Patents
Literature
30results about How to "No need to increase the number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
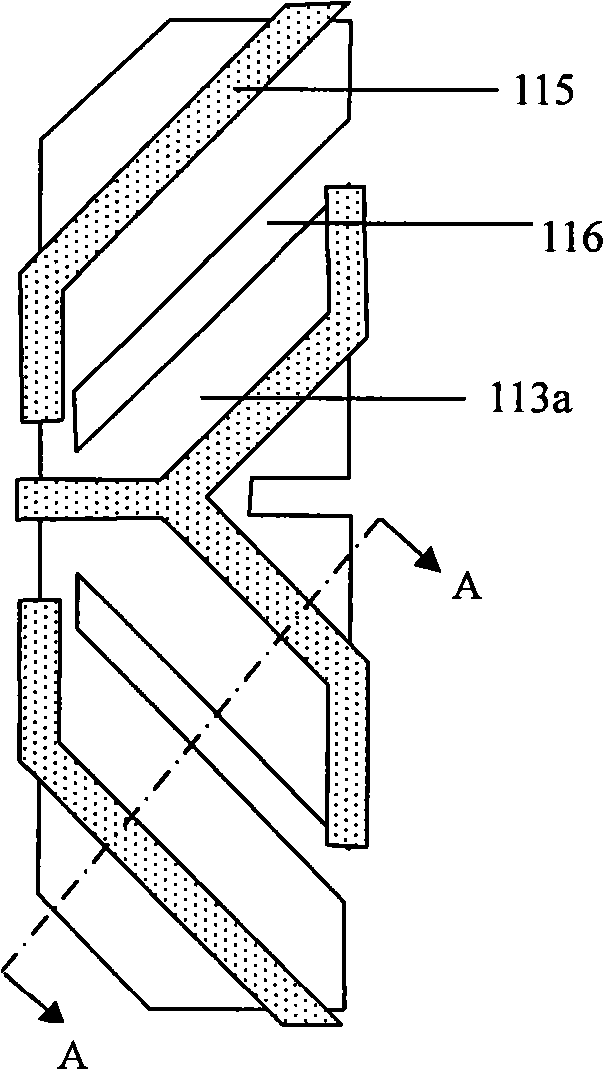
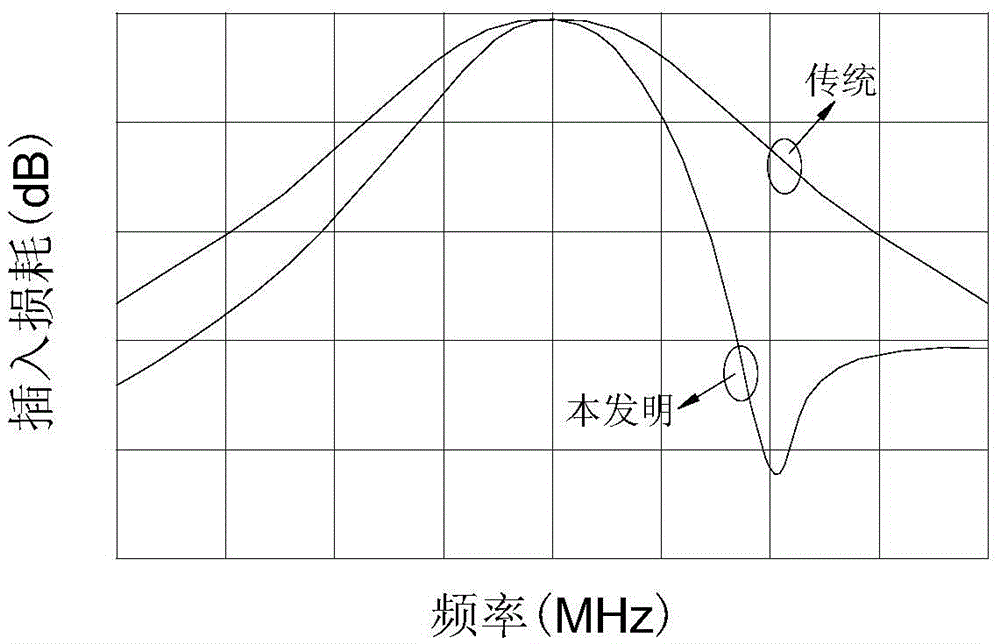
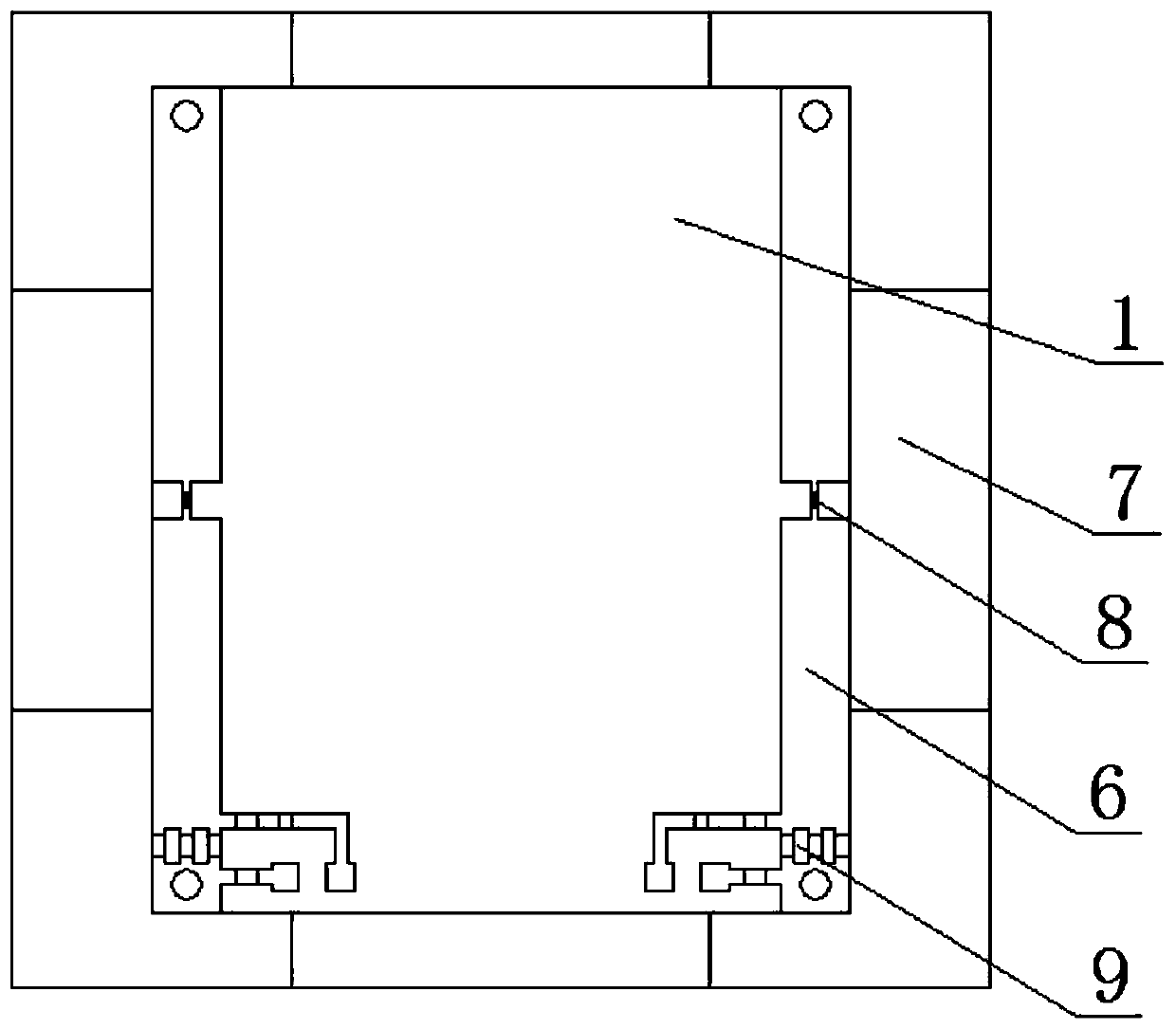
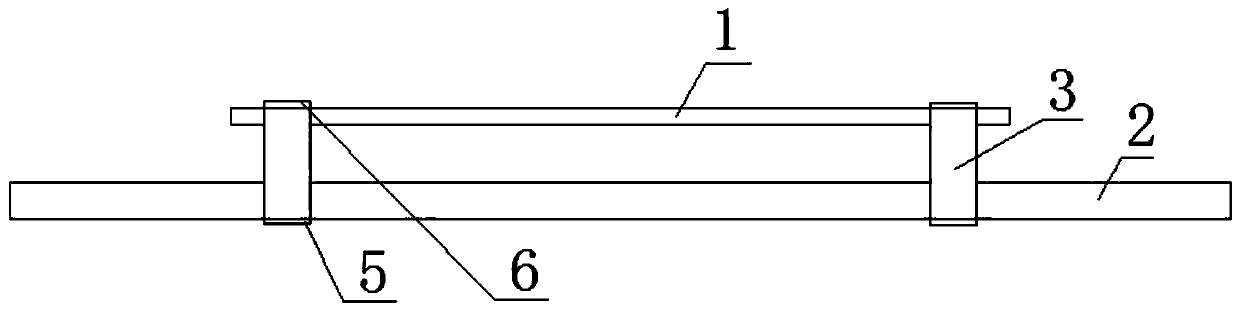
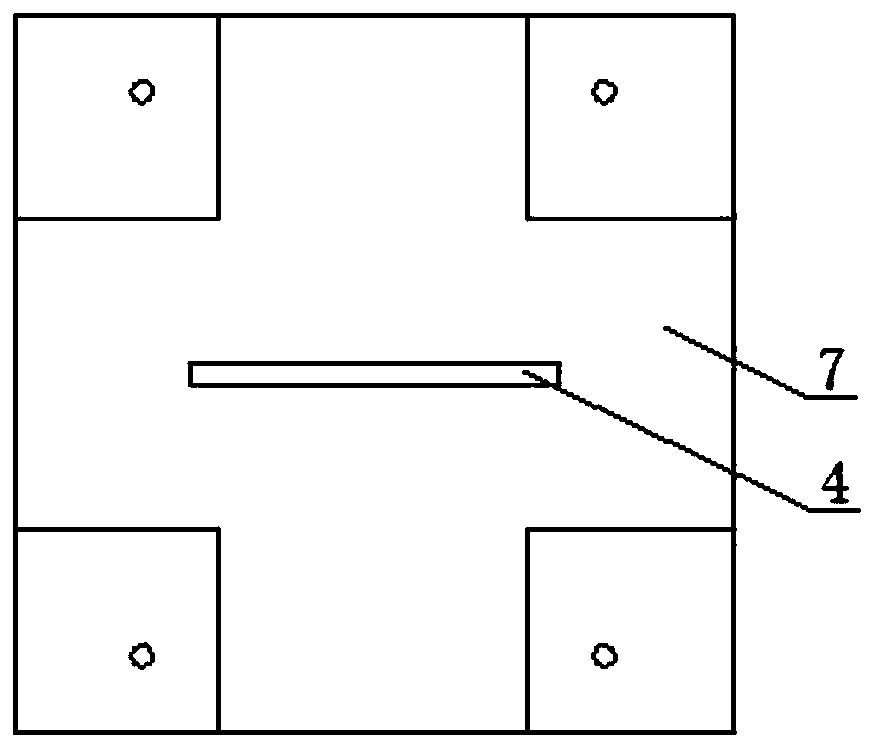
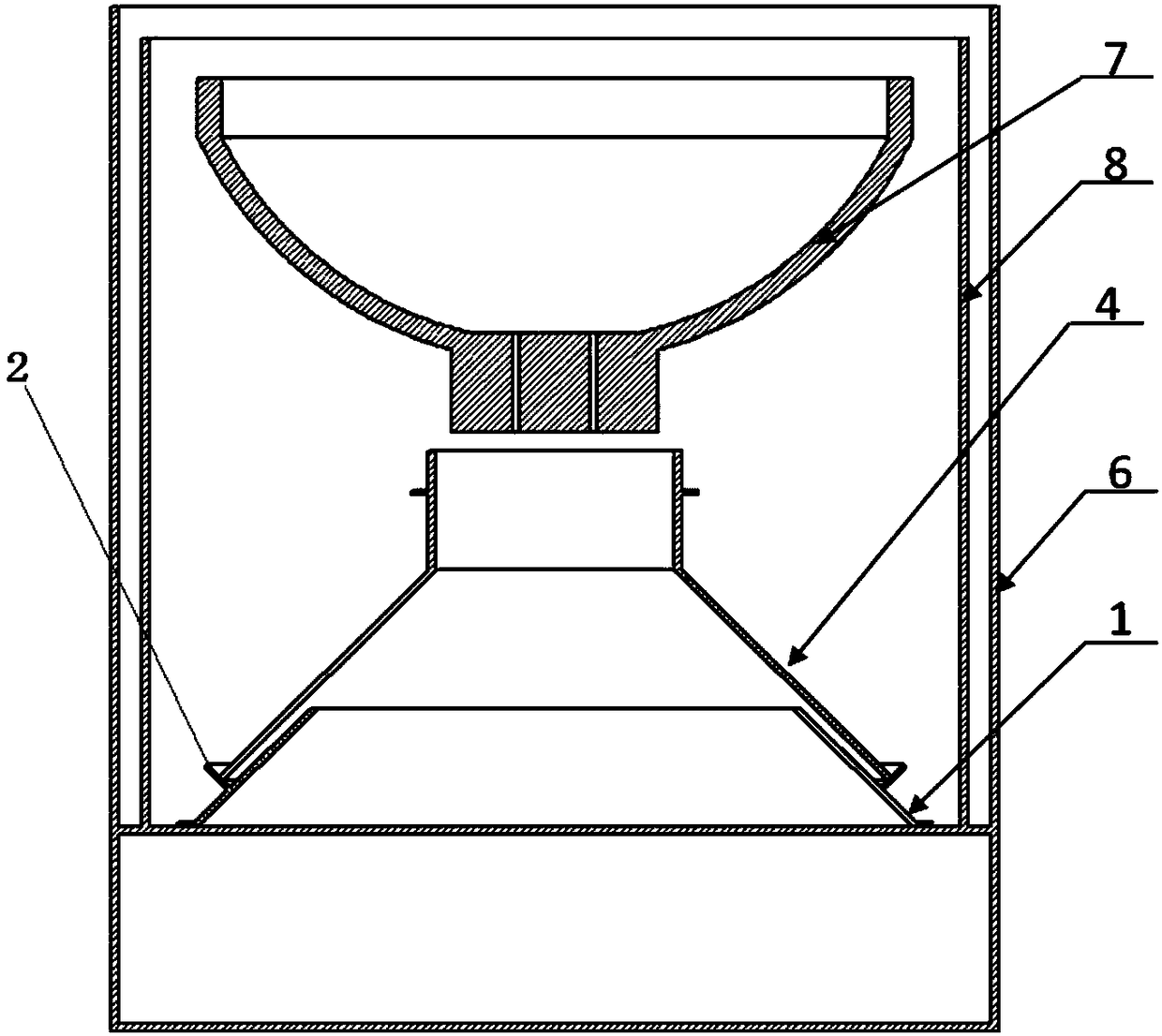
Substrate integrated waveguide filter
InactiveCN103904392AHigh selectivityNo need to increase the numberWaveguide type devicesUltrasound attenuationResonant cavity
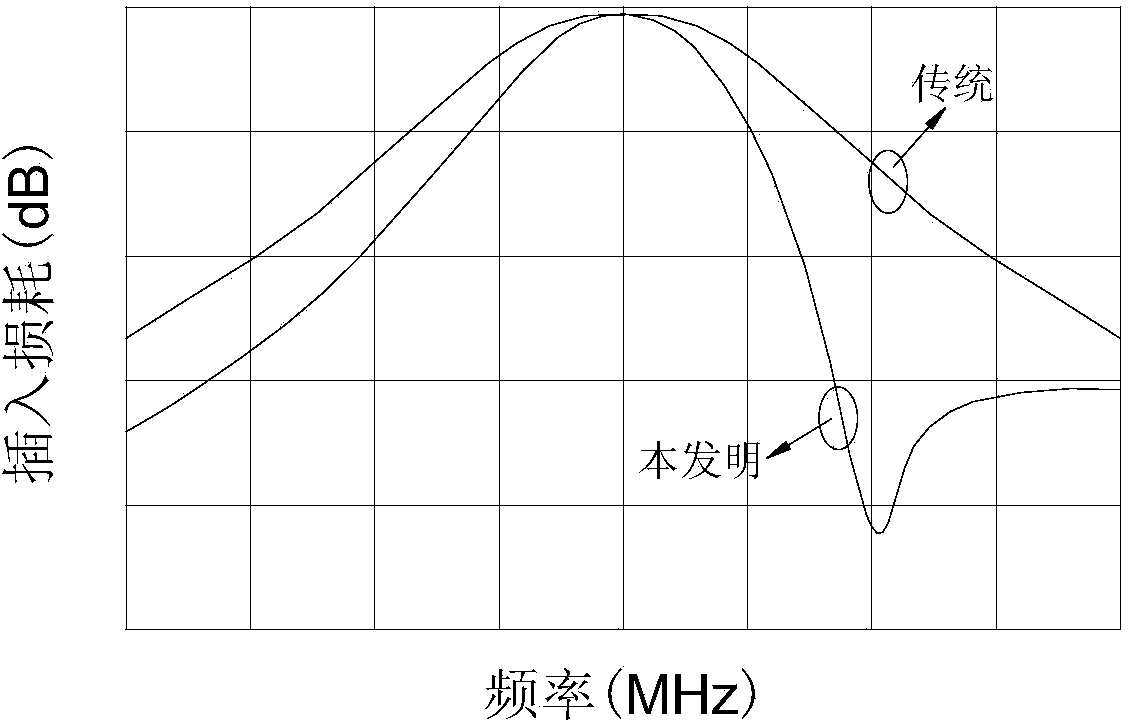
The invention discloses a substrate integrated waveguide filter which is high in selectivity, small in size and low in loss. The substrate integrated waveguide filter comprises a first metal layer, a first dielectric substrate, a second dielectric substrate, a second metal layer and a metallization through hole array, the first metal layer, the first dielectric substrate, the second dielectric substrate, the second metal layer and the metallization through hole array are sequentially stacked from top to bottom, and a first band-shaped coupling unit and a second band-shaped coupling unit are arranged between the first dielectric substrate and the second dielectric substrate. By means of the substrate integrated waveguide filter, the LTCC technology is adopted for integrating the band-shaped coupling units into resonant cavities of the substrate integrated waveguide filter, a signal transmission channel can be added without increasing the number of the resonant cavities, a transmission null point can be accordingly obtained in an attenuation band, and the selectivity of the filter is improved; meanwhile, the position of the transmission null point can be flexibly controlled by adjusting the resonant frequencies of the band-shaped coupling units, more stages of the resonant cavities are not needed, and the substrate integrated waveguide filter has the advantages of being small in size, light in weight and low in loss. The substrate integrated waveguide filter is suitable for popularization and application in the microwave millimeter wave technical field.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
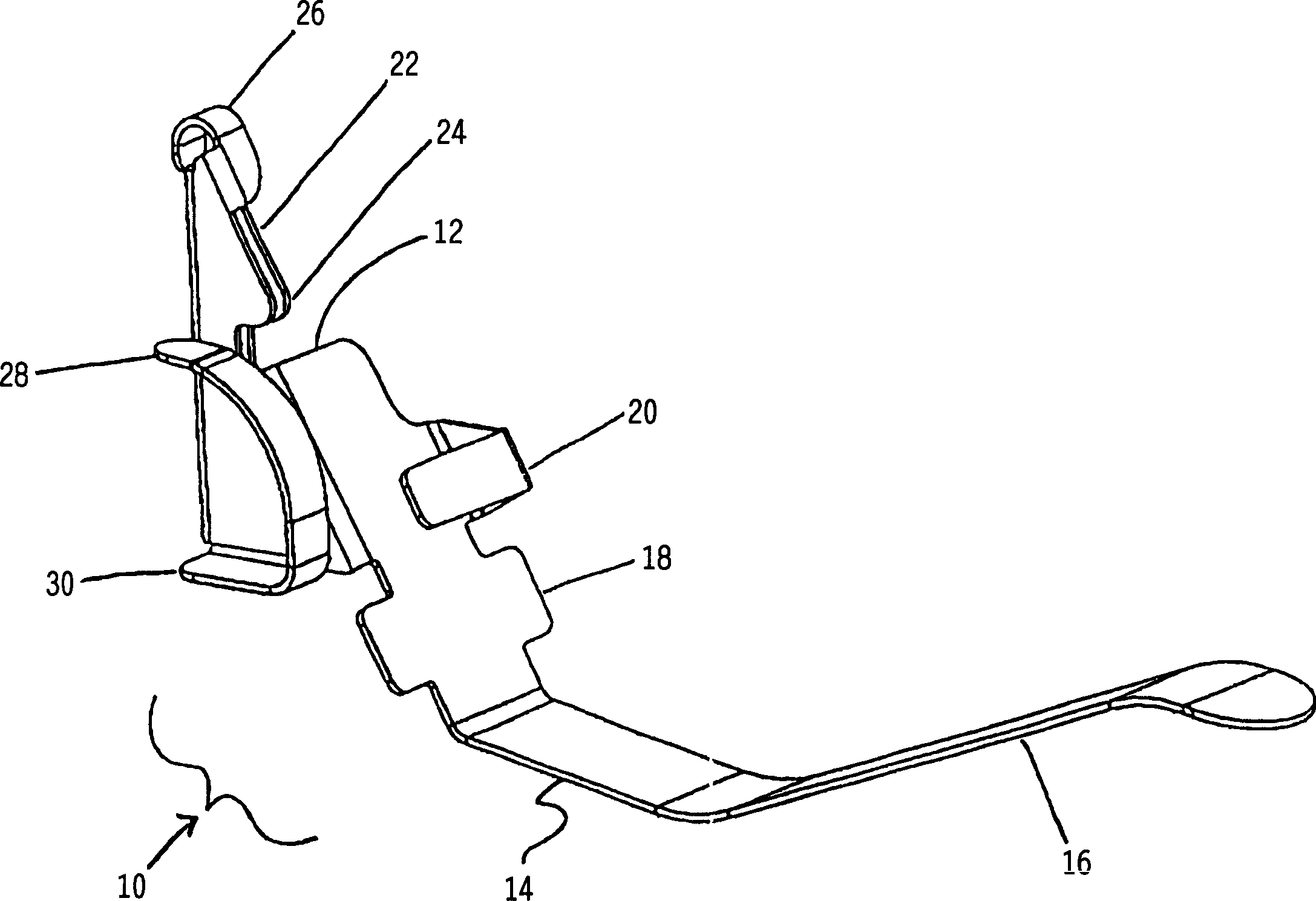
Antenna mounting structure
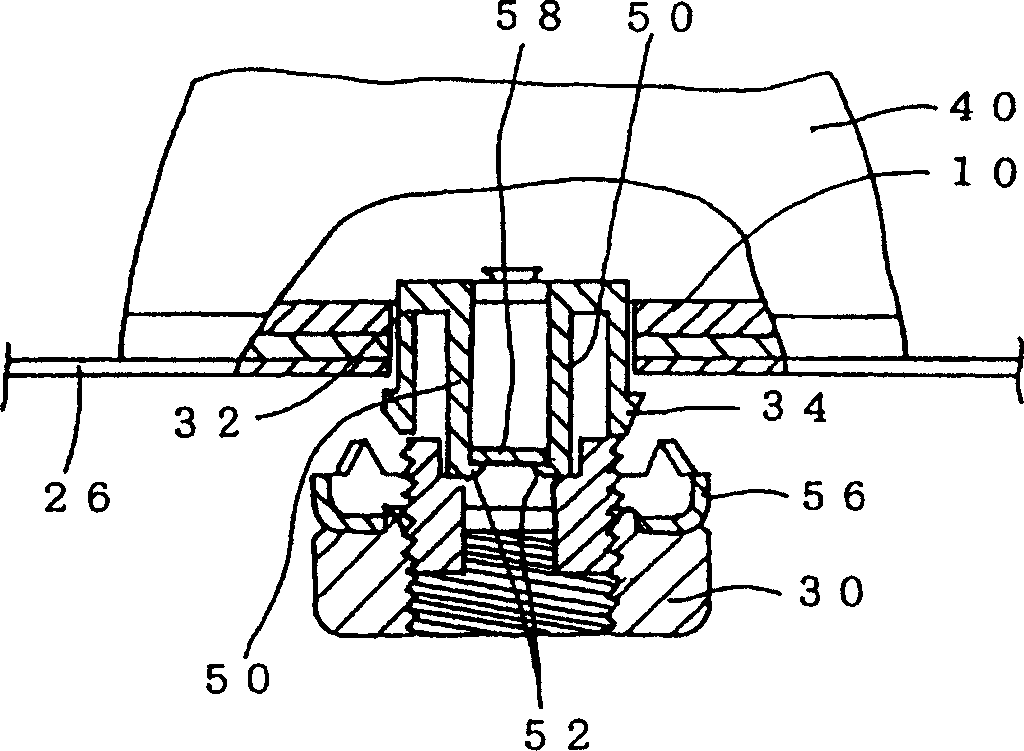
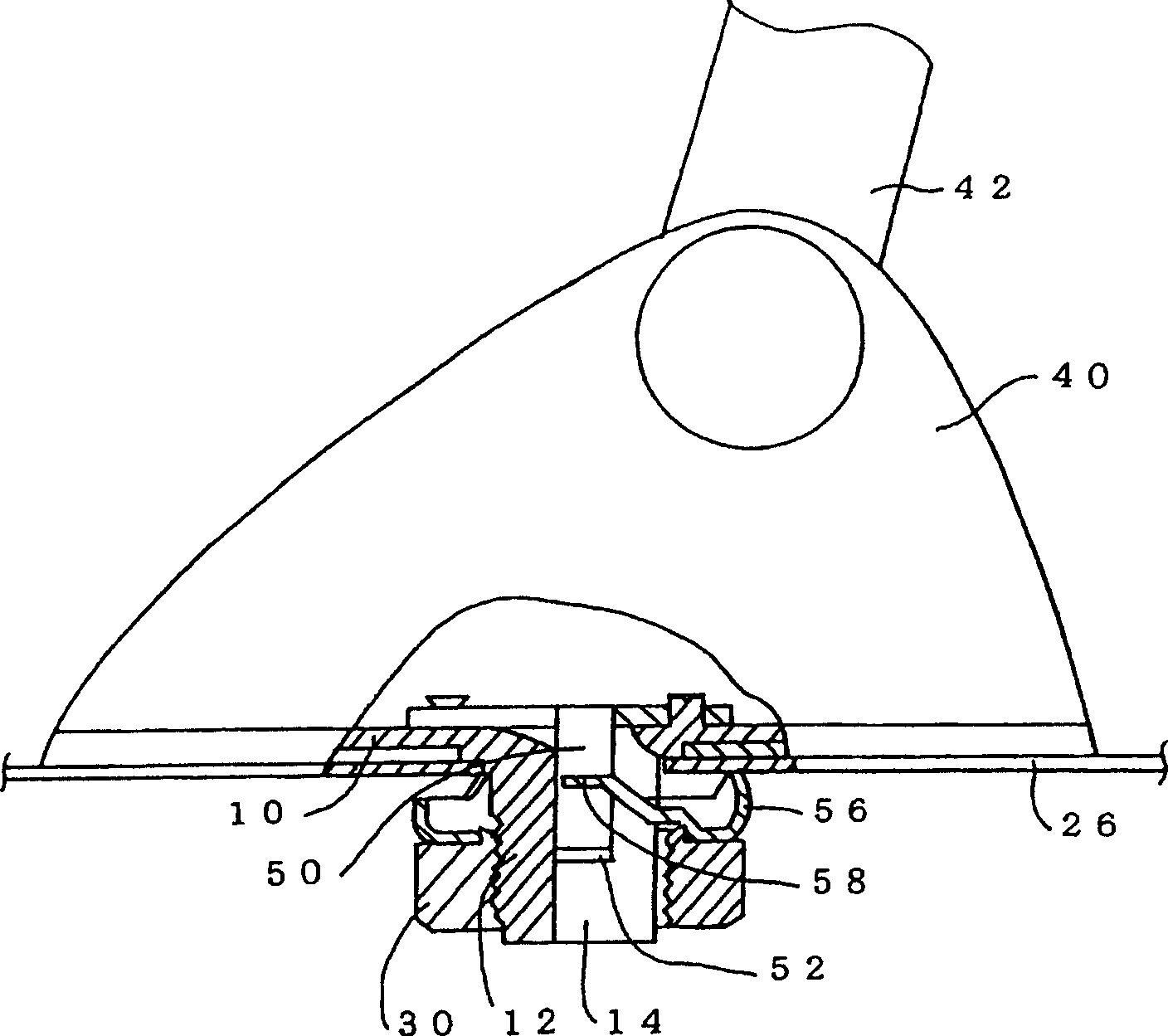
For mounting an antenna device on a first side of a panel body, a mount screw is protruded from the antenna device and formed with a slit extending from a distal end face thereof in an axial direction thereof. A washer has a first engagement member extended from a main body The washer is adapted to be fitted with the mount screw such that the first engagement member is inserted into the slit from the distal end face of the mount screw in a first direction. A second engagement member is provided in the slit, and elastically deformable so as to allow the first engagement member to move within the slit in the first direction. The second engagement member is adapted to engage with the first engagement member at a first position within the slit so as to prevent the first engagement member from moving in a second direction which is opposite to the first direction. A nut is adapted to be screwed to the mount screw while being interconnected with the washer.
Owner:YOKOWO CO LTD
LCD device with multi-domain vertical orientation mode
InactiveCN101256330AReduce the numberNo need to increase the numberNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
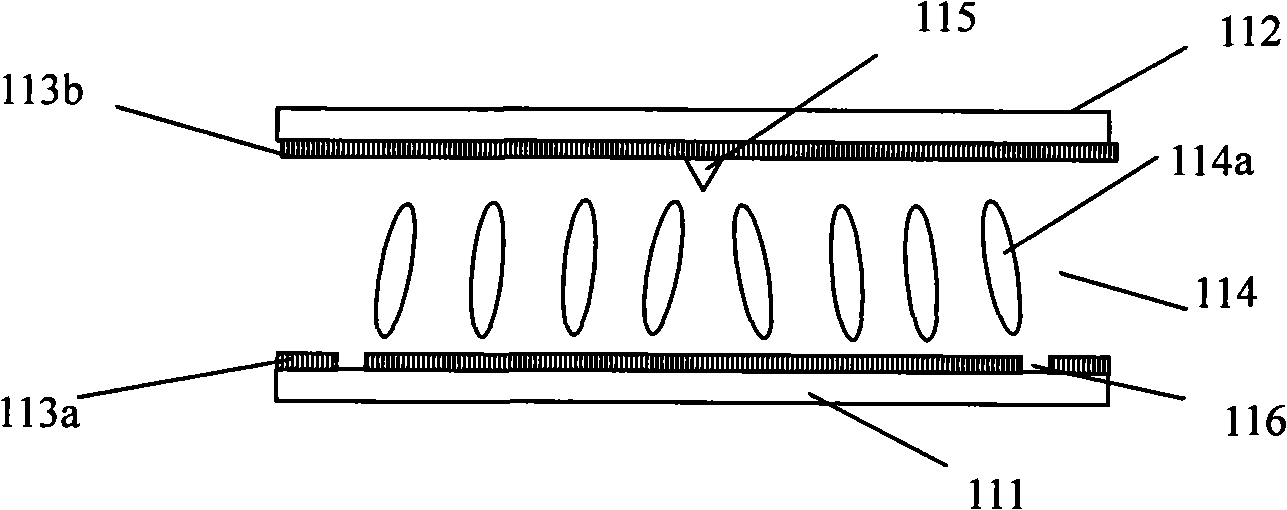
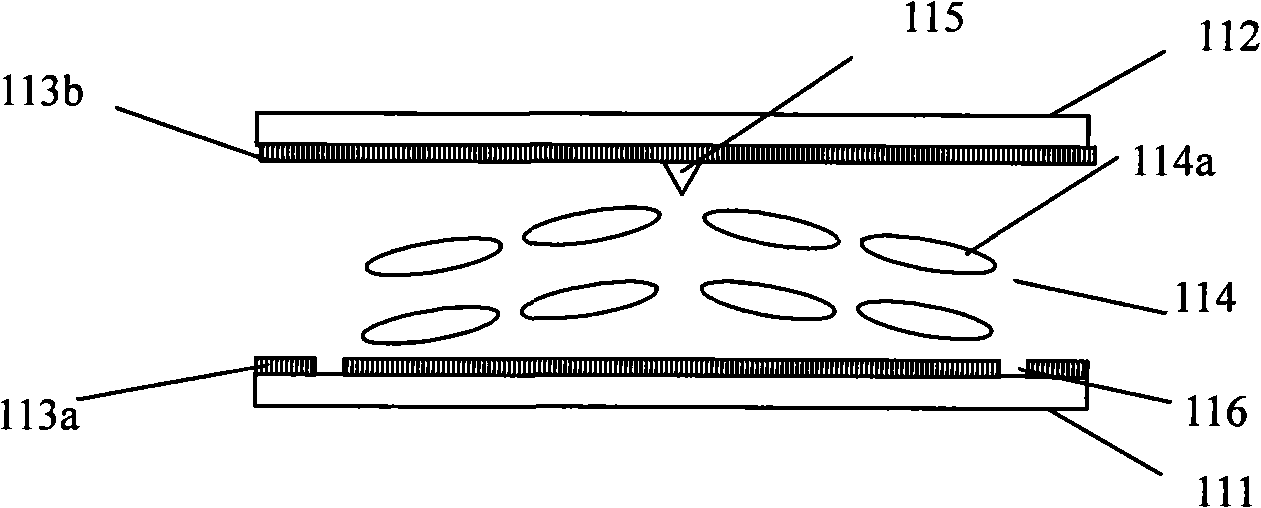
The invention relates to a liquid crystal display device of polydomain vertical orientation mode, comprising a first substrate and second substrate oppositely disposed; a liquid crystal layer between the first substrate and second substrate; a pixel electrode formed on the first substrate; a common electrode formed on the second substrate; a groove or protrusion graved on the pixel electrode or common electrode; a first protrusion and second protrusion alternatively oppositing to the said groove or protrusion on the pixel electrode or common electrode; the first protrusion having first height and the protrusion having second height and the first height is higher than the second height and the first protrusion being alternatively arranged with the second protrusion. The liquid crystal display device can realize 8-domain display without increasing the drive cost and reducing the production good ratio, in order to improve the aberration.
Owner:上海广电光电子有限公司
Screw-less mainframe board fixing device
InactiveCN1402104ANo need to increase the numberDigital data processing detailsSupport structure mountingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A fixer for fixing motherboard without screw is composed of head part for matching with motherboard, a tail part for matching with bottom plate, and a spring part for forcing its head part to match with motherboard. Its fixing method includes arranging one or more said fixer on bottom plate, pivoting their tail parts to bottom plate, matching their head parts with the installation holes on motherboard, and detachably locking the motherboard and bottom plate.
Owner:富骅企业股份有限公司
Display device
InactiveCN102737557ANo need to increase the numberImprove efficiencyPlanar/plate-like light guidesIdentification meansLight guideDisplay device
A display device includes: a casing configured by at least one chassis; a display arranged inside the casing; a light guiding plate arranged on a rear face side of the display and has an outer peripheral face at least a part of which is formed as an incident face on which light is incident; a light source unit including a light source arranged to face the incident face of the light guiding plate on a lateral side of the light guiding plate; and a heat dissipating member, to which the light source unit is attached, that dissipates heat generated when the light source is driven. The heat dissipating member or the light source unit is attached to the light guiding plate, and the heat dissipating member and the light source unit can be moved with respect to the chassis in accordance with expansion or shrinkage of the light guiding plate.
Owner:SONY CORP
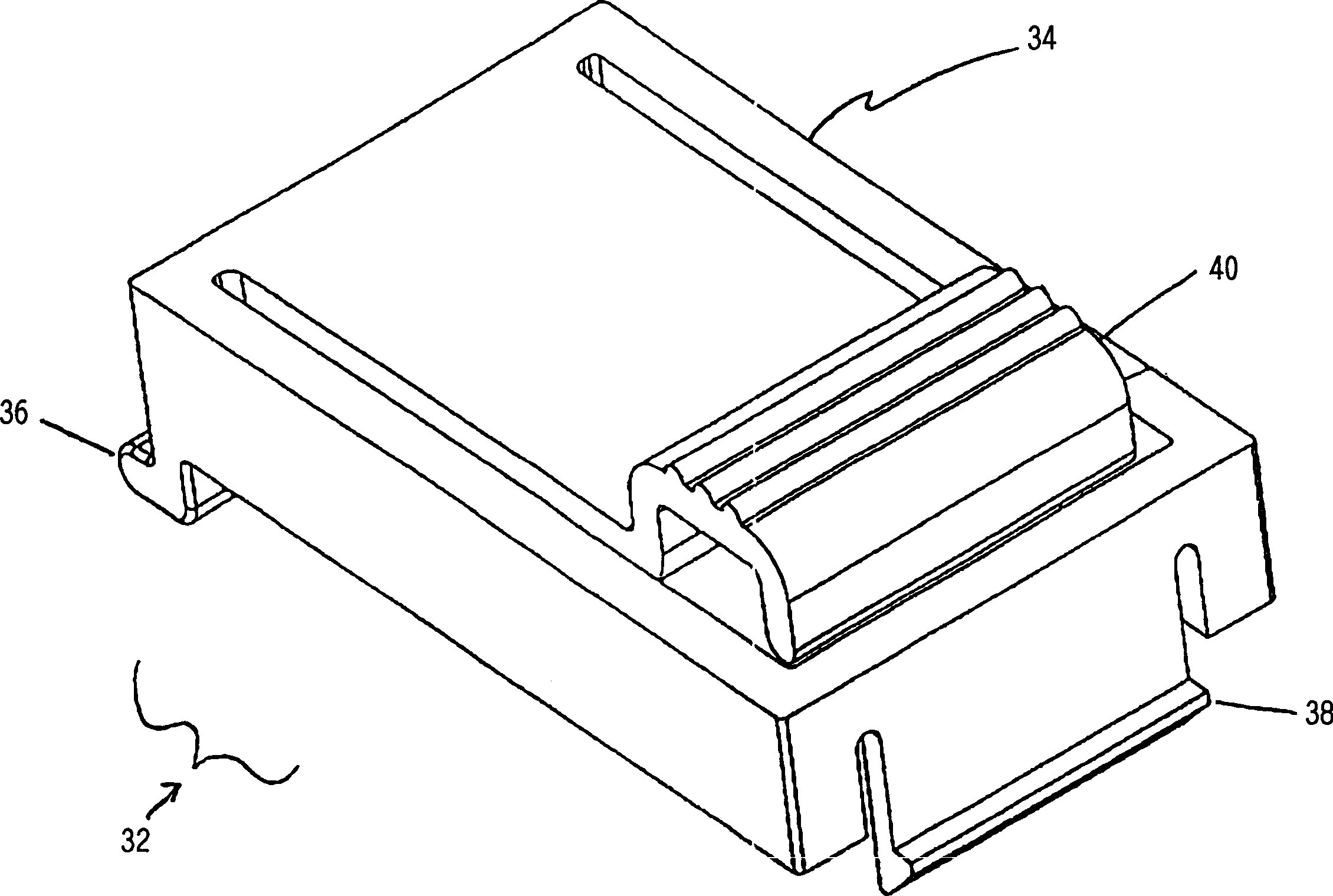
Ultrasonic sensor
InactiveCN102692623AAvoid deformationNo need to increase the numberWave based measurement systemsSound producing devicesTransceiverUltrasonic sensor
An ultrasonic sensor includes a transceiver block having a transceiver device for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves, and a circuit board mounted with an electronic circuit for processing ultrasonic signals transmitted and received through the transceiver device. A housing of the ultrasonic sensor includes a storing portion having an opening. The circuit board is stored within the storing portion, and the opening of the storing portion is closed by the transceiver block.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
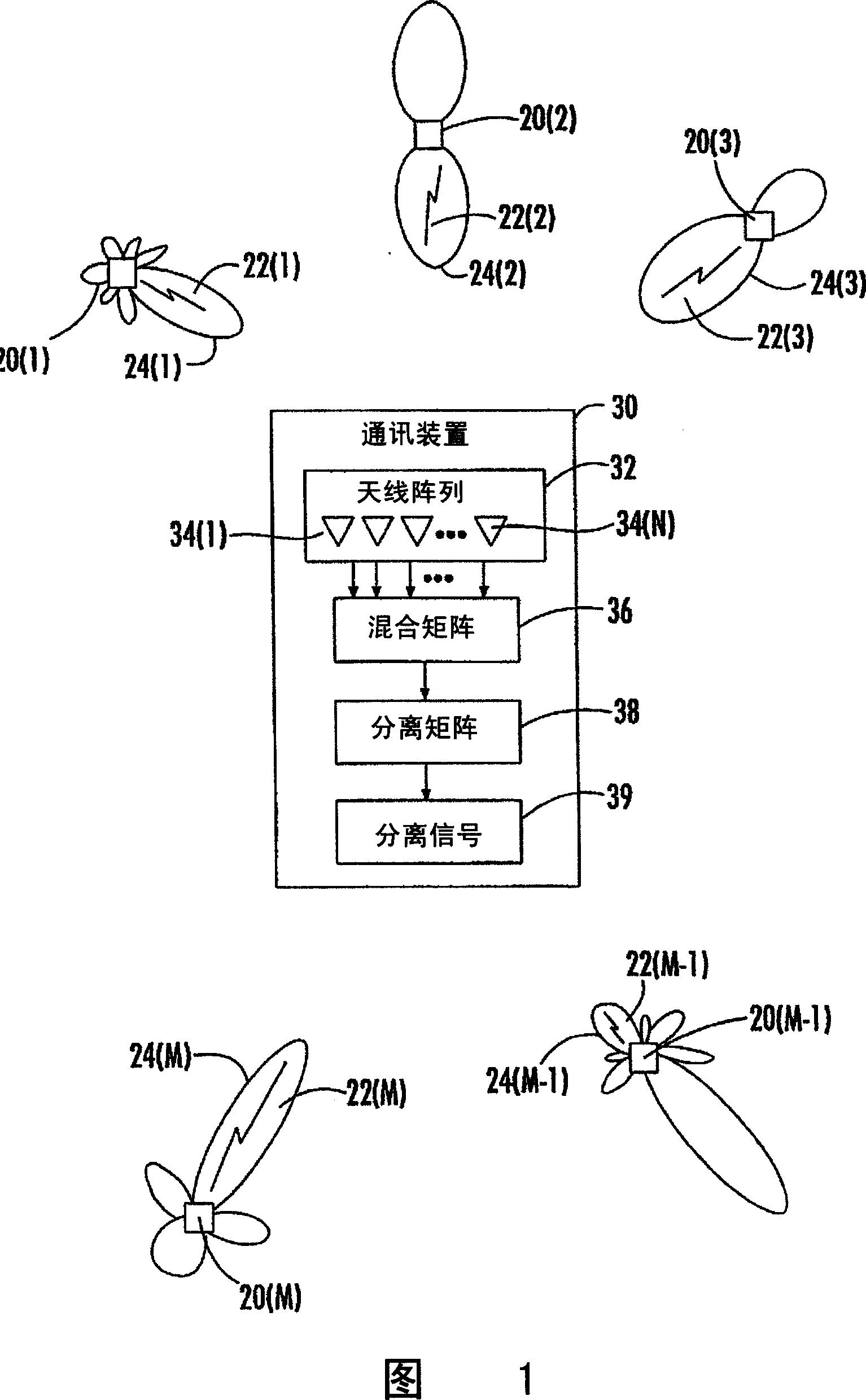
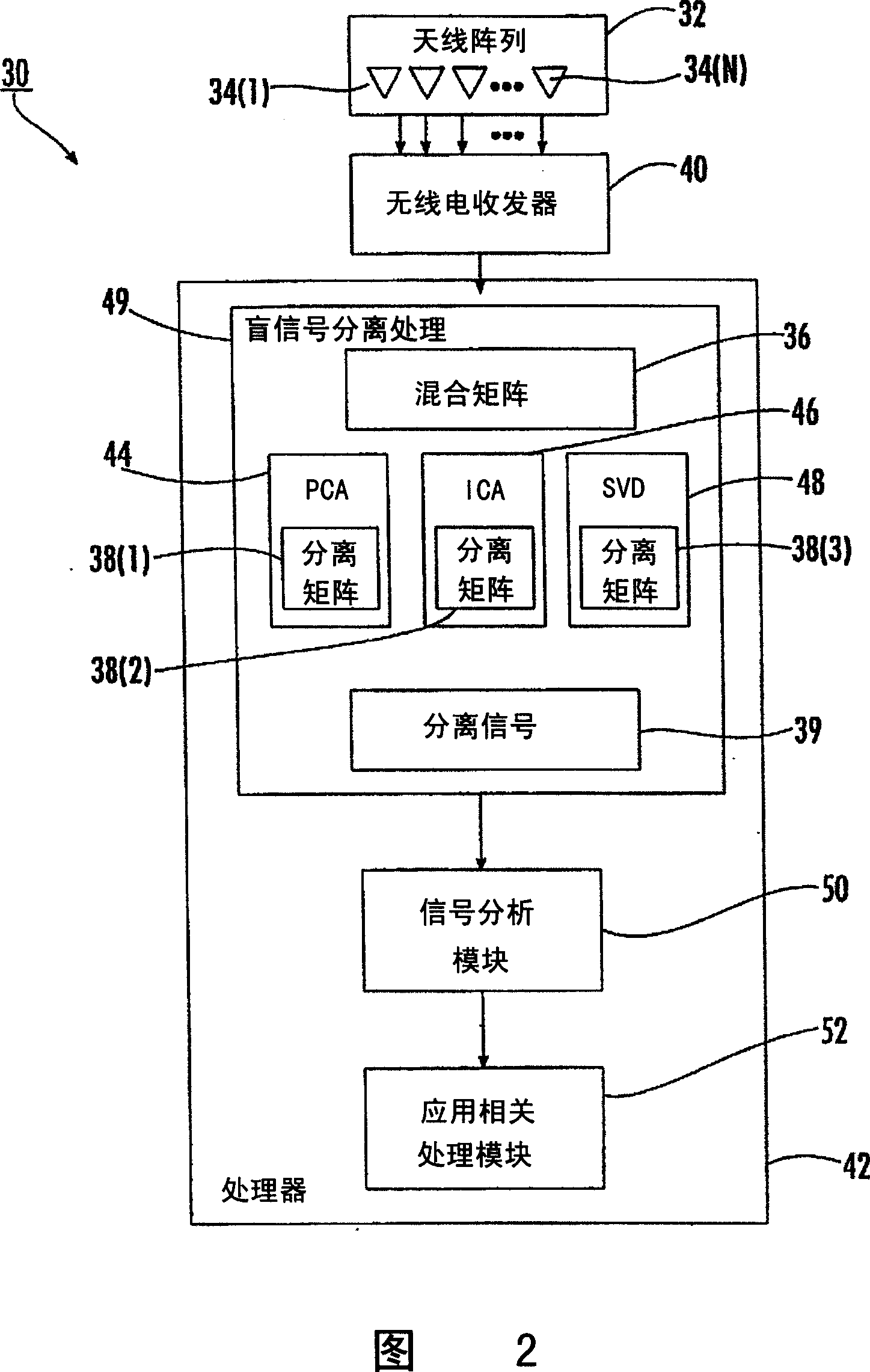
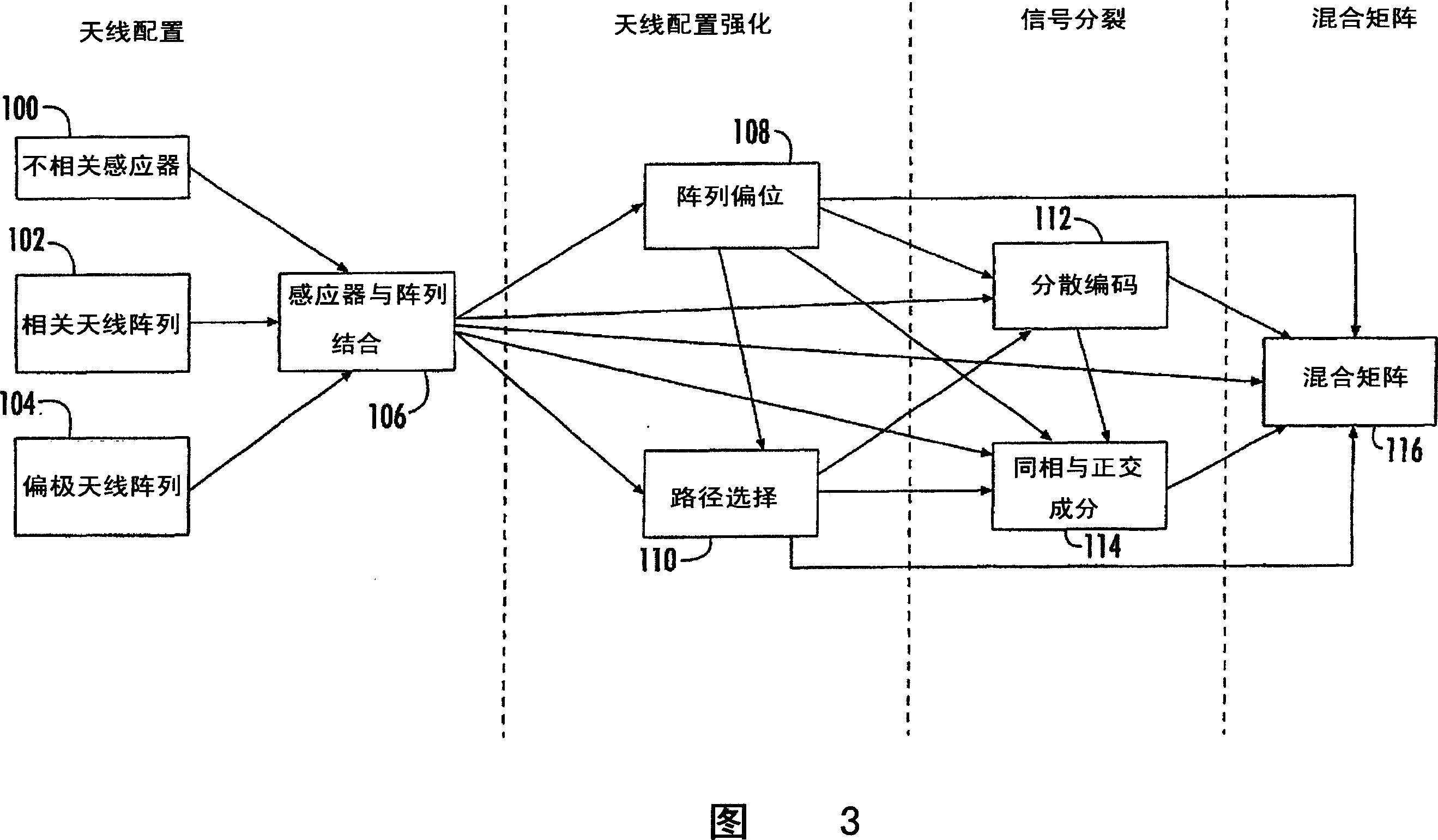
Blind signal separation using array deflection
A communications device for separating source signals provided by M signal sources includes an antenna array comprising N elements for forming at least N antenna beams for receiving at least N different summations of the M source signals, with N and M being greater than 2. A controller is connected to the antenna array for selectively forming the at least N antenna beams. A blind signal separation processor forms a mixing matrix comprising up to the at least N different summations of the M source signals. The blind signal separation processor also determines if the different summations of the M source signals are correlated or statistically independent, and if not, then cooperates with the controller for forming different beams for receiving new different summations of the M source signals to replace the different summations of the M source signals that are not correlated or statistically independent in the mixing matrix. The desired source signals are separated from the mixing matrix by the blind signal separation processor.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
A dual-rotor internal combustion engine
ActiveCN113027601BCompact structureEnough displacementInternal combustion piston enginesDifferential gearingsCombustion chamberGear wheel
The invention discloses a double-rotor internal combustion engine, which comprises a cylinder, a main shaft, left and right rotors, and a left and right intermittent motion mechanism. The cylinder includes an axially penetrating cylinder hole, the rotor includes blades and a support body, and the intermittent motion mechanism is a closed differential gear train including a non-circular gear pair, which can realize continuous and smooth shifting. The left rotor, right rotor and main shaft are located inside the cylinder and have coaxial rotation degrees of freedom. The blades of the two left and right rotors are radially juxtaposed, and the space between the blades constitutes a combustion chamber. The two rotors rotate periodically and intermittently during the ignition, power, exhaust, suction, and compression processes of the internal combustion engine, and the left rotor moves When the right rotor is stationary, the left rotor is stationary when the right rotor is moving. The left and right rotors transmit their respective intermittent rotations to the main shaft through the left and right intermittent motion mechanisms, and convert them into constant rotational speeds. Under the action of inertia, the main shaft feeds back its own rotation to the left and right rotors to control its acceleration, deceleration and static process.
Owner:杨文通
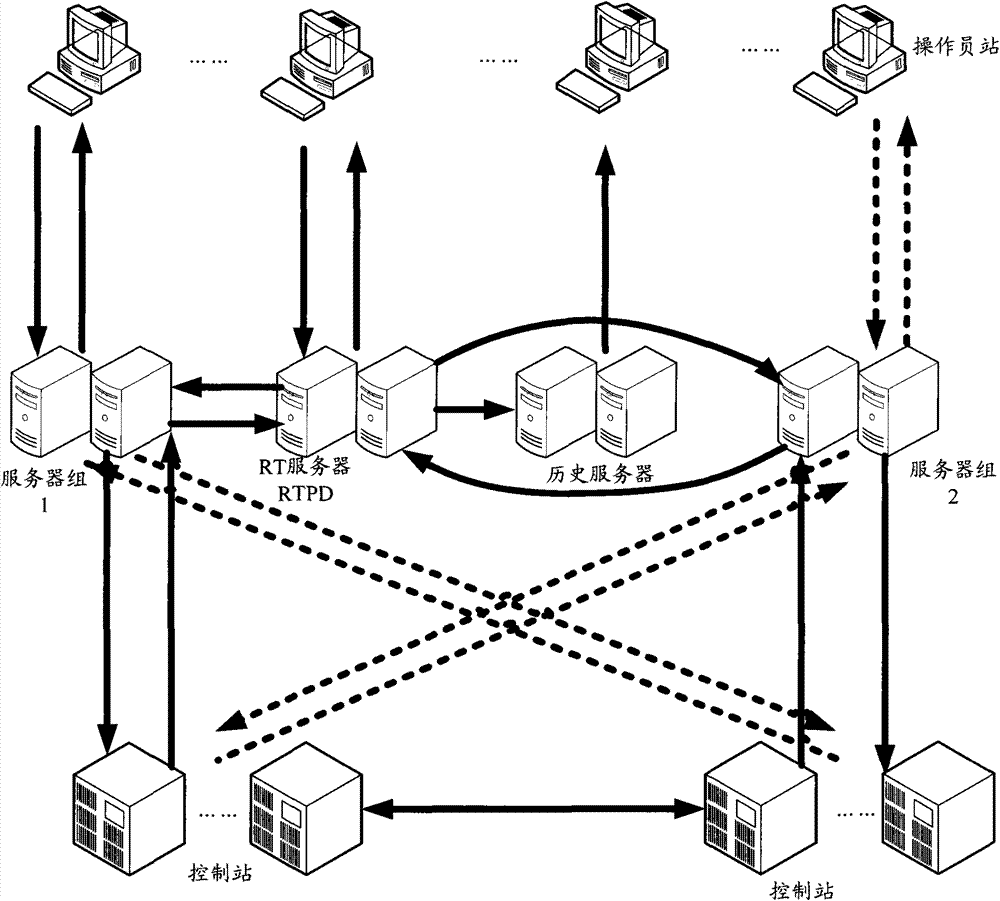
Data acquisition system and device thereof
ActiveCN101741616BRelieve stressNo need to increase the numberData switching networksCommunications systemData acquisition
The invention discloses a data acquisition system and a device thereof, belonging to the technical field of communication. The invention solves the problem of poor system stability due to frequent switching of an active / standby server in a data acquisition system in the prior art. The data acquisition system comprises at least two data acquisition servers, wherein at least two data acquisition servers form at least two server groups which are both under operation condition and acquire data from a control station in the management scope. The technical scheme of the invention can be applied to the communication system with high requirement for reliability.
Owner:北京和利时控制技术有限公司
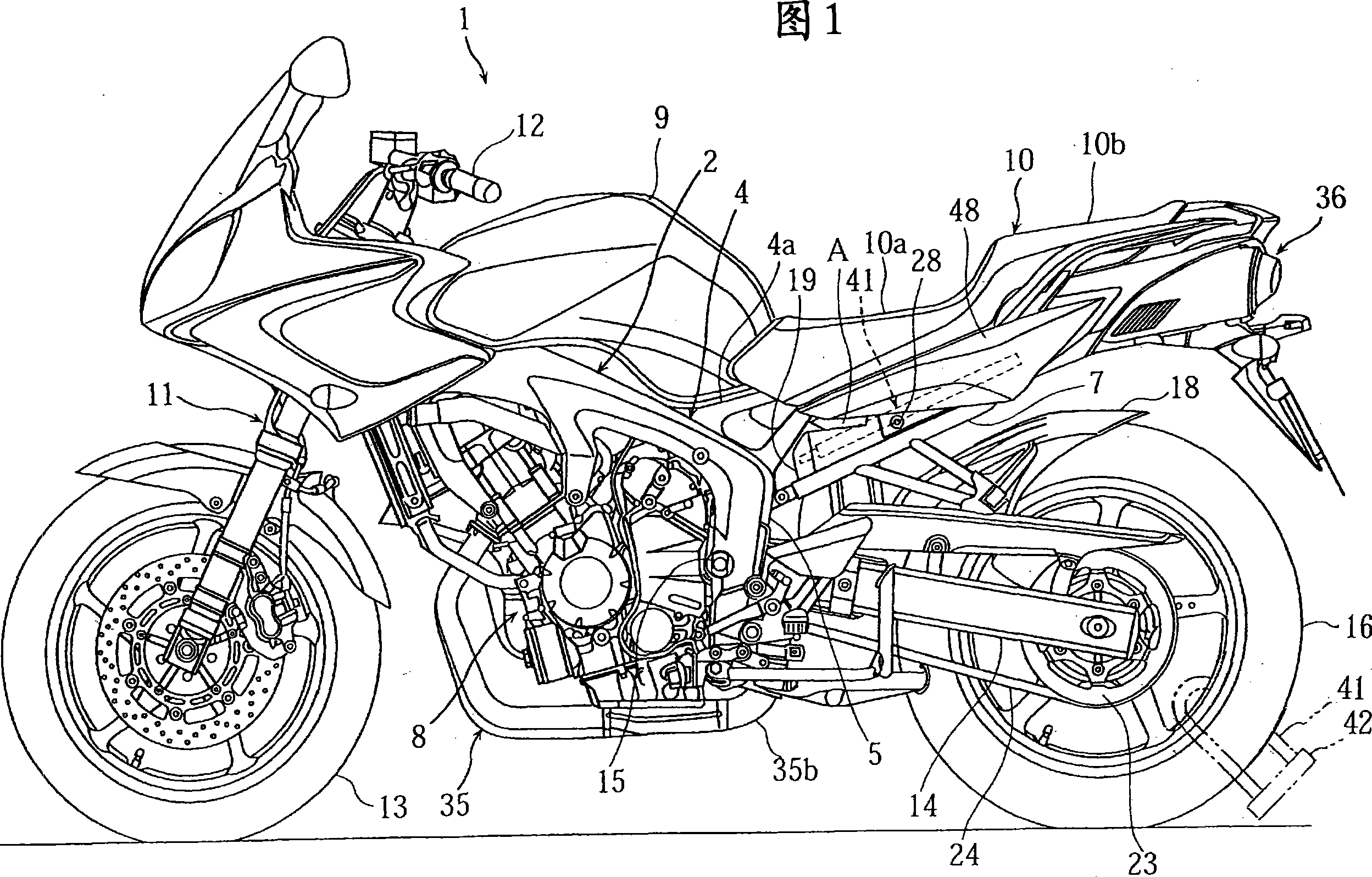
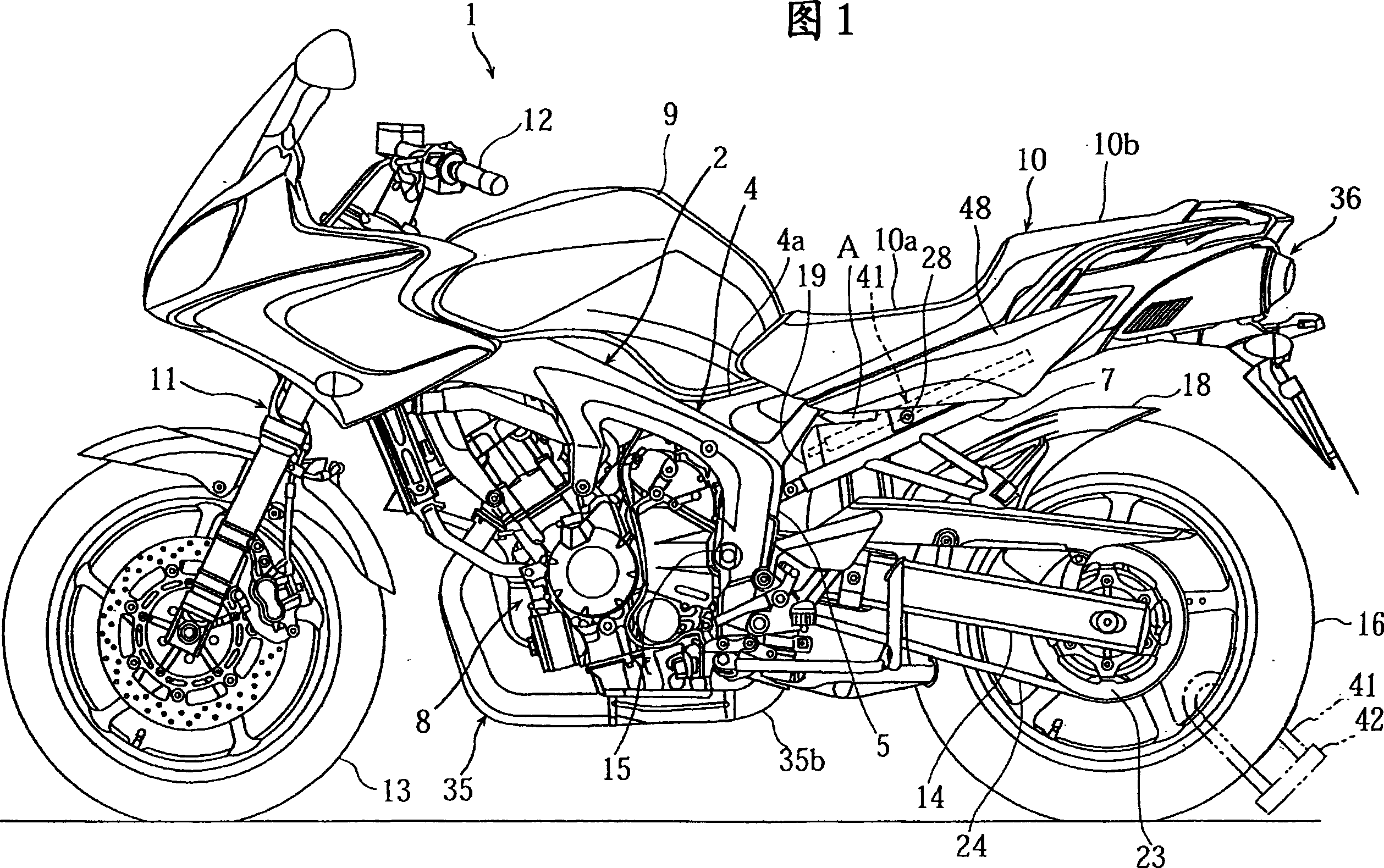
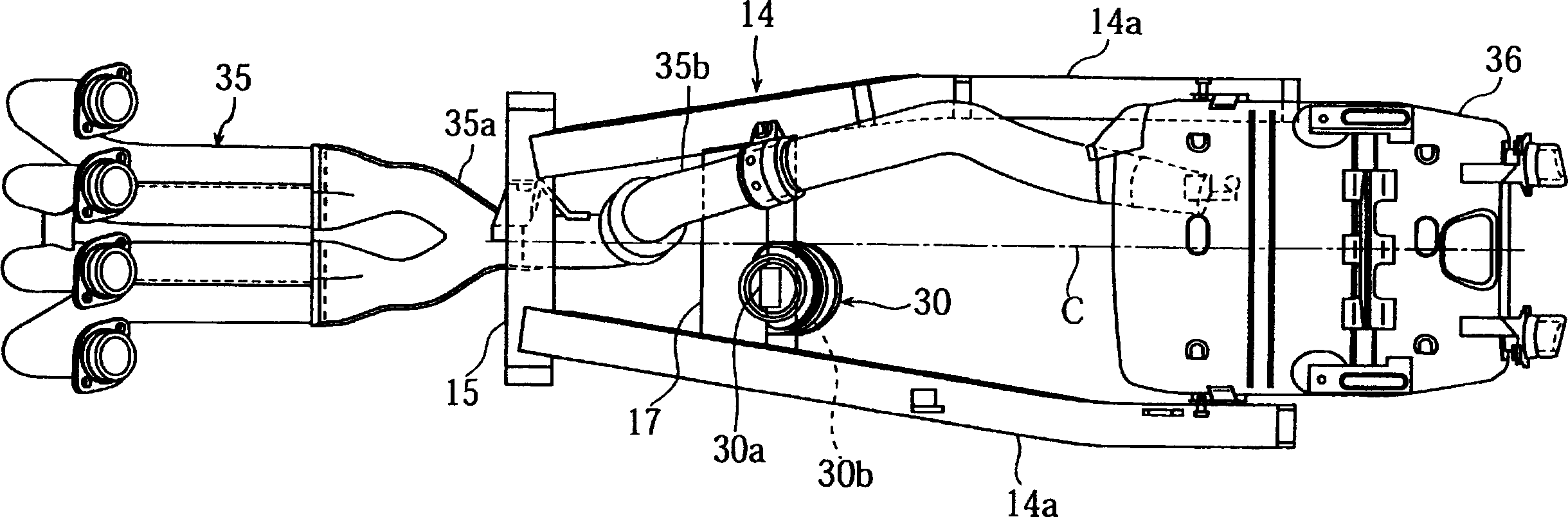
Motorcycle
InactiveCN101181918ALower the altitudeReduce thicknessAnti-theft cycle devicesMotorcyclesMufflerExhaust pipe
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Rotary valve
InactiveCN101608701BBalanced and Stable WorkReduce switching resistanceOperating means/releasing devices for valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyLow noiseRotary valve
The invention discloses a rotary valve, which comprises a stator, a rotor arranged in the stator, a driving mechanism for driving the rotor to rotate, and a sealing cover connected with the stator; a small gap exists between the stator and the rotor; a gas channel is arranged in the rotor; a high pressure gas buffer chamber and a low pressure gas buffer chamber are arranged in the circumferentialdirection of the rotor, and are respectively provided with a notch; the circumferential direction of the rotor is also provided with a groove communicated with the gas channel; and the stator is provided with a high pressure gas inlet communicated with the high pressure gas buffer chamber, a low pressure gas inlet communicated with the low pressure gas buffer chamber, and a gas trough communicated with the groove. The rotary valve can reduce the switching resistance between high pressure and low pressure in the rotary valve, improves switching efficiency, reduces the complexity of a rotary valve system, and has reliable operation, long service life and low noise.
Owner:LIHAN CRYOGENICS
Waterproof type electronic device
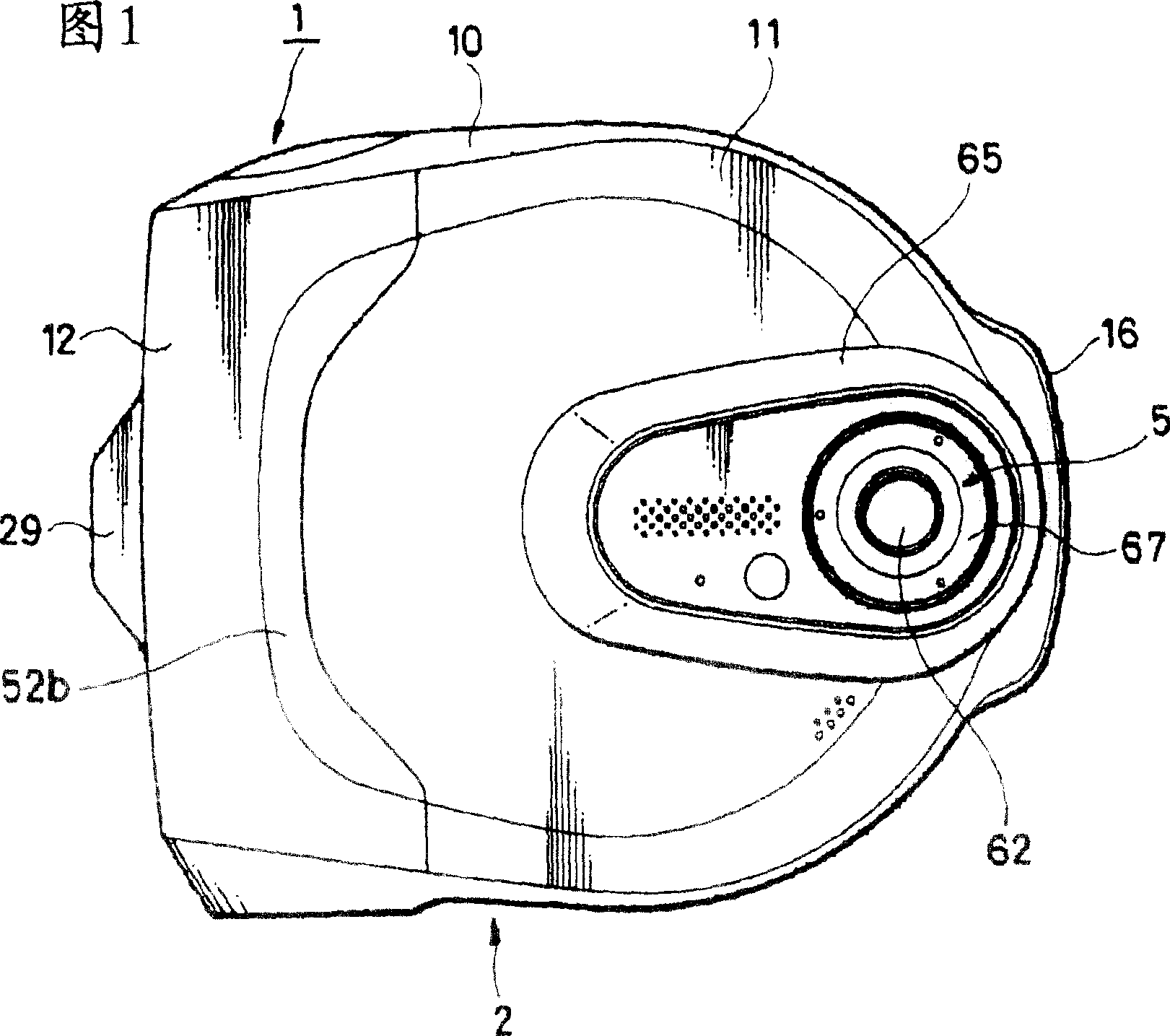
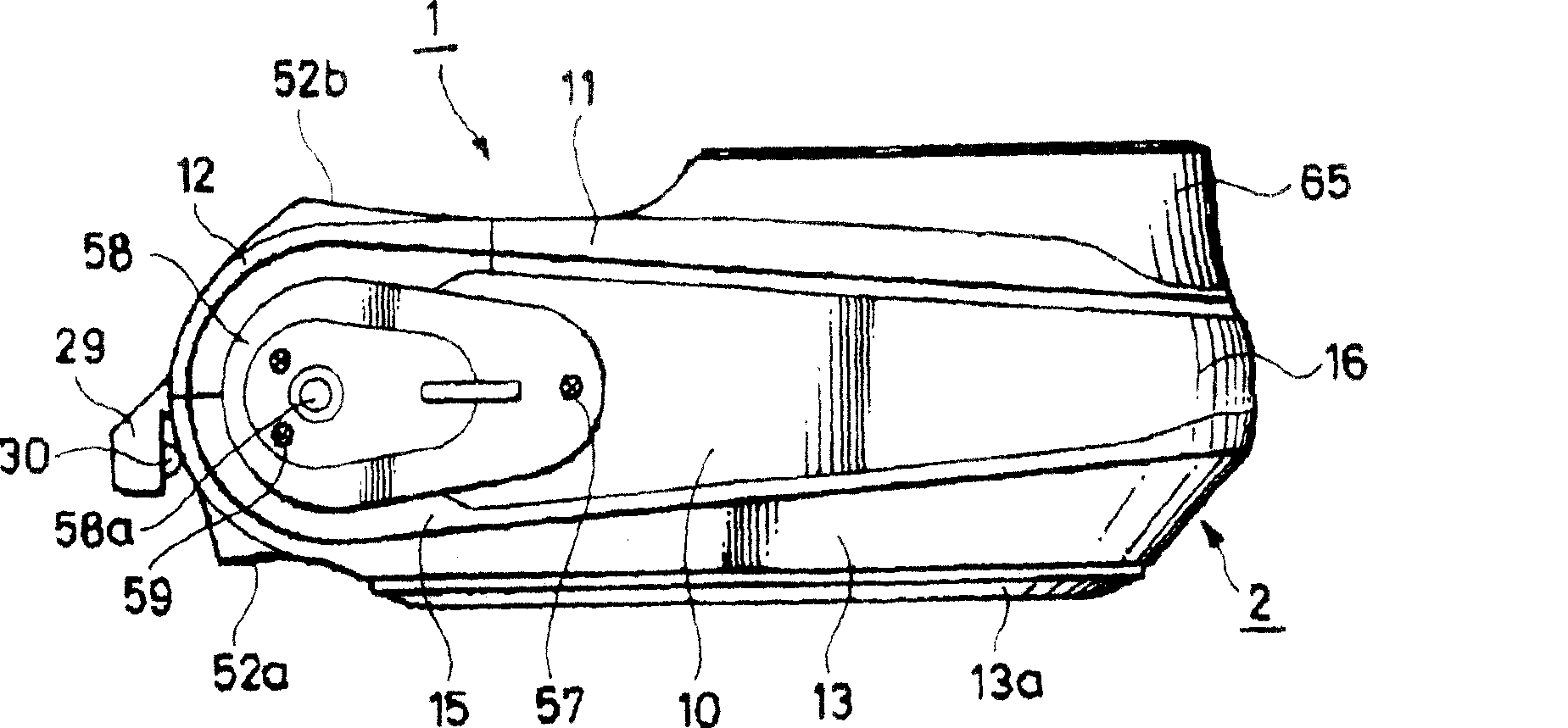
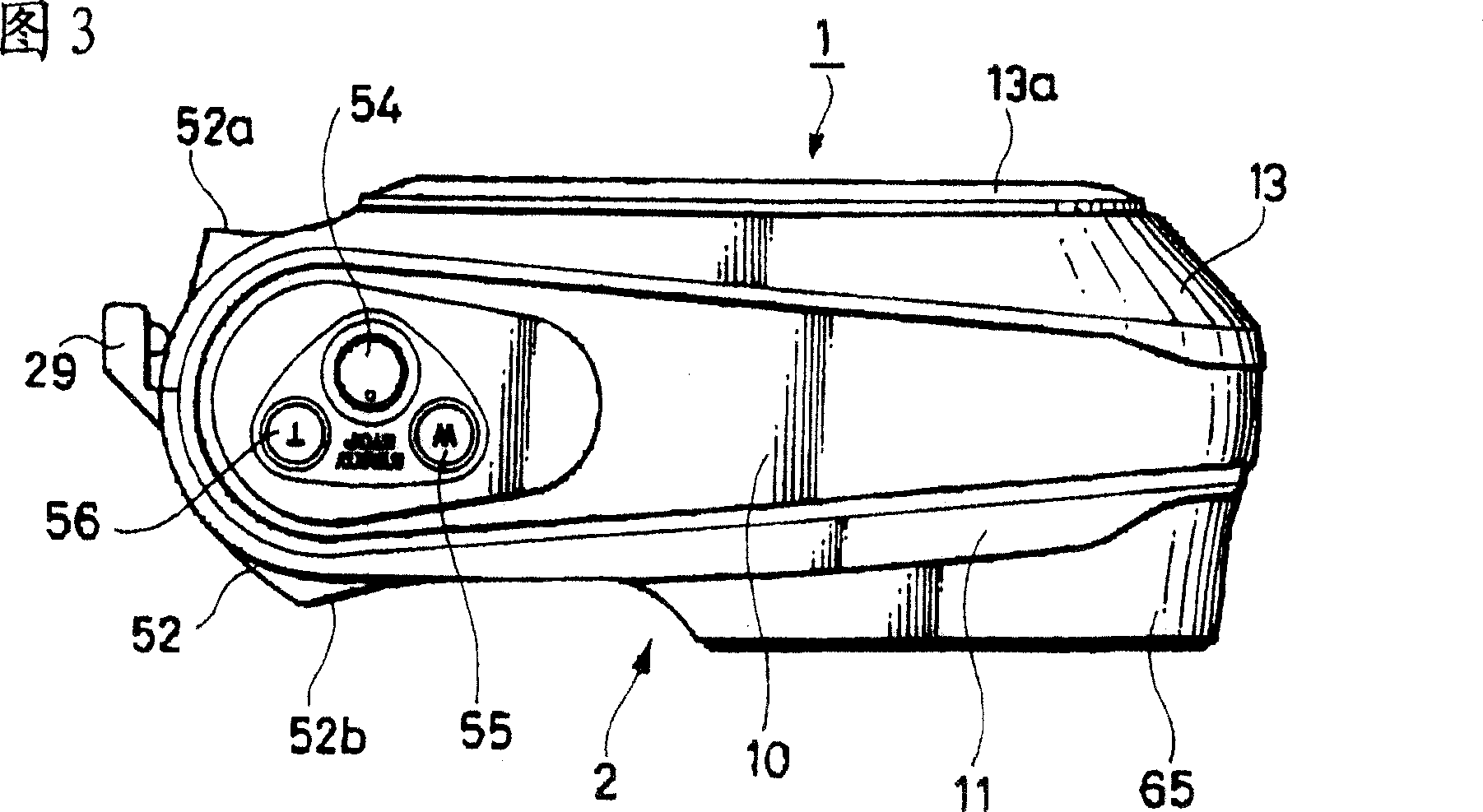
InactiveCN1773365AExcellent waterproof (water resistance) functionEasy to replaceCarrier coversReducing carrier contaminationEngineeringMechanical engineering
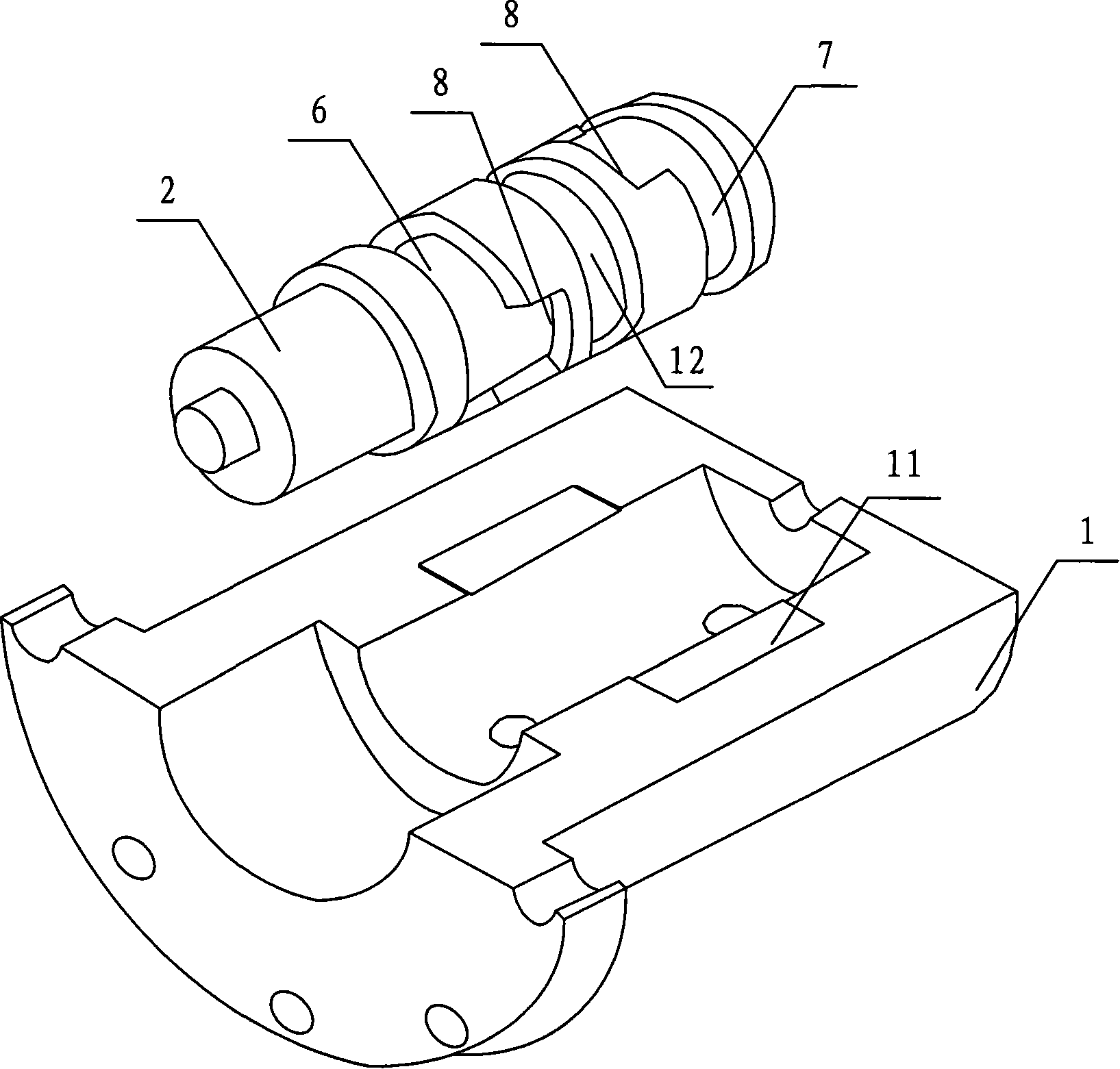
A waterproof electronic device, comprising: a disk cover (13), which can open and close an opening (17) of a camera device main body (2); a fastener (12), which detachably connects the disk cover (13 ) is fastened to the camera device body (2); and a sealing member (24), which is provided on at least one of the fastener 12 and the camera device body (2), the fastener 12 and the camera device body ( 2) Hermetically sealed. When the disc cover (13) is fastened to the camera device main body (2) by the fastener (13), the camera device main body (2) is airtight at least at a part of its portion covered by the fastener (12). seal. In such waterproof electronic devices of the related art, the operation buttons are not formed to have a waterproof structure, so water and water components can relatively easily enter such waterproof electronic devices. If the operating device is made to have a waterproof structure, such a waterproof mechanism will increase the space from a structural point of view, and therefore, the entire device cannot be made compact in size.
Owner:SONY CORP
a node device
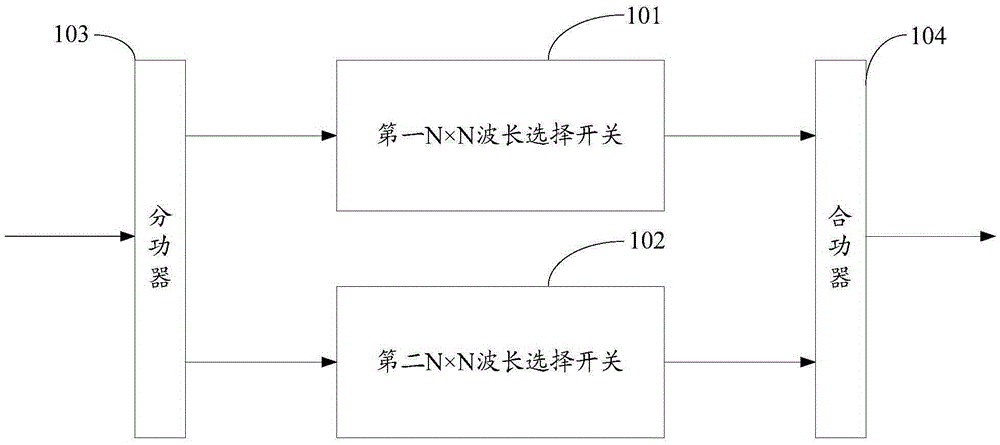
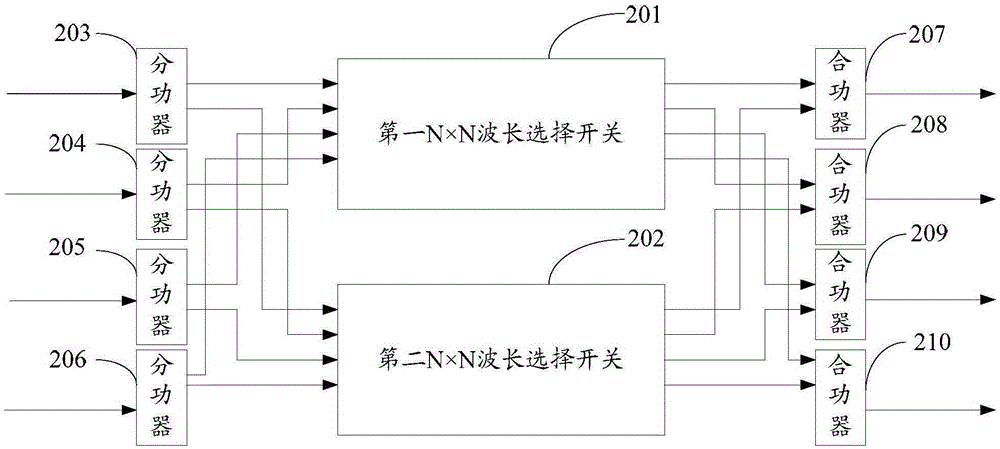
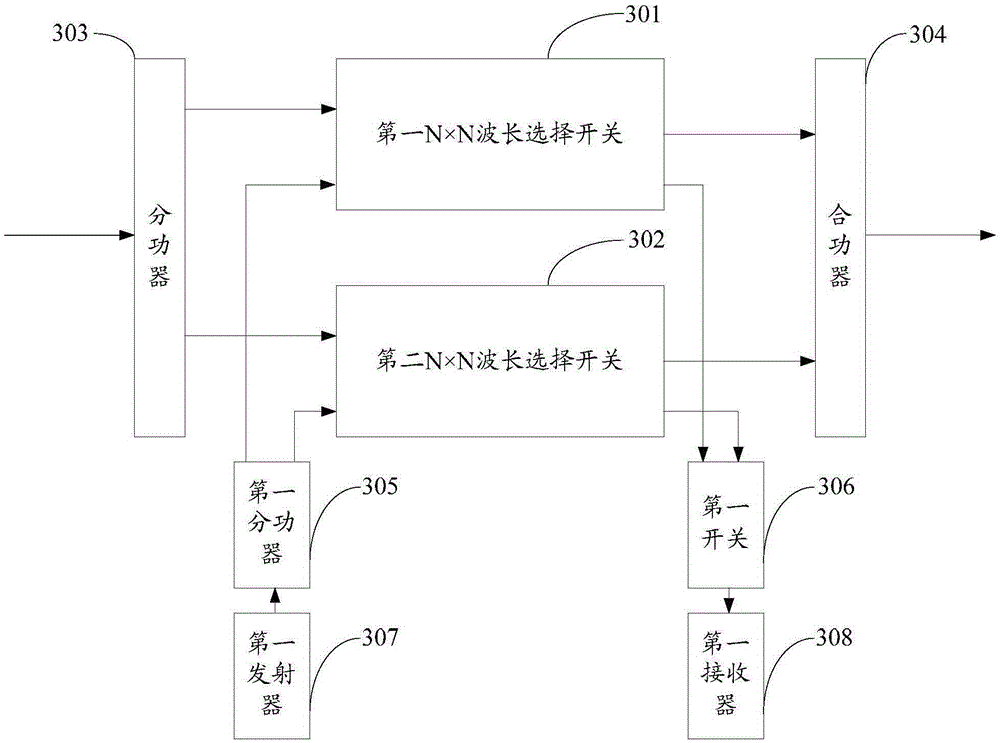
ActiveCN103718479BNo need to increase the numberReduce use costMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsPower combinerComputer module
The present invention provides a node device, which relates to the communication field. Two N×N wavelength selective switches are used to form a parallel structure, and the two ends of each power divider are respectively connected to the input ends of the N×N wavelength selective switches, so that The two ends of each power combiner are respectively connected to the output ends of N×N wavelength selective switches, so that the routing switching selection work originally performed before multiple 1×M wavelength selective switches is transferred to the internal implementation of N×N wavelength selective switches Compared with the original structure using discrete devices, the purpose of simplification is achieved, and when the business volume expands, there is no need to increase the number of line-side module slots, which ultimately reduces the cost of use. The invention is used for signal transmission within a node.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
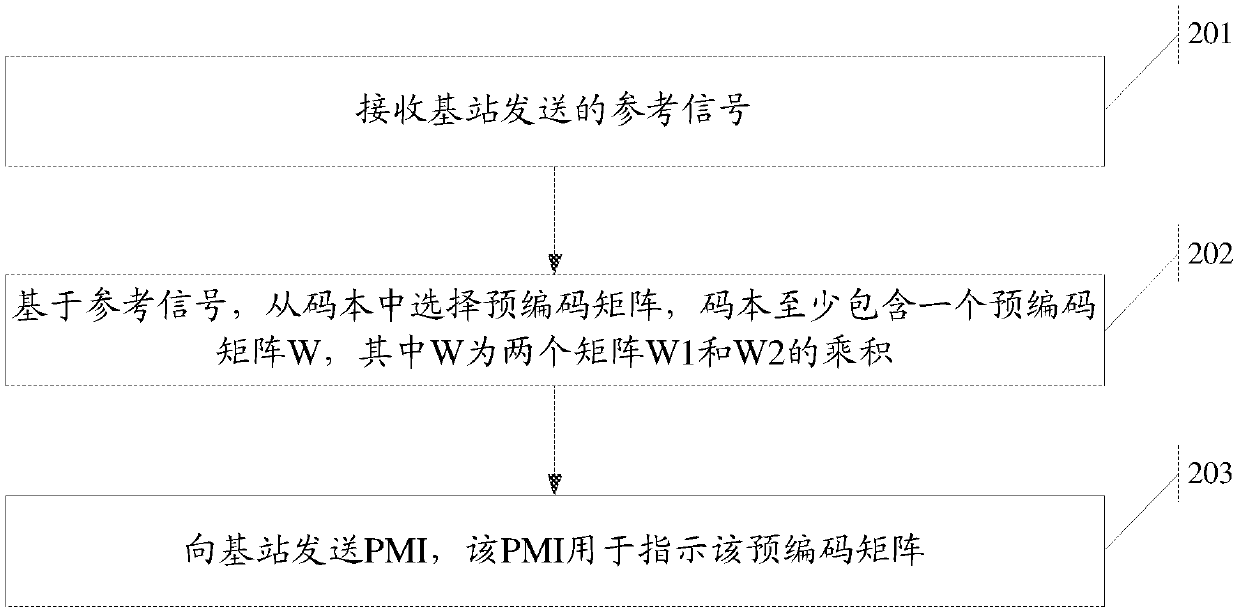
A precoding method and device
InactiveCN107113104BNo need to increase the numberNo need to downsampleError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPrecodingTelecommunications
The present invention relates to the technical field of mobile communications, and in particular to a precoding method and apparatus for solving the technical problem that an existing codebook solution is not applicable to a new antenna form under 3D-MIMO anymore. Provided is a new form W1, wherein W1 can contain a plurality of block matrices, and each of the block matrices can be represented as a Kronecker product of a matrix Ai and a matrix Bi, so that W can not only support an antenna in a horizontal dimension, but can also support an antenna in a vertical dimension, thereby providing a new codebook for a 3D-MIMO system.
Owner:江苏星地通通信科技有限公司
Double-rotor internal combustion engine
ActiveCN113027601ACompact structureEnough displacementInternal combustion piston enginesDifferential gearingsCombustion chamberGear wheel
The invention discloses a double-rotor internal combustion engine which comprises an air cylinder, a main shaft, a left rotor, a right rotor, a left intermittent motion mechanism and a right intermittent motion mechanism. The air cylinder comprises an axially-through air cylinder hole, each rotor comprises blades and a supporting body, and each intermittent motion mechanism is a closed differential gear train comprising a non-circular gear pair and can achieve continuous and stable speed change. The left rotor, the right rotor and the main shaft are located in the air cylinder and have coaxial rotational degrees of freedom. The blades of the left rotor and the right rotor are parallel in the radial direction, a combustion chamber is formed by the space between the blades, the two rotors intermittently rotate periodically in the ignition work, air exhaust, air suction and compression processes of the internal combustion engine, the right rotor is static when the left rotor moves, and the left rotor is static when the right rotor moves. The left rotor and the right rotor transmit respective intermittent rotation to the main shaft through the left intermittent motion mechanism and the right intermittent motion mechanism respectively, and the intermittent rotation speed is converted into a constant rotation speed. Under the action of inertia, the main shaft feeds rotation of the main shaft back to the left rotor and the right rotor to control the acceleration, deceleration and static processes of the rotors.
Owner:杨文通
Waterproof type electronic device
InactiveCN100470353CExcellent waterproof (water resistance) functionEasy to replaceCarrier coversReducing carrier contaminationAir tightness
Owner:SONY CORP
Power supply circuit, terminal and voltage output method
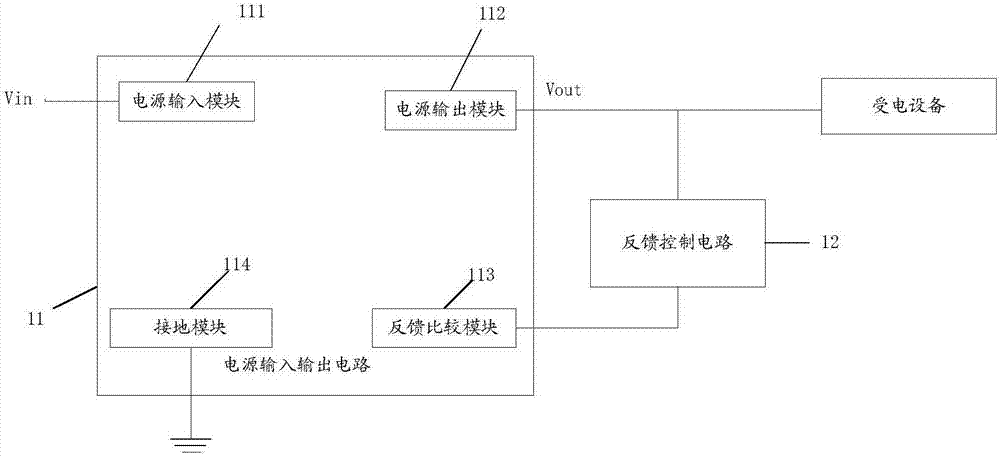
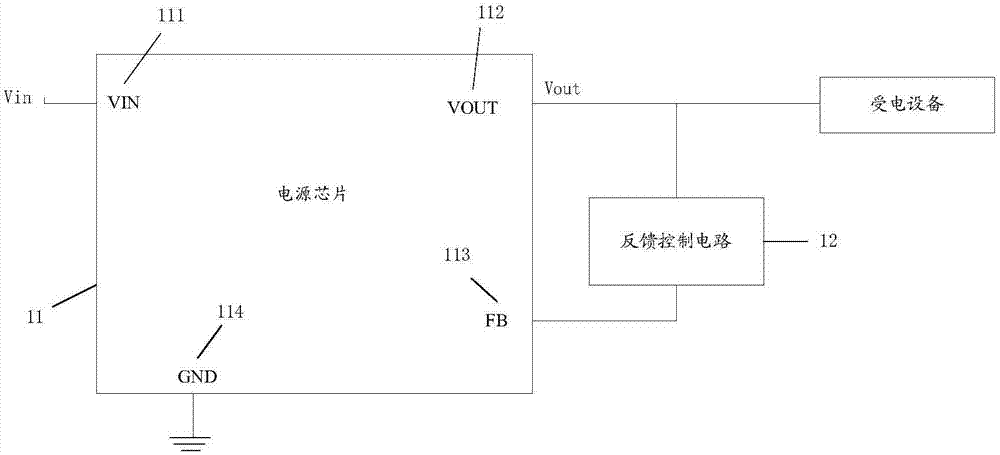
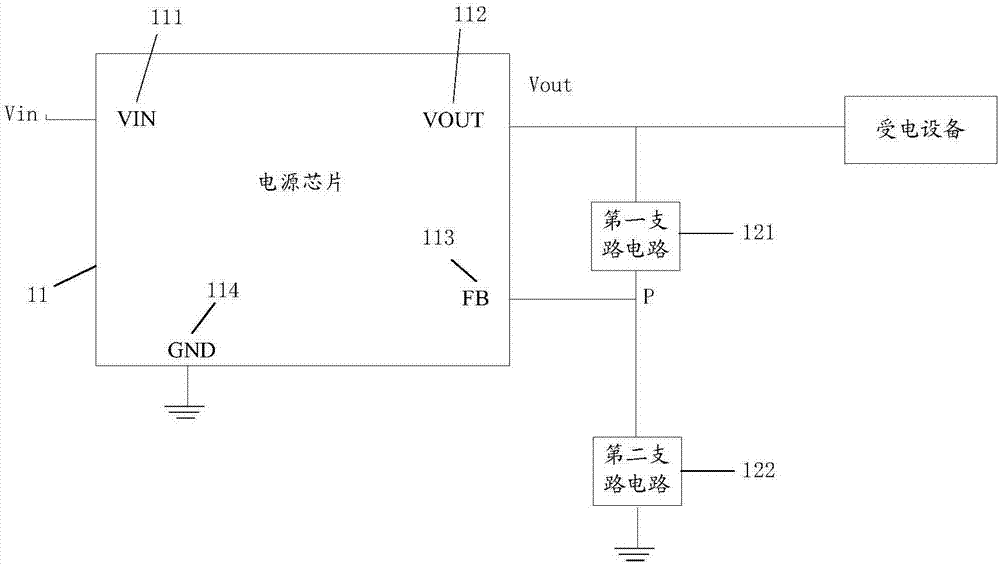
PendingCN107045369ANo need to increase the numberMeet power needsElectric variable regulationElectricityComputer module
The invention discloses a power supply circuit, a terminal, and a voltage output method. The power supply circuit includes a power supply input output circuit and a feedback control circuit; the power supply input output circuit includes a power supply input module, a power supply output module, a feedback comparison module, and a grounding module; the power supply output module is connected to a power receiving device; one end of the feedback control circuit is connected to the power supply output module, and the other end of the feedback control circuit is connected to the feedback comparison module; the feedback control circuit is used for inputting the corresponding feedback voltage to the feedback comparison module according to the output voltage of the power supply output module; the feedback voltage and the output voltage meet at least one preset calculation formula, the feedback comparison module compares the feedback voltage and the preset reference voltage, and when the comparison result is different, the power supply output module adjusts the output voltage till the feedback voltage is identical to the reference voltage. According to the invention, the feedback control circuit is improved so as to achieve output of voltages at different levels, and the feedback control circuit is simple in design, is easy to achieve, can avoid an additional power supply input output circuit, and can save the cost.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
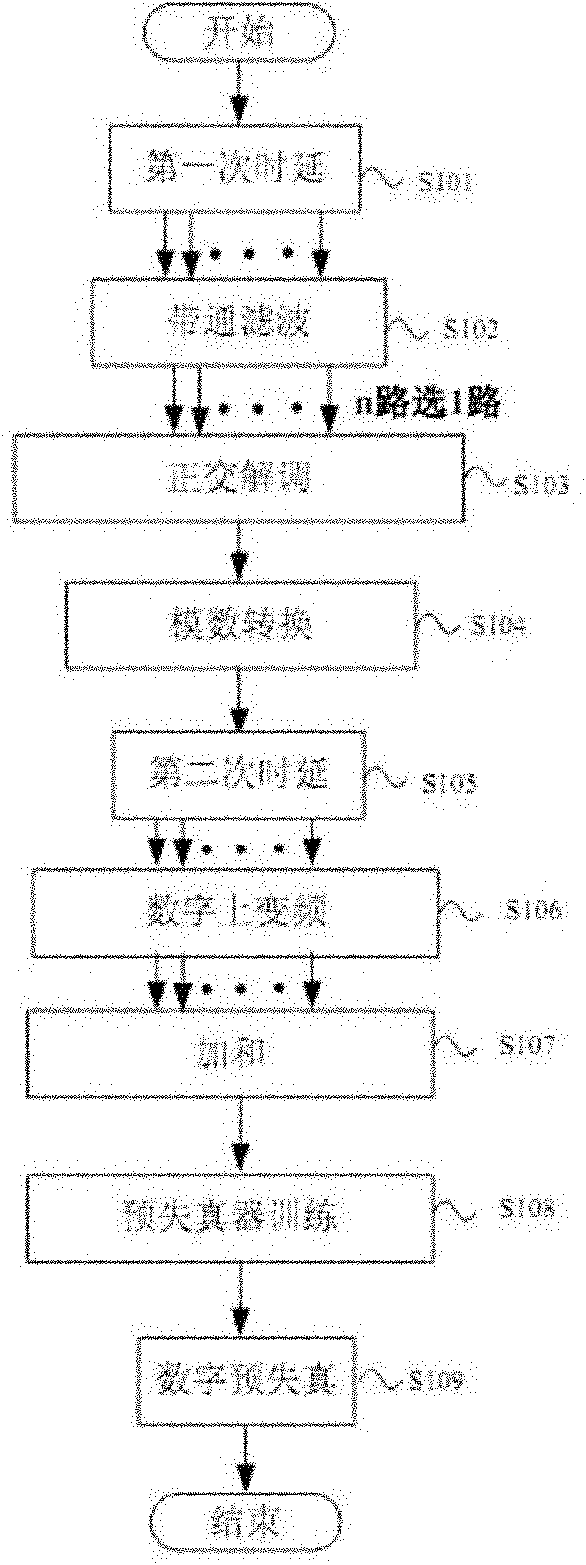
Digital predistortion device and method
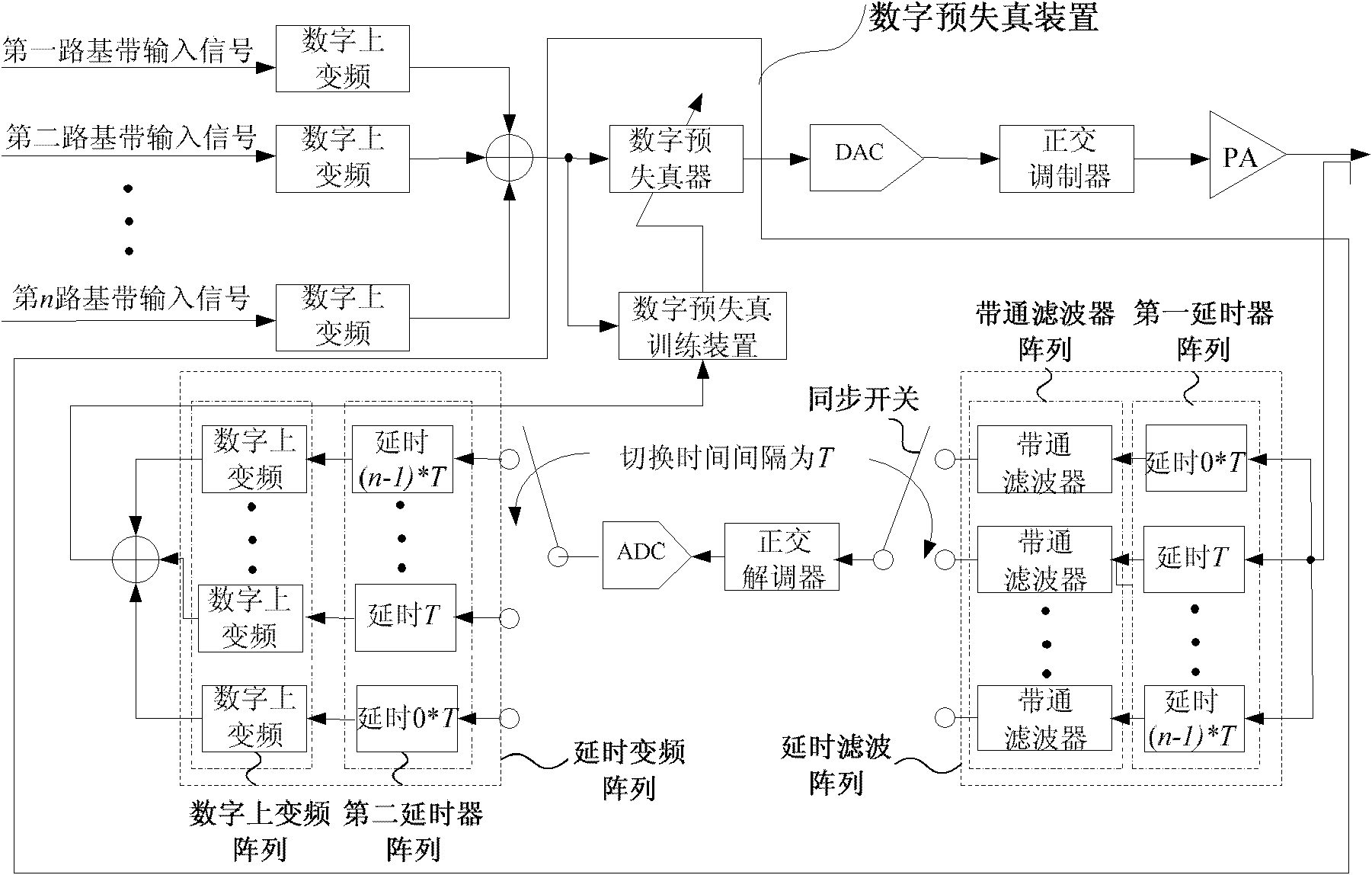
ActiveCN102088427BNo reduction in power utilizationNo need to increase the numberSynchronous/start-stop systemsAudio power amplifierCommunications system
The present invention relates to a digital predistortion device and a method, which are applied to a multichannel single amplifier broadband digital wireless communication system and belong to the technological field of wireless communication. The device includes a time-delay filtering array, a synchronization switch, a quadrature demodulator, an analog-to-digital converter, a time-delay frequency conversion array connected with the synchronization switch and a digital predistortion unit, wherein all the units are connected in order, the input end of the time-delay filtering array is connected with the output end of a power amplifier of the multichannel single amplifier broadband digital wireless communication system, the input end of the digital predistortion unit receives the frequency conversed digital baseband signal, and the output end of the digital predistortion unit outputs a digital carrier. The digital predistortion device and the method resolve the predistortion problem of a multichannel single amplifier broadband digital wireless communication system.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUDAN COMM
Substrate Integrated Waveguide Filter
InactiveCN103904392BHigh selectivityNo need to increase the numberWaveguide type devicesUltrasound attenuationResonant cavity
The invention discloses a substrate integrated waveguide filter which is high in selectivity, small in size and low in loss. The substrate integrated waveguide filter comprises a first metal layer, a first dielectric substrate, a second dielectric substrate, a second metal layer and a metallization through hole array, the first metal layer, the first dielectric substrate, the second dielectric substrate, the second metal layer and the metallization through hole array are sequentially stacked from top to bottom, and a first band-shaped coupling unit and a second band-shaped coupling unit are arranged between the first dielectric substrate and the second dielectric substrate. By means of the substrate integrated waveguide filter, the LTCC technology is adopted for integrating the band-shaped coupling units into resonant cavities of the substrate integrated waveguide filter, a signal transmission channel can be added without increasing the number of the resonant cavities, a transmission null point can be accordingly obtained in an attenuation band, and the selectivity of the filter is improved; meanwhile, the position of the transmission null point can be flexibly controlled by adjusting the resonant frequencies of the band-shaped coupling units, more stages of the resonant cavities are not needed, and the substrate integrated waveguide filter has the advantages of being small in size, light in weight and low in loss. The substrate integrated waveguide filter is suitable for popularization and application in the microwave millimeter wave technical field.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Motorcycle
InactiveCN1791530ALower the altitudeReduce thicknessAnti-theft cycle devicesArticle supporting devicesMechanical engineering
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
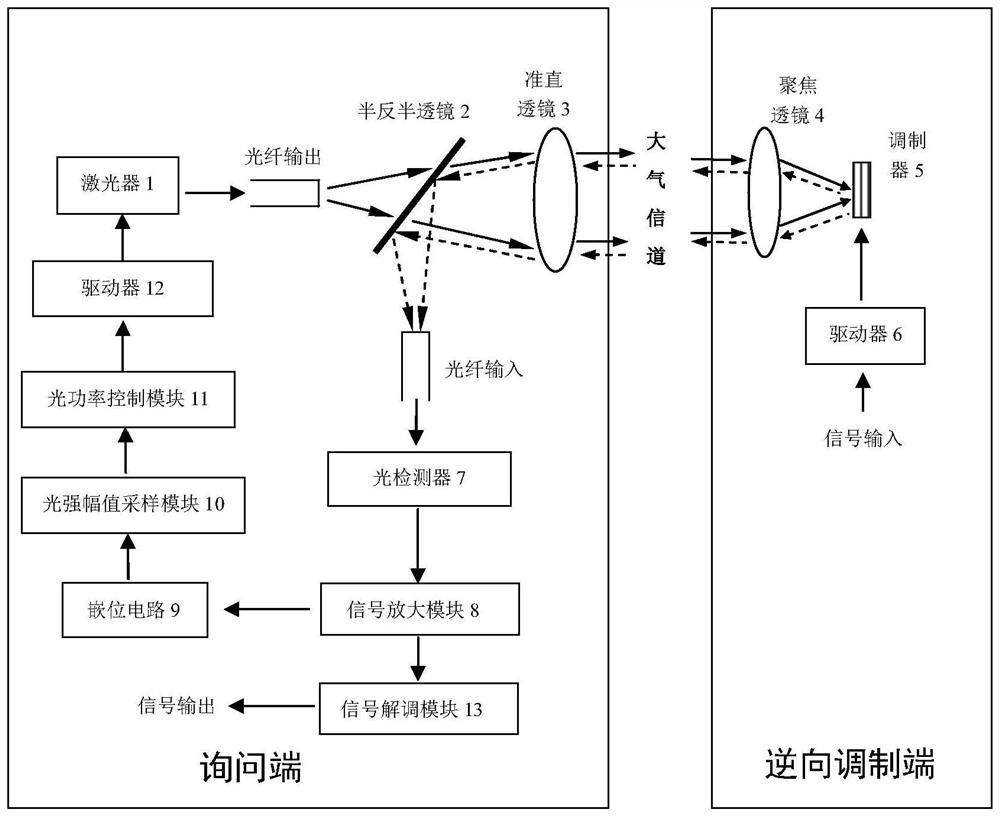
Turbulence suppression method and device for precompensating transmitted optical power in reverse modulation optical communication
ActiveCN110289904BCounteract flickerNo need to increase the caliberFree-space transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersOptical antennaOptical power
The invention discloses a turbulence suppression method and device for pre-compensating transmitted optical power in reverse modulation optical communication. The device is divided into an inquiry end and a reverse modulation end. The inquiry end emits laser light, which is transmitted to the reverse modulation after the beam is collimated through an optical antenna. At the end, the modulator at the reverse modulation end modulates the input signal onto the laser light sent from the inquiring end, and reflects back the original direction of the laser light sent from the inquiring end through the "cat's eye" effect; The mechanism senses the size of the received signal through the light intensity amplitude sampling module, so that the transmitted optical power can be adaptively changed. The invention can maintain the received light intensity at a constant value, thereby suppressing the influence of atmospheric turbulence on reverse modulation wireless optical communication, and realizing reverse modulation wireless optical communication with better performance.
Owner:ARMY ENG UNIV OF PLA
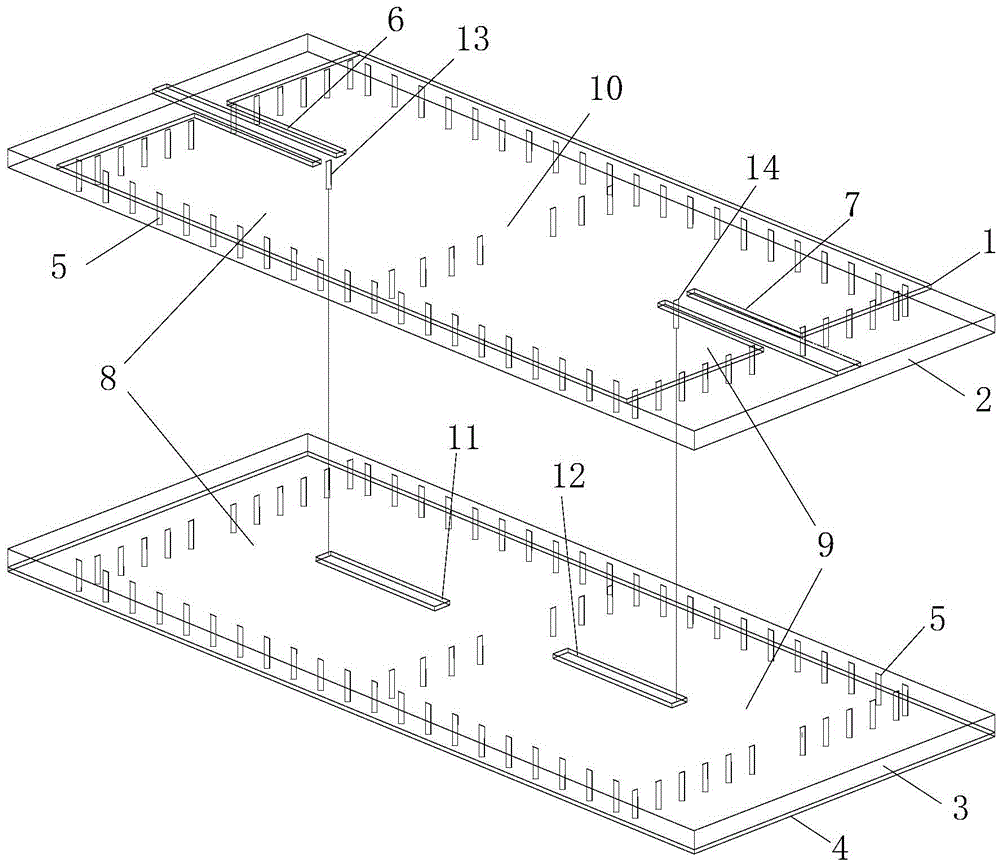
Detachable quenching tank built-in combination type flow guiding cover
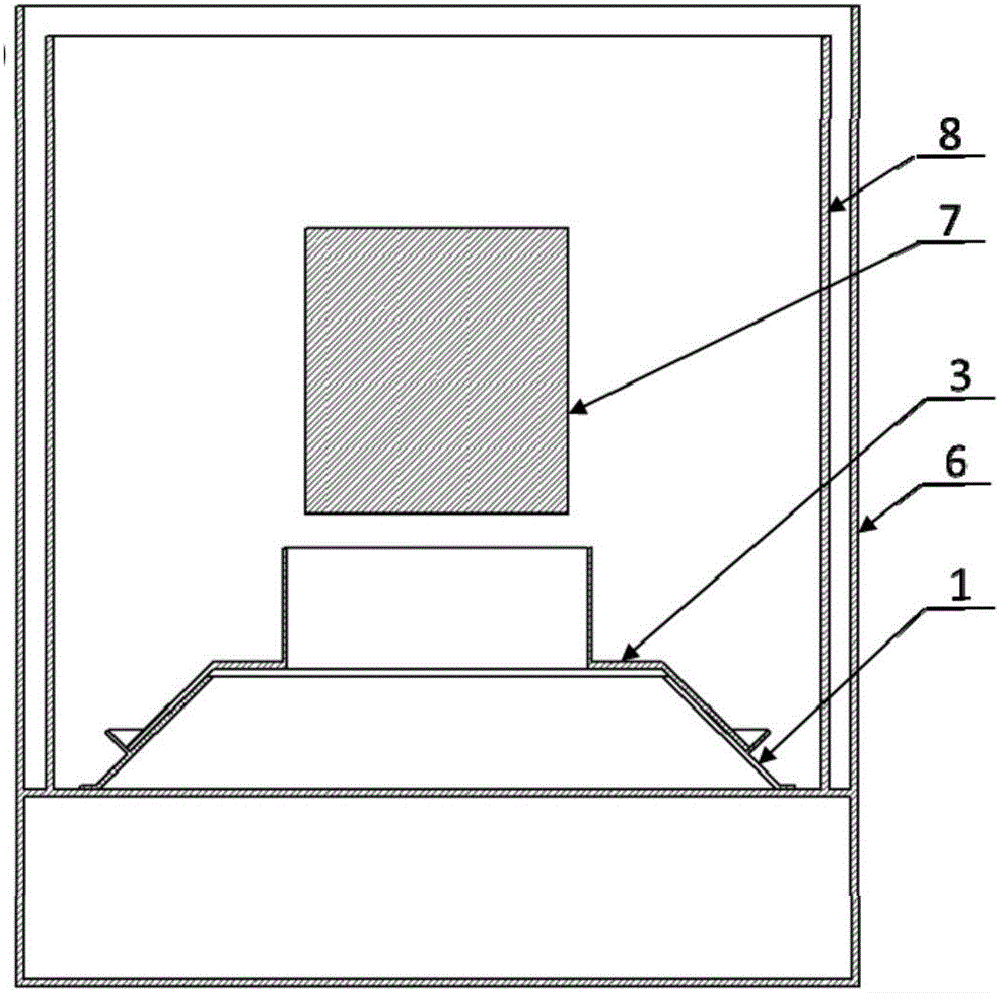
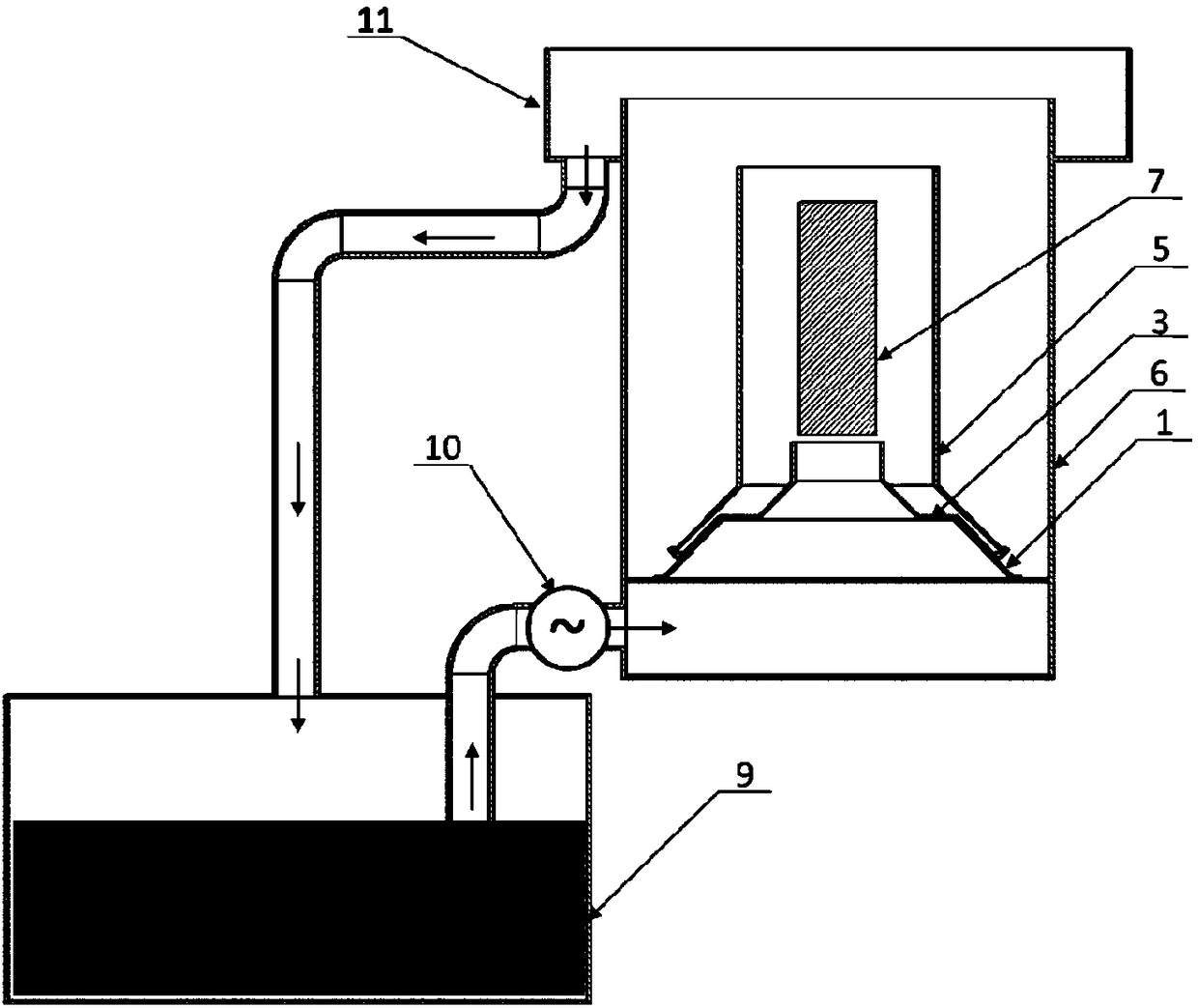
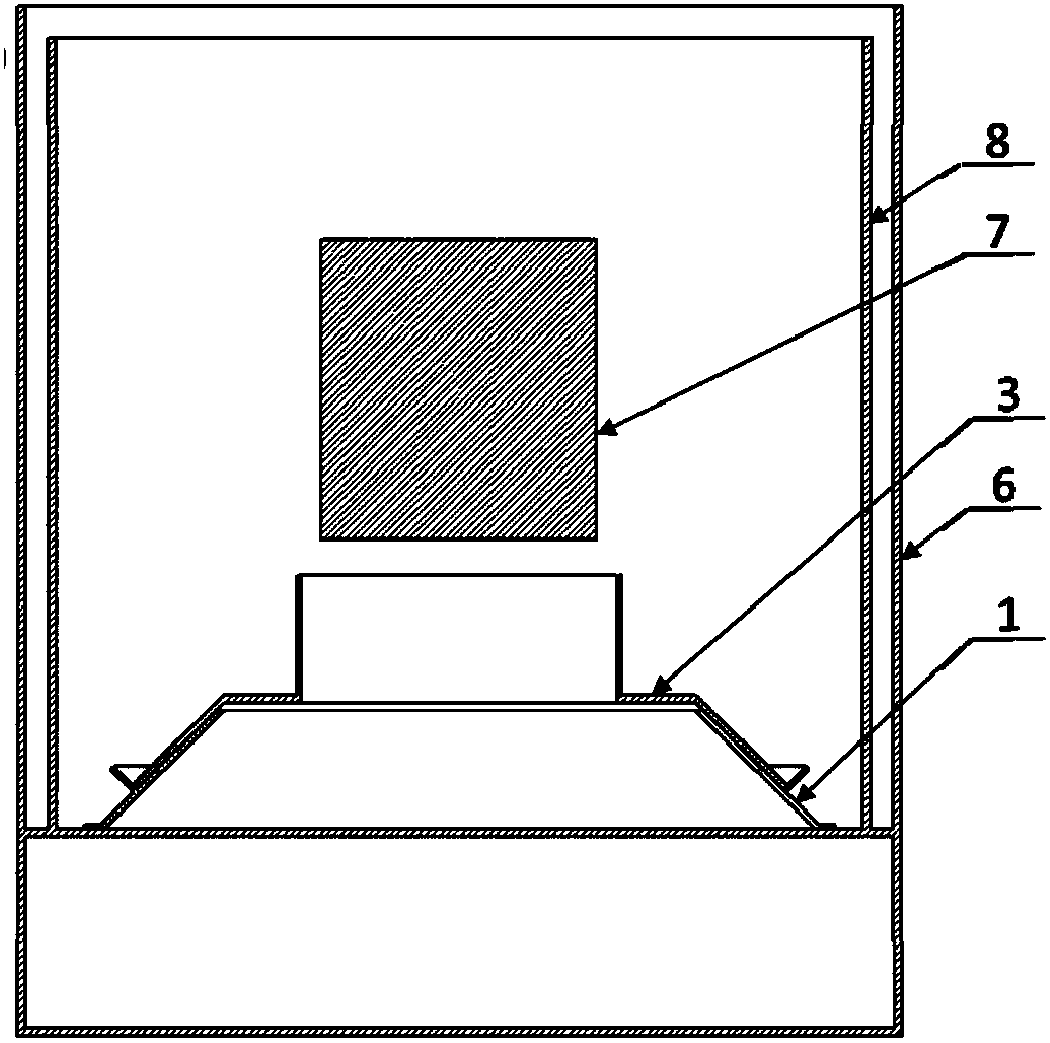
ActiveCN106755824ANo need to increase the numberReduce lossesQuenching devicesQuenchingWaste management
The invention relates to a detachable quenching tank built-in combination type flow guiding cover. The flow guiding cover comprises a conical base fixed to the lower part of a quenching tank and a flow guiding cover unit detachably arranged on the conical base in a sleeving manner in a vertical direction, wherein the flow guiding cover unit comprises at least one flow guiding cover assembly; the flow guiding cover assembly comprises a conical body section and a vertical outlet section which are sequentially arranged from the bottom to the top; the bottom diameter and conicity of the conical body section are matched with those of the conical base, and the shape and size of the vertical outlet section of each flow guiding cover assembly are matched with those of a to-be-quenched workpiece; and the outer side surface of the conical base is provided with a locating cone, and the bottom edge of the flow guiding cover assembly is pressed against the locating cone and is fixedly connected with the conical base. Compared with the prior art, the flow guiding cover has the advantages that the structure is flexible, can be timely changed and regulated, is convenient to assemble and disassemble and has great applicability; the defects of the existing fixed type flow guiding and equalizing device can be overcome under the condition of ensuring economical benefit; and the universality of the quenching tank is improved, and the application prospect is great.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Binding post and wiring terminal
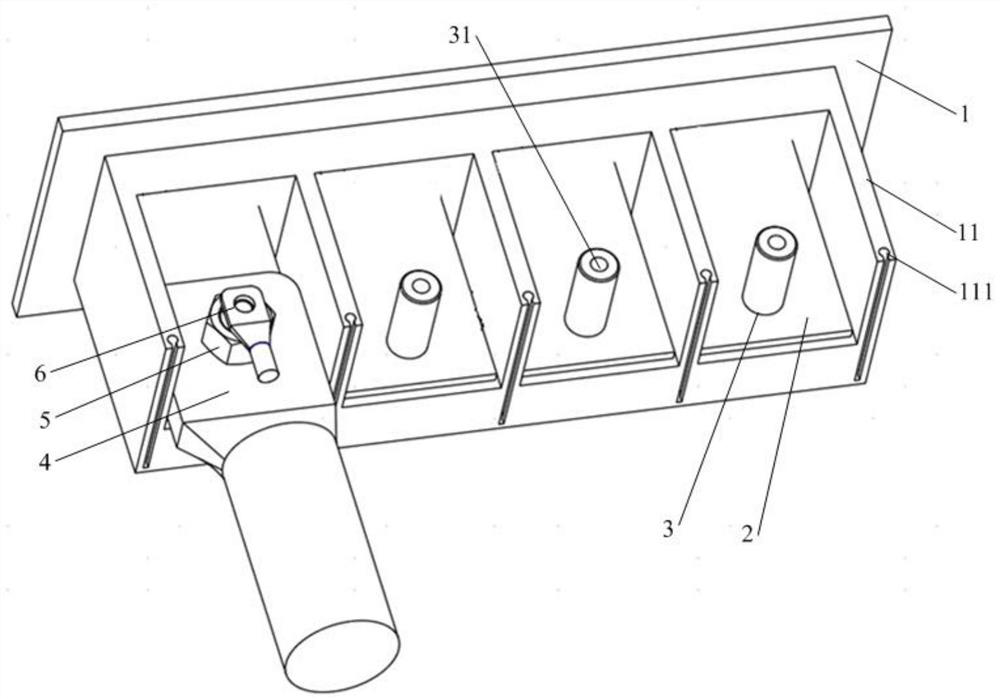
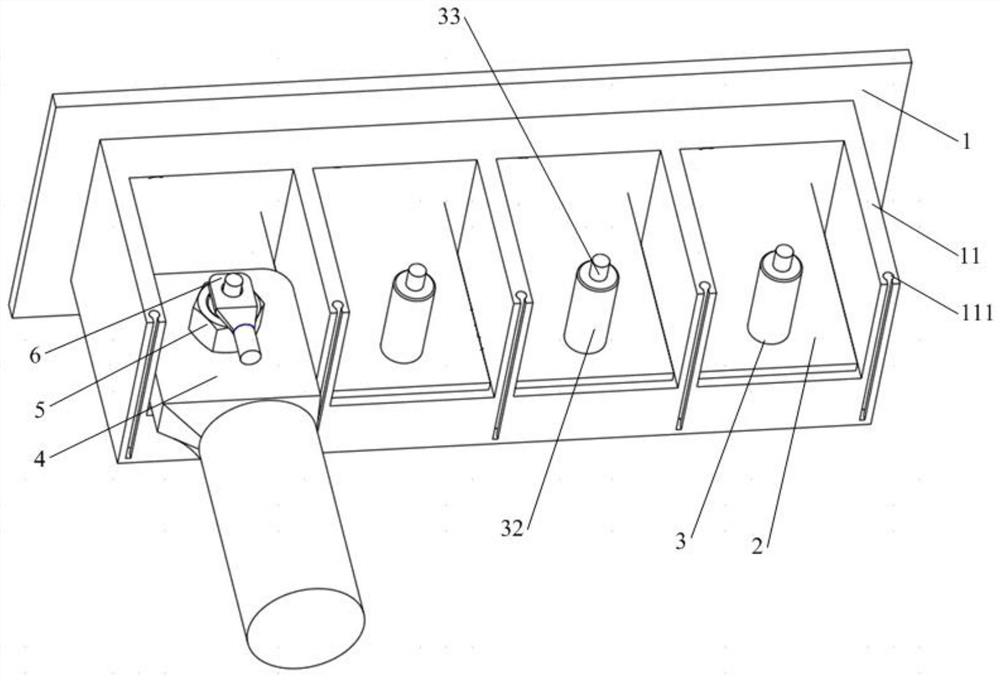
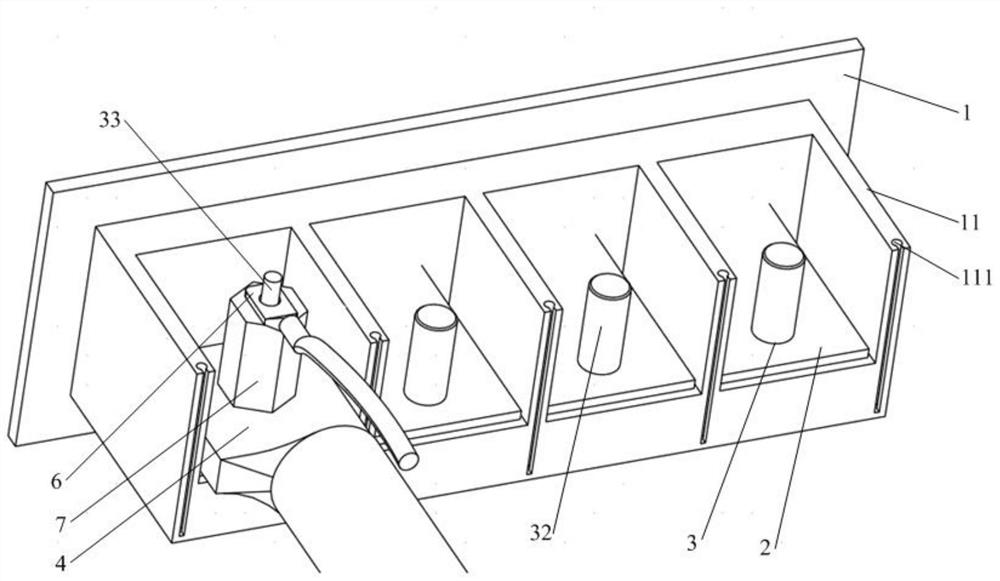
PendingCN112103672ASmall footprintNo need to increase the numberCoupling contact membersClamped/spring connectionsStructural engineeringBinding post
The invention discloses a binding post and a wiring terminal. The binding post comprises at least two wiring structures used for being connected with cables, and the wiring structures are used for being matched with fixing holes of different cables respectively. According to the binding post disclosed by the invention, by arranging the wiring structures connected with the cables and selecting theat least two wiring structures to be respectively matched with the fixing holes of the different cables, the binding post can be connected with the different cables, and the number of the binding posts or the number of the wiring terminals does not need to be increased, so that the space occupied by wiring is reduced; and wiring cost reduction is achieved.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
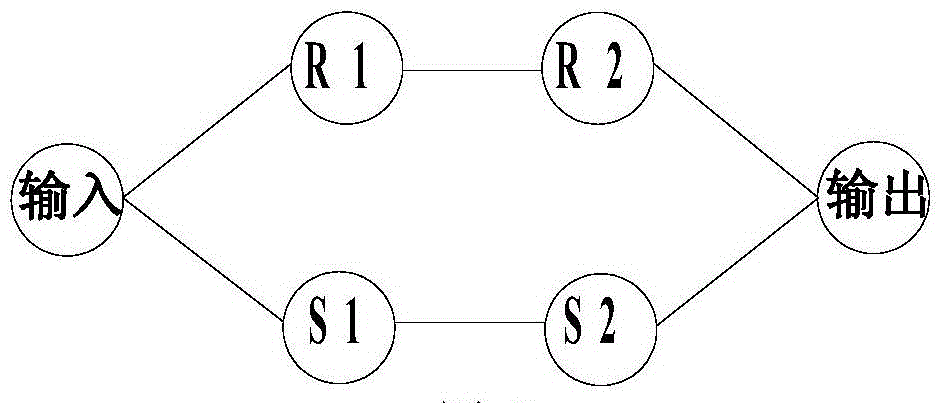
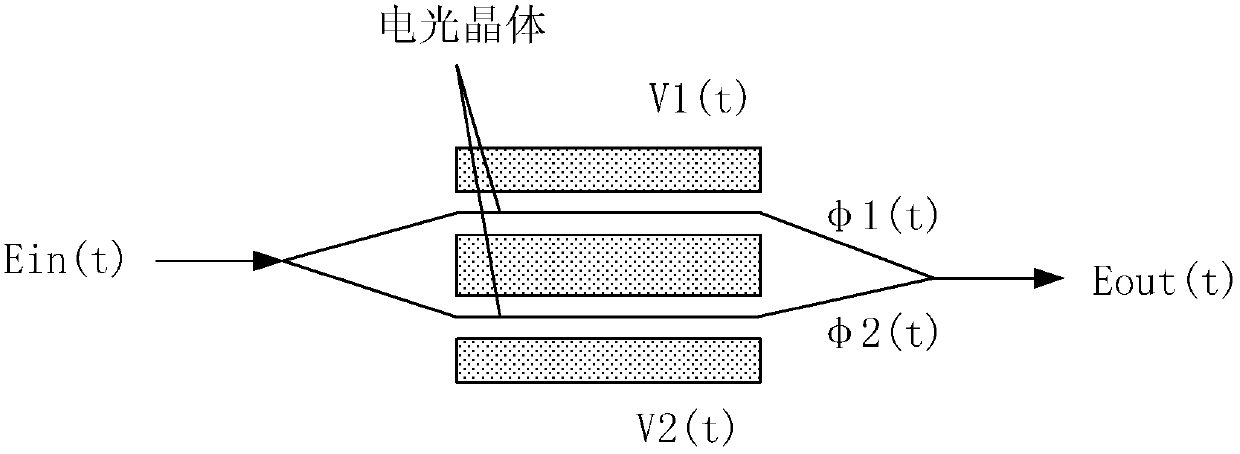
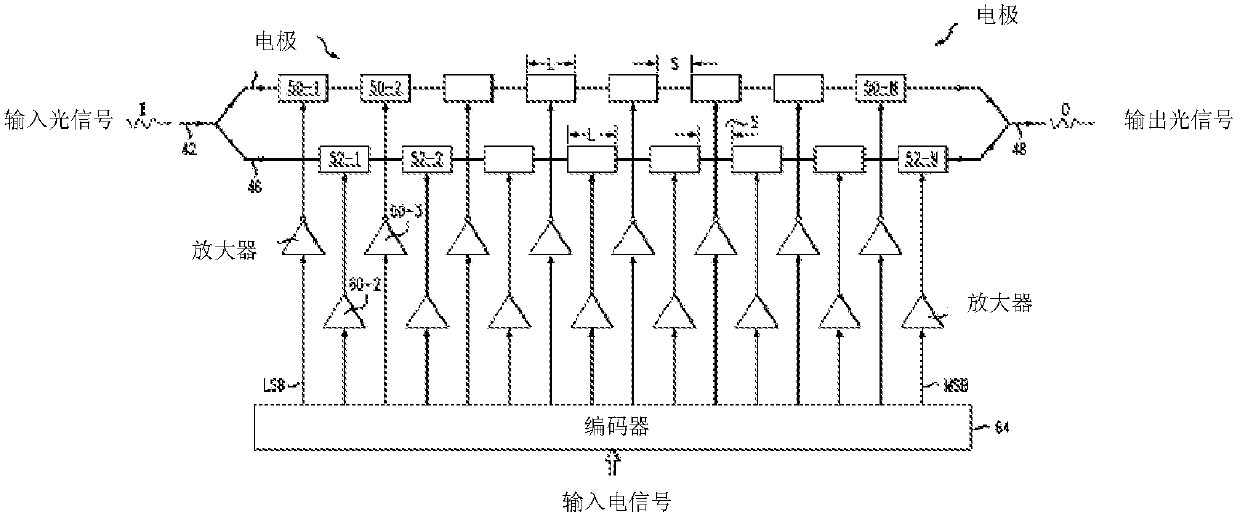
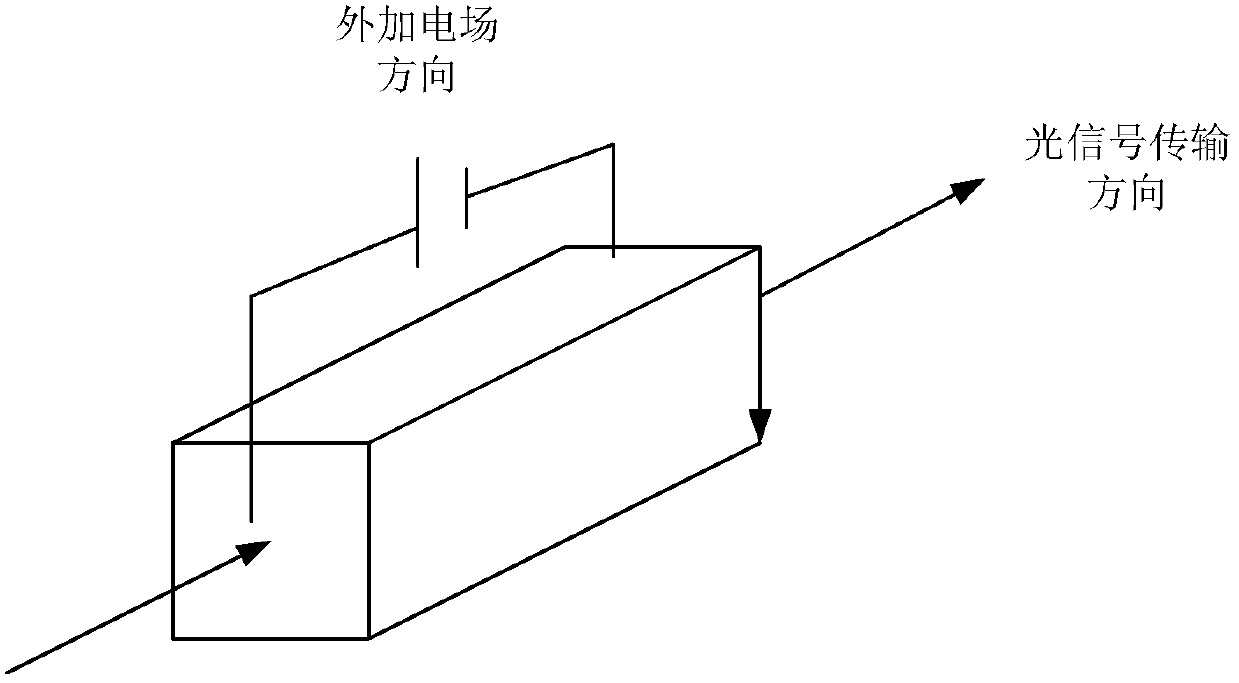
An optical signal modulation path, electro-optic modulator and optical transmitter
ActiveCN105209963BNo need to increase the numberIncrease phase sizeNon-linear opticsLight signalElectro-optic modulator
An optical signal modulation pathway, an electro-optic modulator and an optical transmitter. All electrodes on the optical signal modulation pathway except a reference electrode differ from the reference electrode in the material parameters of electro-optic crystals and / or the width of an electric field when the electric field acts in the transverse direction. The phases of input light signals varied by the other electrodes are greater than the phase of the input light signal varied by the reference electrode. In the case that a particular space is occupied by the entire optical signal modulation pathway, when a high level is accessed to the electrodes on the optical signal modulation pathway, as compared to the situation where only the reference electrode is present on the optical signal modulation pathway, the accumulated value of the phases of the input light signals that can be varied by the entire optical signal modulation pathway can be increased by increasing the phases of the input light signals varied, with no need of the increase in the number of electrodes or the length of individual electrodes.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
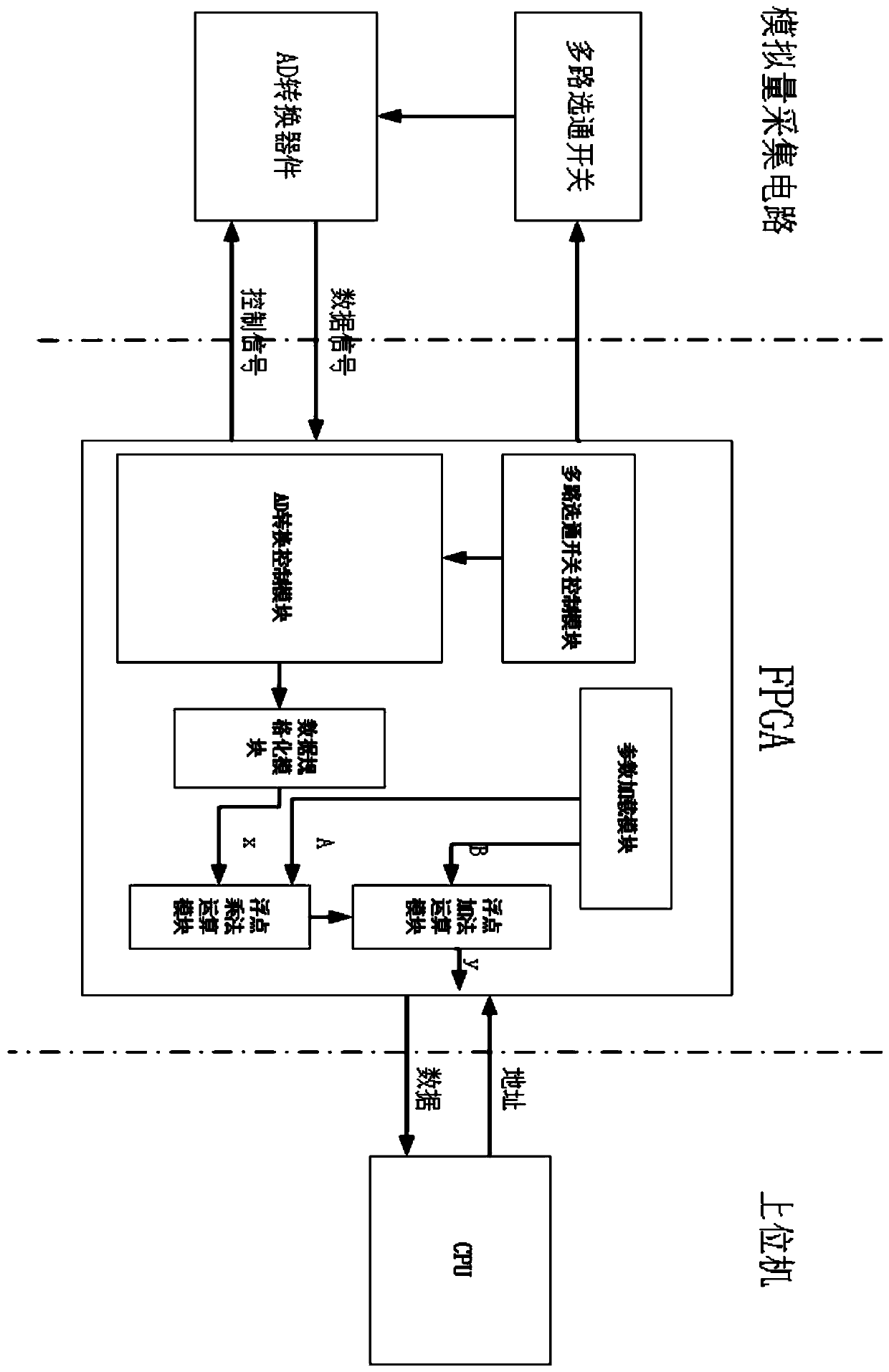
Hardware acceleration method
ActiveCN110147219AReduce resource overheadReduce task cycle timeDigital data processing detailsFloating pointData format
The invention provides a hardware acceleration method, and the method comprises the steps: collecting an analog quantity, wherein the data format of the analog quantity is a binary format; convertingthe data format of the analog quantity into a floating-point number; and according to preset parameters, performing parallel operation on floating-point number multiplication and floating-point numberaddition, and obtaining a calculation result.
Owner:XIAN AVIATION COMPUTING TECH RES INST OF AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
a slot antenna
ActiveCN108511895BNo need to increase the numberBig room for changeRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsMetal stripsHemt circuits
The invention discloses a double-loop structure and a slot antenna based on the structure. The double-loop structure includes two lower metal strips and an upper metal strip corresponding to the lower metal strips. The upper metal strip and the lower metal strip The two ends of the strip are respectively connected by metal pillars to form two symmetrical parasitic rings, and a switch tube for controlling the switching of the parasitic ring and a bias circuit for controlling the switch tube are arranged on the parasitic rings. It forms parasitic ring pairs by upper metal strips, lower metal strips and metal posts, and realizes pattern reconstruction by controlling the disconnection of parasitic ring pairs. Since it depends on the original working mode of the gap, the pattern points to There is more room for change; in addition, there is no need to increase the number of networks and array elements, and the structure is simple and the occupied area is small.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A detachable quenching tank built-in combined shroud
ActiveCN106755824BNo need to increase the numberReduce lossesQuenching devicesQuenchingWaste management
The invention relates to a detachable quenching tank built-in combination type flow guiding cover. The flow guiding cover comprises a conical base fixed to the lower part of a quenching tank and a flow guiding cover unit detachably arranged on the conical base in a sleeving manner in a vertical direction, wherein the flow guiding cover unit comprises at least one flow guiding cover assembly; the flow guiding cover assembly comprises a conical body section and a vertical outlet section which are sequentially arranged from the bottom to the top; the bottom diameter and conicity of the conical body section are matched with those of the conical base, and the shape and size of the vertical outlet section of each flow guiding cover assembly are matched with those of a to-be-quenched workpiece; and the outer side surface of the conical base is provided with a locating cone, and the bottom edge of the flow guiding cover assembly is pressed against the locating cone and is fixedly connected with the conical base. Compared with the prior art, the flow guiding cover has the advantages that the structure is flexible, can be timely changed and regulated, is convenient to assemble and disassemble and has great applicability; the defects of the existing fixed type flow guiding and equalizing device can be overcome under the condition of ensuring economical benefit; and the universality of the quenching tank is improved, and the application prospect is great.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Liquid level tracking type multi-point temperature measuring device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN110118613AReduce stressReduced tightnessThermometer detailsThermometers using physical/chemical changesEngineeringThermal fluids
The invention discloses a liquid level tracking type multi-point temperature measuring device and a manufacturing method thereof. The liquid level tracking type multi-point temperature measuring device comprises an optical fiber temperature measuring wire, and the two ends of the optical fiber temperature measuring wire are connected with a liquid surface floating device and an elastic spring correspondingly; when the liquid level tracking type multi-point temperature measuring device is located in a liquid,the liquid surface floating device floats on the liquid surface, the elastic spring sinks inside the liquid, and the optical fiber temperature measuring wire is straightened. The invention providesthe liquid level tracking type multi-point temperature measuring device and the manufacturing method thereof.The problems that a temperature measuring device of a thermal fluid experiment in the prior art cannot track liquid level change, causes serious interference to the fluid around a measuring point, and influences pressure-bearing and sealing of a pressure vessel, the tracking of the height position of the liquid surface is realized, the stability of the measuring point from the liquid surface is ensured, the number of openings of a container are decreased, sealing is easy, and the fluid interference around the measuring point is reduced.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
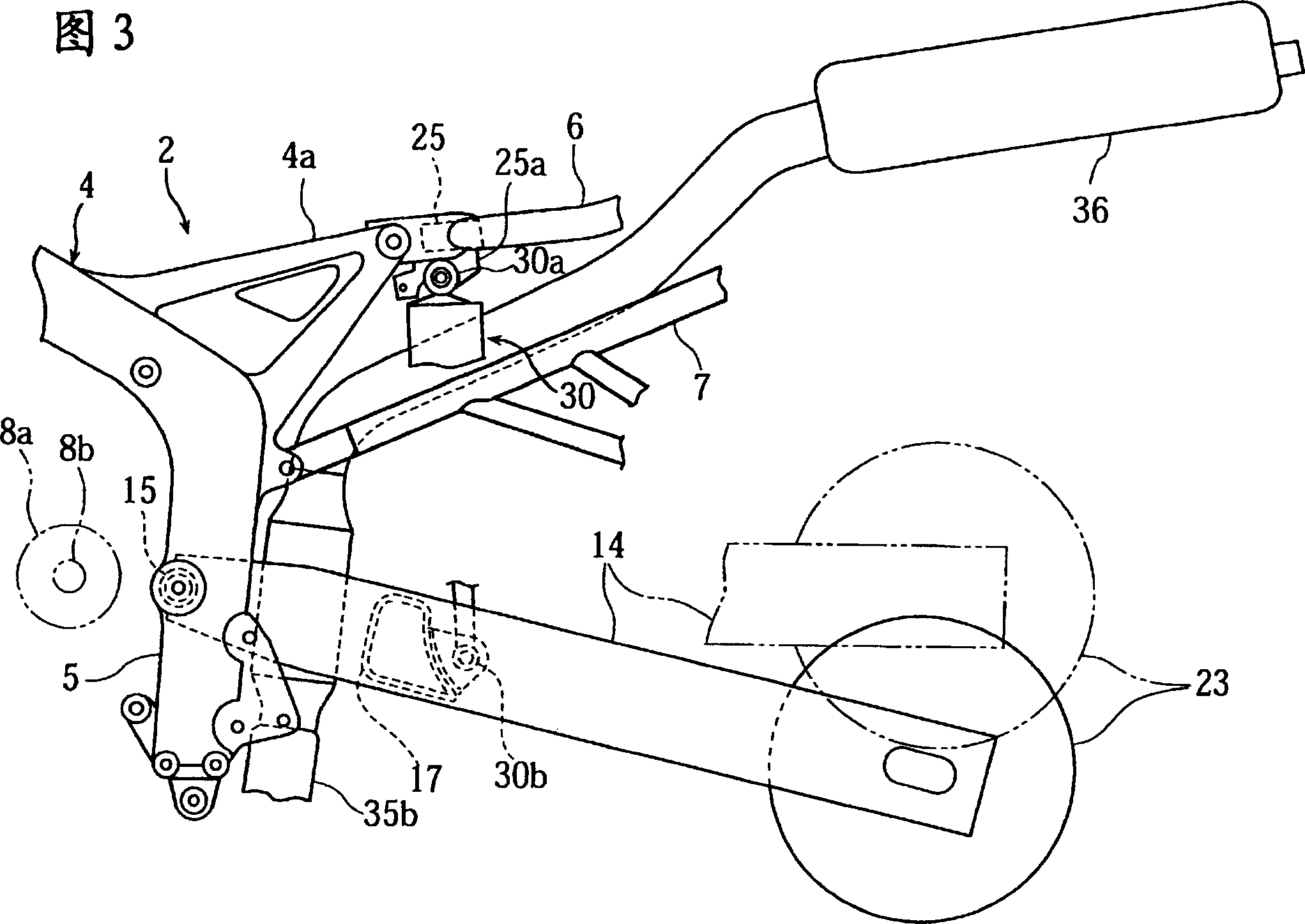
Motorcycle
InactiveCN100393570CLower the altitudeReduce thicknessAnti-theft cycle devicesArticle supporting devicesBody frameEngineering
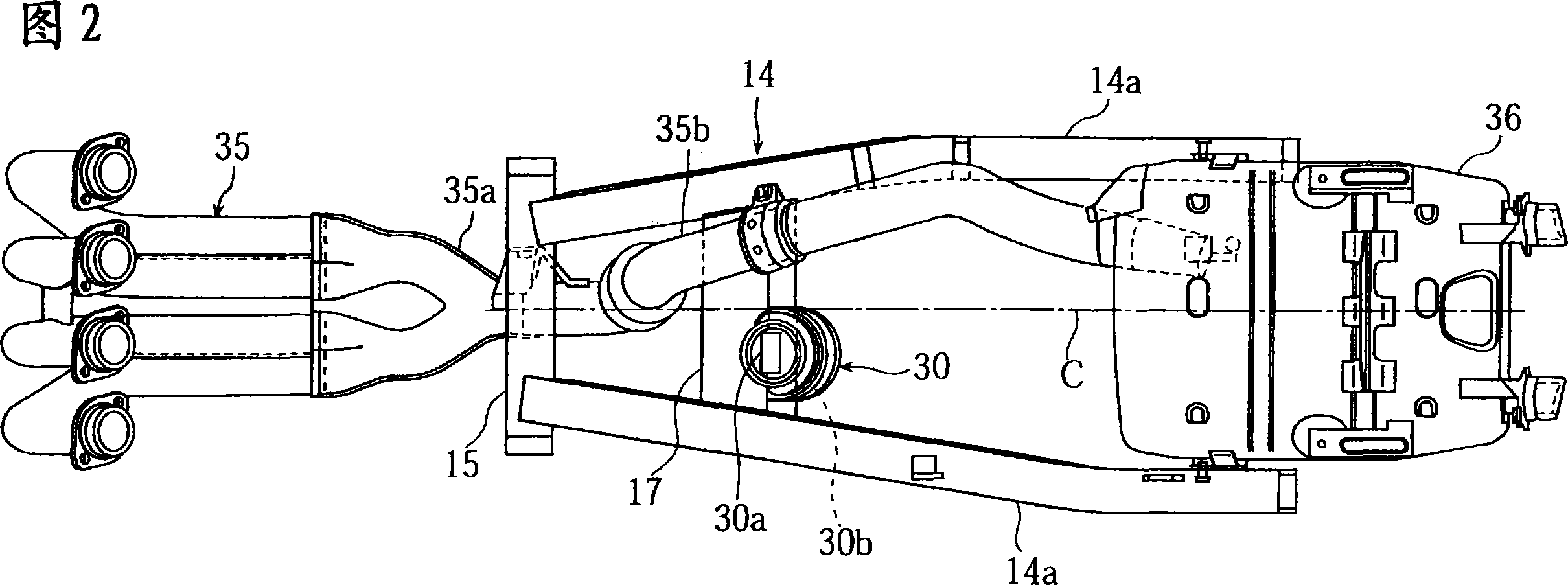
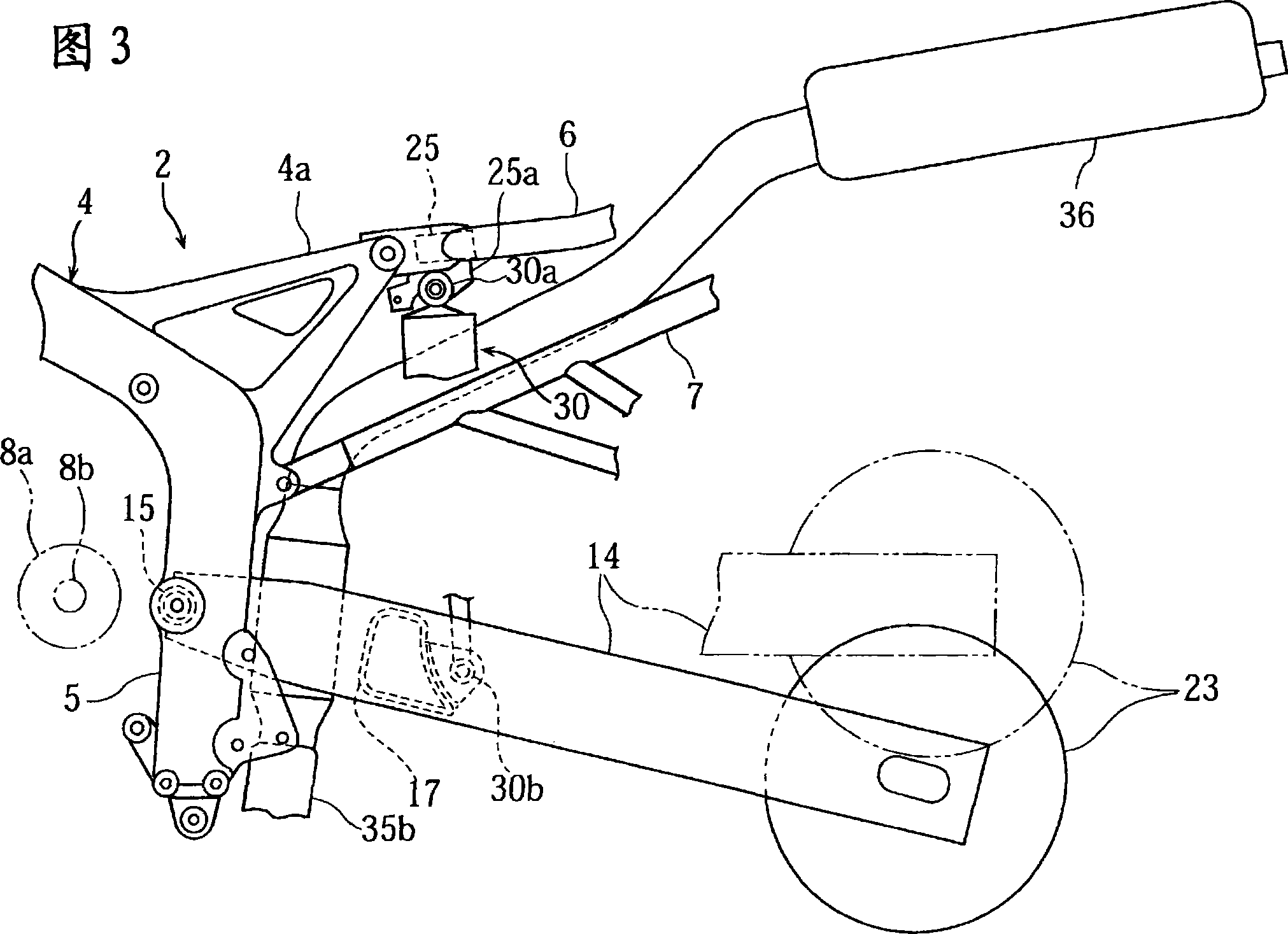
A motorcycle, comprising a rear arm (14) having one end pivotally supporting a rear wheel and the other end pivotally supported on a body frame (2) through a pivot shaft, a cushion unit (30) installed between the rear arm (14) and the body frame (2) so as to be positioned between the pivot shaft and the rear wheel, and a lock arm placing part storing a theft prevention lock arm (41) having left and right arm parts (41a) and (41b) and a bent part (41c) connecting the end parts of the left and right arm parts (41a) and (41b) to each other. The lock arm placing part is formed to store the lock arm (41) so that the left and right arm parts (41a) and (41b) of the lock arm (41) can be positioned on both sides of the cushion unit (30).
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
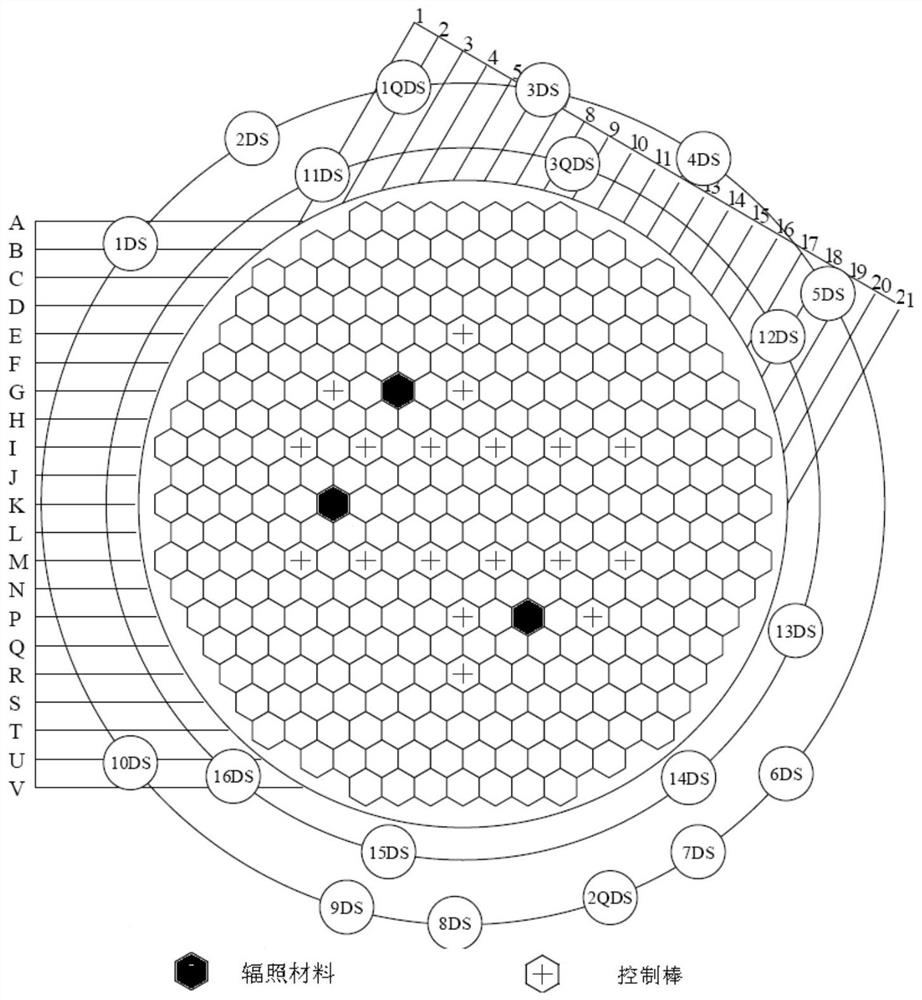
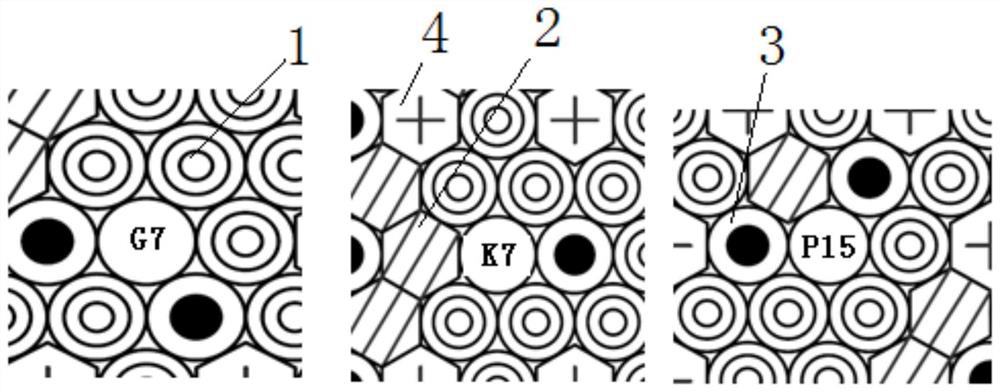
A multi-irradiation target material irradiation test core structure, arrangement and operation method
ActiveCN110211710BNo need to increase the numberAchieve economyNuclear energy generationShieldingIrradiationMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a multi-irradiation target material irradiation test core structure, arrangement and operation method, which solves the problem that materials with different target fluence requirements cannot be simultaneously put into the pile and transferred at the same time in the current HFETR material irradiation. The problem of stacking and stacking at the same time. In the present invention, the horizontal cells of the HFETR core are numbered with letters from A to V from top to bottom, the oblique cells of the HFETR core are numbered with numbers 1 to 12 from left to right, and G7, P15 and K7 are set as irradiation tunnels, and irradiation devices with target materials are installed in the irradiation tunnels; two strong absorber targets are set at the positions adjacent to G7, and one is set at the positions adjacent to K7 A strong absorber target and a beryllium block, and a beryllium block and two strong absorber targets are set adjacent to P15. The present invention can meet the effect that three batches of materials are simultaneously put into the pile, turned and turned out of the pile at the same time, and reach the target value at the same time without changing the number of fuel elements.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com