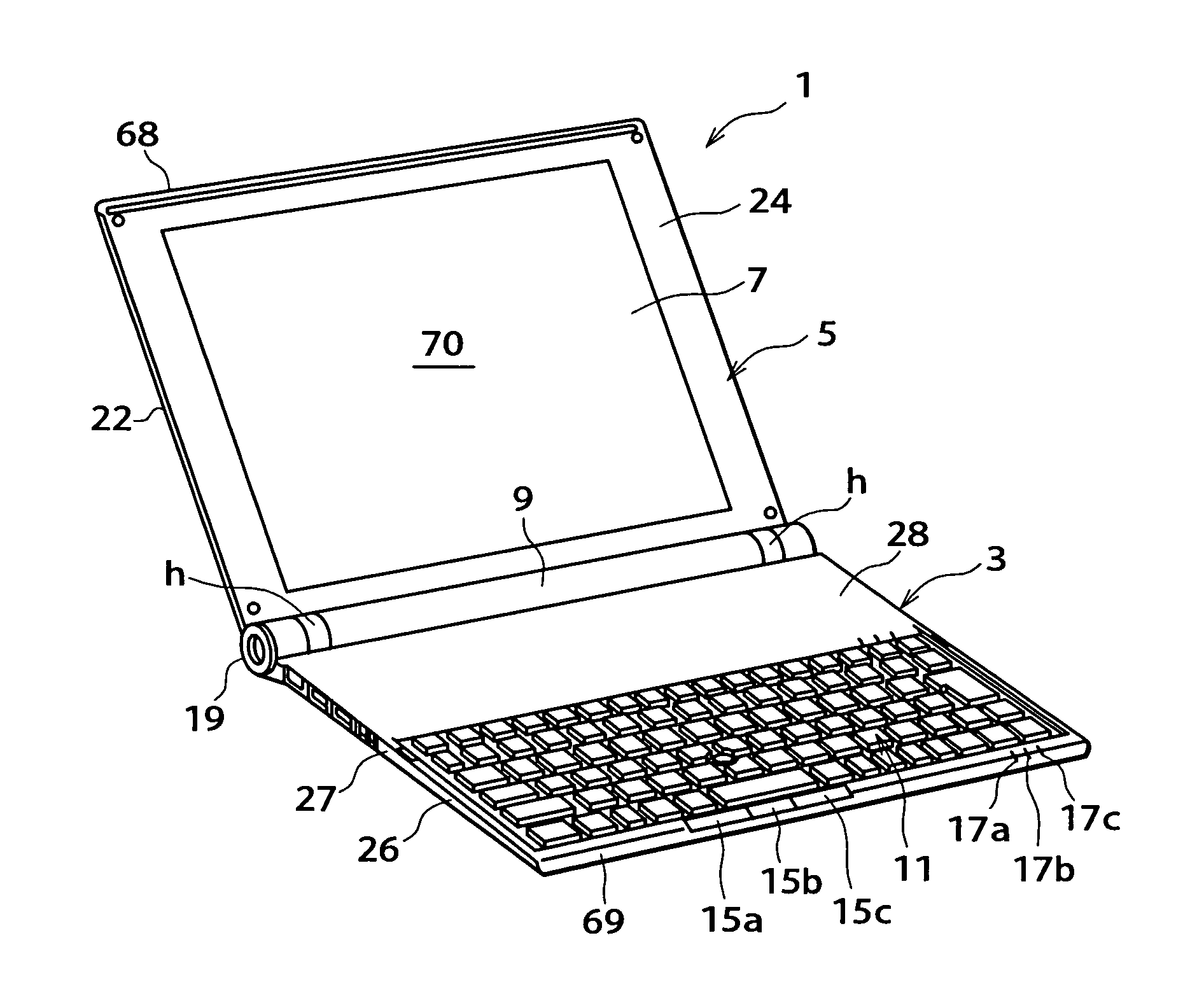
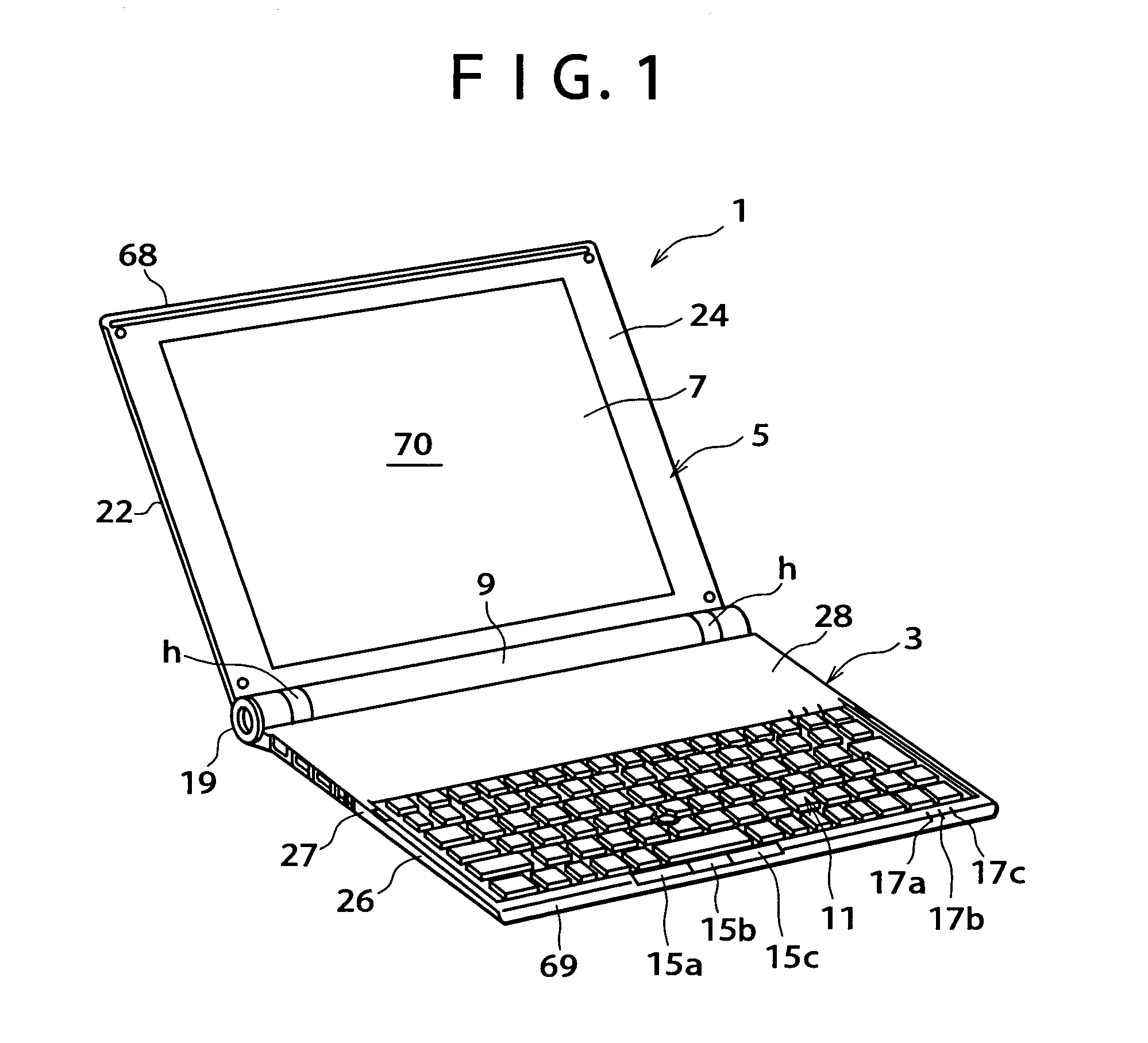
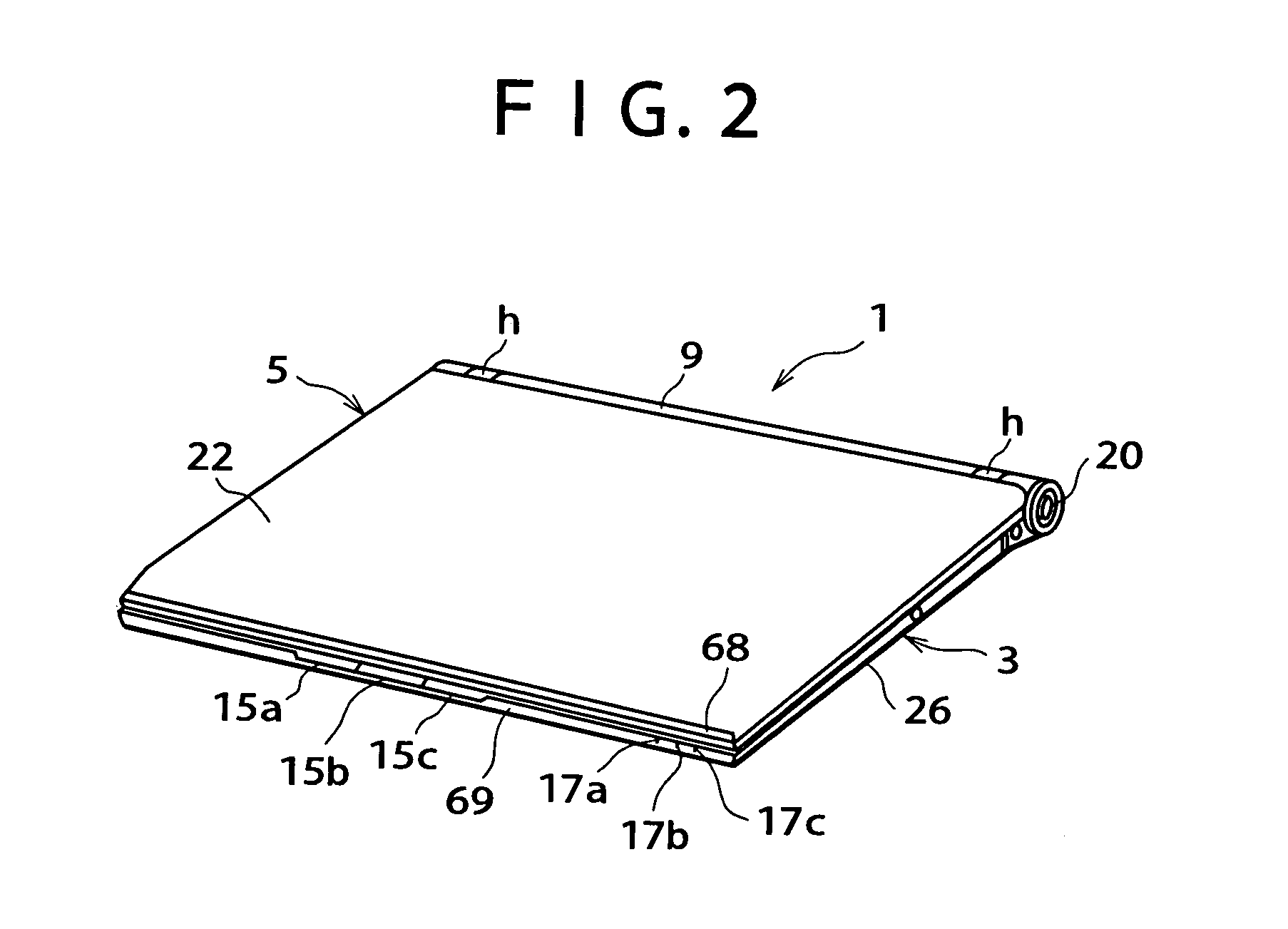
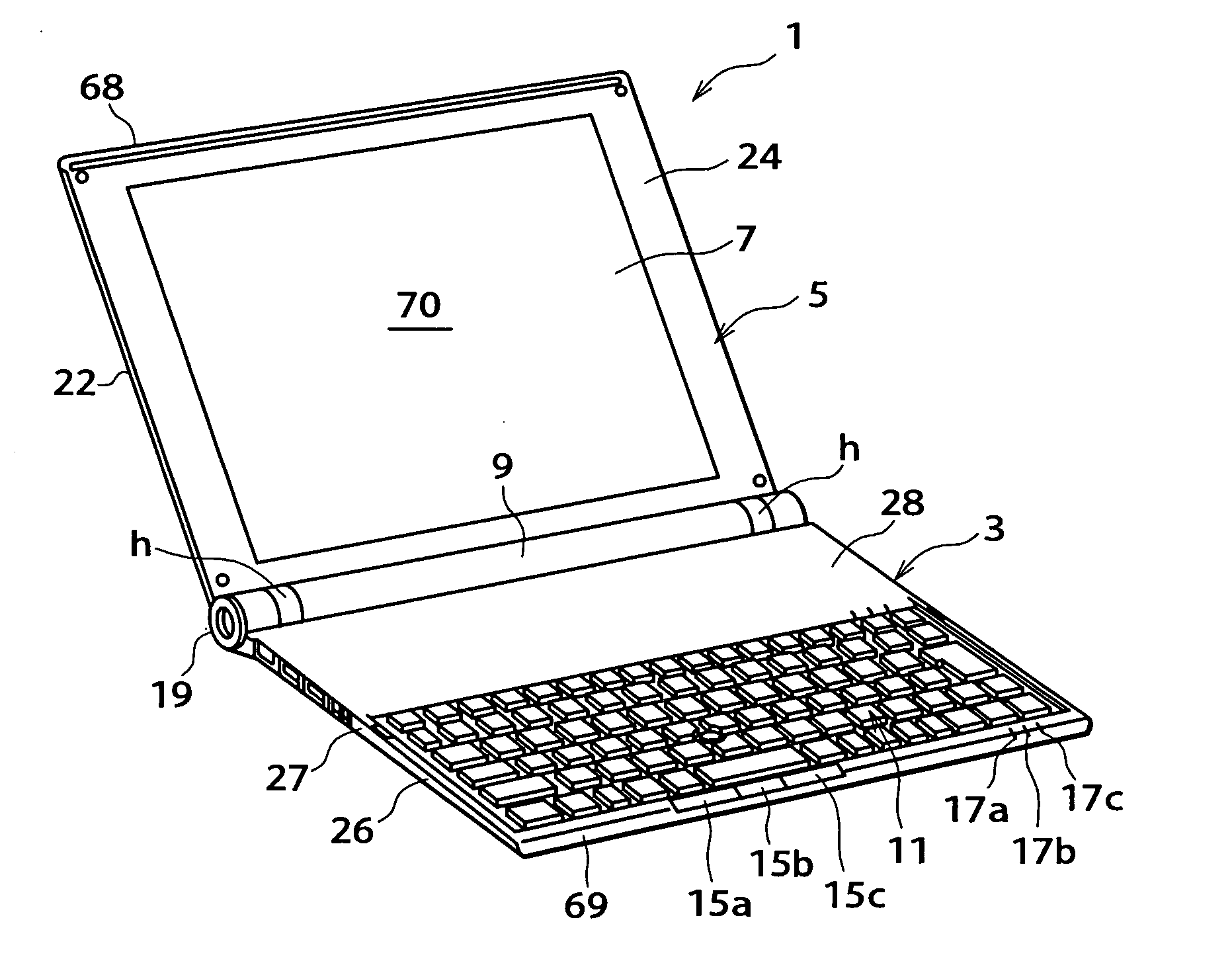
Patents
Literature
76results about How to "Thin display" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
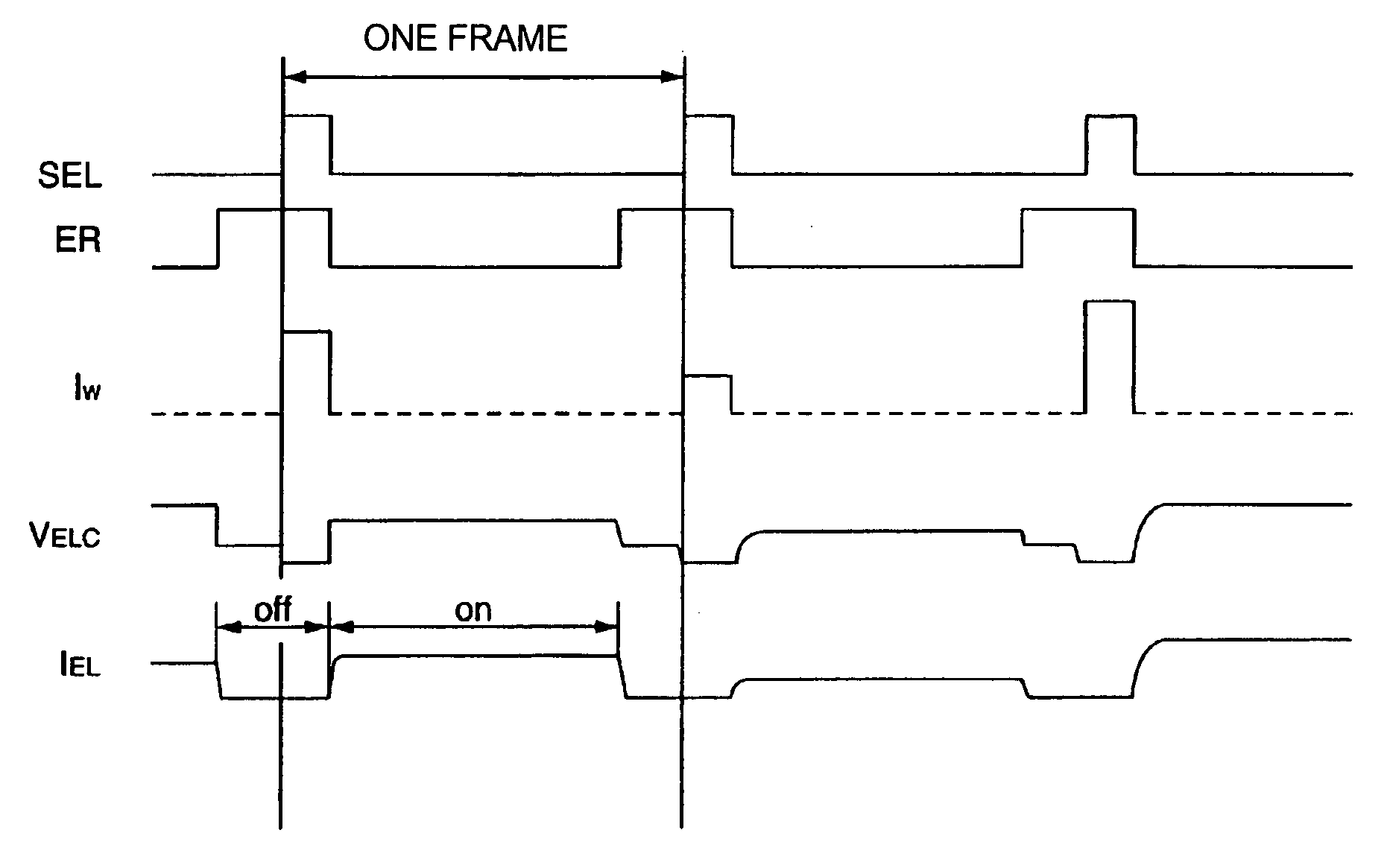
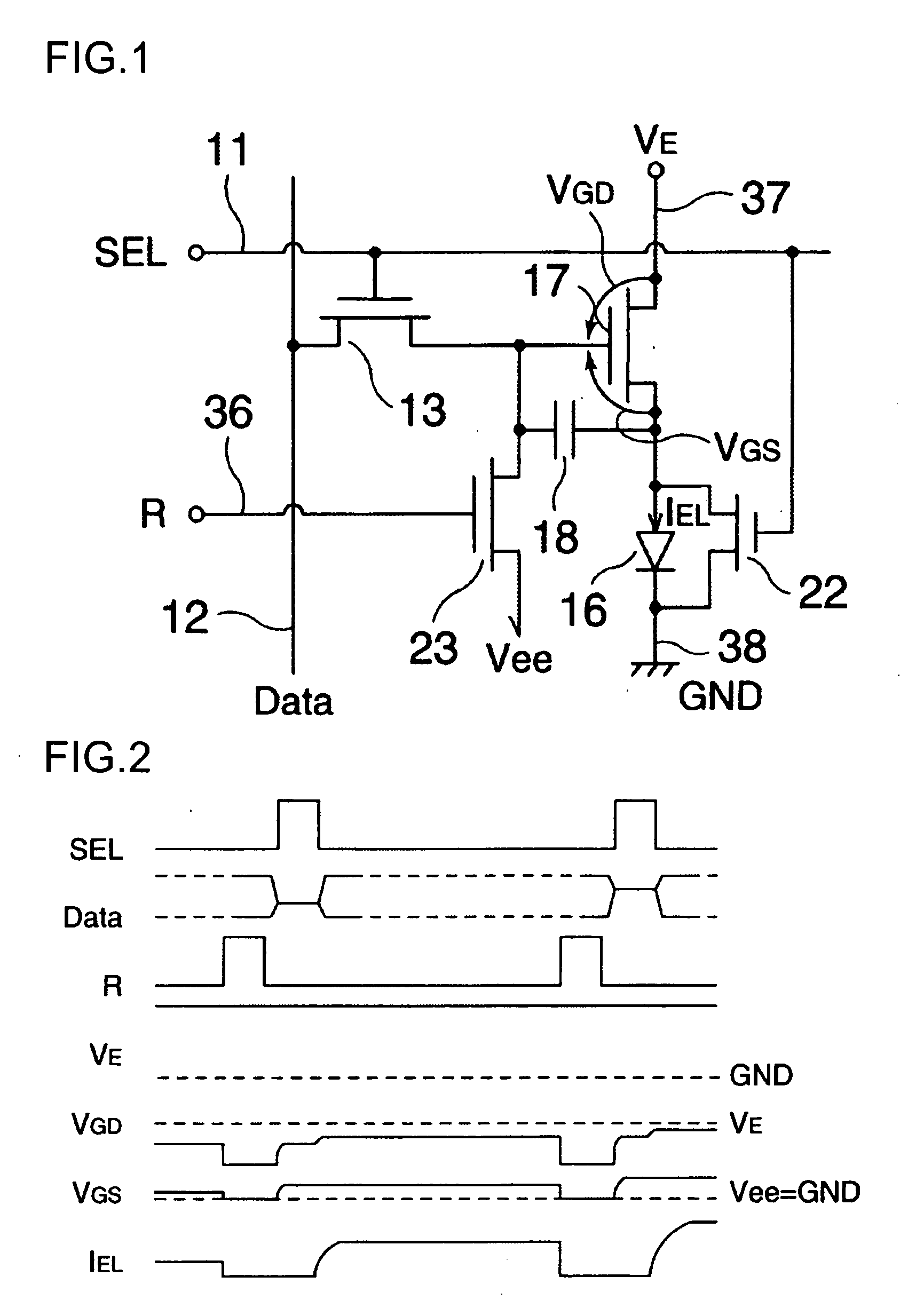
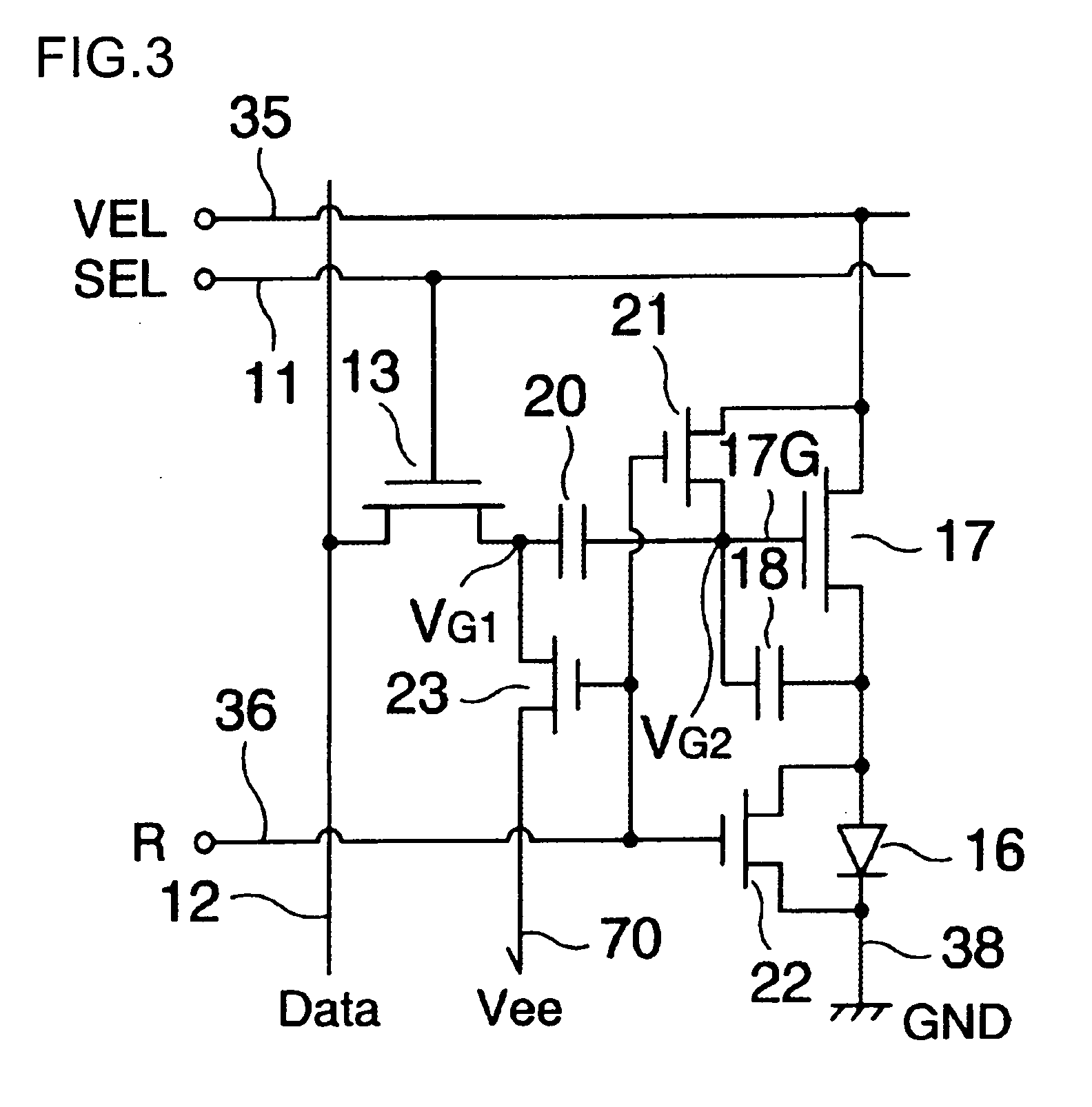
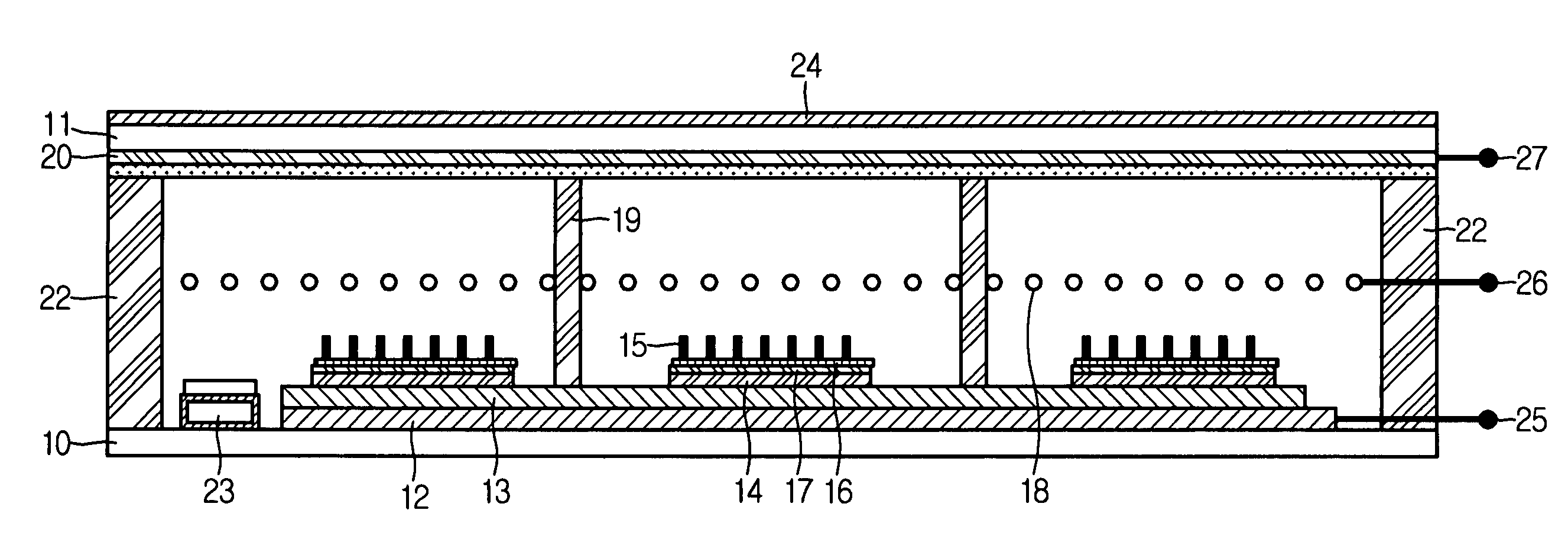
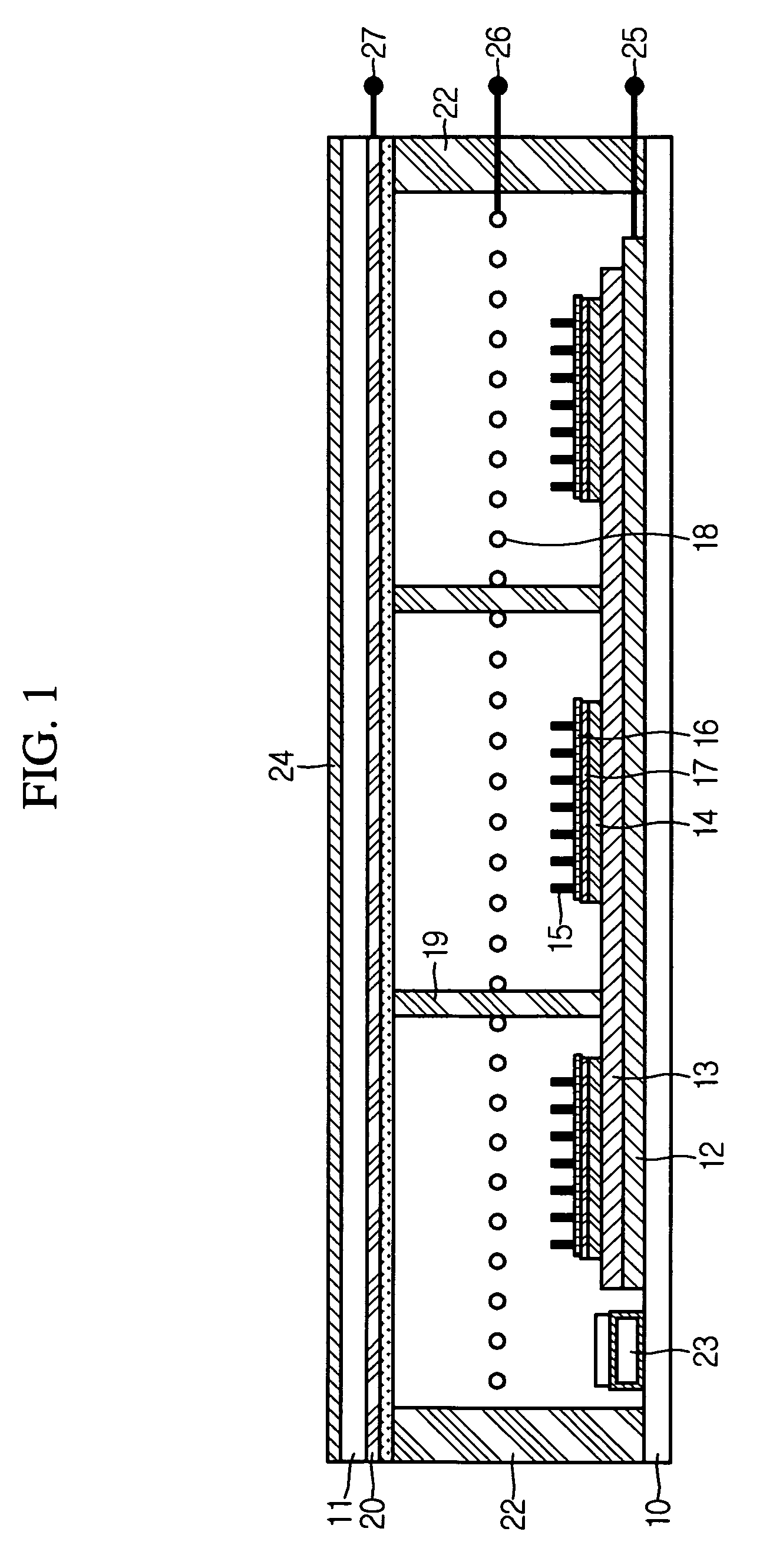
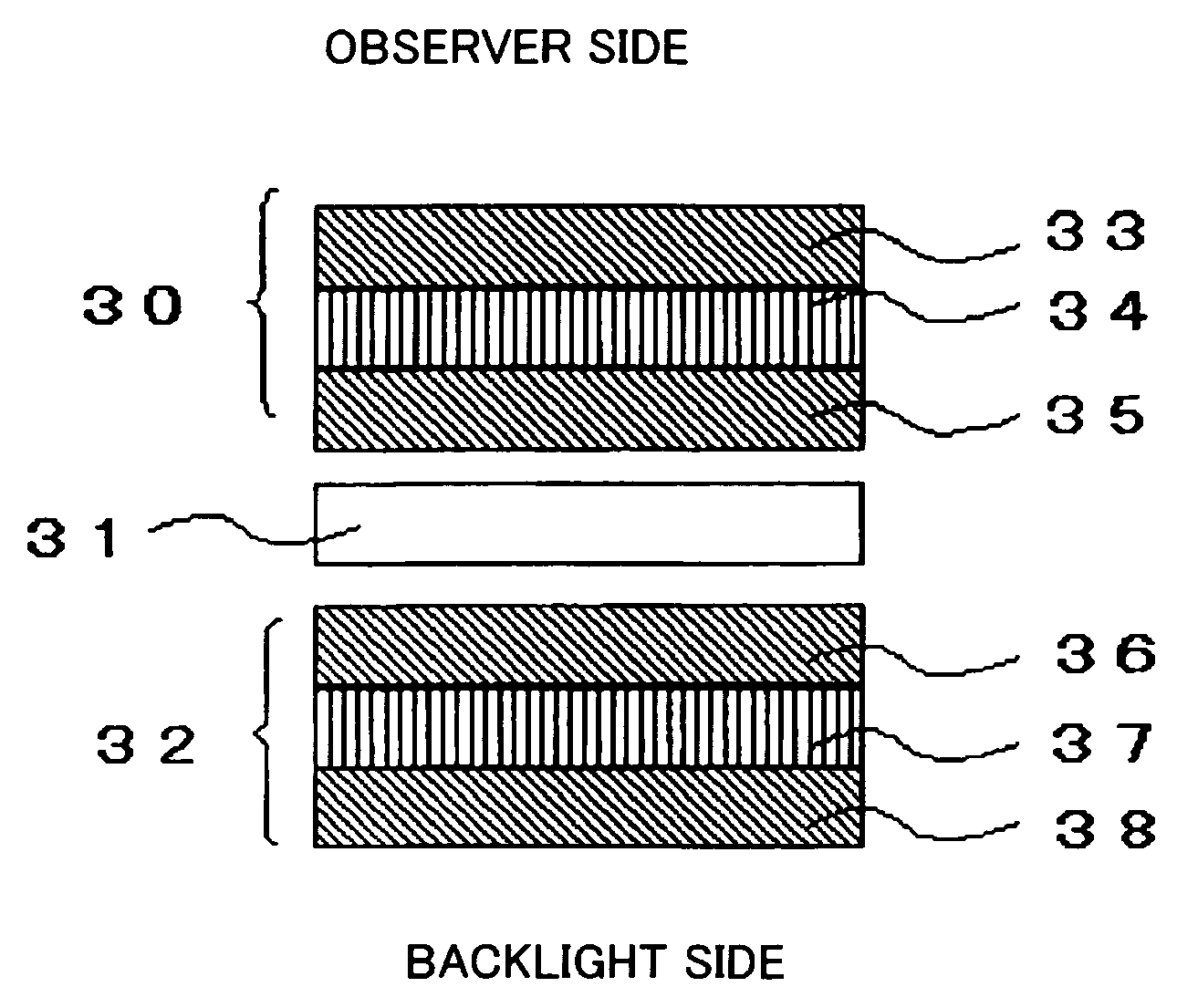
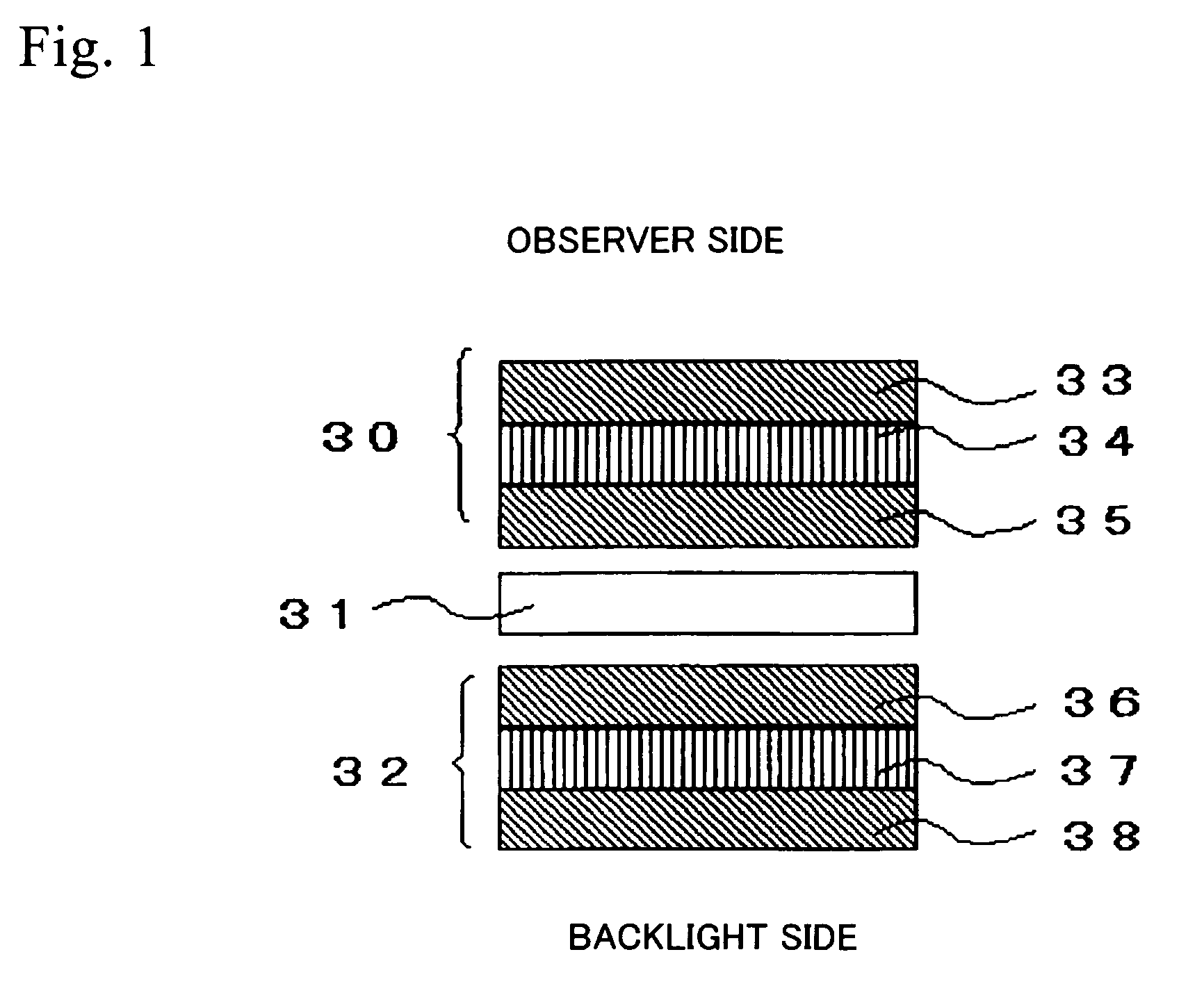
Electro-optical device and driving device thereof
ActiveUS7274345B2Improve display qualityMore accuracyDecorative surface effectsElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentDriven element
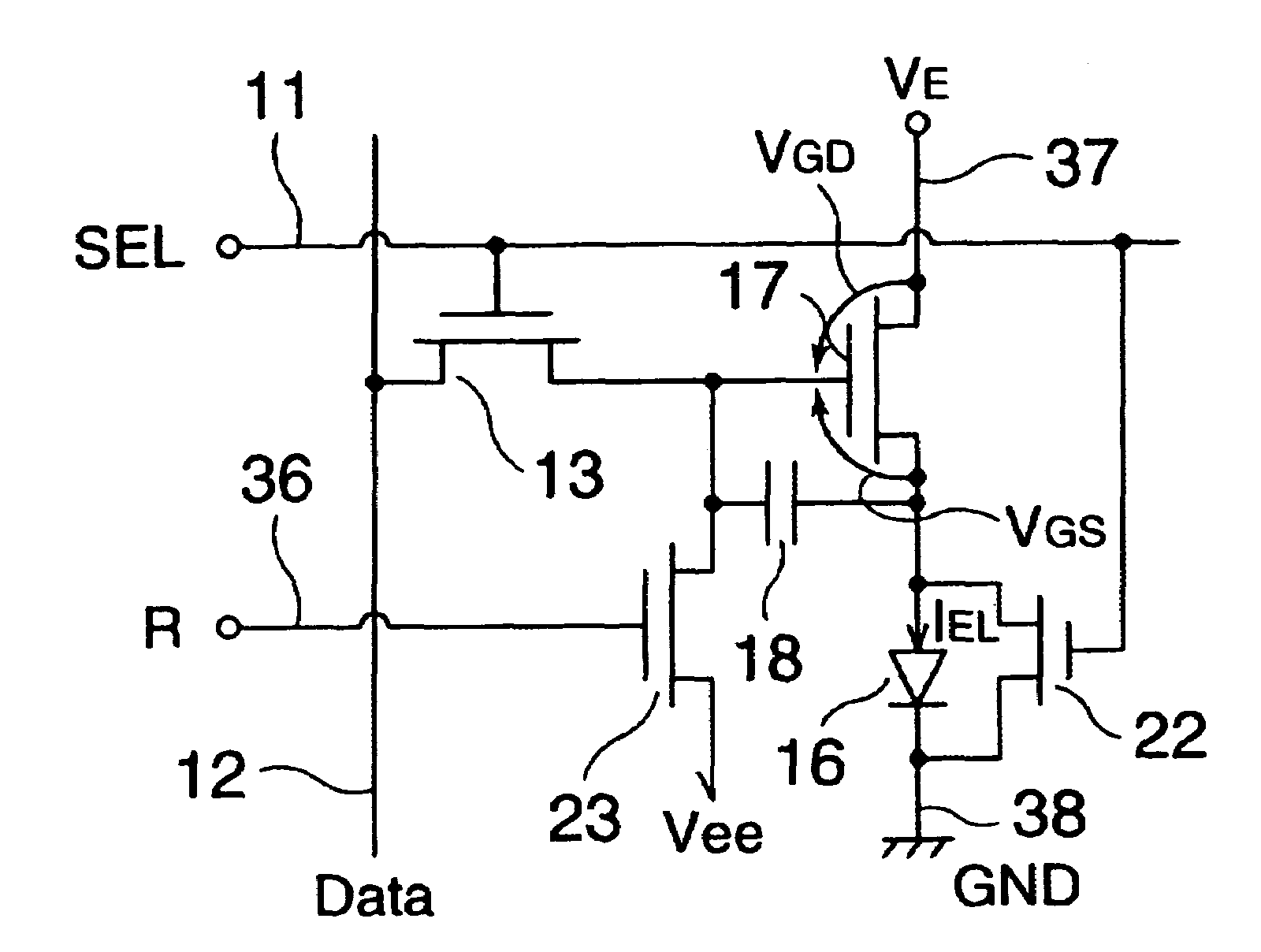
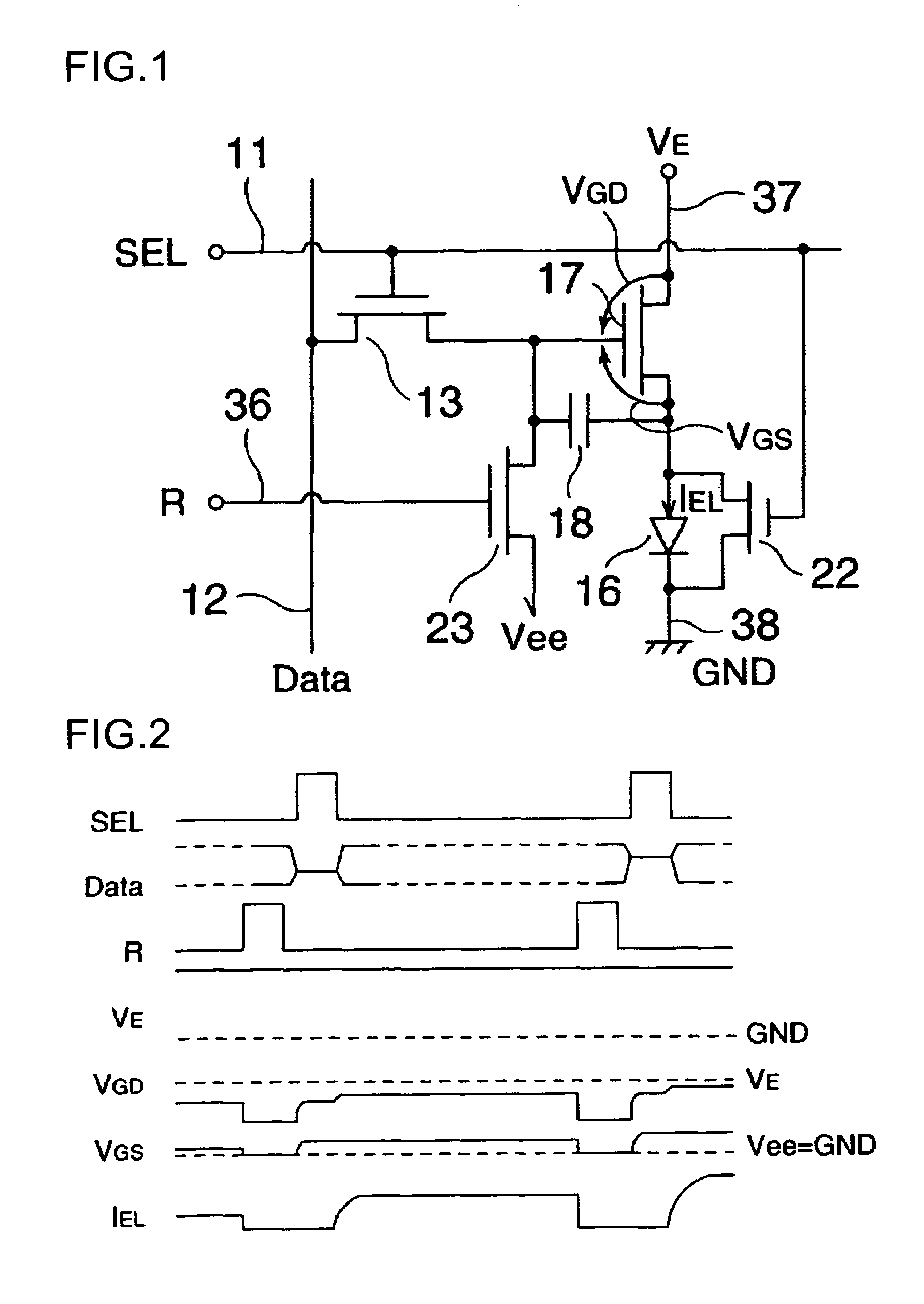
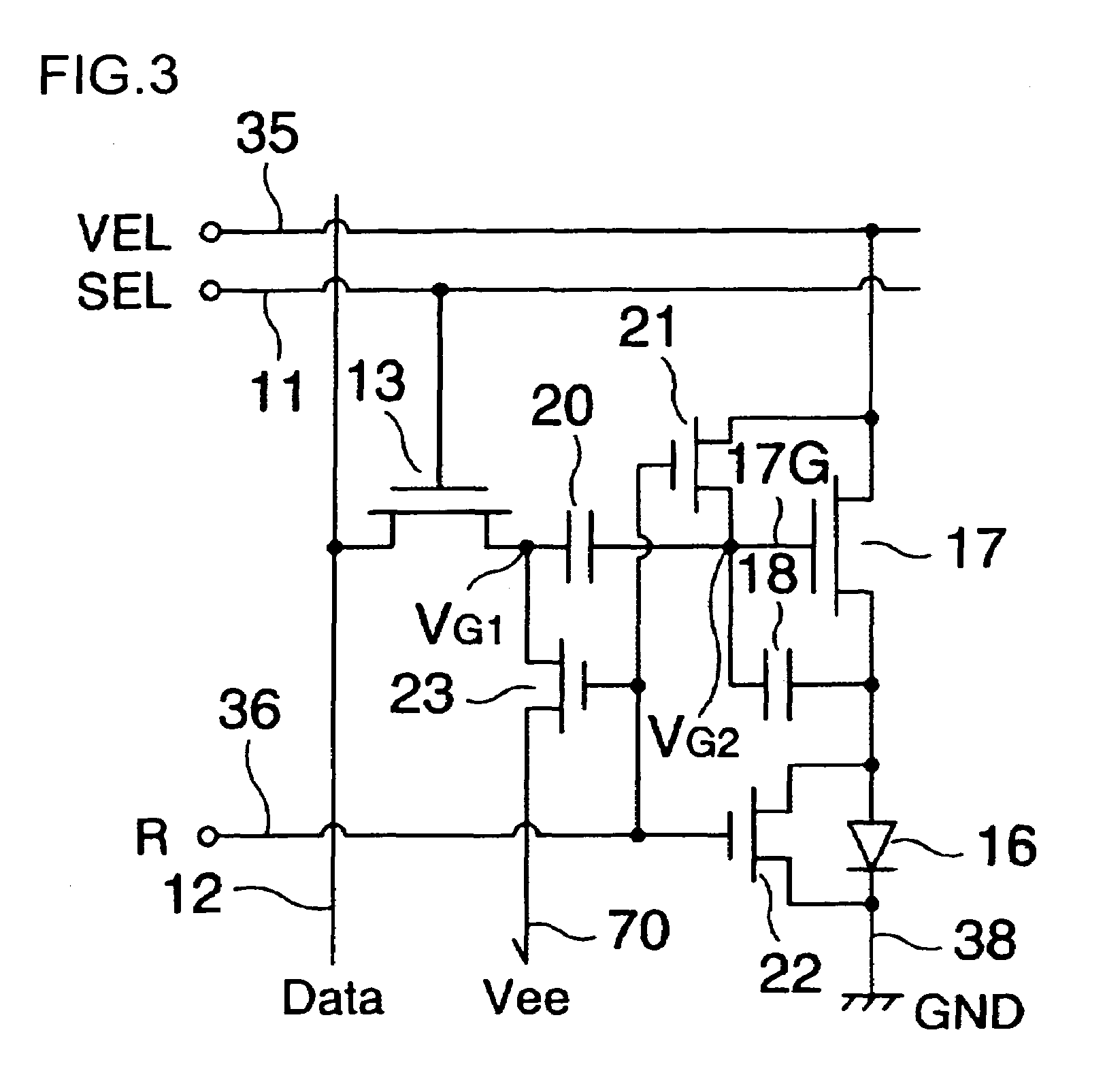
The invention provides an electro-optical device having circuits for driving electro-optical elements, such as organic EL elements, and a driving device, which can employ driving elements having low driving ability, such as α-TFTs. By providing a charge storage capacitor between the source electrode and the gate electrode of a driving transistor which is between power sources, the electro-optical device can allow the driving transistor to control a driving current, even when an electro-optical element is connected to the source side of the driving transistor. In addition, driving data can be stored in the charge storage capacitor by applying a predetermined voltage to the source electrode of the driving transistor.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
Light guide plate, surface light source device, and liquid crystal display device
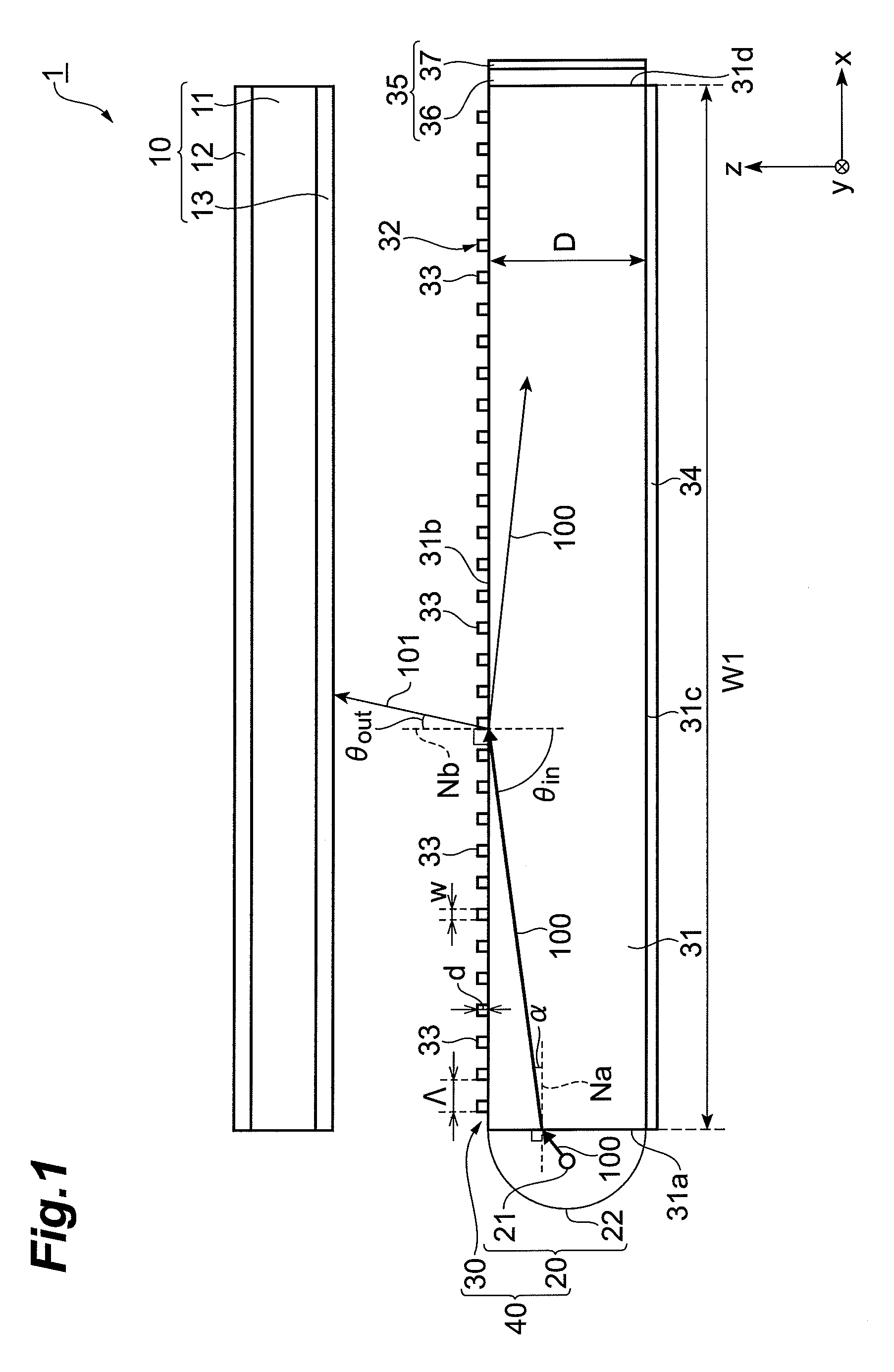
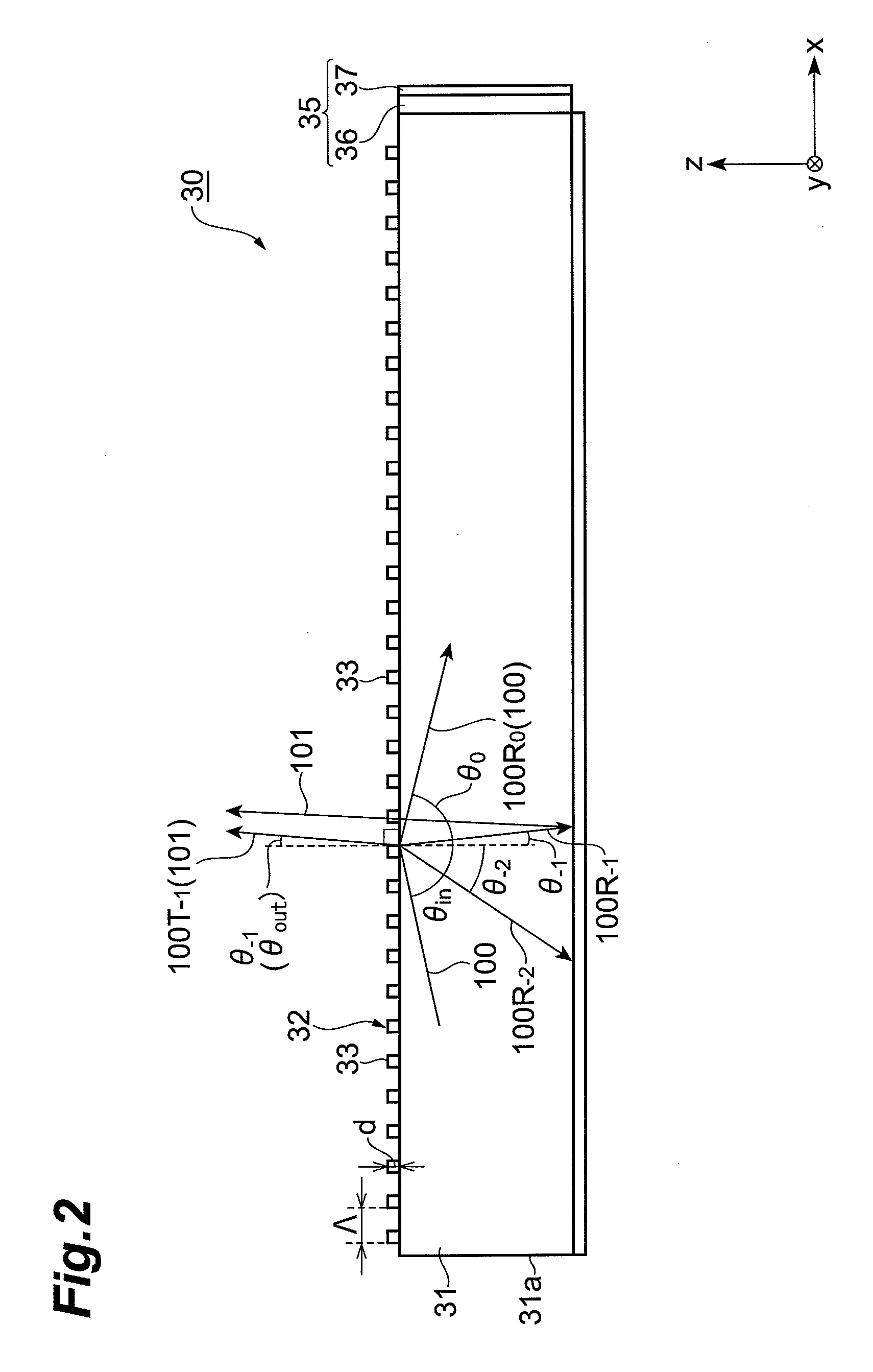
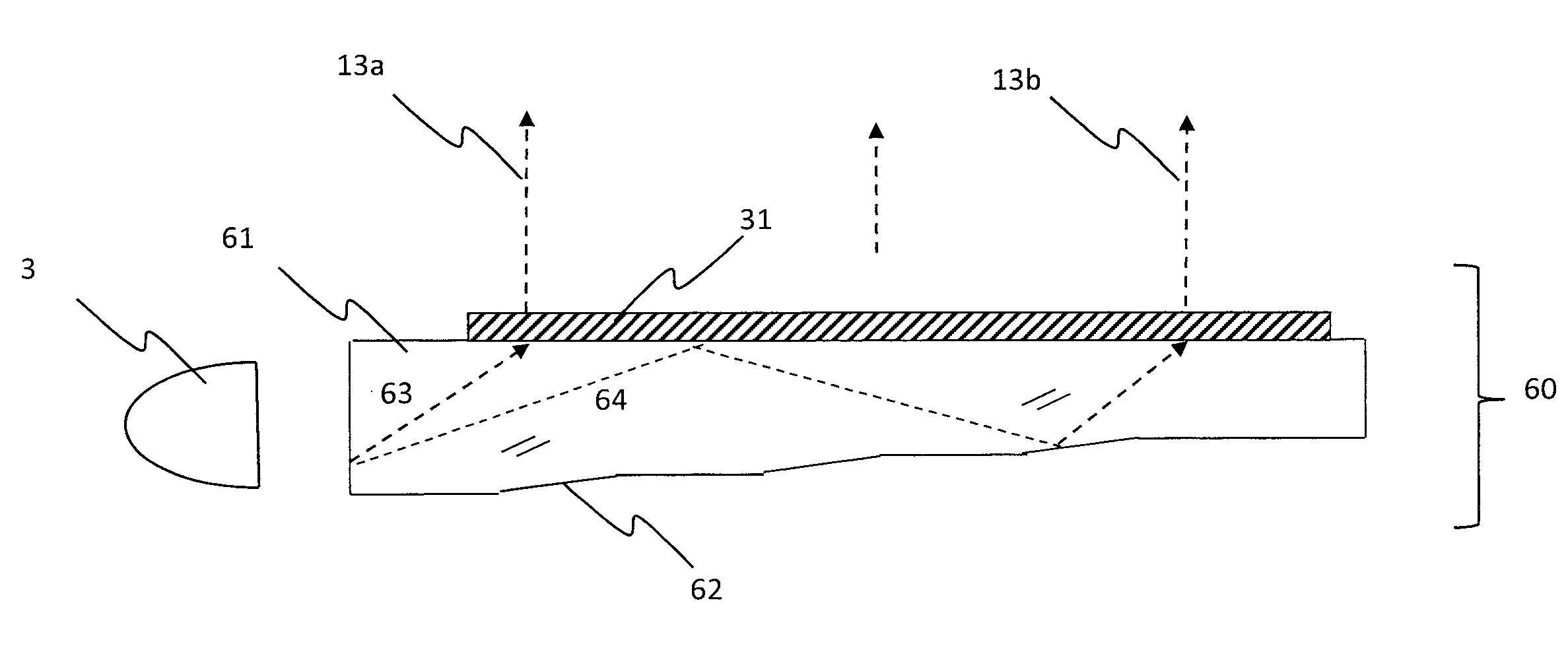
InactiveUS20090129116A1Possible to separateThin displayMechanical apparatusDiffraction gratingsLiquid-crystal displayDielectric
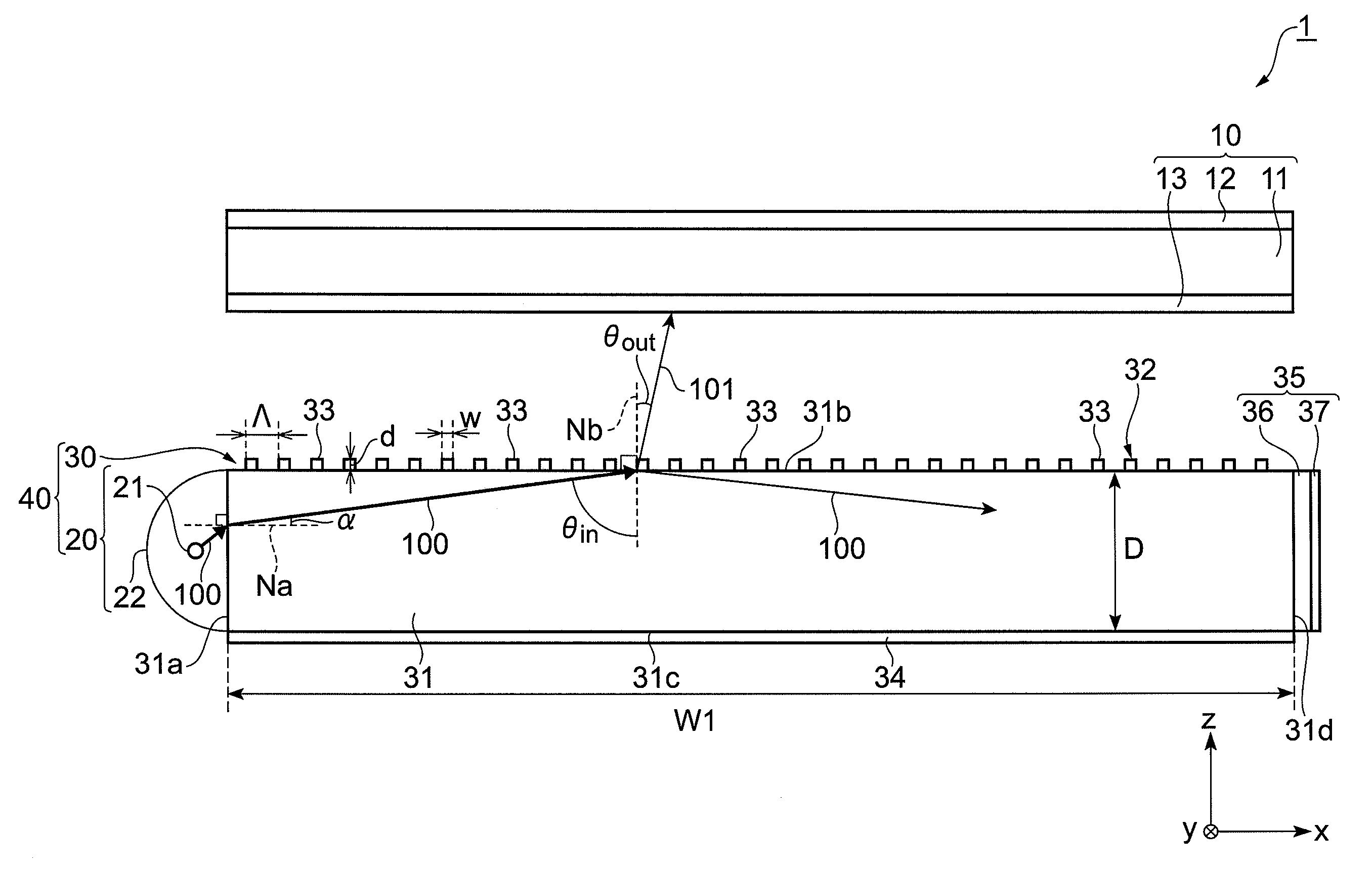
The present invention provides a light guide plate which can process in polarization separation, and emit a light in a desirable direction, a surface light source device, and a liquid crystal display device. A light guide plate 30 includes a light guide plate main body 31 including a first surface 31a on which a light 100 output from a light source section 20 is made incident, a second surface 31b adjacent to the first surface, a third surface 31d which faces the first surface, and is adjacent to the second surface, and a fourth surface which faces the second surface, and is adjacent to the third surface, and a diffraction grating section 32 arranged on the second surface 31b wherein; the diffraction grating section 32 is configured in such a way that a plurality of gratings 33 consisting of a dielectric is arranged in parallel at an interval Λ along a predetermined direction facing from the first surface to the third surface, wherein; when a wavelength of a visible region possessed by a light 100 is set to be λ, the interval Λ satisfies 1≧Λ / λ≧0.5, and when a refractive index of the light guide plate main body 31 is set to be ns, and a refractive index of the grating 33 is set to be ng, the refractive index ng satisfies ng-ns≧0.15.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
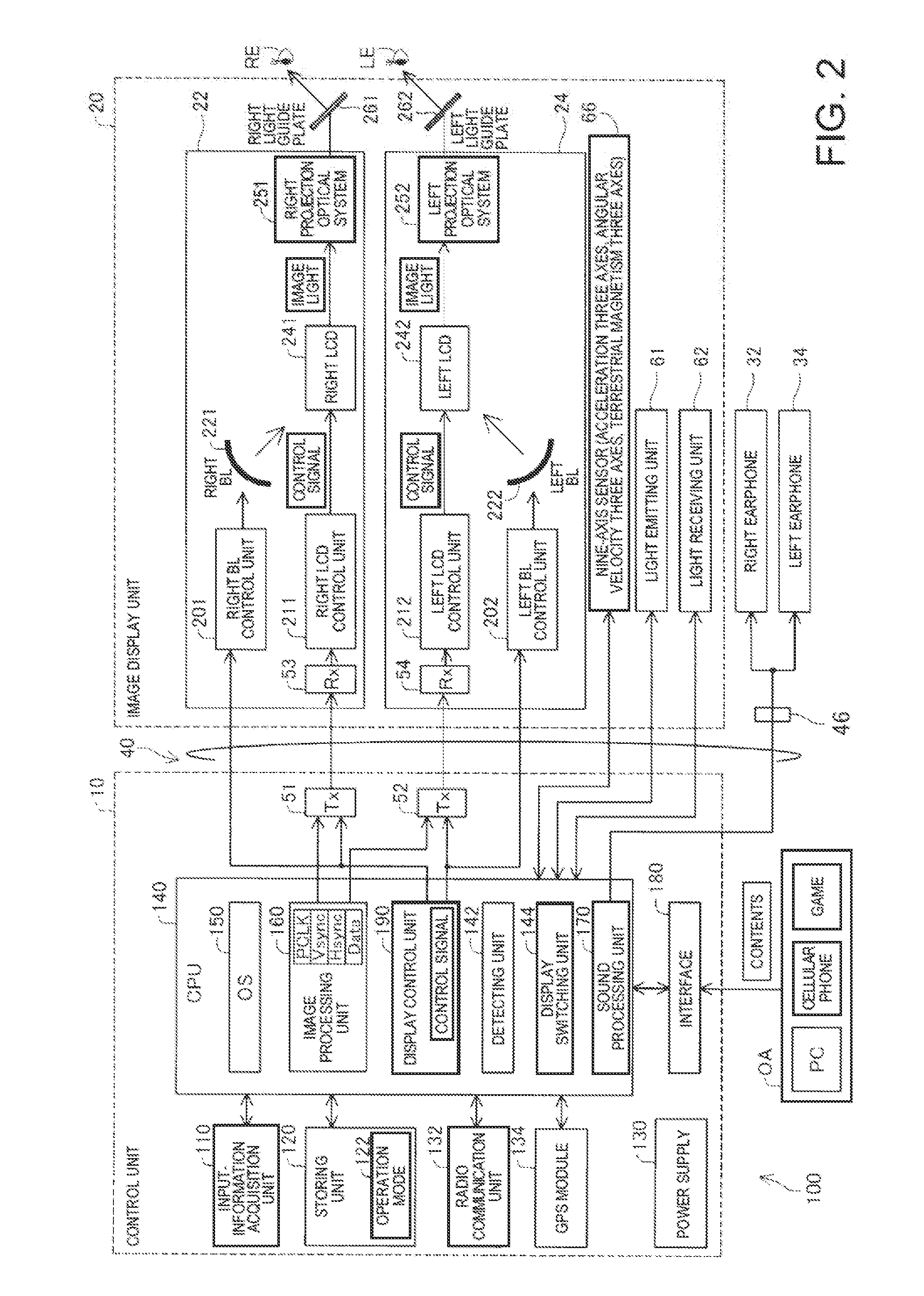
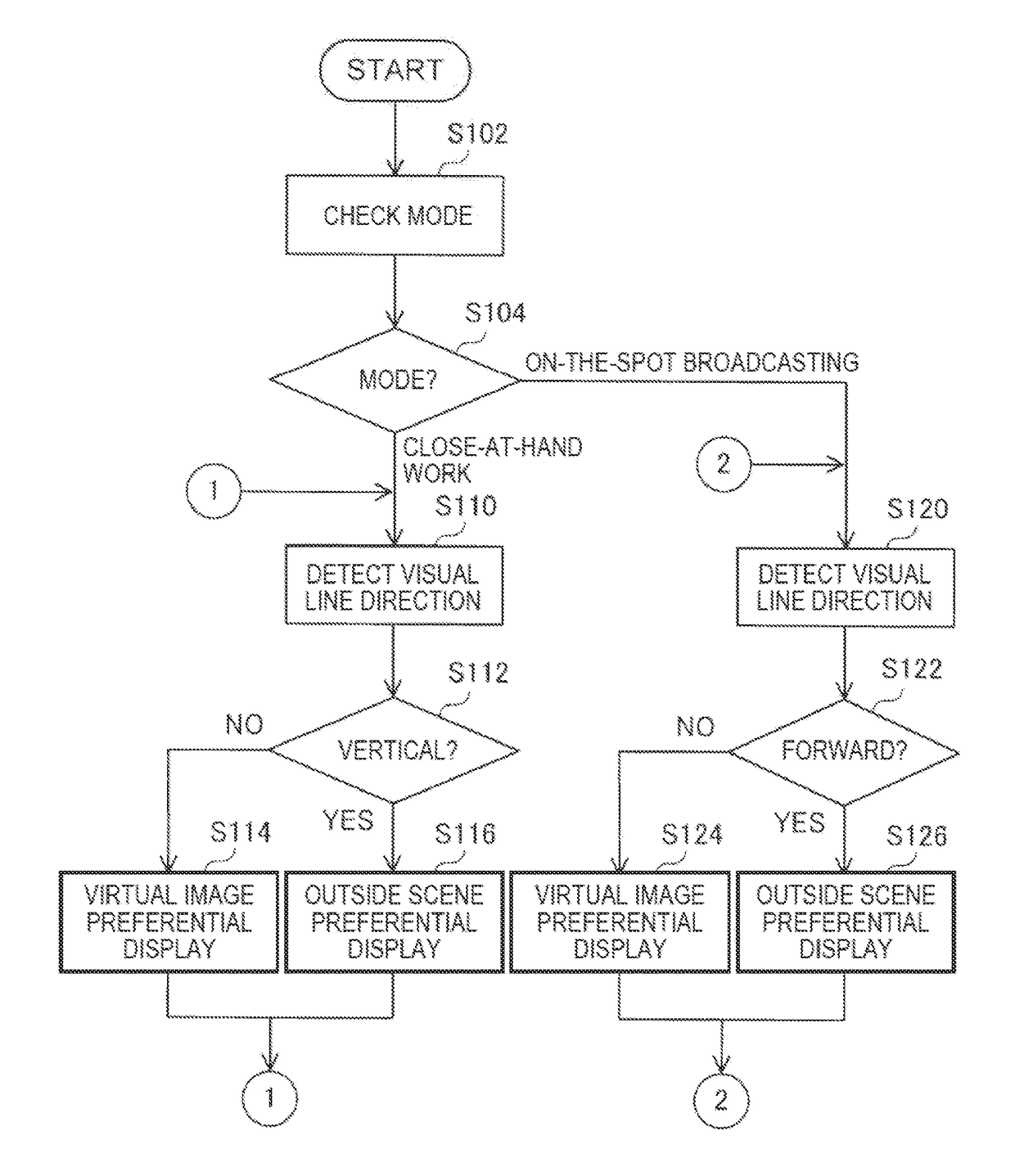
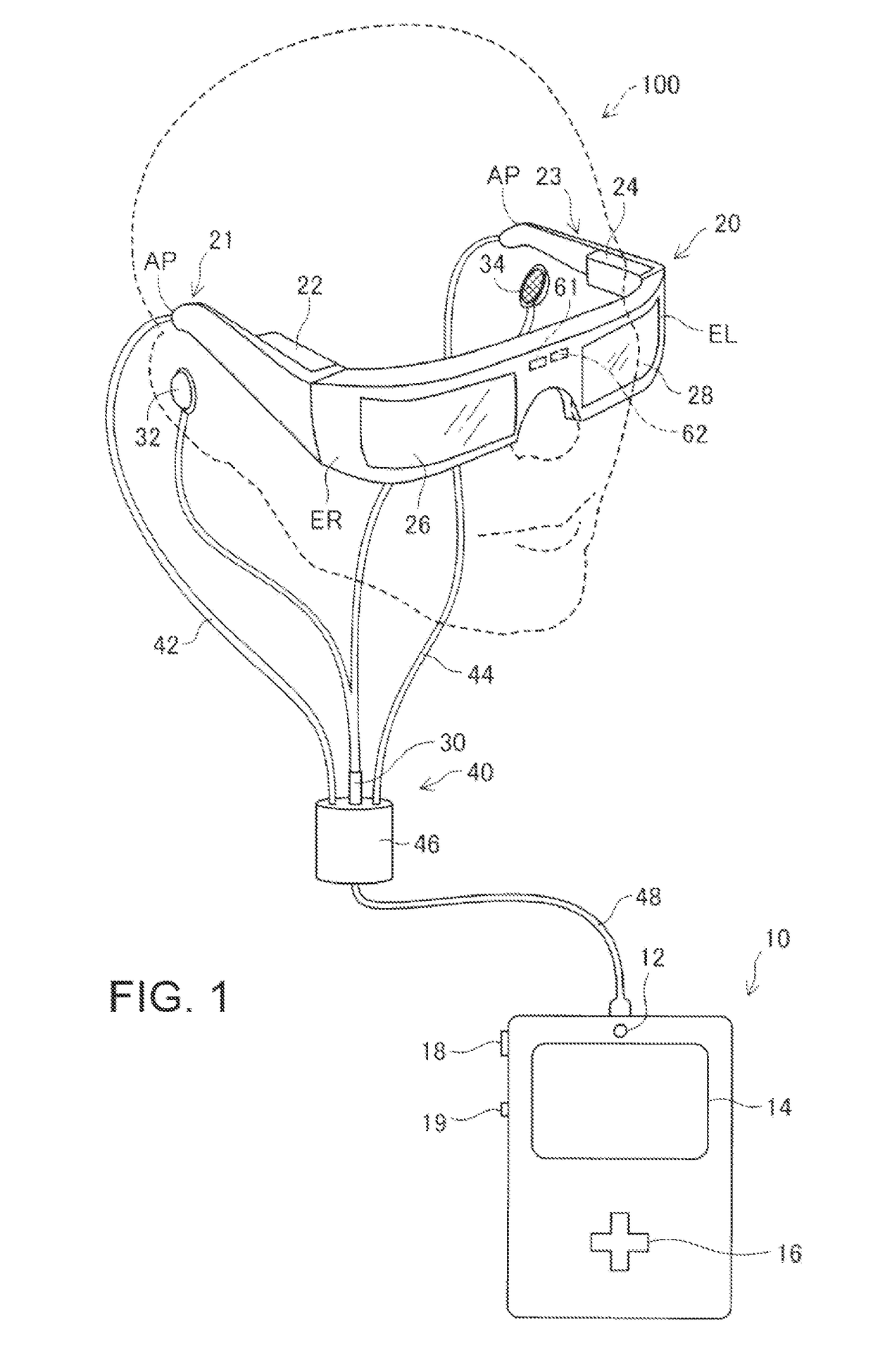
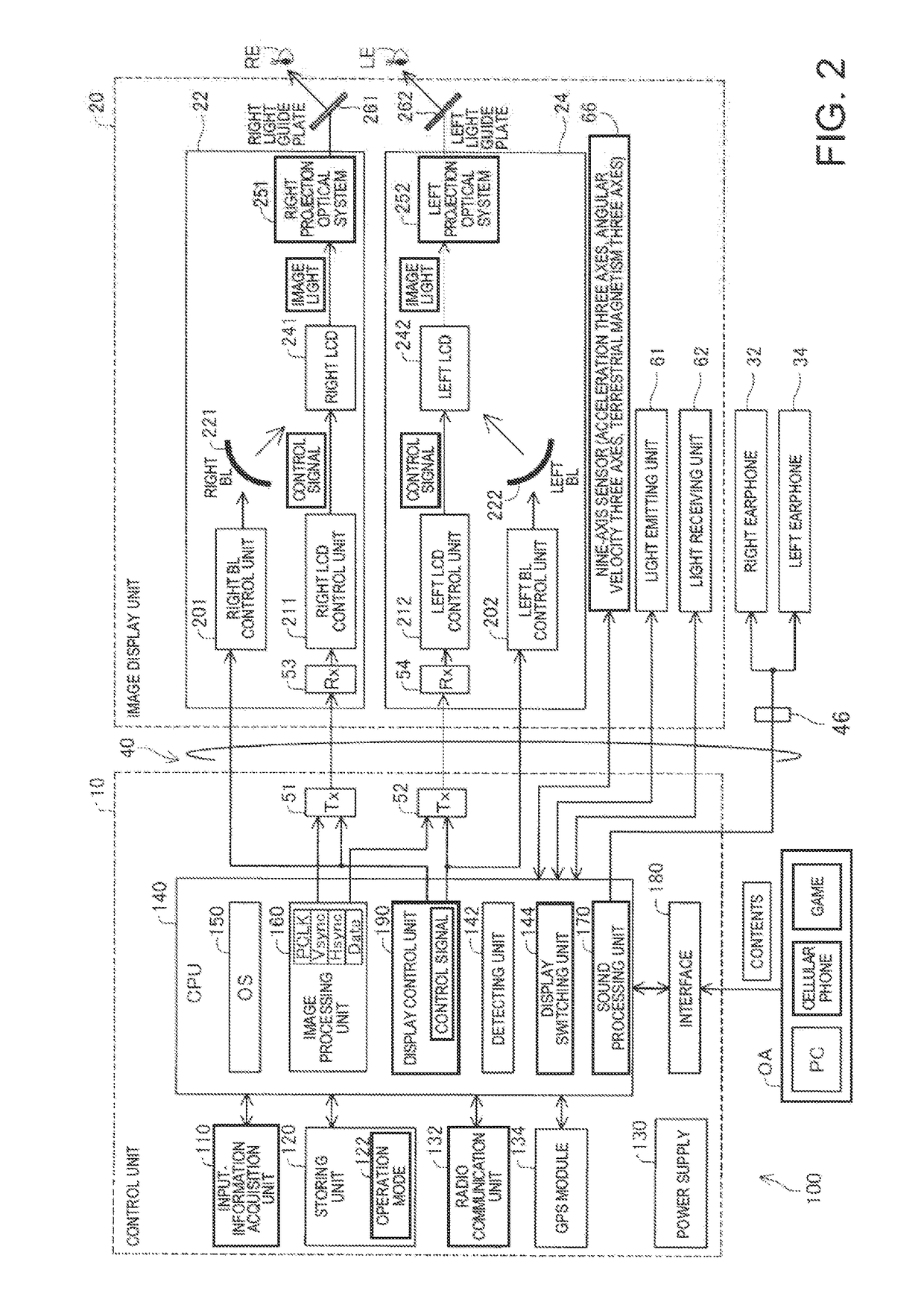
Head-mounted display device and control method for head-mounted display device
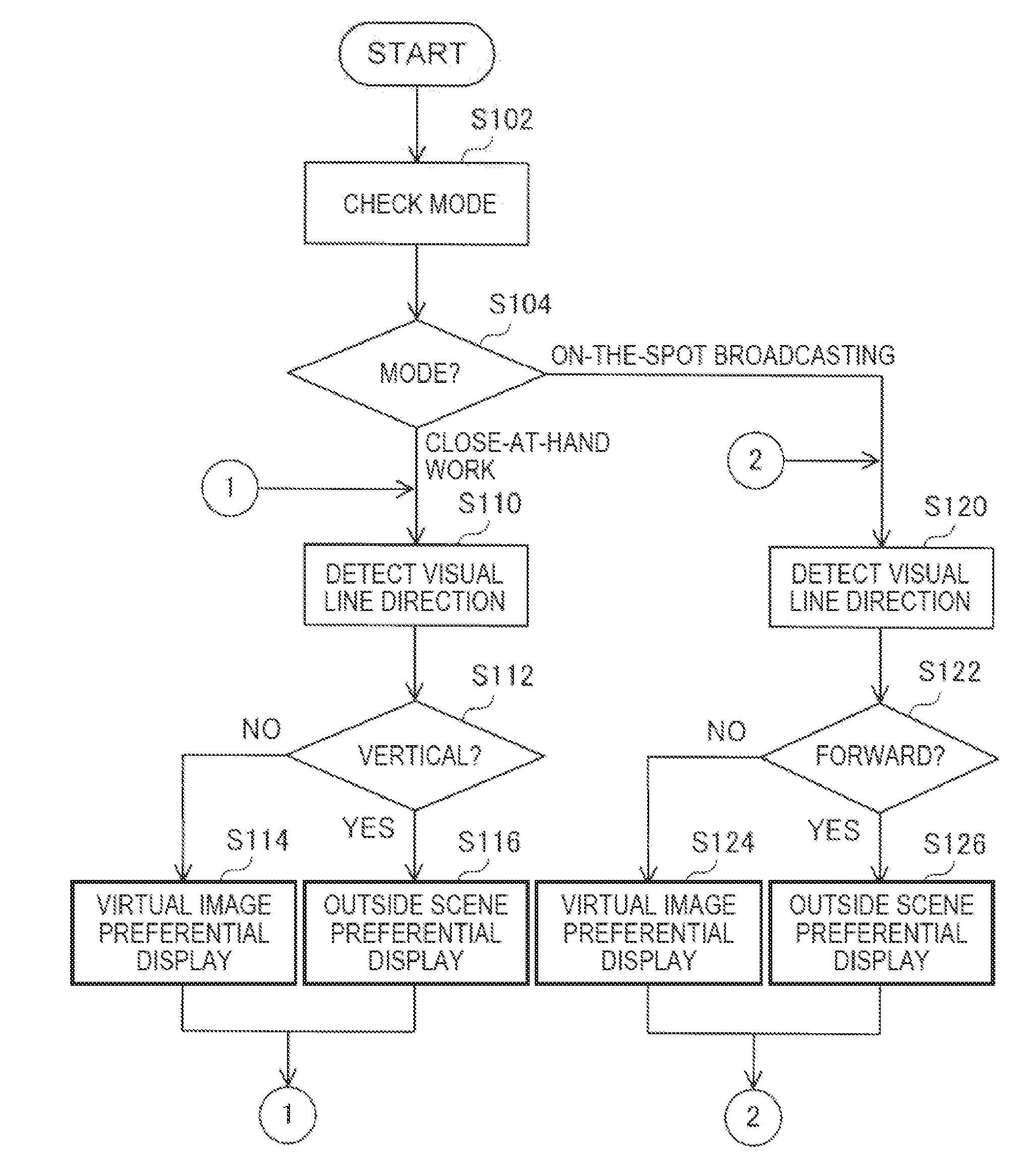
ActiveUS20140285403A1Increase awarenessImprove ease of useCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceVirtual image
A head-mounted display device that enables a user to visually recognize a virtual image and an outside scene includes an image display unit configured to cause the user to visually recognize the virtual image, a detecting unit configured to detect a visual line direction of the user, and a display switching unit configured to switch, according to the detected visual line direction, display of the virtual image by the image display unit between outside scene preferential display for preferentially displaying the outside scene and virtual image preferential display for preferentially displaying the virtual image.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electro-optical device and driving device thereof
InactiveUS20070296652A1Improve display qualityMore accuracyDecorative surface effectsOrnamental structuresDriving currentDriven element
The invention provides an electro-optical device having circuits for driving electro-optical elements, such as organic EL elements, and a driving device, which can employ driving elements having low driving ability, such as α-TFTs. By providing a charge storage capacitor between the source electrode and the gate electrode of a driving transistor which is between power sources, the electro-optical device can allow the driving transistor to control a driving current, even when an electro-optical element is connected to the source side of the driving transistor. In addition, driving data can be stored in the charge storage capacitor by applying a predetermined voltage to the source electrode of the driving transistor.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Composition for polarizing film, polarizing film, method of manufacturing the same, and liquid crystal display provided with the polarizing film
ActiveUS20120050652A1Decrease production costSimplify processSynthetic resin layered productsPolarising elementsPolypropylenePolyolefin
A composition for a polarization film including a polyolefin component including polypropylene and a polyethylene-polypropylene copolymer; and a dichroic dye.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Biaxial-optical polynorbornene-based film and method of manufacturing the same, integrated optical compensation polarizer having the film and method of manufacturing the polarizer, and liquid crystal display panel containing the film and/or polarizer
ActiveUS20060105117A1High light transmittanceUniform in-plane retardation valueLiquid crystal compositionsOptical articlesIn planePolymer dissolution
A method of manufacturing a biaxial-optical polynorbornene-based film is provided, including: preparing a polynorbornene-based polymer containing composition by dissolving a polynorbornene-based polymer in a mixed solvent containing a high-boiling solvent and a low-boiling solvent, with a difference in boiling points of the two solvents of 20° C. or greater and an amount of the high-boiling solvent being 0.1 to 15 wt % based on a weight of the polynorbornene-based polymer; casting and partially drying the composition to obtain a polynorbornene-based film containing 1 to 6 wt % of the mixed solvent based on a total weight of the polynorbornene-based film; and uniaxially stretching the partially dried film in one direction parallel with the surface of the film at a stretching temperature less than or equal to the boiling point of the high-boiling solvent +20° C. and drying the stretched film at a temperature greater than or equal to the boiling point of the high-boiling solvent. According to the method of manufacturing a biaxial polynorbornene-based film, a compensation film which has good light transmittance and a uniform in-plane retardation value and can function as both a negative C-plate and an A-plate can be obtained.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Electronic device
InactiveUS7489507B2Components in expandedImprove the display effectFurniture partsCabinetsDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:SONY CORP
Electronic device
InactiveUS20050117286A1Manipulation is accurateReduce component countDetails for portable computersElectrical apparatus contructional detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:SONY CORP
Flat lamp device with multi electron source array
InactiveUS20060244357A1Excellent light emission uniformityImprove uniformity of light emissionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesCarbon nanotubeEngineering
Disclosed is a flat lamp device, including lower and upper glass plates facing each other in parallel; spacers interposed between the plates to keep distance therebetween; a cathode electrode singly formed over the entire upper surface of the lower glass plate; an insulation film formed on the cathode electrode; semiconductor films independently patterned on the insulation film at intervals; a catalyst-metal layer laminated on the buffer metal to improve the adhesion of catalyst metal formed on the semiconductor films; carbon nano-tubes formed on the catalyst-metal layer; a grid electrode installed on the carbon nano-tubes between the plates to guide electron emission from the carbon nano-tubes with a mesh shape having an opening for passage of the emitted electrons; an anode electrode formed below the upper glass plate to accelerate the emitted electrons; and a fluorescent layer formed below the anode electrode to emit light by collision with the accelerated electrons.
Owner:LEE SEUNG HO
Display apparatus
InactiveUS20130242542A1Thin displayMaintain performanceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsIlluminated signsEmbedded systemChassis
A display apparatus includes a display unit; a chassis member provided at the rear side of the display unit; a fan attached to the chassis member; a first circuit substrate that is provided between the display unit and the chassis member and of which the component-mounting surface is arranged at a position facing the fan side; and a second circuit substrate that is provided between the display unit and the chassis member and of which the component-mounting surface is arranged to face the display unit side.
Owner:CANON KK
Illumination apparatus
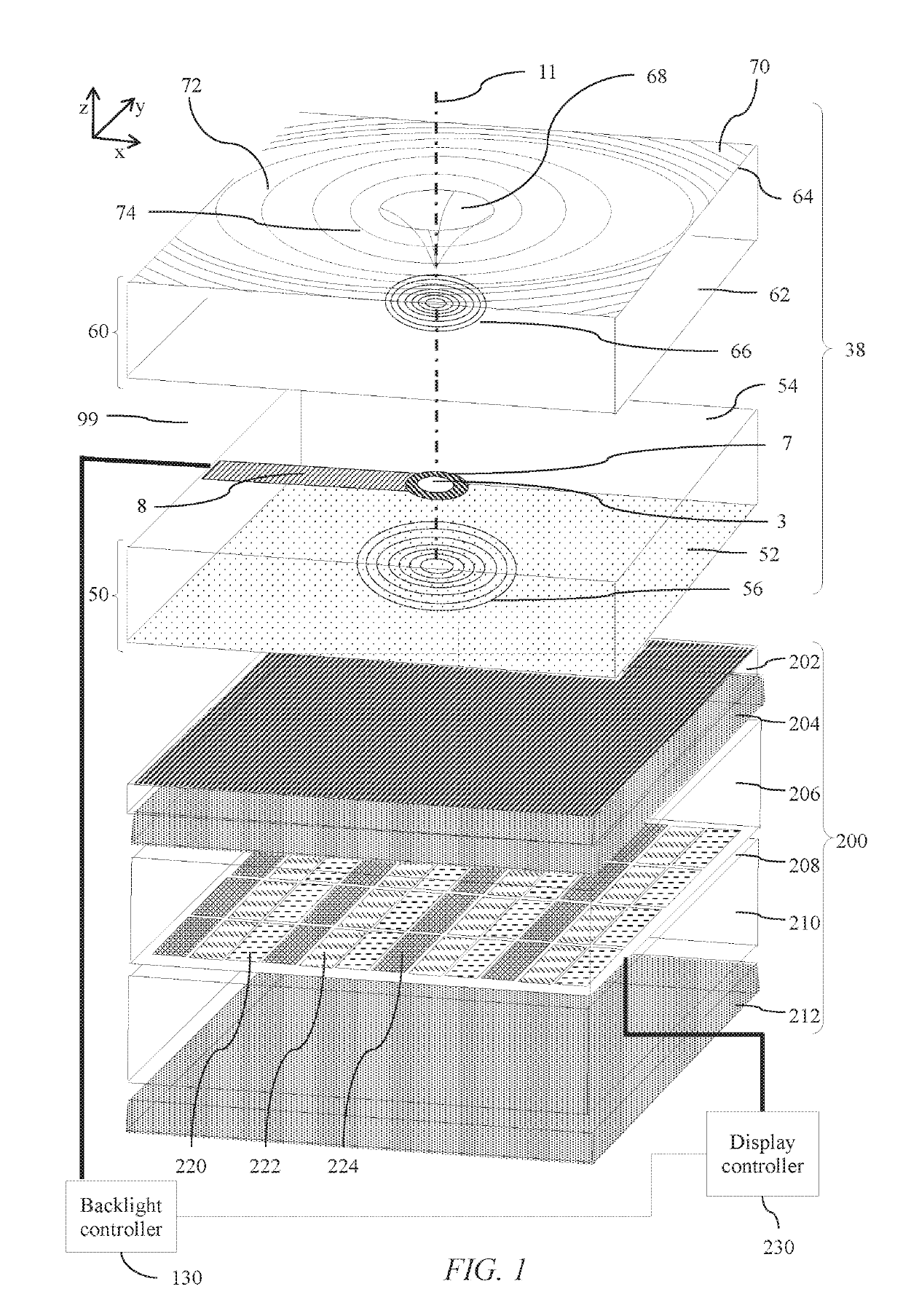
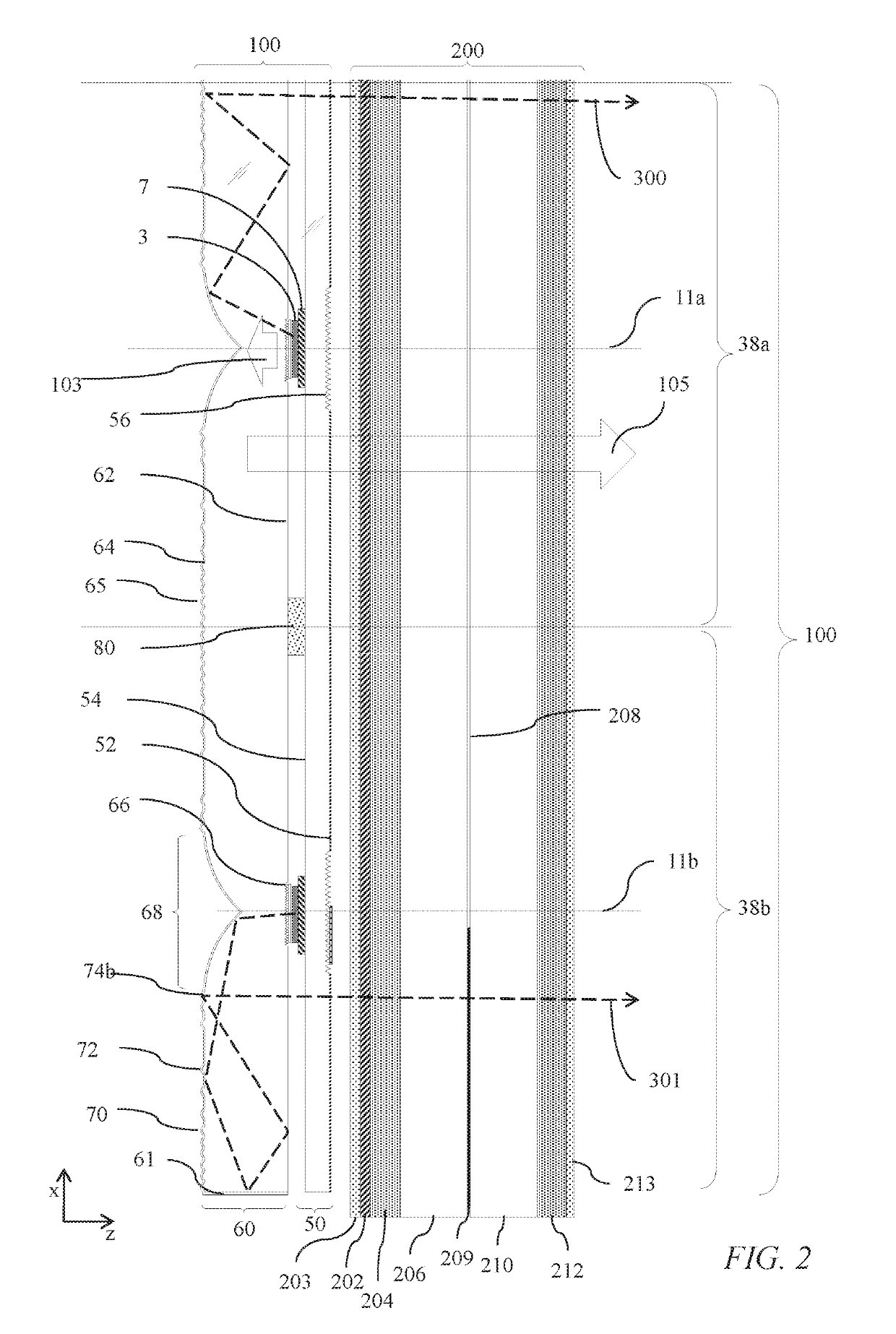
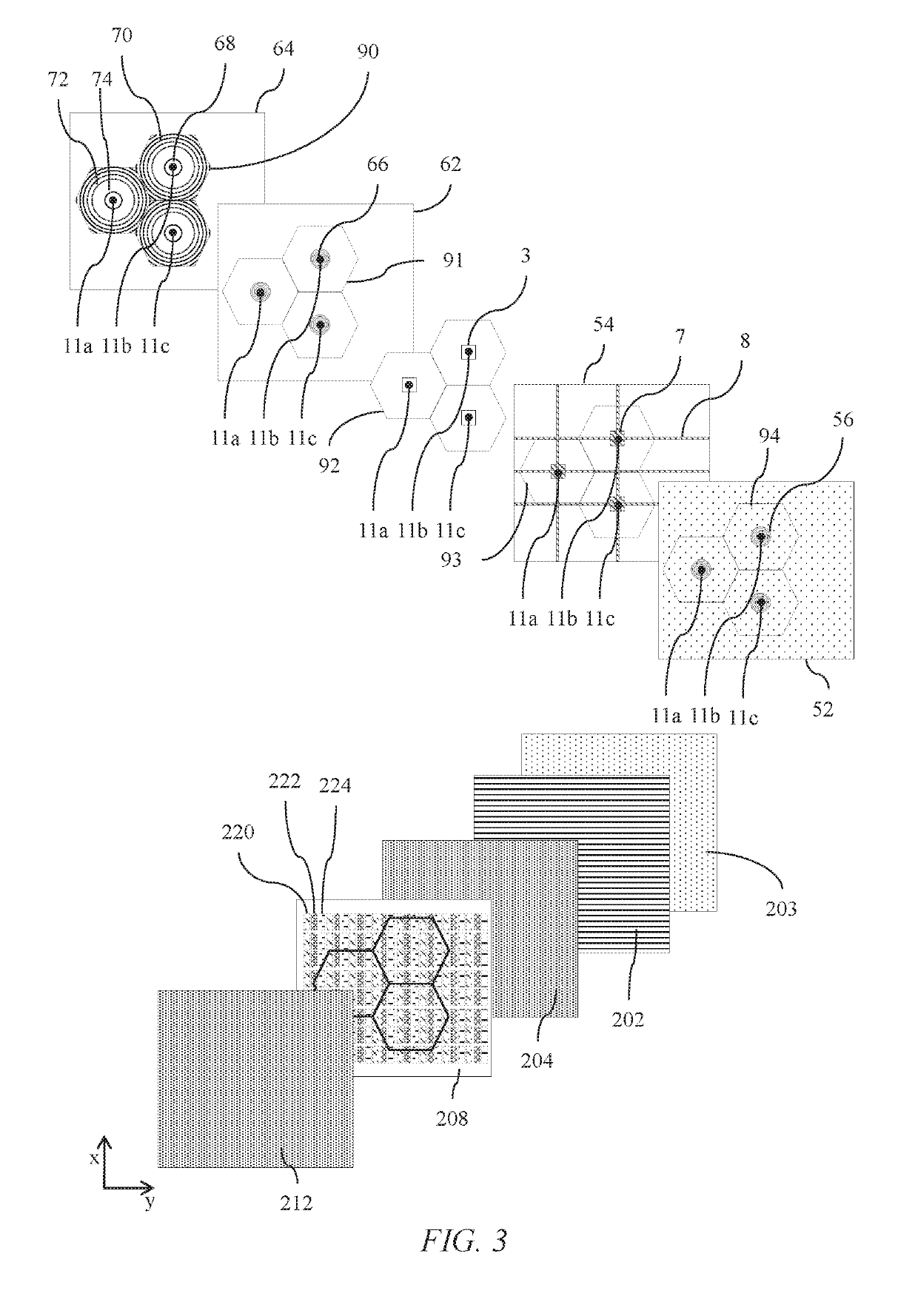
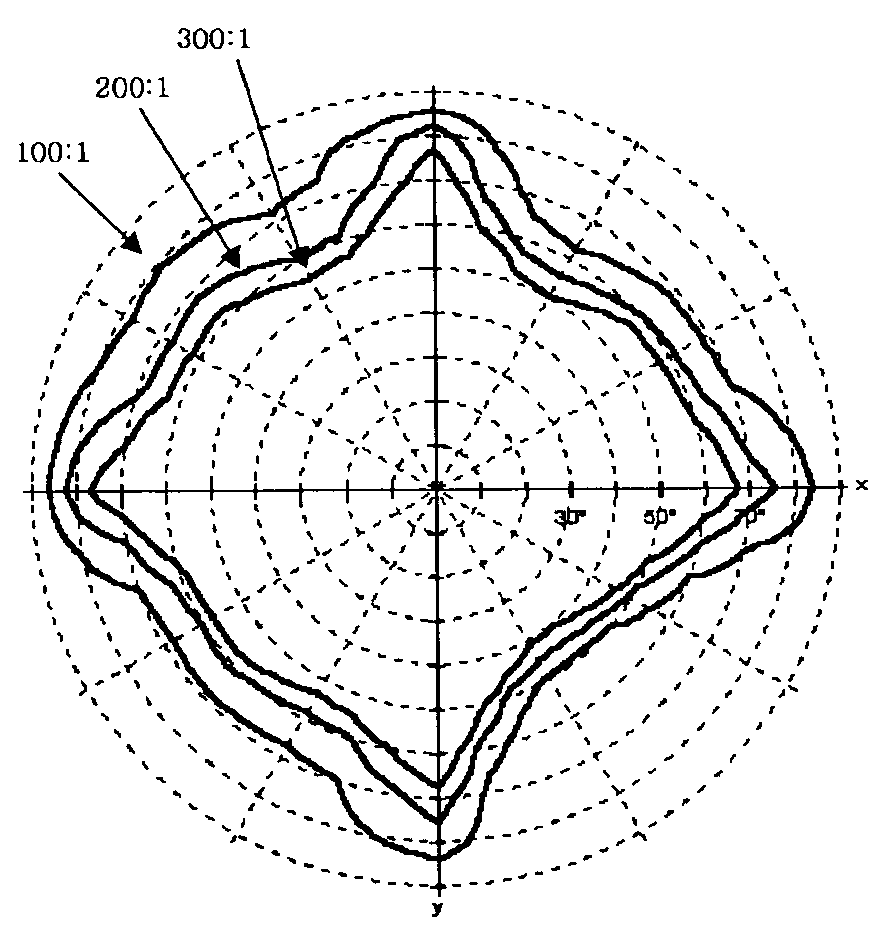
ActiveUS20190278135A1Reduce edge widthSmall bezel widthCondensersNon-linear opticsLight equipmentLed array
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Biaxial-optical polynorbornene-based film and method of manufacturing the same, integrated optical compensation polarizer having the film and method of manufacturing the polarizer, and liquid crystal display panel containing the film and/or polarizer
ActiveUS7582339B2High light transmittanceUniform in-plane retardation valueLiquid crystal compositionsOptical articlesIn planePolynorbornen
Disclosed is a method of manufacturing a biaxial polynorbornene-film having a compensation film which has good light transmittance and a uniform in-plane retardation value and can function as both a negative C-plate and an A-plate.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
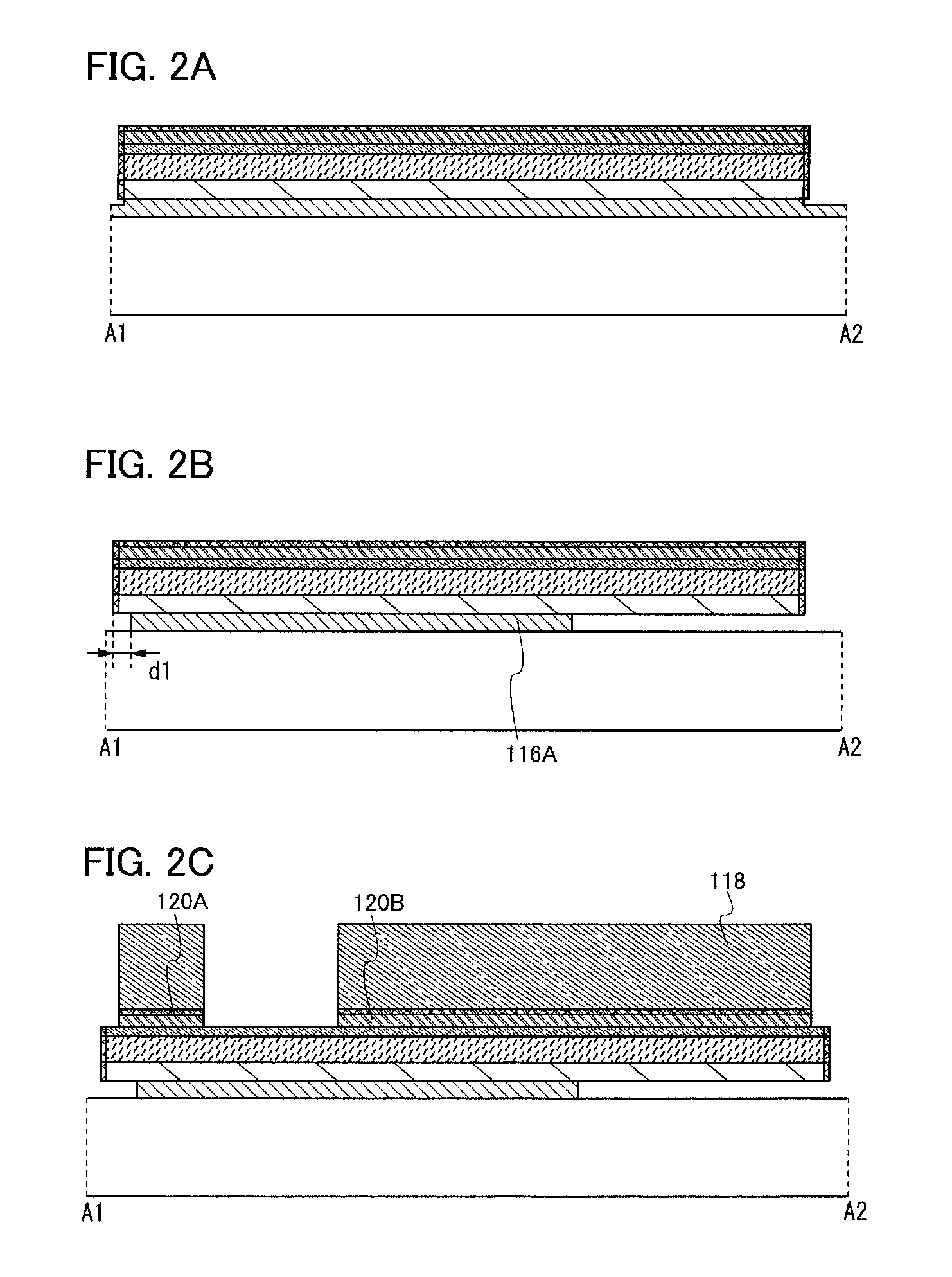
Manufacturing method of thin film transistor and manufacturing method of display device
ActiveUS20100187535A1Improve throughputLeakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesResistDisplay device
To provide a method for manufacturing a thin film transistor and a display device using a small number of masks, a thin film transistor is manufactured in such a manner that a first conductive film, an insulating film, a semiconductor film, an impurity semiconductor film, and a second conductive film are stacked; then, a resist mask is formed thereover; first etching is performed to form a thin-film stack body; second etching in which the first conductive film is side-etched is performed by dry-etching to form a gate electrode layer; and a source electrode, a drain electrode, and the like are formed. Before the dry etching, it is preferred that at least a side surface of the etched semiconductor film be oxidized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
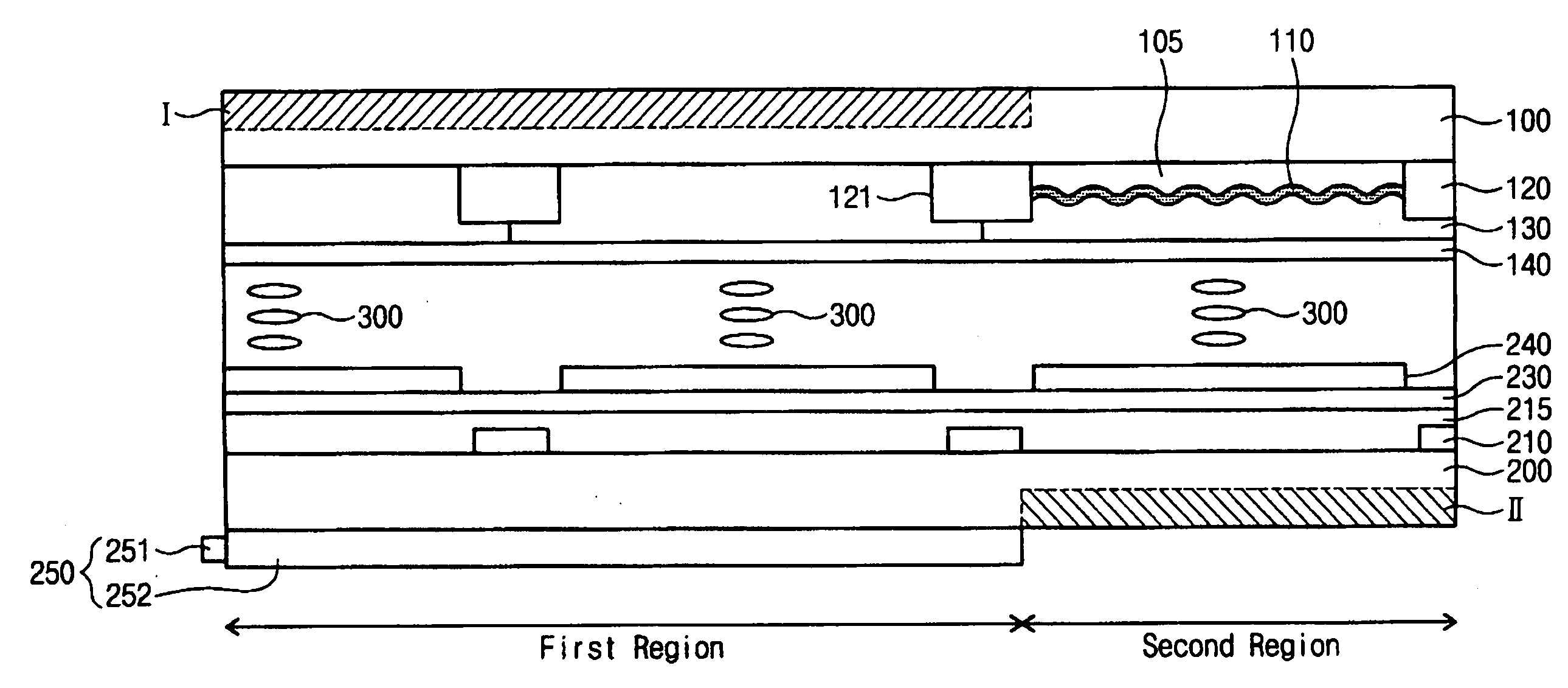
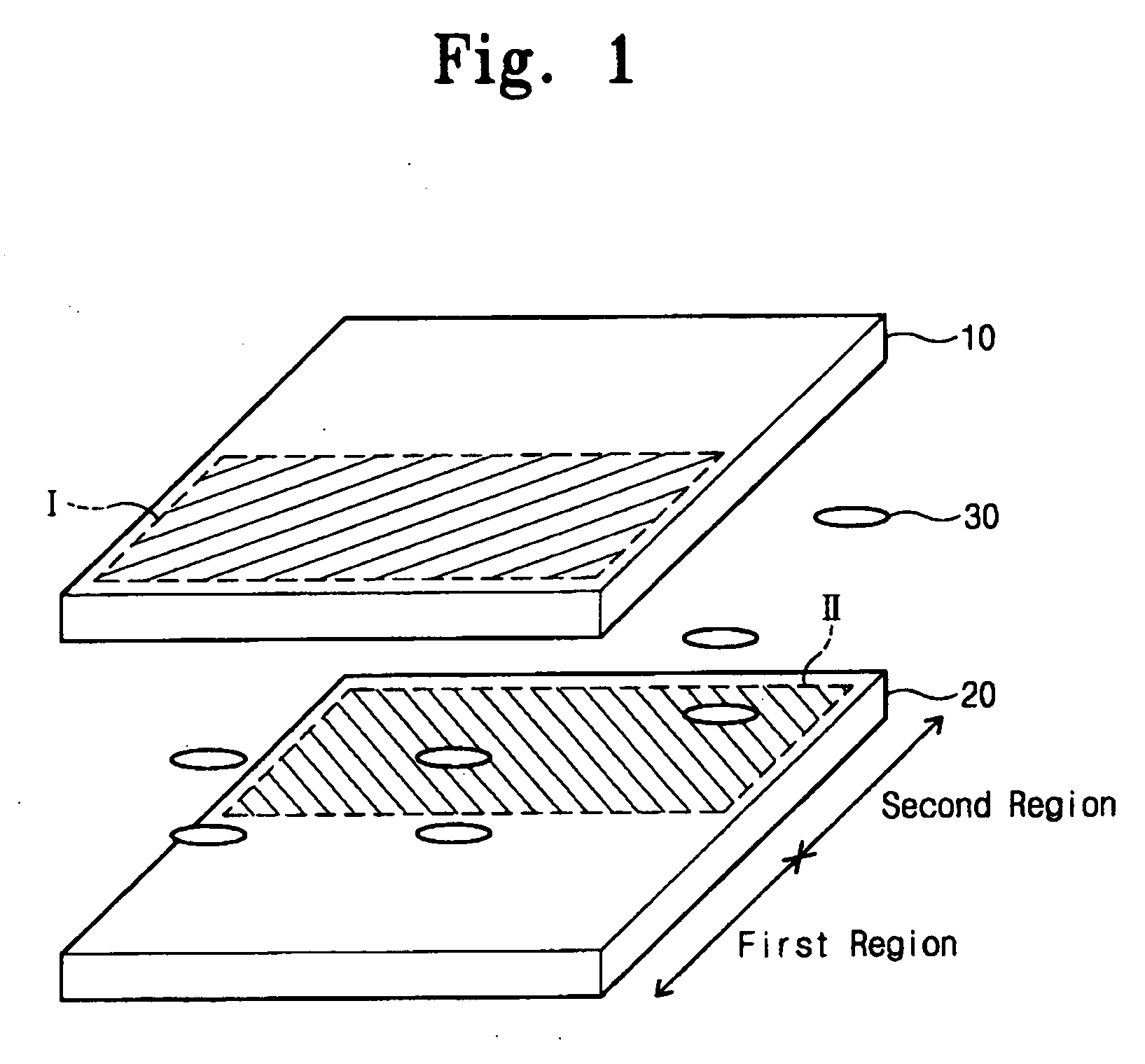
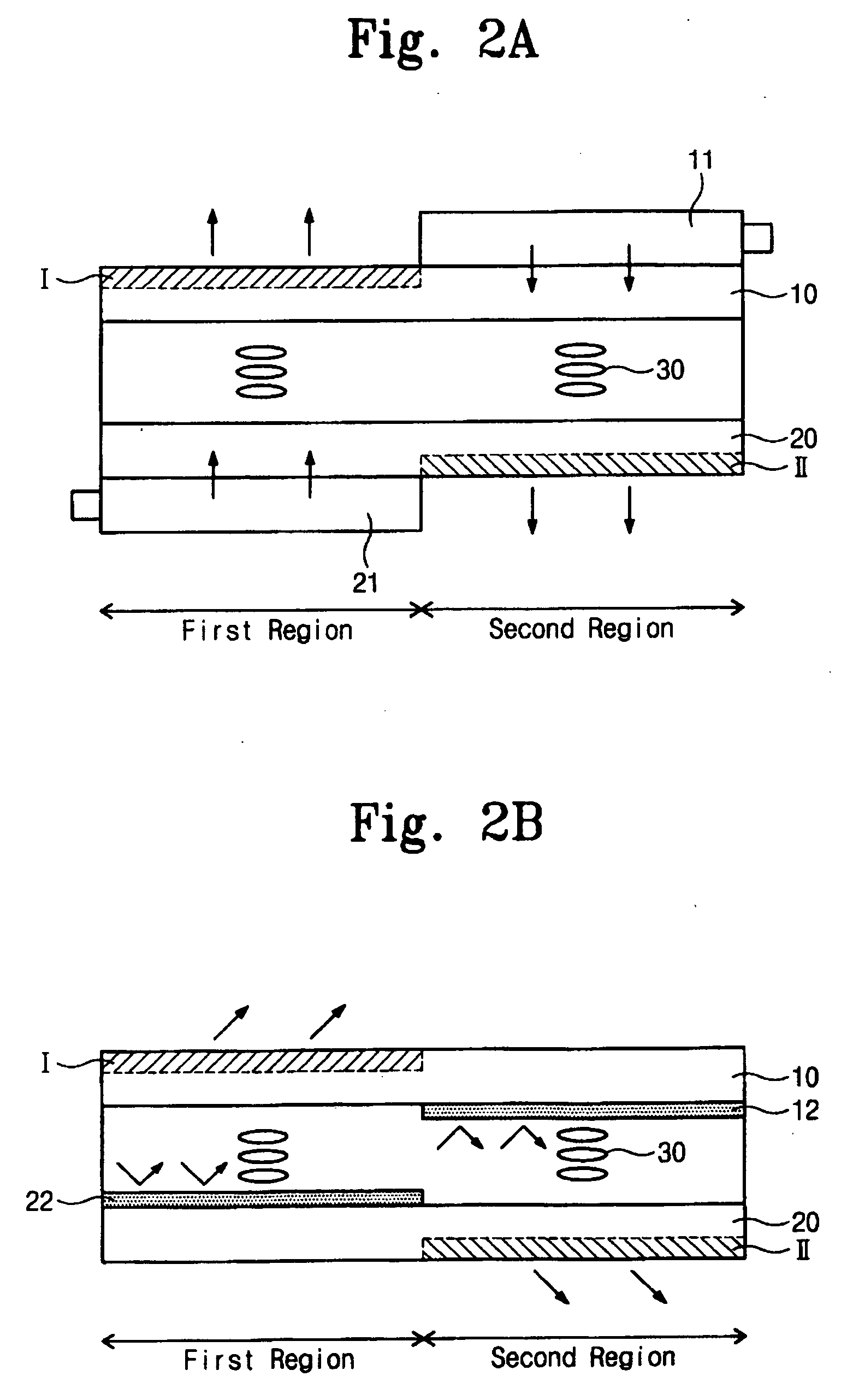
Display apparatus
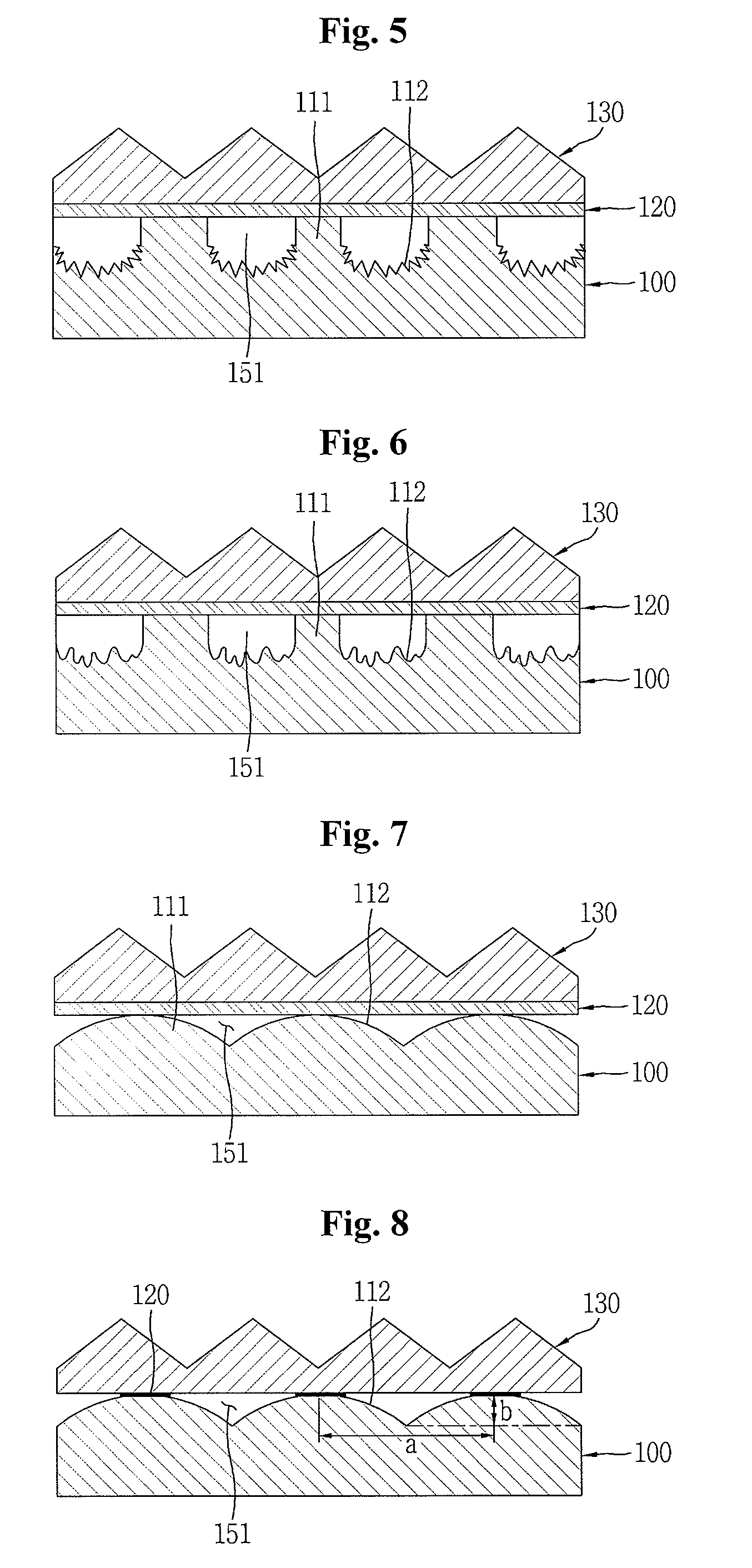
The display apparatus includes a first substrate and a second substrate. The first substrate is divided into a first region and a second region, and a reflection layer pattern is formed in the second region of the first substrate. The second substrate faces the first substrate. Pixel regions are defined on the second substrate, and a pixel electrode is formed on each of the pixel regions. A transmission type image is displayed on a first region of the first substrate and, on a second region of the second substrate, a reflection type image is displayed, so that a two-sided image is displayed using only two substrates thereby reducing the overall thickness of the display apparatus.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Cellulose acylate film, polarizing plate, and liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS7501167B2Reduction in yieldThin displayLiquid crystal compositionsCellulose/protein filament chemical after-treatmentCelluloseLiquid-crystal display
A cellulose acylate film comprising cellulose acylate which has a degree of crystallinity represented by the following expression (I) of 0.9 or more, and satisfies the following expressions (II) and (III):Degree of crystallinity=(X-ray diffraction intensity at 2θ of 13°) / (X-ray diffraction intensity at 2θ of 12°); Expression (I)2.6≦A+B≦3.0; and Expression (II)0.5≦B≦1.2 Expression (III)wherein A represents a substitution degree by an acetyl group of a hydroxyl group in a glucose unit of the cellulose acylate, and B represents a substitution degree by a substituent having from 3 to 4 carbon atoms of a hydroxyl group of a glucose unit of the cellulose acylate.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electronic device
InactiveUS20090040707A1Components in expandedImprove the display effectDetails for portable computersMulti-purpose toolsDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:SONY CORP
Display Apparatus
ActiveUS20160259122A1Uniform white lightAvoid expansionMechanical apparatusStatic indicating devicesEngineeringGlass sheet
Provided is a display apparatus having a structure capable of realizing reduction in thickness and border width.A display apparatus having a liquid-crystal panel prepared by enclosing a liquid-crystal material between a pair of glass substrates opposing to each other, a transparent plate opposed to the liquid-crystal panel, and an optical sheet arranged between the liquid-crystal panel and the transparent plate, and having a face smaller than the liquid-crystal panel, wherein the transparent plate is a glass plate having a wide surface of substantially a same shape as a wide surface of each of the glass substrate, and the display apparatus further comprises a frame body arranged between the liquid-crystal panel and the transparent plate, the frame body surrounding an outer periphery of the optical sheet, the frame body being thicker than the optical sheet.
Owner:SAKAI DISPLAY PROD
Organic Light Emitting Diode Display Device
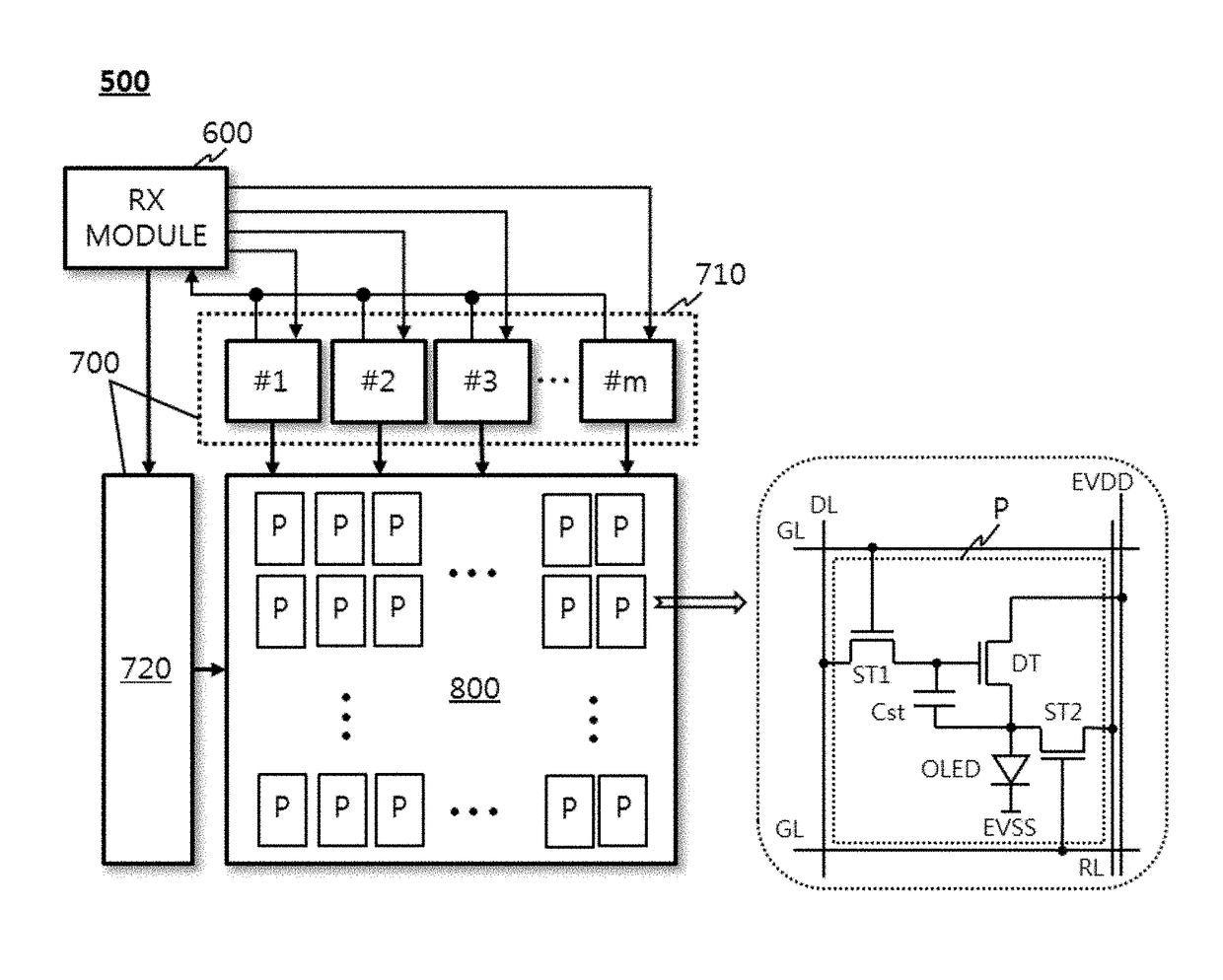
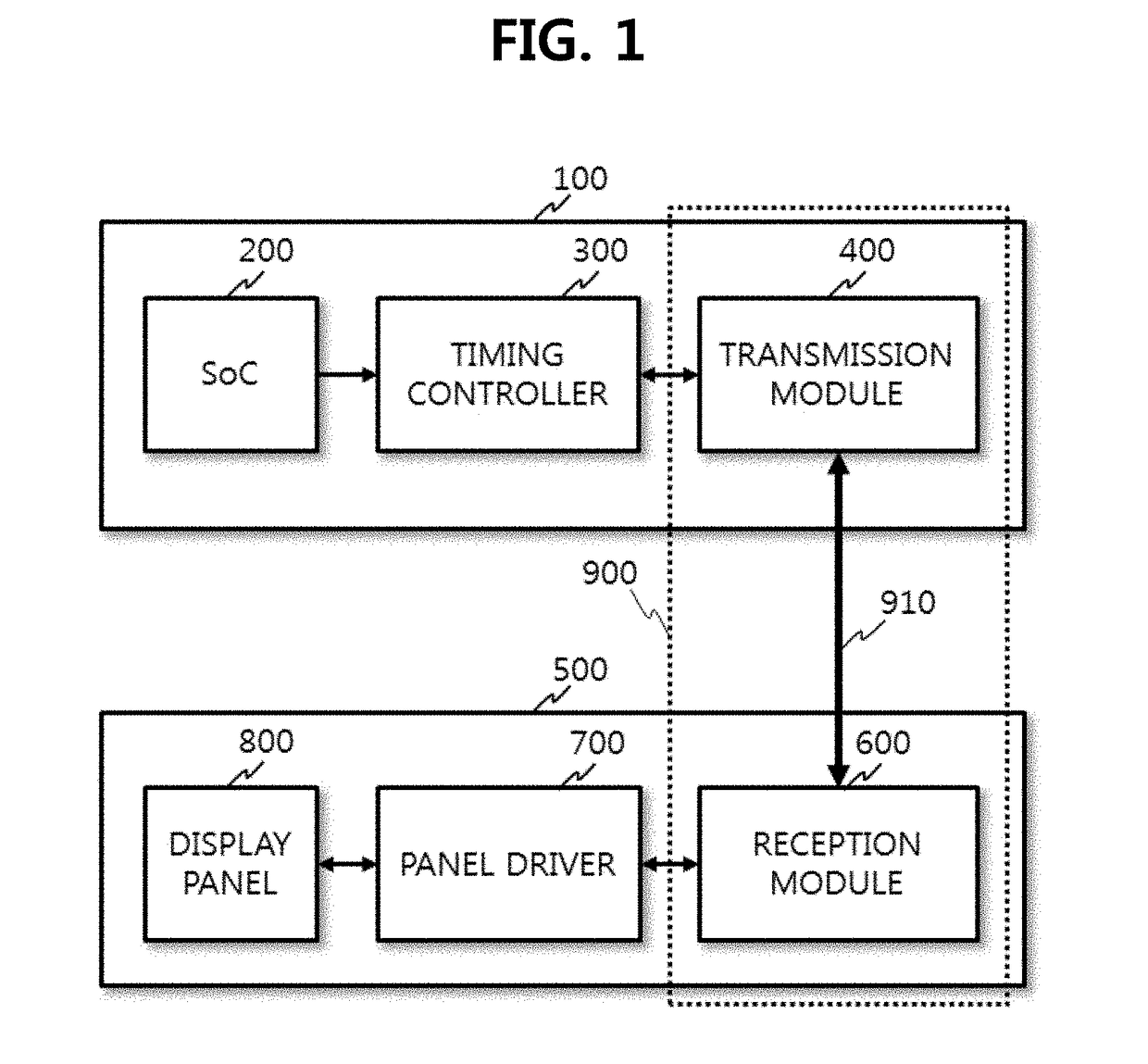
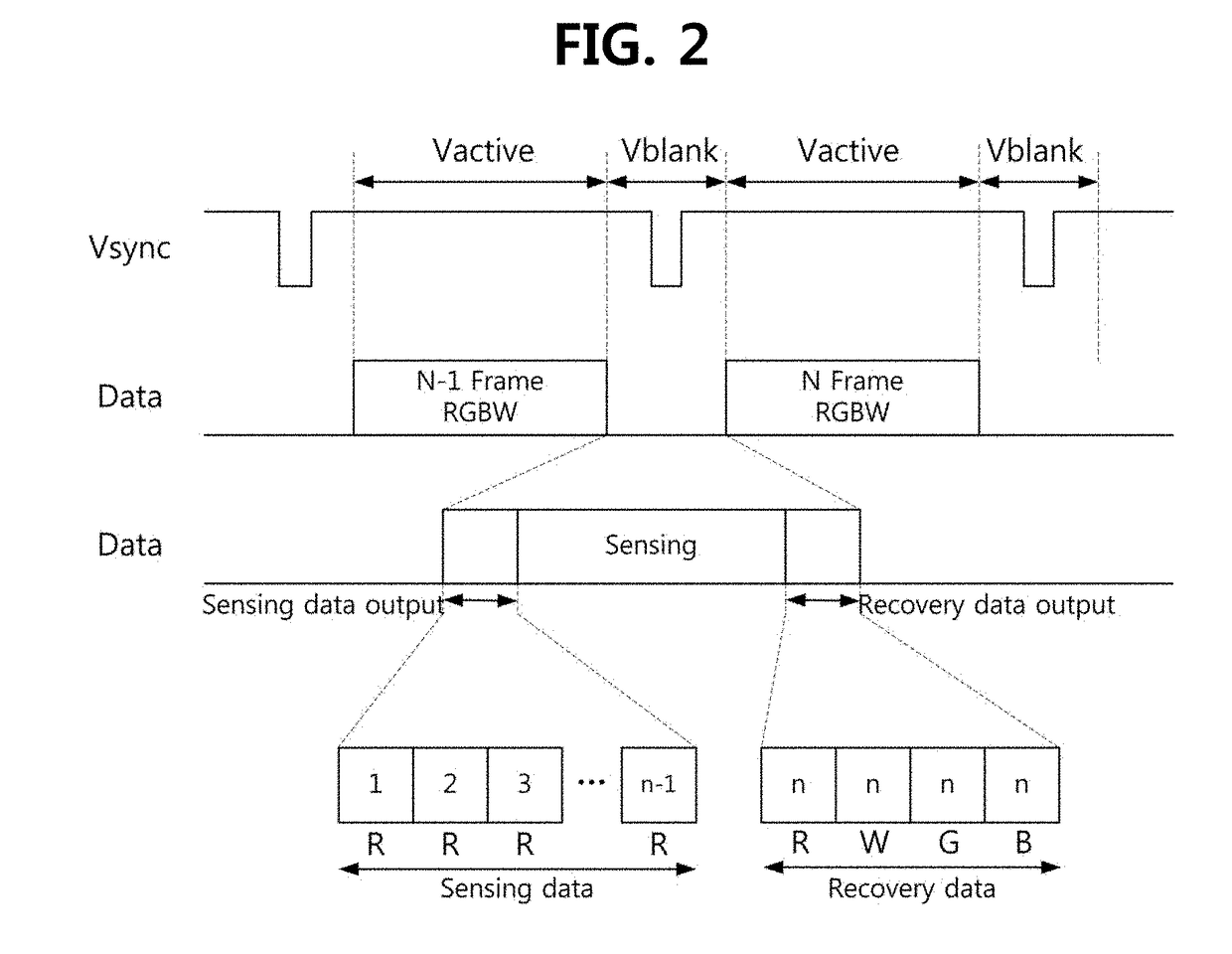
ActiveUS20170193877A1Thin profileEfficient data transferStatic indicating devicesSensing dataDisplay device
An organic light emitting diode display device includes a display module having a display panel and a panel driver; a host system separated from the display module with a timing controller to control the panel driver; and an interface device between the host system and the display module. The interface device includes a cable between the host system and the display module, a transmission module to compress display data from the timing controller in an active period of each frame without compressing sensing data and recovery data supplied in a blank period of the frame and to transmit the compressed display data, the non-compressed sensing data and recovery data via the cable, and a reception module to decompress the compressed data transmitted via the cable, to supply the decompressed data to the panel driver, and to supply the non-compressed data to the panel driver without data processing.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device
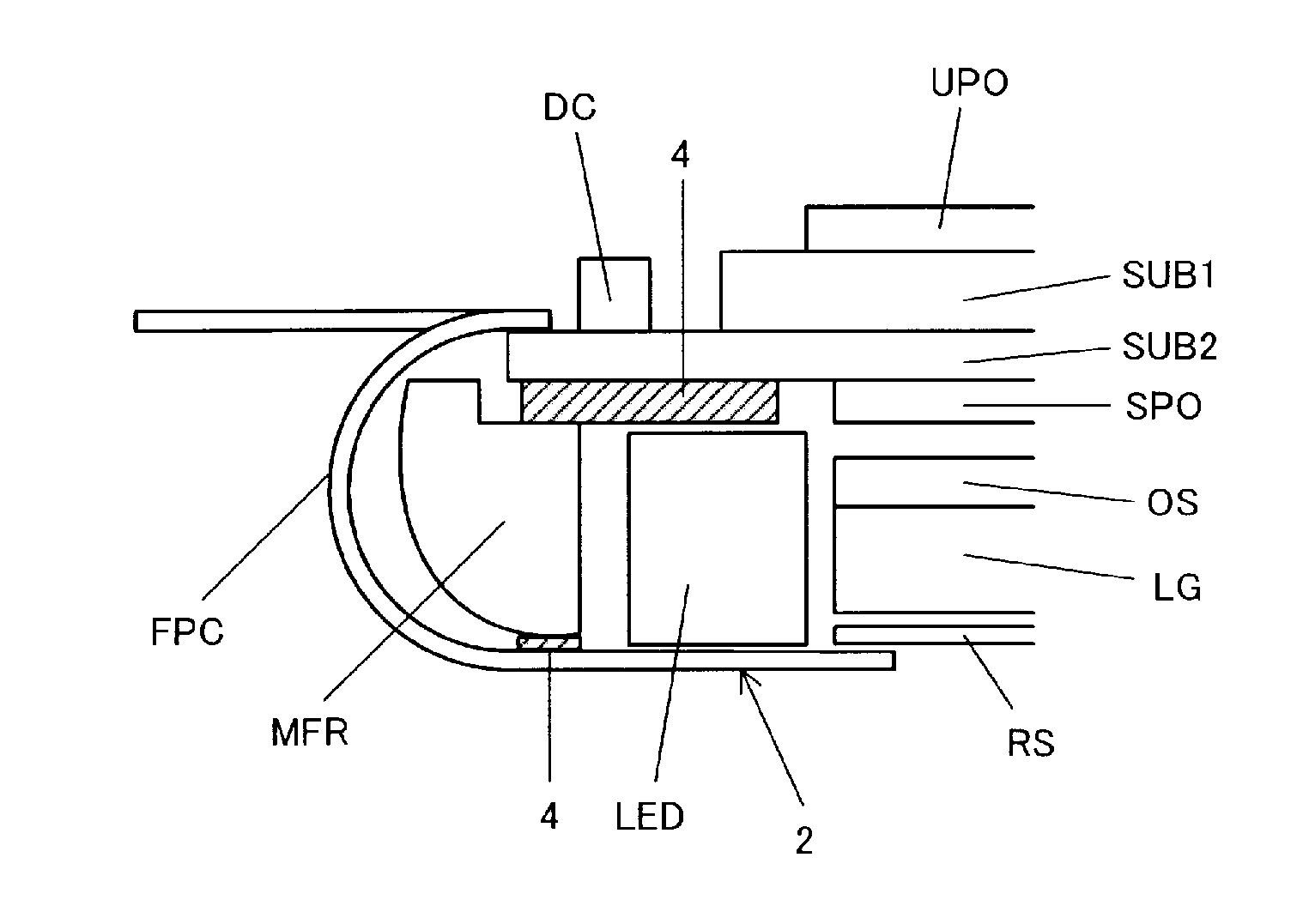
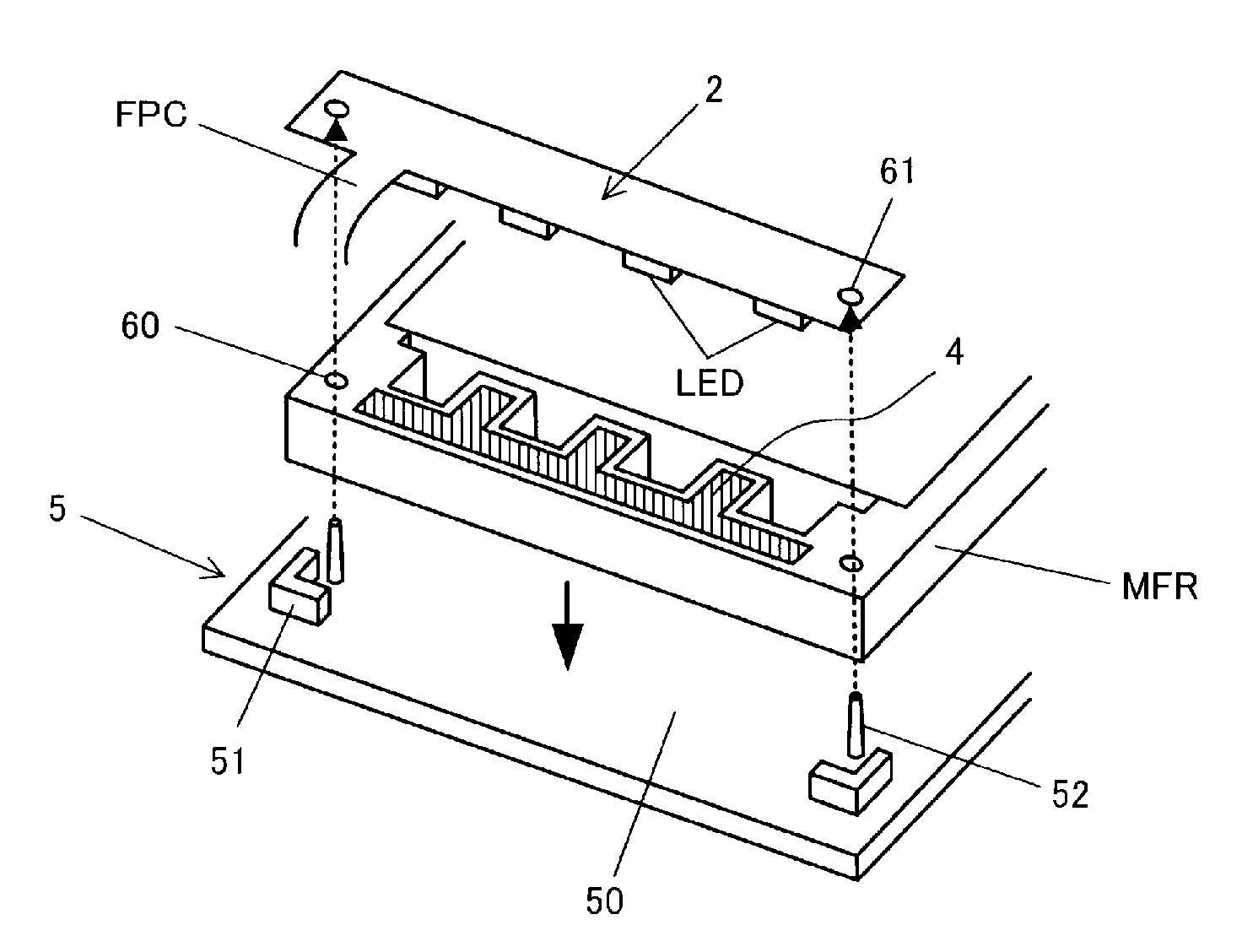
ActiveUS20110242448A1Precise positioningThin displayNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
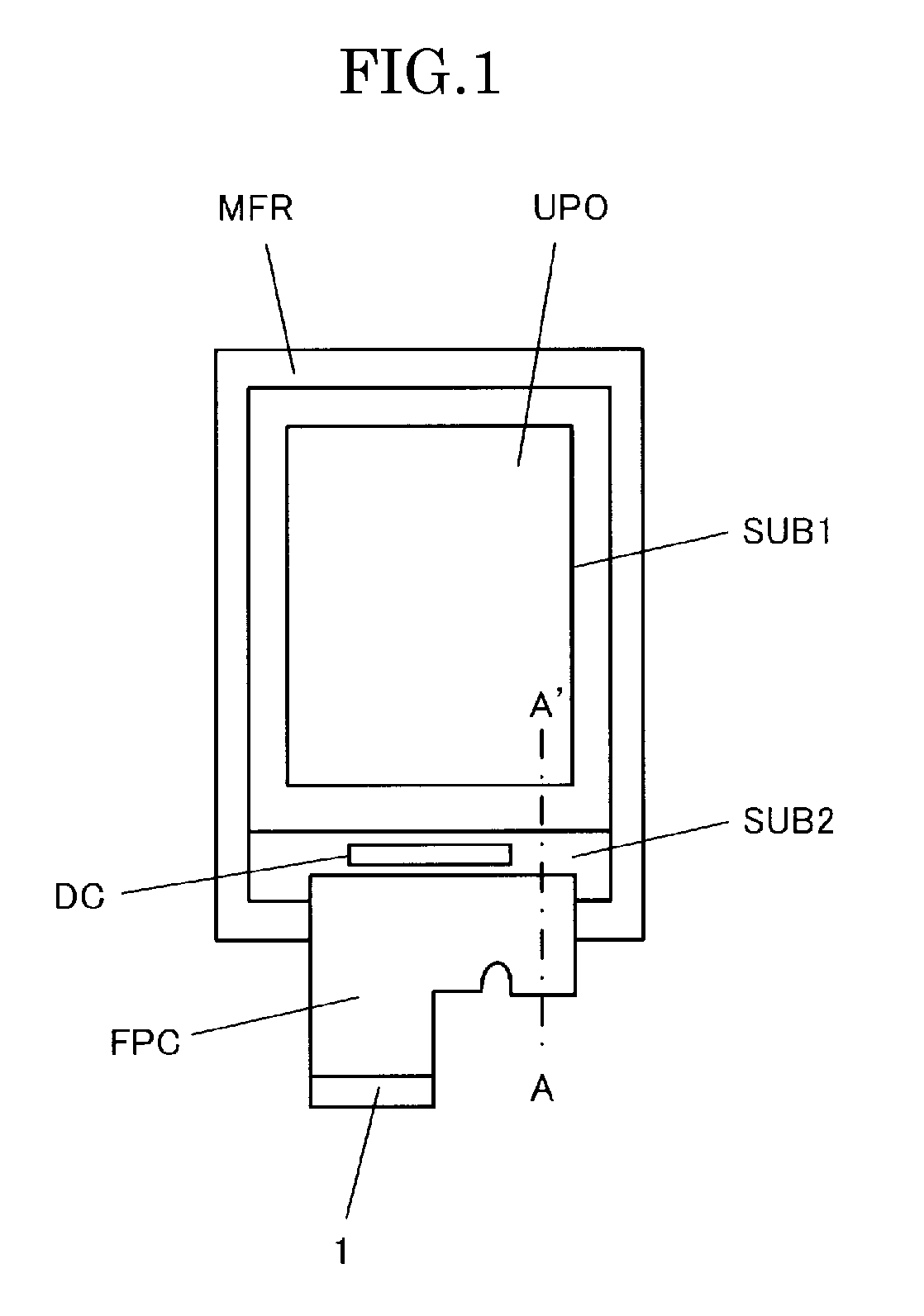
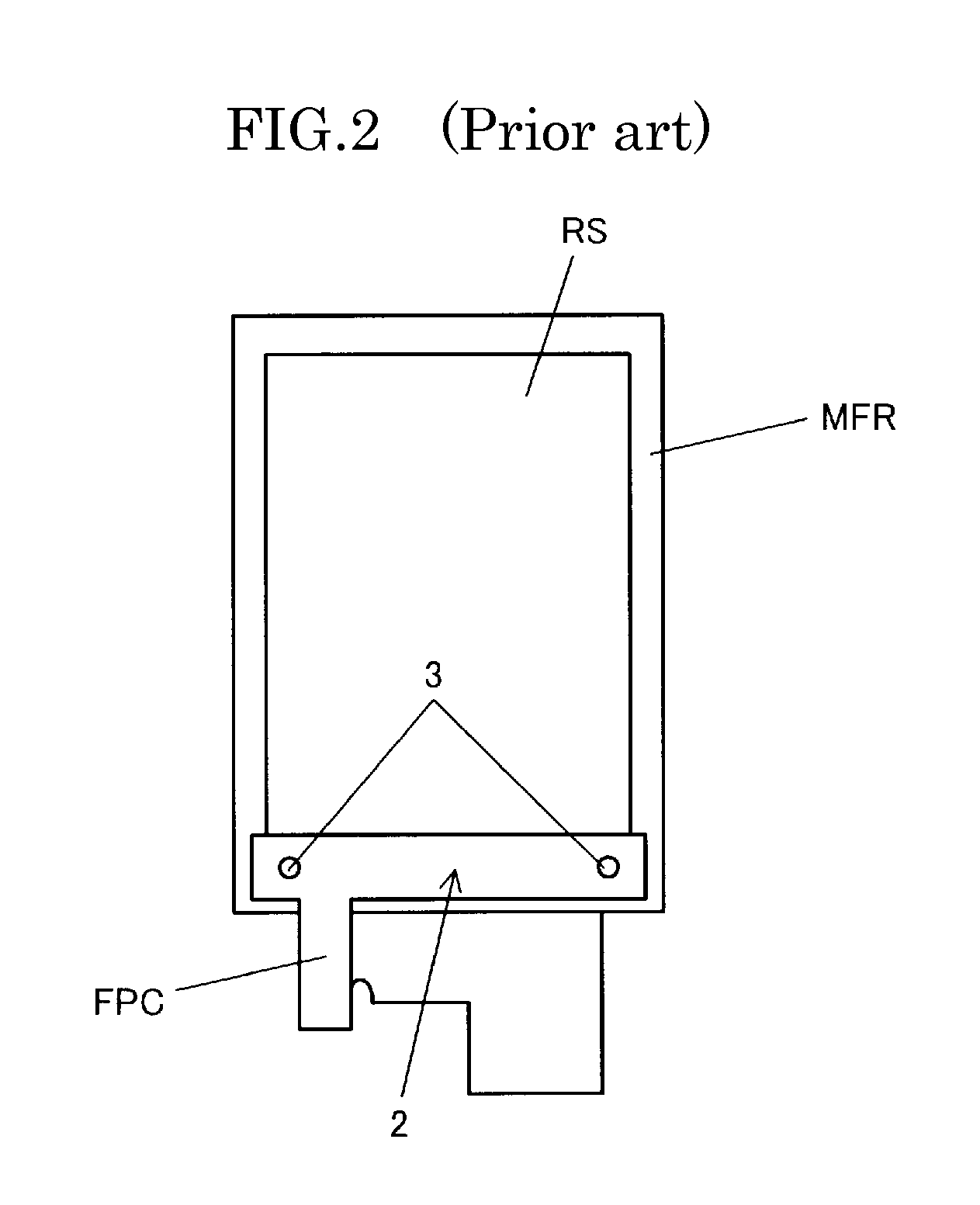
The liquid crystal display device according to the present invention is a thin liquid crystal display device where it is easy to position the flexible printed circuit on which light emitting diodes are mounted. In the liquid crystal display device having a liquid crystal display panel and a flexible printed circuit (FPC) that is connected to the liquid crystal display panel and supplies power for driving display pixels, light emitting diodes (LED) are mounted on a portion of the flexible printed circuit, a mold frame MFR is provided to contain the light emitting diodes, and through holes (60, 61) for positioning are created in both the flexible printed circuit and the mold frame.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Optical composite and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100055409A1Improve work efficiencyLuminance can be restrainedDiffusing elementsSynthetic resin layered productsLiquid-crystal displayPrism
Disclosed is an optical composite for use in a backlight unit of a liquid crystal display or an illumination apparatus, which is able to sufficiently increase luminance and in which adhesion portions are regularly arranged to thus induce an optical illusion effect so that scratches or stains cannot be seen clearly. A method of manufacturing such an optical composite is also provided. There is no need to additionally use optical films or prism sheets, thus making it possible to inexpensively manufacture optical devices, such as backlight units.
Owner:KOLON IND INC
Fresnel lens sheet, transmission screen and rear projection display
ActiveUS20070002439A1Facilitated releaseImprove efficiencyBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsLensFresnel lensProjection image
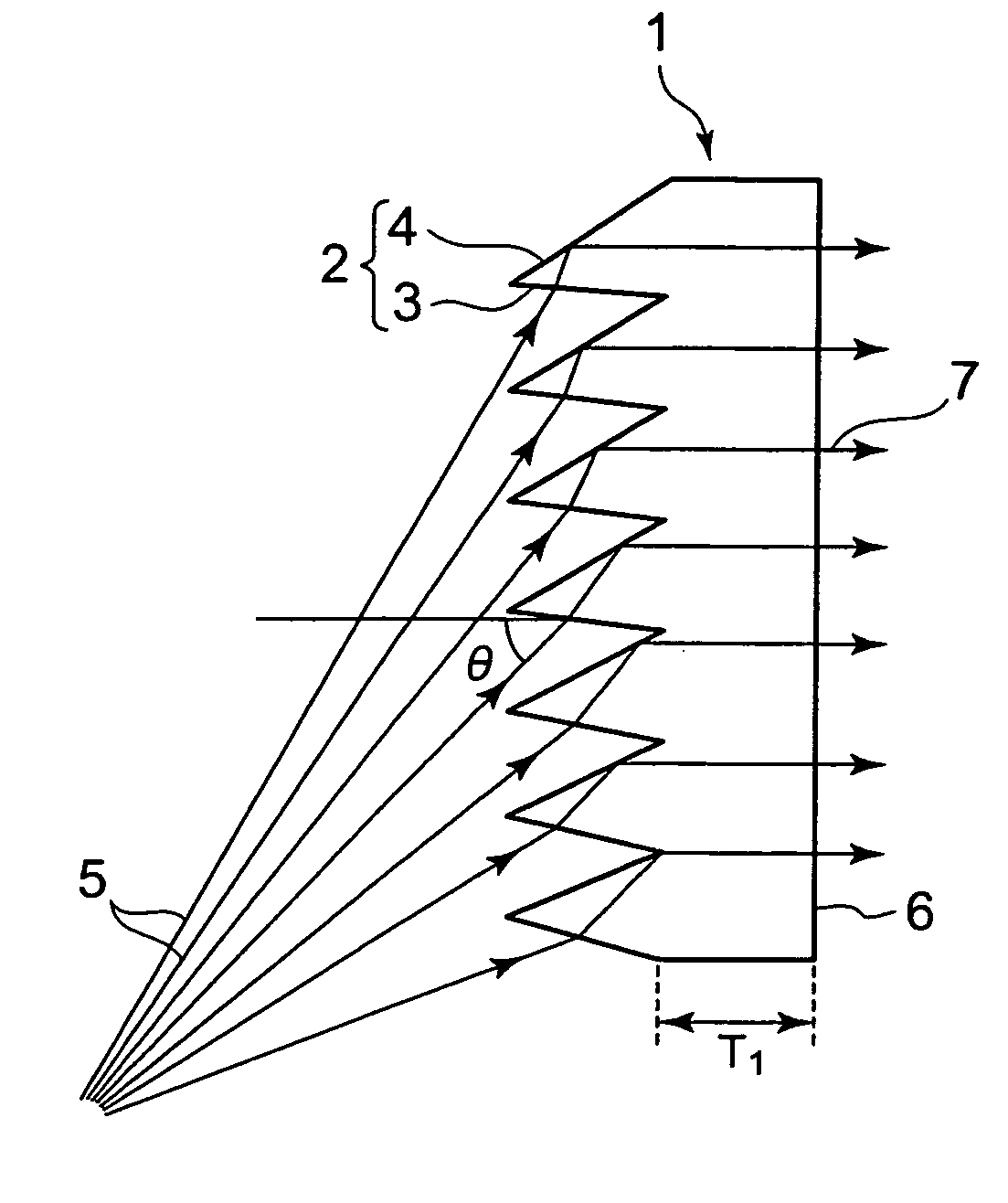
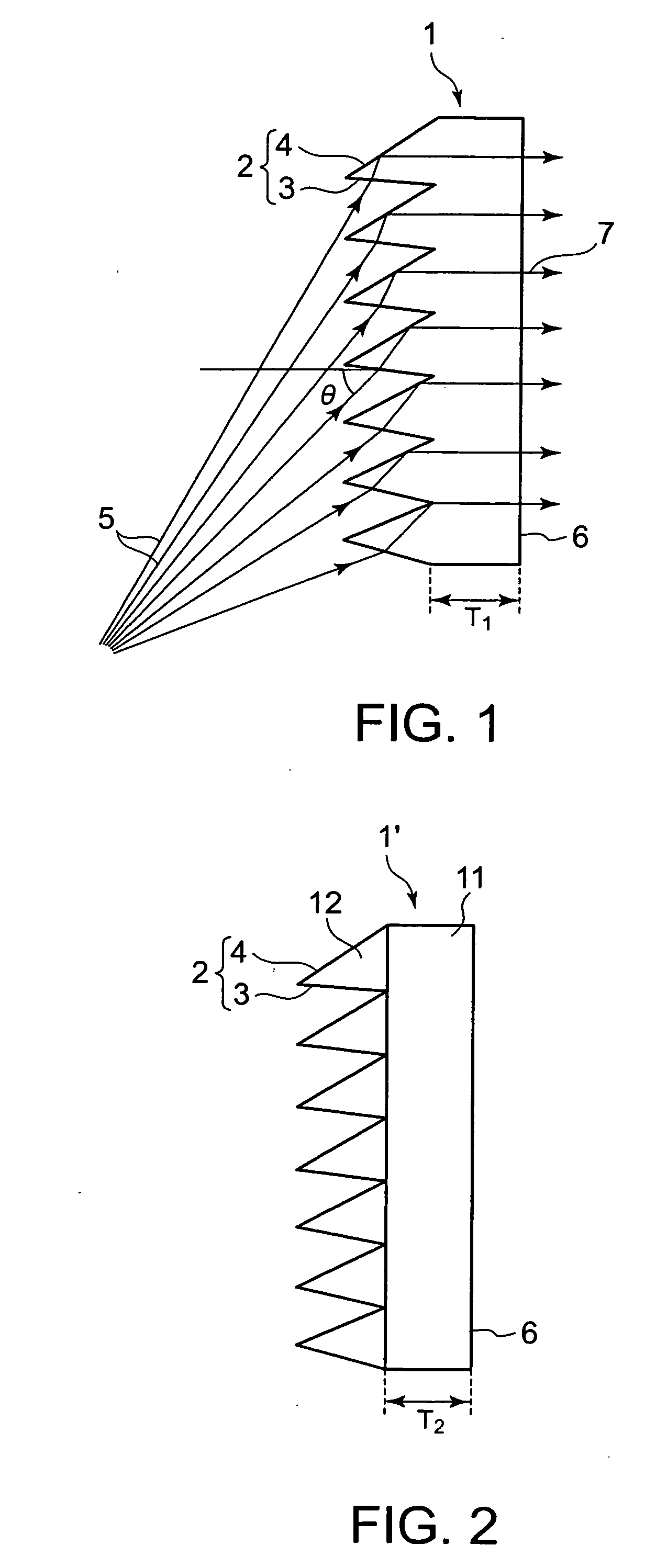
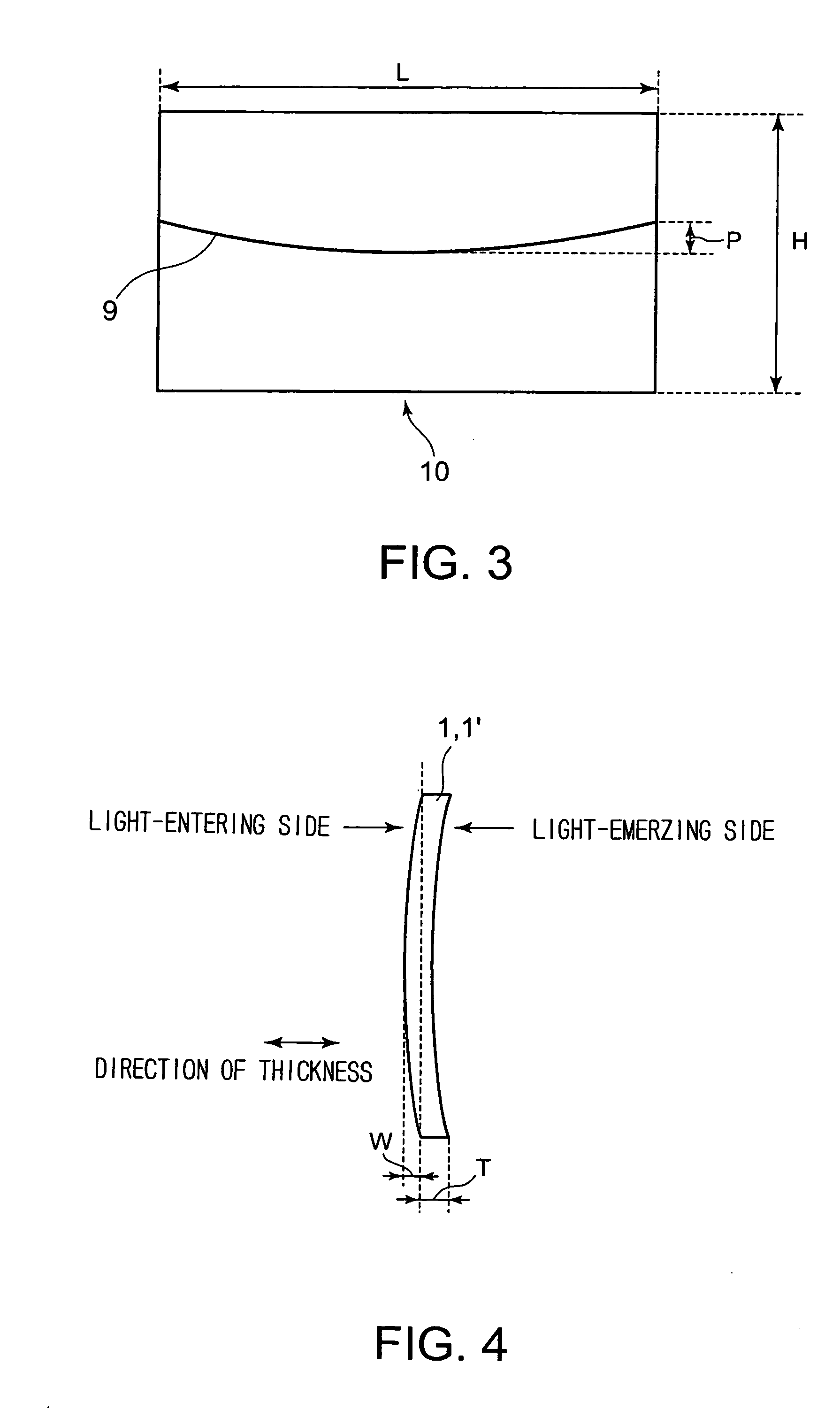
The present invention provides a Fresnel lens sheet that scarcely makes the projected image distorted, and others. The Fresnel lens sheet has a plurality of unit total reflection Fresnel lenses arranged on the light-entering side, each unit lens having a light-entering surface and a total reflection surface that totally reflects a part of or all of the imaging light that has passed through the light-entering surface to deflect the light in the desired direction. This Fresnel lens sheet is formed so that it fulfills the relationship H1×H1 / (10×E1×T1×T1)≦3L / 2000, where H1 represents the length (cm) in the vertical direction of the Fresnel lens sheet; L1, the length (cm) in the horizontal direction of the Fresnel lens sheet; T1, the thickness (cm) of the Fresnel lens sheet; and E1, the modulus of elasticity (kgf / cm2) of the Fresnel lens sheet. Further, by using, to make up the Fresnel lens sheet, a Fresnel-lens-molded sheet having unit total reflection Fresnel lenses and a backing sheet laminated to the light-emerging surface of the Fresnel-lens-molded sheet, improvement in the efficiency of mold releasing operation that is conducted in the production of the Fresnel lens sheet is achieved.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Uniform diffractive backlight
InactiveUS20110051035A1Light extraction efficiency can be improvedMaintain consistencyOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsTotal internal reflectionEdge surface
A backlight is provided for illuminating an at least partially transmissive display. The backlight includes a light source. A light guide receives the light from an edge surface and guides the light by total internal reflection. The light is extracted from the lightguide using sub-wavelength extraction features designed on the basis of one grating structure with a second interlinks structure cut into the first structure. The first structure determines the extraction properties. The second structure determines the extraction efficiency and uniformity of the system. Higher efficiency and more uniform sub-wavelength extraction are possible with a device in accordance with the invention.
Owner:SHARP KK
Light-emitting device, illuminating device comprising same, and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20090052165A1Reduce the overall heightThinner backlightLighting support devicesElectric lightingLiquid-crystal displayElectrical conductor
Owner:SHARP KK
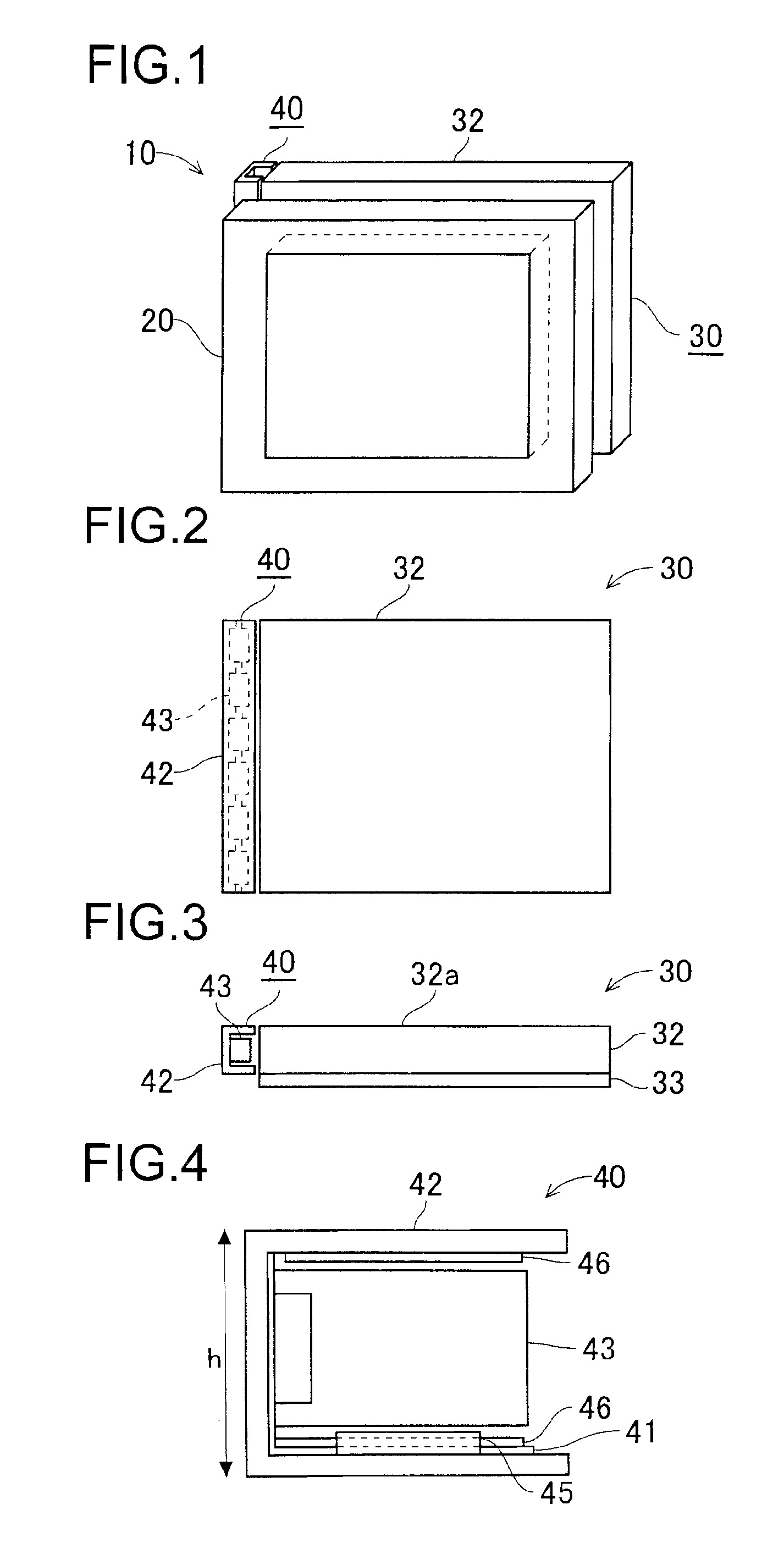
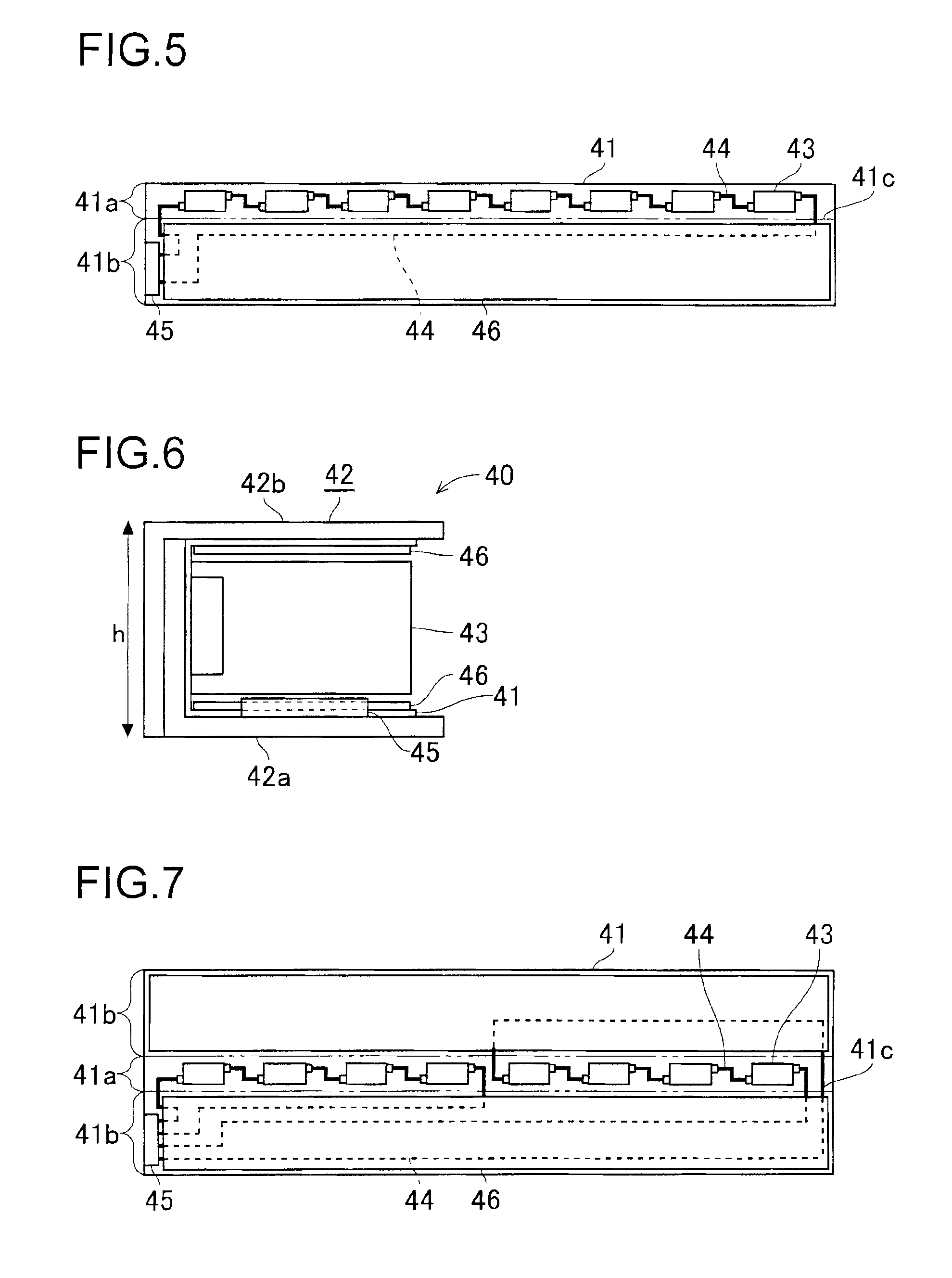
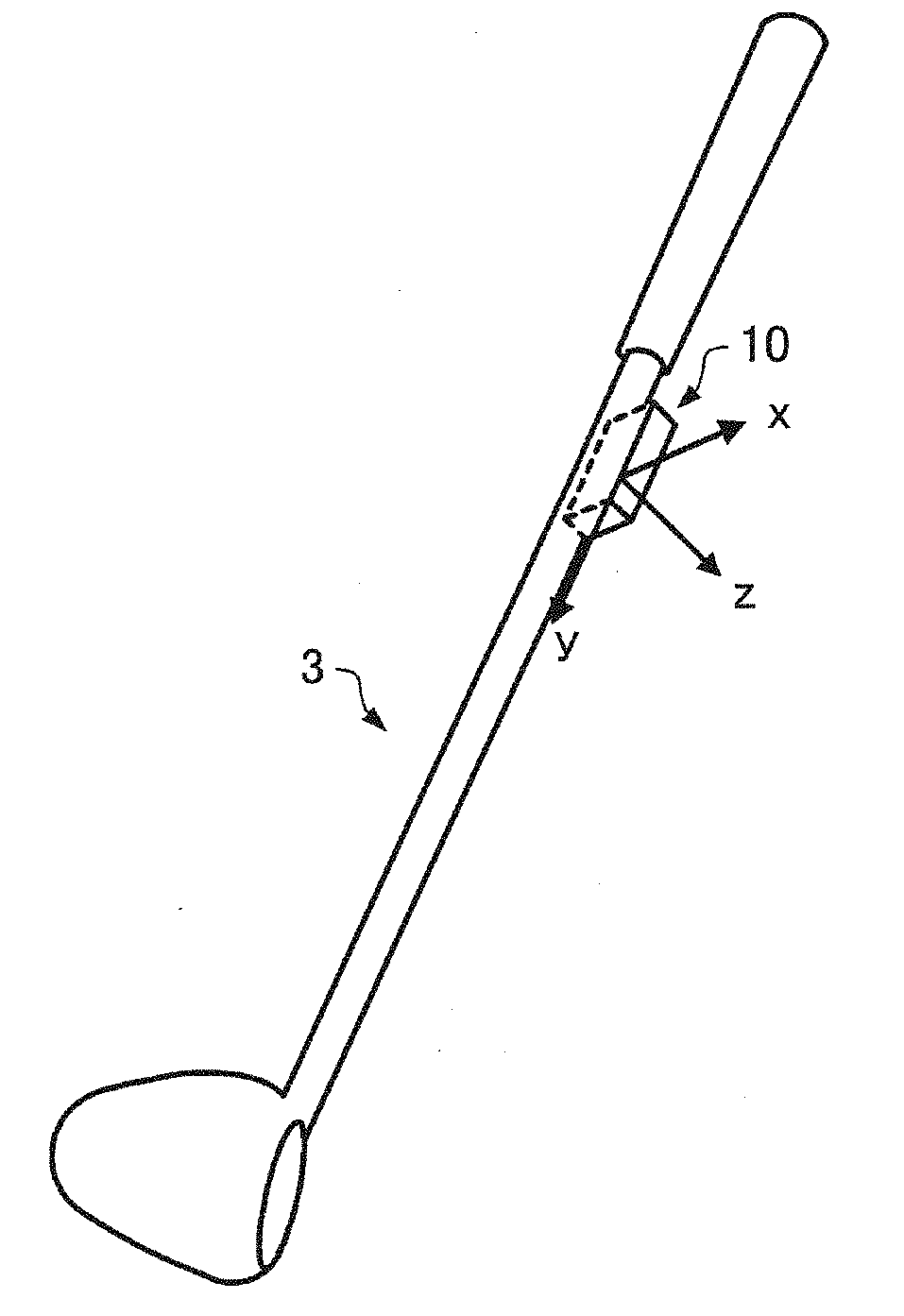
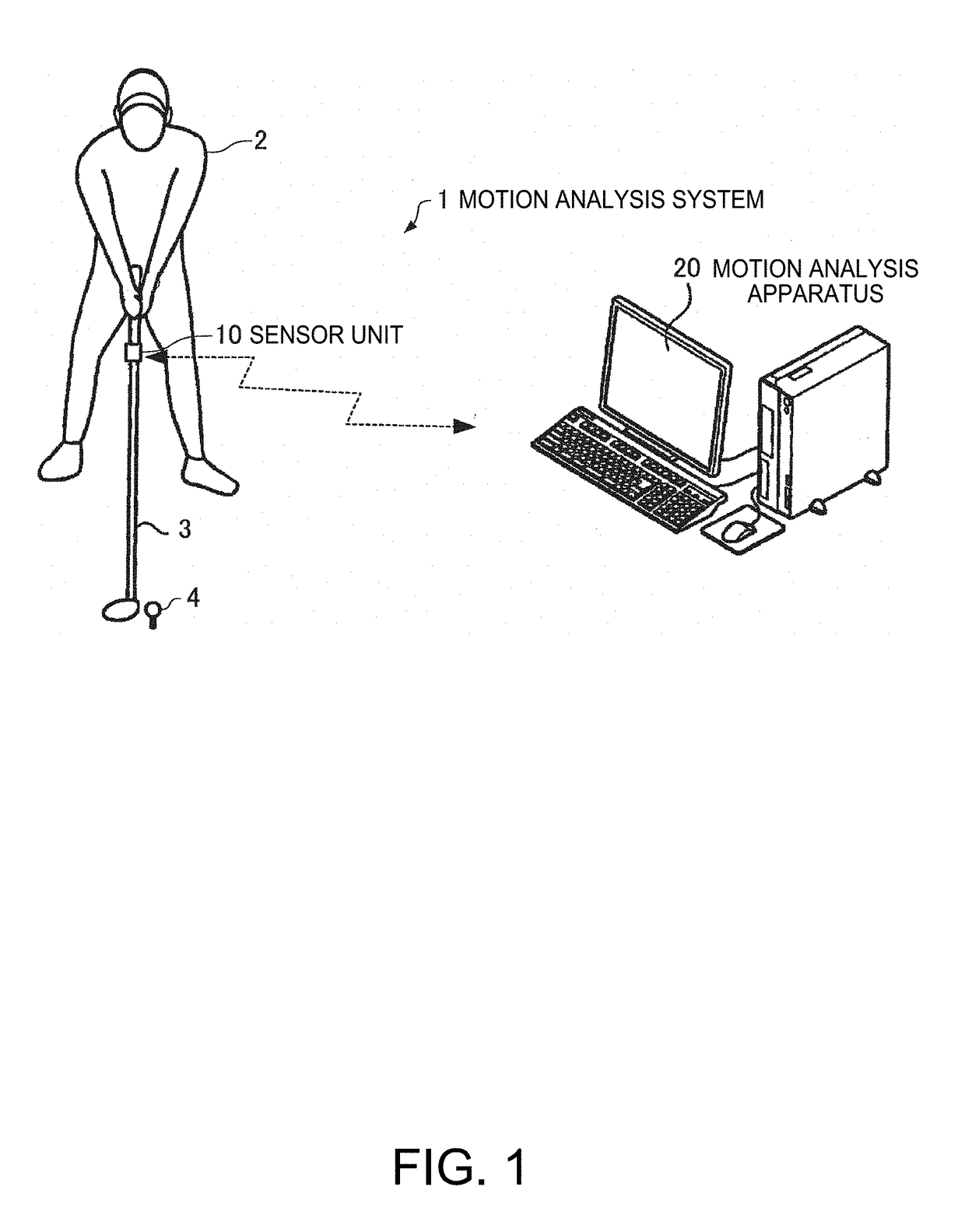
Motion analysis method and display method
ActiveUS20180221711A1Short timeReduce the numberAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGymnastic exercisingNormal modeEngineering
A motion analysis method includes a normal mode in which first motion information in a swing is measured by using an output from a sensor unit in a state in which a standing still action is detected, and a simple mode in which second motion information in a swing is measured by using an output from the sensor unit in a state in which the standing still action is not detected, and the number of analysis items is smaller than in the normal mode.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Head-mounted display device and control method for head-mounted display device
ActiveUS9823473B2Increase awarenessImprove ease of useInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceVisual perception
A head-mounted display device that enables a user to visually recognize a virtual image and an outside scene includes an image display unit configured to cause the user to visually recognize the virtual image, a detecting unit configured to detect a visual line direction of the user, and a display switching unit configured to switch, according to the detected visual line direction, display of the virtual image by the image display unit between outside scene preferential display for preferentially displaying the outside scene and virtual image preferential display for preferentially displaying the virtual image.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Liquid crystal display device
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC +1
Turnable wall mount for display
InactiveUS20130119218A1Less complicatedThin displayStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentDisplay deviceEngineering
A display mount (1) comprising a first device to be fastened on a mounting surface is described. The display mount comprises a second device to be fastened to a display (8) and an arm (10). A first end (11) of the arm (10) is rotatably arm ranged on the first device and a second end (13) of the arm (10) is rotatably arranged on the second device. The first device comprises a first bracket (5) and the second device comprises a second bracket (5) to be attached to the display (8) and sleds (9) which are slidably arranged on the second bracket (5). The second end (13) of the arm (10) is rotatably arranged on the sleds (9). In a folded state the display mount (1) has the display (8) close to and essentially parallel to the mounting surface.
Owner:SMS SMART MEDIA SOLUTIONS
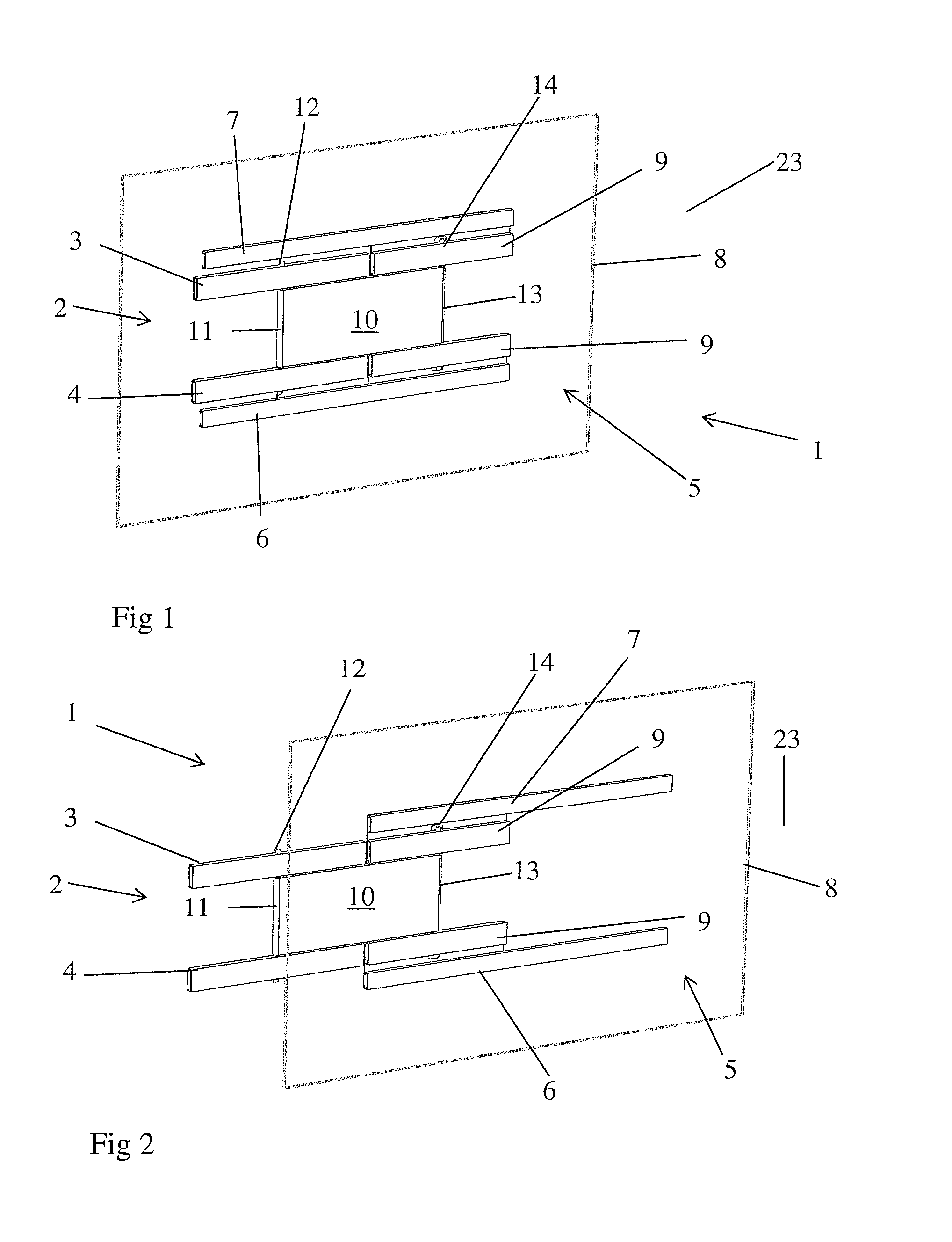
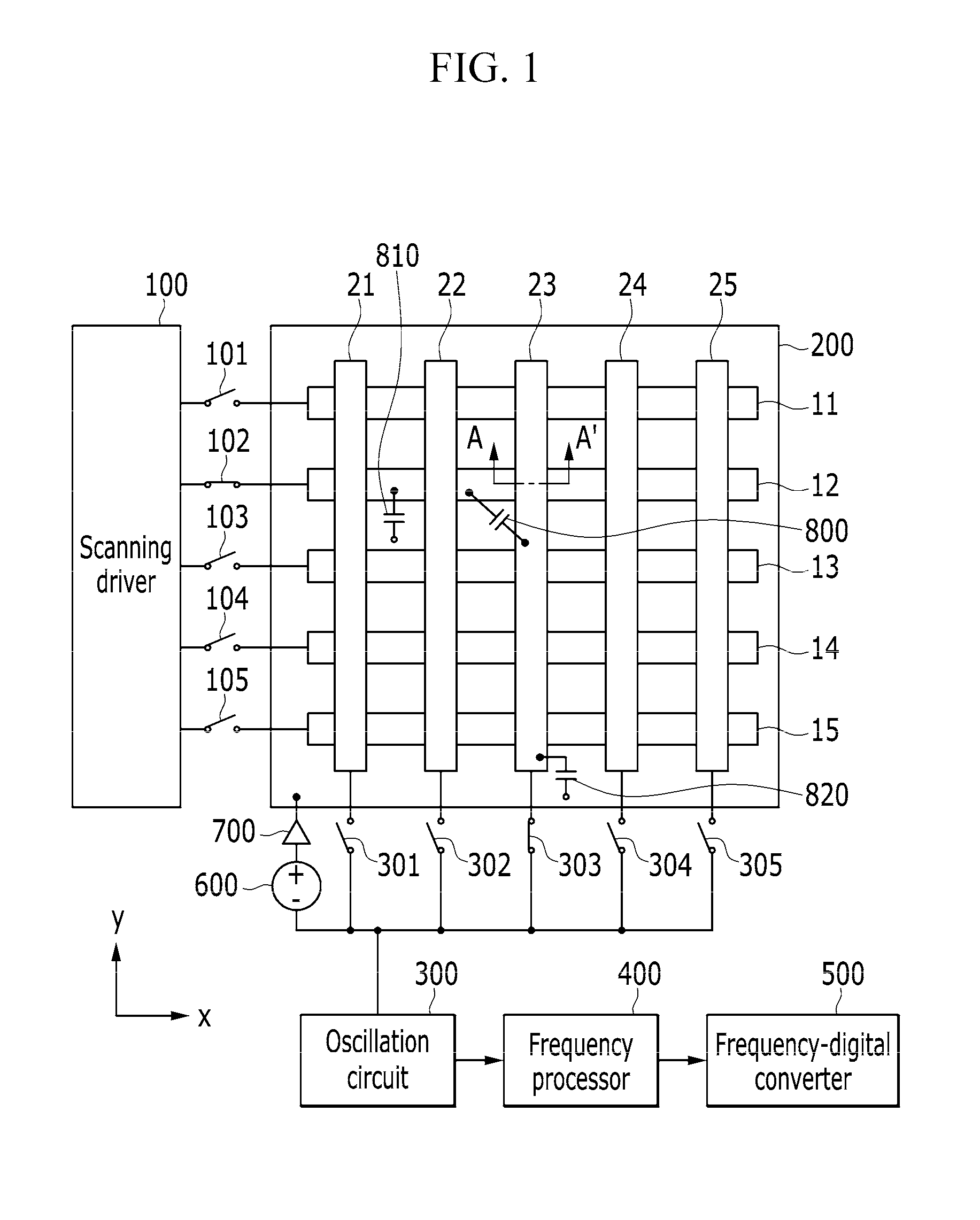
Touch display device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20160216798A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSolve the thickerNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingParasitic capacitanceDisplay device
A touch display device including: a plurality of first sensing electrodes; a plurality of second sensing electrodes forming a mutual capacitance with the plurality of first sensing electrodes; an oscillation circuit connected with the plurality of second sensing electrodes and supplying energy so as to generate a first sinusoidal wave signal; a first electrode plate forming a parasitic capacitance with the first and second sensing electrodes and receiving a second sinusoidal wave signal corresponding to the first sinusoidal wave signal; and a scanning driver configured to sequentially select the plurality of first sensing electrodes one-by-one, apply a reference voltage to the selected first sensing electrode, and float the first sensing electrodes which are not selected.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
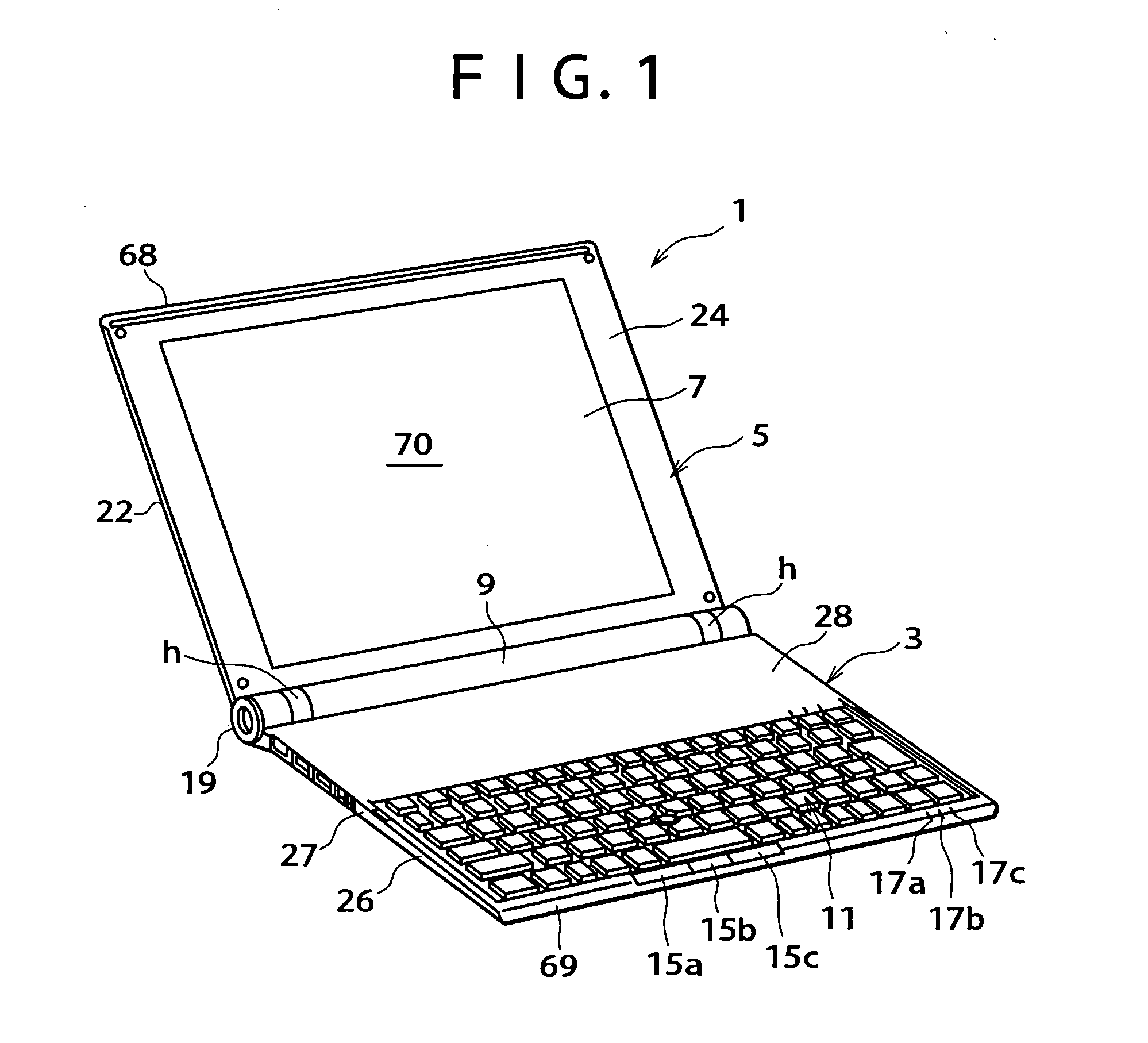
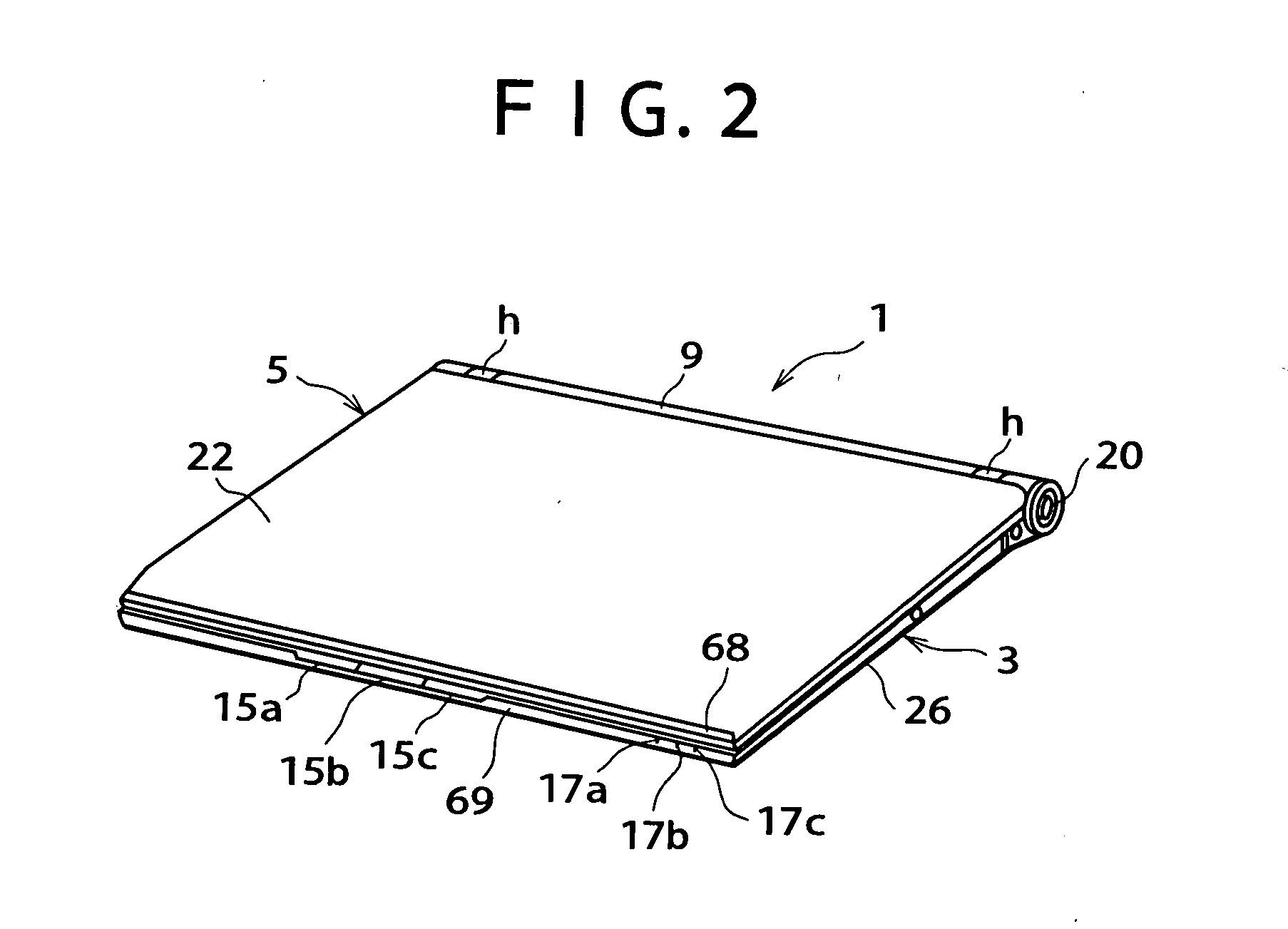
Optimized designs for embedding webcam modules with superior image quality in electronics displays
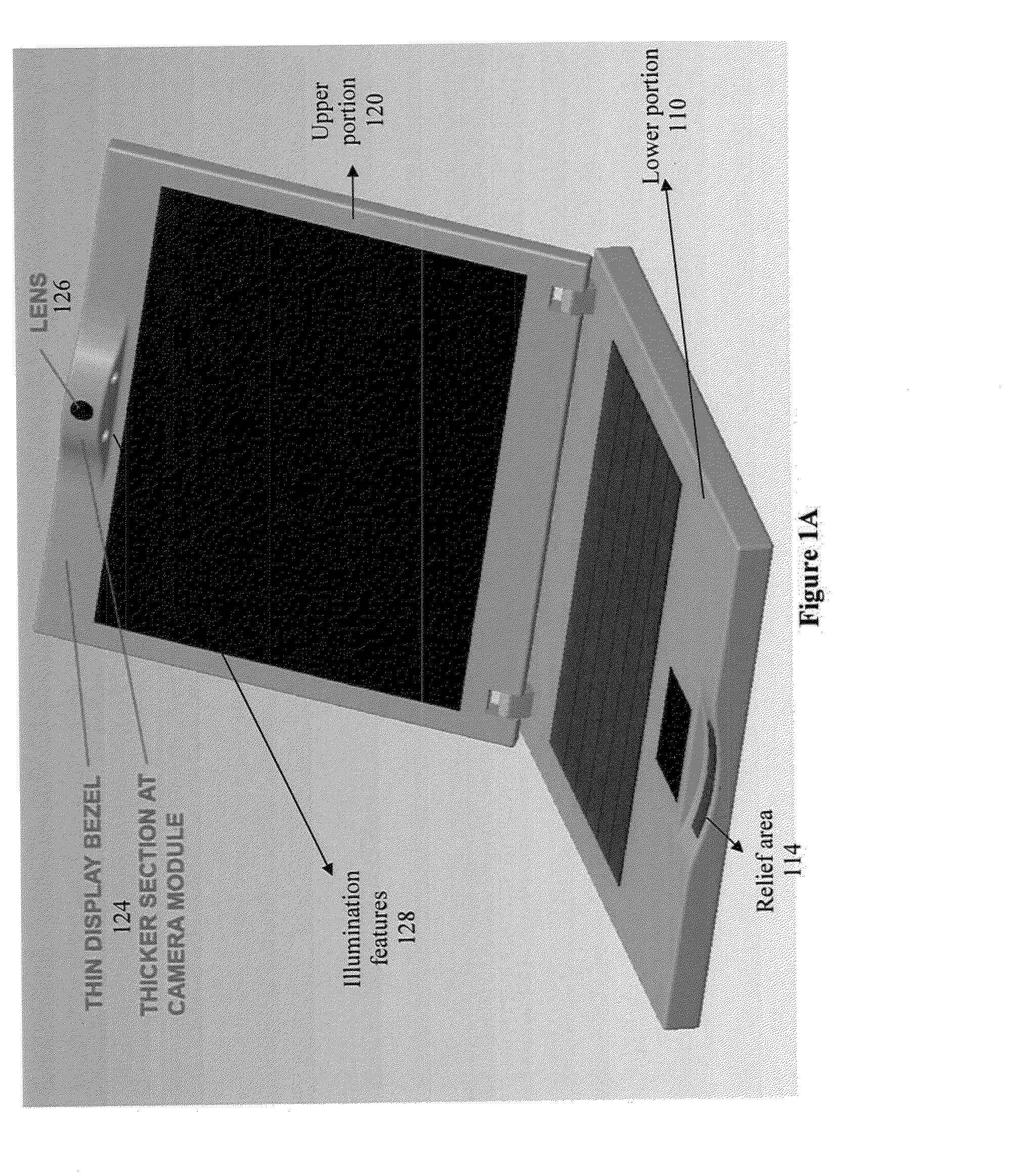
InactiveUS20130229571A1OptimizationIncrease distanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging qualityDisplay device
The present invention is an apparatus and method of manufacture for providing image capturing modules which can be embedded into thin displays (e.g., in laptop computers) while providing for improved image quality. In accordance with several embodiments, a webcam module embedded in a display has multiple positions. A first position (or a “rest” or “park” position) is the position of the webcam module when it is not in use. In this first position of the webcam module, it is in its most compact configuration, and lends itself to integration into a very thin display. In other positions, the webcam module has a more expanded configuration, thus leading to better image quality. Such an expanded configuration leads, amongst other things, to a larger depth of focus. In one embodiment, a stepped PCB is used to provide good image quality while maintaining a compact form factor as well as structural rigidity.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Scanning Field Emission Display
InactiveUS20080211380A1Low-voltage driving capabilityReduce power consumptionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectrode and associated part arrangementsField emission displayDisplay device
Owner:KIM HO SEOB +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com