Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Few rejection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
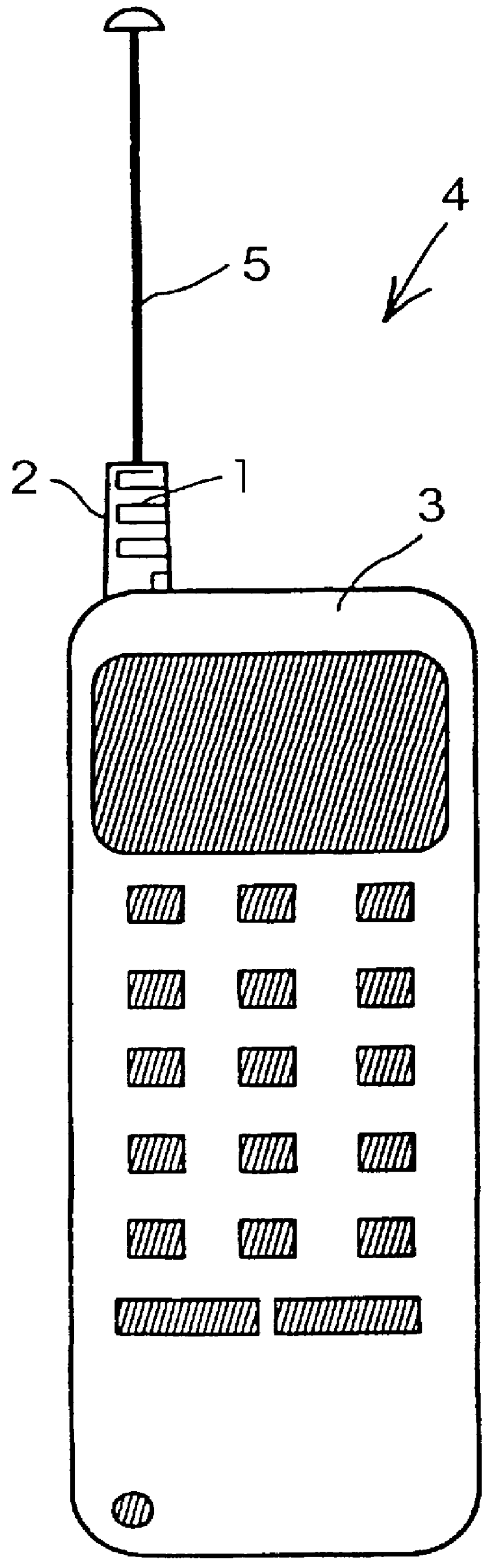
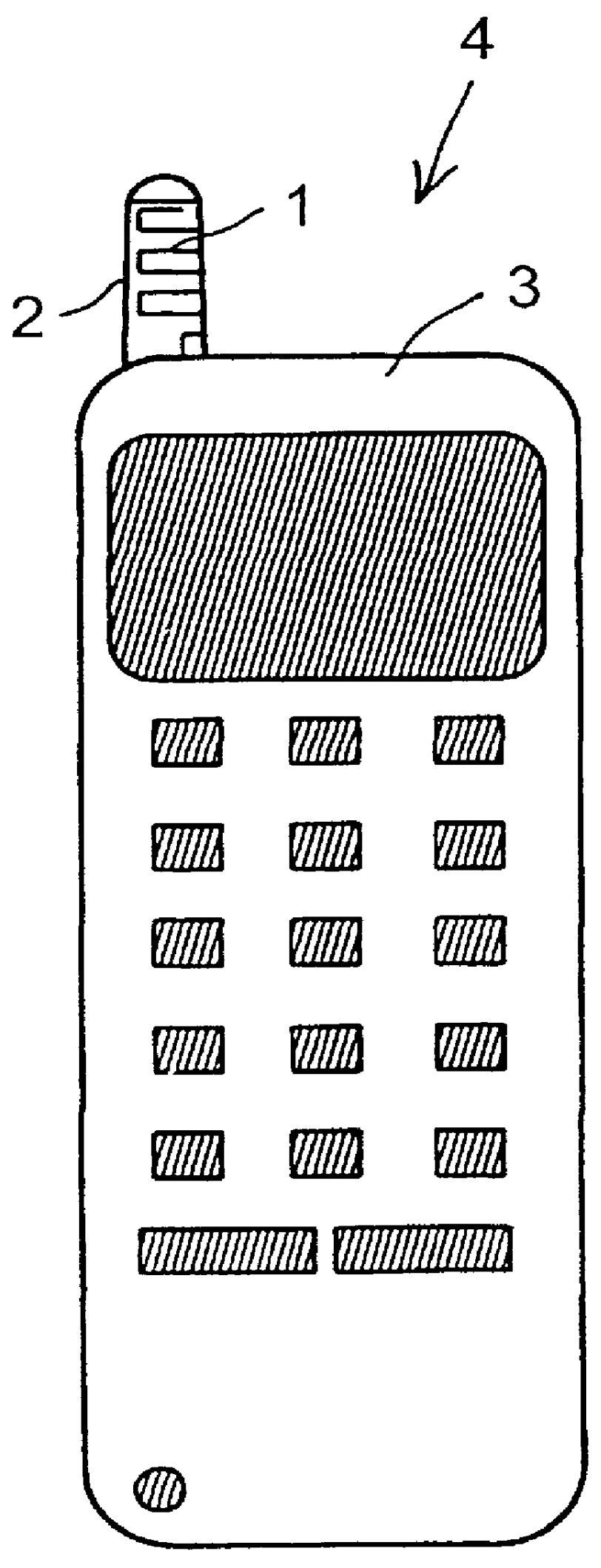
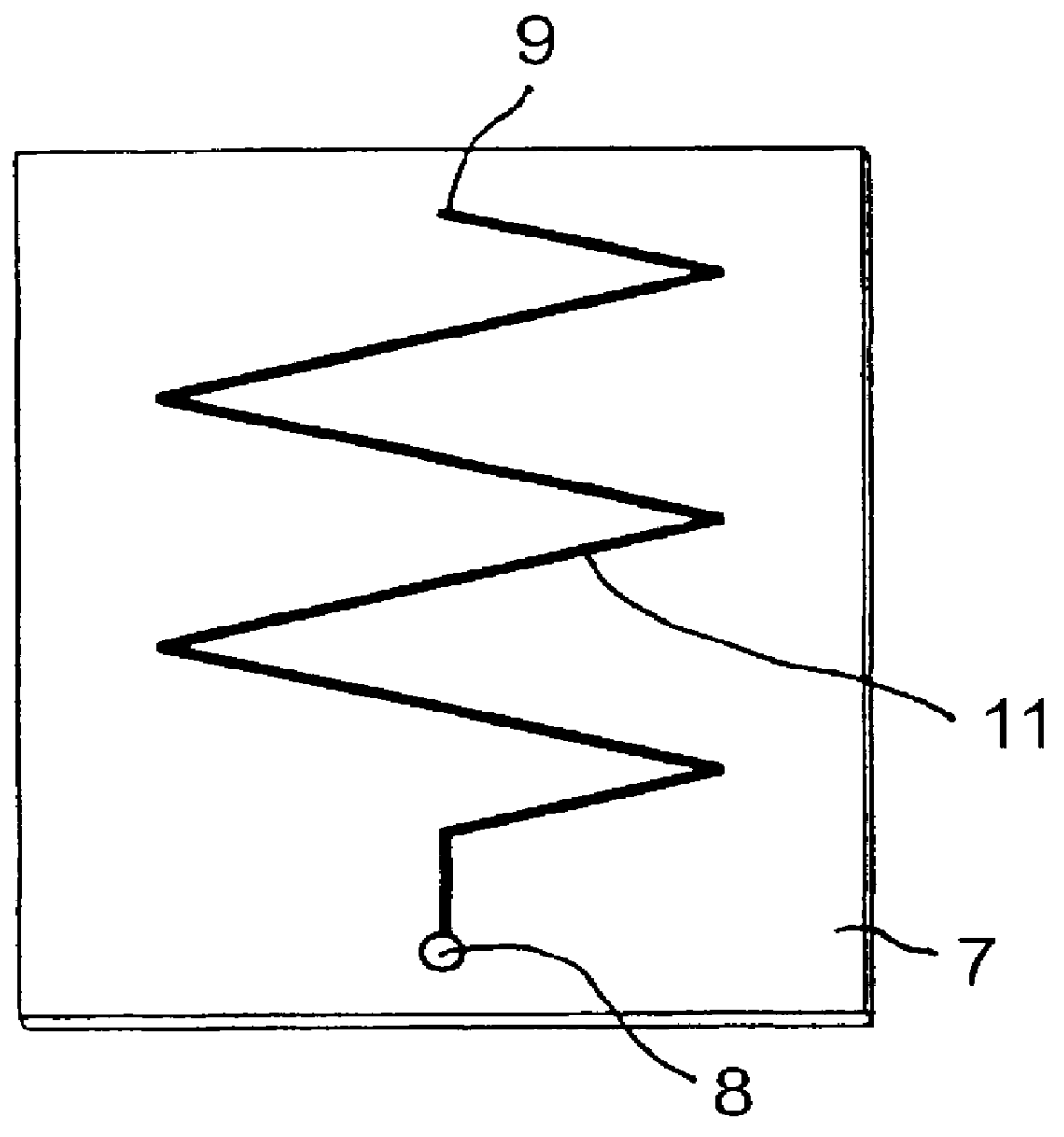
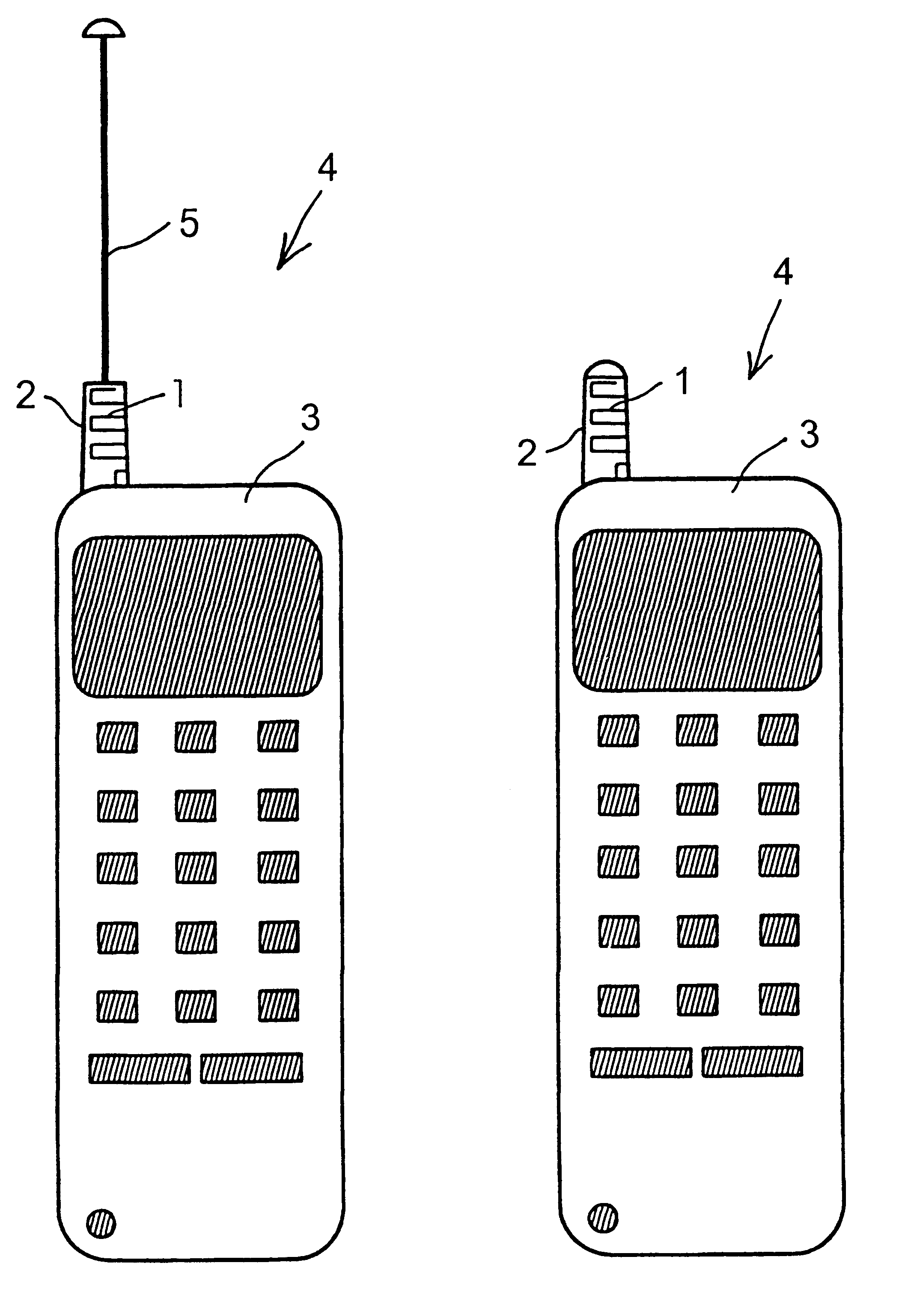
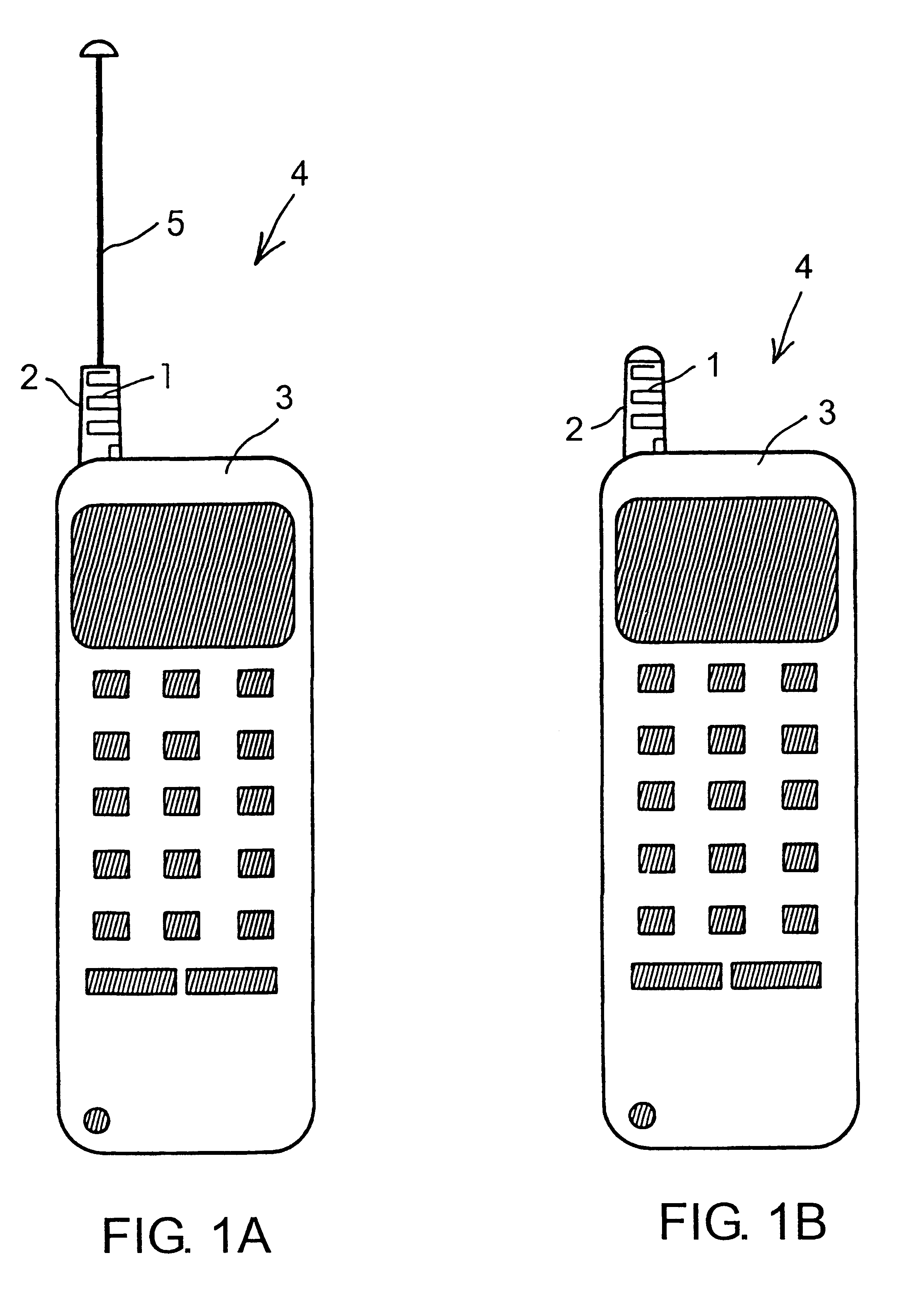
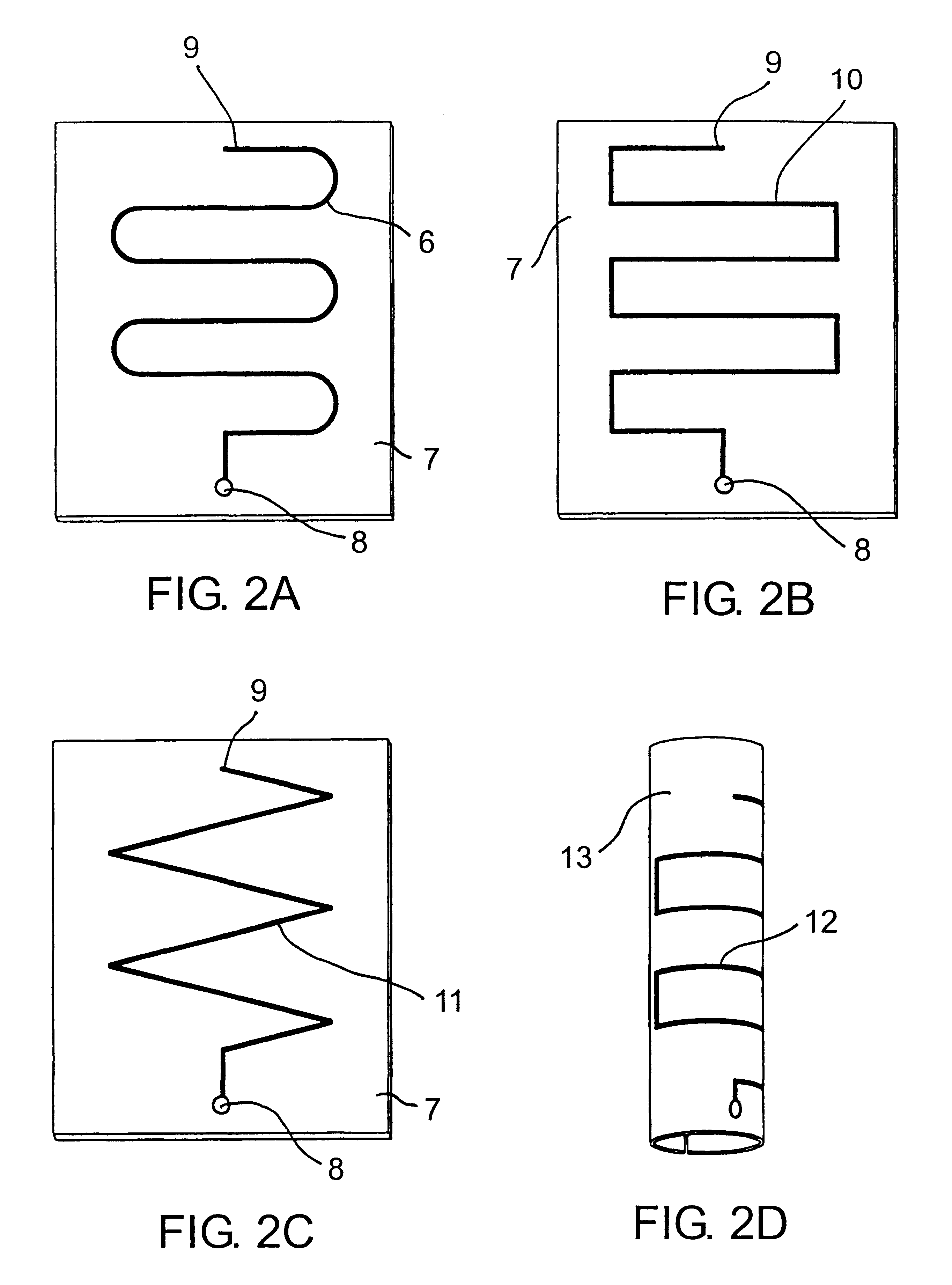
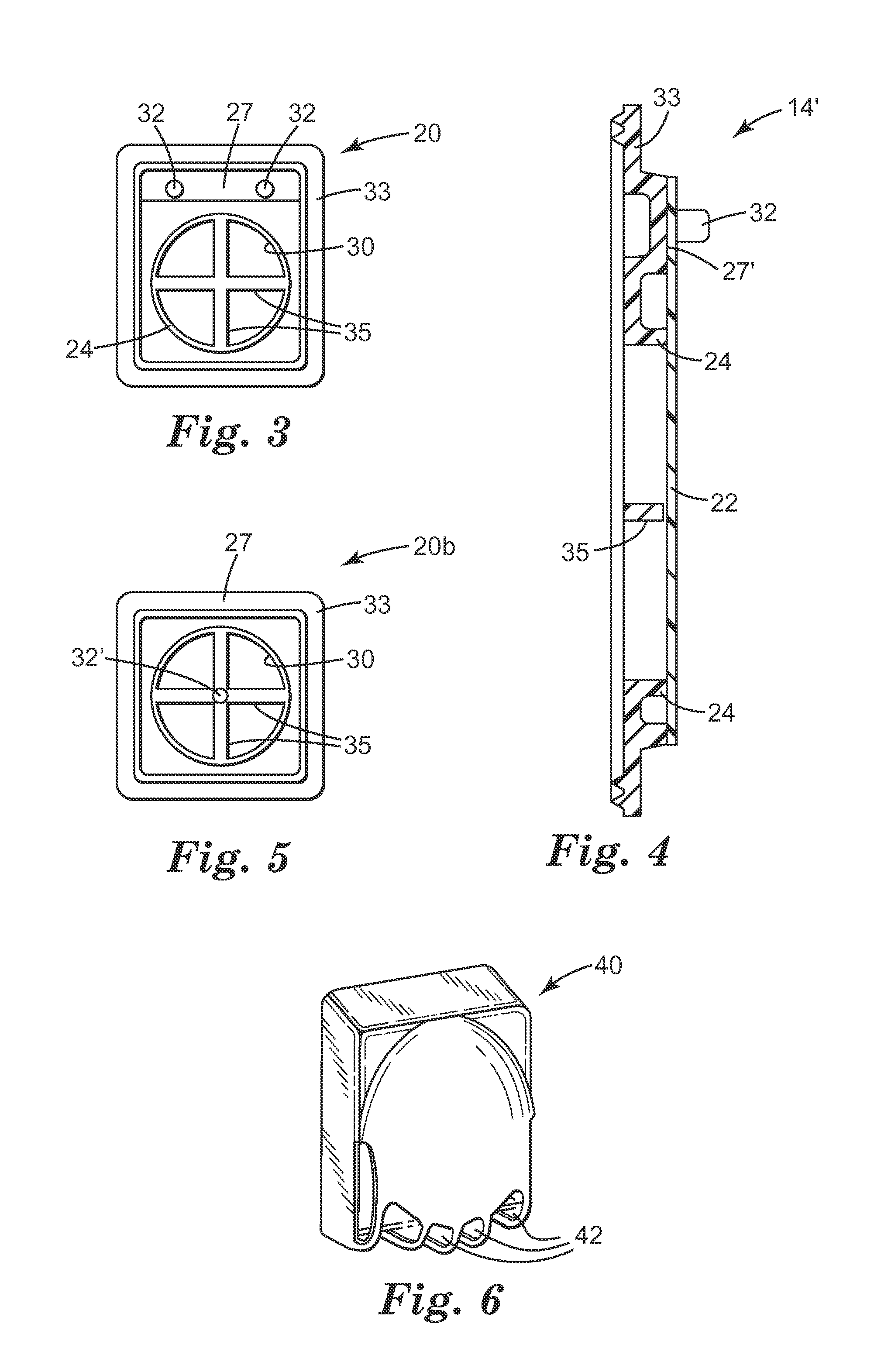
Meander antenna device
InactiveUS6069592AImprove antenna performanceEfficient and impedanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandMeander
An antenna means for a portable radio communication device, in particular a hand-portable mobile telephone, having at least one radiating element that has a meandering and cylindrical configuration. This structure is specifically advantageous in combination with an extendable and retractable whip antenna and, when having two or more meandering radiating elements, in multi-band radiating structures. The antenna device is suitable for manufacturing in large quantities, for example by a flexible printed circuit board technique.
Owner:LAIRD TECH AB (SE)
Meander antenna device
InactiveUS6351241B1High bandwidthMaintain good propertiesSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandMeander
An antenna means for a portable radio communication device, in particular a hand-portable mobile telephone, having at least one radiating element that has a meandering and cylindrical configuration. This structure is specifically advantageous in combination with an extendable and retractable whip antenna and, when having two or more meandering radiating elements, in multi-band radiating structures. The antenna device is suitable for manufacturing in large quantities, for example by a flexible printed circuit board technique.
Owner:LAIRD TECH AB (SE)
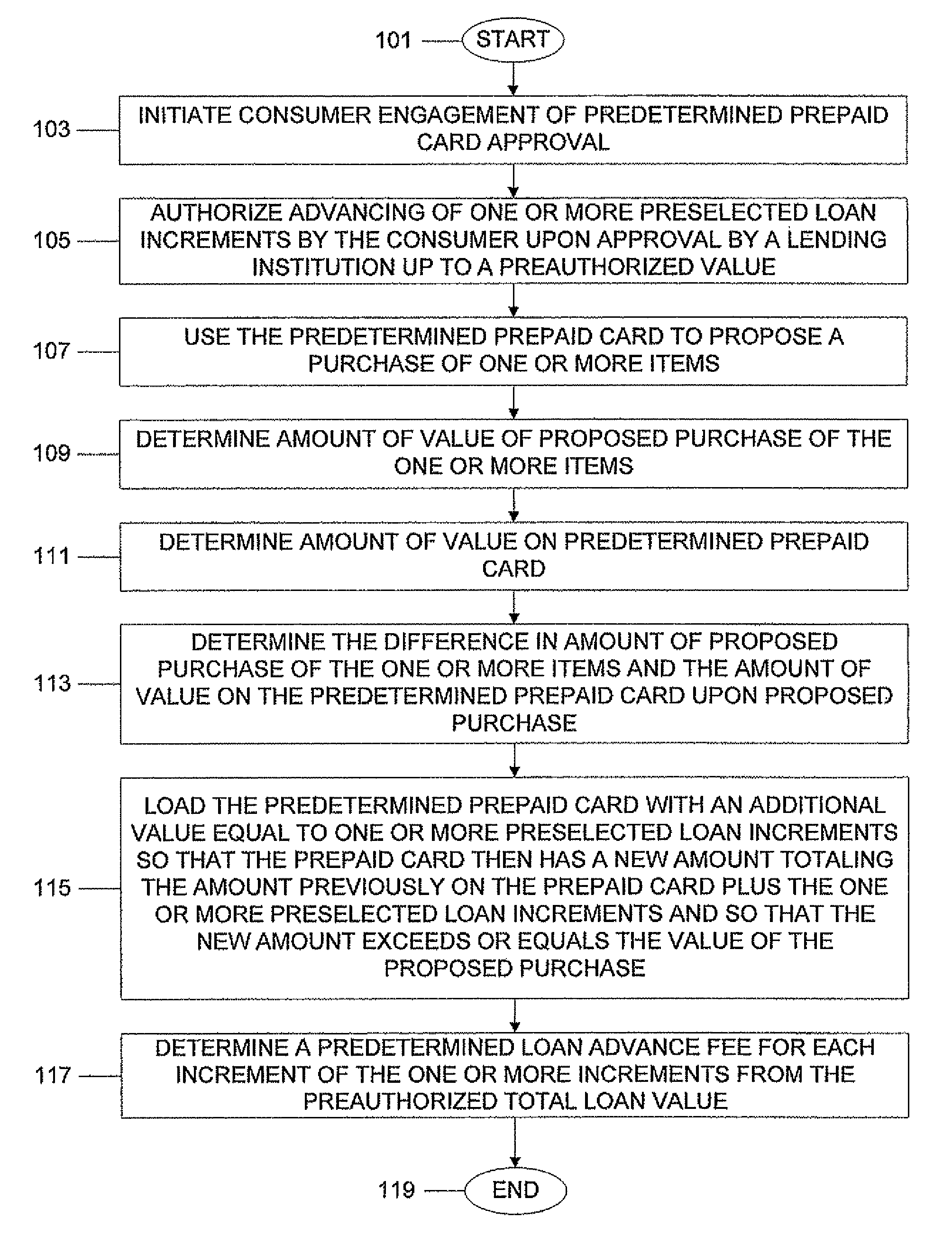
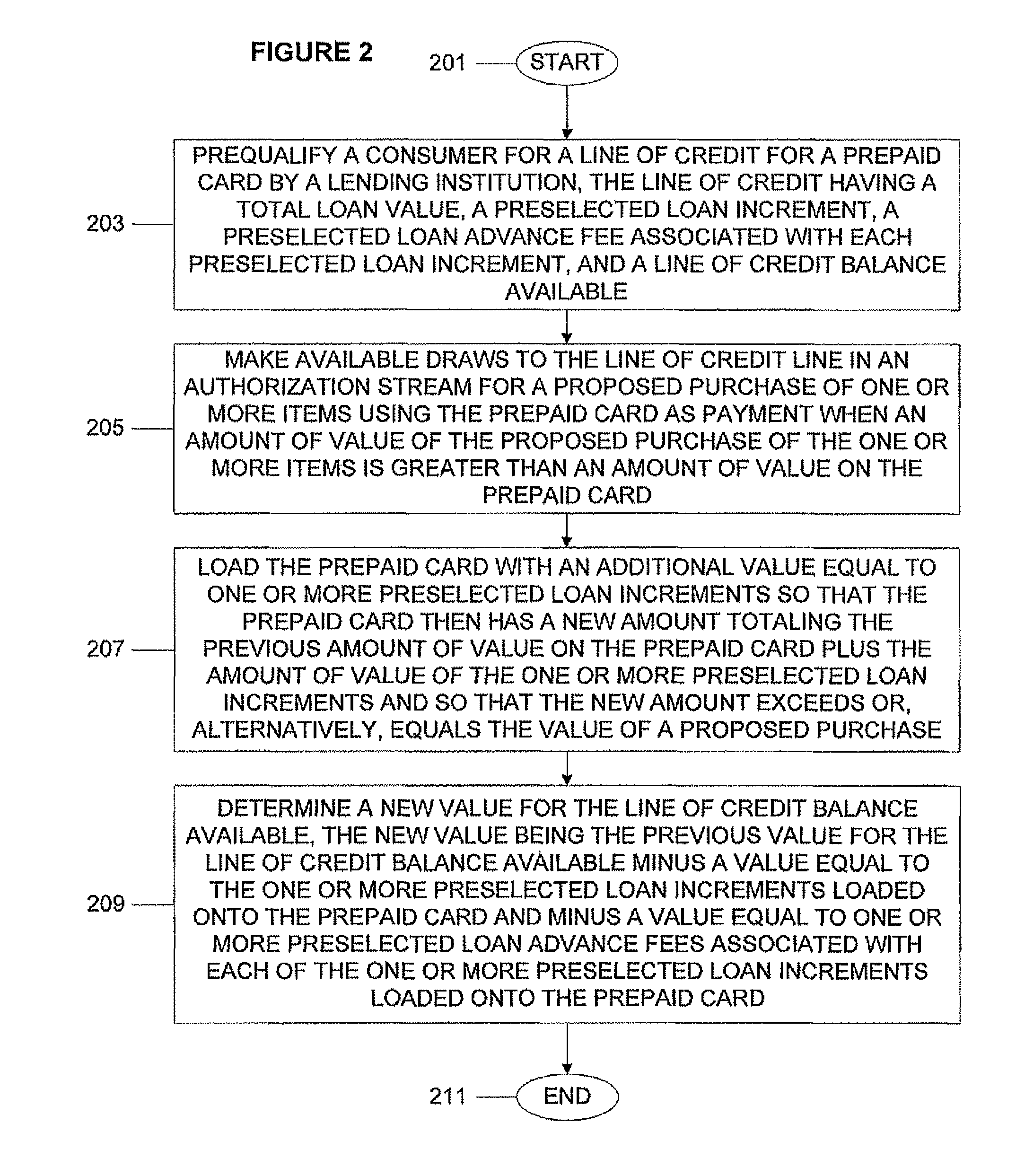
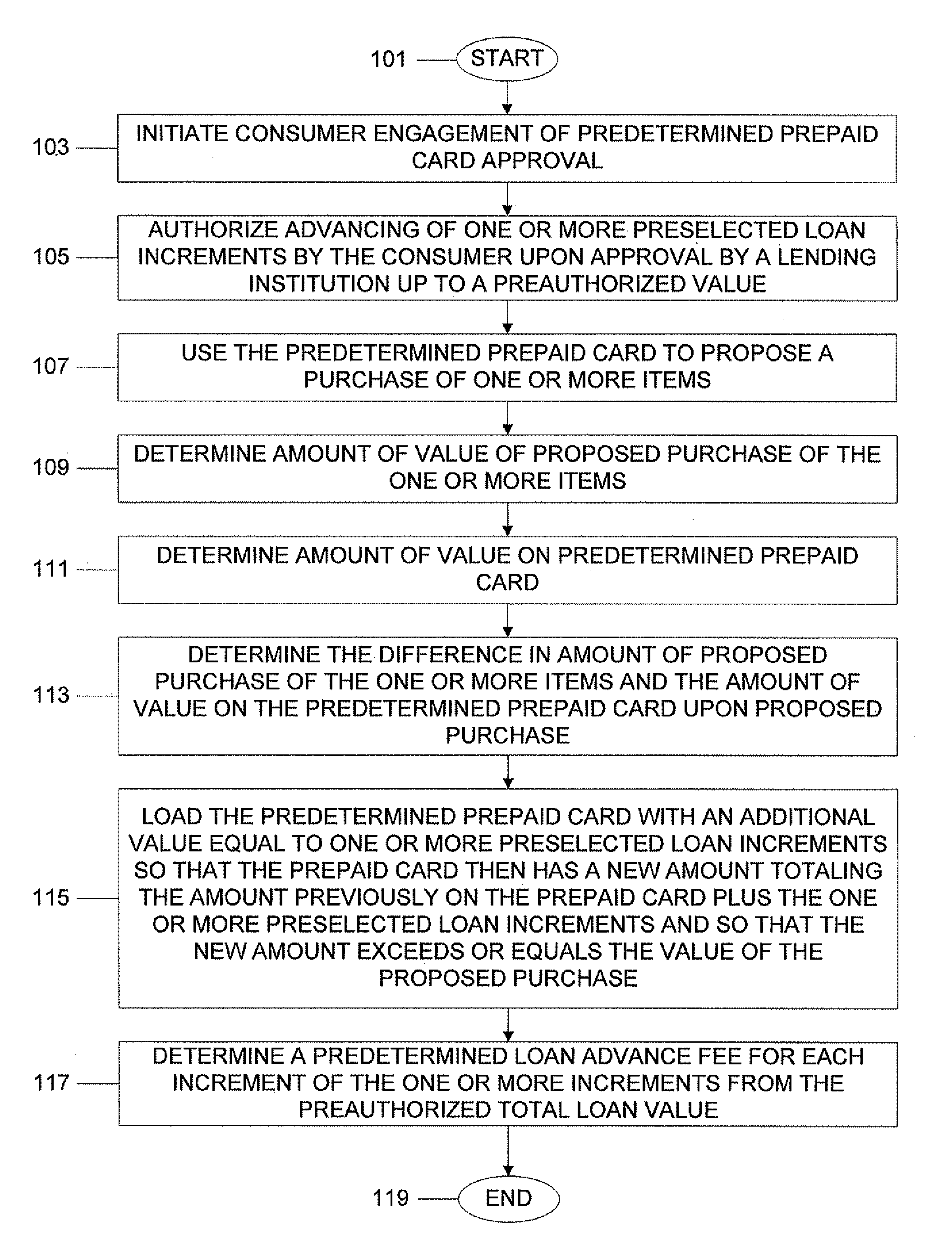
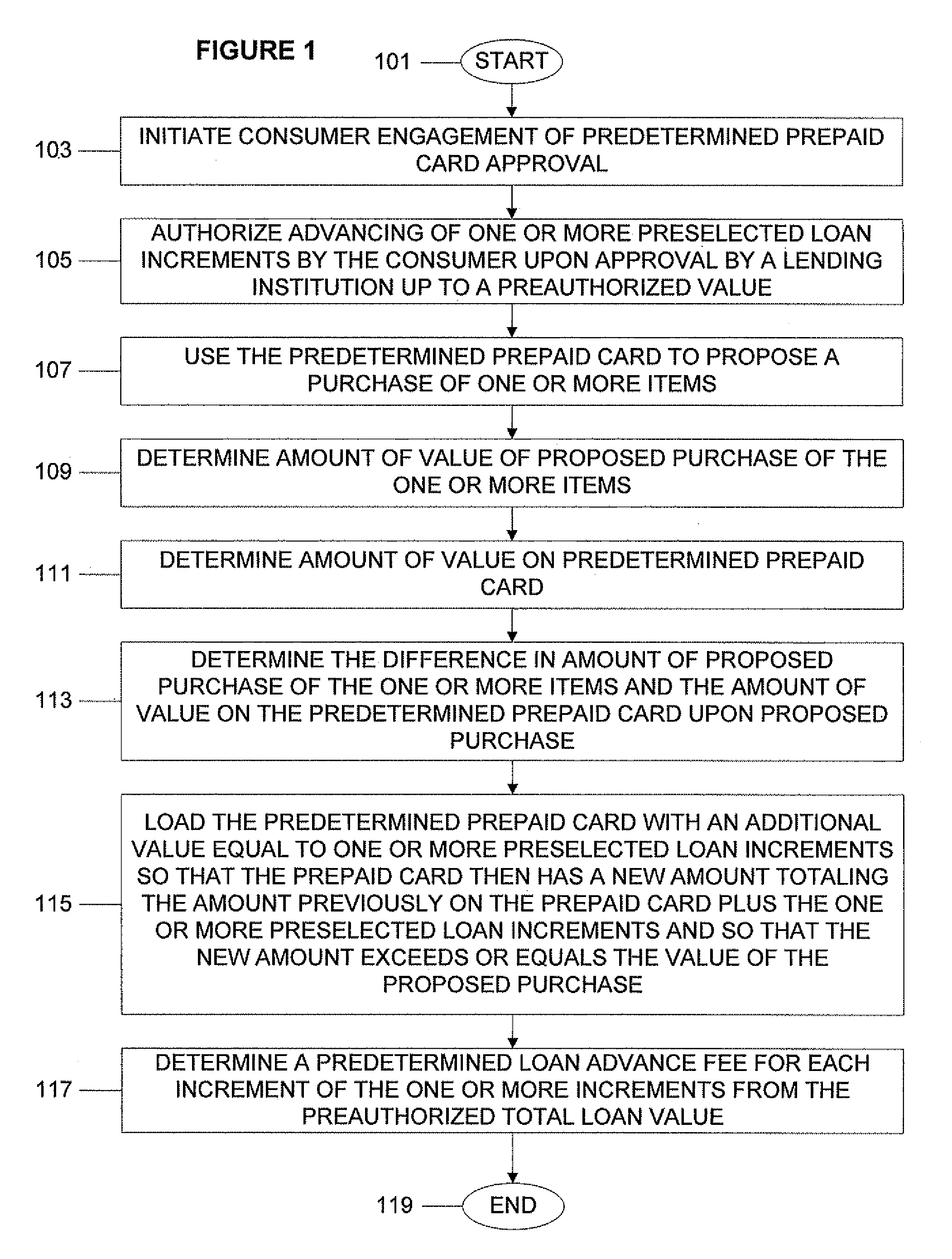
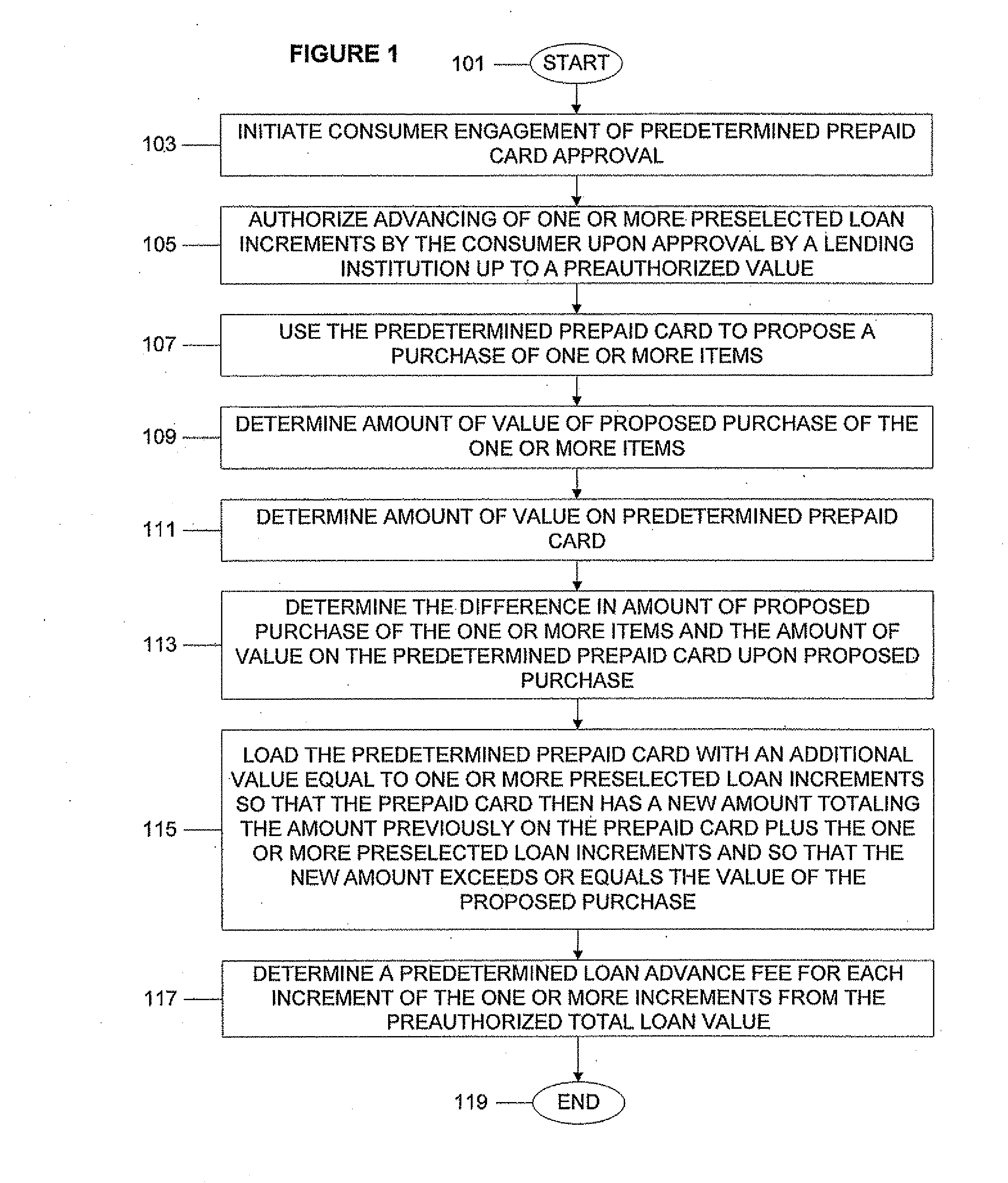
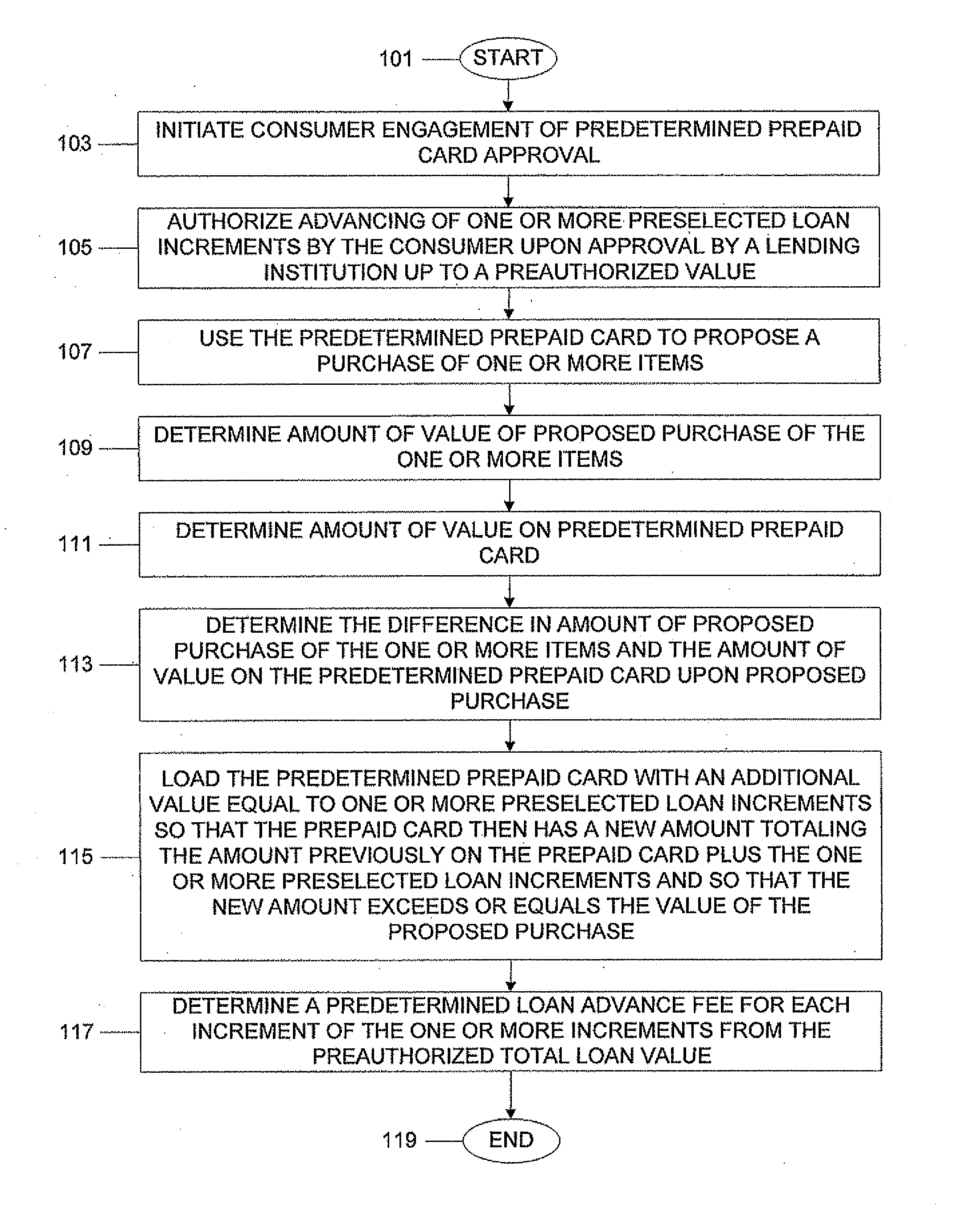
System, program product, and associated methods to autodraw for micro-credit attached to prepaid card
ActiveUS8103549B1Avoid hassleAvoid planningFinancePoint-of-sale network systemsPaymentAdditional values
A consumer is prequalified for a line of credit attached to a prepaid card by a lending institution. The lending institution computer makes available draws to the line of credit line in an authorization stream for a proposed purchase using the prepaid card as payment. When the line of credit is accessed, the prepaid card is loaded with an additional value equal to one or more preselected loan increments so that the prepaid card then has a new amount totaling a previous amount plus the amount of value of the one or more preselected loan increments and so that the new amount exceeds or equals the value of a proposed purchase. Next, a new value for the line of credit balance available is determined, accounting for value loaded onto the prepaid card and a preselected loan advance fee for each loan increment loaded onto the prepaid card.
Owner:PATHWARD NAT ASSOC
System, program product, and associated methods to autodraw for micro-credit attached to a prepaid card
ActiveUS8065187B2Avoid hassleAvoid planningHand manipulated computer devicesFinancePaymentAdditional values
Owner:PATHWARD NAT ASSOC
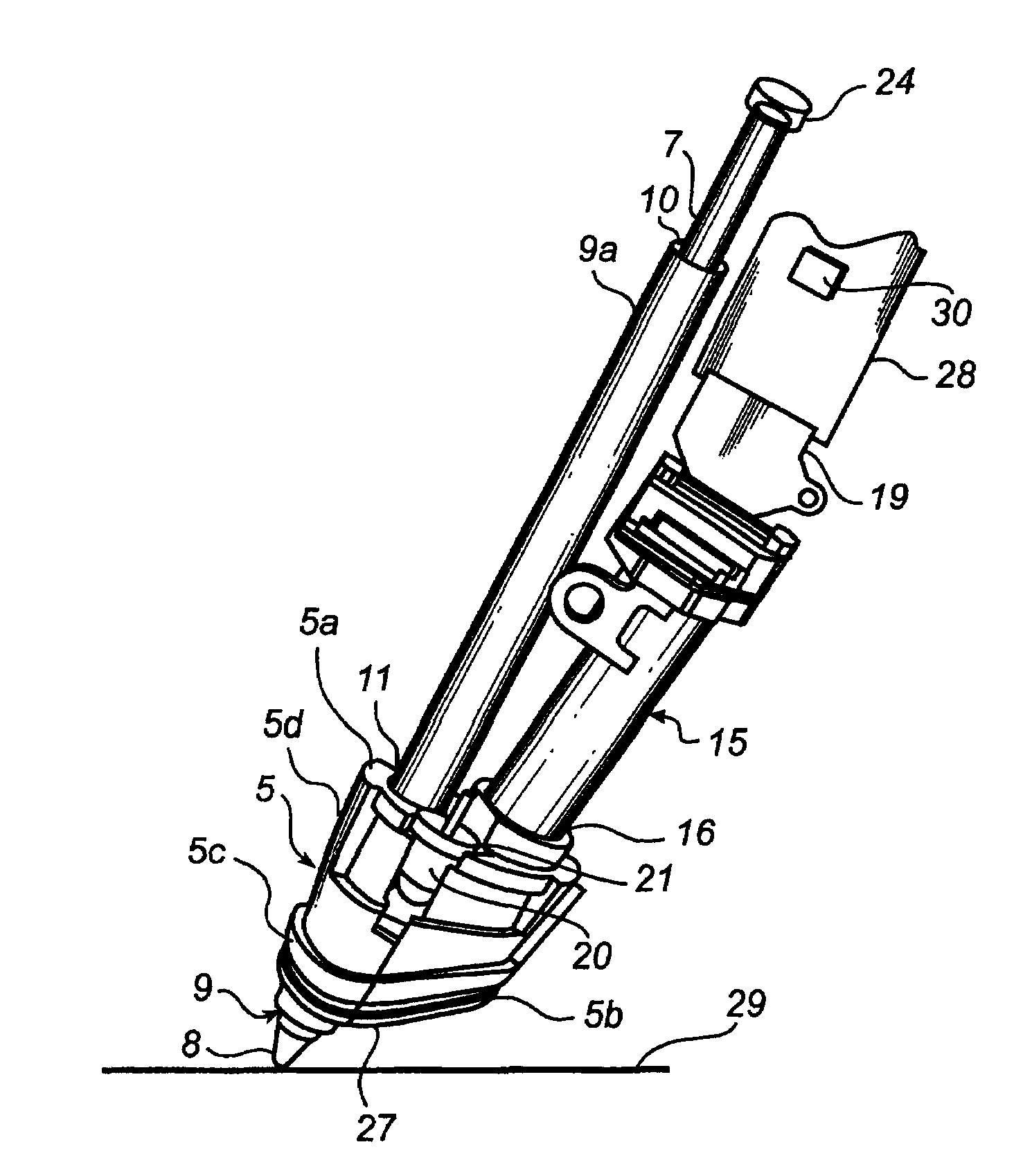
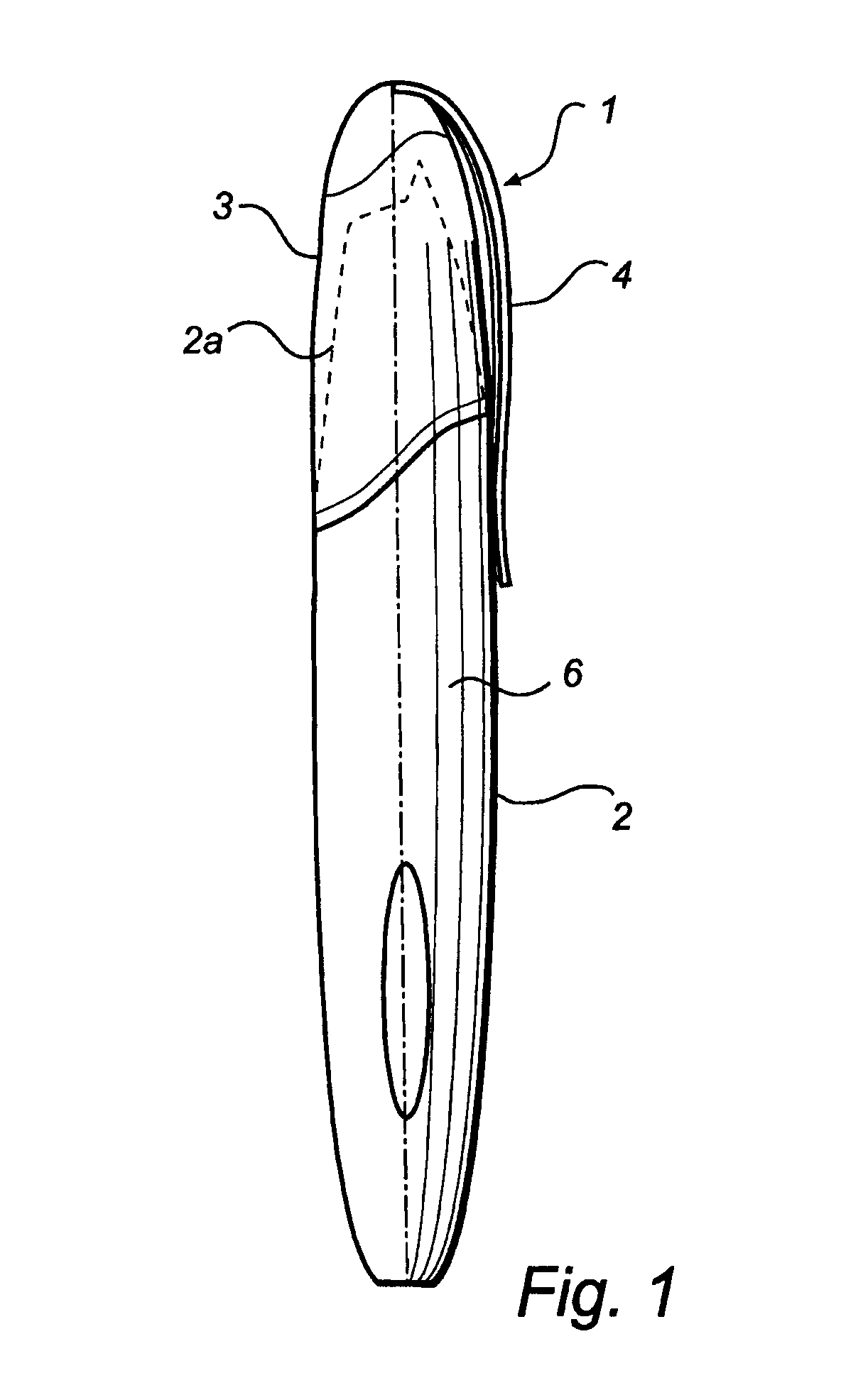
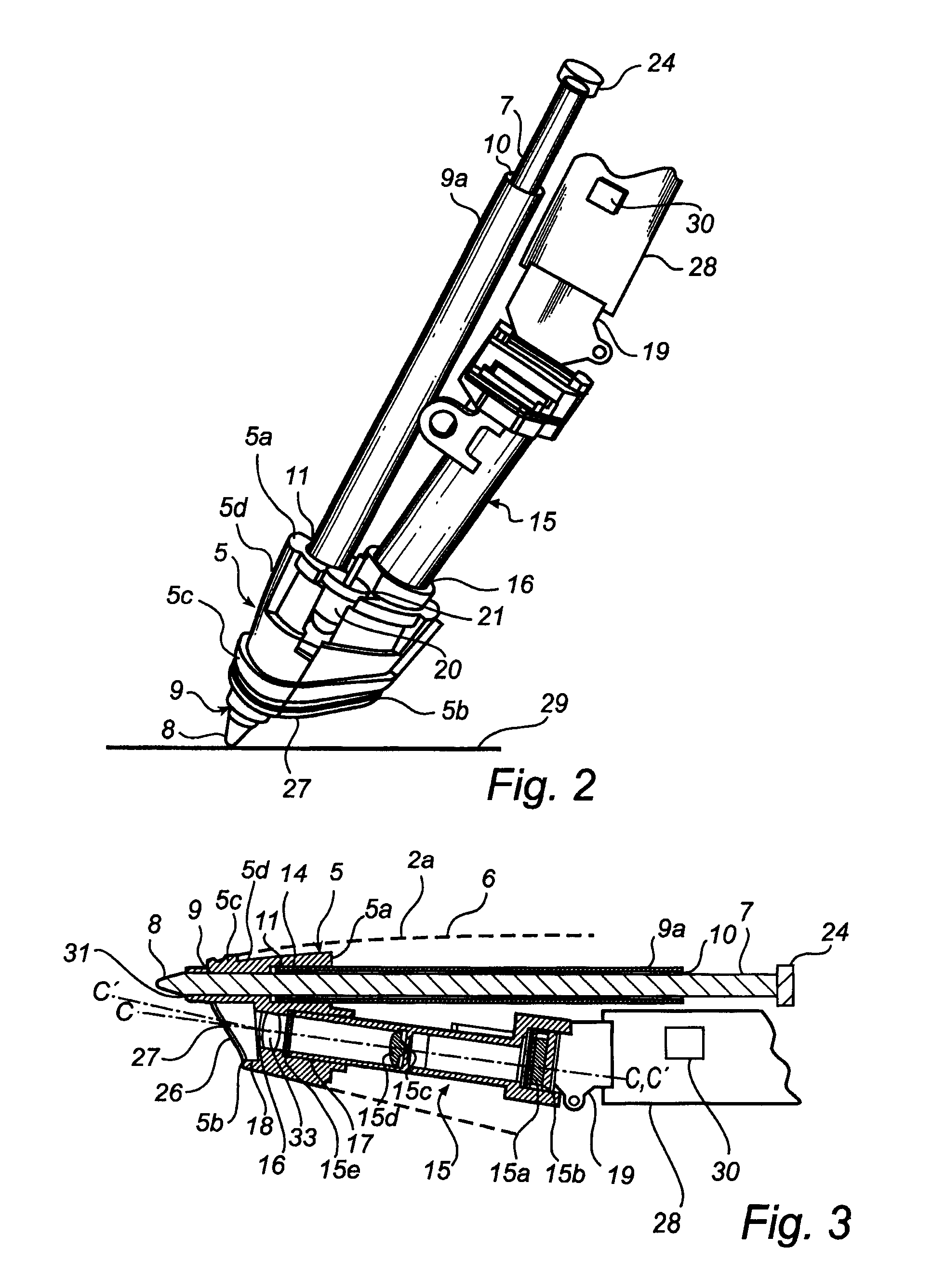
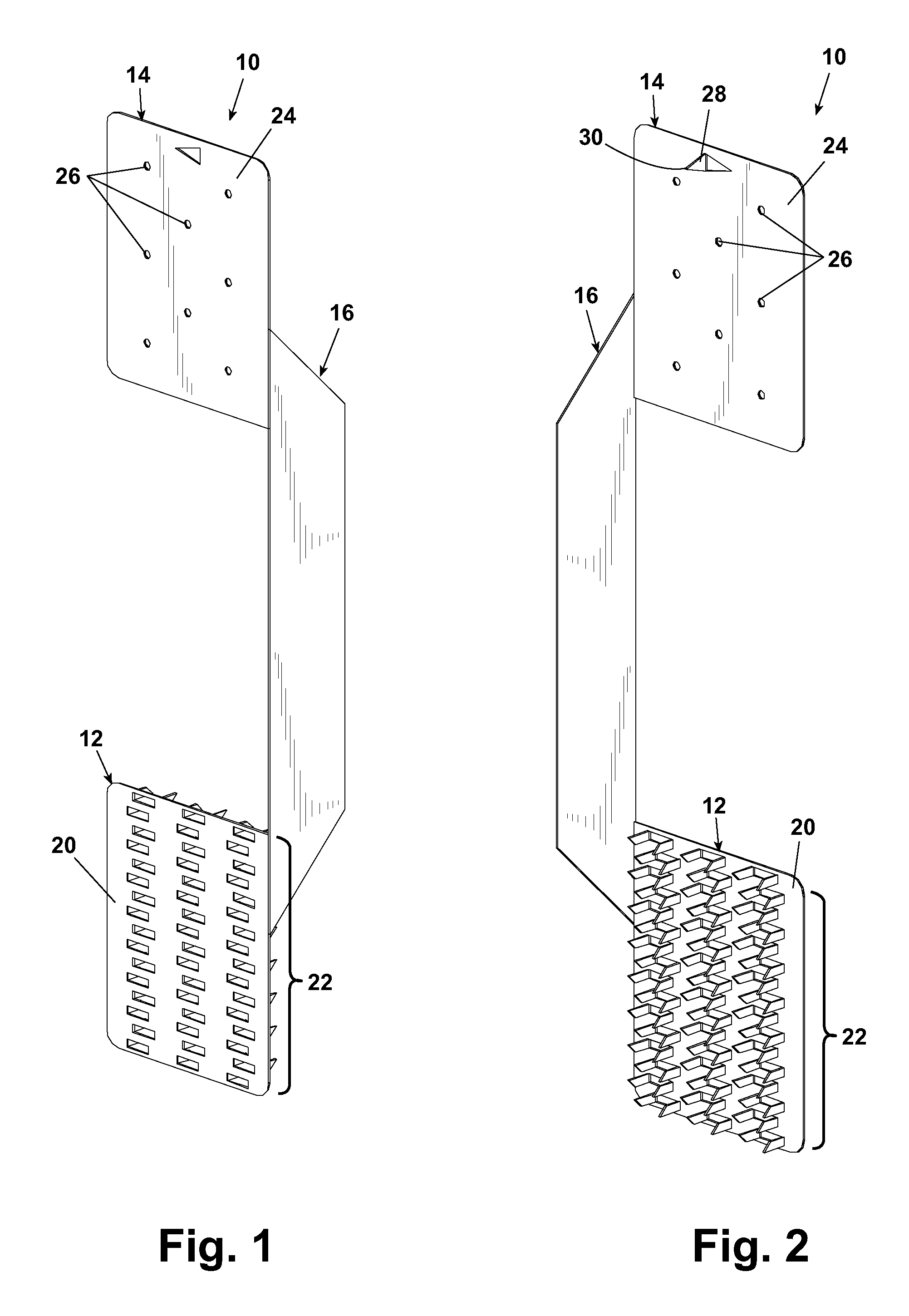
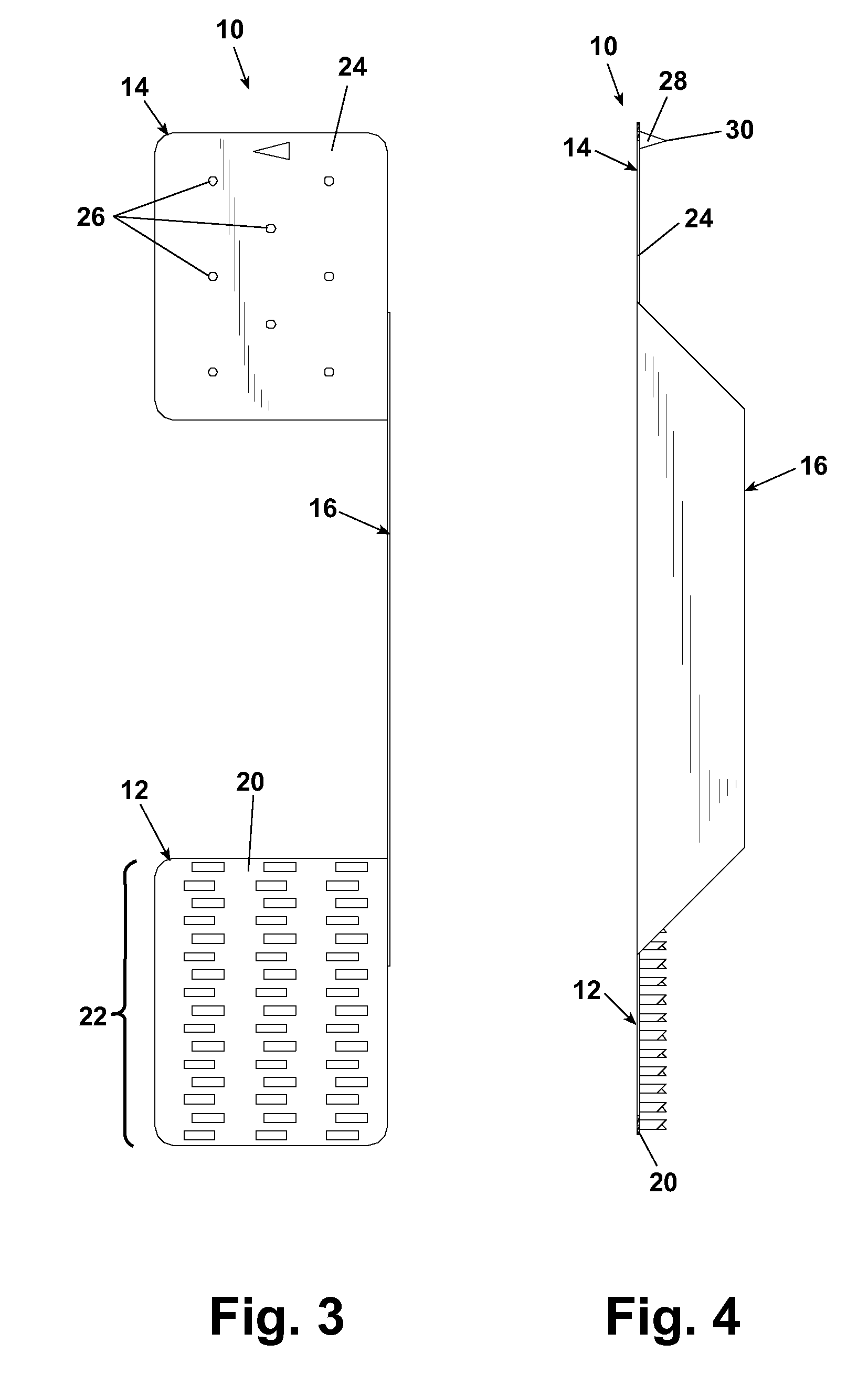
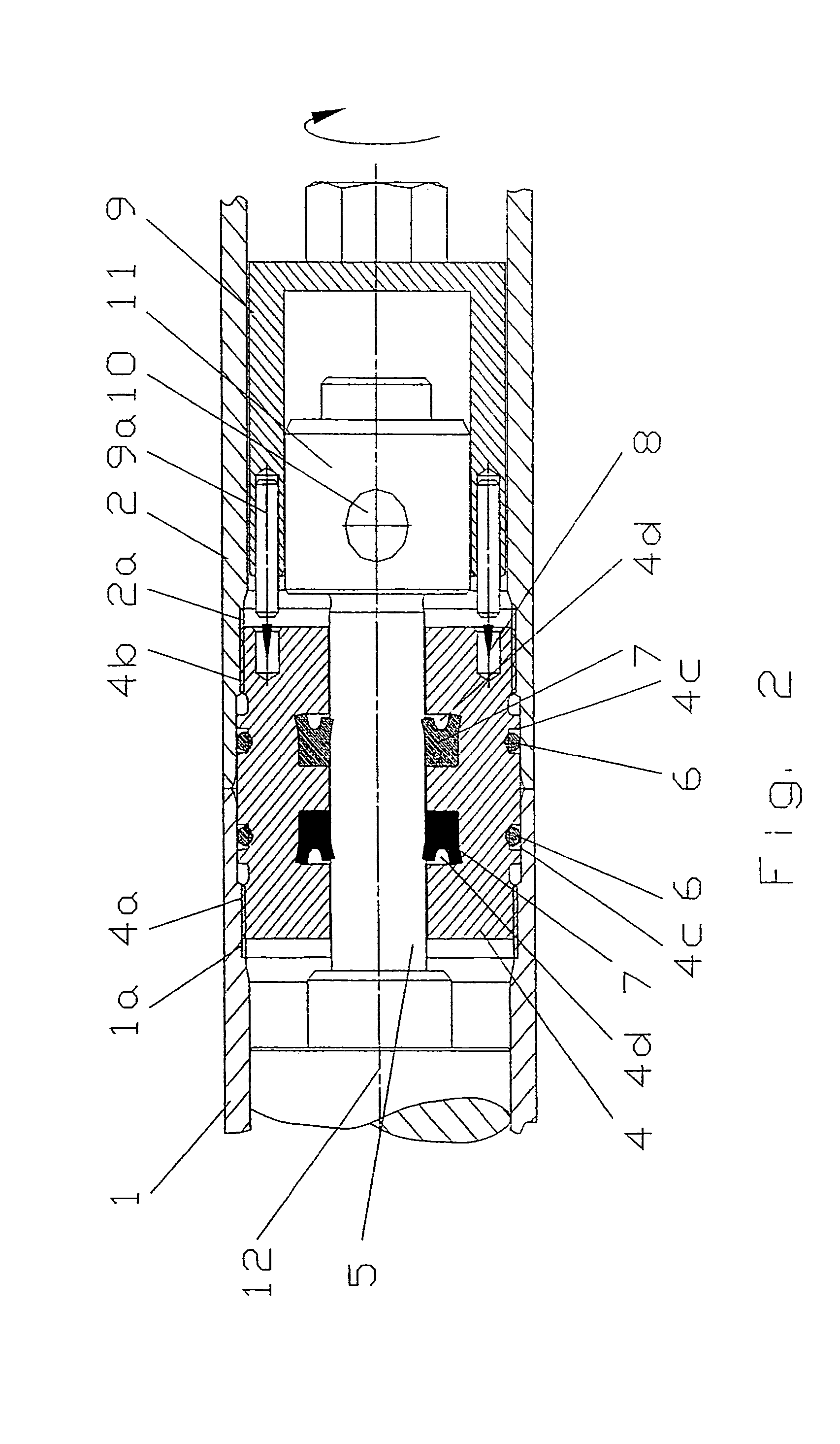
Electronic pen, mounting part therefor and method of making the pen
InactiveUS7180509B2Improve accuracyFew rejectionTransmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringDetector cell
An electronic pen comprises a writing means (7) which extends into the interior of the pen, a guiding element (9) for the writing means (7), a sensor (15a) for recording images and an image processor (30) for calculating positions of the pen based on said images. The sensor (15a) is part of an imaging detector unit (15). The guiding element (9) and the detector unit (15) are arranged in a common mounting part (5) which is fixedly mounted in the interior of the pen. In such a pen, it is possible to minimize the tolerance chain between the components that convert a pen stroke on a base into a sequence of positions. This enables serial production of the pen with a small number of rejects.
Owner:ANOTO AB
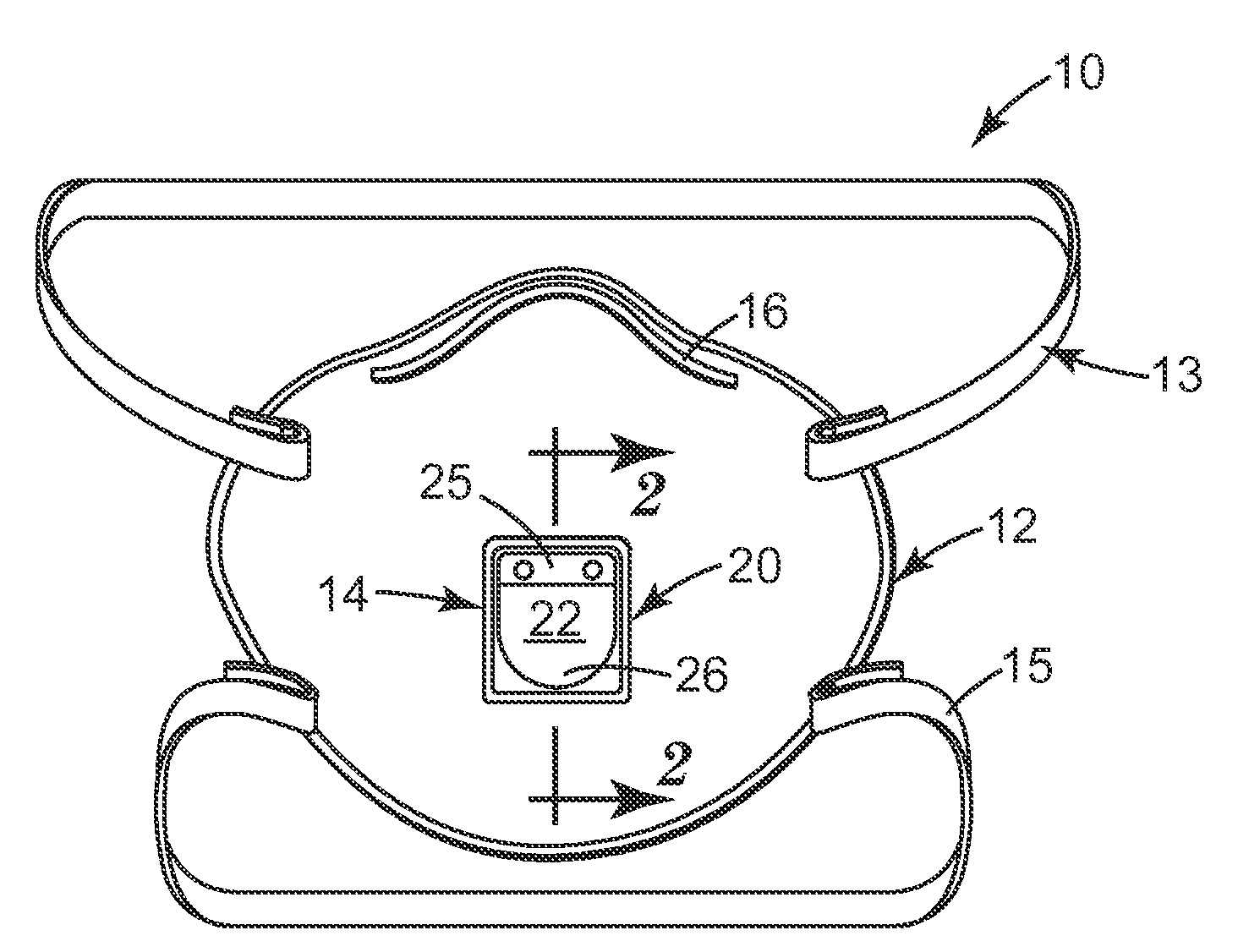
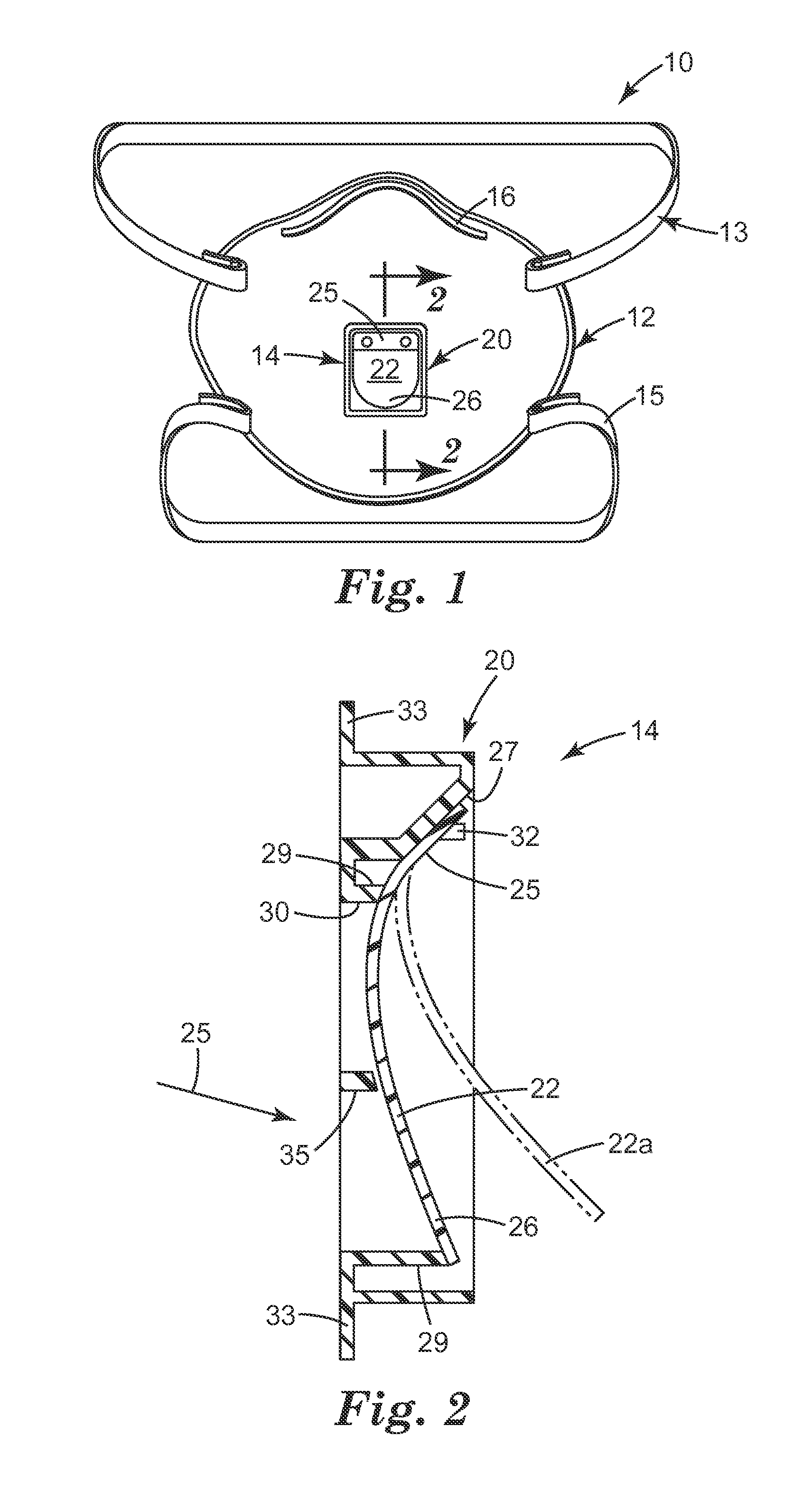
Respirator having valve with an ablated flap
InactiveUS20120167890A1Small pressure dropLess energyRespiratory device testingBreathing filtersRespiratorEngineering
A respirator 10 that has a mask body 12, a harness 13, and an exhalation valve 14. Both the harness 13 and the exhalation valve 14 are secured to the mask body 12. The exhalation valve 14 comprises a valve seat 20 and a flap 22 that has a surface 57 that has been ablated. Through use of an ablated flap, the flap characteristics can be better fashioned to achieve desired valve performance. The valve flap can be fashioned to remain closed under any orientation but also to open with minimal force or pressure from the wearer's exhaled air. A valve having these qualities provides a respirator that is more comfortable for a person to wear, which can be particularly beneficial to workers who wear respirators for extended time periods.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
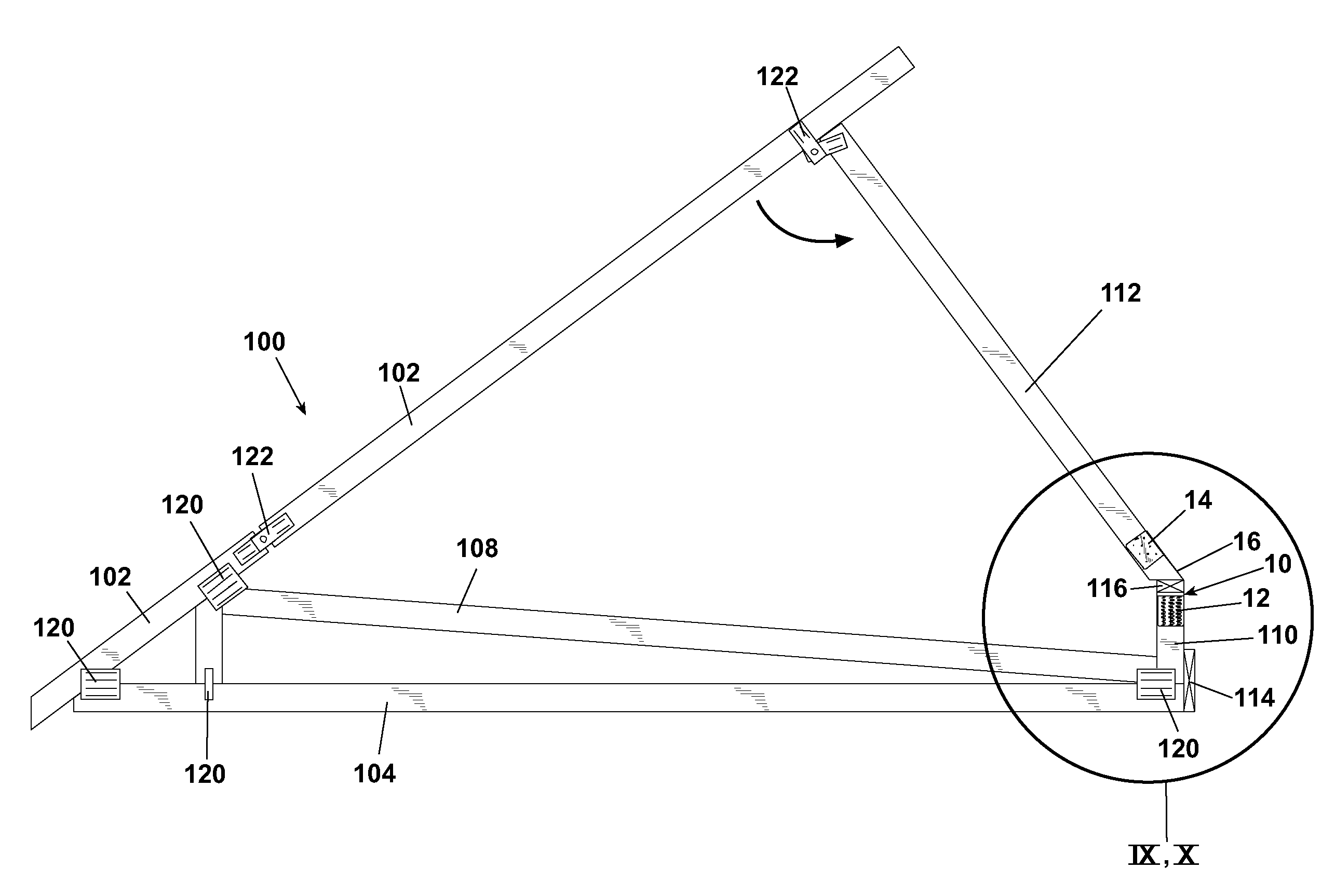
Building truss having a connector with an integral mounting to supporting structure
ActiveUS7200972B1Shorten the timeFew rejectionBuilding roofsArched girdersEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A truss and connector assembly for use in housing structures is shown. The connector provides a direct and integral mounting of the truss to the wall studs to provide increased mounting strength for the roof assembly to the side walls of a structure. A connector according to the invention can be integrally preassembled to a truss at one location and connected to remaining portions of the truss at a separate location.
Owner:UFP IND INC
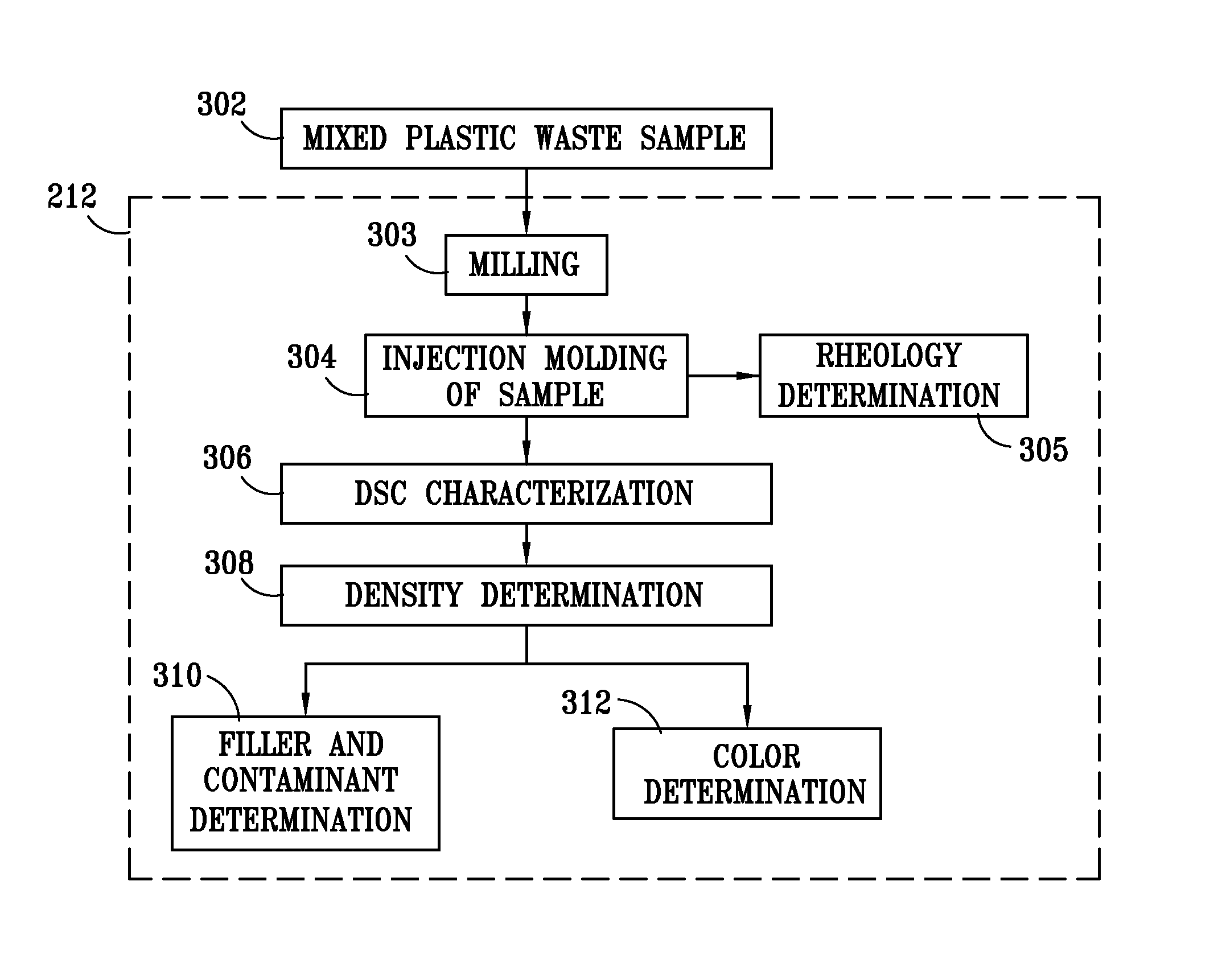
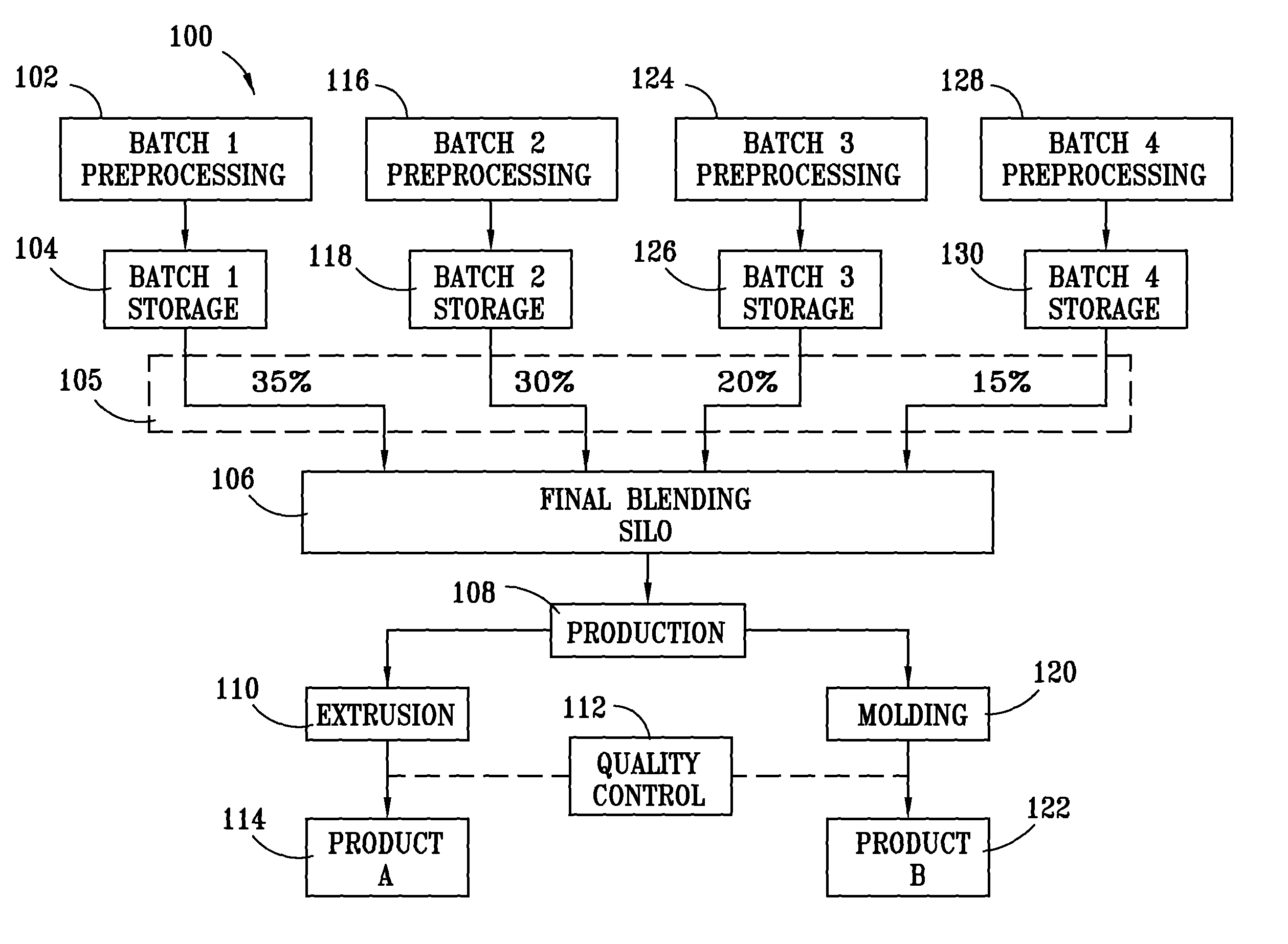
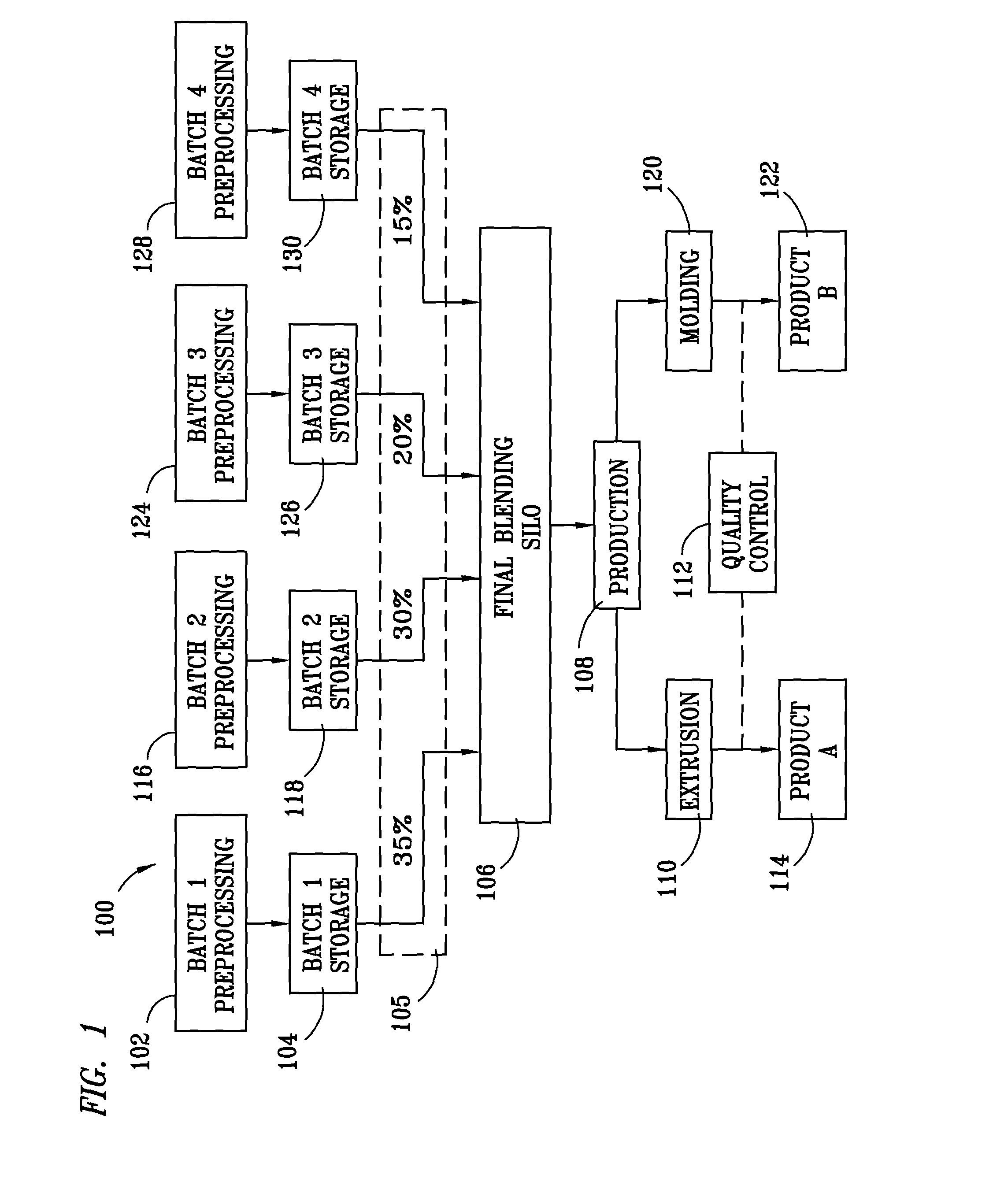
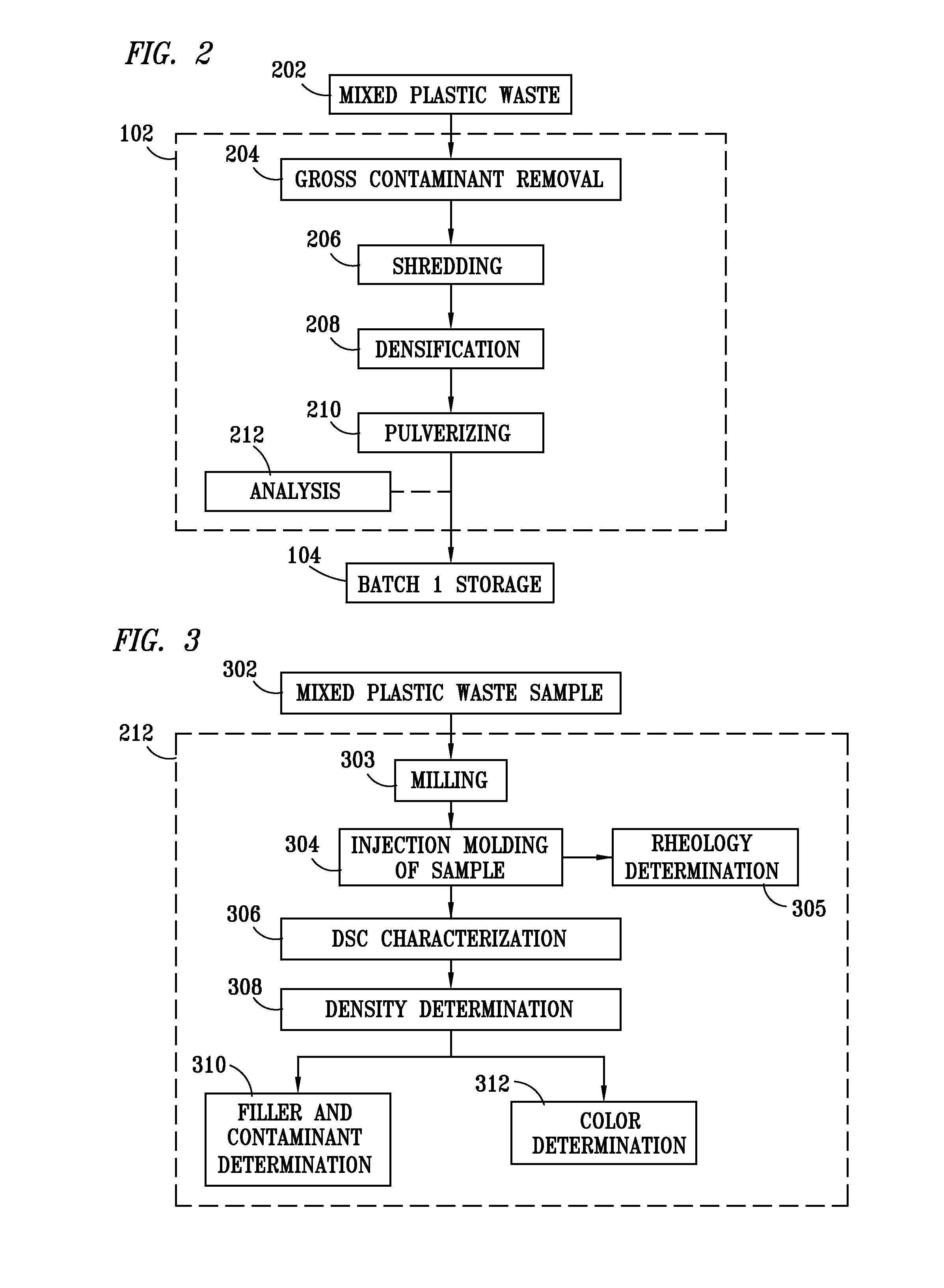
Method for processing and analyzing contaminated mixed waste plastics to produce reformulated blended feed materials having a desired rheology
ActiveUS7968022B1Increase percentageImprove consistencyArtificial filament recoveryPlastic recyclingApparent densityProcess engineering
A method for reformulating reclaimed, contaminated mixed waste plastics into useful articles wherein a plurality of batches of the mixed waste plastics are preprocessed to produce substantially homogeneous mixtures of a desired particle size range that are characterized according to their respective apparent densities, and are thereafter blended to produce a mixed plastic feed material having a rheology predetermined to be desirable for reprocessing into at least one of such useful articles.
Owner:MOISTURESHIELD INC
Top tri-metal system for silicon power semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20120049372A1Not easy to scratchFew wafer rejectionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal silicideScratching
A titanium-nickel-palladium solderable metal system for silicon power semiconductor devices (10), which may be used for one or both of the anode (20) or cathode (30). The metal system includes an outer layer of palladium (40,70), an intermediate layer of nickel (50,80), and an inner layer of titanium (60,90). For certain applications, the nickel may be alloyed with vanadium. The metal system may be deposited on bare silicon (100) or on one or more additional layers of metal (110) which may include aluminum, aluminum having approximately 1% silicon, or metal silicide. The use of palladium, rather than gold or silver, reduces cost, corrosion, and scratching.
Owner:DIODES INC
Infant formula containing an aroma composition for use as fragrance
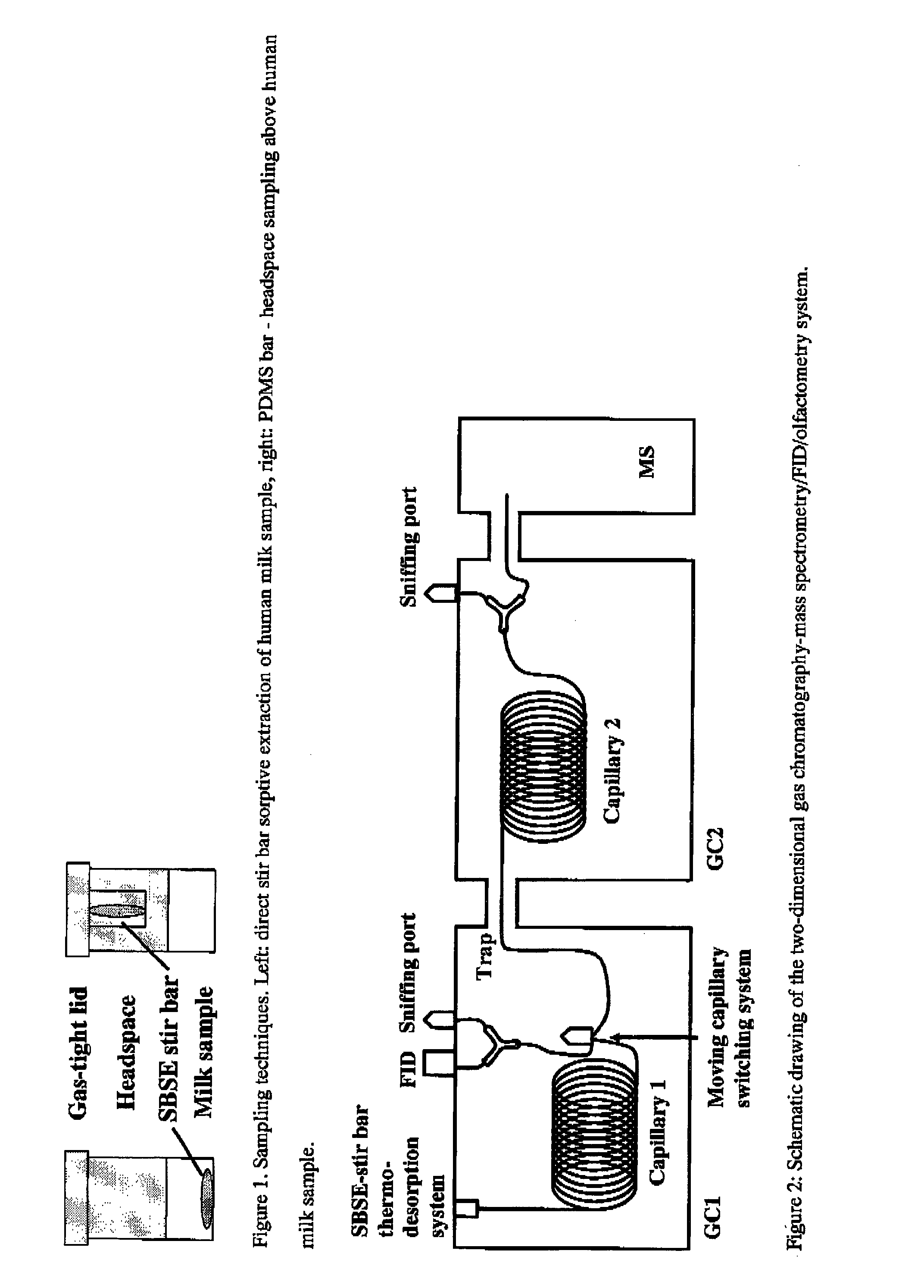
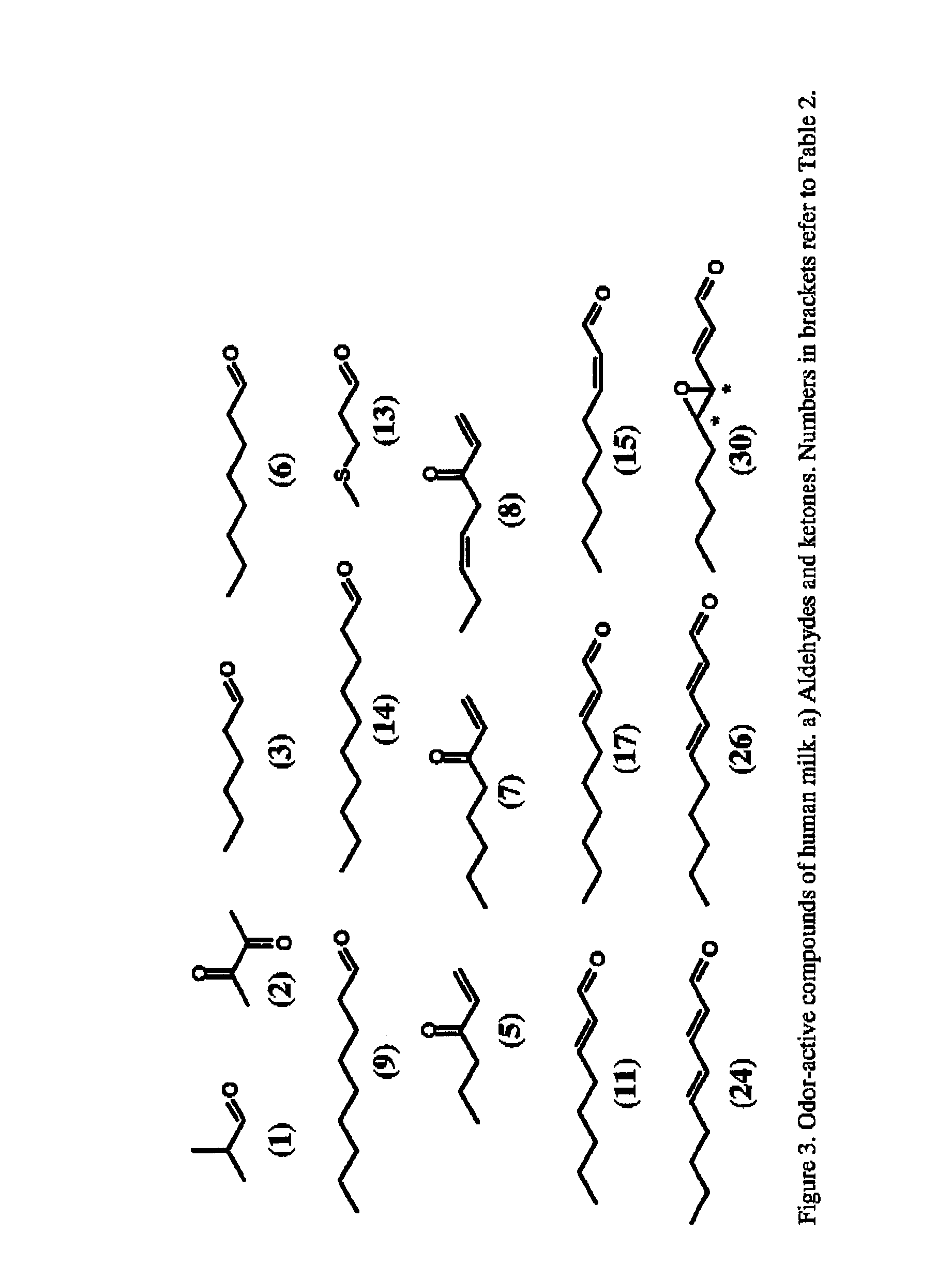
The invention relates to a nutraceutical composition such as infant formula or infant food comprising a) a defined aroma composition; b) a methodology for developing, maintaining certain aroma constituents in the infant formula and an aroma or fragrance composition to be used to increase the acceptance of a person or an object by the baby or new born.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
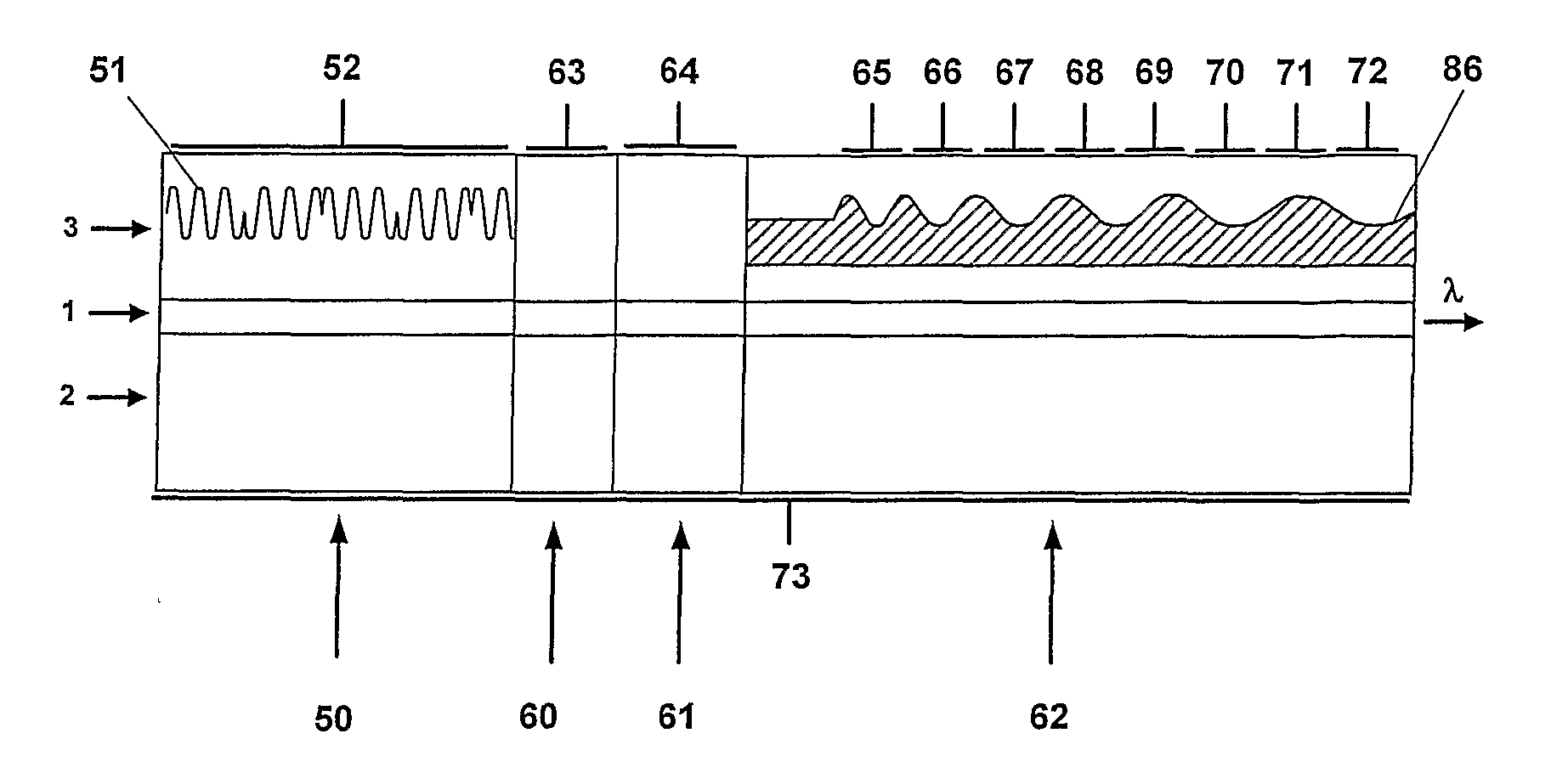
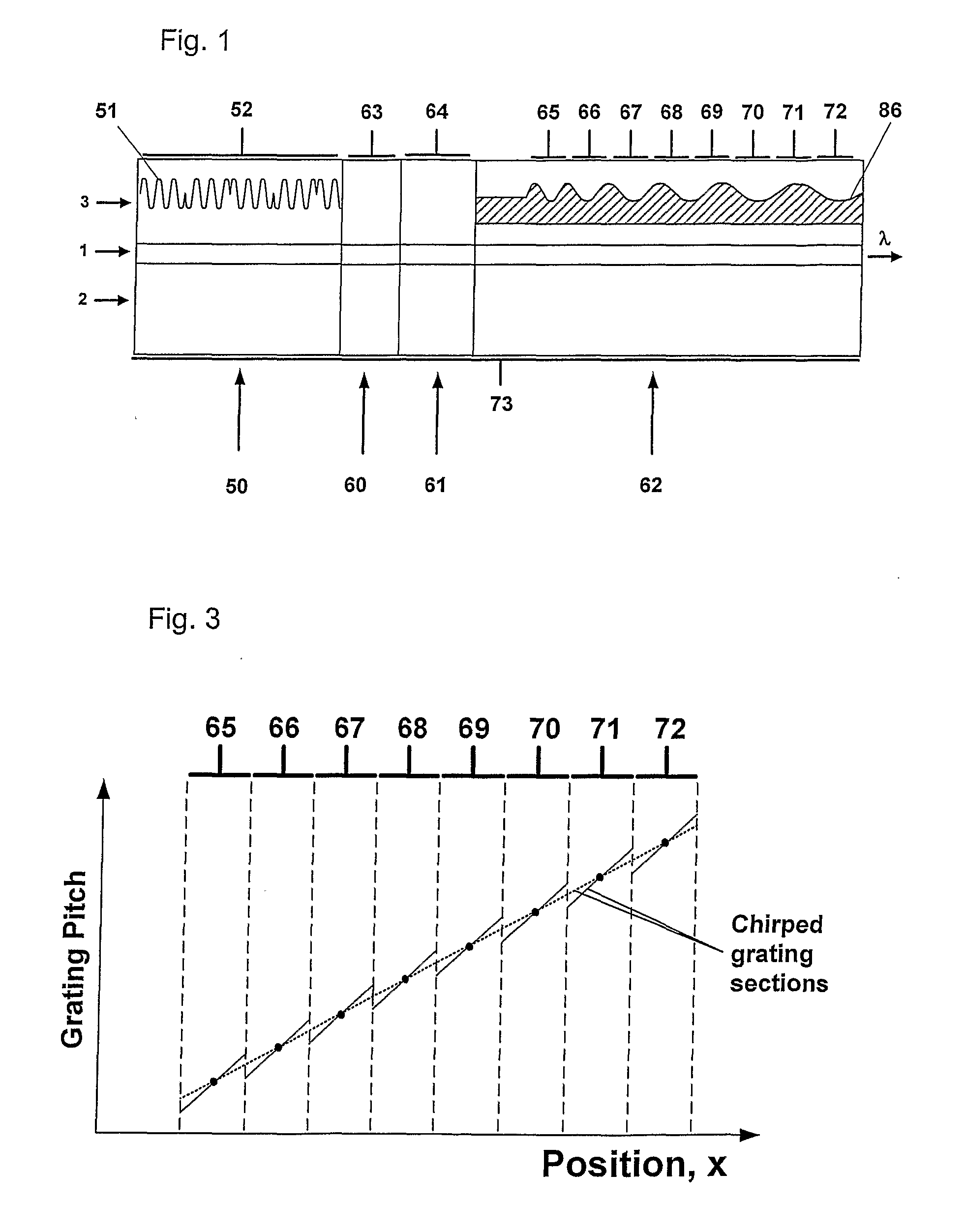
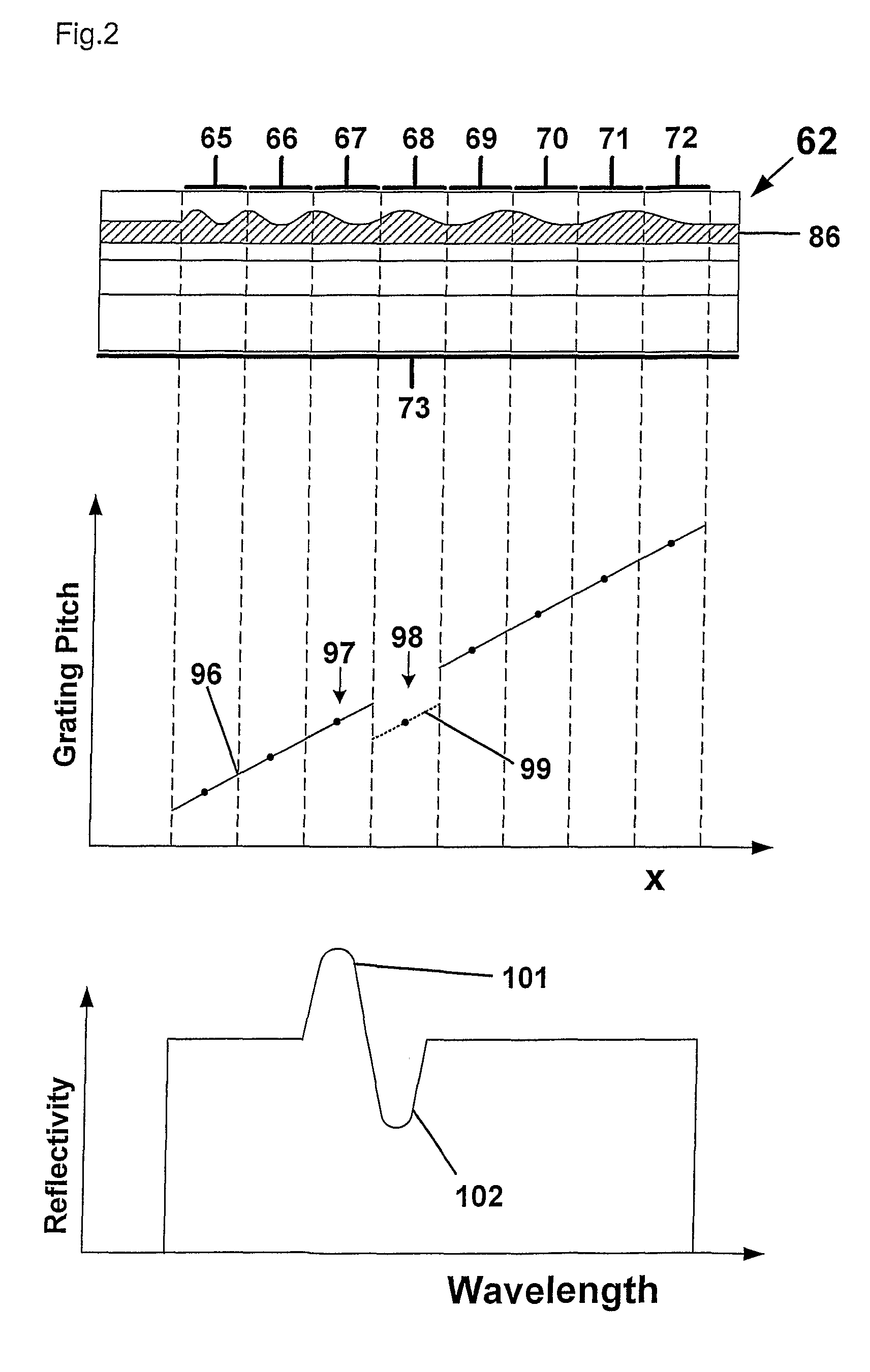
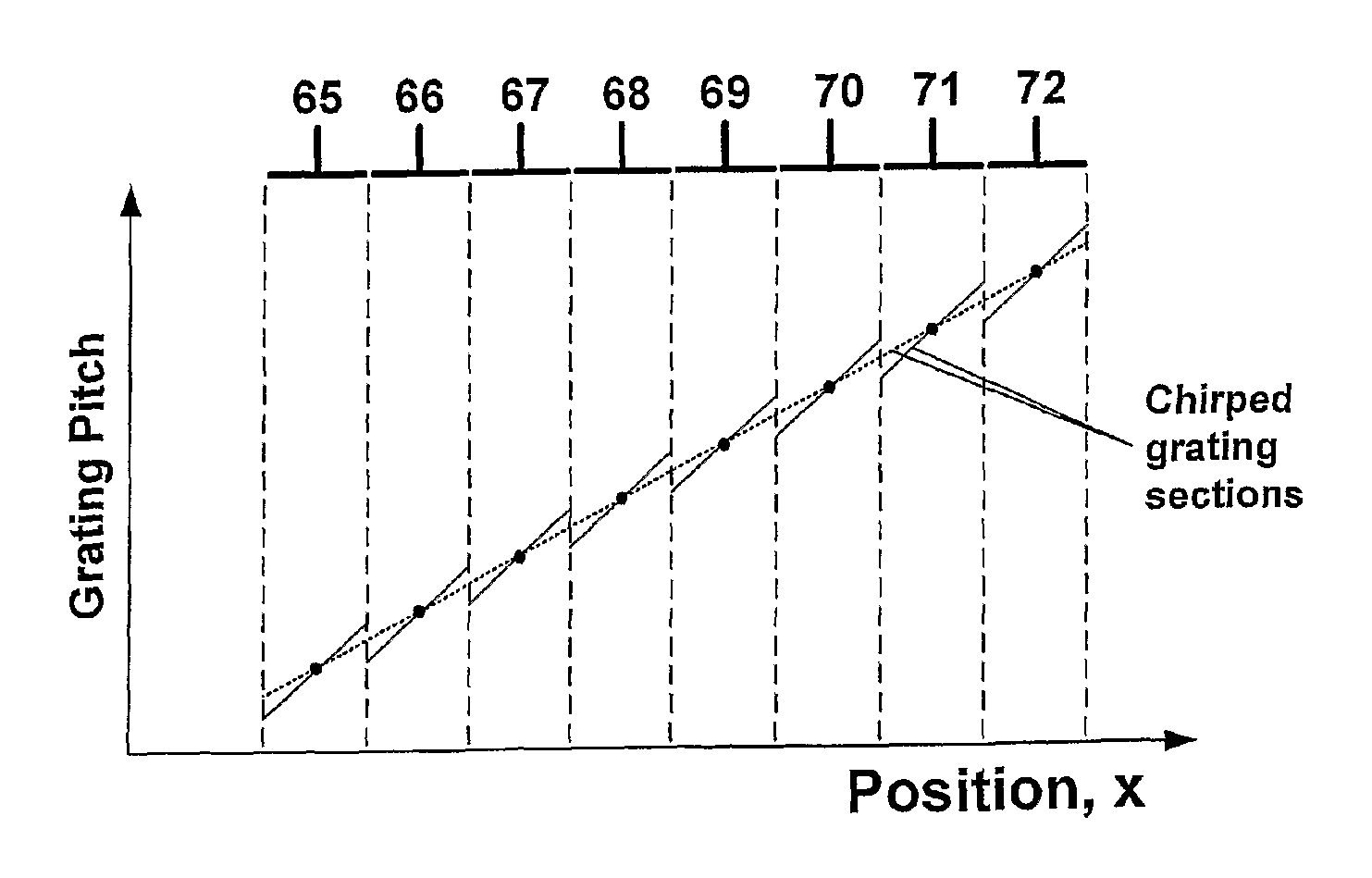
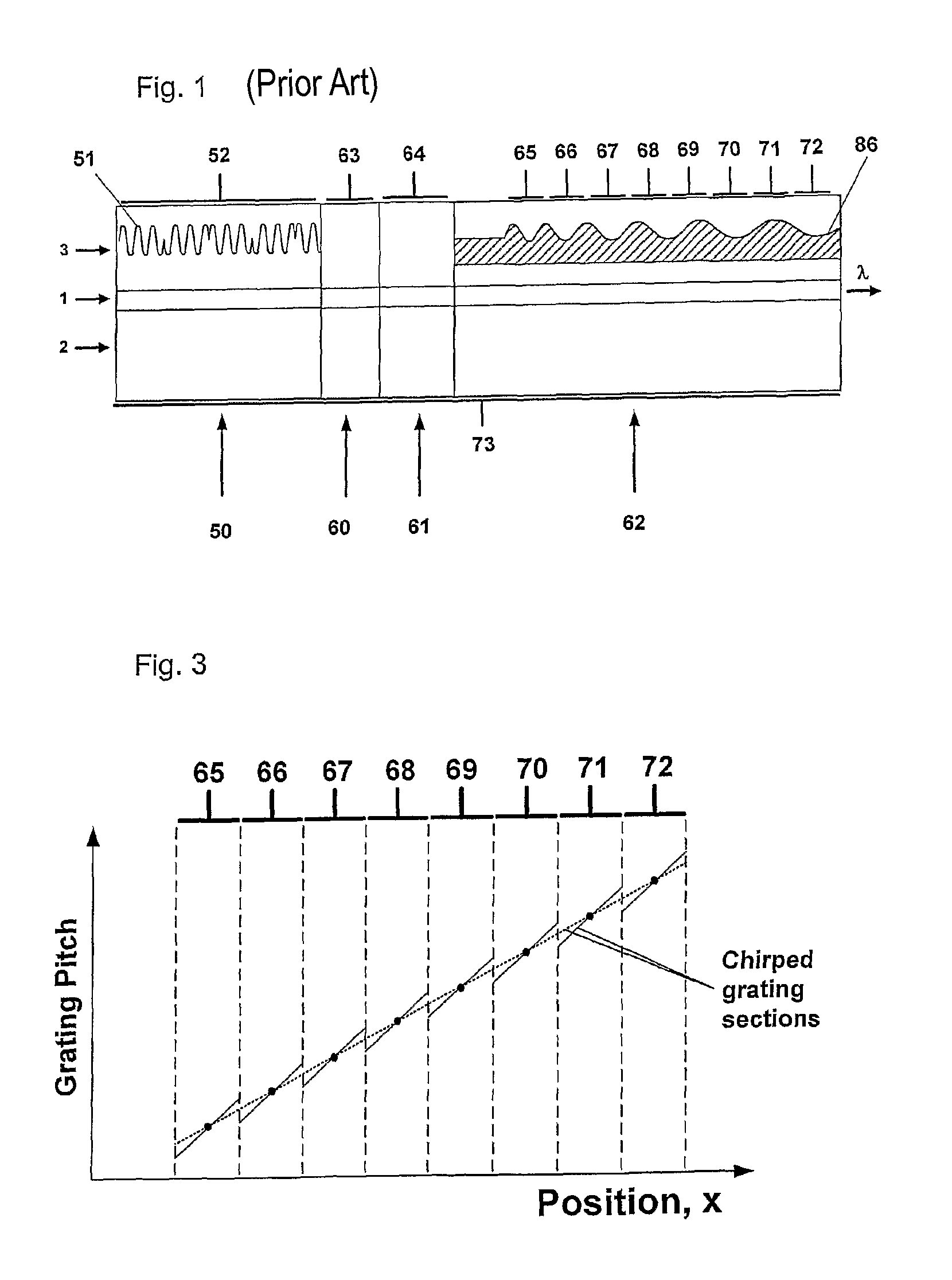
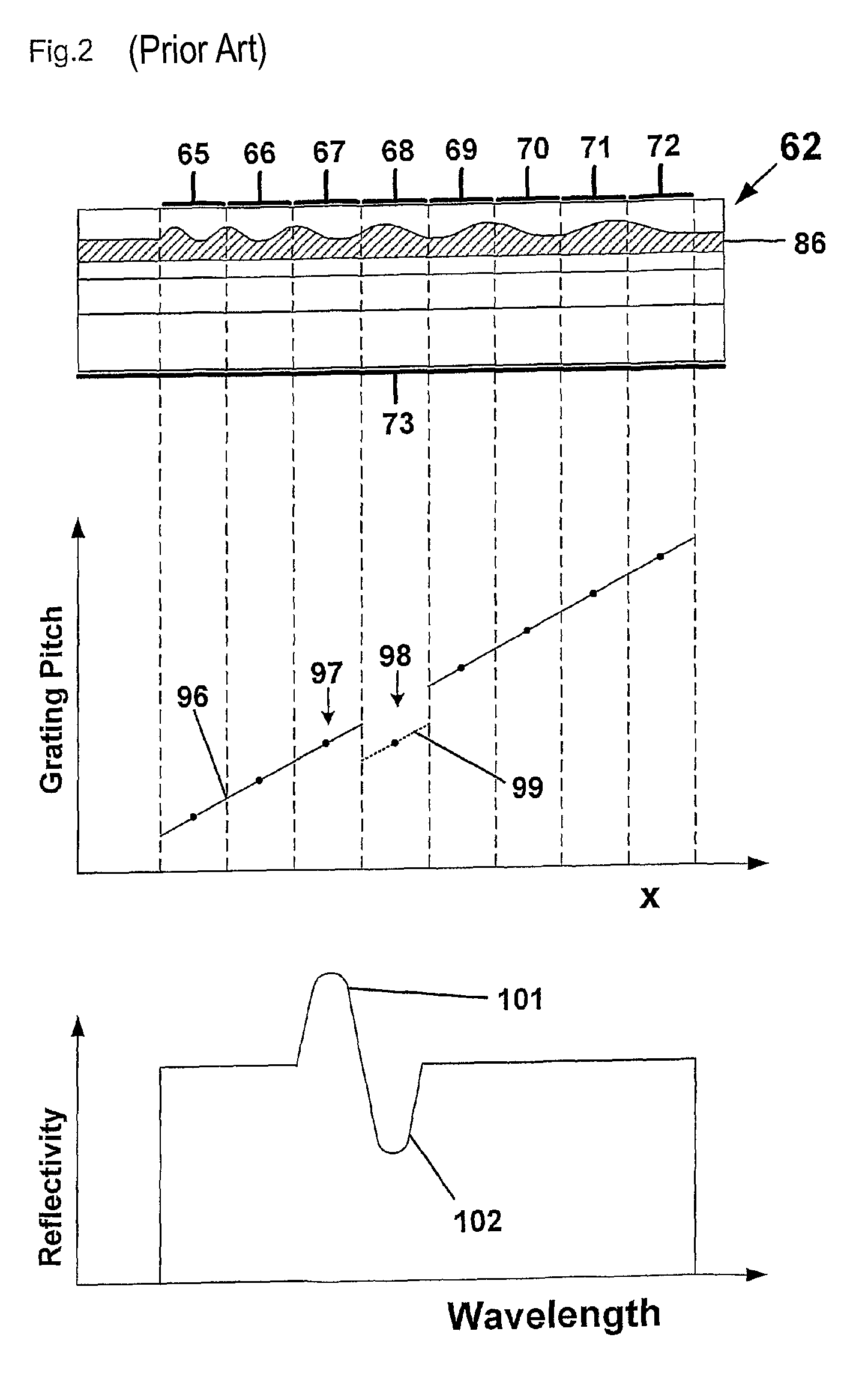
Bragg reflector grating
ActiveUS20090161717A1Large tuning rangeLess sensitiveOptical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsGrating
A Bragg reflector grating comprises a plurality of chirped grating sections (65-72), in which at least a first chirped grating section and a second chirped grating section have differing ranges of grating pitches. The combined range of grating pitches provided by the first and second chirped grating sections includes at least one discontinuity, such that the first and second chirped grating sections have one or more grating pitches in common and / or there are one or more ranges of grating pitches within the combined range of grating pitches that are absent.
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD
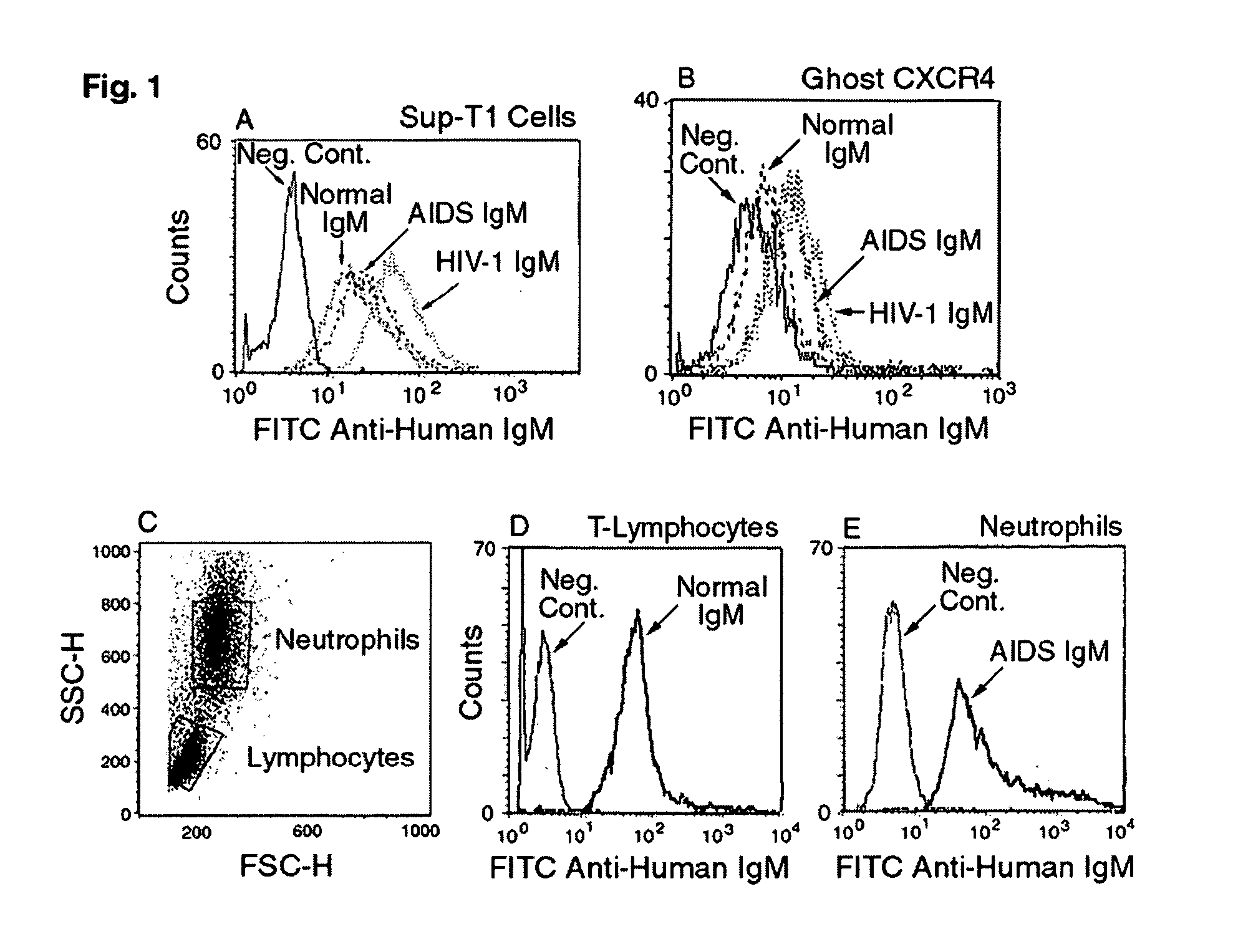
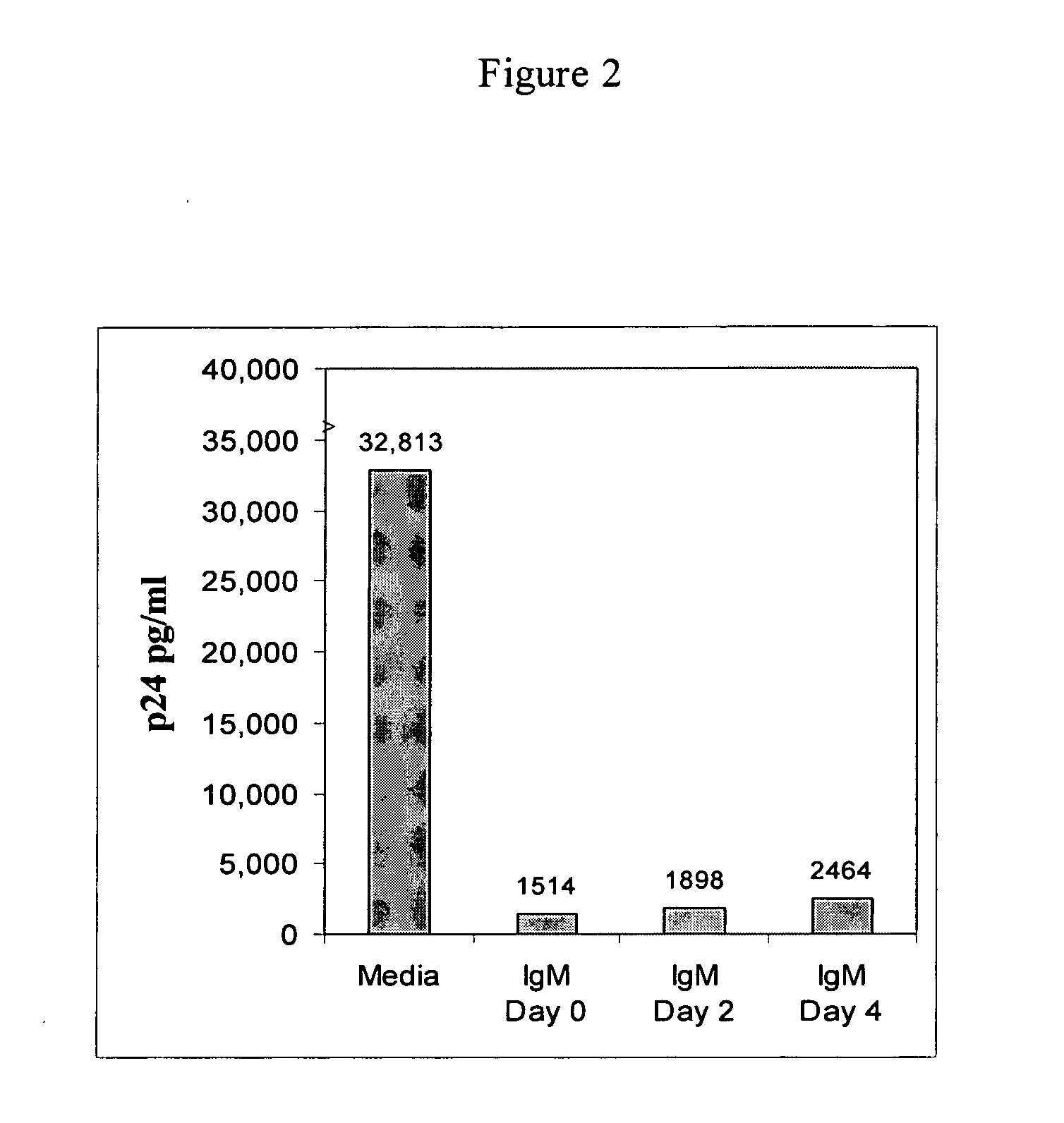
Naturally occurring IgM antibodies that bind lymphocytes
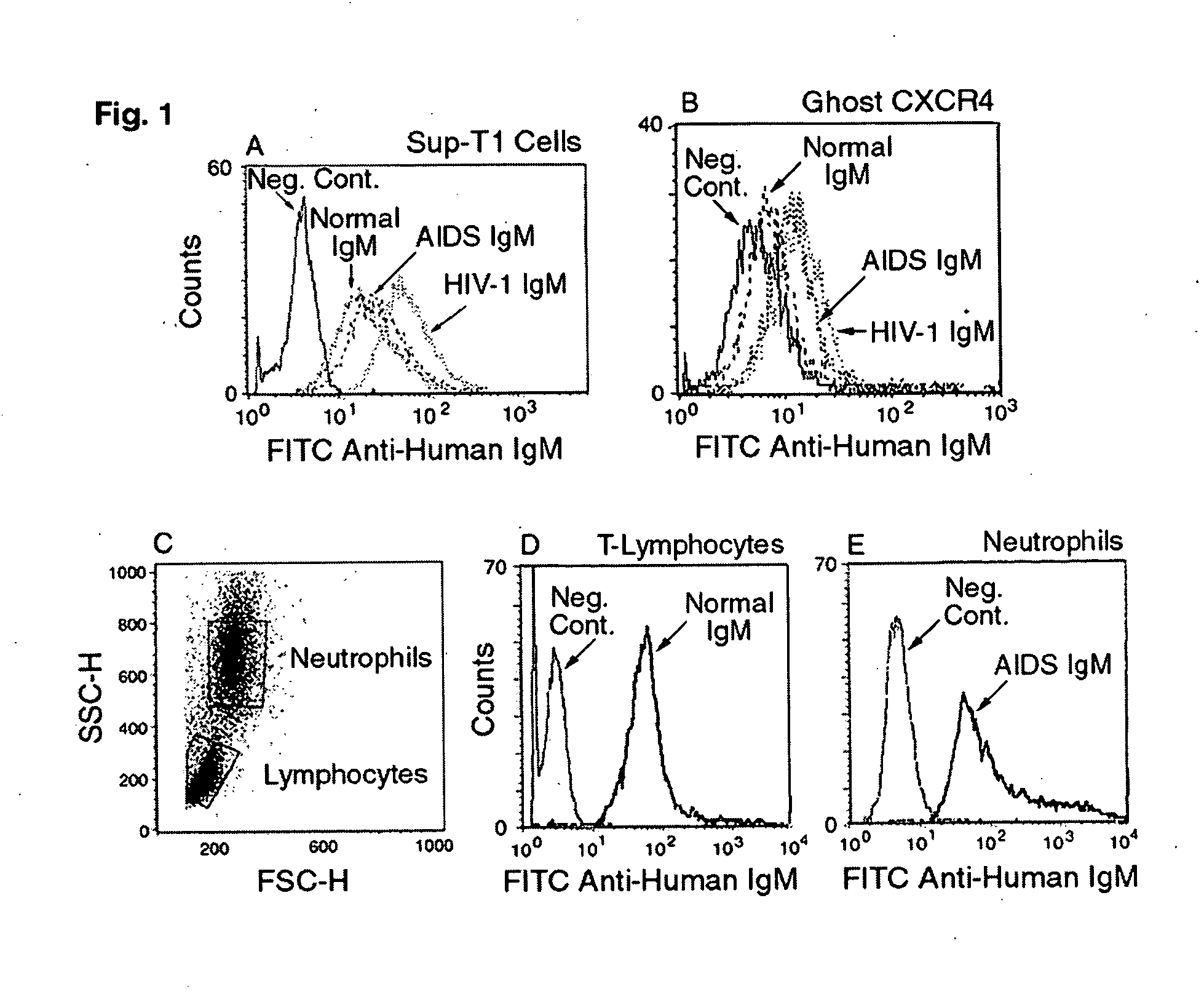
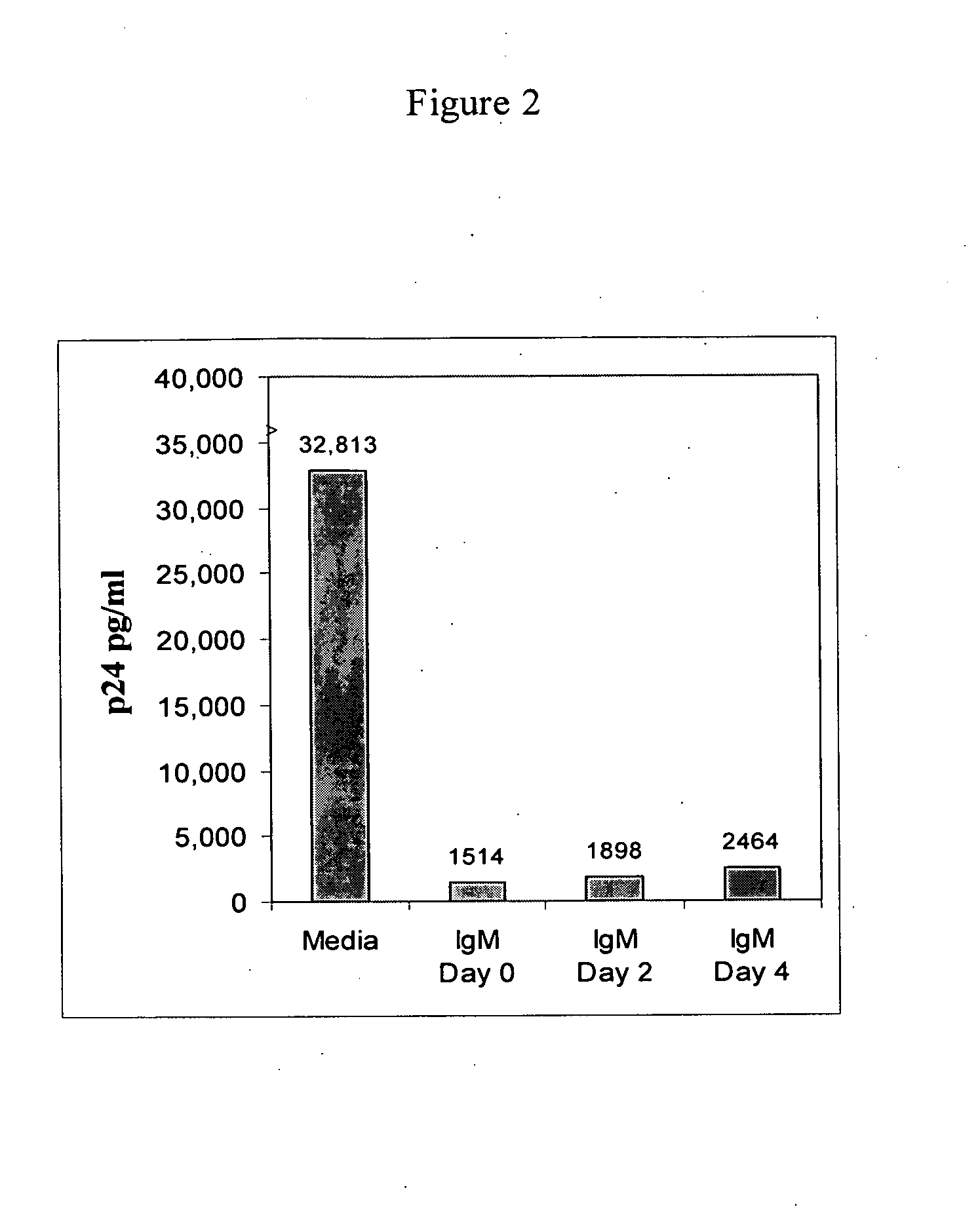
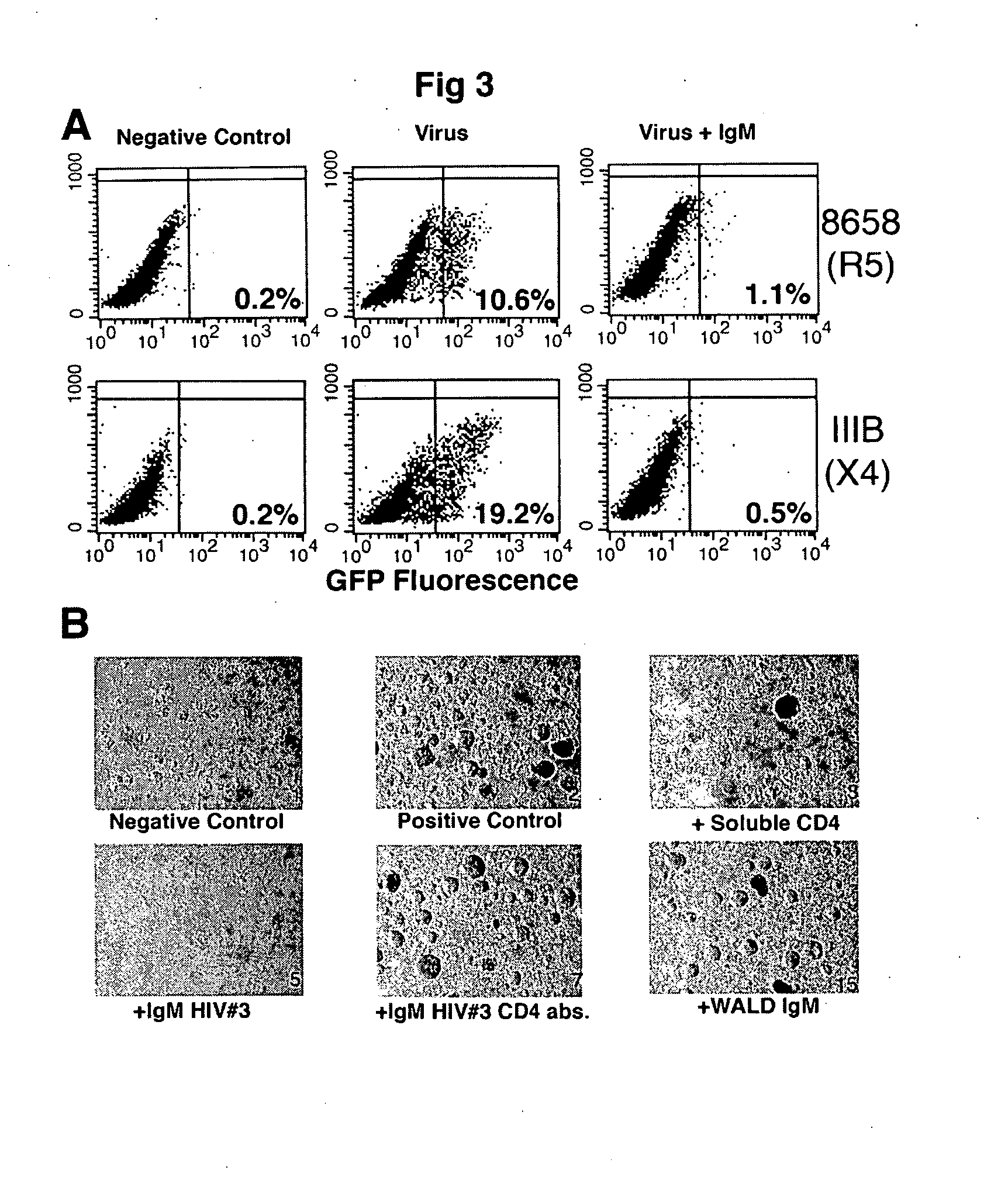
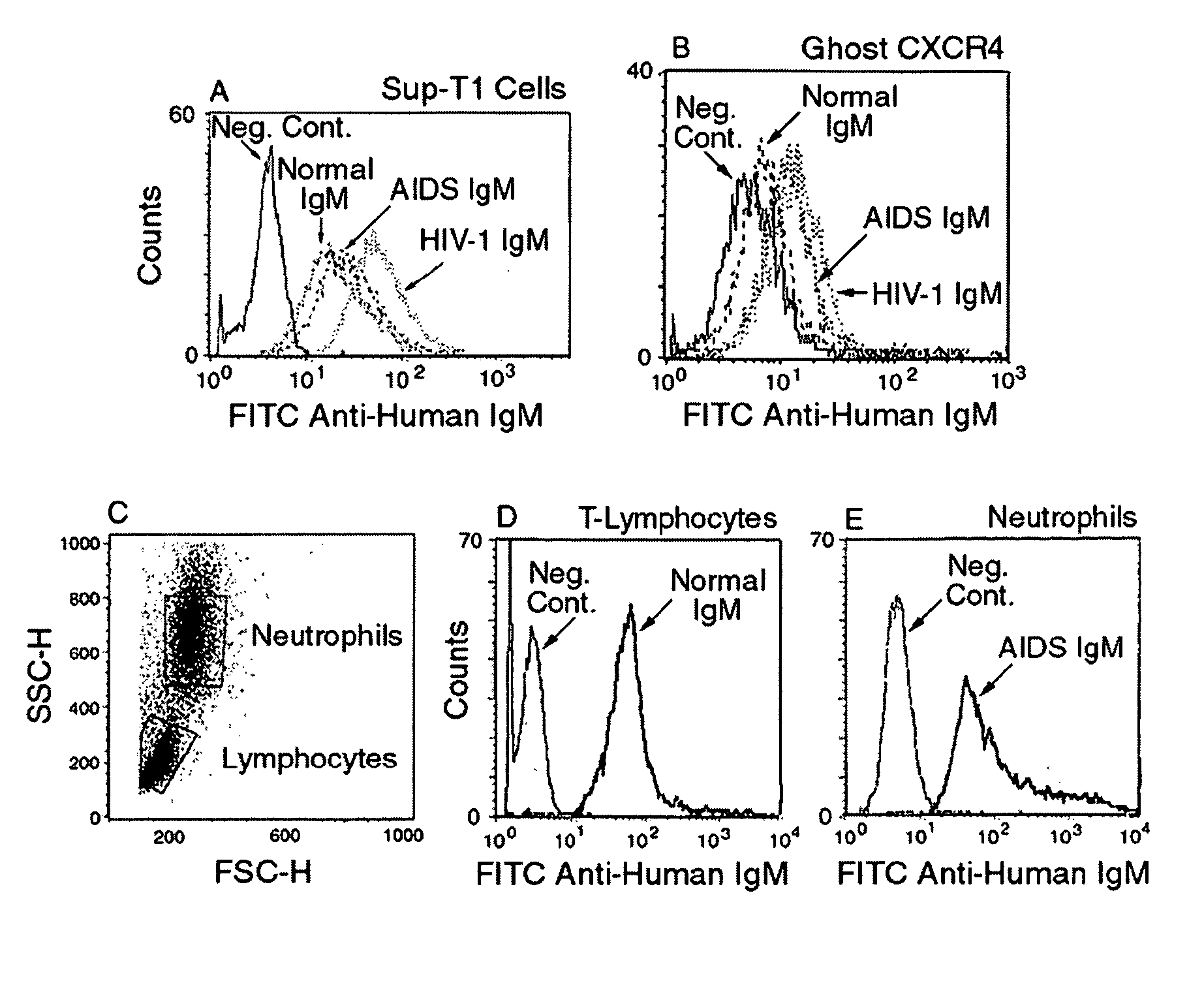
InactiveUS20080112950A1Inhibits Hepatitis CInhibit binding of chemokinesVertebrate antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeterologousLymphocyte Antibody
Human and animal serum contains naturally occurring autoantibodies that develop at birth in absence of deliberate immunization. These antibodies are predominantly of IgM isotype but can include all immunoglobulin isotypes such as IgD, IgA and IgG. Here we describe IgM anti-lymphocyte autoantibodies (IgM-ALA) and show that these antibodies are heterogenous with some antibodies binding to chemokine receptors such as CCR5 and CXCR4 and others binding to other lymphocyte receptors including CD3, CD2, CD4 and CD81. These IgM-ALA, unlike IgG antibodies, are not cytolytic to cells at 37 C and hence function to alter lymphocyte function including cytokine production and act as “blocking antibodies to inhibit binding of chemokines and viruses including HIV-1 and Hepatitis C. IgM antibodies that bind to receptors on lymphocyte also bind to the same or similar class of receptors on other leucocytes and other cells such as cancer cells and endothelial cells. The inventor claims that naturally occurring anti-lymphocyte antibodies inhibit viral infections, cancer and several inflammatory states by binding to chemokine receptors and other cell membrane receptors that activate cells or promote viral entry and replication. Inventor also claims methods for quantitating levels of IgM-ALA with different receptor specificities to aid in preventing disease progression and also claims methods to enhance in-vivo or in-vitro production of IgM-ALA.
Owner:LOBO
Naturally occuring IgM antibodies that bind lymphocytes
InactiveUS20080118522A1Eliminate side effectsInhibit inflammationBiocideAntipyreticLymphocyte AntibodyWhite blood cell
Human and animal serum contains naturally occurring autoantibodies that develop at birth in absence of deliberate immunization. These antibodies are predominantly of IgM isotype but can include all immunoglobulin isotypes such as IgD, IgA and IgG. Here we describe IgM anti-lymphocyte autoantibodies (IgM-ALA) and show that these antibodies are heterogenous with some antibodies binding to chemokine receptors such as CCR5 and CXCR4 and others binding to other lymphocyte receptors including CD3, CD2, CD4 and CD81. These IgM-ALA, unlike IgG antibodies, are not cytolytic to cells at 37 C and hence function to alter lymphocyte function including cytokine production and act as “blocking antibodies to inhibit binding of chemokines and viruses including HIV-1 and Hepatitis C. IgM antibodies that bind to receptors on lymphocyte also bind to the same or similar class of receptors on other leucocytes and other cells such as cancer cells and endothelial cells. The inventor claims that naturally occurring anti-lymphocyte antibodies inhibit viral infections, cancer and several inflammatory states by binding to chemokine receptors and other cell membrane receptors that activate cells or promote viral entry and replication. Inventor also claims methods for quantitating levels of IgM-ALA with different receptor specificities to aid in preventing disease progression and also claims methods to enhance in-vivo or in-vitro production of IgM-ALA.
Owner:LOBO
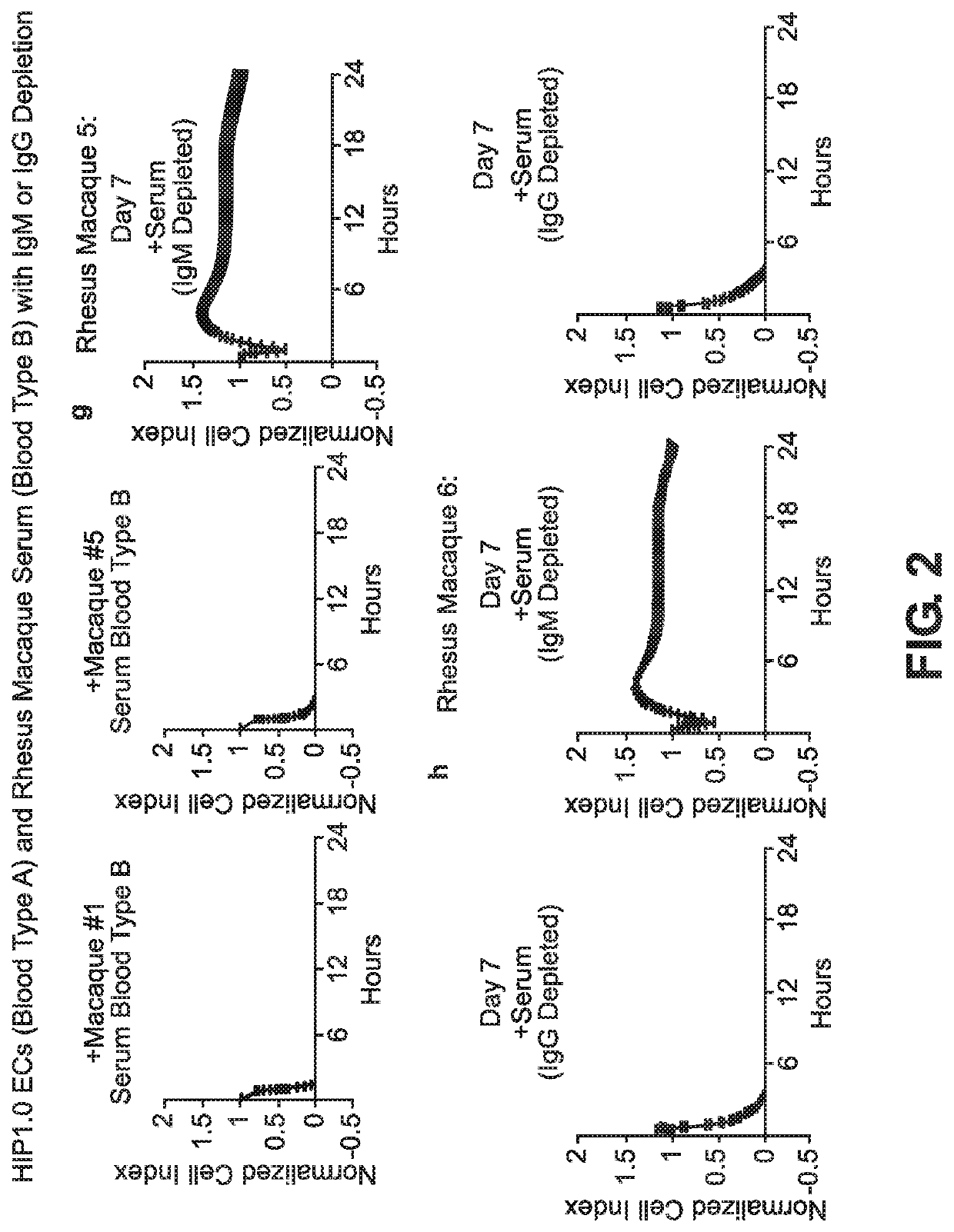
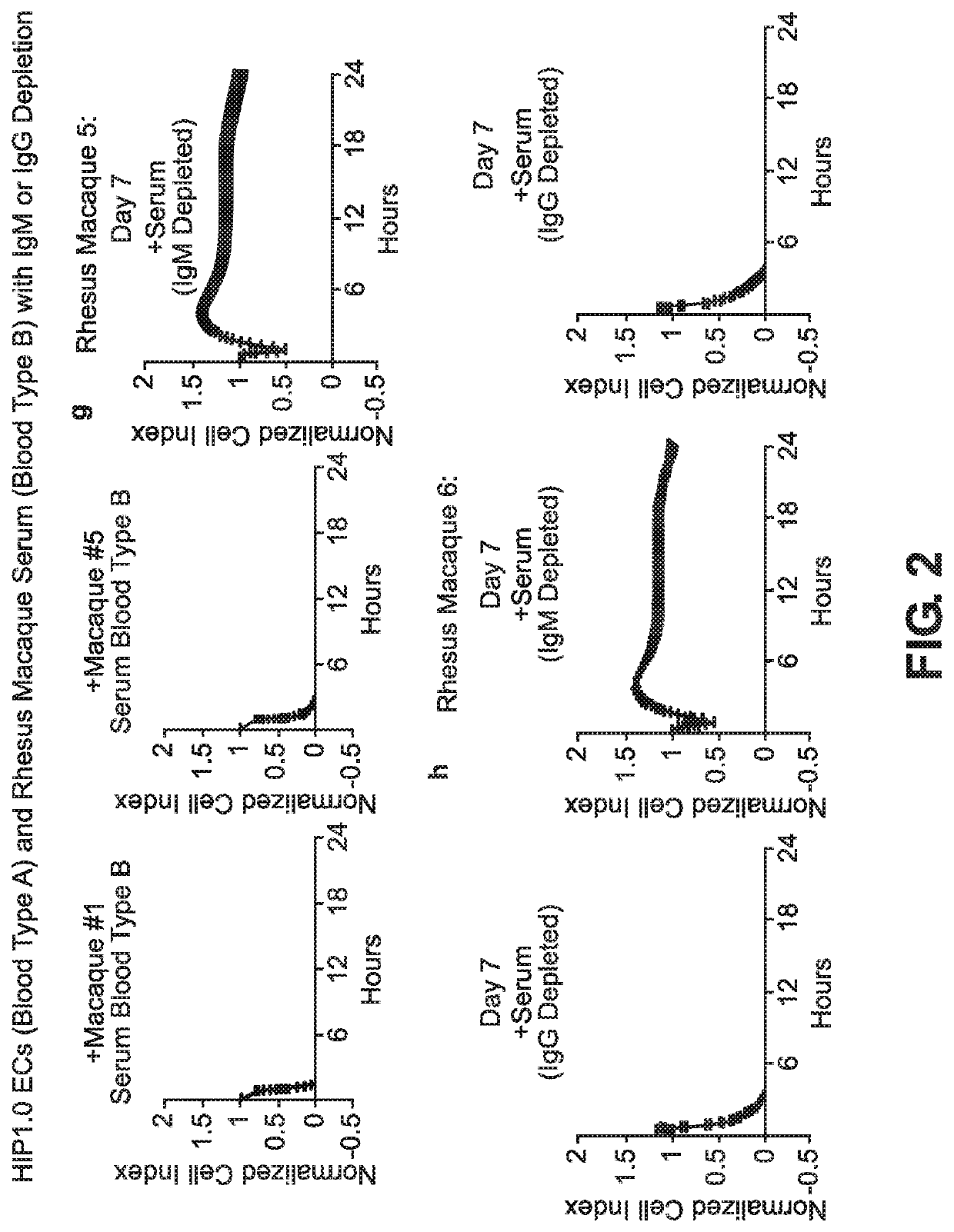
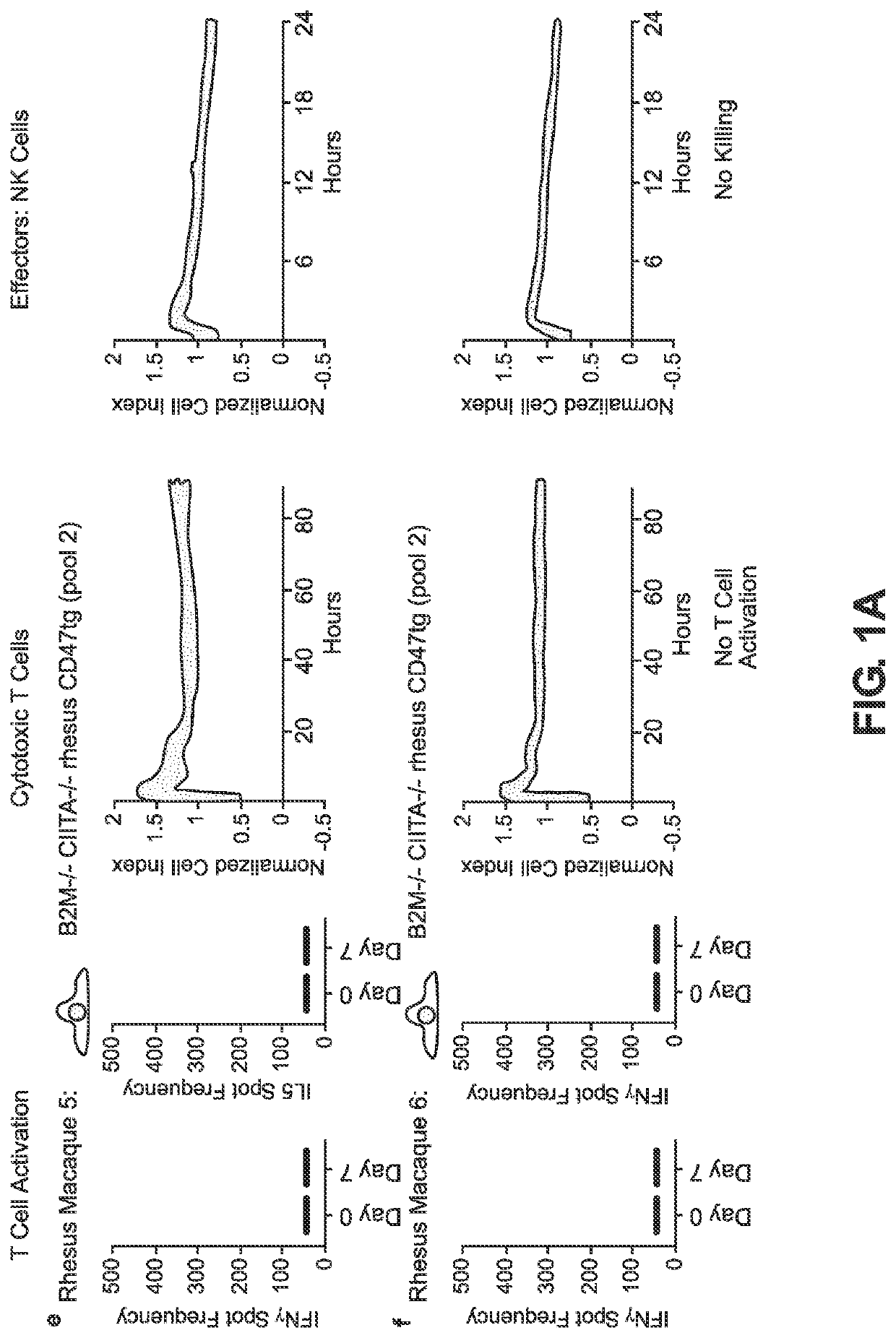
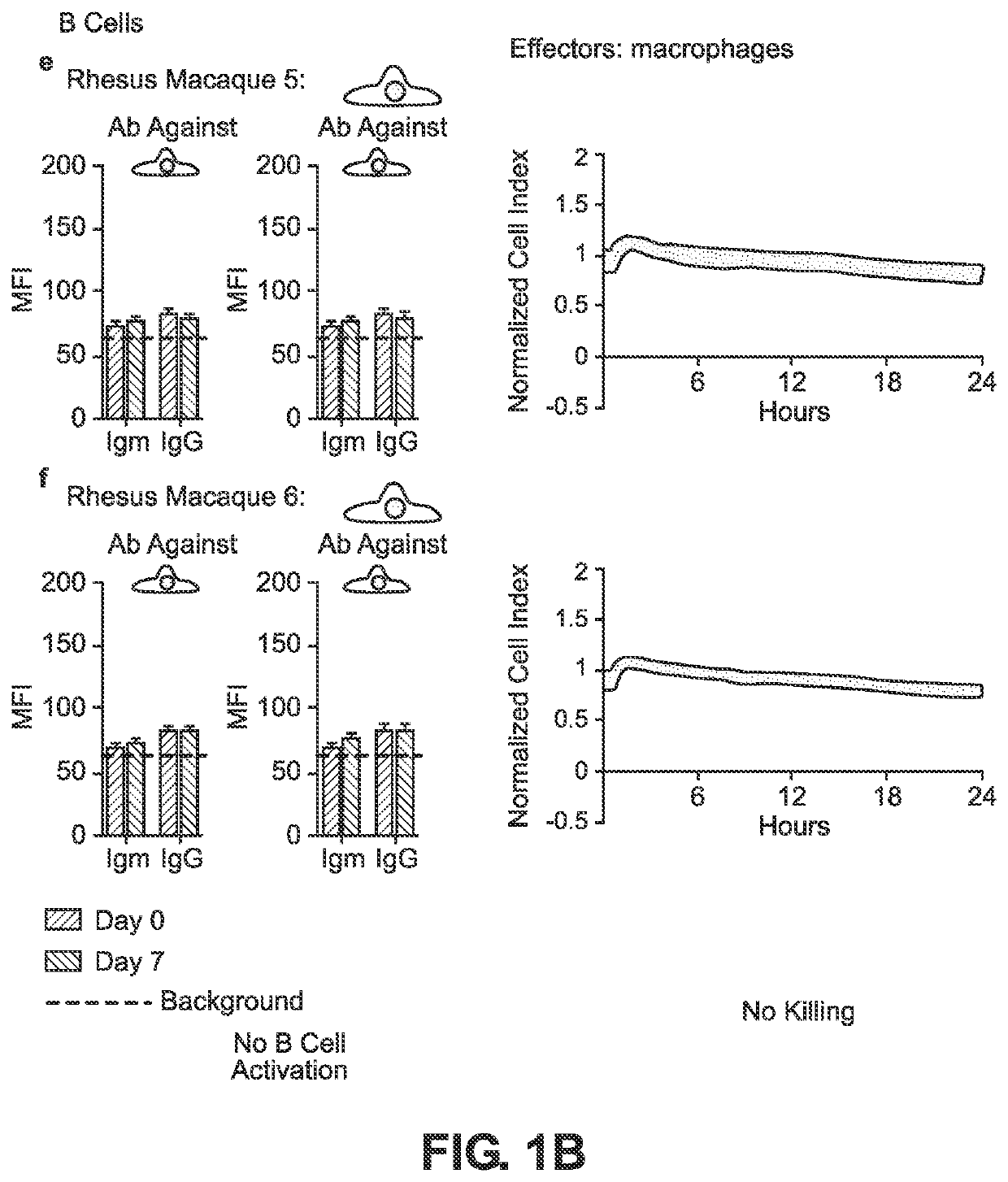
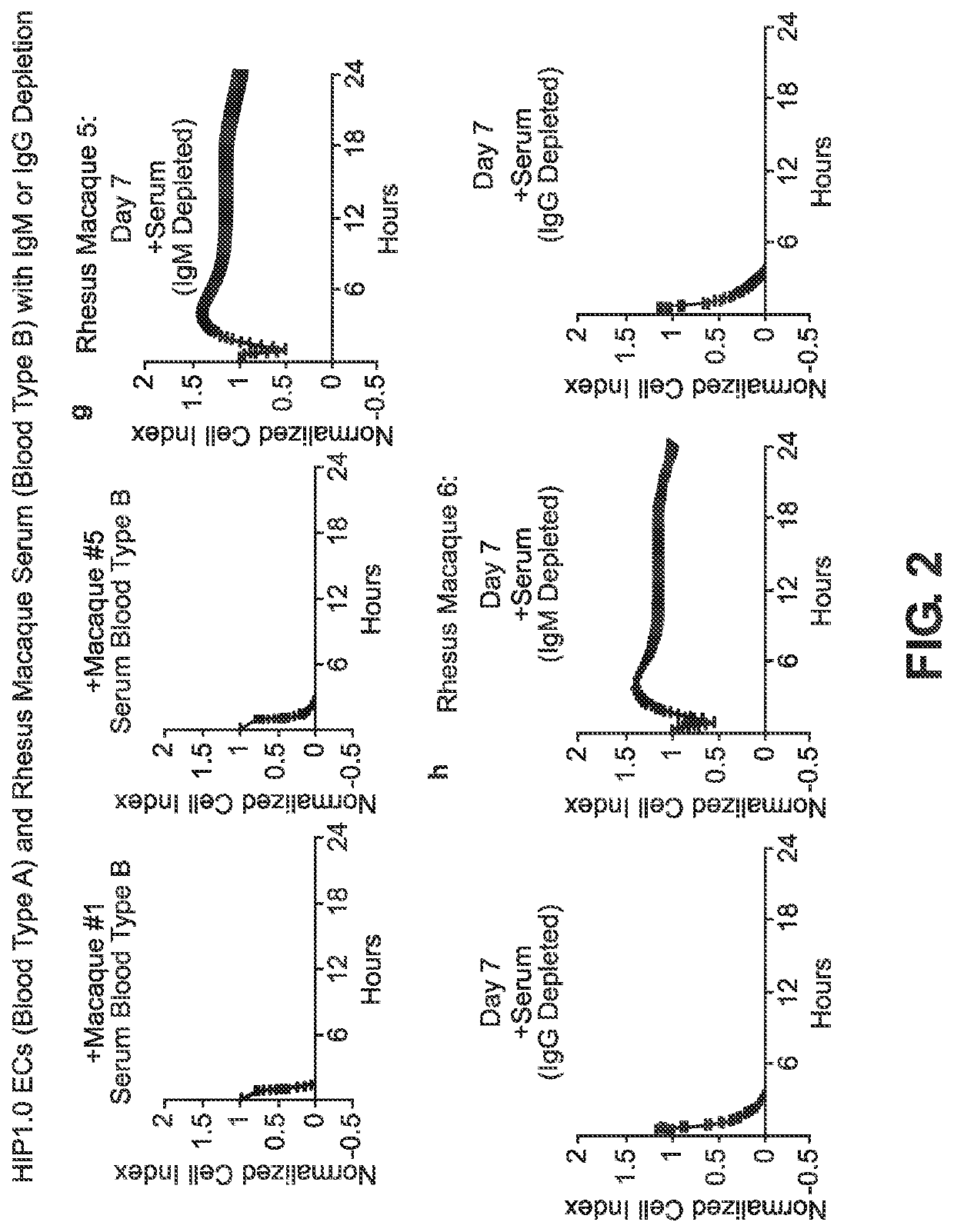
BLOOD TYPE O Rh- HYPO-IMMUNOGENIC PLURIPOTENT CELLS
ActiveUS20200354684A1Reduce functionReduce expressionHydrolasesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPluripotential stem cellImmune clearance
The invention discloses for the first time pluripotent cells, including hypoimmune pluripotent ABO blood type O Rhesus Factor negative (HIPO−) cells, that evade rejection by the host allogeneic immune system and avoid blood antigen type rejection. The HIPO− cells comprise reduced HLA-I and HLA-II expression, increased CD47 expression, and a universal blood group O Rh−(“O−”) blood type. The universal blood type is achieved by eliminating ABO blood group A and B antigents as well as eliminating Rh factor expression, or by starting with an O− parent cell line. These new, novel HIPO− cells evade host immune rejection because they have an impaired antigen presentation capacity, protection from innate immune clearance, and lack blood group rejection. The cells of the invention also include O− pluripotent stem cells (iPSCO−) and O− embryonic stem cells (ESCO−). The invention further provides universally acceptable “off”-the-shelf pluripotent cells and derivatives thereof for generating or regenerating specific tissues and organs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
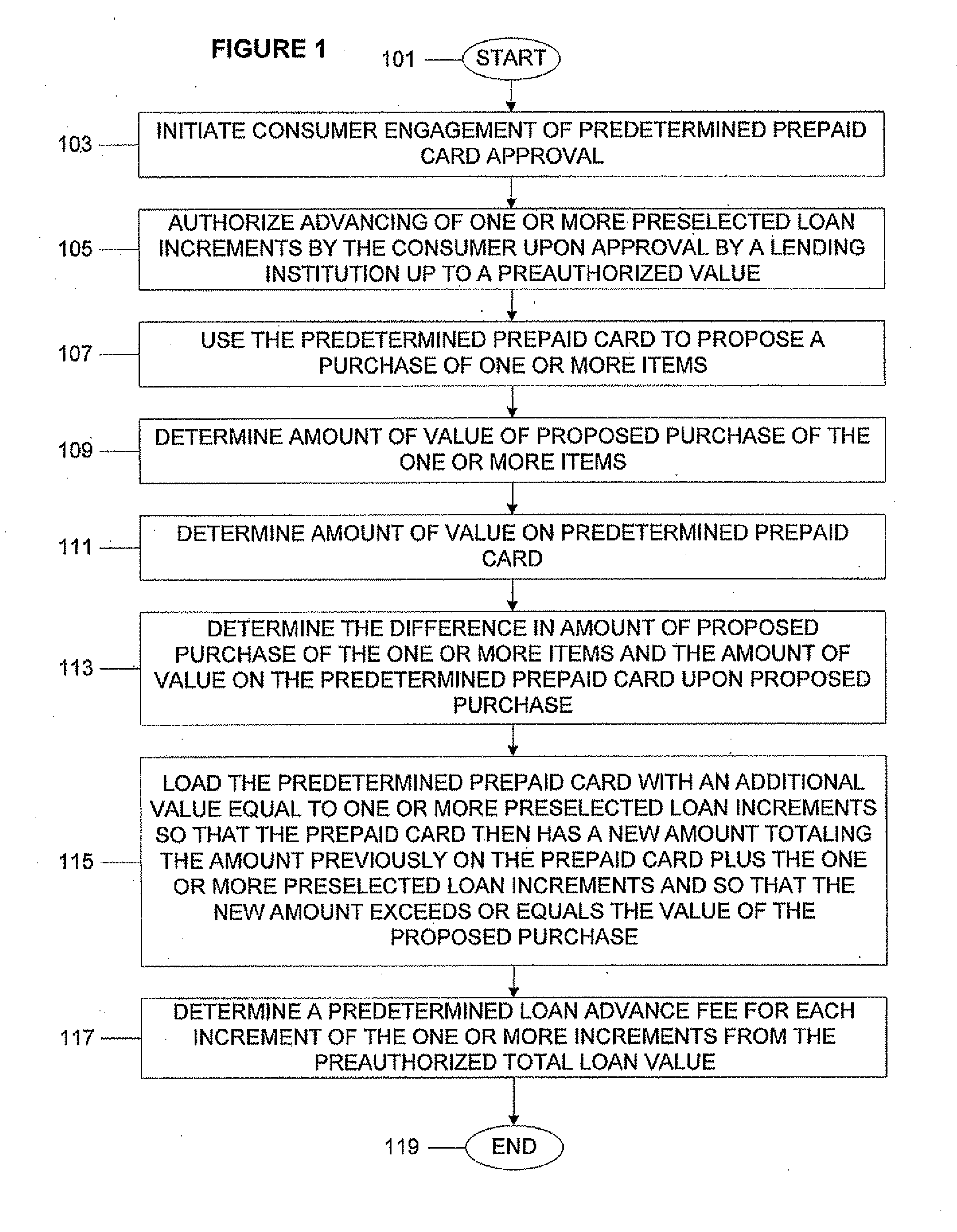
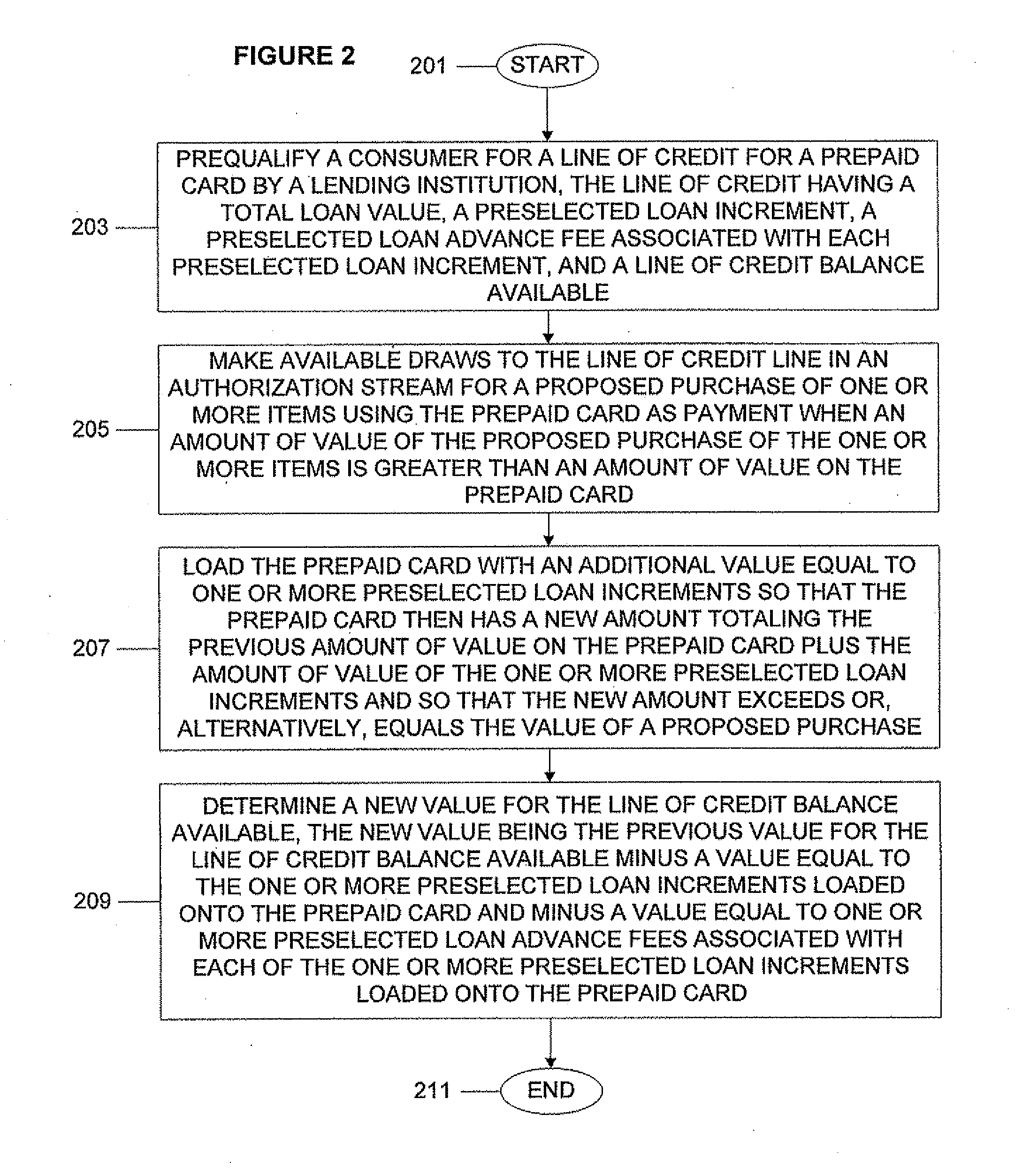
System, Program Product, and Associated Methods to Autodraw for Micro-Credit Attached to Prepaid Card
ActiveUS20120005072A1Avoid hassleAvoid planningFinancePoint-of-sale network systemsPaymentAdditional values
A consumer is prequalified for a line of credit attached to a prepaid card by a lending institution. The lending institution computer makes available draws to the line of credit line in an authorization stream for a proposed purchase using the prepaid card as payment. When the line of credit is accessed, the prepaid card is loaded with an additional value equal to one or more preselected loan increments so that the prepaid card then has a new amount totaling a previous amount plus the amount of value of the one or more preselected loan increments and so that the new amount exceeds or equals the value of a proposed purchase. Next, a new value for the line of credit balance available is determined, accounting for value loaded onto the prepaid card and a preselected loan advance fee for each loan increment loaded onto the prepaid card.
Owner:PATHWARD NAT ASSOC
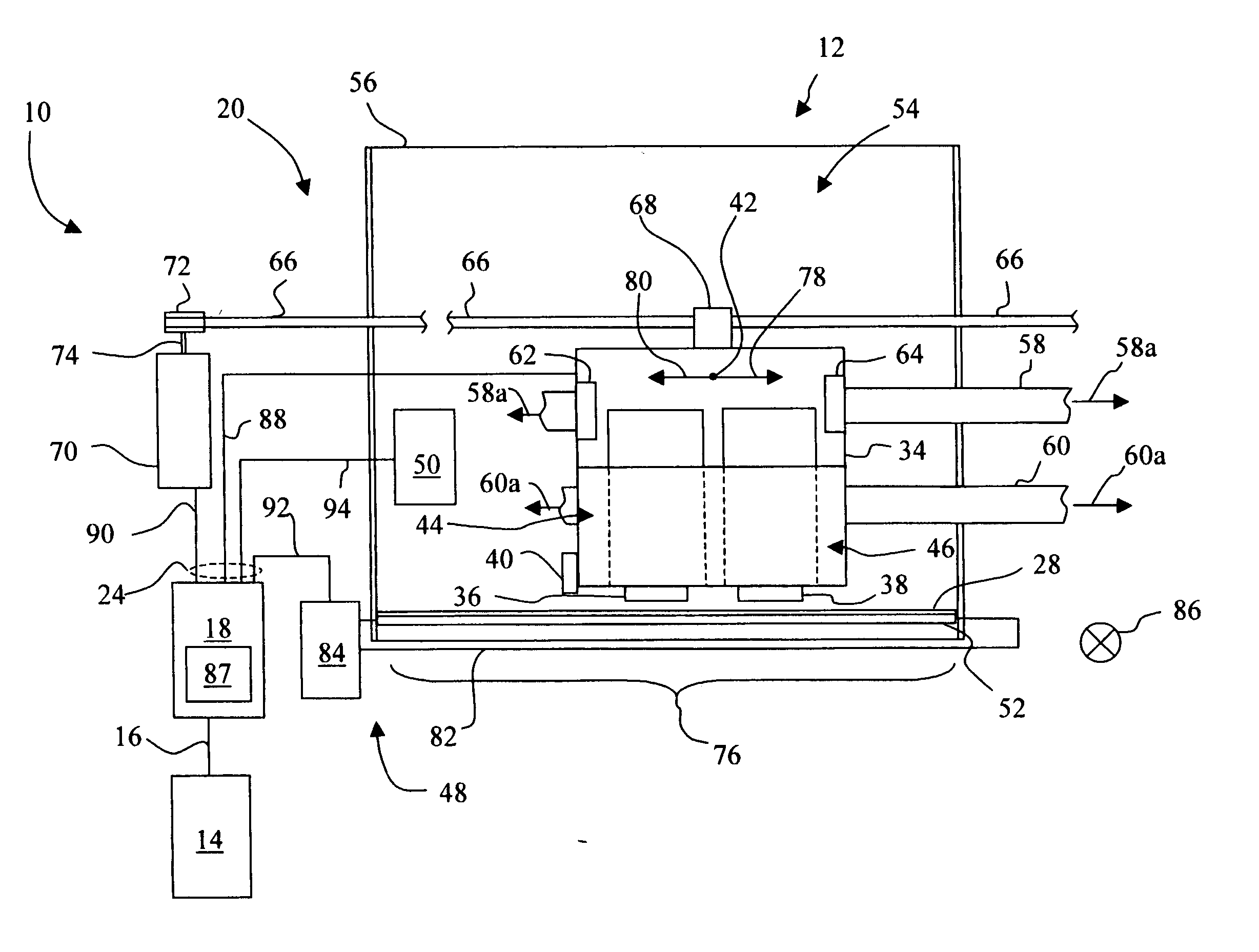
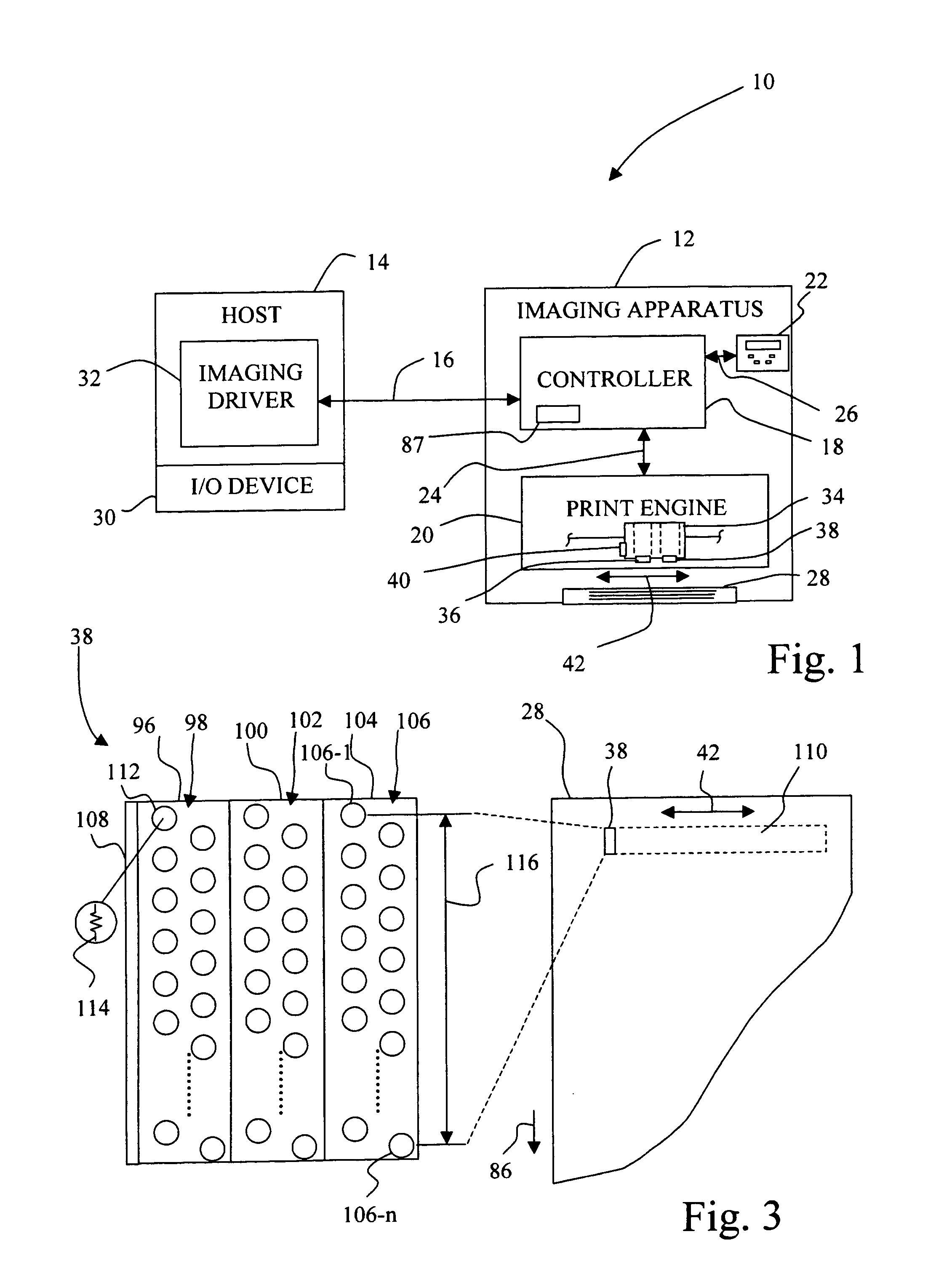
Method for facilitating swath height compensation for a printhead
InactiveUS20060061607A1Reduce generationPrinthead size tolerances may be less closely controlledPower drive mechanismsEngineering
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
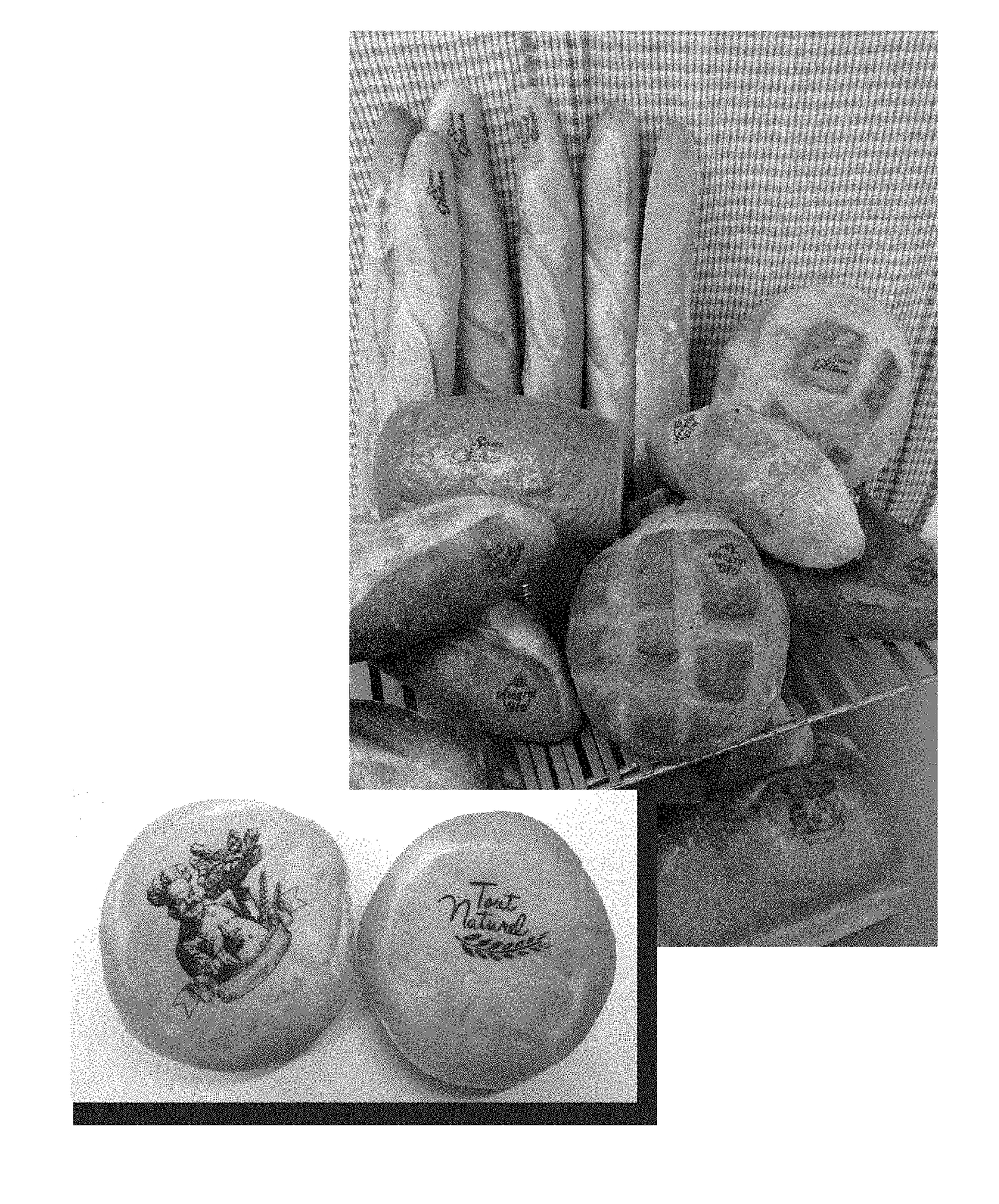
Method for Printing and Transfer Onto a Food Item
InactiveUS20180236801A1Maintain necessary ink viscosityEfficient and highly reproducible transferStampsConfectioneryEngineeringFood item
Owner:9083 8319 QUEBEC INC FASRS SIGNATURE PASQUIER
Door operator
ActiveUS8393054B2Compact structureWide applicabilityBuilding braking devicesPower-operated mechanismCouplingEngineering
A door operator includes a first component having a right-hand thread, a second component having a left-hand thread, and a plug-in or rotatable coupling having two complementary threads. The first and second compartments are interconnected to each other by the coupling when the right-hand thread of the first compartment and the left-hand thread of the second compartment engage the respective complementary threads of the coupling.
Owner:DORMAKABA DEUT GMBH
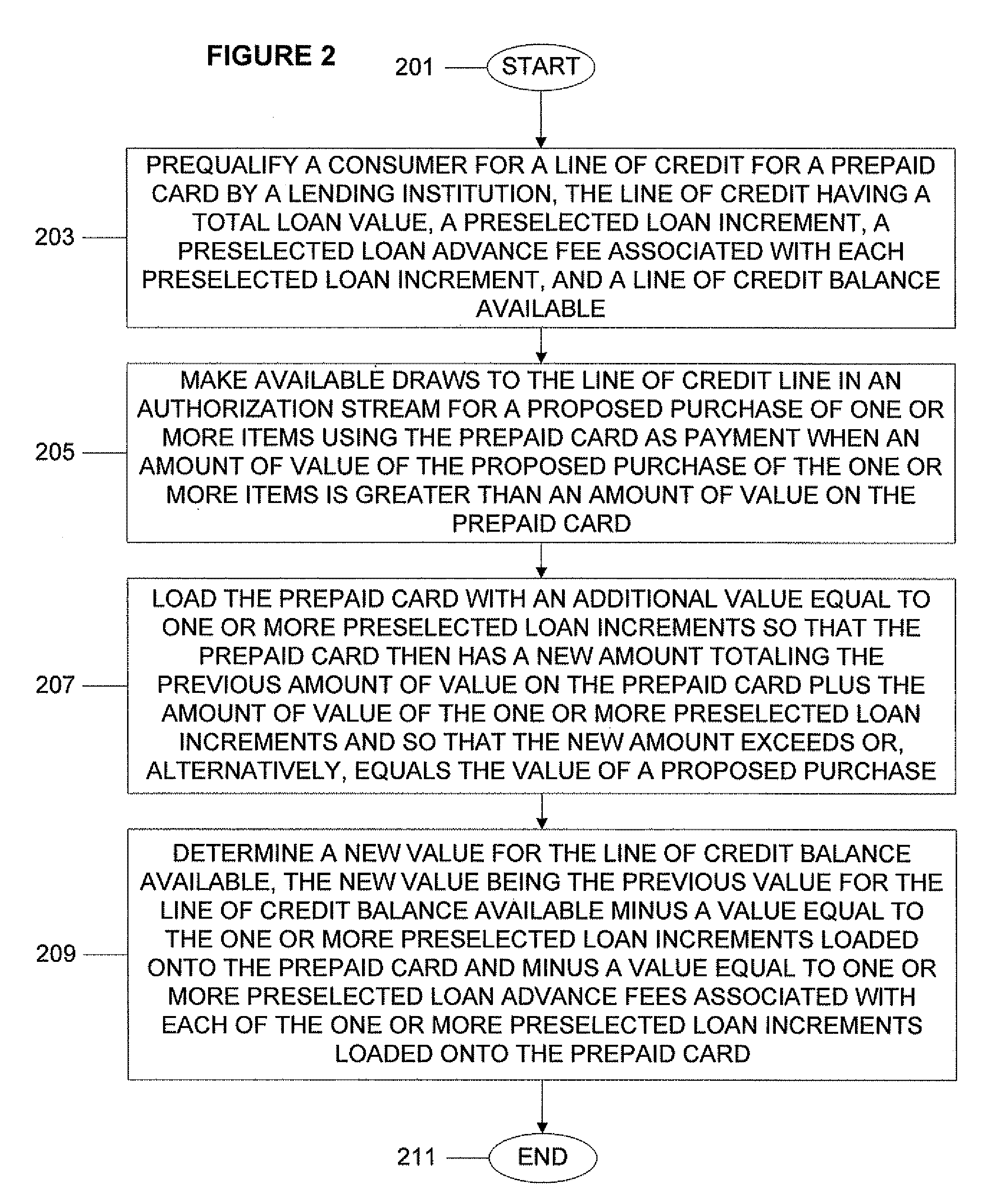
System, Program Product, and Associated Methods to Autodraw for Micro-Credit Attached to Prepaid Card
ActiveUS20120005094A1Avoid hassleAvoid planningFinancePoint-of-sale network systemsPaymentAdditional values
A prepaid card processor receives data for a line of credit for a prepaid card from a lending institution computer. The prepaid card processor makes available draws to the line of credit line on behalf of the lending institution computer in an authorization stream for a proposed purchase using the prepaid card as payment. When the line of credit is accessed, the processor loads the prepaid card with an additional value equal to one or more preselected loan increments so that the prepaid card then has a new amount totaling a previous amount plus the amount of value of the one or more preselected loan increments and so that the new amount exceeds or equals the value of a proposed purchase. Then the processor notifies the lending institution so that the line of credit balances on the lending institution computer and the prepaid card processor are kept in sync.
Owner:PATHWARD NAT ASSOC
Polypeptide specifically binding to cd34 molecule and use thereof
InactiveUS20180169177A1Improve binding efficiencySmall toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisMolecular biologyAcid amino sequences
A polypeptide is provided specifically binding to CD34 molecule and use thereof, the polypeptide is selected from at least one of polypeptide 17 and polypeptide 19, amino acid sequences of the polypeptide 17 and the polypeptide 19 are as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 in sequence listing. The polypeptide provided by the present application can specifically bind to CD34, and can be produced by artificial synthesis or genetic engineering method. Compared with antibody, the polypeptide provided by the present invention has characteristics such as low molecular weight, easy preparation and less immunological rejection; and it has little toxic side-effects, its binding to the CD34+ cell won't obviously kill the target cell and inhibit its proliferation. The polypeptide provided by the present invention can be used as markers for CD34 positive expression cells, and also can be used as substitute of immunofluorescence CD34 antibody.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YIDAI PHARMA +1
Sheet metal section
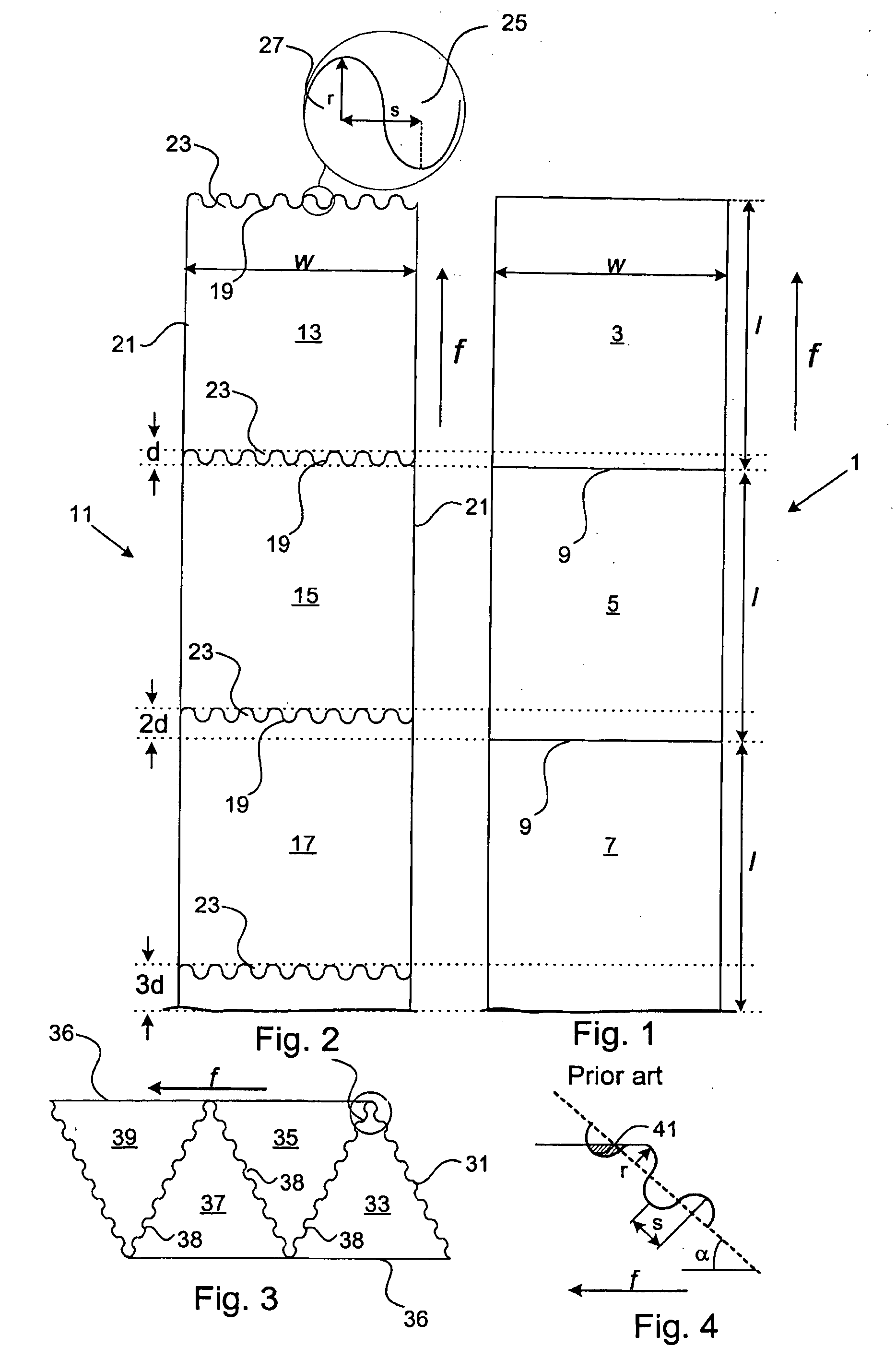
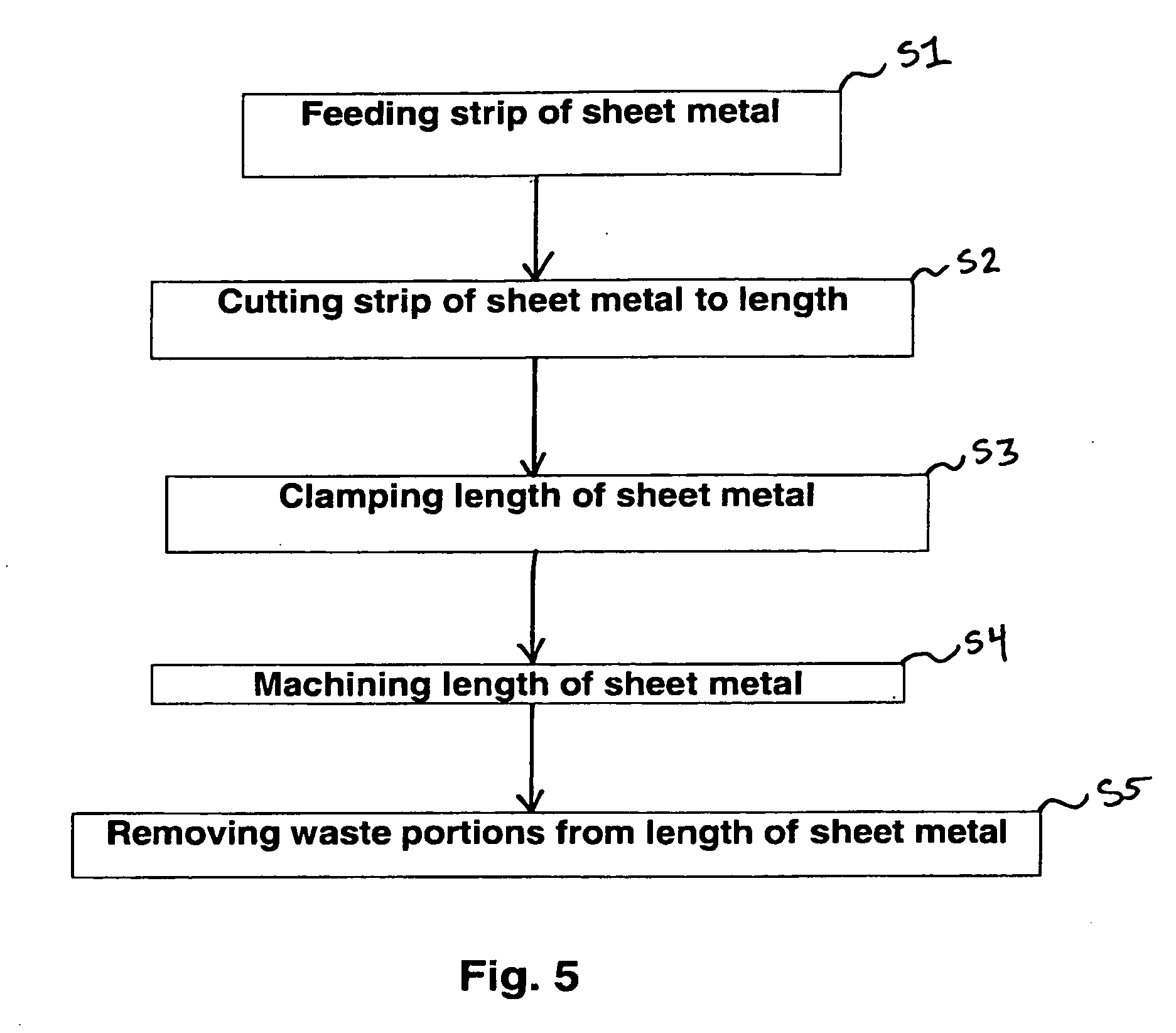
A method of cutting a strip of sheet metal, including feeding out a continuous strip of sheet metal in a feeding direction, cutting the strip into a plurality of lengths, including making a wave shaped cut between each length and an adjacent length, wherein each of a forward edge and a following edge of each length include a plurality of waves, and selecting at least one of a radius of each of the plurality of waves and a spacing between adjacent ones of the plurality of waves based on a cutting angle, wherein the cutting angle is oblique with respect to the feeding direction.
Owner:SAAB AUTOMOBILE AB
Blood type O Rh-hypo-immunogenic pluripotent cells
ActiveUS11162079B2Reduce sensitivityFunction increaseHydrolasesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPluripotential stem cellImmune clearance
The invention discloses for the first time pluripotent cells, including hypoimmune pluripotent ABO blood type O Rhesus Factor negative (HIPO−) cells, that evade rejection by the host allogeneic immune system and avoid blood antigen type rejection. The HIPO− cells comprise reduced HLA-I and HLA-II expression, increased CD47 expression, and a universal blood group O Rh− (“O−”) blood type. The universal blood type is achieved by eliminating ABO blood group A and B antigents as well as eliminating Rh factor expression, or by starting with an O− parent cell line. These new, novel HIPO− cells evade host immune rejection because they have an impaired antigen presentation capacity, protection from innate immune clearance, and lack blood group rejection. The cells of the invention also include O− pluripotent stem cells (iPSCO−) and O− embryonic stem cells (ESCO−). The invention further provides universally acceptable “off”-the-shelf pluripotent cells and derivatives thereof for generating or regenerating specific tissues and organs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
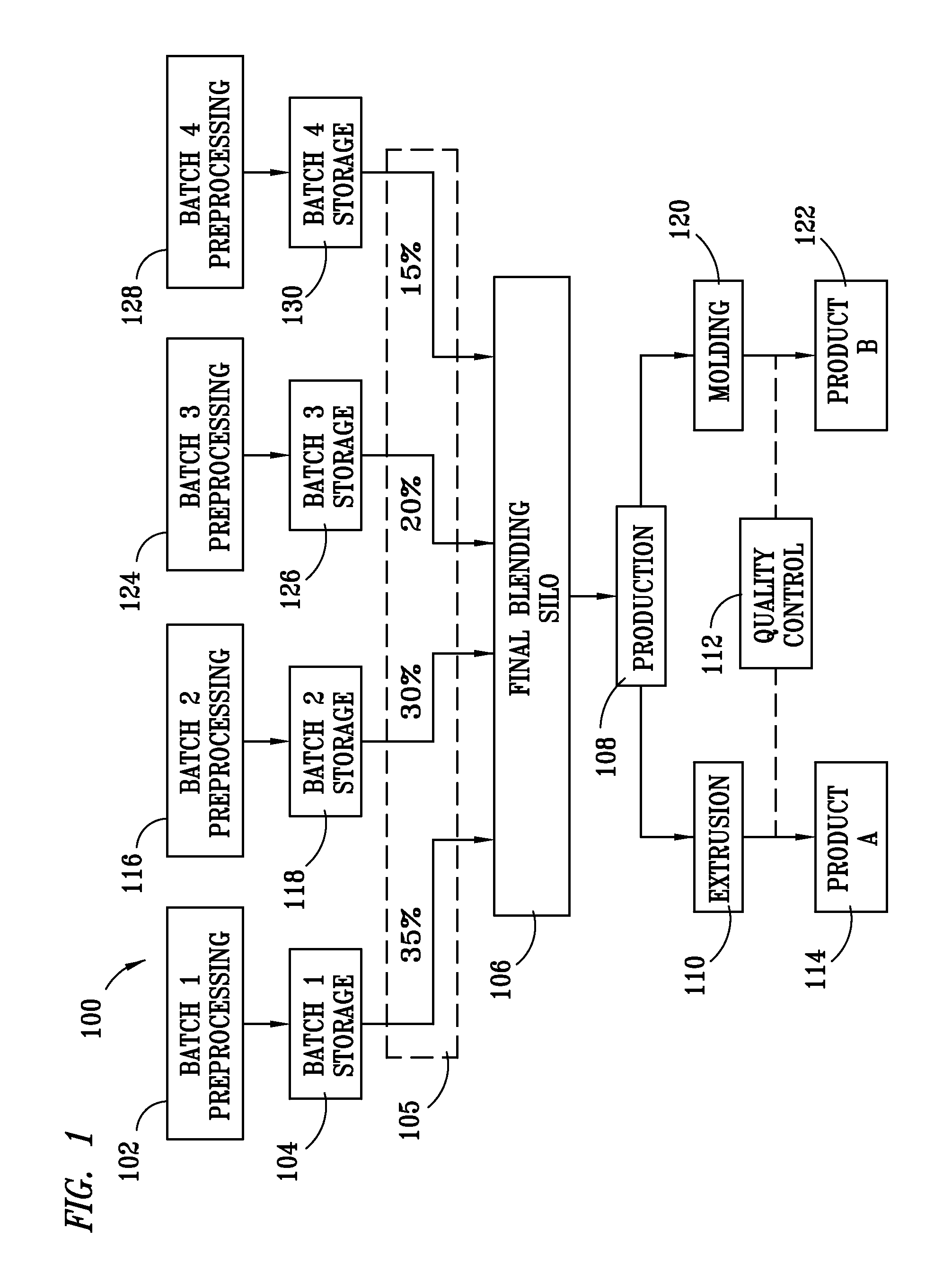
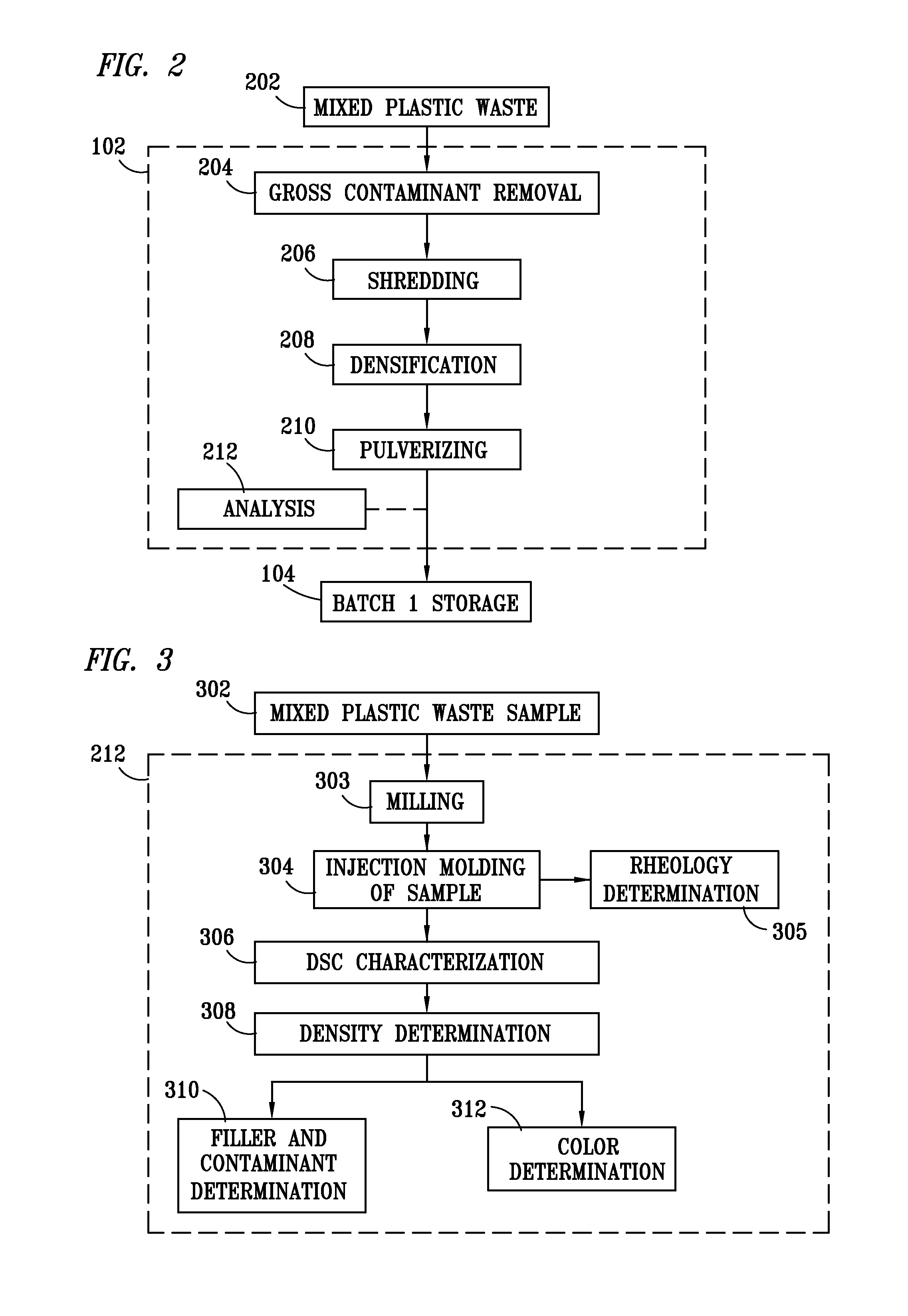
Method for processing and analyzing contaminated mixed waste plastics to produce reformulated, blended feed materials having desired physical properties
InactiveUS8066207B1Increase percentageImprove consistencyPlastic recyclingCocoaEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
A method for reformulating reclaimed, contaminated mixed waste plastics into useful articles wherein a plurality of batches of the mixed waste plastics are preprocessed to produce substantially homogeneous mixtures of a desired particle size range that are characterized according to at least one of their respective plastic content, densities, color and degree of contamination, and are thereafter blended to produce a mixed plastic feed material having properties predetermined to be desirable for reprocessing into at least one of such useful articles.
Owner:MOISTURESHIELD INC
Bragg reflector grating
ActiveUS8160410B2Large tuning rangeLess sensitiveOptical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsGrating
A Bragg reflector grating comprises a plurality of chirped grating sections (65-72), in which at least a first chirped grating section and a second chirped grating section have differing ranges of grating pitches. The combined range of grating pitches provided by the first and second chirped grating sections includes at least one discontinuity, such that the first and second chirped grating sections have one or more grating pitches in common and / or there are one or more ranges of grating pitches within the combined range of grating pitches that are absent.
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD
Infant formulation containing an aroma composition for use as fragrance
InactiveUS9167838B2High acceptanceFew rejectionEssential-oils/perfumesFood preparationFlavorBaby food
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
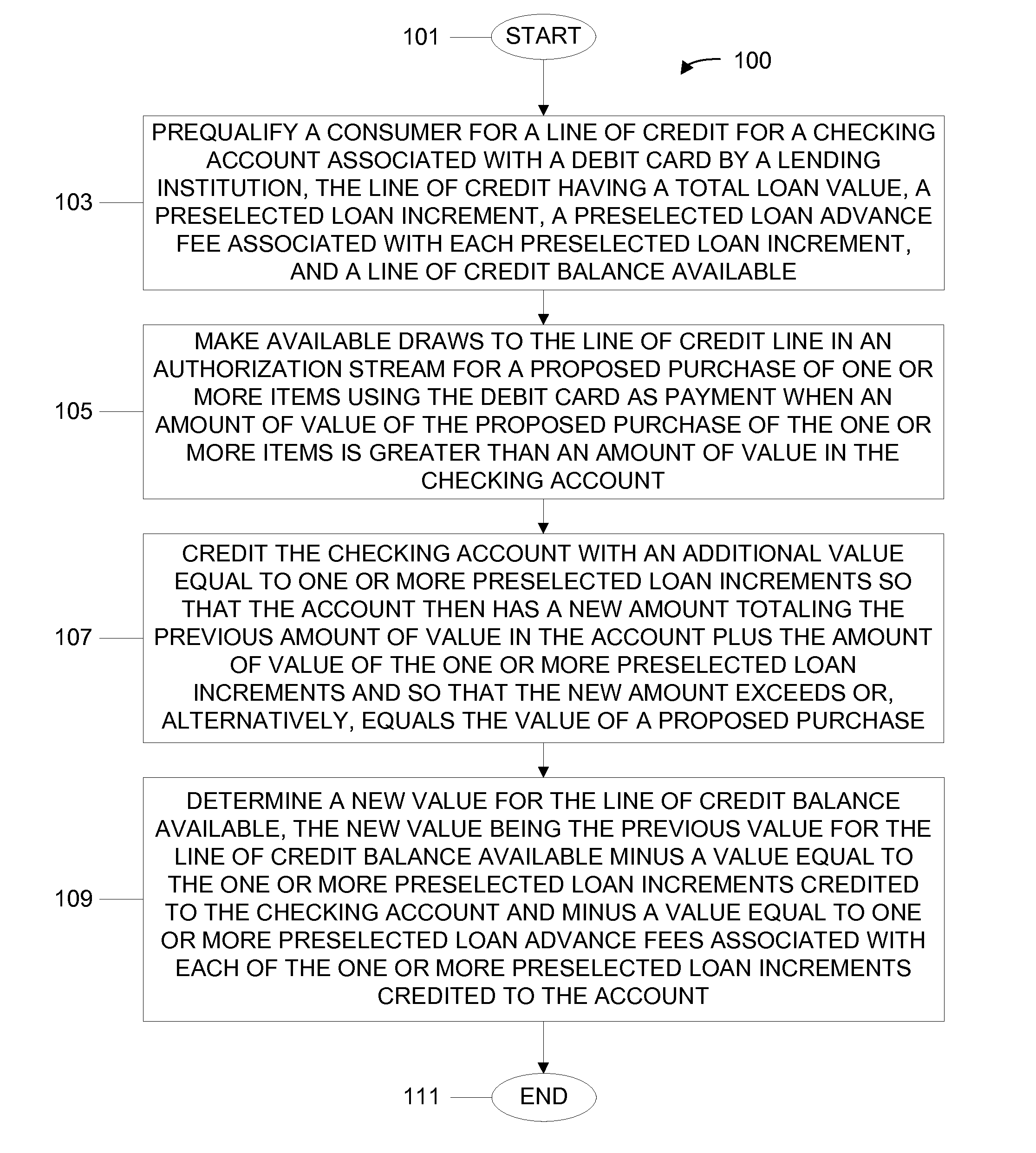
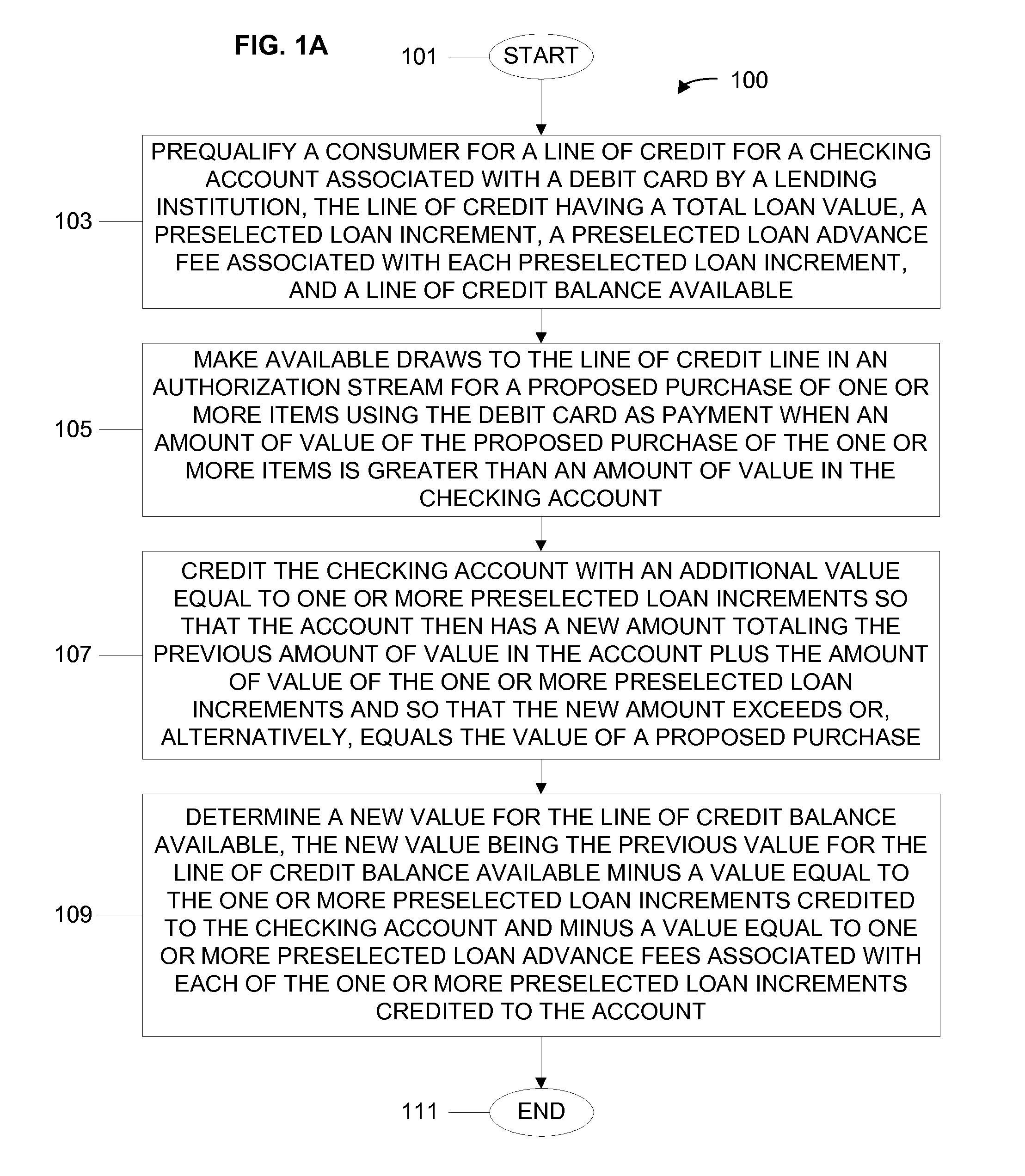
System, Program Product, and Method for Debit Card and Checking Account Autodraw
A consumer is prequalified for a line of credit attached to a checking account by a lending institution computer responsive to consumer underwriting data. The lending institution computer makes available draws to the line of credit line in an authorization stream for a proposed payment from the checking account. When the line of credit is accessed, the checking account is credited with an additional value equal to one or more preselected loan increments so that the account then has a new amount totaling a previous amount plus the amount of value of the one or more preselected loan increments and so that the new amount exceeds or equals the value of a proposed payment. Next, a new value for the line of credit balance available is determined, accounting for value credited to the checking account and a preselected loan advance fee for each loan increment credited to the account.
Owner:PATHWARD NAT ASSOC
BLOOD TYPE O Rh- HYPO-IMMUNOGENIC PLURIPOTENT CELLS
PendingUS20220049227A1Reduce sensitivityFunction increaseHydrolasesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPluripotential stem cellImmune clearance
The invention discloses for the first time pluripotent cells, including hypoimmune pluripotent ABO blood type O Rhesus Factor negative (HIPO−) cells, that evade rejection by the host allogeneic immune system and avoid blood antigen type rejection. The HIPO− cells comprise reduced HLA-I and HLA-II expression, increased CD47 expression, and a universal blood group O Rh− (“O−”) blood type. The universal blood type is achieved by eliminating ABO blood group A and B antigents as well as eliminating Rh factor expression, or by starting with an O− parent cell line. These new, novel HIPO− cells evade host immune rejection because they have an impaired antigen presentation capacity, protection from innate immune clearance, and lack blood group rejection. The cells of the invention also include O− pluripotent stem cells (iPSCO−) and O− embryonic stem cells (ESCO−). The invention further provides universally acceptable “off-the-shelf” pluripotent cells and derivatives thereof for generating or regenerating specific tissues and organs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for positioning a carrier with electronic components and electronic component produced with such method
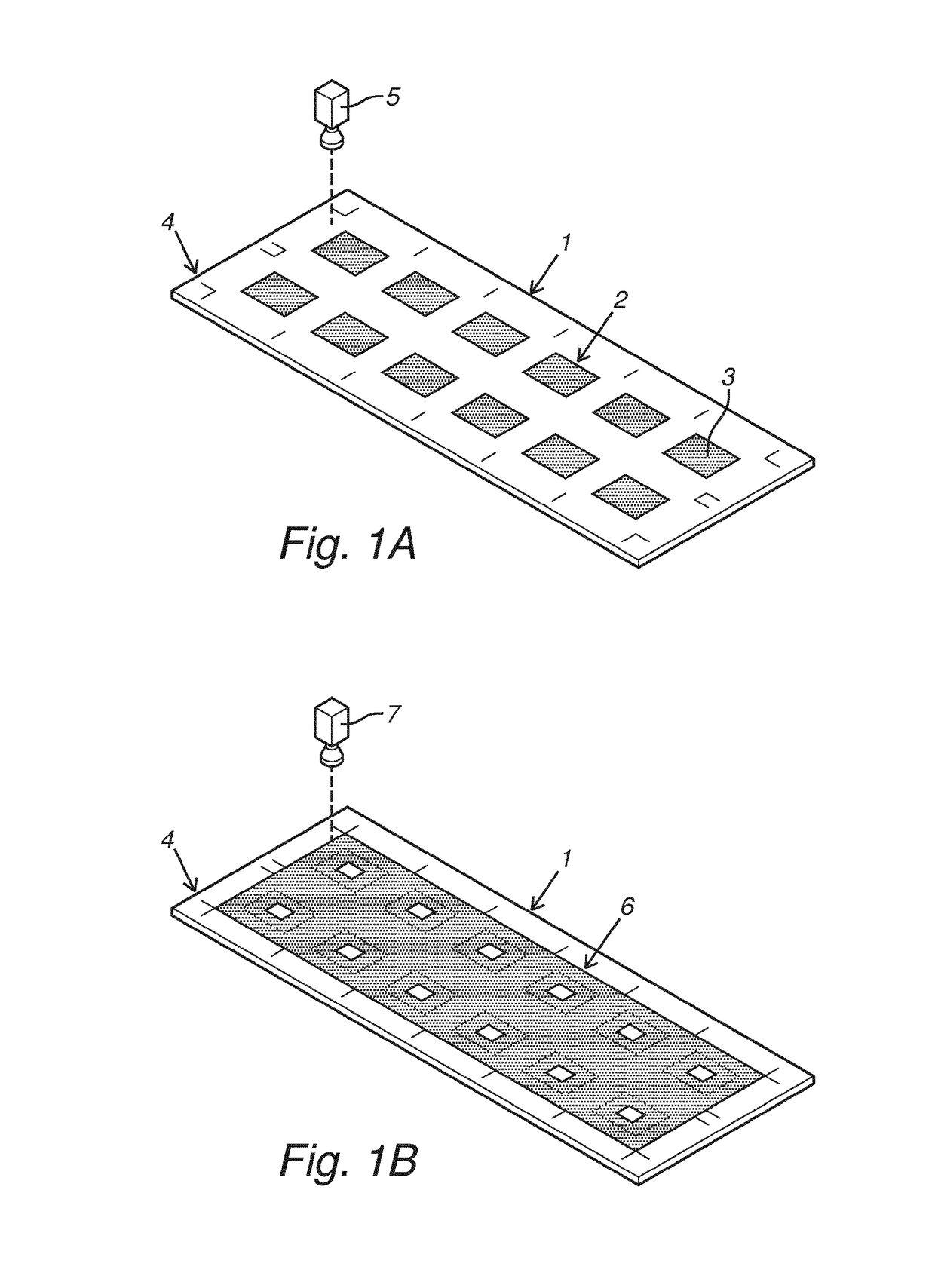
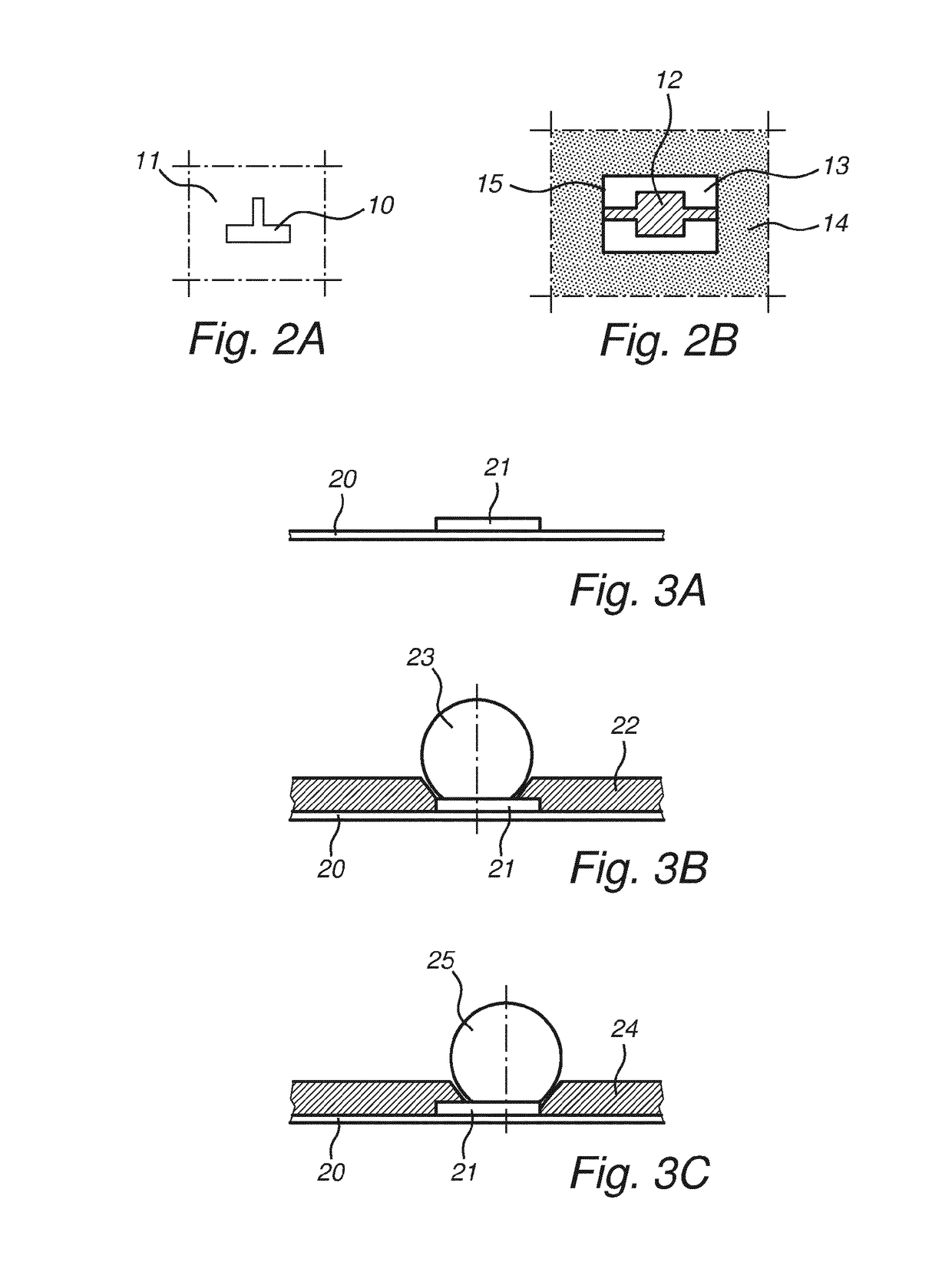
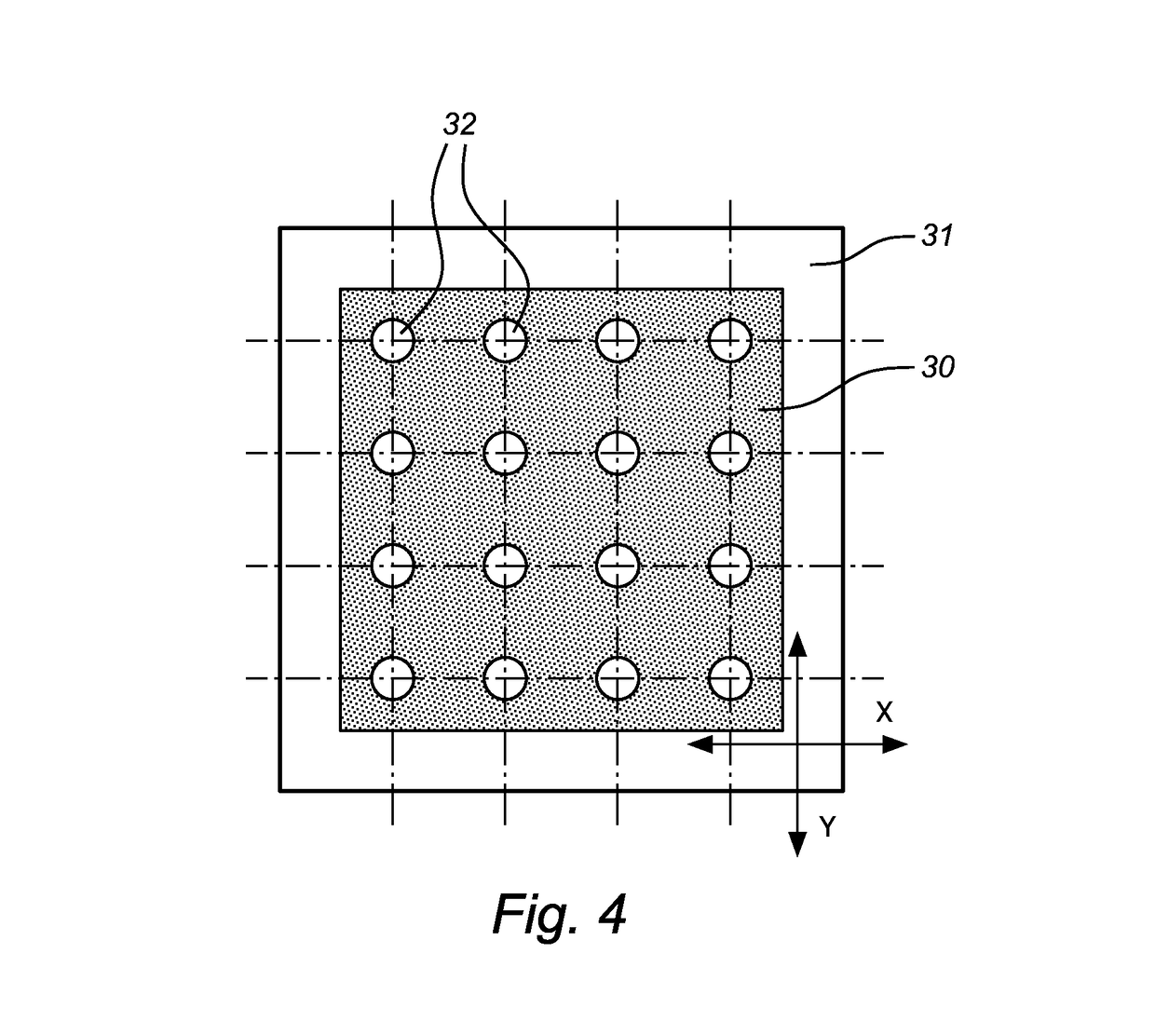
ActiveUS10217679B2Improve detection qualityHigh feasibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder maskElectronic component
The present invention relates to a method of processing a solder masked carrier with electronic components, comprising the detection of a carrier related reference and the detection of a solder mask dependent reference, which detected reference are used for processing the position of the solder mask on the carrier. The invention also relates to an electronic component as produced with such method.
Owner:BESI NETHERLANDS BV
Top tri-metal system for silicon power semiconductor devices
InactiveUS8426971B2Low costHigh of tendencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal silicideScratching
Owner:DIODES INC
Method for the treatment of a surface of a metal-carbide substrate for use in semiconductor manufacturing processes as well as such a metal-carbide substrate
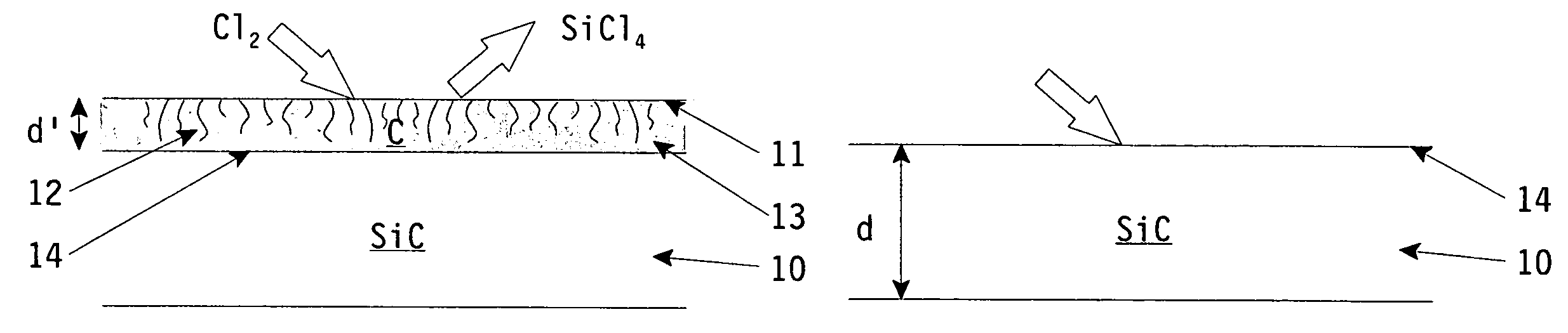
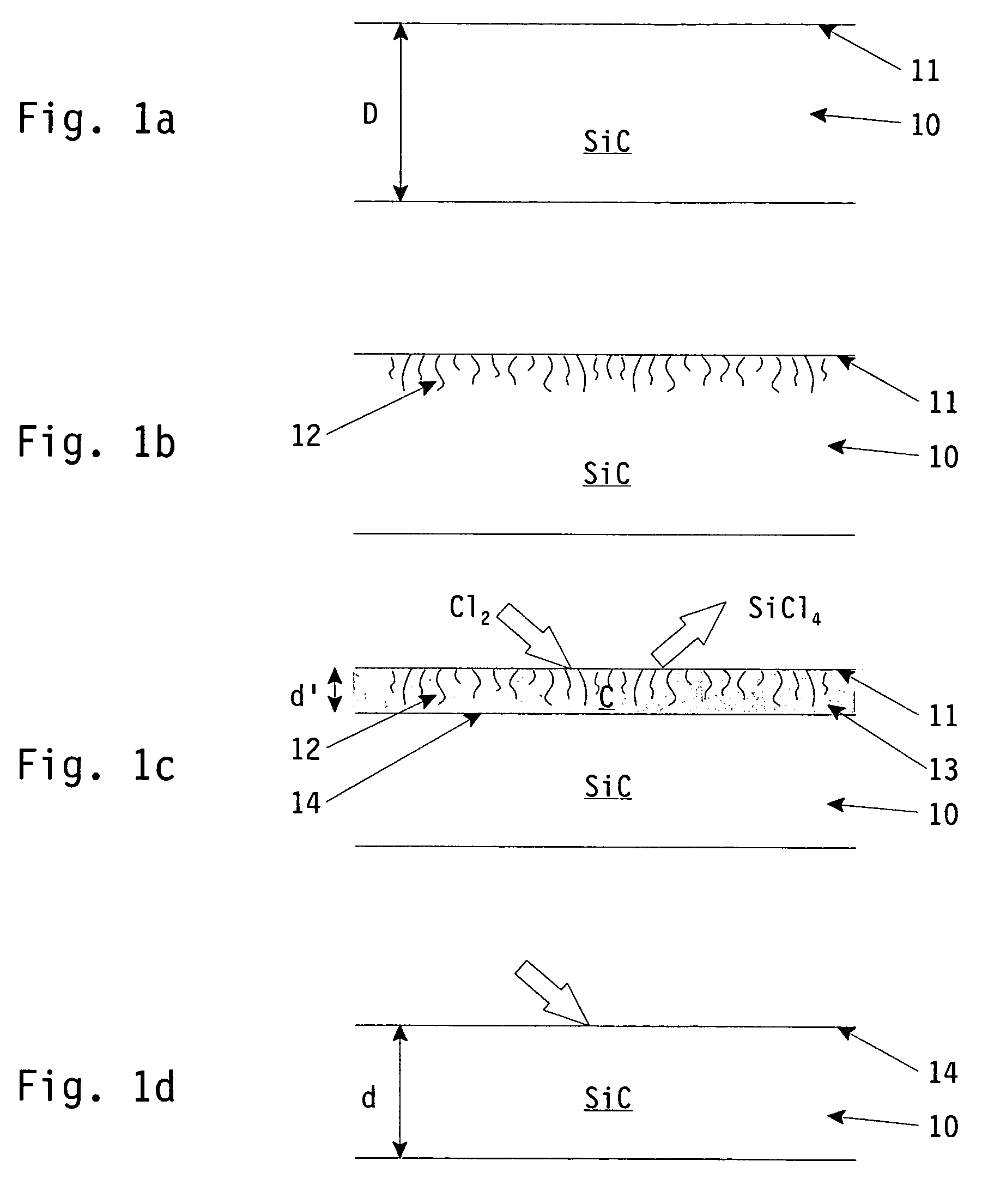
ActiveUS7723155B2High purityFew rejectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSurface layerReactive gas
The invention relates to a method for the treatment of a surface of a silicon carbide (SiC) substrate, said substrate being used in semiconductor manufacturing processes. The invention also relates to a SiC substrate for use in semiconductor manufacturing processes treated with the method according to the invention. According to the invention, said method comprising the steps of selective etching the surface of said SiC substrate using a reactive gas mixture, thereby creating a carbon surface layer on said substrate, and removing said carbon surface layer being created on said substrate. Thus, with the method steps according to the invention, SiC substrates can be obtained with a surface structure that complies with the highest standards as regard to dimensions and purity as required in semiconductor manufacturing processes. In particular, SiC substrates treated according to the steps of the invention are highly suitable for use as wafer boats for handling and containing semiconductor wafers on which subsequent treatment process steps of the semiconductor manufacturing processes (such as semiconductor layer deposition or temperature annealing) are performed under accurate, well controlled working conditions (temperature, pressure and vacuum).
Owner:XYCARB CERAMICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com