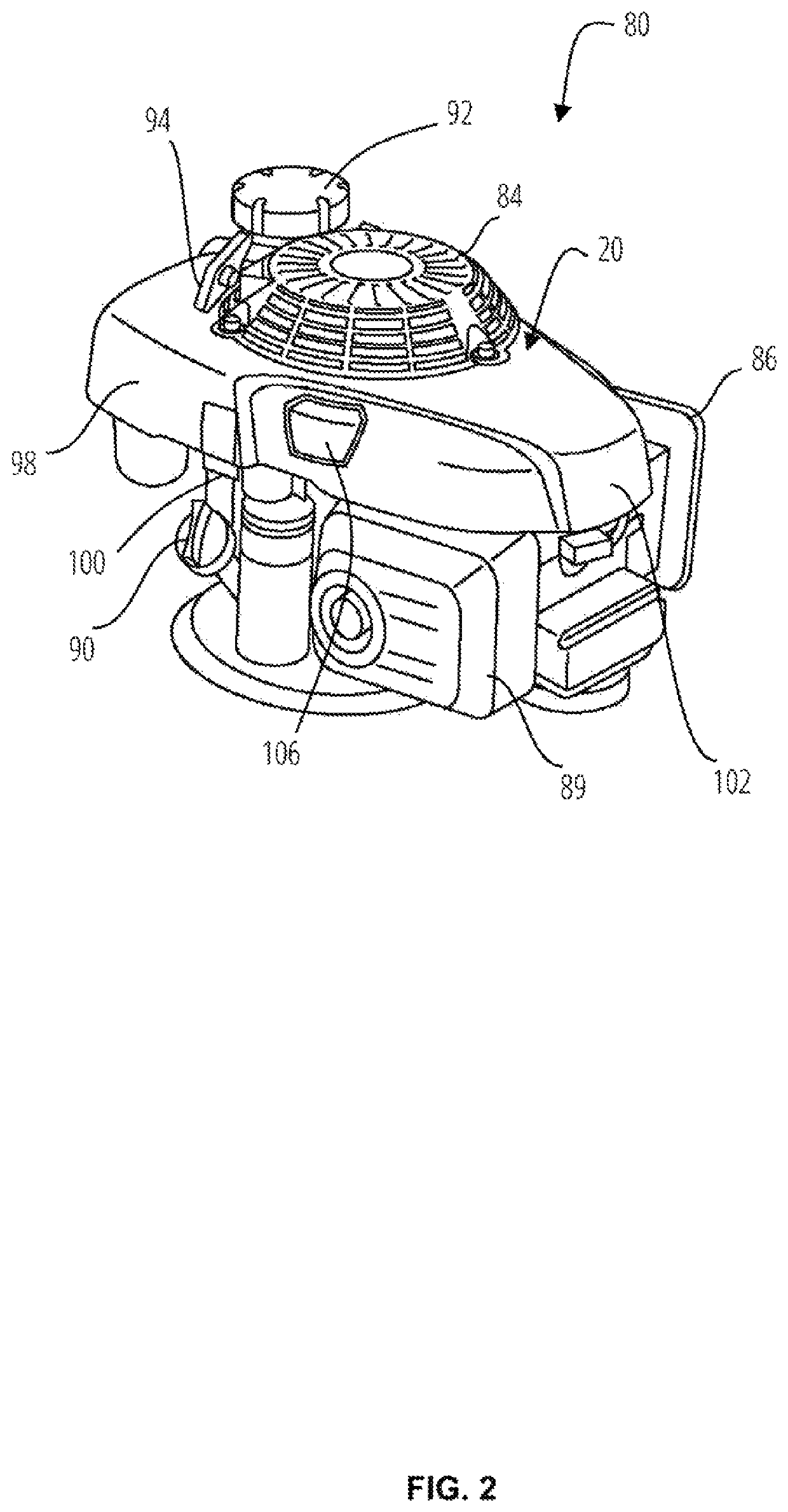
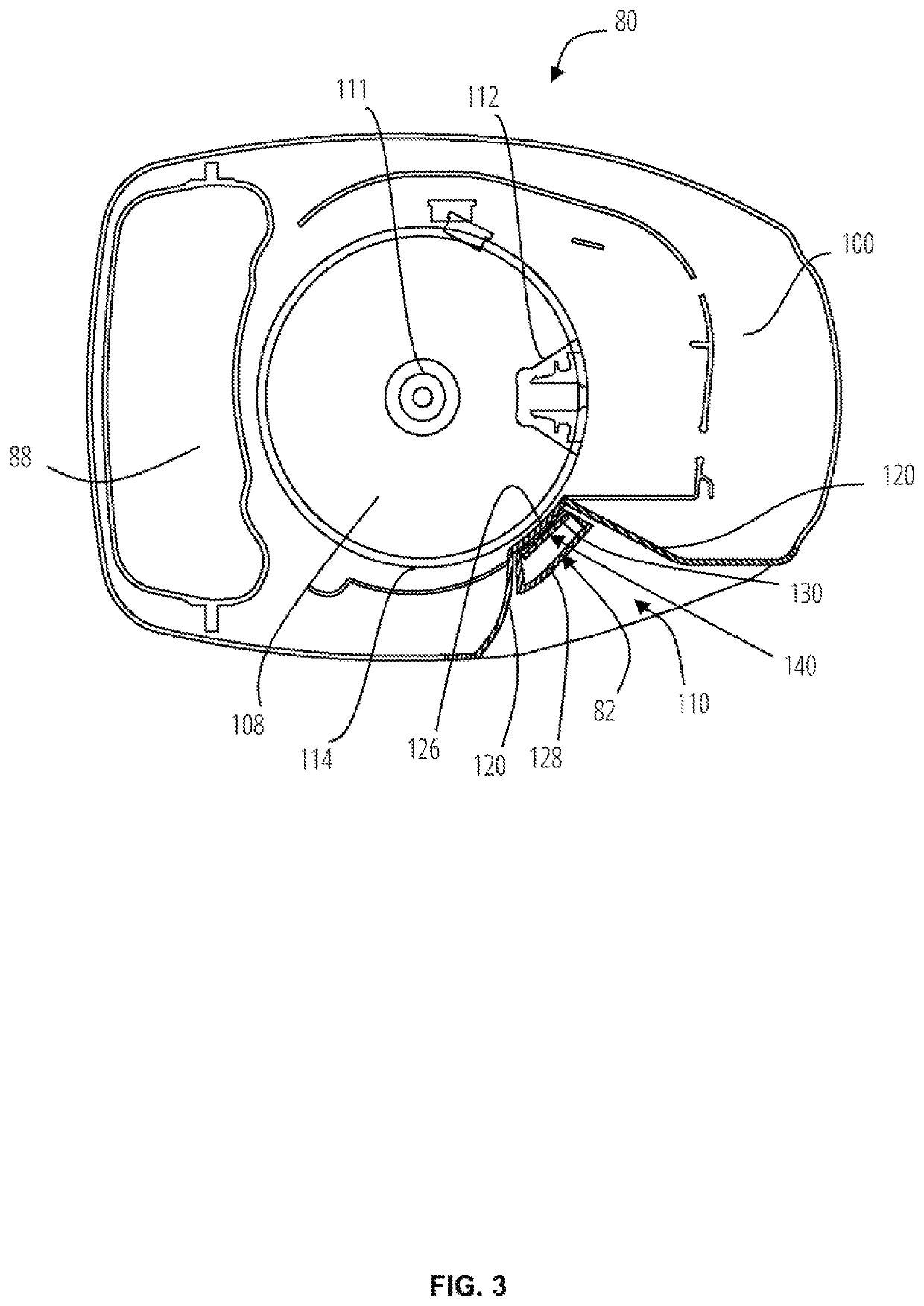
Motorcycle air intake component cooling system
ActiveUS7527115B2Effectively cools vehicle partImprove cooling effectCylinder headsCombustion-air/fuel-air treatmentAlternatorElectric generator
A motorcycle that effectively cools vehicle parts without a special cooling duct has a body frame, an engine and an intake system that supplies air to the engine. A parts cooling system makes air diverge from the intake system, and introduces the diverging air to vehicle parts such as electrical parts and an alternator.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Outboard motor
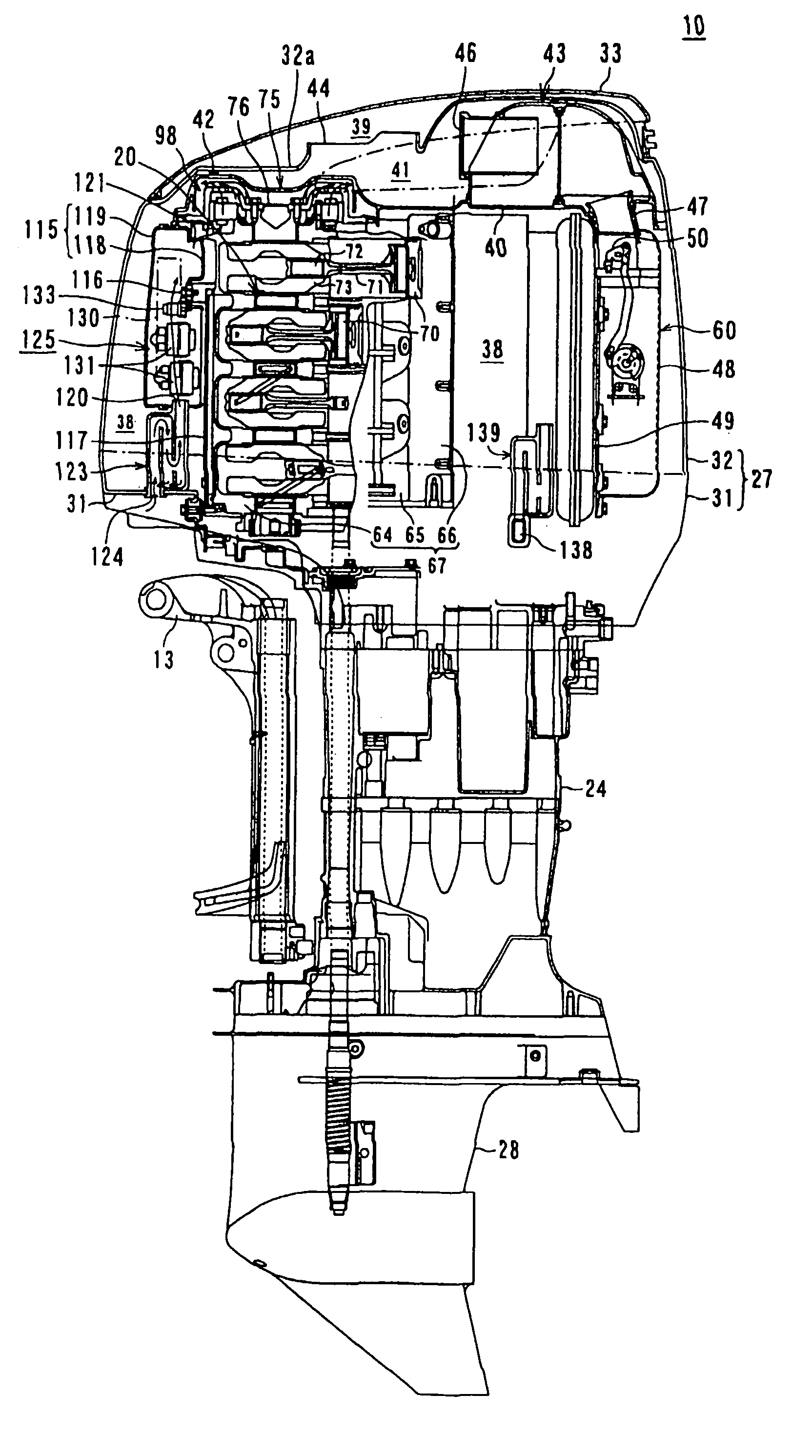
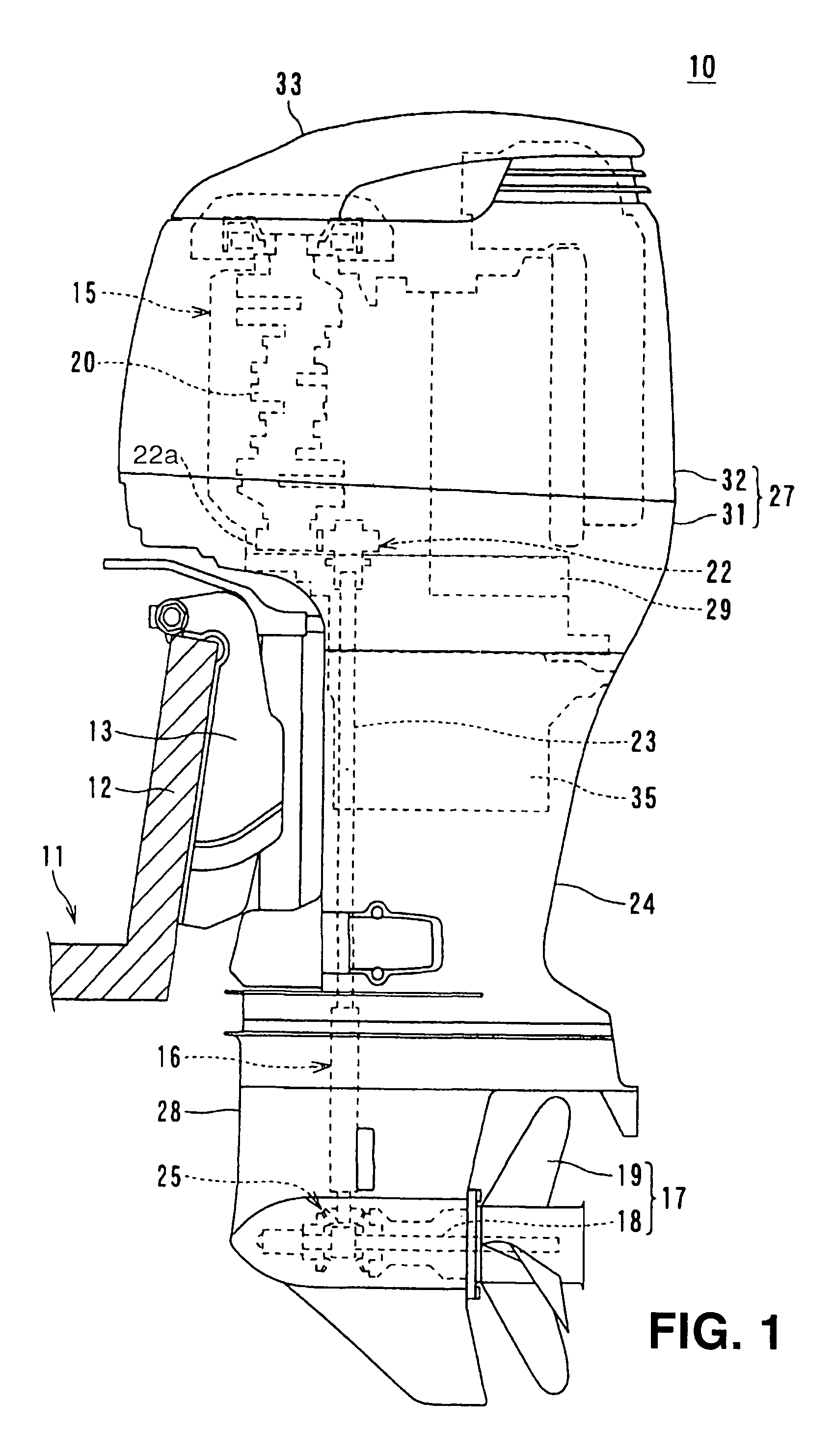
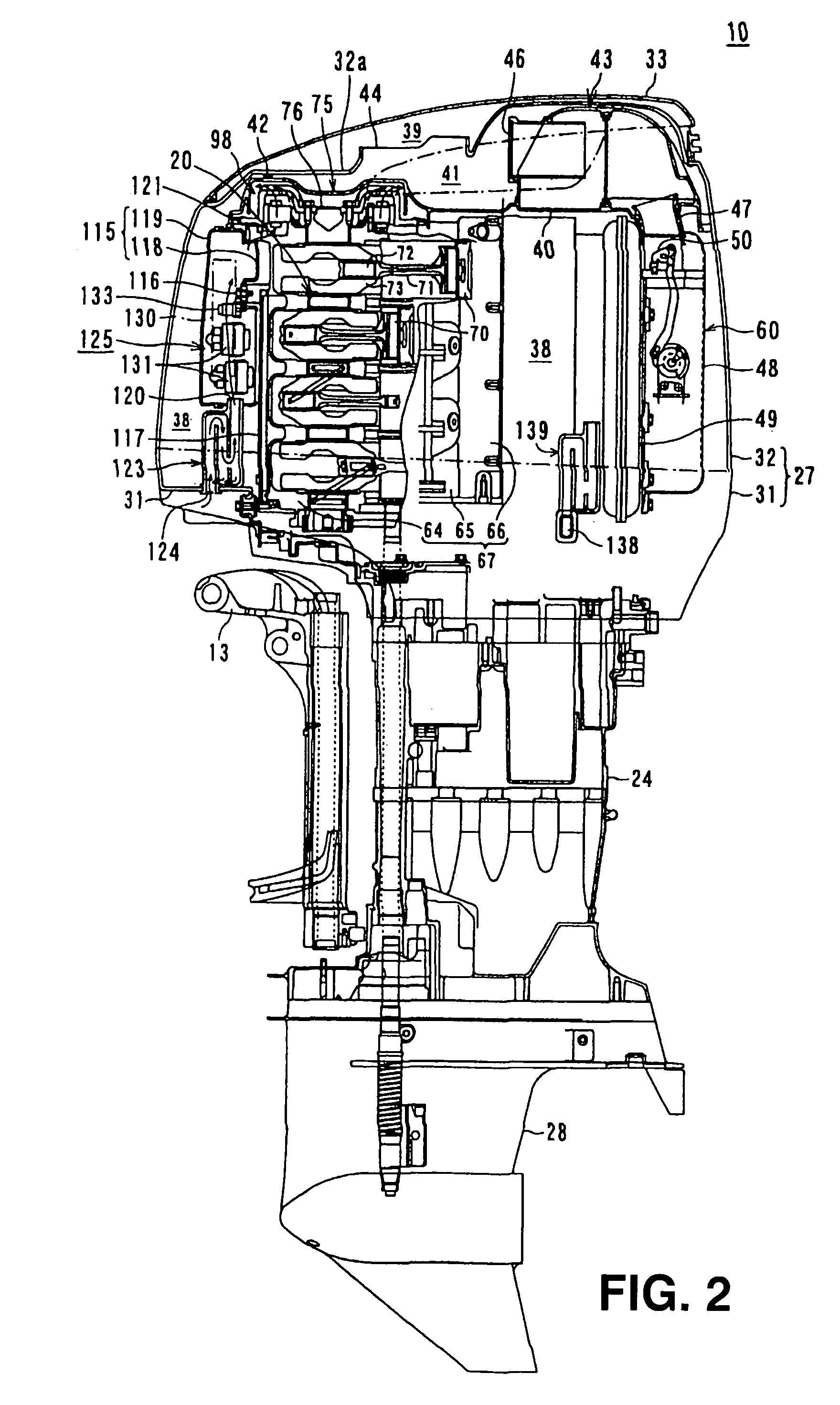
ActiveUS6964255B2Effectively and forcibly ventilateAvoid overall overheatingLiquid coolingNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCrankcaseEngineering
An outboard motor includes a vertical multi-cylinder engine, a fly-wheel magneto device, a partition plate, and a ventilation fan. The vertical multi-cylinder engine is disposed in an engine cover and comprises a crank case and a crank shaft, the crank shaft being rotatably disposed and protruding upward from the crank case. The fly-wheel magneto device is disposed on the protruding portion of the crank shaft. The partition plate is disposed in the engine cover and partitions the inside of the engine cover into an engine air-inlet space and a space including a heat-generating source, the engine air-inlet space being disposed at the upper portion of the engine cover, and the space including a heat-generating source being disposed at the lower portion of the engine cover. The ventilation fan is disposed in the lower space below the partition plate.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Method for Operating a Two-Stroke Engine
ActiveUS20090012699A1Guaranteed uptimeGood choiceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberIgnition timing
A two-stroke engine has a cylinder with a combustion chamber delimited by a reciprocating piston, wherein the piston drives in rotation a crankshaft, and wherein a spark plug projects into the combustion chamber and ignites a fuel / air mixture. The two-stroke engine further has devices for supplying fuel and combustion air to the combustion chamber and a control unit that determines the ignition timing based on an ignition map. The ignition map indicates the ignition timing as a function of the engine speed for at least one first and one second operating states and for at least one first and one second engine speed ranges. The engine is controlled in that for an engine cycle the ignition timing is set in the second operating state at least within the first engine speed range based on the engine speed and on the number of engine cycles since the last combustion.
Owner:ANDREAS STIHL AG & CO KG
Two-stroke internal combustion engine with crankcase lubrication system
InactiveUS20170362972A1Avoid burnsFully lubricatedOilsumpsMachines/enginesTop dead centerExternal combustion engine
A two-cycle internal combustion engine with rear compression chamber, other than that of a crank case. This present engine has valves that can be screwed on the engine block near top dead center, and is actuated by air pressure. This present two-cycle engine yet uses an oil sump similar to that of a four-cycle engine, which eliminating the need to premix oil with the fuel. This present engine has a stationary piston which operates within a movable piston to form a rear-compression chamber. The movable piston has ports near its crown to transfer charge to the combustion chamber. The movable piston also has ports near bottom of its skirt to allow the fuel and air mixture to enter the rear compression chamber. This engine has a piston seat which is adapted to connect the movable piston to the connecting rod.
Owner:MERCIER CESAR
Engine exhaust control
InactiveUS6508214B1Reduce the possibilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemEngineering
An engine has an exhaust control valve which is moved by a control system according to a predetermined control strategy. The control system obtains data from sensors that help the control system to identify certain characteristics of engine operating conditions. The control strategy involves cycling the exhaust control valve under predetermined engine operating conditions to clean the surface of the valve while reducing the impact of the cycling on engine performance. The cycling generally occurs during engine start-up and following engine shutdown. The cycling may be aborted during periods of rapid acceleration.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
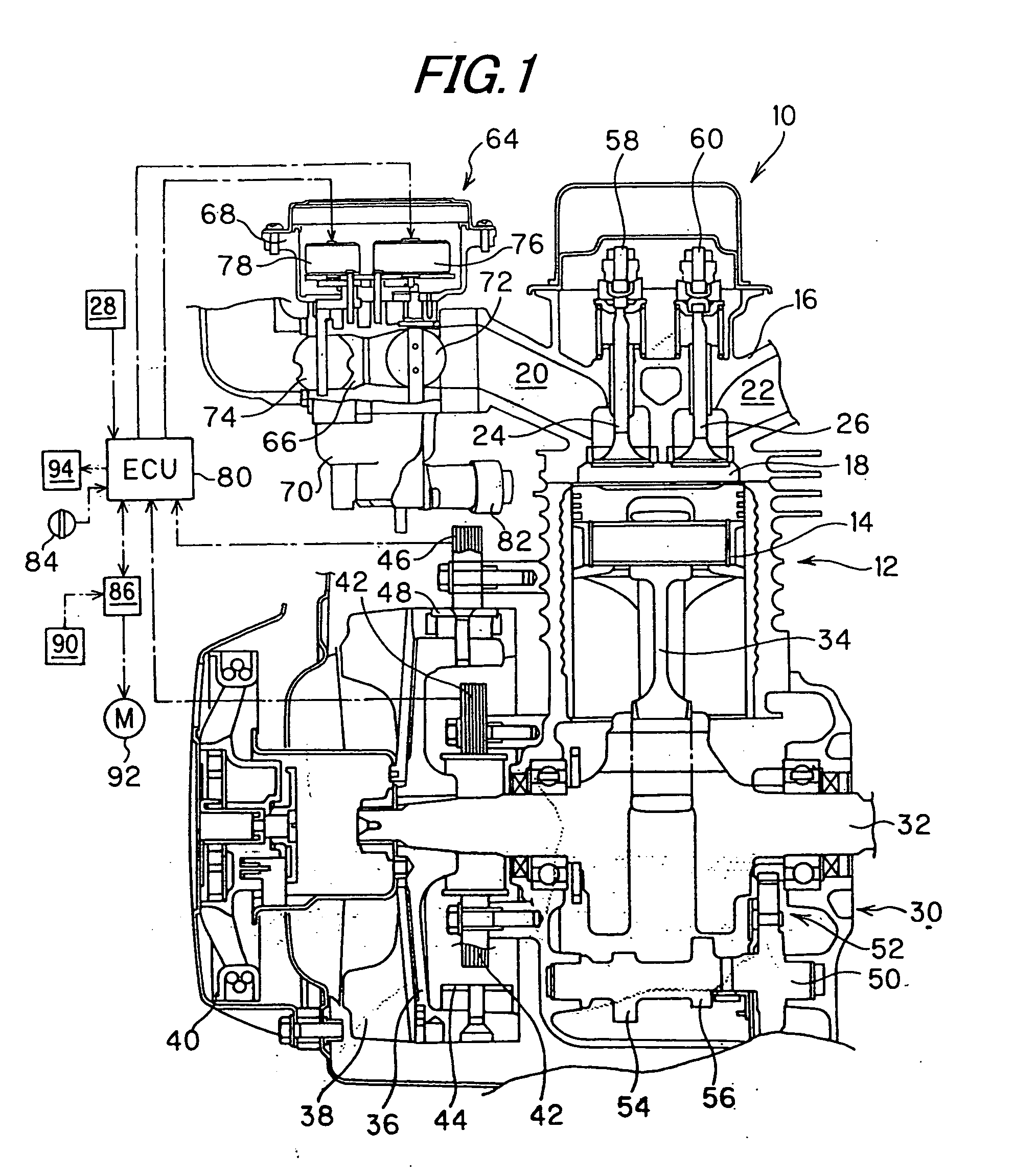
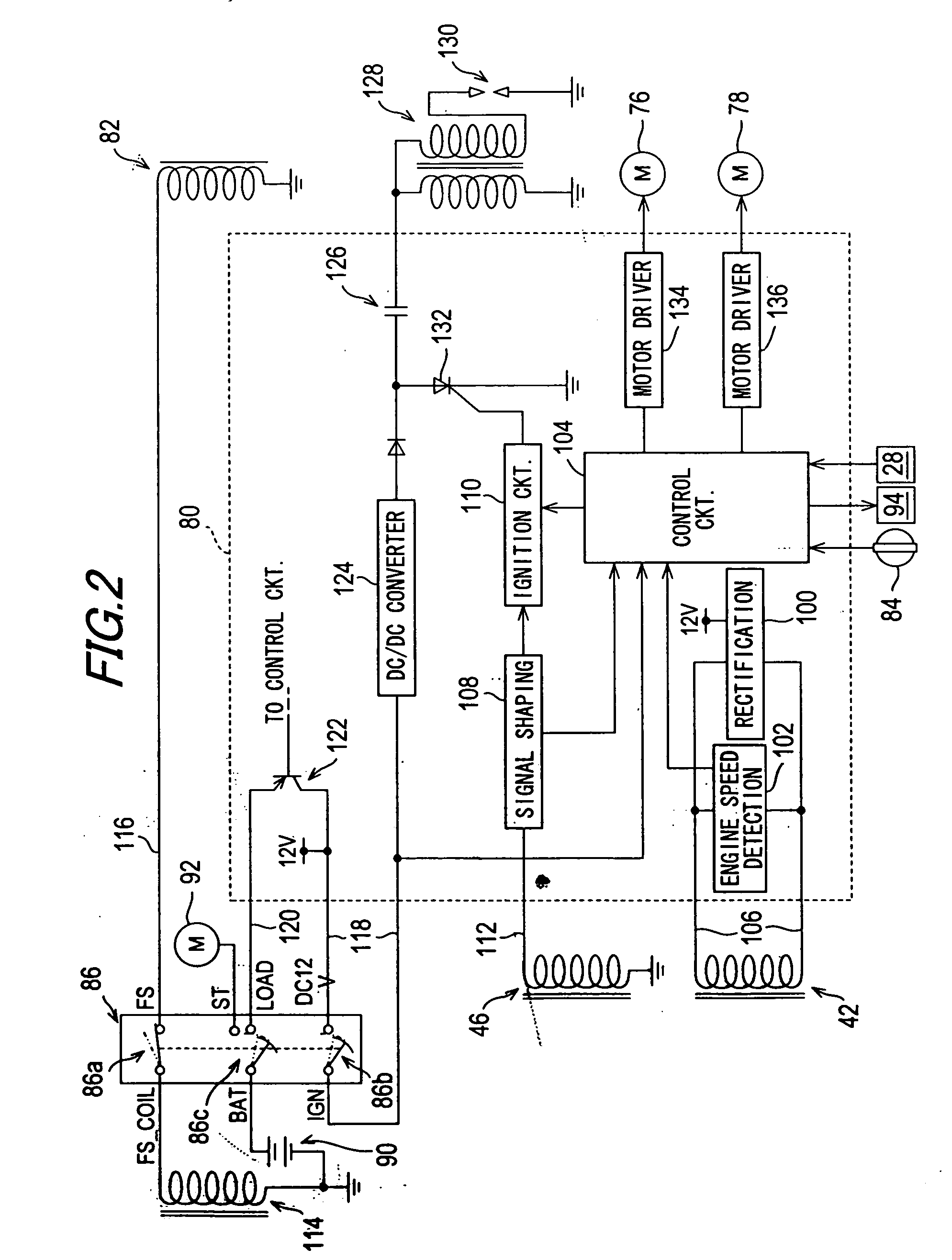
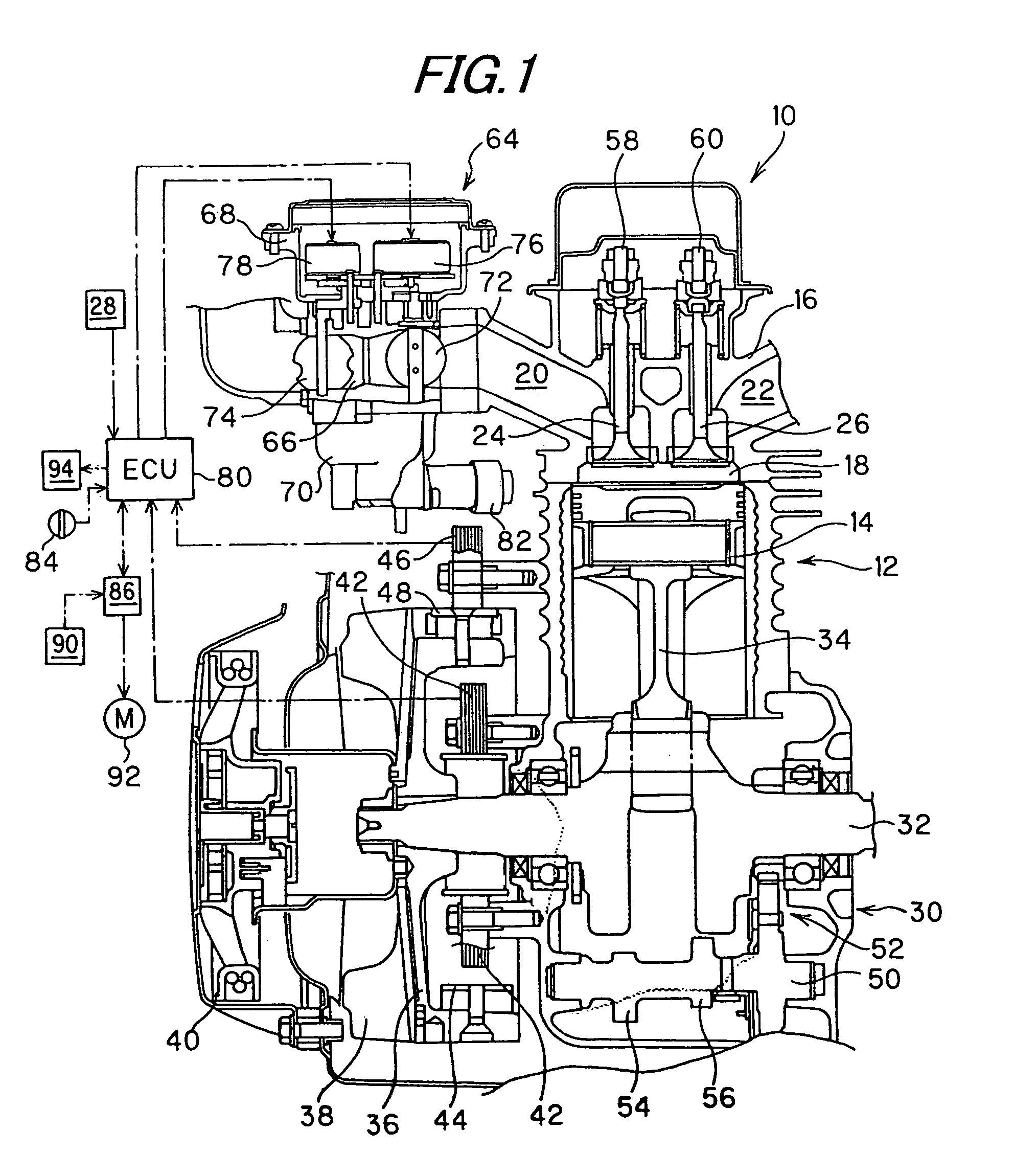
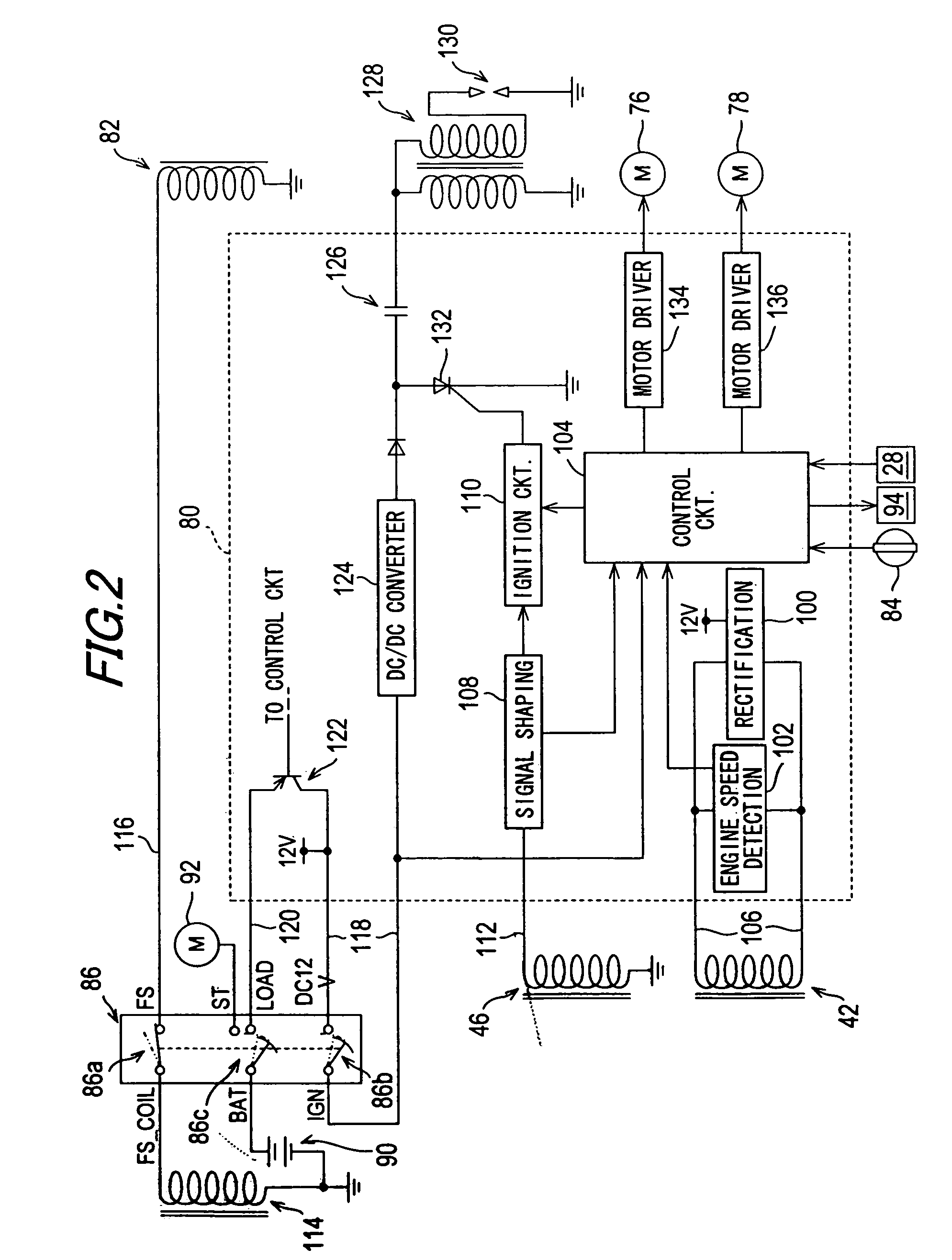
Battery-less power generation control system and straddle type vehicle having the same
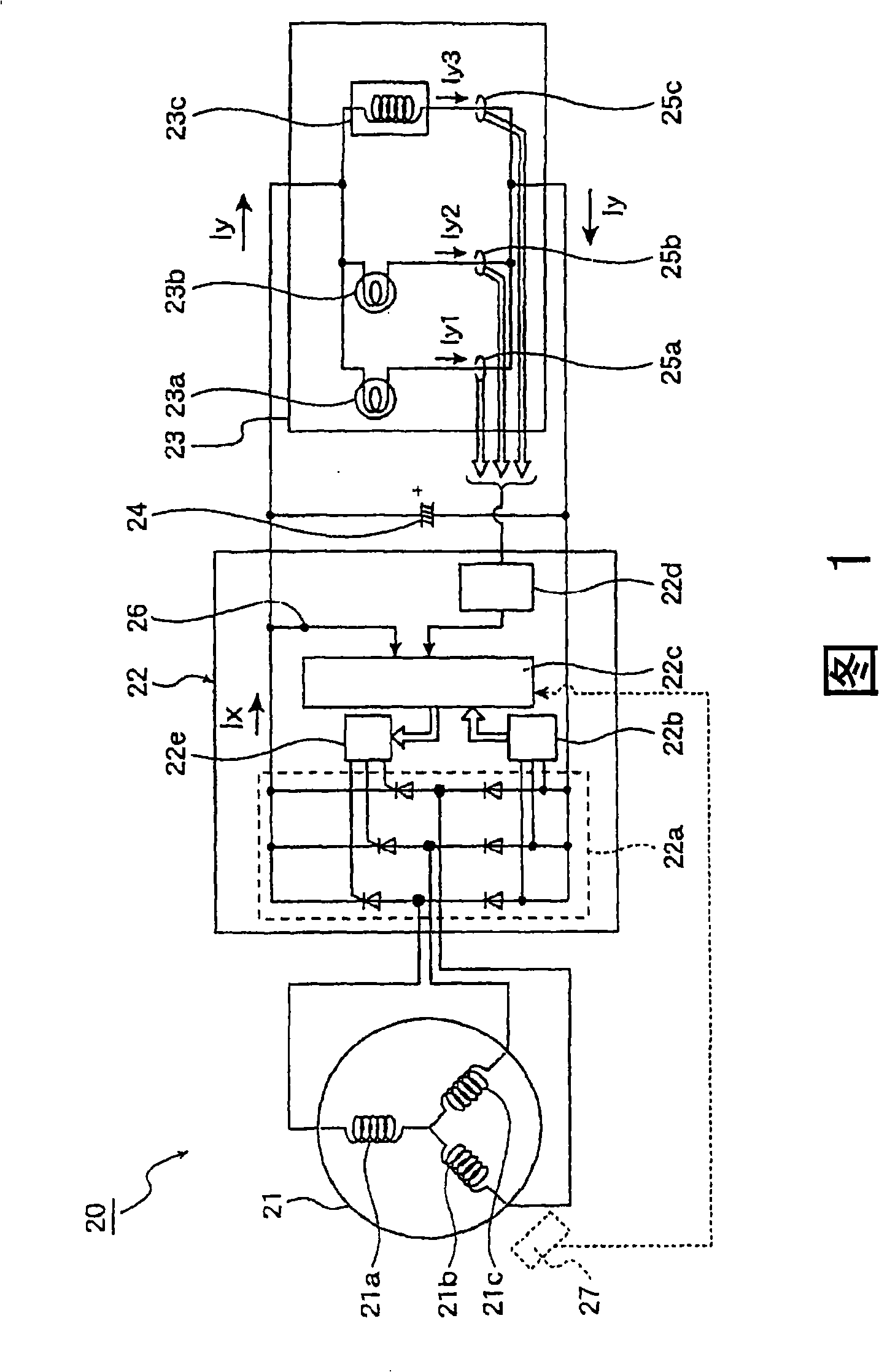
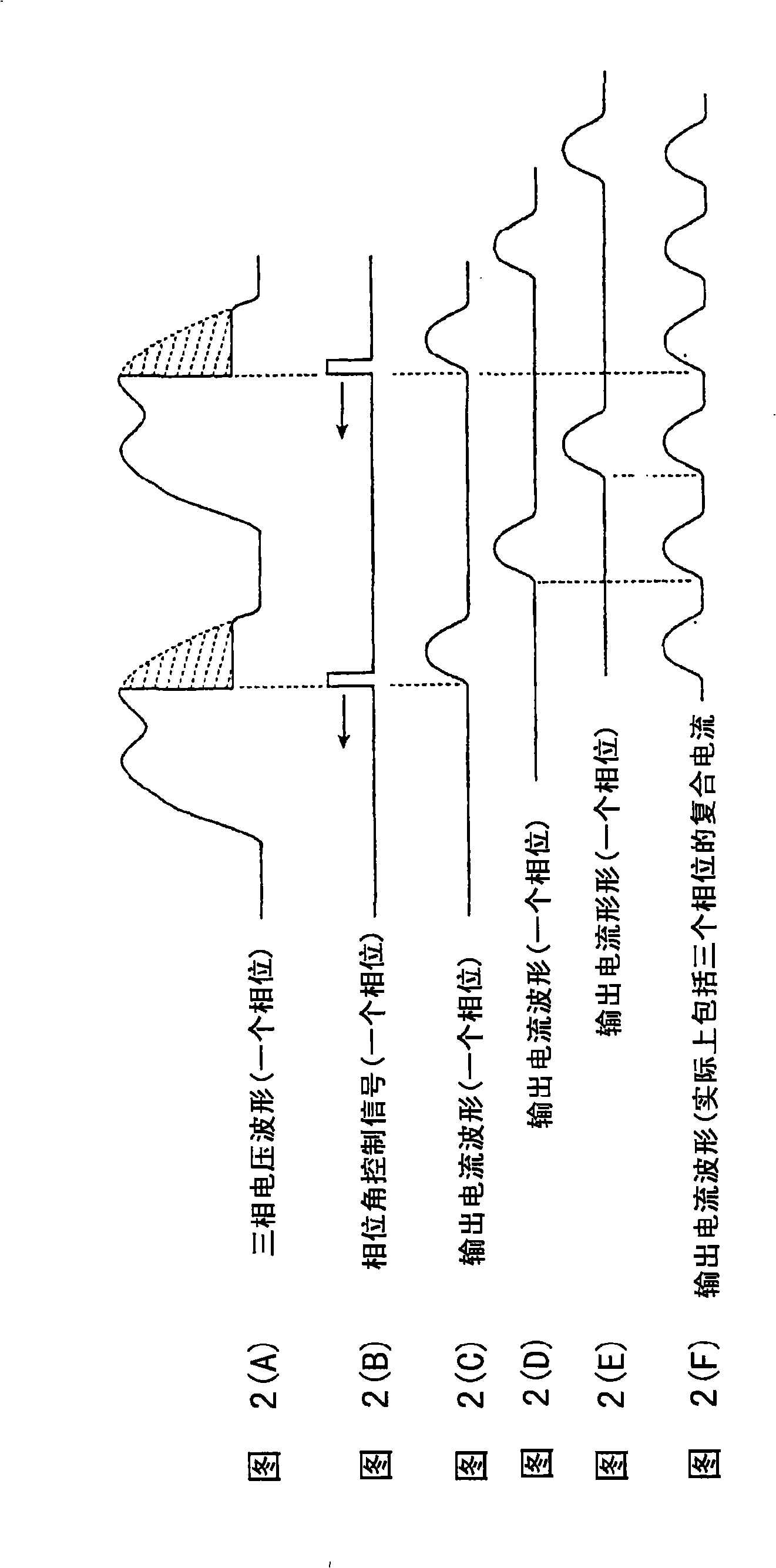
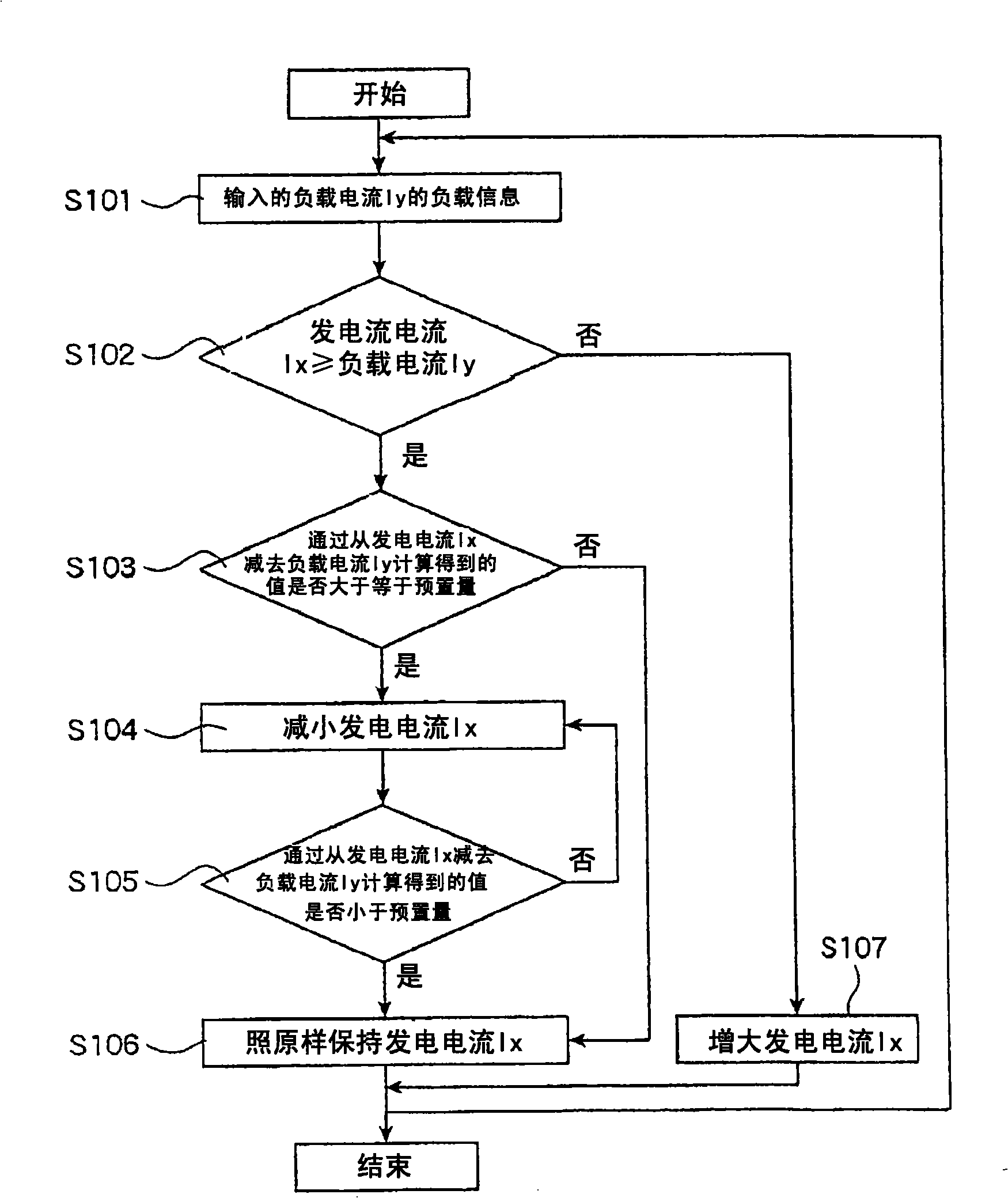
InactiveUS20080180069A1Raises any losses in the horsepower generatedImprove economyEmergency protective circuit arrangementsIgnition generator rotorControl systemStraddle
A battery-less power generation control system that maintains fuel economy and minimizes losses in horsepower generated by engine operation includes a magnet-type generator driven by an internal combustion engine and a controller for rectifying the alternating current generated by the generator to a direct current, the controller supplying the generated direct current to electric equipment. The controller includes a rectifying section for converting the alternating current generated by the generator to direct current, and a control section for controlling the generated current output by the rectifying section. The battery-less power generation control system detects a load current flowing through the electric equipment and the control section controls the rectifying section so that the generated current is generally equal to the load current.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Coil failure detection system for general-purpose engine
In a failure detection system of coils that produce outputs in response to rotation of a crankshaft of a general-purpose engine (including a power coil that produces an output indicative of the engine speed), the outputs produced by the coils are inputted to determine whether the coils produce the outputs, and it is discriminated that one of the coils (i.e., power coil) has failed when the coil does not produce the output, thereby enabling detection of failure such as wire breaking of the power coil and preventing overrunning of the engine and other such problems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Two-stroke internal combustion engine with crankcase lubrication system
InactiveUS20180347415A9Avoid burnsFully lubricatedCombustion enginesIgnition generator rotorTop dead centerExternal combustion engine
A two-cycle internal combustion engine with rear compression chamber, other than that of a crank case. This present engine has valves that can be screwed on the engine block near top dead center, and is actuated by air pressure. This present two-cycle engine yet uses an oil sump similar to that of a four-cycle engine, which eliminating the need to premix oil with the fuel. This present engine has a stationary piston which operates within a movable piston to form a rear-compression chamber. The movable piston has ports near its crown to transfer charge to the combustion chamber. The movable piston also has ports near bottom of its skirt to allow the fuel and air mixture to enter the rear compression chamber. This engine has a piston seat which is adapted to connect the movable piston to the connecting rod.
Owner:MERCIER CESAR
Method for operating a two-stroke engine
ActiveUS7894974B2Guaranteed uptimeSimple methodElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFour-stroke engineIgnition timing
A two-stroke engine has a cylinder with a combustion chamber delimited by a reciprocating piston, wherein the piston drives in rotation a crankshaft, and wherein a spark plug projects into the combustion chamber and ignites a fuel / air mixture. The two-stroke engine further has devices for supplying fuel and combustion air to the combustion chamber and a control unit that determines the ignition timing based on an ignition map. The ignition map indicates the ignition timing as a function of the engine speed for at least one first and one second operating states and for at least one first and one second engine speed ranges. The engine is controlled in that for an engine cycle the ignition timing is set in the second operating state at least within the first engine speed range based on the engine speed and on the number of engine cycles since the last combustion.
Owner:ANDREAS STIHL AG & CO KG
Flywheel with triggering ignition of gasoline engine generator
InactiveCN102116240AEasy to manufactureManufacturing flexibilityIgnition generator rotorEpoxyGasoline
The invention discloses a flywheel with triggering ignition of a gasoline engine generator, which comprises a gasoline engine; a piston is arranged in the gasoline engine; the piston is connected with one end of a connecting bar; the other end of the connecting bar drives a crank; a rare earth generator is arranged at one side of the gasoline engine; a flywheel body is arranged in the rare earth generator; a stator is arranged in the flywheel body; the front end of the flywheel body is provided with a start drum and a start pull plate; and the stator is fixed with a case of the gasoline engine. The flywheel with triggering ignition of the gasoline engine generator is characterized in that fourteen pieces of magnetic steel made of rare earth ferrite are arranged at the inner wall of the flywheel body; the magnetic steel made of ferrite and the flywheel body are fixed by epoxide resin adhesives; a caulking groove is made on an outer wall at one side of the flywheel body; rare earth magnetic steel for ignition is arranged in the caulking groove; counterweight iron with same weight is arranged at the other side of the flywheel body; and the counterweight iron is matched with the rare earth magnetic steel for ignition.
Owner:徐查庆
Coil failure detection system for general-purpose engine
In a failure detection system of coils that produce outputs in response to rotation of a crankshaft of a general-purpose engine (including a power coil that produces an output indicative of the engine speed), the outputs produced by the coils are inputted to determine whether the coils produce the outputs, and it is discriminated that one of the coils (i.e., power coil) has failed when the coil does not produce the output, thereby enabling detection of failure such as wire breaking of the power coil and preventing overrunning of the engine and other such problems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Multiple-keyed flywheel and engine crankshaft
A multiple-keyed crankshaft and flywheel provides for different ignition timing options for an internal combustion engine. The crankshaft of the engine includes multiple keyways set at designated angular displacements of the crankshaft that correspond with keyways on a flywheel for providing different timing options for the engine. The flywheel may be mounted to the crankshaft by aligning one of the keyways of the flywheel to one of the keyways of the crankshaft related to a particular ignition timing selection.
Owner:KOHLER CO
Engine
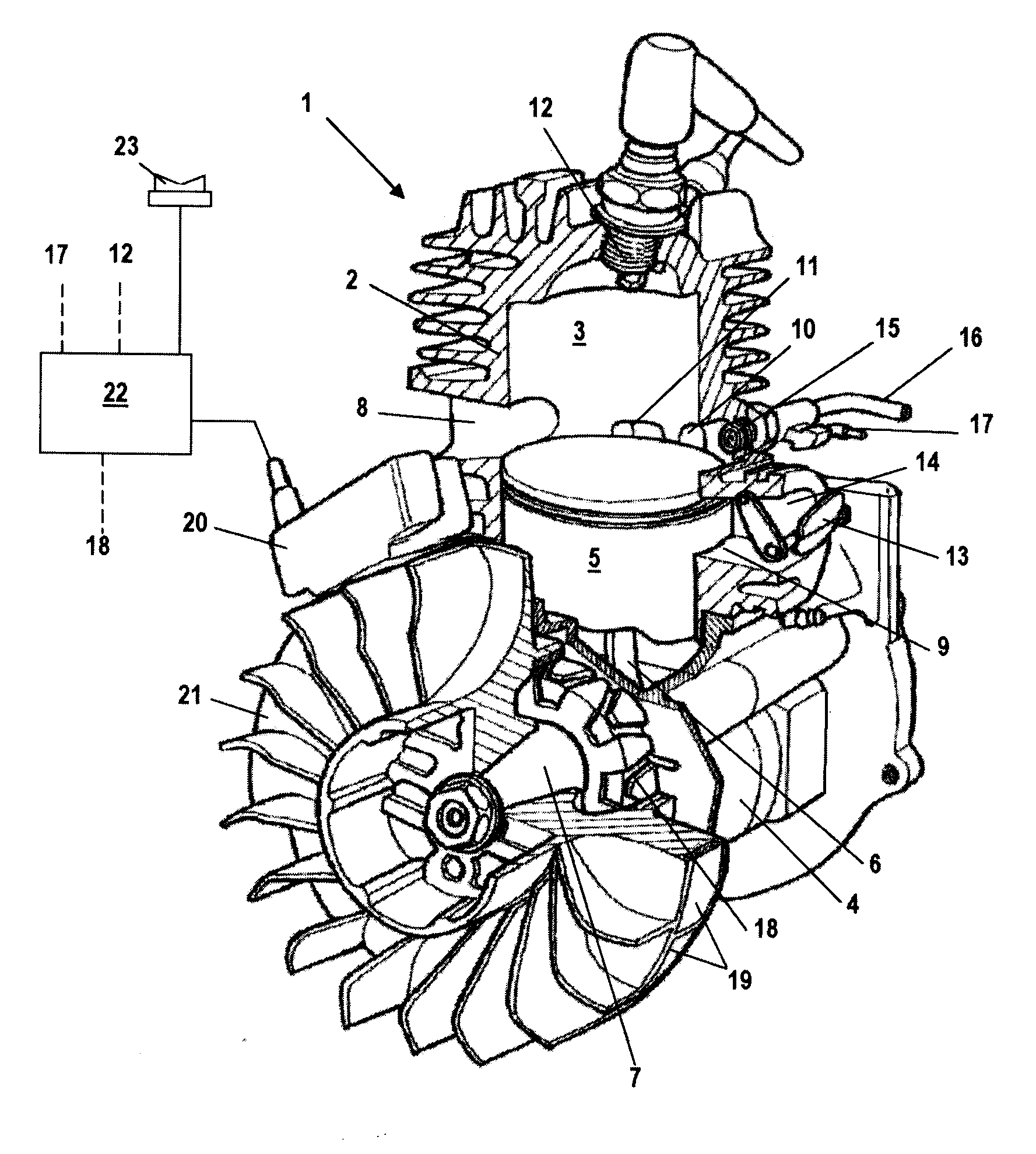
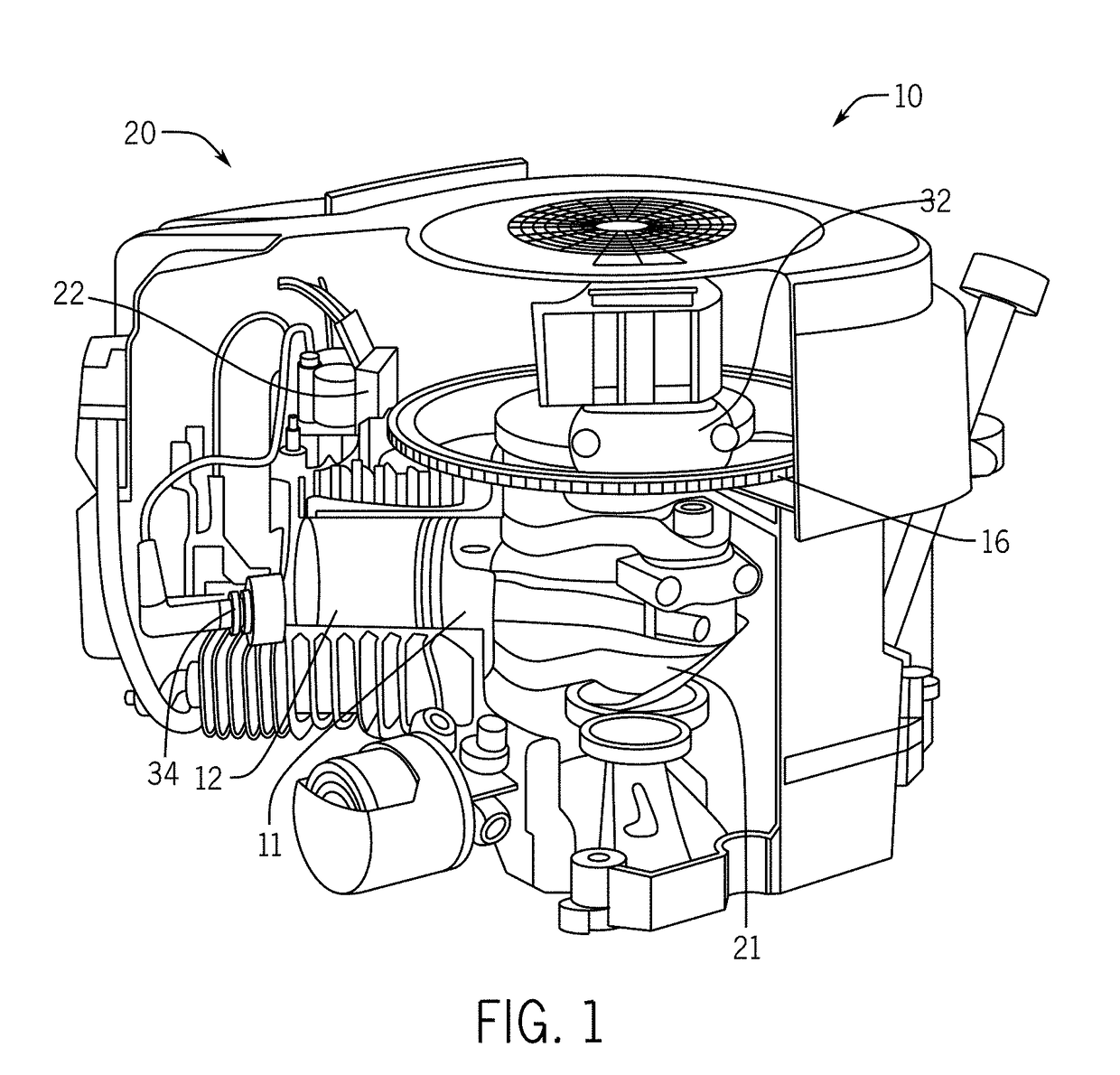
ActiveUS10240509B2Improve maintenance efficiencyImprove efficiencyCasingsAir coolingCrankcaseEngineering
An engine includes a crankcase with cylinders and fins on outer circumferences of the cylinders. A crank shaft penetrates the crankcase. A cooling fan is provided on an outer side of the crankcase and arranged coaxially with the crank shaft. A first cover covers an outer side of the cylinders and the crankcase, and the cooling fan. A second cover capable of being detached from / attached to the first cover. The first cover includes a first opening facing the cooling fan, and second openings facing the fins. The second cover includes an air inlet facing the first opening, and attached to the first cover to cover the first opening and the second openings.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR POWER PROD KK
High-power motorboat outboard engine flywheel
InactiveCN103104395ASmall sizeReduce consumptionIgnition generator rotorFlywheelsEngineeringFlywheel
The invention discloses a high-power motorboat outboard engine flywheel. An outer circumference face, matched with an inner hole of a cylinder body, of a shaft sleeve is arranged to be in a step structure and is composed of an outer layer disc, an outer edge boss and an inner layer disc, wherein the an outer layer disc, the outer edge boss and the inner layer disc are arranged in sequence, the diameter of the outer edge boss is larger than the diameter of the outer layer disc and the diameter of the inner layer disc, and a plurality of sections of cutting string grooves are formed in the outer circumference face of the outer edge boss. When the high-power motorboat outboard engine flywheel is assembled, the outer layer disc of the shaft sleeve is placed in a step small hole of the cylinder body. A plurality of sections of gaps are formed on the corresponding portions of the cutting string grooves of the outer edge boss and a large hole of the cylinder body. A die is composed of an upper die and a lower die which are arranged in a matched mode. An upper convex die is arranged on the upper die, and a lower convex die is arranged on the lower die. The shaft sleeve and the cylinder body are connected into a whole through an upper baffle block, a lower baffle block and a rotation-stopping baffle block, wherein the upper baffle block and the lower baffle block are formed on the outer edge boss. According to the connecting method, a die stamping method is adopted, the shaft sleeve and the cylinder body are firmly connected into the whole, the size of the shaft sleeve is obviously decreased, consumed materials of the shaft sleeve are reduced, and precious resources and machining work hours are saved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Ignition device
ActiveUS20190390642A1Increase output powerStartability is improvedInternal combustion piston enginesIgnition generator rotorFlywheelMagnet
In an ignition device, a proportion of a yoke end width defined as a distance from one end to another end of an end portion of each of a pair of yokes in the circumferential direction to a magnet width defined as a distance from one end to another end of a permanent magnet disposed on the outer circumferential surface of a flywheel, in the circumferential direction is in a range of 60% to 100%. Moreover, a proportion of the magnet width to a yoke interval between the pair of yokes is in a range of 95% to 100%.
Owner:TOYO DENSO
Flywheel arrangement for engine
An engine has a crankshaft journaled on an engine body. The crankshaft has an end portion that extends outward beyond the engine body. In some embodiments, a flywheel has a hub portion and a wheel portion which are unitarily formed with each other. The hub portion has a cylindrical shape that extends generally along an axis of the crankshaft and is coupled with the end portion of the crankshaft. The hub portion has a uniform thickness and a nut or bolt fastens the hub portion onto the end portion of the crankshaft. In other embodiments, the flywheel has a wheel portion and a coupling portion which are unitarily formed with each other. The coupling portion extends over the end portion of the crankshaft and intersects an axis of the crankshaft. Multiple bolts fasten the coupling portion onto the end portion of the crankshaft.
Owner:YAMAHA MARINE KK
Battery-less power generation control system and straddle type vehicle having the same
The present invention provides a battery-less power generation control system that maintains fuel economy and minimizes losses in horsepower generated by engine operation includes a magnet-type generator driven by an internal combustion engine and a controller for rectifying the alternating current generated by the generator to a direct current, the controller supplying the generated direct current to electric equipment. The controller includes a rectifying section for converting the alternating current generated by the generator to direct current, and a control section for controlling the generated current output by the rectifying section. The battery-less power generation control system detects a load current flowing through the electric equipment and the control section controls the rectifying section so that the generated current is generally equal to the load current.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Engine system
ActiveUS10808669B2Increasing size and costImproving startabilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Ignition device, internal combustion engine and method for its operation
ActiveUS20190338746A1High energy demandSafe operation of loadElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesVoltage converterElectricity
Owner:PRUFREX ENG E MOTION
Saddle-ride type vehicle
In an outside air intake duct, a duct body extends intersecting with a part of a vehicle body frame in a top view of a vehicle body. The vehicle body frame includes a duct holding portion. The duct holding portion is formed so as to surround the duct body at an intersecting site with the duct body. The duct body includes an air intake opening and a discharge port. The air intake opening projects outside the vehicle body frame. The discharge port is positioned inside the vehicle body frame. The duct holding portion includes a plurality of duct securing portions to secure the duct body. The duct securing portions are disposed so as to be positioned on both sides of the duct body nipping the duct body.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
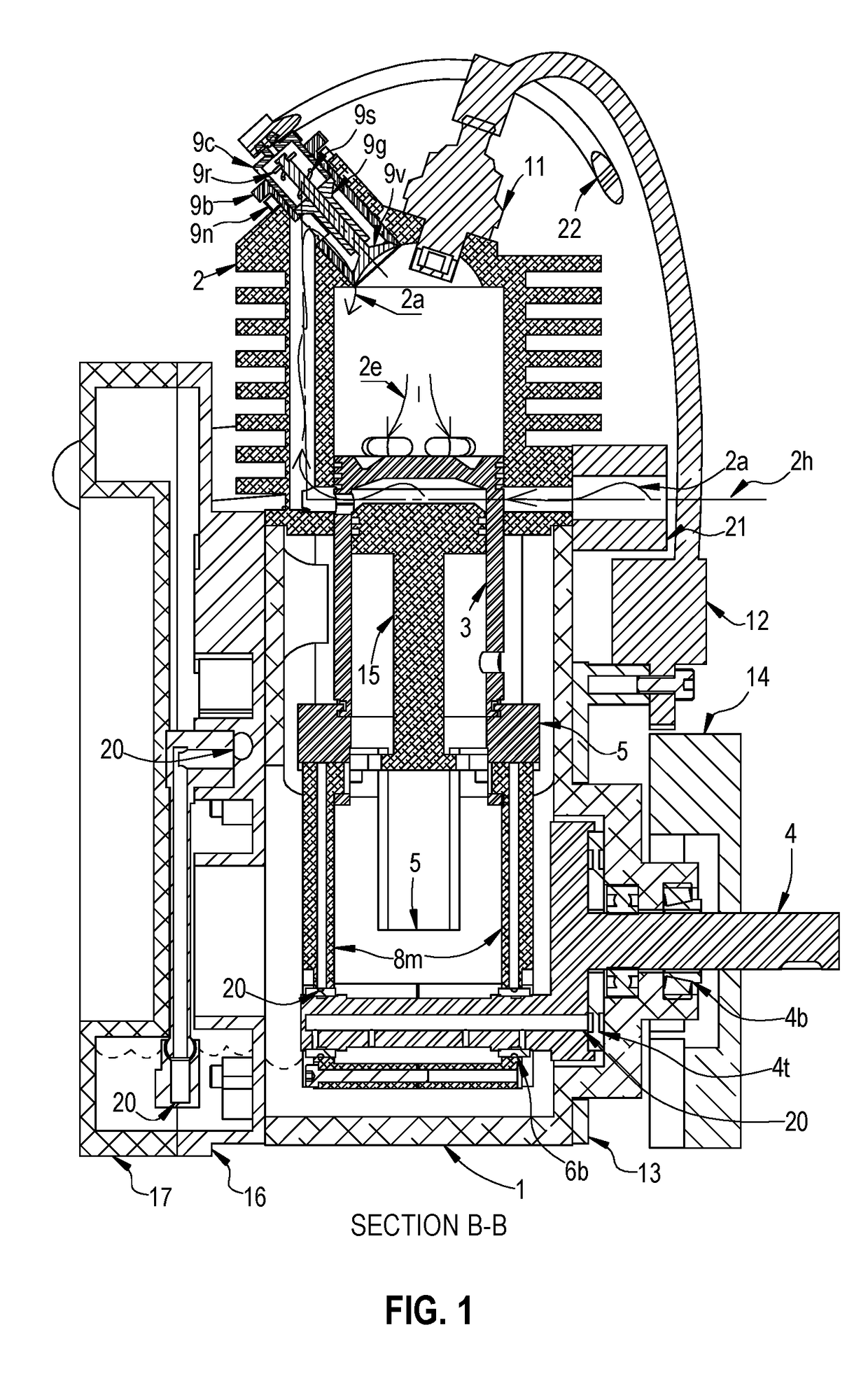
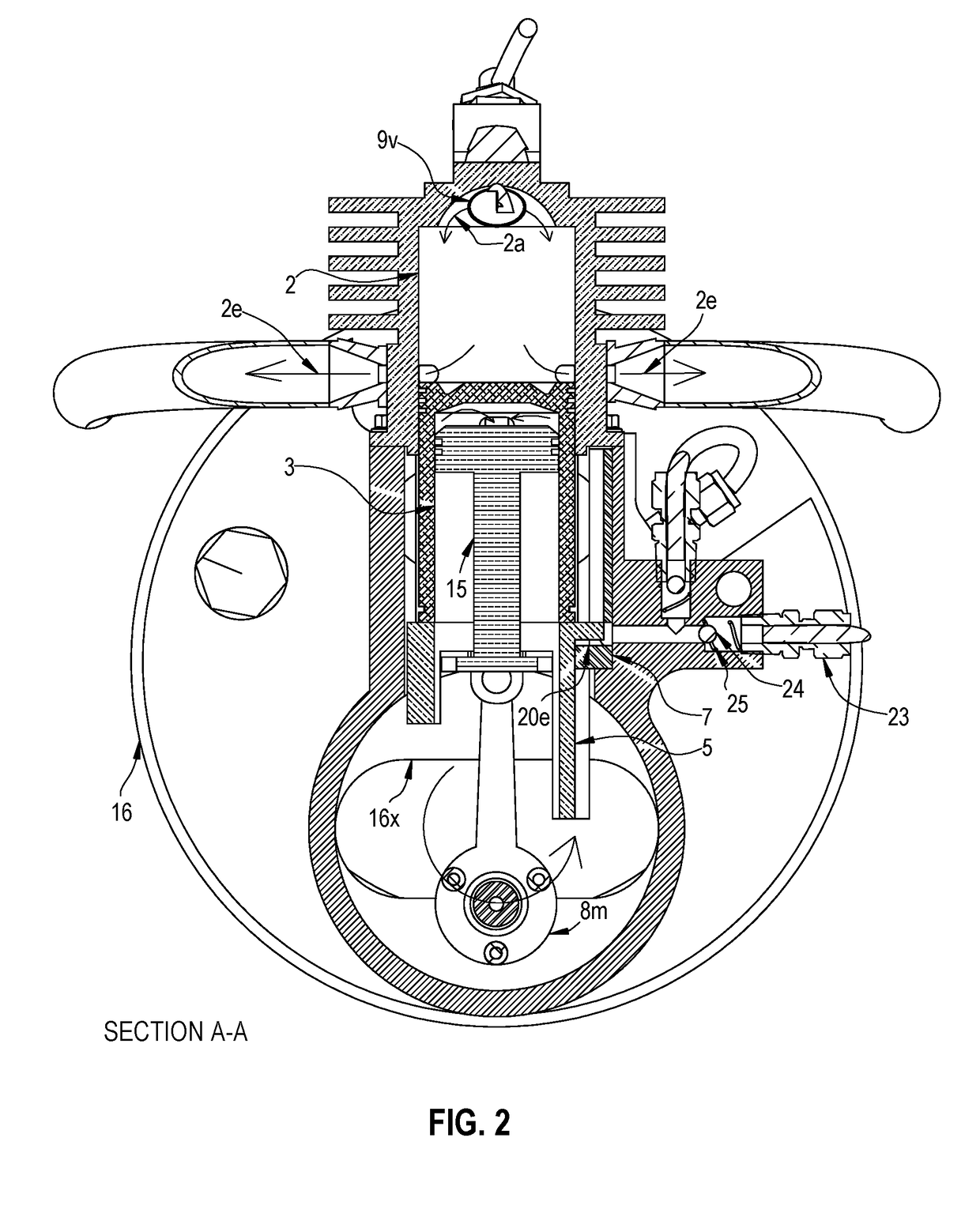
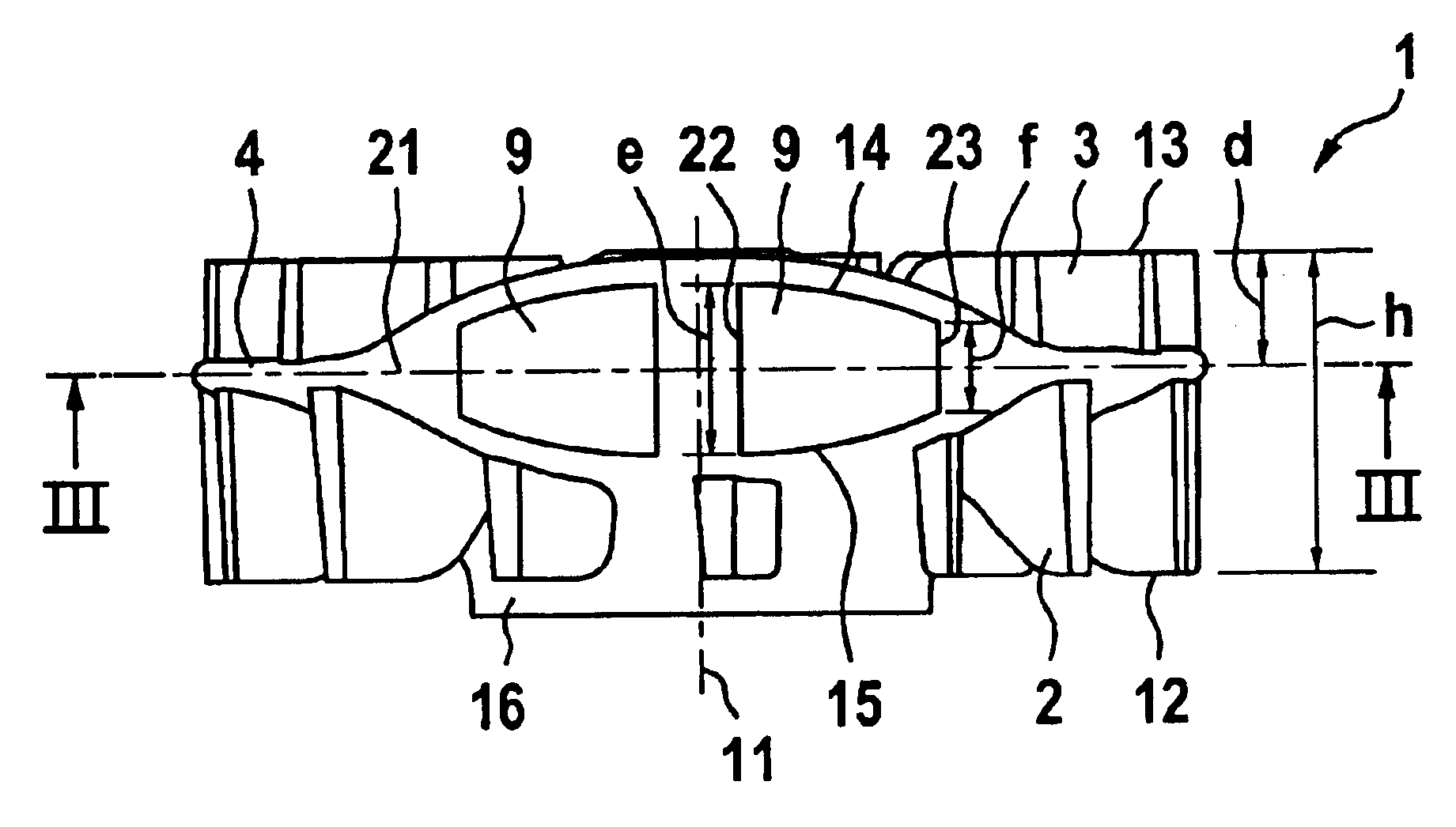
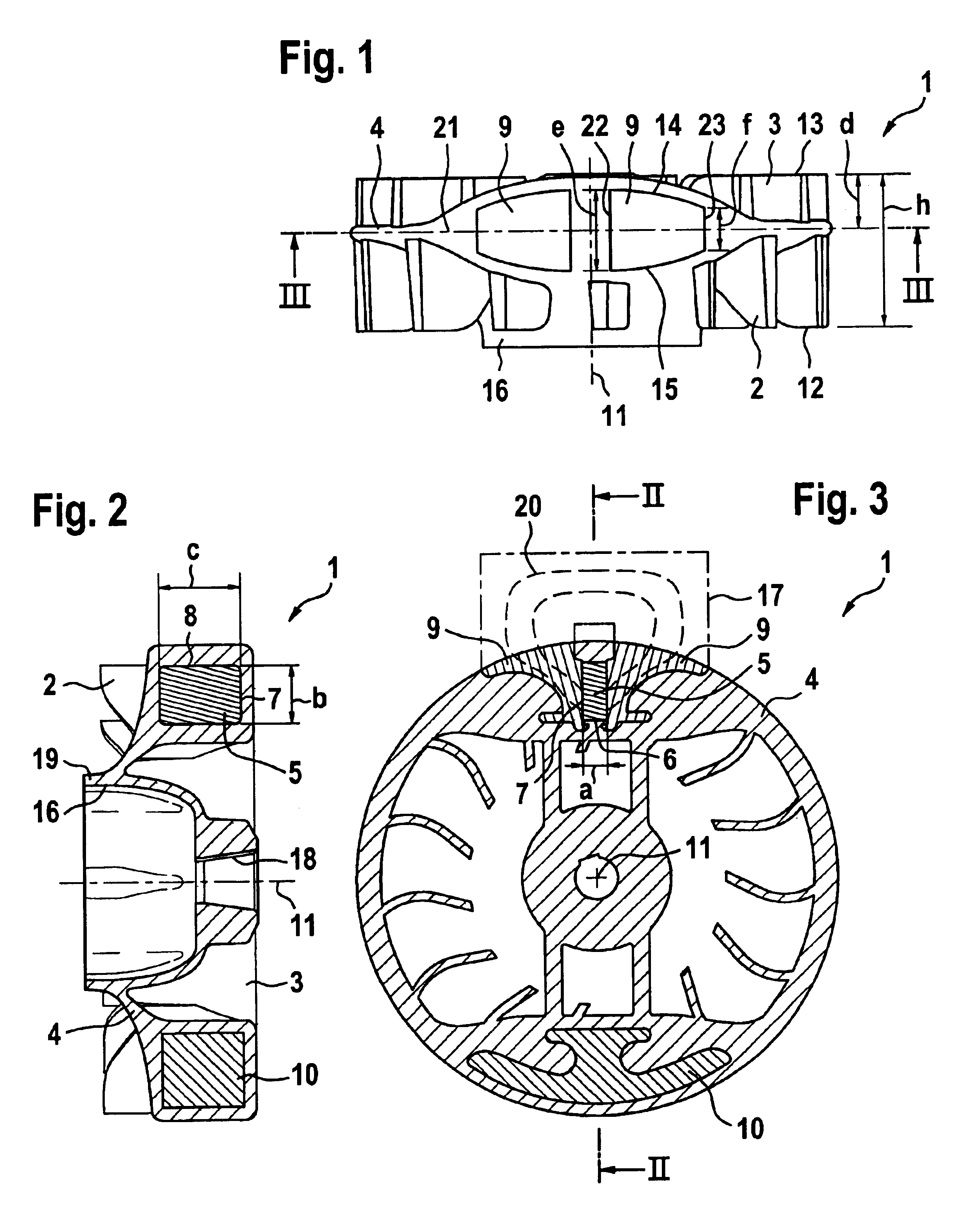
Flywheel for an internal combustion engine
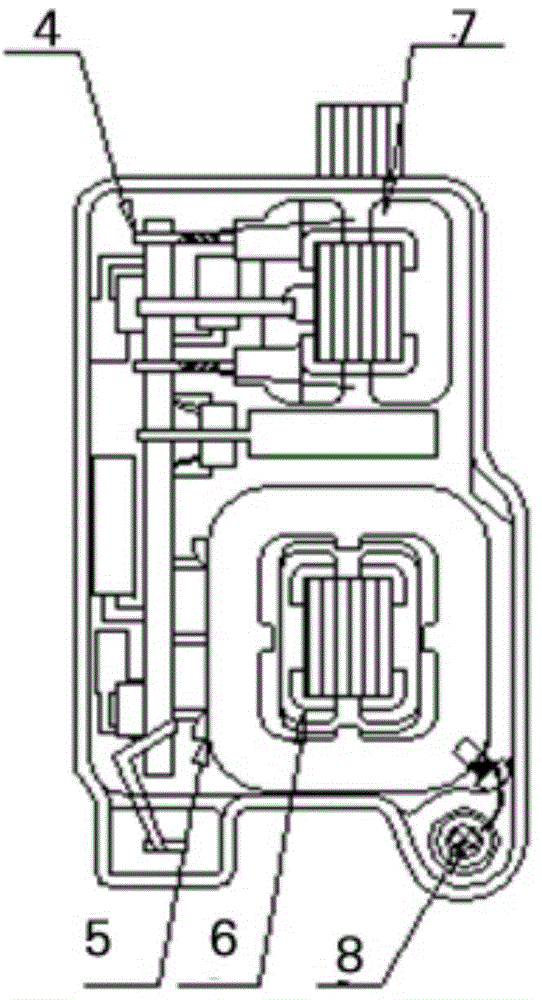
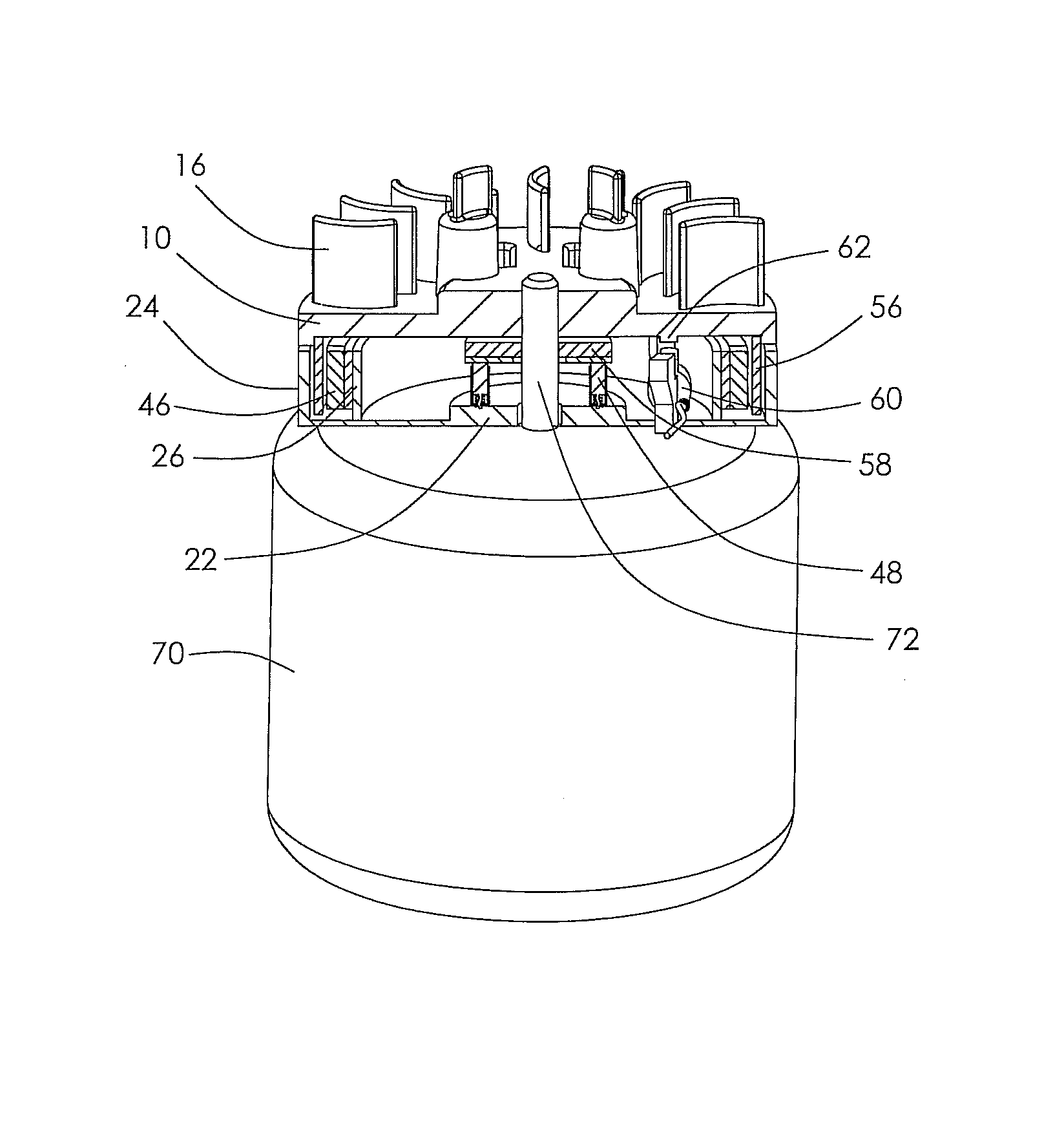
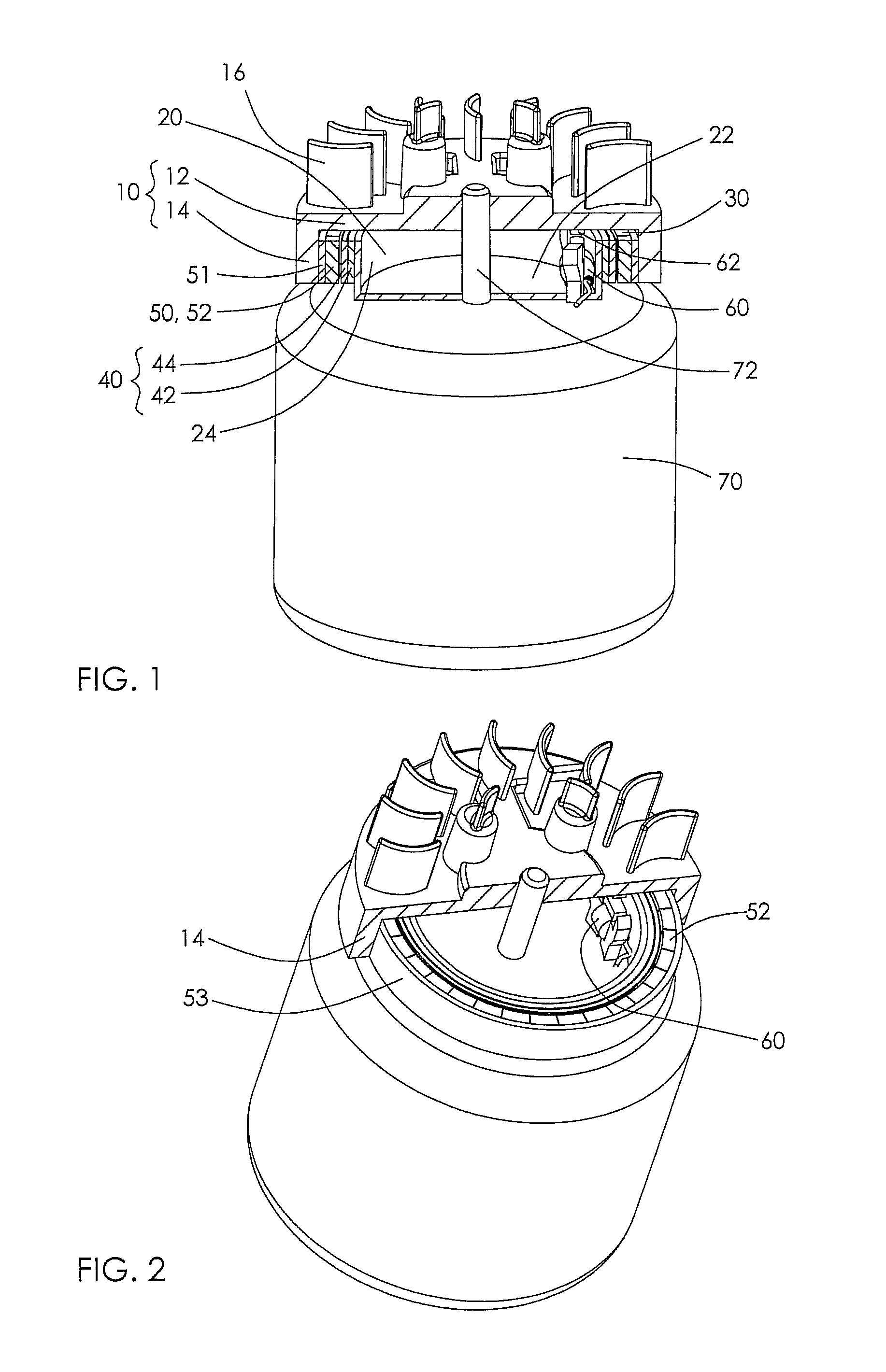
InactiveUS6915764B2High moment of inertiaReduce weightCoolant flow controlIgnition generator rotorRotational axisHand held
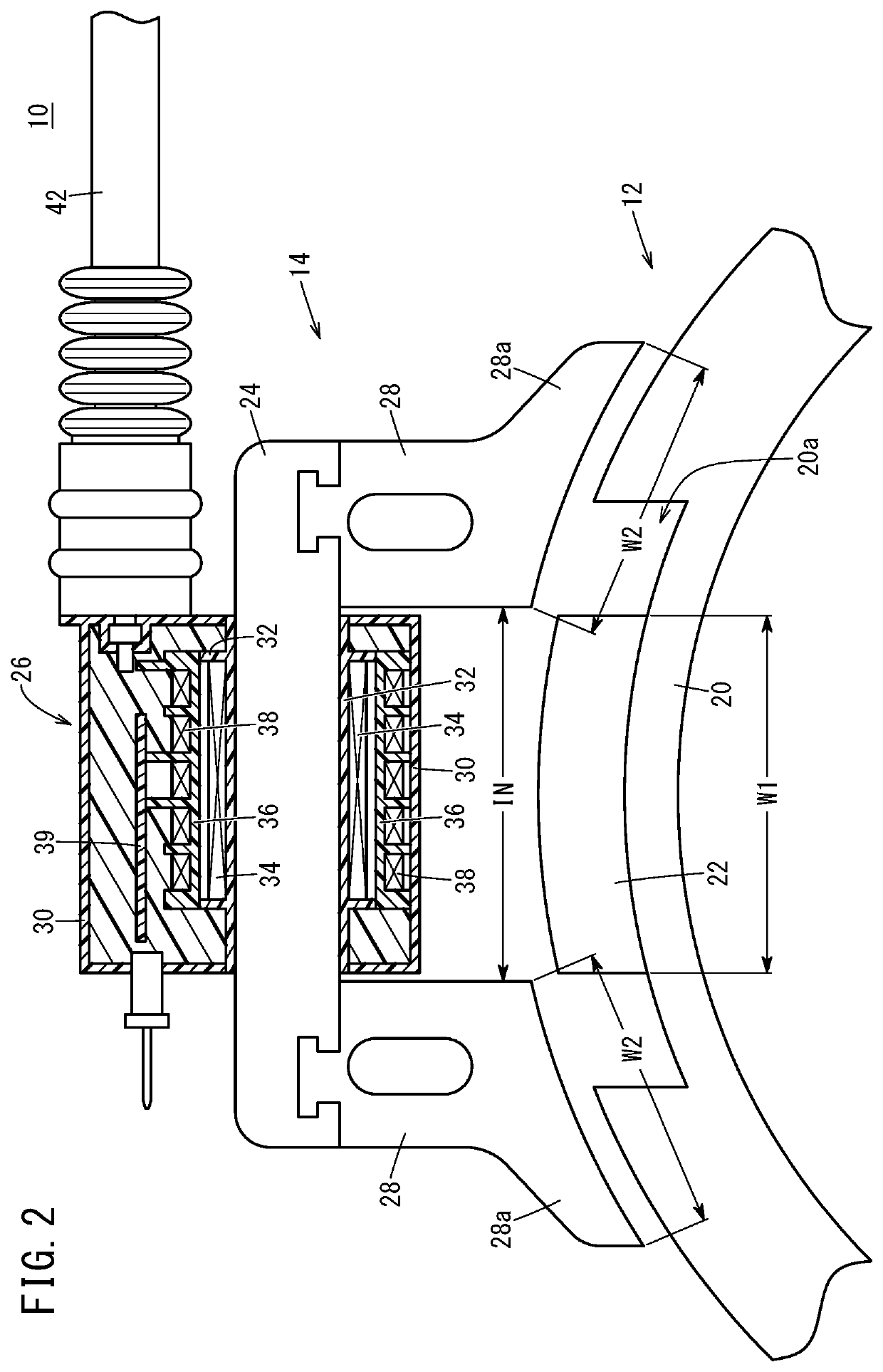
A flywheel (1) for an internal combustion engine is provided for generating a cooling air flow and is especially for a two-stroke engine on a portable handheld work apparatus such as a motor-driven chain saw, cutoff machine or the like. The flywheel (1) carries a parallelopipedly-shaped permanent magnet (5) for a magnetic ignition system. The permanent magnet has a short edge (6), a center edge (7) and a long edge (8). The permanent magnet (5) is polarized in the direction of the short edge (6). To provide a high moment of inertia of the flywheel (1) while achieving a low weight, the short edge of the permanent magnet (5) runs tangentially to the peripheral direction of the flywheel (1) and that the long edge (8) of the permanent magnet (5) is aligned parallel to the rotational axis (11) of the flywheel (1).
Owner:ANDREAS STIHL AG & CO KG
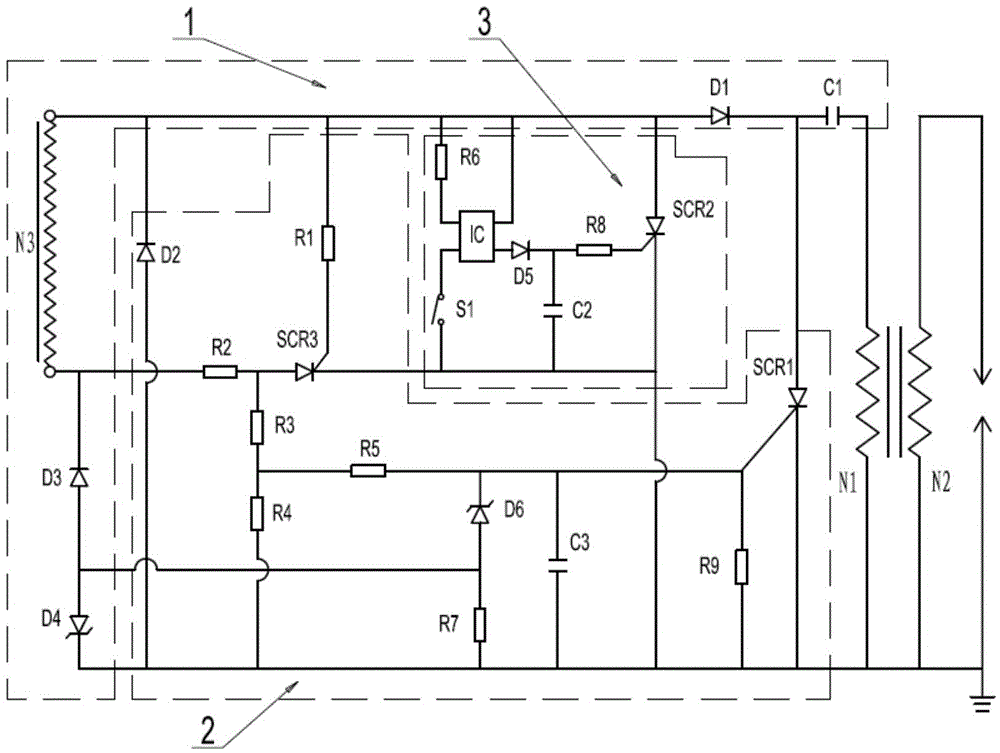
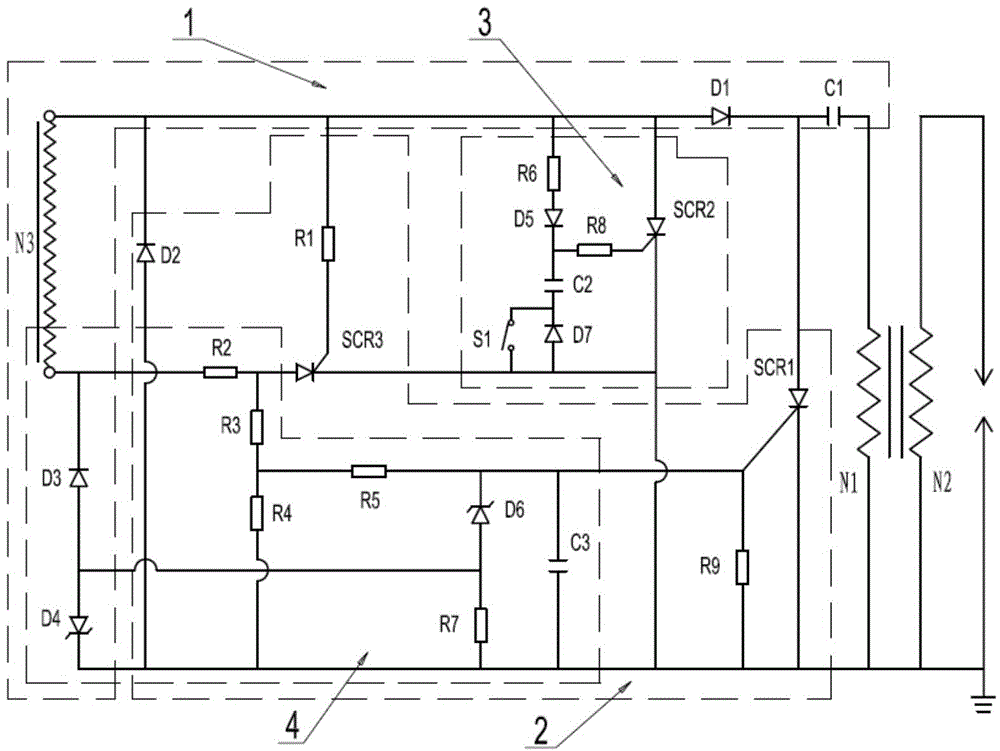
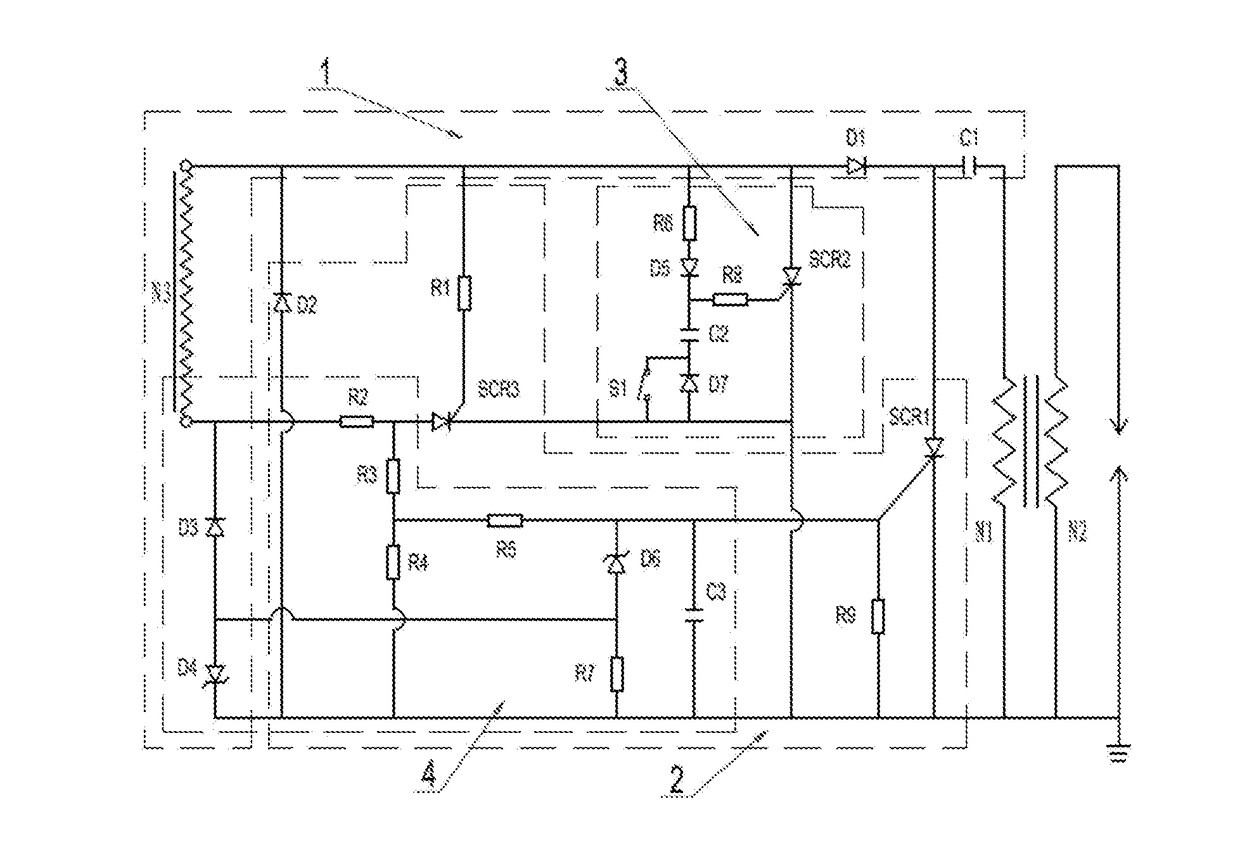
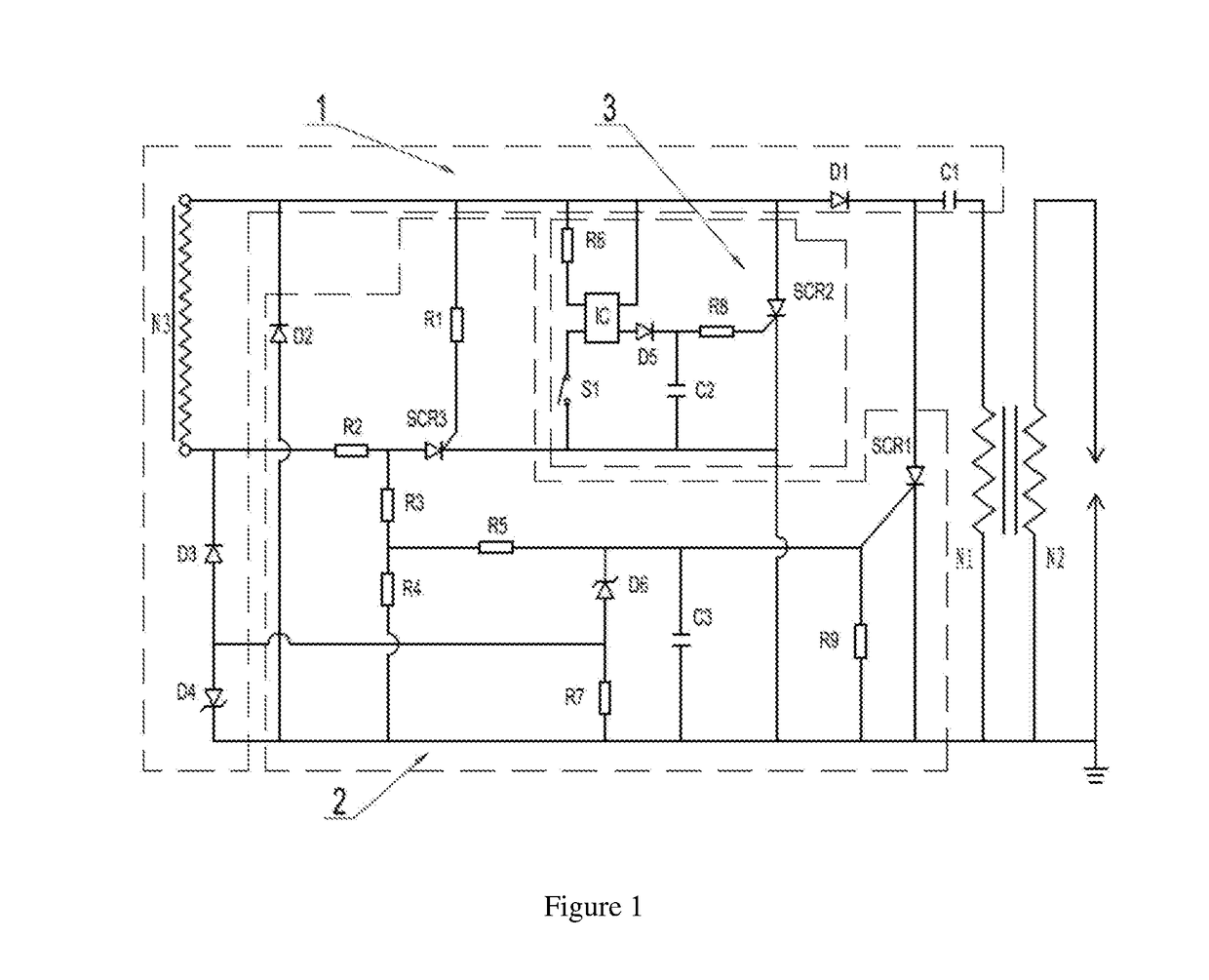
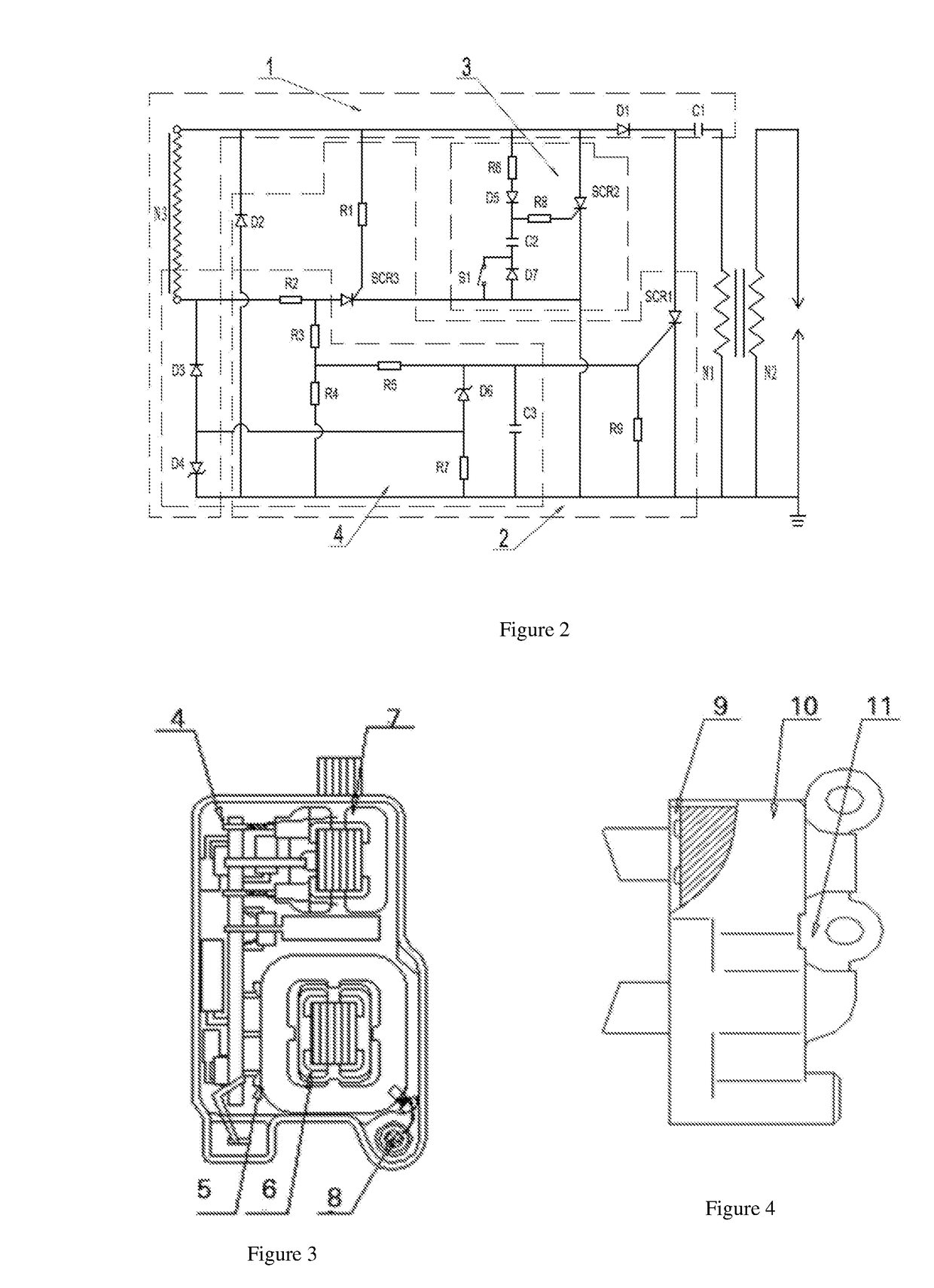
Delayed ignition control device
A delayed ignition control device comprises a charging circuit (1) and a delayed ignition control circuit (3). The charging circuit (1) comprises a power supply circuit N3, an energy storage capacitor C1 and a diode D1, wherein the positive electrode of the diode D1 is connected with the start end of the power supply coil N3, the negative electrode of the diode D1 is connected with the energy storage capacitor C1, and the other end of the energy storage capacitor C1 is connected with an ignition coil. The delayed ignition control circuit (3) comprises a silicon controlled rectifier SCR2, an optical coupler IC, a diode D5, a voltage keeping capacitor C2, a flameout switch S1, a resistor R6 and a resistor R8, wherein the resistor R6 is connected between the positive electrode of the input end of the optical coupler IC and the start end of the power supply coil N3, the flameout switch S1 is connected between the negative electrode of the input end of the optical coupler IC and the ground, the collector of the optical coupler IC is connected with the start end of the power supply coil N3, the output end of the optical coupler IC is connected with the positive electrode of the diode D5, the voltage keeping capacitor C2 is connected between the negative electrode of the diode D5 and the ground, and the resistor R8 is connected between the negative electrode of the diode D5 and the control electrode of the silicon controlled rectifier SCR2. The delayed ignition control device has the advantages of being simple in structure, capable of easily adjusting the delayed time and reliable in operation.
Owner:YUYAO AOXIN ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE
Starter motor
A starter motor for engine has a flywheel fixed to a shaft of the engine. A support is fixed relative to the engine. A space is formed between the flywheel and the support and a driving device is installed in the space. The driving device includes a stator fixed to the support and a rotor fixed to the flywheel.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
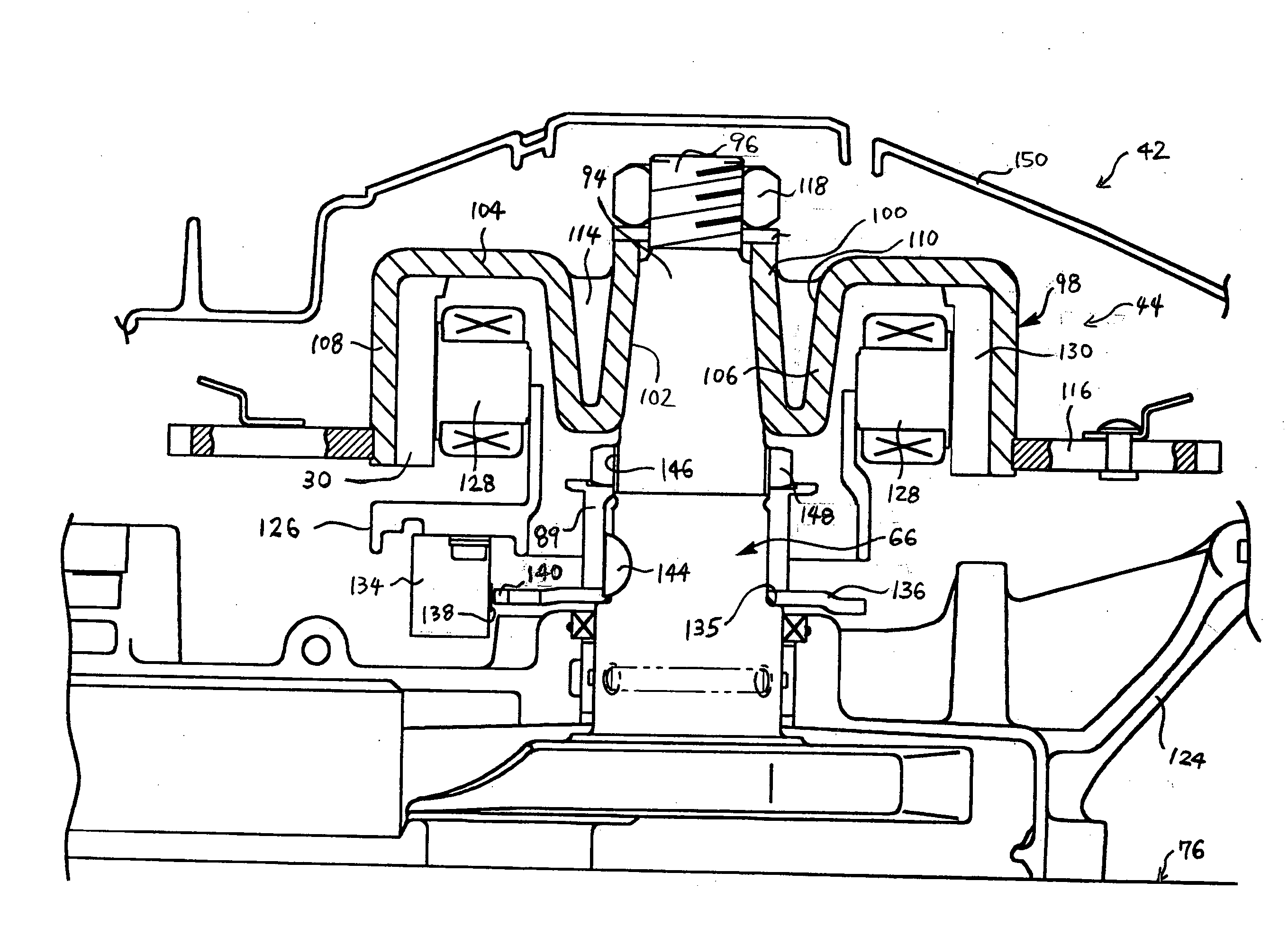
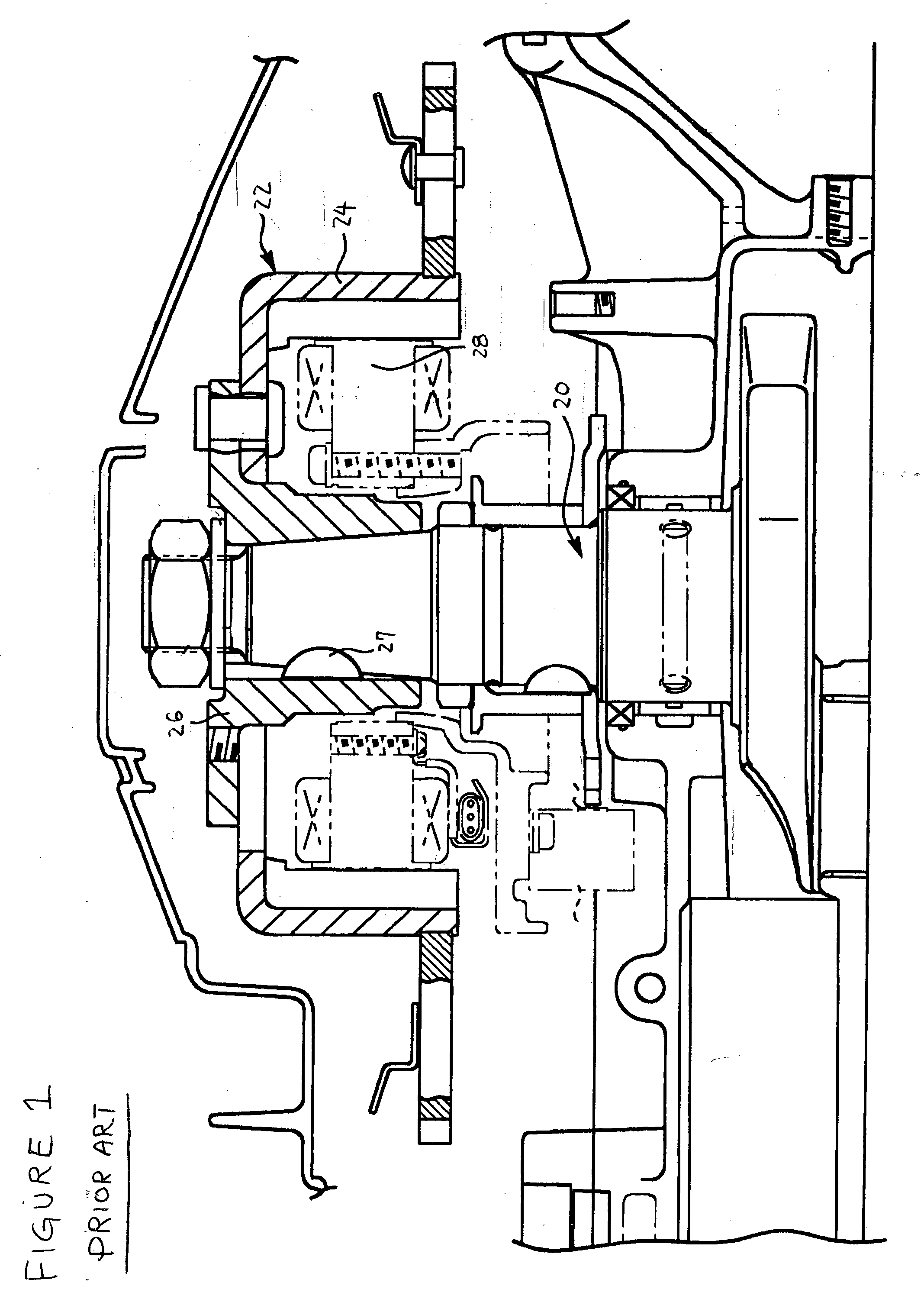
Crankshaft driven flywheel magneto generator with circular winding for power supply in handheld batteryless combustion engines
ActiveUS11391259B2Eliminating weak pointRapid productionIgnition generator rotorMagnetic circuit stationary partsIgnition coilElectrical battery
A magneto ignition system for battery less hand-held combustion engines includes a claw generator with a stationary circular power coil winding enclosed by two iron claw halves and with a rotating flywheel magnet ring with multiple magnetic poles. The stationary circular coil winding includes a trigger coil with a stationary coil winding arranged in a plane orthogonal to the stationary circular power coil winding. The magneto ignition system further includes an engine control module ECM for establishment of appropriate ignition timing, and an ignition coil module ICM. The stationary circular power coil winding may provide the electrical power supply to both the ignition timing module ECM and the ignition coil module ICM.
Owner:SEM AB
Delayed Ignition Control Device
InactiveUS20170107965A1Simple structureEasy to adjustIgnition generator rotorMachines/enginesCapacitorSilicon
A delayed ignition control device comprises a charging circuit and a delayed ignition control circuit. In the delayed ignition control circuit, the resistor R6 is connected between the positive electrode of the input end of the photo coupling IC and the initial end of the power coil N3; the shut-off switch S1 is connected between the negative electrode of the input terminal of the photo coupling IC and the ground; the collector electrode of the photo coupling IC is connected with the initial end of the power coil N3; the output end of the photo coupling IC is connected with the anode of the diode D5; the voltage holding capacitor C2 is connected between the negative electrode of the diode D5 and the ground; and the resistor R8 is connected with the negative electrode of the diode D5 and the controller electrode of the silicon controlled SCR2.
Owner:YUYAO AOXIN ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE
Internal combustion engine with integrated connectivity device
ActiveUS10785908B2Association with control/drive circuitsIgnition generator rotorInternal combustion engineFlywheel
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Lubricating system for air-cooled general-purpose engine
An air-cooled general-purpose engine includes: a cooling fan fixed to one end portion, protruding outward from one end wall of an engine main body, of a crankshaft; and a shroud which is mounted to the engine main body, and which defines a cooling-air path between the shroud and the one end wall, the cooling-air path guiding a cooling air blown under pressure from the cooling fan. The air-cooled general-purpose engine includes: an oil pump which pumps up an oil from an oil reservoir; and an oil-supply path which is formed in the one end wall, facing the cooling-air path, of the engine main body, and configured to guide the oil discharged from the oil pump to a valve operating chamber in a head portion of the engine main body, and a jet for jetting the oil is provided in an opening of the oil-supply path, the opening being open to the valve operating chamber. Accordingly, it is possible to be excellent in cooling oil and to preferably lubricate a valve operating system in addition to the surrounding of a crankshaft.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Popular searches
Plural diverse prime-mover propulsion mounting Advancing/retarding ignition Vehicular energy storage Mechanical energy handling Electric energy management Electric energy vehicles Synchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnets Synchronous generators Electric devices Gas pressure propulsion mounting
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com